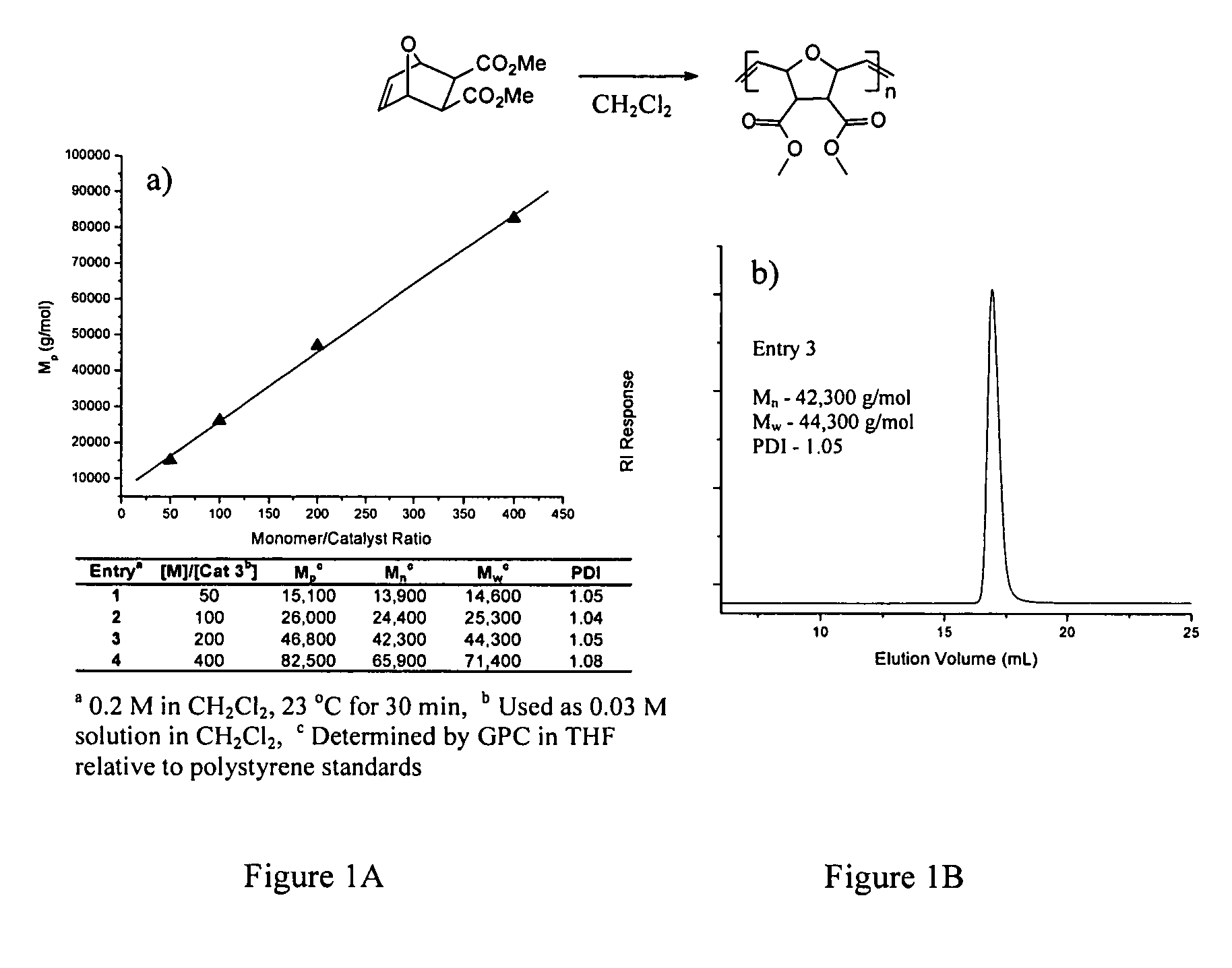
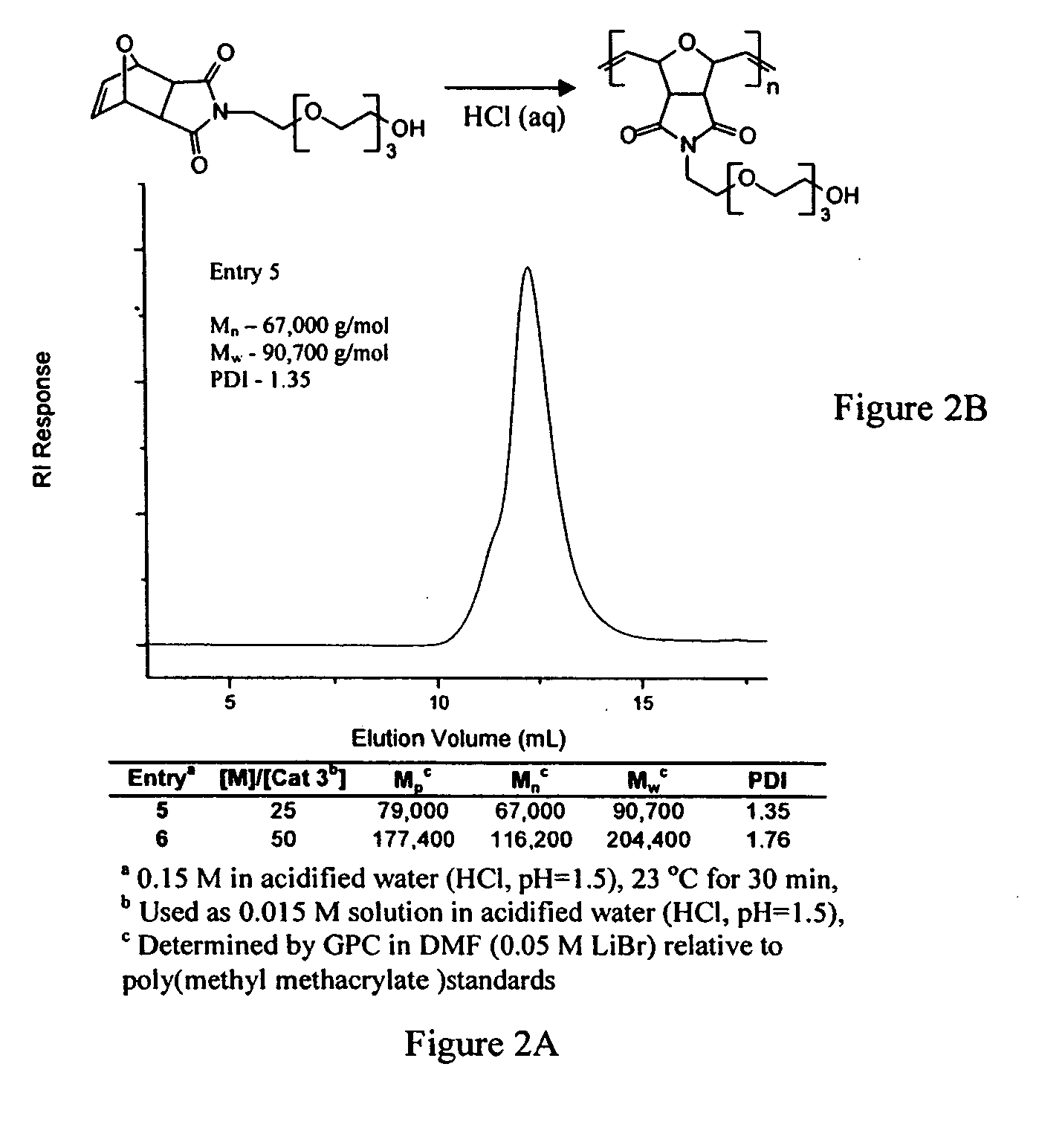
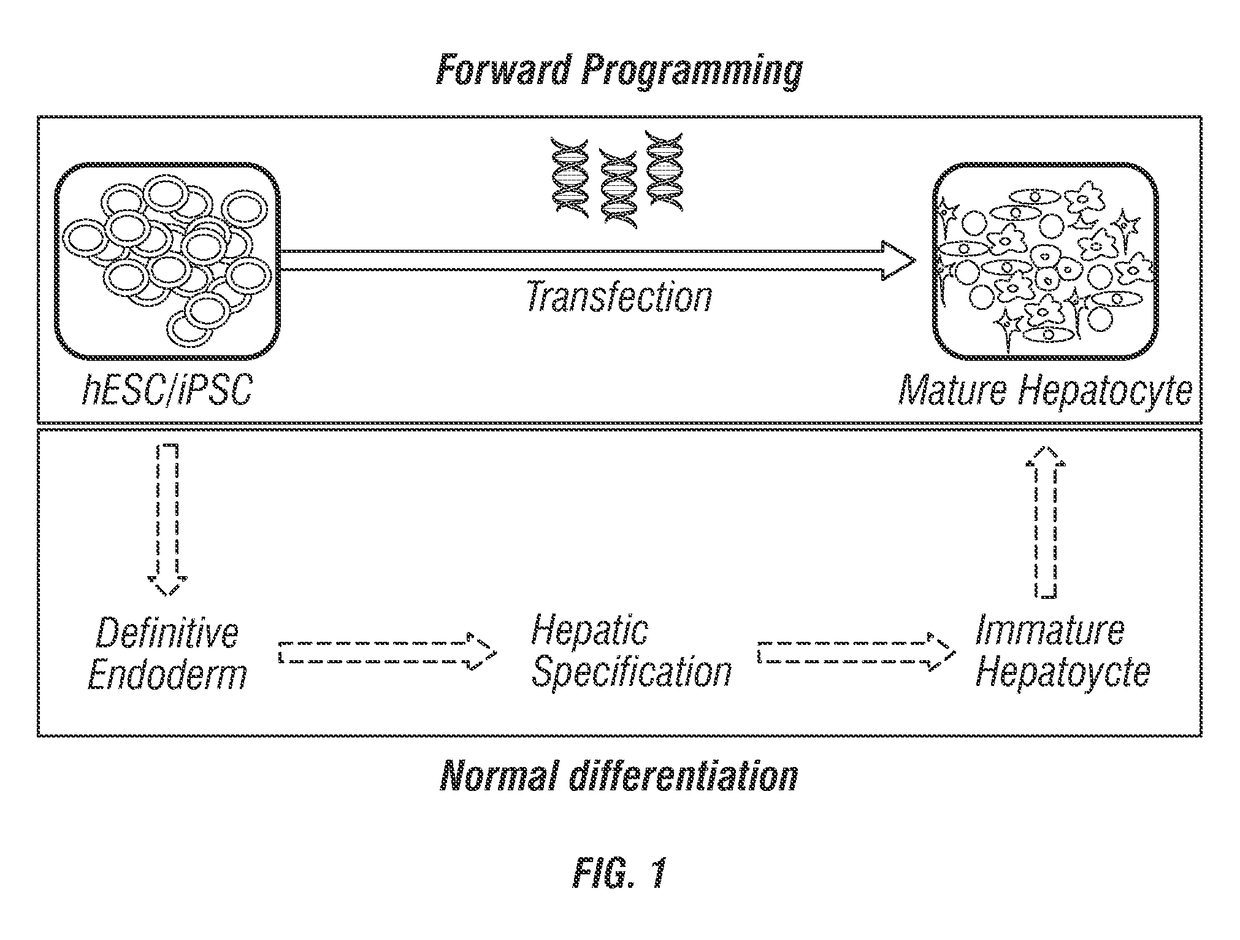
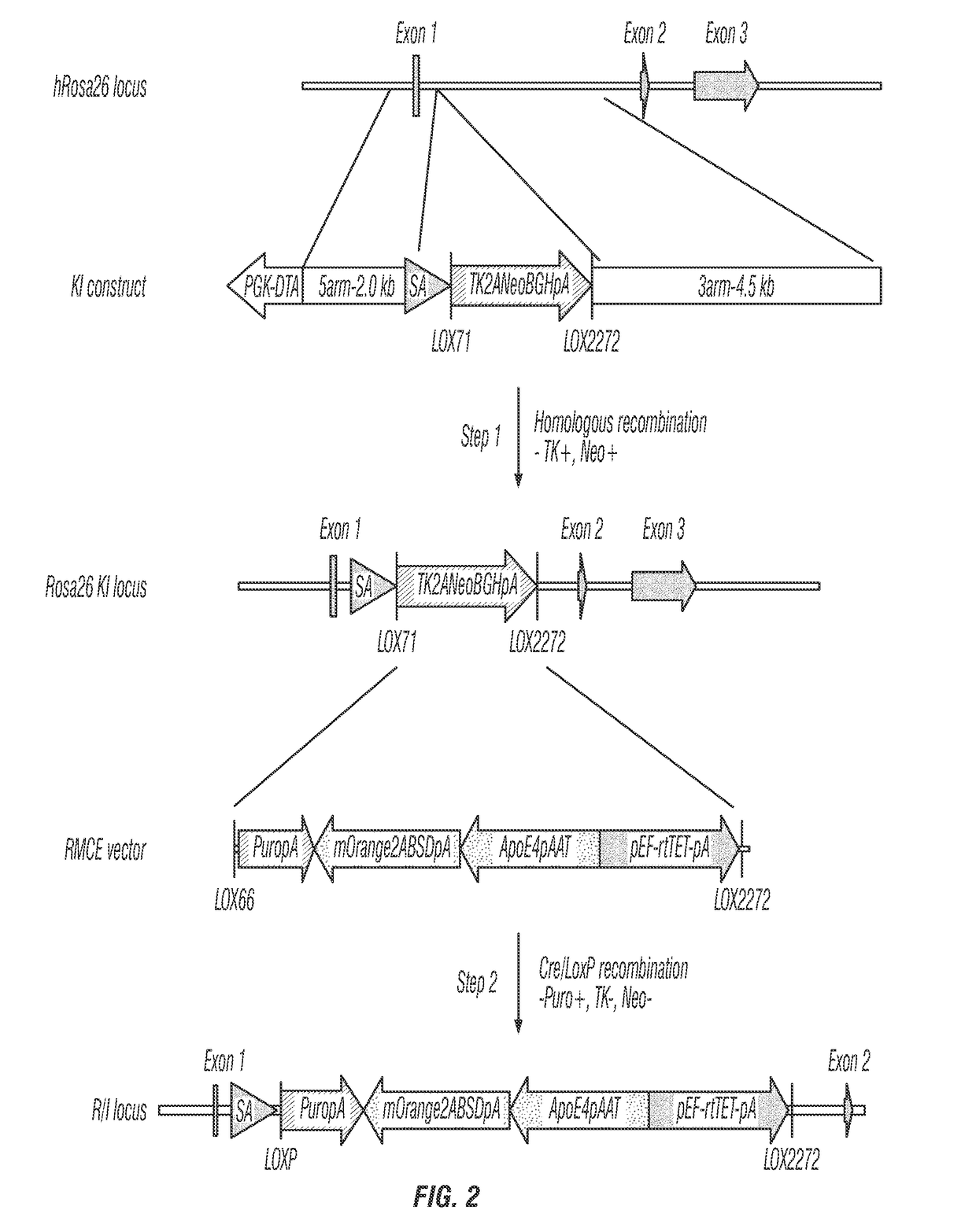
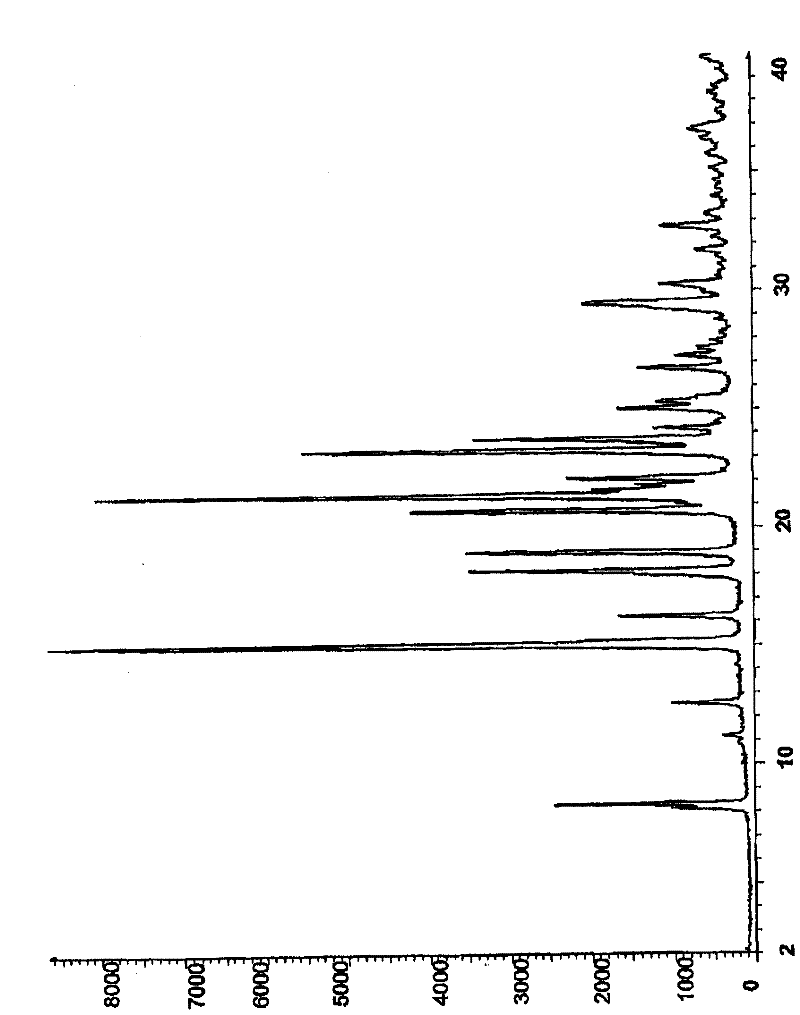
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Chemical methodology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microchemical method and apparatus for synthesis and coating of colloidal nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080087545A1Aggressive processing conditionsRealize the structureFlow mixersVolume/mass flow measurementCrystallographyBatch processing
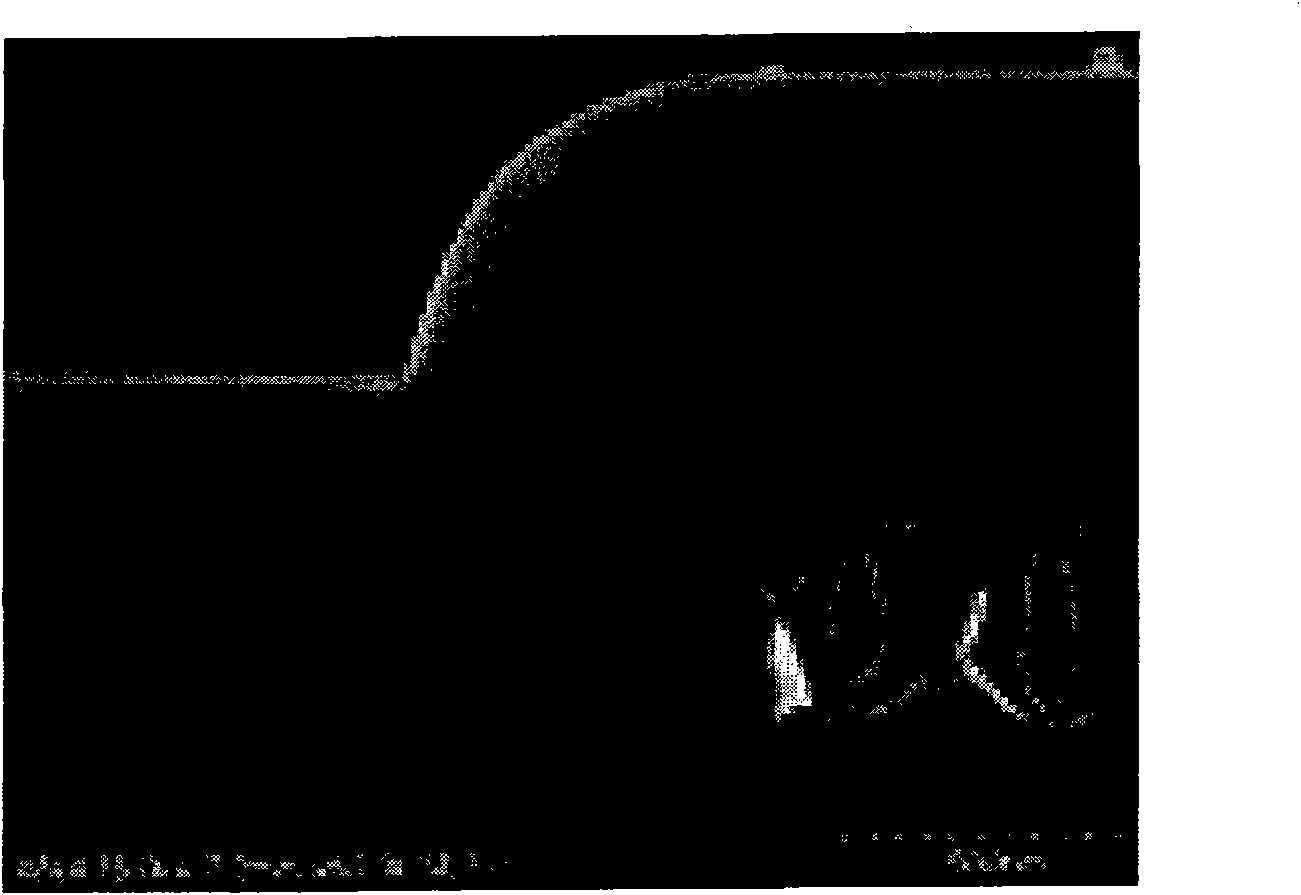
The present invention represents a radical departure from most conventional macro-scale batch processing methods employed to synthesize and coat colloidal nanoparticles. Synthesis and coating are in series and in-situ, obviating the need for numerous cumbersome, and often expensive intermediate-processing steps. In one embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for synthesizing colloidal nanoparticles. In another embodiment, the invention is a method and apparatus for enabling coating of colloidal nanoparticles using an electrophoretic switch for contacting and separating said colloid nanoparticles.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Use of restriction enzymes and other chemical methods to decrease non-specific binding in dual bead assays and related bio-discs, methods, and system apparatus for detecting medical targets
InactiveUS20060068409A1Decrease non-specific bindingEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsValve arrangementsAssayChemical methodology
Methods for decreasing non-specific bindings of beads in dual bead assays and related optical bio-discs and disc drive systems. Methods include identifying whether a target agent is present in a biological sample and mixing capture beads each having at least one transport probe affixed thereto, reporter beads each having at least one signal probe affixed thereto, and a biological sample. Mixing is performed under binding conditions to permit formation of a dual bead complex if the target agent is present in the sample. The reporter bead and capture bead each are bound to the target agent. Denaturing the target agent and keeping it in the denatured form by use of a specialized hybridization buffer is also provided. A denaturing agent is guanidine isothiocynate. Methods further include isolating the dual bead complex from the mixture to obtain an isolate, exposing the isolate to a capture field on a disc, and detecting the presence of the dual bead complex in the disc to indicate that the target agent is present in the sample. The methods may further include selectively breaking up non-specific binding between capture beads and reporter beads employing a digestion agent. Also employed is a method for selectively breaking up non-specific binding between capture beads and reporter beads using a wash buffer containing a chemical agent. The methods are applied to detecting medical targets.
Owner:NAGAOKA
Chemical method
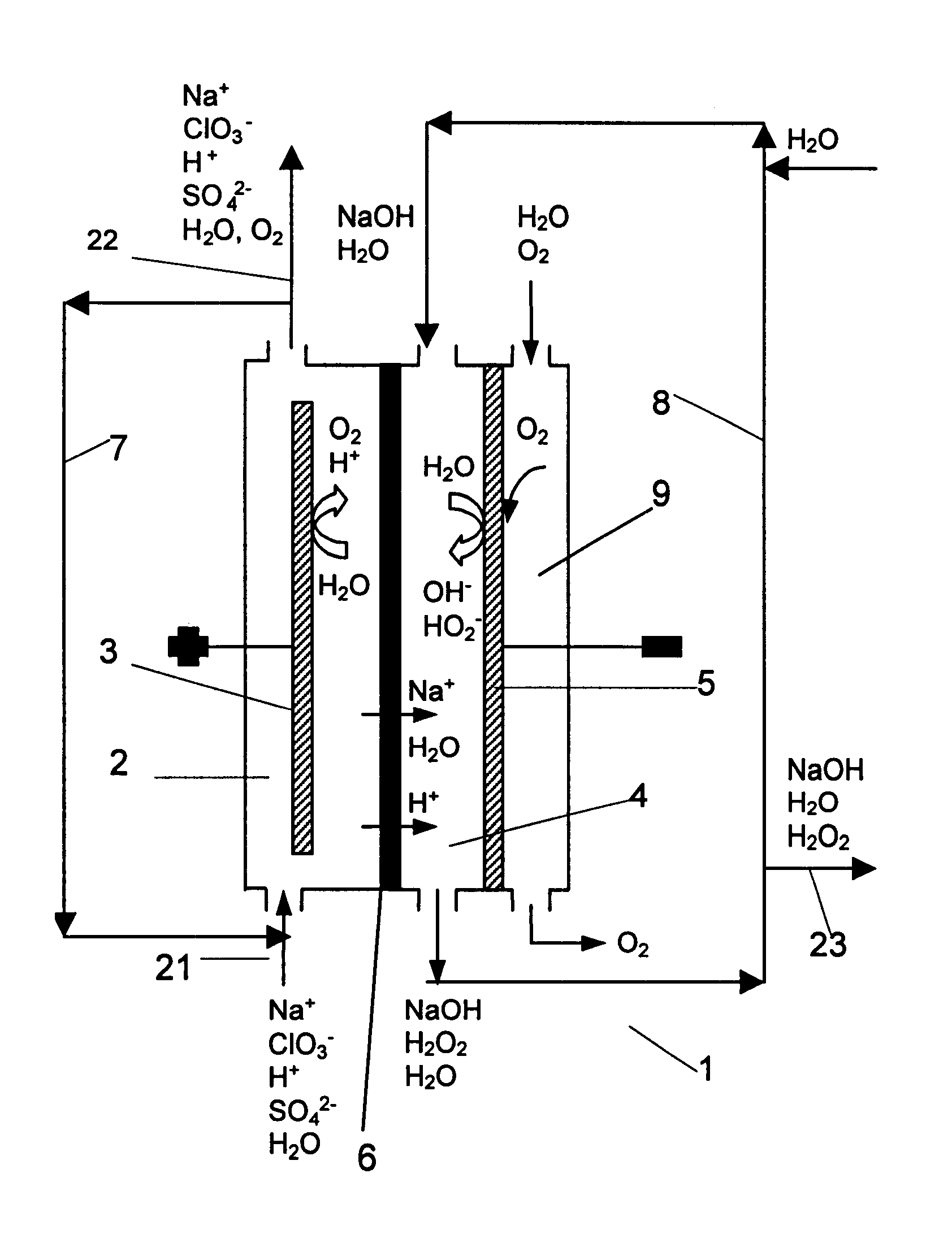
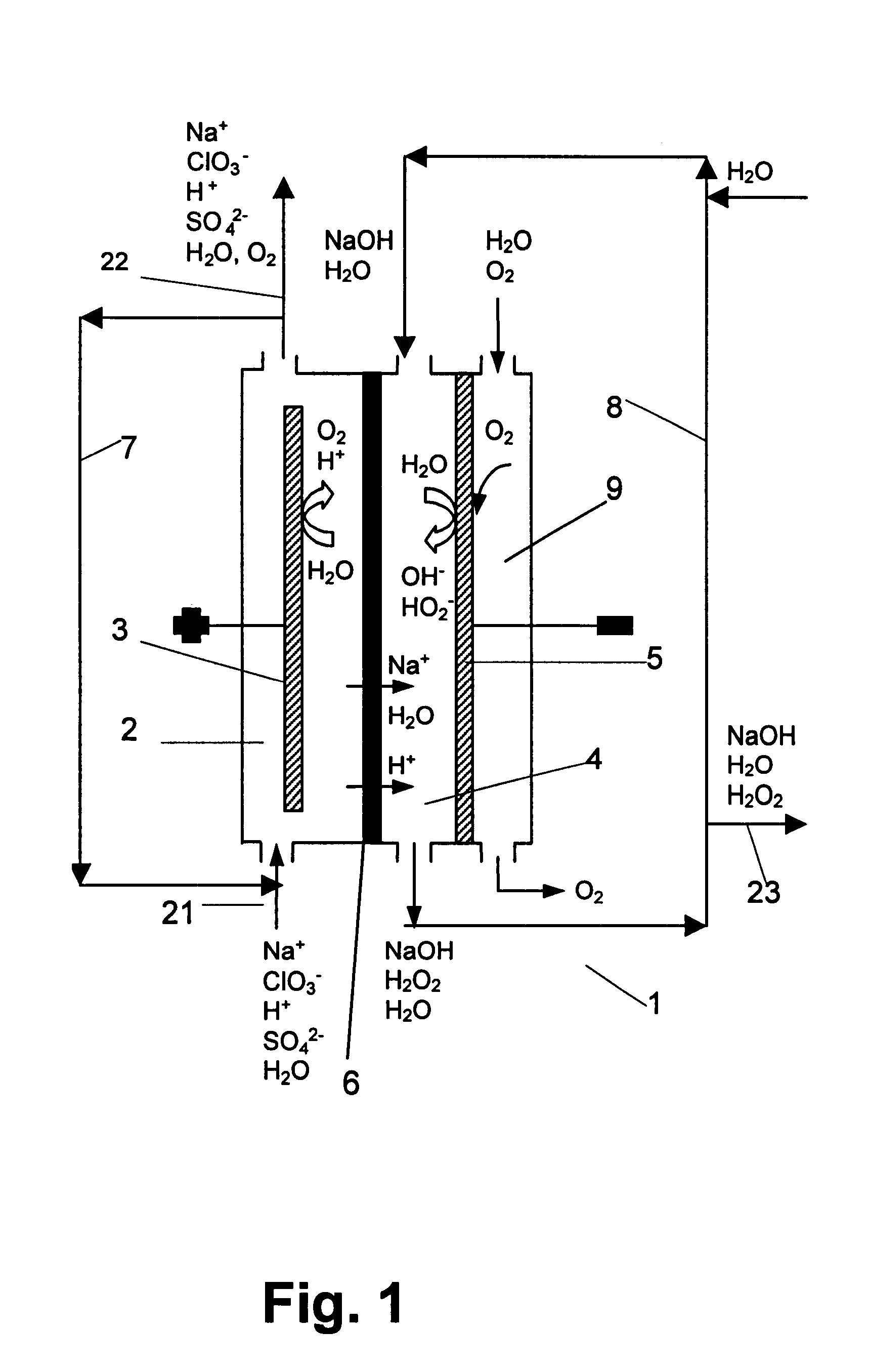
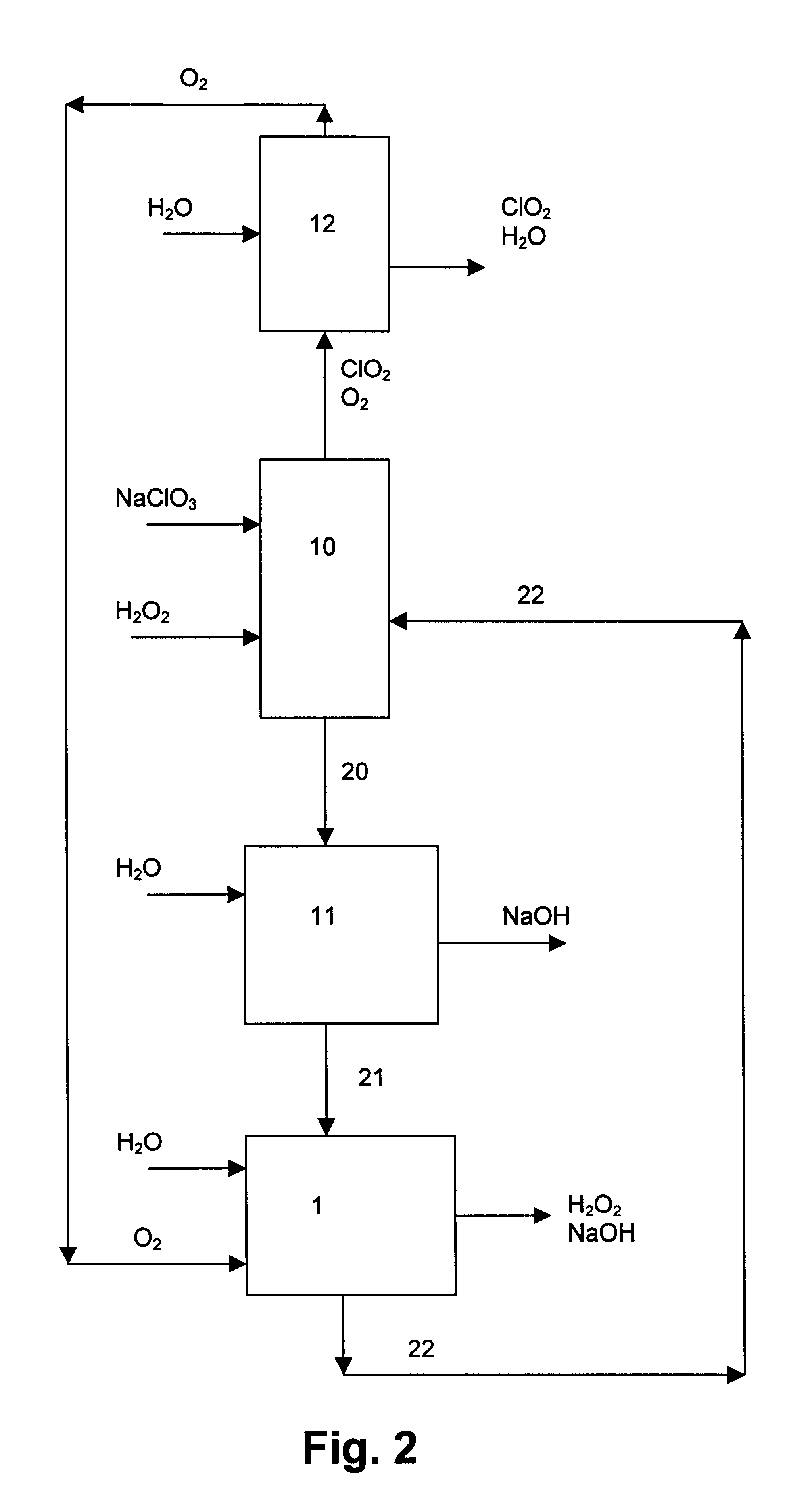
InactiveUS6322690B1Avoiding net productionEliminate needElectrolysis componentsChlorine dioxideChlorate ionChlorine dioxide
The invention relates to a process for production of an alkaline hydrogen peroxide solution and an acidified alkali metal salt solution containing chlorate in an electrochemical cell including an anode compartment provided with an anode and a cathode compartment provided with an oxygen reducing cathode. In the cathode compartment an aqueous alkali metal hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide is formed, wherein the molar ratio MOH:H2O2 for the net production thereof is maintained from about 0.1:1 to about 2:1. Also a process for simultaneous production of chlorine dioxide is disclosed.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
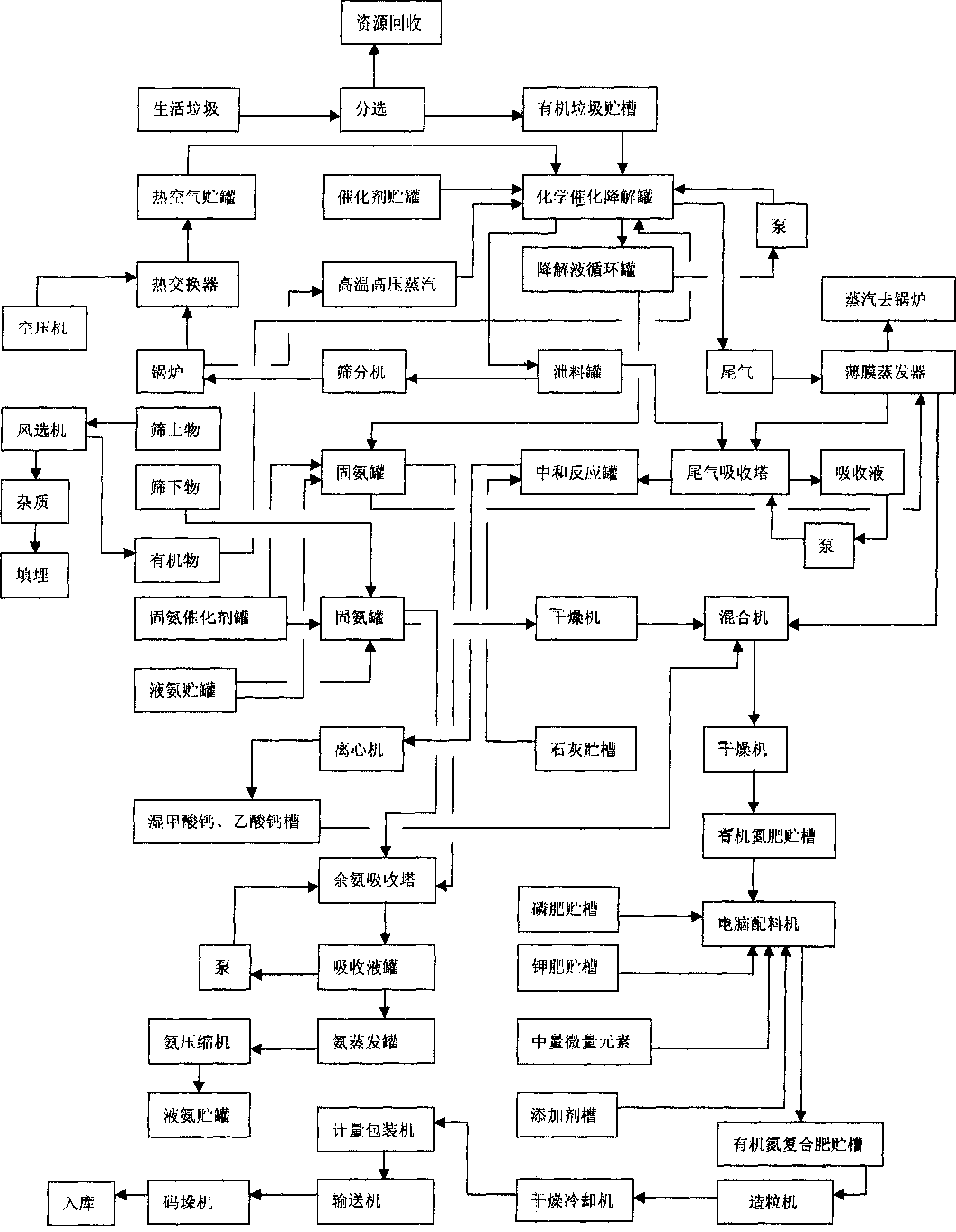
Household gabbage chemical stability treatment technology
ActiveCN1686624ANo parasitismSmall footprintSolid waste disposalMaillard reactionChemical methodology
A process for chemically stabilizing the life garbage includes such steps as quickly degradating the organic high-molecular compound containing C and N to become micro moleculae, and Maillard reaction to generate micro-molecular C-N compound to be used as fertilizer.
Owner:刘文治 +1
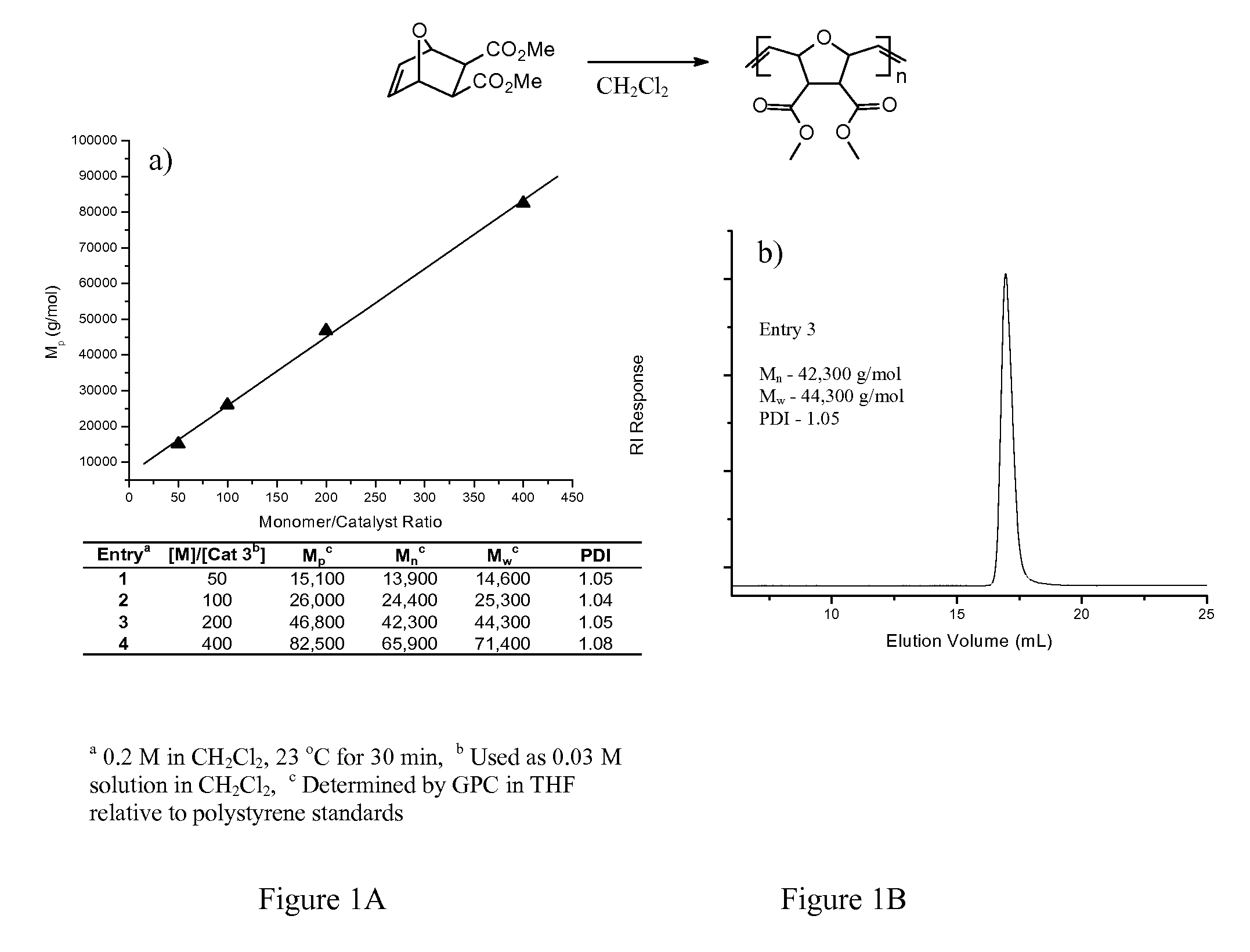
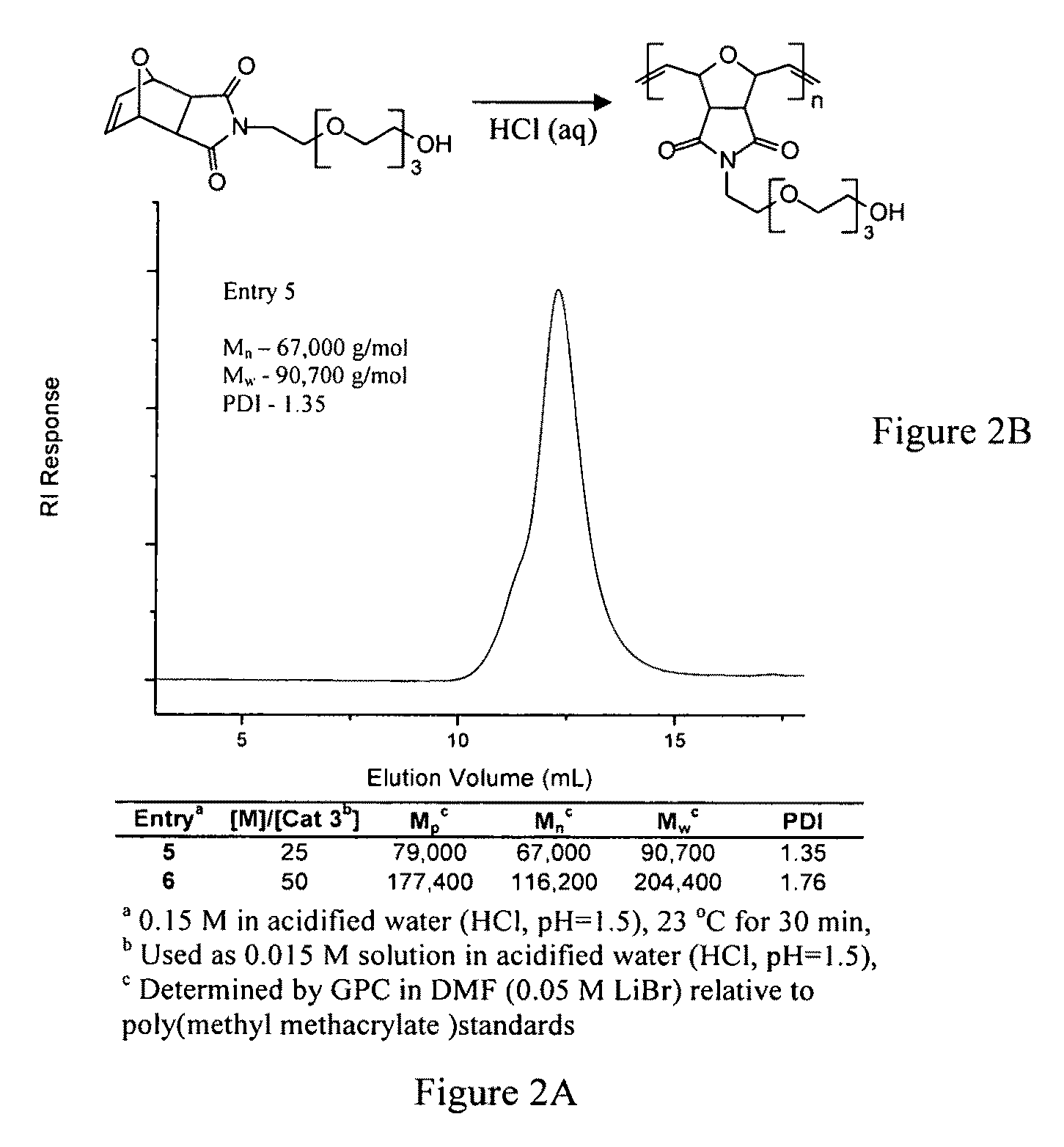
PEG-substituted pyridine ligands and related water-soluble catalysts
InactiveUS7332609B2Good timesReduce yieldRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationCompound (substance)Chemical methodology
Amphiphilic Group VIII metathesis catalysts, as can be used in a range of polymerization reactions and other chemical methodologies.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Substituted pyridine ligands and related water-soluble catalysts
InactiveUS7960555B2Good timesReduce yieldRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationChemical methodologyWater soluble
Versatile Group VIII metathesis catalysts, as can be used in a range of polymerization reactions and other chemical methodologies.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
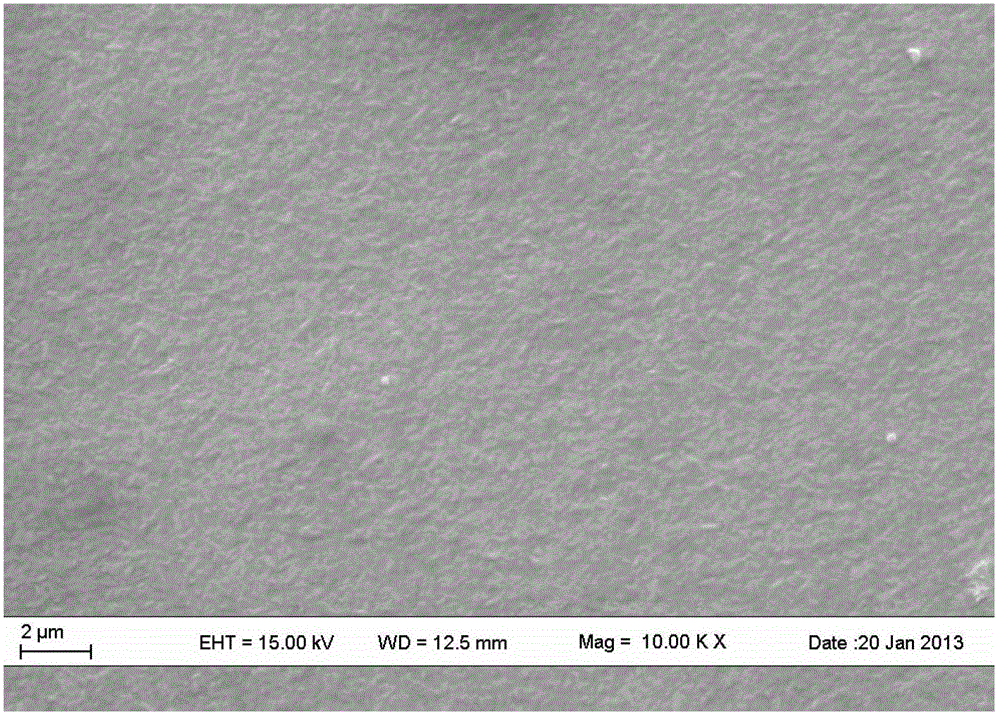
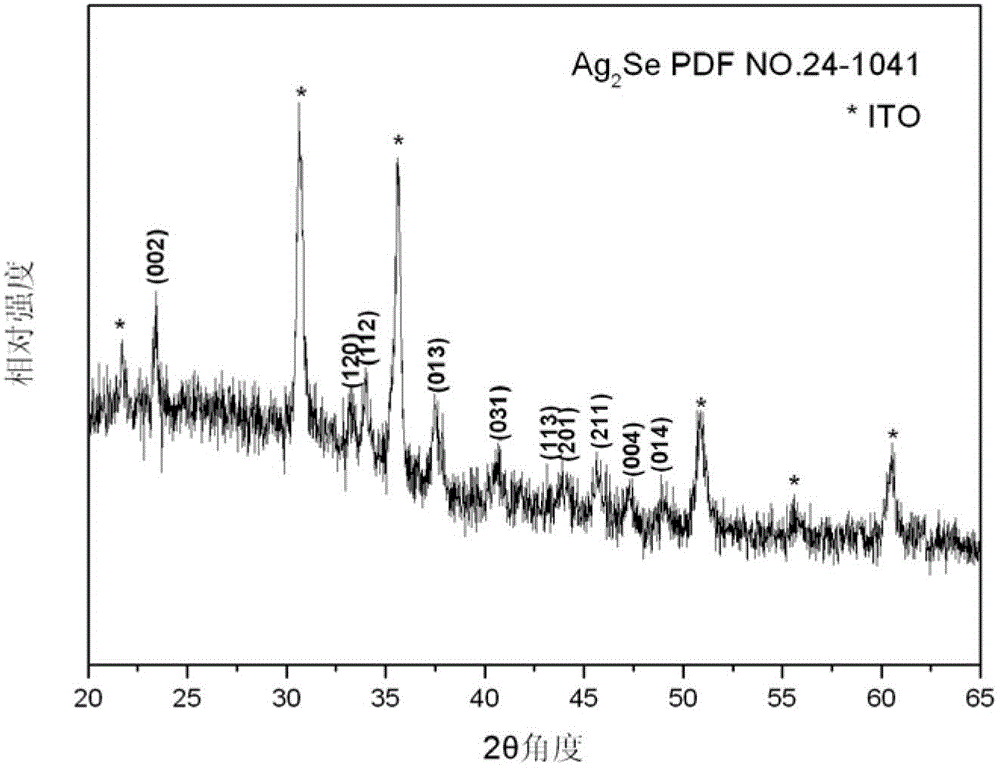
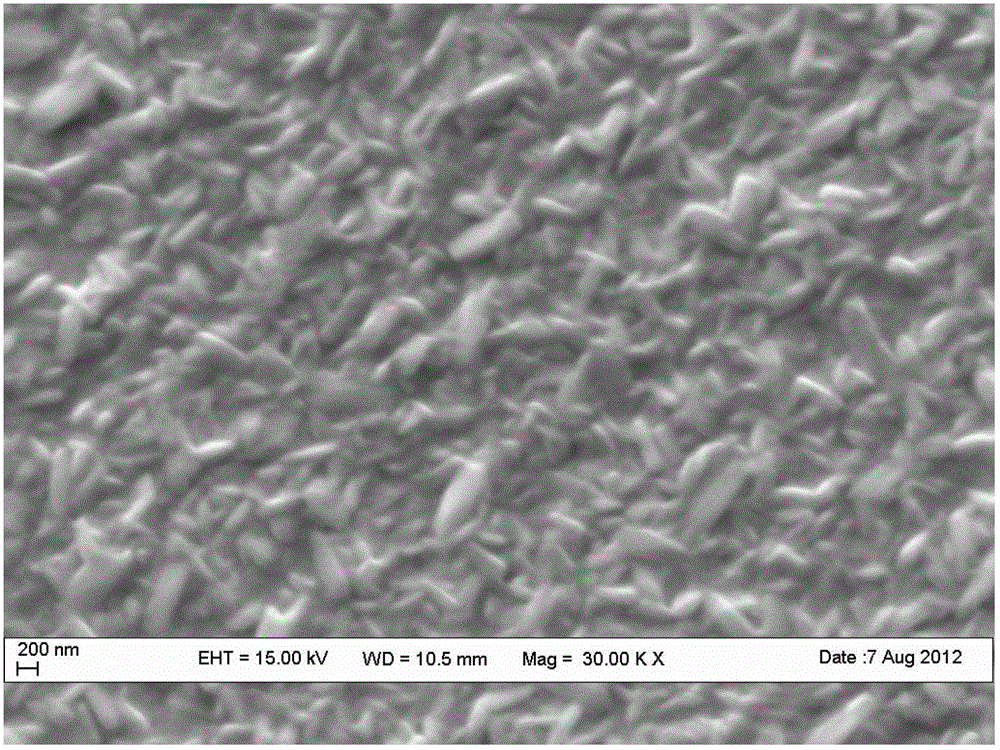
Chemical method for synthesising silver selenide semiconductor photoelectric film material in situ at room temperature
The invention provides a chemical method for synthesising a silver selenide semiconductor photoelectric film material in situ at a room temperature. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving elementary-substance Se powder in Na2S aqueous solution to form orange-yellow solution; placing a substrate material sputtered with an elementary-substance silver film on the surface and the solution aforementioned in the same container; and growing the Ag2Se semiconductor photoelectric film material on the surface of the substrate in situ via a short-time reaction in a temperature range from 7 to 35 DEG C. The reactants are low in price, has no need of being further purified, green and environment-friendly, and any surfactant or other chemical additives are not required; room-temperature reaction conditions are moderate, energy consumption is little, and influence on a conducting substrate is avoided; and the chemical method is fast in reaction, convenient in operation, and controllable in process. The chemical method provided by the invention overcomes the defects of dependence on high vacuum, high energy consumption and high production cost, high reactant toxicity, complex film-forming process and the like of the existing preparation process for an Ag2Se semiconductor photoelectric film material, and is beneficial to large-scale production and industrial application.
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
Swerianmarin injectio, its preparation process and application
InactiveCN1634099AAbundant medicinal resourcesSmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemAdjuvantMedicine
The invention discloses a Swerianmarin injection, its preparation process and application, wherein the preparing process comprises using Gentianaceae, Scrophulariaceae or Oleaceae plants as raw material, employing conventional phytochemical method for extraction, segregation and purification, thus obtaining swertiamarin, weighing swertiamarin and medicinal adjuvant, charging water for injection, thermal insulating 10-20 minutes at 30-60 deg. C, cooling down, filtering, dispensing the filter liquor 1-48 hours at 0-5 deg. C, filtering, encapsulating, drying in frozen, sterilizing, and packaging.
Owner:昆明同持医药研究有限公司
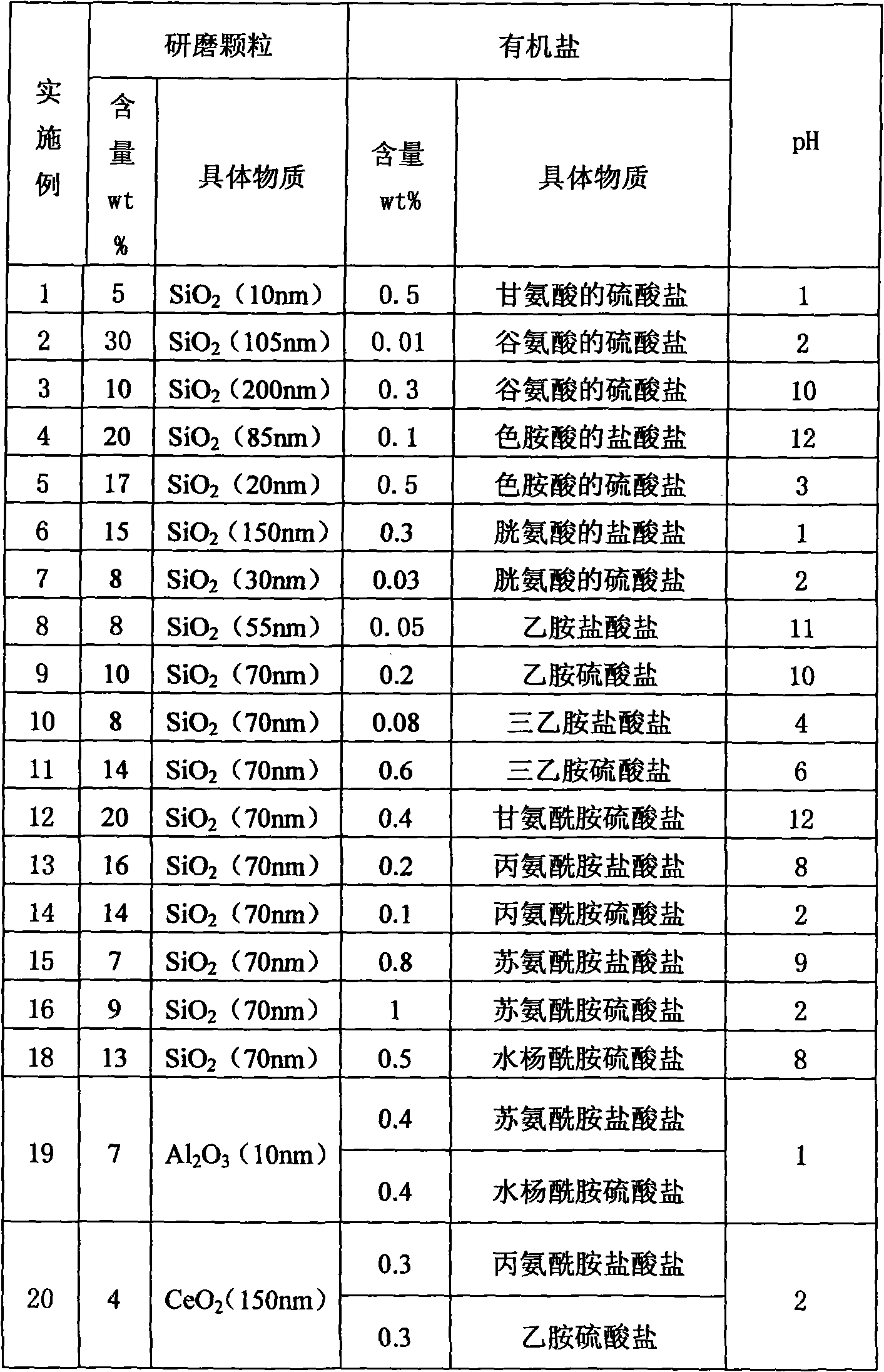
Chemical mechanical polishing solution
InactiveCN101684391AImprove removal rateImprove planarization efficiencyPolishing compositions with abrasivesDielectricSulfate
The invention discloses chemical mechanical polishing solution containing abrasive grains and one or more of the following organic salts: hydrochlorides of aliphatic amines, sulfates of aliphatic amines, hydrochlorides of amides, sulfates of amides, hydrochlorides of amino acids and sulfates of amino acids. The chemical mechanical polishing solution of the invention can increase the removal rate of silica dielectric materials (PETTEOS) by the chemical method under the acidic or alkaline condition and has higher removal rate of silicon oxide and higher planarization efficiency when the contentof the abrasive grains is relatively low. The surfaces of the materials are free of scratch and corrosion.
Owner:ANJI MICROELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
PEG-substituted pyridine ligands and related water-soluble catalysts
InactiveUS20060235235A1Good timesReduce yieldRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationCompound (substance)Chemical methodology
Amphiphilic Group VIII metathesis catalysts, as can be used in a range of polymerization reactions and other chemical methodologies.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Hepatocyte production via forward programming by combined genetic and chemical engineering
InactiveUS20170107486A1Improve expression levelHigh expressionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsChemical methodologyHepatocyte
The present invention provides methods comprising both genetic and chemical means for the production of hepatocytes from a variety of cell sources, particularly pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Injector assembly, chemical reactor and chemical process
An injector assembly for injecting an additional component into a component stream flowing through a reactor conduit along the longitudinal axis thereof. A chemical reactor including an injector assembly for injecting an additional component into a moving component stream and a chemical process are also provided. In one embodiment, the chemical process is a process for producing titanium dioxide.
Owner:TRONOX LLC
Chemical method
InactiveCN103421574ARaise the ash melting pointReduce dust accumulationSolid fuelsHigh sodiumCompound (substance)
The invention provides a chemical method. The chemical method can reduce adverse effects of active sodium-containing components in high-sodium coal on a boiler and other devices in a high-temperature environment, and comprises the following steps: step 1, pretreatment, namely uniformly spraying a certain amount of a silica sol solution containing silica onto the high-sodium coal or soaking the high-sodium coal in the silica sol solution for a period of time to obtain high-sodium coal completely subjected to pretreatment; step 2, drying, namely drying the high-sodium coal completely subjected to pretreatment to obtain dried high-sodium coal; step 3, conveying the dried high-sodium coal to the high-temperature environment for use, wherein in the process, the silica and active sodium-containing components react to generate a sodium-containing substance which is high in melting point and insusceptible to volatilization.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Chemical method for microbial clogging treatment in artificial recharging process
PendingCN109607718AExtended service lifePromotes rapid oxidationWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processSpecific adsorptionChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a chemical method for microbial clogging treatment in an artificial recharging process, and relates to the technical field of microbial clogging treatment. The chemical methodfor the microbial clogging treatment in the artificial recharging process has the advantages that chlorine dioxide is utilized to control microbial clogging in the recharging process, and the effectson prolonging the service life of a recharging facility, reducing the equipment maintenance cost and improving recharging efficiency are positive, a bactericide chlorine dioxide solution can rapidly oxidize and destroy tyrosine in bacterial protein capsid to inhibit the specific adsorption of bacteria, the chlorine dioxide solution reacts with some amino acids in bacteria and other microbial proteins to control the synthesis of microprotein and ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria, the method can be used multiple times for a long time under the condition of meeting the drinking waterstandard, the aquifer and a recharging well system cannot be destroyed, the groundwater quality cannot be adversely affected, the adding dose is small, the cost is low, the unblocking effect is good,and the effect is quick.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Chemical method for clearing sealant and solution prepared by using chemical method
The invention provides a chemical method for clearing sealant and solution prepared by using the chemical method and relates to the field of chemical clearing, in particular to the sealant clearing field. Liquid paraffin, methylbenzene, ethyl acetate, acetone, phenol, ethylalcohol and ammonia water are prepared into organic solution according to proportioning; the sealant which needs clearing is soaked in the solution or degreasing cotton soakage solution is applied on the surface of the sealant, the soak time is thirty minutes. After the sealant is softened, the degreasing cotton soakage solution can be eliminated. After the degreasing cotton soakage solution can be eliminated, deionized water is used for washing and compressed air is used for drying the parts. The chemical method can simply, rapidly, efficiently wipe the sealant on the surface of the parts; the prepared organic solution has no corrosion on the high-temperature alloy 4648, DZ4 and other high-temperature alloy materials referred to the parts.
Owner:CHINA HANGFA GUIZHOU LIYANG AVIATION POWER CO LTD
Stable radioiodine conjugates and methods for their synthesis
InactiveUS6858705B2Increase productionEasy to oxidizeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioimmunodetectionAntibody conjugate
Methods are described for conjugating radioiodinated non-metabolizable peptides to proteins and antibodies with improved yields and qualities of conjugates. Radioiodinated residualizing antibody conjugates comprising any aminopolycarboxylate-appended peptide, or any carbohydrate-appended peptide, are also provided. Additionally, methods are described for conjugating radioiodinated aminopolycarboxylates to proteins and antibodies, as well as for conjugating radioiodinated non-metabolizable carbohydrates to proteins and antibodies by a variety of chemical approaches. The instant radioiodinated residualizing antibody conjugates are particularly stable in vivo and are suitable for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
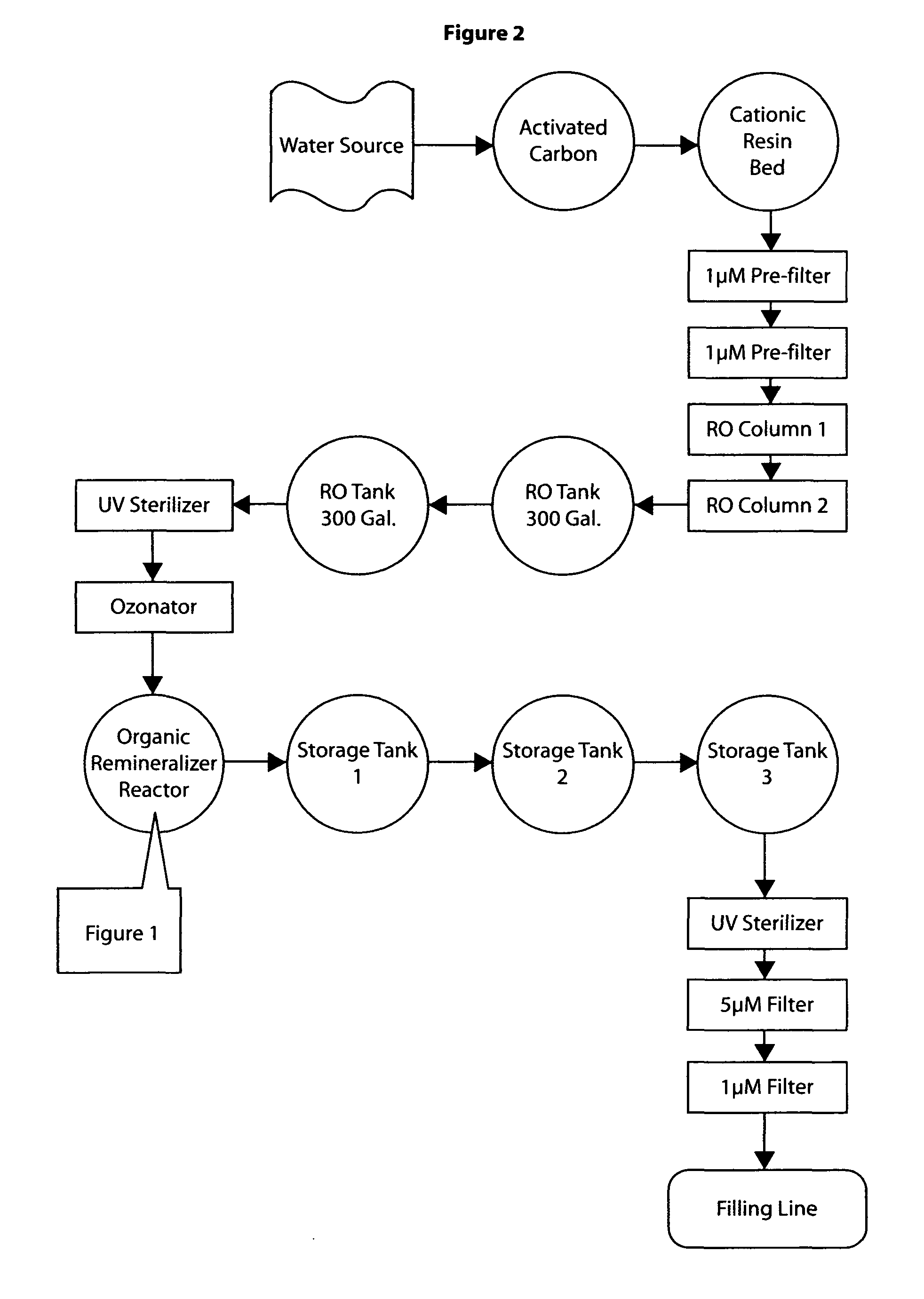
Organic remineralizer reactor
InactiveUS7887696B1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationChemical methodologyElectrolyte
This disclosure describes a commercial / industrial remineralizer designed to be added to a purification system that raises the pH by non-chemical methodology while replacing important electrolytes to the water that were extracted along with the toxic, non-essential minerals from the water. The remineralizer can be designed for heavy commercial continuous production.
Owner:CWP HLDG
Substituted pyridine ligands and related water-soluble catalysts
InactiveUS20090156767A1Promote conversionImprove production yieldRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationChemical methodologyWater soluble
Versatile Group VIII metathesis catalysts, as can be used in a range of polymerization reactions and other chemical methodologies.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Chemical process
ActiveCN102503933AQuality improvementImprove the situationSenses disorderOrganic chemistryChemical methodologyCompound (substance)
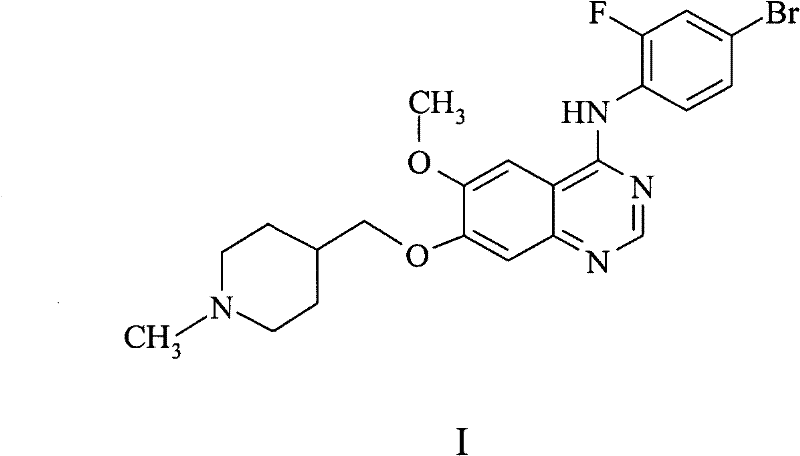
The present invention relates to chemical processes for the manufacture of certain quinazoline derivatives, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. The invention also relates to processes for the manufacture of certain intermediates useful in the manufacture of the quinazoline derivatives and to processes for the manufacture of the quinazoline derivatives utilising said intermediates. In particular, the present invention relates to chemical processes and intermediates useful in the manufacture of the compound 4-(4- bromo-2-fluoroanilino)-6-methoxy-7-(1-methylpiperidin-4-ylmethoxy)quinazoline.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Chemical processes generating solid (s) carried out continuously within microreactors
InactiveCN102858450AFlexible ScalingPrecise stoichiometric controlChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsPeptide preparation methodsMicroreactorChemical reaction
Owner:CORNING INC
System for implementing biological or chemical methods
PendingUS20210053055A1Complicated cleaningComplicated sterilization processLaboratory glasswaresChemical reactionLaboratory scale
The invention having functional vertical disposable reaction systems having a vertically mounted semipermeable membrane for sample preparation, chemical reactions, dialysis, enzymatic / microbiological fermentation, multistage processes, in vitro protein biosynthesis on a laboratory scale, formed from a base body and an exchangeable lid having different functions. For exchange across the membrane, the system is placed vertically into an outer volume consisting of gas, liquid or solid constituents. The system consists of a dimensionally stable base body and a liquid-tight lid having a functional support going toward the base of the base body, the dimensionally stable base body forming at least one noncapillary reaction space as inner volume with at least one semipermeable membrane as lateral wall. The high flexibility in use results from the combination of variants of the base bodies with different lid variants for different areas of use. The base bodies having different membranes and volumes can be coupled with lids having different feeding openings, contacts, sensor supports, gas supply means, circulation means, etc. This yields, in the case of m different base bodies and n different lid variants, m×n combinations having different properties.
Owner:SCIENOVA
A kind of processing method of modified graphene
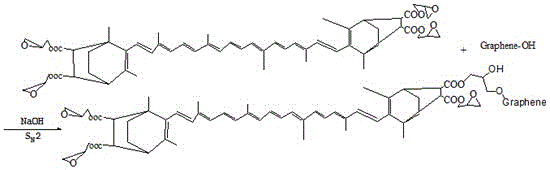
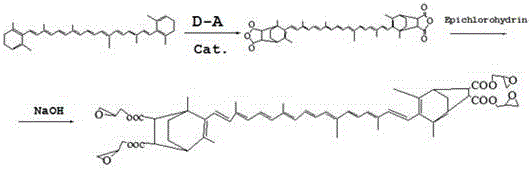
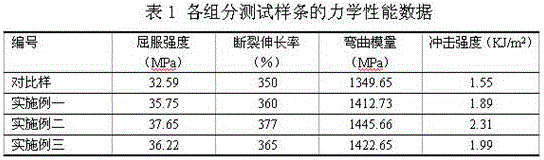
InactiveCN104629496BGood dispersionGood biocompatibilityPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsChemical methodologyGraphene
The invention discloses a treatment method for modified graphene. The invention pretreats and oxidizes graphite to obtain purified graphene containing hydroxyl groups on the surface, and obtains long-chain molecular products through chemical methods, and then design conditions to trigger reactions through chemical methods, so that long-chain molecules are grafted onto graphene. This method can improve the dispersibility of graphene and avoid agglomeration. The modified long-chain molecules come from a wide range of sources, are environmentally friendly, and are also conducive to improving the biocompatibility of graphene, and the modified long-chain molecules provided have more activity. It can provide more graphene modification, so that the obtained modified graphene can adjust the viscosity of the matrix, and can improve the processing and use performance. The method of the invention is simple and has good application effect.
Owner:贵州一当科技有限公司
Chemical method of chemical protein carrier of plant Chinese herb medicine and carrier chemical protein
InactiveCN101590204AQuick resultsGood effectDigestive systemMammal material medical ingredientsHerb medicineEgg protein
The invention discloses a chemical method of a chemical protein carrier of plant Chinese herb medicines and a carrier chemical protein. The carrier chemical protein is prepared in such a way that an egg protein absorbs and carries refined substances in plants necessary for human living cells and is prepared into various prescriptions according to human needs. The chemical method obviously improves the utilization rate of the plant Chinese herb medicines, improves the functions of the treatment and the health care of the plant Chinese herb medicines for human bodies, reduces the side effect of the plant Chinese herb medicines, and has quick and good effect and convenient and easy application. The invention is realized by the following scheme: the prepared plant Chinese herb medicines are put in a utensil according to a prescription by a metering standard of 10g / dose, 120-160 uniform eggs without egg shells are put on the plant Chinese herb medicines, water is added to the range which is 1-1.5 centimeters higher than the eggs, the plant Chinese herb medicines are heated to 100 DEG C, the water temperature is kept at the range of 95 DEG C-100 DEG C for 3.5-4 hours, the color of the egg protein is changed into flesh red, then the egg protein has the functions of the plant Chinese herb medicines of the prescription, and the carrier chemical protein is prepared accordingly.
Owner:甄兆玄
Chemical methods and apparatus
InactiveCN101563357ARadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsChemical methodologyCopper
The invention relates to methods and apparatus for labelling a biologically active vector such as a peptide with reporter moiety such as a radionuclide. The methods comprise reaction of a compound of formula (I) with a compound of formula (II), a compound of formula (III) with a compound of formula (IV) wherein: L1, L2, L3, and L4 are each Linker groups; R is a reporter moiety; in a narrow bore copper vessel. Microfluidic devices for performing the methods of the invention are also claimed.
Owner:HAMMERSMITH IMANET
Chemical process
InactiveUS20080230487A1Do not damage the environmentConveniently disposedRefining by heating/coolingLubricating oils distillationCost effectivenessChemical methodology
A novel chemical process has been developed for the first time for the disposal of greases and manufacture of industrial fuels therefrom. Details of the method for disposing by the new chemical approach have been described. The “degrading agent” used in this method ruptures soap matrices and helps the separation of soap and base oil. The solution derived from the research work is waste-to-energy process and can be used as cost effective fuel for industrial purpose.
Owner:MALHOTRA OIL
Method of biomolecule immobilization on polymers using click-type chemistry
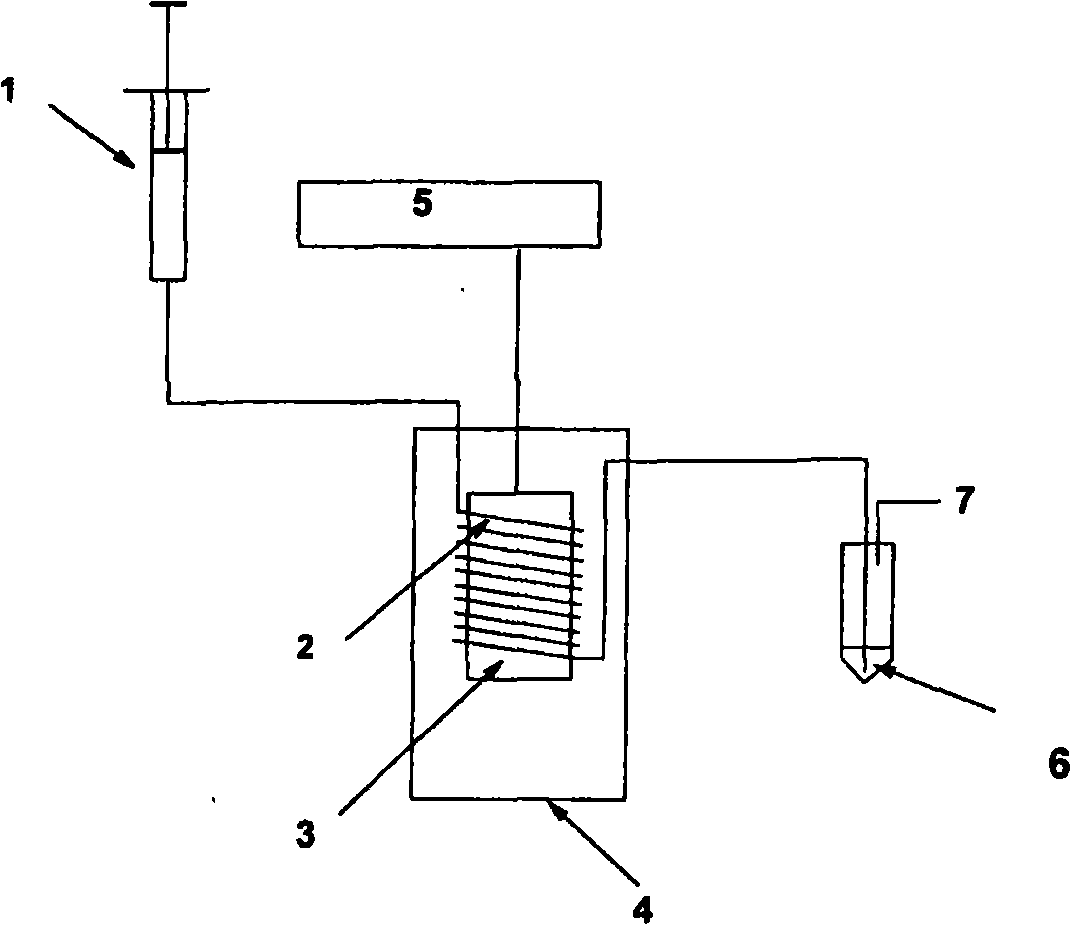
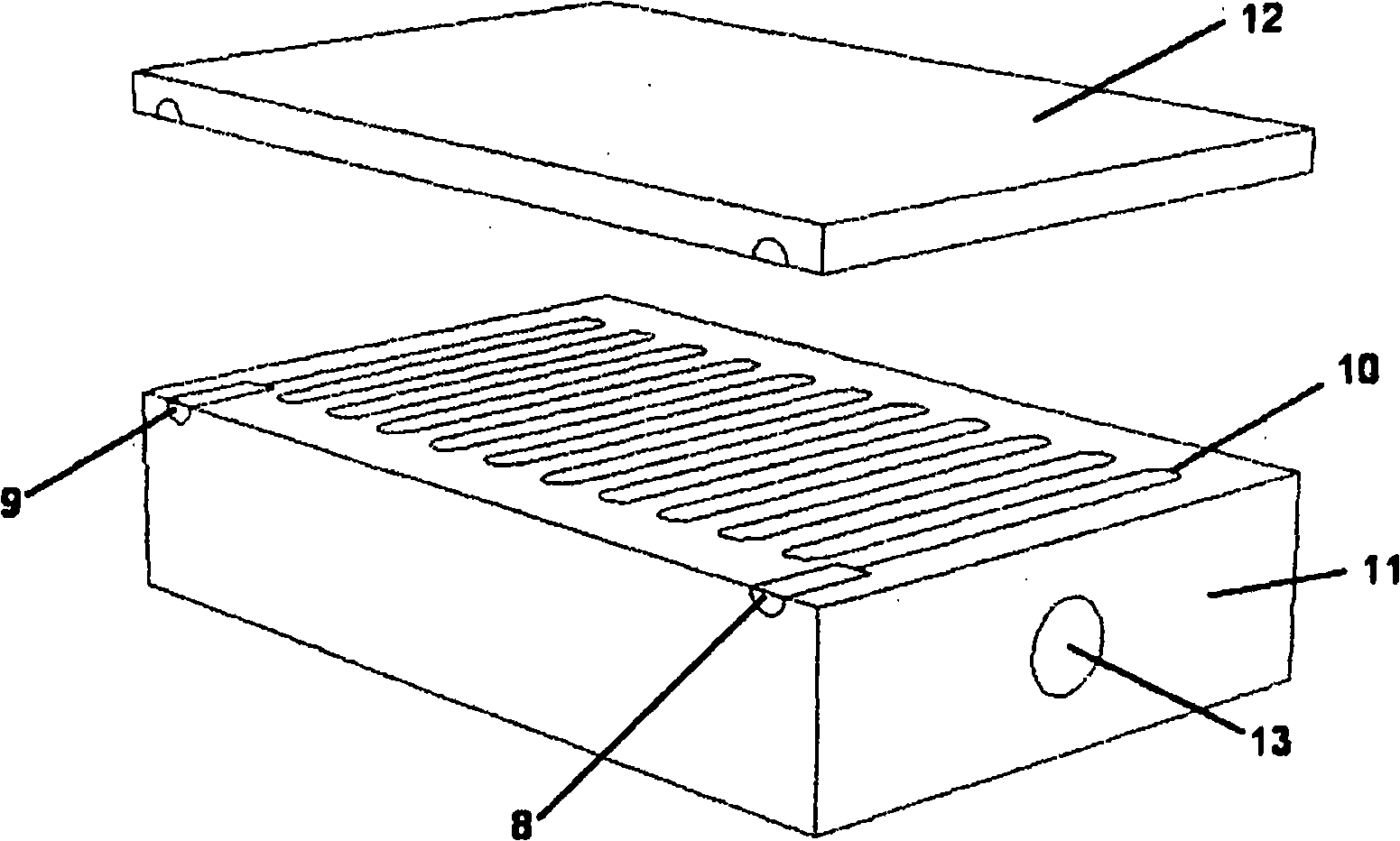
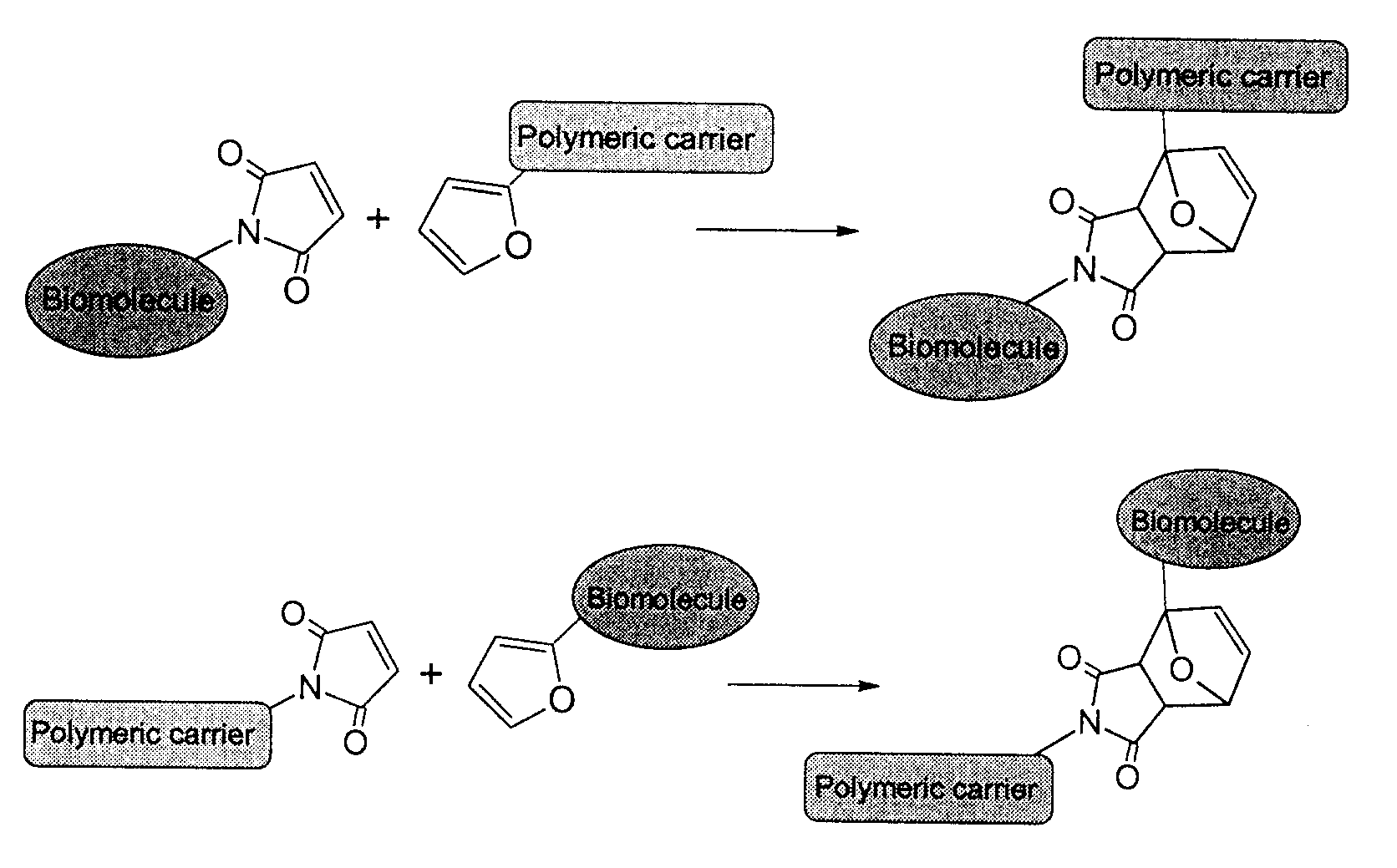
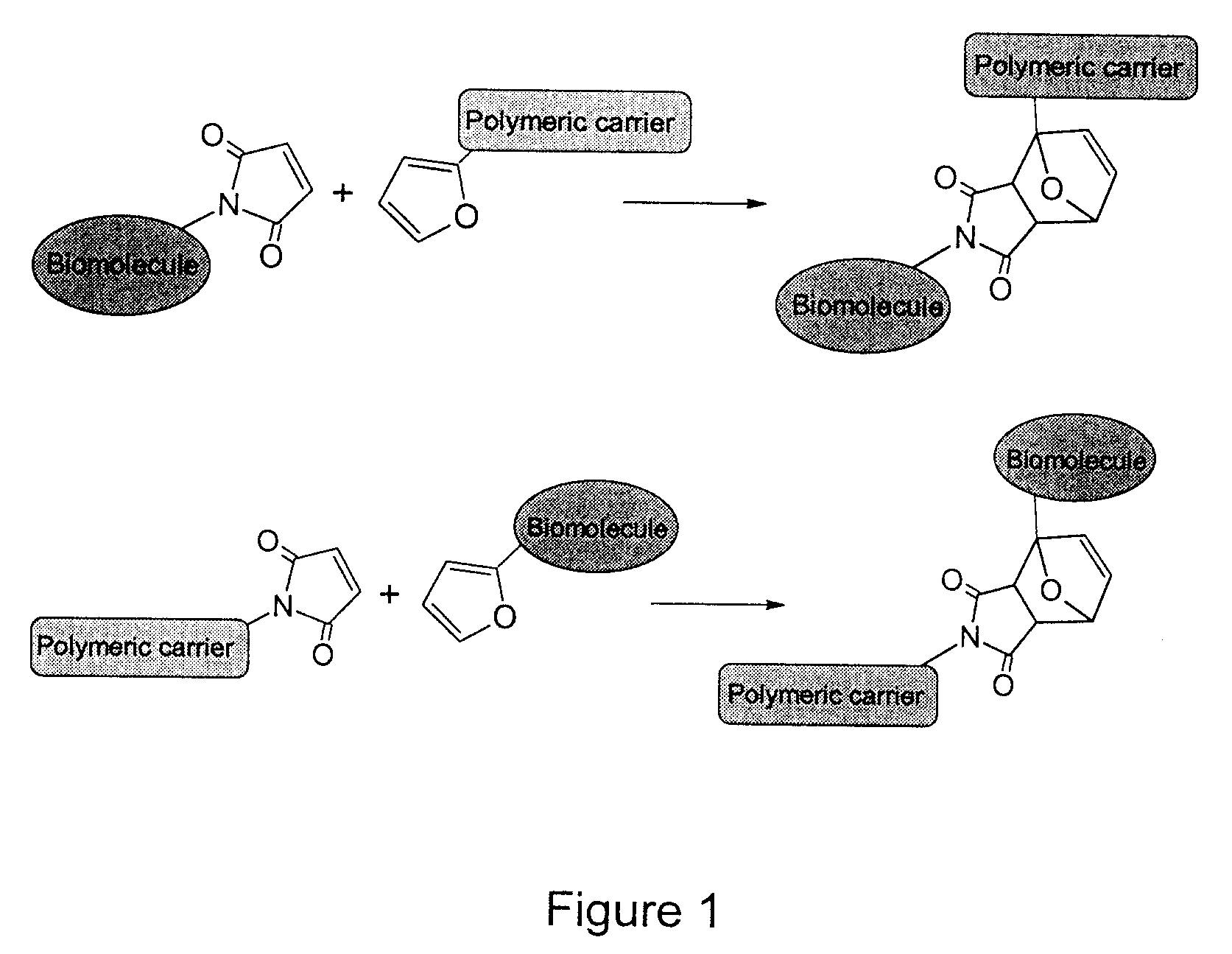
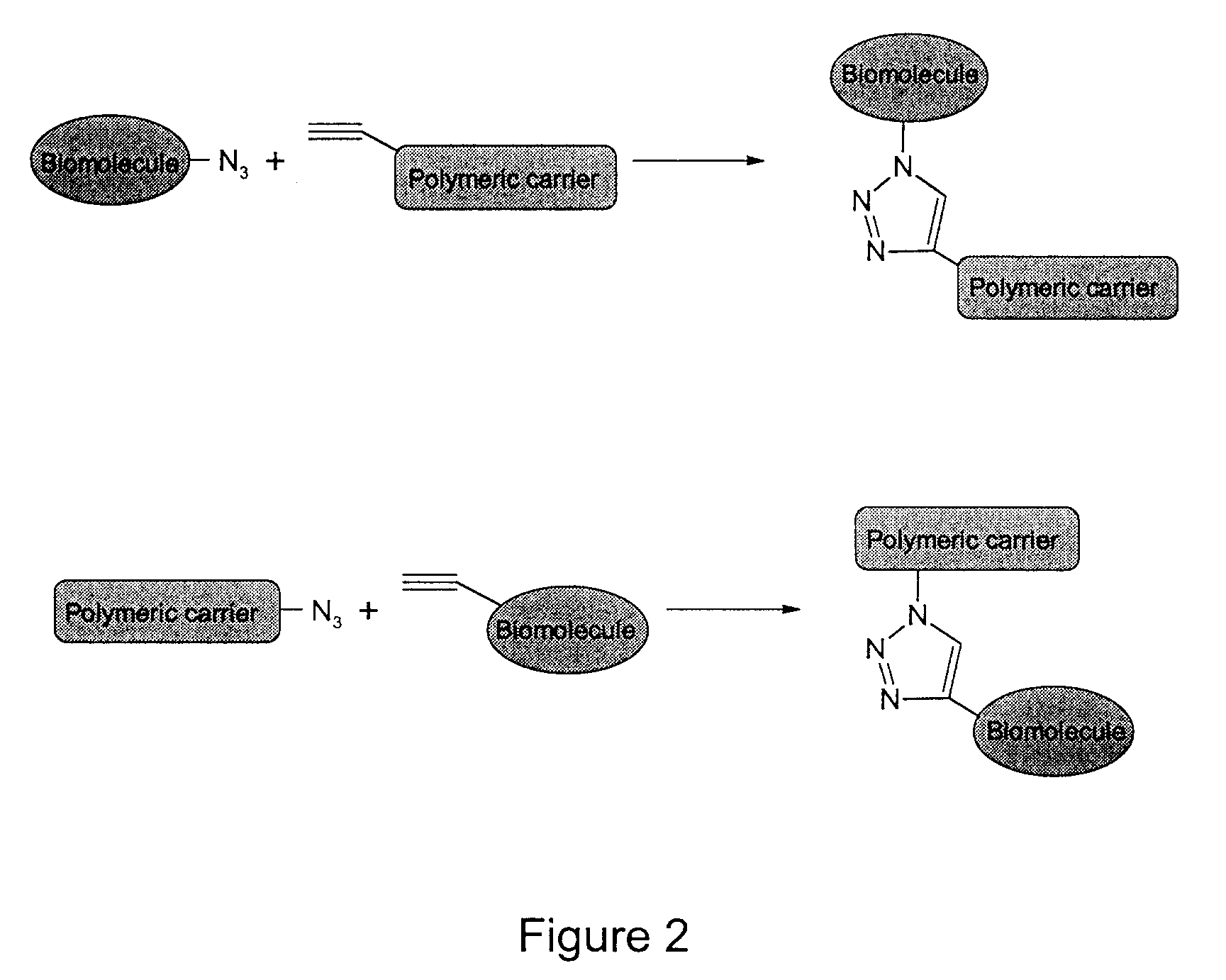
ActiveUS9290617B2Improve efficiencyProcess environmental protectionPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsChemical methodologyMolecular binding
The present invention provides a method for the covalent immobilization of biomolecules on polymers for delivery of the biomolecules, which has the advantage of being simple, highly efficient, environmentally friendly and free of side products relative to traditional immobilization techniques. The invention provides a modified micro / nanoparticle system, which uses a functionalized polymer formed into micro or nanoparticles to bind a molecule to the particles using uses facile chemistry, the Diels-Alder cycloaddition between a diene and a dienophile with the polymer being functionalized with one of them and the molecule with the other, or the Huisgen 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between a terminal alkyne and an azide to bind the molecule to the particle. The molecules and / or other therapeutic agents may be encapsulated within the polymer particles for intravenous therapeutic delivery. The invention also provides a novel synthetic biodegradable polymer, a furan / alkyne-functionalized poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC)-based polymer, whose composition can be designed to meet the defined physical and chemical property requirements. In one example, the particle system self-aggregates from functionalized PTMC-based copolymers containing poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) segments. The composition of the copolymers can be designed to meet various particle system requirements, including size, thermodynamic stability, surface PEG density, drug encapsulation capacity and biomolecule immobilization capacity.
Owner:SHOICHET MOLLY S +2
Probes, system and methods for drug discovery
InactiveCN1533400ATake advantage ofSearch applicableOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsScreening methodChemical methodology
Owner:TRANSTECH PHARMA INC
System and method for simulating chemical or biochemical process
InactiveCN114223037ASimulator controlChemical processes analysis/designChemical speciesChemical methodology
The present invention relates to a system for computer simulation of a chemical method, the system comprising: a plurality of functional modules for completing respective simulation levels of the chemical method; a storage module that stores experimental data related to chemical species in a data structure that can be used by the at least one functional module; the method is defined by a set of files shared by all modules of the system, each file comprising a description of the feedstock and a description of the decomposition of such feedstock into chemical species, said files being the input and output of said modules of the system and always remaining decomposed into chemical species during processing operations.
Owner:YF1
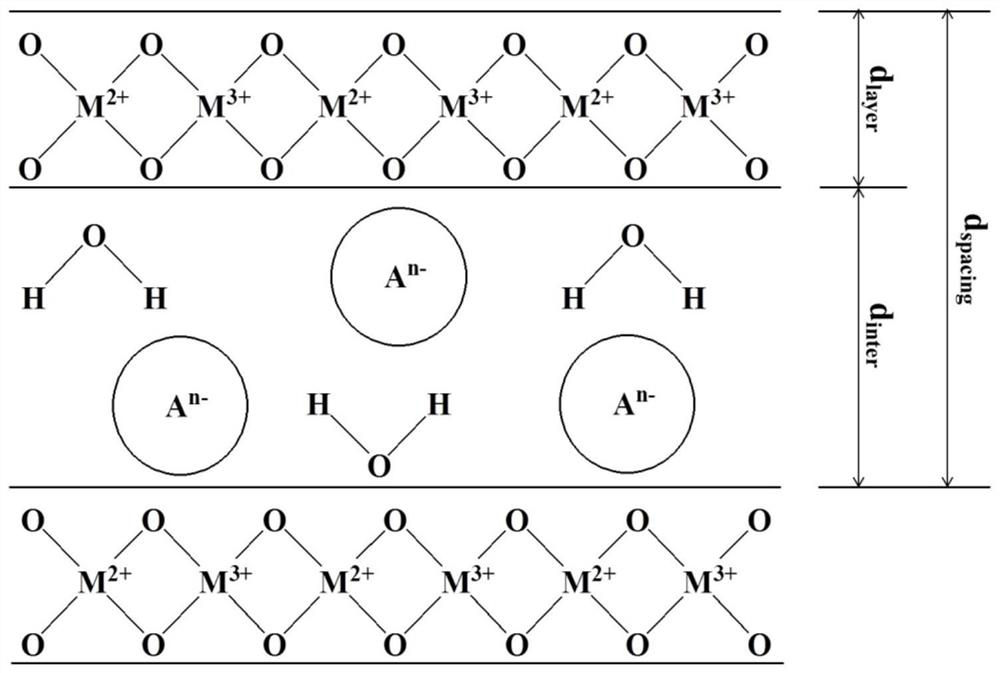
Method for predicting interlayer spacing size mode of layered bimetal oxide through non-chemical experiment method
InactiveCN113707237ALow costEasy to operateChemical property predictionPhysical realisationChemical methodologyArtificial neuronal network
The invention aims to overcome the defects of a mode for detecting the interlayer spacing of the layered bimetal oxide by a chemical method, and provides a method for predicting the interlayer spacing mode of the layered bimetal oxide by a non-chemical experiment method which is low in cost, free of pollution, simple in test, simple, convenient and quick. The whole process comprises the following steps of: forming basic data by taking atomic parameters as independent variables and an interlayer spacing size mode as dependent variables; the atomic parameter data in the basic data are combined and converted, an obtained comprehensive variable, and the comprehensive variable and the interlayer spacing size mode form intermediate data; and based on the intermediate data, an artificial neural network algorithm is utilized to establish a quick recognition model of the interlayer spacing size mode of the layered bimetal oxide, and the model can predict a new interlayer spacing size mode of the layered bimetal oxide.
Owner:上海真谱信息科技有限公司
Rice production place tracing method based on B-Z oscillation system
PendingCN112113815ADistinctive Fingerprint FeaturesHigh identification accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesMalonic acidOscillatory reaction
The invention discloses a rice production place tracing method based on a BZ oscillation system, and belongs to the technical field of food identification. According to the present invention, the BZ chemical oscillation reaction in which malonic acid participates is interfered by rice, and the oscillation reaction conditions are strictly controlled to obtain the electrochemical fingerprint with the significant fingerprint characteristic so as to provide the experimental basis for the identification of rice from different production places. Compared with other chemical methods for identifying the rice, the method only needs to treat the rice into powder, and other tedious, complex and consumable pretreatment is not needed. Meanwhile, the electrochemical fingerprint spectrum can reflect thedifference of rice component types and contents and can also reflect the difference of chemical properties of components, the identification accuracy is higher than 80%, the effect is good, and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com