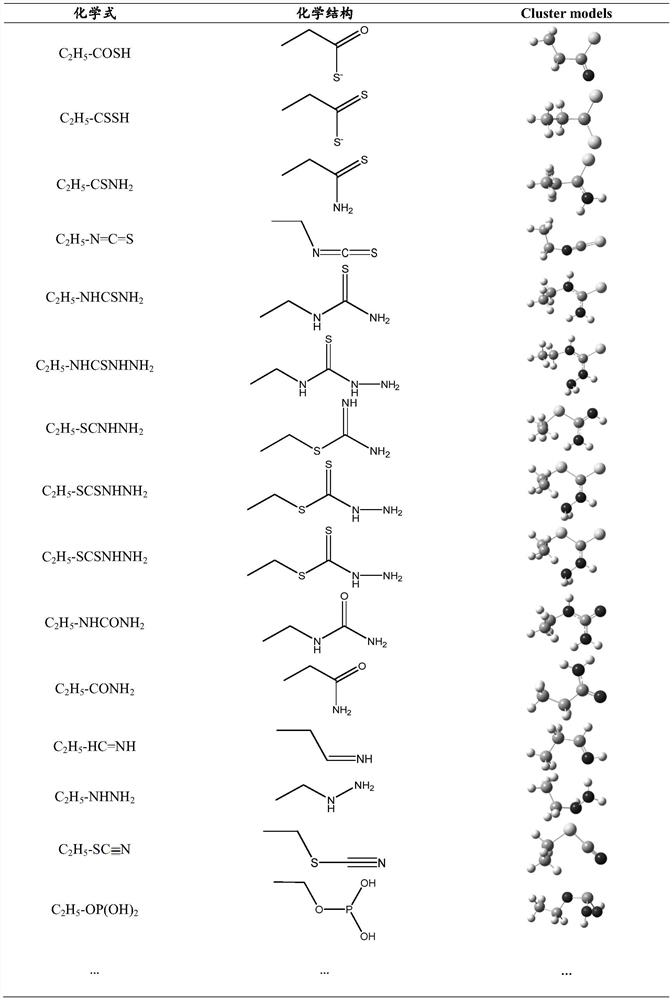
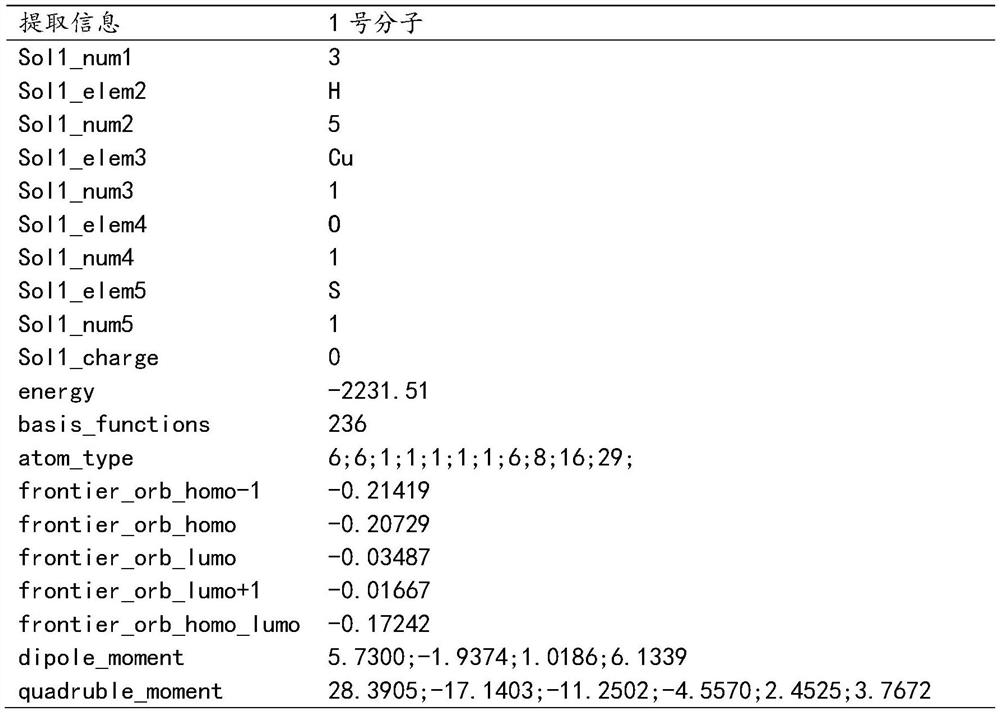
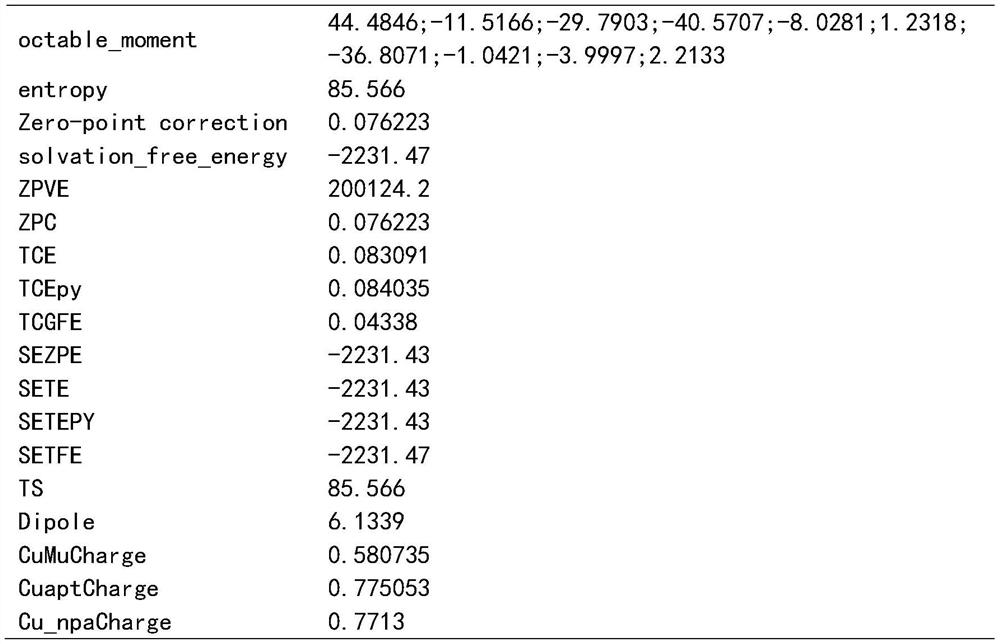
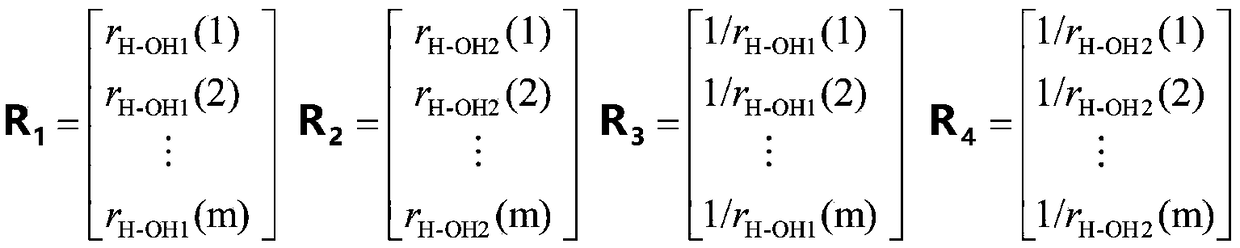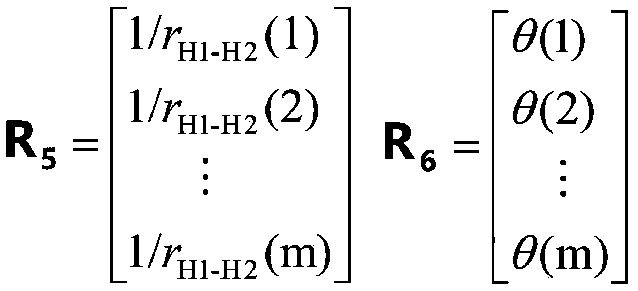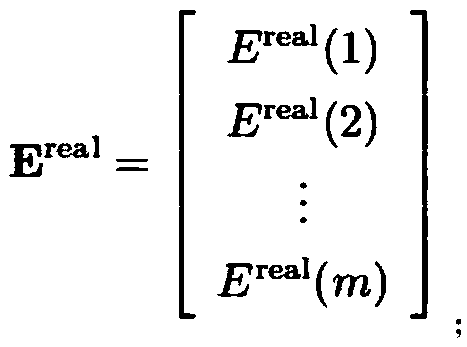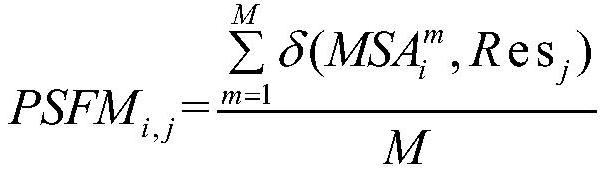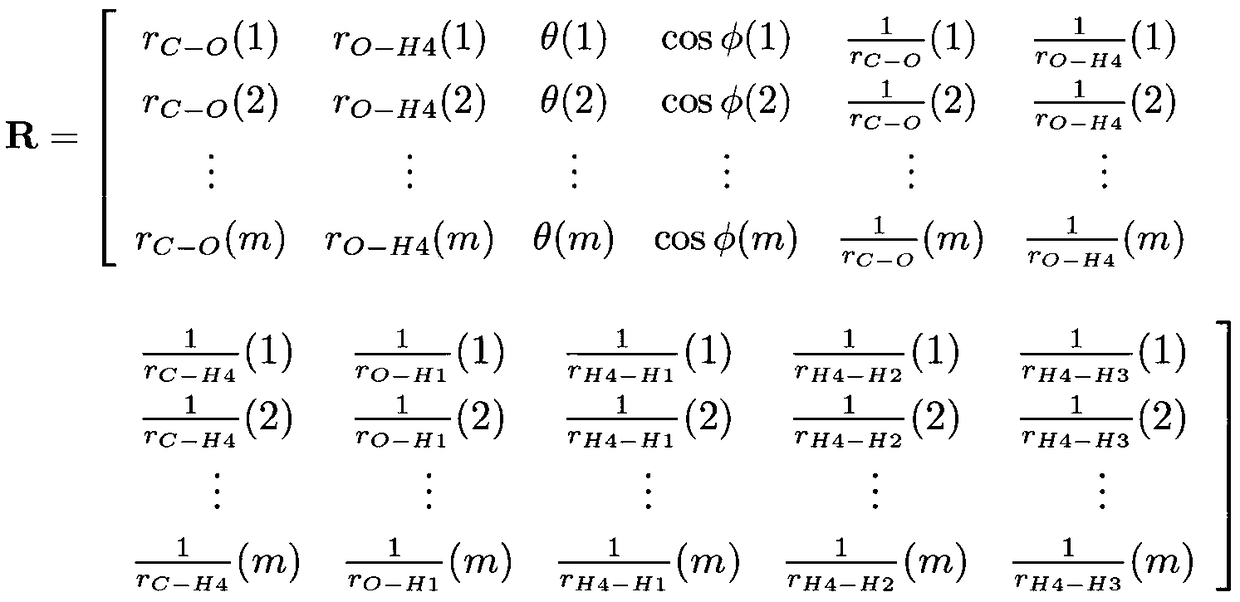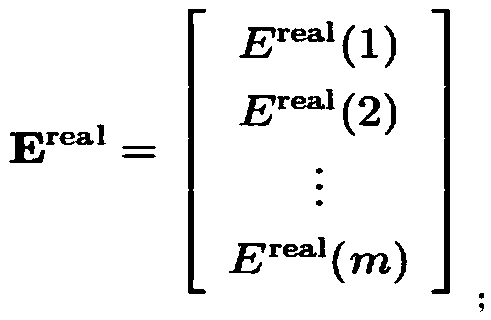Patents
Literature
32 results about "Molecular Databases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molecular database for antibody characterization
InactiveUS7058658B2Weight increaseHigh degreeData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementData setInput selection
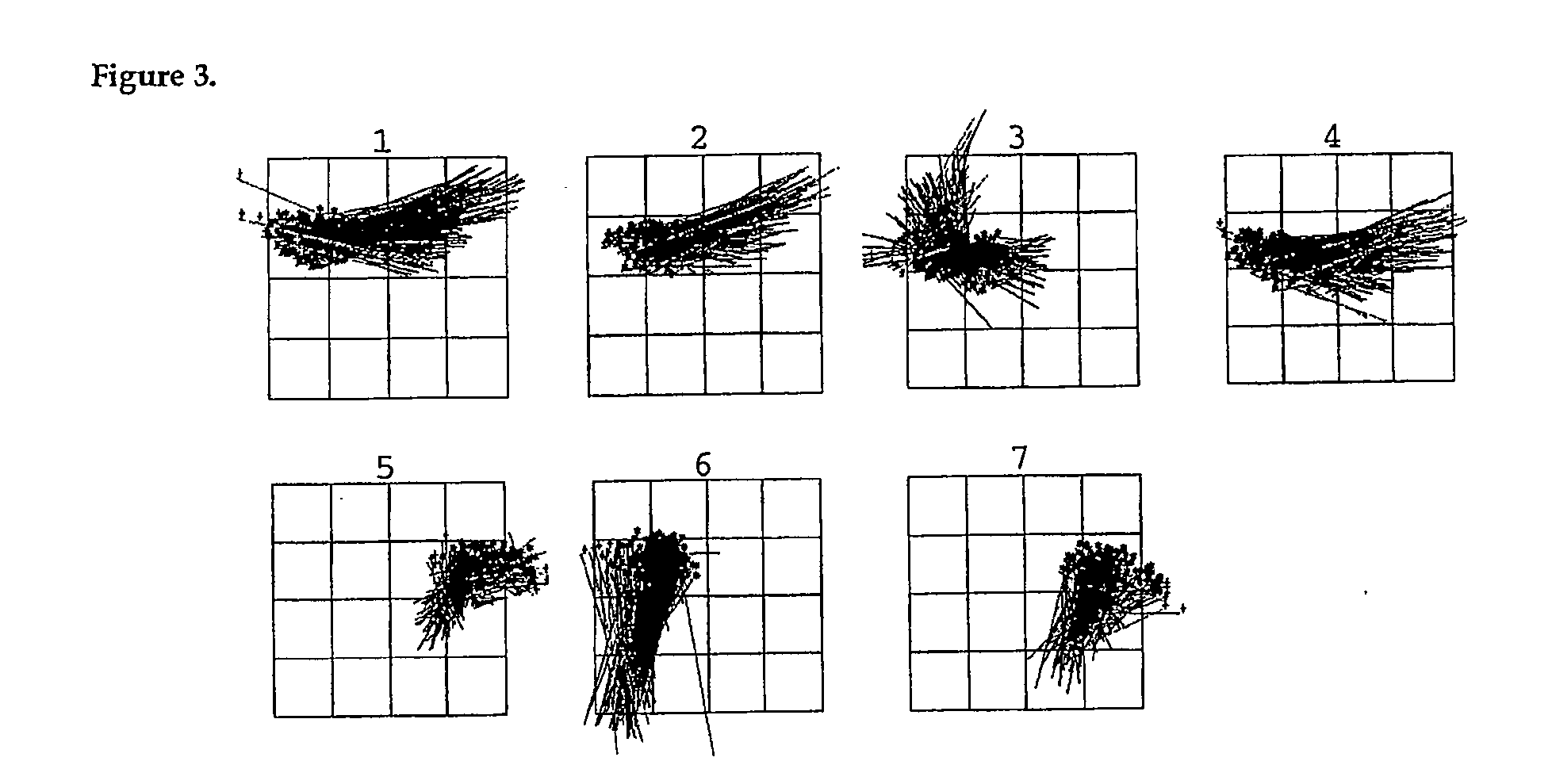
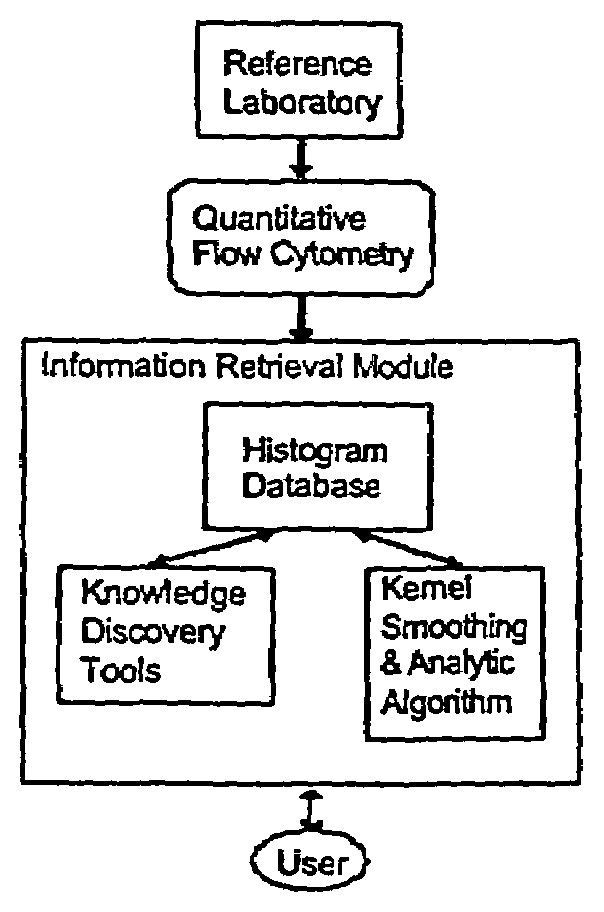
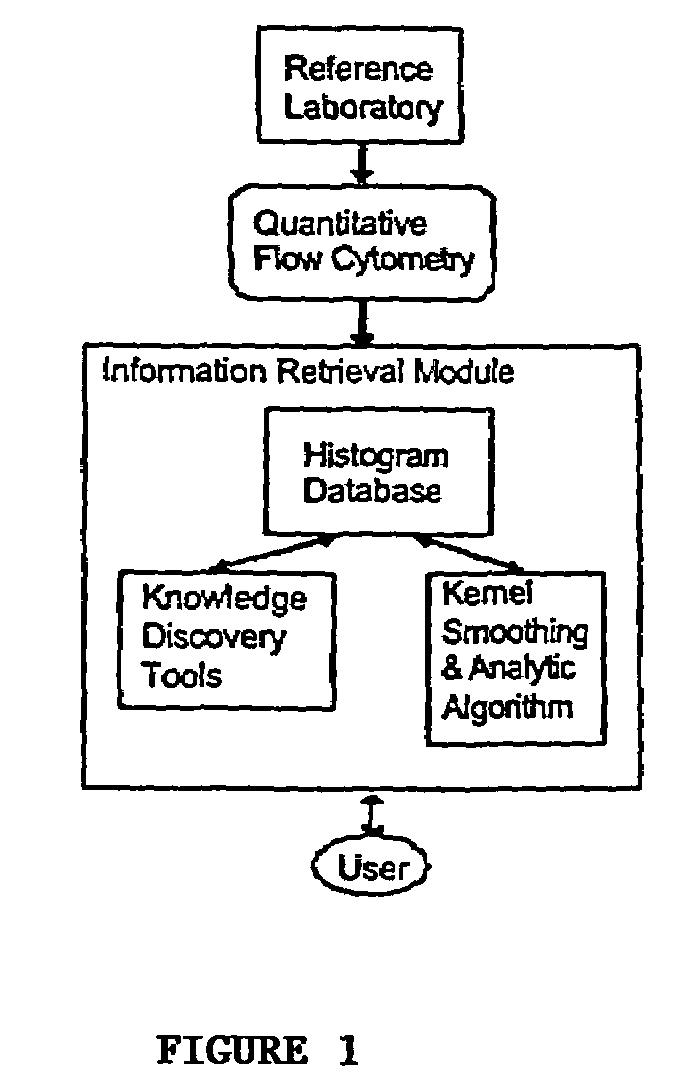
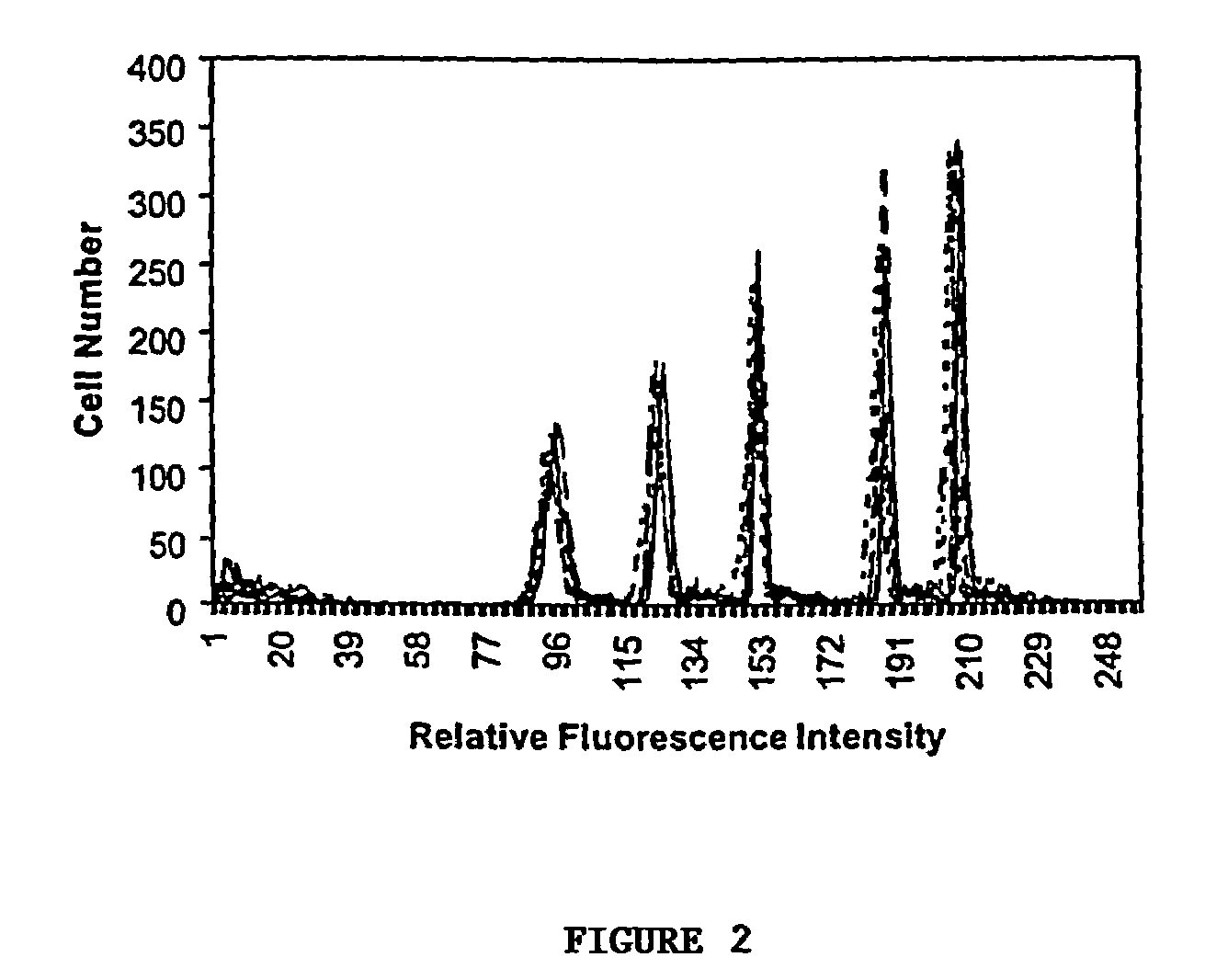
The invention relates to a cumulative, evolving molecular database of monospecific probes and their characteristics. In particular, the invention relates to a computer repository of histograms based upon quantitative flow cytometry. The invention further relates to a system containing a database of monospecific probe properties, the database connected to users through a network to allow users to enter selection criteria and retrieve monospecific probe properties. The invention further relates to a data set useful to refine existing analytic algorithms. The refinement of these algorithms enables computer searches for relationships between known and unknown monospecific probes. Thus, the invention also provides for searching in the database to identify relationships between monospecific probes, groups of probes, and their targets.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
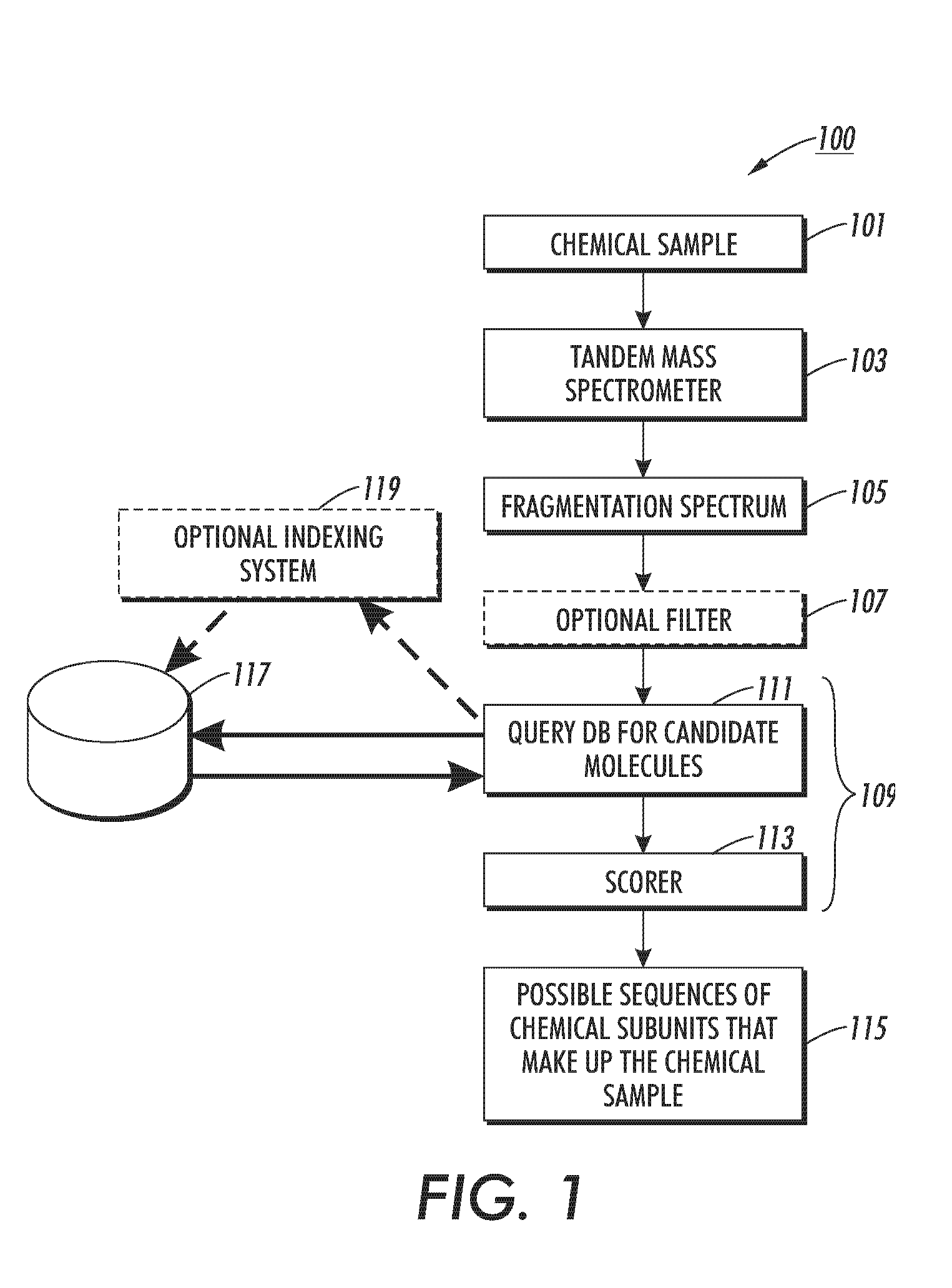
Method, apparatus, and program product for quickly selecting complex molecules from a data base of molecules
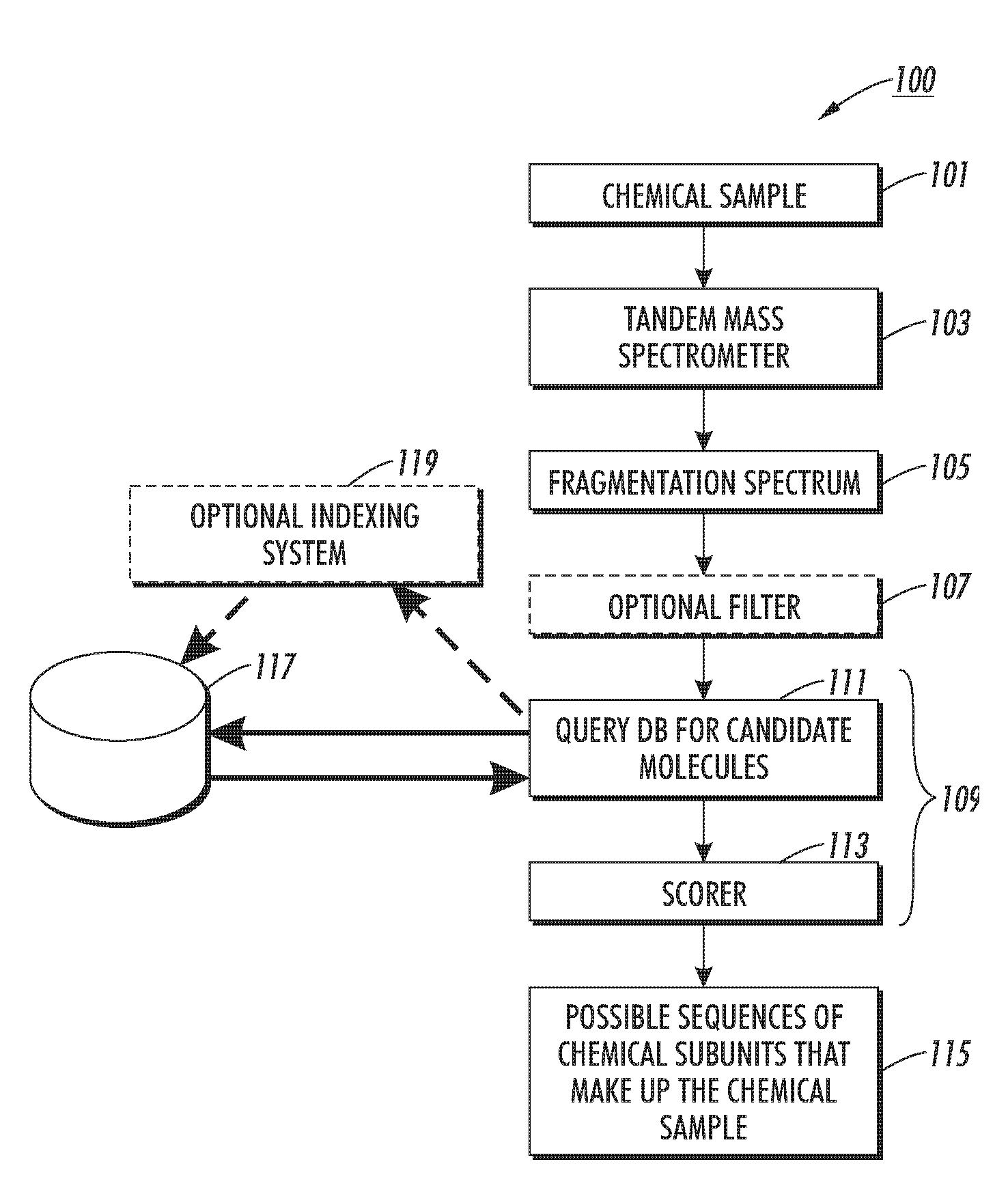
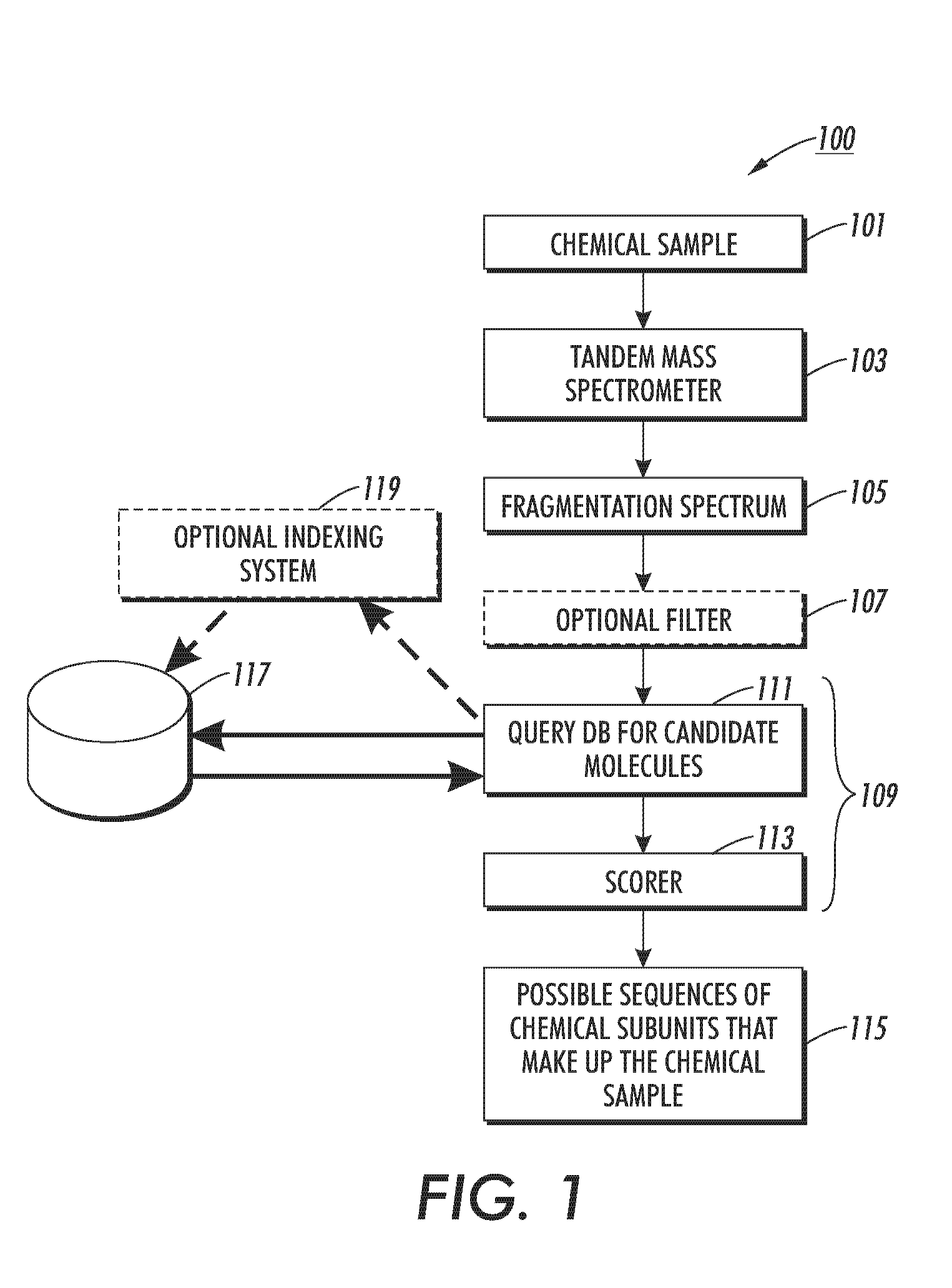
ActiveUS7429727B2Particle separator tubesAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputer scienceIon
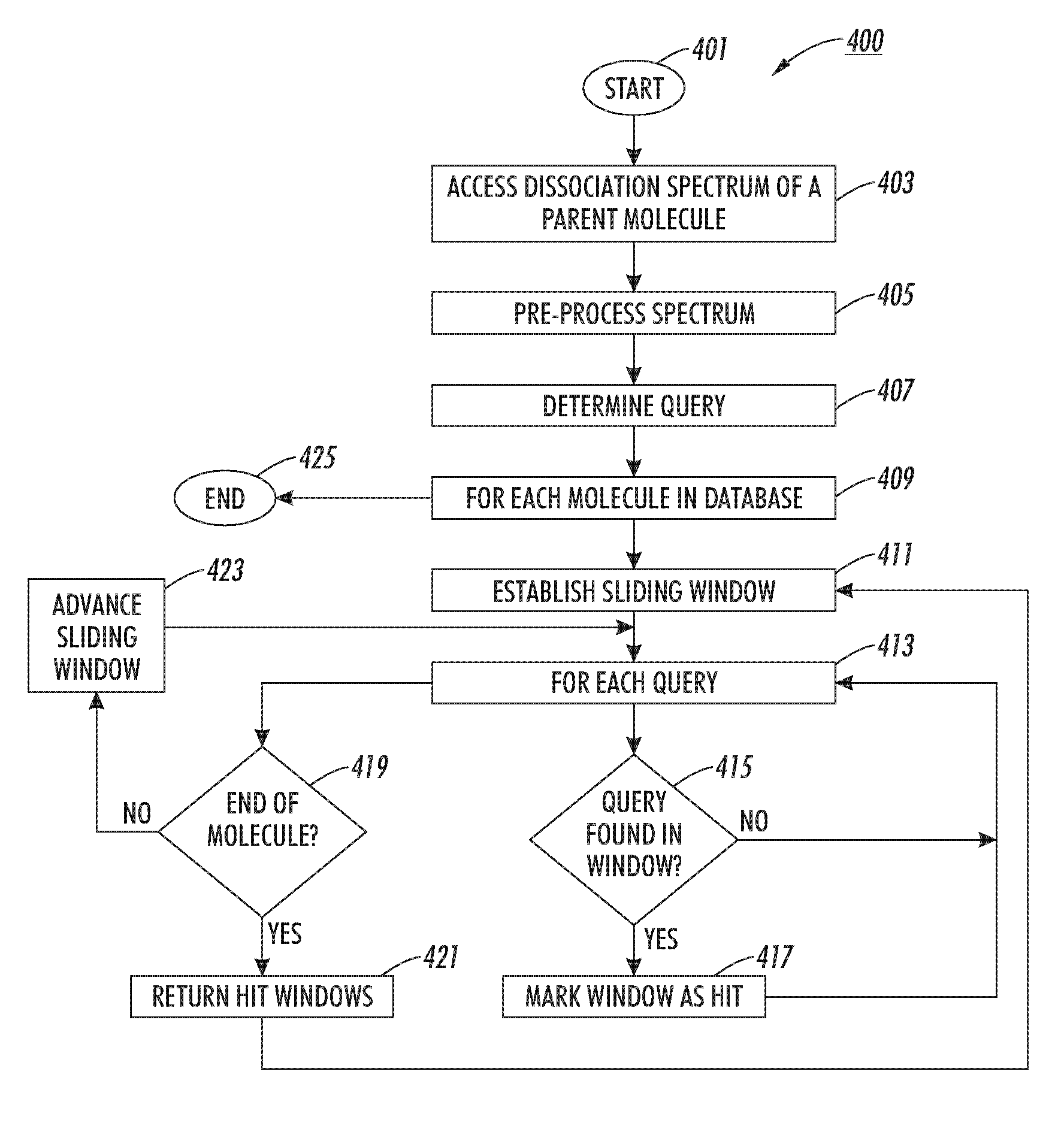
The disclosed technology relates to the analysis of dissociation spectrum data that includes spectral peaks that represent fragments of a parent ion. The parent ion includes molecular subunits that are connected at cleavage sites. The technology accesses the dissociation spectrum data and determines a reference mass of one of the fragments where at least one of the molecular subunits in the fragment is unknown. The technology also selects a candidate parent ion description from a database of molecule descriptions where a computed ion mass of the candidate parent ion description matches the reference mass and scores the candidate parent ion description.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method for determining a shape space for a set of molecules using minimal metric distances
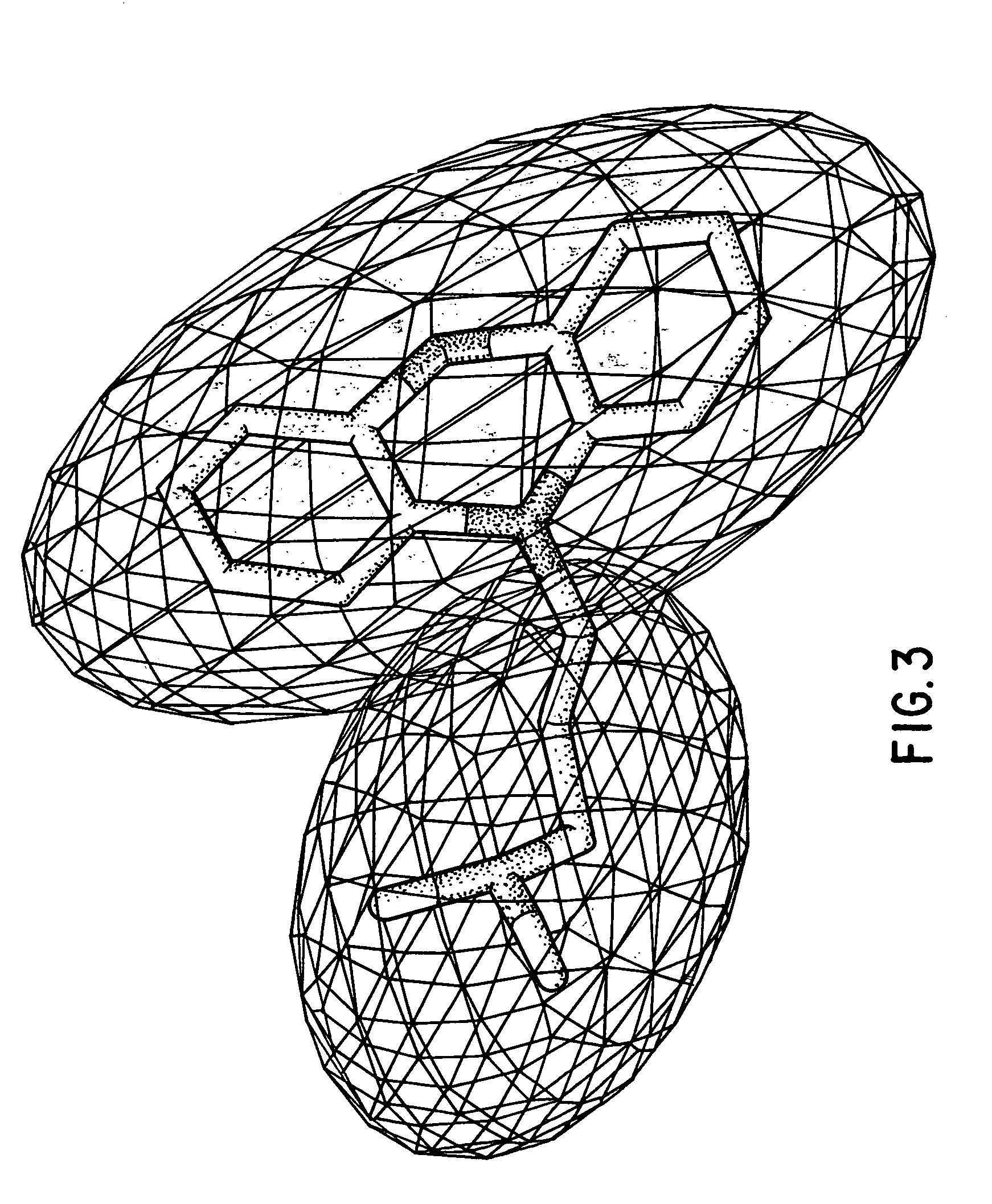
I describe several techniques for characterizing molecules based on the shapes of their fields. The minimal distance between two molecular fields is used as a shape-based metric, independent of the underlying chemical structure, and a high-dimensional shape space description of the molecules is generated. I then show how these attributes can be used in creating, characterizing, and searching databases of molecules based on field similarity. In particular, they allow searches of a database in sublinear time. Next, I extend the utility of this approach by describing a way to automatically break molecules into a series of fragments by using an ellipsoidal Gaussian decomposition. Not only can these fragments then be analyzed by the shape metric technique described above, but the parameters of the decomposition themselves can also be used to further organize and search databases. The most immediate application of these techniques is to pharmaceutical drug discovery and design.
Owner:OPENEYE SCIENTIFIC SOFTWARE
Searchable molecular database
InactiveUS20060116974A1Level be differentRaise the possibilityChemical library matterChemical structure searchChemical structureGraphical user interface
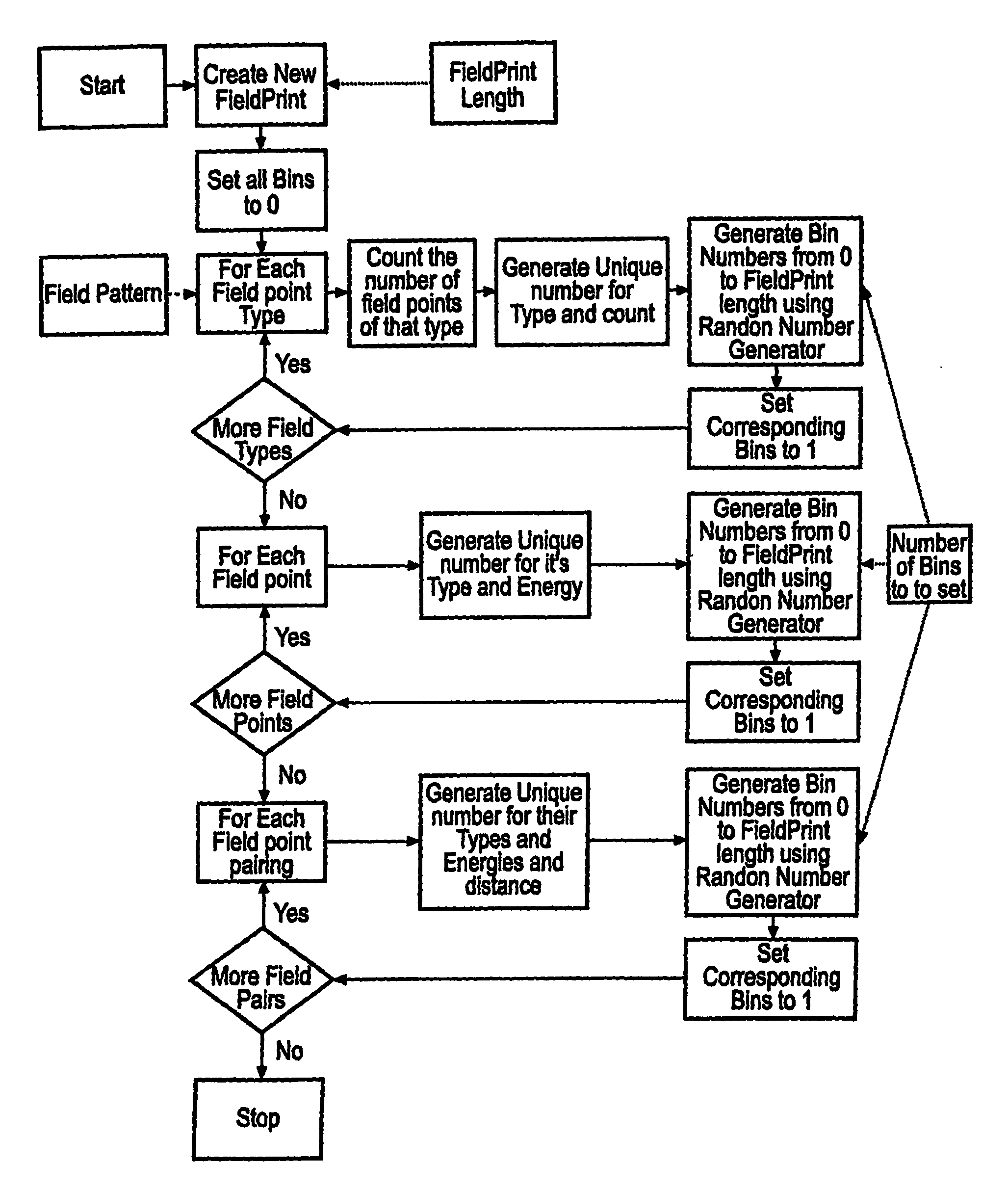
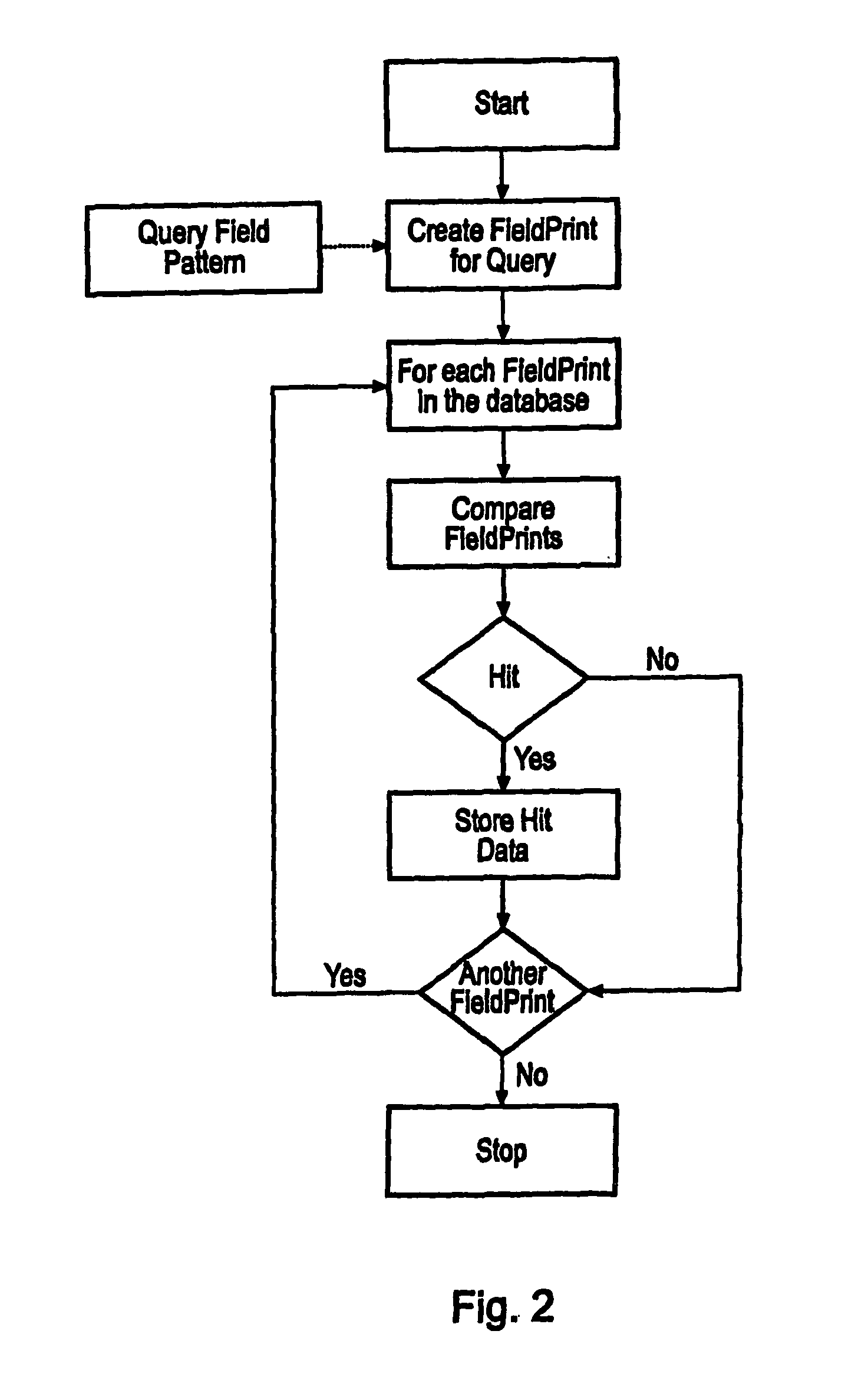
A computer system comprising a database (100) having a plurality of records, is provided. Each record comprises a filed point representation representing field extrema for a conformation of a chemical structure. The database may include records for multiple conformations of the same chemical structure. Each record can have a searchable index of the filed point representation. In one embodiment the index is bit string. An indexing mechanism for generating an index, a searching mechanism for searching the database and a graphical user interface to enable a user to interface with the database (100) are also provided.
Owner:CRESSET BIOMOLECULAR DISCOVERY
System and method for modelling a molecule with a graph
InactiveUS20110264432A1Analogue computers for chemical processesChemical data visualisationGraphicsMolecular modelling
Modelling a molecule by means of a graph, said graph comprising vertices and edges, each edge having a specific type, and said graph having cyclic orderings on the half-edges about at least one of the vertices, said system comprising means for determining the cyclic orderings on the half-edges about said at least one vertex by means of the spatial coordinates of the constituent atoms of the molecule, and means for determining the type of each edge of the graph by means of the relative spatial location of the constituent atoms of the molecule. Thereby automatic classification, comparison, specification, analysis and / or prediction of molecular structures can be provided because these molecular structures are represented by explicit combinatorial objects, and descriptors can be derived from the graph constructed in this manner. The descriptors are automatically computable from molecular databases, such as PDB or CATH, with no qualitative human intervention or subjective criteria. The invention can be applied to macromolecular structures such as proteins, protein globules, ligands, polymers, nucleotides, nucleic acids, RNA and DNA.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Ellipsoidal gaussian representations of molecules and molecular fields
InactiveUS20060195267A1Improve utilizationMolecular designChemical structure searchDecompositionReactive site
I describe several techniques for characterizing molecules based on the shapes of their fields. In particular, I describe a way to automatically break molecules into a series of fragments by using an ellipsoidal Gaussian decomposition. These fragments can then be analyzed by a shape metric technique, and the parameters of the decomposition can be used in creating, characterizing, and searching databases of molecules based on field similarity. The ellipsoidal Gaussian representations can also be used to describe binding or active sites on macromolecules, thereby providing a template for searching for complementary molecules in a database. The most immediate application of these techniques is to pharmaceutical drug discovery and design.
Owner:OPENEYE SCIENTIFIC SOFTWARE
Method and apparatus for searching molecular structure databases
I describe several methods for organizing databases of molecular structures and searching such structures. Also described are methods for characterizing molecules based on the shapes of their fields that can be used in conjunction with the methods of organizing and searching databases. In particular, the databases of molecular structures can be analyzed by a shape metric technique, and the parameters of the decomposition can be used in creating, characterizing, and searching databases of molecules based on field similarity. The most immediate application of these techniques is to pharmaceutical drug discovery and design.
Owner:OPENEYE SCIENTIFIC SOFTWARE
System for the efficient discovery of new therapeutic drugs
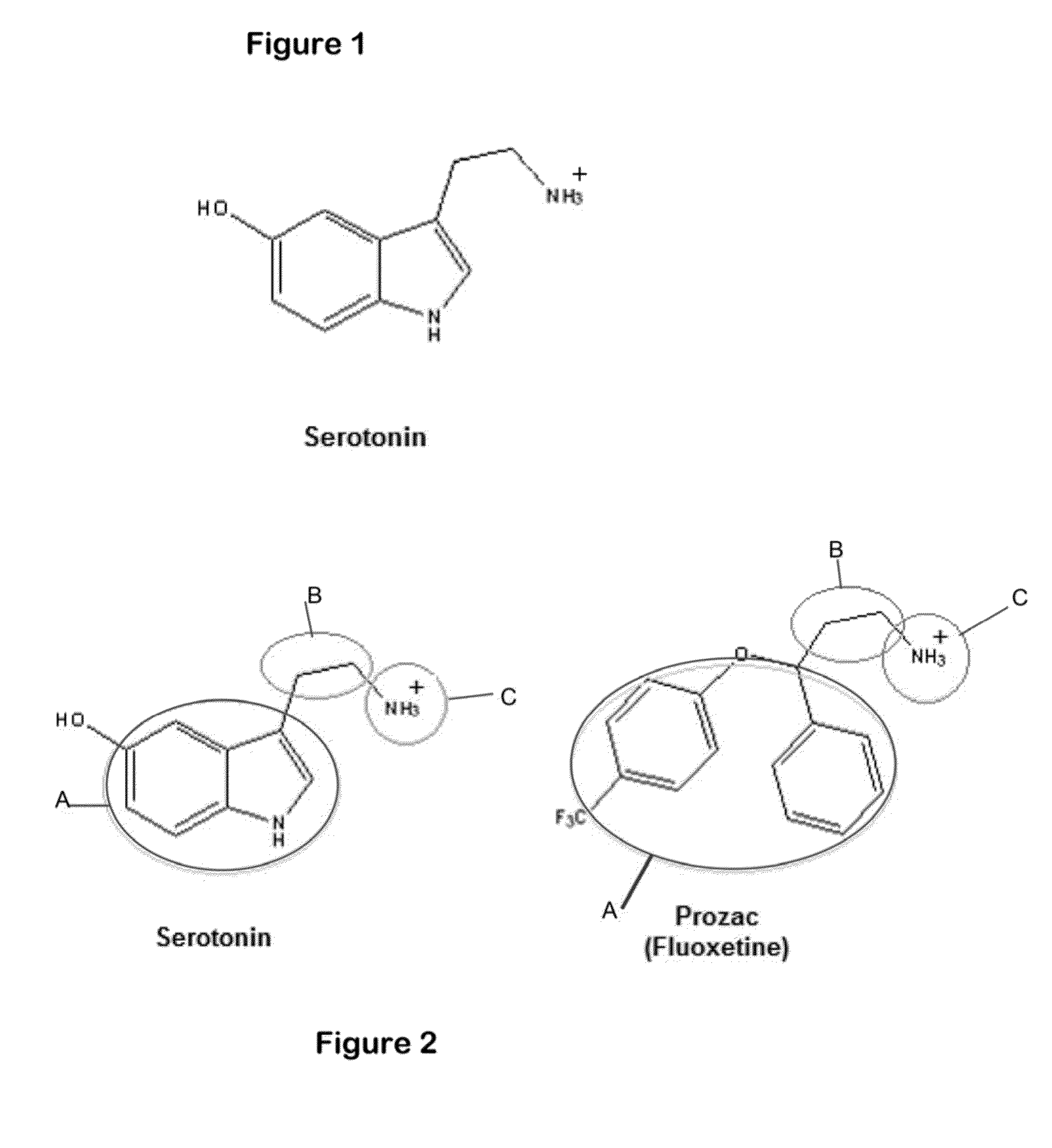
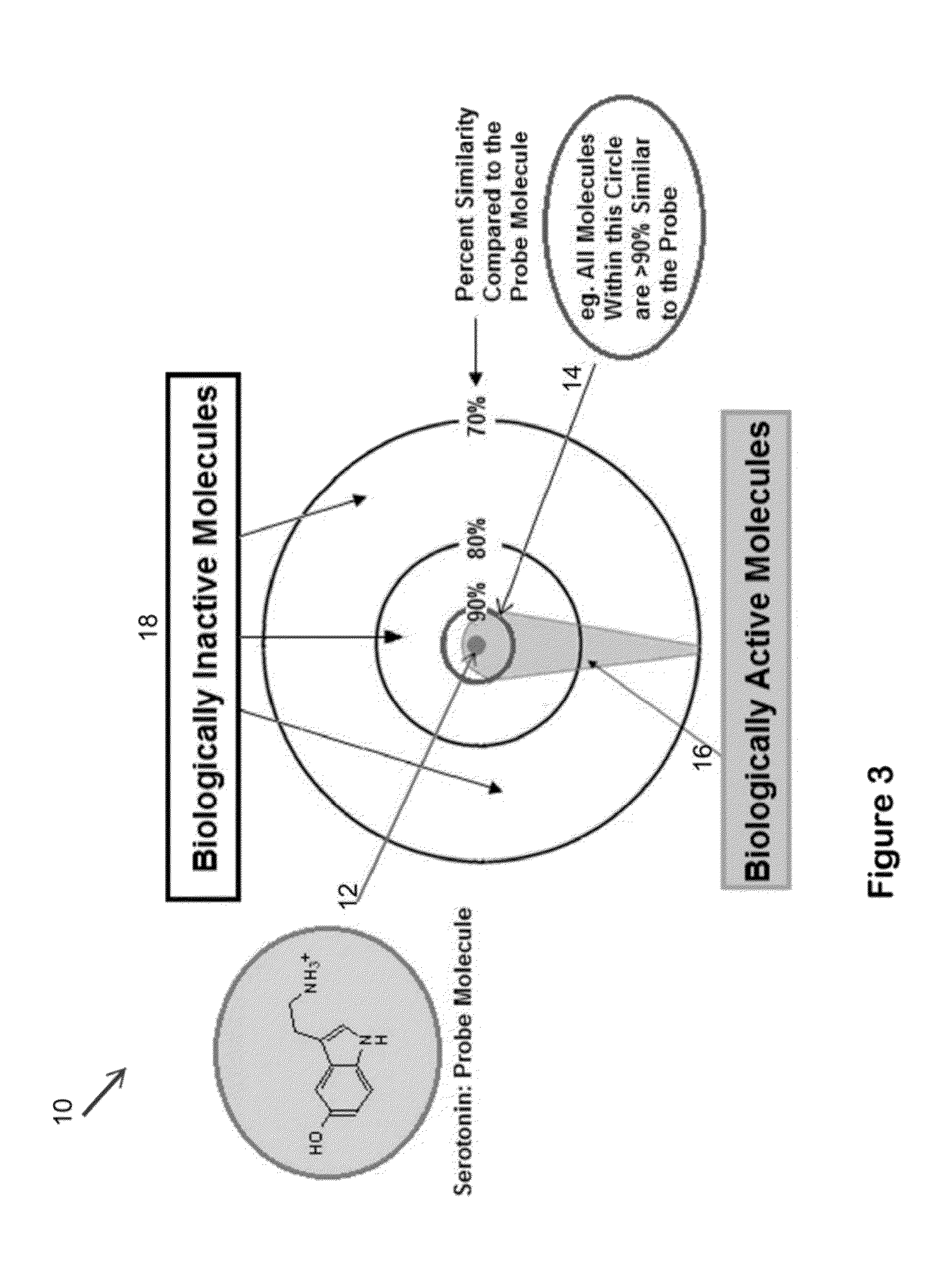
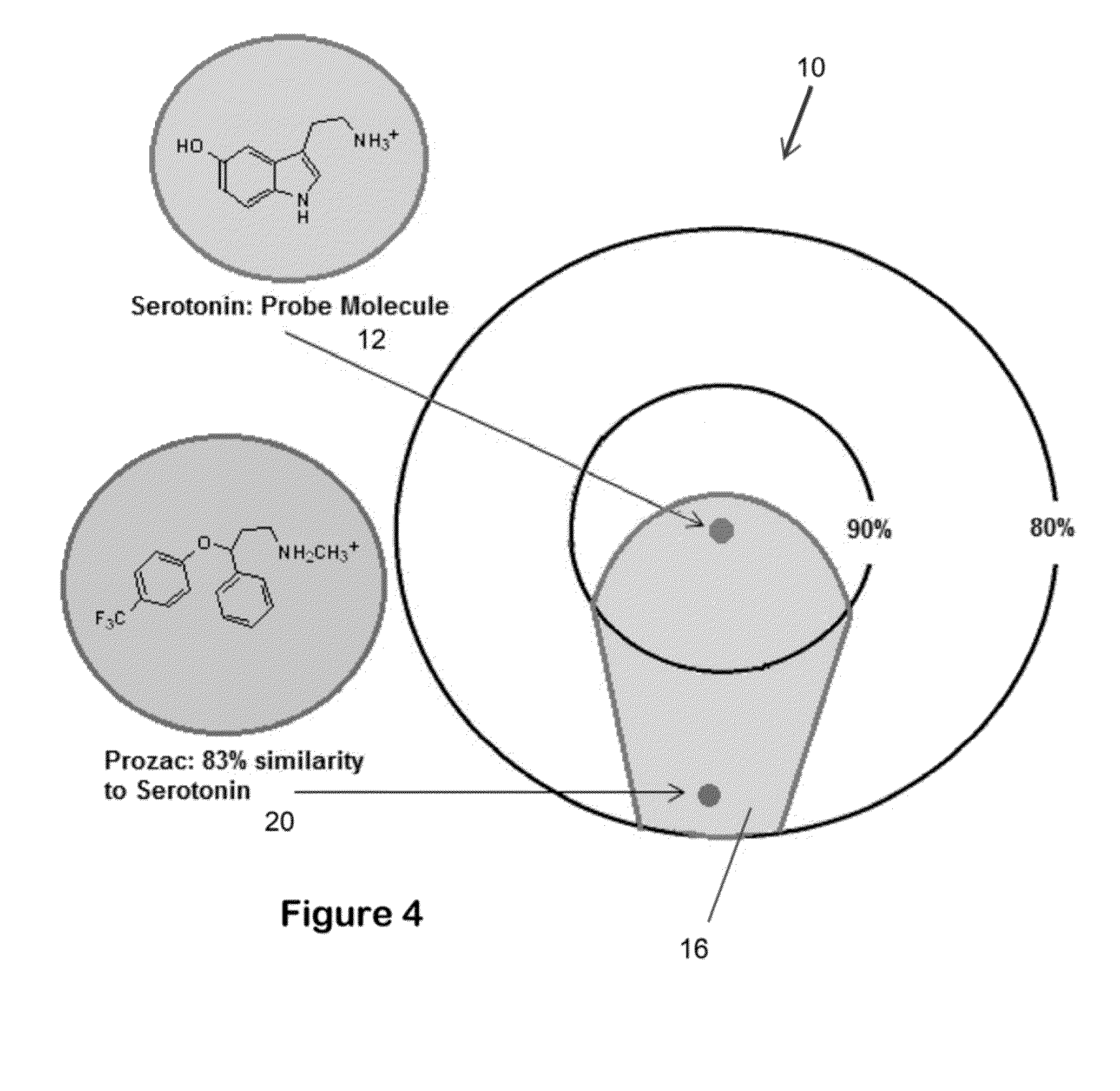
The invention provides for carrying out 3-dimensional similarity searching by comparing a probe molecule to each member of a 3-dimensional database. The probe molecule is overlapped with each member of a database of molecules and then the database molecule is rotated and translates until its similarity with the probe molecule is maximized. The system can contain ten different scoring functions to rate the similarity between the two molecules. Each function employs different molecular features when scoring a particular comparison. Some methods are based on the relative shape of the two molecules, and some are based on the overlap of key atoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and / or halogens.
Owner:HUDSON ROBOTICS
Molecular marker combination for Litopenaeus vannamei germplasm identification and application thereof
ActiveCN105861729AOvercoming the inability to identify Litopenaeus vannamei germplasmOvercoming germplasm problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUnknown Source
The invention relates to a germplasm identification technology in the field of aquatic animal genetic breeding, in particular to a molecular marker combination for Litopenaeus vannamei germplasm identification and application thereof. The molecular marker combination is formed by 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite locus primers. A method for germplasm identification is established with the 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite markers, microsatellite typing is carried out on existing foreign imported germplasms including but not limited to the Zhengda breed, the SIS breed, the Kona Bay breed and the Molokai breed, and domestic artificially-selected germplasms including but not limited to the Kehai-1 breed and the Guihai-1 breed, molecular databases of different germplasm resources are established with obtained typing data, and different germplasms are identified with the molecular markers. The germplasm sources of Litopenaeus vannamei with unknown sources can be identified by comparing panel typing results with the established databases of different germplasm resources. The method for accurately identifying different germplasm materials of Litopenaeus vannamei with the molecular means has great significance on tracing, evaluation, protection and utilization of different germplasms.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Common protein surface shapes and uses therefor
ActiveUS20090318311A1Raise the possibilityLibrary creationSpecial data processing applicationsAmino acid side chainThree-dimensional space
A method of determining common three-dimensional structural features of protein surfaces is provided, as is use of representations of these common structures in molecular database searching and in designing focused molecular libraries. The method is particularly concerned with the analysis and representation of protein surfaces such as b-turns, loops and contact surfaces. In one form, the method identifies common locations and orientations of amino acid side-chains, simplified as Cα-Cβ vectors. In another form, the method identifies common regions of surface charge represented by grid points in three-dimensional space. Further provided are common three dimensional structural features of proteins that can be used to search molecular databases for the purposes of identifying molecules that match these common three dimensional structural features. The common three dimensional structural features can also be used to focus de novo molecular generation to produce libraries containing molecules that have these common three dimensional structural features. Libraries of these structurally-related molecules may then be produced for the purposes of drug discovery.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for calculating water molecule energy based on molecular degree-of-freedom depth learning
InactiveCN109411028AGet rid of constraintsFlexible useMolecular entity identificationChemical physicsEnergy based
The invention discloses a method for calculating water molecule energy based on molecular degree-of-freedom depth learning, and belongs to the technical field of molecular energy calculation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, a water molecular database is established; S2, m configurations and corresponding energy are selected at random to serve as a training group, remaining 1000-m configurations and corresponding energy serve as a test group; S3, spatial coordinates of water molecules in the training group are transformed and serve as starting of calculation; S4, energy data of the training group are extracted to serve as training group output energy matrixes corresponding to column configuration parameter input matrixes in an one-to-one mode; S5, test group configuration parameter input matrixes and test group output energy matrixes are established; and S6, an energy matrix Ecalc is obtained through double neural layer calculation. According to the method, the influence of the ratio of the training group to the test group on accuracy of training results is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Method, apparatus, and program product for quickly selecting complex molecules from a data base of molecules
ActiveUS20070145261A1Particle separator tubesAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputer scienceIon
The disclosed technology relates to the analysis of dissociation spectrum data that includes spectral peaks that represent fragments of a parent ion. The parent ion includes molecular subunits that are connected at cleavage sites. The technology accesses the dissociation spectrum data and determines a reference mass of one of the fragments where at least one of the molecular subunits in the fragment is unknown. The technology also selects a candidate parent ion description from a database of molecule descriptions where a computed ion mass of the candidate parent ion description matches the reference mass and scores the candidate parent ion description.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Intelligent prediction method for small molecule-protein binding affinity
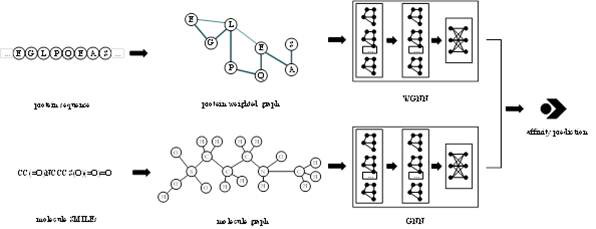
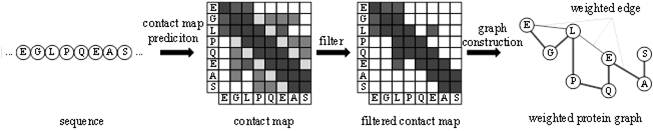
PendingCN114333984ASolve the problem that it is difficult to quickly mine protein structure informationAccurate Sequence CharacterizationNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
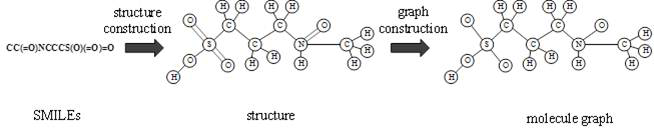
The invention provides a protein weight graph-based small molecule-protein binding affinity intelligent prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a small molecule graph based on SMILES, constructing a protein weight graph based on a sequence, and secondly, respectively extracting the characteristics of the small molecule graph and the protein weight graph by adopting two graph convolutional neural networks; and constructing a graph convolutional neural network to extract the features of the two, splicing the obtained feature vectors, and further predicting the affinity of the two. According to the protein weight graph constructed by the invention, more accurate representation of the sequence is realized, and the interaction among amino acid residues is more intuitively and effectively represented by a graph structure; the constructed protein weight graph does not need to be subjected to an extremely complex sequence alignment process, so that data processing is quicker, the method is suitable for a virtual screening process of a large molecular database, and more accurate small molecule-protein affinity prediction can be realized.
Owner:QINGDAO TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Computer drug design method using P2Y12 as target and application thereof
InactiveCN106407737AInhibition of P2Y12 activitySpecial data processing applicationsProtein targetStructure function
The invention relates to a computer drug design method using a P2Y12 as a target and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of target computer-aided drug design, small molecule drug virtual screening, molecular docking and full atom molecular dynamics. The computer drug design method is a drug virtual screening design method including using the P2Y12 as the target and using a Chembridge small molecule database as a search database. The invention includes target protein spatial structure analysis, a binding pocket definition method and a structure-function relationship analysis method. The computer drug design method has been verified for many times in a drug design method of associated protein targets, and is high in success rate. The computer drug design method has been used for virtual screening of inhibitors of GPCRs.
Owner:张崇骞
Application of small molecule compounds in preparation of silkworm antiviral drug
ActiveCN109223784AInhibition of replicationHas curative effectOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsCell invasionCore gene
The invention discloses an application of a small molecular compound in the preparation of silkworm antiviral drug. The present invention relates to obtaining small molecular compounds based on mainstream molecular docking techniques, Aiming at the core gene of Bombyx mori baculovirus, the three-dimensional structure of the core gene is obtained by using the virtual modeling technology, the molecular docking screening small molecular database is used for detecting the activity of the obtained small molecular compound, and the small molecular compound with effective effect in the invention is finally obtained. At a final concentration of 1 [mu]g / mL or more, that small molecule compound can completely inhibit replication of BmNPV, and can continue to inhibit replication of BmNPV aft BmNPV completes cell invasion, and has therapeutic effect. The invention can be used for the research and development and production of medicines for preventing and treating blood type pus of silkworm, and has application and popularization value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
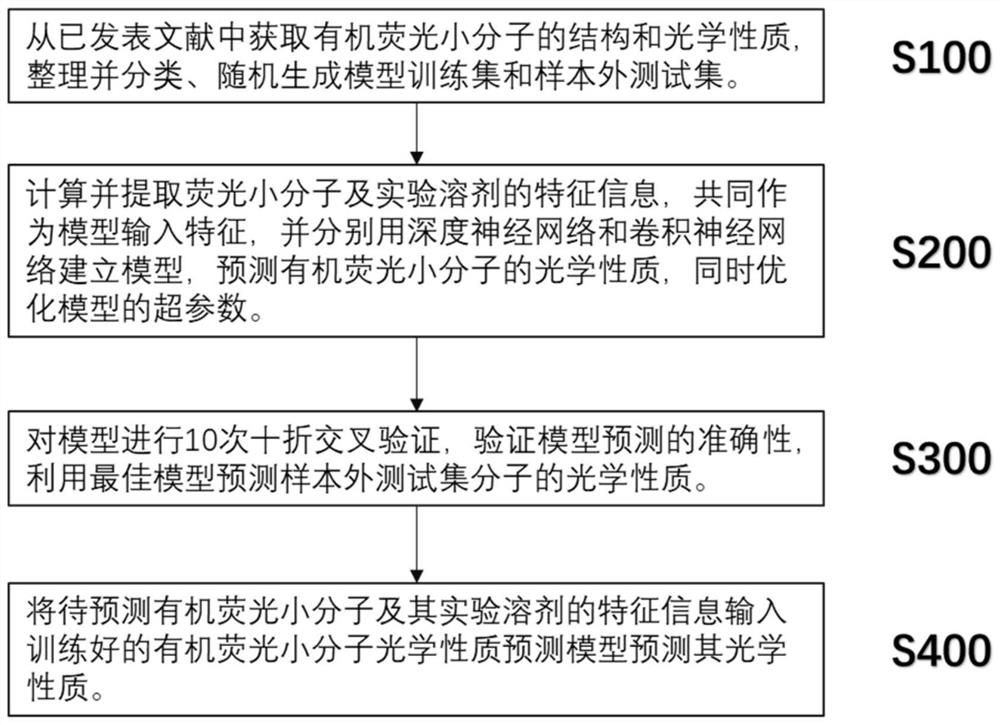
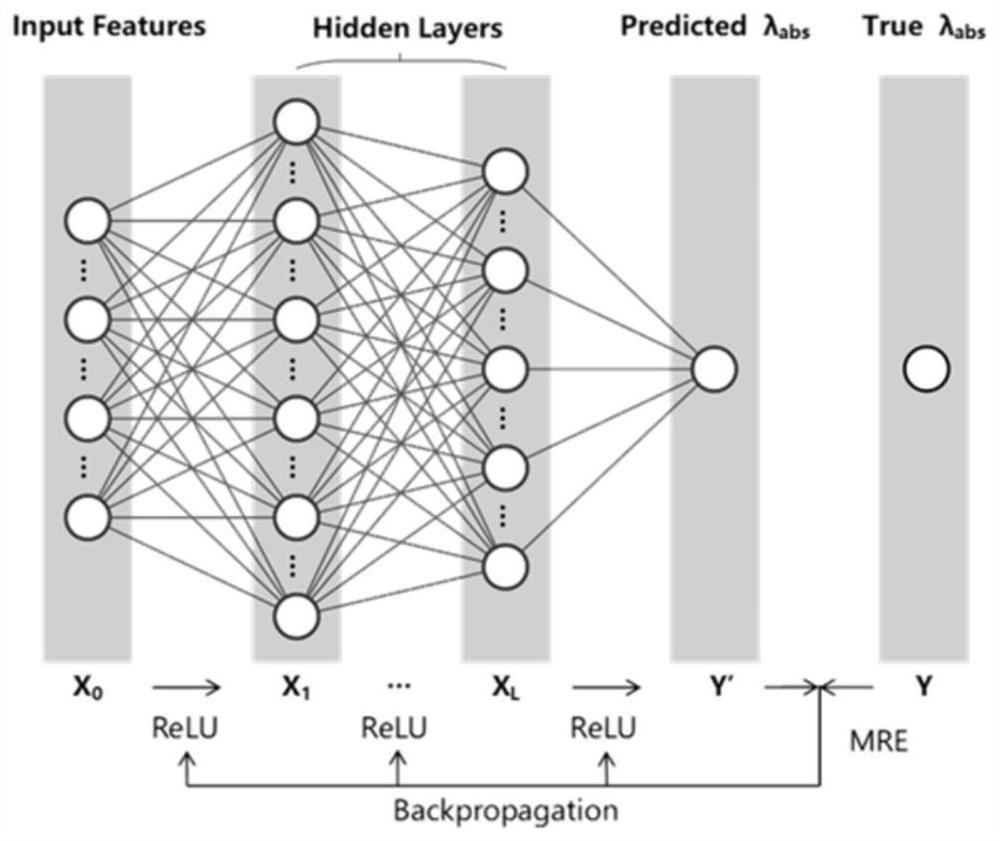
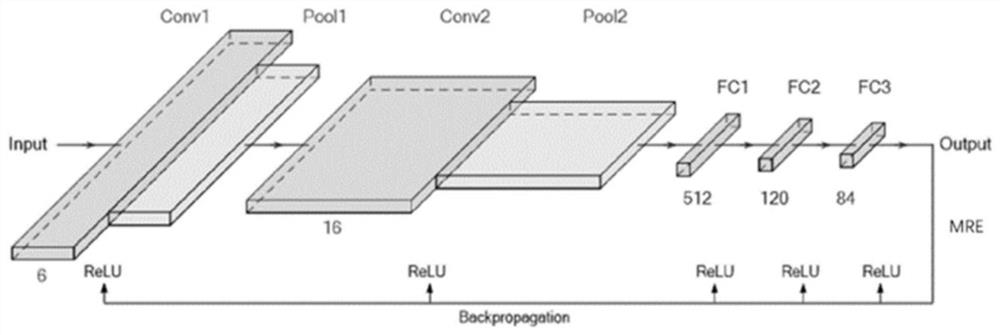
Organic fluorescent small molecule optical property prediction method based on deep neural network
PendingCN113380337AReduce deletionEasy to learnChemical property predictionNeural architecturesOptical propertyNeural network nn
The invention provides an organic fluorescent small molecule optical property prediction method based on a deep neural network. According to the method, a new organic fluorescent small molecule database is established, molecular descriptors and molecular fingerprints are adopted to extract molecular information, and a multi-layer neural network and a convolutional neural network are input for deep learning training to obtain an organic fluorescent small molecule optical property prediction model; the characteristic information of the to-be-predicted organic fluorescent micromolecules and the experimental solvent thereof are input into the trained organic fluorescent micromolecule optical property prediction model so as to predict the optical property of the to-be-predicted organic fluorescent micromolecule. The method can accurately predict the optical properties (the average relative error is less than 5%) of the organic fluorescent small molecules, so that the development efficiency of the organic fluorescent small molecules is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
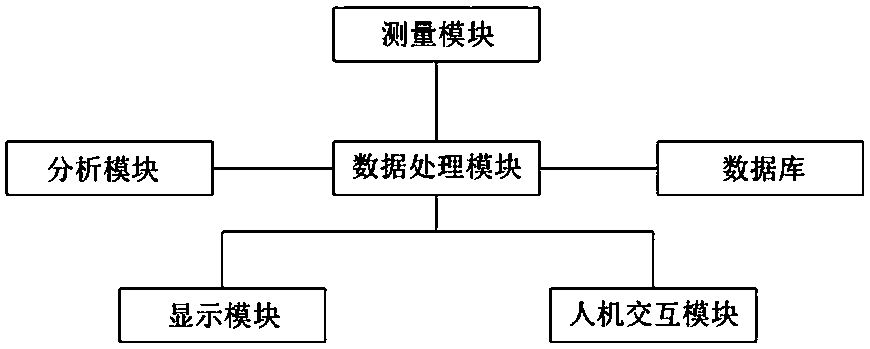
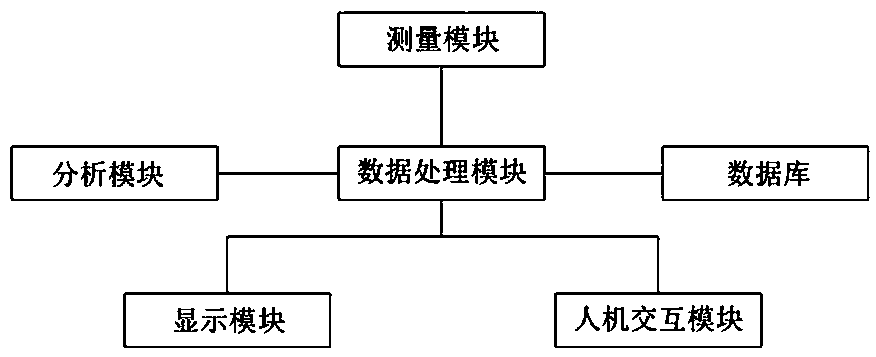
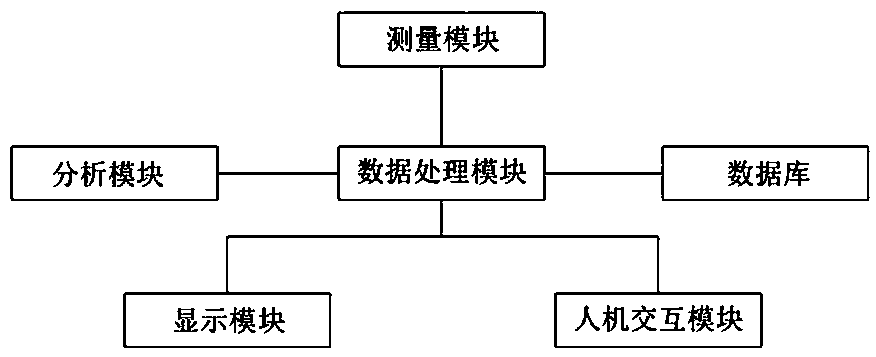
Positron emission medical imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN107647877AAccurate locationPrecise positioningComputerised tomographsTomographyCompanion animalImaging technology
The invention relates to the technical field of molecular imaging and medical image imaging technology, in particular to a positron emission medical imaging system and an imaging method. The positronemission medical imaging system comprises a measurement module, a data processing module, an analysis module and a database. The data processing module is respectively connected with the measurement module, the analysis module and the database for analyzing and processing the information obtained by the measurement module and obtaining wave functions and momentum distribution information of the electrons and positrons in the molecule. The database is the lesion molecular database and the analysis module is used for comparing the wave functions with the momentum distribution information, and locating the exit position of the gamma photon and the location of the lesion molecules. Compared with other positron emission tomography medical imaging methods, the positron emission medical imaging system and the imaging method can accurately locate the lesion molecules by only using PET method, and overcome the defect that the traditional single-mode PET can not form clear image. Meanwhile, theobtained gamma spectrum is compared with the lesion molecules in the database so as to determine the structure of lesion molecules, therefore physiological anatomy is avoided.
Owner:唐山斯腾光电科技有限公司
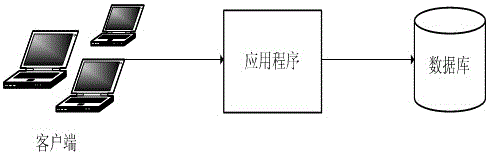
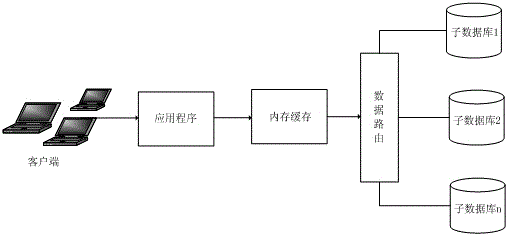
Distributed database storage architecture system
InactiveCN105589937AImprove usabilityImprove acceleration performanceSpecial data processing applicationsComputer clusterHigh availability
The invention discloses a distributed database storage architecture system, comprising a plurality of sub-databases, wherein the connection between each sub-database and an application program is established via a data routing; and the sub-databases are obtained after horizontally segmenting data. The distributed database storage architecture system has the advantages that the database storage system in a computer cluster with high availability and expansibility is constructed by relatively low-cost devices, and the expansion capability of the cluster is so strong that linear expansion can be almost achieved, thus even part of sub-database nodes is failed, the other sub-database nodes are not influenced, and the reading-writing efficiency of the data is also improved without being influenced by data size.
Owner:JIANGSU DINGFENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
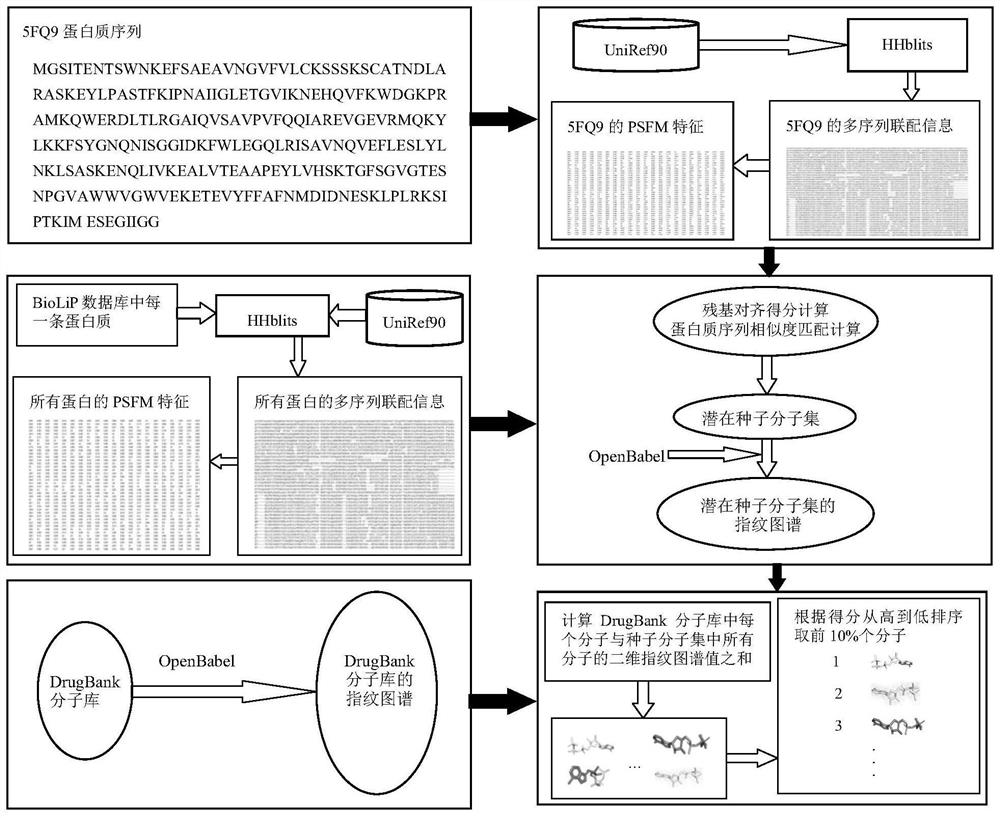
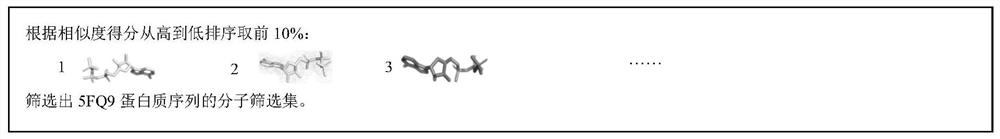
Molecular virtual screening method based on protein sequence alignment
PendingCN112820355AAvoid malfunctionScreening helpsCharacter and pattern recognitionSequence analysisMolecular sieveVirtual screening
The invention relates to a molecular virtual screening method based on protein sequence alignment, which comprises the following steps: according to an input protein sequence to be subjected to molecular screening, acquiring multi-sequence coupling information of protein by using an HHbits program; the frequency PSFM of the same residues appearing at the corresponding positions of the protein sequence to be predicted and the multi-sequence coupling information being calculated; by using the same method, generating the PSFM of each protein sequence in a protein-ligand interaction database BioLiP; calculating the residue alignment score and similarity matching quality of the to-be-predicted protein and each protein in BioLiP, and obtaining a potential seed molecule set according to the matching quality score; and calculating the sum of the two-dimensional fingerprint values of each molecule in the molecule database and all the molecules in the seed molecule set, sorting all the molecules in the DrugBank according to scores, and obtaining x.NDrugBank molecules with the top scores as a molecular sieve selection set of protein sequences to be subjected to molecular screening. The method can be used for any screening scene.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Common protein surface shapes and uses therefor
InactiveUS20050154533A1Raise the possibilityAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingAmino acid side chainThree-dimensional space
A method of determining common three-dimensional structural features of protein surfaces is provided, as is use of representations of these common structures in molecular database searching and in designing focussed molecular libraries. The method is particularly concerned with the analysis and representation of protein surfaces such as b-turns, loops and contact surfaces. In one form, the method identifies common locations and orientations of amino acid side-chains, simplified as Cα-Cβ vectors. In another form, the method identifies common regions of surface charge represented by grid points in three-dimensional space. Further provided are common three dimensional structural features of proteins that can be used to search molecular databases for the purposes of identifying molecules that match these common three dimensional structural features. The common three dimensional structural features can also be used to focus de novo molecular generation to produce libraries containing molecules that have these common three dimensional structural features. Libraries of these structurally-related molecules may then be produced for the purposes of drug discovery.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Method for calculating molecular energy of ethane by deep learning
InactiveCN109147877ASolve the problem of relying on CPU single-core main frequencyGet rid of constraintsMolecular entity identificationChemical machine learningComputer scienceEnergy analysis
The invention discloses a method for calculating molecular energy of ethane by deep learning, and belongs to the technical field of molecular energy calculation. The method comprises steps as follows:S1, an ethane molecule database is constructed; S2, m configurations and corresponding energy are selected randomly as a training group, and the other (1000-m) configurations and corresponding energyare taken as a testing group; S3, molecular space coordinates of the training group are converted to form a training group configuration parameter input matrix; S4, energy data of the training groupis extracted as a training output energy matrix and the training output energy matrix is in one-to-one correspondence with the training group configuration parameter input matrix; S5, a testing groupconfiguration parameter input matrix and an output energy matrix are constructed, and the line number of the matrixes is 1000-m; S6, the ethane molecule energy matrix E<calc> is obtained by calculation of double nervous layers. According to the method, the influence of a ratio of the training group to the testing group on accuracy of a training result is reduced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
A combination of molecular markers for germplasm identification of Litopenaeus vannamei and its application
ActiveCN105861729BAccurate identificationOvercoming the inability to identify Litopenaeus vannamei germplasmMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceUnknown Source
The invention relates to a germplasm identification technology in the field of aquatic animal genetic breeding, in particular to a molecular marker combination for Litopenaeus vannamei germplasm identification and application thereof. The molecular marker combination is formed by 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite locus primers. A method for germplasm identification is established with the 13 pairs of high-polymorphism microsatellite markers, microsatellite typing is carried out on existing foreign imported germplasms including but not limited to the Zhengda breed, the SIS breed, the Kona Bay breed and the Molokai breed, and domestic artificially-selected germplasms including but not limited to the Kehai-1 breed and the Guihai-1 breed, molecular databases of different germplasm resources are established with obtained typing data, and different germplasms are identified with the molecular markers. The germplasm sources of Litopenaeus vannamei with unknown sources can be identified by comparing panel typing results with the established databases of different germplasm resources. The method for accurately identifying different germplasm materials of Litopenaeus vannamei with the molecular means has great significance on tracing, evaluation, protection and utilization of different germplasms.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for calculating methanol molecular energy through deep learning
InactiveCN109326334AReduce the impact of accuracyAvoid convergenceComputational theoretical chemistryChemical machine learningTest groupMethanol
The invention discloses a method for calculating methanol molecular energy through deep learning, and belongs to the technical field of molecular energy calculation. The method comprises the followingsteps: S1, building a methanol molecular database; S2, randomly selecting m configurations and corresponding energy as a training group, and taking the rest of 1000 to m configurations and corresponding energy as a test group; S3, transforming coordinates of a methanol molecular space in the training group into 11 parameters for building training group configuration parameter input matrixes; S4,extracting the energy data of the training group as a training group output energy matrixes corresponding to the training group configuration parameter input matrixes one by one; S5, building test group configuration parameter input matrixes and test group output energy matrixes, wherein the matrixes include 1000 to m lines; S6, learning the methanol molecular energy by adopting a dual-nervous layer calculation structure. By adopting the method, the influence of the ratio of the training group to the test group on the training result accuracy is lowered.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
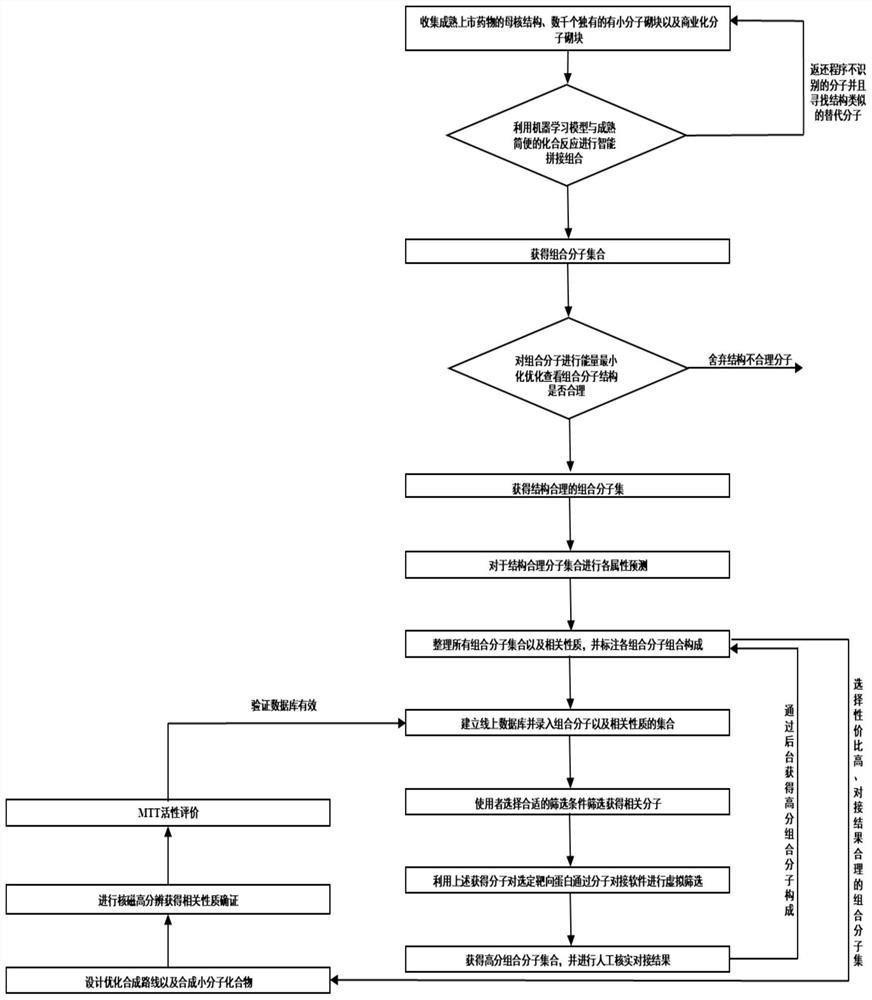
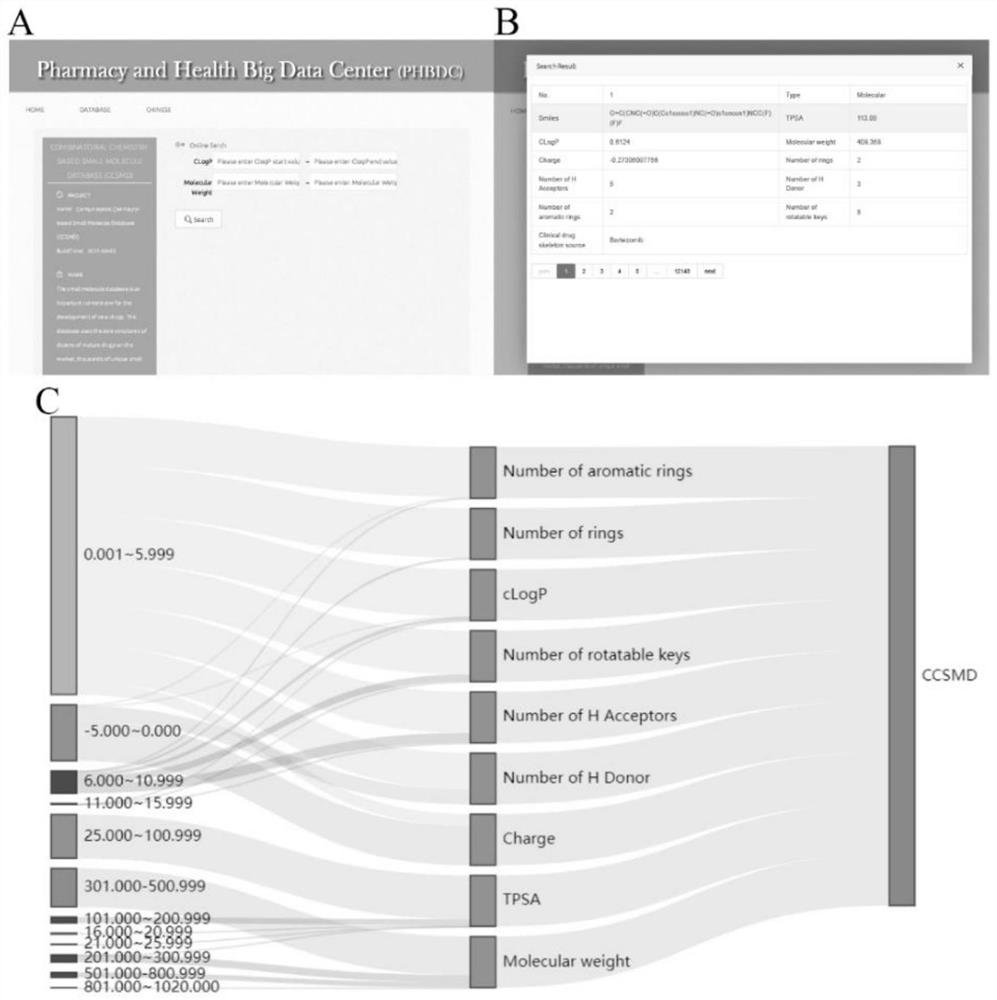
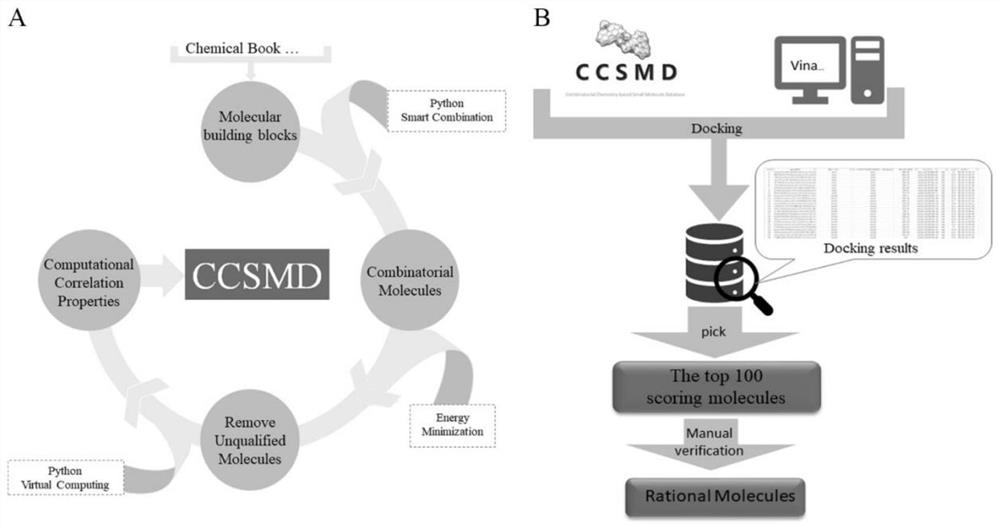
Combined chemical molecule database CCSMD for screening small molecules with anticancer activity and application of combined chemical molecule database CCSMD
PendingCN114783546AEasy to synthesizeImprove securityMolecular entity identificationIn silico combinatorial chemistryHigh activityPharmacology
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, and particularly relates to a method for establishing a library through an intelligent combination method, and finding small molecules with anticancer activity by using the library. According to the method, a virtual database with 12904 molecules is established, the virtual molecules of the database are combined by using Python through molecular blocks which exist actually and can be purchased, and the condition of intelligent combination is a mature and simple reaction condition, so that the small molecules of the database have the characteristic of easiness in synthesis, and the method has more practical significance. The database is used for virtual screening, the screened molecules are synthesized to obtain high-activity anticancer active small molecules, and the molecules are basically non-toxic to normal gastric mucosa cells; the compound has a remarkable gastric cancer treatment effect which is superior to that of cis-platinum, so that the compound has a good application prospect.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Expression method of efficient molecular three-dimensional conformation
The invention relates to the technical field of computer-aided drug research and development, in particular to an efficient molecular three-dimensional conformation expression method, which comprises the following steps of: A, establishing a basic fragment library auxiliary file; step B, constructing a molecular three-dimensional conformation; step C, recording metadata for generating the three-dimensional conformation of the molecule; and step D, compressing and storing the metadata. According to the method, explicit recording of the three-dimensional coordinates of each atom in each molecular conformation is avoided, the meta information for efficiently restoring the three-dimensional coordinates of each conformation is recorded, and the memory space of the meta information is 100-1000 times smaller than explicit expression of the three-dimensional conformation; and the speed of recovering the three-dimensional coordinates by the meta data is more than one order of magnitude faster than that of the fastest three-dimensional conformation generation algorithm. Therefore, the method breaks through the storage limitation of the molecular three-dimensional conformation of a super-large-scale chemical molecule database, and provides an effective solution for three-dimensional screening of drug molecules.
Owner:北京中大唯信科技有限公司
Quantum chemistry high-throughput screening method for chalcopyrite inhibitor
The invention discloses a quantum chemistry high-throughput screening method for a chalcopyrite inhibitor. The quantum chemistry high-throughput screening method comprises the steps of S1 establishing a molecular database of flotation reagents; S2 performing coarse optimization to obtain an optimized molecular database; S3 respectively making corresponding input files for molecules of the initial structure in two states of being neutral and losing one proton to obtain a first molecule database; S4 docking the molecules with metal ions to form alkyl-functional group-metal to obtain a second molecular database; S5 optimizing and analyzing the molecules to obtain quantum chemical parameters and a log file; S6 reading the log file to obtain an output file, and analyzing the output file to extract molecular structure property parameters; and S7 predicting and reflecting Gibbs free energy, and screening flotation reagents. According to the method, typical functional group molecules are analyzed and screened by adopting a quantum chemistry method, so that the technical problems of low success rate, low screening efficiency, risk of synthesizing unknown toxic substances, huge resource waste and safety problems existing in a traditional trial and error method are solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
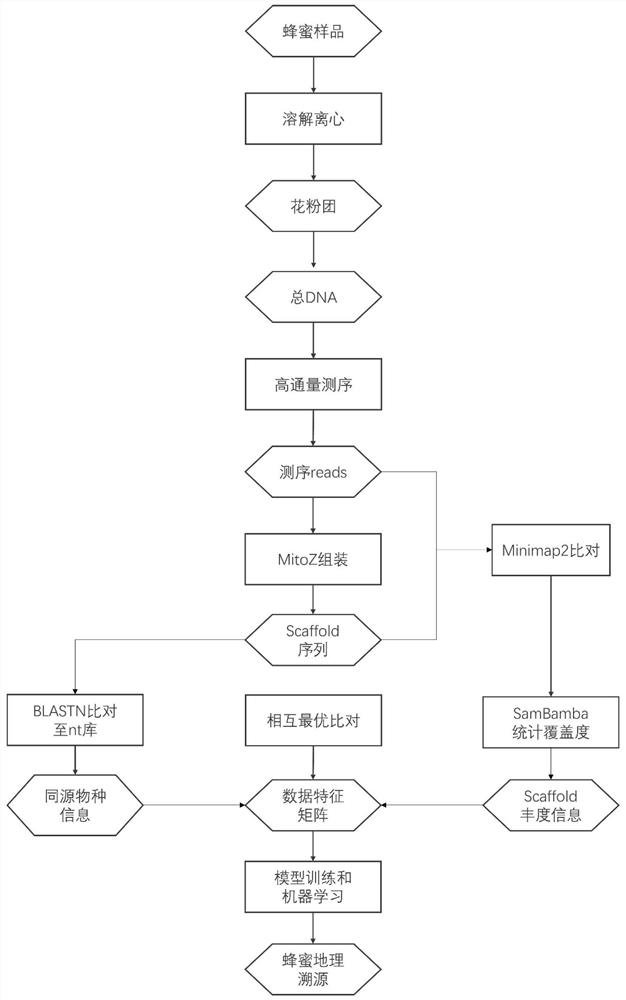
Method for tracking honey source of honey by utilizing metagenome and machine learning
PendingCN113674003ASolve labor costsHigh feasibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsBiotechnologySequence analysis
The invention discloses a method for tracking a honey source of honey by utilizing metagenome and machine learning. According to the method, the problem that molecular databases of plant species are deficient in honey sources, especially remote mountainous areas, is fully considered, and sequence information of nucleic acid substances in honey is analyzed, so that plant sequences contained in honey are obtained; and calculation is performed by a machine learning method to obtain a weight relationship between the plant-derived nucleic acid sequence (without a specific species identification result) in the honey and the honey source, and the honey source of the honey sample is tracked by using the weight relationship as a reference database. The method does not depend on an existing honey source plant molecular database, honey source place information of honey can be directly obtained through honey plant sequence analysis and machine learning, and the method has extremely important value for honey product identification and market standardization.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A kind of positron emission medical imaging system and imaging method
ActiveCN107647877BAccurate locationPrecise positioningComputerised tomographsTomographyGamma photonMolecular imaging
Owner:唐山斯腾光电科技有限公司
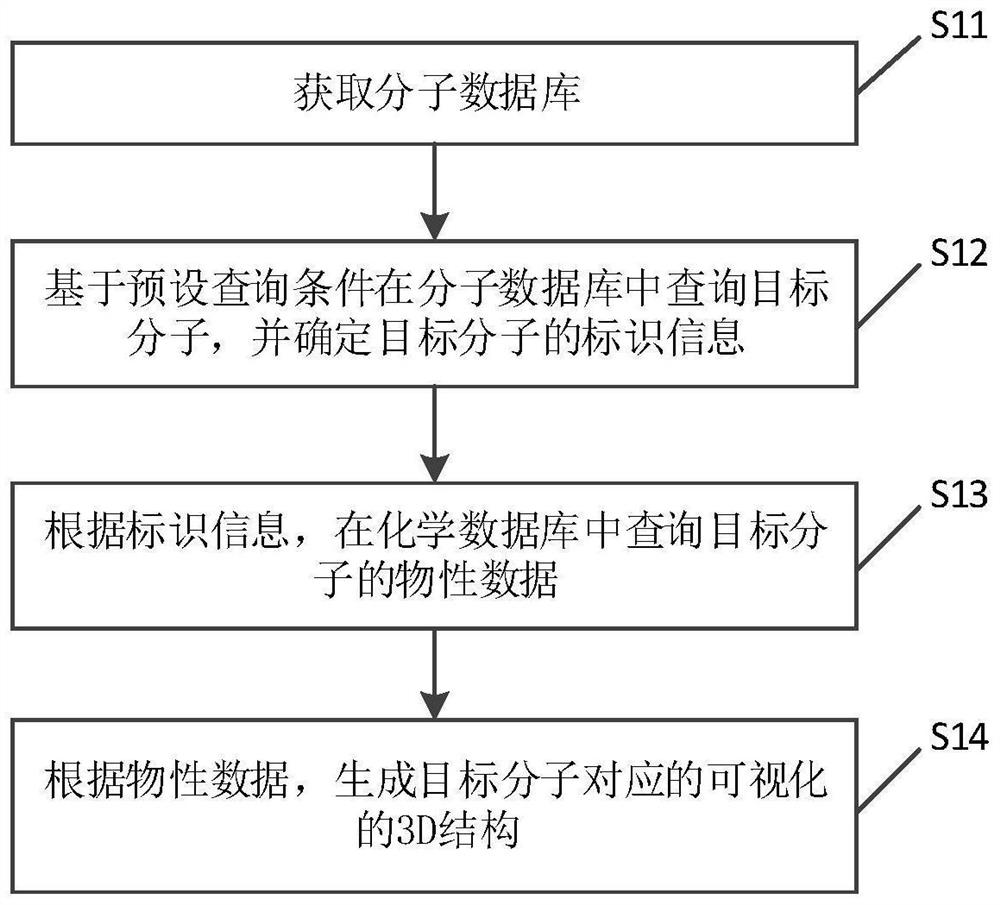
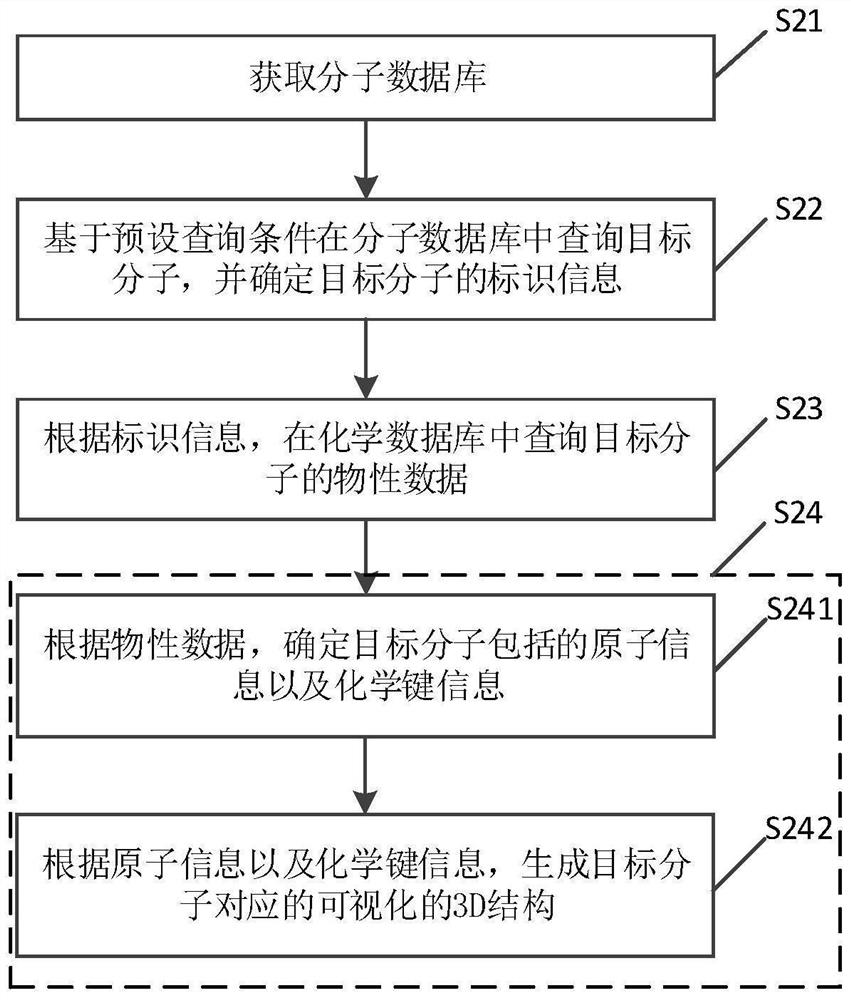
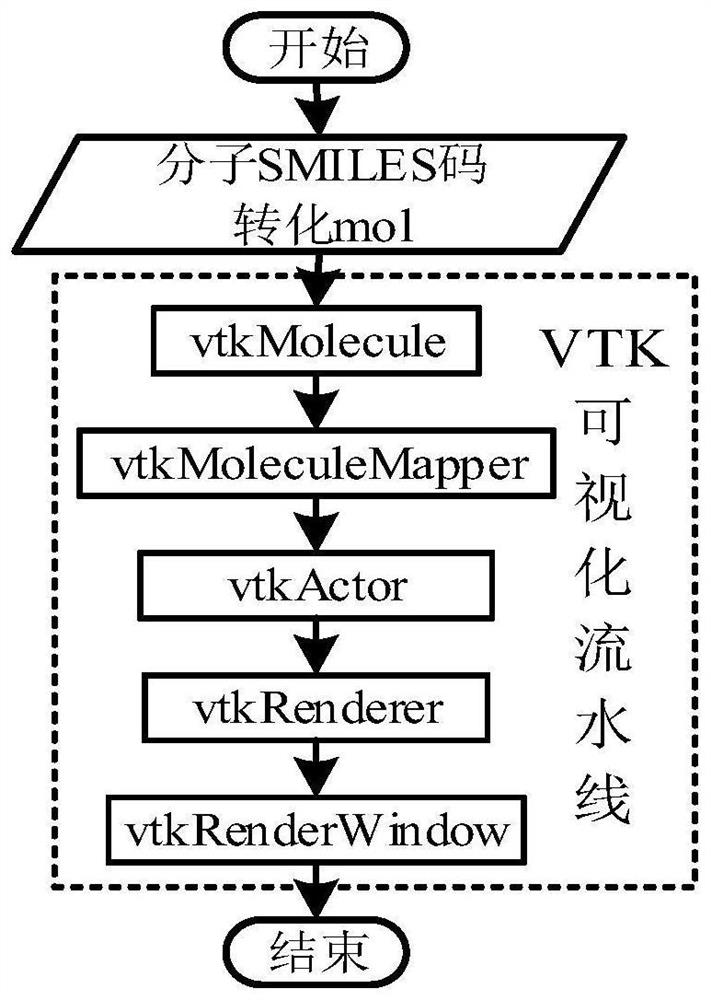
Molecular structure database construction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114464273AGuaranteed accuracyAccurate accessMolecular designCheminformatics data warehousingChemical databaseGraph theoretic
The invention discloses a molecular structure database construction method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and is suitable for the field of chemistry. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a molecular database; the molecular database is associated with the chemical database; querying a target molecule in a molecule database based on a preset query condition, and determining identification information of the target molecule; querying physical property data of the target molecule in a chemical database according to the identification information; and according to the physical property data, generating a visual 3D structure corresponding to the target molecule. By adopting the method, the 3D structure of the target molecule does not need to be generated from the beginning based on the graph theory data structure of the molecule, so that the molecular structure database construction method greatly reduces the complexity of generating the visual 3D structure corresponding to the target molecule, and occupies less storage space of the system.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CLOUD TECH CO LTD
A quantum chemical high-throughput screening method for chalcopyrite inhibitors
The invention discloses a quantum chemical high-throughput screening method for chalcopyrite inhibitors. The molecules in the two states are respectively prepared corresponding input files to obtain the first molecular database; S4 docks the molecules with metal ions to form an alkyl-functional group-metal to obtain the second molecular database; S5 optimizes and analyzes the molecules to obtain Quantum chemical parameters and log files; S6 reads the log files to obtain the output files, and by analyzing the output files, extracts the molecular structure and property parameters; S7 predicts the Gibbs free energy of the reaction and screens the flotation reagents. The invention adopts the quantum chemical method to analyze and screen typical functional group molecules, and avoids the technical problems of low success rate, low screening efficiency, risk of synthesizing unknown toxic substances, huge waste of resources and safety problems of traditional trial and error methods.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com