Lactobacillus plantarum, method for fermenting and preparing bacteriocin of Lactobacillus plantarum, and application of Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocin
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocin, applied in the field of microbial application, can solve the problems of poor pertinence, difficulty in obtaining strains that meet production requirements, and large workload.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Screening and identification of strains of embodiment 1
[0047] 1. Isolation of Lactobacillus in Habitat
[0048] In the initial screening, the collected samples are first diluted with physiological saline, generally 3 to 4 orders of magnitude (depending on the sample, the bacteria in the sample can be diluted to 5 orders of magnitude, and the rare content can be diluted to 2 orders of magnitude), Add 100ul of the last two dilutions of the bacteria-containing solution to the modified MRS plate containing 0.02% bromocresol purple indicator, spread evenly, and select on the MRS medium for 24 hours at 37 °C to change the bromocresol purple from purple. The yellow colonies were isolated and cultured, and the obtained pure bacteria were marked and numbered respectively.
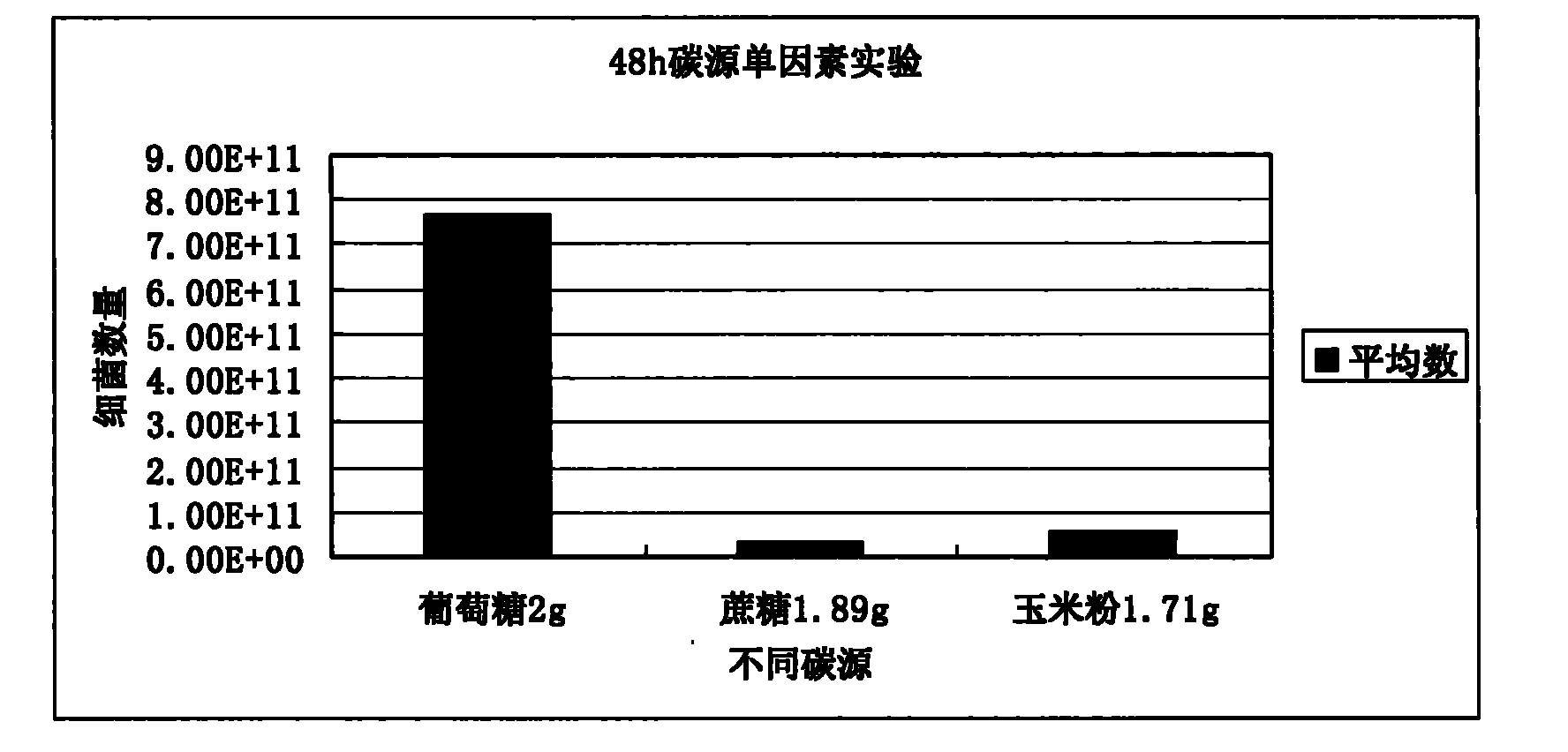
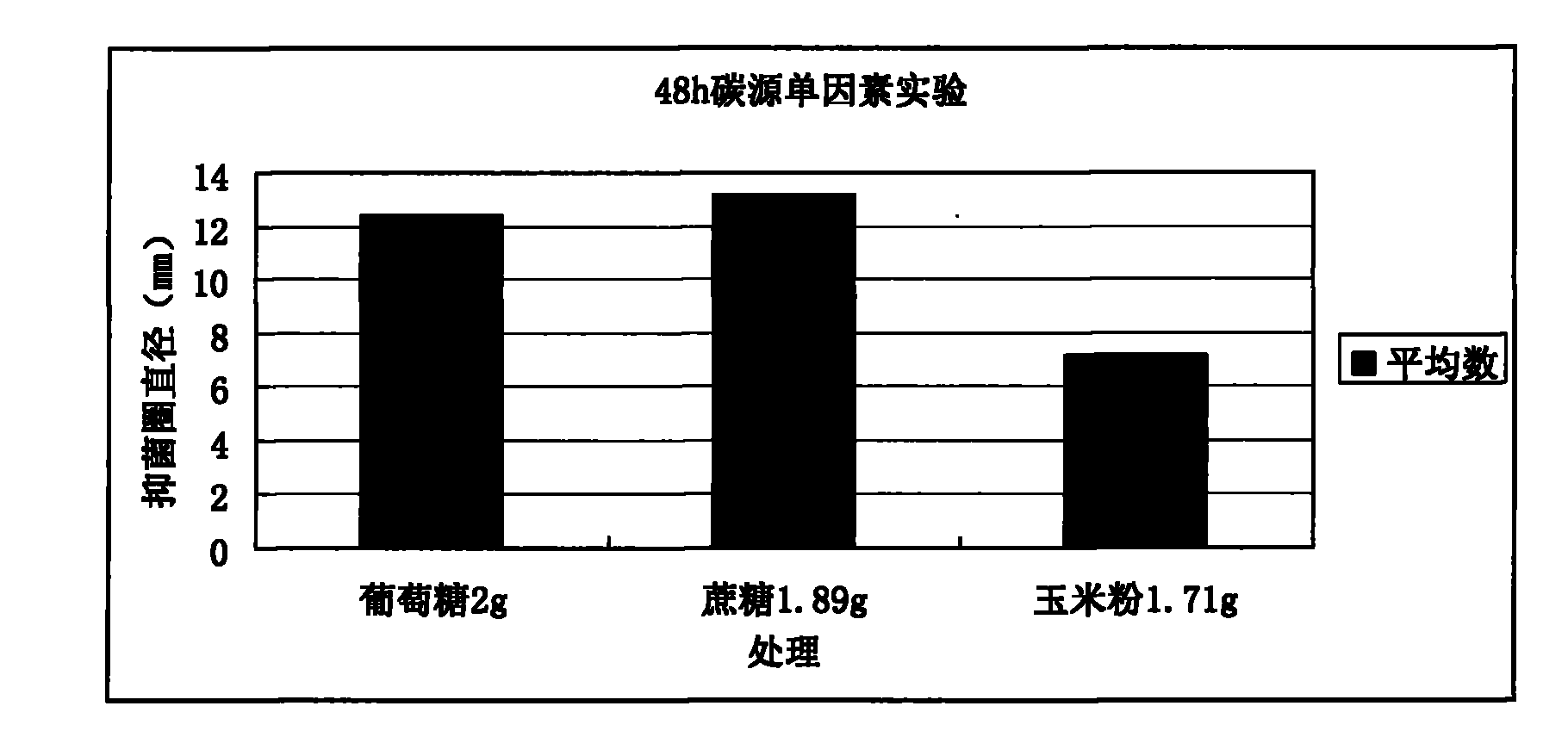
[0049] 2. Preliminary screening of antibacterial by seeding method
[0050] Take pathogenic Escherichia coli CVCC195 and Salmonella pullorum CVCC79301 as indicator bacteria, take their seed bacteria liqu...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Physiological and biochemical properties of Lactobacillus plantarum strain YJG
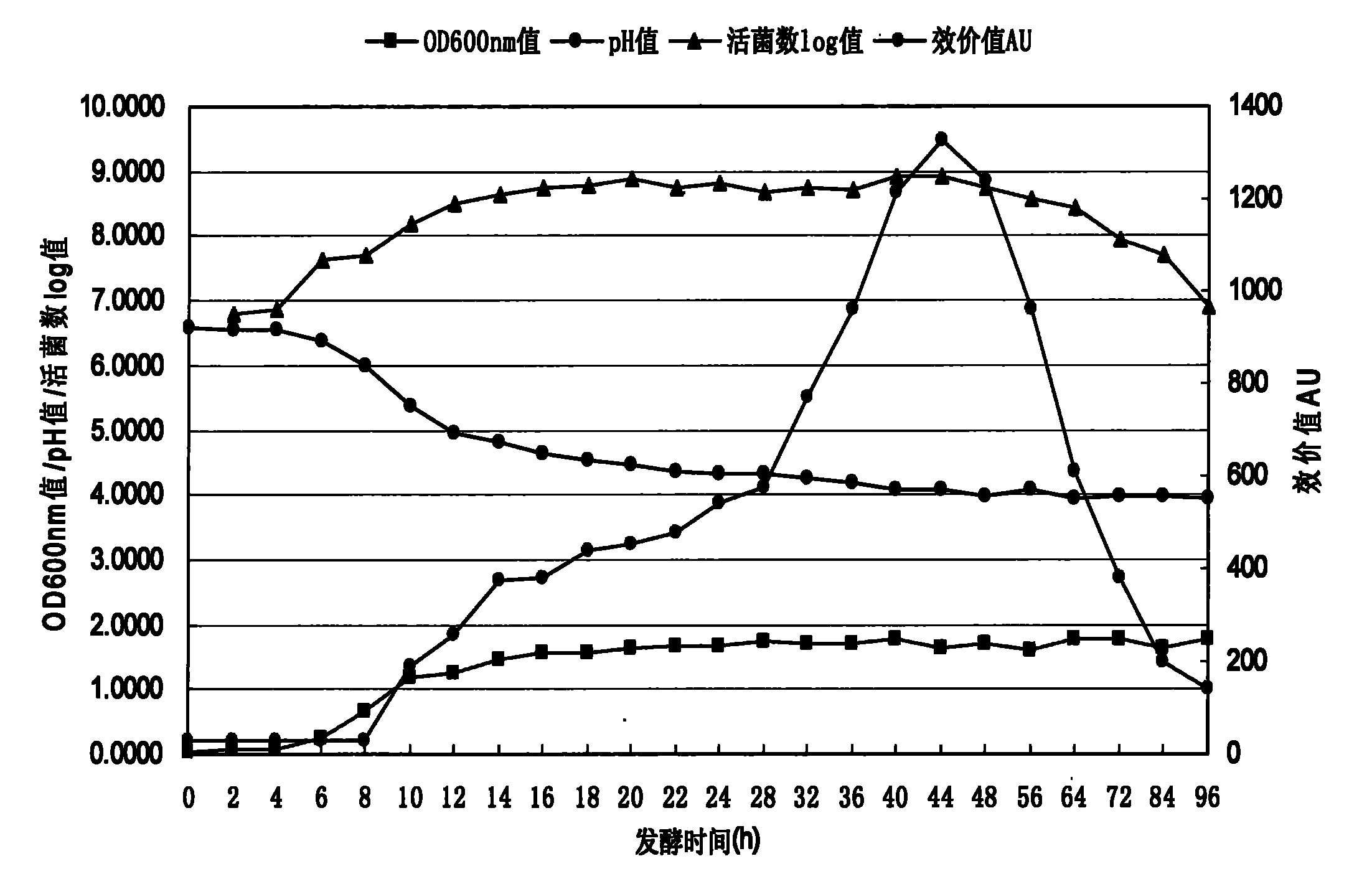
[0059] 1 titer standard curve and fitting equation
[0060] After the fermentation of strain YJG, the centrifuged supernatant still had bacteriostatic activity at a dilution of 1 / 128, but no bacteriostatic activity at a dilution of 1 / 256, and the bacteriostatic activity of YJG was 1280AU. / mL.
[0061] The standard curve was made by measuring the potency value by one-dose method, and the titer fitting equation of strain YJG was obtained by SAS statistical analysis of the measured data:
[0062] y=2.8540+0.0862xR 2 =0.9392
[0063] x- The diameter difference of the inhibition zone between the sample to be tested and the central concentration bacteriocin solution
[0064] y - the value of the sample to be tested is the value obtained by taking log10
[0065] R 2 - Correlation coefficient
[0066] 2. Growth curve and titer change curve
[0067] The growth curve and antibacter...
Embodiment 3
[0068] The preparation of embodiment 3 lactobacillus and its bacteriostatic effect
[0069] 1. Preparation of Lactobacillus
[0070] 1. Preparation of Seed Liquid
[0071] The YJG was inserted into the sterilized liquid medium and cultivated at 30°C for 36 hours to obtain the seed liquid, and the number of viable bacteria was about 10. 7 ~10 9 cfu / ml.
[0072] The liquid culture medium is prepared according to the following proportions: 10 g of peptone, 10 g of beef extract, 5 g of yeast extract, 18 g of glucose, 2 g of ammonium citrate, 4 g of sodium acetate trihydrate, 2 g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 801 mL of Tween, and 0.2 g of magnesium sulfate. g, manganese sulfate 0.04, water 1000mL.
[0073] 2. Large-scale fermentation preparation of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation broth
[0074] Take 5kg of soybean meal, 3kg of corn gluten, 10kg of brown sugar, and 10kg of molasses into the fermentation tank, add 280kg of water and mix, sterilize at 0.1-0.13MPa, 115-1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com