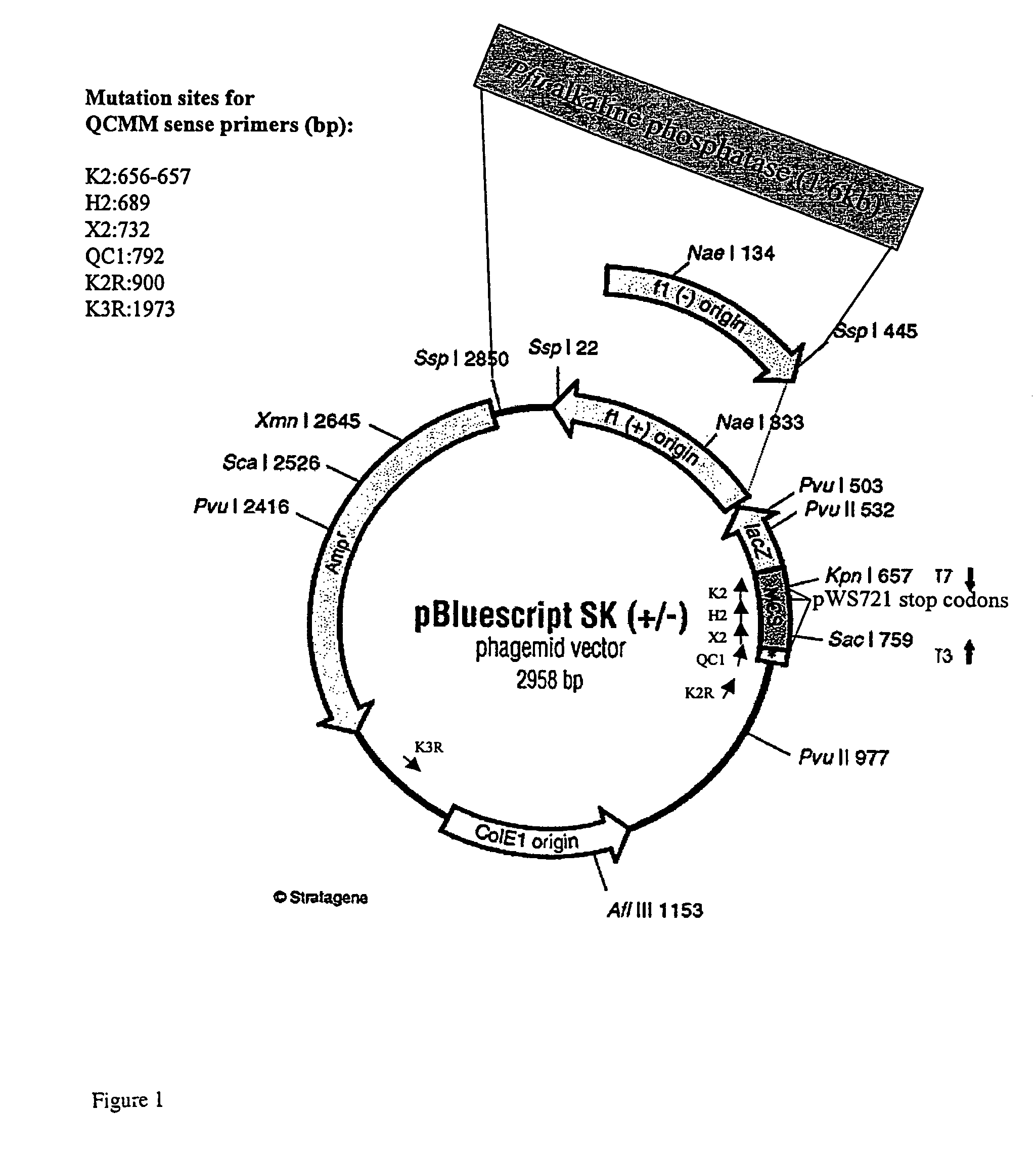
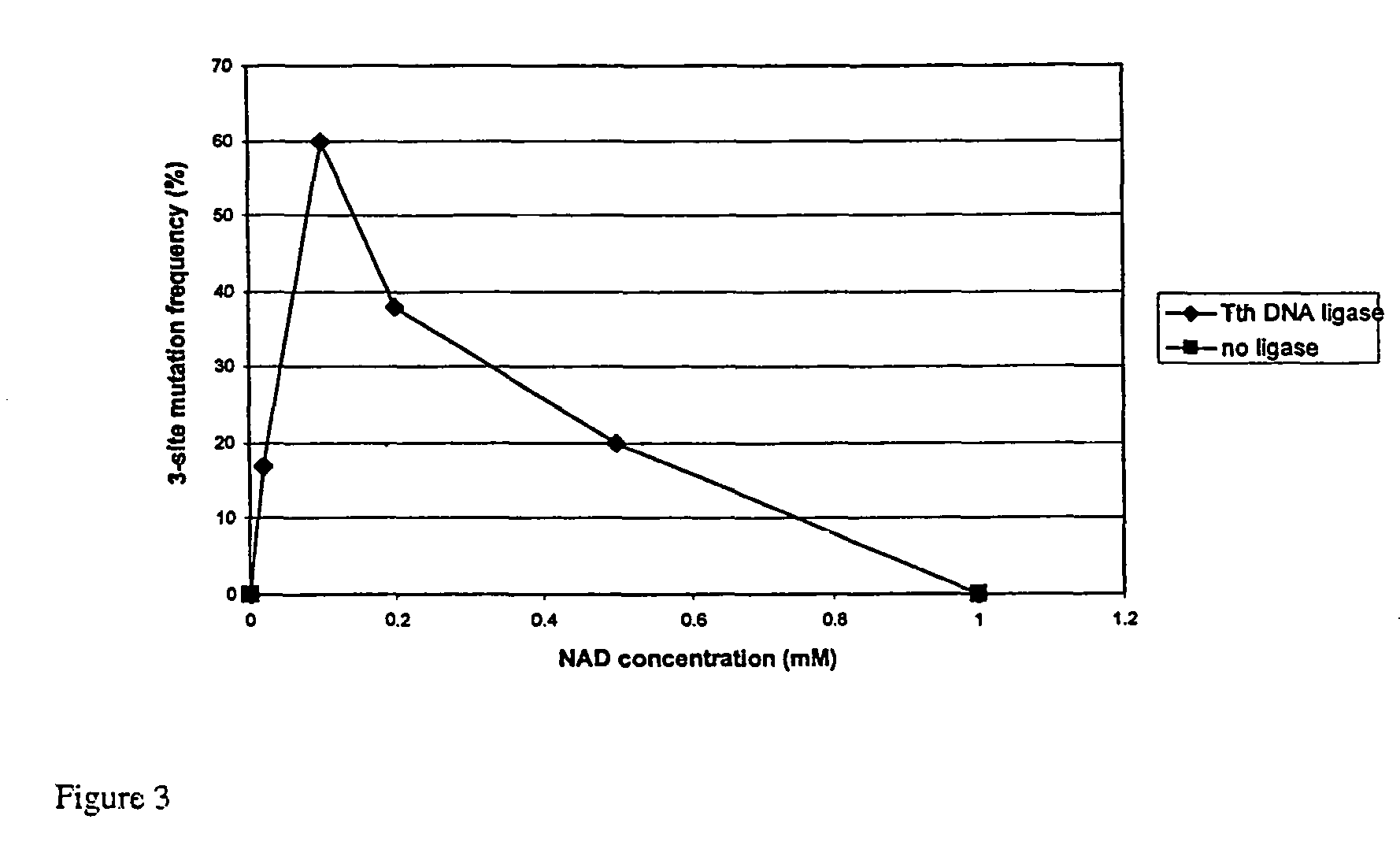
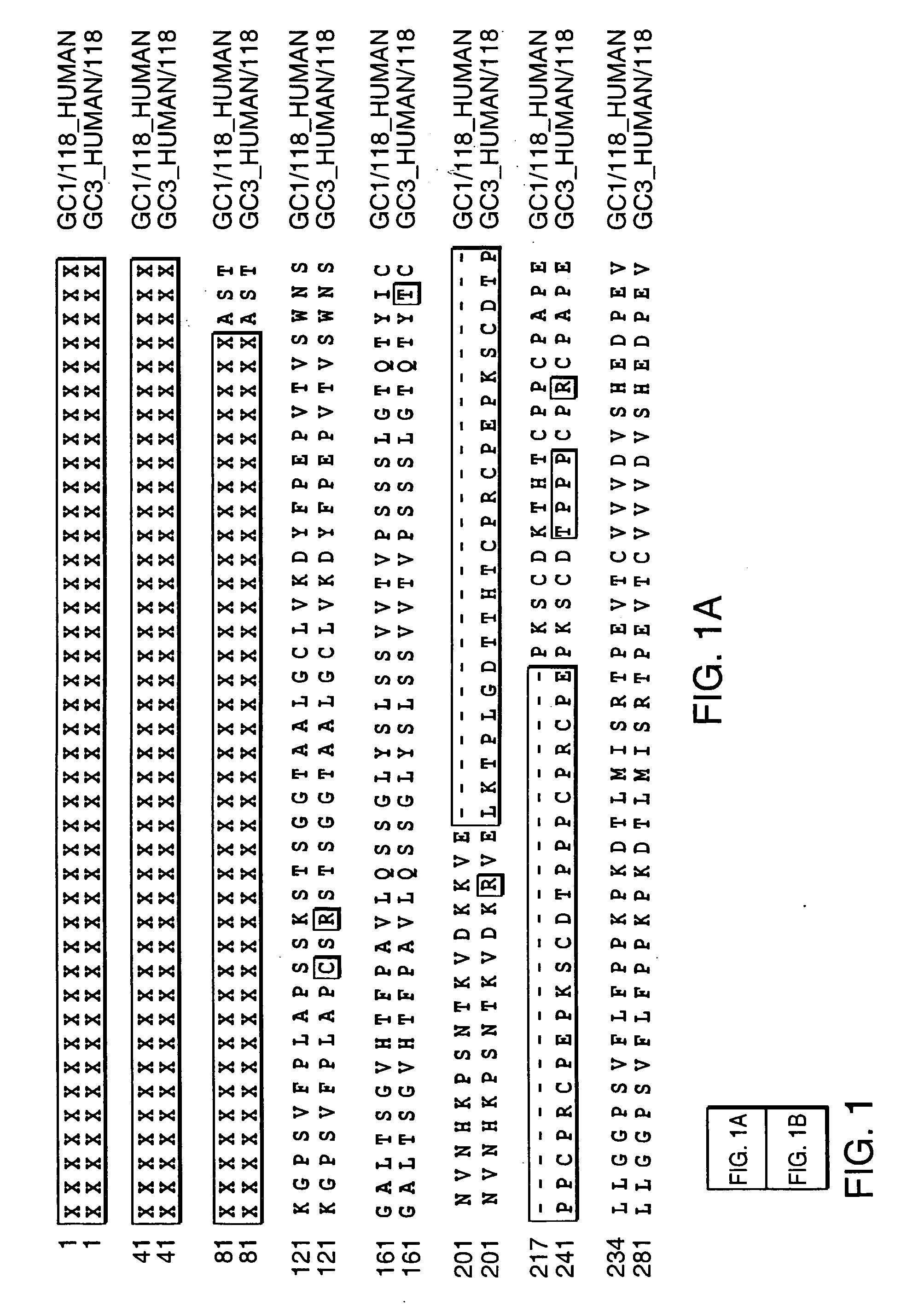
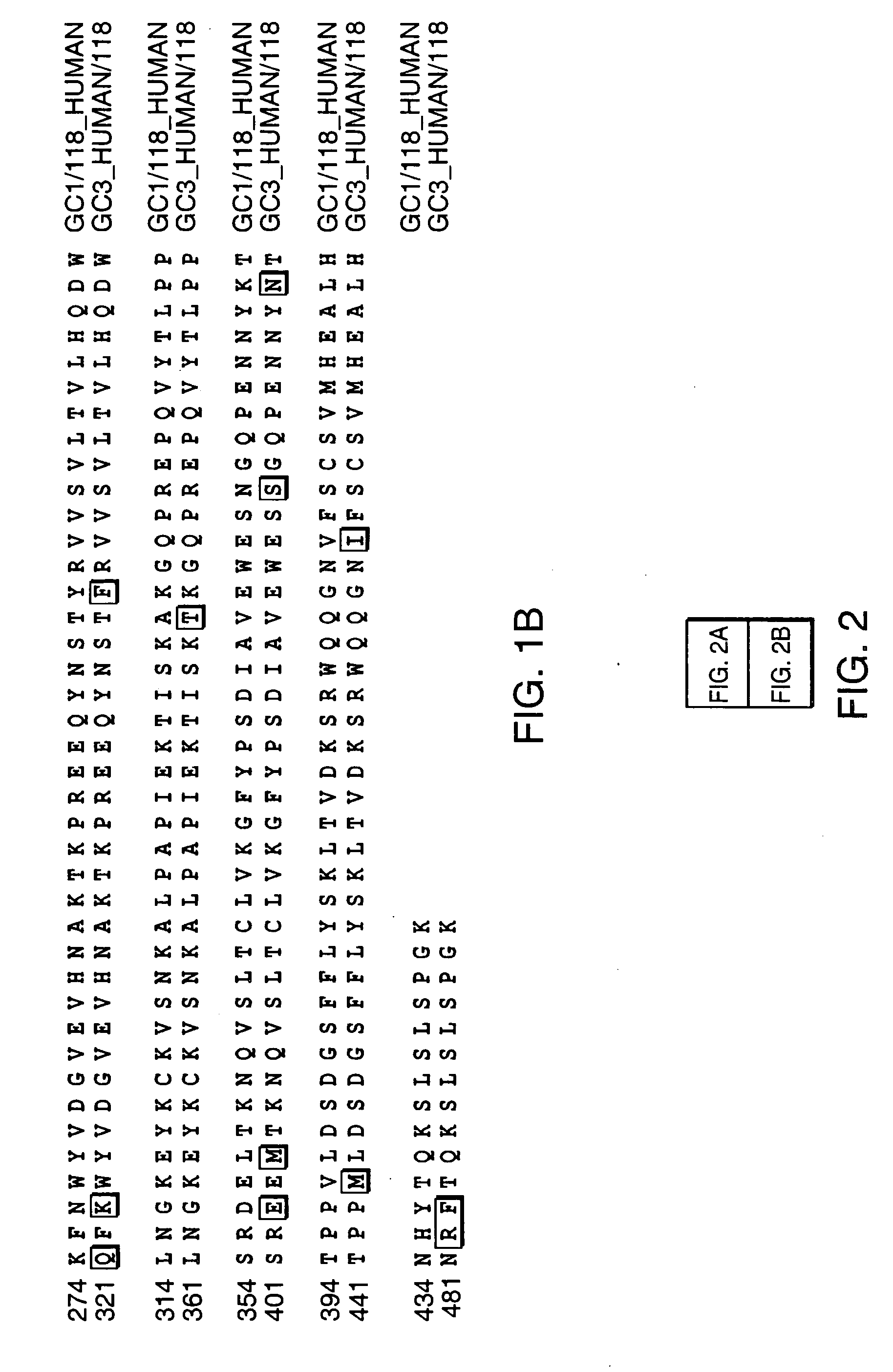
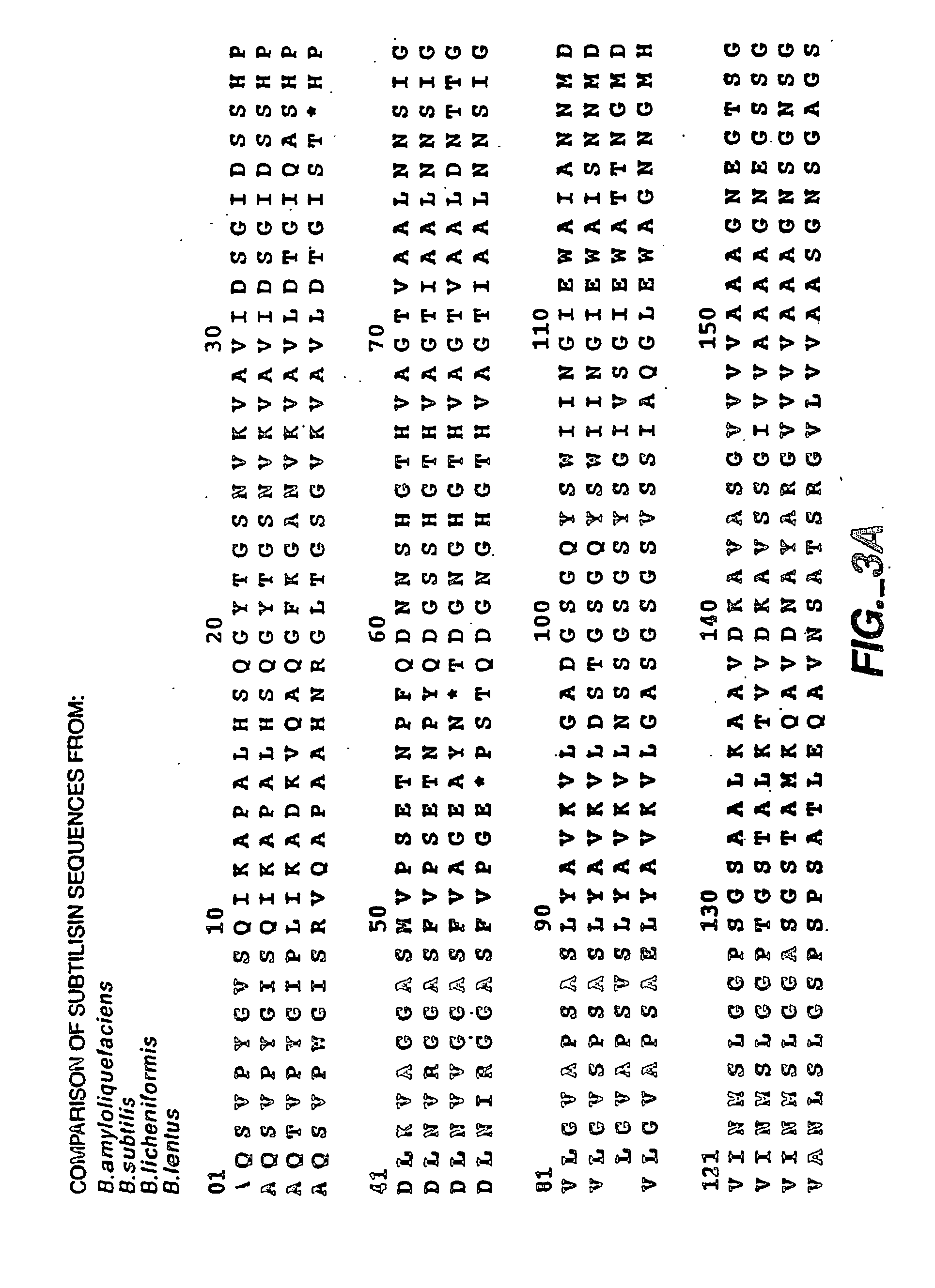
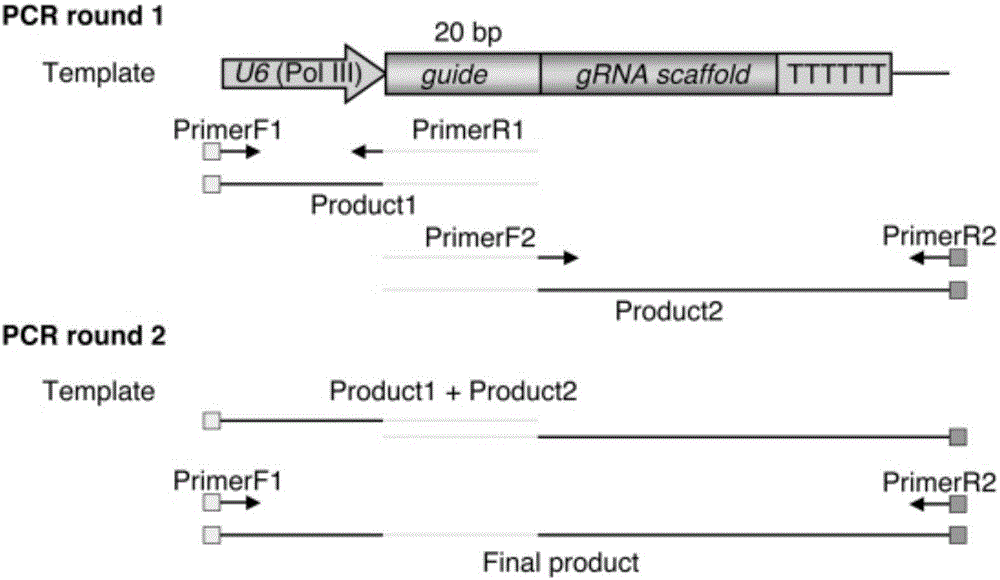
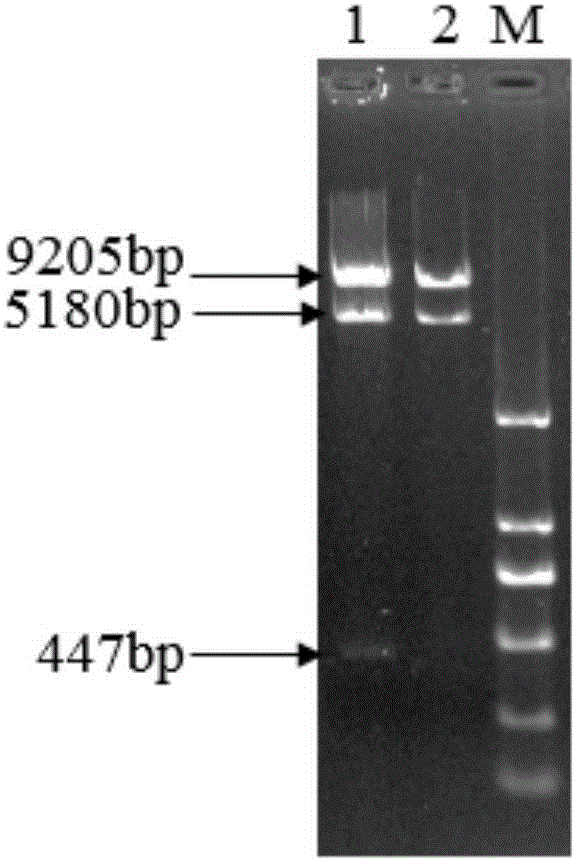
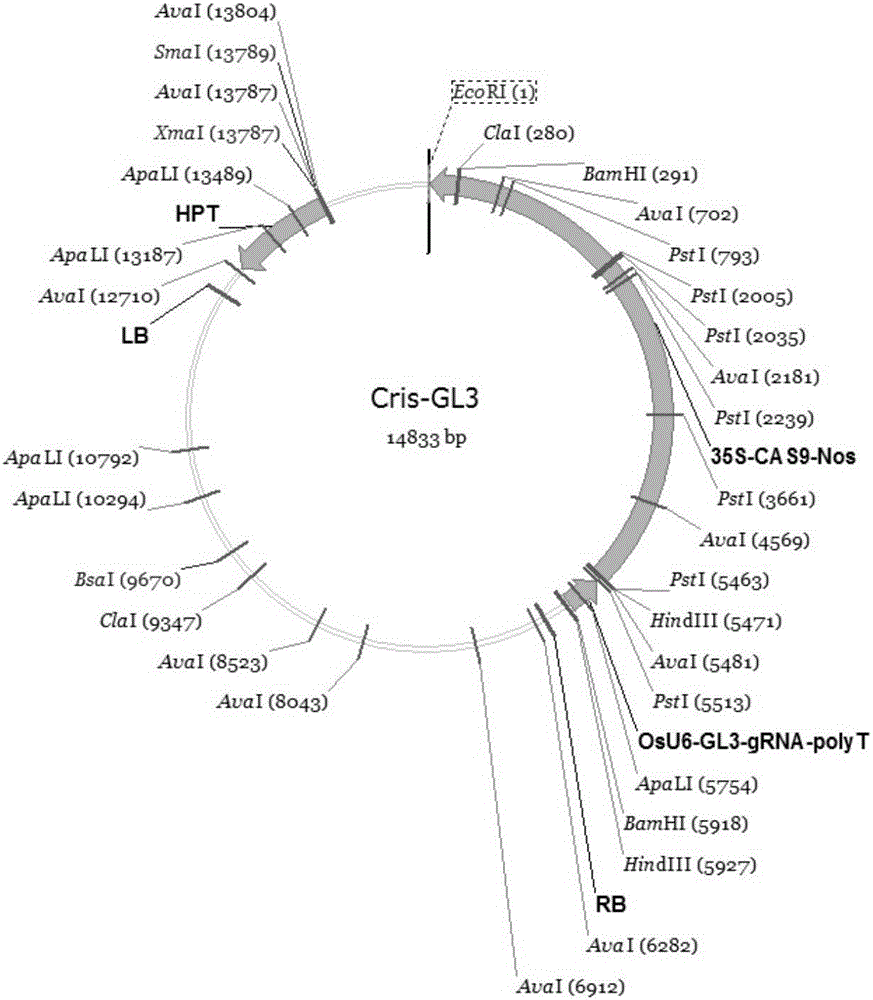
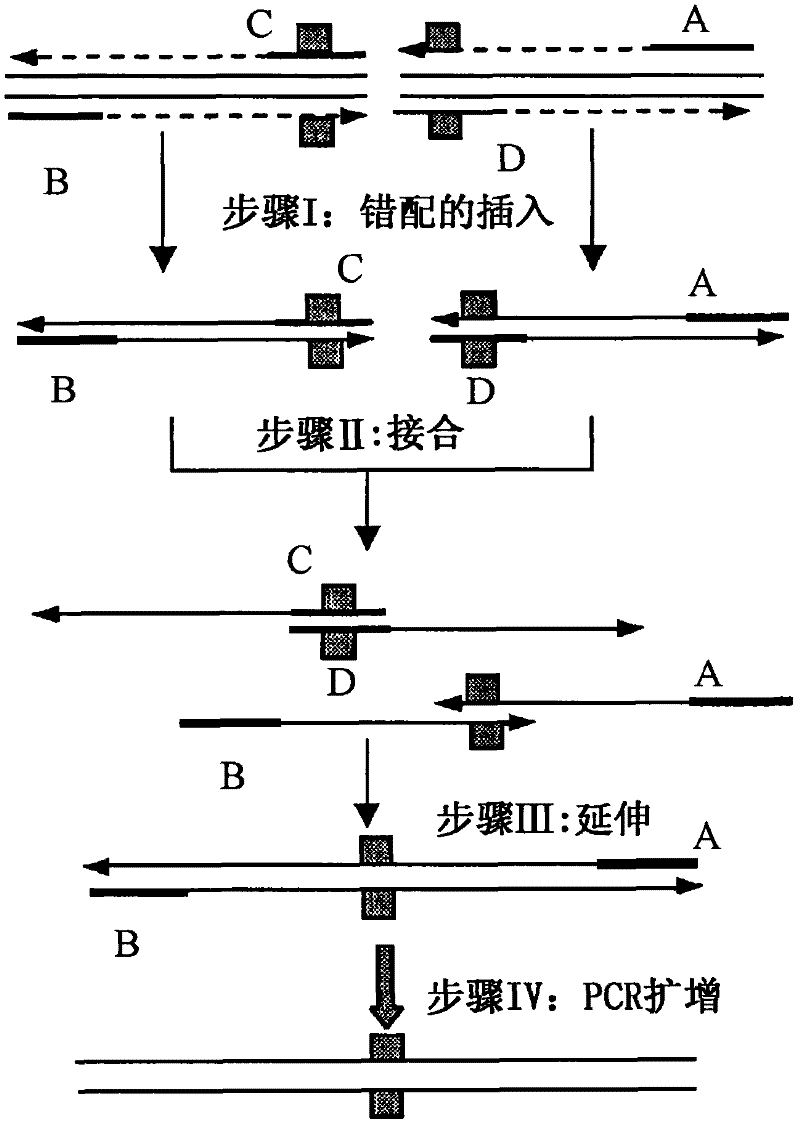
Patents
Literature
355 results about "Directed mutagenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Directed mutagenesis, also known as directed mutation, was a hypothesis proposing that organisms can respond to environmental stresses by orthogenetically directing mutations to certain genes or areas of the genome.
Multi-site mutagenesis
The present invention provides compositions and improved methods for multi-site directed mutagenesis and DNA shuffling. The present compositions and methods provide increased mutation frequency and increased number of transformants which allow one to sequence only a few clones in order to identify the correct mutants and to obtain the desired mutant by screening large number of transformants in a short time. Moreover, the inclusion of FEN-1, PEF and optimized buffer and cycling conditions provided in the present invention should also facilitate random mutagenized library construction and the mutagenesis of large or difficult templates.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Enhancing the circulating half-life of antibody-based fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060194952A1Extended half-lifeReduced binding affinityHybrid immunoglobulinsSugar derivativesFc(alpha) receptorFc receptor
Disclosed are methods for the genetic construction and expression of antibody-based fusion proteins with enhanced circulating half-lives. The fusion proteins of the present invention lack the ability to bind to immunoglobulin Fc receptors, either as a consequence of the antibody isotype used for fusion protein construction, or through directed mutagenesis of antibody isotypes that normally bind Fc receptors. The fusion proteins of the present invention may also contain a functional domain capable of binding an immunoglobulin protection receptor.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
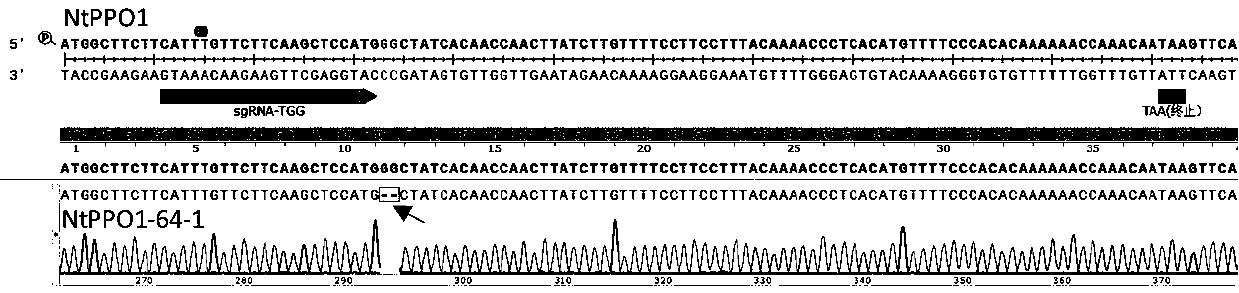
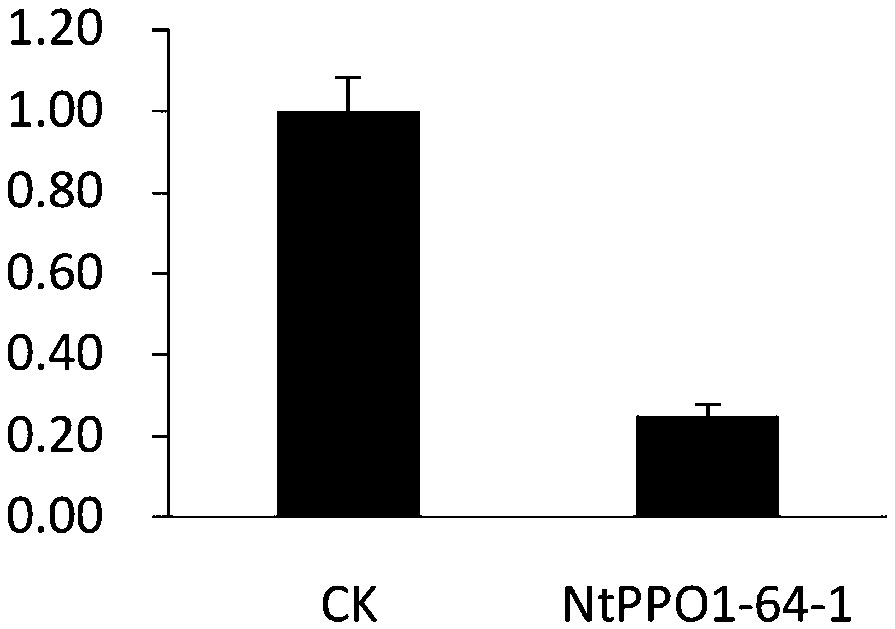
Tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 and site-directed mutagenesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN107653256AReduce expressionReduce PPO enzyme activityHydrolasesOxidoreductasesNicotiana tabacumPolyphenol oxidase
The invention discloses a tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 and a site-directed mutagenesis method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 is shown in SEQ ID:No.1, the coded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID:No.2. The invention further discloses a clone method of the tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1. The clone method comprisesthe specific steps that firstly, cDNAs of tobacco leaves are synthesized; secondly, PCR amplification of the NtPPO1 gene is conducted; thirdly, a CRISPR / Cas9 carrier of the NtPPO1 gene is constructed;fourthly, sequencing detection of the NtPPO1 gene mutation is conducted. The NtPPO1 gene has a wide application prospect in preventing tobacco browning. The tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene and the encoded protein thereof provide the gene and technology support for crops especially for anti-browning breeding of tobaccos.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Antineoplastic dibasic polypeptide and application and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101139613ASpecific targetingWon't attackPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid peptidesNucleotideDouble chain
The invention provides a gene, recombinant plasmid and polypeptide for an anti-tumor binary polypeptide. The gene of the recombinant anti-tumor binary polypeptide is obtained by connecting in an operable way the gene of a coding antibody simulator with a recombinant bacillus anthraci protein antigen gene. The recombinant plasmid of the invention is formed by inserting the gene of the coding antibody simulator by double-chain oligomeric nucleotide directed mutagenesis method into the recombinant bacillus anthraci protein antigen gene. The obtained recombinant plasmid is infected into engineering bacillus coli BL-21 to get engineering bacillus coli cell of anti-tumor binary polypeptide; the anti-tumor binary polypeptide can be obtained by expanding the bacillus coli, settling in centrifugal way the bacillus coli body, crushing in altrasonic way, settling and crushing bacillus coli body by hi-speed centrifuging and treating the upper clean solution. The anti-tumor binary polypeptide is of special targeting characteristic, higher efficiency in killing special physical tumor than prior anti-tumor medicine, and will not attack normal cells, and has much lower toxicity and poor-reaction than prior anti-tumor medicine.
Owner:姜荣锡
Perhydrolase providing improved specific activity
An acetyl xylan esterase variant having perhydrolytic activity is provided for producing peroxycarboxylic acids from carboxylic acid esters and a source of peroxygen. More specifically, a Thermotoga maritima acetyl xylan esterase gene was modified using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create an enzyme catalyst characterized by an increase in specific activity. The variant acetyl xylan esterase may be used to produce peroxycarboxylic acids suitable for use in a variety of applications such as cleaning, disinfecting, sanitizing, bleaching, wood pulp processing, and paper pulp processing applications.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Multi-site mutagenesis
ActiveUS20060051748A1Optimized cycling conditionSimple methodSugar derivativesHydrolasesMulti siteMutation frequency
The present invention provides compositions and improved methods for multi-site directed mutagenesis and DNA shuffling. The present compositions and methods provide increased mutation frequency and increased number of transformants which allow one to sequence only a few clones in order to identify the correct mutants and to obtain the desired mutant by screening large number of transformants in a short time. Moreover, the inclusion of FEN-1, PEF and optimized buffer and cycling conditions provided in the present invention should also facilitate random mutagenized library construction and the mutagenesis of large or difficult templates.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Mutation penicillin G acylase, recombinant expression plasmid and transformation engineering strains thereof
ActiveCN101177688AImprove synthesis abilityMaximum conversion rate increaseBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolysatePolymerase L
The invention relates to a gene, mutant plasmid and engineering bacteria which have improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase and are obtained by a gene site-directed mutagenesis method, and mutant enzyme can also be obtained with improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase by fermenting and purifying the engineering bacteria. Two enzymes Kpn I and Pst I are firstly used for cutting pUC18 by the invention, then T4 polymerase is adopted to make the ends blunt, and pZ01 is obtained through self-linkage; the enzyme of EcoR I is used for cutting pZ01, and then connected with pEES102 that is also cut by the enzyme of EcoR I, thereby obtaining the recombinant plasmid pY020; the pY020 is adopted as a template plasmid, and TaKaRa MuTanBEST Kit is utilized for conducting the site-directed mutagenesis to B.megaterium PGA, thereby obtaining the mutant plasmid with improved synthesis performance to the penicillin G acylase. The mutant plasmid is transformed to bacillus subtilis to obtain the required engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria are amplified and fermented, and the mutant enzyme with improved maximum conversion rate of 7-ADCA and the ratio of synthetic product / hydrolysate can be obtained after the engineering bacteria are purified.
Owner:SHANXI WEIQIDA PHARMA IND
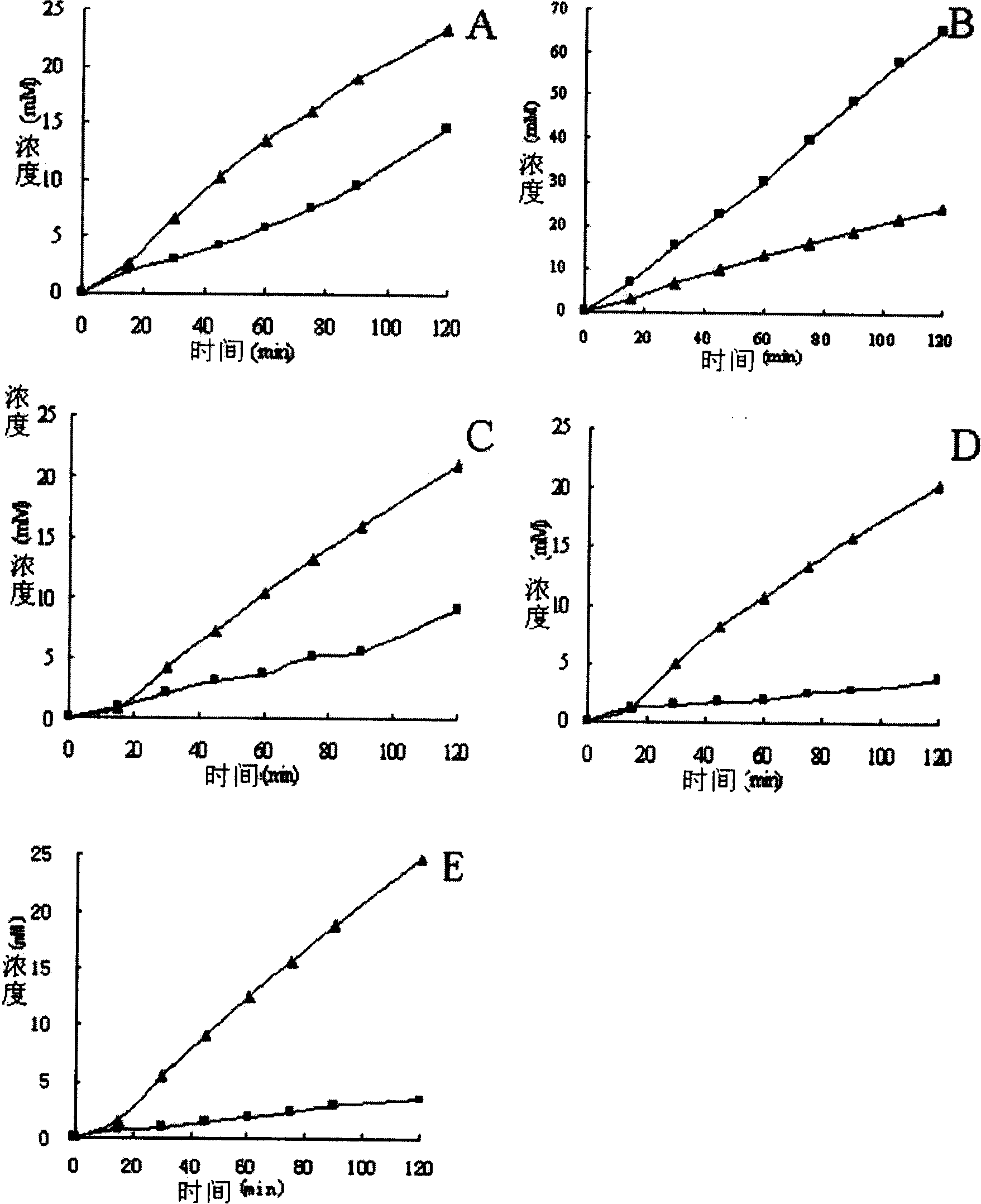
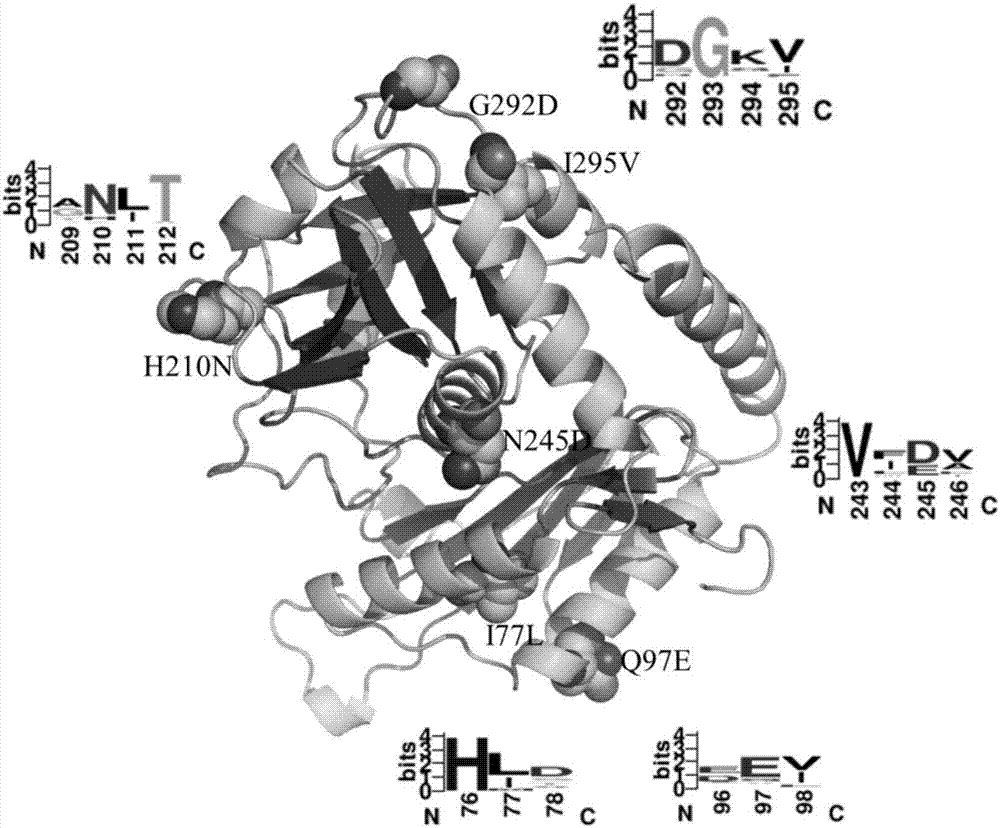
Omega-transaminase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107058256AIncrease the probability of positive mutationImprove experimental efficiency and feasibilityTransferasesFermentationSite-directed mutagenesisEnzyme
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant and a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The amino acid sequence of the omega-transaminase mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, SEQ ID No. 4, SEQ ID No. 6, SEQ ID No. 8, SEQ ID No. 10 or SEQ ID No. 12. The invention further provides the gene of the omega-transaminase mutant, an expression unit containing the gene, recombinant plasmid and a transformant. The preparation method includes: using an NCBI database and BLAST software to perform comparison screening to obtain the homologous amino acid sequence of omega-transaminase, using a Weblogo program to obtain a sequence consistency result, using the homologous amino acid sequence, the sequence consistency result and the sequence of the omega-transaminase to determine amino acid residue sites which need to be mutated, and using site-directed mutagenesis technology to perform experimental verification. The method has the advantages direct mutation probability can be increased effectively, experiment efficiency and feasibility are increased, and mutant enzymes whose thermodynamic stability is evidently better than that of wild enzymes can be screened out.
Owner:上海邦林生物科技有限公司
Methods for site-directed mutagenesis and targeted randomization
InactiveUS20060252155A1Efficient conversionAvoid the needOther foreign material introduction processesMedical preparationsEscherichia coliRandomization
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the construction and direct transformation of site-saturation libraries into Bacillus. This method avoids the need for the use of intermediate hosts, such as E. coli for the development of Bacillus strains suitable for the production of proteins.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Mutant of cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase having highly beta-cyclodextrin yielding property and mutation method
InactiveCN101503680AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesWild typeSite-directed mutagenesis
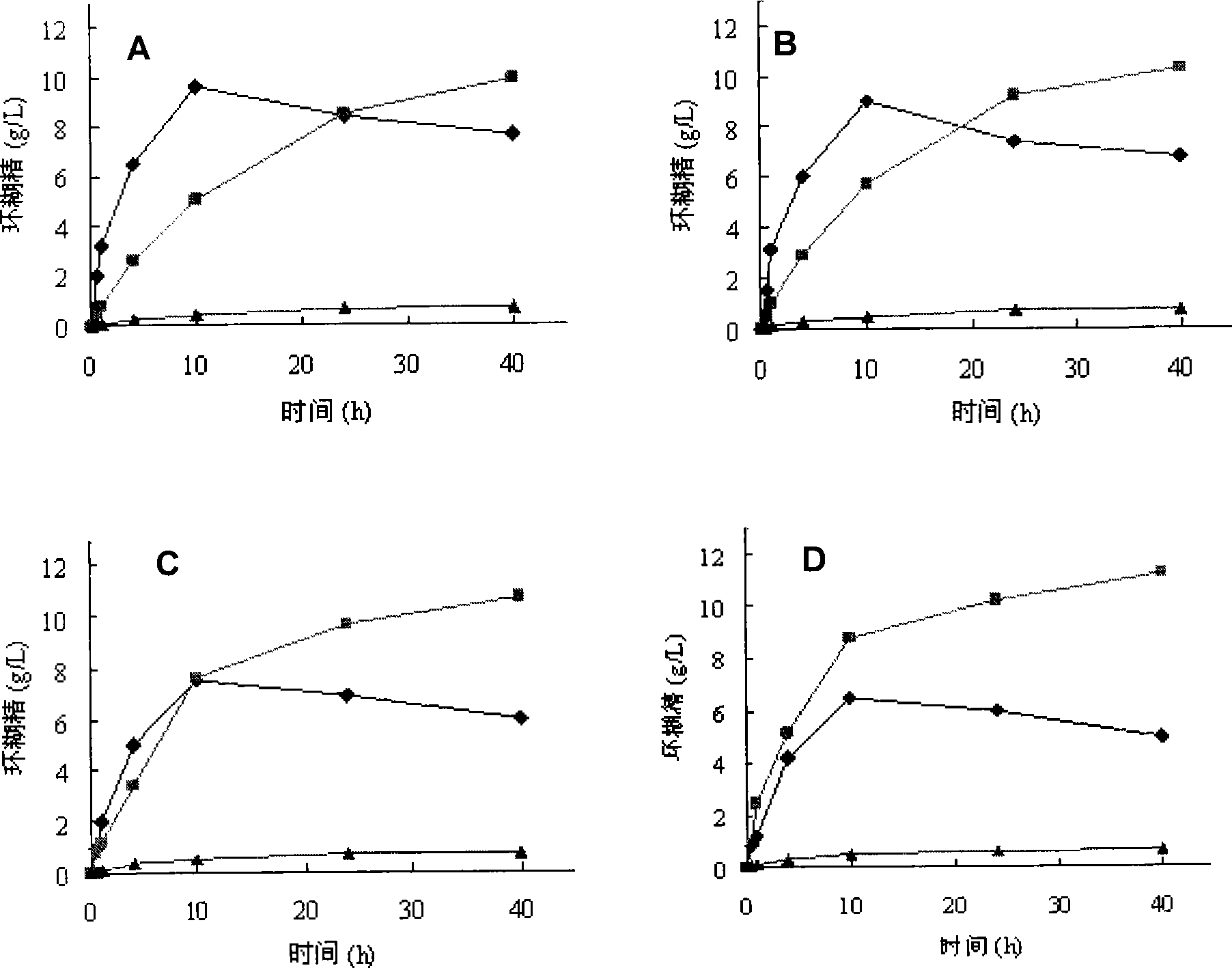
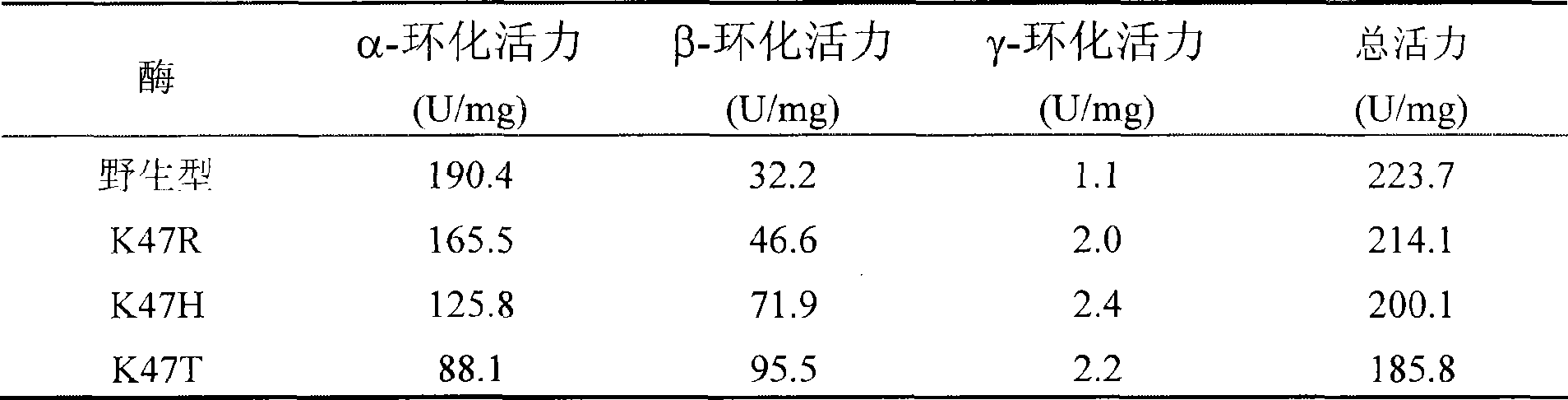
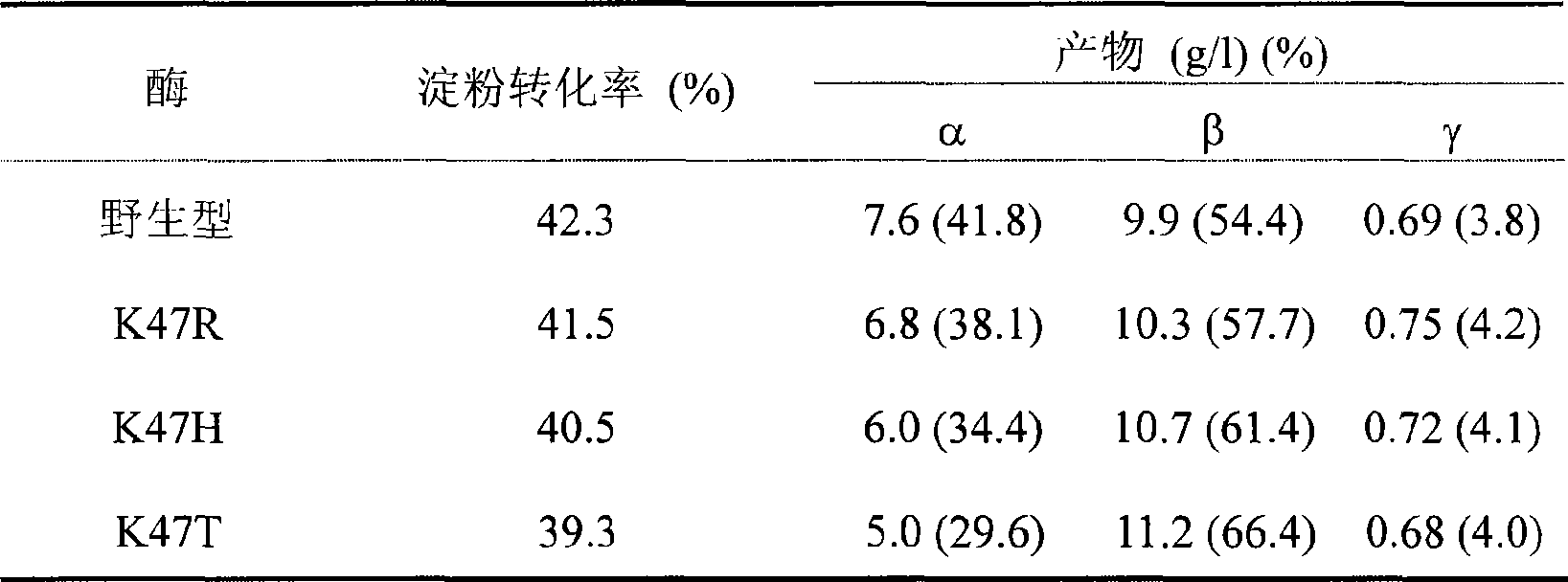
The invention relates to a mutant of a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with the capability of highly yielding beta-cyclodextrin and a mutation method, which belong to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention improves the capability of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin by a rite-directed mutagenesis method, provides a mutant proposal for improving the capability of CGT enzyme from Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M 208063) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin, and substitutes Lys on the 47 position of the CGT enzyme for Arg, His and Thr respectively; the beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the obtained three mutant enzyme of K47R, K47H and K47T is improved compared with wild type CGT enzymes, wherein the mutant enzyme K47T is particularly obvious. The mutant enzymes are more favorable for industrial production of the beta-cyclodextrin than the wild type CGT enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Paddy rice BADH2 gene site-directed mutagenesis method through using CRISPR-CAS9 technology
InactiveCN106676130ACreate Fragrant Rice Germplasm Resources Conveniently and EfficientlyImplement site-directed mutagenesisPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMutantSite-directed mutagenesis
The invention provides a paddy rice BADH2 gene site-directed mutagenesis method through using CRISPR-CAS9 technology. According to the fact that a paddy rice BADH2 gene is designed based on a sgRNA sequence of CRISPR / Cas9, a DNA fragment with the sgRNA sequence coded is connected to a carrier carrying CRISPR / Cas, and paddy rice is transformed, thereby achieving site-directed mutagenesis of the paddy rice BADH2 gene. The nucleotide sequence of a sgRNA acting site is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The paddy rice endogenous gene BADH2 is edited through CRISPR-CAS9 technology to obtain a BADH2 mutant, which is convenient and efficient in creation of jasmine rice germplasm resources.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
Acid resistant medium temperature alpha-amylase and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses acidproof medium-temperature alpha-amylase and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: A1, amplifying a precursor alpha-amylase gene; A2, performing site-directed mutagenesis on the precursor alpha-amylase; A3, constructing a mutant alpha-amylase expression vector; and A4, transforming bacillus subtilis by using the expression vector. A recombinant strain obtained by the method can be used for industrialized production of an acidproof alpha-amylase mutant. The required acidproof alpha-amylase mutant can be obtained by the following steps of: culturing recombinant cells in a liquid culture medium with selection pressure without induced expression, precipitating supernatant by using ammonium sulfate, dialyzing a precipitate, desalting, adding an allyl dextran S300 gel column, and eluting by using eluent.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Feruloyl esterase and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109652392AIncrease enzyme activityHigh hydrolytic activityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCefazolin
The invention provides feruloyl esterase and a preparing method and application thereof. A feruloyl esterase gene coming from a soil macro gene library have the nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The gene contains a tetrapeptide SXXK sequence motif which is rarely seen, and after the esterase gene is inserted into plasmid pET28a(+), the gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21(DE3) to achieve heterogeneous expression. The molecular weight of purified recombinase (DLFae4) is 38.3 kDa. Besides, it is put forward for the first time that novel feruloyl esterase can hydrolyze penbritin, penicillin, cefazolin and other lactam antibiotics. As is shown by site-directed mutagenesis experiments, a catalysis triplet of DLFae4 is composed of serine(S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302), and the mutation of any of serine (S11), histidine (H74) and aspartic acid (D302) can cause loss of the catalysis capability of DLFae4. DLFae4 has a high hydrolytic activity on methyl ferulate and has good heat stability. In the presence of cellulase, DLFae4 can obviously increase the amount of ferulic acid released from destarched wheat bran. Due to peculiar activities and enzymatic characteristics of novel feruloyl esterase, novel feruloyl esterase can be applied to feed, paper making, food, pharmacy and other fields.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
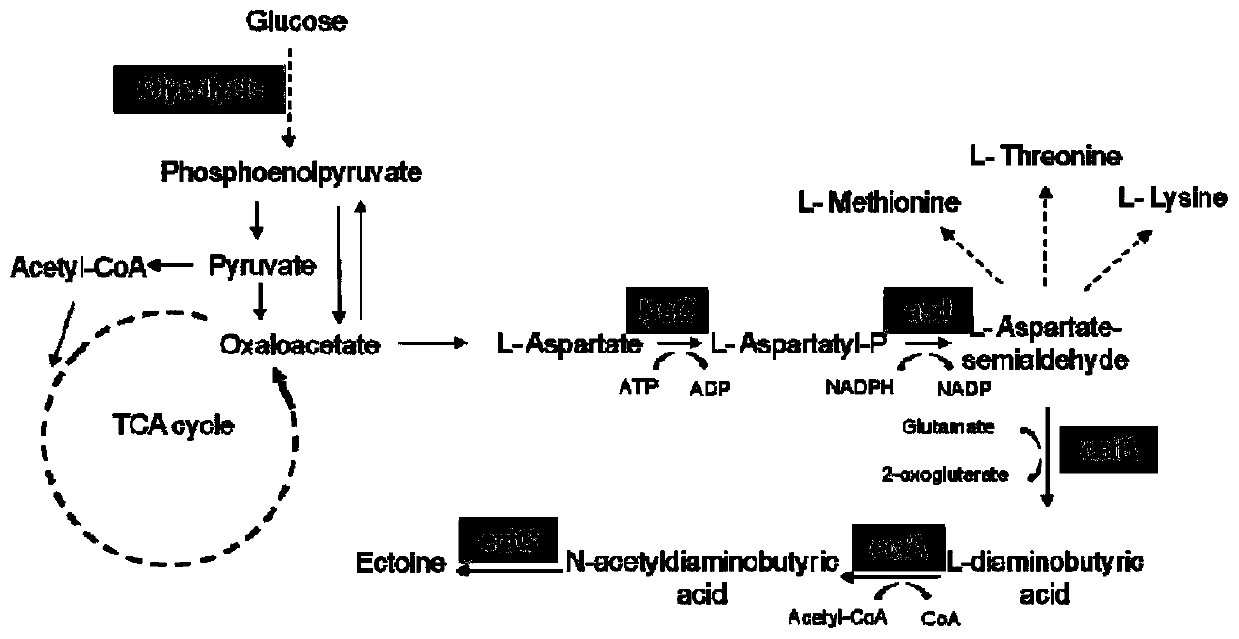
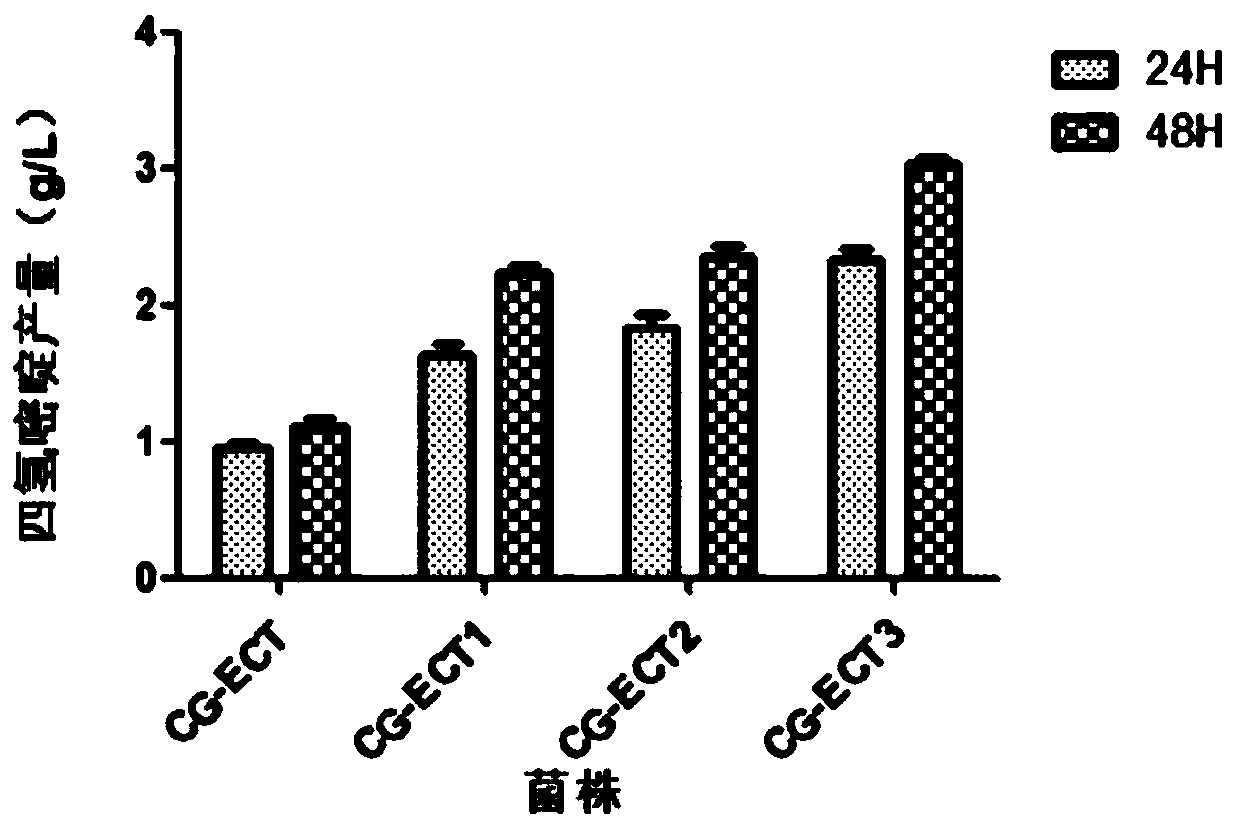
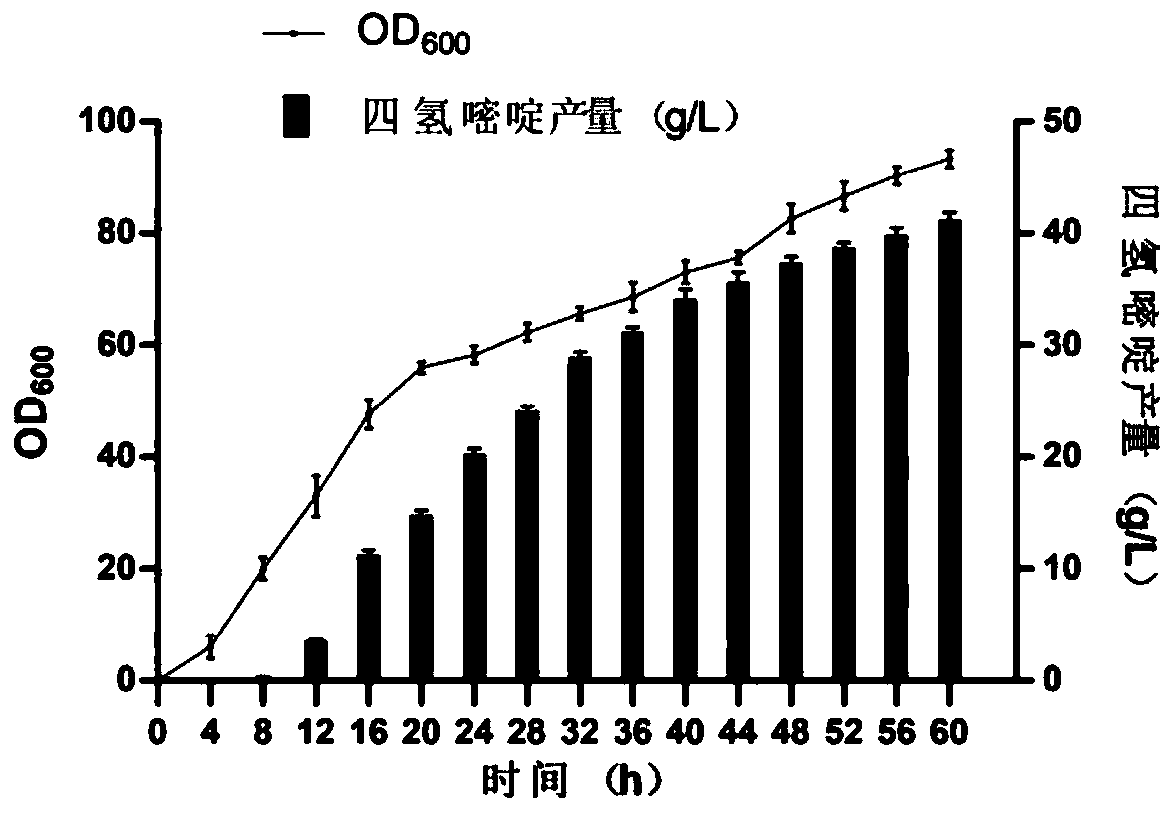
Tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
ActiveCN110699310APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBacilliBiological safety
The invention discloses tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Feedback inhibition is relieved through site-directed mutagenesis of Corynebacterium glutamicum aspartokinase gene lysC, and expression of mutational LysC is intensified through promoter replacement. Further, pentose phosphate pathway of host bacteriais further intensified through promoter replacement to meet needs on reducing power NADPH in efficient synthesis of tetrahydropyridine. Finally, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by transferring tetrahydropyridine synthetic gene cluster ectABC of P. stutzeri into recombinant bacteria. By recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum, tetrahydropyridine can be efficiently synthesized by utilizing cheap raw materials like glucose and maize plasm; compared with recombinant Escherichia coli produced strains, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum hasbetter bio-safety and is of great significance to industrial production and large-scale application of tetrahydropyridine.
Owner:无锡晶扬生物科技有限公司
Immunogenic detoxified mutant e. coli lt-a toxin
InactiveUS20030113338A1Maximise adjuvanticityMaximise immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliAdjuvant
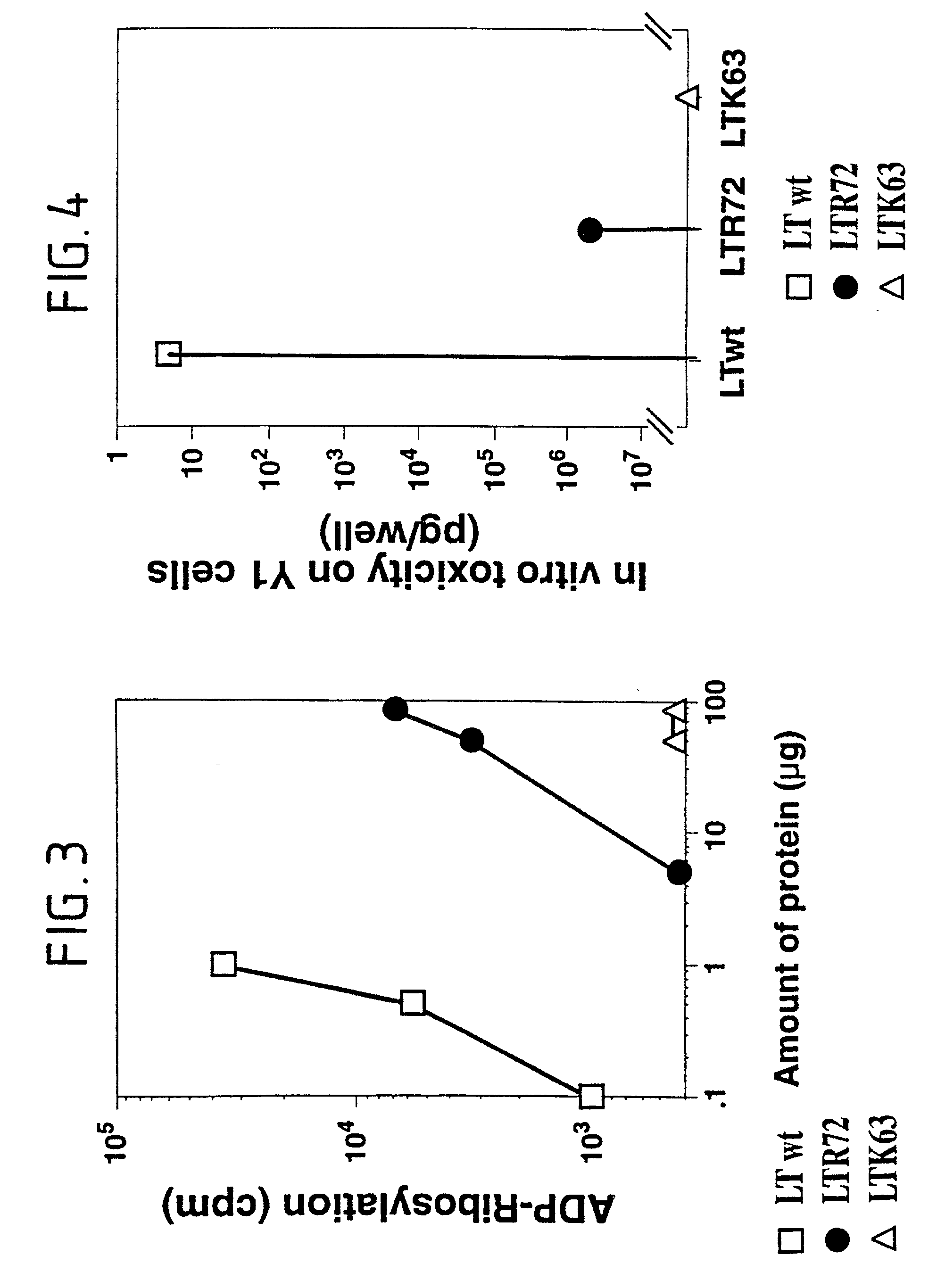
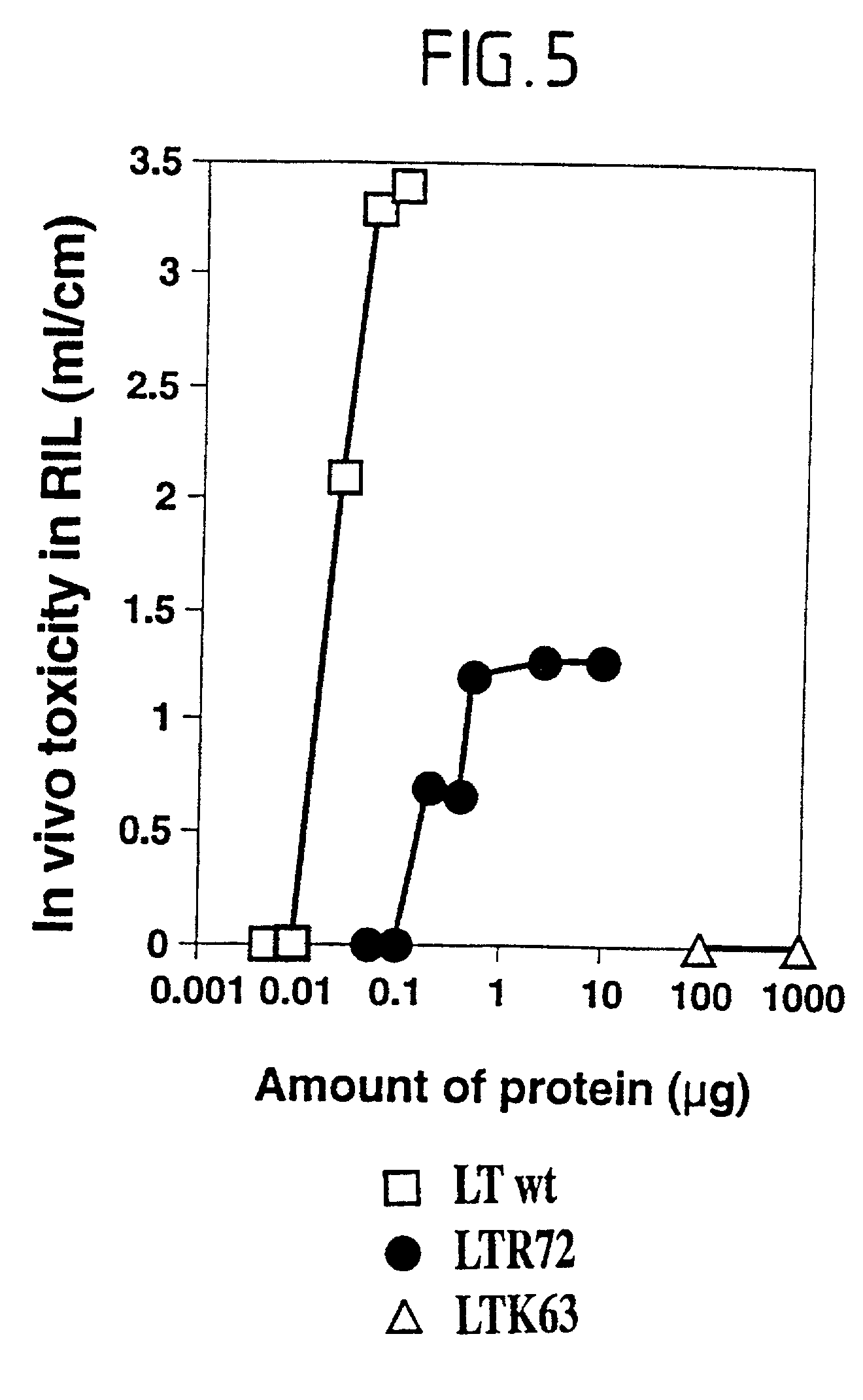
An immunogenic detoxified protein is provided which comprises the amino acid sequence of subunit A of an E. coli heat labile toxin (LT-A) or a fragment thereof in which at least amino acid Ala-72 of the A subunit is mutated, preferably by substitution with Arg. The toxoid is useful as vaccine against an enterotoxigenic strain of E. coli and is produced by recombinant DNA means by site-directed mutagenesis. It is also an effective adjuvant.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Fixedpoint mutation modified phytase
InactiveCN101144072AImprove heat resistanceWide pH rangeHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffPhytaseAspergillus niger
The present invention relates to phytase which is obtained through the gene engineering reconstruction, and provides the phytase which is reconstructed through the rite-directed mutagenesis, the phytase is produced by manufacturing a plurality of amino acids in the phytase which is derived from aspergillus niger and has the serial number of the amino acid of EQ ID No.1 to be replaced, and the replacement of the amino acid comprises a 23rd replacement, a 53rd replacement, a 136th replacement, a 137th replacement, and a 195th replacement. The present invention discloses the optimal and reconstructive phytase and the corresponding DNA sequence, and also discloses the production method and the application of the phytase. The phytase of the present invention is better in the stand up quality of the temperature, and the pH range which is most suitable for the enzyme activity is also improved; further, a mutant gene is highly and effectively expressed through a bioreactor, to lead the phytase after the reconstruction and the rite-directed mutagenesis to be highly and effectively expressed, thereby finally achieving the requirement of industrialized production.
Owner:广东中大南海海洋生物技术工程中心有限公司
Directional modification method of specific gene of animal genome and application thereof
ActiveCN102653756AInefficient cutting mutagenesisHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementZinc finger nucleaseEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for modifying an animal genome by directed mutagenesis, in particular relates to a novel directional transformation method of a specific gene of an animal genome by utilizing zinc finger nuclease. The method comprises the following steps: designing the zinc finger nuclease which specifically identifies and cuts a targeting gene according to a sequence in a target animal target gene region; validating the directional cutting capability and efficiency of the zinc finger nuclease to the target gene by using an independent expression system; and carrying out directional genetic modification on the target gene of the embryo of a target animal to obtain a stable genetic character by utilizing the selected zinc finger nuclease. Furthermore, the invention also relates to a main gene mutation mode which is obtained by using the independent expression system, selecting and utilizing the zinc finger nuclease, and a filial generation obtained through efficient screening and oriented genetic modification by utilizing the selected gene mutation mode. On the other hand, the invention relates to the zinc finger nuclease which is obtained by utilizing the method and is capable of specifically identifying the myostatin gene of pelteobagrus fulvidraco and directionally knocking out the myostatin gene of the pelteobagrus fulvidraco.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Production method of organic potassium fertilizer strain agent and biologic organic fertilizer
The invention relates to an organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent. The organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent is characterized by being prepared by the following steps: after salt-tolerance colloid bacilli are activated on a nitrogen-free culture medium, the salt-tolerance colloid bacilli are transferred into a liquid culture medium and cultured, thalluses are collected by centrifugation, then kieselguhr, active carbon or plant ash with equivalent quantity is added as an adsorbent, and the mixture is dried at low temperature to obtain the organic potassium fertilizer strain agent. The invention also relates to a production method of biologic organic fertilizer. The organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent is prepared by combining a culture medium prepared by adopting seawater or bittern and the salt-tolerance colloid bacilli which are obtained by chemomorphosis or radialization mutagenesis and directed mutagenesis, can adapt to the seawater with a certain concentration and contain potassium bittern, the potassium content of the organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent is higher, and the organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent can be used as the biologic organic fertilizer, can be directly applied to common soil and salt alkali soil and can promote the absorption of plants to the soil and potassium in the microbial agent. The organic potassium fertilizer microbial agent also can be used as the organic fertilizer microbial agent and can produce organic potassium fertilizer and composite potassium fertilizer.
Owner:肖君
Glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN105462949AGood thermal stabilityHigh application valueFermentationGenetic engineeringGlutamate decarboxylaseMutant
The invention discloses a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and a preparation method thereof and application. An amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and a nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention further discloses an expression unit containing genes for encoding the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant, a recombinant plasmid and a transformant. According to information of comparison with a thermococcus kodakarensis glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) amino acid sequence, a method of site-directed mutagenesis is adopted to introduce proline residue at an amino acid locus corresponding to lactobacillus brevis GAD, and the thermal stability of the GAD is improved through rational design. The mutant has better thermal stability in the process of catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof to generate gamma-aminobutyric acid and is favorable for industrial production of gamma amino acid butyric acid (GABA).
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Molecular internal standard quality control method and kit for biological sample nucleic acid detection
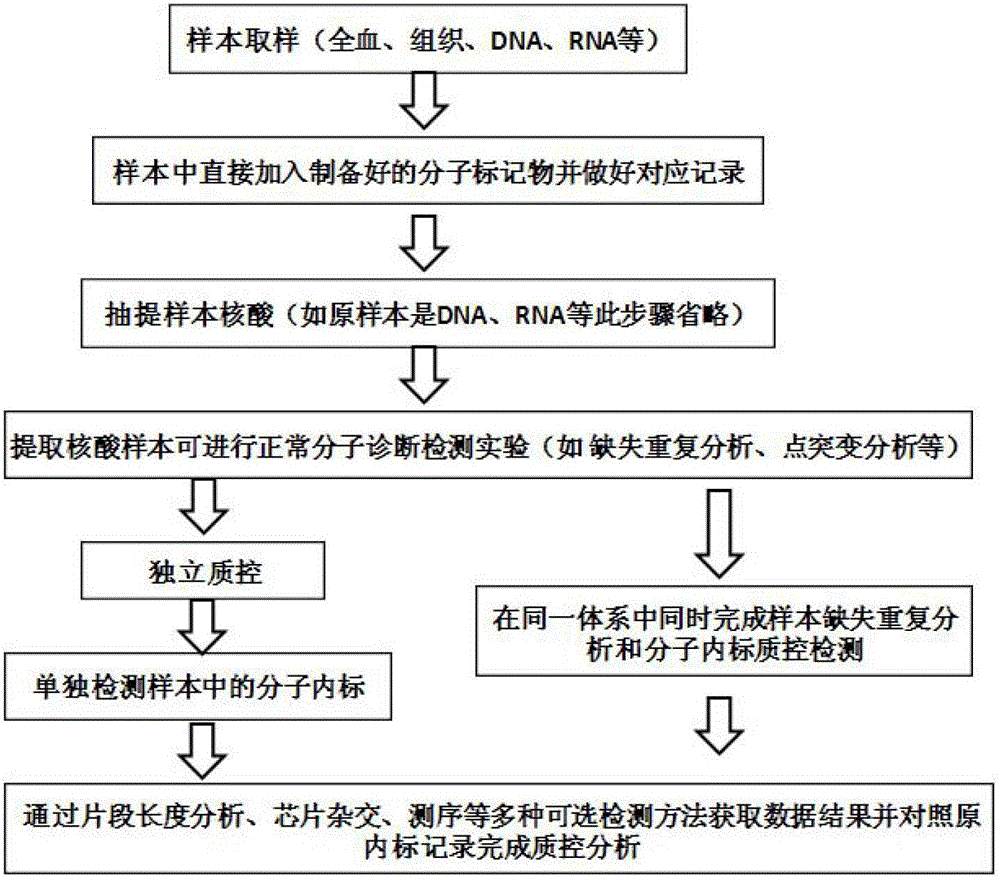
The invention provides a molecular internal standard quality control method and a kit for biological sample nucleic acid detection. The molecular internal standard quality control method and the kit can realize sample quality control such as sample identification and detection analysis. Quality control molecular internal standards are specific exogenous nucleotide sequences different from nucleotide sequences of tested samples and have homology less than or equal to 99% with the tested samples. The specific exogenous nucleotide sequences are mixed with the tested samples uniformly, and corresponding records are made and simultaneously, follow-up treatment is carried out. Through DNA synthesis, site-directed mutagenesis and gene cloning technologies, the quality control molecular internal standards are prepared. The quality control molecular internal standards are used in an identifier quality control system for biological sample nucleic acid detection. Through common technologies of amplification, fragment length analysis, SNP typing, multiple fluorescent polymerase chain reaction (PCR), capillary electrophoresis and sequencing, quality control molecular internal standard information can be obtained and be used for sample verification so that quality control processes of identification and acceptance inspection of a sample are realized simply and easily.
Owner:GENESKY DIAGNOSTICS SUZHOU
Recombined alkaline pectinase with high pH stability and specific enzyme activity and construction method thereof
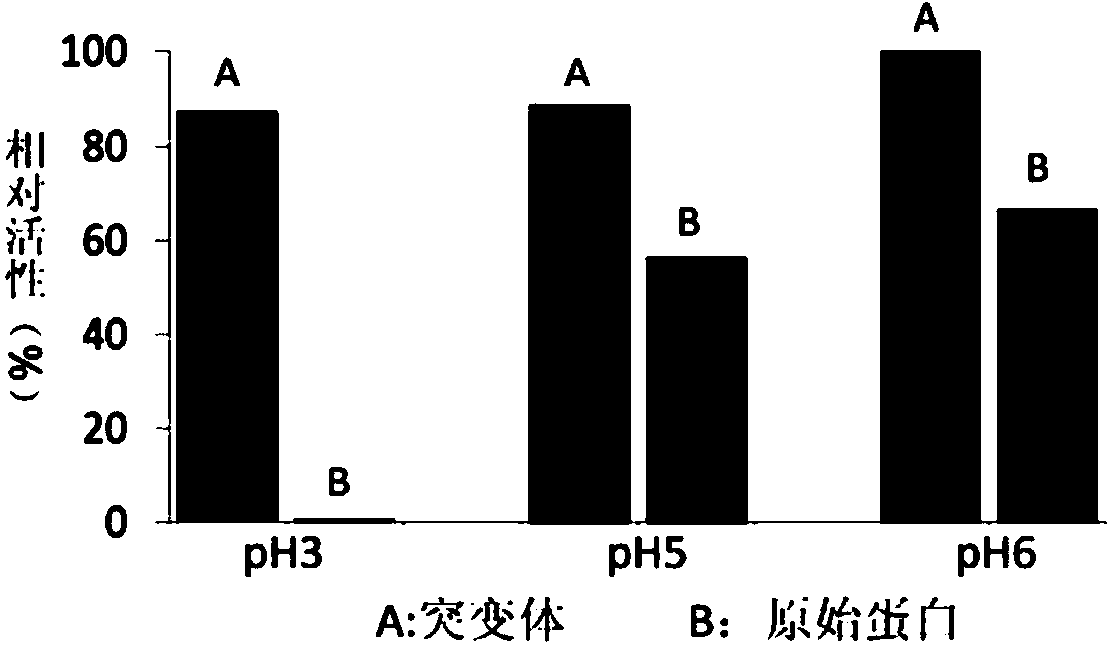
InactiveCN103881996AImproves pH stabilityImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionPectinaseA-site
The invention discloses recombined alkaline pectinase with good pH stability and high specific enzyme activity and a construction method thereof. A Site-directed mutagenesis technique is adopted for mutagenesis of an alkaline pectinase coding gene pel168 of bacillus subtilis 168 and 457-bit guanine G is transformed into thymine T so that the 132-bit valine V of the mature peptide of the coded pectinase is mutated into phenylalanine F, a mutant gene pel168V132F is expressed in colon bacillus Rosset Blue (DE3) and subjected to inducible expression, bacterium breaking and purification, the purified enzyme is subjected to enzyme activity measurement, and the relative activity of the obtained pectinase mutant PEL168V132F is much higher than that of the original pectinase PEL168 when the pH is 3, 5 and 6; and meanwhile, the specific enzyme activity is 2.25 times that of the original pectinase, thus good foundation is laid for wide application of the alkaline pectinase.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Sucrose hosphorylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and construction method and application of sucrose phosphorylase mutant
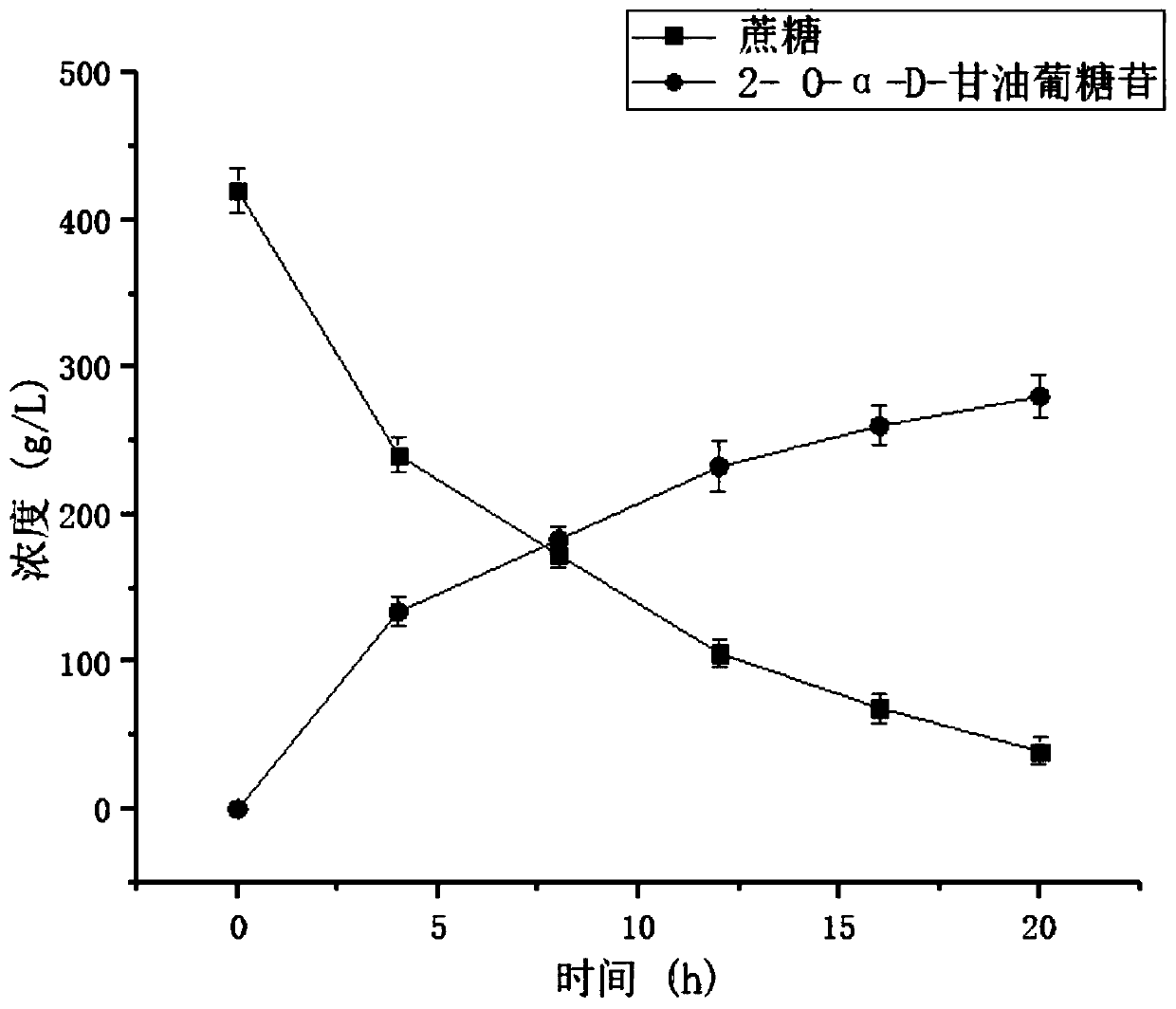
ActiveCN110734899AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased potential for industrial applicationsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSucrose phosphorylasePhosphorylation
The invention relates to a sucrose phosphorylase mutant with improved enzyme activity and a construction method and application of the sucrose phosphorylase mutant, and belongs to the technical fieldof genetic engineering. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. Based on sucrose phosphorylase which is derived from Leuconostoc mesenteroides, site-directed mutagenesis is performed on the mutant so as to improve the enzyme activity of sucrose phosphorylase, the mutant is expressed in Corynebacterium glutamicum, and is used as a whole-cell catalyst for production of 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol, and a large amount of 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol can be produced efficiently in a short period of time at the level of a fermenter of 5 L, so that industrial application prospects for 2-O-alpha-D-glycosylglycerol production from sucrose phosphorylase is expanded, and large-scale industrial application is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
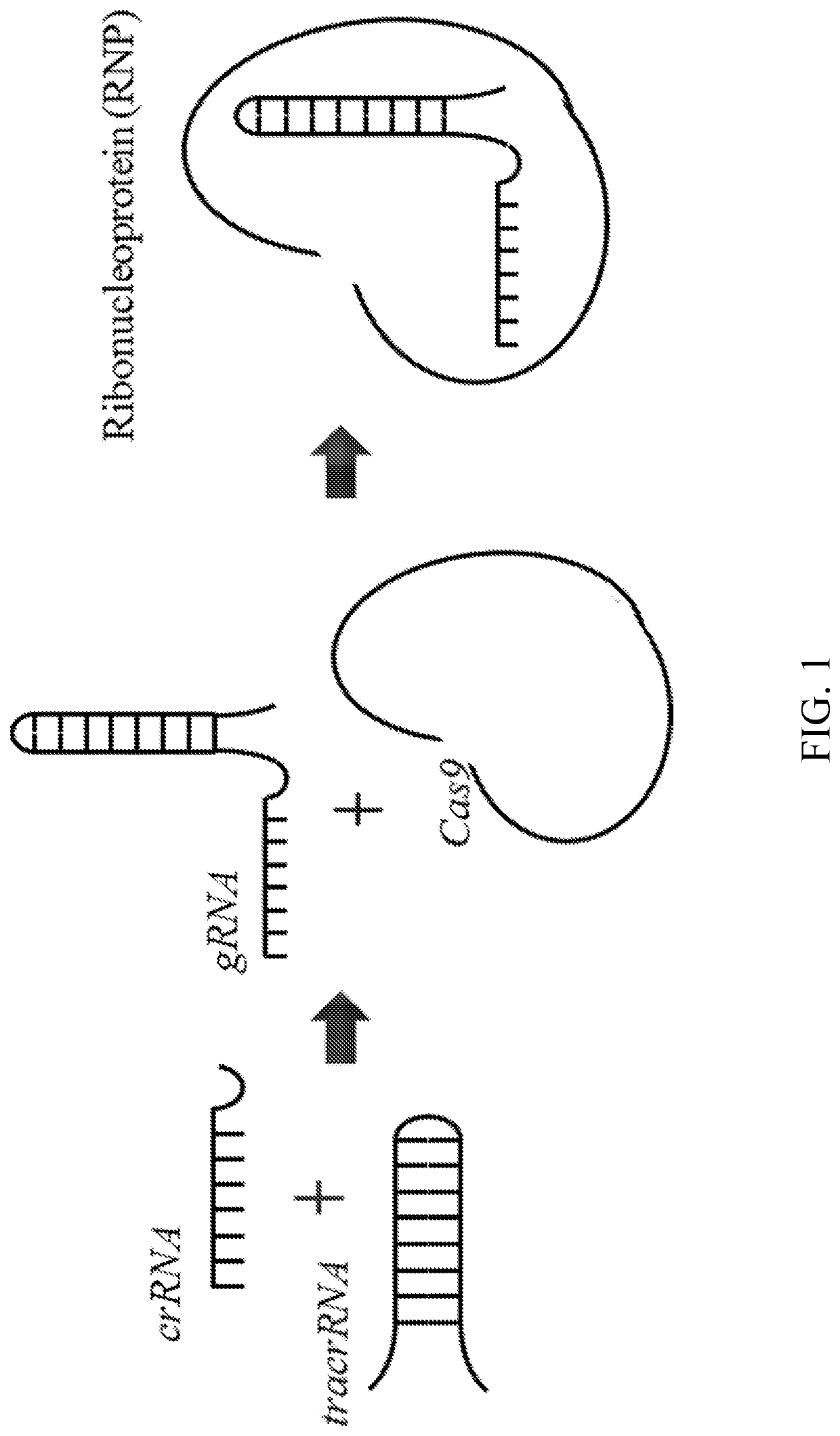
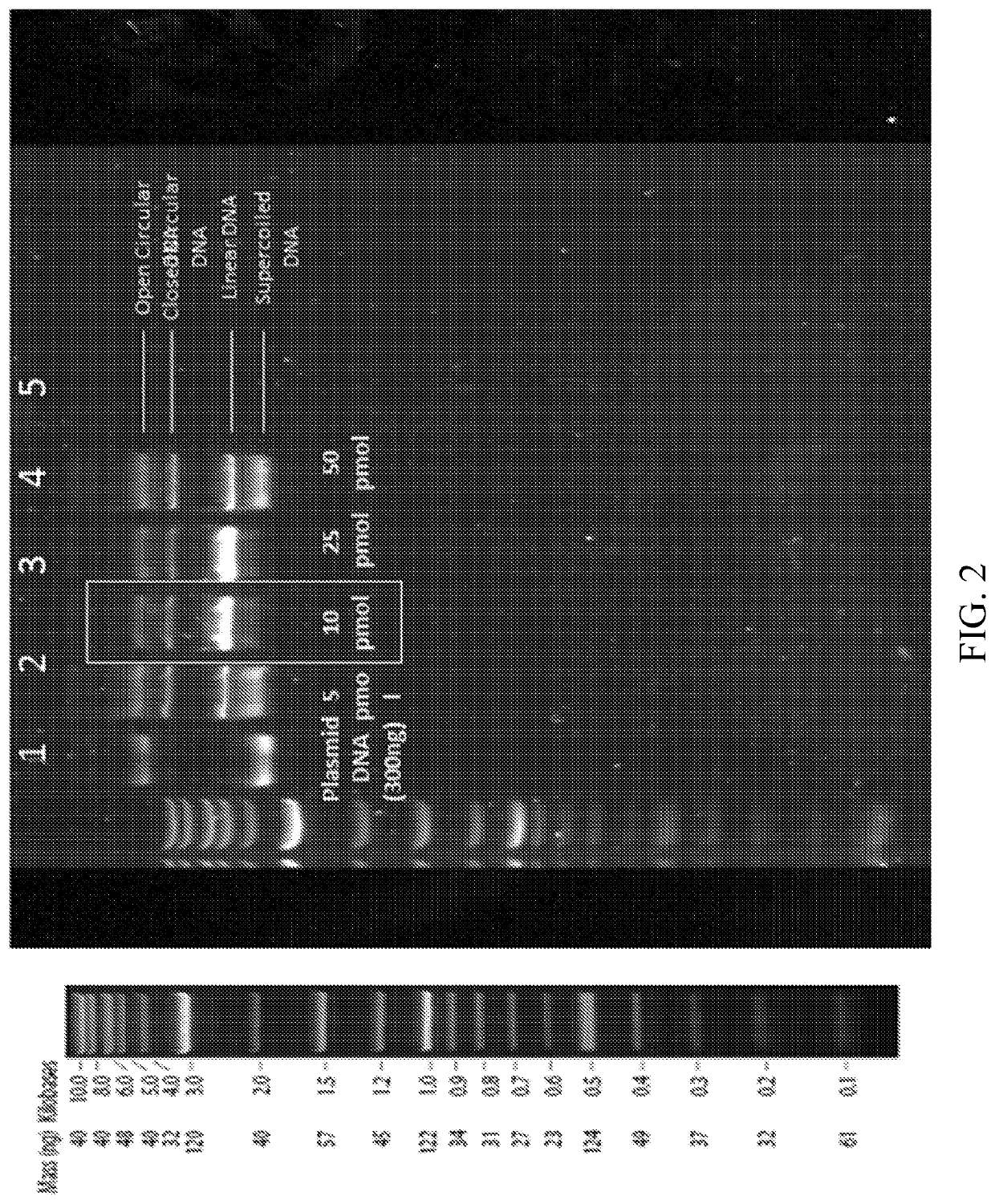
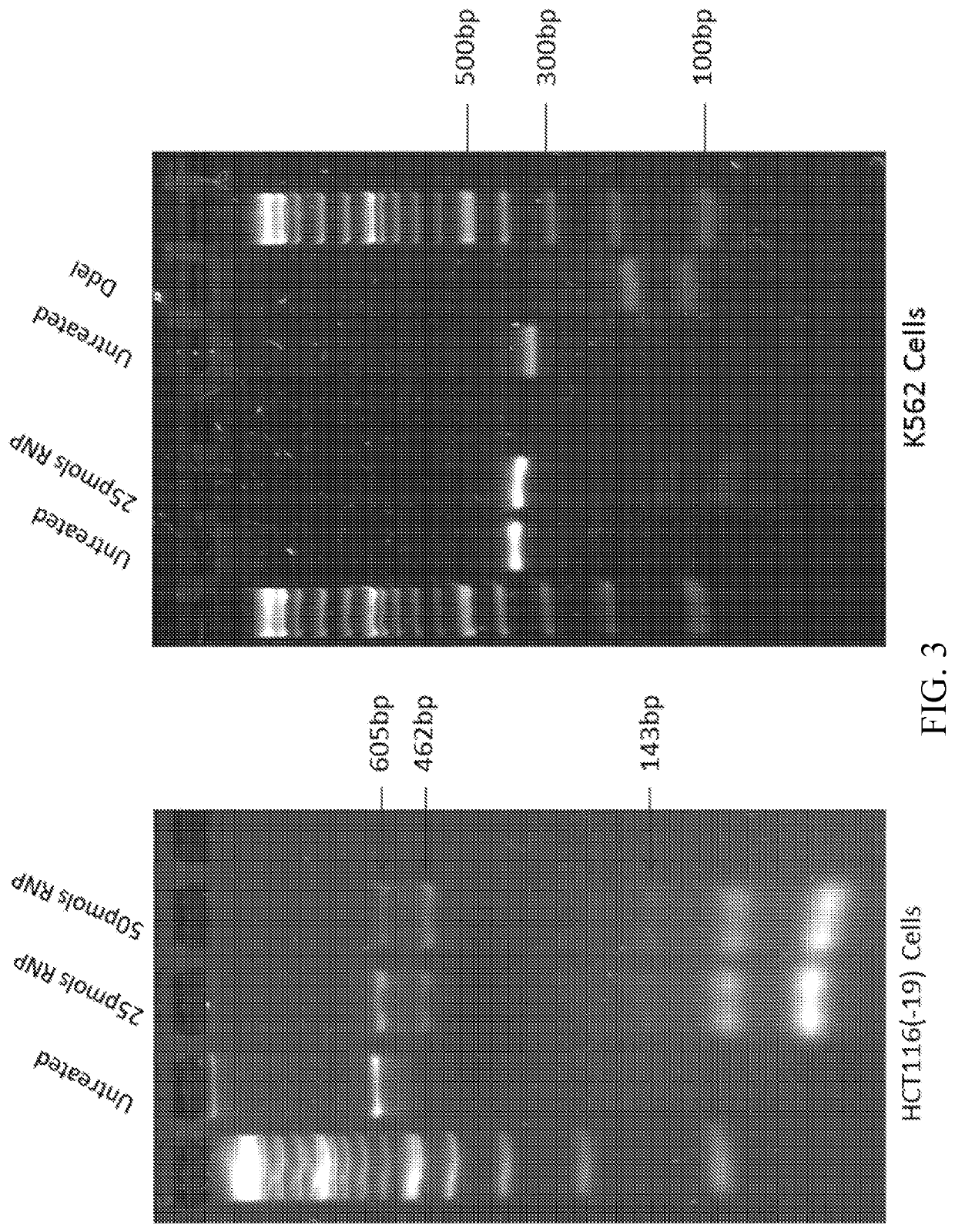
Methods for in vitro site-directed mutagenesis using gene editing technologies
The invention relates to methods for performing in vitro site-directed mutagenesis of a targeted gene or genes. In another aspect, the invention includes in vitro site-directed mutagenesis kits comprising a ribonucleotide particle (RNP), an oligonucleotide, a buffer, a cell-free extract, and instructional material for use thereof.
Owner:F O R E BIOTHERAPEUTICS LTD +1
Method for effecting site-directed mutagenesis
InactiveUS6448048B1Easy to confirmEfficiently obtainedSugar derivativesBacteriaDNA fragmentationSite-directed mutagenesis
A method for performing site-directed mutagenesis characterized in that the method includes the step of carrying out PCR by the use of a double-stranded DNA vector having one or more amber codons, the vector resulting from insertion of a target DNA fragment for site-directed mutagenesis, and at least two kinds of selection primers; and a kit for site-directed mutagenesis for use in the above method, characterized in that the kit includes amber codon reversion primers. According to the present invention, there can be provided a method for performing site-directed mutagenesis and a kit, which is useful for genetic engineering or protein engineering, more simply and rapidly. By using the method and the kit of the present invention, it is possible to efficiently obtain a mutation-introduced gene at the desired position by simply transforming a host with a PCR product obtained by PCR.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Method of constructing vectors for homologous recombination directed mutagenesis
InactiveUS6924146B1Easy constructionAvoid disadvantagesSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsVector systemOrganism
The present invention provides a novel vector system and thereby a novel method for the simplified construction of recombinant vectors for directed mutagenesis. Said vector system is used to modify the eukaryotic genome, particularly of embryonic stem cells, at precise and predefined loci by the means of homologous recombination. Furthermore, said system finds its usage in the generation of new strategies for gene therapy and in the generation of genetically modified higher eukaryotic organisms.
Owner:WATTLER SIGRID +1
Leukemia mouse model based on gene co-transfection technology and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102864172AIncrease success rateImprove featuresFermentationGenetic engineeringBone marrow cellViral vector
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a leukemia mouse model based on a gene co-transfection technology and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the leukemia mouse model comprises the following steps: performing construction and packaging of K-ras mutants and AML1-ETO fusion gene lentivirus vectors; performing bone marrow cell separation and virus infection condition monitoring; implanting infection cells in a mouse to build a leukemia animal model; and performing model identification. The method of building the leukemia mouse model in a mode of utilizing caudal vein injection to lead in the manual site-directed mutagenesis K-ras mutants and AML1-ETO fusion gene lentivirus vectors is adopted initiatively. The leukemia mouse model is high in success rate, pathological characteristics are high in similarity to morbidity conditions of clinical leukemia, and the novel animal model can be provided for leukemia extramedullary infiltration mechanism research, leukemia medicine screening and gene and molecule target treatment.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
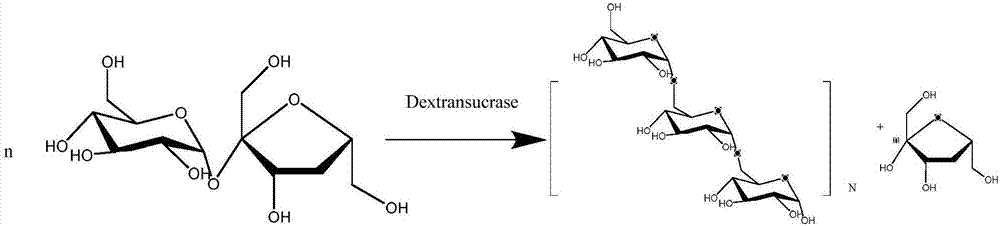
Genetically engineered bacterium for expressing heat resistant type dextransucrase, as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN107201332AIncrease enzyme activitySave production capitalBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEngineered genetic
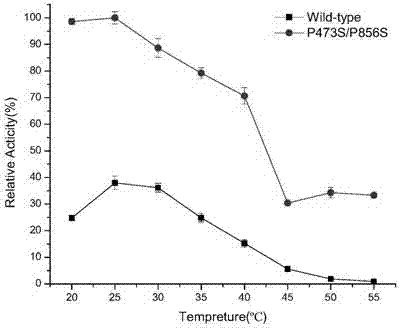
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for expressing heat resistant type dextransucrase, as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The genetically engineered bacterium for expressing the heat resistant type dextransucrase is constructed as follows: a dex-YG gene obtained by cloning is inserted into an expression vector pET28(+)a, so as to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid pET28(+) / dex-YG which is taken as a template; site-directed mutagenesis is performed on a 473-site and a 856-site, heat-resistant double-mutants P473S / P856S with high enzyme activity is obtained after screening, and a recombinant engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 is obtained from the conversion of a host bacterium E.ColiBL21(DE3). The genetically engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 disclosed by the invention have the characteristics of heat resistance and high enzyme activity, and provide a certain basis for application of the genetically engineered bacterium dex-YG-thMu01 to industrial production of the dextransucrase; the productive capital can be saved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
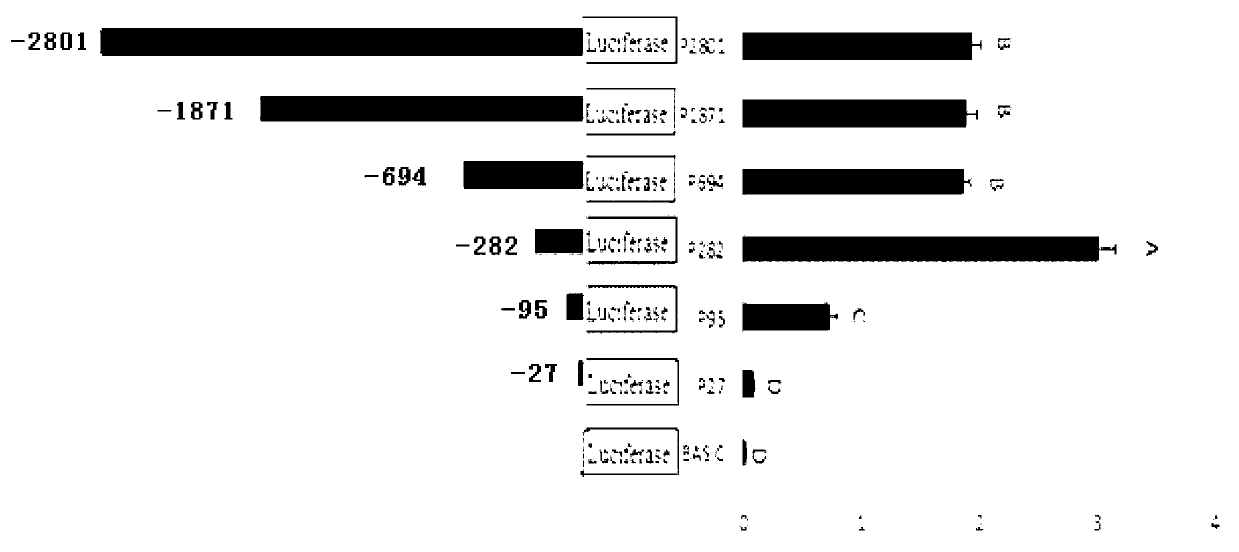
CYP3A88-molecular-marker breeding method for sorting porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS)-resistant pigs and application thereof
ActiveCN103131772AReduced activitySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePromoter activity
The invention relates to the field of molecular genetics, in particular to the application of a molecular marker method in pig breeding for disease resistance, wherein according to the molecular marker method, the molecule at a mutation site in a CYP3A88 gene 5' regulatory region of a pig is marked. The inventor of the method discovers that the CYP3A885' regulatory region of a large Chinese streaky-head pig and the CYP3A885' regulatory region of a Duroc long hybrid pig have a plurality of differences, wherein an A-to-T mutation exists at the -78 site, through a luciferase reporter gene system, the fact that promoter activity of the -78 site is lowered remarkably after an A at the -78 site is mutated into a T in a site-directed mutagenesis mode is found, and the promoter activity of the -78 site is the same as the low level of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression of a CYP3A88 gene of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS)-resistant large Chinese streaky-head pig. Therefore, through genotype detection of the -78 site of the CYP3A88 regulatory region in a pig genome, the genotype of the -78 site of the CYP3A88 regulatory region can be used as a modular marker associated with traits of the PPRS, the molecular marker method not only is simple, convenient and rapid, but also cannot be affected by the environment, and early selection for breeding can be realized.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for directed gene assembly
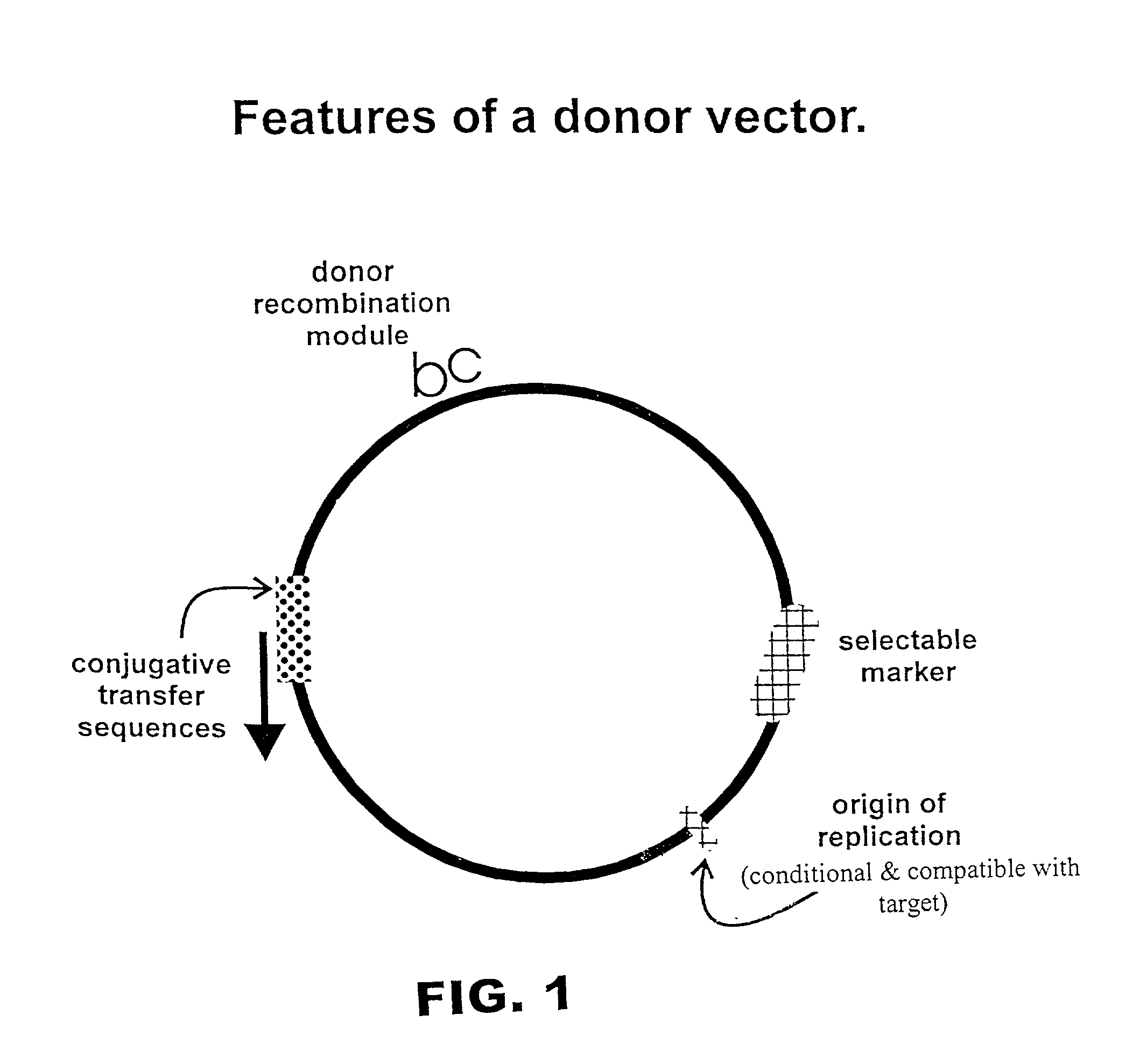
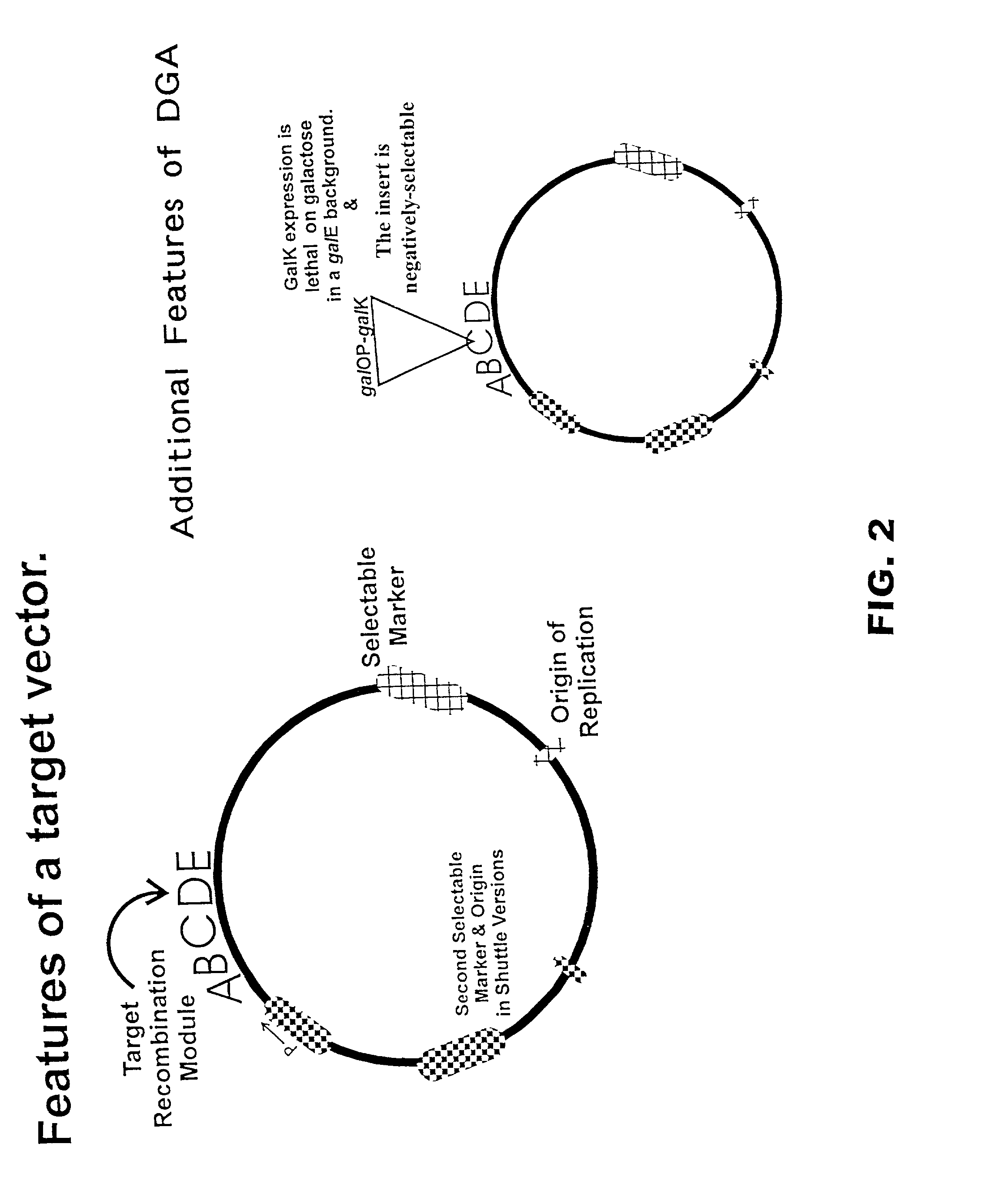
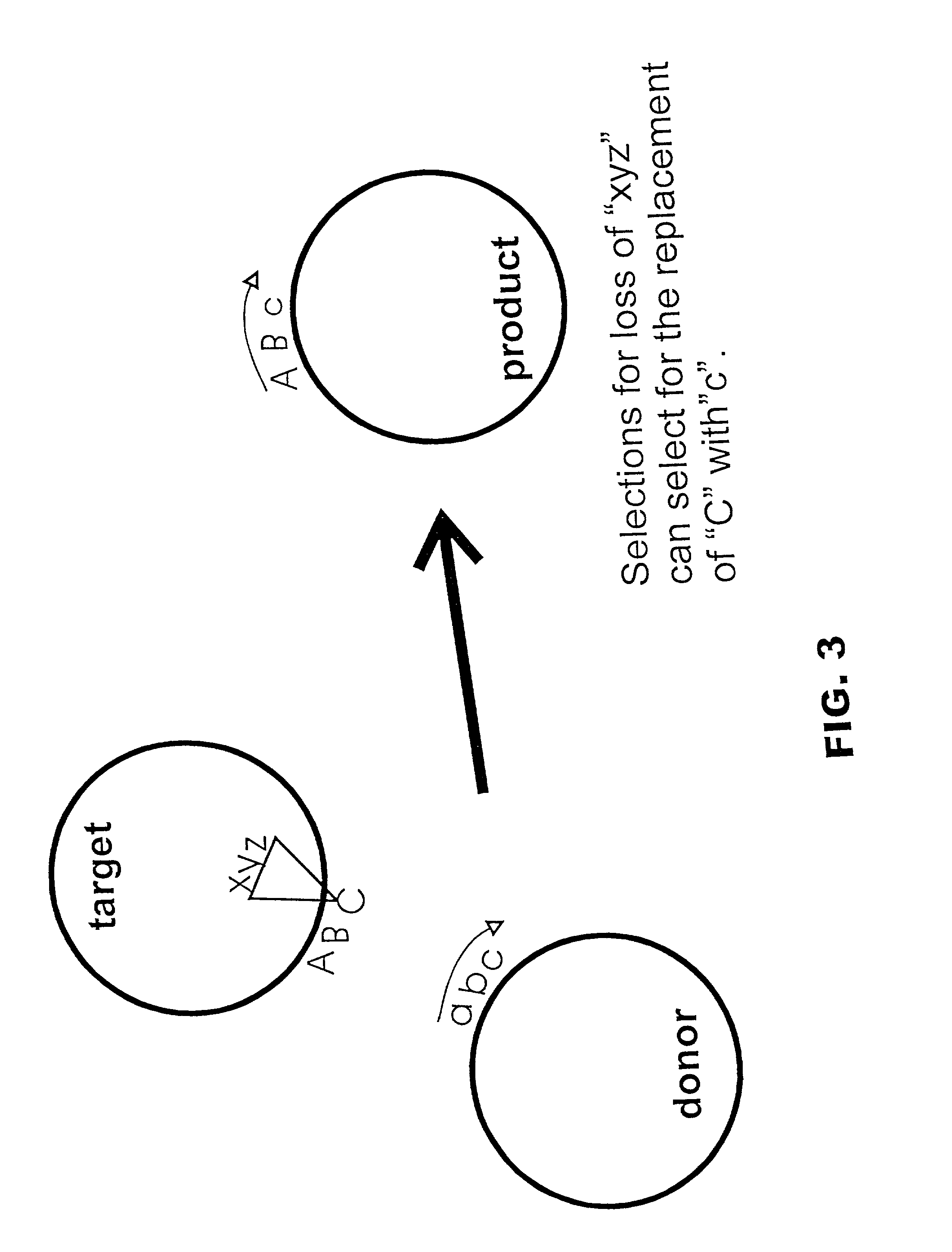
InactiveUS20020102734A1Reduce the burden onBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGene assemblyDirected evolution
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for use of homologous recombination for directed evolution, gene reassembly, and directed mutagenesis. One aspect of the present invention relates to methods for use of bacterial conjugative transfer and homologous recombination for directed evolution, gene reassembly, and directed mutagenesis. Another aspect of the present invention relates to compositions for use in or produced by the methods of the present invention, including libraries, archives and databases.
Owner:ATHENA BIOTECH INC
High-specific-activity endo-xylanase NPWXynB, and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106834255ATaller than aliveReduce the cost of fermentation productionFungiMicroorganism based processesSite-directed mutagenesisRumen
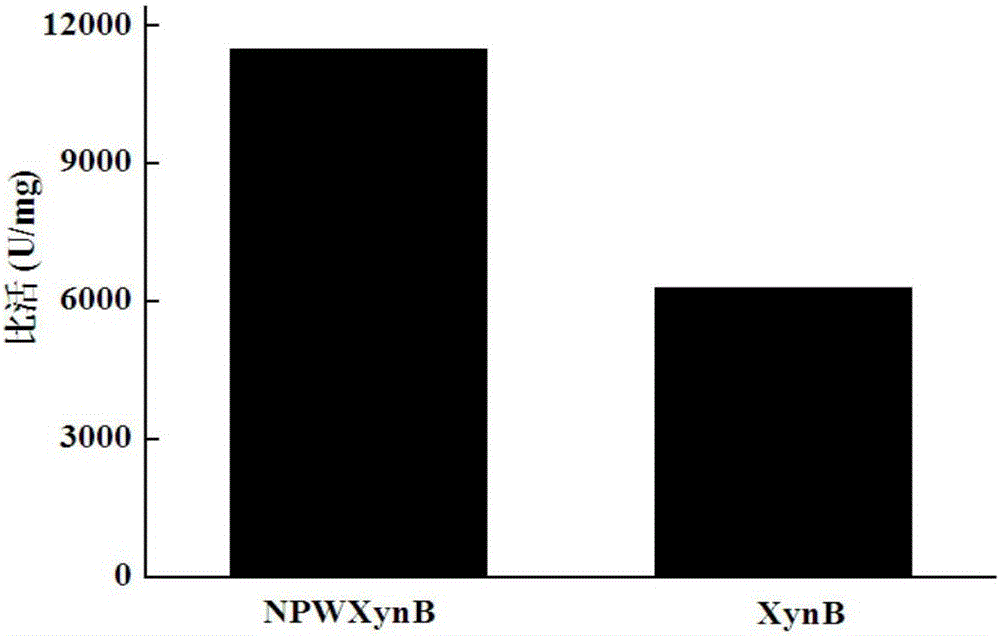
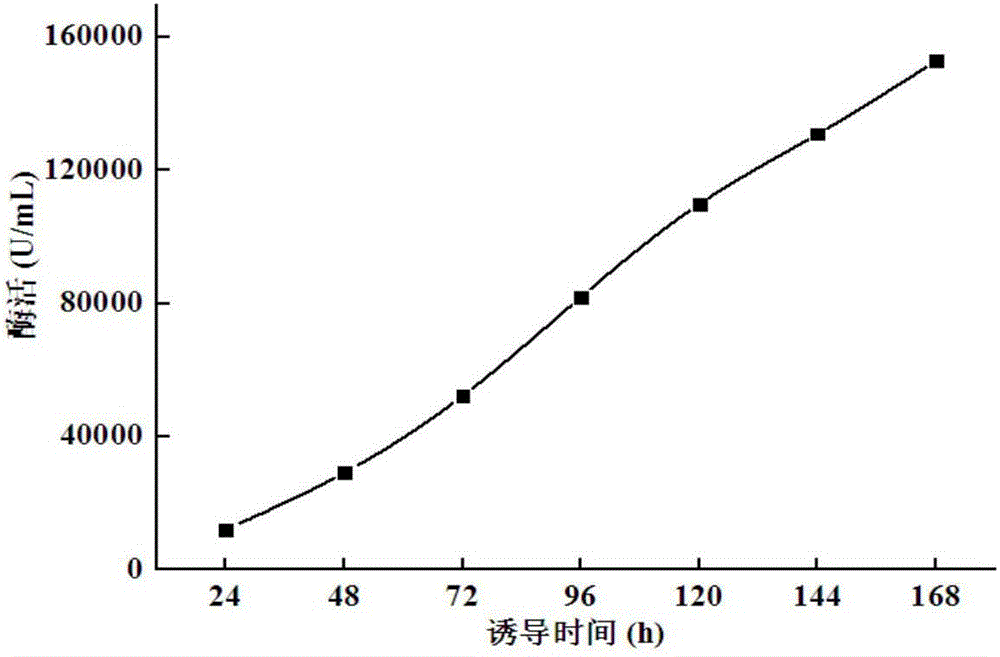
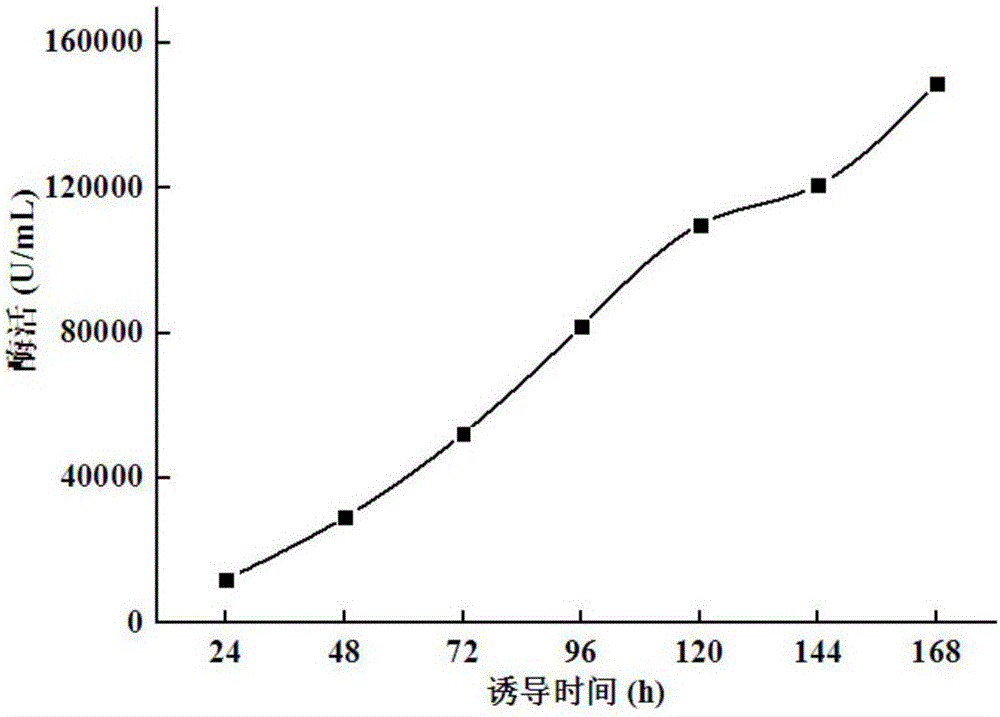
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, particularly a high-specific-activity endo-xylanase NPWXynB, and a gene and application thereof. Orthogenesis and site-directed mutagenesis are utilized to perform molecular modification on endo-xylanase XynB derived from rumen fungus Neocallimastix patriciarum to obtain the high-specific-activity xylanase NPWXynB. In the amino acid sequence, the 58th site Y is substituted by F, the 78th site M is substituted by Y, the 94th site Y is substituted by S, the 143rd site V is substituted by L, the 145th site E is substituted by R, and the 182nd site D is substituted by R. The specific activity of the endo-xylanase mutant NPWXynB provided by the invention is 11500 U / mg under the condition of 37 DEG C, which is enhanced by 82.5% as compared with the specific activity of the original endo-xylanase XynB. The maximum enzyme activity of the NPWXynB-gene-containing recombinant engineering bacterium can reach 153000 U / mL, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTR BIO TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com