Patents
Literature
1477 results about "Salmonella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Salmonella is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of Salmonella are Salmonella enterica and Salmonella bongori. Salmonella enterica is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,500 serotypes.
Method for treatment of disorders of the gastrointestinal system
There are provided novel synthetic stool preparations comprising bacteria isolated from a fecal sample from a healthy donor. The synthetic stool preparations are used for treating disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, including dysbiosis, Clostridium difficile infection and recurrent Clostridium difficile infection, prevention of recurrence of Clostridium difficile infection, treatment of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and diverticular disease, and treatment of food poisoning such as salmonella. Methods of preparation and methods of use of the synthetic stool preparations are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH +2
Nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules and methods for preparing and using the same
InactiveUS6379712B1Improve solubilityPreventing mold build-upPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliDisease
The present invention relates to nanosilver-containing antibacterial and antifungal granules ("NAGs"). The NAGs have longlasting inhibitory effect on a broad-spectrum of bacteria and fungi, which include, but are not limited to, Escherichia coli, Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Providencia stuartii, Vibrio vulnificus, Pneumobacillus, Nitrate-negative bacillus, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Bacillus cloacae, Bacillus allantoides, Morgan's bacillus (Salmonella morgani), Pseudomonas maltophila, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus foecalis alkaligenes, Streptococcus hemolyticus B, Citrobacter, and Salmonella paratyphi C. The NAGs contain ground stalk marrow of the plant Juncus effusus L. which has been dispersed with nanosilver particles. The nanosilver particles are about 1-100 nm in diameter. Each of the nanosilver particles contain a metallic silver core which is surrounded by silver oxide. The present invention also provides a process for making the NAGs. The NAGs can be used in a variety of healthcare and industrial products. Examples of the healthcare products include, but are not limited to, ointments or lotions to treat skin trauma, soaking solutions or cleansing solutions for dental or women hygiene, medications for treating gastrointestinal bacteria infections, sexual related diseases, and eye diseases. Examples of industrial products include, but are not limited to, food preservatives, water disinfectants, paper disinfectants, construction filling materials (to prevent mold formation).
Owner:LEGEND WIN FINANCE
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS6080849AImprove securityReduce capacityBiocideBacteriaTumor targetVirulent characteristics
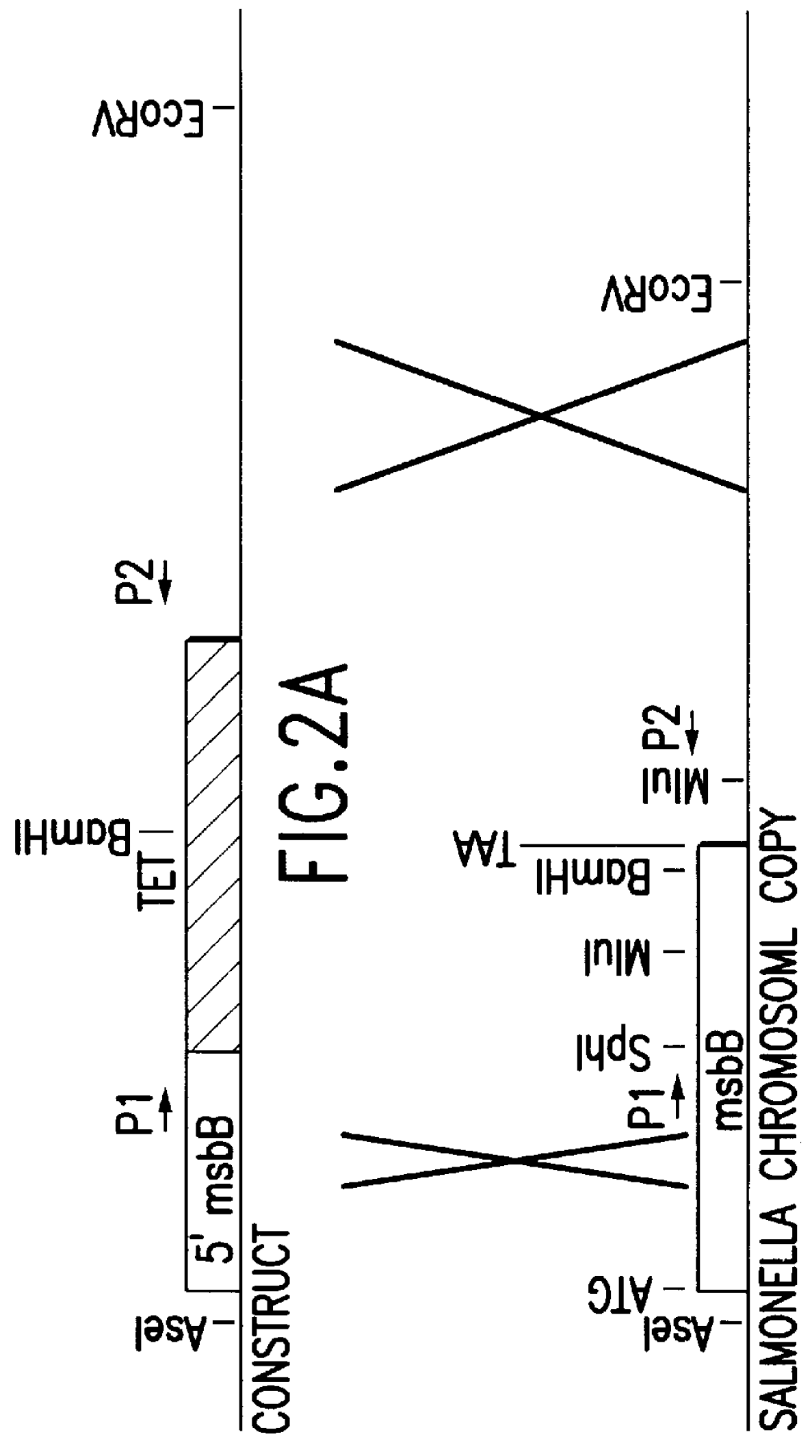
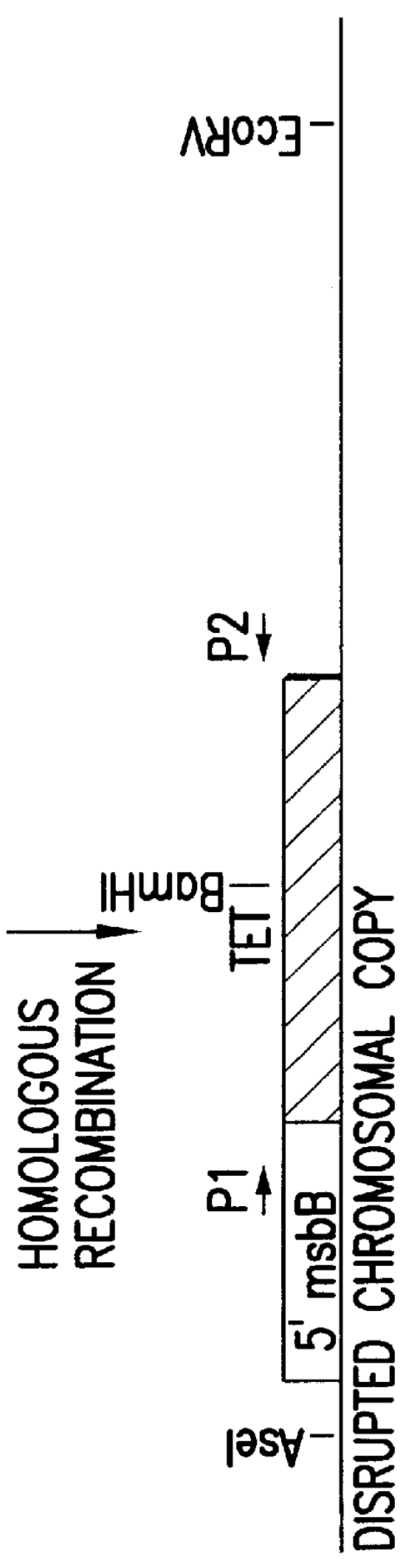
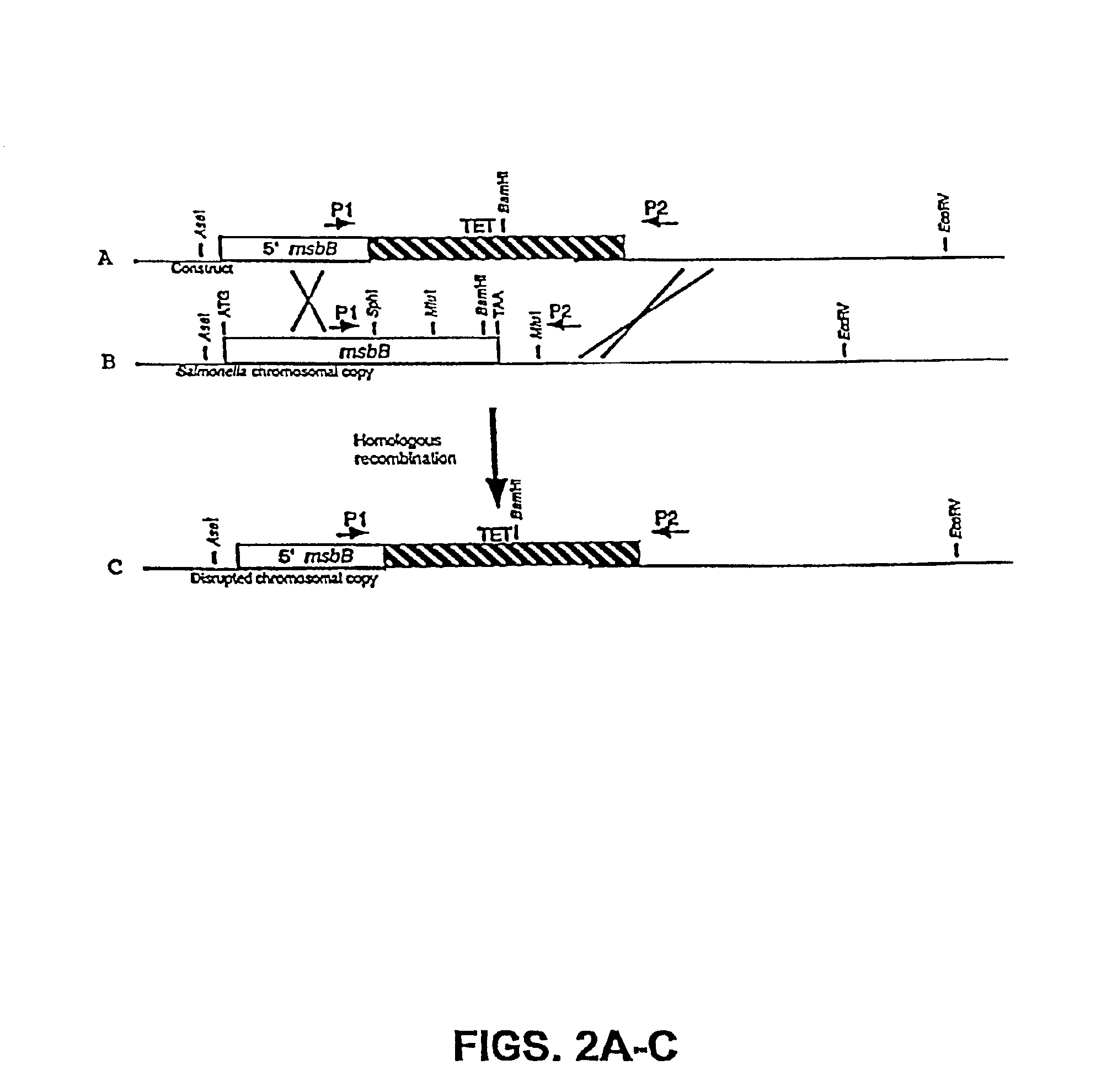
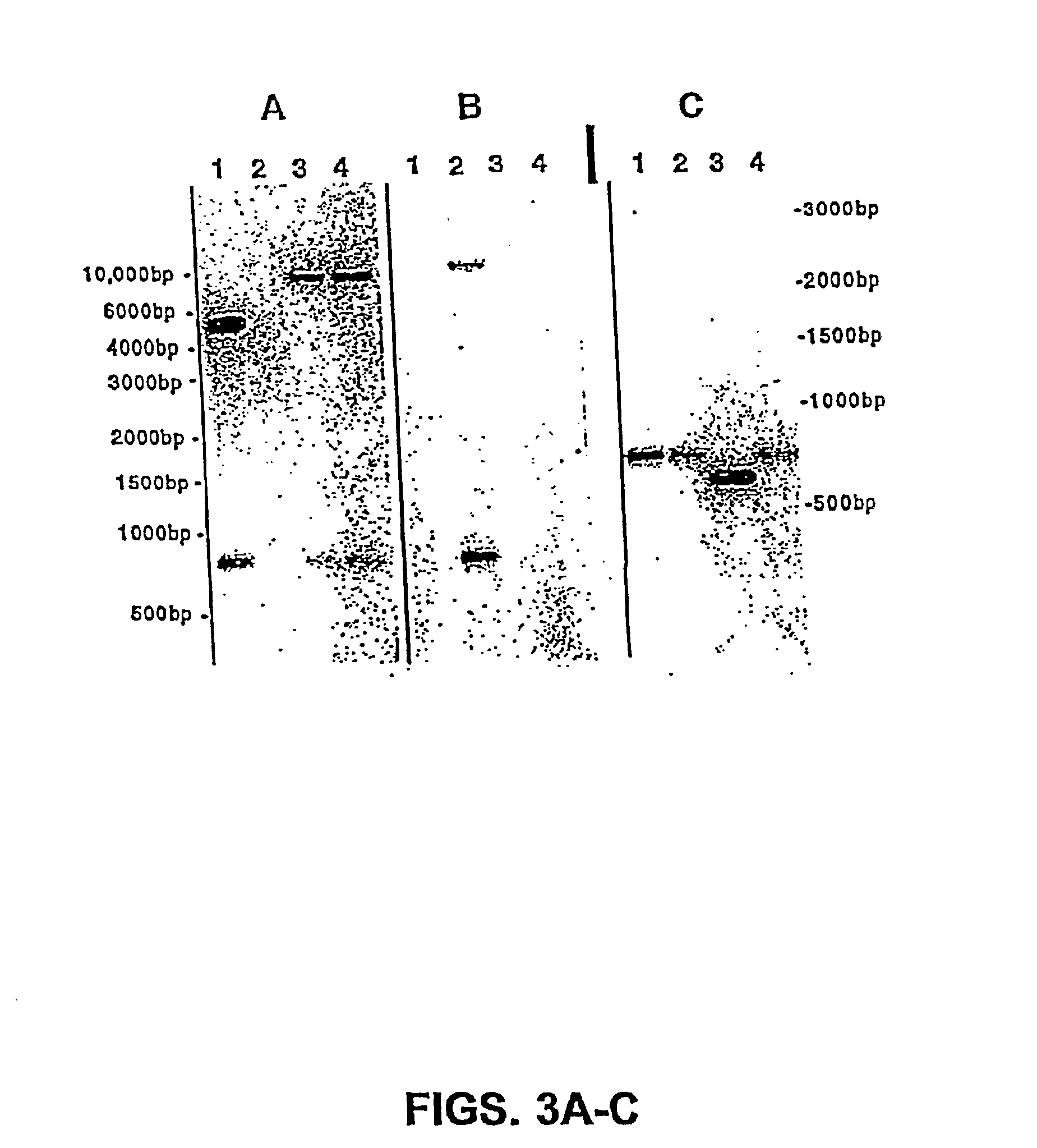
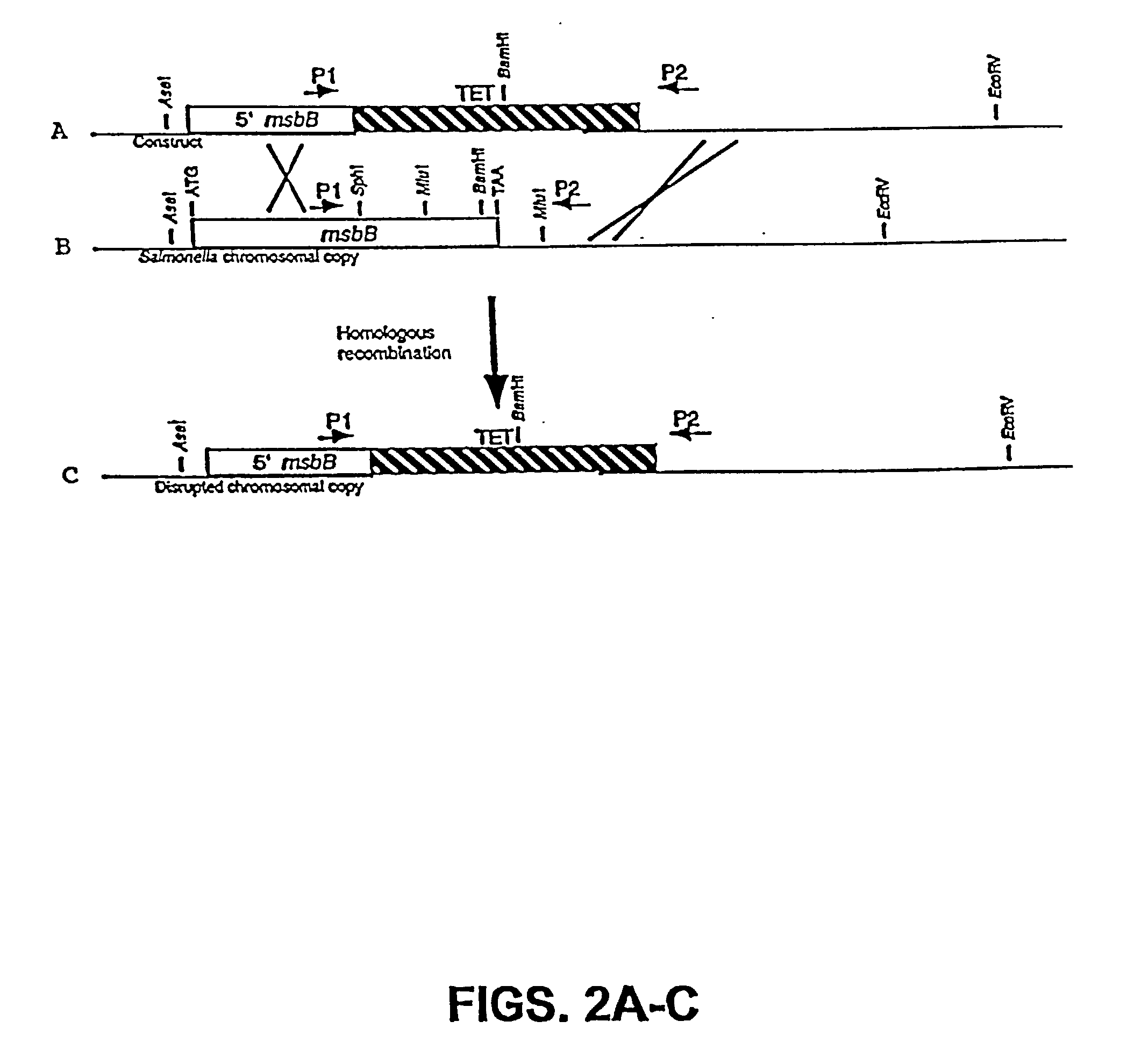
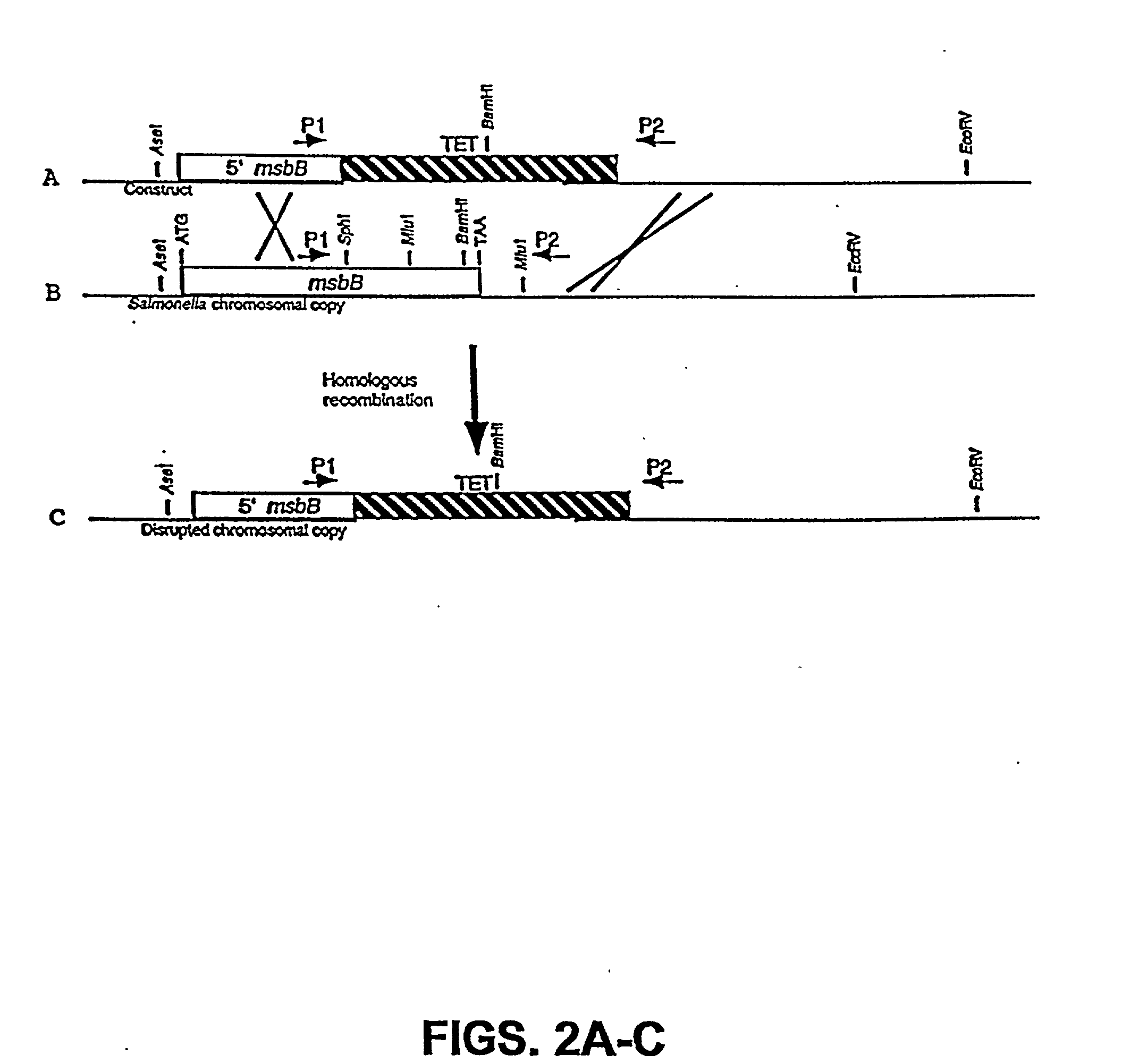
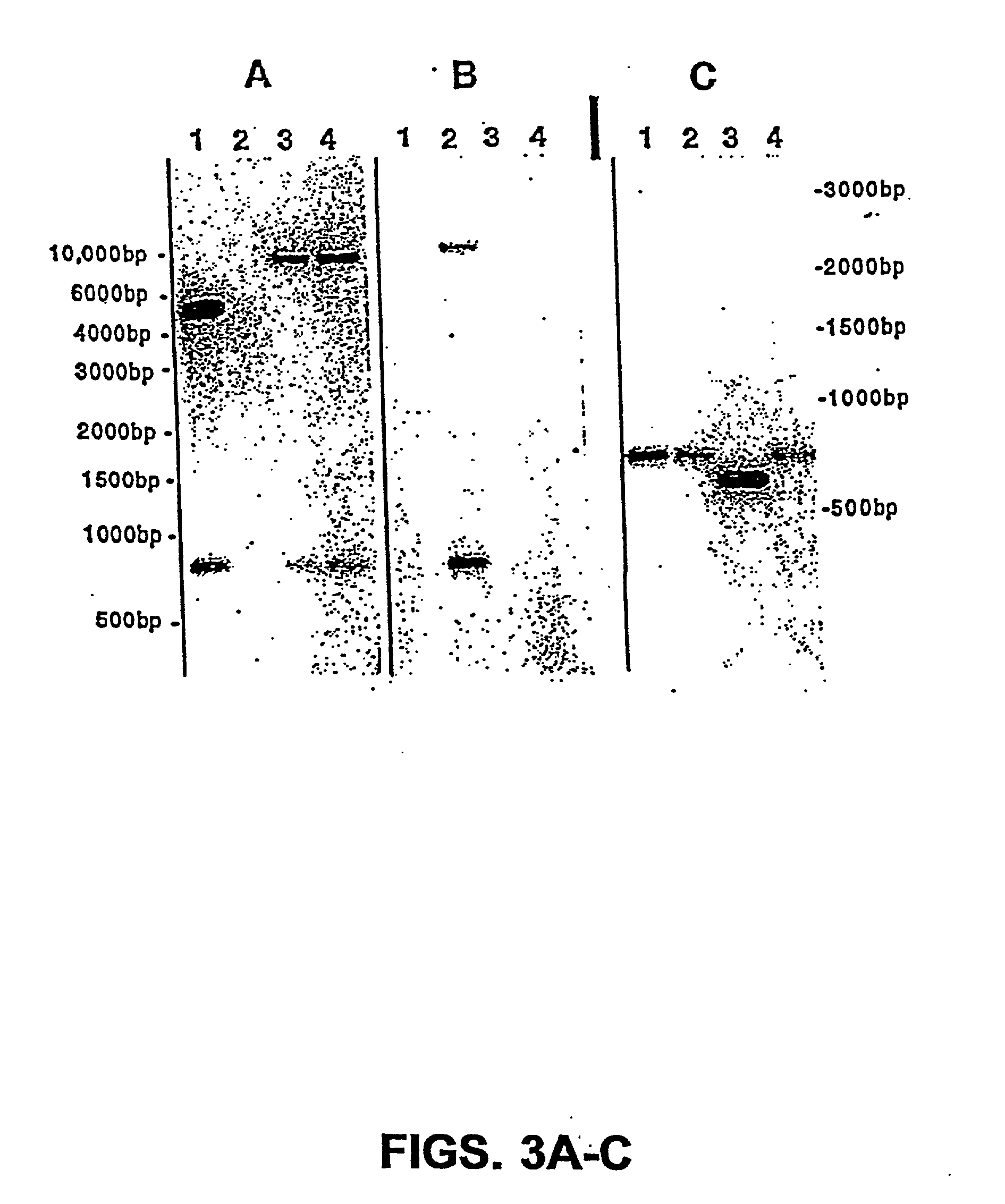
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Vectors for the diagnosis and treatment of solid tumors including melanoma
The present invention is directed to the isolation and use of super-infective, tumor-specific vectors that are strains of parasites including, but not limited to bacteria, fungi and protists. In certain embodiments the parasites include, but are not limited to, the bacterium Salmonella spp., such as Salmonella typhimurium, the bacterium Mycobacterium avium and the protozoan Leishmania amazonensis. In other embodiments, the present invention is concerned with the isolation of super-infective, tumor-specific, suicide gene-containing strains of parasites for use in treatment of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV
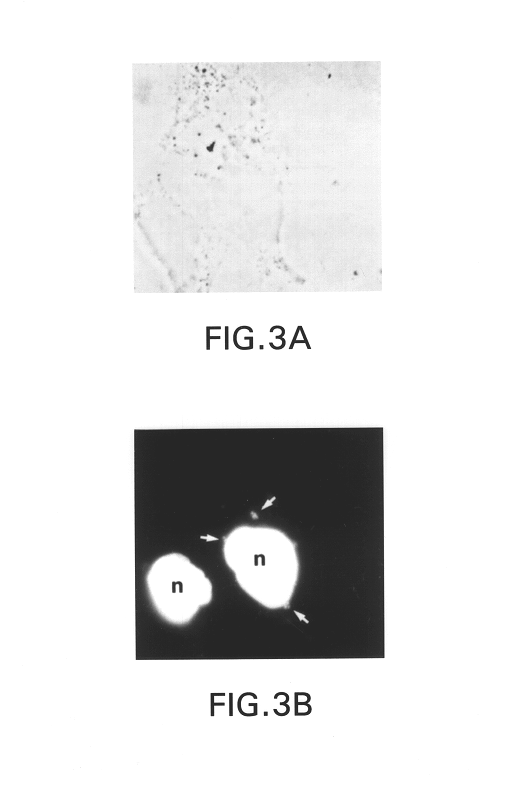
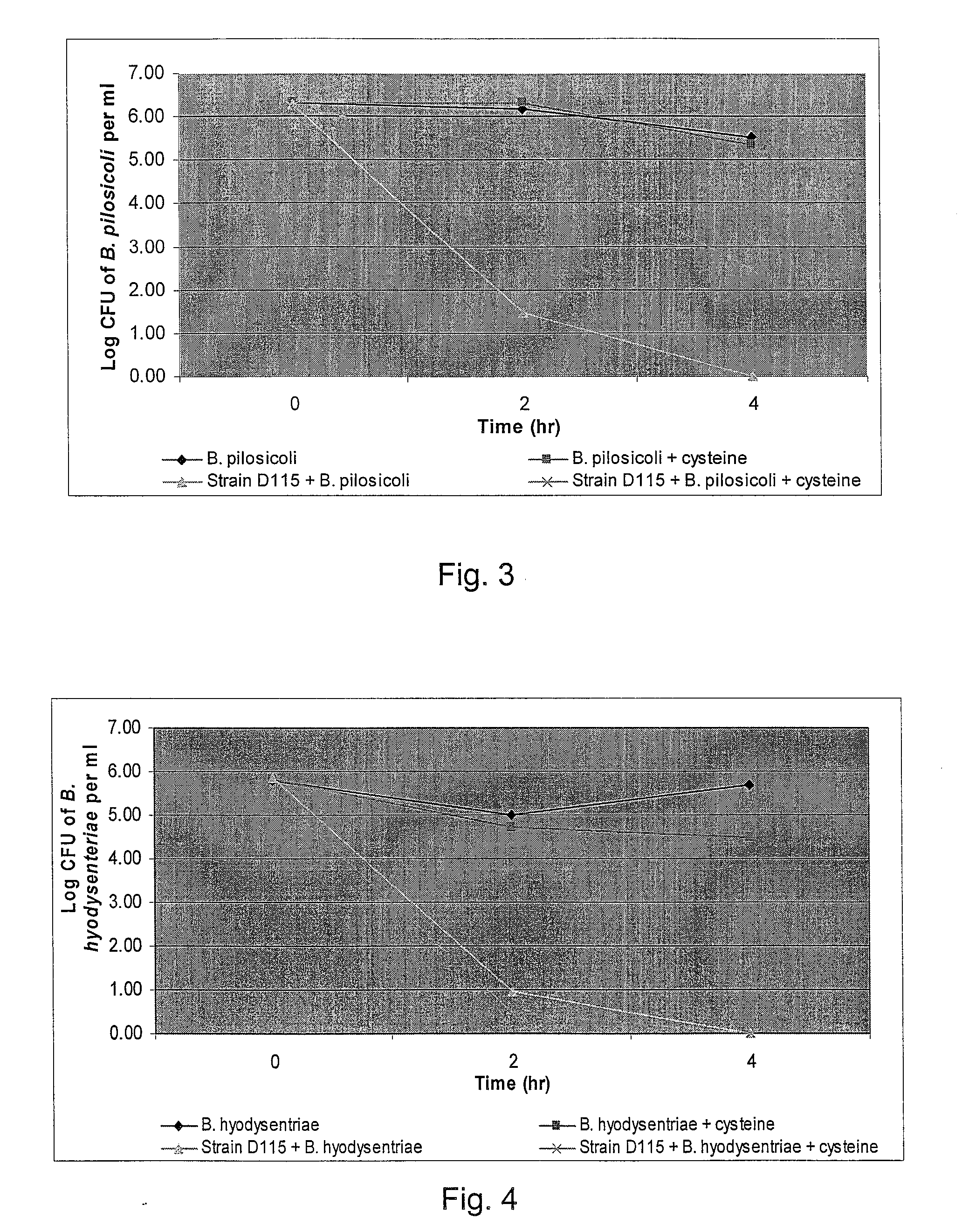
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Compositions and methods for delivery of an agent using attenuated Salmonella containing phage
The present application generally discloses delivery of an agent which can be therapeutic or prophylactic and, more particularly, the preparation and use of attenuated bacteria, such as Salmonella, containing a bacteriophage in which the genome of the bacteriophage has been modified to encode for a gene product of interest, e.g., an antigen or an anti-tumor protein. The bacteria functions as a vector for delivering the bacteriophage encoded gene product of interest to an appropriate site of action, e.g., the site of a solid tumor.
Owner:NANOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Vaccination by topical application of recombinant vectors
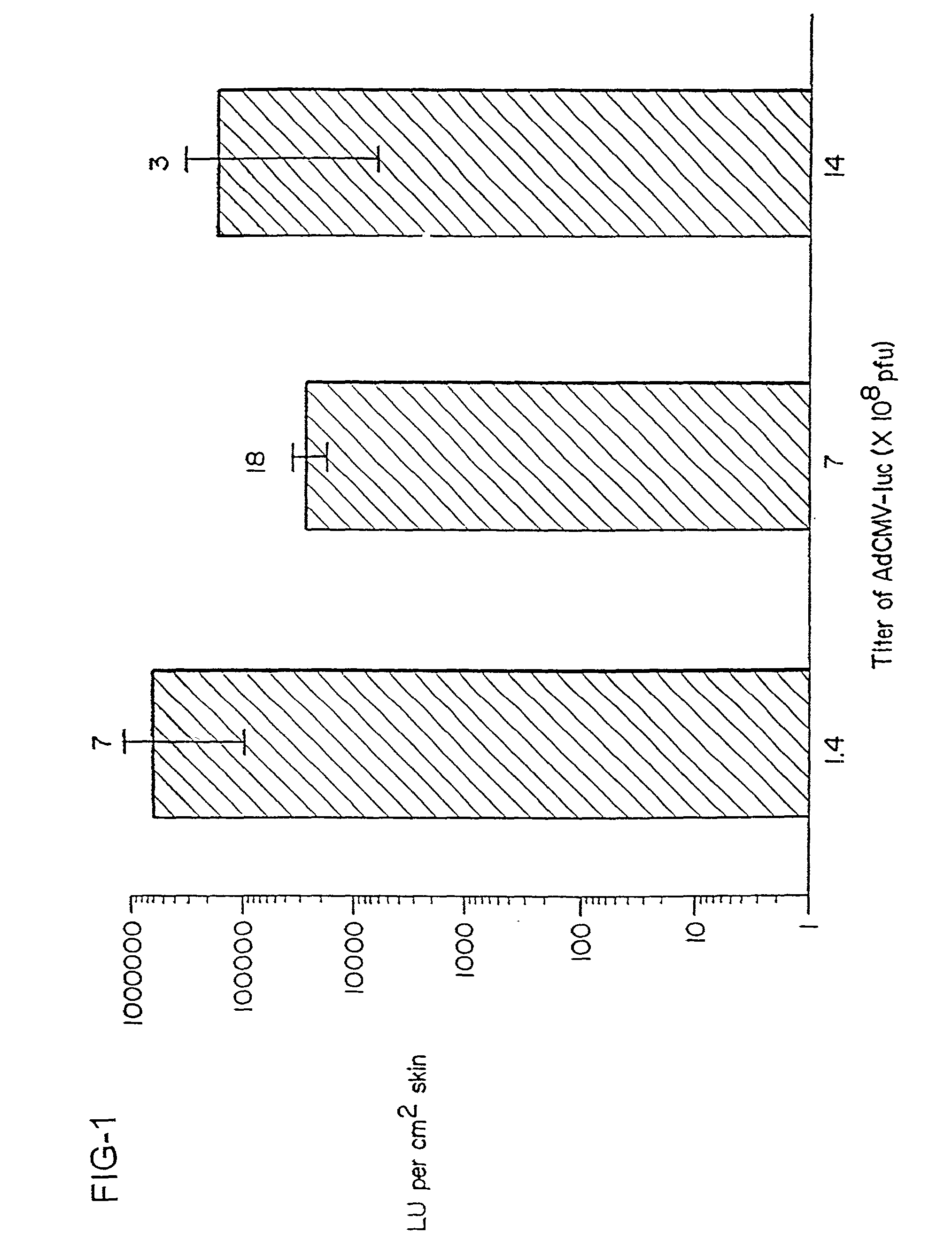
InactiveUS20030045492A1Improve vaccination schemeEfficient methodSsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryVaccination
The present invention relates to techniques of skin-targeted non-invasive gene delivery to elicit immune responses and uses thereof. The invention further relates to methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal following topical application of vectors, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can be gram negative bacteria, preferably Salmonella and most preferably Salmonella typhimurium.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS6863894B2Effective concentration and/or duration of the therapeutic vectorBiocideBacteriaTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purI gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:VION PHARMA INC +1
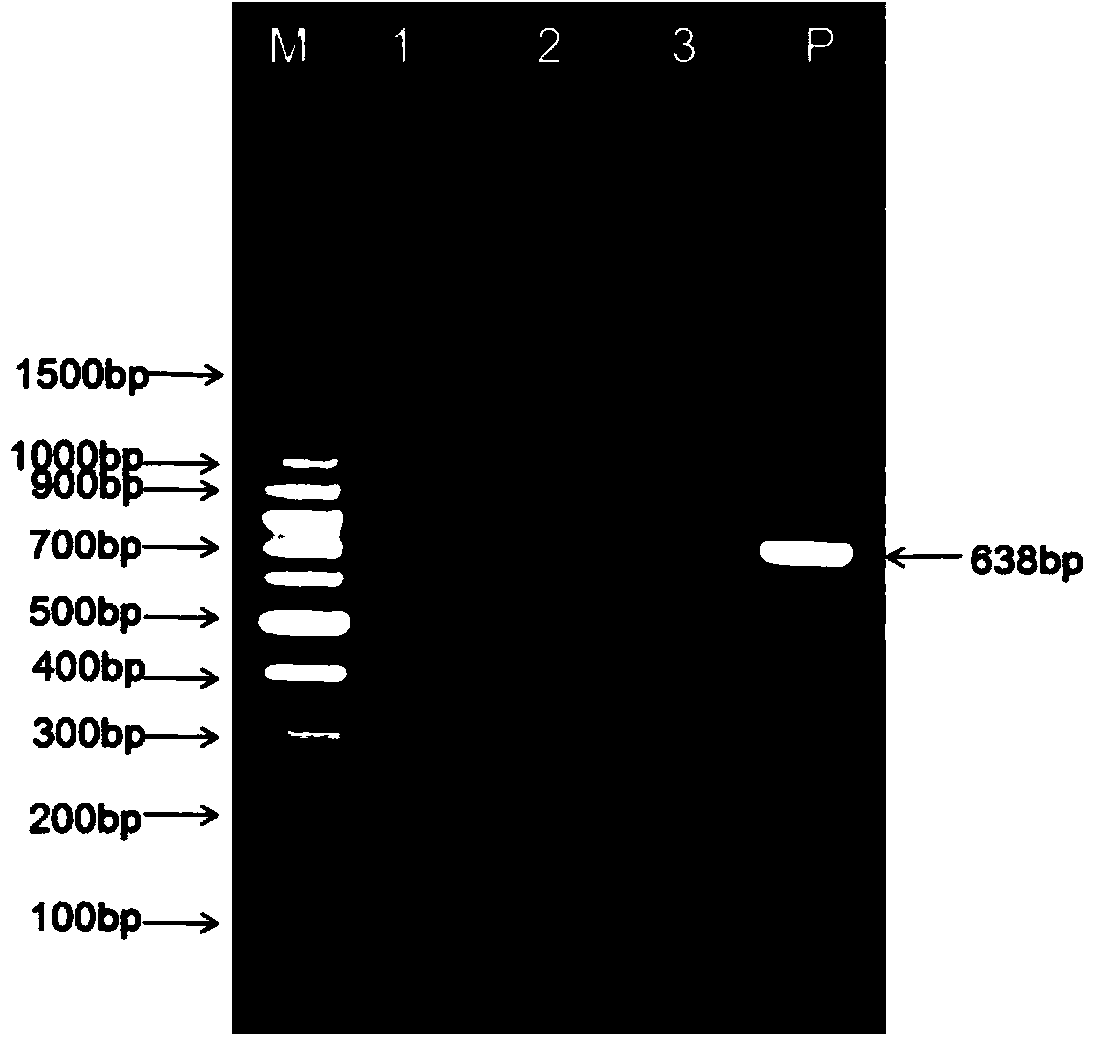
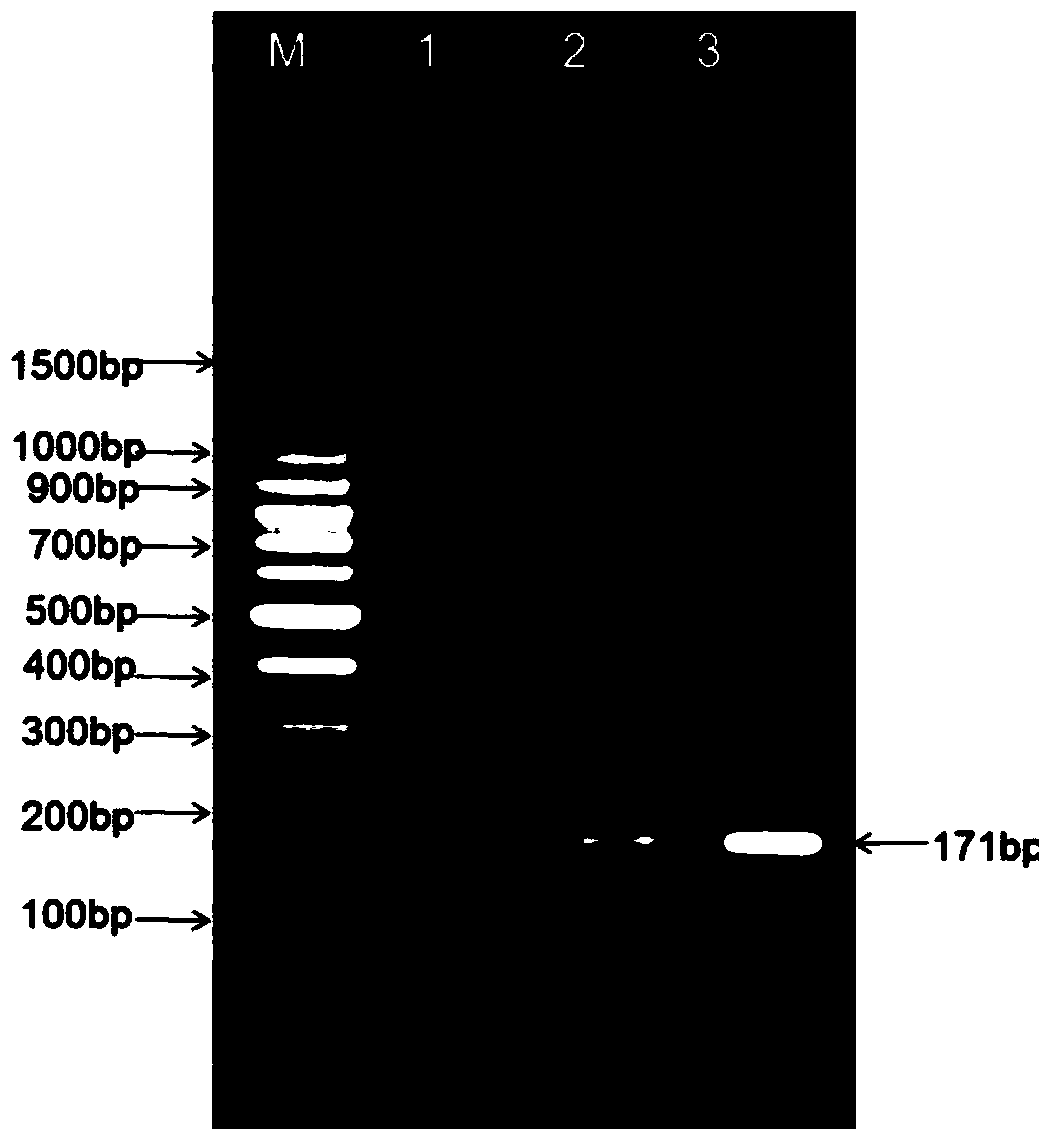
Primer, detection method and detection reagent kit for detecting salmonella
InactiveCN101153327AStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood borneLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a technique for fast detecting food-borne pathogens based on a loop-mediated isothermal amplification, LAMP technique. A primer for detection of salmonella can augment the specific base sequence of a target gene which is the invA-GenBank (accession no. DQ644633) of the salmonella, and the primer is complementary to a part of or a complementary chain of the nucleic acid sequence on the 382-580bp loci on the target gene. The invention provides a primer unit having specificity to a specific gene fragment of the salmonella, and through detecting whether or not the detecting specimen in a reagent box of the primer unit contains the specific gene fragment of the salmonella, determines whether the salmonella exists in the specimen or not.
Owner:ZHUHAI DISEASE PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Active peptide feed additive and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN1579198APromote growthPromote growth and differentiationHydrolasesFood processingAnimal proteinDigestion
The present invention relates to an active peptide feed addictive, as a mixture of one or more plant protein and animal protein, which is the product of the following steps: fermenting and degrading the mixture through bacillus and the like, controlling the degree of hydrolysis at 20-35%, obtaining a fermentation supernatant after a separation post-processing process, concentrating drying the supernatant or directly adsorbing the supernatant onto the carrier, and then low temperature drying it. Said active peptide feed addictive is capable of obviously depressing development of bacillus coli and salmonella, and can prevention and cure diarrhea caused by bacilli or lienteric diarrhea; can exert its functions at a very low concentration, with a very intense effect; can regulate stomach and intestine bacterium group and promote animals digestion functions; can excite animal immune function, reinforce animal disease resistance against a plurality of epidemic diseases and greatly reduce the morbidity and death rate; can promote animal development and improve the growth velocity; can improve the feed use ratio and reduce production costs. Applications of the microorganism fermentation degradation method provided by the present invention have a low fabricating cost, and the obtained peptides have many kinds and high content, without environment pollutions.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Immunogenic compositions and vaccines comprising carrier bacteria that secrete antigens
InactiveUS20040101531A1Snake antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesMucosal Immune ResponsesAntigen delivery
Disclosed are vaccines and immunogenic compositions which use live attenuated pathogenic bacteria, such as Salmonella, to deliver ectopic antigens to the mucosal immune system of vertebrates. The attenuated pathogenic bacteria are engineered to secrete the antigen into the periplasmic space of the bacteria or into the environment surrounding the bacteria. The vertebrate mounts a Th2-mediated immune response toward the secreted antigen.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Microorganisms and methods for treating poultry
ActiveUS20070202088A1Increasing low G+CImprove feed conversionBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliFeed conversion ratio
An isolated Bacillus strain LSSAO1 is provided. When fed to a bird, this and other Bacillus strains described herein provide benefits to the birds. For example, administration of the one or more Bacillus strain can increase low G+C, gram positive bacteria in the gastrointestinal flora of the bird. These type of bacteria are increased by antibiotics and include beneficial Clostridium. Administration of the one or more Bacillus strain can also inhibit pathogen in the bird, such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Clostridium. These benefits can enhance feed conversion in poultry. Useful combinations of Bacillus strains and methods of using one or more Bacillus strain are also provided.
Owner:AGTECH PRODS
Peptide-based vaccine for influenza
A human synthetic peptide-based influenza vaccine for intranasal administration comprises a mixture of flagella containing at least four epitopes of influenza virus reactive with human cells, each expressed individually in Salmonella flagellin, said influenza virus epitopes being selected from the group consisting of: (i) one B-cell hemagglutinin (HA) epitope; (ii) one T-helper hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleo-protein (NP) epitope that can bind to many HLA molecules; and (iii) at least two cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) nucleoprotein (NP) or matrix protein (M) epitopes that are restricted to the most prevalent HLA molecules in different human populations.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Antimicrobial food additive and treatment for cooked food, water and wastewater
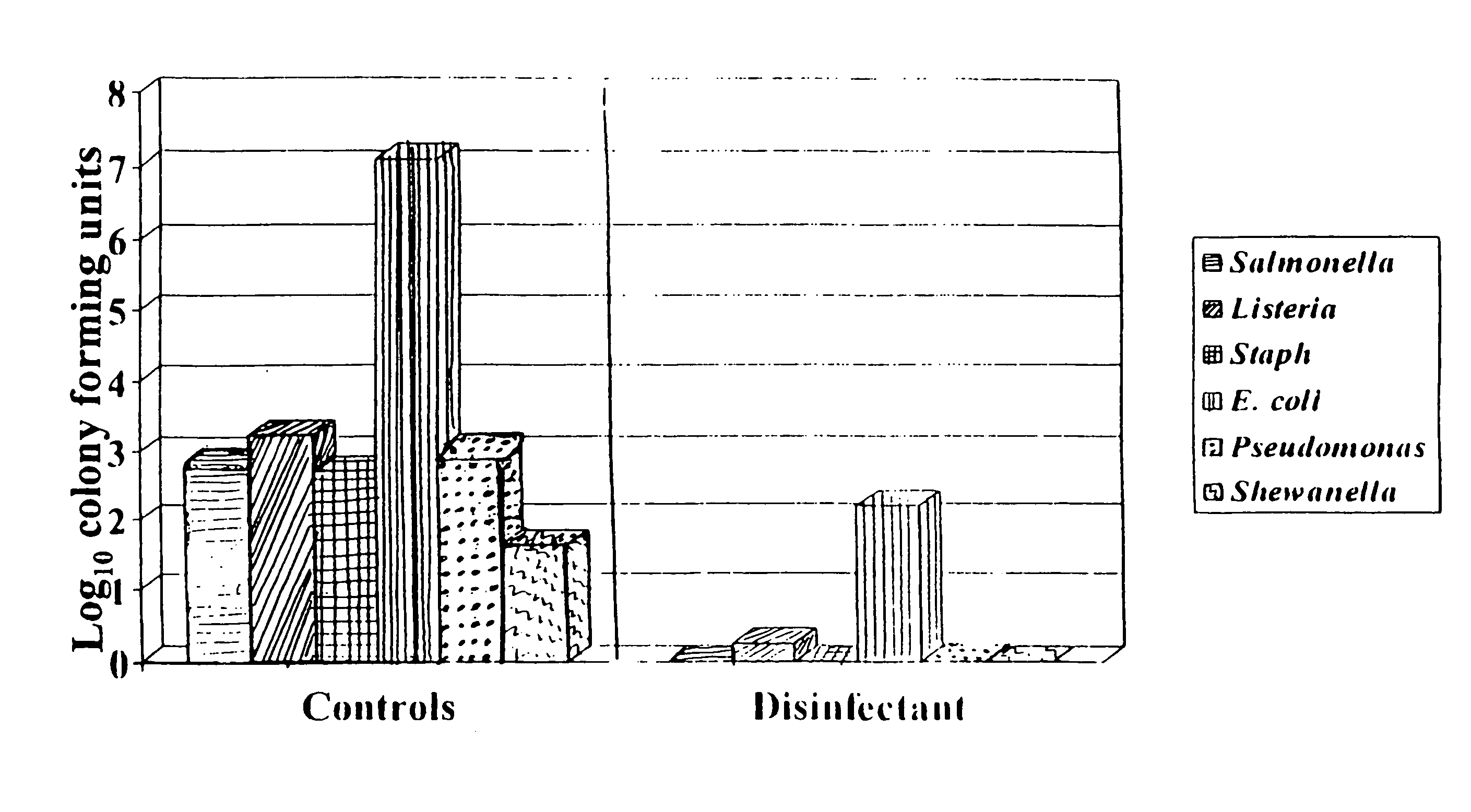
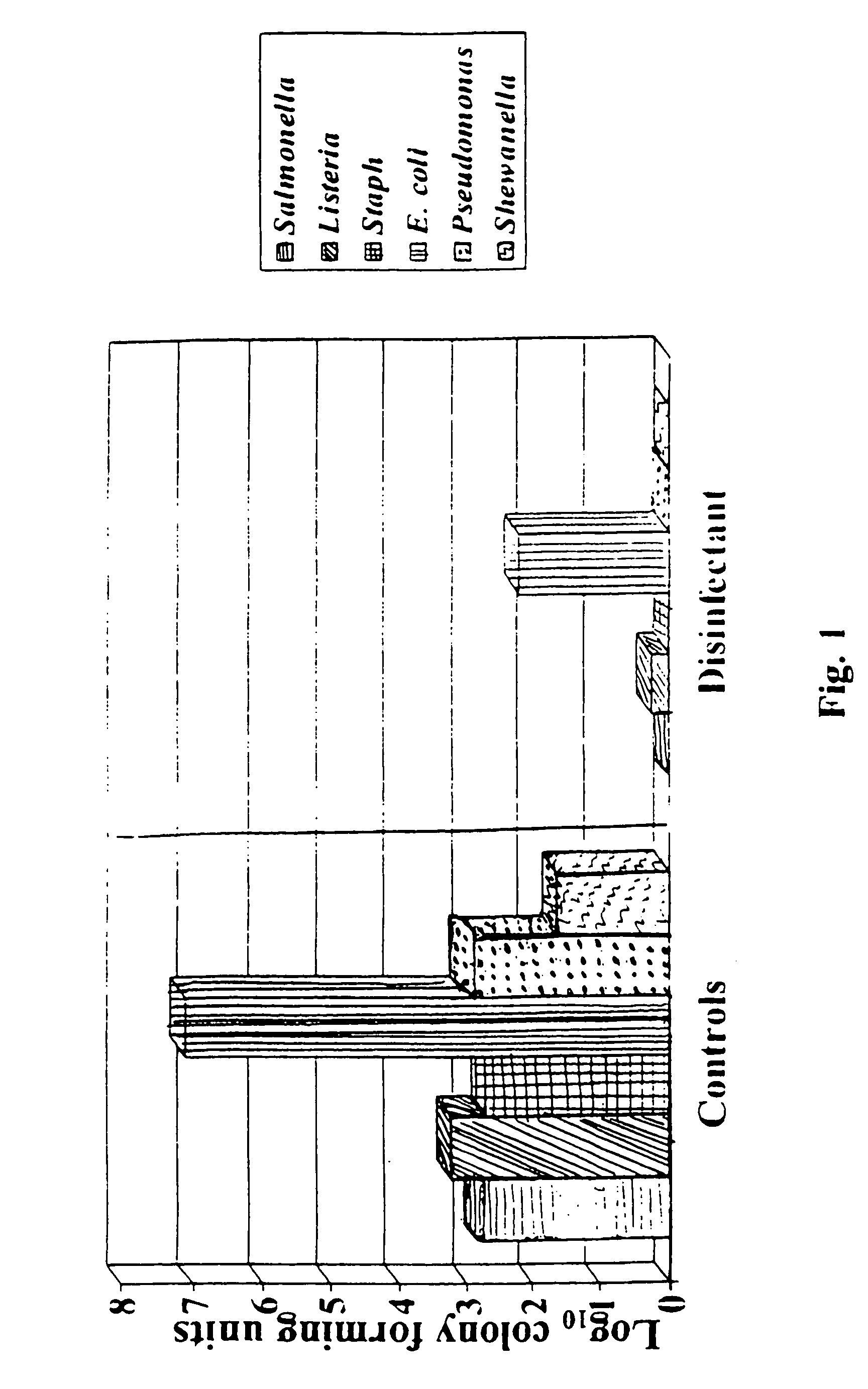
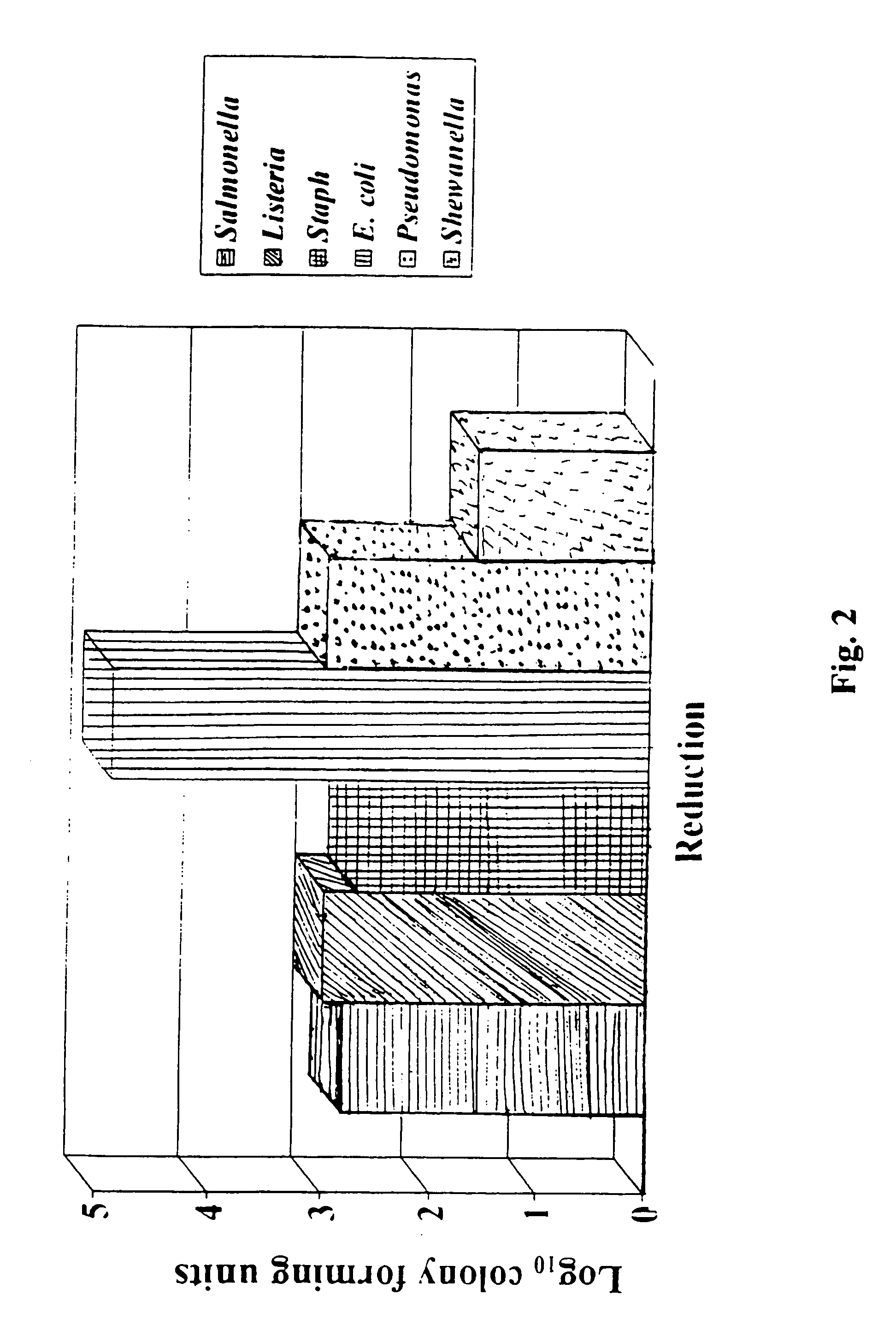
A composition of matter with antimicrobial and antibacterial properties for treatment of water, wastewater, processed food and for use as a food additive is provided. The antimicrobial composition inhibits cellular growth of known pathogenic, indicator and spoilage organisms, such as salmonella, stahphylococcus, listeria, E-coli, aerobic and anerobic organisms in wastewater and the like. The antimicrobial composition of the present invention is useful in many situations and conditions in need of disinfectants and sanitizers. One of the primary benefits of the antimicrobial agent is that it inhibits the growth of bacteria that have become antibiotic resistant. In addition, the antimicrobial composition herein does not have any known toxicity to man or the environment.
Owner:TASKER PRODS IP HLDG CORP
Compositions and methods for delivery of an agent using attenuated Salmonella containing phage
InactiveUS20040219169A1Reduce Toxicity RiskReduce riskBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaGene productBacteriophage
Owner:NANOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Probiotic composition suitable for animals
InactiveUS20100047209A1Reduce pollutionPathogen transmission can be reducedBiocideBacteriaLactobacillus salivariusProbiotic bacteria
The invention provides a probiotic composition to alleviate Salmonella infection in farm animals. The composition may comprise at least one of Lactobacillus murinus, Lactobacillus pentosus, Lactobacillus salivarius sub-species salivarius, and Pediococcus pentosaceus. The composition maybe formulated as an animal feedstuff, or as a pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:TEAGASC THE AGRI & FOOD DEVMENT AUTHORITY +1
Feed additive containing microbe and biological enzyme
InactiveCN1579201AReduce dosageMaintain natural healthAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsEscherichia coliDisease
The invention is a feed additive containing microbe and bio-enzyme, and its character: it is composed of beneficial bacteria, functional enzyme, mineral trace elements, and feed carrier. It has multielements to cooperate with one another, and thus it has good synthetic effect, and its microbes are obtained by solid fermentation, and thus the device investment is low, the low-temperature drying effectively assures the nutrient constituents, and the variety and activity of the microbes and bio-enzymes from not being lost, and simultaneously reduces enzyme extraction procedures, and extremely reduces the production cost; the product meets the dispersion of various effective constituents in the raw materials on the carrier as far as possible, so as to fully use them to achieve the best effect. It uses the addition of beneficial bacteria to regulate the balance of bacteria crowd in the stomach intestine of the domestic animal and fowl, improves the micro-ecological environment, and makes the domestic animal and fowl keep naturally healthy physique; inhibits and prevents the occurrence of the bacterial diseases, such as Escherichia coli disease, salmonella disease, etc, reducing antibiotic usage, reducing therapeutic expenses and improving the productivity of the animal.
Owner:ENZYME ENG INST SHAANXI PROVINCE ACAD OF SCI
Live attenuated salmonella vaccines to control avian pathogens
A vaccine for protecting birds against infection by avian pathogenic gram negative microbes is disclosed. The vaccine is a recombinant Salmonella strain expressing O-antigen of an avian pathogenic gram negative microbe such as an E. coli strain that is pathogenic in poultry. The recombinant Salmonella strain also does not express Salmonella O-antigen. Methods of using the vaccine to immunize birds are also disclosed.
Owner:AVANT IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS
Recombinant bacterial vaccine system with environmentally limited viability
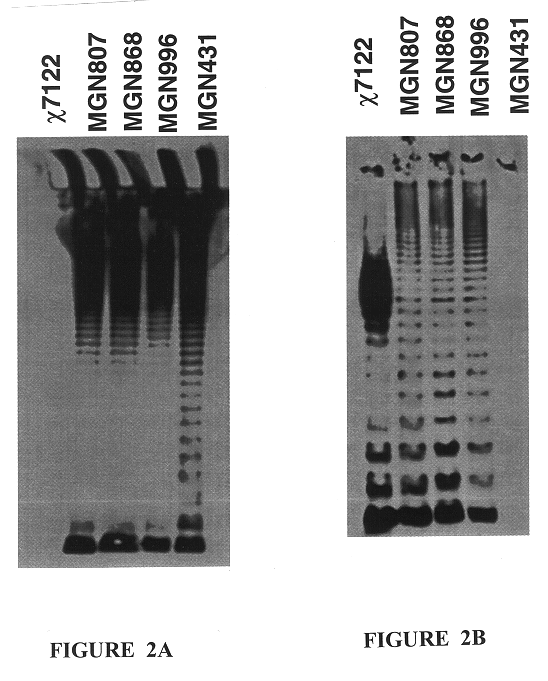
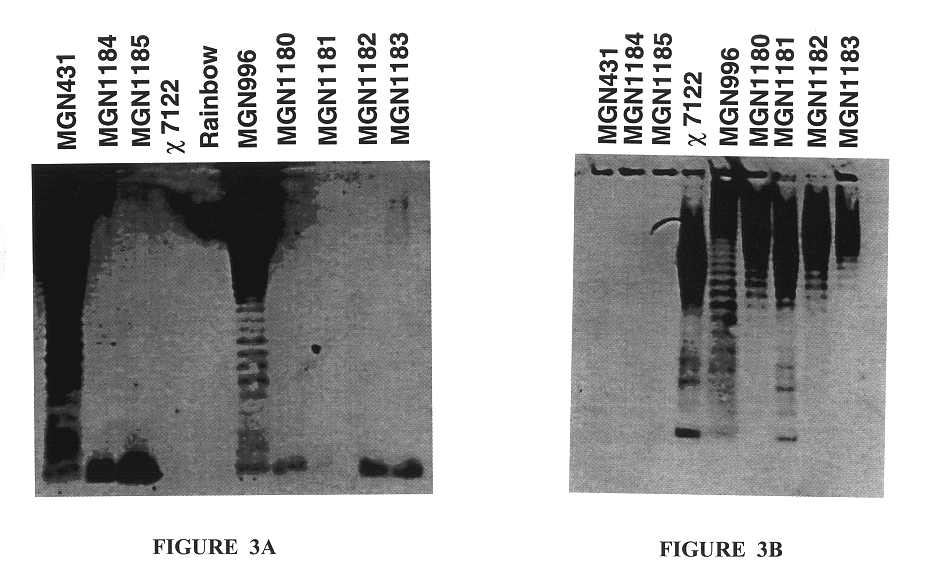
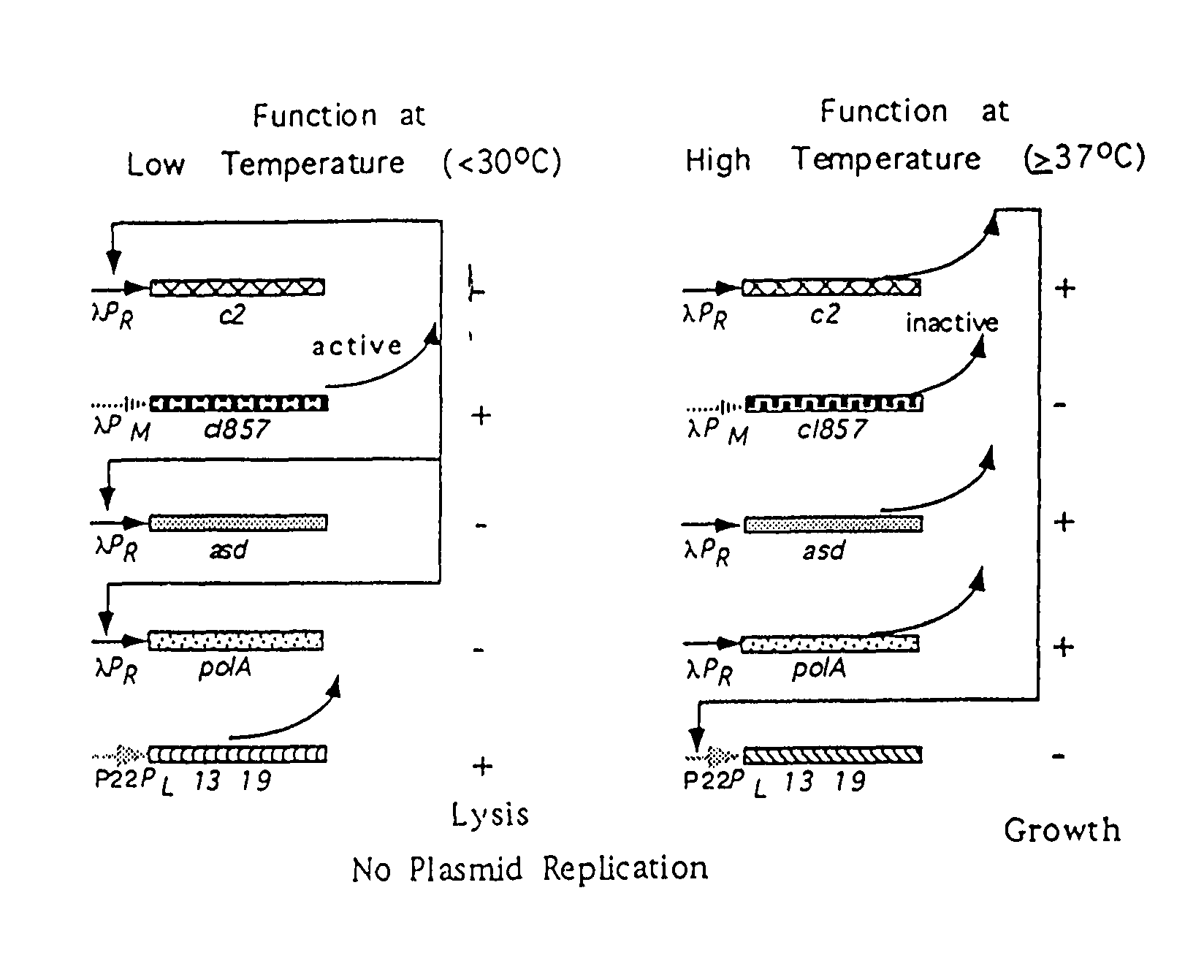
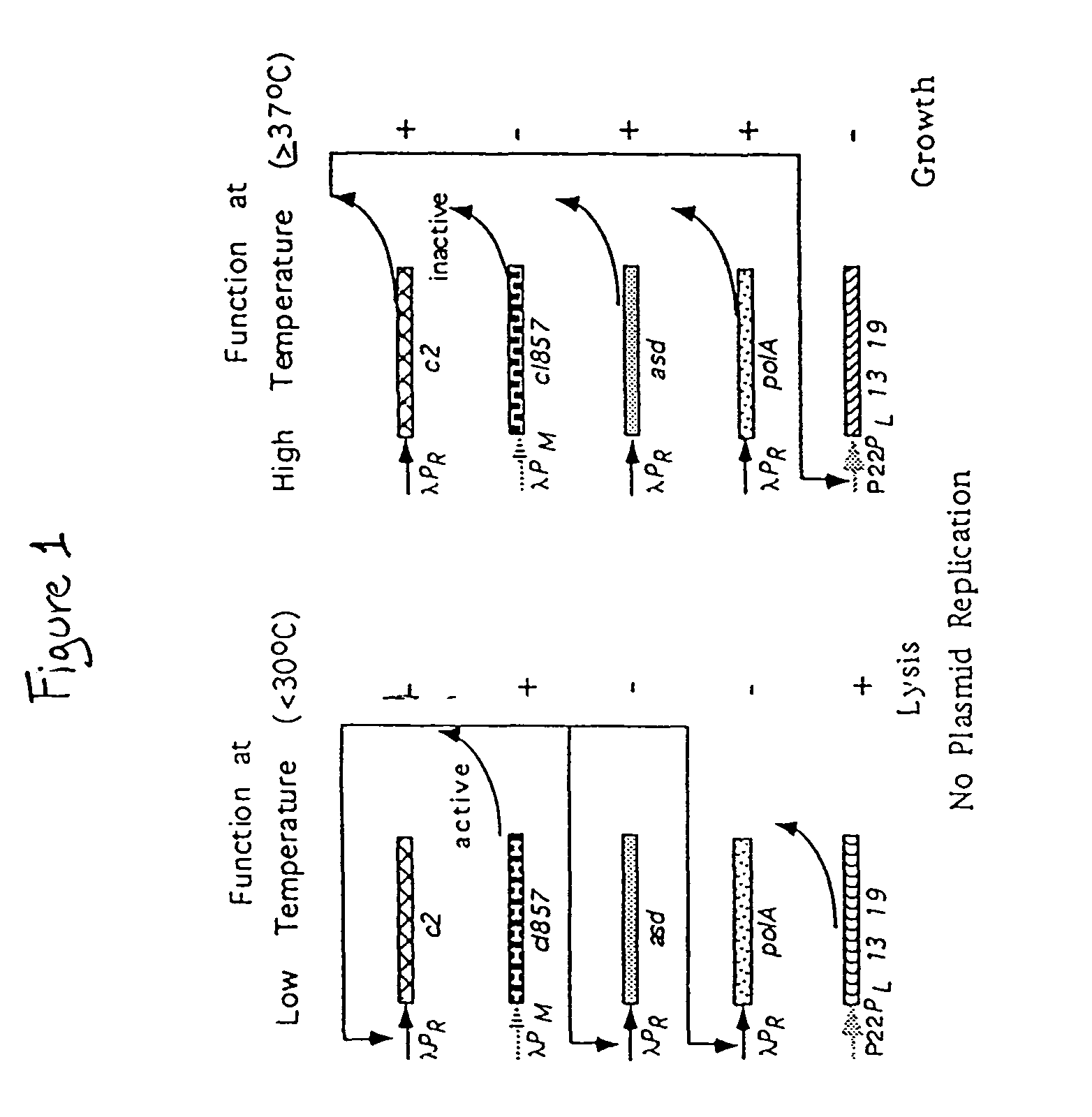
Disclosed is an Environmentally Limited Viability System (ELVS) for microorganisms based on temperature differences between permissive and non-permissive environments. Viability of the microorganisms are limited to the permissive environment by specifically expressing one or more essential genes only in the permissive environment, or expressing one or more lethal genes only in the non-permissive environment. Environmentally Limited Viability Systems are also disclosed involving coordinate expression of a combination of required genes and lethal genes. Microorganisms containing an Environmentally Limited Viability System are useful for release into a permissive environment. Temperature regulated Environmentally Limited Viability Systems are particularly suited for use with recombinant avirulent Salmonella vaccines by limiting their growth to the warmer environment inside the host. Such vaccines can be administered to protect humans or warm-blooded animals against bacterial, viral, mycotic and parasitic pathogens, especially those that colonize on or invade through mucosal surfaces. This antigen delivery system can also be used for expression of gamete-specific antigens to induce immune responses to block fertilization, or to induce immune responses to tumor antigens. In the event that an individual sheds live vaccine into the environment, the presence of the ELVS prevents survival of the vaccine. When environmentally regulated lethal genes are present on an extrachromosomal element and are regulated by chromosomal genes, transfer of the extrachromosomal element to other microorganisms will be limited by unregulated expression of the lethal genes in the recipient microorganism.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Attenuated salmonella as a delivery system for sirna-based tumor therapy
InactiveUS20090208534A1Promote growthConducive to survivalBacteriaSpecial deliveryTumor targetTumor targeting
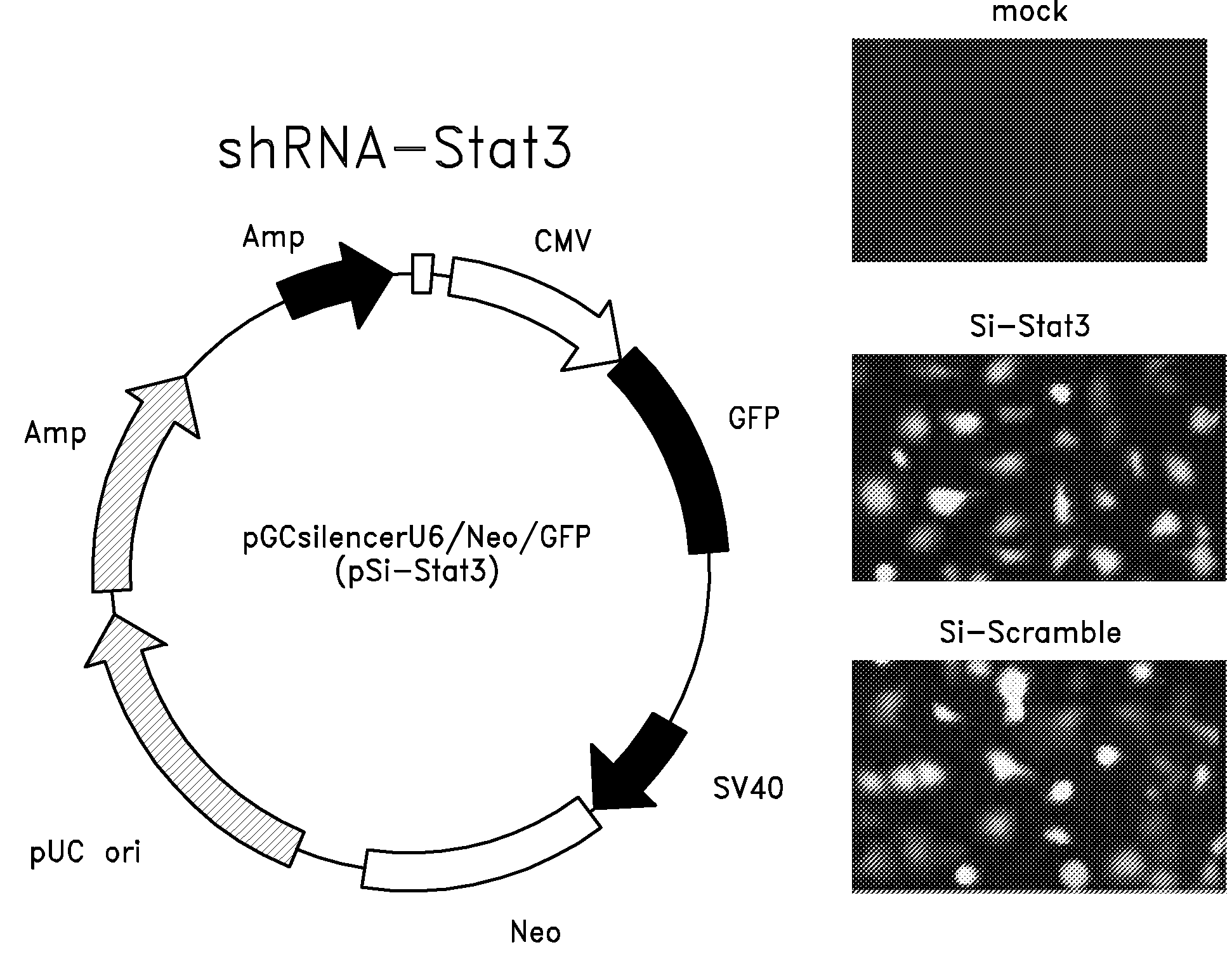
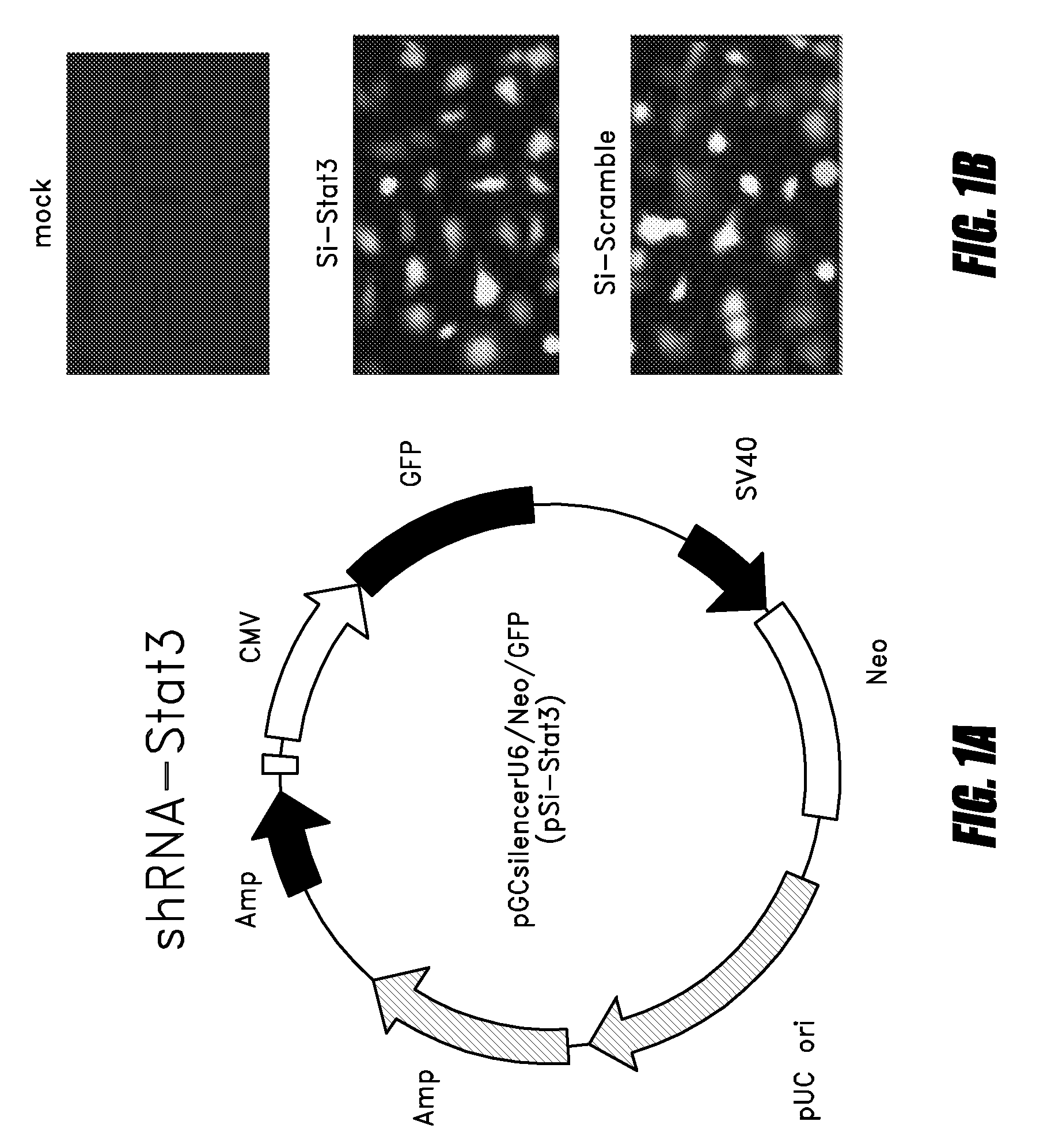
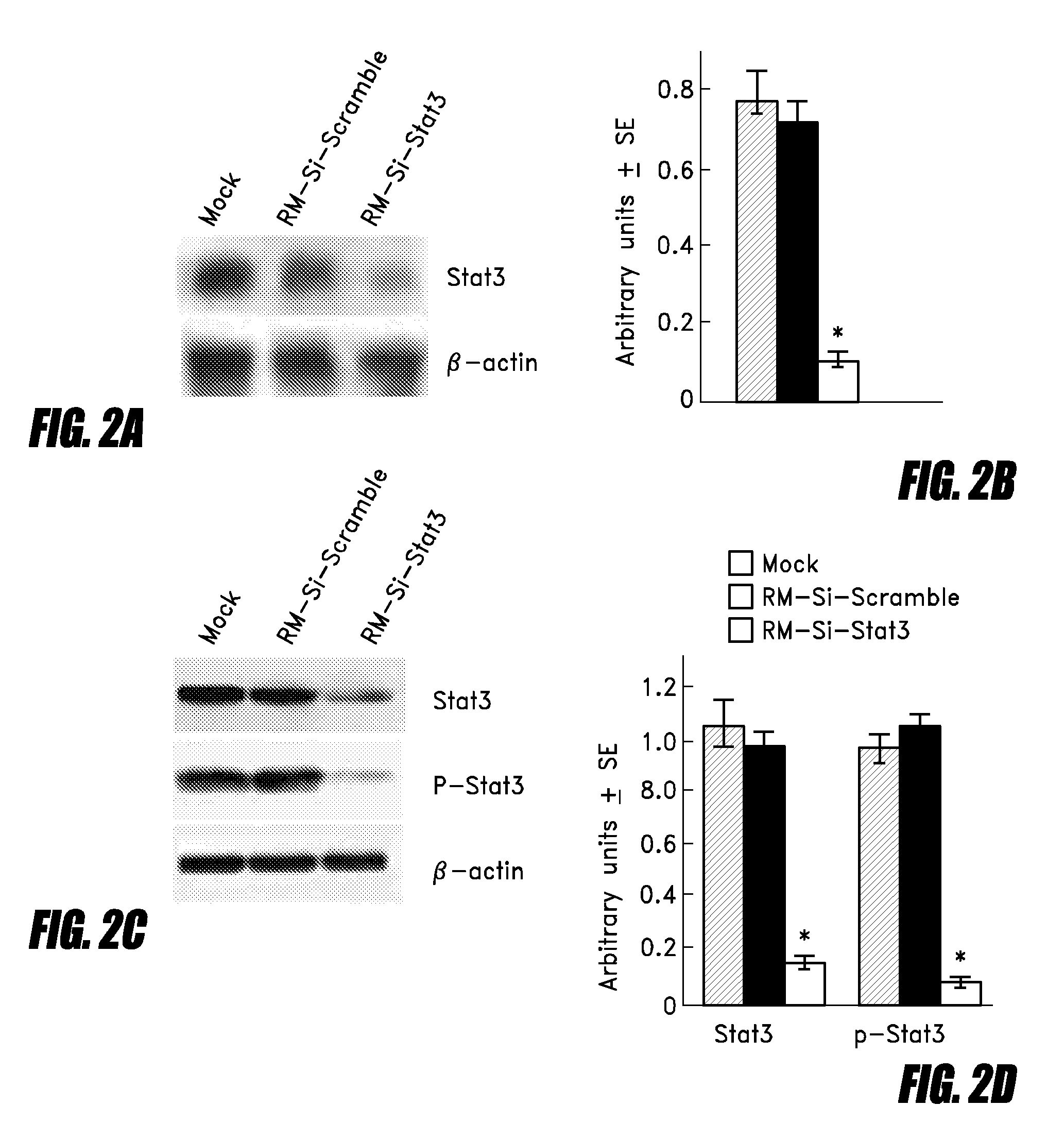
The invention relates to an attenuated Salmonella sp. that is capable of targeting a solid tumor when administered in vivo comprising a short hairpin (sh) RNA construct, and methods of inhibiting the growth or reducing the volume of a solid tumor cancer comprising administering an effective amount of an attenuated Salmonella sp. to a patient having a solid tumor cancer, wherein said attenuated Salmonella sp. is a tumor targeting attenuated Salmonella sp. expressing a short hairpin (sh) RNA which attenuated Salmonella sp. is capable of inhibiting the growth or reducing the volume of the solid tumor cancer when administered in vivo.
Owner:JILIN UNIV +2
Recombinant vector for eliminating activity of kanamycin drug resistance gene and building method of recombinant vector
InactiveCN105463003AInhibitory activityHigh copy numberNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionNovel geneOrganism
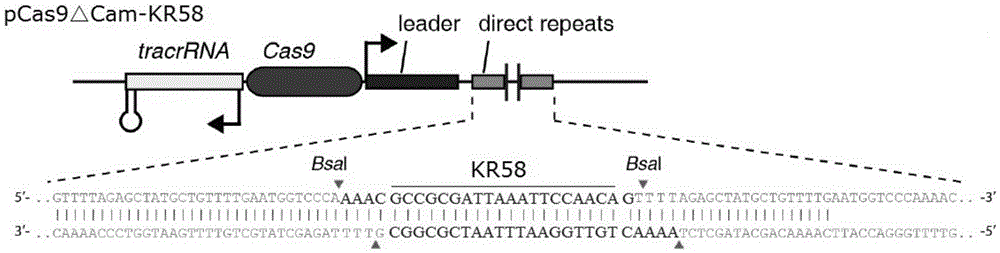
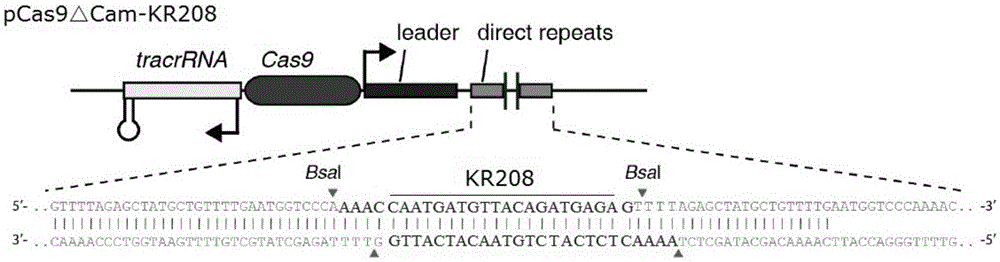
The invention provides a recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of a kanamycin drug resistance gene, and aims at eliminating drug resistance germs in organisms and solving the problem of kanamycin drug resistance of the germs. The recombinant vector for eliminating the activity of the kanamycin drug resistance gene is characterized by comprising a pCas9 vector subjected to chloramphenicol resistance elimination and a gRNA nucleotide sequence KR58 or KR208 aiming at a kanamycin resistance gene kan; the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR58 is GCCGCGAT TAAATTCCAACA, and the concrete nucleotide sequence of the KR208 is CAATGATG TTACAGATGAGA. A building method of the recombinant vector mainly comprises the steps of carrying intergenic region nucleic acids by a novel gene editing tool CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 system; removing a chloramphenicol resistance gene on the recombinant vector; transforming the gene into vaccine vector bacteria such as attenuated salmonella typhimurium; performing co-culture on the recombinant bacteria and the kanamycin drug resistance gene so that the recombinant vector in the recombinant bacterium cell enters the kanamycin drug resistance bacteria in an engaging mode. The activity of the kanamycin resistance gene kan is effectively inhibited, so that the original drug resistance bacterium cannot grow on a kanamycin culture medium.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Intranasal recombinant Salmonella vaccine encoding heterologous polysaccharide antigens
InactiveUS20050260225A1Promote robust immune responseReduce deliveryBacterial antigen ingredientsAgainst vector-borne diseasesHeterologousAntigen
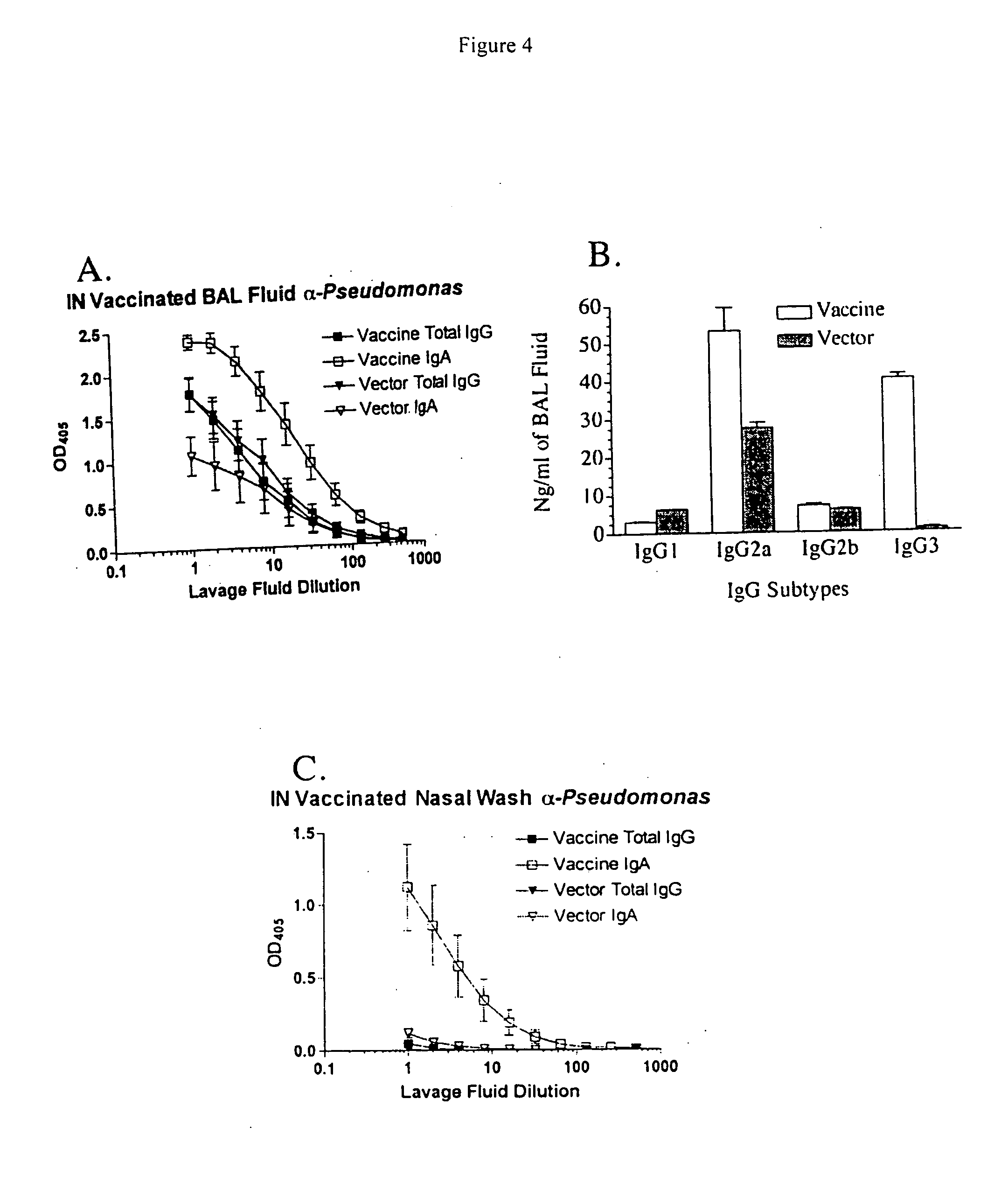
The invention relates of administration of an attenuated Salmonella strain expressing a lipopolysaccharide O antigen from a suitable pathogen, in particular Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the use of the same as a vaccine to promote sterile immunity to the pathogen, e.g., P. aeruginosa, via intranasal vaccination. In one embodiment, the present invention is directed to a unique intranasal route of immunization for the delivery of relevant heterologous polysaccharide antigens via a live, attenuated Salmonella strain.
Owner:GOLDBERG JOANNA B +2
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20030109026A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purI gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:VION PHARMA INC +1
Antimicrobial composition for pre-harvest and post-harvest treatment of plants and animals
ActiveUS7192618B2Minimize growth and spreadReduce Microbial ContaminationHeavy metal active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationFood additiveDisinfectant
Owner:CMS TECH INC +1
Immunization of animals by topical applications of a salmonella-based vector
InactiveUS20030125278A1Efficient methodSimple and effective and economical and immunizationSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacterial antigen ingredientsGene deliveryWhole body
The present invention relates to techniques of skin-targeted non-invasive gene delivery to elicit immune responses and uses thereof. The invention further relates to methods of non-invasive genetic immunization in an animal and / or methods of inducing a systemic immune or therapeutic response in an animal following topical application of vectors, products therefrom and uses for the methods and products therefrom. The methods can include contacting skin of the animal with a vector in an amount effective to induce the systemic immune or therapeutic response in the animal as well as such a method further including disposing the vector in and / or on the delivery device. The vector can be gram negative bacteria, preferably Salmonella and most preferably Salmonella typhimurium.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and kit
ActiveCN103484546ATo achieve the detection effectMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a fourteen-food-borne pathogenic bacterium multiplex PCR detection primer set and a kit. The detection primer set is composed of primer pairs for detecting salmonella, Shigella, Vibrio parahemolyticus, campylobacter jejuni, campylobacter coli, staphylococcus aureus, bacillus cereus, Listeria monocytogenes, yersinia enterocolitica, enterobacter sakazakii, Escherichia coli, vibrio cholerae, Escherichia coli O157, aeromonas hydrophila and internal positive control. A multiplex PCR detection method based on an ordinary PCR platform is built, multiplex PCR reactions are carried out on genomic DNA, extracted from a sample to be tested, of bacteria in the same reaction system through the primer pairs acquired through analysis and design, and whether the food-borne pathogenic bacteria are contained in the sample or not is judged through the electrophoretic analysis of reaction products.
Owner:北京卓诚惠生生物科技股份有限公司
Methods of reducing porcine circovirus-associated disease outbreaks
InactiveUS20100136060A1Reduce severityOvercome problemsViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseClinical manifestation
The present invention relates to the use of an immunogenic composition that comprises a salmonella antigen for treatment of several clinical manifestations (diseases). Preferably, the clinical manifestations are associated with a PCV2 infection, even more preferably PCVAD. The use relates to a method comprising the steps of administering the composition to an animal in need thereof, preferably prior to disease exposure. Administration of salmonella antigen, preferably a salmonella vaccine, lessens the incidence and reduces the severity of PCVAD.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Genetically modified tumor-targeted bacteria with reduced virulence
InactiveUS20020026655A1Improve securityReduce capacityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetVirulent characteristics
The present invention is directed to mutant Salmonella sp. having a genetically modified msbB gene in which the mutant Salmonella is capable of targeting solid tumors. The invention is also directed to Salmonella sp. containing a genetically modified msbB gene as well as an genetic modification in a biosynthetic pathway gene such as the purl gene. The present invention further relates to the therapeutic use of the mutant Salmonella for growth inhibition and / or reduction in volume of solid tumors.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Lactobacillus plantarum, method for fermenting and preparing bacteriocin of Lactobacillus plantarum, and application of Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocin
The invention provides a new Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG which was preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGNCC) with the collection number of CGMCC No. 2994 on march, 30th, 2009. The Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG can produce broad-spectrum bacteriostatic activity bacteriocin with high yield, and can express bacteriostasis for staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and E.coli of gram-negative bacterium, L. plantarum, L.brevis, Streptococcus and Bacillus of gram-positive bacterium, and the like. A virus attacking tests with high dosage proves that the Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG is safe to animal bodies. The Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG and a zymophyte liquid thereof can be used for preparing additives of green animal feeds, and the bacteriocin of the Lactobacillus plantarum bacterial strain YJG can be used for preparing green biological veterinary drugs, environmental-friendly biopreservatives, biocontrol drugs and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plating media for the identification of Salmonella
InactiveUS7150977B2Reduce and eliminate responseElimination reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementAdditive ingredientBeta-Galactosidases
An isolation plating medium for the identification of Salmonella bacteria in a sample containing a plurality of different bacteria comprising a mixture of a carbohydrate capable of being a metabolic source for Salmonella bacteria and supporting colonies of Salmonella bacteria, a pH indicator dye that changes the color of the plating medium to a first color different from the color of the medium responsive to a change in the pH of the medium, a first substrate that does not react with Salmonella bacteria and injects color into the medium of a second color responsive to the presence of beta-galactosidase, the second color contrasting with the first color and the color of the medium, a second substrate that does not react with Salmonella bacteria and injects color into the medium of substantially the same color as the second color responsive to the presence of beta=galactosidase, and an ingredient for thickening the mixture in sufficient quantity to solidify the mixture.
Owner:R&F PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com