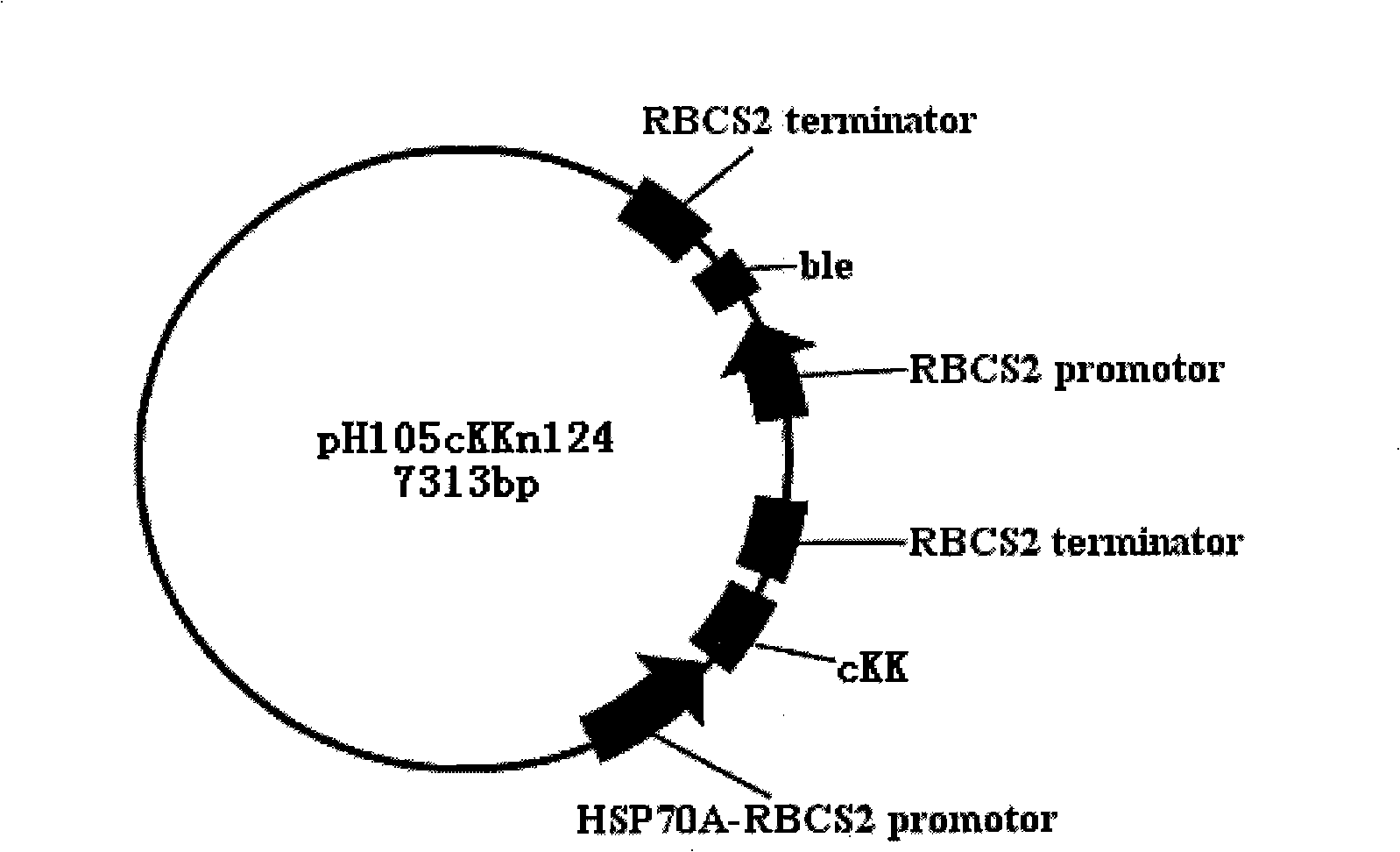
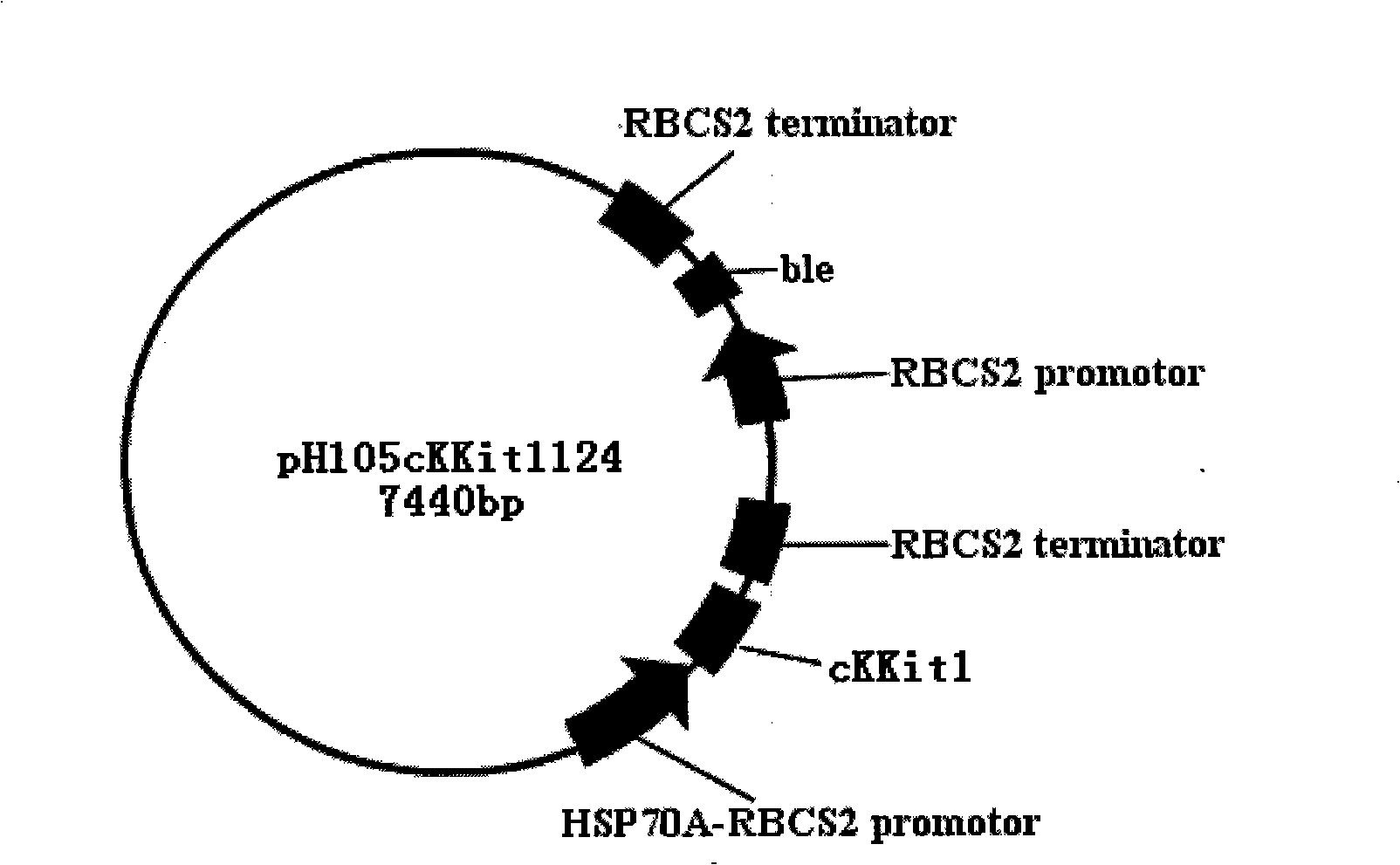
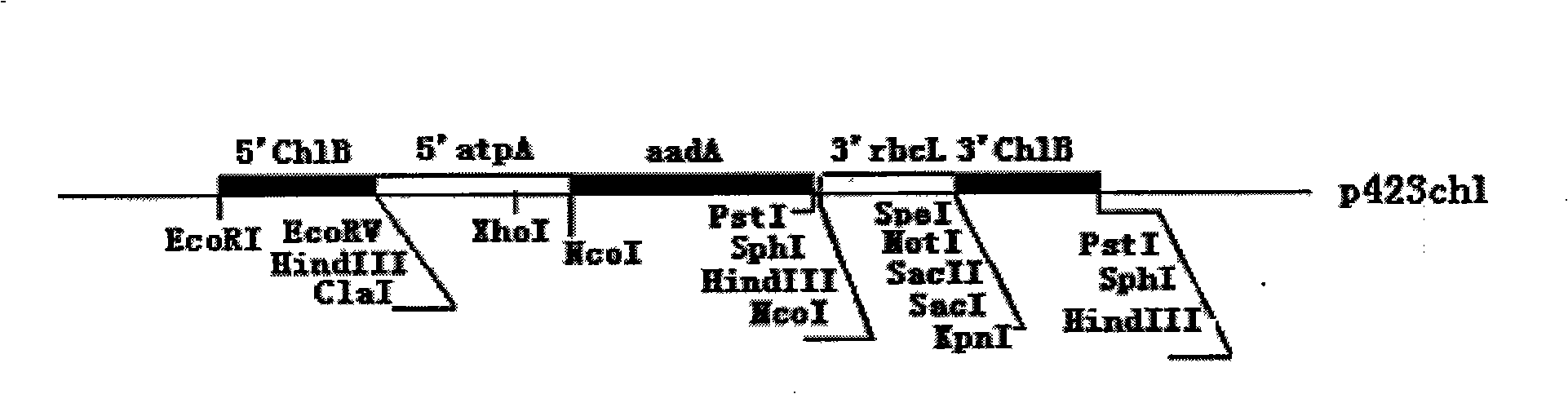
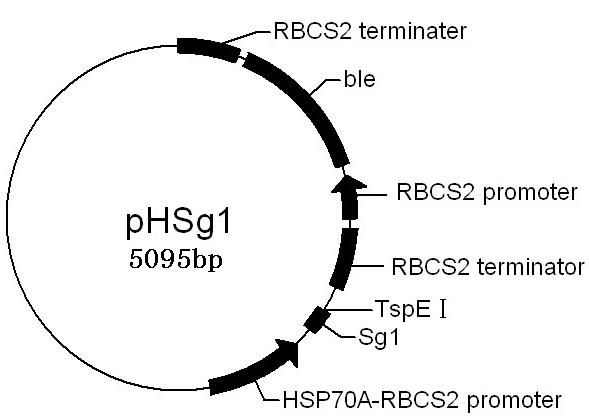
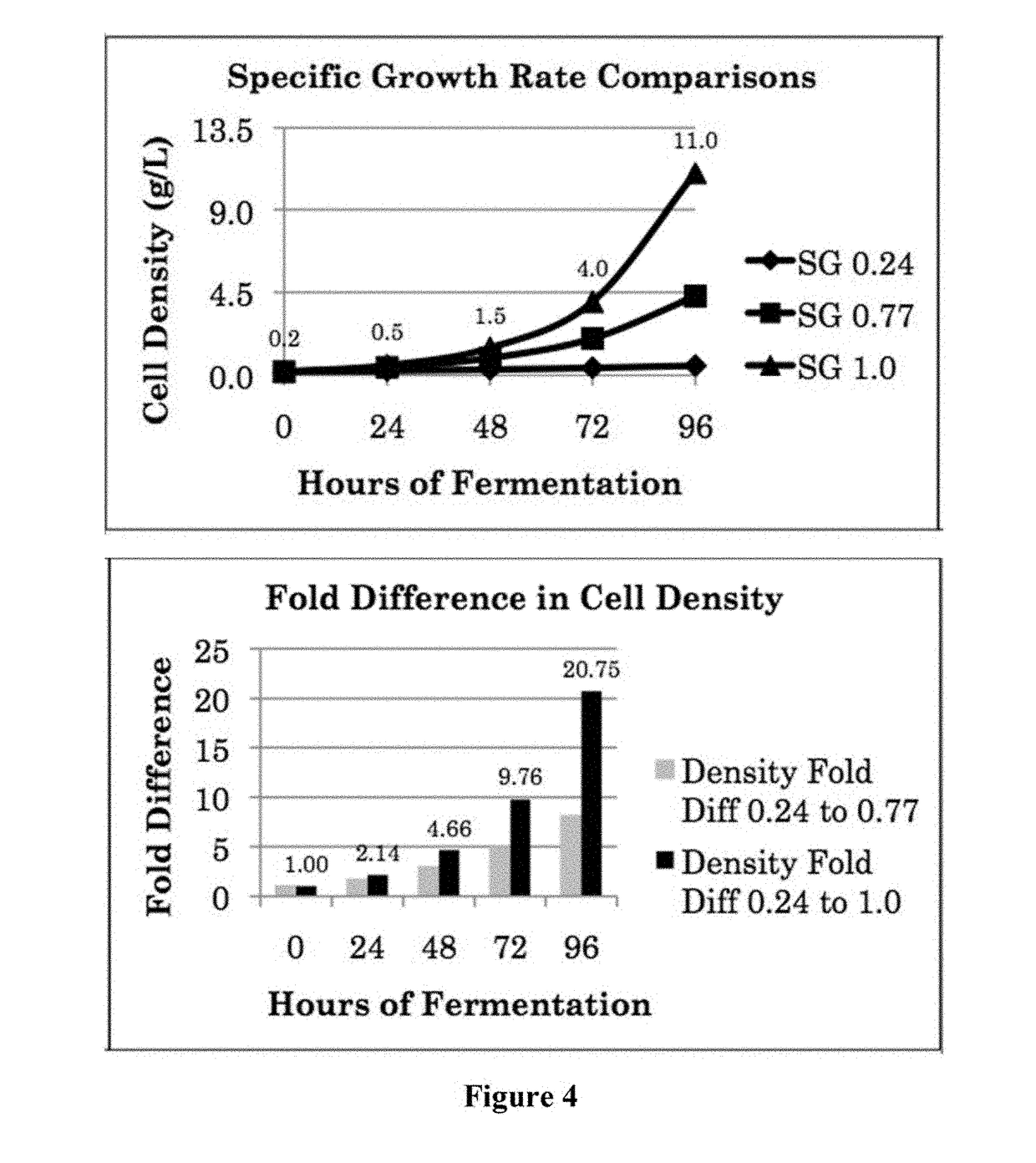
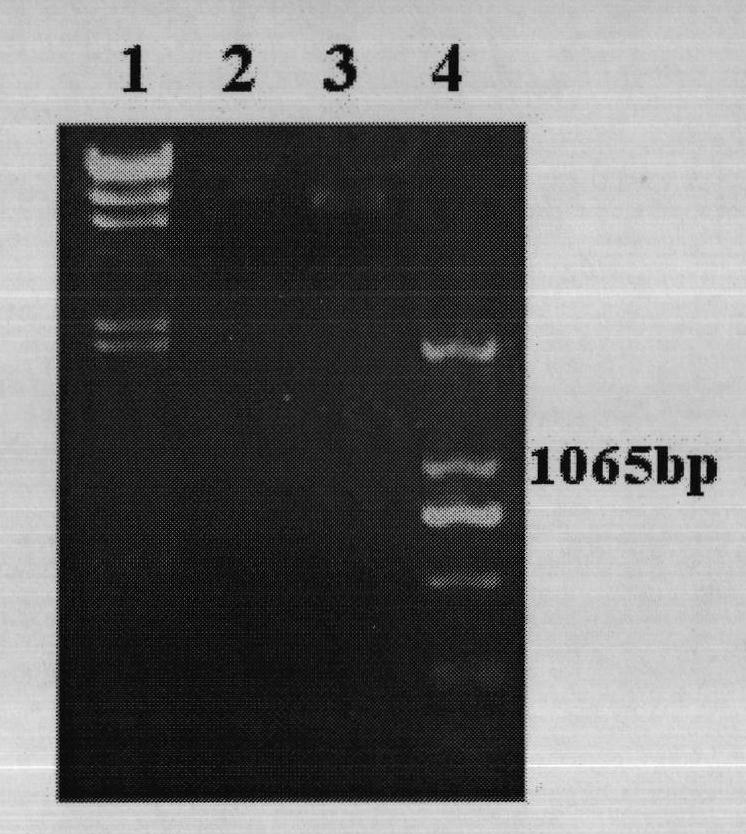
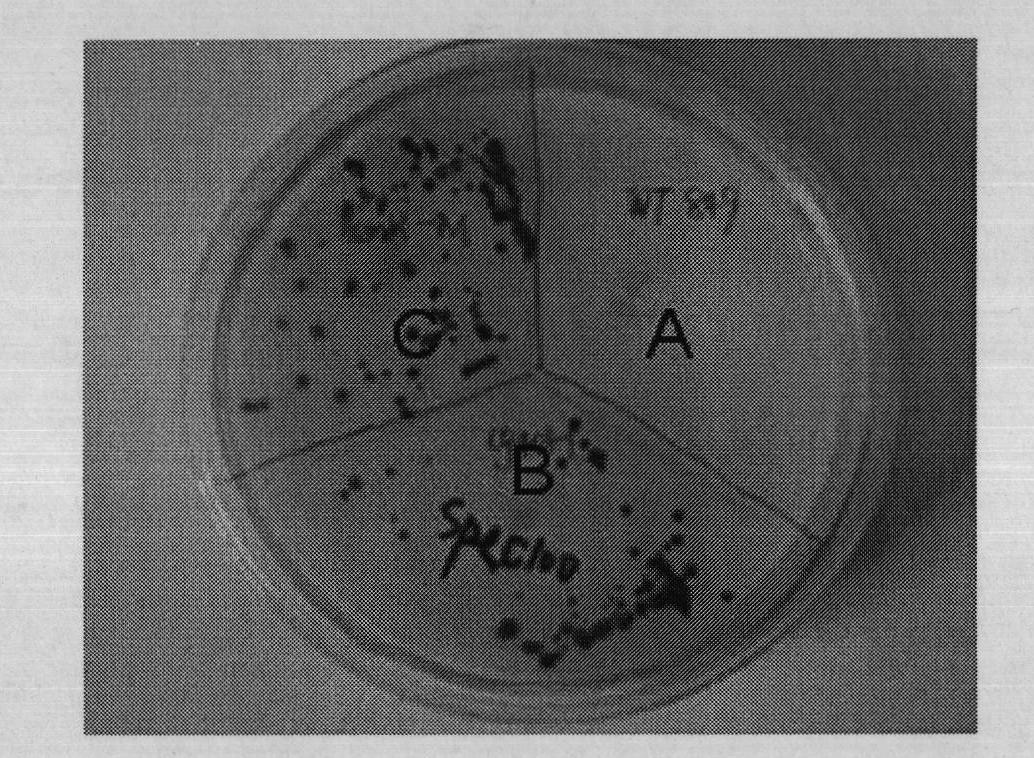
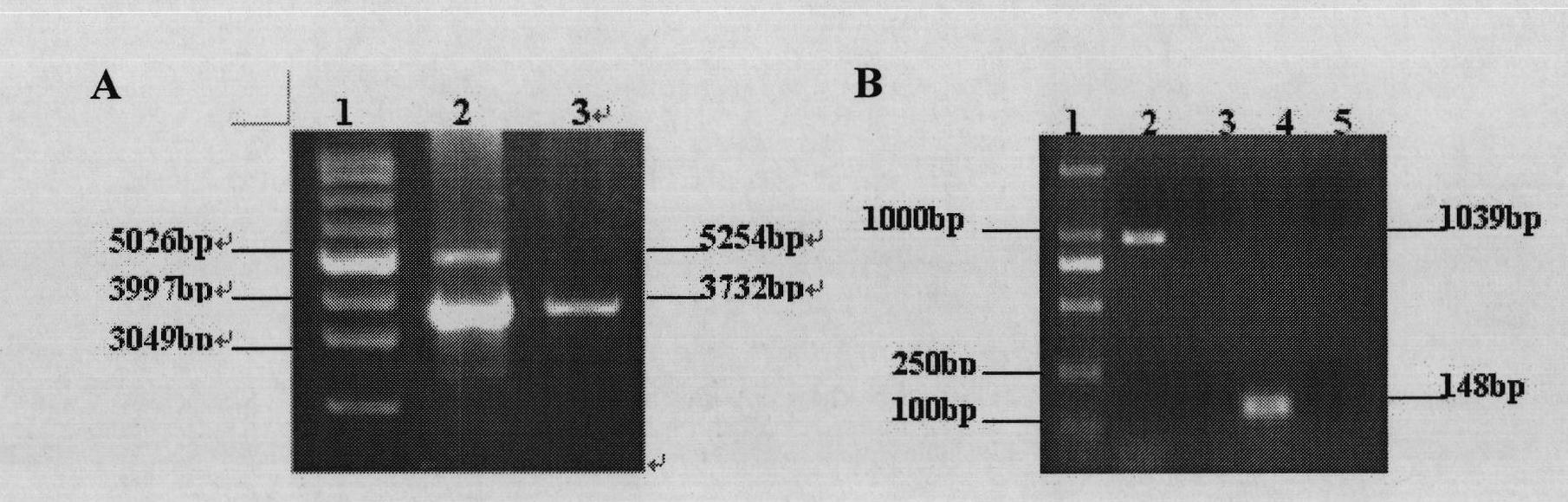
Patents
Literature
179 results about "Chlamydomonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 325 species all unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.
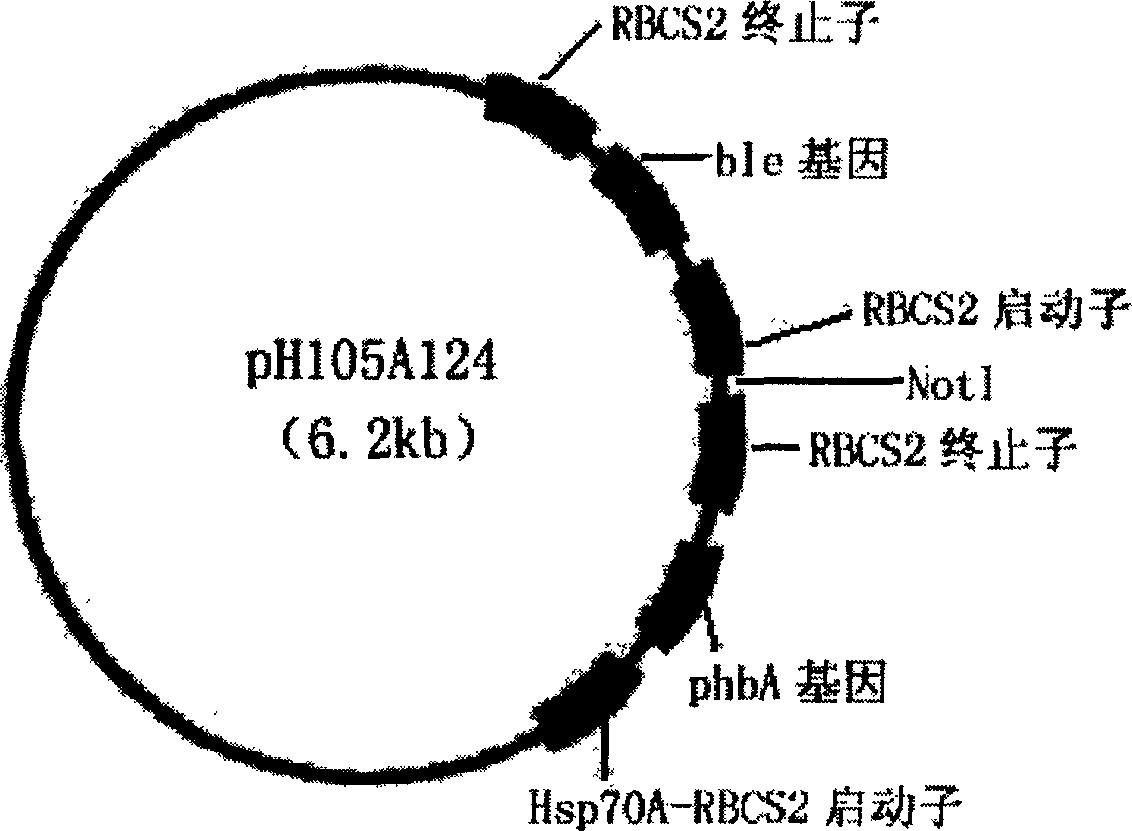
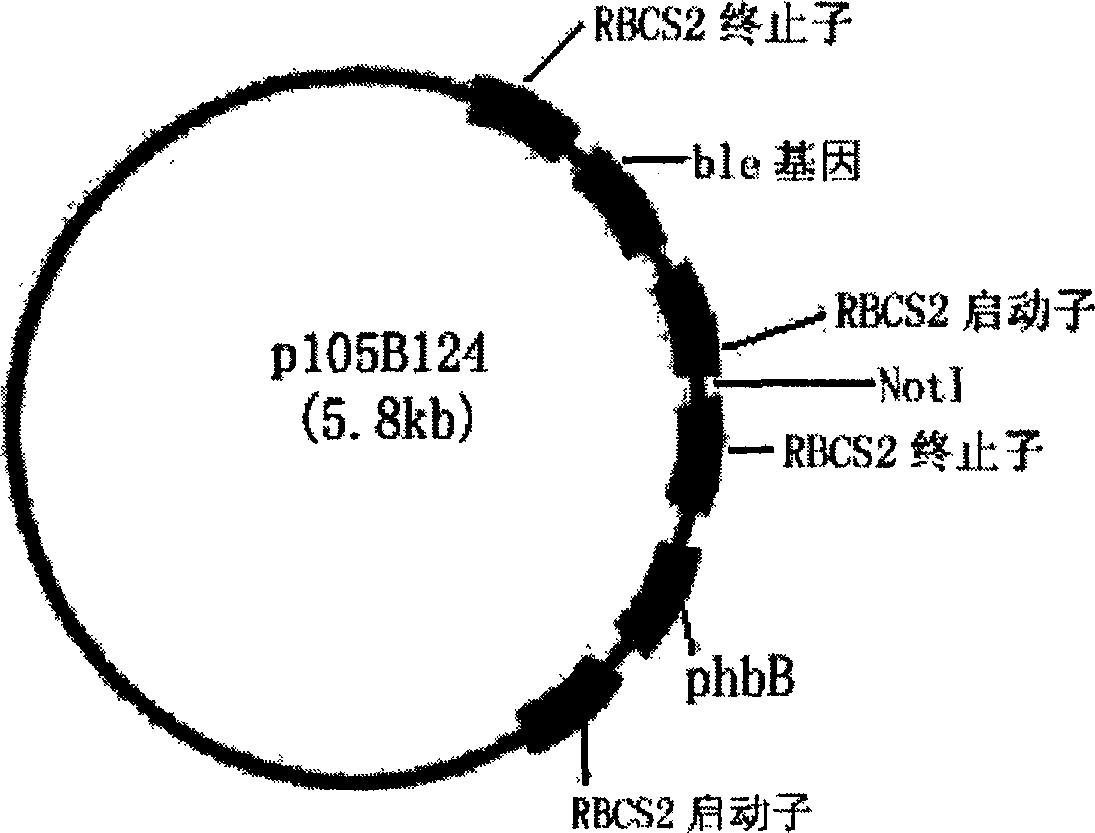
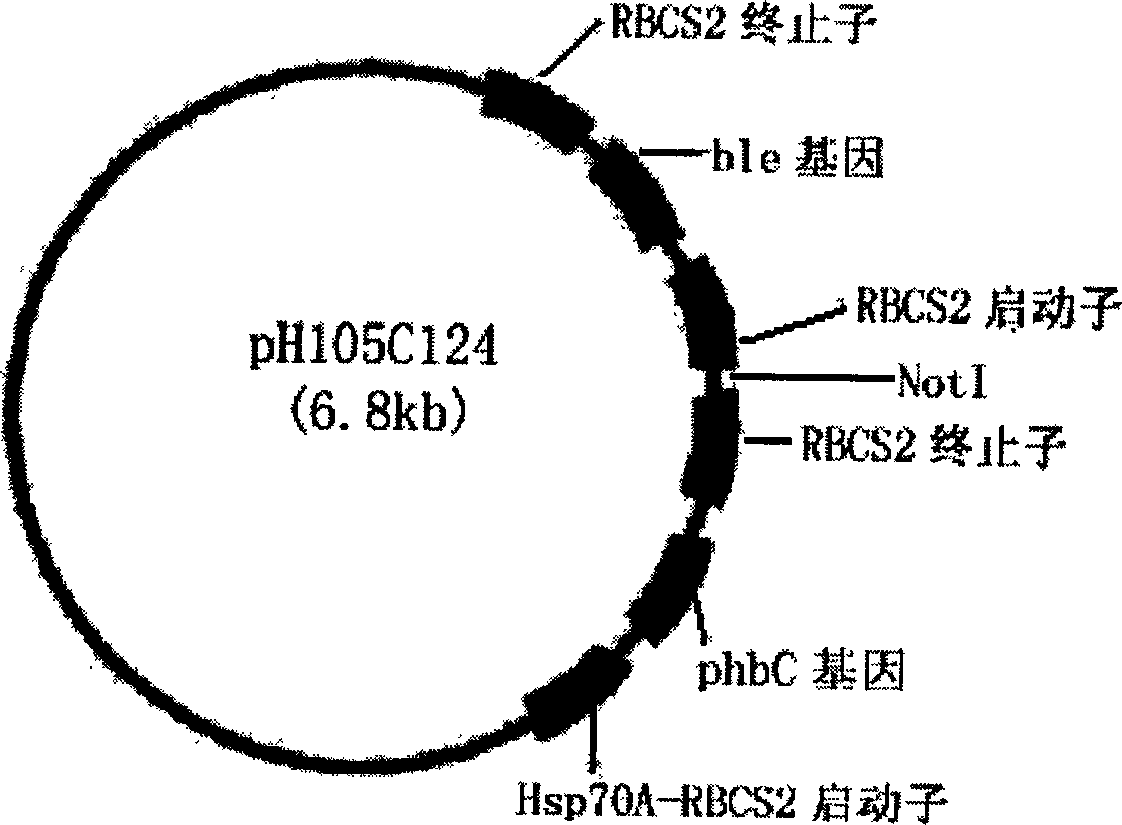
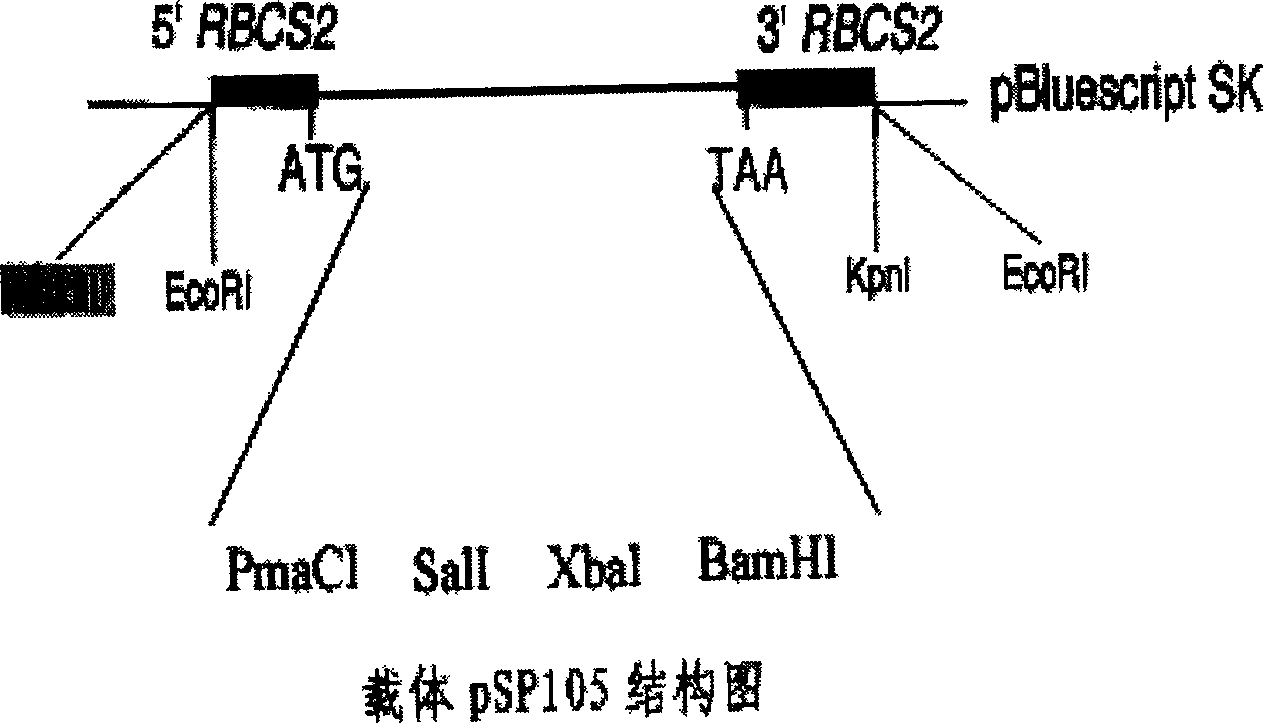
Exogenous gene expression system of Chlamydomonasreinhardtii and method for constructing and producing PHB transgenic algae
ActiveCN1807649AImprove expression efficiencyIncrease productionUnicellular algaeFermentationHydroxybutyric acidChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses an expression system and constructing PHB transgene algae method of rhine chlamydomonas exogenesis gene, which comprises the following parts: promotor, exogenesis-goal gene, screening badge and rhine chlamydomonas acceptor algae strain, wherein the method comprises the following: A, selecting and cultivating acceptor algae strain; B, cloning key enzyme gene by PHB biosynthesizing; C, expressing carrier of PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme rhine chlamydomonas; D, using PHB biosynthesizing key enzyme to lead in rhine chlamydomonas from fungus Bacillus alcaligenes with bead-milling method, gene-gun method or electrization; obtaining bivalence or transgene Chlamydomonas of producing PHB by screen selecting and molecule detecting. The poly-hydroxybutyric acid is compounded by acting in conjunction of PHB compounding key enzyme of phbA, phbB and phbC gene coding, which uses acetylcoenzyme A as substrate by photosynthesis. The method simplifies the operating, which reduces cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Rapana venosa ecological breeding method
InactiveCN101999328AIncrease perversion rateGrow fastClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRapanaWater temperature
The invention relates to the field of Rapana venosa artificial breeding, in particular to a Rapana venosa ecological breeding method. The method comprises: transferring egg bags into a plastic basket or net cage (10-20mesh) for suspended hatch in a nursery pond and charging air continuously, wherein the density of the egg bags is 5,000 to 8,000 / m<3>; breeding larvae at a density of 1 / ml with bait made of chlamydomonas (diatom and tetraselmis are preferred) in an amount of 1.0 to 12.0*10<4> / ml every day at a water temperature of 22 to 26 DEG C; continuously charging air, changing 1 / 2 of water every day; and when the larvae grow three whorls to a size of 700 to 800 micrometers, placing the larvae in to 60-mesh net bags, cages or tanks together with double-shell spats (animal baits for transformed Rapana venosa) for sea breeding.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV AT WEIHAI
Constructing method for transgene Chlamydomonas reinhardtii bioreactor
InactiveCN1827769AEasy point-to-point integrationSolve training difficultiesUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementChlamydomonas reinhardtiiVaccination
The invention relates the construct method for transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The method comprises the following steps: using the rhinestone algae as transgenosis receptor biology, highly effective expressing the carrier construct by constructing the exogenesis gene containing screening mark expression frame, leading the destination genes in rhinestone algae with bead milling method, electric punching method and other methods, integrating them into nucleus genome or chloroplast genome, and adopting a series of gene expression regulate and control technology to construct the transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor possesses the characters of fast growth rate, short breeding cycle, easy segregation, photoautotroph and large scale culture, fast and cheap producing medicinal protein, industrial raw materials, and feeding vaccination, and possessing the bioactivity secondary metabolite.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Light-receiving channel rhodopsin having improved expression efficiency
Disclosed is a Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin with an improved expression efficiency on a cell membrane. Specifically disclosed is a modified Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin protein. The protein is modified to contain an N-terminal region of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii-derived channel rhodopsin-1 at the N-terminal of the Volvox carteri-derived light-receiving channel rhodopsin protein, wherein the N-terminal region is involved in cell membrane-localized expression and contains no transmembrane domain of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii-derived channel rhodopsin-1.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Construction method of transgenic chlamydomonas reinhardtii for expressing human tissue kallikrein
ActiveCN101255438ARich in nutrientsReasonable structureUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesDiseaseChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention is a constructing method of a genetic modified chlamydomonas reinhardtii to express kallikrein of human tissue. Firstly kallikrein gene sequence suitable for expression of chlamydomonas reinhardtii kernel genome or expression of chloroplast genome or expression of mitochondrial is designed according to kallikrein gene sequence of human tissue and preferred codon table of chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the gene sequence is synthesized by artificial synthesis, kallikrein gene of human tissue containing non-coded sequence is artificially synthesized, then expression vector of chlamydomonas reinhardtii kernel genome or expression vector of chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast genome or expression vetor of chlamydomonas reinhardtii mitochondrial with mention foreign gene is constructed, then transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii by genetic transformation, and genetic modified algal strains capable of expressing kallikrein of human tissue is obtained after screening. The invention lays foundation of treating and preventing some diseases such as hypertention, glomerulonephritis with human original kallikrein gene chlamydomonas reinhardtii and products there.
Owner:深圳市微宇生物科技有限公司
Cultivating method of sinocyclocheilus grahami seedling
InactiveCN101822230AImprove survival rateIncrease growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaCarpWater quality
The invention relates to a cultivating method of a sinocyclocheilus grahami seedling, belonging to the technical field of fish culture. The cultivating method comprises the steps of the cultivation of fish fries growing mouths in rich water, artificial cultivation of fish fries, the rearing of fish fries at middle and rear stages and pest control. In the cultivation of fish fries growing mouths in rich water, a temporarily-cultivating pond is arranged in a tunnel, bait for fish fries growing mouths is chlamydomonas and rotatoria cultivated in rich water and the fish fries are cultivated at water temperature of 15 DEG C for 10-12 days. In the artificial cultivation of fish fries, the fish fries are cultivated by eel powder feed with the protein content of 40 percent for 40 days. The feed in the fish fries at middle and rear stages is carp crushed feed with the protein content of 39 percent. In the pest control, the water quality and the conditions of fish bodies are detected every three days, 50-80ml / mu of povidone iodine for controlling bacterial infection and 50-50ml / mu of rotatoria one-time removal (ammonium ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate) for controlling balantidiasis are splashed every 15 days. The invention can effectively improve the survival rate and the growth speed of inocyclocheilus grahami seedlings, is simple and convenient, and is beneficial to being popularized and generalized. Bacterial.
Owner:云南省水产技术推广站
Method for constructing secretory expression carrier and secretory expression system of Chlammydomonas reinhardtii
ActiveCN102181471AEasy to separate and purifyHigh recovery rateMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSequence signalChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for constructing a secretory expression carrier and secretory expression system of Chlammydomonas reinhardtii. In the invention, the method comprises the steps of predicating a signal peptide gene sequence by using an amino acid sequence from a secretory protein of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii through signal peptide predicating software; artificially synthesizing a signal peptide gene obtained by predicating; and inserting the signal peptide gene between a promoter and a cloning site of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii expression carrier to construct the secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii; meanwhile, detecting the expression efficiency of the constructed secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii by using an exogenous gene; converting the secretory expression carrier of the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii, containing the exogenous gene, to the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii by using a Chlammydomonas reinhardtii genetic conversion method; and screening the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii to obtain a transgene engineering strain capable of expressing the exogenous gene in a secretory way. By using the invention, the basis is laid for using the Chlammydomonas reinhardtii as the secretory expression exogenous gene of a bioreactor.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
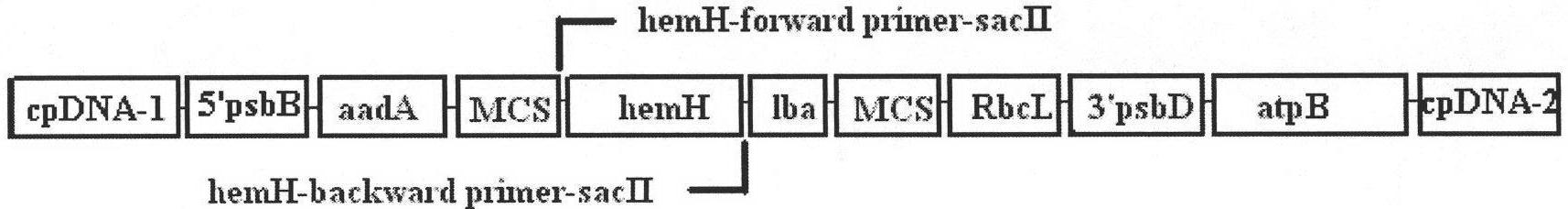
Method for improving chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene
InactiveCN101775407ALower oxygen levelsIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeFermentationEnzyme GeneChlamydomonas reinhardtii
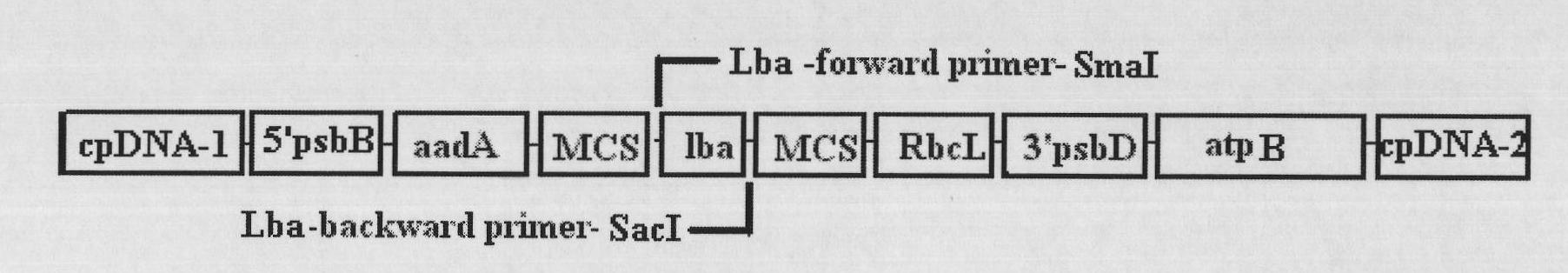
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for improving the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production method has the defects that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen enzymes are sensitive to oxygen and easily restricted by the oxygen to lose activity, and the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production effect is limited. The invention discloses an application of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene and a globulin subunit gene to hydrogen production by constructing the leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene hemH and the globulin subunit gene lba in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, transferring the expression vector in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast and expressing the hemH-lba gene in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The invention has the advantages that the content of oxygen in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is reduced obviously faster than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of an un-transformed gene, the oxygen content is kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen production amount is obviously increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
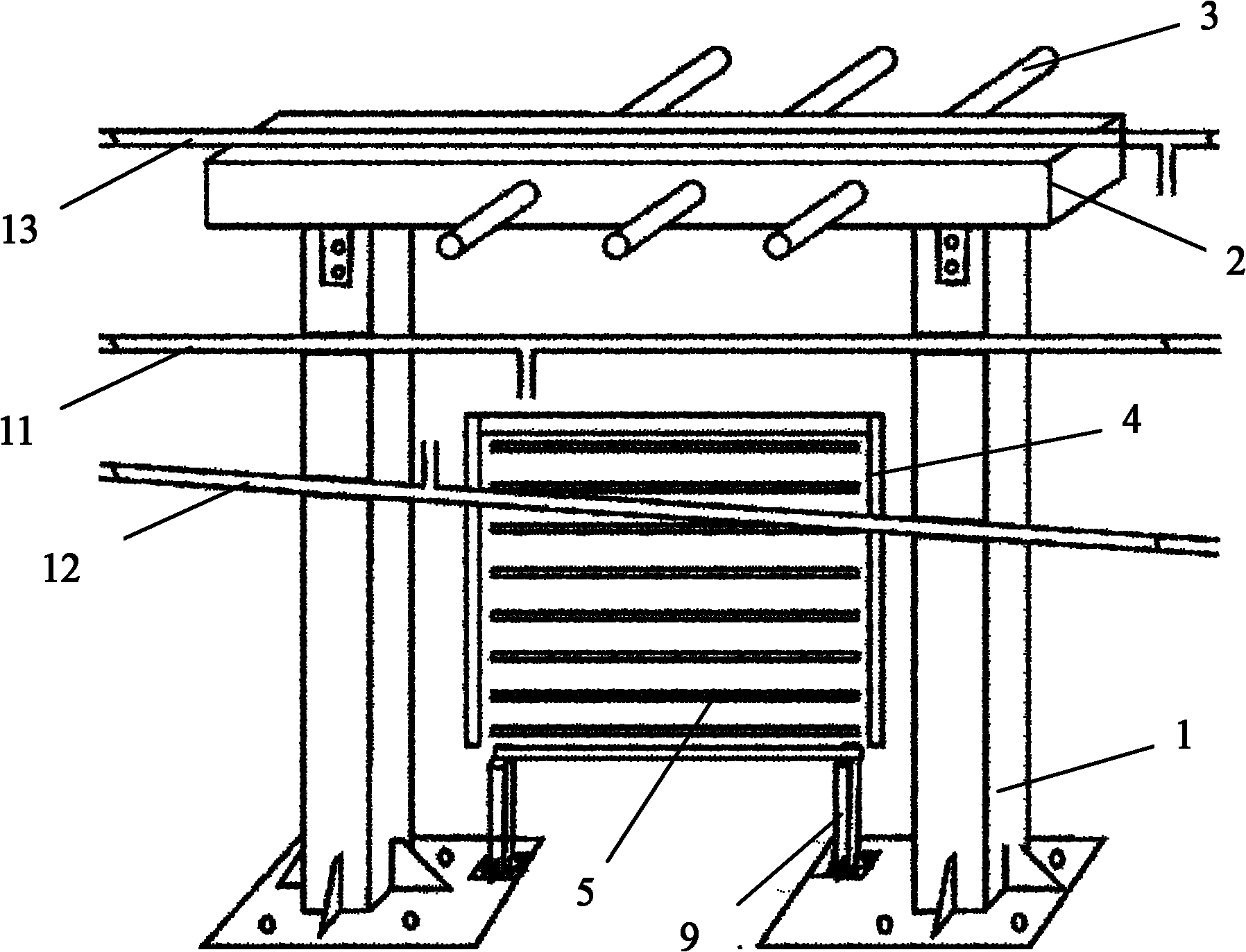
Hanging bag-type chlamydomonas culturing bracket
InactiveCN102071133AAchieve integrationClear wiringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringReaction system
The invention discloses a hanging bag-type chlamydomonas culturing bracket. The hanging bag-type chlamydomonas culturing bracket comprises at least two upright posts and a beam fixed to the top ends of the upright posts, wherein 3 to 5 supporting rods are arranged on the beam; a lamp hanger in which lamp tubes are arranged is arranged under the beam between two adjacent upright posts; a feed liquor inlet pipe and an algal liquid discharge pipe are arranged below the beam in turn; a breathing pipe is also arranged above the beam; and 6 to 8 lamp tubes are horizontally arranged on the lamp hanger from the top to the bottom. The hanging bag-type chlamydomonas culturing bracket has a simple structure and low cost, is convenient to use and is firm and durable, provides an effective support structure for continuous cultivation of chlamydomonas, realizes layered fixed circuits, waterways and gas circuits, has clear routing, distinct levels, less space occupation and clear wiring conduit in the continuous cultivation of the chlamydomonas, fully utilizes light sources, can support an overall reaction system in all directions, and is convenient to operate and effectively control in a cultivation process of the chlamydomonas.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
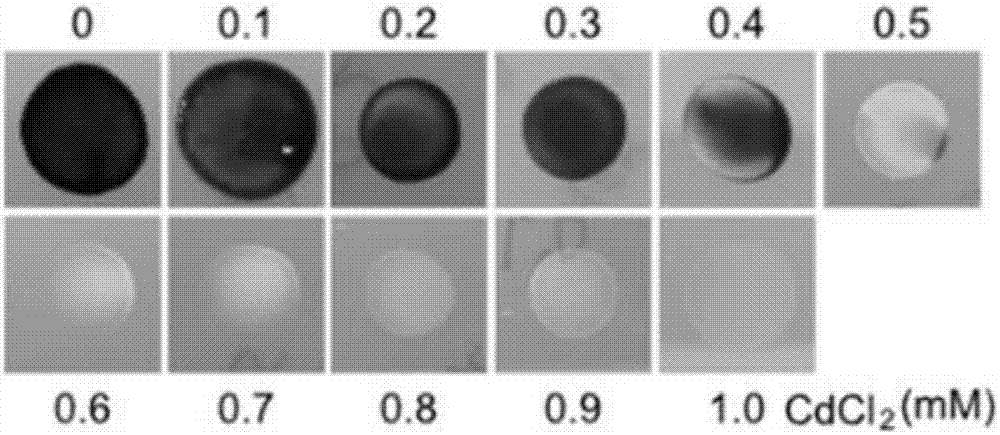
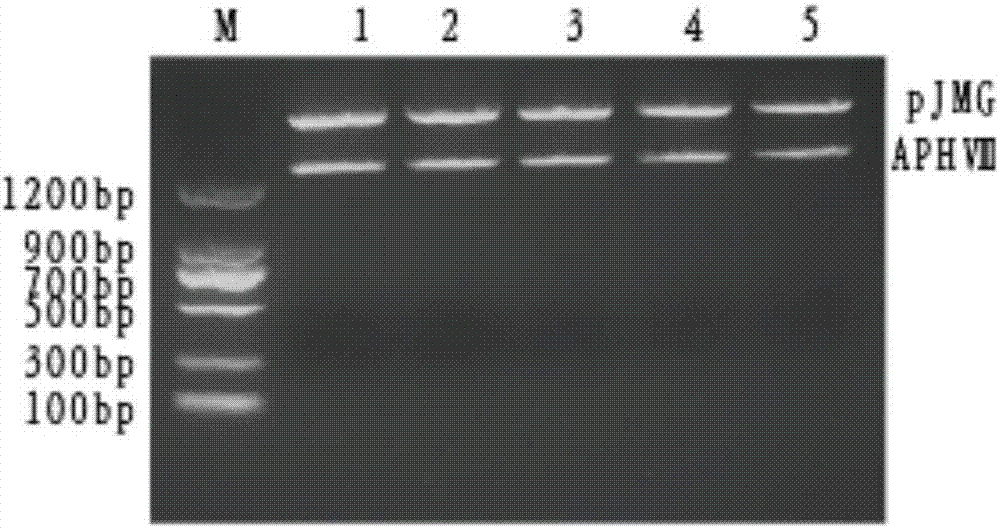
Screening method of chlamydomonas reinhardtii heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants
InactiveCN106967749ASimple stepsImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCadmium adsorptionChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a screening method for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The screening method comprises: selecting a suitable screening concentration for heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants according to the influence of different cadmium chloride concentrations on the growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii; Transformation to obtain Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutants; screening out heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the screening of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii includes screening heavy metal cadmium sensitive mutants and screening heavy metal cadmium resistant mutants; identification screening Mutant genes of heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention achieves the technical effect of being able to obtain a large amount of Chlamydomonas heavy metal cadmium adsorption mutants simply and efficiently.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Litopenaeus vannamei ecological breeding method based on live food and water quality bio-regulation
InactiveCN110292009APhysically strongStrong resistanceClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseWater quality
The invention discloses a litopenaeus vannamei ecological breeding method based on live food and water quality bio-regulation. The method includes following steps: (1), treating water before breeding,and performing live food culture; (2), arranging larvae; (3), breeding, regulating water quality, and preventing and controlling pest and disease; (4), marking thickness, desalting, and transferring.An ecological breeding technique of chlamydomonas plus artemia plus probiotics plus compound Chinese herbal medicine is provided, and natural protein, trace elements and minerals are provided for theshrimp larvae, so that the shrimp larvae have strong physique and resistivity, and ecological shrimp larvae bred by the method are big in size, orderly in specification, quick in growth and high in survival rate. The breeding method is advanced in concept, scientific, reasonable, easy in implementation and suitable for large-scale application in high-health breeding of litopenaeus vannamei and has good social benefit and economic benefit.
Owner:GUANGXI ACADEMY OF FISHERY SCI
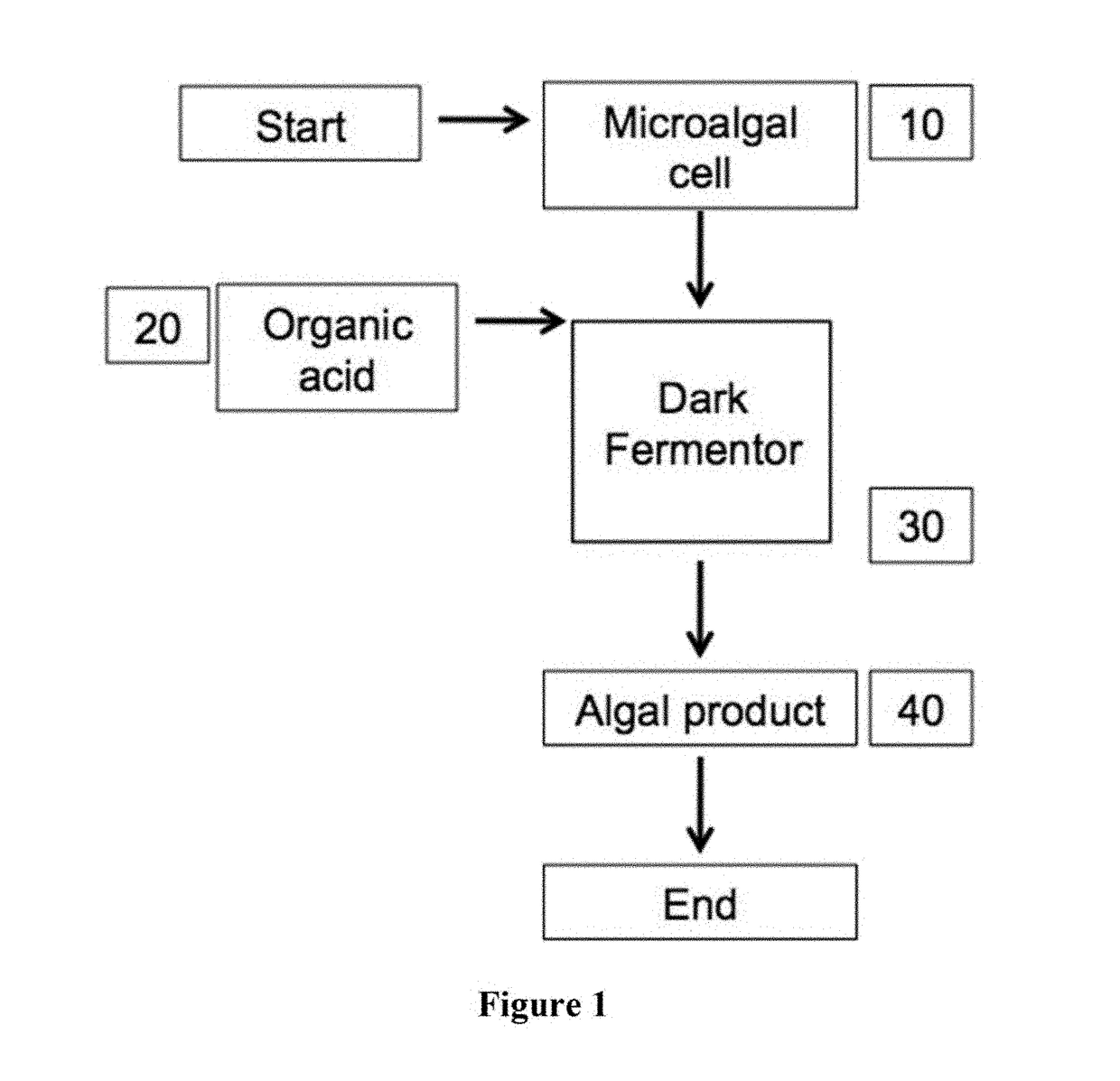
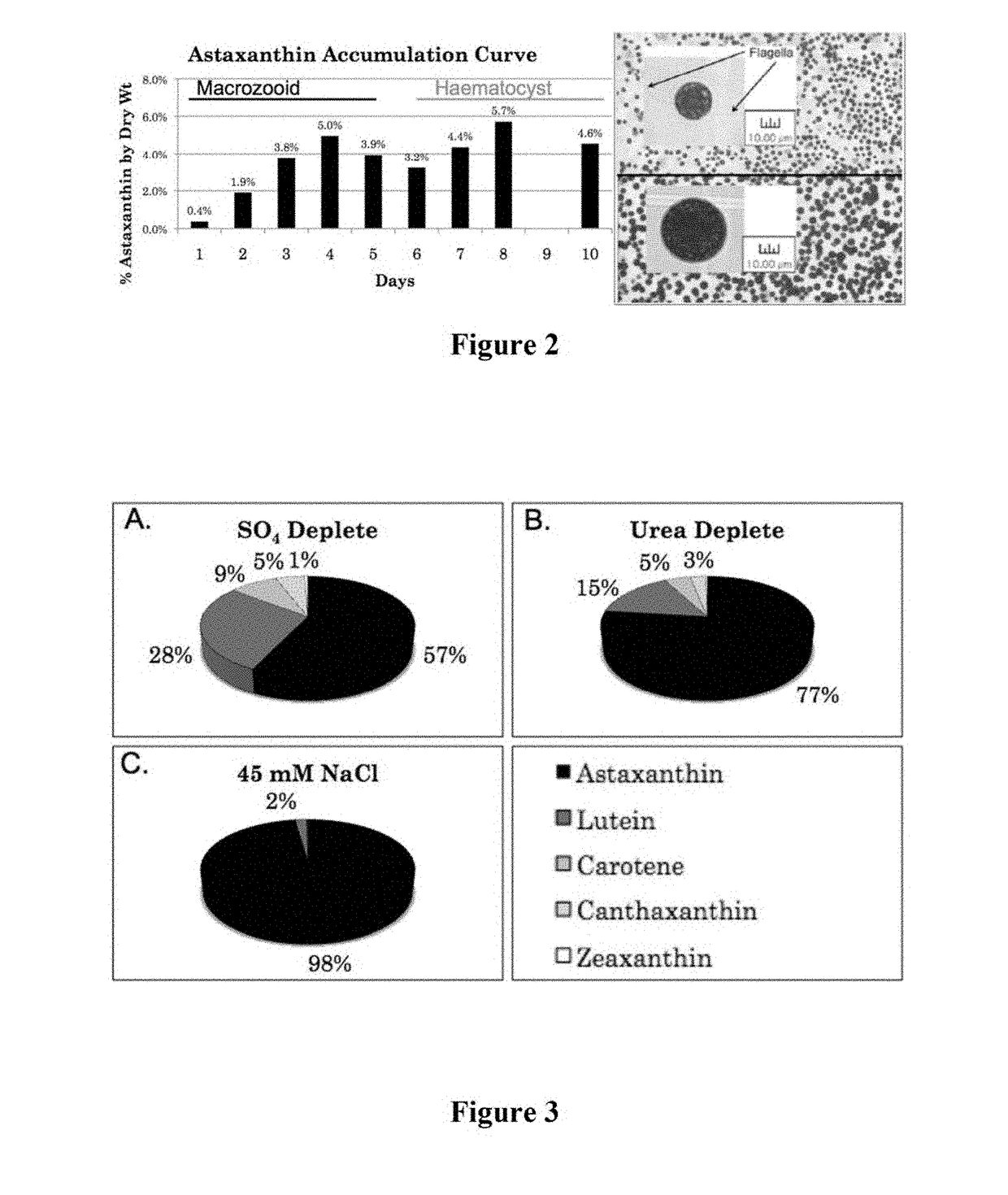
Heterotrophic production methods for microbial biomass and bioproducts
The invention pertains to a method for synthesizing a product of interest by culturing a microalgal cell producing the product of interest in the dark in a culture medium comprising an organic acid as a fixed carbon source, wherein the microalgal cell is a facultative heterotroph. The product of interest can be a microalgal biomass, a pigment, terpene, recombinant molecule, biogas, or a precursor thereof. In an embodiment, the culture medium comprises urea as a primary source of nitrogen. In one embodiment, the microalgal cell belongs to the order Chlamydomonadales. A method of identifying and isolating a microalgal cell having a preferred characteristic that is suitable for synthesis of a product of interest is also provided, the method comprising identifying and isolating a non-mutagenized or recombinant microalgal cell from a microalgal culture using a fluorescence activated cell sorting technique and / or a phototaxic response.
Owner:KUEHNLE AGROSYST
Enzyme Directed Oil Biosynthesis In Microalgae
The present invention is related to biosynthetic oil compositions and methods of making thereof. In some embodiments, the invention relates to the use of endogenous enzymes in plants capable of synthesizing oil. In preferred embodiments, said plants are algae. In further embodiments, said algae are from the family Chlamydomonas, Nannochloropsis, Dunaliella, Chlorella and Scenedesmus. In still further embodiments, said endogenous enzymes are diacylglycerol acyltransferases.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for artificial oxytocin and fertilization of Mytilus coruscus
InactiveCN103548720AAccurately determine the time of artificial induced laborImprove efficiencyAnimal reproductionClimate change adaptationMytilus coruscusOxytocin
A method for artificial oxytocin and fertilization of Mytilus coruscus comprises the following steps of a parent cultivating pool: building an outdoor cultivating cement pool with the dimension of 10cmx1.5mx1m, stocking inflatable stones, covering canvas above the cement pool to prevent rain and sunlight, and shading the periphery of the cement pool by dark cloth to regulate strength of light; selecting Mytilus coruscus which has new and integral shell surfaces, full gonads, complete gill, light red ovaries and white testes, and is free of damage and powerful in closure of double shells; preparing baits, wherein chlamydomonas live baits including cultured Dunaliella viridis, latymonas subcordiformis and Chaetoceros serve as primary baits, and artificial compound feed including spirulina powder, chlorella powder and yeast tablets serves as secondary baits; drying parent Mytilus coruscus with developed gonads in the shade for 6-8 hours, stimulating the parent parent Mytilus coruscus for 1 hour through running water, and feeding the parent parent Mytilus coruscus into prepared warming seawater.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENG LAKE FISHERIES TECH CENTCO
Artificial breeding method for tuba false fusus
InactiveCN101946720ARealize indoor artificial seedling cultivationShorten the artificial breeding cycleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater flowSalinity
The invention relates to an artificial breeding method for tuba false fusus, which comprises the following steps of: on the basis of investigating tuba false fusus resources along the coast of Hainan and reproductive biology, finding out the thriving propagation season of the tuba false fusus, and catching parent tuba false fusus in the season; putting healthy adult tuba false fusus into a nursery pond for intensified breeding, and optimizing breeding conditions such as water flow, illumination, water temperature, and salinity; after the tuba false fusus is mated and lays eggs, cutting off an egg capsule, and transferring to an incubation basket for flowing water breeding; after young tuba false fusus is hatched, transferring to a breeding basket, feeding concentrated chlamydomonas in first 4 to 6 days, and then feeding fresh clam and Sinonovacula constricta; when the young tuba false fusus grows to 2.0-2.5cm, dividing the young tuba false fusus; and when the young uba false fusus grows to about 4.0cm in the breeding basket, entering a culture stage. Based on the reproductive biological process of the tuba false fusus, the method realizes indoor artificial breeding of the tuba false fusus, shortens the artificial breeding cycle, is suitable for mass production, and has the advantages of simpleness, practicability, convenient operation, low production cost, and high survival rate of the bred tuba false fusus.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization
InactiveCN102146344AHigh expressionLower oxygen levelsUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to exogenous gene expression and biological hydrogen production technologies, in particular to a method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization. In the prior art, the expression efficiencies of exogenous leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast are low, thus influencing the increase of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity. The invention discloses a method for respectively optimizing the codon bias of the leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba. The codon-optimized hemHc and lbac genes are transferred into the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast to be expressed. The invention obviously increases the expression quantity of the exogenous recombinant protein; the expression quantity of the exogenous leghemoglobin hemH and Lba in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast is increased by 6.8 times; and compared with the non-codon-optimized hemH and lba transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity is increased by 22%. The invention is applicable to regulating and controlling the exogenous gene expression of more species having codon bias.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
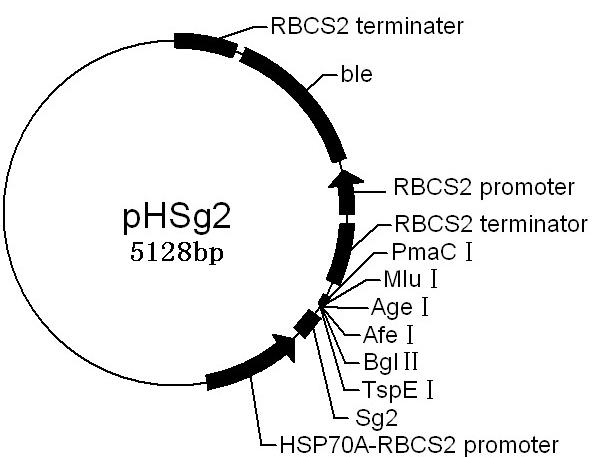
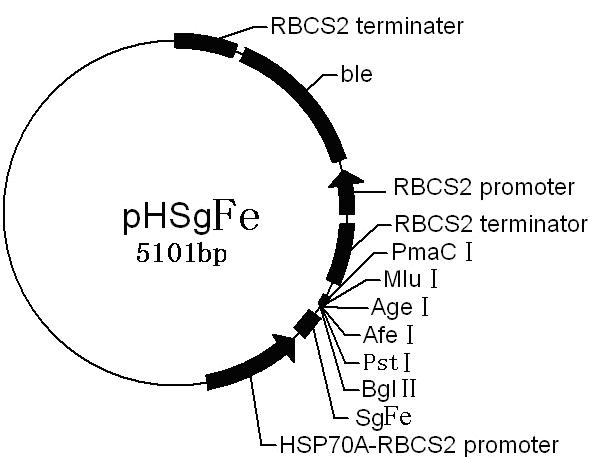
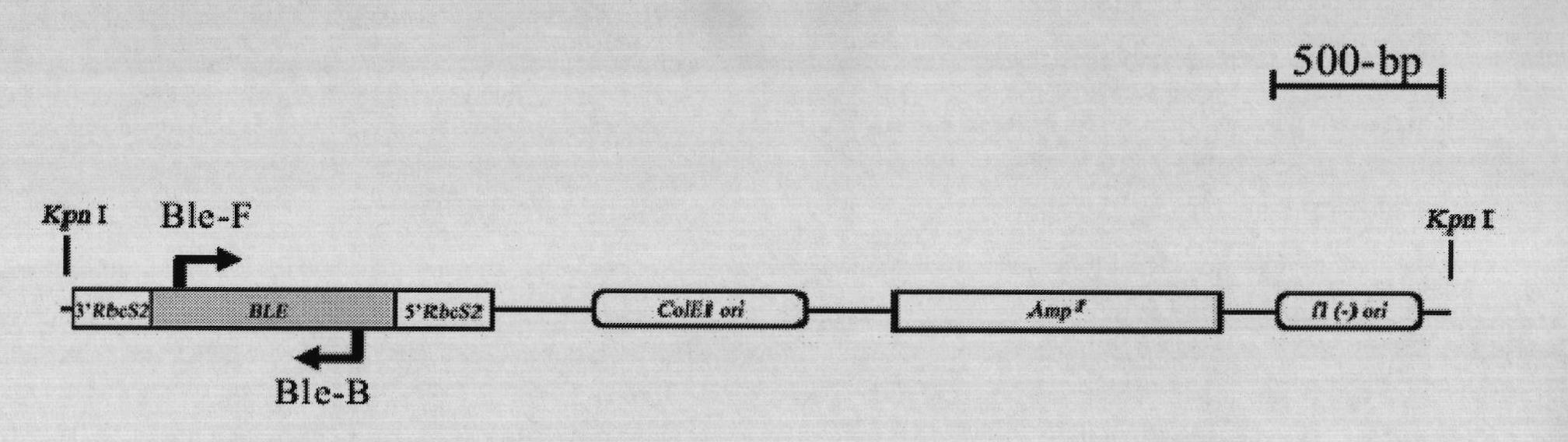
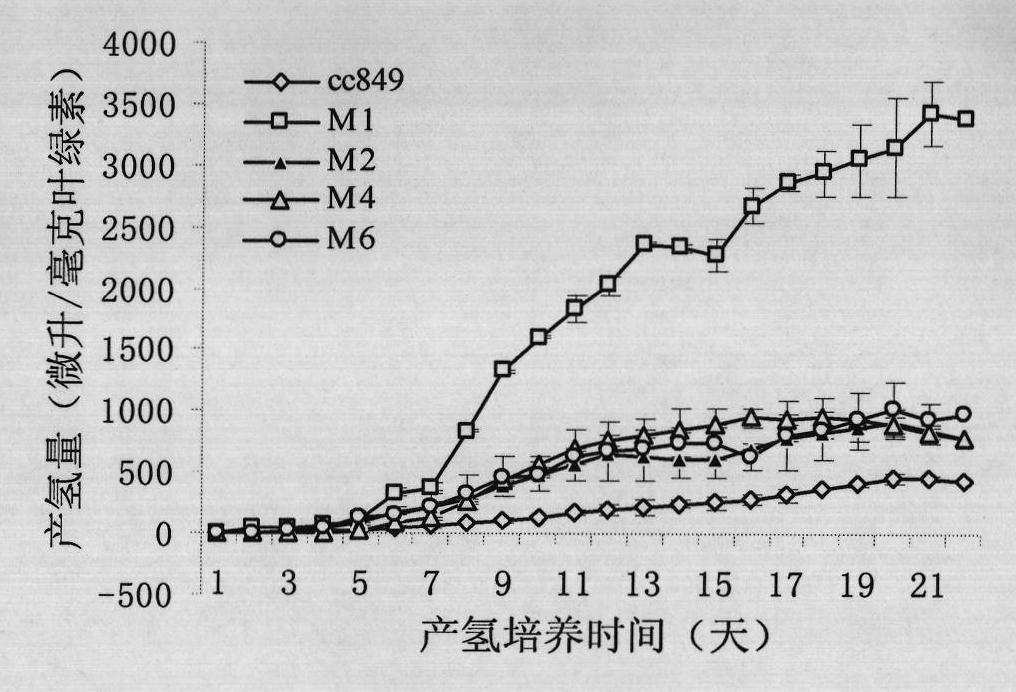
Method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis
InactiveCN101864365AHigh biohydrogen productionGood experimental materialUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii has low hydrogen production rate and limits the application and the development of a biological and photosynthetic hydrogen production technology. The method for obtaining a high-hydrogen-production mutant strain through the random insertion mutagenesis of chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nuclei comprises the following steps: cultivation of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii; preparation of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation vector and a glass bead; chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation and transformant screening; analysis of the hydrogen yield and the oxygen consumption of chlamydomonas reinhardtii transformant hydrogen-production cultivation; analysis of the integration and the expression thereof of ble genes in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant strain; and analysis of the influence of recombinant leghemoglobin hemH-1ba on the growth of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention has the advantages that the biological hydrogen production yield of the obtained high-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii is 7 times of the original yield; the method provides a good experimental material and a good basic condition for deeply researching the hydrogen-production metabolic mechanism of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka
InactiveCN102100195ALow costIncrease productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAuriculariaFishing
The invention aims to provide a method for breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka. The method comprises the following steps of: placing oosperms of the apostichopus japonicus selenka in an hatching slot for hatching; breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka larvae in a breading tank after small auricularia larvae are produced by hatching the oosperms; putting attaching bases for collecting young apostichopus japonicus selenka when 20 to 30 percent of the apostichopus japonicus selenka larvae grow into doliolaria larvae; and screening and taking the young apostichopus japonicus selenka out of the tank when the young apostichopus japonicus selenka grow to the length of between 2 and 4cm, and transferring the young apostichopus japonicus selenka into a pool for breeding. The apostichopus japonicus selenka bred in the pool is not required to be fed, and natural basic bait organisms brought by water changing are taken as feeds such as chlamydomonas and benthic diatoms primarily. The apostichopus japonicus selenka is harvested by an artificial diving fishing method when growing to the weight of between 4 pieces / kg and 6 pieces / kg.
Owner:SHANDONG HAIYIBAO AQUATIC PROD
Soilless Nereid larva breeding method
The invention relates to a soilless Nereid larva breeding method. According to the method, with 27-29 DEG C of water temperature, 7.8-8.6 of pH and 28-30 of salinity, larva breeding water undergoes dark precipitation and secondary sand filtration and is then filtered for further use by a 300-mesh bolting-silk bag; large and vigorous heteronereis bodies with no exterior wounds are selected and positioned in a plastic bucket containing 0.5 m3 of sea water for oviposition and insemination according to a proportion of 3:1 between the female and the male heteronereis bodies; oosperms undergo three times of egg washing and then are moved into a larva breeding pond; larva in a roaming period are mainly fed with chlamydomonas together with a certain amount of artificially mixed feed; when the larva grow into five-setiger nectochaeta larva, gracilaria is put in the pond as an attachment substrate, and a small amount of fish paste is also fed; and during the Nereid larva breeding, according to larva growing periods, the light illumination is controlled in a range of 300-1000 Lux. When the gracilaria is used for replacing silt as the Nereid perching place, as the gracilaria can utilize the metabolic products of the Nereids as the nutrients to promote self growth and is easily cleaned, the living environment of the larva can be bettered, the diseases and the damage to the larva during larva generation can be reduced, and the survival rate of the larva can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Method for constructing artificial algal crusts by utilizing mixed algae
InactiveCN102613065ARapid multiplicationLarge biomassClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsNaviculaRefrigerated temperature
The invention discloses a method for constructing artificial algal crusts by utilizing mixed algae. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting sufficiently developed algal crusts on the desert, collecting the algal crusts, and grinding the algal crusts after air-drying the algal crusts; sieving bare sand with a 0.2mm sieve, then adding 1 liter of BG11 liquid culture medium to 100g of bare sand, and collecting the algae together with the grains of sand fixed on the algae three weeks later, wherein the inoculum size is 50g dry soil per liter of culture medium, the culture temperature is the room temperature, the illumination intensity is 4000lux, and in the cultured mixed algae, the dominant species are filamentous algae which are mainly microcoleus, lyngbya and phormidium and account for 80% of the total biomass, and species such as oscillatoria, chlorococcum humicola, chlorella, chlamydomonas, Navicula, hantzschia and the like account for 20% of the total biomass; grindingthe collected algae into alga powder after air-drying the collected algae, and putting the alga powder in a refrigerator at minus 20 DEG C; and carrying out inoculation on the bare sand when the soiltemperature is 20 DEG C, wherein the inoculum size is 80g.m<-2>, and the moisture applied daily is 3L.m<-2>. The method successfully avoids the problems of purification and separation of the algae, and has wide applicability.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
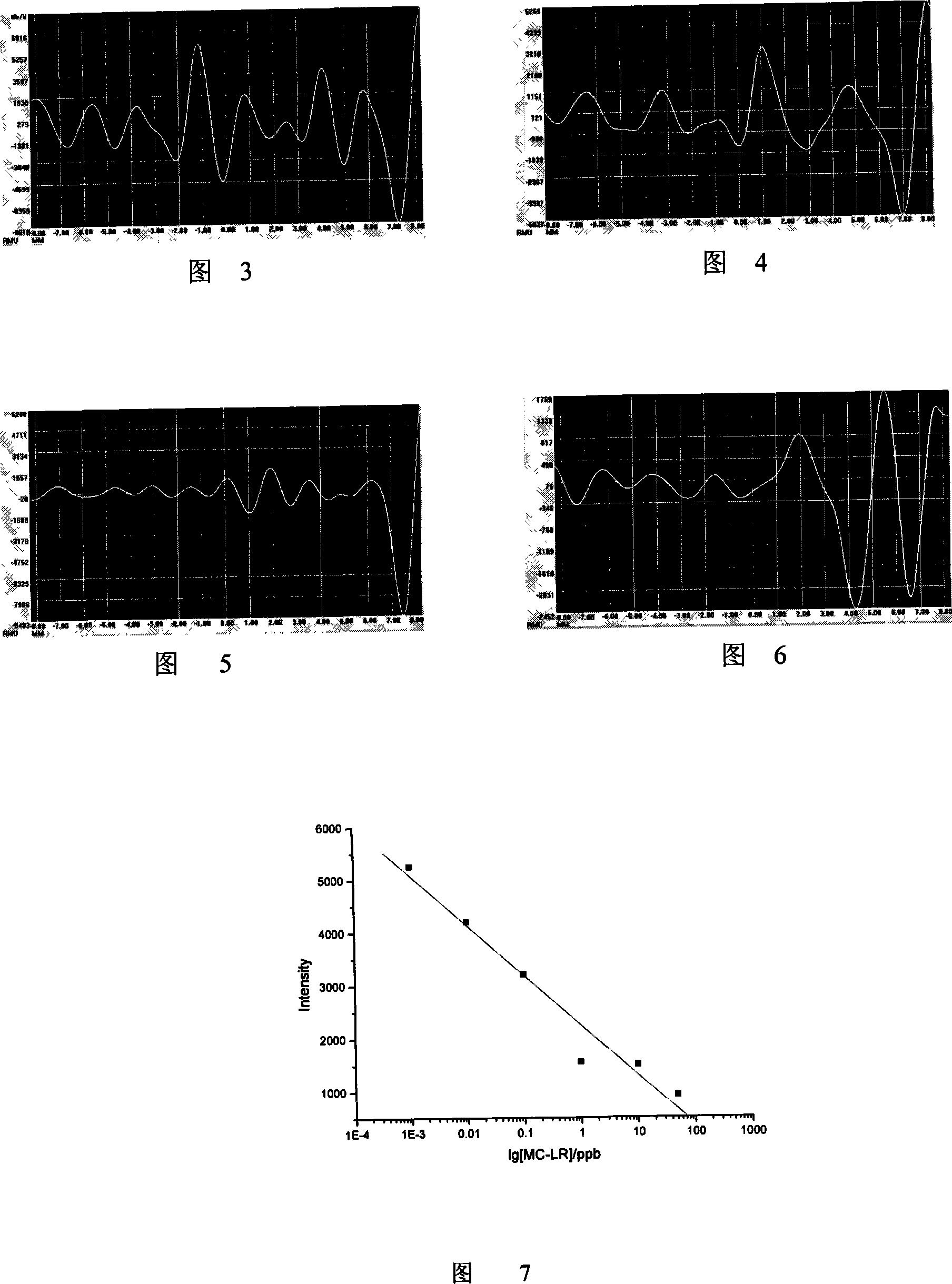
Water body Chlamydomonas reinhaidtii toxin detection method
The invention relates to a measuring method of micro-capsule alga toxin in water. The method includes the steps as follows: firstly, compounding and appraising of the micro-capsule alga toxin; secondly, preparing and purifying of polyclonal antibody antibody: immunizing the New-Zealand rabbit by making the micro-capsule alga toxin holoantigen MC-LR-KLH as the immunity resource, and preparing the polyclonal antibody and purifying by ammonium sulphate according to the normal method; thirdly, preparing immune bead: coupling the micro-capsule alga toxin holoantigen MC-LR-BSA and the nanometer bead, and preparing the immune bead containing MC-LR-BSA; fourthly, embedding the antibody to the pyroxylin film; fifthly, producing testing board, combing the coupling mat of the magnetic scale MC-LR-BSA, the pyroxylin film embedding the polyclonal antibody, the sample mat, the sopping mat, the covering film, the testing board out card into a testing board; sixthly, sample testing, respectively adding standard goods and testing samples with different concentrations into the sampling holds on the testing board, the samples flow on the test paper through the chromatography effect, after 3 to 5 minutes of the reaction under the room temperature, the testing board is put into a magnetic single testing apparatus to be tested, and the testing apparatus can further output the biology reaction signals being transferred to the magnetic field signals by the way of the electric signals; after the standard curve being drawn, the specific value of the micro-capsule alga toxin content in the sample to be tested is counted based on the standard curve.
Owner:嘉兴博泰生物科技发展有限公司
Method for preparing dried chlamydomonas products, its products and use thereof
InactiveCN1632100AExtended shelf lifeGood dispersionUnicellular algaeAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceNitzschia closterium
Disclosed are a preparing method and its product and application. Firstly, condense the pelagic unicellular alga in 1~2 degree, which is made into cream-condensed alga product, the dry it in low temperature or in vacuum, making the products which will not become harmful substance to juvenile of animal culture and can be diffused into alga juvenile of animal culture single cell with complete cell, finally, package it in vacuum or in nitrogen. The invention can be applied in all kinds of pelagic unicellular alga, and the products includes chlorella, nitzschia, chaetocero, can replace live pelagic unicellular alga to be applied in culture of seedling of animal culture in water, cultivation and strengthening of diet animal, especially for feeding diet animal .
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Anti-stress health agent for pomfret
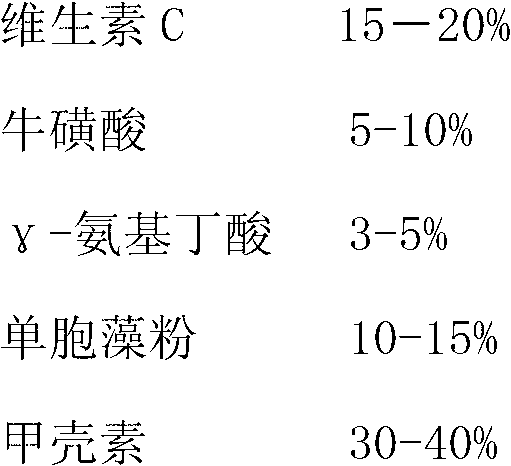
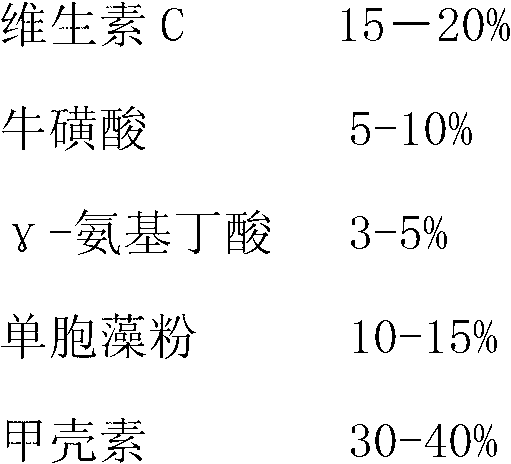
The invention relates to an anti-stress health agent for pomfret. The anti-stress health agent for pomfret comprises, on the basis of weight percentage of dry matters, 15 to 20% of vitamin C, 5 to 10% of taurine, 3 to 5% of gamma-aminobutyric acid, 10 to 15% of Chlamydomonas powder and 30 to 40% of chitin, with the balance being a diluent. The above mentioned components are uniformly mixed and then added into a feed for pomfret, wherein the components account for 1 to 4% of the total weight of the feed. The anti-stress health agent provided in the invention has good anticonvulsant and tranquillization-promoting effects, enables the survival rate of cultured pomfret to be obviously increased, improves the feeding rate of pomfret and promotes growth of pomfret; and the agent has the advantages of stable sources of raw materials, low price and a simple production process.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
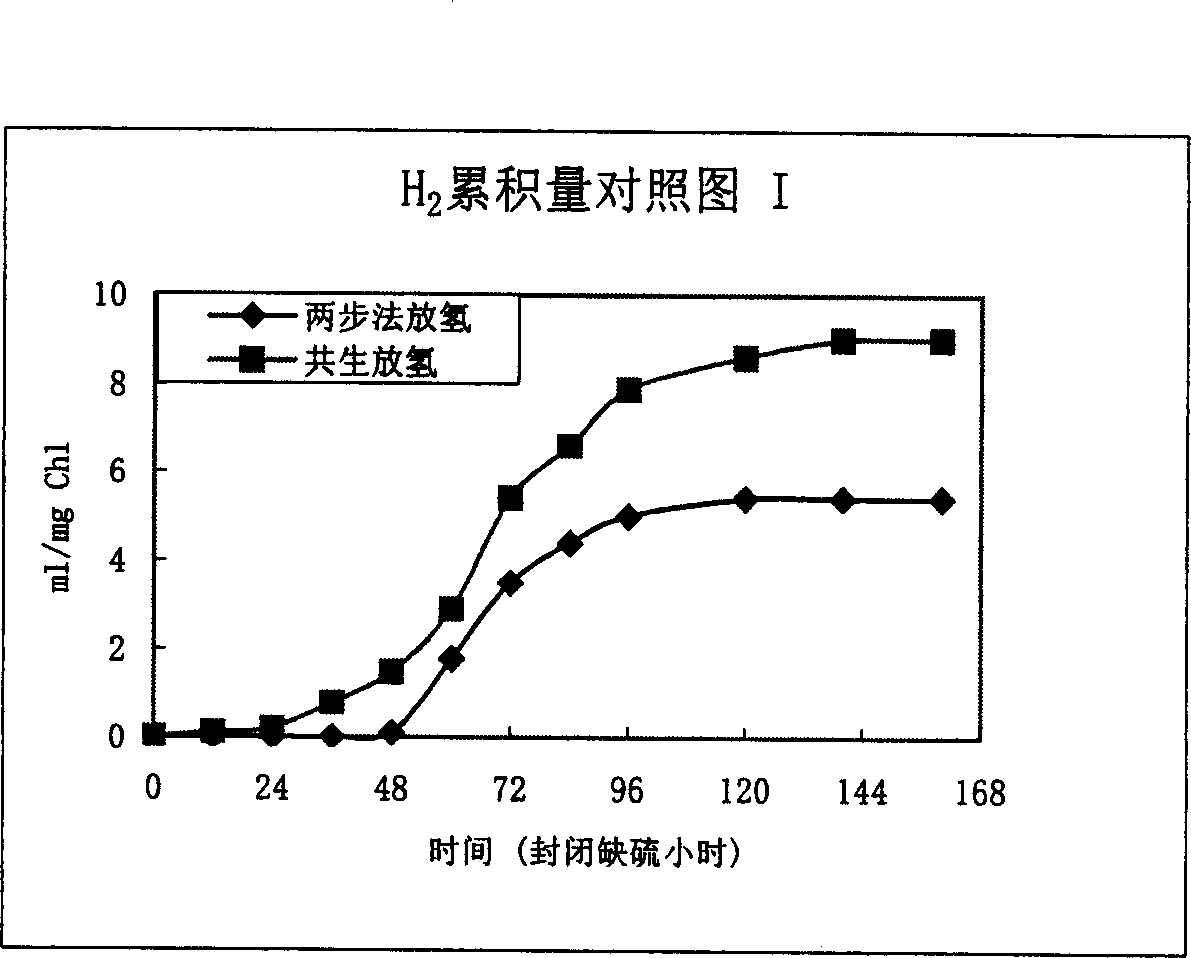
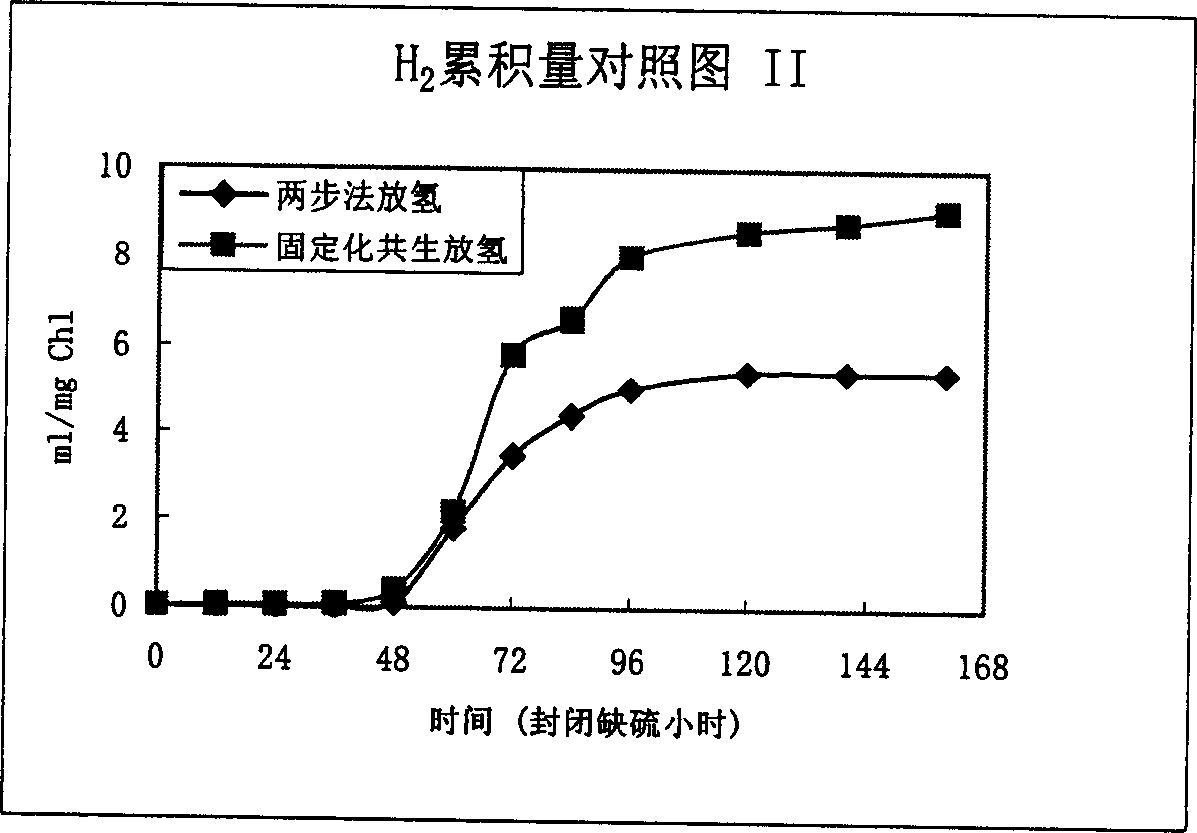
Method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102559832AIncrease hydrogen productionReduce the greenhouse effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamyodomonas reinhardtii. Through mixing aerobic bacteria represented by bradyrhizobium japonicum with the chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to a certain proportion for culture, the hydrogen output can be remarkably improved. The invention provides a new method for further improving the hydrogen output in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii twp-step-method hydrogen production technology.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for improving yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes
InactiveCN101845461AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiChloroplast
The invention belongs to a biological hydrogen production technology, particularly to a method for improving the yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes. Traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production has the disadvantages that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogenase is sensitive to oxygen and is easily inhabited by the oxygen to inactivate; and the hydrogen production effect of chlamydomonas is limited. The invention discloses application of soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes in chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production, the soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes lba are constructed in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, and the expression vector is transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast, so that the lba genes are expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The decrease of the oxygen content in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is markedly quicker than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of the untransformed genes, the oxygen content can be kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen yield is markedly increased; the method is applicable for all microalgae for hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of increasing hydrogen releasing efficient of chlamydomonas
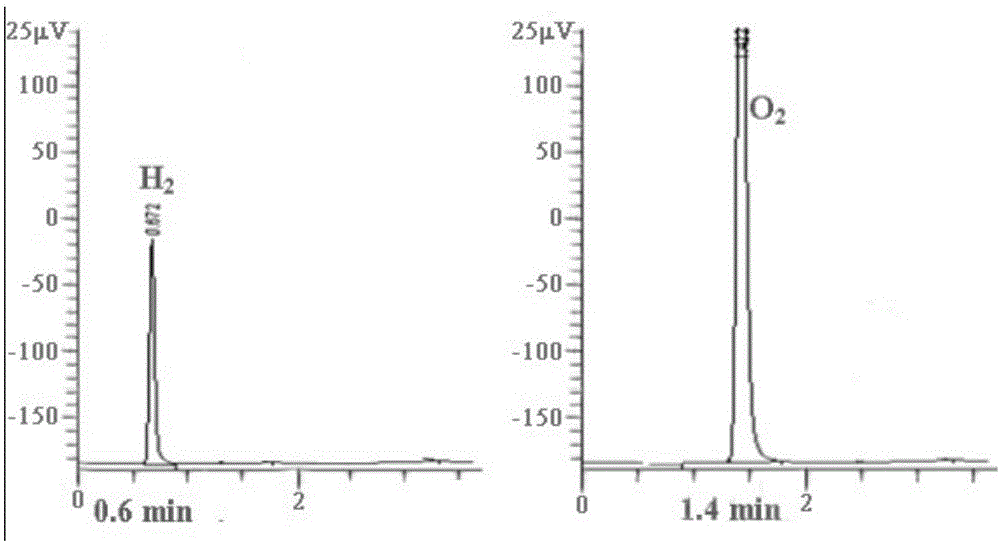
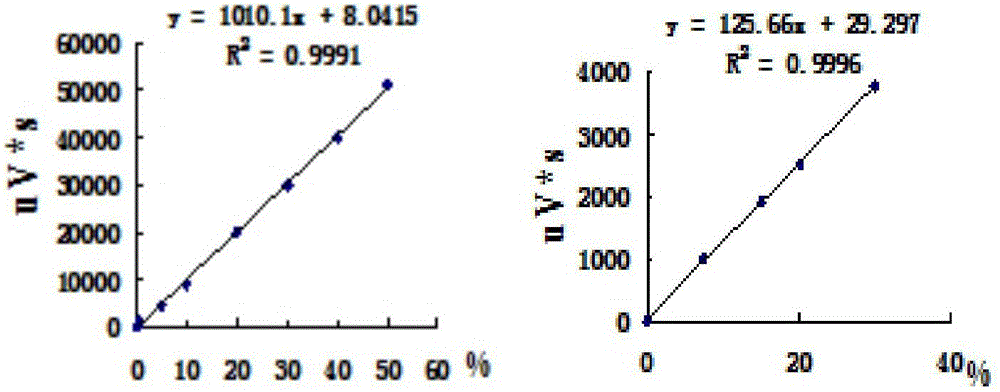
InactiveCN1657605AImproved hydrogen release efficiencyUnicellular algaeHydrogen productionHydrogenChlamydomonas
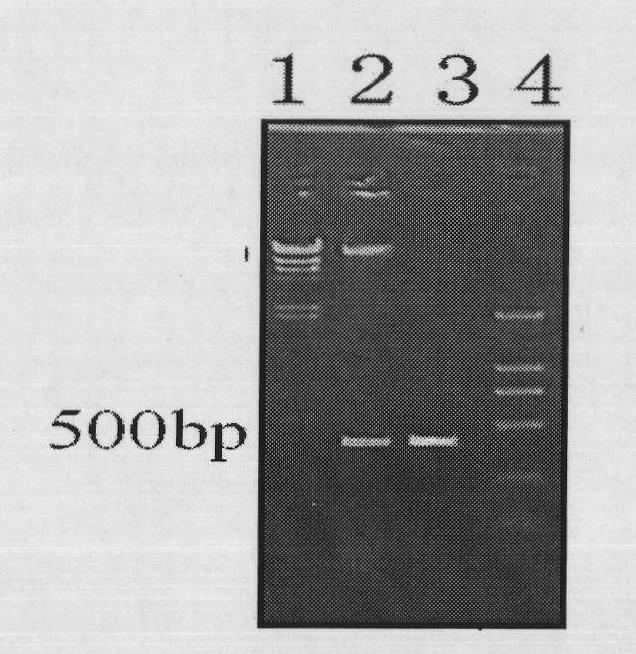
A process for increasing the hydrogen releasing efficiency of chlamydomonas features use of the dominant complementation between phycobionts.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chlamydomonas strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101892159AImprove liquidityImprove qualityFatty acid esterificationUnicellular algaeBiodieselEdible oil
The invention provides a chlamydomonas strain. Through authentication, the chlamydomonas strain is a novel strain, and the collection number of the chlamydomonas strain is CGMCC No.3577. The chlamydomonas strain has higher grease content and can be applied to preparing biodiesel, feed or edible oil.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
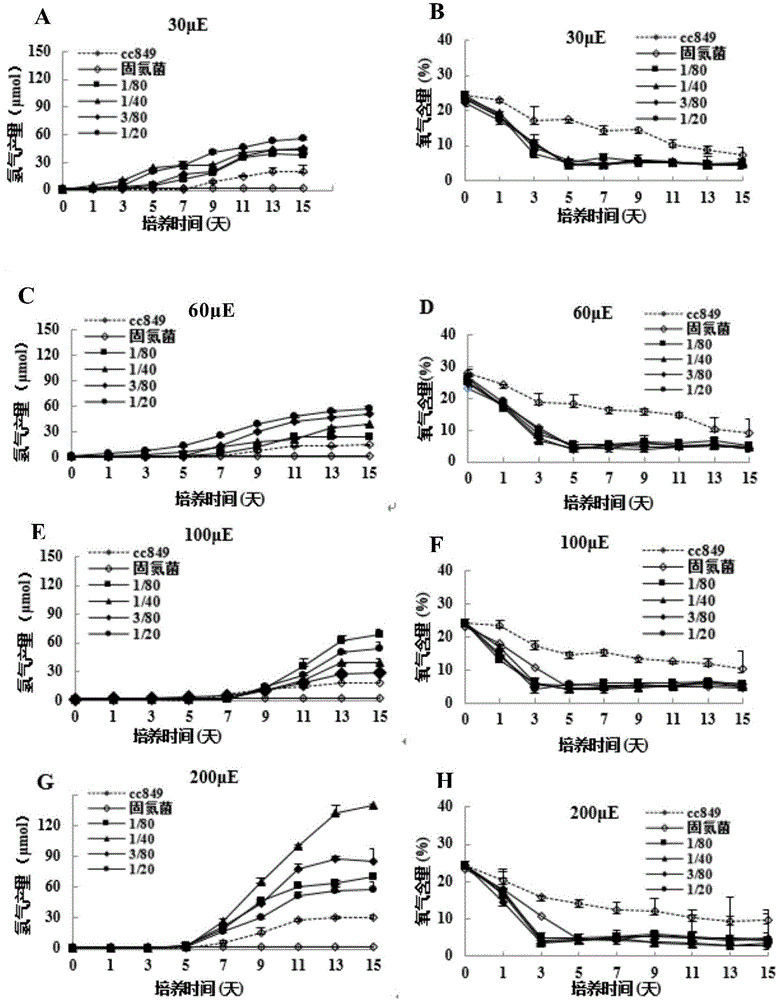
Method for improving hydrogen production of chlamydomonas
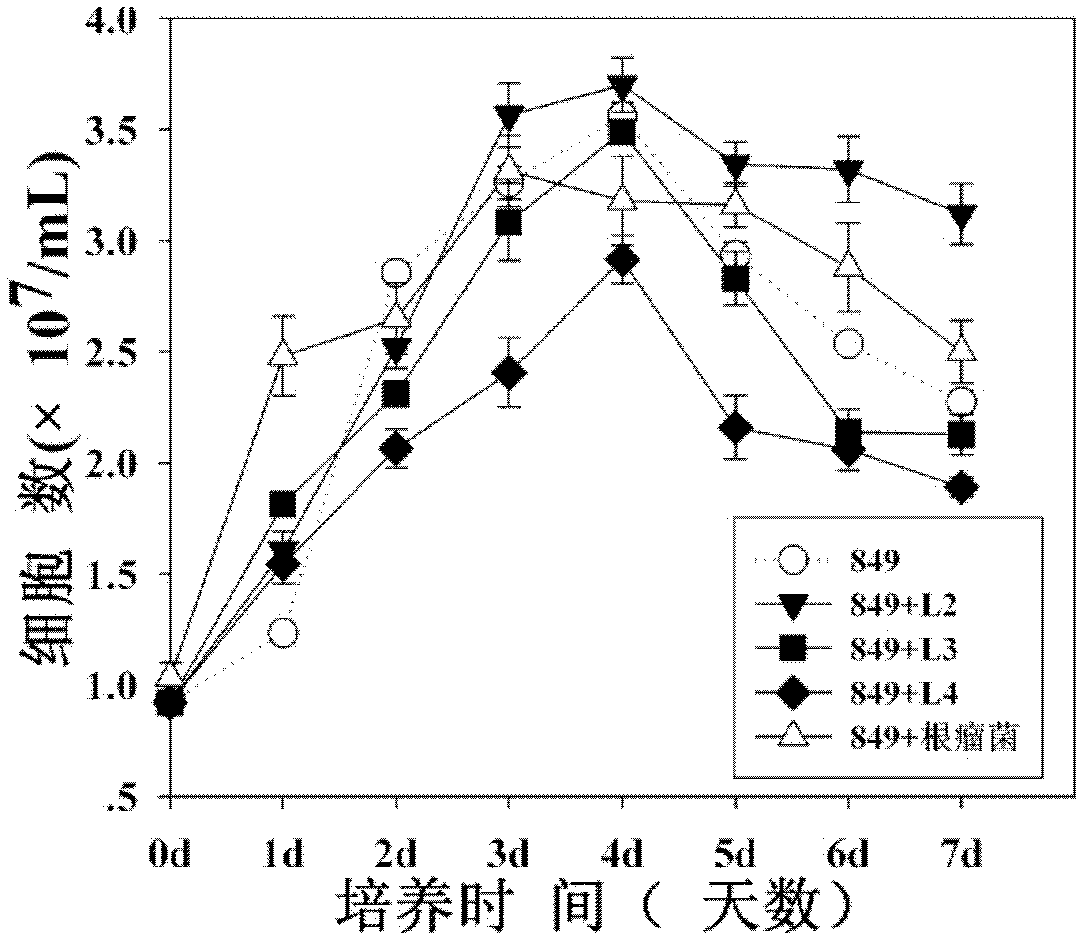
ActiveCN106520897ABroaden the range of symbiotic objectsPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention discloses a method for improving hydrogen production of chlamydomonas. The method includes steps of commonly cultivating chlamydomonas and nitrogen-fixing bacteria; before commonly cultivating, cultivating chlamydomonas to a saturated period and cultivating nitrogen-fixing bacteria to a logarithmic phase, wherein the nitrogen-fixing bacteria is round brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria; the chlamydomonas is Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cc849 (with cell wall type) and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cc124 (cell wall defective type). The method can effectively improve the hydrogen production of chlamydomonas; in relative to the hydrogen production of independent chlamydomonas, the maximum hydrogen production can be improved by 16 times.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Soilless Nereid breeding method
InactiveCN101622973AImprove the breeding environmentIncrease productionAnimal husbandryFiltrationFish paste
The invention relates to a soilless Nereid breeding method. A cement pond is used as a Nereid breeding pond. Sea water undergoes dark precipitation and secondary sand filtration and is then filtered for further use by a 300-mesh bolting-silk bag. Gracilaria is selected as a Nereid perching environment. The breeding pond and the gracilaria are sterilized. The gracilaria is paved at the bottom of the pond. The filtered sea water is added. Yong Nereids with 2-3-meter bodies are put in the pond according to a density of 1500-2000 Nereids per square meter. During the Nereid breeding, chlamydomonas, artificially mixed feed and fish paste are used for feeding the Nereids. Water in the pond is changed each day. The breeding pond is cleaned regularly. The light illumination is controlled in a range of 400-1000 Lux. Meanwhile, as the Nereid grow, the number of the Nereids is added. After 8-10 months of breeding, the Nereid yield rate can reach 5-7 kg / m2, which is 40 percent higher than the traditional breeding methods. The method adopts the gracilaria in place of silt as the Nereid perching place, thereby facilitating the cleaning, reducing a great amount of man power, fully improving the breeding environment, decreasing the possibility of diseases and being good for the growth of the Nereids and the breeding density increase. Meanwhile, the gracilaria can also be sold as commodity.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
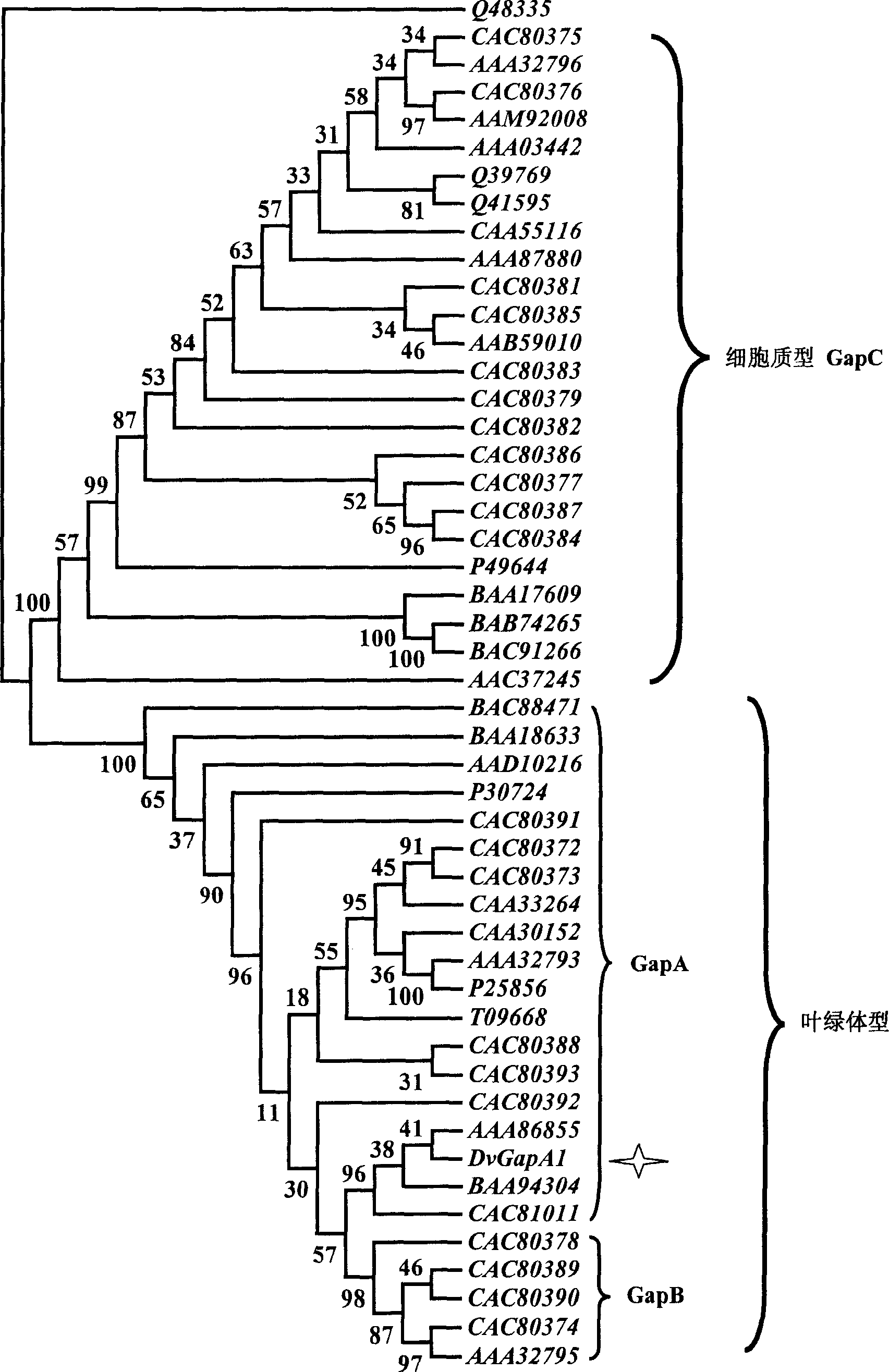
Salt algae NADP glyceral dehyde-3-phosdehydrogenase gene clone and protein expression method
The present invention relates to a kind of saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene, coded protein and its clone and protein expression method. The invented saline alga photosynthetic metabolic pathway key enzyme NADP-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene has the base sequence showed by SEQ NO 5, and its coded protein has the amino acid sequence showed by SEQ NO 6. Said invention uses homologous fragment of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene originated from chlamydomonas as probe and firstly clones a glyceraldehydes-3 phosphate dehydrogenase specialized by saline alga. Besides, said invention makes primary analysis for its sequence and coded protein sequence, at the same time makes primary function analysis for said gene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com