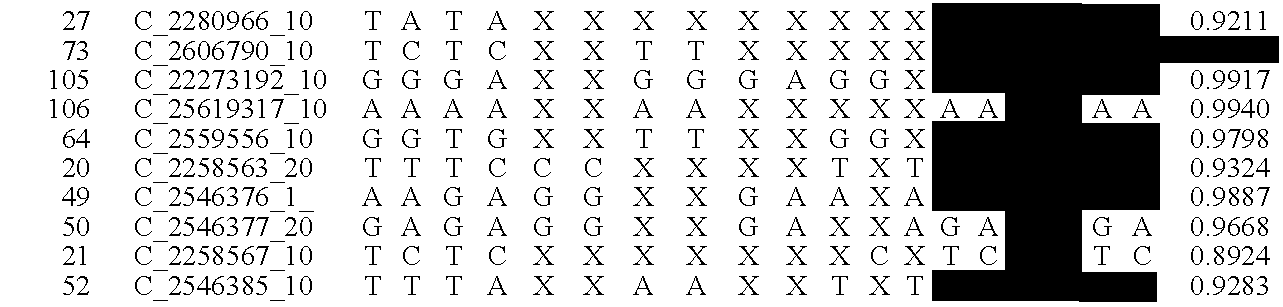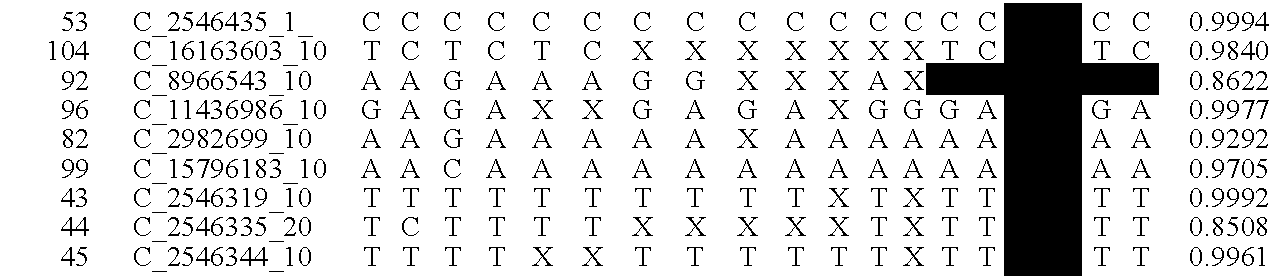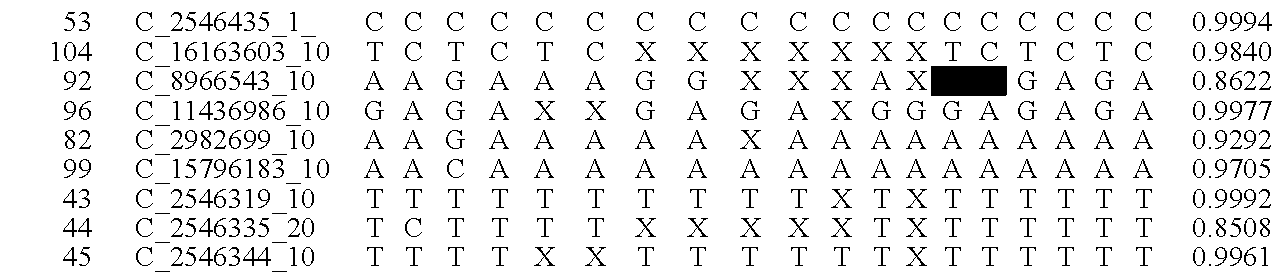Patents
Literature
6405 results about "Embryo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An embryo is an early stage of development of a multicellular diploid eukaryotic organism. In general, in organisms that reproduce sexually, an embryo develops from a zygote, the single cell resulting from the fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The zygote possesses half the DNA from each of its two parents. In plants, animals, and some protists, the zygote will begin to divide by mitosis to produce a multicellular organism. The result of this process is an embryo.
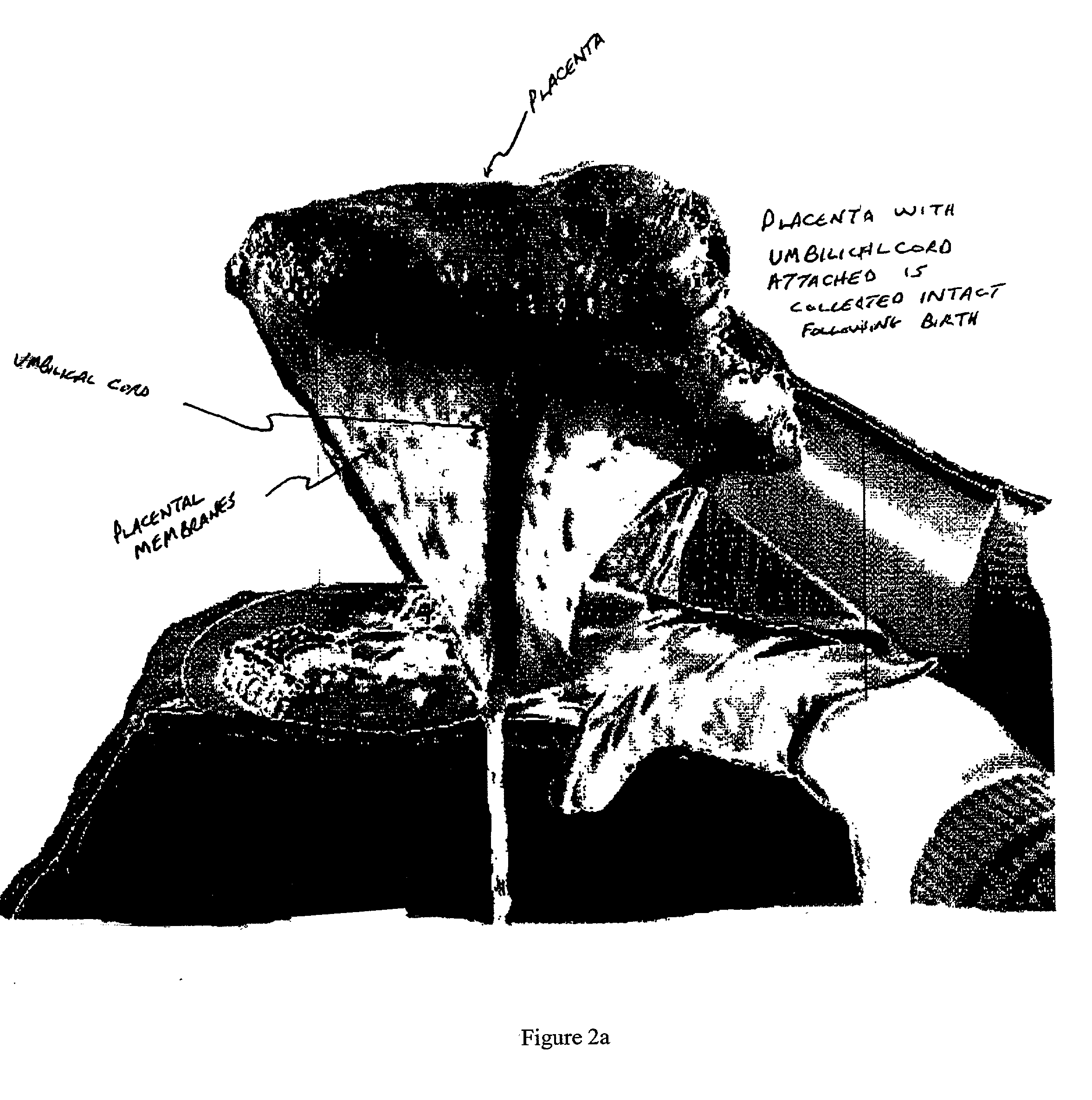
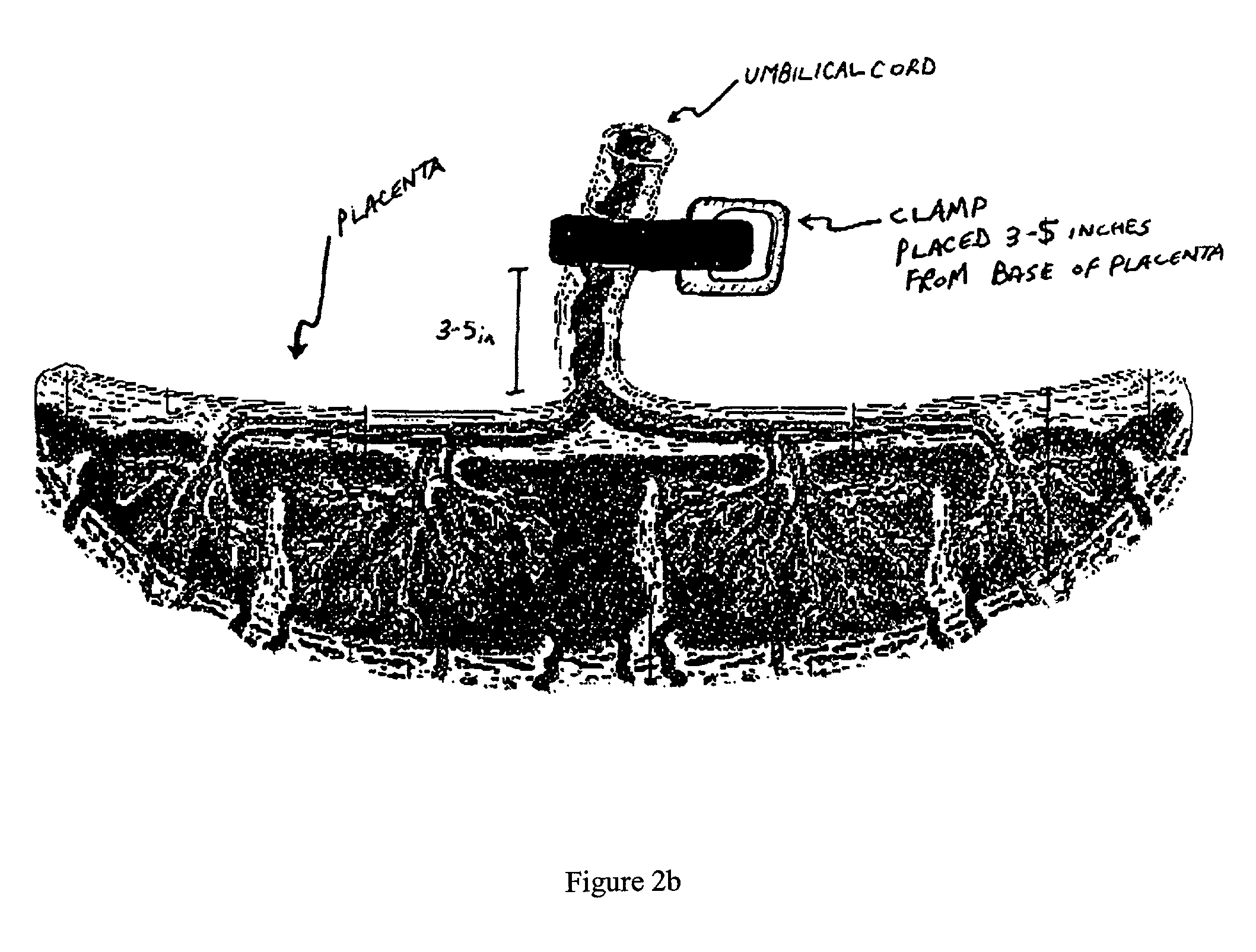
Post-partum mammalian placenta, its use and placental stem cells therefrom
InactiveUS20030032179A1Enhance exsanguinationEnhance sterile conditionSenses disorderAntipyreticAnticoagulant AgentEmbryo
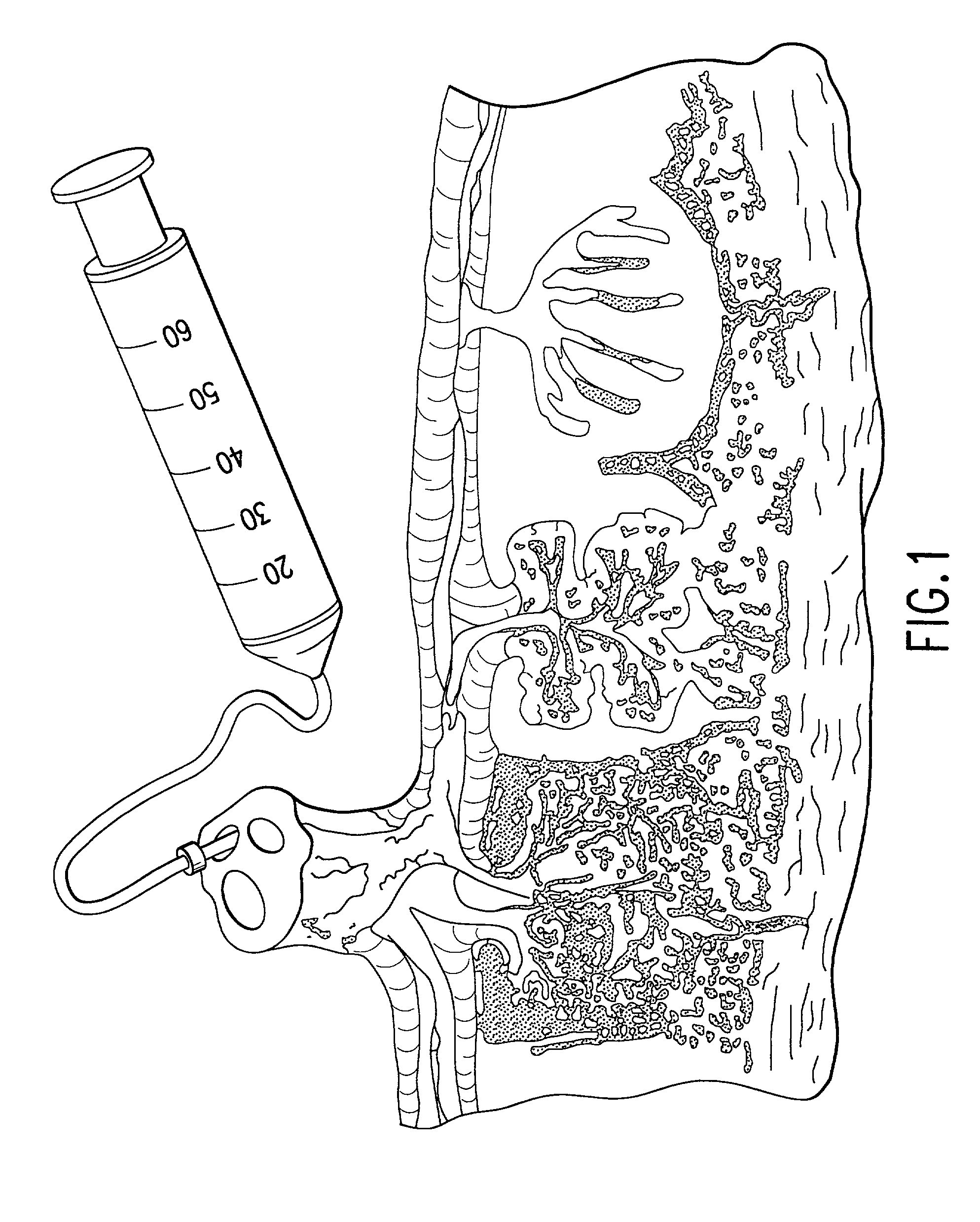
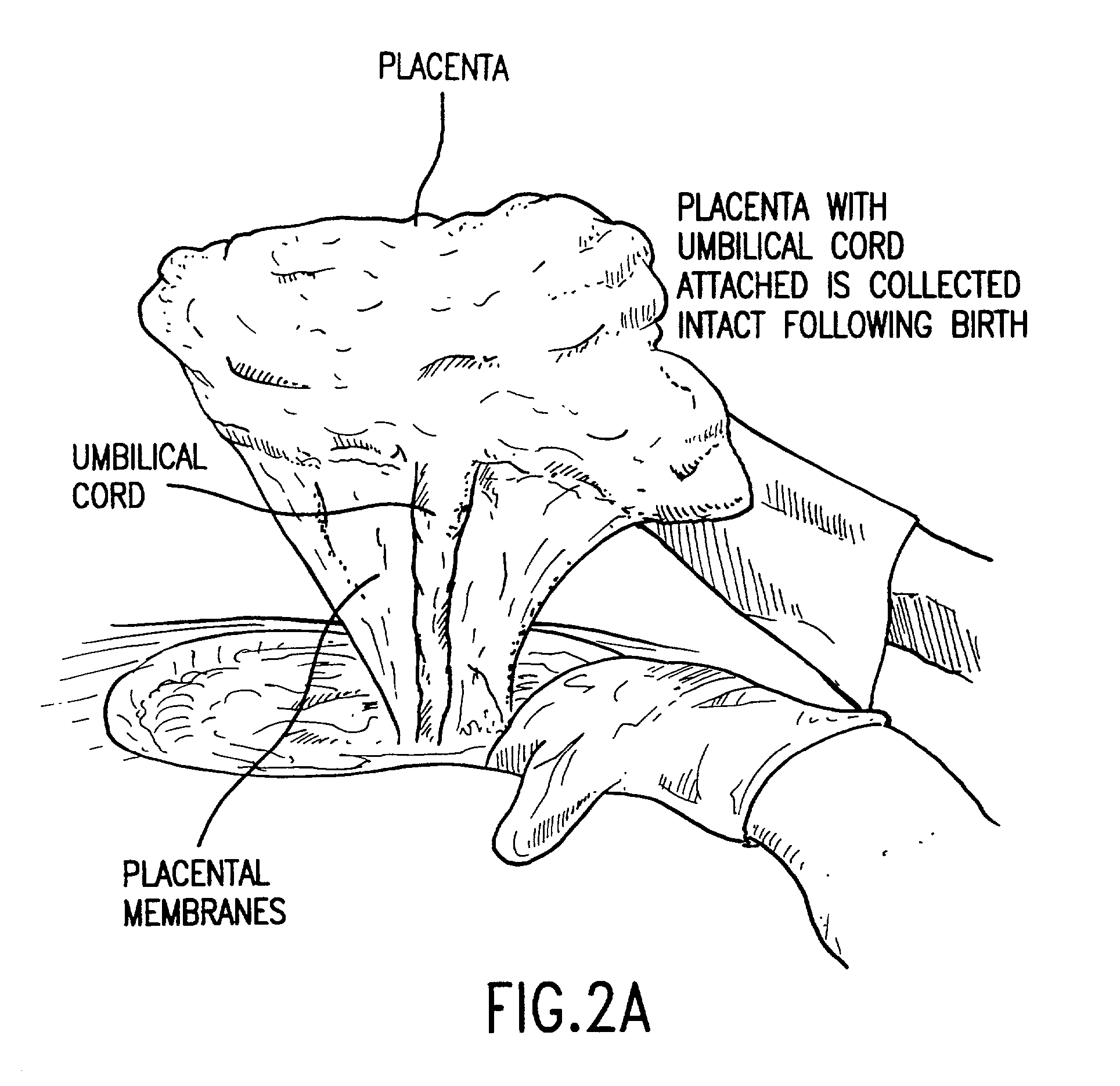
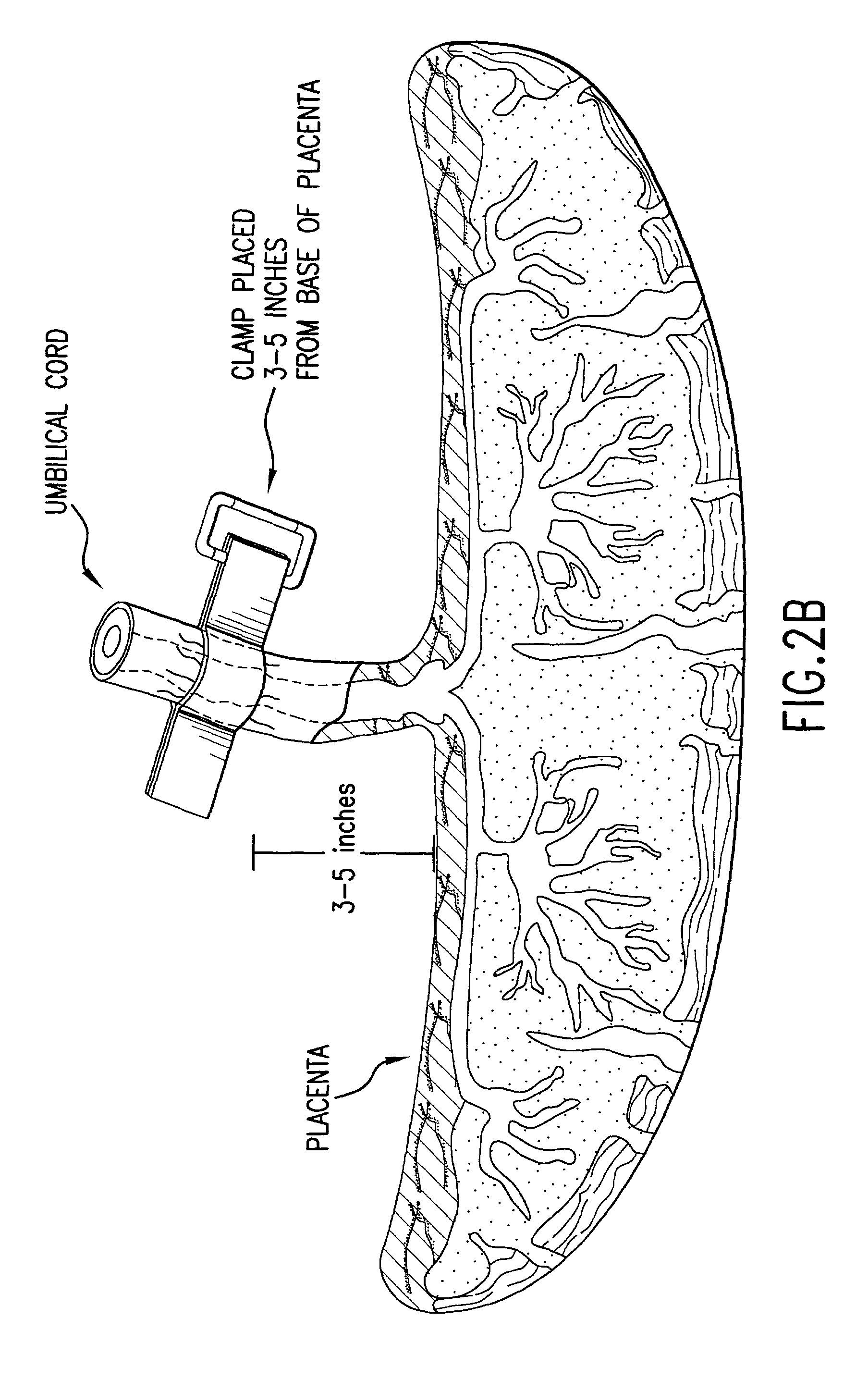
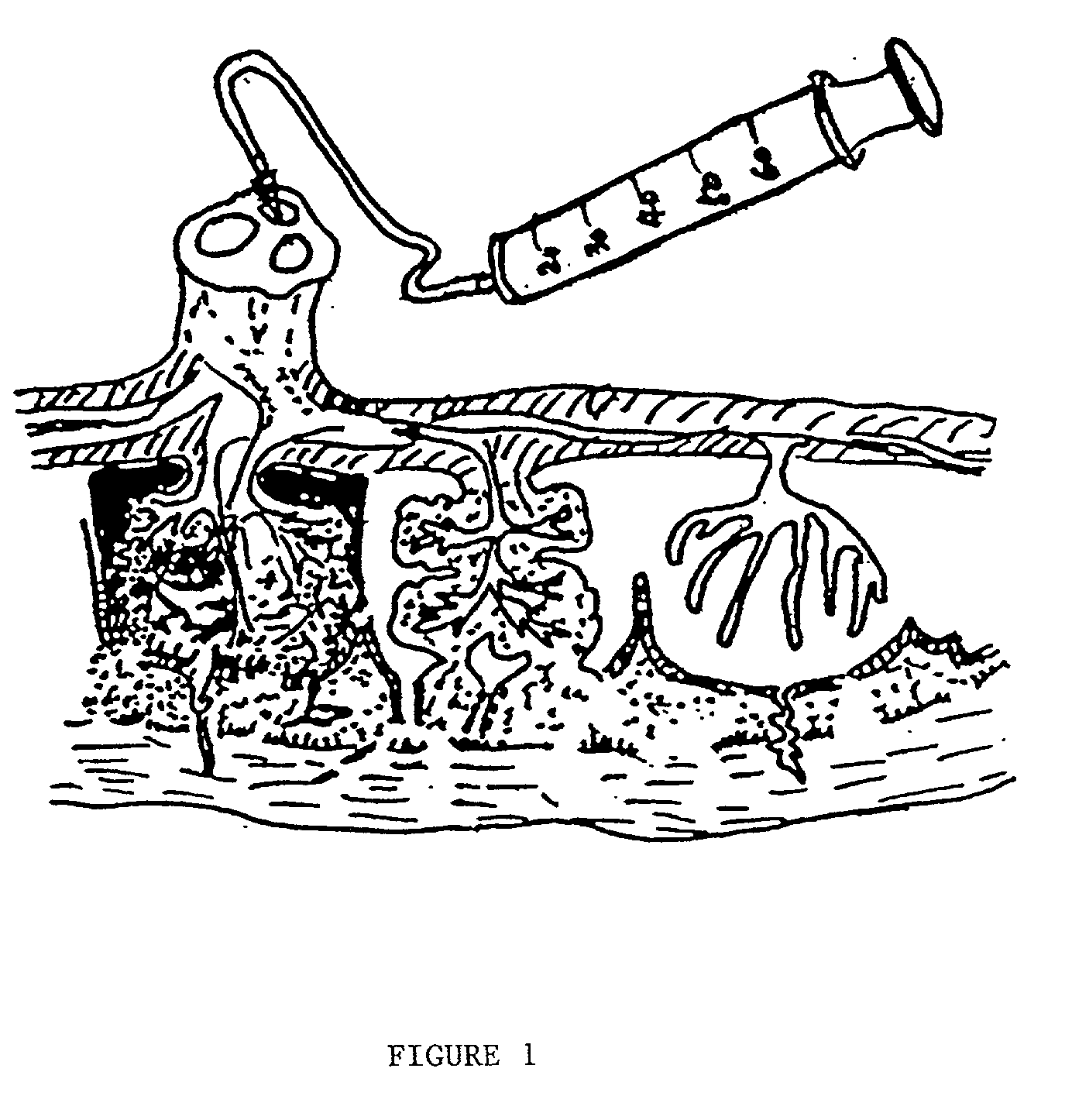
The present invention provides a method of extracting and recovering embryonic-like stem cells, including, but not limited to pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, from an exsanguinated human placenta. A placenta is treated to remove residual umbilical cord blood by perfusing an exsanguinated placenta, preferably with an anticoagulant solution, to flush out residual cells. The residual cells and perfusion liquid from the exsanguinated placenta are collected, and the embryonic-like stem cells are separated from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. The invention also provides a method of utilizing the isolated and perfused placenta as a bioreactor in which to propagate endogenous cells, including, but not limited to, embryonic-like stem cells. The invention also provides methods for propagation of exogenous cells in a placental bioreactor and collecting the propagated exogenous cells and bioactive molecules therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Method of collecting placental stem cells
InactiveUS20020123141A1Increase concentrationImprove the environmentSenses disorderAntipyreticCord blood stem cellEmbryo
A method of collecting embryonic-like stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood by perfusing the drained placenta with an anticoagulant solution to flush out residual cells, collecting the residual cells and perfusion liquid from the drained placenta, and separating the embryonic-like cells from the residual cells and perfusion liquid. Exogenous cells can be propagated in the placental bioreactor and bioactive molecules collected therefrom.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
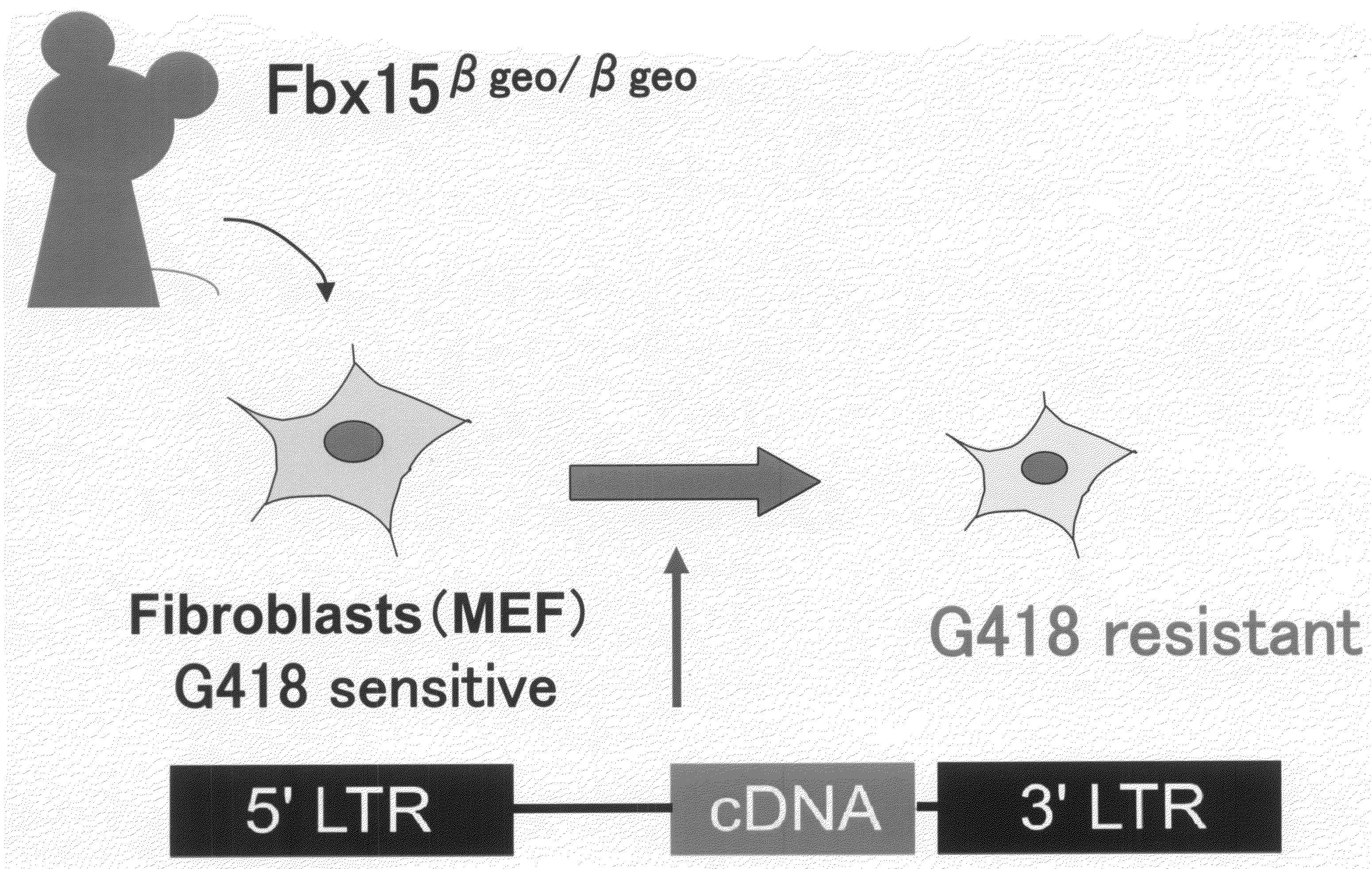
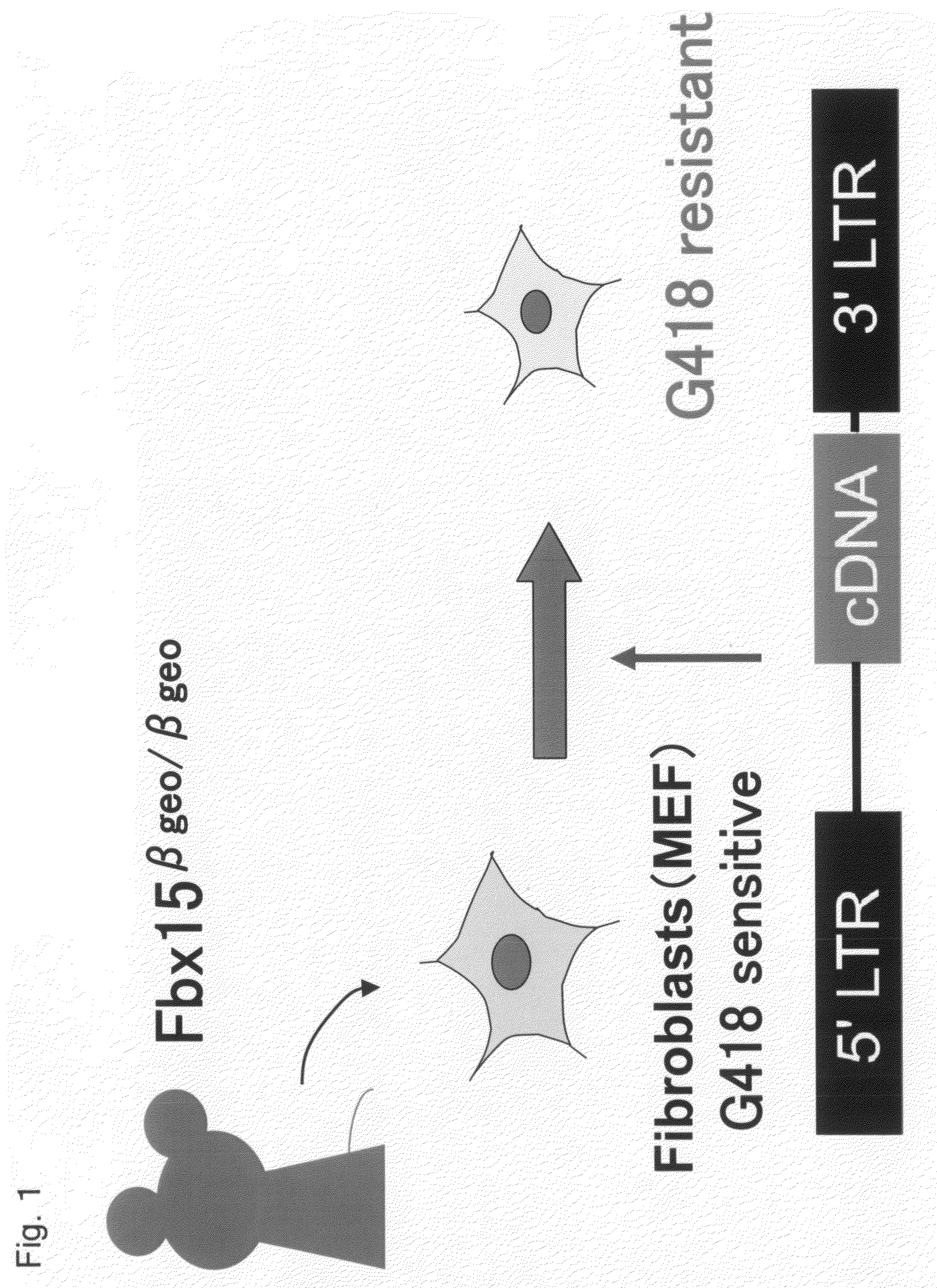
Nuclear Reprogramming Factor
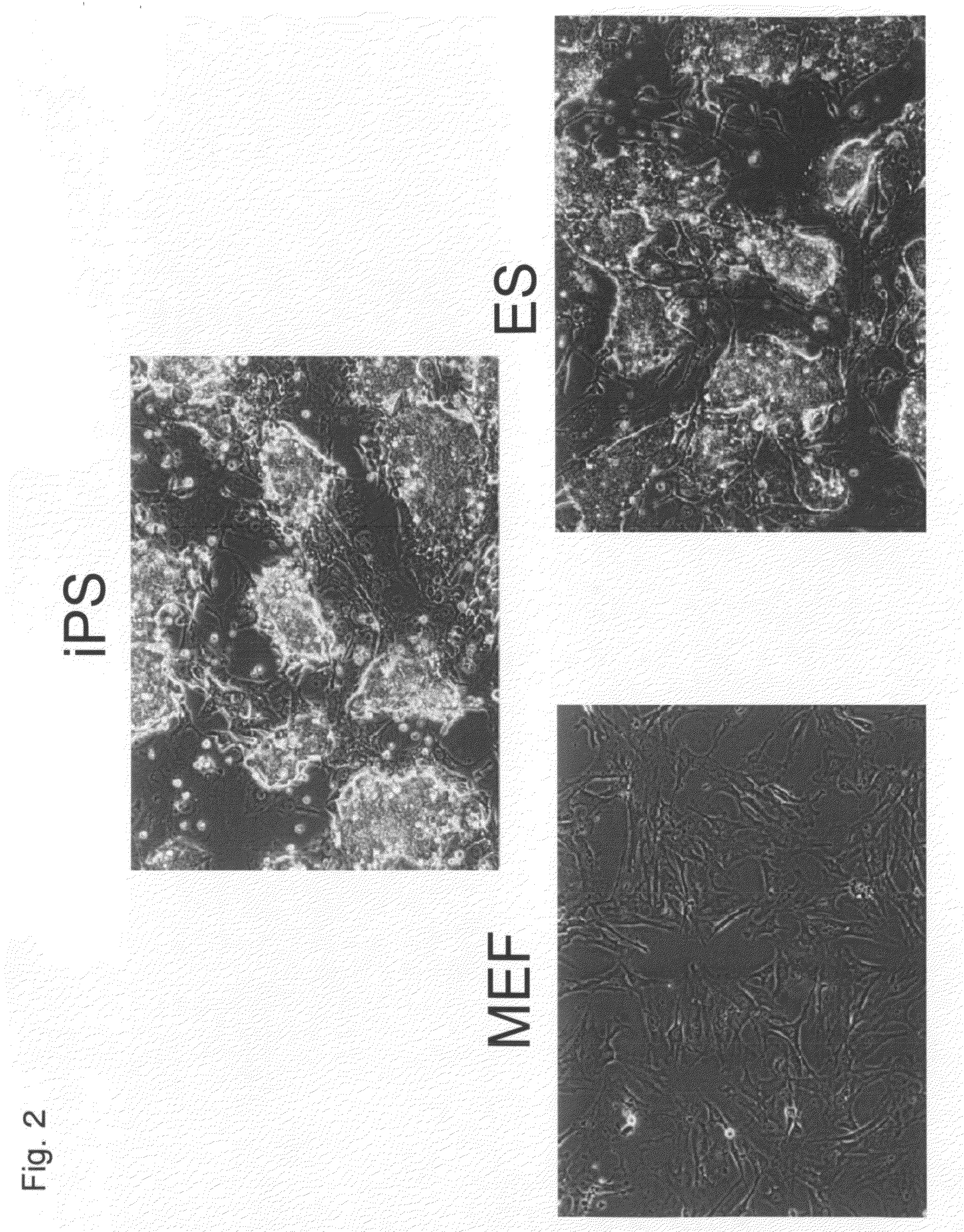
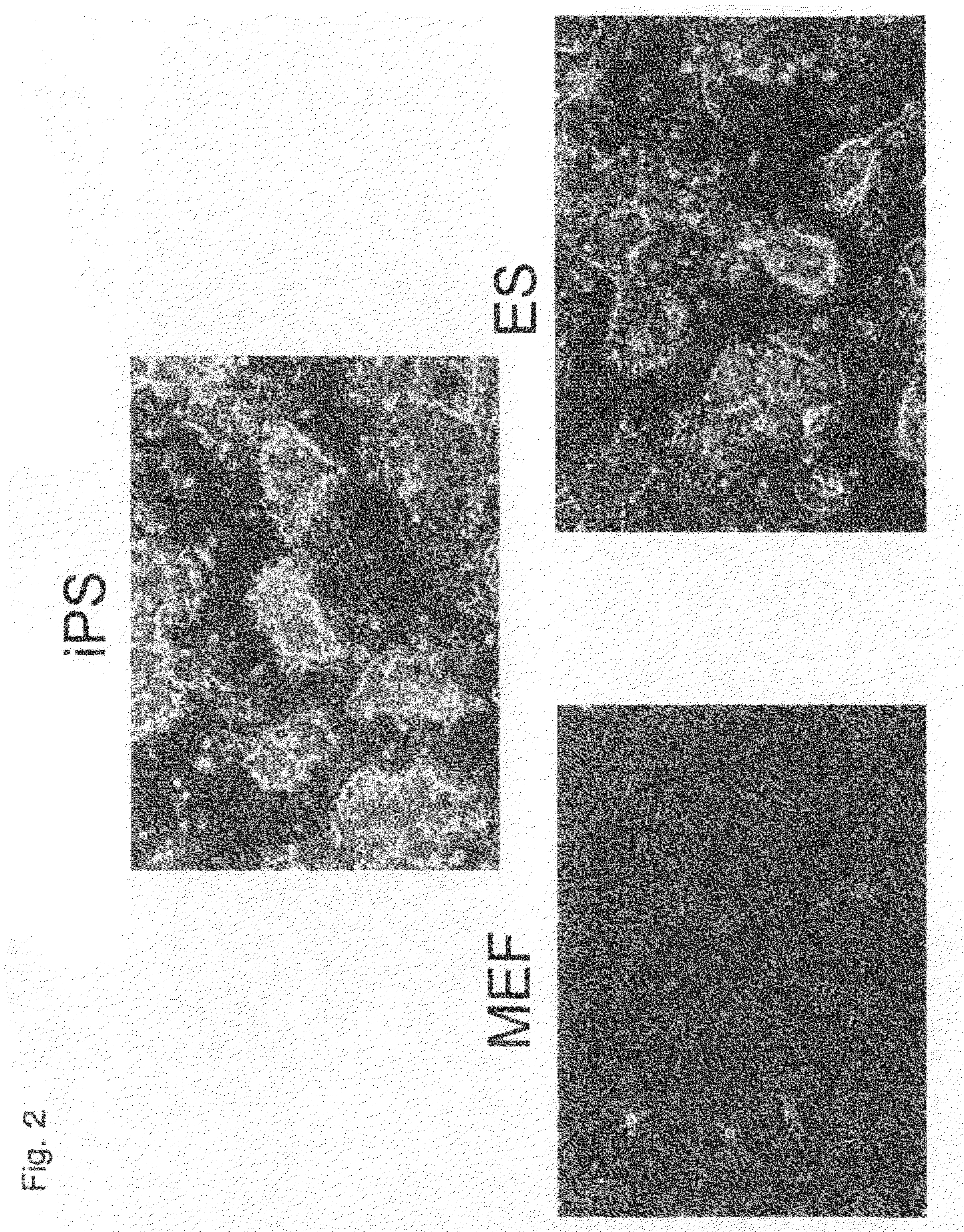
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Embryonic-like stem cells derived from post-partum mammalian placenta, and uses and methods of treatment using said cells
Owner:CELULARITY INC
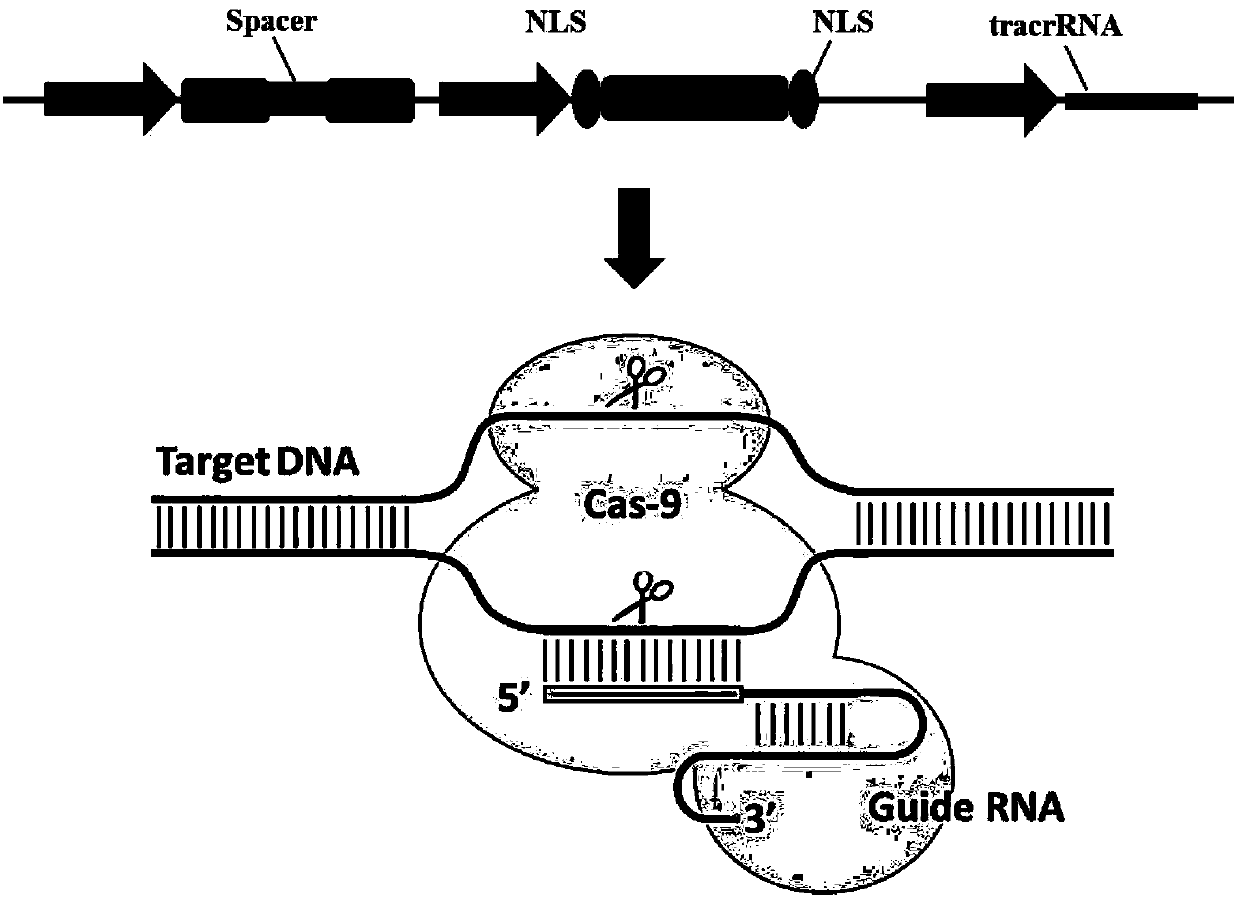
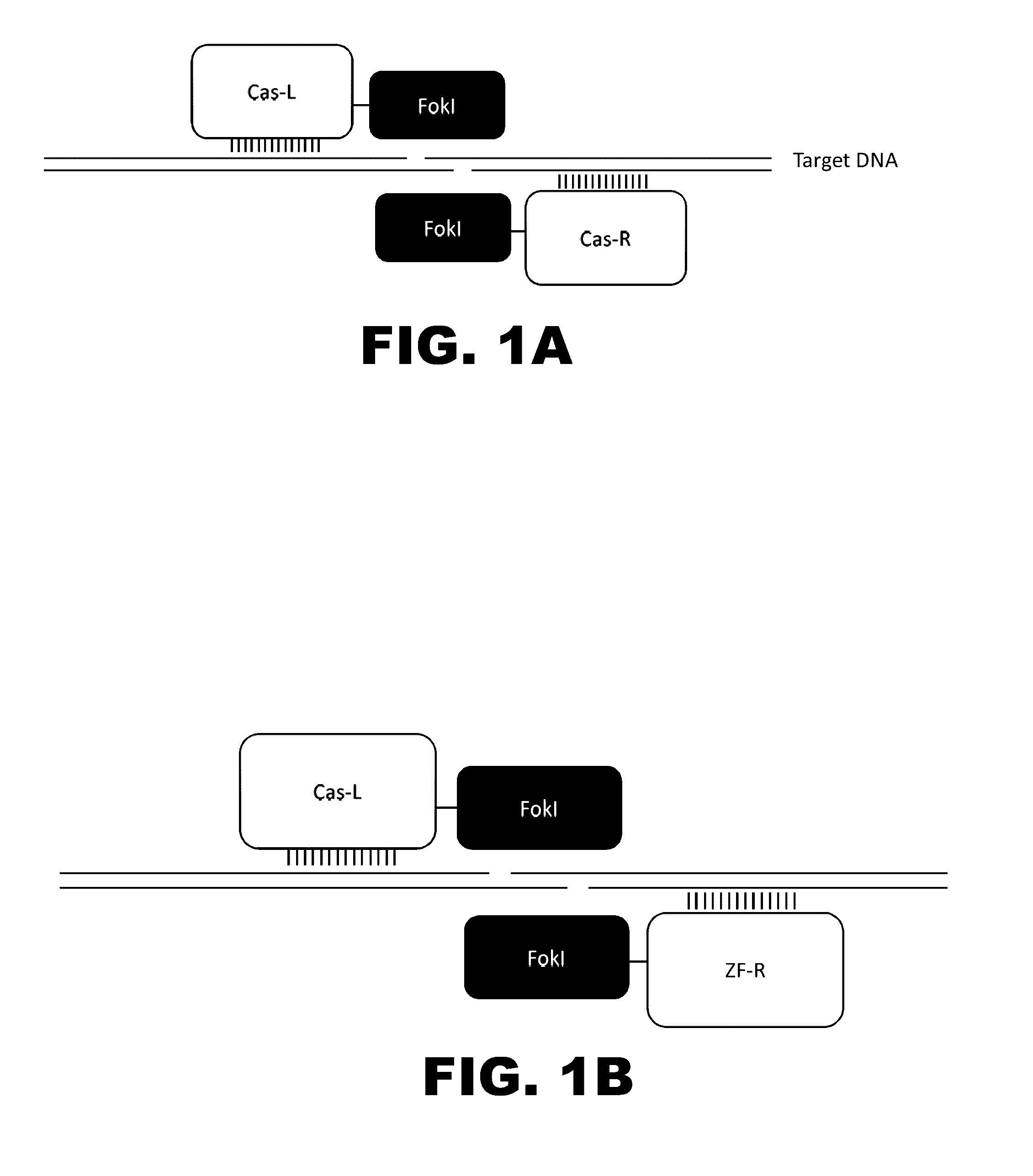
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
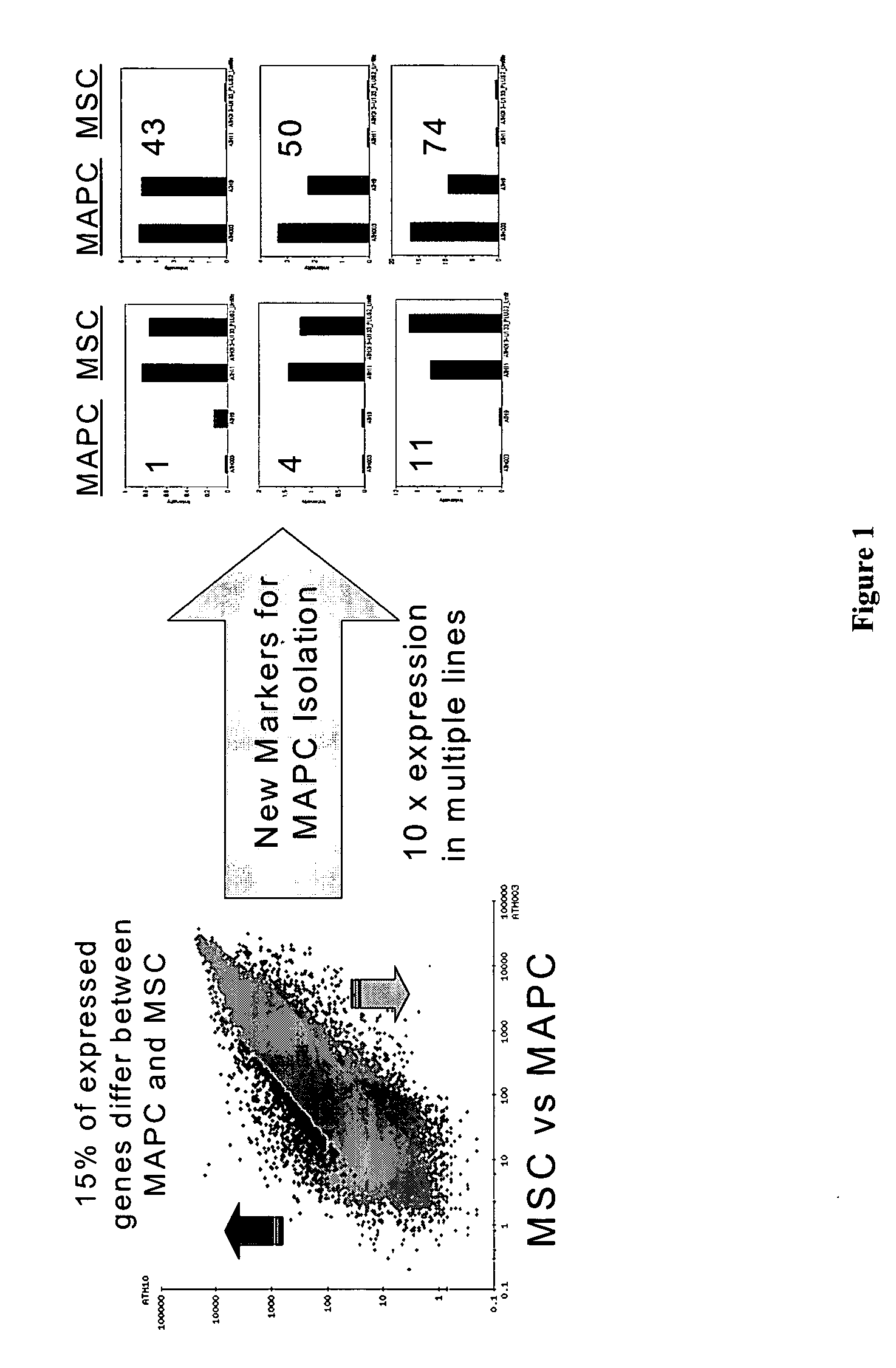
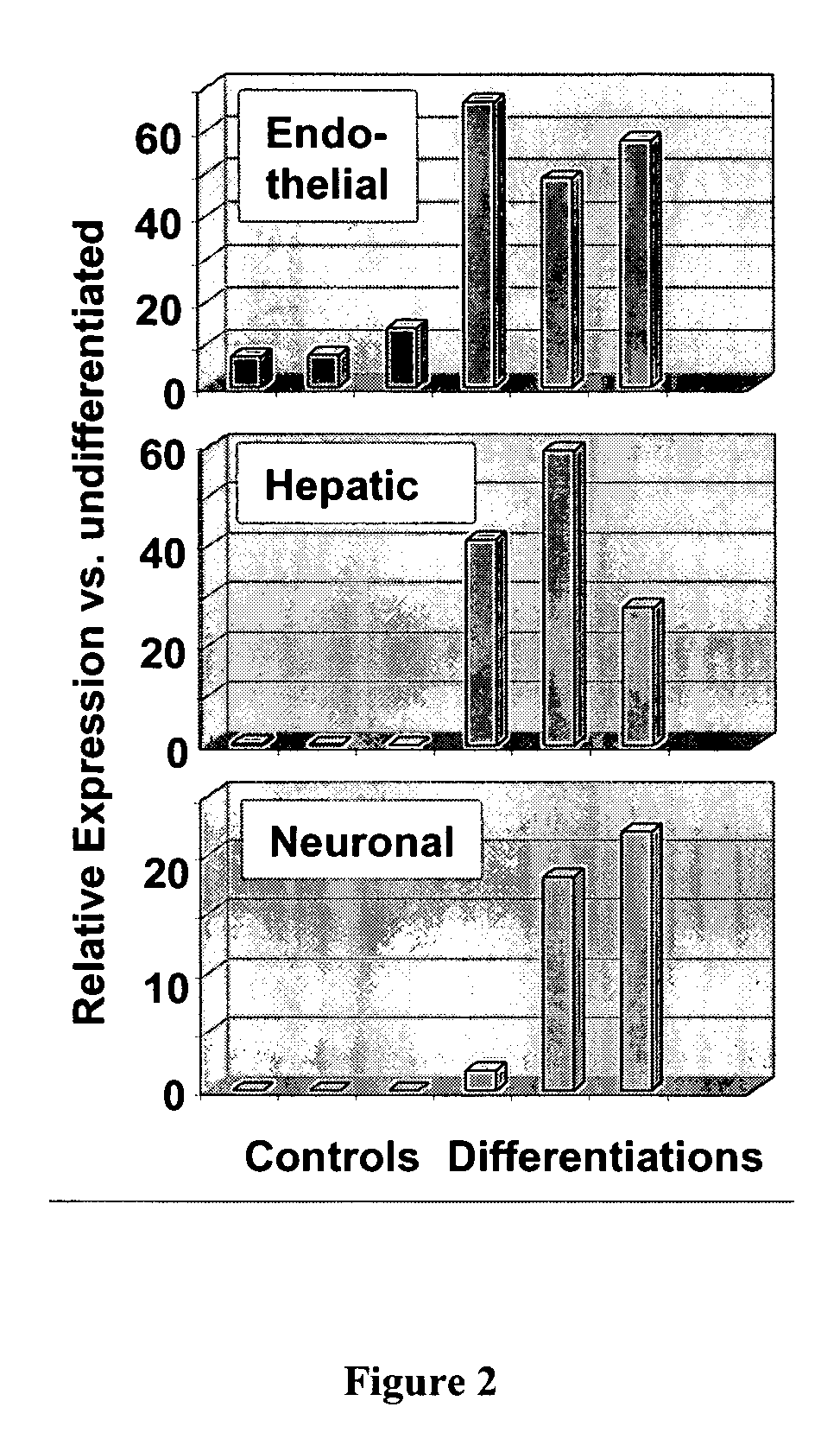
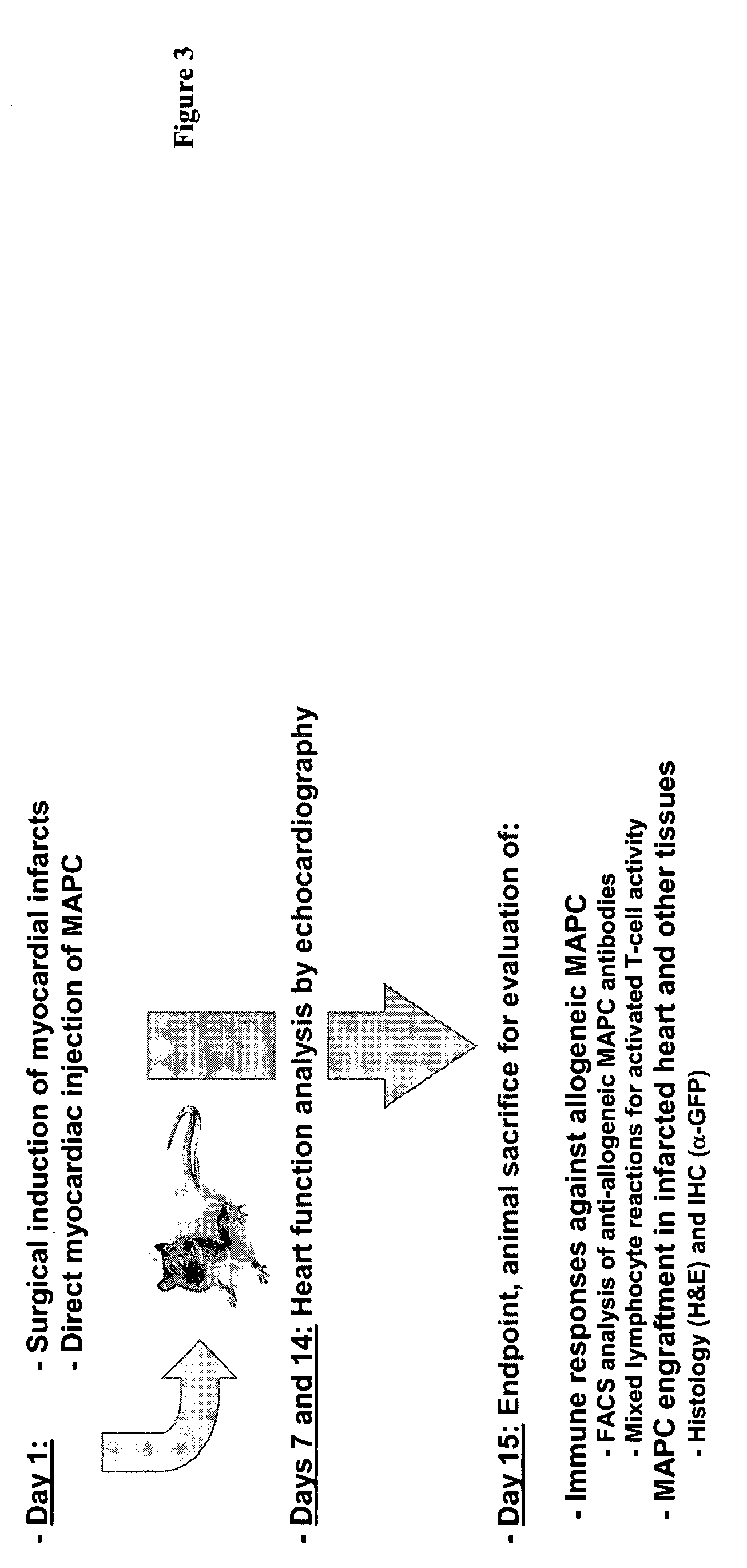
Use of multipotent adult stem cells in treatment of myocardial infarction and congestive heart failure
ActiveUS20060008450A1Restore and enhance cardiac muscle functionRapid responseBiocideGenetic material ingredientsTissues typesEmbryo
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
ActiveUS20070184467A1Significant resultMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsUniparental disomyEmbryo
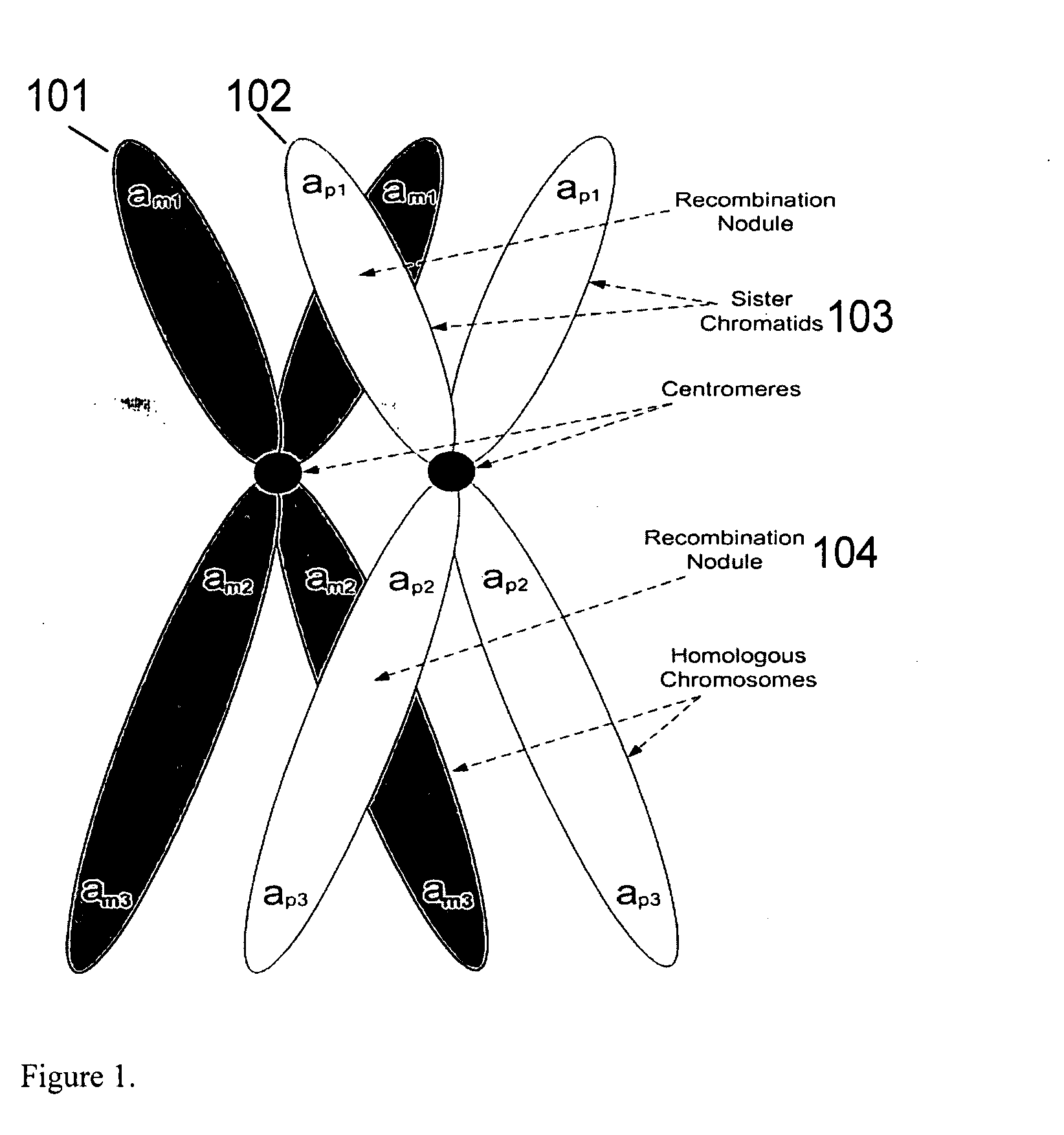
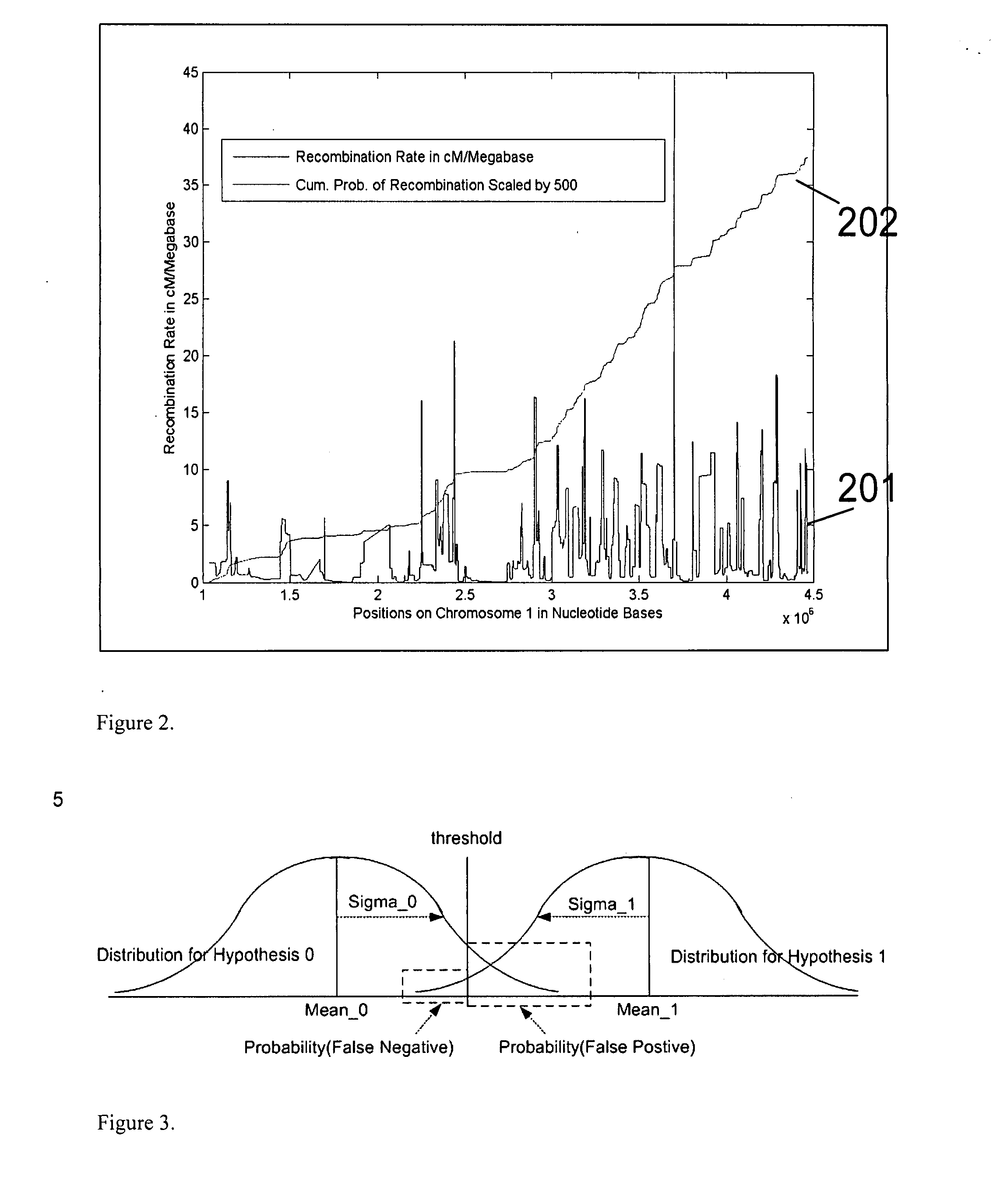
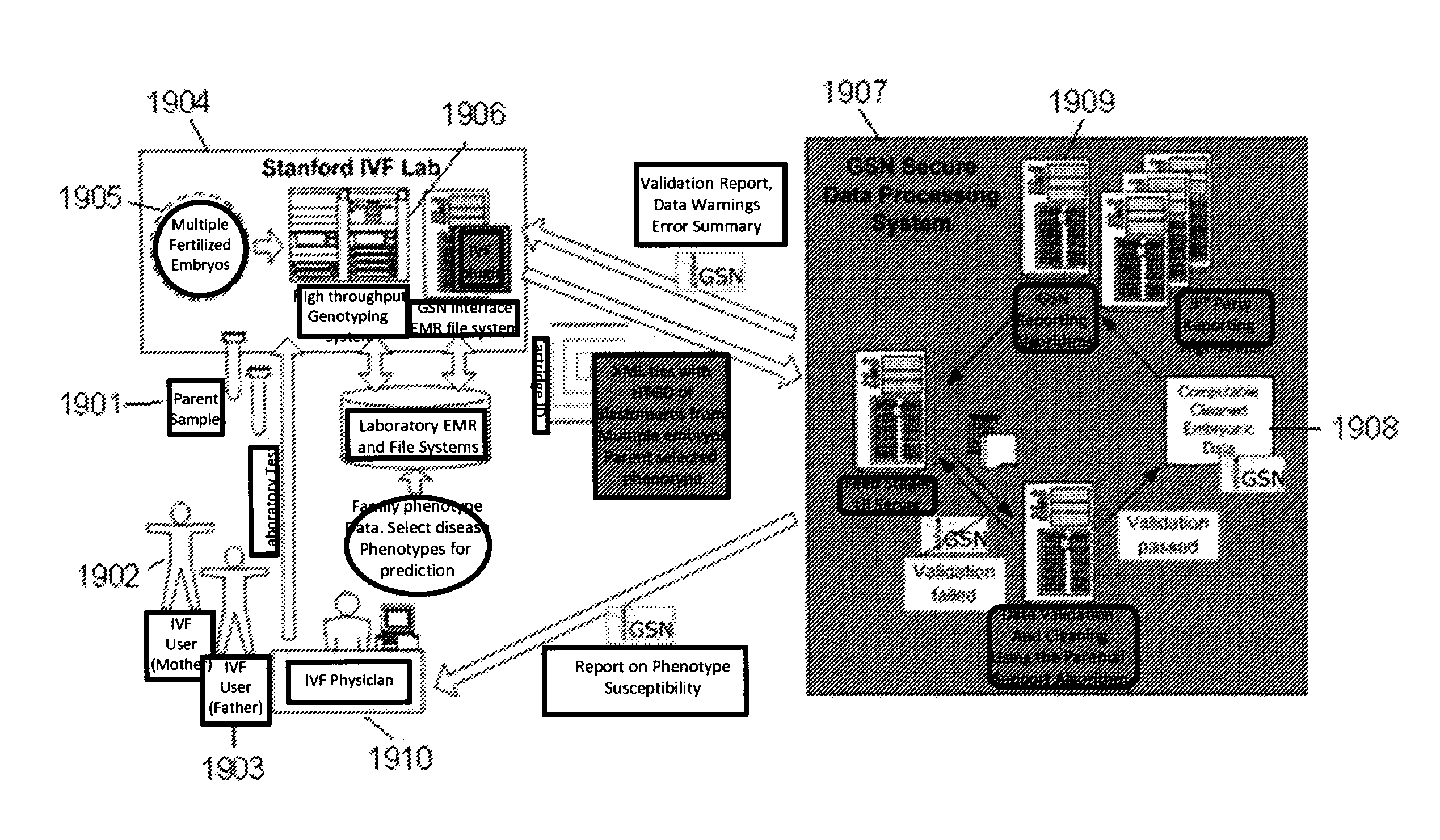
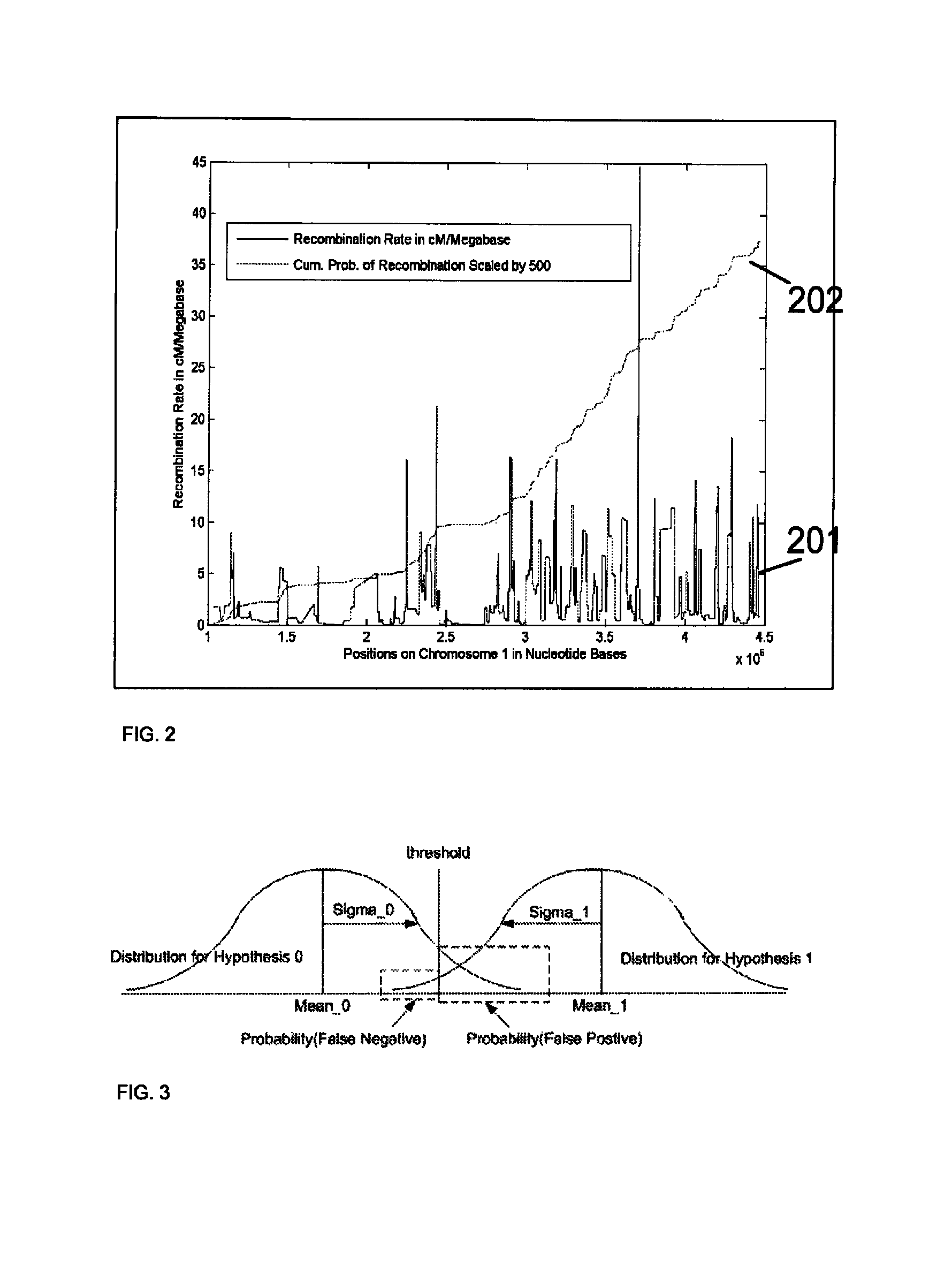
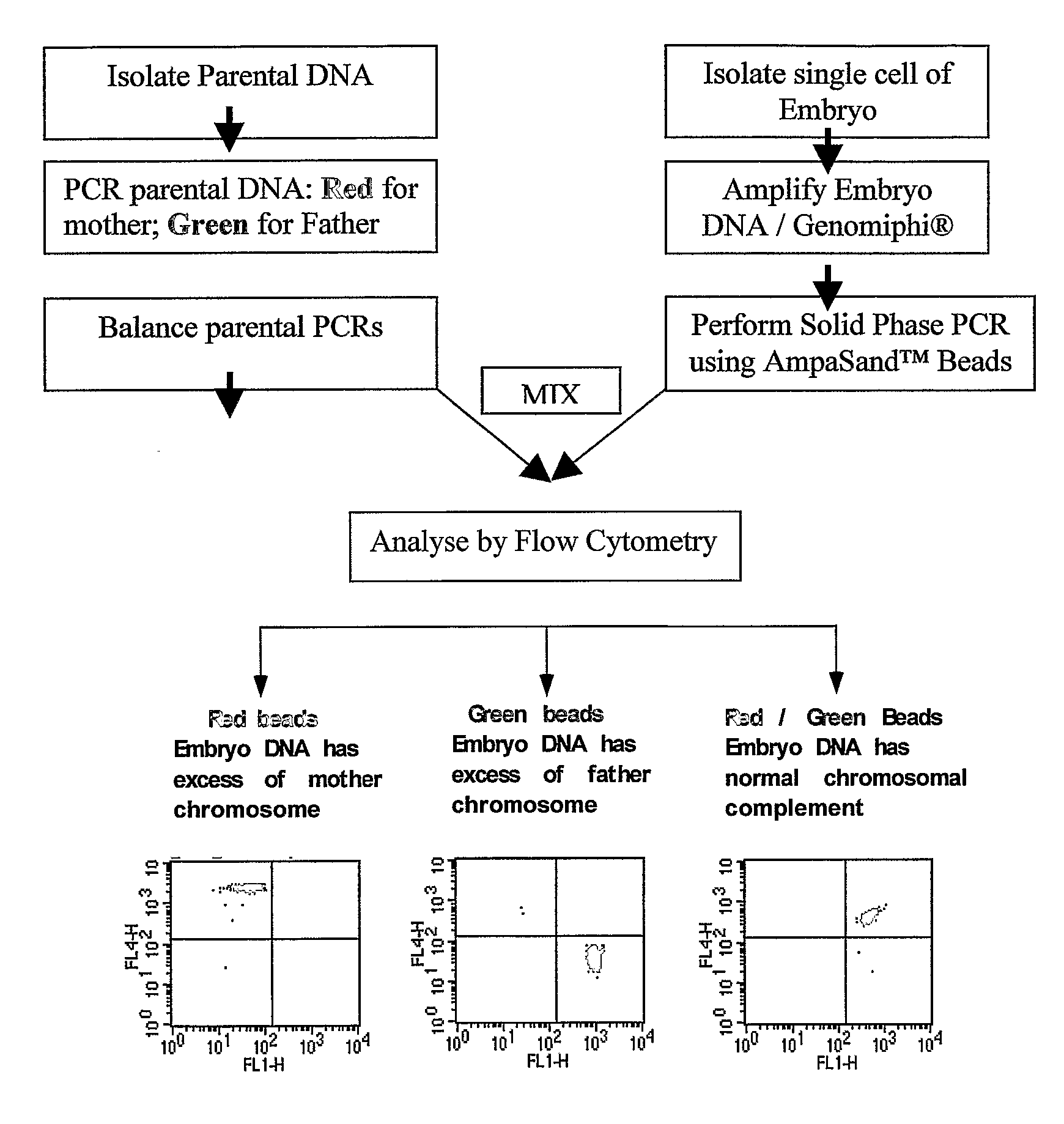
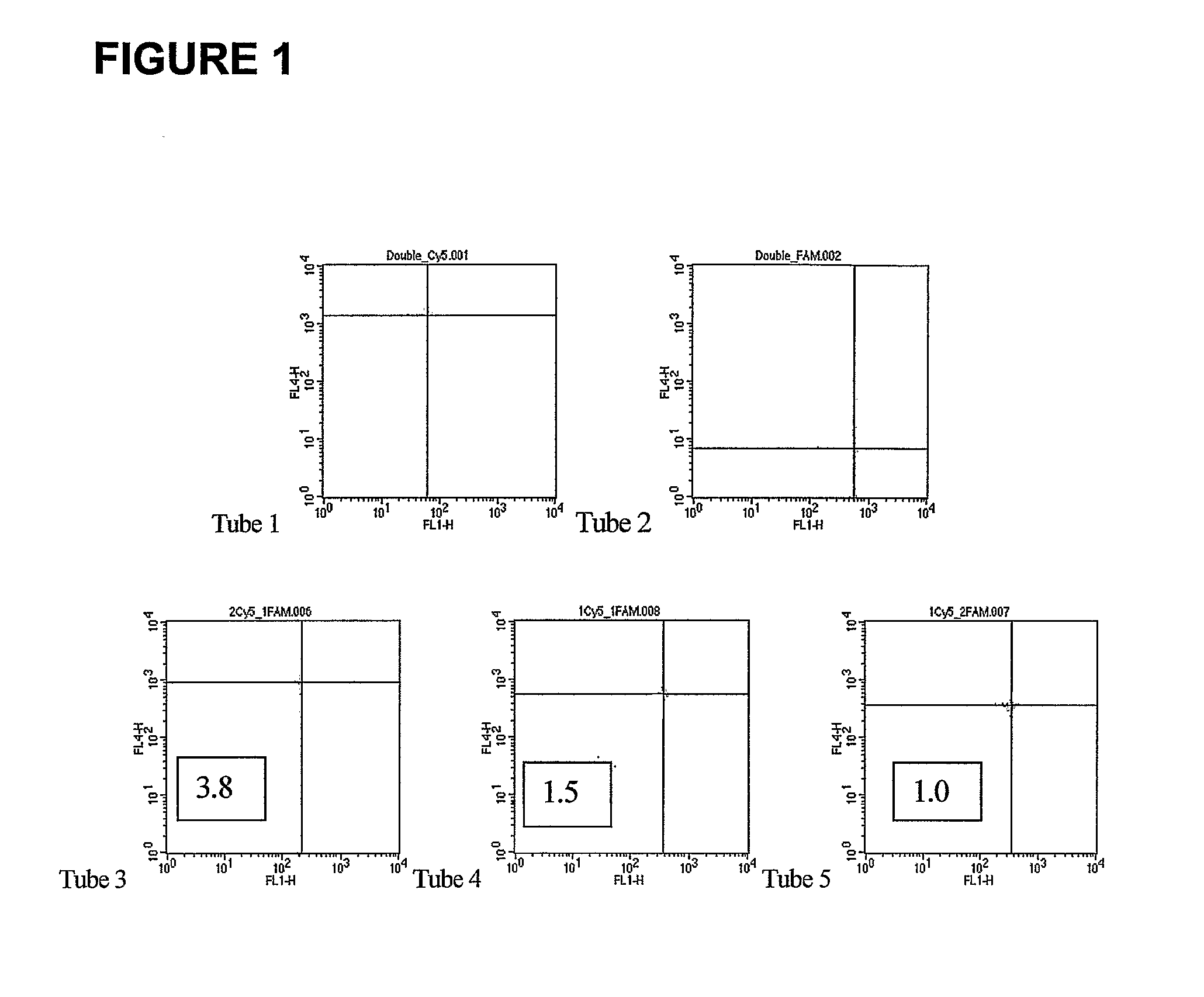
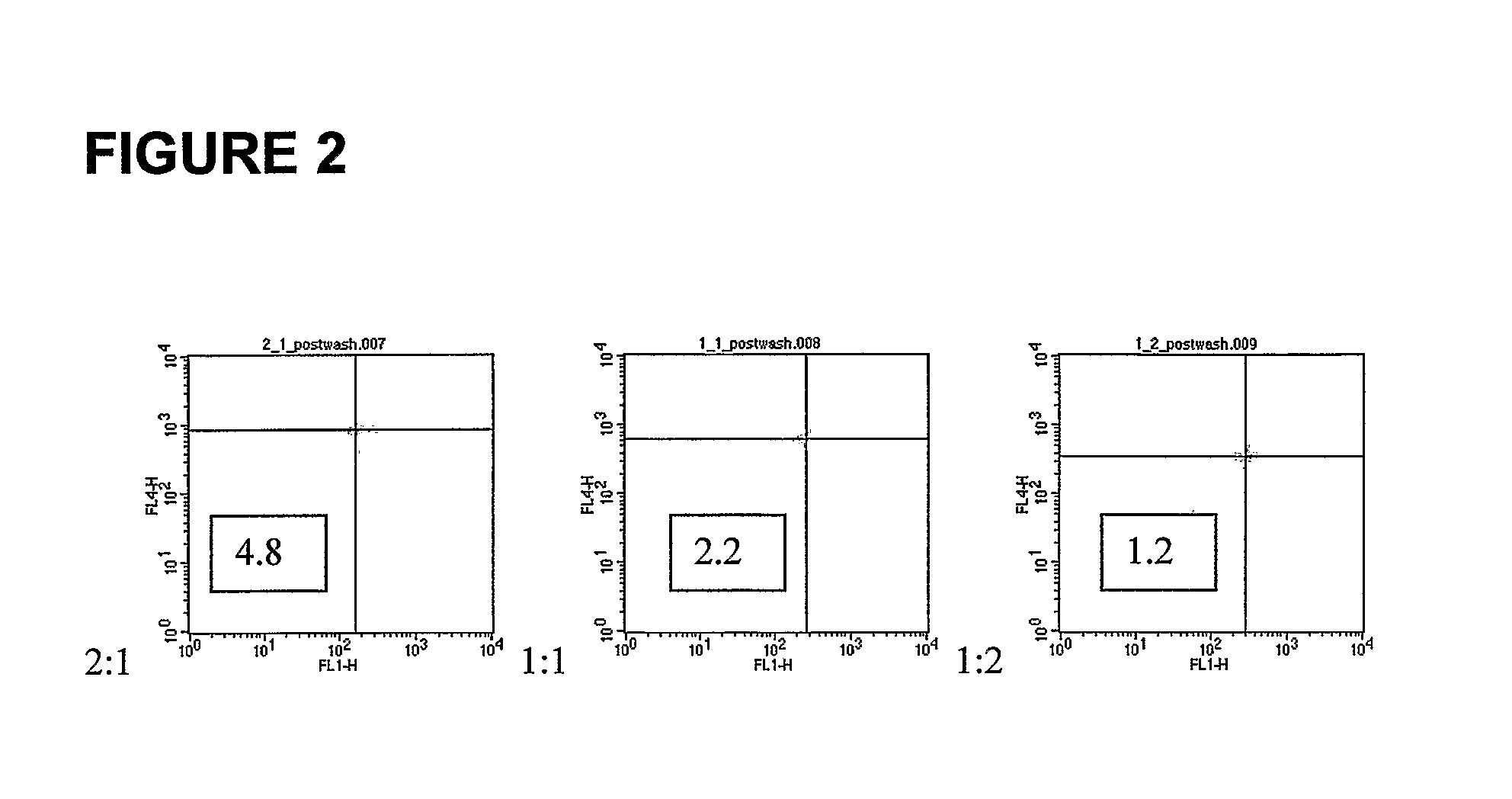
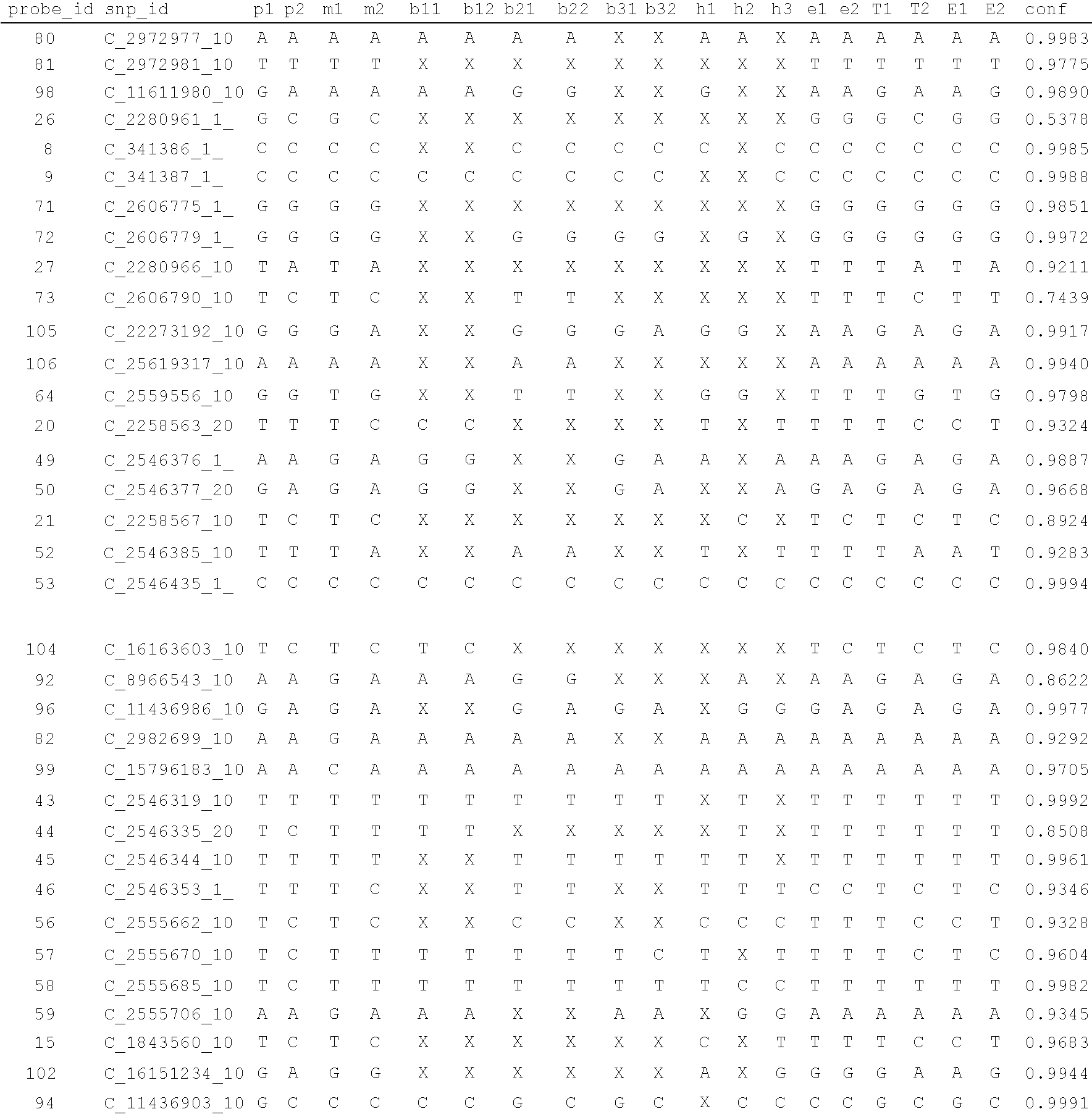
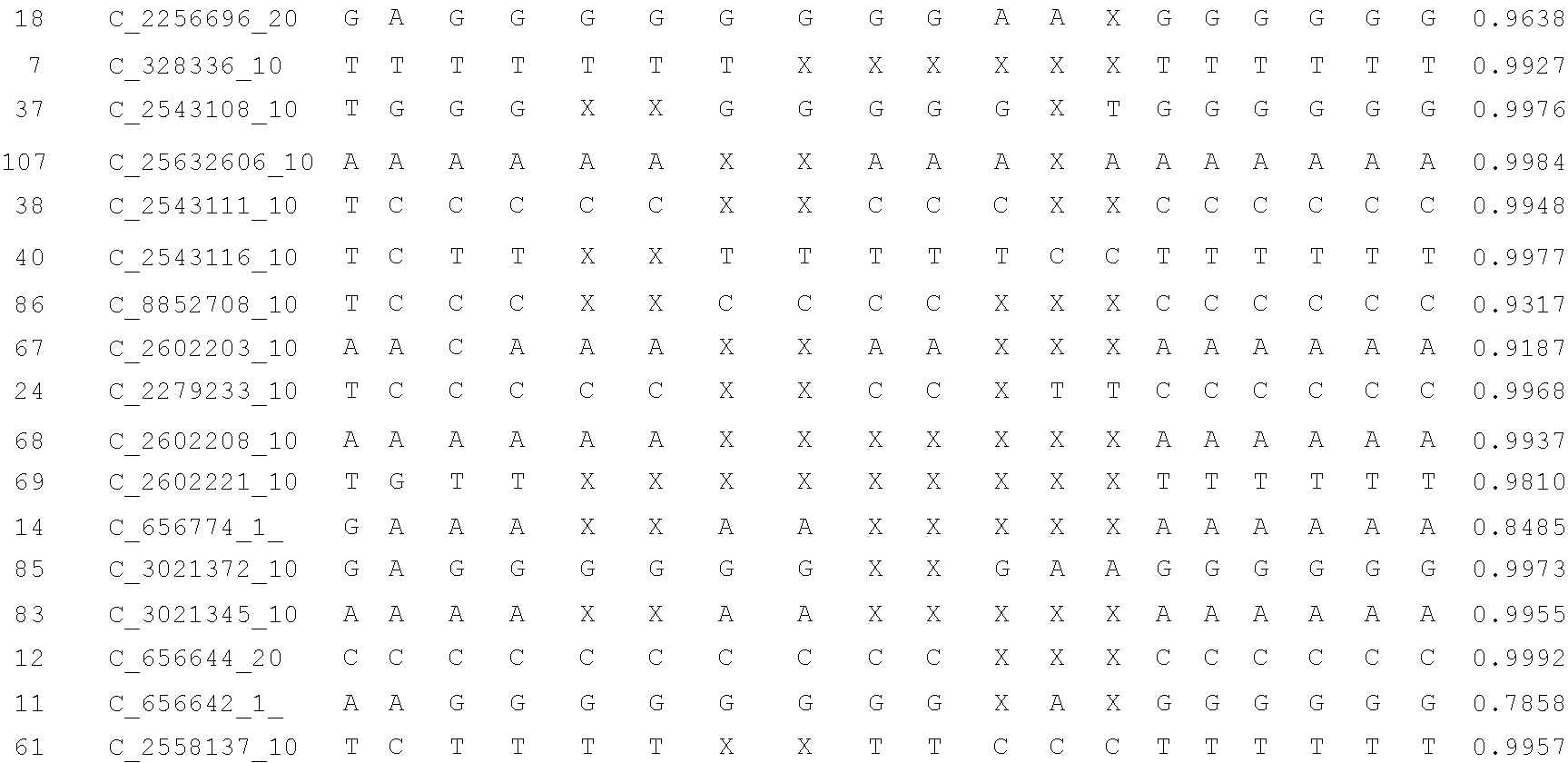
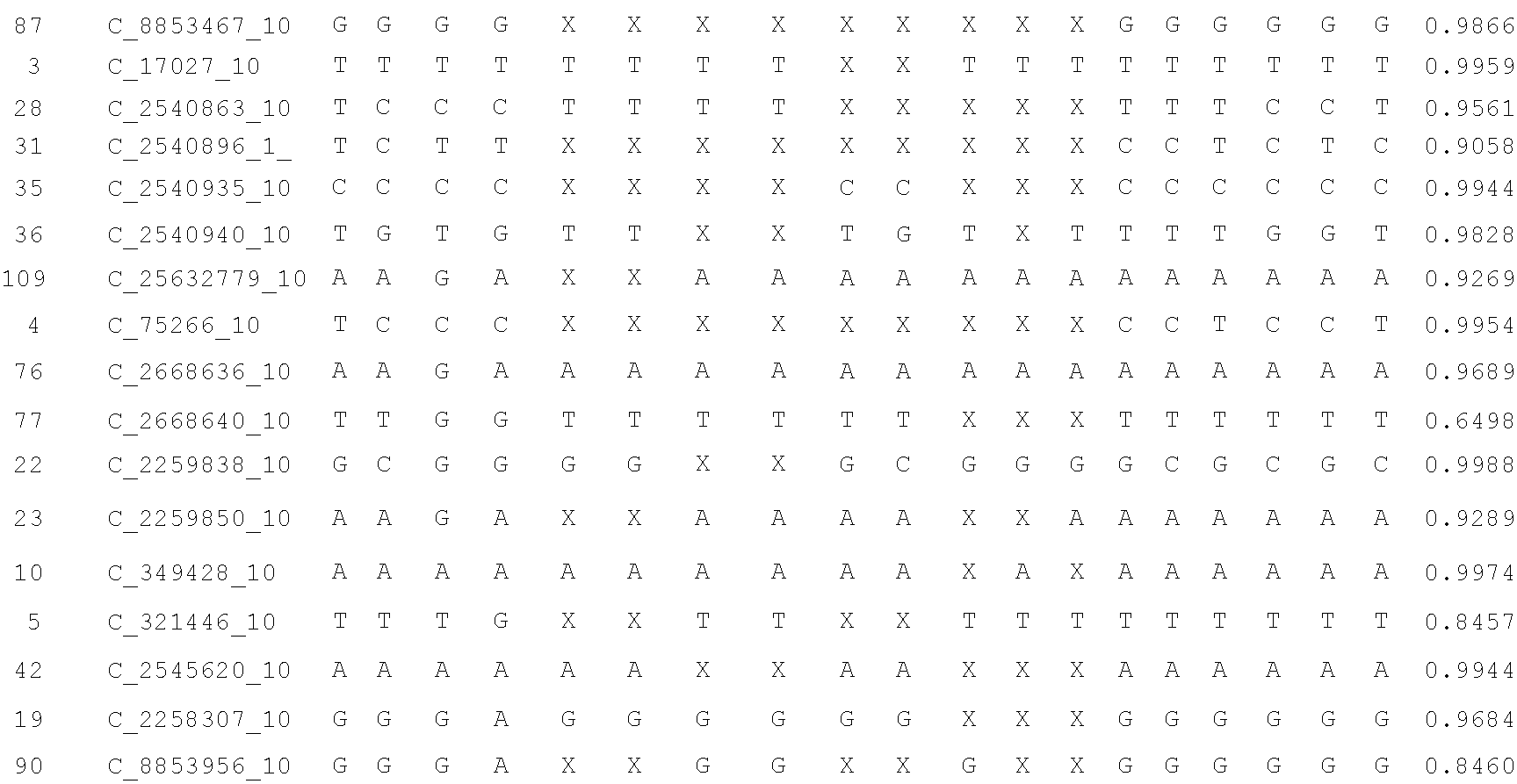
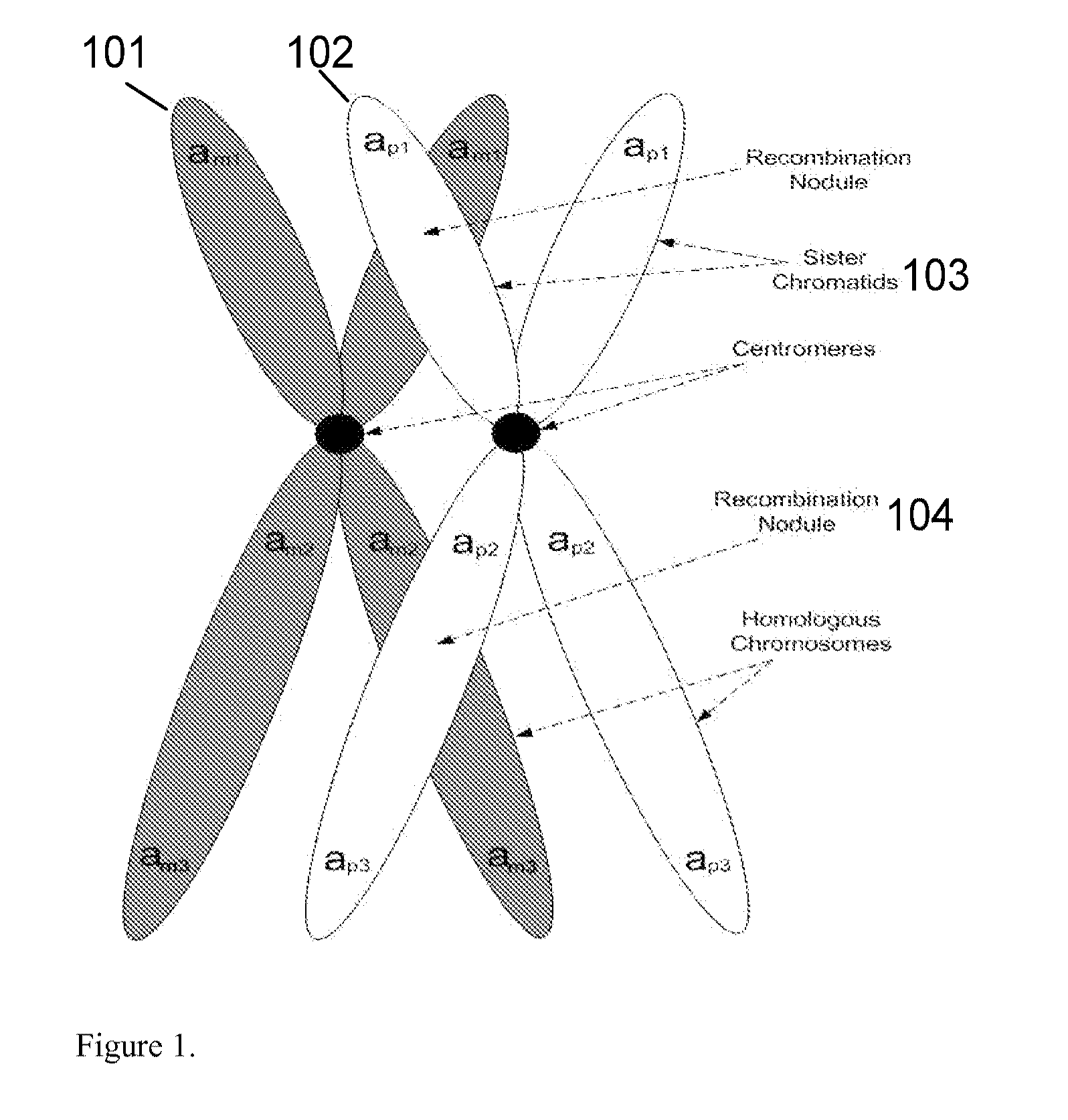
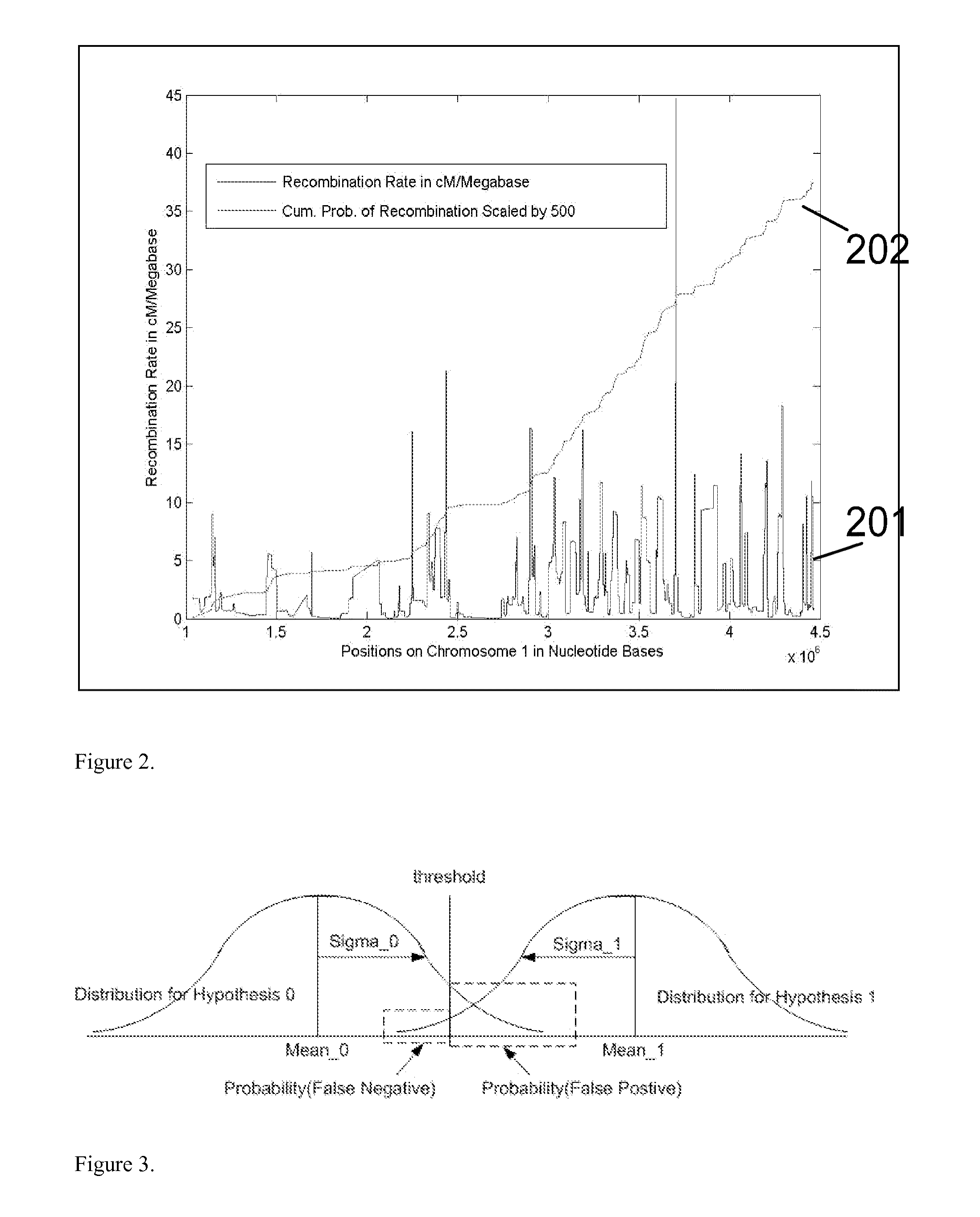
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20080243398A1Significant resultImprove fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsEmbryo
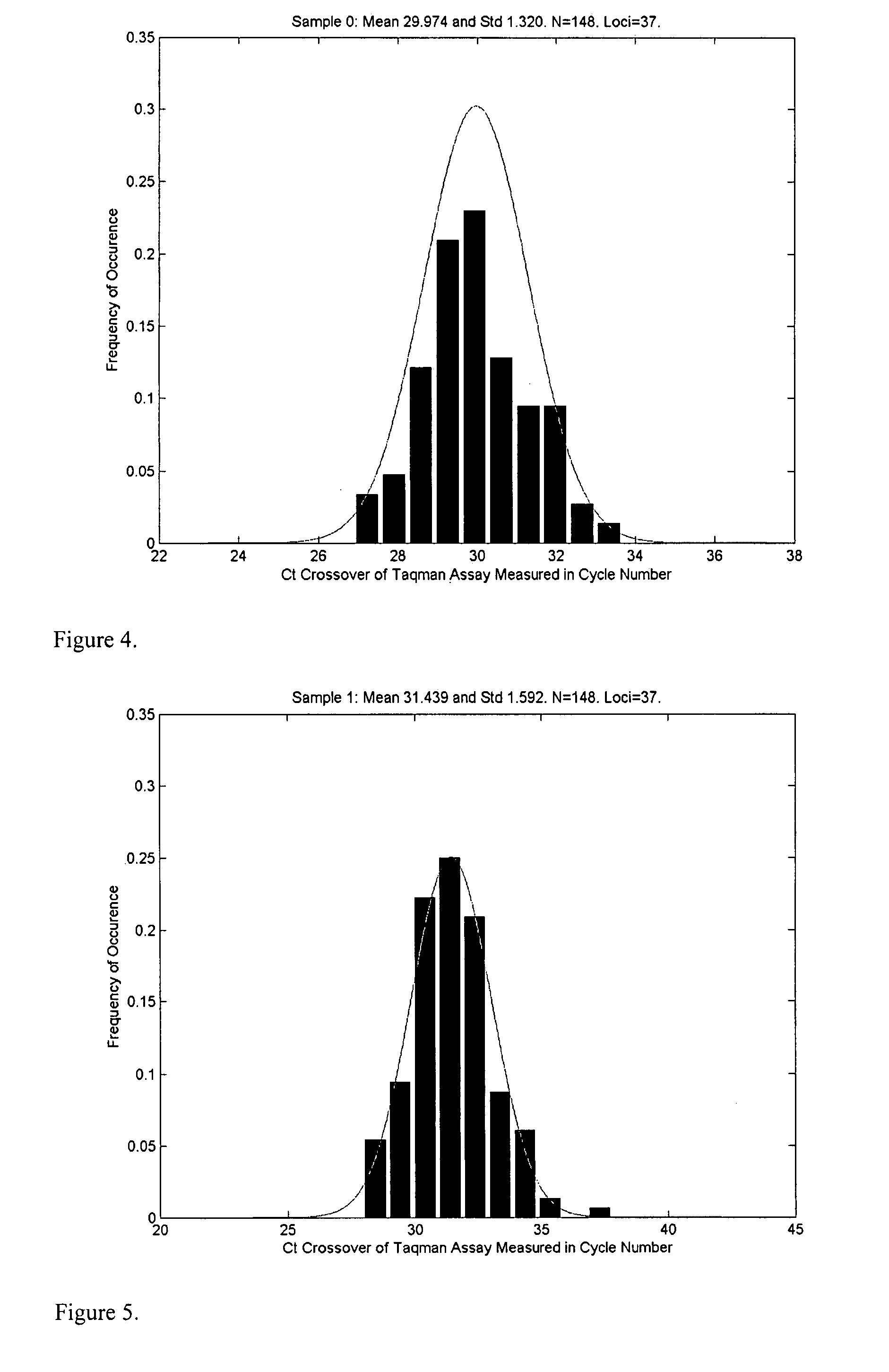
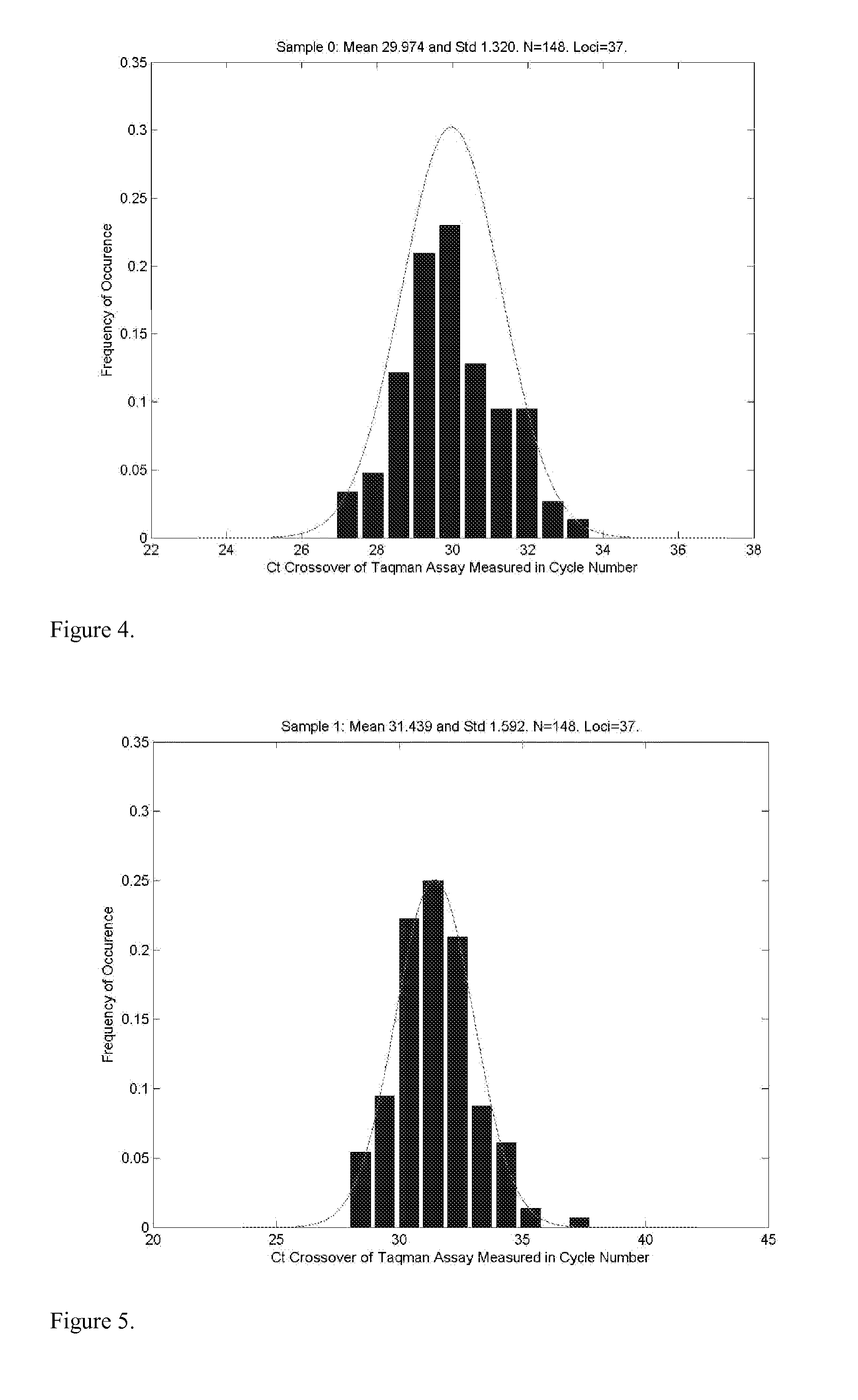
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic material from the target individual is acquired, amplified and the genetic data is measured using known methods. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data of a single or small number of cells, with or without genetic information from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, these determinations are made for the purpose of embryo selection in the context of in-vitro fertilization. In another embodiment of the invention, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions.
Owner:NATERA
Nuclear reprogramming factor
ActiveUS8048999B2Improve abilitiesPromote growthNervous disorderVirusesGene productNuclear reprogramming
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Multipotent adult stem cells and methods for isolation
ActiveUS20050181502A1Improve the level ofLong telomereGenetically modified cellsDiagnosticsTissues typesEmbryo
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY +1
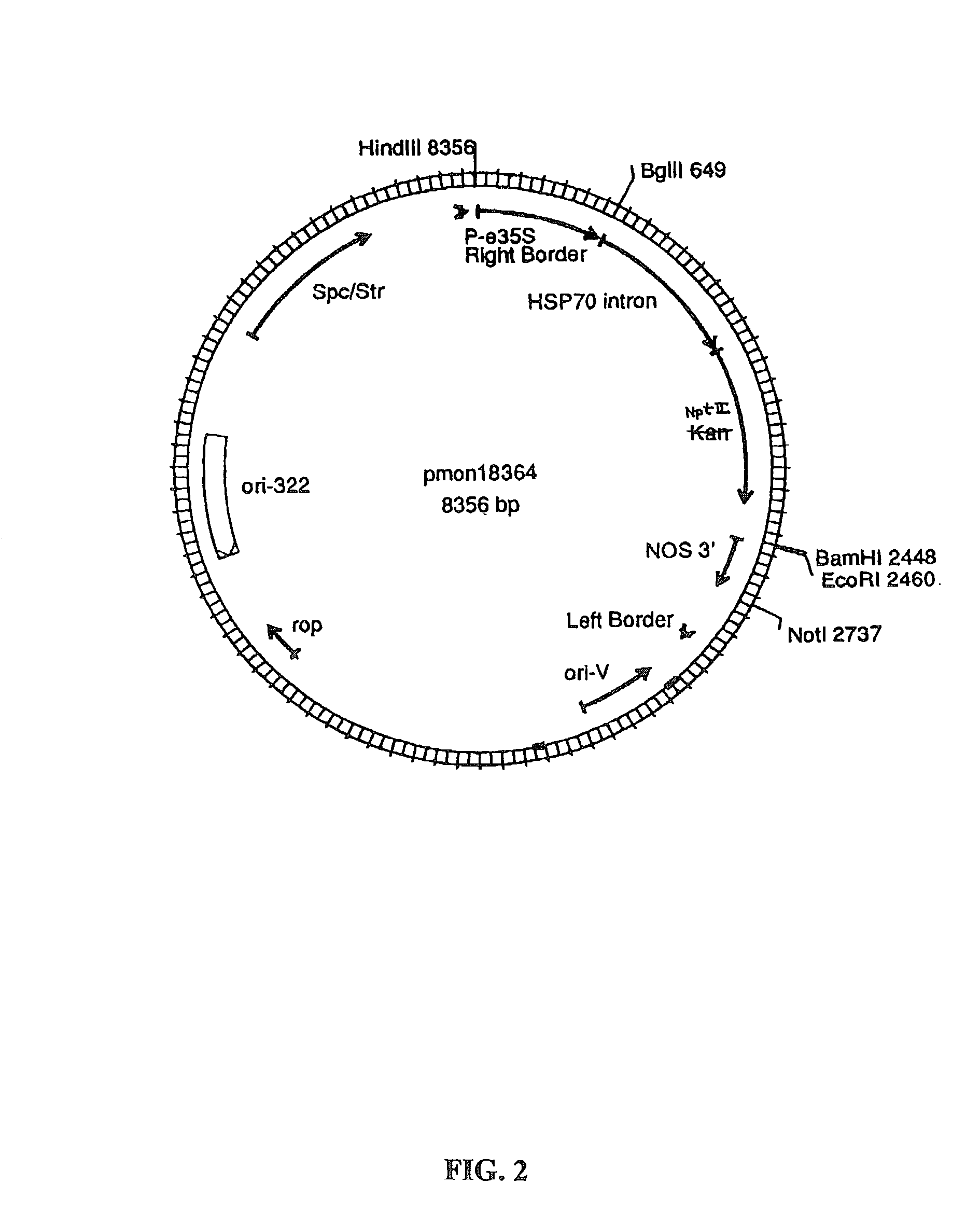
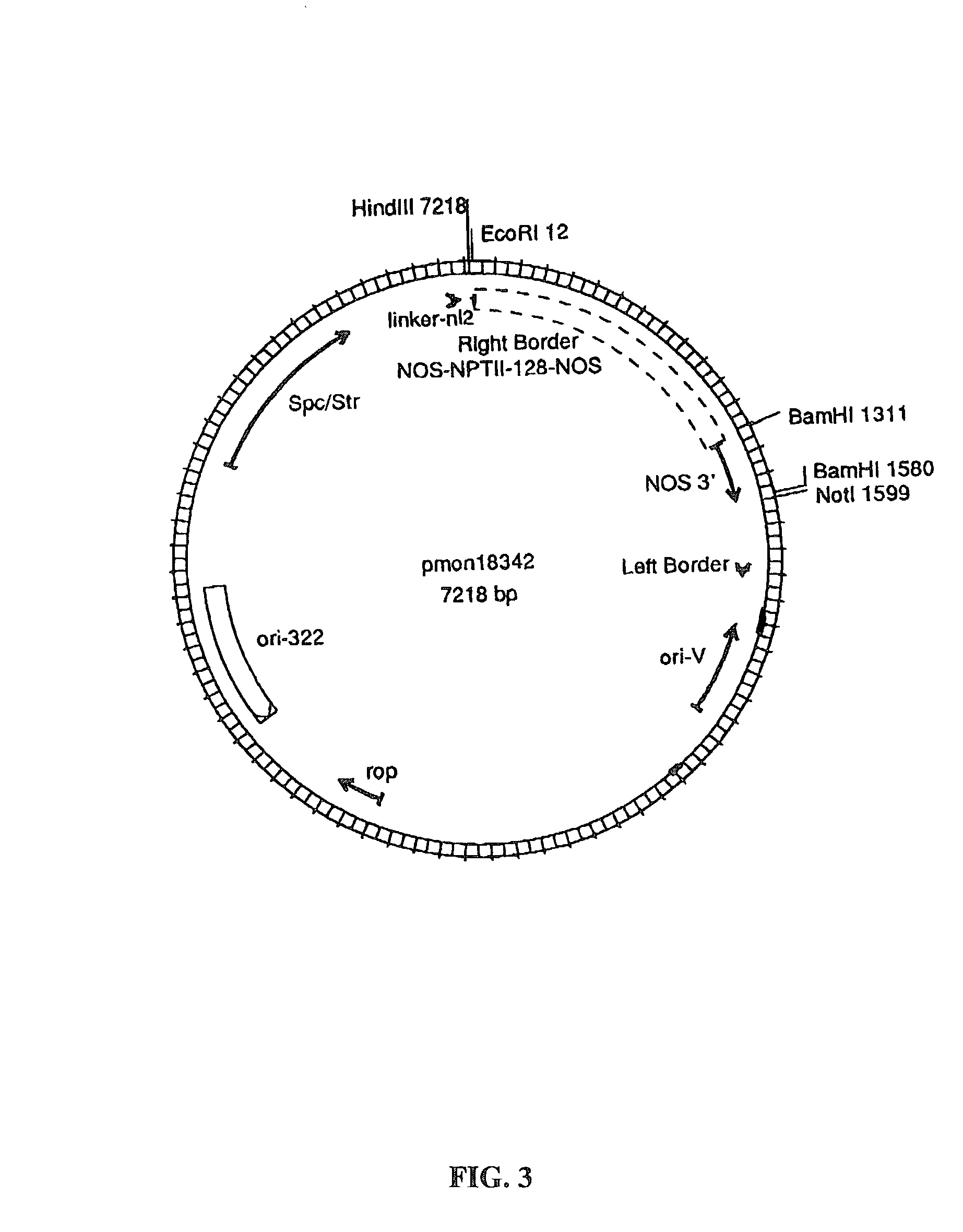
Methods for the production of stably-transformed, fertile wheat employing agrobacterium-mediated transformation and compositions derived therefrom
InactiveUS7026528B2Tissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologySomaclonal variation
Disclosed are processes for producing stably transformed fertile wheat a system of transforming wheat via Agrobacterium. This invention provides methods transforming a variety of explants, such as freshly isolated or pre-cultured immature embryos, embryogenic callus and suspension cells. Also disclosed are methods for recovering transgenic plants after transformation within a short period of time, if the explants are regenerable at the time of transformation. Thus the frequency of somaclonal variation associated with prolonged in vitro culture period is significantly reduced. The transformation frequency using this system is comparable to or better than published methods using other systems, such as microprojectile bombardment.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for constructing gene site-directed mutation
ActiveCN103388006AEfficient constructionRaise the ratioVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMulti siteEmbryo
Owner:BIORAY LABORATORIES INC
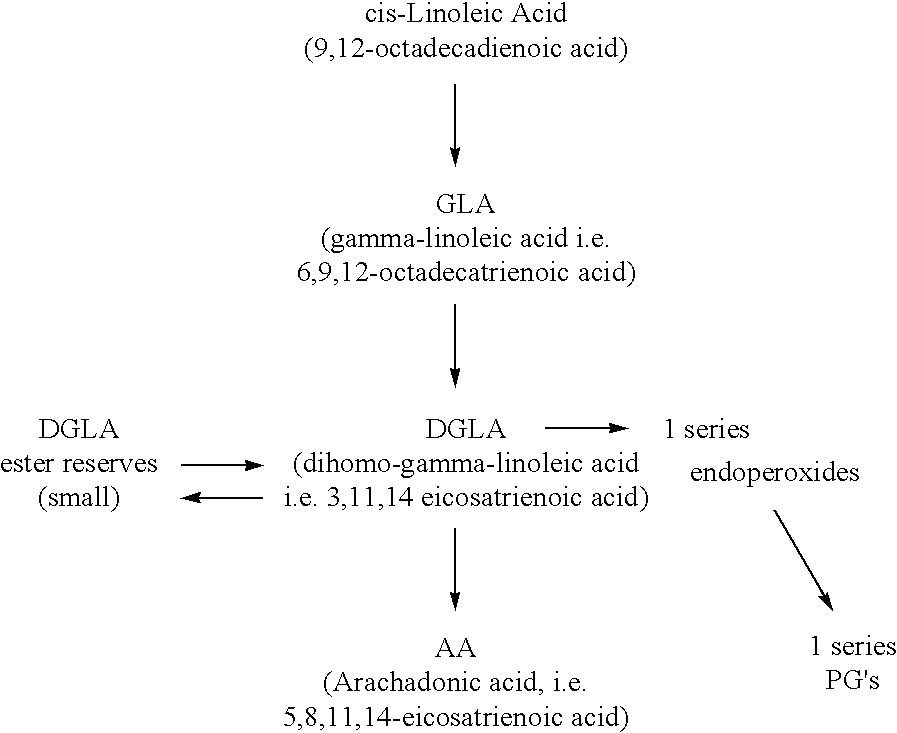
Nutritional supplements
The present disclosure relates to novel nutritional methods and compositions containing essential fatty acids which optimize embryonic, fetal and child neurological development and provide improved nutritional support for women prior to and during lactation. Further the methods and compositions improve gestational length and birth weight. The nutritional methods and compositions are also intended for use by women to optimize infant neurological development and provide improved nutritional support for women prior to, during and after lactation.
Owner:AMAG PHARMA USA INC
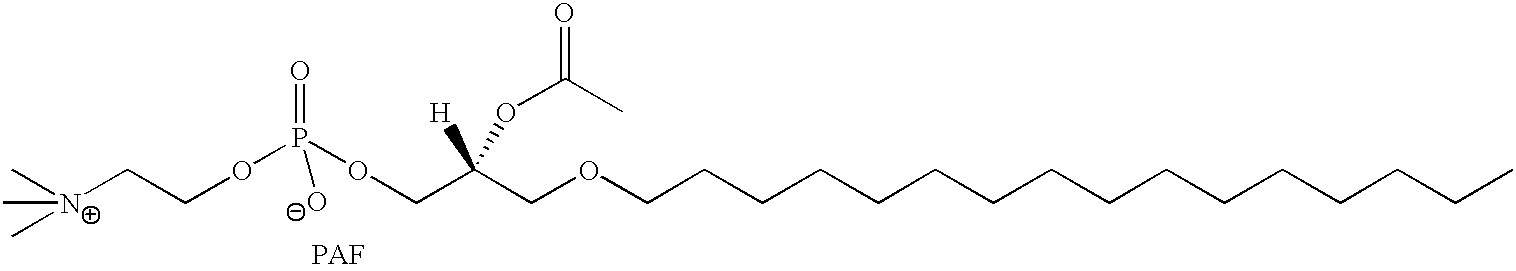
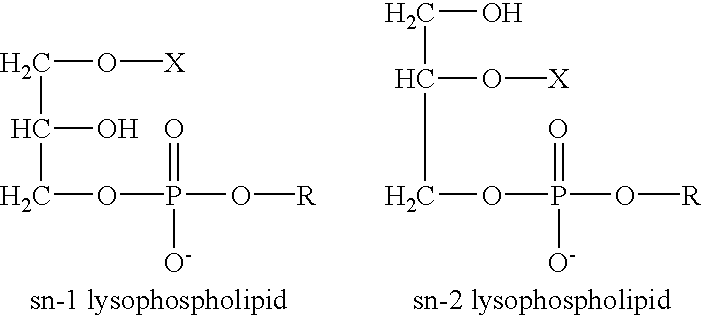
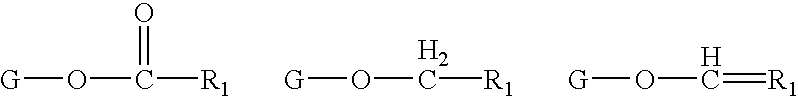
Determination of biological characteristics of embryos fertilized in vitro by assaying for bioactive lipids in culture media
InactiveUS6489135B1Increase the likelihood of successAffect viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiological propertyEmbryo
The present invention provides methods for determining various biological characteristics of in vitro fertilized embryos, including overall embryo health, implantability, and increased likelihood of developing successfully to term. More specifically, the present invention concerns analyzing media specimens of in vitro fertilization cultures for levels of bioactive lipids in order to determine these characteristics.
Owner:LPL TECH
Methods for the culture of human embryonic stem cells on human feeder cells
InactiveUS7432104B2Artificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsBone Marrow Stromal CellCell culture media
Methods and cell culture medium for the generation of human pluripotent embryonic stem cells are disclosed. Human embryonic stem cells are cultured with human granulosa feeder cells, muscle cells, Fallopian ductal epithelial cells, bone marrow stromal cells, and skin fibroblasts and the embryonic stem cells maintain their pluripotent phenotype. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be cultured without feeder cells, and in the presence of supplemental growth factors. The human pluripotent embryonic stem cells can be alternatively cultured with conditioned medium obtained from a cell culture capable of maintaining human embryonic stem cells in a pluripotent state, wherein the cell culture is a human granulosa cell culture.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
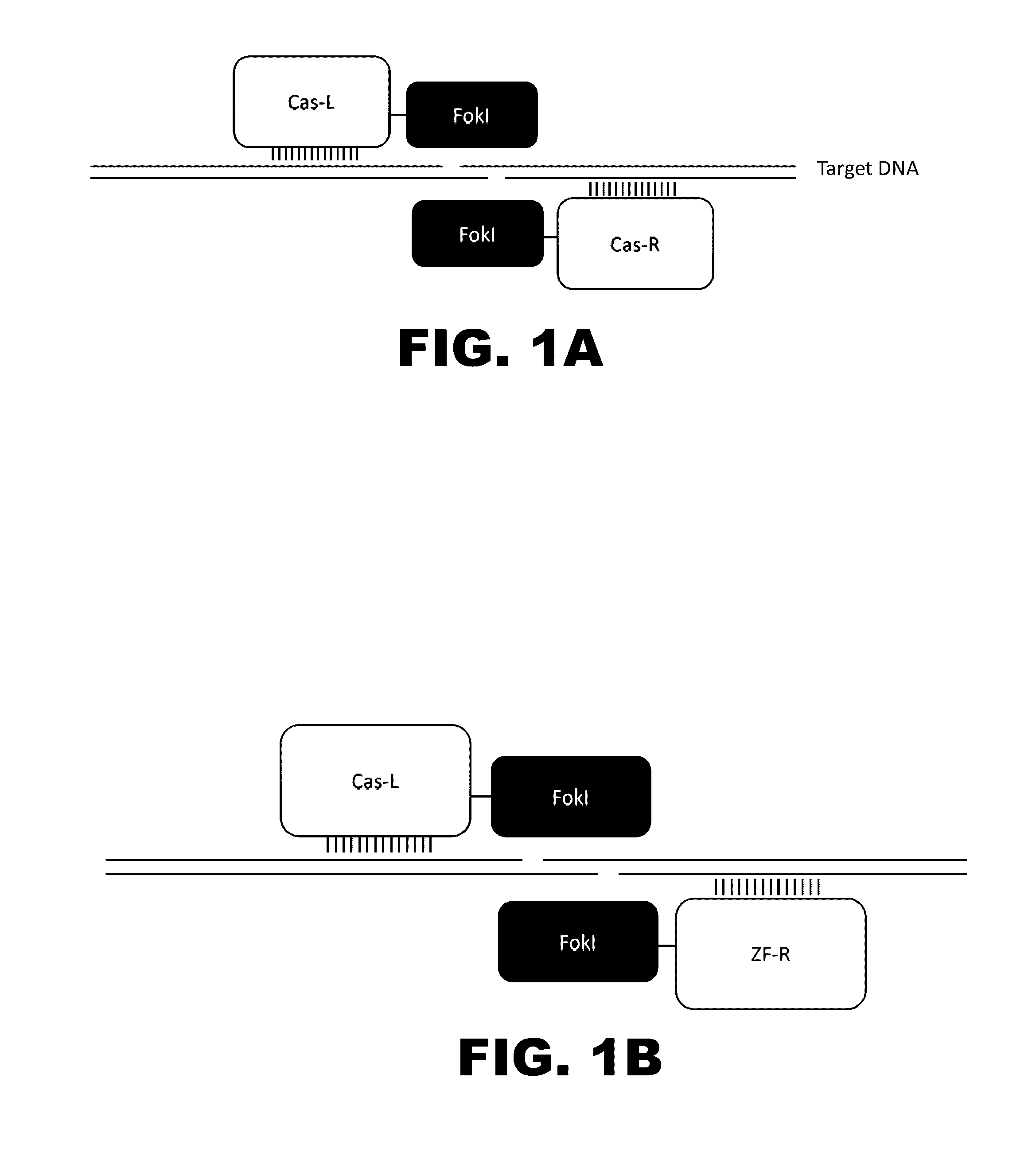
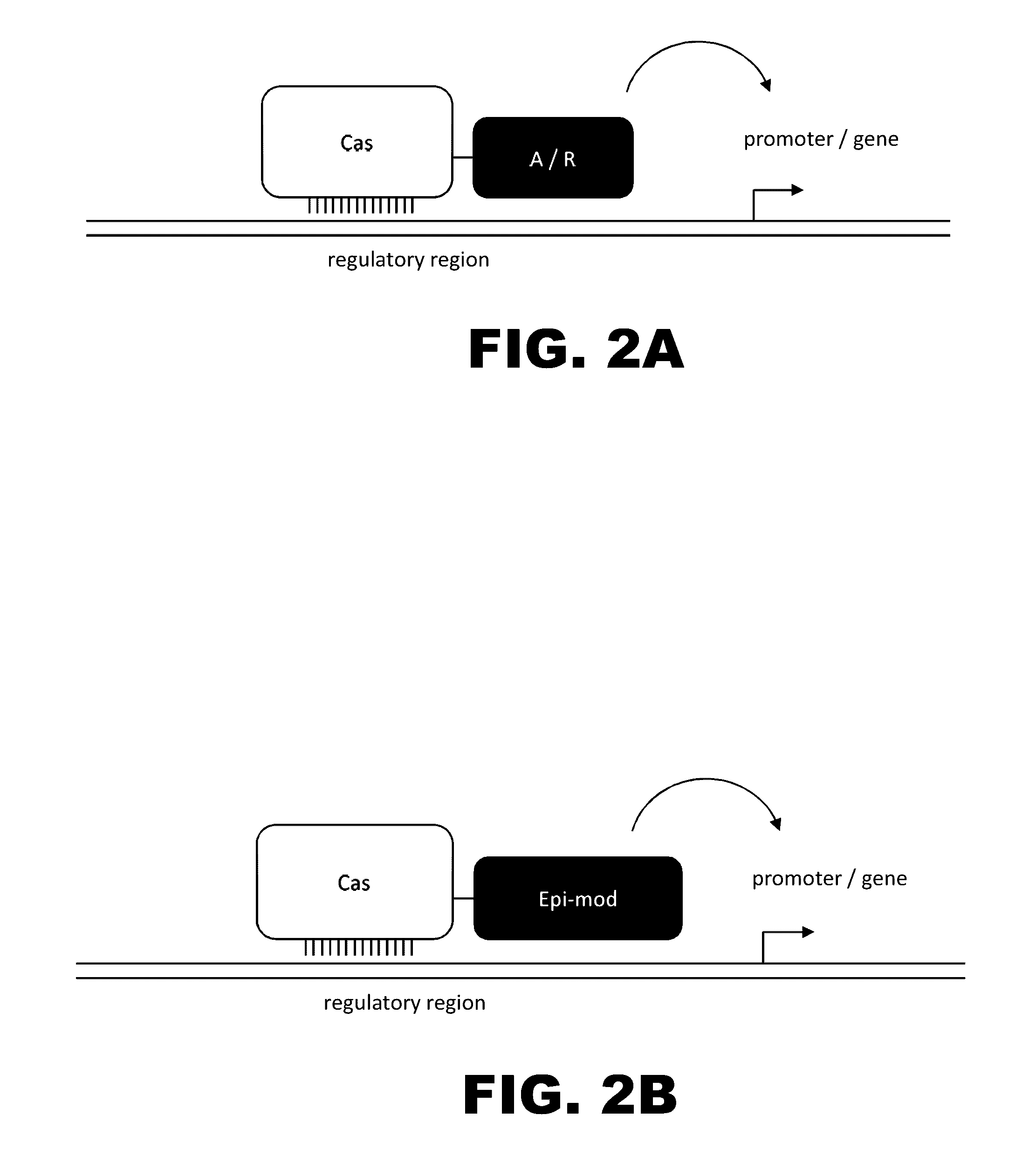
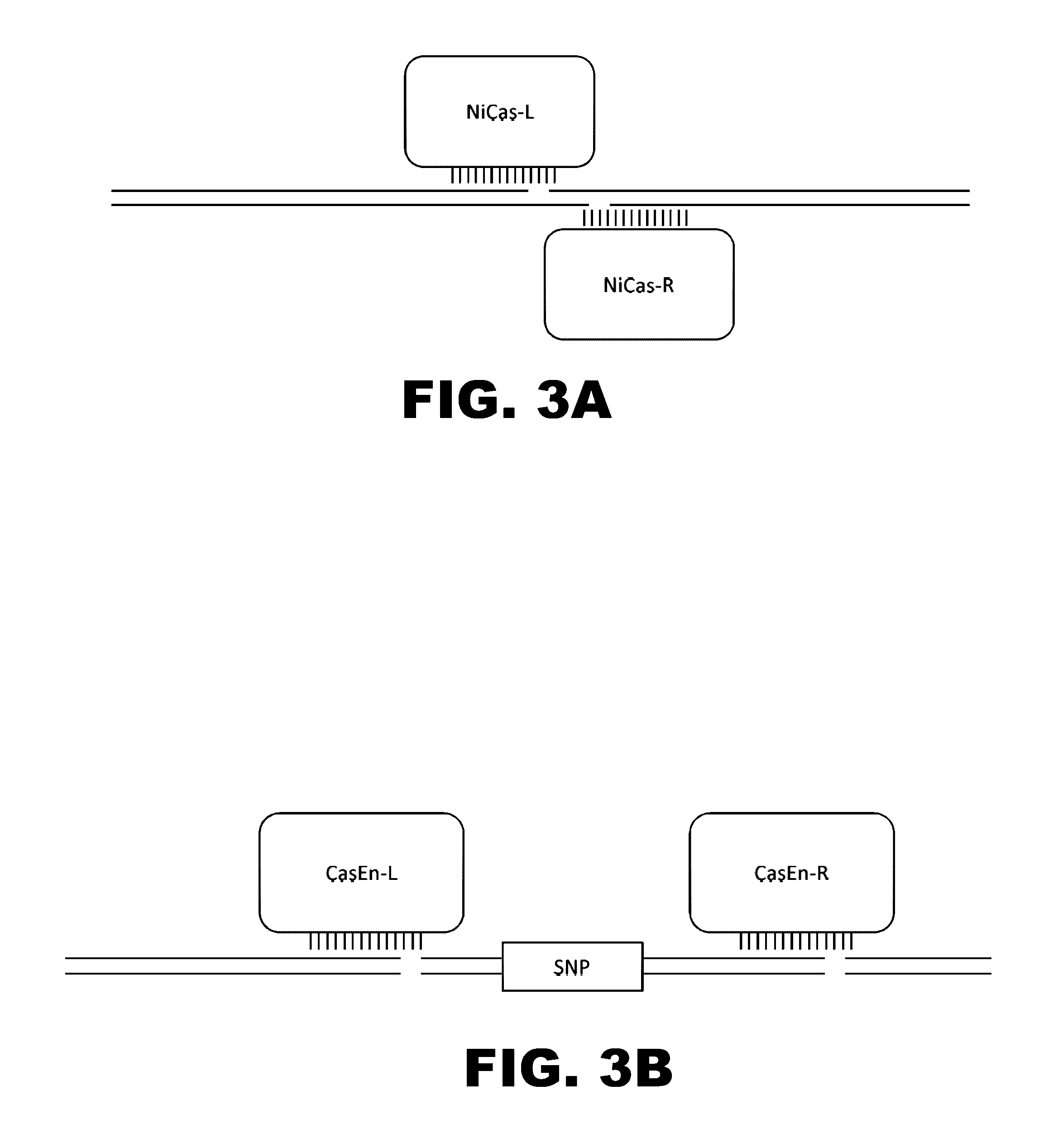
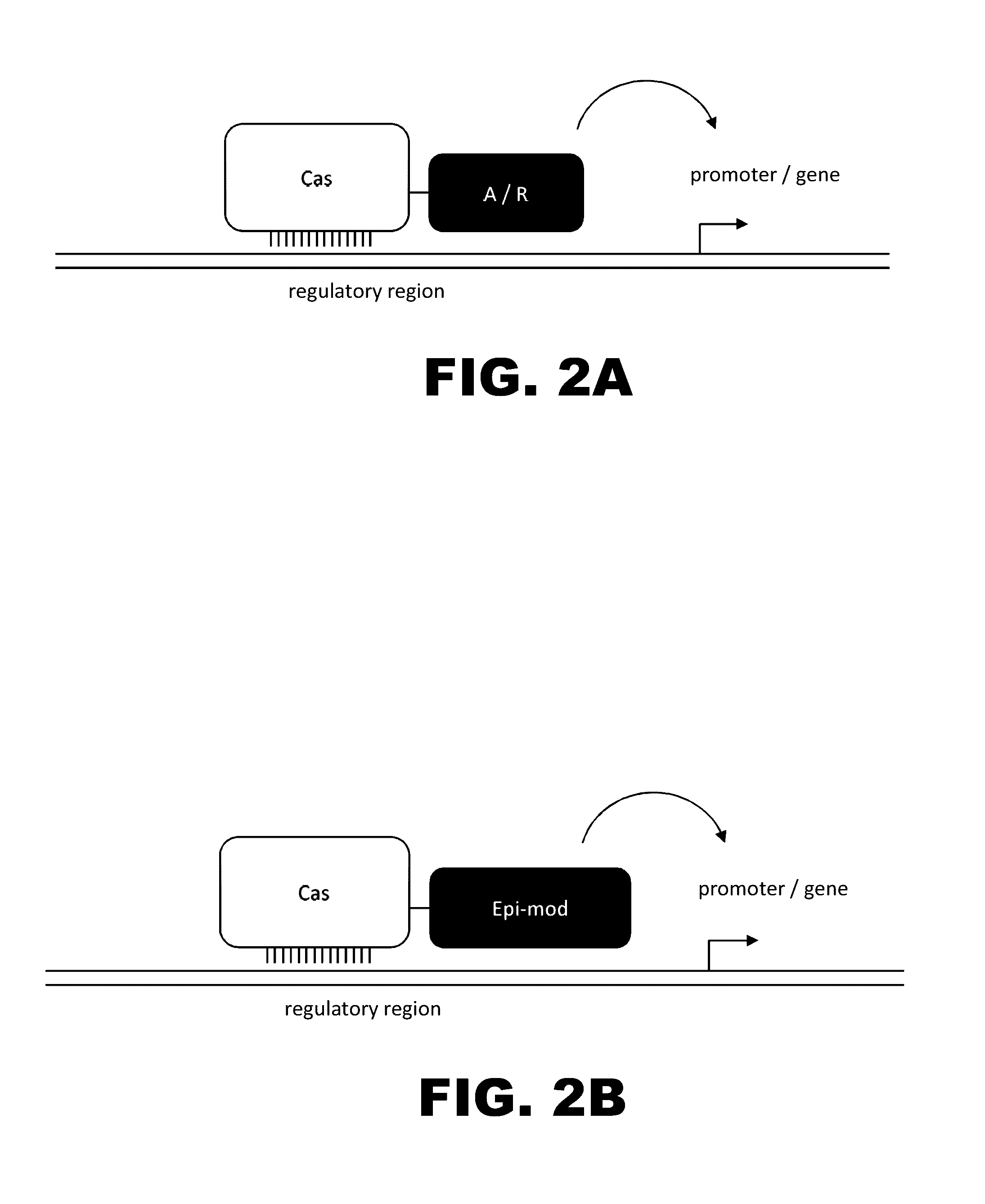
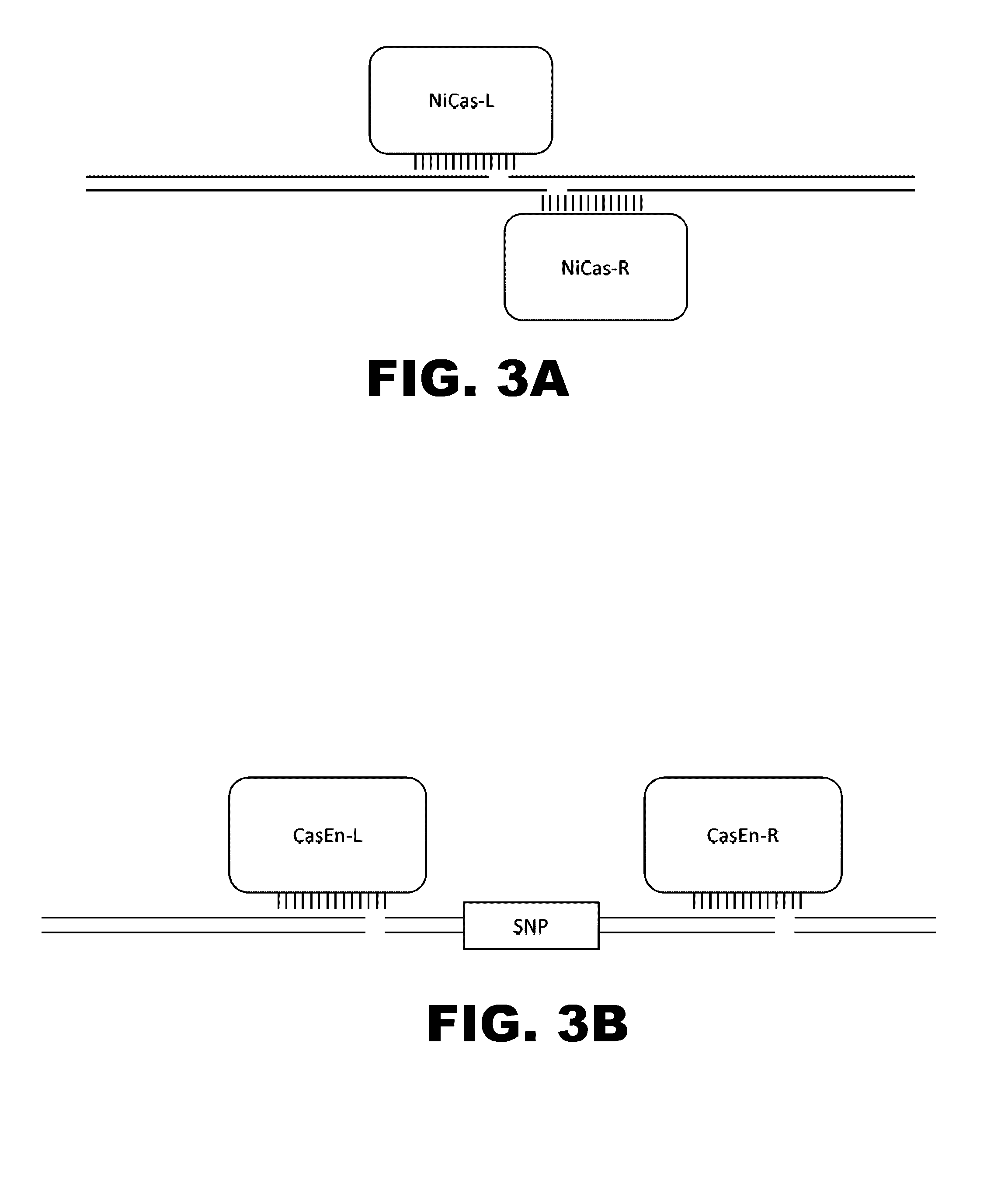
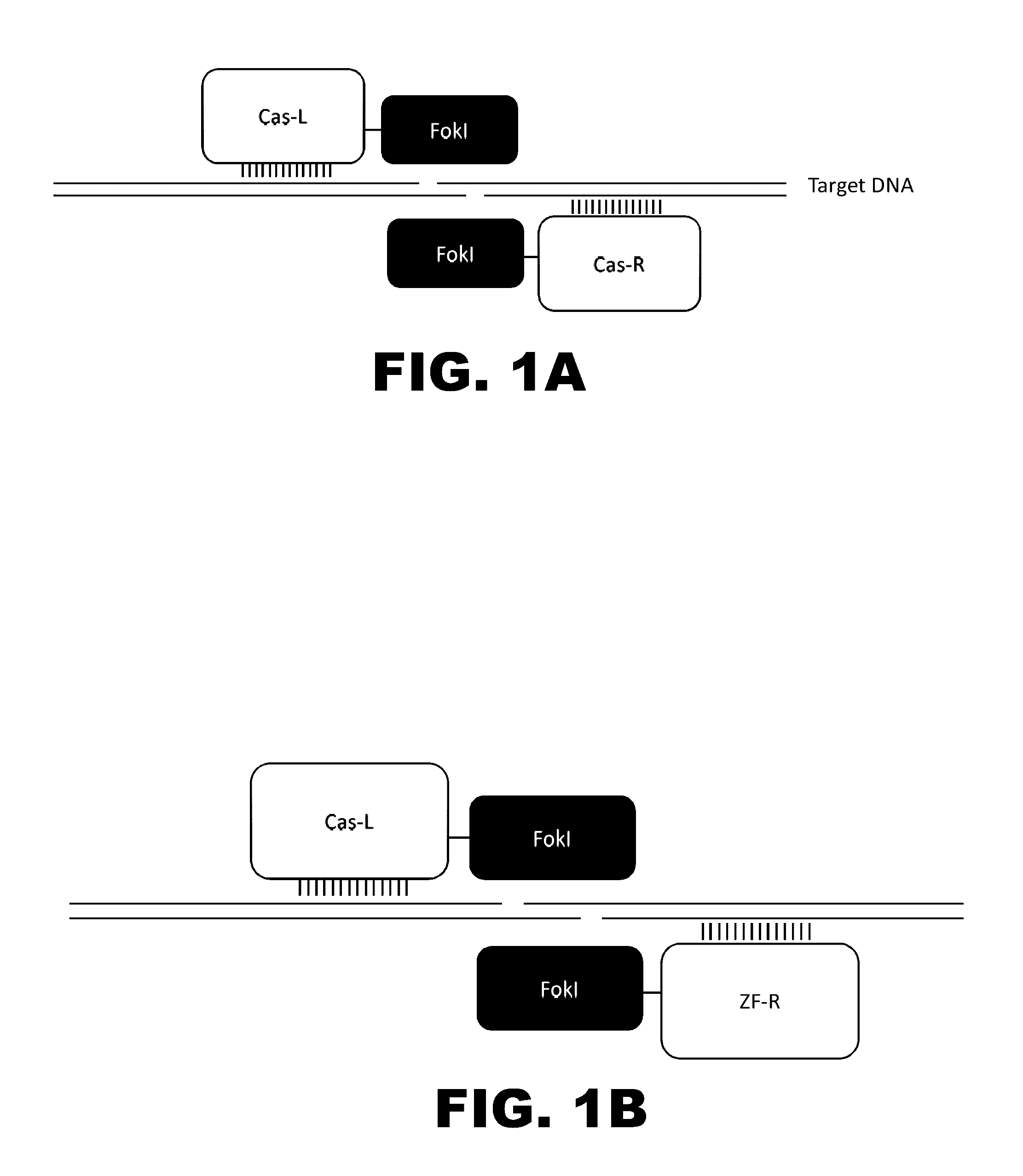
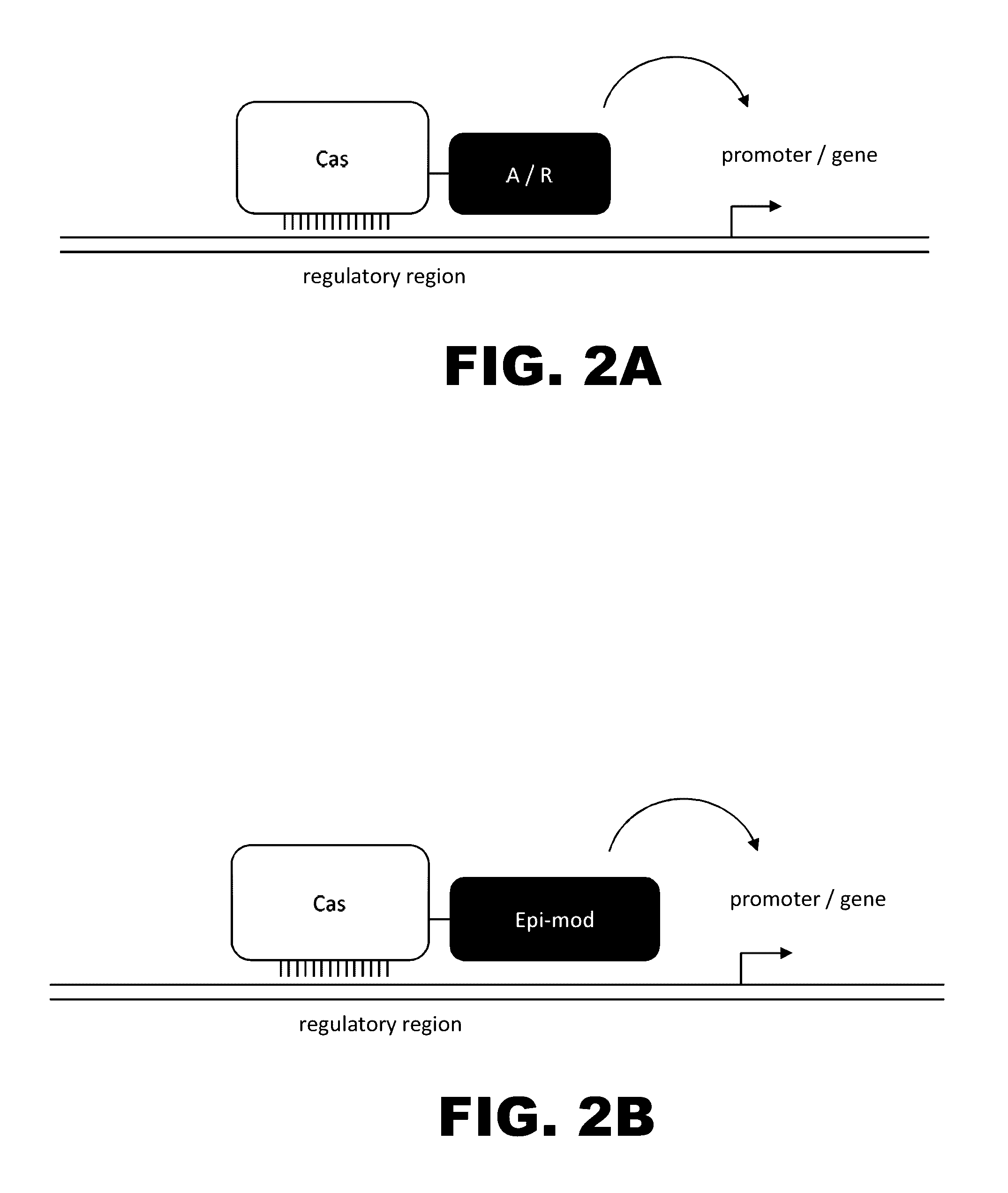
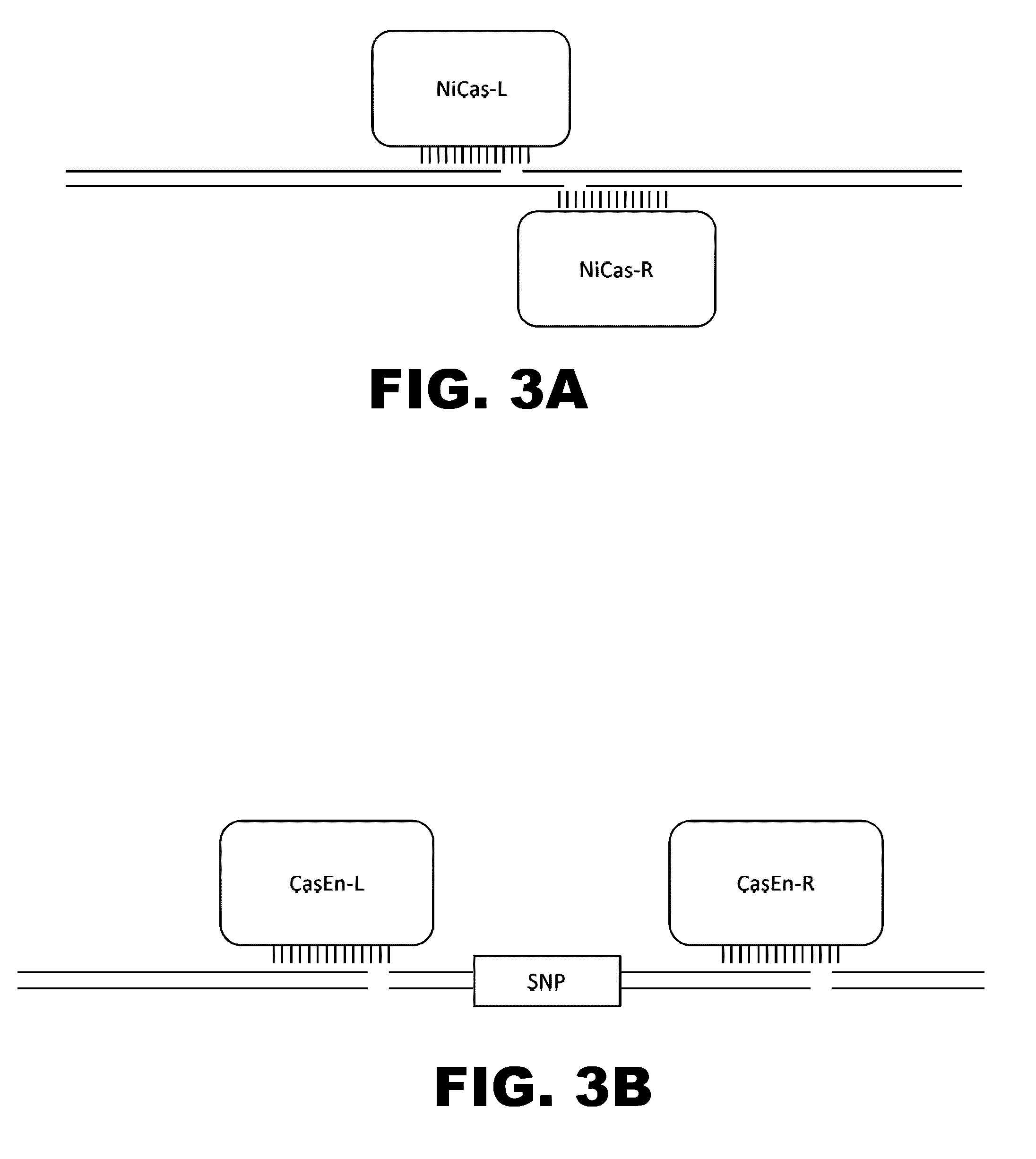
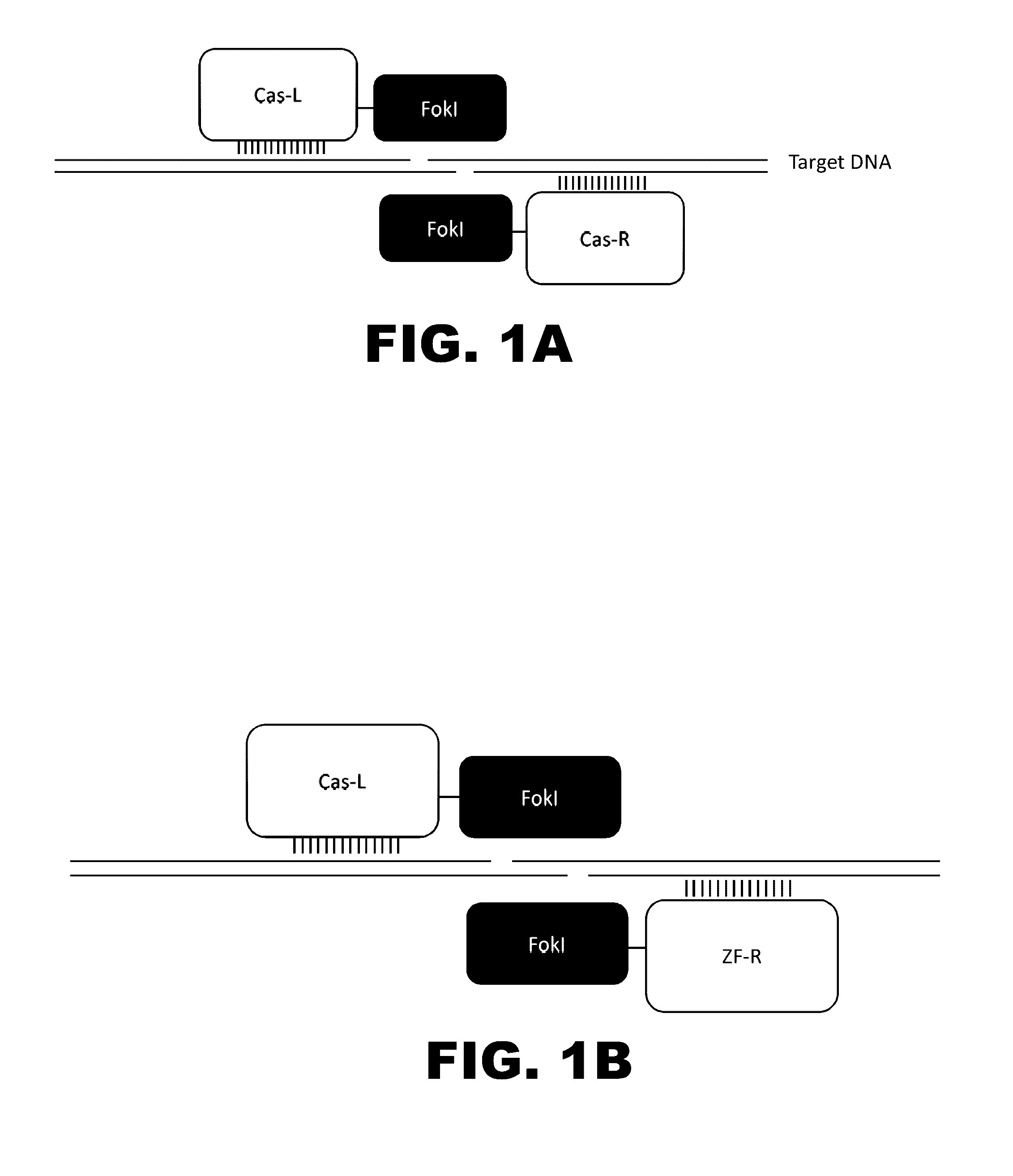
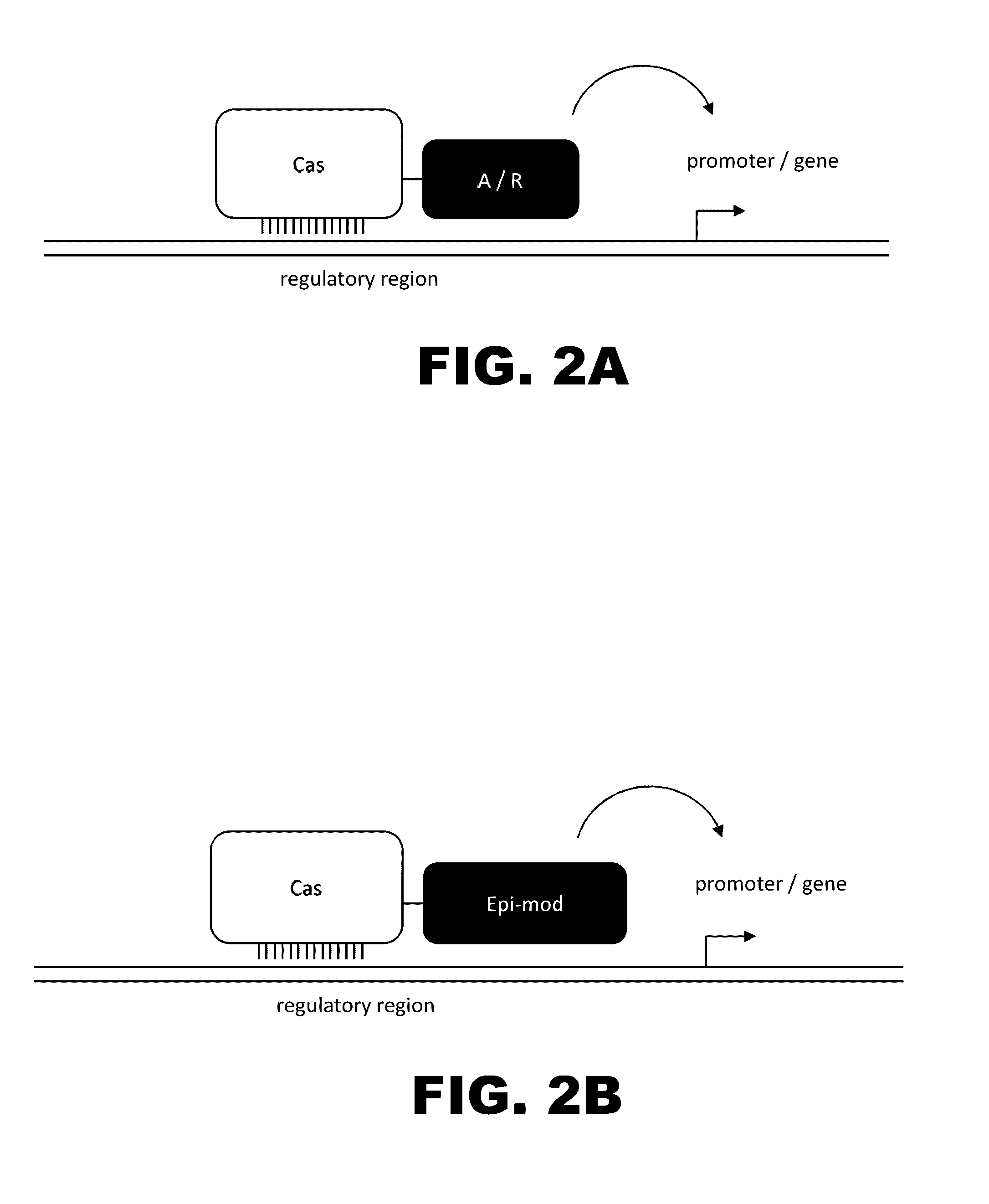
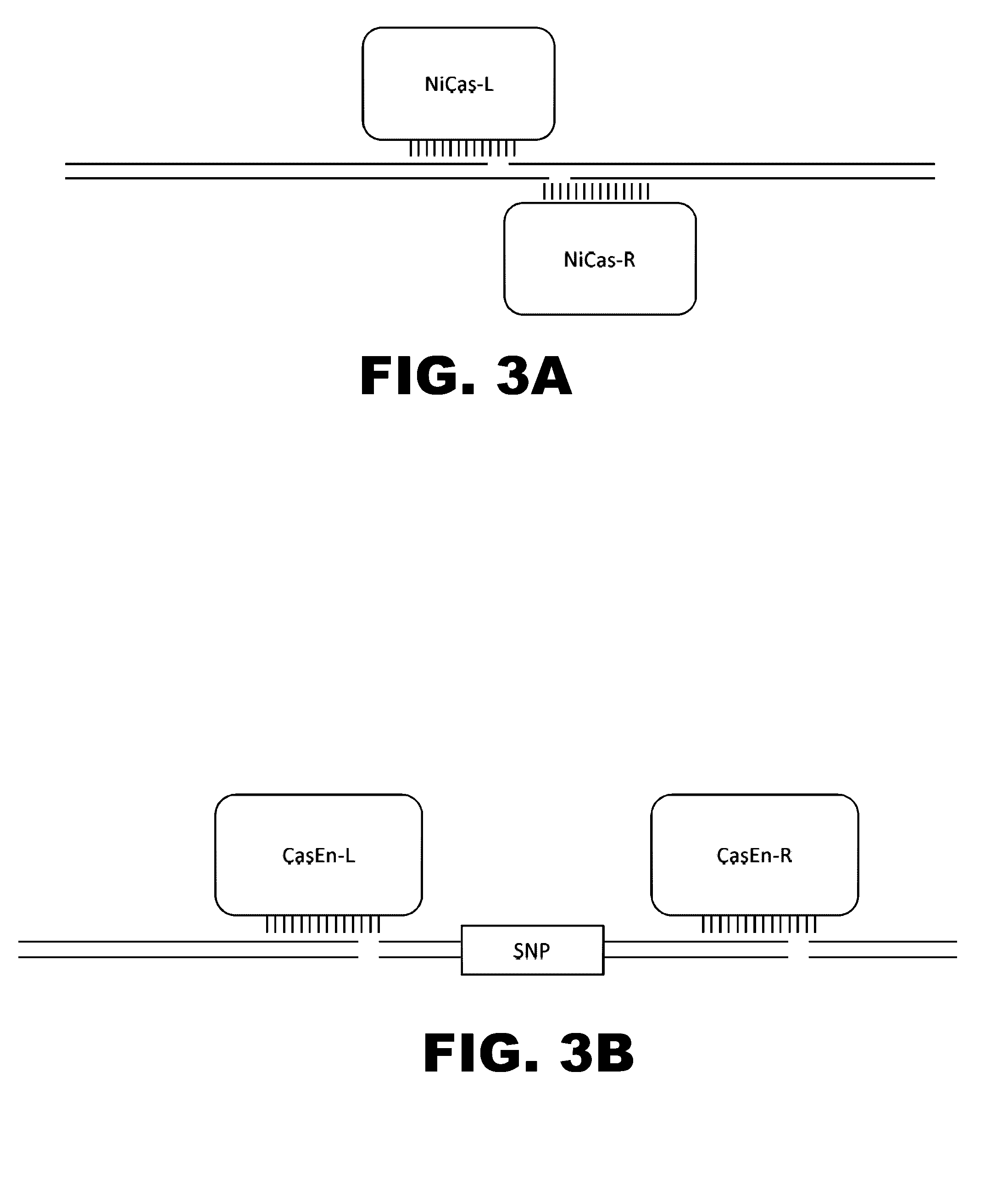
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Method for determining the number of copies of a chromosome in the genome of a target individual using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS8515679B2Improve fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic material from the target individual is acquired, amplified and the genetic data is measured using known methods. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data of a single or small number of cells, with or without genetic information from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, these determinations are made for the purpose of embryo selection in the context of in-vitro fertilization. In another embodiment of the invention, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions.
Owner:NATERA
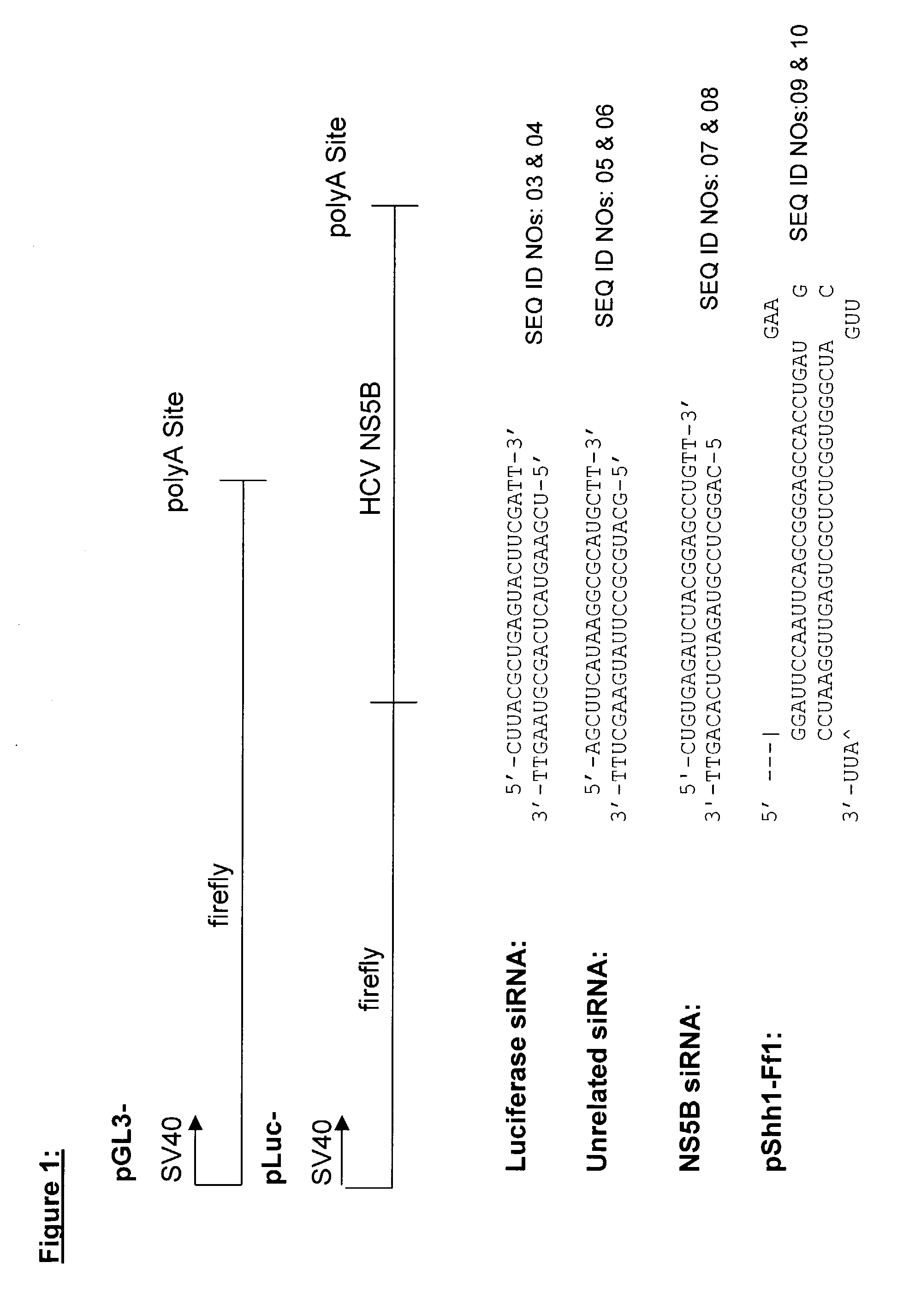
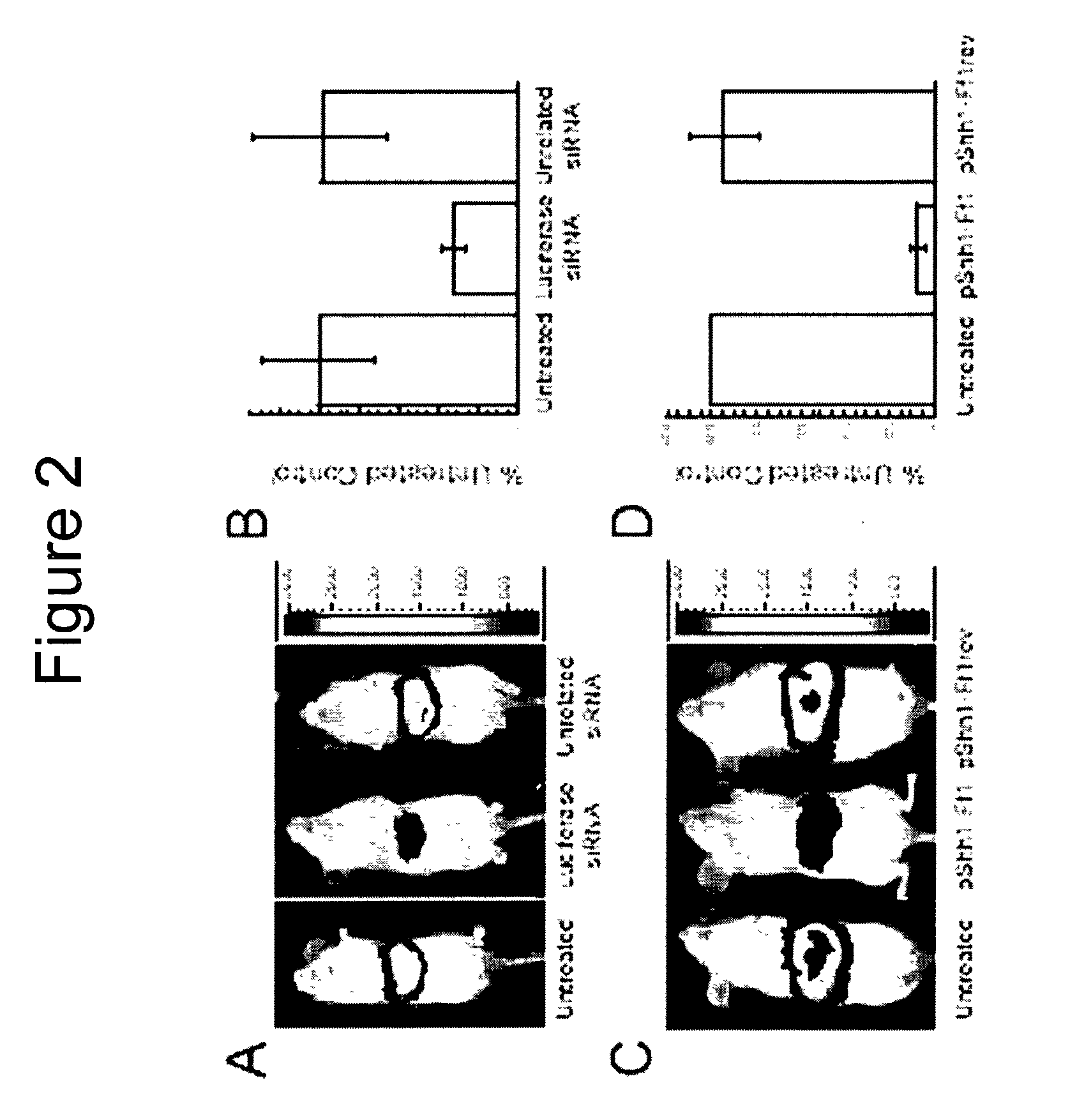
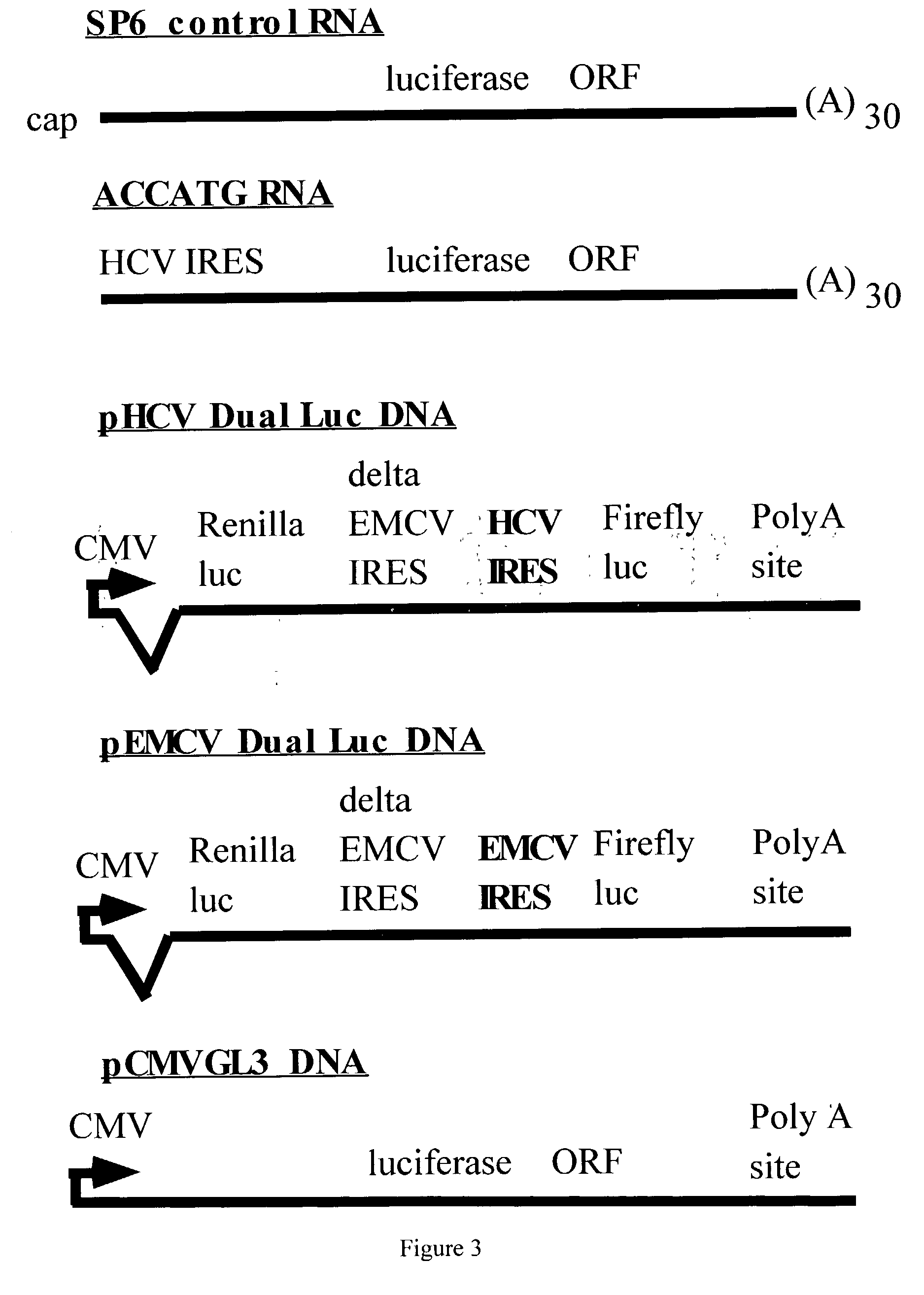
Methods and compositions for RNAi mediated inhibition of gene expression in mammals
Methods and compositions are provided for modulating, e.g., reducing, coding sequence expression in mammals. In the subject methods, an effective amount of an RNAi agent, e.g., an interfering ribonucleic acid (such as an siRNA or shRNA) or a transcription template thereof, e.g., a DNA encoding an shRNA, is administered to a non-embryonic mammal, e.g., via a hydrodynamic administration protocol. Also provided are RNAi agent pharmaceutical preparations for use in the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including academic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Gynogenetic or androgenetic production of pluripotent cells and cell lines, and use thereof to produce differentiated cells and tissues
InactiveUS20040014206A1Rejection is prevented and reducedEliminate, orMammal material medical ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPrimateEmbryo
Methods for obtaining pluripotent (embryonic stem) cells from parthenogenetic embryos, especially primates, are provided. These cells are useful for producing differentiated cells, tissues and organs, especially human and non-human primate cells, tissues and organs.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method Of Detecting Aneuploidy
InactiveUS20080102455A1Quick checkCheap methodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyIvf treatment
The present invention provides a method for detecting aneuploidy in a subject. This method has applications for the detection of aneuploidy in single cells, embryos and complete organisms. The present invention has particular application for the detection of aneuploidy in human and other animal embryos generated by in-vitro fertilization. Pre-implantation screening for aneuploidy has the potential to significantly increase the rate of successful carriage to term after IVF treatment, and significantly reduce the incidence of birth defects in children conceived with the assistance of IVF treatment. Kits for the detection of aneuploidy are also provided.
Owner:GENERA BIOSYSTEMS LTD
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20140032128A1Significant resultImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiploid cellsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
Embryo modification and implantation
InactiveUS7819796B2Low specificityNanomedicinePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsIvf treatmentEmbryo
The present invention relates to constructs and methods used to enhance the attachment and implantation of an embryo. It is shown that modified glycolipids and glycolipid-attachment molecule constructs can be used to modify embryos, or localised to target tissues, to enhance interaction between the embryo and the target tissue, (typically the endometrium). The invention may advantageously be used to enhance implantation of embryos in the uterus, for example, in IVF treatments.
Owner:KODE BIOTECH
Cloning pigs using donor nuclei from non-quiescent differentiated cells
InactiveUS6235969B1Superior genotypes of pigsSpeed up genetic progressNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPresent method
An improved method of nuclear transfer involving the transplantation of donor differentiated pig cell nuclei into enucleated pig oocytes is provided. The resultant nuclear transfer units are useful for multiplication of genotypes and transgenic genotypes by the production of fetuses and offspring. Production of genetically engineered or transgenic pig embryos, fetuses and offspring is facilitated by the present method since the differentiated cell source of the donor nuclei can be genetically modified and clonally propagated.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050158852A1Improve breeding conditionsImprove survival rateGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsCell-Extracellular MatrixIn vitro growth
The present invention discloses a method for improving growth and survival of single human embryonic stem cells. The method includes the step of obtaining a single undifferentiated HES cell; mixing the single undifferentiated cell with an extracellular matrix (ECM) to encompass the cell; and inoculating the mixture onto feeder cells with a nutrient medium in a growth environment. Therefore the single cells can survive, proliferate and grow in vitro.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Manufacturing method for crystallized fruit
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for crystallized fruit, which comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the following raw materials by weight percent: 20-67.7% of fruit embryos, 32.05-53.0% of sugar crops, 0.1-5% of filling materials, 0-5% of medicinal and food homologous traditional Chinese medicines, 0.05-10% of seasoning spices, 0.1-2.0% of preservatives and 0-5% of pigments; (2) pre-treating the raw materials by preparing liquid sugar, filling material liquid, traditional Chinese medicine extracts and preservative solution; (3) soaking: adding the liquid sugar material,the seasoning spices, the pigments, the liquid sugar, the filling material liquid and the traditional Chinese medicine extracts into a soaking cylinder and mixing uniformly to form the mixed materialliquid, adding the fruit embryos into the soaking cylinder, increasing the temperature of the mixed material liquid to 50-60 DEG C and keeping the temperature for 10-15 hours; (4) leaching and drying; and (5) drying to obtain the crystallized fruit. The manufacturing method for crystallized fruit is easily performed, the full utilization of fruit resource is realized, and the manufactured crystallized fruit is full of nutrition and tastes fresh and cool.
Owner:汕头市天悦轻工技术科技有限公司 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com