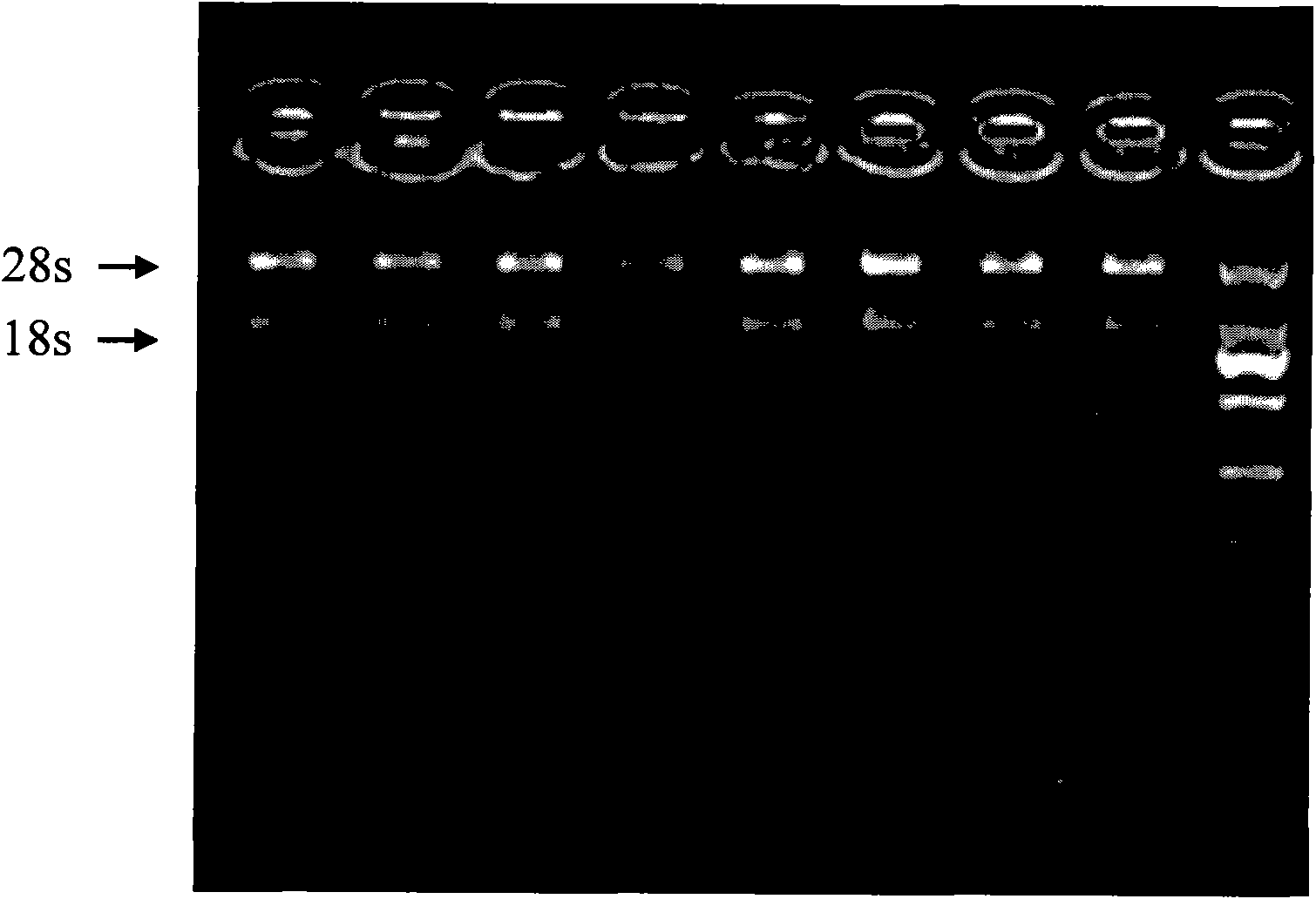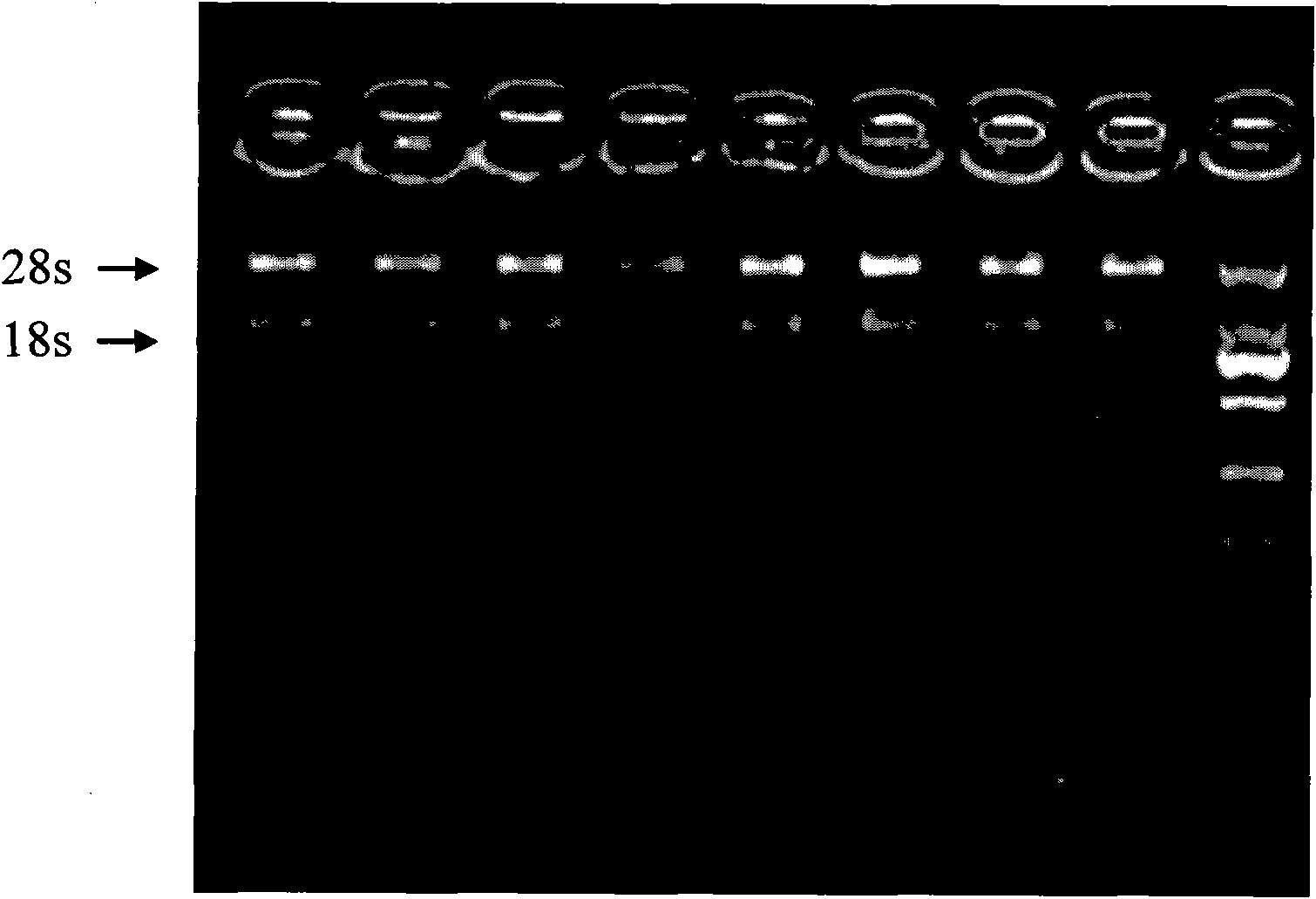Patents
Literature
111 results about "Apostichopus japonicus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apostichopus japonicus is a species of sea cucumber in the family Stichopodidae. It is found in shallow temperate waters along the coasts of south east Asia and is commonly known as the Japanese spiky sea cucumber or the Japanese sea cucumber.
Sandy pool Apostichopus japonicus ecological regulation and cultivation method
InactiveCN101305696ACreate a natural ecological environmentImprove qualityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffPolycultureEcological environment
The invention relates to an ecological trepang culture method in silt sandy ponds in coastlands, which belongs to the aquaculture field. The method comprises the steps of setting a pond, setting trepang reefs, disinfect the pond, controlling feed water, cultivating feedstuff, stocking young trepang and managing culture. The feedstuff culture which is performed in April to May comprises the following steps: firstly, transplanting benthic diatom in a height of 0.8 to 1 m feed water depth in the pond in the prior period, with 5 to 10 L of benthic diatom liquid per Chinese acre; secondly, transplanting ruppia maritime and amphilhoe japonice, especially, integrally transplanting ruppia maritime through pulling up by the roots according to the quantity of 5 to 15m per square meter, and transplanting amphilhoe japonica according to the quantity of 1.5 to 3 kg per Chinese acre after the transplanting of ruppia maritime; thirdly, poly-culturing mussel organism; fourthly, feeding water to the pond to the depth of 3 to 4 m, and stocking prawns according to the quantity of 500 to 1500 per Chinese acre. In the method of the invention, ecological feedstuff is adopted for transplanting and polyculture, therefore, not only the cost of artificial feedstuff is saved, but also the natural ecological environment is created for trepang culture.
Owner:张士华
Method for preparing sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha
InactiveCN101579057AImprove survival rateLow costFood processingClimate change adaptationAdditive ingredientSargassum thunbergii
The invention discloses a method for preparing sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha. In the method, sea cucumber compound feed is added and mixed with dry Enteromorpha powder to form the sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha, the coefficient of variation of the obtained sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha after being fully mixed is less than or equal to 10 percent, and the obtained sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha are made into grains with a diameter of 3 millimeters by using 2 percent sodium alginate as a binder. The added dry Enteromorpha powder accounts for 30 percent of the weight of the sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha. The sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha comprises the following ingredients by weight percentage: 10 percent of fish meal, 5 percent of Sargassum thunbergii powder, 20 percent of vinasse, 15 percent of sea mud, 10 percent of bean pulp, 30 percent of Enteromorpha powder, 8 percent of bran, 1 percent of vitamin mix and 1 percent of inorganic slat mix. In the sea cucumber compound feed with additional Enteromorpha prepared by the formulation, the Enteromorpha powder used to replace kelp powder can reduce the cost of feed prepared by the conventional formulation (not using the Enteromorpha powder) and avoids influencing the growth of Apostichopus japonicus Selenka; and the survival rate of the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka is improved remarkably (P is less than 0.05).
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA
InactiveCN101864414AMeet Gene Expression AnalysisFulfil requirementsDNA preparationWater bathsTotal rna
The invention discloses a high-extraction-purity, good-integrity and high-yield extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps of: quickly freezing apostichopus japonicus body-wall tissue in liquid nitrogen; grinding and putting the frozen tissue in lysate to homogenate, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding chloroform to the supernatant fluid and centrifugating to take the supernatant fluid to another centrifuge tube; then, adding a high-salt solution and isopropyl alcohol and filtering precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the precipitation with DEPC (diethypyrocarbonate) treated water to have constant volume; sequentially adding a DNA enzyme buffer solution without RNA enzymes, DNA enzymes without RNA enzymes and an RNA enzyme inhibitor to the dissolved solution to mix; carrying out a water bath at 37 DEG C to obtain DNA lysate; adding phenol and chloroform in a ratio of 5:1 to the DNA lysate to mix, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding a glycogen solution, a potassium acetate solution and pre-cooling ethanol to the supernatant fluid; mixing and staying over night; centrifugating to discard the supernatant fluid; washing and dying the precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the solution with the DEPC treated water to have constant volume of 20 mu l; and storing at 80 DEG C below zero.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Anti-oxidation and DPP-IV inhibition active peptide derived from apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN109400678AHigh puritySmall molecular weightPeptide preparation methodsFermentationDiseaseSeparation technology
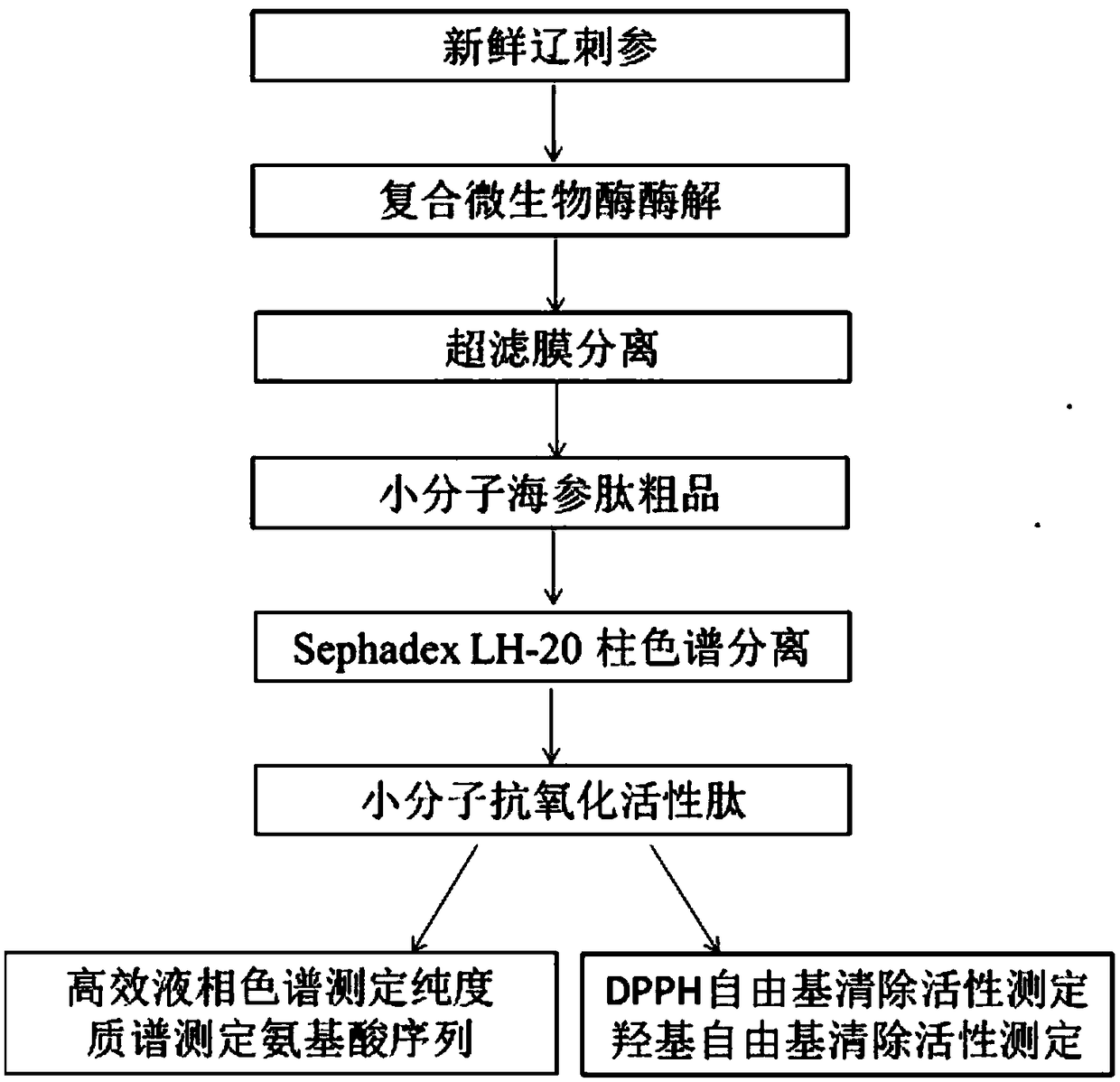
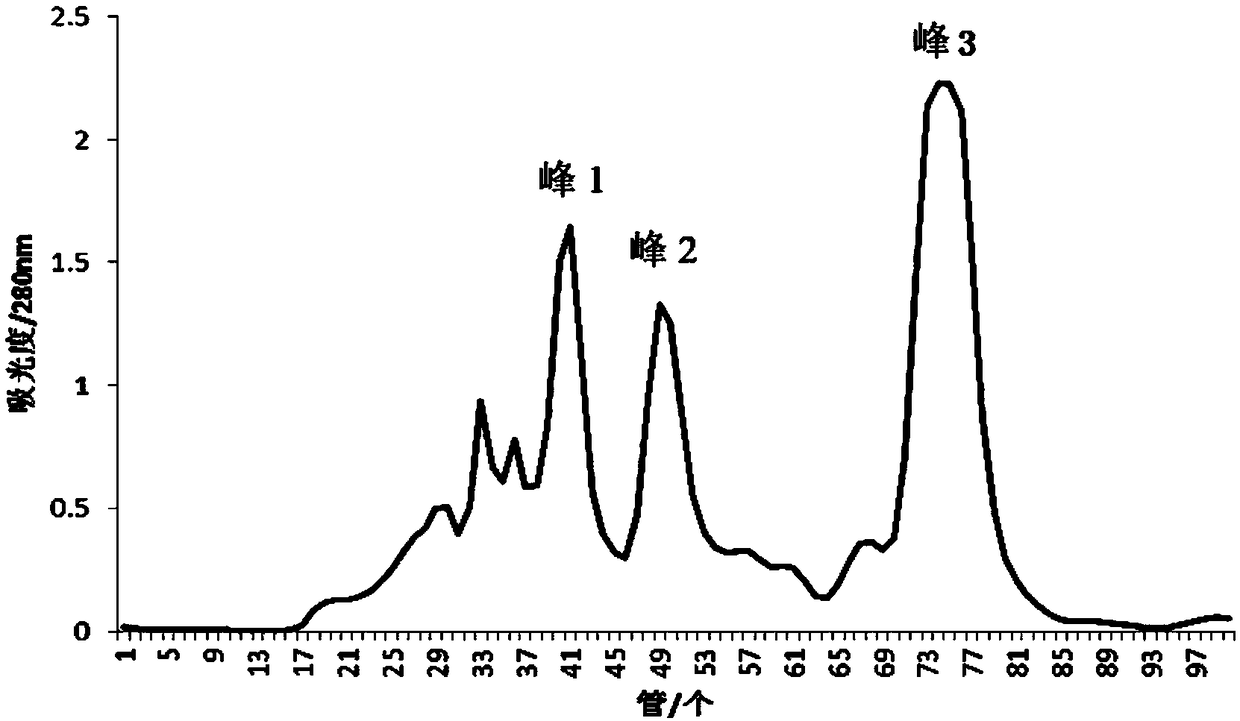
The invention belongs to the field of marine organism small-molecular active peptides, and particularly relates to an anti-oxidation and DPP-IV inhibition active peptide derived from apostichopus japonicus by enzymolysis. The amino acid sequence of the anti-oxidation and DPP-IV inhibition active peptide is Ser-Arg-Pro-Gln-Tyr-Pro-Gln-Tyr-Pro-Ser. The anti-oxidation and DPP-IV inhibition active peptide is prepared by the following steps: adding water into fresh apostichopus japonicus for homogenizing, and placing the homogenate in an enzymolysis tank; performing enzymolysis with compound protease to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; treating the enzymatic hydrolysate with a membrane separation technology to obtain a small-molecular active peptide crude product; separating the crude product through Sephadex LH-20 to obtain a small-molecular active peptide. The purity of the small-molecular active peptide as measured by adopting RP-HPLC (Reversed-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography)is greater than 95 percent, and the amino acid composition of the active peptide is measured by high performance liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry, so that the amino acid sequence of the small-molecular peptide is determined finally. The active small-molecular peptide derived from the apostichopus japonicus has the advantages of small molecular weight, simple separating-purifying steps, easiness in preparation, high purity and higher oxidization resistance and DPP-IV inhibition activity, has the characteristics of naturalness, safety and high efficiency, can be applied to the preventionand treatment of relevant diseases such as diabetes mellitus as an antioxidant as well as a DPP-IV inhibitor, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of foods, health care products and medicines.
Owner:DALIAN SHENLAN PEPTIDE TECH R & D CO LTD
Bacillussubtilis and application thereof in raising Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN102134558AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of reproductionBiocideBacteriaEcological environmentMetabolite
The invention relates to separation of Bacillussubtilis and application of the Bacillussubtilis in raising Apostichopus japonicus. The Bacillussubtilis can effectively inhibit vibriones and other pathogenic bacteria from breeding, and promote the growth of the Apostichopus japonicus. The strain is separated from gills of fished captured in the Dalian sea area, and is preserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number of CGMCC No.3498. The Bacillussubtilis can be widely applied to breeding and production links in the fishery industry, can degrade, convert and metabolize metabolic products in the breeding and production processes, creates good ecological environment, and improves, preserves and repairs the ecological environment of water resources to fulfill the aims of reducing self-pollution, reducing medicinal harm, reducing cost, lightening the pollution of the aquaculture to the whole ecological environment and improving the quality of cultured products.
Owner:LIAONING OCEAN & FISHERIES SCI RES INST
Antibacterial immune double-effect compound Chinese herb for skin ulcerative syndrome of apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN101623315AImprove immunity of sea cucumberEasy to useImmunological disordersDermatological disorderDiseaseSide effect
The invention discloses an antibacterial immune double-effect compound Chinese herb for skin ulcerative syndrome of apostichopus japonicus. The herb comprises the following components: common andrographis herb, dyer woad leaf, honeysuckle and szechuan lovage rhizome; the weight ratio of the components is 2:1:3:2; and the herb is powered, wherein granularity is 200 mesh. The herb is orally taken to prevent and cure the skin ulcerative syndrome of apostichopus japonicus, wherein each kilogram feed is added with 20g of herb powder for the mild sea cucumber and each kilogram feed is added with 30g of herb powder for the critical sea cucumber. When in use, the herb is weighed according to required dosage and is fed after being evenly stirred with stichopus japonicus feed one time per day, wherein continues 20 days are a period of treatment. The Chinese herb is special for the skin ulcerative syndrome of apostichopus japonicus, which can be used for the young sea cucumbers and the adult sea cucumbers, has good protection effect during the peak period of the skin ulcerative syndrome, and has cure rate high to 80-90% and survival rate high to more than 85% for the apostichopus japonicus having the skin ulcerative syndrome within 2-3 weeks. The compound herb has a double effect for immunity and disease resistance, has no poison and side effect, convenient use, can reduce or replace the use of antibiotics, and is suitable for breeding the young sea cucumbers and controlling diseases during breeding and producing.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Antioxidant active peptide fragment derived from sea cucumbers and extraction method
ActiveCN108129552ANo bitternessNo fishy smellPeptide preparation methodsFermentationDPPHProtease preparation
The invention belongs to the fields of preparation and identification of antioxidant active peptides, and particularly relates to an antioxidant active peptide fragment derived from sea cucumbers andan extraction method. The amino acid sequence of the peptide fragment is NH2-Gly-Pro-Ala-Gly-Pro-Cys, and the peptide fragment is obtained by enzymolysis by using a compound protease preparation, andhas a good scavenging effect on DPPH free radicals, hydroxyl free radicals and superoxide anion free radicals. Sea cucumber oligopeptides with the molecular weight of 400-800 account for 57%-68% of the total sea cucumber oligopeptides prepared by the method provided by the invention. The sea cucumber oligopeptides prepared by the method have no bitterness or fishy smell, and can be directly eatenas a protein nutritional supplement. The peptide fragment obtained by the method is derived from apostichopus japonicus, has strong antioxidant activity and a clear sequence, and can be produced massively by using prokaryotic expression or polypeptide synthesis method.
Owner:DALIAN SHENLAN PEPTIDE TECH R & D CO LTD
Method for breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka
InactiveCN102100195ALow costIncrease productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAuriculariaFishing
The invention aims to provide a method for breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka. The method comprises the following steps of: placing oosperms of the apostichopus japonicus selenka in an hatching slot for hatching; breeding apostichopus japonicus selenka larvae in a breading tank after small auricularia larvae are produced by hatching the oosperms; putting attaching bases for collecting young apostichopus japonicus selenka when 20 to 30 percent of the apostichopus japonicus selenka larvae grow into doliolaria larvae; and screening and taking the young apostichopus japonicus selenka out of the tank when the young apostichopus japonicus selenka grow to the length of between 2 and 4cm, and transferring the young apostichopus japonicus selenka into a pool for breeding. The apostichopus japonicus selenka bred in the pool is not required to be fed, and natural basic bait organisms brought by water changing are taken as feeds such as chlamydomonas and benthic diatoms primarily. The apostichopus japonicus selenka is harvested by an artificial diving fishing method when growing to the weight of between 4 pieces / kg and 6 pieces / kg.
Owner:SHANDONG HAIYIBAO AQUATIC PROD
Chinese herbal medicine feed additive capable of improving survival rate of Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN101433269ANo pollution in the processNo residueFood processingClimate change adaptationSide effectSurvival ratio
The invention discloses a Chinese herbal medicine feed additive for improving the survival ratio of apostichopus japonicus selenka. The Chinese herbal medicine feed additive comprises the following compositions in weight mixture ratio: 10 to 16 percent of Wu Chia Pee, 9 to 13 percent of angelica, 9 to 11 percent of codonopsis pilosula, 7 to 12 percent of cortex eucommiae, 7 to 10 percent of herba houttuyniae, 6 to 9 percent of bunge corydalis herb, 4 to 7 percent of areca, 3 to 7 percent of dried orange peel, 3 to 8 percent of radix bupleuri, 2 to 6 percent of herba eupatorii, 2 to 5 percent of cortex fraxini, 2 to 5 percent of radix stemonae, 1 to 4 percent of purslane, 1 to 5 percent of rhizoma Ligustici Wallichi, 3 to 7 percent of gallnut, 1 to 4 percent of radix scutellariae, 1 to 3 percent of snphora angustifolia, 1 to 5 percent of garlic, 0.6 to 1 percent of herba taching, 0.4 to 0.8 percent of rhizoma aspidii, 0.3 to 0.6 percent of honeysuckle, 0.2 to 0.7 percent of fructus aristolochiae, 0.1 to 0.6 percent of oregon grape root and 0.1 to 0.4 percent of rhubarb. The Chinese herbal medicine feed additive has the advantages of no pollution, no residue, no drug resistance, no side effect and the like and is a green feed additive worthy of the name. The Chinese herbal medicine feed additive has compatibility of various compositions, is used as a common feed additive to feed sea cucumber; juvenile sea cucumber has rapid discoloration, good extension rate, high survival ratio and rapid weight increment; and the Chinese herbal medicine feed additive in particular has good feed inducement to the juvenile sea cucumber and has remarkable effect on improving the survival rate of the seedling.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Method of cultivating fry of Apostichopus japonicus by floating cages in ponds
InactiveCN103518658AImprove survival rateIncrease productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater qualityFishery
A method of cultivating fry of Apostichopus japonicus by floating cages in ponds includes: 1, producing and placing cages, and producing floating cages; 2, stocking fry of Apostichopus japonicus reasonably; 3, controlling water quality reasonably; 4, managing cultivation of the fry of Apostichopus japonicus reasonably; 5, adjusting cage level reasonably. The method has the advantages that survival rate, yield and fry quality of the fry of Apostichopus japonicus are increased, the method has good effect and is convenient to popularize, the floating cages can sink to proper levels in hot periods of summer and cold periods of winter so that water temperature and water quality are maintained, and growing period of cage-cultivated fry can also be prolonged.
Owner:JINZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Multiple PCR method for rapidly identifying four varieties of sea cucumbers
ActiveCN101942510AShorten the timeLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisPcr method
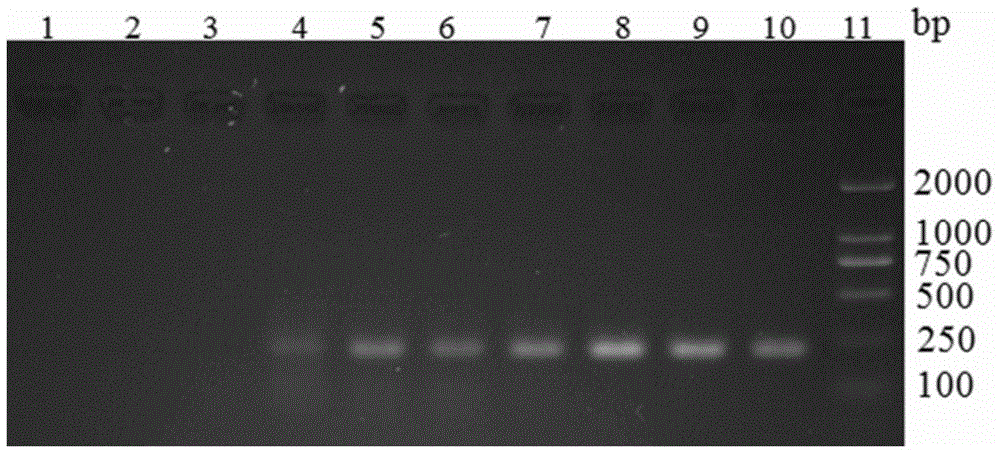
The invention relates to a multiple PCR method for rapidly identifying four varieties of sea cucumbers and belongs to the field of molecular biology. The method adopts mitochondria CO I genes of four varieties of sea cucumbers as target DNA, and by sequence comparison, species specificity primers of the four varieties of sea cucumbers are designed respectively. The CO I genes of the sea cucumbers are extracted, multiple-PCR detection is carried out, thus judging the varieties of the sea cucumbers according to the molecular weight of PCR products. After the multiple-PCR detection is carried out on apostichopus japonicus, thelenota ananas, California apostichopus japonicus and Iceland sea cucumbers, the molecular weights of characteristic electrophoretic bands are 202bp, 301bp, 261bp and 358bp sequentially. The identification method has simple operation, low cost, short inspection period, good specificity and repeatability and high sensitivity, overcomes the defects of large workload, long consumed time, high cost and the like of the traditional sea cucumber morphology identification method and can realize rapid and accurate identification of the varieties of the sea cucumbers.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Feed additive for improving growth and immunity of Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN102715371AImprove immunityPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyAcanthopanax japonicus
The invention discloses feed additive for improving growth and immunity of Apostichopus japonicus. The feed additive for improving growth and immunity of Apostichopus japonicus is characterized by comprising, by weight, 0.1-0.3 part of chitosan oligosaccharide, 0.1-0.3 part of bacillus, 1-3 parts of astragalus root, 1-3 parts of licorice root, and 1-3 parts of radix angelicae sinensis. The feed additive is capable of improving growth and stress resistance of Apostichopus japonicus, reducing harm caused by stress and enhancing body immunity to increase survival rate of the Apostichopus japonicus. The compound feed additive mainly comprises the bacillus, the chitosan oligosaccharide, the manyprickle acanthopanax root, the astragalus root, fructus lycii, licorice root, lily bulb, the radix angelicae sinensis and root of bidentate achyranthis. The ingredients are made into the additive for common feed used to feed the Apostichopus japonicus according to a best proportion, and accordingly the Apostichopus japonicus grows well, weight gain is high, immuno-enzyme activity, and body immunity of the Apostichopus japonicus is improved. The feed additive has the advantages of no pollution, no residue, no side effects and the like.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Bechedemer breeding feed formula
InactiveCN101331922AMeet growth needsFast growthClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYeastAquatic product
The invention relates to a feed formula for holothurian culture feed used in the aquiculture field, in particular to a feed formula for apostichopus japonicus culture. The technical proposal is that each component has the following weight percentages: 28 to 30 percent of strong flour, 12 to 14 percent of fish powder, 16 to 20 percent of beer yeast, 21 to 25 percent of soybean meal, 4.5 to 8.5 percent of zeolite powder elements and 1.5 to 5.5 percent of compound microelement; each component is mixed evenly, is passed 80 mesh sieve and then is sealed and packaged. The formula has the effect of meeting the growth needs of the apostichopus japonicus, accelerating the growth speed, causing good development and greatly improving the productivity of the apostichopus japonicus culture.
Owner:张士华
Industrialized comprehensive breeding method for apostichopus japonicus Selenka and octopus vulgaris Cuvier
PendingCN110495412AIncrease profitLow costClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHabitSeedling
The invention relates to an industrialized comprehensive breeding method for apostichopus japonicus Selenka and octopus vulgaris Cuvier. The method comprises the steps that an indoor industrialized breeding pond and a shelter in the pond are built; the octopus vulgaris Cuvier is put into the pond, wherein seedlings of the octopus vulgaris Cuvier are put into the indoor industrialized breeding pondand fed with fresh and live baits; the apostichopus japonicus Selenka is put into a pond, wherein when the outdoor water temperature exceeds 22 DEG C, 20-50 g of the apostichopus japonicus Selenka istransferred into the indoor industrialized breeding pond where the octopus vulgaris Cuvier is added from the outdoor breeding pond; the octopus vulgaris Cuvier and the apostichopus japonicus Selenkaare bred, wherein the weight of the octopus vulgaris Cuvier is increased by 10-15 times to reach the commercial specification of 1,500-2,000 g through 3-4 months of breeding in the indoor industrialized breeding pond; when the outdoor water temperature is lower than 22 DEG C, the apostichopus japonicus Selenka is put back to the outdoor breeding pond. According to the method, biological habits that the octopus vulgaris Cuvier and the apostichopus japonicus Selenka do not struggle for feed, the shelter is shared, the baits are complementary without competition, and the suitable growth temperature and light intensity are consistent are fully utilized, conditions suitable for the growth of the octopus vulgaris Cuvier and the apostichopus japonicus Selenka are provided in an artificially-controllable environment, and the utilization rate of the industrialized breeding ponds is effectively increased.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY +2
Method for identifying apostichopus japonicus by means of specific peptide fragment group
ActiveCN106008688APreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBacteroidesPeptide fragment
The invention relates to a method for identifying apostichopus japonicus by means of a specific peptide fragment group, and a group of marker peptides capable of being used for identifying apostichopus japonicus when used alone or otherwise. The marker peptides are low-homology polypeptide fragments of apostichopus japonicus protein, wherein the low-homology polypeptide fragments are exclusive to apostichopus japonicus with a length of 5-30 amino acids. Even though it is found that there are plants or bacteria having the same protein, the marker peptides are exclusive to apostichopus japonicus by comparison with thelenota ananas, acaudina molpadioidea, isostichopus badionotus and holothuria Mexicana.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for breeding juvenile Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN105557566AIncrease oxygen contentIncrease dissolved oxygenClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseHigh density
The invention relates to a method for breeding juvenile Apostichopus japonicus and belongs to the technical field of sea cucumber culture. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out density control; (2) carrying out feedstuff control; (3) carrying out adhering apparatus drop-off; (4) carrying out inflation; (5) carrying out pond changing; and (6) carrying out sheet changing. According to the method, through taking the measures of controlling temperature, controlling light, strengthening feeding, and the like, diseases can be effectively prevented and treated, and the high-density breeding of offspring is achieved; and healthy juvenile Apostichopus japonicus is bred by taking the technical measures of carrying out water quality regulation and control, carrying out scientific feeding, carrying out ecological disease prevention, and the like. The utilization ratio of water is effectively increased, the disadvantages of the traditional extensive culture are overcome, the quality of cultured Apostichopus japonicus is adequately guaranteed, and the factory, industrialized and modernized culture of the Apostichopus japonicus is promoted.
Owner:王娟
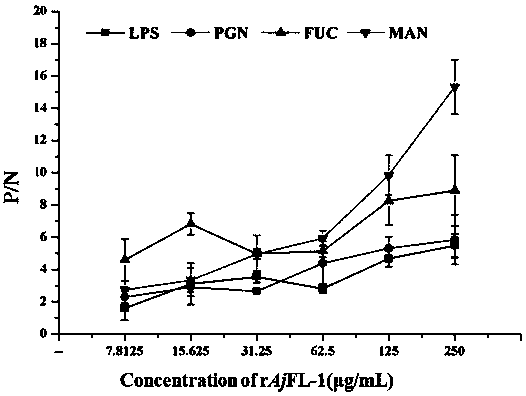
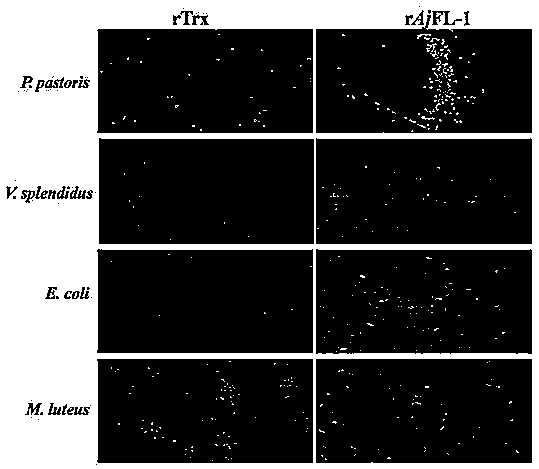
Apostichopus japonicus F type lectin AjFL-1 as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN108191964APreferential bindingEnhanced inhibitory effectAntimycoticsPeptide/protein ingredientsPichia pastorisEscherichia coli
The invention discloses apostichopus japonicus F type lectin AjFL-1. The amino acid sequence is shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing PCR amplificationon a coding region fragment of apostichopus japonicus F type lectin AjFL-1 by using specific primers P1 and P2, wherein the DNA sequence of the primer P1 is shown by SEQ ID NO.2, and the DNA sequenceof the primer P2 is shown by SEQ ID NO.3; performing Nde1 and Xho1 digestion on the PCR amplification product and a pET-22b(+) carrier; then connecting through T4 ligase, transforming, sequencing andidentifying the recon; transferring the recon into an escherichia coli Transetta (DE3) expression strain, and performing induction culture; then performing purification and renaturation to obtain recombinant protein with an amino acid sequence in the sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The apostichopus japonicus F type lectin AjFL-1 can be used for preparing a pichia pastoris inhibiting drug.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Plant type apostichopus japonicus compound immunizing booster
InactiveCN101147531AImprove antibacterial propertiesEnhance resistance to heat stressClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffCrataegus FruitAngelica sinensis
The present invention discloses a plant-type compound schlepper for stichopus japonicus. It is characterized by that its raw material composition includes (by wt%) 25%-35% of astragalus root, 20%-25% of crataegus fruit, 15%-20% of isatis root, 10%-20% of Chinese angelica root and 10%-20% of schisandra berry. The invented compound schlepper can be used as additive and can be added into the feed of stichopus japonicus for raising immunity of stichopus japonicus body, resistance to bacteria and heat resistance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apostichopus japonicus lectin gene, recombinant fusion protein and preparation method
InactiveCN105349546ALow costHigh agglutination activityFermentationHybrid peptidesTotal rnaNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses an Apostichopus japonicus lectin gene. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and an amino acid sequence of recombinant fusion protein of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The preparation method of the gene includes: extracting Apostichopus japonicus body wall total RNA; synthesizing a first strand of cDNA; using cDNA as a template to respectively obtain 5'RACE and 3'RACE products; using a RT-PCR primer for amplification to obtain a complete lectin gene segment, and obtaining a complete lectin sequence through sequencing and splicing; connecting the lectin gene onto a PMD19-T vector, and subjecting a product to positive colon expression and purification to obtain the Apostichopus japonicus lectin recombinant fusion protein rAj-MBCL. The preparation method is simple and high in purification rate, and the obtained Apostichopus japonicus lectin recombinant fusion protein is low in cost, high in agglutinating activity, high in expression quantity, small in experiment repeated difference, stable in result and high in controllability.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Beche-de-mer pool crag cage rearing method
InactiveCN101491220APromote growthImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZooplanktonHectare
The invention discloses an Apostichopus japonicus Selenka pond reef cage culture method capable of improving the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka survival rate and recapture rate, reducing the culture cost, facilitating Apostichopus japonicus Selenka commodity harvest, and benefiting the timely pond cleaning treatment. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an Apostichopus japonicus Selenka culture pond; cleaning the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka culture pond and discharging the water; placing reef cages according to the pitch of 2 to 3m and the density of 1,200pcs / hectare, admitting 0.45 to 0.55m natural seawater and culturing the water so as to have 10 to 20mg / L of phytoplankton biomass, less than 10mg / L of zooplankton, 50 to 60g / m of attaching organism, and less than 70mg / m benthos in the seawater; placing the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka seedlings in the reef cages with the dosage specification of 50pcs of Apostichopus japonicus Selenka for each reef cage, 100 to 500pcs of Apostichopus japonicus Selenka being equal to 1kg, then closing the reef cages with webs, and then admitting natural seawater to the depth of at least 1.5m; culturing the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka to reach the commodity specifications; and during harvesting the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka, taking out the reef cages, taking out the anchoring beds, catching the bigger Apostichopus japonicus Selenka and leaving the smaller Apostichopus japonicus Selenka, and catching and stocking the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka in rotation.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Microecological preparation used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus putrid skin syndrome and preparation method of microecological preparation
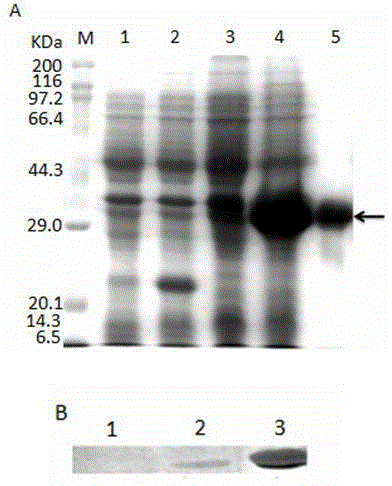
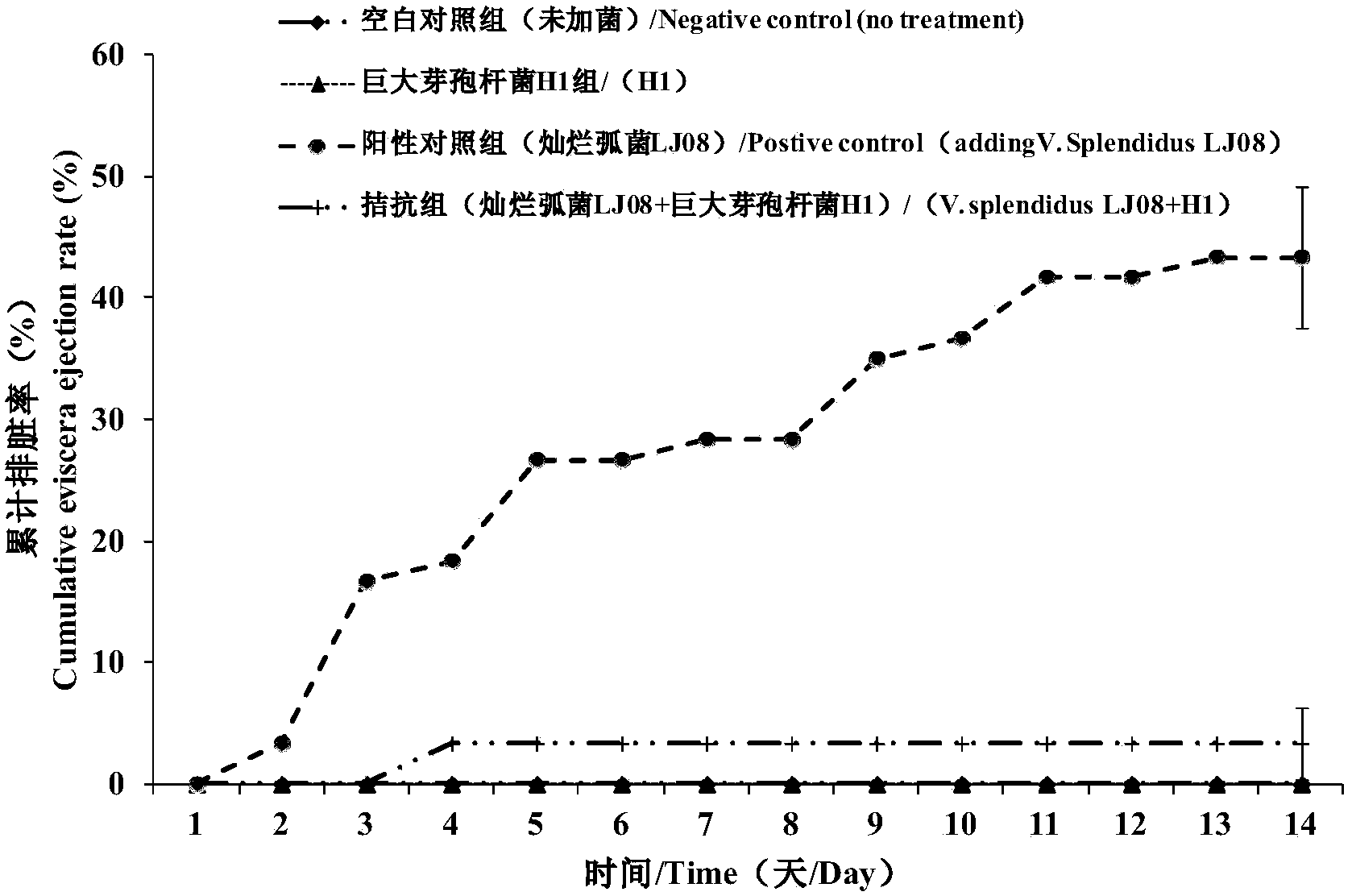
The invention relates to a microecological preparation used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus putrid skin syndrome and a preparation method of the microecological preparation and belongs to the field of aquatic microorganisms. Active ingredients of the microecological preparation are thalli of bacillus megatherium H1 and extracellular metabolites of the bacillus megatherium H1; the bacillus megatherium strain is separated from intestinal tract excrement of apostichopus japonicus which is healthily cultivated in Penglai, Shandong, detection of safety, bacteriostatic activity and toxicity and artificial antagonistic vibrio splendidus experiments verify that the bacillus megatherium H1 is antagonistic to vibrio splendidus, young apostichopus japonicus is effectively protected, the bacillus megatherium H1 can be used for preventing and treating apostichopus japonicus 'putrid skin syndrome' caused by vibrio splendidus and survival rate of an apostichopus japonicus seedling protecting stage is increased.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Apostichopus japonicus Selenka feed by replacing sargassum thunbergii for terrestrial plants
InactiveCN101869209AIncrease special growth rateImprove digestibilityAnimal feeding stuffAmylasePapaya family
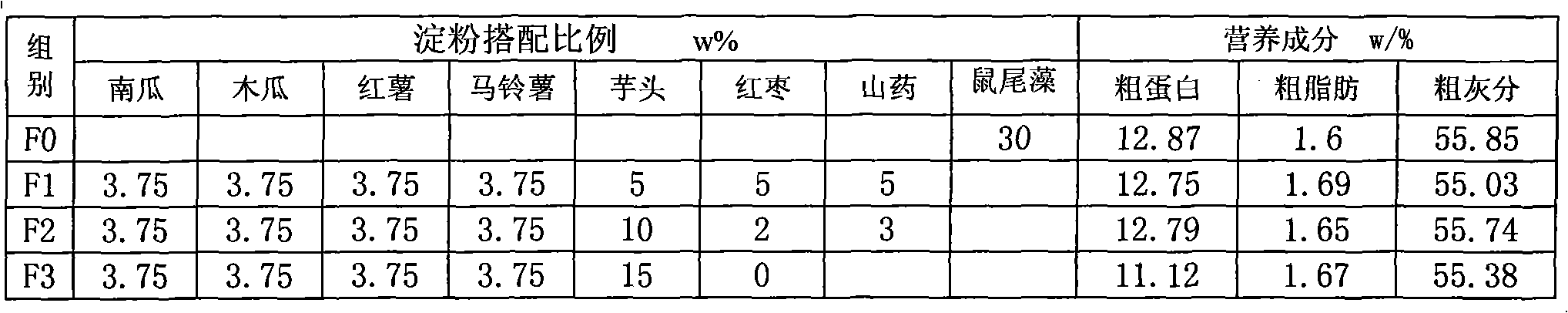
The invention discloses an Apostichopus japonicus Selenka feed by replacing sargassum thunbergii for terrestrial plants, which has low cost and high nutritional value and can obviously improve the special growth rate, amylase activity, digestibility and immunity of the Apostichopus japonicus Selenka. The Apostichopus japonicus Selenka feed consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 11 percent of fish meal, 7 percent of soybean protein, 40 percent of sea mud, 5 percent of shrimp, 1 percent of yeast, 0.2 percent of xanthan gum, 0.8 percent of mineral, 5 percent of shell powder, 3.75 percent of pumpkin starch, 3.75 percent of papaya starch, 3.75 percent of sweet potato starch, 3.75 percent of potato starch, 10 percent of taro starch, 2 percent of red date starch and 3 percent of yam starch, wherein the starch is powder which is prepared by pasting, drying, grinding and crushing.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
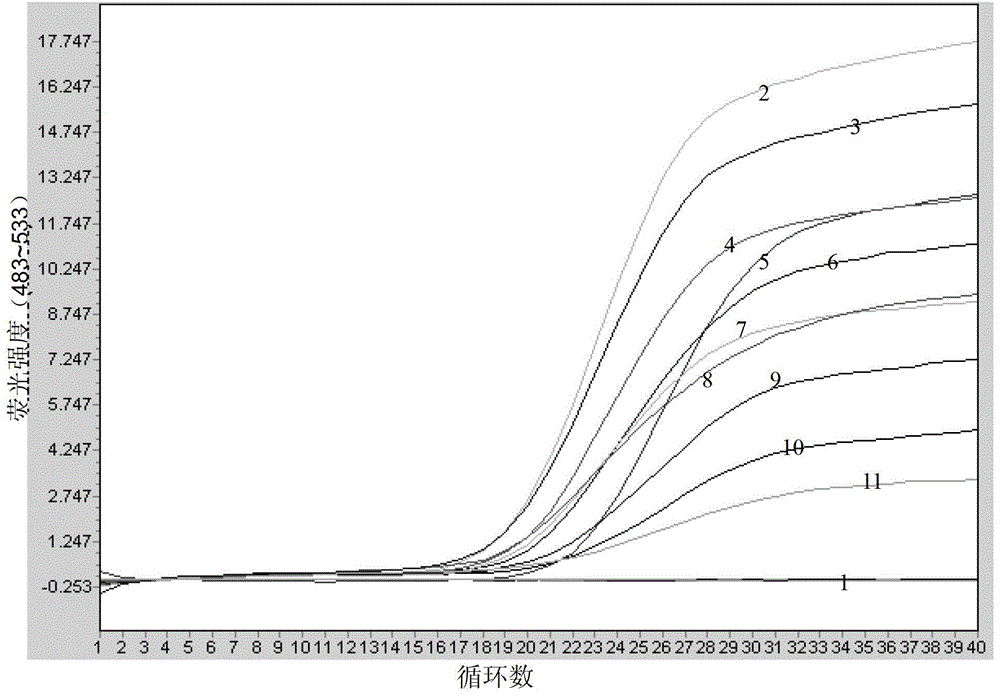
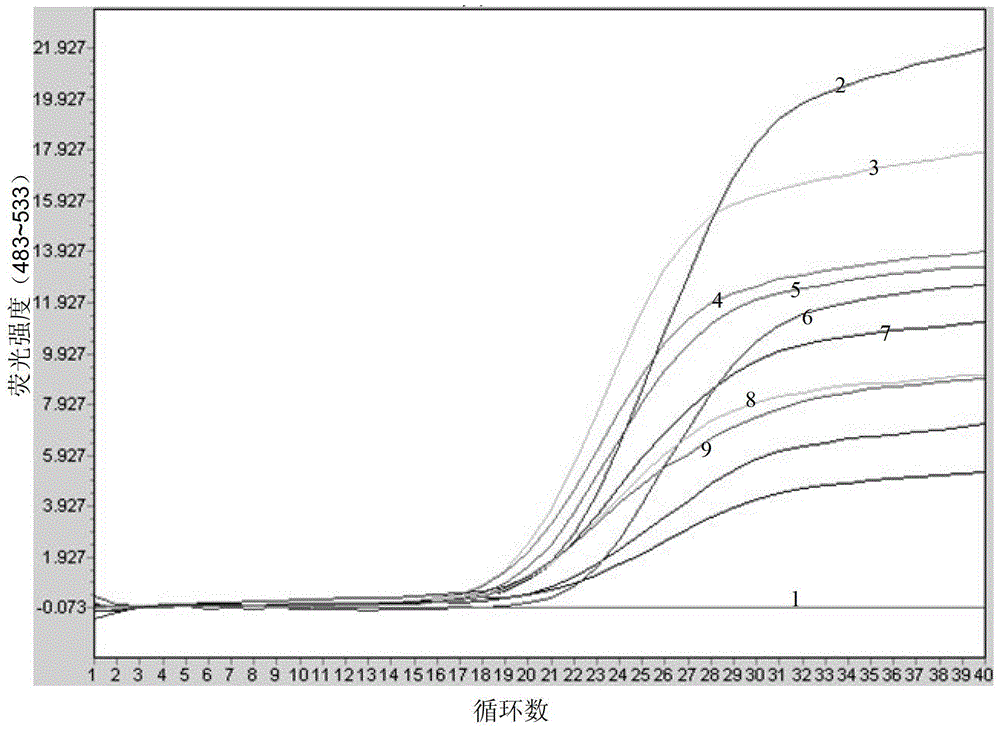
Apostichopus japonicus detection primer, kit and real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method
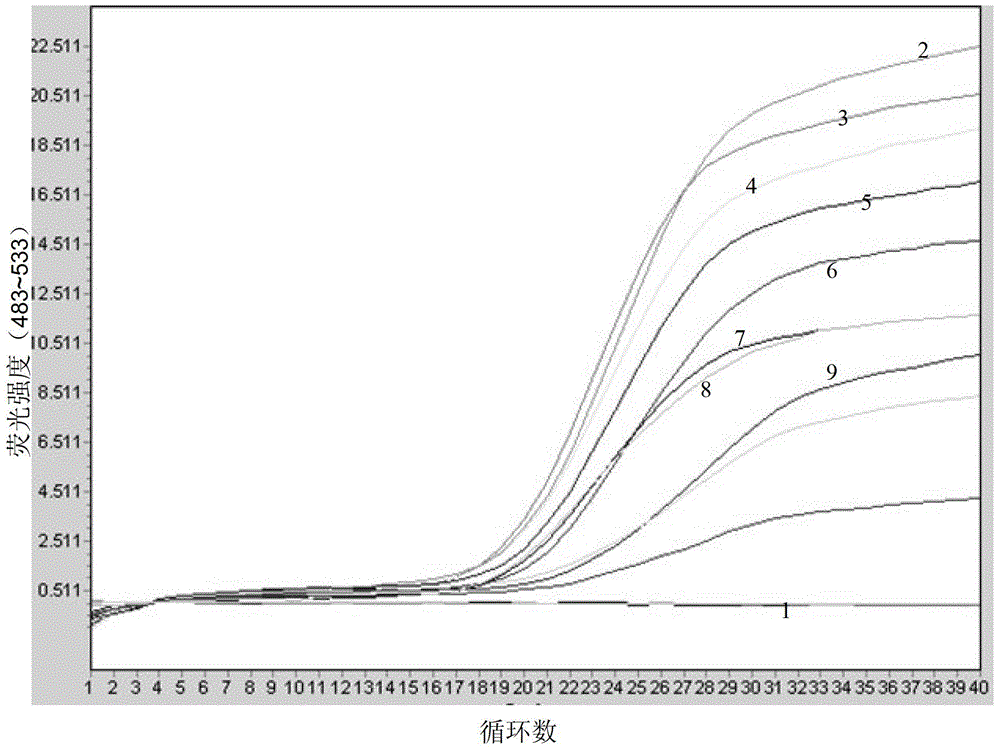
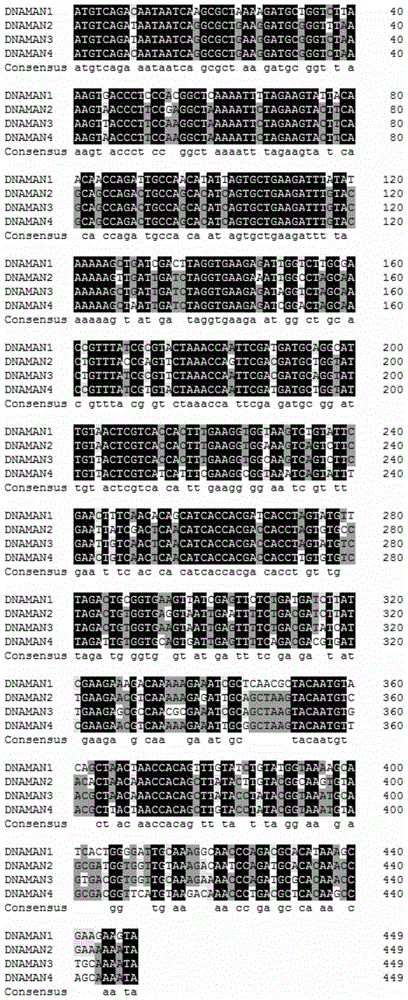
InactiveCN103333966AImprove detection efficiencyHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceCox1 gene
The invention discloses an apostichopus japonicus detection primer, a kit and a real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method. On the basis of design systems 1 to 3 of apostichopus japonicus parameter mitochondria COX1 gene and NAD4 gene, a probe method in the fluorescent PCR technology is used for carrying out the specificity identification experiment of the apostichopus japonicus. On the basis of design systems of 12 sea cucumber mitochondria 16S rRNA genes, a green I embedded fluorescent method in the fluorescent PCR technology is used for monitoring the sea cucumber nucleic acid extraction situation. The invention particularly designs a primer for detection, namely SEQ ID NO. 1 to No. 13, and a method for quickly detecting the apostichopus japonicus is established by utilizing the real-time fluorescent PCR technology. The manual operation time is less than 60 minutes in the entire detection process. The method has a wide application prospect in the authenticity identification of the apostichopus japonicus.
Owner:曹际娟 +3
Eukaryotic expression method of sea cucumber cathepsin
InactiveCN105385706AReduce manufacturing costQuality controllableHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPichia pastorisProtein target
The invention relates to an eukaryotic expression method of sea cucumber cathepsin. The method comprises the following steps: screening a cathepsin gene EST sequence on the basis of an Apostichopus japonicus transcriptome database obtained through early stage working according to a bioinformatics analysis result; acquiring gene full-length sequence information by adopting an RACE full-length cloning technology on the basis of a fragment sequence; predicating and analyzing the structure characters and function activity of an encoded protein according to the full-length sequence information, and searching and determining a key structural domain; determining a gene sequence fragrance accessed to an expression system according to the predication and analysis result; constructing a Pichia pastoris eukaryotic expression system, and expressing a target protein in vitro; and detecting and explicating the activity and function characters of the protease obtained after expression. The sea cucumber protease expressed through the method has the characteristics of low production cost, easy quality control, increase of the selectable kinds of collagen proteolysis proteases, increase of the enzymatic hydrolysis production benefit, and important economic and social values.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
PCR detection primer and method of Vibro Splendidus and application of PCR detection primer
ActiveCN105039547AEasy to observeSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesApplications of PCRBiology
The invention discloses a PCR detection primer and method of Vibro Splendidus and application of the PCR detection primer. The PCR detection primer is characterized by being designed according to the DNA sequences of a fur gene of Vibro Splendidus, the sequences of the designed PCR detection primer are VSFur RTF3:5'-ACAACAACCAGATTGCCAACA-3' and VSFurRTR3:5'-GATAACTTCACCGCAGTCTAAACAT-3'. The PCR detection method includes the following steps of firstly, preparing a matrix of seawater, apostichopus japonicus epidermis, apostichopus japonicus muscle or apostichopus japonicus coelomic fluid; secondly, establishing a 25-microlitre PCR reaction system; thirdly, conducting a PCR reaction, and finally conducting agarose gel electrophoresis to conduct result analysis. The PCR detection primer can be used for detecting Vibro Splendidus in seawater, apostichopus japonicus epidermis, apostichopus japonicus muscle or apostichopus japonicus coelomic fluid and has the advantages of being high in detection speed and sensitivity.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility and aquacultural method
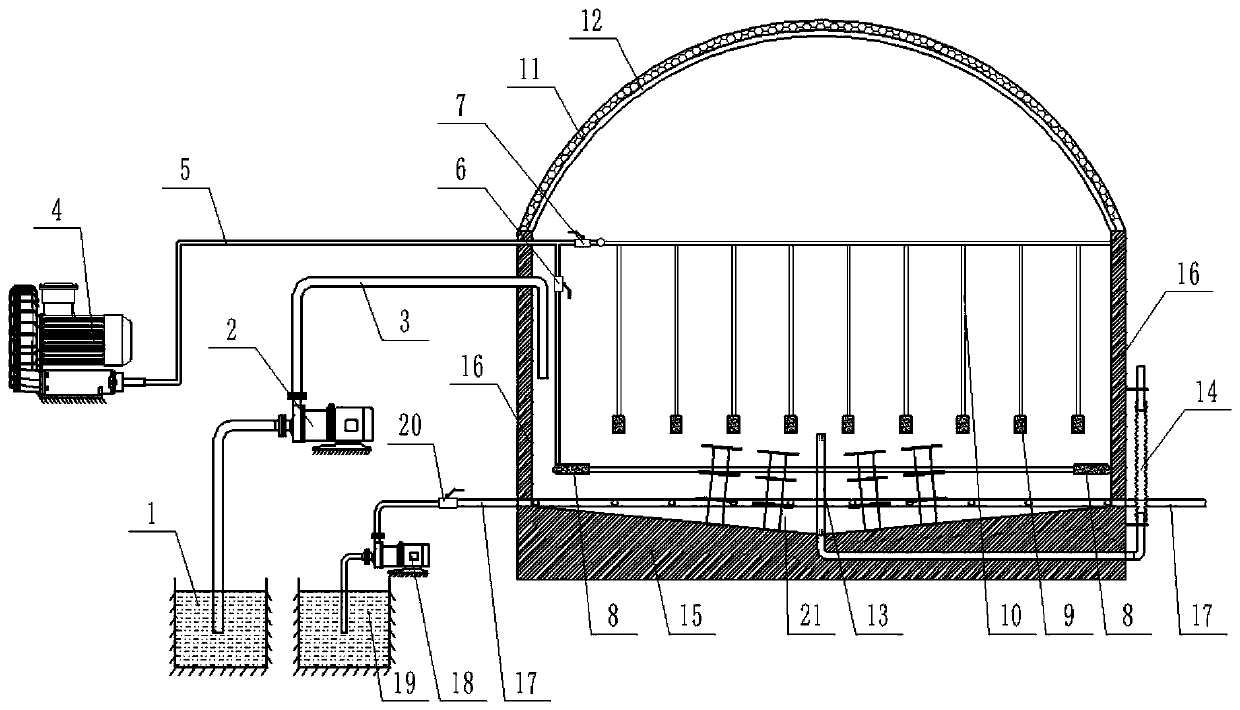
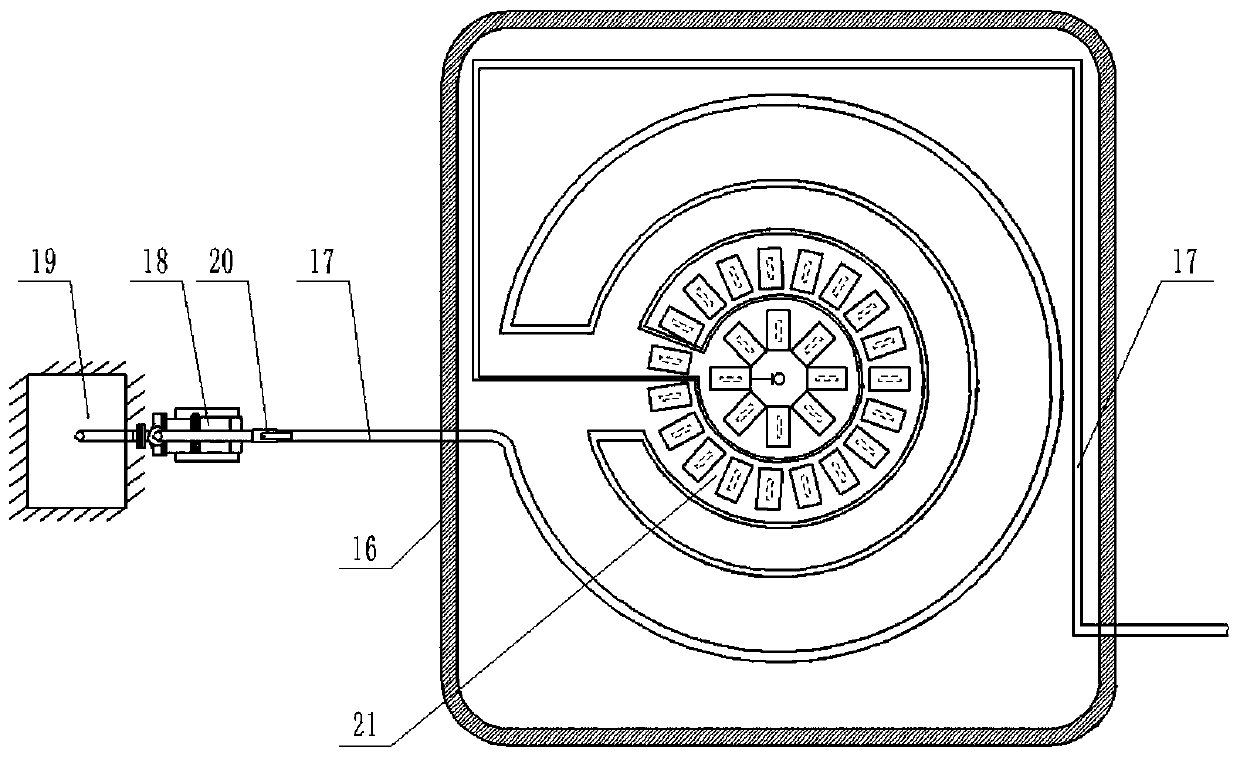
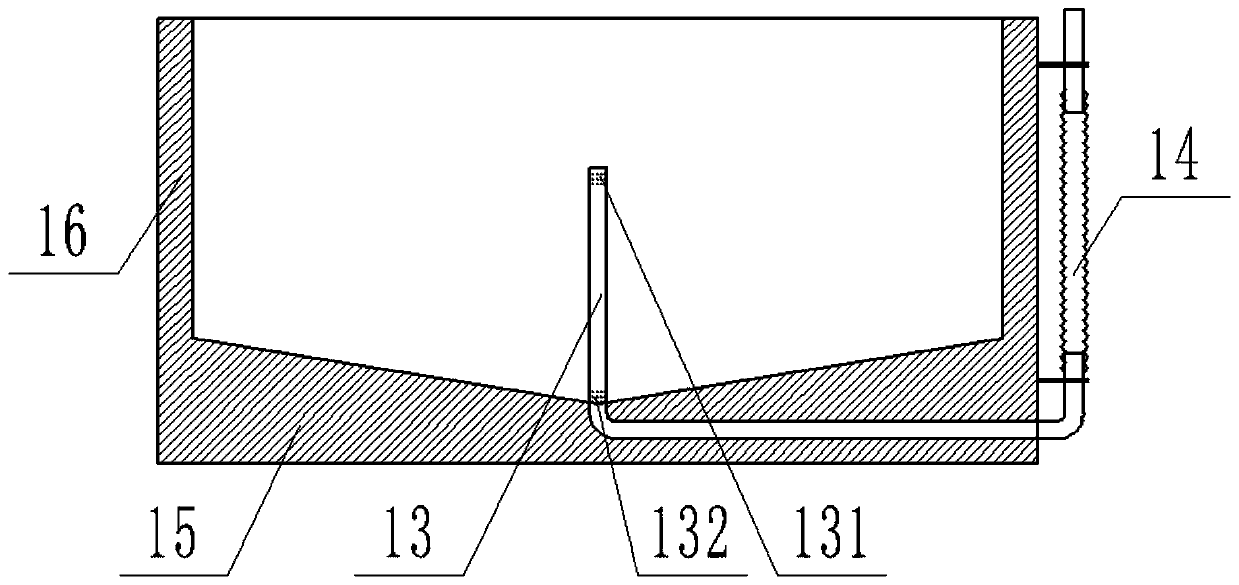
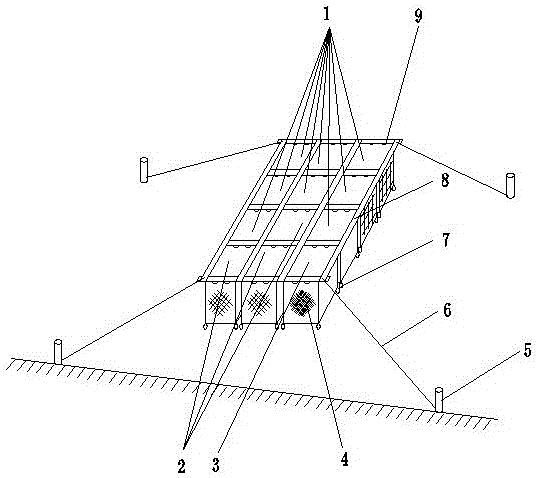
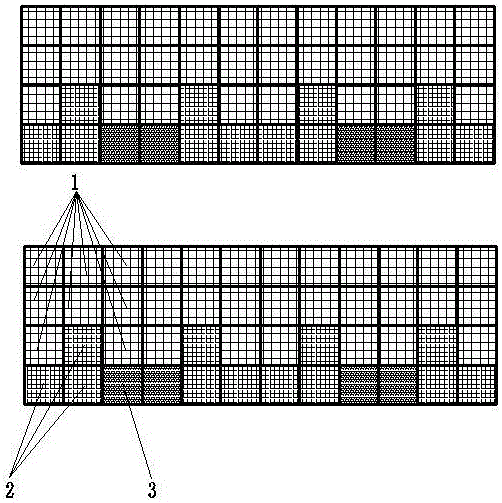
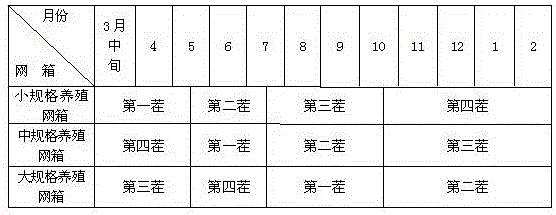
ActiveCN105660494ASafe sheltered habitatIncrease attachment spaceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShallow seaEngineering
The invention provides a shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility and an aquacultural method. The shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility comprises a plurality of cages. The shallow sea cage apostichopus japonicus recirculating aquacultural facility is characterized in that the plurality of cages comprise small, medium and large aquacultural cages which are respectively used for aquaculture of small, medium and large juvenile apostichopus japonicus, the small, medium and large aquacultural cages are connected in proportional allocation that quantity of the small aquacultural cages is lower than quantity of the medium aquacultural cages and the quantity of the medium aquacultural cages is lower than quantity of the large aquacultural cages to form aquacultural units, and the aquacultural units are connected and then are fixed under the sea through piling. In March, April and May every year, the small, medium and large juvenile apostichopus japonicus are put into the cages to be cultivated according to specific density, and cultivation in each stage can provide enough juvenile apostichopus japonicus for the next stage; and then the small juvenile apostichopus japonicus are continuously supplemented and put into the cages, and the process is repeated, so that ecological efficient continuous product is realized. Aqucultural facility utilization rate is greatly improved, production cost is greatly reduced, growth rate of the juvenile apostichopus japonicus is improved, survival rate of the juvenile apostichopus japonicus is greatly improved, operation management is convenient, and comprehensive benefits are obviously improved.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Apostichopus-japonicus glucan binding protein and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110066330AGood for healthPromote sustainable developmentAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliVibrio anguillarum
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and gene engineering, and specifically discloses an apostichopus-japonicus glucan binding protein and a preparation method and application thereof. Through the in-vitro recombinant expression technology, the apostichopus-japonicus glucan binding protein (AJ-GBP) is obtained for the first time, and preferably the amino acid sequenceof the apostichopus-japonicus glucan binding protein (AJ-GBP) is shown in a sequence table SEQIDNO.1. The recombinant protein has an agglutination effect on bacillus subtilis, staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, curtobacterium luteum and vibrio anguillarum, can inhibit bacillus subtilis, escherichia coli, curtobacterium luteum and vibrio anguillarum, and has potentialapplication value in the fields of development of novel broad-spectrum antibiotics and feed additives.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Separation and purification method of antibacterial peptides in bodily wall of Apostichopus japonicus
InactiveCN108570101ASmall molecular weightBroad spectrum antibacterialPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesPurification methodsAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to separation and purification of polypeptides and discloses a separation and purification method of antibacterial peptides in bodily wall of Apostichopus japonicus, comprising the steps of 1) pretreating a material; 2) performing acetic acid extraction; 3) performing ultrafiltration; 4) performing macroporous adsorbing resin chromatography; 5) performing high-speed counter-current chromatography purification; 6) performing sephadex chromatography. Live Apostichopus japonicus is stimulated to produce massive antibacterial peptides; a most suitable separation and purification method is selected according to the properties of the most effective ingredient T1 in the antibacterial peptides in the bodily wall of Apostichopus japonicus to acquire high-purity antibacterial peptides; the antibacterial peptides have best antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella enteritidis and Bacillus subtilis and can replace drugs fed during farming of Apostichopus japonicus, thereby reducing medicine residue in Apostichopus japonicus, and promoting the ensuring of quality safety of Apostichopus japonicus products and healthy development of the food industry.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
Preparation method for fermentation-type peony tender-bud tea composite beverage
A preparation method for a fermentation-type peony tender-bud tea composite beverage comprises preparation step of shelled peony seed powder, preparation step of apostichopus japonicus powder, preparation step of ant powder, preparation step of fruit pulp, extraction preparation step of the peony tender-bud tea, homogenizing and packaging step of a finished product. The extraction preparation step of the peony tender-bud tea also comprises performing tedding withering, enzyme-deactivating and rolling on fresh peony tender buds; performing primary fermentation on rolled tender buds; after preliminary fermentation is performed, drying by a drying baker and performing microwave processing; and after microwave processing is performed, adding shelled peony seed powder, ant powder and fruit pulp for secondary fermentation, and drying to prepare an extraction liquid. The prepared fermentation-type peony tender-bud tea composite beverage finished product is rich in tea flavor, abundant in nutrition and unique in flavor, and has health-care control functions, and the additional utilization value of peony industry is improved.
Owner:LUOYANG CHUNKUI AGRI DEV
Breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus
ActiveCN105613383AStrong selection purposeImprove efficiencyPisciculture and aquariaF1 generationPhenotypic trait
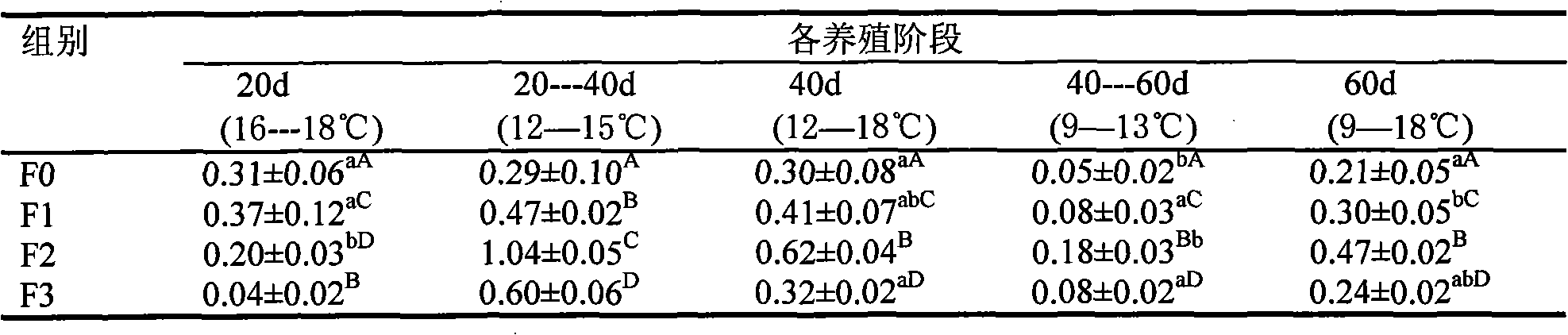
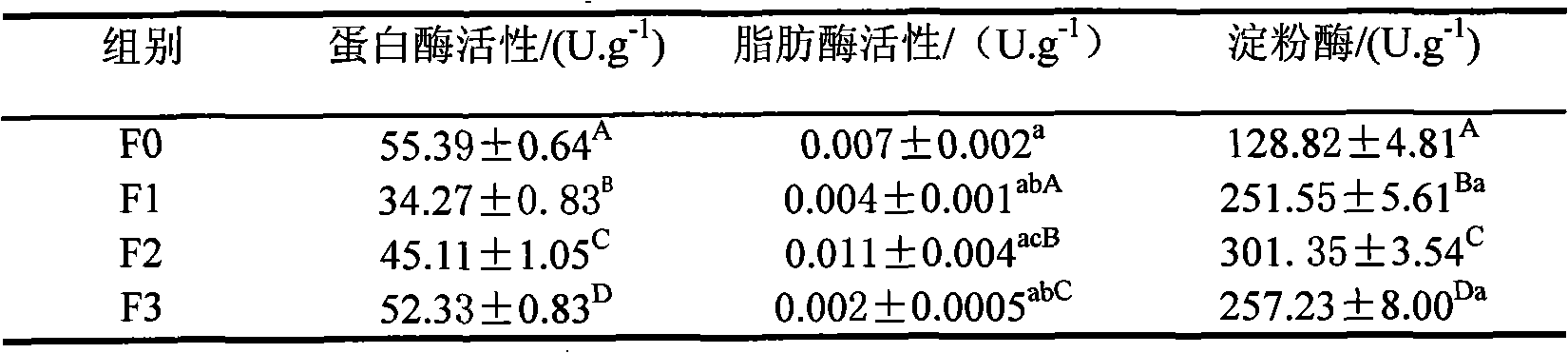
The invention provides a breeding method of purple apostichopus japonicus. The breeding method is characterized by collecting purely wild apostichopus japonicus individuals of which the back part and the abdomen part are totally purple, and transplanting the apostichopus japonicus individuals into a breeding pond for carrying out independent separation, temporary rearing and preserving; screening breeding base populations in the middle of May, and carrying out artificial spawning, hatching and breeding; when 30 percent of planktonic larvae develop to be doliolaria, feeding an adhering substrate, changing water and feeding fodder; recording the body color and the growth and development situation of the doliolaria at a fixed period, and screening and weeding out weak individuals; performing an overall breeding process in a purple environment, and strengthening the coloring of young purple apostichopus japonicus by feeding the fodder containing purple natural pigment components in an assisting manner; respectively carrying out selfing on bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and hybridization on the bred F1-generation purple apostichopus japonicus and preserved base populations, thus forming F2 filial generations, wherein a breeding technology and breeding conditions of the F2 filial generations are the same as those of F1 generations; carrying out three times of high-strength standard breeding, thus obtaining F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus, wherein the selection and reservation rate is 90 percent or more, and no significant difference of the growing speed and the anti-capability is generated between the F3-generation new varieties of the purple apostichopus japonicus and original apostichopus japonicus.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com