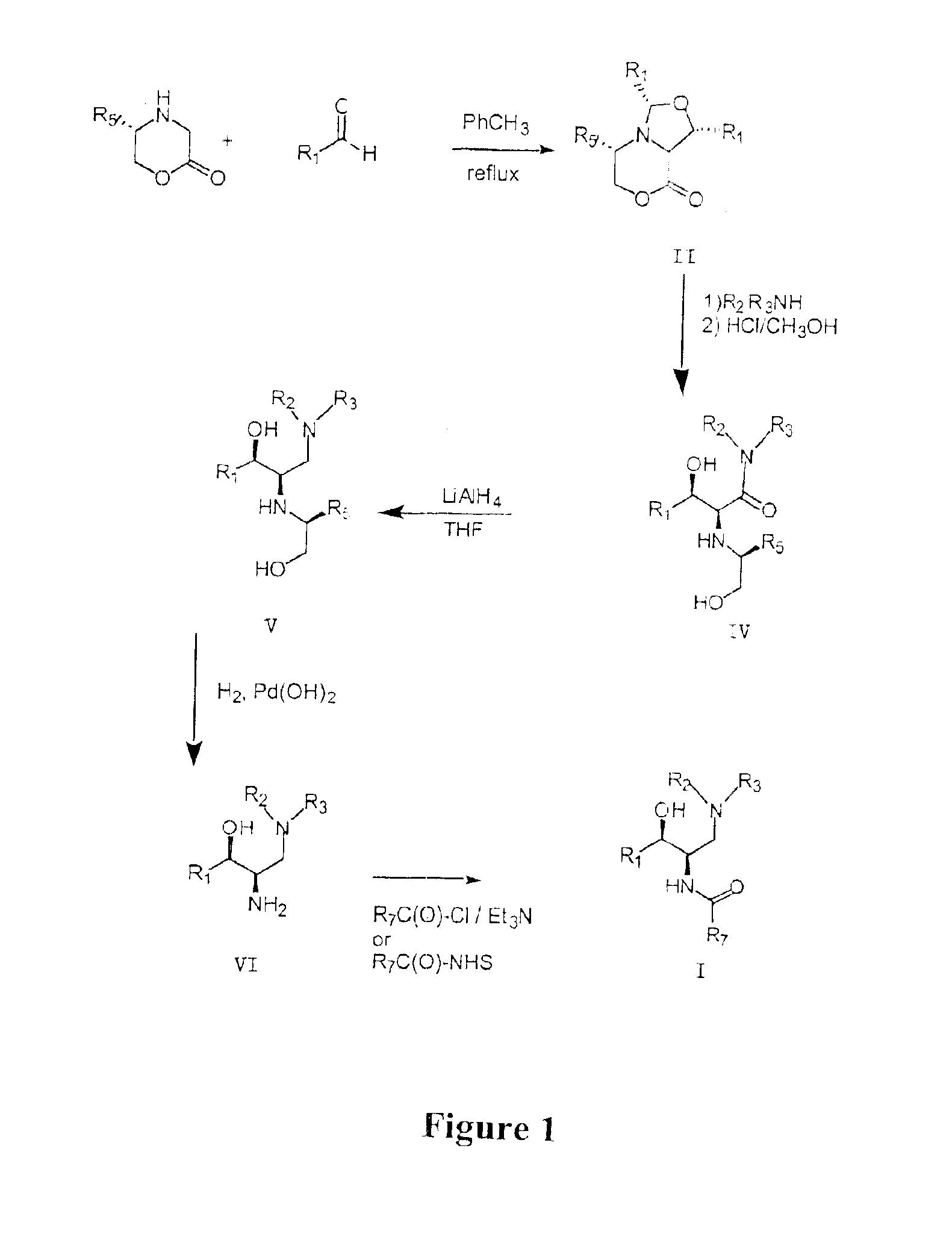
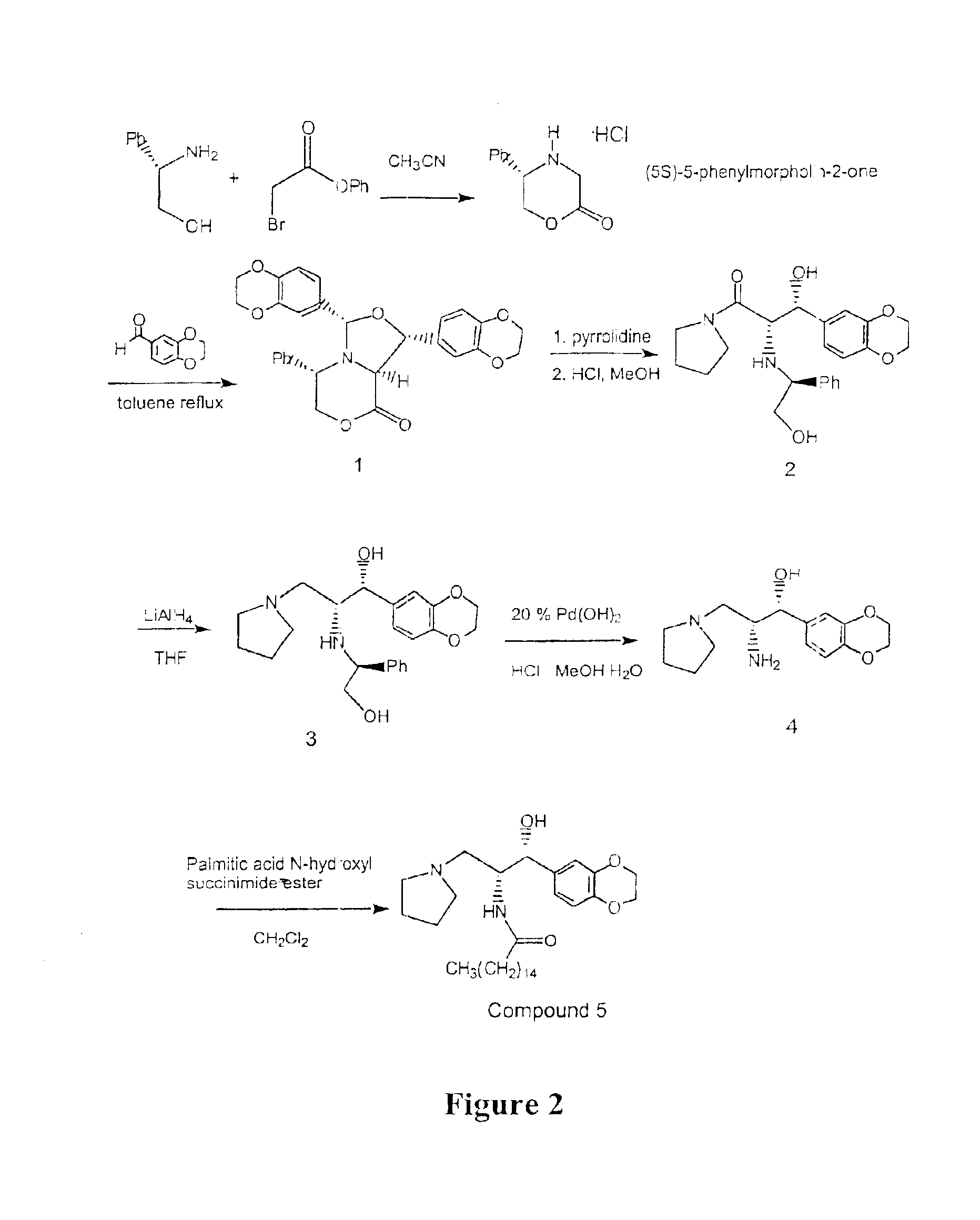
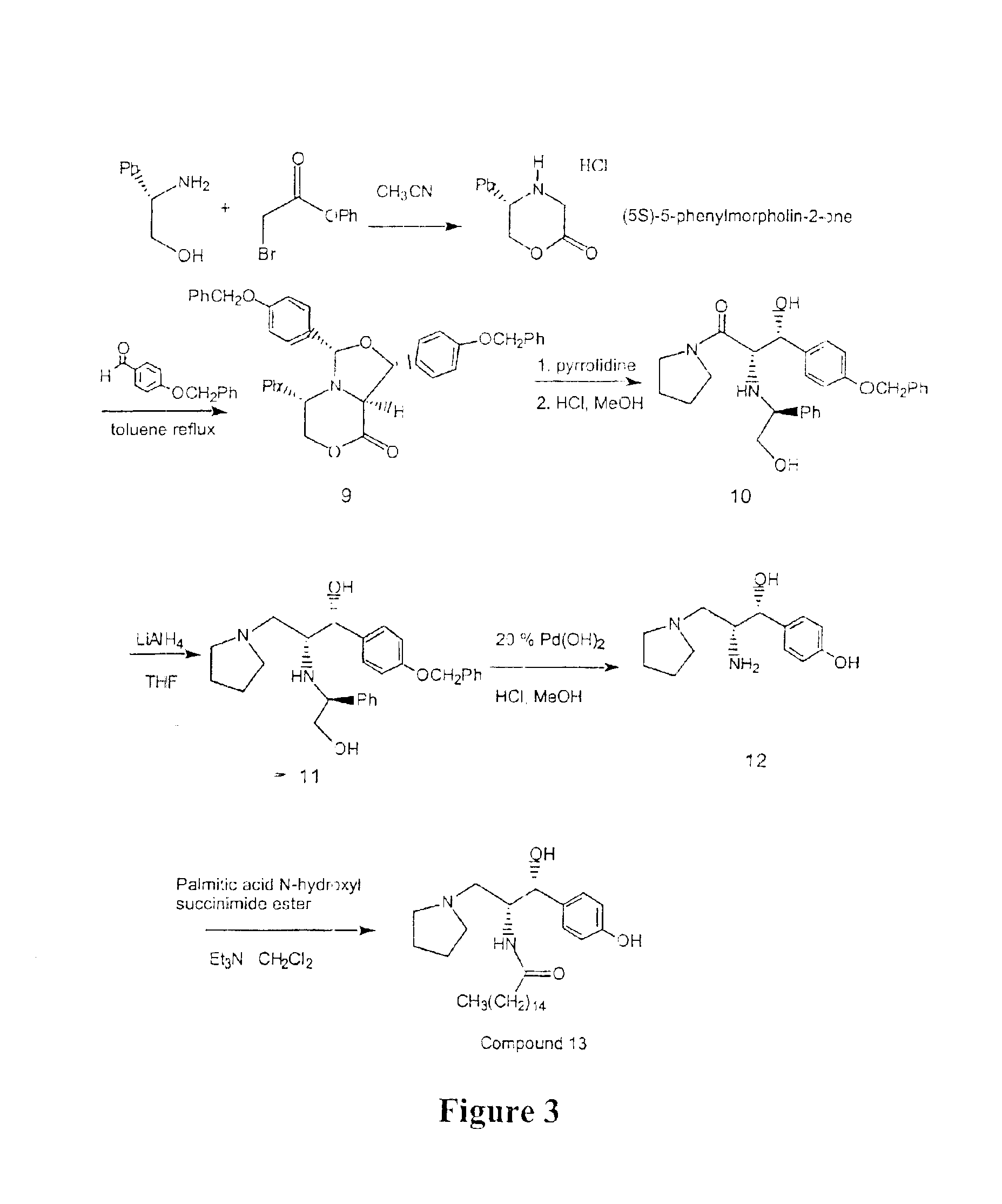
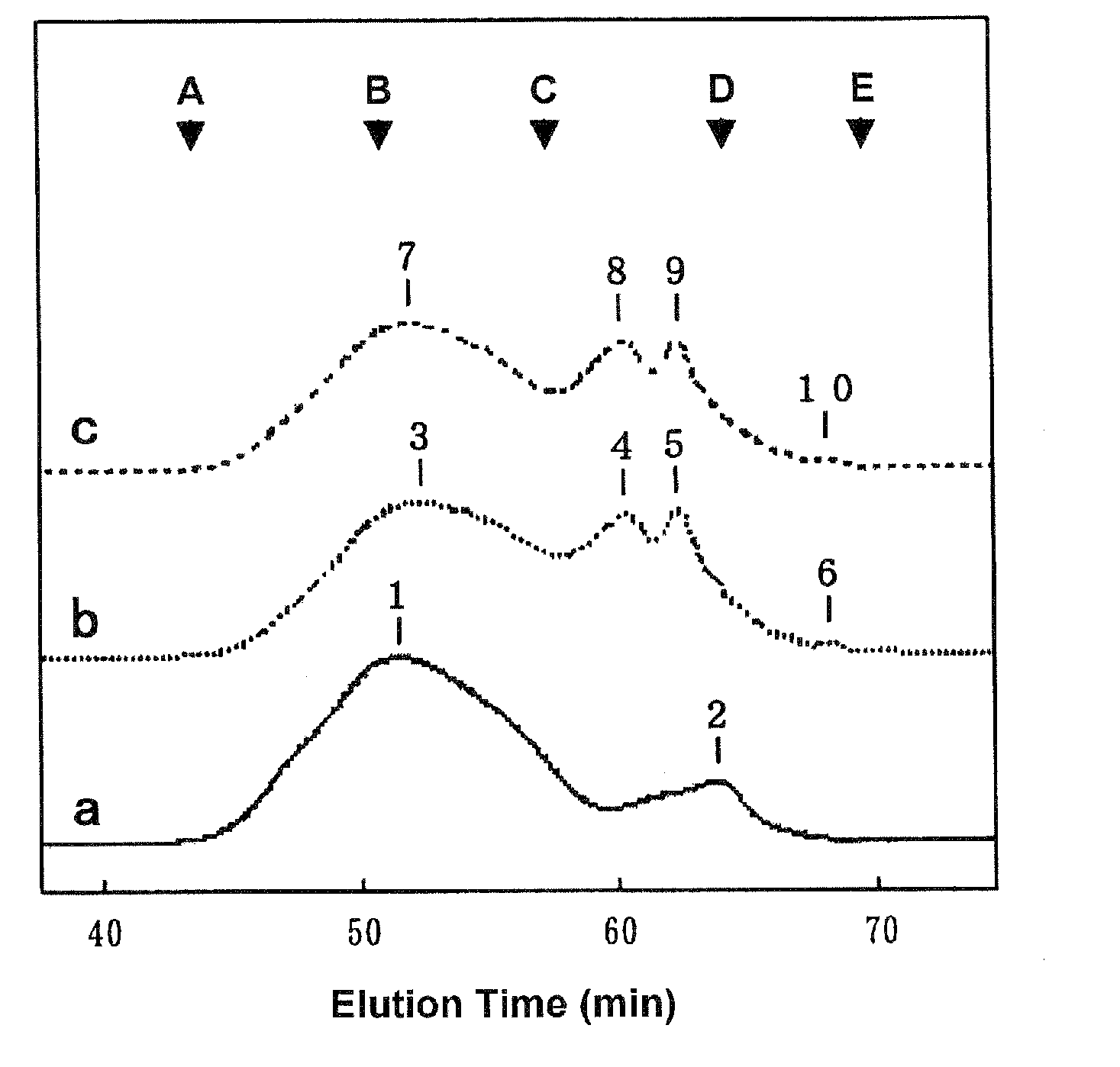
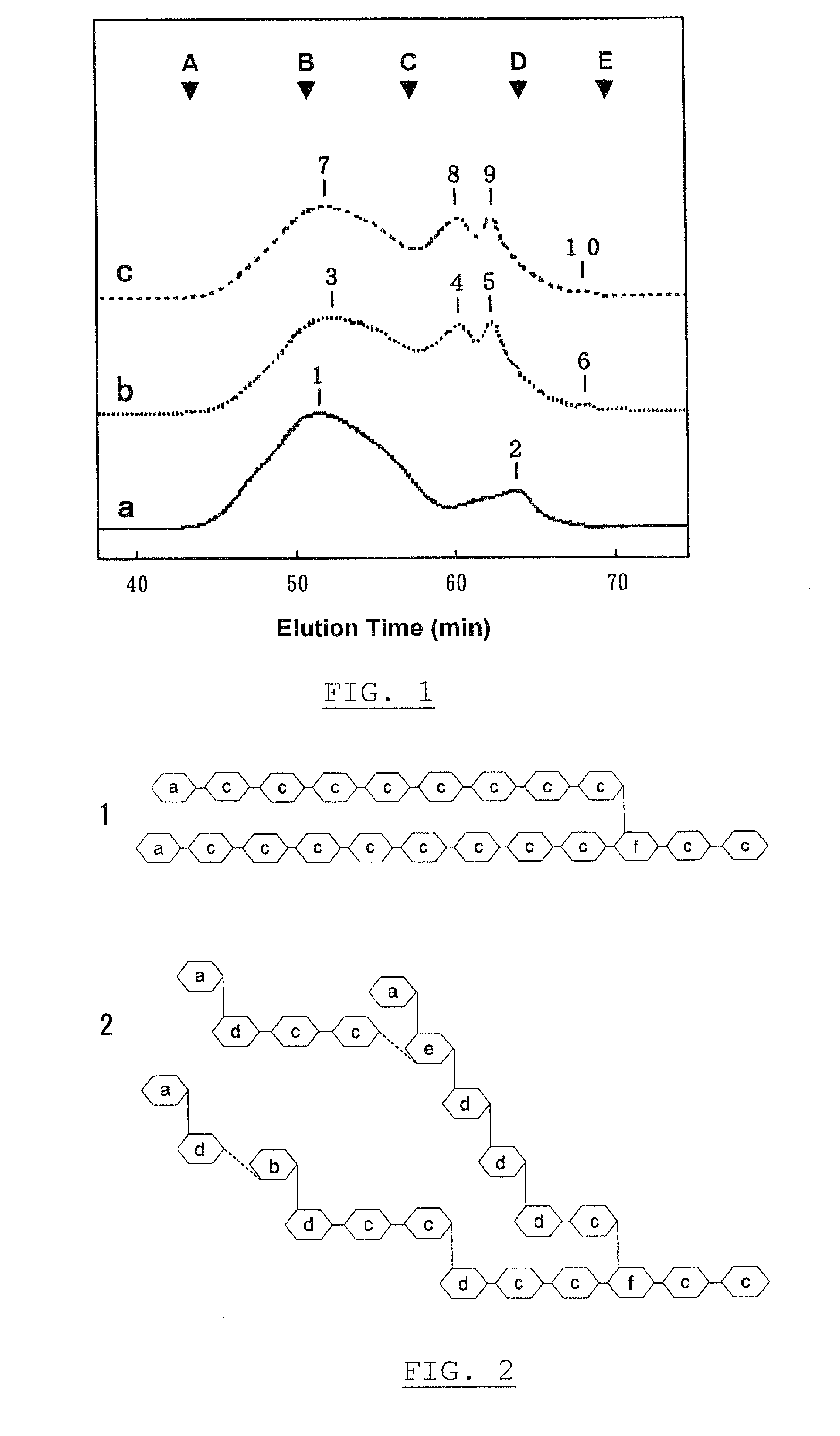
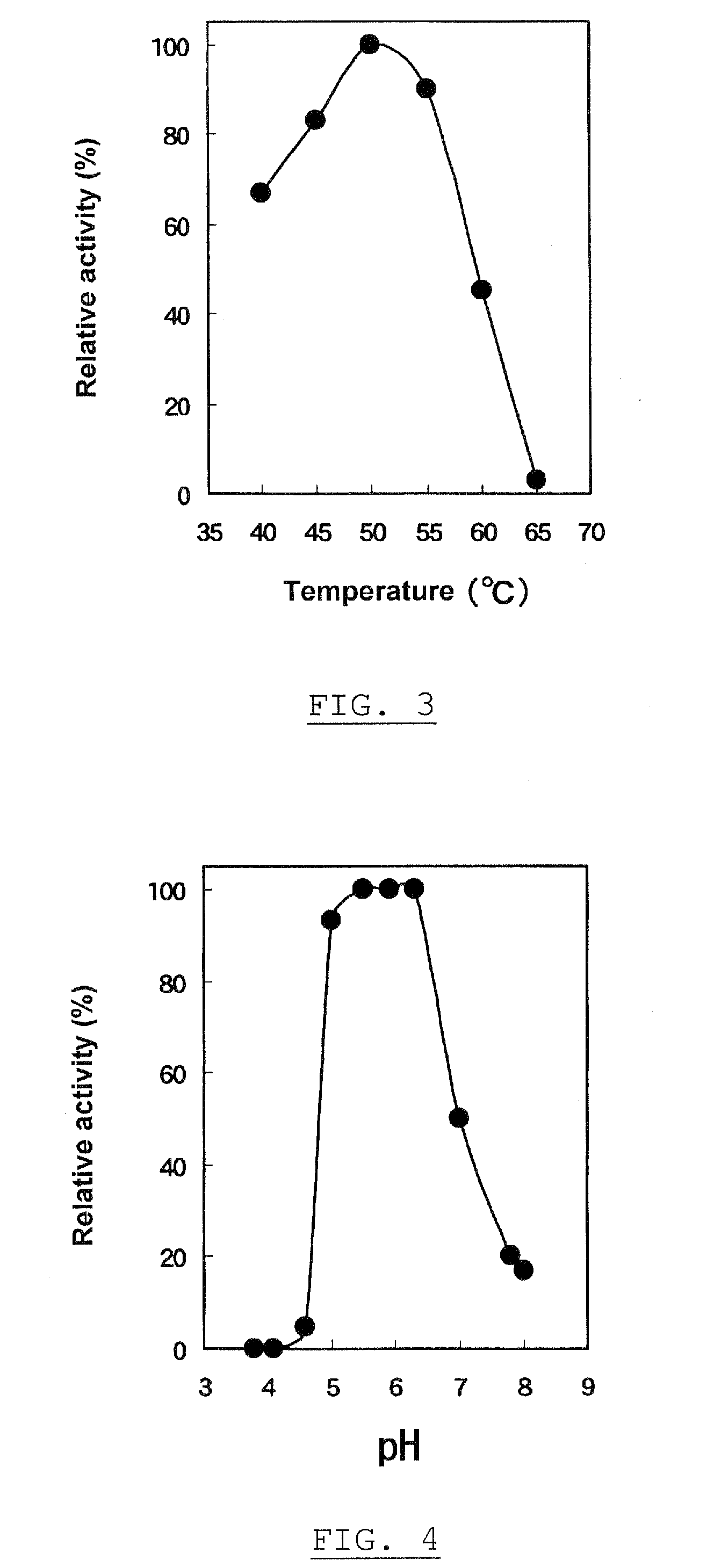
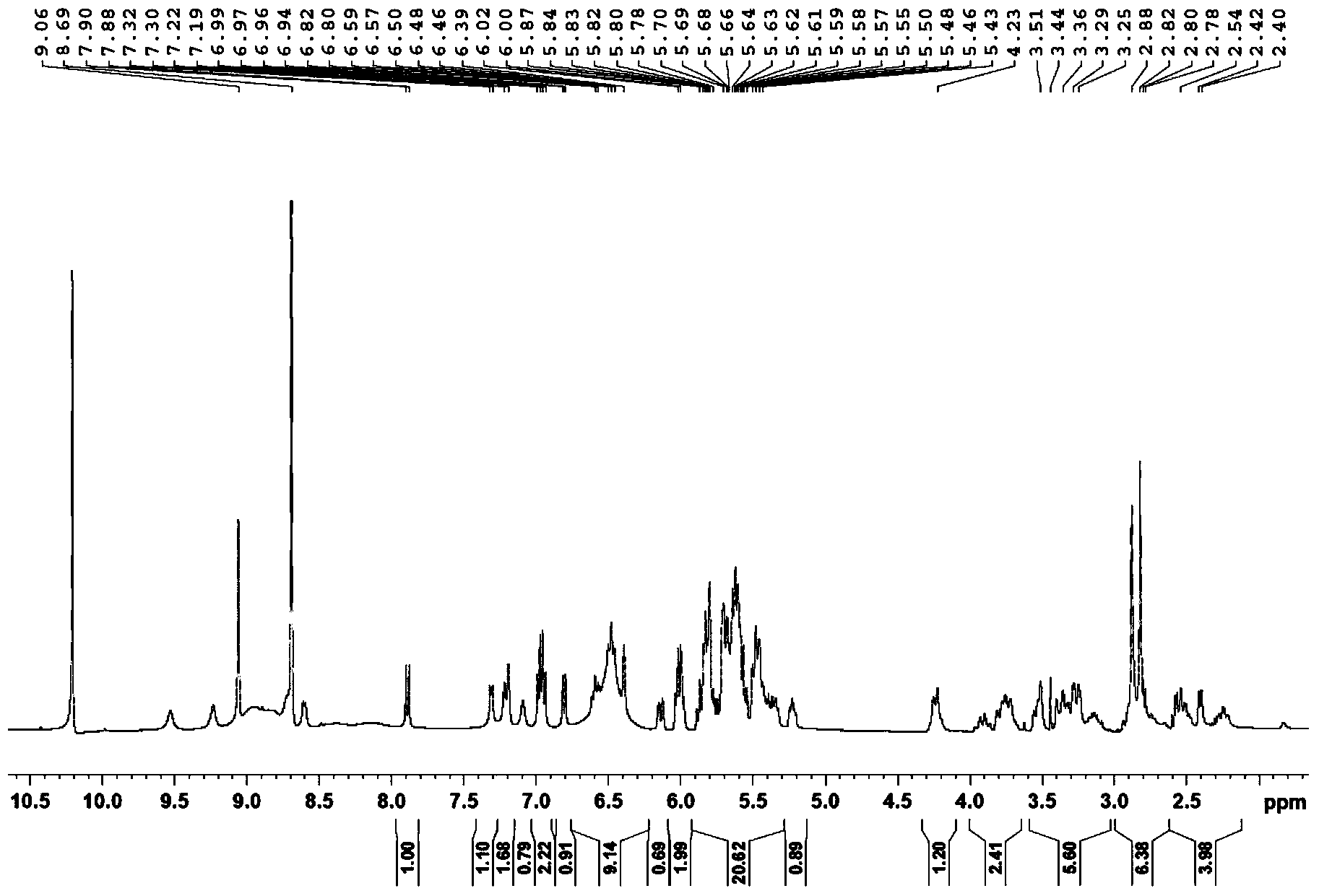
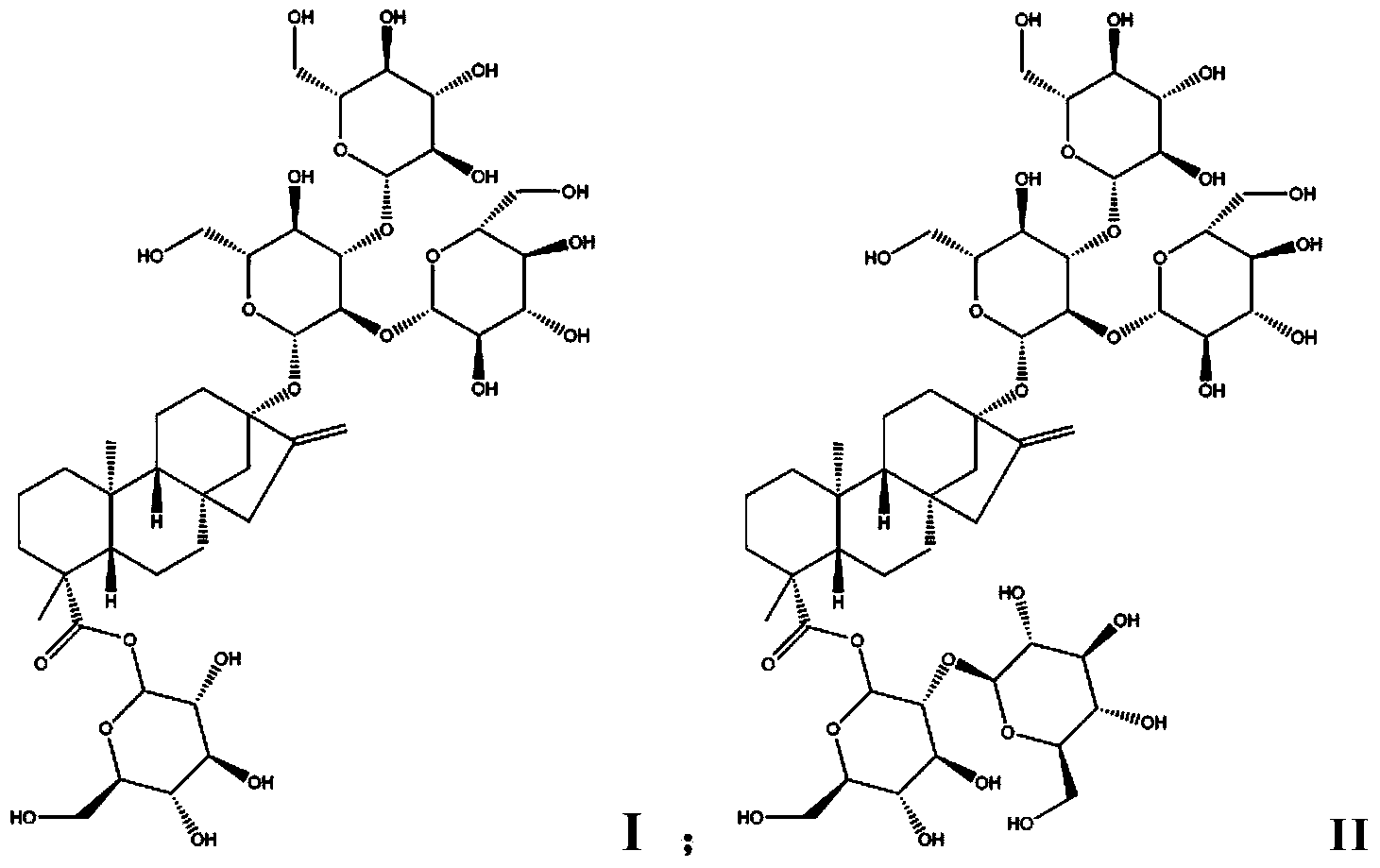
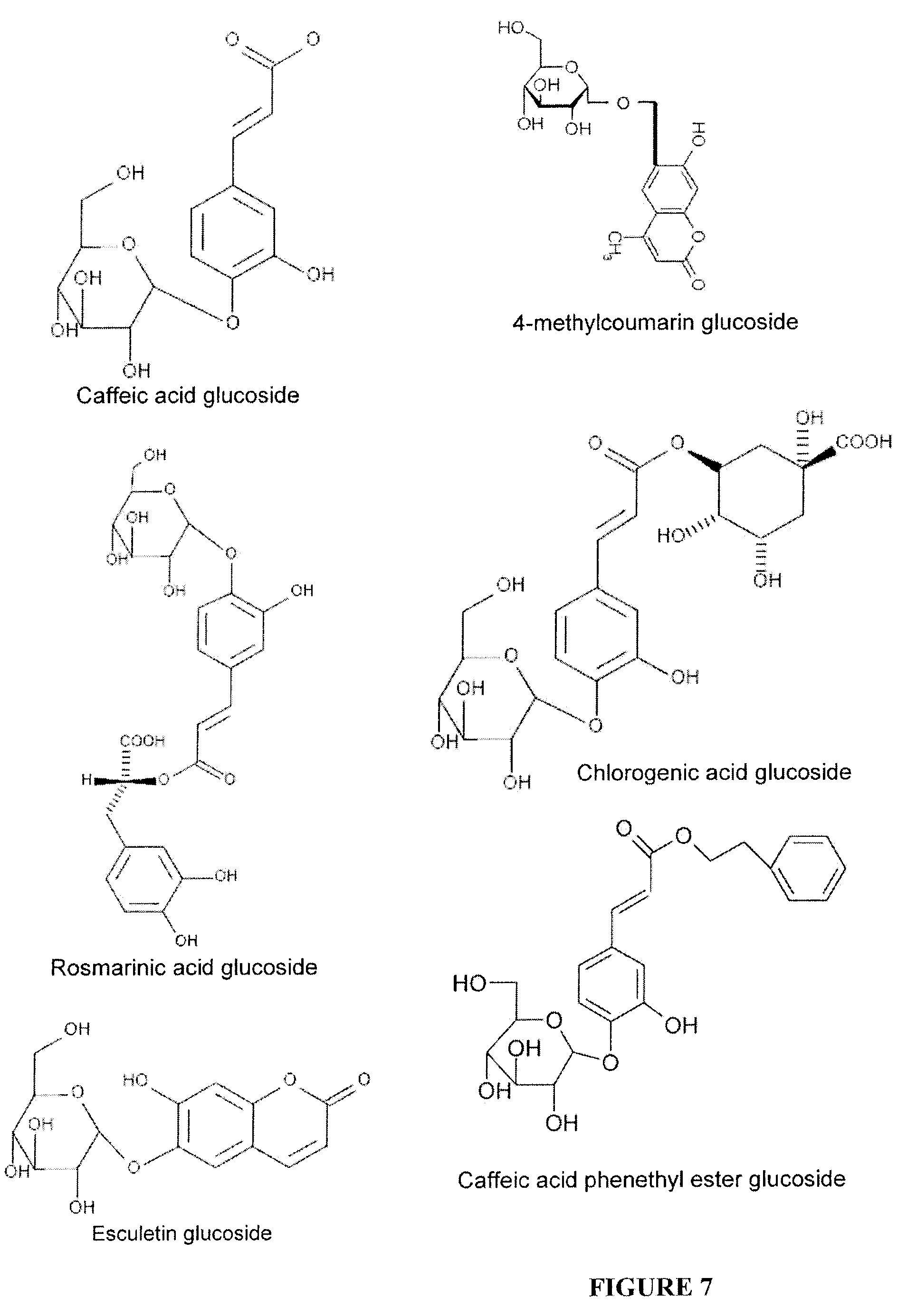
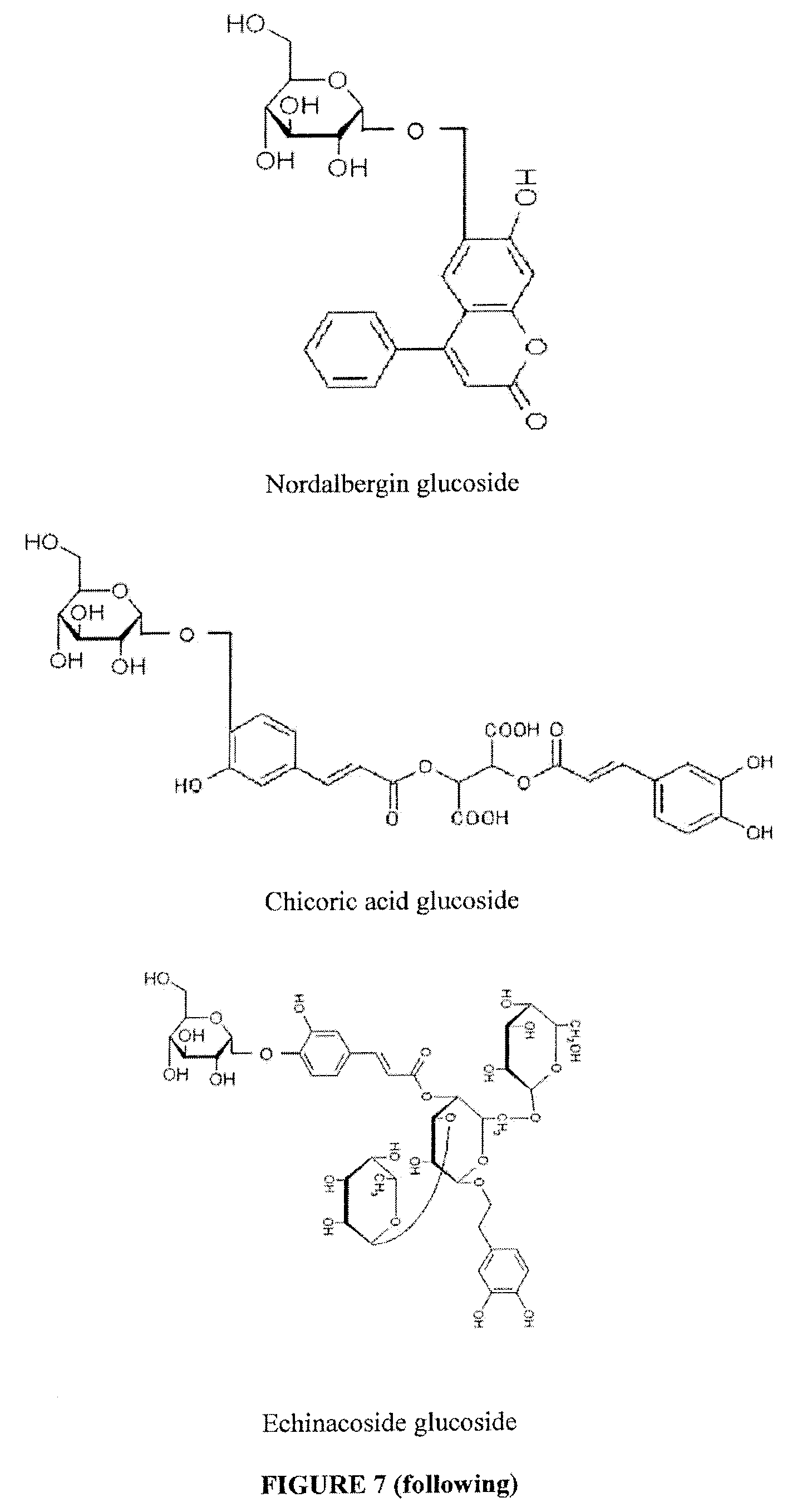
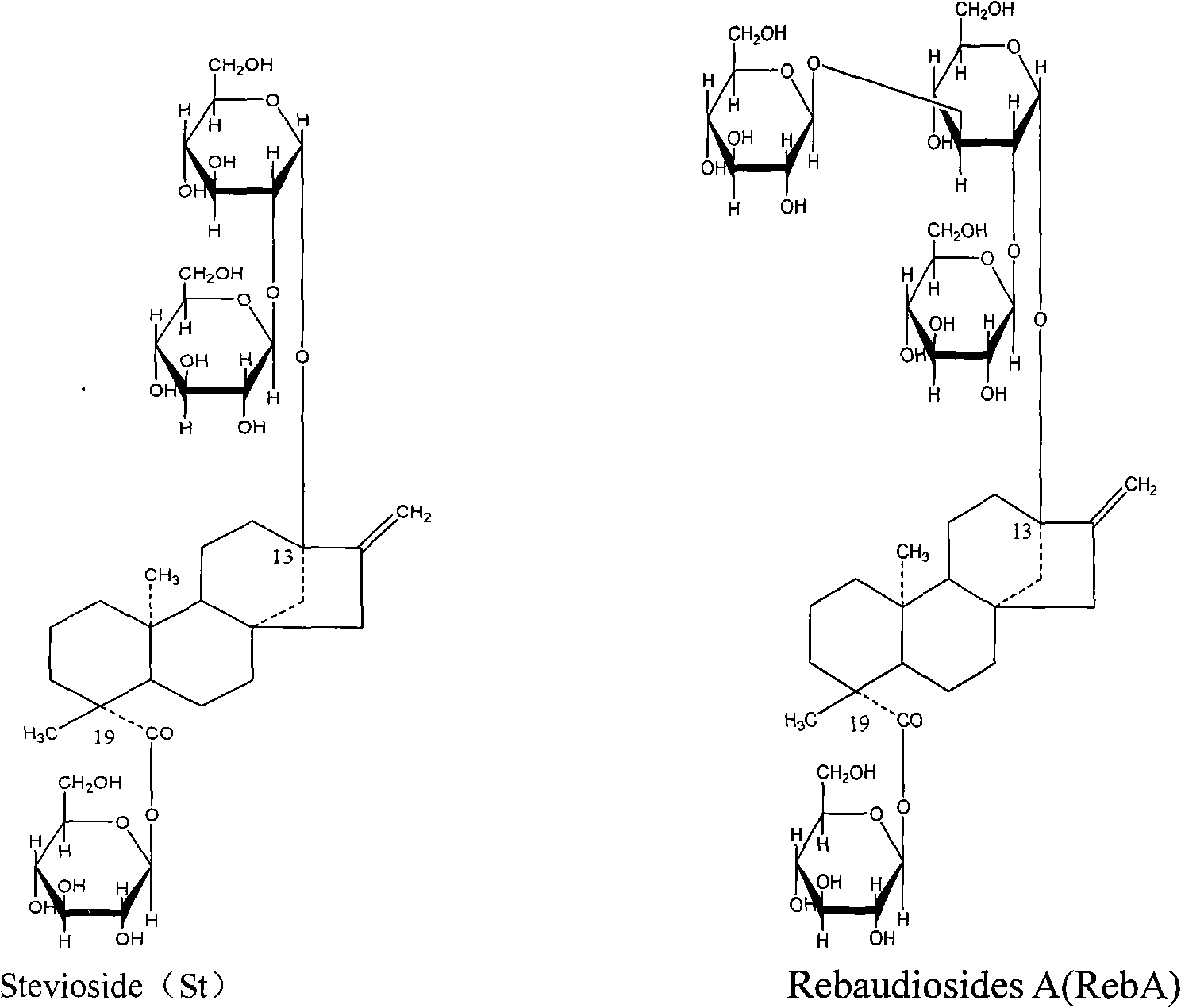
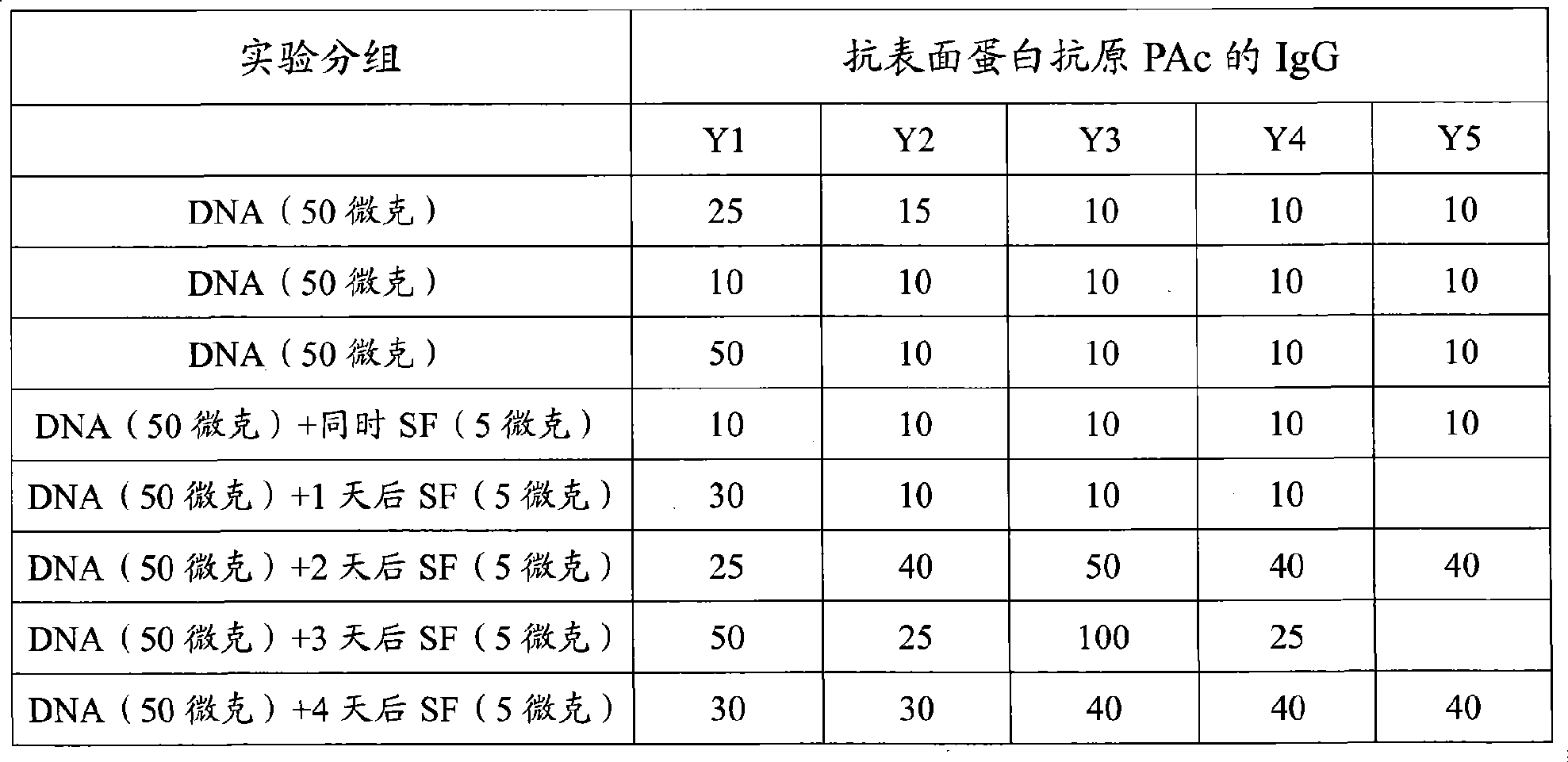
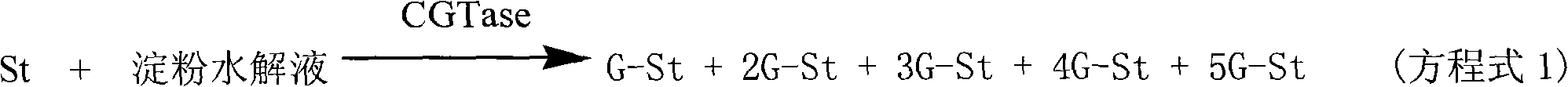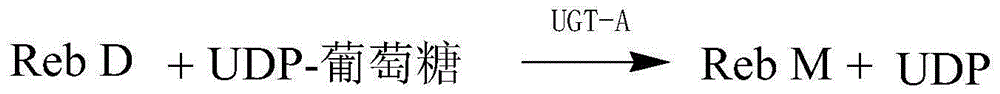Patents
Literature
281 results about "Glucosyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
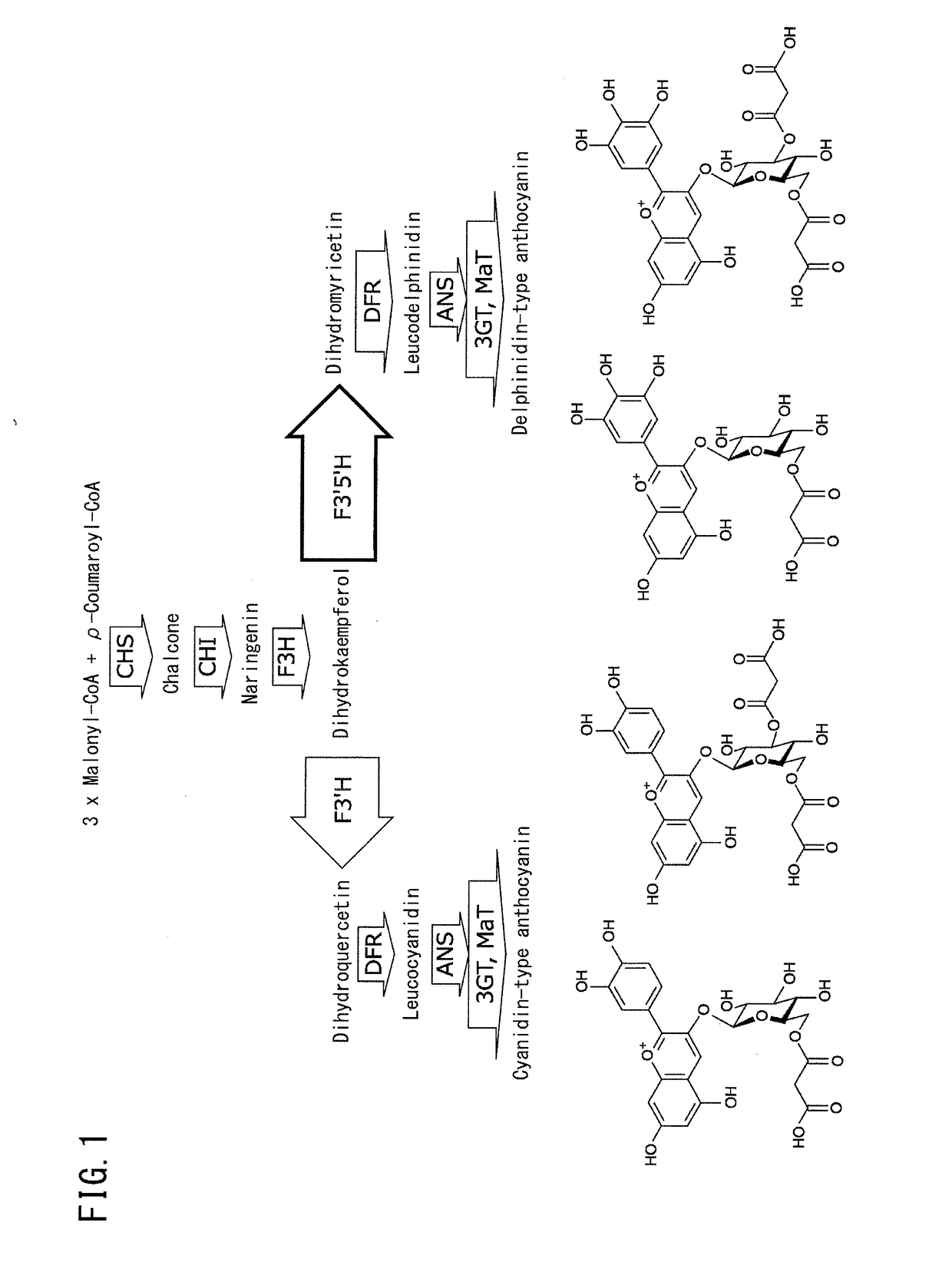
Glucosyltransferases are a type of glycosyltransferase that enable the transfer of glucose.
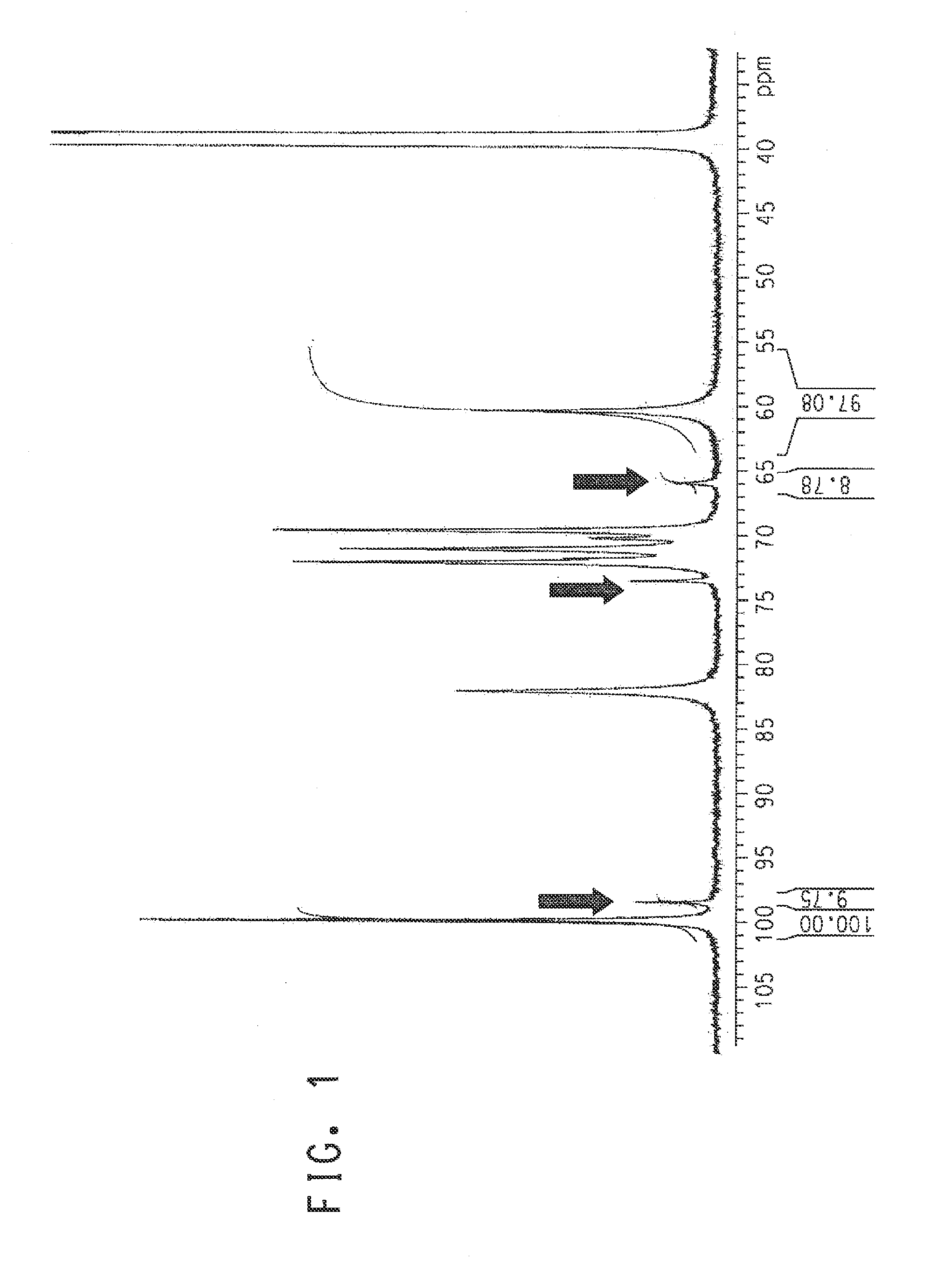
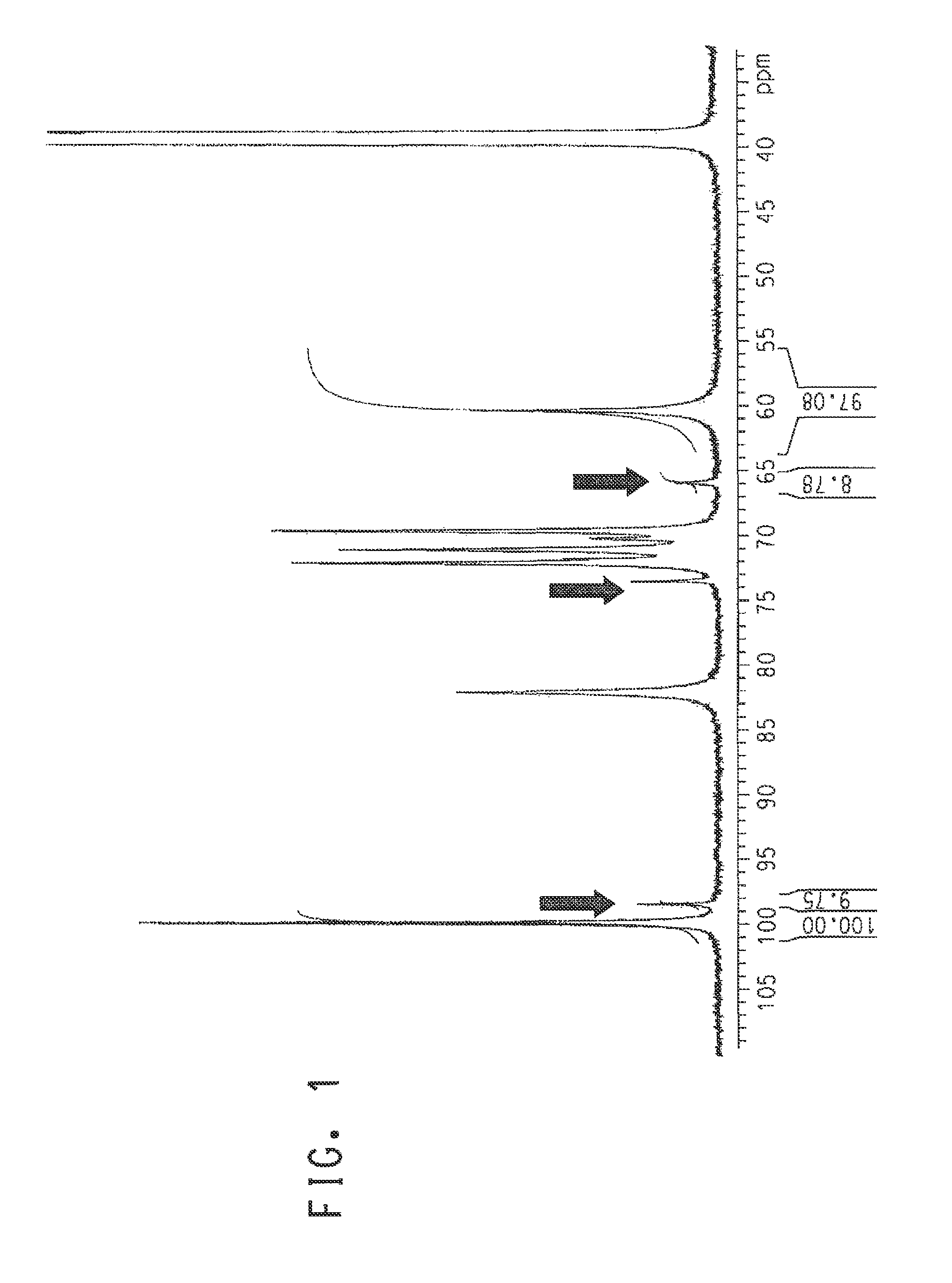
High titer production of highly linear poly (alpha 1,3 glucan)
ActiveUS20130244287A1Improve mechanical propertiesMore amenable to preparing fibersTransferasesFermentationSucroseSaccharophagus degradans
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
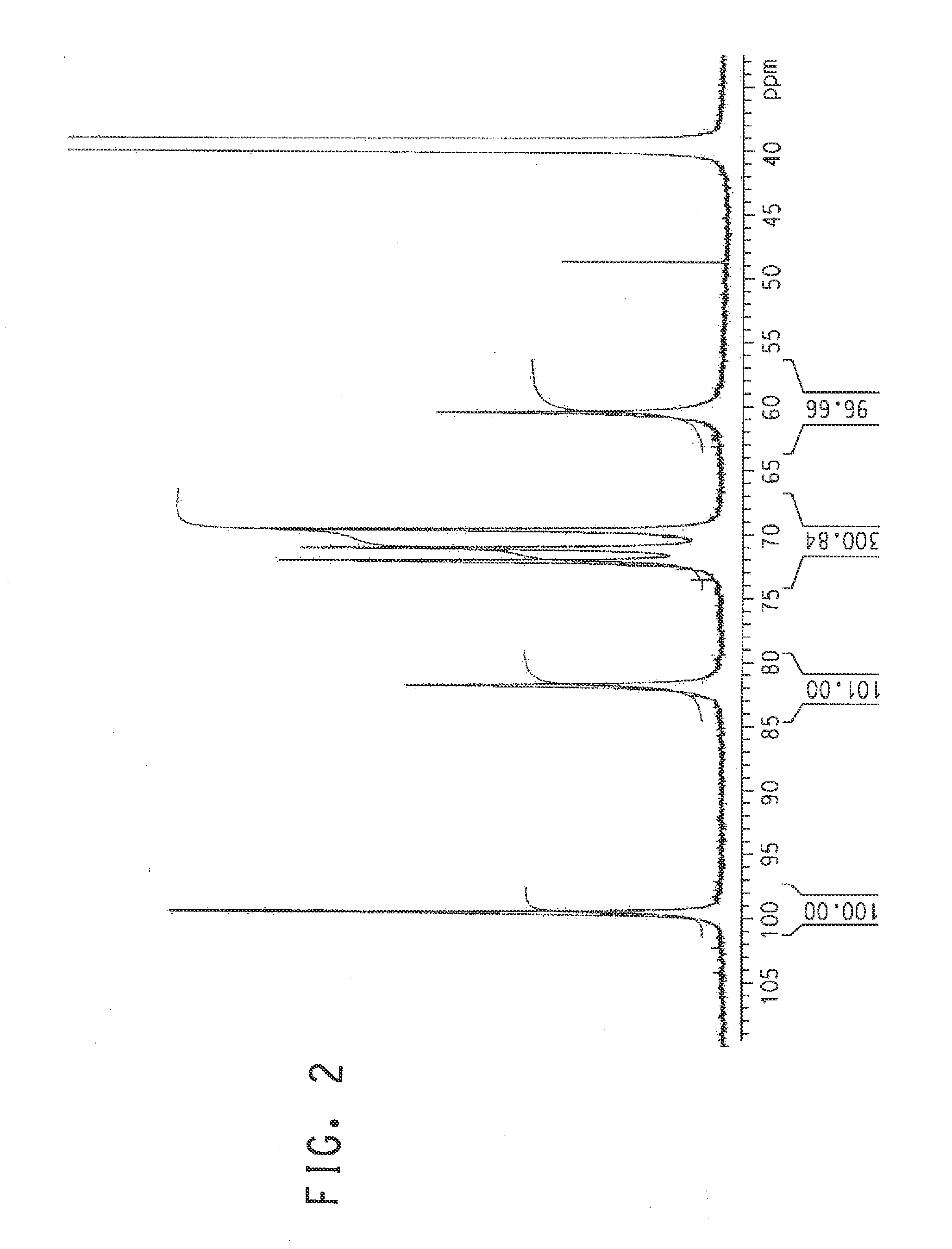
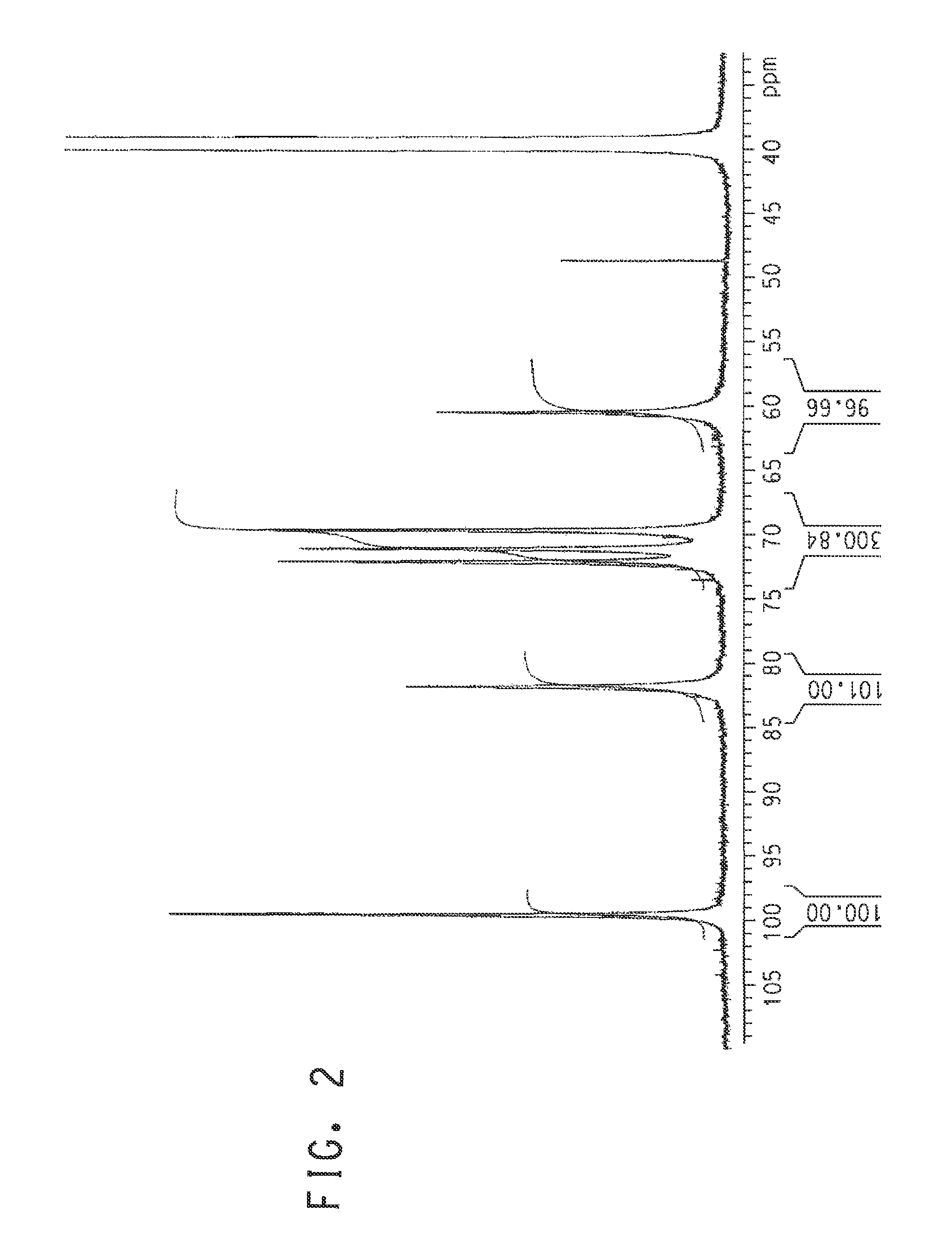
High titer production of poly (α 1,3 glucan)
A process for enzymatic preparation of poly (α1, 3 glucan) from sucrose is disclosed. The glucosyltransferase enzyme (gtfJ) from Streptococcus salivarius is used to convert sucrose to fructose and poly (α1, 3 glucan). Application of semi-permeable membranes to continuously remove fructose, a by-product of the gtf enzyme, thus increasing the poly (α1, 3 glucan) liter, is disclosed.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
High titer production of highly linear poly (alpha 1,3 glucan)
ActiveUS8642757B2Improve mechanical propertiesMore amenable to preparing fibersSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsSucroseSaccharophagus degradans
A process for enzymatic preparation of a highly linear poly(α1,3 glucan) from sucrose is disclosed. The glucosyltransferase enzyme (gtfJ) from Streptococcus salivarius is used to convert sucrose to a highly linear poly(α1,3 glucan) in high titers. Hydrolyzed poly(α1,3 glucan) is used as the primer for the gtfJ enzyme reaction resulting in the formation of highly linear poly(α1,3 glucan).
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
Synthesis of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors
Disclosed is a novel enantiomeric synthesis cermamide-like inhibitors of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase. Also disclosed are novel intermediates formed during the synthesis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Branched alpha-glucan, alpha-glucosyltransferase which forms the glucan, their preparation and uses
ActiveUS20100120710A1High yieldA large amountOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
The present invention has objects to provide a glucan useful as water-soluble dietary fiber, its preparation and uses. The present invention solves the above objects by providing a branched α-glucan, which is constructed by glucose molecules and characterized by methylation analysis as follows:(1) Ratio of 2,3,6-trimethyl-1,4,5-triacetyl-glucitol to 2,3,4-trimethyl-1,5,6-triacetyl-glucitol is in the range of 1:0.6 to 1:4;(2) Total content of 2,3,6-trimethyl-1,4,5-triacetyl-glucitol and 2,3,4-trimethyl-1,5,6-triacetyl-glucitol is 60% or higher in the partially methylated glucitol acetates;(3) Content of 2,4,6-trimethyl-1,3,5-triacetyl-glucitol is 0.5% or higher but less than 10% in the partially methylated glucitol acetates; and(4) Content of 2,4-dimethyl-1,3,5,6-tetraacetyl-glucitol is 0.5% or higher in the partially methylated glucitol acetates; a novel α-glucosyltransferase which forms the branched α-glucan, processes for producing them, and their uses.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA CO LTD
Method for preparing rebaudioside M through enzyme method
ActiveCN103757074AImprove conversion rateHigh purityFermentationSucrose synthetaseUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention relates to a method for preparing rebaudioside M through an enzyme method. According to the method, rebaudioside A or rebaudioside D is used as a substrate, and the substrate reacts to generate the rebaudioside M in the presence of sucrose and UDP under the catalytic action of a mixture of UDP-glucosyltransferase and sucrose synthetase or recombinant cells containing the UDP-glucosyltransferase and the sucrose synthetase, wherein the reaction is performed in a water-phase system having a pH value of 5.0-9.0 at 20-60 DEG C. The method for preparing rebaudioside M through an enzyme method has important application value; and compared with the existing technology of extracting rebaudioside M from stevia rebaudian leaves, the method provided by the invention obviously shortens the production cycle, improves the productivity and lowers the cost, and can provide products having higher purity. Thus, the method can be used in the food and beverage industry in a more economical manner.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
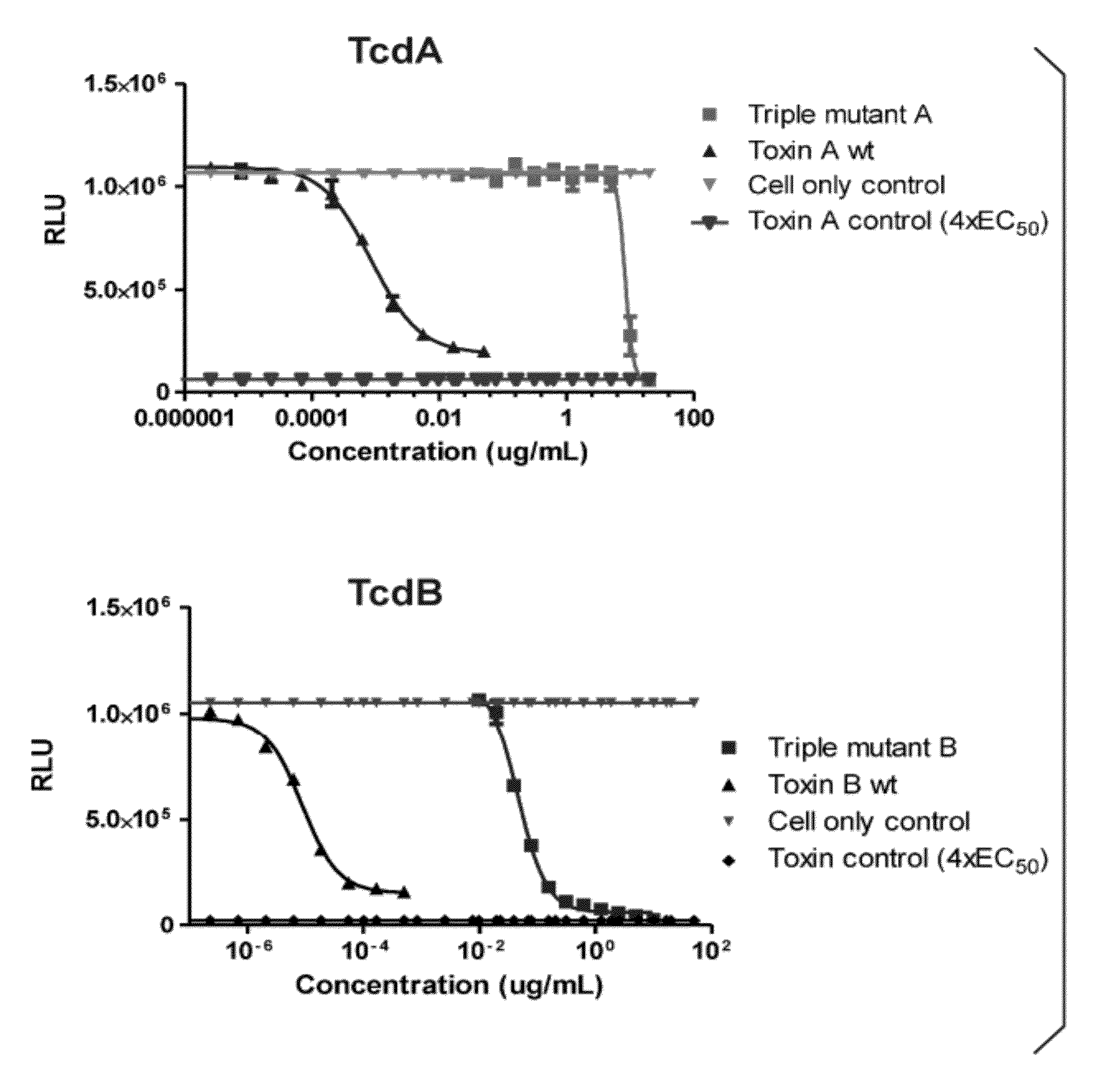
Compositions relating to a mutant clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
ActiveUS20120269841A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNucleotide
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Sugar reduction of food products
ActiveUS20180146699A1Hydrolytic activity was lowHigh activityConfectionerySweetmeatsFood materialSugar
A process for reducing the monosaccharide and / or disaccharide content in a food material, the process comprising contacting the food material with a glucosyltransferase that comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 95% identity to SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Steviol glucosyltransferases and genes encoding the same
ActiveUS20150159188A1Efficient extractionImprove efficiencyBiocideCosmetic preparationsGeneSteviol glycoside
Steviol glucosyltransferases and methods for producing steviol glycosides using the enzymes are provided.The present invention provides steviol glucosyltransferases and methods for producing steviol glycosides using the enzymes. The invention also provides transformants into which steviol glucosyltransferase genes are introduced and methods for preparing the transformants.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Compositions relating to a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method for preparing rebaudioside-M by enzymic method
ActiveCN104726523AHigh reaction conversion rateReduce manufacturing costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionUdp glycosyltransferaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preparing rebaudioside-M by an enzymic method. The method comprises the steps of utilizing tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase and potato sucrose synthetase, and using rebaudioside-A and sucrose as raw materials for producing rebaudioside-M. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the high-yield recombinant strain of UDP-glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthase is obtained by virtue of a genetic engineering technology at first, then a bio-enzyme crude product is collected, a catalytic reaction is directly carried out, UDP or UDP-glucose is not added in the reaction system, the rebaudioside-A and the sucrose are used as the raw materials, and the rebaudioside-A is catalyzed to generate the rebaudioside-M through the efficient circulation of catalyzing the UDP-glucose by the sucrose synthase, and through the action of the tomato UDP-glycosyltransferase. Compared with the existing preparation method for rebaudioside-M, the process is short in steps, low in cost, important in application value, and good in economical efficiency.
Owner:XINGHUA GL STEVIA CO LTD
Method for improving taste quality of stevioside by using beta-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
InactiveCN102492757AVarious catalytic activitiesAbundant resourcesMicroorganism based processesFermentationSweetnessBeta-Cyclodextrins
The invention relates to a method for improving taste quality of stevioside by using beta-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase. The method is characterized by comprising steps of: preparing a reaction solution containing 2-5wt% of stevioside and 2-5wt% of starch with water; adding beta-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with enzyme activity of 60-70 U / ml into the reaction solution and mixing uniformly, wherein an addition of the transferase is 300-500 U / stevioside weight g; carrying out conversion reaction at 37-50 DEG C for 48-72 h; and carrying out separation and purification to obtain a single transformation product glucosyl-stevioside. The method has advantages and effects of simple method, easy control, good product mouthfeel and high sweetness.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
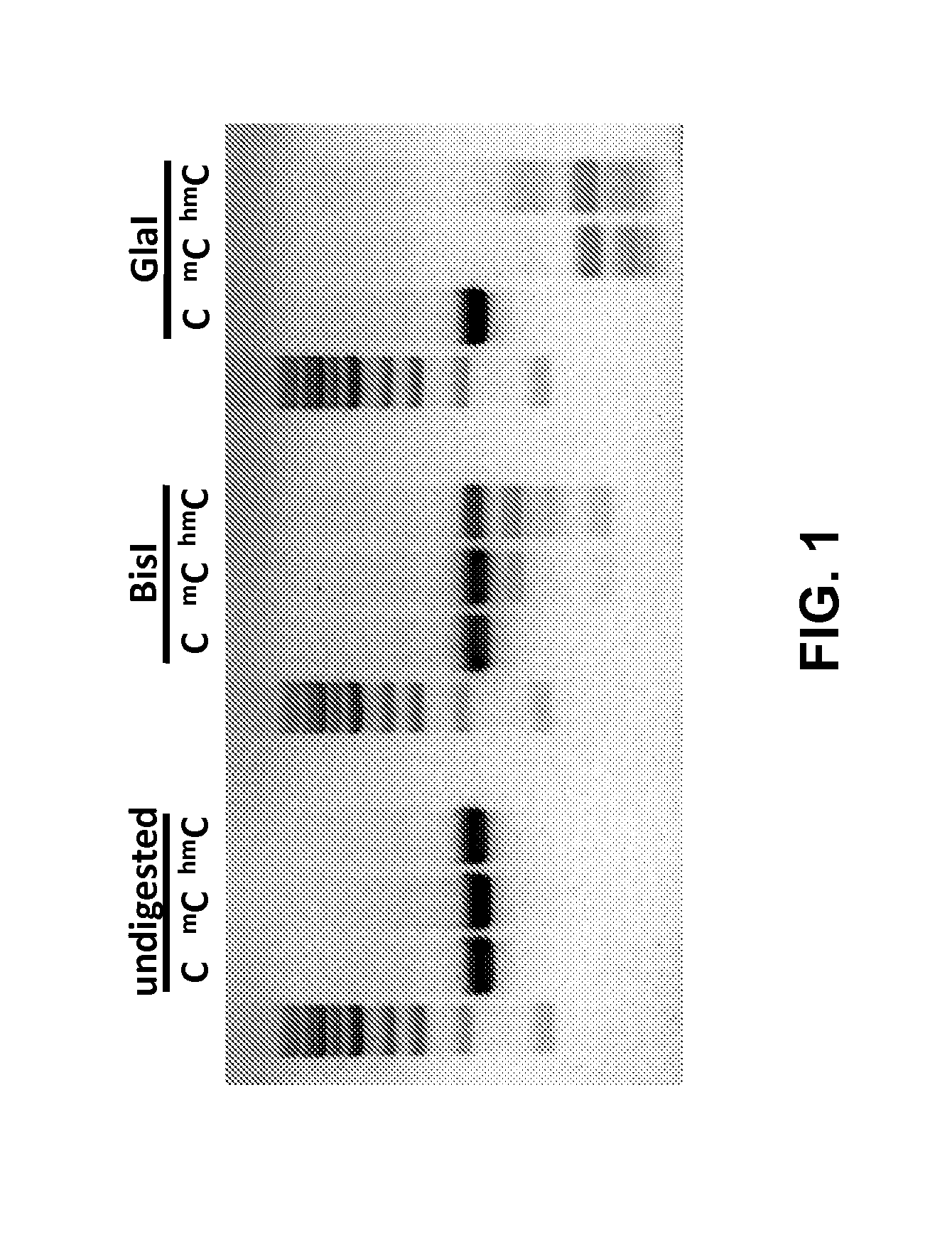
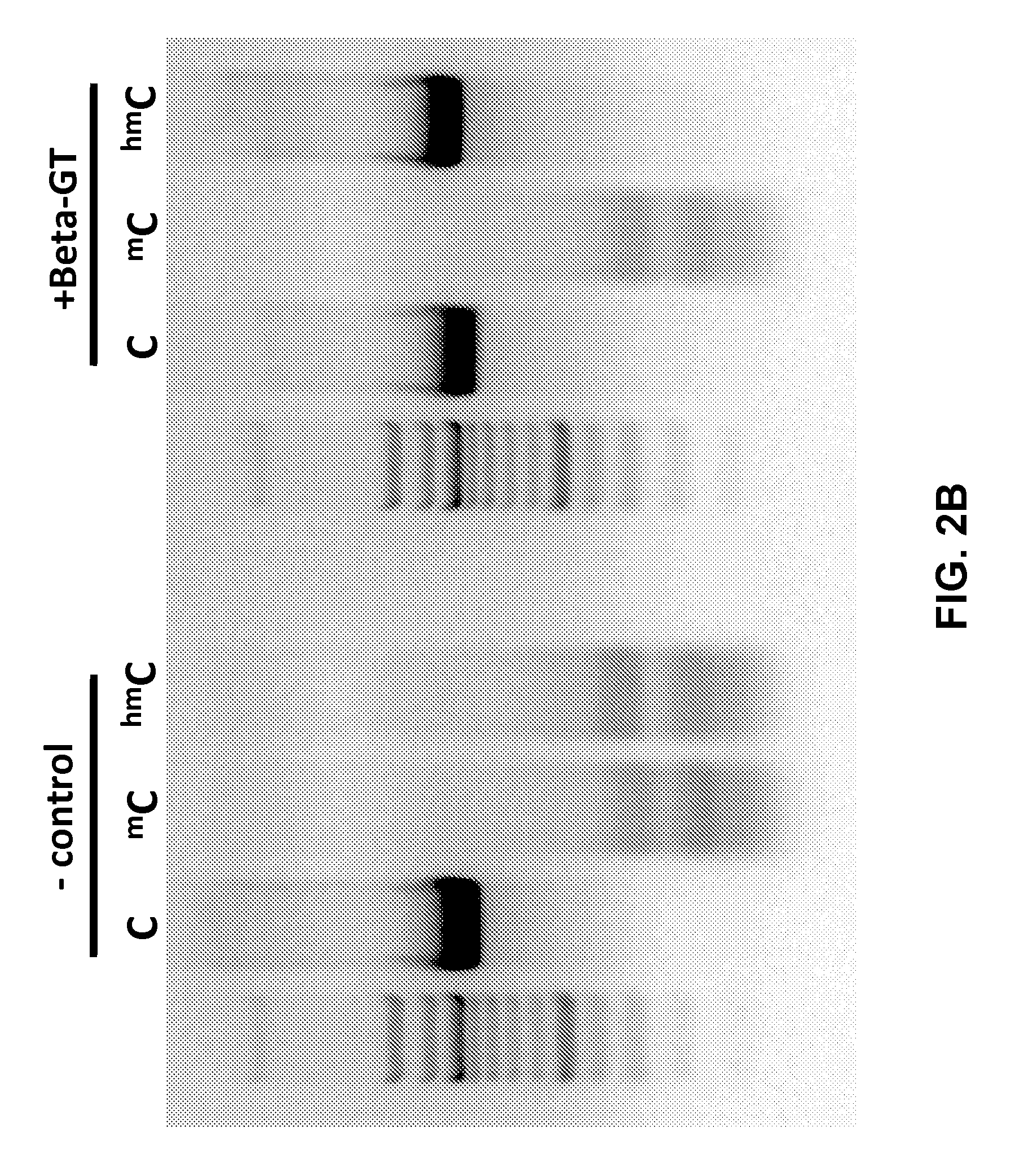
Detection of DNA hydroxymethylation
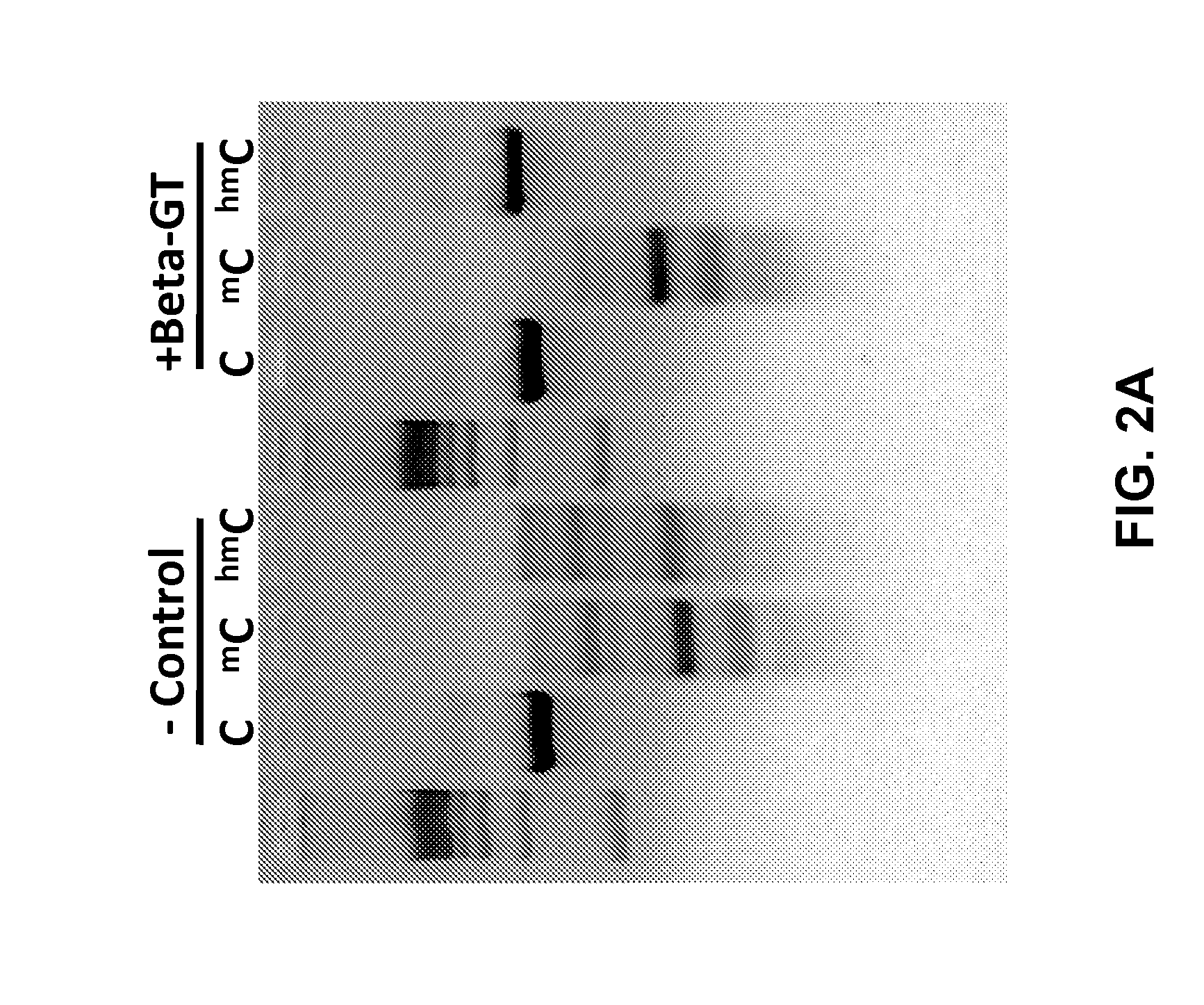
Reagents and methods for analysis of DNA hydroxymethylation are provided. Methods comprise modification of hydroxymethylated cytosine residues with a bulky moiety to protect hydroxymethylated positions from cleavage with a DNA endonuclease. For example, methods may comprise contacting DNA with a glucosyltransferase to glucosylate hydroxymethylated DNA positions and digesting the DNA with a DNA endonuclease to cleave DNA in positions lacking hydroxymethylation. Reagents and kits for hydroxymethylated DNA analysis are also provided.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
Recombinant Escherichia coli producing salidroside, construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN107435049AMetabolic pathway optimizationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliSalidroside
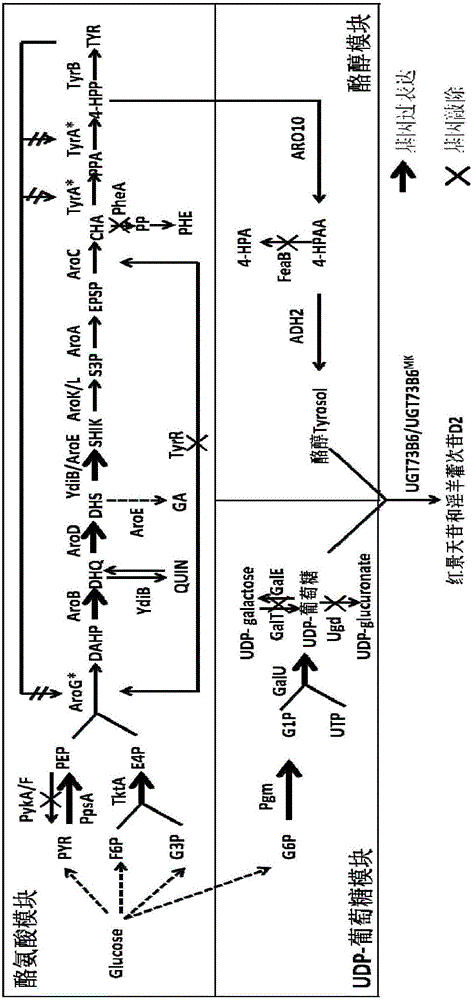
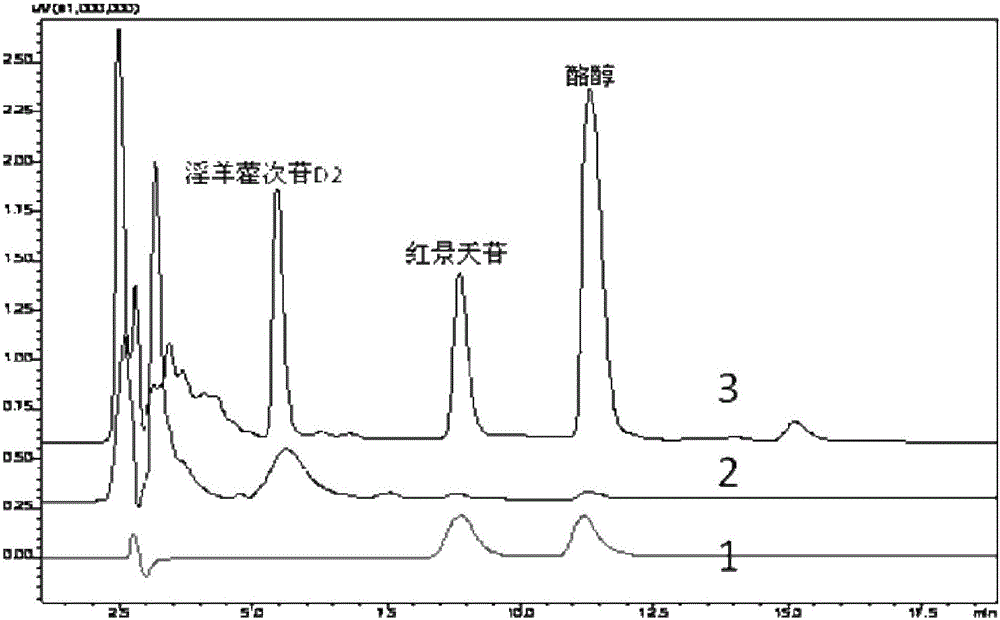
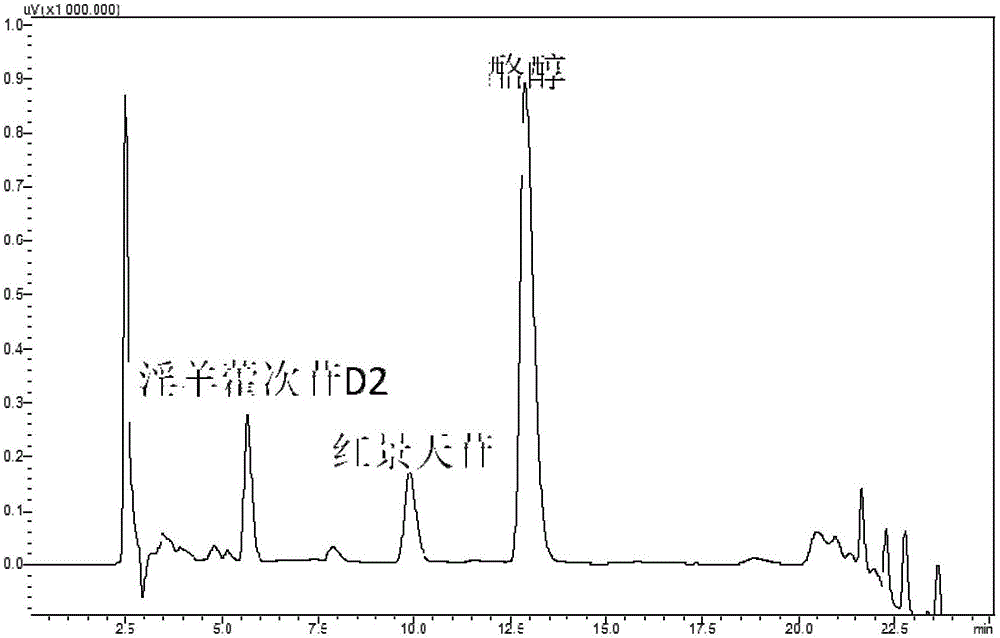
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli producing salidroside, a construction method and applications thereof. The construction method comprises: (1) using Escherichia coli [delta]A as a starting strain, and carrying out gene knockdown or gene silencing to make the galE gene, the galT gene and the ugd gene on the Escherichia coli chromosome be not expressed to obtain an Escherichia coli strain BMGU; and (2) introducing genes such as ARO10, UGT73B6MK, pgm, galU and T7Polymerase to over-express the genes such as ARO10, UGT73B6MK, pgm, galU and T7Polymerase so as to achieve the heterologous synthesis of salidroside, such that the recombinant Escherichia coli producing salidroside is obtained. According to the present invention, the efficient UDP-glucosyltransferase mutant UGT73B6MK is introduced, and the glucose metabolism pathway is optimized, such that the yield of salidroside is significantly improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Water Soluble and Activable Phenolics Derivatives with Dermocosmetic and Therapeutic Applications and Process for Preparing Said Derivatives
InactiveUS20090233876A1Reduce allergic reactionsPotent immunosuppressive effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilitySucrose
The invention relates to the preparation of phenolics derivatives by enzymatic condensation of phenolics selected among pyrocatechol or its derivatives with the glucose moiety of sucrose. The production of said phenolics derivatives is achieved with a glucosyltransferase (EC 2.4.1.5). These O-α-glucosides of selected phenolics are new, have a solubility in water higher than that of their parent polyphenol and have useful applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical compositions, such as antioxidative, antiviral, antibacterial, immune-stimulating, antiallergic, antihypertensive, antiischemic, antiarrhythmic, antithrombotic, hypocholesterolemic, antilipoperoxidant, hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory, anticarcinogenic antimutagenic, antineoplastic, anti-thrombotic, and vasodilatory formulations, or in any other field of application.
Owner:LIBRAGEN SA
Method for catalyzing and synthetizing modified stevioside by using microwave auxiliary cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
A method for catalyzing and synthetizing modified stevioside by using microwave auxiliary cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase relates to the technical field of biosynthesis of organic compounds, and comprises the following steps: taking stevioside aqueous solution and starch hydrolyzates as raw materials, and synthetizing stevioside replaced by glucose residue under the combined action of microwave radiation and CGTase catalysis in a microwave reaction device. In the process condition provided by the invention, enzyme catalysis reaction can be remarkably quickened, and the phenomenon that microwave of a water system enable enzyme to be inactive under the usual condition. Through tasting, the bitter taste of the synthetic modified stevioside is greatly reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +2
Process for producing alpha-1,3-glucan polymer with reduced molecular weight
A process for producing poly alpha-1,3-glucan with reduced molecular weight is disclosed. The process comprises contacting water, sucrose, a polar organic solvent, and a glucosyltransferase enzyme in a solution to produce poly alpha-1,3-glucan. This contacting step results in the production of poly alpha-1,3-glucan having a reduced molecular weight compared to the molecular weight of a poly alpha-1,3-glucan made in the absence of the polar organic solvent.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
Method for preparing rebaudioside M according to saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymatic method
InactiveCN105200098AImprove securitySave fermentation timeMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesFood additiveUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention discloses a method for preparing rebaudioside M according to a saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymatic method. The method for preparing rebaudioside M comprises the following steps: utilizing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae containing UDP-glucosyltransferase or UDP-glucosyltransferase prepared from the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae to catalyze rebaudioside A or rebaudioside D in the presence of a glucosyl group donor, so as to generate rebaudioside M. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained by introducing a strong promoter into a plasmid to obtain a vector plasmid, inserting a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene into the vector plasmid through a restriction site to obtain an expression vector under the control the strong promoter, and carrying out saccharomyces cerevisiae transformation. The method for preparing rebaudioside M has the advantages that the high-safety recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is utilized for catalytic production; the produced UDP-glucosyltransferase is higher in expression level and activity; the produced rebaudioside M can be directly utilized as a food additive, and is short in production period, higher in yield, and relatively low in cost.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
Process for extracellularly producing recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
ActiveCN101831414AReduce pollutionImprove purification efficiencyTransferasesMicroorganism based processesHybrid proteinOxygen
The invention discloses a process for producing recombinant alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase in a fermenting way by culturing escherichia coli in high density through a temperature two-stage control strategy and a constant oxygen-dissolved and feed-supplemented batch technology, belonging to the technical field of fermentation engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating recombinant escherichia coli BL21(DE3) as a production strain at the inoculation quantity of 5-10 percent and fermenting in batch; starting adding a supplementing liquid in a flowing mode when dissolved oxygen rises to about 80-100 percent, ensuring that a strain body exponentially grows, controlling the temperature of the growth phrase of the strain body to be 33-37DEG C and maintaining the dissolved oxygen to 20-30 percent; adding 0.75-1.5 percent (mass volume percent) of glycine when the strain body OD600 reaches about 15-30; reducing the temperature to be 23-27DEG C and continuously supplementing 0.2-0.4g.l<-1>.h<-1> when the strain body OD600 reaches 45-60 and supplementing the supplementing liquid by adopting a gradient diminishing mode at the same time; and enabling the enzymeactivity of the extracellular alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to reach 200-280U / ml by fermenting culture for 30-35 hours. By adopting the strategy to ferment, the invention realizes the high-efficiency extracellular expression of the alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase and greatly improves the production intensity. The invention has the advantages of wide source of raw materials, simple and feasible process and suitability for large-scale production; with effective extracellular expression, the pollution on host bacteria hybrid proteins can be greatly reduced and the purification efficiency of the protein can be improved. The invention lays a foundation for large-scale production of the alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutant of cyclodextrin glucosyl transferase having highly beta-cyclodextrin yielding property and mutation method
InactiveCN101503680AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityTransferasesMicroorganism based processesWild typeSite-directed mutagenesis
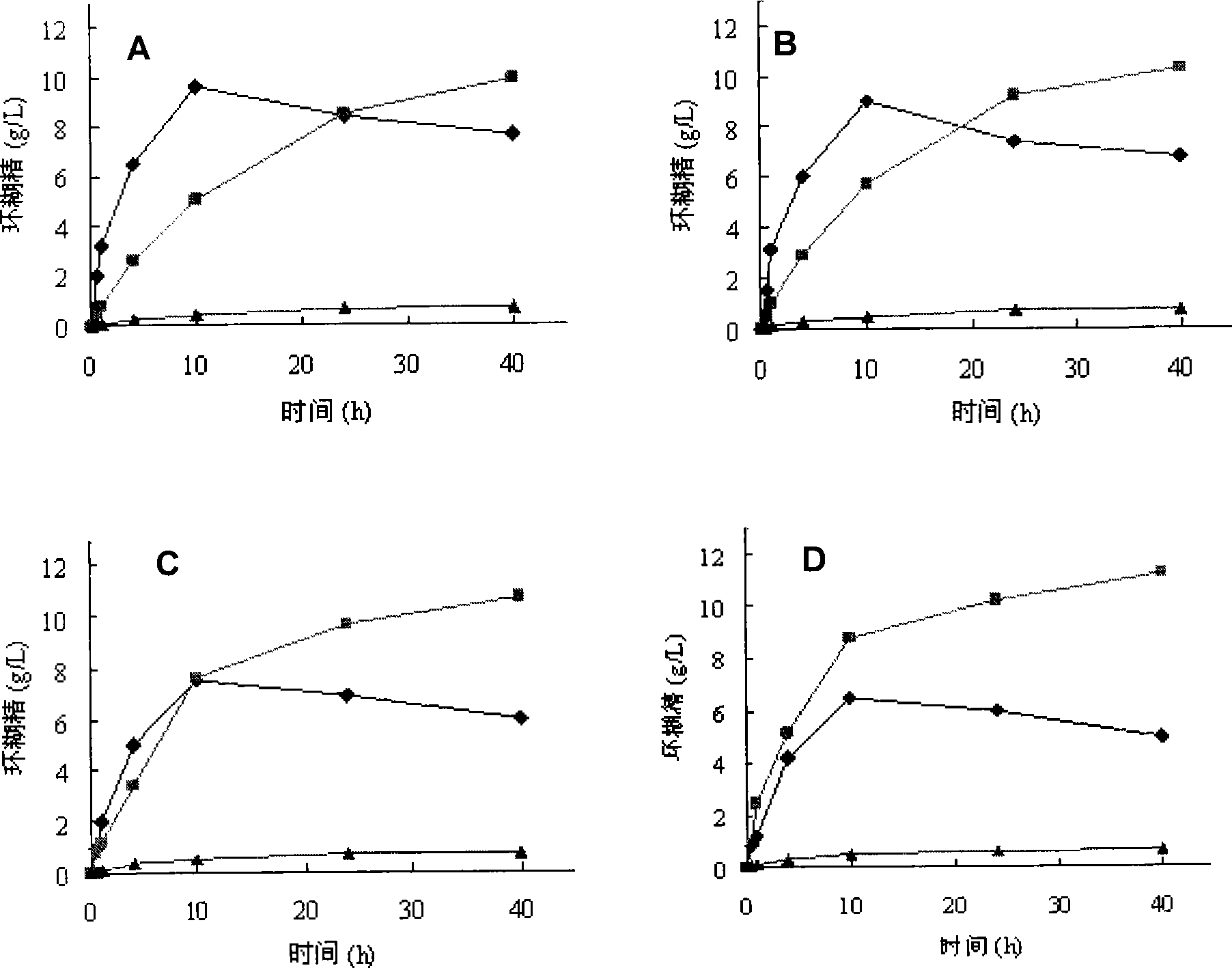
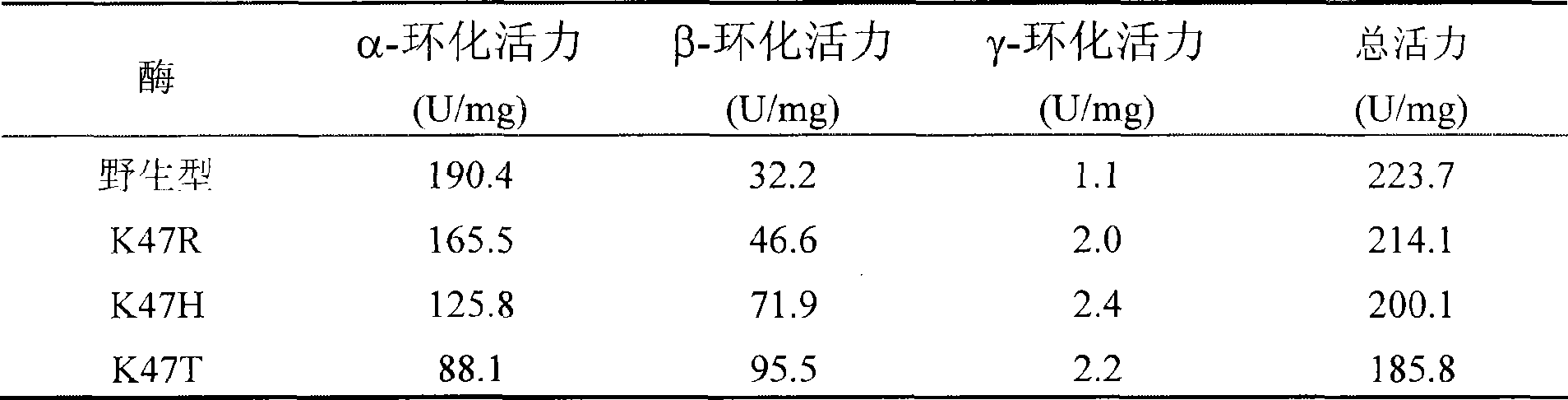
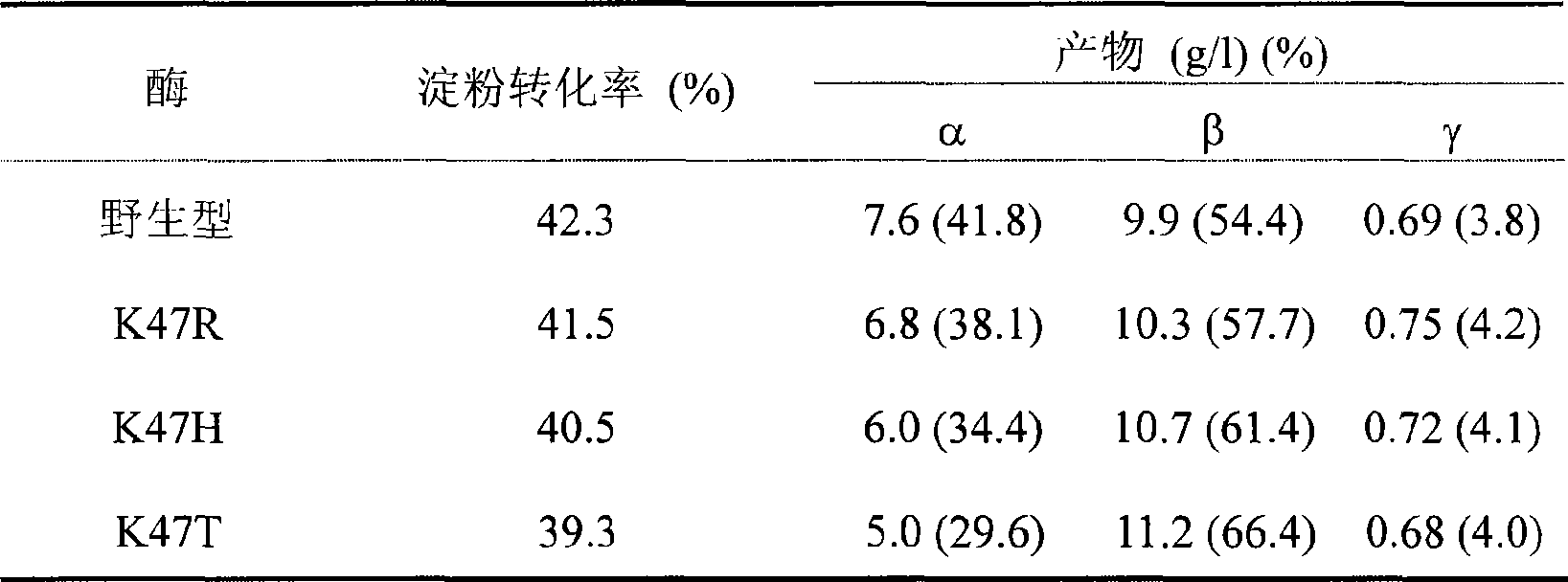
The invention relates to a mutant of a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with the capability of highly yielding beta-cyclodextrin and a mutation method, which belong to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention improves the capability of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin by a rite-directed mutagenesis method, provides a mutant proposal for improving the capability of CGT enzyme from Peanibacillus macerans JFB05-01 (CCTCC NO: M 208063) for producing the beta-cyclodextrin, and substitutes Lys on the 47 position of the CGT enzyme for Arg, His and Thr respectively; the beta-cyclodextrin production capacity of the obtained three mutant enzyme of K47R, K47H and K47T is improved compared with wild type CGT enzymes, wherein the mutant enzyme K47T is particularly obvious. The mutant enzymes are more favorable for industrial production of the beta-cyclodextrin than the wild type CGT enzymes.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
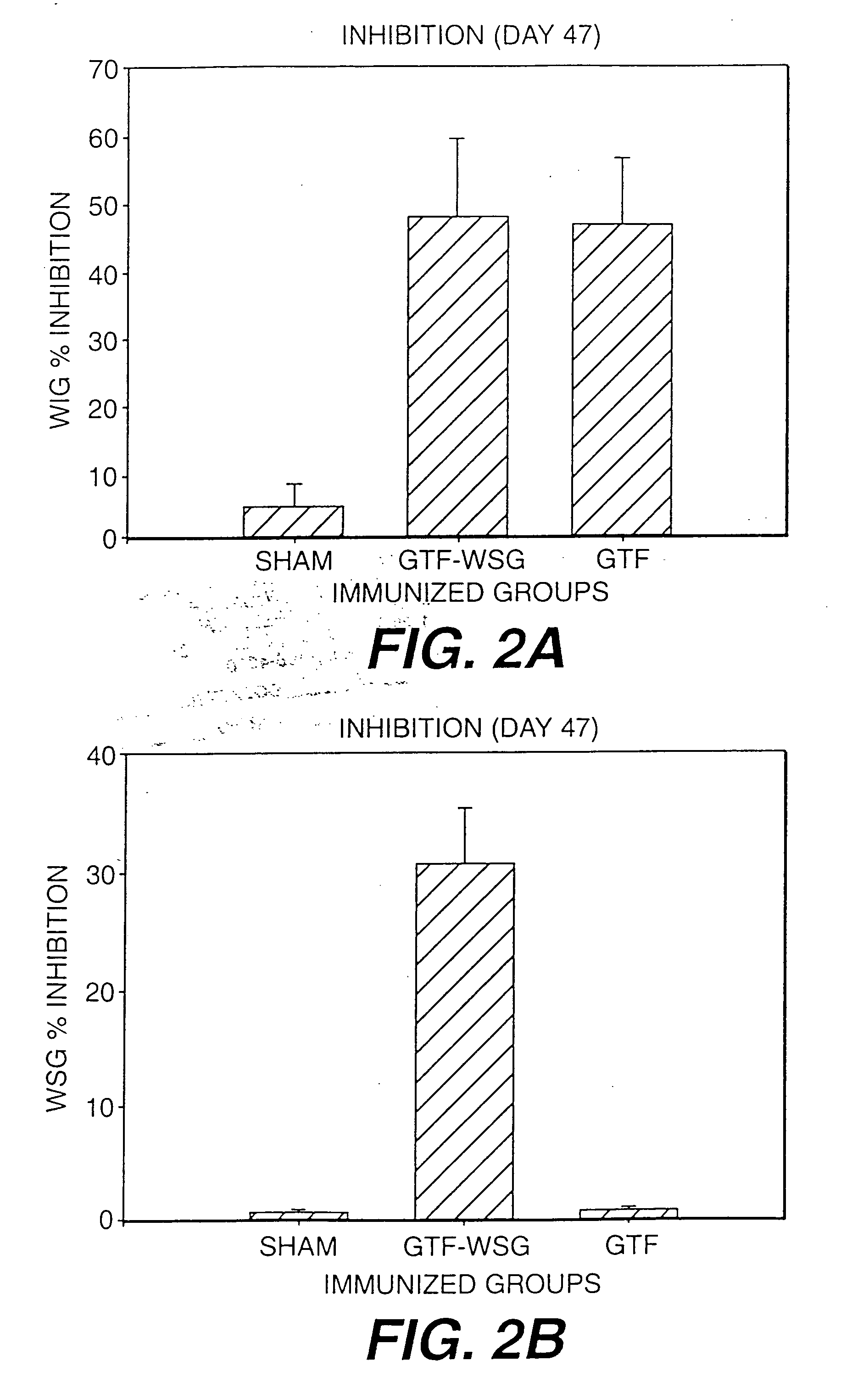
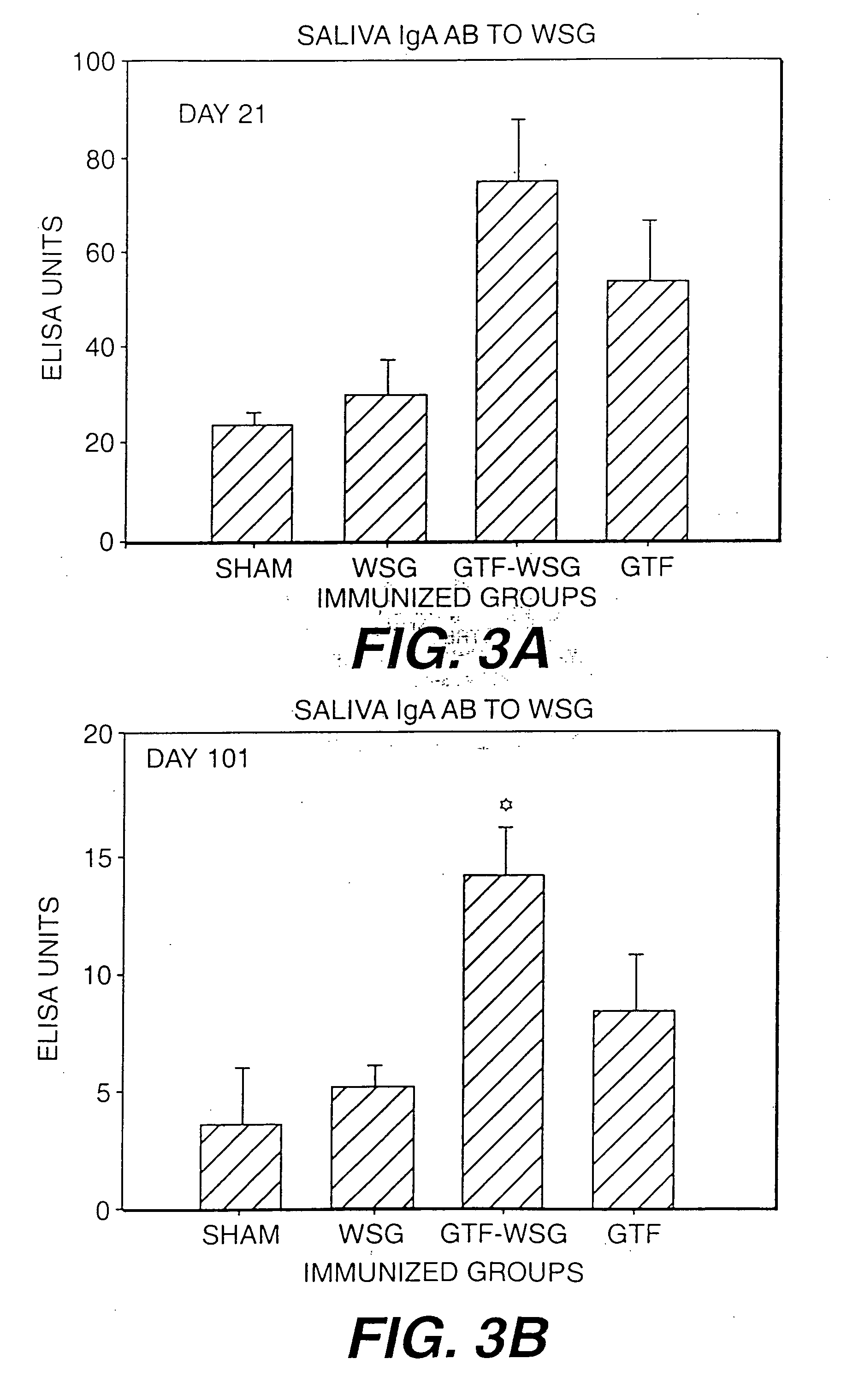
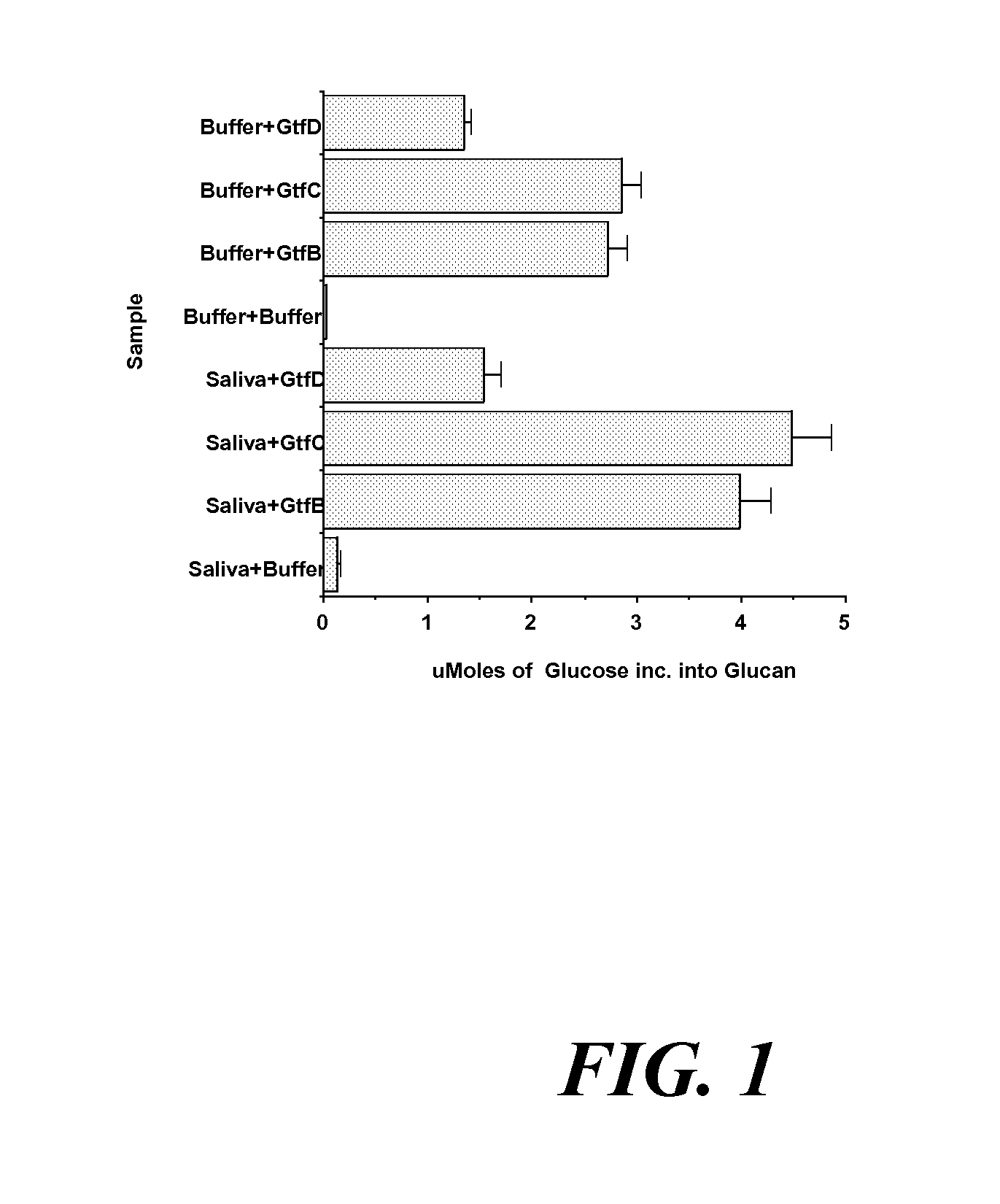
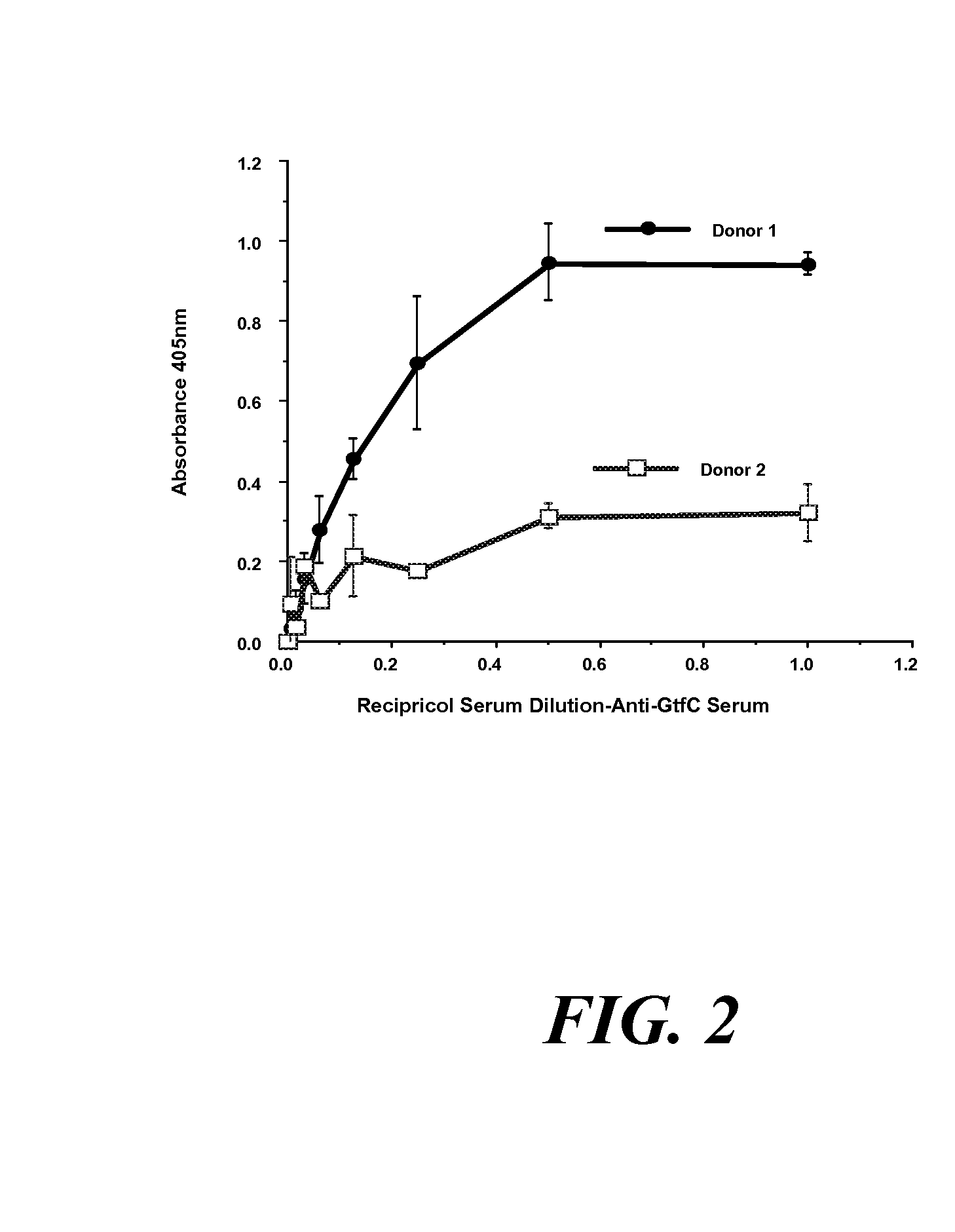
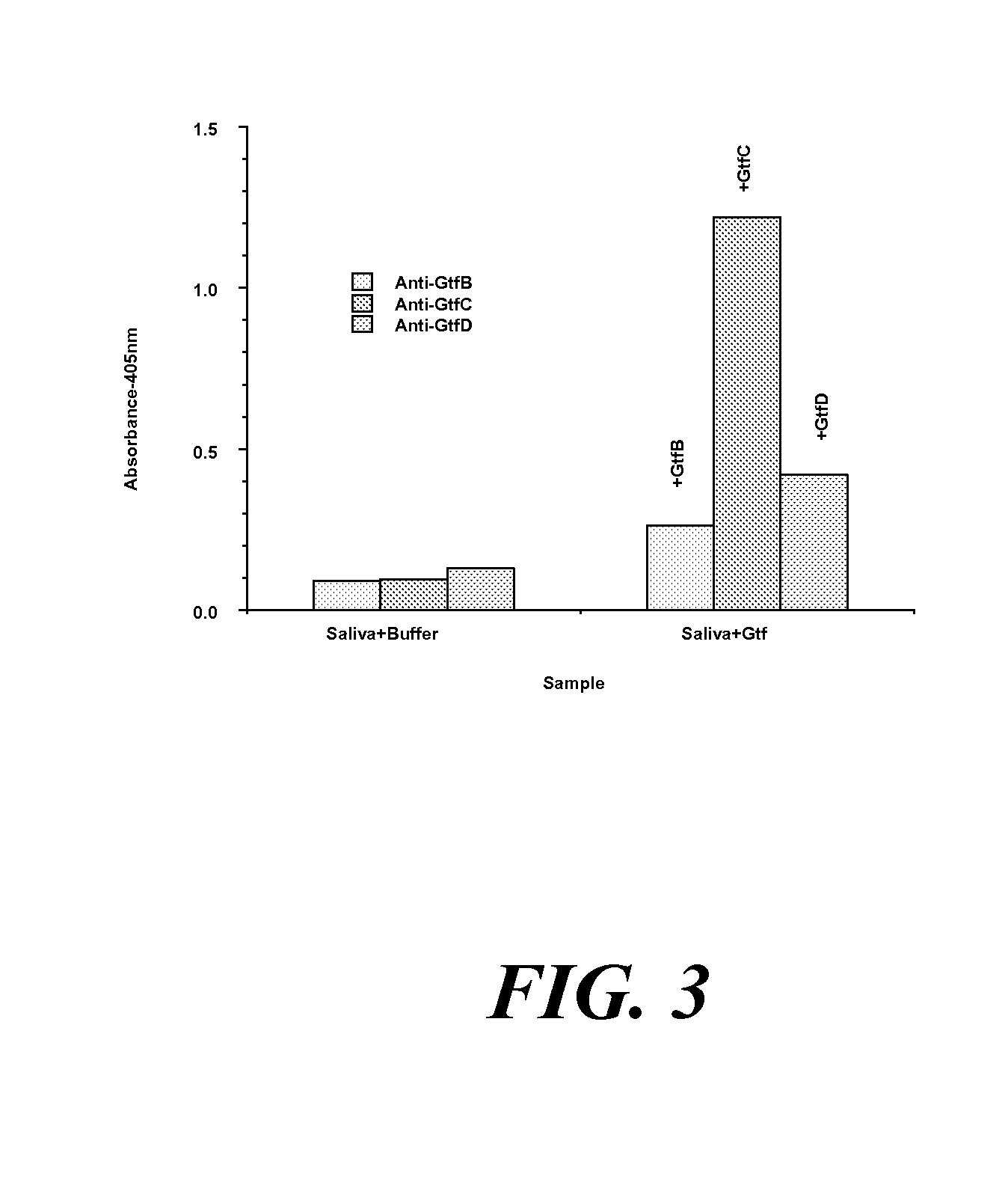
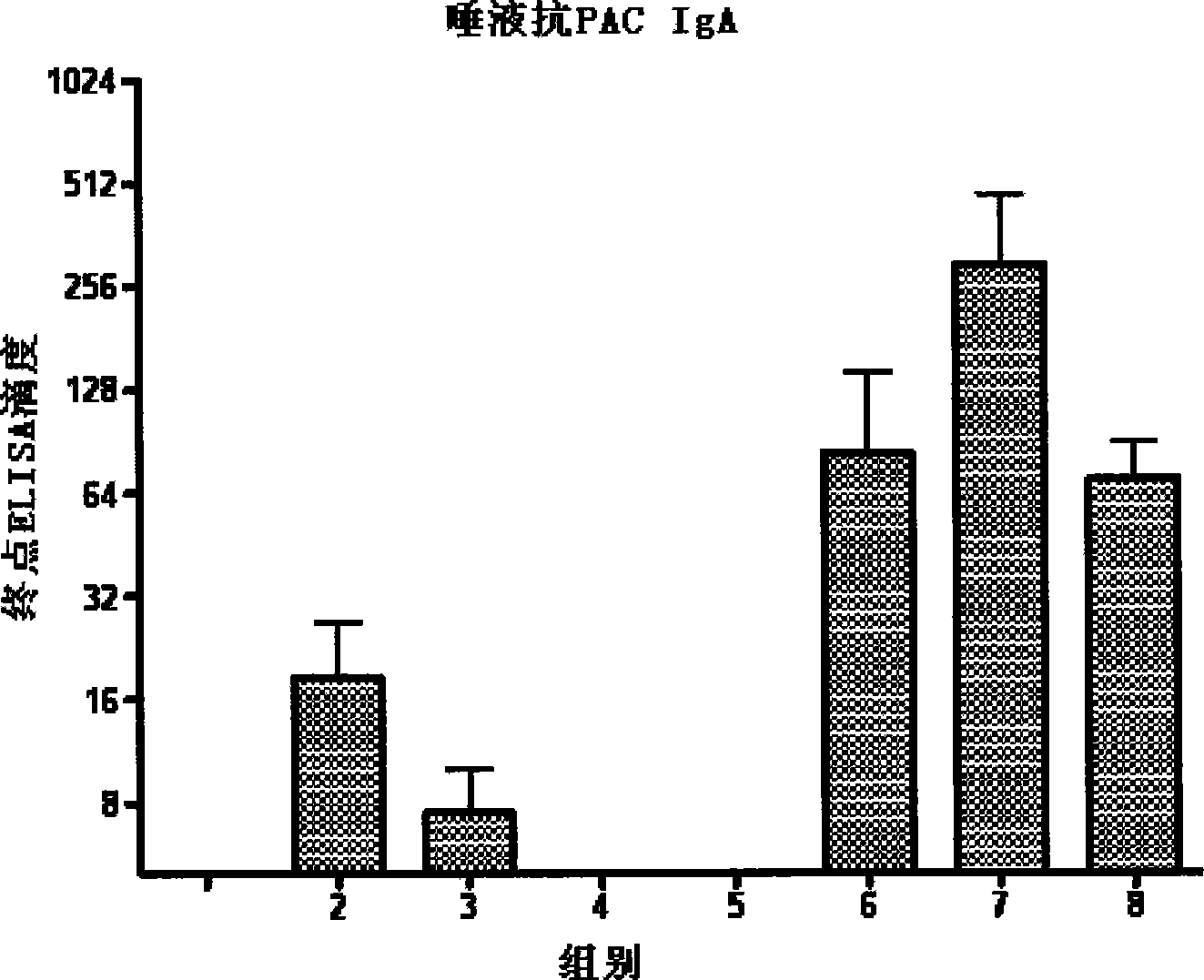
Conjugate vaccines for the prevention of dental caries
InactiveUS20070065465A1Organic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsConjugate vaccineEpitope
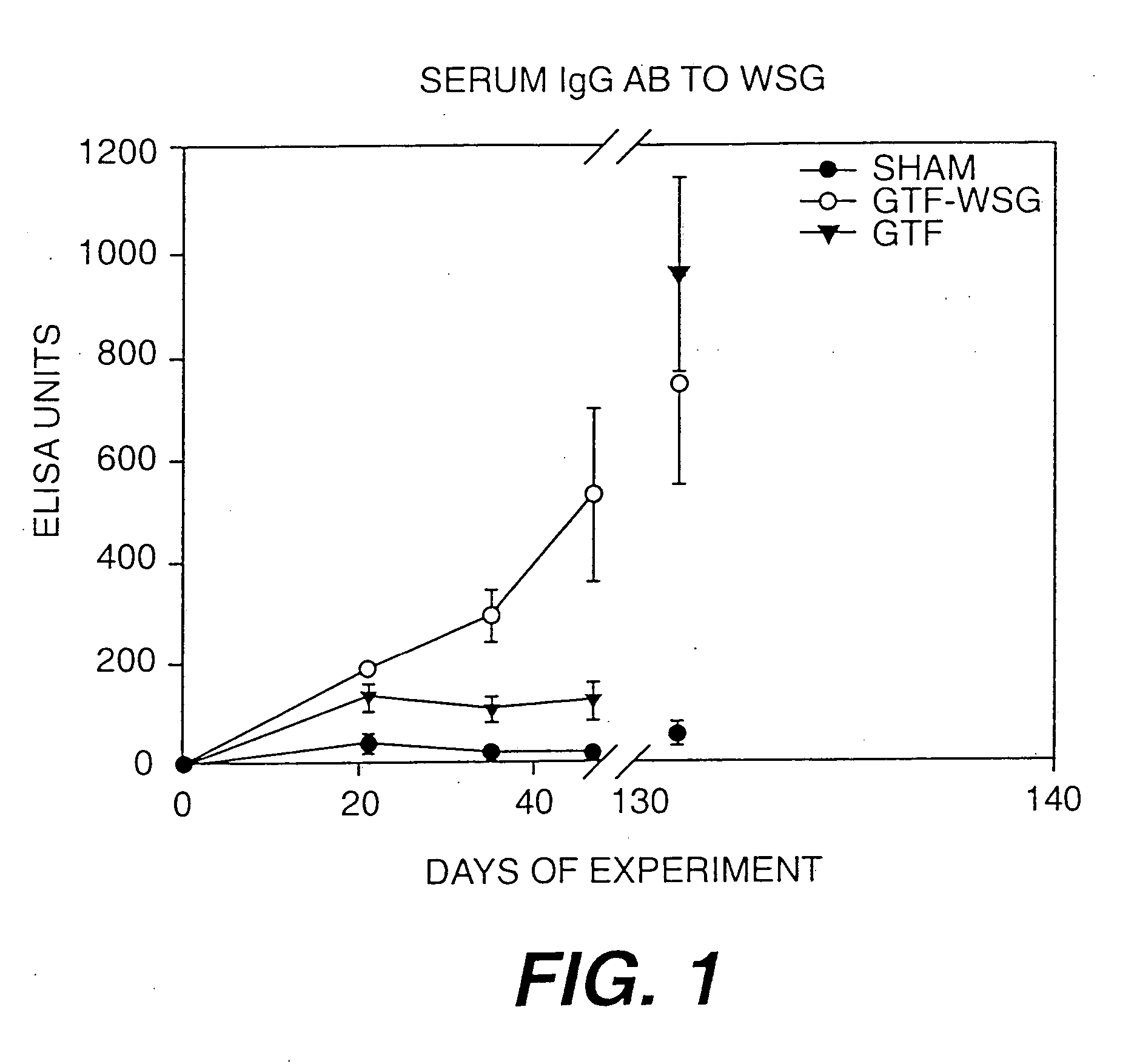
The present invention provides glucan-based compositions and methods for stimulating an immune response against mutans streptococci components and vaccines and methods for the treatment and prevention of dental caries. In a preferred embodiment, a glucan polymer, preferably WSG, is covalently bound to one or more T cell-dependent antigens to form a conjugate vaccine. The T cell-dependent antigen preferably contains epitopes of one or more mutans streptococcal proteins, such as a glucosyltransferase. Moreover, one or more moieties, including haptens, may be conjugated to the glucan or to the glucan-T cell-dependent composition. In a preferred embodiment, these moieties are peptides which contain immunogenic epitopes corresponding to components of a mutans streptococcus.
Owner:LEES ANDREW +2
Method for producing isomalto-oligosaccharide by using high-concentration starch
InactiveCN104212854ARaise the initial concentrationReduce energy consumptionFermentationHigh concentrationLiquid glucose
The invention relates to a method for producing isomalto-oligosaccharide by using high-concentration starch and belongs to the field of production of isomalto-oligosaccharide. By improving the initial concentration of starch milk, through performing insulation liquification and spraying liquification to prepare a high-concentration maltodextrin solution, by virtue of a synergistic effect of beta-amylase and pullulanase (incisal enzyme) in a process of converting glucoside by saccharifying, the content and the concentration of maltose in liquid glucose are increased; meanwhile, due to the fact that the pullulanase is added, the viscosity of the high-concentration liquid glucose can be reduced, and an optimal substrate environment is provided for alpha-glucosyltransferase, thus the yield of the isomalto-oligosaccharide is improved, and the time of converting glucoside by saccharifying is shortened. The starch resource is wasted due to the fact that a separation and purification technology of the isomalto-oligosaccharide is not enough advanced. According to the method disclosed by the invention, by adopting a nanofiltration membrane technology, the purity of the isomalto-oligosaccharide is increased, crystalline dextrose can be co-produced when high-purity liquid glucose can be produced as a byproduct, and thus the problem of low resource utilization rate is effectively solved.
Owner:吉林省轻工业设计研究院
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate
ActiveCN104531629AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant, the 228th lysine near the active center of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase of thermophilic fat bacillus (Bacillus stearotherm opilus NO2) is mutated into arginine to obtain a mutant K228R, the 367th aspartic acid is mutated into serine to obtain a mutant D367S and amphimutation is carried out on the basis to obtain a mutant D367S / K228R. The mutant can be used for realizing the improvement of the AA-2G conversion rate and has relatively high industrial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Antibodies and methods for predicting dental caries
ActiveUS20070065886A1Simple diagnostic testReduce morbidityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCementum cariesEarly childhood caries
The present invention relates to antibodies, binding portions thereof, or probes that bind specifically to glucosyltransferase enzymes, and uses of these agents for detecting glucosyltransferase enzyme(s) in a sample and for diagnosing predisposition of a human child to early childhood caries. The present invention also relates to a kit for detecting a glucosyltransferase enzyme in an oral sample from an animal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Vaccine reagent kit for preventing carious tooth and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101411872AImproving immunogenicityComprehensive persistent immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantA-DNA
The invention relates to a vaccine reagent kit for preventing decayed tooth, which comprises antigen and adjuvant, wherein the antigen is a dna recombinant plasmid of at least one surface proteantigen and at least one glucosyltransferase which co-express decayed tooth streptococcus mutans; and the adjuvant is flagellins of one or more than one germ. The vaccine reagent kit for preventing the decayed tooth has strong immunogenicity, can excite comprehensive and lasting immune response, and has strong specificity, even immune effect and simple and convenient operation. The invention also provides an application method for the vaccine reagent kit for preventing the decayed tooth, and the vaccine reagent kit has good immune effect and simple and convenient operation.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for preparing isomaltitol
ActiveCN1884561AIncrease contentIncrease profitMicroorganism based processesFermentationIsomaltEnergy conservation
This is the preparation method of isomalttulose. The steps includes: (1) the raw material is aqueous sucrose solutions, make it through the stablized alpha-glucosyltransferase reaction column or can to produce the transformation liquid which contains isomaltose and other sugers that transformed from enzyme; (2) make the prepared transformation liquid through de-sugers reactor with yeast immobilization in it, to get rid of the sugers other than isomaltose in transformation liquid; (3) then remove the residua in the acentric transformation liquid and get the clear liquid that contains isomaltose, then catalytic hydrogenation to produce isomalttulose. The content of isomaltose in the transformation liquid can reach more than 98%, then after catalytic hydrogenation, the obtained isomalttulose can increase the utilization rate of sucrose. Besides, it can also save energy and increase productivity.
Owner:LIFECOME BIOCHEM
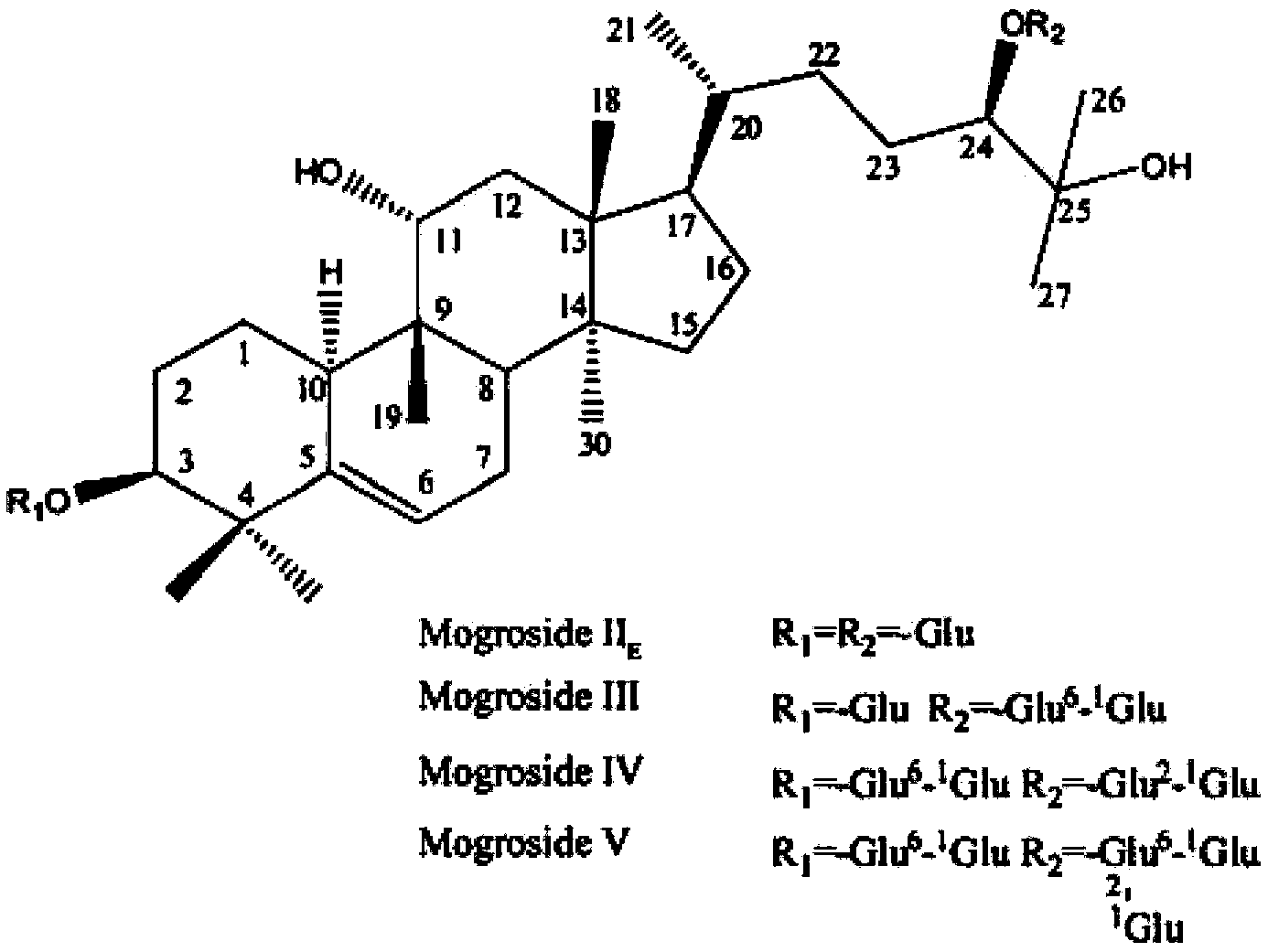
Methods of producing mogrosides and compositions comprising same and uses thereof
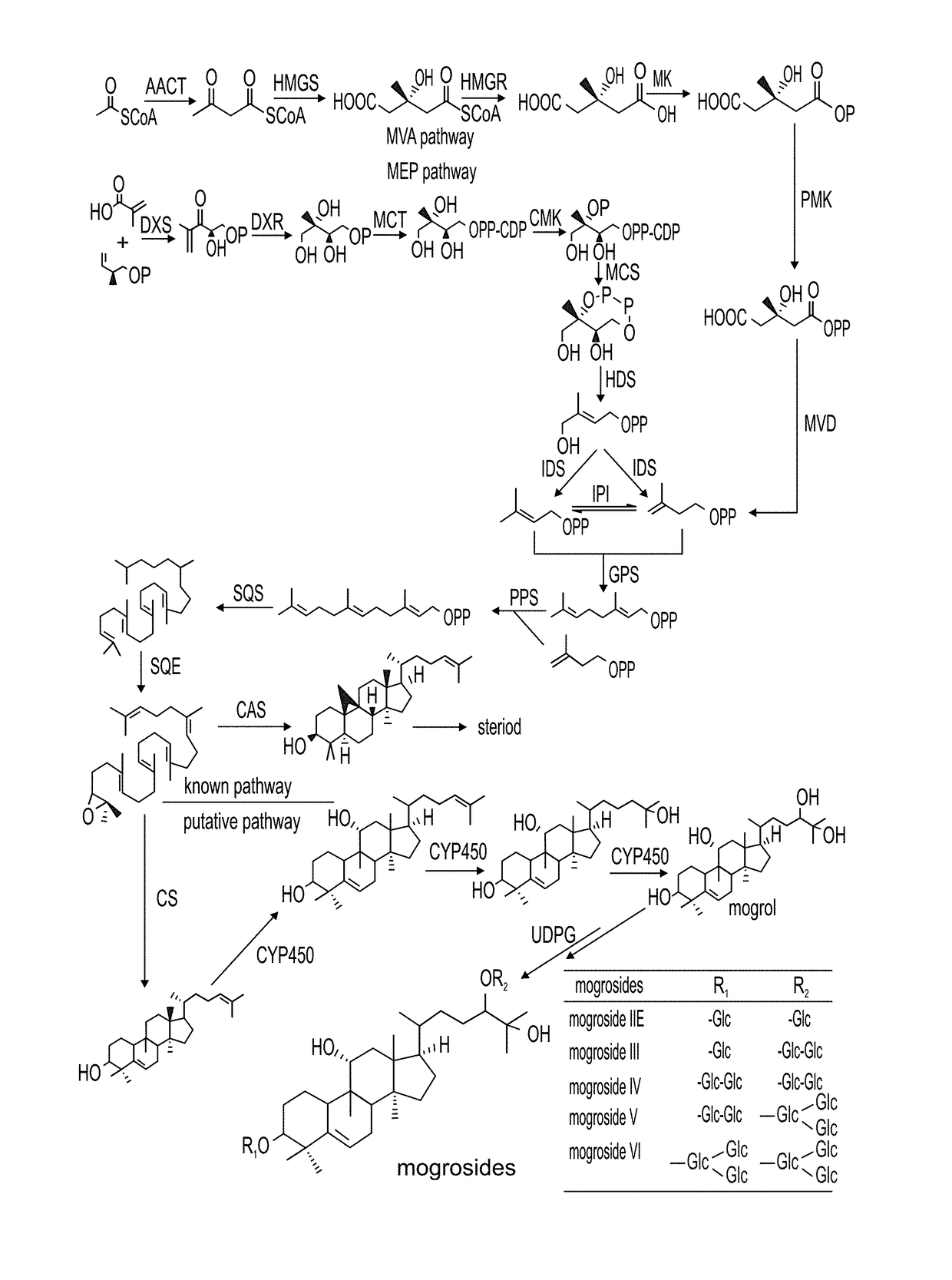
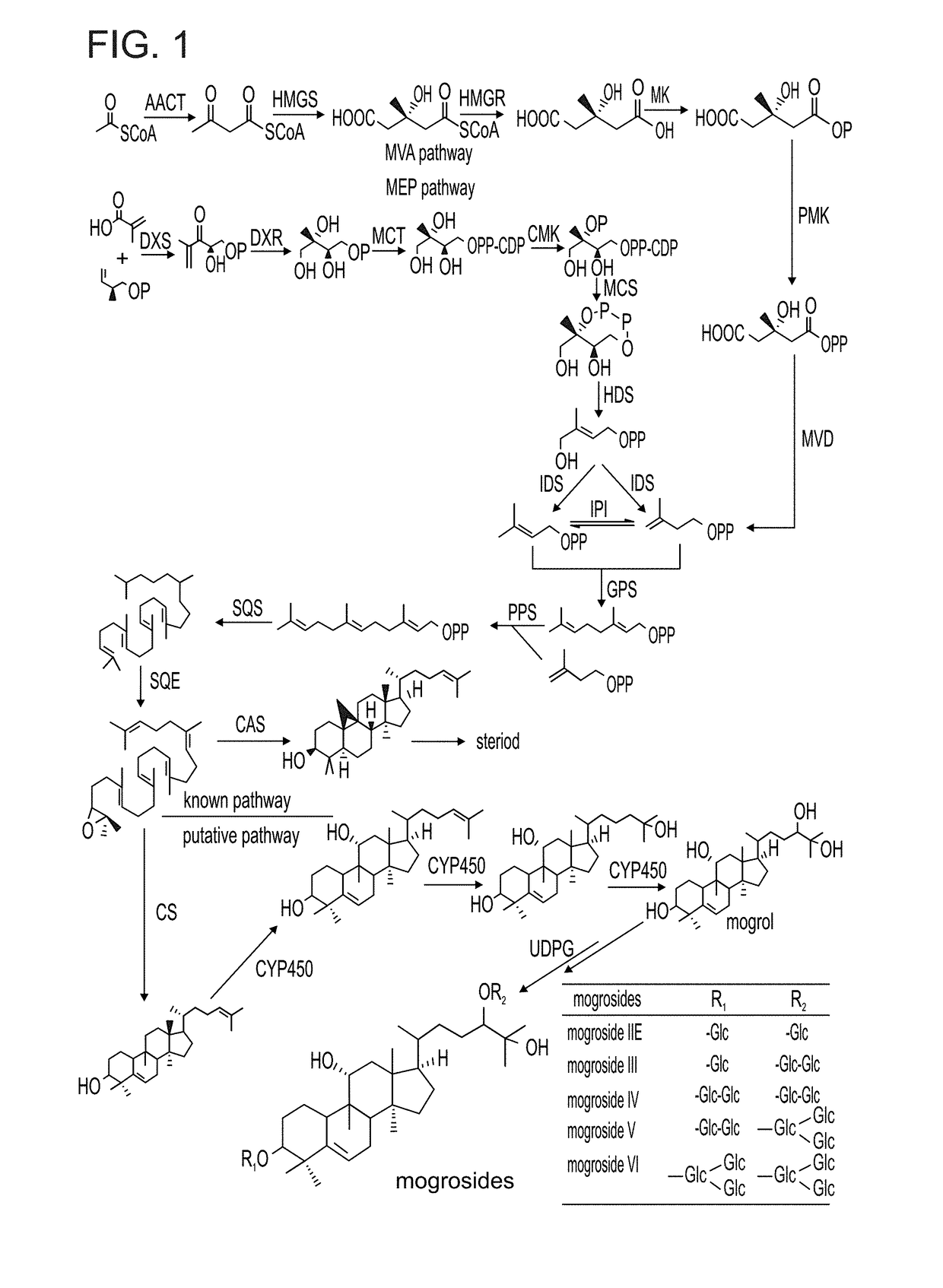
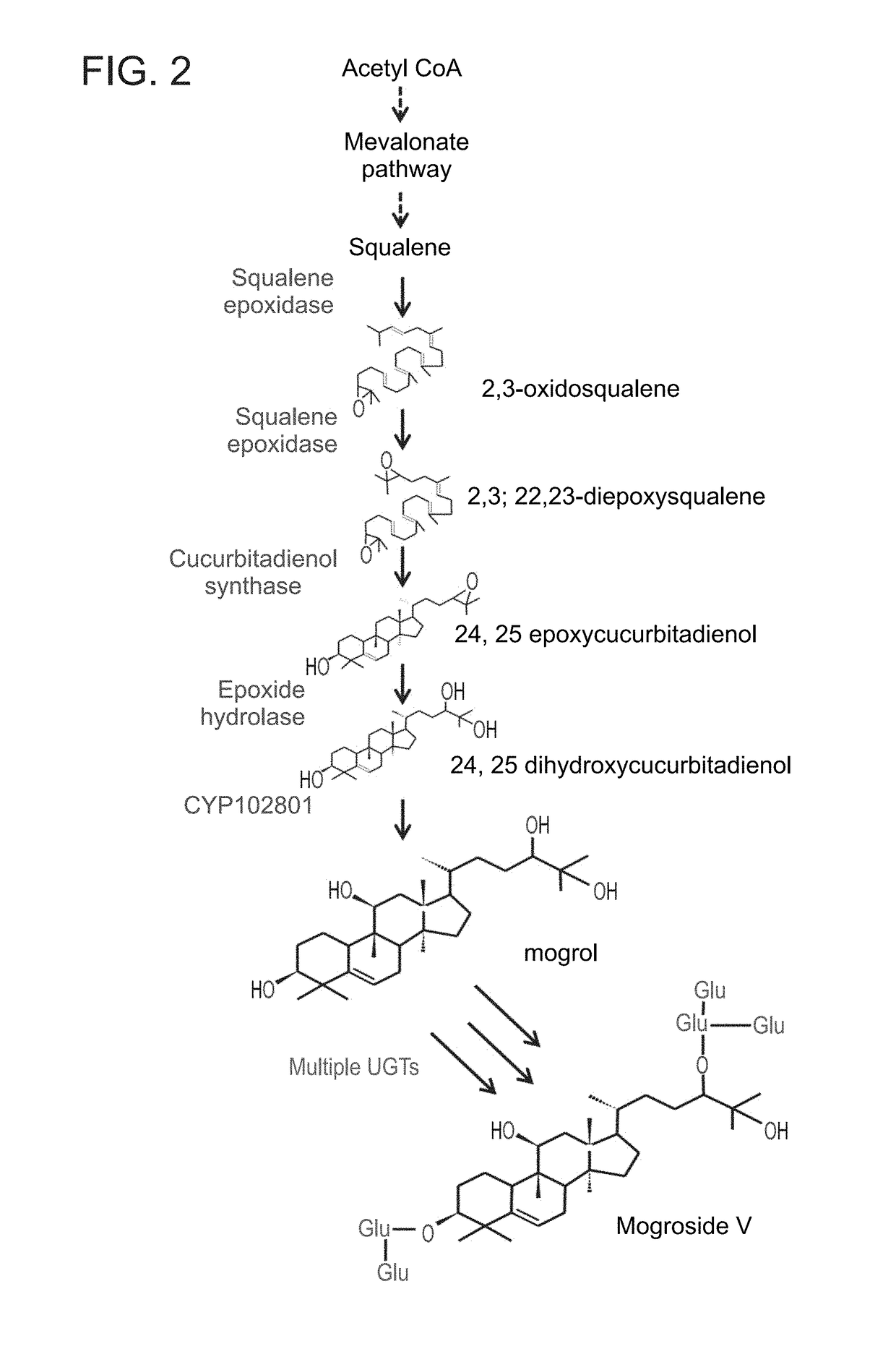
Isolated mogroside and mogrol biosynthetic pathway enzyme polypeptides useful in mogroside biosynthesis are provided. Mogroside biosynthetic pathway enzymes of the invention include squalene epoxidase (SE), expoxy hydratase (EH), cytochrome p450 (Cyp), cucurbitadienol synthase (CDS) and udp-glucosyl-transferase (UGT). Also provided are methods of producing a mogroside using the isolated mogroside and mogrol biosynthetic enzyme polypeptides, the methods comprising contacting a mogrol and / or a glycosylated mogrol (mogroside) with at least one UDP glucose glucosyl transferase (UGT) enzyme polypeptide of the invention catalyzing glucosylation of the mogrol and / or the glucosylated mogrol to produce a mogroside with an additional glucosyl moietie(s), thereby producing the mogroside. Alternatively or additionally provided is a method of synthesizing a mogrol, the method comprising contacting a mogrol precursor substrate with one or more mogrol biosynthetic pathway enzyme polypeptides as described herein catalyzing mogrol synthesis from the mogrol precursor substrate, thereby synthesizing the mogrol.
Owner:THE STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG ARO VOLCANI CENT
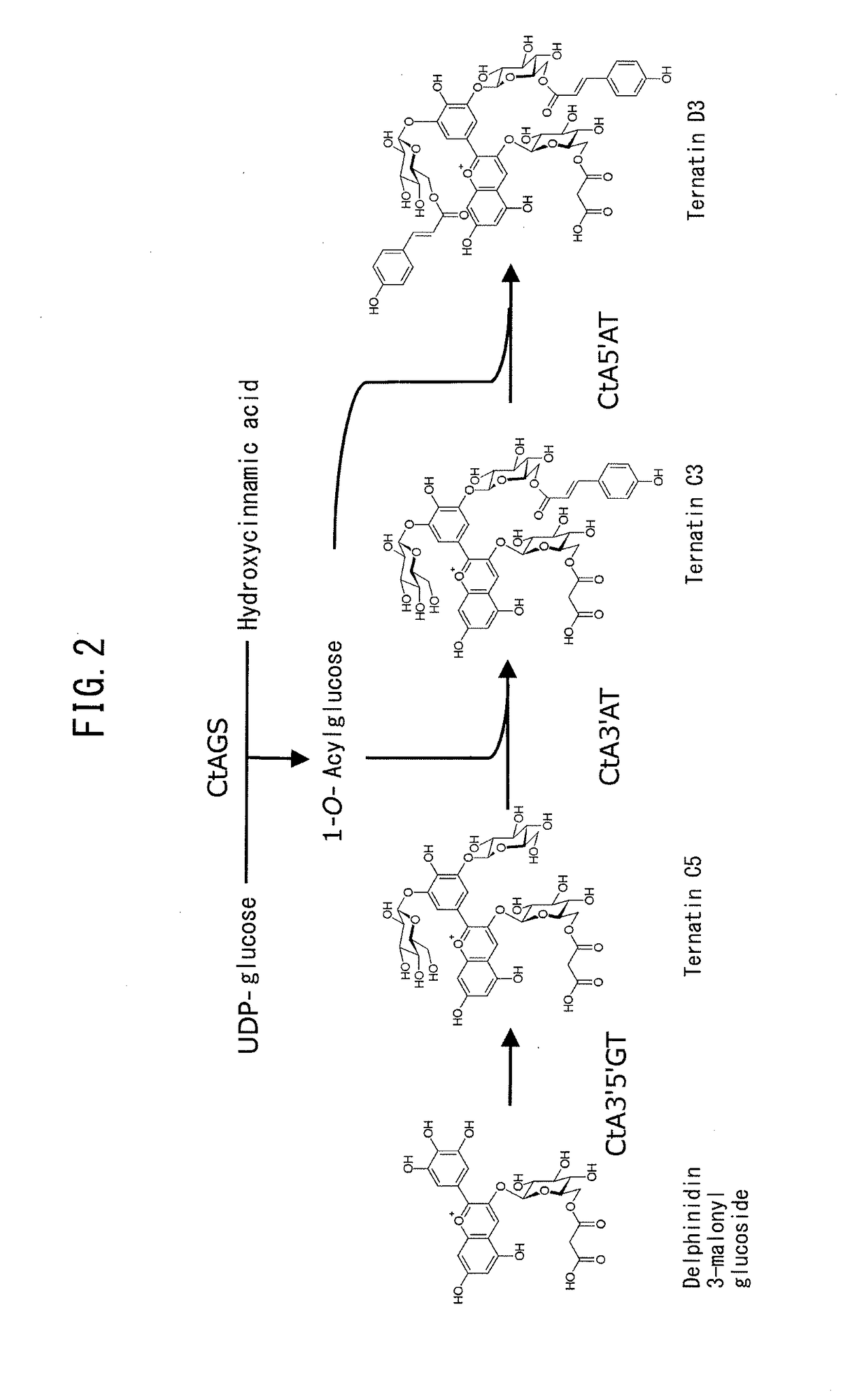
Creation of chrysanthemum with blue flower color
Provided are transformed chrysanthemum plants having blue flower color, their self-fertilized progenies or cross-fertilized progenies thereof, a vegetative propagated plants thereof, and a part, a tissue or a cell of the plant body. Anthocyanin 3′,5′-O-glucosyltransferase gene (CtA3′5′GT) derived from Clitoria ternatea and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene derived from Campanula (CamF3′5′H) are coexpressed in chrysanthemum petals.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
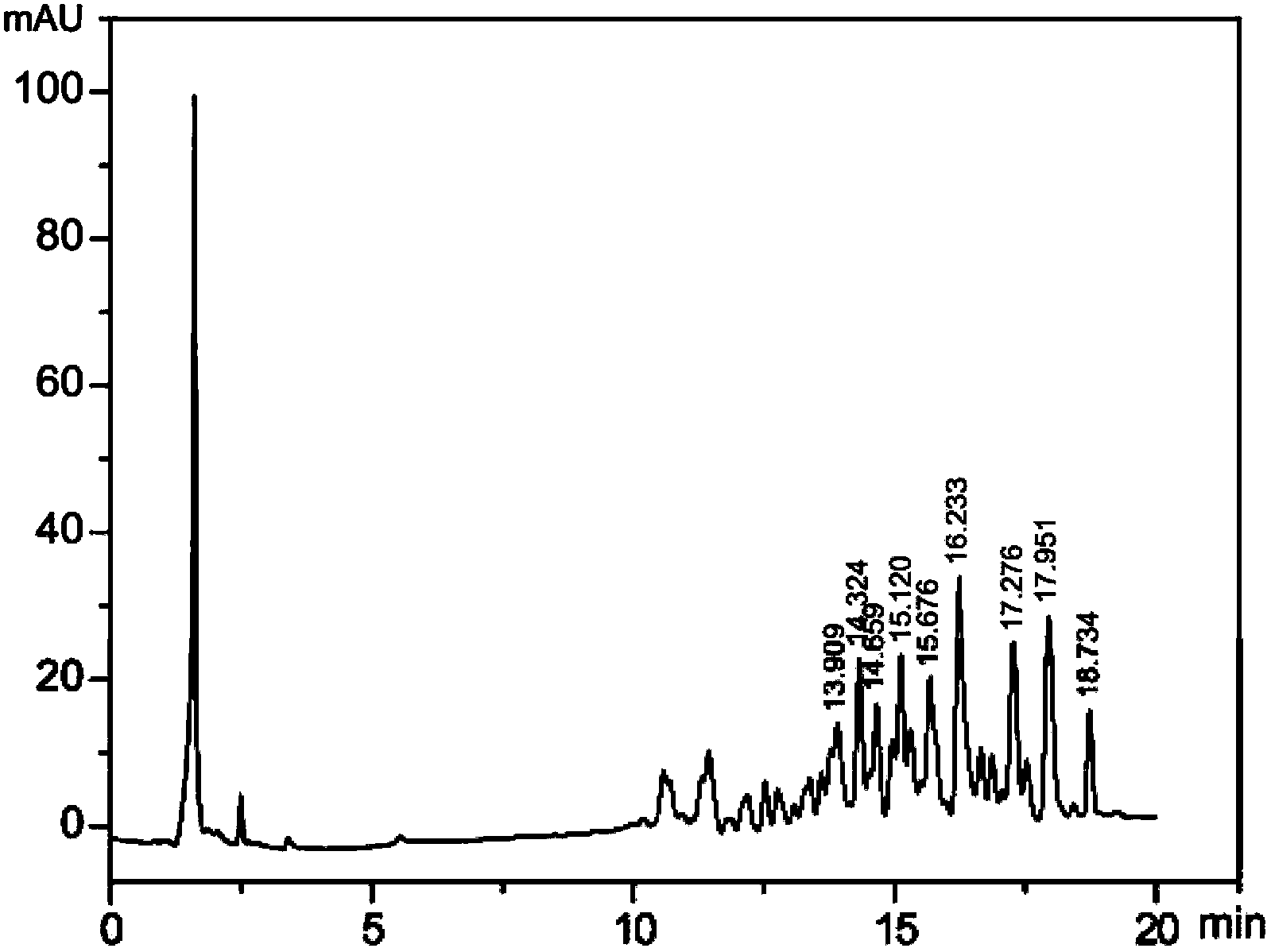
Method for synthesizing sweet saponin with bitter and fallen grosvenor momordica fruit as raw material
InactiveCN104059959AExtend the length of the glucose chainIncrease incomeFermentationMomordicaCyclodextrin
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing sweet saponin with bitter and fallen grosvenor momordica fruit as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) weighing and crushing bitter or fallen grosvenor momordica fruit, adding water or ethanol with a volume of 45 to 55% for extraction and subjecting obtained extract to macroporous resin column chromatography so as to obtain bitter grosvenor momordica fruit saponin, wherein the content of mogroside II and / or III is no less than 50%; 2) dissolving bitter grosvenor momordica fruit saponin in water, adding starch and cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, carrying out an enzymic catalytic reaction at 60 to 65 DEG C until the reaction is completely finished, killing enzyme activity, carrying out filtering and collecting filtrate; and 3) subjecting the filtrate to macroporous resin or silica gel column chromatography, carrying out rinsing and collecting ethanol eluate with a volume of 30 to 40%, or directly allowing the filtrate to pass through an alumina column or active carbon column and collecting effluent, and concentrating and drying the collected ethanol eluate with the volume of 30 to 40% or the collected effluent. The method provided by the invention fundamentally overcomes the problem of bitter and fallen fruit in growth of grosvenor momordica fruit.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF BOTANY THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
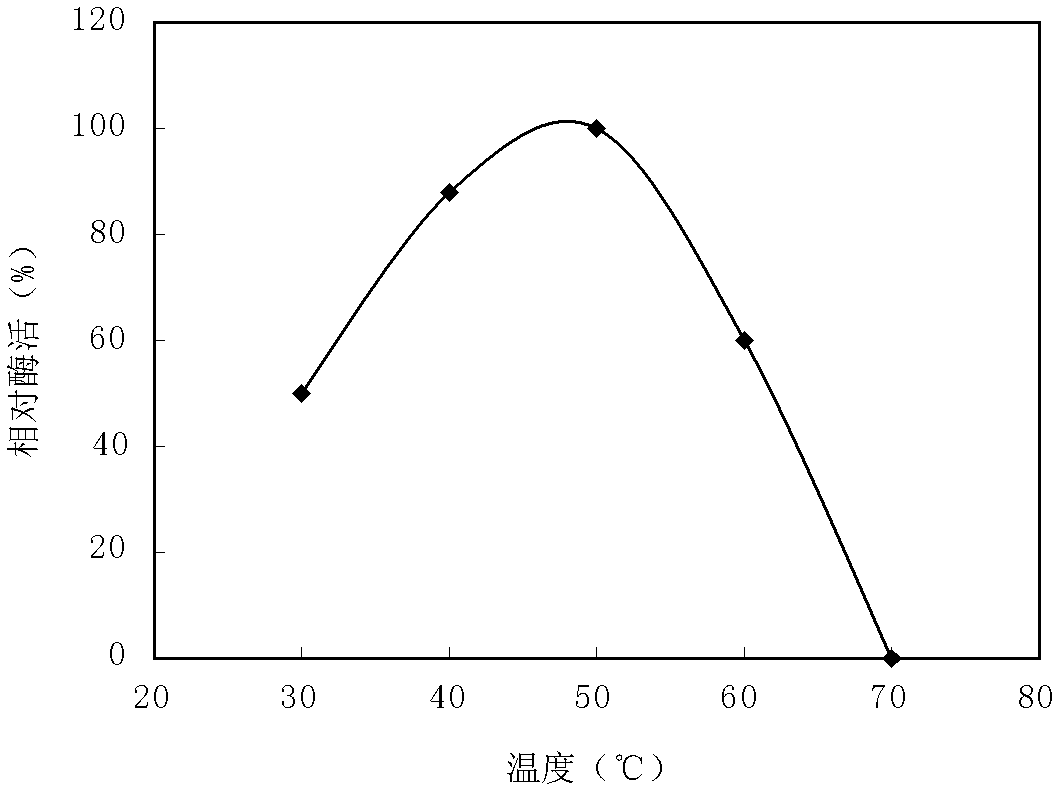
Acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN102559568AIncrease enzyme activityHas starch amylopectin hydrolysis activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisGenetic engineering
The invention relates to an acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and an application thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a Tfu_1891 encoding gene sequence of isoamylase is obtained by chemical synthesis; culture is carried out in an industrial fermentation culture medium by taking pT7-7 as an expression vector and E.coli BL21 (DE3) as an expression host; and by virtue of inductive recombination, the fermentation vigor of the isoamylase reaches 3185U / mL. The recombinase has hydrolysis activity of a starch alpha-1,6 glucoside bond; the optimum temperature is 40-50 DEG C, and the optimum pH value is 5.5; after heat preservation is carried out for 30 hours at the temperature of 50 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the recombinase still maintains more than 50%; the recombinase has starch debranching activity and can hydrolyze branched starch in starch so as to form amylose; and the recombinase is combined with alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to be used, thereby obviously improving the conversion rate of cyclodextrin and being suitable for industrial production of cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com