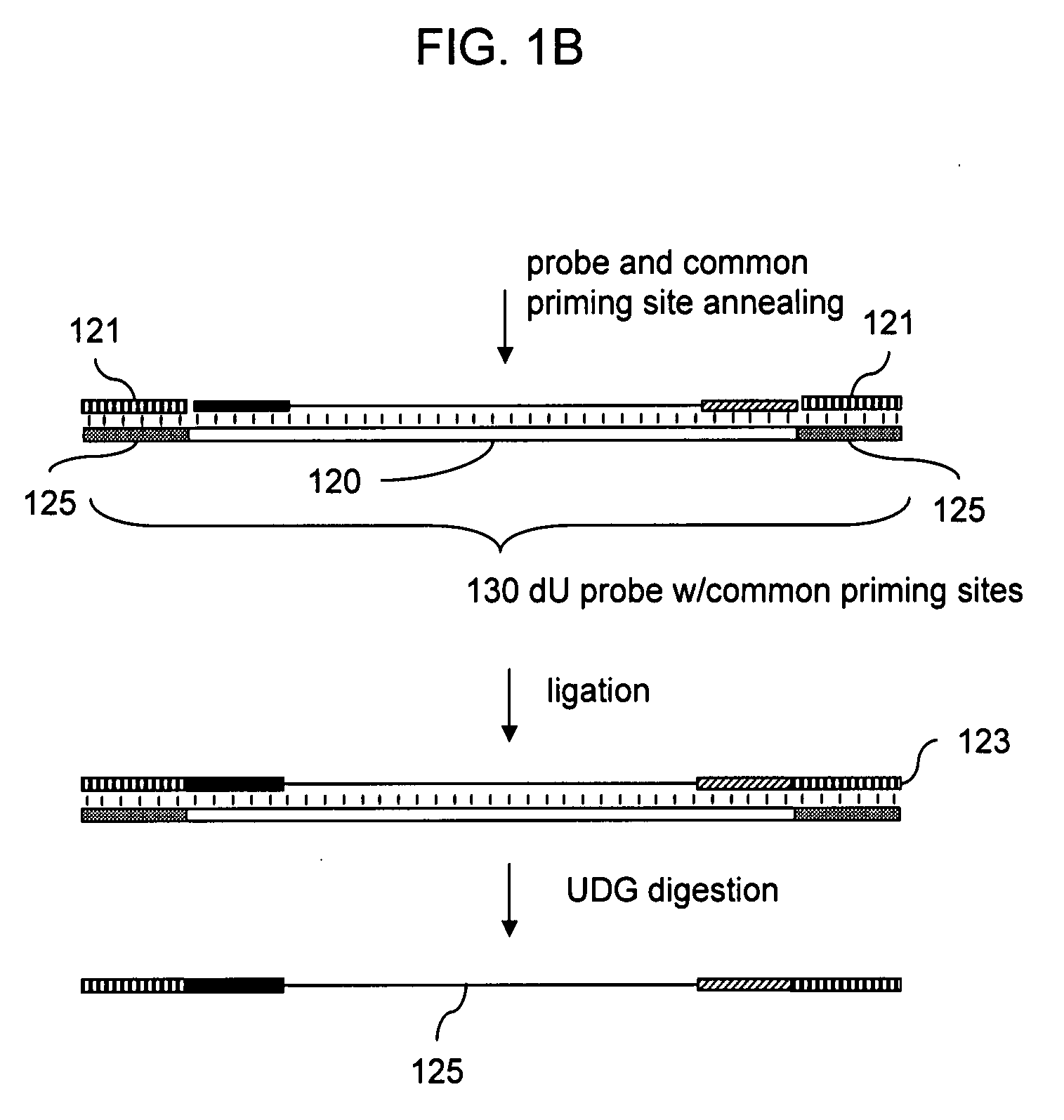
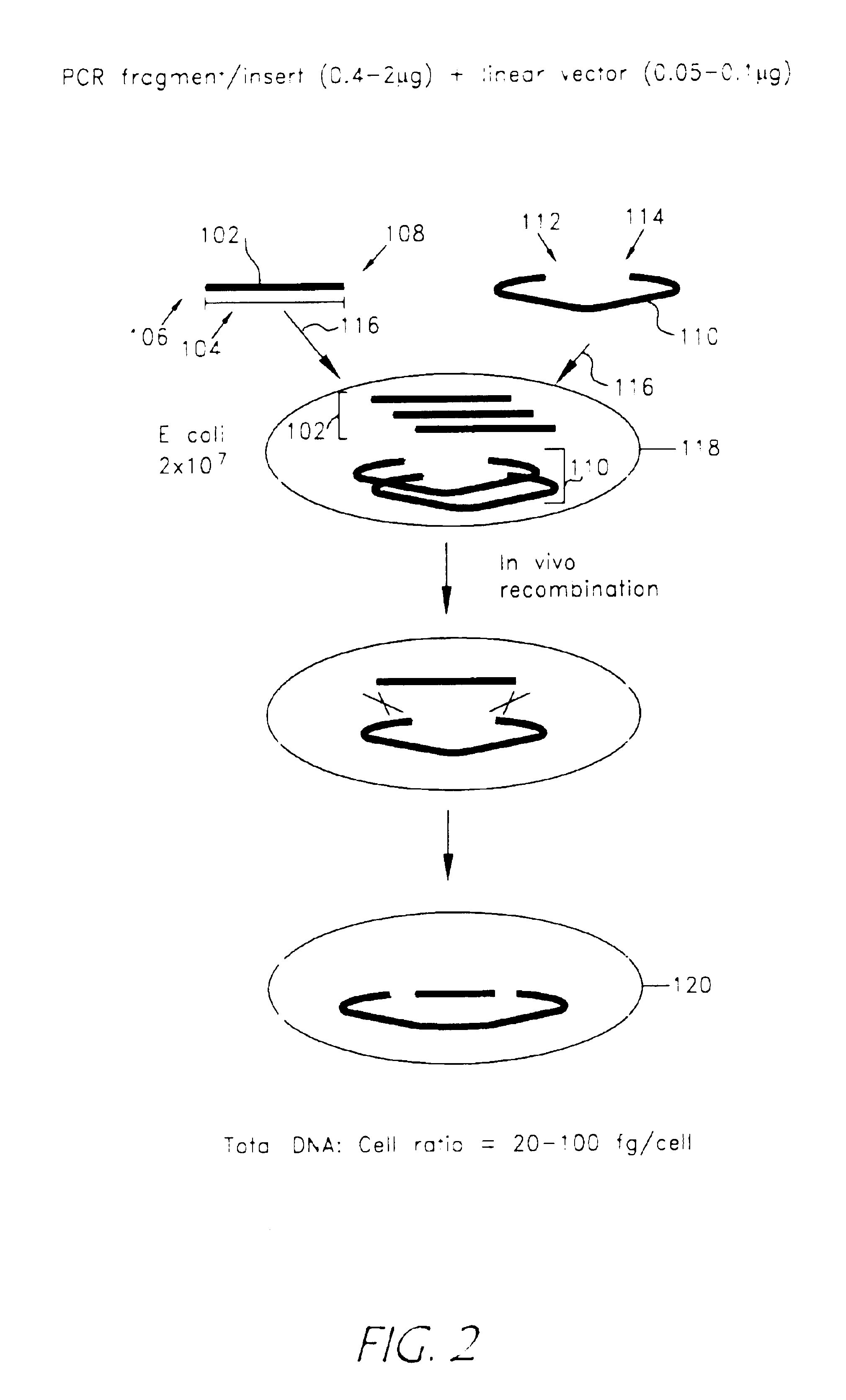
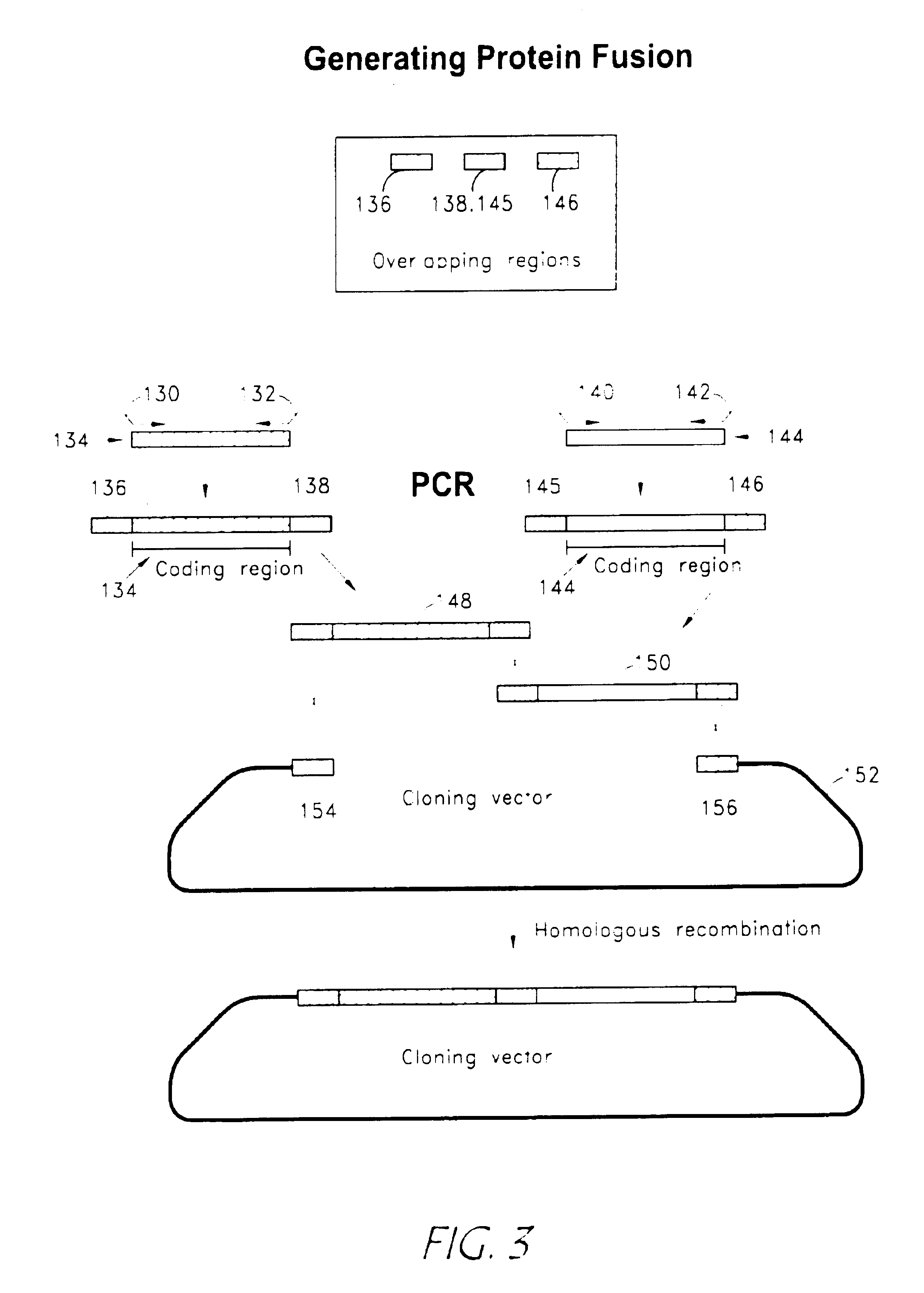
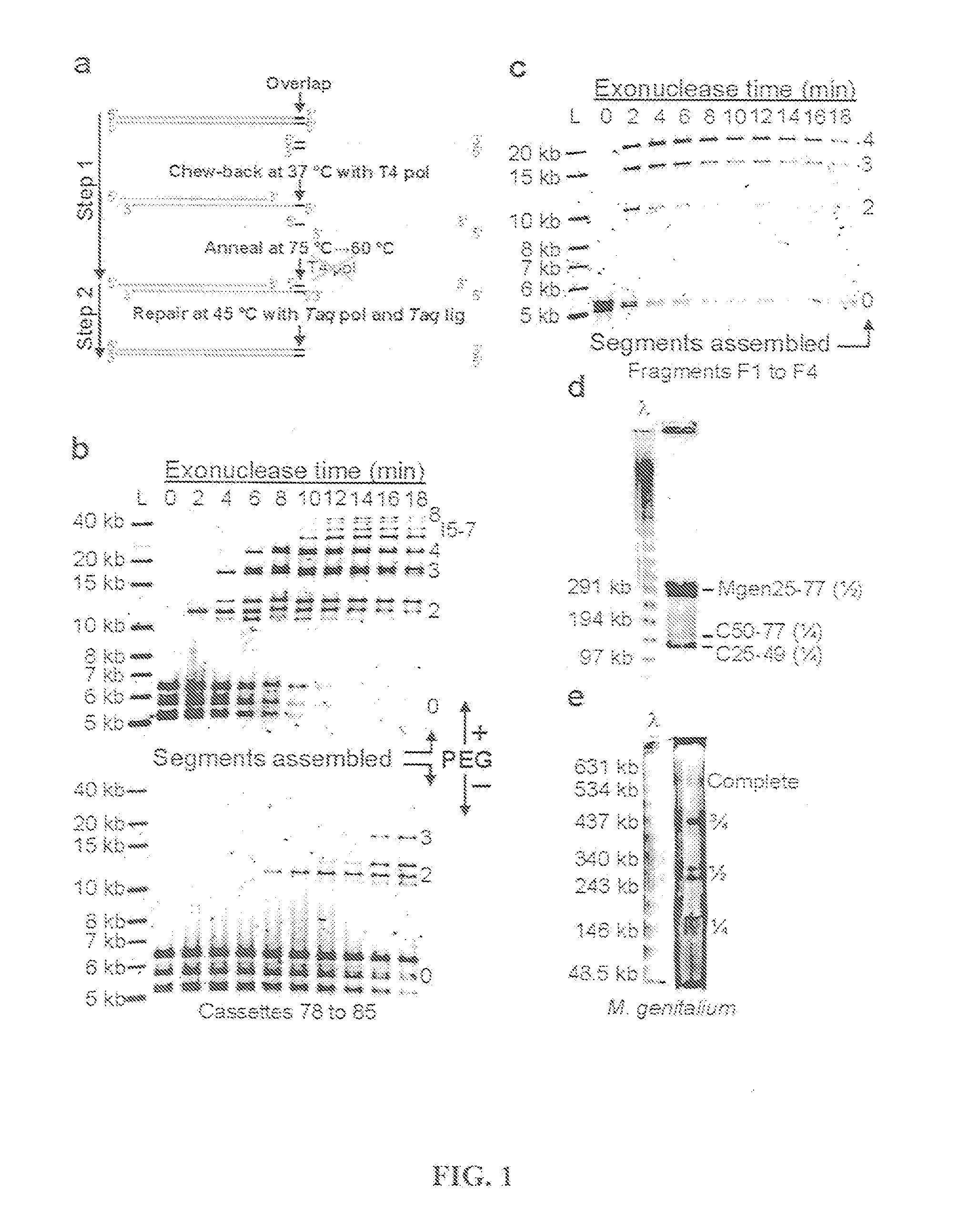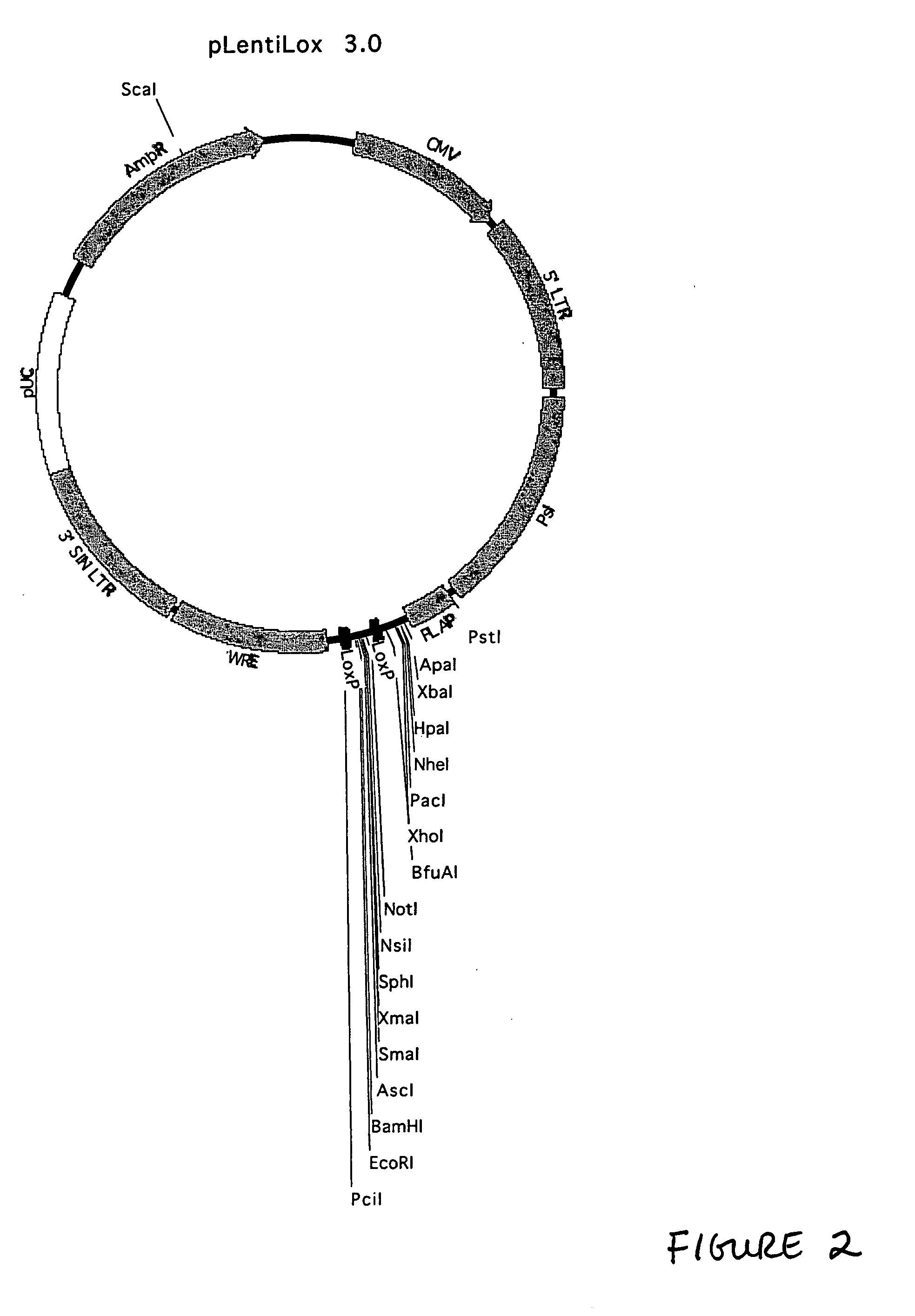Patents
Literature
1076 results about "Restriction enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
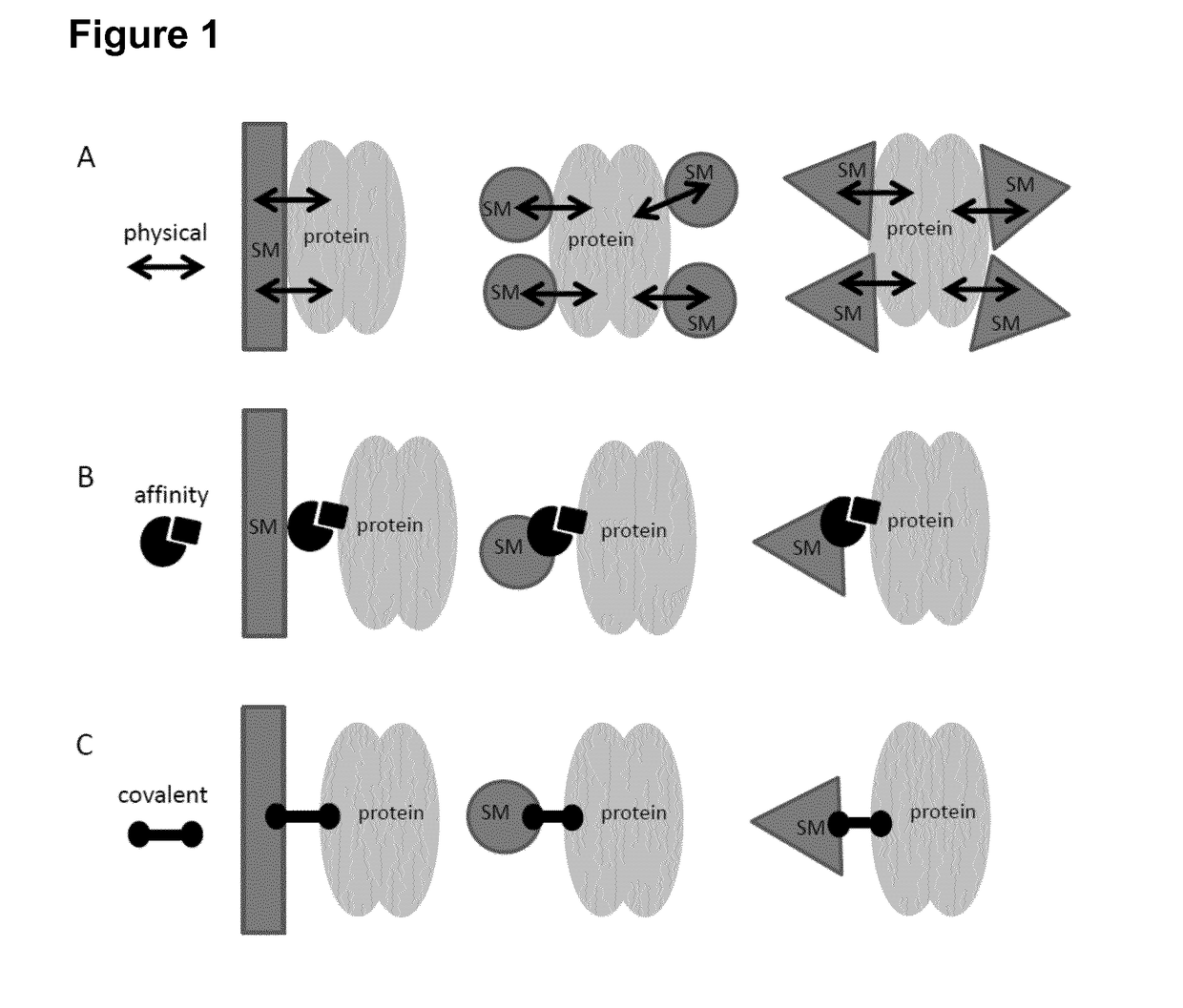
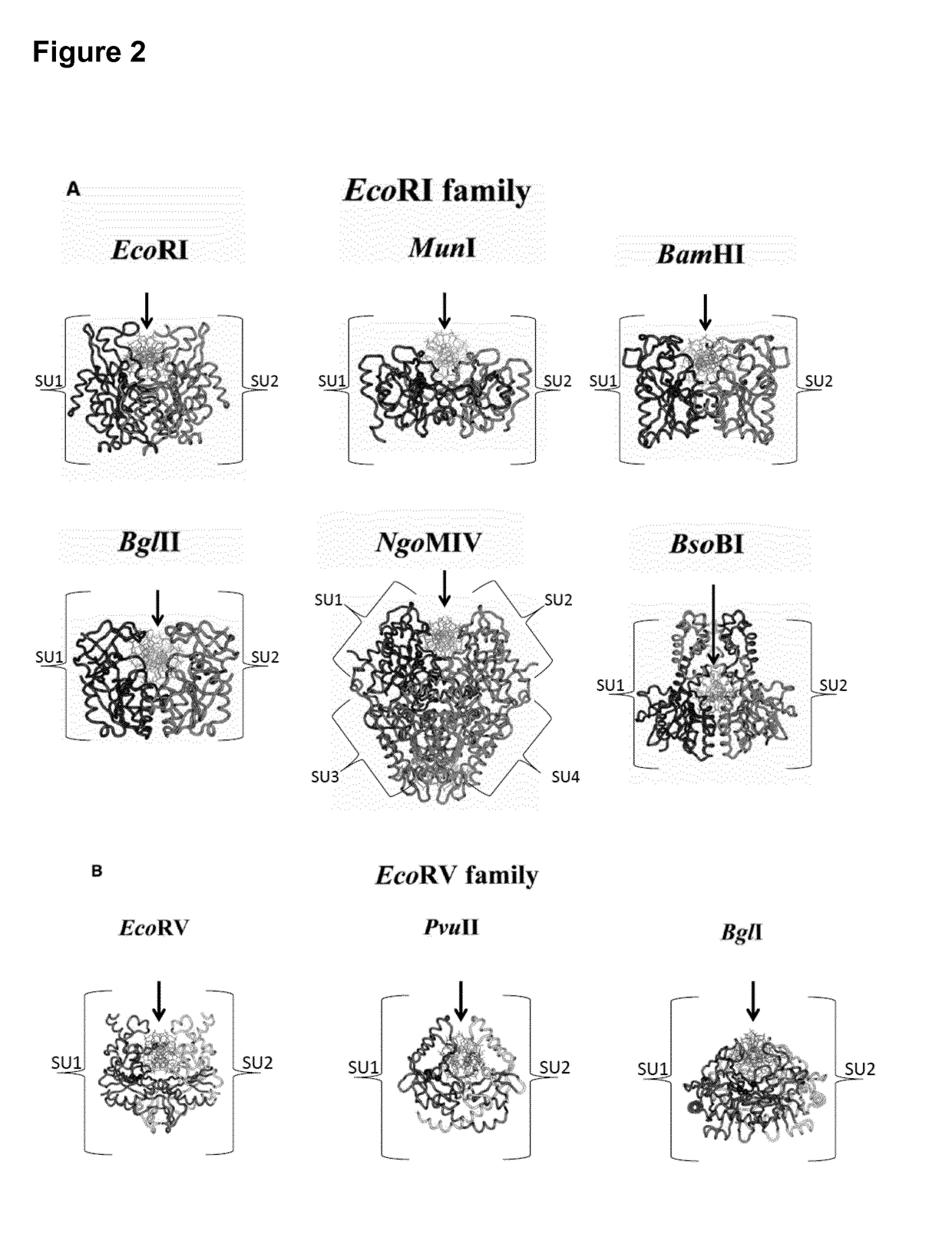
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, or restrictase is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each sugar-phosphate backbone (i.e. each strand) of the DNA double helix.
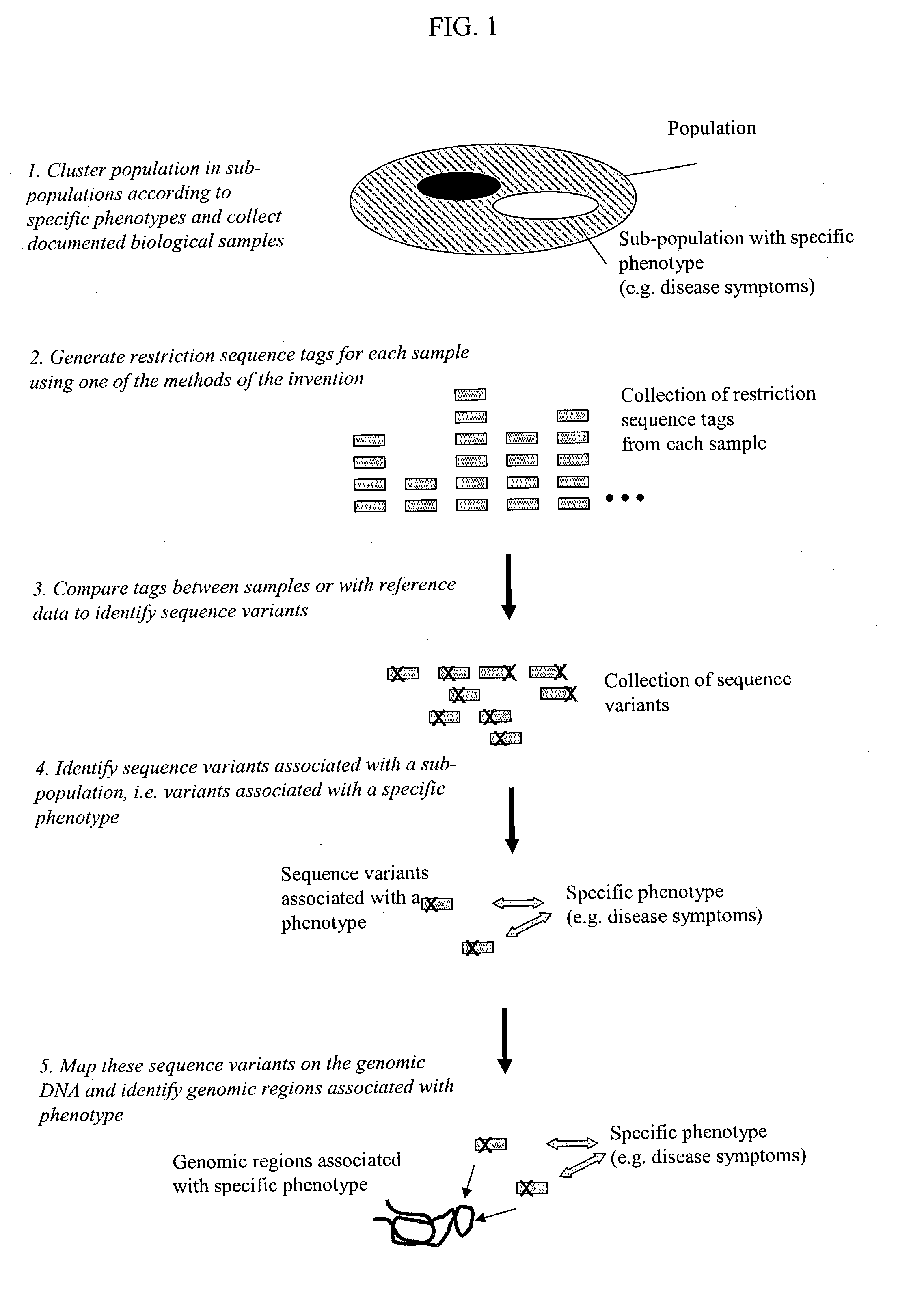
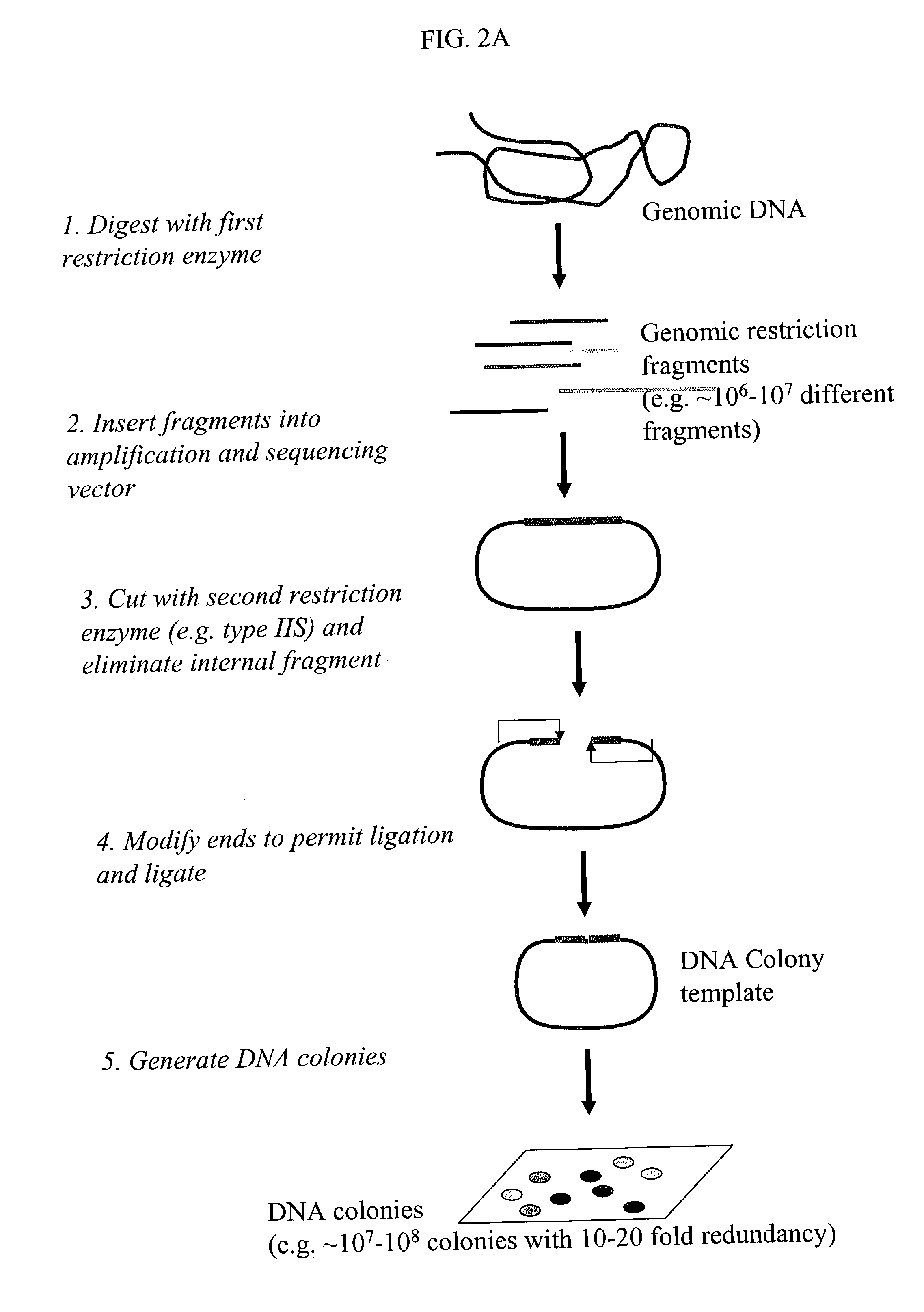
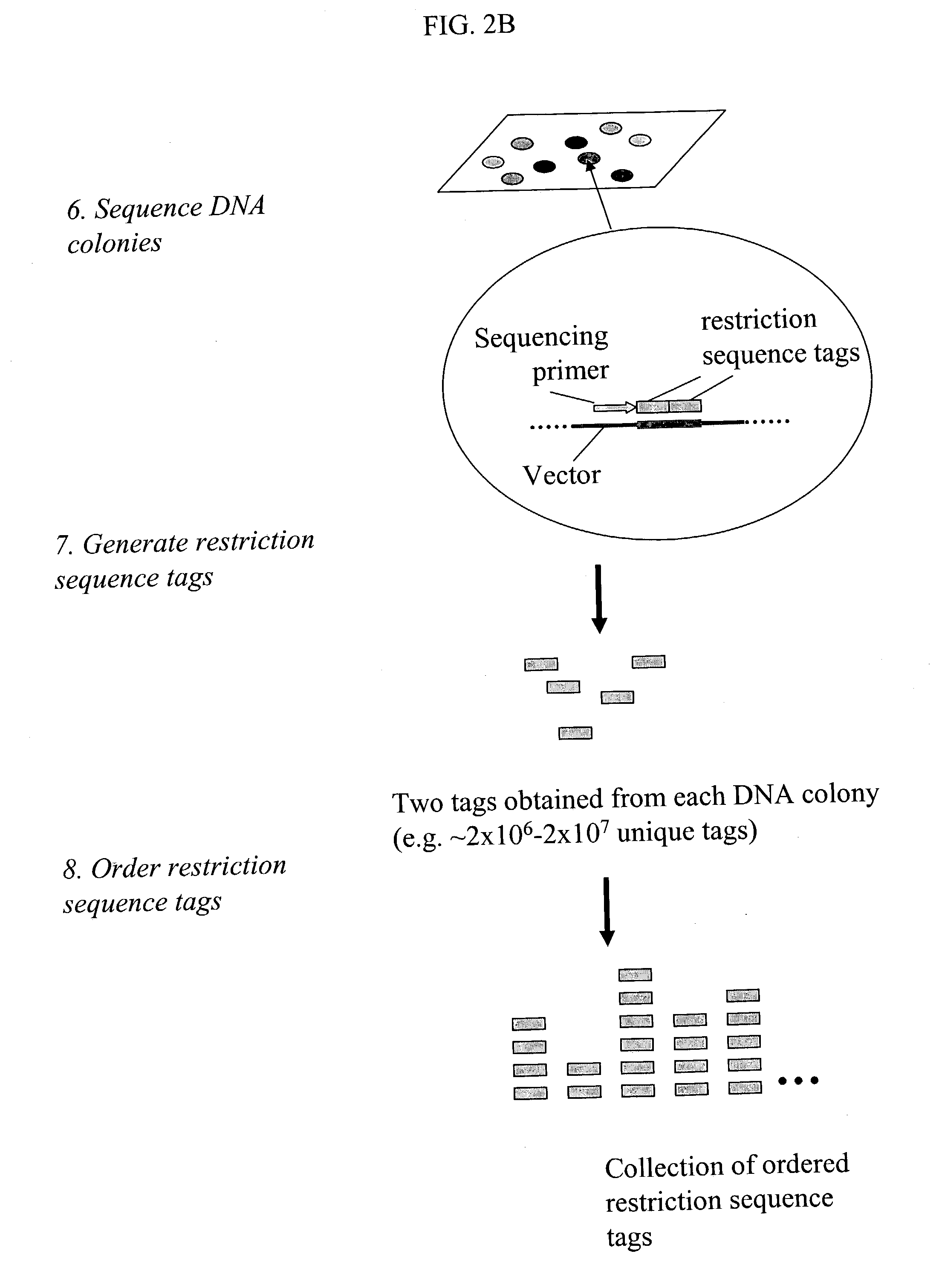
Methods for detecting genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype
InactiveUS20040002090A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationSub populationsGenetic risk factor
The invention provides methods for determining genome-wide sequence variations associated with a phenotype of a species in a hypothesis-free manner. In the methods of the invention, a set of restriction fragments for each of a sub-population of individuals having the phenotype are generated by digesting nucleic acids from the individual using one or more different restriction enzymes. A set of restriction sequence tags for the individual is then determined from the set of restriction fragments. The restriction sequence tags for the sub-population of organisms are compared and grouped into one or more groups, each of which comprising restriction sequence tags that comprise homologous sequences. The obtained one or more groups of restriction sequence tags identify the sequence variations associated with the phenotype. The methods of the invention can be used for, e.g., analysis of large numbers of sequence variants in many patient samples to identify subtle genetic risk factors.
Owner:SOLEXA
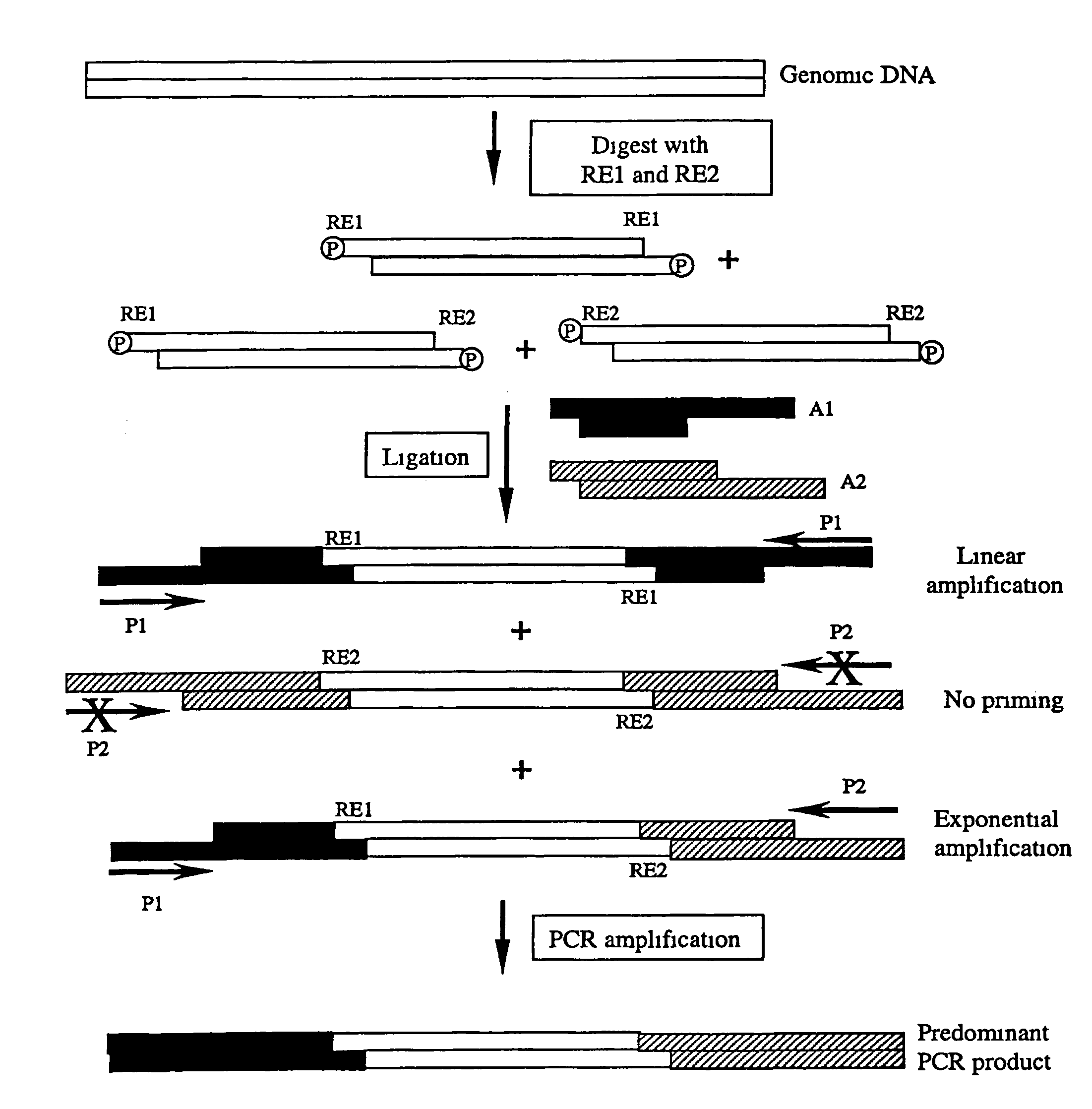
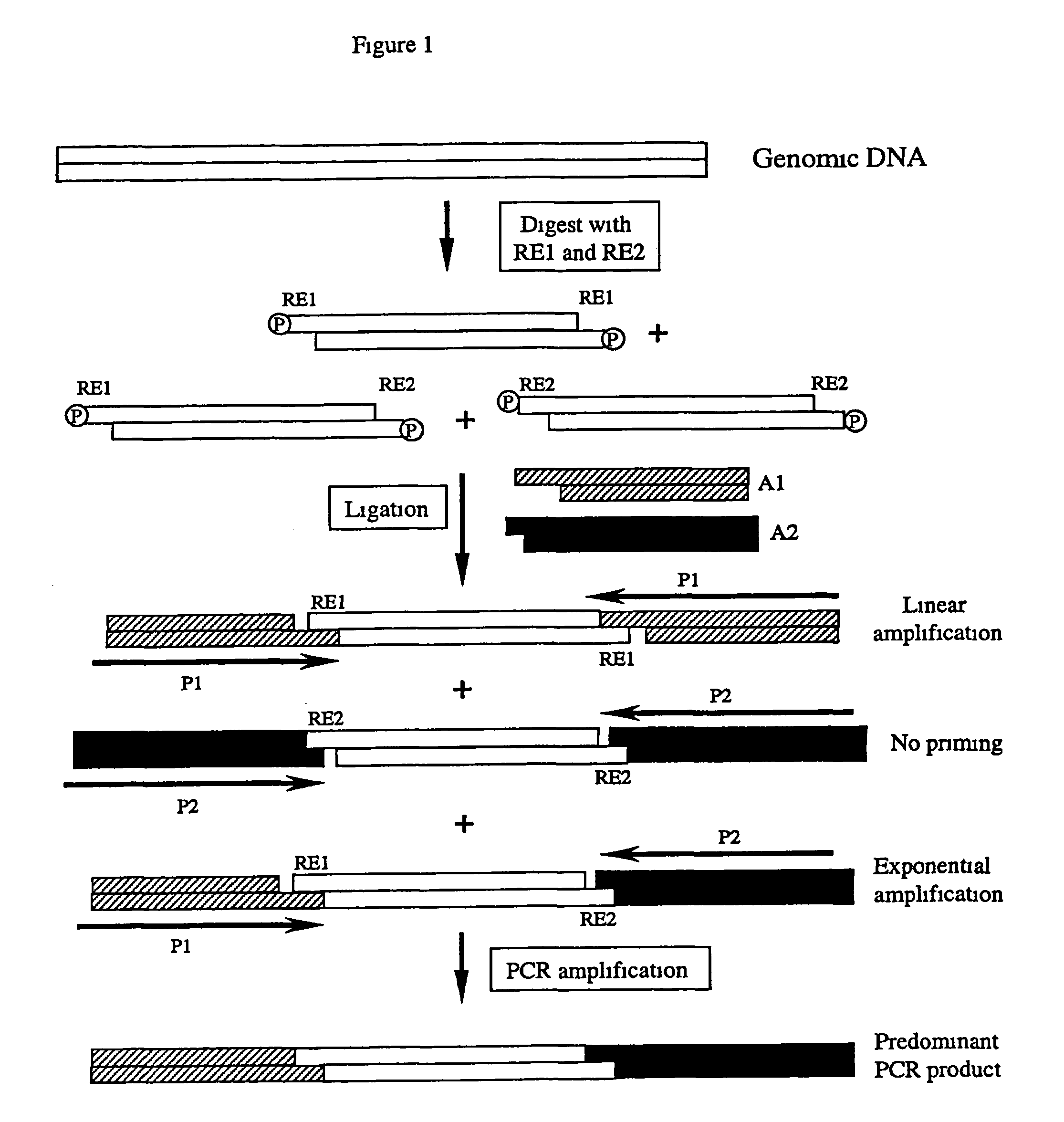
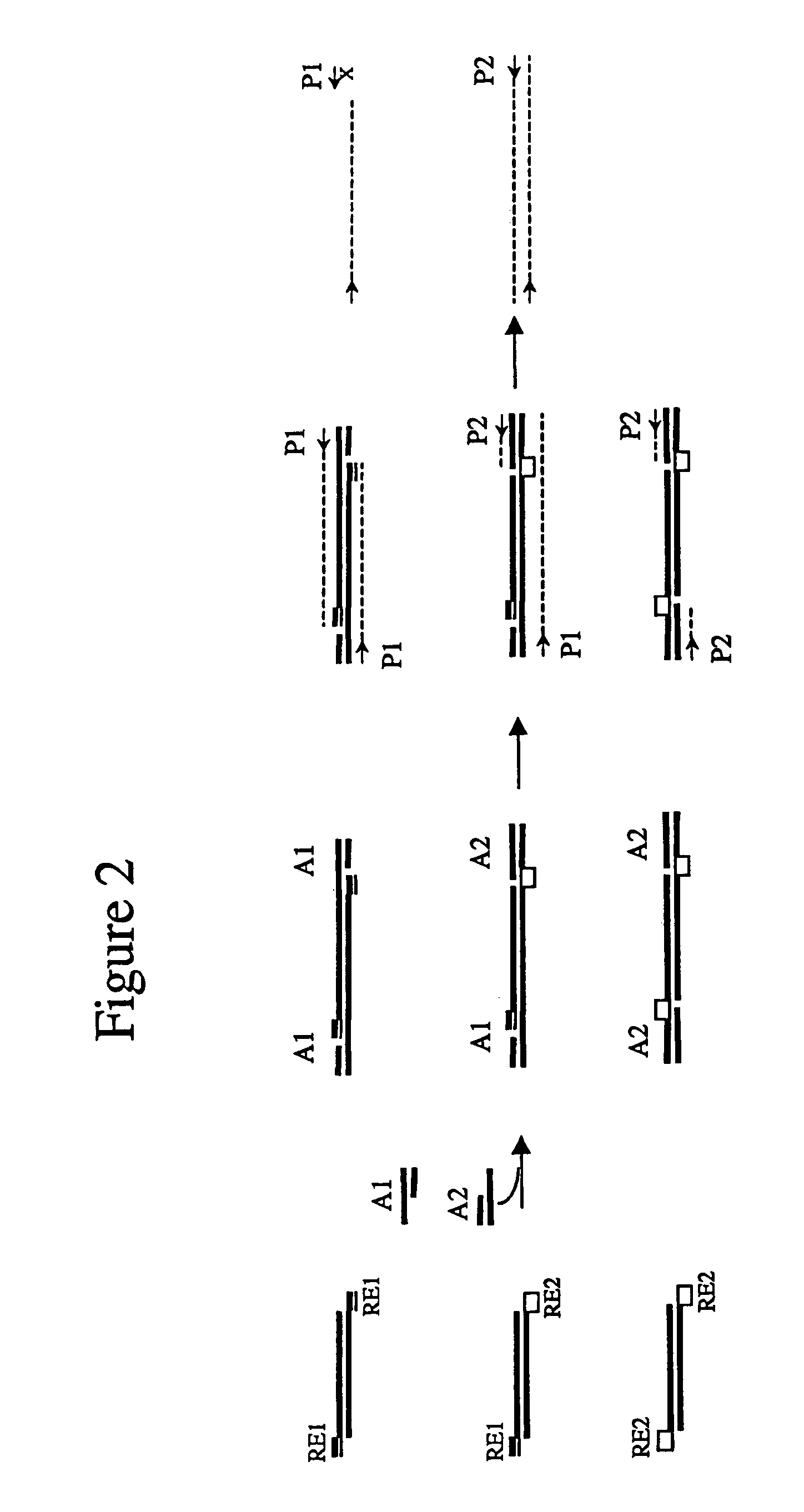
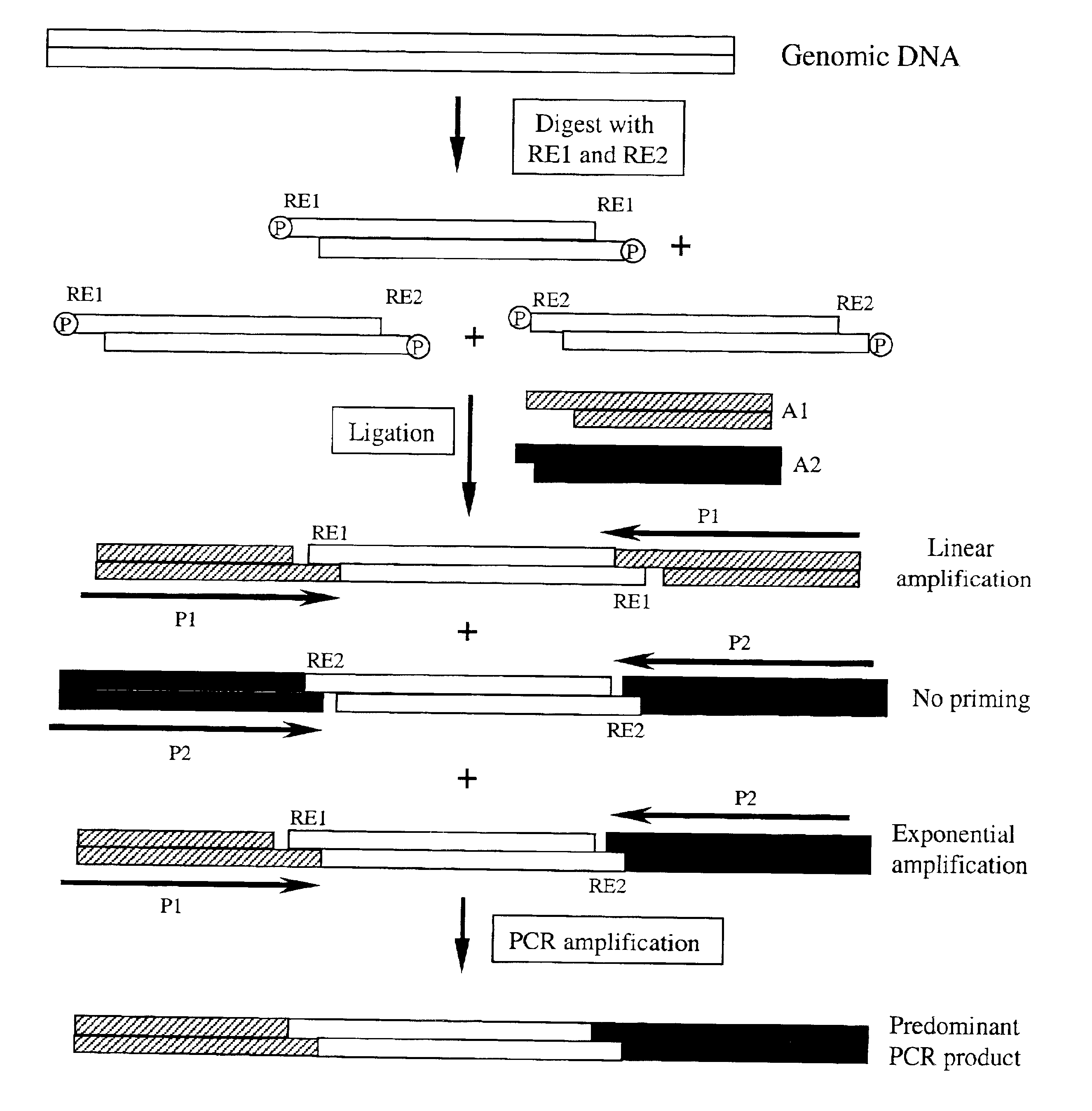
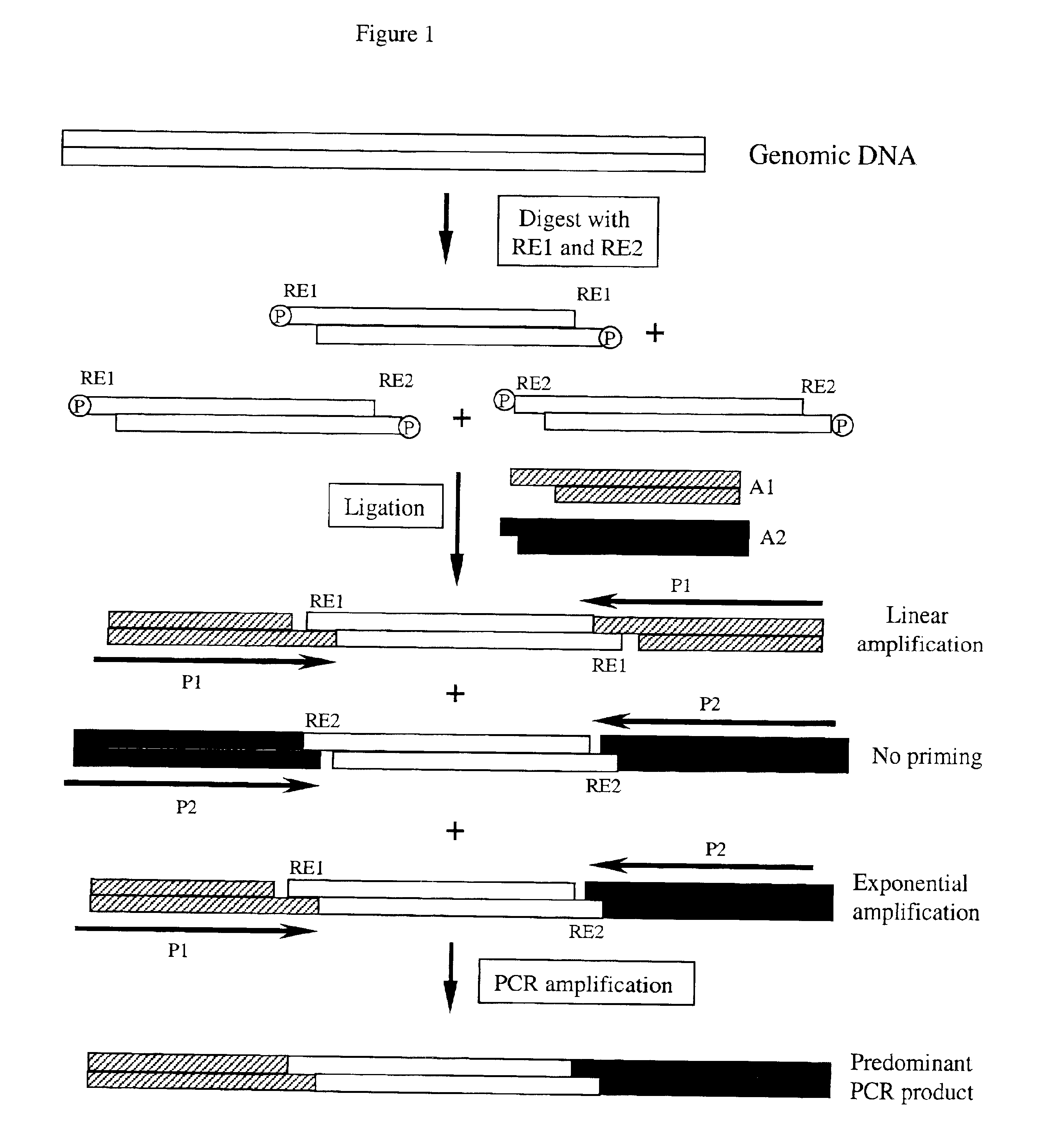
Complexity management of genomic DNA
InactiveUS7745178B2Reduce complexityComplexity of resultingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGel basedGenomic DNA
The presently claimed invention provides for novel methods and kits for reducing the complexity of a nucleic acid sample by providing non-gel based methods for amplification of a subset of the sequences in a sample. In a preferred embodiment, amplification of a subset can be accomplished by digesting a sample with two or more restriction enzymes and ligating adaptors to the fragments so that only a subset of the fragments can be amplified. The invention further provides for analysis of the above amplified sample by hybridization to an array, which may be specifically designed to interrogate the desired fragments for particular characteristics, such as, for example, the presence or absence of a polymorphism.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
In vitro recombination method
ActiveUS20070037197A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand DNA-binding proteinSequence identity
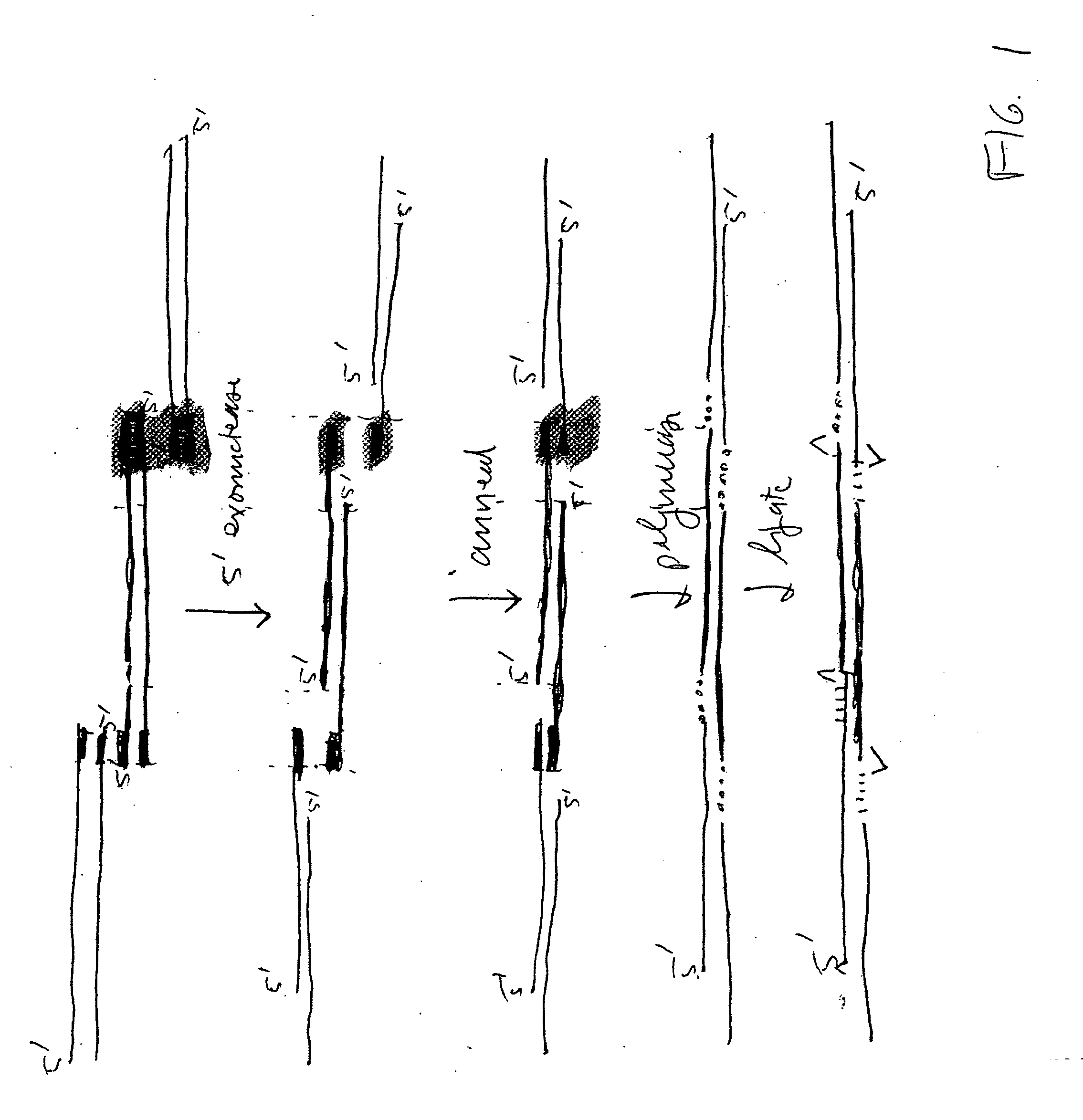
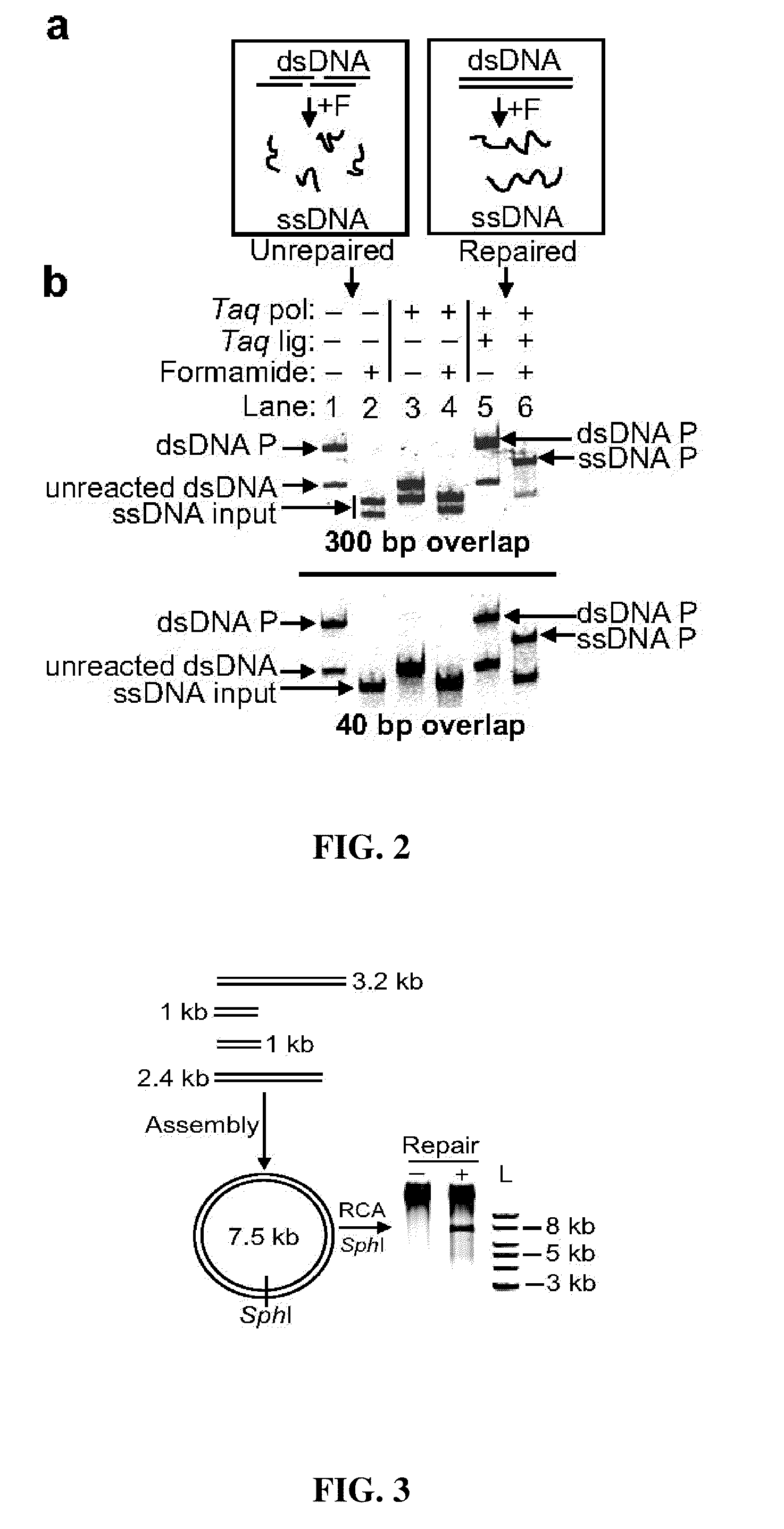
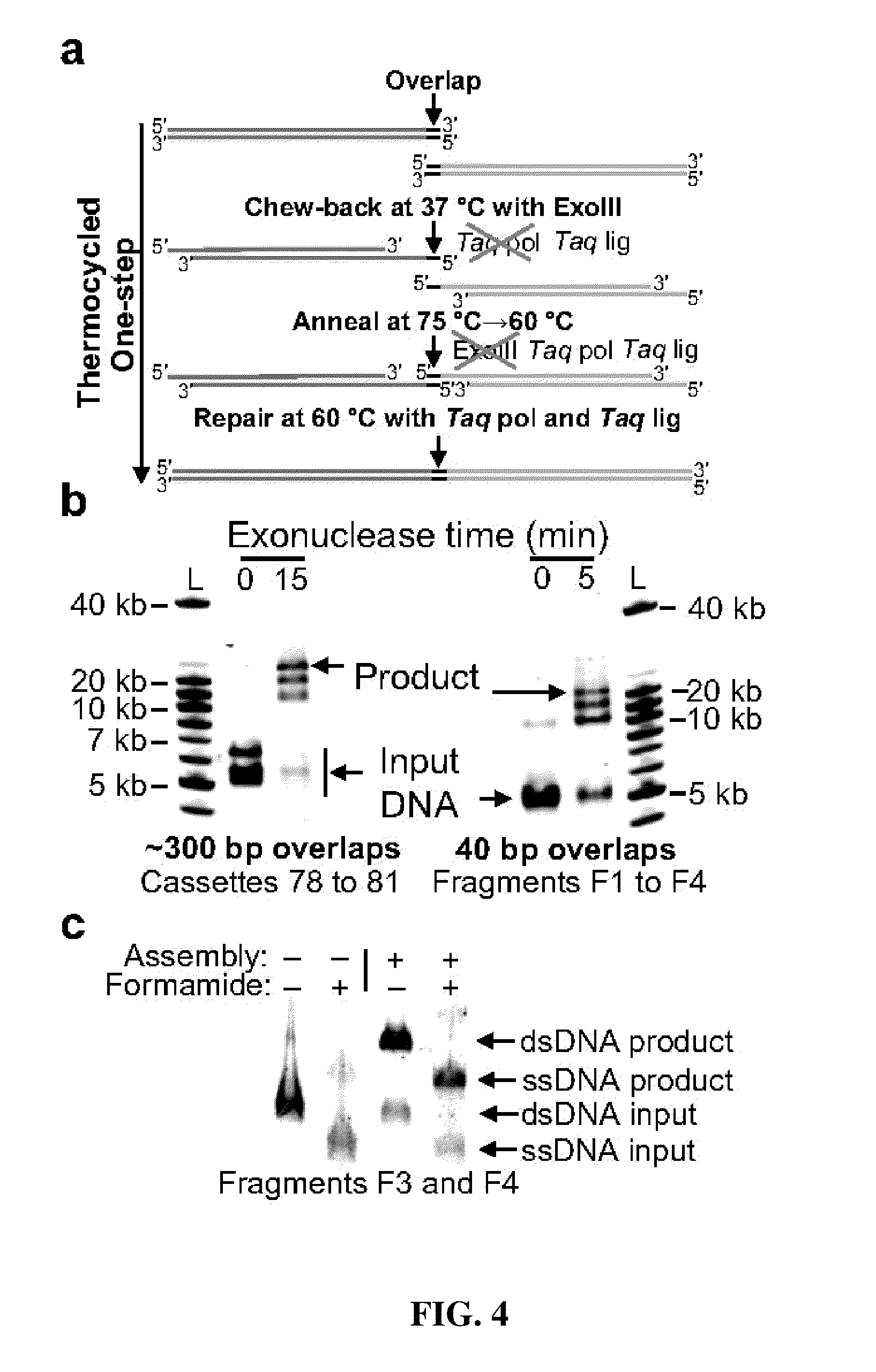
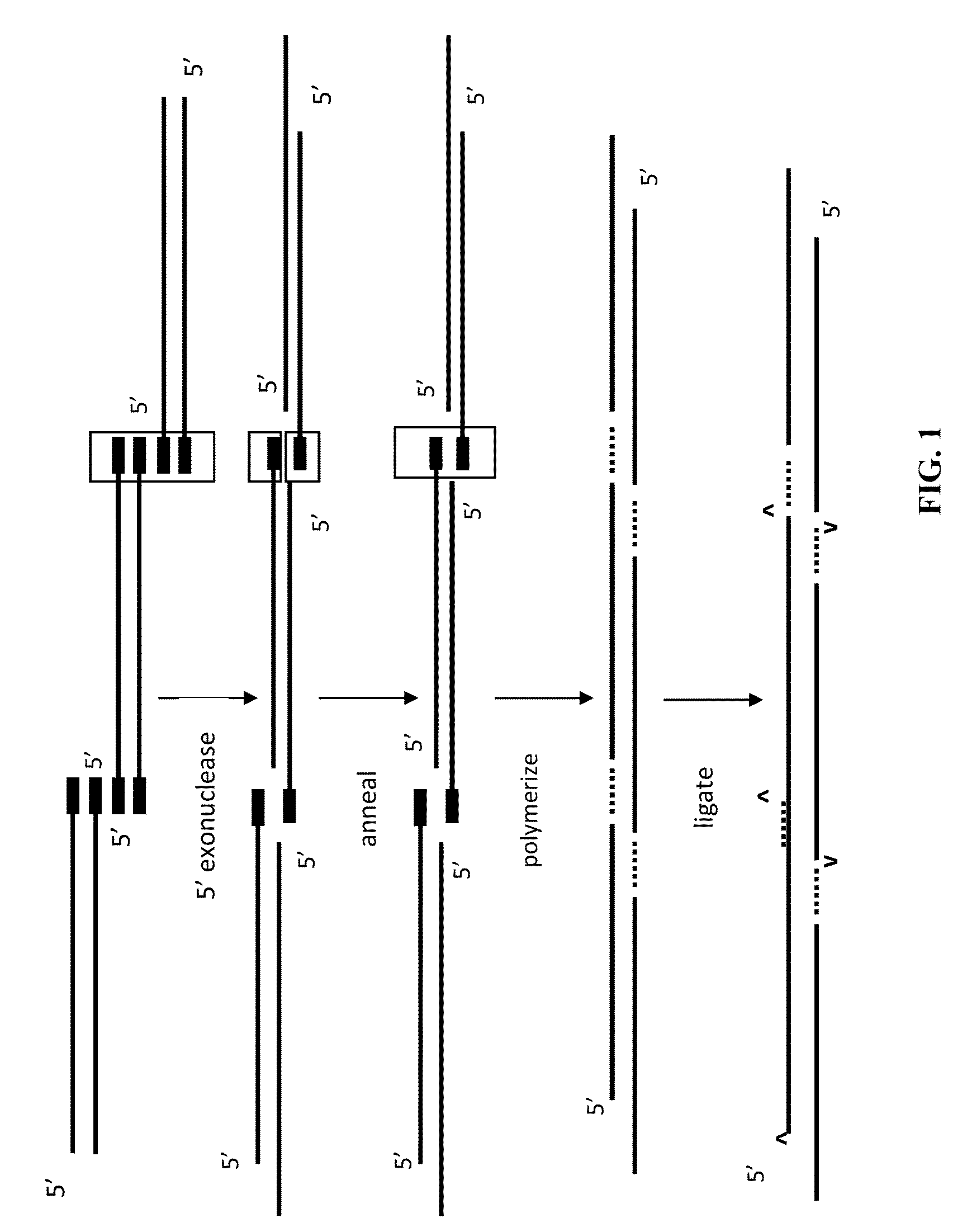
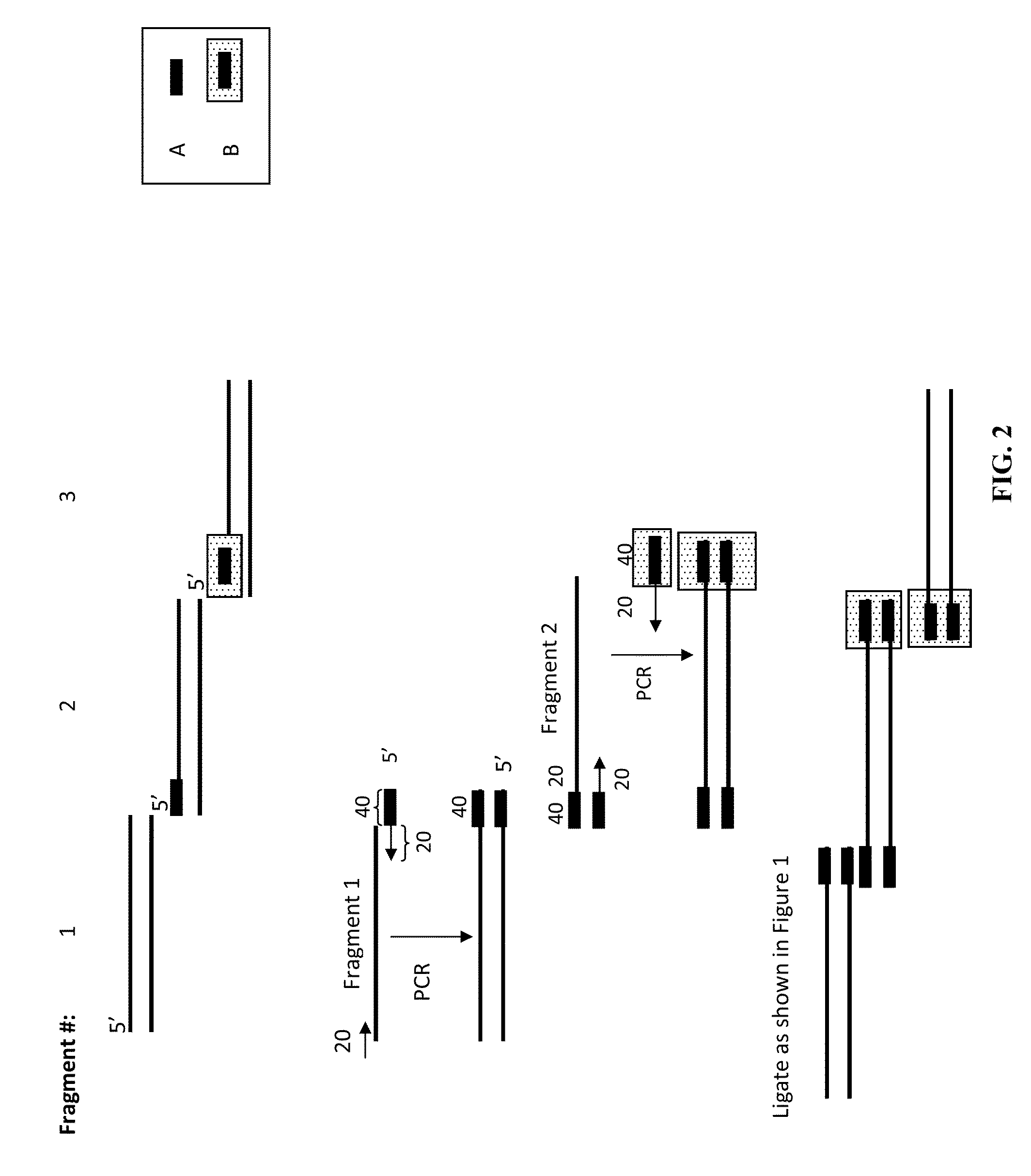
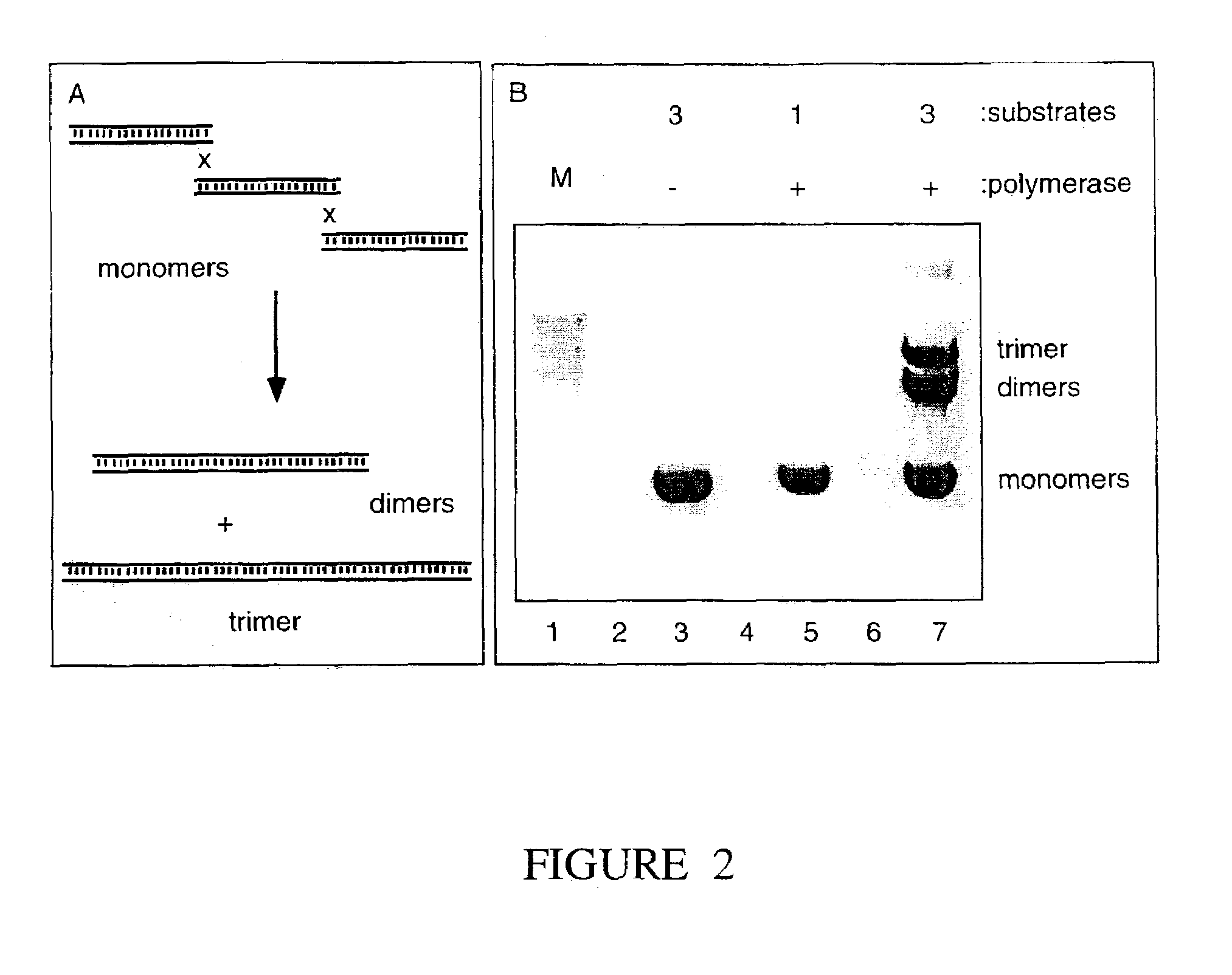
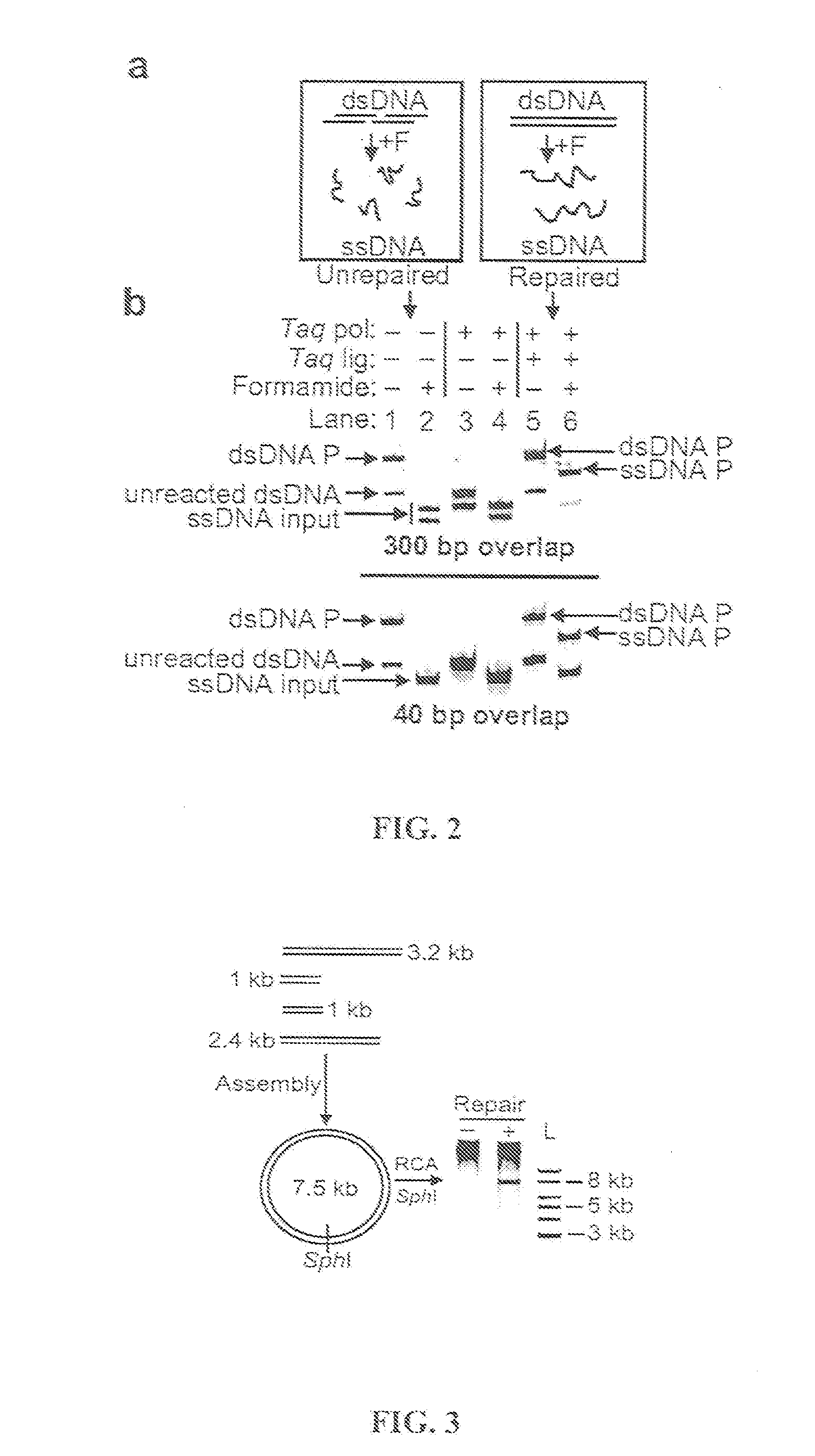
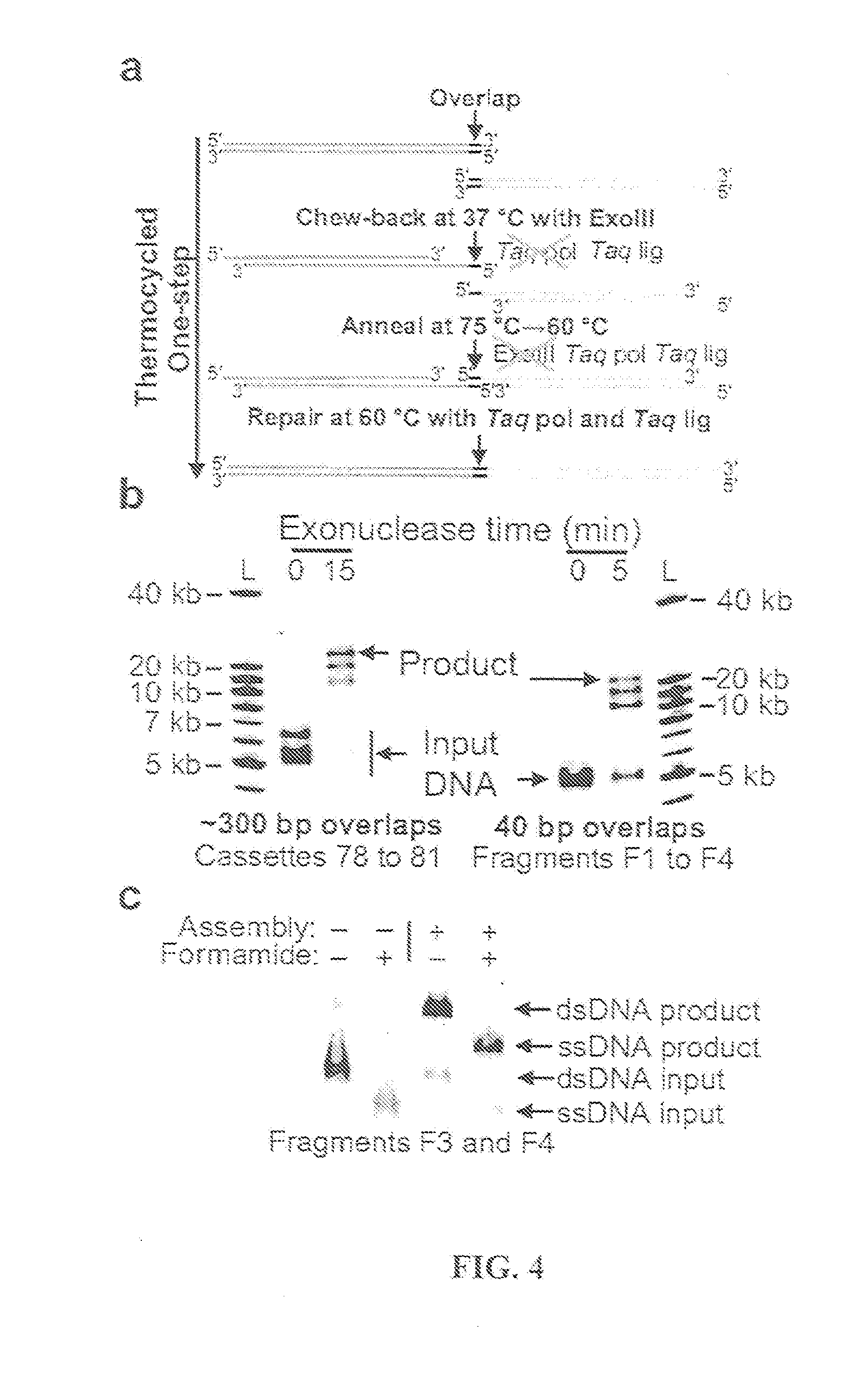
The present invention relates, e.g., to in vitro method, using isolated protein reagents, for joining two double stranded (ds) DNA molecules of interest, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule share a region of sequence identity, comprising contacting the two DNA molecules in a reaction mixture with (a) a non-processive 5′ exonculease; (b) a single stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) which accelerates nucleic acid annealing; (c) a non strand-displacing DNA polymerase; and (d) a ligase, under conditions effective to join the two DNA molecules to form an intact double stranded DNA molecule, in which a single copy of the region of sequence identity is retained. The method allows the joining of a number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
MULTIPLEX BARCODED PAIRED-END DITAG (mbPED) LIBRARY CONSTRUCTION FOR ULTRA HIGH THROUGHPUT SEQUENCING
Multiplex barcoded Paired-End Ditag (mbPED) library construction for ultra high throughput sequencing is disclosed. The mbPED library comprises multiple types of barcoded Paired-End Ditag (bPED) nucleic acid fragment constructs, each of which comprises a unique barcoded adaptor, a first tag, and a second tag linked to the first tag via the barcoded adaptor. The two tags are the 5′- and 3′-ends of a nucleic acid molecule from which they originate. The barcoded adaptor comprises a barcode, a first polynucleotide sequence comprising a first restriction enzyme (RE) recognition site, and a second polynucleotide sequence comprising a second RE recognition site and covalently linked to the first polynucleotide sequence via the barcode. The two REs lead to cleavage of a nucleic acid at a defined distance from their recognition sites. The length of the adaptor is set so that the bPED nucleic acid fragment fits one-step sequencing.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Methods and compositions for segregating target nucleic acid from mixed nucleic acid samples
InactiveUS8927218B2Rapid and efficient isolation and identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDNA EndonucleaseMethylation
The invention provides methods, compositions and kits for segregating a target nucleic acid from a mixed nucleic acid sample. The methods, compositions and kits comprise a non-processive endonuclease (e.g., a restriction enzyme) or an antibody that binds the target nucleic acid (e.g., has methylation specificity). The mixed nucleic acid sample can comprise prokaryotic and eukaryotic nucleic acid and / or nucleic acid from more than one prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms.
Owner:FLIR DETECTION
Complexity management of genomic DNA
InactiveUS6958225B2Reduce complexityComplexity of resultingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGel basedGenomic DNA
The presently claimed invention provides for novel methods and kits for reducing the complexity of a nucleic acid sample by providing non-gel based methods for amplification of a subset of the sequences in a sample. In a preferred embodiment, amplification of a subset can be accomplished by digesting a sample with two or more restriction enzymes and ligating adaptors to the fragments so that only a subset of the fragments can be amplified. The invention further provides for analysis of the above amplified sample by hybridization to an array, which may be specifically designed to interrogate the desired fragments for particular characteristics, such as, for example, the presence or absence of a polymorphism.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods for in vitro joining and combinatorial assembly of nucleic acid molecules
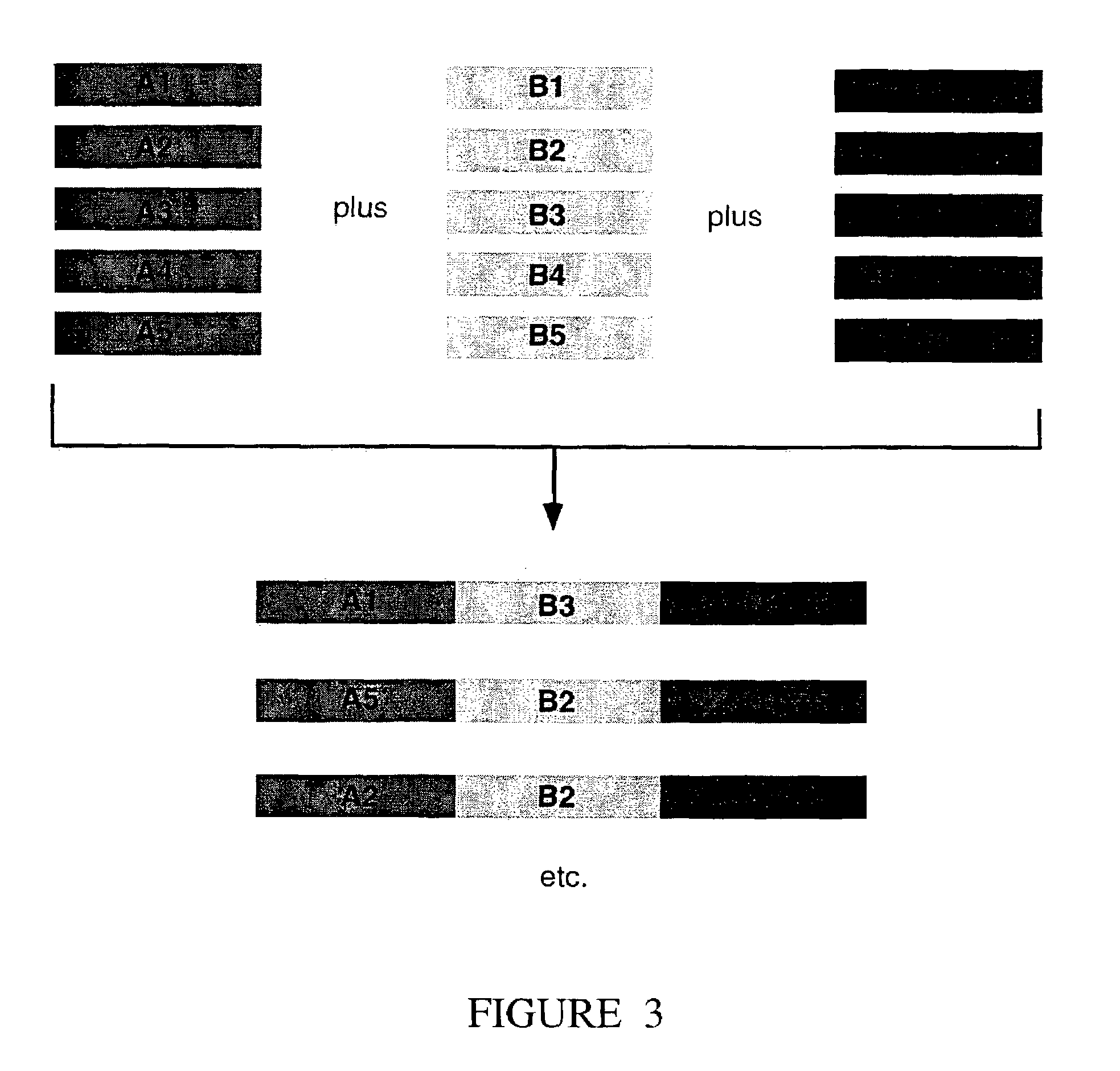
The present invention relates to methods of joining two or more double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) DNA molecules of interest in vitro, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule of each pair share a region of sequence identity. The method allows the joining of a large number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes. It can be used, e.g., to join synthetically produced sub-fragments of a gene or genome of interest. Kits for performing the method are also disclosed. The methods of joining DNA molecules may be used to generate combinatorial libraries useful to generate, for example, optimal protein expression through codon optimization, gene optimization, and pathway optimization.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
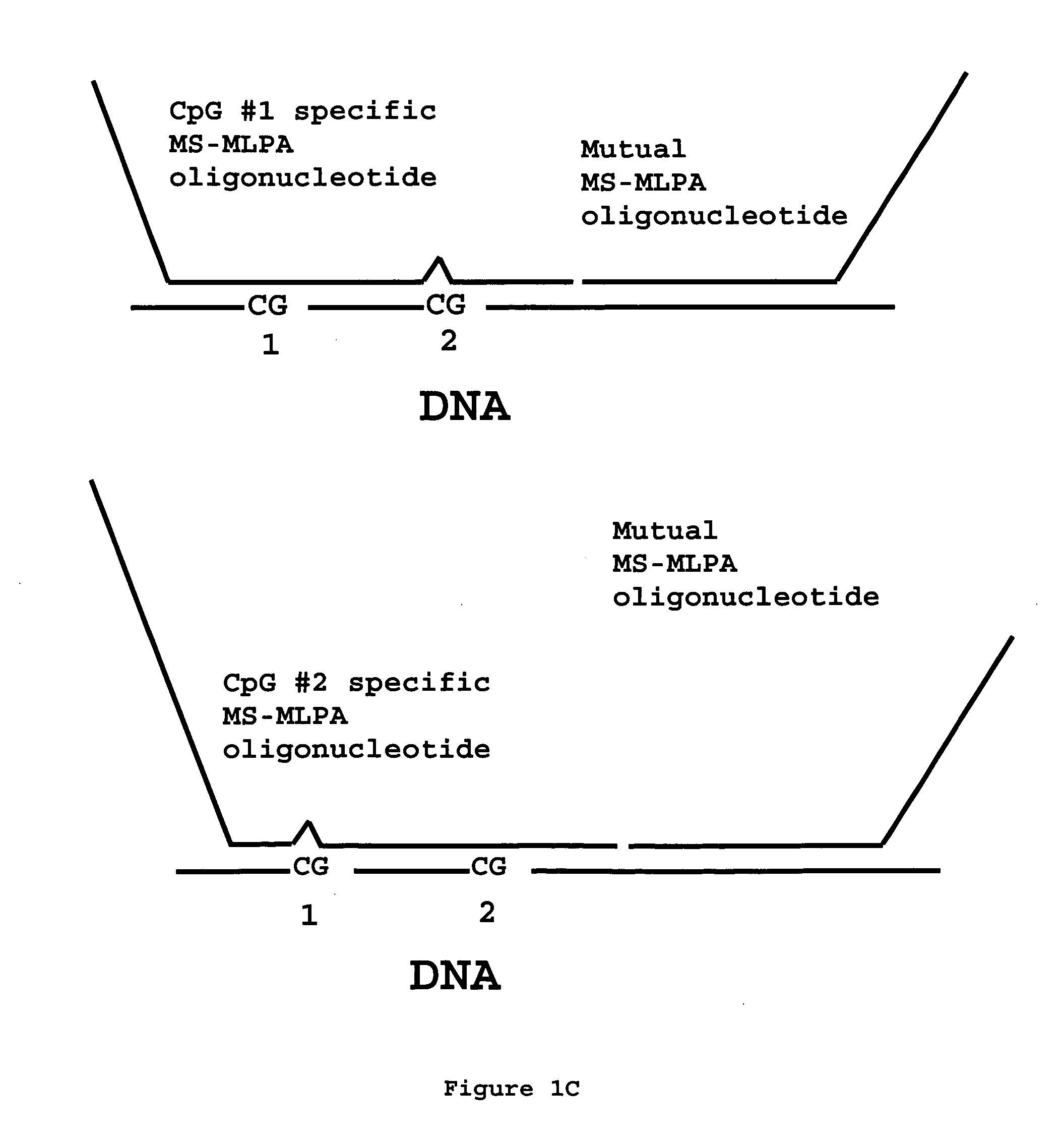
Methylation specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA)
InactiveUS20070092883A1Rapid and easy to applyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMultiplex ligation-dependent probe amplificationNucleic acid sequencing
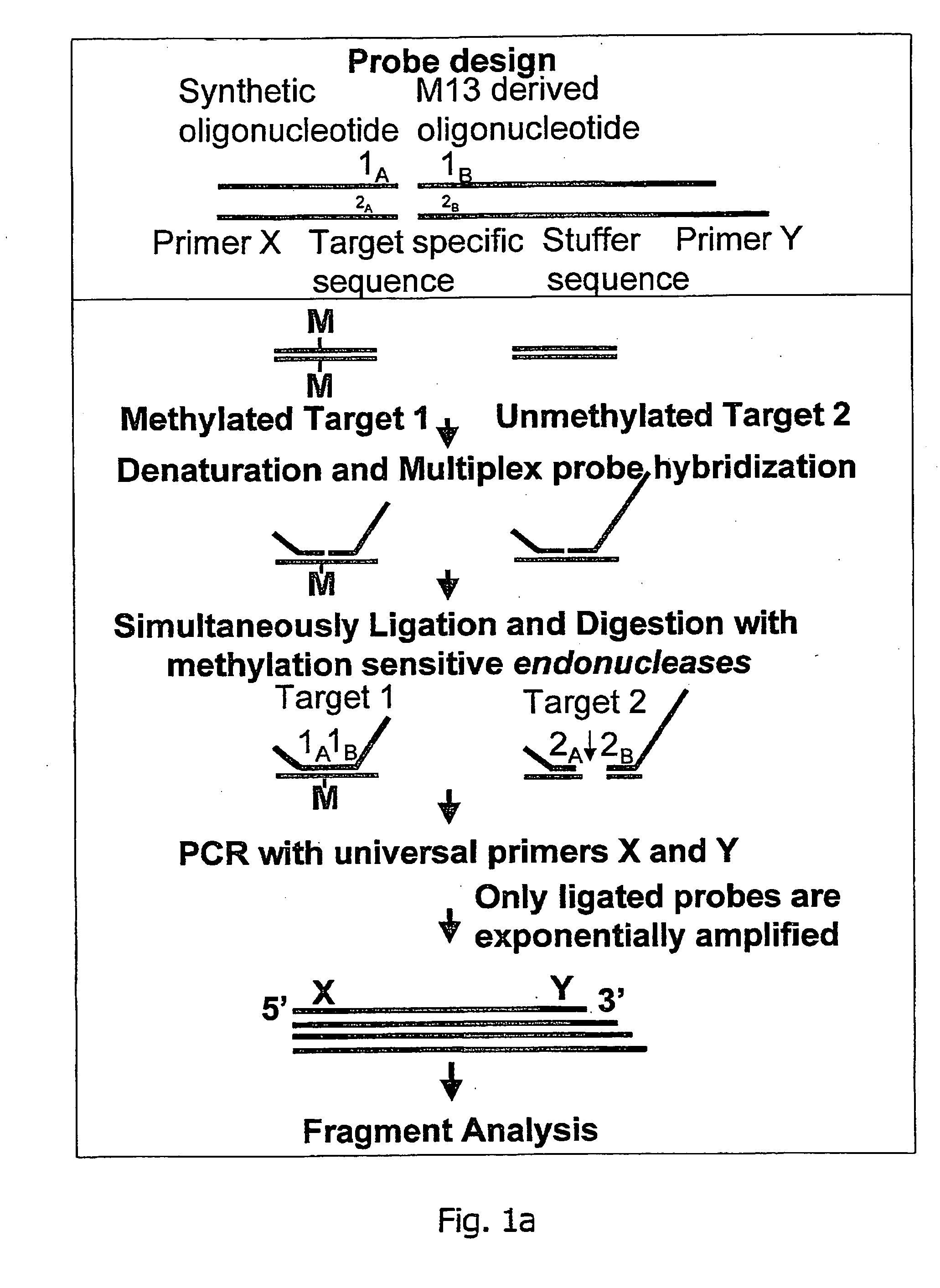
An improved multiplex ligation-dependent amplification method is disclosed for detecting the presence of specific methylated sites in a single stranded target nucleic acid, while simultaneously, the quantification of the target nucleic acid sequence can be performed, using a plurality of probe sets of at least two probes, each of which includes a target specific region and non-complementary region containing a primer binding site. At least one of the probes further includes the sequence of one of the strands of a double stranded recognition site of a methylation sensitive restriction enzyme. The probes belonging to the same set are ligated together when hybridised to the target nucleic acid sequence, the hybrid is subjected to digestion by the methylation sensitive restriction enzyme, resulting in non-methylated recognition sites being cleaved. The probes of the uncleaved (methylated) hybrid are subsequently amplified by a suitable primer set.
Owner:DE LUWE HOEK OCTROOIEN
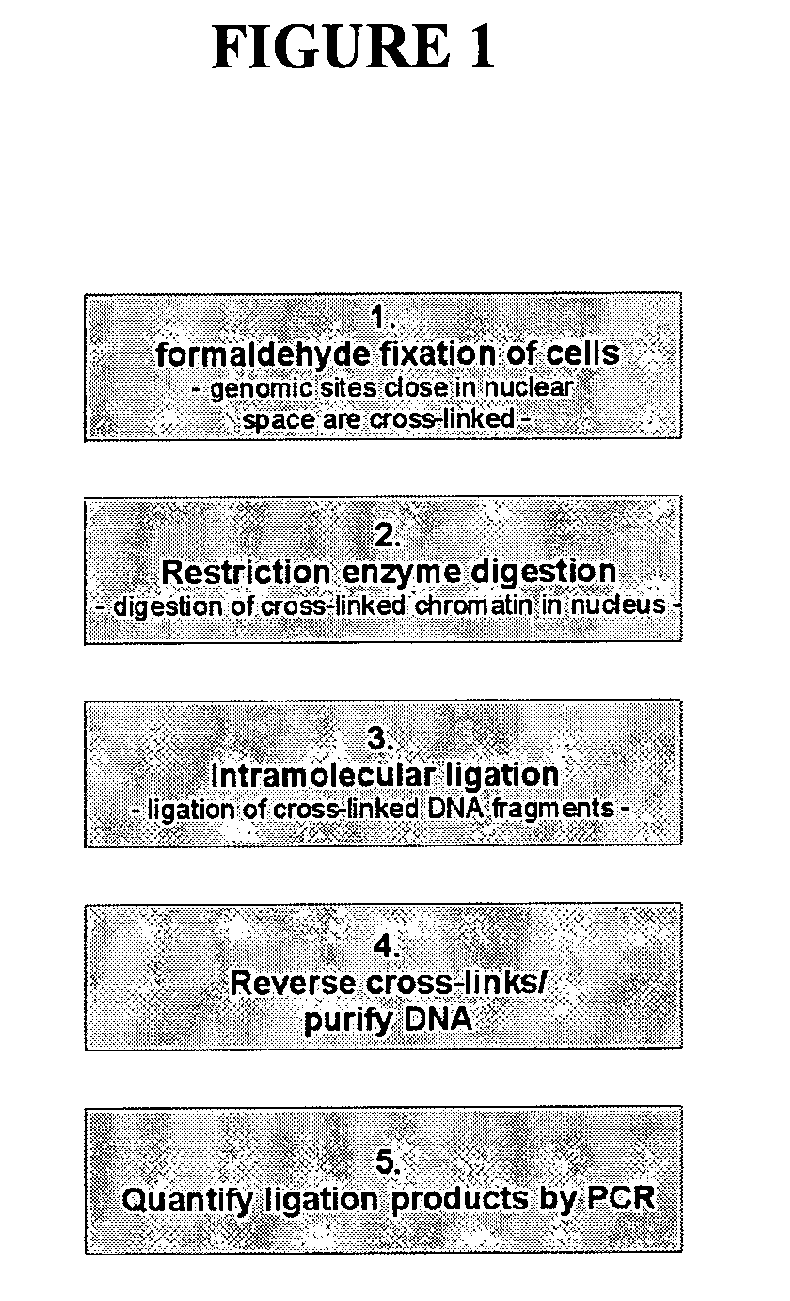
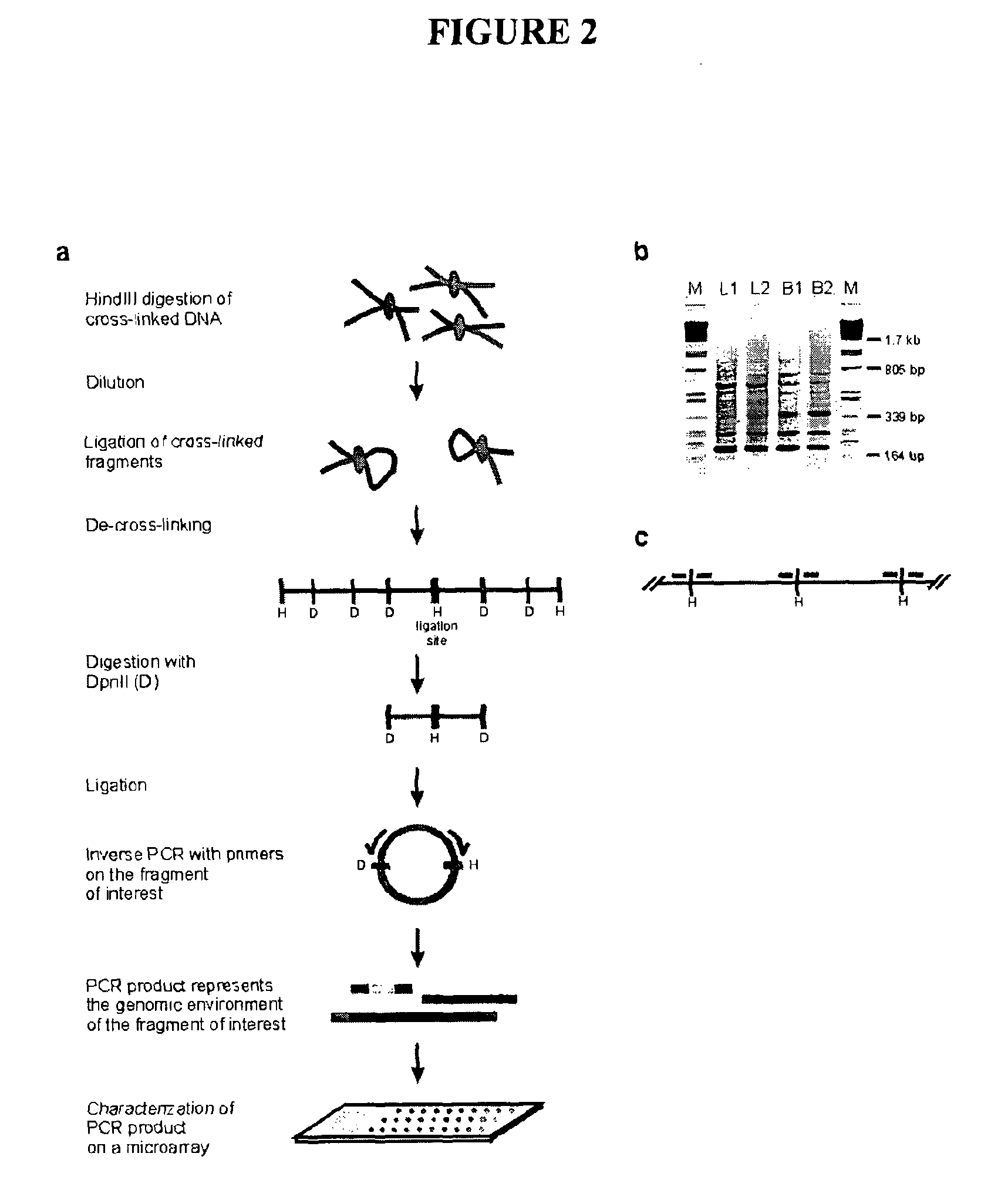
Circular chromosome conformation capture (4C)
ActiveUS8642295B2High throughput analysisAccurate mappingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionRestriction enzyme digestion
The present invention relates in one aspect to a method for analyzing the frequency of interaction of a target nucleotide sequence with one or more nucleotide sequences of interest (eg. one or more genomic loci) comprising the steps of: (a) providing a sample of cross-linked DNA; (b) digesting the cross-linked DNA with a primary restriction enzyme; (c) ligating the cross-linked nucleotide sequences; (d) reversing the cross linking; (e) optionally digesting the nucleotide sequences with a secondary restriction enzyme; (f) optionally ligating one or more DNA sequences of known nucleotide composition to the available secondary restriction enzyme digestion site(s) that flank the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest; (g) amplifying the one or more nucleotide sequences of interest using at least two oligonucleotide primers, wherein each primer hybridises to the DNA sequences that flank the nucleotide sequences of interest; (h) hybridising the amplified sequence(s) to an array; and (i) determining the frequency of interaction between the DNA sequences.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
In vitro recombination method
The present invention relates, e.g., to in vitro method, using isolated protein reagents, for joining two double stranded (ds) DNA molecules of interest, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule share a region of sequence identity, comprising contacting the two DNA molecules in a reaction mixture with (a) a non-processive 5′ exonculease; (b) a single stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) which accelerates nucleic acid annealing; (c) a non strand-displacing DNA polymerase; and (d) a ligase, under conditions effective to join the two DNA molecules to form an intact double stranded DNA molecule, in which a single copy of the region of sequence identity is retained. The method allows the joining of a number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes.
Owner:TELESIS BIO INC
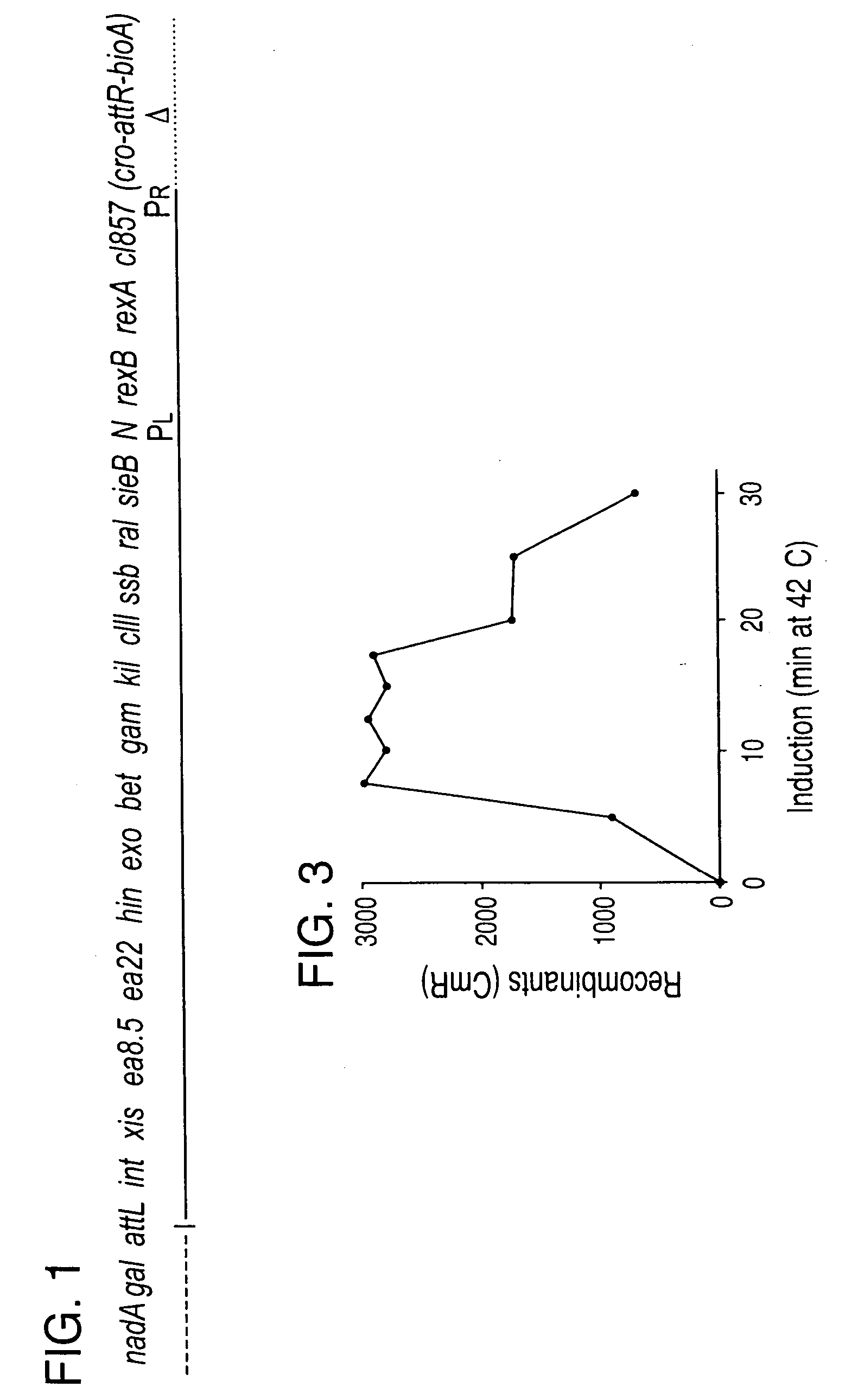
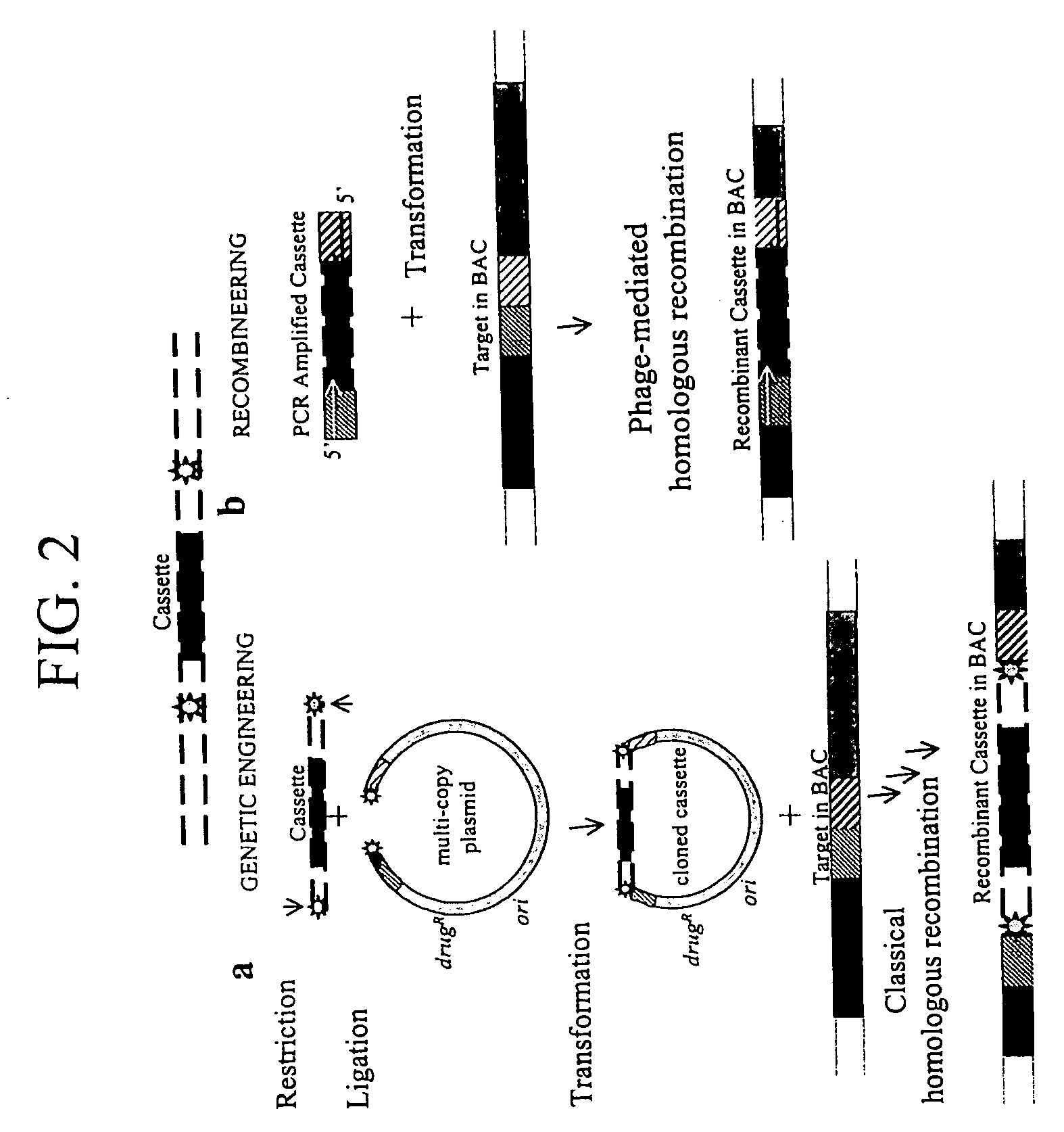
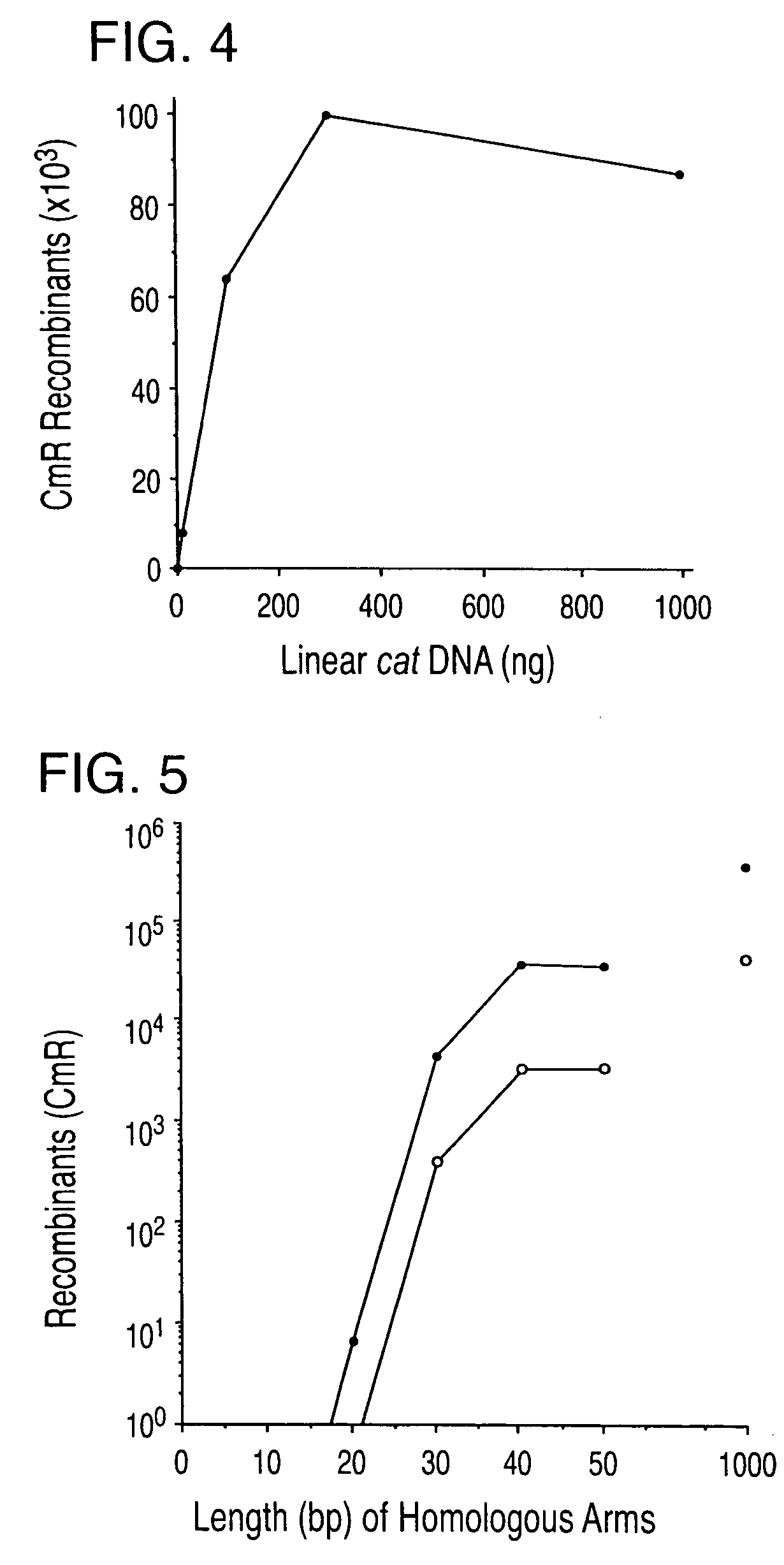
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20030224521A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredFungiBacteriaMammalKnockout animal
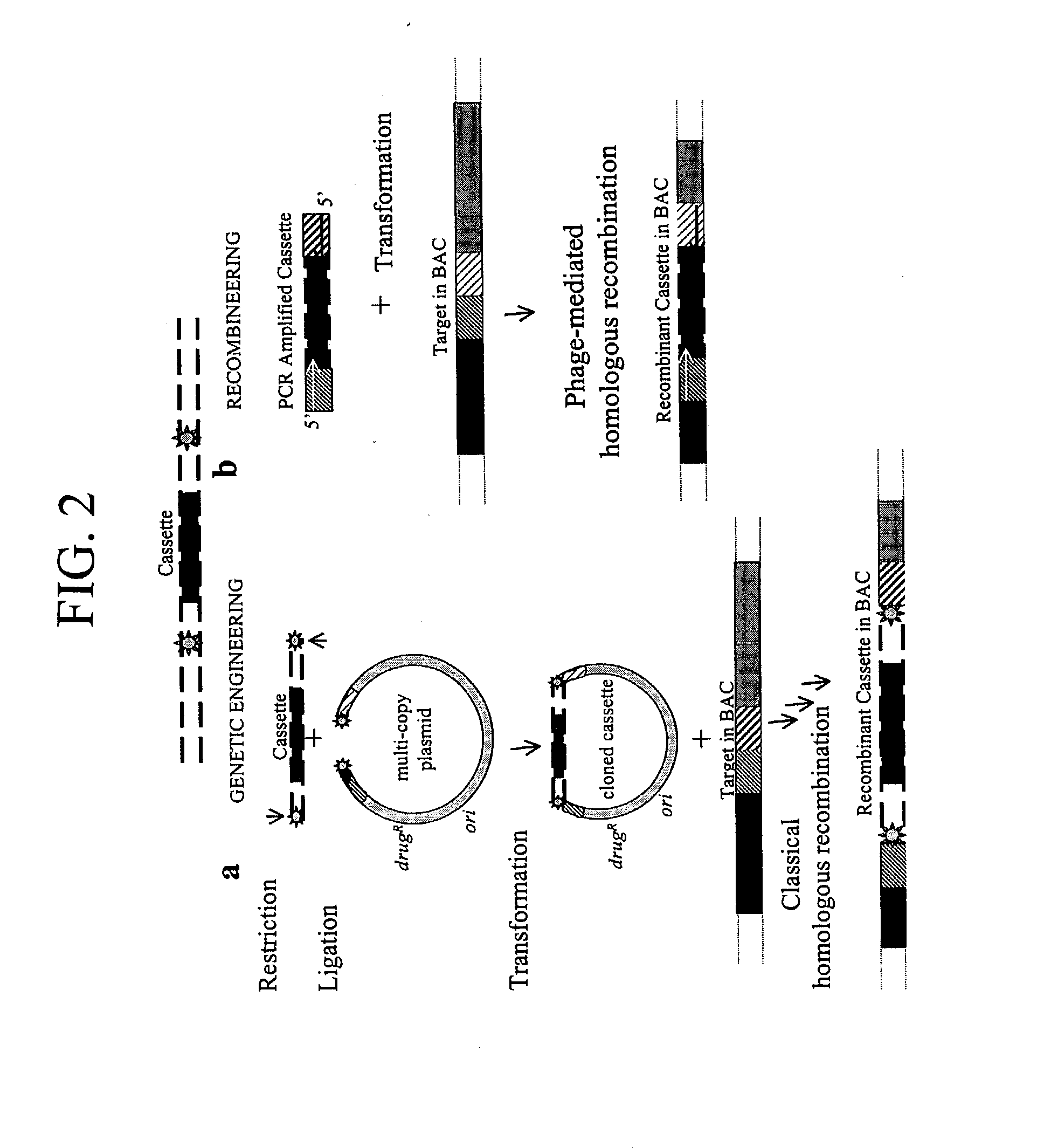
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Generation of recombinant DNA by sequence-and ligation-independent cloning
InactiveUS20070292954A1Efficient conversionGenerate efficientlyTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesRecombinant DNAEnzyme
The present invention is directed methods for cloning DNA by homologous recombination. The methods can be used without a need for ligases or restriction enzymes and allow for the rapid alignment of multiple DNA fragments.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
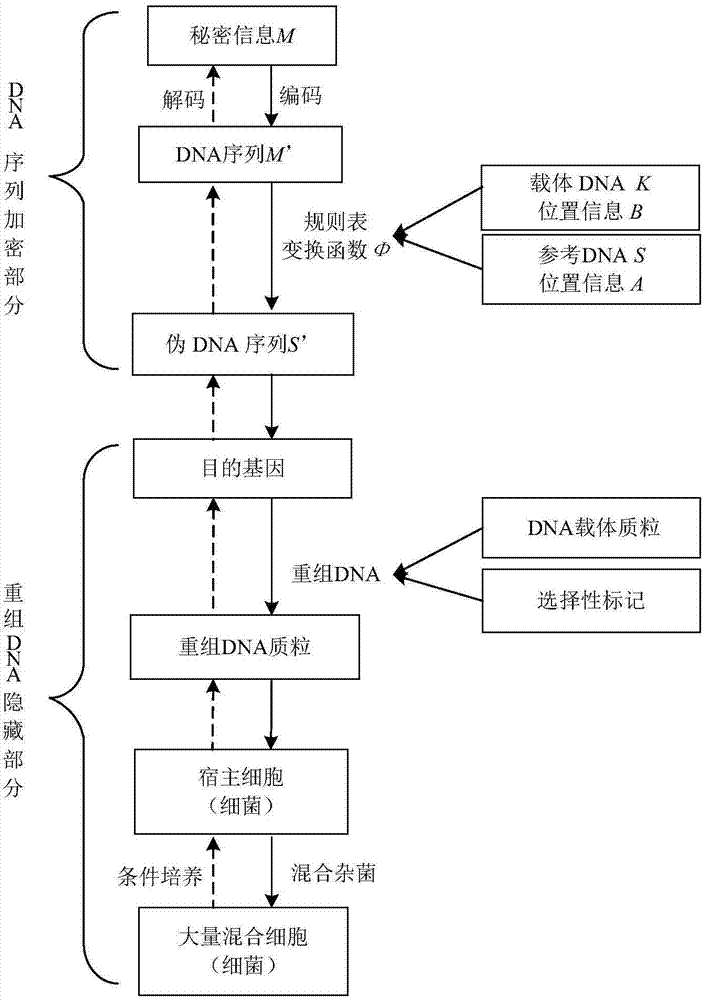
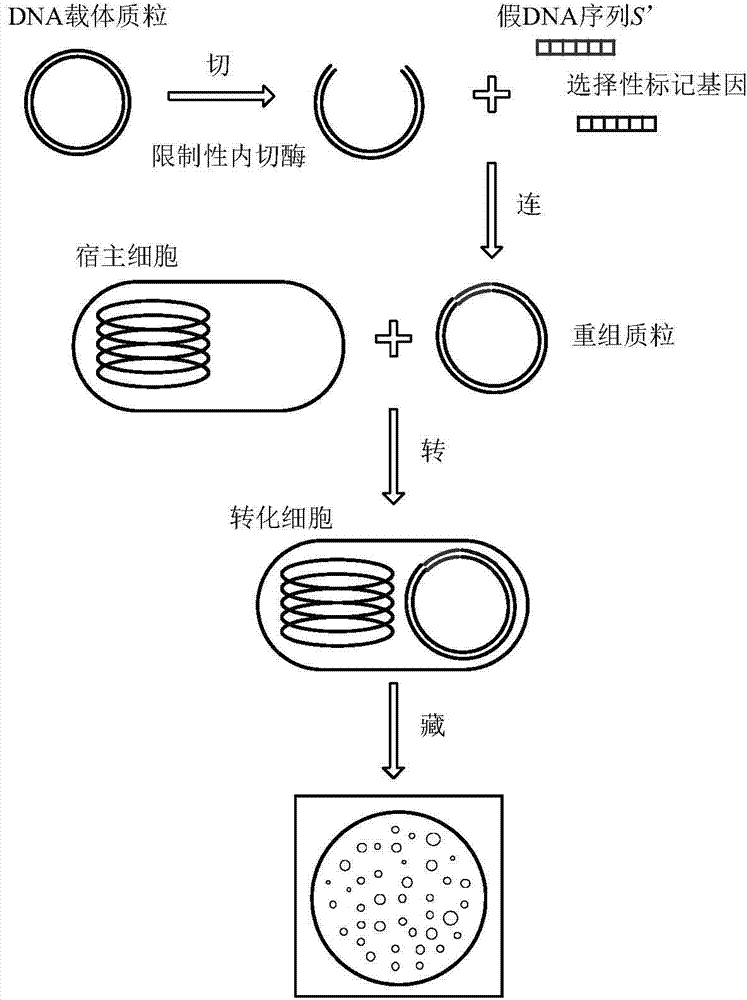
Recombinant DNA technology based information encrypting and hiding method and application
InactiveCN104734848AMeet safety requirementsIncrease the difficulty of crackingVector-based foreign material introductionSecuring communicationPlasmid VectorDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a recombinant DNA technology based information encrypting and hiding method and an application. Firstly, a plain text is coded into a DNA sequence, preprocessing is carried out on the DNA sequence by adopting the encryption algorithm, and a pseudo-DNA segment is generated; and then the pseudo-DNA segment and a marker gene segment are connected to a DNA plasmid vector by using the restriction enzyme and the ligase, and an obtained recombinant plasmid is further hided into a germ body; finally, a cell which contains confidential information is hided into a large number of irrelevant pseudo-cells, and the hided cells can be screened out by the selective cultivation. The encrypting and hiding method is applied to the authentication and signature technology. Encrypting, hiding and transmitting of the confidential information are achieved, and the cracking difficulty of a system is enhanced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
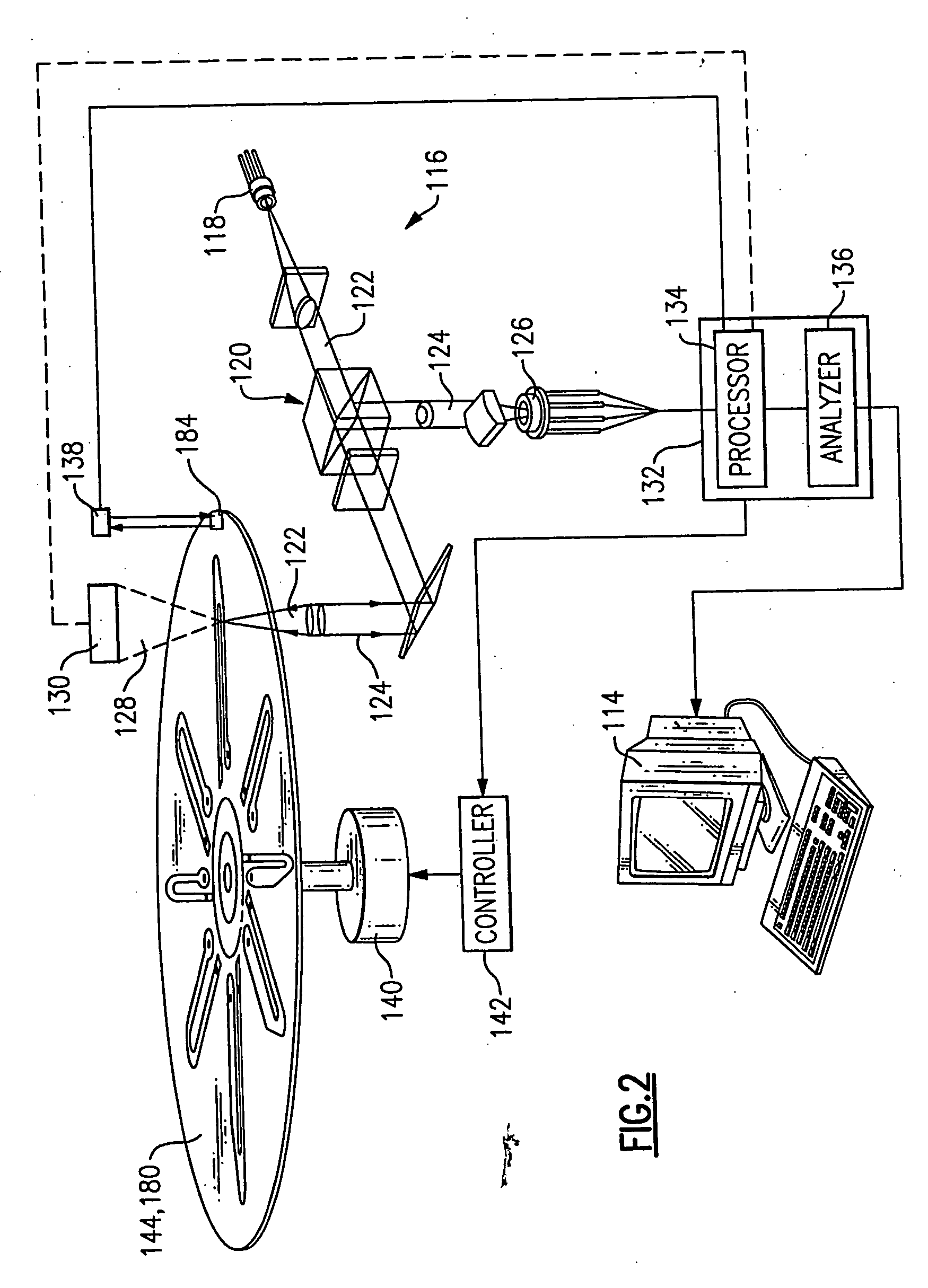
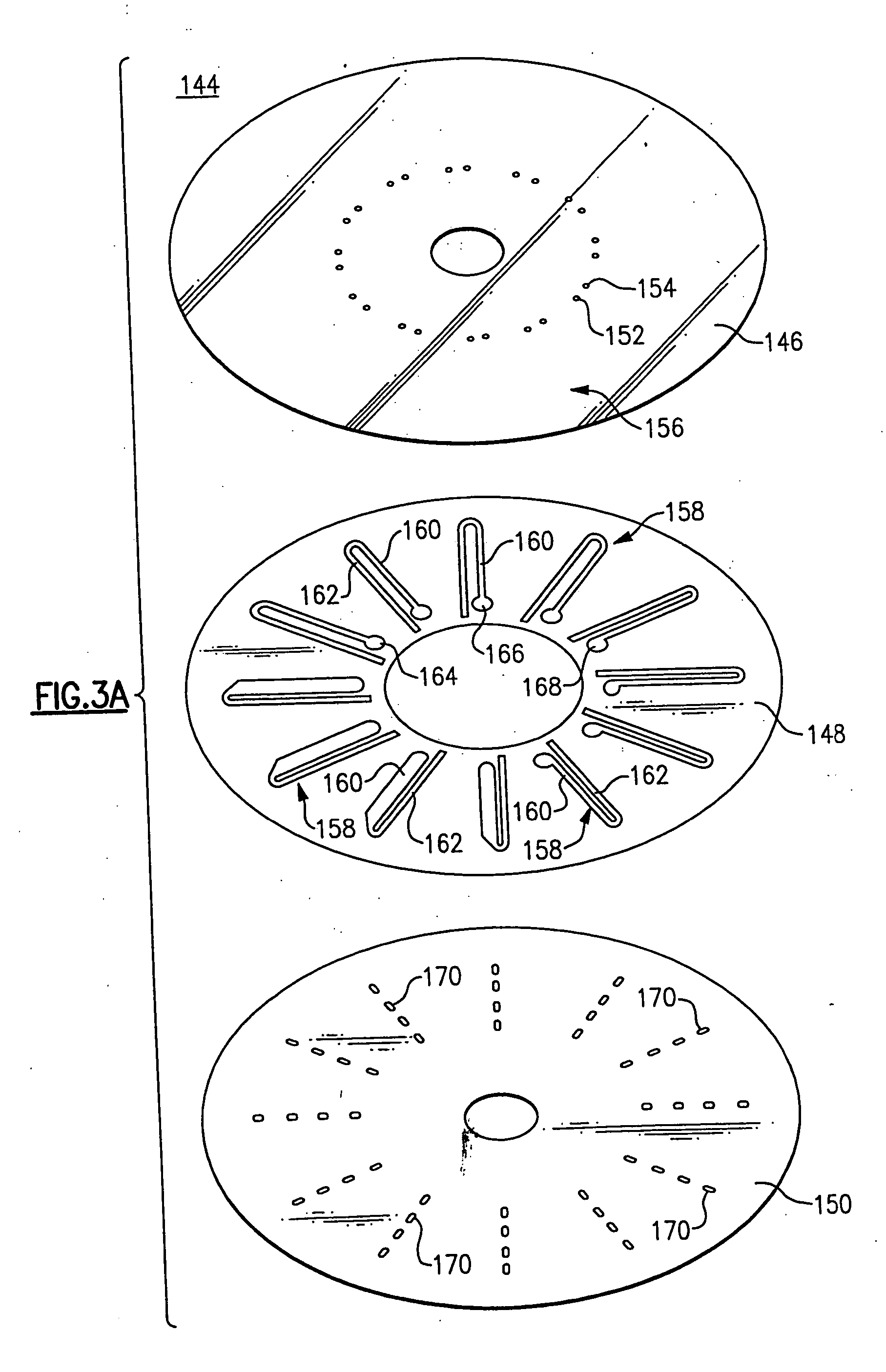
Use of restriction enzymes and other chemical methods to decrease non-specific binding in dual bead assays and related bio-discs, methods, and system apparatus for detecting medical targets
InactiveUS20060068409A1Decrease non-specific bindingEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsAssayChemical methodology
Methods for decreasing non-specific bindings of beads in dual bead assays and related optical bio-discs and disc drive systems. Methods include identifying whether a target agent is present in a biological sample and mixing capture beads each having at least one transport probe affixed thereto, reporter beads each having at least one signal probe affixed thereto, and a biological sample. Mixing is performed under binding conditions to permit formation of a dual bead complex if the target agent is present in the sample. The reporter bead and capture bead each are bound to the target agent. Denaturing the target agent and keeping it in the denatured form by use of a specialized hybridization buffer is also provided. A denaturing agent is guanidine isothiocynate. Methods further include isolating the dual bead complex from the mixture to obtain an isolate, exposing the isolate to a capture field on a disc, and detecting the presence of the dual bead complex in the disc to indicate that the target agent is present in the sample. The methods may further include selectively breaking up non-specific binding between capture beads and reporter beads employing a digestion agent. Also employed is a method for selectively breaking up non-specific binding between capture beads and reporter beads using a wash buffer containing a chemical agent. The methods are applied to detecting medical targets.
Owner:NAGAOKA
Rice blast resistance gene Pi9 gene specificity molecular marker Pi9SNP as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN103305510AStrong specificityImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a rice blast resistance gene Pi9 gene specificity molecular marker Pi9SNP as well as preparation and application thereof. The molecular marker Pi9SNP is prepared by amplifying from total DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a rice blast resistant variety with rice blast resistance gene Pi9 by using a primer pair F1 and R1 so as to obtain a nucleotide segment I, and carrying out digestion on the nucleotide segment I by using restriction enzyme Hind III, so as to obtain a nucleotide segment II which is in specificity banding pattern with the obtained rice blast resistance gene Pi9. The molecular marker is the first one which is developed for marking Pi9 gene specificity SNP (Signal Nucleotide Polymorphism) for an internal sequence of the Pig gene, and has the following advantages that the specificity is high, the cost is low and the flux is high in practical application, and the molecular marker is widely applied to colonies of different genetic backgrounds. By utilizing the molecular marker, the efficiency in auxiliary molecular marker selective breeding, gene pyramiding breeding and transgenosis breeding is improved.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
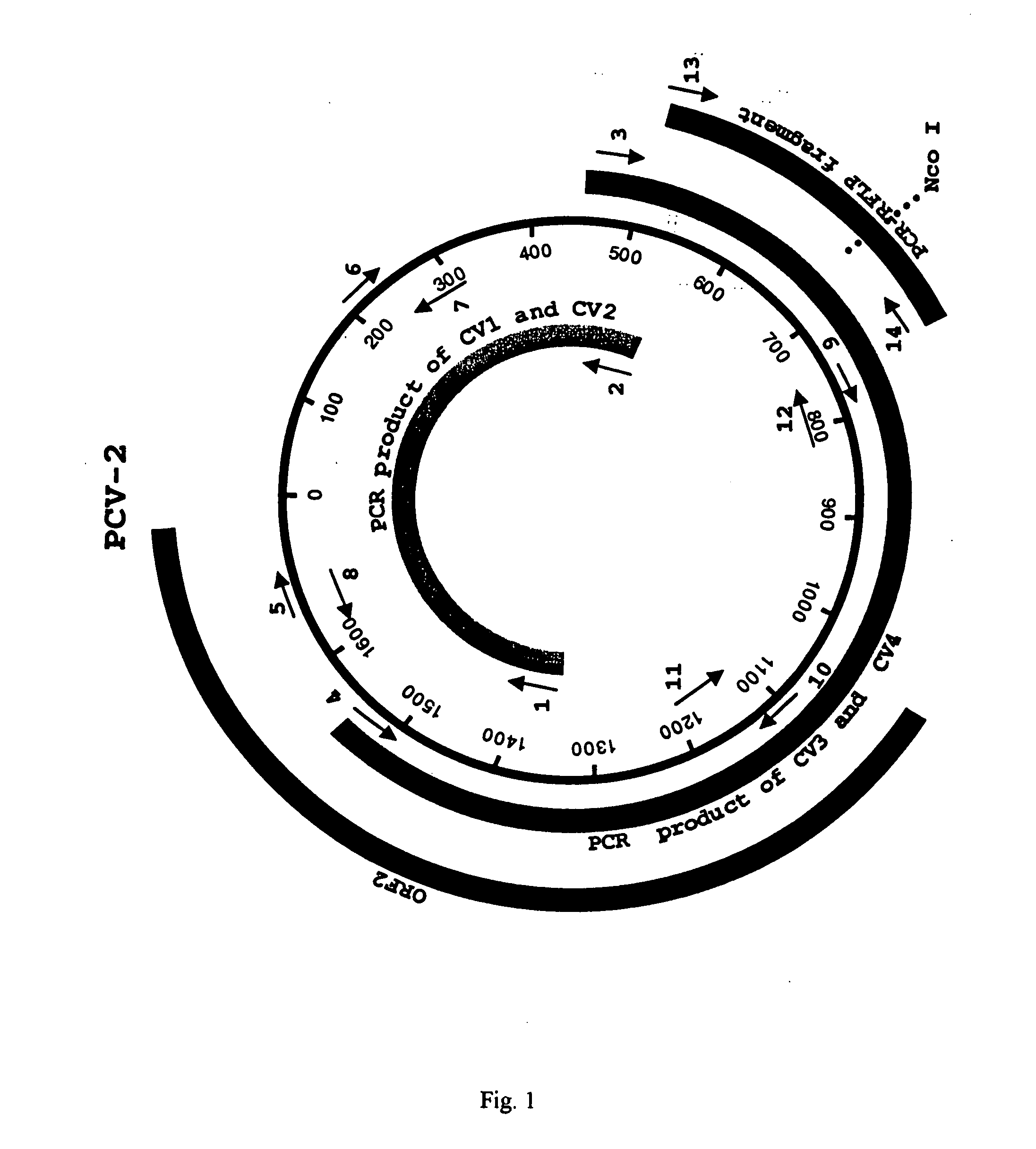
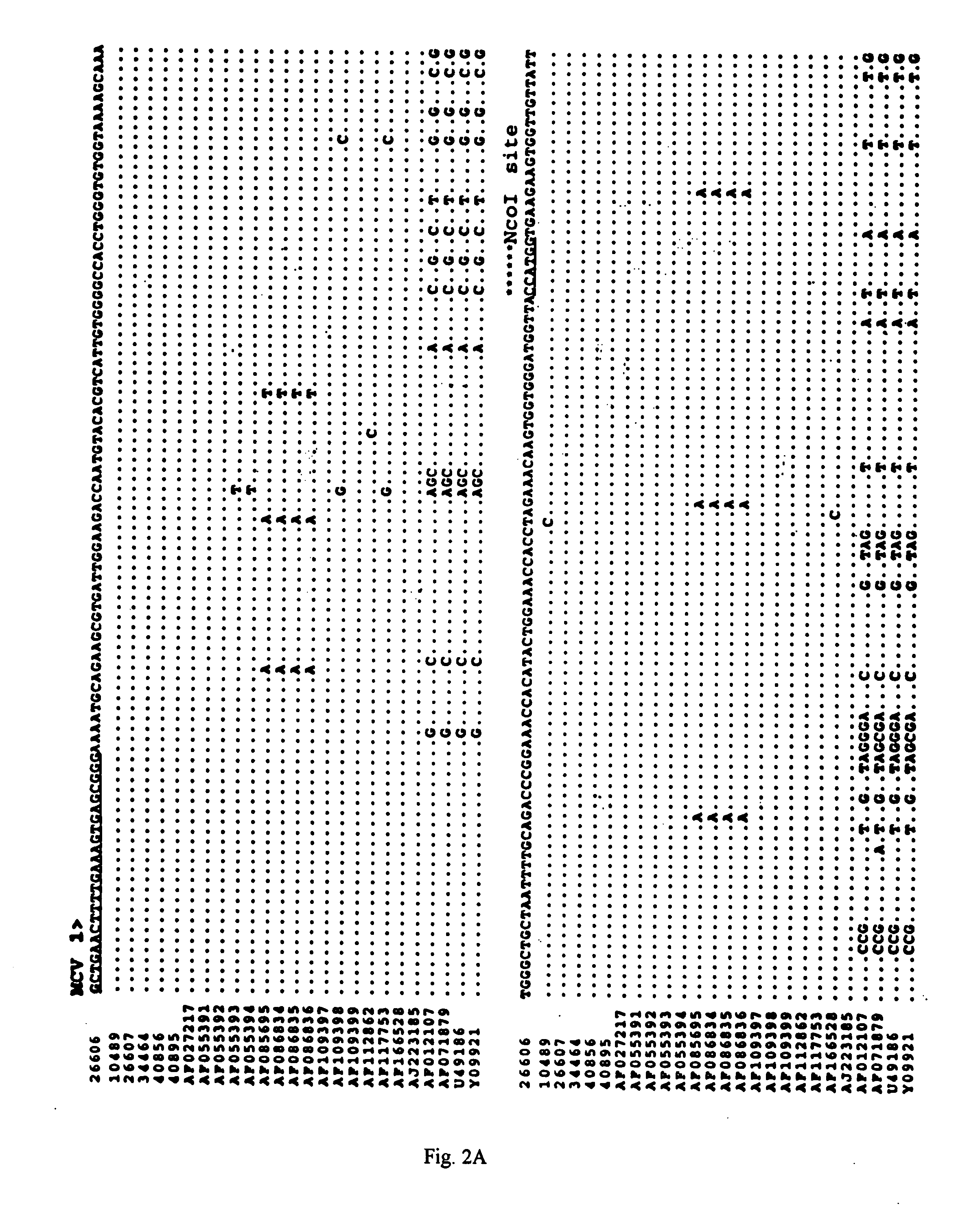
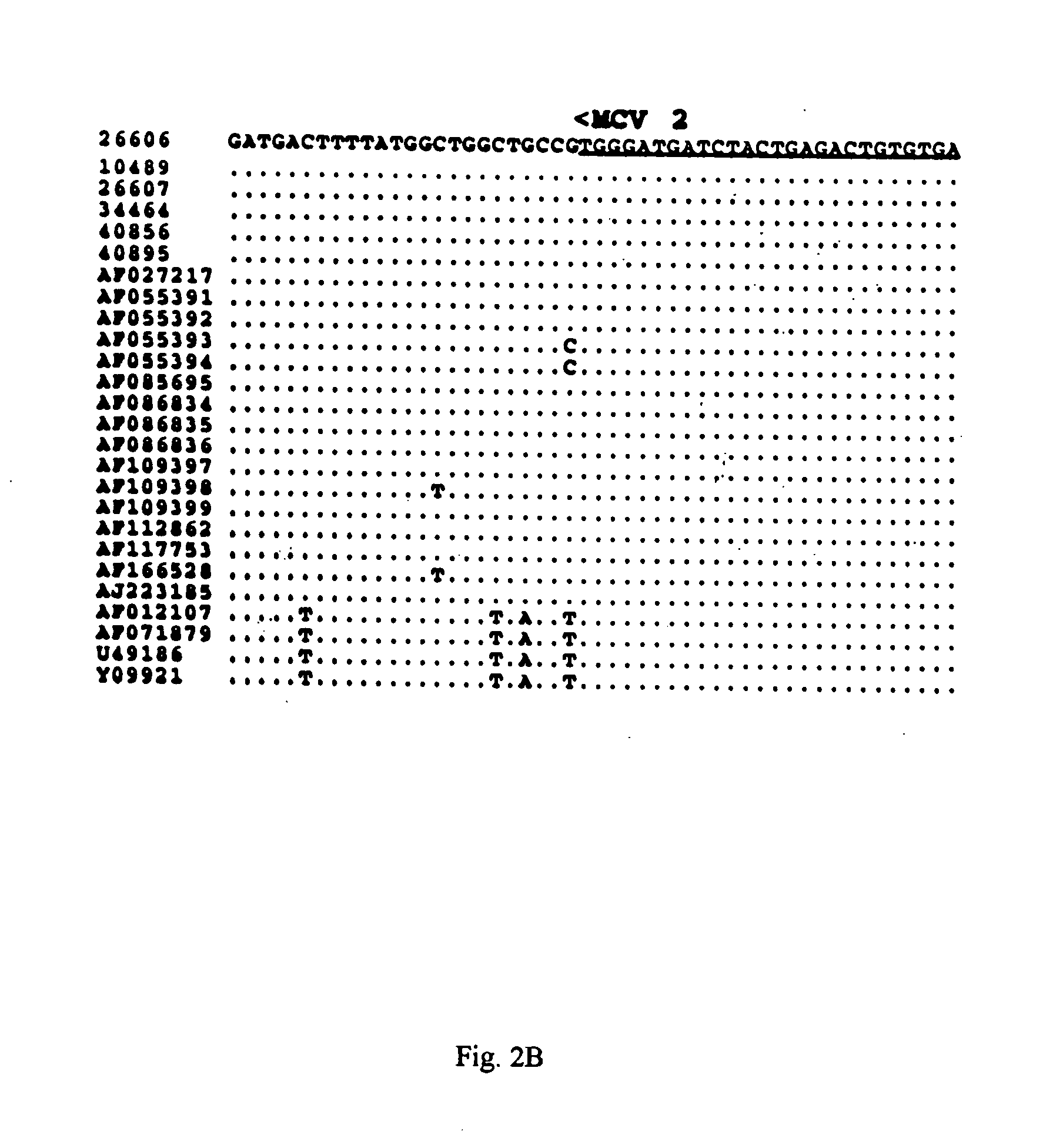
Differential PCR-RFLP assay for detecting and distinguishing between nonpathogenic PCV-1 and pathogenic PCV-2
InactiveUS20050147966A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The present invention relates to a method for detecting and differentiating PCV infections in a biological sample taken from a pig which involves amplifying a fragment from an extracted nucleic acid; digesting the fragment with a suitable restriction enzyme such as the unique NcoI restriction enzyme; forming a restriction fragment length polymorphism pattern; and then detecting the presence or absence of a PCV isolate. The invention further concerns the new oligonucleotide primers for differentiating PCV infections comprising a nucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of MCV1 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:1 and MCV2 having a nucleotide sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO:2. Moreover, this invention provides a novel kit for detecting and distinguishing PCV infections that includes the new oligonucleotide primers and the suitable restriction enzyme.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
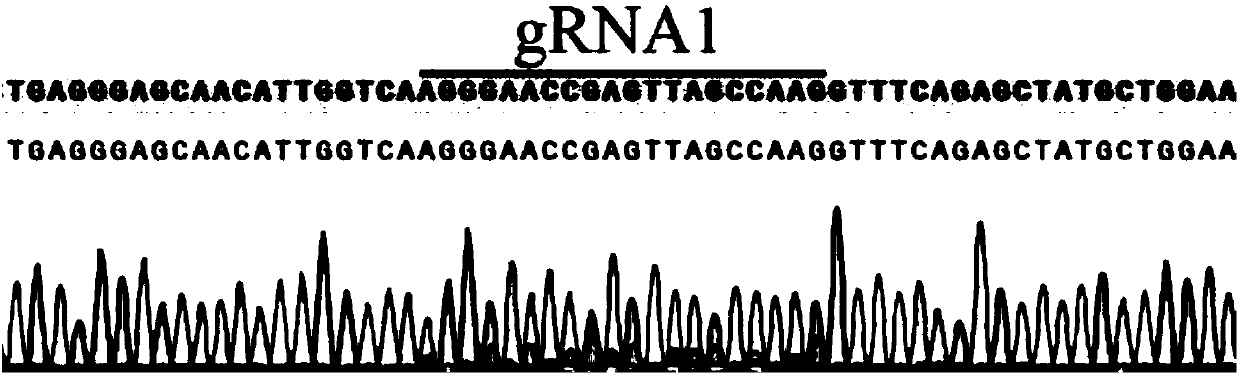
CRISPR/Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes
InactiveCN105400773AHigh infection efficiencyMeet the packaging ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationInfected cellCancer cell
The invention relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 enrichment sequencing method applied in large-scale screening of cancer genes. Firstly, an sgRNA library is established; then the sgRNA library is packaged by lentiviruses, and viruses are collected; the sgRNA library is screened in a cancer cell line, the obtained cells are extracted and screened, and genome DNAs of precancerous cells are screened; finally, enrichment of sgRNAs in the genome DNAs is carried out. When the provided method is compared with the prior art, the screening process of CRISPR / Cas9 cells is improved, the virus infection efficiency is determined and the virus MOI value is determined through a simple method and by utilization of puromycin resistance of infected cells, importantly, the restriction enzyme cutting method and a high flux method are combined, correct chromatin fragments can be obtained effectively, false positive caused by non-specific PCR amplification can be lowered, a DNA template of sgRNAs can be amplified efficiently, and a library establishment efficiency is raised.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
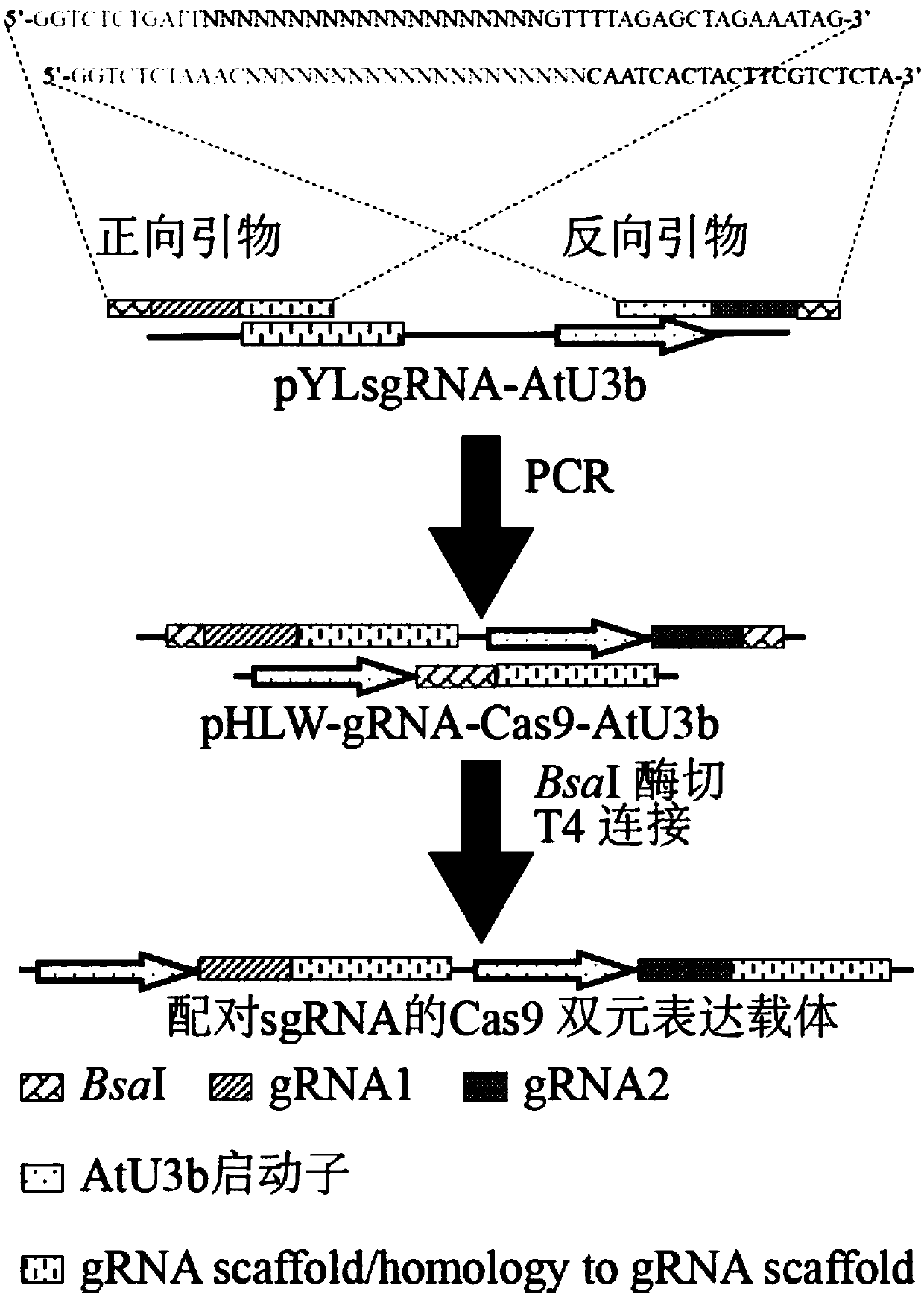
Method for rapidly establishing Cas9 dual-element expression carrier library of paired sg RNA
ActiveCN107893086AEfficiently buildEfficient constructionHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteGene engineering
The invention discloses a method for rapidly establishing a Cas9 dual-element expression carrier library of paired sg RNA, and relates to a method for rapidly establishing a dual-element carrier in the gene engineering field. According to the method, on the basis of establishing a CRISPR-Cas9 dual-element expression carrier, corresponding positive and negative primers are designed according to a specific gene design target sequence and have two BsaI restriction enzyme cutting sites; through one-step PCR, the target sequence and target segments of two BsaI sites are obtained, and the segments enter the dual-element expression carrier with a Cas9 gene through a simple restriction enzyme cutting and connecting mode to form the Cas9 carrier of the paired sg RNA. A random library and a non-random library can be efficiently established and can be used for large-scale screening of gene functions in plants and meanwhile can be used for establishment and research of a gene interoperation network among multiple genes; it is proved through experimental results that the Cas9 dual-element expression carrier library of the randomly-paired sg RNA of 14 target spots (from 14 genes) is successfullyand efficiently established through the method.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
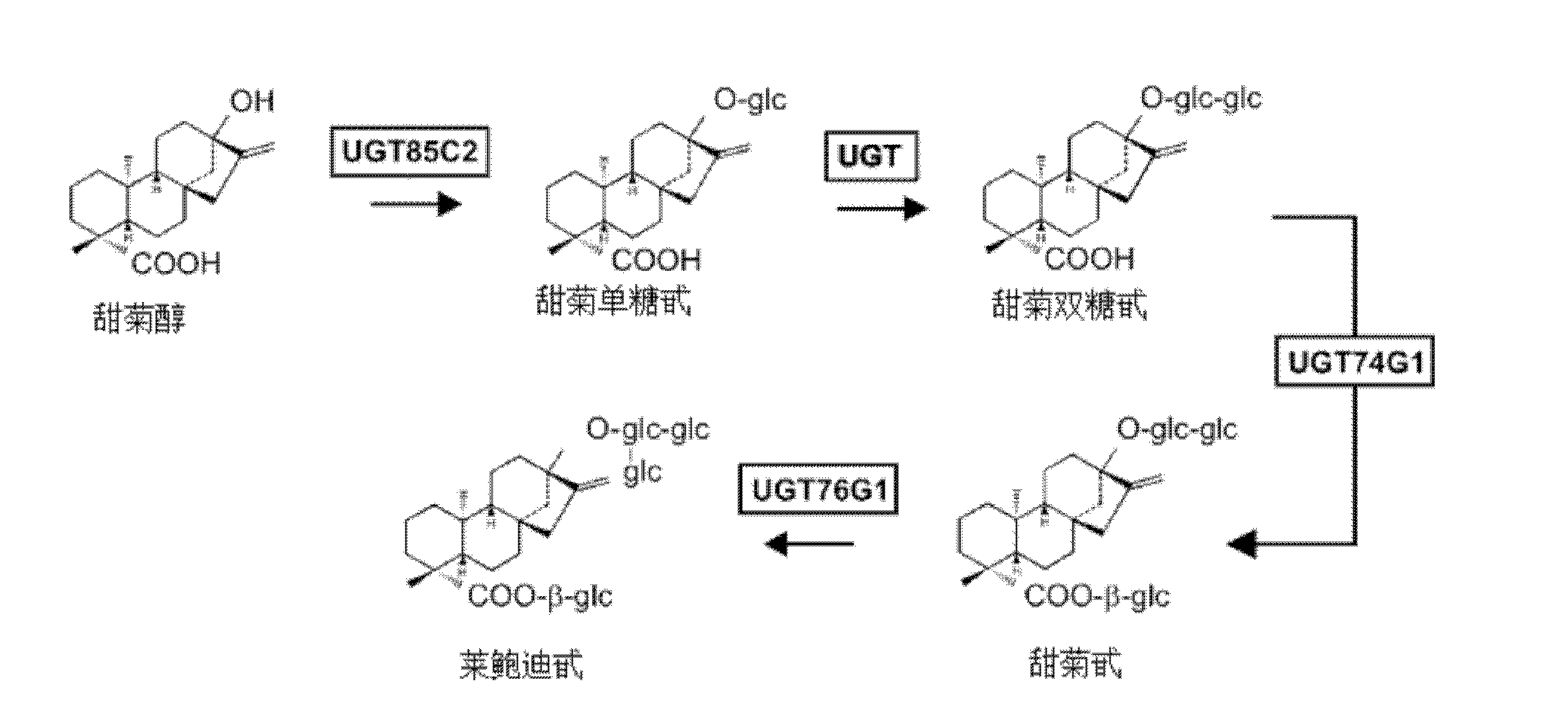
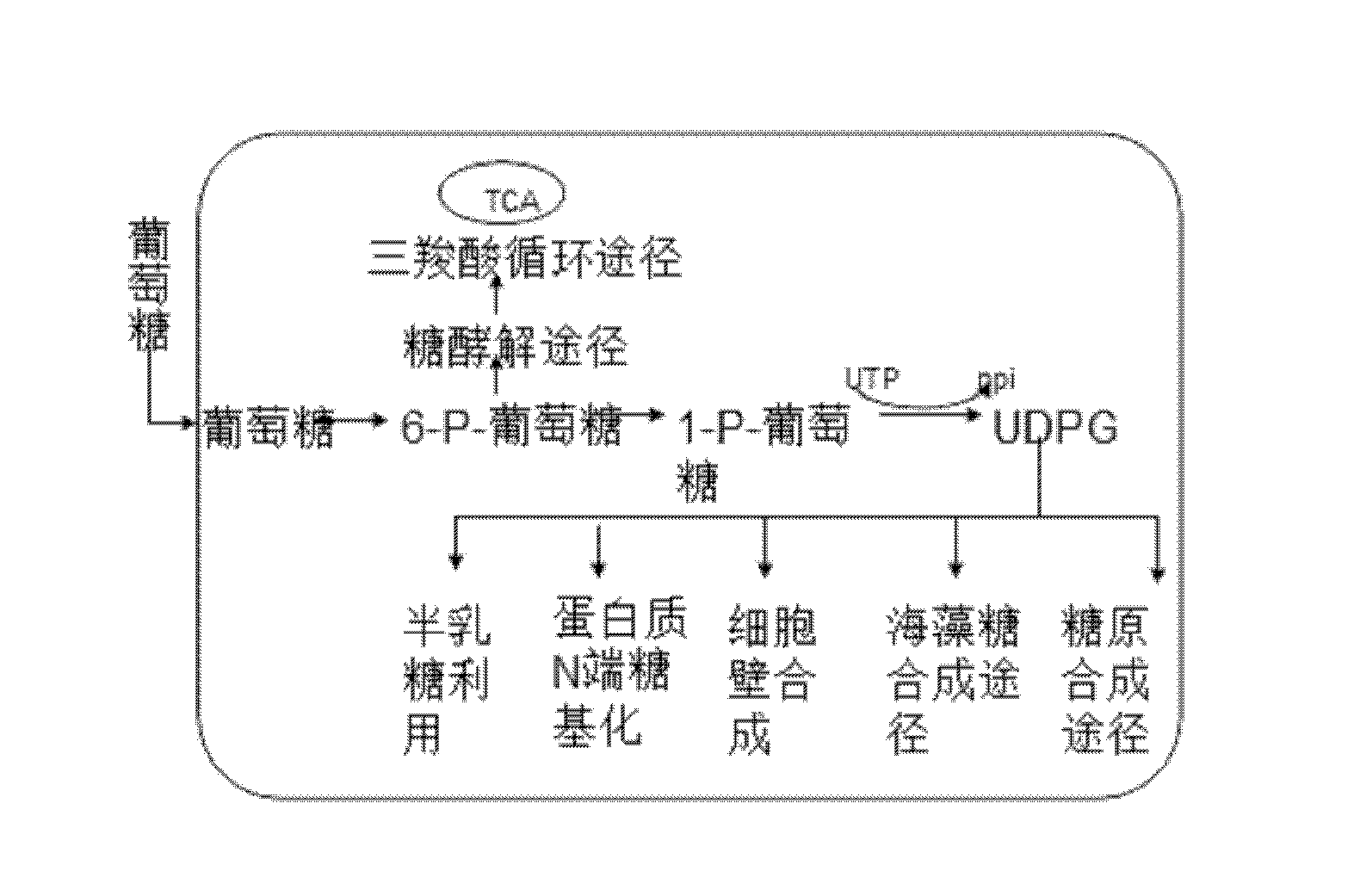
Genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1 and application thereof
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacteria used for producing stevia glycosyltransferase UGT76G1; a UGT76G1 coding gene is inserted between the restriction enzyme cutting sites EcoRI and XhoI of a PYes2 carrier, so as to construct a recombinant plasmid, and then the recombinant plasmid is introduced to expression host Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPH499 to obtain the engineered bacteria; and the coding gene of the UGT76G1 is GenBank, No. GenBank: AY345974.1, and the gene sequence of the coding gene is named as UGT (Udp Glucuronyl Transferase). The invention also discloses a construction method of the genetically engineered bacteria and the application of the bacteria to the production of rebaudioside A. According to the invention, under the condition that expensive UDPG (Uridine Diphosphate Glucose) is not added, cheap carbon source glucose is used as a substrate, the metabolic pathway of UDPG in the yeast is regulated, and then the rebaudioside A is produced from St glycosides through whole cell catalysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
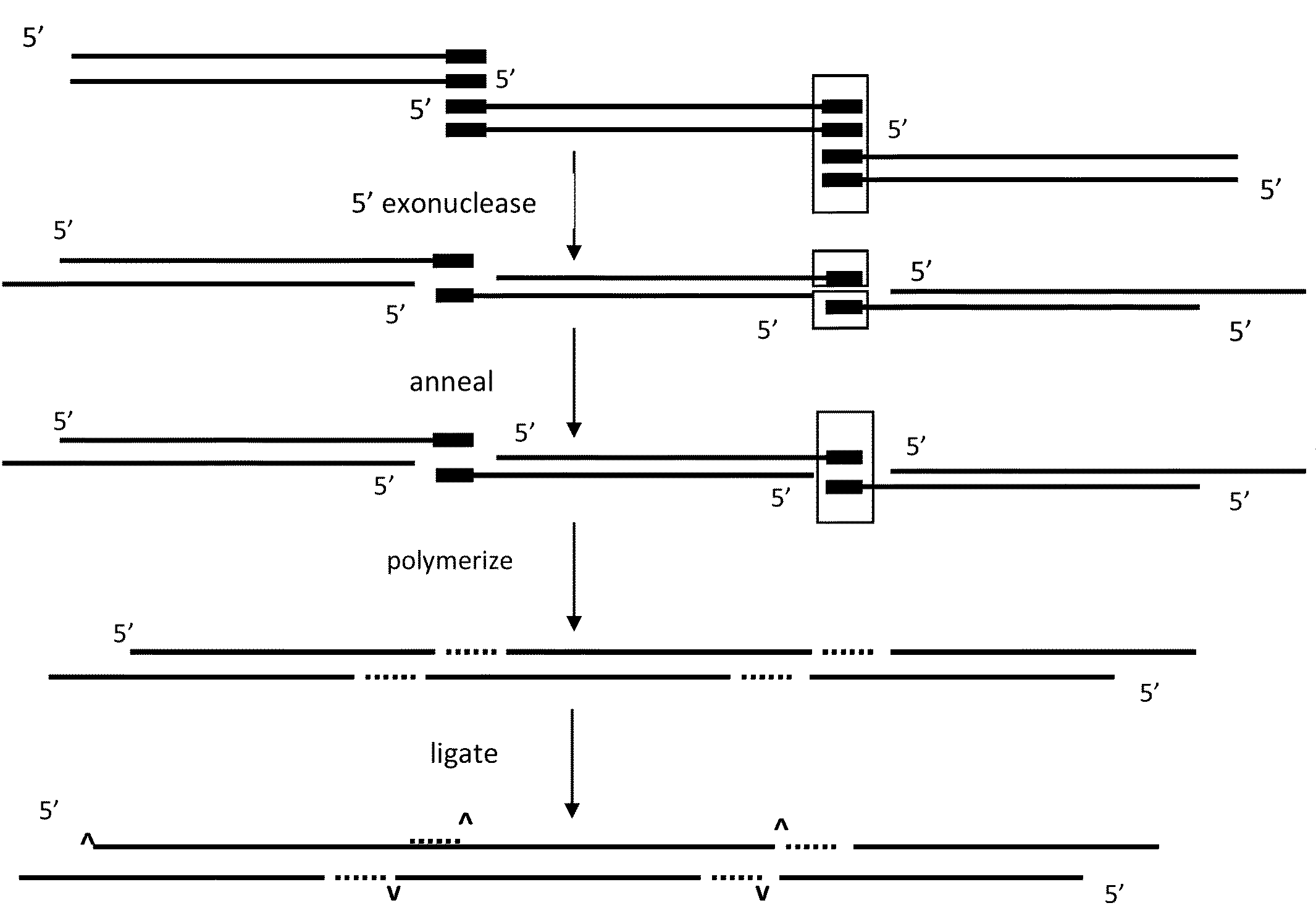
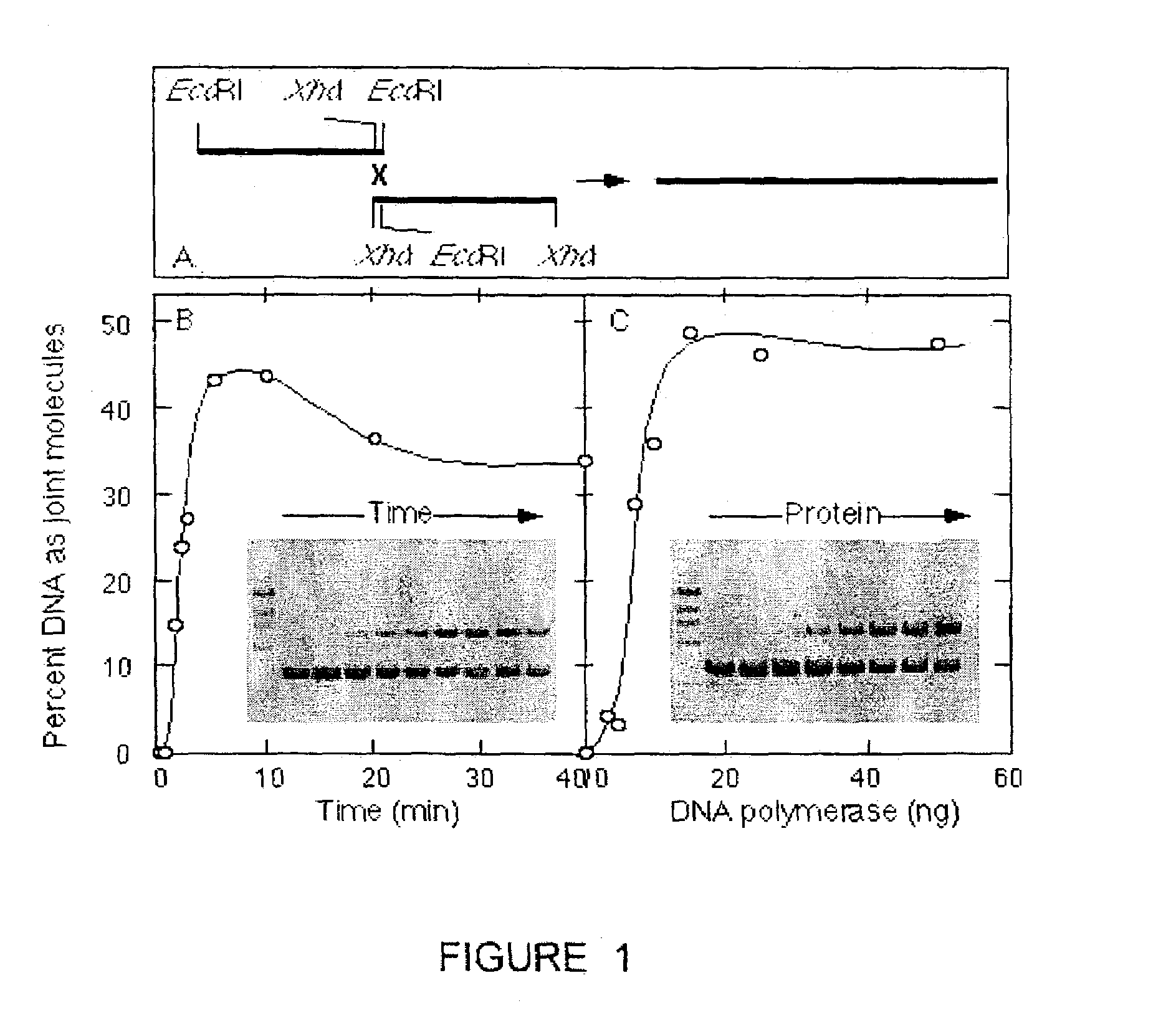
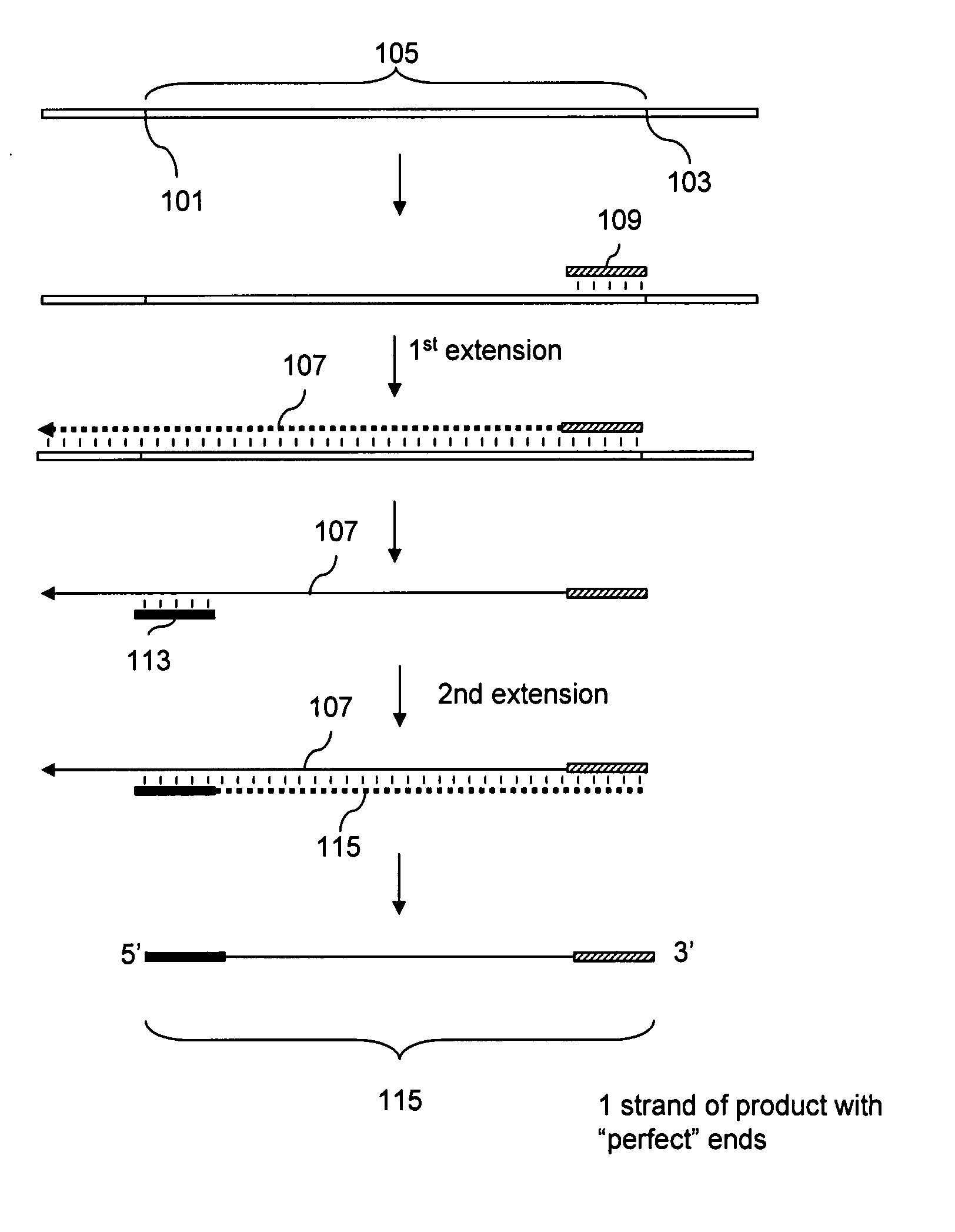
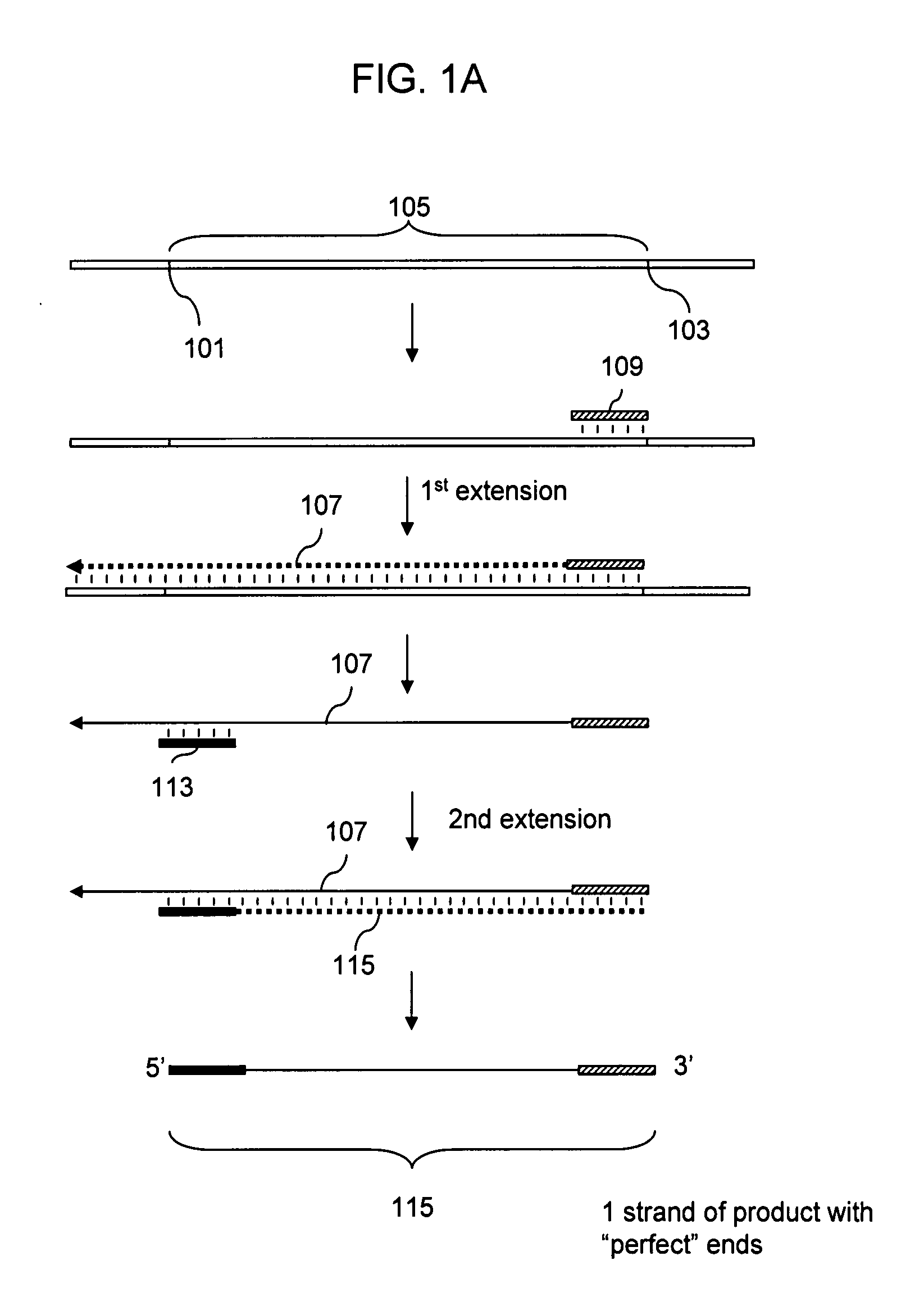
DNA joining method
InactiveUS7575860B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzymeExonuclease
The present invention provides a method to directionally clone any linear template DNA molecule into any linearized vector. The vector ends may be generated from any restriction enzyme cleavage. The method does not require a ligation step nor the use of carefully controlled conditions as is required with methods involving specific exonucleases alone. It has been determined that specific DNA polymerases are able to efficiently join one or more linear DNA molecules sharing ends with appropriate complementation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Methods for in vitro joining and combinatorial assembly of nucleic acid molecules
The present invention relates to methods of joining two or more double-stranded (ds) or single-stranded (ss) DNA molecules of interest in vitro, wherein the distal region of the first DNA molecule and the proximal region of the second DNA molecule of each pair share a region of sequence identity. The method allows the joining of a large number of DNA fragments, in a predetermined order and orientation, without the use of restriction enzymes. It can be used, e.g., to join synthetically produced sub-fragments of a gene or genome of interest. Kits for performing the method are also disclosed. The methods of joining DNA molecules may be used to generate combinatorial libraries useful to generate, for example, optimal protein expression through codon optimization, gene optimization, and pathway optimization.
Owner:SYNTHETIC GENOMICS INC
Novel reaction system for rapidly constructing plant gene site-directed knockout carrier
InactiveCN107254485AHigh speedImprove efficiencyHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyDouble chain
The invention discloses a novel reaction system for rapidly constructing a plant gene site-directed knockout carrier. The system comprises 1) based on a CRISPR-Cas system carrier, the carrier comprises the DNA molecules having the following characteristics: an agrobacterium infection method is used for carrier conversion to the plant, a carrier capable of simultaneously realizing driving of SgRNA by an OsU3 promoter for transcription and driving of Cas9 protein by an Ubiquitin promoter for expression; 2) restriction enzyme AarI; 3) buffer and Oligo required by a reaction of the restriction enzyme AarI; 4) target gene site specific DNA double chain; and 5) T4DNA ligase and ATP required by an enzyme reaction. The system only requires 5-10 reaction cycles for rapidly and efficiently completing a construction process of plasmid, greatly simplify the operation flow, and satisfies the requirement of rapid construction with high flux for plant gene site-directed knockout plasmid.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
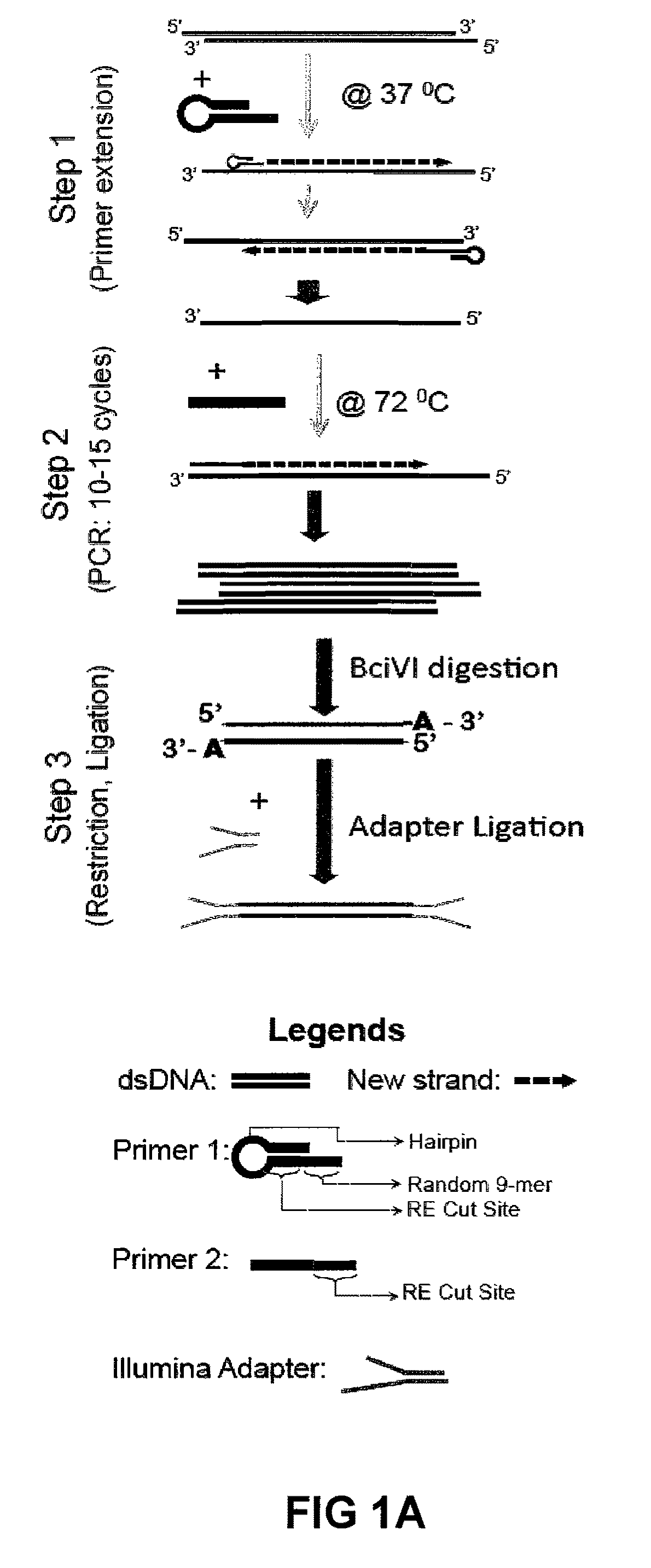
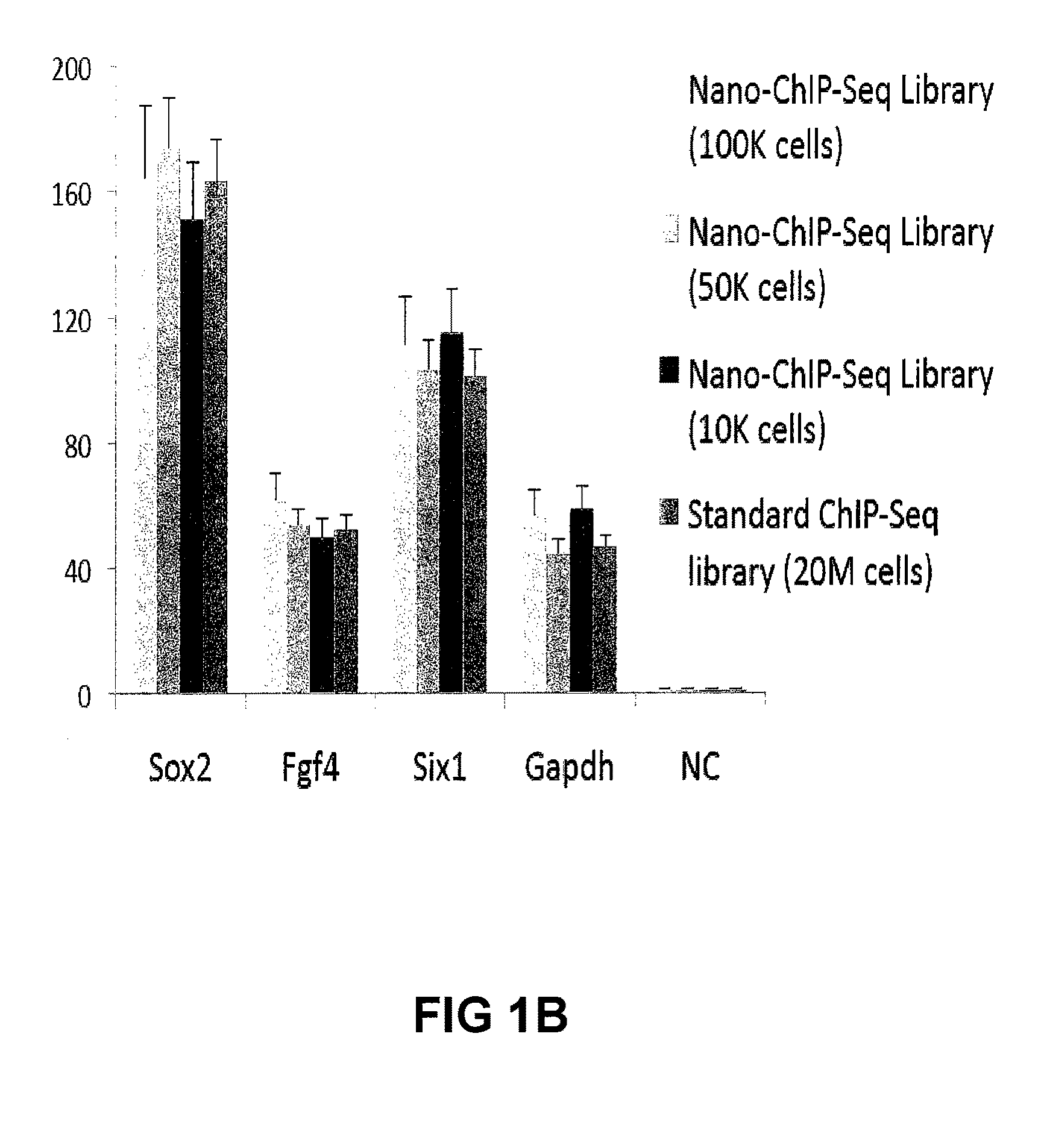
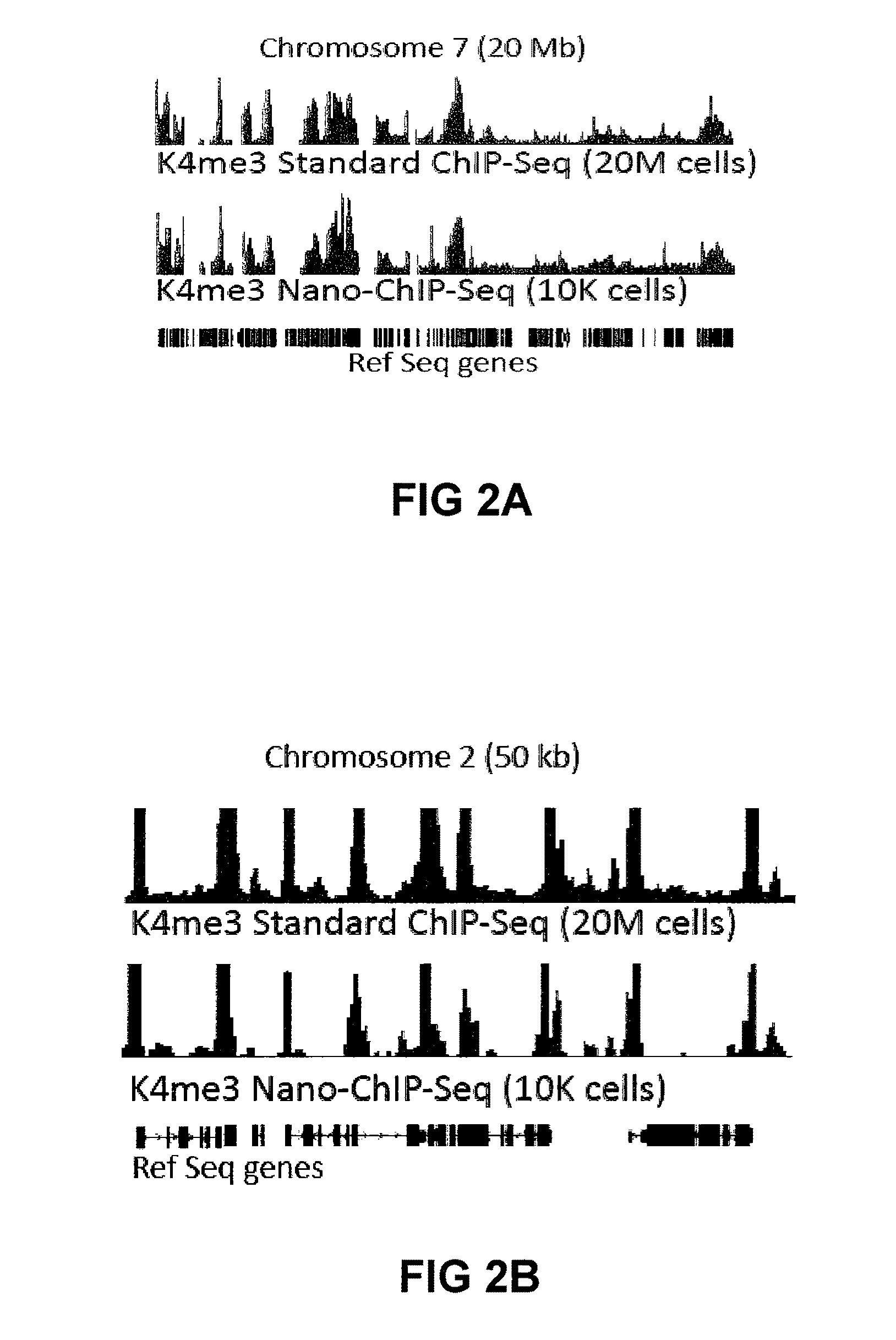
Methods For Preparing Sequencing Libraries
ActiveUS20110189677A1Reduce the amount requiredSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementImproved methodOrder of magnitude
Improvements in chromatin immunoprecipitation-high throughput sequencing techniques has allowed the creation of chromatin maps from limited biological sample sizes that cannot be evaluated using conventional chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing protocols. For example, a modified universal primer is utilized that incorporates restriction enzymes into chromatin immunoprecipitation fragments before amplification. The improved method allows the sample sizes to be several orders of magnitude less than that required for standard ChIP-Seq techniques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Method for in vitro transcription using an immobilized restriction enzyme
InactiveUS20180208957A1Enhancing and improving linearizationLow costHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierDNA EndonucleaseRestriction enzyme
The present invention relates to a method for in vitro transcription of a linear template DNA which is produced using an immobilized restriction endonuclease. The invention also relates to mutated restriction enzymes which are suitable for immobilization and a solid support to which these restriction enzymes are immobilized. Further, the present invention relates to an enzyme reactor containing said immobilized restriction endonuclease which enzyme reactor can be used for preparing linearized template DNA. Finally, the present invention relates to the use of said enzyme reactor for preparing a linear template DNA for in vitro transcription. In addition, the present invention relates to a kit comprising the immobilized restriction endonuclease.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Methods of Analysis of Methylation
InactiveUS20080108073A1Uniformly amplifyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexCytosine
Methods for determining the methylation status of a plurality of cytosines are disclosed. In some aspects genomic DNA target sequences containing CpGs are targeted for analysis by multiplex amplification using target specific probes that can be specifically degraded prior to amplification. The targets may be modified with bisulfite prior to amplification. In another aspect targets are cut with methylation sensitive or insensitive restriction enzymes and marked with a tag using the target specific probes. The presence or absence of methylation may be determined using methylation sensitive restriction enzyme or bisulfite treatment. Detection in many embodiments employs hybridization to tag arrays, genotyping arrays or resequencing arrays.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Rapid and enzymeless cloning of nucleic acid fragments
InactiveUS6936470B2Recovery functionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoSingle strand dna
A method for cloning a nucleic acid fragment into a vector by flanking the fragment with first and second adapter sequences, and contacting the fragment with the vector having sequences homologous to the first and second adapter sequences under conditions such that the nucleic acid fragment is incorporated into the vector by homologous recombination in vivo in a host cell. Additionally, a method for selecting for a successful transformation of a vector by a nucleic acid insert. Also, systems for cloning a nucleic acid fragment into a vector without at least one of a restriction enzyme, a ligase, a gyrase, a single stranded DNA binding protein, or other DNA modifying enzymes. Further, a kit for cloning a nucleic acid fragment into a vector.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20040092016A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredBacteriaStable introduction of DNAMammalKnockout animal
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods and adaptors for generating specific nucleic acid populations
InactiveUS6017701APreventing replication and amplificationEasy to findSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingEndonuclease
The present invention relates to methods and kits for generating or analyzing nucleic acid populations or desired nucleic acid sequences based upon replication or amplification reactions. The invention comprises methods employing adaptors ligated to nucleic acids that preferentially permit replication or amplification of desired nucleic acid sequences or preferentially eliminate undesired nucleic acids from replication or amplification. The invention also comprises adaptors useful in the methods and in kits for replicating or amplifying nucleic acids. In one embodiment, the adaptors function to protect desired nucleic acids from cleavage by a restriction enzyme while other nucleic acids are cleaved. The protected, desired nucleic acids can then be preferentially replicated or amplified. Accordingly, the invention can be used for the amplification of desired nucleic acids and the effective removal of undesired nucleic acids from a population.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Method for constructing high-flux simplified genome sequencing library
ActiveCN104694635AReduce the impact of quantitative accuracy before mixingImprove uniformityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGenomic sequencingPhosphorylation
The invention provides a method for constructing a high-flux simplified genome sequencing library. The method comprises the following steps: digesting genome DNA of different samples by using restriction enzymes, thereby obtaining blunt-end DNA fragments with phosphorylation modification at the 5' end; adding the base A at the 3' end, connecting the DNA fragments of different samples with 5' phosphorylation and 3' cohesive ends A with joints containing different bar code sequences, connecting the products PCR, purifying and mixing the amplification products, performing low-cycle PCR amplification, thereby obtaining a target fragment amplification product of which the ratio of the joints to joint dimers is greatly reduced; and separating, purifying, and forming the high-flux simplified genome sequencing library from the purified products. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the flux is high, the cost is low, and the generated library is high in sequencing quality and has very wide application prospects in researches such as high-flux SNP detection and marker development, genetic map drawing and functional gene location.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
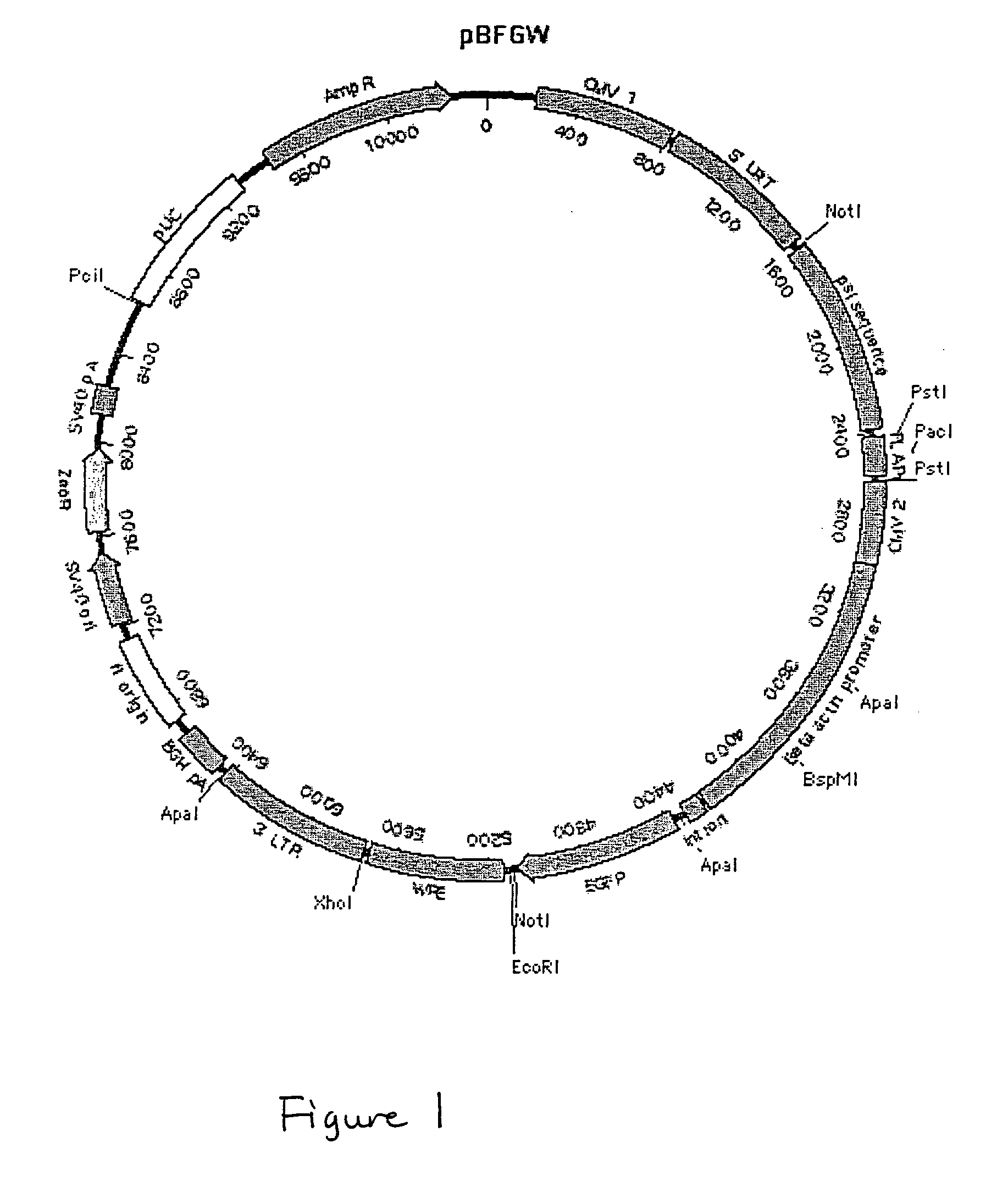
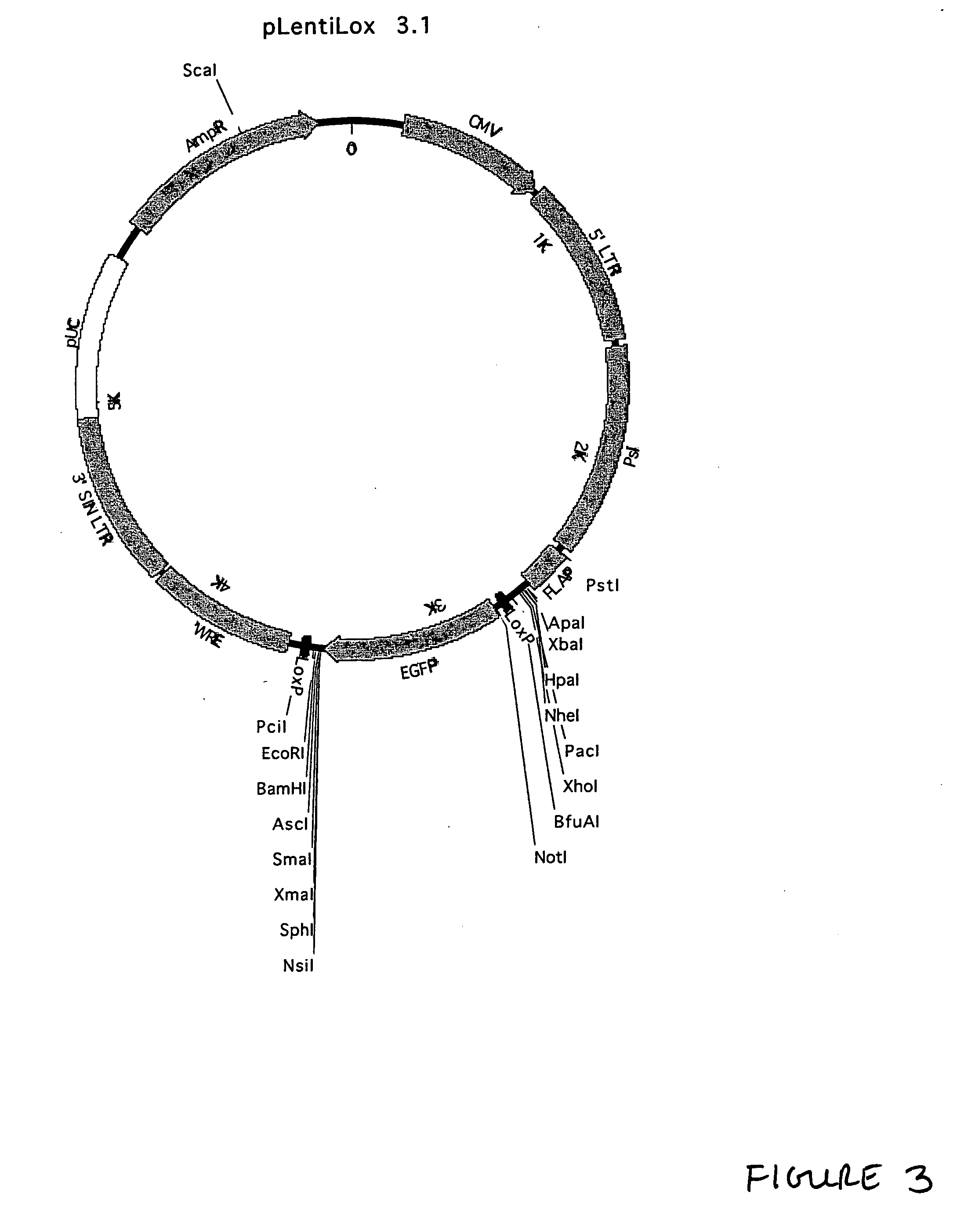
Lentiviral vectors, related reagents, and methods of use thereof
The present invention provides new lentiviral vectors, including lentiviral transfer plasmids and infectious lentiviral particles. Lentiviral vectors of the invention were designed to offer a number of desirable features including reduced size, convenient cloning sites (including multiple cloning sites and sites for particularly useful restriction enzymes), loxP sites, self-inactivating LTRs, etc. Certain of the vectors are optimized for expression of reporter genes and / or for expression of siRNAs or shRNAs within eukaryotic cells. The invention also provides three and four plasmid lentiviral expression systems. In addition, the invention provides a variety of methods for using the vectors including gene silencing in cells and transgenic animals, and methods of treating disease.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com