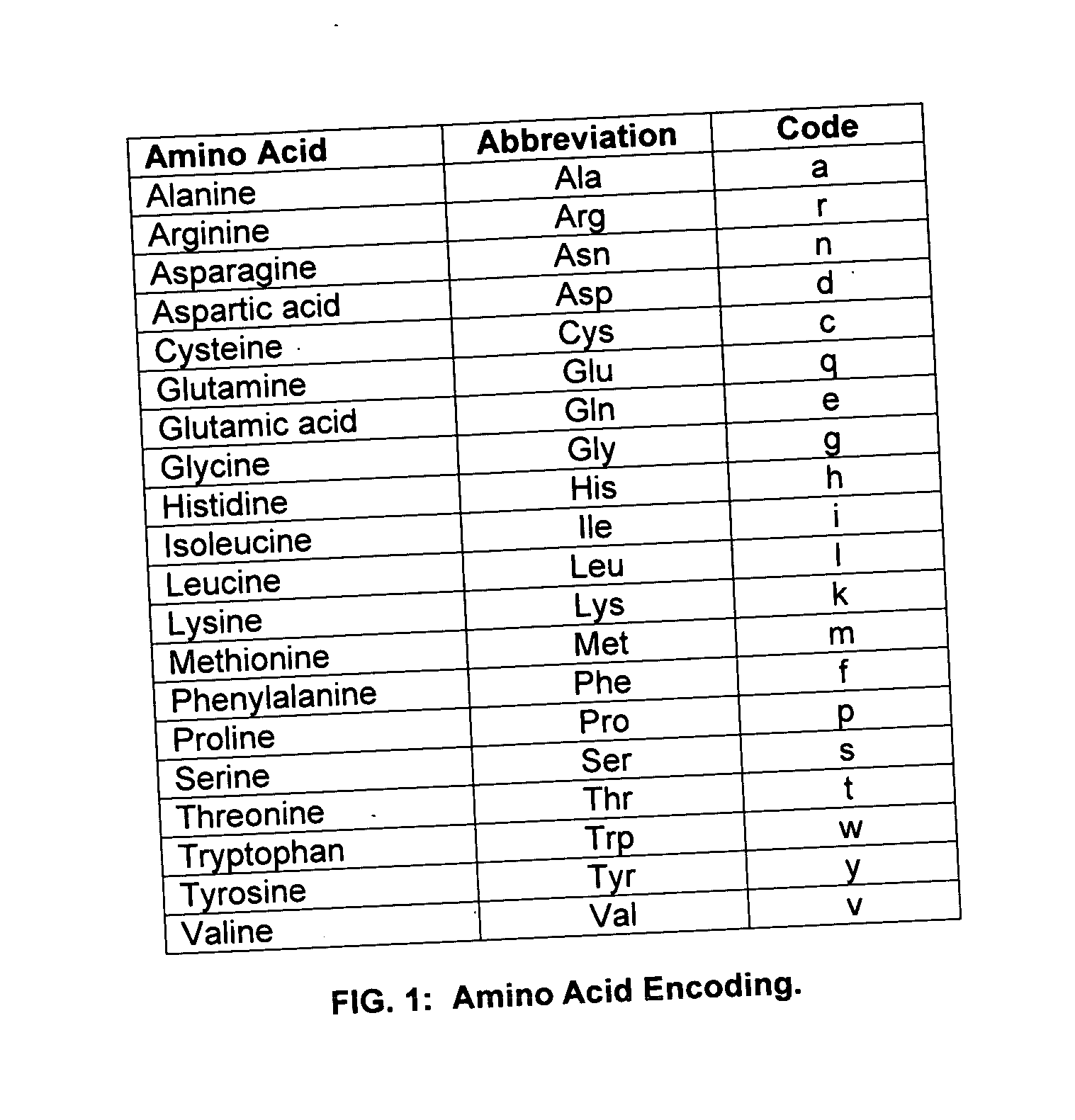
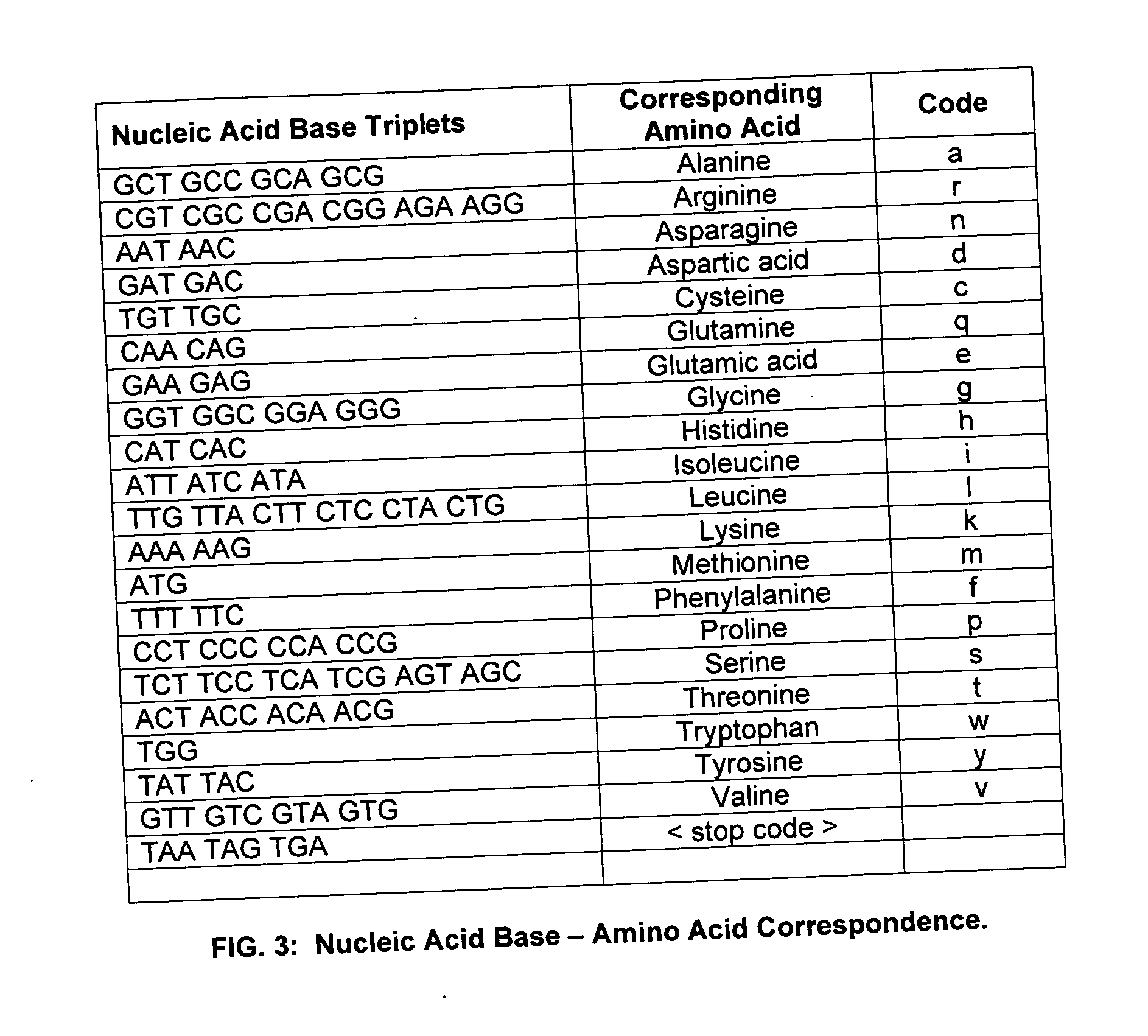
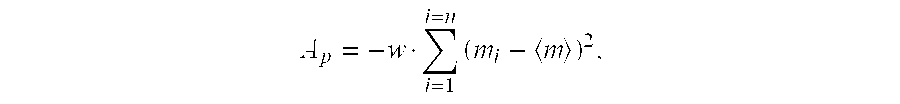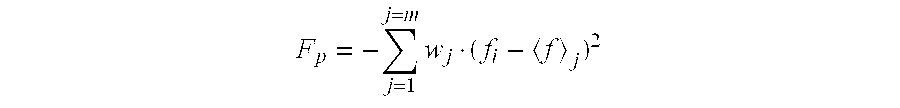Patents
Literature
512results about "In silico combinatorial chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
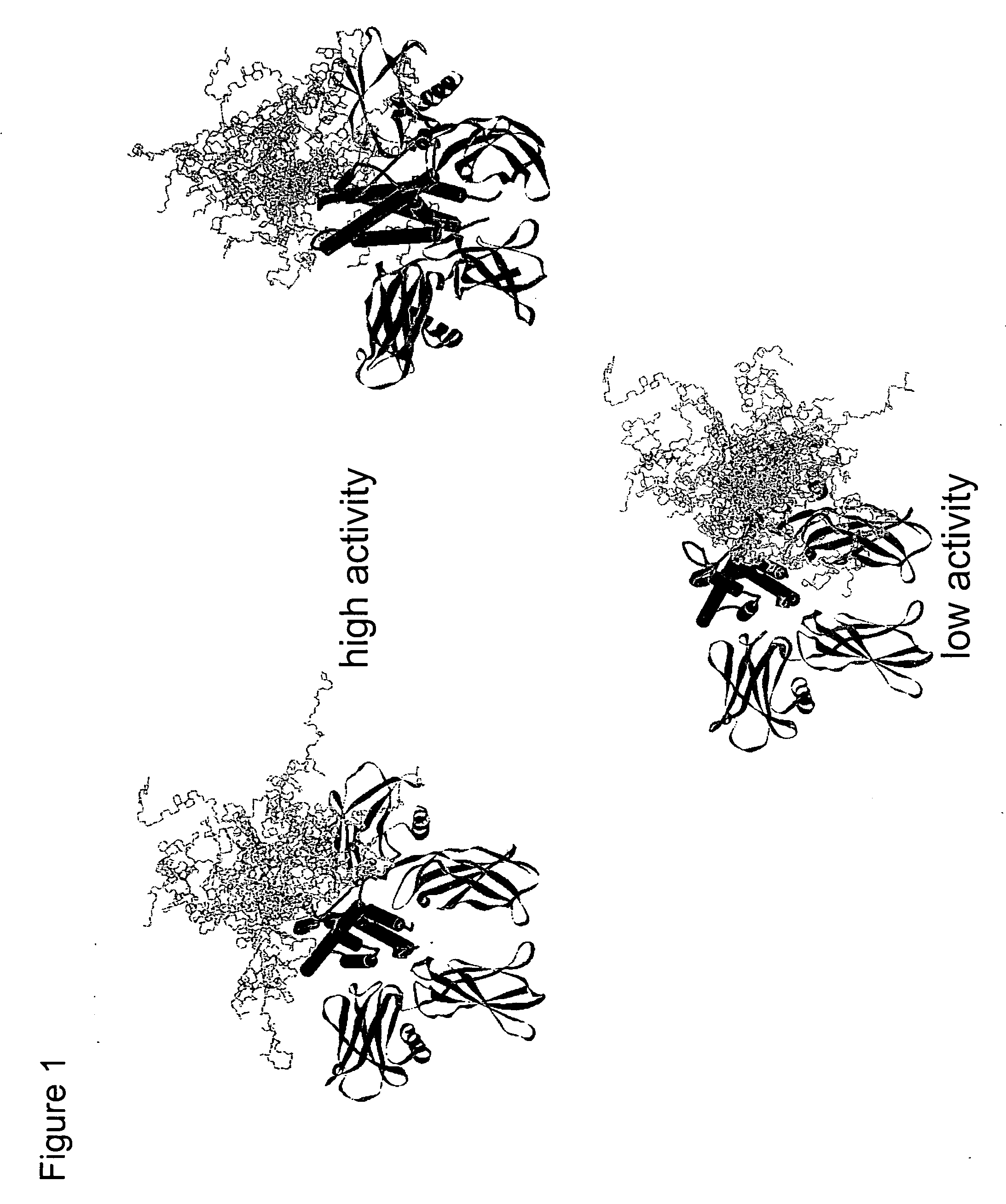
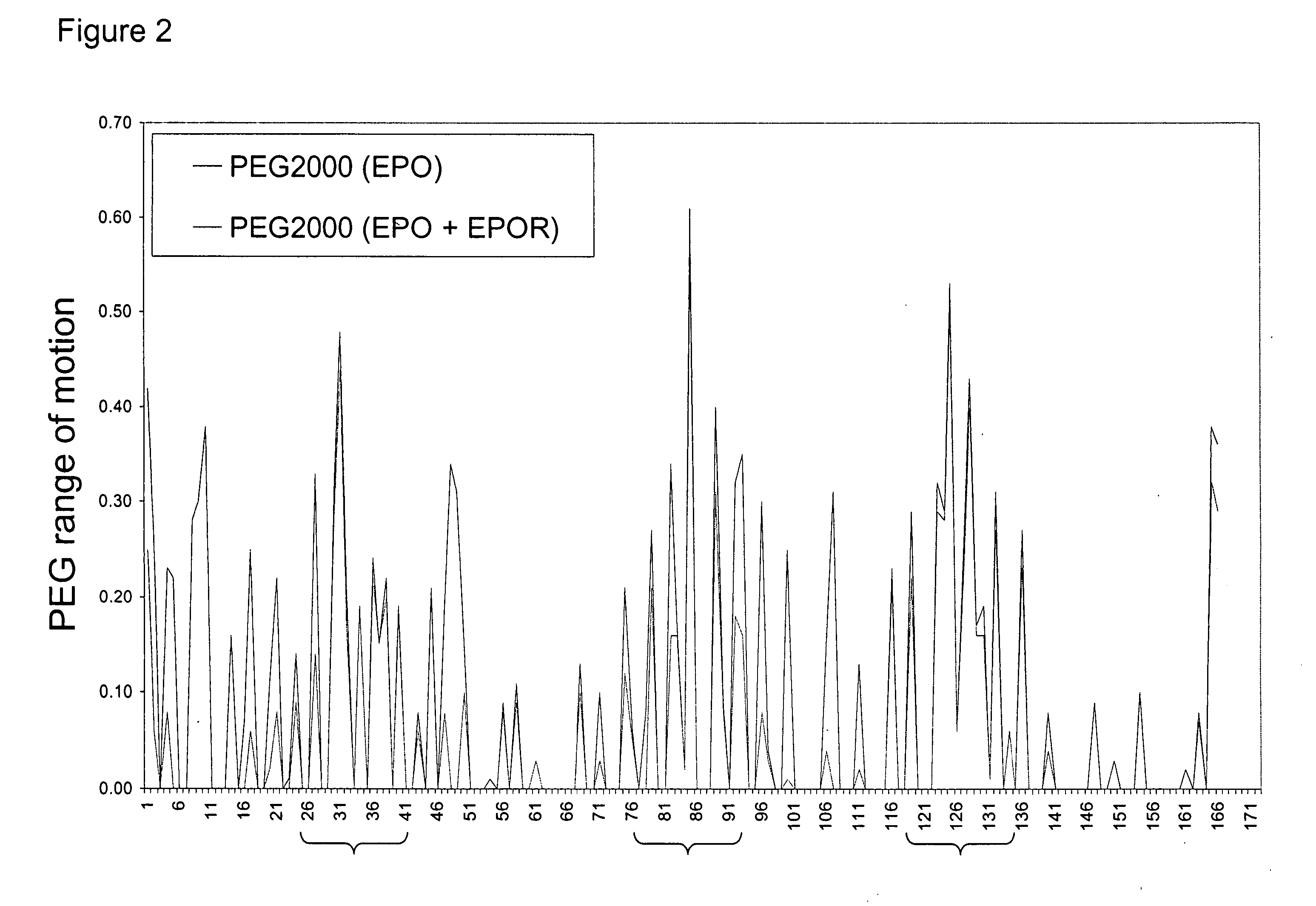
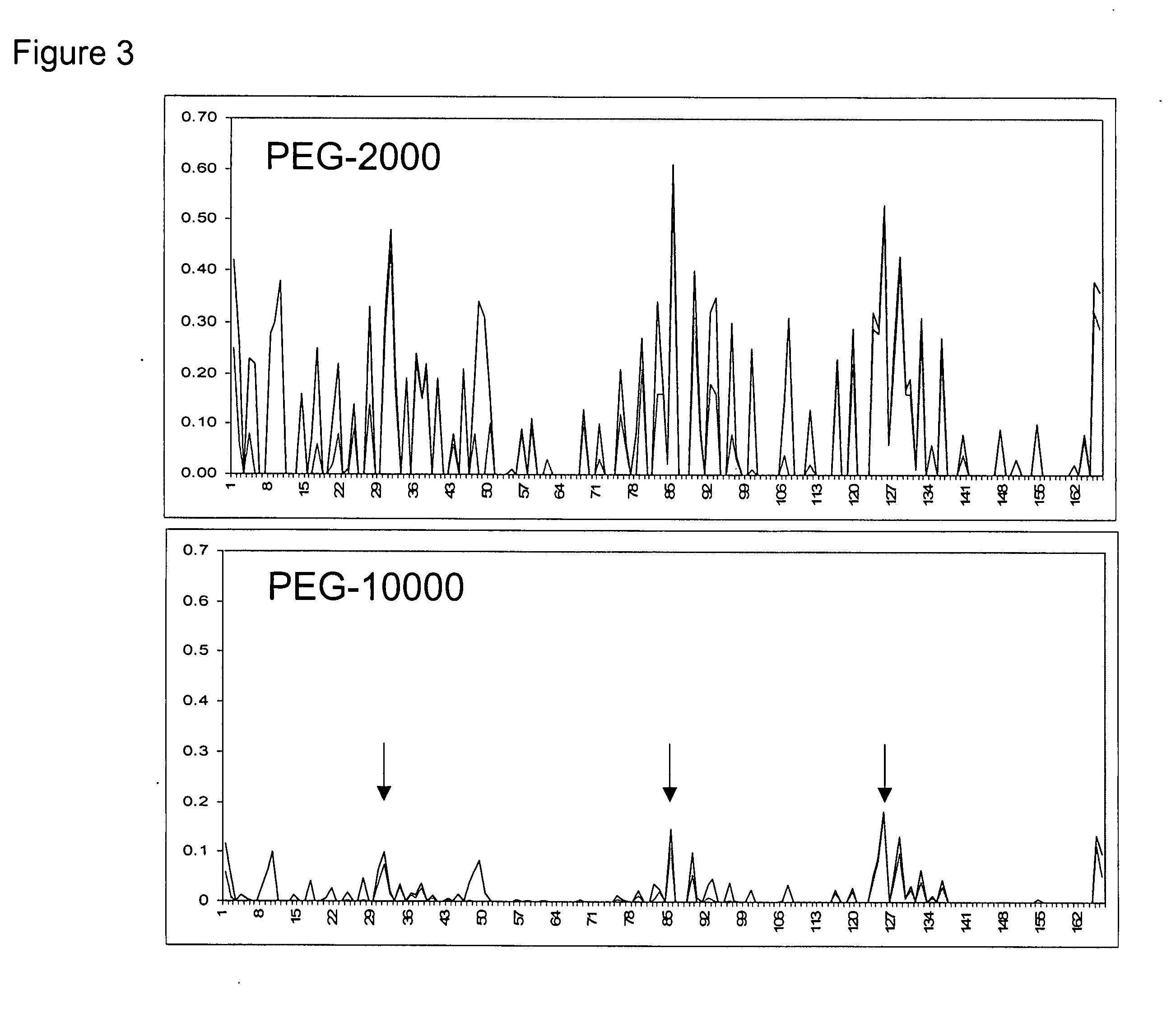
Methods for rational pegylation of proteins
The present invention relates to the use of simulation technology to rationally optimize the locations and sizes of attached polymeric moieties for modification of therapeutic proteins and the proteins generated from this method.
Owner:XENCOR
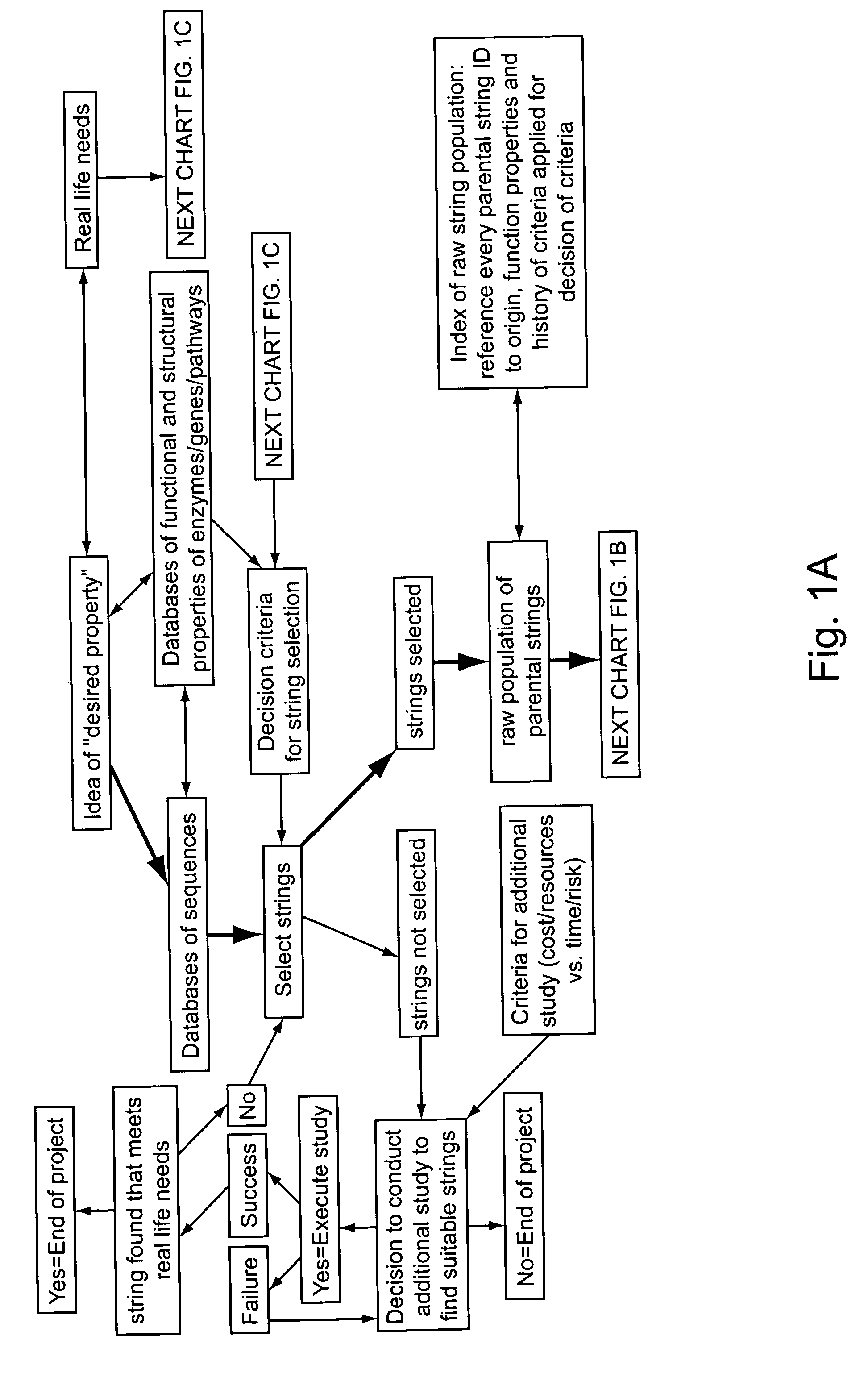
Methods for making character strings, polynucleotides and polypeptides having desired characteristics
InactiveUS7024312B1Simplifies overall synthesis strategyLow levelPeptide/protein ingredientsBiostatisticsPolynucleotideIn silico
“In silico” nucleic acid recombination methods, related integrated systems utilizing genetic operators and libraries made by in silico shuffling methods are provided.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
System of components for preparing oligonucleotides
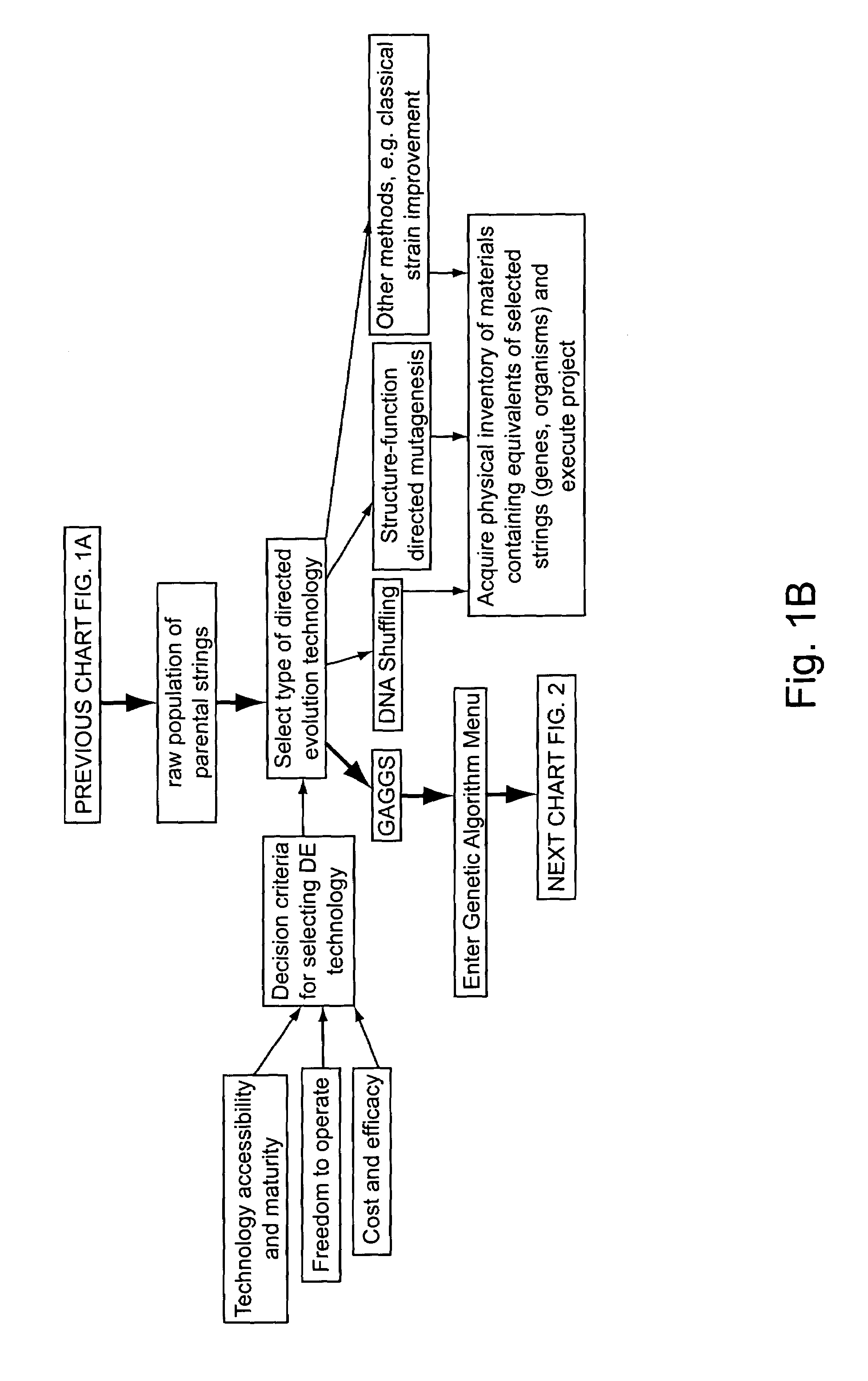
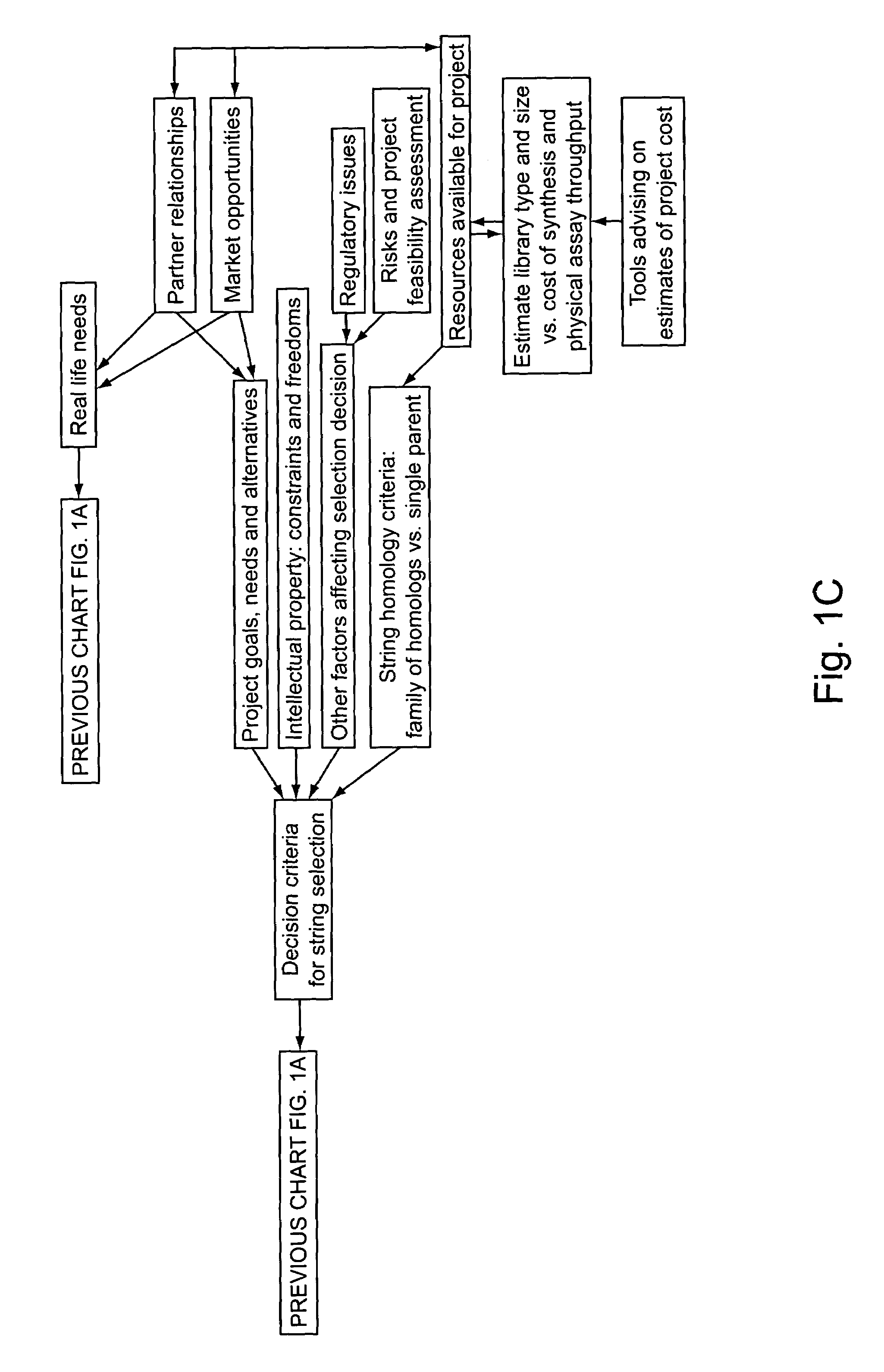
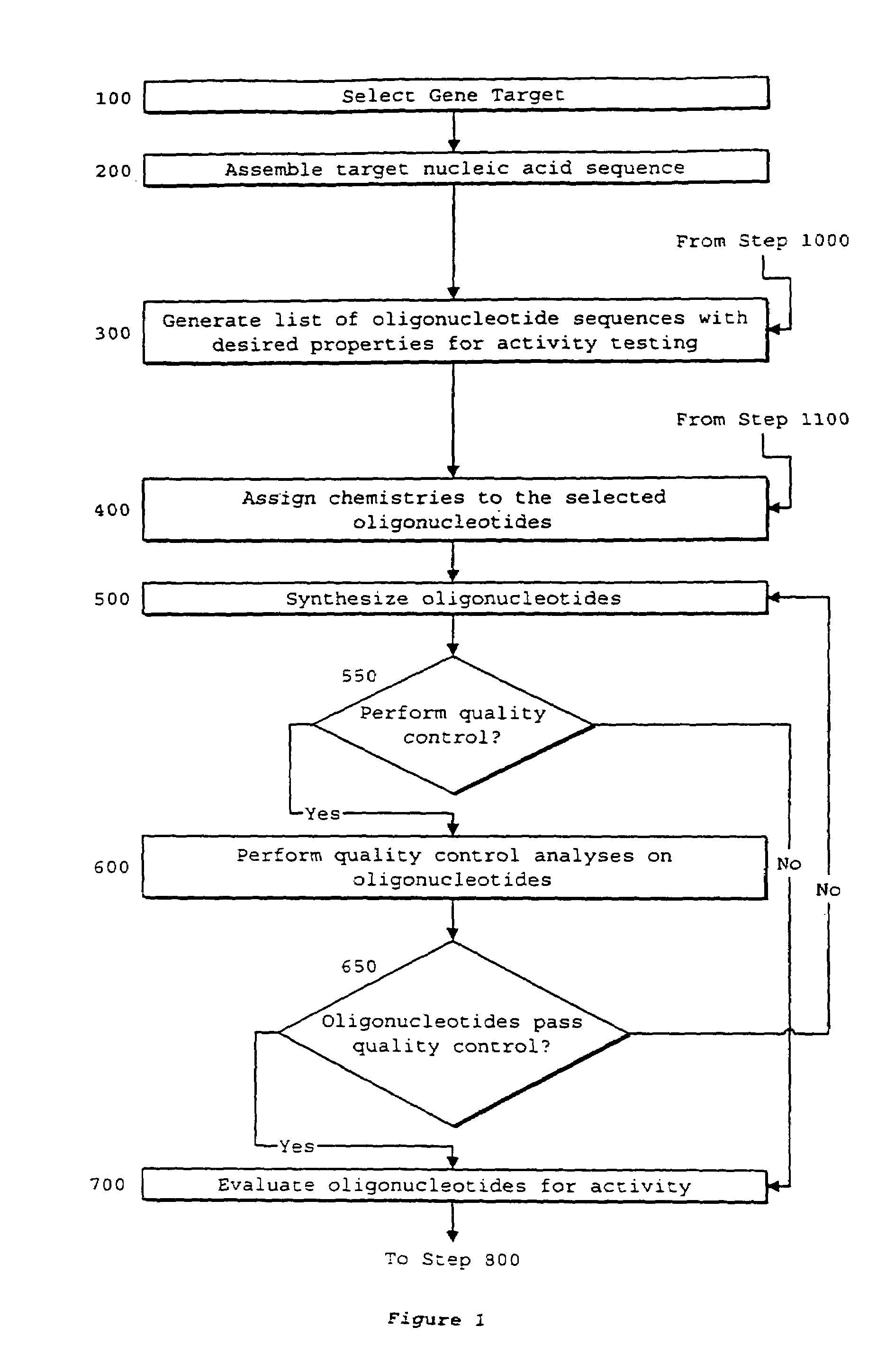
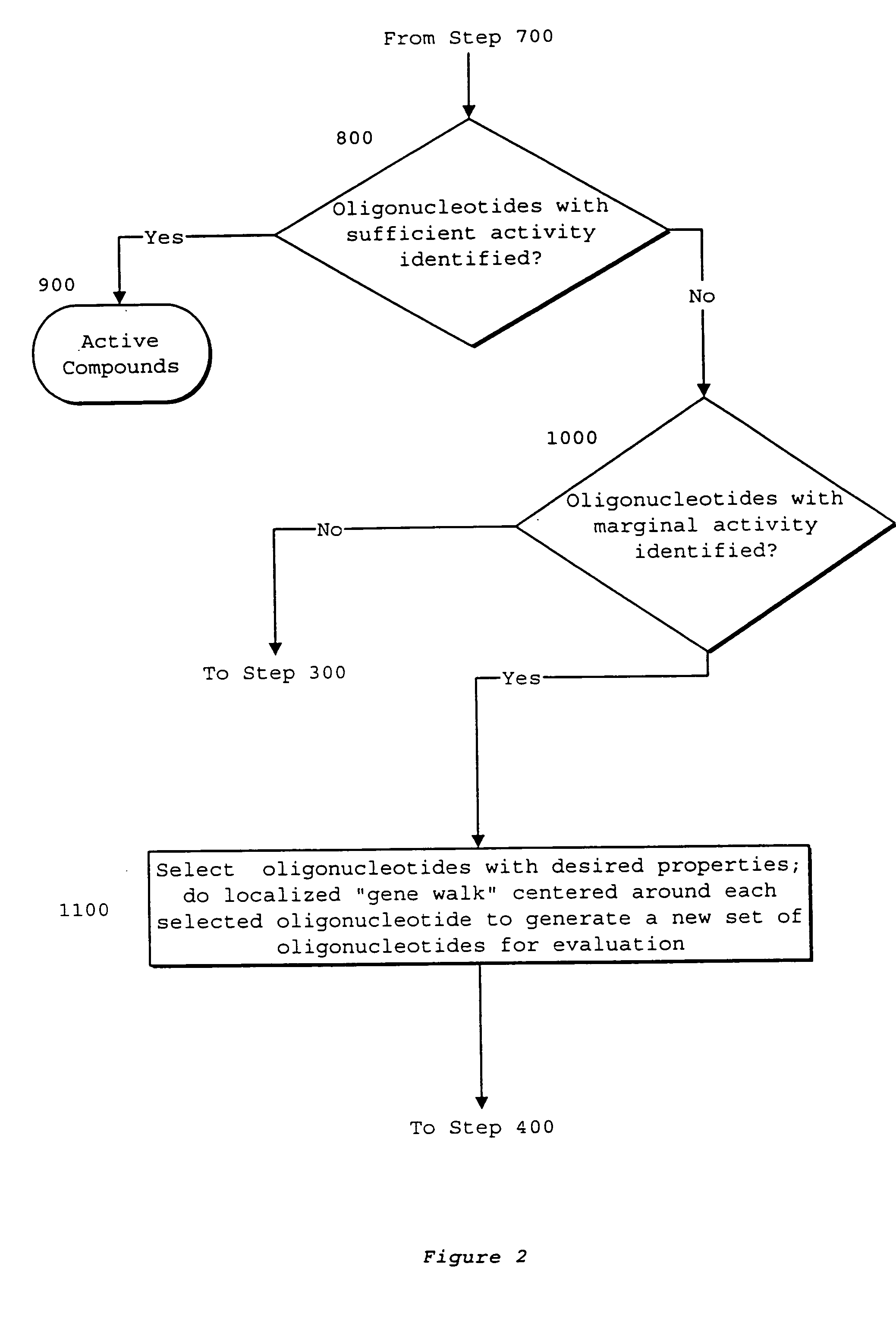
Interative, preferably computer based iterative processes for generating synthetic compounds with desired physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties, i.e., active compounds, are provided. During iterations of the processes, a target nucleic acid sequence is provided or selected, and a library of candidate nucleobase sequences is generated in silico according to defined criteria. A “virtual” oligonucleotide chemistry is chosen and a library of virtual oligonucleotide compounds having the selected nucleobase sequences is generated. These virtual compounds are reviewed and compounds predicted to have particular properties are selected. The selected compounds are robotically synthesized and are preferably robotically assayed for a desired physical, chemical or biological activity. Active compounds are thus generated and, at the same time, preferred sequences and regions of the target nucleic acid that are amenable to oligonucleotide or sequence-based modulation are identified.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
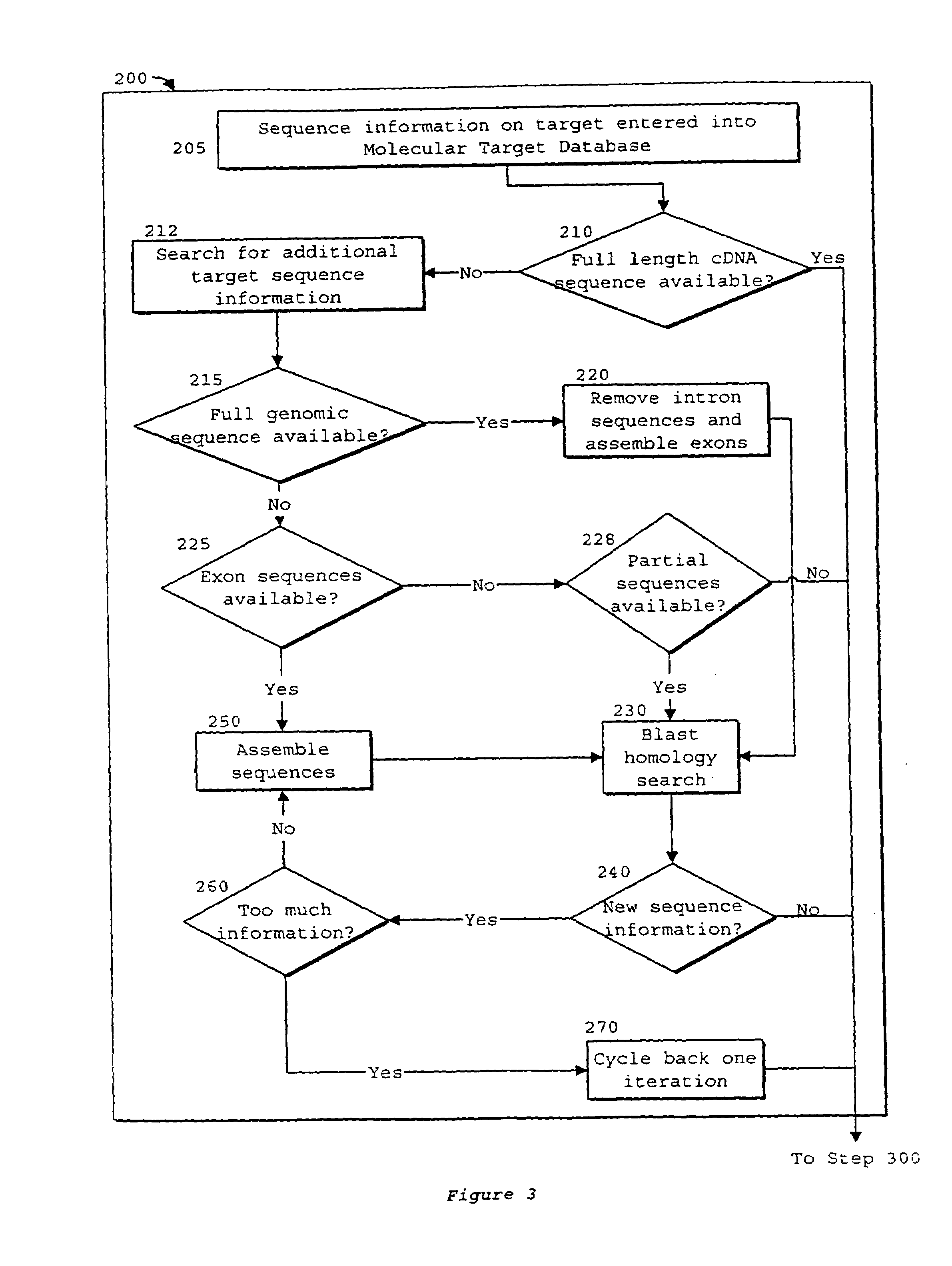
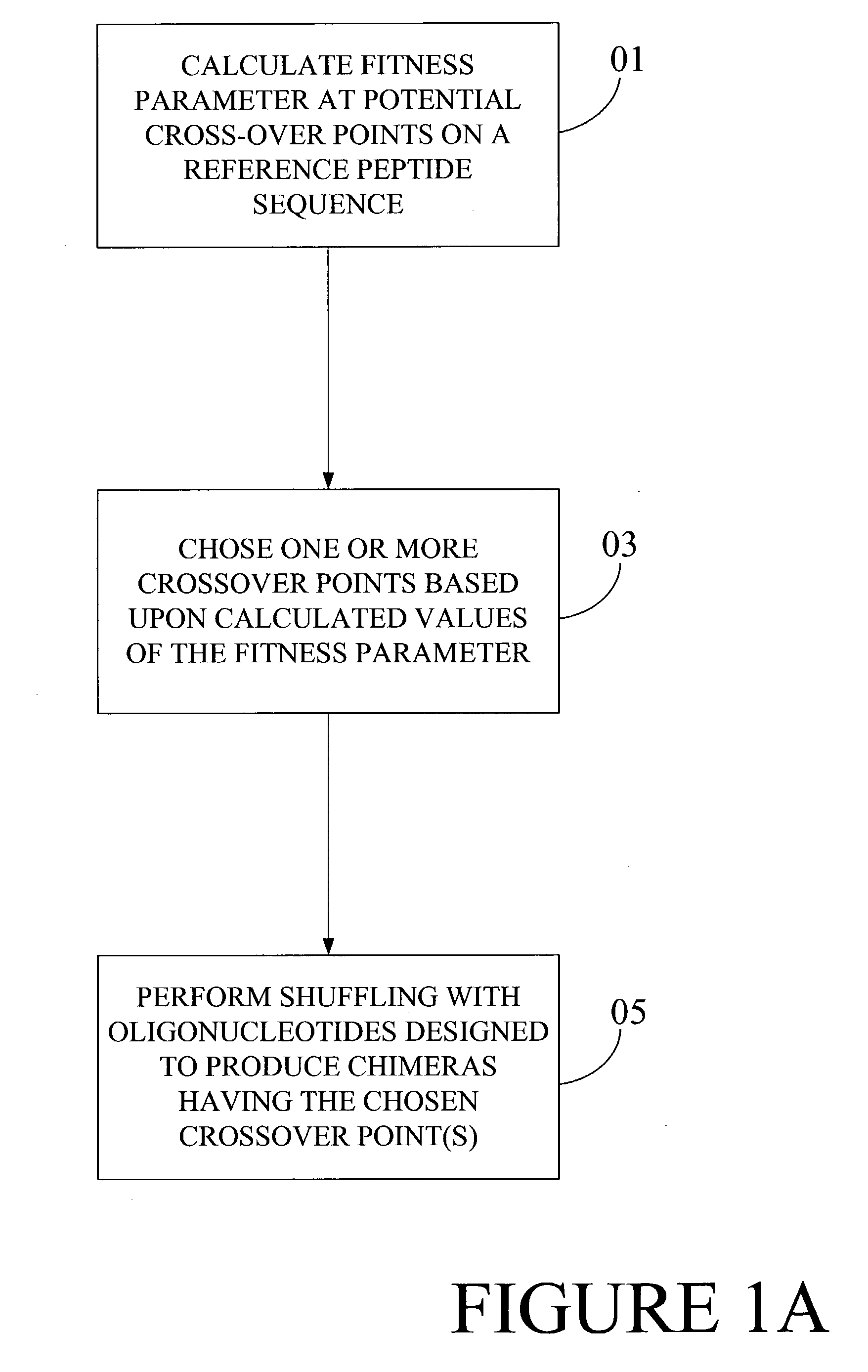
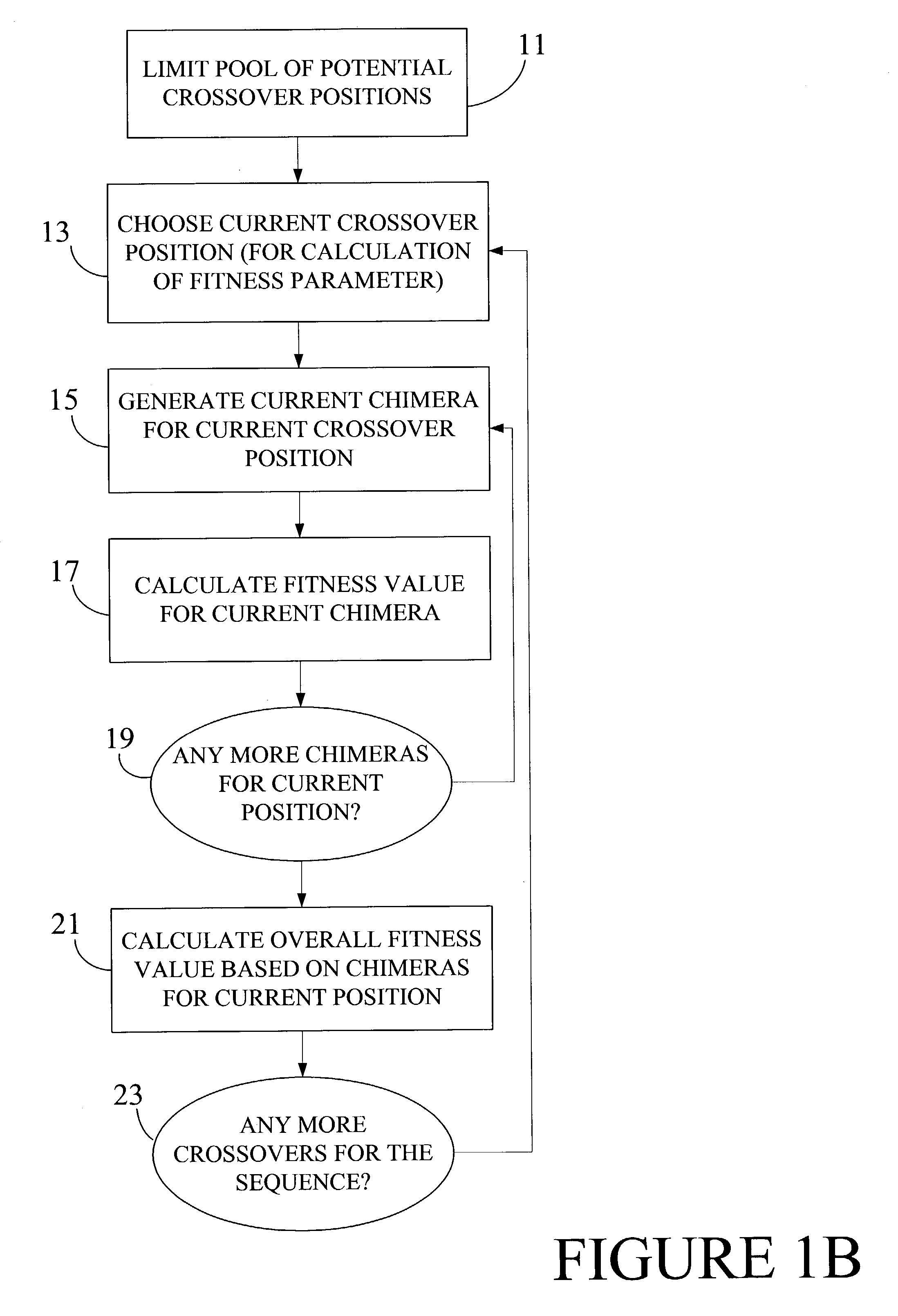
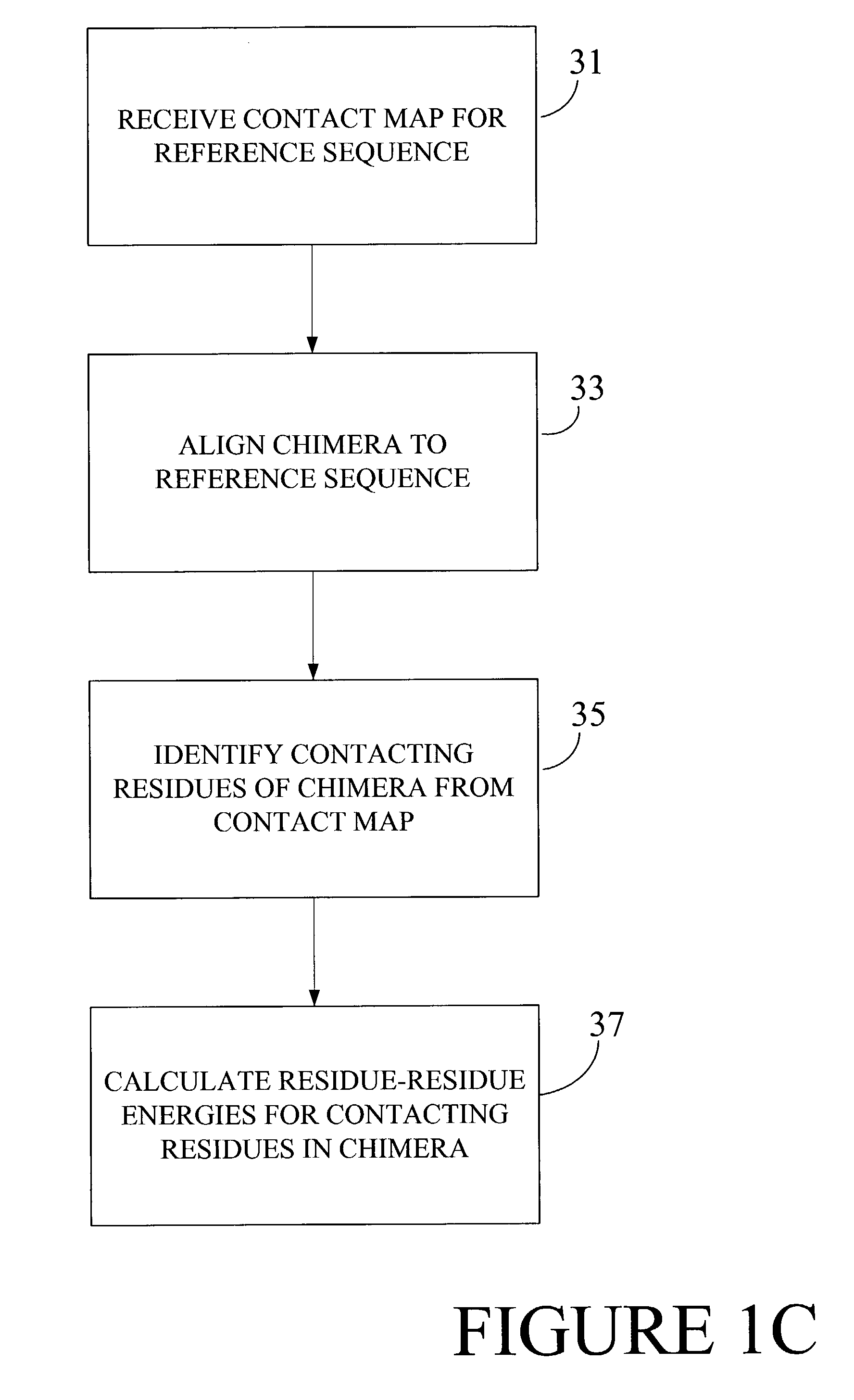
Optimization of crossover points for directed evolution
ActiveUS7620500B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
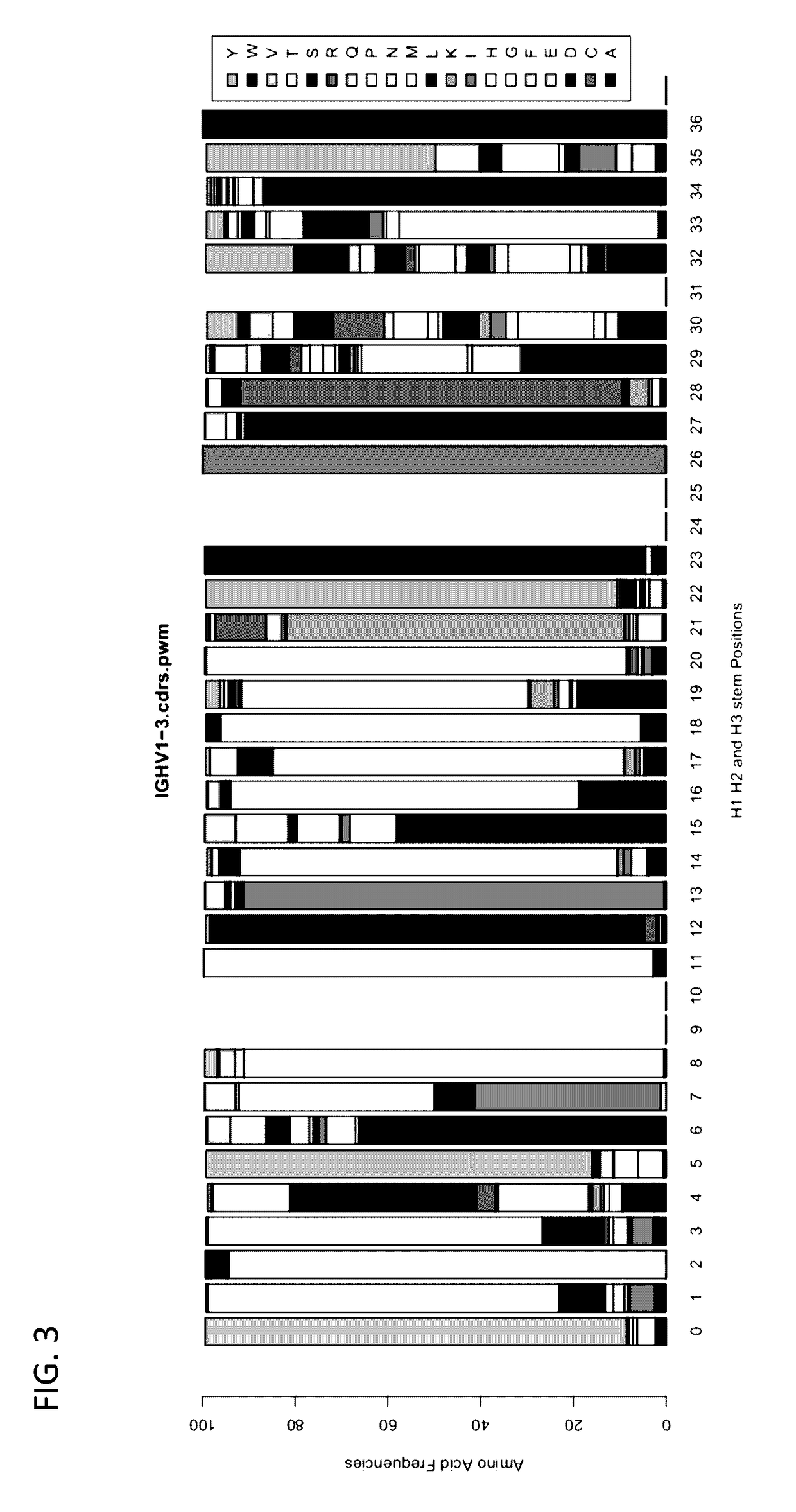
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
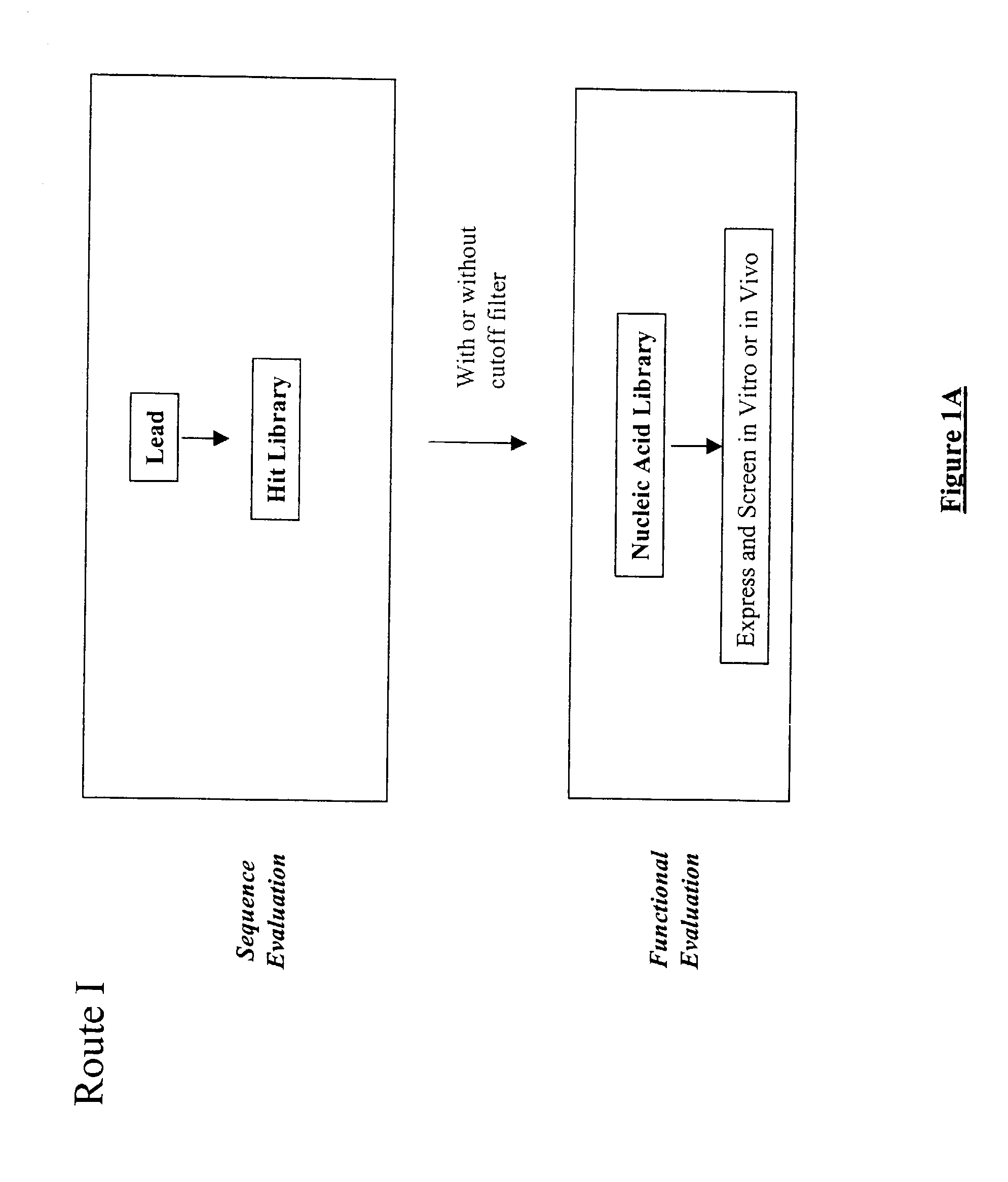
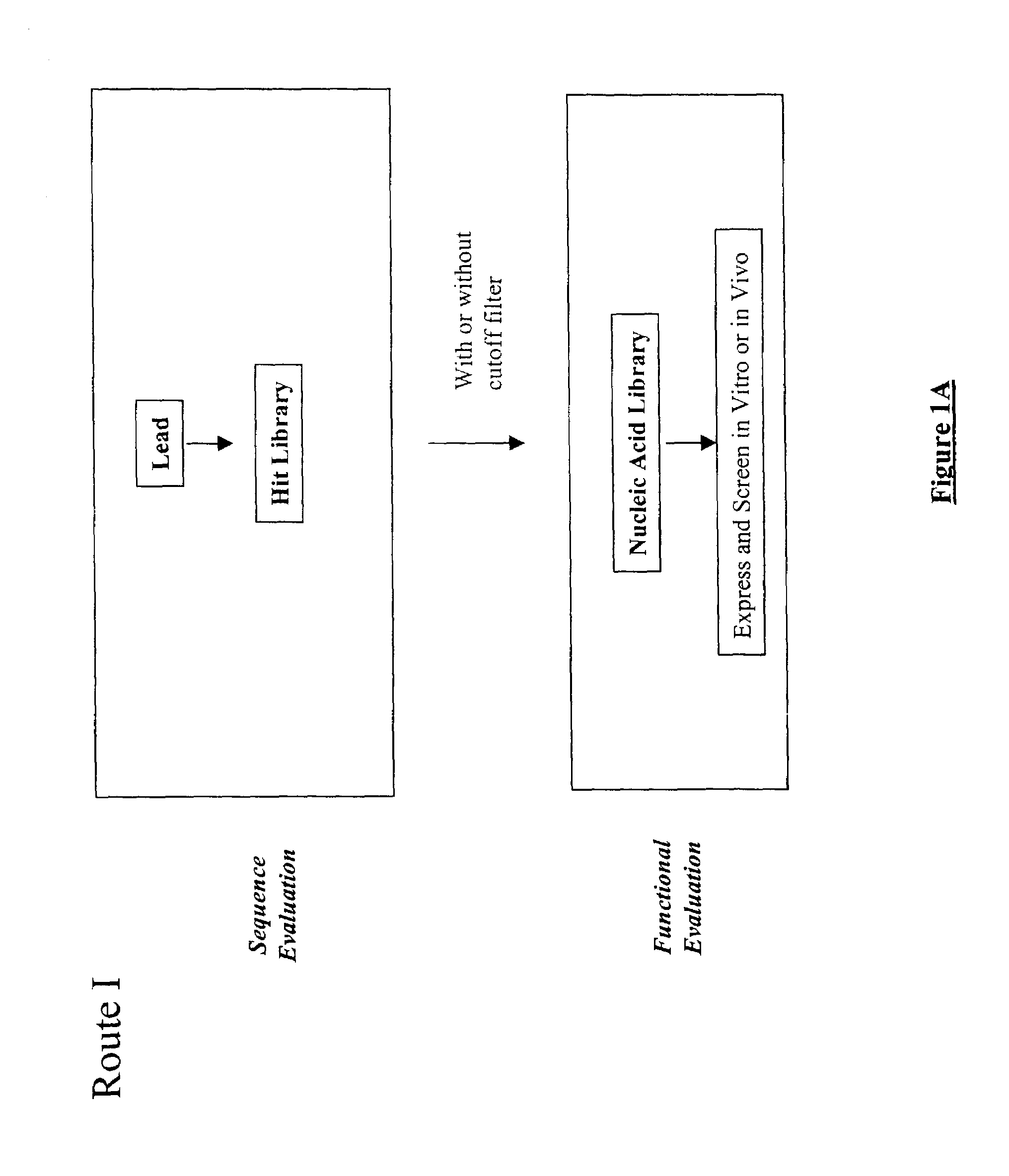
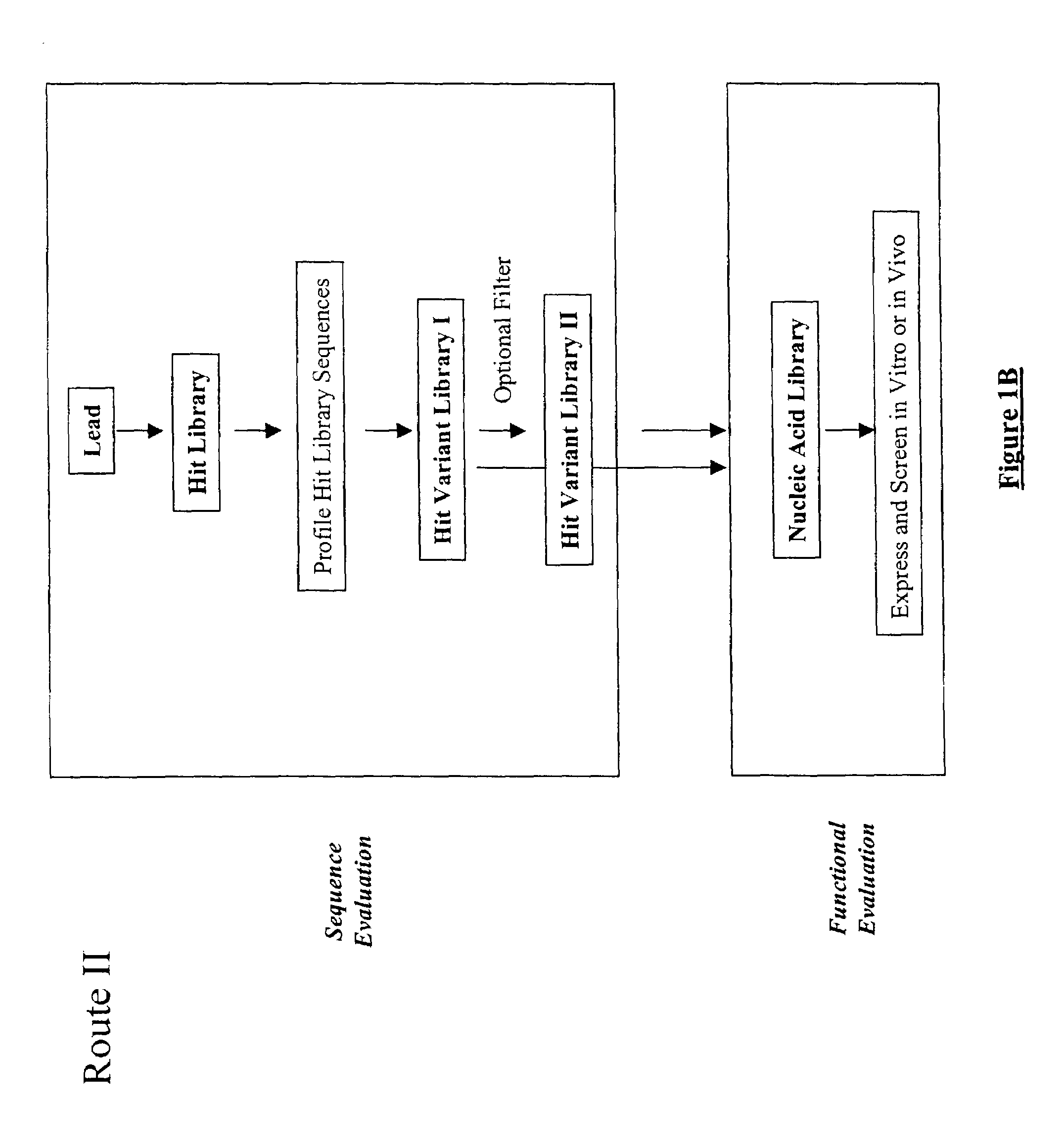
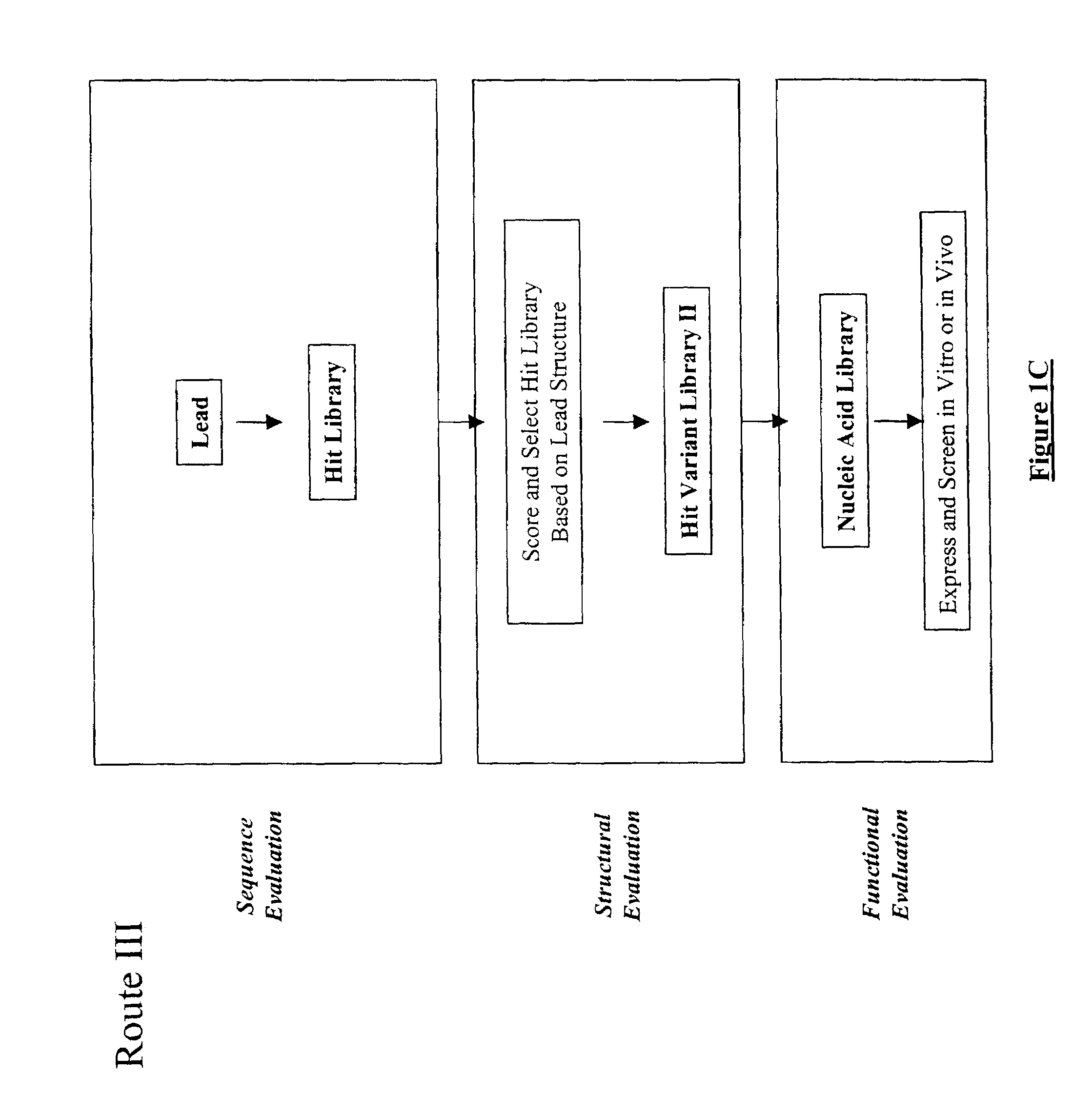
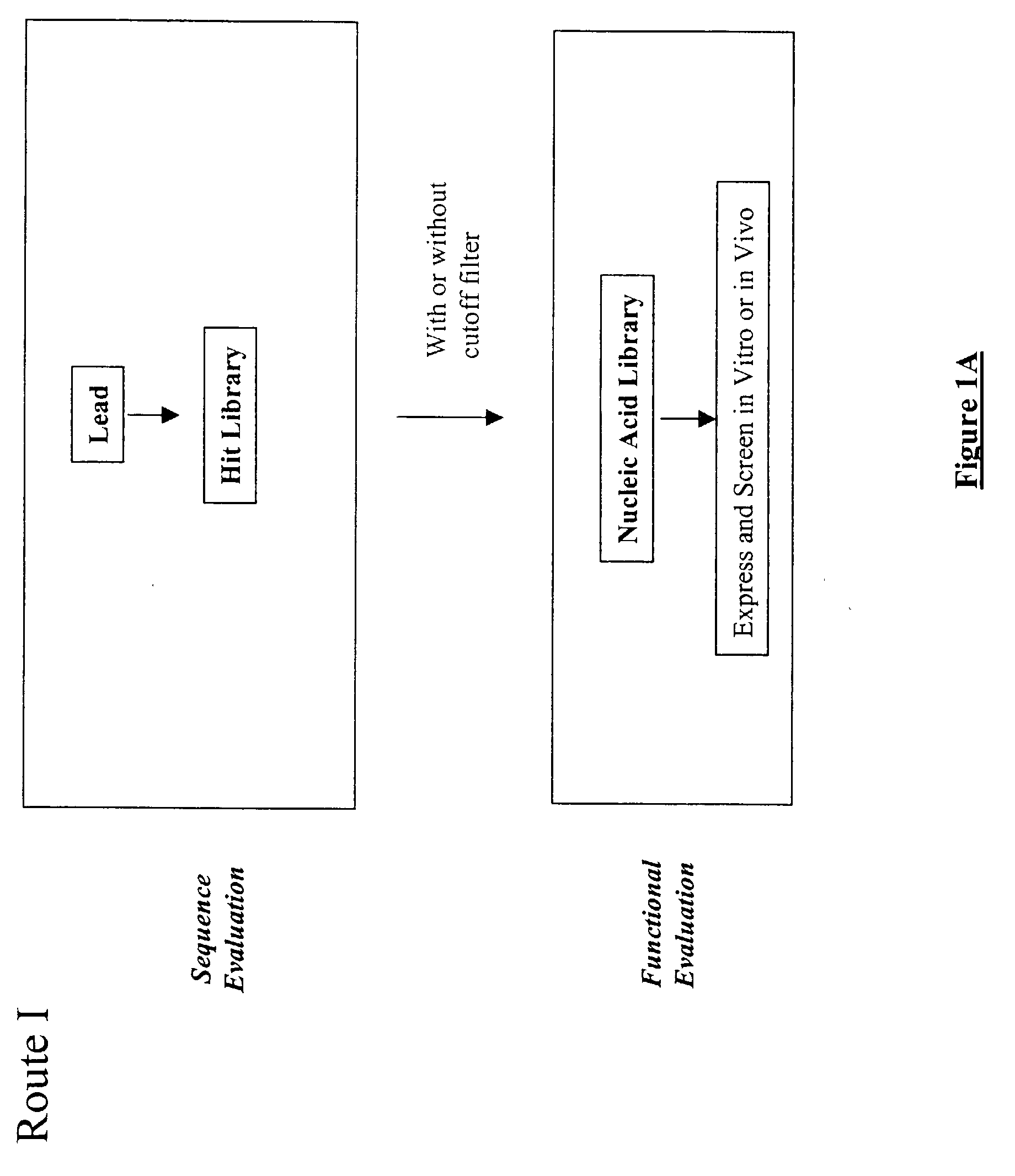
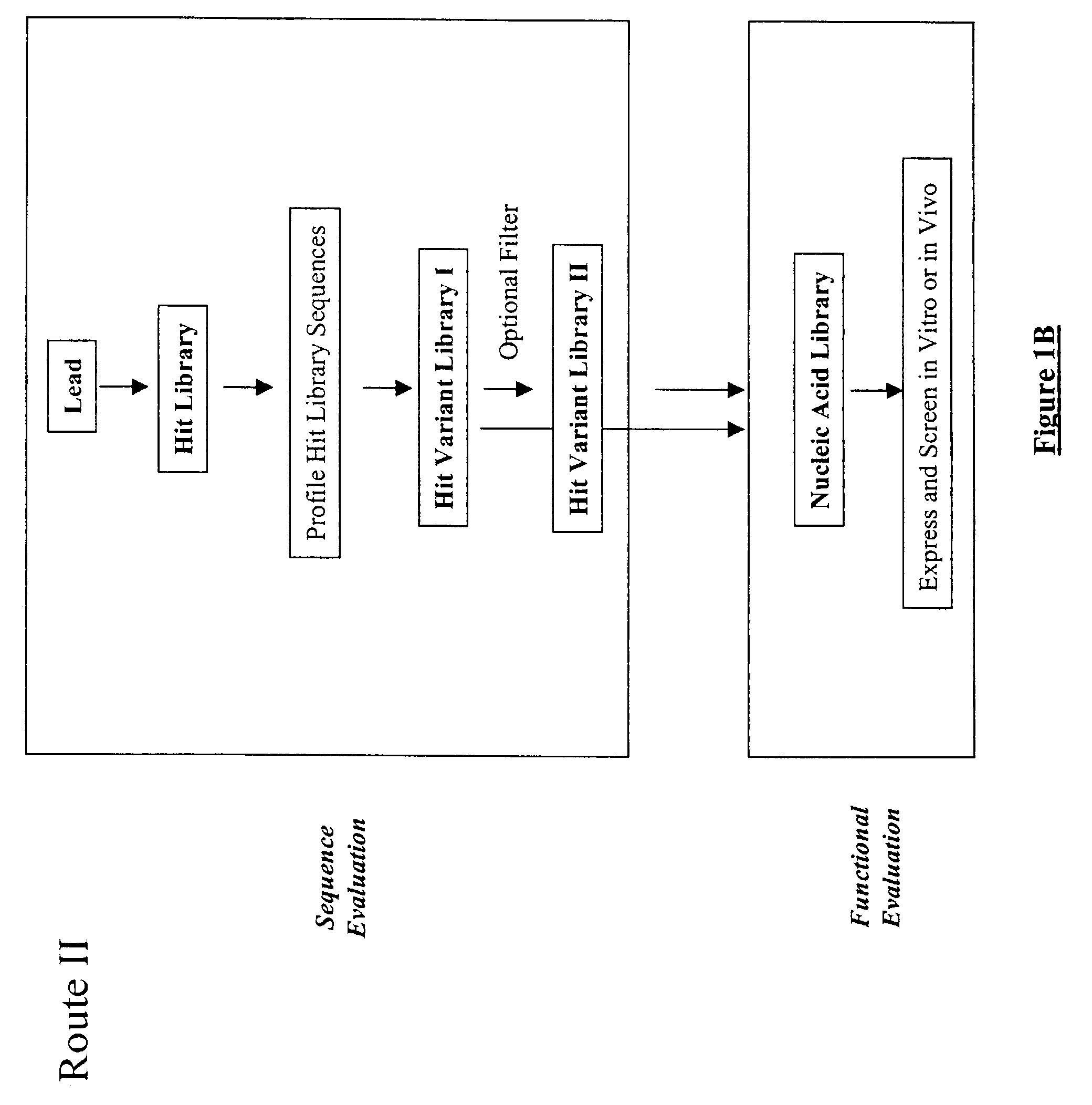
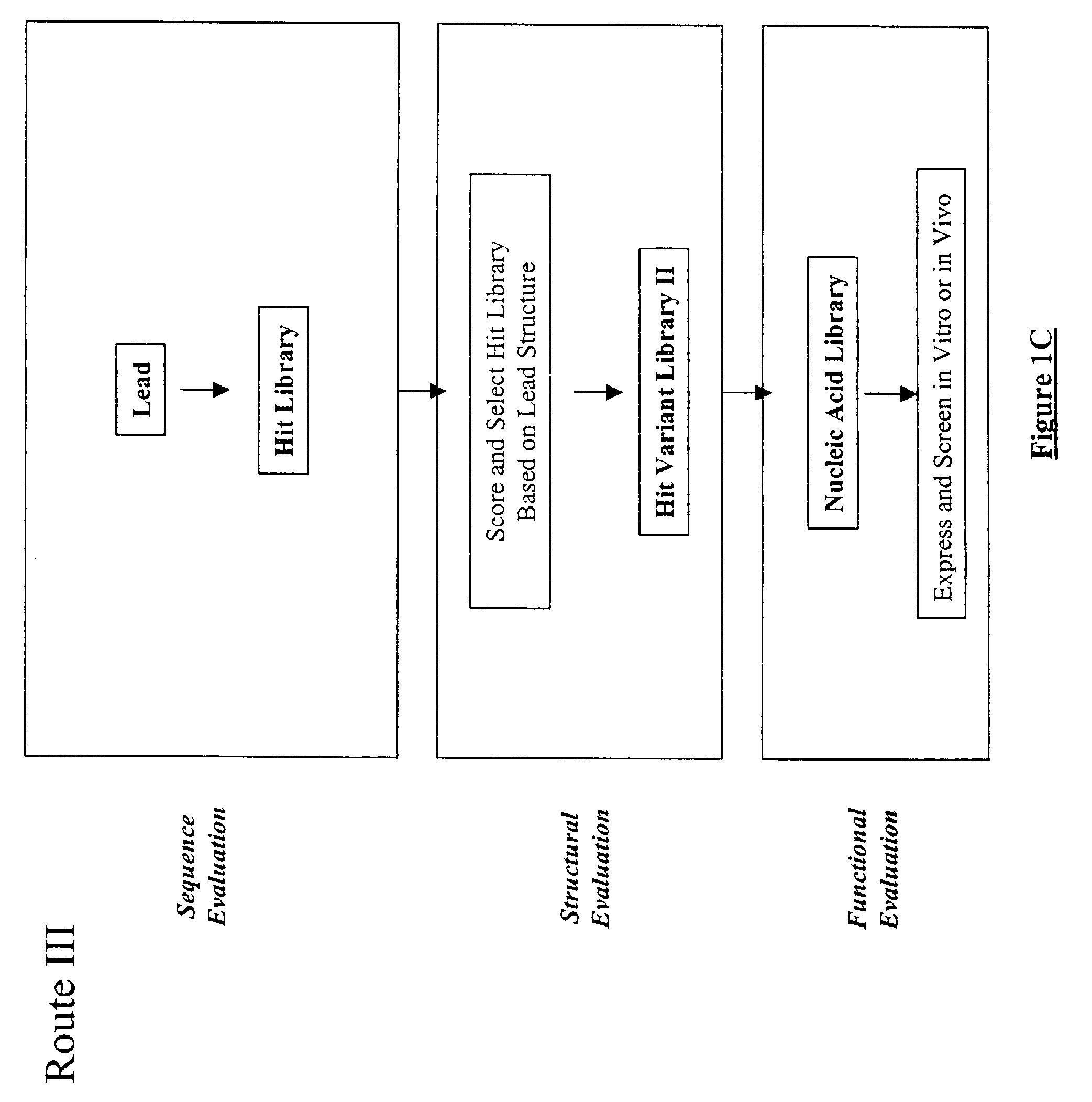
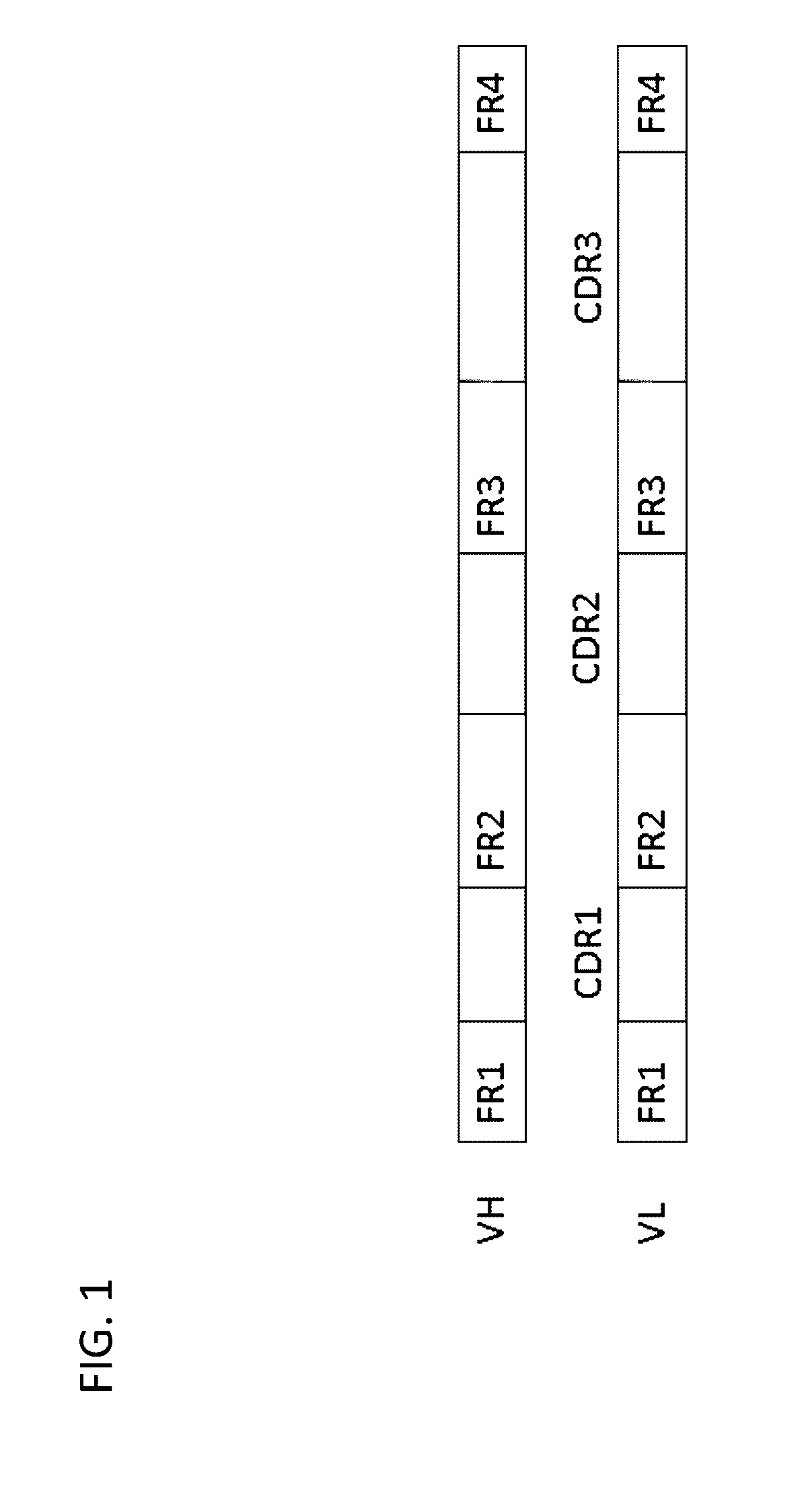
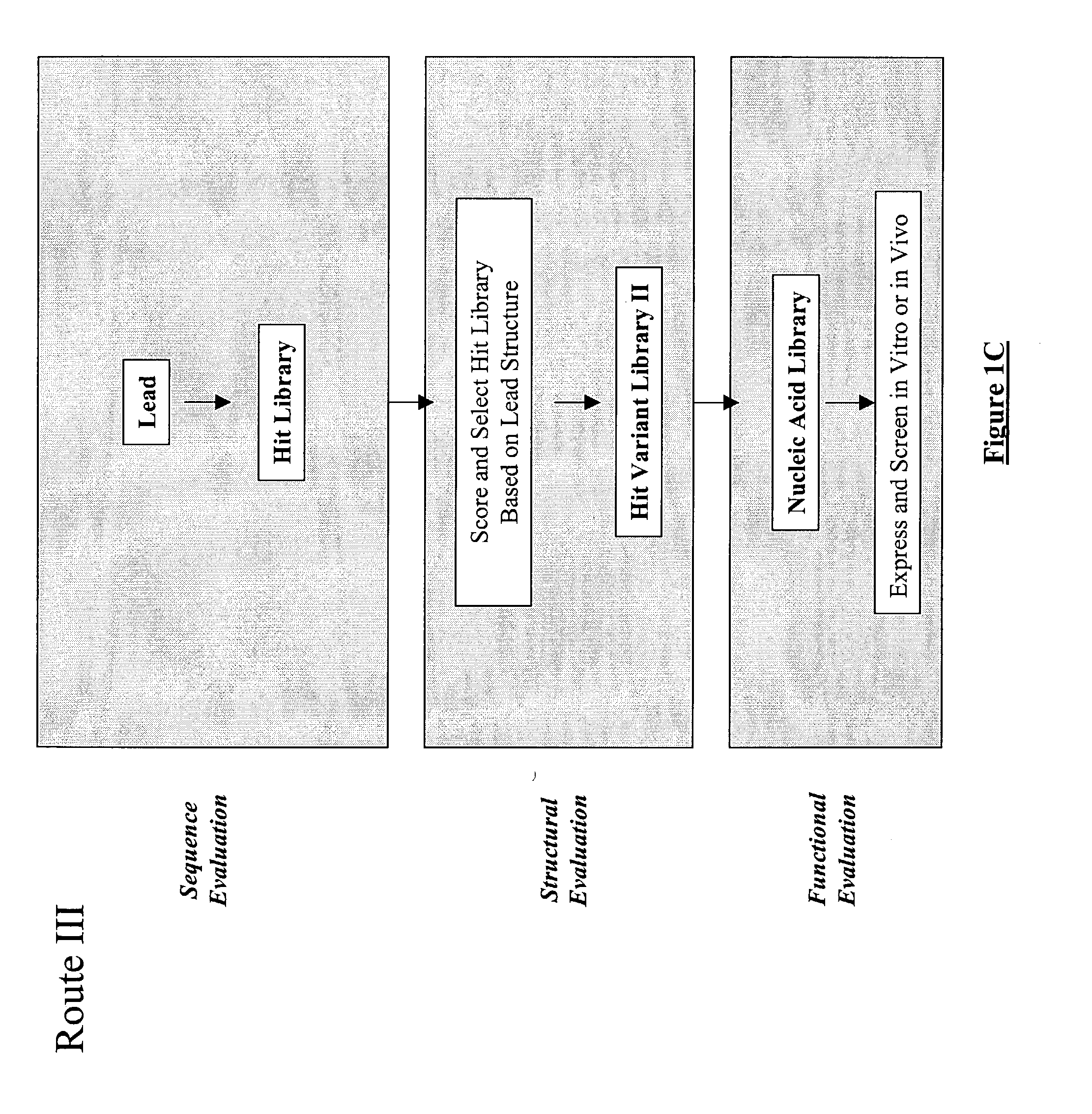
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Structure-based selection and affinity maturation of antibody library
InactiveUS7117096B2High affinityImprove throughputPeptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein insertionIn vivo
The present invention provides a structure-based methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as antibodies with high binding affinity and low immunogenicity in humans. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on a three dimensional structure of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody, the lead antibody having a known three dimensional structure which is defined as a lead structural template; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence profile with a plurality of tester protein sequences; selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 10% sequence identity with lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; determining if a member of the hit library is structurally compatible with the lead structural template using a scoring function; and selecting the members of the hit library that score equal to or better than or equal to the lead sequence. The selected members of the hit library can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
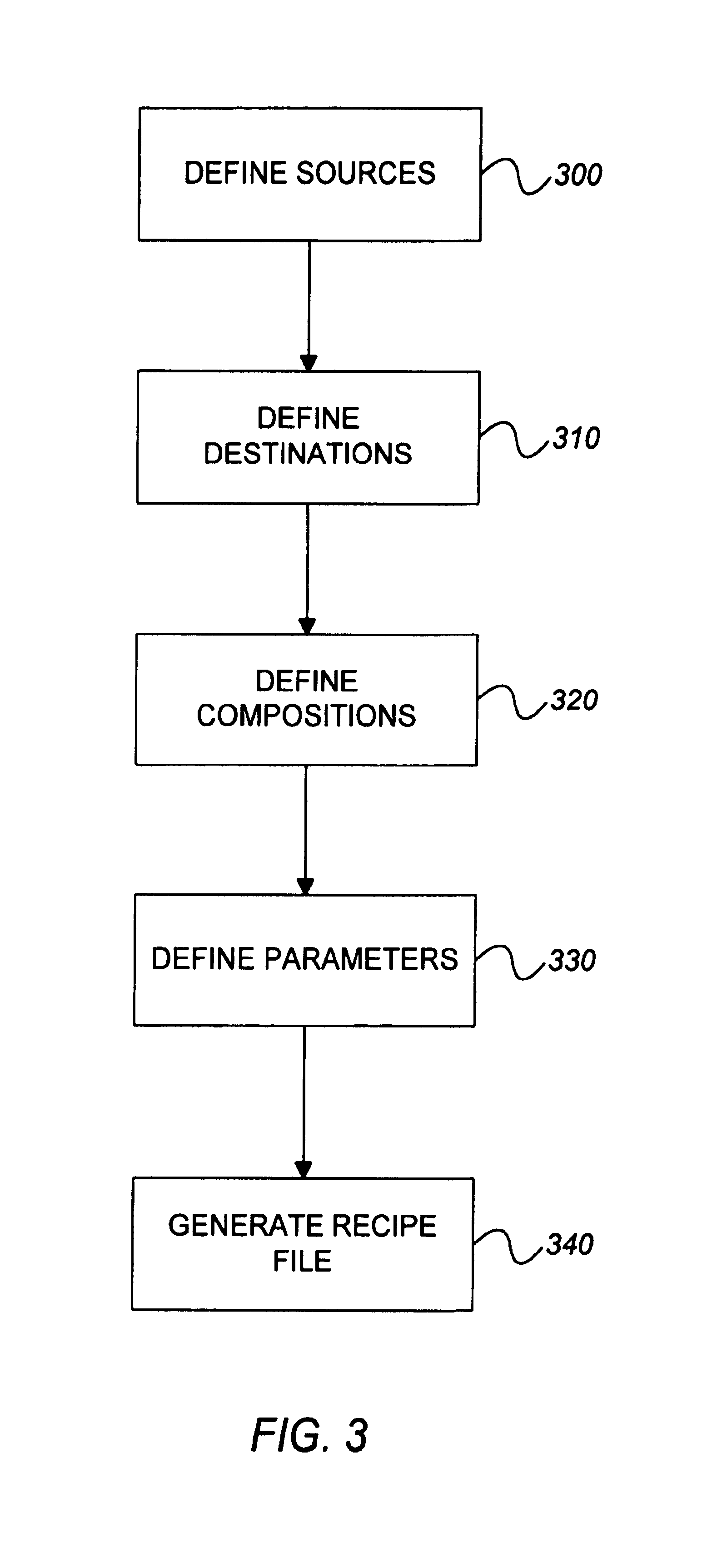
Graphic design of combinatorial material libraries
InactiveUS7199809B1Flexible definitionSpeed up library designOrganic chemistry methodsLibrary screeningGraphicsData file
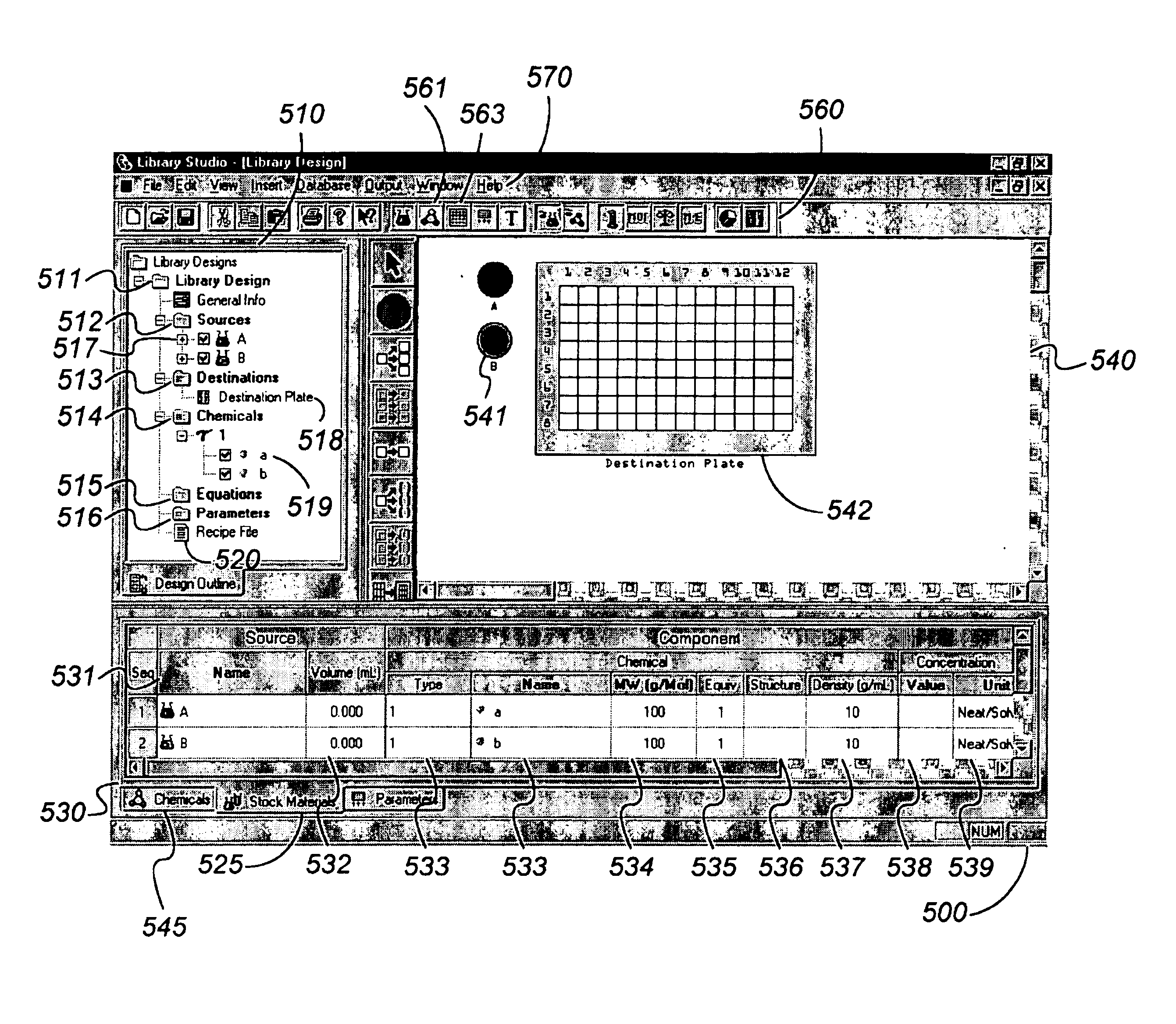
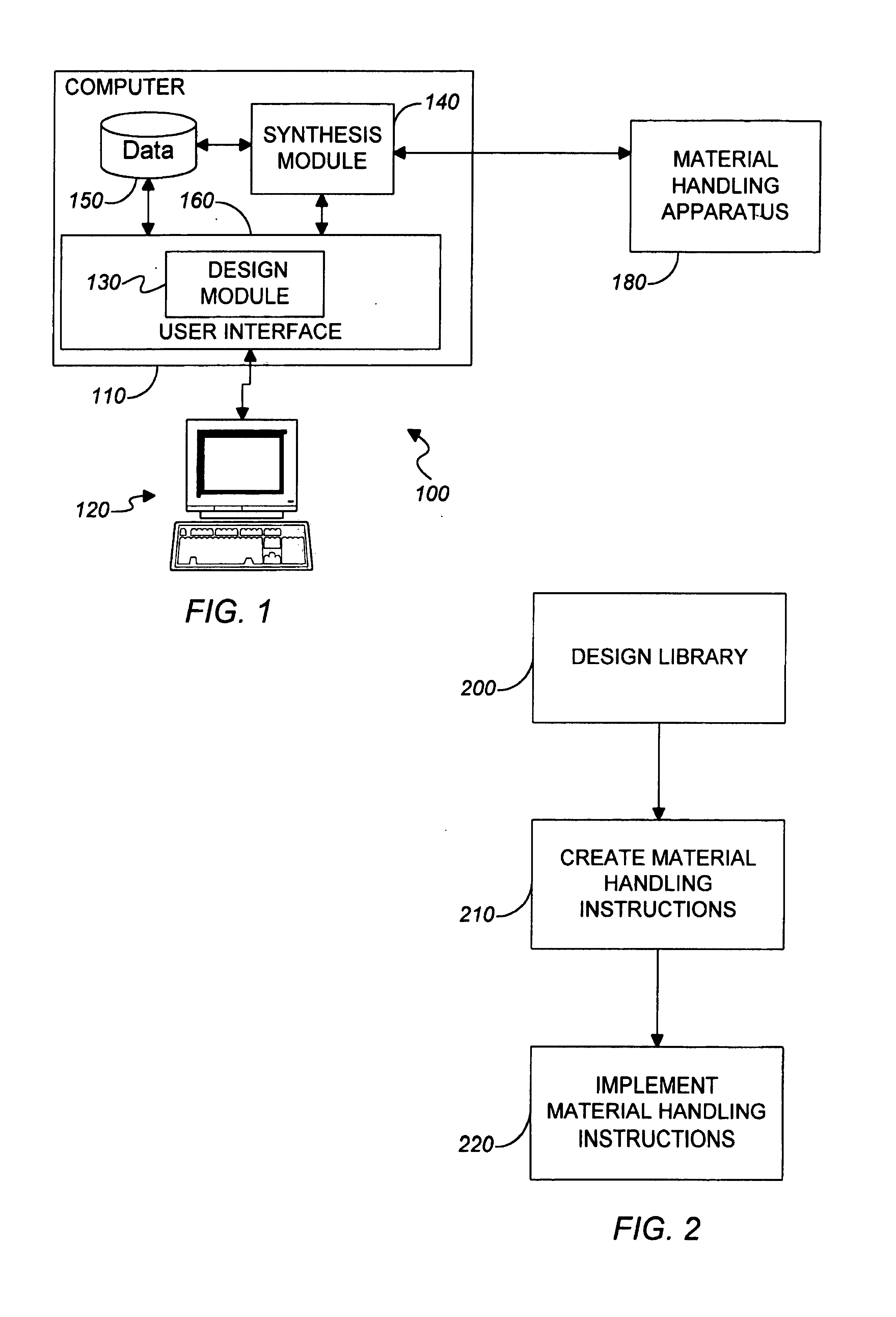
Computer-implemented methods, programs and apparatus for generating a library design for a combinatorial library of materials. A library design includes a set of sources representing components to be used in preparing the combinatorial library, destinations replying arrangements of cells and mappings, defining one or more distribution patterns for assigning components to cells in the destination arrangement or arrangements. Mappings include gradients and sets of user-defined equations, and are used to calculate the amount of on components to be assigned to a cell or cells in an arrangement. A library design can also include one or more process parameters defined to vary over time or across a plurality of destination cells. The invention outputs a data file defining the library design, including electronic data representing the sources, the destinations and the mapping, in a format suitable for implementing manually or using automated material handling apparatus.
Owner:UNCHAINED LABS
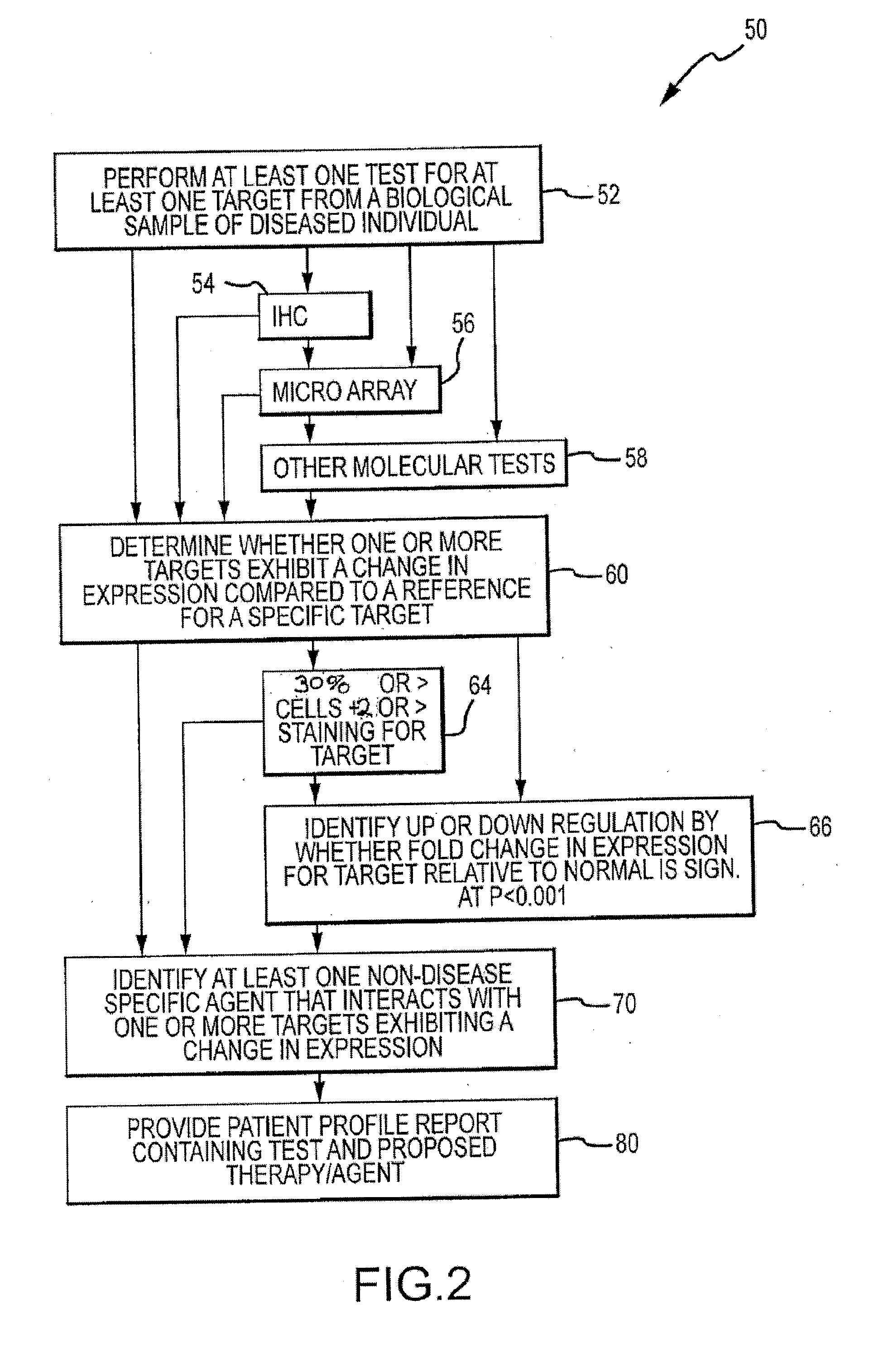
Molecular profiling of tumors
Provided herein are methods and systems of molecular profiling of diseases, such as cancer. In some embodiments, the molecular profiling can be used to identify treatments for a disease, such as treatments that were not initially identified as a treatment for the disease or not expected to be a treatment for a particular disease.
Owner:CARIS MPI INC
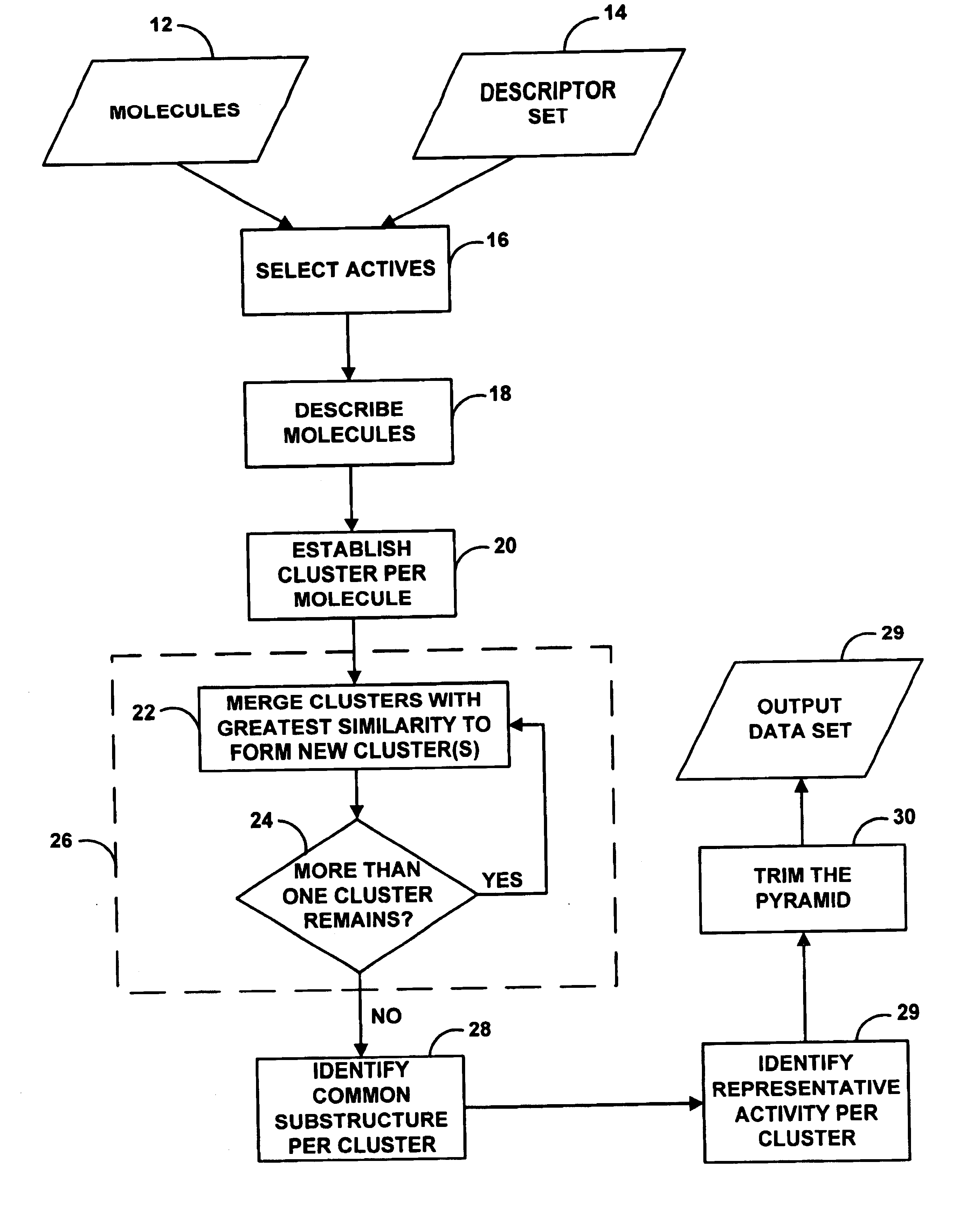
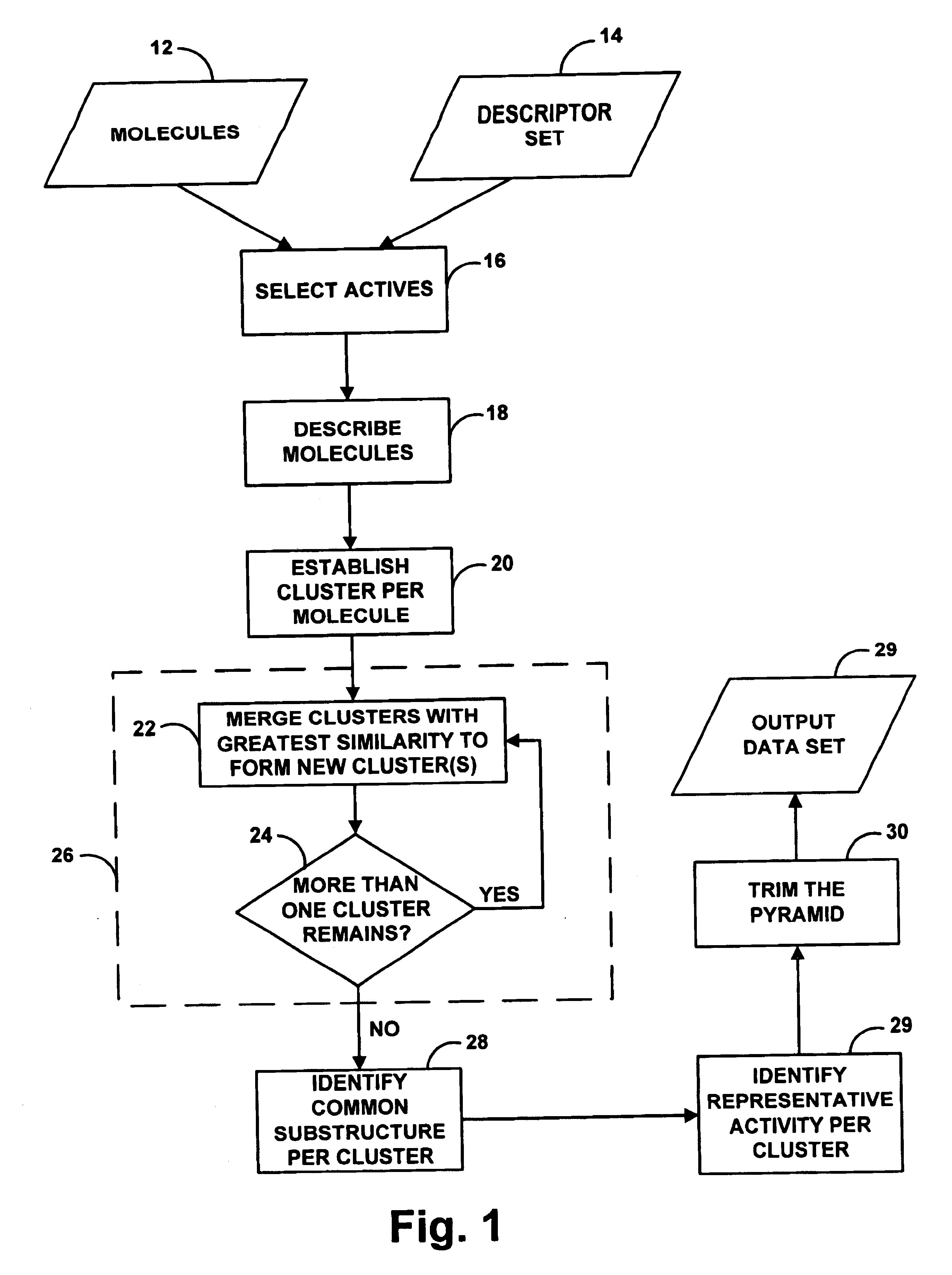
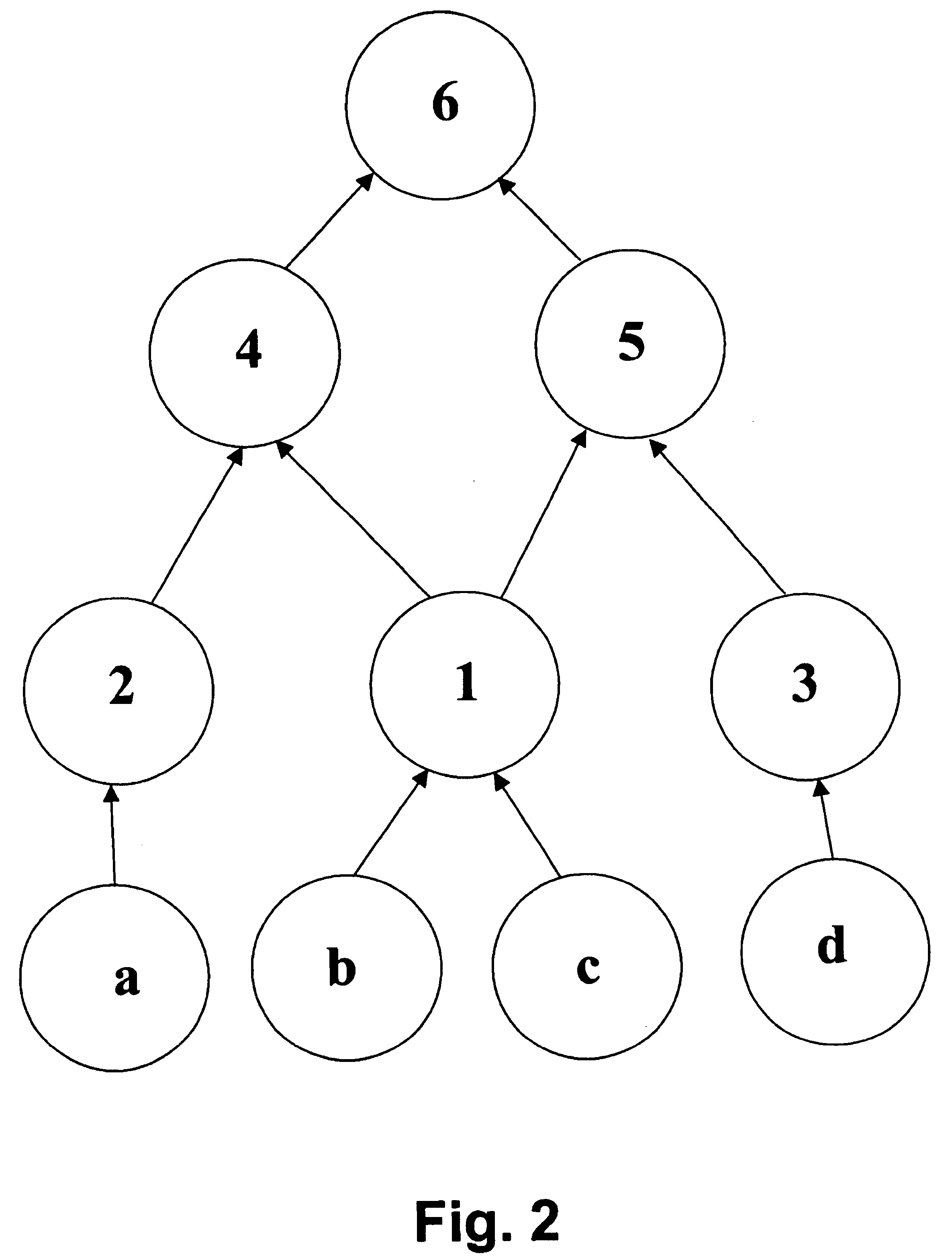
Method and system for artificial intelligence directed lead discovery though multi-domain agglomerative clustering
A system for helping a chemist to identify pharmacophoric mechanisms, based on a set of input data representing many chemical compounds. Given an input data set defining for each compound a feature characteristic and an activity characteristic, a computer agglomeratively clusters representations of the molecules based on their feature characteristics. The result of this process is a multi-domain pyramid structure, made up of a number of nodes each representing one or more molecules. For each node, the computer identifies a representative feature set (such as a largest substructure common among the molecules in the node) and a representative activity level (such as an average of the activity levels of the molecules in the node). The computer then provides as output to a chemist a description of all or part of the pyramid. This process thus converts a large set of raw data into an understandable and commercially useful form, which can assist the chemist in developing beneficial new pharmaceuticals.
Owner:SIMULATIONS PLUS +6
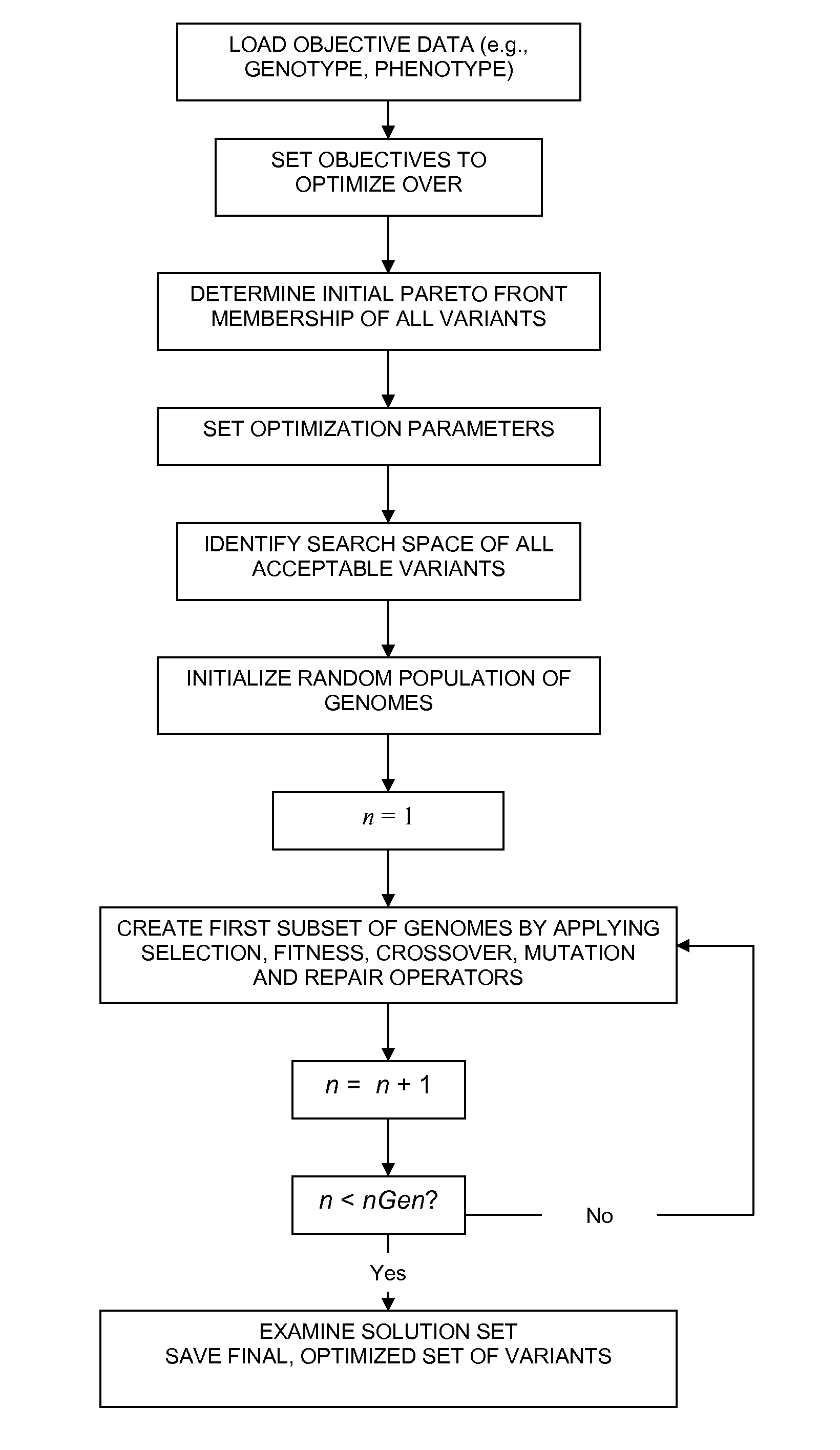
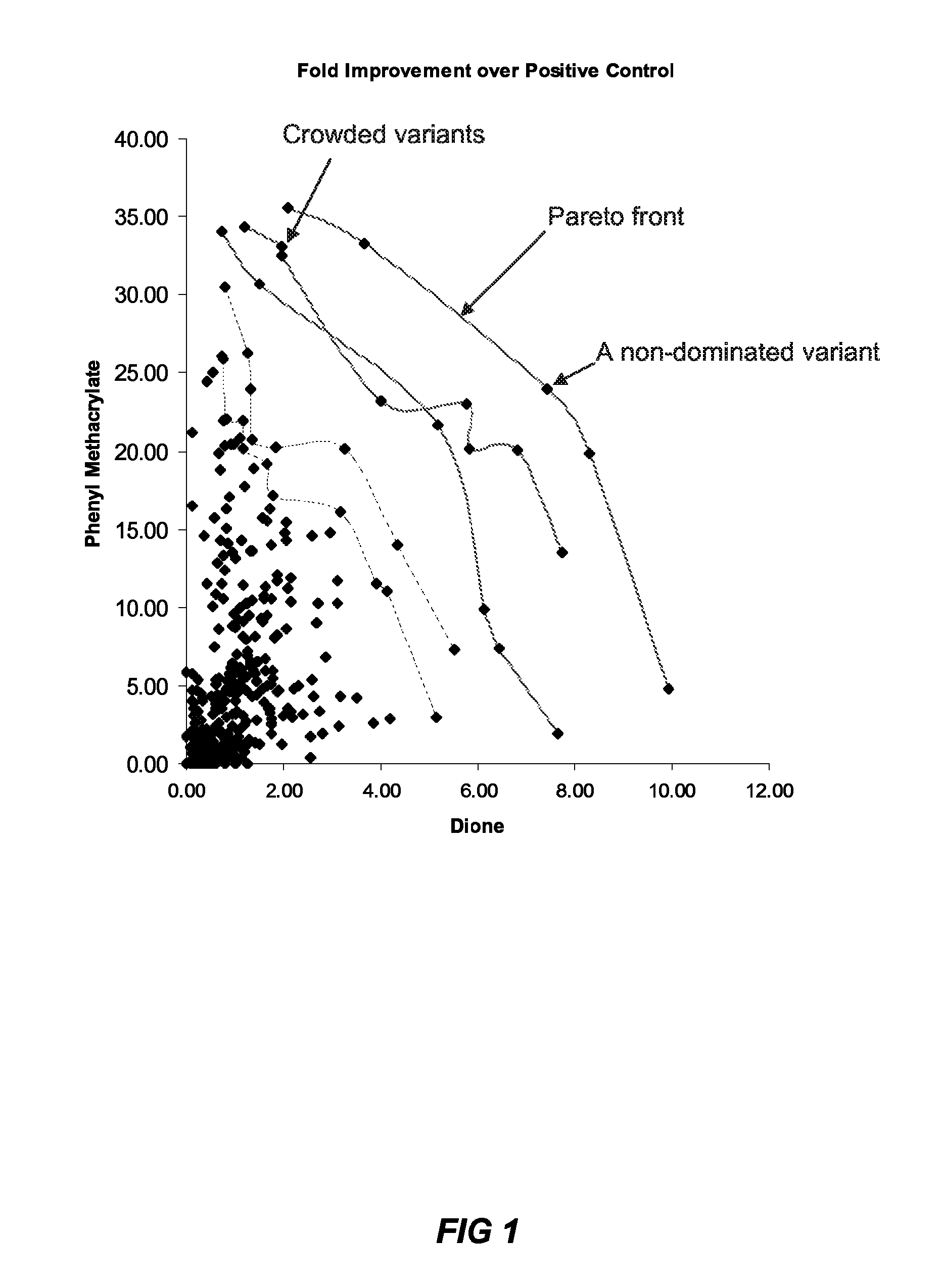
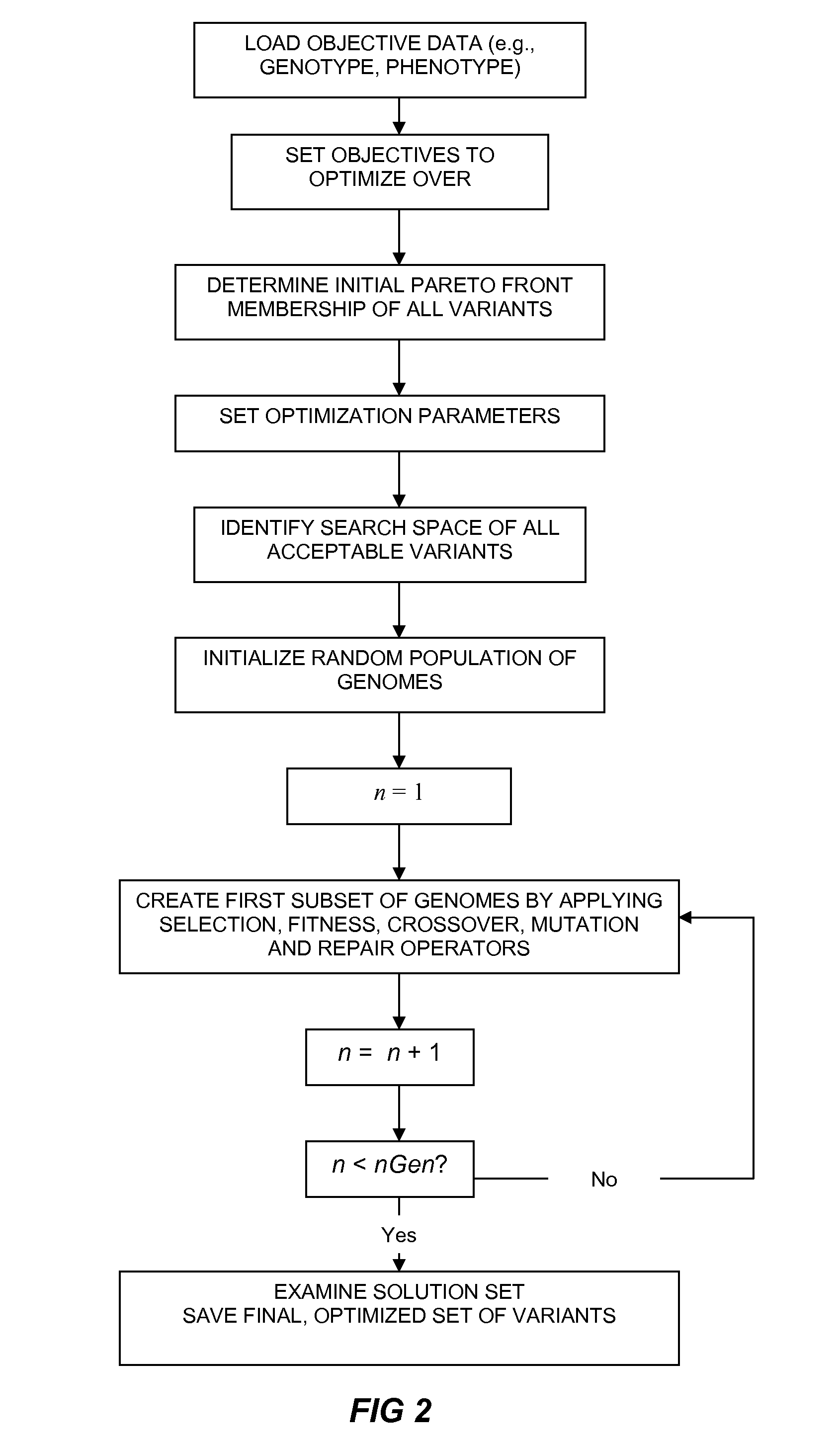
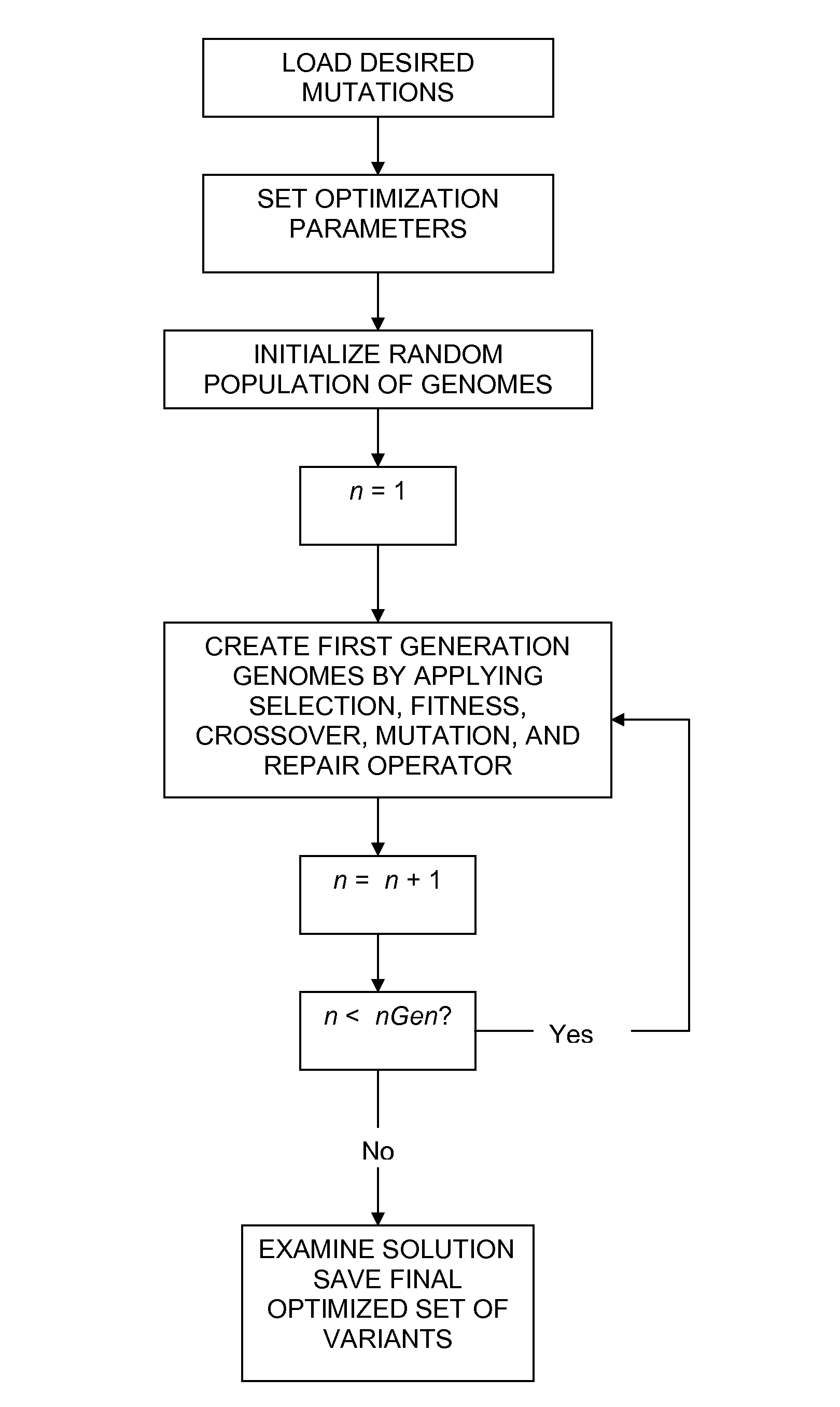
Method of generating an optimized, diverse population of variants
The present disclosure relates to methods of rapidly and efficiently searching biologically-related data space to identify a population set maximally diverse and optimized for sets of desired properties. More specifically, the disclosure provides methods of identifying a diverse, evolutionary separated bio-molecules with desired properties from complex bio-molecule libraries. The disclosure additionally provides digital systems and software for performing these methods.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Method of generating an optimized, diverse population of variants
The disclosure relates to a method of generating a diverse set of variants to screen improved and novel properties within the variant population, a system for creating the diverse set of variants, and the variant peptides.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
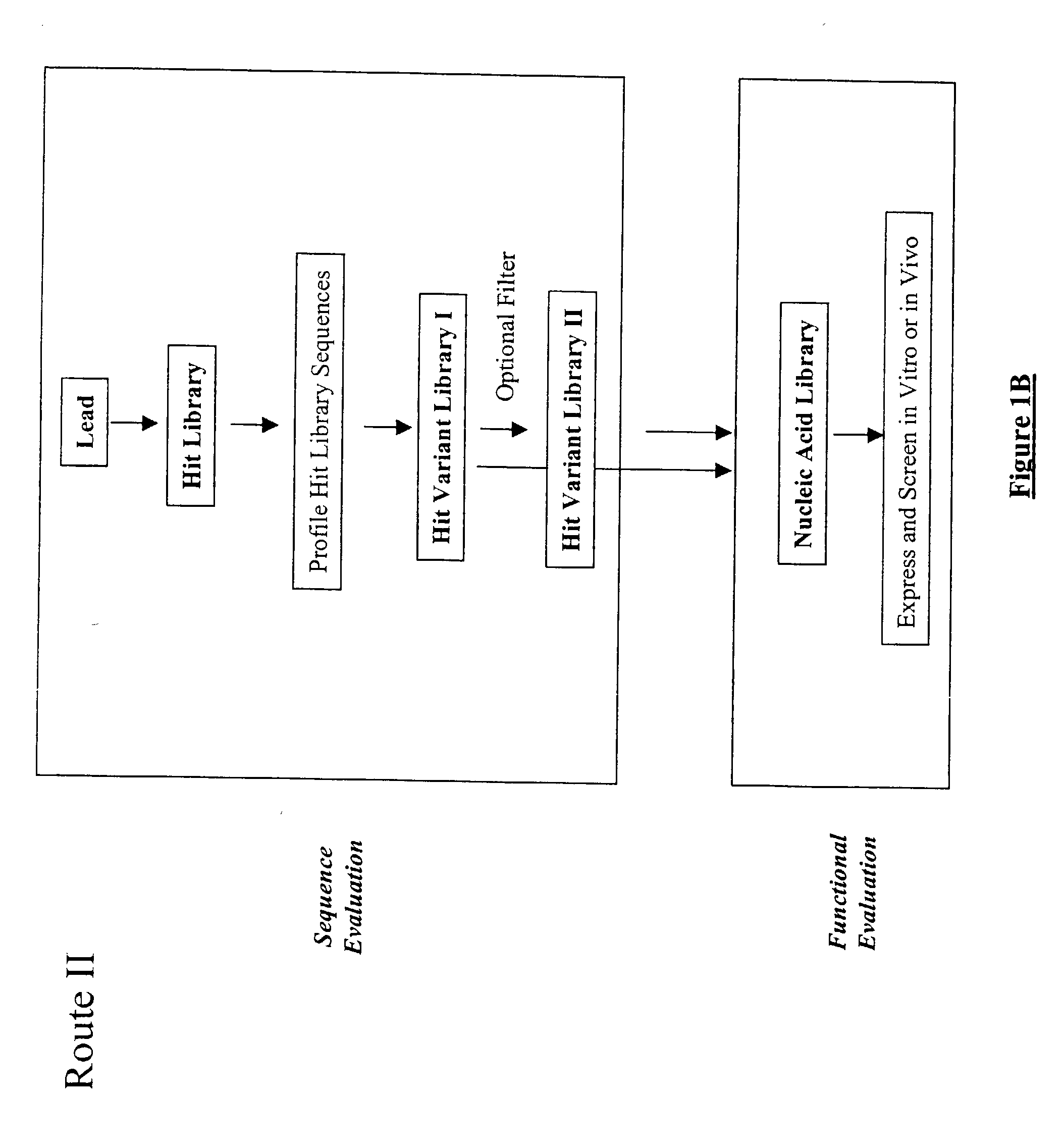
Generation and affinity maturation of antibody library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method is provided for constructing a library of antibody sequences based on the amino acid sequence of a lead antibody. The method comprises: providing an amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) of a lead antibody; identifying the amino acid sequences in the CDRs of the lead antibody; selecting one of the CDRs in the VH or VL region of the lead antibody; providing an amino acid sequence that comprises at least 3 consecutive amino acid residues in the selected CDR, the selected amino acid sequence being a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library. The hit library of antibody sequences can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant antibodies that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead antibody.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Comparative gene transcript analysis
InactiveUS6114114ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisDisease cause
A method and system for quantifying the relative abundance of gene transcripts in a biological sample. One embodiment of the method generates high-throughput sequence-specific analysis of multiple RNAs or their corresponding cDNAs (gene transcript imaging analysis). Another embodiment of the method produces a gene transcript imaging analysis by the use of high-throughput CDNA sequence analysis. In addition, the gene transcript imaging can be used to detect or diagnose a particular biological state, disease, or condition which is correlated to the relative abundance of gene transcripts in a given cell or population of cells. The invention provides a method for comparing the gene transcript image analysis from two or more different biological samples in order to distinguish between the two samples and identify one or more genes which are differentially expressed between the two samples.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Methods of selection, reporting and analysis of genetic markers using borad-based genetic profiling applications
ActiveUS20070042369A1Economical and effective genetic profilingGuaranteed economic efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomePhenotype
Owner:FABRIC GENOMICS INC
Method and system using systematically varied data libraries
InactiveUS7873477B1Reduce the amount requiredProteomicsBiological testingComputer scienceData library
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
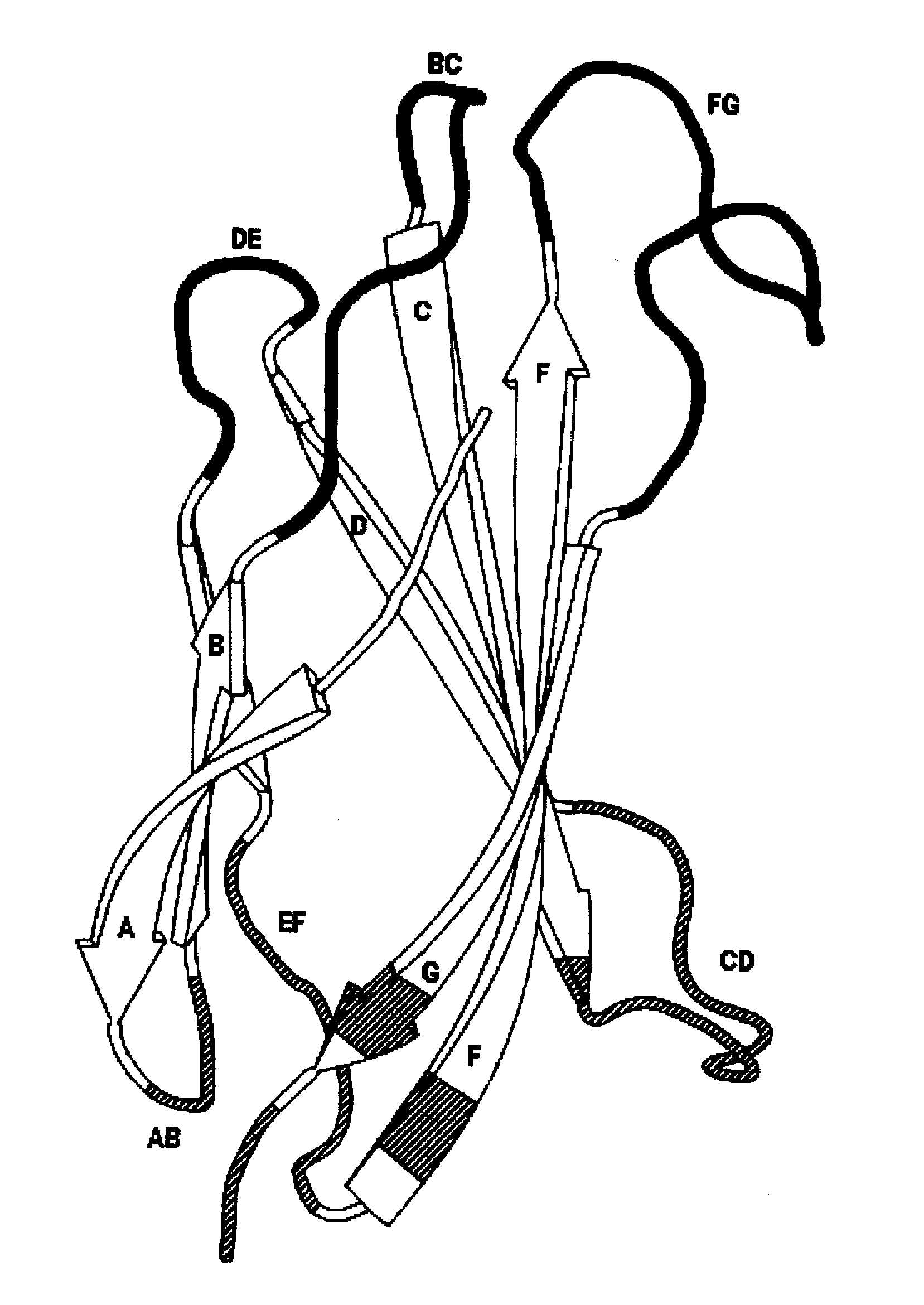
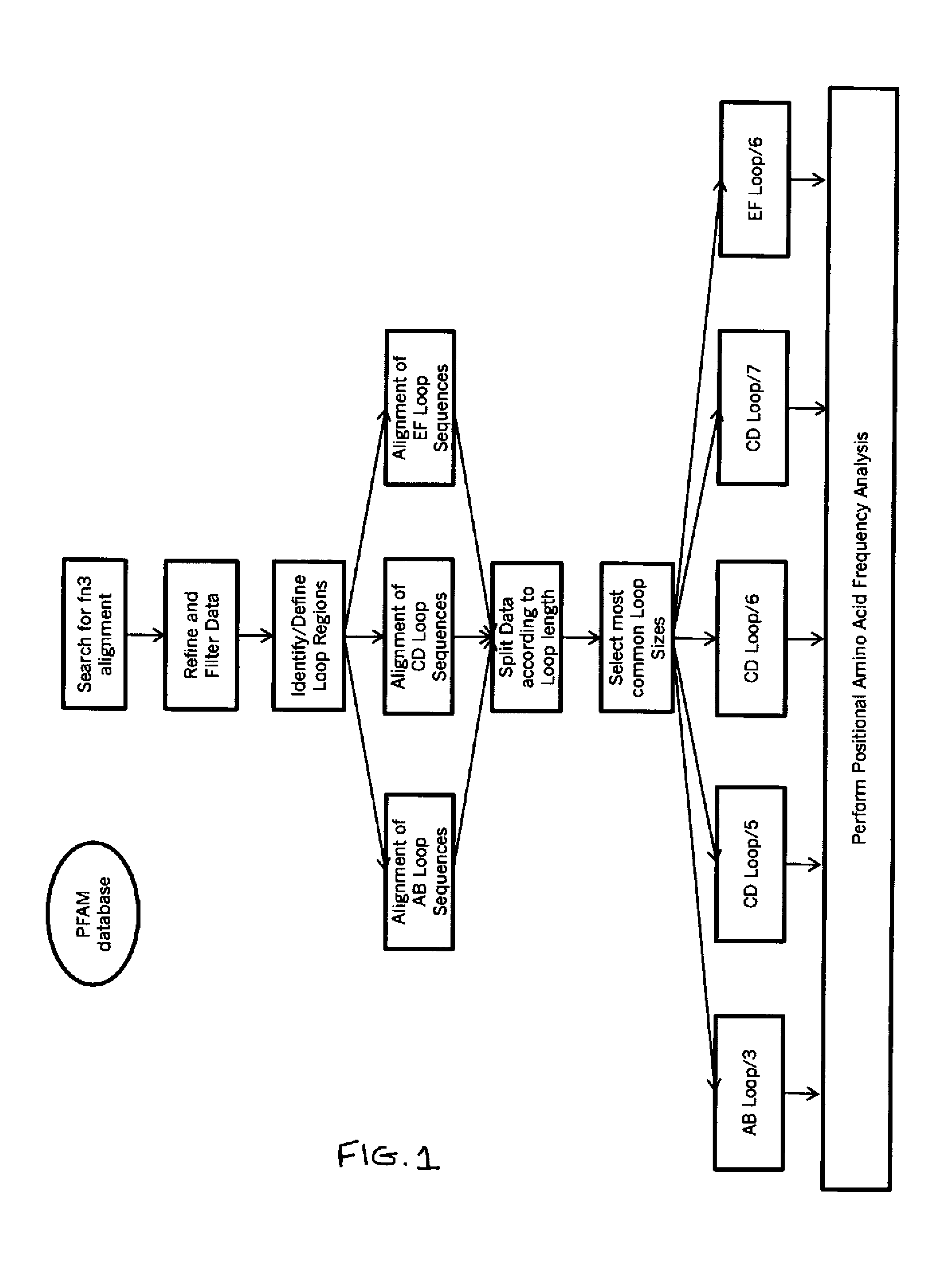
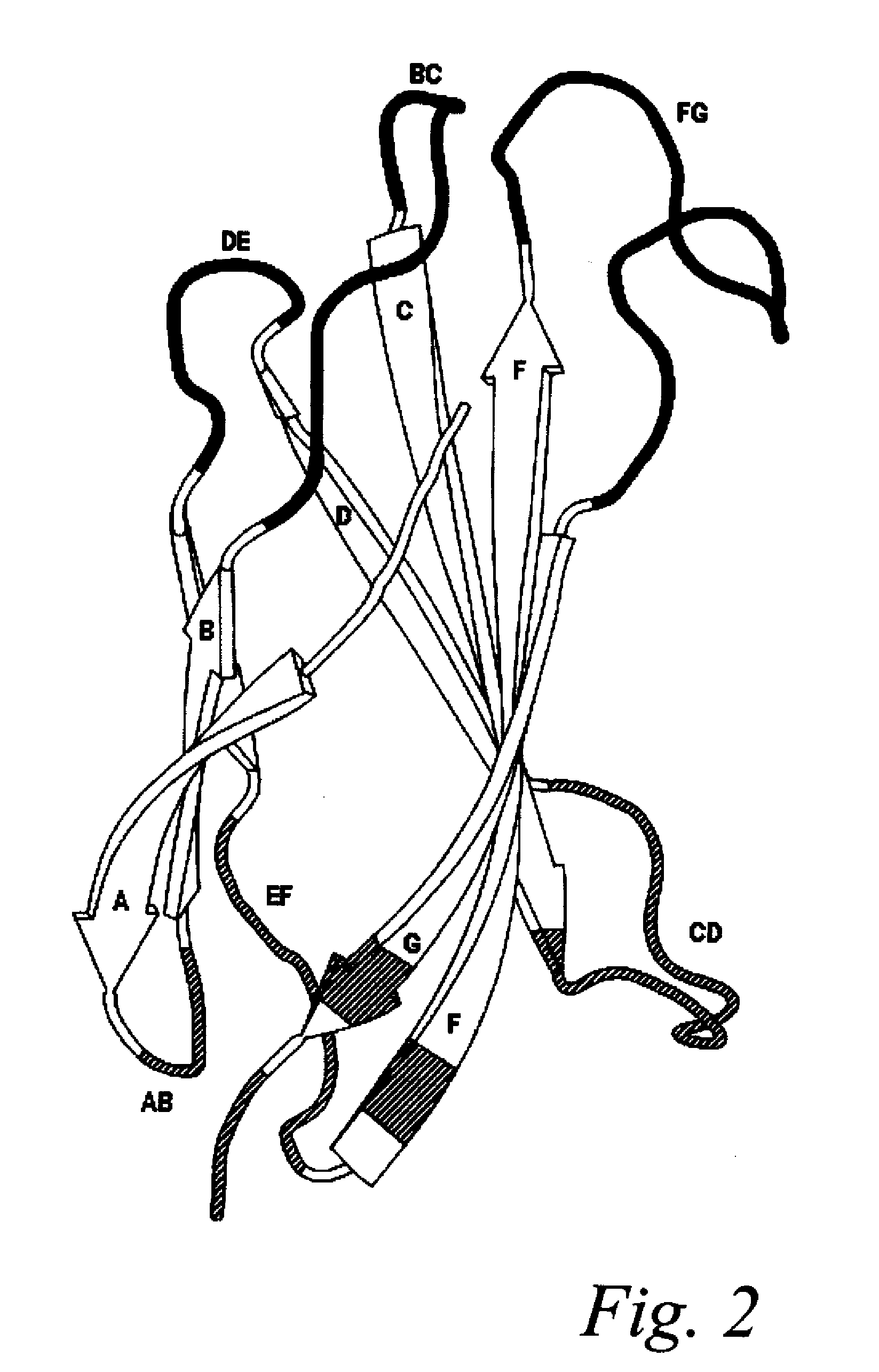
Universal fibronectin type iii bottom-side binding domain libraries
The invention pertains to a natural-variant combinatorial library of fibronectin Type 3 domain (Fn3) polypeptides useful in screening for the presence of one or more polypeptides having a selected binding or enzymatic activity. The library polypeptides include (a) regions A, AB, B, C, CD, D, E, EF, F, and G having wildtype amino acid sequences of a selected native fibronectin Type 3 polypeptide or polypeptides, and (b) loop regions AB, CD, and EF having selected lengths (Bottom Loops). The Fn3 may also have loop regions BC, DE, and FG having wildtype amino acid sequences, having selected lengths, or mutagenized amino acid sequences (Top Loops).
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method to clone mRNAs
InactiveUS6261770B1Convenient verificationHigh homologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
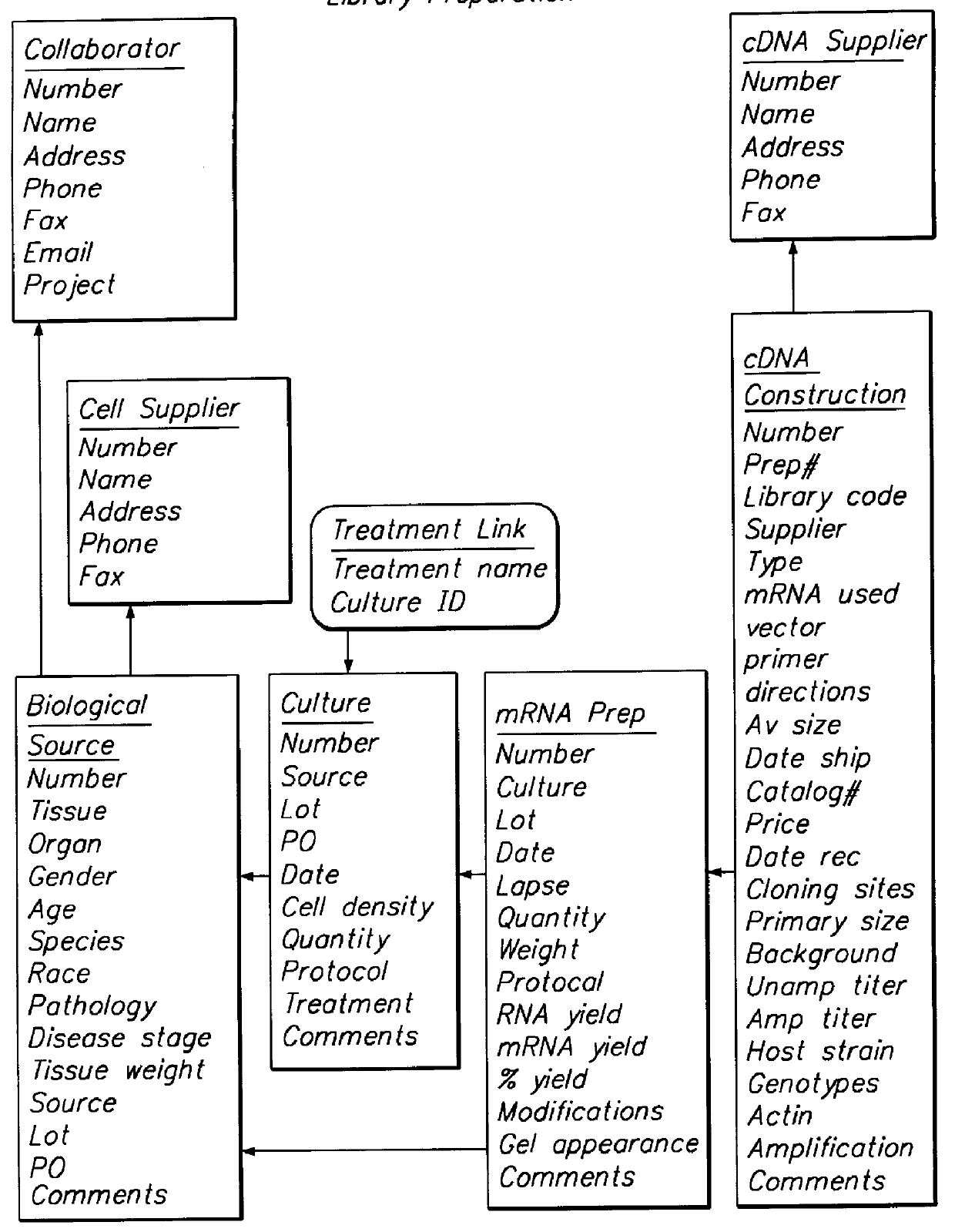
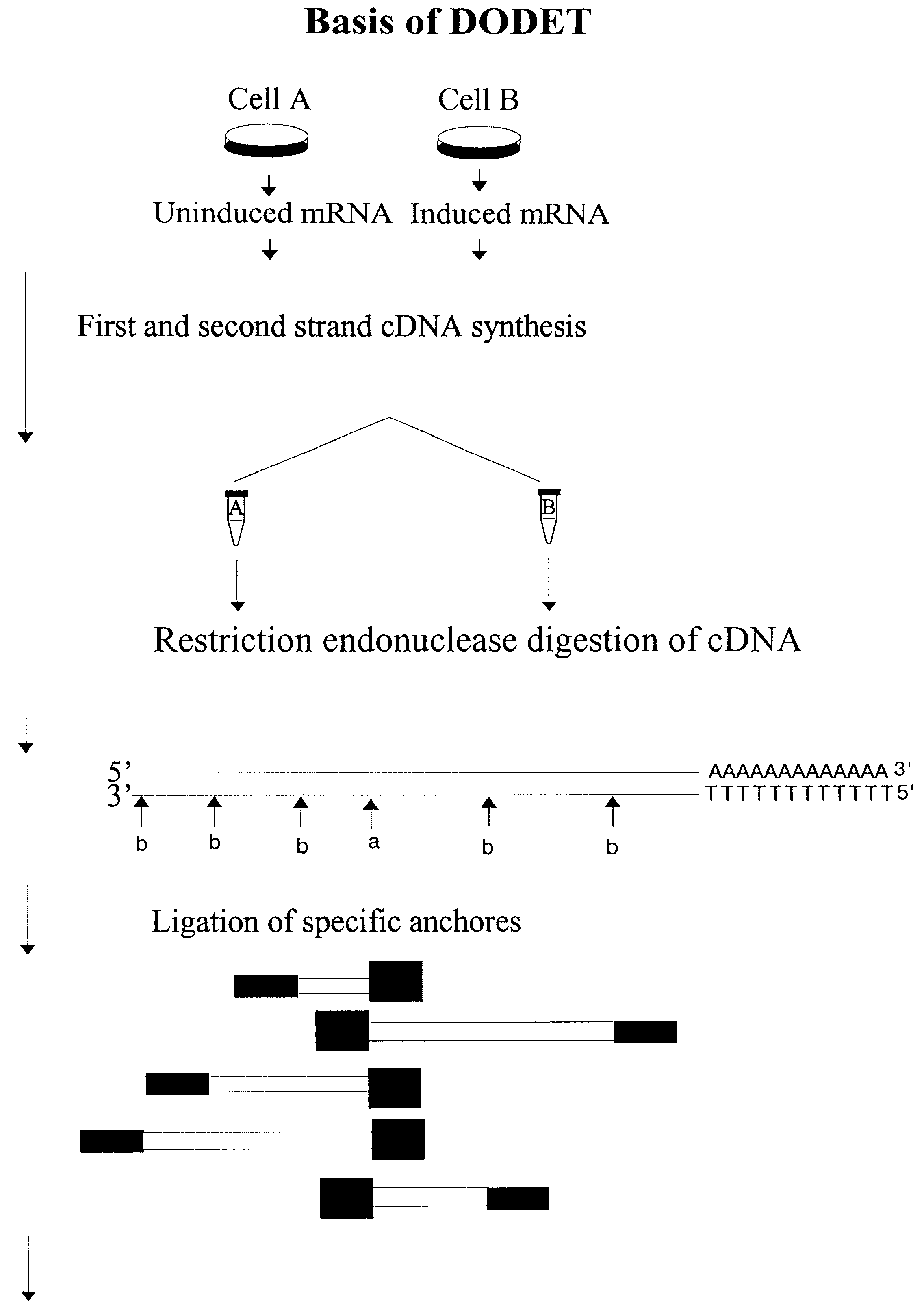
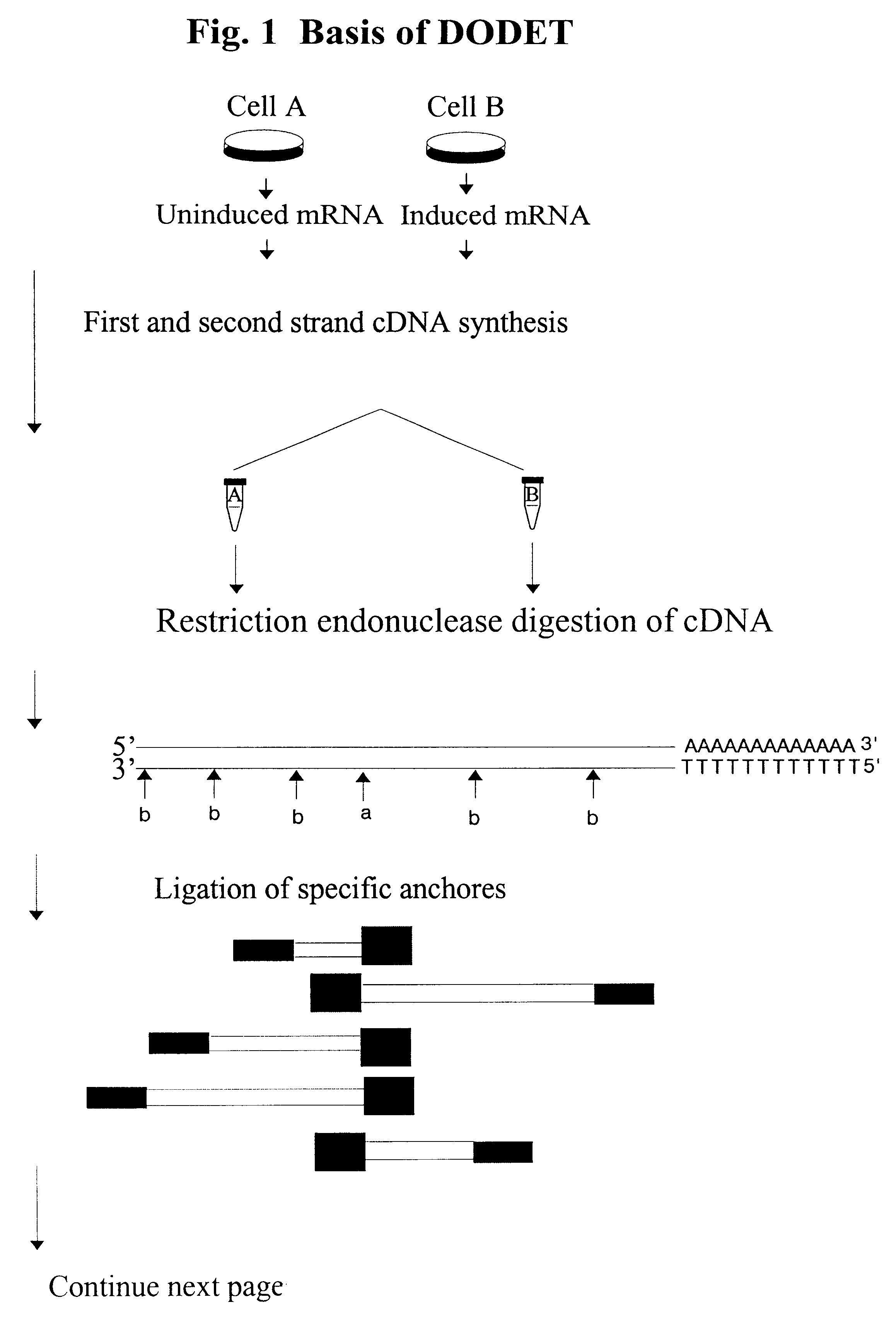
Disclosed and claimed is a method for preparing a normalized sub-divided library of amplified cDNA fragments from the coding region of mRNAs contained in a sample. The method includes the steps of: a) subjecting the mRNA population to reverse transcription using at least one cDNA primer, thereby obtaining first strand cDNA fragments, b) synthesizing second strand cDNA complementary to the first strand cDNA fragments by use of the first strand DNA fragments as templates, thereby obtaining double stranded cDNA fragments, c) digesting the double stranded cDNA fragments with at least one restriction endonuclease, the endonuclease leaving protruding sticky ends of similar size at the termini of the DNA after digestion, thereby obtaining cleaved cDNA fragments, d) adding at least two adapter fragments containing known sequences to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c), the at least two adapter fragments being able to bind specifically to the sticky ends of the double stranded cDNA produced in step c), the one adapter fragment being able to anneal to the primer having formula I in step f), the second adapter fragment being a termination fragment introducing a block against DNA polymerization in the 5'->3' direction setting out from said termination fragment and the termination fragment being unable to anneal to any primer of the at least two primer sets in step f) during the molecular amplification procedure, the at least two adapter fragments being ligated to the cleaved cDNA fragments obtained in step c) so as to obtain ligated cDNA fragments, e) sub-dividing the ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step d) into 4n1 pools where 1<=n1<=4, and f) subjecting each pool of ligated cDNA fragments obtained in step e) to a molecular amplification procedure so as to obtain amplified cDNA fragments, wherein is used, for an adapter fragment used in step d), a set of amplification primers having the general formula Iwherein Com is a sequence complementary to at least the 5'-end of an adapter fragment which is ligated to the 3'-end of a cleaved cDNA fragment, N is A, G, T, or C, the one primer having the general formula I where n1=0, and the second primer having the general formula I where 1<=n1<=4, the second primer being capable of priming amplification of any nucleotide sequence ligated in its 3'-end to the adapter fragment complementary in its 5'-end to Com.
Owner:AZIGN BIOSCI
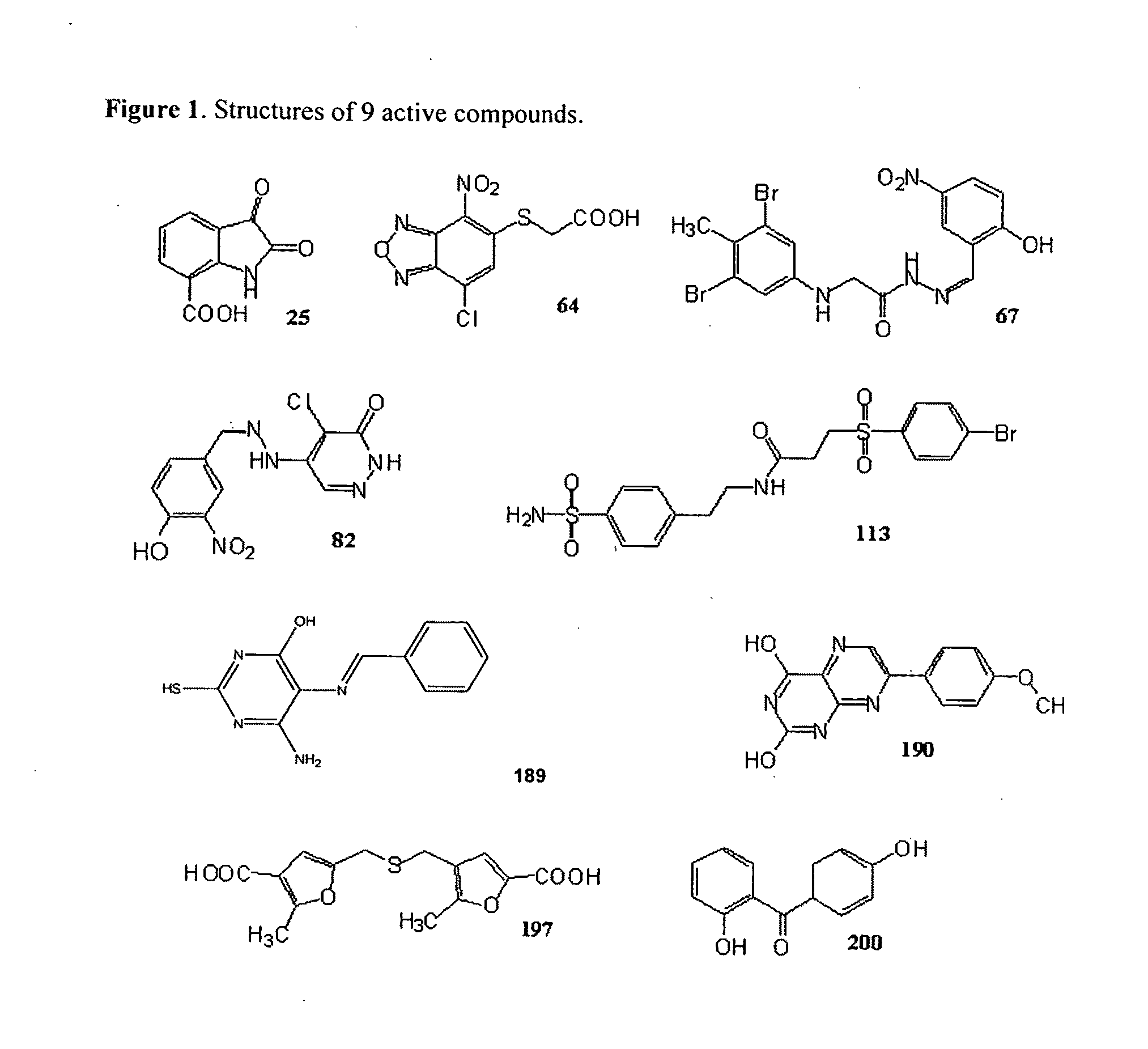
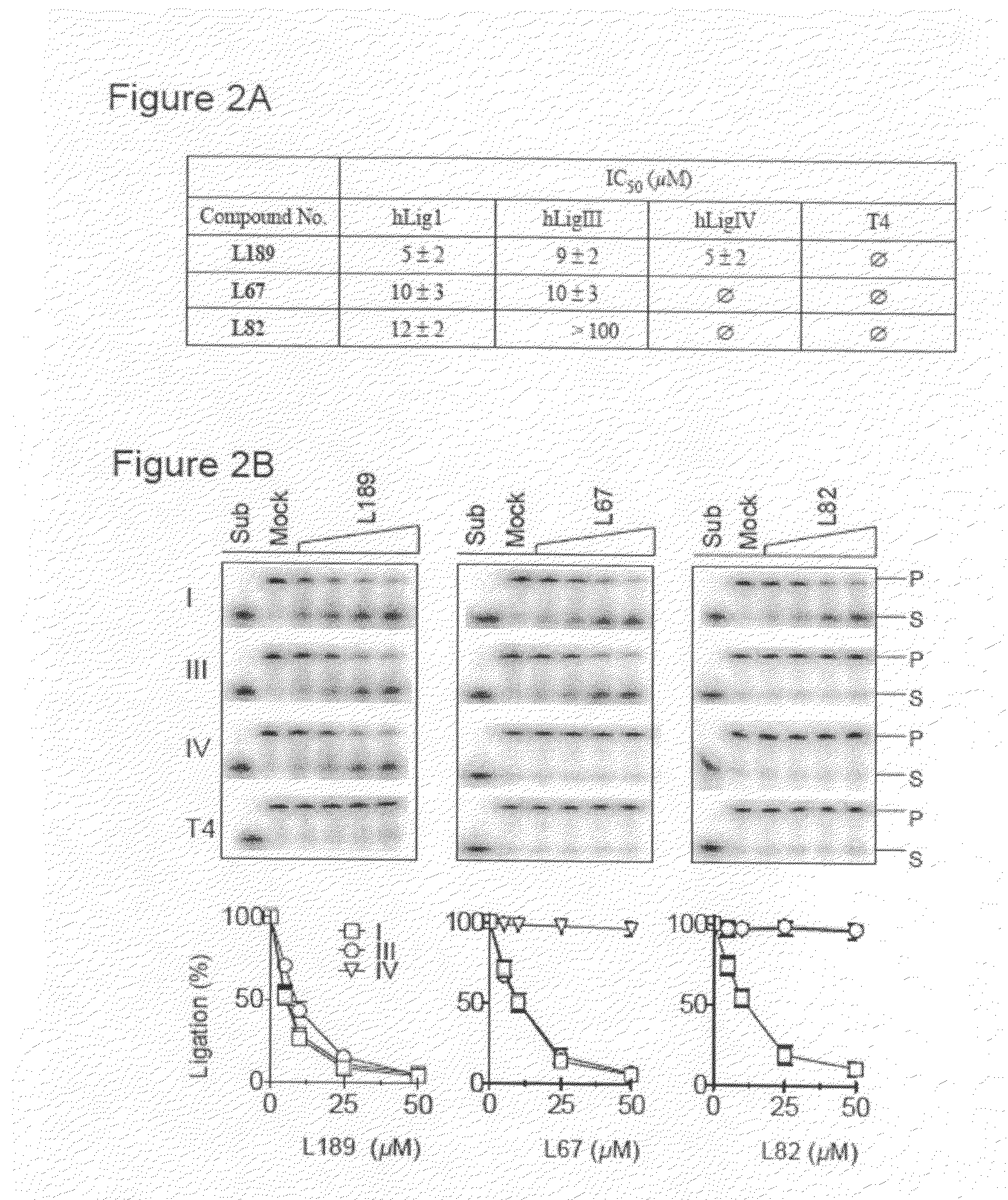
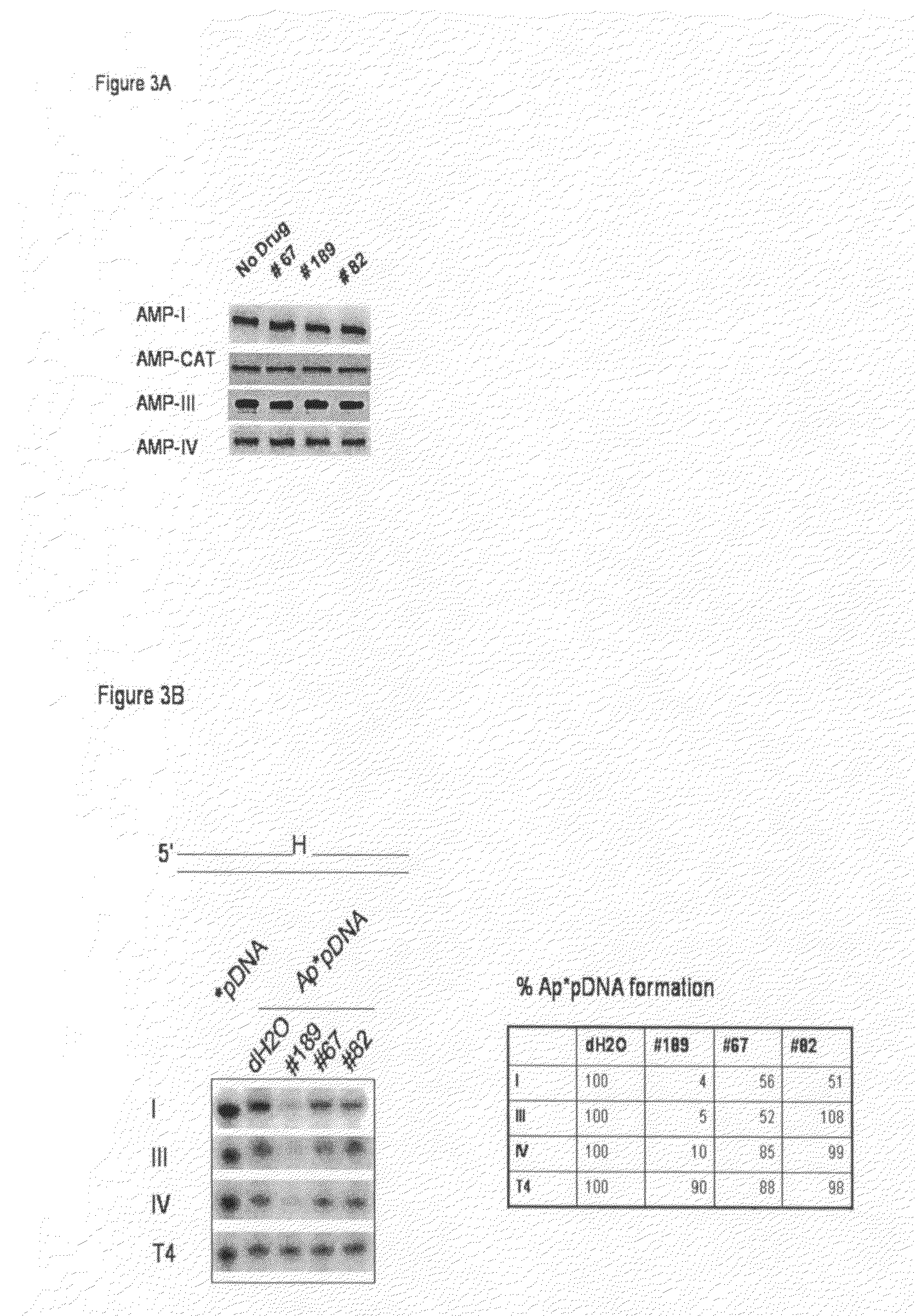
Compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases and methods of treating cancer
ActiveUS20100099683A1Strong cytotoxicityInhibit cell growthBiocideOrganic chemistryScreening methodBiochemistry
Methods for treating cancer using compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases. Methods for using compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases to provide insights into the reaction mechanisms of human DNA ligases, for example to identify the human DNA ligase involved in different DNA repair pathways. Screening methods for compounds that inhibit human DNA ligases.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
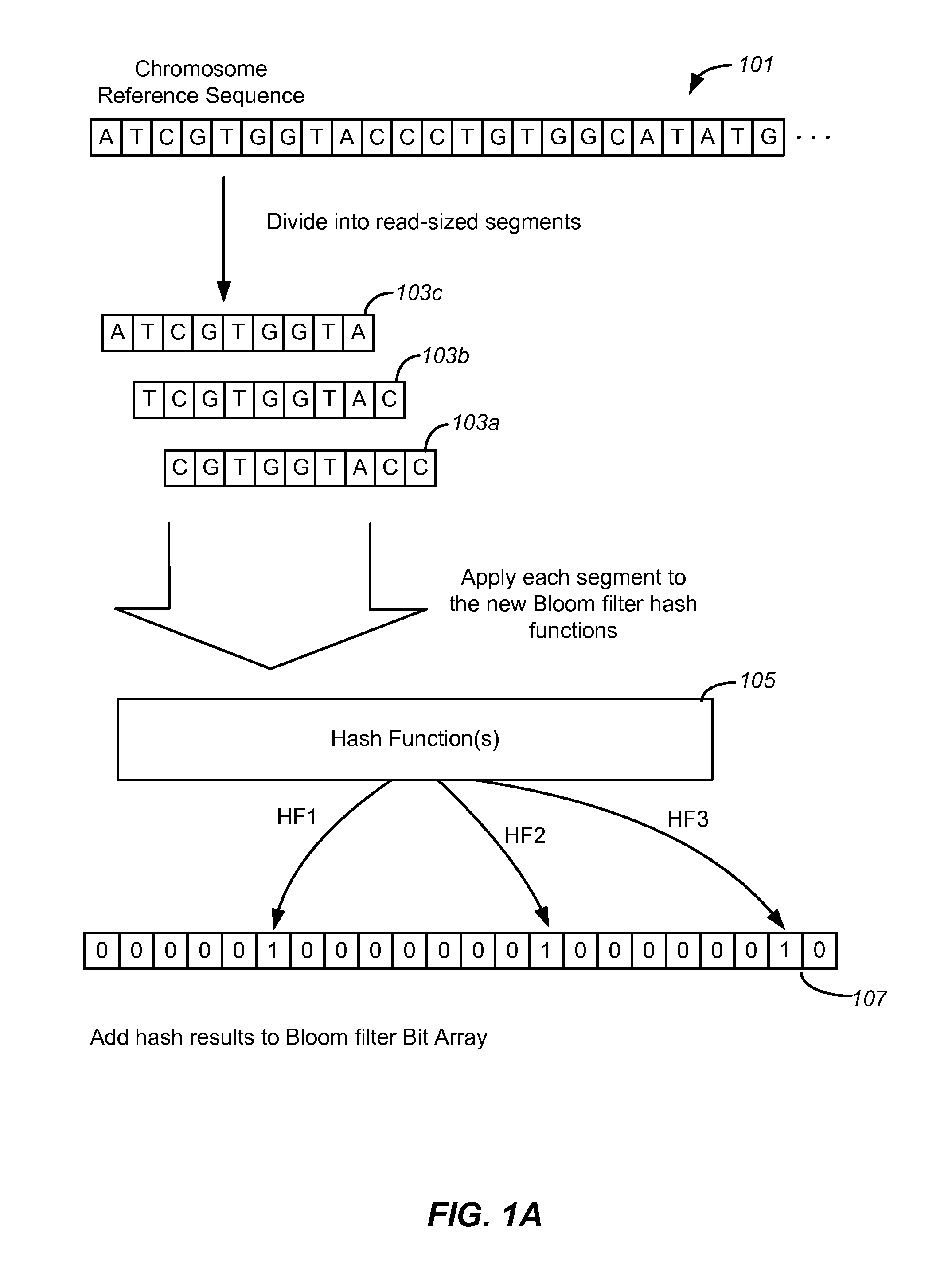
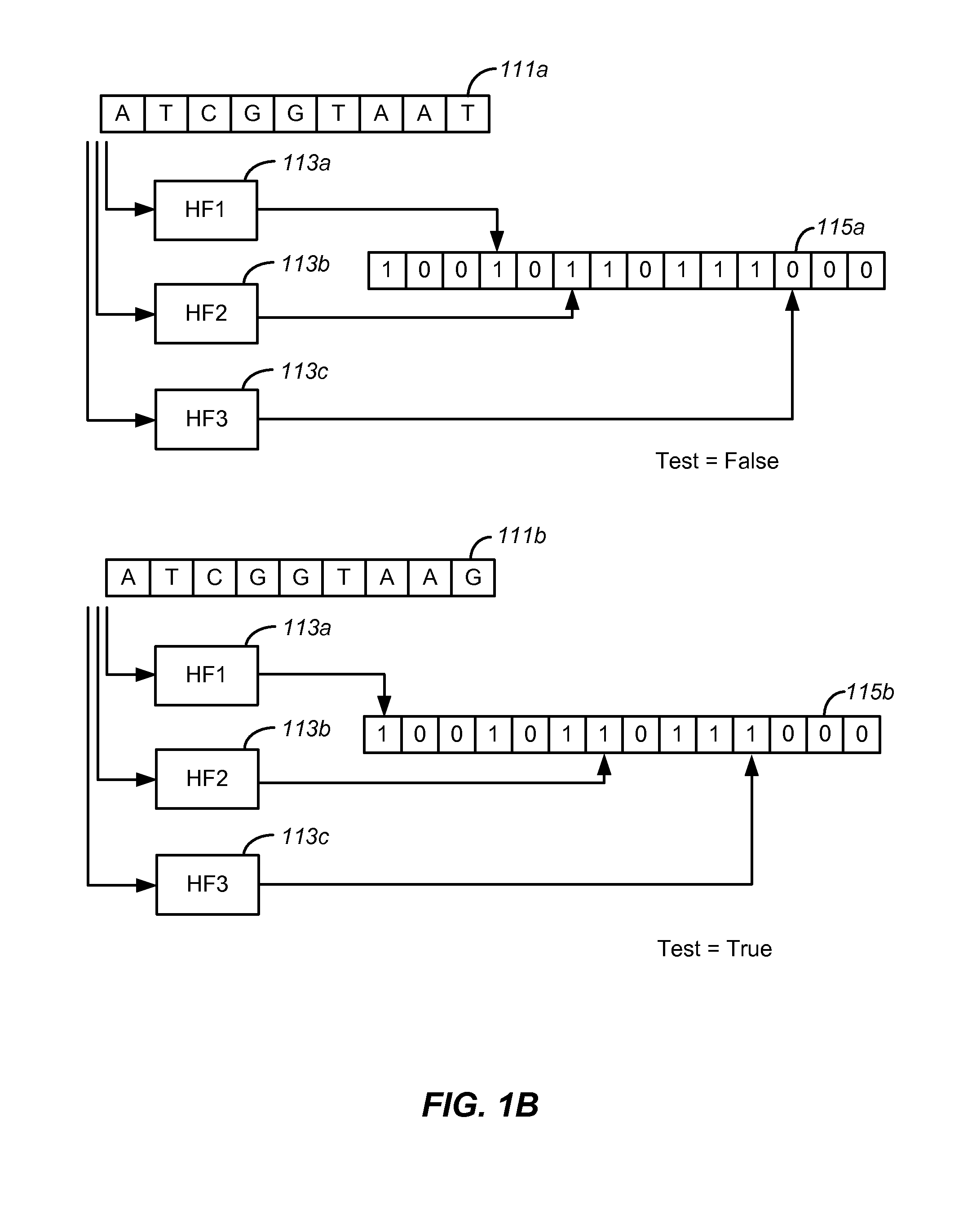
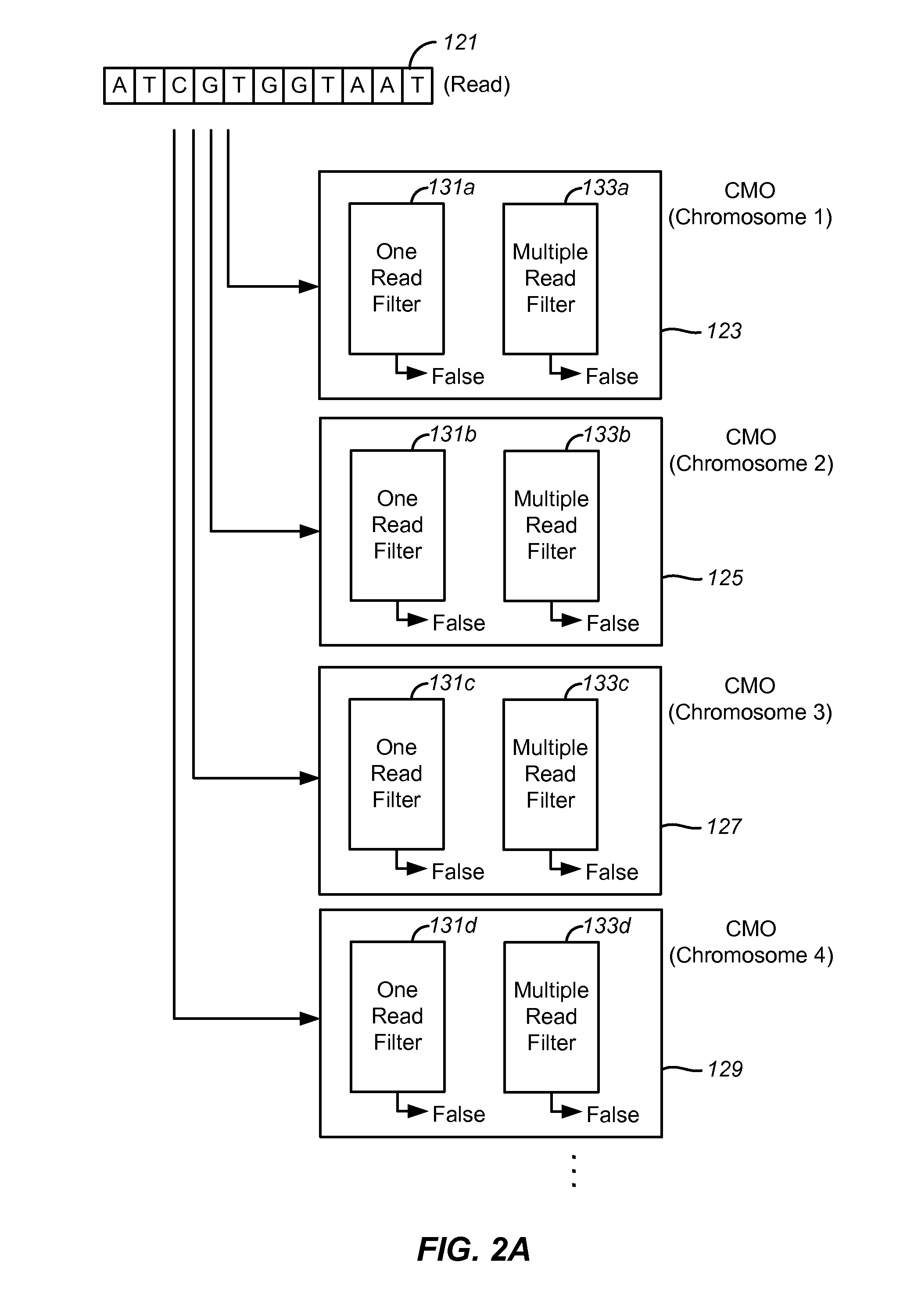
Set membership testers for aligning nucleic acid samples
Disclosed are methods and tools for rapidly aligning reads to a reference sequence. These methods and tools employ Bloom filters or similar set membership testers to perform the alignment. The reads may be short sequences of nucleic acids or other biological molecules and the reference sequences may be sequences of genomes, chromosomes, etc. The Bloom filters include a collection of hash functions, a bit array, and associated logic for applying reads to the filter. Each filter, and there may be multiple of these used in a particular application, is used to determine whether an applied read is present in a reference sequence. Each Bloom filter is associated with a single reference sequence such as the sequence of a particular chromosome. In one example, chromosomal abundance is determined by aligning reads from a sequencer to multiple chromosomes, each having an associated Bloom filter or other set membership tester.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Method and/or apparatus for determining codons
InactiveUS8457903B1Efficiently determinedEfficient identificationBiostatisticsProteomicsData needsClient-side
Computer processing methods and / or systems for minimizing and / or optimizing data strings in accordance with rules and options. Minimized data strings can represent data sequences important in certain biologic analyses and / or syntheses. In specific embodiments, a request is generated by a user at a client system and received by a server system. The server system accesses initial data indicated or provided by the client system. The server system then performs an analysis to minimize the data needed for further reactions. In specific embodiments, a server can use proprietary methods or data at the server side while protecting those proprietary methods and data from access by the client system.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
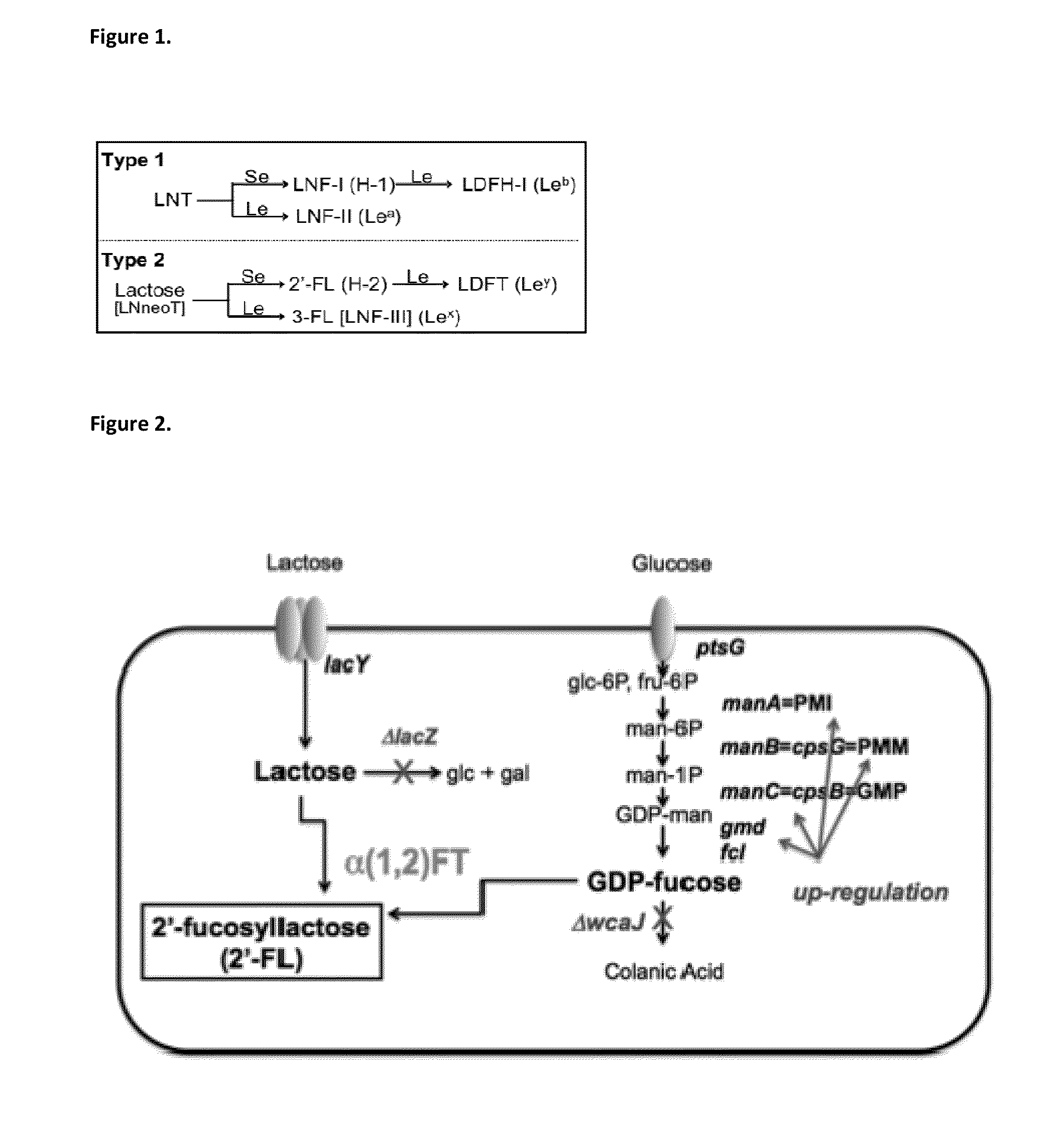
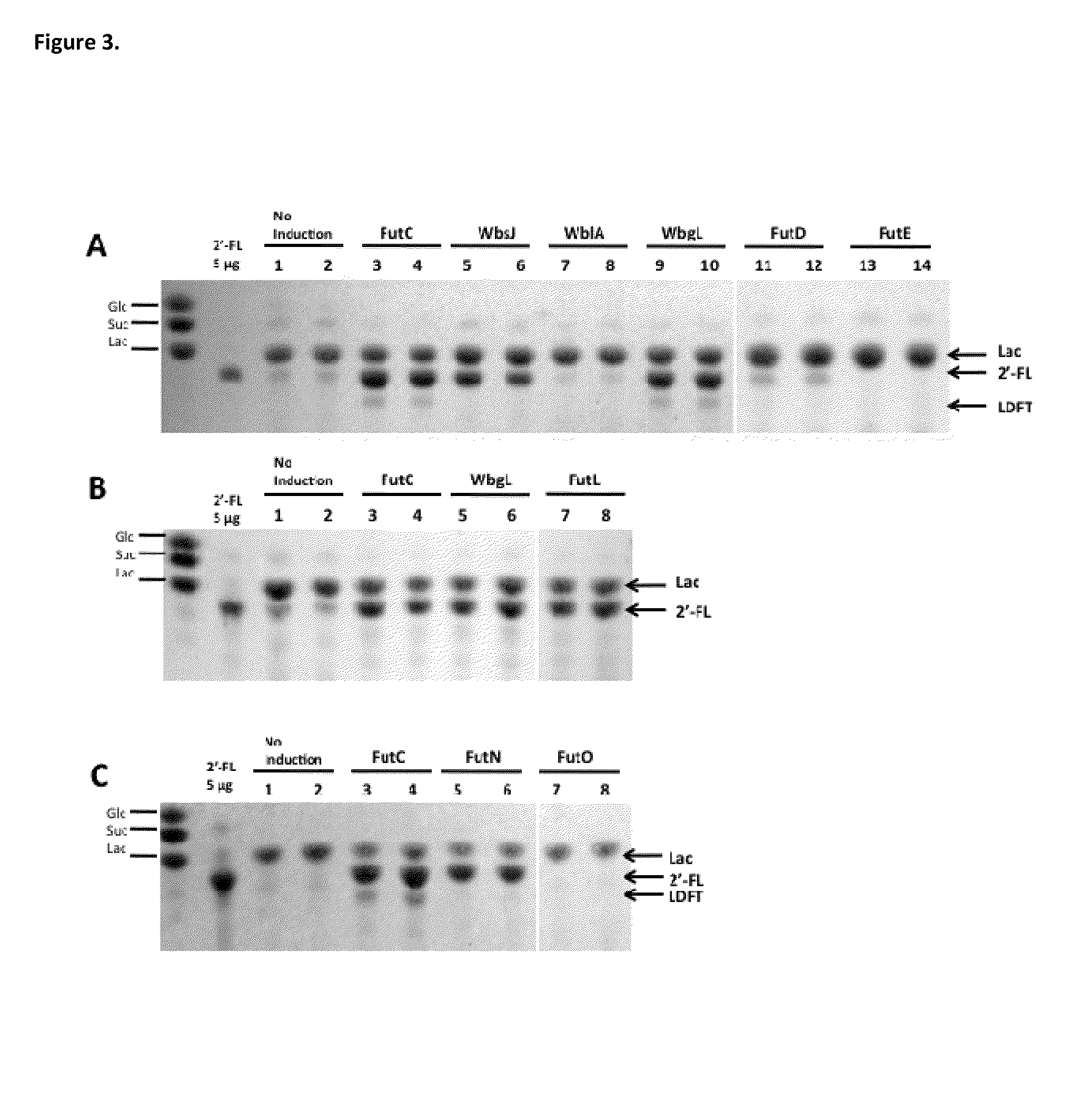
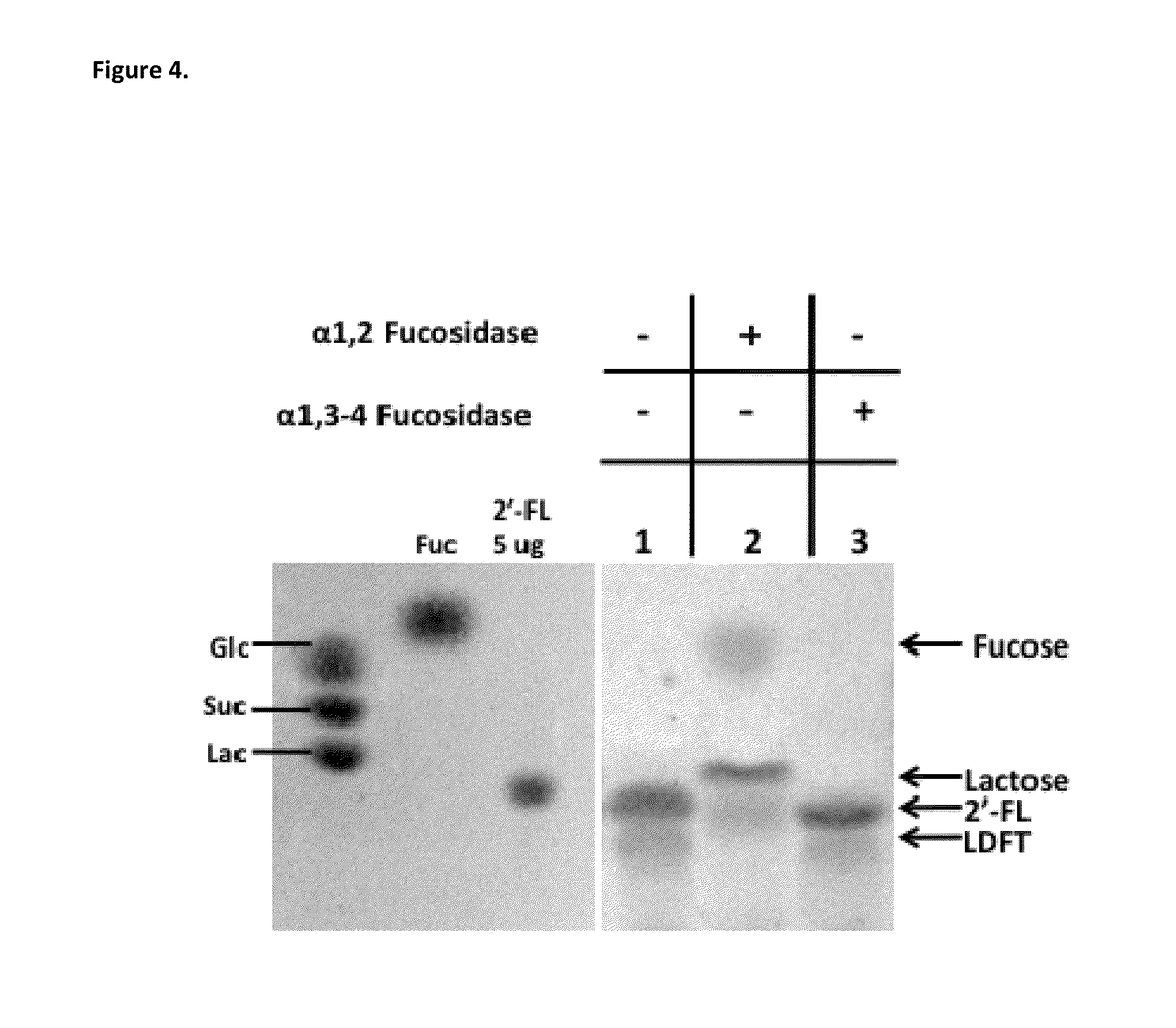
Alpha (1,2) Fucosyltransferases Suitable for Use in the Production of Fucosylated Oligosaccharides
ActiveUS20140031541A1Reduce severityReduce frequencyBacteriaLibrary screeningEscherichia coliFucosylation
The invention provides compositions and methods for engineering E. coli or other host production bacterial strains to produce fucosylated oligosaccharides, and the use thereof in the prevention or treatment of infection.
Owner:GLYCOSYN
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
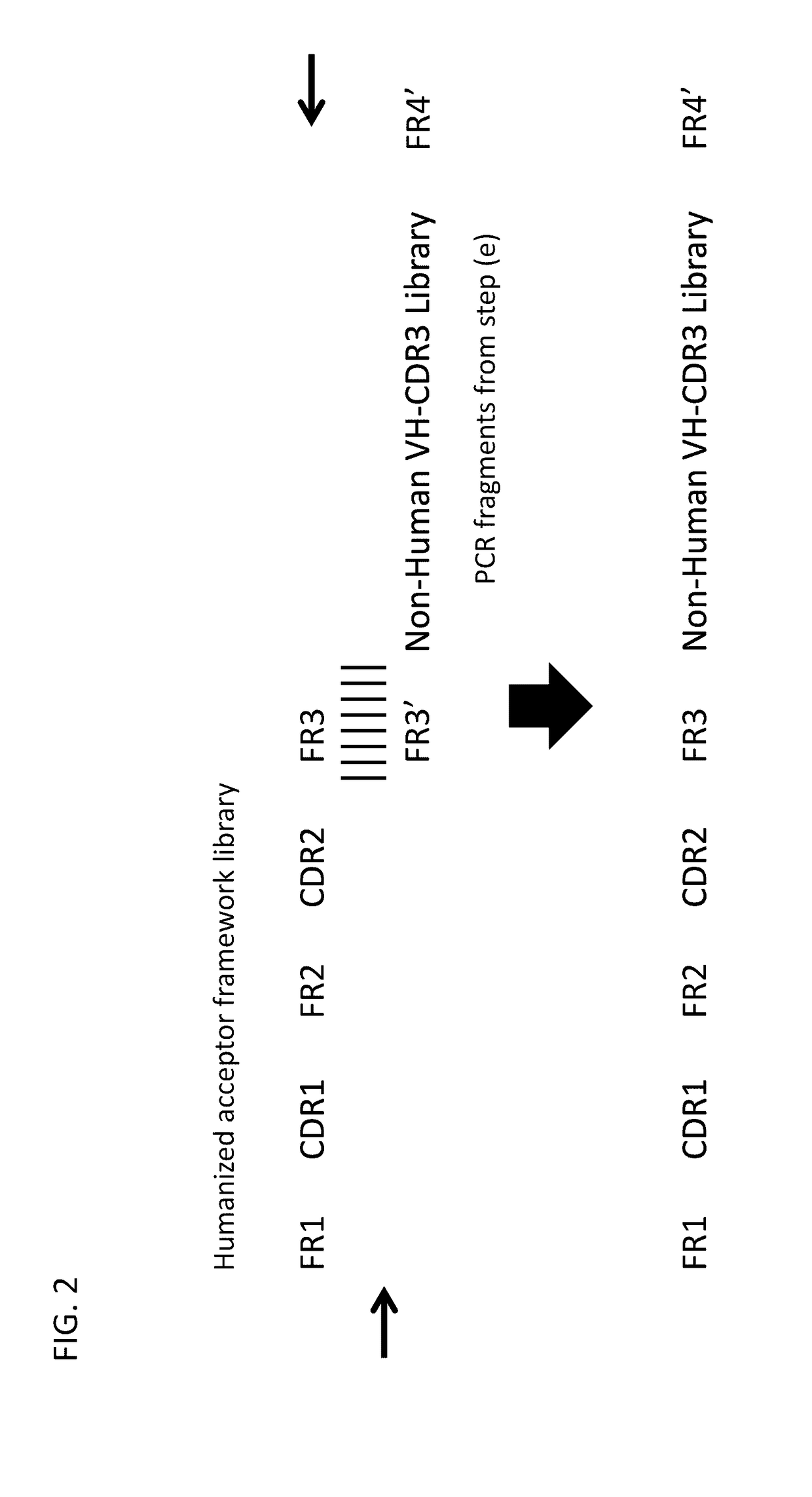
Method for mass humanization of non-human antibodies
The present invention relates to a method for producing a population of nucleic acids encoding at least one protein comprising at least one immunoglobulin variable domain having a non-human-derived CDR3 amino acid sequence embedded in essentially human framework sequences, as well as to a population of nucleic acids and a population of proteins relates thereto and uses thereof.
Owner:CHARLES RIVER LAB INC
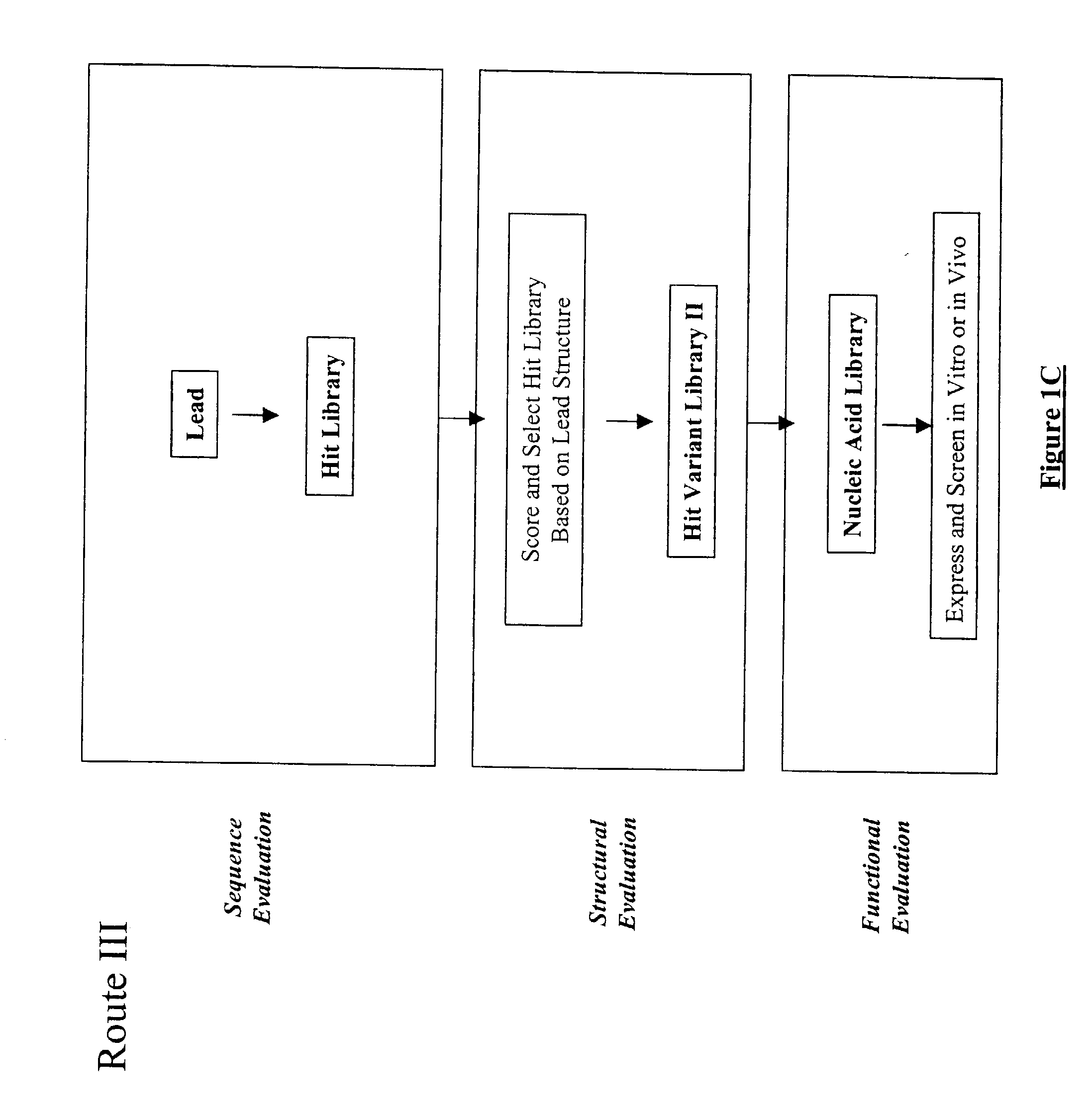
Generation and selection of protein library in silico
The present invention provides a methodology for efficiently generating and screening protein libraries for optimized proteins with desirable biological functions, such as improved binding affinity towards biologically and / or therapeutically important target molecules. The process is carried out computationally in a high throughput manner by mining the ever-expanding databases of protein sequences of all organisms, especially human. In one embodiment, a method for constructing a library of designed proteins, comprising the steps of: providing an amino acid sequence derived from a lead protein, the amino acid sequence being designated as a lead sequence; comparing the lead sequence with a plurality of tester protein sequences; and selecting from the plurality of tester protein sequences at least two peptide segments that have at least 15% sequence identity with the lead sequence, the selected peptide segments forming a hit library; and forming a library of designed proteins by substituting the lead sequence with the hit library. The library of designed proteins can be expressed in vitro or in vivo to produce a library of recombinant proteins that can be screened for novel or improved function(s) over the lead protein, such as an antibody against therapeutically important target.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Programmable iterated elongation: a method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries
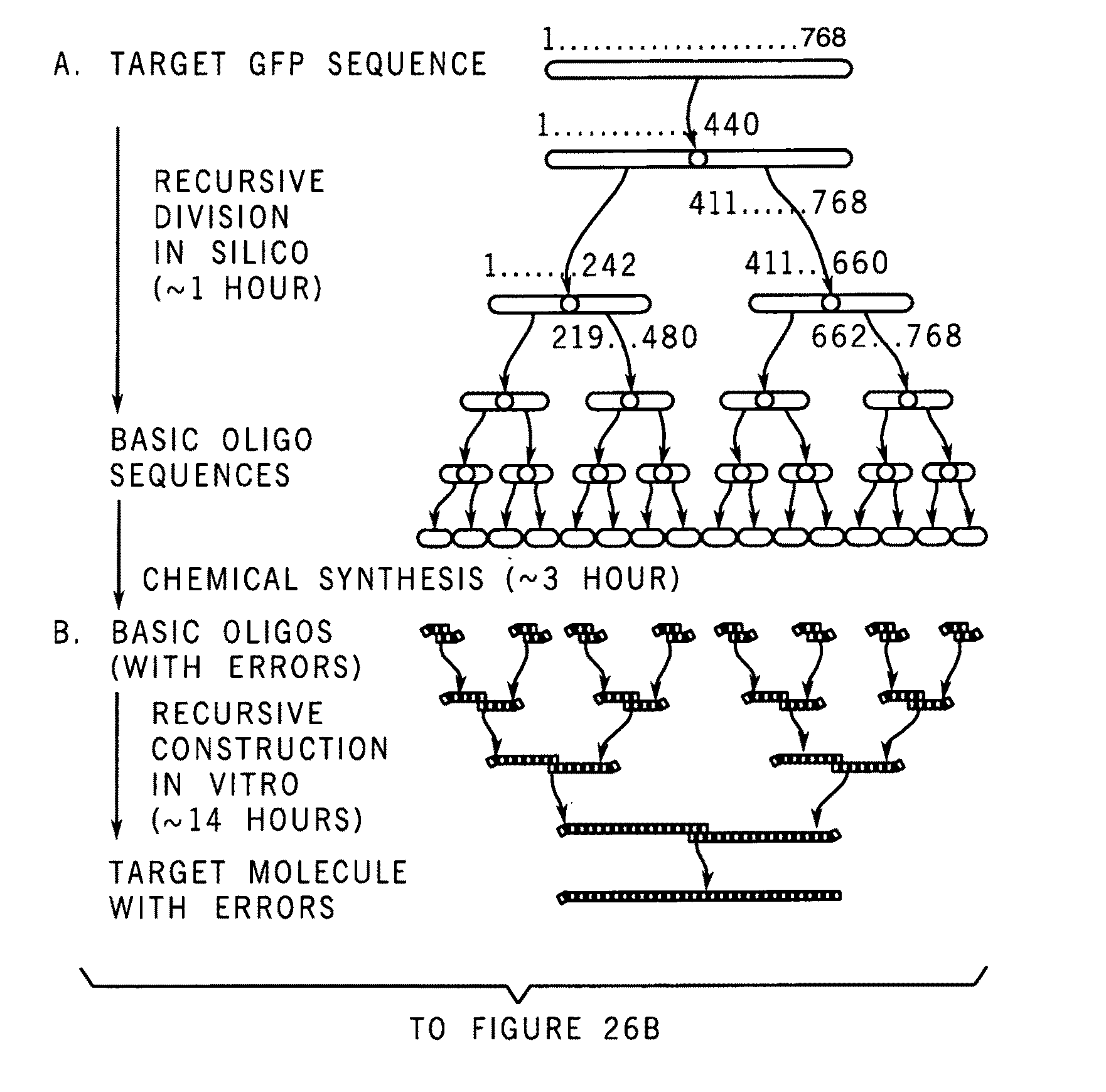
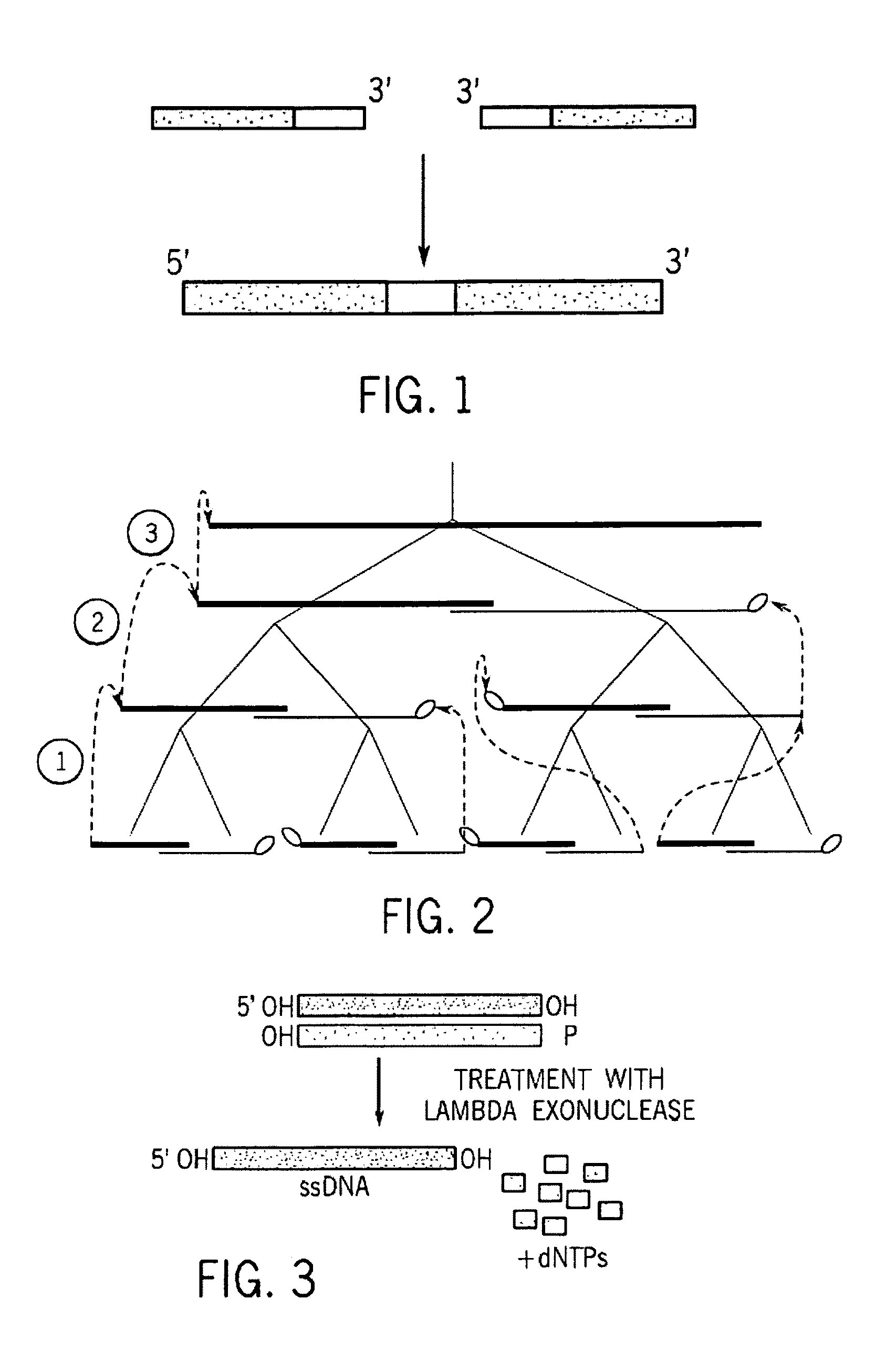
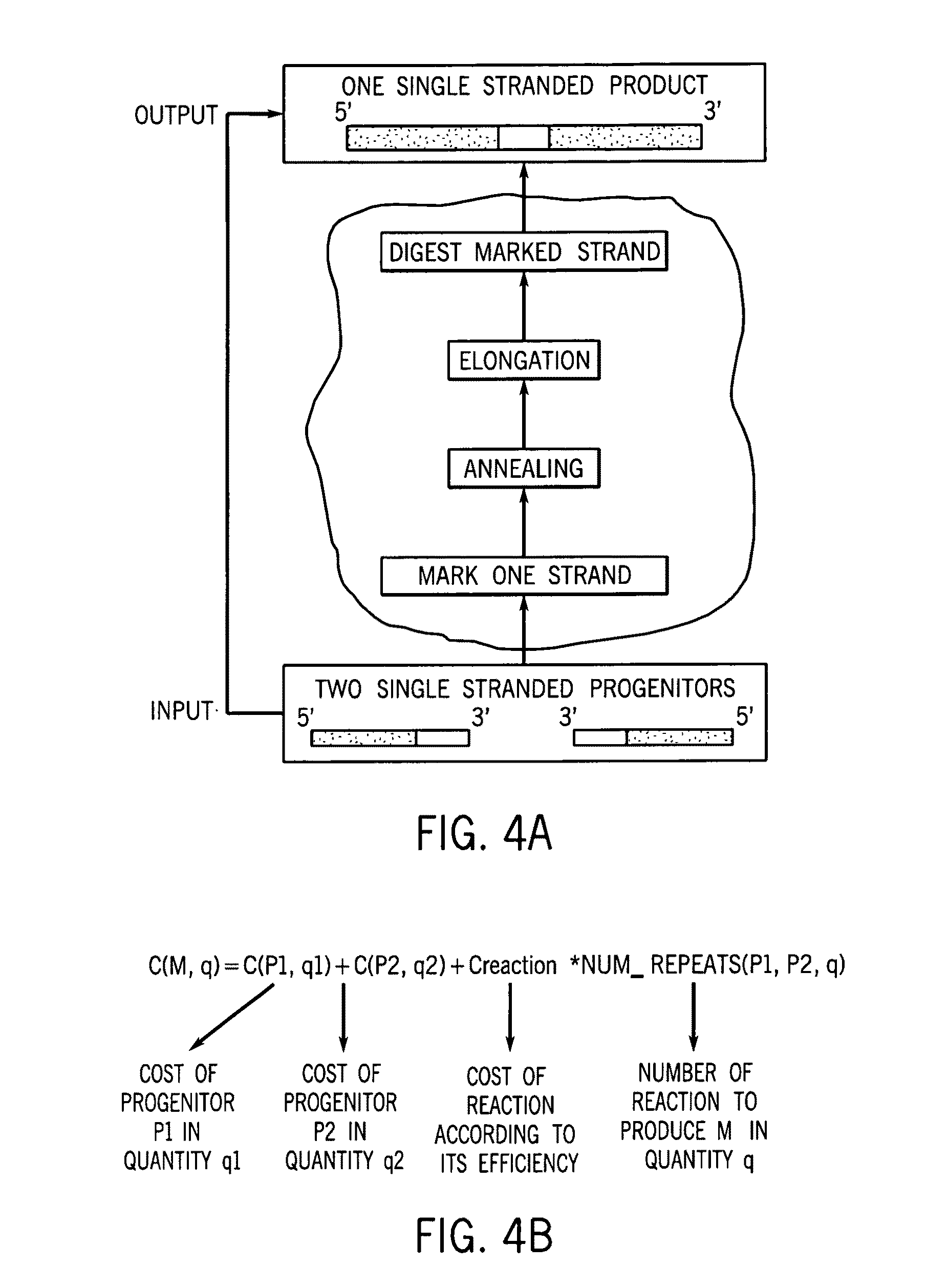
A method for manufacturing synthetic genes and combinatorial DNA and protein libraries, termed here Divide and Conquer-DNA synthesis (D&C-DNA synthesis) method. The method can be used in a systematic and automated way to synthesize any long DNA molecule and, more generally, any combinatorial molecular library having the mathematical property of being a regular set of strings. The D&C-DNA synthesis method is an algorithm design paradigm that works by recursively breaking down a problem into two or more sub-problems of the same type. The division of long DNA sequences is done in silico. The assembly of the sequence is done in vitro. The D&C-DNA synthesis method protocol consists of a tree, in which each node represents an intermediate sequence. The internal nodes are created in elongation reactions from their daughter nodes, and the leaves are synthesized directly. After each elongation only one DNA strand passes to the next level in the tree until receiving the final product. Optionally and preferably, error correction is performed to correct any errors which may have occurred during the synthetic process.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Drug discovery methods
ActiveUS20070178473A1Raise priorityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningDrug responseDisease cause
Owner:INGENUITY SYST INC
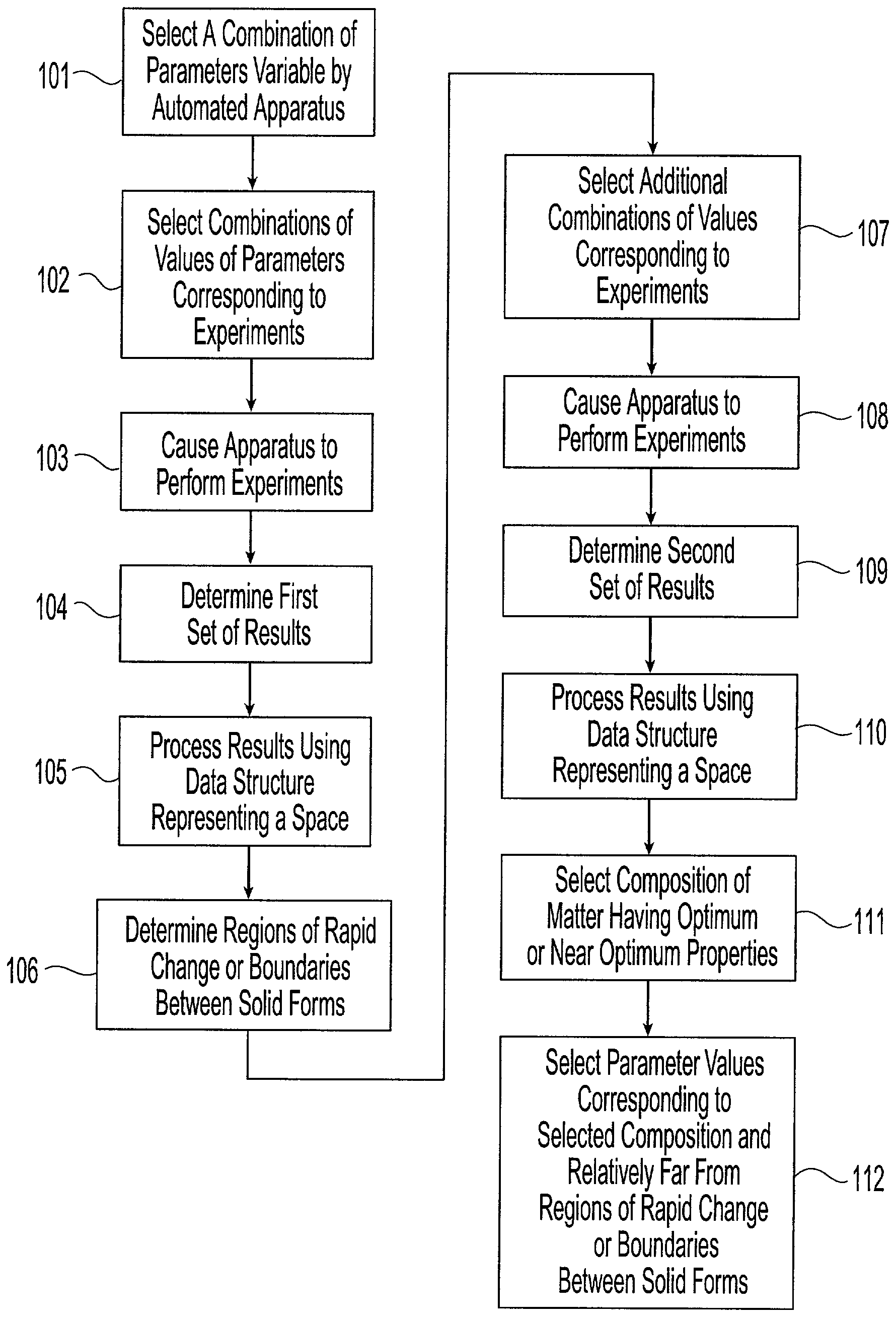
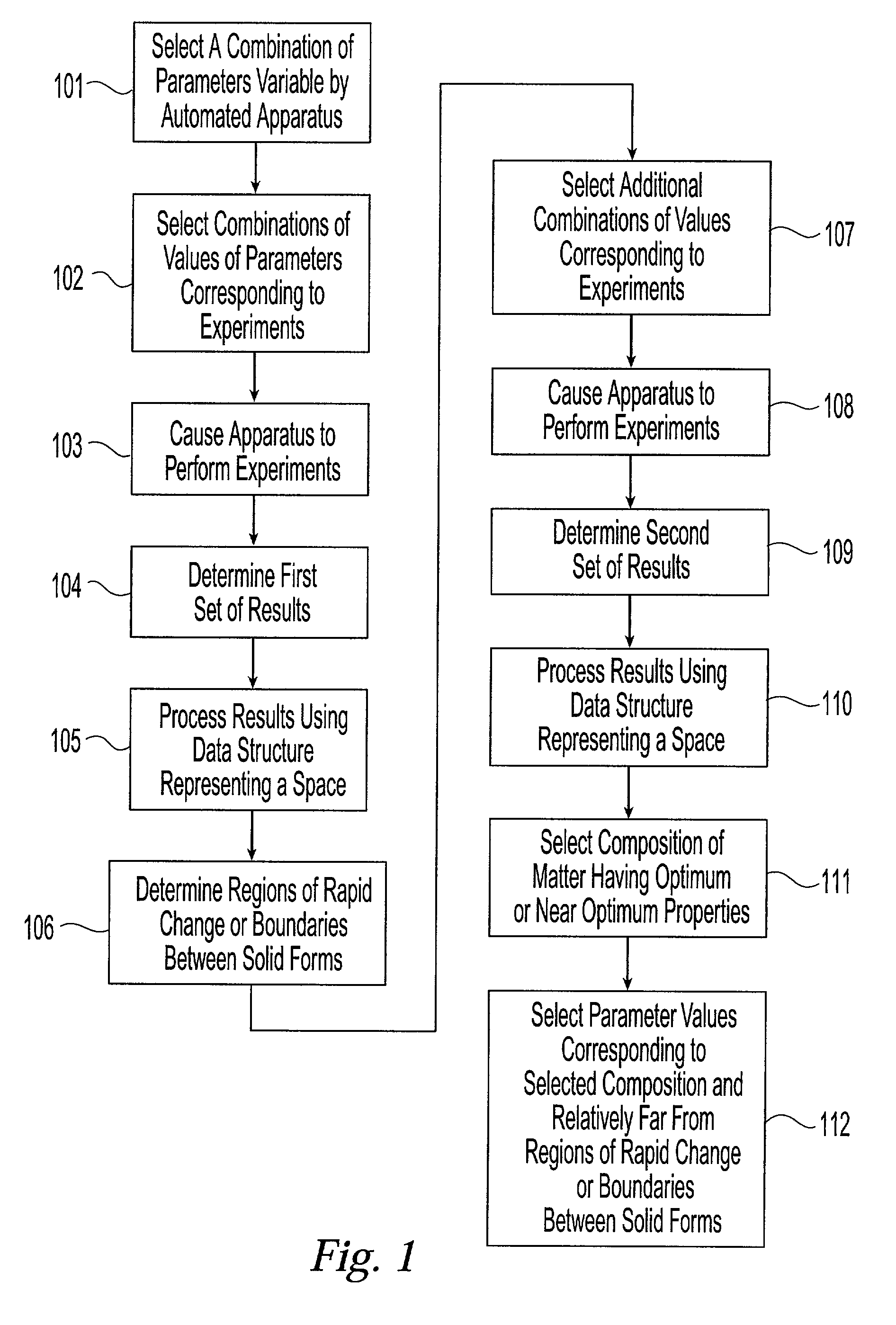
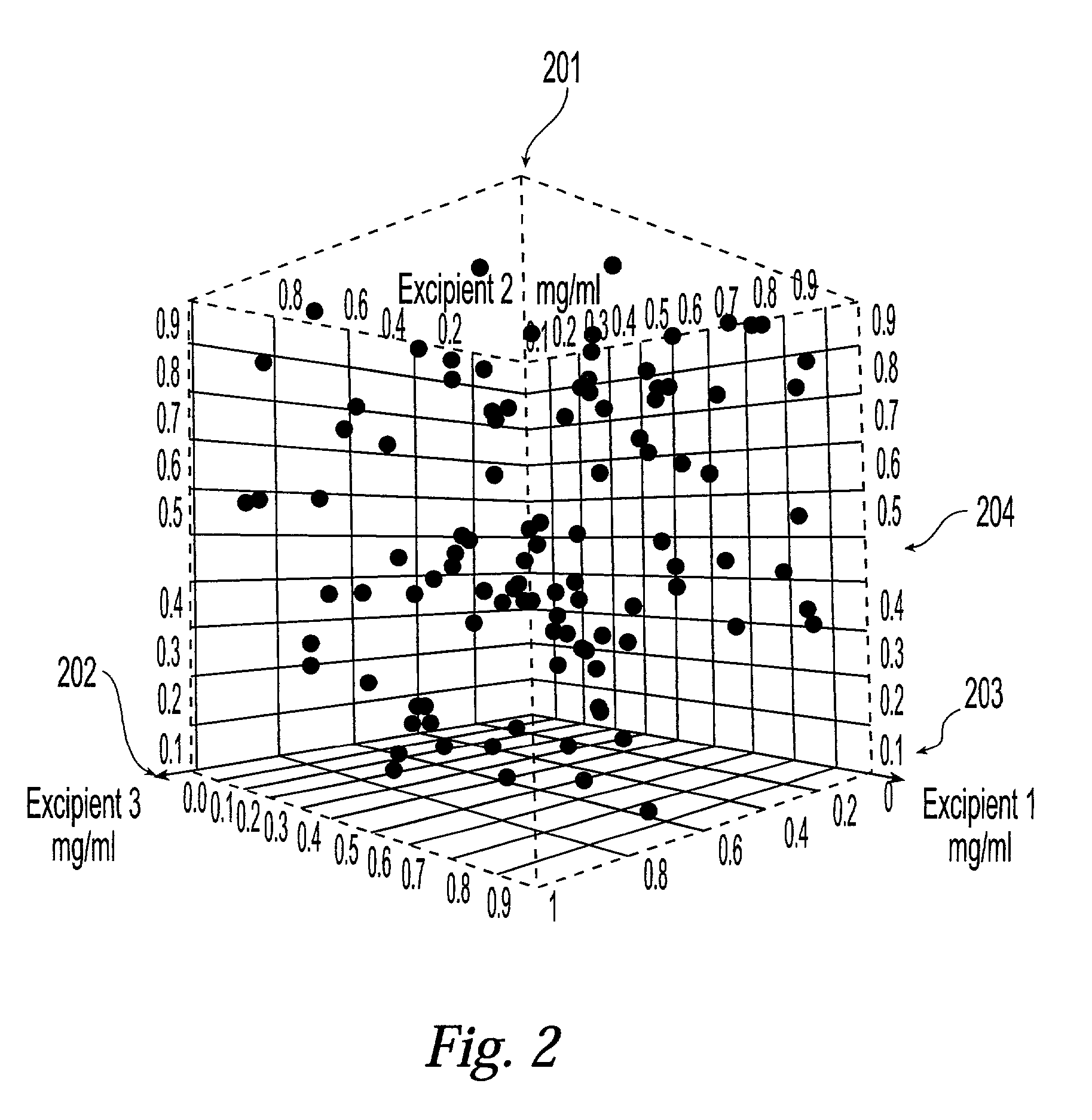
Method and system for planning, performing, and assessing high-throughput screening of multicomponent chemical compositions and solid forms of compounds
InactiveUS20050089923A9Chemical property predictionComponent separationCompound aChemical composition
A method and system for planning and assessing the results of high-throughput solid form screening and high-throughput formulation screening are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods and systems for using high-throughput solid form screening and high-throughput formulation screening to select compounds and formulations for further testing, or to prioritize testing.
Owner:TRANSFORM PHARMACEUTICALS INC
System and method for identifying complex patterns of amino acids
InactiveUS7774144B2SsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsProtein DatabasesHistidine residue
A method and system are disclosed for identifying and / or locating complex patterns in an amino acid sequence stored in a computer file or database. According to an aspect of the present invention, techniques are provided to facilitate queries of protein databases. For protein descriptions received in response to the queries, embodiments of the present invention may scan the received protein descriptions to identify and locate Replikin patterns. A Replikin pattern is defined to be a sequence of 7 to about 50 amino acids that include the following three (3) characteristics, each of which may be recognized by an embodiment of the present invention: (1) the sequence has at least one lysine residue located six to ten amino acid residues from a second lysine residue; (2) the sequence has at least one histidine residue; and (3) at least 6% of the amino acids in the sequence are lysine residues.
Owner:BOGOCH SAMUEL +3
Method and device for partitioning a molecule
ActiveUS20050228592A1Efficient and fast transmissionWide range of usesMolecular designDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceDrug discovery
A method for partitioning a molecular subset is described. The partitioning method takes into account molecular structure and its manner of storage and transmission, transformations to be applied to the molecular subset and their implementation, and constraints imposed by the implementation of the partitioning method. Using this method, a molecular subset can be stored, transmitted, and processed more efficiently. The resulting efficiency makes it possible to design and run applications which require complex molecular processing, such as rational drug discovery, virtual library design, etc.
Owner:VERSEON INT CORP
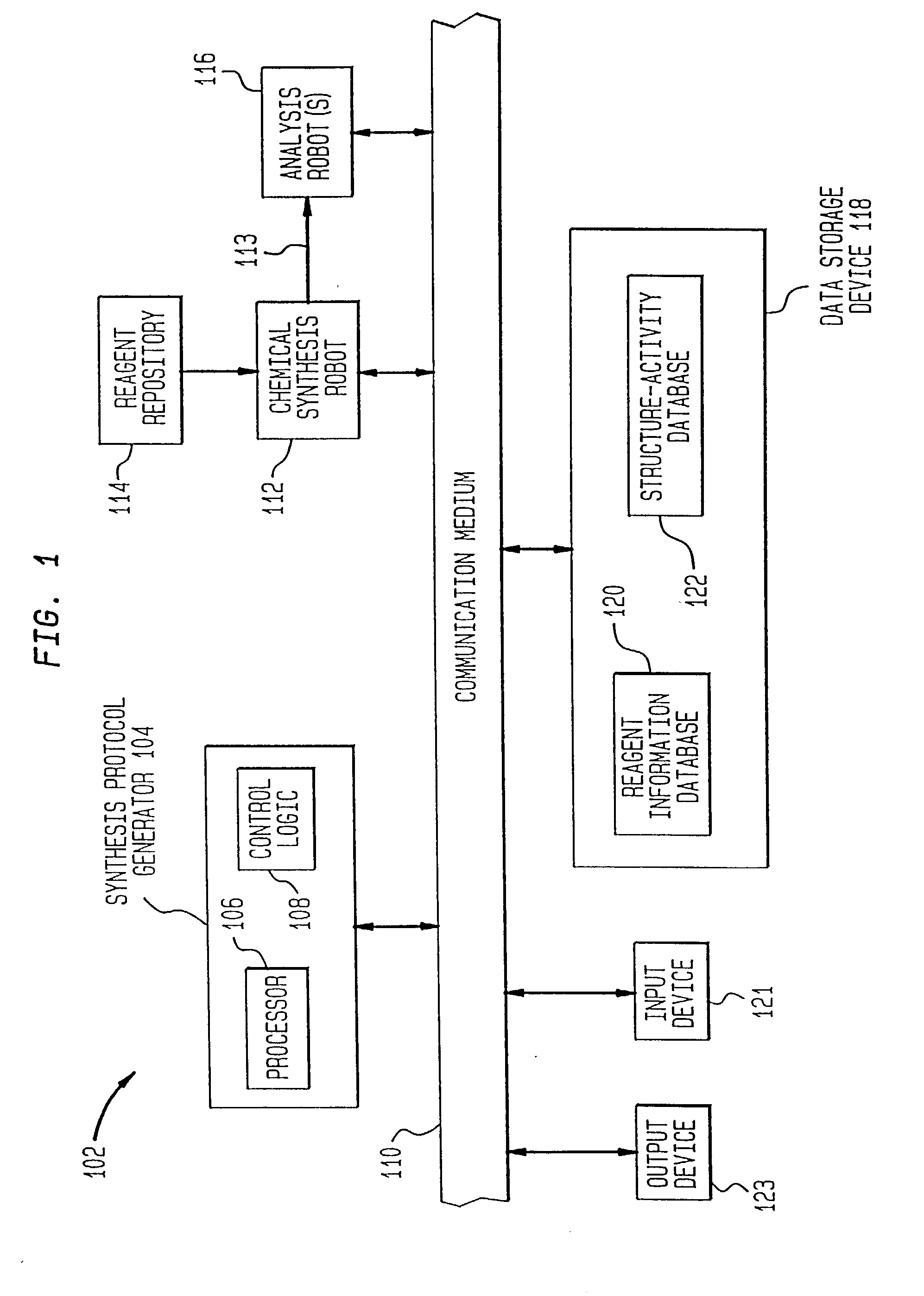
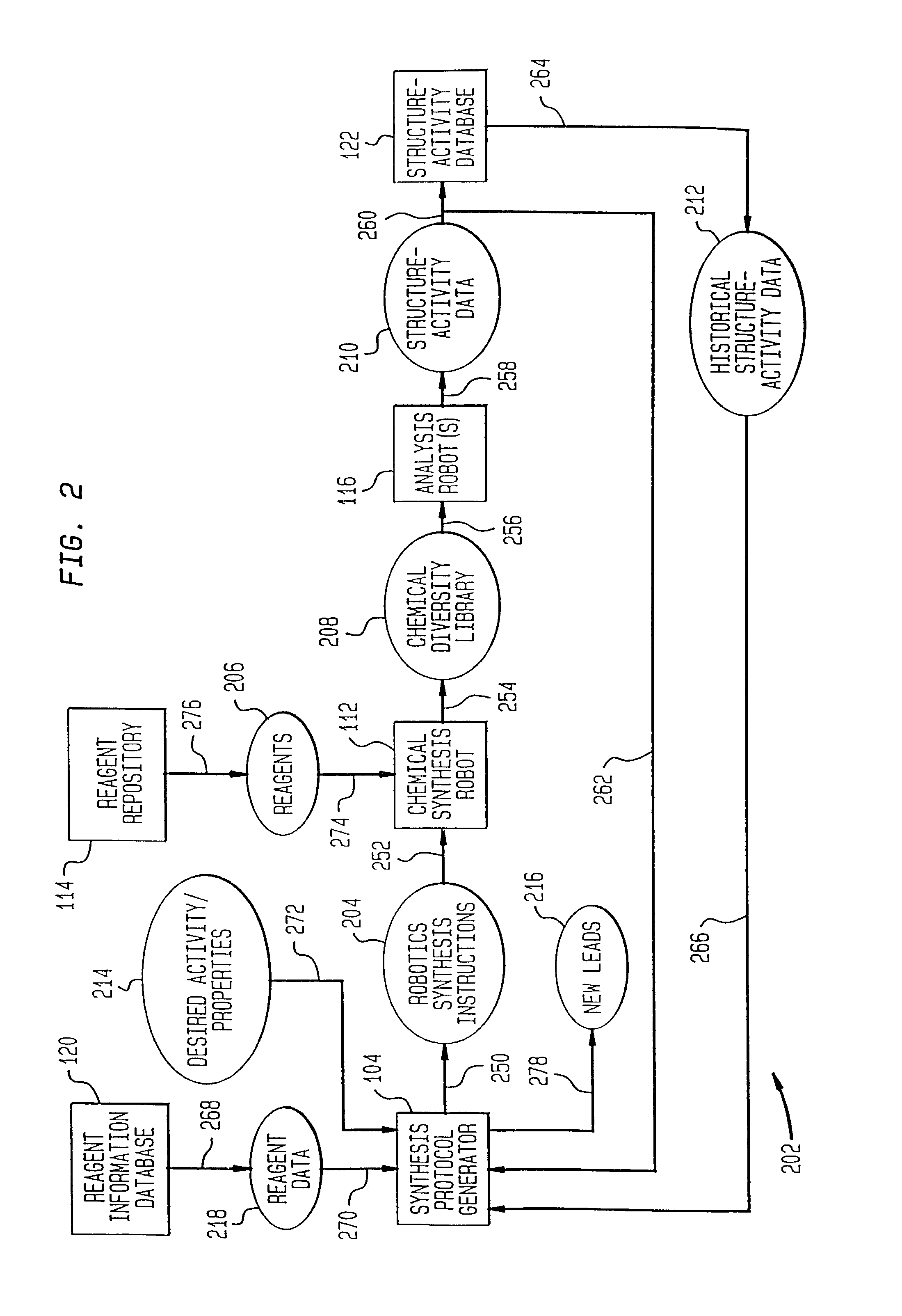
Method of generating chemical compounds having desired properties
InactiveUS20030033088A1Chemical property predictionSequential/parallel process reactionsStructure propertyChemical compound
A computer based, iterative process for generating chemical entities with defined physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties. During each iteration of the process, (1) a directed diversity chemical library is robotically generated in accordance with robotic synthesis instructions; (2) the compounds in the directed diversity chemical library are analyzed to identify compounds with the desired properties; (3) structure-property data are used to select compounds to be synthesized in the next iteration; and (4) new robotic synthesis instructions are automatically generated to control the synthesis of the directed diversity chemical library for the next iteration.
Owner:AGRAFIOTIS DIMITRIS K +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com