Bacillus stearothermophilus and method for antibiotic residue detection
A technology of stearothermophilic spore and detection method, which is applied in the field of microorganism detection of antibiotics, and achieves the effects of good dispersibility, strong diffusivity, and simple and feasible method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
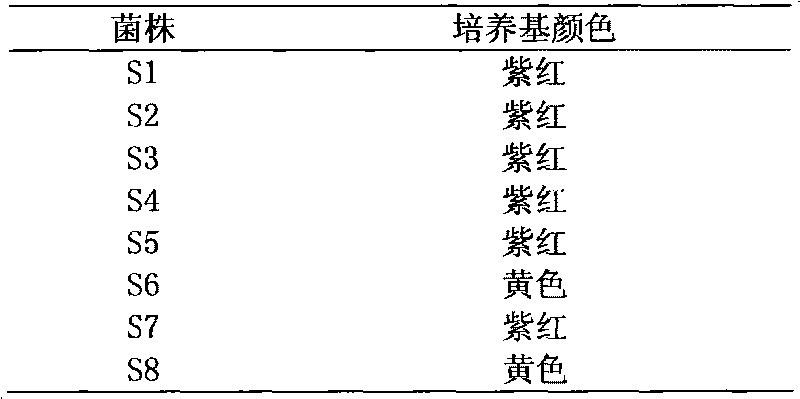
[0031] Example 1 Screening of strains
[0032] (1) Medium preparation
[0033] ①Nutrition agar medium peptone 10g, beef extract 3g, sodium chloride 5g, agar 20g, distilled water 1000mL, add the above ingredients to distilled water, mix well, and autoclave at 120°C for 15min.
[0034] ②Soybean tryptone agar medium tryptone 17.0g, vegetable peptone 3.0g, sodium chloride 10.0g, glucose 2.5g, agar 20g, distilled water 1000mL, add the above ingredients into distilled water, mix well, and autoclave at 120°C for 15min.
[0035] ③Manganese salt nutrient agar medium peptone 10g, beef extract 3g, sodium chloride 5g, agar 20g, distilled water 1000mL, add the above ingredients to distilled water, add 0.5% manganese sulfate solution 1mL, mix well, autoclave at 120°C for 15min .
[0036] ④Potassium bromide phenol purple glucose peptone medium peptone 10g, glucose 5g, 2% potassium bromide phenol purple ethanol solution 0.6mL, agar 4.0g, distilled water 1000mL, add peptone, glucose, agar to distilled ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2 Strain identification
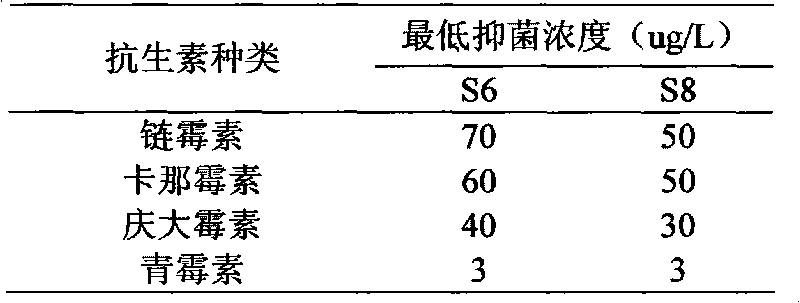
[0055] The strain S8 isolated in Example 1 was further morphologically identified through observation of biological characteristics, and the results are as follows:
[0056] (1) Physiological identification
[0057] Cultivated on Tryptone Soy Agar Medium, only a needle-sized colony is formed. The bacterial body is rod-shaped and does not form filaments. It has flagella all over the body and can move. The spores are oval, sub-terminal or terminal, which usually enlarge the cysts , Can cause high-temperature sterilization milky acid spoilage and sweet curd and other deterioration; the minimum growth temperature is 28 ℃, the optimum growth temperature is 50 ~ 65 ℃, the maximum growth temperature is 70 ~ 77 ℃, at pH 6.8 ~ 7.2 It grows well in the medium and cannot grow when the pH is close to 5.
[0058] (2) Biochemical identification:
[0059] Cultivation at 65°C can grow rapidly: glucose produces acid;
[0060] Sabouraud dextrose broth, negative; ...
Embodiment 3
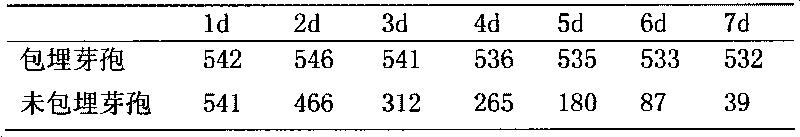
[0069] Embodiment 3 A method for detecting antibiotic residues includes the following steps:
[0070] (1) Strain activation
[0071] Bacillus stearothermophilus CGMCC NO.3287 strain was inoculated on the slant medium of tryptone soybean, adjusted the pH of the medium to 7.2, and optimized culture at 65℃, and planted once a week;
[0072] (2) Spore enrichment and suspension
[0073] Heating and centrifugation: culture the slant strain at 65°C for 4 days, wash the lawn with 10 mL of physiological saline, transfer it to a sterile Erlenmeyer flask with a small amount of glass beads, shake, filter sterile cotton into a sterile container, Prepare a suspension with a certain concentration, heat the suspension at 70~80℃ for 10min, let it stand overnight, centrifuge at 2000r / min for 15min, take the supernatant, centrifuge at 4000r / min for 15min, and repeat the centrifugation and washing for 4 to 5 times. Suspend the centrifugal sediment into a spore suspension with physiological saline and ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com