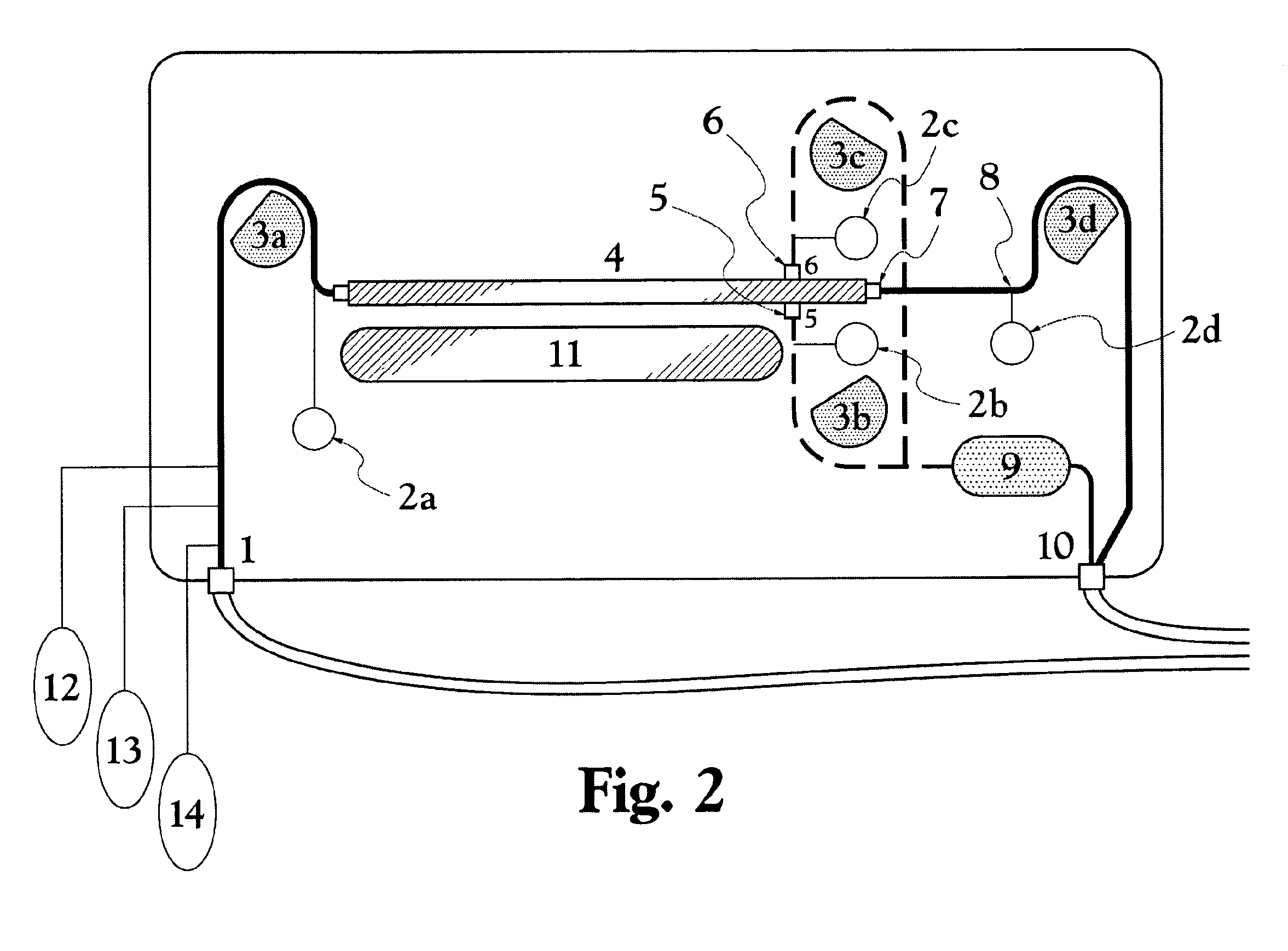
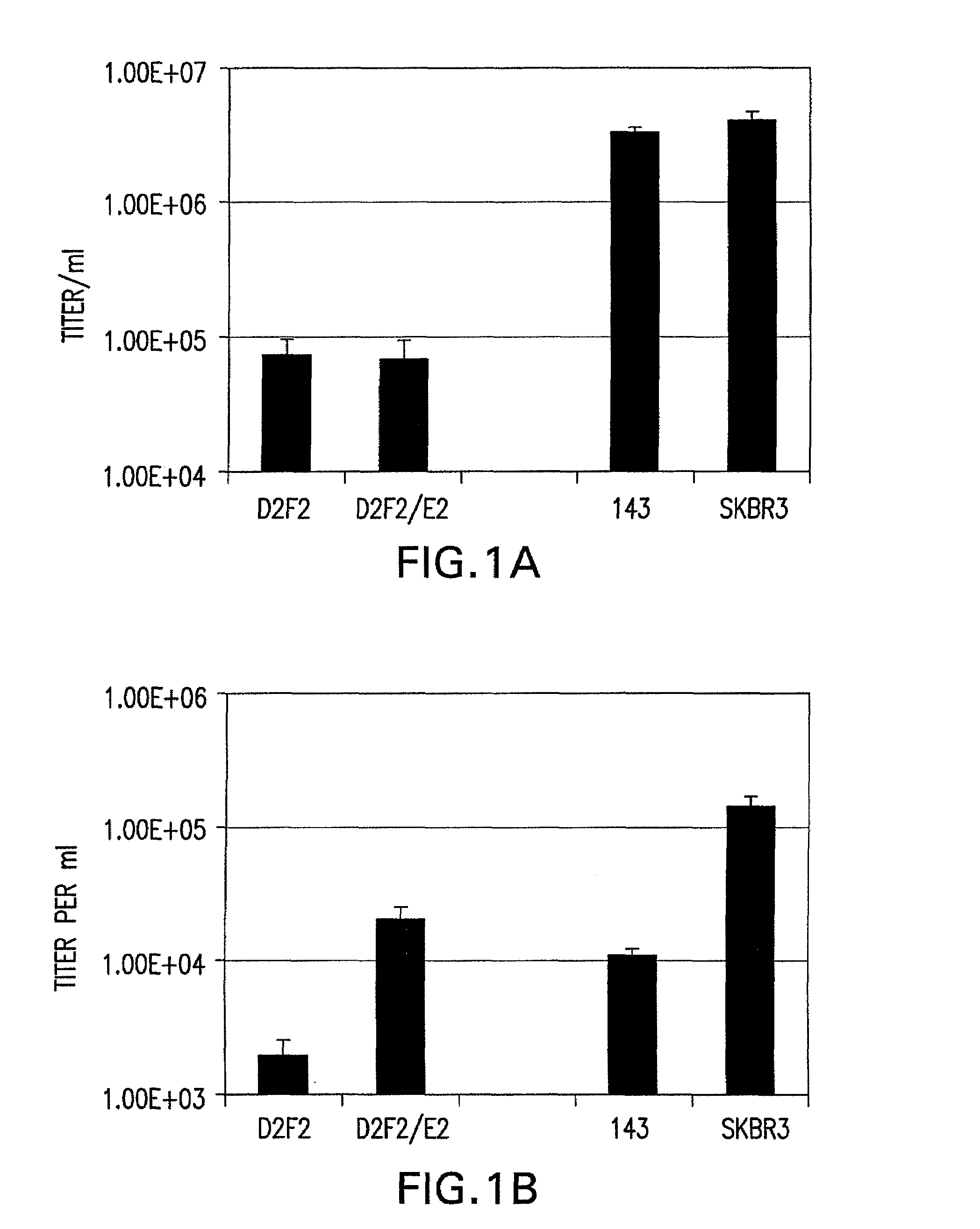
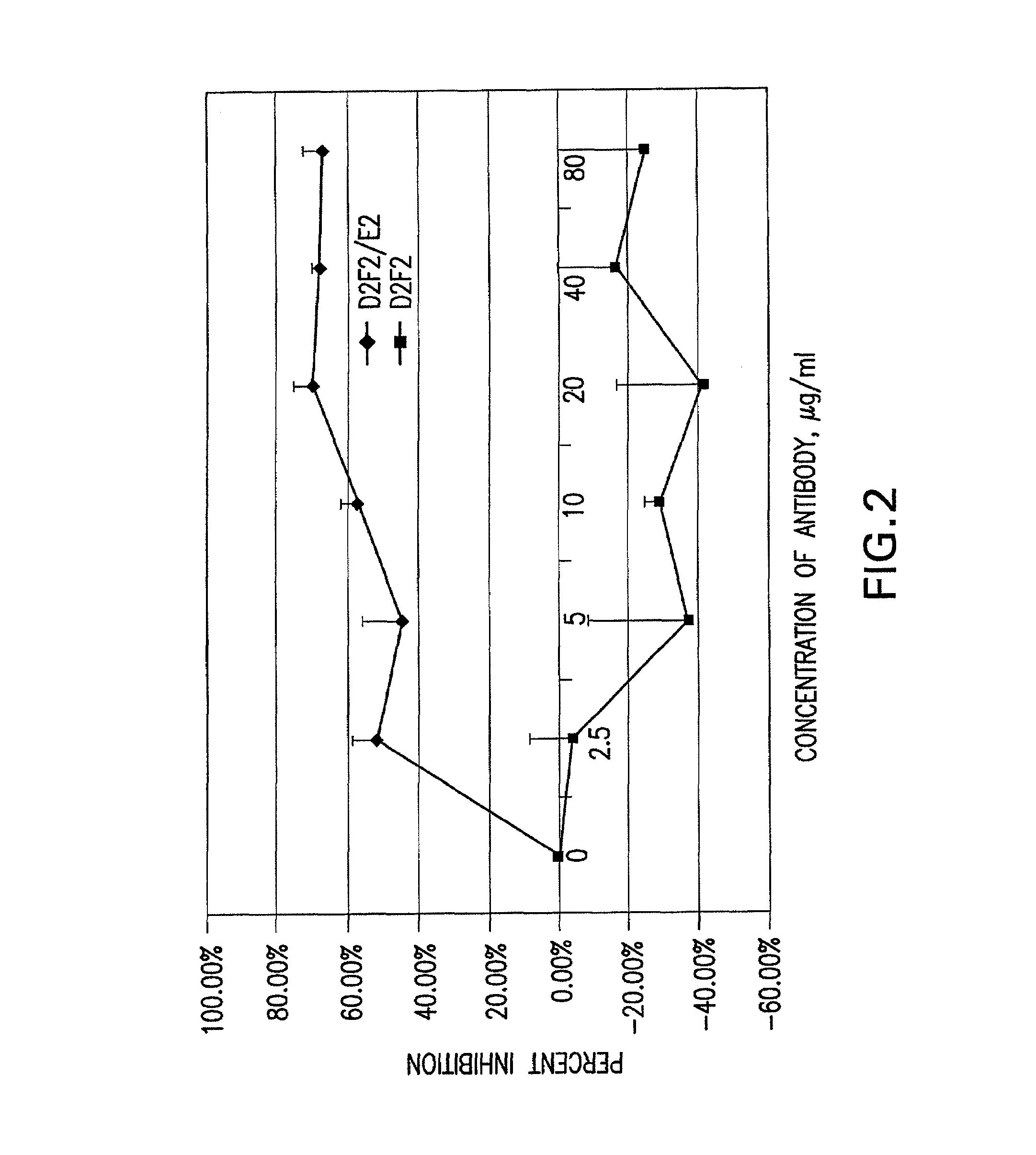
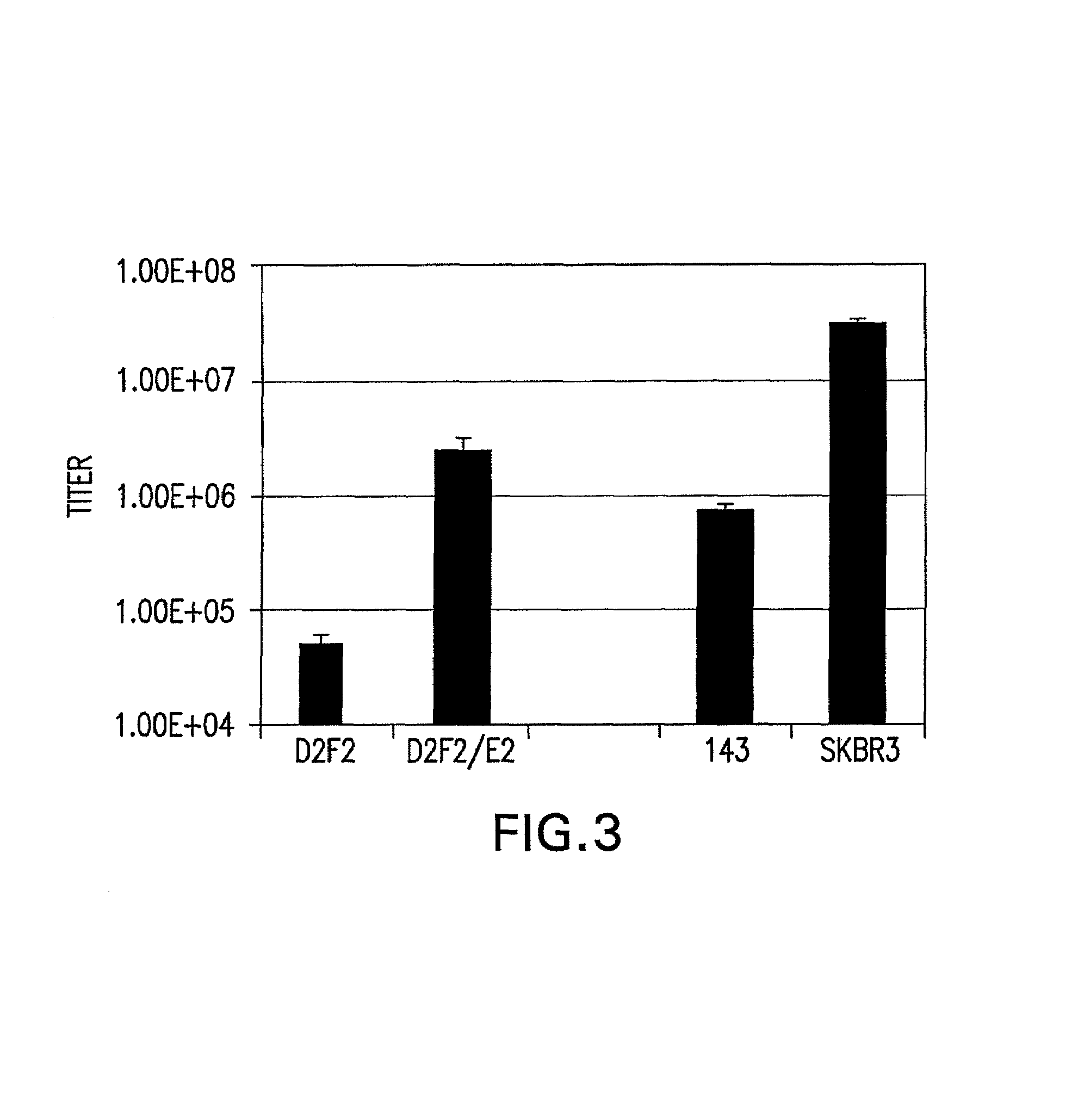
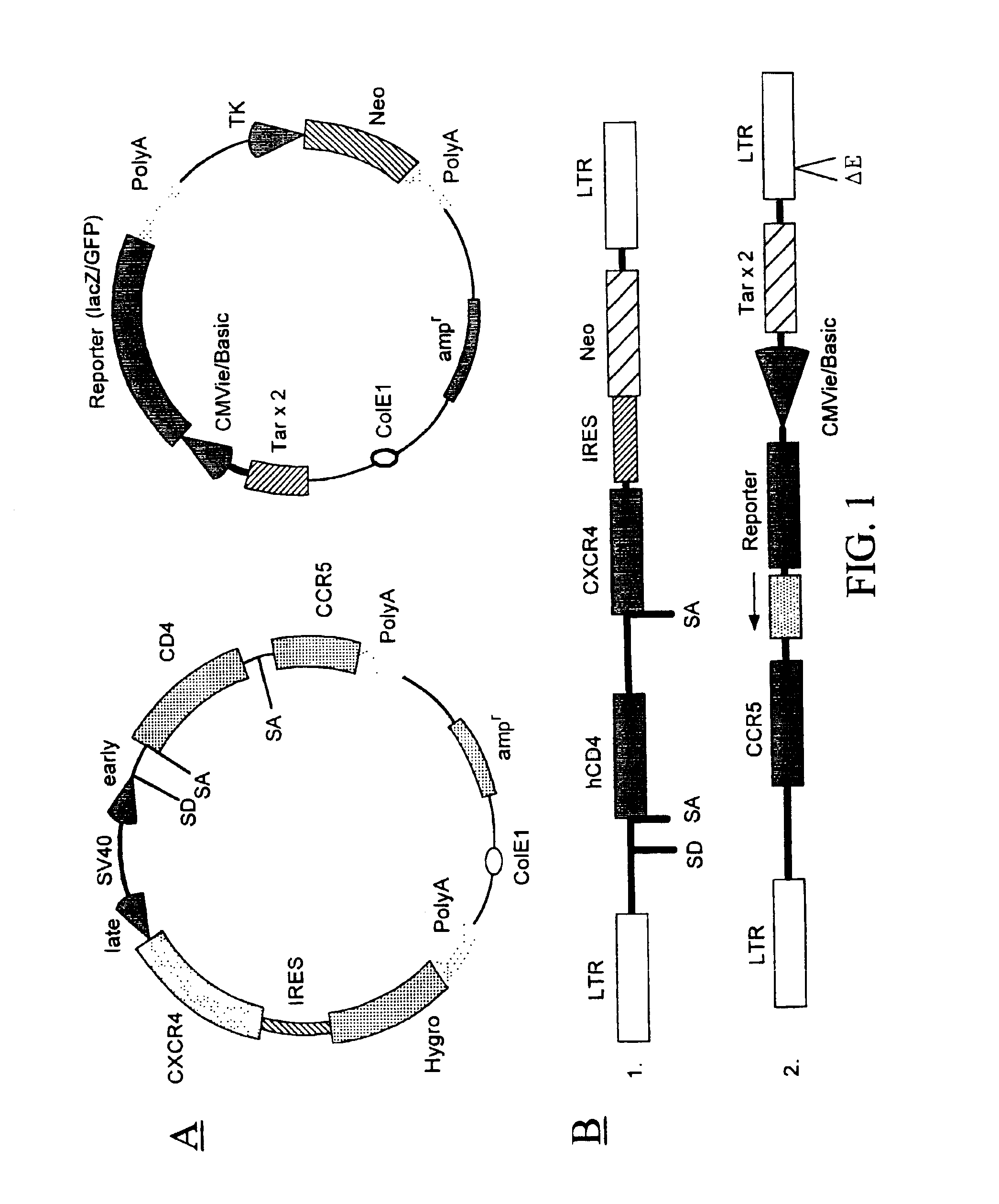
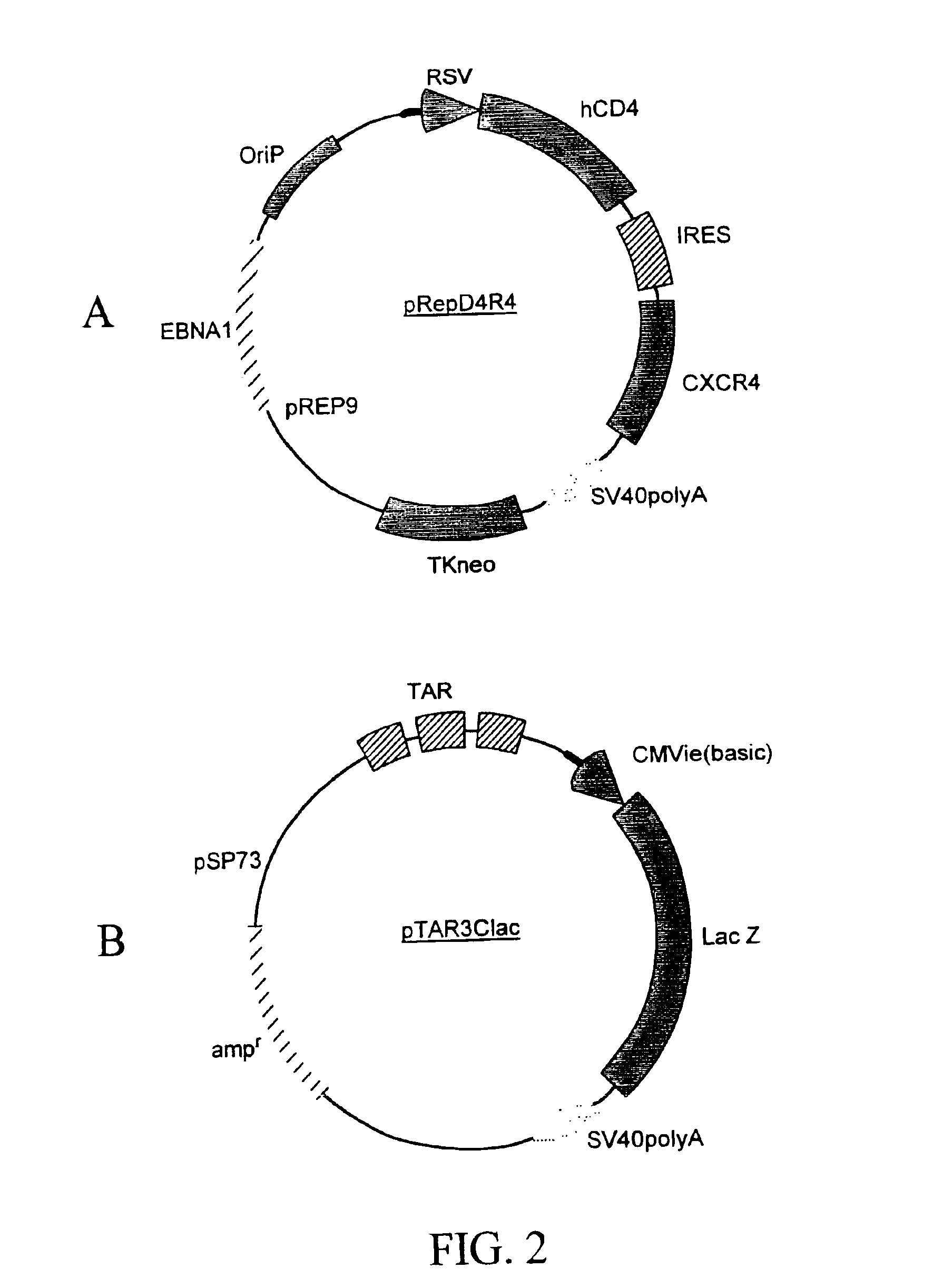
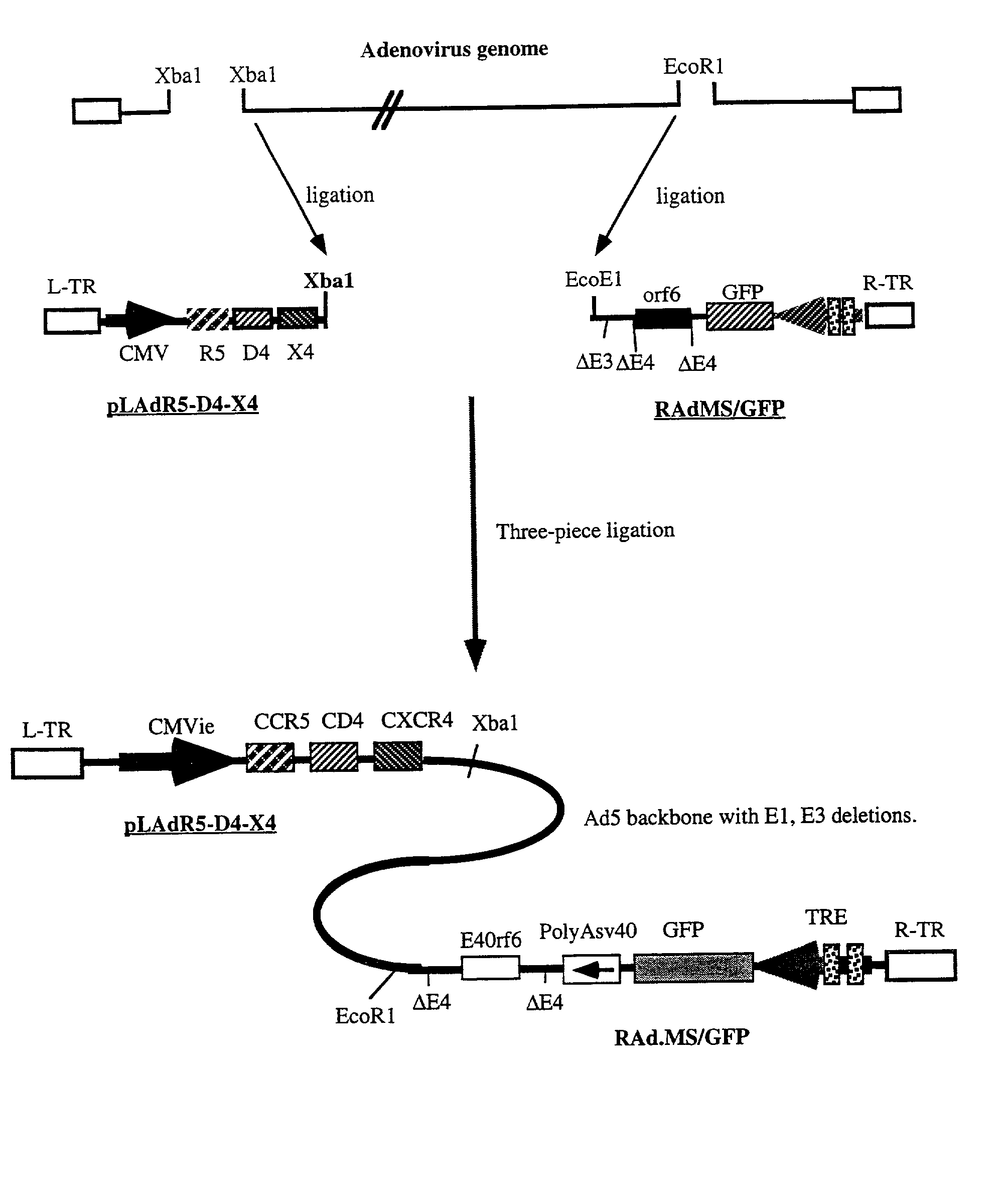
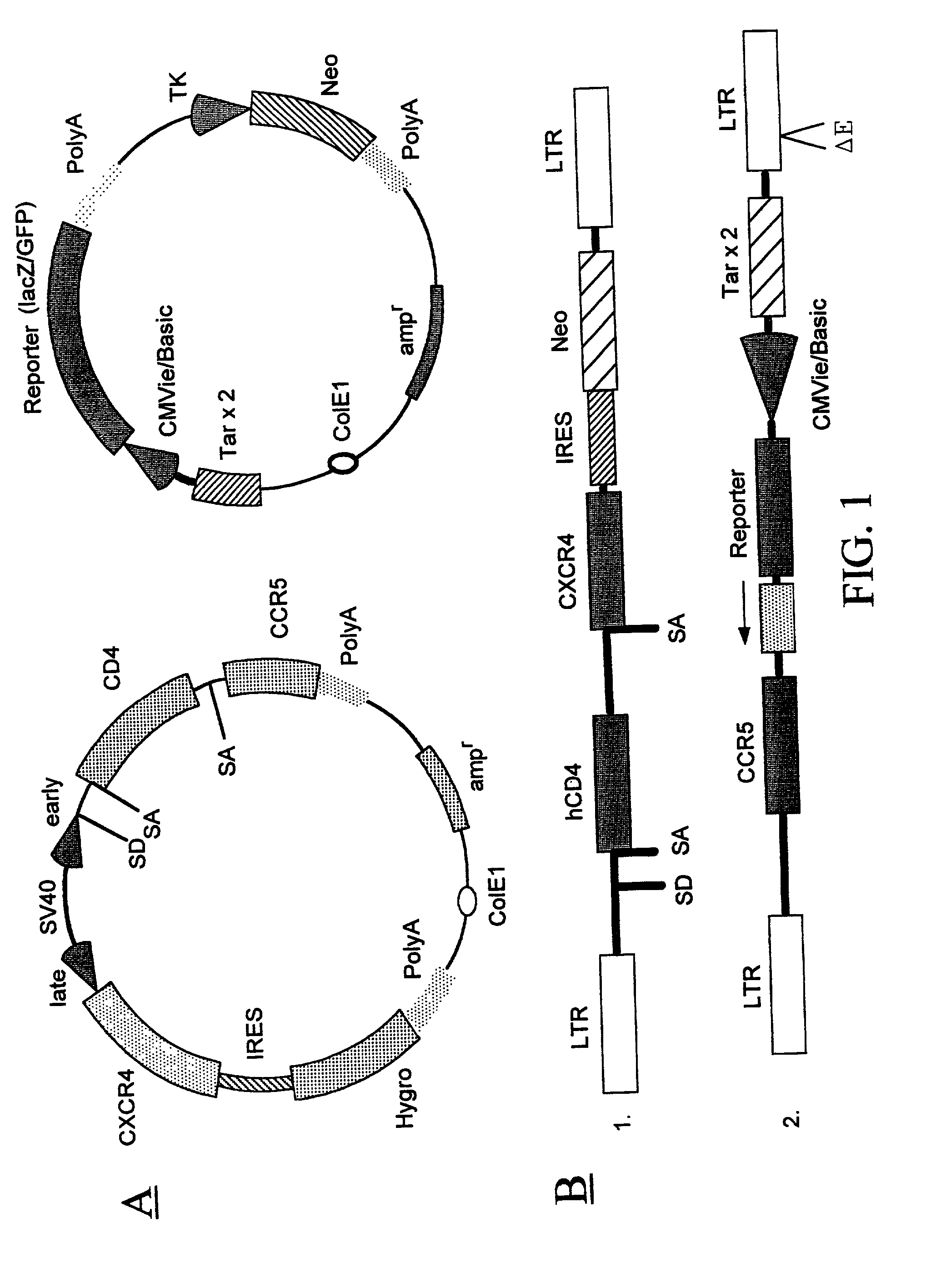
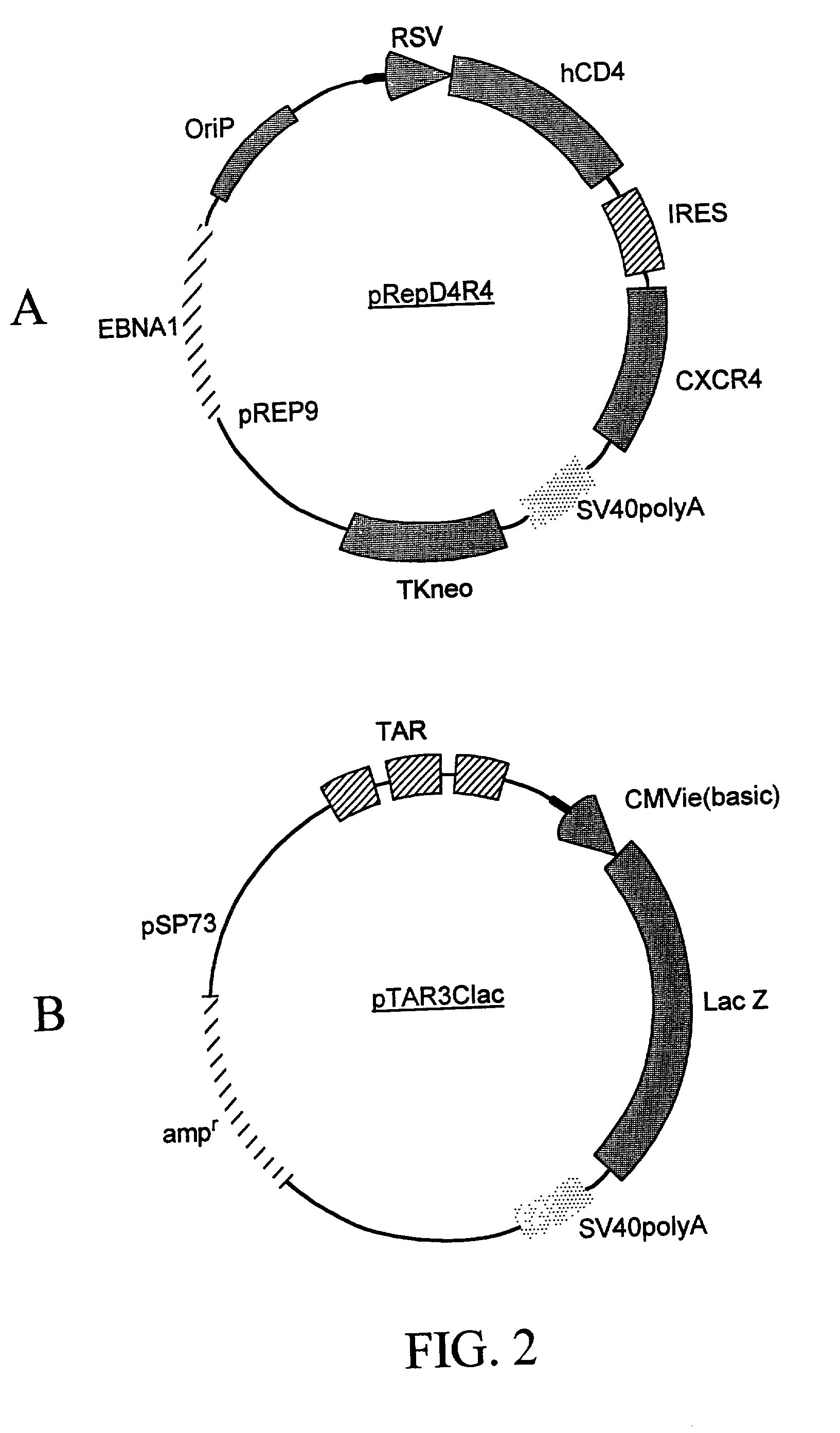
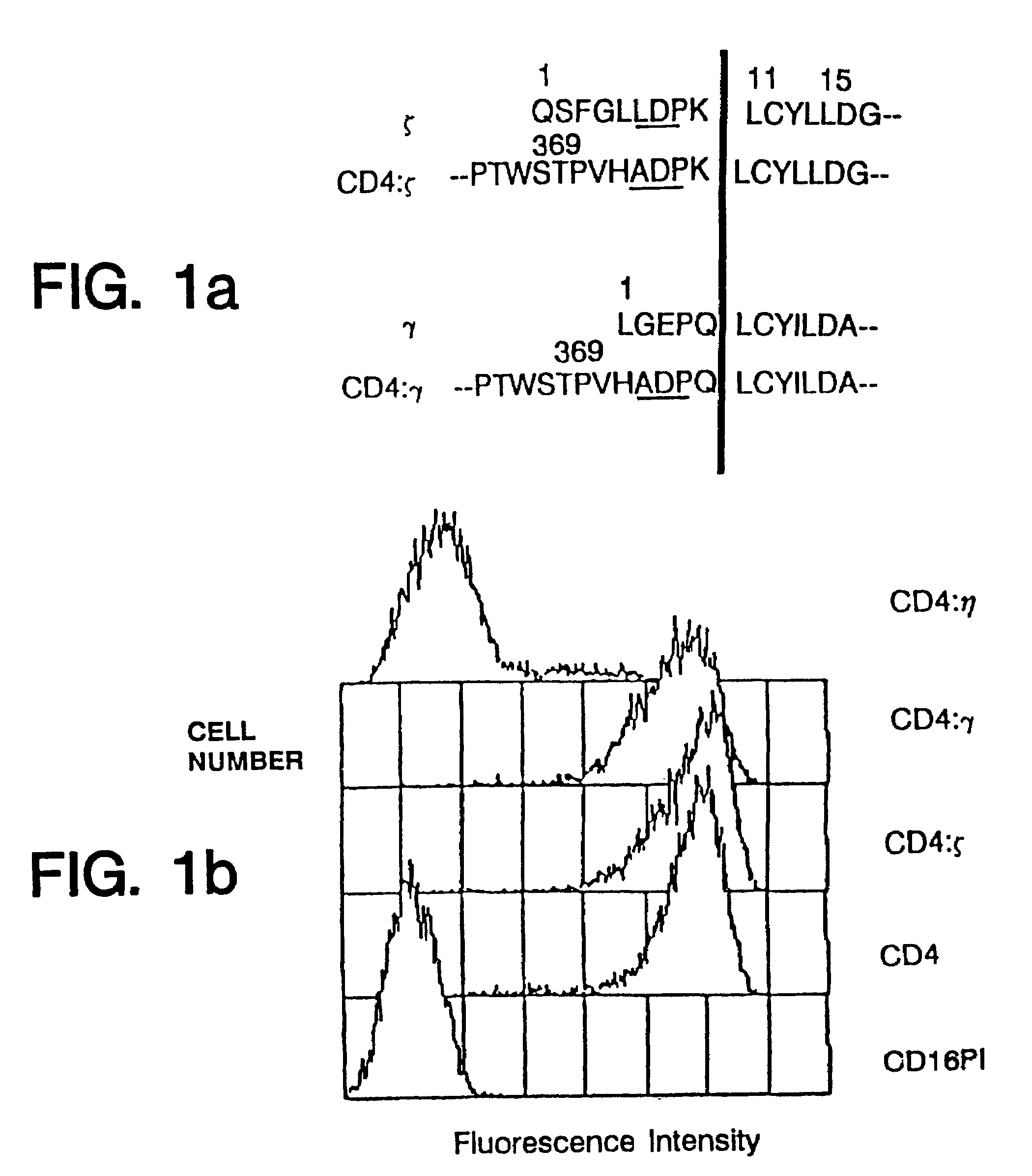
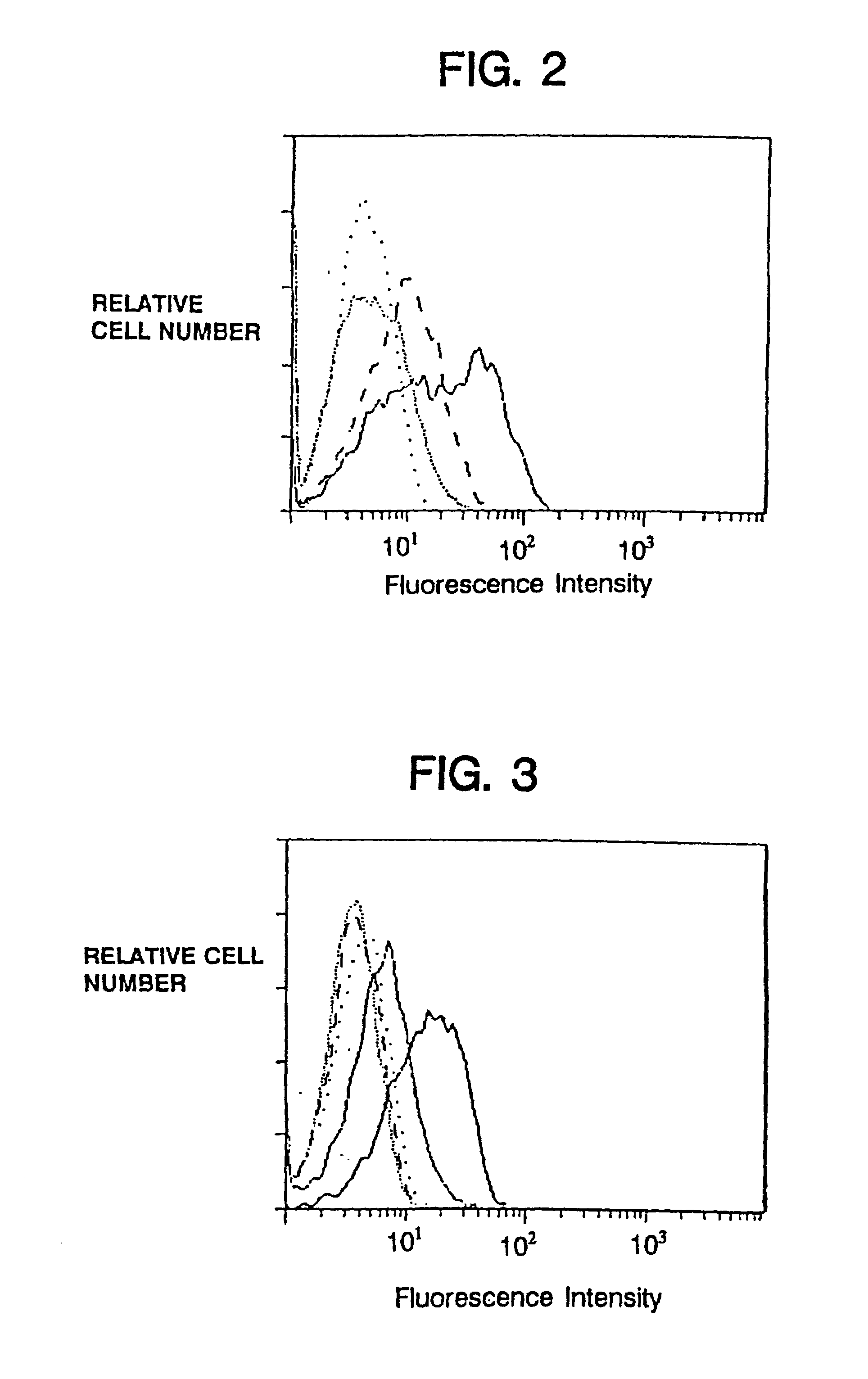
Patents
Literature
415 results about "Infected cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
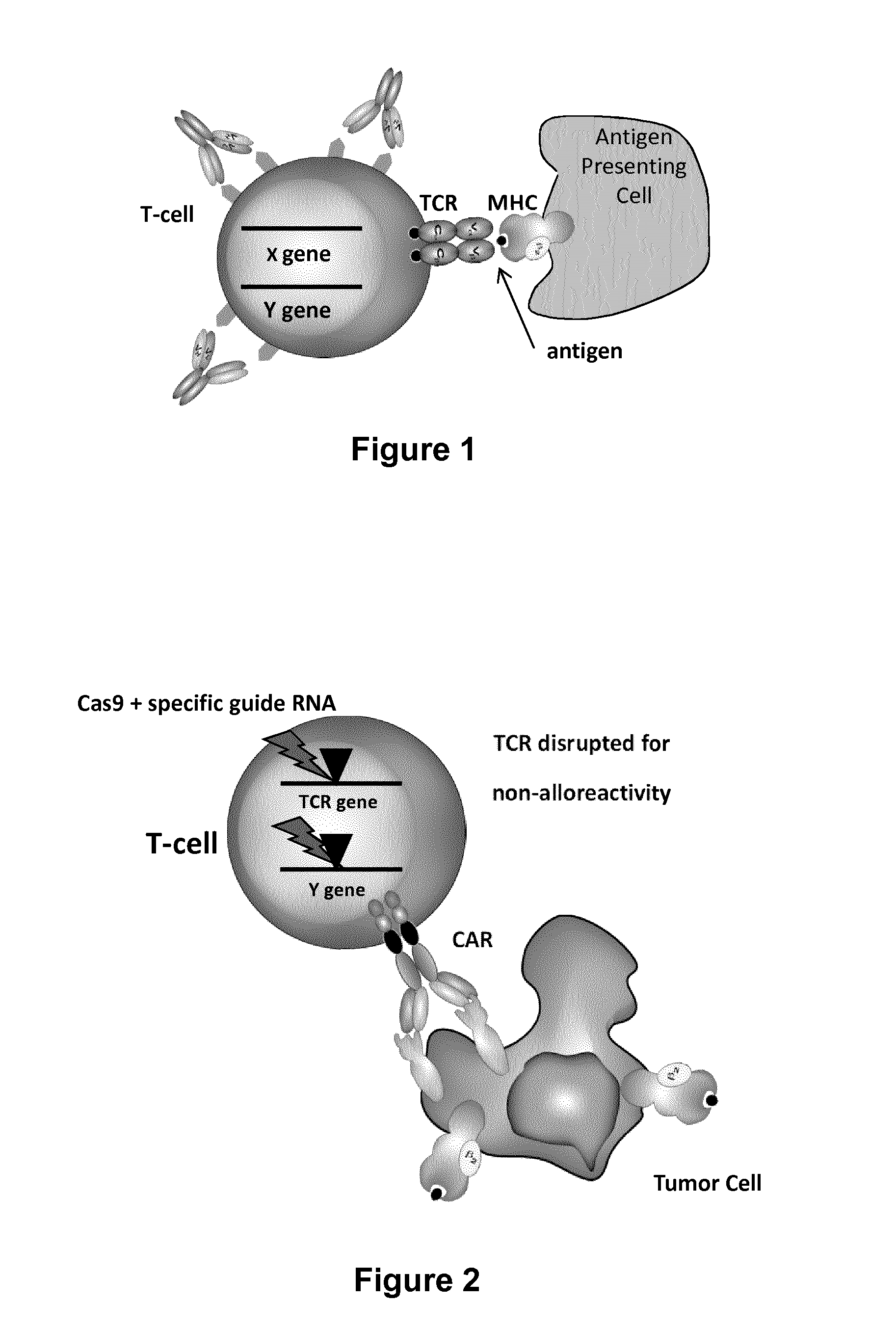
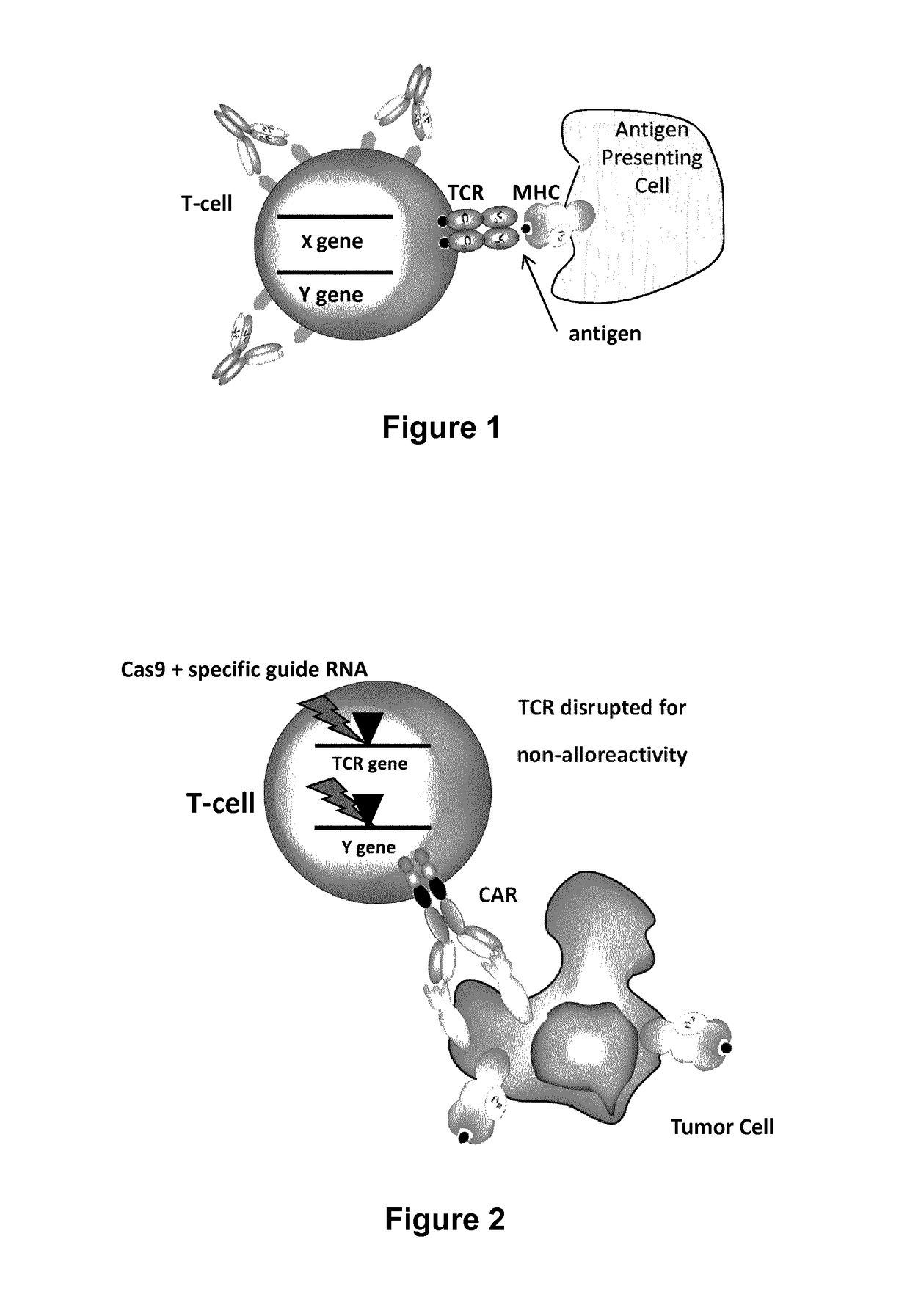
Infected cell. A virus is a small infectious agent that needs other cells to replicate. The virus gets its genetic material inside the cell and the cell then uses its machinery to read the genetic code and create virus proteins that will form new viral particles.
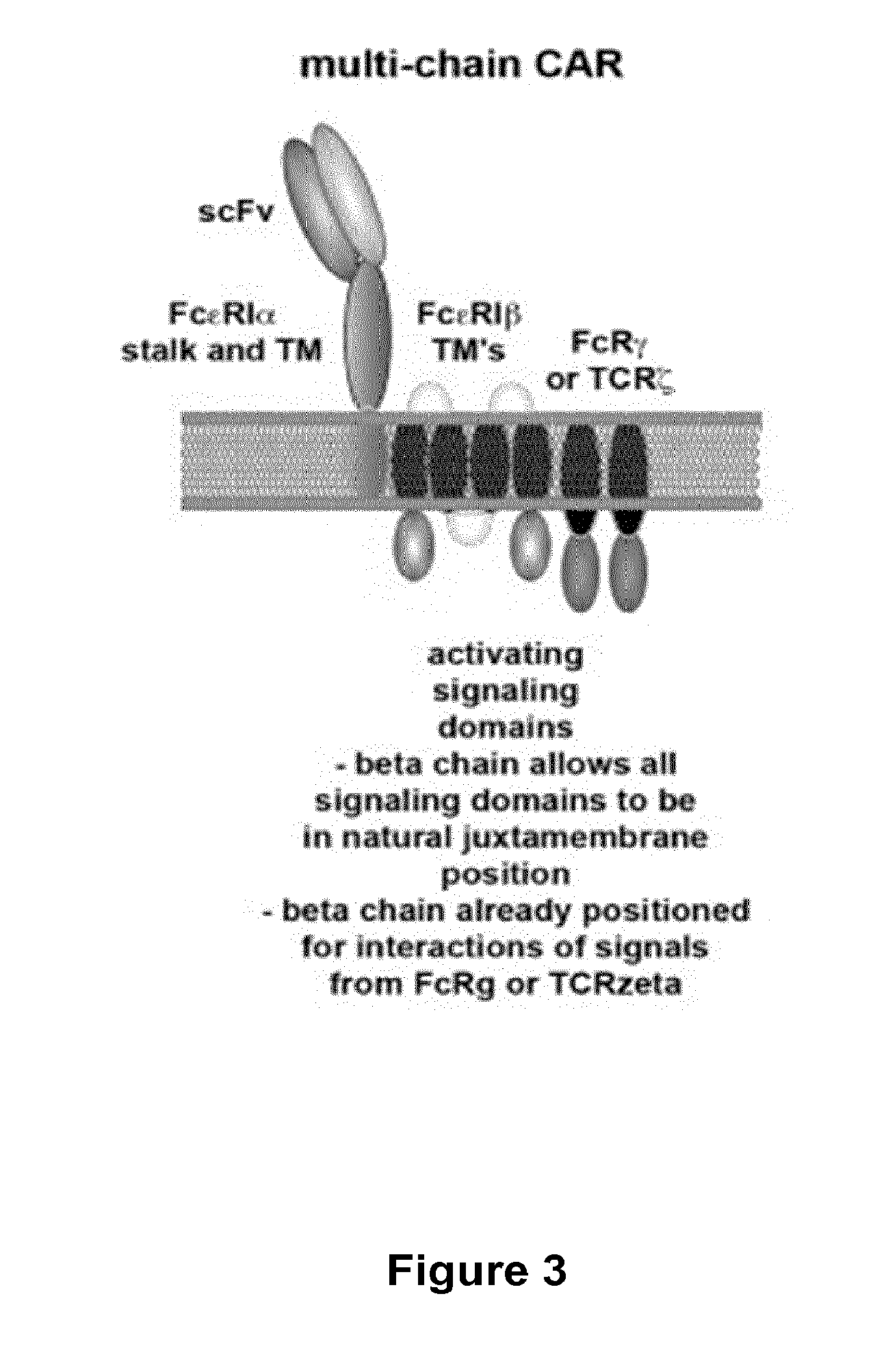
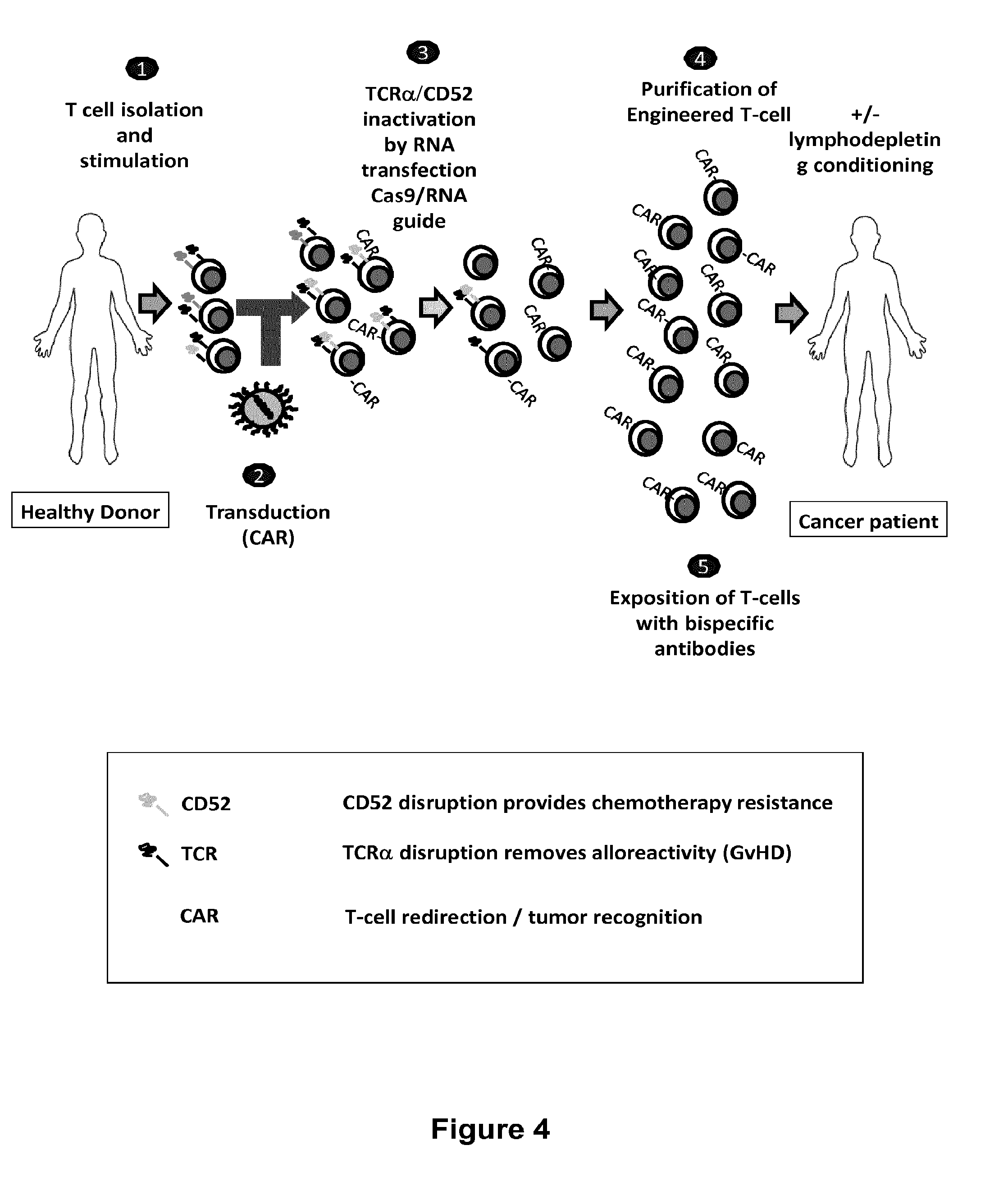
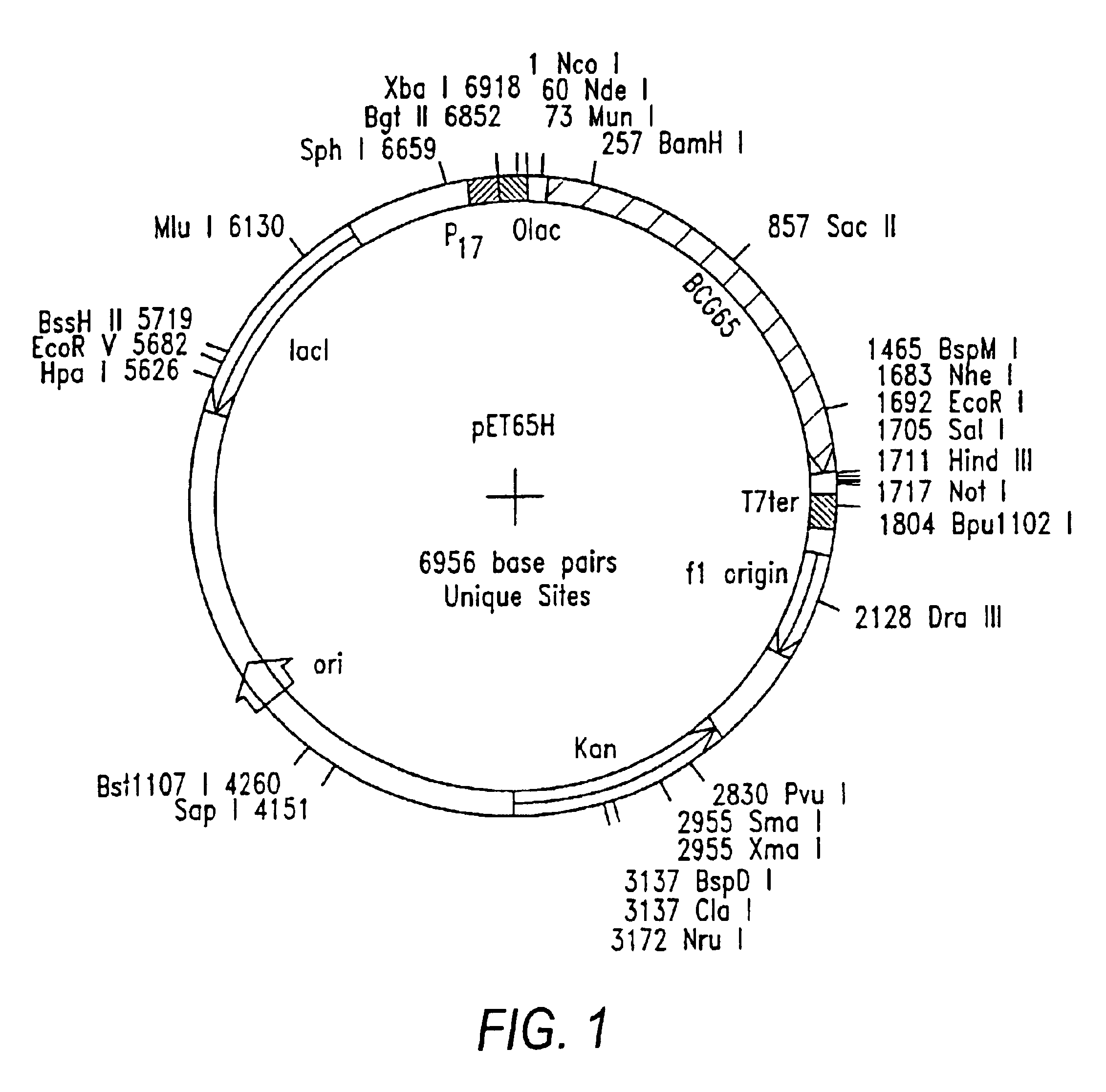
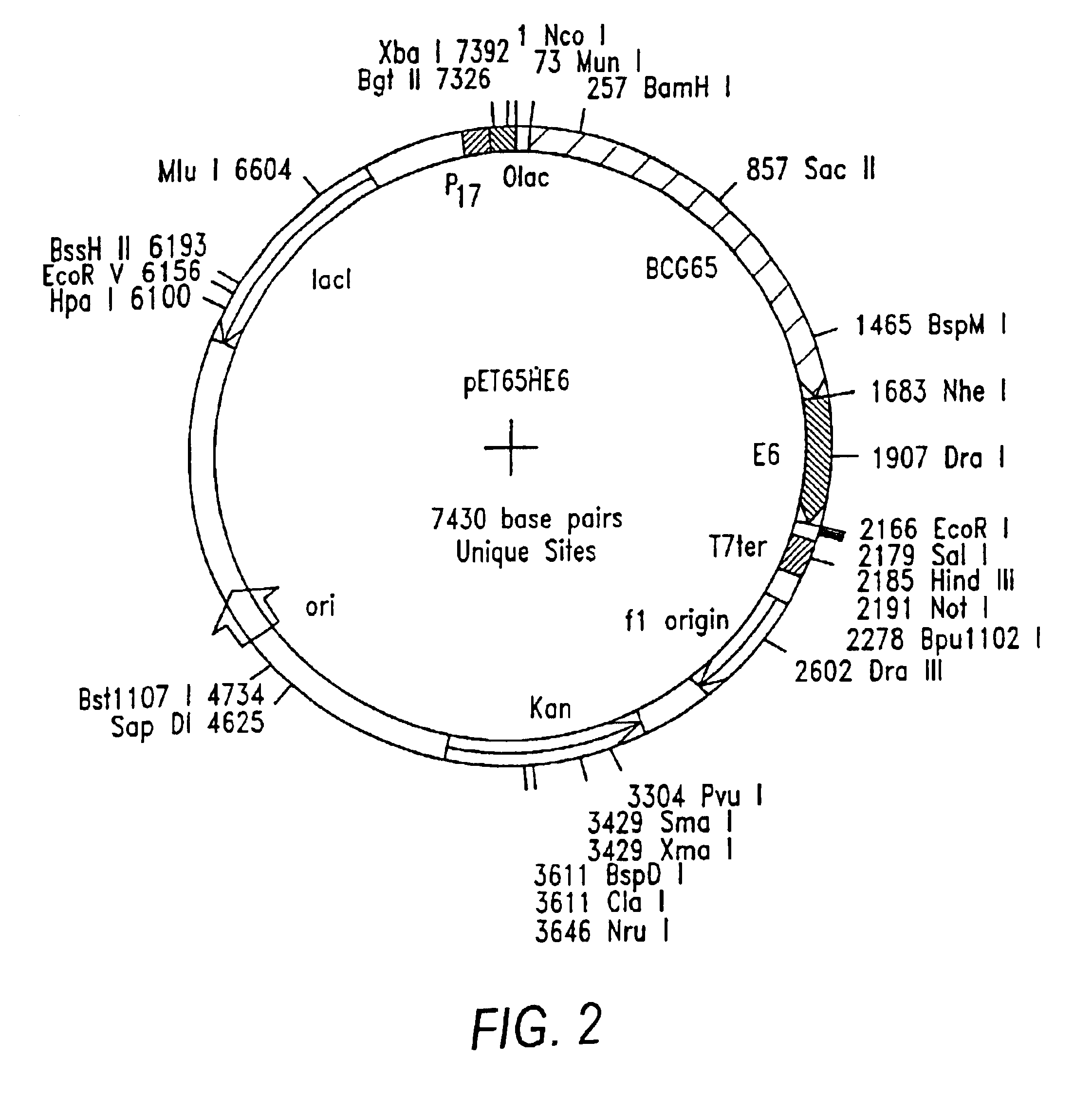
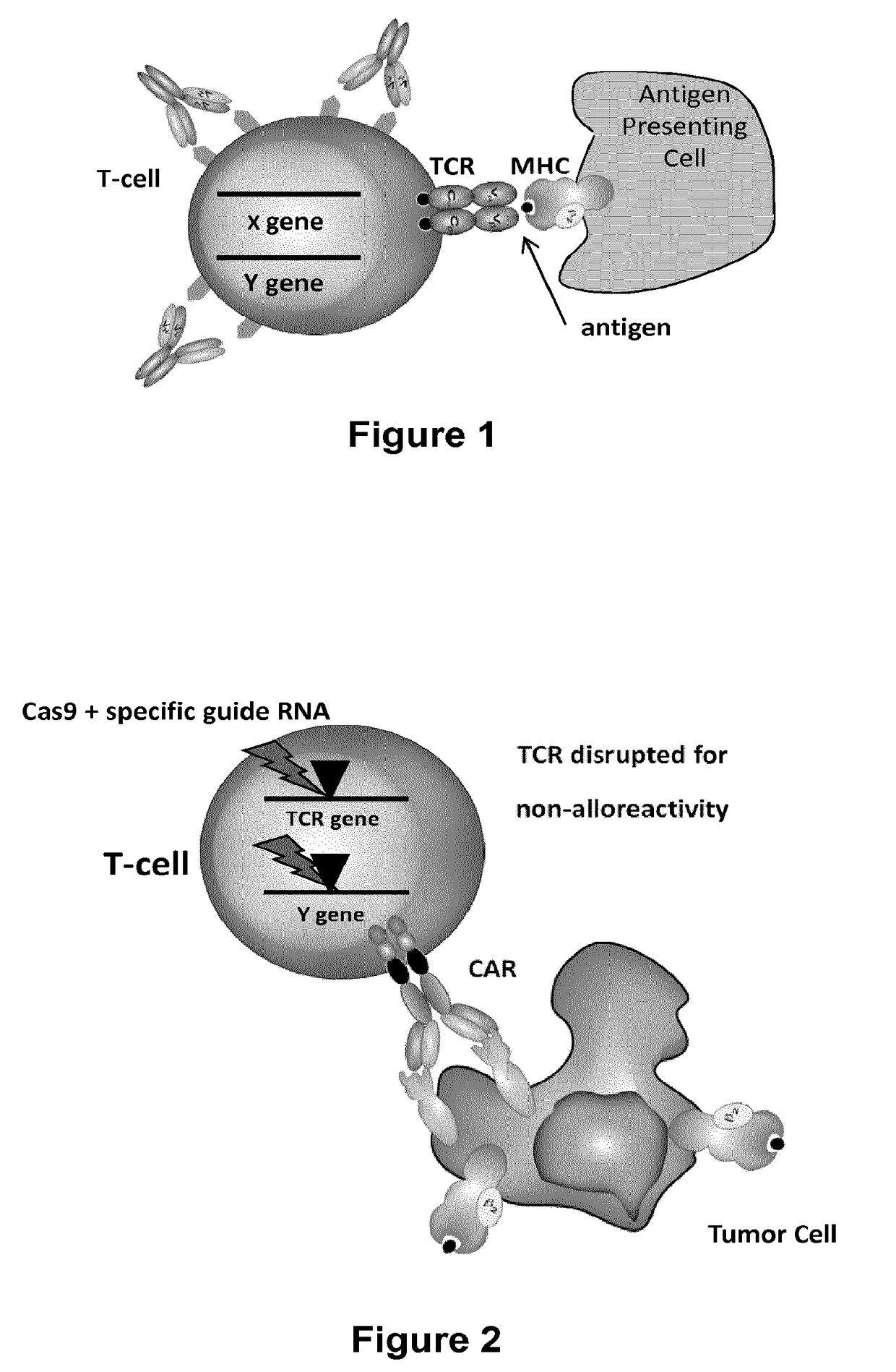
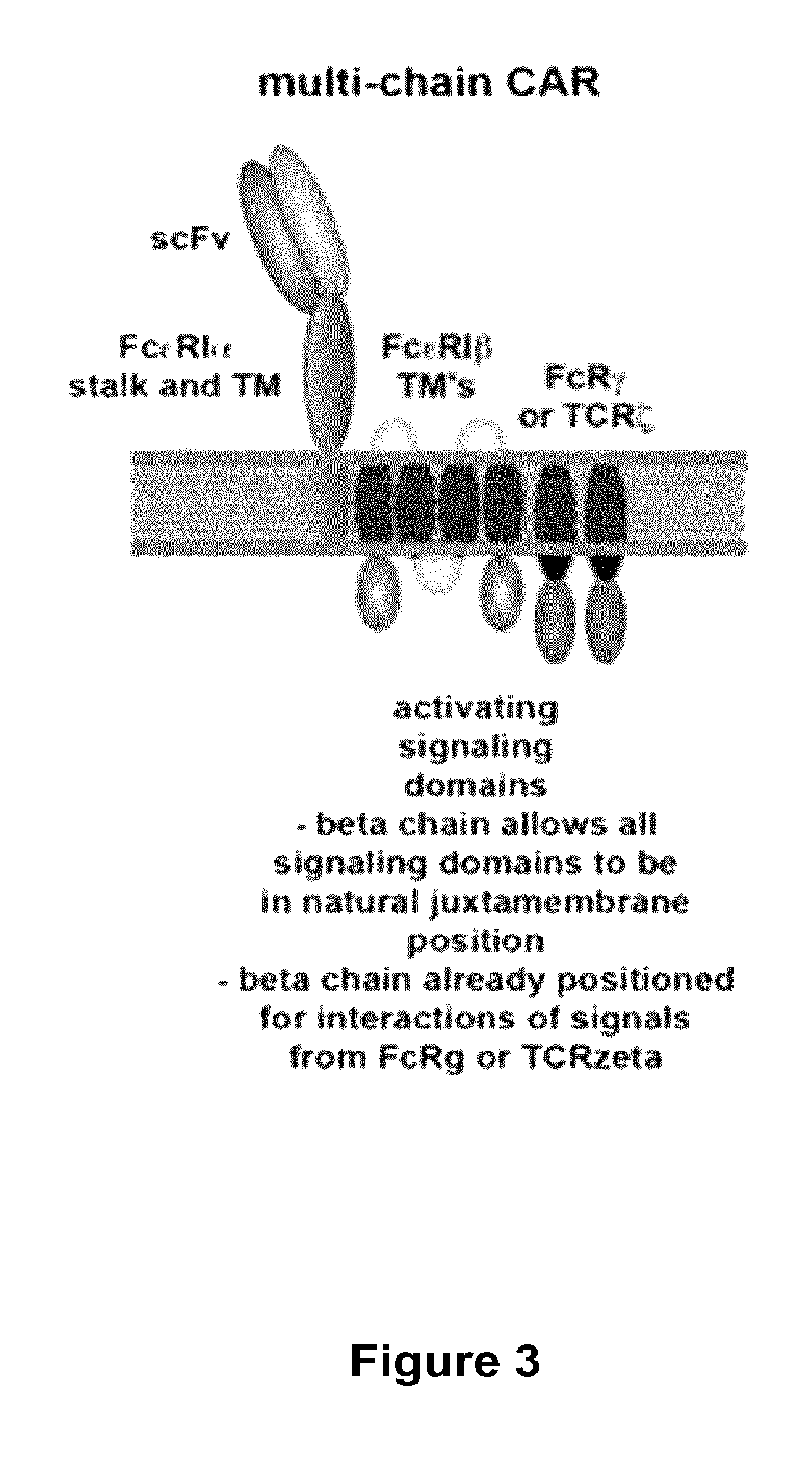
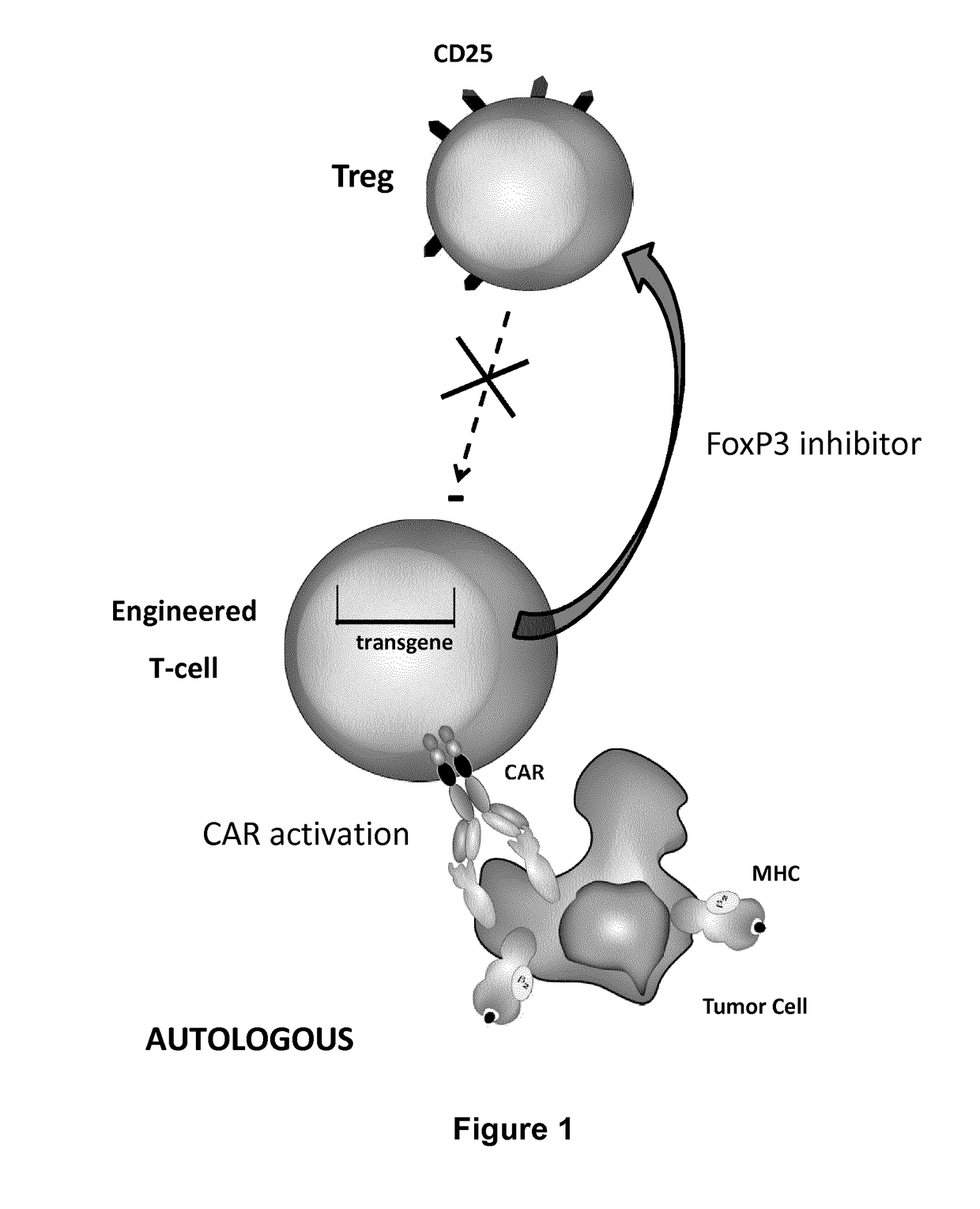
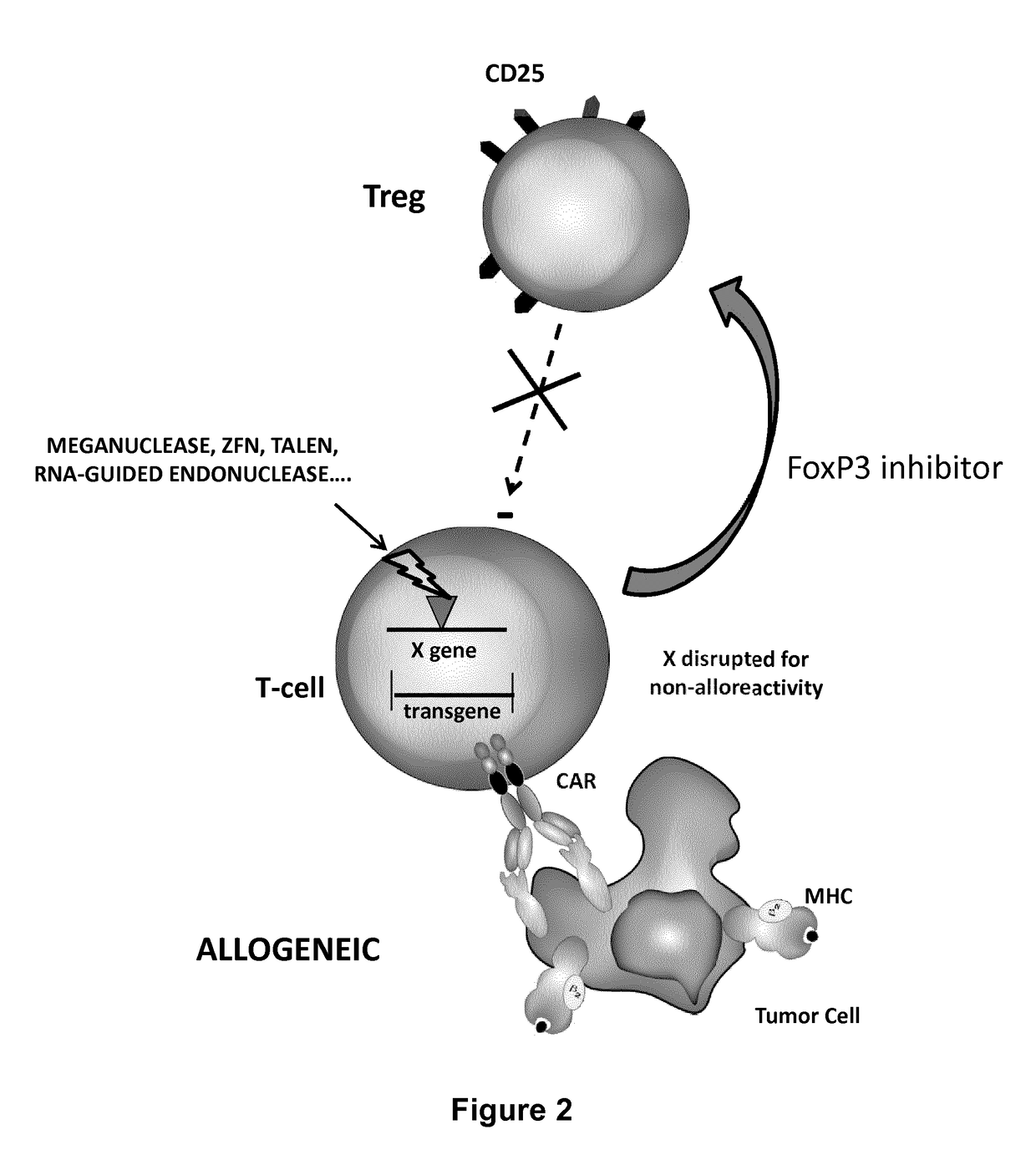
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160272999A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
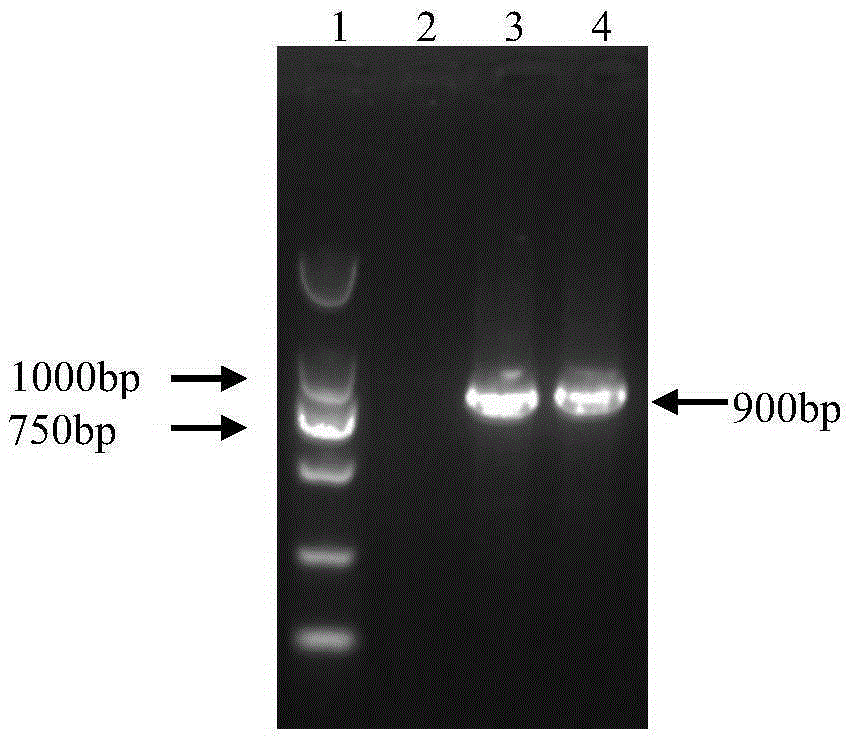
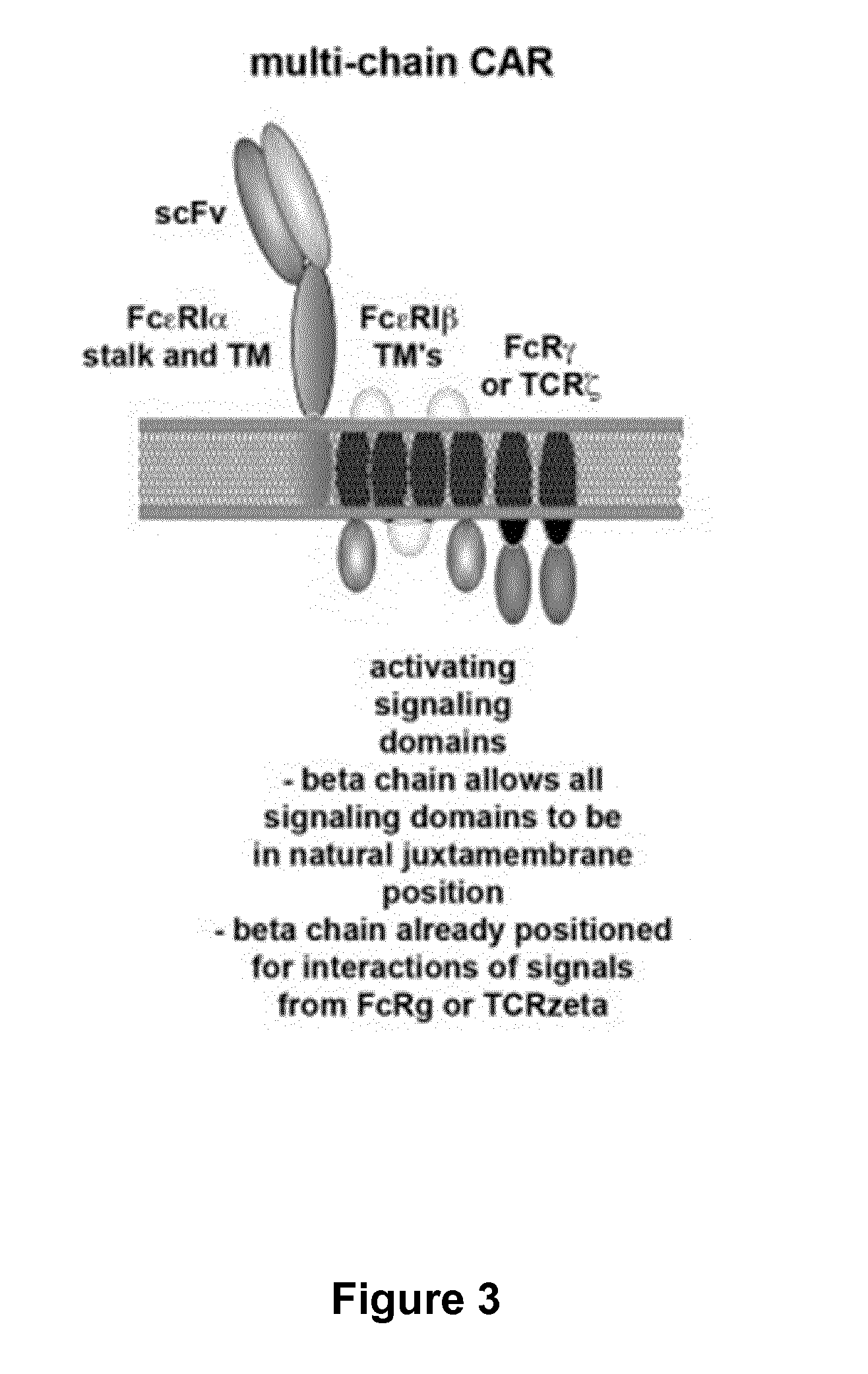
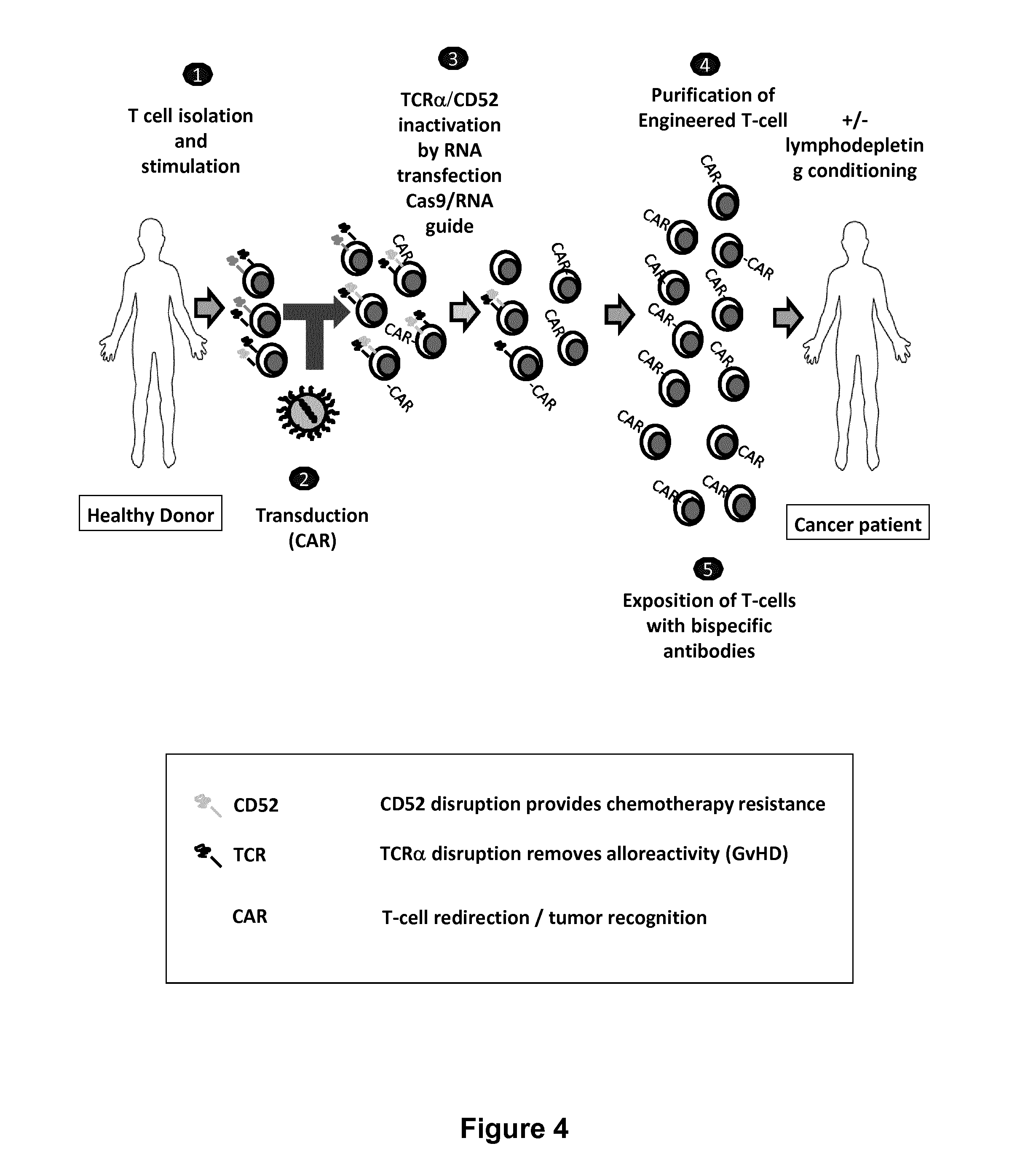
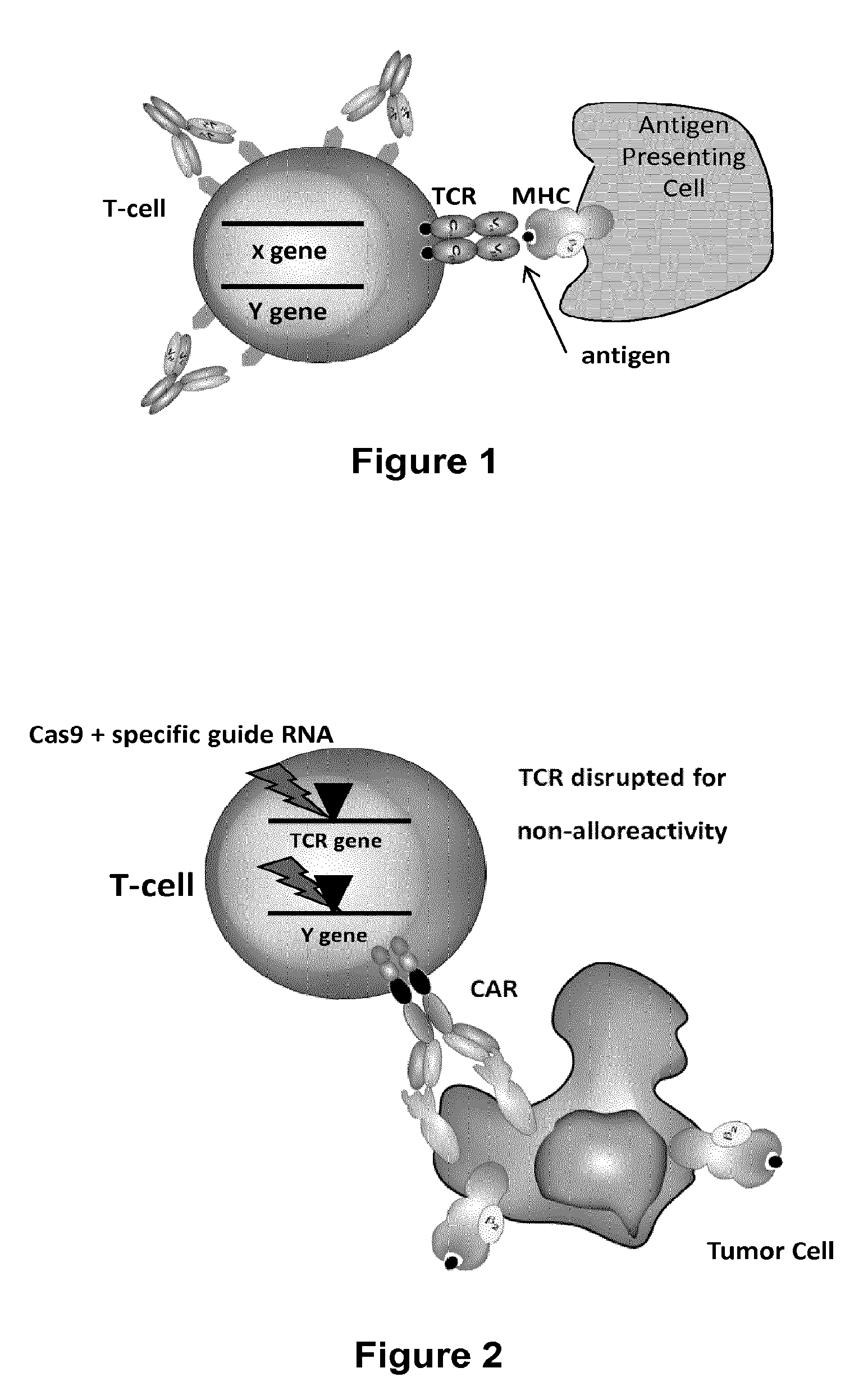
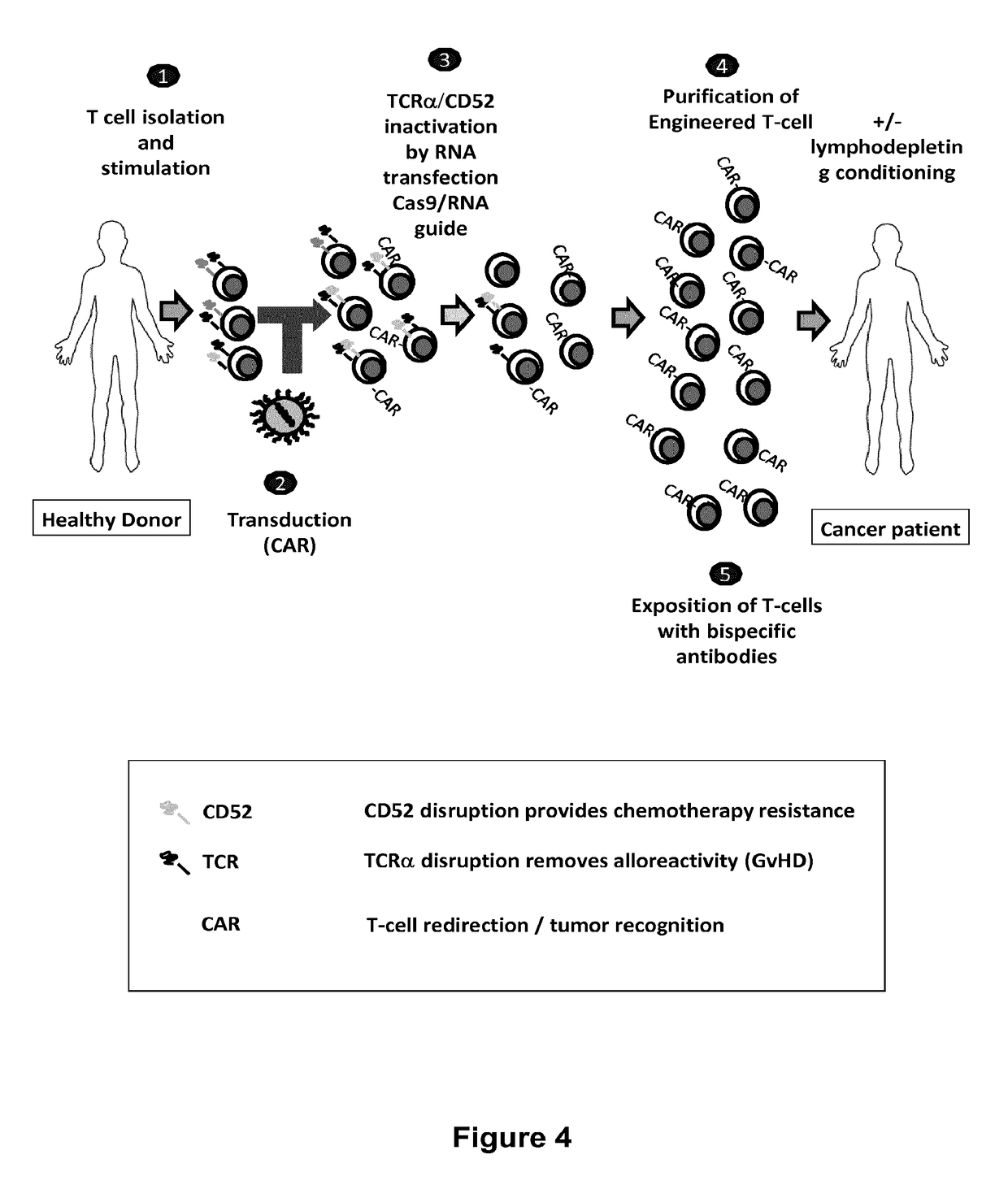
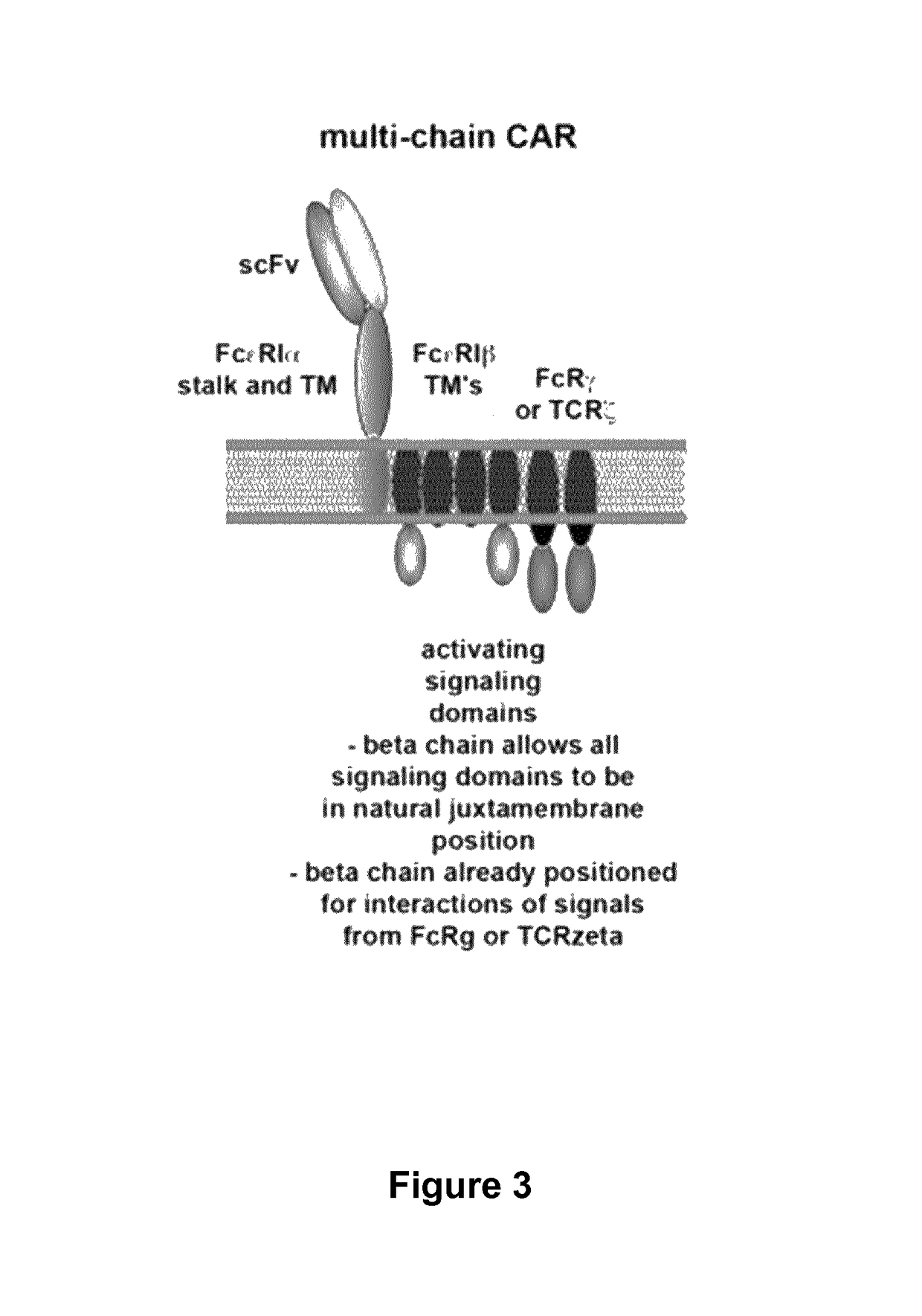
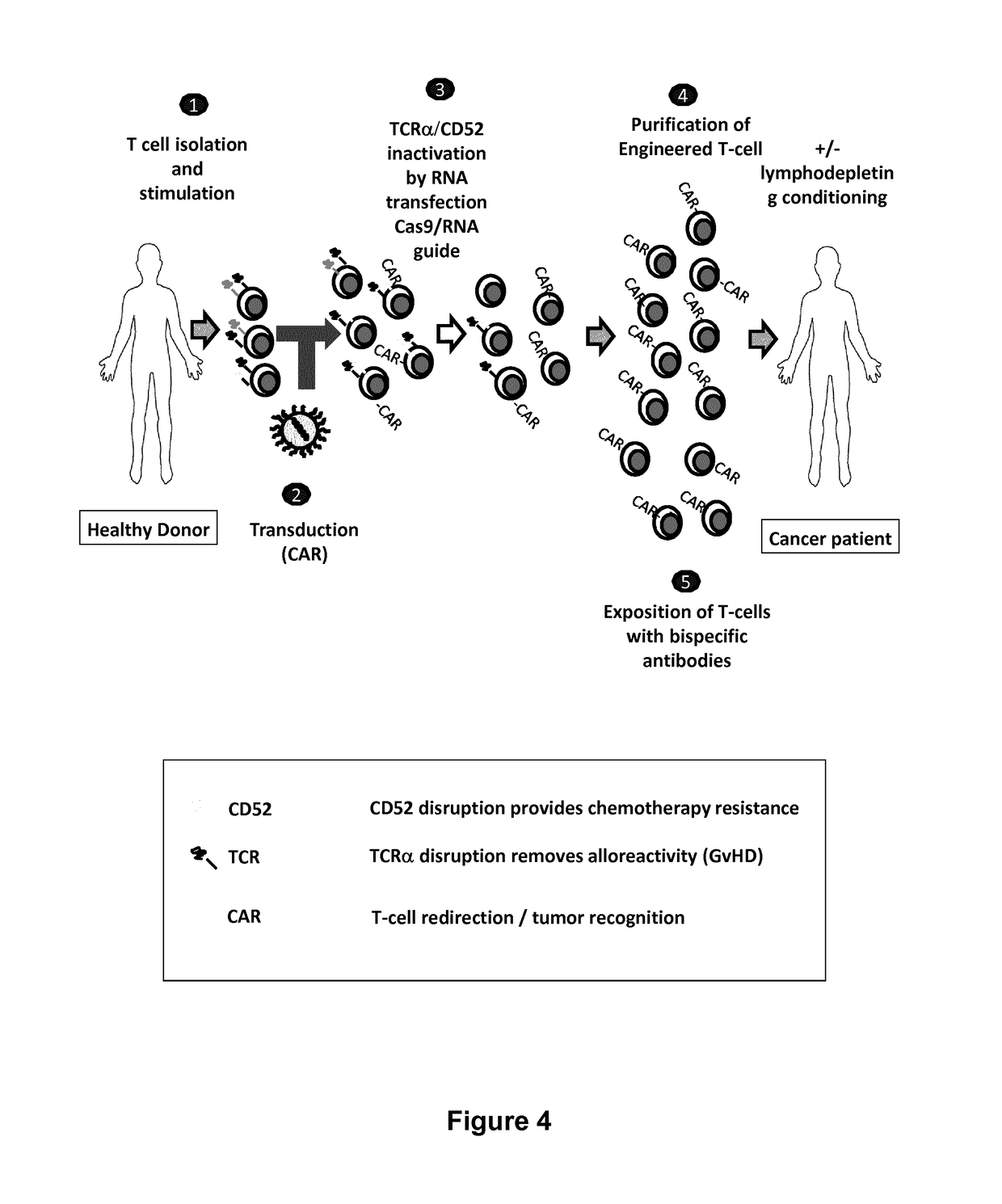
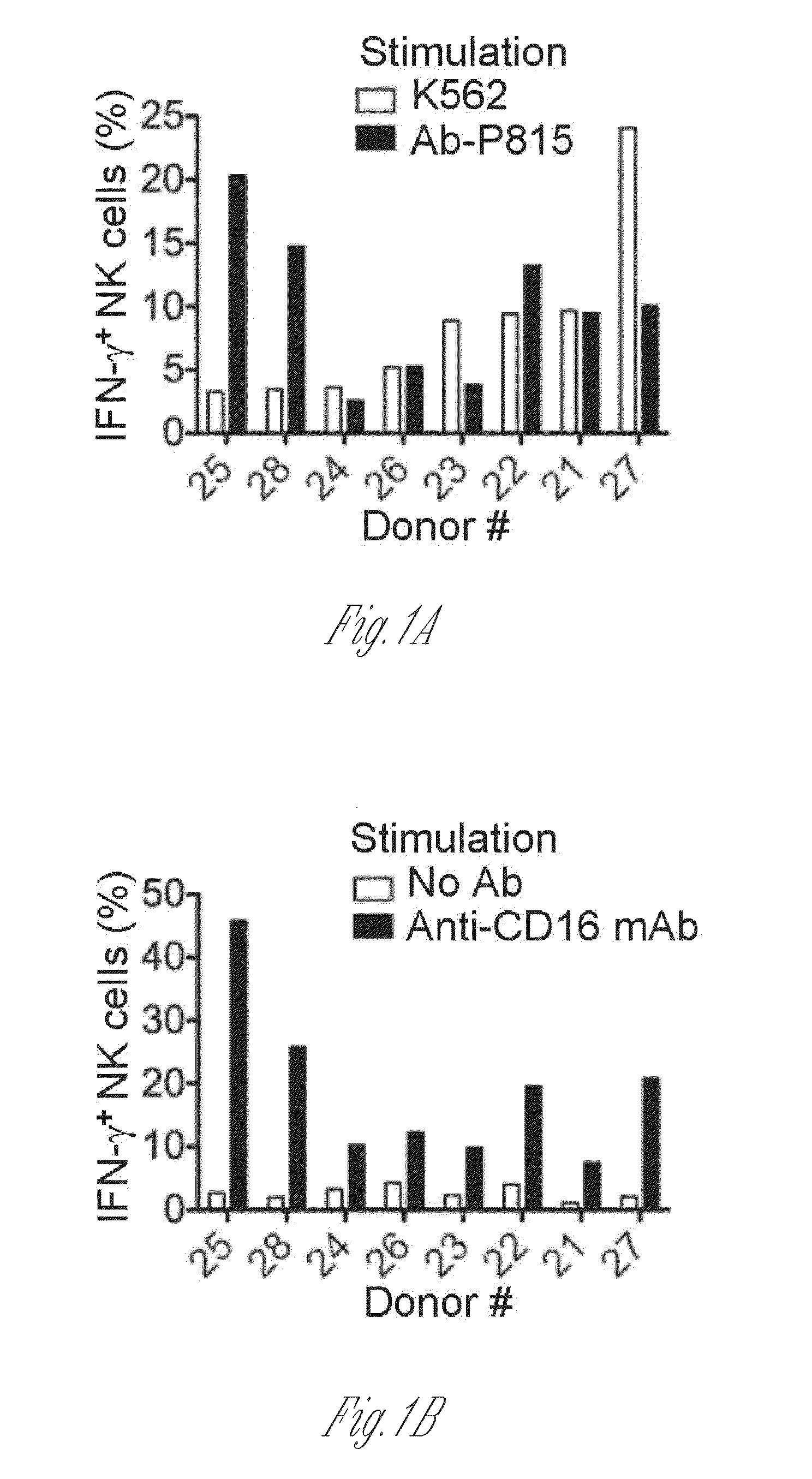
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160184362A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Uses of DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR for inhibiting hepatitis C virus infection
InactiveUS20060198855A1Prevent hepatocellular carcinomaTreating or preventing hepatocellular carcinomaCompound screeningSsRNA viruses positive-senseInfected cellImmunoglobulin superfamily
This invention provides a method of inhibiting HCV infection of a cell susceptible to HCV infection which comprises contacting the cell with an amount of a compound effective to inhibit binding of an HCV envelope glycoprotein to a DC-SIGN protein present on the surface of the cell, so as to thereby inhibit HCV infection of the cell susceptible to HCV infection. This invention provides a method of inhibiting HCV infection of a cell susceptible to HCV infection which comprises contacting the cell with an amount of a compound effective to inhibit binding of an HCV envelope glycoprotein to a DC-SIGNR protein present on the surface of the cell, so as to thereby inhibit HCV infection of the cell susceptible to HCV infection. Compounds of the present invention inhibit HCV infection of cells susceptible to HCV infection. The compounds of the present invention preferably have specificity for preventing or inhibiting infection by HCV and do not inhibit infection by other viruses, such as HIV, that may utilize DC-SIGN or DC-SIGNR for infection. Moreover the compounds of the present invention preferably do not interfere or inhibit members of the immunoglobulin superfamily, in particular, the compounds do not interfere with ICAM-2 or ICAM-3 or with ICAM-2-ilke, or ICAM-3-like molecules.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
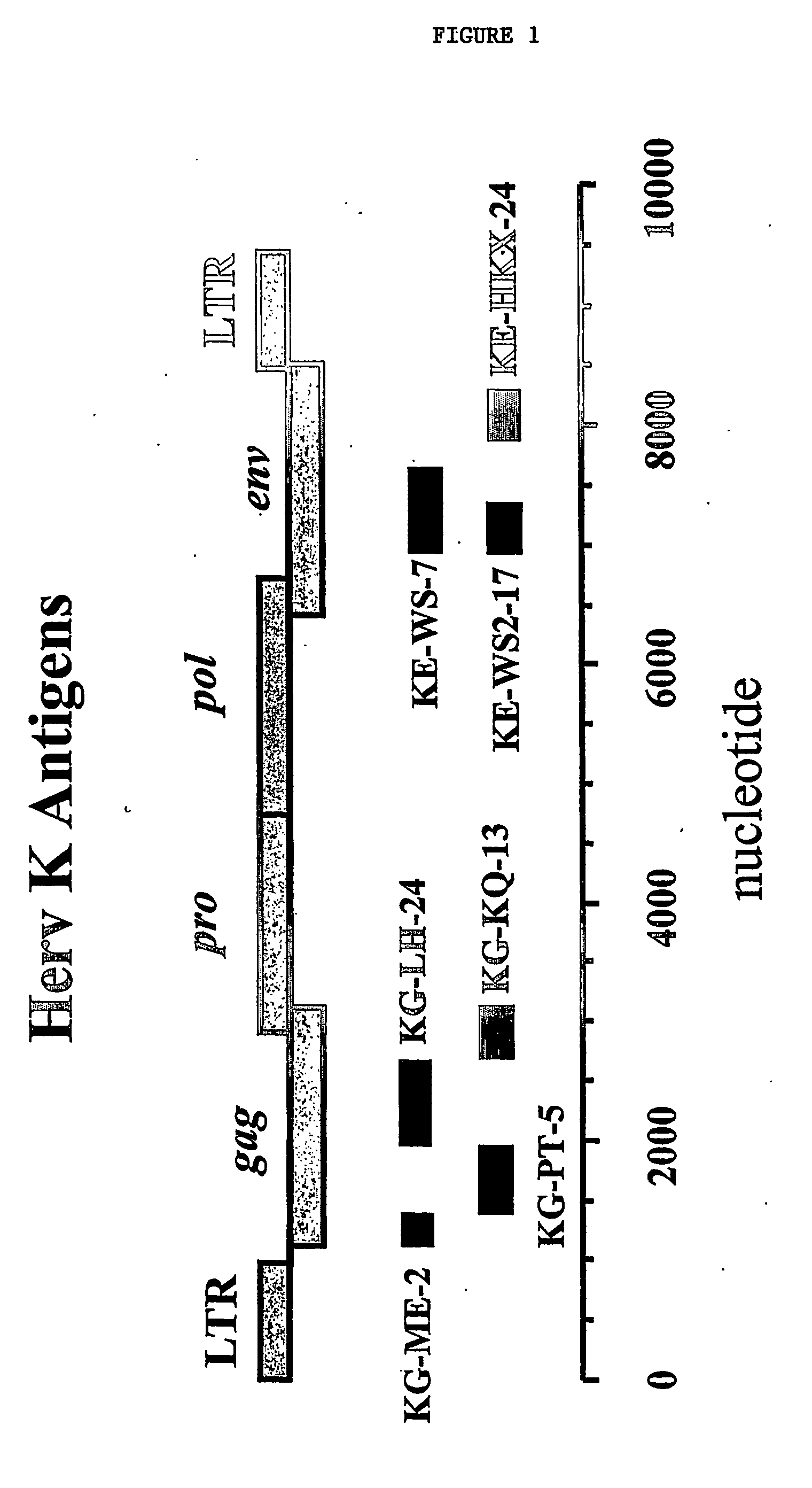
Monitoring and treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
InactiveUS20060160087A1Reduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInfected cellAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis
The invention provides methods of monitoring amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) disease development or progression and monitoring an ALS therapy in an individual by determining the presence or absence of Herv-K / HML-2 expression in a biological sample from the individual. The invention is also directed to methods for aiding diagnosis of ALS by determining expression of Herv-K / HML-2 in a biological sample from the individual. The invention is also directed to methods of reducing Herv-K / HML-2 expression in infected cells and individuals. The invention includes reagents for use in these methods.
Owner:PATHOLOGICA
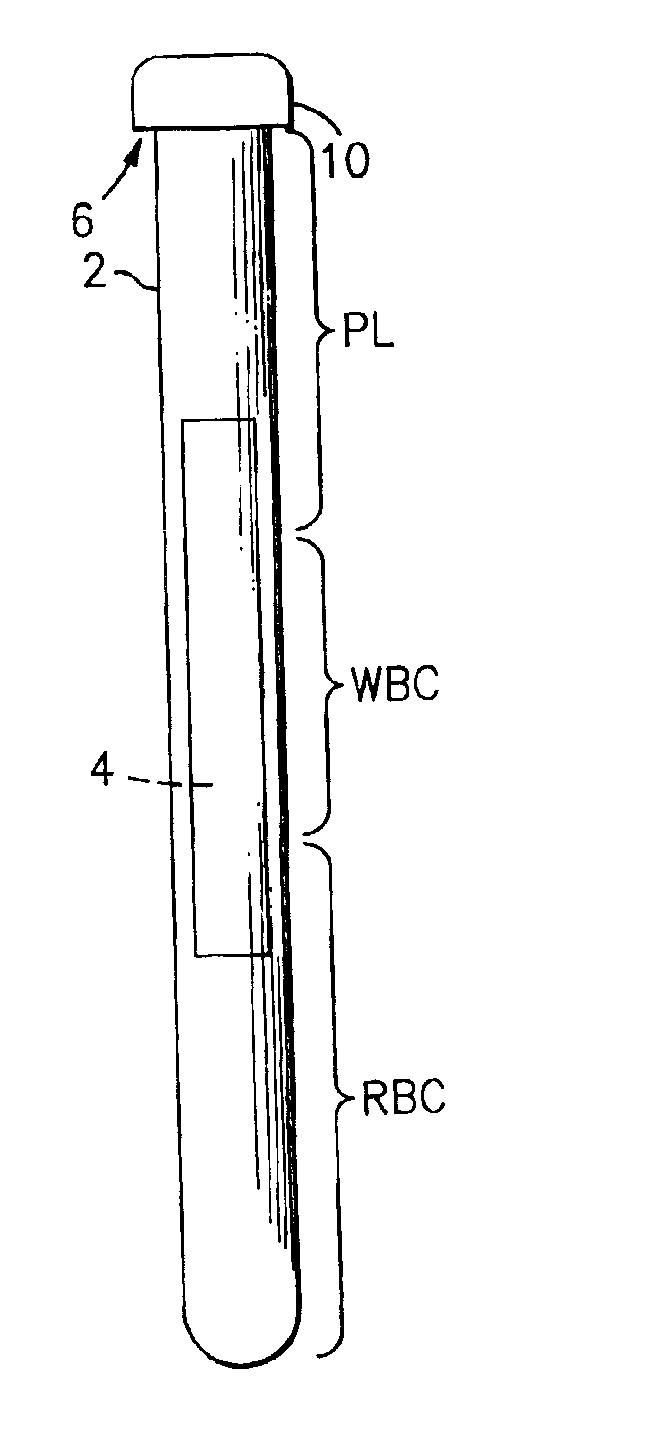
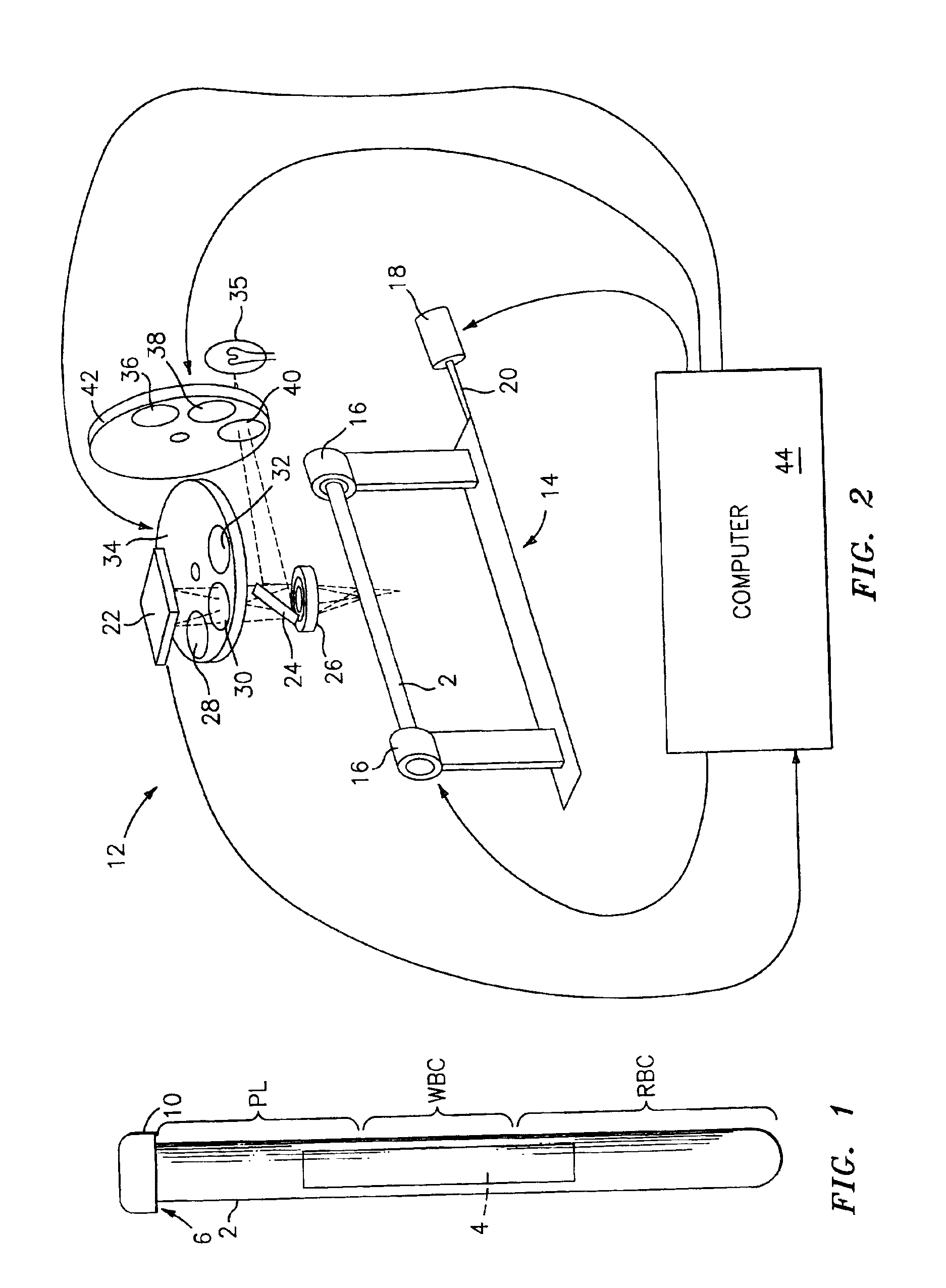
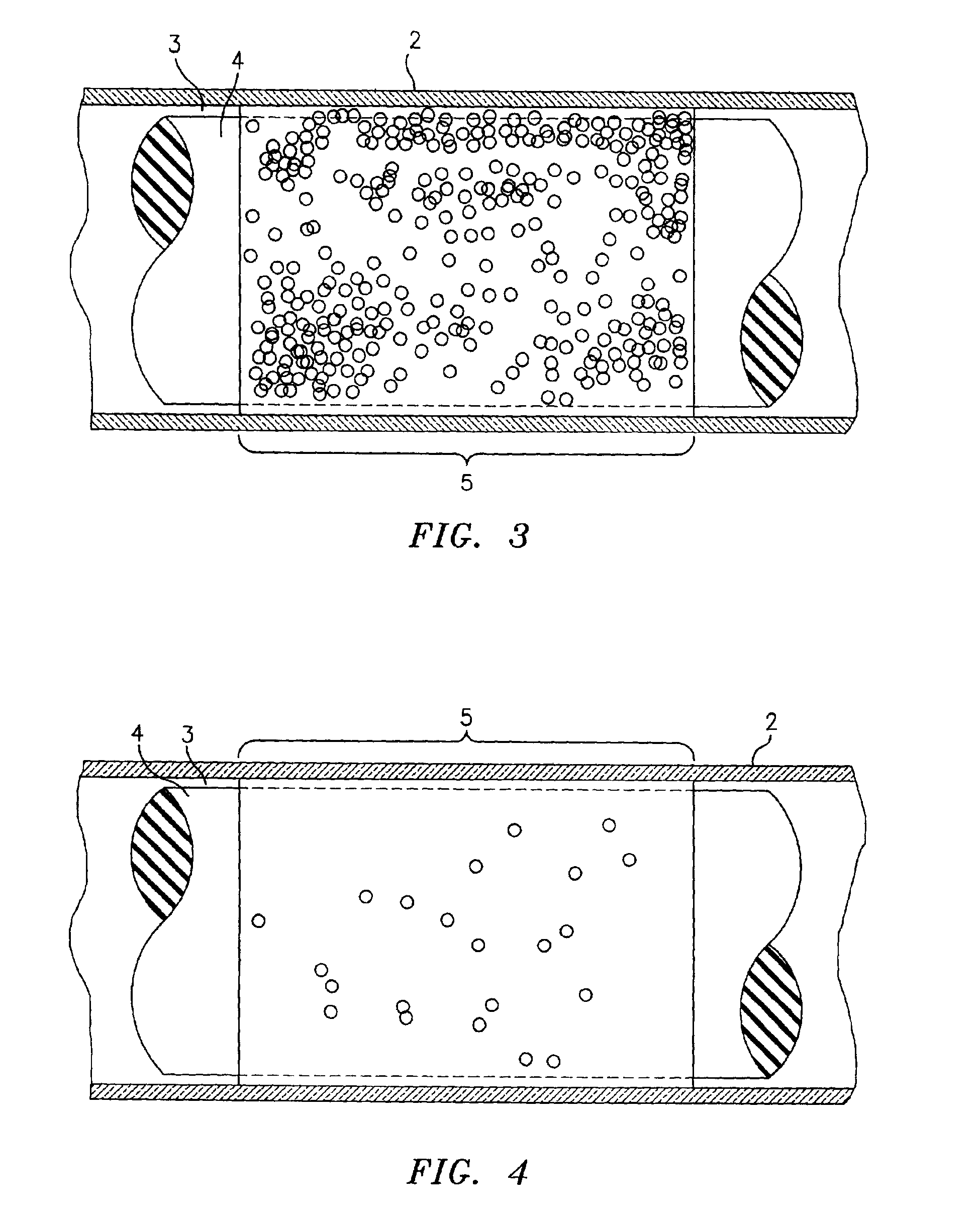
Method for the detection, identification, enumeration and confirmation of virally infected cells and other epitopically defined cells in whole blood
InactiveUS6911315B2Reduce the possibilityAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesInfected cellFluorophore
A method for analyzing blood enables one to isolate, detect, enumerate and confirm under magnification the presence of target cells which have expressed surface epitopes that indicate intracellular infection by various viruses or other infectious agents, and also cells which have expressed surface epitopes that indicate the presence of non-infectious medical conditions. The analysis involves the examination of cells in the blood sample for the presence or absence of particular surface epitopes while the blood sample is disposed in a centrifuged blood sampling container. The epitopic analysis for the presence or absence of infected cells, or cells which indicate the presence of non-infectious medical conditions relies on the detection of known target expressed epitopes. The target epitopes on the target cell types are epitopes which are also known to be absent on normal circulating cells in the blood. Fluorophores or other labels with distinct wavelength emissions are coupled with specific binding agents such as lectins, antibodies, aptamers, or the like, which are directed against the target expressed epitopes. The epitopic analyses may be performed in or near the expanded buffy coat layer in the centrifuged blood sample. The epitopic analysis may be performed under magnification either visually and / or photometrically. The blood sampling container is sized to hold between about 1 and about 20 ml, preferably about 10 ml of blood, and contains an insert that occupies about 90-98% of the volume of the container bore in the area of the container where the target cells will, if present, be detected. The insert forces the target cells in question to reside in an annular space in the container which is adjacent to the circumference of the container bore. The entire analysis can be performed in a relatively short period of time which is typically a matter of minutes to single digit hours.
Owner:LEVINE ROBERT A +1
Method for screening drug target genes based on CRISPR/Cas9 high-throughput technology
InactiveCN106399377ADetermining infection efficiencyDetermine the MOI valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a method for screening drug target genes based on a CRISPR / Cas9 high-throughput technology. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing a sgRNA library; secondly packaging the sgRNA library by using slow viruses, and collecting the viruses; thirdly screening the sgRNA library in a cancer cell line; fourthly extracting cells obtained by screening and genome DNA of the cells before screening; and finally enriching sgRNA in genome DNA. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that a CRISPR / Cas cell screening process is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined with a simple and convenient method by utilizing puromycin resistance of infected cells, and MOI values of the viruses are determined; more importantly, a virus packaging method is greatly optimized, so that the virus packaging efficiency is improved to be more than 5 times that of a conventional method, and large-scale drug target screening cost can be greatly reduced; and the method is used for promoting industrialization of cancer drug target screening.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
CRISPR/Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes
InactiveCN105400773AHigh infection efficiencyMeet the packaging ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes. Firstly, an sgRNA library is established; then the sgRNA library is packaged by lentiviruses, and viruses are collected; the sgRNA library is screened in a cancer cell line, the obtained cells are extracted and screened, and genome DNAs of precancerous cells are screened; finally, enrichment of sgRNAs in the genome DNAs is carried out. When the provided method is compared with the prior art, the screening process of CRISPR / Cas9 cells is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined and the virus MOI value is determined through a simple method and by utilization of puromycin resistance of infected cells, importantly, the restriction enzyme cutting method and a high flux method are combined, correct chromatin fragments can be obtained effectively, false positive caused by non-specific PCR amplification can be lowered, a DNA template of sgRNAs can be amplified efficiently, and a library establishment efficiency is raised.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Immune responses against HPV antigens elicited by compositions comprising an HPV antigen and a stress protein or an expression vector capable of expression of these proteins
InactiveUS6900035B2Enhance immune responseVirusesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHPV AntigenInfected cell
This document describes compositions and methods for inducing an immune response (e.g., a cellular response such as a cell-mediated cytolytic immune response) to a human papillomavirus (HPV) antigen, which can be displayed by HPV or exhibited by infected cells (e.g., cells from cervical and other tumors). The HPV protein can be joined to a stress protein by chemical conjugation or noncovalently using linking moieties, or by fusion (e.g., a recombinant fusion protein). Also described are expression vectors containing sequences encoding HPV antigens and stress proteins, which can be introduced into cells of a subject or cells ex vivo. Also described are compositions that include a stress protein linked to an HPV antigen and another pharmacologically acceptable component and stress protein—HPV antigen fusions and conjugates. These compositions can be used to induce or enhance an immune response against HPV and cells that exhibit HPV antigens, including HPV-associated tumors.
Owner:NVENTA BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CORP
Methods for engineering T cells for immunotherapy by using RNA-guided CAS nuclease system
ActiveUS9855297B2Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Recombinant virus vectors
InactiveUS6319703B1Risk minimizationReduced zero riskBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInfected cellCytopathic effect
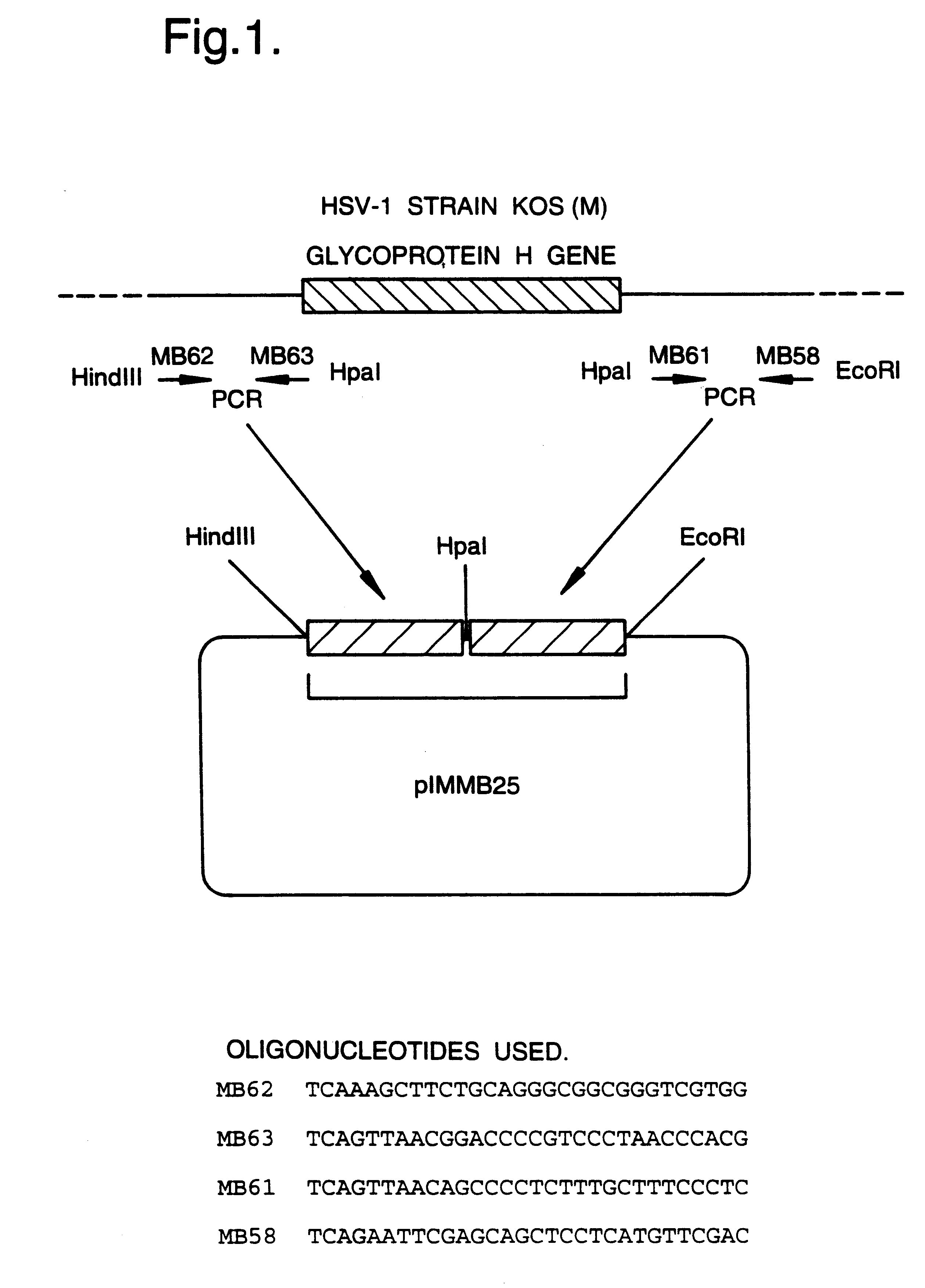
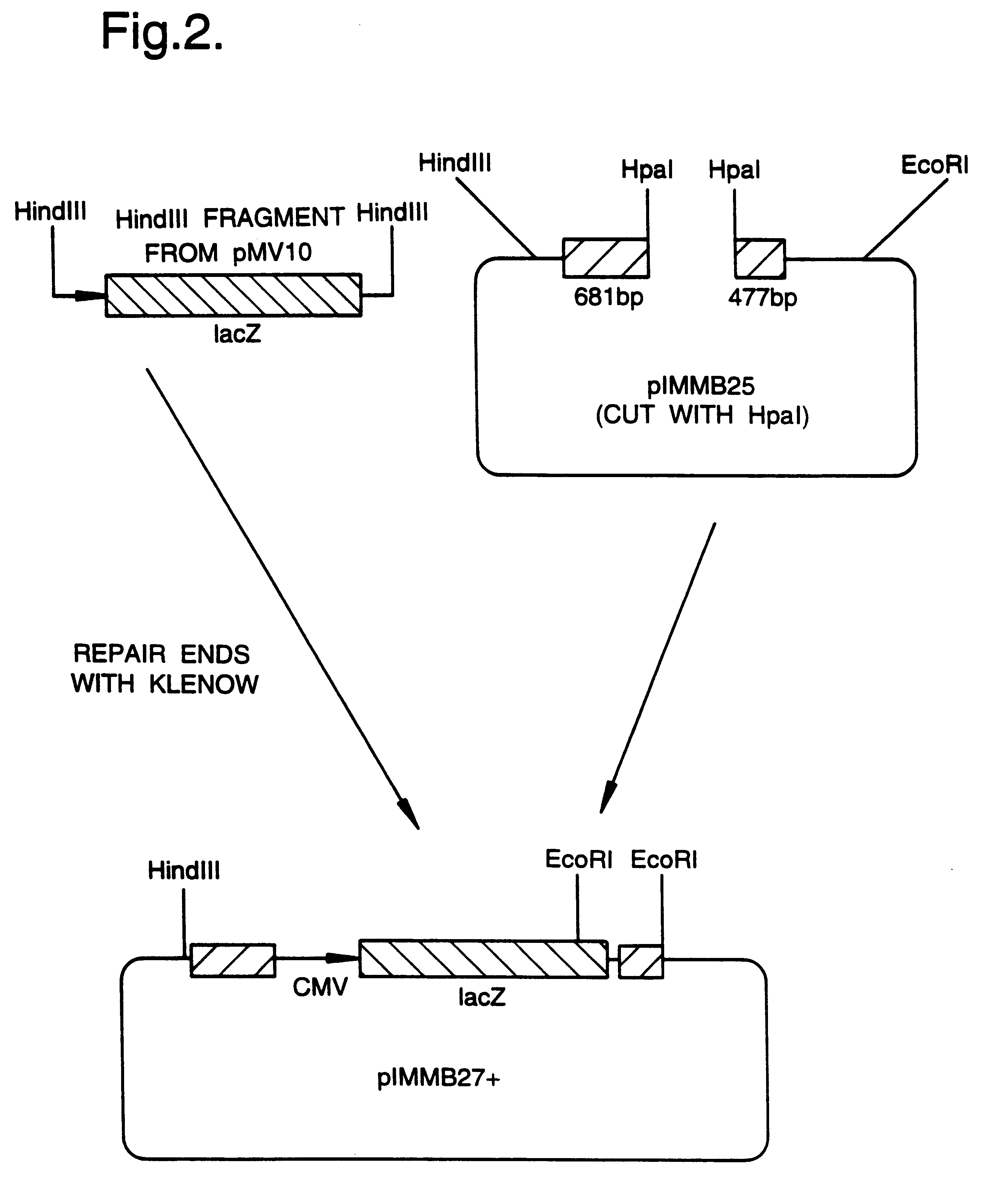
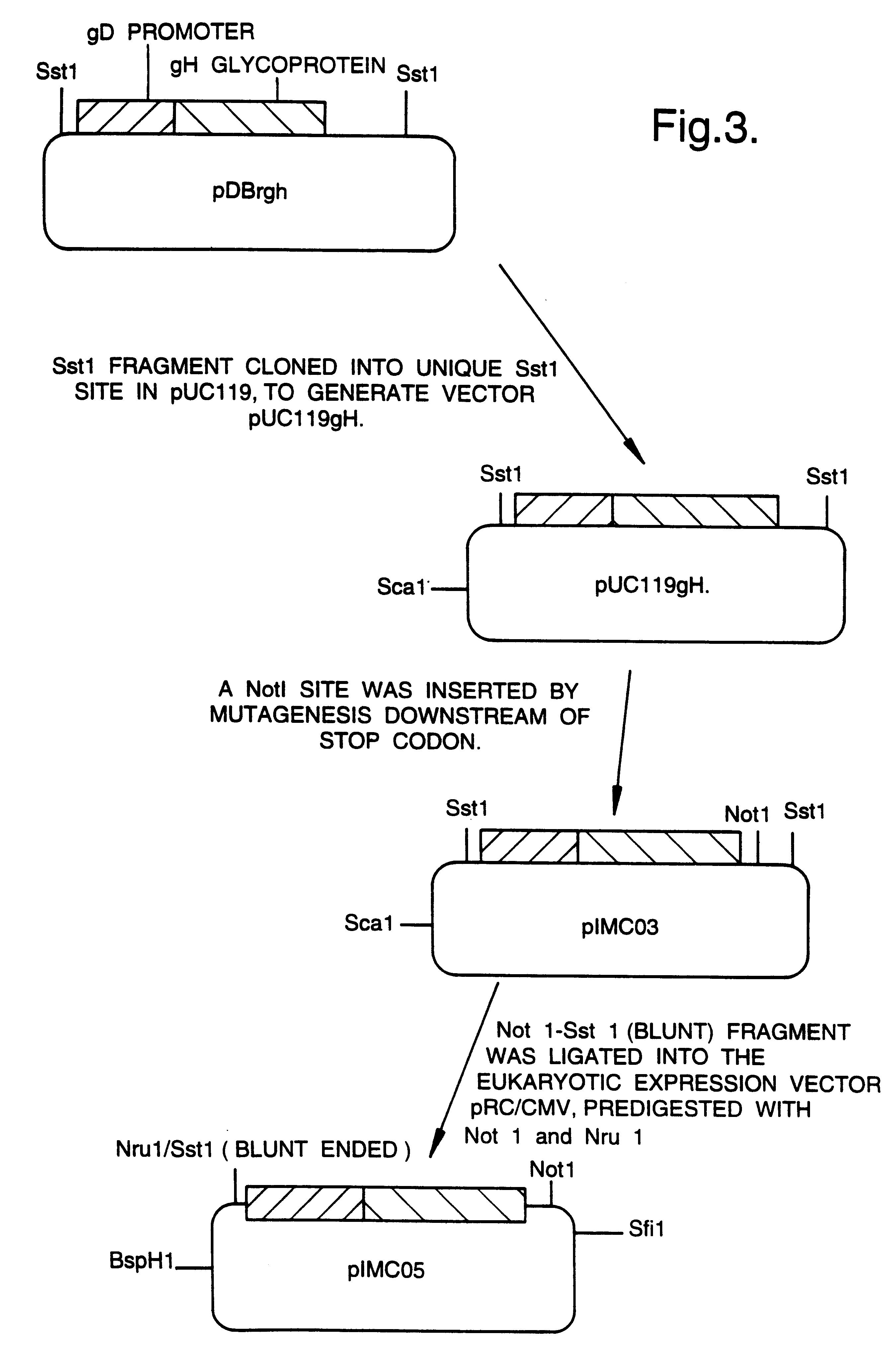
A mutant herpesvirus that can be used a recombinant virus vector includes (a) a mutation such that the mutant virus has a reduced ability in comparison with a parent type to cause lysis of an infected cell, and (b) an inactivating mutation in a gene essential for the production of infectious virus. An example is a HSV1 mutant lacking the essential glycoprotein gH gene and having a mutation impairing the function of the gene product VP16. A heterologous gene can be carried at the site of the inactivated essential gene, e.g. a gene suitable for administering gene therapy. The vector has an increased margin of safety over known herpesvirus vectors in respect of incidence of cytopathic effects and / or risk of infection.
Owner:SPECK PETER G
Replication-defective arenavirus vectors
ActiveUS20100297172A1Enhance protein expressionHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntigenDisease
The invention relates to an infectious arenavirus particle that is engineered to contain a genome with the ability to amplify and express its genetic information in infected cells but unable to produce further infectious progeny particles in normal, not genetically engineered cells. One or more of the four arenavirus open reading frames glycoprotein (GP), nucleoprotein (NP), matrix protein Z and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase L are removed or mutated to prevent replication in normal cells but still allowing gene expression in arenavirus vector-infected cells, and foreign genes coding for an antigen or other protein of interest or nucleic acids modulating host gene expression are expressed under control of the arenavirus promoters, internal ribosome entry sites or under control of regulatory elements that can be read by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, cellular RNA polymerase I, RNA polymerase II or RNA polymerase III. The modified arenaviruses are useful as vaccines and therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Targeting viruses using a modified sindbis glycoprotein
InactiveUS20060127981A1High expressionIncrease infectivitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseInfected cellDisease
The present invention relates to viruses that are engineered to contain a surface ligand molecule which targets the virus to a cell of interest. In particular non-limiting embodiments, the cell of interest is desirably ablated and may be a cancer cell, an infected cell, a cell exhibiting a non-malignant proliferative disorder, or a cell of the immune system. Alternatively, the cell of interest is a target for gene therapy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
A Blood Purification Method and Apparatus for the Treatment of Malaria
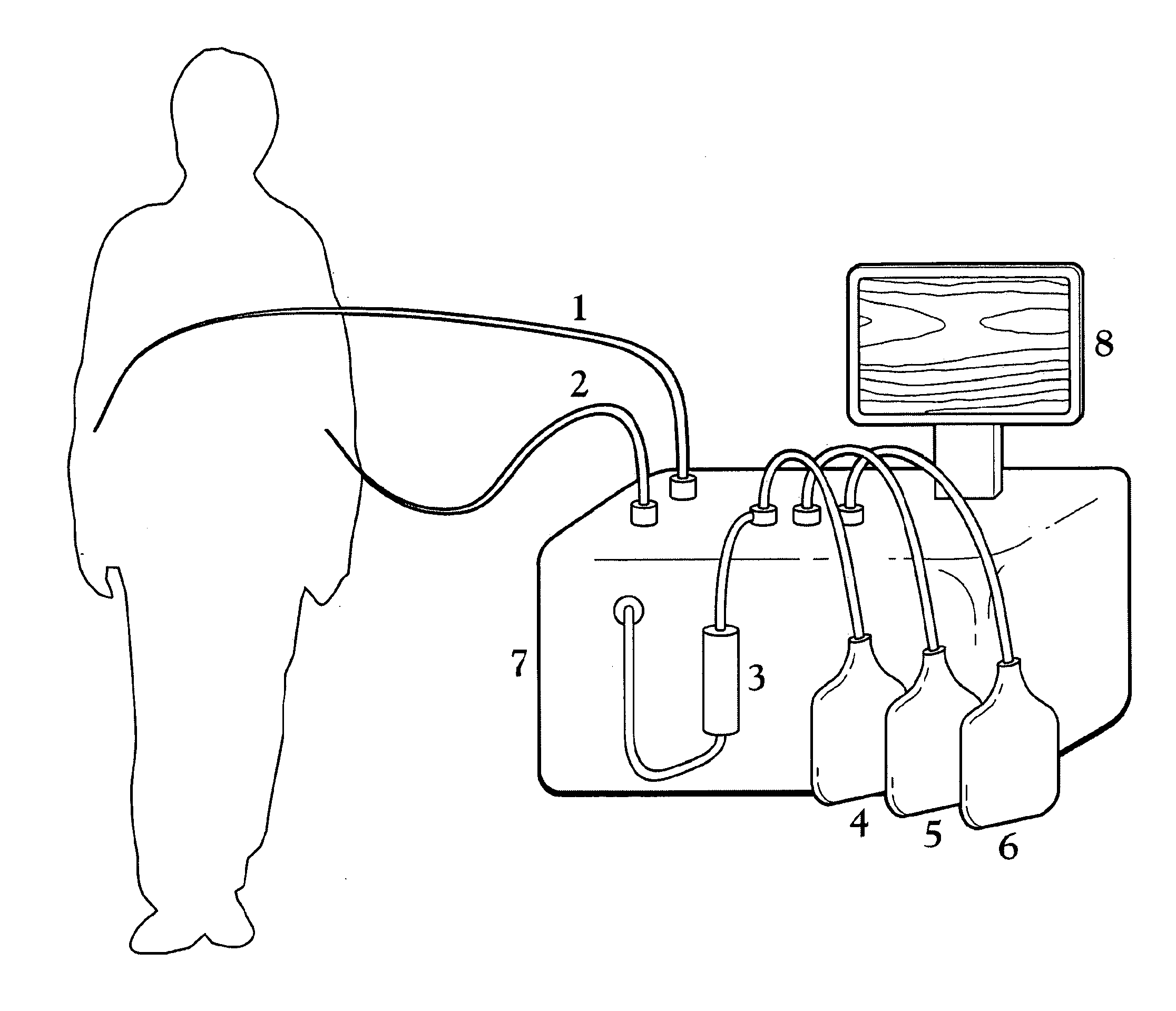
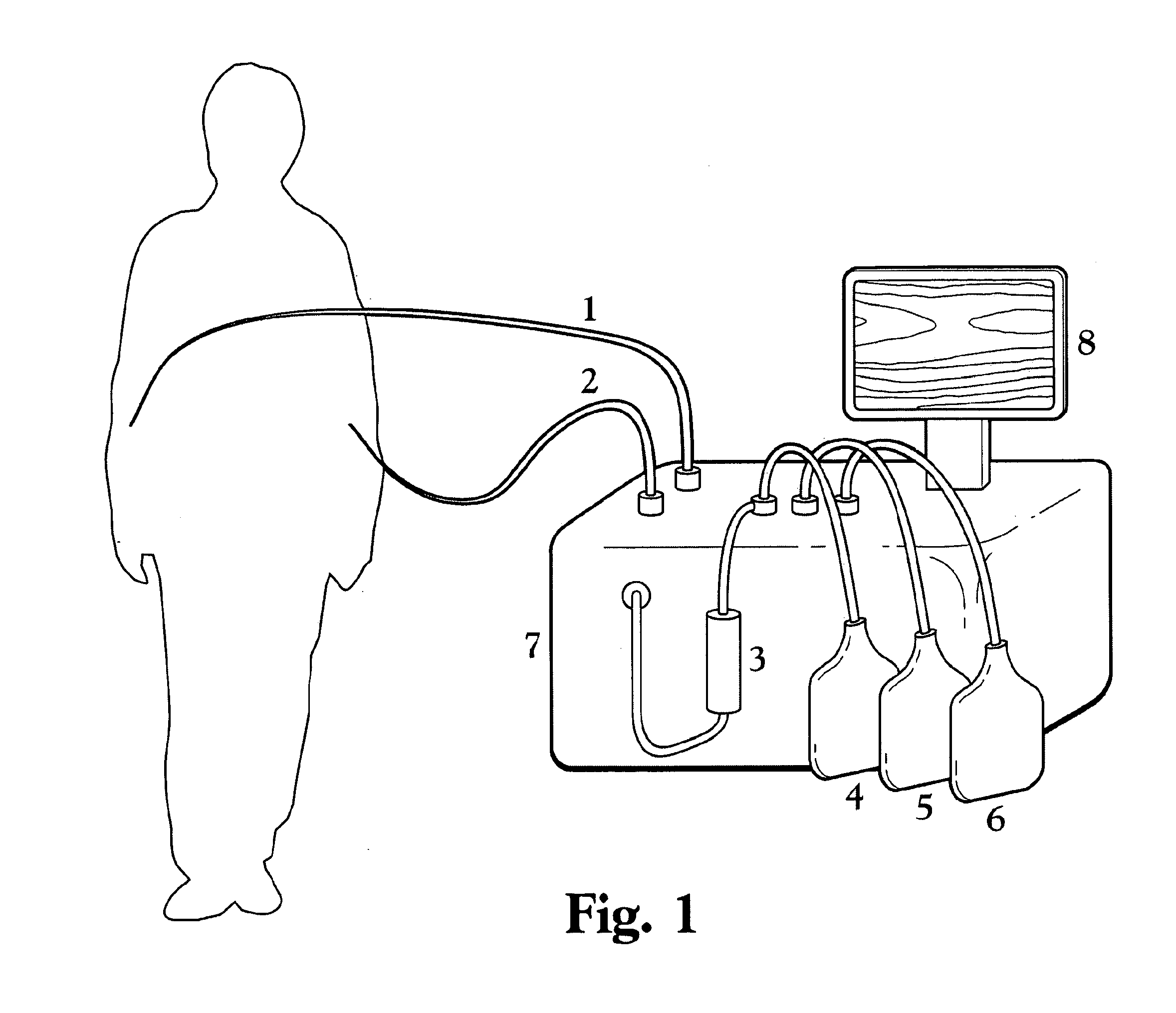
ActiveUS20100331753A1Promote recoveryQuick effectElectrostatic separationMedical devicesDiseaseMagnetic field gradient
Methods for treating malaria are provided, the treatment comprising the step of removing malaria-infected red blood cells from the patient s blood. Blood is drawn from the patient s circulatory system and circulated through a blood purification device that selectively eliminates the infected red blood cells from all other blood s components and replaces the cleansed blood back into the patient s circulatory system. A blood purification device, which is useful to perform the therapeutic methods of the invention, is also provided. The device leverages the magnetic properties of the hemozoin contained within the infected red blood cells and comprises one or more separation chambers (4) though which blood flows through a high-gradient magnetic field generated by an array of wires (5) separated from the chambers and not in contact with the patient blood. The magnetic field gradient acting on the cells magnetic properties displaces the infected and non-infected red blood cells on different layers of the blood flow across the chamber height. The blood flow is split into separated streams and blood streams containing infected cells are filtrated thereby trapping infected cells. Blood containing non-infected red blood cells is circulated back to the patient. The device application is not limited to the treatment of malaria and includes other blood related diseases that affect the magnetic properties of a patient's red blood cells.
Owner:TROPICAL HEALTH SYST
Targeting viruses using a modified sindbis glycoprotein
InactiveUS7429481B2High expressionIncrease infectivitySsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseNon malignantInfected cell
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Nucleic acid delivery with ovine adenoviral vectors
InactiveUS6020172ARich varietyGenetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersInfected cellOvine adenovirus
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00518 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 20, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 20, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 14, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 06826 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 27, 1997A method of delivering a nucleic acid molecule to a human cell which involves exposing to the cell a viral vector containing a DNA molecule including a nucleic acid sequence encoding the genome of an ovine adenovirus capable of infecting human cells or functionally equivalent nucleic acid sequence or portion thereof and at least one nucleic acid sequence encoding a gene to be expressed in the cell, such that the vector infects the cell and the infected cell expresses the gene.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for the recovery and purification of poxviruses from infected cells
InactiveUS7056723B2Easy to controlImprove scalabilityViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsInfected cellVaccinia
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Recombinant cancer cell secreting modified heat shock protein-antigenic peptide complex
InactiveUS20080026012A1Elicit immune responseAntibacterial agentsFungiInfected cellCancer prevention
The present invention relates to methods for purifying immunogenic, prophylactically and therapeutically effective complexes of modified heat shock proteins noncovalently associated with antigenic peptides of cancer or infected cells. The claimed methods comprise the constructing of a nucleotide sequence encoding a secretable modified heat shock protein, expressing the sequence in an appropriate host cell, recovering the immunogenic complexes from the cell culture and the cells, and purifying the immunogenic complexes by affinity chromatography. Large amounts of such immunogenic complexes can be obtained by large-scale culturing of host cells containing the genetic sequence. The complexes can be used as a vaccine to elicit specific immune responses against cancer or infected cells, and to treat or prevent cancer or infectious diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Role of tyrosine phosphorylation of a cellular protein in adeno-associated virus 2-mediated transgene expression
The present invention identifies a protein, designated the D-sequence-binding protein (D-BP), is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues and blocks AAV-mediated transgene expression in infected cells by inhibiting the leading strand viral DNA synthesis. More particularly, the present invention demonstrates that D-BP is phosphorylated by EGF-R protein tyrosine kinase. Methods of increasing transcription and promoting replication of transgenes exploiting this information are disclosed herein.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST
Acidizing fluid for green algae and disease infected cell in porphyra haitanensis cultivation and treating method thereof
The invention discloses an acidizing fluid for green algae and a disease infected cell in porphyra haitanensis cultivation and a treating method thereof. A solvent for the acidizing fluid is clean seawater, and solute for the acidizing fluid is at least one of hydrochloric acid and citric acid, wherein the concentration expressed in percentage by weight of the solute in the acidizing fluid is 0.3 to 1.5 percent. The green algae and the disease infected cell can be quickly killed by a treating method of preparing the acidizing fluid, shipping, dipping for 15 to 20 seconds and rinsing, killing effect is better, the killing rate is over 90 percent, and the influence on the growth of the porphyra haitanensis is less. The treating method has the advantages of no restriction of natural condition, labor intensity reduction and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
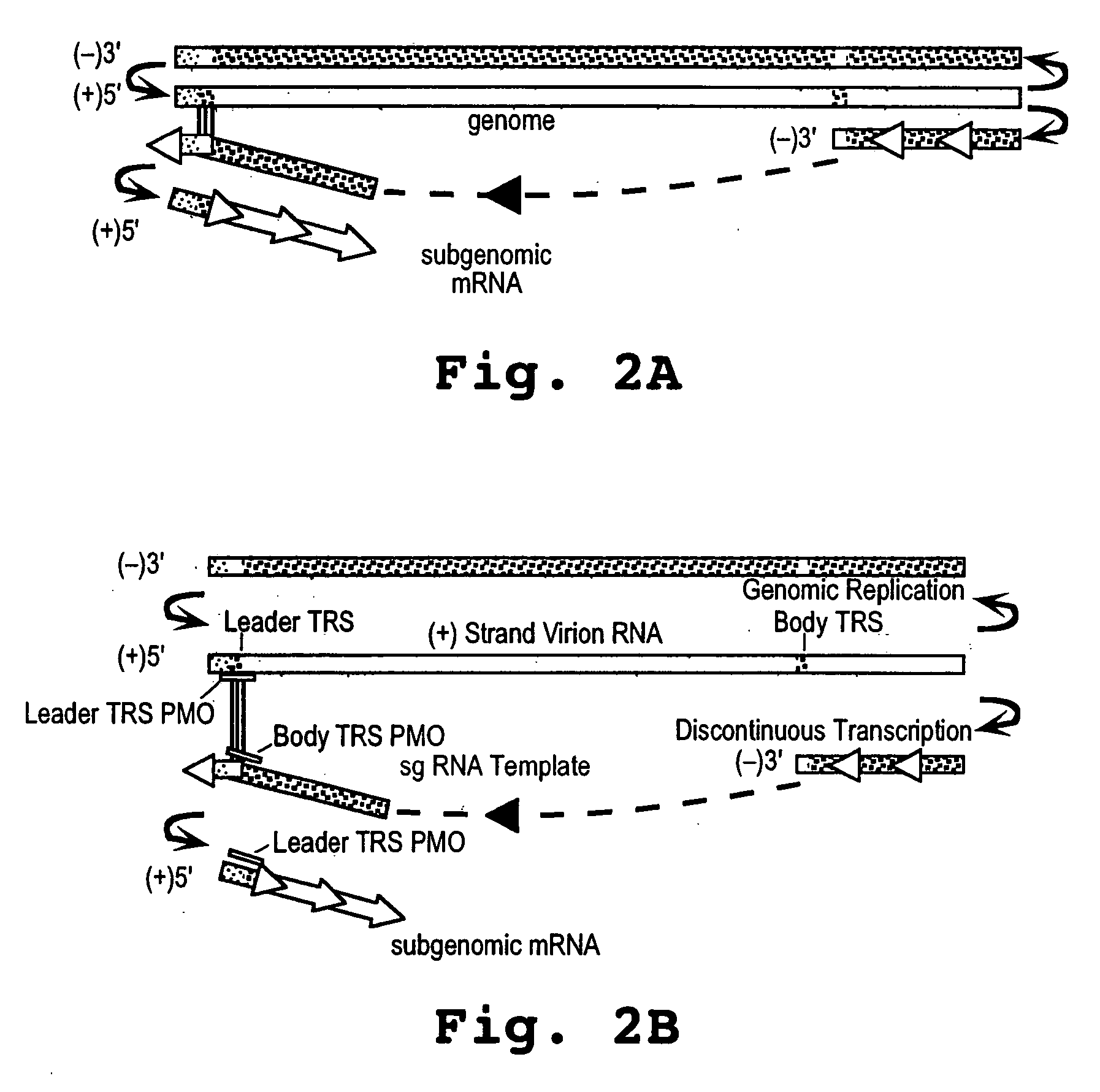
Oligonucleotide compound and method for treating nidovirus infections
A method and oligonucleotide compound for inhibiting replication of a nidovirus in virus-infected animal cells are disclosed. The compound (i) has a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) is capable of uptake by the infected cells, (iii) contains between 8-25 nucleotide bases, and (iv) has a sequence capable of disrupting base pairing between the transcriptional regulatory sequences in the 5′ leader region of the positive-strand viral genome and negative-strand 3′ subgenomic region. In practicing the method, infected cells are exposed to the compound in an amount effective to inhibit viral replication.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
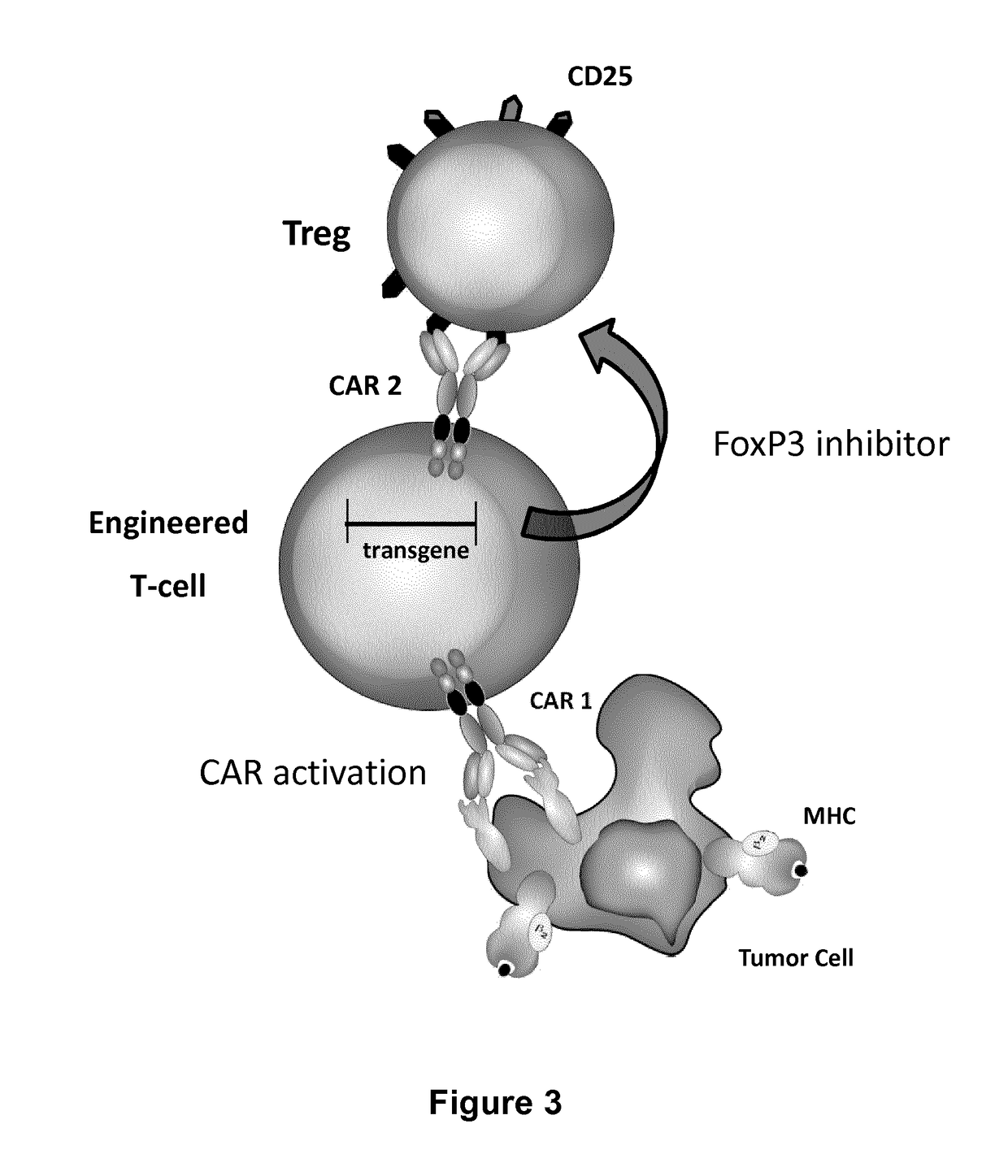
Method for in situ inhibition of regulatory t cells
ActiveUS20170067022A1Reducing FoxP transcriptional activityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenInfected cell
The present invention pertains to engineered T-cells, method for their preparation and their use as medicament, particularly for immunotherapy. The engineered T-cells of the invention are designed to express both a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) directed against at least one antigen expressed at the surface of a malignant or infected cell, and a secreted inhibitor of regulatory T-cells (Treg). Preferably, such secreted inhibitor is a peptide inhibitor of forkhead / winged helix transcription factor 3 (FoxP3), a specific factor involved into the differentiation of T-cells into regulatory T-cells. The engineered T-cells of the invention direct their immune activity towards specific malignant or infected cells, while at the same time will prevent neighbouring regulatory T-cells from modulating the immune response. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies, especially for treating or preventing cancer, and bacterial or viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
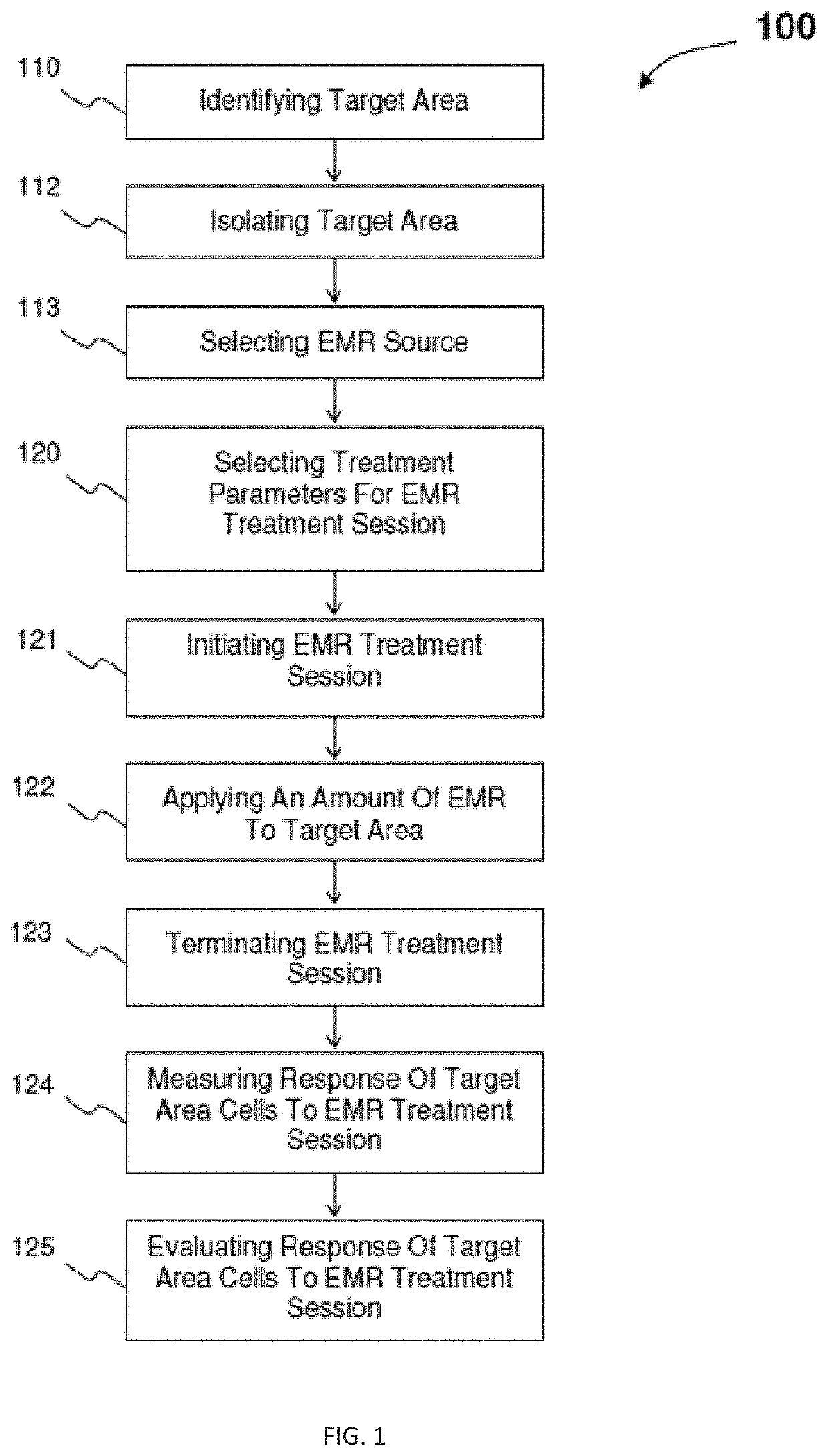
Electromagnetic radiation treatment
InactiveUS20200330782A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsInfected cellEngineering
An electromagnetic radiation treatment regime includes identifying a target area of a patient. In one embodiment, the target area is a virally-infected cell or tissue. An electromagnetic radiation source, for example, a low frequency and / or radio frequency electromagnetic radiation source, is selected, along with treatment session parameters, such as, pulse frequency, pulse duration, electrical current, magnetic flux density, and / or treatment session exposure time. An amount of electromagnetic radiation is applied to the target area, and a response to the electromagnetic radiation in the target area is measured. Based on an evaluation of the measured response, the treatment parameters may be modified for one or more subsequent electromagnetic radiation treatment session.
Owner:ZABARA JACOB
Methods for engineering T cells for immunotherapy by using RNA-guided CAS nuclease system
ActiveUS9890393B2Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Natural killer cells with enhanced immune response
ActiveUS20130295044A1Avoiding unnecessary treatmentAvoid treatmentBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsInfected cellNatural killer cell
The invention relates to a specialized subpopulation of natural killer cells that have enhanced effector functions and the potential to kill malignant tumor cells or infected cells when the natural killer cells are exposed to an antibody bound to the tumor cells or the infected cells.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Herpes virus vectors for dendritic cells
InactiveUS6641817B1Efficient infectionLow toxicityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseInfected cell
An attenuated herpes virus capable of efficiently infecting a dendritic cell without preventing antigen processing occurring within the infected cell. The attenuated herpes virus and dentrictic cells infected with the virus are useful in immunotherapeutic methods of treating disease.
Owner:BIOVEX LTD
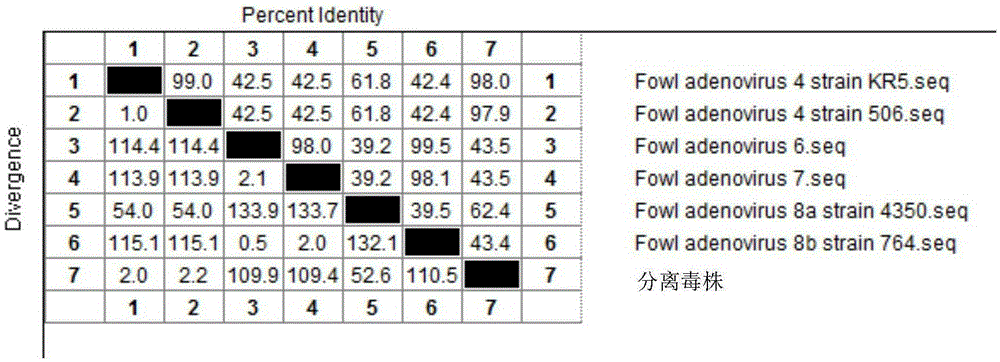
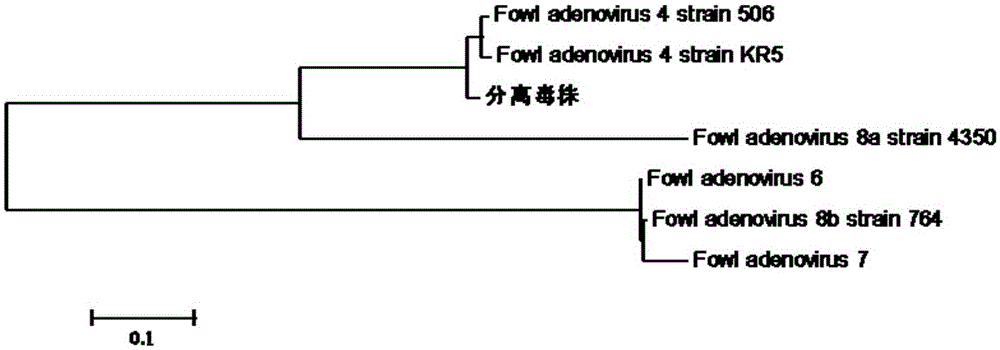
I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain and application thereof
ActiveCN105368795AImprove featuresImproving immunogenicityViral antigen ingredientsBiological material analysisInfected cellLaryngotracheitis virus
The invention aims at providing an I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 strain, which is preserved with preservation number of CCTCC No. V201541. The I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 YBAV-4 strain disclosed by the invention is excellent in specificity and immunogenicity; a specific precipitation line does not appear in specific positive serum chicken SPF chicken serum such as infected cell sap and egg drop syndrome resisting virus, chicken infectious bursal disease virus, Newcastle disease virus, chicken infectious laryngotracheitis virus, chicken Marek's disease virus, avian influenza and the like, while an obvious specific precipitation line appears in I-colony fowl adenovirus 4 specific serum. The strain disclosed by the invention, as a vaccine strain which is good in manufacturing effect, is capable of preventing chicken hydropericardium syndrome, and the strain is applicable to identification of virus serotype and investigation on epidemiology.
Owner:YEBIO BIOENG OF QINGDAO
Compositions and methods for detecting human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS6900010B2Robust and efficient and sensitive in detectionEarly diagnosisBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHeterologousInfected cell
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Methods of monitoring HIV drug resistance using adenoviral vectors
InactiveUS20020168345A1Easy to produceEasy maintenanceVirusesDiagnosticsInfected cellProtein regulation
Recombinant expression vectors and methods are provided for detecting HIV and monitoring HIV drug resistance. The method comprises: taking a culture of cells; adding a recombinant viral vector into the culture to transduce the cells, the recombinant viral vector comprising a reporter sequence comprising a reporter gene whose expression is regulated by a protein specific to HIV viruses which is expressed from a genome of an HIV virus upon infection of a cell in the culture that is transduced by the recombinant viral vector, and a receptor sequence comprising CD 4 and one or more coreceptor genes, expression of the coreceptor genes facilitating productive infection of the transduced cell and enabling HIV virus which has infected the transduced cell to replicate and infect non-infected cells in the culture of the cells transduced by the recombinant viral vector; infecting the transduced cells with a sample containing HIV; adding one or more anti-HIV agents to the cell culture; and detecting a change in a level of expression of the reporter gene in cells.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Targeted cytolysis of HIV-infected cells by chimeric CD4 receptor-bearing cells
InactiveUS7094599B2Promote absorptionProlong lifeVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEphA Receptors
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular immune response against an HIV-infected cell in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells which express a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising (a) an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection and (b) an intracellular portion which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy the receptor-bound HIV-infected cell. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA and vectors encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods and Systems for Detection of Microorganisms
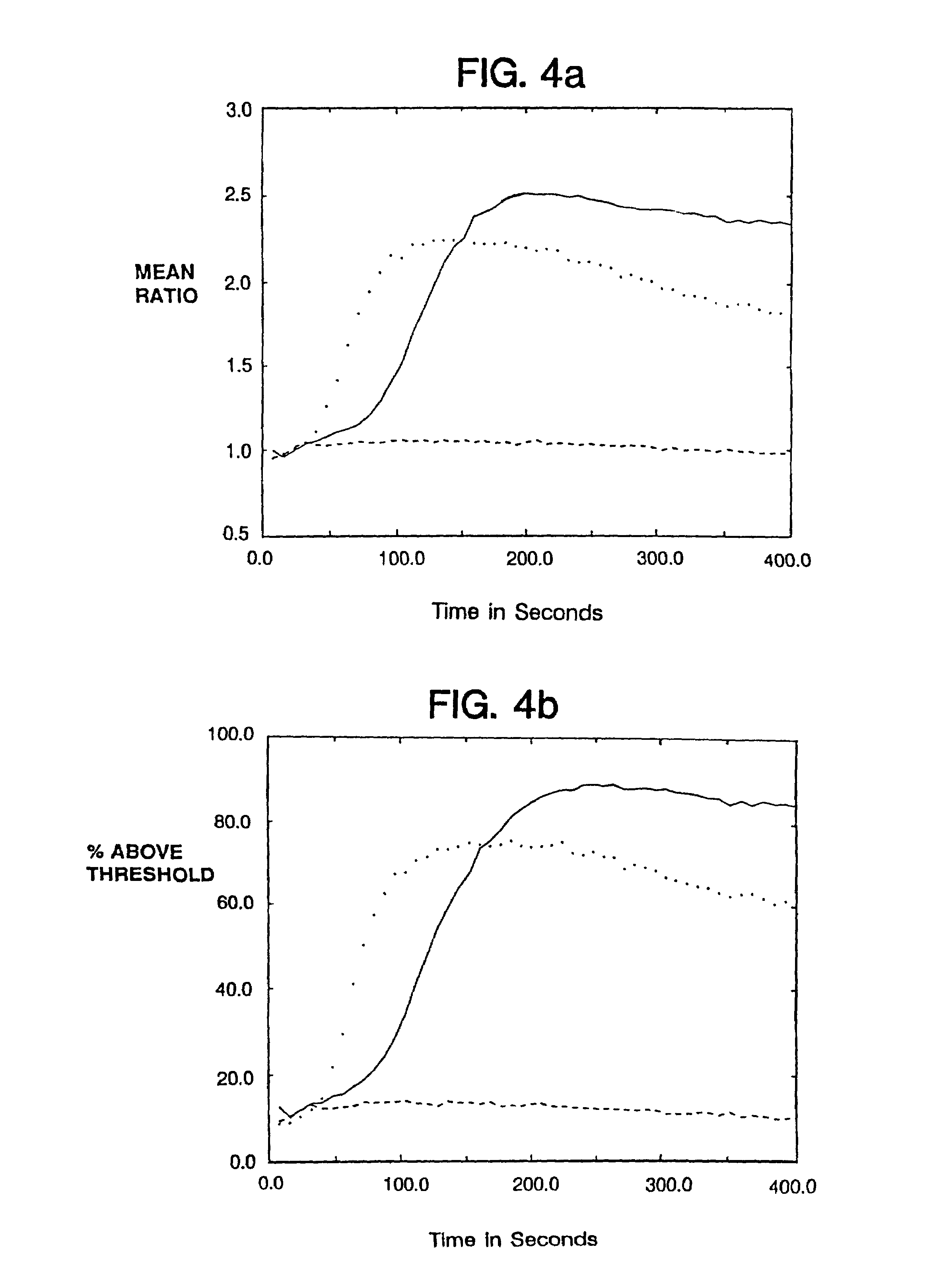
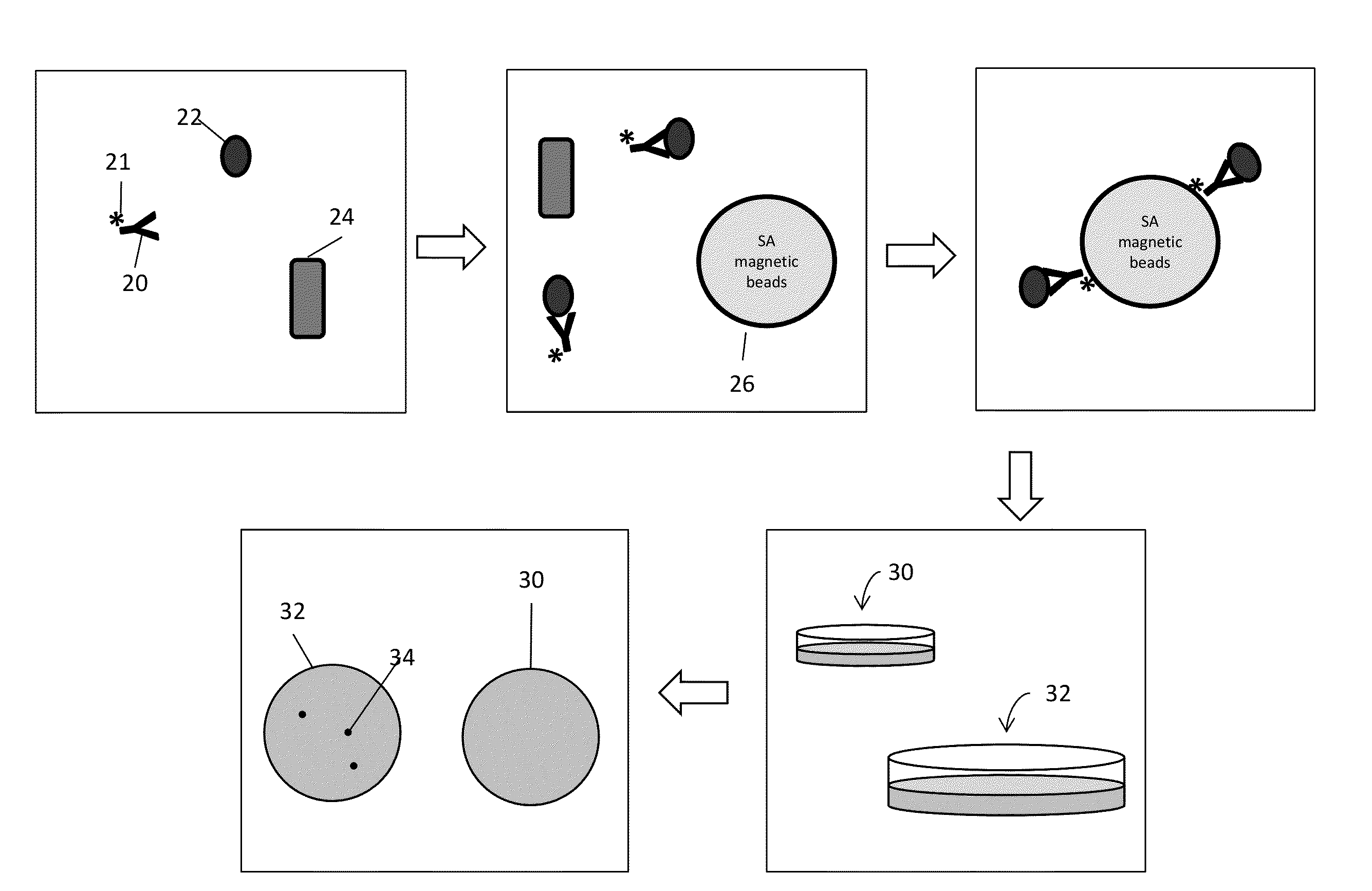
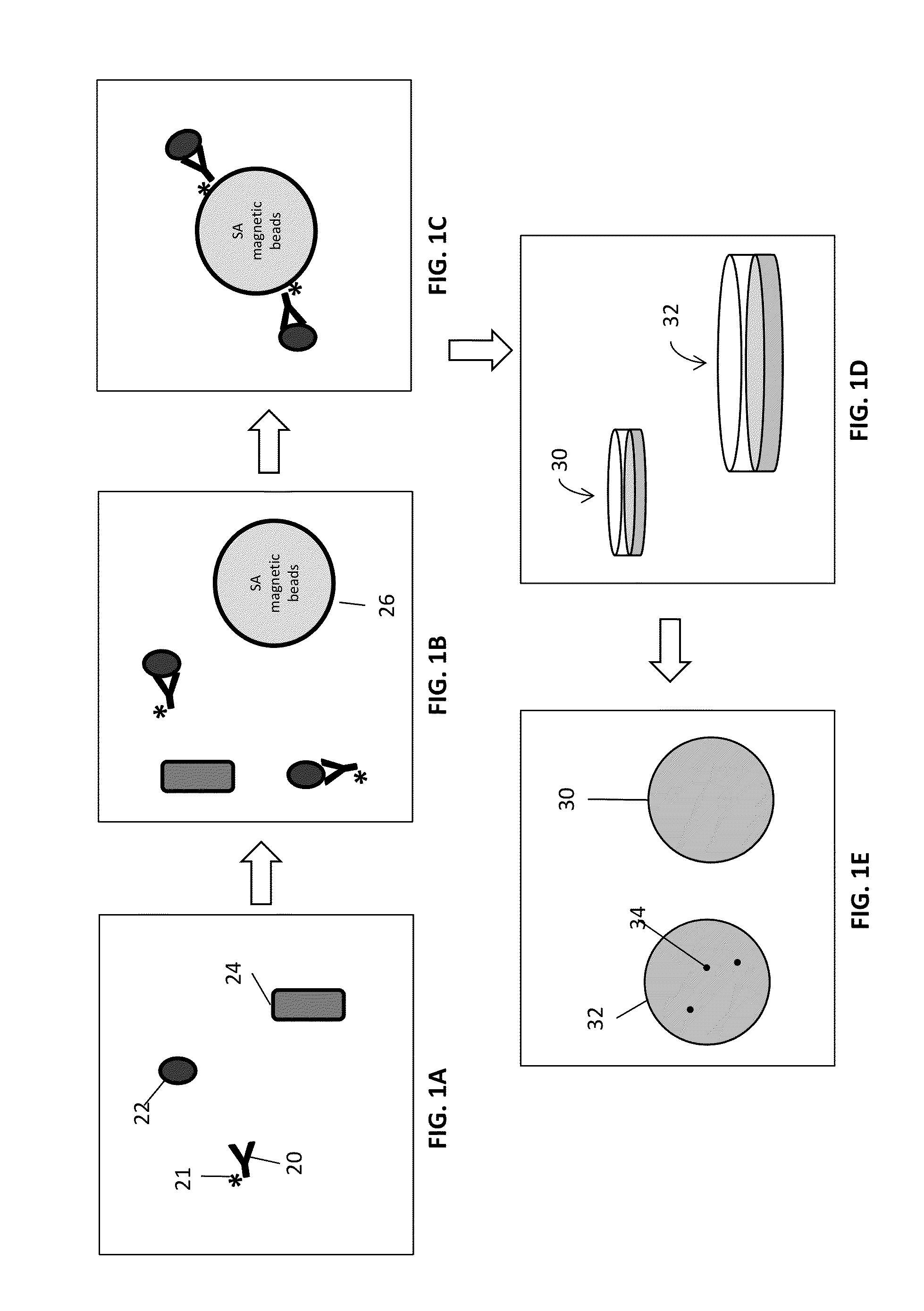
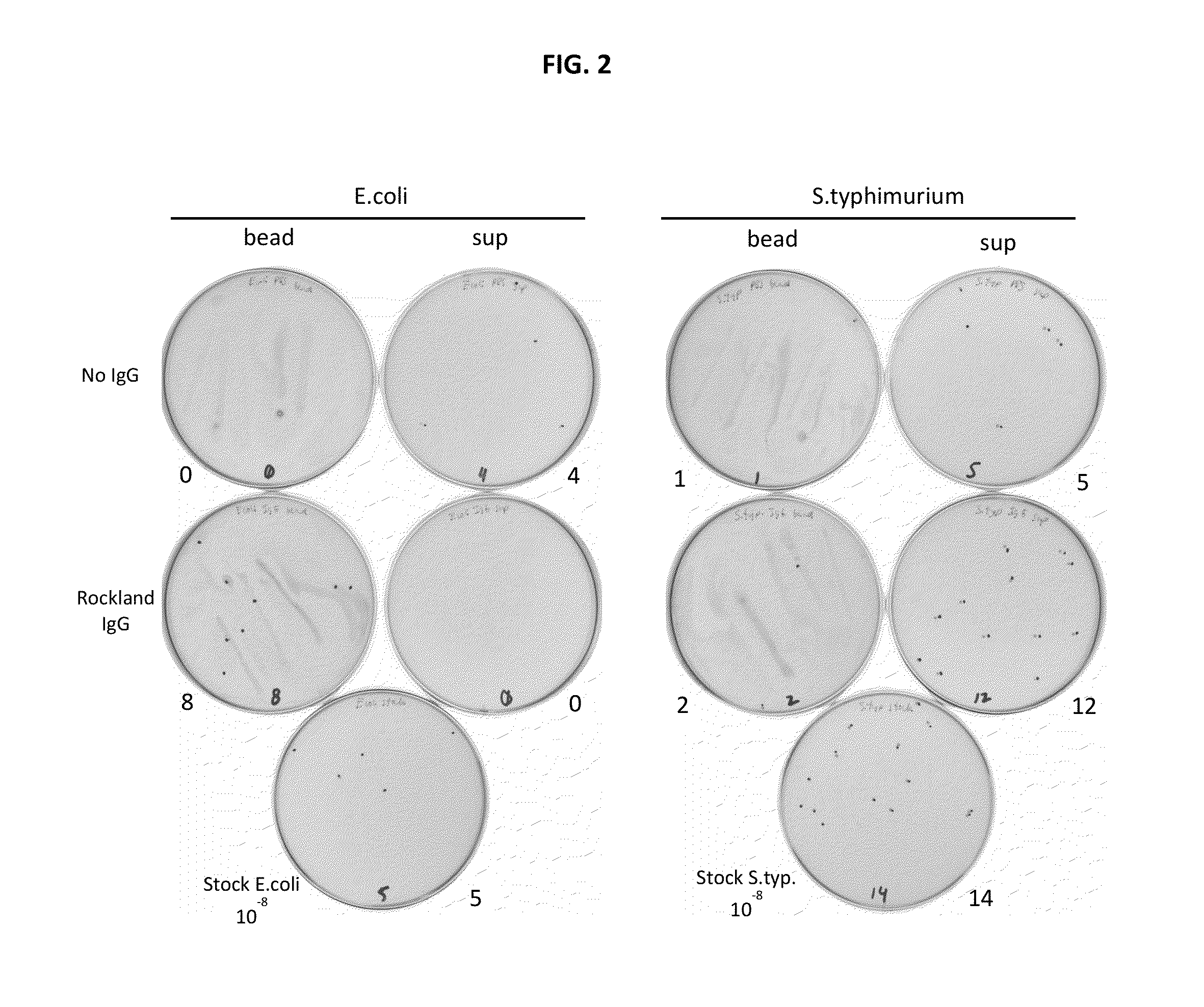
ActiveUS20130216997A1Easy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicroorganismInfected cell
Disclosed are methods and systems for the isolation and detection of microbes from a sample. The use of binding agents for isolation of a microbe of interest from a sample are described. In certain embodiments, the methods use ribosome-based and / or bacteriophage-based amplification of the signal in detection of bacteria and other microorganisms. For example, embodiments of the present invention can achieve total amplification of at least 10,000 from a single infected cell.
Owner:LAB OF AMERICA HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com