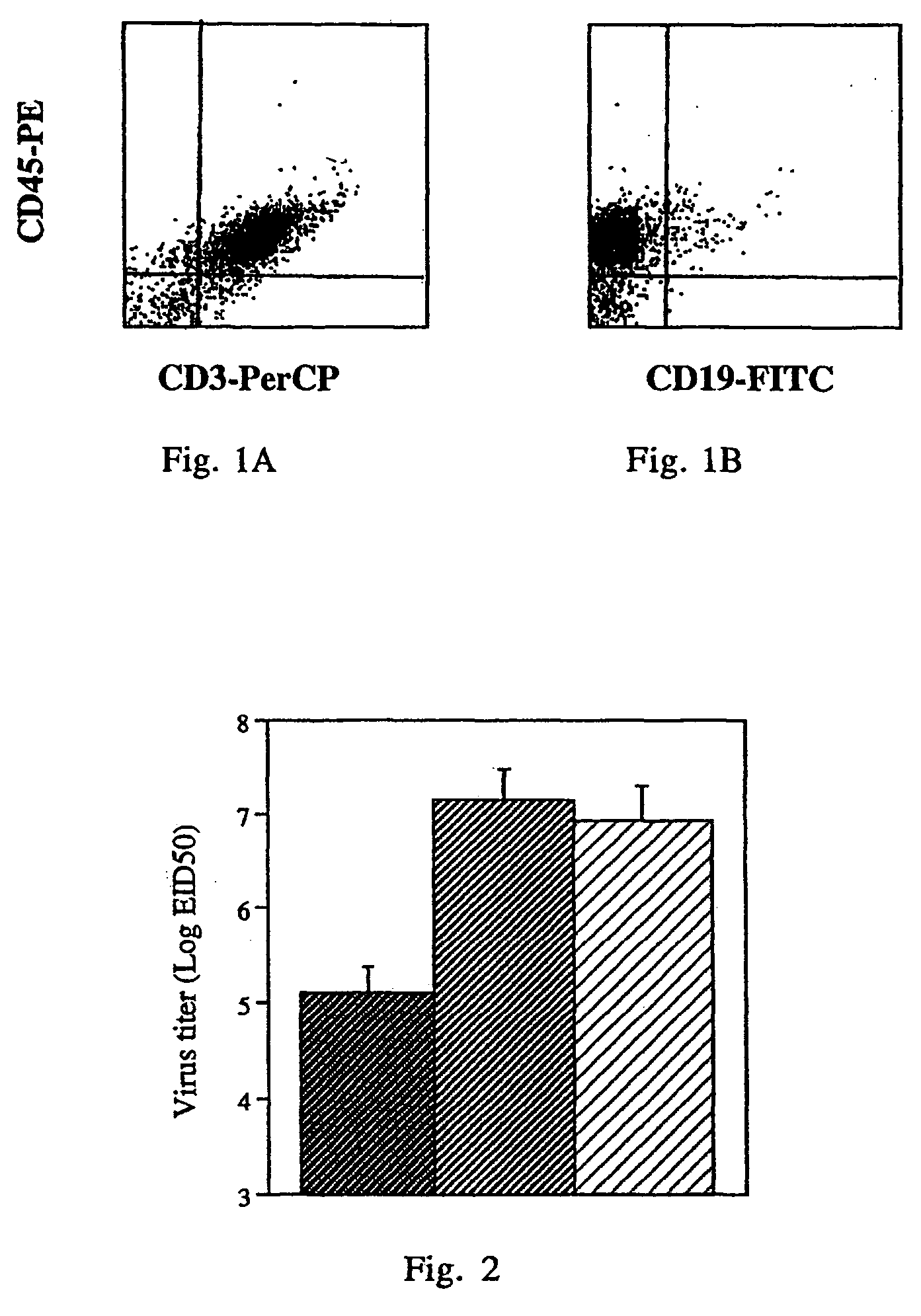
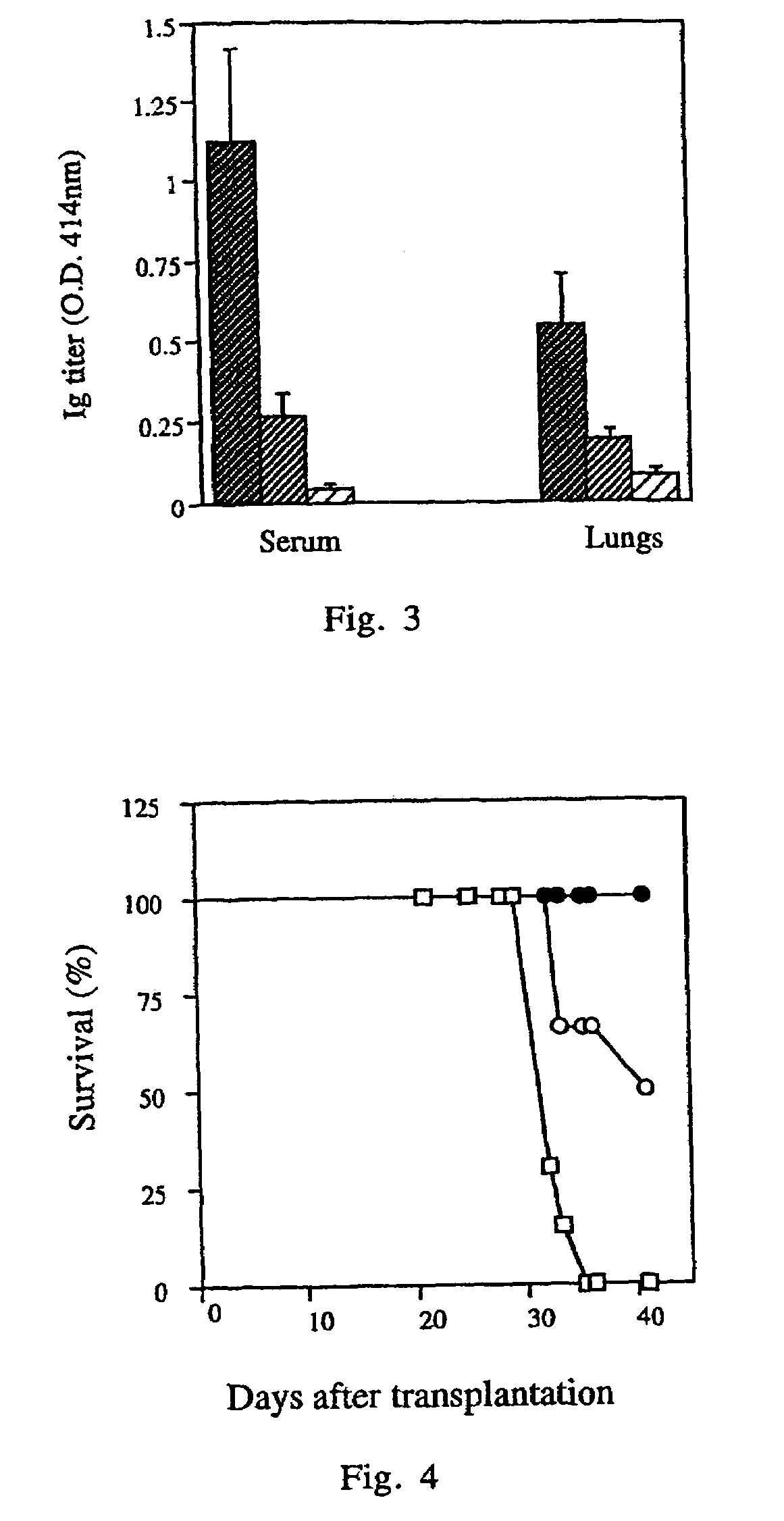
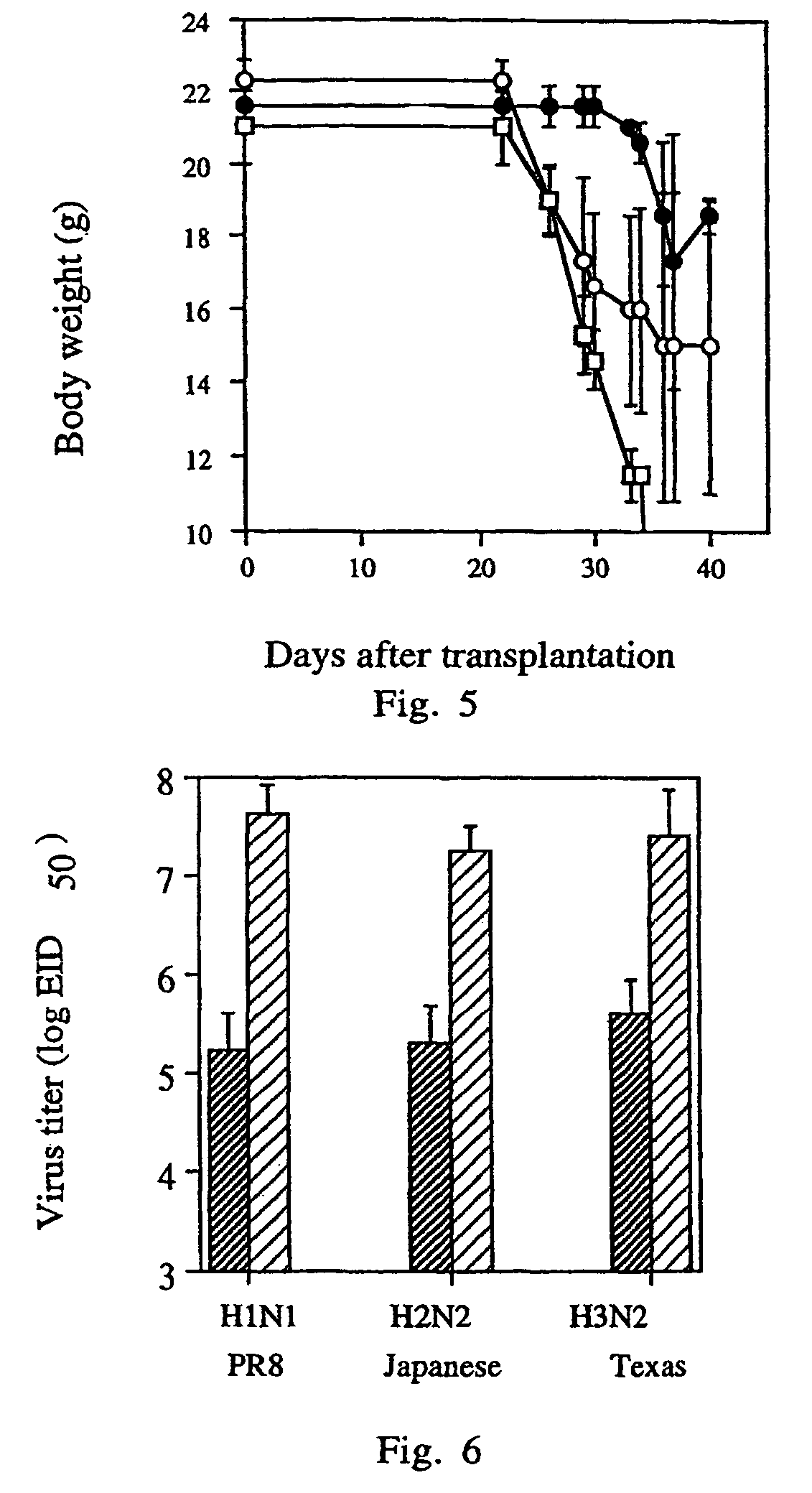
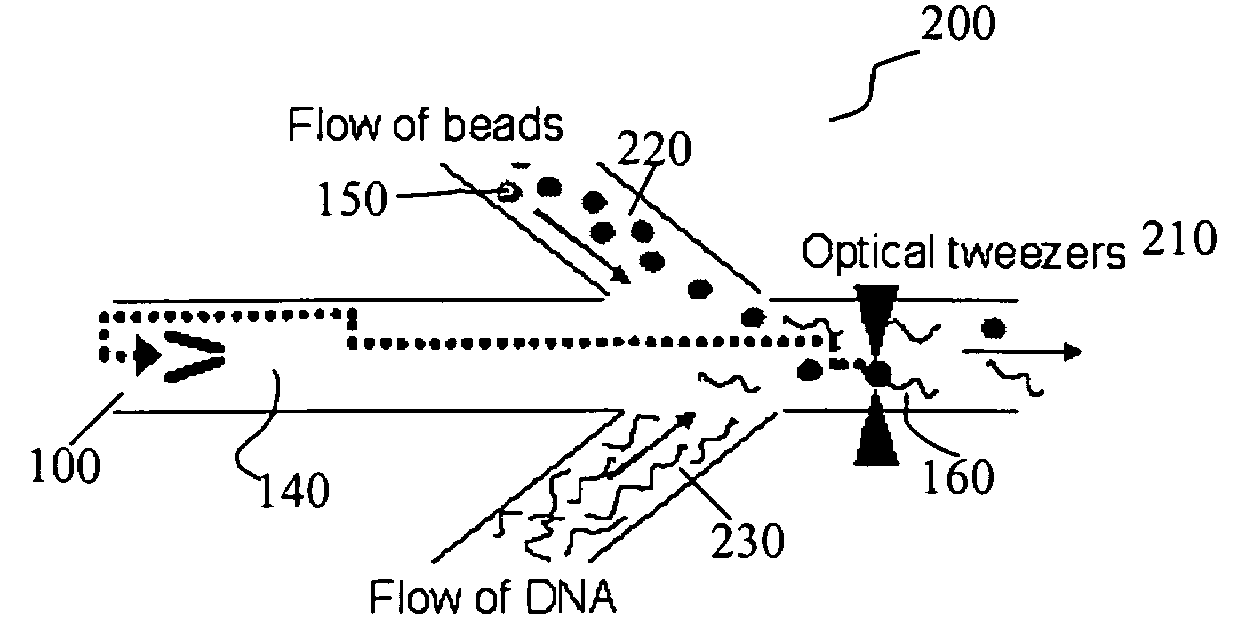
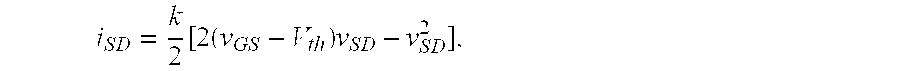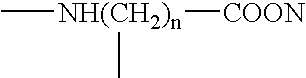Patents
Literature
529 results about "Molecular binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
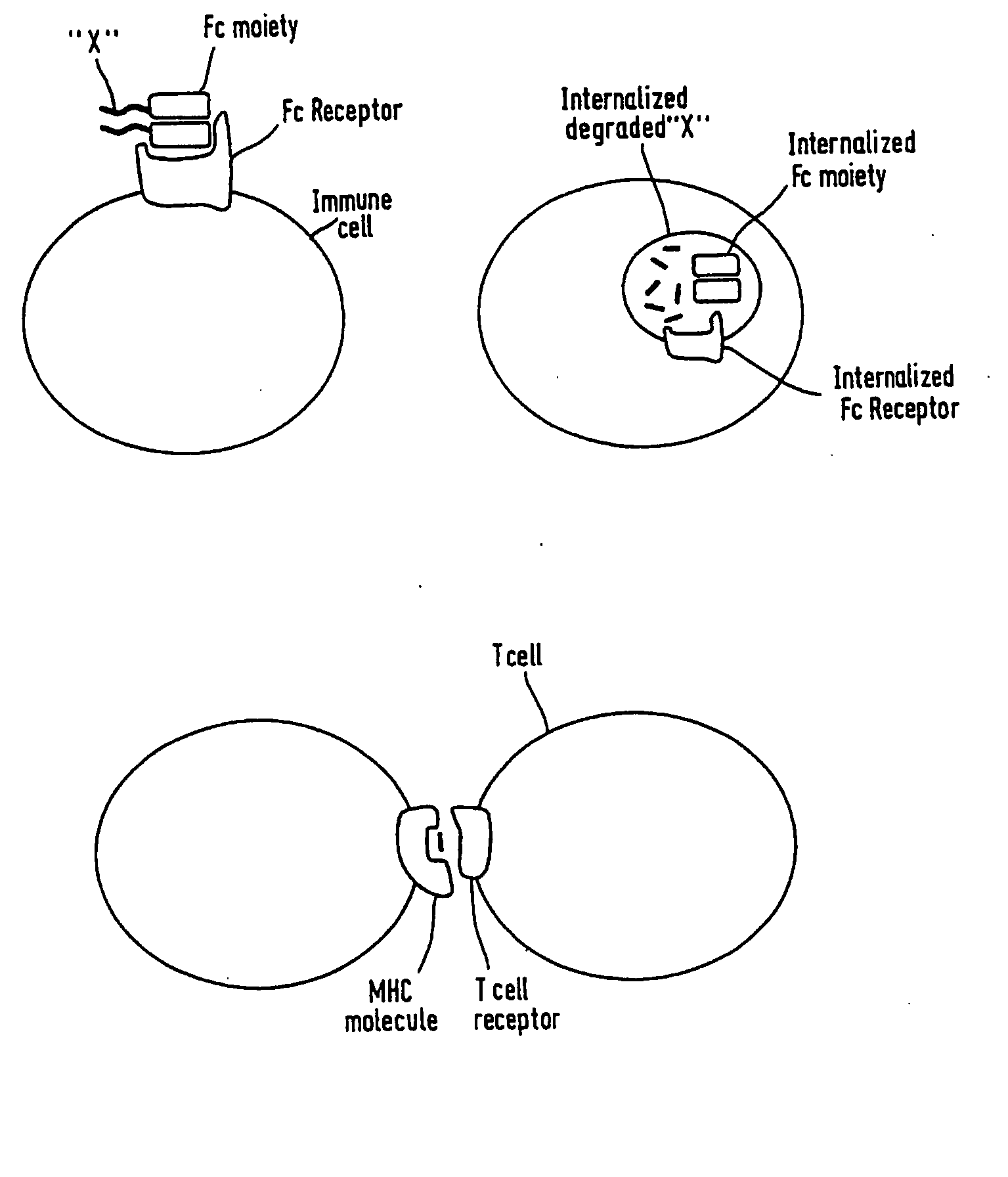
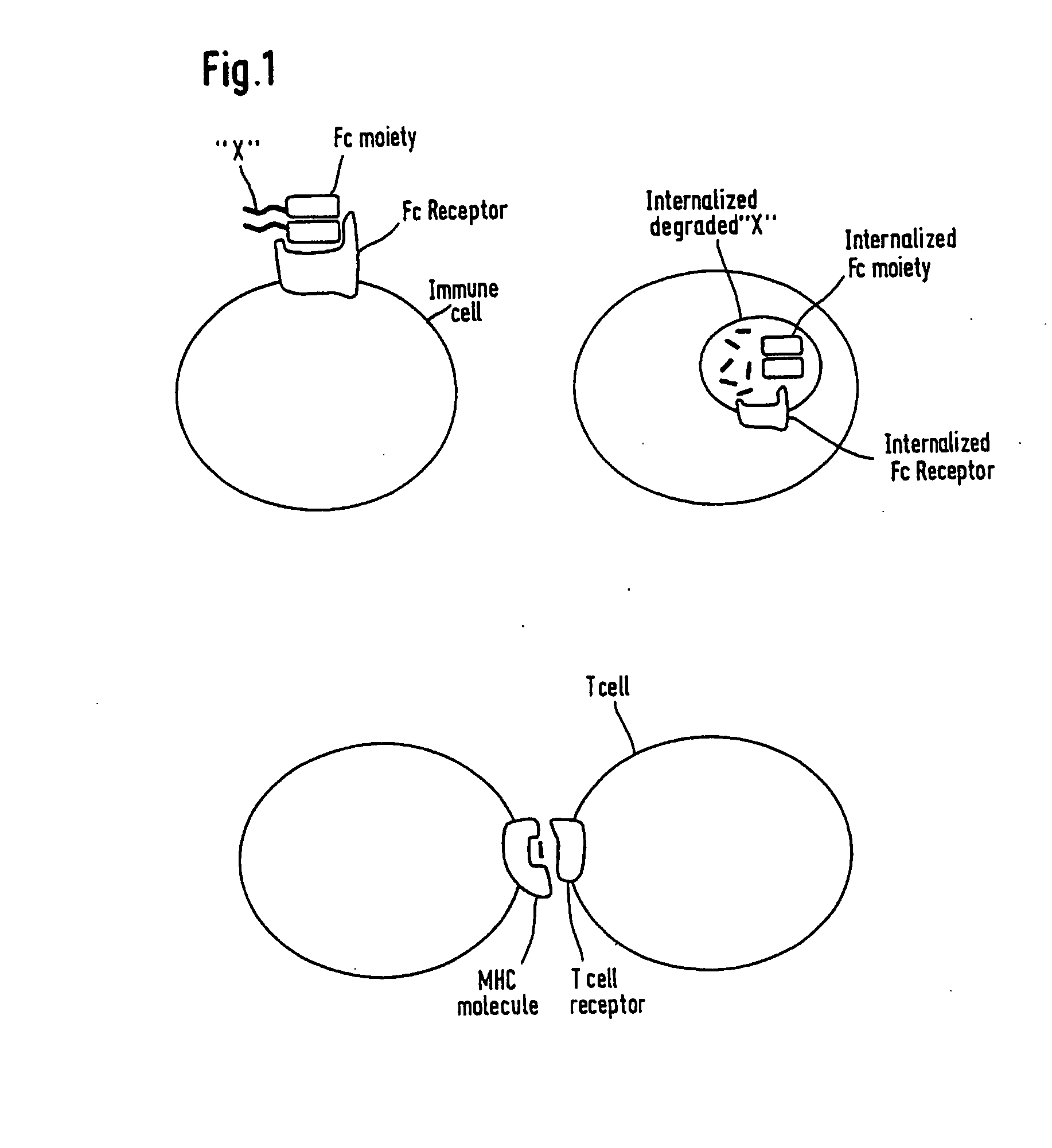
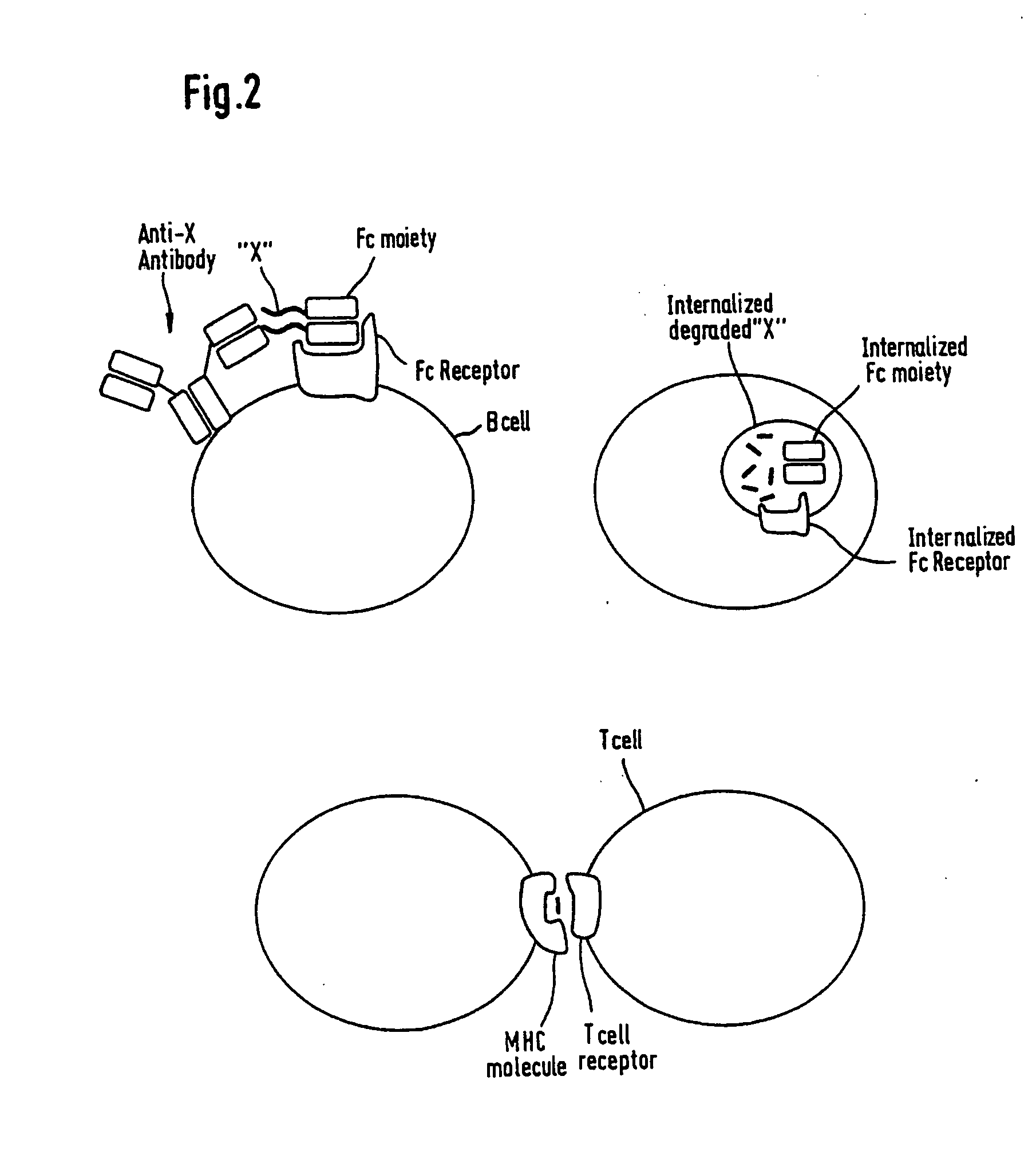
Molecular binding is an attractive interaction between two molecules that results in a stable association in which the molecules are in close proximity to each other.It is formed when atoms or molecules bind together by sharing of electrons. It often but not always involves some chemical bonding.
Single chain fc, methods of making and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20080260738A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilityAnimal cellsFungiAntigen bindingStereochemistry
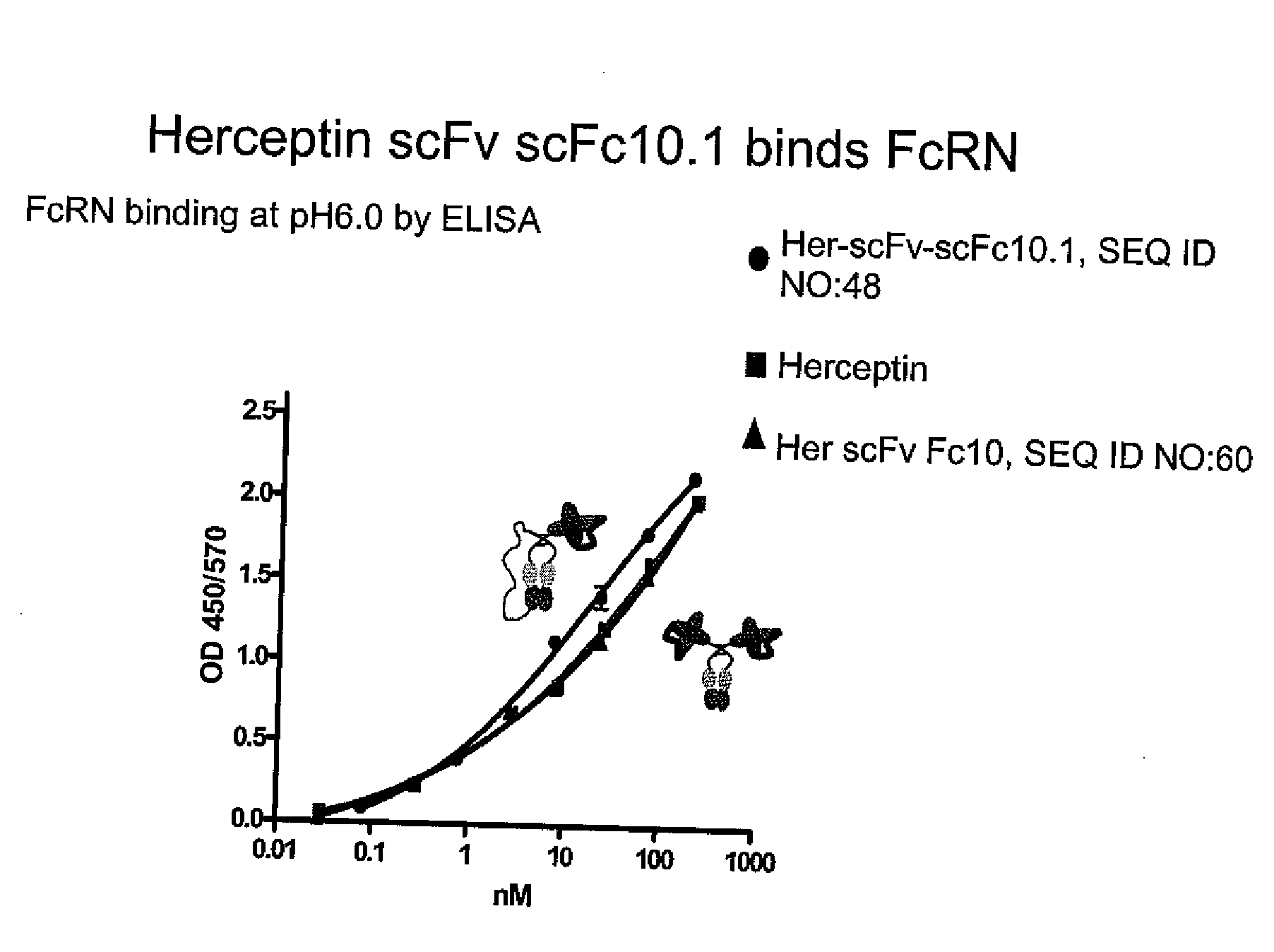
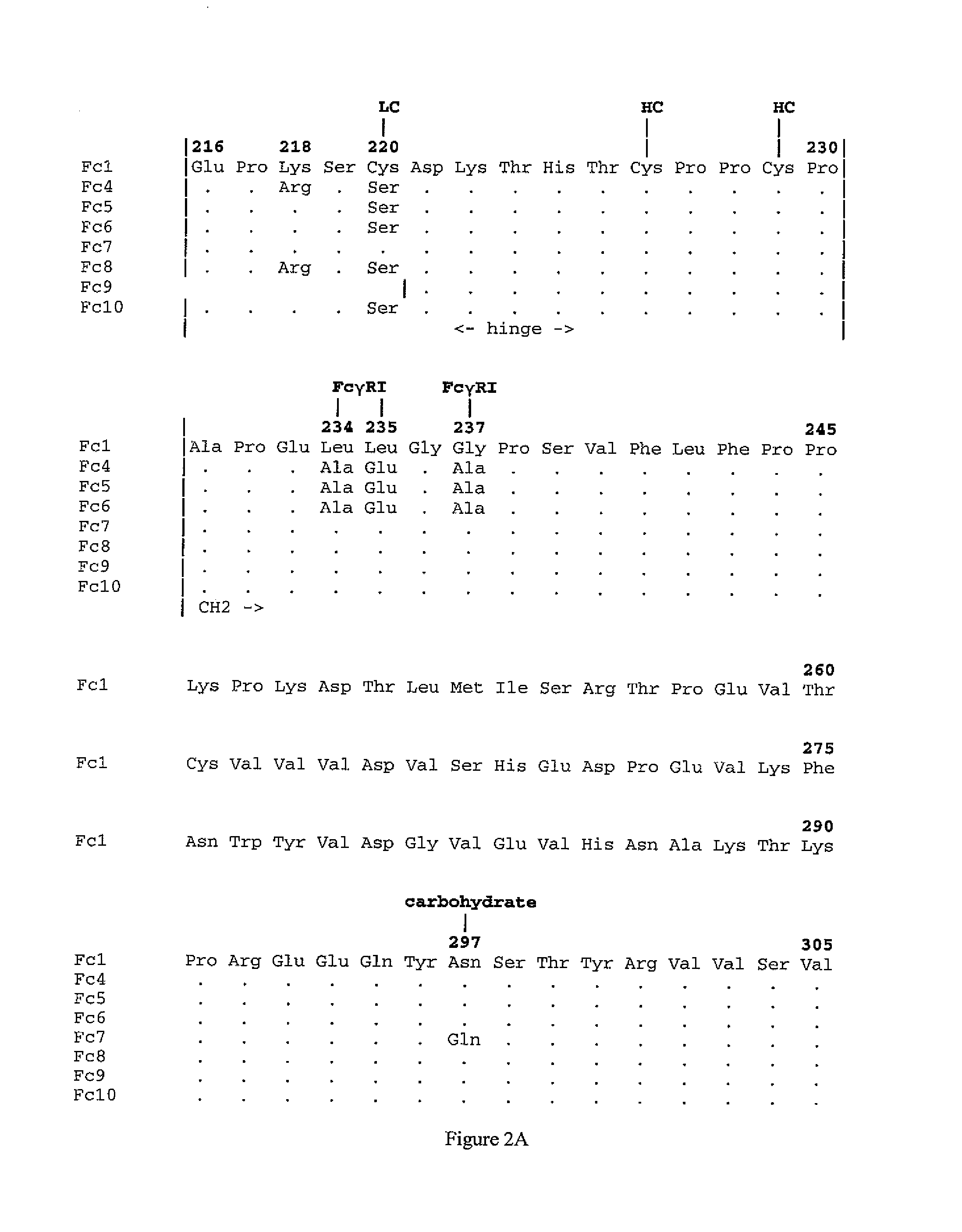
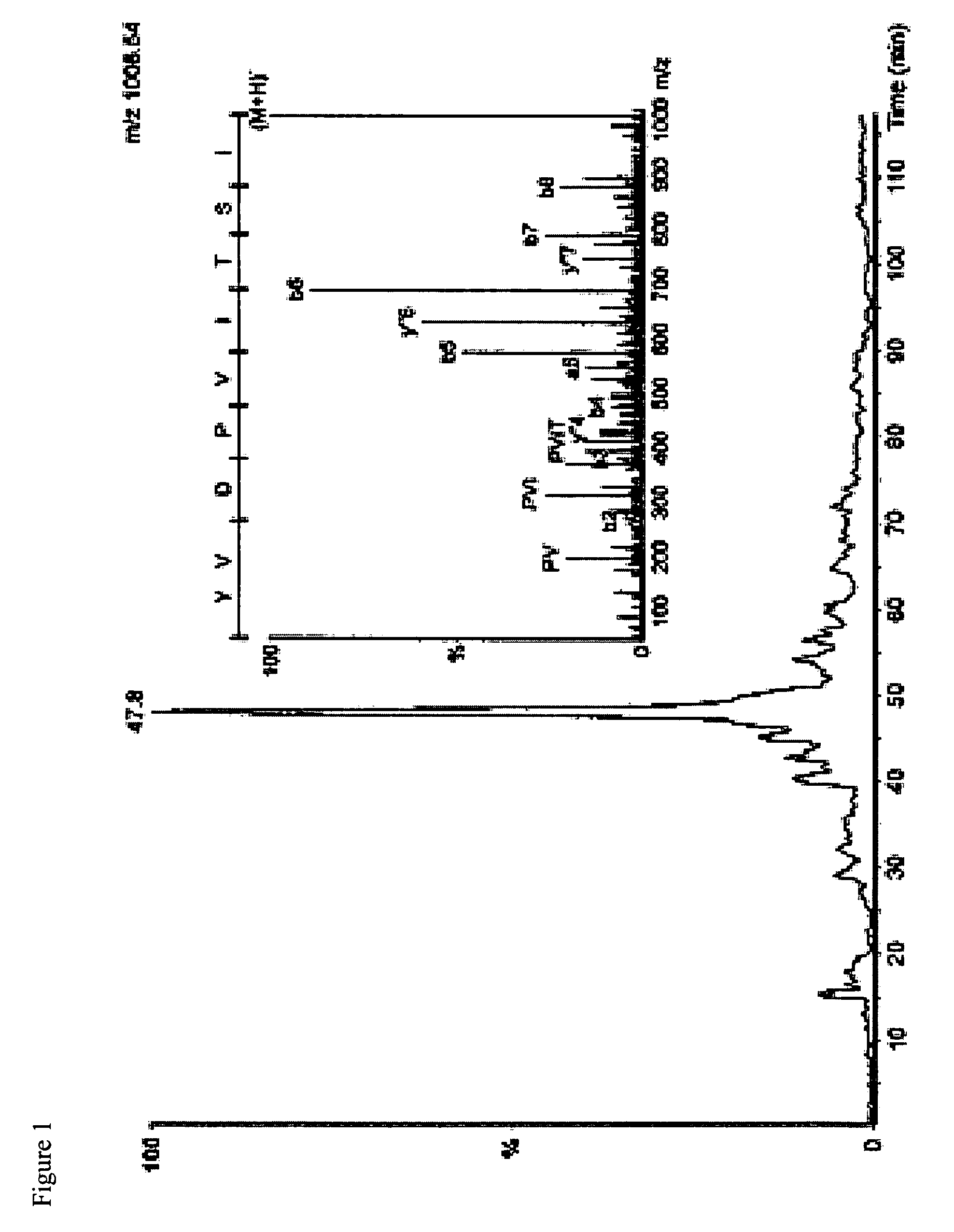
The present invention relates generally to scFc molecules. The scFc molecules comprise at least two Fc regions and at least one linker, and can be produced in a variety of single chain configurations. The scFc molecules can further comprise at least one binding entity and / or at least one functional molecule. Binding entities can be fused to the scFc molecule in a variety of configurations. The present invention also relates generally to methods for making such molecules and methods for their use. The scFc molecules provided herein can be recombinantly produced. Also provided are monovalent forms of the scFc molecules that have an equivalent or superior ADCC and / or CDC response than do bivalent molecules targeting the same antigens. Provided herein are improved antigen binding compositions. Methods for using the scFc molecules of the present inventions are provided
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against small cell lung cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS20170096461A1High error rateIncrease in motilityNervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptideDrug
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Tumour-associated peptides binding to human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class i or ii molecules and related Anti-cancer vaccine
InactiveUS20090274714A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsHla class iiAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to immunotherapeutic methods, and molecules and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumour-associated T-helper cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumour-associated peptides, that serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions which stimulate anti-tumour immune responses. In particular, the present invention relates to two novel peptide sequences derived from HLA class II molecules of human tumour cell lines, which can be used in vaccine compositions for eliciting anti-tumour immune responses.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Antibody complexes
InactiveUS20070036783A1Reduce needImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsCell adhesionAdhesion process
This invention is directed to a soluble complex of ligands that binds to surface molecules of hemopoietic cells and result in their activation or expansion. The complex may be used in the activation and / or expansion of hemopoietic cells, optionally in combination with their transduction. The complex of ligands bind at least two cell surface molecules, such as one that plays a role in cell-cell adhesion and one that may or may not activate or stimulate the cell to promote growth and / or proliferation after binding to a ligand. A complex of ligands that bind two hemopoietic cell stimulatory molecules is also provided. The invention further provides for the use of the complex to target vectors to hemopoietic cells.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Co-localization affinity assays
The invention provides a new assay format for high throughput molecular binding studies at a single molecule level. The invention enables creation of binding event identifiers in a highly parallel way. Individual binding events occur between two agents of a binding pair, e.g., a protein-based binding pair or a binding pair comprising a protein and a chemical moiety. The binding event identifier created through the binding of the two binding agents is unique to that pair, and identification of the binding event identifier is indicative of the binding of these specific may be assessed through a readout that is digital in nature. The invention enables very large sets of thousands or more of different binding agents or potential binding agents to be assayed simultaneously, resolving millions or more of potential interactions, and distinguishing specific interactions from those that are less specific.
Owner:PROGNOSYS BIOSCI
Microelectronic device and method for label-free detection and quantification of biological and chemical molecules
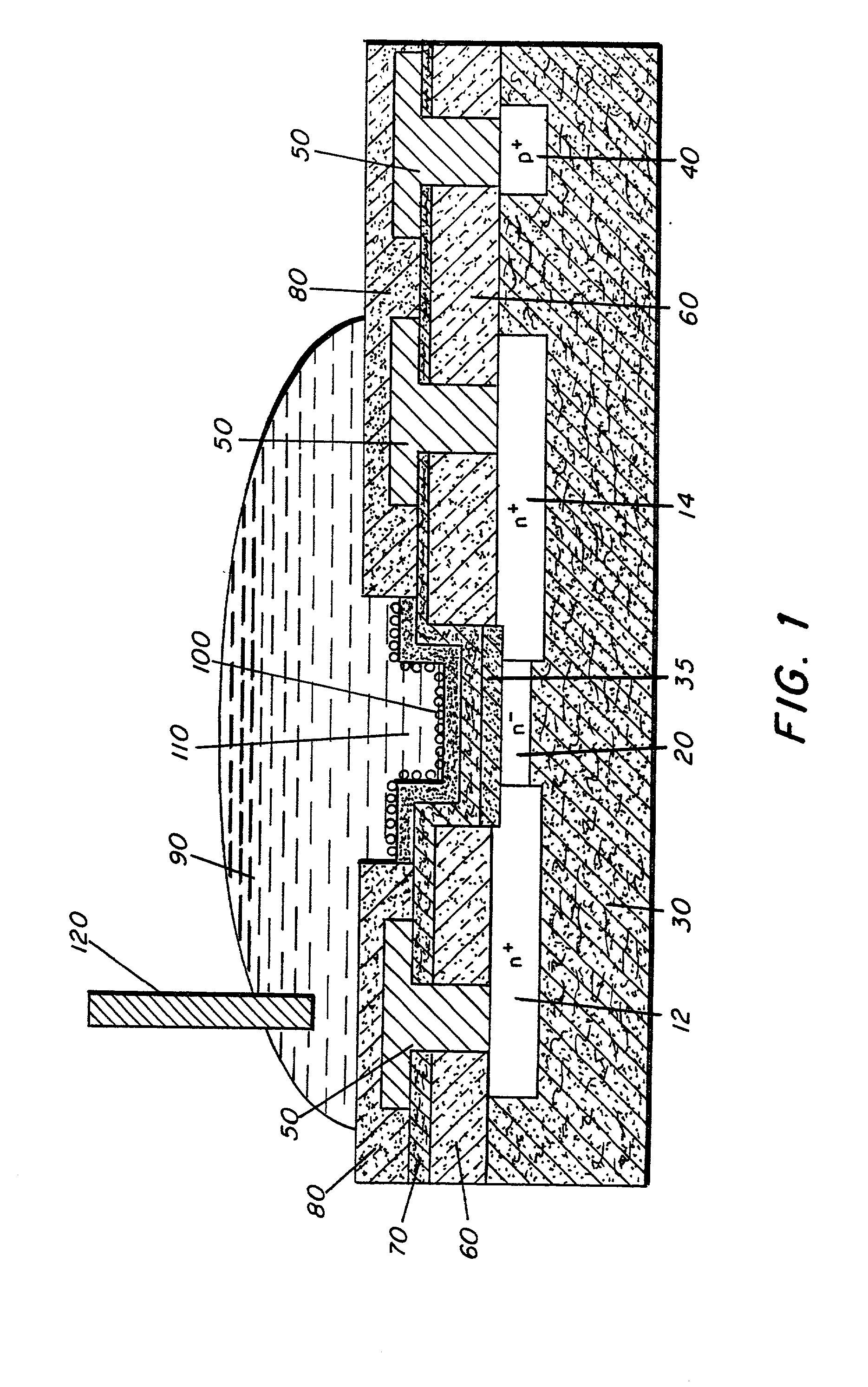
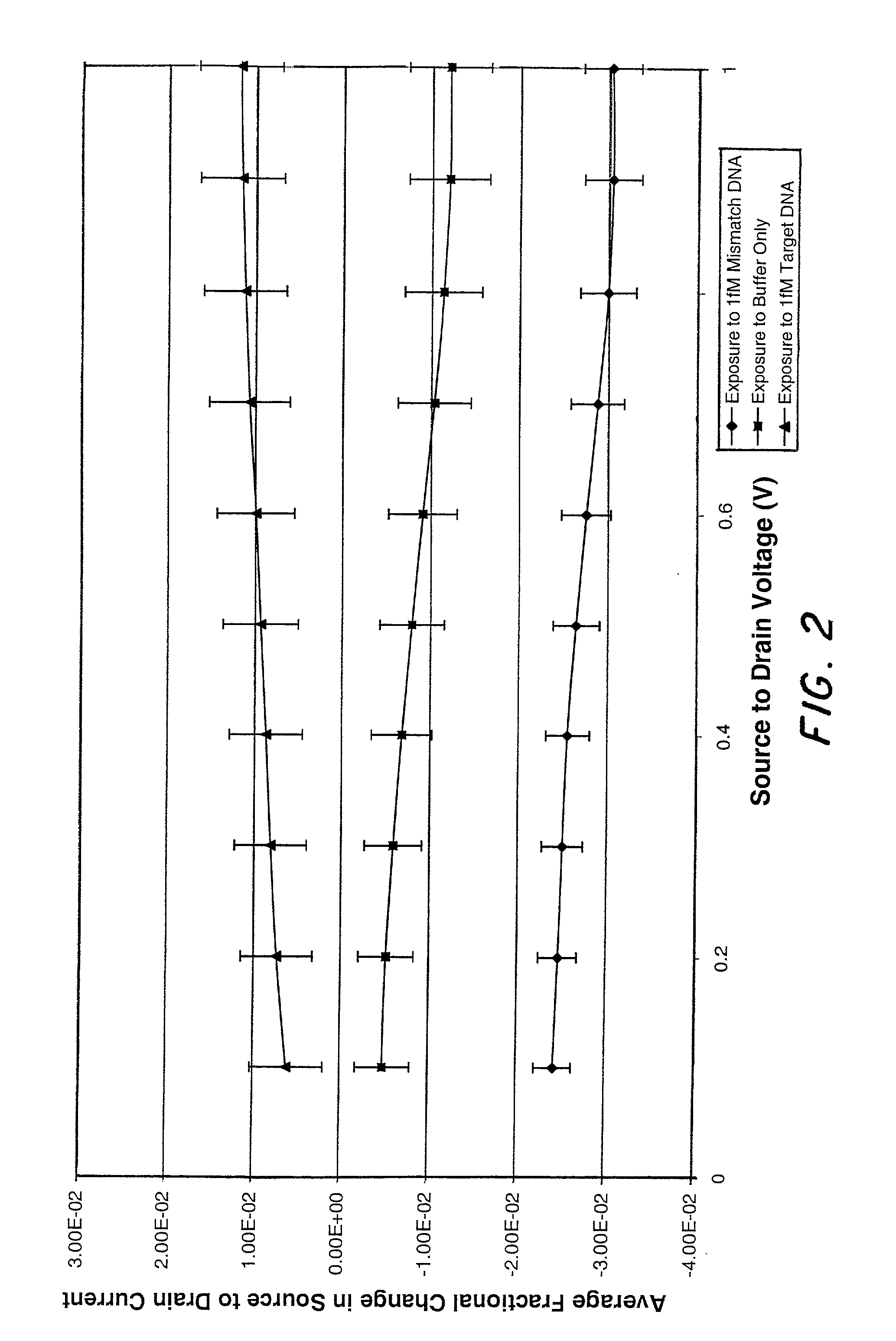
InactiveUS20020012937A1Wide scope of practicalWide scope of worthwhile utilizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceField-effect transistor
Molecular recognition-based electronic sensor, which is gateless, depletion mode field effect transistor consisting of source and drain diffusions, a depletion-mode implant, and insulating layer chemically modified by immobilized molecular receptors that enables miniaturized label-free molecular detection amenable to high-density array formats. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The conductivity of the active channel is determined by the potential of the sample solution in which the device is immersed and the device-solution interfacial capacitance. The conductivity of the active channel modulates current flow through the active channel when a voltage is applied between the source and drain diffusions. The interfacial capacitance is determined by the extent of occupancy of the immobilized receptor molecules by target molecules. Target molecules can be either charged or uncharged. Change in interfacial capacitance upon target molecule binding results in modulation of an externally supplied current through the channel.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Nucleic acid ligands to complex targets
InactiveUS20050069910A1Improve abilitiesIncrease capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiologyNucleic acid
The present invention relates to a method for isolating a pool of nucleic acid ligands capable of binding to one or more target molecules in a complex mixture.
Owner:TURNER JOHN +4
Method of identifying peptides capable of binding to MHC molecules, peptides identified thereby and their uses
A method of identifying peptides originating from a particular cell type and being capable of binding to MHC molecules of a particular haplotype is disclosed. The method comprises obtaining a cell type expressing a soluble and secreted form of the MHC molecules of the particular haplotype; collecting the soluble and secreted form of the MHC molecules of the particular haplotype; and analyzing peptides bound to the soluble and secreted form of the MHC molecules of the particular haplotype, thereby identifying the peptides originating from the particular cell type and being capable of binding to MHC molecules of the particular haplotype.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
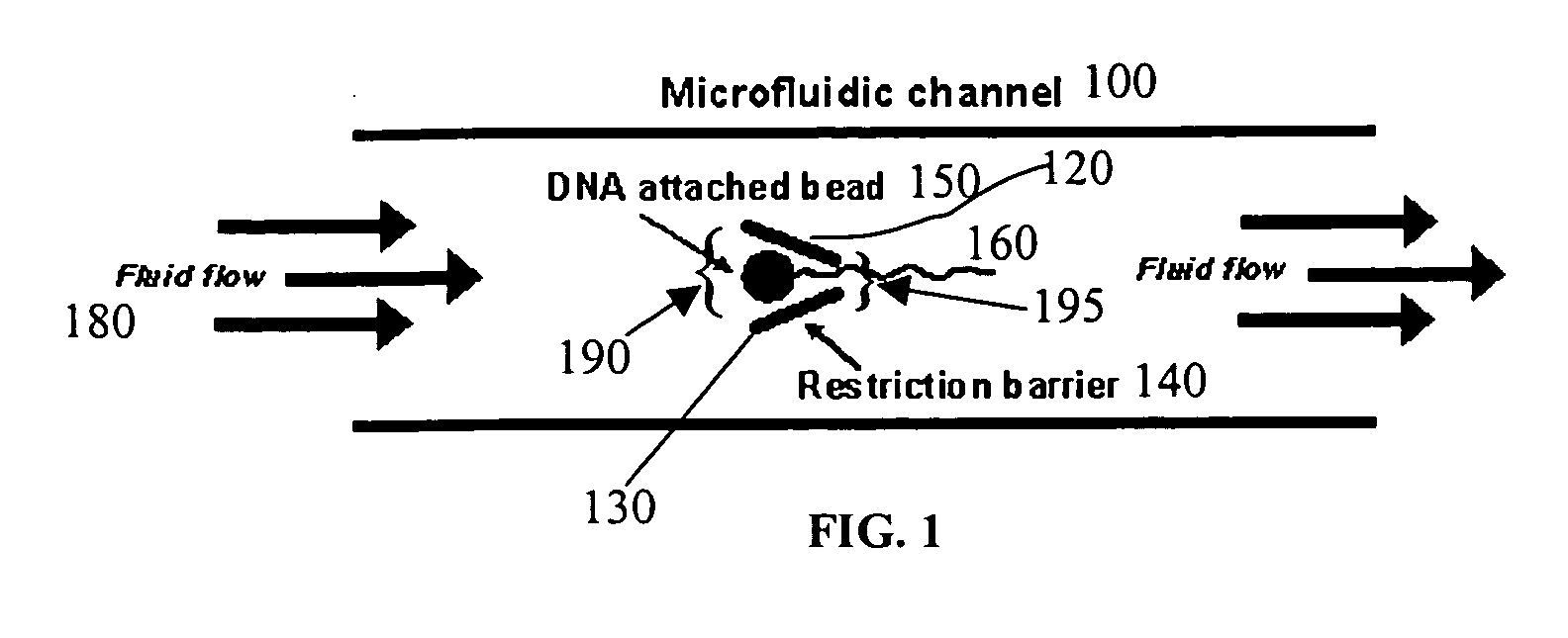
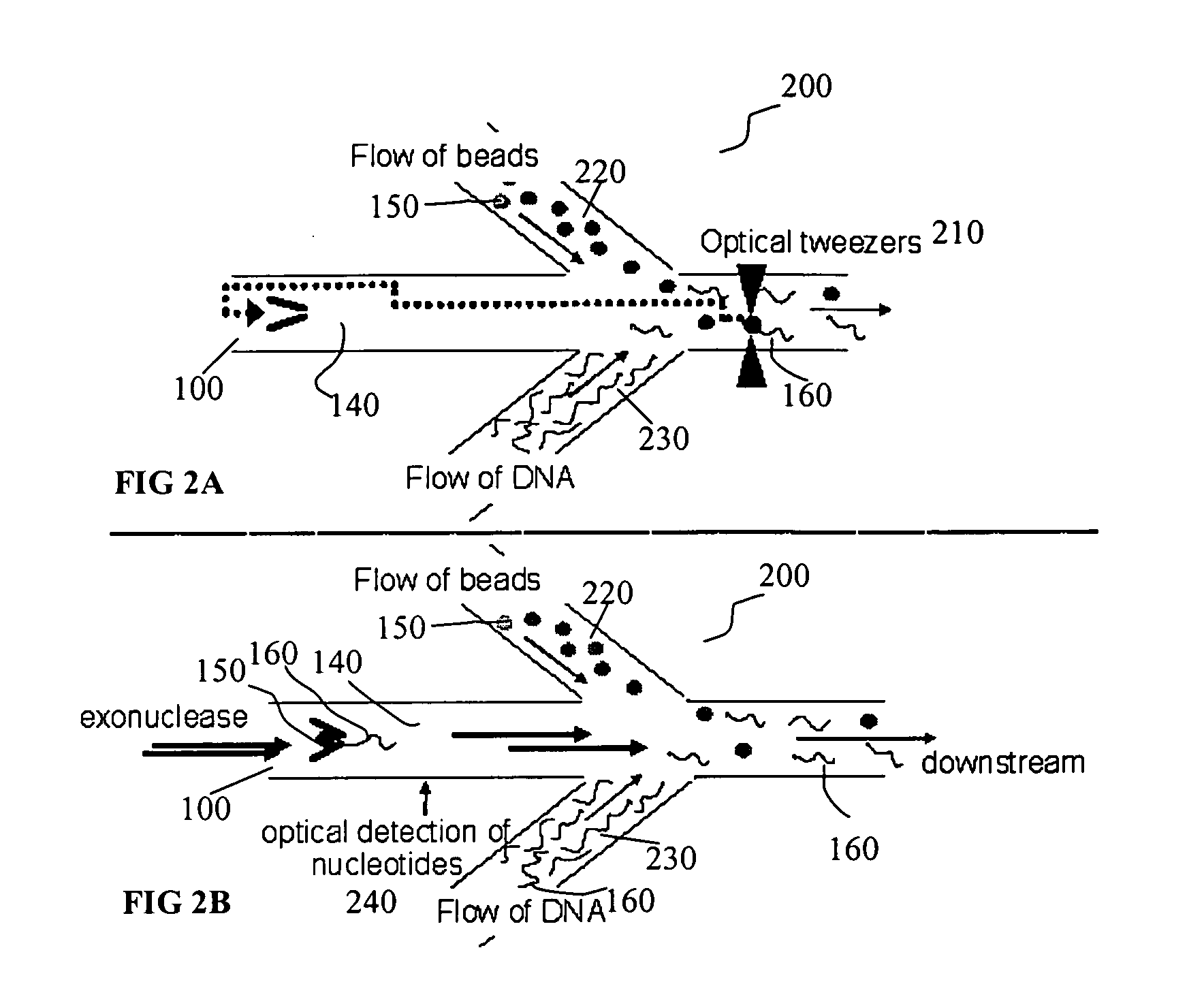
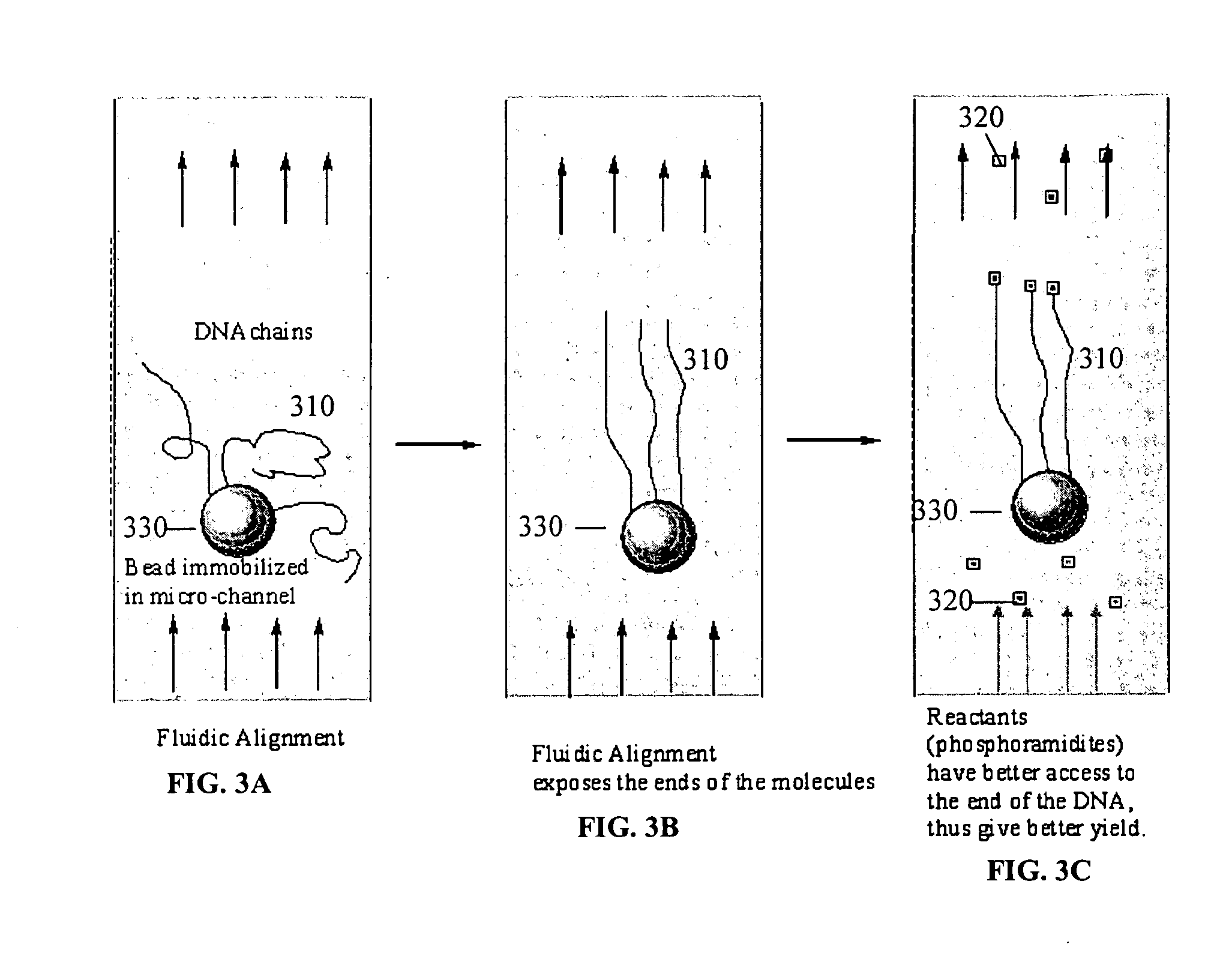
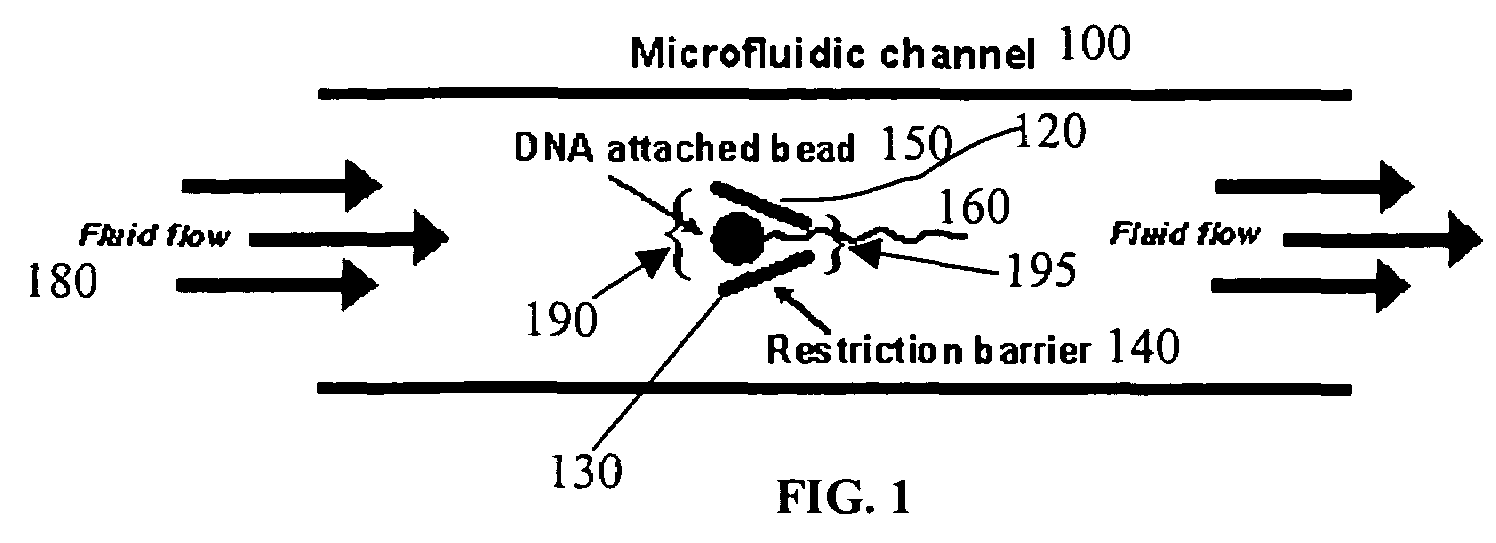
Microfluidic apparatus, systems, and methods for performing molecular reactions
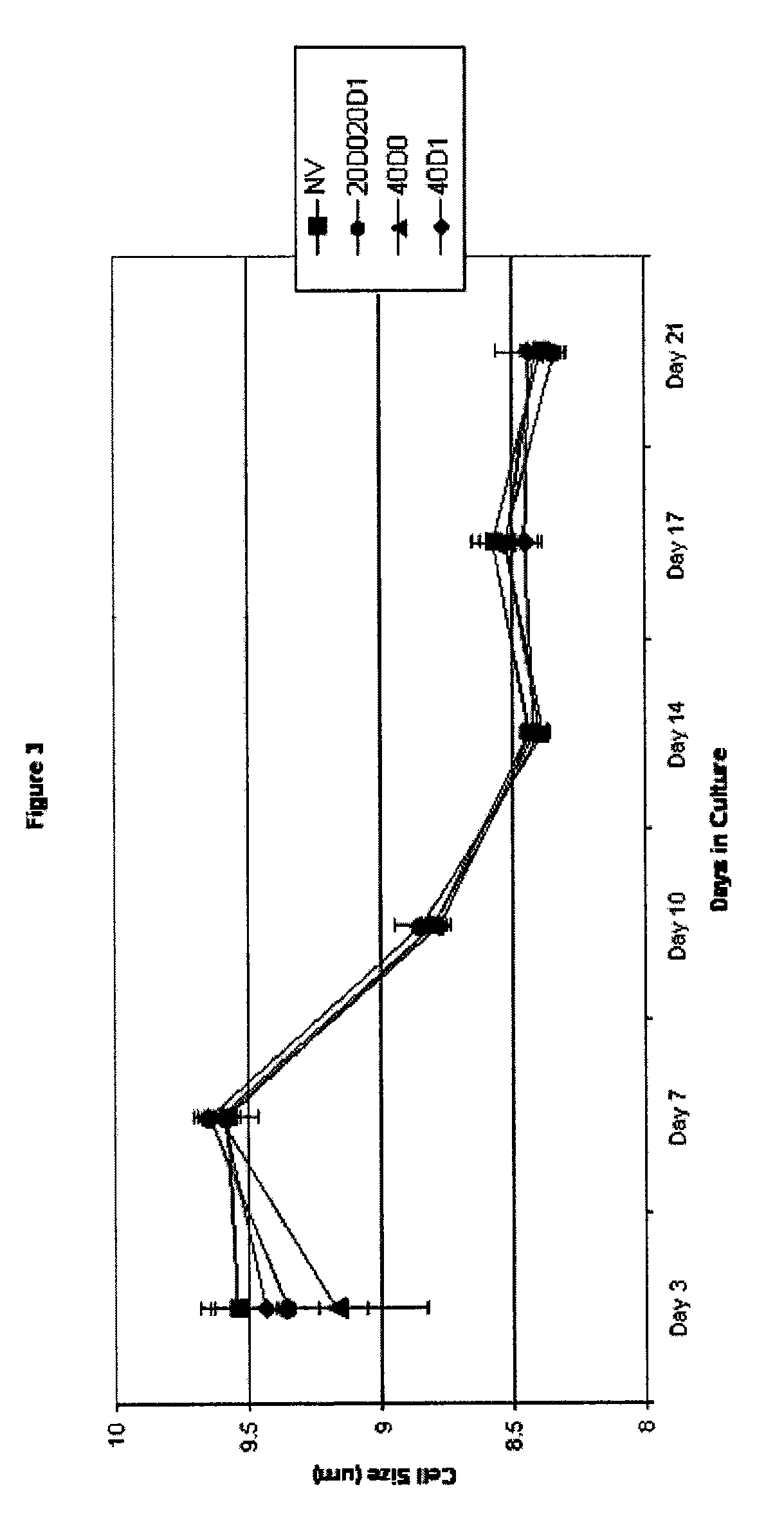
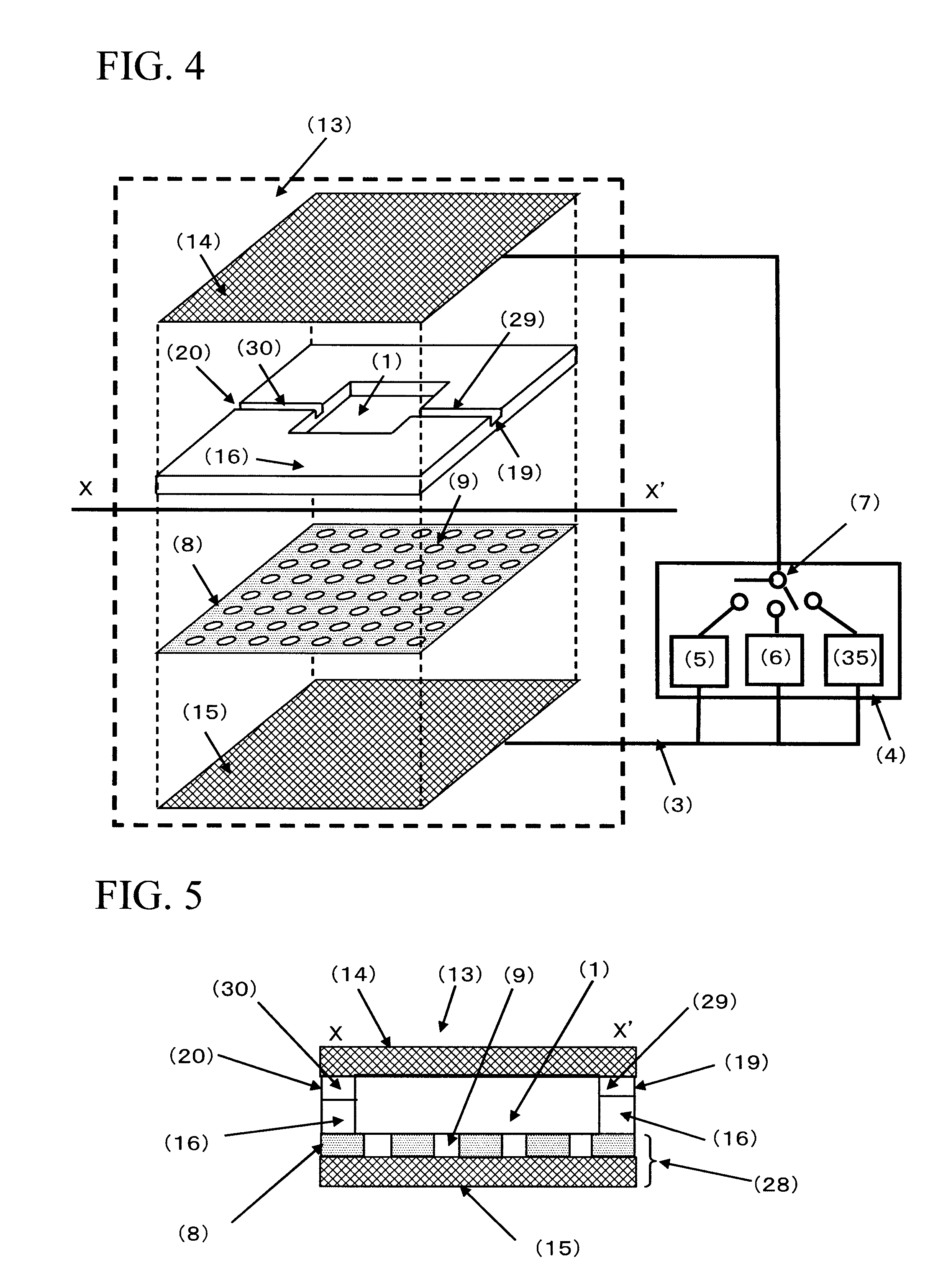
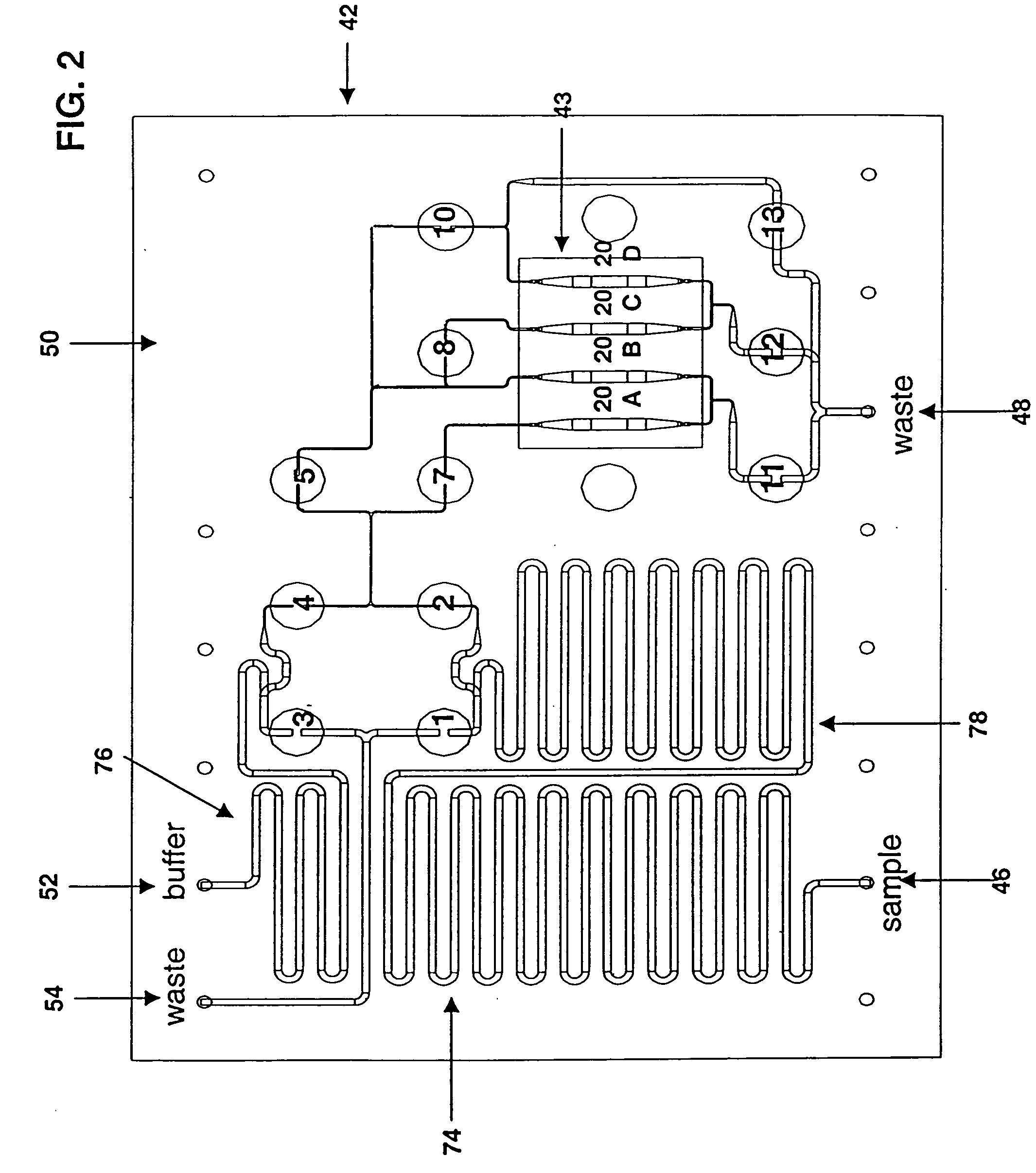
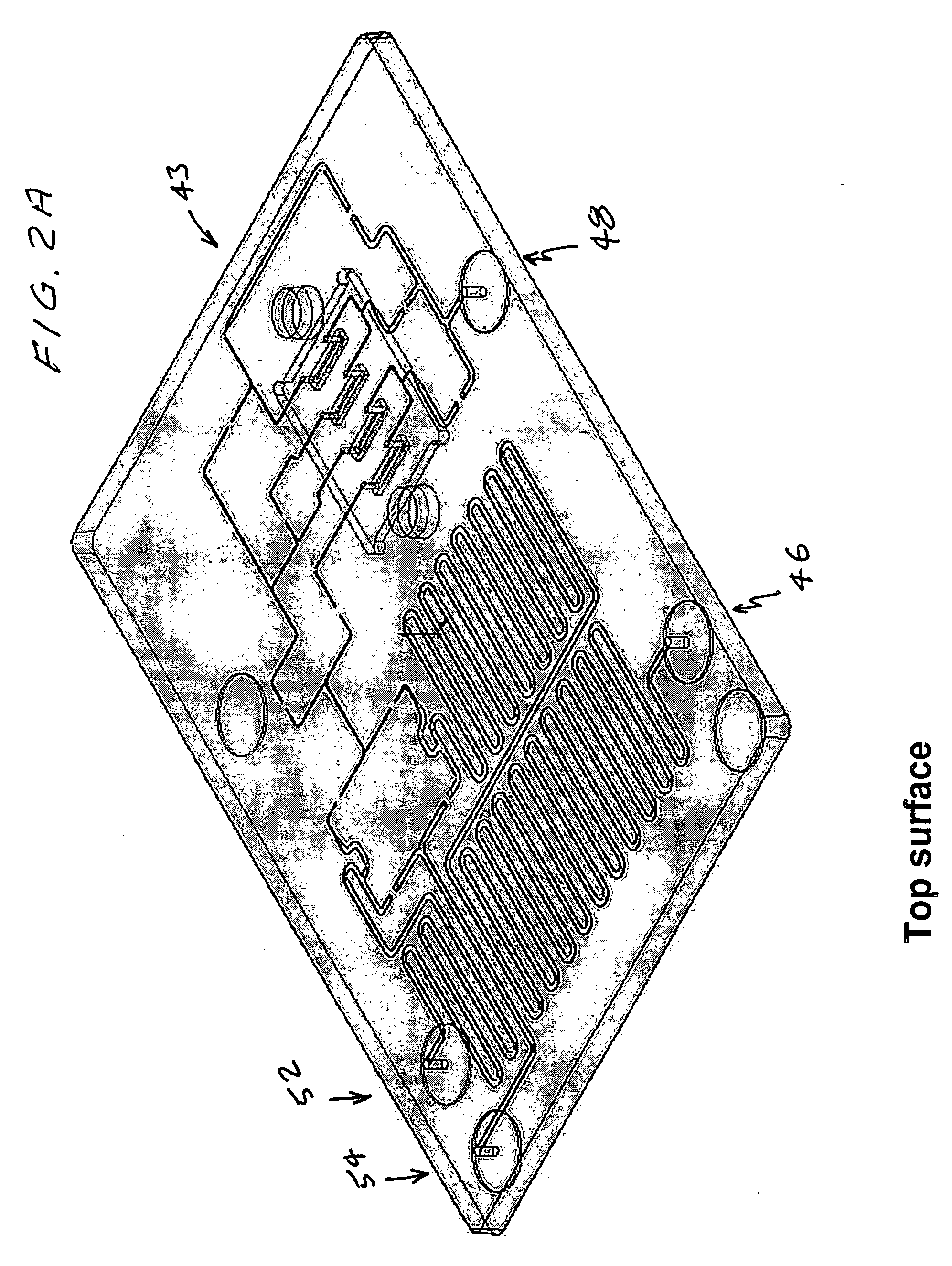
ActiveUS20050221333A1Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular bindingNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing nucleic acid sequencing reactions and molecular binding reactions in a microfluidic channel. The methods, apparatuses, and systems can include a restriction barrier to restrict movement of a particle to which a nucleic acid is attached. Furthermore, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can include hydrodynamic focusing of a delivery flow. In addition, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can reduce non-specific interaction with a surface of the microfluidic channel by providing a protective flow between the surface and a delivery flow.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for reading reporter labeled beads
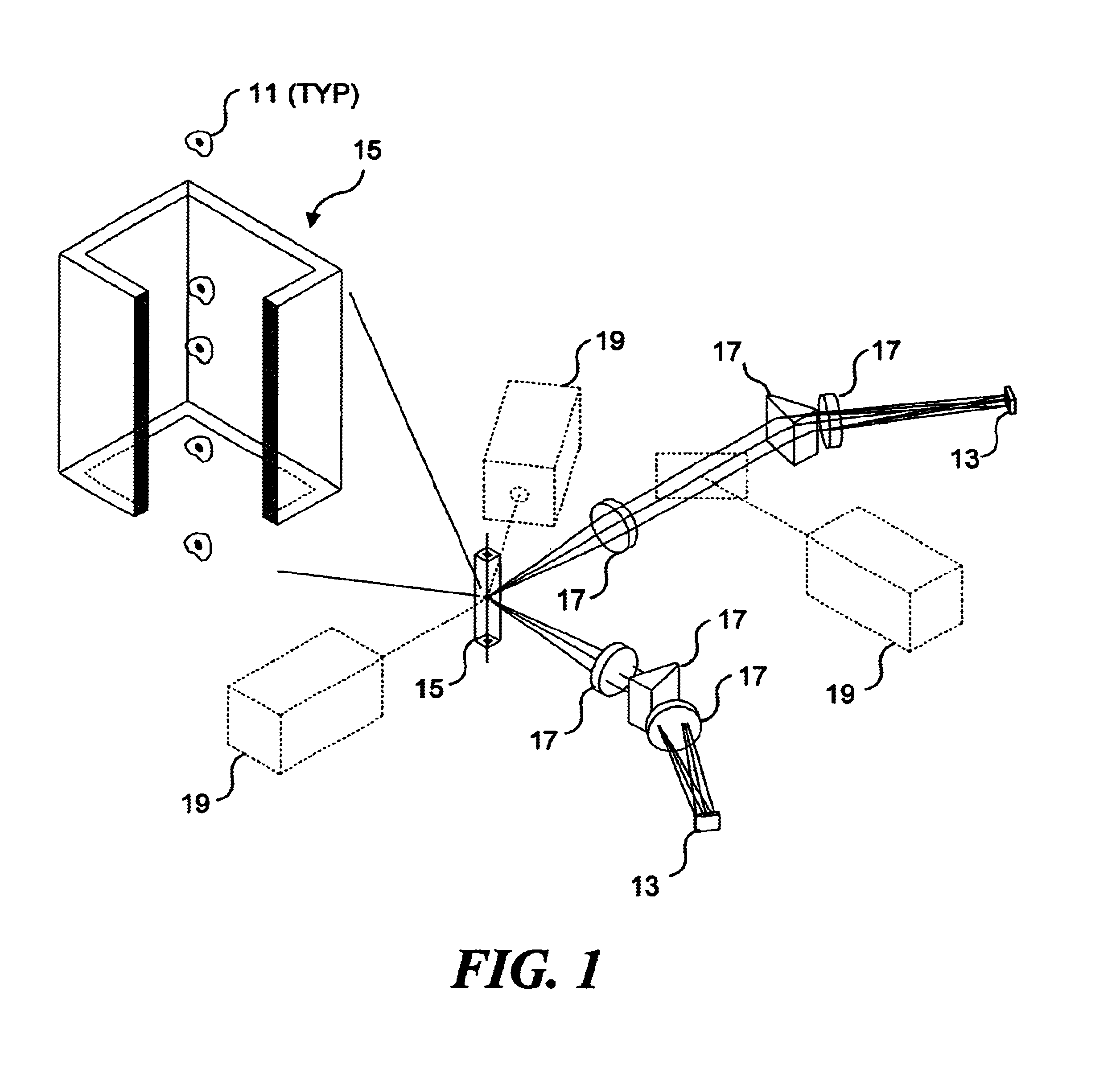
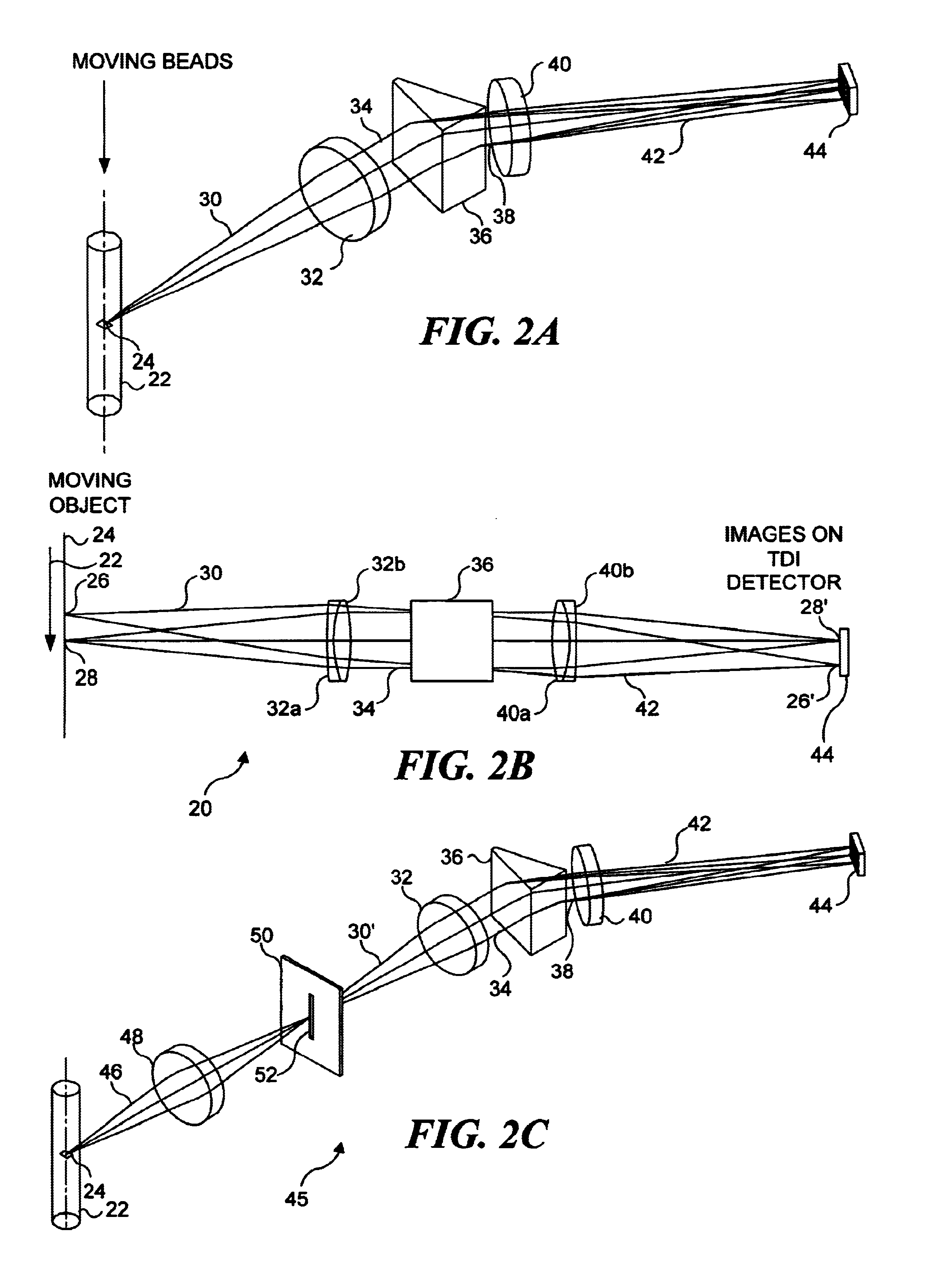
Combinatorially-synthesized deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) oligonucleotides attached to encoded beads that are hybridized to amplified and labeled genomic DNA or ribonucleic acid (RNA) are analyzed using a flow imaging system. Oligonucleotides and corresponding reporters are bound to the surfaces of a plurality of small beads such that different beads bear different oligo sequences. Each bead bears a unique optical signature comprising a predefined number of unique reporters, where each reporter comprises a predefined combination of different fluorochromes. The composite spectral signature in turn identifies the unique nucleotide sequence of its attached oligo chains. This optical signature is rapidly decoded using an imaging system to discriminate the different reporters attached to each bead in a flow in regard to color and spatial position on the bead.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Novel peptides and combination of peptides and scaffolds thereof for use in immunotherapy against colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and other cancers
ActiveUS20160346371A1Reduce releaseImprove discriminationImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor rejection antigen precursorsEpitopeMajor histocompatibility
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Method for producing reagent for antibody detection and use thereof
ActiveUS20150064801A1Efficiently solubilizeEffective recoveryTumor rejection antigen precursorsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsProtein moleculesAntigenic protein
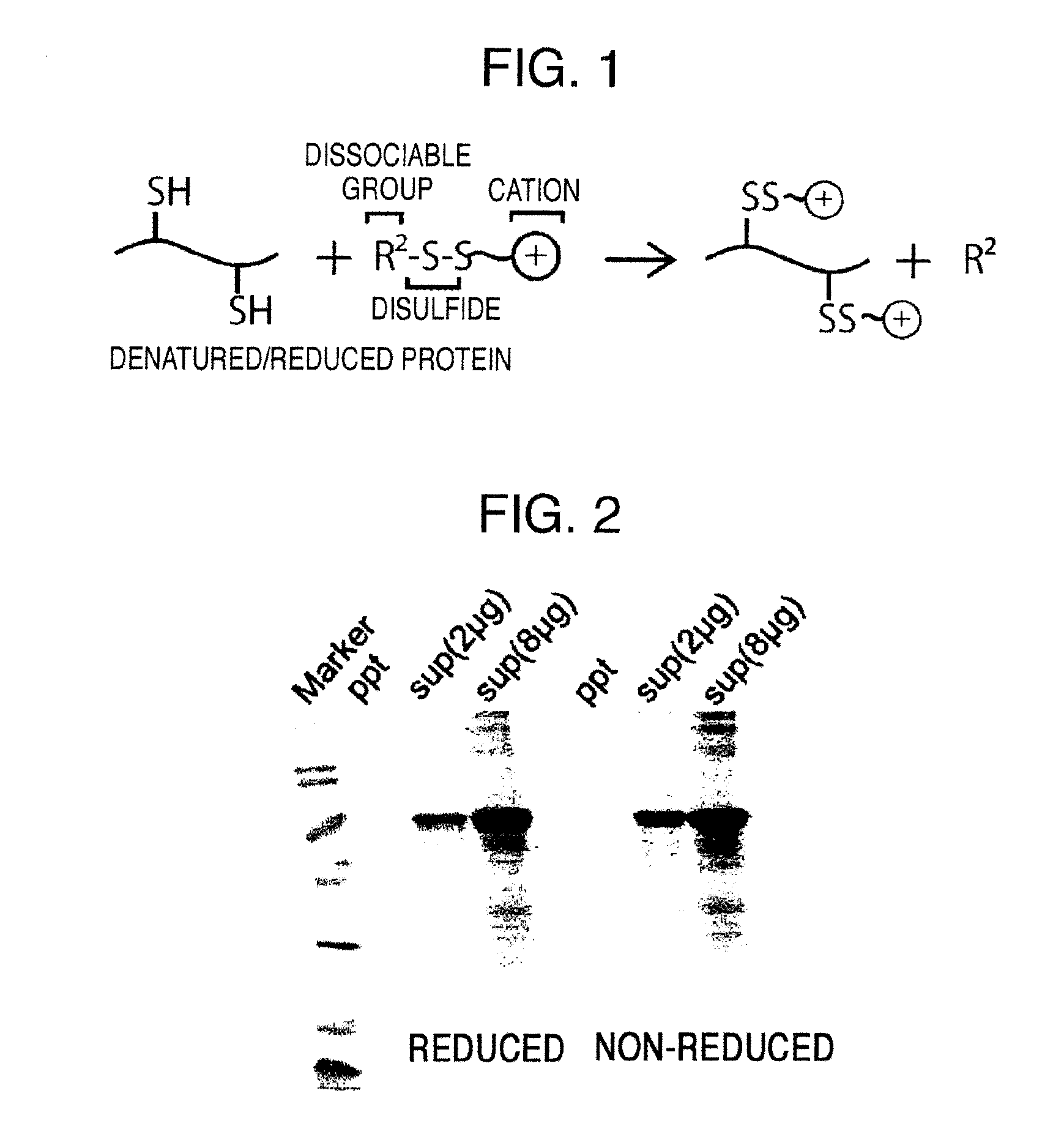
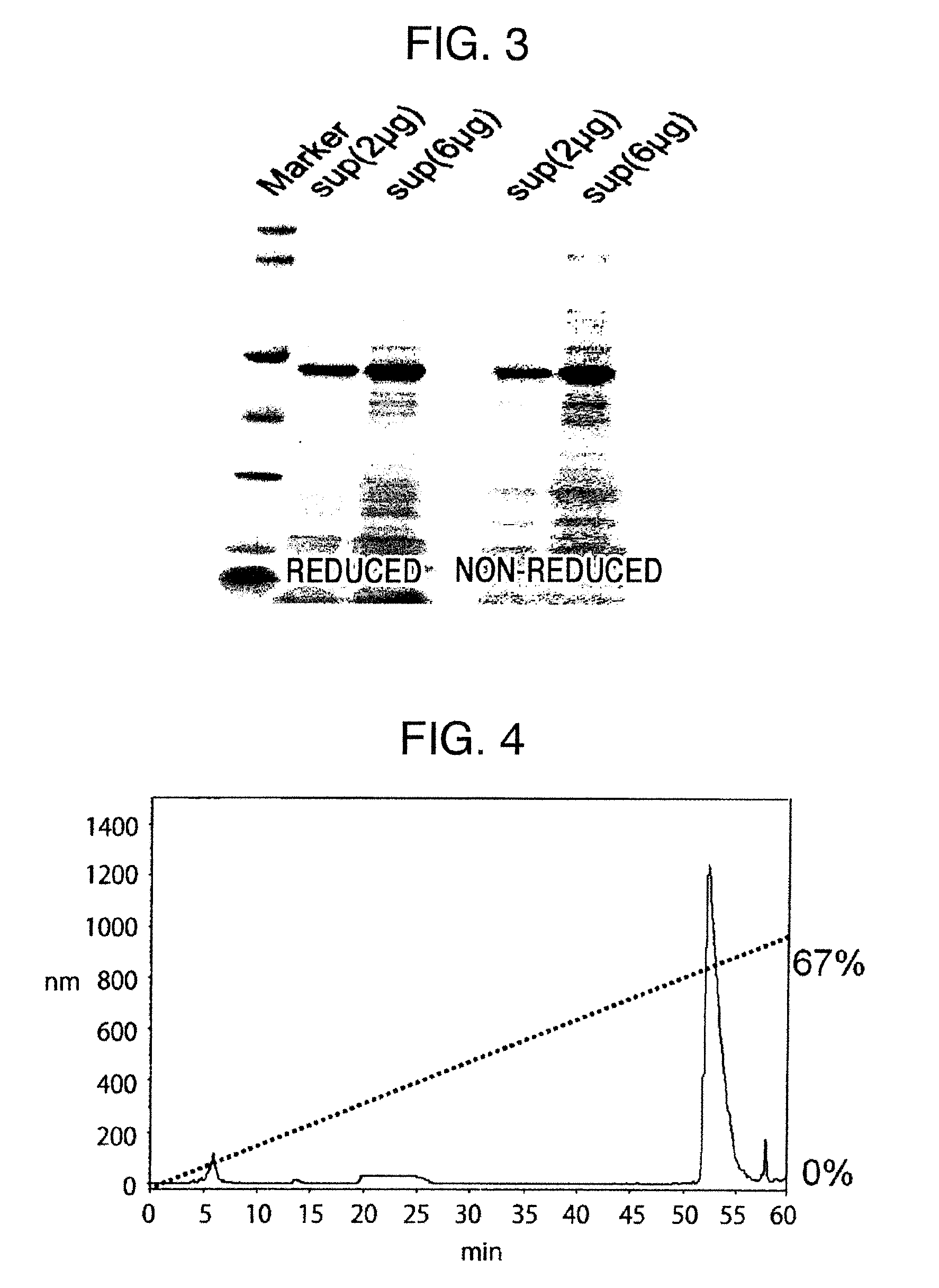
The present invention provides the following: a method for efficiently producing a reagent for detecting an antibody that specifically binds with an insoluble antigen protein present in a liquid sample; a reagent for antibody detection produced by the production method; and a use of the antibody. In a step for solubilizing an antigen protein, it is possible to efficiently solubilize and recover the antigen protein by using a cationizing agent; therefore, when compared to conventional methods, it is possible to efficiently produce a reagent for detecting an antibody that has bound to multiple antigen protein molecules in a carrier.
Owner:FUTAMI JUNICHIRO +1
Nanoscale transduction systems for detecting molecular interactions
InactiveUS20050176029A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular bindingNanostructure
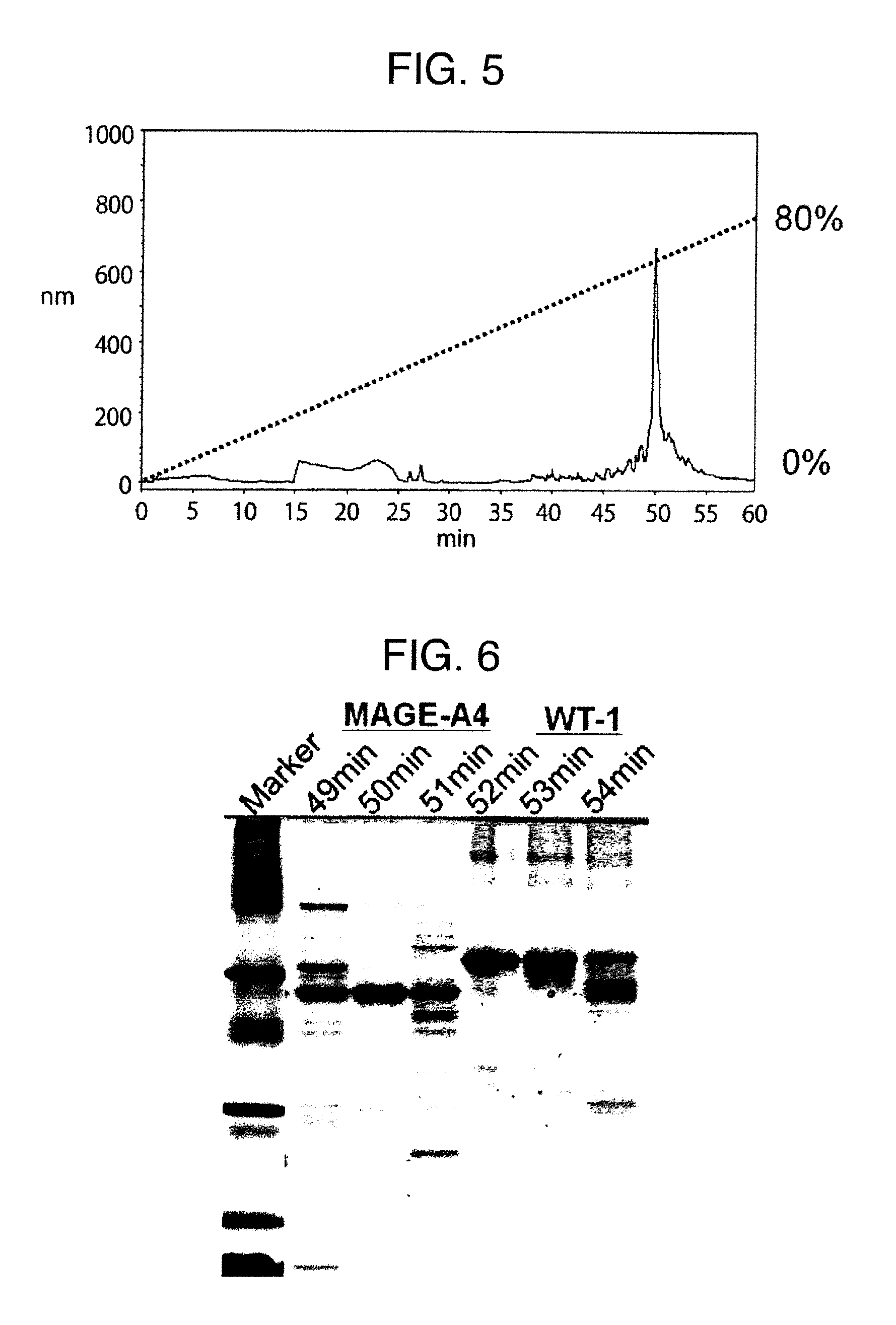
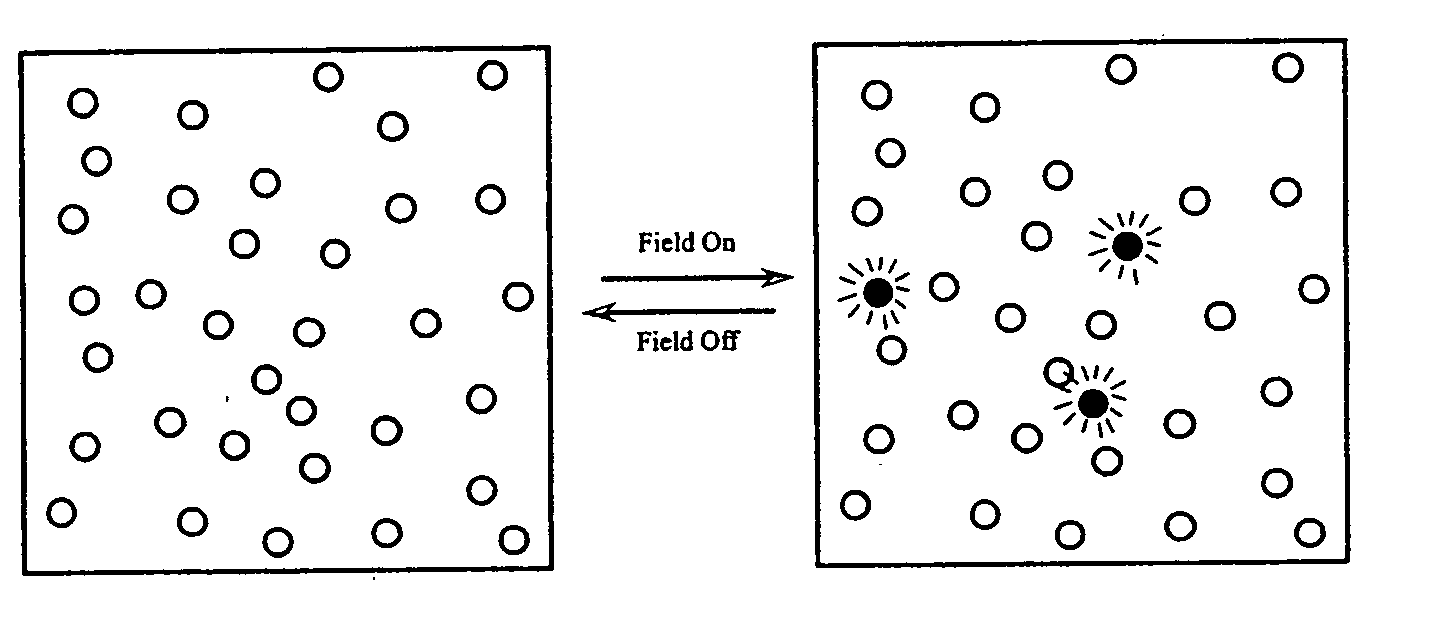
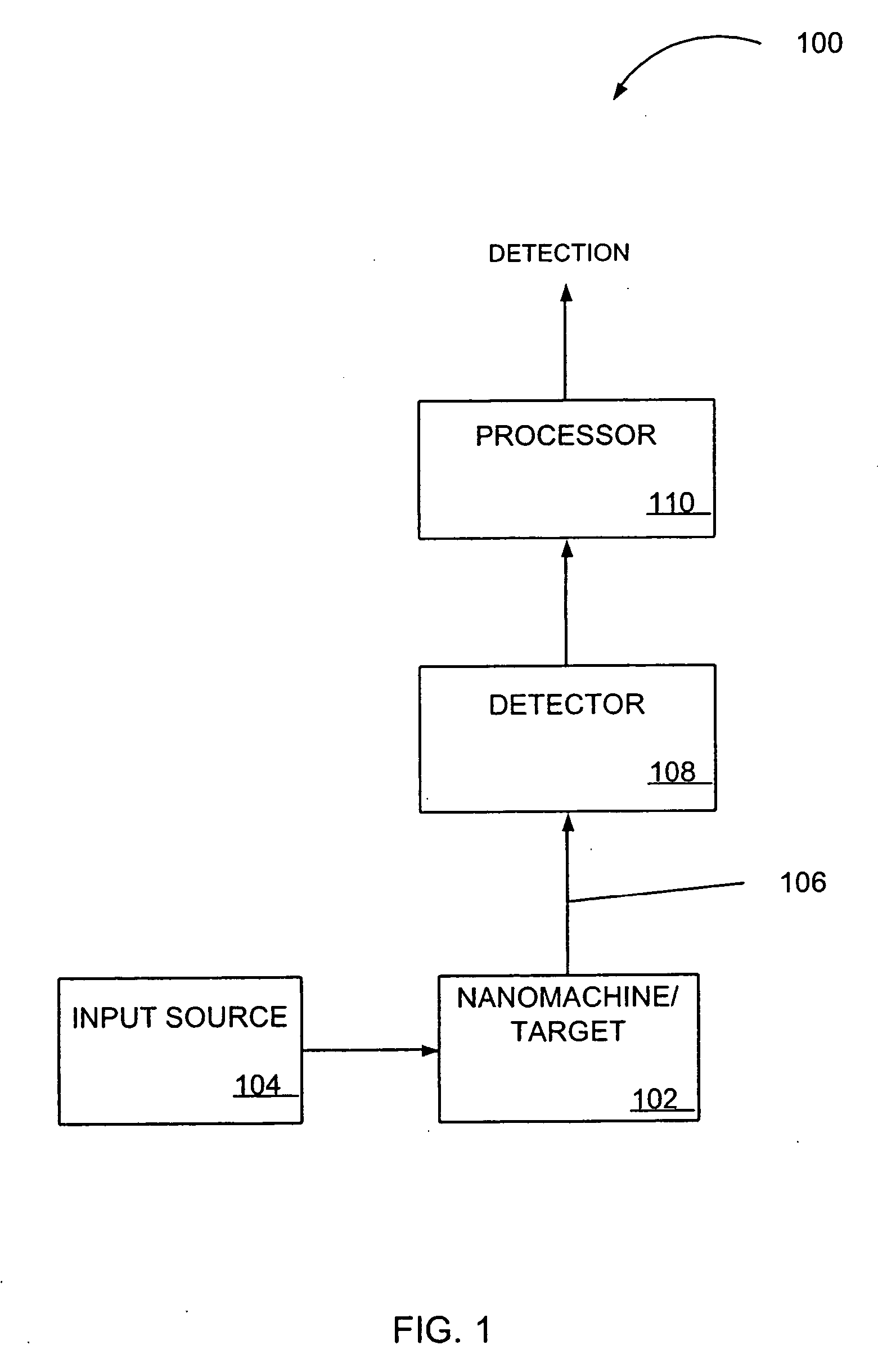
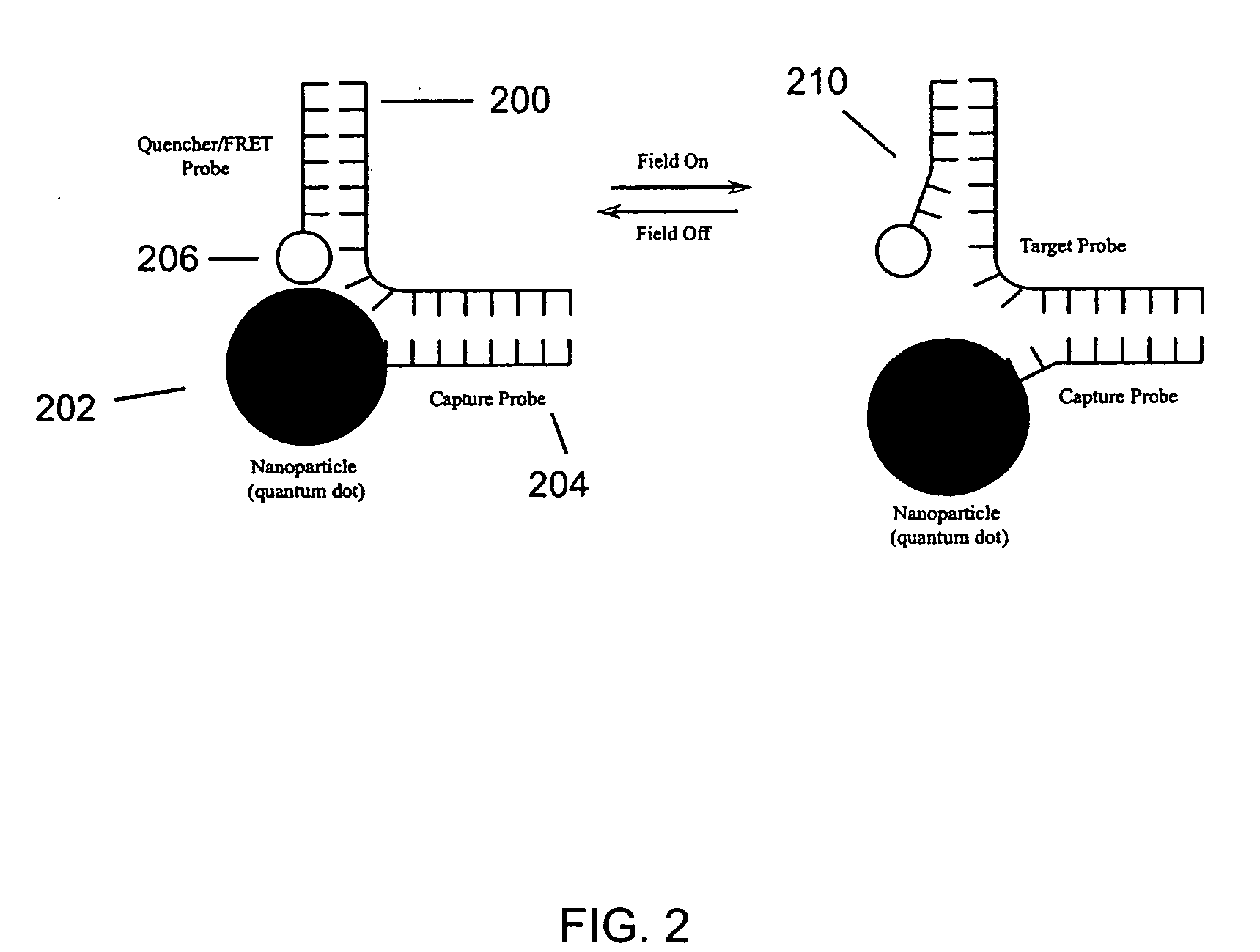
The present invention relates to nanoscale transduction systems that produce reversible signals to facilitate detection. In one respect, the invention relates to the analysis of molecular binding events using higher order signaling nanoscale constructs, or “nanomachines”, that allow nanostructures to be individually detectable, even in the midst of high background noise. Such systems are particularly useful for improving the performance of rare target detection methods, as well as being generally useful in any field in which sensitivity, discrimination and confidence in detection are important.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Peptide-based vaccine for influenza
A human synthetic peptide-based influenza vaccine for intranasal administration comprises a mixture of flagella containing at least four epitopes of influenza virus reactive with human cells, each expressed individually in Salmonella flagellin, said influenza virus epitopes being selected from the group consisting of: (i) one B-cell hemagglutinin (HA) epitope; (ii) one T-helper hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleo-protein (NP) epitope that can bind to many HLA molecules; and (iii) at least two cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) nucleoprotein (NP) or matrix protein (M) epitopes that are restricted to the most prevalent HLA molecules in different human populations.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
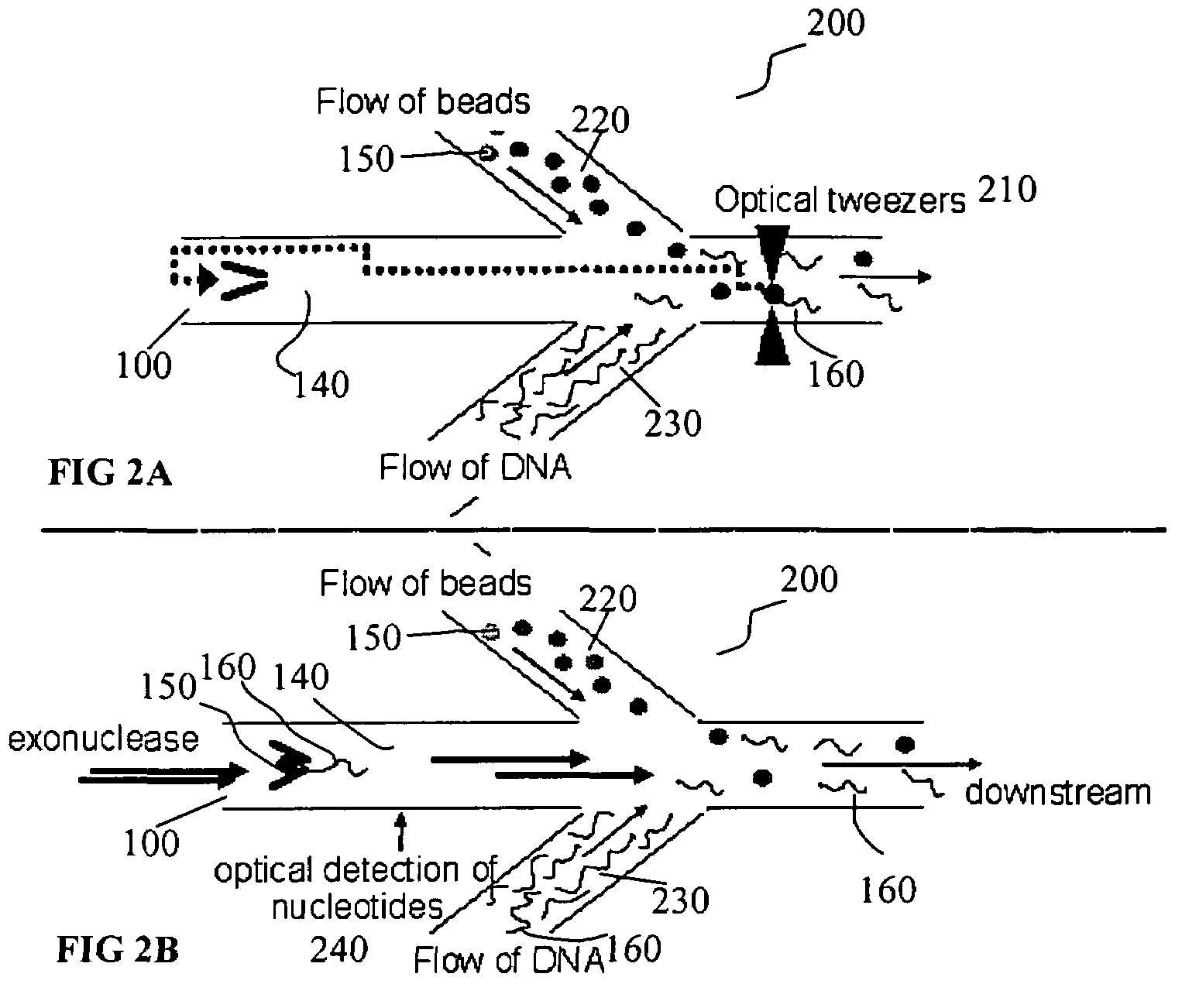
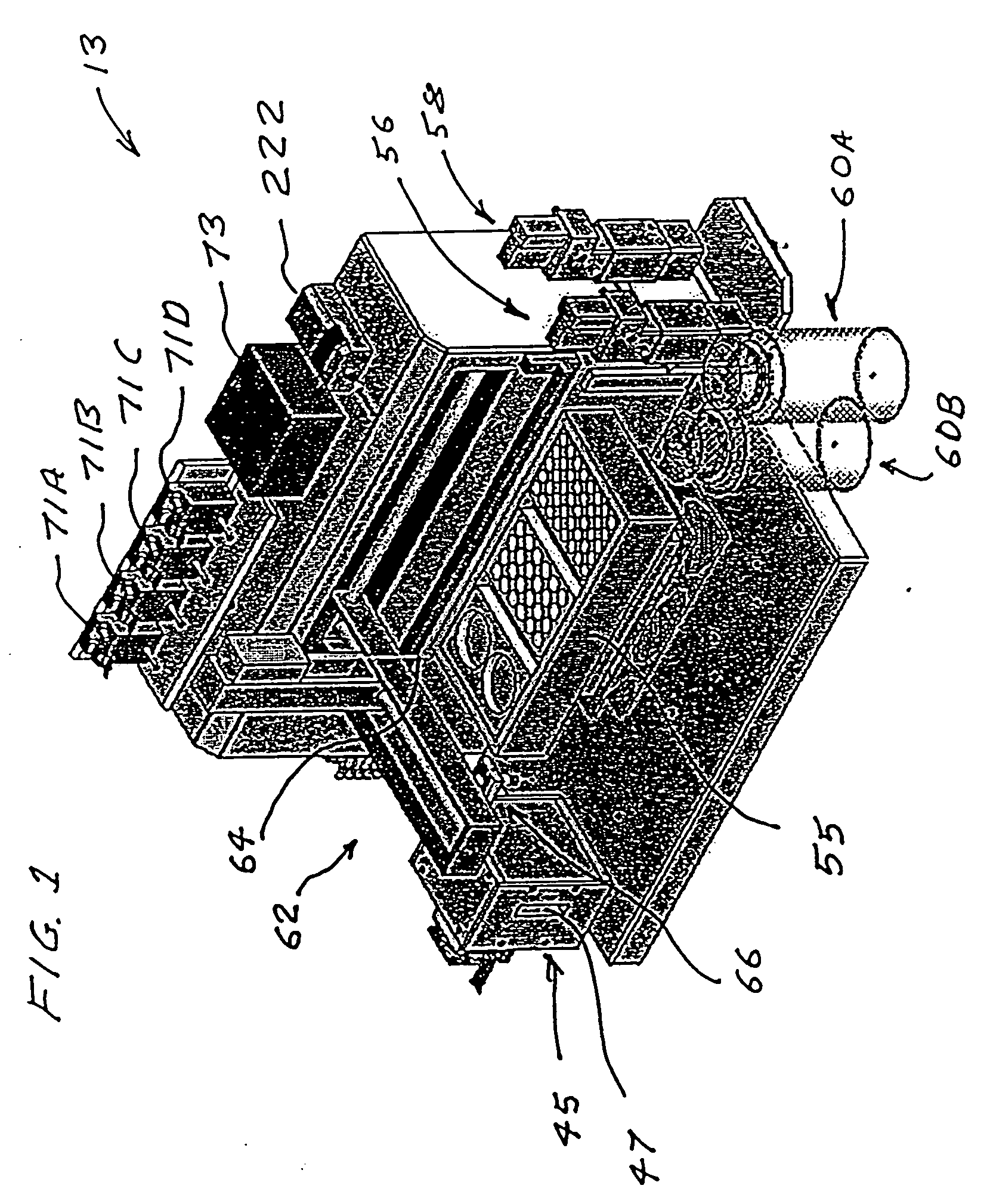
Microfluidic apparatus, Raman spectroscopy systems, and methods for performing molecular reactions
ActiveUS7442339B2Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular bindingNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for performing nucleic acid sequencing reactions and molecular binding reactions in a microfluidic channel. The methods, apparatuses, and systems can include a restriction barrier to restrict movement of a particle to which a nucleic acid is attached. Furthermore, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can include hydrodynamic focusing of a delivery flow. In addition, the methods, apparatuses, and systems can reduce non-specific interaction with a surface of the microfluidic channel by providing a protective flow between the surface and a delivery flow.
Owner:INTEL CORP
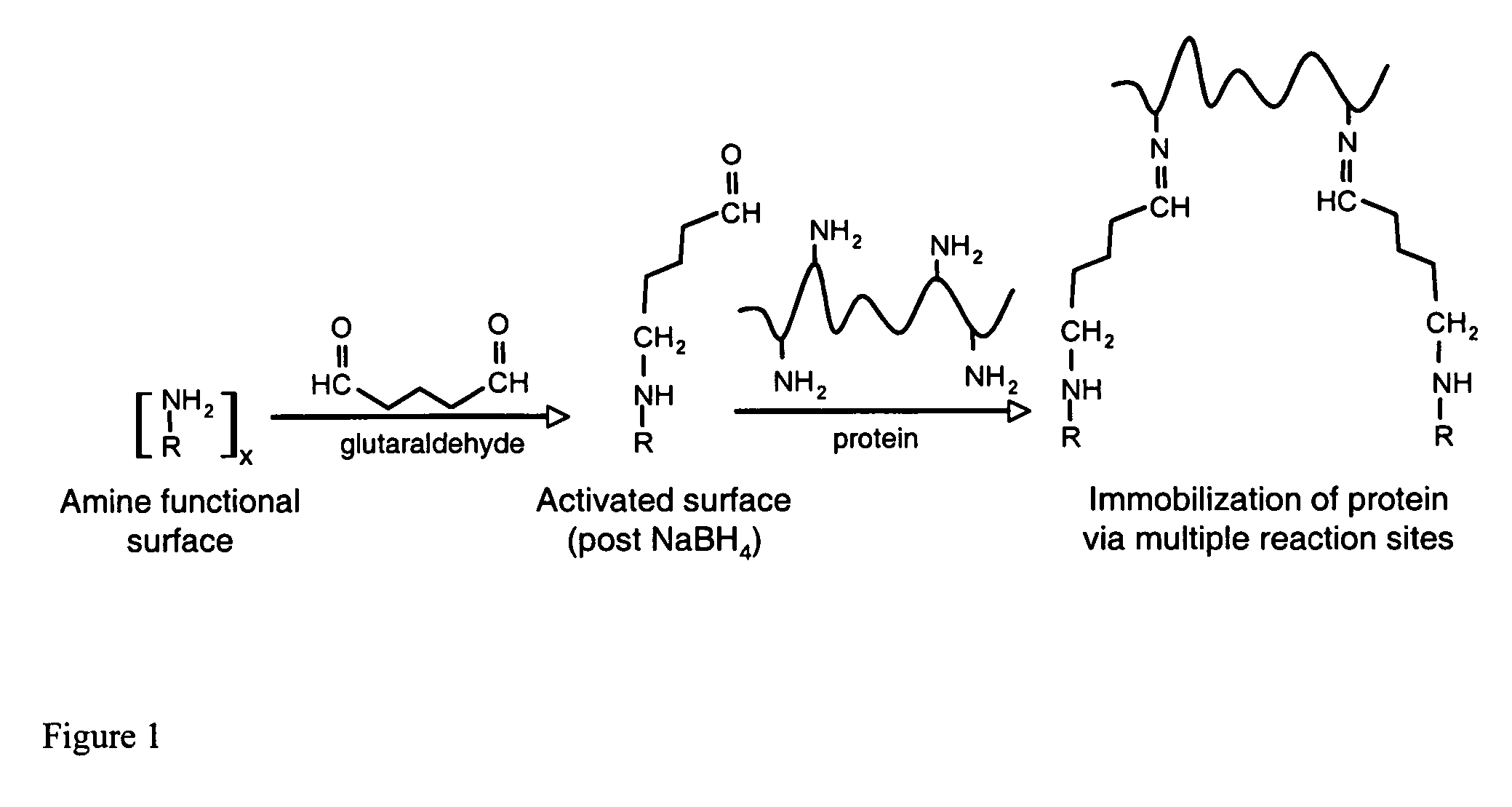
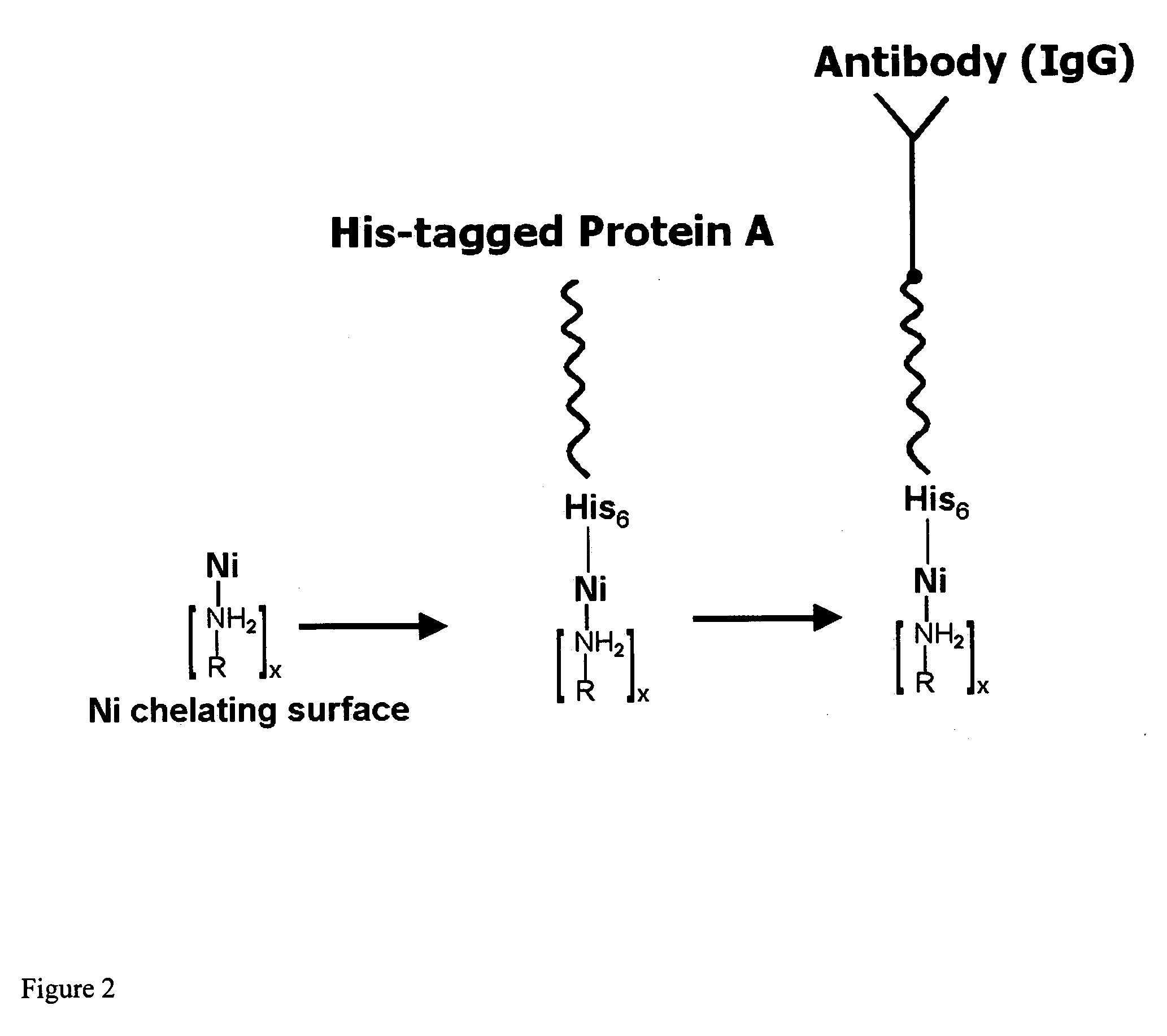
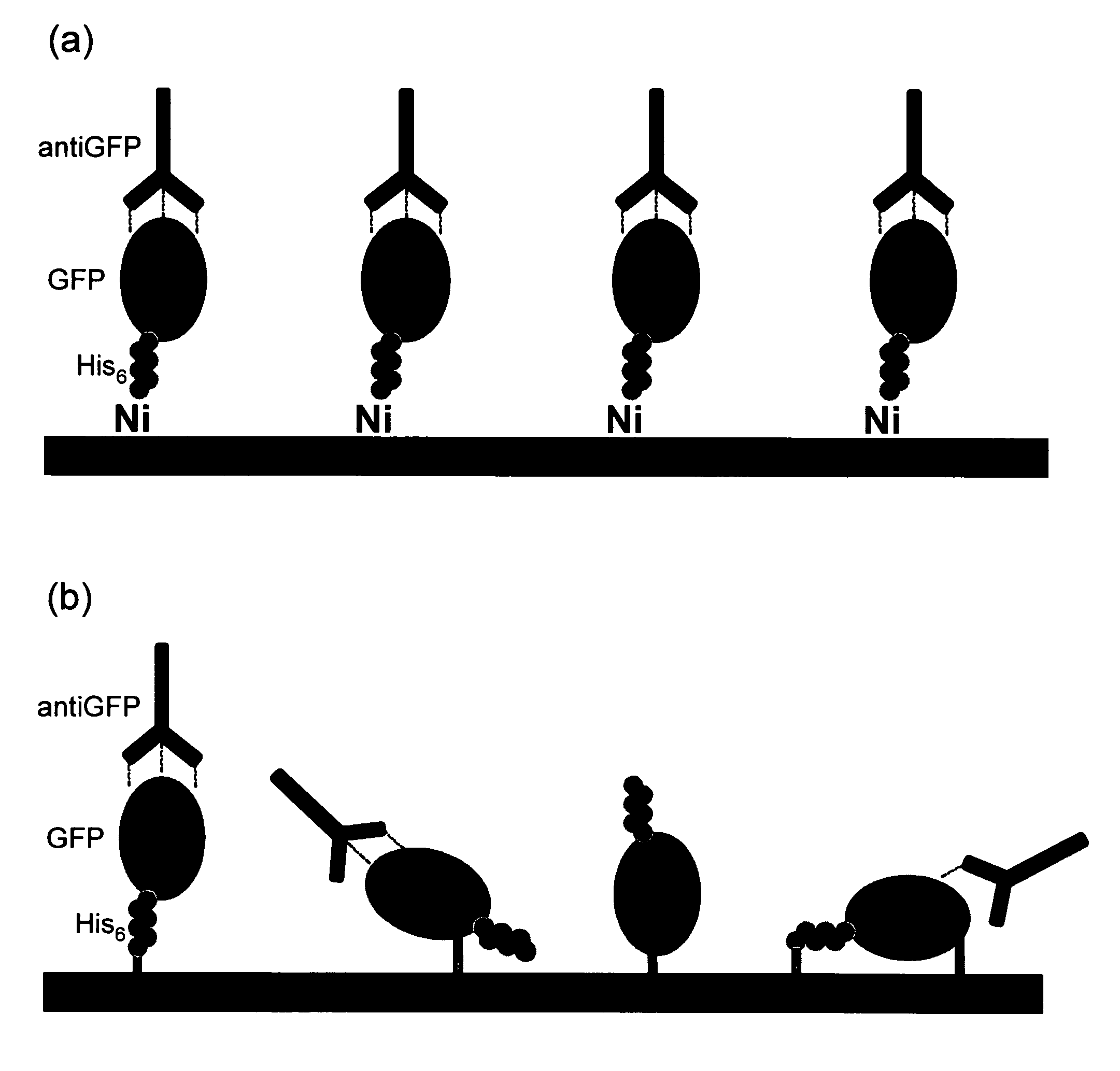
Affinity membrane for capture of a target biomolecule and formation thereof by site-directed immobilization of a capture biomolecule
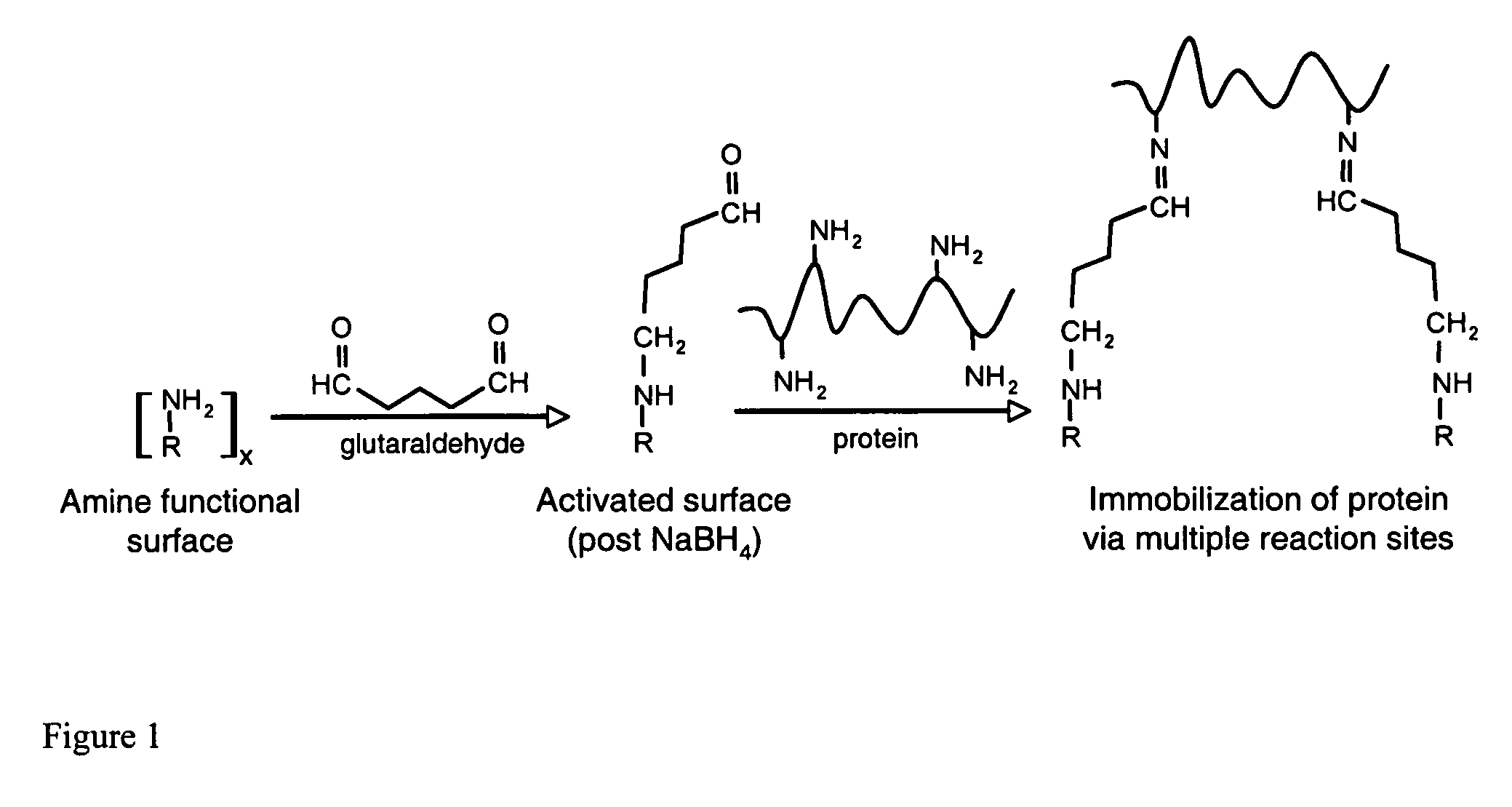
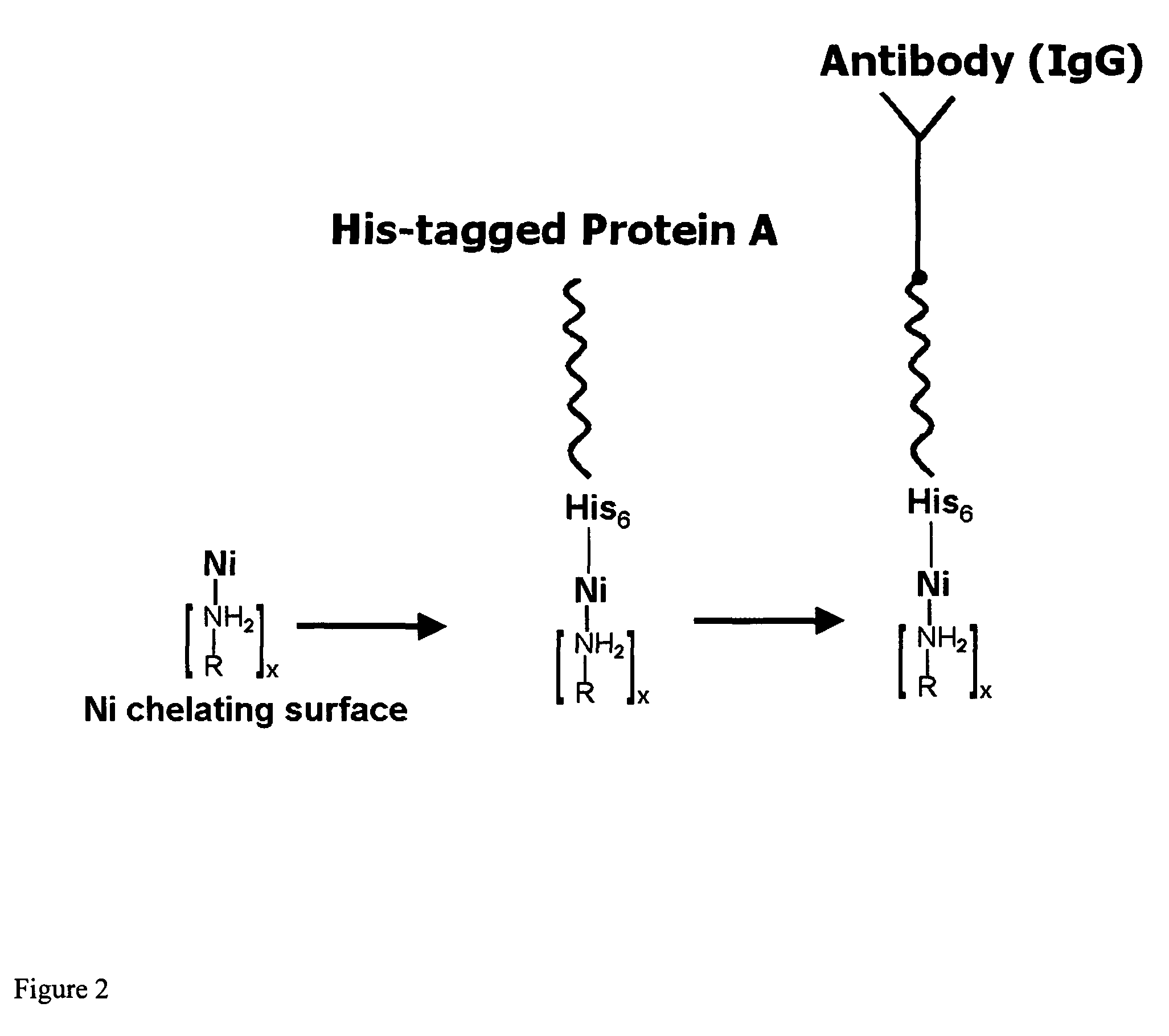
InactiveUS20060292680A1Increase the number ofEasy to captureGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesTyrosineTyrosinase activity
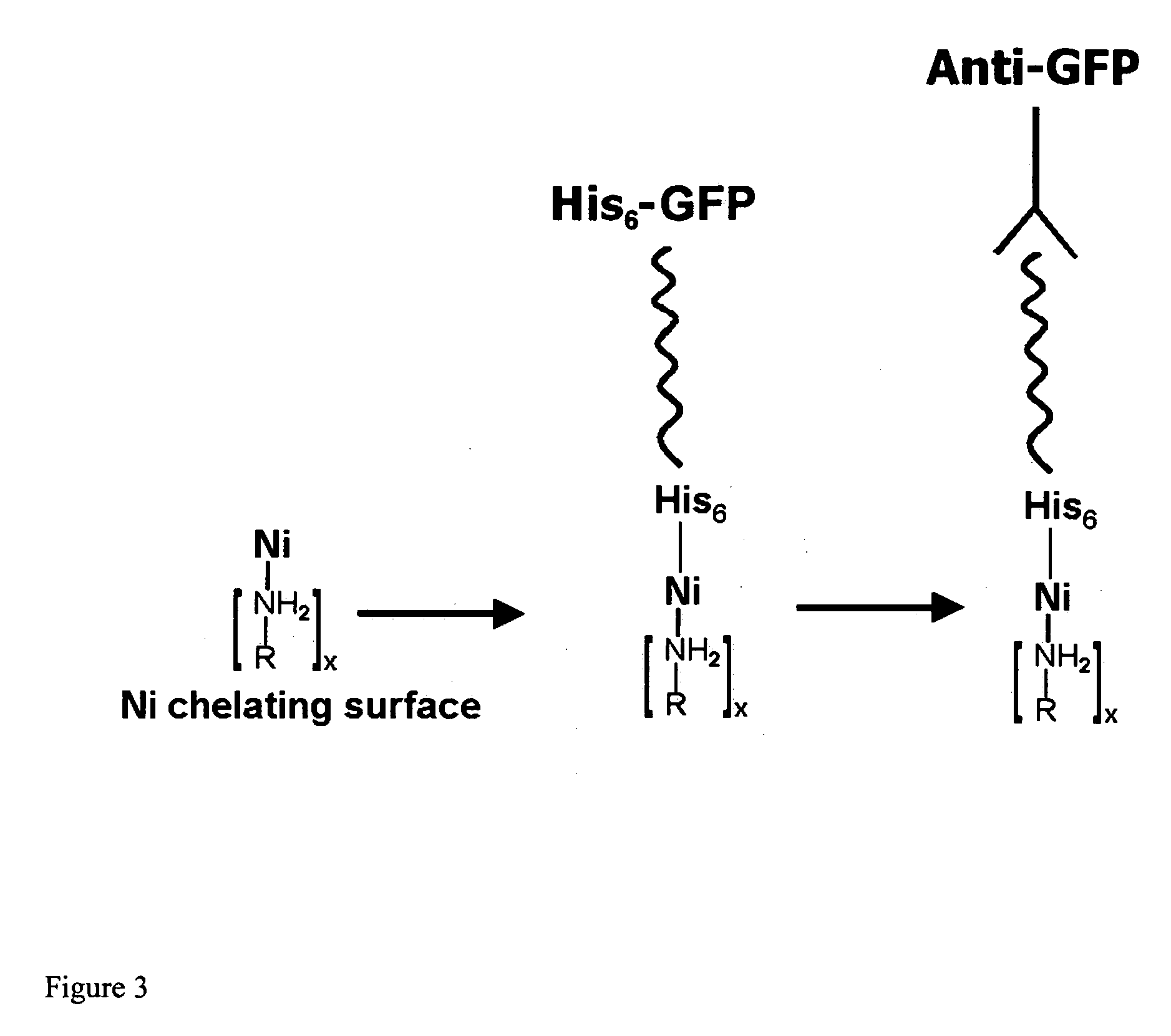
Compositions and methods are taught for directing the orientation of an immobilized capture biomolecule on a hydrophobic membrane. The method comprises layering at least one tie layer on a hydrophobic membrane, adding an amine functional layer on top of at least one tie layer; and attaching an alignment biomolecule to the amine functional layer. The alignment biomolecule has the ability to either capture a target biomolecule itself and thus be considered a capture biomolecule, or bind and orient the immobilized capture biomolecule so as to maximize the binding activity of the immobilized capture biomolecule. In one embodiment, a nickel-coordinated amine functional layer binds with a histidine-tagged alignment biomolecule. In another embodiment, an amine functional layer reacts, via tyrosinase catalysis, with a tyrosine residue in an alignment biomolecule.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Novel peptides and combination of peptides for use in immunotherapy against breast cancer and other cancers
ActiveUS20170173132A1High error rateImmunoglobulin superfamilyTumor rejection antigen precursorsAdditive ingredientNeoplasm
The present invention relates to peptides, proteins, nucleic acids and cells for use in immunotherapeutic methods. In particular, the present invention relates to the immunotherapy of cancer. The present invention furthermore relates to tumor-associated T-cell peptide epitopes, alone or in combination with other tumor-associated peptides that can for example serve as active pharmaceutical ingredients of vaccine compositions that stimulate anti-tumor immune responses, or to stimulate T cells ex vivo and transfer into patients. Peptides bound to molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or peptides as such, can also be targets of antibodies, soluble T-cell receptors, and other binding molecules.
Owner:IMMATICS BIOTECHNOLOGIES GMBH
Biological component comprising artificial membrane
InactiveUS7713544B2Improved performance characteristicsMinimize adhesionMaterial nanotechnologyMicroorganismsAmount of substanceMembrane mimetic
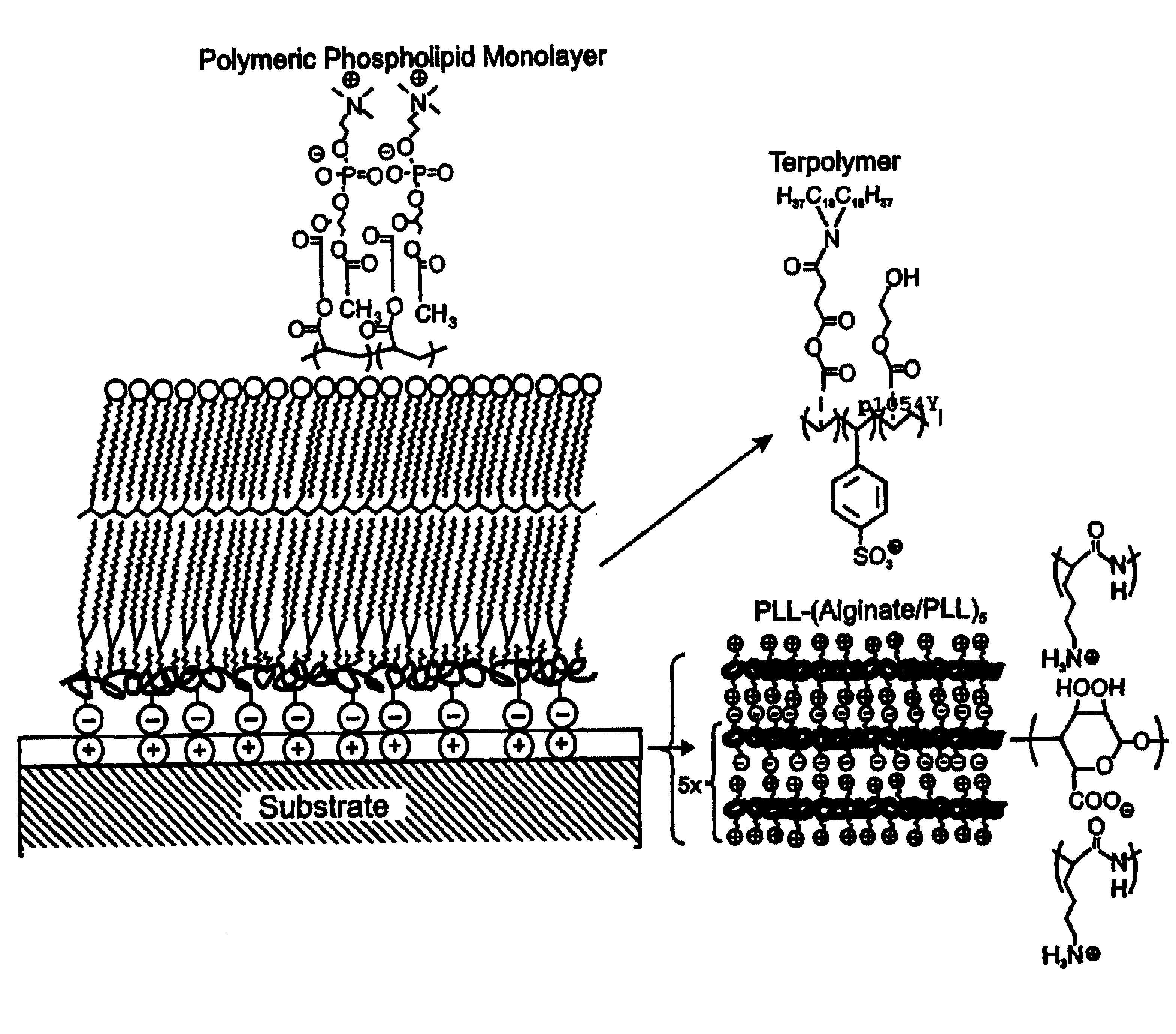
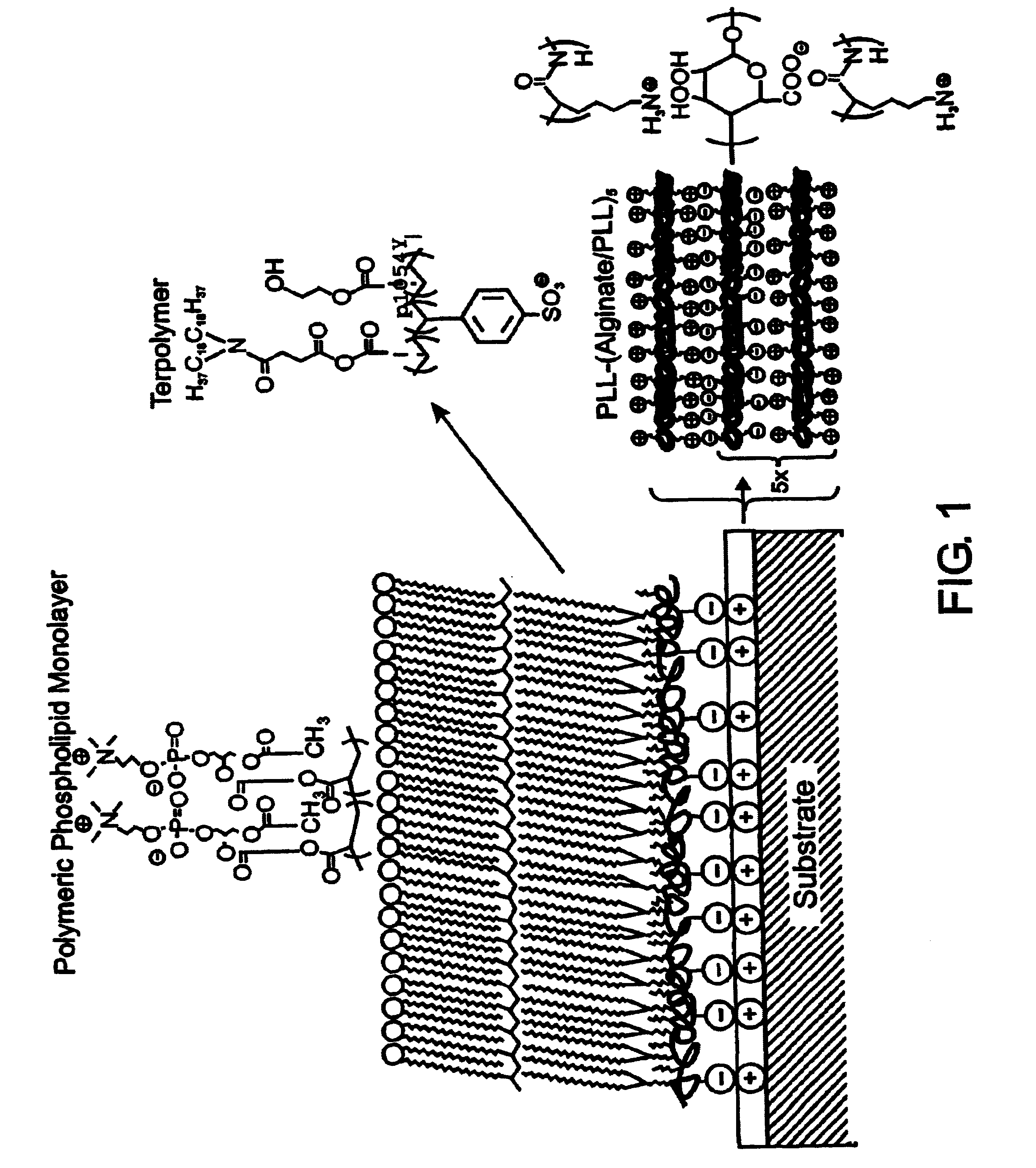
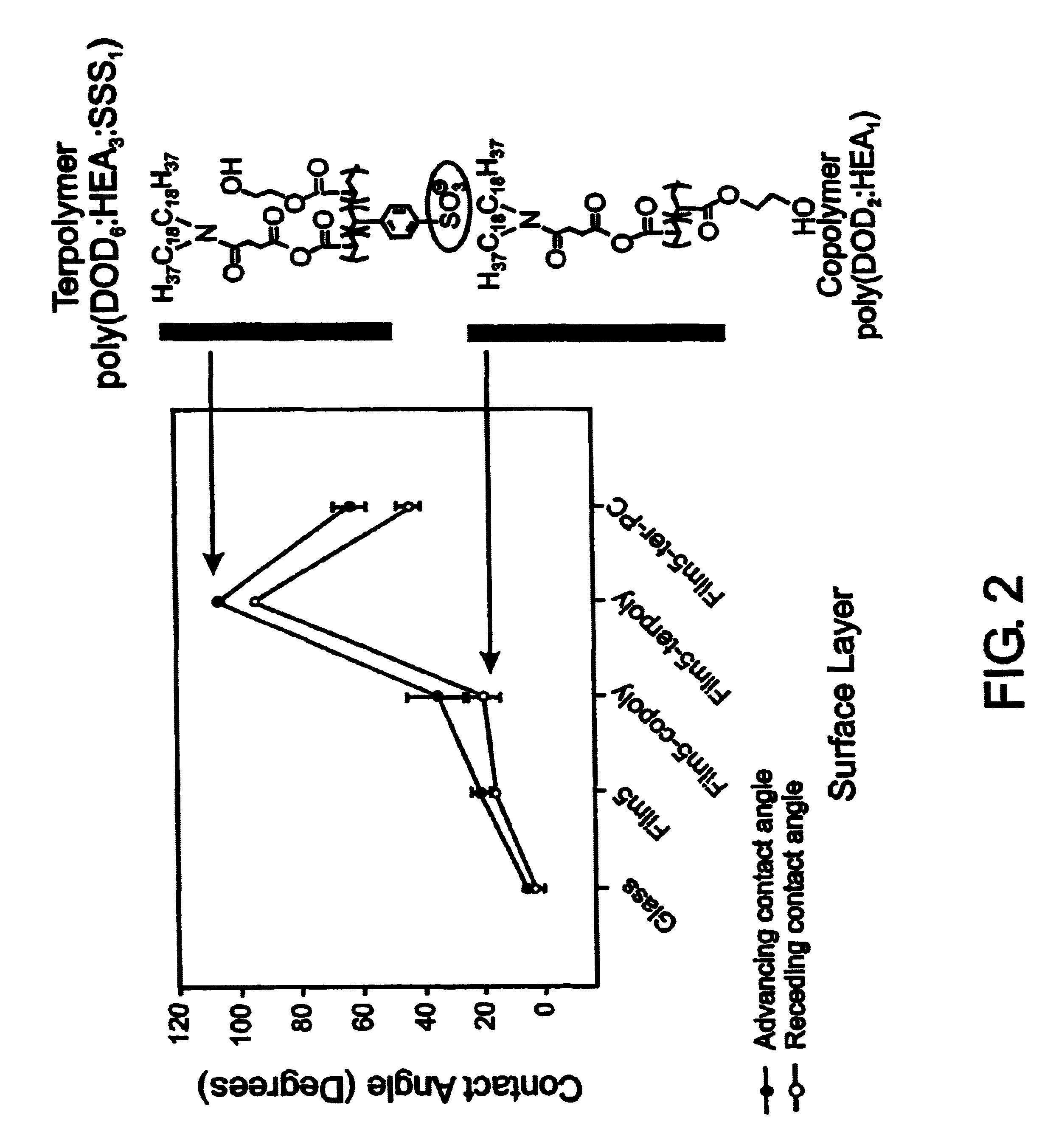
A biocompatible biological component is provided comprising a membrane-mimetic surface film covering a substrate. Suitable substrates include hydrated substrates, e.g. hydrogels which may contain drugs for delivery to a patient through the membrane-mimetic film, or may be made up of cells, such as islet cells, for transplantation. The surface may present exposed bioactive molecules or moieties for binding to target molecules in vivo, for modulating host response when implanted into a patient (e.g. the surface may be antithrombogenic or antiinflammatory) and the surface may have pores of selected sizes to facilitate transport of substances therethrough. An optional hydrophilic cushion or spacer between the substrate and the membrane-mimetic surface allows transmembrane proteins to extend from the surface through the hydrophilic cushion, mimicking the structure of naturally-occurring cells. An alkylated layer directly beneath the membrane-mimetic surface facilates bonding of the surface to the remainder of the biological component. Alkyl chains may extend entirely through the hydrophilic cushion when present. To facilitate binding, the substrate may optionally be treated with a polyelectrolyte or alternating layers of oppositely-charged polyelectrolytes to facilitate charged binding of the membrane-mimetic film or alkylated layer beneath the membrane-mimetic film to the substrate. The membrane-mimetic film is preferably made by in situ polymerization of phospholipid vesicles.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of hydrophobic modified guar gum
InactiveCN102827300ANot easy to degradePreserve macromolecular quality propertiesWater-repelling agents additionCelluloseOrganic acid
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of hydrophobic modified guar gum. The method comprises the following steps of: suspending guar gum in an ionic liquid, adding a basic catalyst, and alkalifying at the temperature of 10-40 DEG C; gradually heating under the protection of nitrogen, dropwise adding a modifying agent slowly, and heating to 30-80 DEG C for performing a modification reaction; and after the reaction, adding organic acid for adjusting the pH to 5-7, soaking and washing with ethanol, filtering, and drying a filter cake in vacuum to obtain the hydrophobic modified guar gum. A hydrophobic alkyl long chain is introduced into guar gum hydroxyl, and a terminal group is a carboxylic acid group, so that the water dissolving speed of the guar gum is increased, the macromolecular quality characteristic of the guar gum is protected to the maximum extent, and the guar gum is endowed with hydrophobic performance. Compared with other modified guar gum, the hydrophobic guar gum has the advantages of high molecular weight, high compatibility with cellulose, increase in the molecular bonding force of cellulose-guar gum, improvement on the paper strength and applicability to a paper-making wet part chemical process as a reinforcing agent and a surface sizing agent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
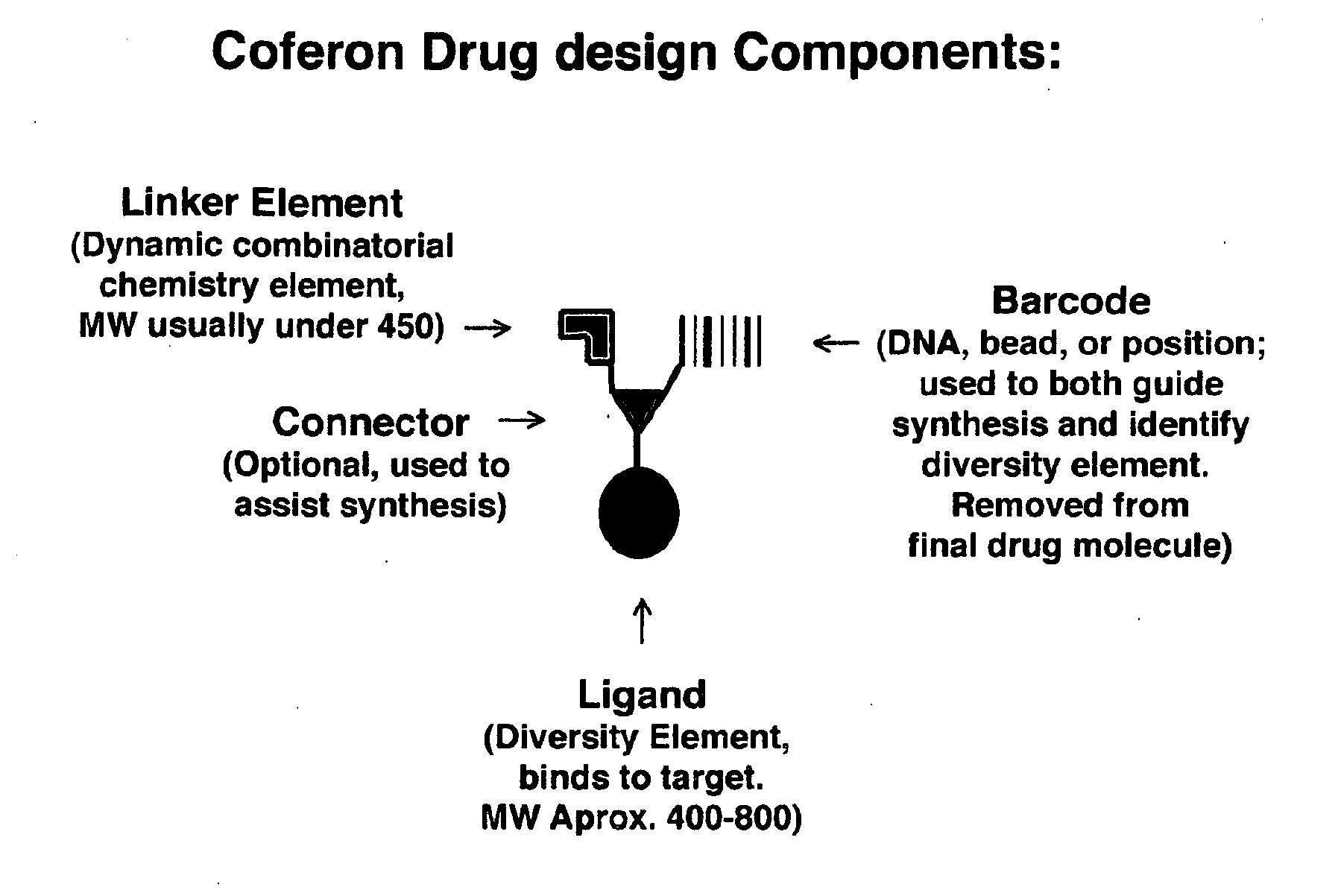
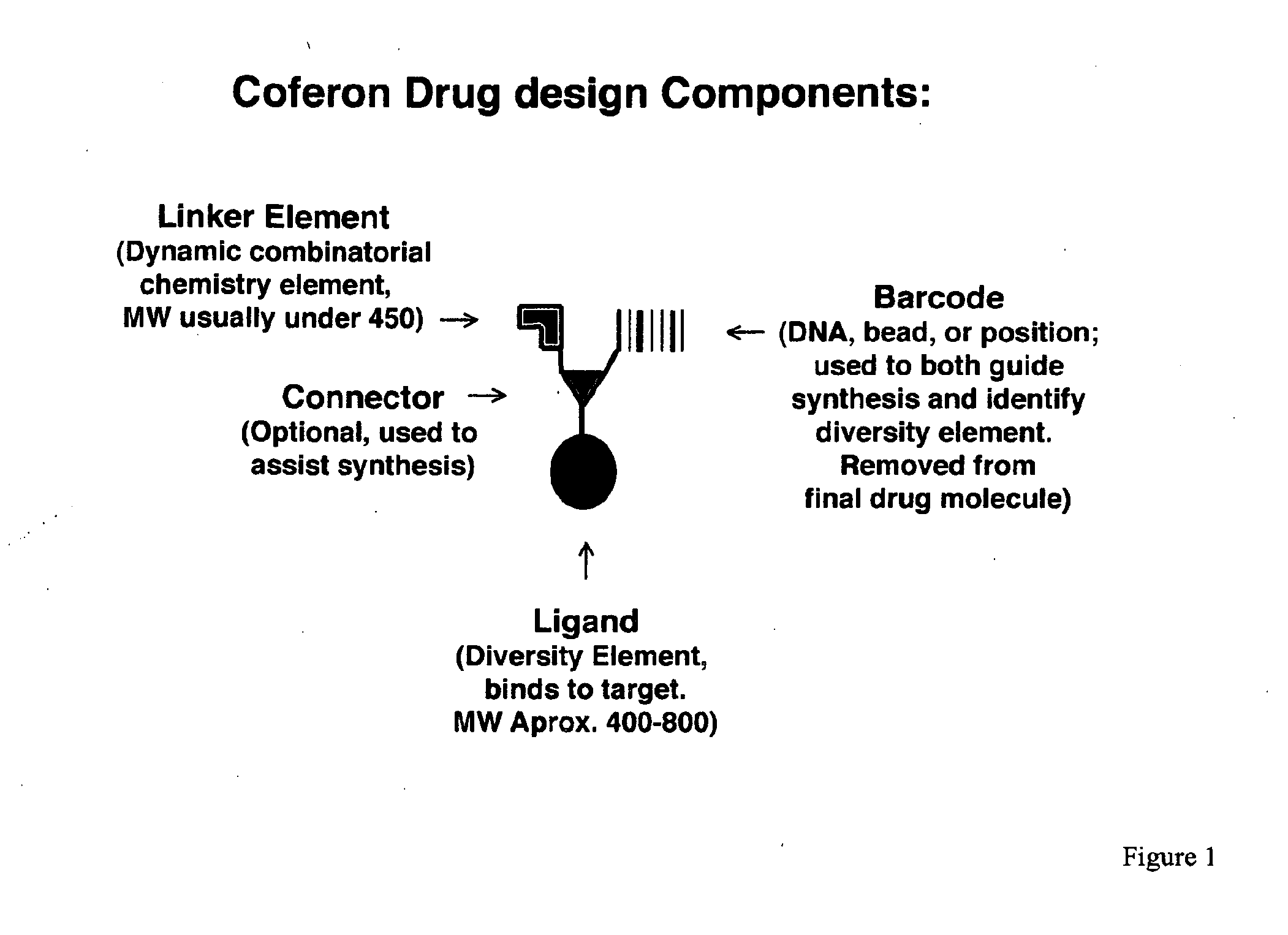
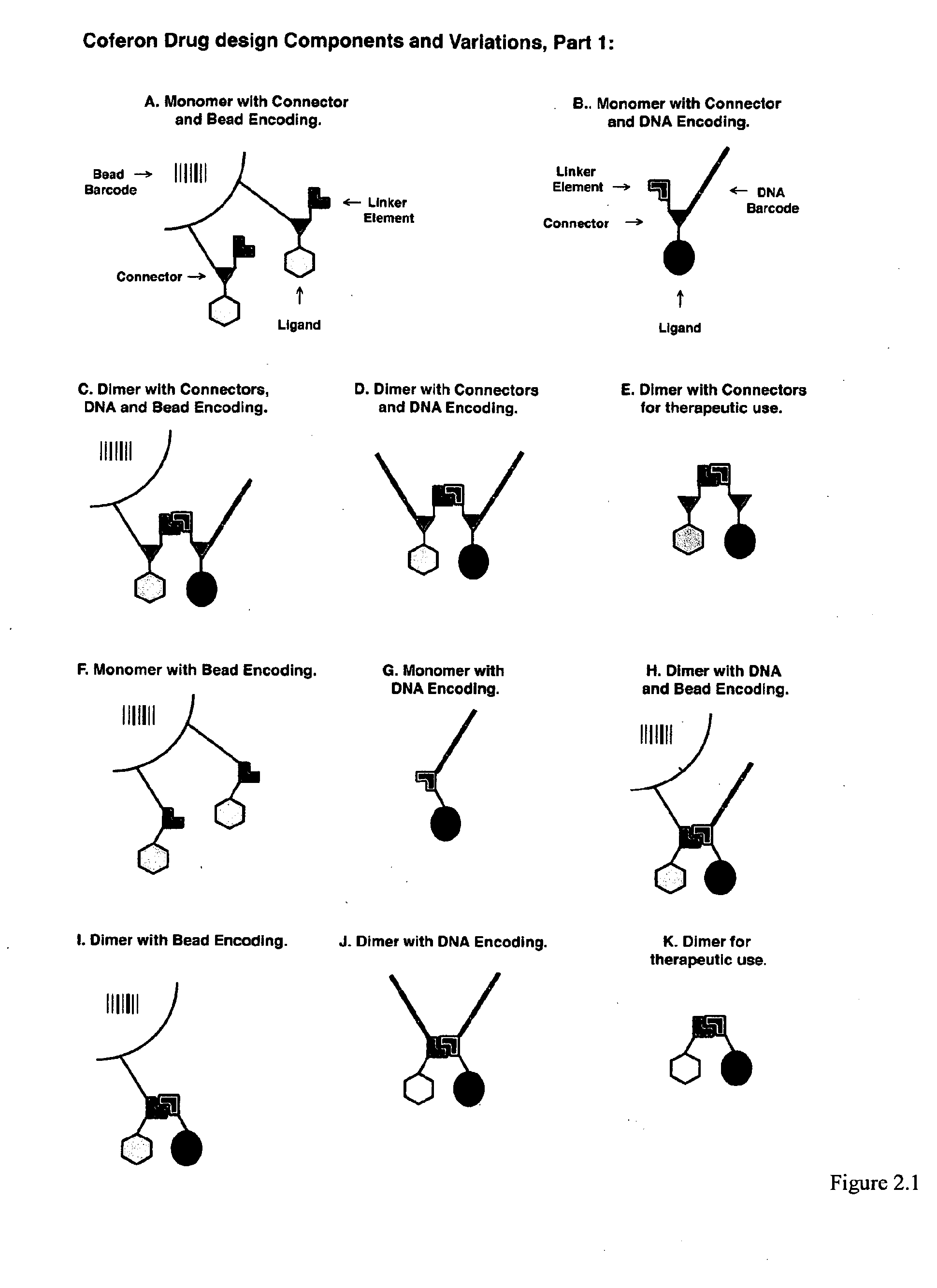
Coferons and methods of making and using them
ActiveUS20110263688A1Easy to modifyDisrupt interactionSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical compoundCombinatorial chemistry
A monomer useful in prepaπng therapeutic compounds includes a diversity element which potentially binds to a target molecule with a dissociation constant of less than 300 11 M and a linker element connected to the diversity element The linker element has a molecular weight less than 500 daltons, is connected, directly or indirectly through a connector, to said diversity element, and is capable of forming a reversible covalent bond or noncovalent interaction with a binding partner of the linker element The monomers can be covalently or non-covalently linked together to form a therapeutic multimer or a precursor thereof
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Cell selection apparatus, and cell selection method using the same
InactiveUS20110033910A1Avoid difficult choicesMaintain activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell selectionEngineering
The cell selection apparatus includes: a cell selection vessel which has a pair of electrodes and a sheet-like insulating material having a plurality of micropores, with a recognition molecule bindable to the specific substance being disposed on a bottom face of the micropore; and a power supply, wherein the power supply includes a cell-immobilization power supply and a cell-taking power supply. The cell selection method uses the cell selection apparatus, including; introducing cells into a cell selection area; immobilizing these cells in the micropores; effecting a binding reaction between the specific substance and the recognition molecule; thereafter, taking out a cell of which the specific substance is not or is weakly bound to the recognition molecule, from the micropore; otherwise alternatively, leaving a cell of which the specific substance on the surface of the cell is strongly bound to the recognition molecule, behind in the micropore.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
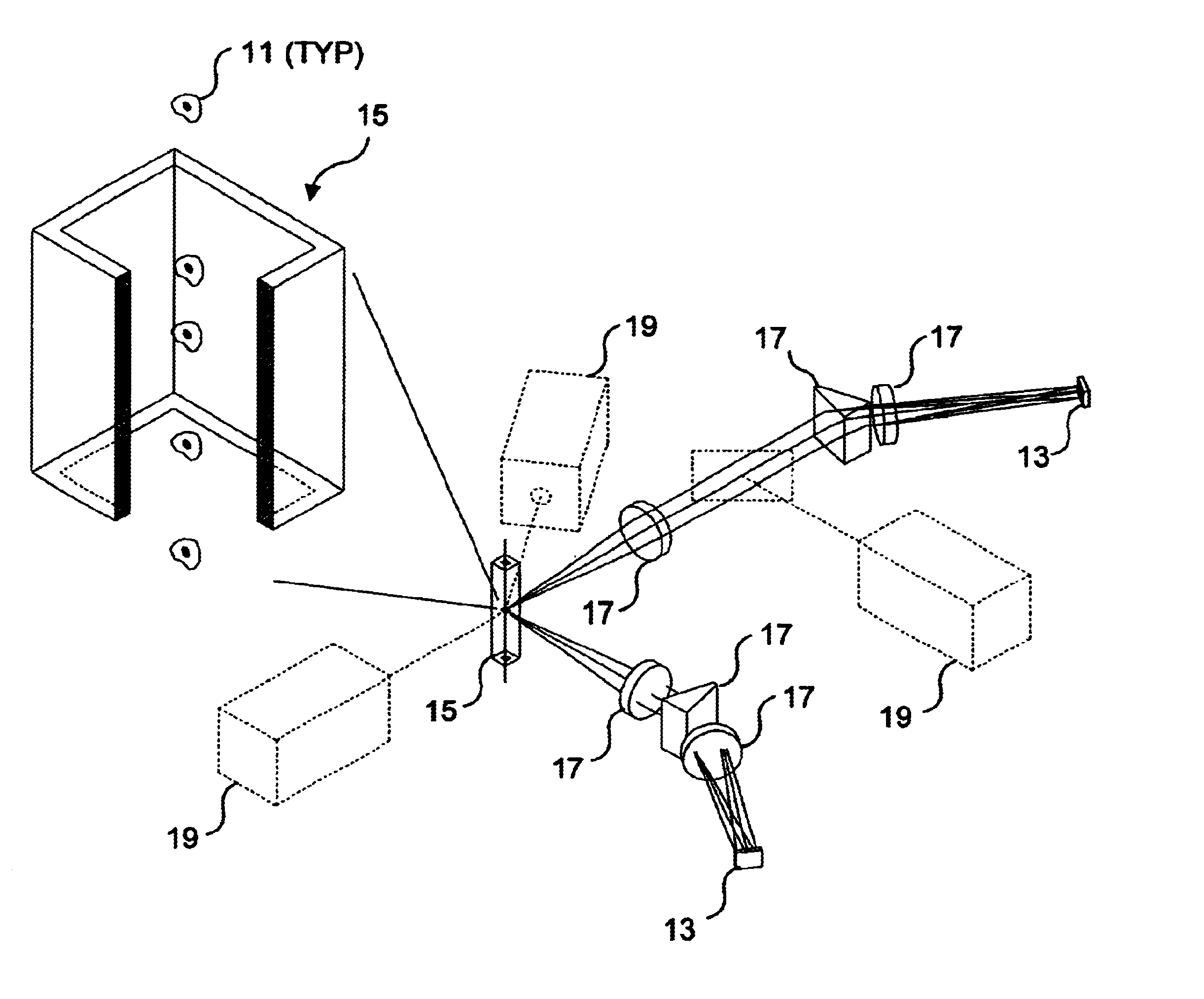
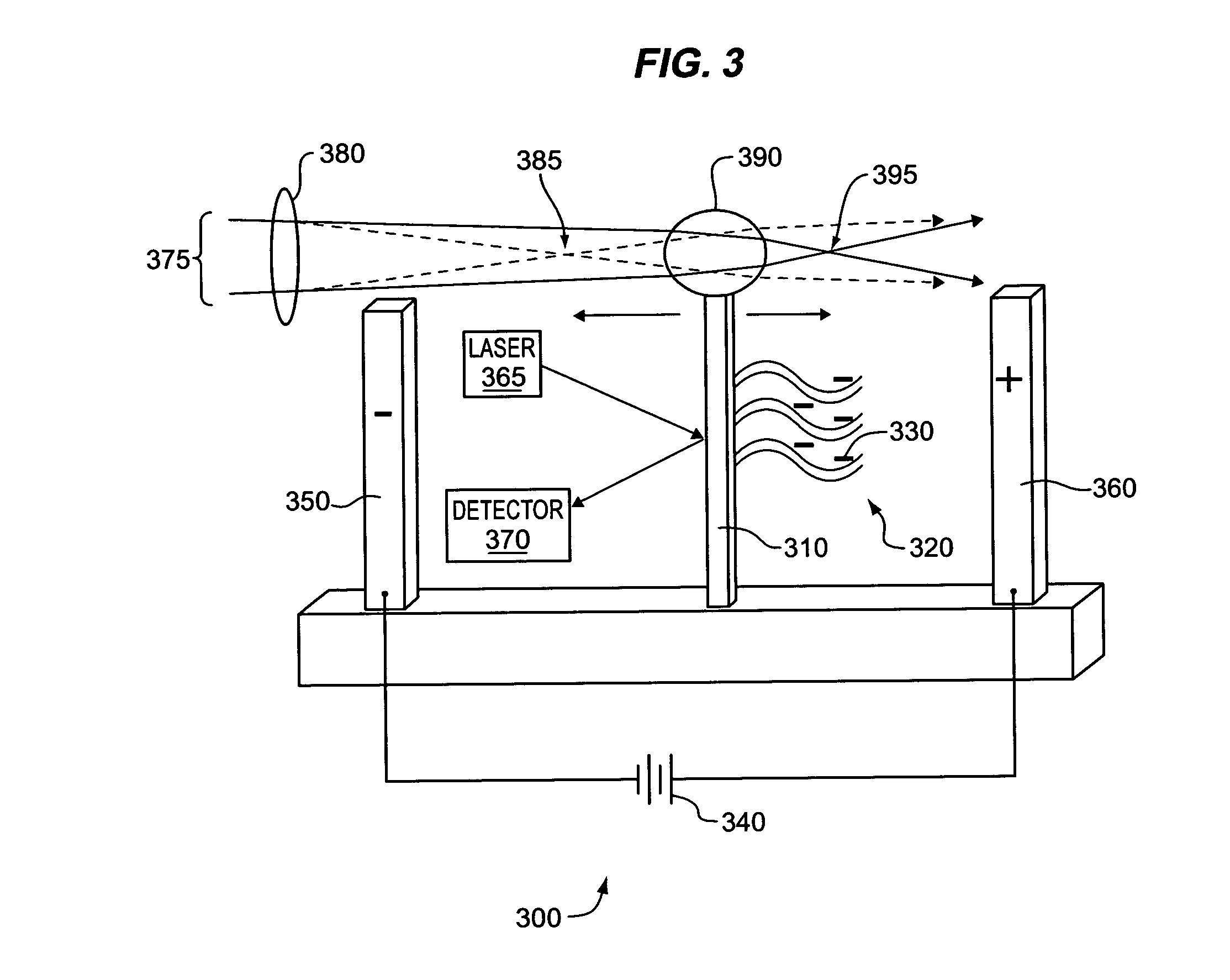
Optical sensor and methods for measuring molecular binding interactions
InactiveUS20060063178A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsProtein molecules
Methods and devices for the measurement of molecular binding interactions. Preferred embodiments provide real-time measurements of kinetic binding and disassociation of molecules including binding and disassociation of protein molecules with other protein molecules and with other molecules. In preferred embodiments ligands are immobilized within pores of a porous silicon interaction region produced in a silicon substrate, after which analytes suspended in a fluid are flowed over the porous silicon region. Binding reactions occur when analyte molecules diffuse closely enough to the ligands to become bound. Preferably the binding and subsequent disassociation reactions are observed utilizing a white light source and thin film interference techniques with spectrometers arranged to detect changes in indices of refraction in the region where the binding and disassociation reactions occur. In preferred embodiments both ligands and analytes are delivered by computer controlled robotic fluid flow control techniques to the porous silicon interaction regions through microfluidic flow channels.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Bi-specific fusion proteins
ActiveUS20110293579A1Promotes cell recruitment and inhibitionPromote cell growthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPharmaceutical drugMolecular binding
Owner:SILVER CREEK PHARMA INC
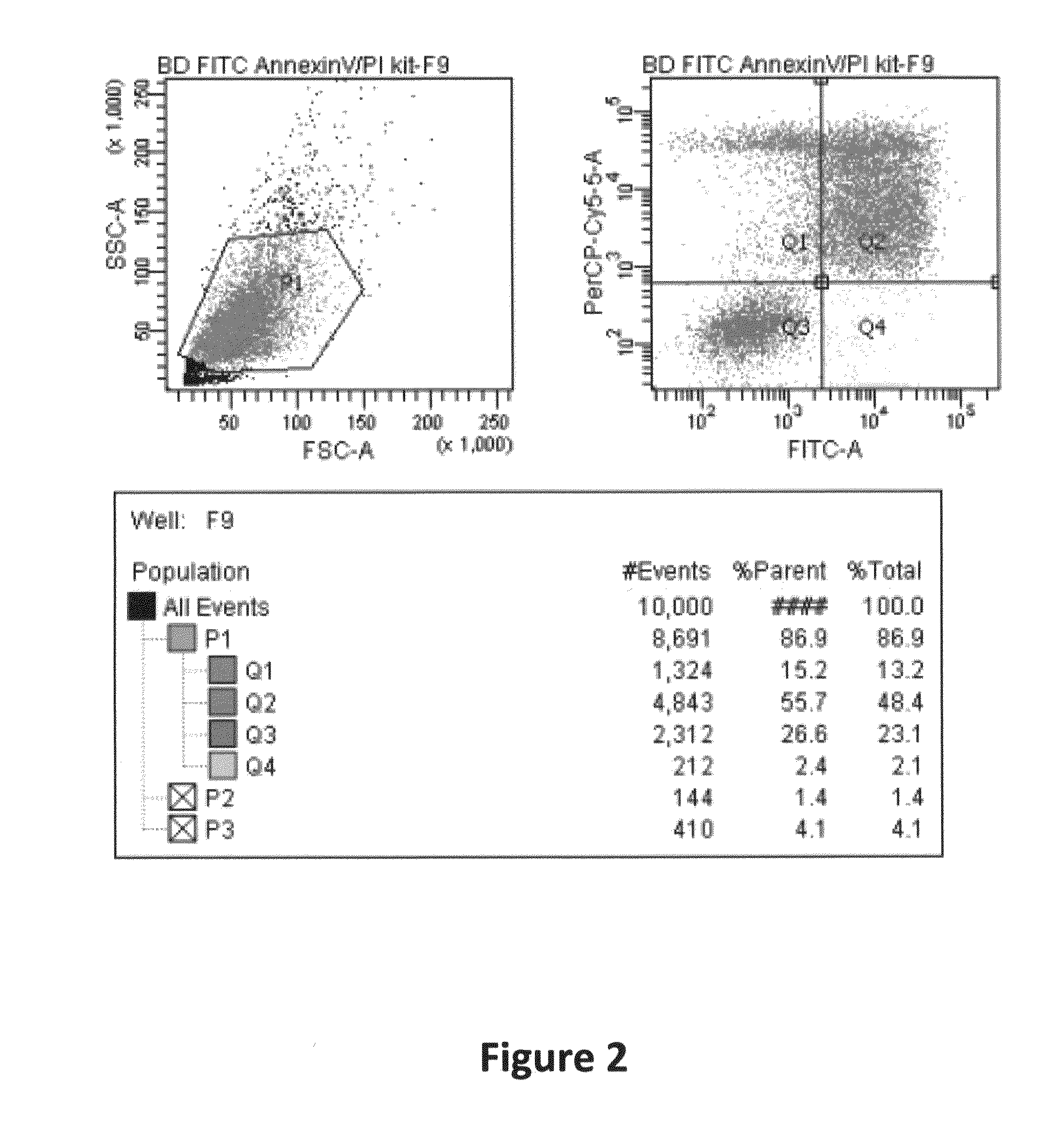
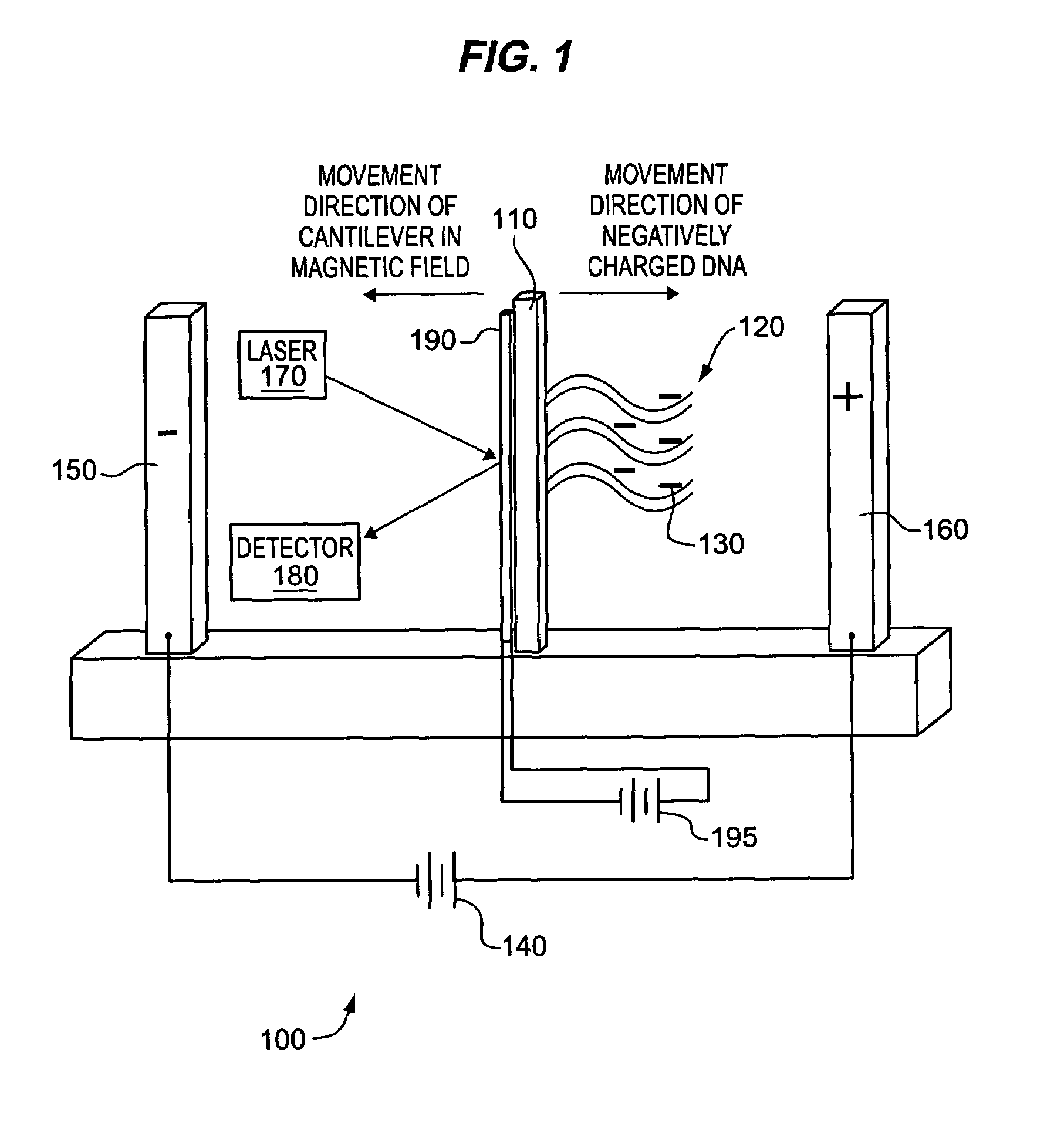
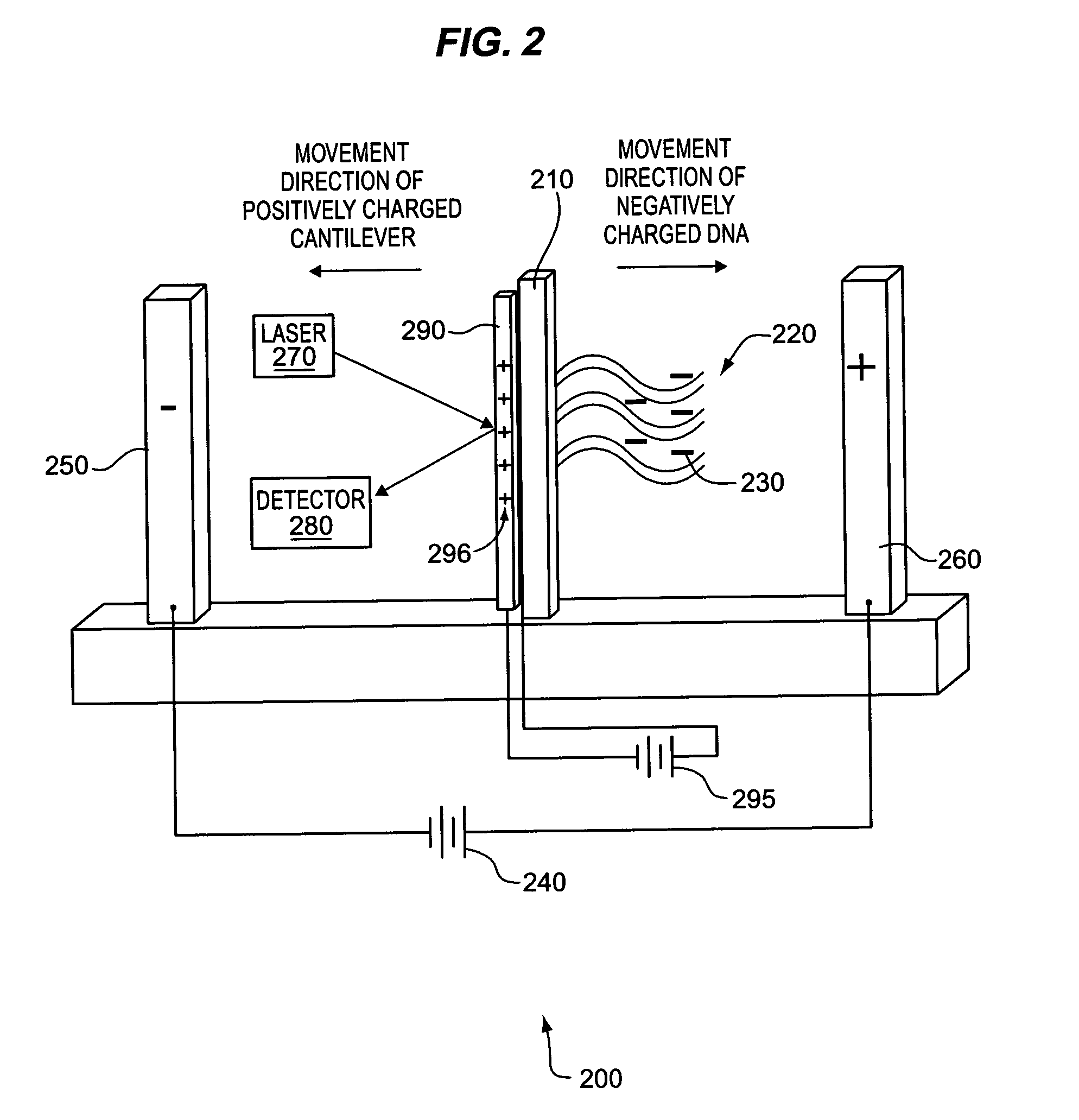
Detecting molecular binding by monitoring feedback controlled cantilever deflections
InactiveUS7105301B2Microbiological testing/measurementNanomedicineInformation processingPresent method
The present methods and apparatus concern the detection and / or identification of target analytes using probe molecules. In various embodiments of the invention, the probes or analytes are attached to one or more cantilevers. Binding of a probe to an analyte results in deflection of the cantilever, detected by a detection unit. A counterbalancing force may be applied to restore the cantilever to its original position. The counterbalancing force may be magnetic, electrical or radiative. The detection unit and the mechanism generating the counterbalancing force may be operably coupled to an information processing and control unit, such as a computer. The computer may regulate a feedback loop that maintains the cantilever in a fixed position by balancing the deflecting force and the counterbalancing force. The concentration of analytes in a sample may be determined from the magnitude of the counterbalancing force required to maintain the cantilever in a fixed position.
Owner:INTEL CORP
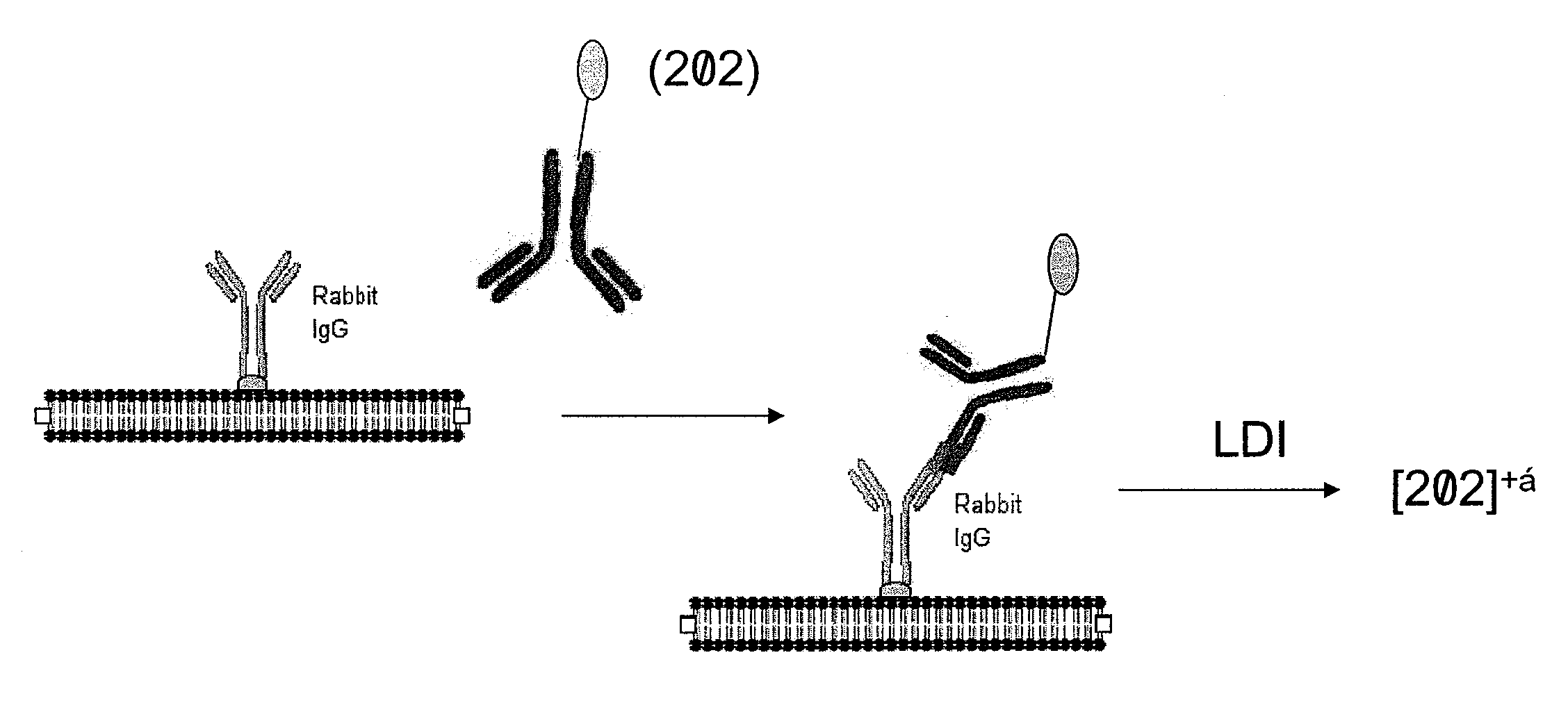
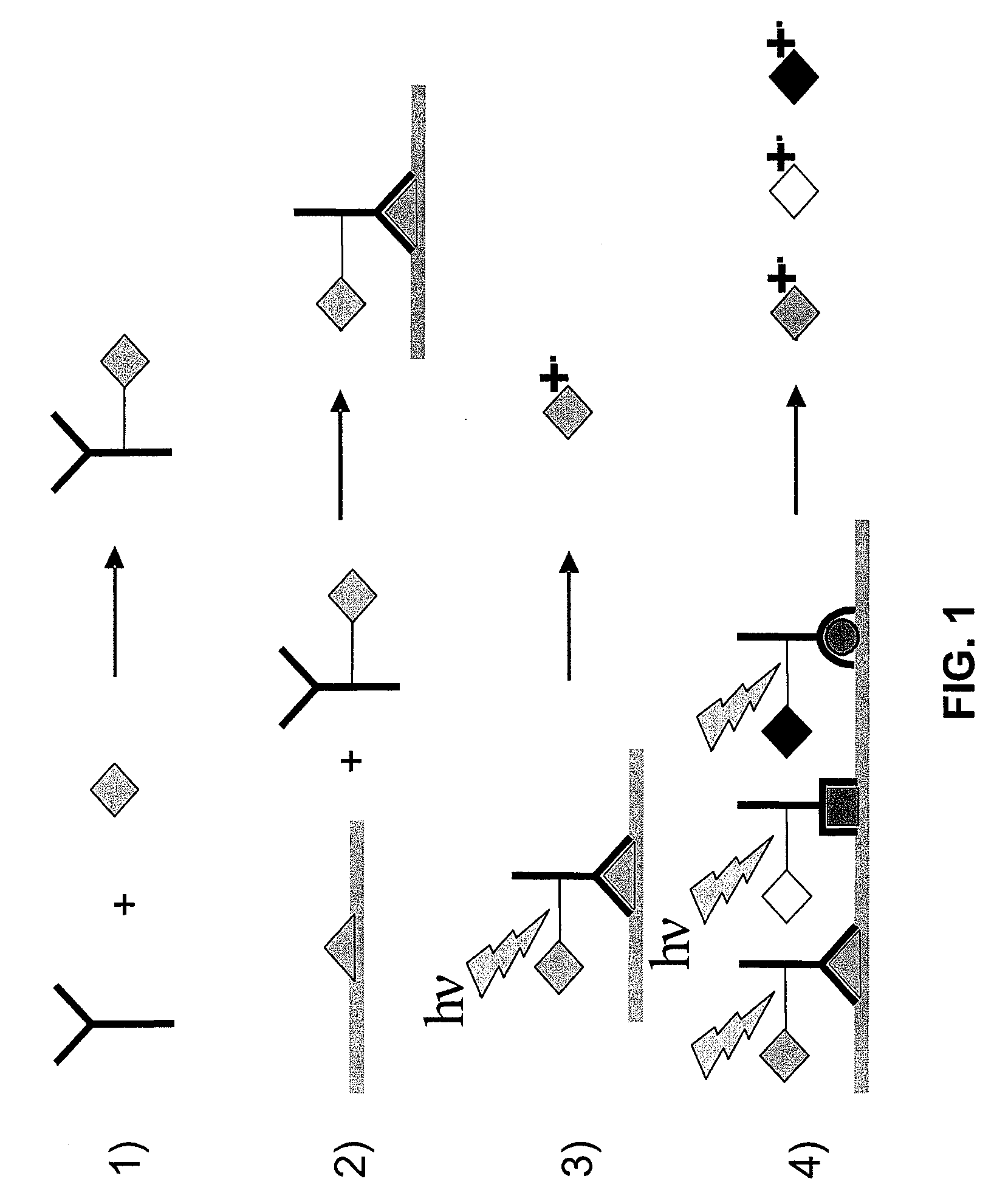
Molecular detection by matrix free desorption ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080113875A1High sensitivityLibrary screeningBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMolecular binding
The present invention provides methods for obtaining information of a plurality of target molecules by matrix free LDI MS. Mass tagged complexes for detection of target molecules comprise a target molecule binding domain, and a mass tag separated by a cleavable linker. Methods of the invention may be used for example to analyze the distribution of a multiple target molecules in a complex sample, such as a tissue section.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Artificial proteins with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS20070269435A1Improve propertiesLow immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding sitePharmacometrics
The invention relates to artificial modified proteins, preferably fusion proteins, having a reduced immunogenicity compared to the parent non-modified molecule when exposed to a species in vivo. The invention relates, above all, to novel immunoglobulin fusion proteins which essentially consist of an immunoglobulin molecule or a fragment thereof covalently fused via its C-terminus to the N-terminus of a biologically active non-immunoglobulin molecule, preferably a polypeptide or protein or a biologically active fragment thereof. In a specific embodiment, the invention relates to fusion proteins consisting of an Fc portion of an antibody which is fused as mentioned to the non-immunological target molecule which elicits biological or pharmacological efficacy. The molecules of the invention have amino acid sequences which are altered in one or more amino acid residue positions but have in principal the same biological activity as compared with the non-altered molecules. The changes are made in regions of the molecules which are identified as T-cell epitopes, which contribute to an immune reaction in a living host. Thus, the invention also relates to a novel method of making such fusion proteins by identifying said epitopes comprising calculation of T-cell epitope values for MHC Class II molecule binding sites in a peptide by computer-aided methods.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Affinity membrane for capture of a target biomolecule and formation thereof by site-directed immobilization of a capture biomolecule
InactiveUS7771955B2Increase the number ofPrecise positioningNickel organic compoundsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesTyrosineTyrosinase
Compositions and methods are taught for directing the orientation of an immobilized capture biomolecule on a hydrophobic membrane. The method comprises layering at least one tie layer on a hydrophobic membrane, adding an amine functional layer on top of at least one tie layer; and attaching an alignment biomolecule to the amine functional layer. The alignment biomolecule has the ability to either capture a target biomolecule itself and thus be considered a capture biomolecule, or bind and orient the immobilized capture biomolecule so as to maximize the binding activity of the immobilized capture biomolecule. In one embodiment, a nickel-coordinated amine functional layer binds with a histidine-tagged alignment biomolecule. In another embodiment, an amine functional layer reacts, via tyrosinase catalysis, with a tyrosine residue in an alignment biomolecule.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF +1
Enhanced biologically active conjugates
InactiveUS20050260651A1Improve propertiesImprove abilitiesOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAptamerComparable size
The invention provides compositions and methods for making and using sterically enhanced antagonist aptamer conjugates that include a nucleic acid sequence having a specific affinity for a target molecule and a soluble, high molecular weight steric group that augments or facilitates the inhibition of binding to, or interaction with, the target molecule binding partner by the target molecule when bound to the aptamer conjugate. The present invention also provides methods and formulations for ocular delivery of a biologically active molecule by attaching a charged moiety to the biologically active molecule and delivering the biologically active molecule by iontophoresis. Iontophoresis of a biologically active molecule that is conjugated to a high molecular weight neutral moiety, in enhanced by substituting the high molecular weight neutral moiety with a charged molecule of comparable size.
Owner:EYETECH
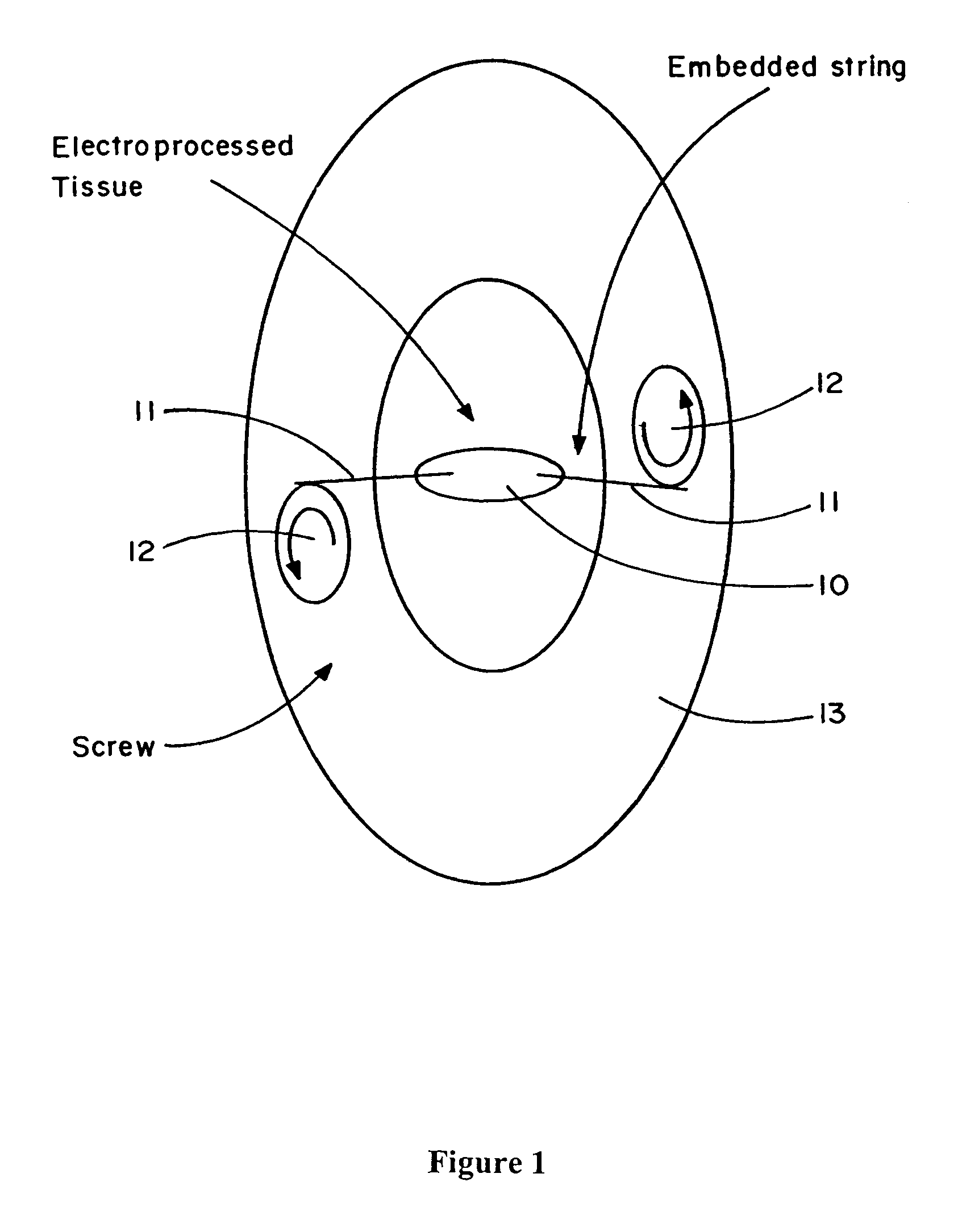
Electroprocessed fibrin-based matrices and tissues
InactiveUS7759082B2Minimizing chanceCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
The invention is directed to formation and use of electroprocessed fibrin as an extracellular matrix and, together with cells, its use in forming engineered tissue. The engineered tissue can include the synthetic manufacture of specific organs or tissues which may be implanted into a recipient. The electroprocessed fibrin may also be combined with other molecules in order to deliver the molecules to the site of application or implantation of the electroprocessed fibrin. The fibrin or fibrin / cell suspension is electrodeposited onto a substrate to form the tissues and organs.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV INTPROP FOUND INC
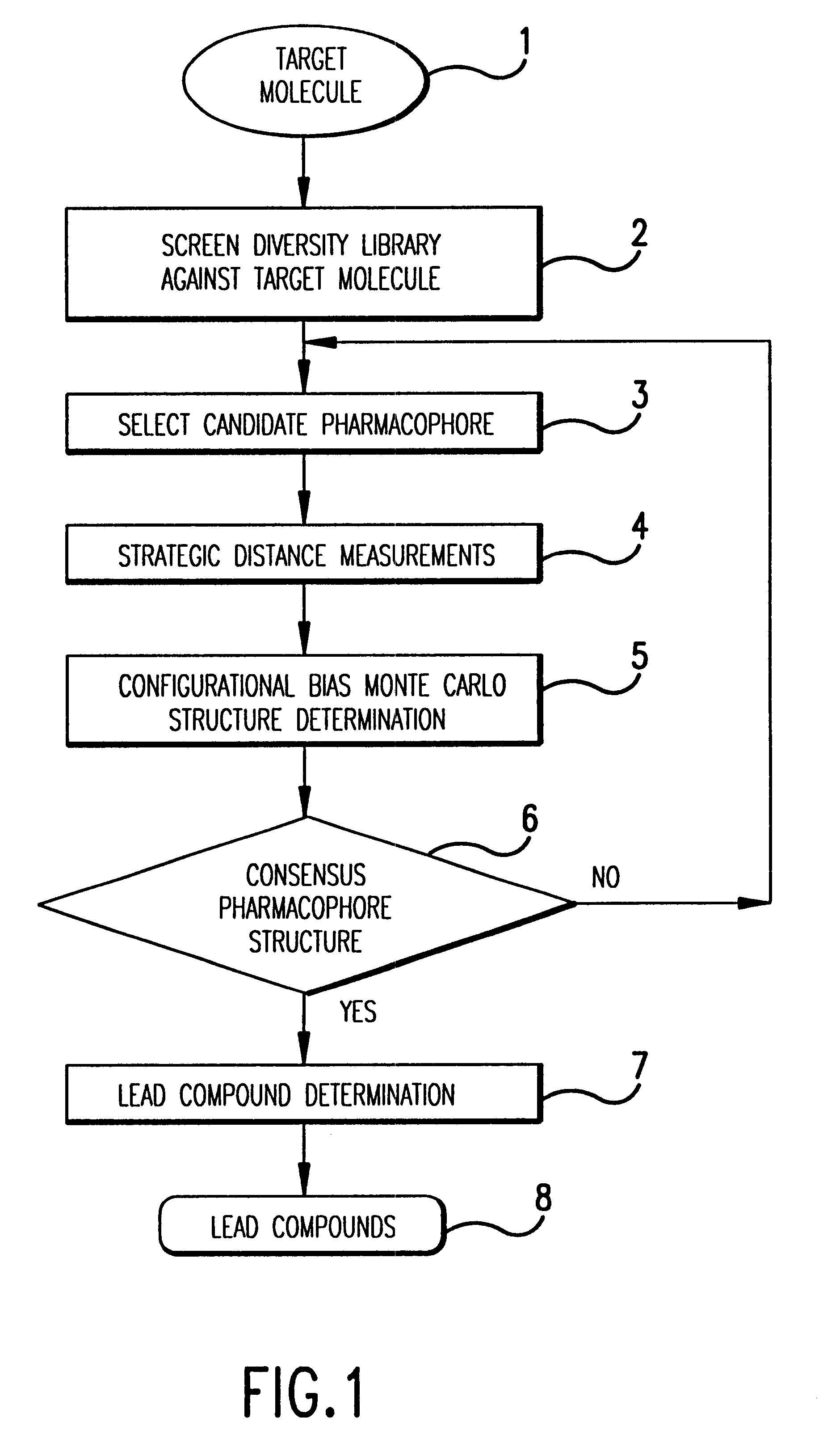
Consensus configurational bias Monte Carlo method and system for pharmacophore structure determination
InactiveUS6341256B1Accurate distance measurementMake a pharmacophore structure determinationPeptide librariesNanotechNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePeptide
In a specific embodiment, this invention includes a method for determining an accurate, consensus pharmacophore structure shared by compounds that bind selectively to a target molecule. Optionally, the method begins with screening a diversity library against the target molecule of interest to pick the selectively binding members. Next the structure of the selected members is examined and a candidate pharmacophore responsible for the binding to the target molecule is determined. Next, preferably by REDOR nuclear magnetic resonance, several highly accurate interatomic distances are determined in certain of the selected members which are related to the candidate pharmacophore. A highly accurate consensus, configurational bias, Monte Carlo method determination of the structure of the candidate pharmacophore is made using the structure of the selected members and incorporating as constraints the shared candidate pharmacophore and the several measured distances. This determination is adapted to efficiently examine only relatively low energy configurations while respecting any structural constraints present in the organic diversity library. If the diversity library contains short peptides, the determination respects the known degrees of freedom of peptides as well as any internal constraints, such as those imposed by disulfide bridges. Finally, the highly accurate pharmacophore so determined is used to select lead organics for drug development targeted at the initial target molecule.
Owner:CURAGEN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com