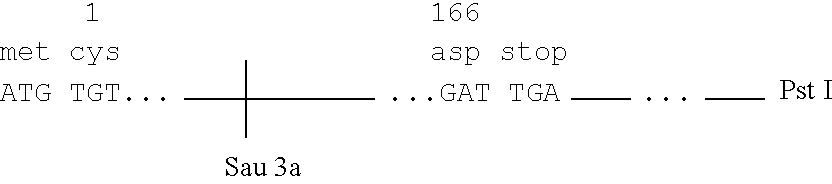Patents
Literature
1182results about "Interferons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
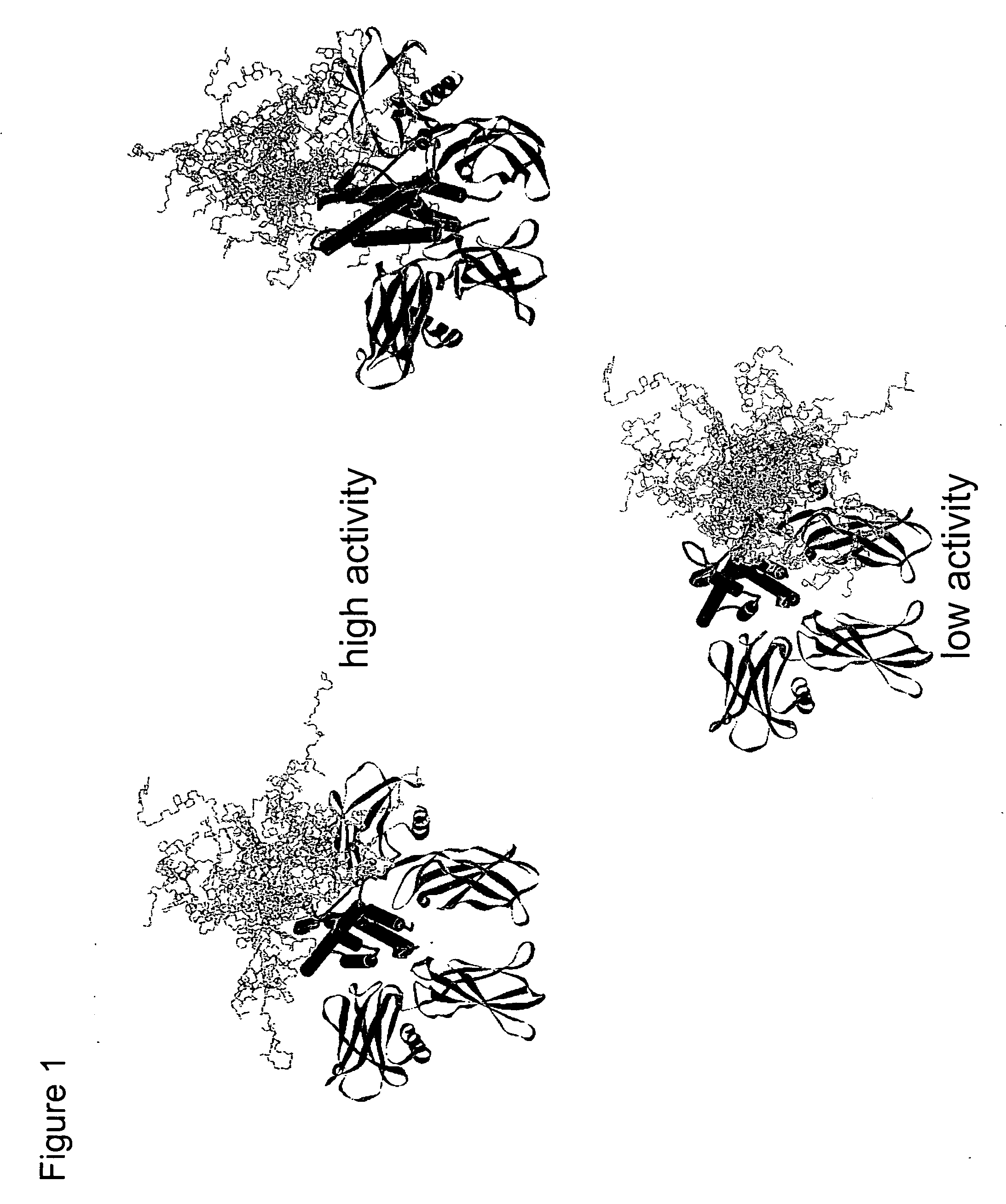
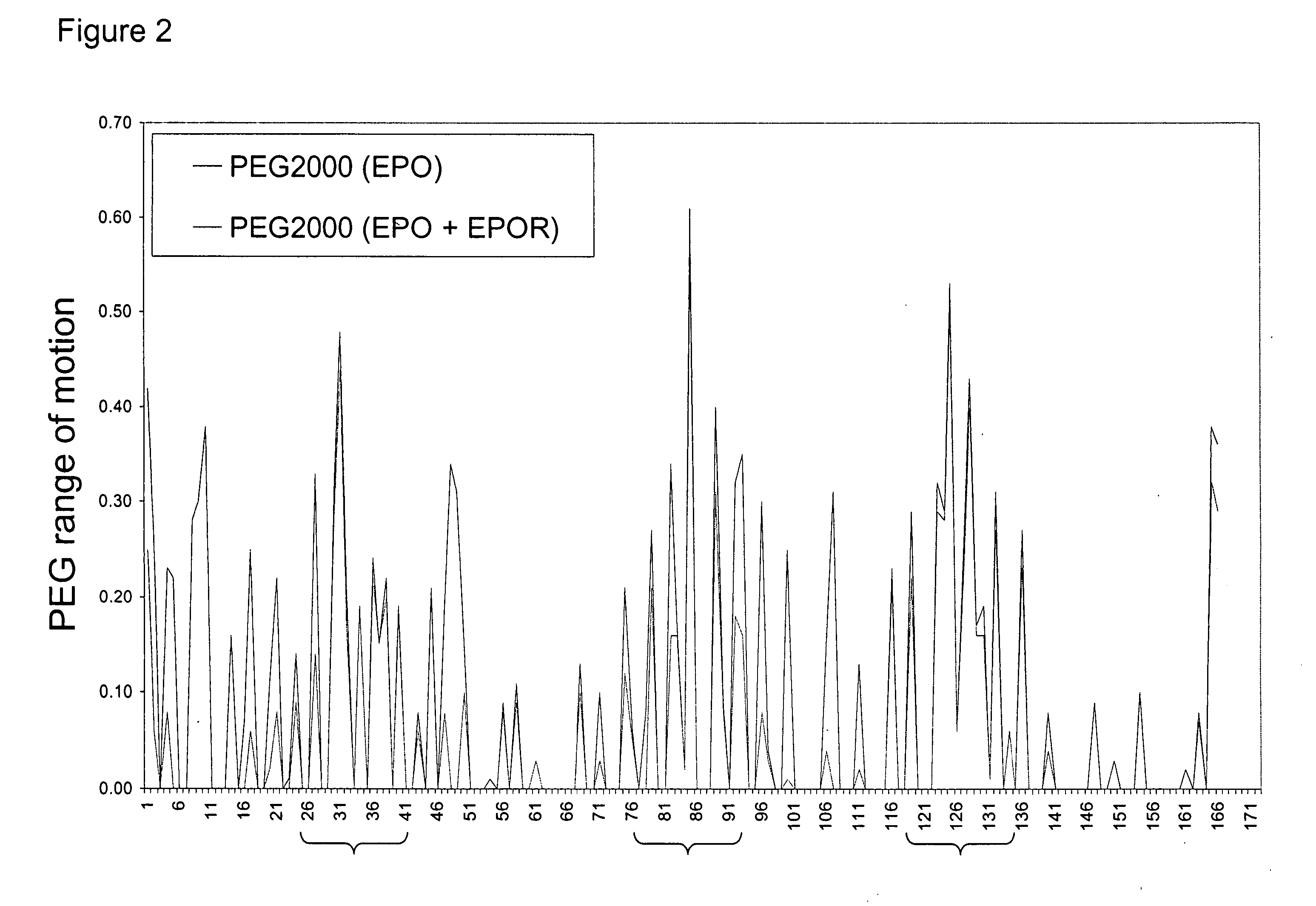
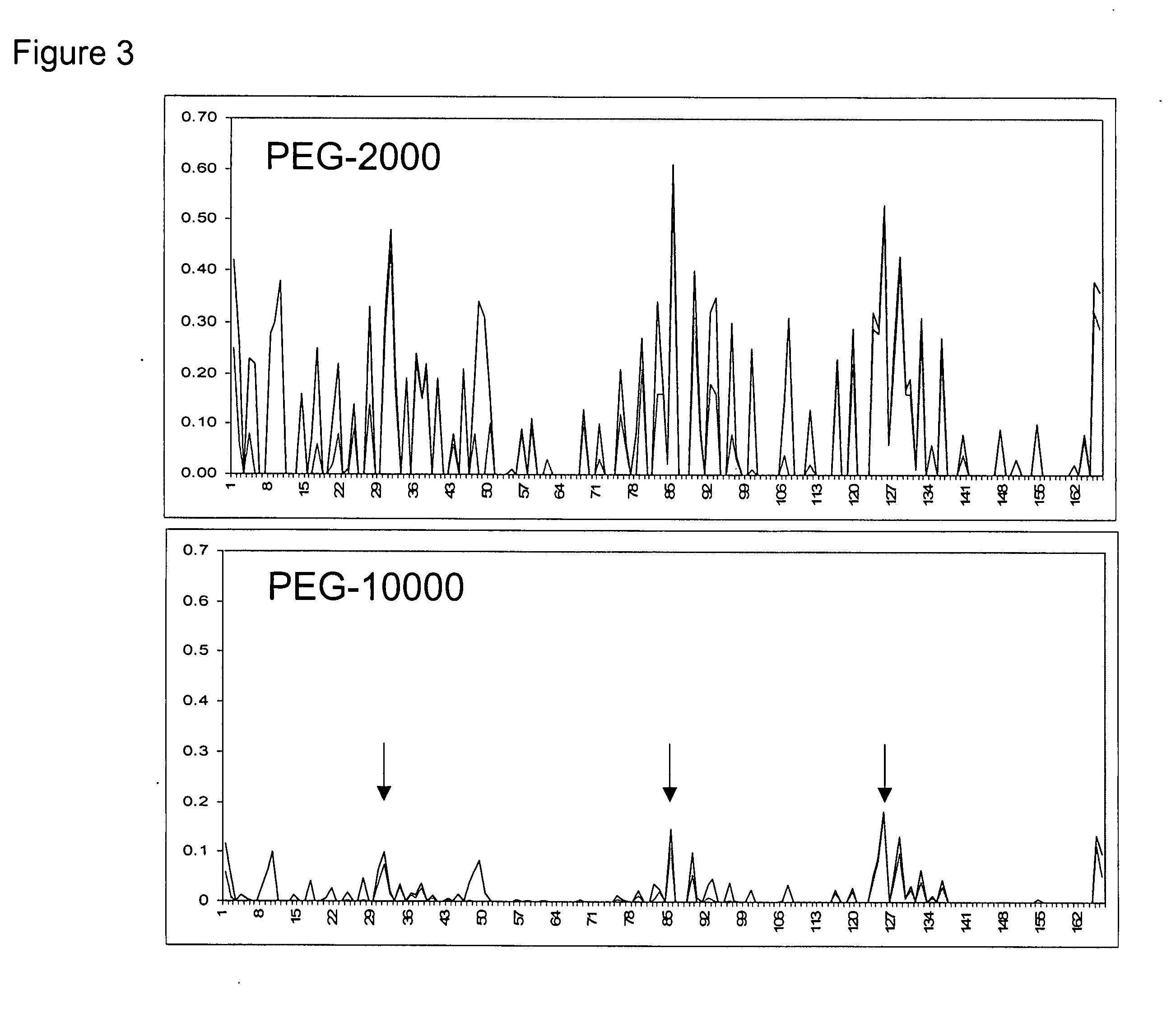
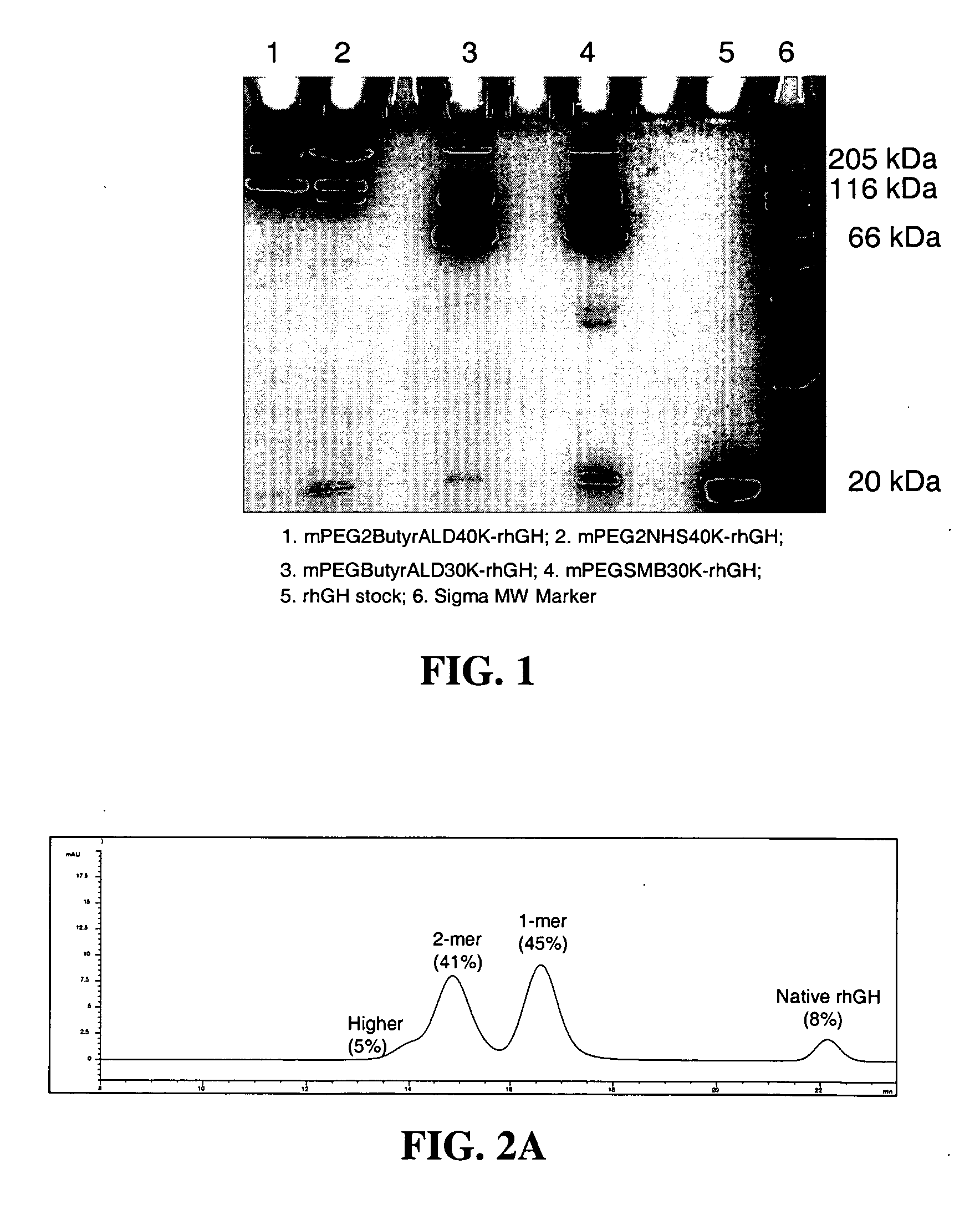
Methods for rational pegylation of proteins
The present invention relates to the use of simulation technology to rationally optimize the locations and sizes of attached polymeric moieties for modification of therapeutic proteins and the proteins generated from this method.
Owner:XENCOR
Methods for making proteins containing free cysteine residues
The present invention relates to novel methods of making soluble proteins having free cysteines in which a host cell is exposed to a cysteine blocking agent. The soluble proteins produced by the methods can then be modified to increase their effectiveness. Such modifications include attaching a PEG moiety to form pegylated proteins.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
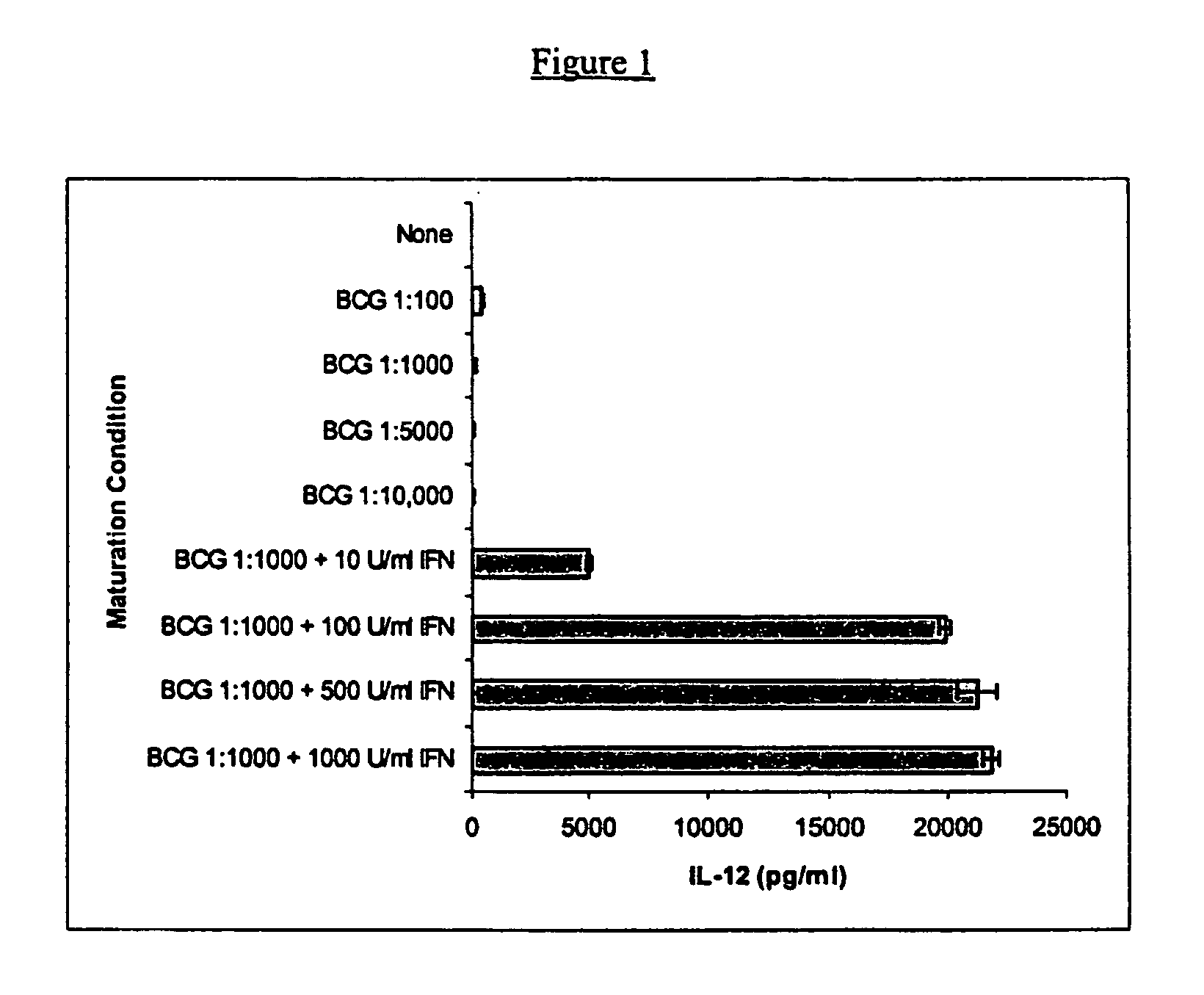
Compositions and methods for priming monocytic dendritic cells and t cells for th-1response
InactiveUS20050059151A1Mammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsDendritic cellMonocyte
The present invention provides compositions and methods for inducing maturation of immature dendritic cells (DC) and for priming those cells for inducing a type 1 immune response. The present invention also provides dendritic cell populations useful for activating and for preparing T cells polarized towards production of type 1 cytokines and / or a type 1 response. Similarly, activated, polarized T cell populations, and methods of making the same are provided.
Owner:NORTHWEST BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7157559B2Improve expression levelIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity. One type of biological activity that is shown is an antiviral activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Microbial production of mature human leukocyte interferons
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Methods for treating cancer using cytokine-expressing polynucleotides
InactiveUS7268120B1Improved in vivo polypeptide expressionMinimizing adverse side effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMammalSodium phosphates
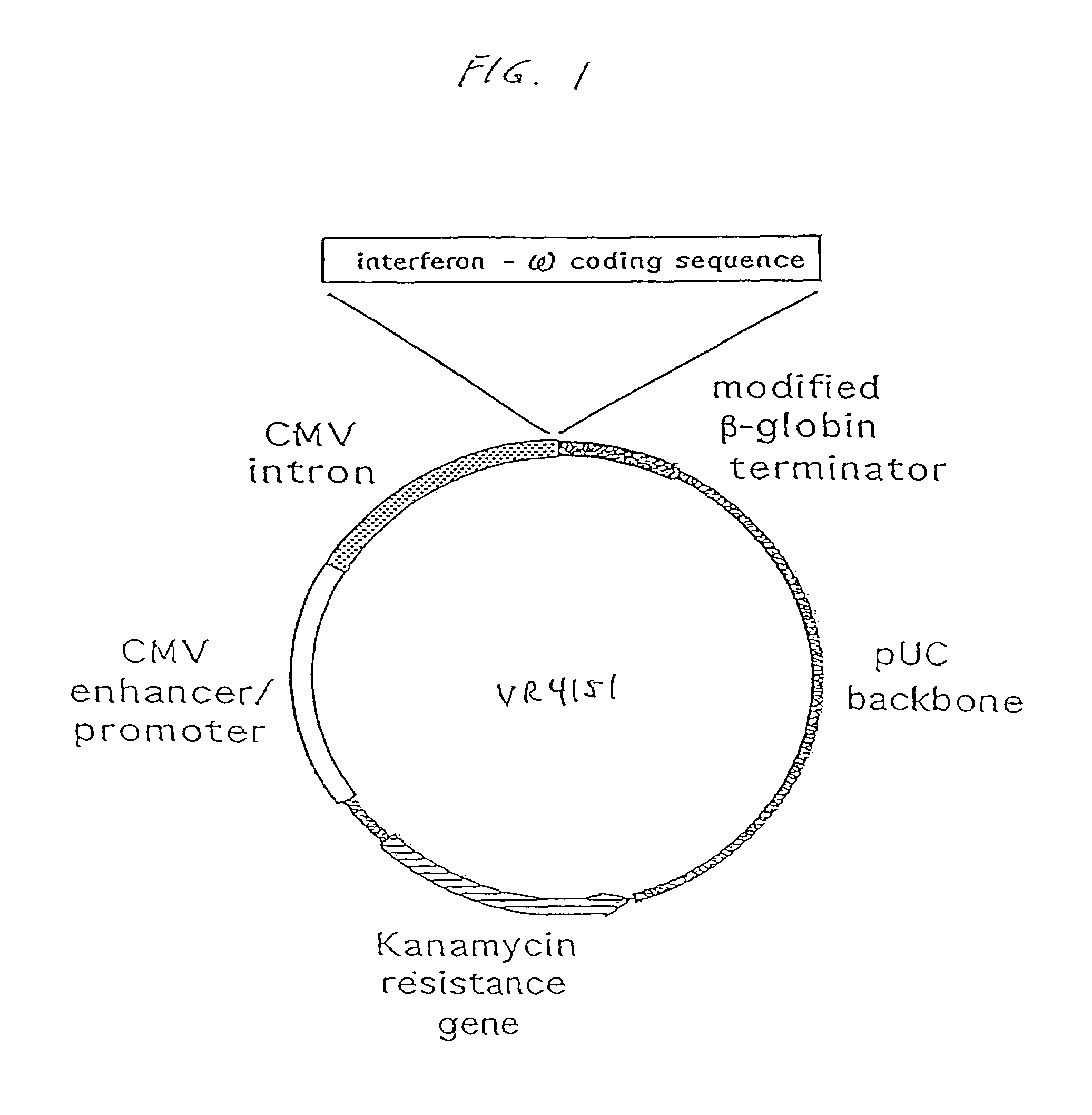
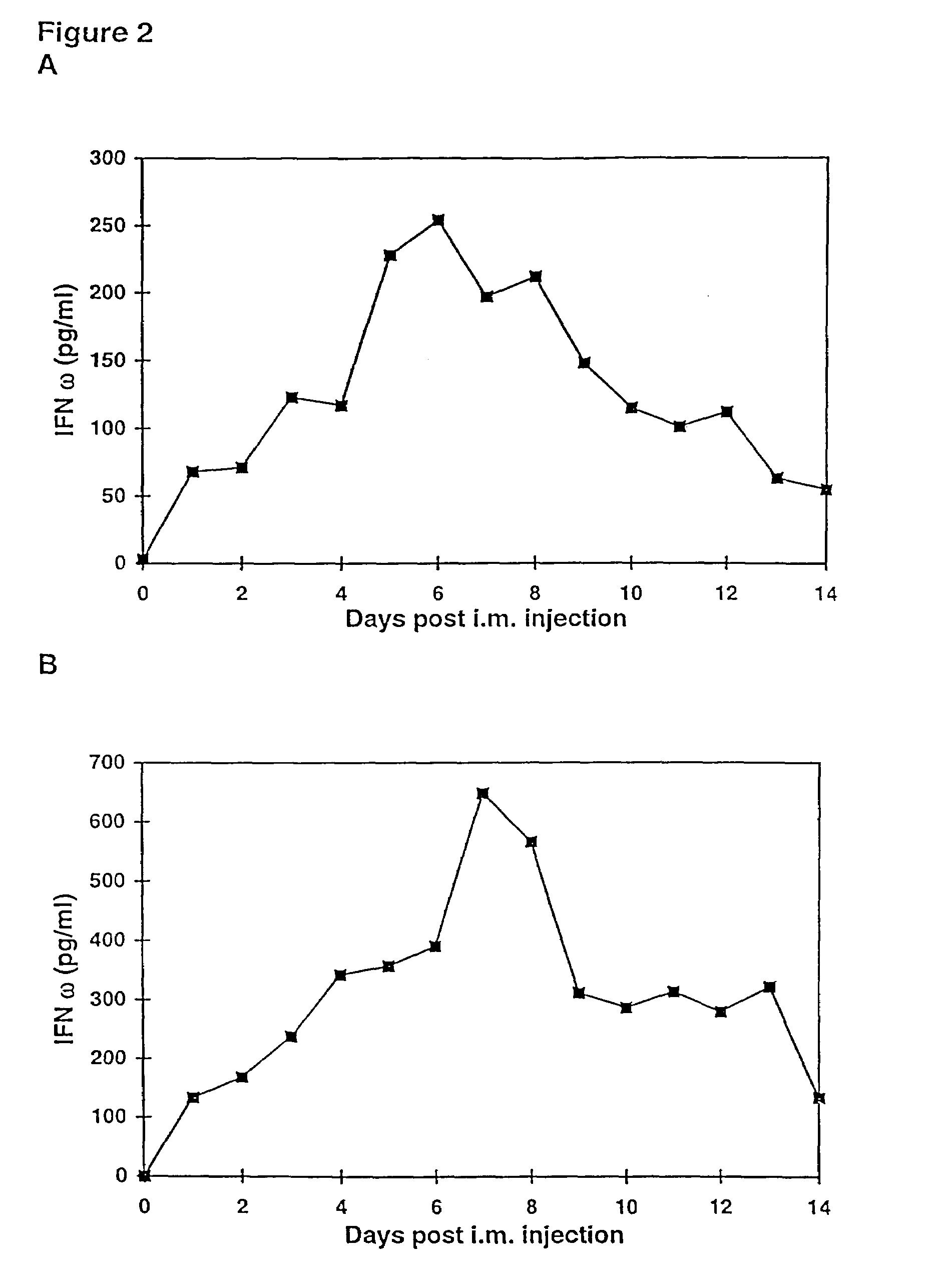
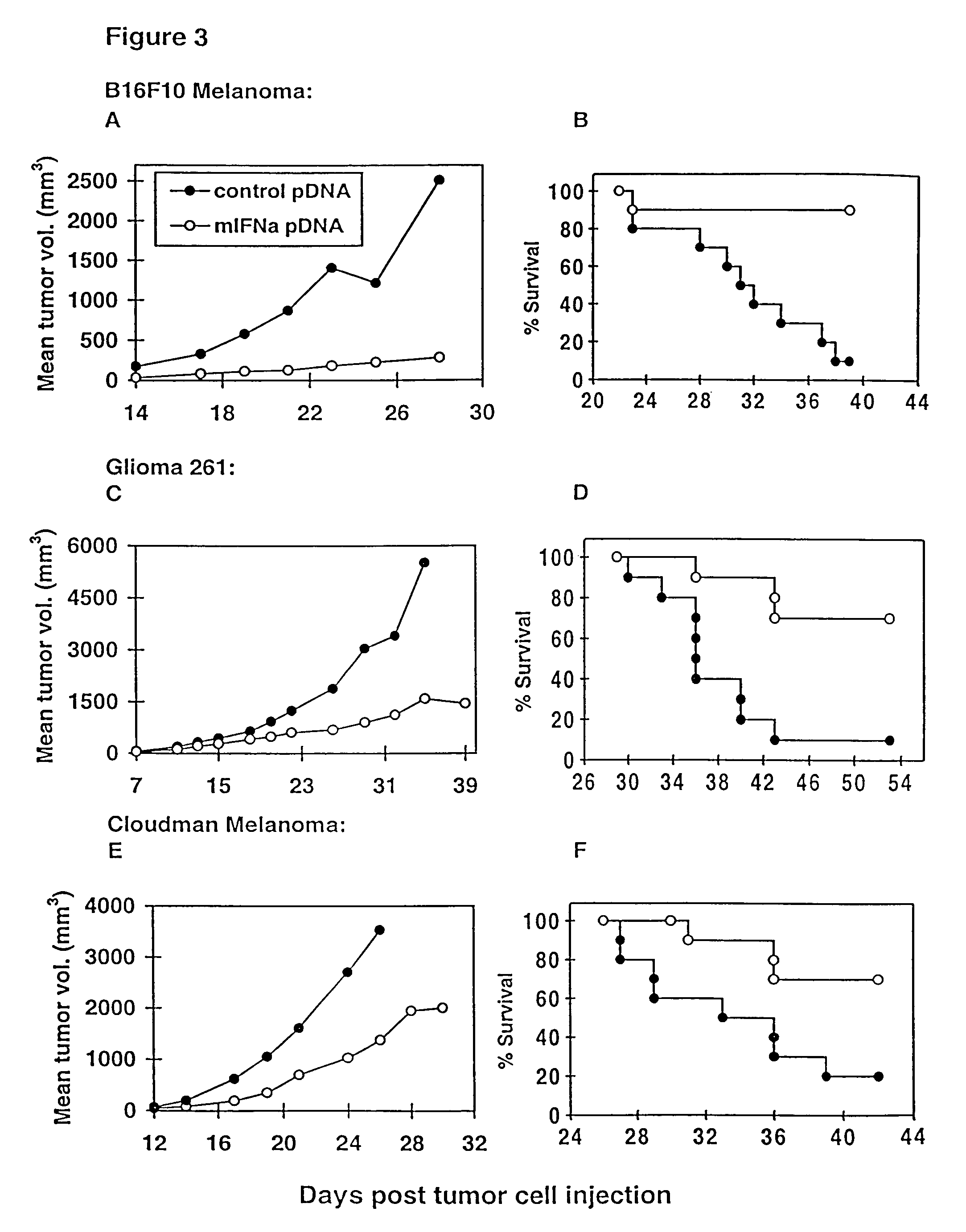
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, comprising a non-infectious, non-integrating polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding an interferon ω and one or more cationic compounds. The present invention also provides methods of treating cancer in a mammal, comprising administering into a muscle of the mammal a non-infectious, non-integrating DNA polynucleotide construct comprising a polynucleotide encoding a cytokine. In addition, the present invention also relates to the methodology for selective transfection of malignant cells with polynucleotides expressing therapeutic or prophylactic molecules in intra-cavity tumor bearing mammals. More specifically, the present invention provides a methodology for the suppression of an intra-cavity dissemination of malignant cells, such as intraperitoneal dissemination. Furthermore, the invention relates to compositions and methods to deliver polynucleotides encoding polypeptides to vertebrate cells in vivo, where the composition comprises an aqueous solution of sodium phosphate.
Owner:VICAL INC
Glycopegylated Interferon Alpha
InactiveUS20090028822A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesInterferon alphaSugar
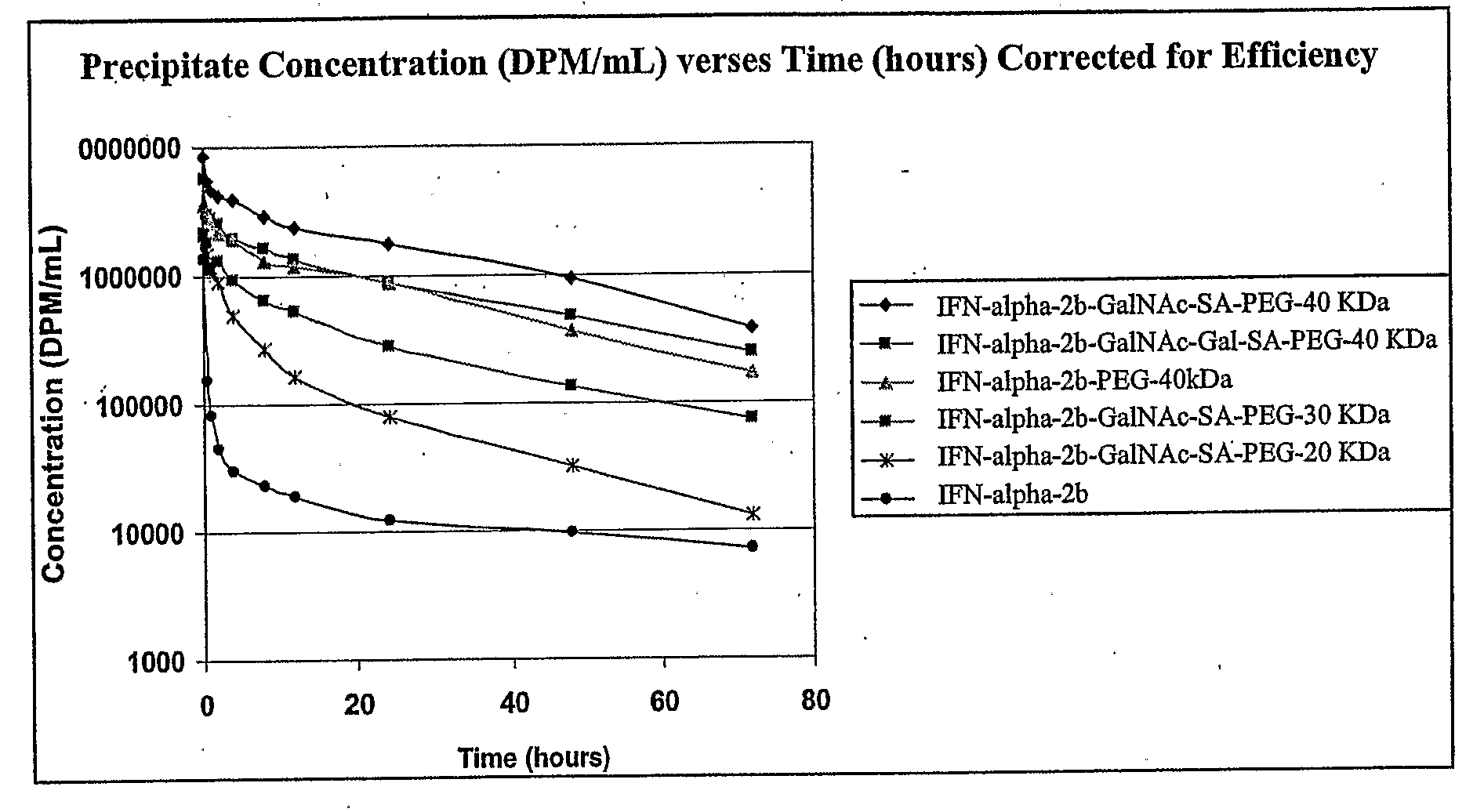
The present invention provides IFN-α conjugates including IFN-α peptides and modifying groups such as PEG moieties. The IFN-α peptide and modifying group are linked via an intact glycosyl linking group interposed between and covalently attached to the IFN-α peptide and the modifying group. The IFN-α conjugates are formed from glycosylated peptides by the action of a glycosyltransferase. The glycosyltransferase ligates a modified sugar onto an amino acid or a glycosyl residue on the IFN-α peptide. Also provided are methods for preparing the IFN-α conjugates, methods for treating various disease conditions with the IFN-α conjugates, and pharmaceutical formulations including the IFN-α conjugates.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin fc region as a carrier
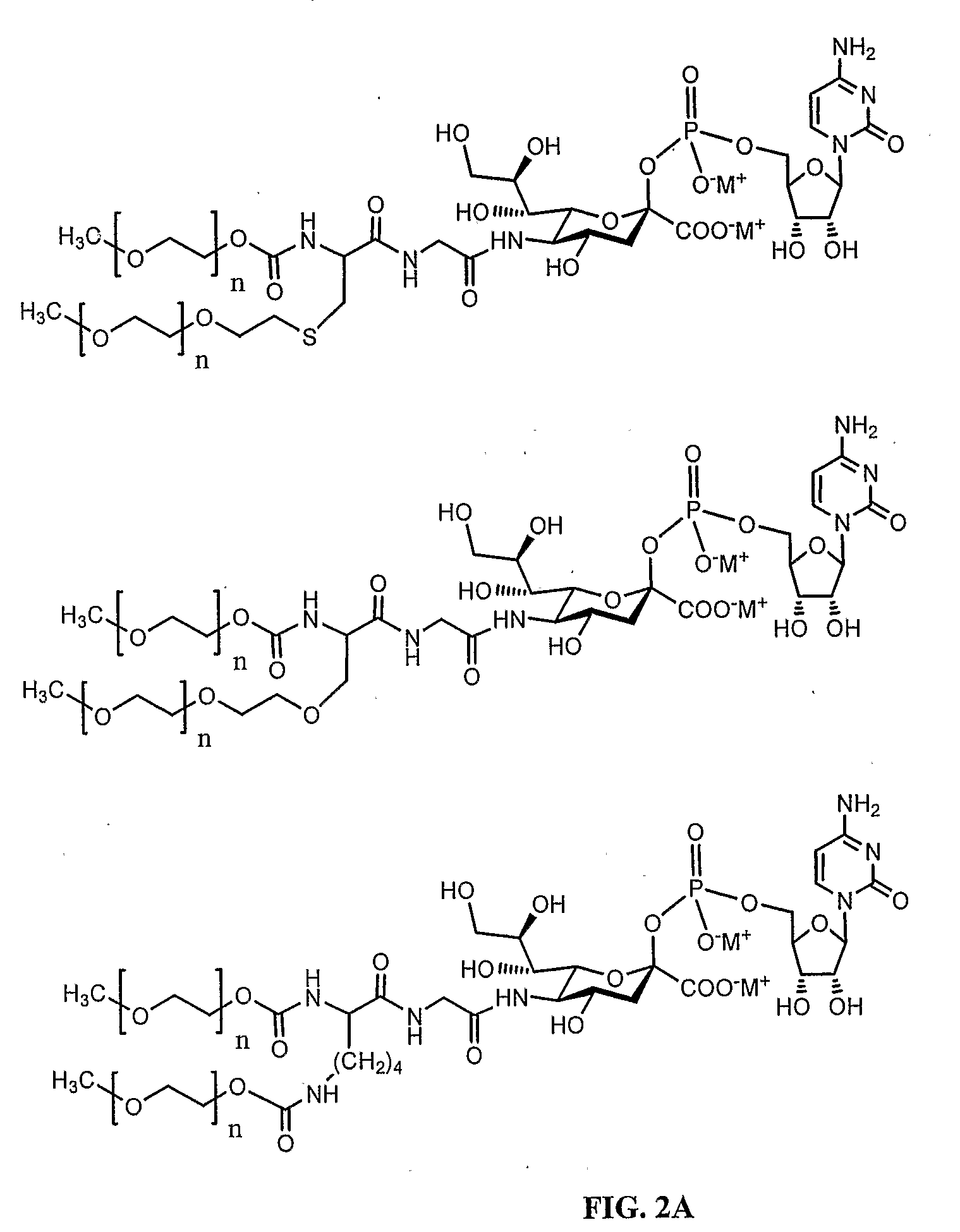
ActiveUS20060275254A1Prolong the action timePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtein targetHalf-life
Disclosed is a novel use of an immunoglobulin Fe fragment, and more particularly, a pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fe fragment as a carrier. The pharmaceutical composition comprising an immunoglobulin Fe fragment as a carrier remarkably extends the serum half-life of a drug while maintaining the in vivo activity of the drug at relatively high levels. Also, when the drug is a polypeptide drug, the pharmaceutical composition has less risk of inducing immune responses compared to a fusion protein of the immunoglobulin Fe fragment and a target protein, and is thus useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
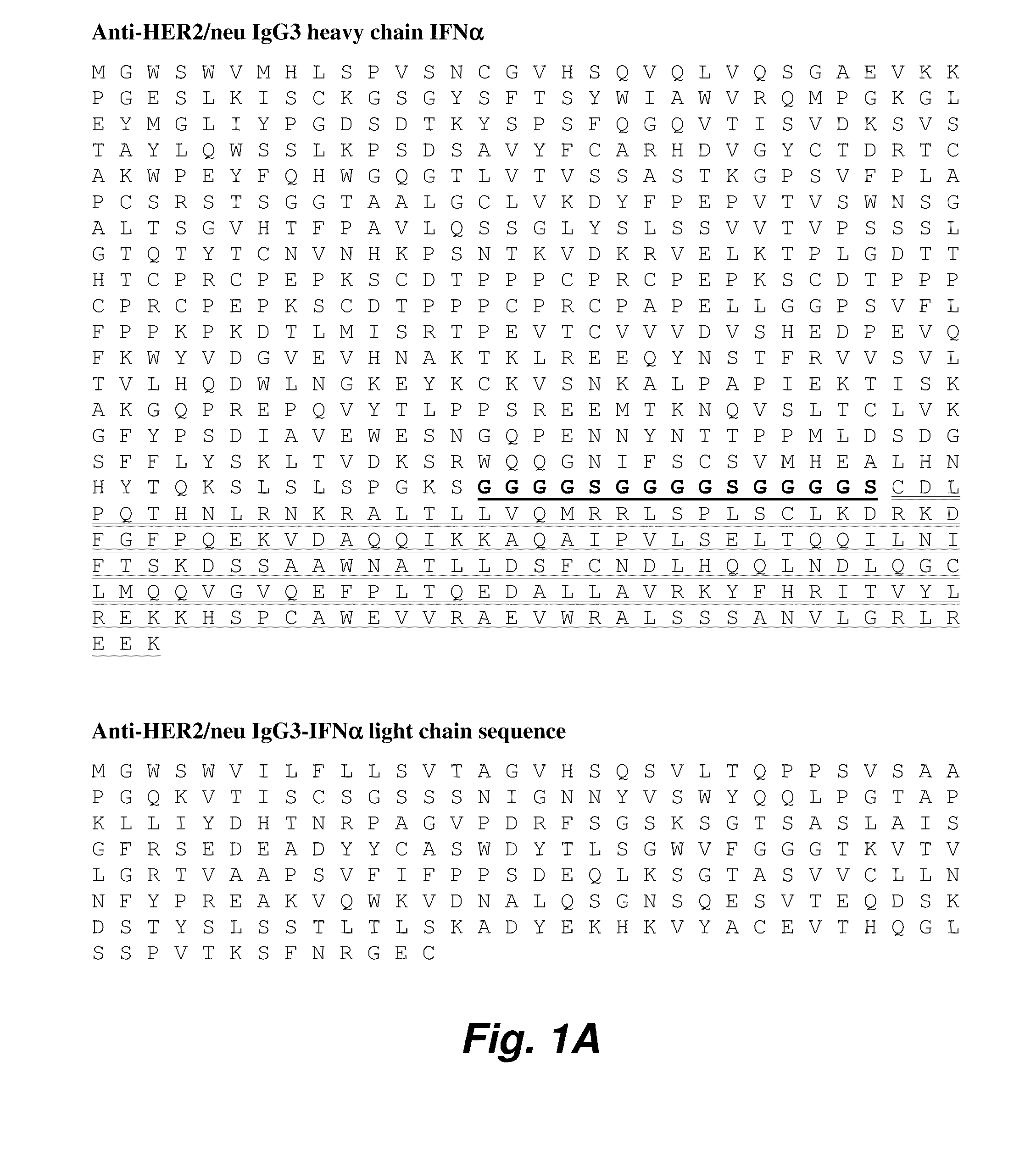
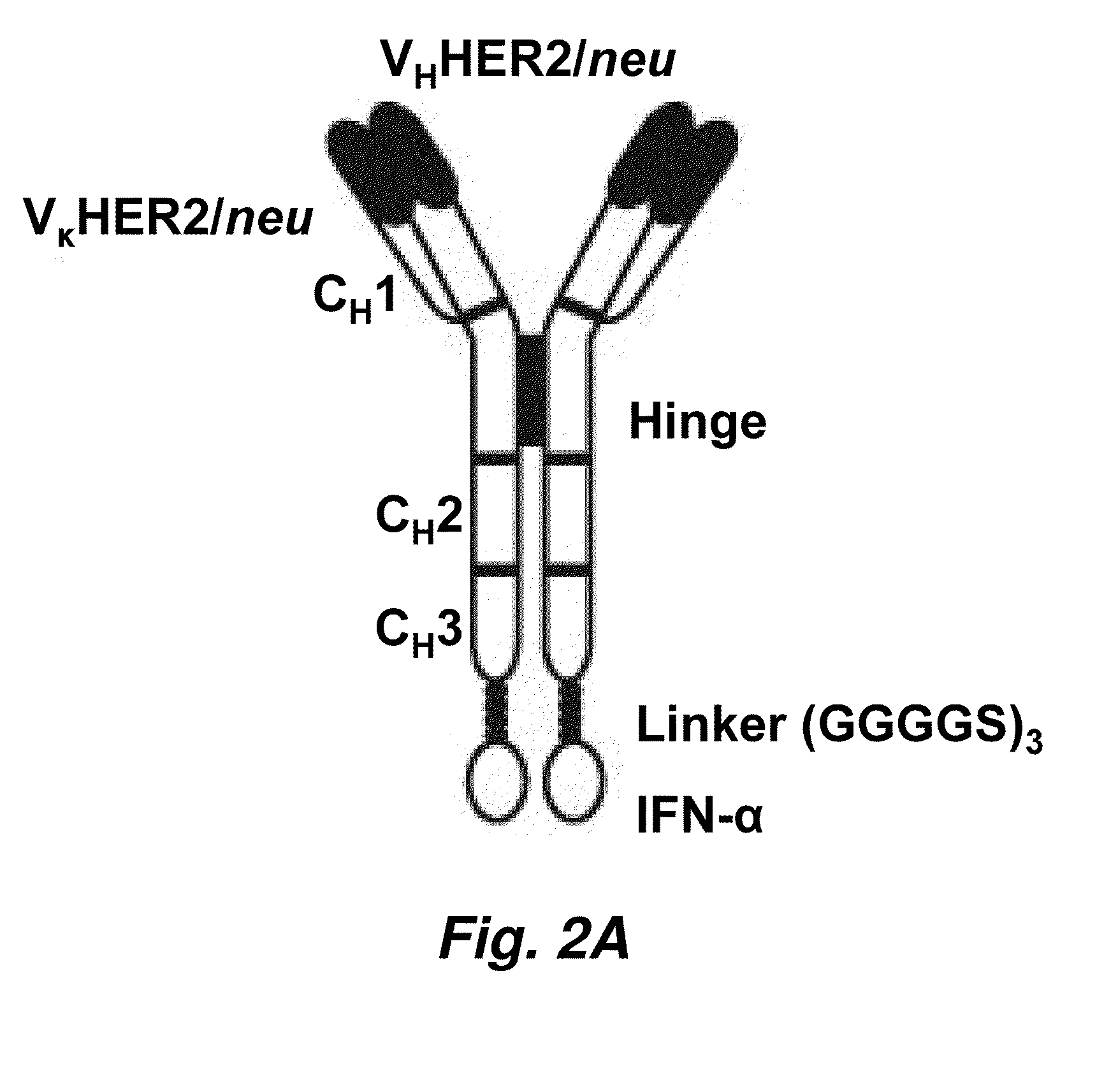
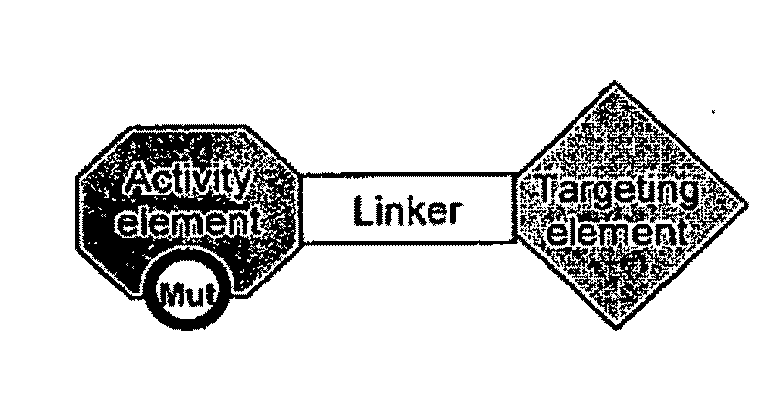
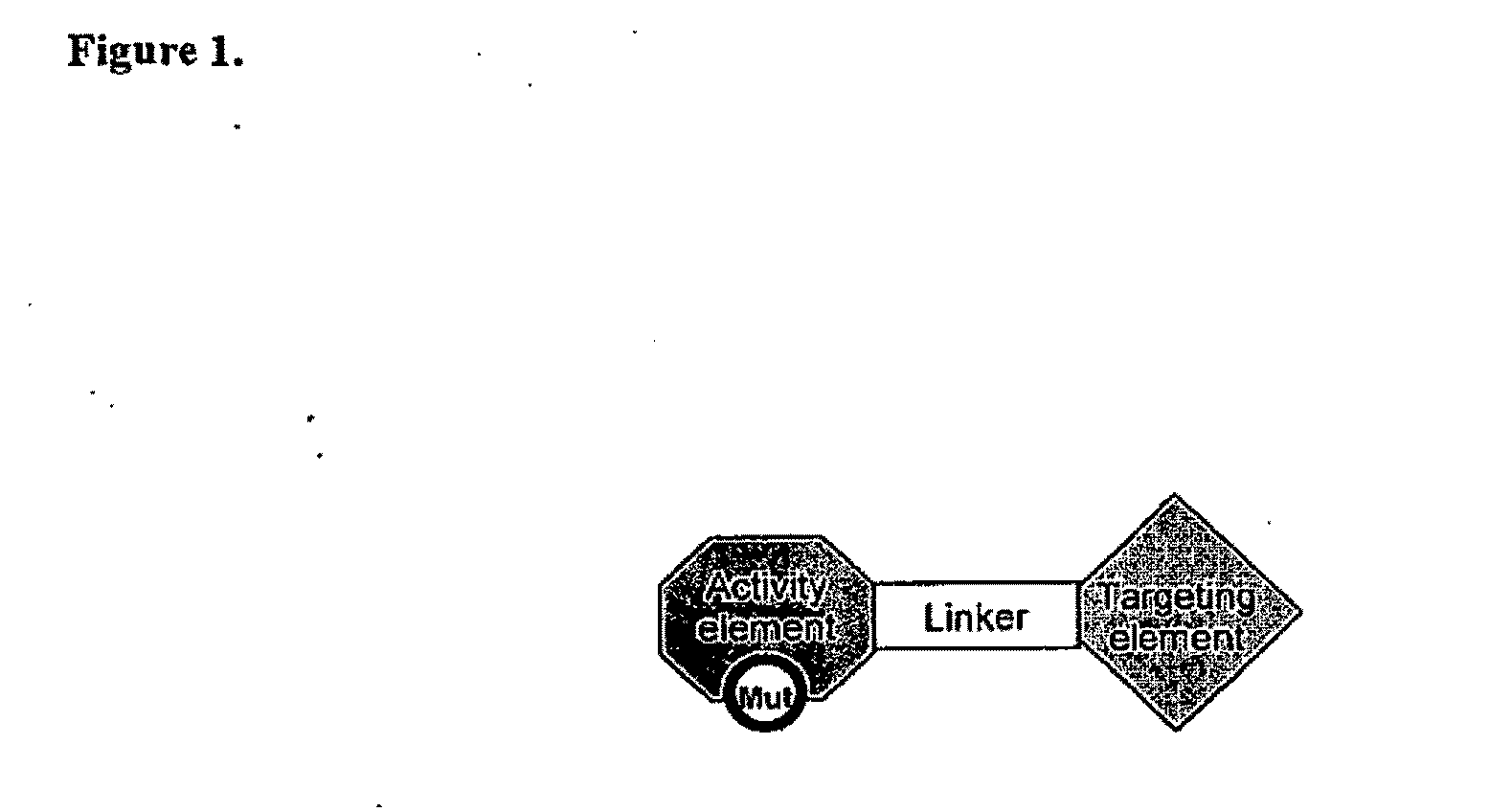
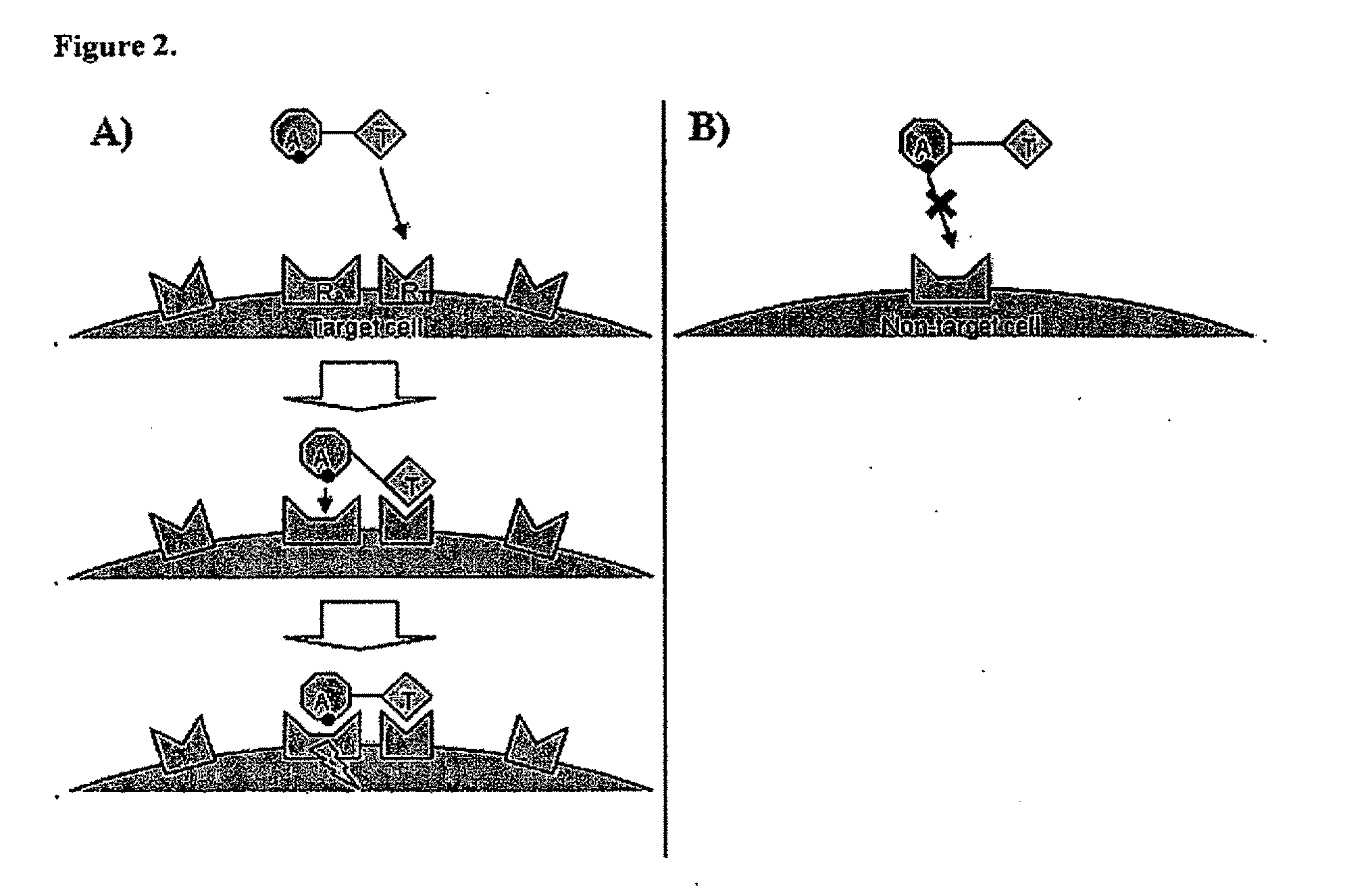
Targeted interferons demonstrate potent apoptotic and Anti-tumor activities
ActiveUS20100172868A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInterferon alphaAntitumor activity
Novel chimeric moieties that show significant efficacy against cancers are provided. In certain embodiments the chimeric moieties comprise a targeting moiety attached to an interferon. In certain embodiments, the chimeric moieties comprise fusion proteins where an antibody that specifically binds to a cancer marker is fused to interferon alpha (IFN-α) or interferon beta (IFN-β).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
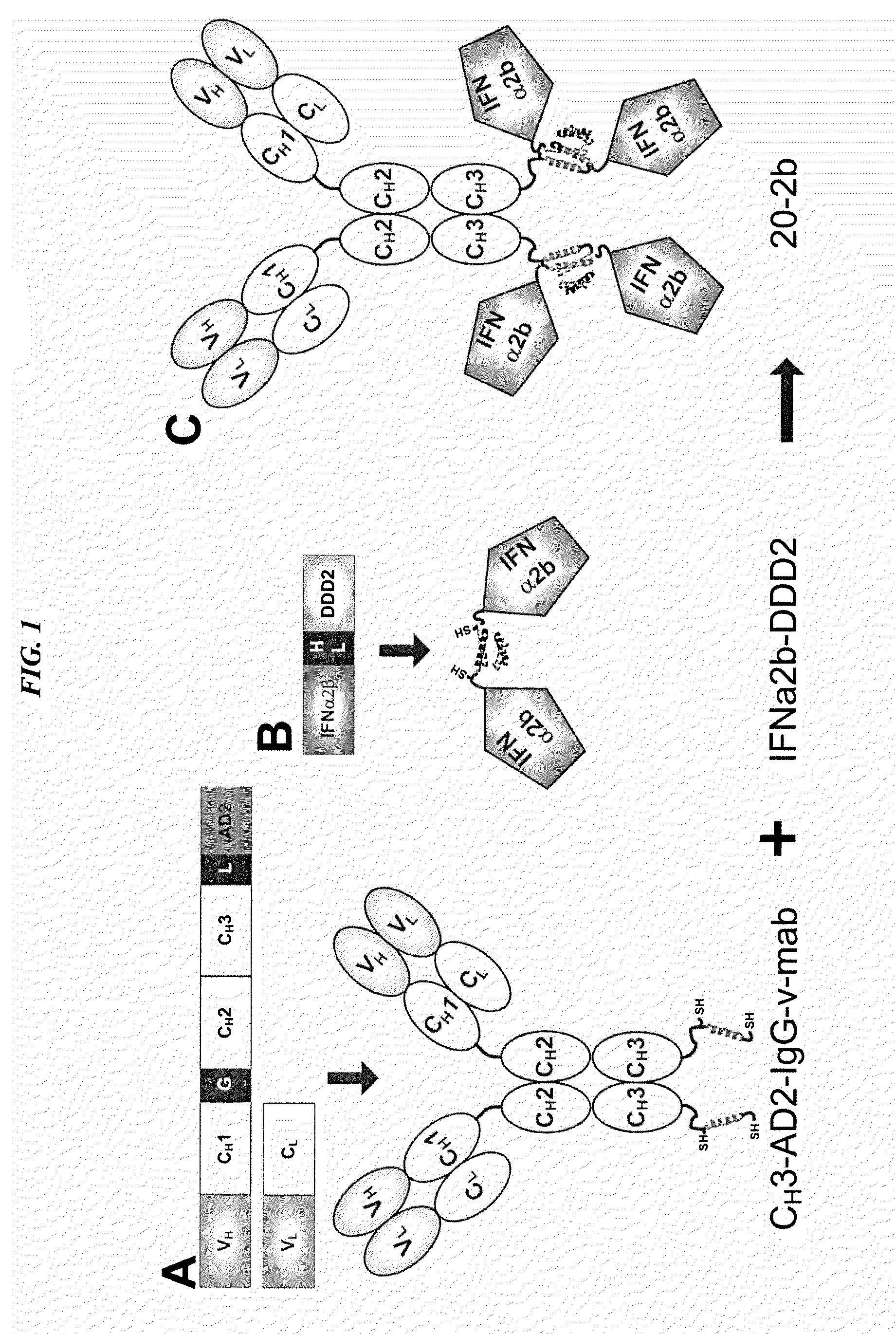
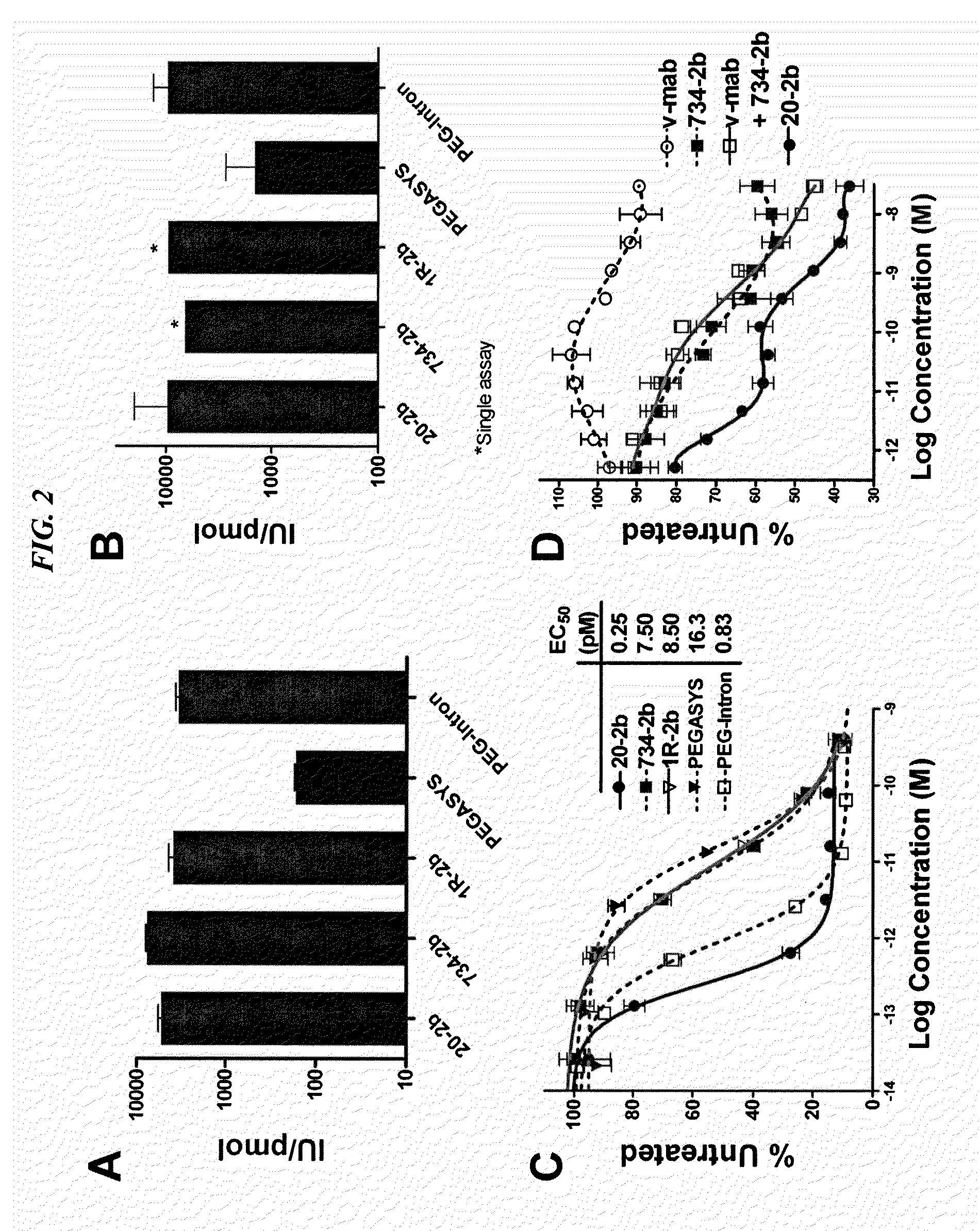
Tetrameric cytokines with improved biological activity
ActiveUS8034352B2Keep for a long timeLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming cytokine-antibody complexes using dock-and-lock technology. In preferred embodiments, the cytokine-MAb DNL complex comprises an IgG antibody attached to two AD (anchor domain) moieties and four cytokines, each attached to a DDD (docking and dimerization domain) moiety. The DDD moieties form dimers that bind to the AD moieties, resulting in a 2:1 ratio of DDD to AD. The cytokine-MAb complex exhibits improved pharmacokinetics, with a significantly longer serum half-life than either naked cytokine or PEGylated cytokine. The cytokine-MAb complex also exhibits significantly improved in vitro and in vivo efficacy compared to cytokine alone, antibody alone, unconjugated cytokine plus antibody or cytokine-MAb DNL complexes incorporating an irrelevant antibody. In more preferred embodiment the cytokine is G-CSF, erythropoietin or INF-α2b.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
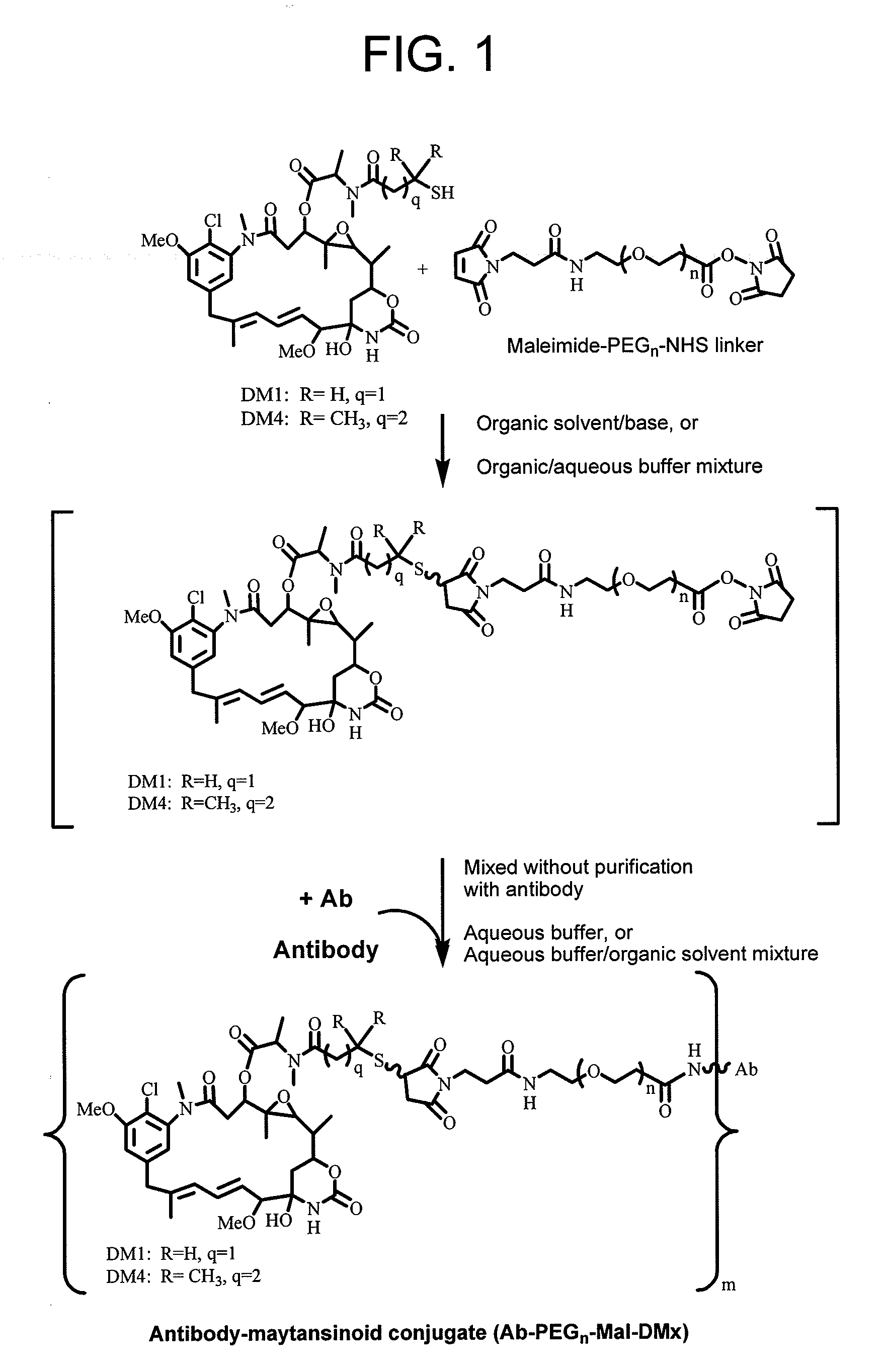
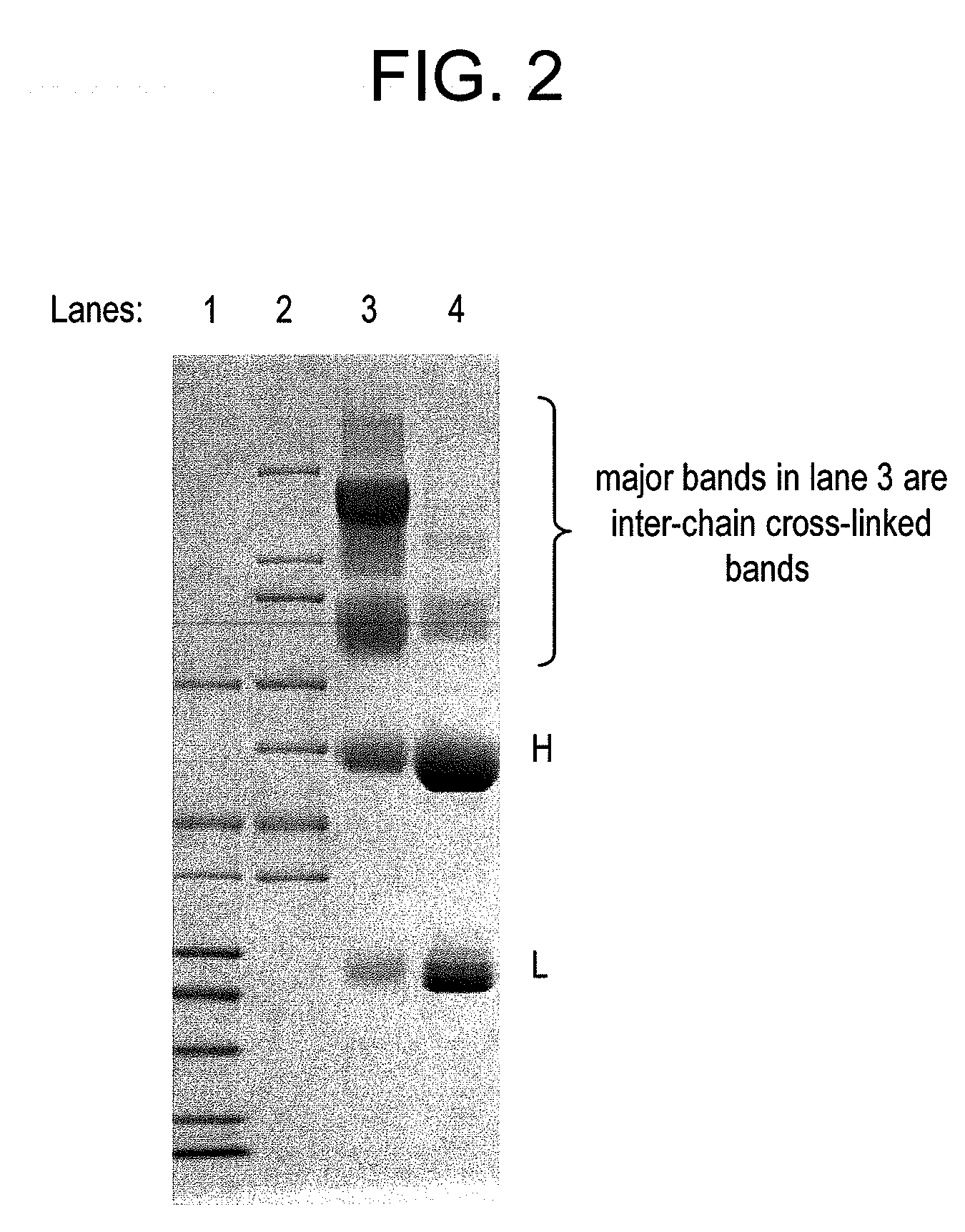
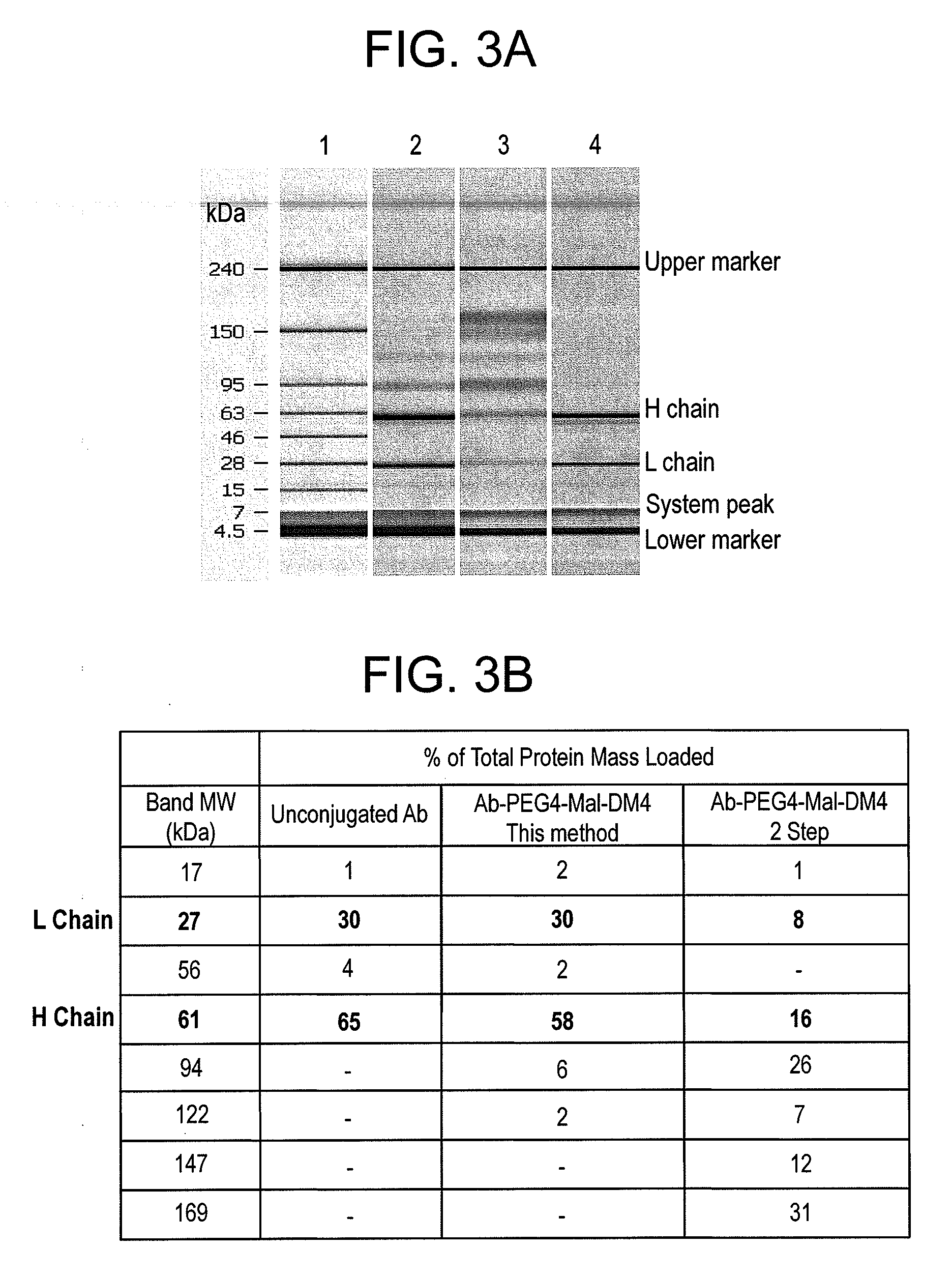
Conjugation methods
ActiveUS20110003969A1Reduce potential steric hindrancePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsBiochemistryAntibody
This invention describes a method of conjugating a cell binding agent such as an antibody with an effector group (e.g., a cytotoxic agent) or a reporter group (e.g., a radionuclide), whereby the reporter or effector group is first reacted with a bifunctional linker and the mixture is then used without purification for the conjugation reaction with the cell binding agent. The method described in this invention is advantageous for preparation of stably-linked conjugates of cell binding agents, such as antibodies with effector or reporter groups. This conjugation method provides in high yields conjugates of high purity and homogeneity that are without inter-chain cross-linking and inactivated linker residues
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
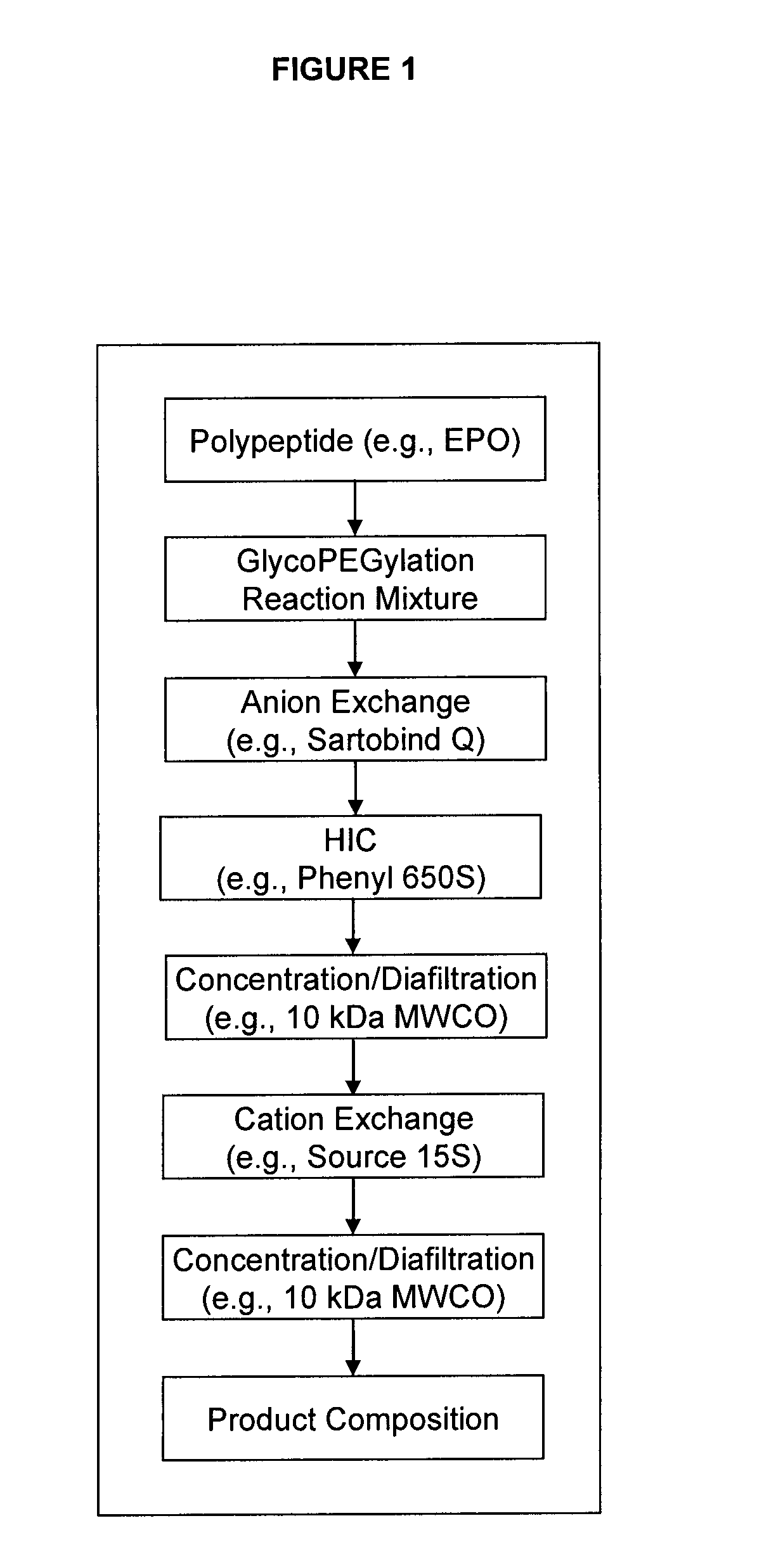
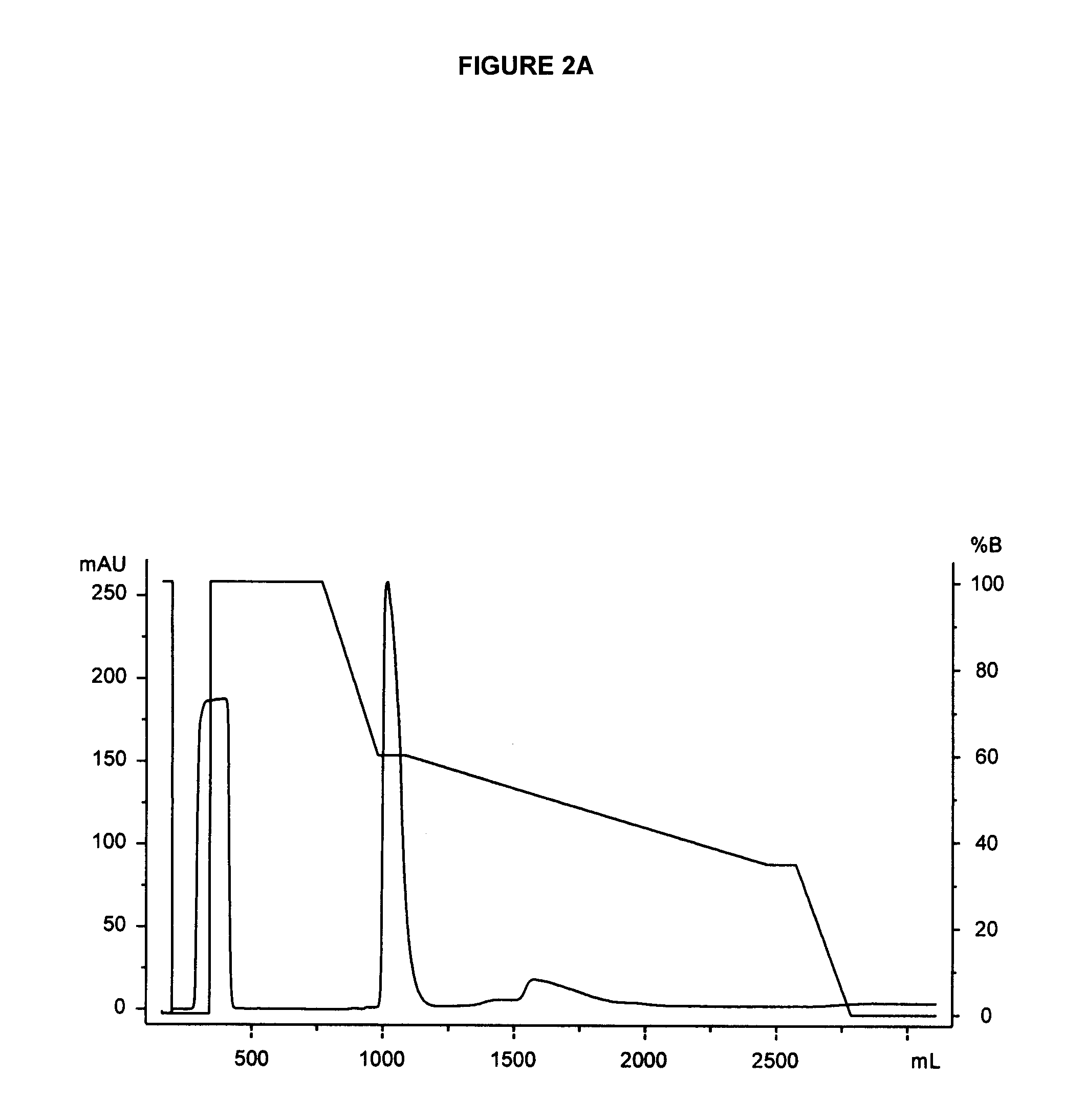
Methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates
InactiveUS20100035299A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPolymer sciencePolypropylene glycol
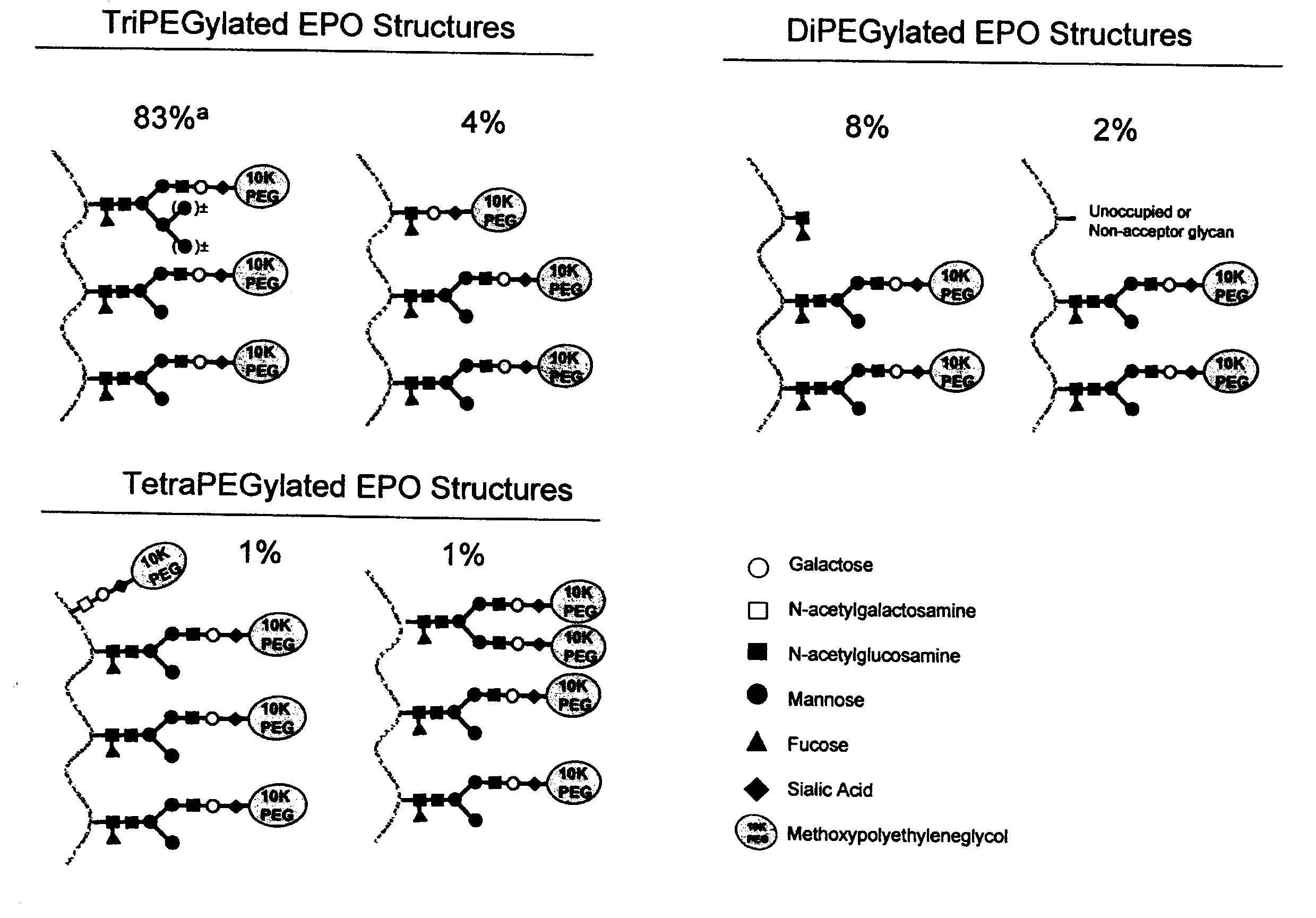
The present invention provides processes for the manufacturing of polypeptide conjugates. In particular, the invention provides methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates, which include at least one polymeric modifying groups, such as a poly(alkylene oxide) moiety. Exemplary poly(alkylene oxide) moieties include poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(propylene glycol). In an exemplary process, hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is used to resolve different glycoforms of glycoPEGylated polypeptides.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
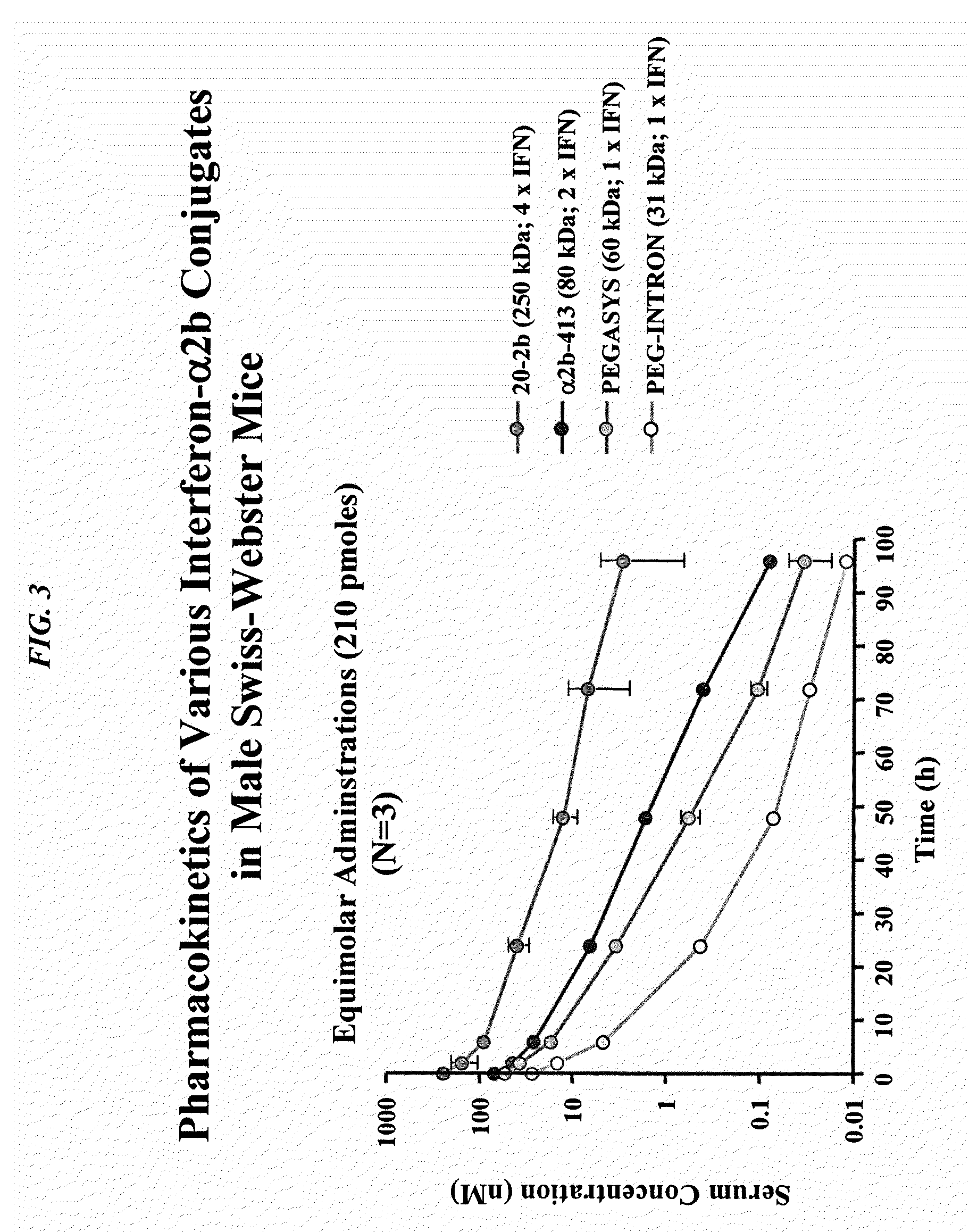
Targeted interferon demonstrates potent apoptotic and Anti-tumor activities
ActiveUS20100297076A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInterferon alphaWilms' tumor
This invention provides novel chimeric moieties that show significant efficacy against cancers. In certain embodiments the chimeric moieties comprise a targeting moiety attached to an interferon. In certain embodiments, the chimeric moieties comprise fusion proteins where an antibody that specifically binds to a cancer marker is fused to interferon alpha (IFN-α).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
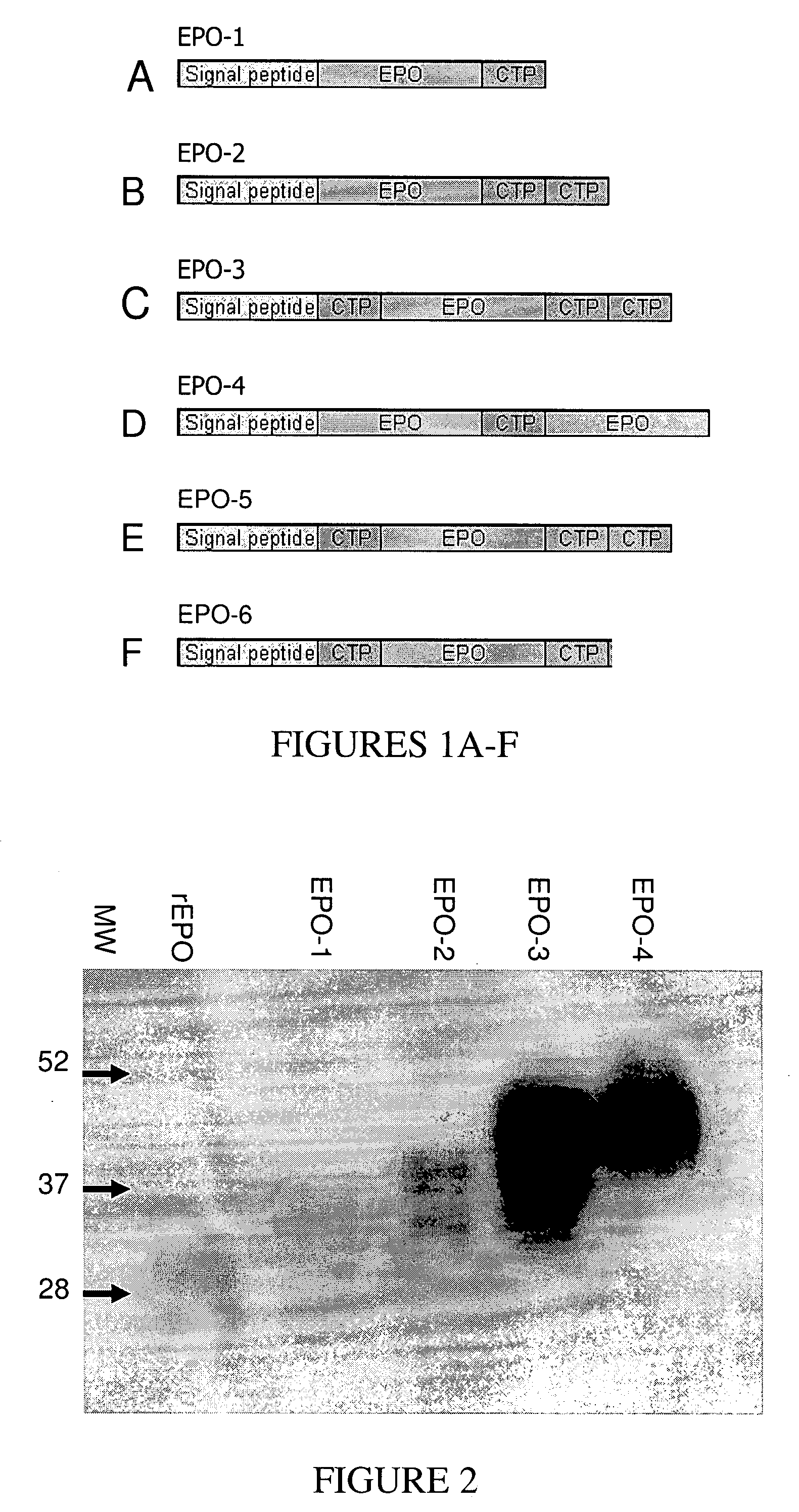
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing and administering same
ActiveUS20130184207A1Reduce dosing frequencyIncrease the areaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
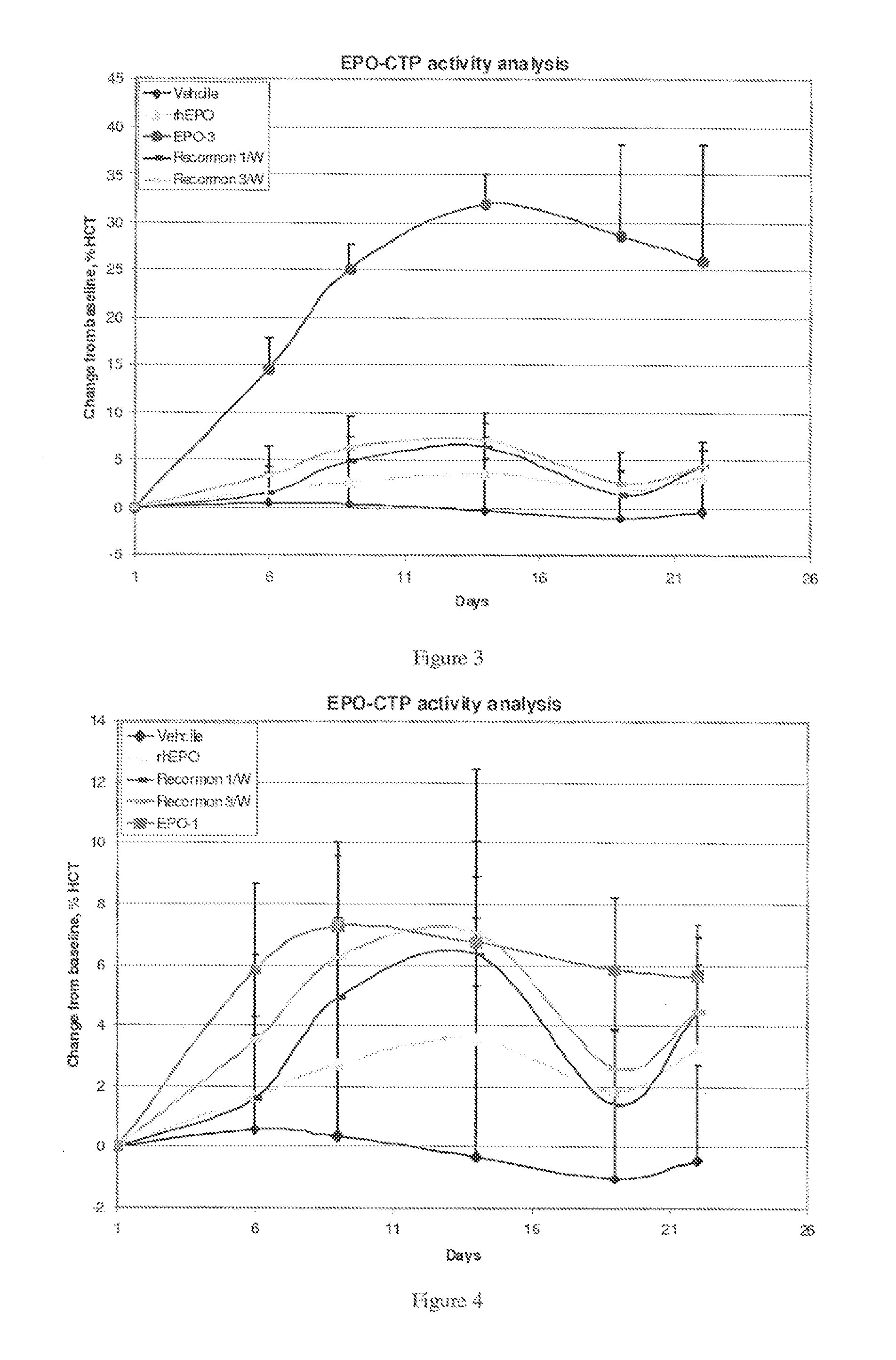
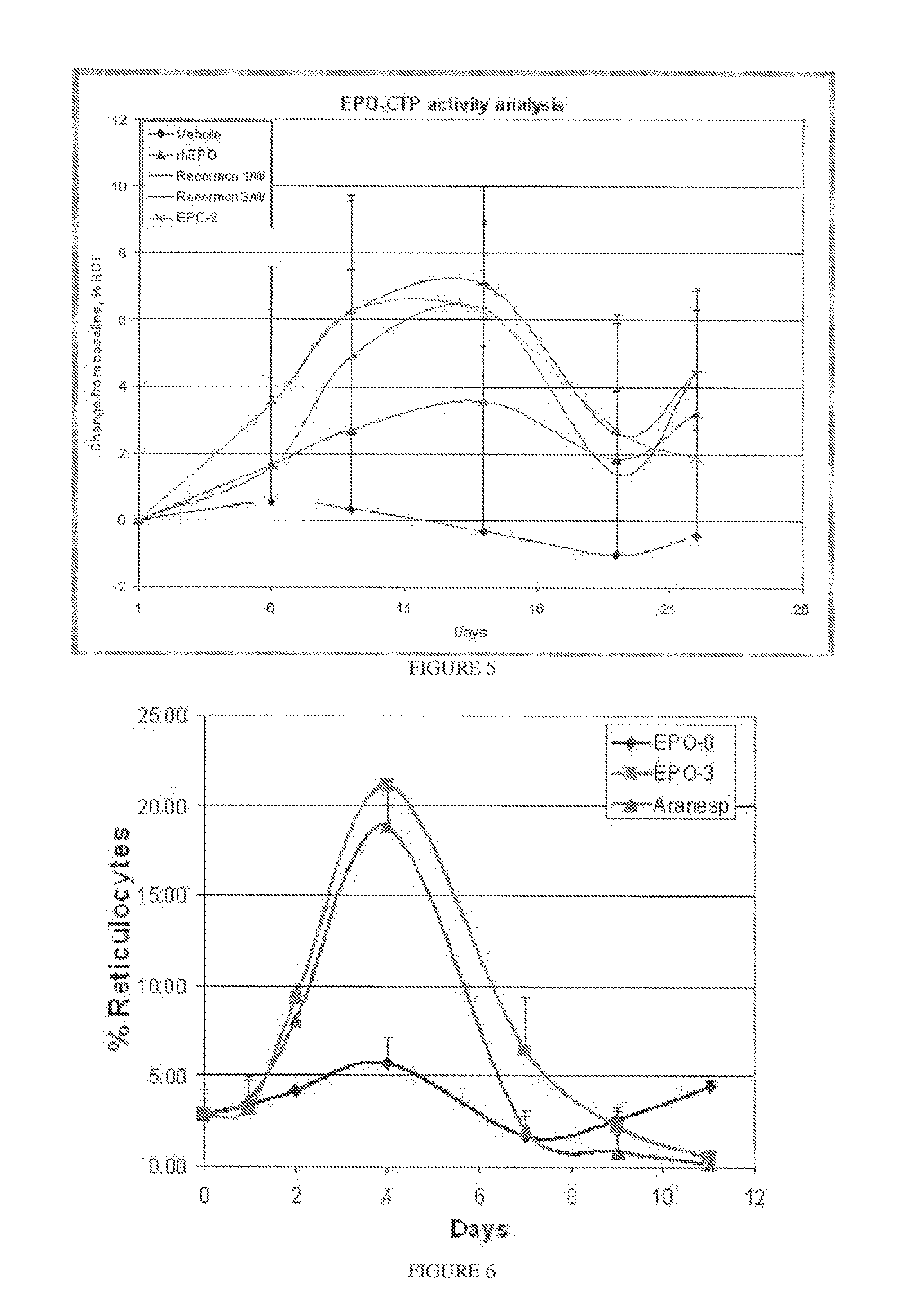
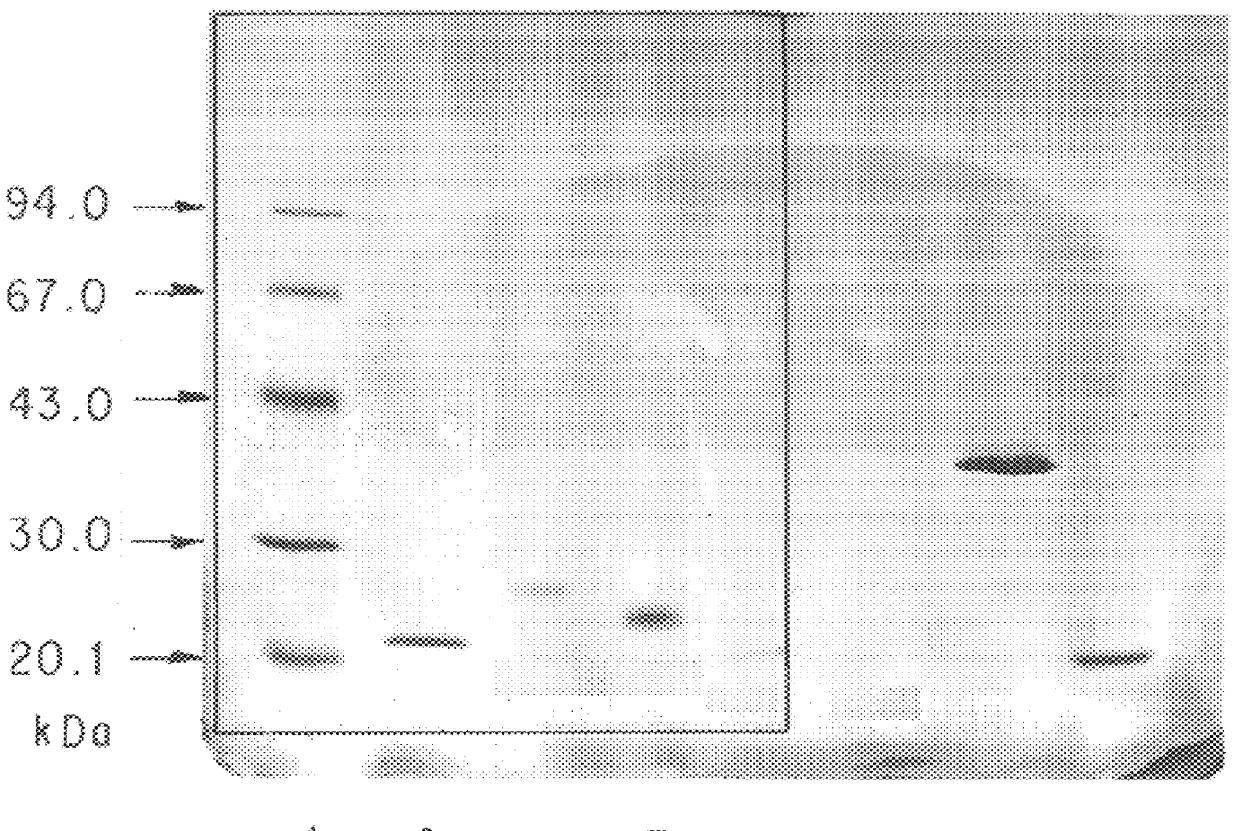
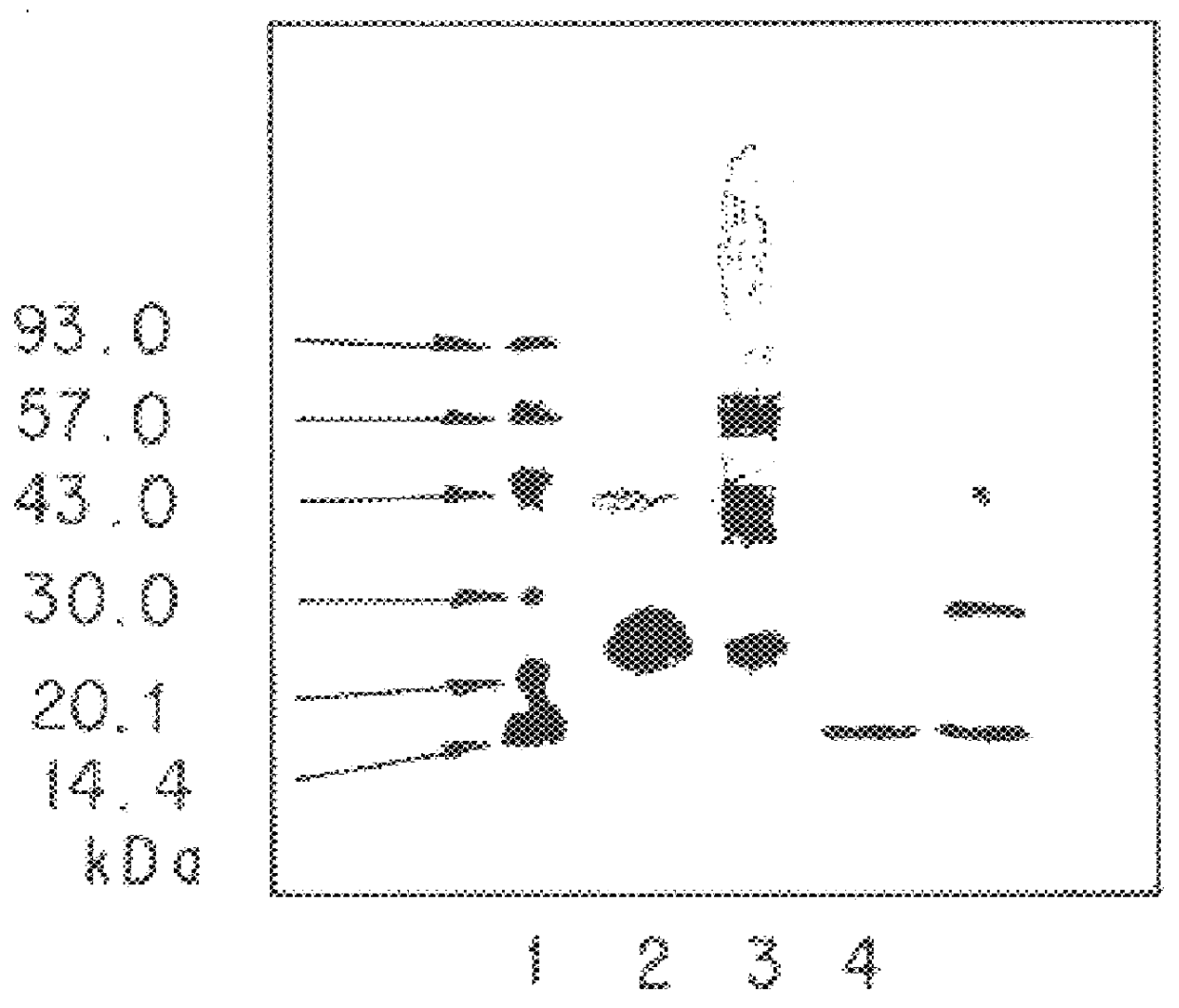
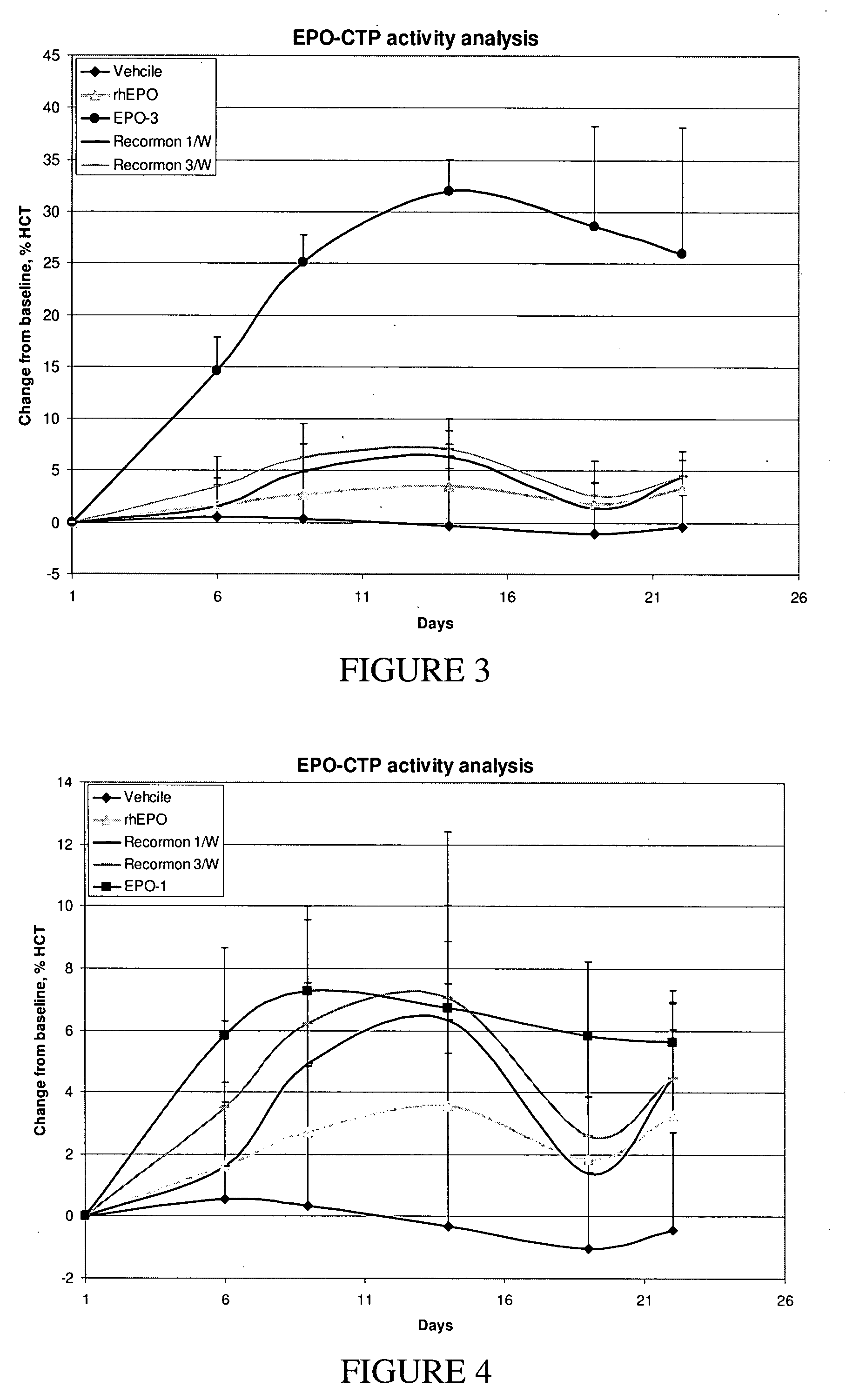
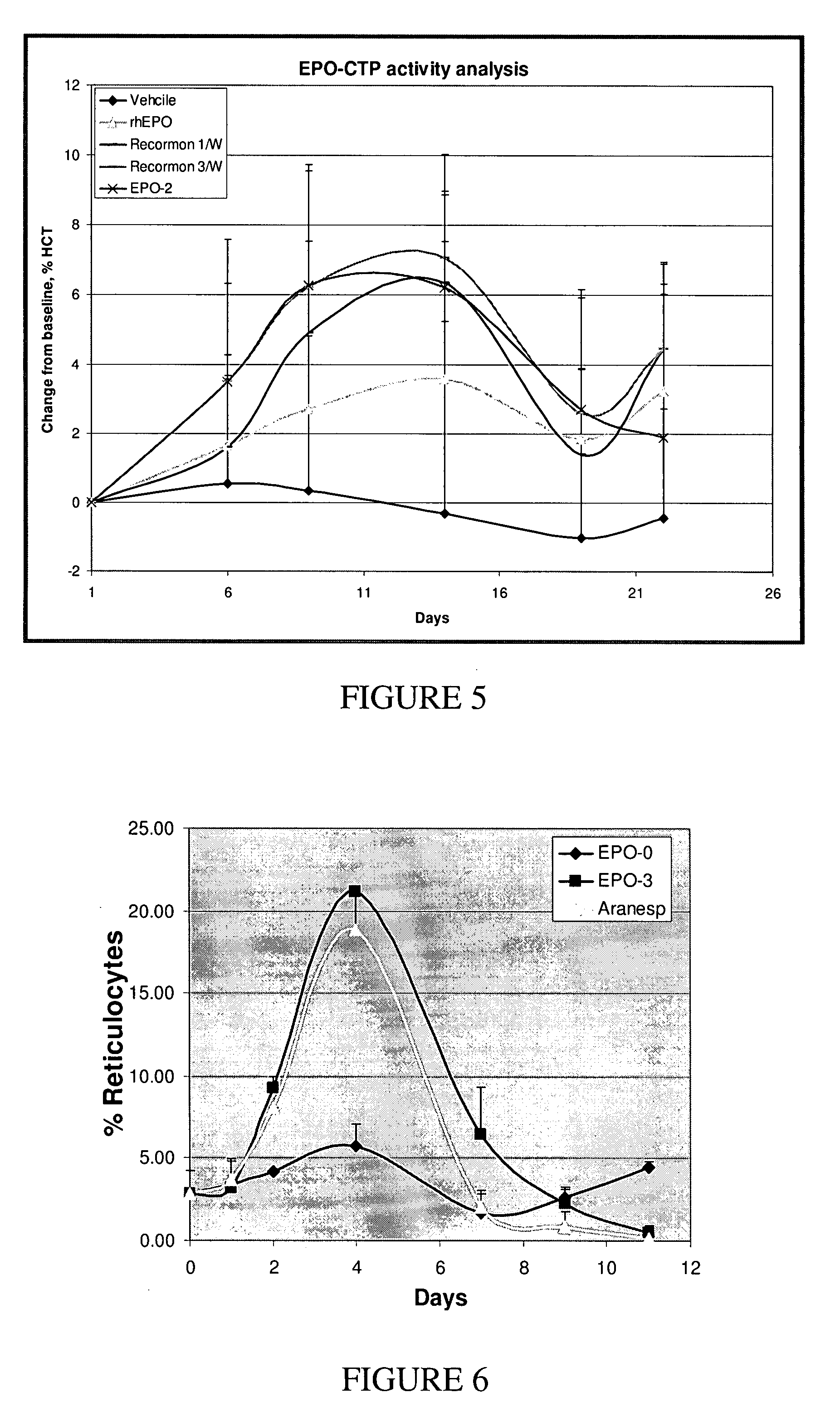
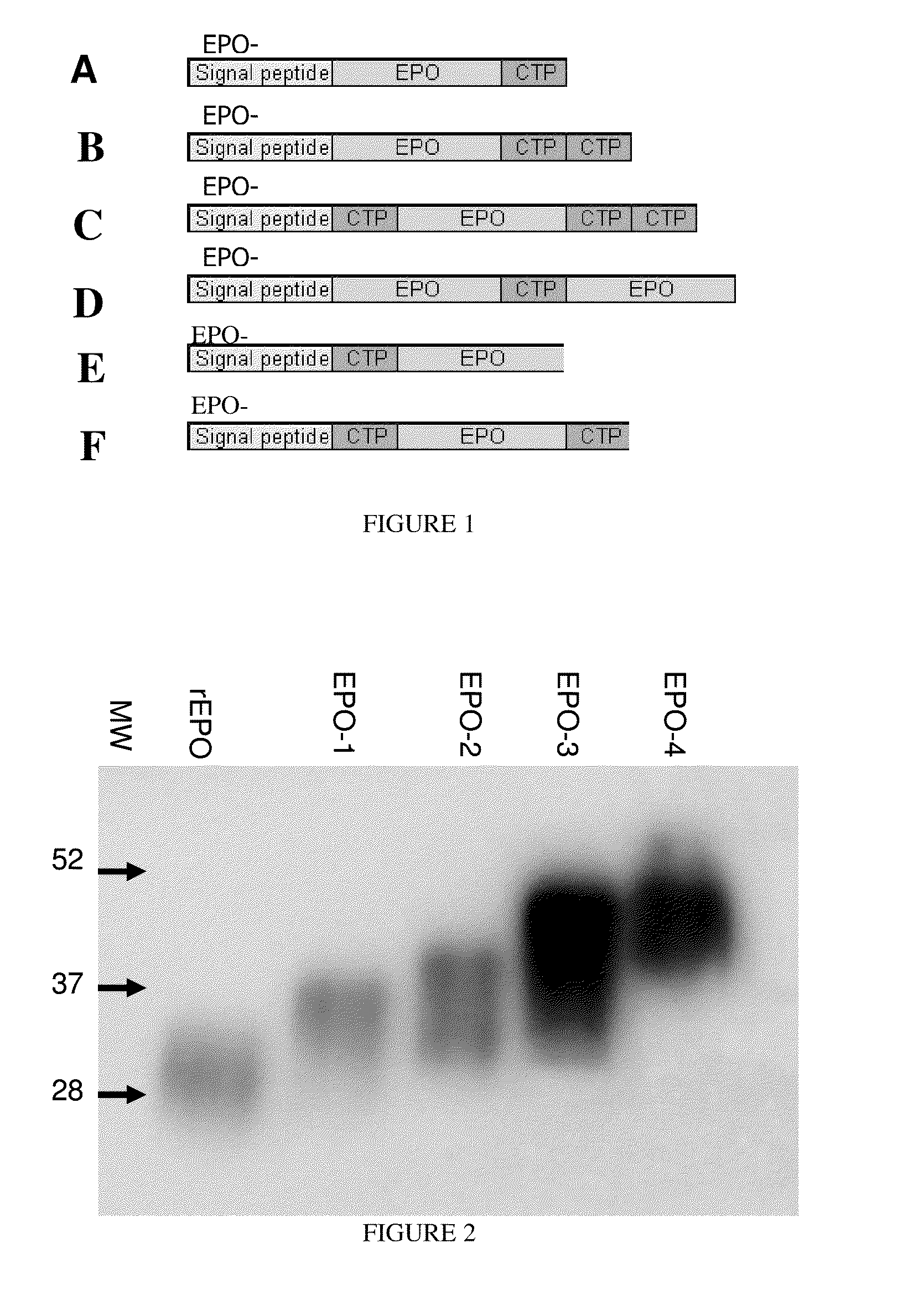
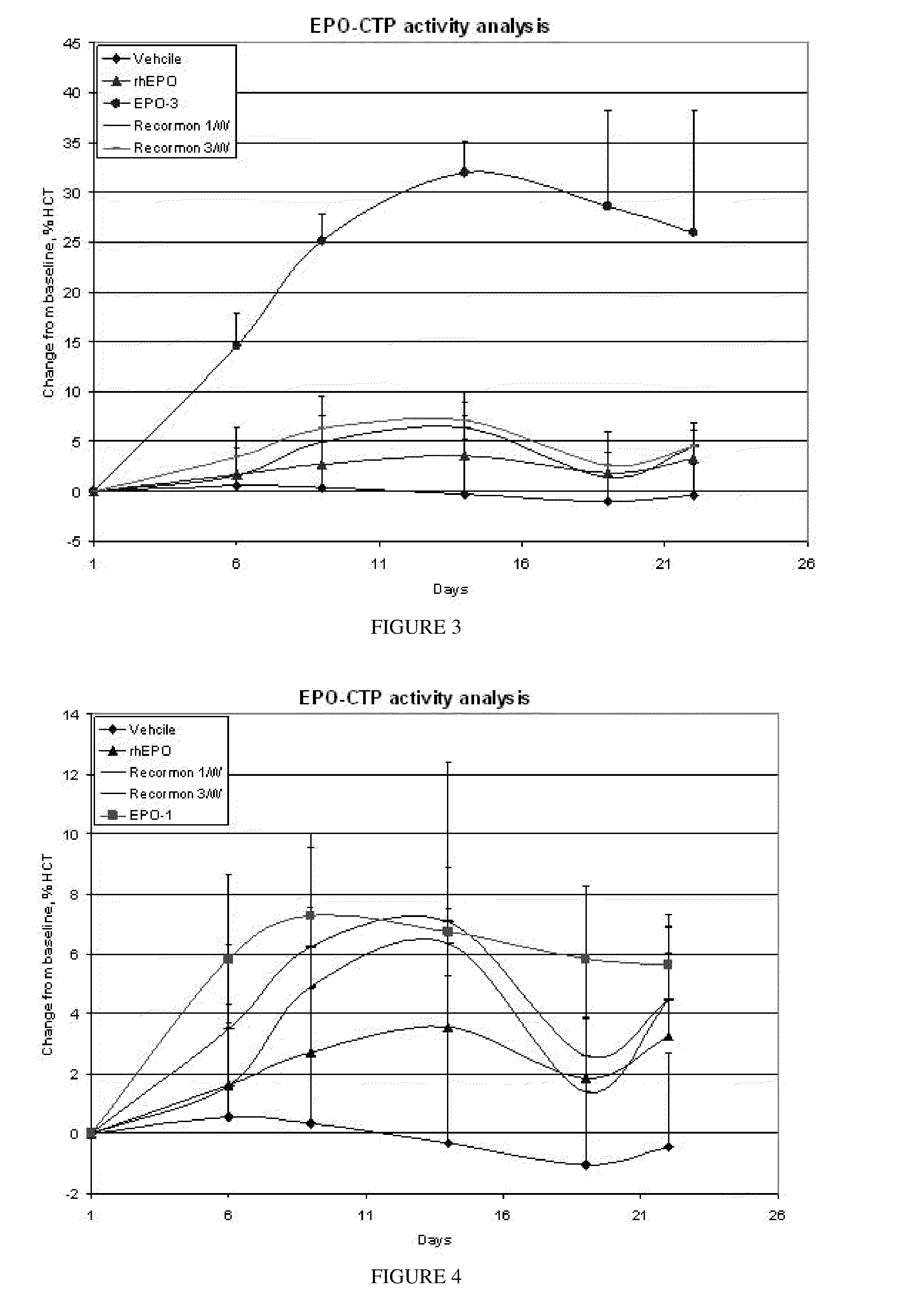
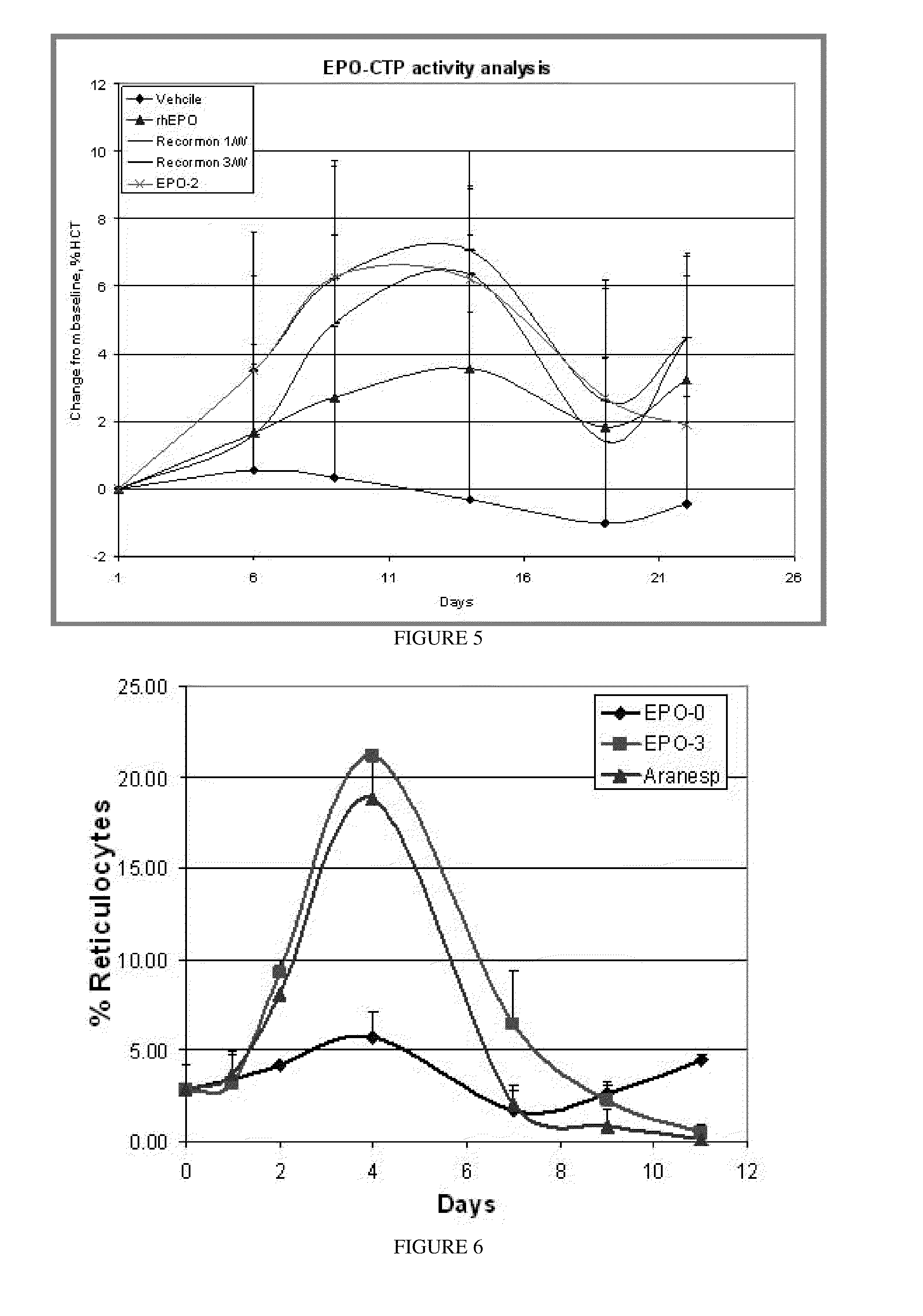
A polypeptide and polynucleotides comprising at least two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a non-human peptide-of-interest are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the non-human polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using both human and non-human polypeptides and polynucleotides are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
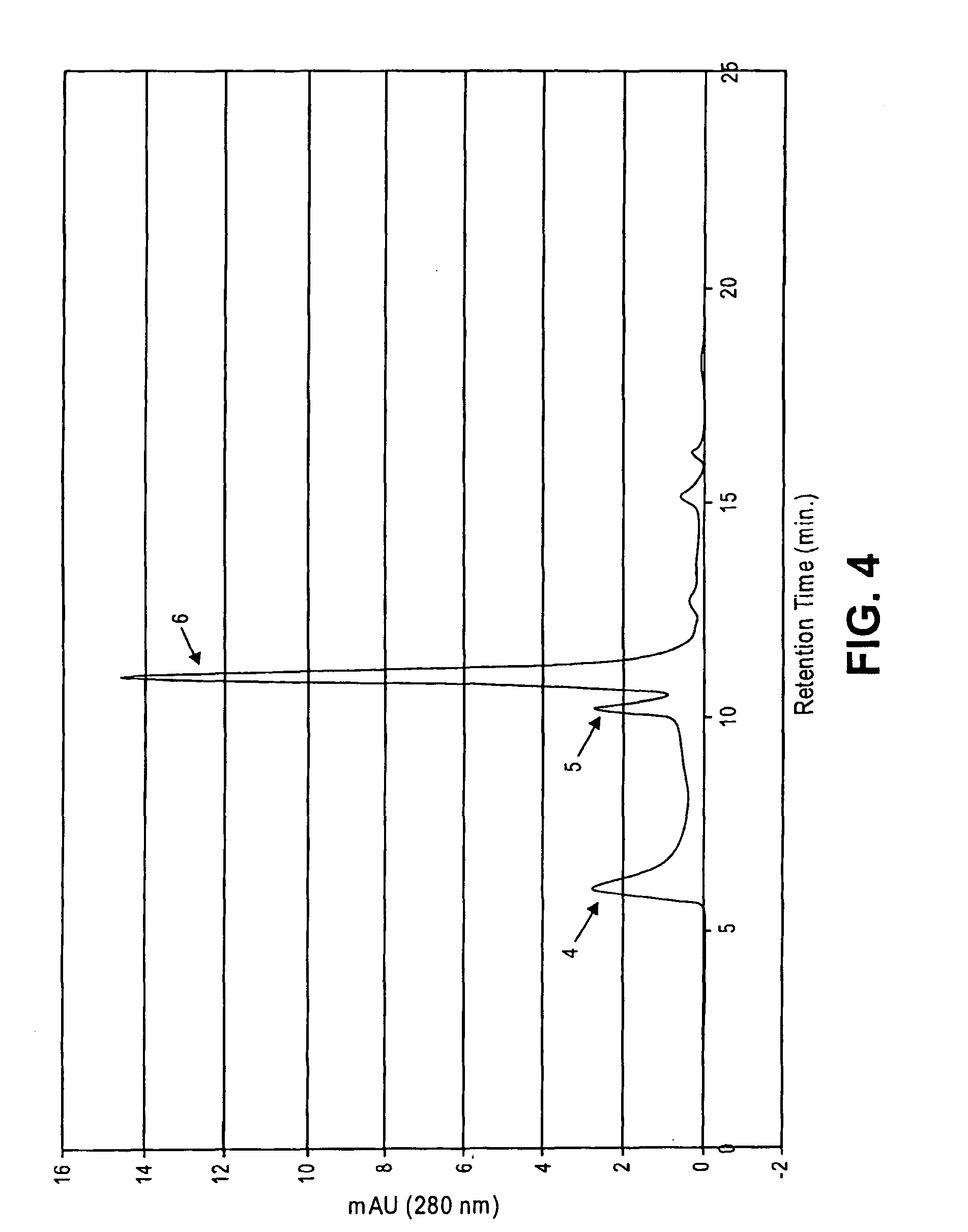
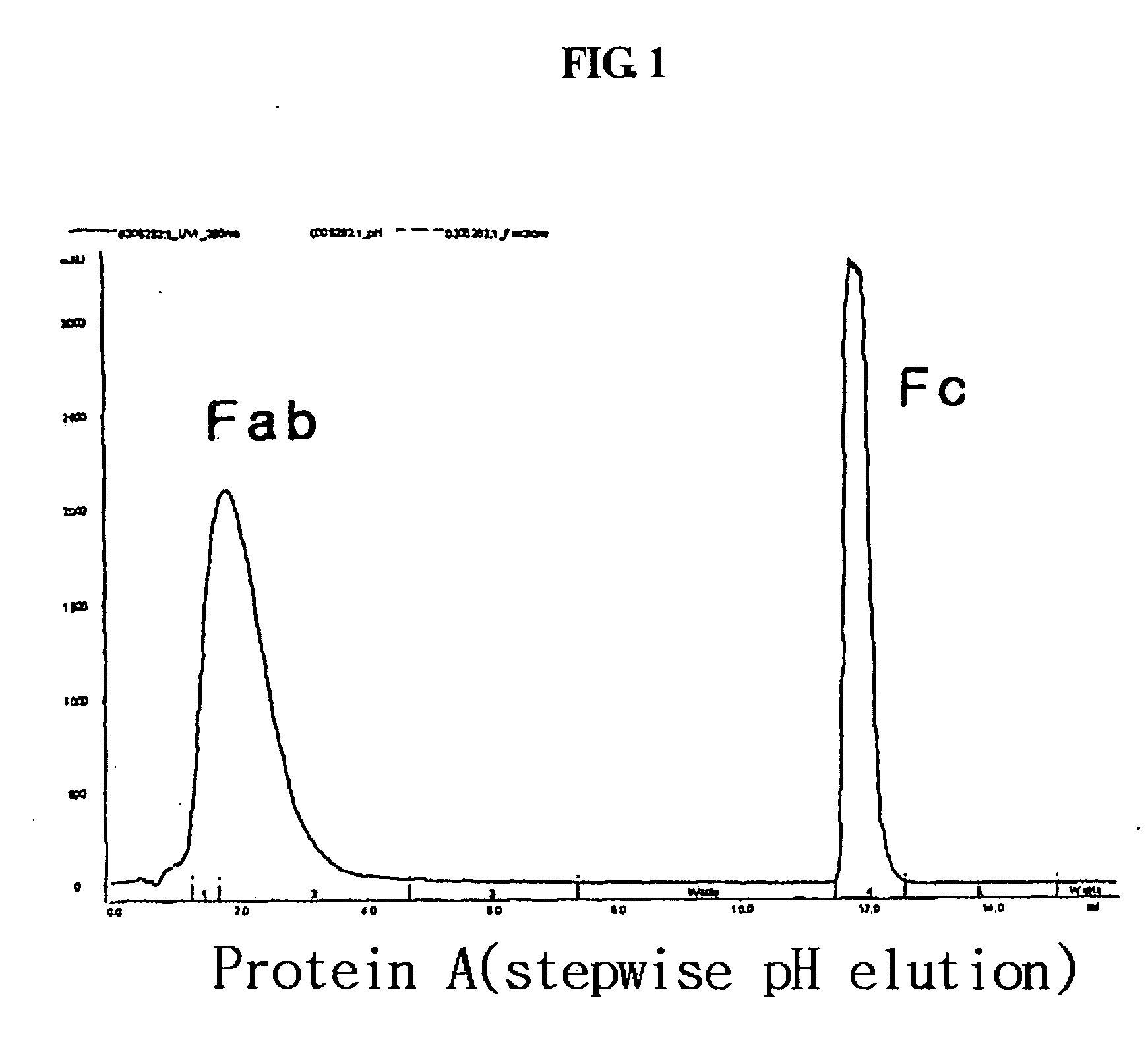
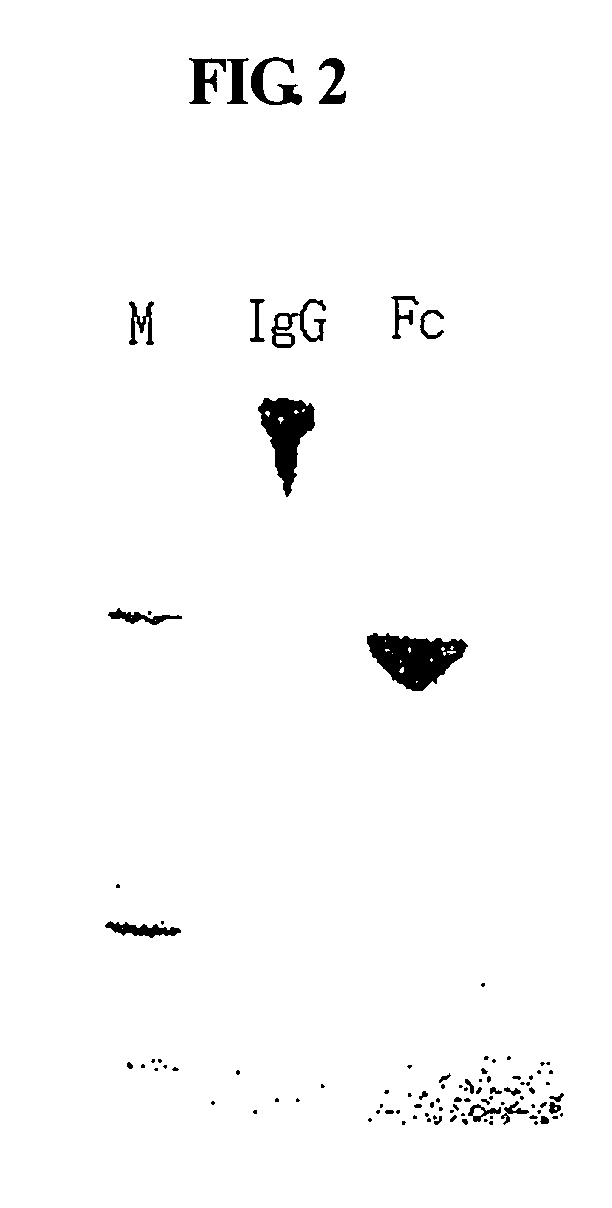
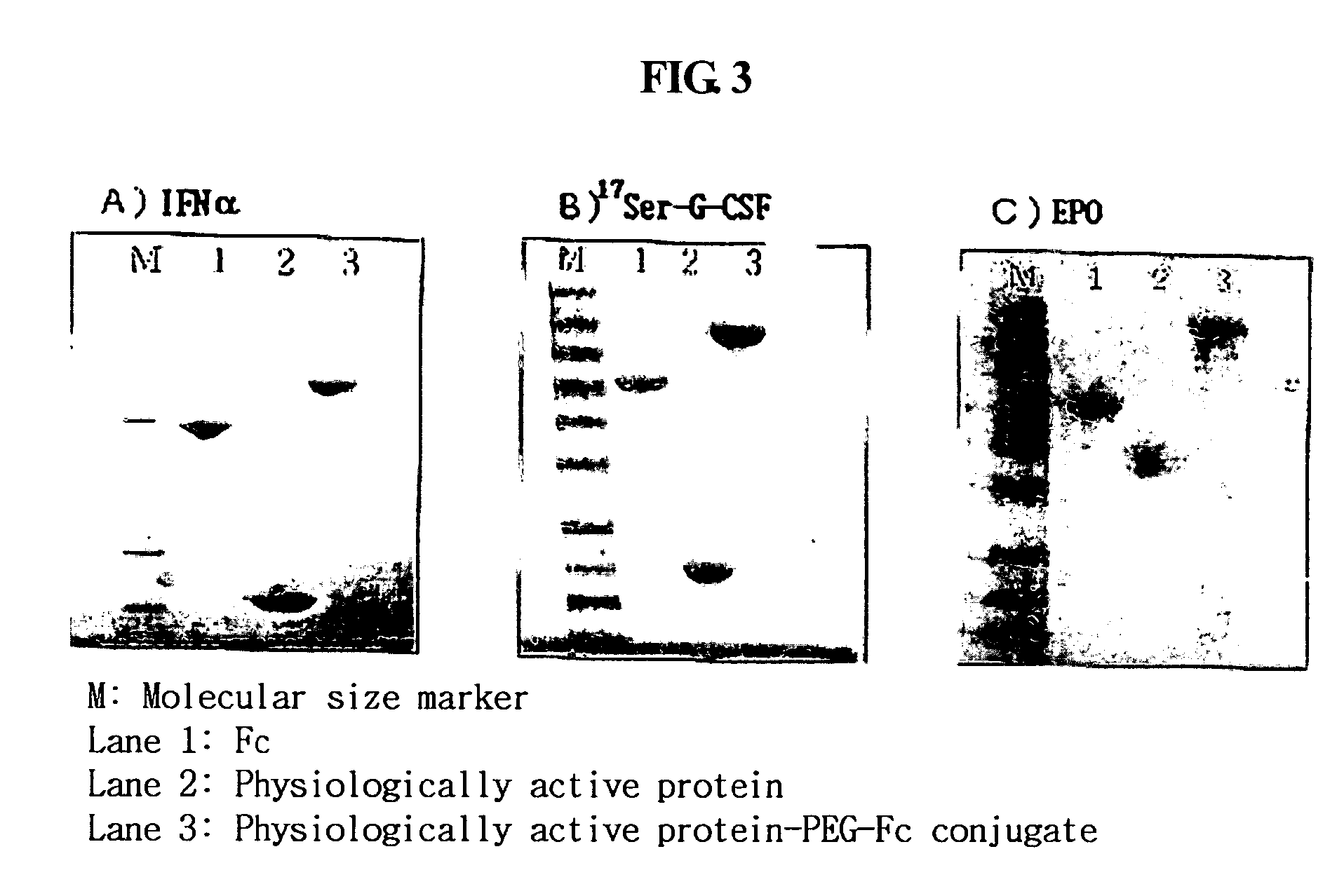
Modification of peptide and protein
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01994 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 8, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 8, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 29, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 10089 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 4, 1996A process for modifying a physiologically active peptide or a physiologically active protein which comprises reacting a physiologically active peptide or a physiologically active protein having at least a glutamine residue with a substance having an amino donor in the presence of a transglutaminase originating in a microorganism to thereby form an acid amide bond at the gamma -position acid amide group of the glutamine residue with the amino group of the amino donor; and the product of modification obtained thereby.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
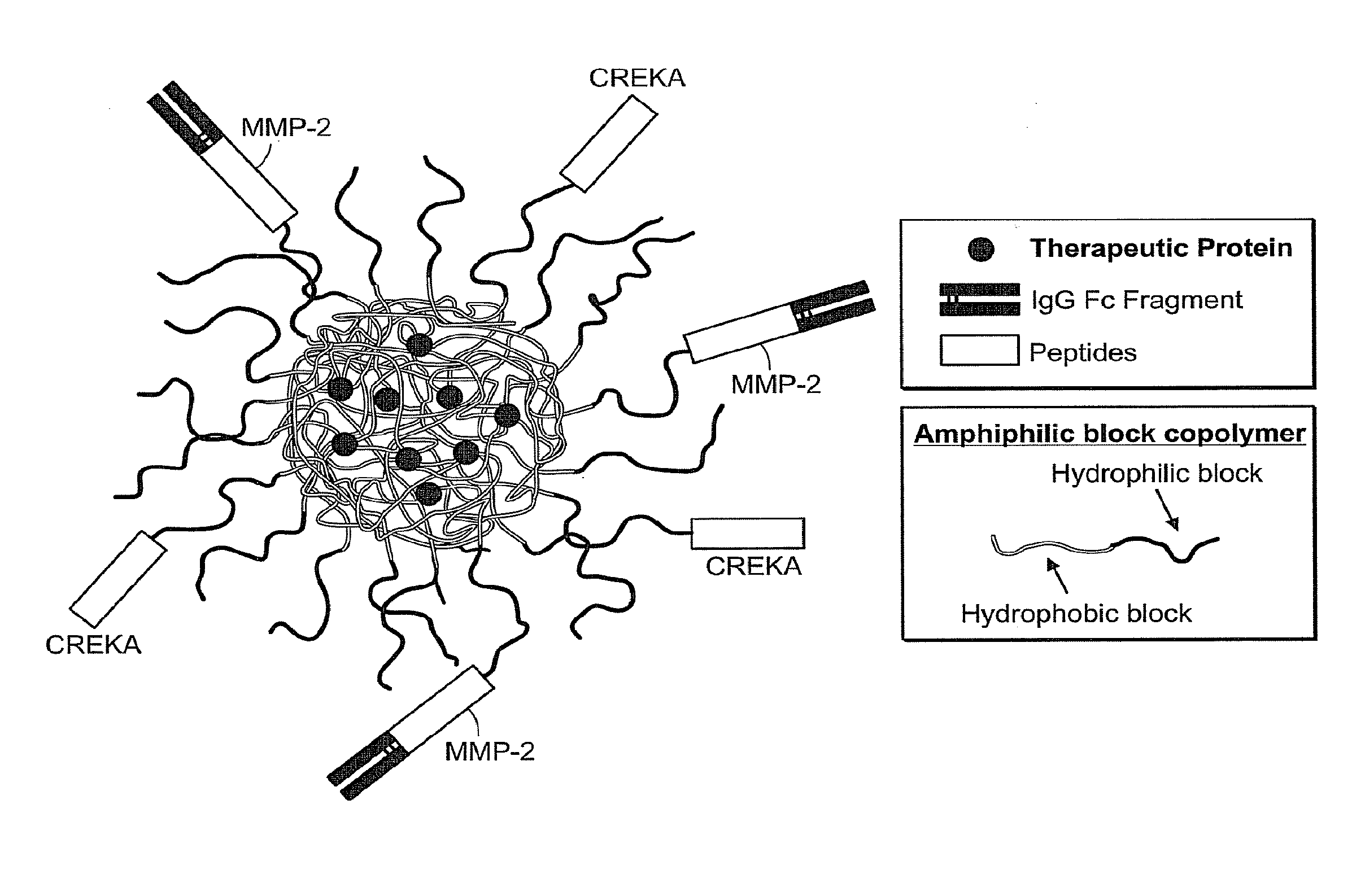
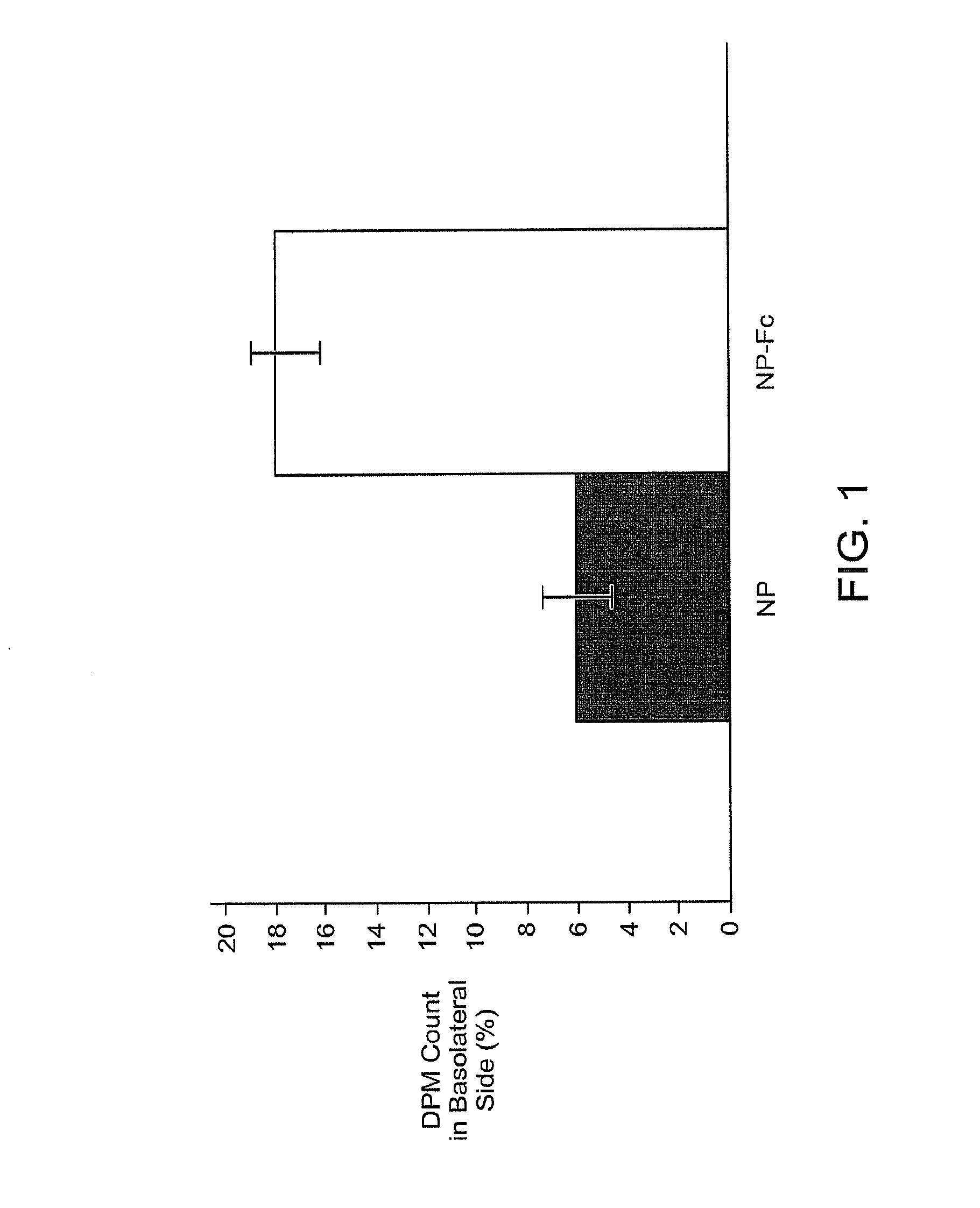
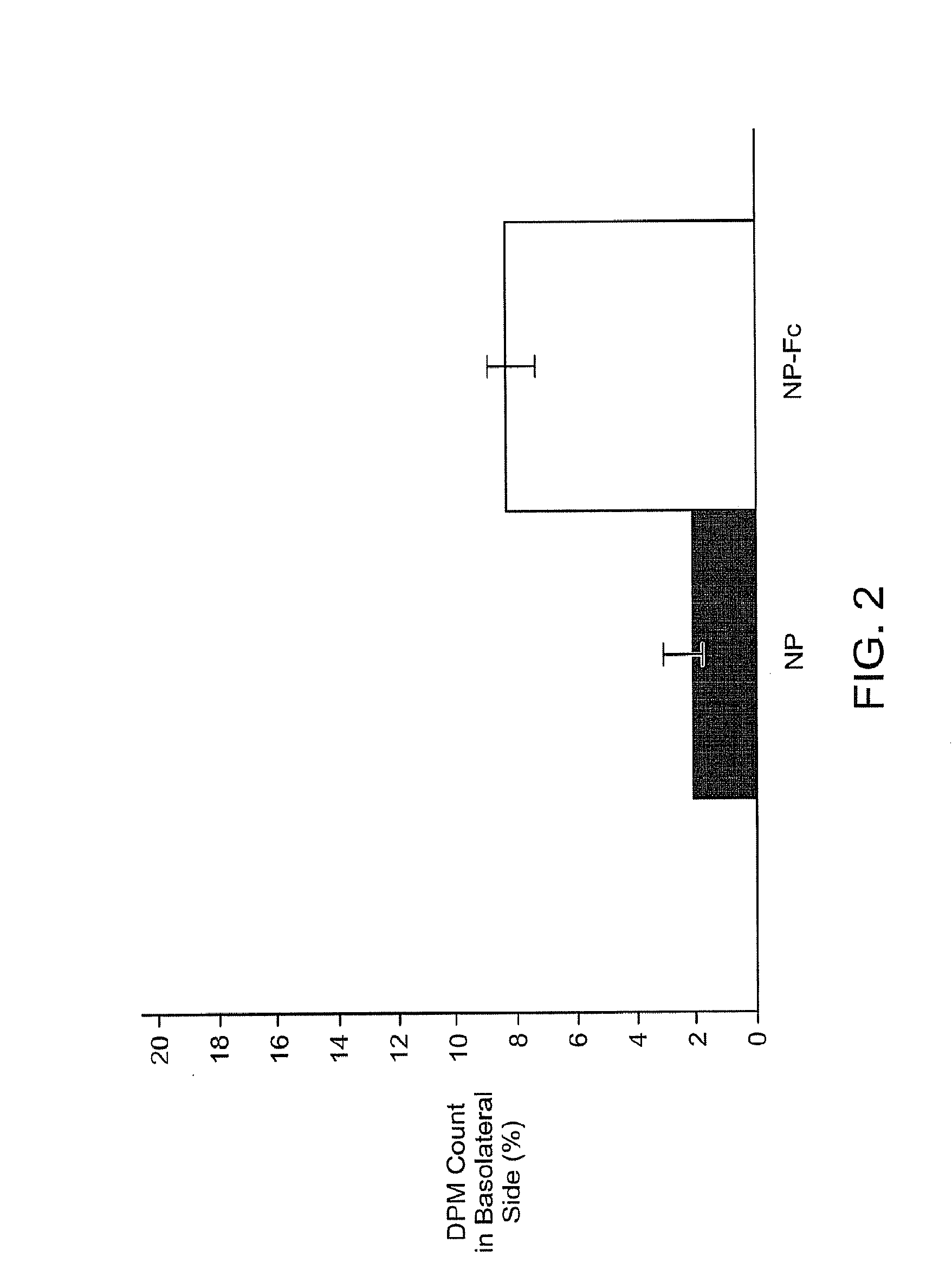
Drug delivery systems using fc fragments
InactiveUS20100303723A1Easy to useEffectively cross epithelial cell layersPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitheliumMedicine
The present invention provides drug delivery systems comprising FcRn binding partners (e.g., FcRn binding partner, Fc fragment) associated with a particle or an agent to be delivered. Inventive drug delivery systems allow for binding to the FcRn receptor and transcytosis into and / or through a cell or cell layer. Inventive systems are useful for delivering therapeutic agents across the endothelium of blood vessels or the epithelium of an organ.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
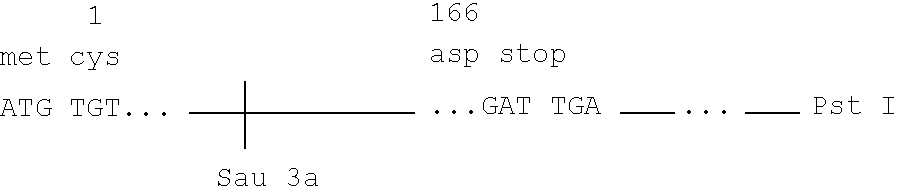
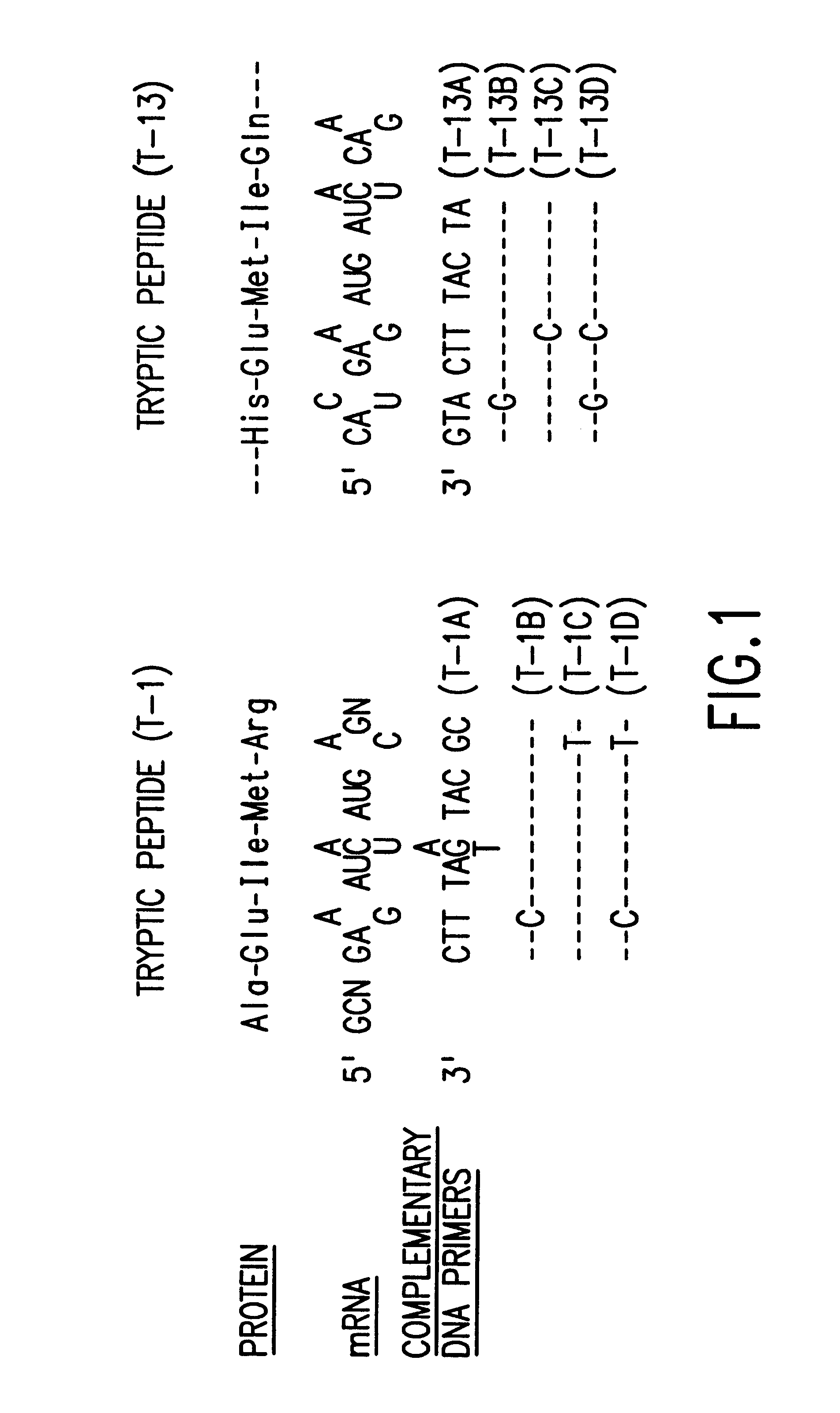
Microbial production of mature human leukocyte interferons
Disclosed herein are methods and means of microbially producing, via recombinant DNA technology, mature human leukocyte interferons, useful in the treatment of viral and neoplastic diseases.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG +1
Conjugates formed from polymer derivatives having particular atom arrangements
Polymeric reagents are provided comprising a moiety of atoms arranged in a specific order, wherein the moiety is positioned between a water-soluble polymer and a reactive group. The polymeric reagents are useful for, among other things, forming polymer-active agent conjugates. Related methods, compositions, preparations, and so forth are also provided.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Acryloyloxyethylphosphorylcholine Containing Polymer Conjugates and Their Preparation
InactiveUS20100166700A1Prevents and reduces efficiencyExtended half-lifeFactor VIINervous disorderPolymer sciencePharmaceutical drug
The present invention relates to polymeric reagents and conjugates thereof, methods for synthesizing the polymeric reagents and conjugates, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the conjugates and methods of using the polymer conjugates including therapeutic methods where conjugates are administered to patients.
Owner:KODIAK SCI
Protein complex using an immunoglobulin fragment and method for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20060269553A1Improve stabilityExtended durationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunological disordersHalf-lifeImmunoglobulin Fc Fragments
Disclosed are a protein conjugate with improved in vivo duration and stability and the use thereof. The protein conjugate includes a physiologically active polypeptide, a non-peptide polymer and an immunoglobulin Fc fragment. Since the three components are covalently linked, the protein conjugate has extended in vivo duration and enhanced stability for the physiologically active polypeptide. The protein conjugate maintains the in vivo activity at relatively high levels and remarkably increases the serum half-life for the physiologically active polypeptide, with less risk of inducing undesirable immune responses. Thus, the protein conjugate is useful for developing long-acting formulations of various polypeptide drugs.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Chimeric activators: quantitatively designed protein therapeutics and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110274658A1Reduced cell-activating propertyAvoid and reduce unwanted side effectObesity gene productsPeptide/protein ingredientsChimerin ProteinsApoptosis
Aspects of the invention provide methods for harnessing the potential of proteins that occur naturally (e.g., in humans) and that have serious but finite toxicity. Aspects of the invention relate to a quantitative systems-biological and structural approach to design a class Mof chimeric proteins that avoid the toxicity of protein drugs while retaining their desired activities. In particular, chimeric proteins containing a variant form of a natural protein fused to a targeting moiety may be administered to a subject to target a signal (e.g., induction of apoptosis) to particular cells without having a generalized toxic effect
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20070190611A1Reduce morbidityProlong lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
A polypeptide and polynucleotides encoding same comprising at least two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a peptide-of-interest are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
Compositions and methods of use of targeting peptides for diagnosis and therapy of human cancer
The present invention concerns compositions comprising and methods of identification and use of targeting peptides selective for cancer tissue, particularly prostate or ovarian cancer tissue. The method may comprise identifying endogenous mimeotopes of such peptides, such as GRP78, IL-11Rα and hsp90. Antibodies against such targeting peptides or their mimeotopes may be used for detection, diagnosis and / or staging of prostate or ovarian cancer. In other embodiments, the compositions and methods concern novel type of gene therapy vector, known as adeno-associated phage (AAP). AAP are of use for targeted delivery of therapeutic agents to particular tissues, organs or cell types, such as prostate or ovarian cancer. In still other embodiments, targeting peptides selective for low-grade lipomas may be used for detection, diagnosis and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20090312254A1Reduce dosing frequencyImprove compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
A polypeptide and polynucleotides encoding same comprising one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to an amino terminus of a cytokine and two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a cytokine are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:MODIGENE LLC +1
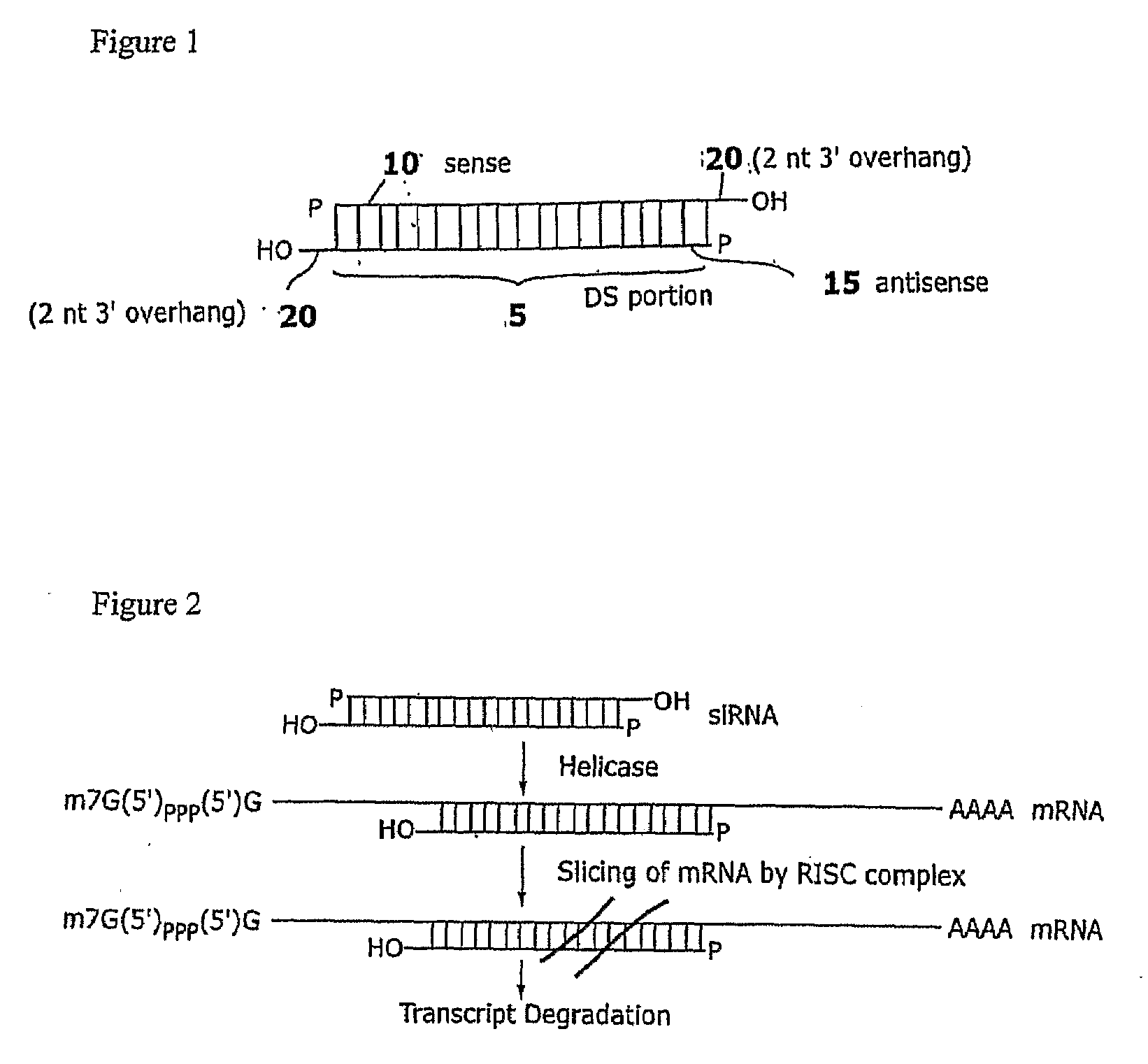
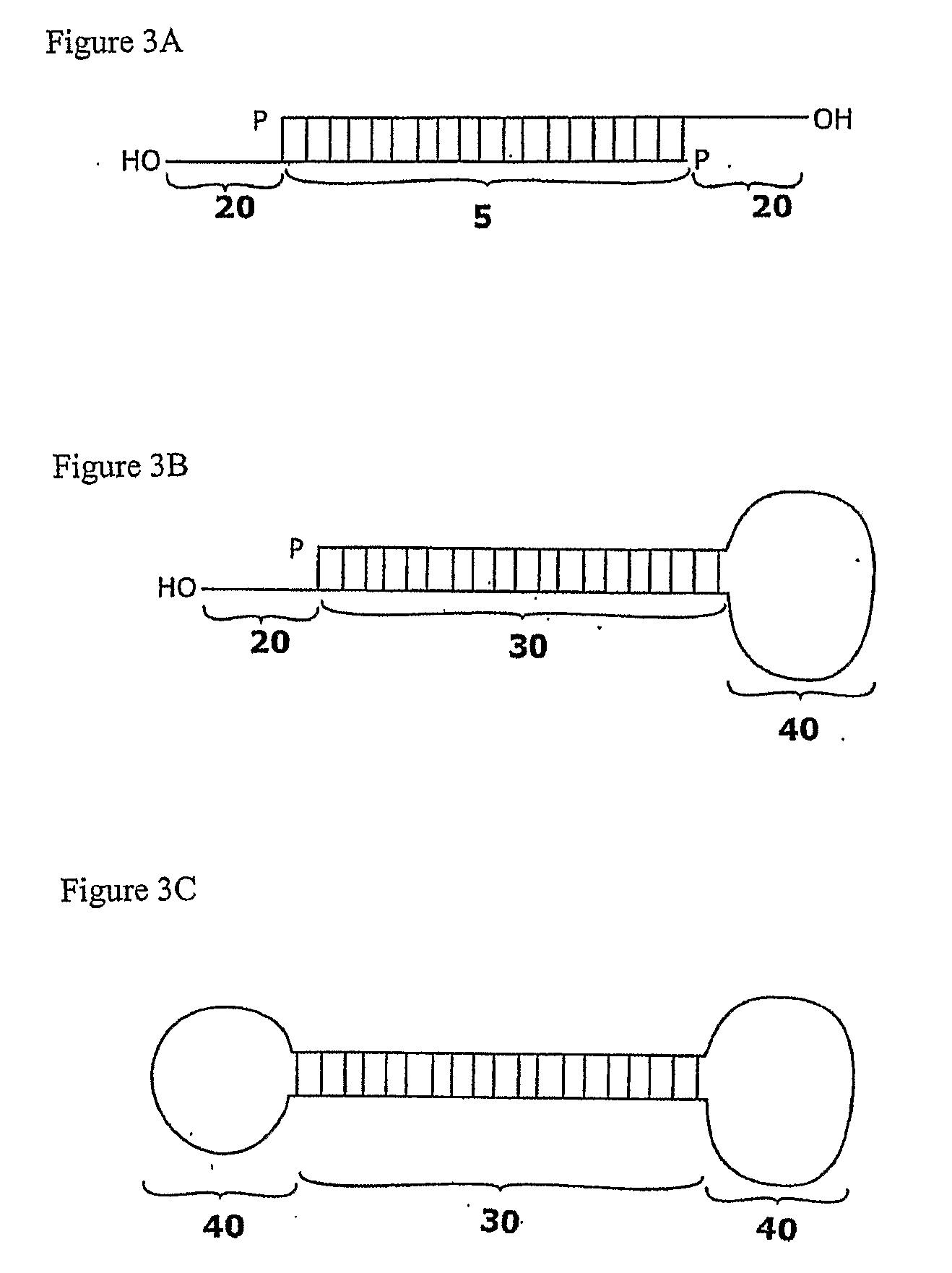
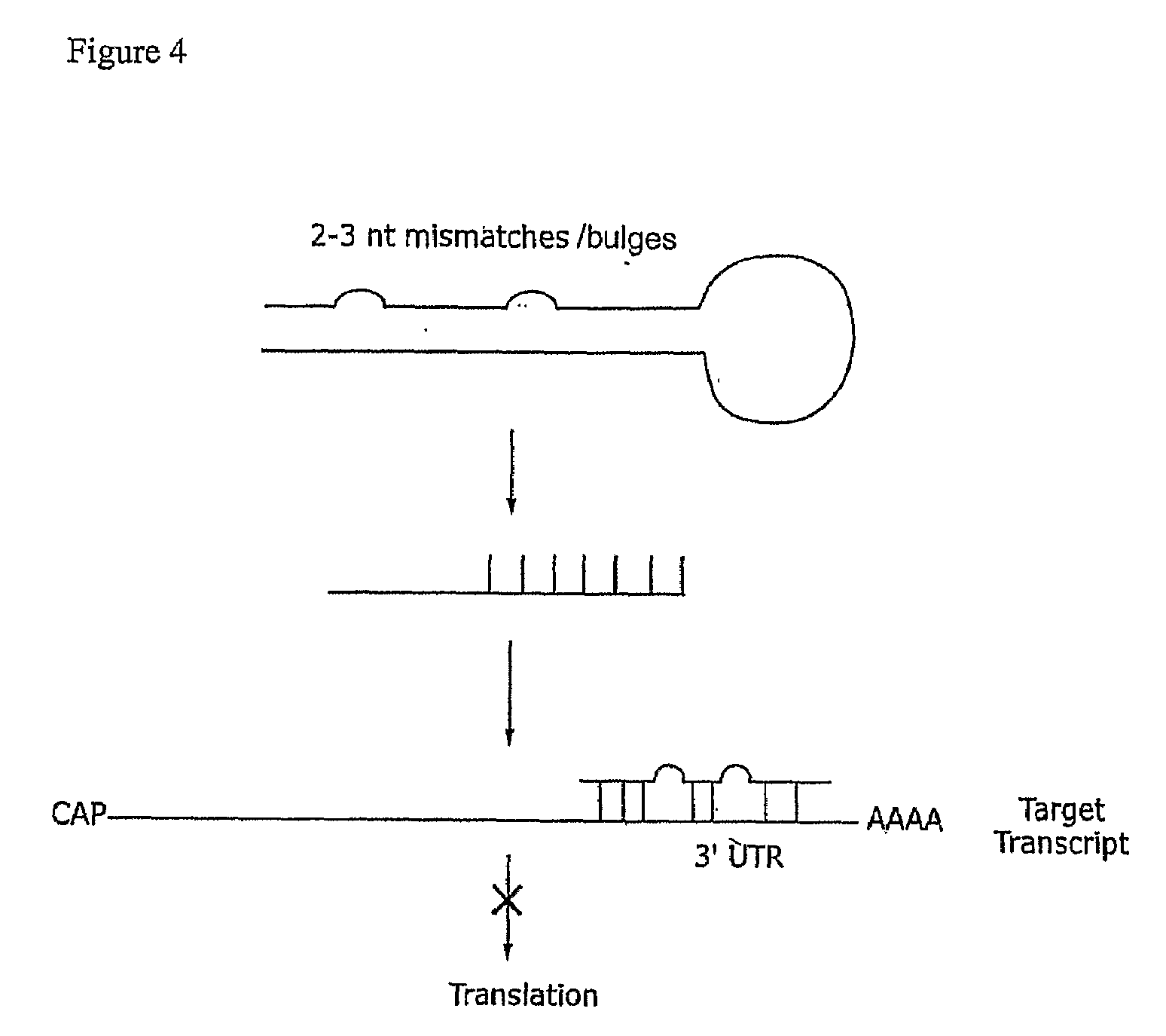
Compositions and methods for RNA interference with sialidase expression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090203055A1Reducing sialidase activityReduce decreaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSialic acidControl cell
The present invention provides RNAi agents targeted to sialidase. The RNAi agents include siRNA, shRNA, and expression vectors that comprise a template for transcription of an siRNA or shRNA. The invention further provides cells and cell lines that comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The cells and cell lines exhibit reduced sialidase activity relative to control cells that do not comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. Certain of the cell lines stably express the RNAi agent. The invention further provides methods of producing the cells and cell lines. The invention further provides methods for producing a glycoprotein in cells that comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The glycoproteins exhibit an improved sialic acid profile relative to glycoproteins produced by cells that do not comprise an RNAi agent targeted to sialidase. The invention further provides glycoproteins, e.g., therapeutic glycoproteins, produced in the cells.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
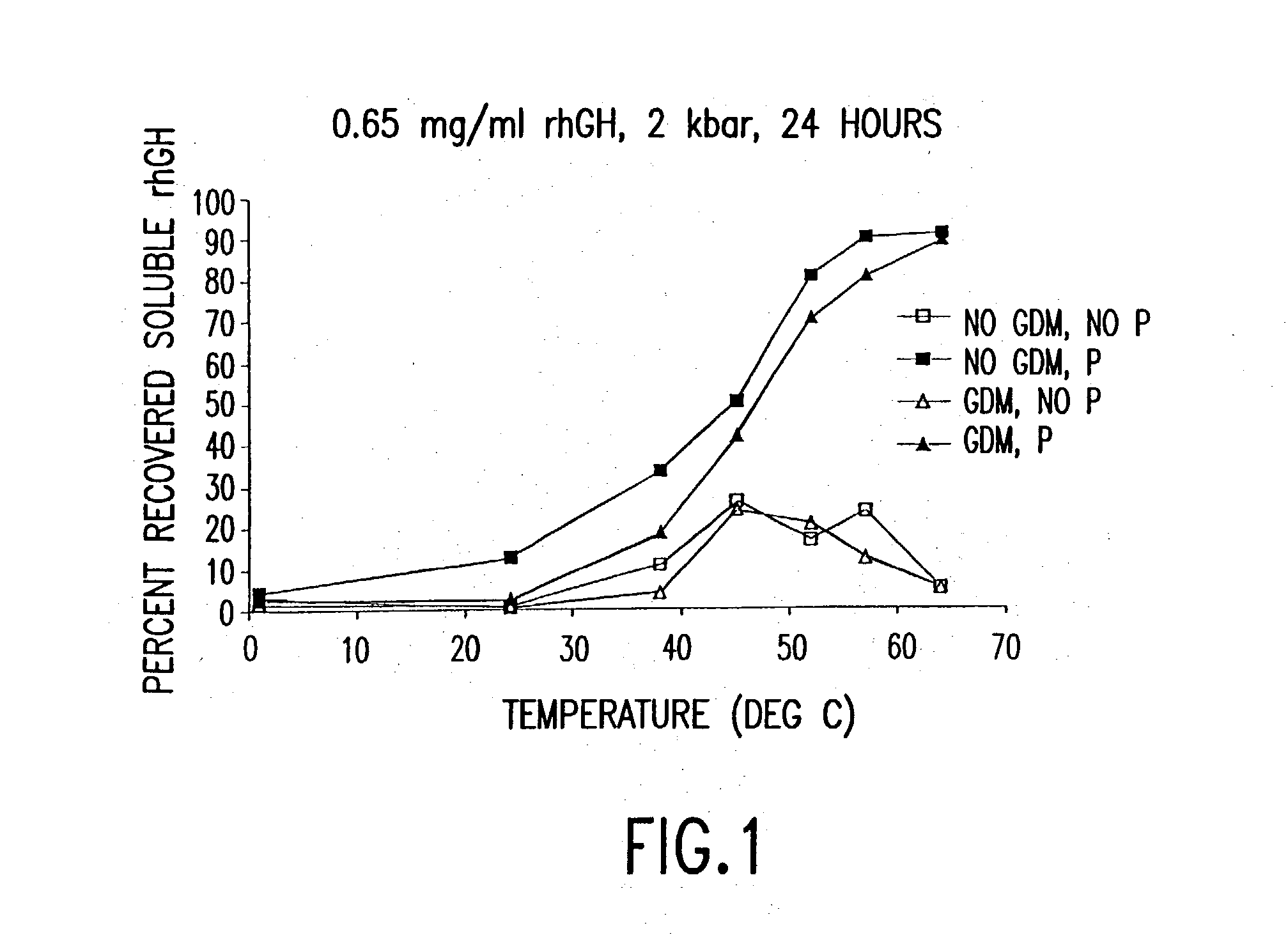
Methods for protein refolding
InactiveUS20040038333A1Decrease product valueDangerous anaphylactic reactionInactivation/attenuationDepsipeptidesDissolutionImproved method
The present invention discloses improved methods of disaggregating protein aggregates, and refolding denatured proteins, using high pressure. In particular, the present invention provides for the use of agitation, high temperature, "stepped" depressurization, dialysis and dilution under pressure to increase the speed and extent of aggregate dissolution and protein refolding.
Owner:BARFOLD INC
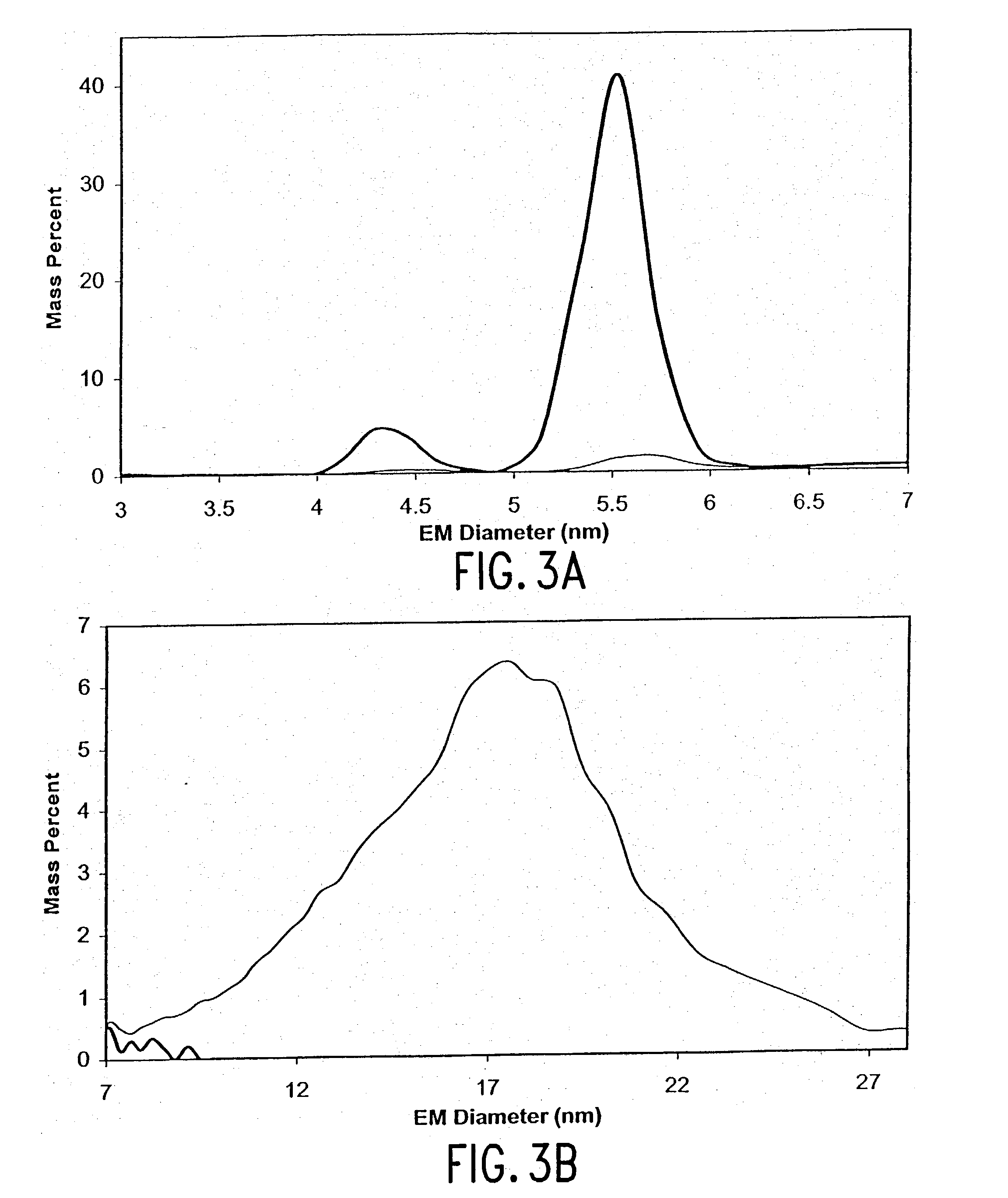
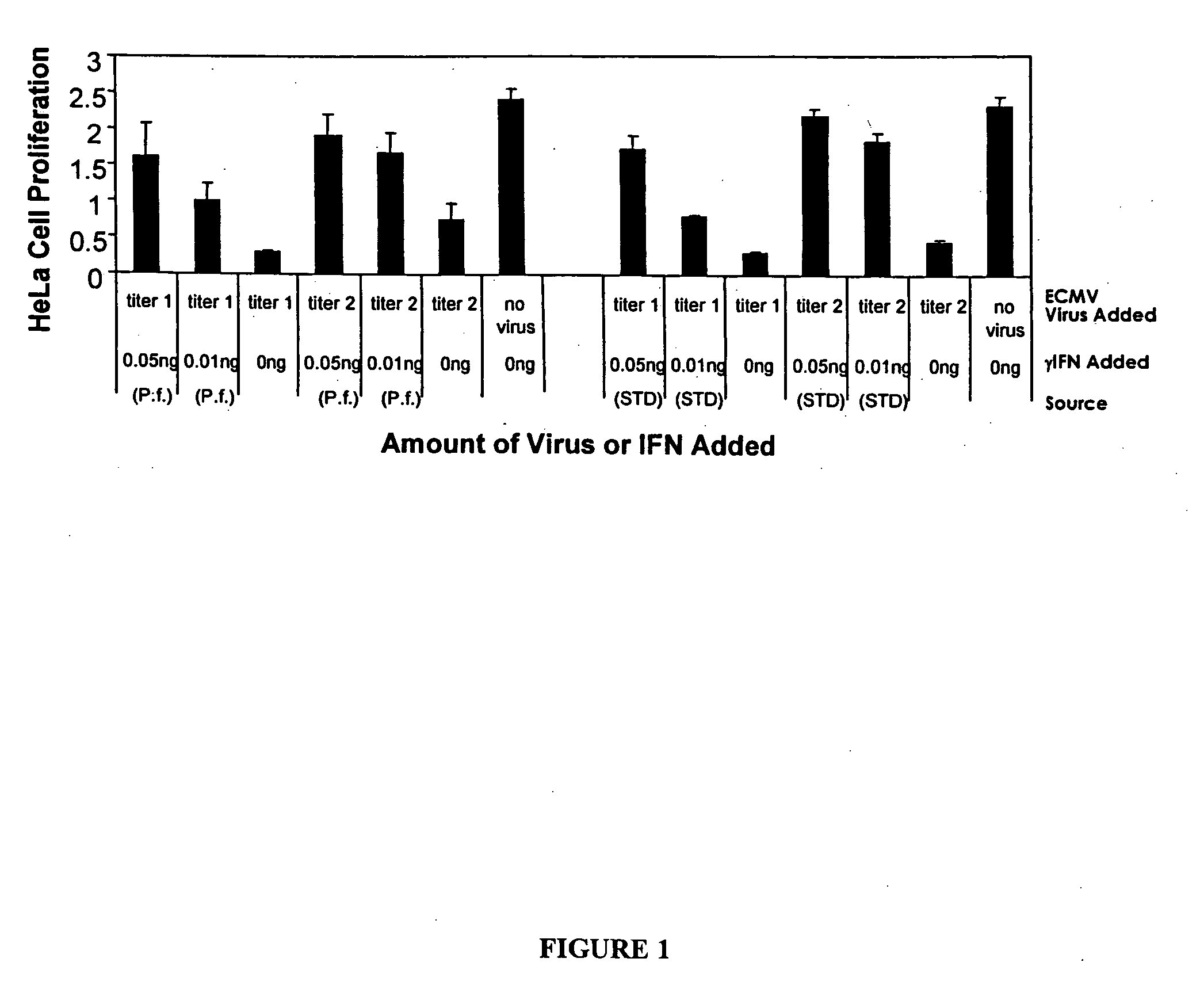
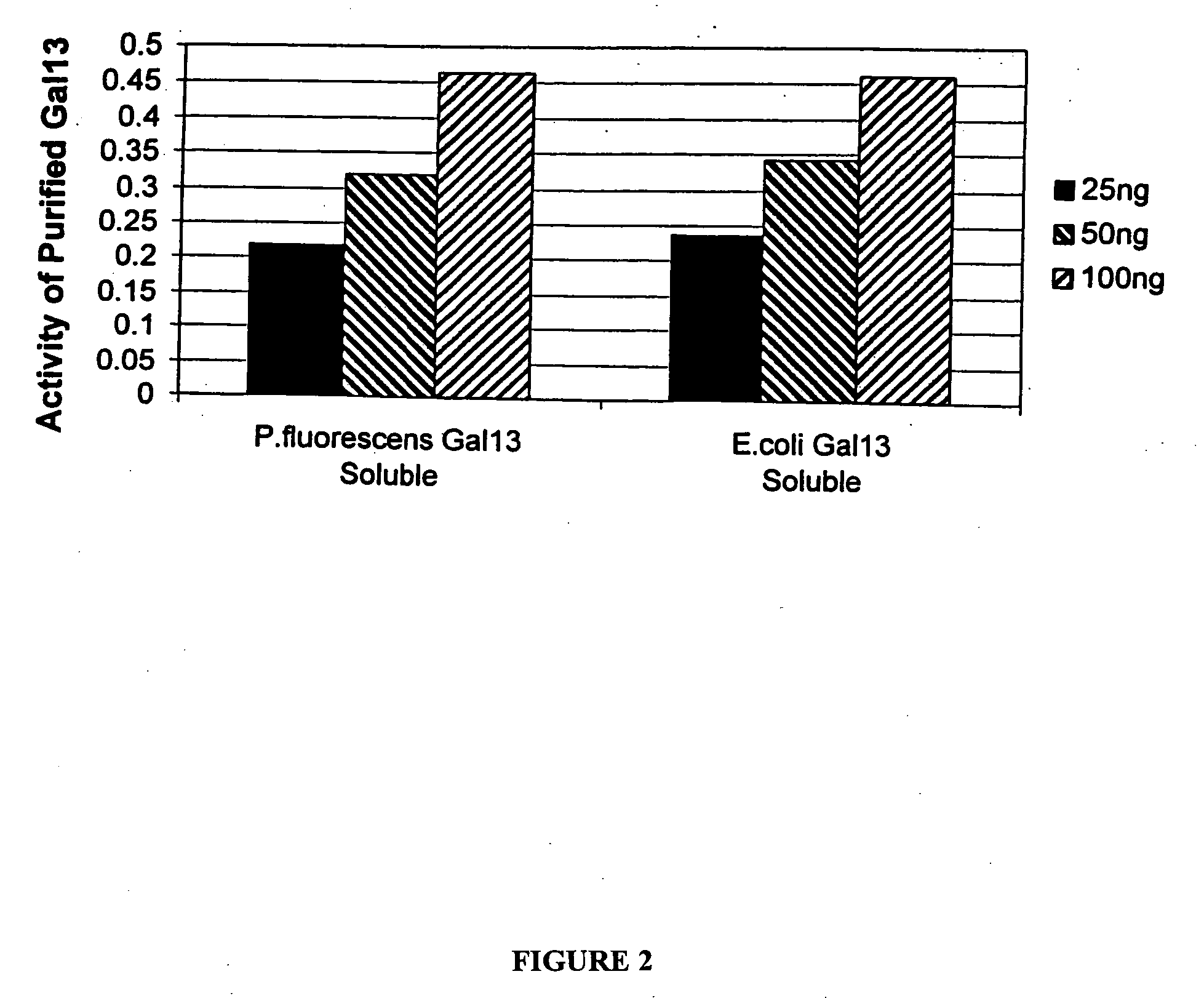
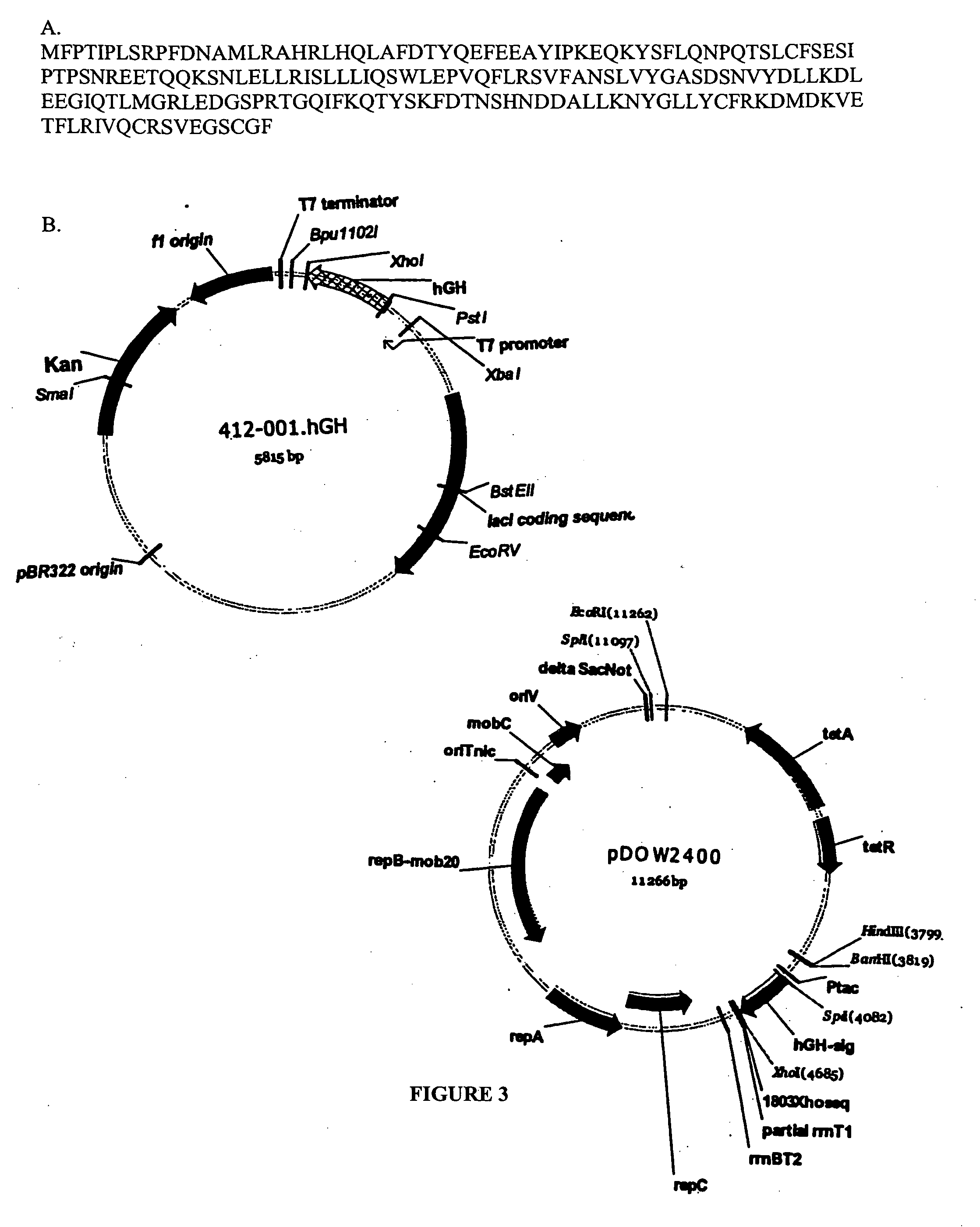
Expression of mammalian proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens
The invention is a process for improved production of a recombinant mammalian protein by expression in a Pseudomonad, particularly in a Pseudomonas fluorescens organism. The process improves production of mammalian proteins, particularly human or human-derived proteins, over known expression systems such as E. coli in comparable circumstances Processes for improved production of isolated mammalian, particularly human, proteins are provided.
Owner:PELICAN TECH HLDG INC
Homogeneous preparations of il-28 and il-29
ActiveUS20070042471A1Improve expression levelIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMutated proteinCysteine thiolate
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com