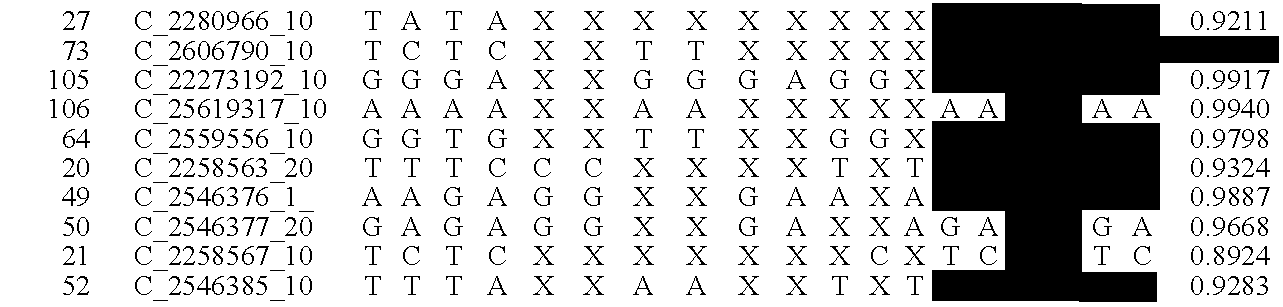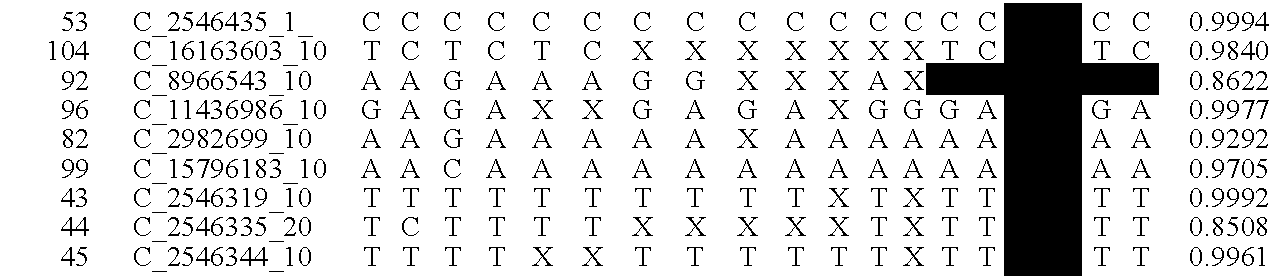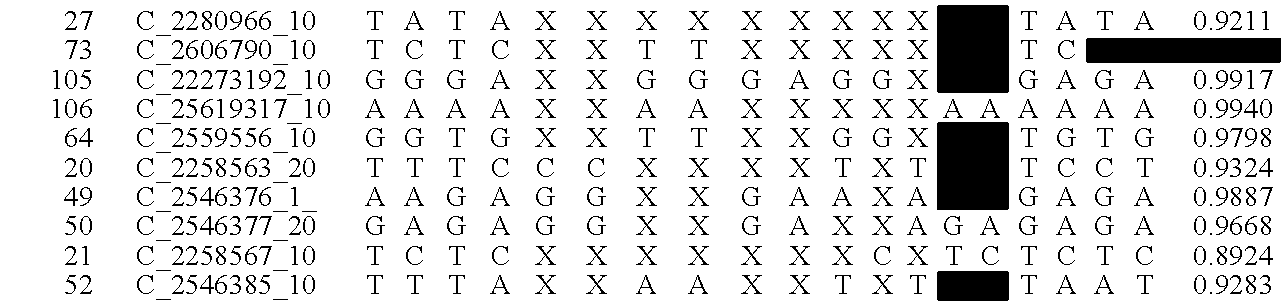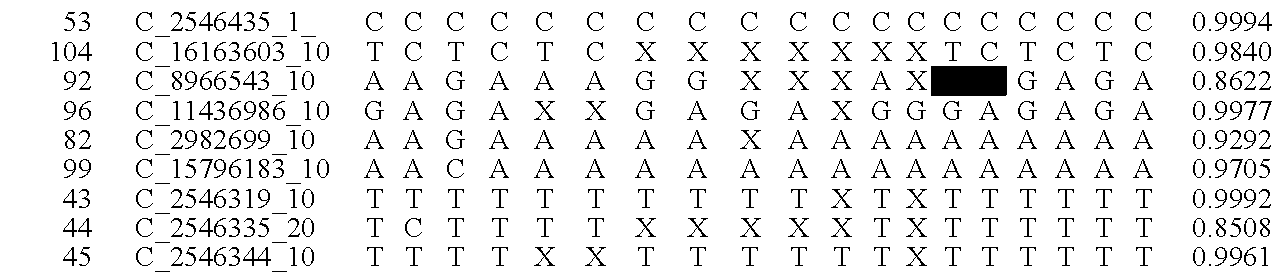Patents
Literature
105 results about "Diploid cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
ActiveUS20070184467A1Significant resultMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsUniparental disomyEmbryo
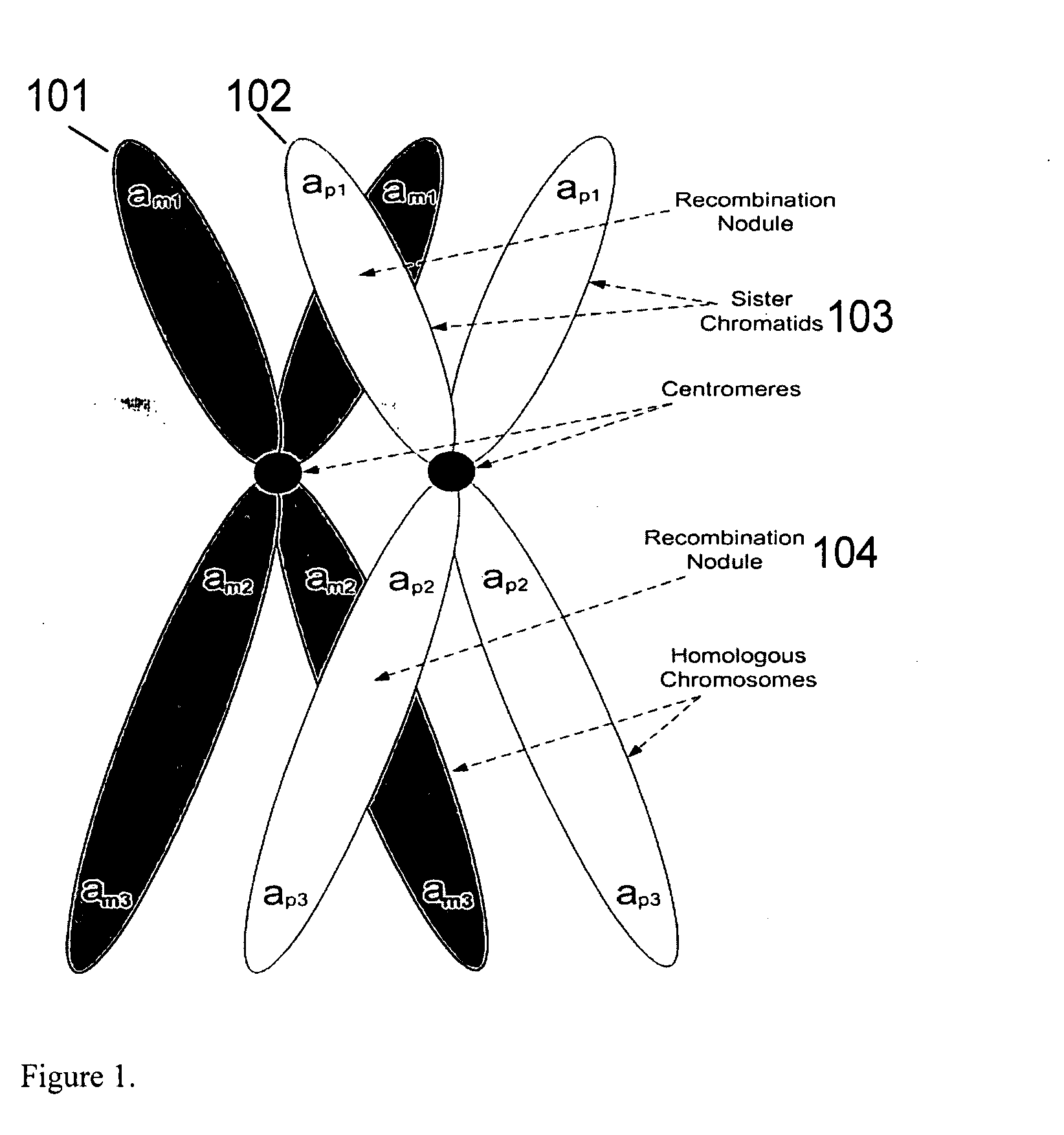
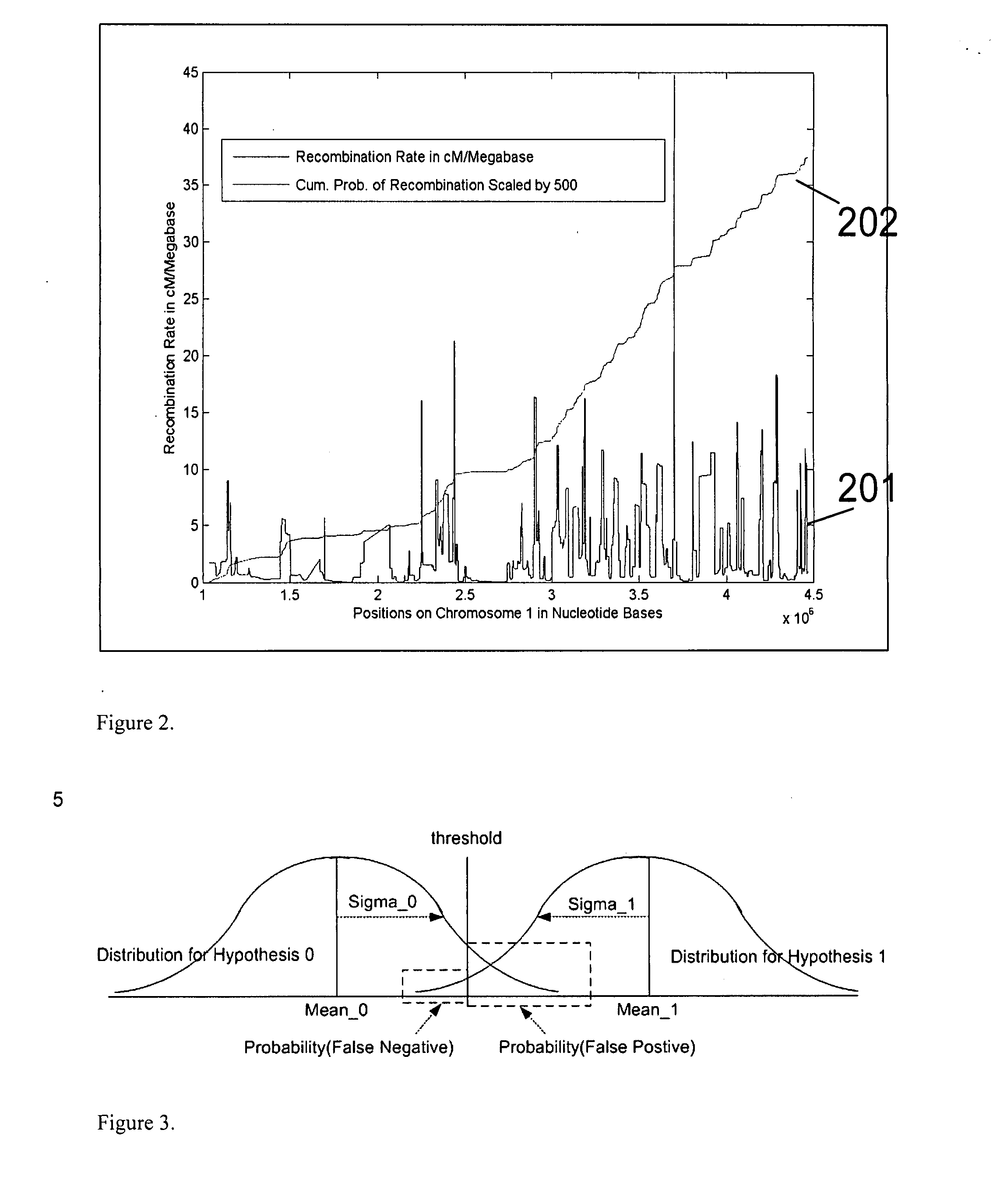
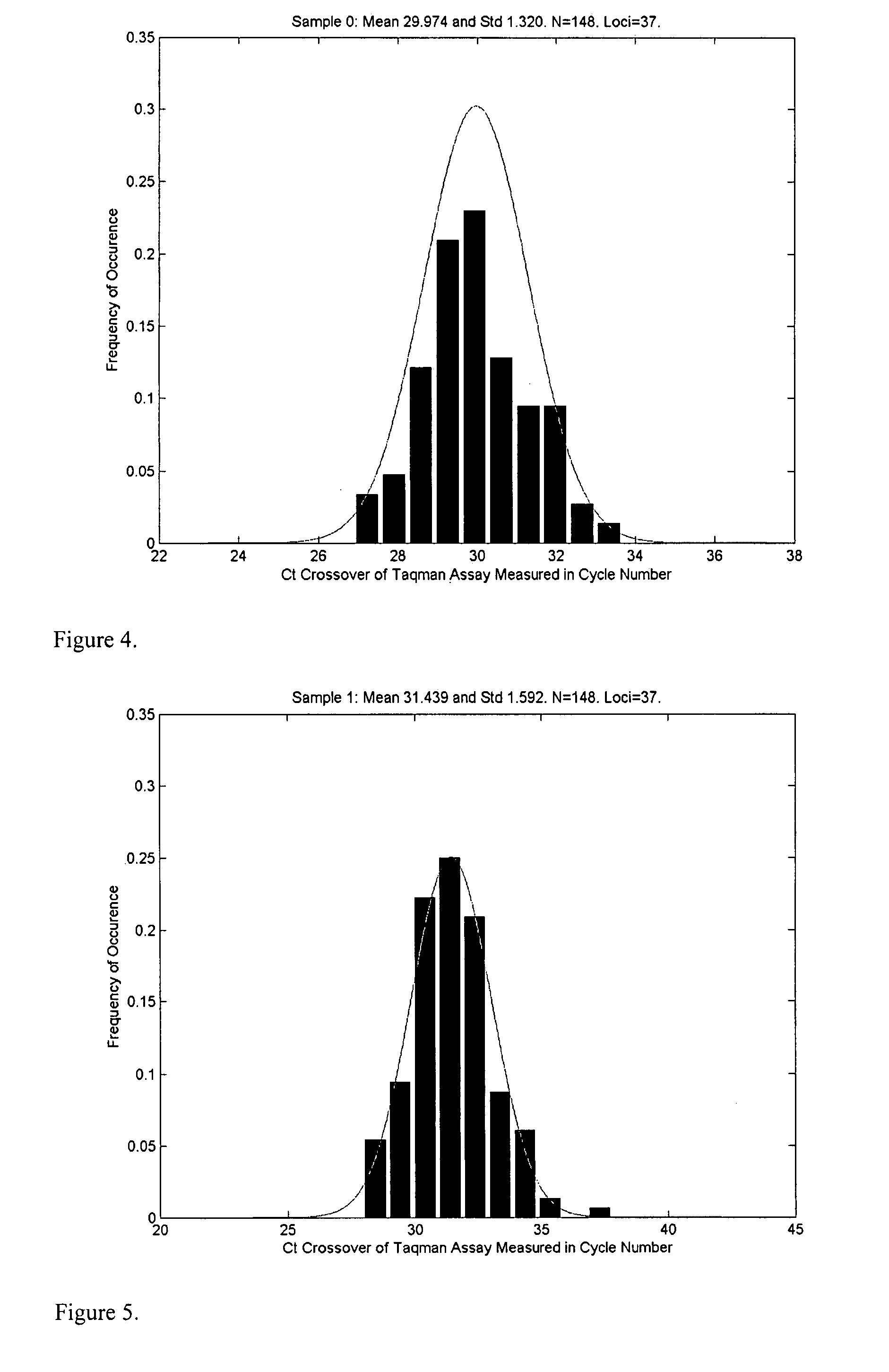
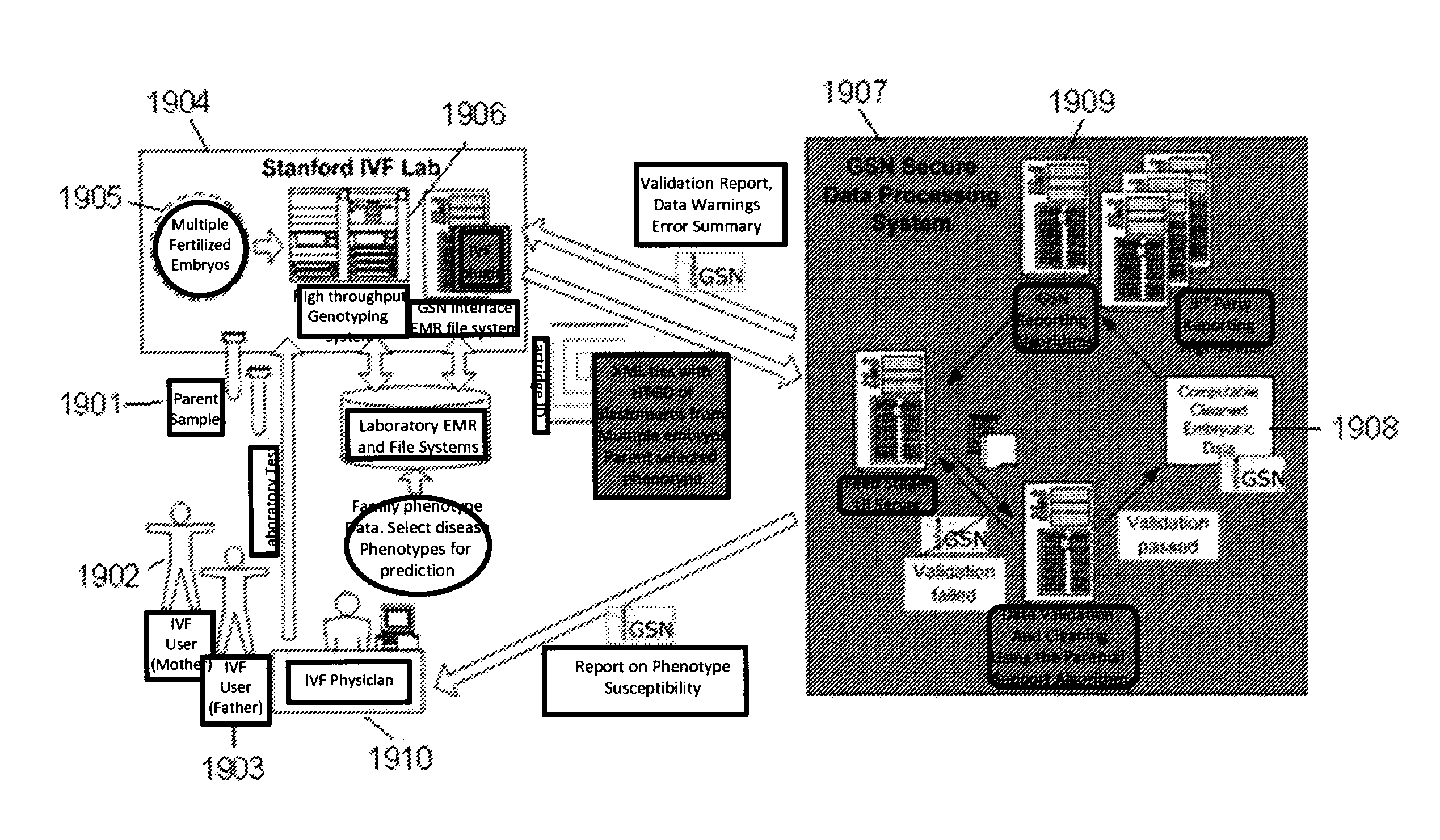
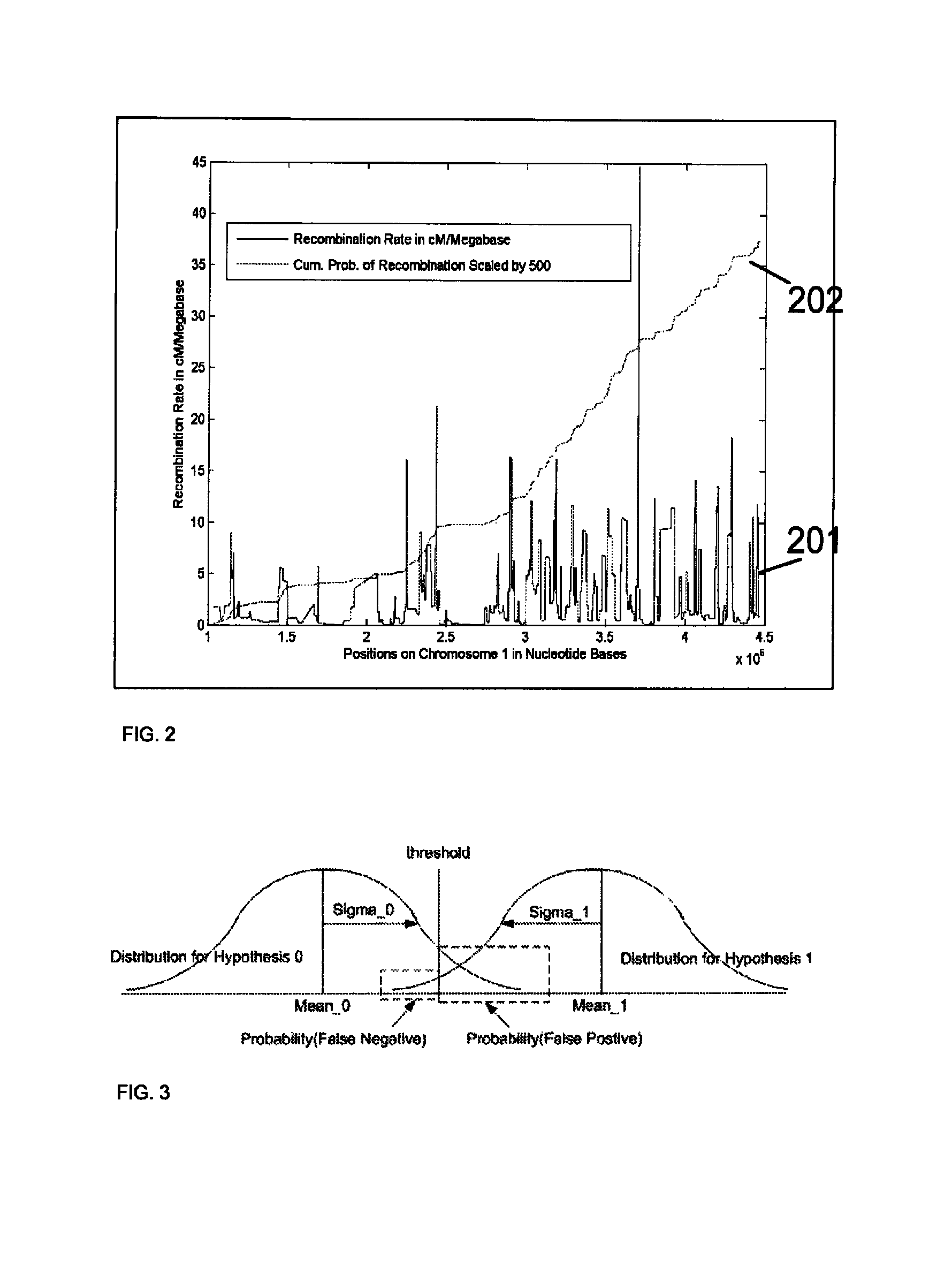
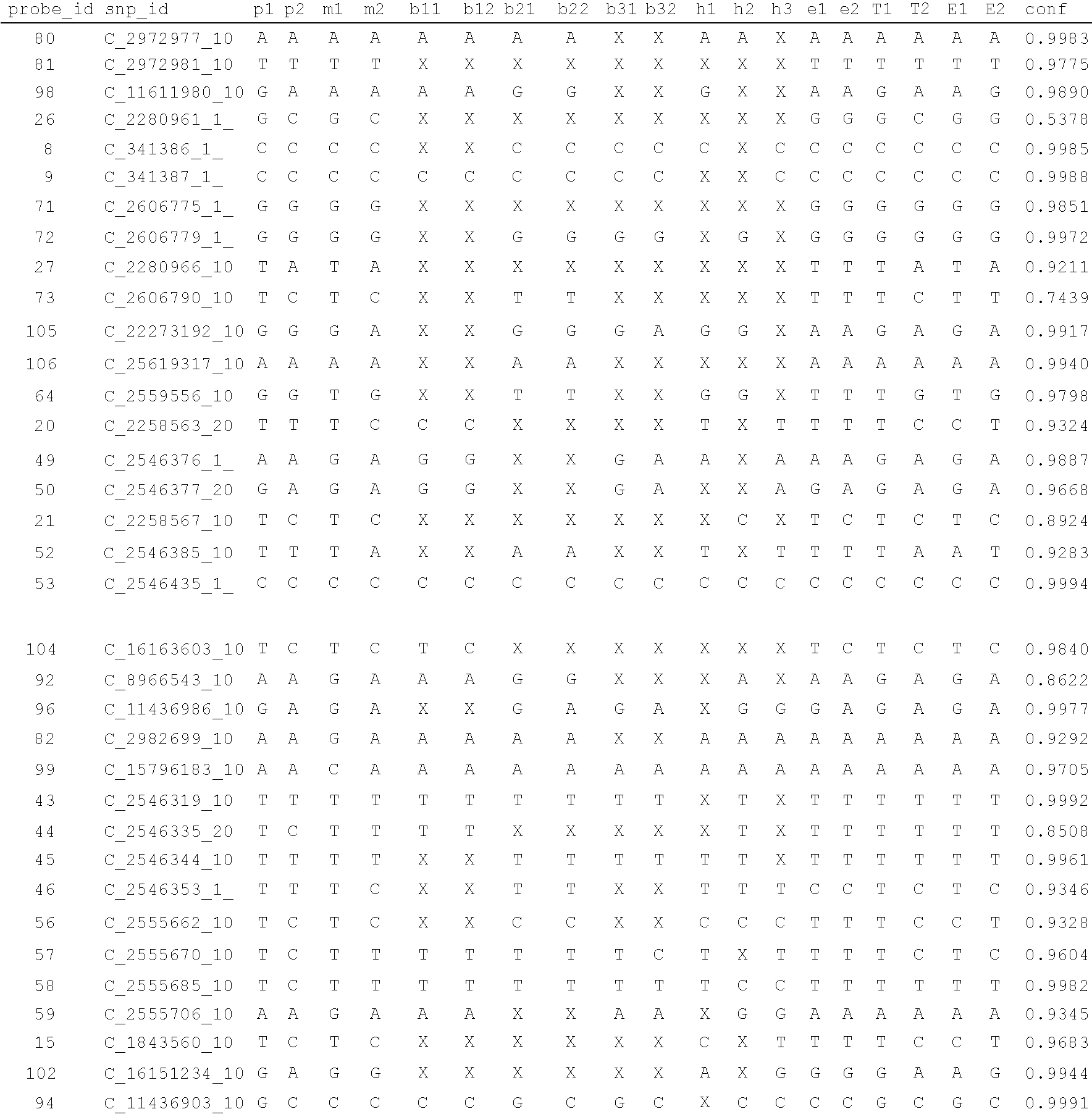
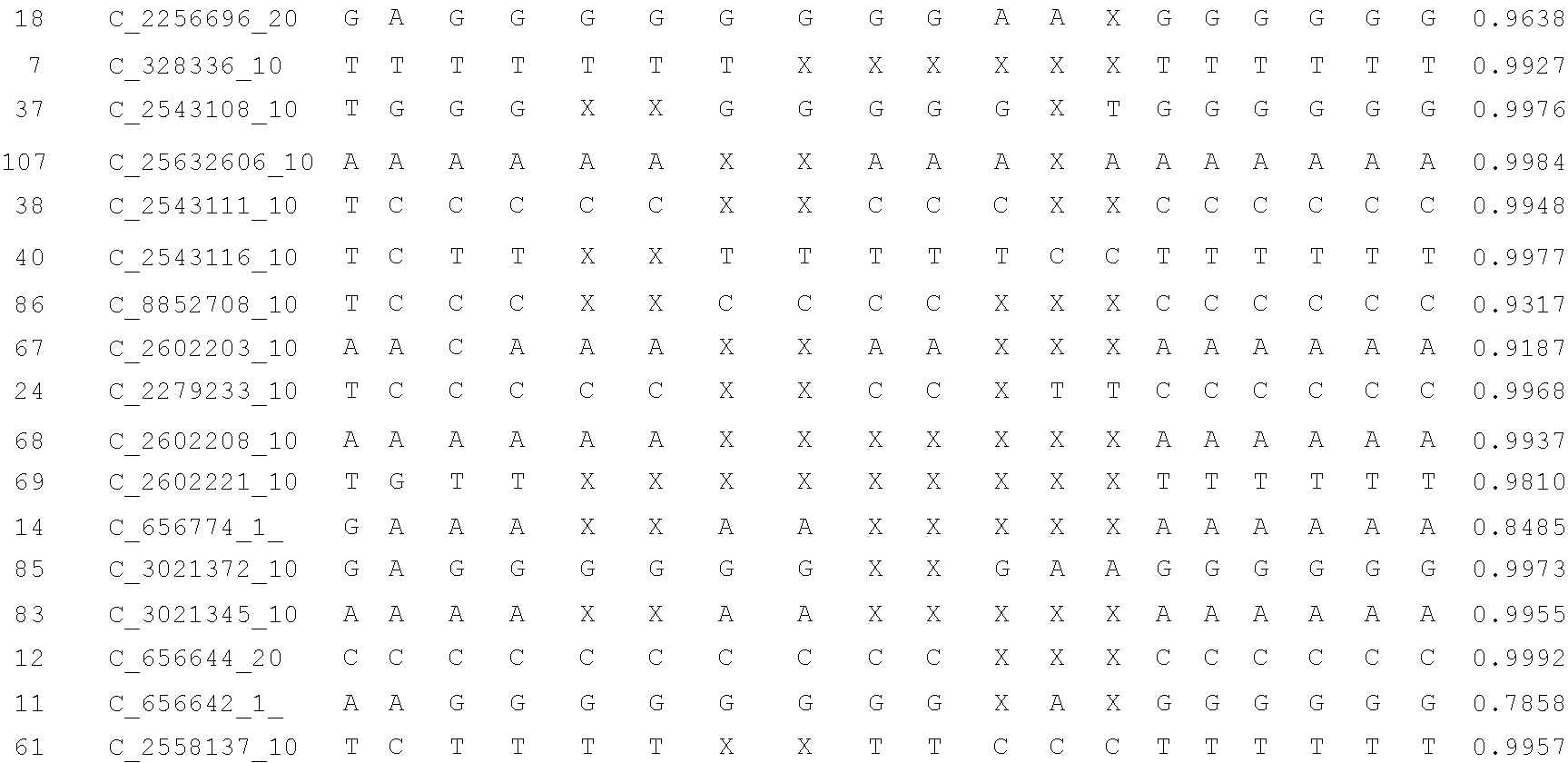
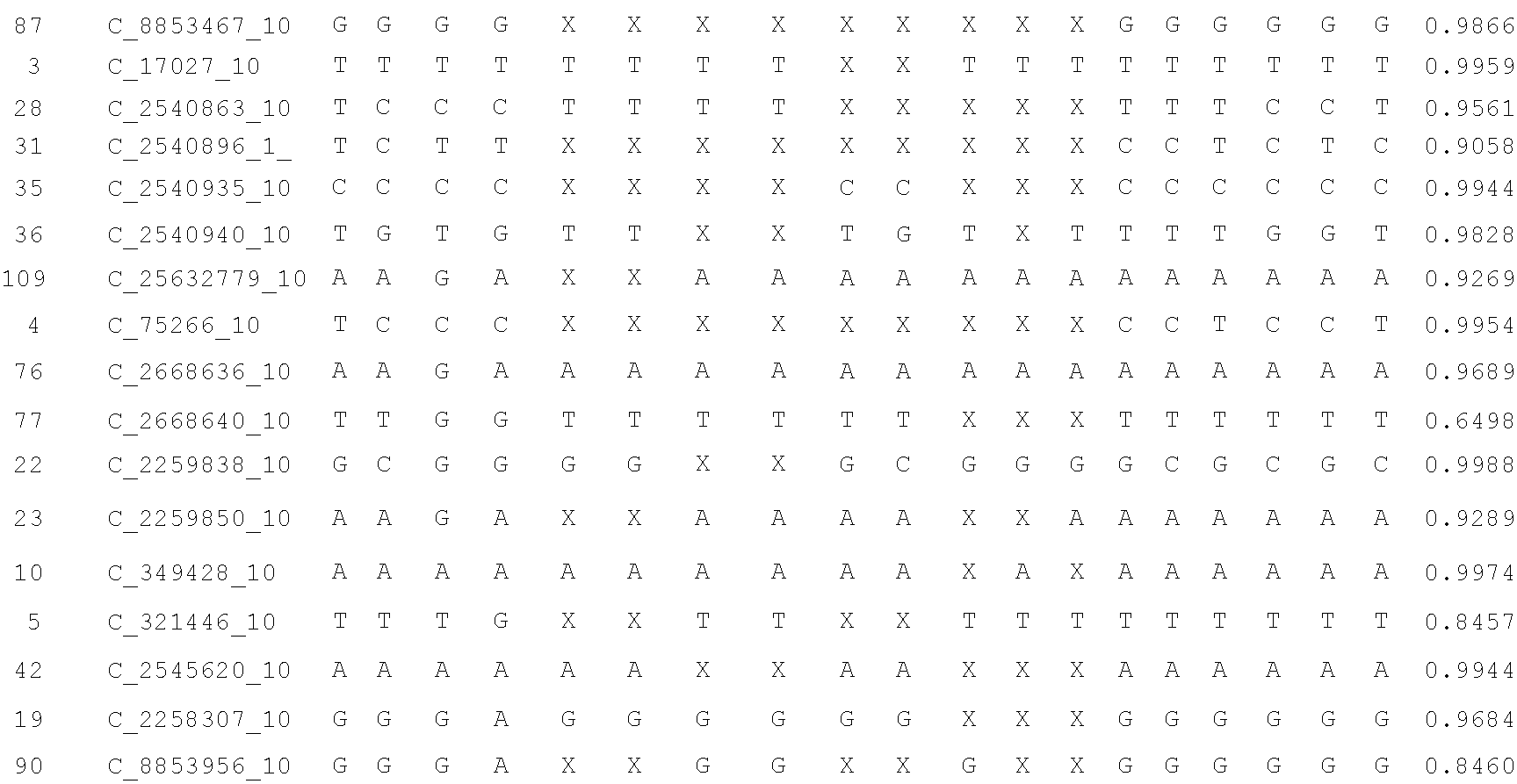
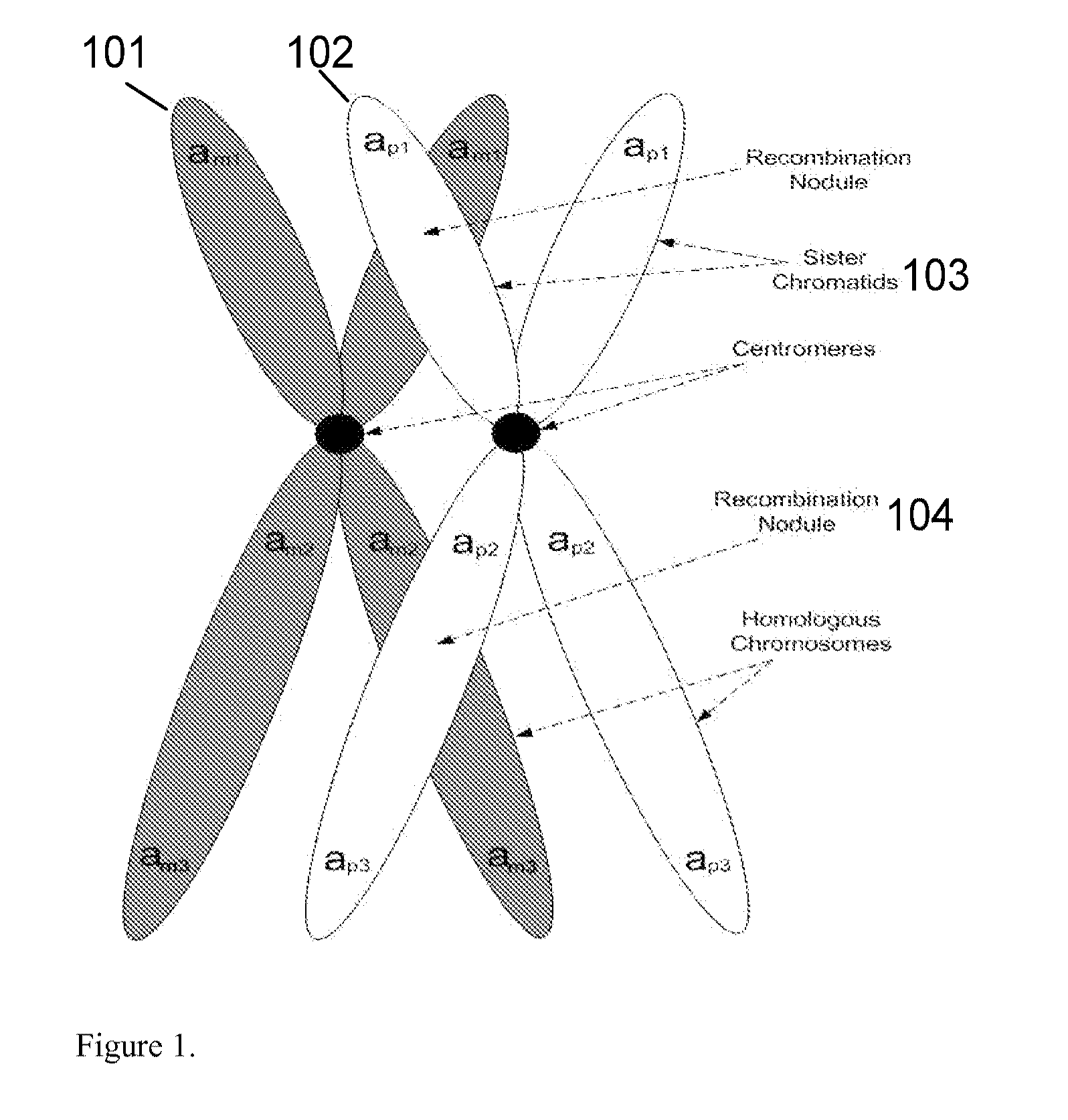
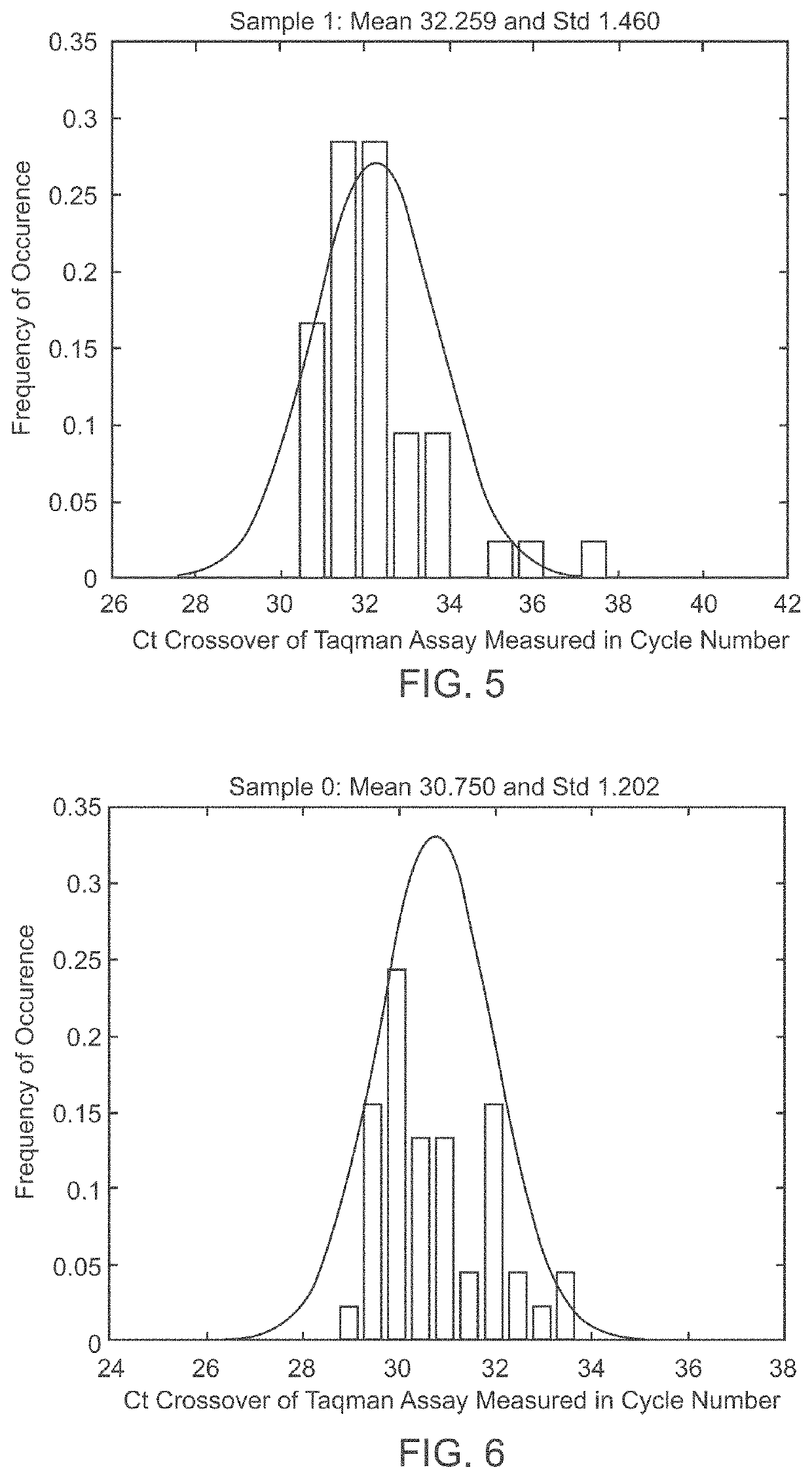
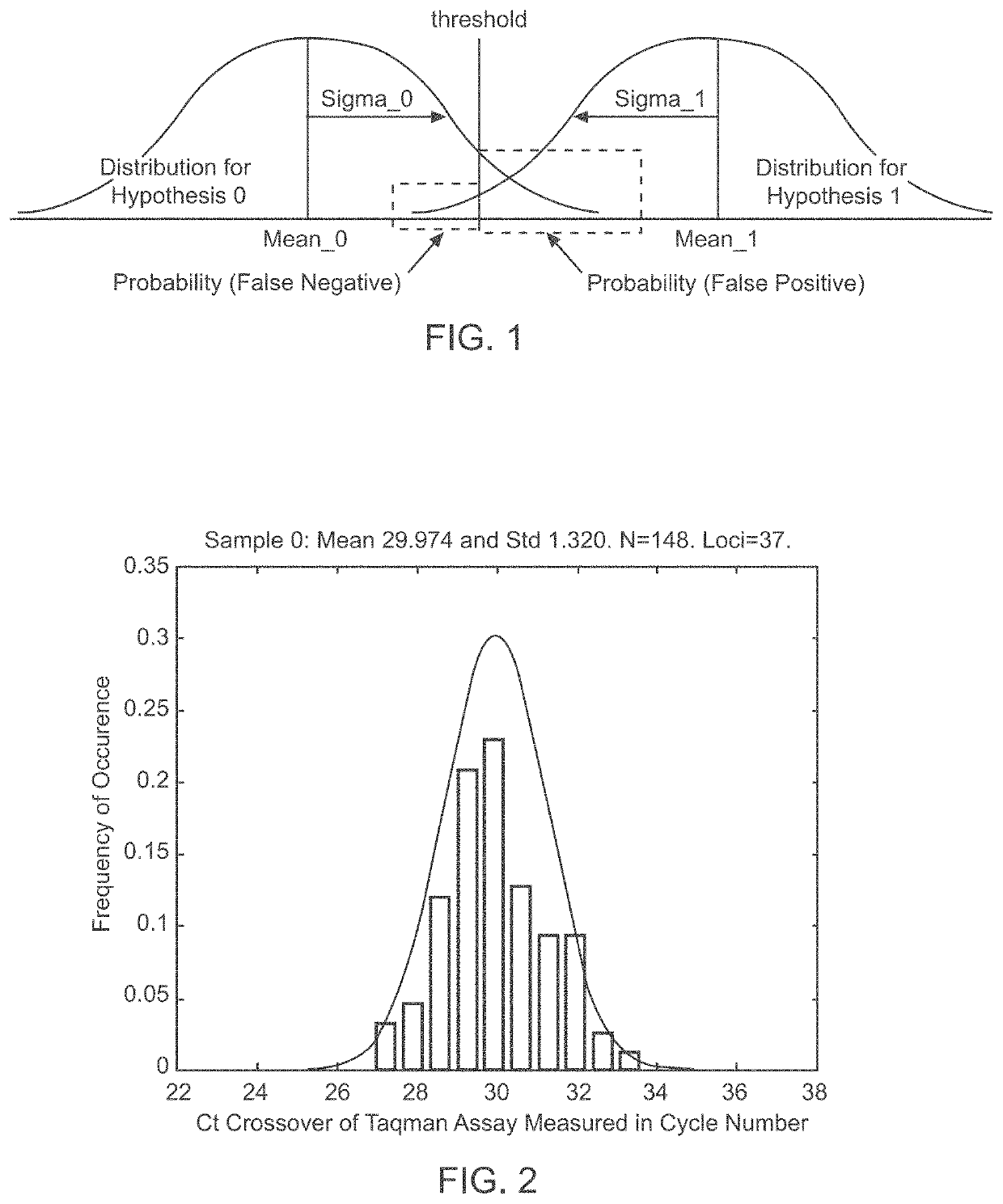
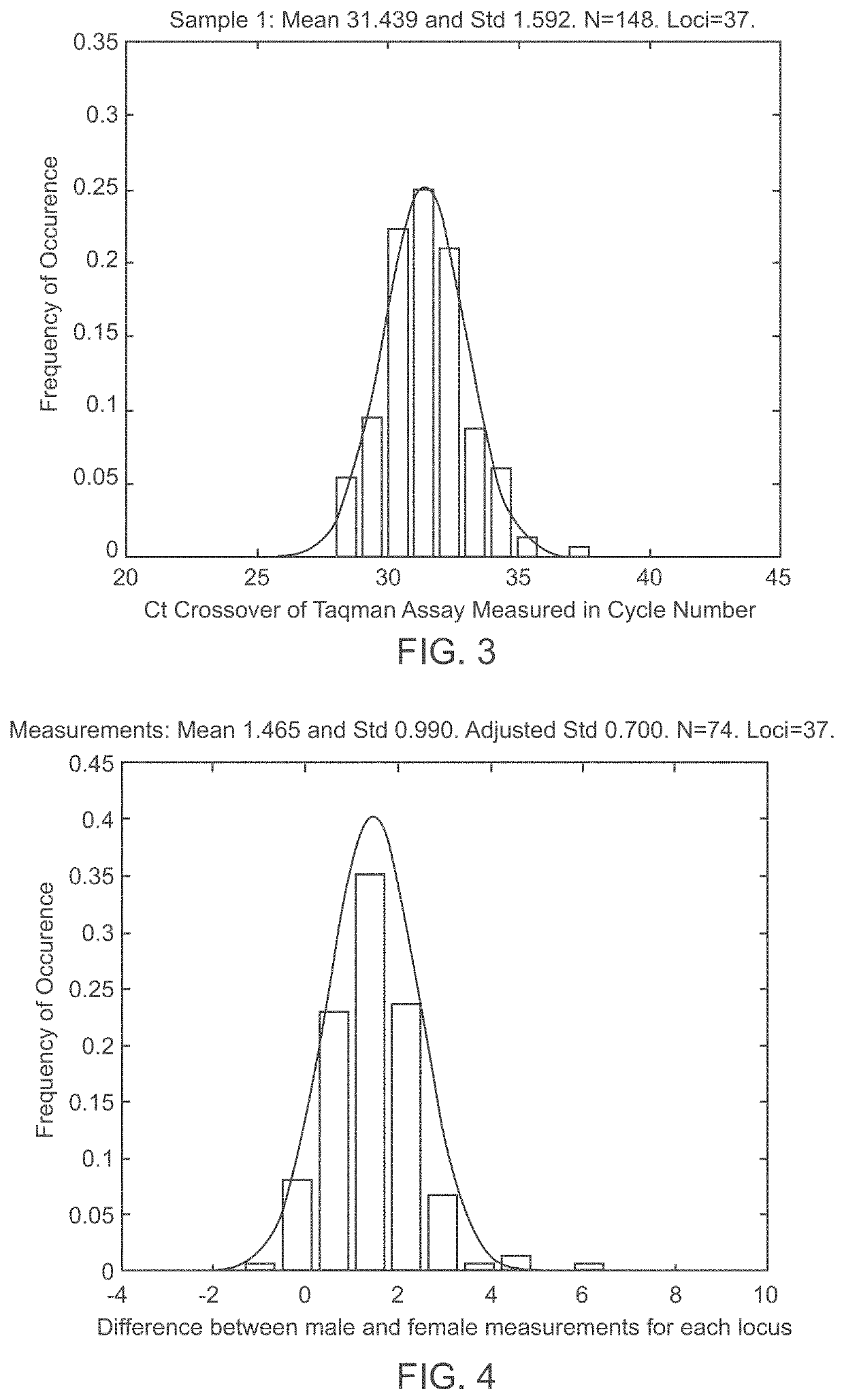
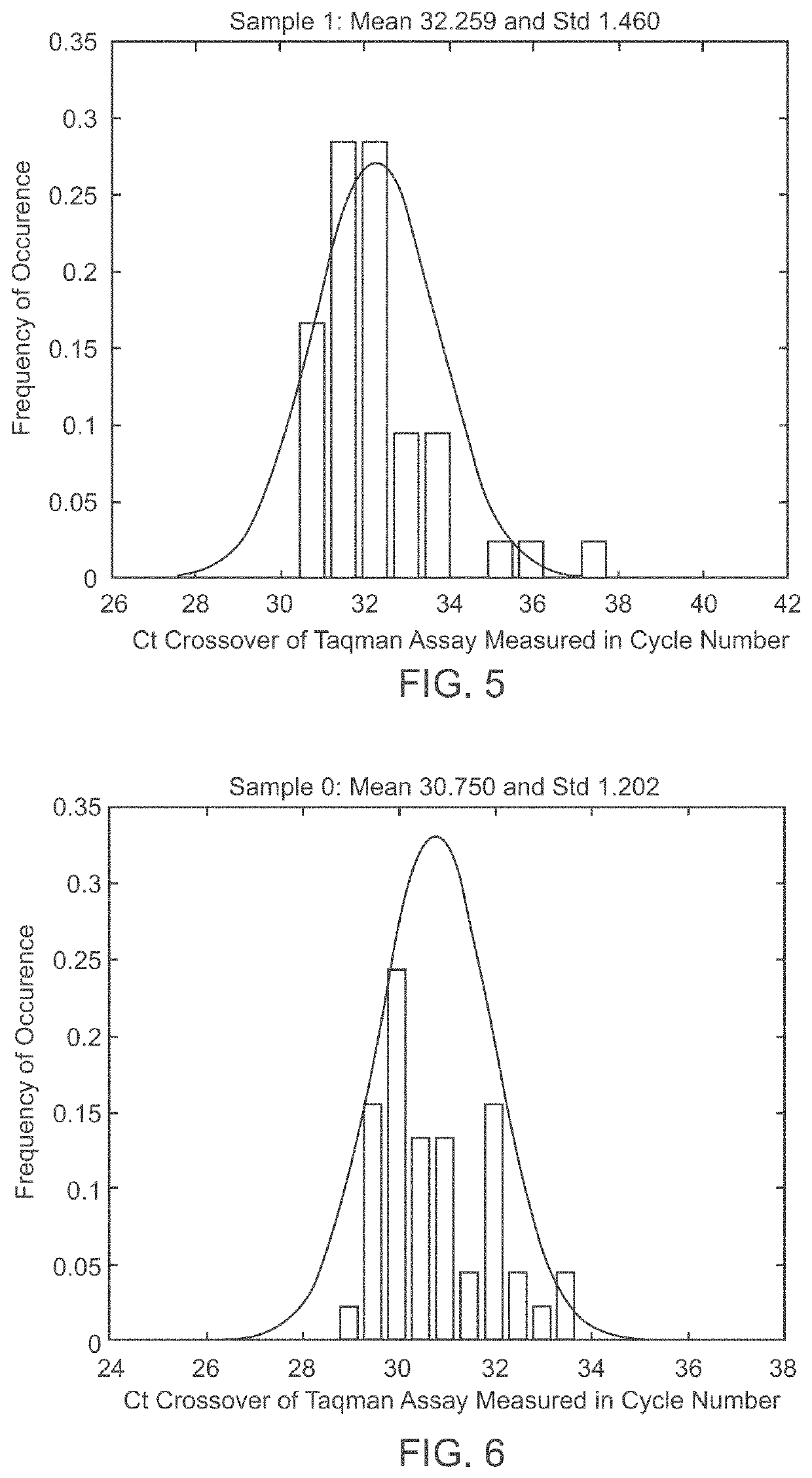
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20080243398A1Significant resultImprove fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsEmbryo
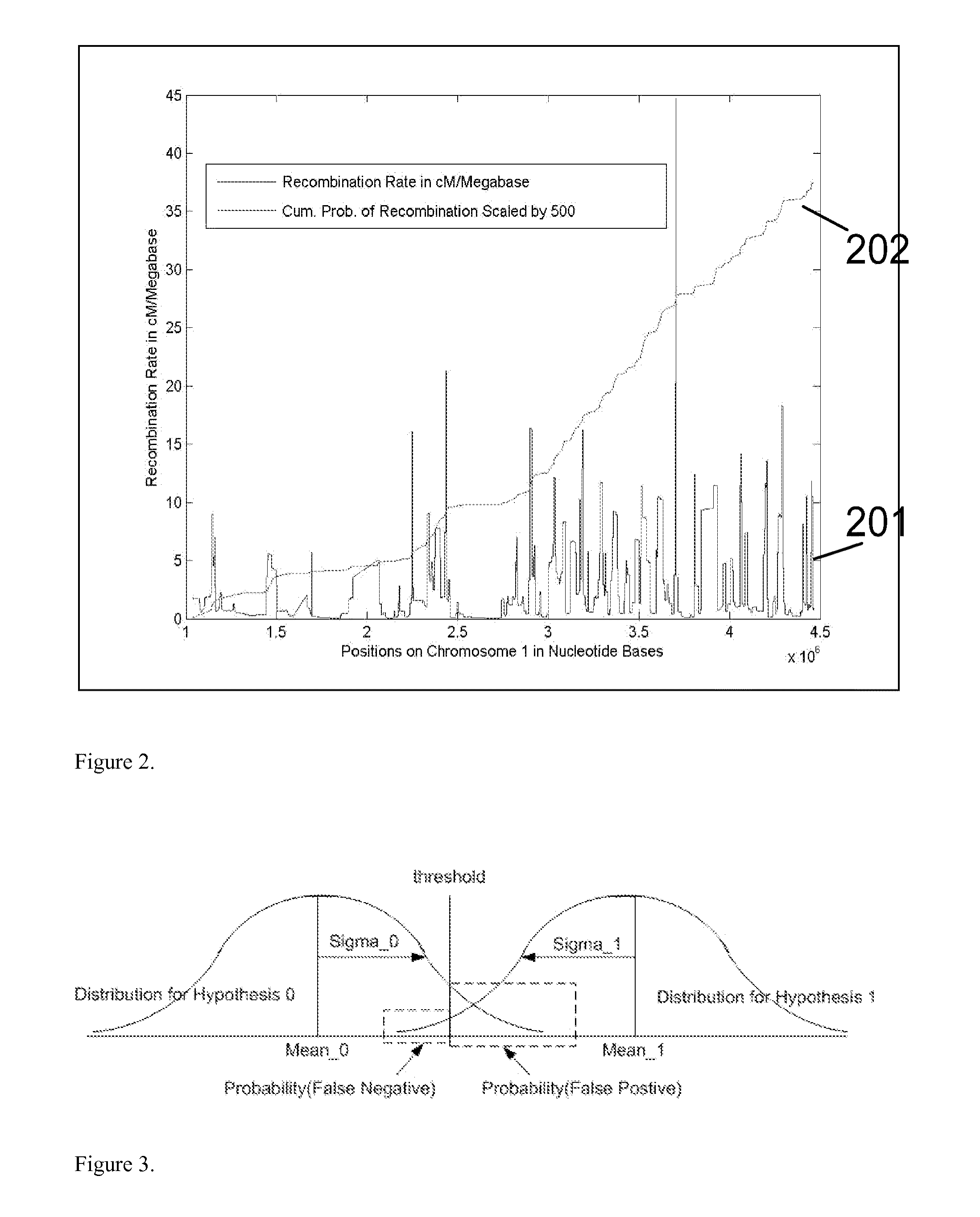
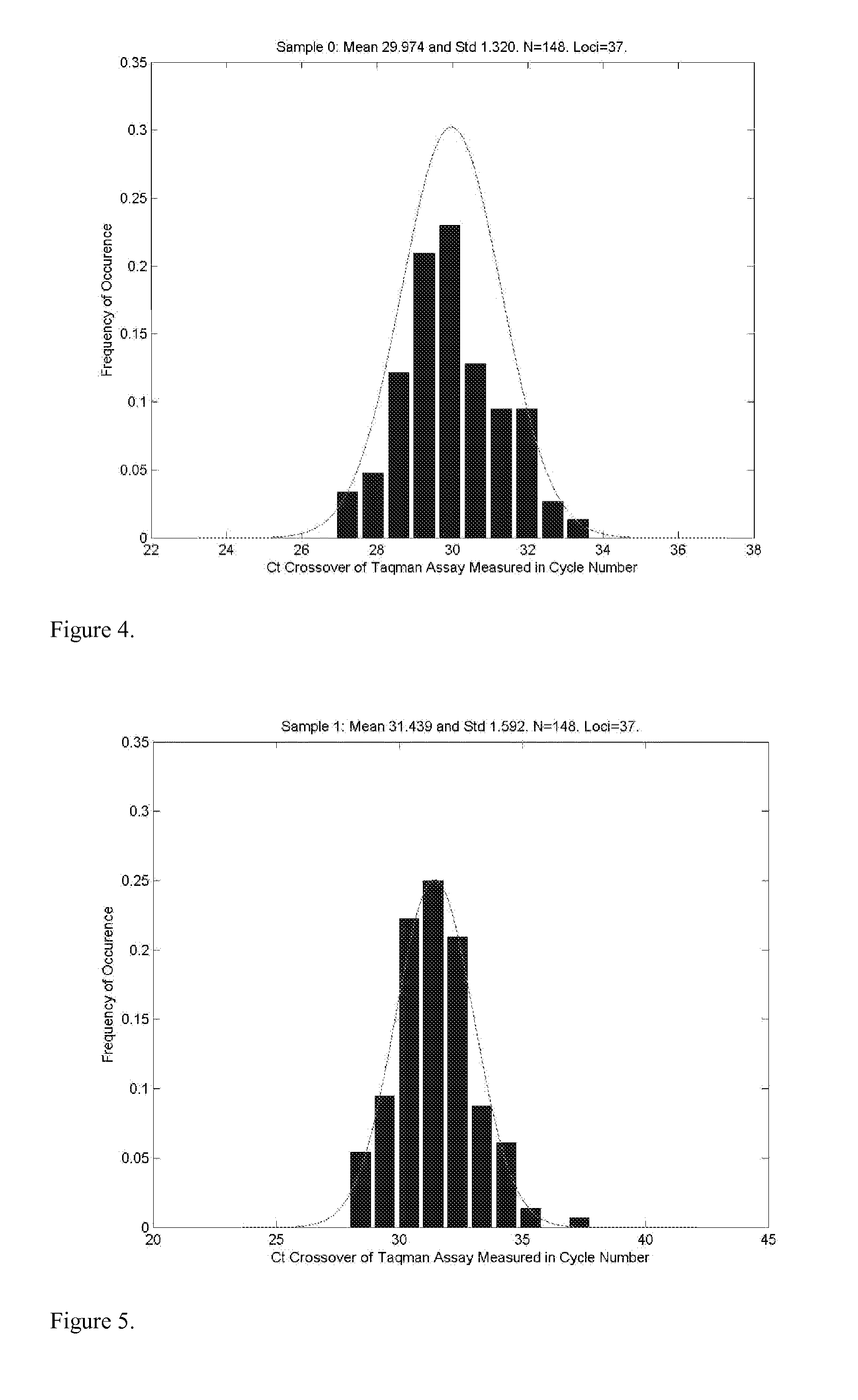
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic material from the target individual is acquired, amplified and the genetic data is measured using known methods. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data of a single or small number of cells, with or without genetic information from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, these determinations are made for the purpose of embryo selection in the context of in-vitro fertilization. In another embodiment of the invention, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions.
Owner:NATERA
Method for determining the number of copies of a chromosome in the genome of a target individual using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS8515679B2Improve fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic material from the target individual is acquired, amplified and the genetic data is measured using known methods. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data of a single or small number of cells, with or without genetic information from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, these determinations are made for the purpose of embryo selection in the context of in-vitro fertilization. In another embodiment of the invention, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20140032128A1Significant resultImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiploid cellsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available, are disclosed. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data is acquired from embryonic cells, fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS10083273B2Improve fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiploid cellsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
InactiveUS20200224273A1Improve fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
PendingUS20200248264A1Improve fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20200232036A1Significant resultImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
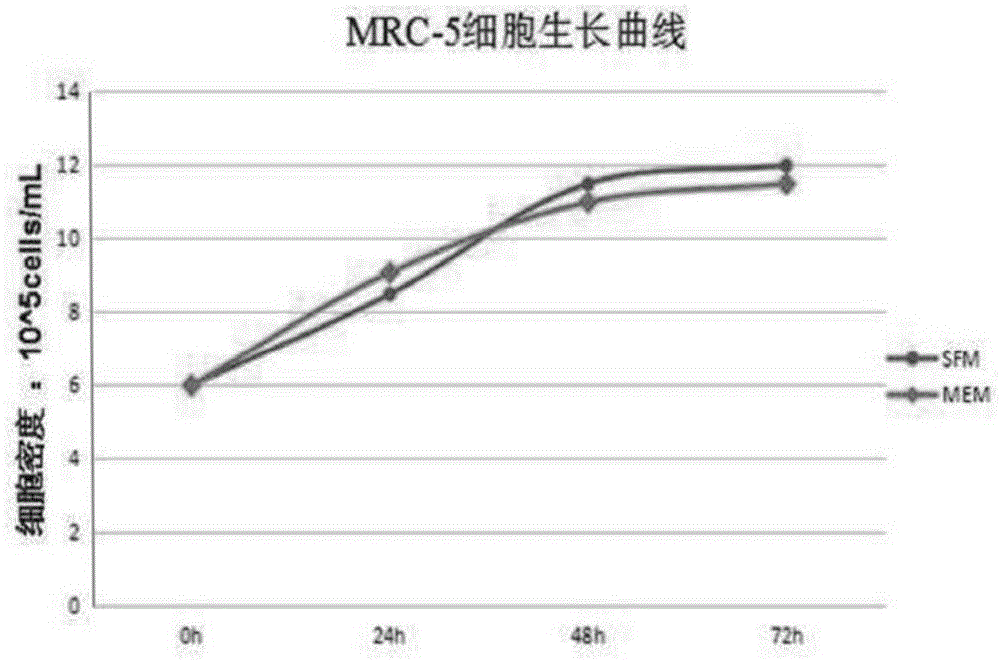
Culture medium for normal epithelial cell of human or mammal, culture methods, normal epithelial cell and application of normal epithelial cell
InactiveCN104694460ANormal differentiation physiological functionMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsMatrigelMammal
The invention relates to a culture medium for a normal epithelial cell of a human or mammal, primary separation culture, subculture, 3D gas-liquid culture and 3D matrigel culture methods, the normal epithelial cell generated by using the culture medium and the culture methods and application of the normal epithelial cell to a toxicological evaluation system. The culture medium is prepared by mixing DMEM and Ham's F-12NUTRIENT MIX according to the volume ratio of 3:1 and also adding 4-6% of fetal calf serum, 1-3nM triiodothyronine, 0.4-0.65% of insulin-transferrin-selenium reagent, 4-6mu g / ml transferrin, 9-11ng / mL epidermal growth factors, 0.3-0.5mu g / mL hydrocortisone, 0.5-1.5nM cholera toxin, 0.4-0.6mu g / mL amphoterrible B, 35-45mu g / mL gentamicin, 45-55nM calpeptin, 35-45ng / ml recombinant human IL-1RA and 3mu g / ml recombinant human R-Spondin-1. The culture medium disclosed by the invention can be used for carrying out separation culture or subculture on the normal epithelial cell of the human or the mammal and any other various tissue source, rapidly proliferating the normal epithelial cell in vitro and establishing a cell line; and the normal epithelial cell is a normal diploid cell and is applied to the toxicological evaluation system of the human or the mammal.
Owner:SHENZHEN RES INST OF WUHAN UNIVERISTY
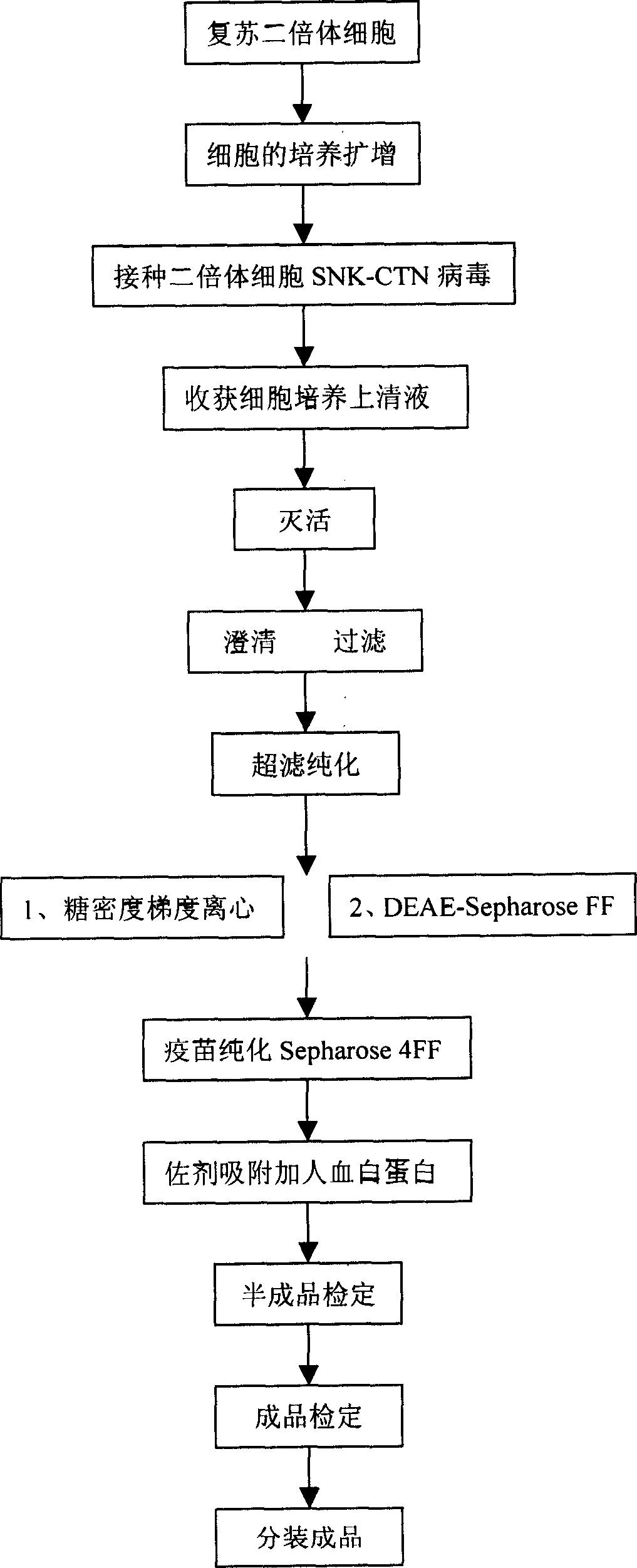
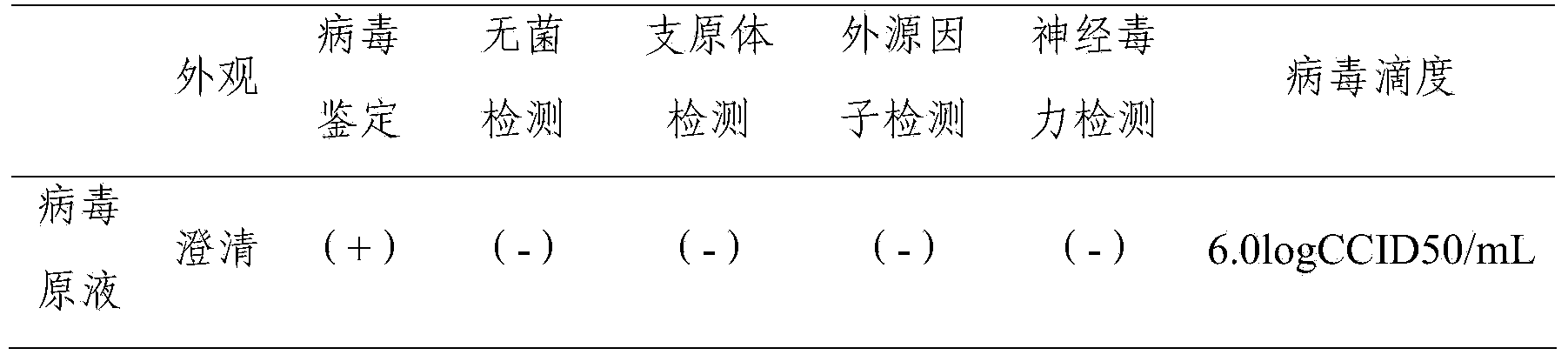
Prepn process of inactivated rotavirus vaccine
ActiveCN101020053APrevent infectious diseasesViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsRotavirus RNAResearch Object
The present invention discloses preparation process of inactivated rotavirus vaccine. Rotavirus strains G1, G2, G3 and G4 are made to adapt human diploid cell line and propagate on human diploid cell line to obtain the producing strain of inactivated rotavirus vaccine, with the human diploid cell line being KMB17. The human diploid cell line used as the cell matrix for producing inactivated rotavirus vaccine is safer compared with available cell matrixes. Therefore, by means of the established technological platform, it is possible to develop inactivated rotavirus vaccine with other serotypes of rotavirus as the target.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
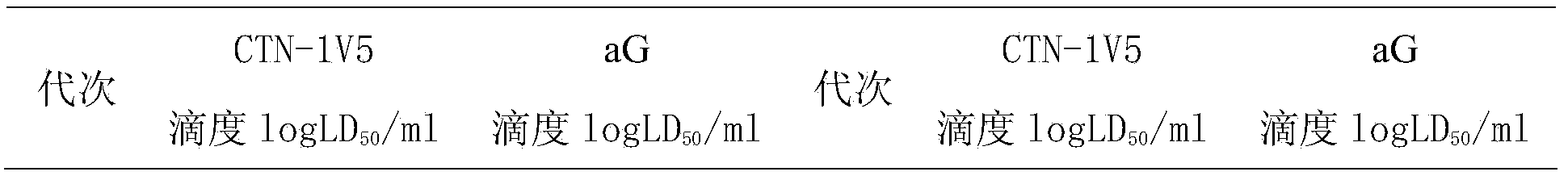
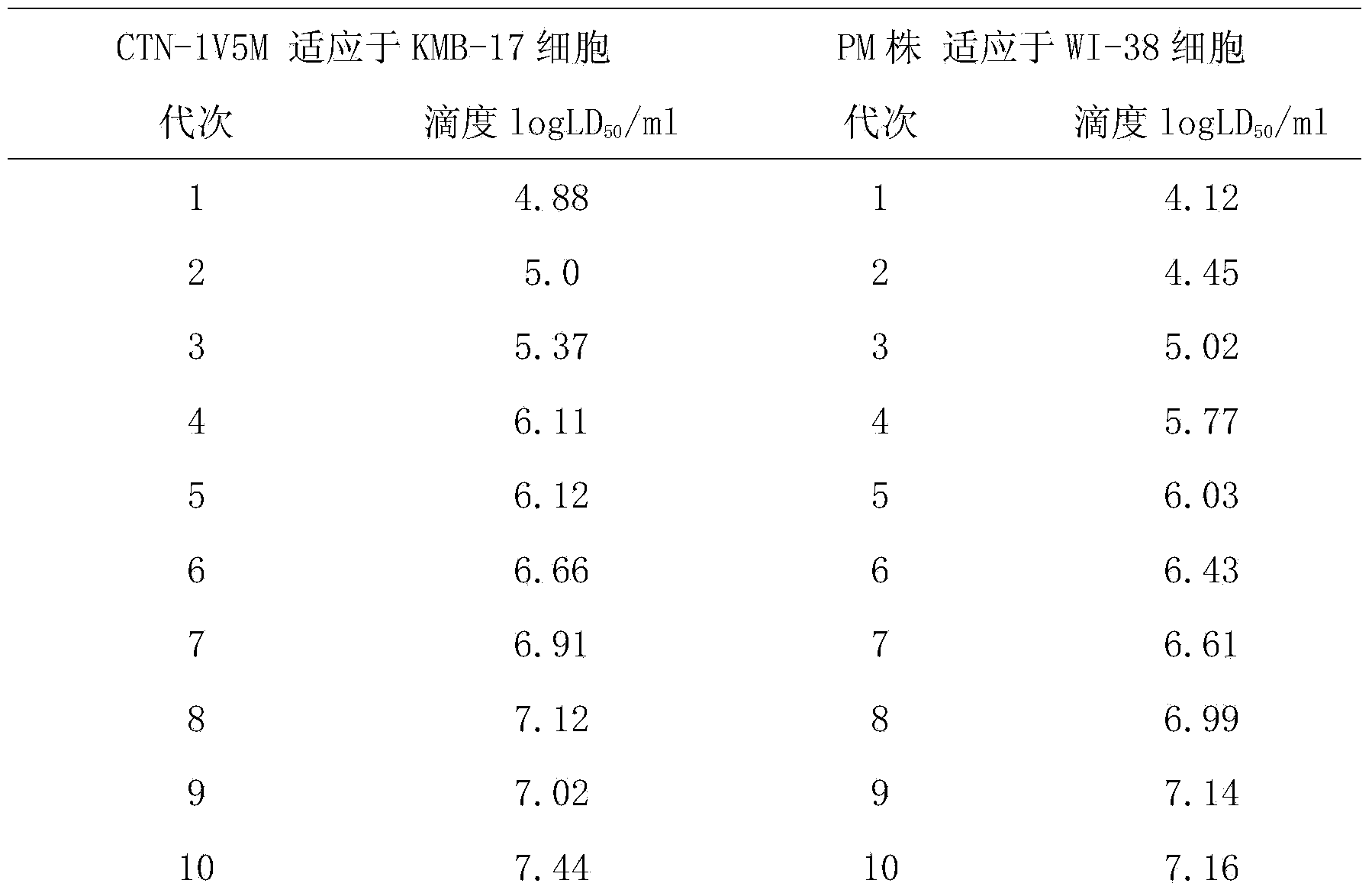
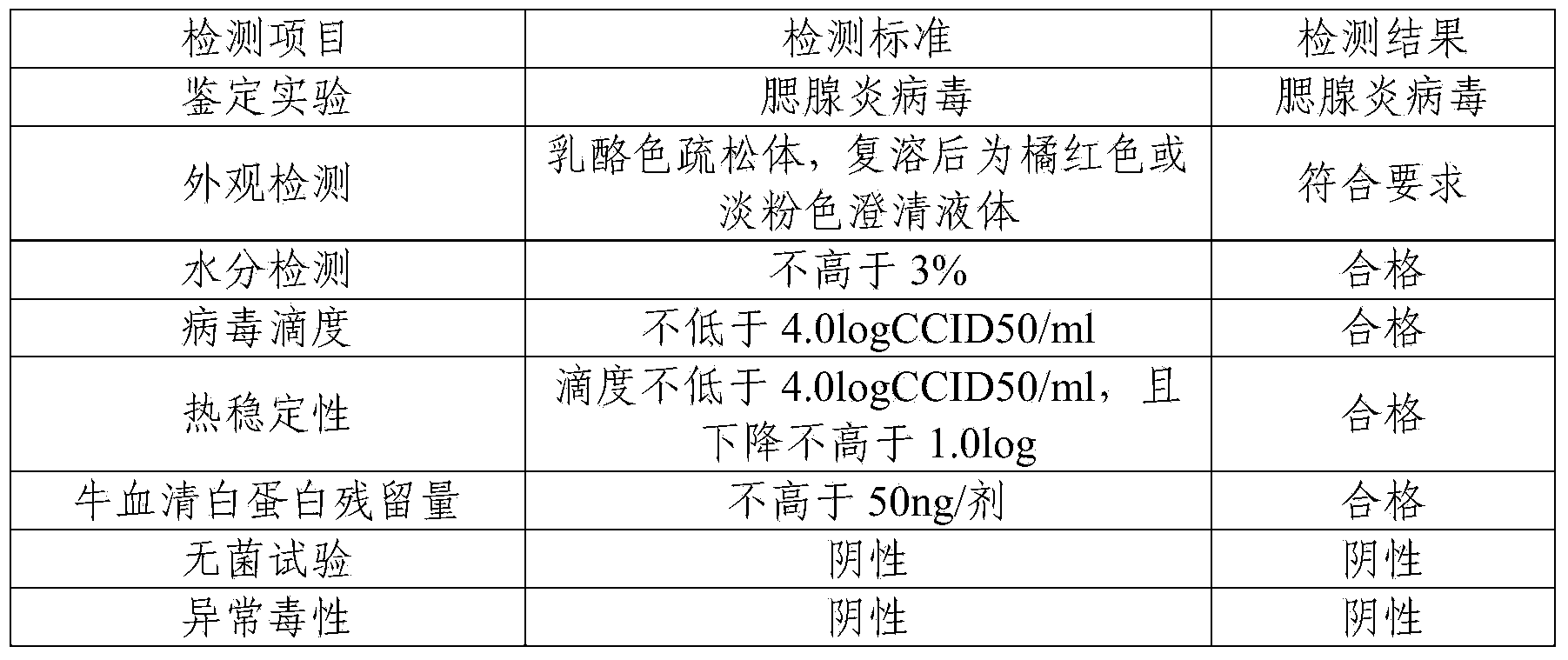
Human diploid cell rabies vaccine virus seed and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102093983ASafeEffectiveMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesBiotechnologyRabies
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a virus seed for producing vaccines for preventing human rabies by utilizing human diploid cells (KMB17) and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, a rabies fixed virus CTN-1V5 strain is continuously subcultured in the human diploid cells (KMB17), and a terminal dilution method is used for screening viruses with highertiter, thereby obtaining a rabies virus strain which is suitable for the human diploid cells (KMB17) and has good immunogenicity and heredity stability, and culturing a rabies vaccine virus seed (CTN-DK strain) capable of efficiently reproducing in the human diploid cells (KMB17). By using the virus seed for producing a human diploid cell (KMB17) rabies vaccine, the risk caused by residual heterogonous DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in the vaccine which is currently used at home can be effectively avoided, and the safety and practicability of the rabies vaccine in China are further improved, thus the invention has great social and economic benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PUKANG BIOTECH
Method for producing rabies vaccine for human
The invention relates to a method for producing a rabies vaccine for human, comprising the following steps of: culturing human diploid cell lines by adopting a linear amplification technique of three or more levels of bioreactors; after the human diploid cell line in each level of bioreactor reaches 106 / ml, carrying out the vaccination on the next level of bioreactor; after the human diploid cell line in the last level of bioreactor grows on a microcarrier until the density reaches 106 / ml, vaccinating rabies virus strains; propagating viruses on cells by vaccinating the rabies virus strains,harvesting virus stock solutions, and inactivating, concentrating and purifying the harvested virus stock solutions to obtain the rabies vaccine for human. By using the linear amplification techniqueof the bioreactor to culture the human diploid cell lines, the cells do not contain exogenous pollution factors and tumorigenicity, and the residual DNA of the cells has no danger, and the rabies vaccine for human has the advantages of good immunizing effect and high safety and meets the requirement of large-scale industrial production of the rabies vaccine.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD +1
Diploid cell rabies vaccine and method for preparing purified rabies vaccine
InactiveCN101352570AIncreased antigenic activityHigh purityAntiviralsTissue cultureSerum free mediaSerum ige
The invention relates to a preparation method for a diploid cell rabies vaccine and a purified rabies vaccine, and the method uses a serum-free medium to culture human diploid cell rabies purified vaccine, thus greatly reducing anaphylactic reaction and being beneficial to purification.
Owner:崔栋
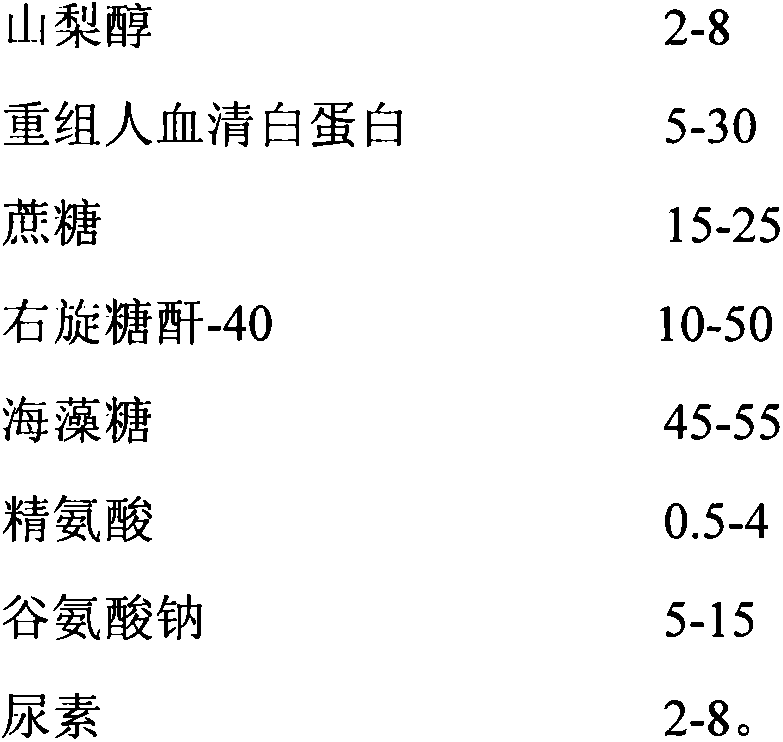
Method for preparation of freeze-dried chickenpox vaccine
The invention relates to the preparative way of a kind of freeze-drying varicella vaccine, which has something to do with the biotechnology. The main making procedures include the following steps: the amplification and passage of Varicellavirus strain Oka to the MRC-5 strain in human's diploid cells; the harvest of the vaccine liquids; freeze-drying. The main property of the vaccine is that it adopts 0.5-1.2%(g / ml) gelatine, 0.6-1.2%(g / ml) glutamic sodium, 0.3-0.9%(g / ml) carbamide and 0.05-0.2%(g / ml) arginine as the freeze-drying protective agents, the previous concentrations stand for the final concentration of the protective agents. The good quality of the vaccine lies in that: the freeze-drying protective agents are developed by the producers themselves to make sure the stability of the vaccine. The result of storage stability test at 2-8DEG C shows that: there's no evident difference between the samples that stored for 18 months and the new-produced samples.
Owner:长春百克生物科技有限公司
Human diploid cell rabies vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102671192AContains less impuritiesPerfect purification processMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesDiploid cells
The invention discloses a human diploid cell rabies vaccine and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of vaccines. A CDKHBP-1 strain is inoculated into a human diploid cell WI-38, and the rabies vaccine is obtained through separation and purification. The human diploid cell does not contain any contaminants or oncogenicity, and is obvious superior to an animal cell serving as a medium for producing the vaccine; and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production, a purification process is perfect, and the vaccine contains a few impurities and has high purity and immunogenicity.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD
Diploid-cell rabies vaccine and purified rabies vaccine, freeze-drying preparation and water injection thereof
InactiveCN1712068ATotal protein content decreasedHigh potencyAntibody medical ingredientsFreeze-dryingDiploid cells
Owner:崔栋
Method for detecting titre of live viruses
InactiveCN101545907AReduce incubation timeThe detection process is fastMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorInfected cellFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting the titre of live viruses, which comprises the following steps: firstly, infecting diploid cells or other adherent cells with dilute viruses to be detected, culturing and fixing the infected cells; secondly, adding virus antiserum (first antibody) into the fixed cells, culturing and washing, adding a second antibody marked by horseradish peroxidase (HRP), culturing and washing, adding coloring solution for color development and producing red or brown spots, or adding virus antiserum marked by the HRP into the fixed cells, culturing the virus antiserum and washing, adding the coloring solution for color development and producing red or brown spots; thirdly, calculating the virus titre according to the quantity of the red or brown spots and the dilution multiple, or calculating the 1gTCID50 value of the viruses according to the dilution degree and the hole numbers of the spots. The detection method can be applicable to the titre detection of various live viruses, can shorten the detection time of the titre of the viruses due to fast detection speed, has good specificity as the immune spots are caused by special immune reaction, low detection cost as well as simple and convenient operation and does not need special instruments of optical or fluorescent microscopes, and the like or other reagents.
Owner:BEIJING WANTAI BIOLOGICAL PHARMACY ENTERPRISE
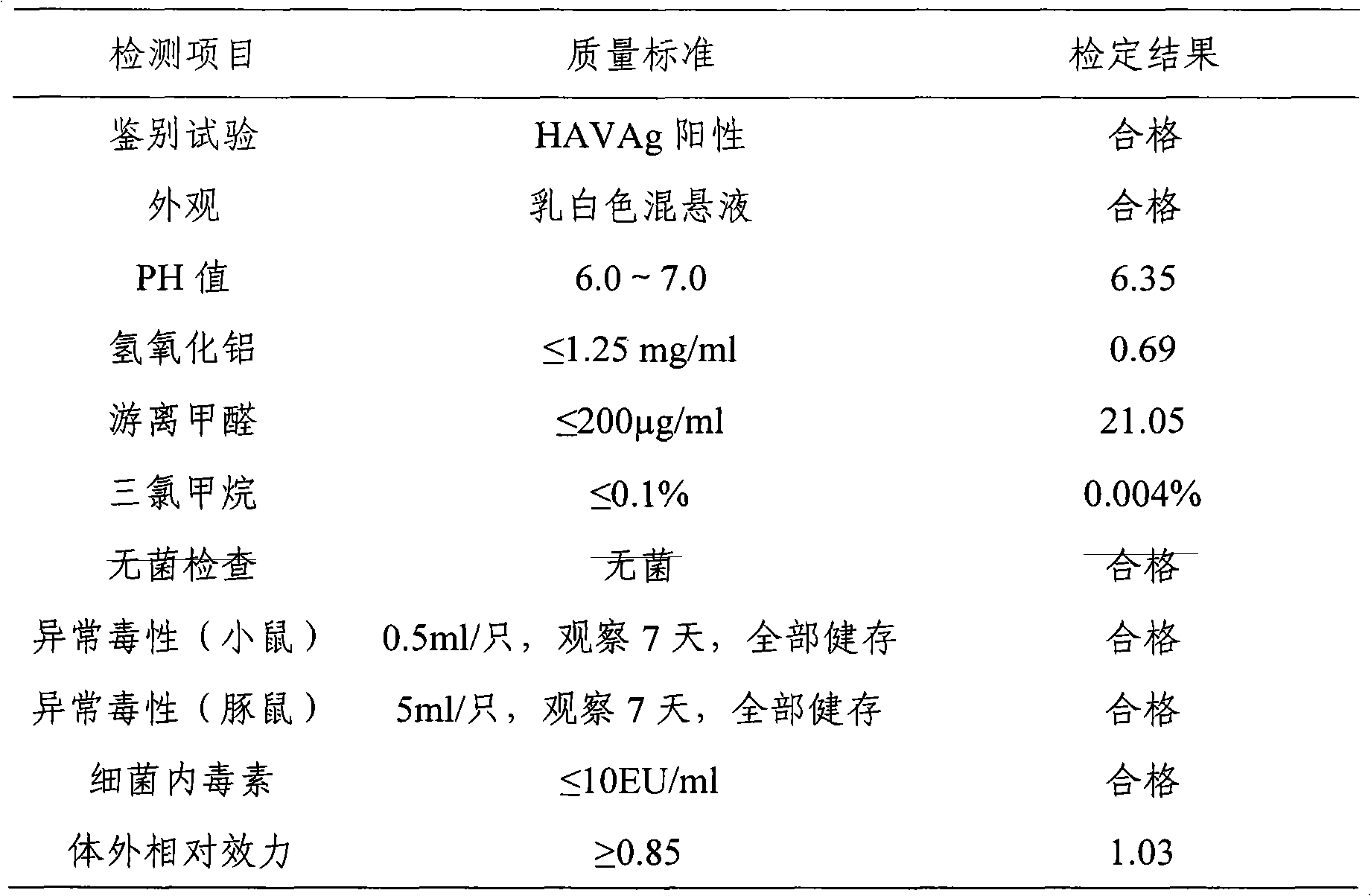
Method of preparing hepatitis A inactivated vaccine
ActiveCN102058882AIncrease production capacityHigh purityAntiviralsViruses/bacteriophagesAdjuvantCell factory
The invention provides a method of preparing a hepatitis A inactivated vaccine, which comprises the following steps of inoculating mixed and absorbed hepatitis A virus strain SH and a human embryo diploid cell MRC-5 to hepatitis A virus propagated in a cell factory, digesting the cell in the virus propagation peak to obtain cell virus liquid, removing impurity proteins of the cell by ultrasonication, chloroform extraction and ultrafiltration through ultrafiltration membranes, degerming and filtering by gel filtration chromatography and purification, and absorbing by an aluminium hydroxide adjuvant so that the hepatitis A inactivated vaccine is prepared. The result of in vivo effectiveness experiments performed on a mouse shows that the hepatitis A inactivated vaccine prepared by the method of the invention has higher ED50 and better immunogenicity than the contract strain. The method of the invention can improve the safety of the vaccine, simplify the technique, shorten the productionperiod, reduce the production cost, and realize the scale production of the hepatitis A inactivated vaccine.
Owner:SHENZHEN KANGTAI BIOLOGICAL PROD
Diploid somatic cell encephalitis B vaccine and method for preparing purified encephalitis B vaccine
ActiveCN101352569ATotal protein content decreasedImprove immunityViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsJapanese encephalitis vaccineSerum ige
The invention relates to a preparation method for diploid cell Japanese encephalitis vaccine and purified encephalitis vaccine. The method uses a serum-free medium to culture human diploid cell Japanese encephalitis purified vaccine, thus greatly reducing anaphylactic reaction and being beneficial to purification.
Owner:崔栋
Method for improving survival rate of human diploid cells
InactiveCN104430301AImprove survival rateDead animal preservationSerum free mediaHydroxyethyl starch
The invention discloses a method for improving a survival rate of human diploid cells. The method comprises the following steps: digesting the cells by using a trypsin solution, centrifuging, and removing supernatant; suspending the cells by using a frozen stock solution, wherein a solvent of the frozen stock solution is normal saline or TC199 serum-free medium, and each milliliter of solvent contains 3 percent of human albumin, 5 percent of dimethyl sulfoxide, 0.5 percent of sodium carbonate, 2 percent of hydroxyethyl starch, 5 percent of serine and 6-10 percent of dimethylacetamide. According to the preservation method provided by the invention, the survival rate of the human diploid cells can be improved.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHUA BIOLOGICAL PROD
Protein-free serum-free medium suitable for diploid cell culture and application
The invention provides a protein-free serum-free medium suitable for diploid cell culture and a preparing method thereof. The medium contains calcium chloride, magnesium sulfate, potassium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, L-arginine hydrochloride, L-asparaginate, L-cystine dihydrochloride, L-histidine hydrochloride, L-leucine, L-isoleucine and the like. The medium can meet the requirement of the growth or maintenance stage of diploid cells and prevents contact with exogenous viruses possibly existing in protein and serum to reduce potential safety hazards; as the components are simple and definite, standard products can be purchased in the market, the difference between different product batches is small, and the step of purifying down-stream products is simplified; a scientific basis is provided for large-scale standard production. In addition, the protein-free serum-free medium can be applied in the growth or maintenance stage of the diploid cells.
Owner:SICHUAN BAINUOJI TECH CO LTD
Method for producing novel freeze-dried live attenuated varicella vaccine
InactiveCN104188923ASolve outputSolve productivityPowder deliveryAntiviralsAdditive ingredientFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for producing a novel freeze-dried live attenuated varicella vaccine. The method is characterized in that a human diploid cell is used as a culture medium, a reactor culture process is applied to inoculate a varicella OKa strain, and an invented freeze-drying protective additive containing sorbitol and recombinant human serum albumin is used to produce the freeze-dried live attenuated varicella vaccine. By applying the reactor culture technology, the production cost is reduced, the defects of low yield, large production occupied area, high labor intensity and the like of a static culturing process can be overcome, the yield of vaccines can be increased, and the virus titer stability can be improved; furthermore, the protective additive containing sorbitol and recombinant human serum albumin is used and does not contain gelatin, so that animal derived ingredients can be removed, the content of toxin in the vaccine can be remarkably reduced, the stimulation and hazard of the vaccine on a human body can be greatly reduced, and the safety and stability of the vaccine can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING HEKANGYUAN BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Application of human embryonic lung fibroblast strains in preparation of rabies inactivated vaccine
InactiveCN103468650ACharacteristics of typical human diploid cells cultured in vitroEasy to shapeMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAntigenImmune effects
The invention discloses an application of human embryonic lung fibroblast strains Walvax-2 in the preparation of a rabies inactivated vaccine. The human embryonic lung fibroblast strains Walvax-2 are susceptible to rabies viruses, and when the human embryonic lung fibroblast strains are used for producing the rabies virus vaccine, the diploid cell rabies virus inactivated purified vaccine for people can be obtained, wherein the vaccine is high in antigen purity, good in immune effect, high in safety and low in price.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
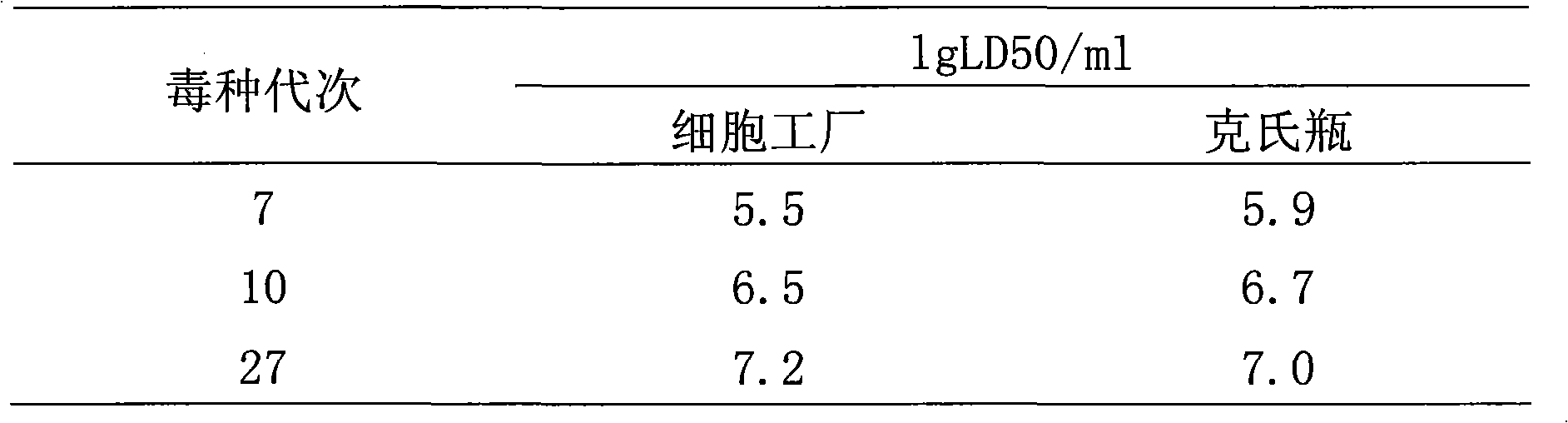
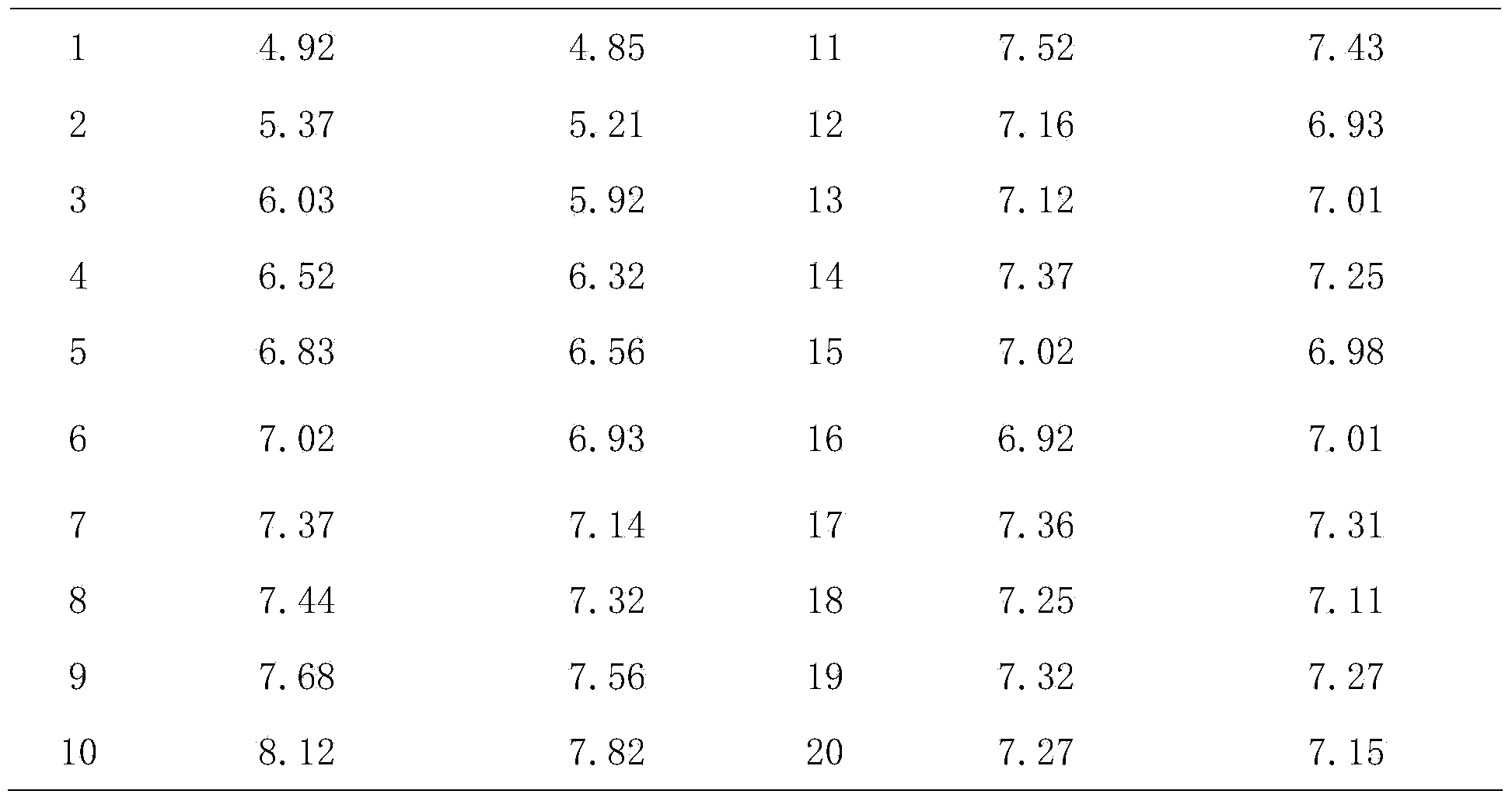
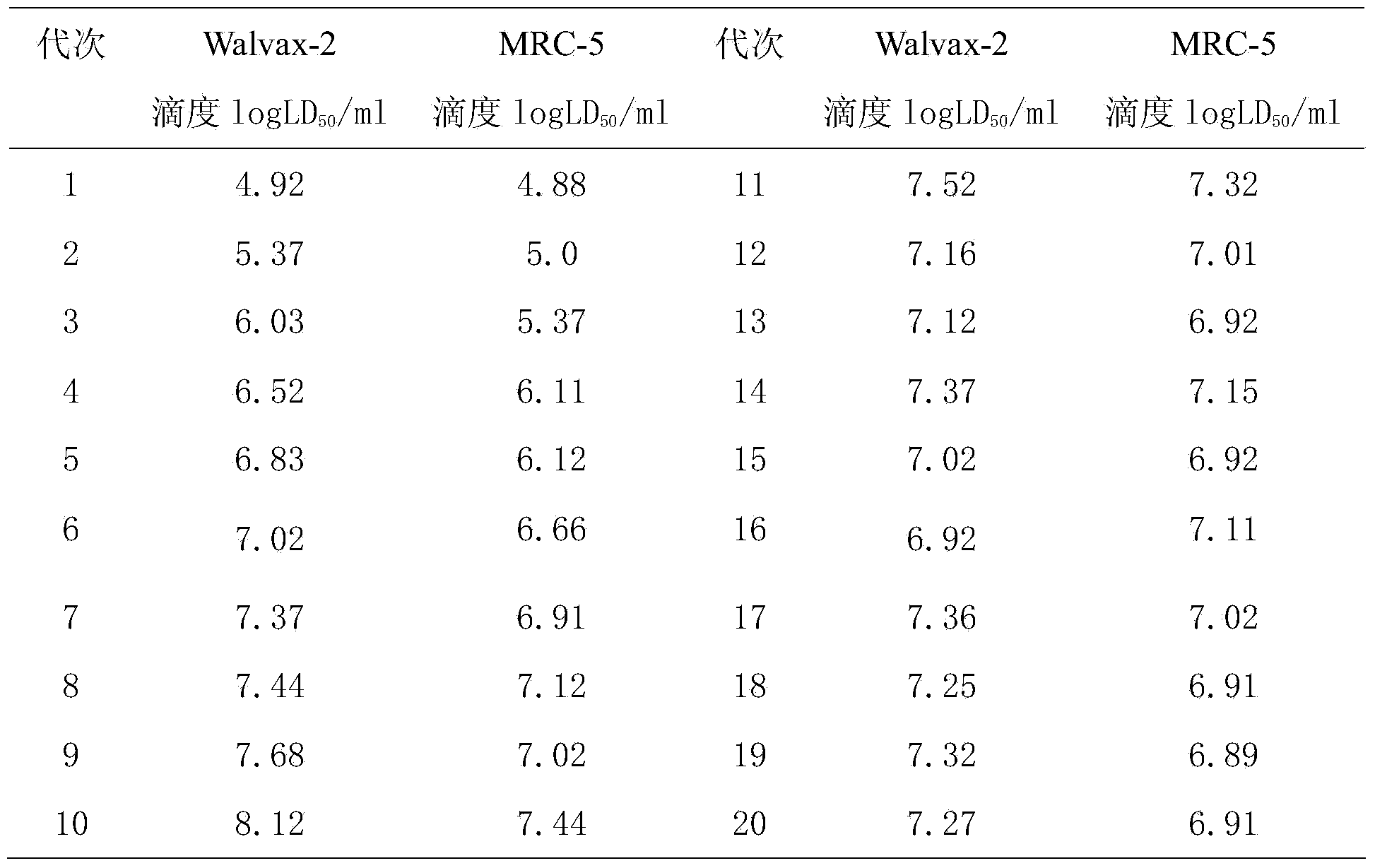
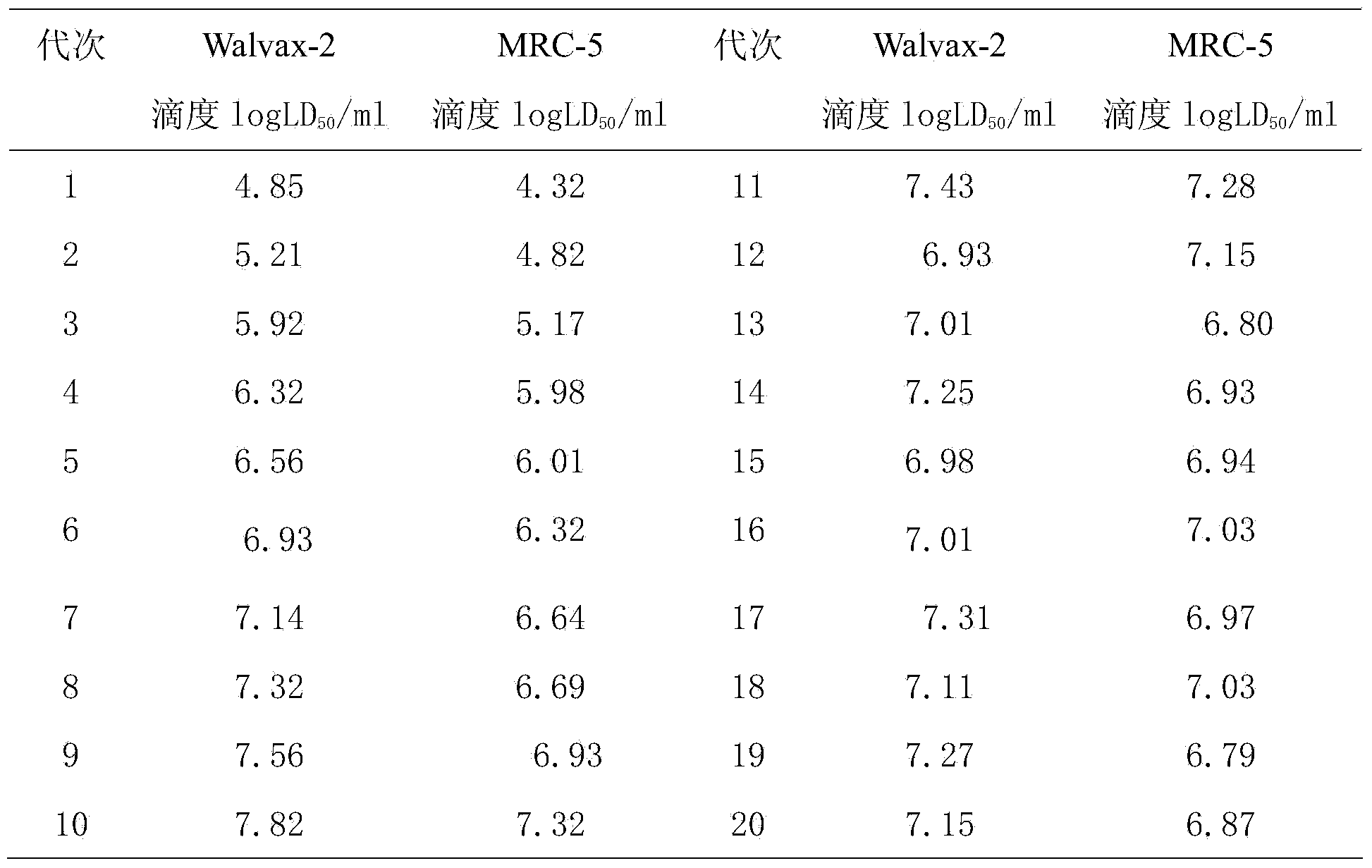
Rapid adaptation method of rabies vaccine virus strains for human body on diploid cells of human body
ActiveCN103468649AImproving immunogenicityShort adaptation timeViruses/bacteriophagesHuman bodyMaterial resources
The invention discloses a rapid adaptation method of rabies vaccine virus strains for the human body on diploid cells of the human body. Fresh rabies viruses are inoculated on the diploid cells of the human body, poisoned passage is carried out, only 4-5 cycles are required, passage is carried out for 12-15 passages, the virus titer rises above 7.0logLD50 / ml of the P15 from 3.0logLD50 / ml of the P1, the adaptation cycle of the viruses is shortened by at least 50%, on the premise that the virus immunogenicity is not affected, the virus yield is rapidly improved, and manpower and material resources are saved.
Owner:云南沃森生物技术股份有限公司
Vaccine for virus of encephalitis B and preparation method
ActiveCN1695736AImproving immunogenicityGood protective effectViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsAcute viral encephalitisDiploid cells
A vaccine of the encephalitis B virus for preventing viral encephalitis B is prepared through inoculating said virus into human diploid cells, culturing, naturalizing, adapting, amplifying, concentrating and purifying.
Owner:复星安特金(成都)生物制药有限公司
Method for cultivating triploid dendrobium huoshanense by fusion breeding method of diploid cells and pollen cells
ActiveCN104429939ABreeding method steps are simpleShorten breeding timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsFiberPlanting seed
The invention discloses a method for cultivating triploid dendrobium huoshanense by a fusion breeding method of diploid cells and pollen cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting dendrobium huoshanense varieties from different producing areas, which are good in stress resistance, quick in growth, thick in stalks, long in stem height, various in tillering, low in fiber content and high in medicinal composition content as a triploid cultivating source plant parent; (2) performing aseptic seeding on source plant seeds in a solid culture medium to obtain protocorm; (3) performing sterile culture on the source plant pollen in the solid culture medium to obtain a pollen cell population; (4) preparing protoplasts of the pollen cells and the protocorm cells to perform cell fusion; (5) culturing the fused cells on the solid culture medium to differentiate the fused cells into young plants, and then detecting the triploid plants; and (6) performing tissue culture on the triploid plants to obtain a large number of triploid young plants.
Owner:WEST ANHUI UNIV
Method for preparing genotype F mumps attenuated live vaccine
InactiveCN103751772AGood humoral immunityImprove securitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsFreeze thawingGenotype
The invention provides a method for preparing genotype F mumps attenuated live vaccine. The method comprises the following steps of inoculating mumps attenuated strain MHM-19 to human embryo lung diploid cell MHL-3 which is cultured to a monolayer; releasing virus through frozen-thawed cell in the peak of viral multiplication; centrifuging and removing cell debris; adding a protective agent to centrifuged virus suspension to obtain a semi-finished product of vaccine; and freezing and drying the semi-finished product to obtain the finished product of genotype F mumps attenuated live vaccine. After a rhesus monkey is injected with the prepared MHM-19 attenuated live vaccine for immunizing, good humoral immunity is induced to be produced, and the detection results obtained at different times after immunization show that the MHM-19 attenuated live vaccine has immunizing potency superior to that of reference mumps vaccine S79; in addition, the safety experiment shows that the rhesus monkey does not suffer from parotitis-related symptom after being injected with MHM-19 attenuated live vaccine, the pathological tissue nearly has no obvious difference with that of S79 strain by observing, so that the MHM-19 attenuated live vaccine has high safety.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com