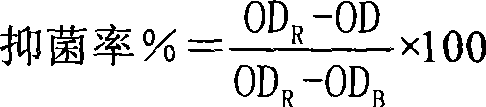Patents
Literature
66 results about "Indicator bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Indicator bacteria are types of bacteria used to detect and estimate the level of fecal contamination of water. They are not dangerous to human health but are used to indicate the presence of a health risk.
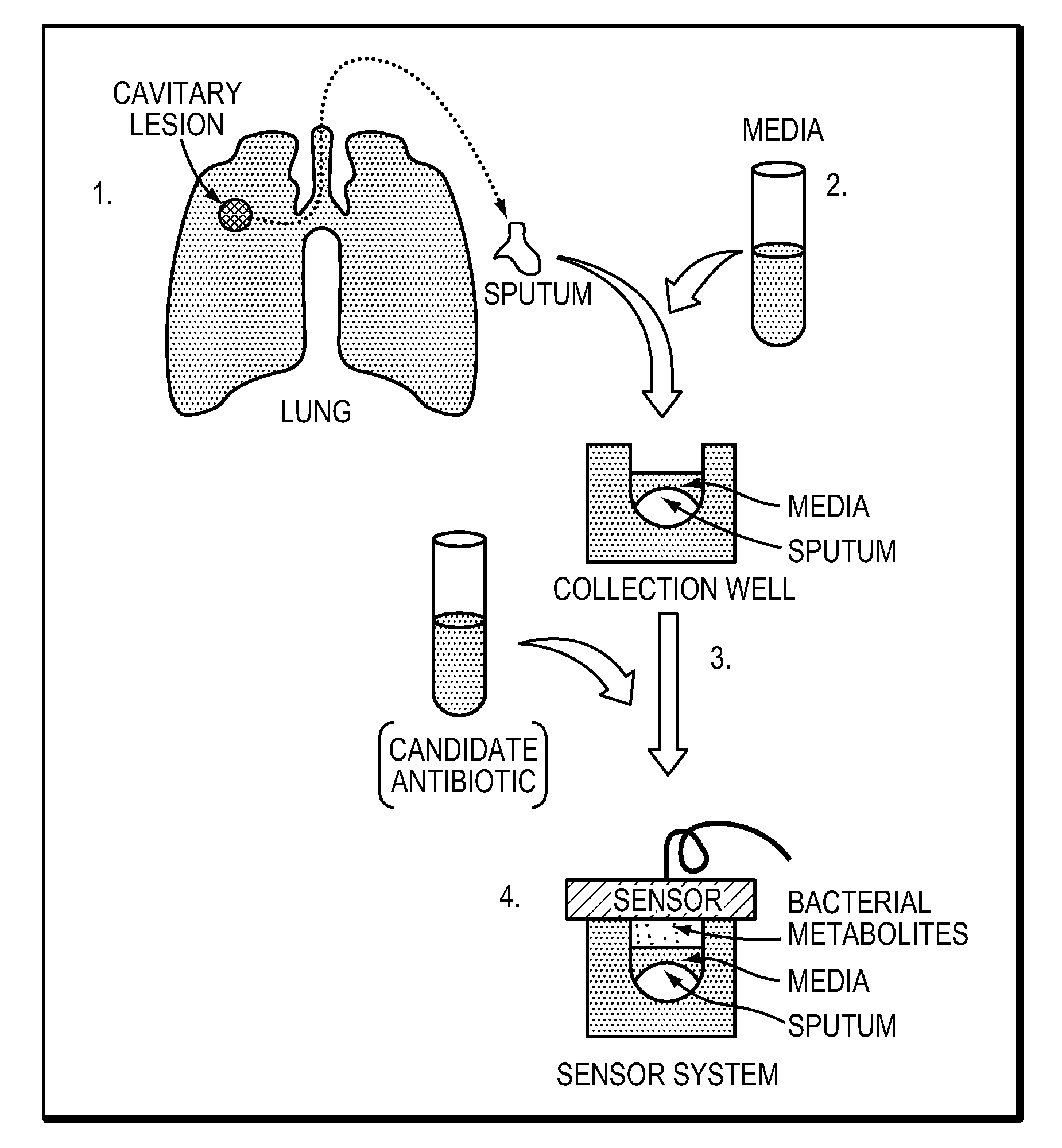
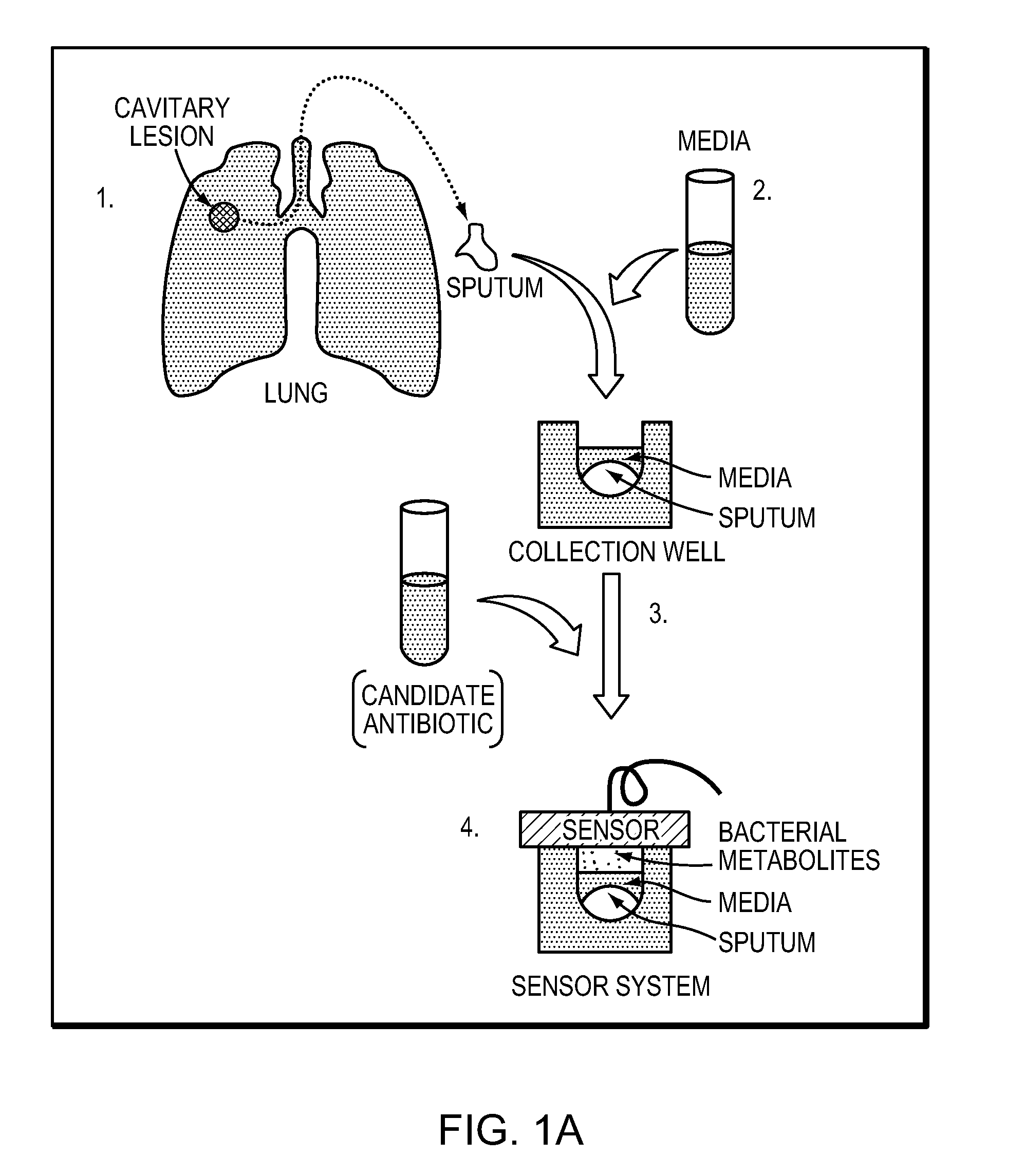
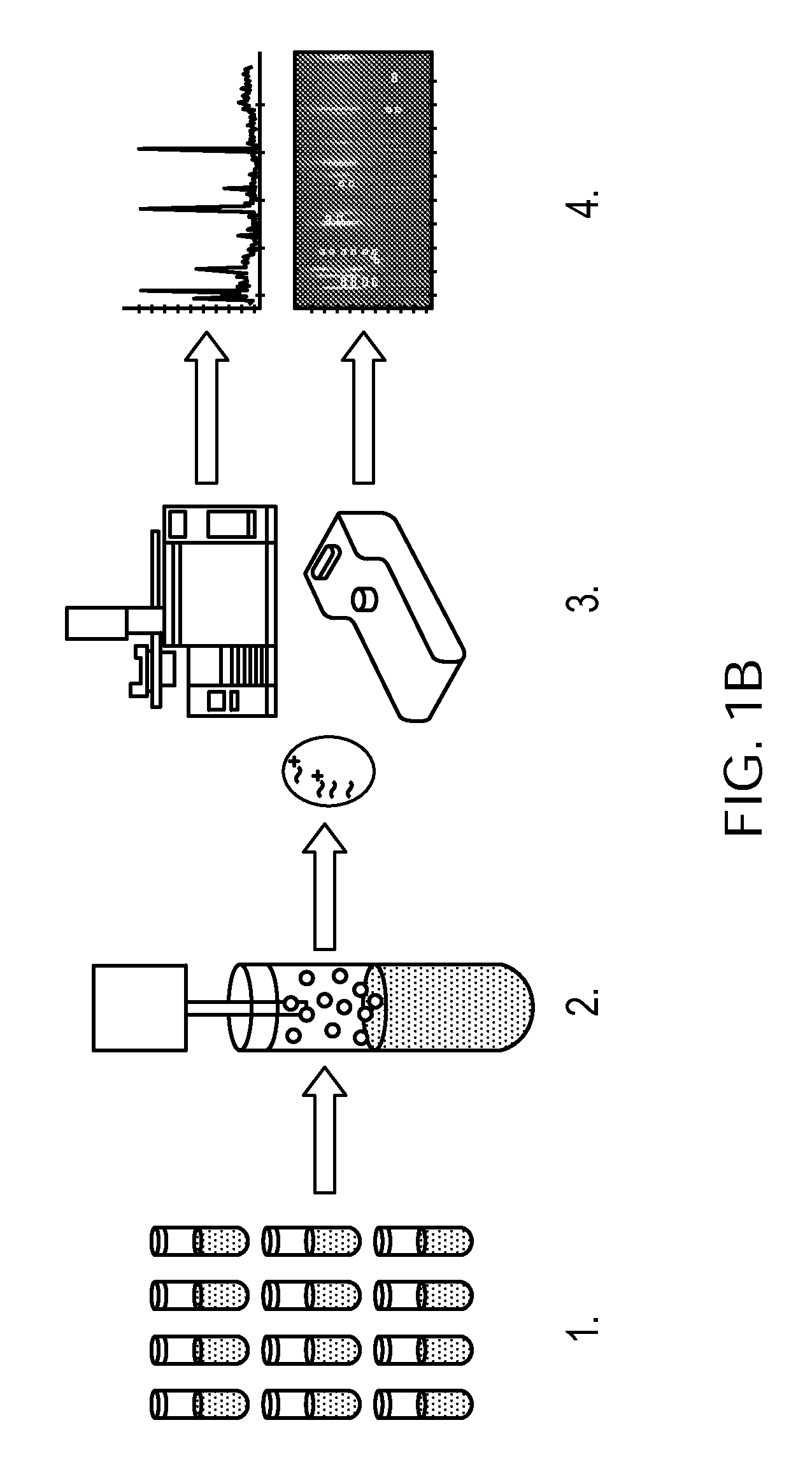
Rapid detection of volatile organic compounds for identification of bacteria in a sample
InactiveUS20090230300A1Change in bacterial burdenChange in efficacyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesMicrobiologyBacteria
In various embodiments, the invention relates to a method for identifying the presence of particular bacteria in a sample. The method includes collecting a sample that includes or has been exposed to the particular bacteria and detecting, in the sample, at least one volatile organic compound indicative of the presence of the bacteria.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
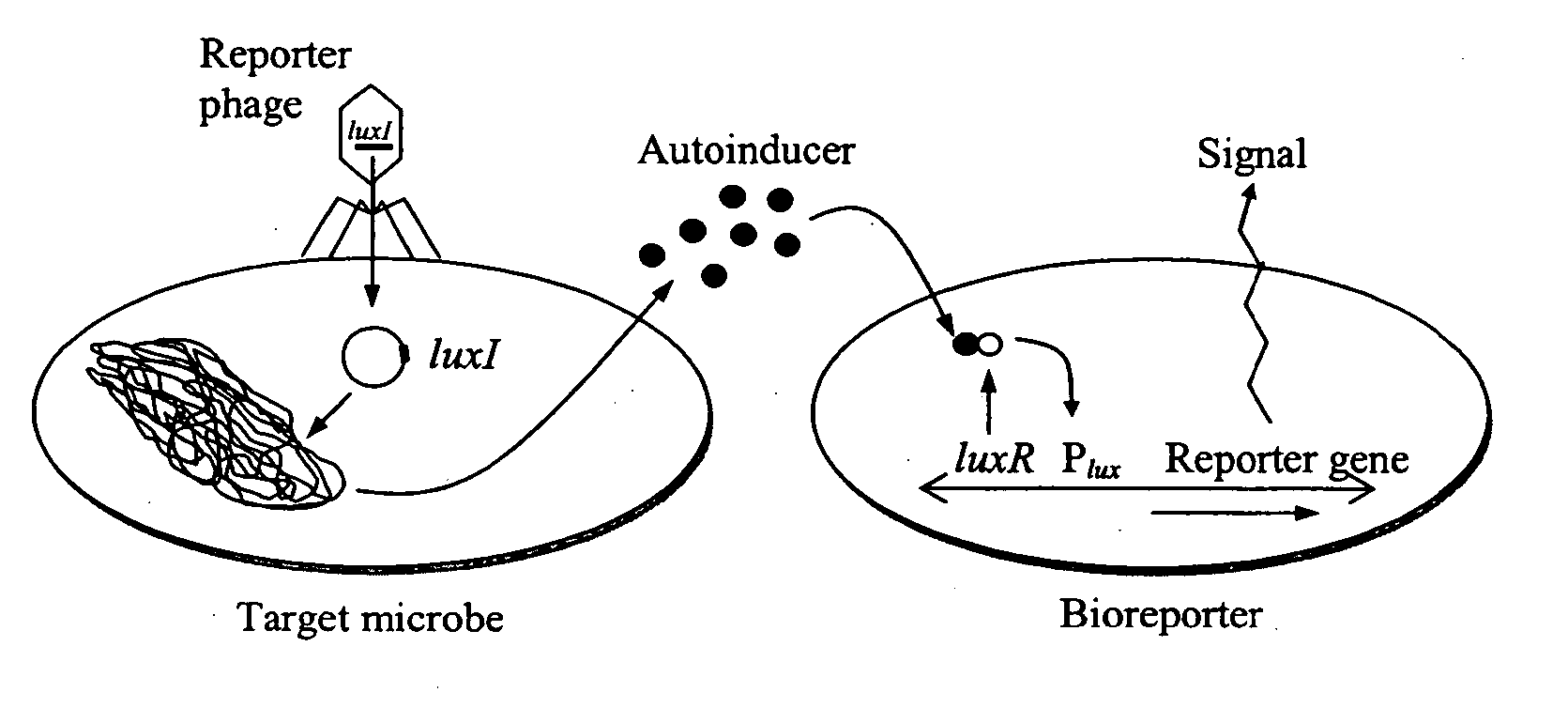
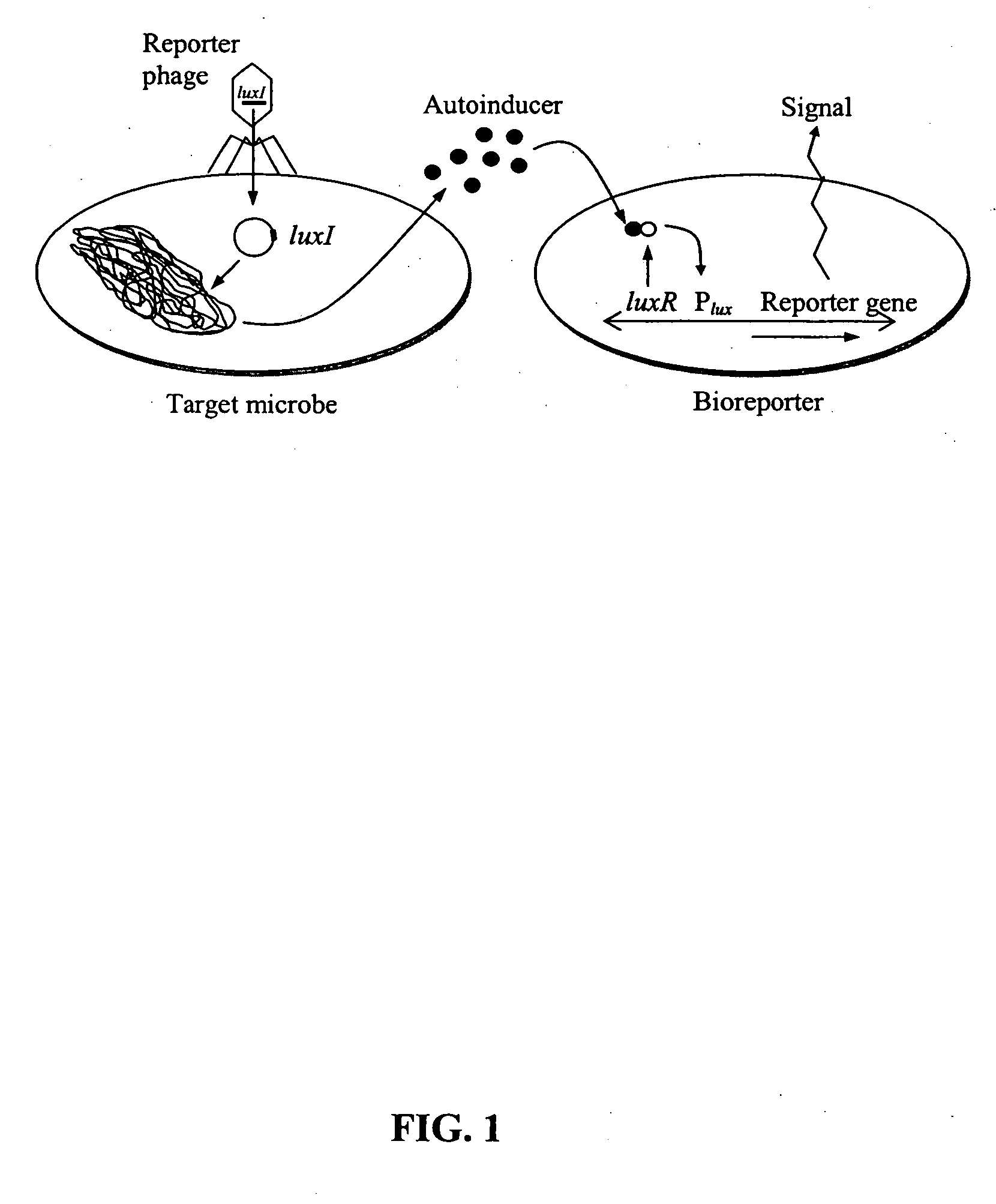
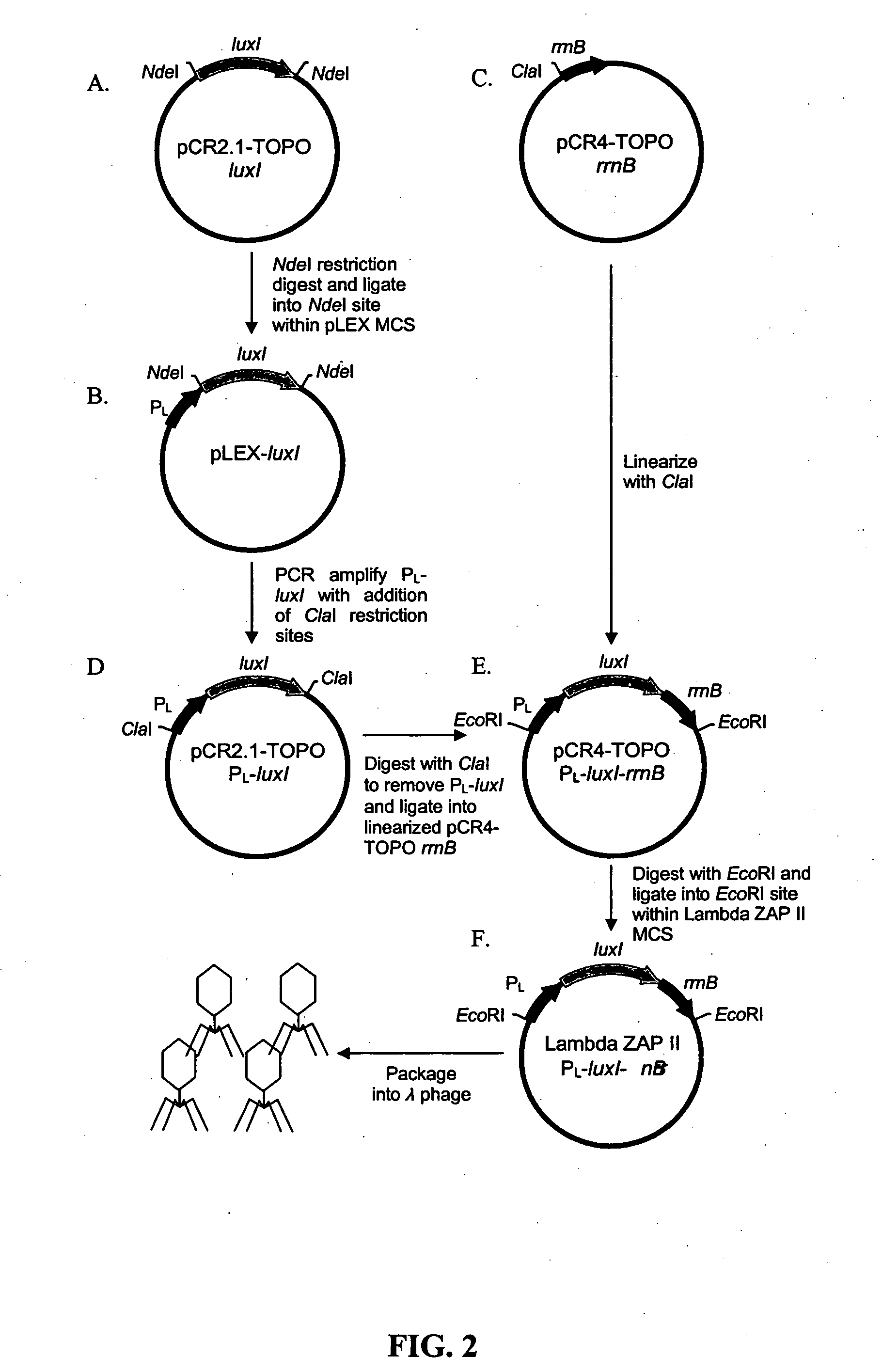
Bioreporter for detection of microbes
InactiveUS20070072174A1Large amplificationGood signal amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSignalling moleculesOrganism
A recombinant phage system has been developed for the rapid detection of bacteria, particularly fecal coliform indicator bacteria. The systems of the invention link phage infection events to quorum sensing signal molecule biosynthesis and bioluminescent bioreporter induction, facilitating the detection of pathogens that may be present in low numbers. The phage-based systems of the invention maintain specificity for the pathogen while still producing significant signal amplification for sensitive and quantitative detection. The systems require only the combination of sample with phage and bioreporter organisms; no extraneous addition of any substrates or user intervention of any kind is necessary, making this approach significantly less technical than standard molecular or immunological methods.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
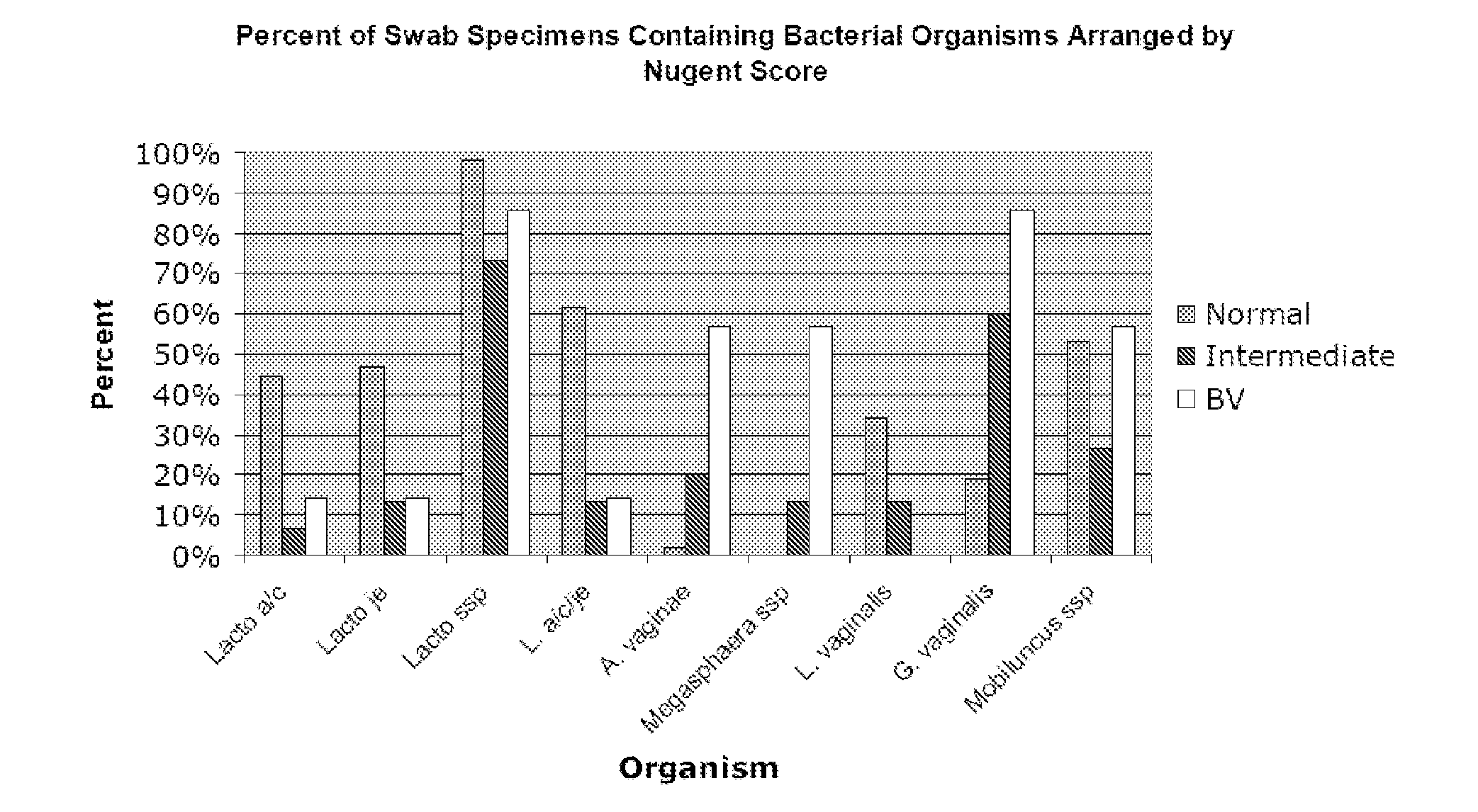
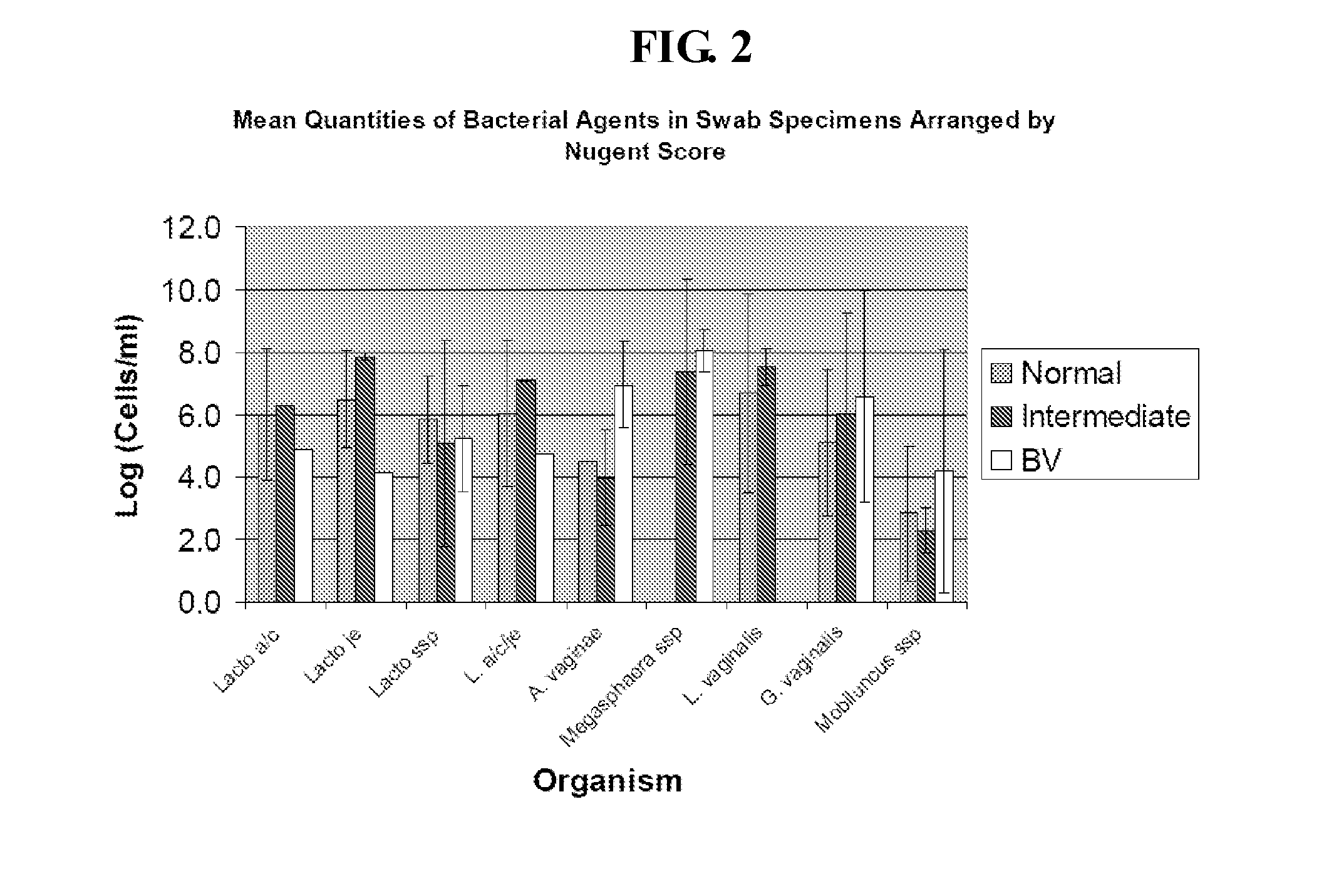
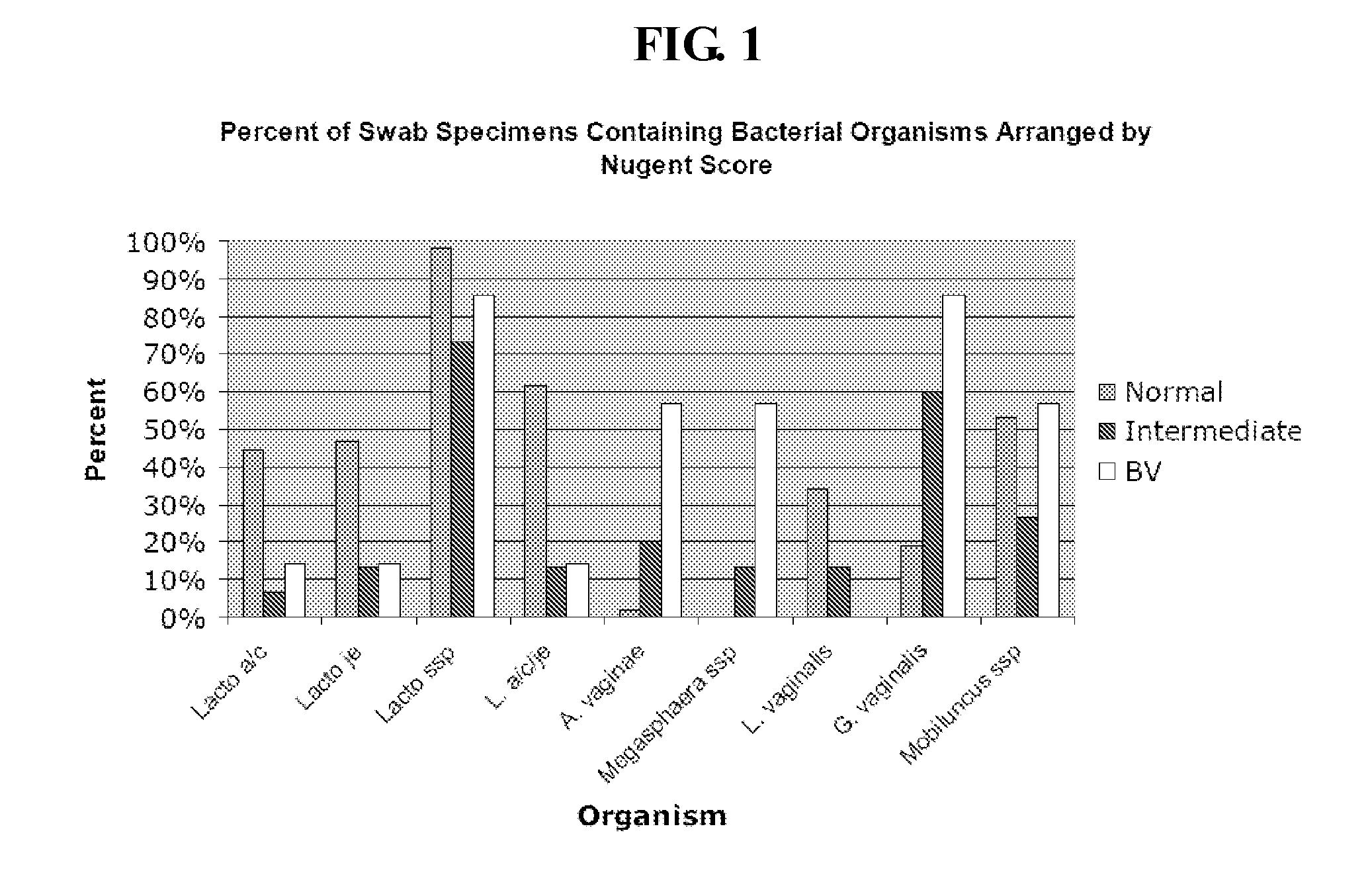
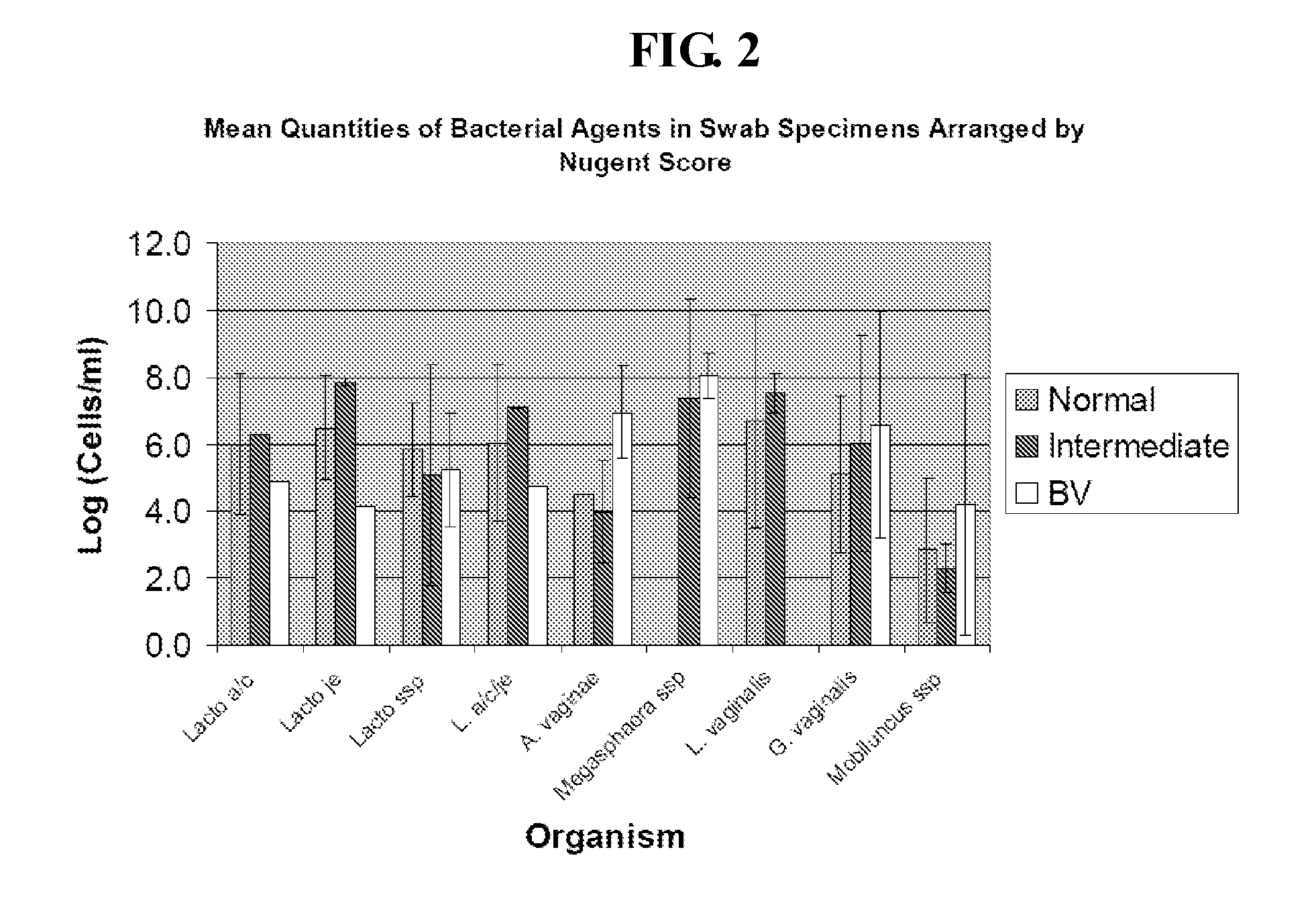
Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis
ActiveUS20120264126A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBacterial vaginosis
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis based on an analysis of a patient sample. For example, patient test samples are analyzed for the presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms. The presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms may be detected using PCR analysis of nucleic acid segments corresponding to each target organism. The quantity of the target organisms can then be used to determine a score which is indicative of a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS LLC
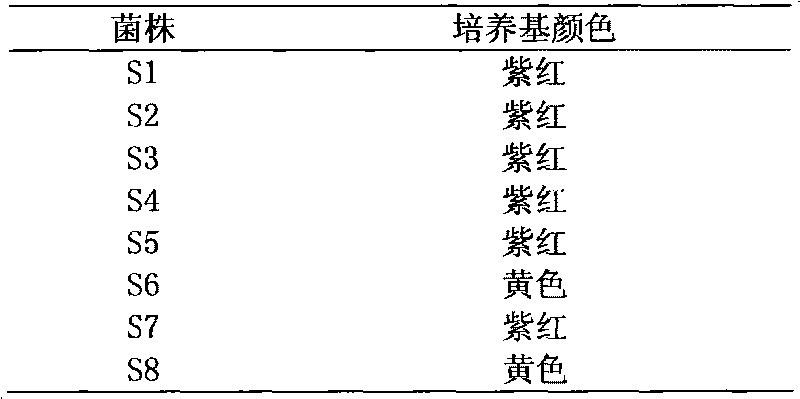
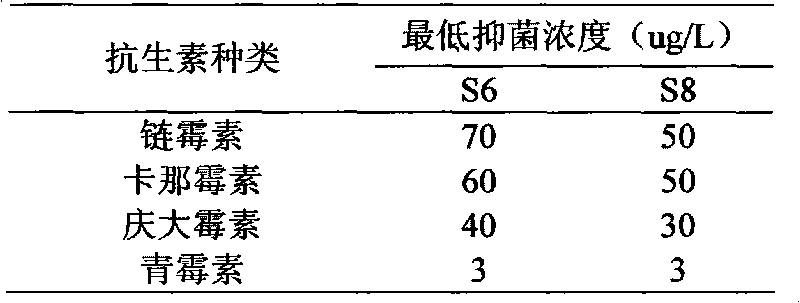
Bacillus stearothermophilus and method for antibiotic residue detection
ActiveCN101724586AStable strainEasy to saveBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyCulture fluid
The invention relates to bacillus stearothermophilus and a method for carrying out antibiotic residue detection by utilizing the same. The preservation number of the screened strain is CGMCC NO.3287; and the antibiotic residue detection method which is established by taking the strain as indicator bacteria comprises the following steps of: rejuvenating and activating the strain; preparing spore suspending liquid in enrichment; preparing a purple culture solution; embedding bacillus; detecting a sample, and the like. The strain CGMCC NO.3287 is stable, easy to store and prepare, highly sensitive to B-lactam antibiotic, good in homogeneity and dispersibility in a culture medium, grows fast at 65 DEG C and has fast metabolism and acid production. Compared with a TIC method and a fermentation test method, the method has convenient operation, high sensitivity, 2-3h time-consumption which is shorter than 4h of national similar methods and is easy to judge the result; compared with a commercial kit, the bacillus stearothermophilus has low cost which is equal to 1 / 7 of the kit in price; and the method is simple and practicable and can be operated in a common laboratory.
Owner:河南花花牛乳业集团股份有限公司
Bacillus subtilis JN005 and application thereof in prevention and control of rice blast
ActiveCN104974965AGood prevention effectAvoid Potential Adverse EffectsBiocideBacteriaDisease riskMetabolite
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis JN005 and application thereof in prevention and control of rice blast. The preservation number of the strain JN005 is CCTCC No: M2015228. According to the invention, the strain JN005 is utilized to prevent and control the rice blast, so as to avoid potential bad influence of chemical prevention and control on environment and rice safety and disease risk of disease-resistant variety utilization. The strain JN005 living bacteria and metabolite thereof have good prevention and control effect on rice blast and have protection and control effects, and can be developed to dosage forms of the living bactericide and metabolite thereof. In addition, the strain JN005 has inhibition effect on multiple pathogeny indicator bacteria.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Suspension type biological indicator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105087361ALower resistanceWon't sproutBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRoom temperatureEngineering
The invention provides a suspension type biological indicator of which the stability is good and spores are not easy to sprout. The biological indicator comprises a plastic tube of which the two ends are sealed by fusing, wherein bacterial tablets and a culture medium ampoule tube are arranged in the plastic tube; the invention further provides the preparation method of the biological indicator, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: sealing one end of the plastic tube by fusing for standby application; allowing a hydrophilic support to carry a specified number of spores and drying the spores to form the bacterial tablets, and encapsulating a recovery medium with pH indicating liquid in a glass tube to form the culture medium ampoule tube; placing the bacterial tablets and the culture medium ampoule tube in the plastic tube, and sealing the other end of the plastic tube by fusing. According to the suspension type biological indicator and the preparation method thereof, provided by the invention, the spores are in a dry state and the quality stability of the products is improved, during storage, the spores are isolated from the liquid recovery medium, therefore the spores do not grow, even the storage temperature is the same as the spore growth temperature, and the biological indicator can be stored at room temperature. The suspension type biological indicator can serve as indicator bacteria of various spores that are different in growth temperatures.
Owner:湖州一控医疗科技有限公司
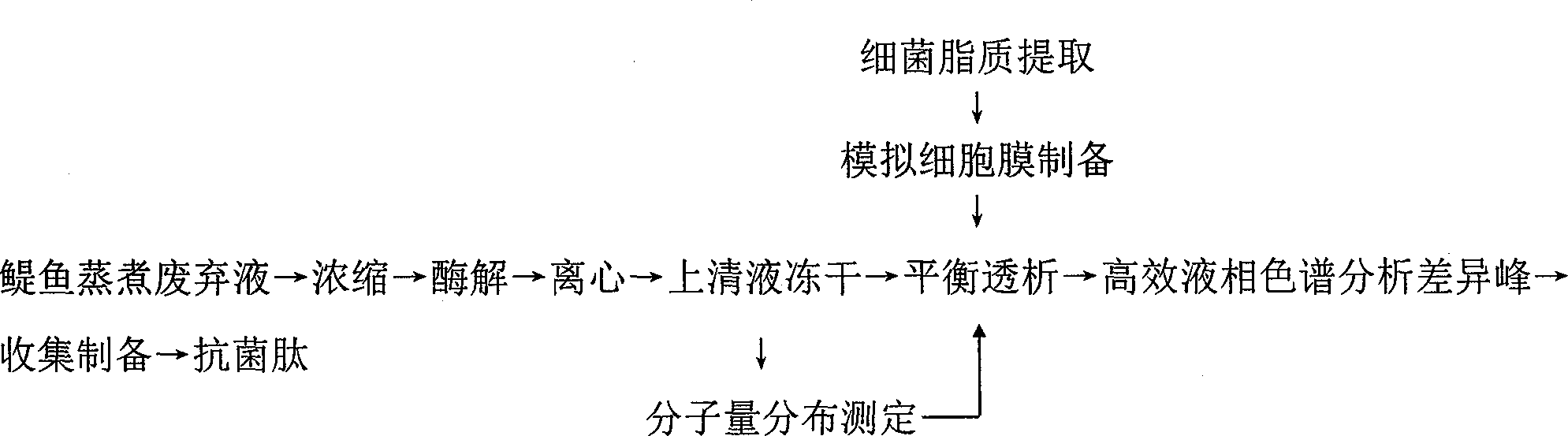
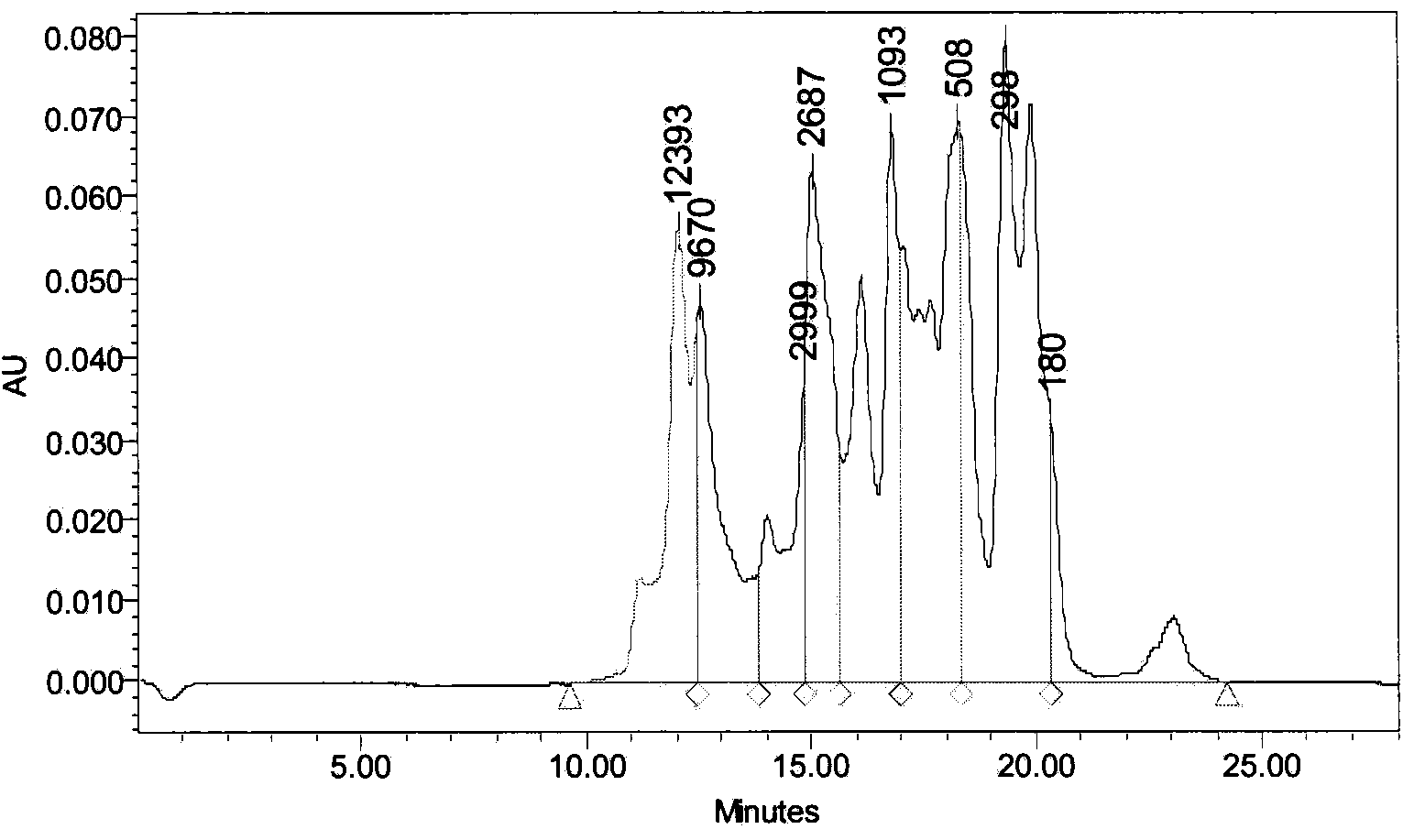
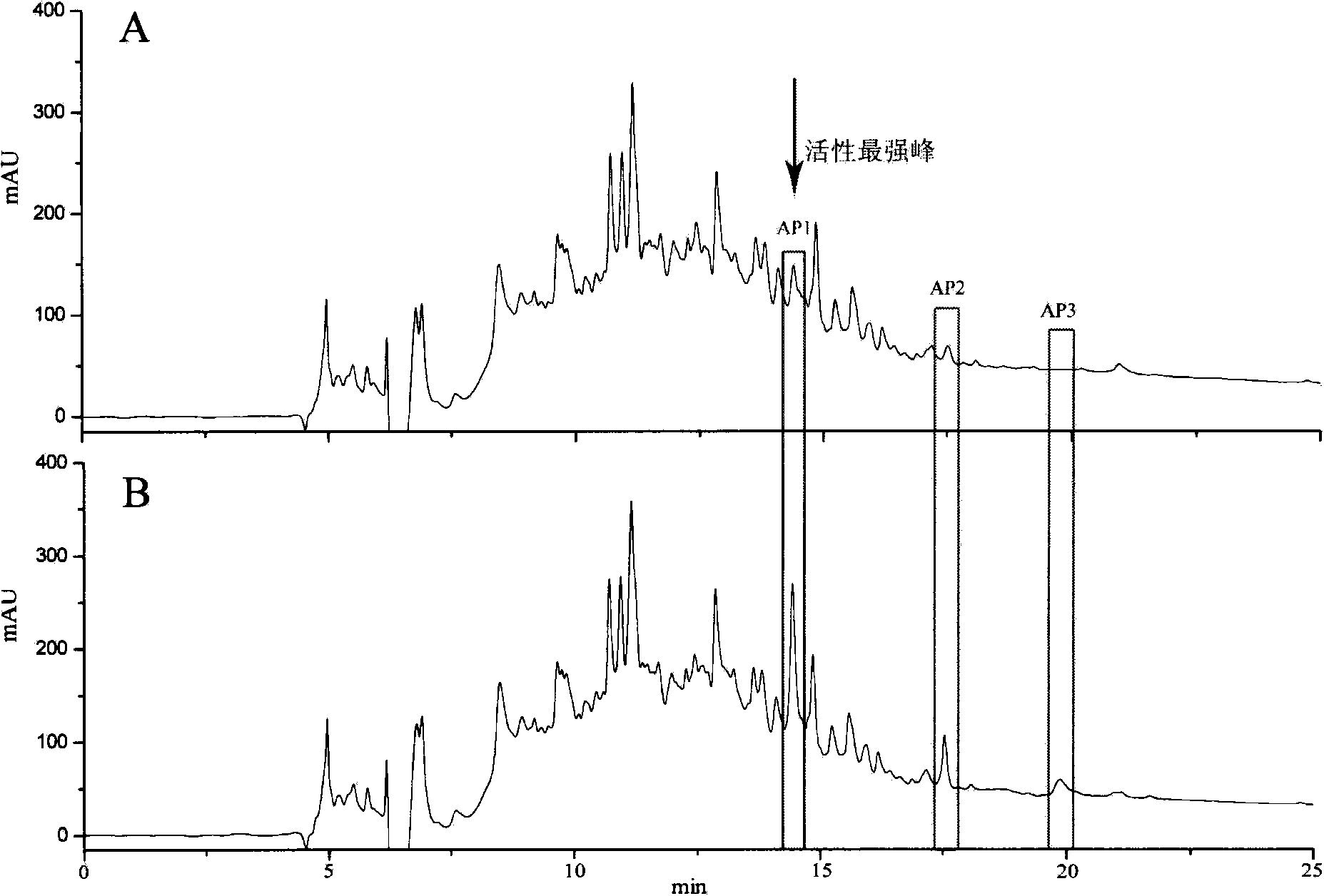
Antibacterial peptide derived from anchovy cooking waste liquid and antibacterial peptide separation method
InactiveCN103936832ARealize the value-added effectSimplify targeted isolation stepsPeptide preparation methodsFermentationEscherichia coliCell membrane
The invention relates to antibacterial peptide derived from anchovy cooking waste liquid and an antibacterial peptide separation method. The antibacterial peptide separation method is characterized in that a food-grade enzymic preparation is used for enzymolysis of anchovy cooking waste liquid concentrate, the antibacterial peptide in the anchovy cooking waste liquid concentrate is separated by combination of simulated cell membrane equilibrium dialysis and high-performance liquid chromatography, the amino acid sequence of the purified peptide is analyized, and the activity of the amino acid sequence is verified. The result shows that the antibacterial peptide is decapeptide, and the amino acid sequence of the antibacterial peptide is GLSRLFTALK. The antibacterial peptide has antibacterial activity to seven types of indicator bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli. The amino acid sequence GLSRLFTALK is obtained through enzymolysis, has the characteristics of high safety and strong antibacterial property and has a potential utilization value in industries such as medicines, food and feed. The antibacterial peptide separation method realizes the targeting separation by using the binding characteristics of a simulated cell membrane of the antibacterial peptide and overcomes the shortcomings of too many steps and long time consumption existing in a conventional peptide separation method. The antibacterial peptide separation method has the advantages that fish processing wastewater is used as a raw material, the environmental pollution is reduced, and the added value of the product is increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
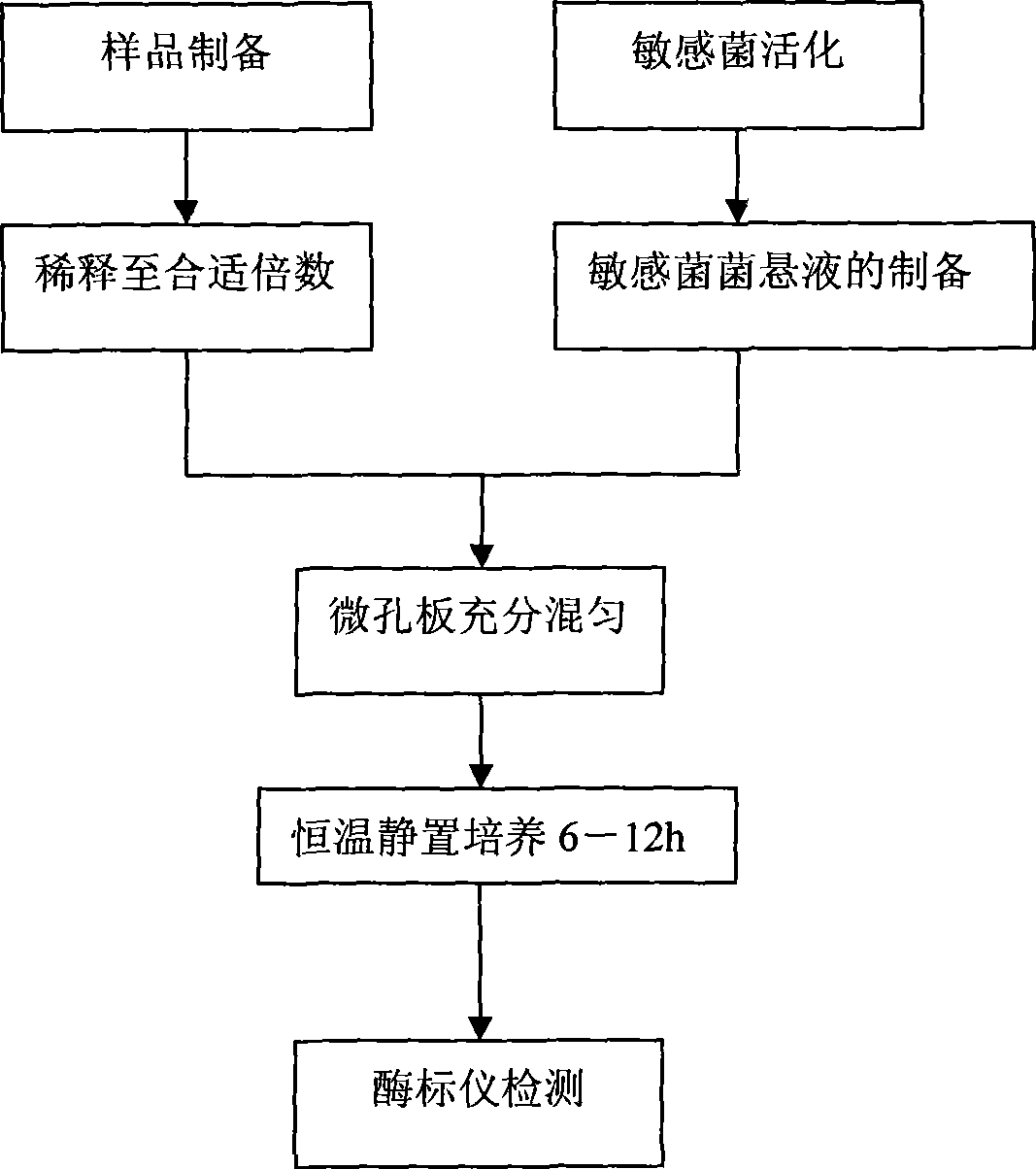
Micropore plate biological detection method for rapidly detecting bacteriostatics activity
InactiveCN101413876AEliminate errorsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansHigh fluxTurbidity
The invention relates to a micro plate biological detection method for rapid detecting bacteriostatic activity of antibacterial substance; in the method, a sample to be tested which has higher antibacterial properties on sensitive indicator bacteria is used; the micro plate with good standardization and parallelization is taken as a detection plate with high flux; after sensitive bacteria indicator solution and the sample to be tested are fully blended and are cultured for a proper time, the bacteriostatic activity of the sample is rapid detected by an ELIASA determining the change of the turbidity of the culture liquid in each hole of the micro plate. The detection method has simple operation, rapid analyzing speed, large primary treatment capacity, high reliability of the result, and overcomes the shortcoming that the existing biological detection method has complex steps and is often interfered by human factors. The detection method has similar analytical accuracy with high performance liquid chromatography but can better reflect the bacteriostatic activity of the sample in a visualized way, can be popularized to high flux screening work of producing bacteria of antibacterial substance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
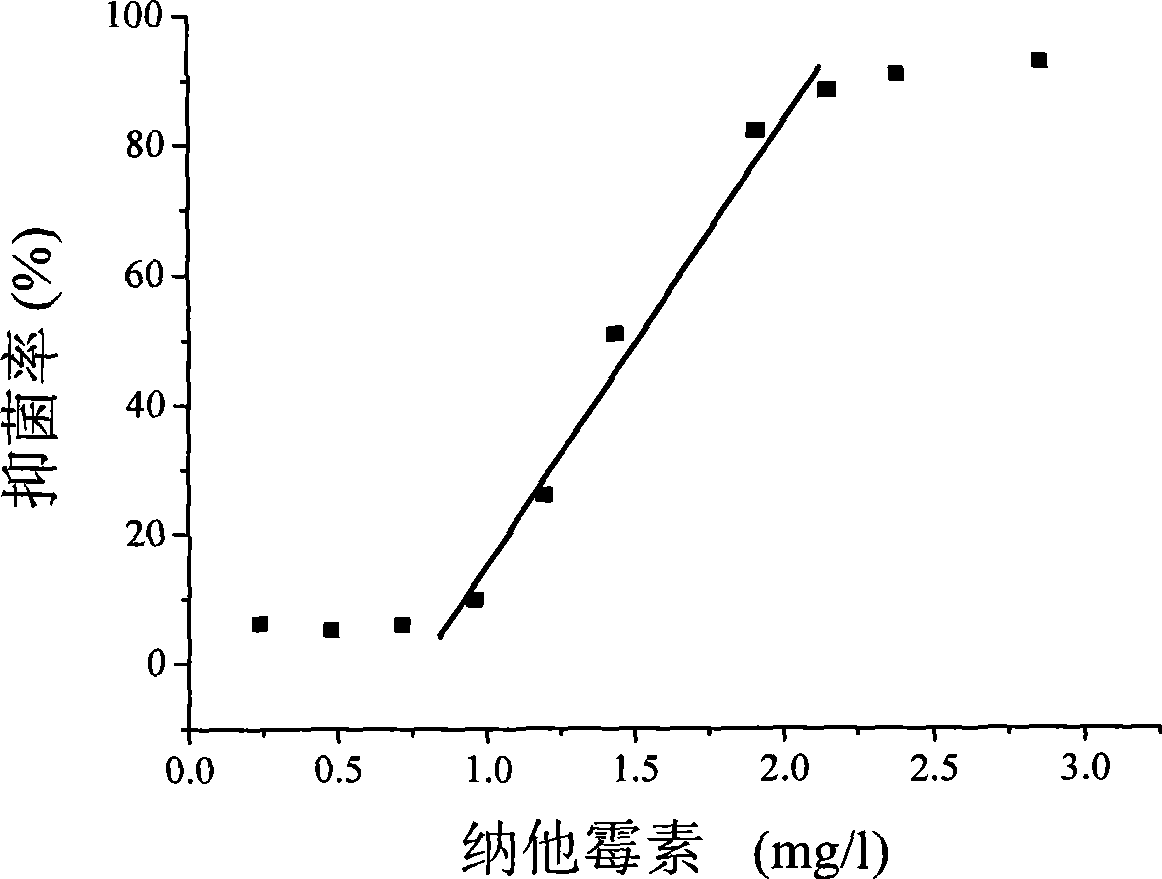
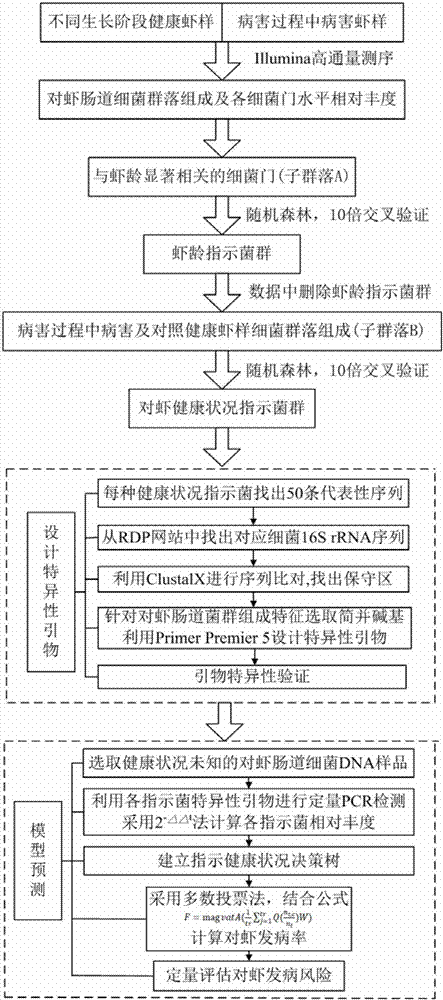
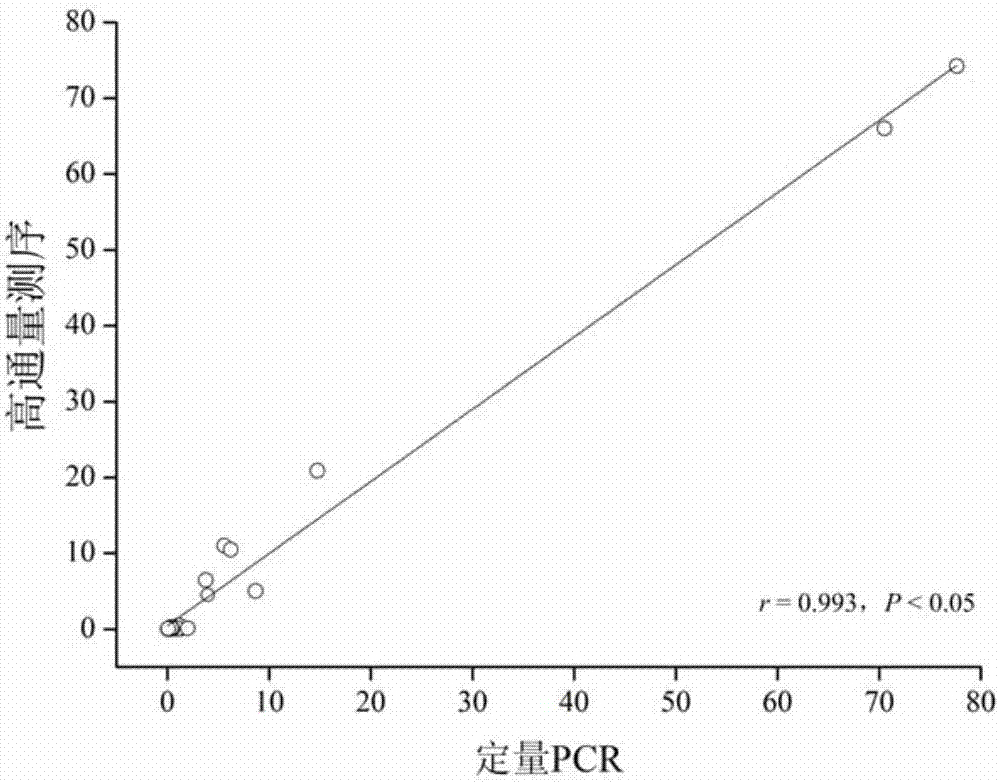
Quantitative prawn disease prediction method based on intestinal tract indicator bacteria
ActiveCN107273711AImprove accuracyReduce riskData processing applicationsSequence analysisIntervention measuresPredictive methods
The invention discloses a quantitative prawn disease prediction method based on intestinal tract bacterial indicators. The quantitative prawn disease prediction method is characterized in that prawn health condition indicator bacteriophyta are screened based on bioinformatics, and characteristic design specific primers are formed based on prawn intestinal flora; real-time quantitative PCR is adopted to detect the relative abundance of the health indicator bacteriophyta, the relative abundance of the health indicator bacteriophyta and its indicating weight are used as independent variables to self-establish a prediction model, and quantitative disease prediction during prawn breeding is achieved. The method has the advantages that the influences of diseases on intestinal flora at different growth stages are distinguished, the accuracy rate of prediction is improved, meanwhile the cheap disease prediction method is established and has a very high actual application value, a basis can be provided for formulation of a coping and intervention measure, for example, design of probiotics, and the method has the good pushing effect on reduction of the prawn breeding risk.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Methods and compositions for the detection and quantification of e.coli and enterococcus
The present invention is drawn to methods and compositions for the rapid assessment of fecal indicator bacteria in a sample. Provided herein are novel primer and probe compositions for use in detecting the presence of these organisms in a sample, particularly using quantitative PCR methods. Provided herein are novel oligonucleotide primers and probes, including the primers set forth in SEQ ID NO:1-4, the novel oligonucleotide probe sequences set forth in SEQ ID NO:5-8, and methods for using these primers and probes for the detection and / or quantification of fecal indicator bacteria, particularly E. coli and Enterococcus spp. in a sample.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Method for screening lactic acid bacteria capable of producing bacteriocin from plant source materials
InactiveCN102250806AKeep activeReduce experimental stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAntibiotic testedPlant Sources
The invention relates to a method for screening lactic acid bacteria capable of bacteriocin from plant source materials. The method comprises the following steps: treating the plant source materials; separating and screening out the lactic acid bacteria; screening a lactic acid bacterium strain capable of producing antibiotic substances by using a method of fermenting a supernatant fluid by use of the strain to carry out an antibiotic test; eliminating interference of small molecules by using dialyzate of the supernatant fluid to carry out the antibiotic test, and screening out the lactic acid bacteria capable of producing the bacteriocin; and performing an antibiotic test by using a protein crude extract which is precipitated by use of ammonium sulfate, and performing a crude extract enzymolysis test by using various proteases to prove that the lactic acid bacterium strain capable of producing the bacterocin can be effectively screened by utilizing the method. In the method, the method for separating and purifying the lactic acid bacteria capable of producing the bacteriocin is improved, the fermented supernatant fluid is dialyzed by a dialysis bag with smaller cut-off molecular weight, so that the inhibition effect of small molecular antibiotic substances in the fermented supernatant fluid on indicator bacteria can be eliminated, and the activity of the bacteriocin can be guaranteed. By utilizing the method, the experimental steps are reduced, and the screening efficiency is improved.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for exploring indicator bacteria by utilizing n-butyl alcohol oxidizing bacteria as oil-gas microorganism
InactiveCN102002519AImprove reliabilityShort training periodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismDistilled water
The invention relates to a method for exploring indicator bacteria by utilizing n-butyl alcohol oxidizing bacteria as oil-gas microorganism, comprising the following steps of: carrying out block process on a soil sample; coating the soil sample in the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium by utilizing a spread-plate method in an aseptic operating room; and putting the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium in a static incubator to cultivate the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria, wherein the n-butyl alcohol is used as the unique carbon and energy source of hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium, the cultivating parameter is set as 30 DEG C, 5 days form a cultivating period, and the needed soil sample is air dried rapidly, then dissolved in distilled water and put in a shaking table to activate for use. The method has the advantages of shortening the cultivating period to 5 days, simplifying the whole experiment operating process, enhancing the safety, accurately obtaining the quantity of the needed objective colony by utilizing the medium with n-butyl alcohol as the unique carbon source, and enhancing the reliability of the colony count data through reducing the cultivating time.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Screening method for clostridium butyricum producing efficient antibacterial peptide butyrisin
InactiveCN104611411AEnhance the effect of non-specific immunityPromote Microecological BalanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a screening method for clostridium butyricum producing efficient antibacterial peptide butyrisin. The method includes the following steps in order: 1) performing preliminary screening based on the bacteriostatic activity of a fermentation bacterial broth: taking Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus as the indicator bacteria to perform preliminary screening on to-be-tested strains, thus obtaining clostridium butyricum having antibacterial activity on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus; and 2) verifying the expression of antibacterial peptide butyrisin protein gene by PCR. The PCR positive strain is clostridium butyricum producing efficient antibacterial peptide butyrisin. By the method provided by the invention, the clostridium butyricum producing efficient antibacterial peptide butyrisin can be obtained. The antibacterial peptide has antibacterial activity on bacteria including but not limited to E.coli ATCC25922, E.coli K88, S.aureus ATCC25923 and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Separation method for soil antagonistic bacteria
InactiveCN109097280AGood antibacterial effectSimplified separation stepsMicroorganism separationMicroorganismPHENOL LIQUID
The invention discloses a separation method for soil antagonistic bacteria, and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The separation method for the soil antagonistic bacteria comprises thefollowing steps: A, preparing raw materials, B, preparing a soil suspension, C, diluting, D, preparing an isolation medium, E, performing culture, F, carrying out selective separation, G, preparing an indicator bacteria plate, and H, screening. According to the invention, the antagonistic bacteria are separated from soil through a dilution separation method, actinomycetes in the medium are screened through adding phenol liquid to the medium, and the antagonistic bacteria with the strongest antibacterial effect in the medium are screened through an indicator bacteria plate confrontation method, and are developed into a biocontrol preparation for biocontrol of plant diseases, thereby having good market application prospects. The separation method for the soil antagonistic bacteria disclosedby the invention simplifies the steps of separating the antagonistic bacteria, can quickly separate the antagonistic bacteria from the soil, and improves the separation success rate and separation efficiency of the antagonistic bacteria.
Owner:NINGDE NORMAL UNIV
Antimicrobial peptide cecropin A mutant and coding gene, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109021086AEfficient expressionStrong gram negativeAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideHeat stability
The invention discloses an antimicrobial peptide cecropin A mutant and a coding gene, a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No: 3. The nucleotide sequence of a gene for encoding the above mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No: 4. Molecular cloning is carried out according to the gene sequence of the antimicrobial peptide mutant PEW300 at the design site, and the gene was cloned into a recombinant expression vector; and through fusion expression with a self-aggregation short-peptide ELK16, high-efficiency expression of the mutant PEW300 is realized. Then, bacteriostasis performance test of 9 indicator bacteria is carried out on the mutant peptide PEW300, and the results show that bacteriostasis performance of the antimicrobial peptide PEW300 is greatly improved and the antimicrobial peptide PEW300 has strong pH and heat stability.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
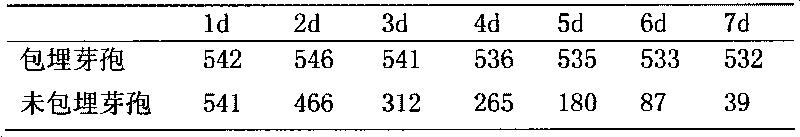
Atmospheric steam sterilizing biological indicator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102041292AAvoid the problem of variable sterilization capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementSporeEmulsion
The invention discloses an atmospheric steam sterilizing biological indicator and a preparation method thereof. The atmospheric steam sterilizing biological indicator comprises a dry culture medium and an indicator bacteria carrier, wherein the indicator bacteria carrier is formed by adhering the spore of the indicator bacteria onto a contaminated carrier sheet the surface of which is coated withparaffin, paraffin emulsion or fatty acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: inoculating the indicator bacteria onto the inclined plane of a bacteria culture medium for generatingthe spore; after the spore is generated, preparing indicator bacteria suspension; adsorbing the indicator bacteria spore suspension, and dripping on the contaminated carrier sheet to prepare the contaminated carrier sheet; dipping the contaminated carrier sheet into melted paraffin or fatty acid liquid or paraffin emulsion; drying to obtain a waterproof indicator bacteria carrier; and combining the waterproof indicator bacteria carrier with the dry culture medium. When determining the atmospheric steam sterilizing effect, the indicator provided by the invention can ensure that time that the indicator bacteria spore is actually in contact with water is basically consistent no matter when water is added to an indicator bottle, thus effectively avoiding the problem that the indicator has different sterilizing abilities because the time when water is added to the indicator in the same autoclave is different.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
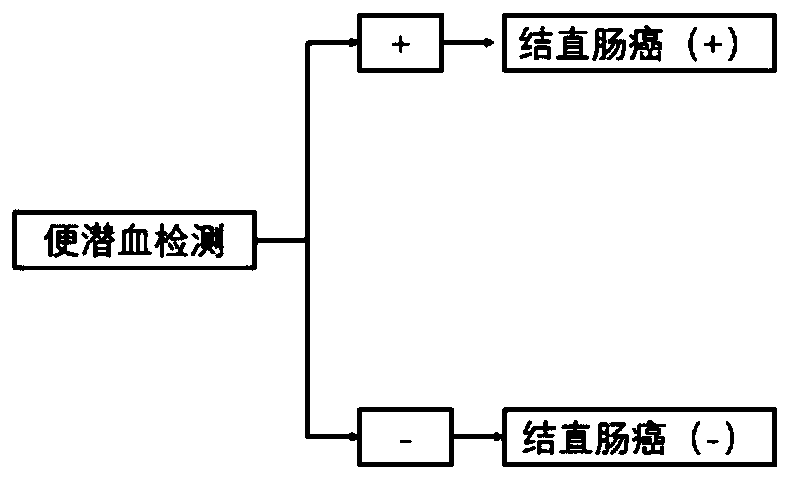
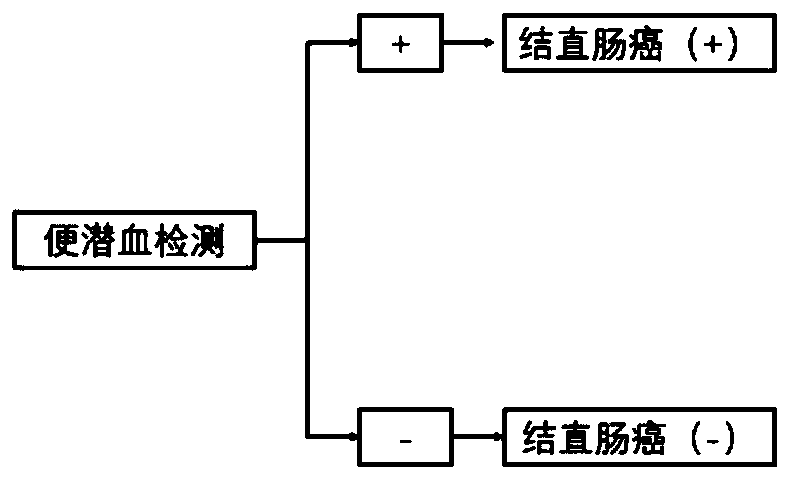
Kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria
InactiveCN110643721AHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium symbiosumFusobacteria
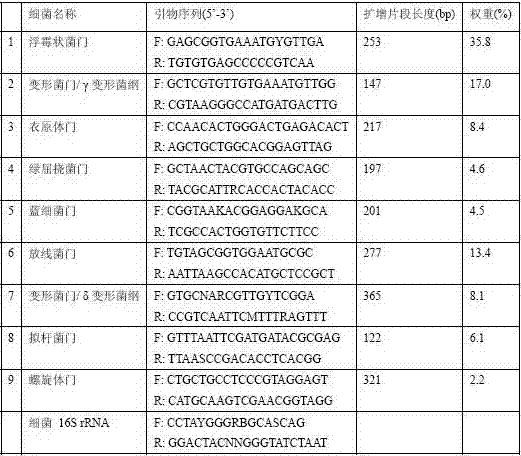
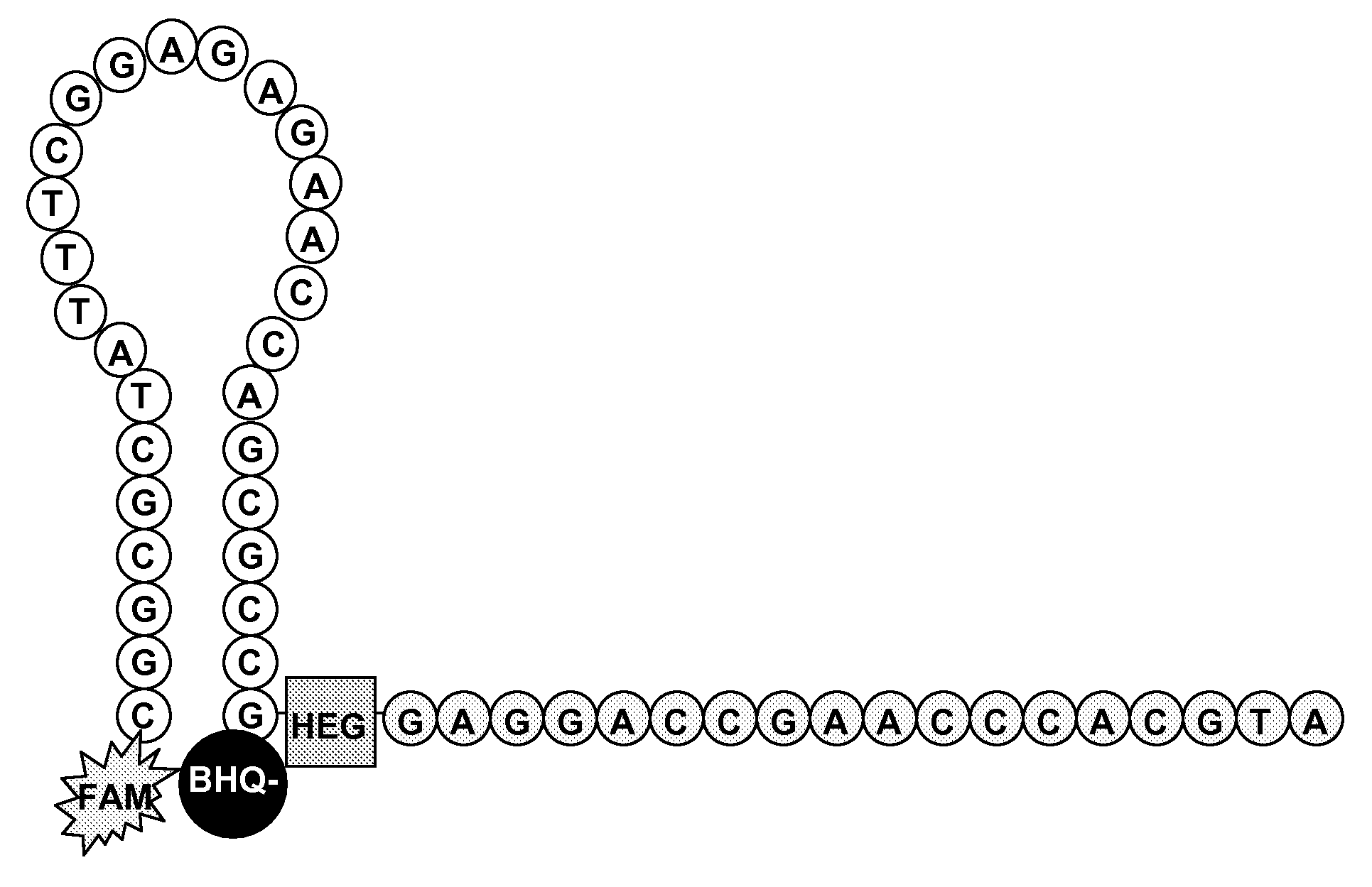
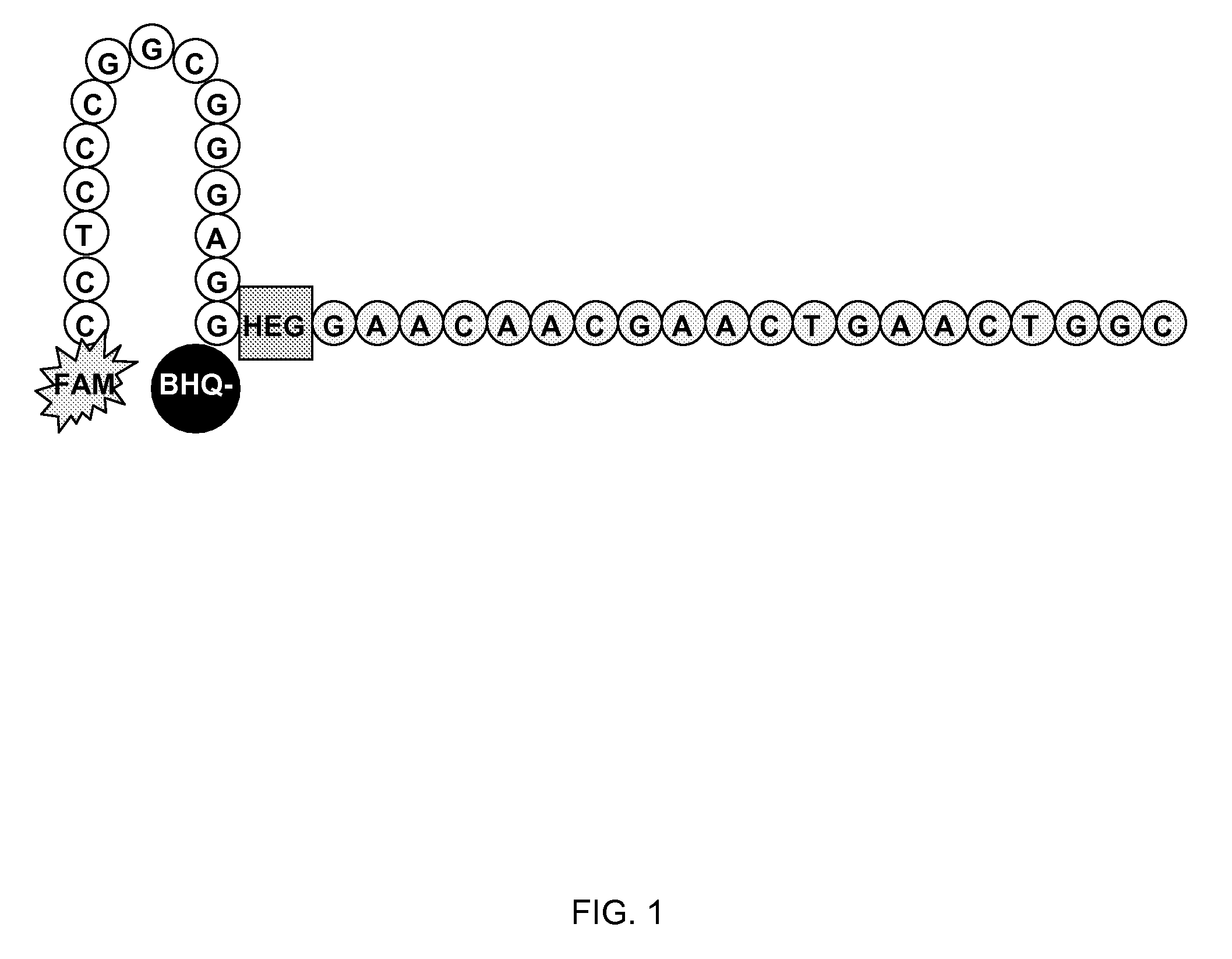
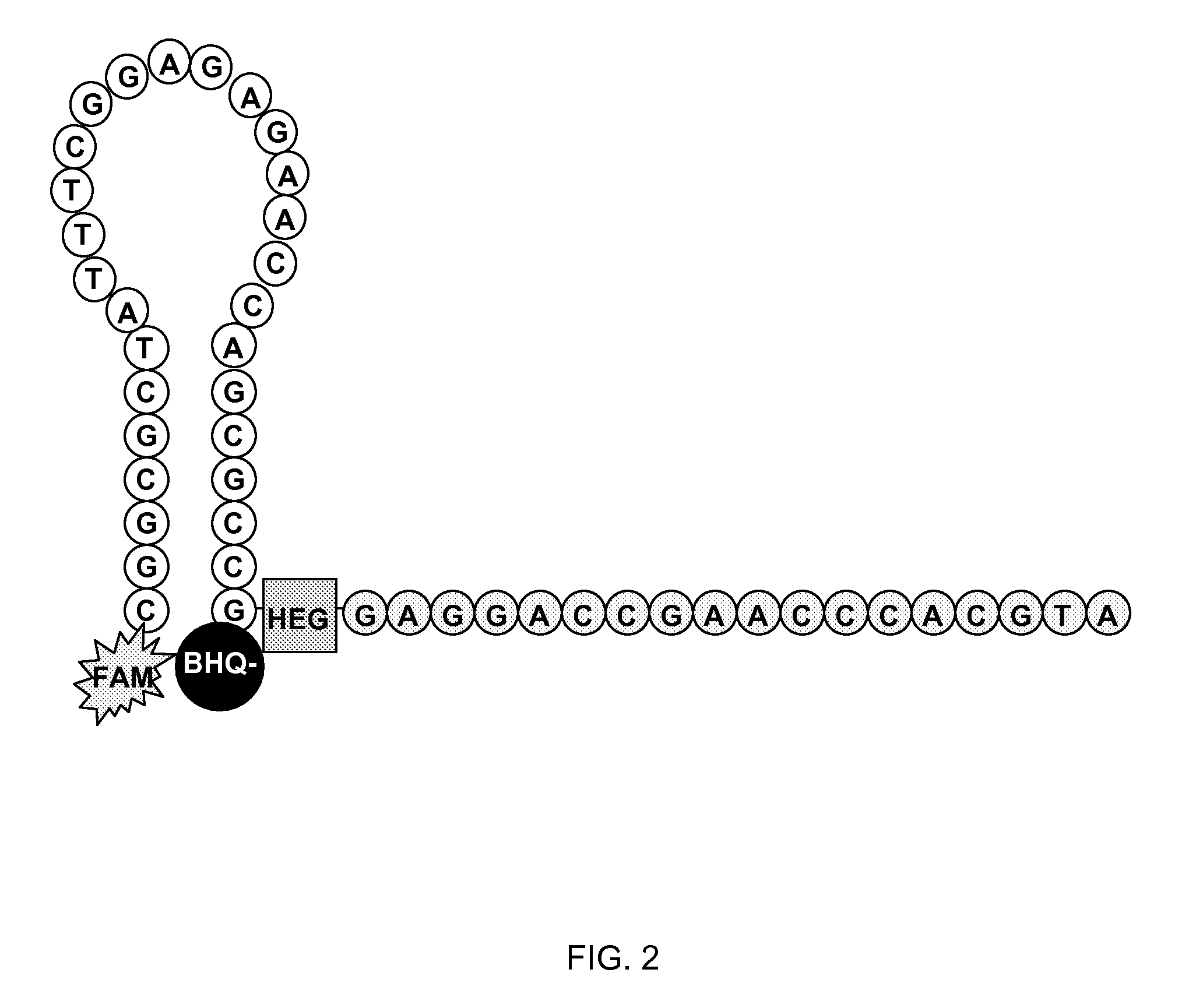
The invention discloses a kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria. The kit is characterized by comprising the following components: a specific primer combination for identifying the indicator bacteria, wherein the primer combination is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1-14, and the indicator bacteria are the combination of fusobacterium nucleatum (F.nucleolus), anaerobic digestion streptococcus(P.anaerobicus), clostridium symbiosum (C.symbiolum), Porphyromonas saccharolytica (P.asaccharolytica), Prevotella intermedia (P.intermedia), Bacteroides fragilis (B.fragilis) and Streptococcus salivarius (S.salivarius). The kit for detecting colorectal cancer indicator bacteria disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the colorectal cancer can be identified only by collecting astool sample. The principle is that the aim of identifying the colorectal cancer by detecting the colorectal cancer pathogenic bacteria in excrement, the sensitivity can reach 92.9%, and the specificity is 92.6%.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Helicobacter pylori rapid-growth additive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103436468AShorten the era timePromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSodium bicarbonateAnimal science
The invention discloses a helicobacter pylori rapid-growth additive. The rapid-growth additive is prepared by the following components in parts by mass: 500 parts of pig stomachs, 500 parts of beef, 7 parts of sodium chloride, 1 part of insoluble starch, 1 part of urea, and right amount pure water and sodium bicarbonate; the pH value is adjusted to be 7.4 to 7.6; after pretreatment, stripping and slicing, boiling for two times, filtering, filter liquor mixing and cold storage, boiling again, cooling, filtering, constant volume, sodium chloride addition, insoluble starch and urea dissolution, pH adjustment, sterilization and storage are performed on raw materials sequentially, the rapid-growth additive is prepared. The rapid-growth additive provided by the invention has the advantages that the lag phase of indicator bacteria is promoted to be shortened when the indicator bacteria are cultured in vitro, the growth and reproduction time of the indicator bacteria on culture medium is shortened effectively, the detection positive rate is improved, the rapid-growth additive is used for preparing high-quality helicobacter pylori isolation medium, and the rapid-growth additive can be prepared through the preparation method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:杭州致远医学检验所有限公司
Method for rapidly detecting polyoxin B using biological value detection and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
InactiveCN109765364AIncrease the areaFacilitate high-throughput screeningComponent separationBiological valueHigh flux
The invention relates to indicator bacteria using alternaria alternata as biological value detection. A high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) chemical detecting method is combined, and the content of polyoxin B in samples can be rapidly and quantitatively detected. The detecting method uses self-made wooden discs as detecting tools, the number of the detected samples is nine times that ofthe a traditional method, corresponding standard curves correspond to the detecting glass wooden discs, the samples with high biological value can be rapidly and precisely screened, the chemical content of the samples with high content is detected by HPLC, the production cost is reduced, the labor intensity is reduced, and the method can be used for monitoring of the polyoxin B bacteria in the high-throughput screen and production processes.
Owner:RUSHAN HANWEI BIO TECHN & SCI
Method for quick combinative monitoring of total coliform and escherichia coli
InactiveCN105907874ASimple application productionSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDuplex pcr
The invention provides a method for quick combinative monitoring of total coliform and escherichia coli. Water fecal pollution indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli are defected through the most probable number duplex PCR (MPN-dulpex PCR) method. The method is simple and quick, only four steps of experiments are needed, and the detection rate is higher than that of the national standard multi-tube fermentation method; specificity is high, repeatability is good, and two alive indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli in water can be monitored at the same time in a combinative and quantitative mode. A new method is provided for quick combinative monitoring of the water fecal pollution indicator bacteria including total coliform and escherichia coli.
Owner:CHONGQING THREE GORGES UNIV
Devices and assays for diagnosis of viral and bacterial infections
ActiveUS20200241010A1Rapid and accurate resultSimple processMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgeryAssayIndicator bacteria
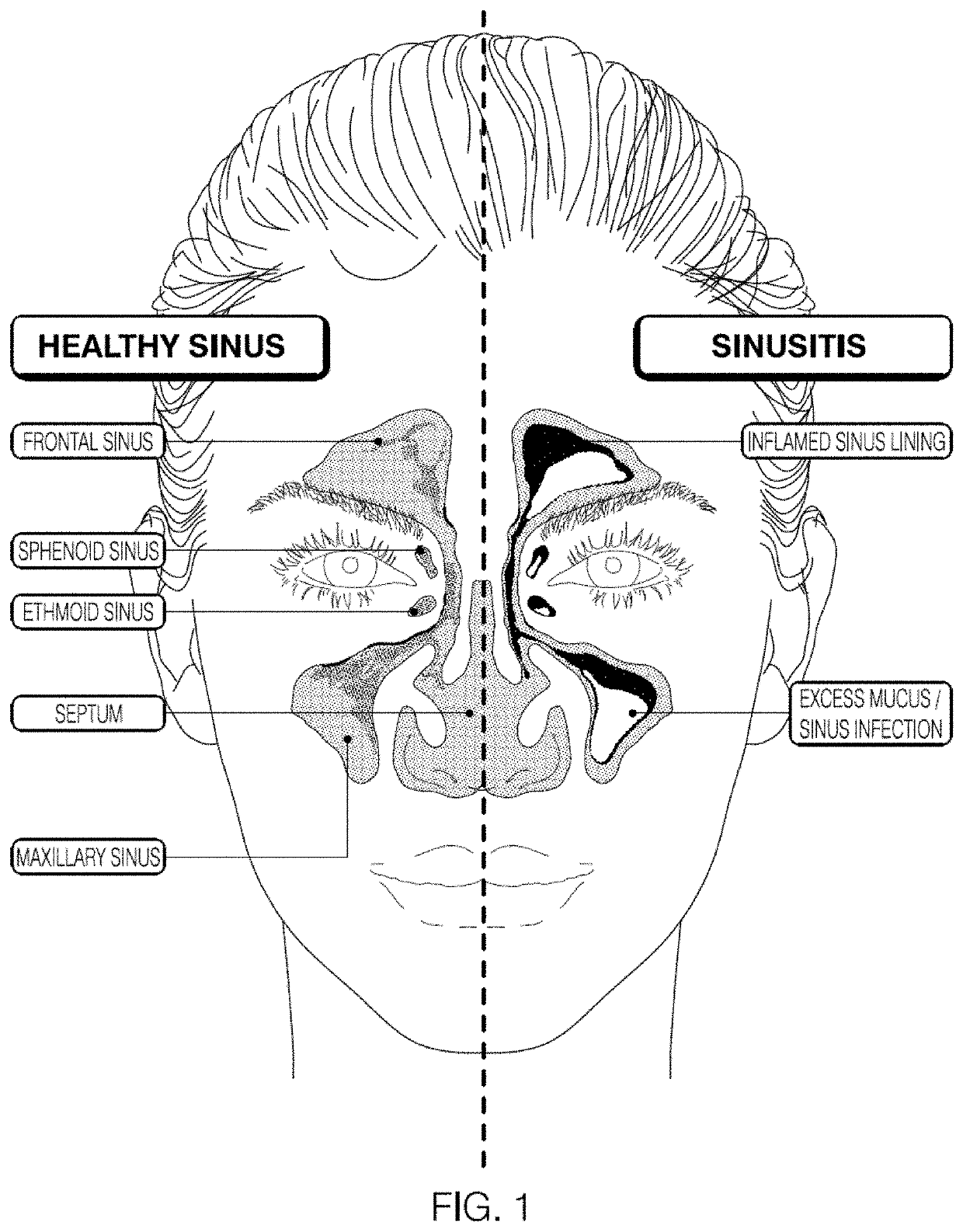
Methods and kits for sampling mucous from within a sinus to determine if a single sample includes one or more bacterial types indicating a bacterial infection, such as bacterial sinusitis, and one or more viruses indicating a viral infection, such as influenza.
Owner:ENTVANTAGE DIAGNOSTICS INC
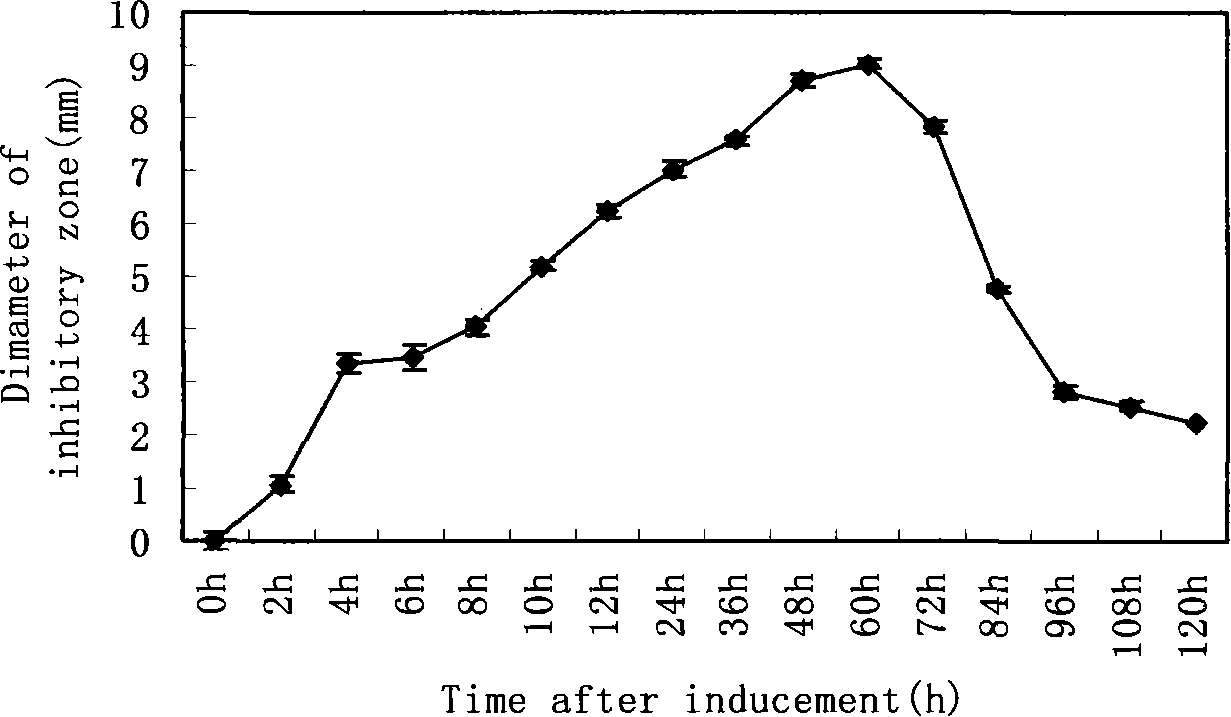
Method for inducing spider to generate antibiotic activity substance
InactiveCN101233838AHigh antibacterial activitySuitable for collectionAntibacterial agentsAnthropod material medical ingredientsRhynchophorusHemolymph
The invention provides a simple and high-efficiency method for inducing spiders to produce antibiotic active substances, which comprises the following steps: a. ultraviolet irradiation is used for inducement: larinioides cornuta is put into a culture vessel and irradiated for 0.5-3 hours under 20W ultraviolet light and in the distance of 1 meter; then the larinioides cornuta is raised continuously; b. hemolymph of the spiders 1-120 hours after induced is extracted and collected by applying a tissue homogenate method; c. B bronchiseptica is employed as indicator bacteria in a coated flat drilling method to test antibacterial activity of the hemolymph. The antibacterial activity of extracted spider hemolymph after irradiated and induced by ultraviolet is high, and the antibiotic active substances can be applied to development of antibiotics.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
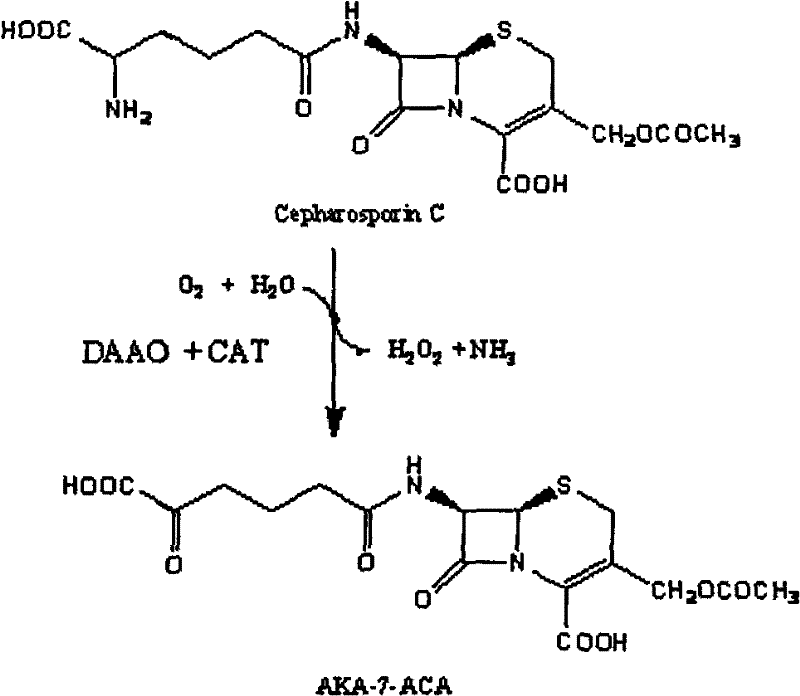
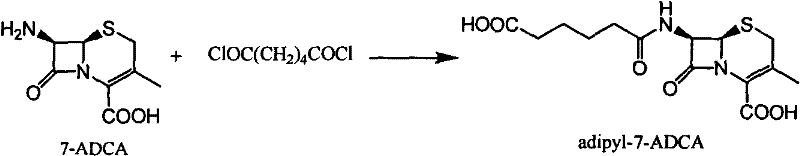
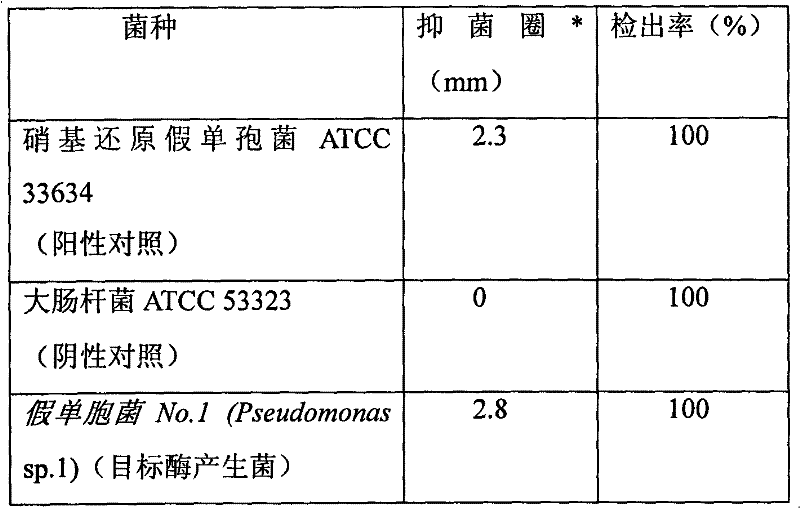
Method for screening alpha-ketone adipoyl-7-aminocephalosporanic acid acylase-producing bacteria
InactiveCN102690859AEasy to operateImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsKetone
The invention discloses a method for screening alpha-ketone adipoyl-7-aminocephalosporanic acid acylase-producing bacteria. The screening process of the method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of alpha-ketone adipoyl-7-aminocephalosporanic acid and structural analogues thereof; (2) selection and culture of screening system indicator bacteria, enrichment culture of candidate bacteria, and selection and culture of positive and negative control strains; (3) preparation of a three-tier agar plate culture medium screening system; (4) judgement of the objective alpha-ketone adipoyl-7-aminocephalosporanic acid acylase-producing bacteria. According to the method, simple operation is achieved, no expensive and complex experimental instrument is needed, 5000 candidate strains can be screened by one person per day, high screening efficiency is achieved and high throughput screening is obtained. Moreover, the method can be used in breeding of industrial strains.
Owner:广西中医学院
Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3 as well as screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN112481165AEnhanced inhibitory effectEfficient degradationBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyVibrio anguillarum
The invention discloses Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3. The preservation number of the Rhodopseudomonas palustris P-3 is CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO: M 2020808. According to the strain, photosynthetic bacteria are separated and purified by adopting a double-layer plate coating method and a streaking method, vibrio parahaemolyticus, vibrio vulnificus and vibrio anguillarum are used as indicator bacteria, and the bacteriostatic action of the marine photosynthetic bacteria strain is determined by adopting an oxford cup method. Naphthalene ethylenediamine hydrochloride spectrophotometry and indophenol blue spectrophotometry are adopted to determine the nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen degradation effects of different strains, and screening is performed to obtain the product. The strain P-3 has the composite functions of resisting vibrio and efficiently degrading nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen, has a strong inhibition effect on vibrio anguillarum, has thestrongest effect on vibrio anguillarum, and also has a certain nitrite nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen degradation effect. The strain P-3 is cultured in a culture medium containing 50mg / L ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen for 4 days, the degradation rates are 89.68% and 94.98% respectively, and the strain P-3 has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV
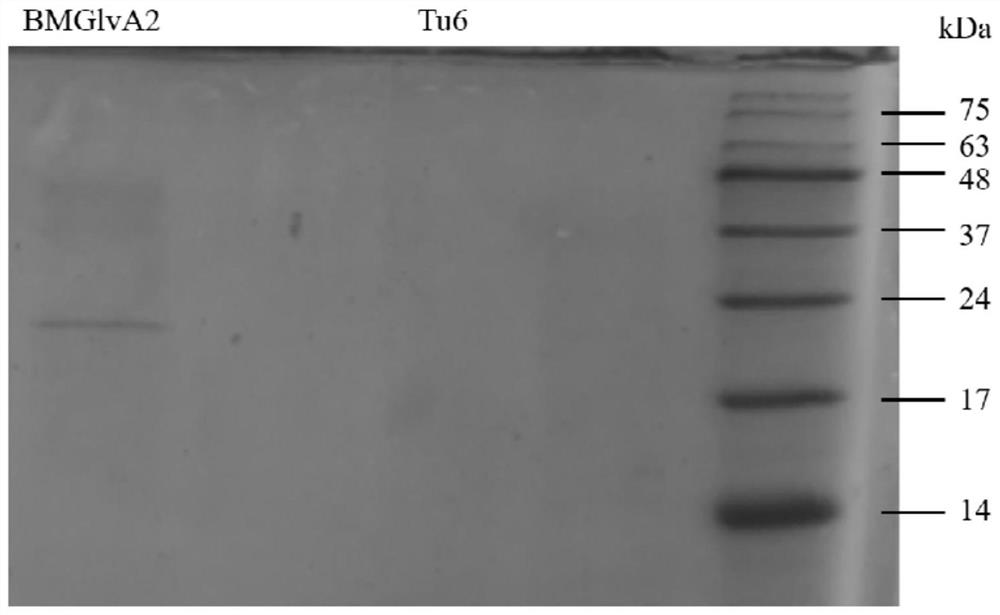
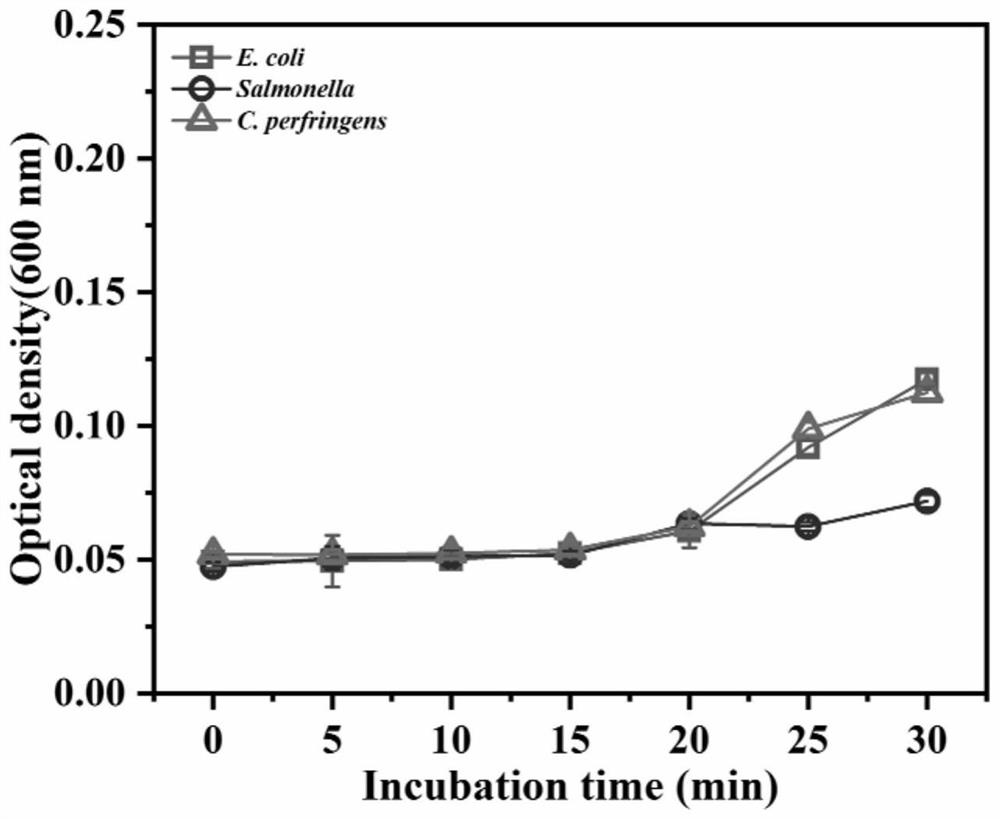
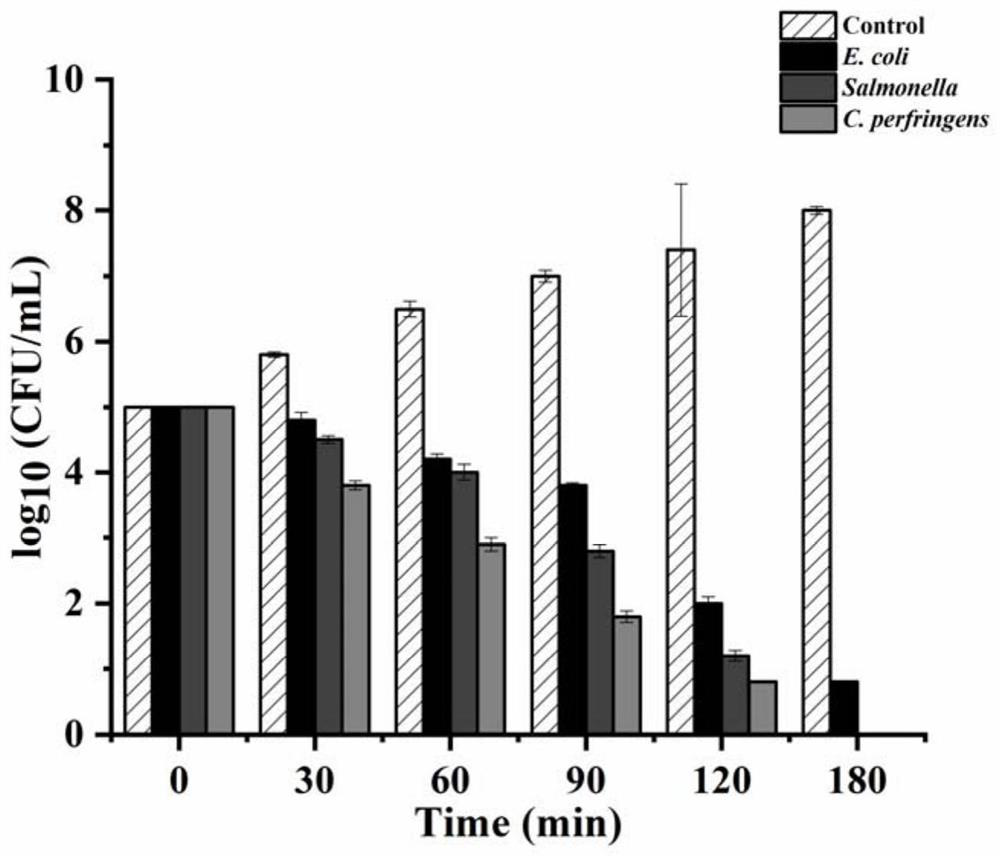
Preparation method and application of bombyx mori antibacterial peptide BMGlvA2 recombinant protein
PendingCN113429469ATo characterize the inhibitory effectImprove featuresAccessory food factorsFermentationEscherichia coliBacillus perfringens
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a bombyx mori antibacterial peptide BMGlvA2 recombinant protein, and the amino acid sequence of the bombyx mori antibacterial peptide BMGlvA2 recombinant protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and an engineering strain Trichoderma reesei is used as an expression host to realize expression of the bombyx mori antibacterial peptide BMGlvA2 recombinant protein. Escherichia coli, salmonella and clostridium perfringens are used as indicator bacteria at the same time for the first time, and it is identified that the antibacterial peptide fermentation product have obvious antibacterial activity on the indicator bacteria. The invention also characterizes the self properties of temperature tolerance, digestive enzyme tolerance, hemolytic activity and the like of the antibacterial peptide, and also preliminarily provides an inhibition mechanism of the antibacterial peptide on clostridium perfringens. The bombyx mori antibacterial peptide BMGlvA2 provided by the invention is beneficial to further development and application in the field of feeds.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Screening method for lactic acid bacteria
PendingCN109837323AHigh screening accuracyStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismLactobacillus
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial screening, and in particular, relates to a screening method for lactic acid bacteria. The method includes the steps: grinding a sample firstly, and then carrying out enlarged cultivation; then growing on a culture medium by a tilt-pour process so as to separate single colonies of lactic acid bacteria; inoculating an MRS flat plate with indicator bacteria with single colonies by a bacteria dotting manner, and covering with MRS soft agar; selecting strains with a bacteriostatic effect, and carrying out purification and preservation of thesingle colonies; and finally, verifying. The strains separated and screened by the method not only can reduce the impact of other miscellaneous bacteria in early stage, but also can eliminate the non-bacteriostatic lactic acid bacteria, can reduce the workload, also can screen the required strains for inhibiting pathogenic bacteria more pertinently.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Method for producing bacteriostatic active substances by bacillus amyloliquefaciens
ActiveCN110790823ALarge damageAntibacterialAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a method for producing bacteriostatic active substances by bacillus amyloliquefaciens and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The method comprises the steps of culturing the bacillus amyloliquefaciens so as to obtain fermentation supernatant, and subjecting the supernatant to separating and purifying, thereby preparing a novel hexapeptide. According to the method provided by the invention, the obtained fermentation supernatant can be directly applied to bacteriostasis, three kinds of bacteriostatic substances can be obtained after further separating and purifying the fermentation supernatant and comprises the novel hexapeptide which similarly has a bacteriostatic action; and when the three kinds of bacteriostatic substances jointly act on indicator bacterium cells, the extent of damage to the cells is greater. Discovered by results of acting on indicator bacteria by pairwise combinations of the three kinds of bacteriostatic substances, lactic acid and Surfactin have a synergistic action, the lactic acid and the hexapeptide have a synergistic action, and the Surfactin and the hexapeptide have an additive action. A theoretical support is provided forcontinuous development of novel antibacterial peptides, and a new way of think is provided for efficient use of natural bacteriostatic substances.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
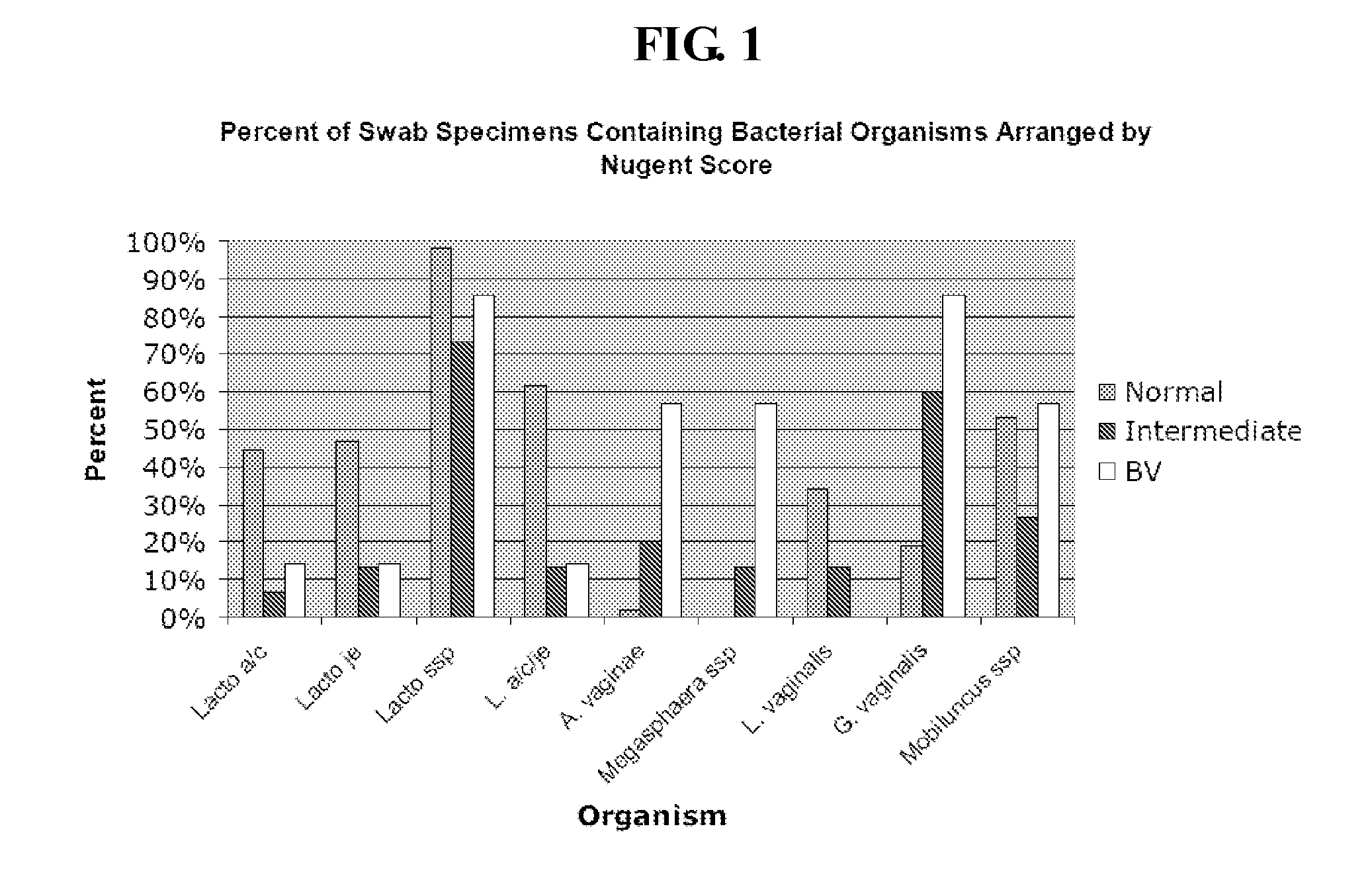
Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis
ActiveUS9200331B2Microbiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBacterial vaginosisTest sample
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis based on an analysis of a patient sample. For example, patient test samples are analyzed for the presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms. The presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms may be detected using PCR analysis of nucleic acid segments corresponding to each target organism. The quantity of the target organisms can then be used to determine a score which is indicative of a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
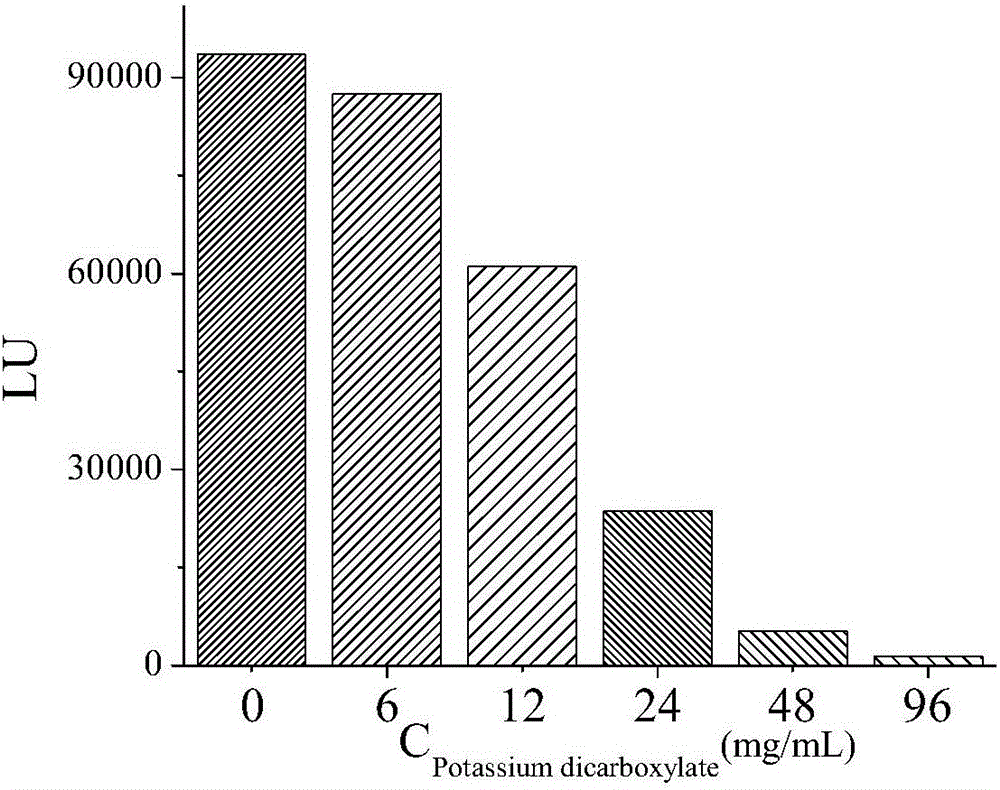
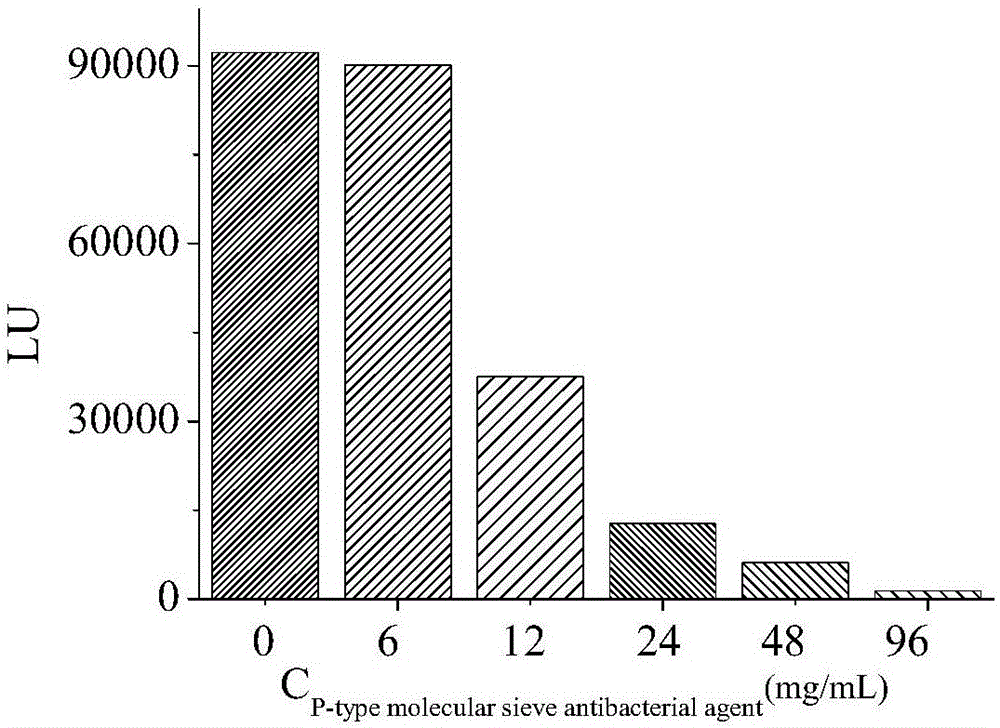
Method for determining antibacterial mechanism of zeolite molecular sieve antibacterial agent by high performance liquid chromatography
The invention discloses a method for determining an antibacterial mechanism of a zeolite molecular sieve antibacterial agent by high performance liquid chromatography. The zeolite molecular sieve antibacterial agent is taken as a research object, escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus are taken as indicator bacteria, and content changes of staphylococcus aureus mycoprotein and content of beta-lactamase in escherichia coli after action of the antibacterial agent are determined by means of high performance liquid chromatography to realize expounding of the antibacterial mechanism of the zeolite molecular sieve antibacterial agent. The method is simple in operation, high in sensitivity, low in sample consumption and quick in detection. Along with increase of the concentration of the antibacterial agent, HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) peak area is reduced, and protein content is decreased, so that the bacterial structure is changed and even completely damaged, bacteria fail to grow normally since cell metabolism and growth are affected, and bacterium inhibition and killing are realized.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
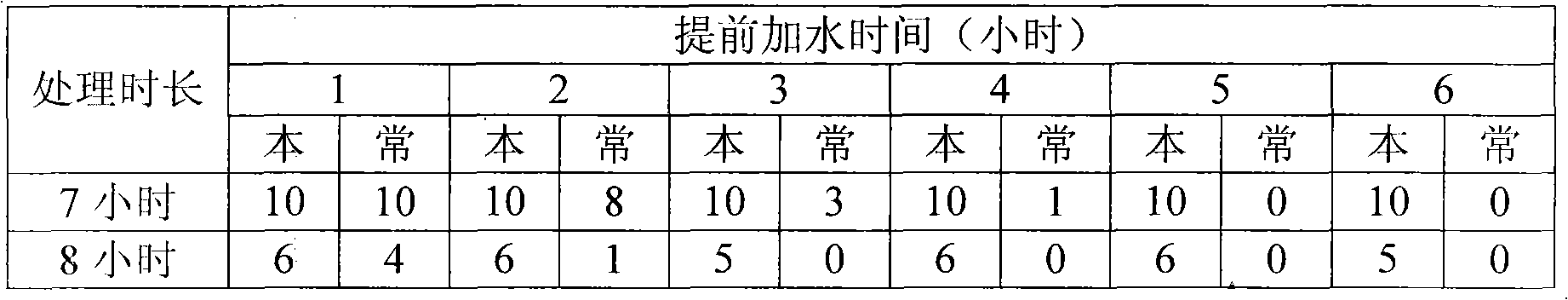
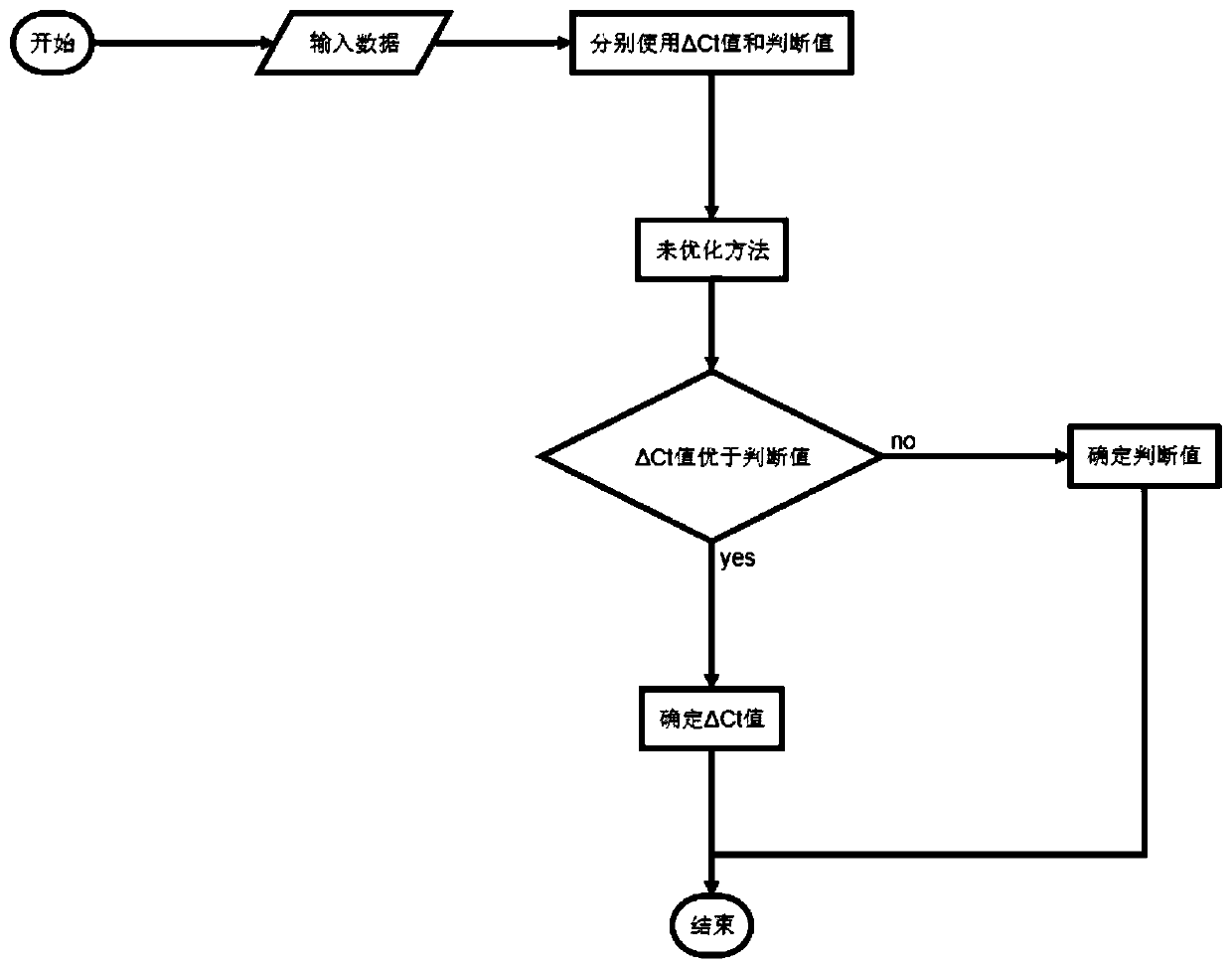
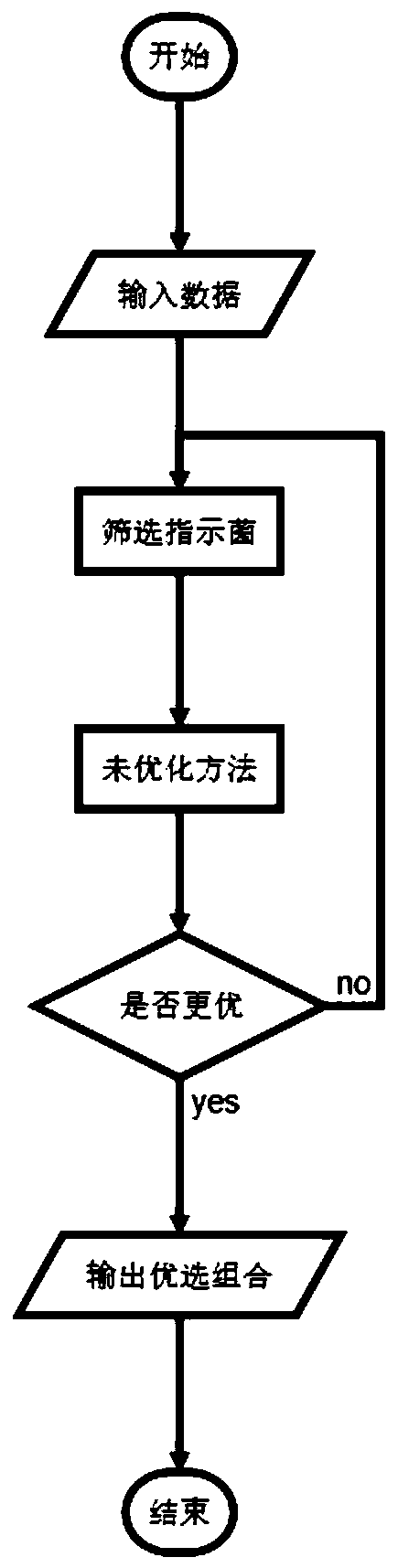
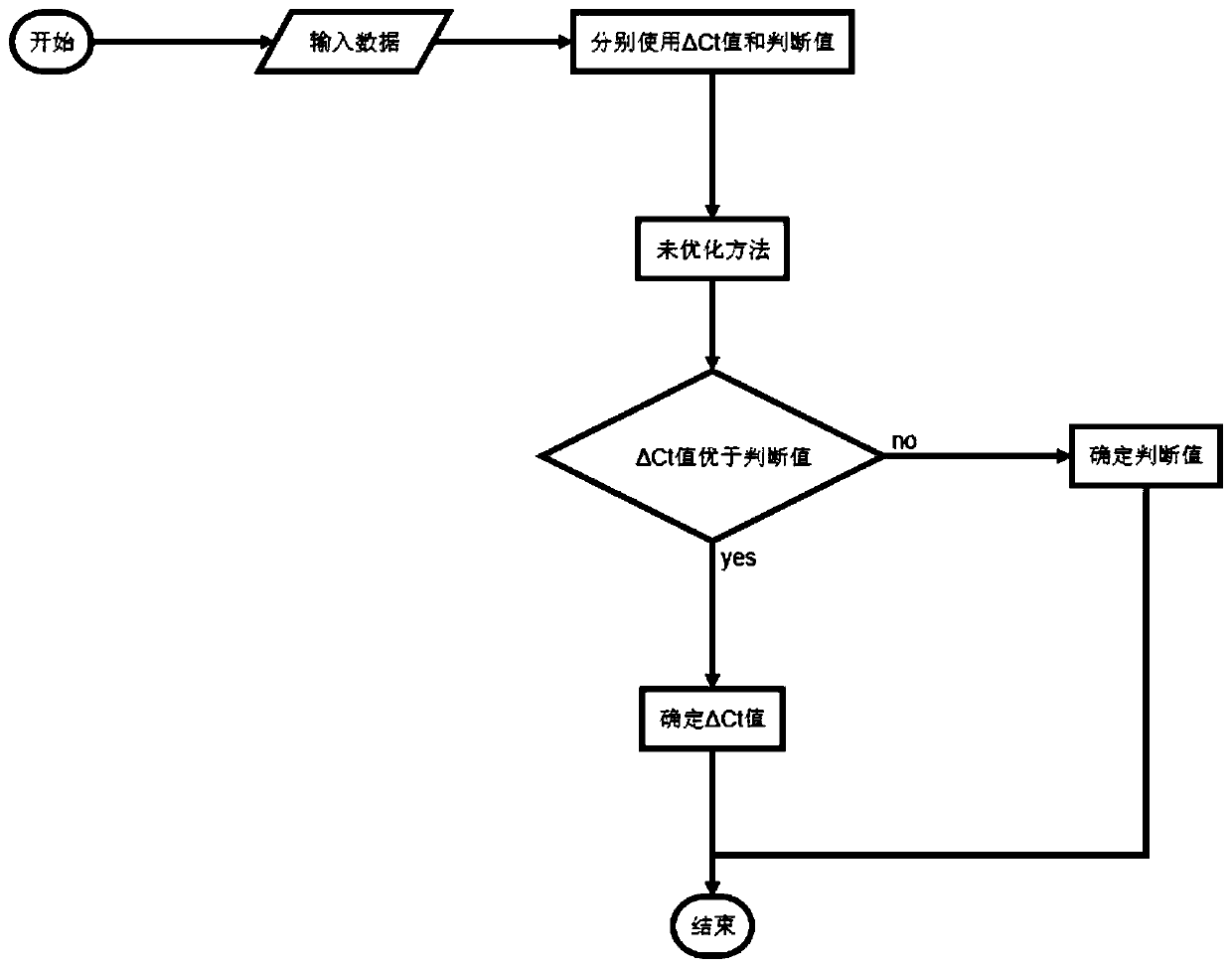
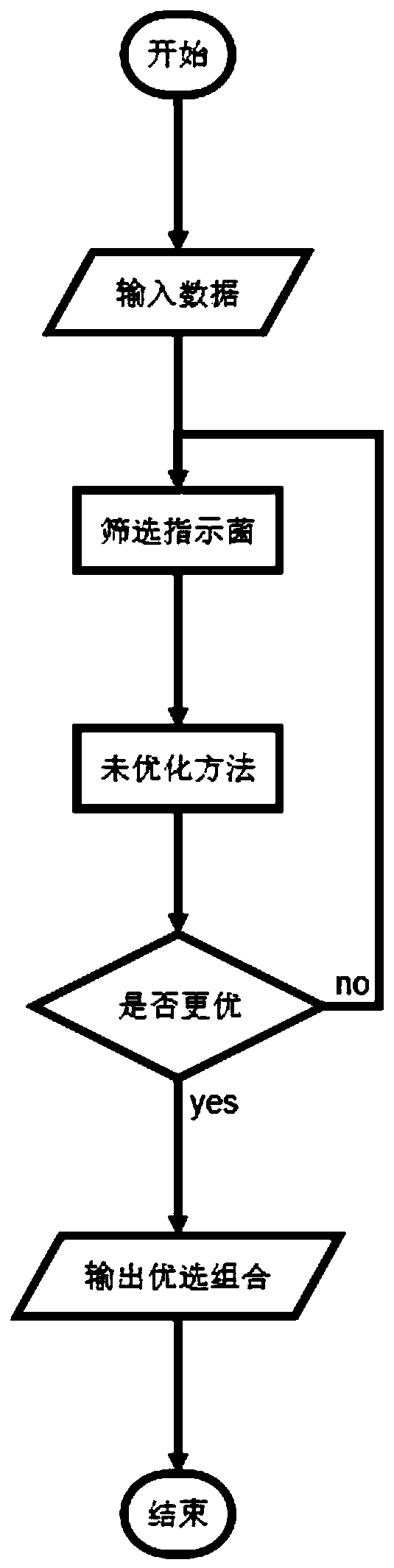
Method for improving detection sensitivity of colorectal cancer indicator bacteria by applying support vector machine algorithm
ActiveCN110781915AImprove detection accuracyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionICT adaptationAlgorithmIndicator bacteria
The invention discloses a method for improving the detection sensitivity of colorectal cancer indicator bacteria by applying a support vector machine algorithm, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: selecting a delta Ct value as a basic numerical value, and selecting a combination of the indicator bacteria and a fecal occult blood FIT (Fitting) index as an indicator index; and a more accurate colorectal cancer recognition method is obtained on the basis of a support vector machine method, parameters of a kernel function, a penalty coefficient and a gamma value and an optimization test of a corresponding model. The method has the beneficial effects that compared with fecal occult blood FIT detection, the SVM optimization algorithm is combined with the optimized indicator primer combination and fecal occult blood FIT index combination, so that the fecal occult blood FIT detection accuracy is higher; the recognition accuracy is higher than that of an unoptimized SVMalgorithm; compared with an unoptimized indicator bacterium primer combination and fecal occult blood FIT index combination, the accuracy is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com