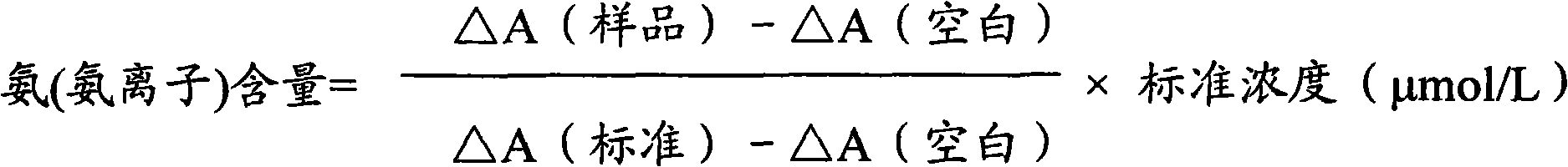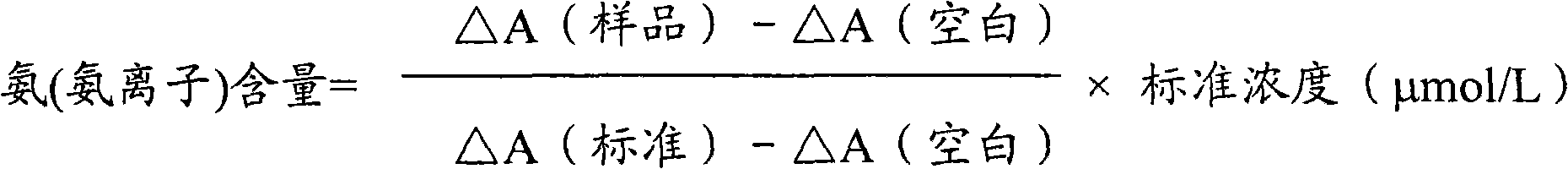Patents
Literature
63 results about "Ferredoxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
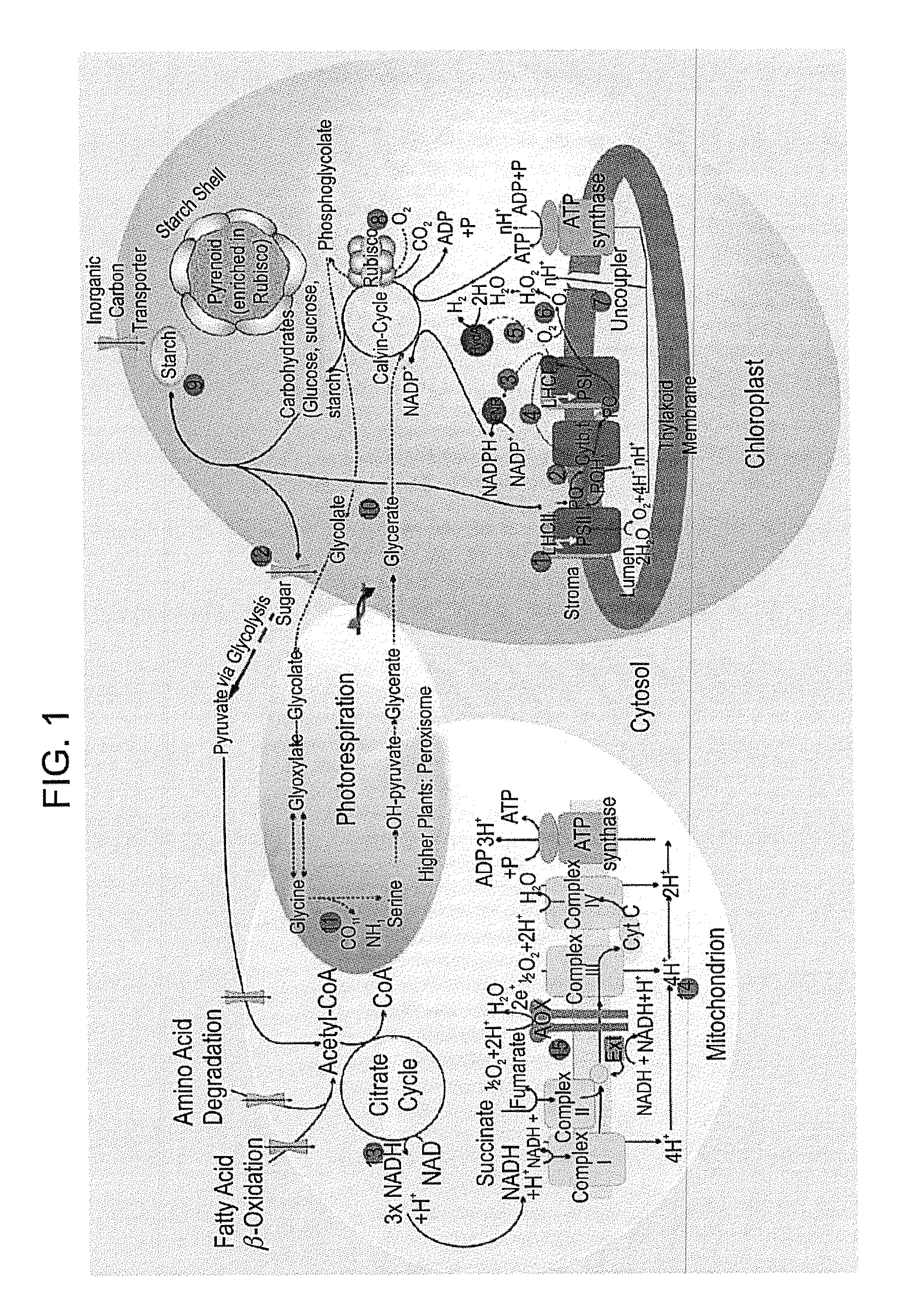
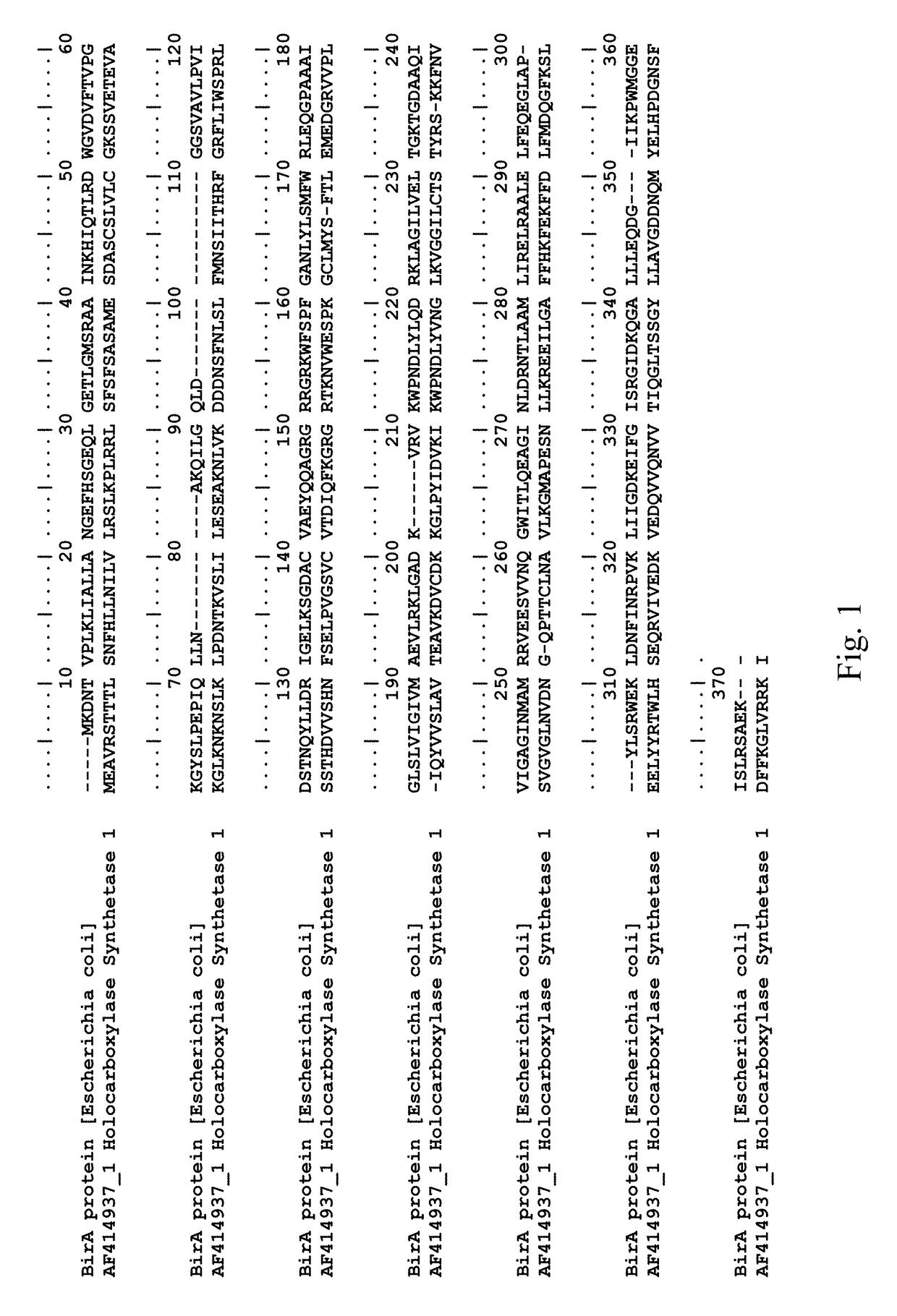
Ferredoxins (from Latin ferrum: iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied to the "iron protein" first purified in 1962 by Mortenson, Valentine, and Carnahan from the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium pasteurianum.
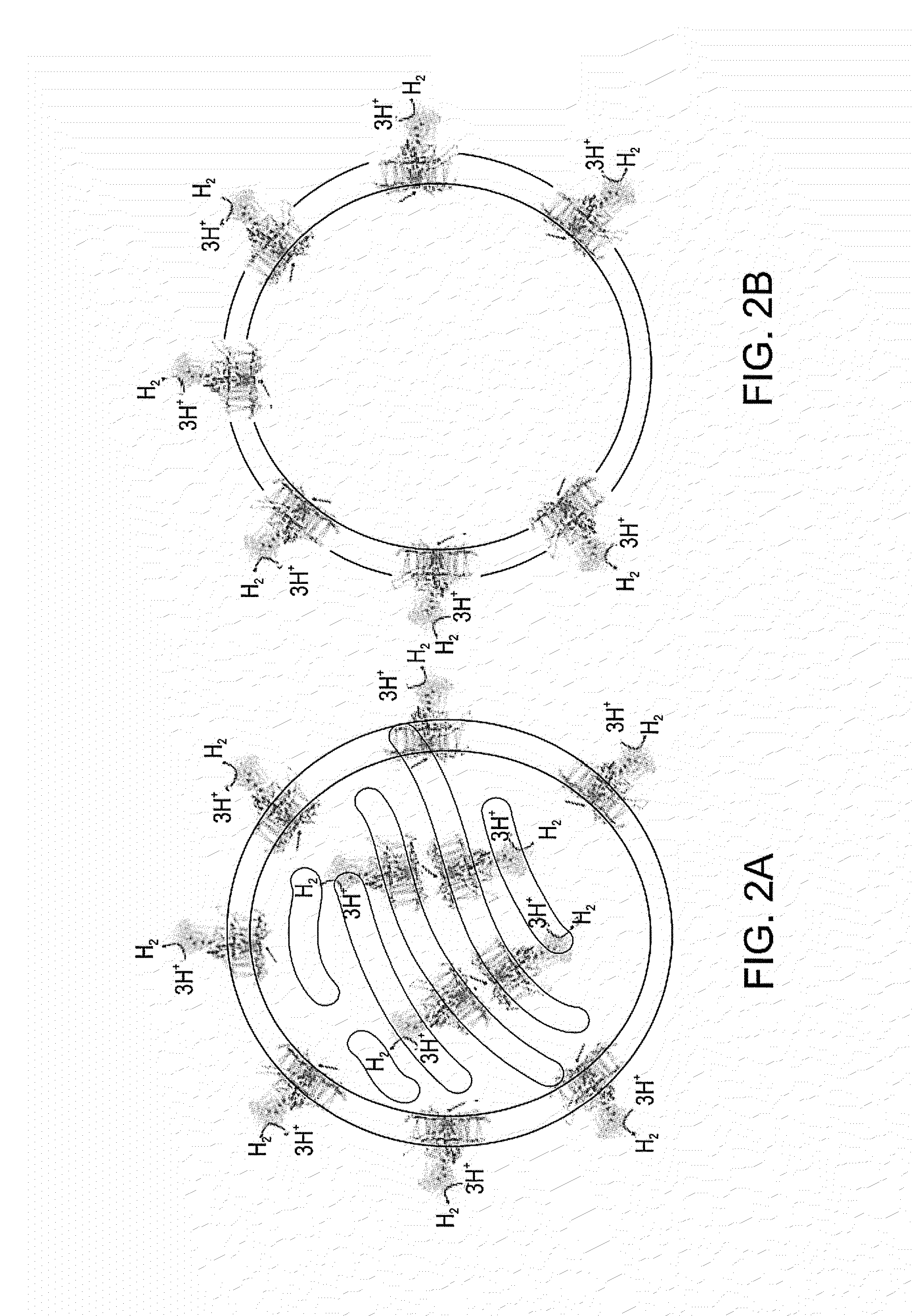
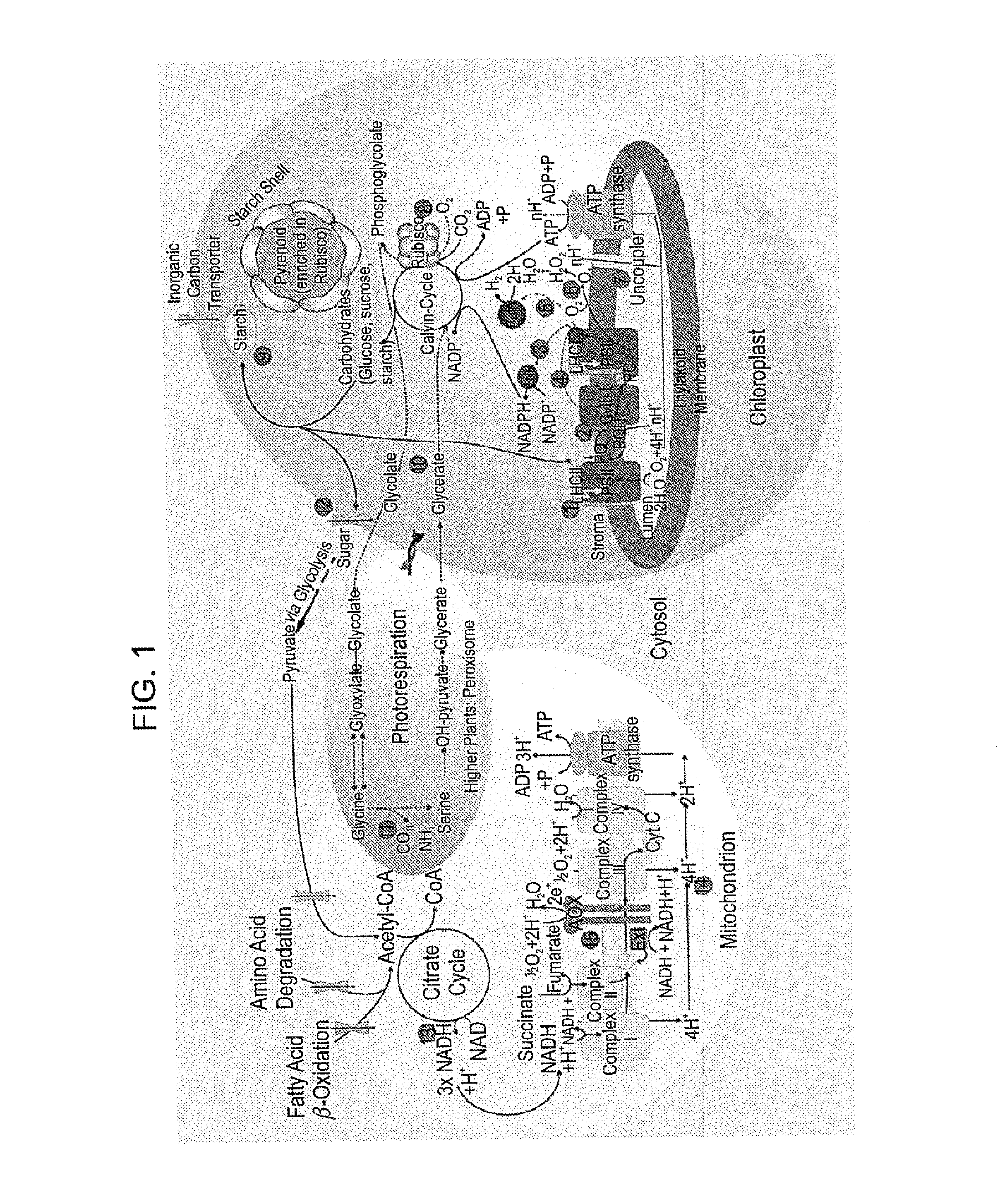
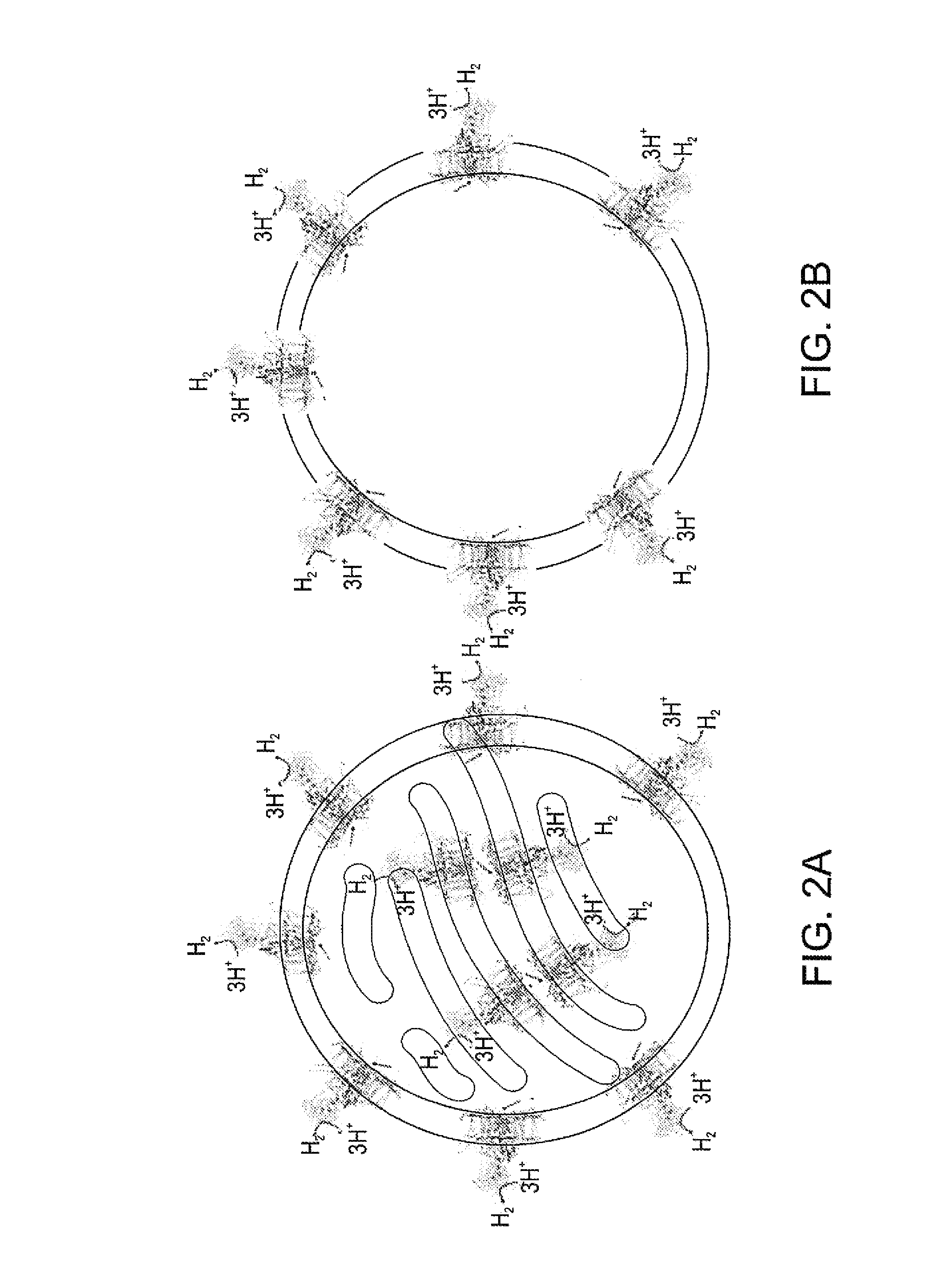
Photocatalytic hydrogen production and polypeptides capable of same
InactiveUS20100203609A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeterologousNucleotide
An isolated polypeptide comprising a hydrogen generating enzyme attached to a heterologous ferredoxin is disclosed, as well as polynucleotides encoding same, nucleic acid constructs capable of expressing same and cells expressing same. A method for generating hydrogen using the isolated polypeptide is also disclosed.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
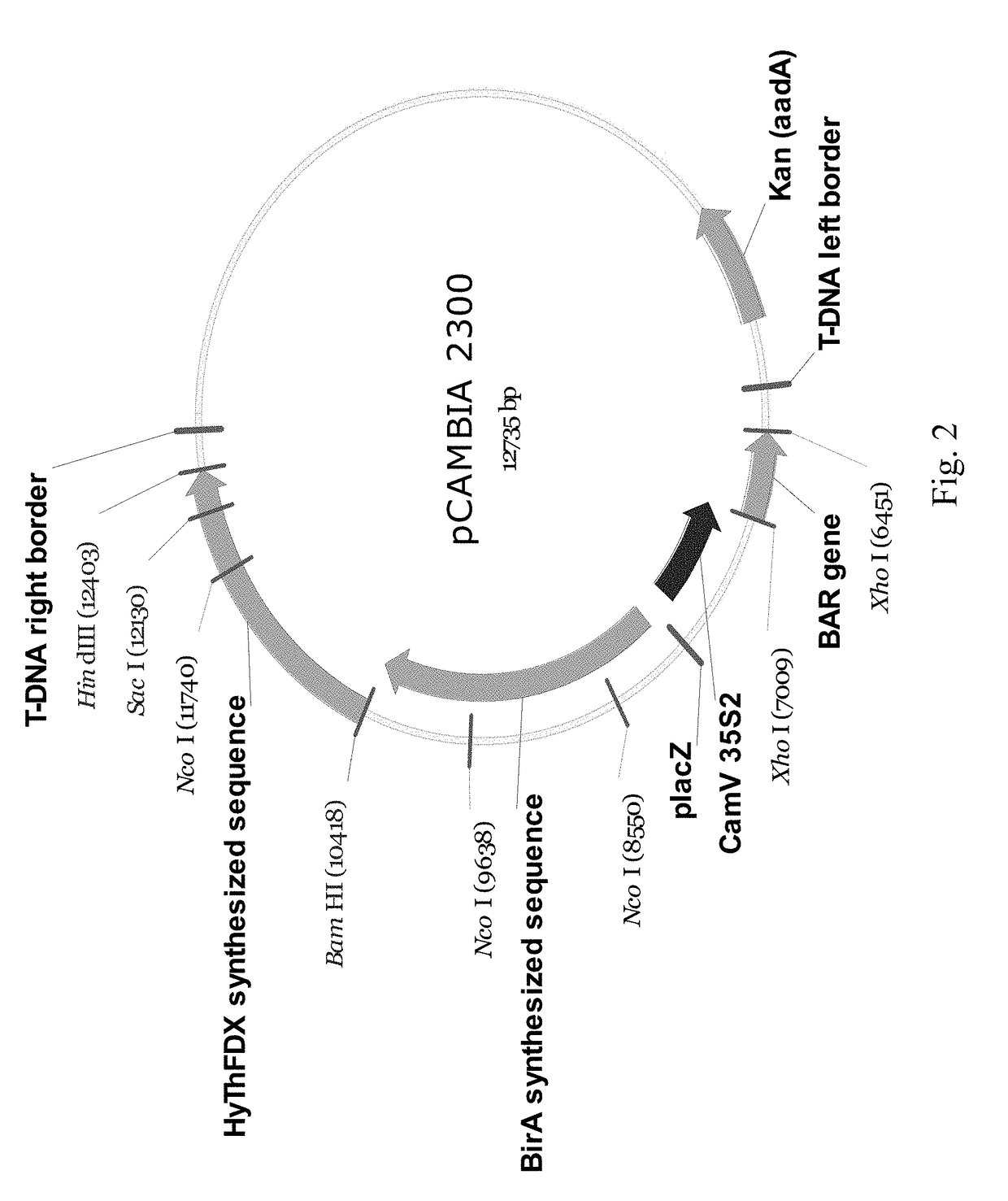
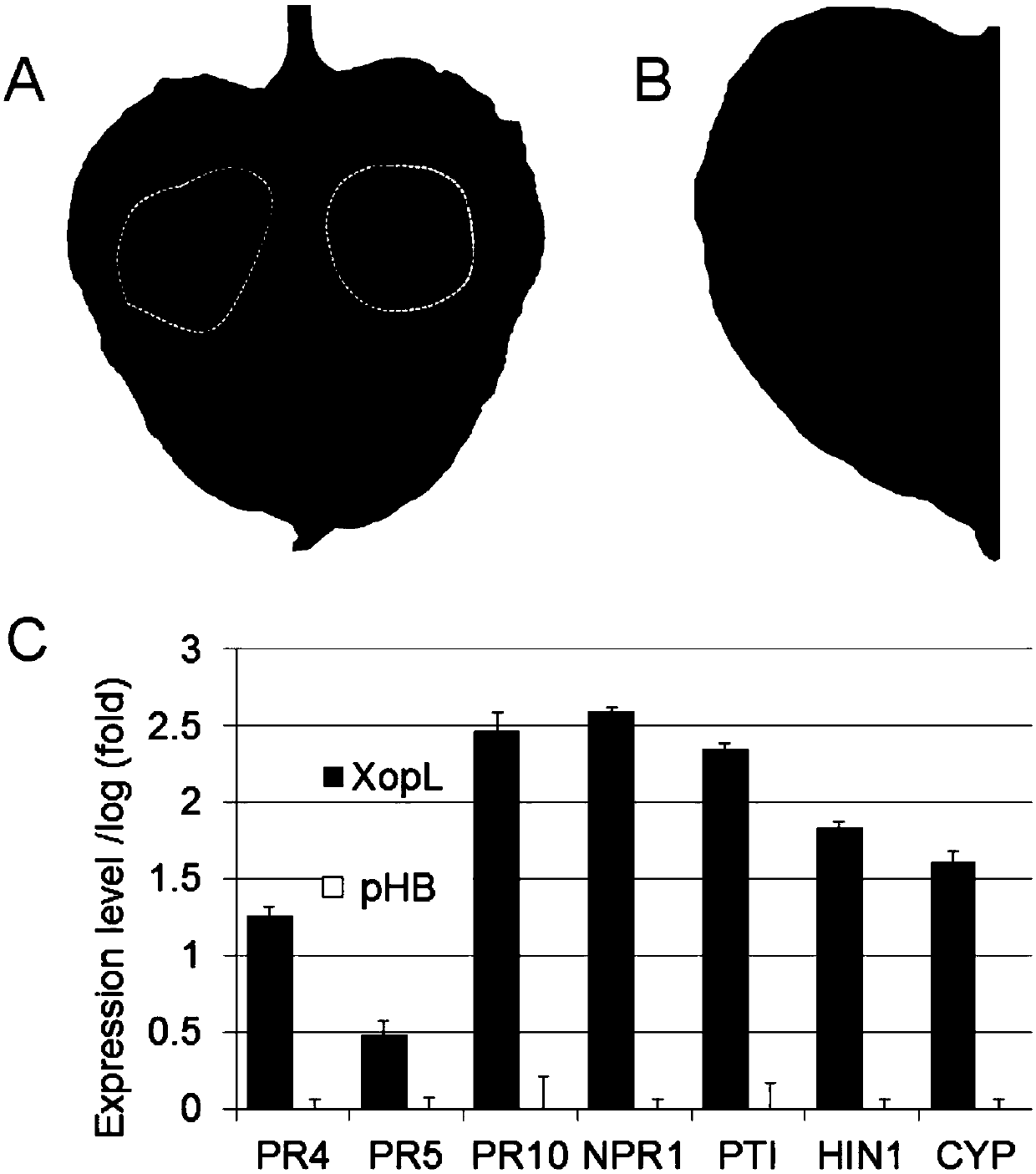
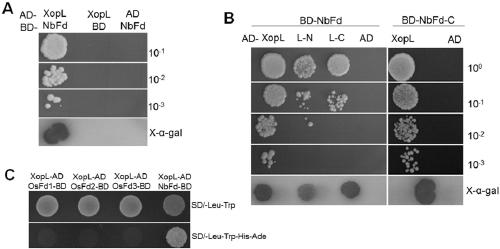
Tobacco ferredoxin capable of improving disease resistance of rice and coding gene of tobacco ferredoxin
InactiveCN109554354ARaise active oxygen levelsIncreased Blight AbilityLigasesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyDisease
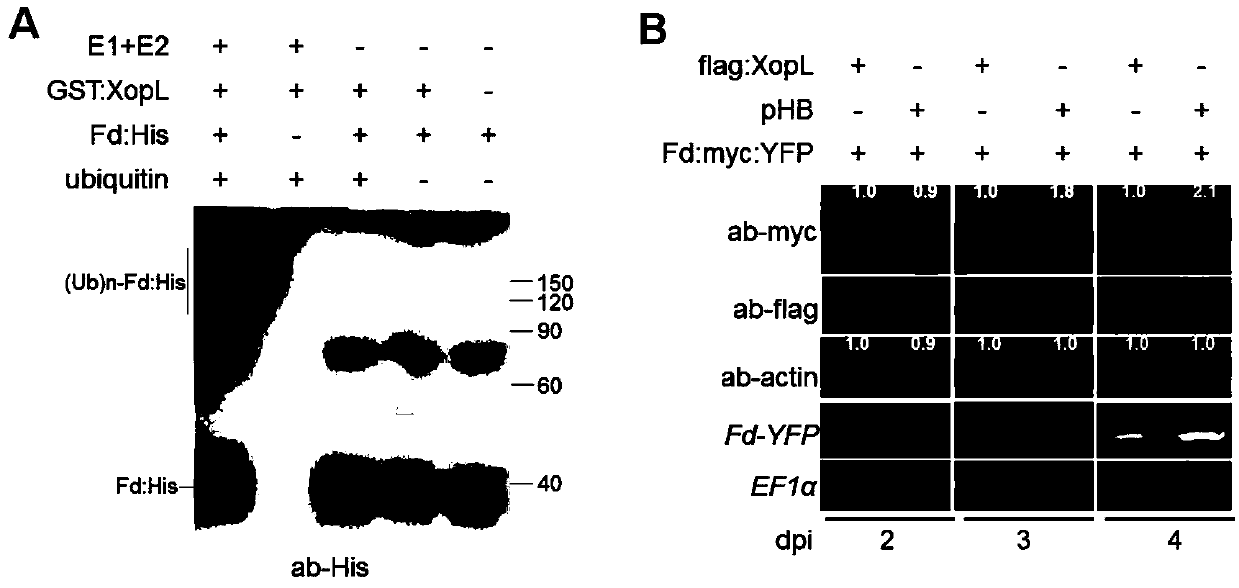
The invention relates to tobacco ferredoxin capable of improving disease resistance of rice and a coding gene of the tobacco ferredoxin, and belongs to the field of disease-resistant genetic engineering of the rice. Tobacco ferredoxin Ferredoxin (NbFd) in effector protein XopL mediated plant cells generates ubiquitination, then the tobacco ferredoxin is degraded by proteasomes, and the number of plant cell chloroplasts entering the NbFd is reduced, so that transmission of electrons in photosynthesis is restrained, accumulation of active oxygen is caused, and plants are induced to produce an allergic reaction (HR) type disease-resistant reaction. Ferredoxin protein in the rice does not interact with XopL, but after Ferredoxin protein coding genes from tobacco are transferred into the rice,the resistance of the rice to bacterial leaf spot can be improved. The tobacco Ferredoxin protein coding gene NbFd obtained in the way of protein interaction can be used as a breeding gene resource ofthe rice for resisting bacterial leaf spots, and the resistance of obtained NbFd transgenic rice to the bacterial leaf spots can be notably improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for producing alkane and recombinant microorganism capable of synthesizing alkane
ActiveUS20140186915A1Efficient productionLowering alkane production costMicroorganismsEnzymesMicroorganismFerredoxin
A method for producing alkane and a recombinant microorganism with good alkane productivity in a reaction system for synthesizing alkane by alkane synthase activity are provided. Alkane productivity is significantly improved in a system for synthesizing alkane by alkane synthase in the presence of ferredoxin. Specifically, the method for producing alkane according to the present invention comprises synthesizing alkane by alkane synthase in the presence of ferredoxin.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
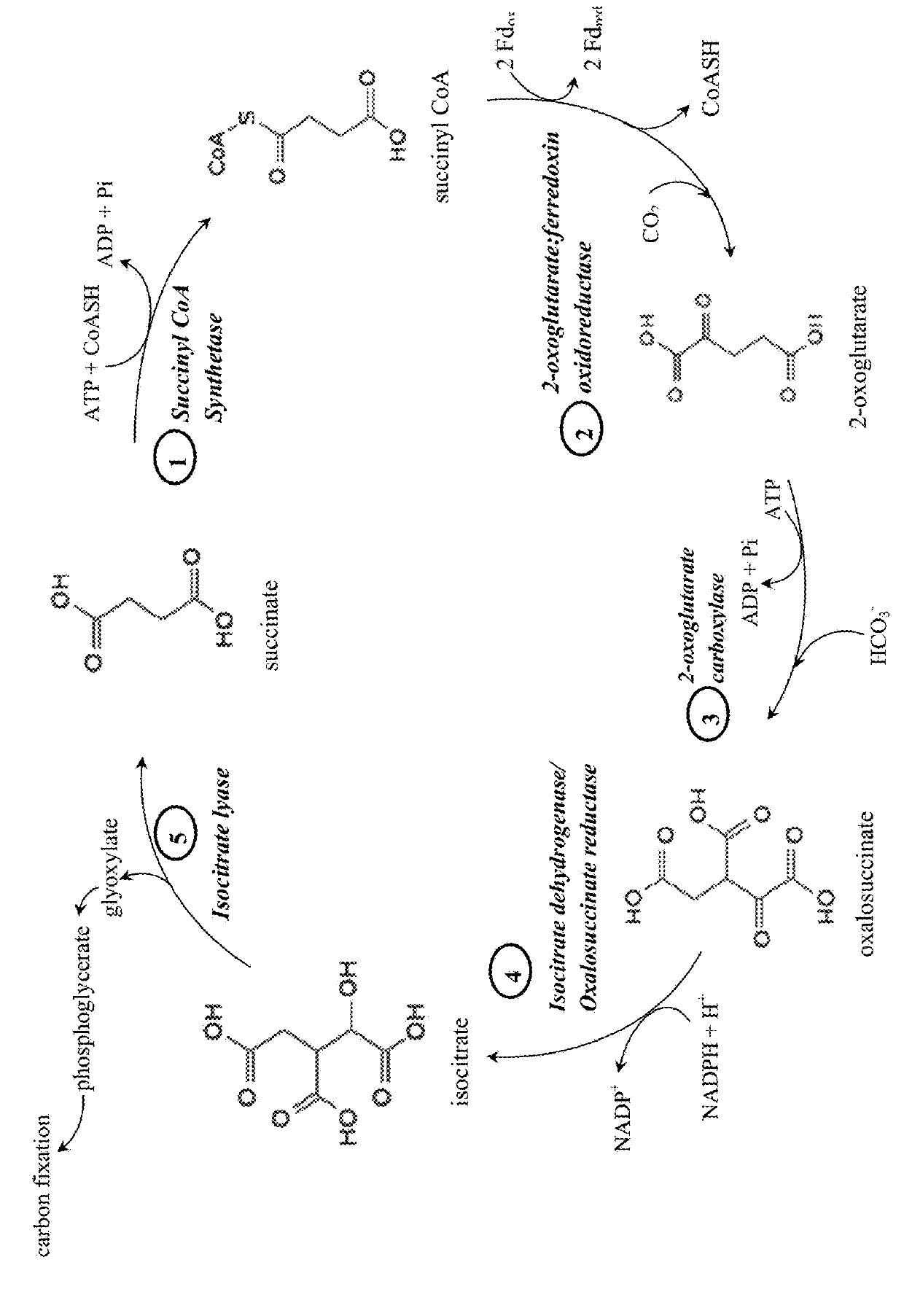
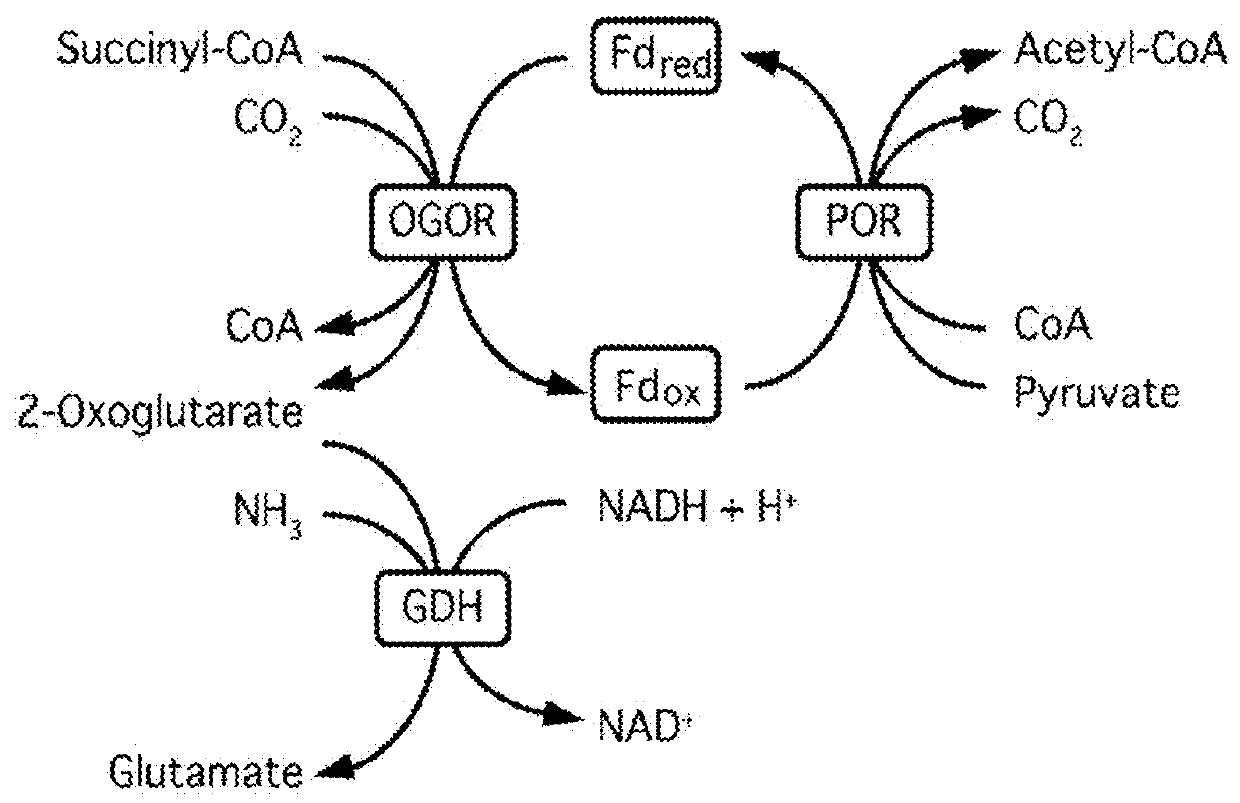
Synthetic Pathway for Biological Carbon Dioxide Sequestration
InactiveUS20140150135A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionBiocideOrganic chemistryHeterologousNucleotide
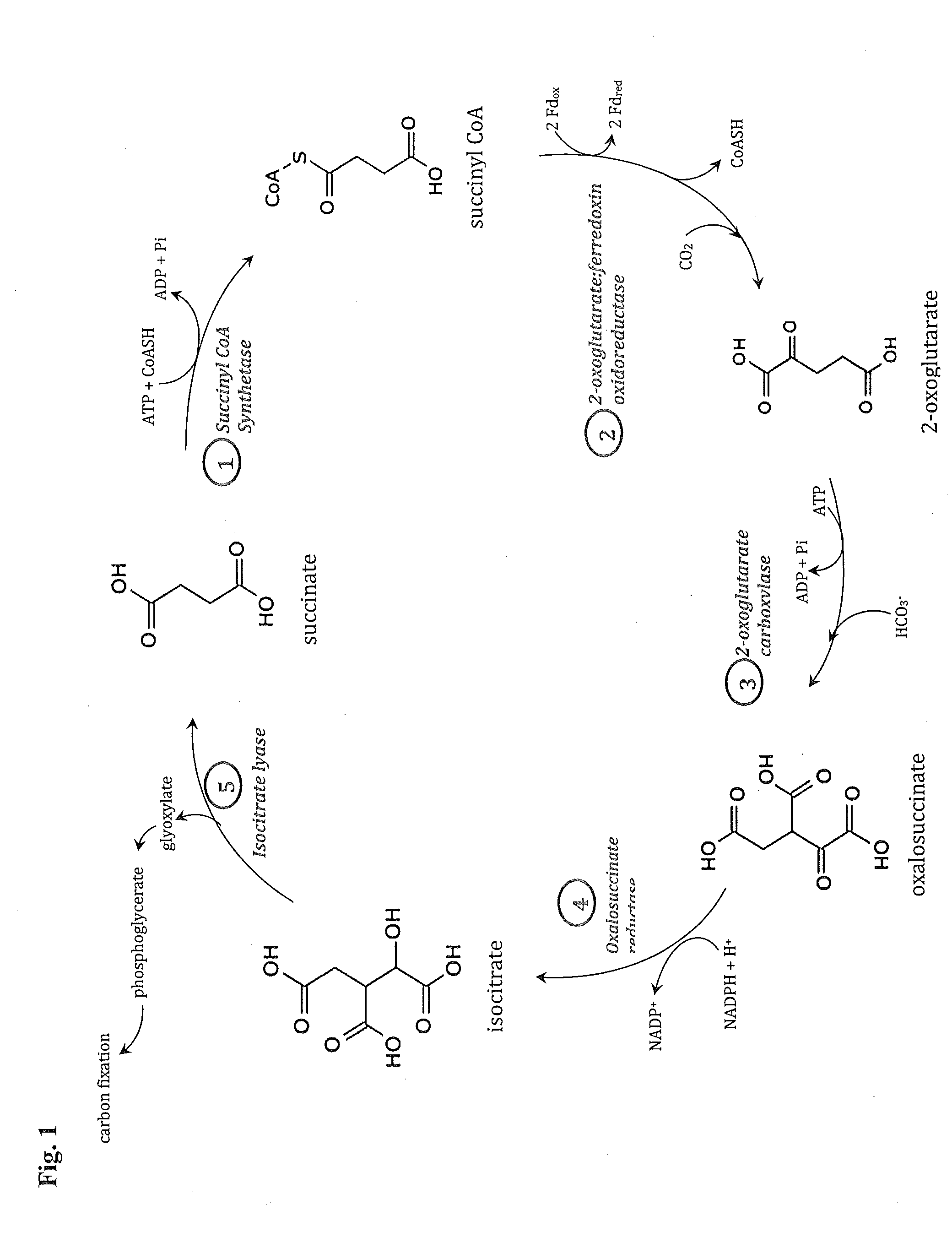
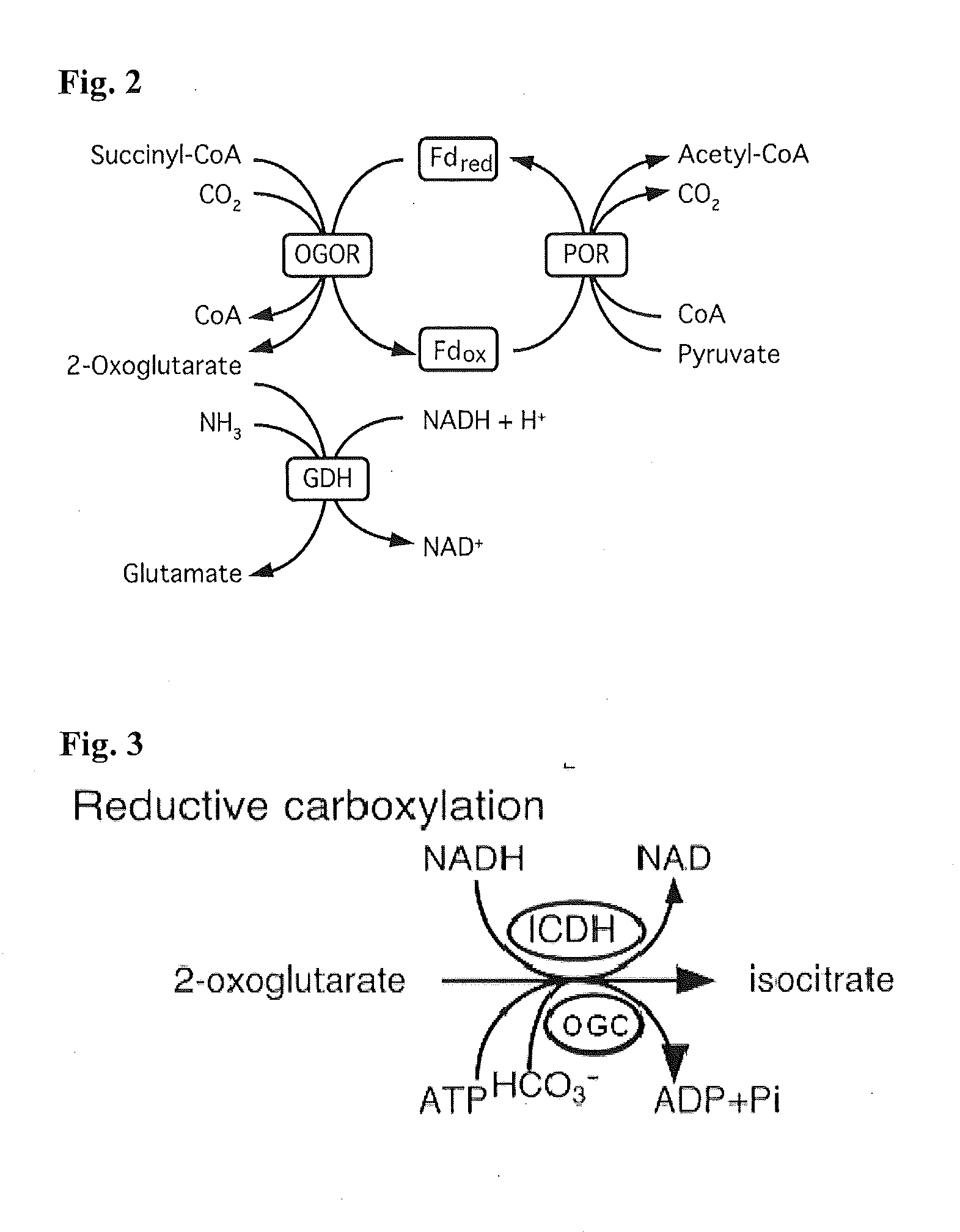
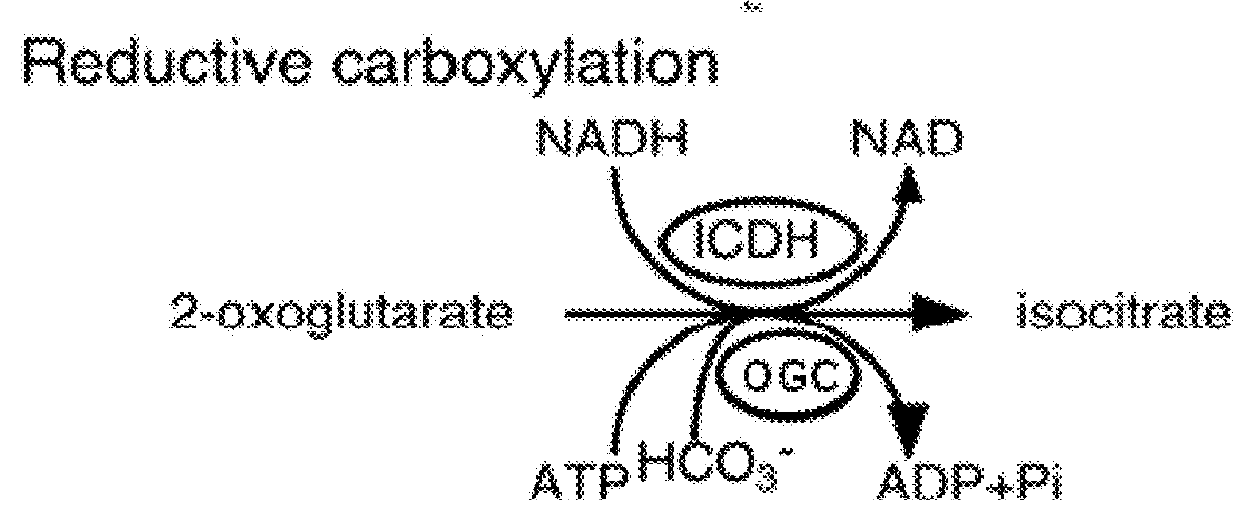
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation and / or increasing biomass production in a plant, comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell one or more heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of succinyl CoA synthetase, 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase, oxalosuccinate reductase and isocitrate lyase to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell expressing the one or more heterologous polynucleotides. The methods further comprise introducing into a plant, plant part or plant cell heterologous polynucleotides encoding polypeptides having the enzyme activity of glyoxylate carboligase and tartronic semialdehyde reductase, and / or heterologous polynucleotides encoding a superoxide reductase from an archaeon species, an aquaporin and / or an inhibitor of cell wall invertase inhibitor. Additionally, transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells are provided as well as products produced from the transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof
InactiveCN102181369AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesGas phaseWild type
The invention discloses a genetic engineering chlamydomonas having increased hydrogen producing capacity and application thereof. The genetic engineering chlamydomonas provided by the invention is a genetic engineering chlamydomonas which is obtained by inhibiting an expression level of ferredoxin-NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) reductase coding genes in a starting chlamydomonas. It is determined by gas chromatography that the hydrogen producing capacity of the genetic engineering chlamydomonas is increased by 6-10 times compared with a wild strain after phosphorus deficiency treatment is carried out for 48 hours. The mutant strain is obtained to lay the basis for industrialization of a microalgal photosynthetic hydrogen production technology.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
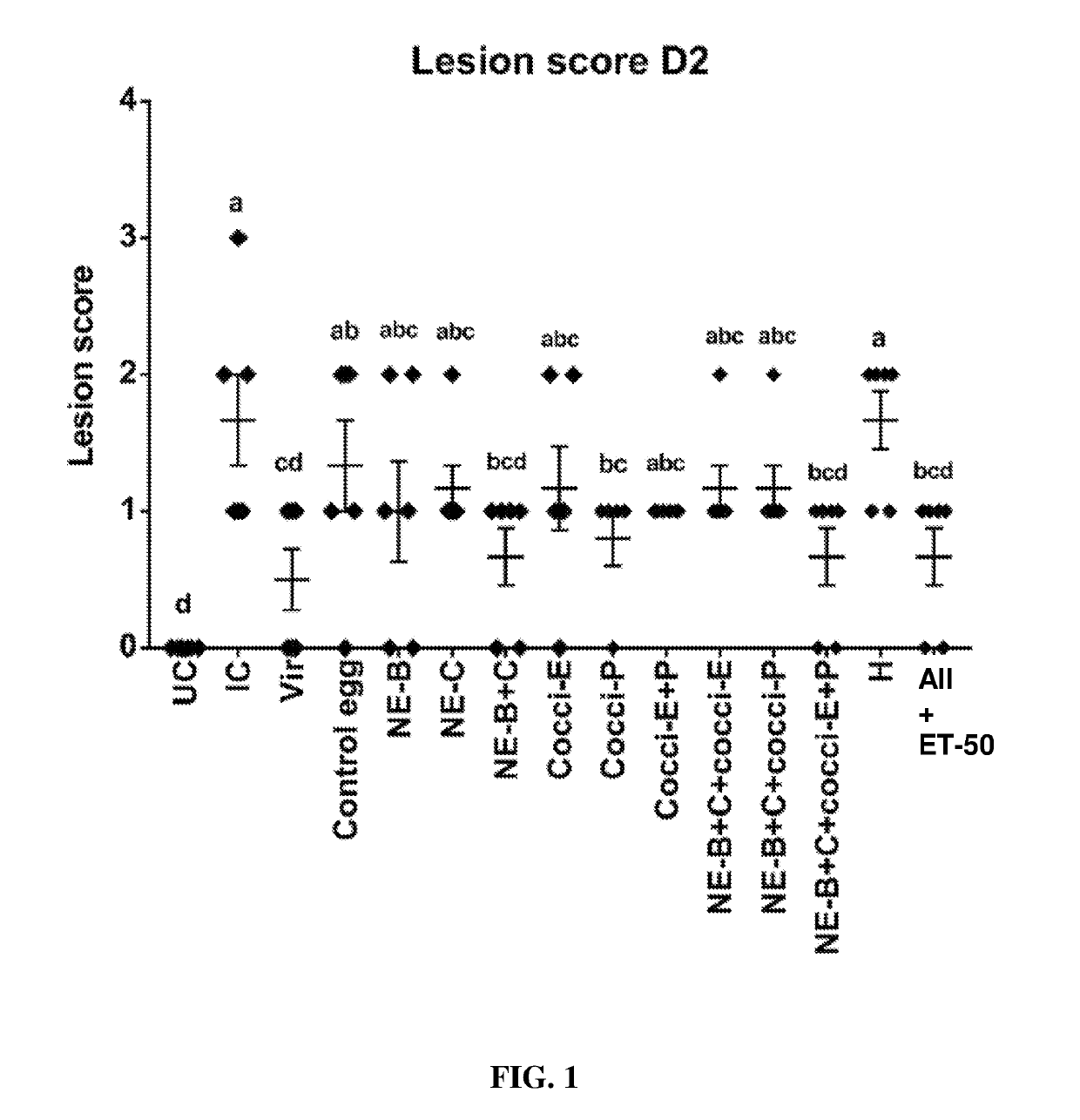
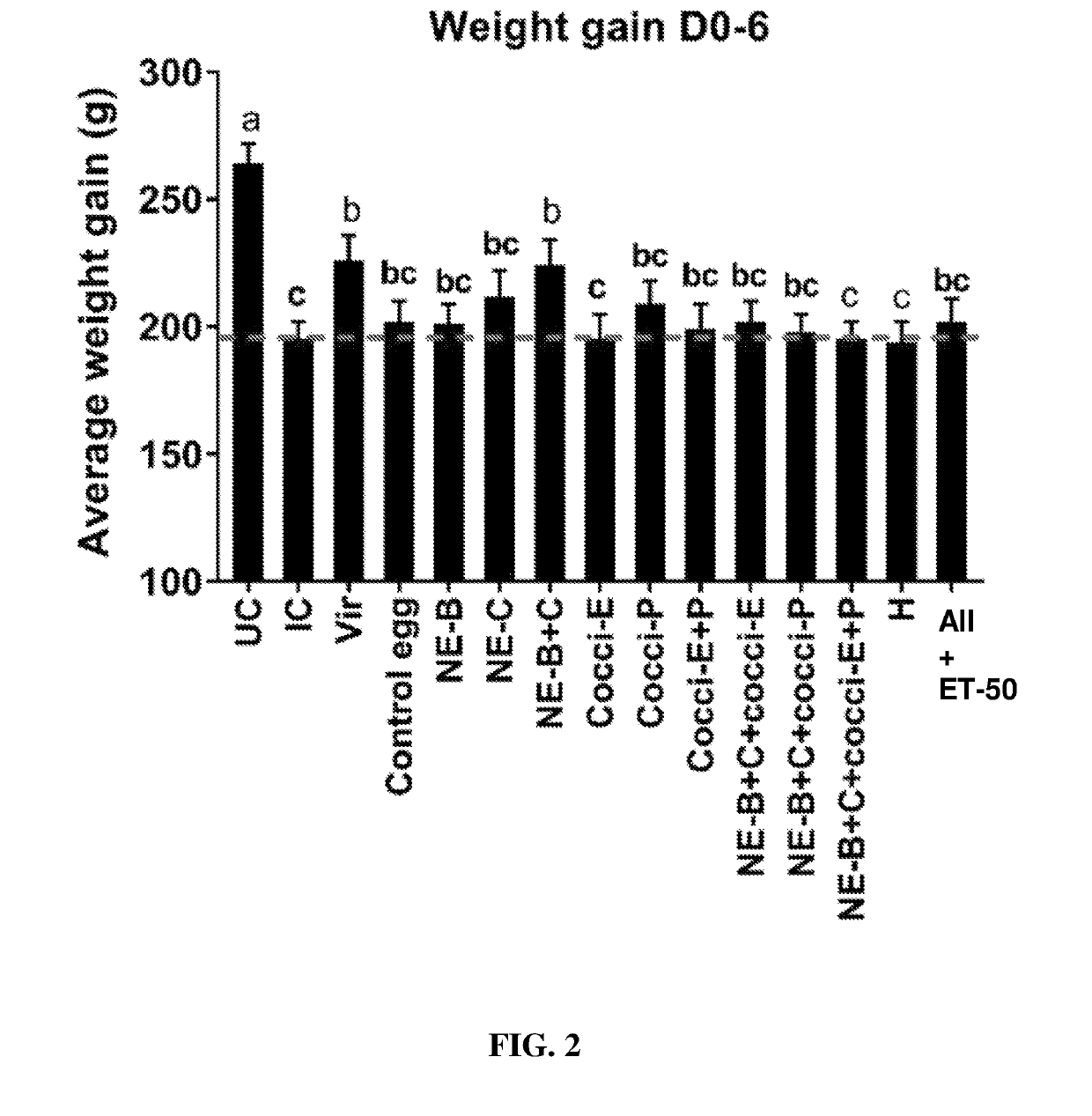
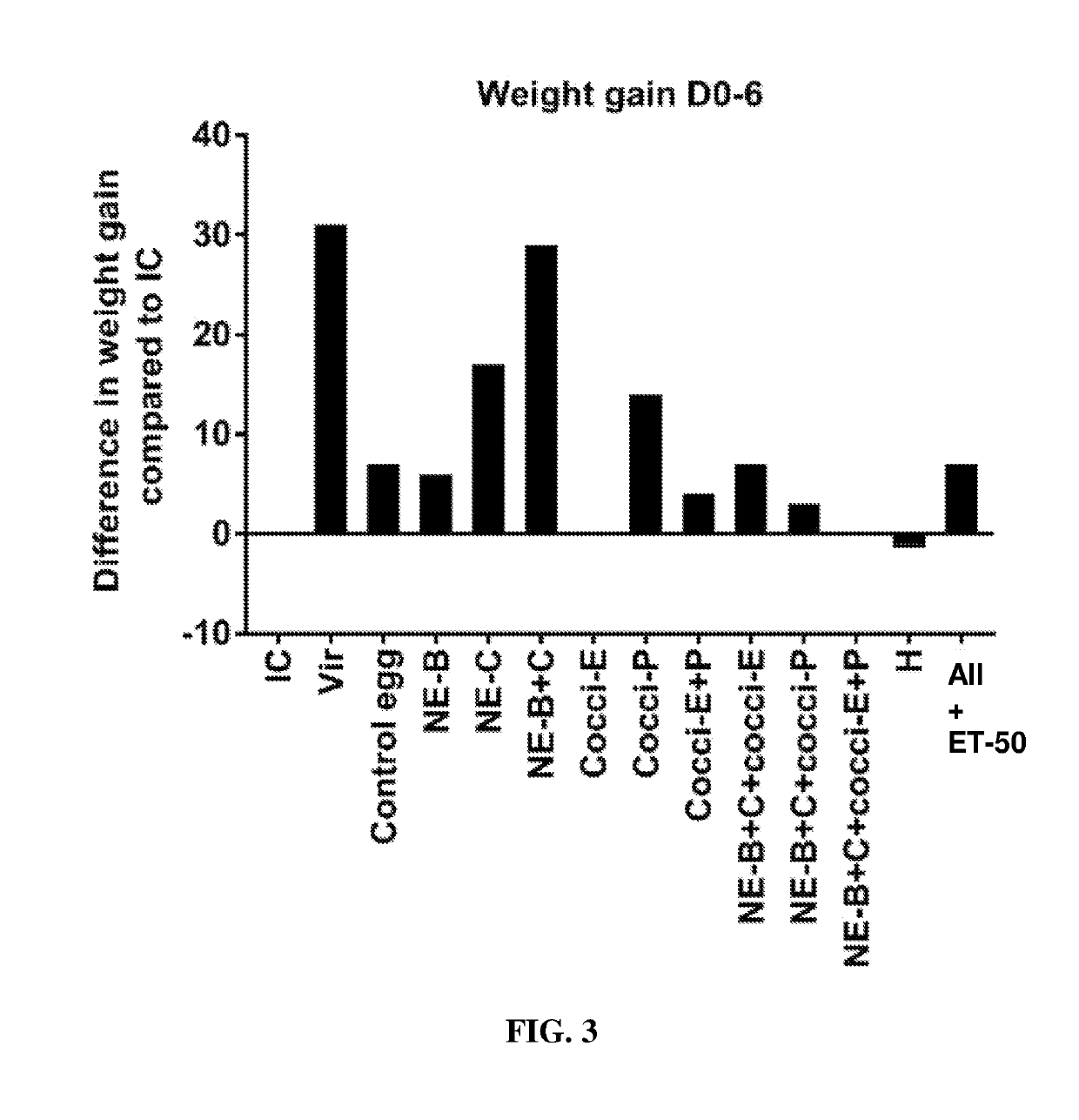
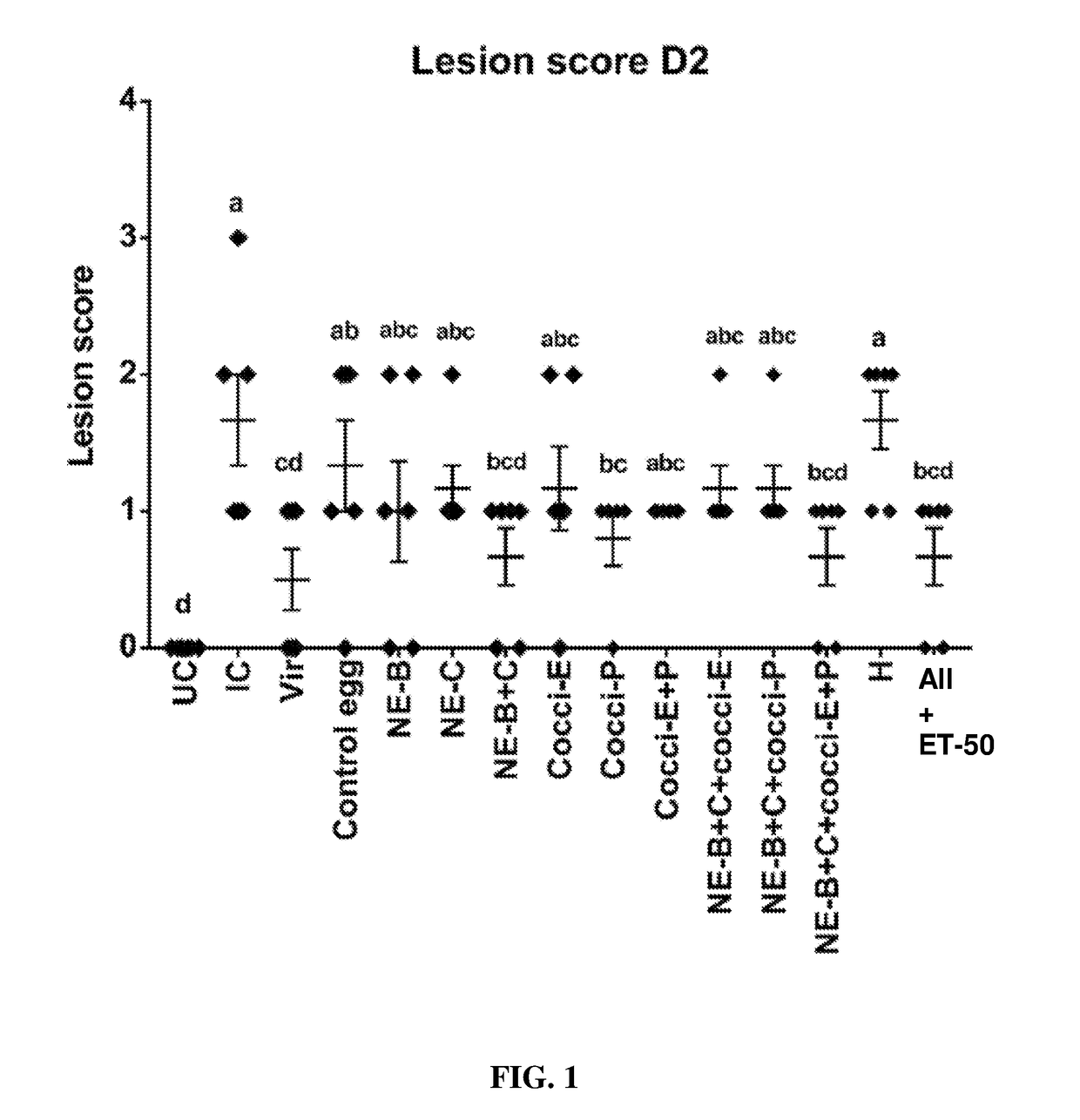
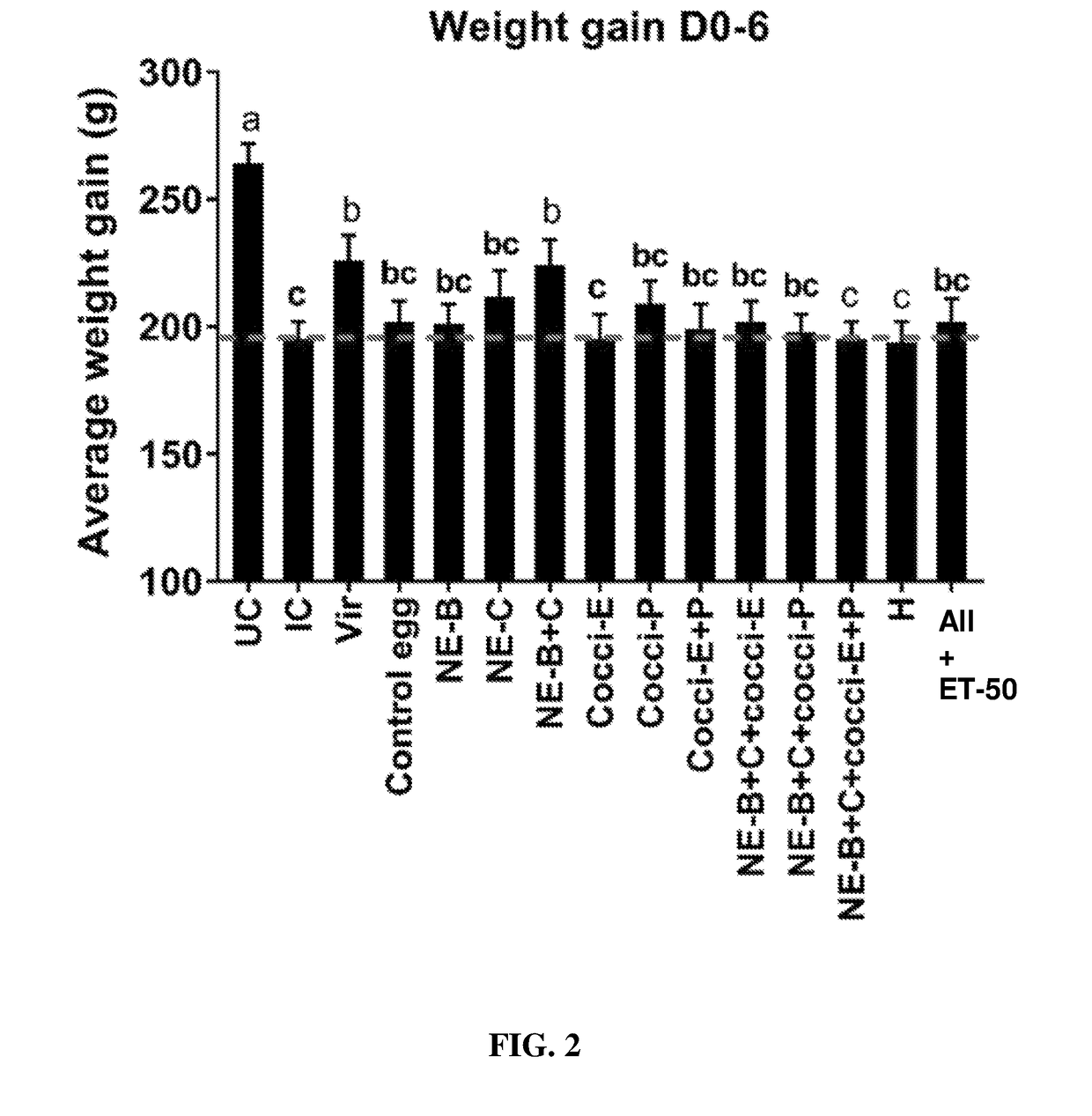
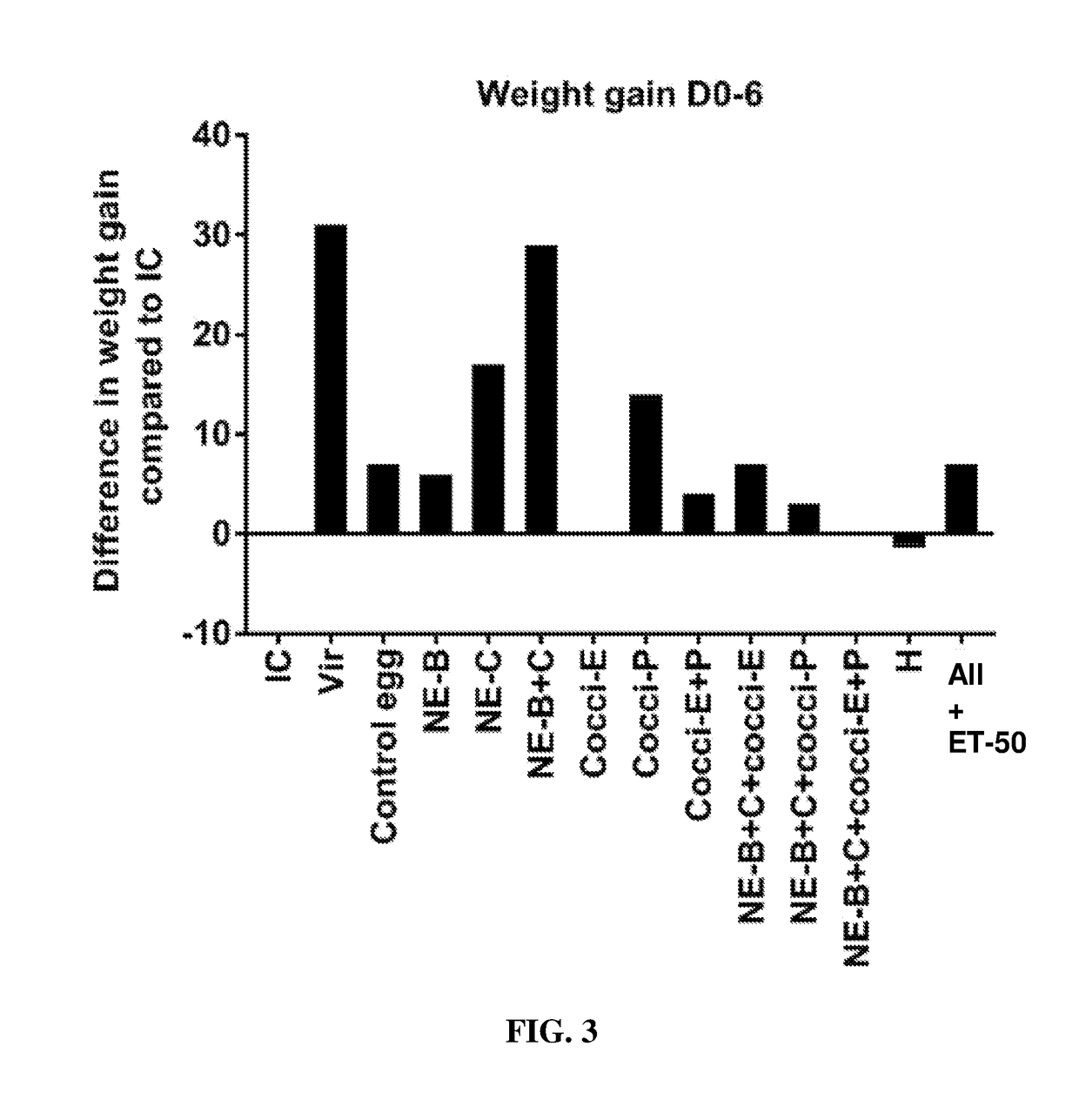
Hyperimmunized egg product for treatment of necrotic enteritis in poultry
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a method for preventing or treating necrotic enteritis by administering a hyperimmunized egg product obtained from an egg-producing animal to an avian. The hyperimmunized egg product may contain an antibody specific to an antigen selected from the group consisting of Clostridium perfringens α-toxin, Clostridium perfringens elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), Clostridium perfringens necrotic enteritis B-like (NetB) toxin, Clostridium perfringens Pyruvate: Ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFO), and Eimeria tenella elongation factor 1-alpha.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC +1
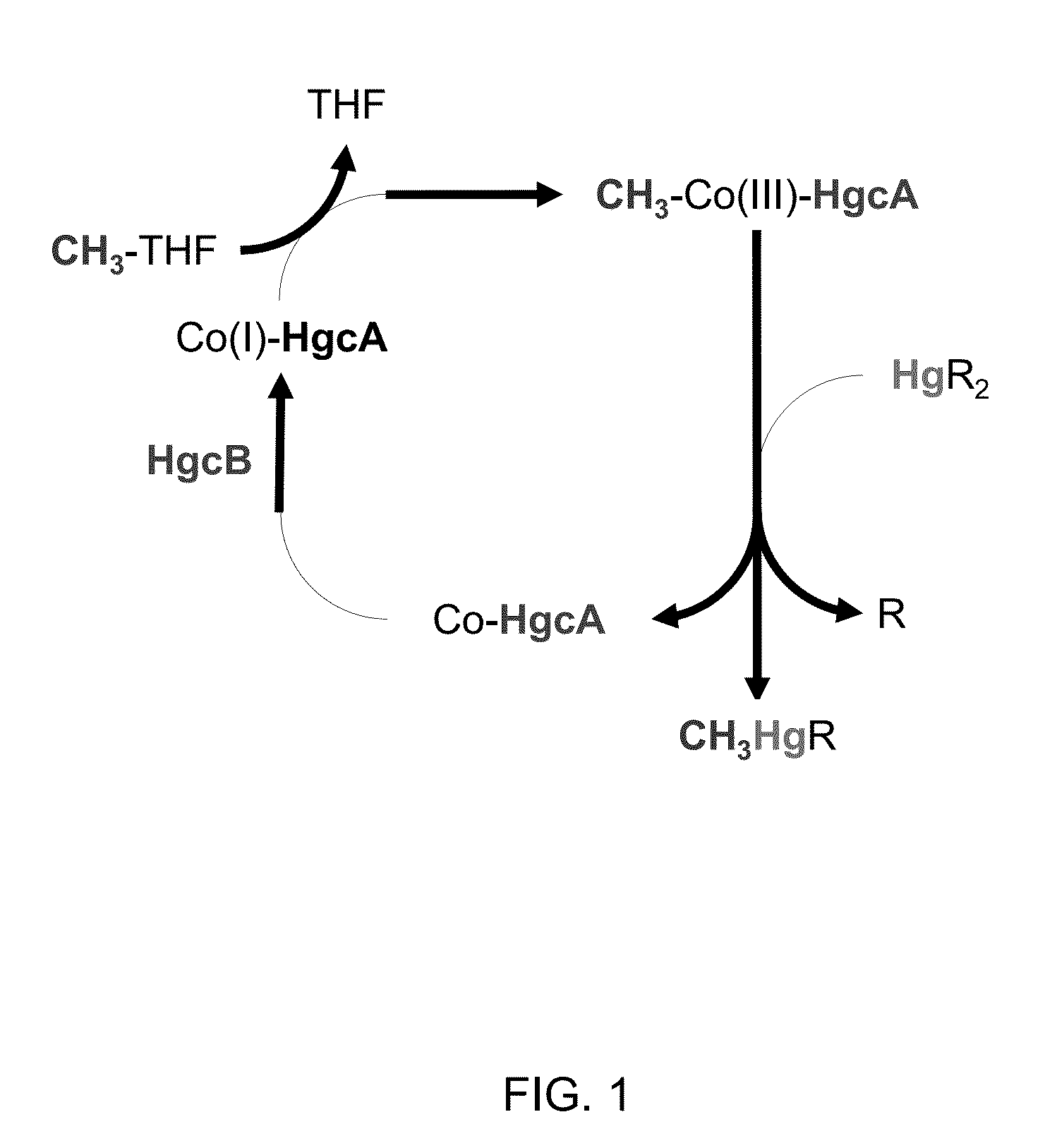
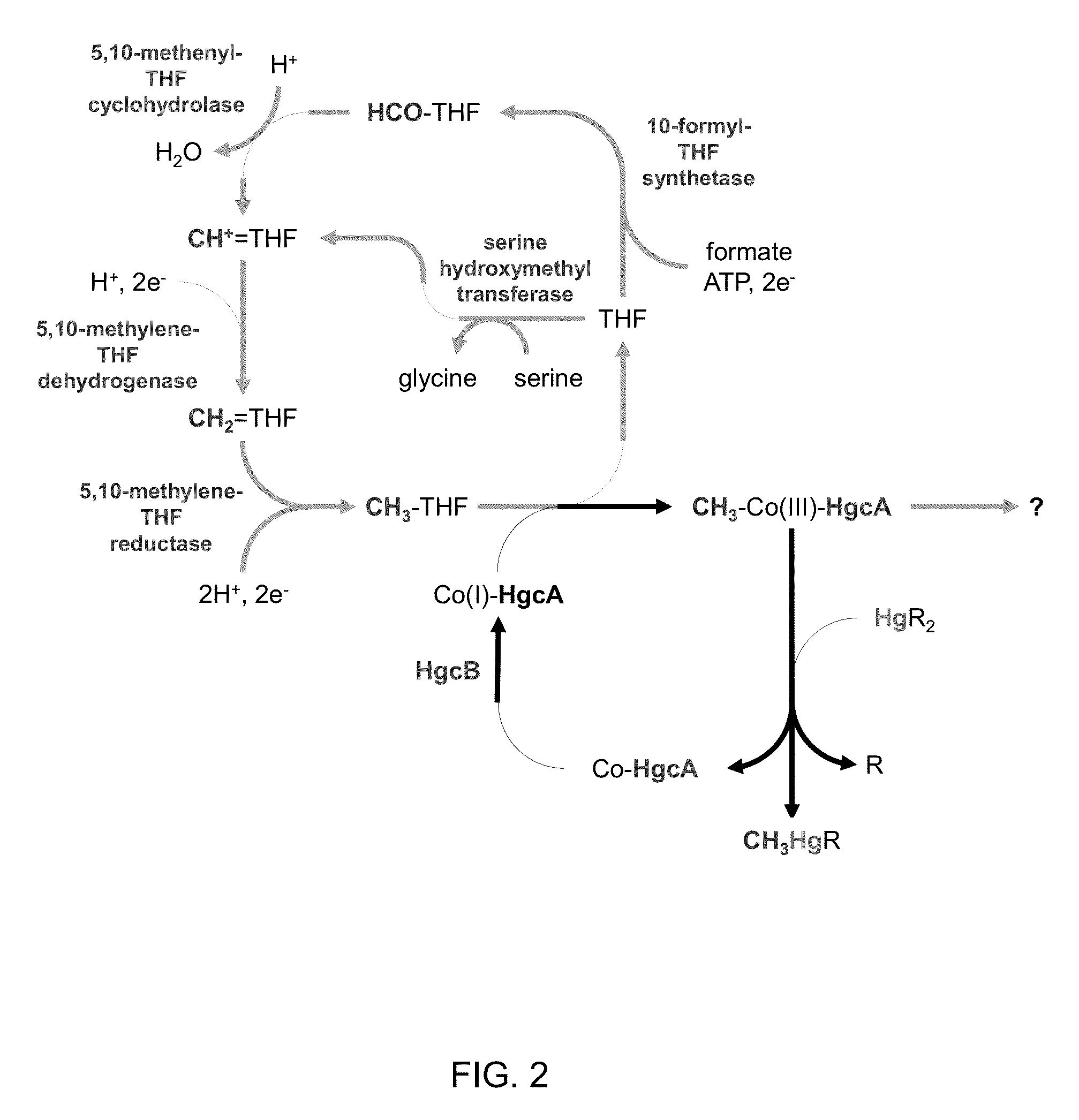
Mercury methylation genes in bacteria and archaea
Two genes required for this mercury methylation have been identified in bacteria and archaea. These genes are the hgcA gene and hgcB, a corrinoid protein that facilitates methyl group transfer to Hg, and a corrinoid protein-associated ferredoxin with two [4Fe-4S] binding motifs involved in generating cob(I)almin, respectively. The invention provides nucleic acid probes and primers for detecting methylmercury and or for assessing mercury methylation potential in environmental, clinical and other samples. The invention also provides antibodies against these proteins, antibodies against these proteins, methods of using the antibodies and methods of biocatalysis.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
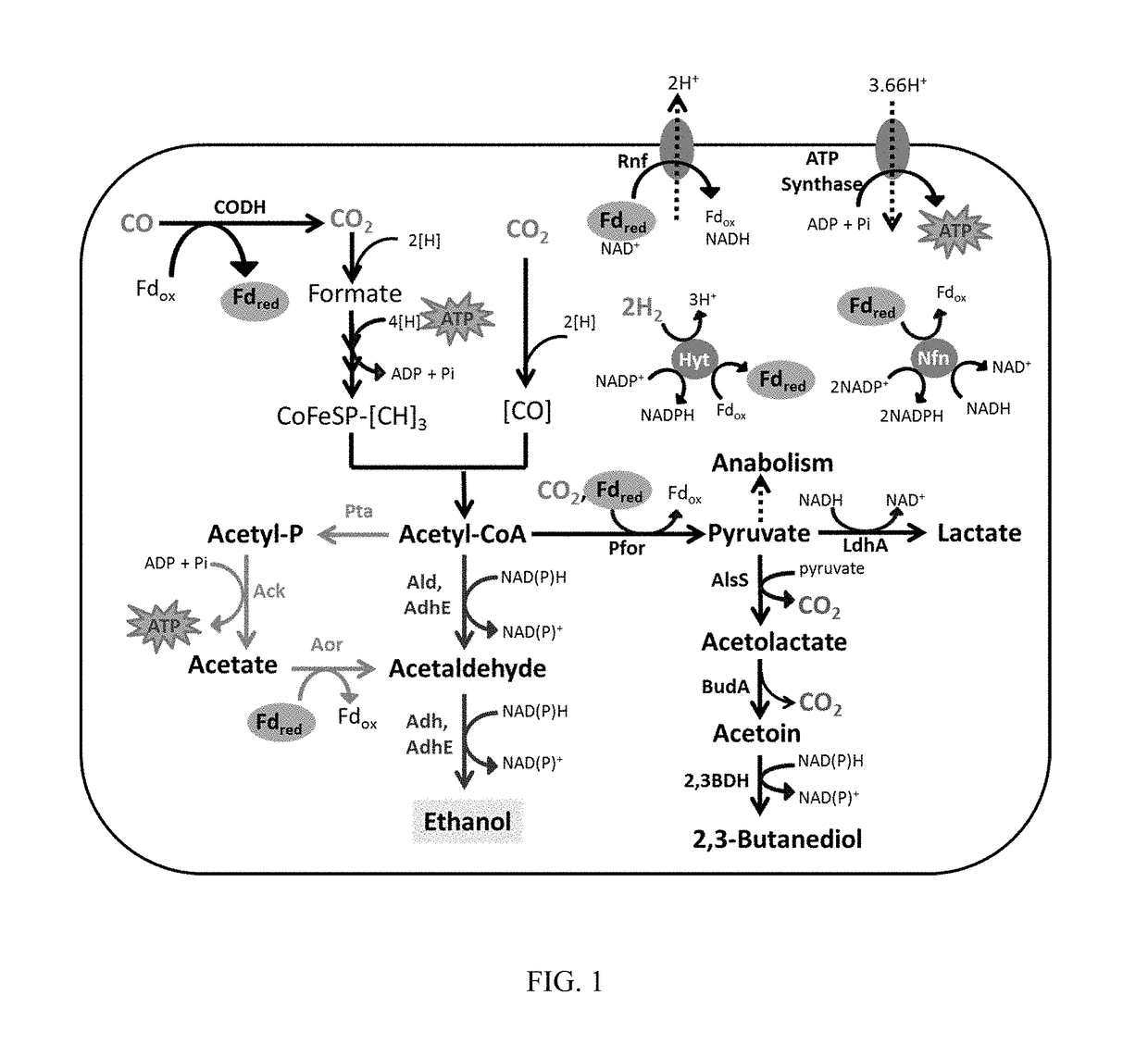
Microorganism with modified aldehyde:ferredoxin oxidoreductase activity and related methods
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring bacterium having decreased or eliminated activity of an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction defined by EC 1.2.7.5, such as aldehyde:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (AOR). Optionally, the bacterium also has decreased or eliminated activity of an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction defined by EC 1.2.1.10 and / or EC 1.1.1.1, such as aldehyde dehydrogenase, alcohol dehydrogenase, or bifunctional aldehyde / alcohol dehydrogenase. The invention further provides methods of producing products by culturing the bacterium in the presence of a gaseous substrate containing one or more of CO, CO2, and H2.
Owner:LANZATECH INC
Creatinine diagnostic/determination reagent (kit) and method for determining concentration of creatinine
InactiveCN101762497AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCreatinine riseEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a creatinine diagnostic / determination reagent (kit) adopting an enzymatic colorimetric method and an enzyme coupling method and simultaneously relates to a method for determining concentration of creatinine and components of the reagent, belonging to the technical field of medical test and determination. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises buffer solution, coenzyme, oxidized ferredoxin, creatinine deiminase, ferredoxin nitrite reductase, nitrate reductase and stabilizing agents. The samples and the reagent are mixed according to certain volume ratio and then carry out a series of enzymatic reactions, then the reactants are placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to test the degree of absorbance rise at the dominant wavelength of 340nm, thus measuring and calculating the concentration of creatinine.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
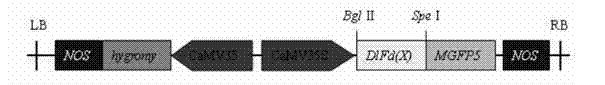
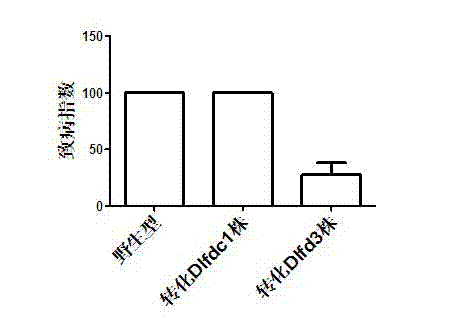
Method for improving disease resistance by transforming arethusa with longan ferredoxin gene
InactiveCN103898156AHigh transplant survival rateImproves resistance to soft rotFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyOncidium
The invention provides a method of improving disease resistance by transforming arethusa with longan ferredoxin gene and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The longan ferredoxin gene (Dlfd3) (Register number: JF733784) is guided to arethusa oncidium by means of a transgenic technology, and the obtained transformed plant represents higher transplanting survival rate and disease resisting capability. Compared with wild plants, the soft rot resistant capability of the transgenic plant is improved from high touch soft rot (Di=100) to intermediate soft rot resistance (Di=27.5). The transplanting survival rate is improved from 79.3% to 95.7%, thereby realizing extremely significant difference.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV +1
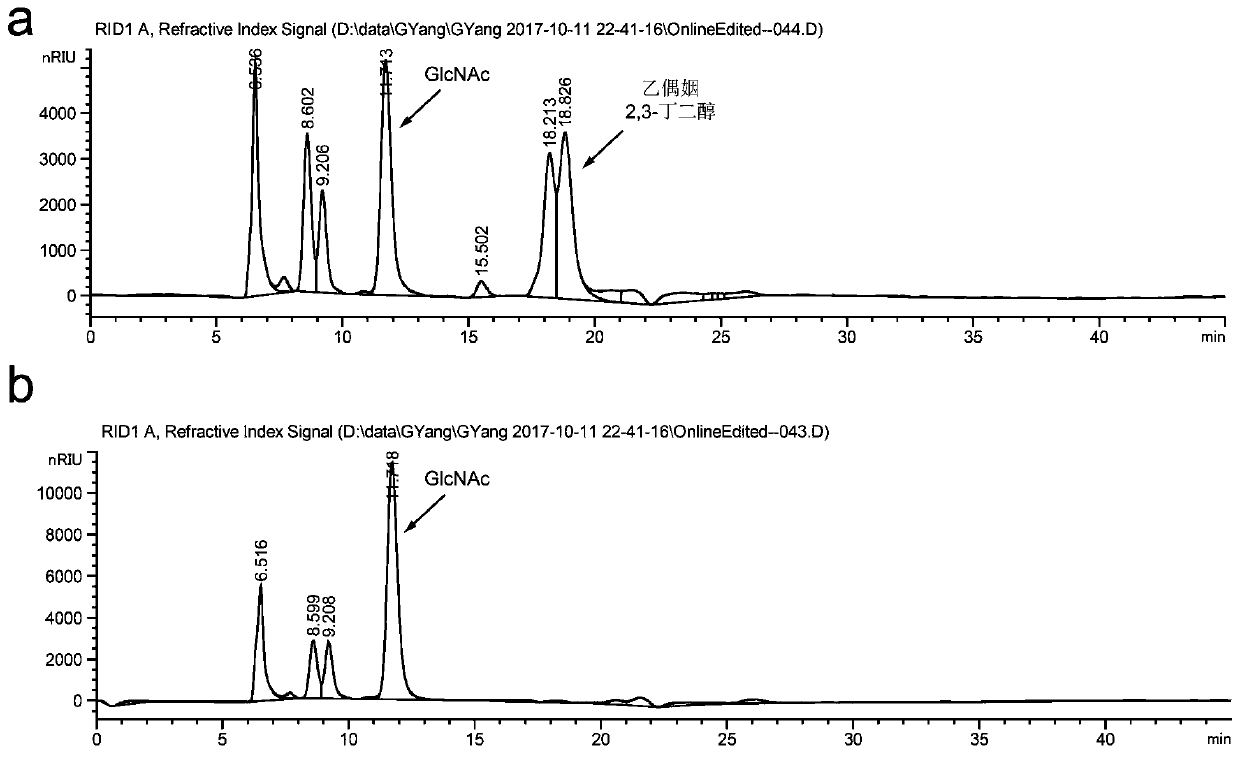
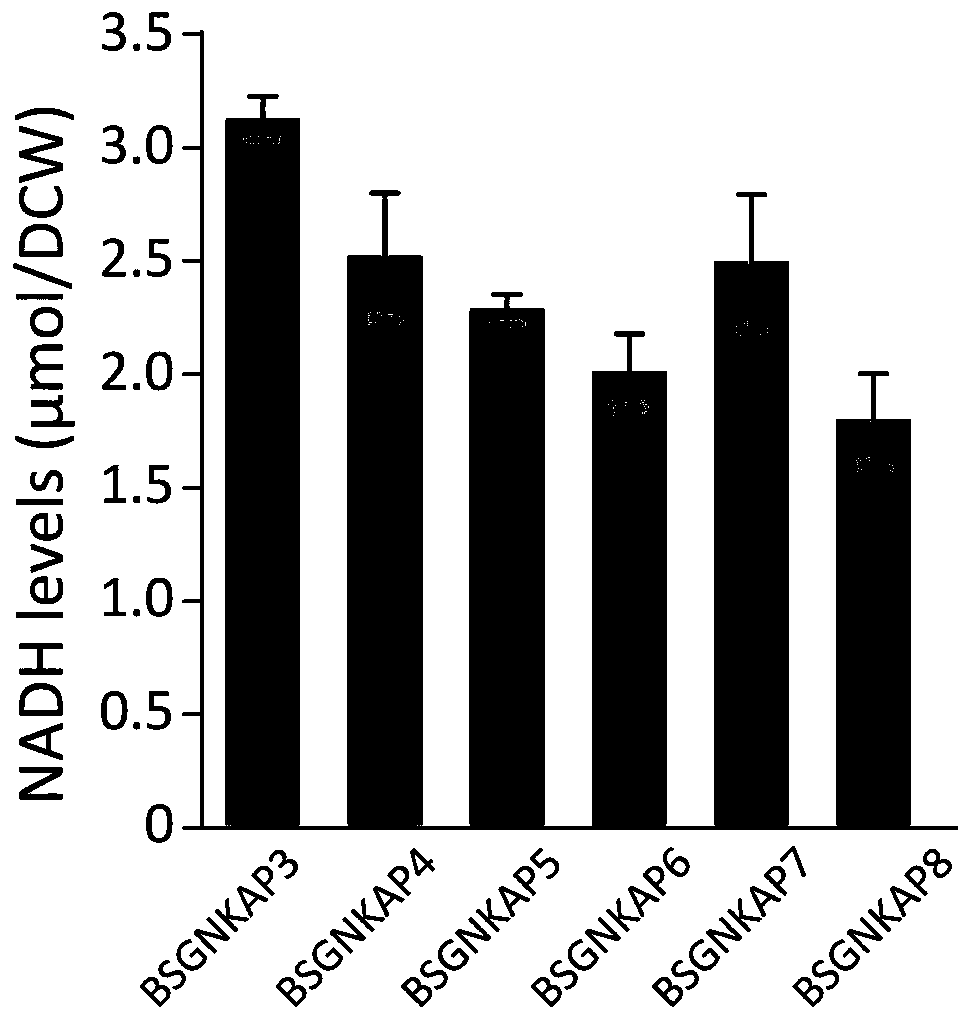
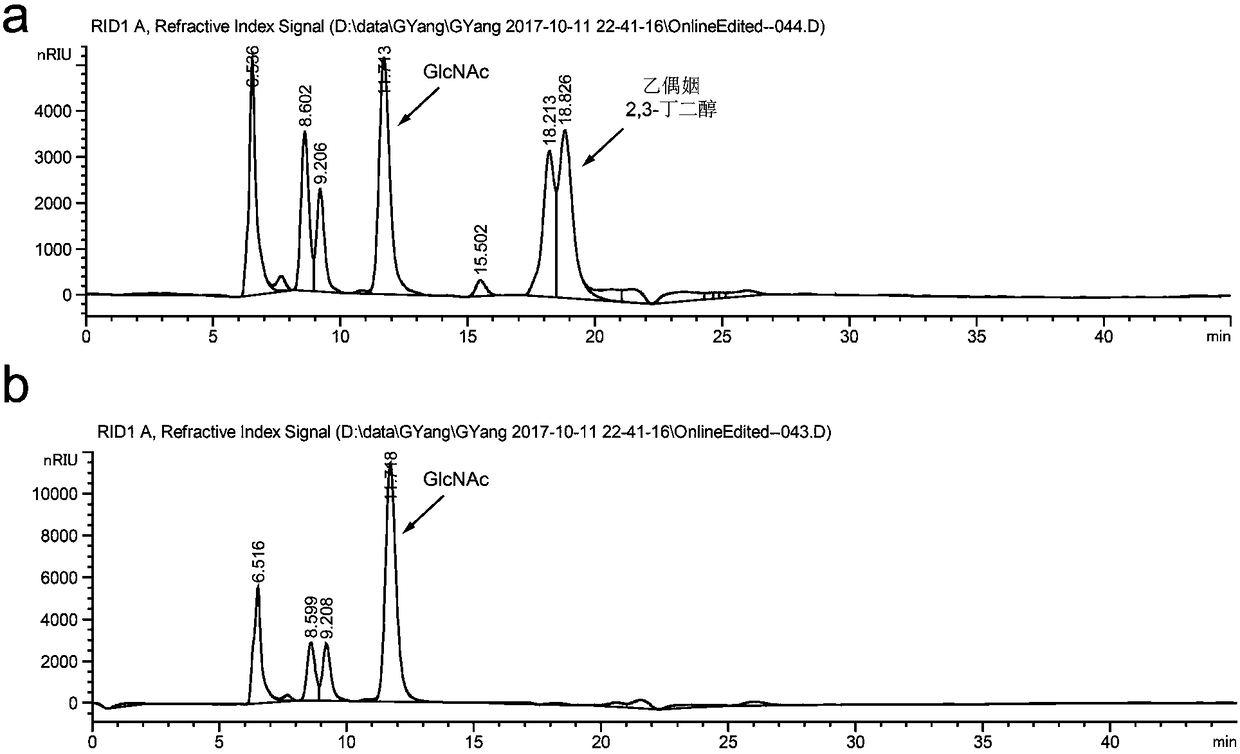
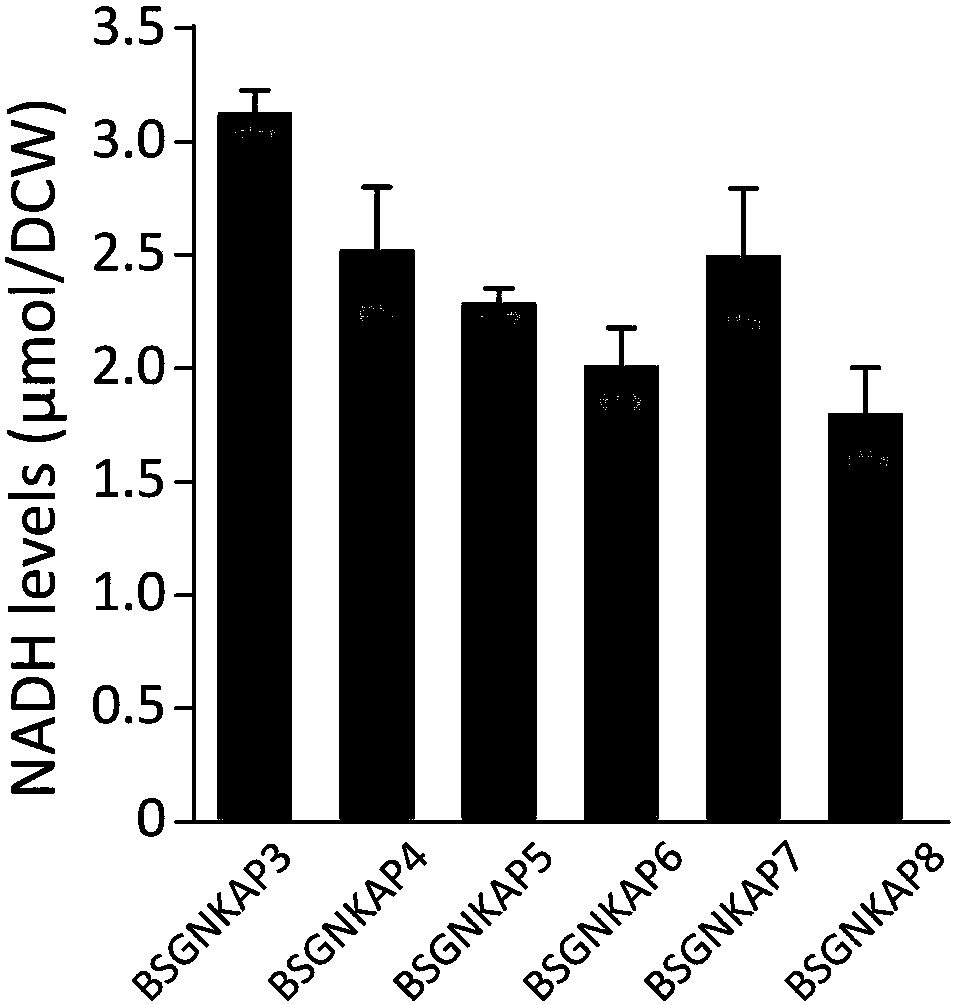
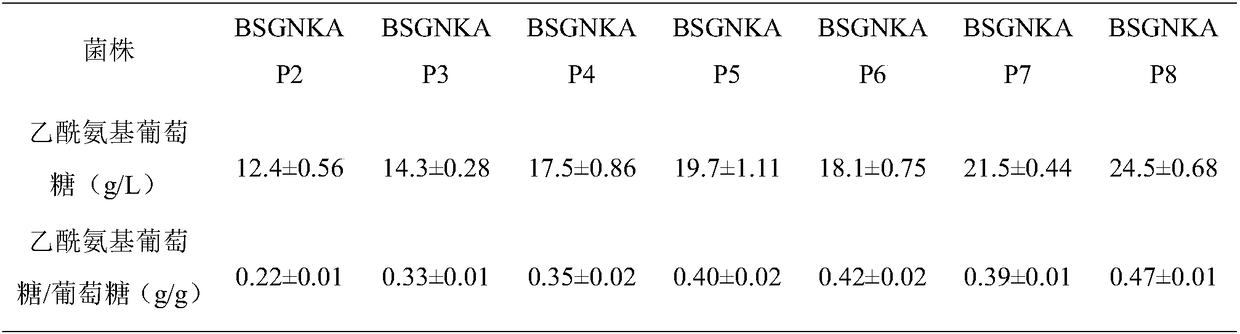
Method for promoting synthesis of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN108424869AEasy to synthesizeInhibit synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesQuinonePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for promoting synthesis of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The method is characterized in that a recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGNKAP2 is taken as a starting strain, and pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA from bacillus cereus is exogenously introduced, so that metabolism overflow of bacillus subtilis central carbon iseliminated and synthesis of acetoin as a byproduct is avoided; furthermore, five exogenous reductive metabolism reactions are introduced to replace a glycolytic pathway and a reaction of producing NADH in tricarboxylic acid cycle and reconstruct intracellular reductive metabolism, wherein the five exogenous reductive metabolism reactions specifically comprise glyceraldehydes-3-ferredoxin phosphate dehydrogenas, isocitric acid NAD<+> dehydrogenas, malic acid quinone dehydrogenas, ketonic acid ferredoxin oxidordeuctase and nitrogenase ferritin. In the shake-flask fermentation process of using acomplex medium, the yield of a recombinant strain BSGNKAP8 acetylglucosamine is 24.50g / L, and the yield of acetylglucosamine / glucose is 0.469g / L, which are 1.97 times and 2.13 times that of the starting strain BSGNKAP2.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Homocysteine diagnosing/measuring reagent (kit) and homocysteine concentration measuring method
InactiveCN101750301AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a homocysteine diagnosing / measuring reagent (kit) using the technologies of an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme linkage method. At the same time, the invention also relates to a homocysteine concentration measuring method, the reagent composition and reagent ingredients, which belong to the technical field of medical detection and measurement. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises the following ingredients: a buffer solution, cozymase, cozymase A, oxidized form ferredoxin, catechol, chlorine, homocysteine desulfhydrase, 2-oxobutyryl synthetase, chlorobenzoic acid-1, 2-dioxygenase and stabilizing agents. The method has the following steps: mixing samples and the reagent by the certain volume percent for making the samples and the reagent take a series of enzymatic reaction, and then, placing reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the rising degree of the light absorbancy in the position with the main wave length of 340 nm, so the concentration of the homocysteine can be measured and calculated.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
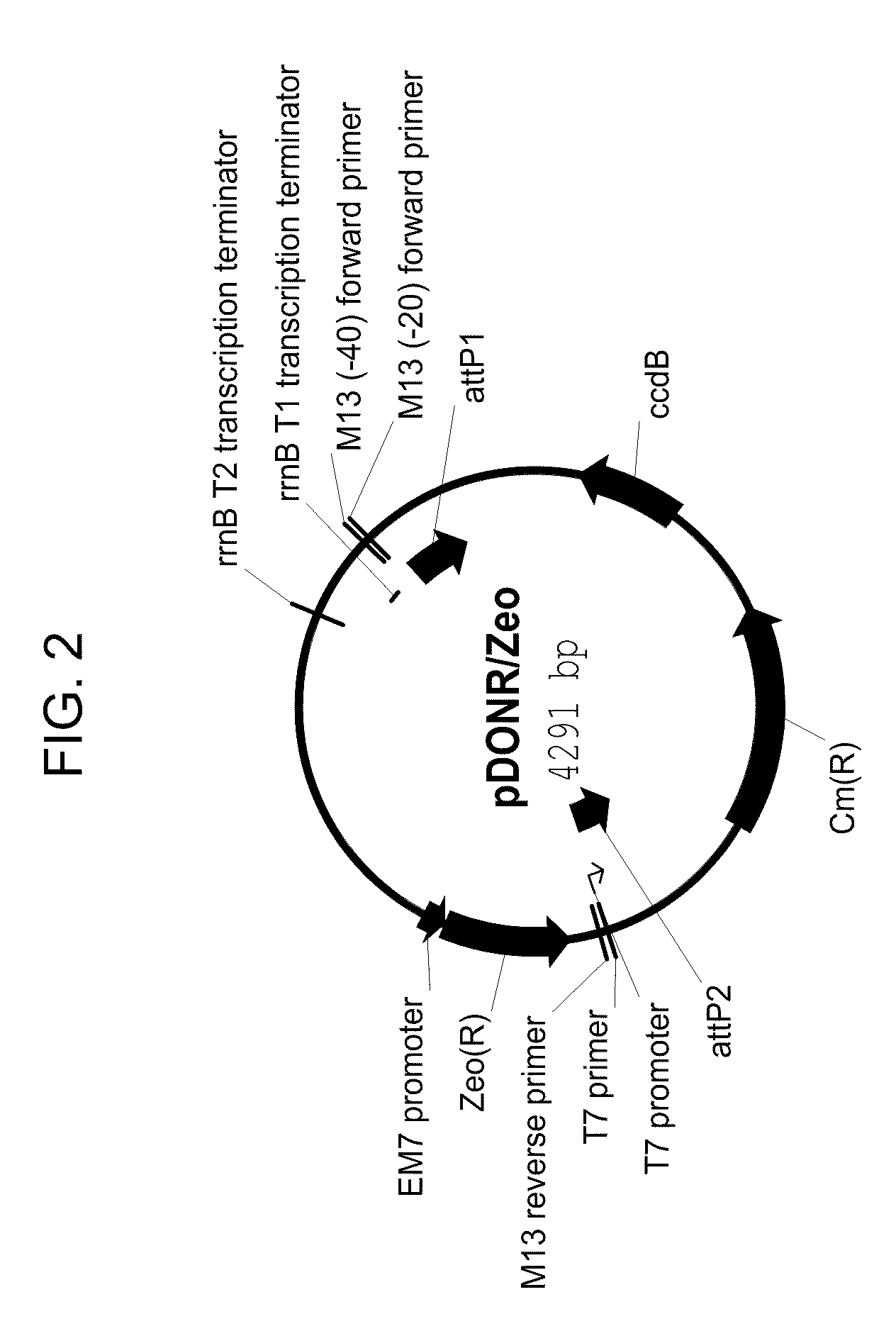
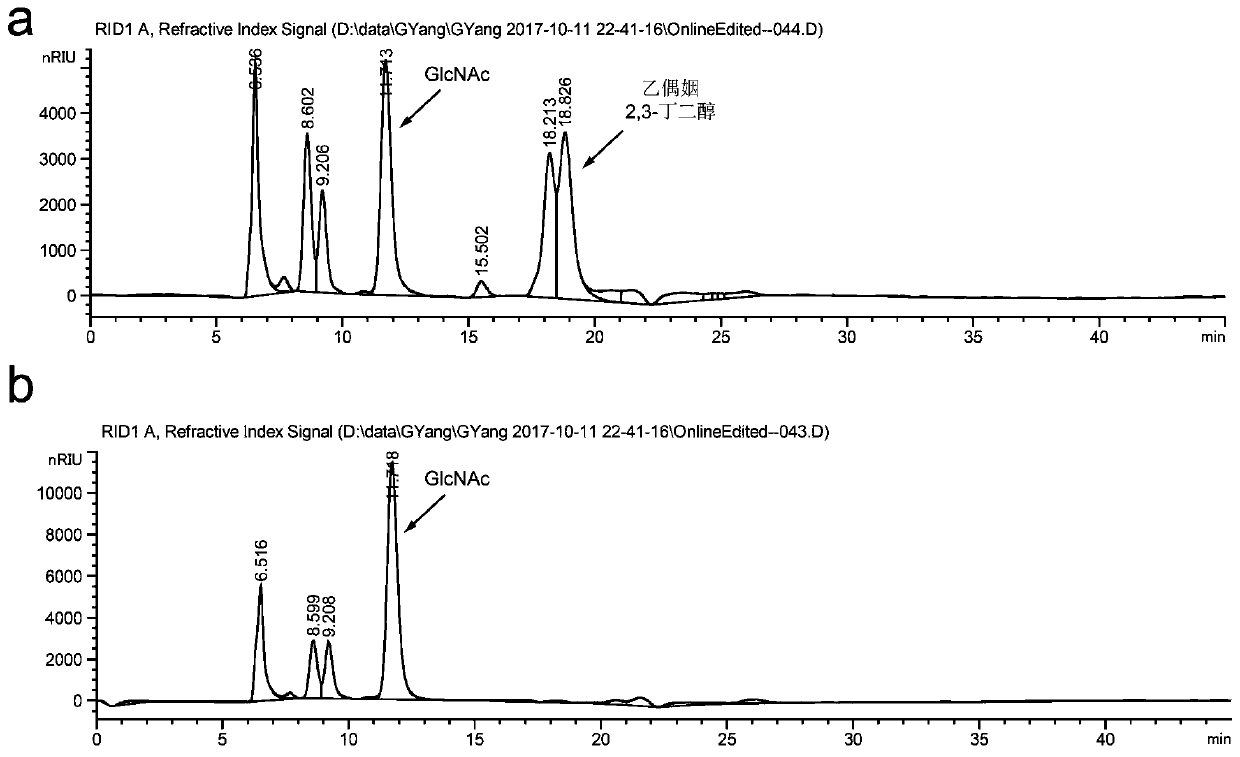
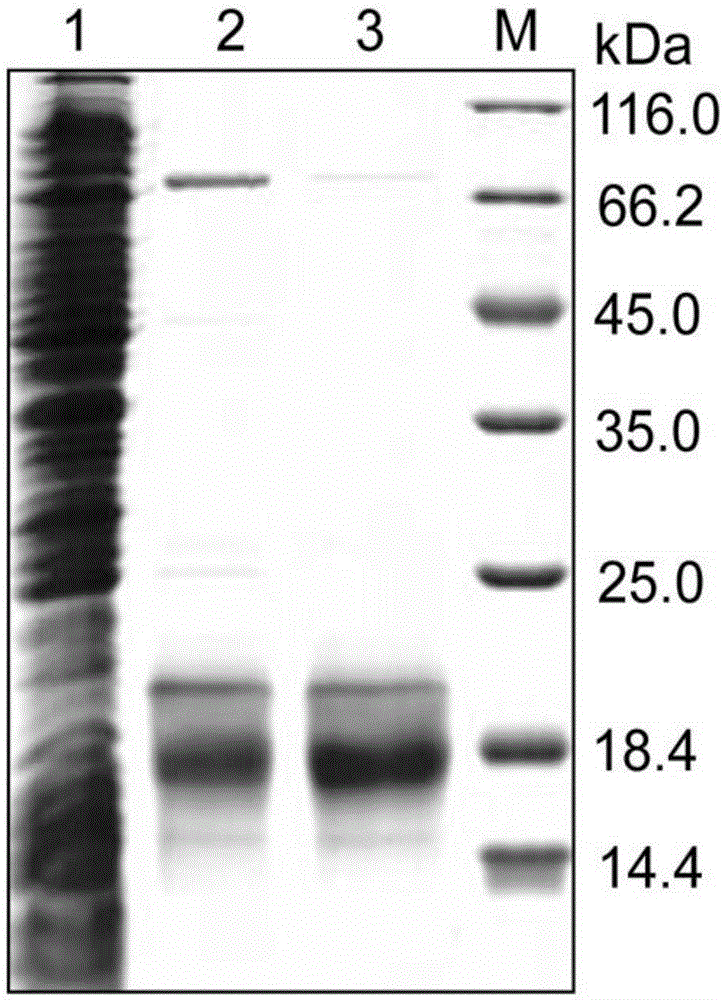
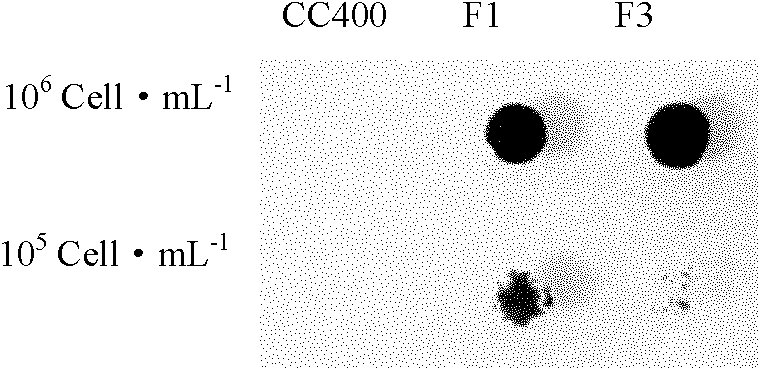
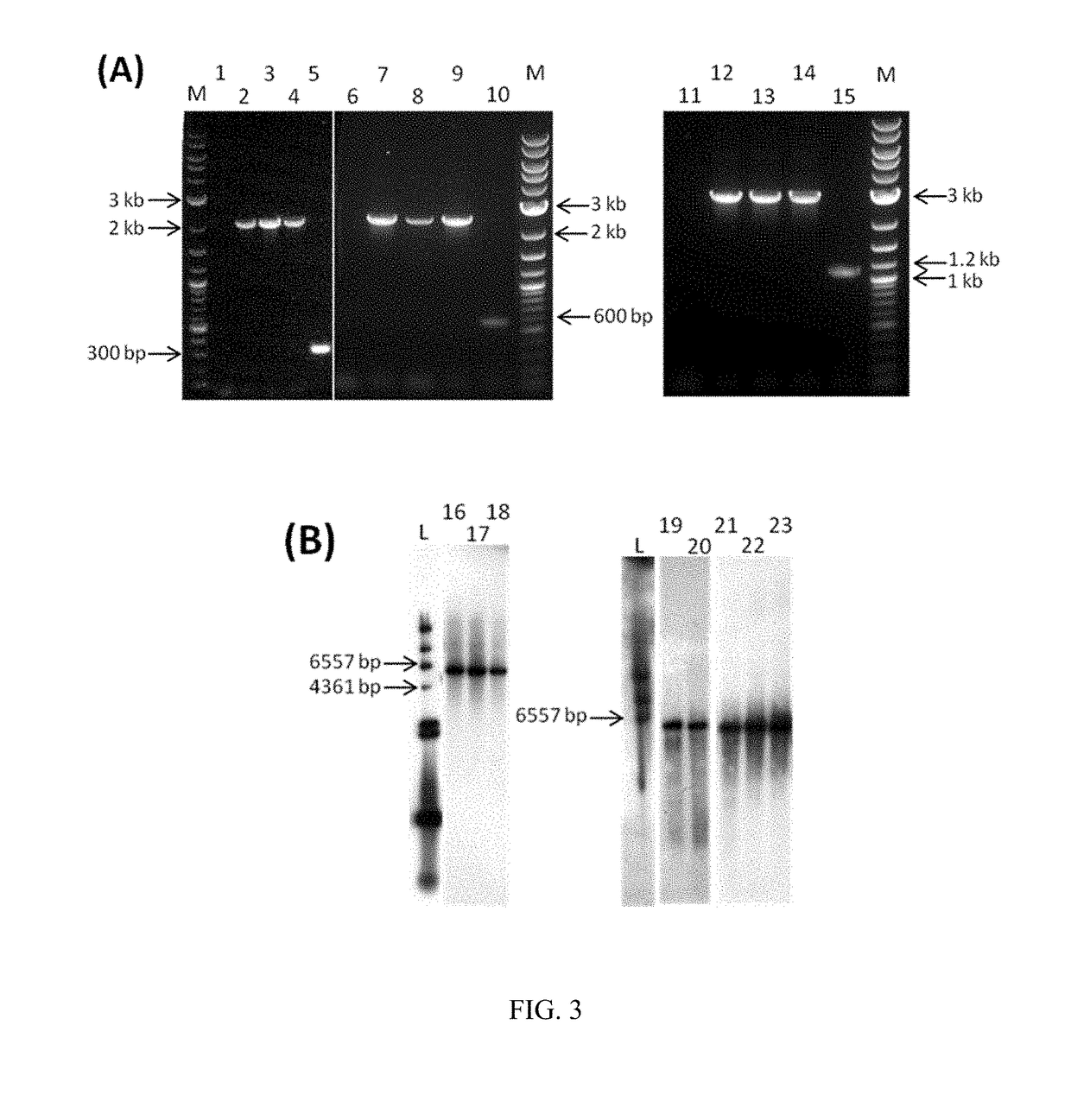
Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin
InactiveCN105274042AIncrease final yieldHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses a recombinant Escherichia coli. The strain contains a 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and is named as Escherichia coli pCodonPlus / pRKISC / pET51b-2[4Fe4S]Fd which is obtained by the steps of connecting the 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin gene into a pET51b carrier to prepare a recombinant plasmid named as pET51b-2[4Fe4S], and transferring the prepared recombinant plasmid to E.coli C41(DE3) containing pCodonPlus and pRKISC plasmids. The invention also discloses application of the recombinant Escherichia coli to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin. Experiments prove that each litre of fermented cultures can be used for generating 3.5mg of purified 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin, and the yield is far higher than 0.5mg of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin purified from wild bacteria, and therefore, the recombinant Escherichia coli disclosed by the invention has a favorable application prospect in industrial production.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICINE OF SAMS
Synthetic pathway for biological carbon dioxide sequestration
ActiveUS20180163220A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionVectorsClimate change adaptationPlant cellFerredoxin
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation and / or increasing biomass production in a plant, comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell heterologous polynucleotides encoding (1) a succinyl CoA synthetase, (2) a 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, (3) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase, (4) an oxalosuccinate reductase, or (5) an isocitrate lyase, or (6) a succinyl CoA synthetase and a 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase, (7) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase and an oxalosuccinate reductase polypeptide, and / or (8) a 2-oxoglutarate carboxylase polypeptide, an oxalosuccinate reductase polypeptide and an isocitrate lyase polypeptide to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell, wherein said heterologous polynucleotides are from a bacterial and / or an archaeal species. Additionally, transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells are provided as well as products produced from the transformed plants, plant parts, and / or plant cells.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
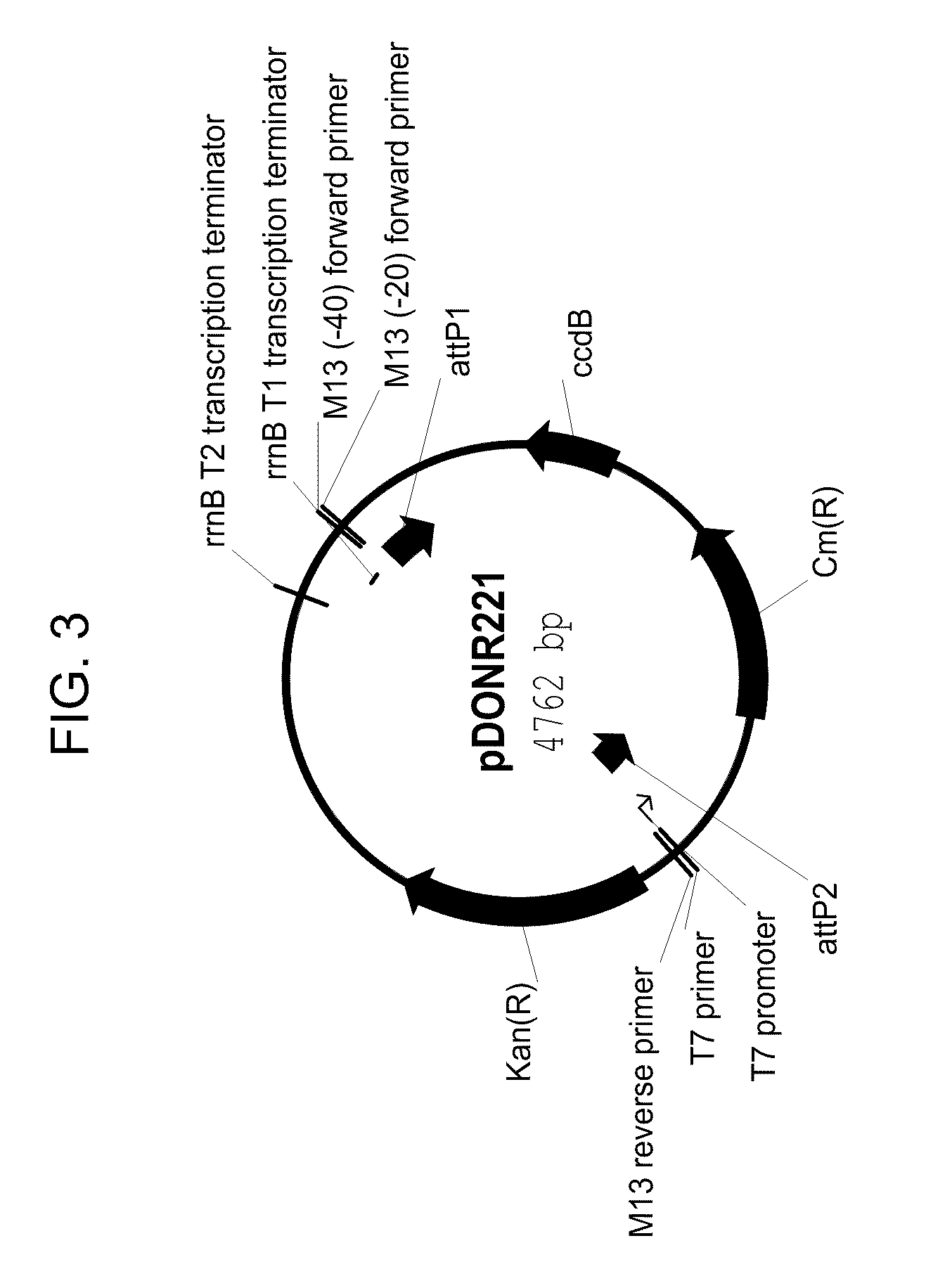
Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli
InactiveCN105349480ABuild completeIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin. The recombinant Escherichia coli is named as Escherichia coli pCodonPlus / pRKISC / pETDuet-[2Fe2S]Fd and contains [2Fe2S] ferredoxin genes. Nucleotide sequences of the recombinant Escherichia coli are shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The [2Fe2S] ferredoxin genes are connected into pETDuet-1 carriers to obtain recombinant plasmids of the recombinant Escherichia coli, and the obtained recombinant plasmids are named as pETDuet-[2Fe2S] and are transferred into E.coli C41(DE3) with pCodonPlus and pRKISC plasmids to obtain the recombinant Escherichia coli. The invention further discloses application of the recombinant Escherichia coli to fermenting and producing the [2Fe2S] ferredoxin. The recombinant Escherichia coli and the application have the advantages that as proved by experiments, 40 mg of purified [2Fe2S] ferredoxin can be ultimately obtained from each liter of fermentation culture, the yield of the purified [2Fe2S] ferredoxin is far higher than previously reported 2mg yield of [2Fe2S] ferredoxin expressed in existing recombinant Escherichia coli and 0.2mg yield of [2Fe2S] ferredoxin purified from wild fungi, and the recombinant Escherichia coli is predicted to have an excellent application prospect in industrial production.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICINE OF SAMS
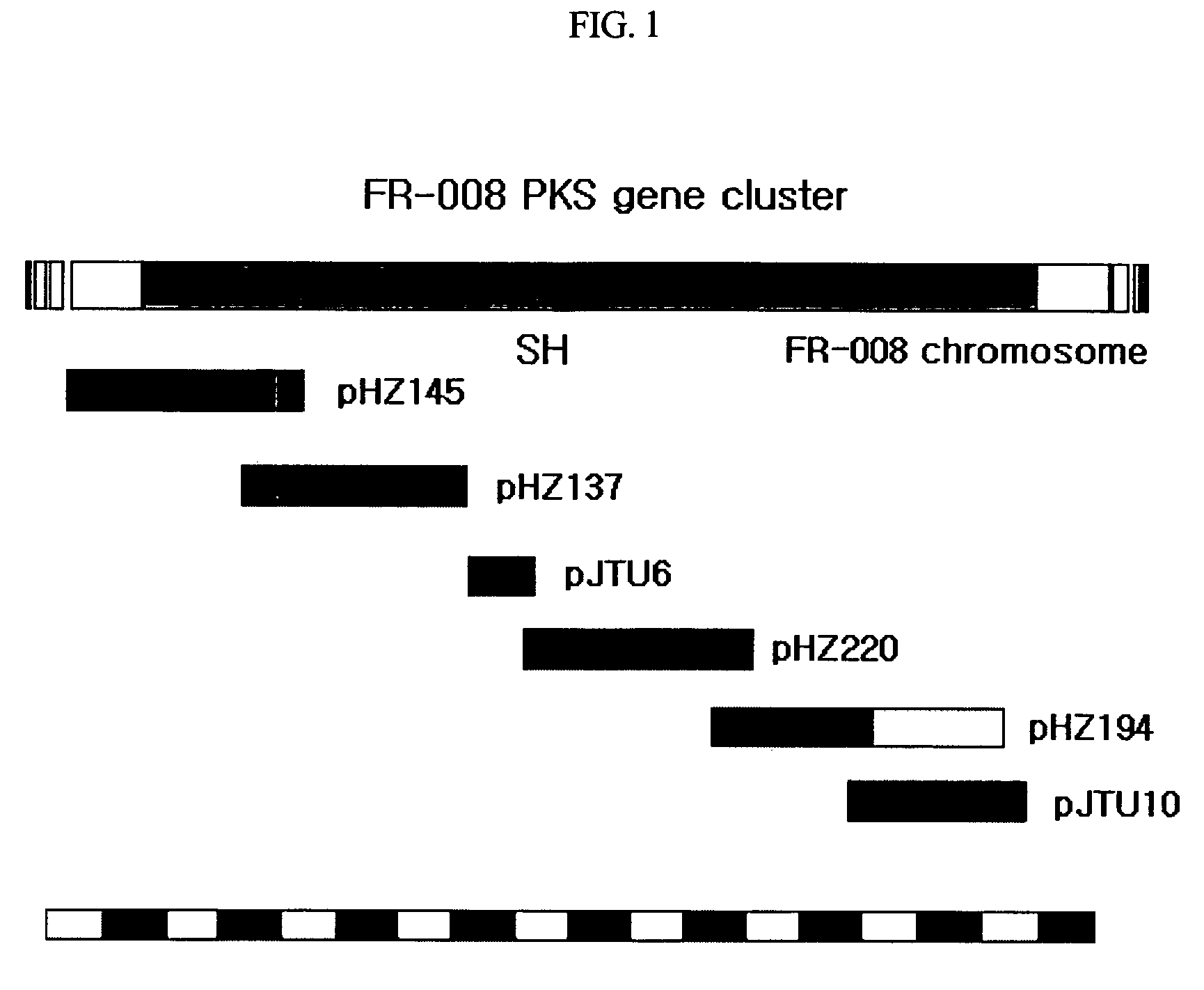
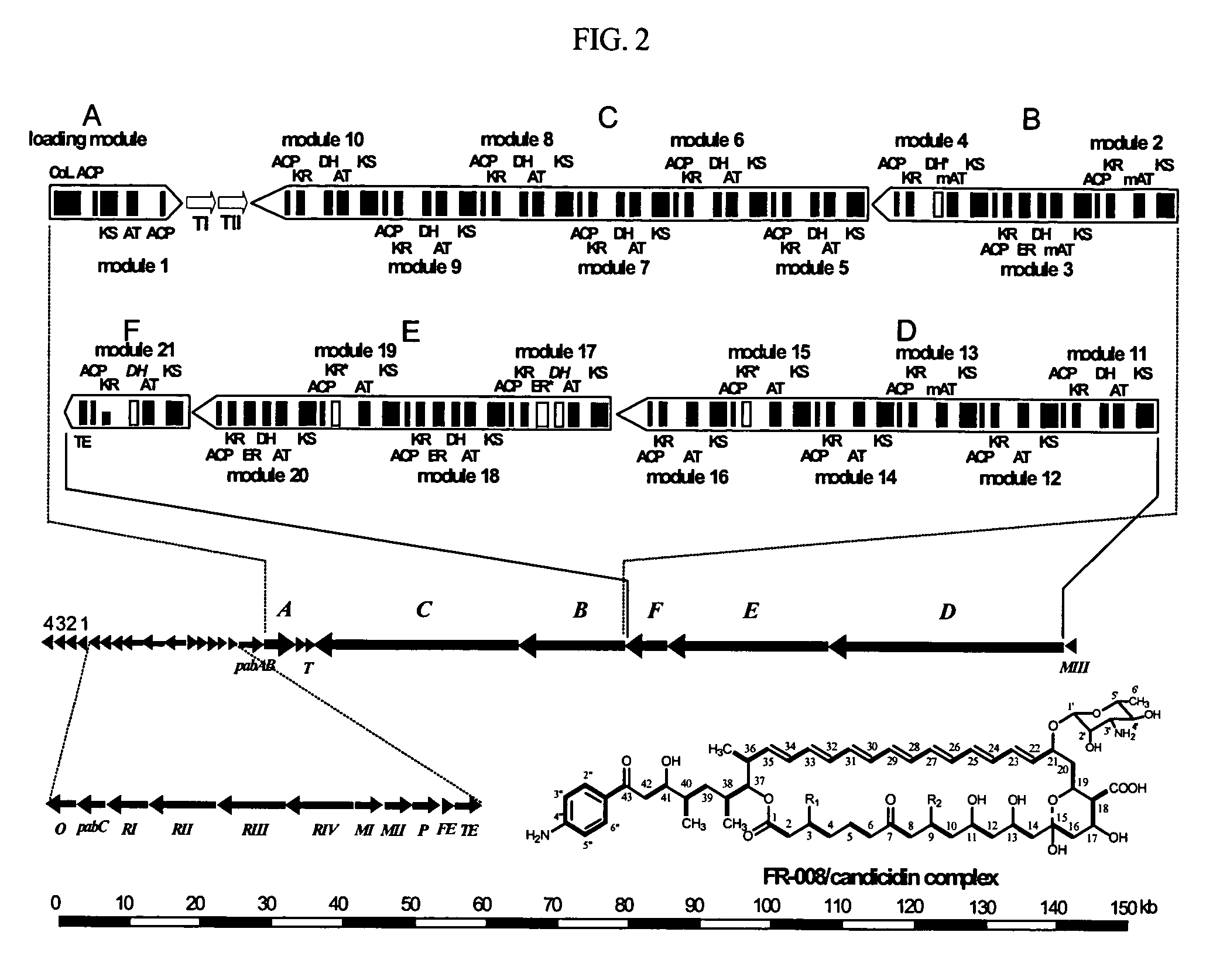
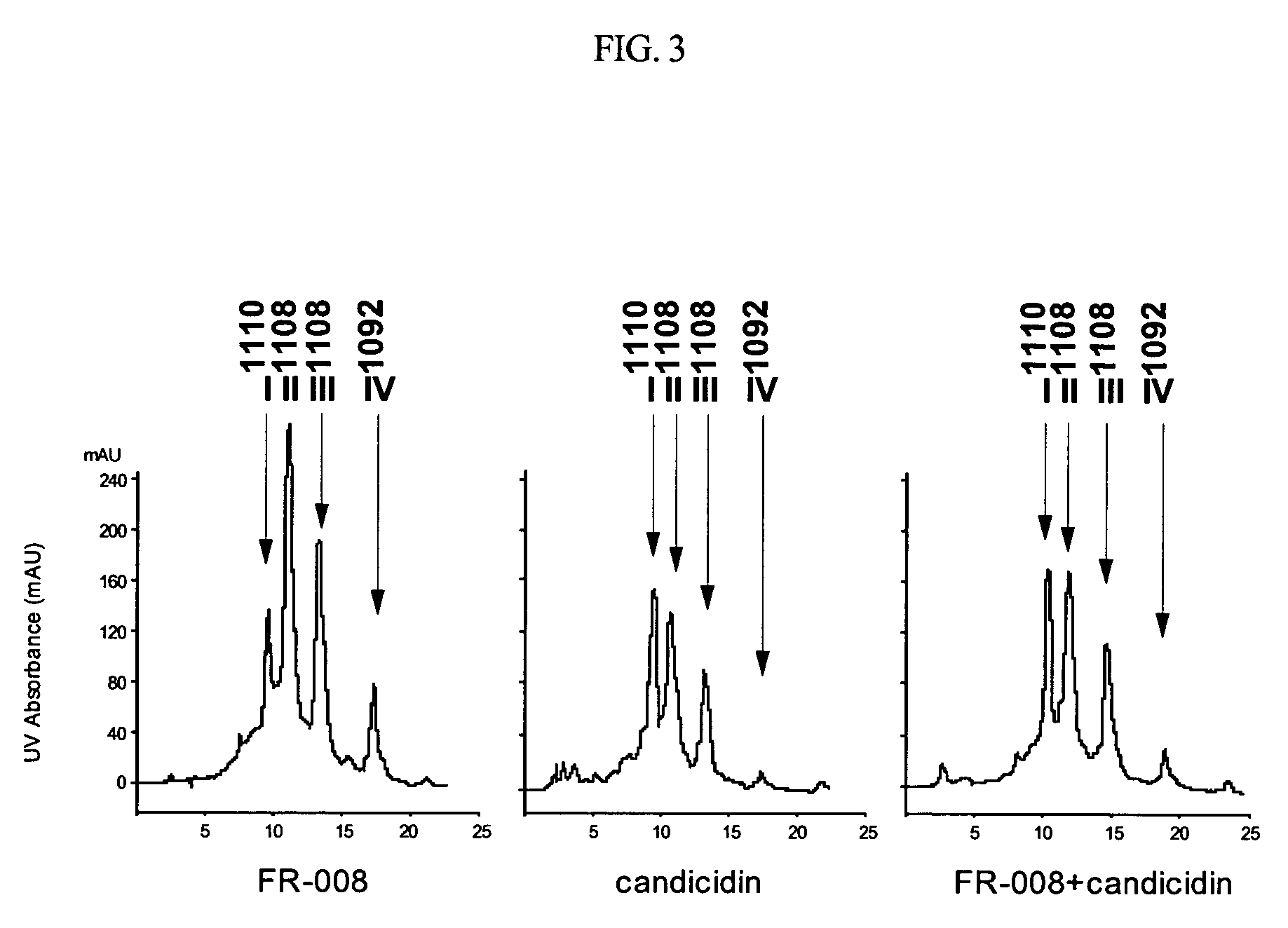
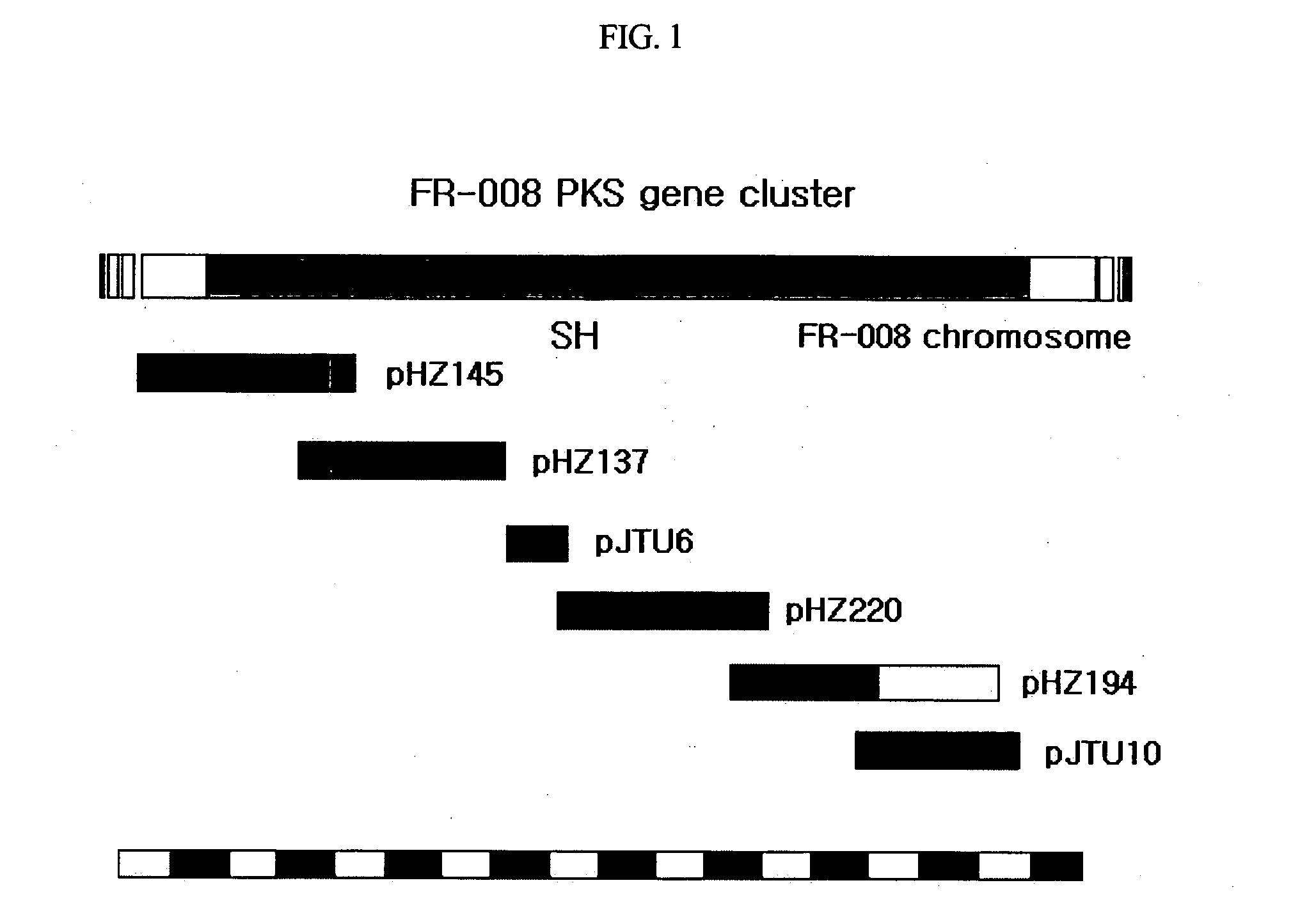
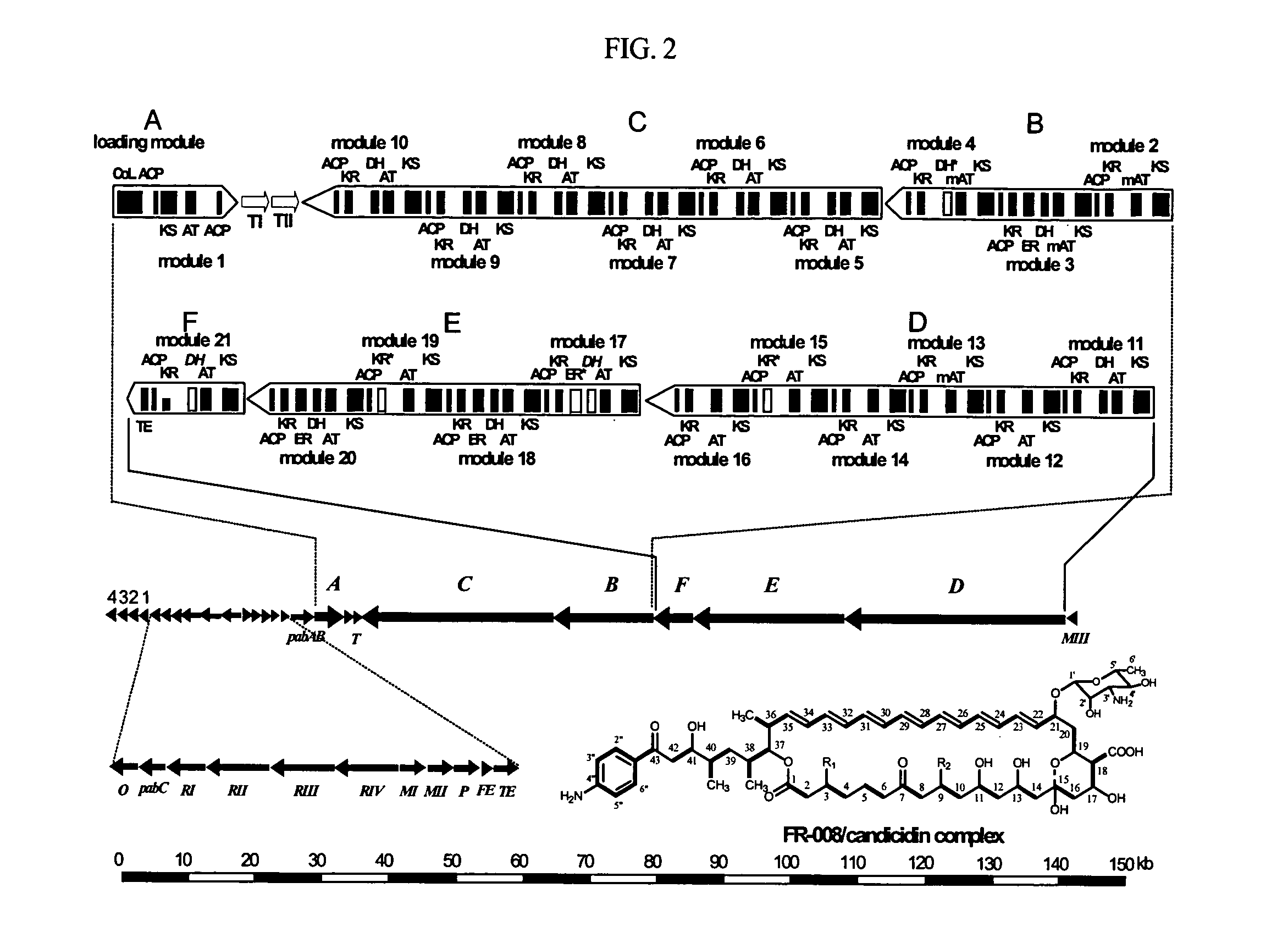
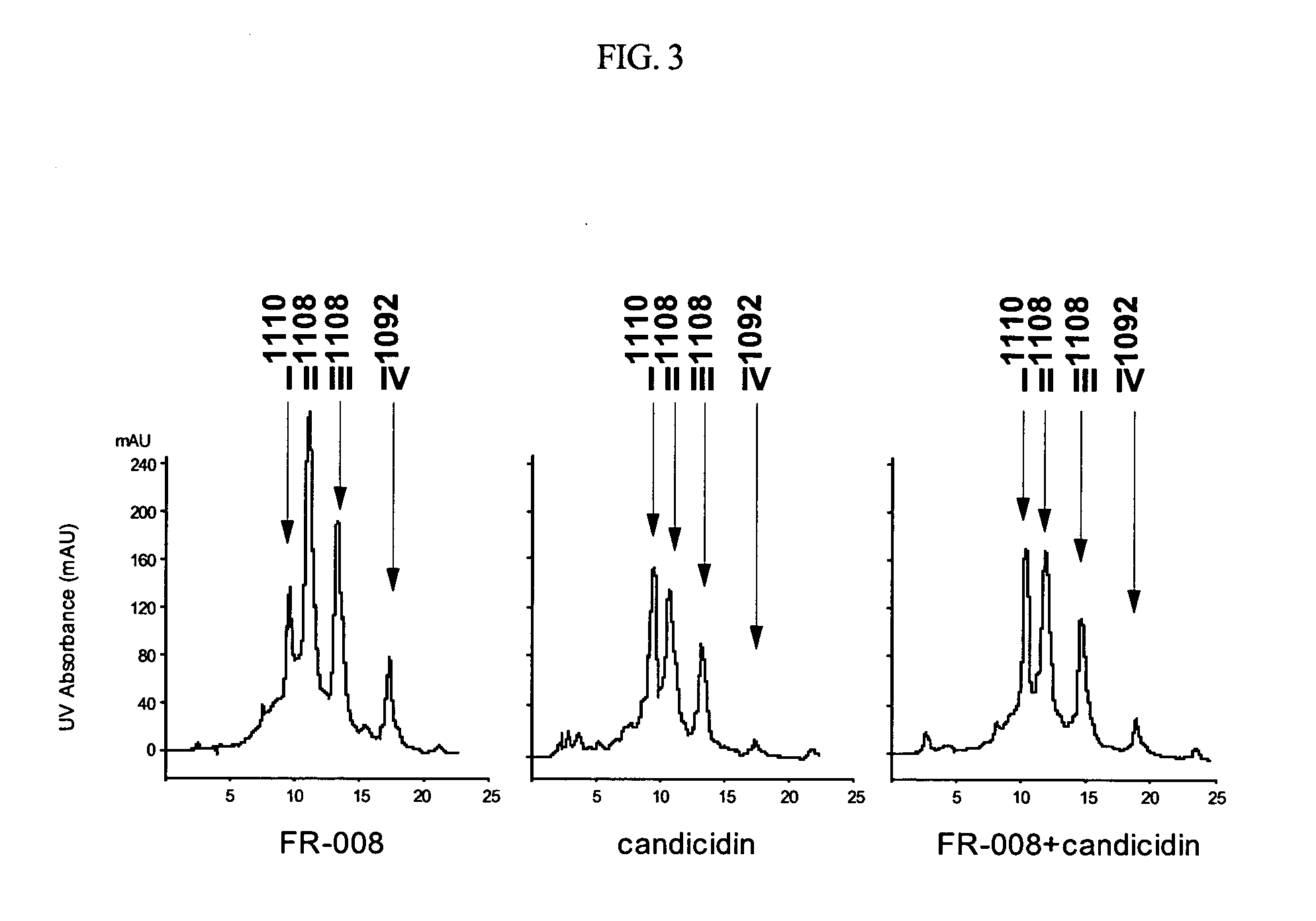
Genes for synthesis of FR-008 polyketides
The present invention relates to the base sequence of whole genes involved in the biosynthesis of FR-008 polyketides derived from Streptomyces sp. FR-008. This base sequence comprises genes coding for ketosynthase (KS), acyl transferase (AT), acyl carrier protein (ACP), ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH) and enoyl reductase (ER) domains, and genes coding for modifier enzymes, such as ABC transporter, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, ferredoxin, thioesterase, sugar synthetic protein, FAD-dependent monooxygenase, 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate (ADC) synthase and ADC lyase. The gene base sequence according to the present invention can be used to increase the productivity of the existing FR-008 polyketides or produce new FR-008 polyketides, through modification of its parts.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Drought tolerant plants and related constructs and methods involving genes encoding ferredoxin family proteins
InactiveUS20120023622A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructNucleotide
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant DNA constructs useful for conferring drought tolerance, compositions (such as plants or seeds) comprising these recombinant DNA constructs, and methods utilizing these recombinant DNA constructs. The recombinant DNA construct comprises a polynucleotide operably linked to a promoter that is functional in a plant, wherein said polynucleotide encodes a ferredoxin family protein.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Photocatalytic hydrogen production and polypeptides capable of same
InactiveUS9181555B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFerredoxinPolynucleotide
An isolated polypeptide comprising a hydrogen generating enzyme attached to a heterologous ferredoxin is disclosed, as well as polynucleotides encoding same, nucleic acid constructs capable of expressing same and cells expressing same. A method for generating hydrogen using the isolated polypeptide is also disclosed.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Genes for synthesis of FR-008 polyketides
The present invention relates to the base sequence of whole genes involved in the biosynthesis of FR-008 polyketides derived from Streptomyces sp. FR-008. This base sequence comprises genes coding for ketosynthase (KS), acyl transferase (AT), acyl carrier protein (ACP), ketoreductase (KR), dehydratase (DH) and enoyl reductase (ER) domains, and genes coding for modifier enzymes, such as ABC transporter, cytochrome P450 monooxygenase, ferredoxin, thioesterase, sugar synthetic protein, FAD-dependent monooxygenase, 4-amino-4-deoxychorismate (ADC) synthase and ADC lyase. The gene base sequence according to the present invention can be used to increase the productivity of the existing FR-008 polyketides or produce new FR-008 polyketides, through modification of its parts.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Hyperimmunized egg product for treatment of necrotic enteritis in poultry
In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a method for preventing or treating necrotic enteritis by administering a hyperimmunized egg product obtained from an egg-producing animal to an avian. The hyperimmunized egg product may contain an antibody specific to an antigen selected from the group consisting of Clostridium perfringens α-toxin, Clostridium perfringens elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), Clostridium perfringens necrotic enteritis B-like (NetB) toxin, Clostridium perfringens Pyruvate: Ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFO), and Eimeria tenella elongation factor 1-alpha.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC +1
Homocysteine diagnosing/measuring reagent (kit) and homocysteine concentration measuring method
InactiveCN101750300AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a homocysteine diagnosing / measuring reagent (kit) using the technologies of an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme linkage method. At the same time, the invention also relates to a homocysteine concentration measuring method, the reagent composition and reagent ingredients, which belong to the technical field of medical detection and measurement. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises the following ingredients: a buffer solution, reduced form cozymase, cozymase A, oxidized form ferredoxin, hanoyl-cozymase A, homocysteine desulfhydrase, 2-oxobutyryl synthetase, malonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase and stabilizing agents. The method has the following steps: mixing samples and the reagent by the certain volume percent for making the samples and the reagent take a series of enzymatic reaction, and then, placing reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the dropping degree of the light absorbancy in the position with the main wave length of 340 nm, so the concentration of the homocysteine can be measured and calculated.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Homocysteine diagnosing/measuring reagent (kit) and homocysteine concentration measuring method
InactiveCN101750298AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a homocysteine diagnosing / measuring reagent (kit) using the technologies of an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme linkage method. At the same time, the invention also relates to a homocysteine concentration measuring method, the reagent composition and reagent ingredients, which belong to the technical field of medical detection and measurement. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises the following ingredients: a buffer solution, cozymase, cozymase A, oxidized form ferredoxin, longchain fatty acid, homocysteine desulfhydrase, 2-oxobutyryl synthetase, fatty acid synthetase and stabilizing agents. The method has the following steps: mixing samples and the reagent by the certain volume percent for making the samples and the reagent take a series of enzymatic reaction, and then, placing reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the rising degree of the light absorbancy in the position with the main wave length of 340 nm, so the concentration of the homocysteine can be measured and calculated.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Methods and compositions for enhanced biomass production and increased abiotic stress tolerance
ActiveUS20180168120A1Improve efficiencyIncreased biomass productionTransferrinsClimate change adaptationHeterologousPlant cell
This invention relates to methods for increasing carbon fixation, increasing biomass production and / or increasing abiotic stress tolerance in a plant comprising: introducing into a plant, plant part, and / or plant cell a heterologous polynucleotide encoding a ferredoxin polypeptide and / or a heterologous polynucleotide encoding a biotin ligase polypeptide to produce a stably transformed plant, plant part, and / or plant cell, wherein said heterologous polynucleotides are from a bacterial and / or an archaeal species. Further provided are plants, plant parts and plant cells produced by the methods of the invention.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Homocysteine diagnosing/measuring reagent (kit) and homocysteine concentration measuring method
InactiveCN101750297AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAcyl-CoA synthetaseAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a homocysteine diagnosing / measuring reagent (kit) using the technologies of an enzyme colorimetric method and an enzyme linkage method. At the same time, the invention also relates to a homocysteine concentration measuring method, the reagent composition and reagent ingredients, which belong to the technical field of medical detection and measurement. The reagent (kit) mainly comprises the following ingredients: a buffer solution, cozymase, cozymase A, oxidized form ferredoxin, longchain-acyl-cozymase A, homocysteine desulfhydrase, 2-oxobutyryl synthetase, fatty acyl-CoA synthetase and stabilizing agents. The method has the following steps: mixing samples and the reagent by the certain volume percent for making the samples and the reagent take a series of enzymatic reaction, and then, placing reactants under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the rising degree of the light absorbancy in the position with the main wave length of 340 nm, so the concentration of the homocysteine can be measured and calculated.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A method for promoting the synthesis of acetylglucosamine in Bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN108424869BEasy to synthesizeInhibit synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus cereusNitrogenase
The invention discloses a method for promoting the synthesis of acetylglucosamine of bacillus subtilis, which belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The present invention uses the recombinant Bacillus subtilis BSGNKAP2 as the starting strain, and exogenously introduces pyruvate carboxylase BalpycA derived from Bacillus cereus to eliminate the overflow of carbon metabolism in the center of Bacillus subtilis, avoid the synthesis of by-product acetoin, and further Introduce 5 exogenous reducing power metabolism reactions to replace the glycolysis pathway, the reaction of NADH in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and reconstruct the intracellular reducing power metabolism, including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin dehydrogenase, iso CitrateNAD + Dehydrogenase, malate quinone dehydrogenase, ketoferredoxin oxidoreductase, and nitrogenase ferritin. During the shake flask fermentation using the compound medium, the yield of acetylglucosamine of the recombinant strain BSGNKAP8 was 24.50g / L, and the yield of acetylglucosamine / glucose was 0.469g / g, which were 1.97 and 2.13 times that of the starting strain BSGNKAP2, respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Determination method of ammonia (ammonia ion) and ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / determination kit
InactiveCN102466684AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsNitric oxideCoupling reaction
The invention relates to a determination method of ammonia (ammonia ion) content utilizing enzymatic colorimetric method and couple reaction, and reagent composition and components. Technical principles of the determination method are in the light of a series of catalytic reactions of ferredoxin-nitrite reductase, nitrite reductase and nitric oxide dioxygenase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / determination kit. The determination method of the present invention has high sensitivity and little error, so the determination method and the kit of the invention can be widely applied to clinic medicine / food examination.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Maize RBCS7A promoter for expressing a ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase in a plant
Compositions and methods for improving plant growth are provided herein. The maize RbcS7A promoter is provided which is a developmentally regulated promoter. Polynucleotides encoding ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase proteins, polypeptides encompassing ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase proteins, and expression constructs for expressing genes of interest whose expression may improve agronomic properties including but not limited to crop yield, biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, and early vigor, plants comprising the polynucleotides, polypeptides, and expression constructs, and methods of producing transgenic plants are also provided.
Owner:BENSON HILL BIOSYST
Detection method of ammonia (ammonia ion) and diagnosis/detection kit of ammonia (ammonia ion)
InactiveCN102466693AMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryBiology
The invention relates to a detection method of the ammonia (ammonia ion) content by enzymatic colorimetry and enzyme coupled reaction technology and composition and components of a reagent. The technology principle of the detection method is based on a series of catalytic reactions of ferredoxin-nitrite reductase, nitrite reductase and nitric oxide synthetase. The invention also relates to an ammonia (ammonia ion) diagnosis / detection kit. The detection method provided by the invention has advantages of high sensitivity and small error. Therefore, the detection method and the kit provided by the invention can be widely applied in clinical medicine / food inspection.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Recombinant escherichia coli and application in fermenting and producing 2Fe2S ferredoxin
InactiveCN105331569AShorten the timeLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses recombinant Escherichia coli, which is named as Escherichia coli pCodonPlus / pRKISC / pETDuet-S33[2Fe2S]Fd, the strain contains [2Fe2S] ferredoxin genes sourced from agrobacterium tumefaciens S33, and a nucleotide sequence thereof is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; the recombinant Escherichia coli is obtained by inoculating the [2Fe2S] ferredoxin into a pETDuet-1 carrier to prepare recombinant plasmids named as pETDuet-[2Fe2S] and transferring the prepared recombinant plasmids into Escherichia coli C41(DE3) containing pCodonPlus and pRKISC plasmids. The invention also discloses an application of the recombinant Escherichia coli in fermenting and producing [2Fe2S] ferredoxin. The experiment proves that 23mg of pure [2Fe2S] ferredoxin can be obtained from every liter of fermented culture, which is far higher than the reported yield 0.03mg of [2Fe2S] purified from wild mushrooms, so that the recombinant Escherichia coli has good application prospect in the industrialized production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
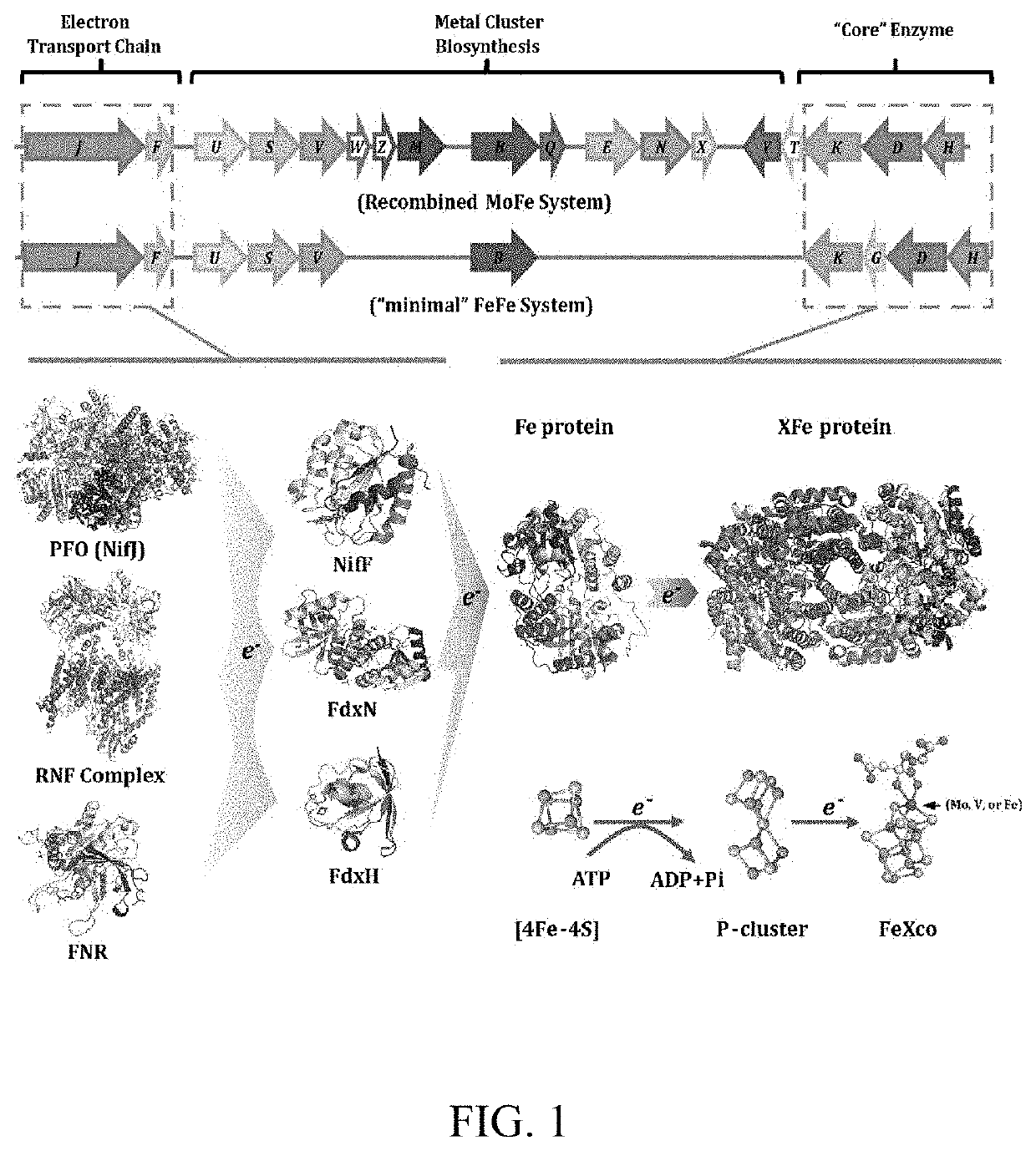
Electron transport chain module from eukaryotic organelle and application thereof
InactiveUS20190338257A1Meet needsHigh energy demandClimate change adaptationOxidoreductasesKlebsiella oxytocaWhite blood cell
Provided are an electron transport chain module from a eukaryotic organelle and an application thereof in biological nitrogen fixation. The electron transport chain (ETC) module is composed of the NifJ protein from Klebsiella oxytoca and a ferredoxin from plant chloroplasts or leucoplasts; plant-type ferredoxin-NADPH reductase (FNR) and the FdxH or FdxB protein from Anabaena; or an FNR and a Ferredoxin protein from plant organelles.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5d703ada-74ac-46ea-82ae-011993502b1d/HDA0000856464100000011.PNG)
![Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5d703ada-74ac-46ea-82ae-011993502b1d/HDA0000856464100000012.PNG)
![Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin Recombinant Escherichia coli and application thereof to fermentative production of 2[4Fe4S]ferredoxin](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5d703ada-74ac-46ea-82ae-011993502b1d/BDA0000856464090000041.PNG)
![Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e5587da5-0c54-4249-9ce1-a1c2170a8dd6/HDA0000856459410000011.PNG)
![Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e5587da5-0c54-4249-9ce1-a1c2170a8dd6/HDA0000856459410000012.PNG)
![Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli Recombinant Escherichia coli with efficiently expressed [2Fe2S] ferredoxin and application of recombinant Escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e5587da5-0c54-4249-9ce1-a1c2170a8dd6/BDA0000856459400000031.PNG)