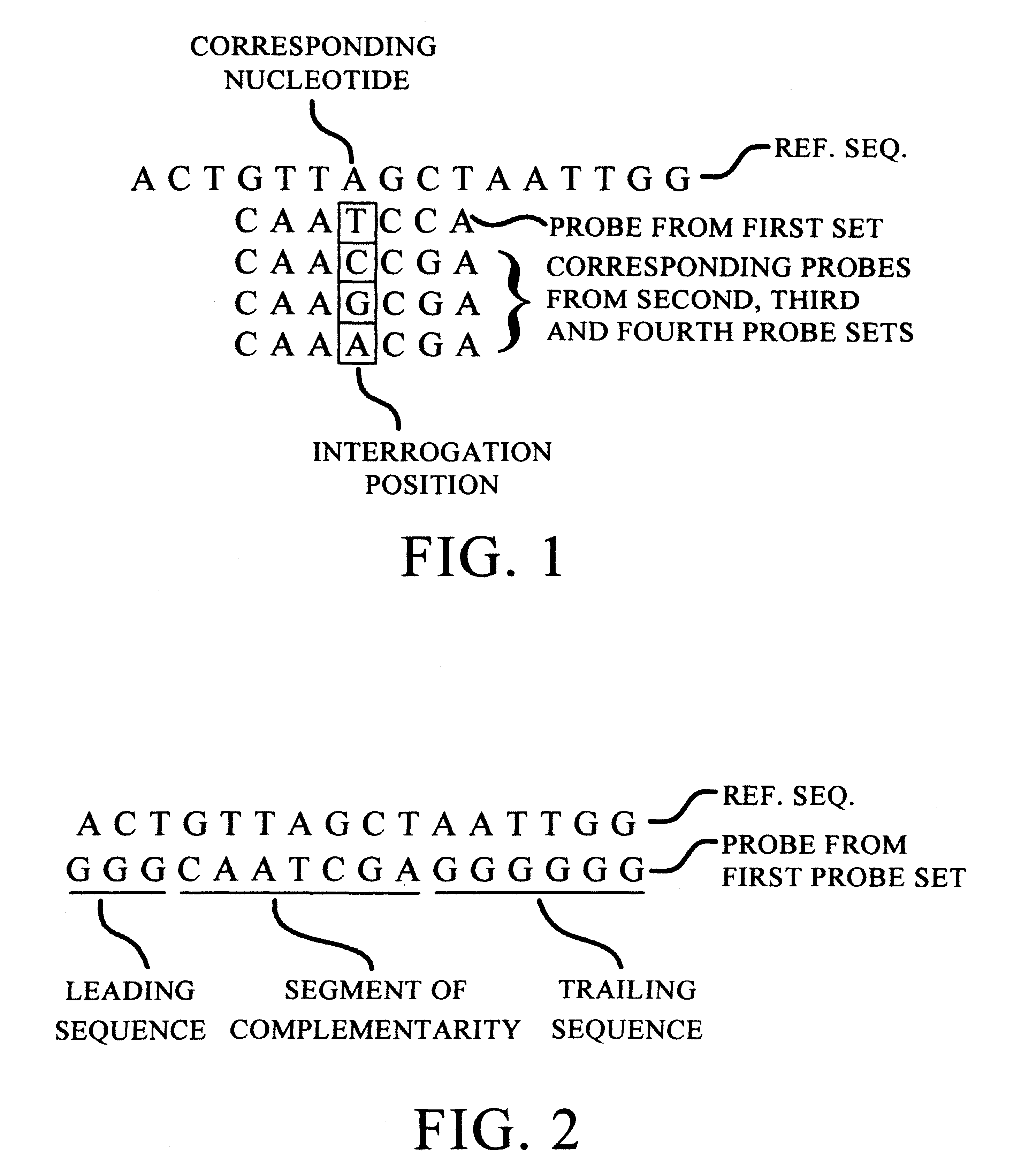
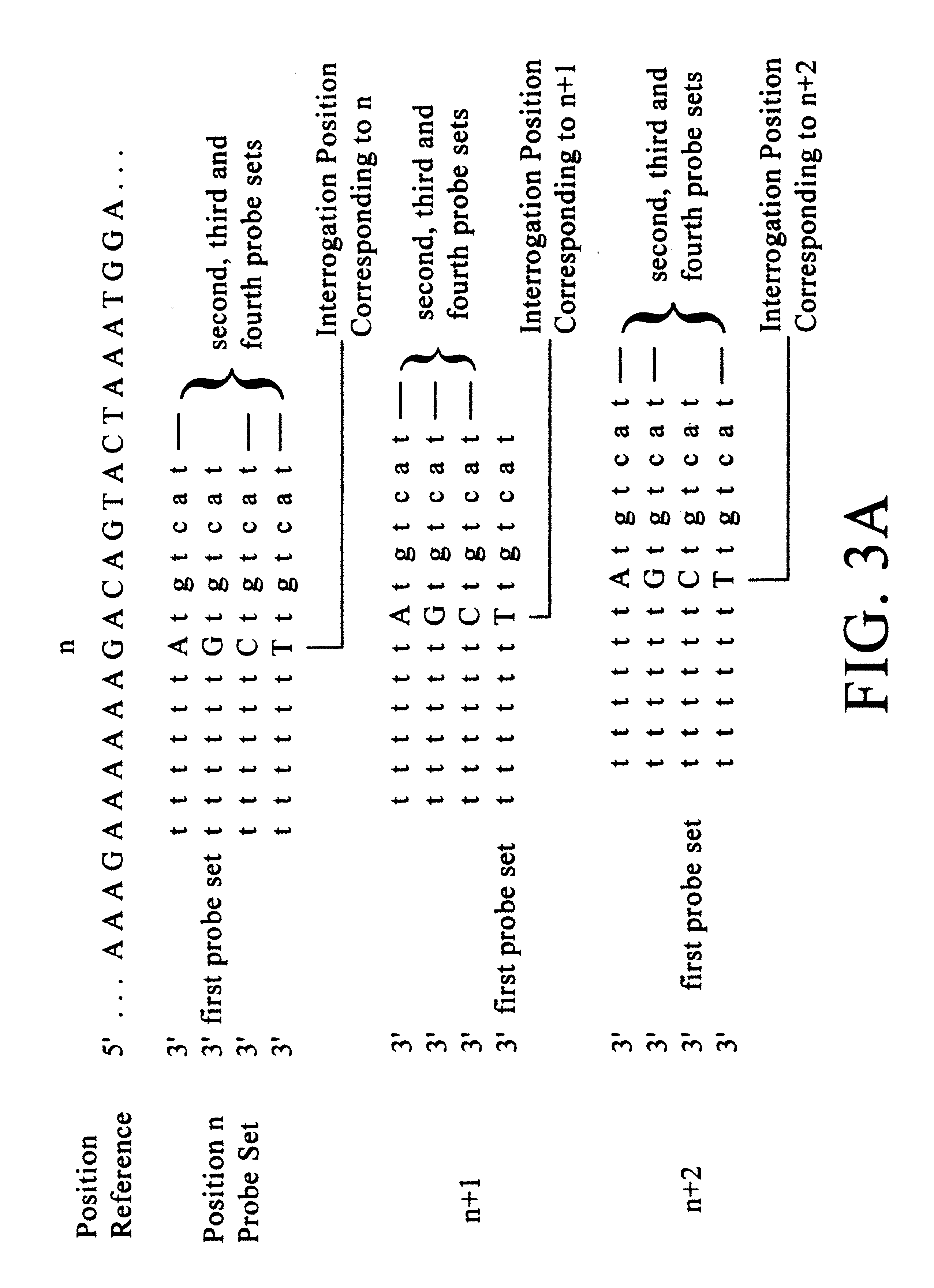
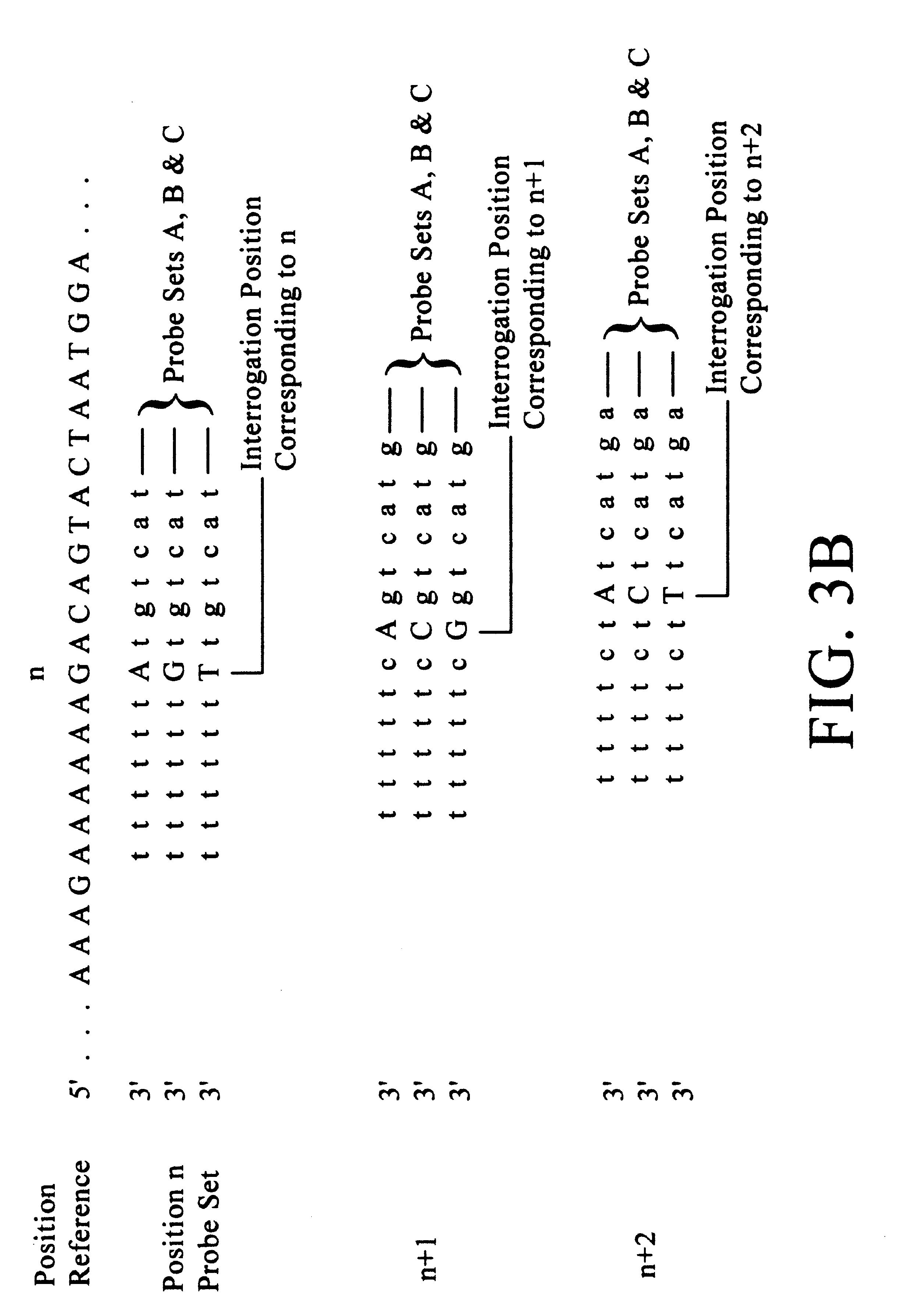
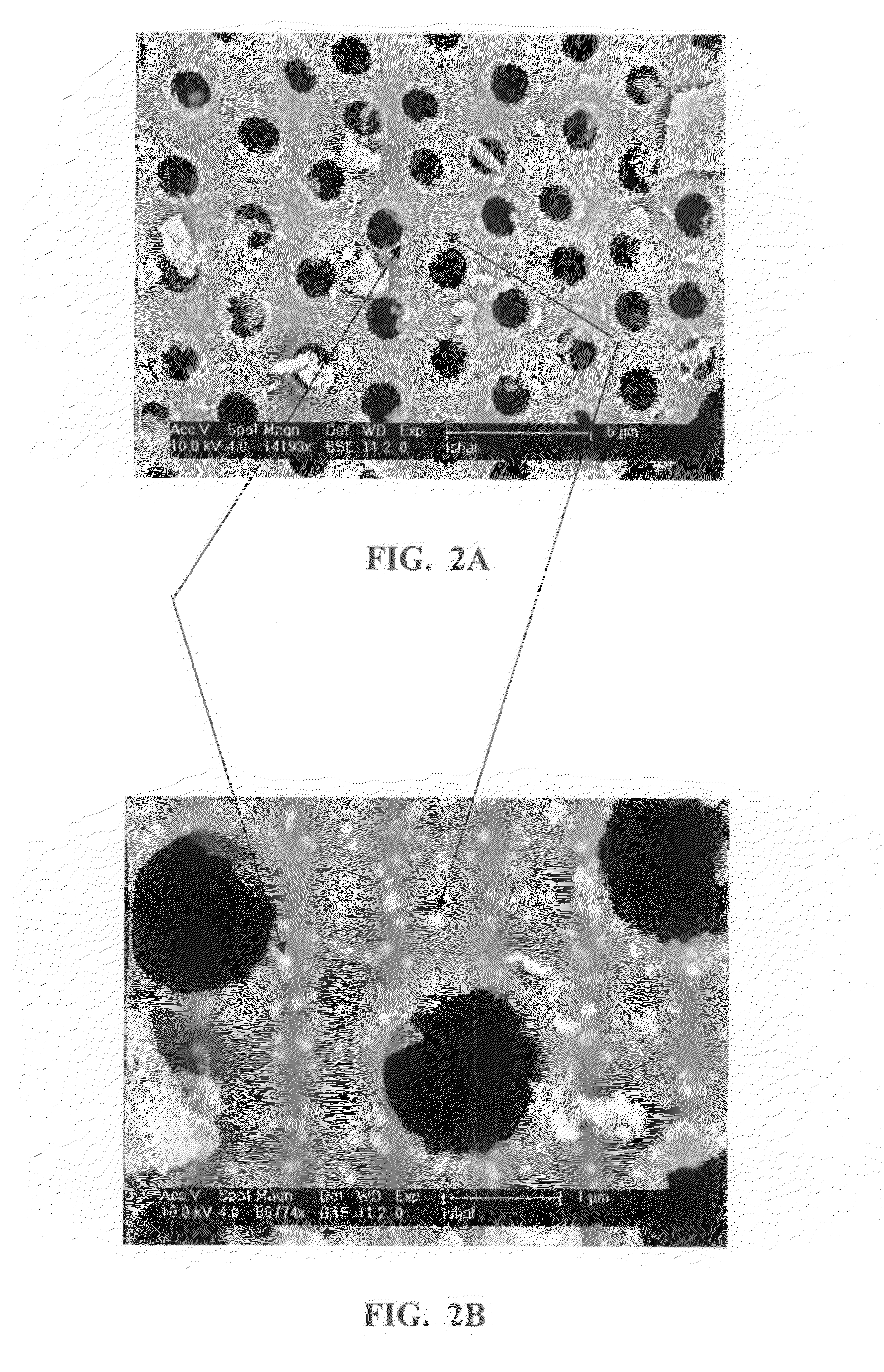
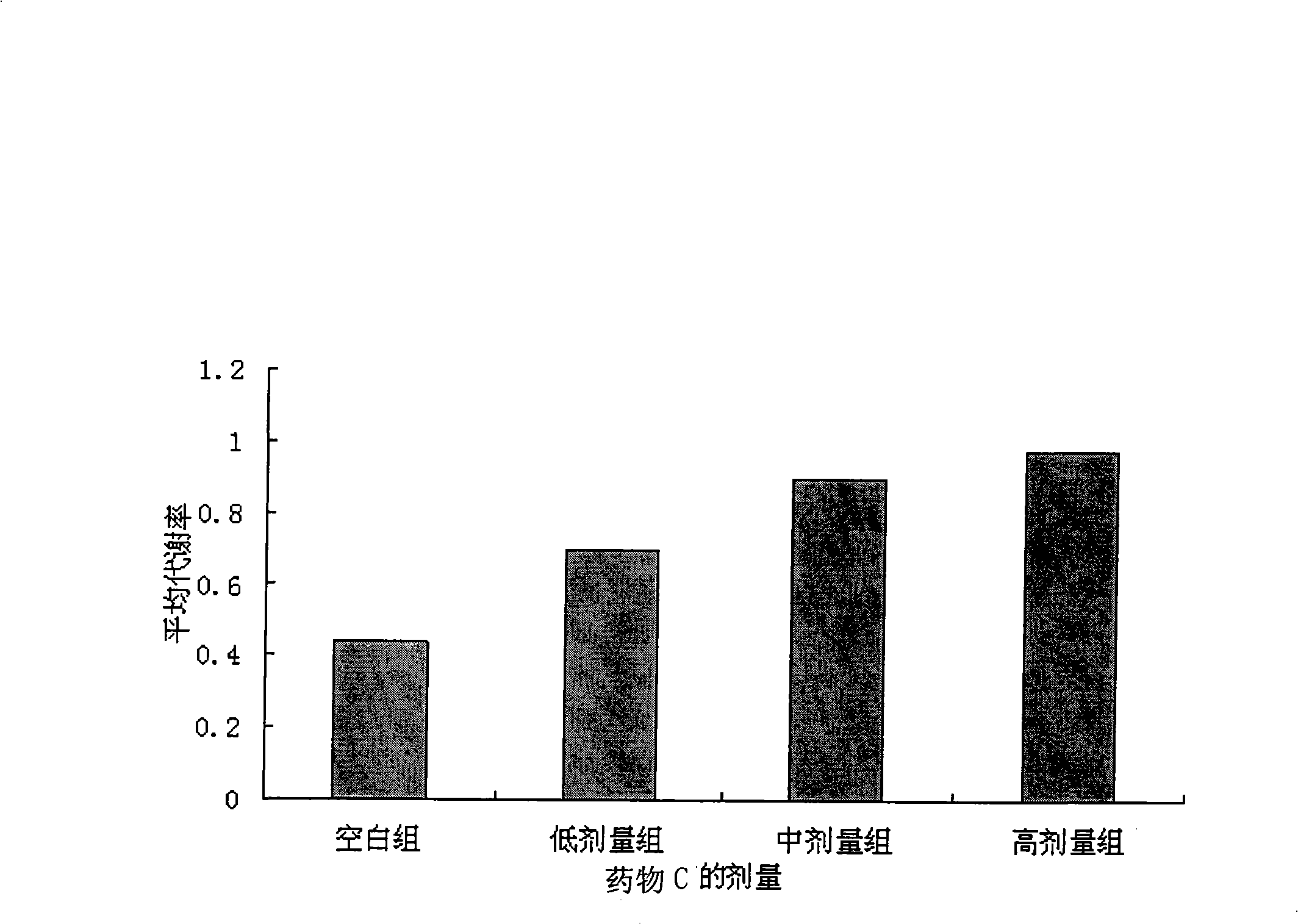
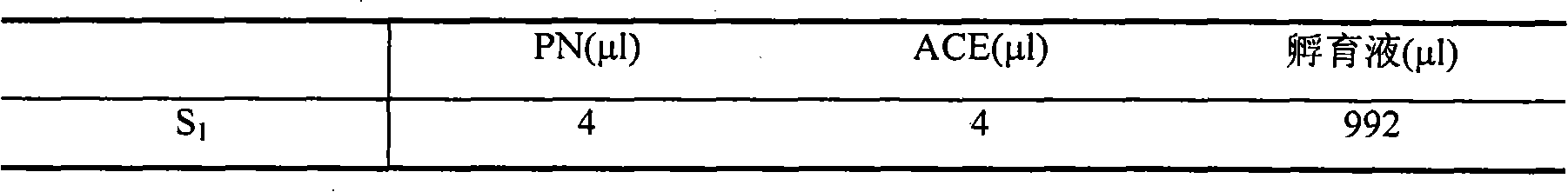
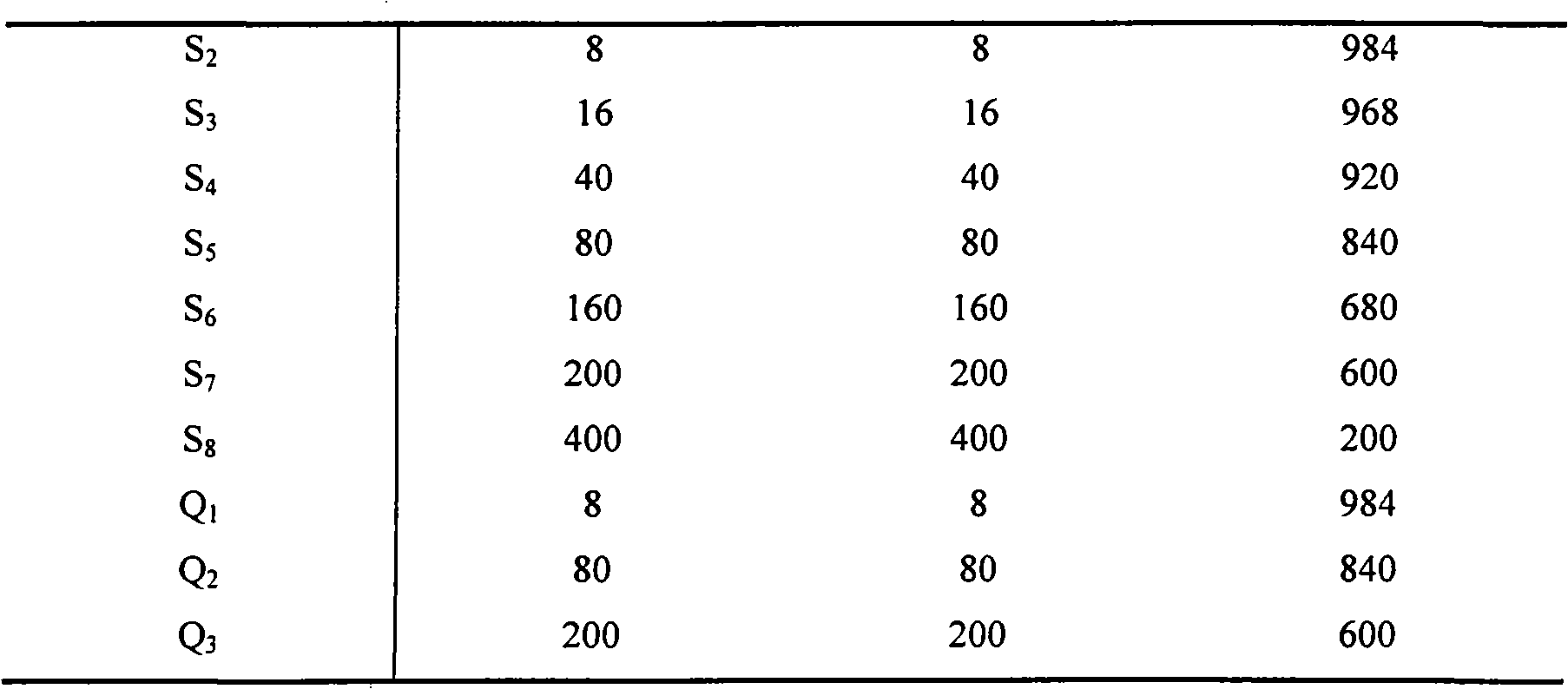
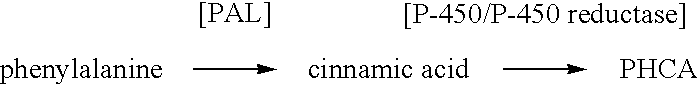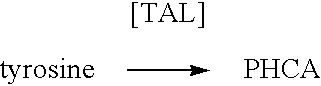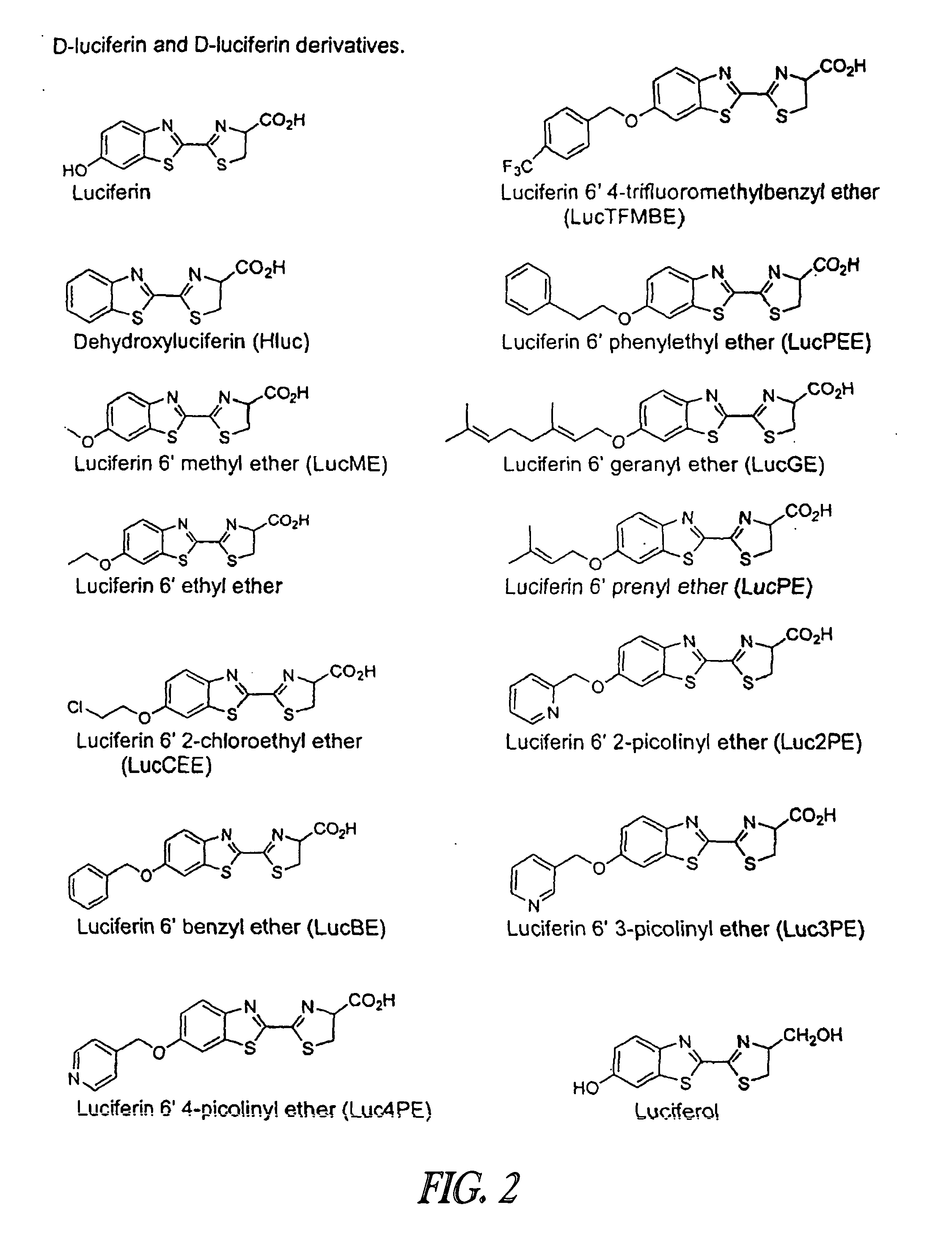Patents
Literature
584 results about "Cytochrome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cytochromes are proteins containing heme as a cofactor. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the IUBMB, cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature.
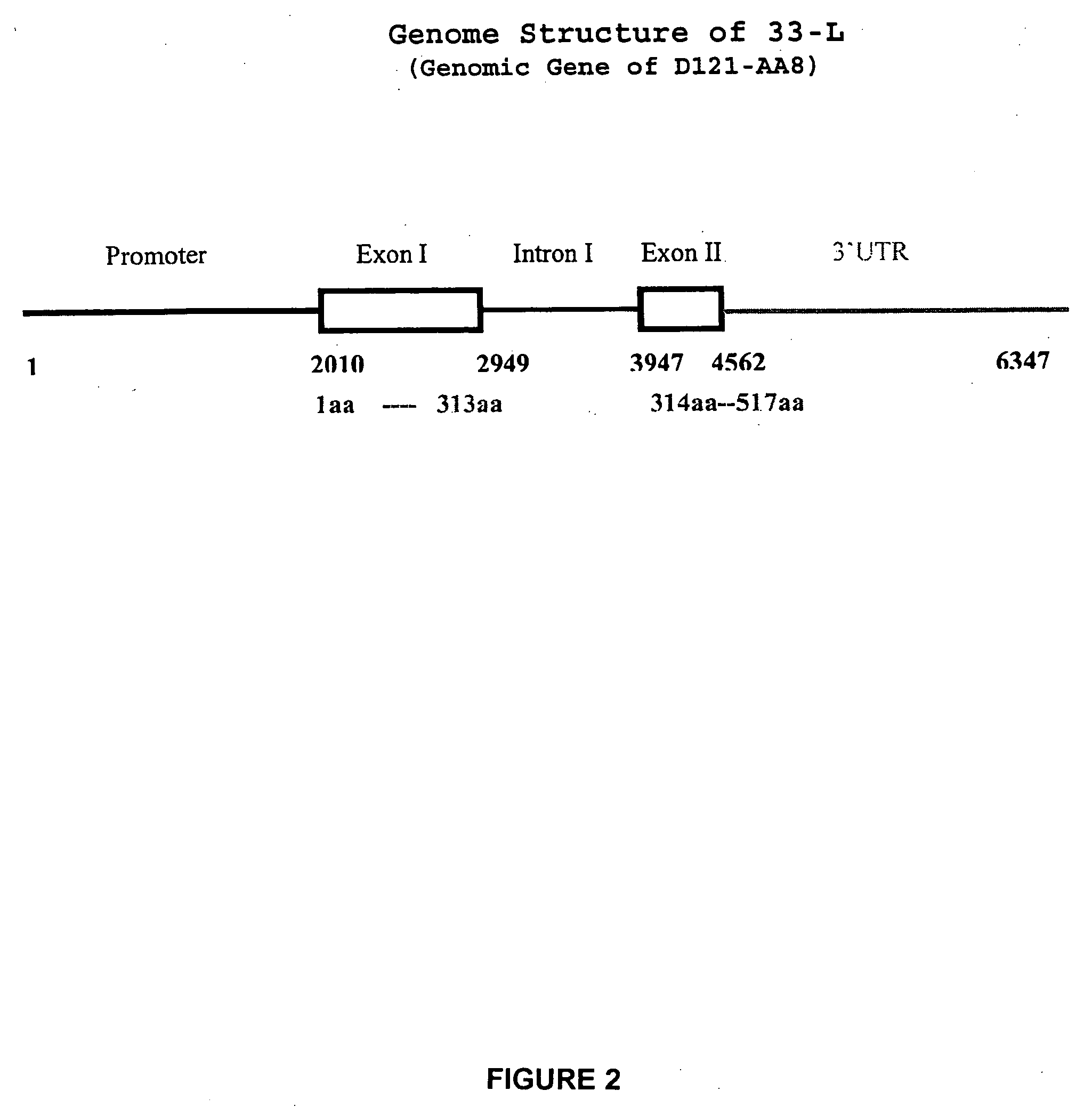
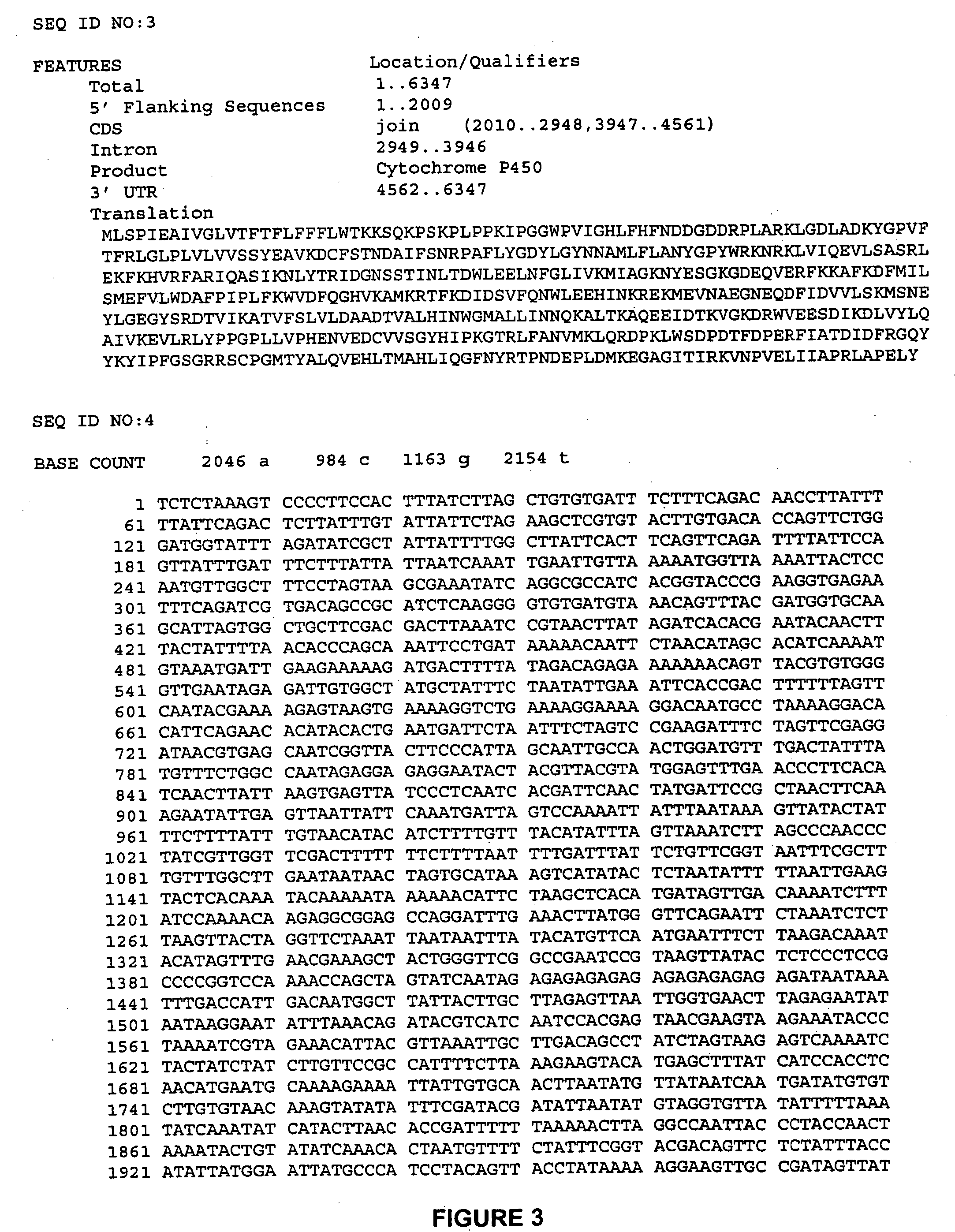
Analysis of genetic polymorphisms and gene copy number
InactiveUS6468744B1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsCytochrome P450Drug biotransformation
The invention provides methods for detecting variations in polymorphic sites and / or variations in gene copy number. The methods are particularly useful for analysis of biotransformation genes, such as cytochromes P450.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
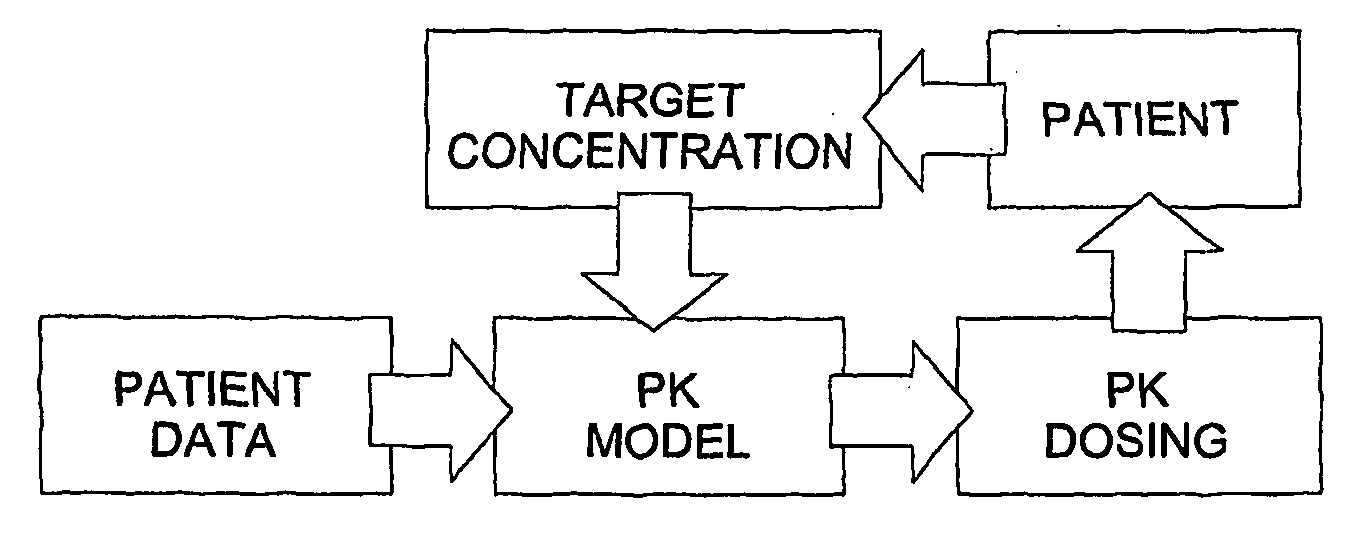
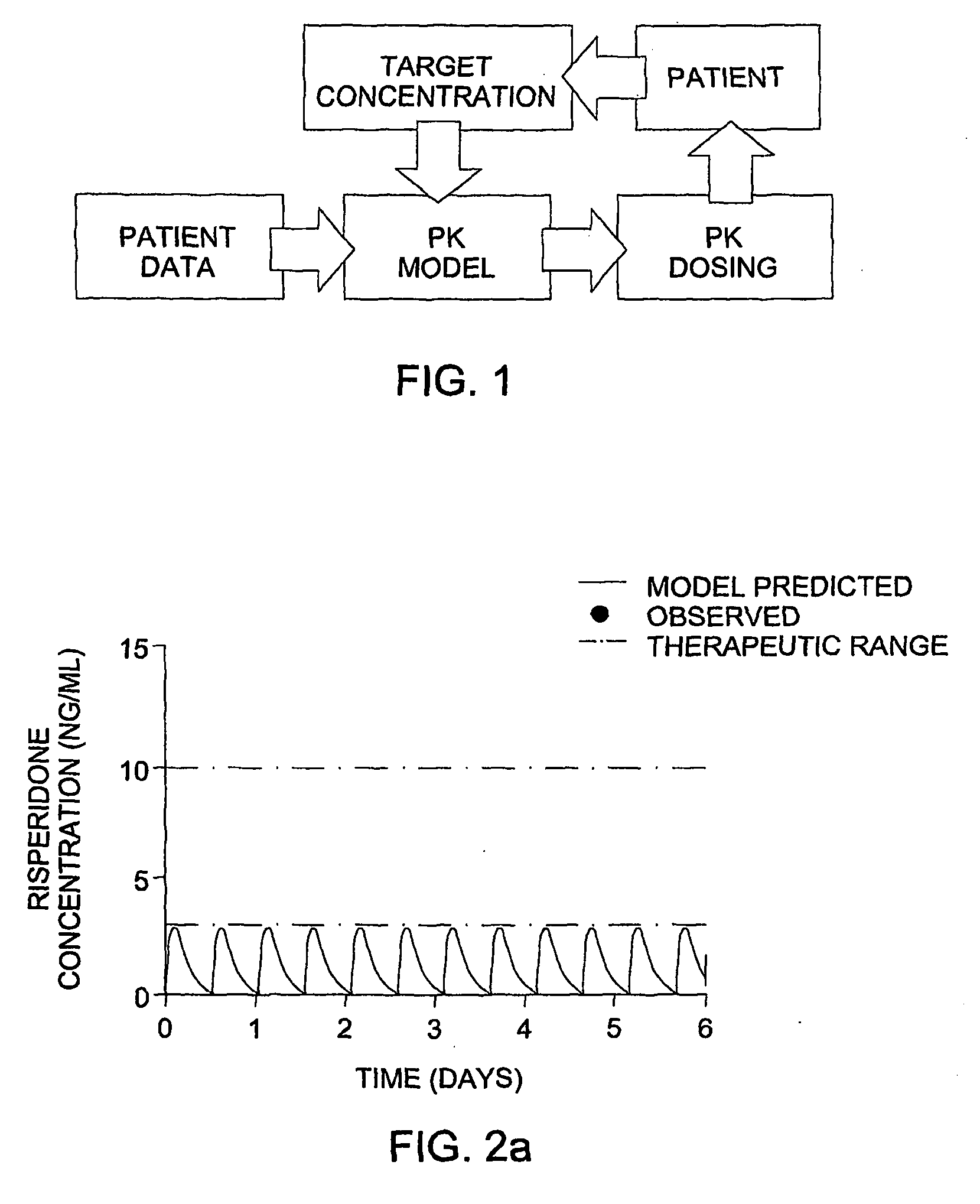
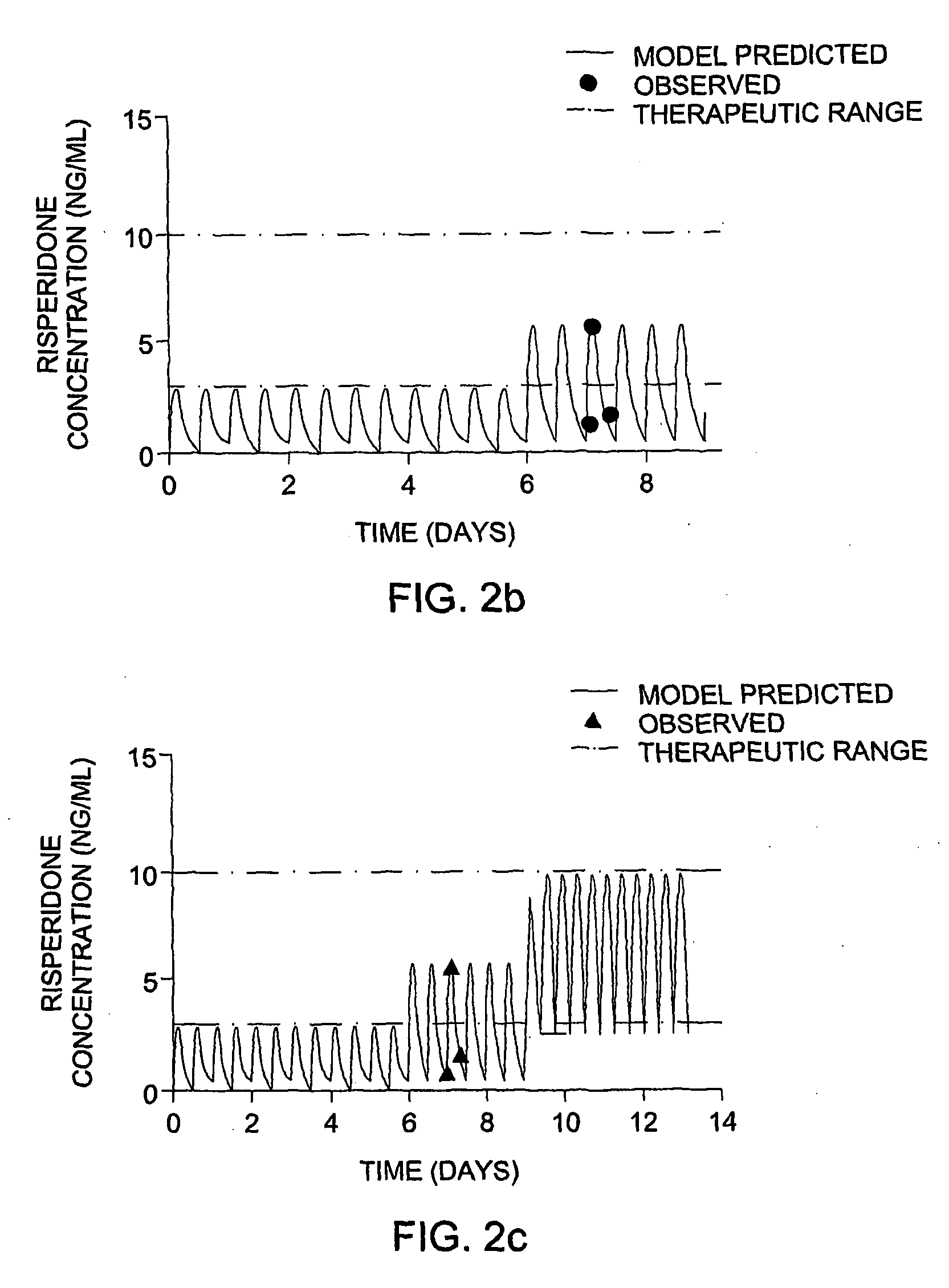
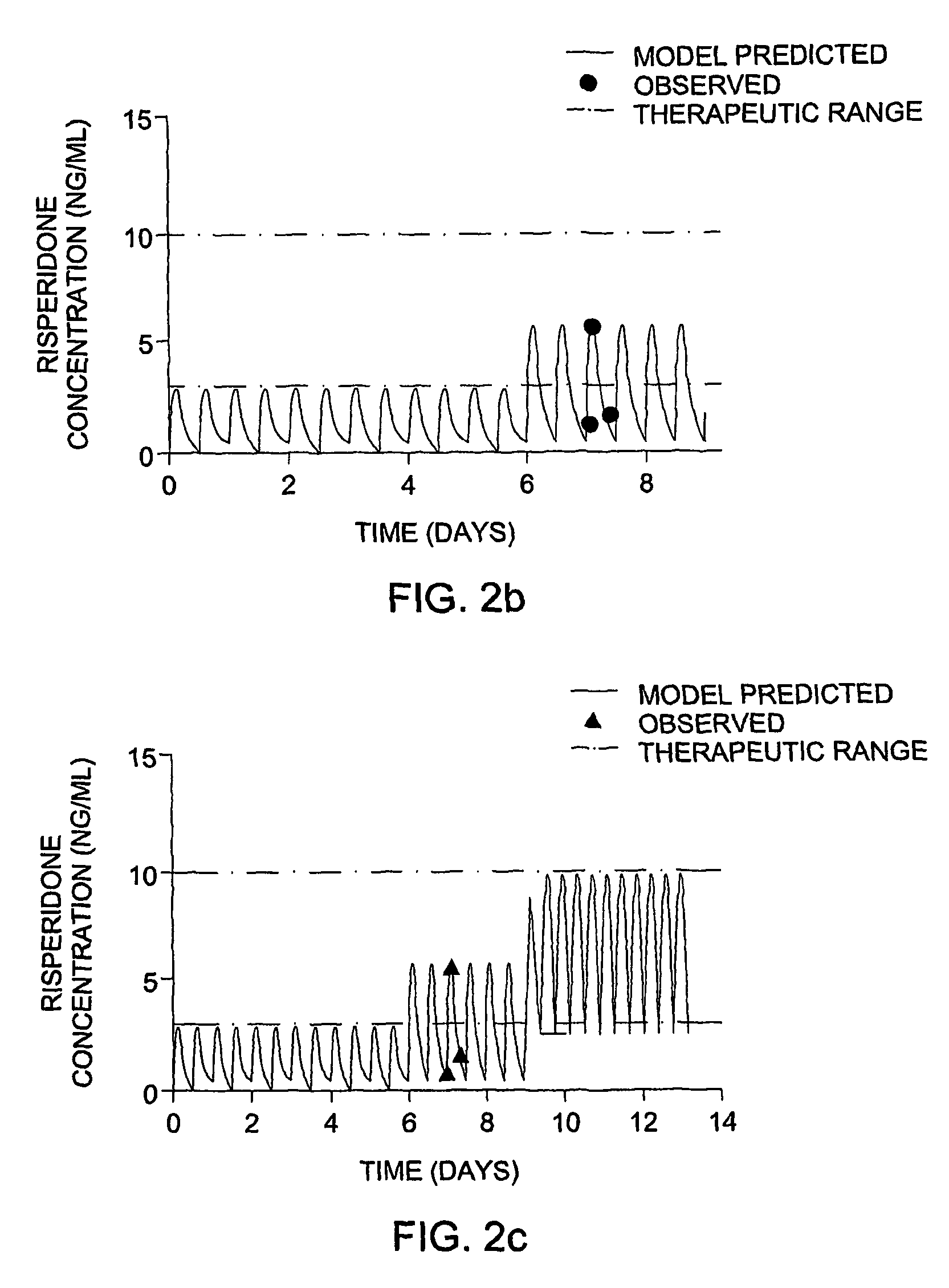
Optimization and Individualization of Medication Selection and Dosing
ActiveUS20090171697A1Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
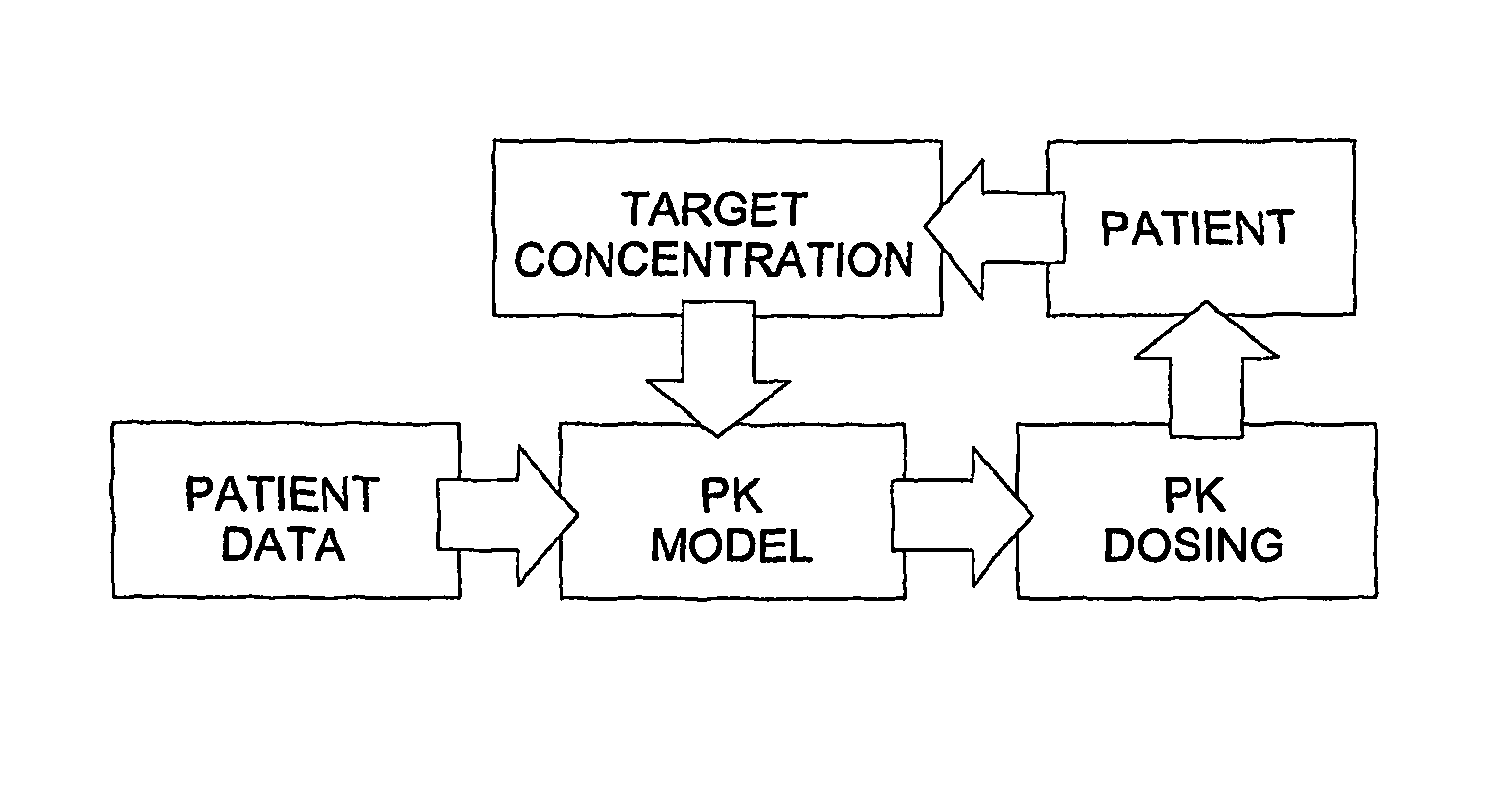
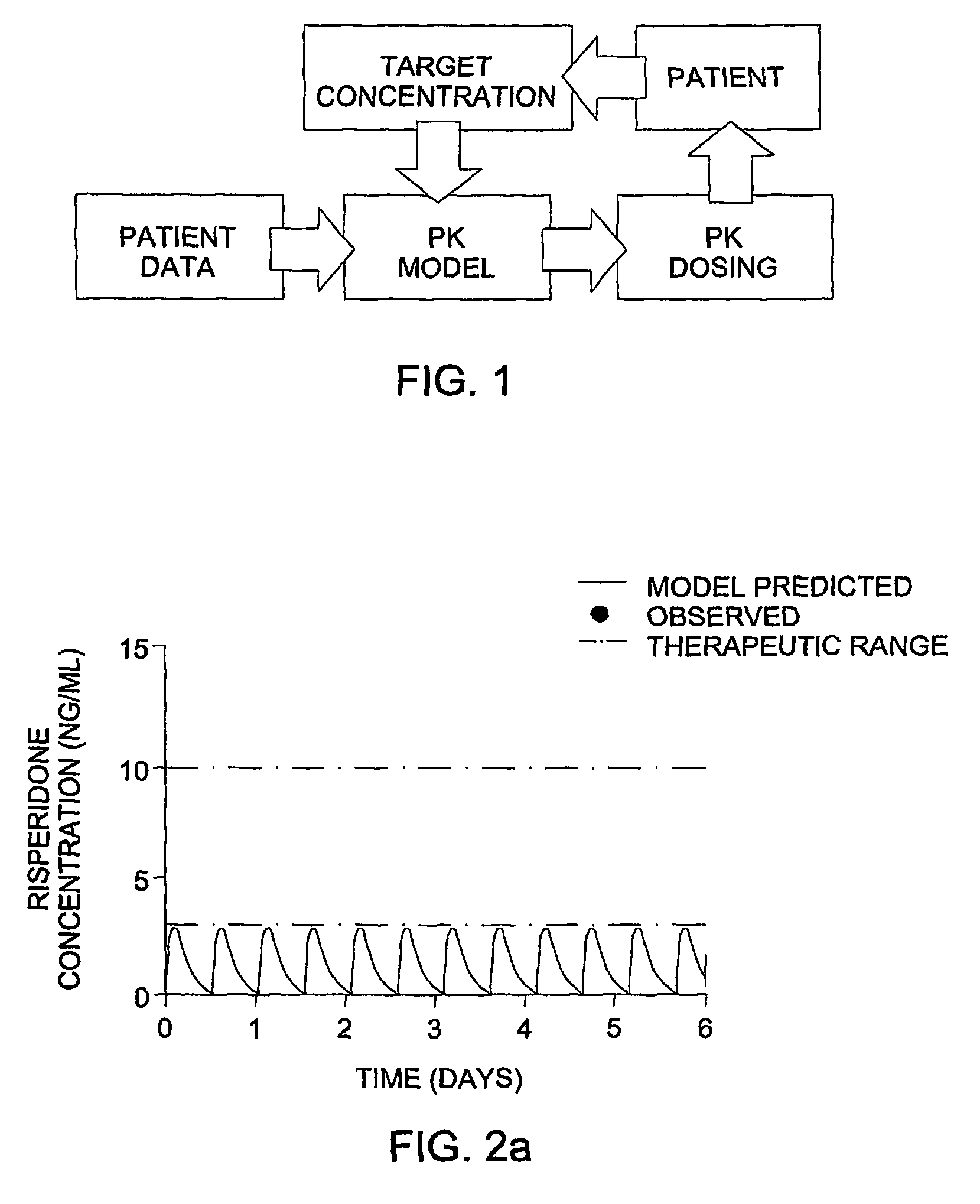
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Nicotiana nucleic acid molecules and uses thereof
ActiveUS20060041949A1Change activityDecrease and increases activityOther foreign material introduction processesPlant peptidesNicotiana tabacumNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention features Nicotiana nucleic acid sequences such as sequences encoding constitutive, or ethylene or senescence induced polypeptides, in particular cytochrome p450 enzymes, in Nicotiana plants and methods for using these nucleic acid sequences and plants to alter desirable traits, for example by using breeding protocols.
Owner:U S SMOKELESS TOBACCO COMPANY LLC
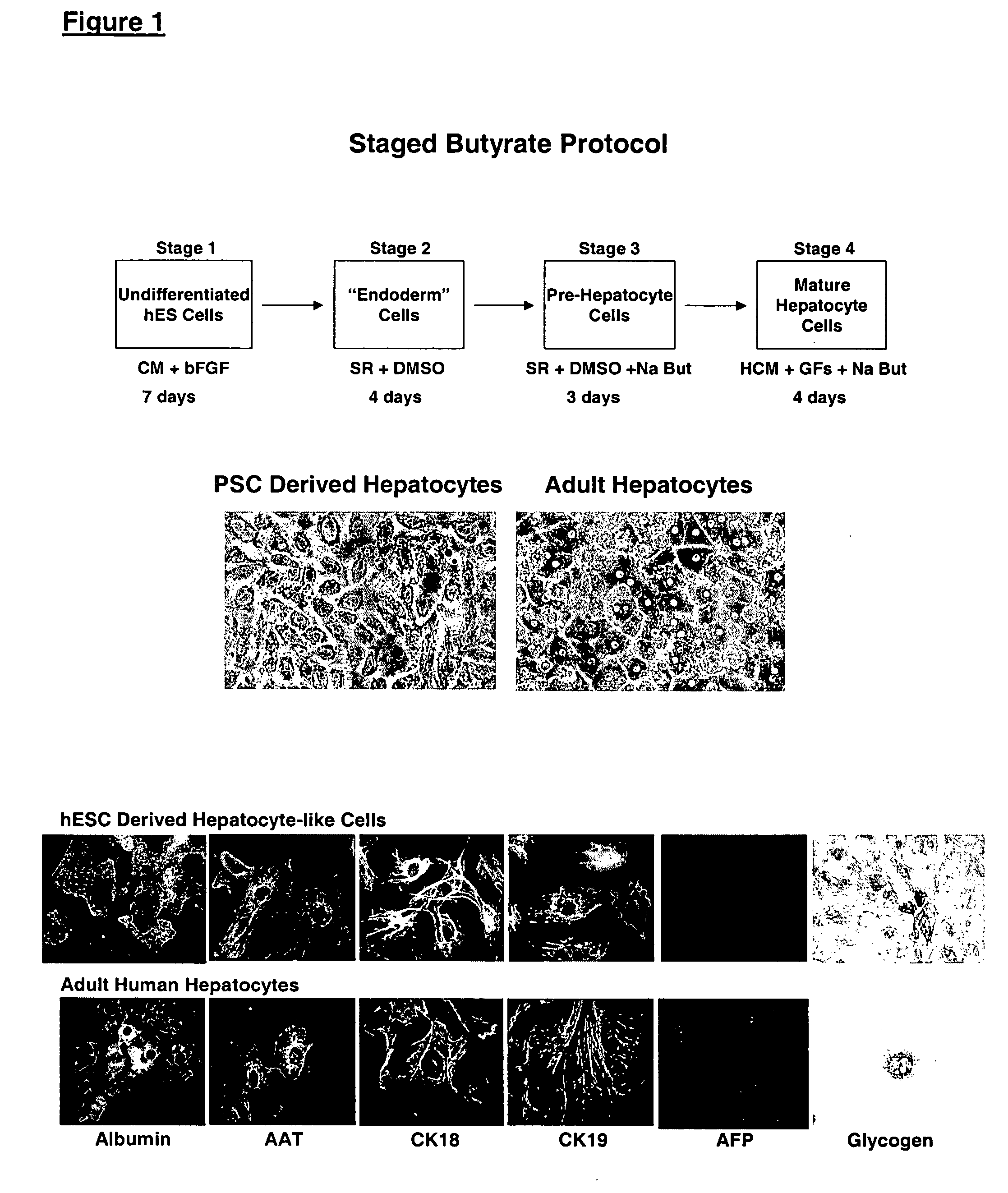
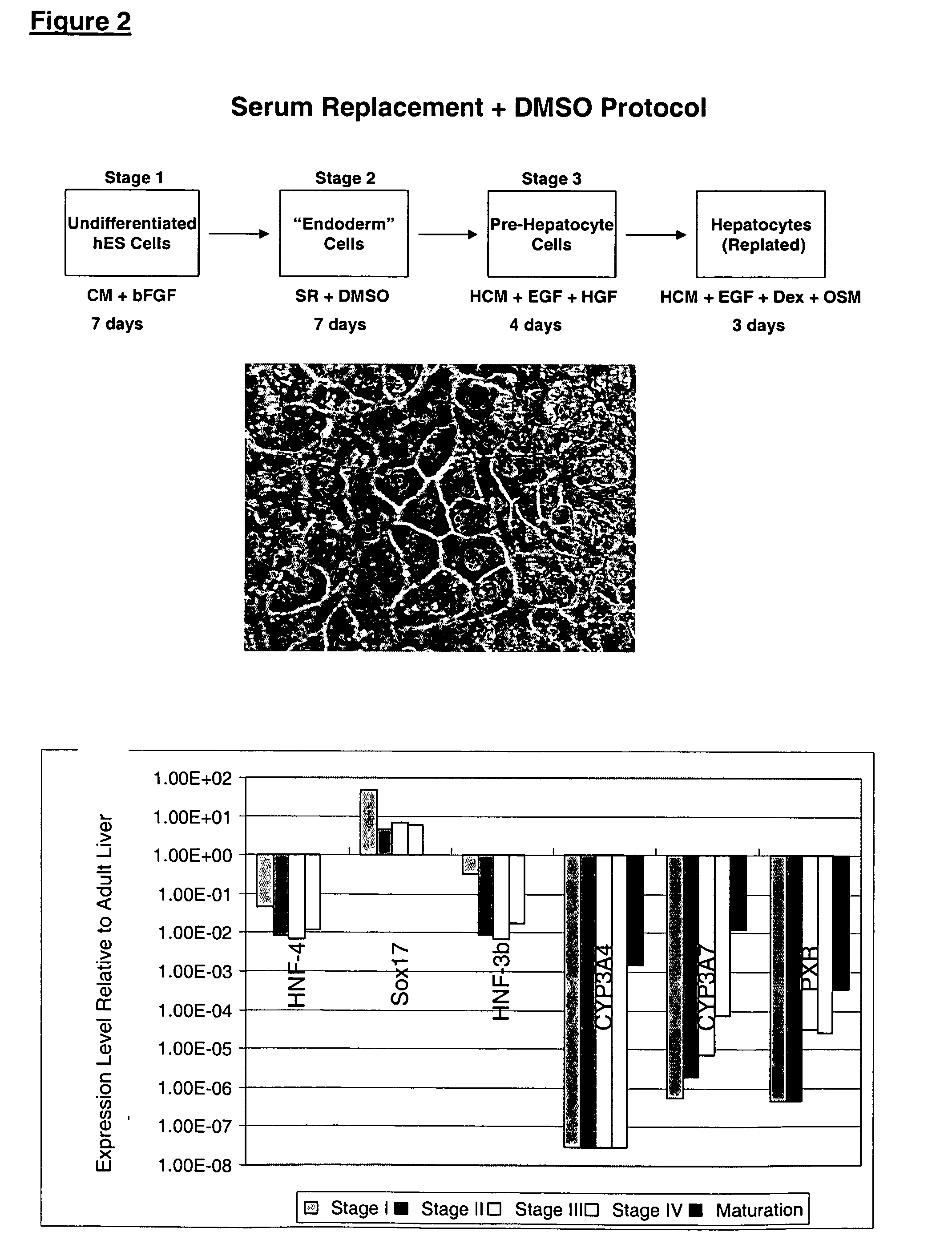
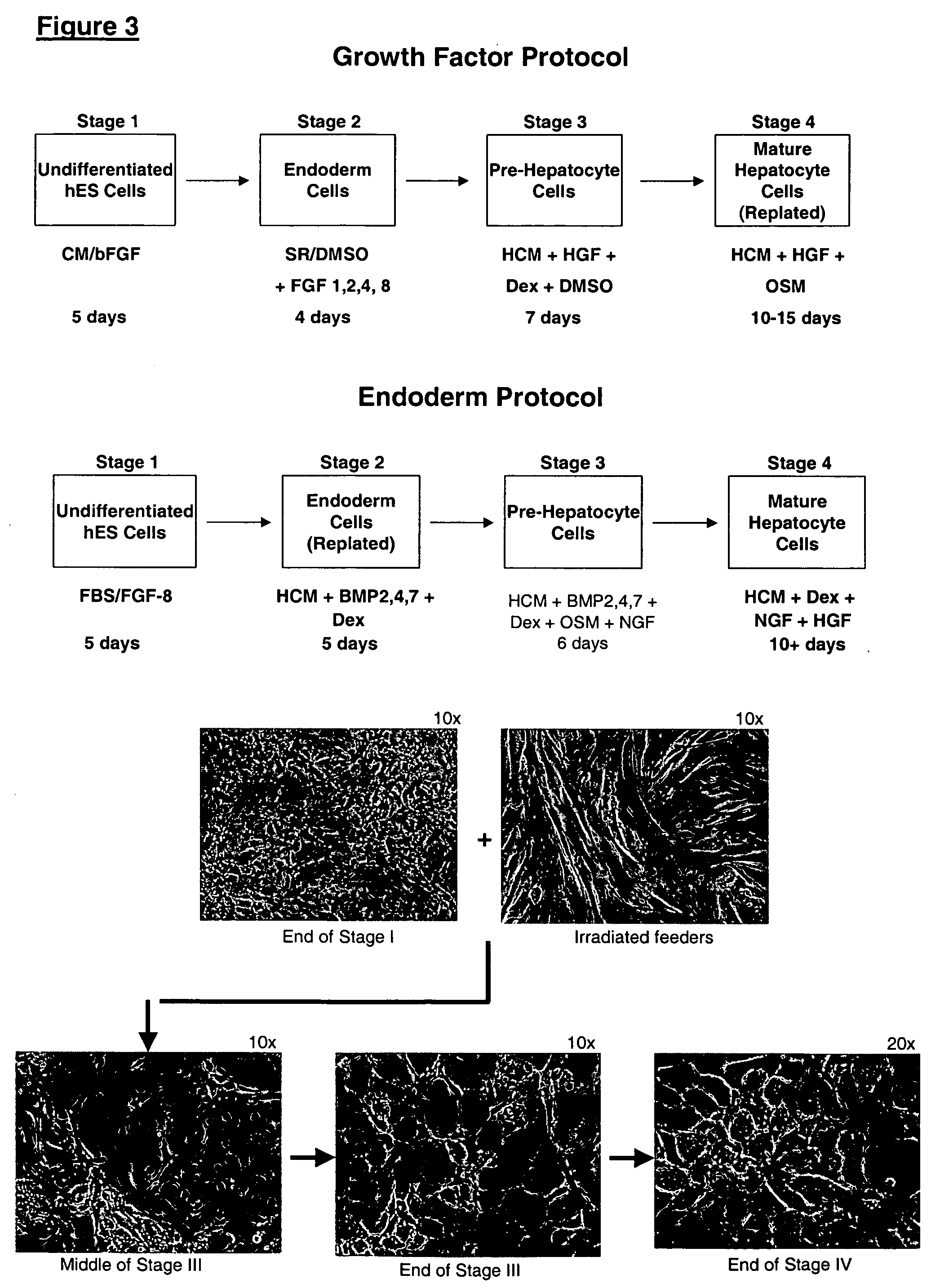
Protocols for making hepatocytes from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050037493A1Promote cell differentiationCulture processDrug screeningGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides a newly developed strategy and particular options for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the hepatocyte lineage. Many of the protocols are based on a strategy in which the cells are first differentiated into early germ layer cells, then into hepatocyte precursors, and then into mature cells. The cells obtained have morphological features and phenotypic markers characteristic of human adult hepatocytes. They also show evidence of cytochrome p450 enzyme activity, validating their utility for commercial applications such as drug screening, or use in the manufacture of medicaments and medical devices for clinical therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
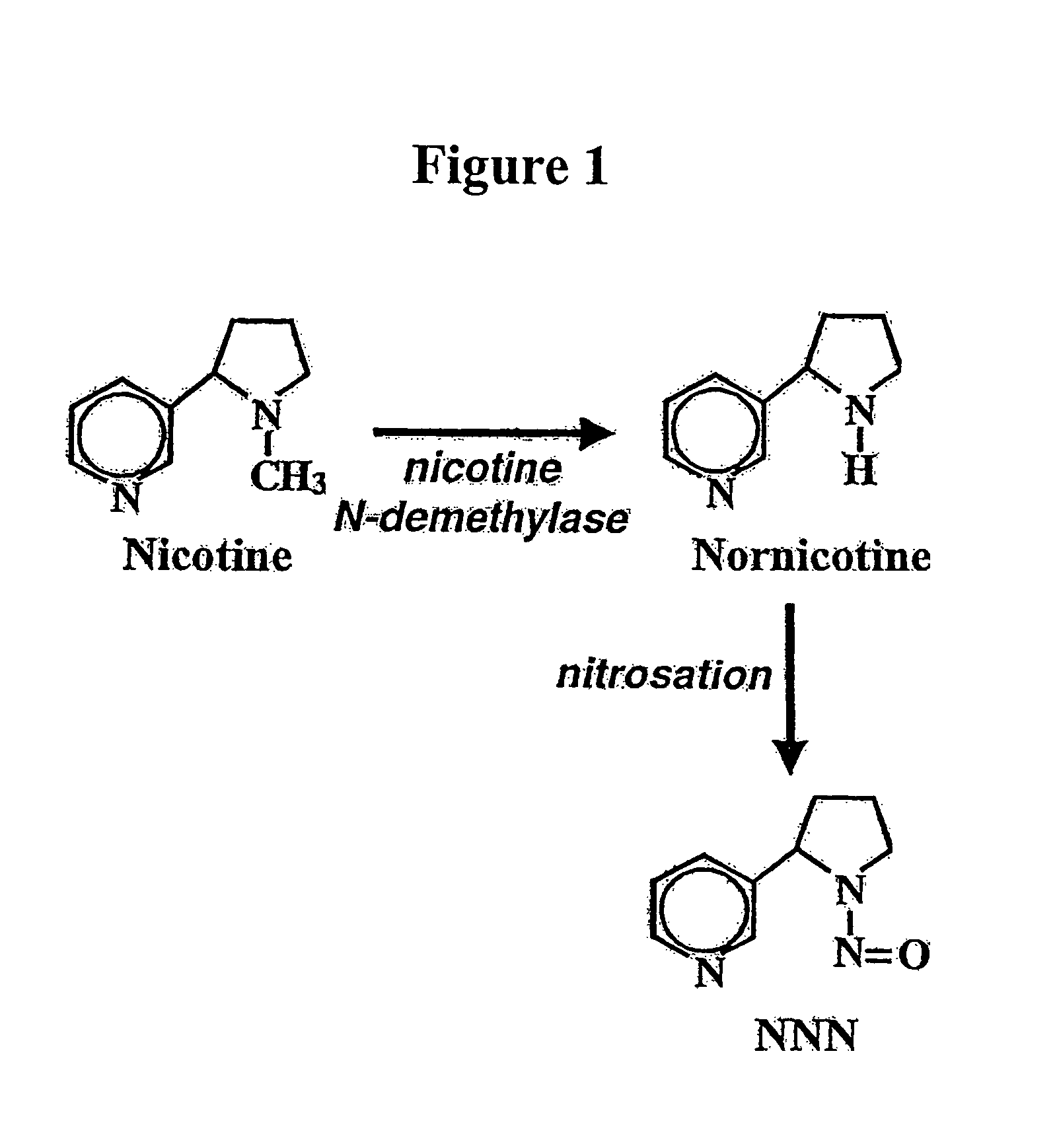
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
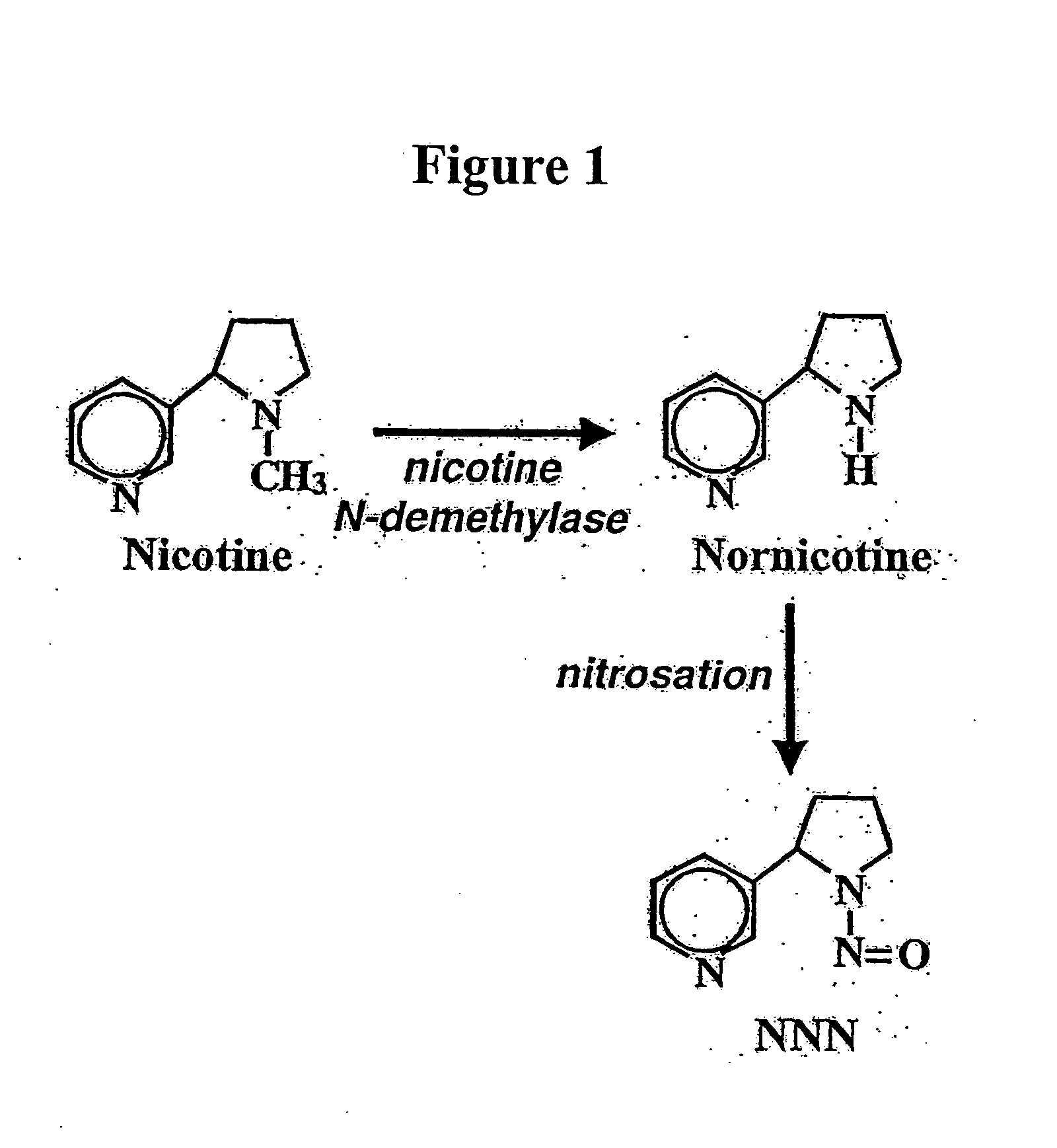
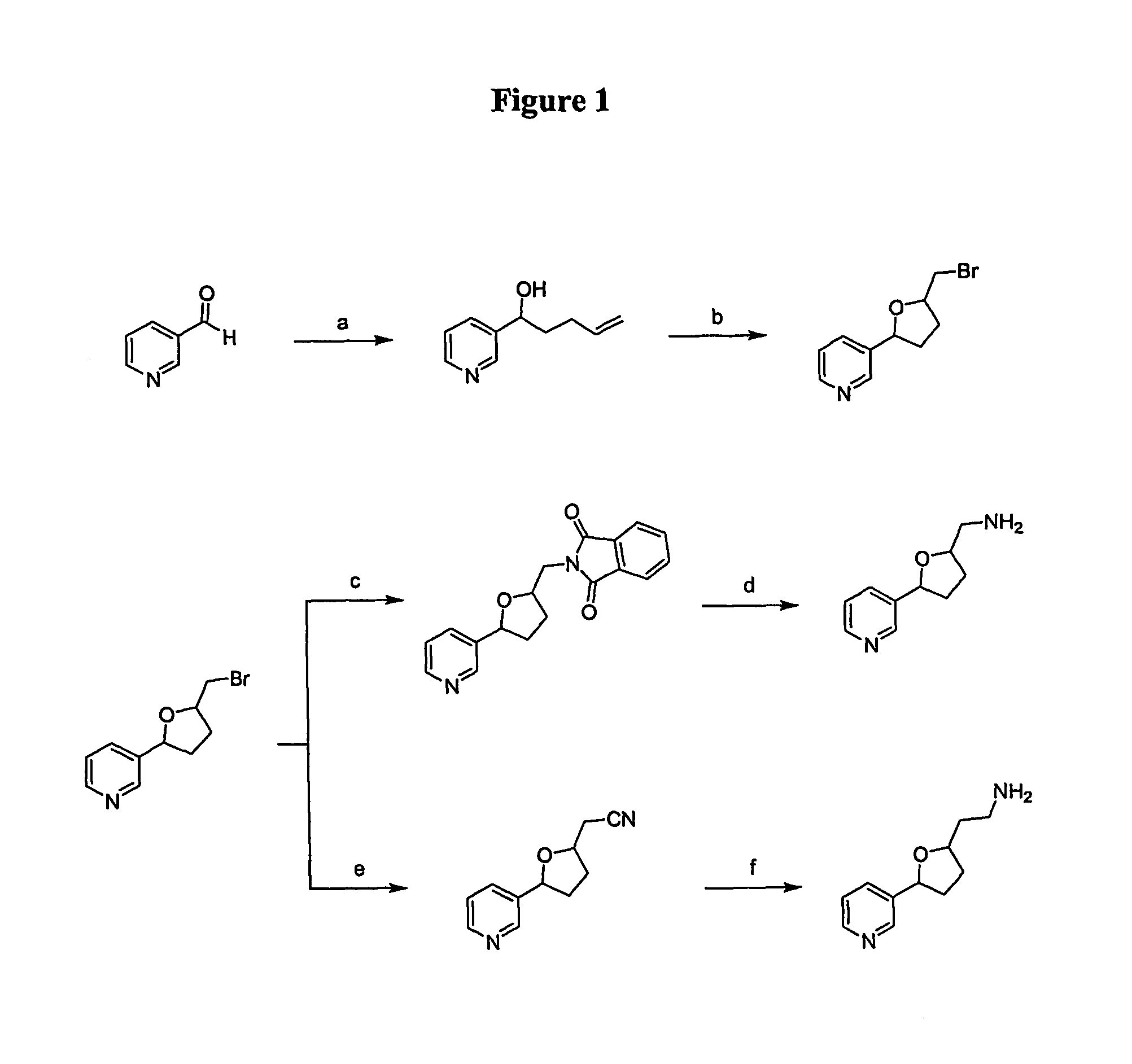
ActiveUS7884263B2Decrease in levelLower Level RequirementsTobacco treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS8124851B2Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNornicotineMetabolite
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Pharmacogenetic DME detection assay methods and kits
InactiveUS20060160074A1Increase nucleic acid synthesis reaction rateHeating evenlySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDrug metabolismPharmacogenetics
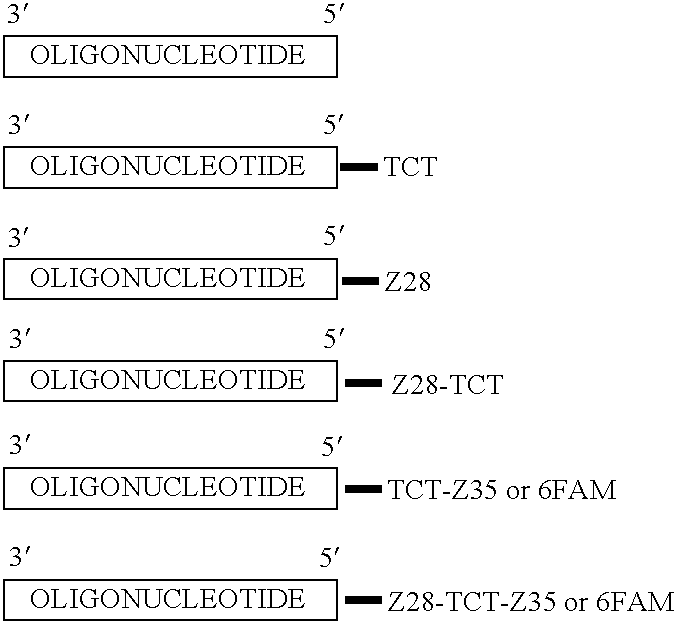
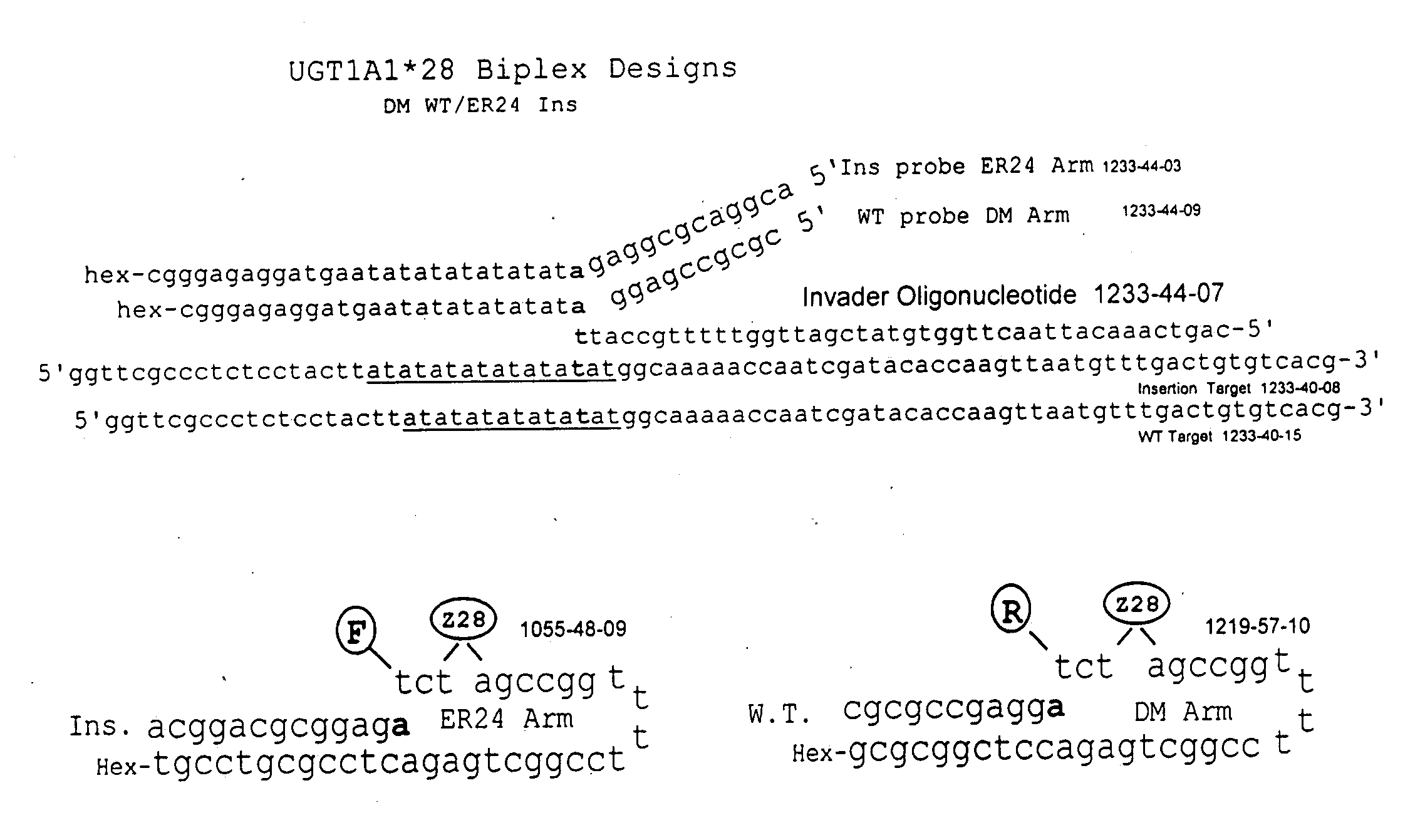
The present invention relates to methods for detecting polymorphisms in enzymes related to drug metabolizm (Drug Metabolizing Enzymes or DMEs) such as uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase (UGT) gene promoter, cytochrome p450, with a non-amplified oligonucleotide detection assays. The present invention also relates to pharmacogenetic DME detection assay kits.
Owner:THIRD WAVE TECH
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
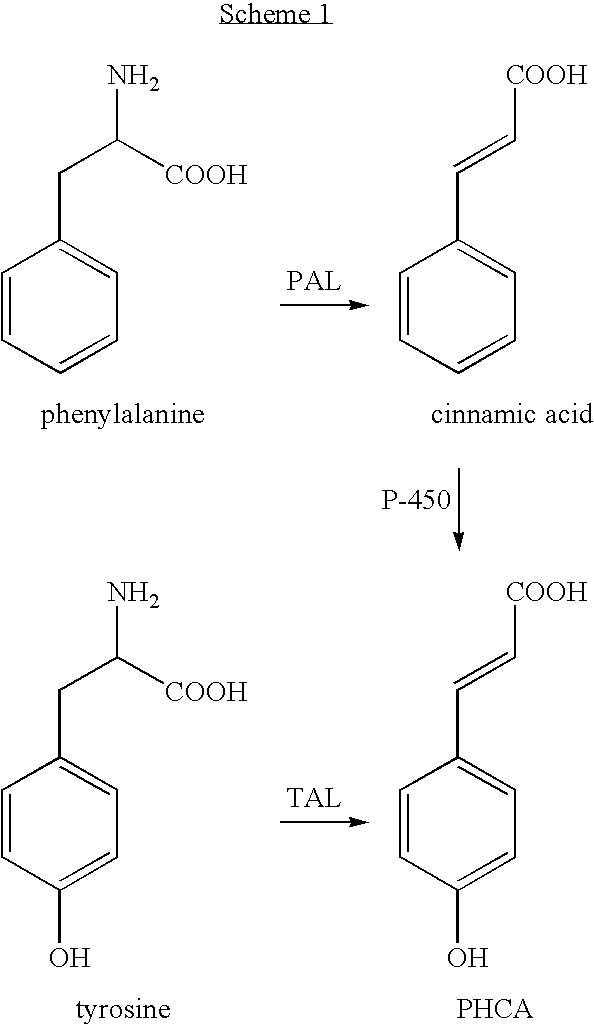
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:GATENBY ANTHONY A +4
Optimization and individualization of medication selection and dosing
ActiveUS8589175B2Easy to understandEasy to recommendationDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsPersonalizationDosing regimen
The invention provides population models, methods, and algorithms for targeting a dosing regimen or compound selection to an individual patient. The methods and algorithms of the invention utilize population models that incorporate genotype information for genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes for one or more compounds of interest. The methods allow integration of genotype information for one or more genes encoding a drug metabolizing enzyme, particularly a cytochrome P450 gene with patient data. The methods allow integration of genotype information and the effect of one or more compounds on one or more drug metabolizing enzymes. The methods allow iterative feedback of drug metabolizing data obtained from a patient into the process of generating a dosage regimen recommendation for a compound of interest for an individual patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Peroxide-driven cytochrome P450 oxygenase variants
InactiveUS20050202419A1Improve abilitiesImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenaseHeme
The invention relates to novel variants of cytochrome P450 oxygenases. These variants have an improved ability to use peroxide as an oxygen donor as compared to the corresponding wild-type enzyme. These variants also have an improved thermostability as compared to the cytochrome P450 BM-3 F87A mutant. Preferred variants include cytochrome P450 BM-3 heme domain mutants having I58V, F87A, H100R, F107L, A135S, M145A / V, N239H, S274T, L324I, I366V, K434E, E442K, and / or V446I amino acid substitutions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
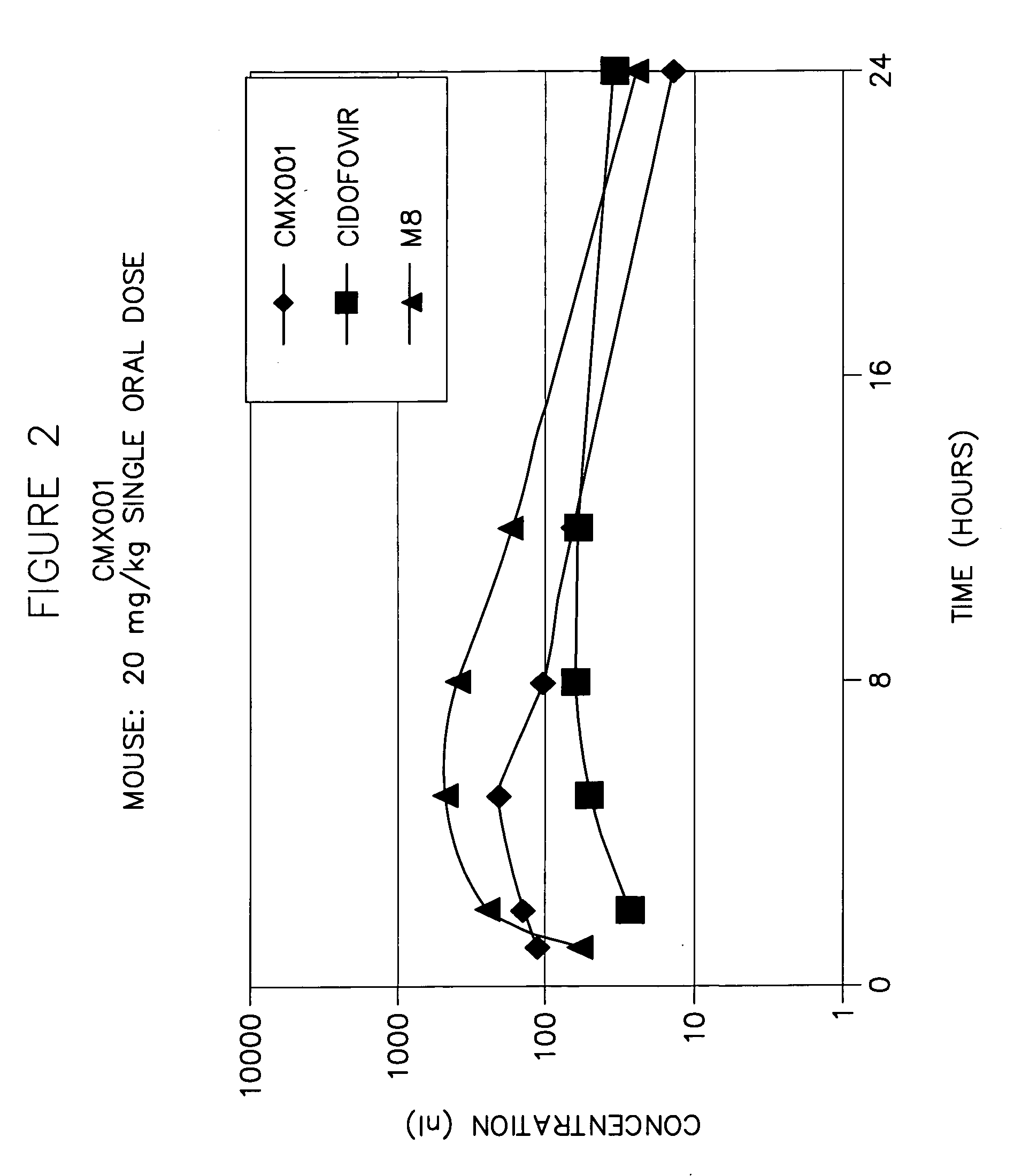
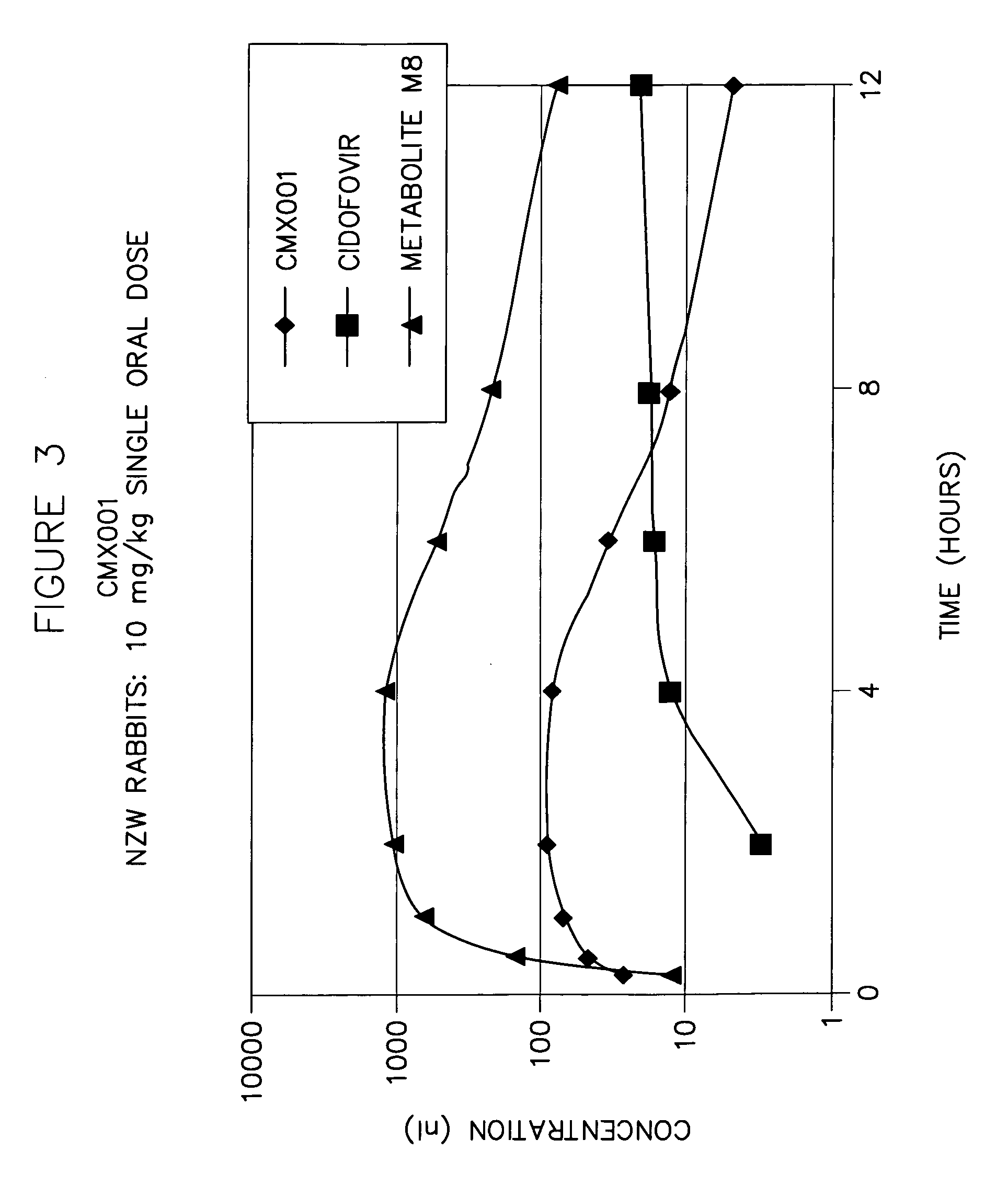
Compounds, compositions and methods for the treatment of viral infections and other medical disorders
InactiveUS20070003608A1Improve bioavailabilityPrevents and minimizes metabolism and degradationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLipid formationMedical disorder
The present application provides methods and compositions for improving the bioavailability of a lipid-containing antiviral compound, and in particular, an antiviral lipid-containing compound. In one embodiment, pharmaceutically acceptable compositions are provided that include an antiviral lipid-containing compound, or salt, ester, or prodrug thereof and one or more bioavailability enhancing compounds, such as inhibitors of cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Owner:CHIMERIX INC
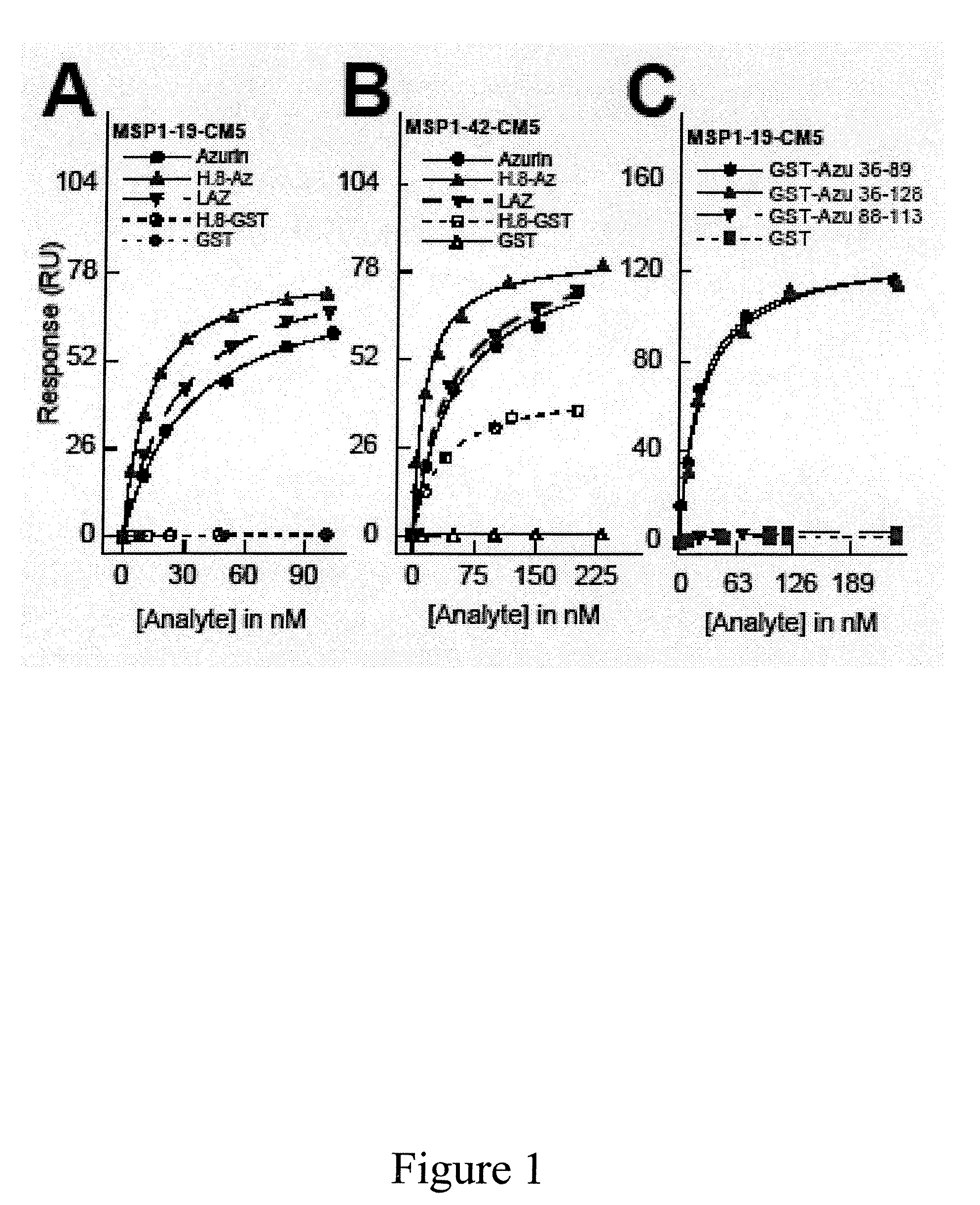
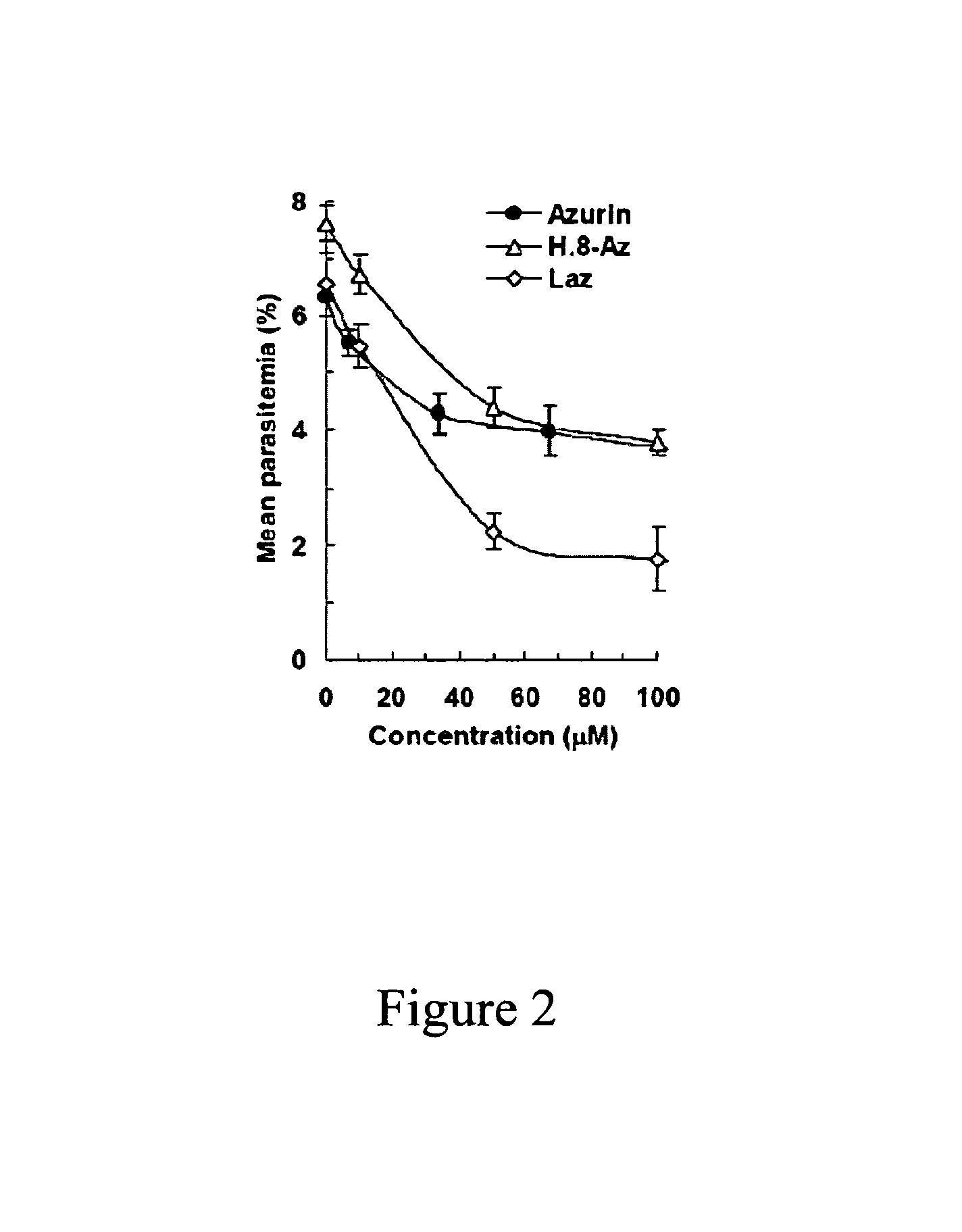
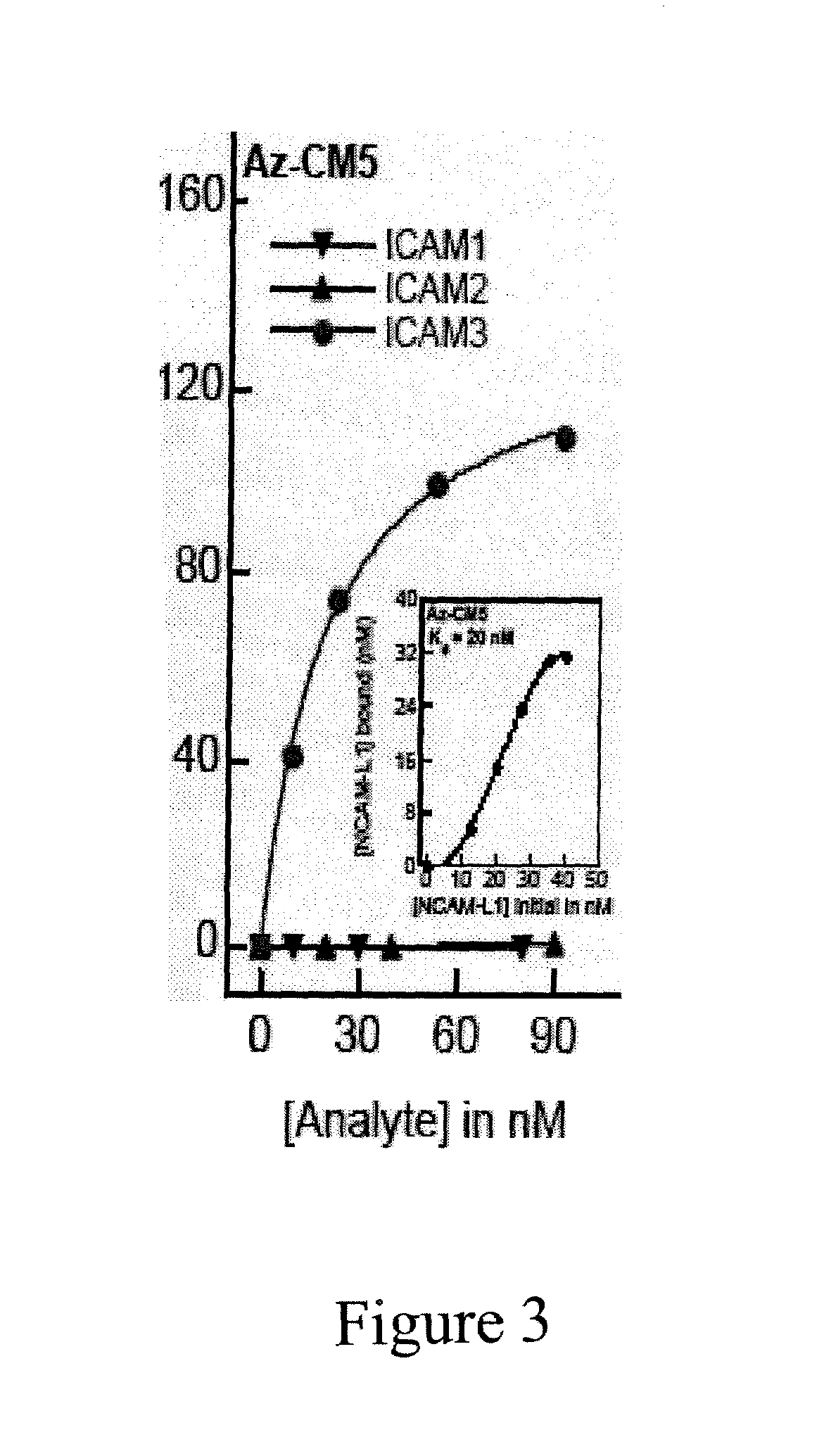
Compositions and methods for treating malaria with cupredoxin and cytochrome
The present invention relates to cupredoxin and cytochrome and their use, separately or together, to inhibit the spread of parasitemia in mammalian red blood cells and other tissues infected by the malaria parasite, and in particular the parasitemia of human red blood cells by P. falciparum. The invention provides isolated peptides that are variants, derivatives or structural equivalents of cupredoxins or cytochrome c, and compositions comprising cupredoxins and / or cytochrome c, or variants, derivatives or structural equivalents thereof, that are useful for treating or preventing malaria infection in mammals. Further, the invention provides methods to treat mammalian patients to prevent or inhibit the growth of malarial infection in mammals. The invention also provides methods to prevent the growth of malaria infection in insect vectors.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Composition for Treatment of Pain Specification
InactiveUS20080096872A1Easy to useRelief the painBiocideNervous disorderCytochrome P450Treatment pain
A method for the treatment of pain and / or inflammation in a subject by the administration of N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) or derivative thereof and a pain and / or anti-inflammatory medication. The pain or anti-inflammatory medication is metabolized by the action of the cytochrome p450 system. The pain medication includes N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist(s). NAC and the pain medicine can be administered concurrently or sequentially. The joint administration can result in the use of lower dosages than typical dosage of the pain and / or anti-inflammatory medication or in enhanced relief from the treated condition.
Owner:FRIEDMAN ROBERT S
Cytochrome P450 oxygenases
ActiveUS7226768B2High activityImprove stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesCytochrome p450 enzymeAmino acid
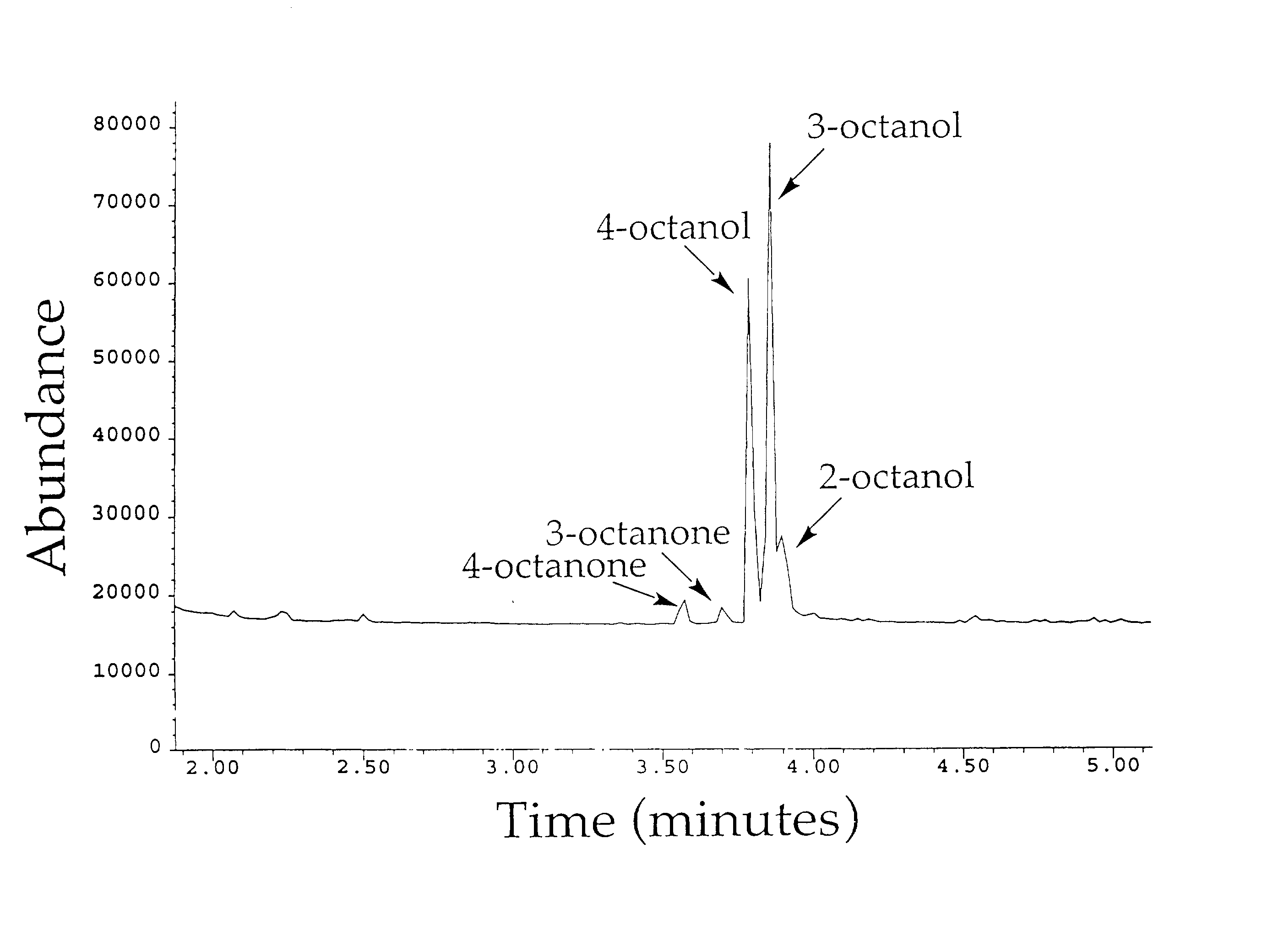
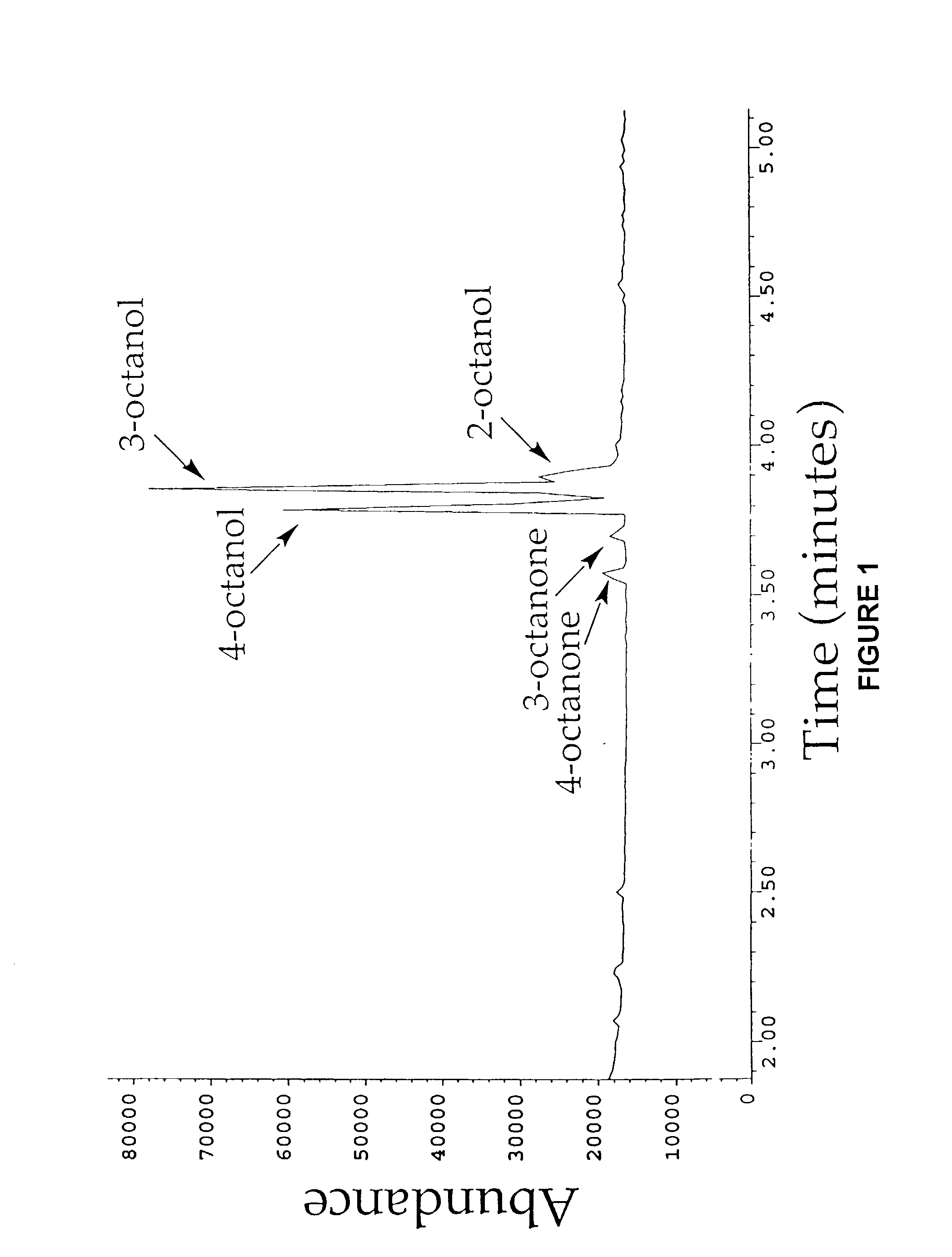
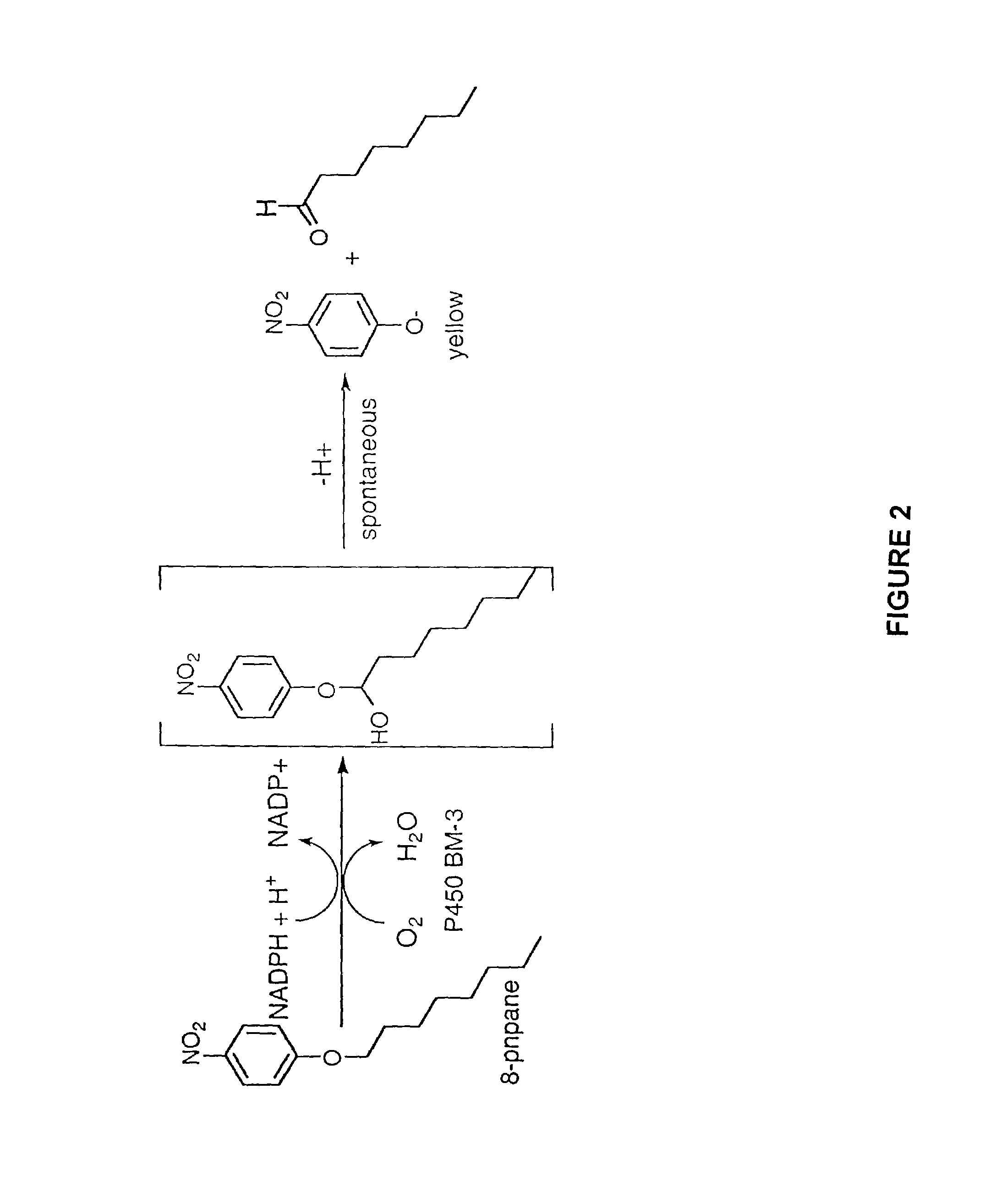
Nucleic acids encoding cytochrome P450 variants are provided. The cytochrome P450 variants of have a higher alkane-oxidation capability, alkene-oxidation capability, and / or a higher organic-solvent resistance than the corresponding wild-type or parent cytochrome P450 enzyme. A preferred wild-type cytochrome P450 is cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants include those having an improved capability to hydroxylate alkanes and epoxidate alkenes comprising less than 8 carbons, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to V78A, H236Q, and E252G of cytochrome P450 BM-3. Preferred cytochrome P450 variants also include those having an improved hydroxylation activity in solutions comprising co-solvents such as DMSO and THF, and have amino acid substitutions corresponding to T235A, R471A, E494K, and S1024E of cytochrome P450 BM-3.
Owner:NORO MOSELEY PARTNERS V +2
Alteration of tobacco alkaloid content through modification of specific cytochrome P450 genes
ActiveUS20080202541A1Lower Level RequirementsReducing nornicotine levelTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesMetaboliteNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in Nicotiana plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for cytochrome P450s that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Expression cassettes, vectors, plants, and plant parts thereof comprising inhibitory sequences that target expression or function of the disclosed cytochrome P450 polypeptides are also provided. Methods for the use of these novel sequences to inhibit expression or function of cytochrome P450 polypeptides involved in this metabolic conversion are also provided. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Synthetic Compounds and Derivatives as Modulators of Smoking or Nicotine Ingestion and Lung Cancer
InactiveUS20080188527A1Reduce formationHarmful effectsBiocideNervous disorderSelective modulationMedicine
Disclosed are nicotine-related compounds that selectively inhibit cytochrome P-450 2A6 (CYP2A6), selectively inhibit cytochrome P-450 2A13 (CYP2A13), and / or selectively modulate a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR). Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising a compound of the invention, as well as methods of using the pharmaceutical compositions for treating or preventing a disease or disorder associated with nicotine-ingestion, or a disease or disorder amenable to treatment by selective modulation of nAChRs.
Owner:HUMAN BIOMOLECULAR RES INST
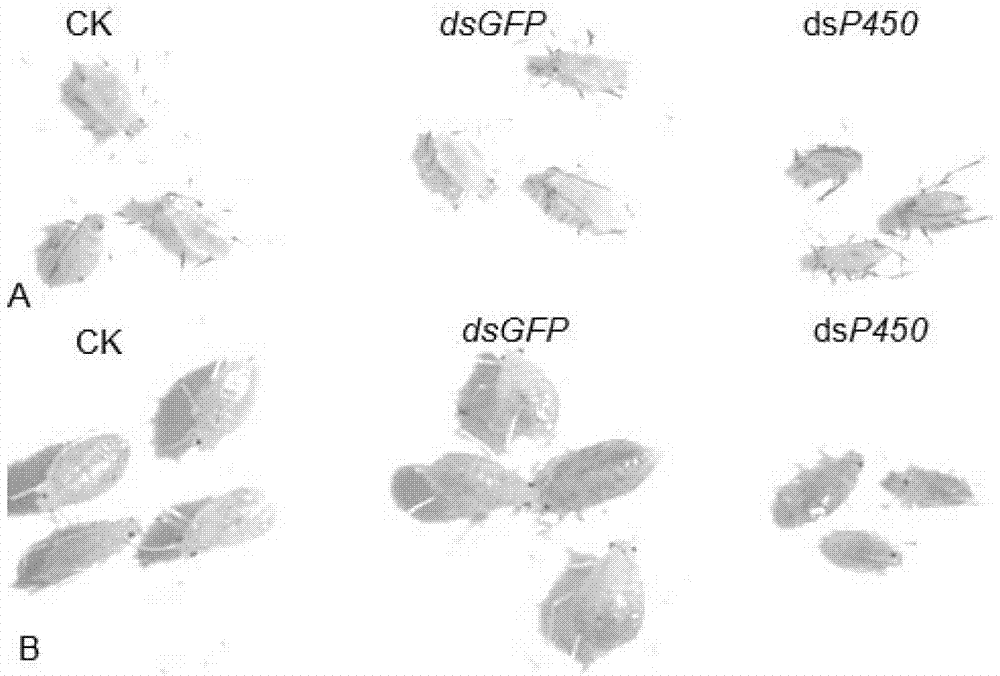
Cytochrome P450 dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition
The invention discloses dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) and application to aphid growth inhibition. The dsRNA provided by the invention is dsRNA as expressed by 1) or 2) as follows: 1) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleic acid as shown by a sequence 4 in a sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 4; and 2) dsRNA consisting of ribonucleicacid as shown by a sequence 5 in the sequence table and ribonucleic acid as shown by a reverse complementary sequence of the sequence 5. According to experiments, the obtained dsRNA of a conserved sequence of cytochrome P450cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) of English grain aphids and green peach aphids can inhibit growth and development of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids and can cause a lethal effect by adopting a method of feeding the dsRNA in vitro and using an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interfere) technology to silence the in-vivo cytochrome p450 of the English grain aphids and the green peach aphids.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
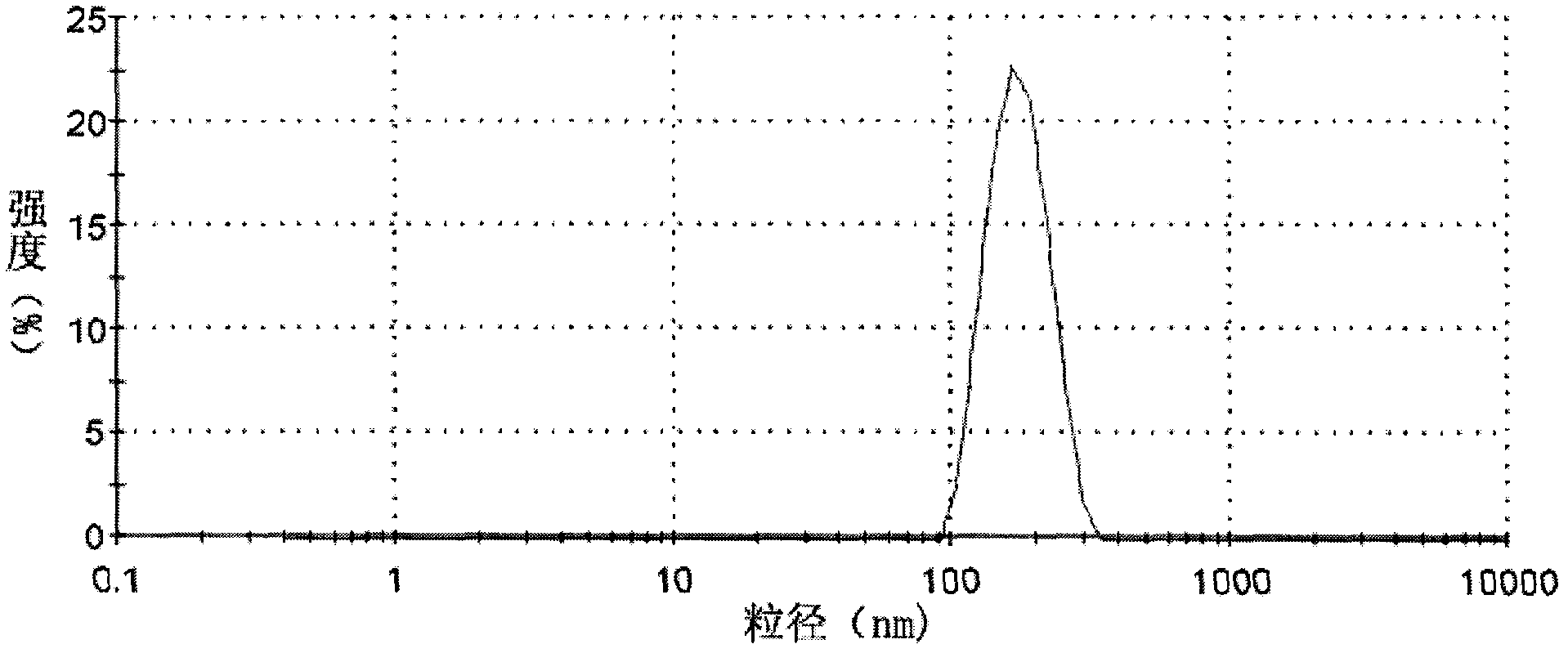
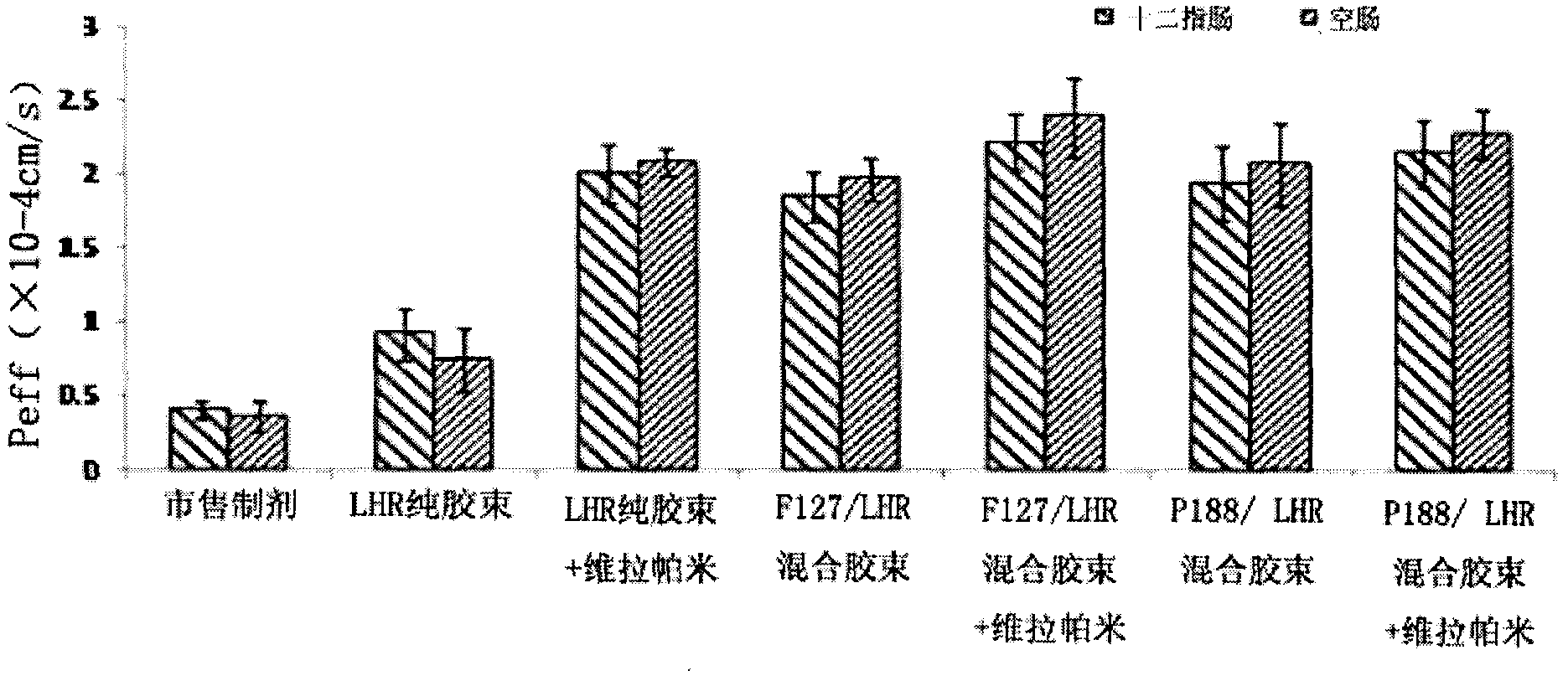
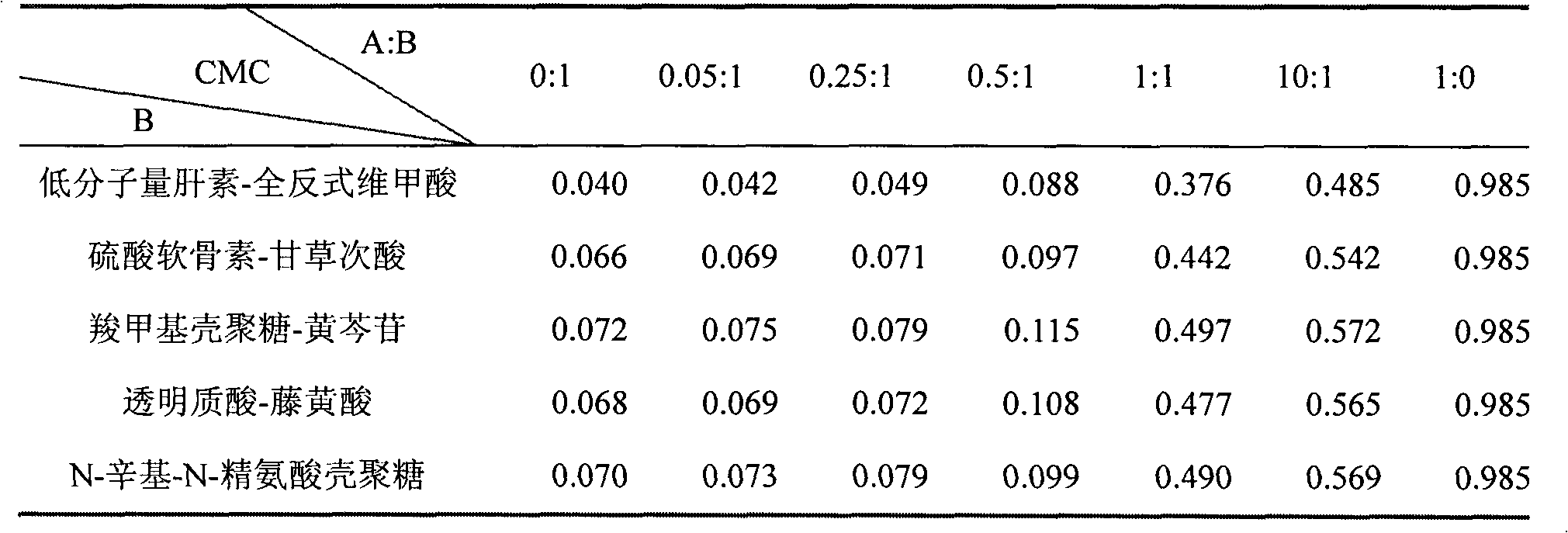
Preparation and application of insoluble drug-entrapped poloxamer/amphiphilic polysaccharide mixed micelle
InactiveCN102626518AOvercome the problems of high critical micelle concentration and low drug loadingImprove oral bioavailabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMixed micelleCytochrome p450 enzyme
The invention discloses preparation and application of an insoluble drug-entrapped poloxamer / amphiphilic polysaccharide mixed micelle. The insoluble drug-entrapped poloxamer / amphiphilic polysaccharide mixed micelle is prepared through a dialysis method or a solvent evaporation method. The mixed micelle is low in critical micelle concentration, is high in drug-loading rate, is capable of obviously prolonging the stabilization time and has the long-circulation function of a nanomicelle and has dual functions of restraining the metabolism of P-glycoprotein and cytochrome P450 enzyme and is capable of increasing the bioavailability of oral administration. The mixed micelle is simple in preparation method, is mature in process and is high in yield and can be prepared into preparations for the oral administration, such as tablets, capsules, pills and syrups.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Primer system for detecting genetic polymorphic sites related to human cytochrome P450 and application of primer system
InactiveCN103233068AHigh detection sensitivityOperational securityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceHuman cytochrome
The invention discloses a primer system for detecting genetic polymorphic sites related to human cytochrome P450. Based on a product prepared by adopting the primer system, seven genetic polymorphic sites related to the human cytochrome P450 can be simultaneously detected. By using the product, through detecting the genetic polymorphic sites related to the human cytochrome P450, clinical medication scheme can be guided and regulated, the basis is provided for clinical personalized medicine, and adverse medicine effects are prevented. The primer system is capable of simultaneously detecting the seven genetic polymorphic sites on different genes in a reaction system, and has the advantages of being lower in cost and more convenient to operate, and increasing the accuracy and the sensitivity in comparison with technologies of sequencing and real-time fluorescence quantification PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction).
Owner:BIOYONG TECH +1
SNP rs762551 of CYP1A2 gene and application thereof in relevant drug metabolism activity detection
InactiveCN101748196AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringDrug metabolismNormal people
The invention discloses SNP rs762551 of a CYP1A2 gene and application thereof in relevant drug metabolism activity detection, and also provides a method for prejudging drug metabolism activity. The method comprises the steps of detecting whether the cytochrome oxidase P4501A2 gene (CYP1A2) and a transcript of a human individual have variation or not compared with a normal cytochrome oxidase P4501A2 gene and a normal transcript, and if so, showing that the drug metabolism activity of the individual is different from common or normal people, for the individual. The invention also discloses a corresponding detection kit used for prejudging the drug metabolism activity of the individual.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
Expression system for actinomycete-origin cytochrome p-450 in escherichia coli
InactiveUS20060234337A1Efficient biotransformationConvenient and rapid enzyme-assaying operationSugar derivativesBacteriaSimple Organic CompoundsEscherichia coli
This invention relates to a system for the expression of cytochrome P-450 gene in host Escherichia coli, and provides Escherichia coli which contains actinomycete ferredoxin gene and also ferredoxin gene and ferredoxin reductase gene which are xenogenic to Escherichia coli. Thus, this invention is useful for the promotion of effective single oxygen atom insertional reaction of a substrate organic compound.
Owner:MERCIAN CORP
Bioproduction of para-hydroxycinnamic acid
InactiveUS20010053847A1Increased substrate specificityEnhanced TAL activitySugar derivativesBacteriaTyrosine ammonia-lyase activityTyrosine
The present invention provides several methods for biological production of para-hydroxycinnamic acid (PHCA). The invention is also directed to the discovery of new fungi and bacteria that possess the ability to convert cinnamate to PHCA. The invention relates to developing of a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wild type PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis into E. coli underlining the ability of the wildtype PAL to convert tyrosine to PHCA. The invention is also directed to developing a new biocatalyst for conversion of glucose to PHCA by incorporation of the wildtype PAL from the yeast Rhodotorula glutinis plus the plant cytochrome P-450 and the cytochrome P-450 reductase into E. coli. In yet another embodiment, the present invention provides for the developing of a new biocatalyst through mutagenesis of the wild type yeast PAL which possesses enhanced tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Protein electron mediator
ActiveUS20110045513A1Easy to collectReduce usageBacteriaBiochemical fuel cellsGlucose MeasurementOxidoreductase
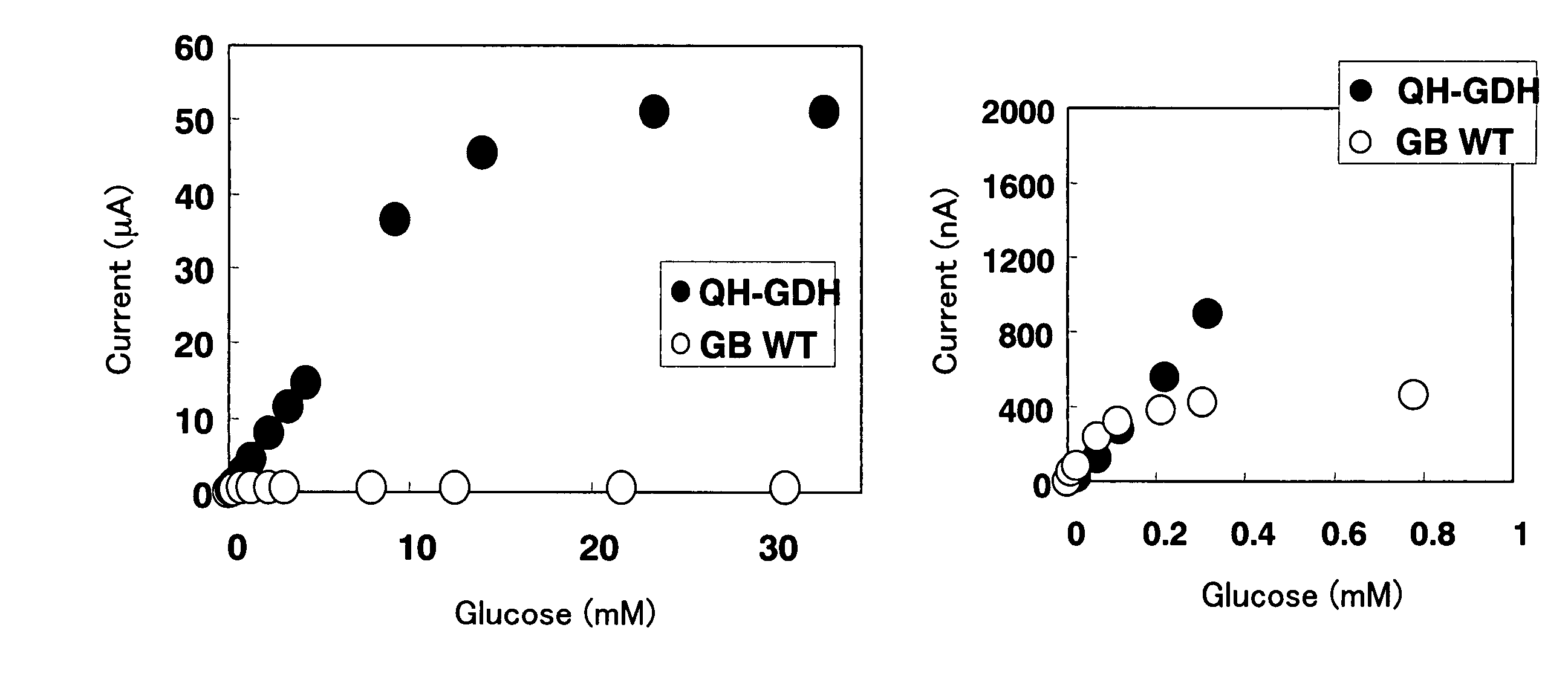
The problem to be resolved is to provide an electron mediator and a fusion body with high affinity with an enzyme, a measuring method using extracellular secretion type cytochrome and an enzyme, an electrode, and a sensor.The present invention relates to an electron mediator for glucose oxidoreductase comprising extracellular secretion type cytochrome, a fusion body in which the electron mediator is fused with glucose oxidoreductase, a composition for glucose measurement including the electron mediator or fusion body, a gene encoding a new extracellular secretion type cytochrome, and a measurement method using extracellular secretion type cytochrome and an enzyme, an electrode, and a sensor.
Owner:IKEDA SHOKKEN KK
Glucose Dehydrogenase/Cytochrome Fusion Protein
A fusion protein of pyrroloquinoline quinone glucose dehydrogenase (PQQGDH) and a cytochrome is disclosed. PQQGDH is, for example, a water-soluble PQQGDH derived from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. The cytochrome is, for example, an electron transfer domain of quinohemoprotein ethanol dehydrogenase from Comamonas testosteroni. The fusion protein of the present invention shows intramolecular electron transfer from PQQ, a redox center, to the cytochrome, which allow construction of a direct electron transfer-type glucose sensor which requires no electron mediators.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Luminescence-based methods and probes for measuring cytochrome P450 activity
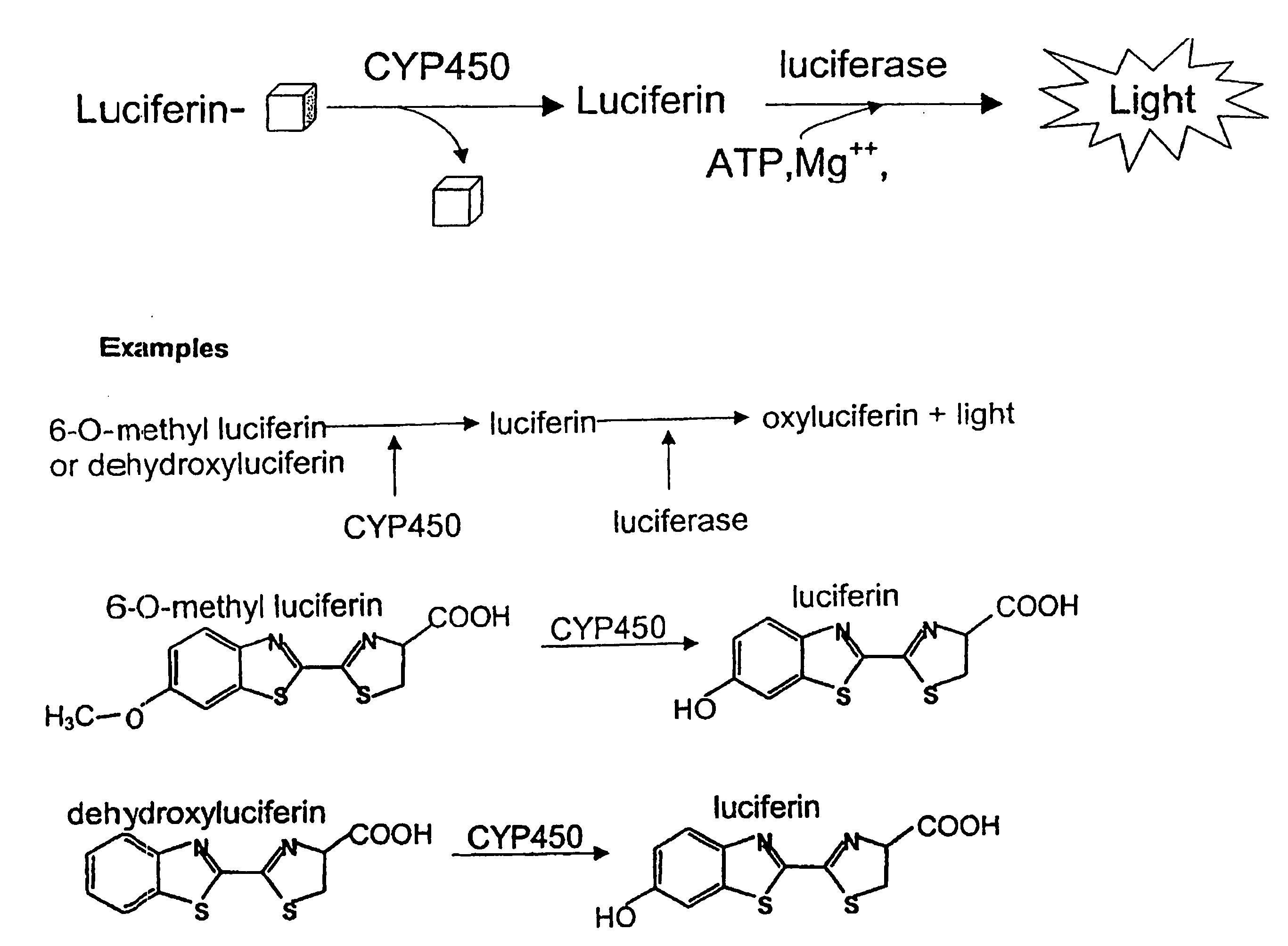
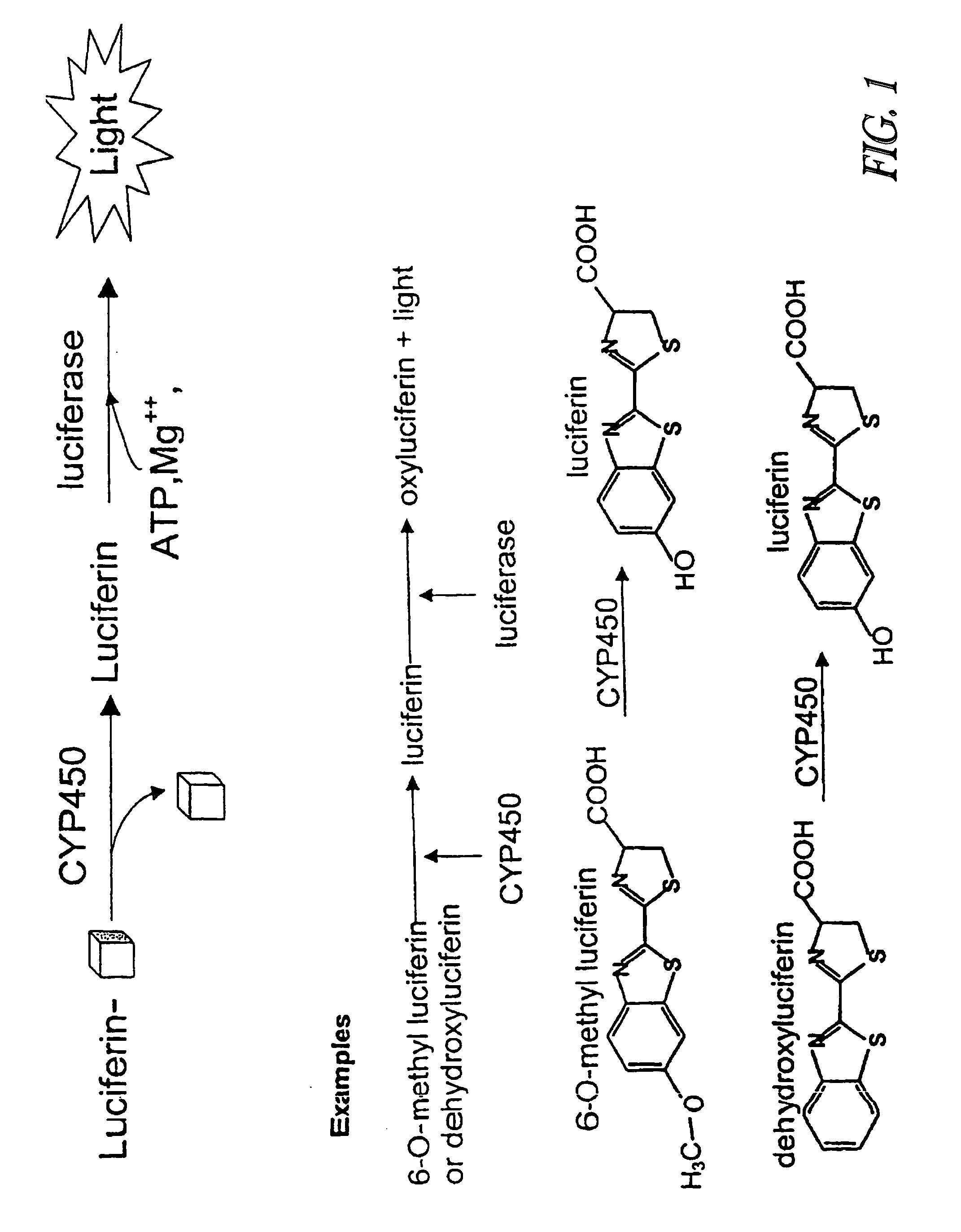
ActiveUS20090023173A1Enhance stabilityProlonged life timeCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningFluoresceinBioluminescence
The invention provides compounds, compositions, methods, substrates, and kits useful for analyzing the metabolic activity in cells, tissue, and animals and for screening test compounds for their effect on cytochrome P450 activity. In particular, a one-step and two-step methods using luminogenic molecules, e.g. luciferins or coelenterazines, that are cytochrome P450 substrates and that are also bioluminescent enzyme, e.g., luciferase, pro-substrates are provided. The present method further provides a method for stabilizing and prolonging the luminescent signal in a luciferase-based assay using luciferase stabilizing agents such as reversible luciferase inhibitors.
Owner:PROMEGA
Isolation and identification of mouse and human transcription control elements associated with cytochrome expression
The present invention relates to transcription control elements derived from mouse and human genes associated with cytochrome expression, e.g., Cyp3A11 and CYP3A4, respectively. Isolated polynucleotides, expression cassettes, vectors, recombinant cells, and transgenic animals, may comprise such transcription control elements as described herein.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
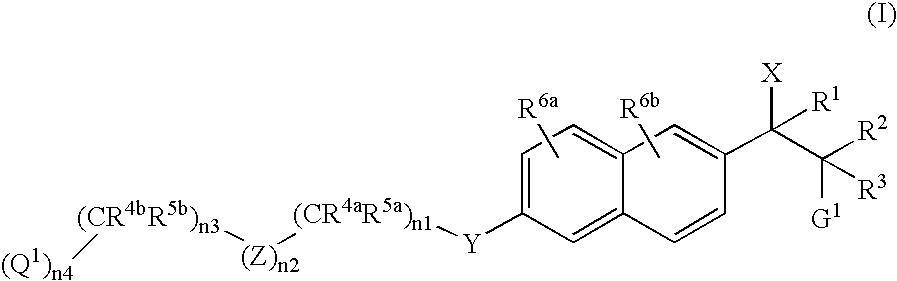
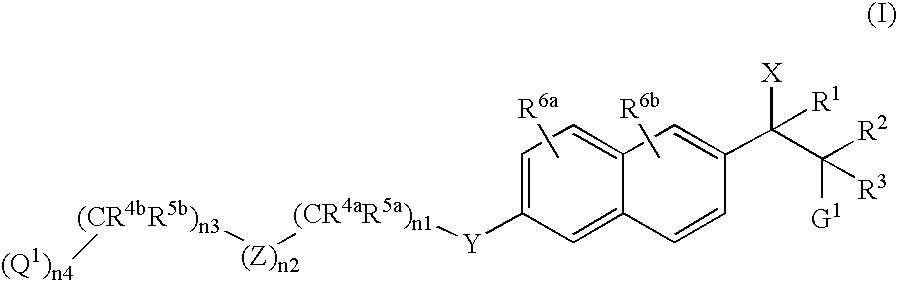
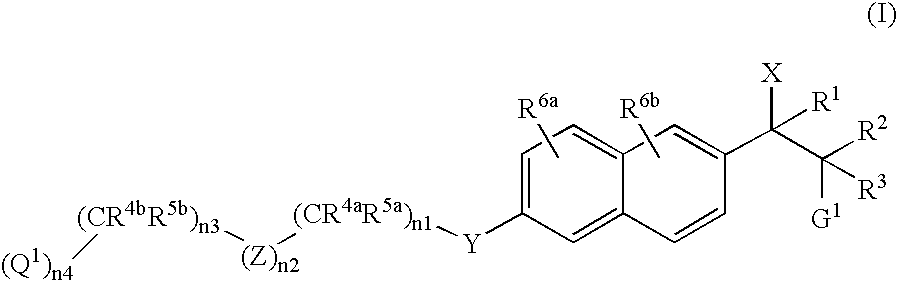
Naphthylene derivatives as cytochrome P450 inhibitors
Compounds of the formula and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof, wherein n1, n2, n3, n4, G1, Q1, Z, R1, R2, R3, R4a, R4b, R5a, and R5b are defined herein, inhibit the cytochrome P450RAI enzyme and are useful for the treatment and / or prevention of various diseases and conditions which respond to treatment by retinoids and by naturally occurring retinoic acid.
Owner:OSI PHARMA INC
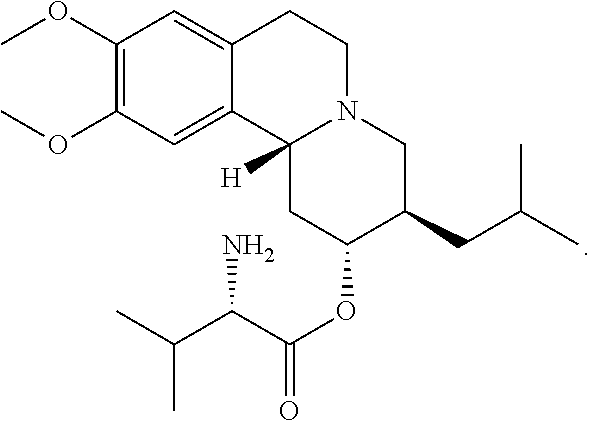
Methods for the Administration of Certain VMAT2 Inhibitors
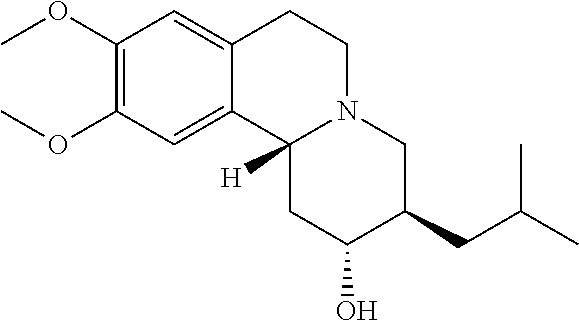
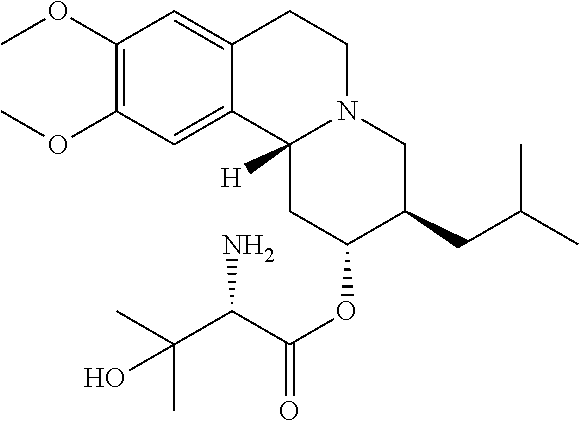
Provided are methods of administering a vesicular monoamine transport 2 (VMAT2) inhibitor chosen from valbenazine and (+)-α-3-isobutyl-9,10-dimethoxy-1,3,4,6,7,11b-hexahydro-2H-pyrido[2,1-a]isoquinolin-2-ol, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and / or isotopic variant thereof, to a patient in need thereof wherein the patient is also being administered a strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitor.
Owner:NEUROCRINE BIOSCI INC
Zero valent metal composite, manufacturing, system and method using thereof, for catalytically treating contaminated water
InactiveUS20090127208A1Reduce concentrationReduce the concentration of pollutantsLayered productsContaminated soil reclamationSurface waterCobalt
Zero valent metal composite, manufacturing thereof, using thereof, and system including thereof, for (in-situ or ex-situ) catalytically treating contaminated water, such as sub-surface water, surface water, above-surface water, water vapor, or / and gaseous water. Composite includes powdered diatomite matrix incorporated with nanometer (1-1000 nm) sized particles of a zero valent (transition) metal (iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc, palladium, platinum, or / and gold) and at least one electron transfer mediator (catalyst) from porphyrinogenic organometallic complexes (e.g., metalloporphyrins (chlorophylls, hemes, cytochromes) or metallocorrins (e.g., vitamin B12), and optionally, includes vermiculite. System includes composite and in-situ or / and ex-situ unit containing the composite, enabling exposure of contaminated water thereto. Applicable to in-situ sub-surface permeable reactive barriers (PRBs). Treatable water contaminants are organics (halogenated organic compounds), or / and inorganics (metal elements, metal element containing inorganic species, nonmetal elements, and nonmetal element containing inorganic species). Applicable to non-aqueous fluids (liquids, vapors, gases), for removing contaminants therefrom.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for minim hepatic tissue in vitro incubation and detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity
InactiveCN101308119AHigh simulationSave costsComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteCytochrome p450 enzyme
Disclosed is a method for detecting CYP450 enzymatic activity by means of micro-liver tissue incubation in vitro, which is characterized in that: a liver trace puncturing method used in clinic takes micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g, or kills a mouse to take out the liver in an animal experiment, and builds a micro-liver tissue in vitro incubation system, then uses a one-probe medicine to perform the liquid phase chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for detecting probe substrates and concentration of corresponding metabolites, and obtains the activity of P450 enzyme according to metabolite ratios thereof. The method has the advantages of: 1. micro scale: only micro-liver tissues of 0.1 to 0.2g are needed for detecting cytochrome P450enzyme activity, and can be used for animal experiment and checking clinic micro-liver tissue liver drug enzyme activity; 2. time saving and convenience: costly ultracentrifugation equipment used in the conventional method is saved, costs and time for detection are greatly saved, and liver enzyme metabolic condition simulation is better; and 3. establishing indexes for evaluating the enzyme metabolic activity: metabolite ratios.
Owner:CENT HOSPITAL XUHUI DISTRICT SHANGHAI CITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com