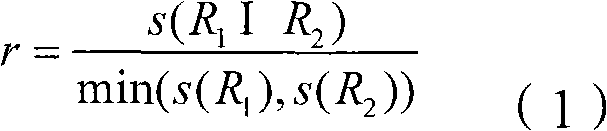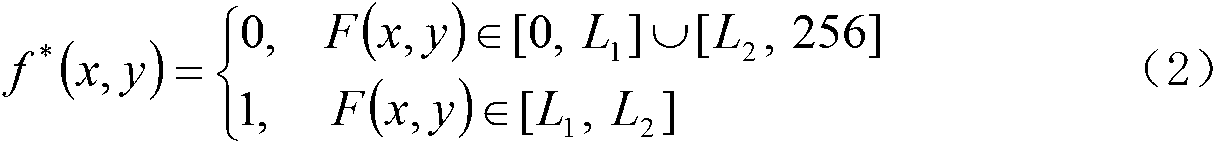Patents
Literature
211 results about "Flow imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
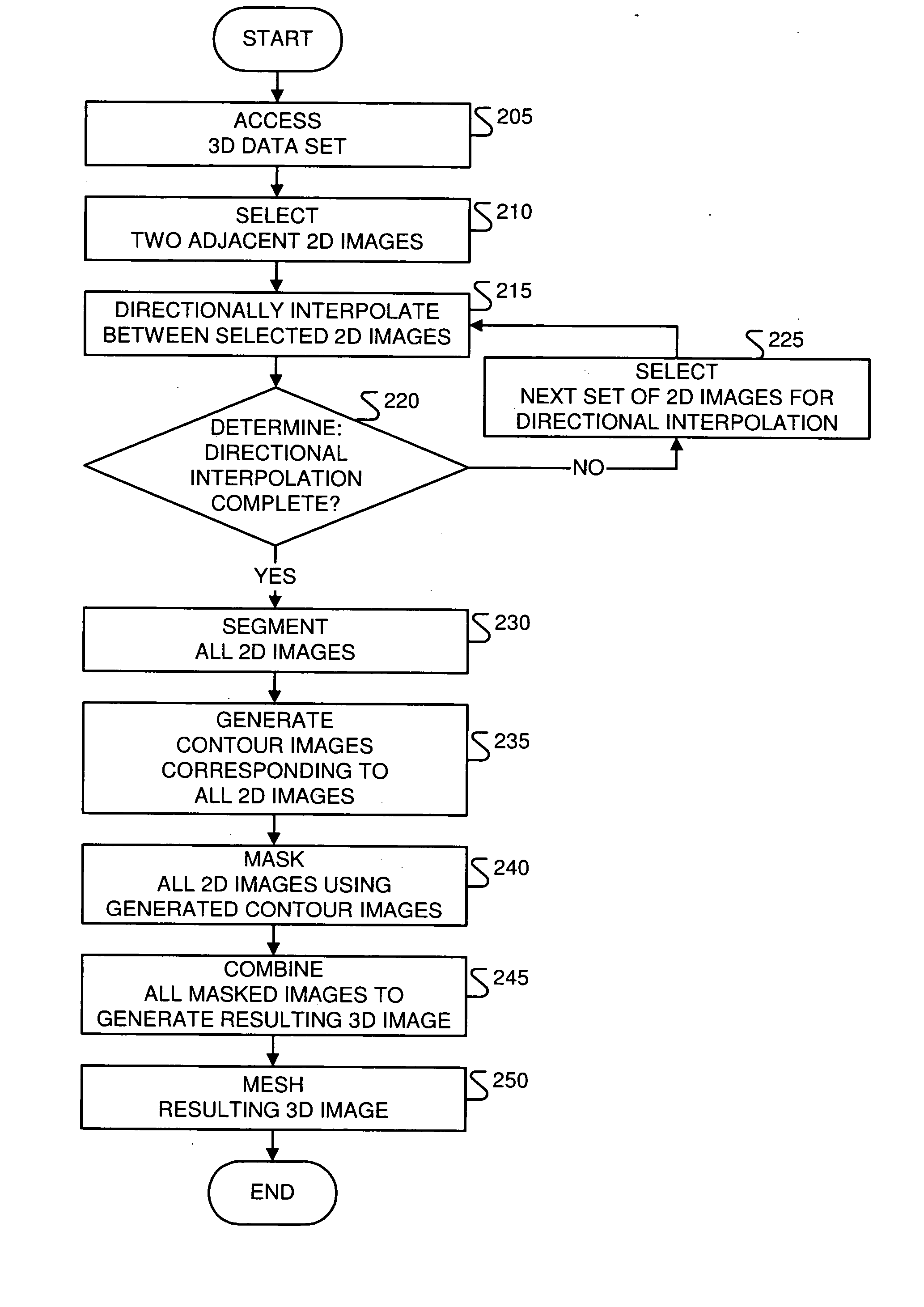
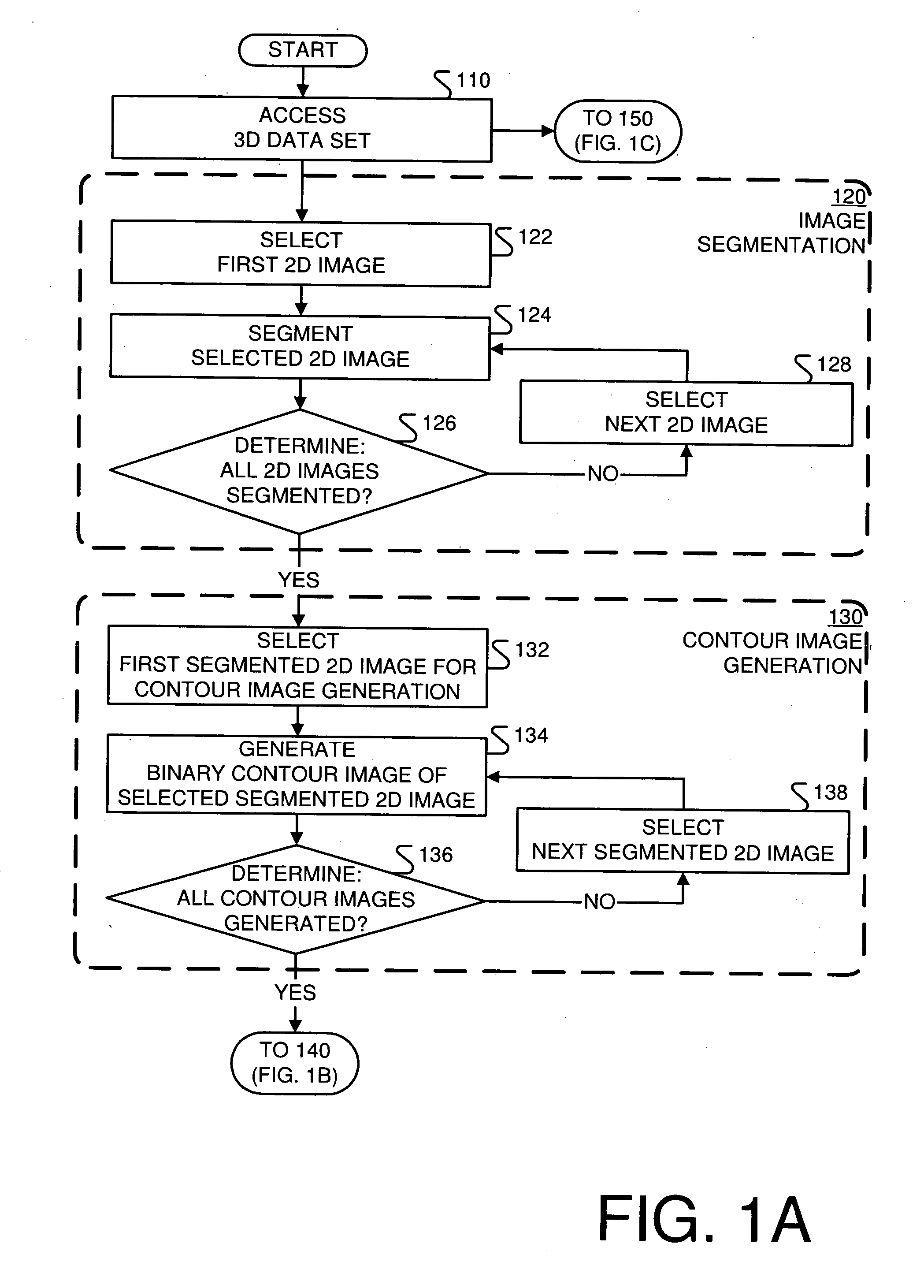
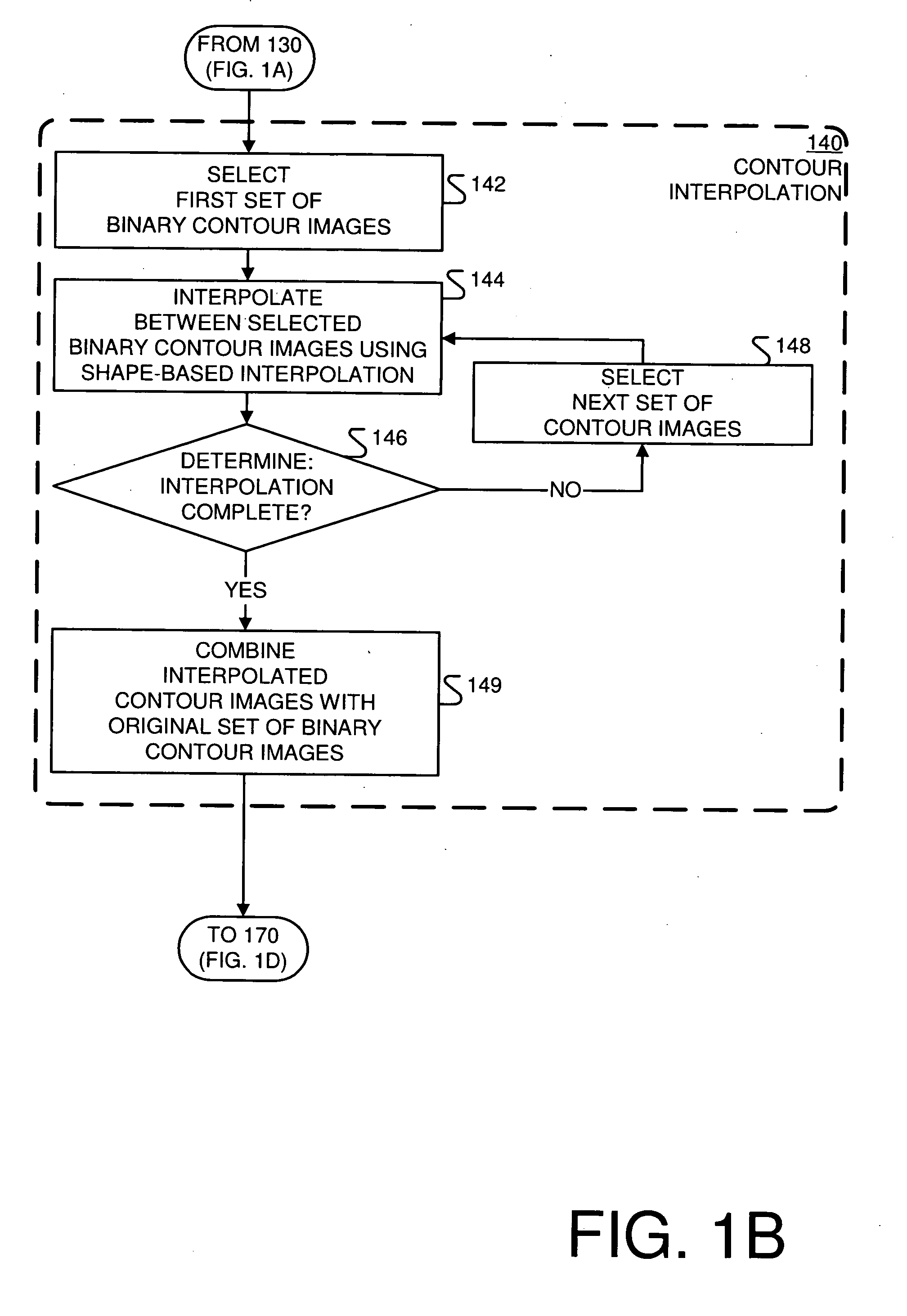
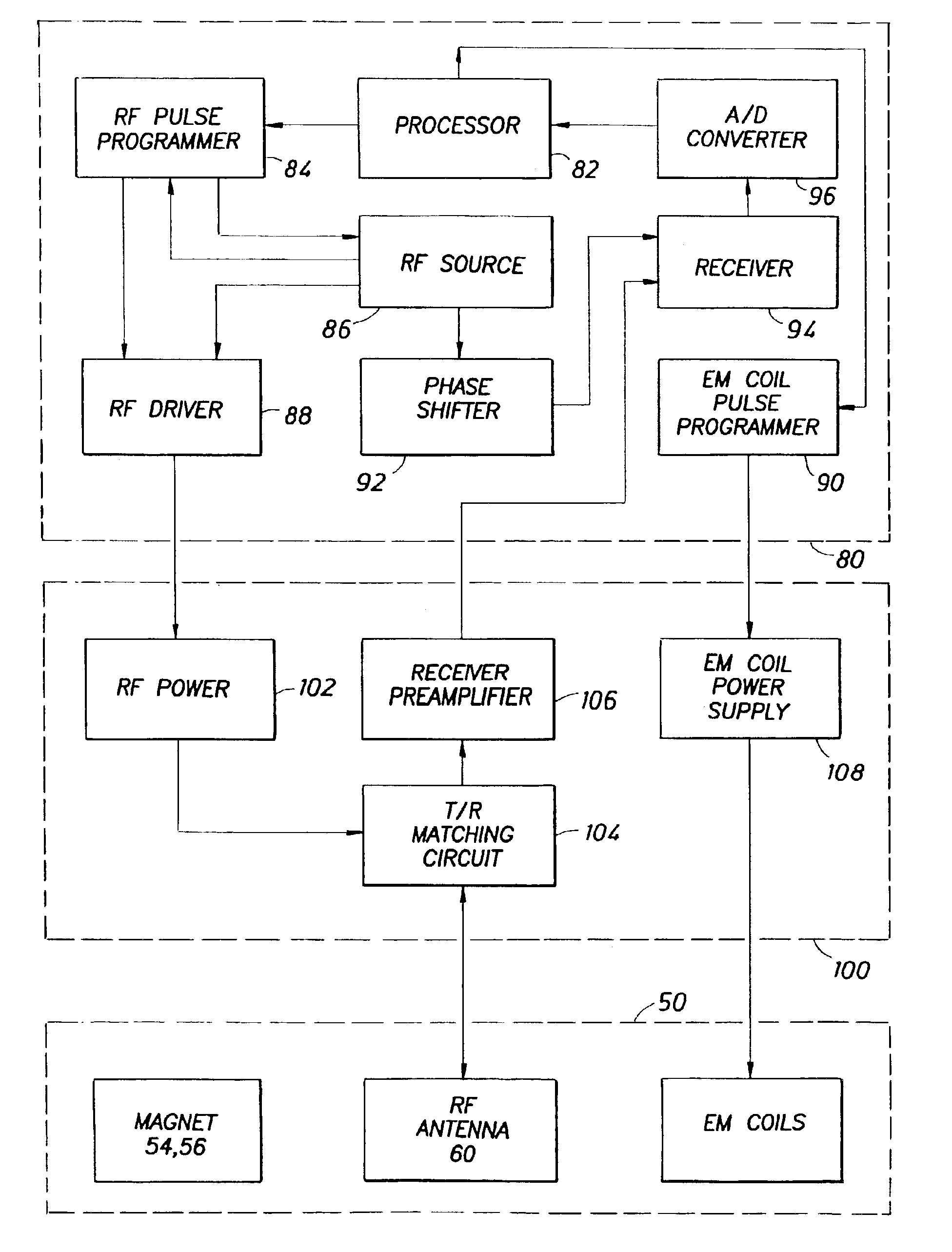
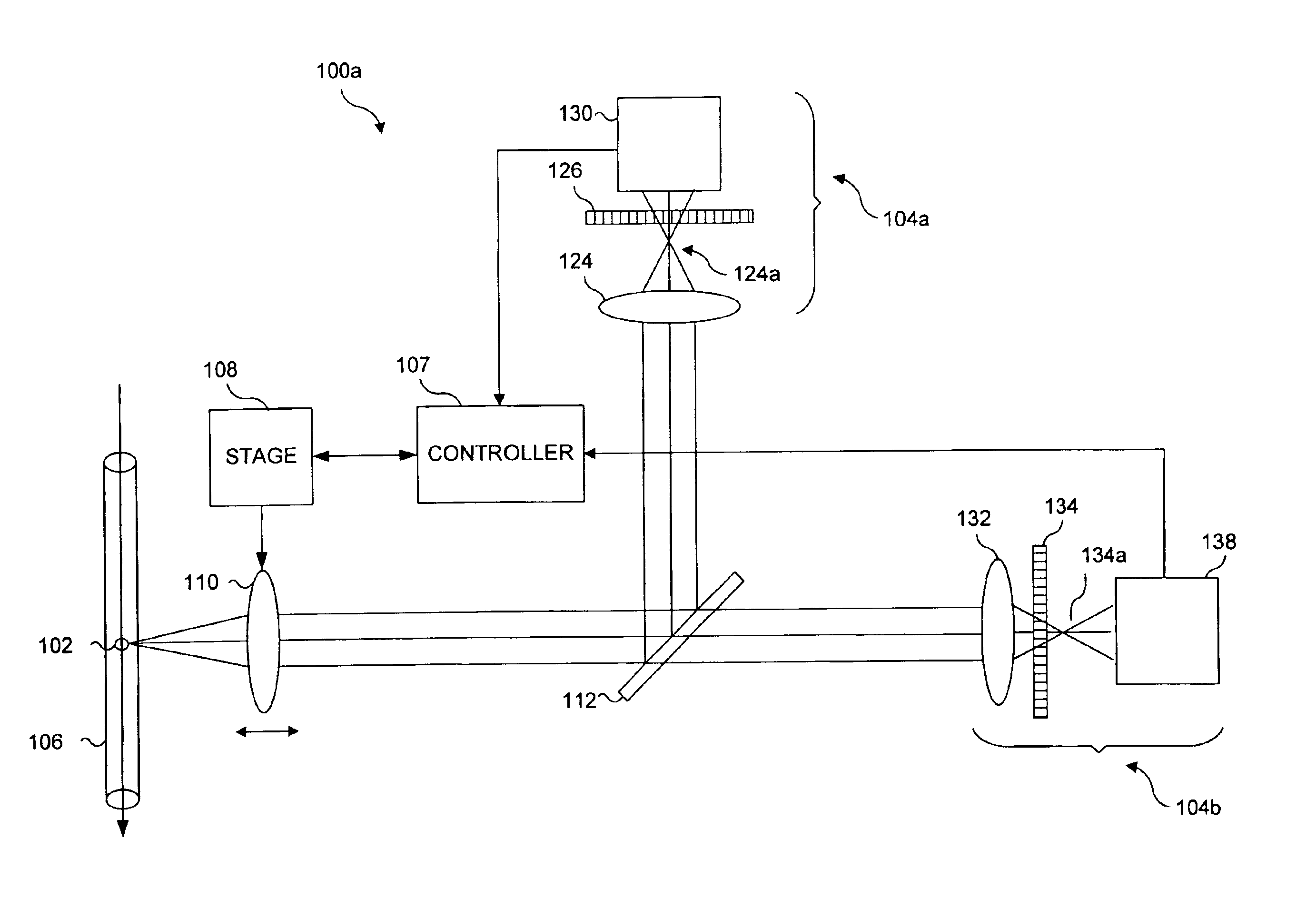
Data reconstruction using directional interpolation techniques
Approaches to three-dimensional (3D) data reconstruction are presented. The 3D data comprises 2D images. In some embodiments, the 2D images are directionally interpolated to generate directionally-interpolated 3D data. The directionally-interpolated 3D data are then segmented to generate segmented directionally-interpolated 3D data. The segmented directionally-interpolated 3D data is then meshed. In other embodiments, a 3D data set, which includes 2D flow images, is accessed. The accessed 2D flow images are then directionally interpolated to generate 2D intermediate flow images.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
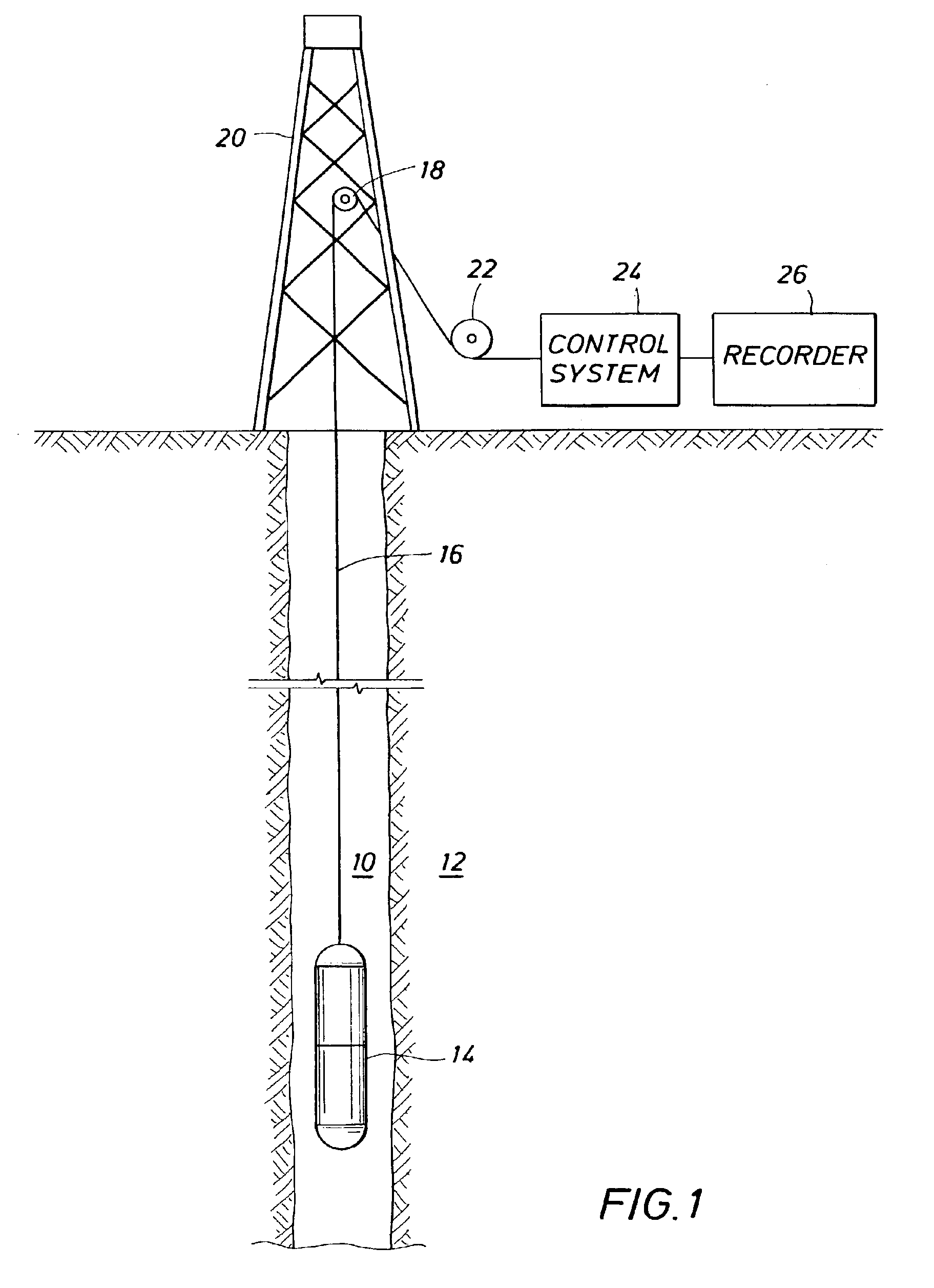
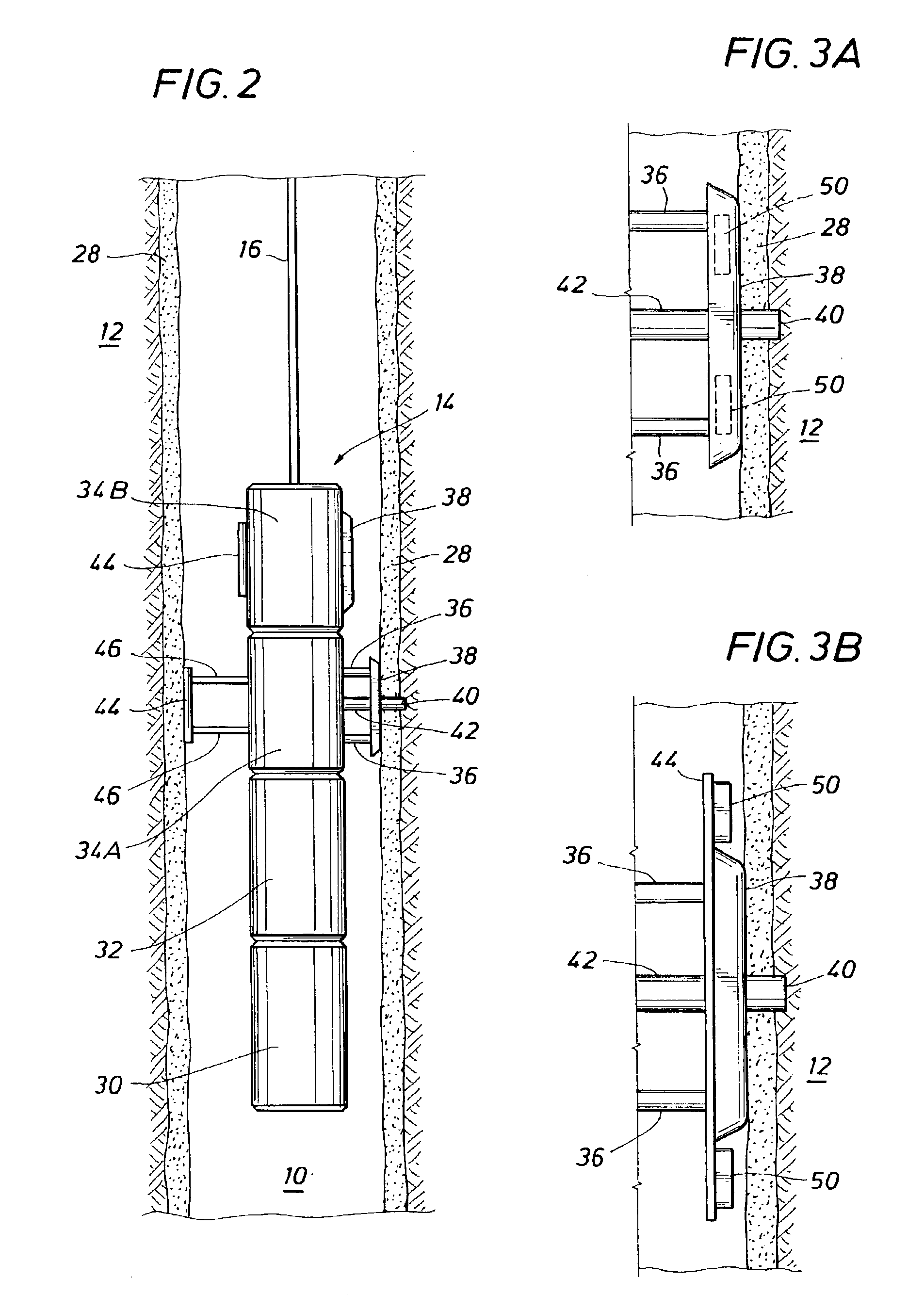
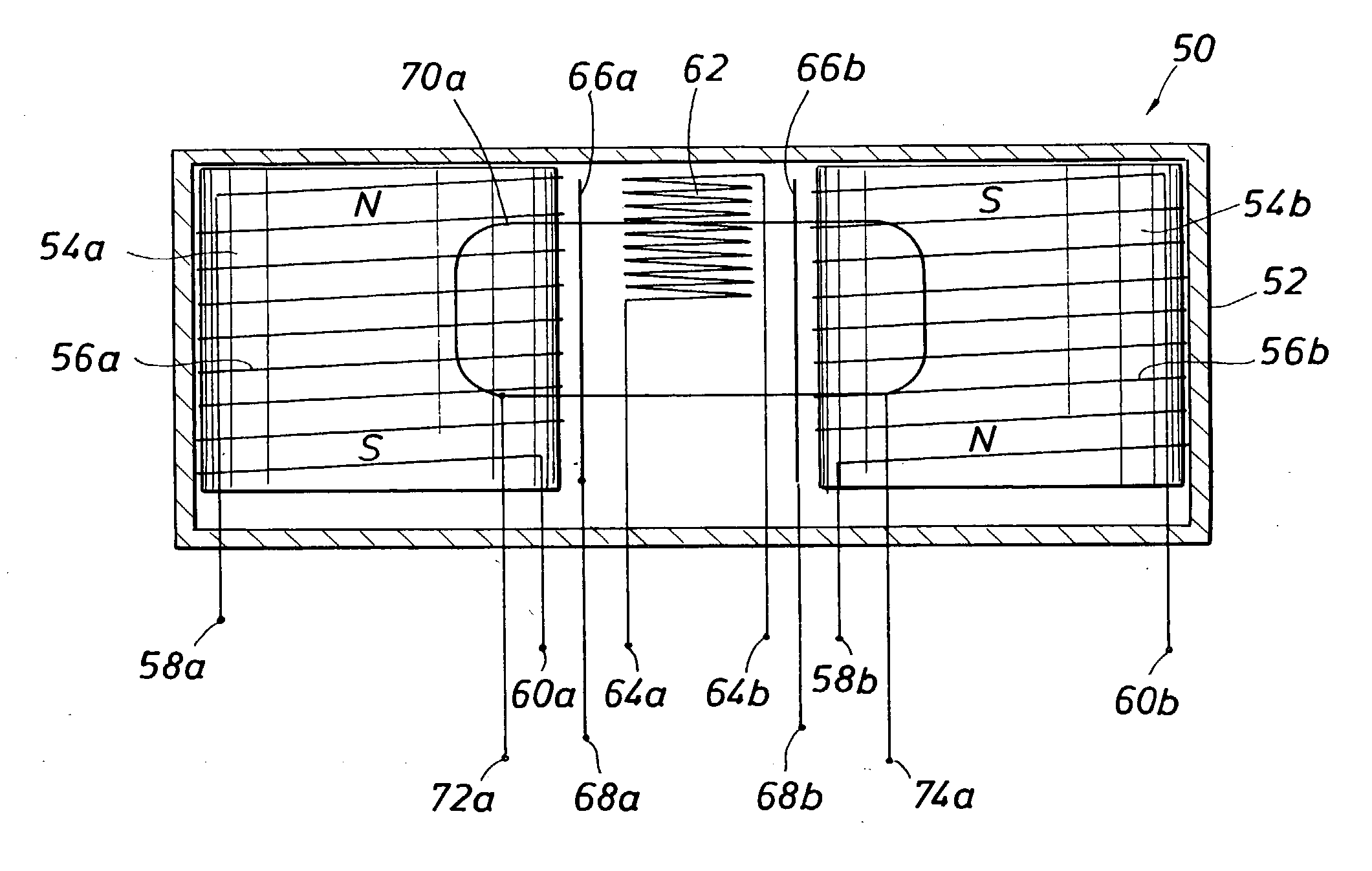
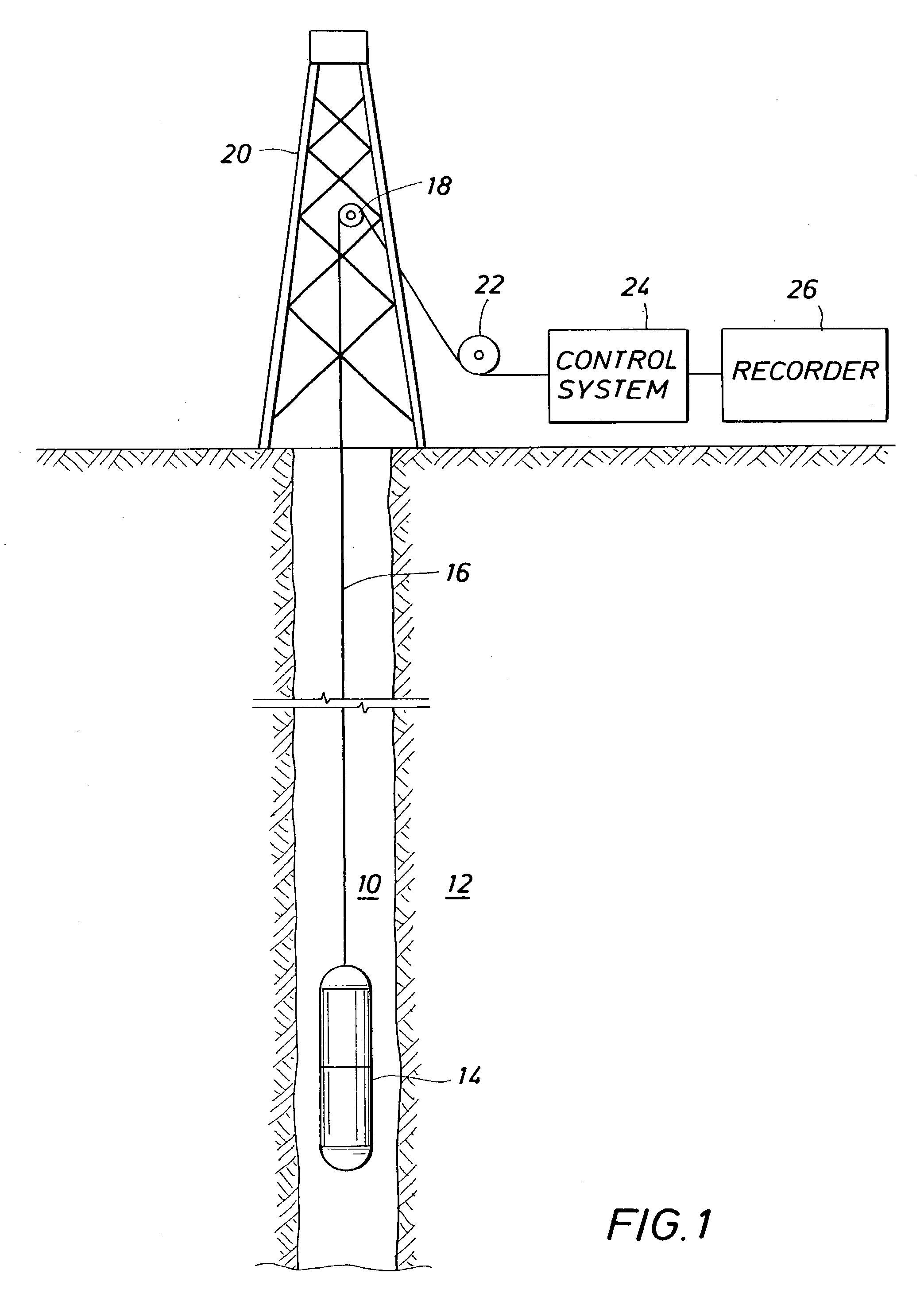
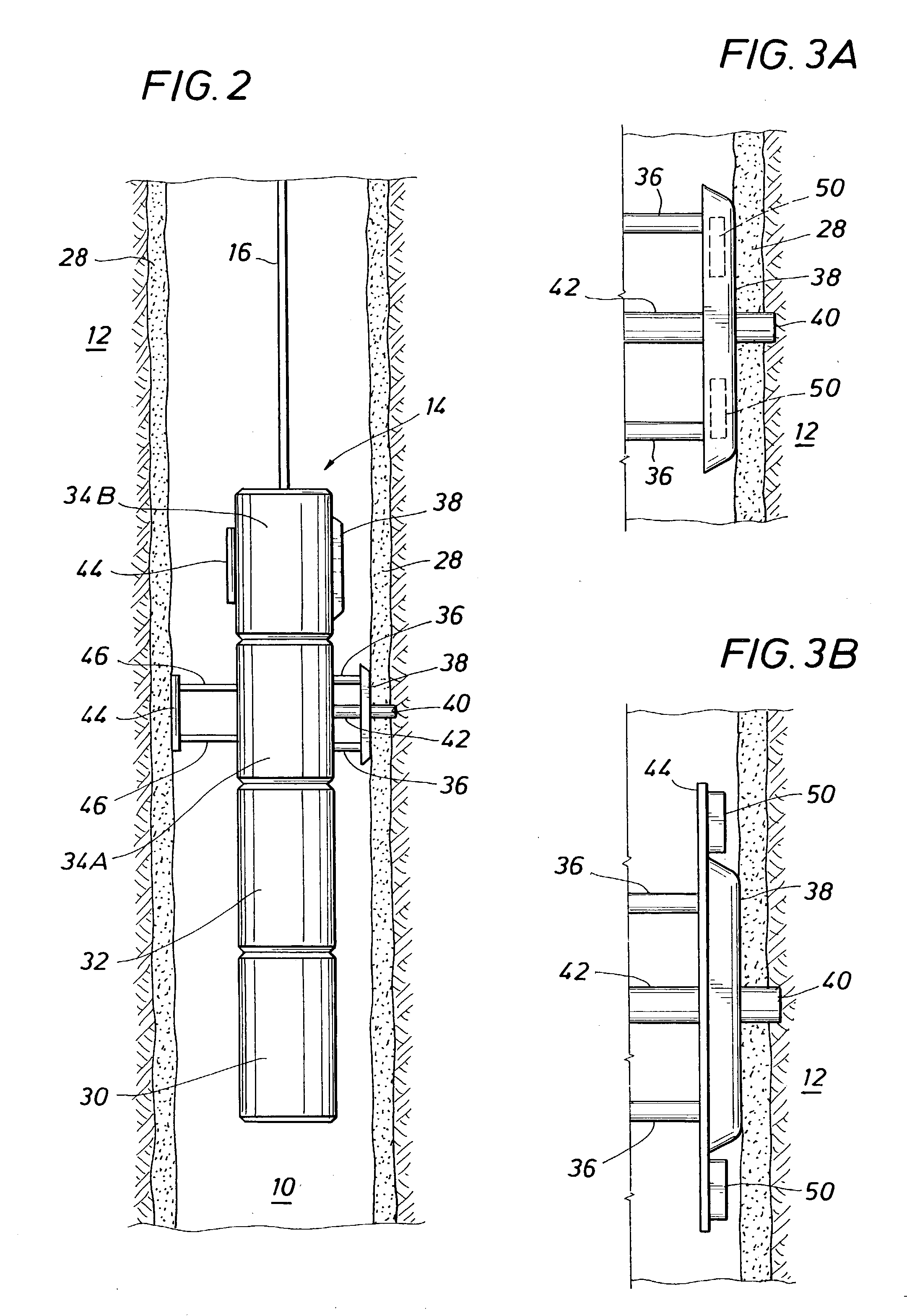
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
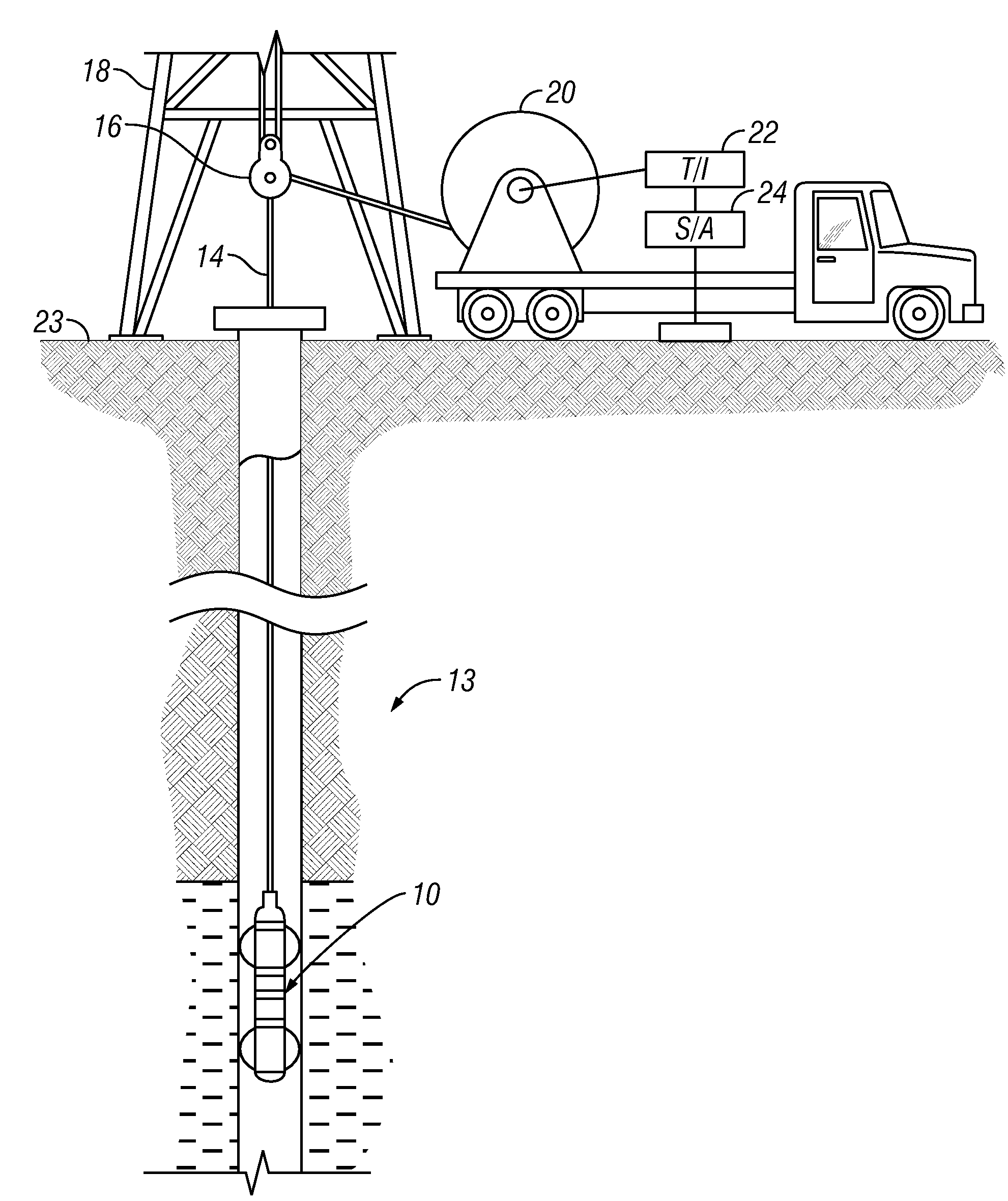
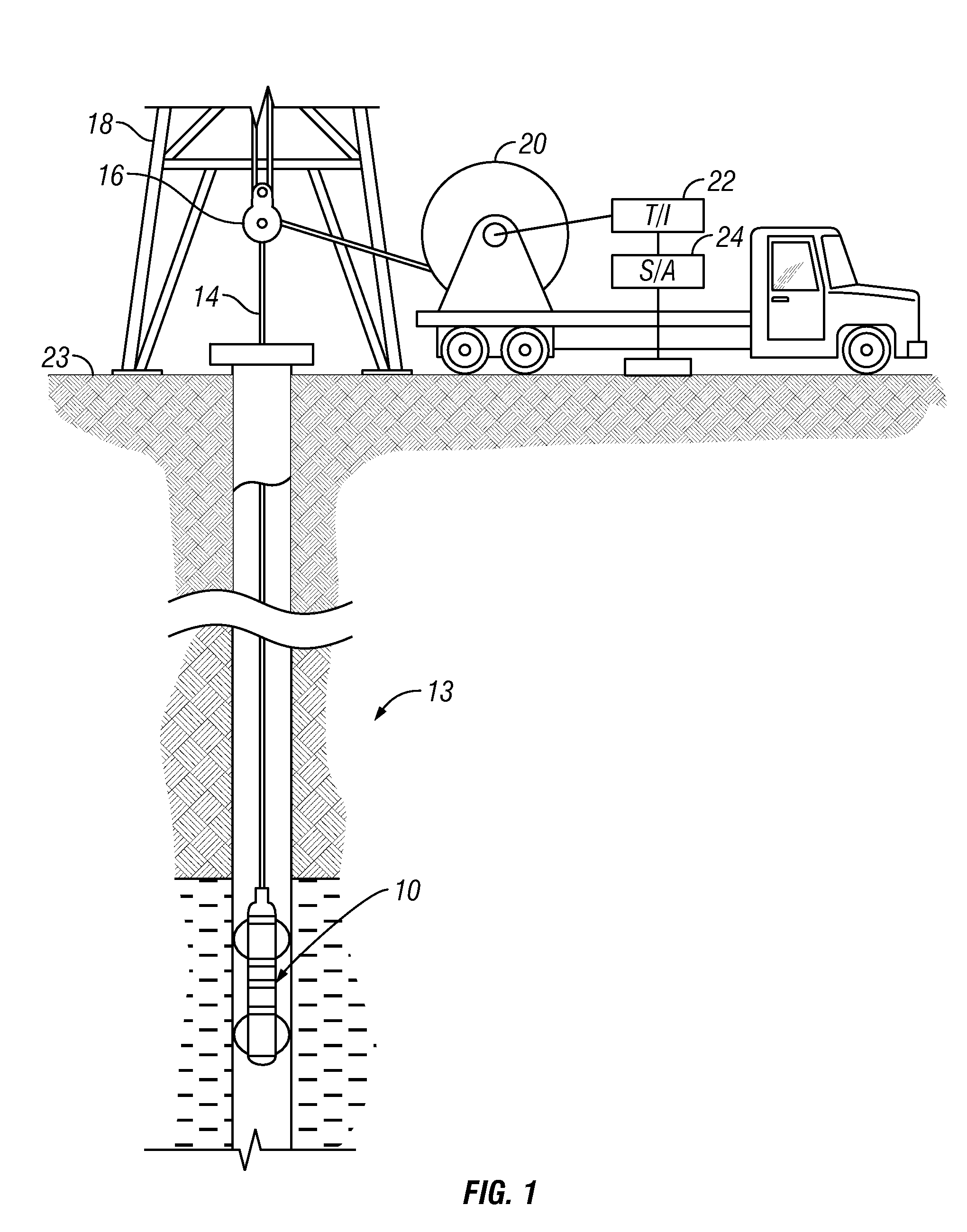
InactiveUS6856132B2Accurate measurementAccurately determineElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method and apparatus for subterranean formation flow imaging
InactiveUS20040090230A1Accurately determine formation parameterAccurate measurementElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceMri imageGeophysics
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring a property relating to fluid flow in an earth formation, more specifically to directly measuring formation permeability and other fluid characteristics. The present invention provides a method for determining the permeability of a hydrocarbon bearing earth formation, which method comprises the steps of: locating a tool at a selected position in a borehole penetrating the earth formation; inducing a flow of fluid within the earth formation to said tool; creating at least two MRI images of said fluid while flowing within the earth formation to said tool, said at least two images being created at different times; determining displacement of said fluid within the earth formation between said different times, using the at least two MRI images.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Methods of calibrating an imaging system using calibration beads
InactiveUS6906792B2Improve liquidityEasy procedureImage analysisIndividual particle analysisPoint spreadSmall sample
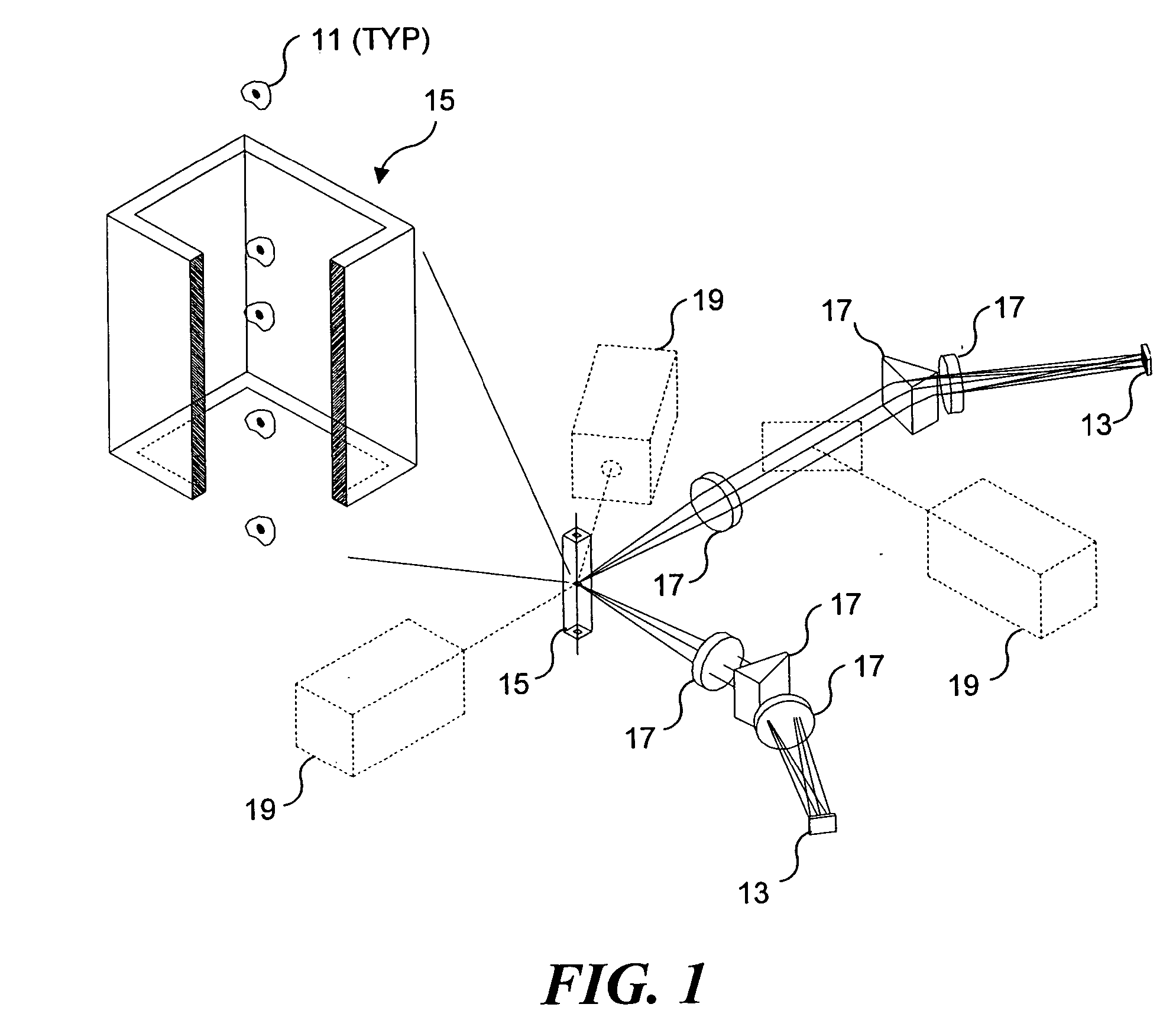
When utilized in a flow imaging instrument, calibration beads provide a known data source that can be employed in various self-diagnostic, calibration and quality metric applications for the both the optical system of the flow imaging instrument, as well as the flow cell of the flow imaging instrument. Such data can be used to determine point spread functions associated with an imaging system, to determine a sensitivity of an imaging system, and to determine a focal point of the imaging system. Imagery collected from calibration beads can be used to determine core size and stability and TDI / flow speed synchronization. Calibration beads can be beneficially employed to enable stable system operation, even when very low sample concentration, or very small sample sizes are to be analyzed.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
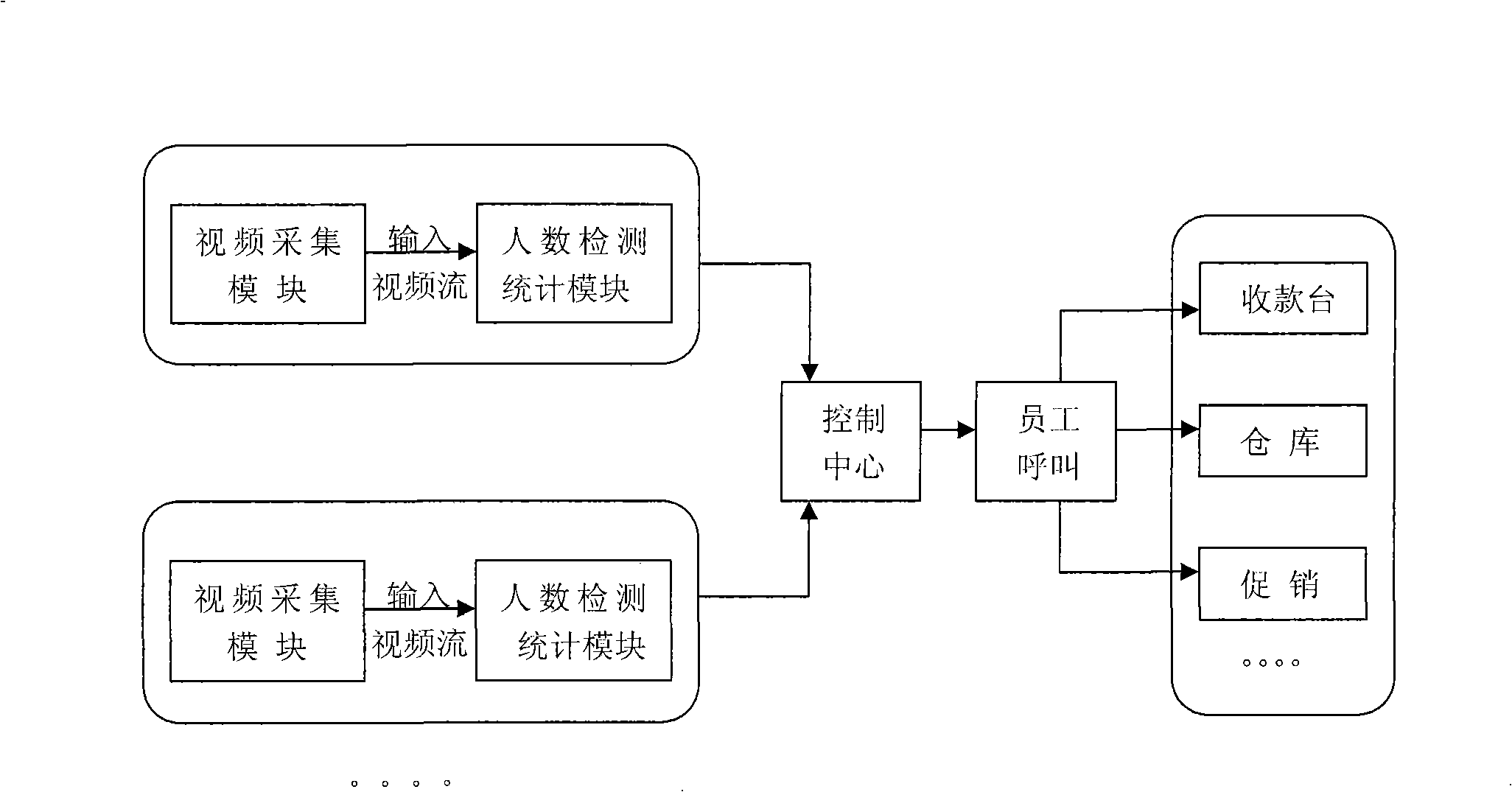
Intelligent management method based on video human number Stat. and system thereof
ActiveCN101303727AImprove management levelImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionIntelligent managementVideo image
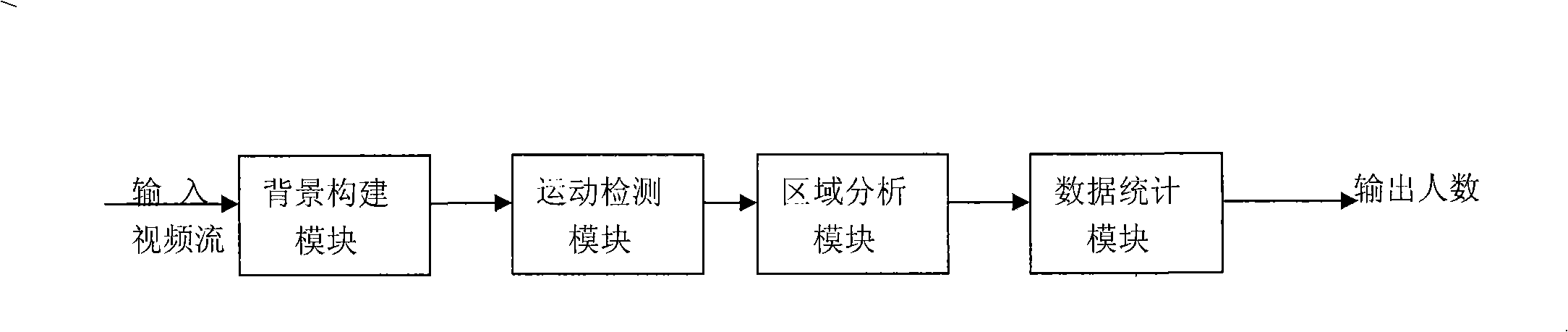
The invention relates to the technical field of video image processing and mode identifying. The invention discloses an intelligent management method based on video people number statistics, which includes the following steps: S1: capturing a video flow image as an input image; S2: carrying out the treatment of people number statistics on the input image to obtain the people flow distribution data in the unit time of each area; S3: a control center carries out adjusting and control on the working personnel according to the people flow distribution data obtained in step S2. A corresponding system includes a video collection module and a people number detecting statistics module; wherein, the people number detecting statistics module include a background construction module, a motion detecting module, an area analyzing module and a data statistics module. The method can be used for reasonably arranging the working number of the personnel of different posts according to the people flow statistic in a scene in a unit time, can better and more reasonably save the manpower cost and effectively improve the management level of public areas.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
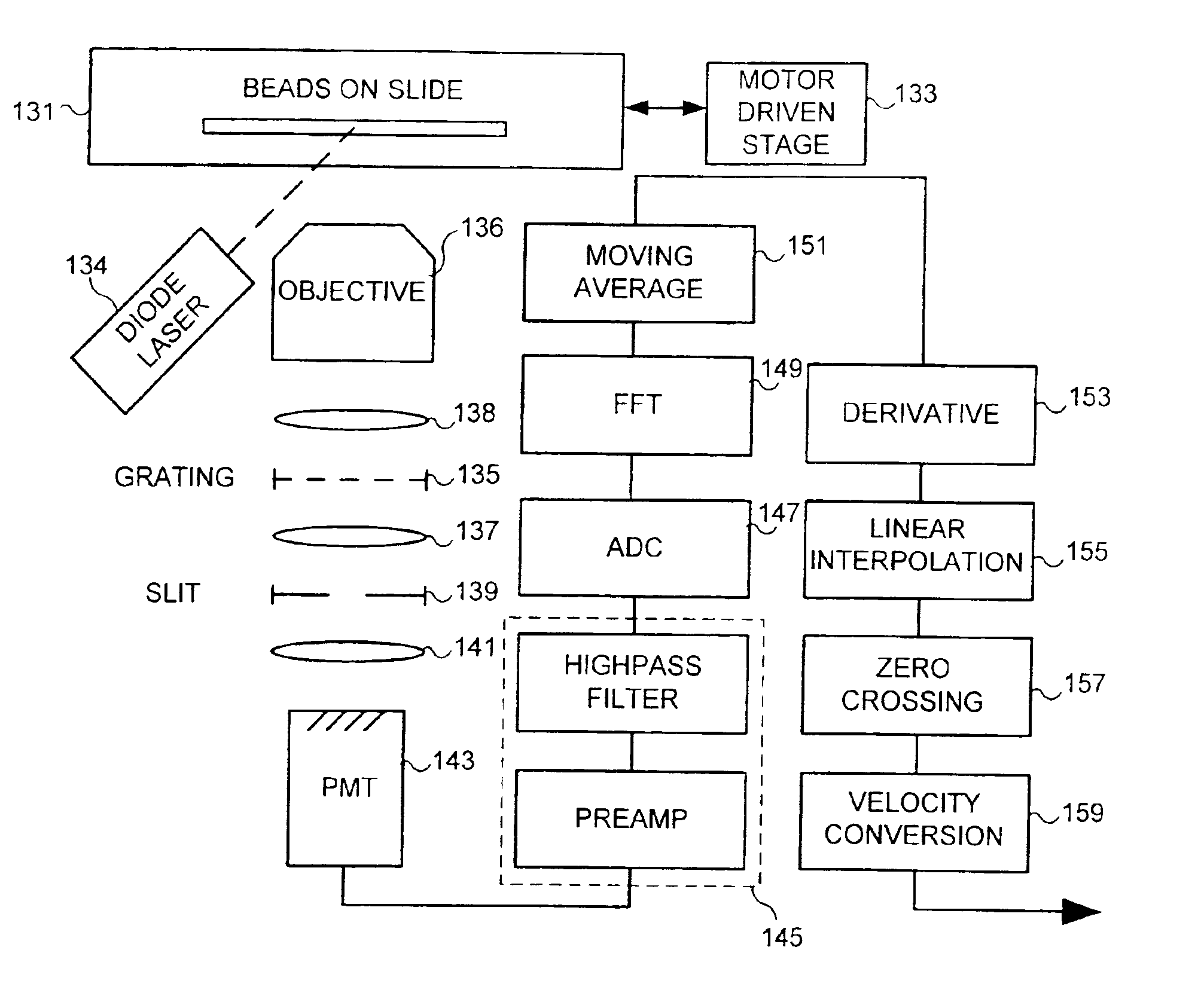
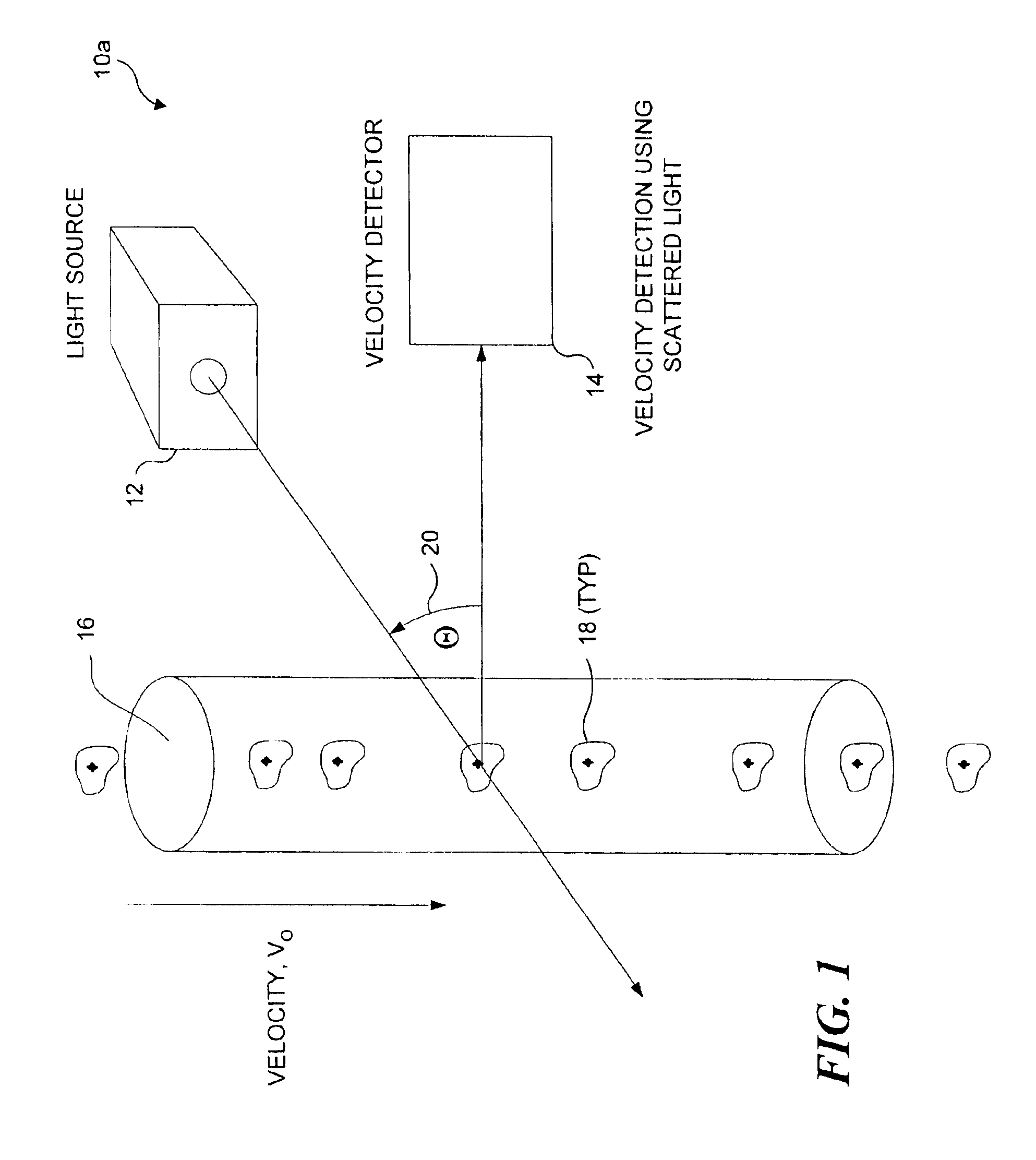
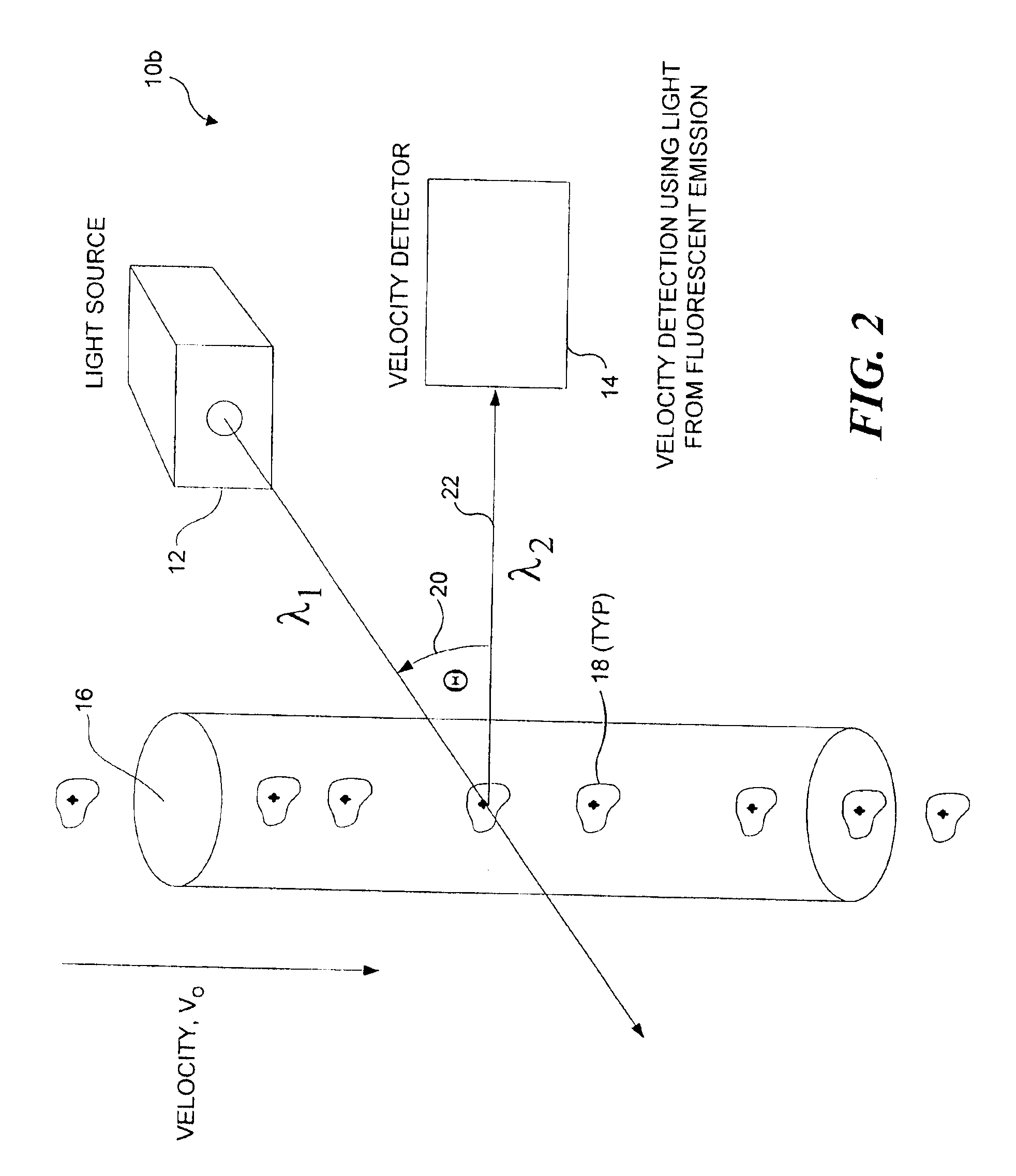
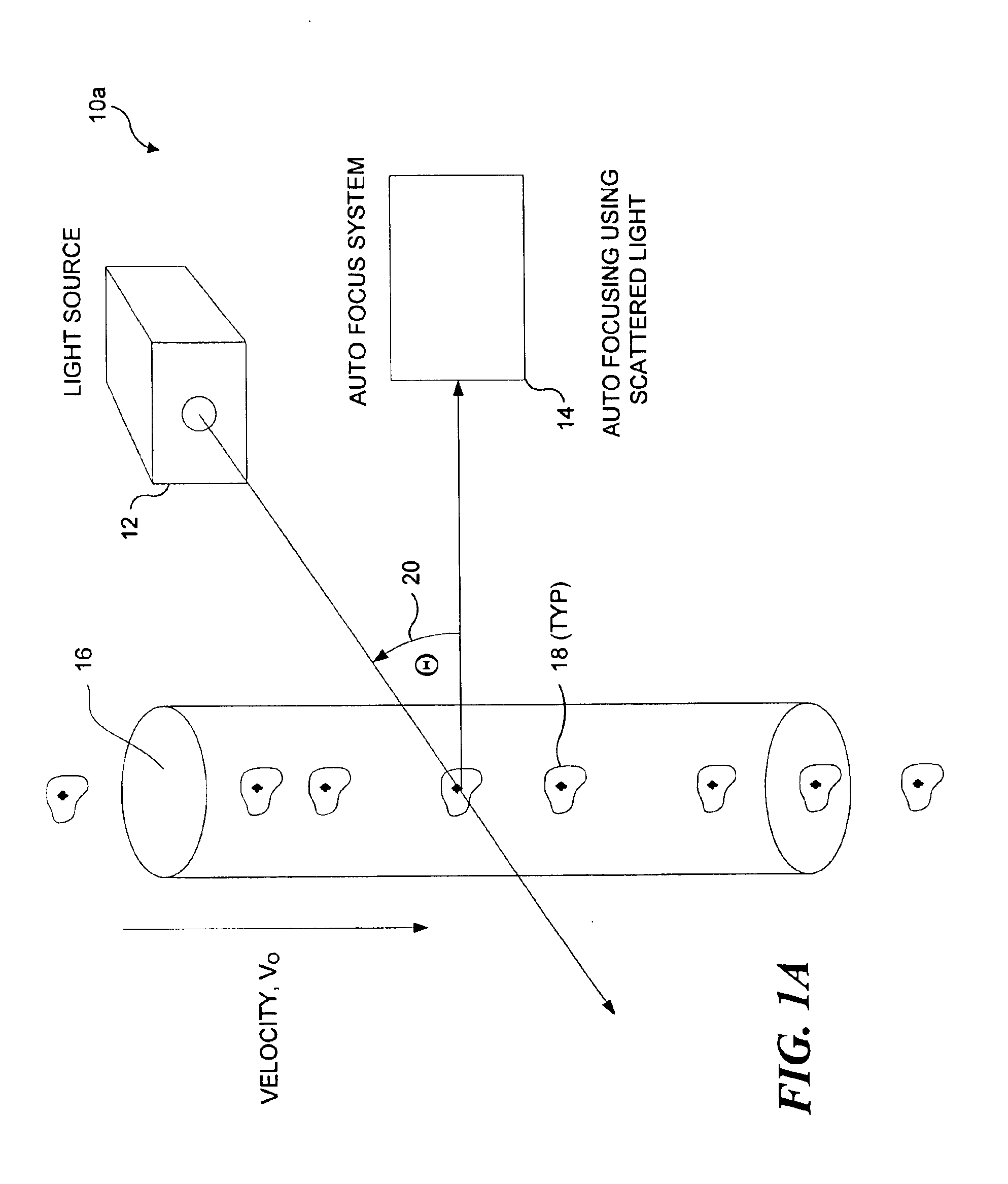
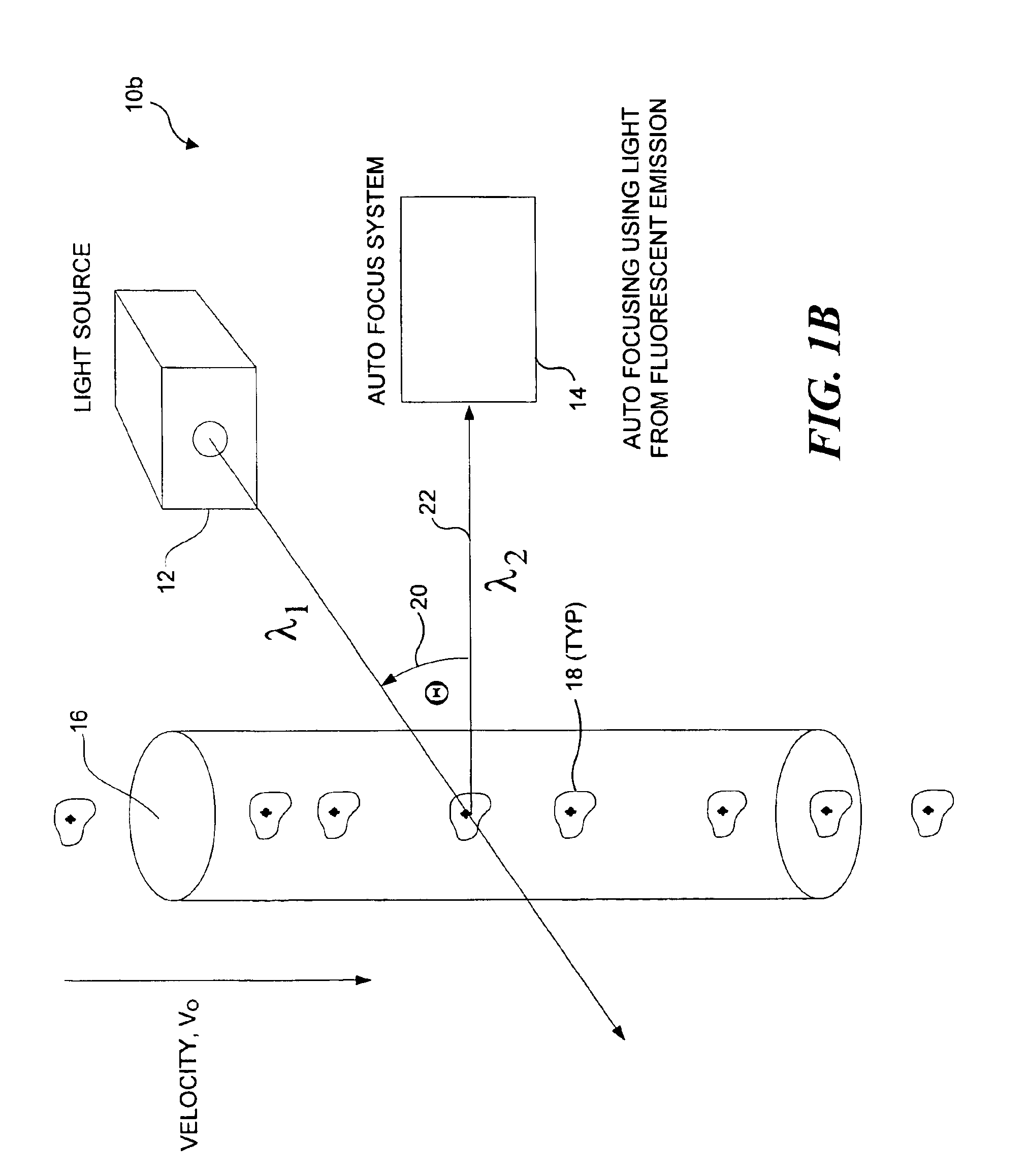
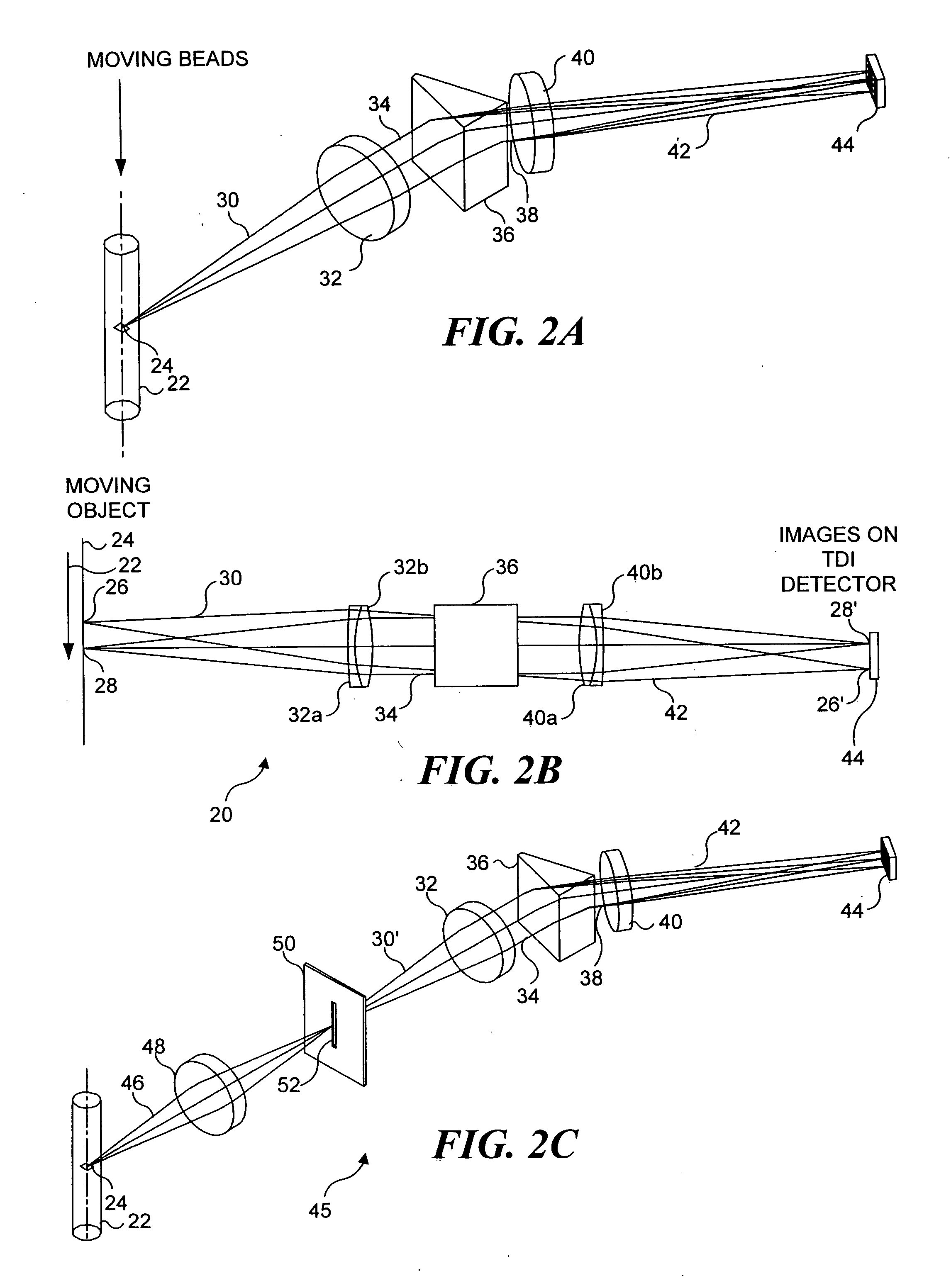
Auto focus for a flow imaging system
A pair of optical gratings are used to modulate light from an object, and the modulated light from either optical is used to determine the velocity of the object. Each optical grating is offset from a reference focal point by the same distance, one grating being offset in a positive direction, the other in a negative direction. Signals produced in response to the modulated light can be processed to determine a direction in which a primary collection lens should be moved in order to improve a focus of the imaging system on the object. The lens is moved incrementally in the direction so determined, and the process is repeated until an optimal focus is achieved. In a preferred embodiment, the signals are weighted, so that the optical grating disposed closest to the optimal focus position contributes the most to velocity detection.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
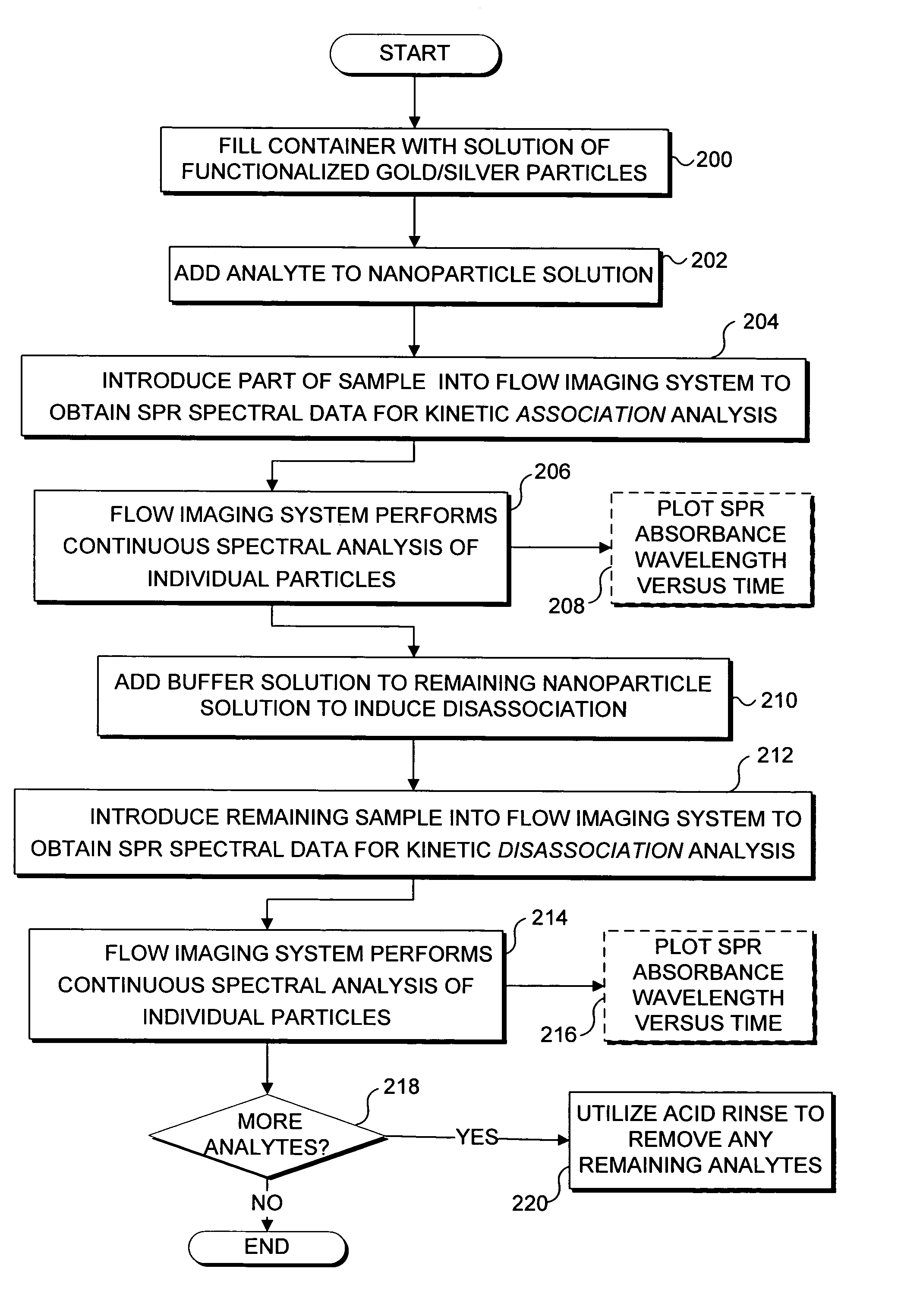
Imaging platform for nanoparticle detection applied to SPR biomolecular interaction analysis
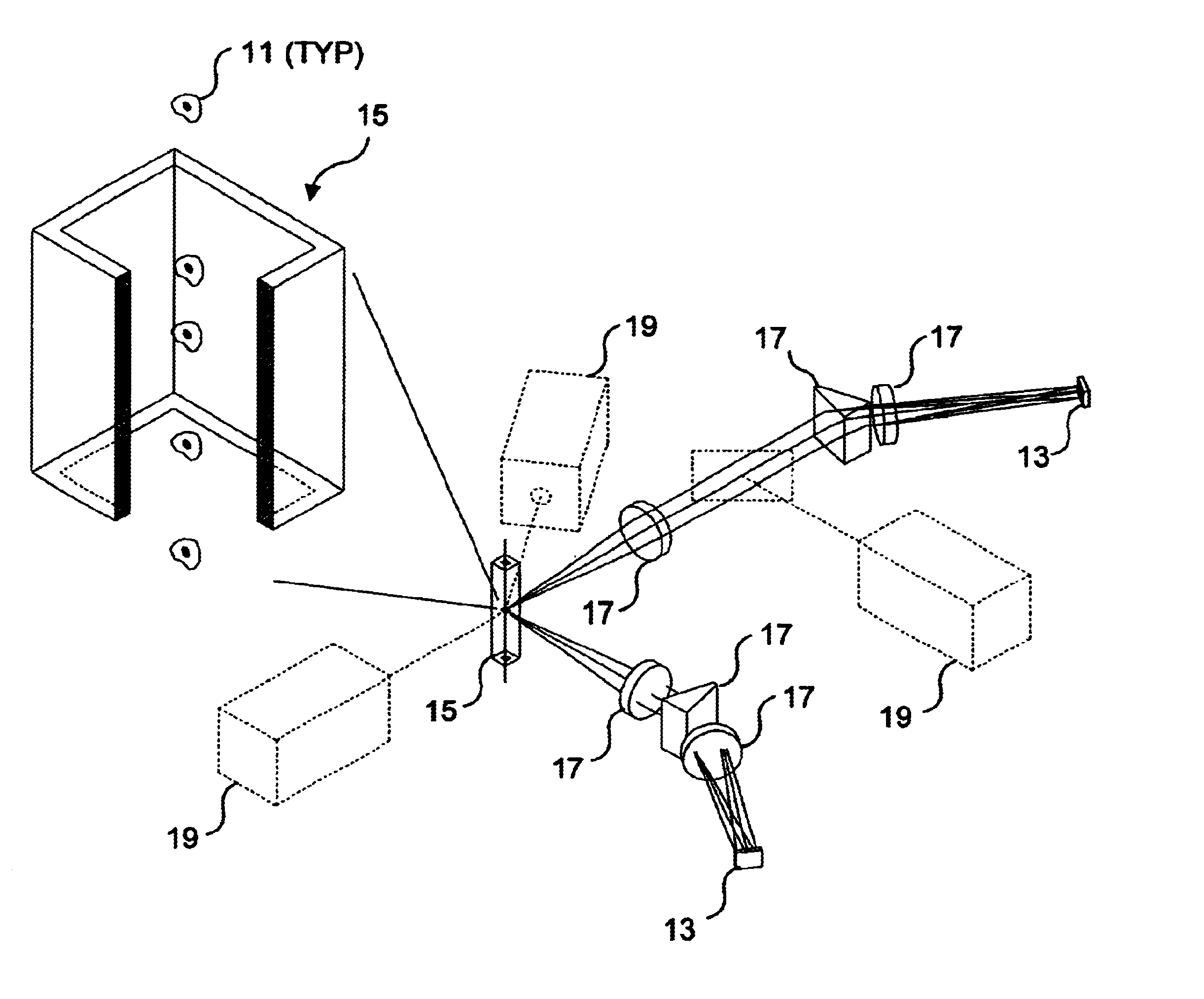
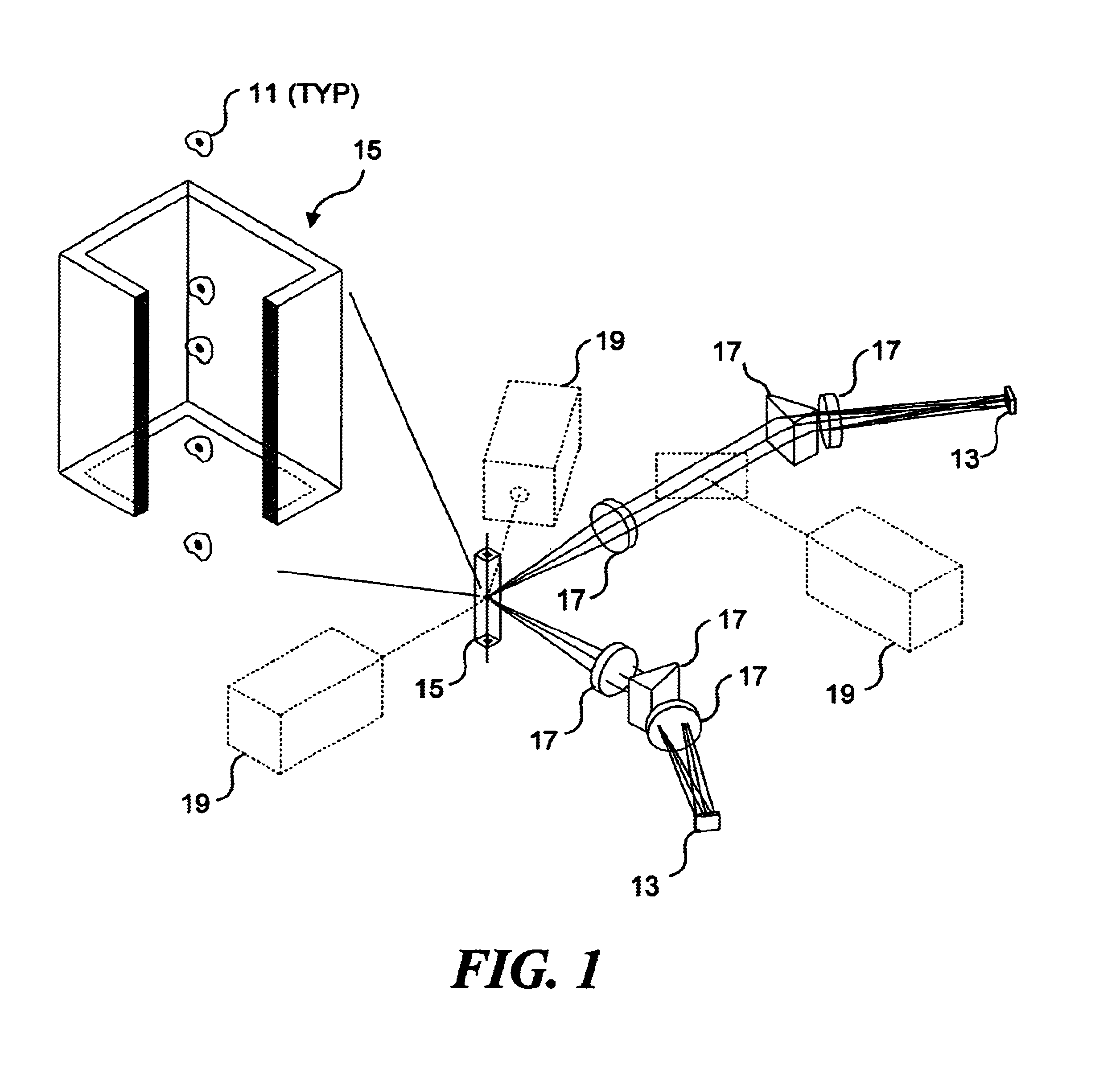
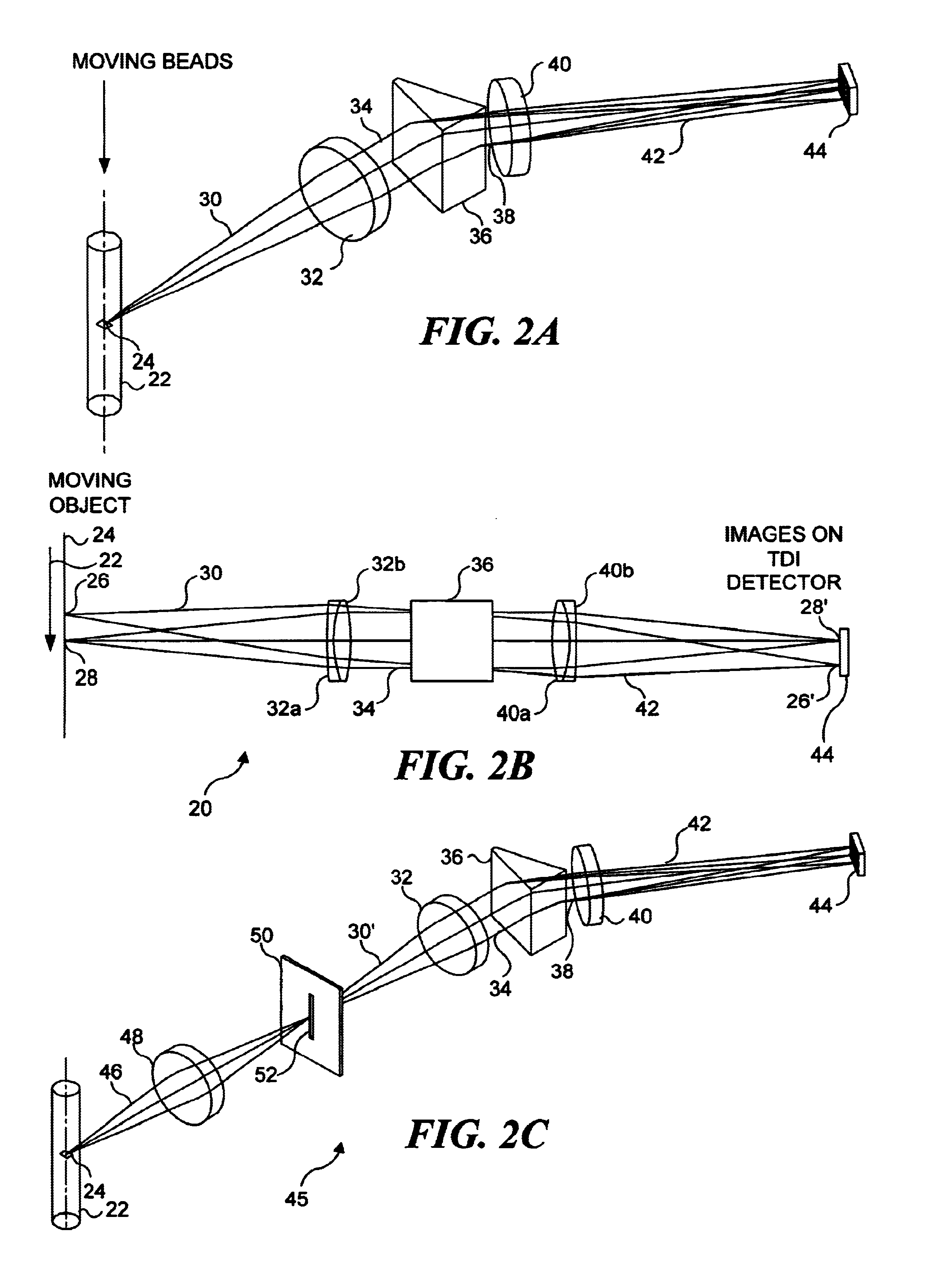
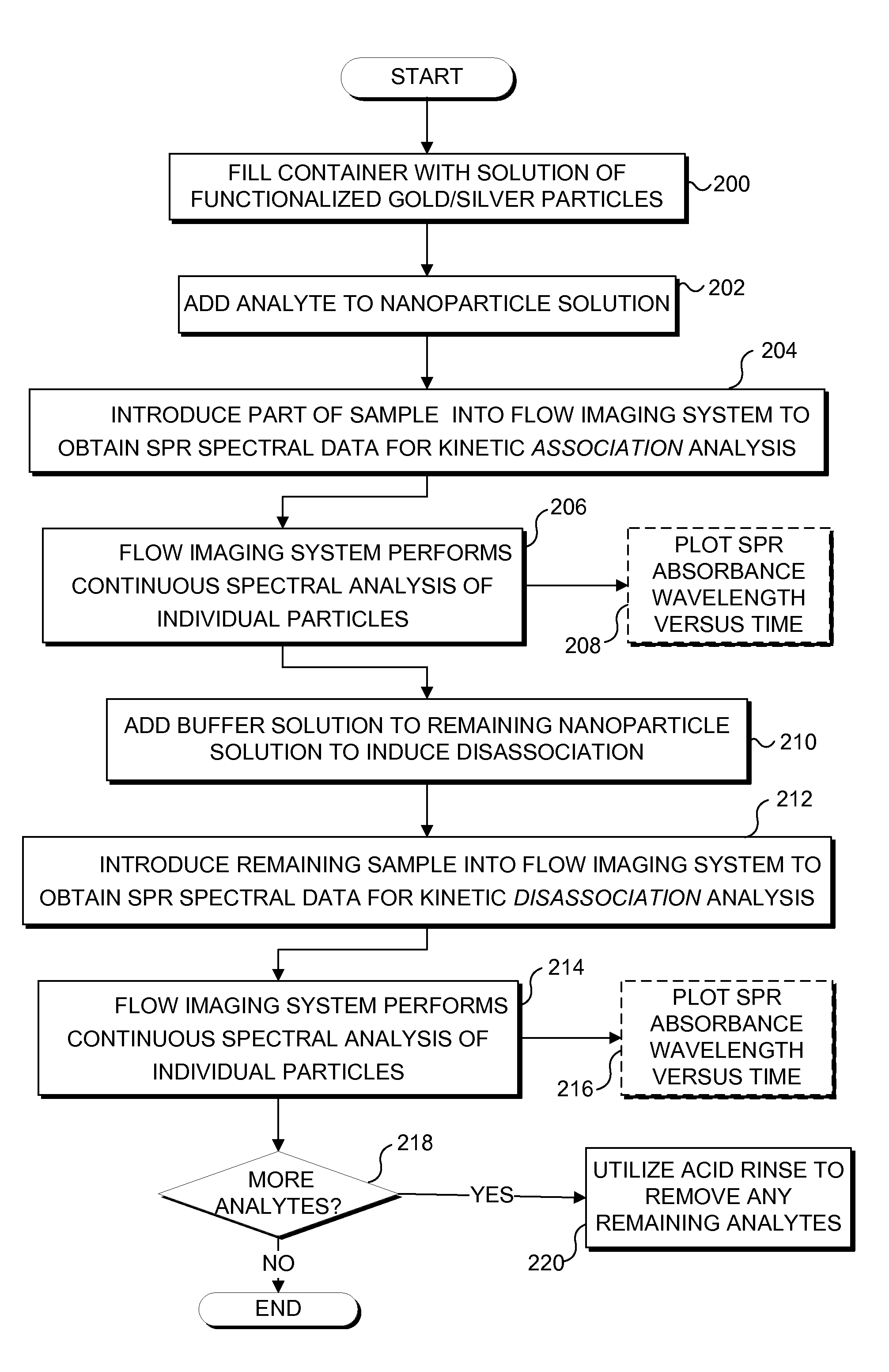
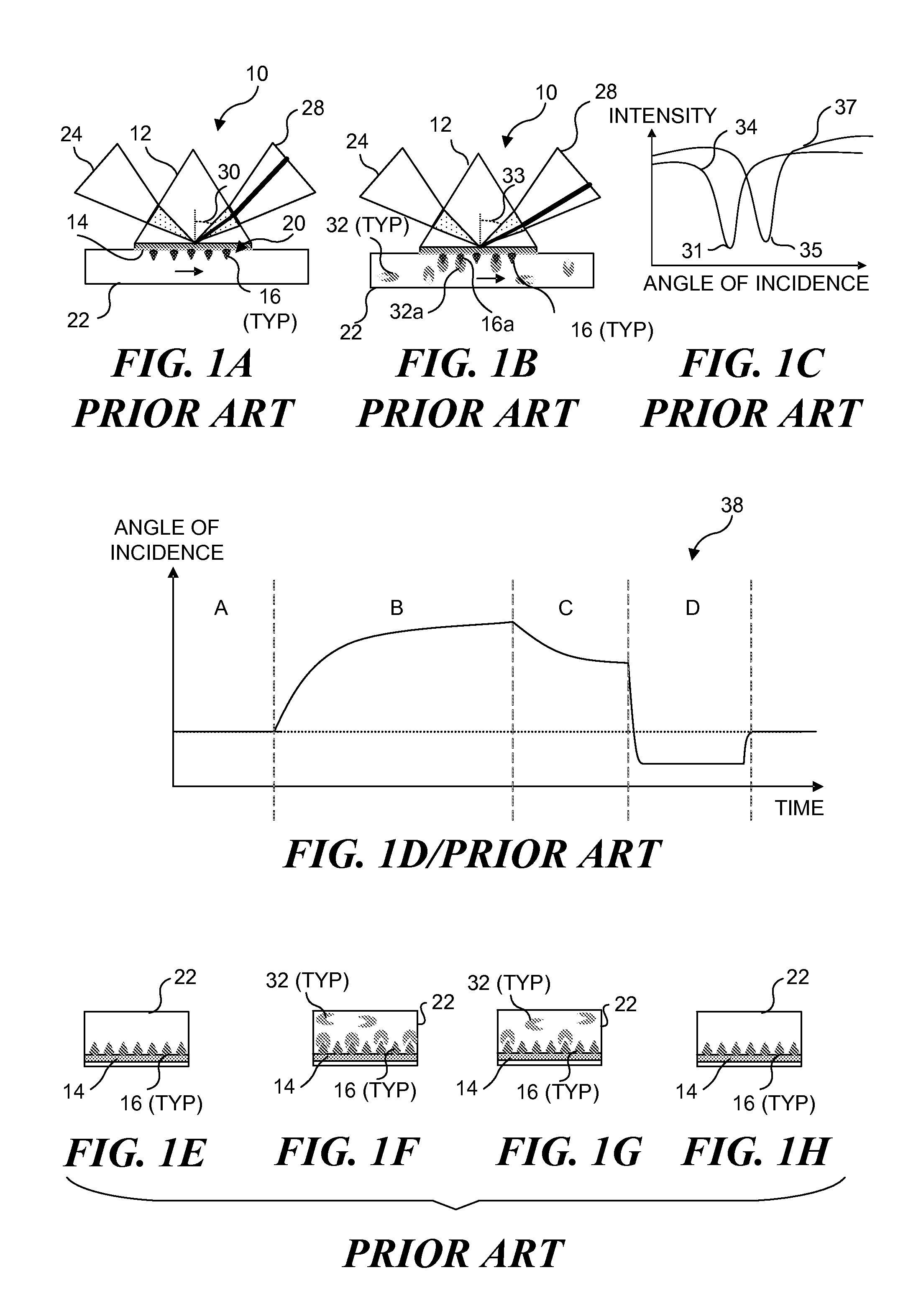
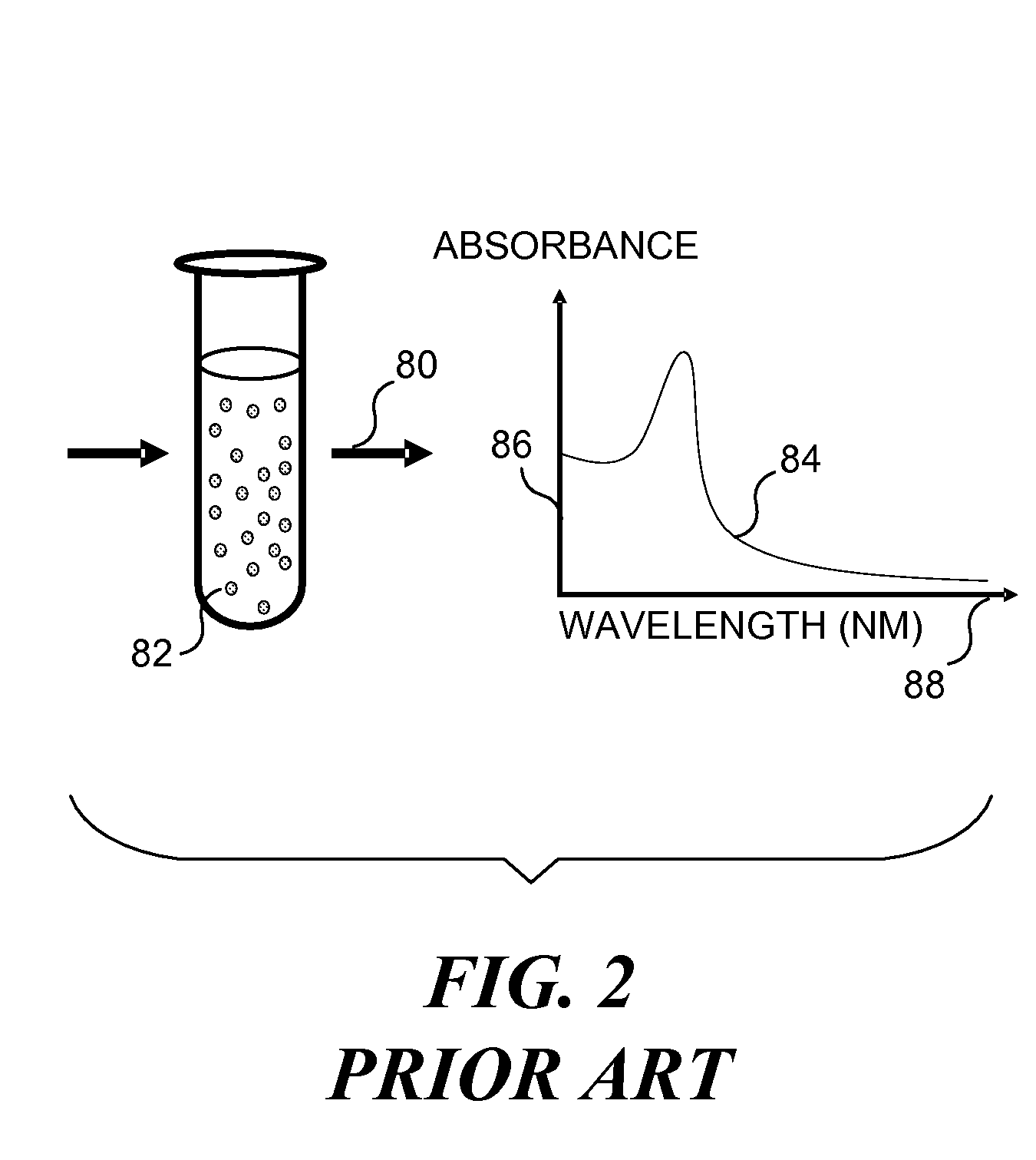
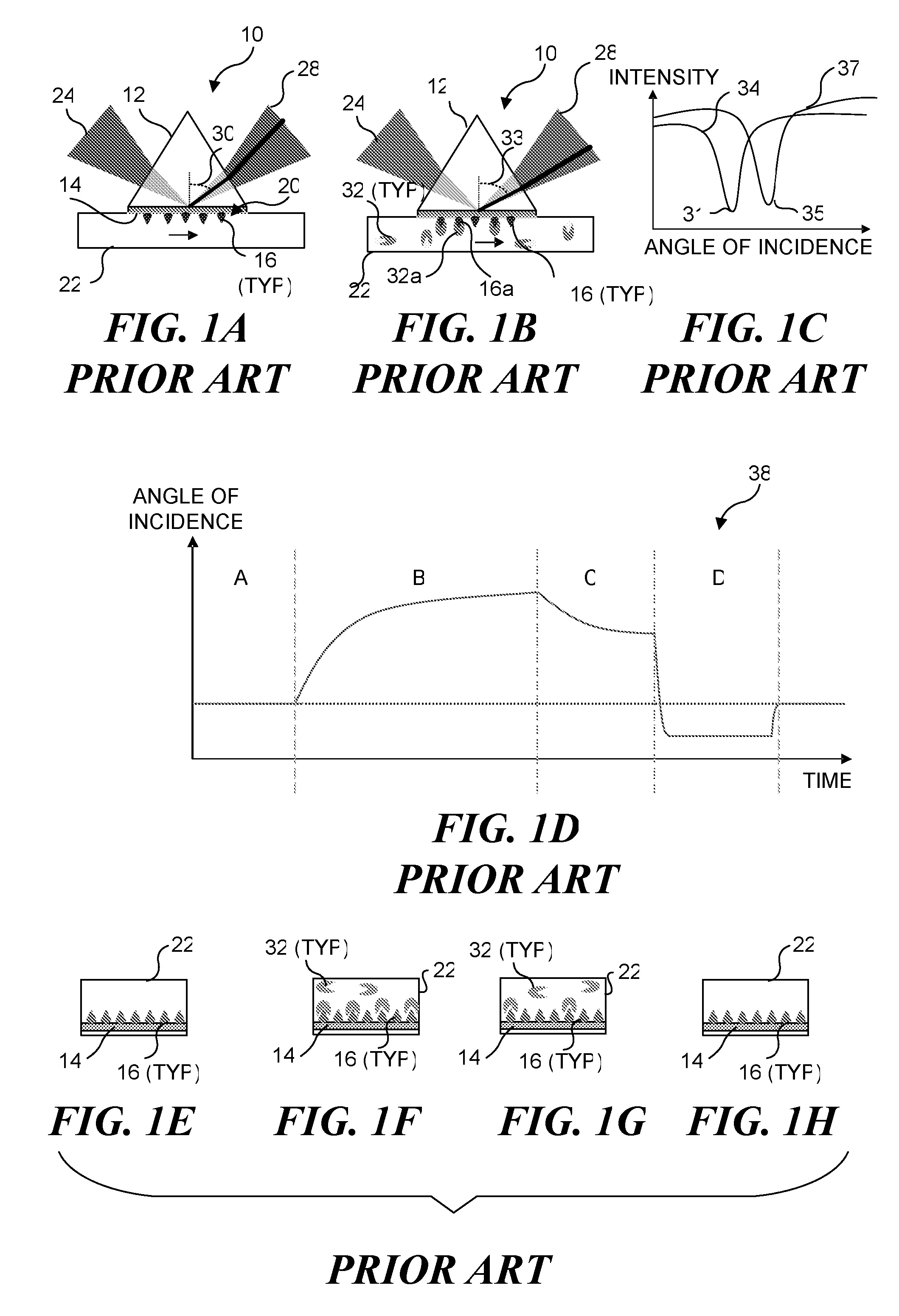
InactiveUS7057732B2Increase curve 's linearityAccurate CalibrationSpectrum investigationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsSurface plasmonic resonanceAnalyte molecule
A flow imaging system is used to implement surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detection to study bio-molecular interactions. The flow imaging system is used to capture SPR absorption spectra of large numbers of objects, where each object includes both a metal film capable of exhibiting SPR, and detecting molecules. Analyte molecules are added to a solution of such objects, and the result is introduced into the flow imaging system which collects full SPR spectral data from individual objects. The objects can be nanoparticles or larger particles that support metal island films. The SPR spectral data can be used to determine specificity, kinetics, affinity, and concentration with respect to the interactions between the detecting molecules and the analyte molecules.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
High resolution flow imaging for ultrasound diagnosis
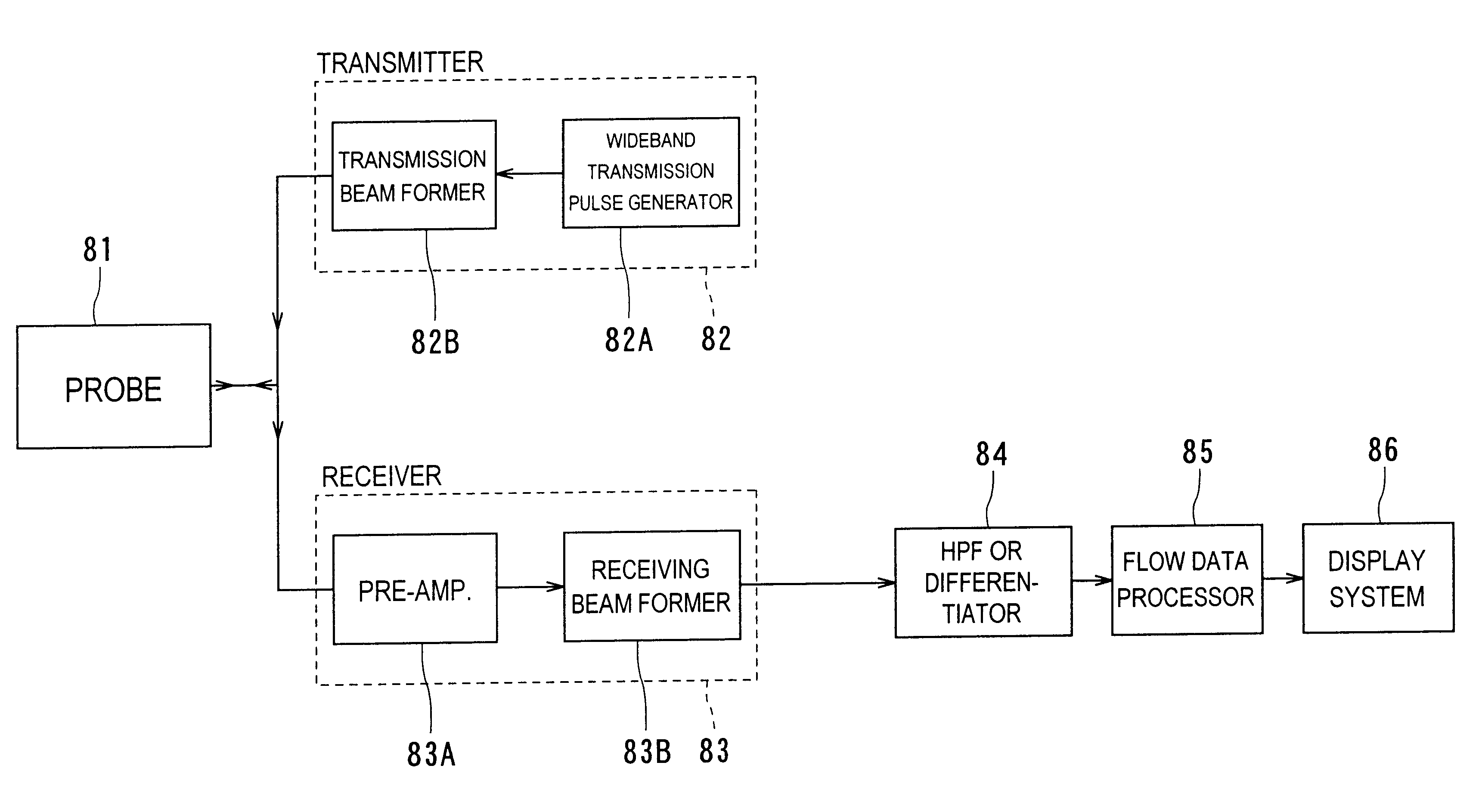
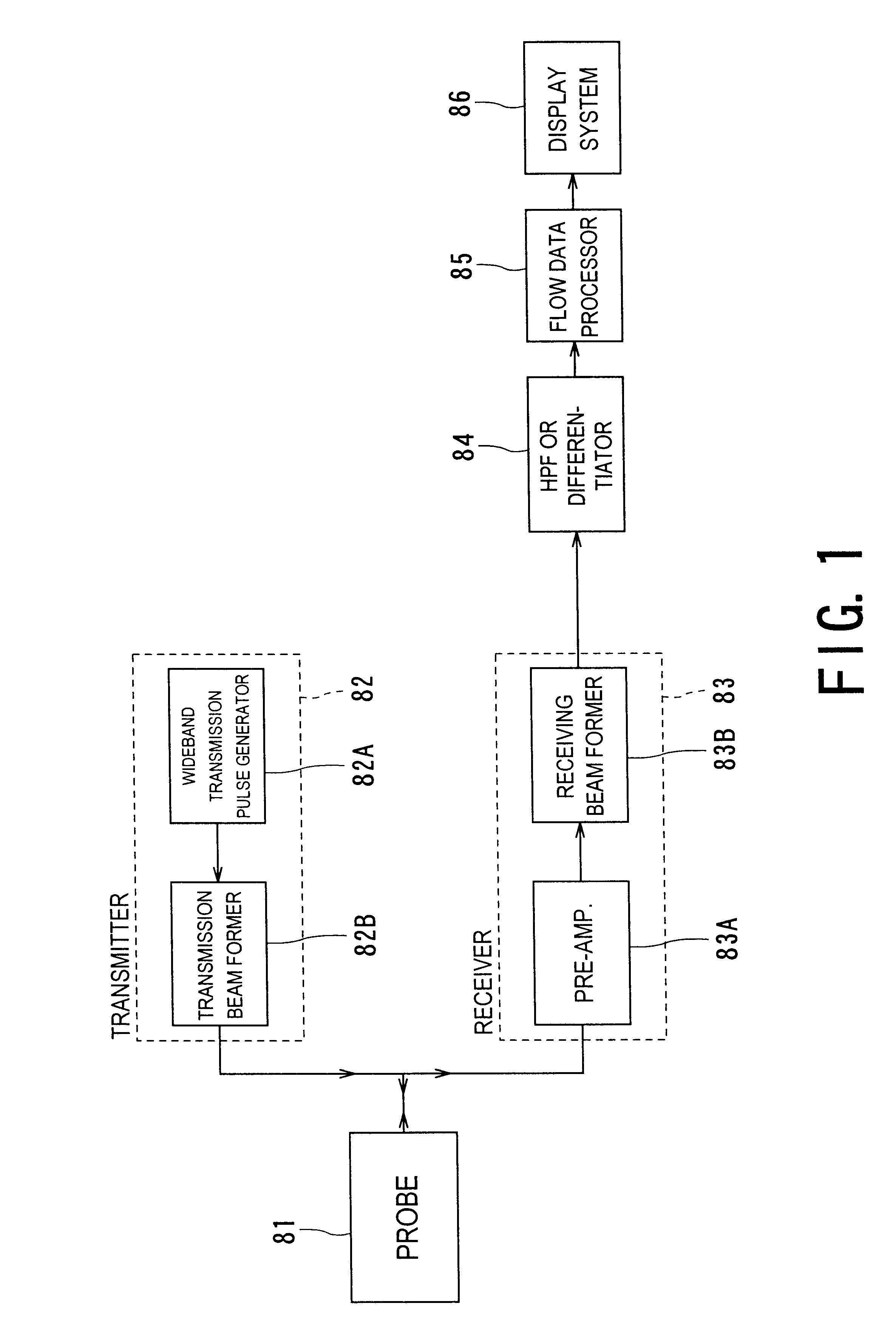
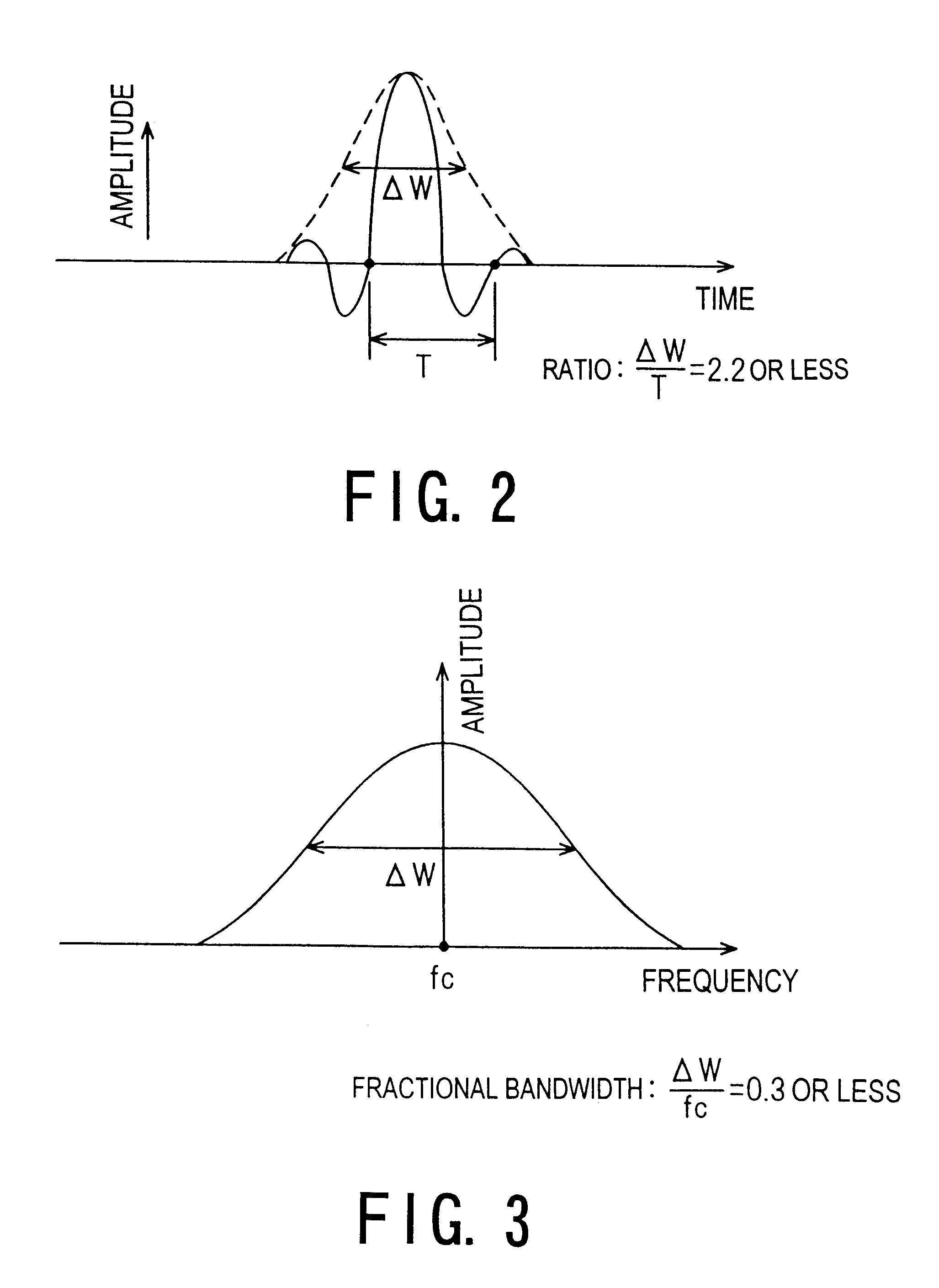
In a high-resolution flow mode, a diagnostic ultrasound apparatus and a diagnostic ultrasound method that provide an image of blood flow or perfusion is provided with higher sensitivity and high resolution, which makes it possible to precisely observe the presence of fine blood vessels. In this apparatus, by scanning means (81 to 83), with a ultrasound pulse having a wideband frequency characteristic transmitting at least two times in the same direction within an object, a cross section to be imaged therein is scanned to obtain an echo signal at each time of transmission. By processing means 84, highpass filtering or differential processing is performed with rows of data in the time axis direction of an echo signal acquired at each sample location in the cross section, so that signals from blood flow are extracted. By producing means 85, the processed signals are produced into data of luminance or power. This data is displayed by displaying means 86 as a high-resolution color (flow) image or grayscale flow image indicative of blood flow or perfusion.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
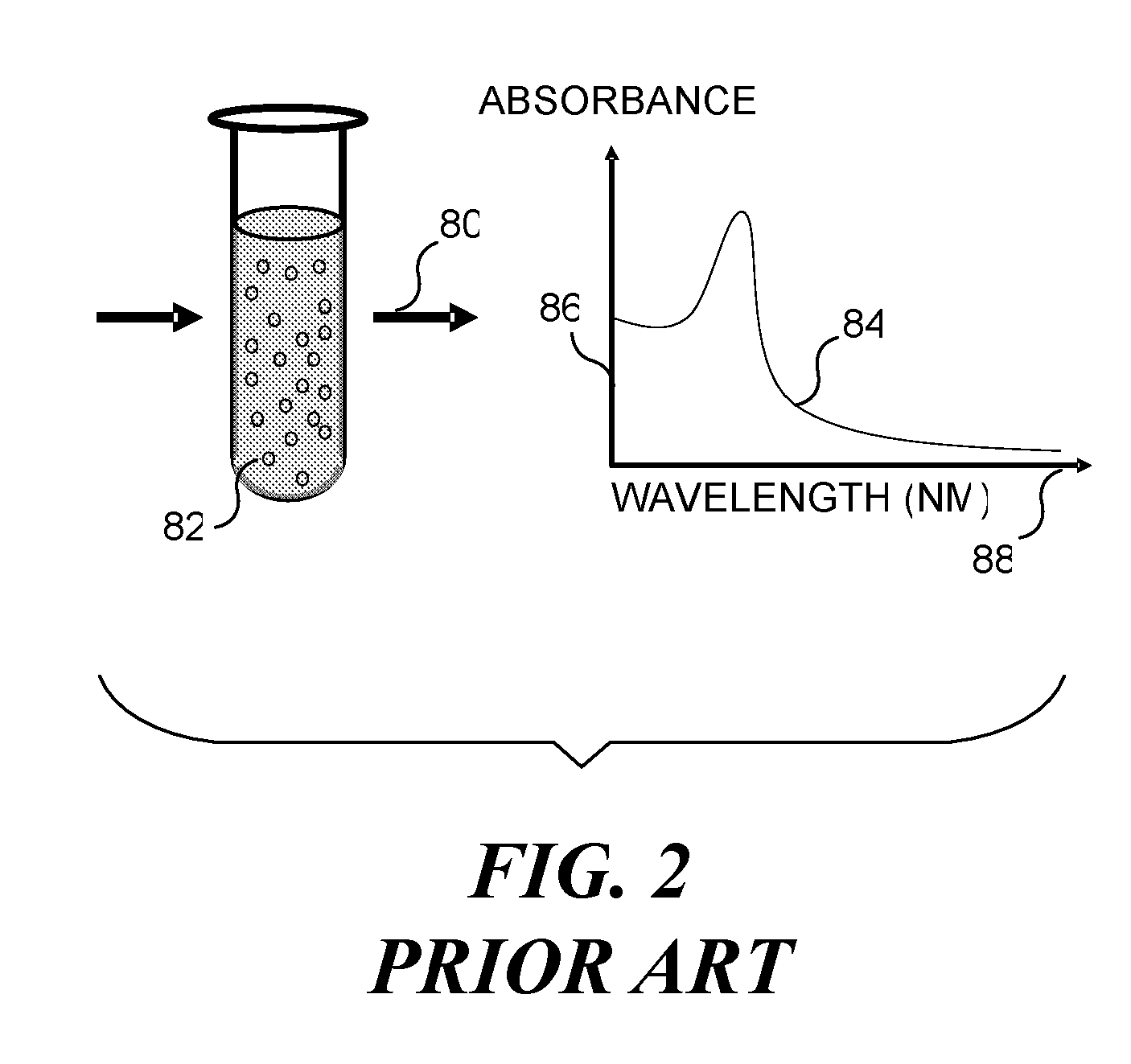
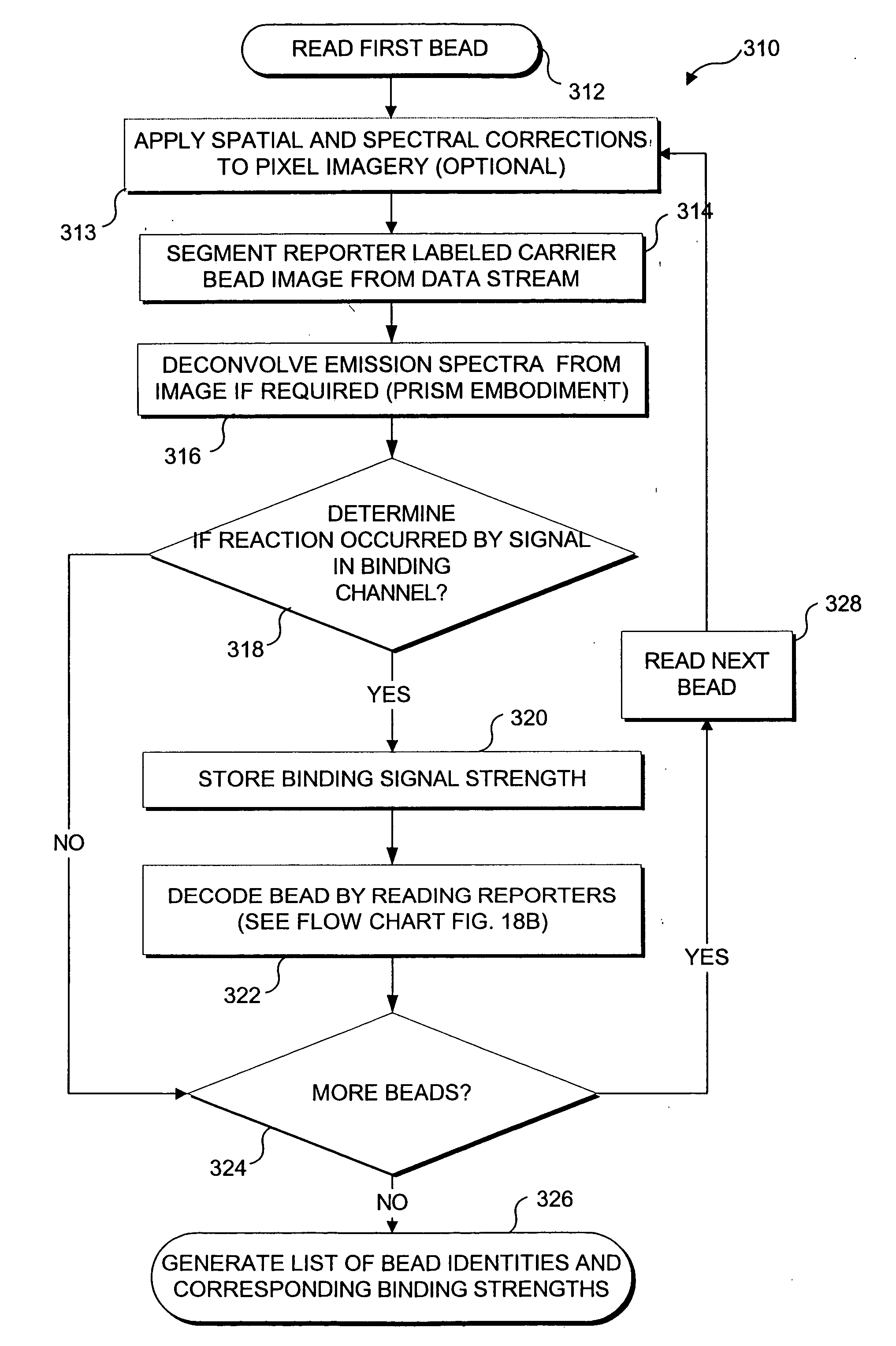
Method and apparatus for reading reporter labeled beads
Combinatorially-synthesized deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) oligonucleotides attached to encoded beads that are hybridized to amplified and labeled genomic DNA or ribonucleic acid (RNA) are analyzed using a flow imaging system. Oligonucleotides and corresponding reporters are bound to the surfaces of a plurality of small beads such that different beads bear different oligo sequences. Each bead bears a unique optical signature comprising a predefined number of unique reporters, where each reporter comprises a predefined combination of different fluorochromes. The composite spectral signature in turn identifies the unique nucleotide sequence of its attached oligo chains. This optical signature is rapidly decoded using an imaging system to discriminate the different reporters attached to each bead in a flow in regard to color and spatial position on the bead.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Imaging platform for nanoparticle detection applied to SPR biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS7221457B2Spectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsAnalyte moleculeLarge particle
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
Imaging platform for nanoparticle detection applied to spr biomolecular interaction analysis
InactiveUS20060192955A1Spectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsMolecular analysisAnalyte molecule
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for reading reporter labeled beads
Combinatorially-synthesized deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) oligonucleotides attached to encoded beads that are hybridized to amplified and labeled genomic DNA or ribonucleic acid (RNA) are analyzed using a flow imaging system. Oligonucleotides and corresponding reporters are bound to the surfaces of a plurality of small beads such that different beads bear different oligo sequences. Each bead bears a unique optical signature comprising a predefined number of unique reporters, where each reporter comprises a predefined combination of different fluorochromes. The composite spectral signature in turn identifies the unique nucleotide sequence of its attached oligo chains. This optical signature is rapidly decoded using an imaging system to discriminate the different reporters attached to each bead in a flow in regard to color and spatial position on the bead.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
Device and method for sorting biological particles
InactiveCN1950690AImprove classification accuracySimple compositionScattering properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisElectrical polarityBiological particles
A device for illuminating a flow of a liquid containing biological particles with light, detecting light from the biological particles, collecting bioinformation on the biological particles, and sorting the biological particles according to the collected bioinformation. The device comprises a light detecting section for detecting light from biological particles, and an imaging section for imaging a flow and a droplet separated from the flow, means for calculating the distance from the detecting position at which a light detector detects light from the biological particles to the flow lower end position and the intervals between particles contained in the flow on the b sis of the flow image captured by the imaging section and calculating the time for the particles to move from the detection position to the lower end position by using the distance and intervals, and means for giving charge of a polarity depending on the properties of the biological particles to the flow after a calculated time from the detection of light from the biological particles by the light detection. Thus, the structure of the biological particle sorting device is simplified, and the accuracy of sorting is improved.
Owner:BAY BIOSCI
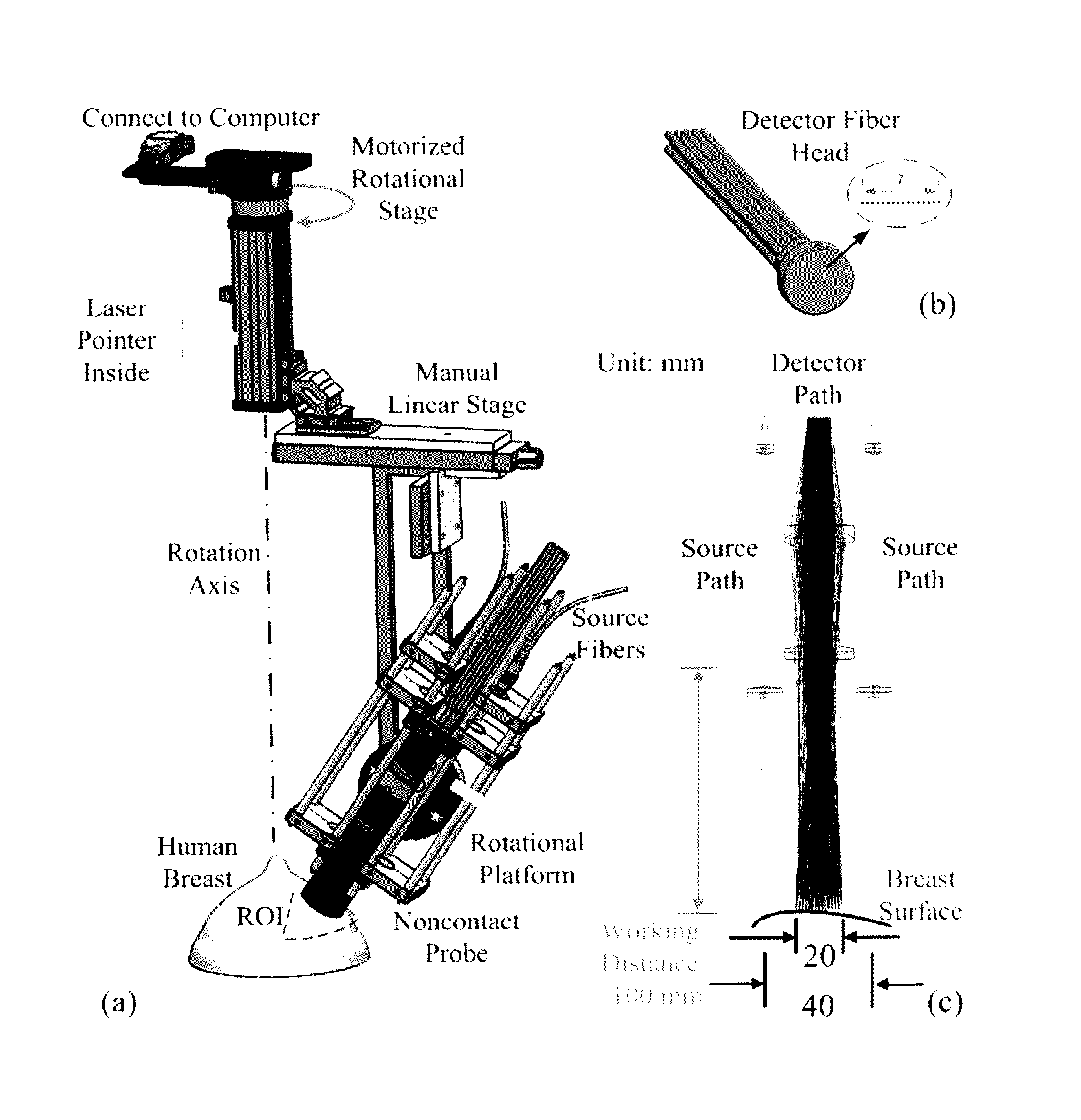
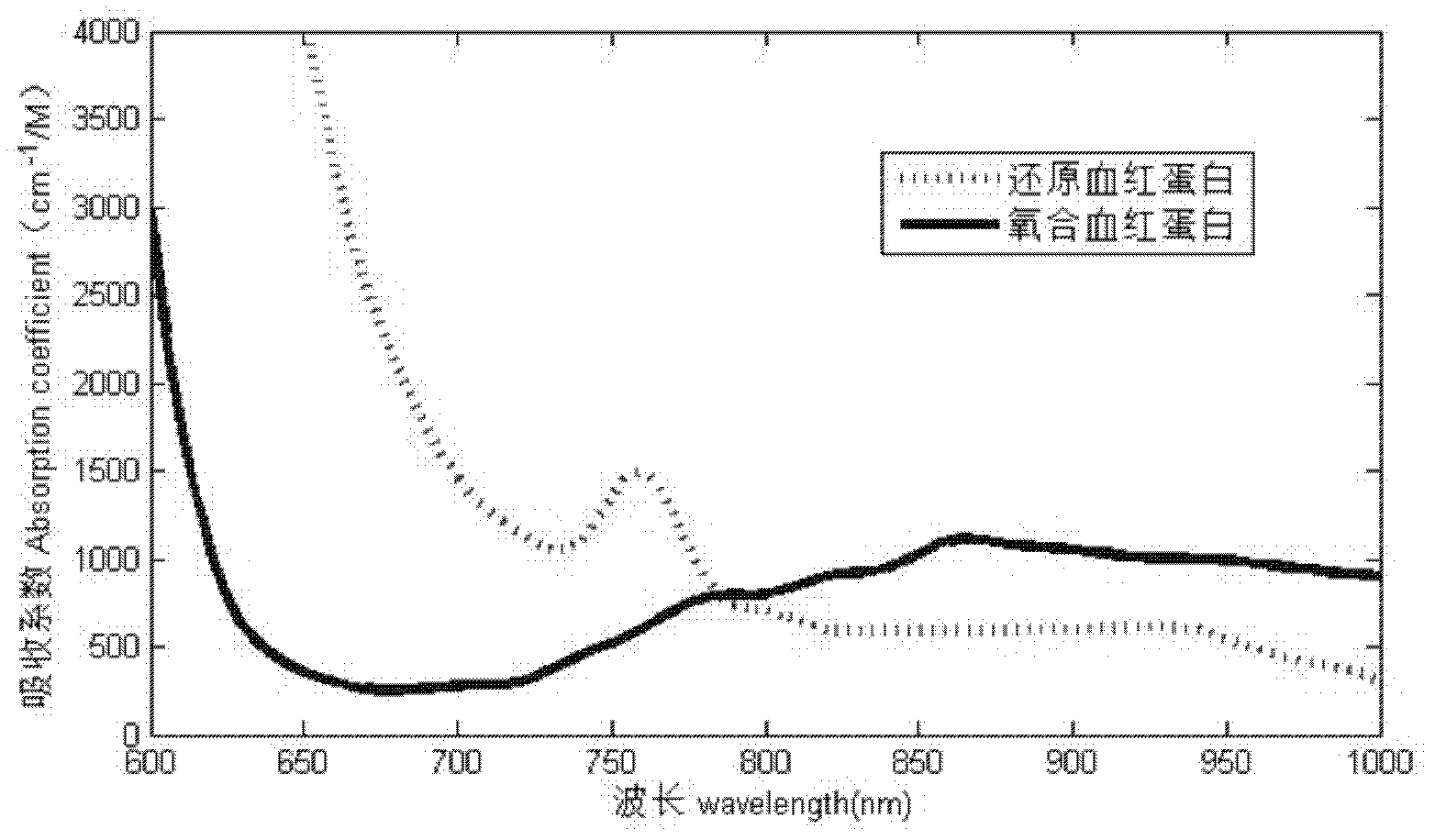
Noncontact Three-dimensional Diffuse Optical Imaging of Deep Tissue Blood Flow Distribution
ActiveUS20160278715A1Avoid contactMedical simulationDiagnostics using spectroscopyFinite element methodDeep tissue
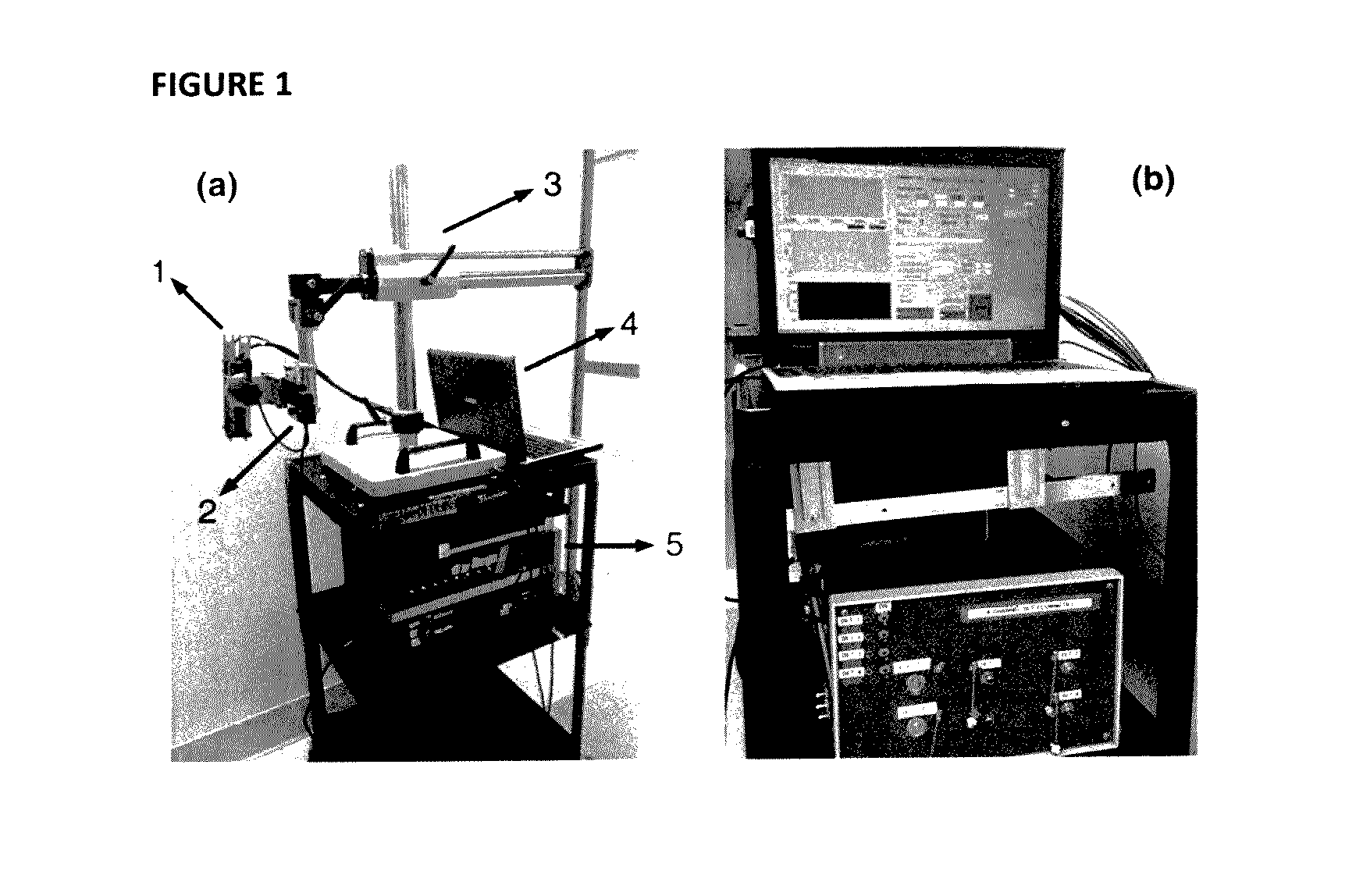
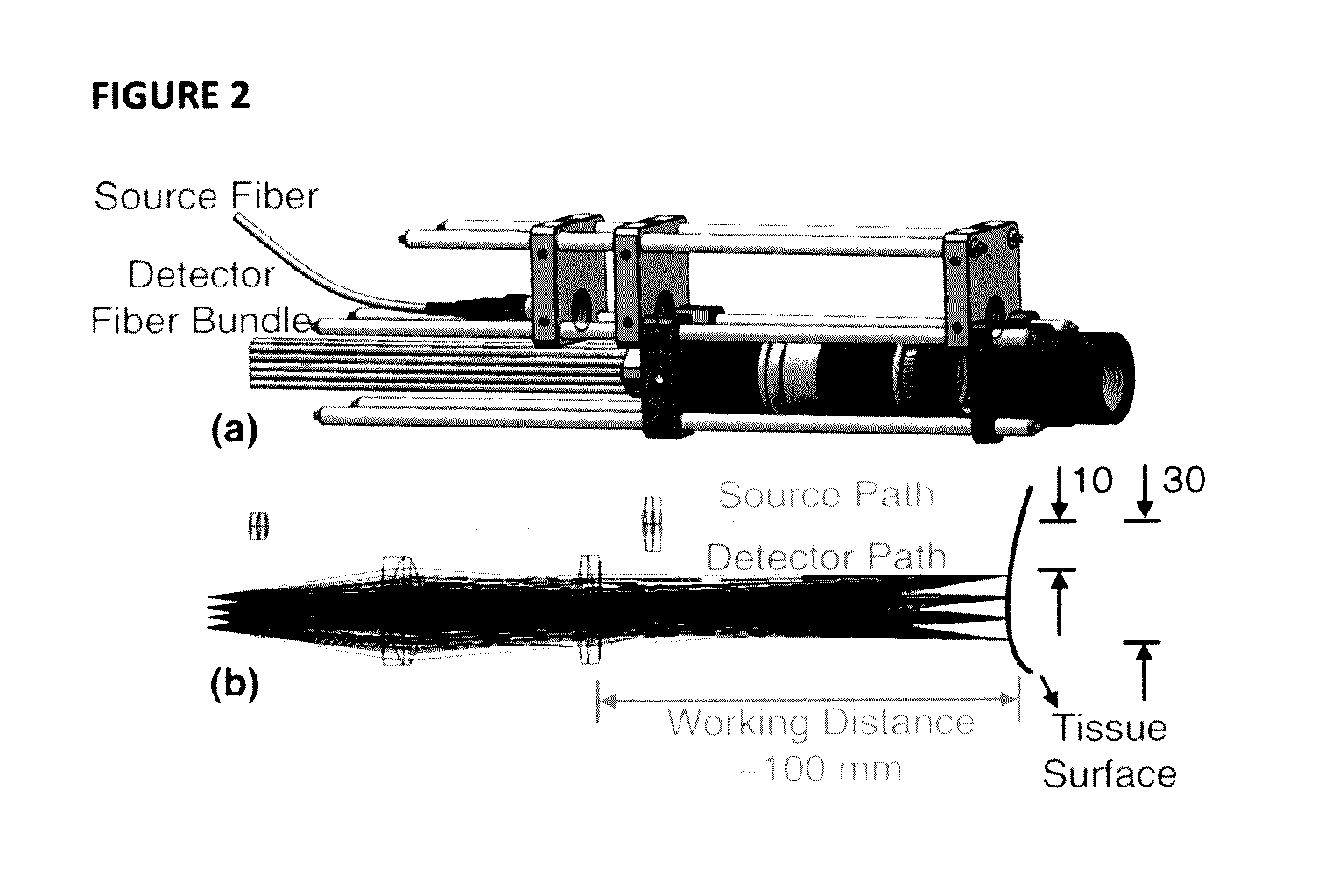
The present invention provides for three-dimensional reflectance diffuse optical imaging of deep tissue blood flow distribution that removes the need for probe-tissue contact, thereby allowing for such technology to be applied to sensitive, vulnerable, damaged, or reconstructive tissue. The systems utilize noncontact application and detection of near-infrared light through optical lens and detection through a linear array or two-dimensional array of avalanche photodiodes or a two-dimensional array of detectors provided by charge-coupled-device (CCD). Both further feature a finite-element-method (FEM) based facilitation to provide for three-dimensional flow image reconstruction in deep tissues with arbitrary geometries.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
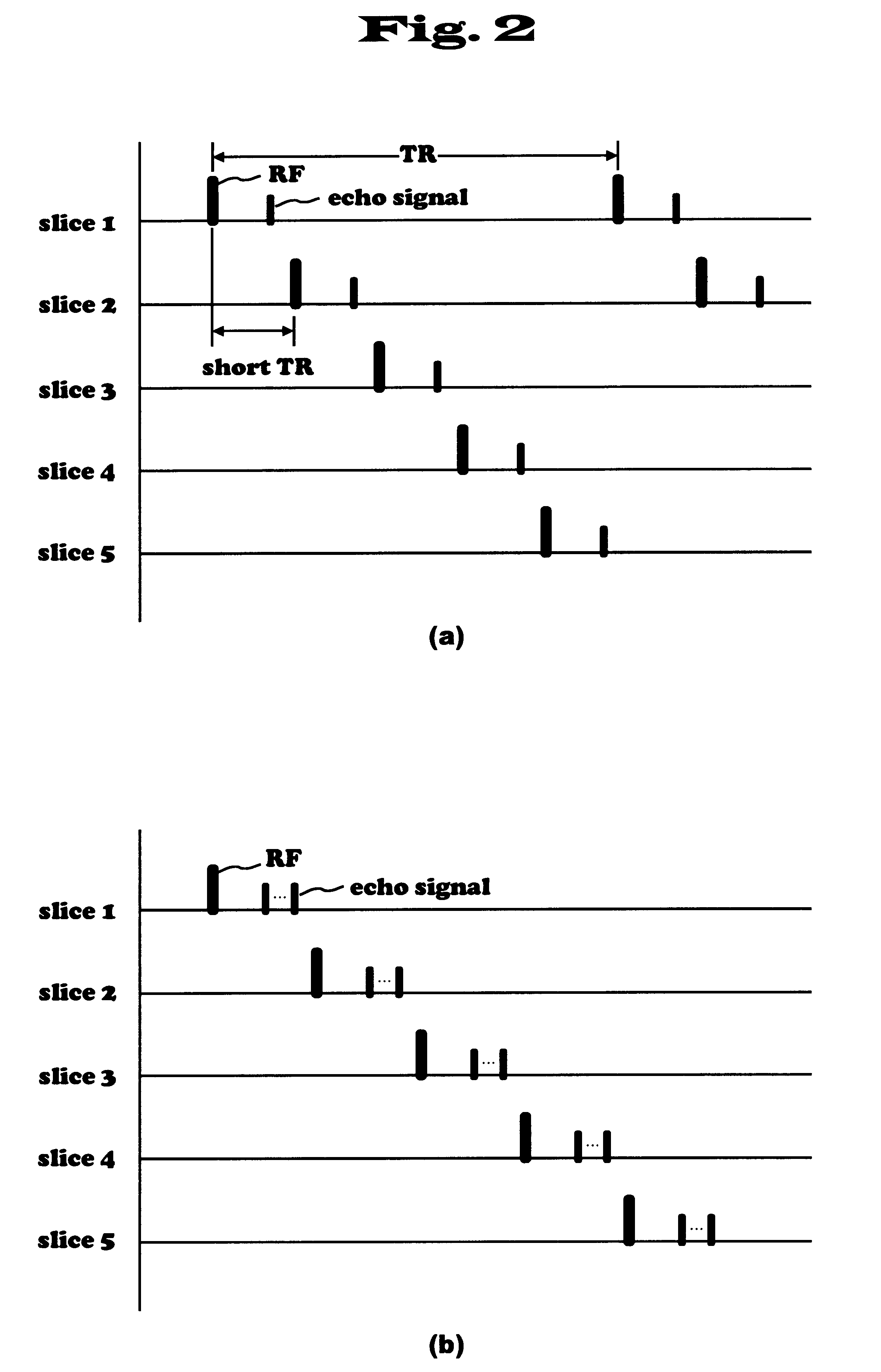
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6442414B1Signal intensity can be more suppressedImprove imaging effectSensorsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMulti sliceReverse order
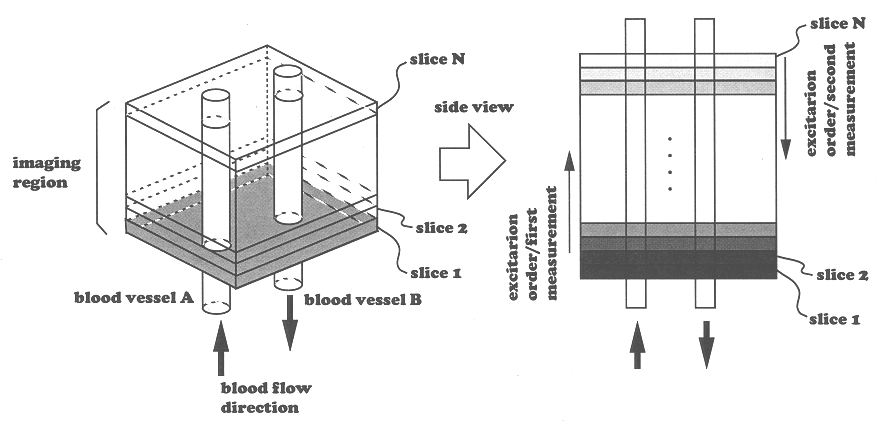
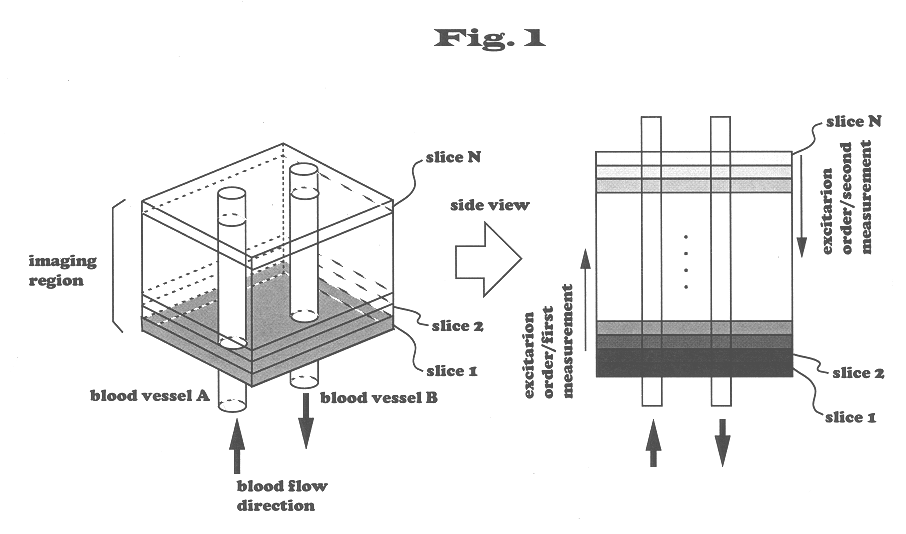
An MRI apparatus having an ability of displaying images of flow in different directions in distinguishable manner. When this MRI apparatus performs multi-slice acquisition with a predetermined repetition time TR by selecting a plurality of slices approximately perpendicular to the flow direction of an object to be examined, it performs a first measurement of exciting the plurality of slices in a first order and a second measurement of exciting the same slices in the opposite order to obtain two kinds of data whose signal intensity differs depending on the flow direction. The two kinds of data obtained by two measurements are subjected to subtraction operation to obtain data with different signs depending on the flow direction. These signs combined with the signal intensity are made into images where flow in opposite directions are distinctively depicted. In the multi-slice acquisition, slices are selected so that adjacent slices partially overlap in the direction of the thickness of the slice. Thereby signals of a static part can be suppressed and contrast of flow images after substraction can be enhanced. EPI method of very short imaging time can be employed for the imaging sequence of MRA according to the present invention.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
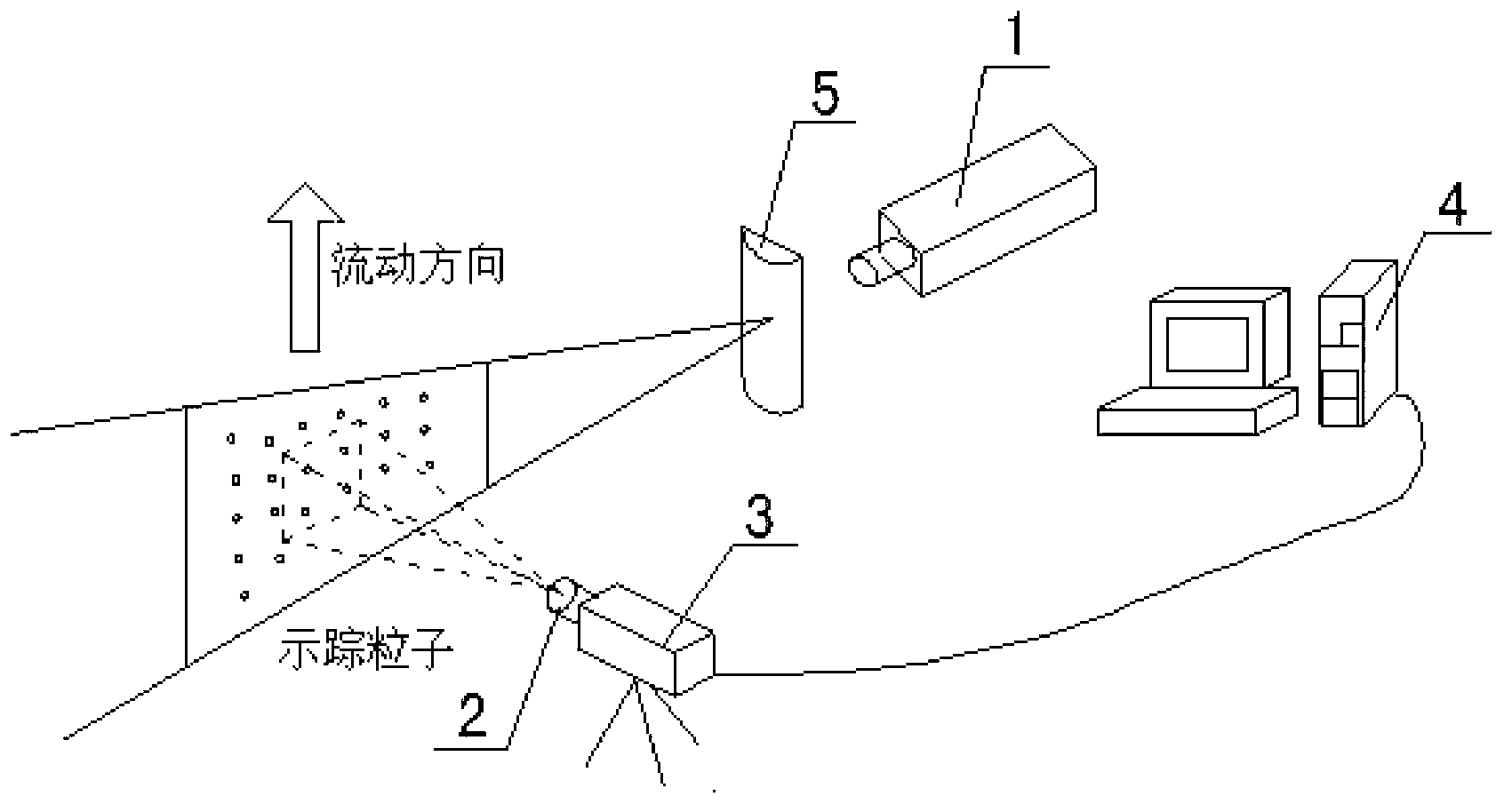
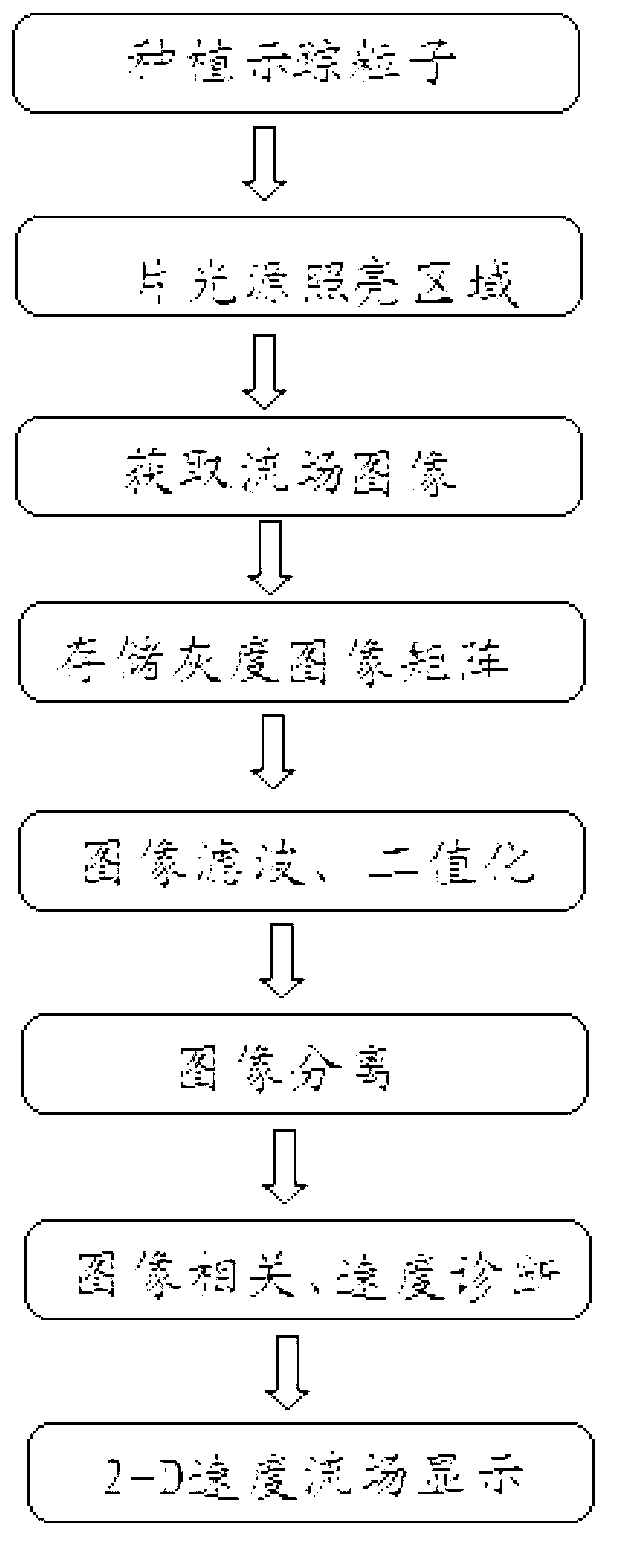
Two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device of interlaced scanning CCD (charge coupled device)
ActiveCN103293333AEnables full-field velocity measurementLow priceFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceHigh power lasers
The invention discloses a two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device of an interlaced scanning CCD (charge coupled device). Trace particles are implanted into a to-be-measured flowing object (gas or liquid) and can move together with fluid due to viscidity. For the measurement device, a continuously light-emitting gas laser (such as He-Ne laser) is used as a light source, and a common interlaced scanning CCD sensor is used as an image detector. A one-frame flowing image including the trace particles is captured transiently, then the flowing image is processed by means of filtering and binaryzation, the interlacedly scanned one-frame image is separated into two images according to odd-even lines, a cross-correlation technology is adopted to perform computation processing, and accordingly a two-dimensional flow velocity field can be obtained. PIV (particle image velocimetry) full-field velocity measurement can be achieved without a high-power laser, a high-resolution CCD and a complex synchronizer; and the two-dimensional flow velocity field measurement method and device is simple in equipment, low in cost and applicable to flow field measurement on different occasions.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Synthetic aperture imaging for fluid flows
InactiveUS8922636B1Increase contrastColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsSynthetic aperture sonarFluid phase
A synthetic aperture three-dimensional fluid flow imaging apparatus is provided. The apparatus includes a plurality of cameras. At least two of the cameras are oriented to view a volume along mutually non-parallel directions. The cameras are connected to a programmable computer. The computer captures images from the cameras to generate three dimensional intensity fields. The computer can refocus the images on at least one refocus plane to generate reconstructed three dimensional intensity fields on a plane within the volume. Intensity field cross-correlation is performed on the reconstructed three dimensional intensity fields to extract velocity fields within the volume. The velocity fields represent velocities of objects or fluid phases within the volume. These velocity fields can be recorded for later use.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
System and method for automatic, non-invasive diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension and measurement of mean pulmonary arterial pressure
InactiveUS20100094122A1Optimize workflowAnalyze moreMagnetic measurementsEvaluation of blood vesselsSystoleCardiac cycle
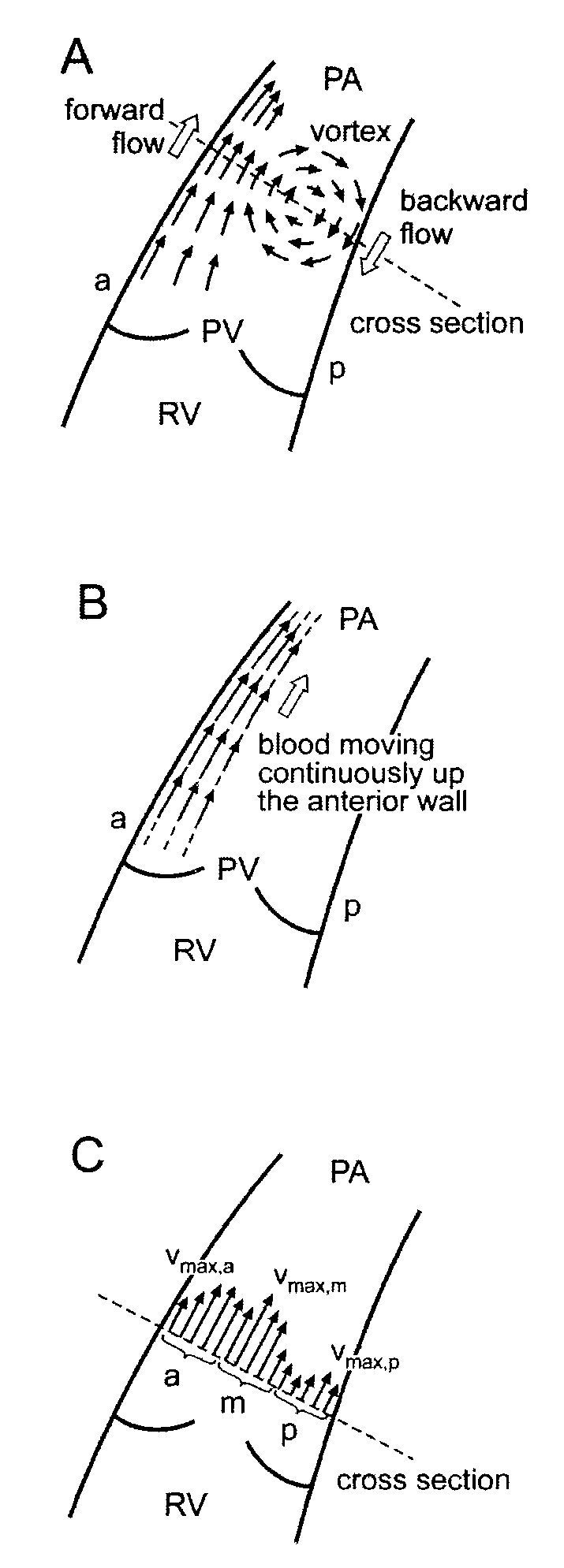
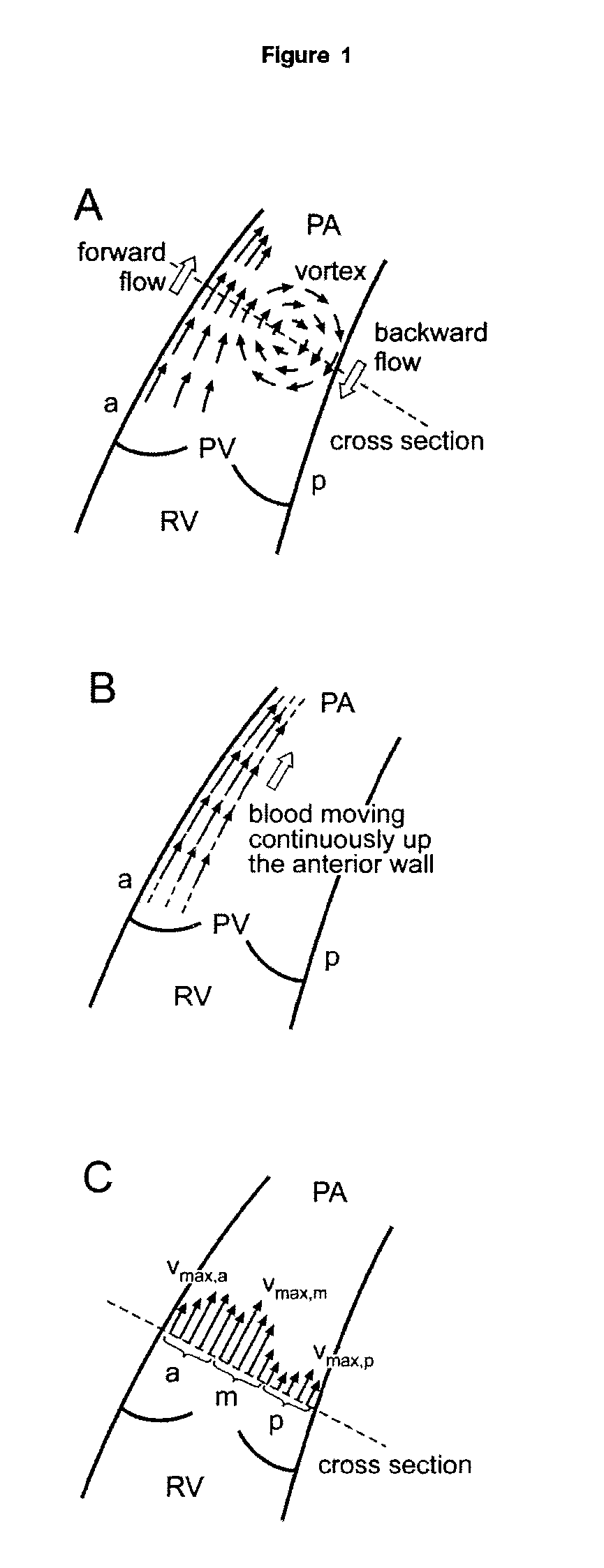
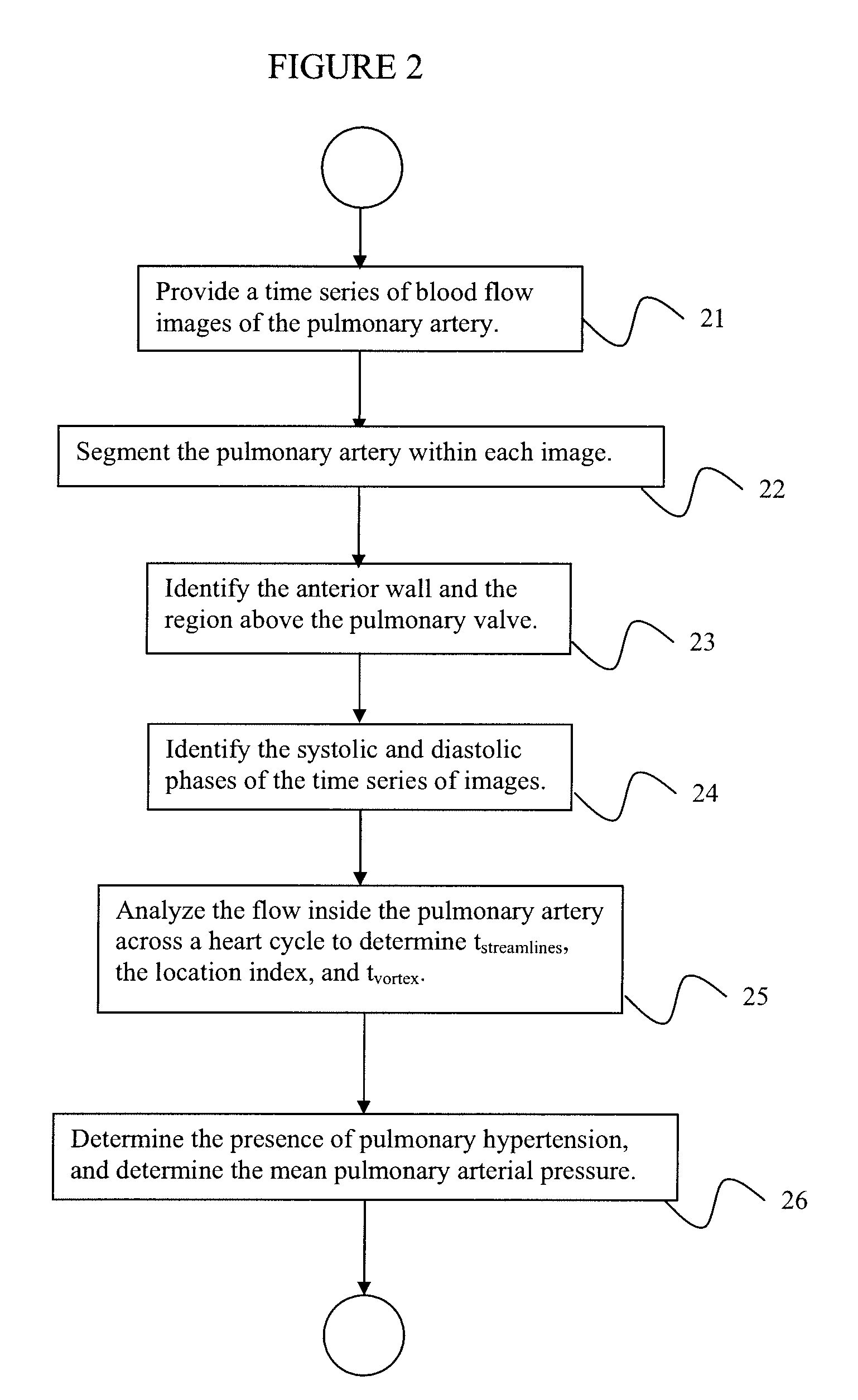
A method for diagnosing pulmonary hypertension from phase-contrast magnetic resonance (MR) images includes providing a time series of one or more magnetic resonance (MR) flow images of a patient's mediastinum during one or more cardiac cycles, segmenting the pulmonary artery within each image of the times series of images, identifying the anterior wall and pulmonary valve within the segmented pulmonary artery, analyzing blood flow during a diastolic phase of the one or more cardiac cycles to determine a relative duration of blood flow, tstreamlines, during the diastolic phase, analyzing blood flow during a latter portion of a systolic phase and a subsequent diastolic phase of the one or more cardiac cycles to detect the presence and duration tvortex of a vortex, and diagnosing the presence of pulmonary hypertension from tstreamlines and tvortex.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
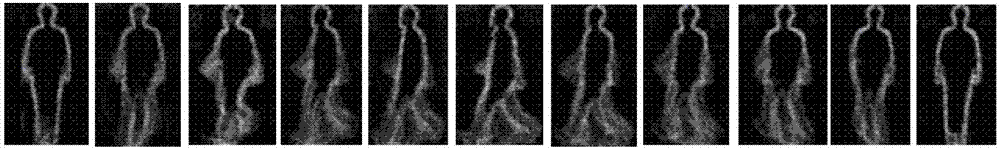
Method for realizing remote authentication by fusing gait flow images (GFI) and head and shoulder procrustes mean shapes (HS-PMS)
InactiveCN103049758ADivisibleEfficient extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionValidation methodsOptical flow
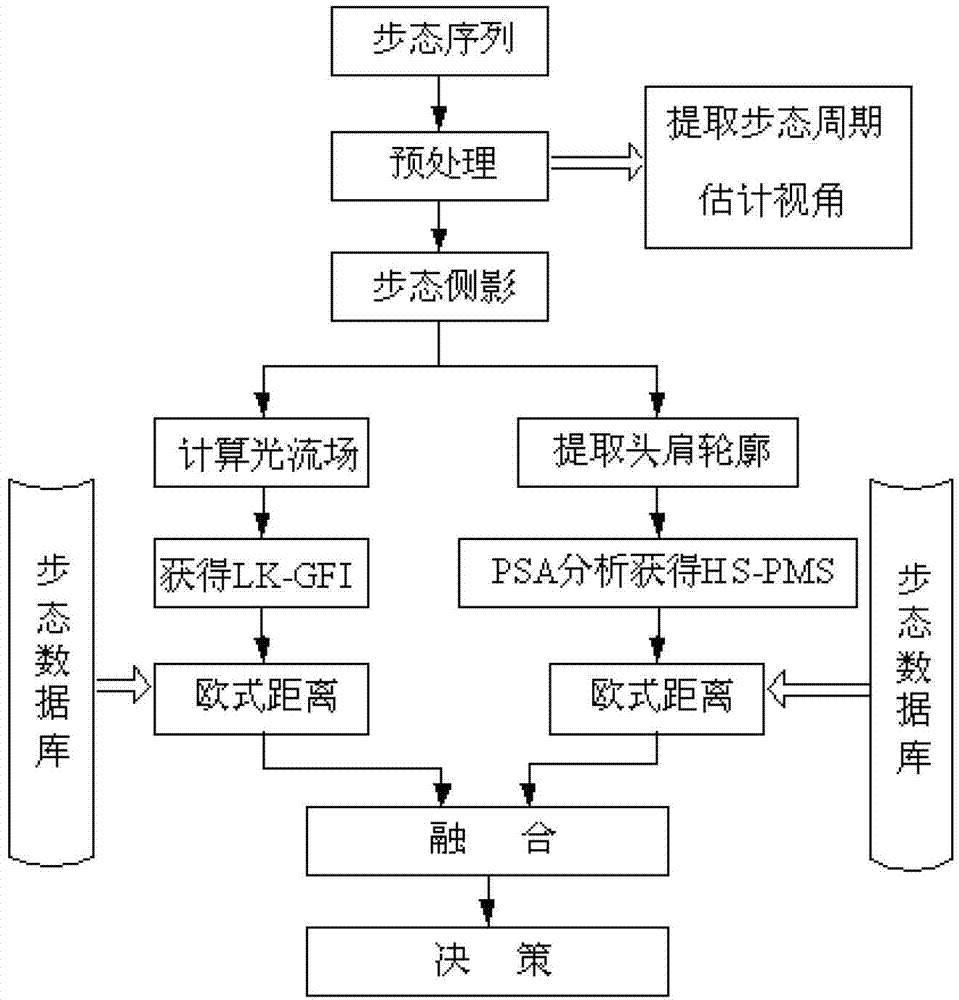
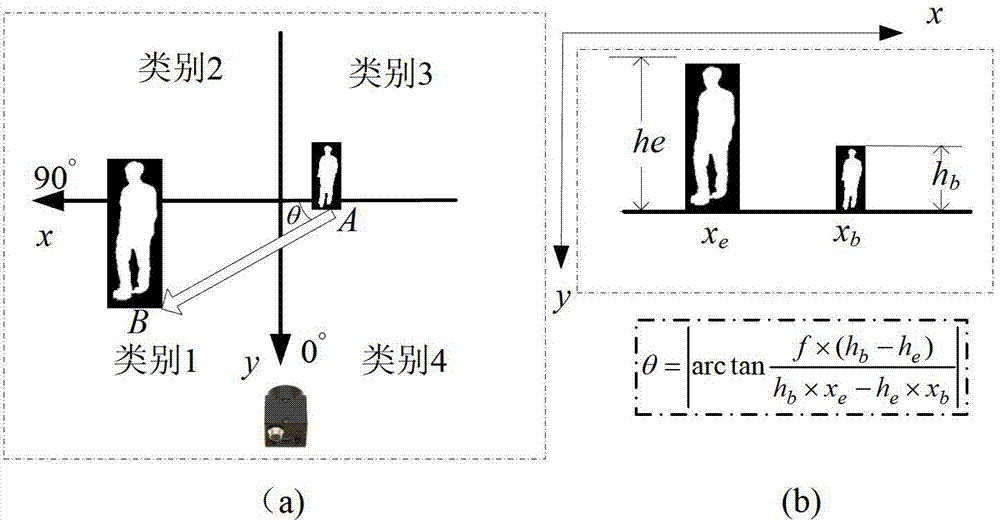
The invention belongs to the field of pattern recognition and particularly relates to a method for realizing remote authentication by fusing gait flow images (GFI) and head and shoulder procrustes mean shapes (HS-PMS). The method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing; estimating walking directions and determining visual angles; establishing a dynamic feature classifier for gaits; establishing a static feature for the gaits; fusing similarities between the dynamic feature classifier and the static feature according to the product rule at a matching layer to obtain decision information. According to the method for realizing remote authentication by fusing the GFIs and the HS-PMSs, the visual angles are introduced to serve as the rules of the classifiers, and thus, the problem that gait recognition is greatly influenced by the visual angle is solved. An optical flow field between adjacent two profile images is calculated by utilizing a Lacus-Kanade optical flow method, so that the real-time processing capacity of an algorithm is improved. The dynamic information and the static information of the gaits are fused, so that the separability of the method is improved, and the recognition performance is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
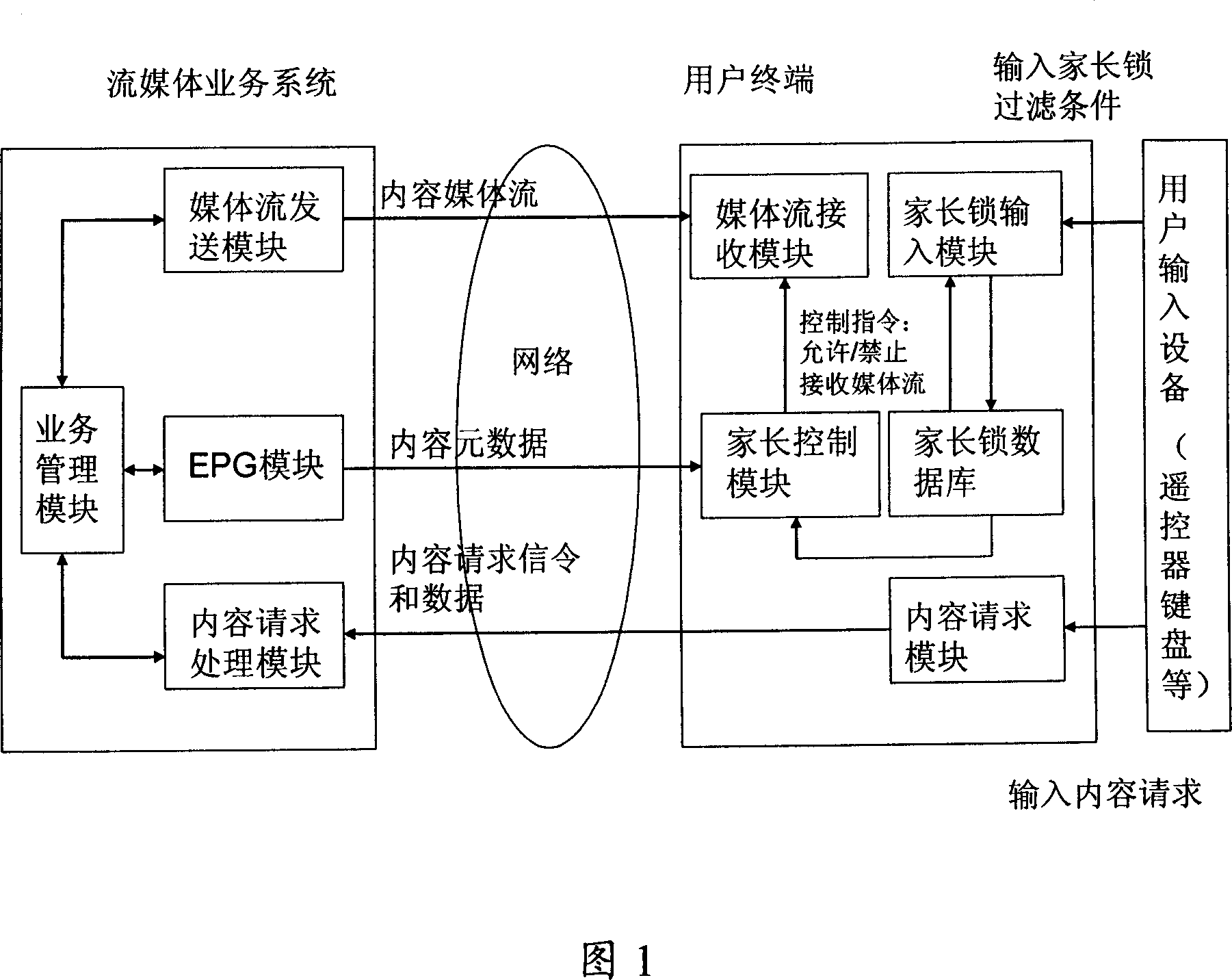
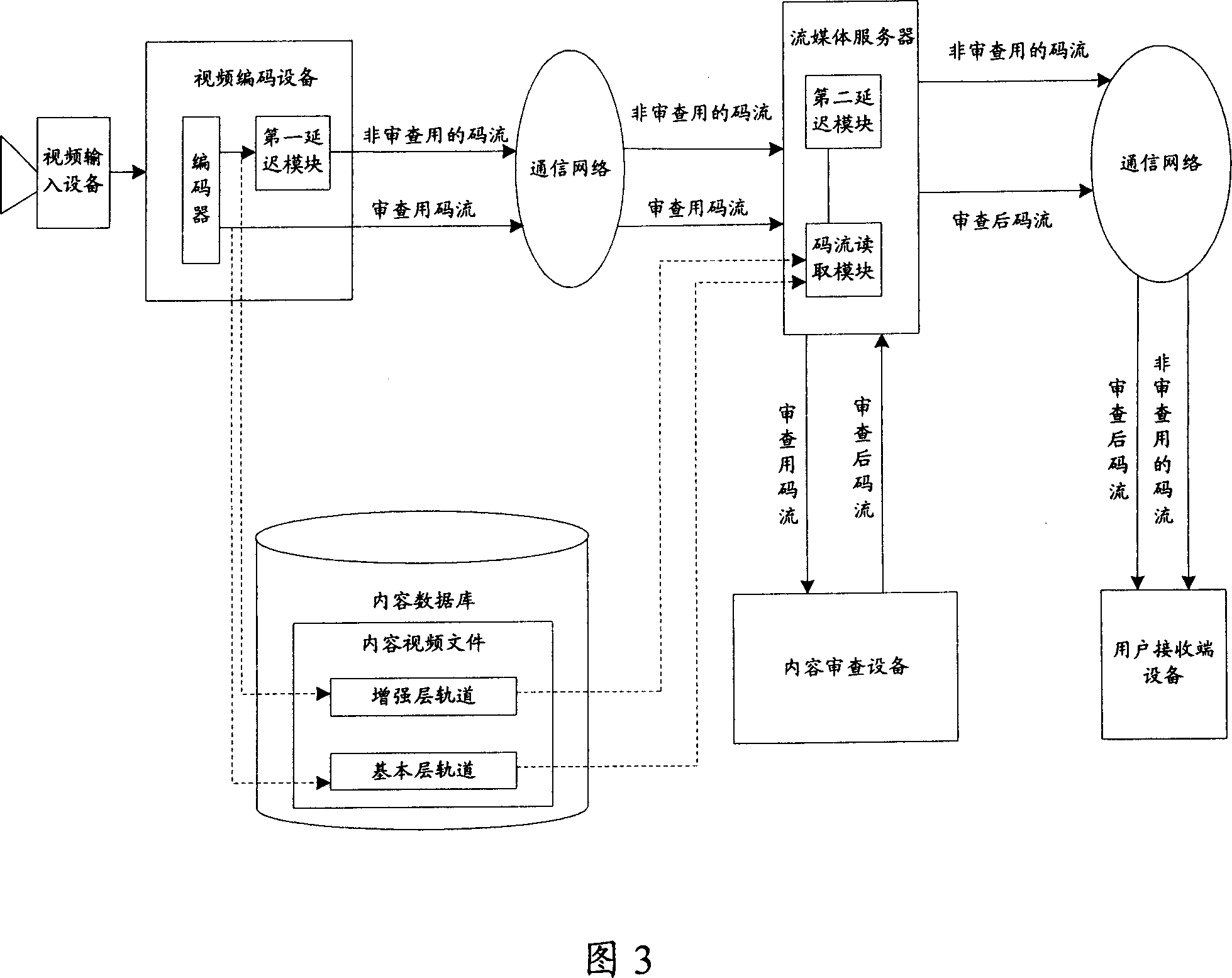
User terminal equipment for stream media content checking and checking method
ActiveCN1968409AImplement local censorshipImprove reliabilityPulse modulation television signal transmissionSimultaneous/sequential multiple television signal transmissionFlow imagingComputer hardware
The invention relates to a user terminal for inquiring the flow media content, and relative inquire method, wherein the user terminal uses the first decoding module, delay module, and the first display module to decode, rebuild and delayed display the original video flow image of flow media service; uses the second decoding module and second display module to synchronously decode and display inquire code image; user inquires said code flow image and sends out control command, when the code flow image contains harmful content; it uses user command processing module to receive and process user control command, to trigger the first display module to stop playing the video code flow image.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Three-dimensional flow radiographic method and system based on optical coherence tomography of feature space
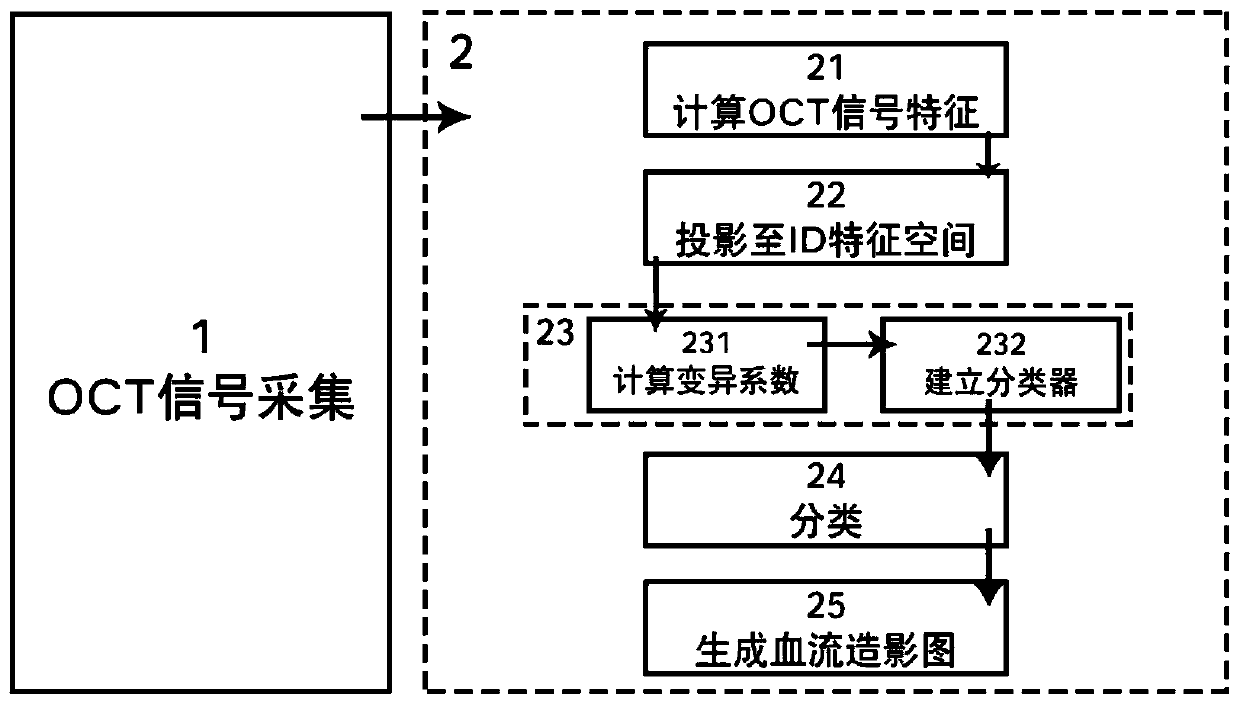
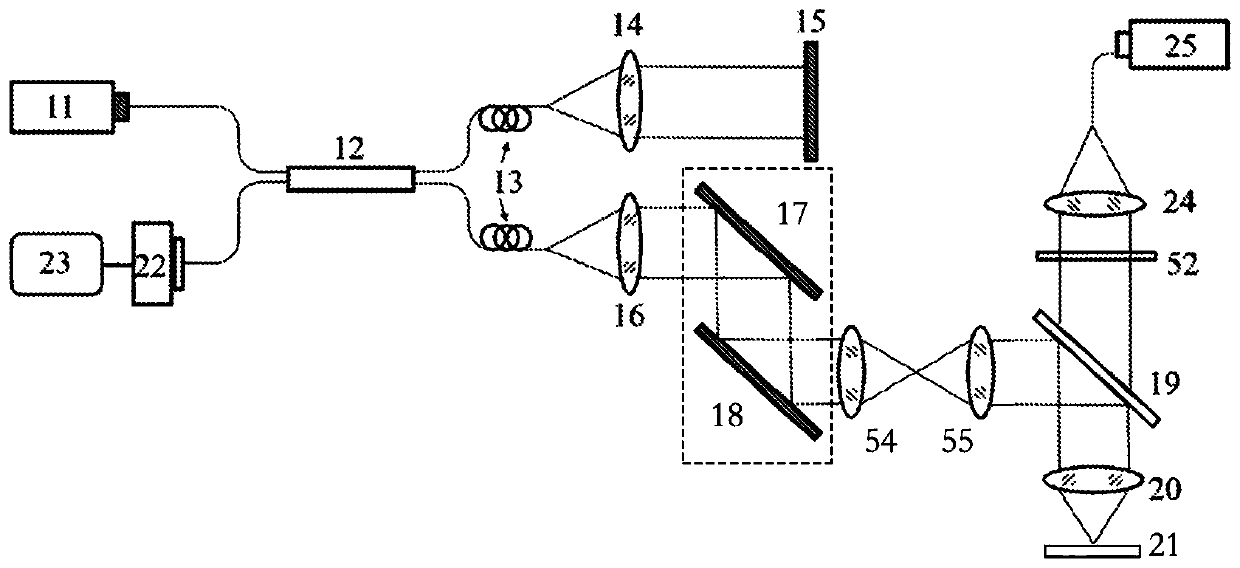
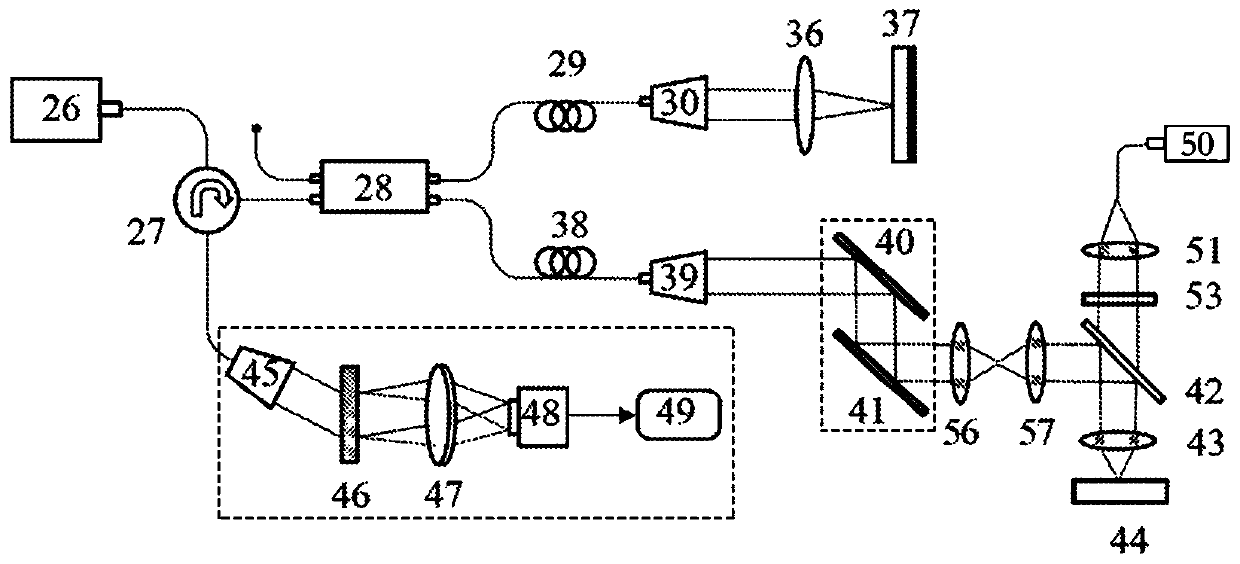
ActiveCN109907731AEliminate the effects of motion artifactsSolve the problem of unsatisfactory suppression effectSensorsAngiographyCovarianceSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a three-dimensional flow radiographic method and system based on optical coherence tomography of feature space. OCT (optical coherence tomography) scattering signals of a scattering signal sample in a three-dimensional space are collected through a collector; a two-dimensional feature space is constructed through a theoretically established classifier in combination with local signal-to-noise ratios of the OCT scattering signals and a decorrelation coefficient; dynamic flow signal and stationary tissue classification is achieved. The specific steps include calculating and analyzing the OCT scattering signals through first-order and zero-order auto-covariance to obtain the signal-to-noise ratios of the OCT scattering signals and two decorrelated features; constructing a signal-to-noise ratio reciprocal-decorrelation coefficient two-dimensional feature space; constructing a linear classifier of ID spaces based on the principle of multivariate time series, and removing background of the stationary surrounding tissues. The method and system herein can evidently inhibit the influence of system noise upon flow radiography, contrast of flow images is increased, vessel visibility of deep tissues is particularly increased, and accuracy of blood flow can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
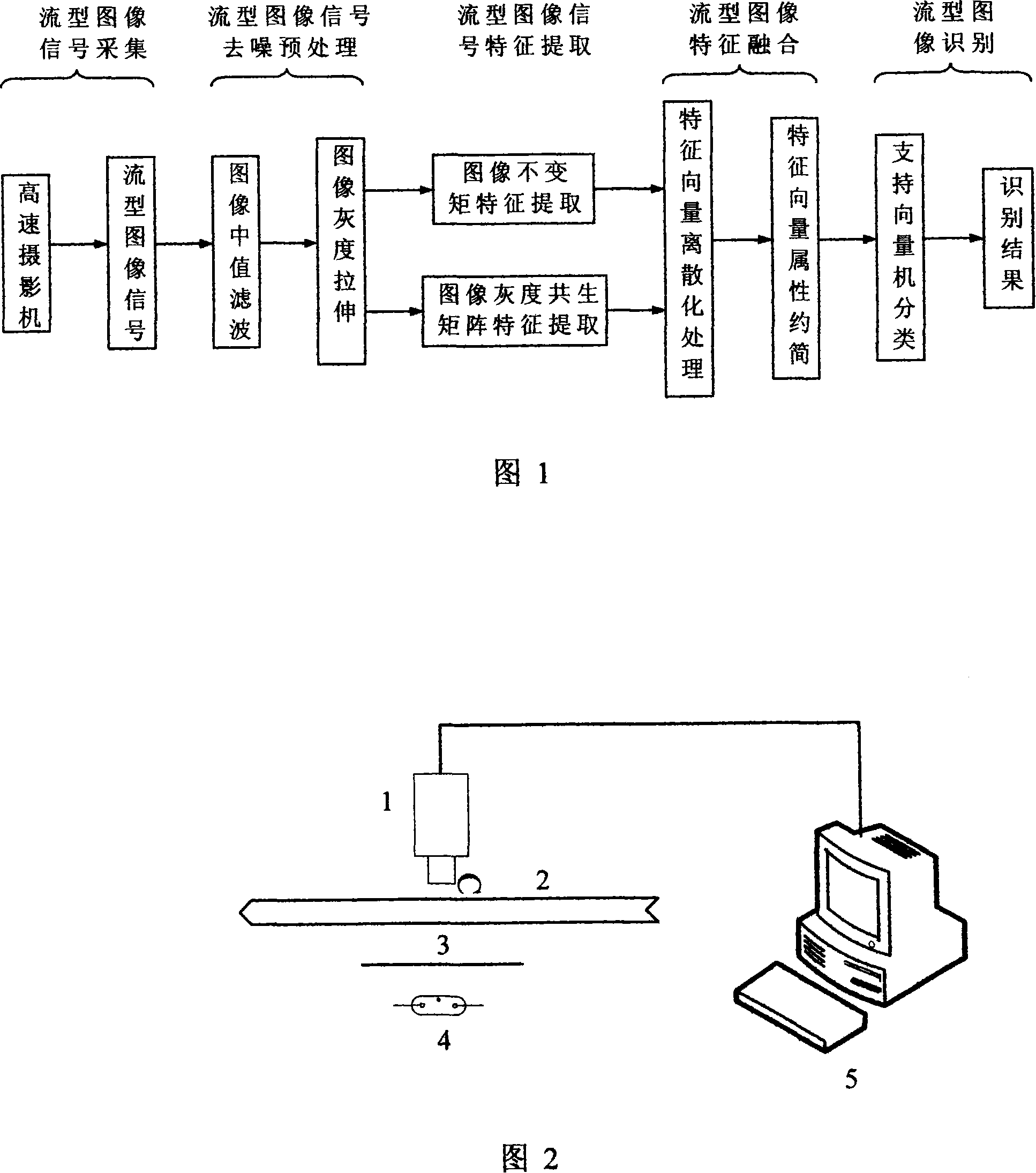
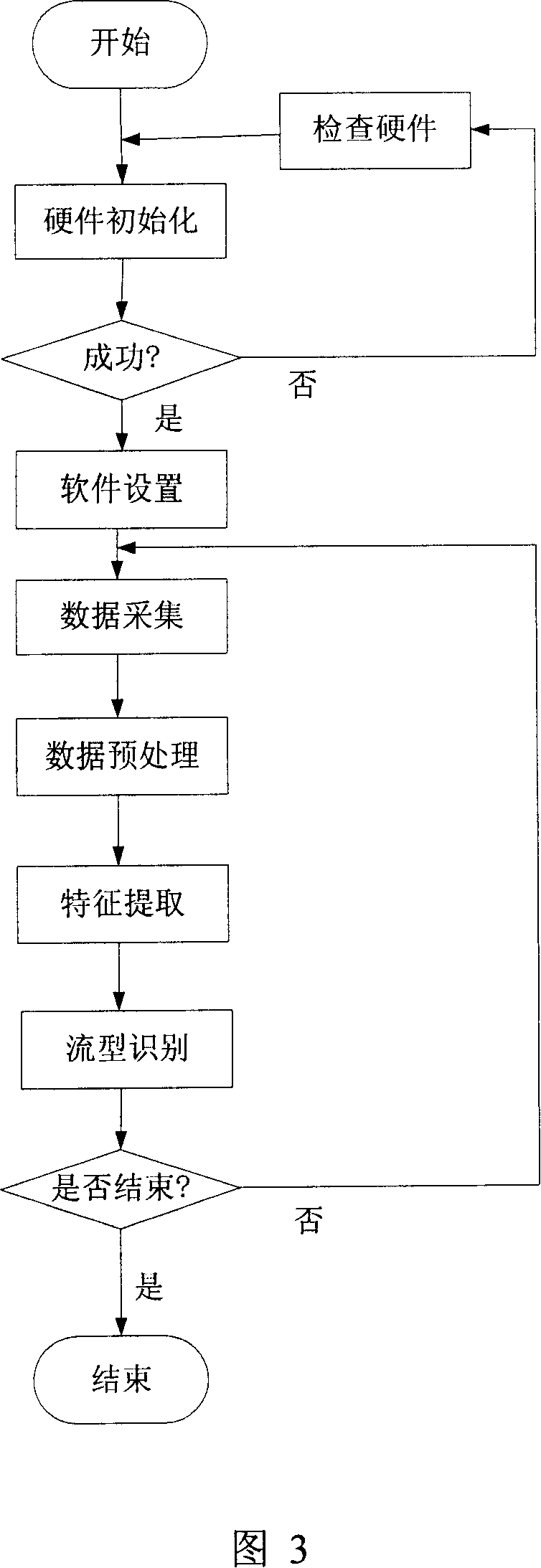
Gas-liquid two-phase flow type recognition method based on digital graphic processing technique
InactiveCN101140216ARealize non-contact measurementClear stream imageFlow propertiesCharacter and pattern recognitionCharacteristic spaceRough set
The invention relates to a gas-liquid two-phase flow pattern recognition method based on digital image processing technology, which is characterized in that the method uses a high-speed camera to gain the gas-liquid two-phase flow image in a horizontal pipeline under the different working conditions; the characteristics of invariant moment and gray level co-occurrence matrix of the image are extracted by the image processing technology; the characteristic fusion is implemented by using a rough set theory to reduce the characteristic dimensions, and the characteristic vector forms a flow pattern sample to implement the training for a support vector machine in order to complete the mapping from the characteristic space to the flow pattern space and finally realize the flow pattern recognition. The adopted rough set theory fuses image texture information and shape information, improves the recognition precision of a classifier, simultaneously reduces the training time, and can roundly reflect the characteristics of flow pattern image; the dependent degree and the generalization capacity of the flow pattern recognition method of the support vector machine for the sample data are better than the BP neural network; the invention has the shorter training time, and is applied to the flow pattern online recognition.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY
Flow imaging and monitoring for synchronized management of wide area drainage
A flow imaging and monitoring system for synchronized management of wide area drainage that includes an interposer for supporting monitoring and management equipment in a manhole, a module for illuminating water flowing in pipes at the base of the manhole, a module for monitoring responses to reflected light, a sealed and rechargeable battery pack, and a data analysis and management system to interpret data streams in real time. The interposer can be adjusted to fit the diameter of the manhole and can be adjusted to be placed under the manhole cover. The module for illuminating the flowing water can be adjusted to generate various frequencies. The support structures for the modules can be adjusted for varying pitch, roll and yaw with respect to the manhole. The data analysis and management system is supported by cloud computing.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY +1
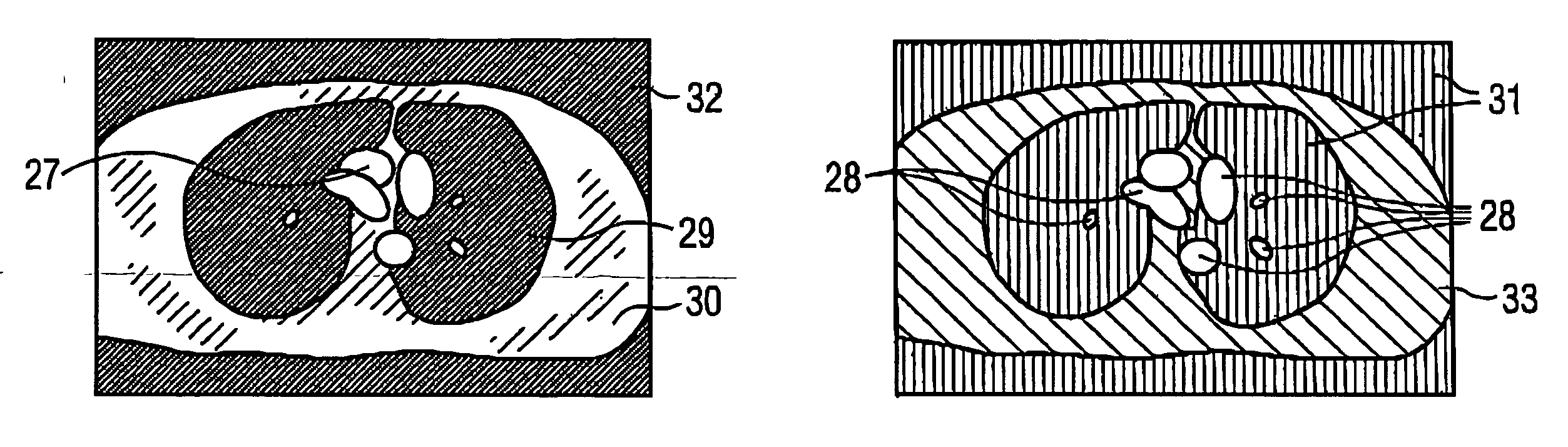
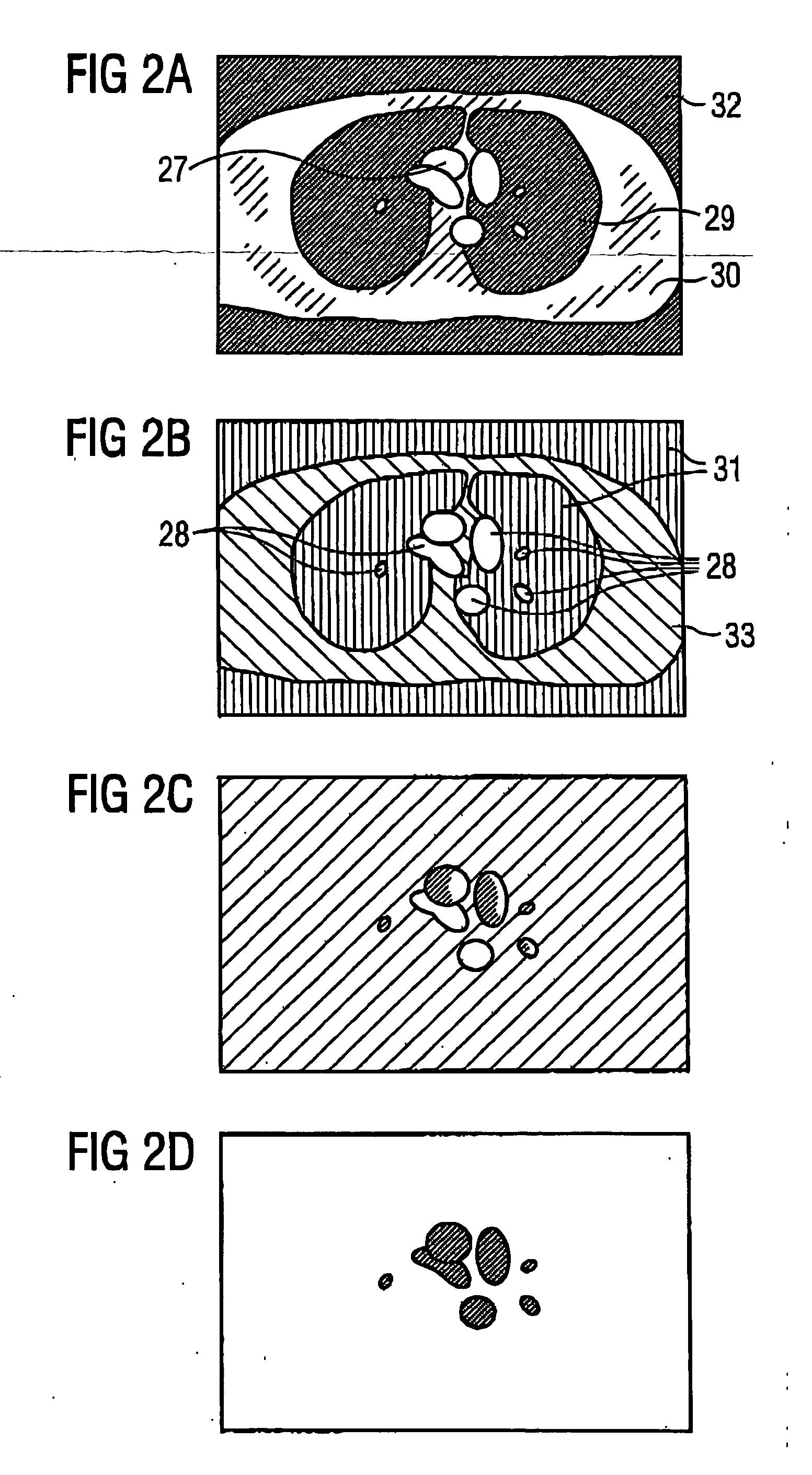
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for producing phase-coded flow images
In a method and MR apparatus for the automatic segmentation of flow images acquired by magnetic resonance tomography for the depiction of tissue or organs traversed with fluid such as blood, at least one phase image of a selected region of the subject is acquired by magnetic resonance tomography, and fluid-traversed regions in the at least one phase image are automatically segmented.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
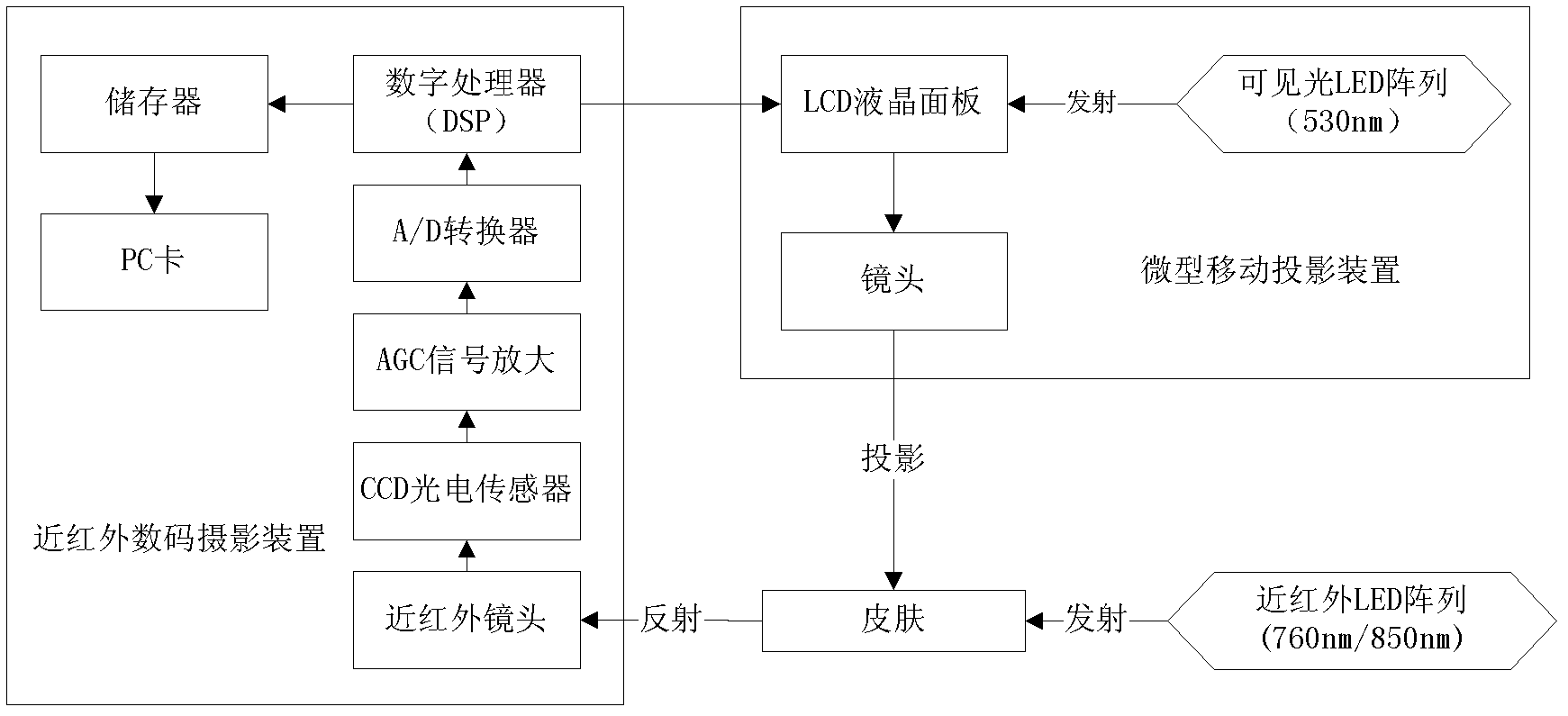
Near-infrared imaging ultrasonic vascular therapeutic apparatus
InactiveCN102871645AReal-time display of flow rateReal-time display of flow directionUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesDisplay deviceThrombus
The invention discloses a near-infrared imaging ultrasonic vascular therapeutic apparatus. A near-infrared surface vessel detection subsystem is used for detecting the surface vessels, and is connected with a near-infrared vessel detection operating interface; the near-infrared vessel detection operating interface is used for controlling focus, thereby achieving the inspection of vessels; according to the set, the surface veins or arteries are likely to be displaced below a projecting device; a color Doppler flowing imaging subsystem is used for detecting the flowing information and is connected with a diagnosis probe; an ultrasonic treatment subsystem is used for treating shallow-layer vascular diseases and is connected with a treatment probe; a keyboard is used for inputting information of patients, achieving switch and control of the color Doppler flowing imaging and the ultrasonic treatment, and respectively displaying on a display; and the display is used for displaying the information of the patients, the color Doppler flowing information and a thrombectomy situation. With the adoption of the near-infrared imaging ultrasonic vascular therapeutic apparatus, the surface veins or arteries distribution can be displayed in real time, the flowing parameters are obtained fast, the focus of infection is located exactly, the ultrasonic density is selected to perform an targeted treatment according to the flowing situation, thereby achieving the best treatment effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
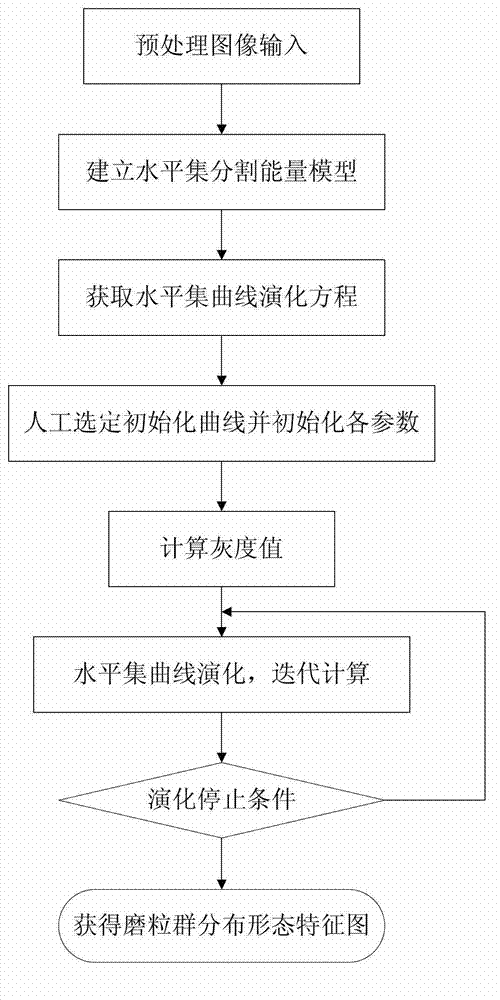
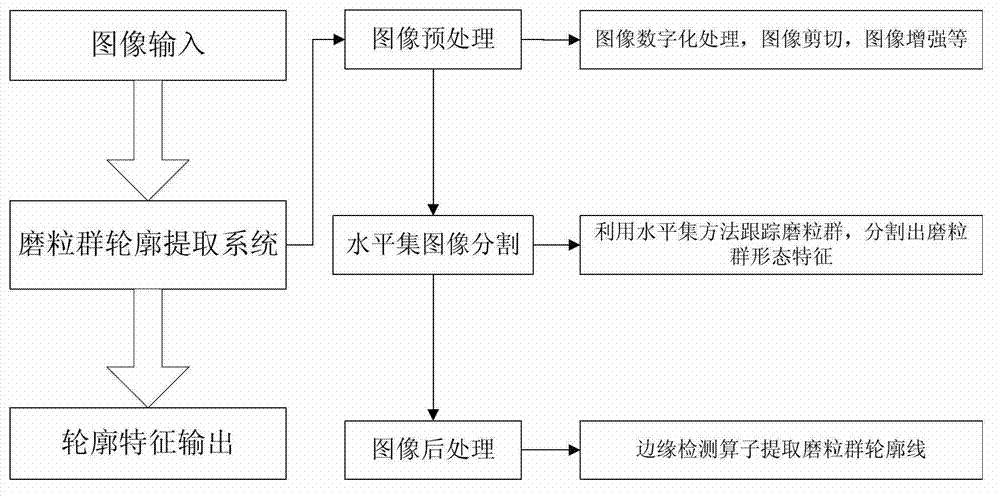
Real-time detection method of soft abrasive flow abrasive group
InactiveCN102830121AEfficient detectionAccurate extractionInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsField functionRunge–Kutta method
A real-time detection method of a soft abrasive flow abrasive group comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a phase-field model two-phase interface mixed energy equation according to the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group, also establishing a control equation of the phase-field function evolution, finally approximating a viscous phase and a surface pressure phase by a traditional second order center difference scheme, performing spatial discretization reconstruction of the control equation by a fifth order WENO scheme, performing discretization in the time direction by a Runge-Kutta method with a TVD property, and thus solving the two-phase interface to obtain a theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution; 2) performing real-time image processing of the distribution area of the abrasive group in a constraint channel obtained by a soft abrasive flow image acquisition device according to the obtained theoretical model of the abrasive group distribution, and thus extracting a contour feature of the abrasive group distribution area to obtain the change condition of the abrasive group dynamic boundary. The invention effectively detects the distribution condition of the soft abrasive flow abrasive group.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Medical image processing system and method for personalized brain disease diagnosis and status determination
InactiveUS20200315455A1Ensure correct executionEfficient analysisImage enhancementMedical imagingFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryImage manipulation
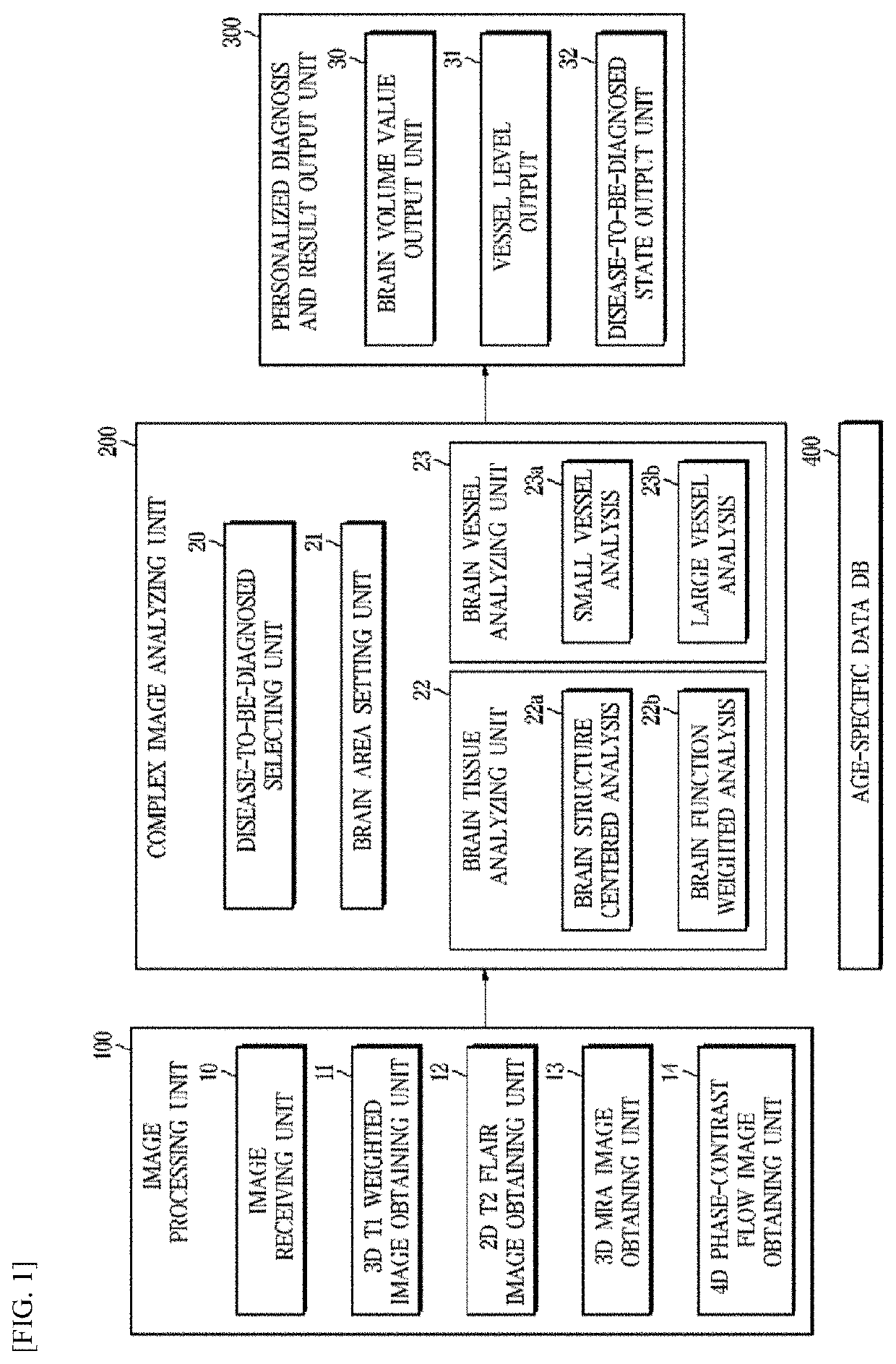
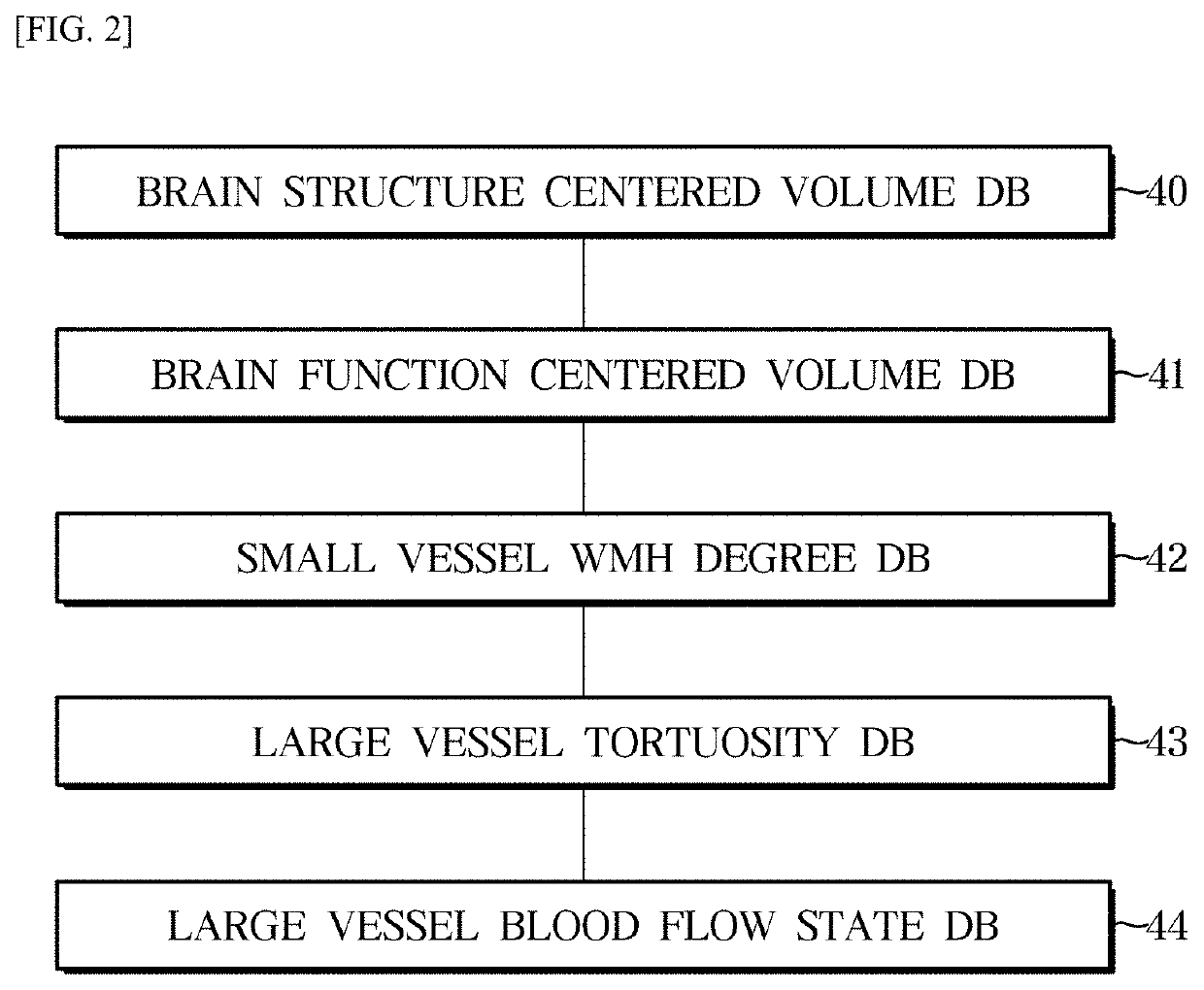
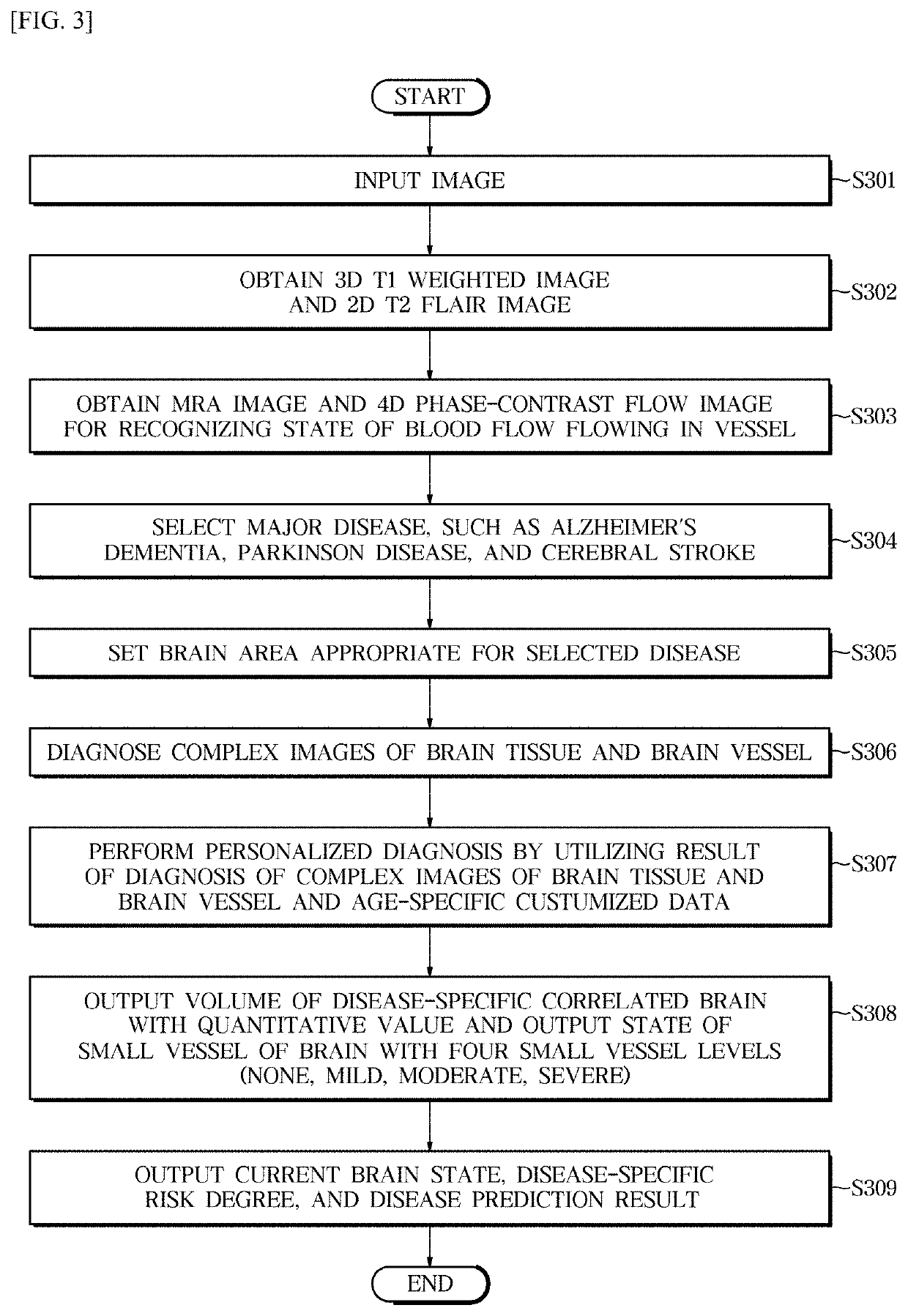
A system for processing a medical image for personalized brain disease diagnosis and status determination, includes: an image processing unit, which obtains a 3D T1 weighted image, a 2D T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image, a magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) image, which images only a vessel for checking abnormality of a brain vessel, and a 4D phase-contrast flow image for recognizing a state of a blood flow in a vessel; a complex image analyzing unit, which selects a disease-to-be-diagnosed, sets a brain area according to the selected disease, and analyzes brain tissue and a brain vessel; and a personalized diagnosis and result output unit, which outputs a brain state, a disease-specific risk degree, a risk of disease, and a disease prediction result through a machine learning algorithm by utilizing an age-specific data DB.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO +1
Downhole Multi-Phase Flow Imager
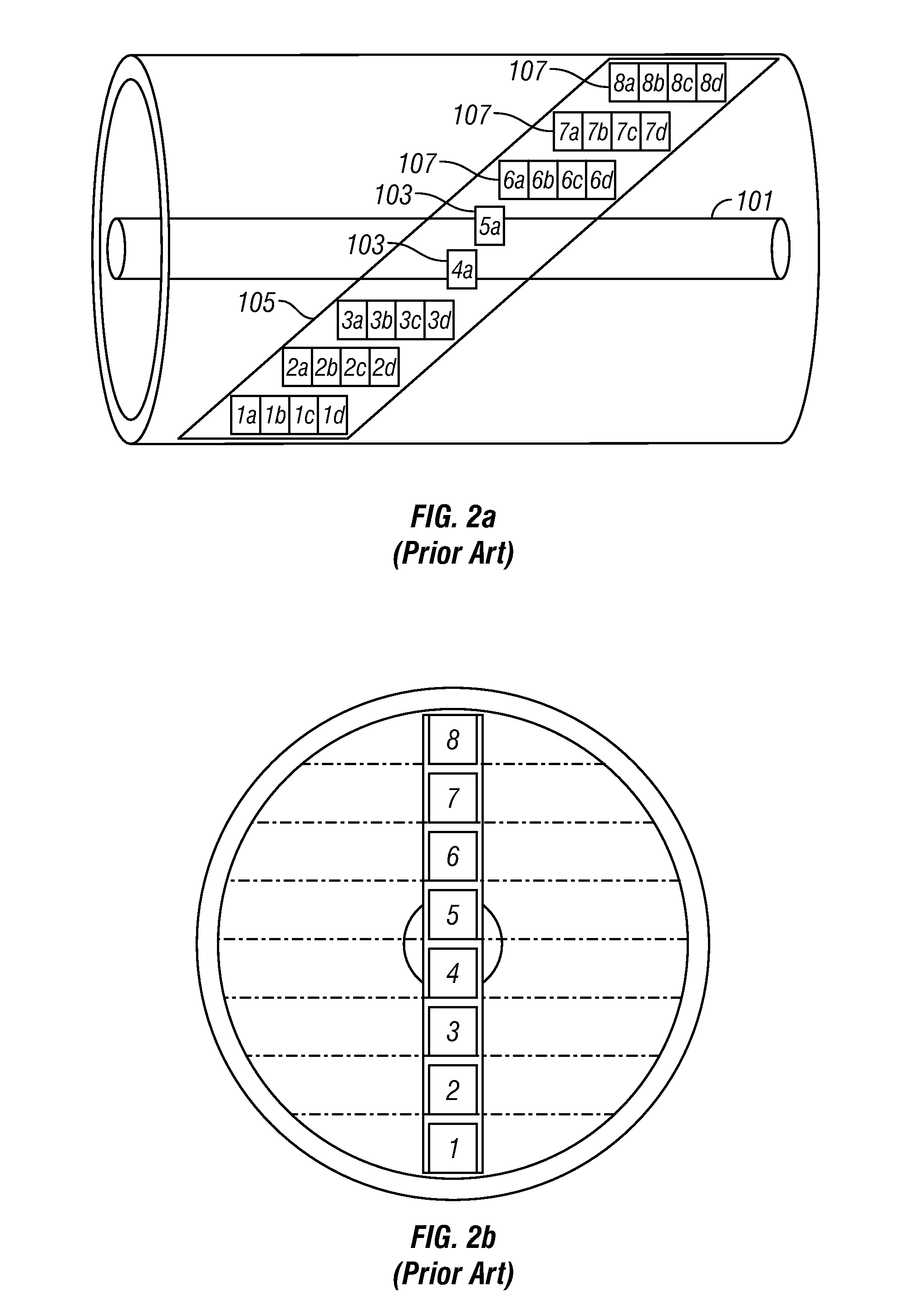
Dynamic gain setting is provided for a multiphase flow measuring device that measures in-phase and quadrature signals. The average current at a plurality of measure electrodes is determined and subtracted from the individual measure currents to give a measurement with improved dynamic range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for segmentation of mr flow data using fluid dynamics and tracking
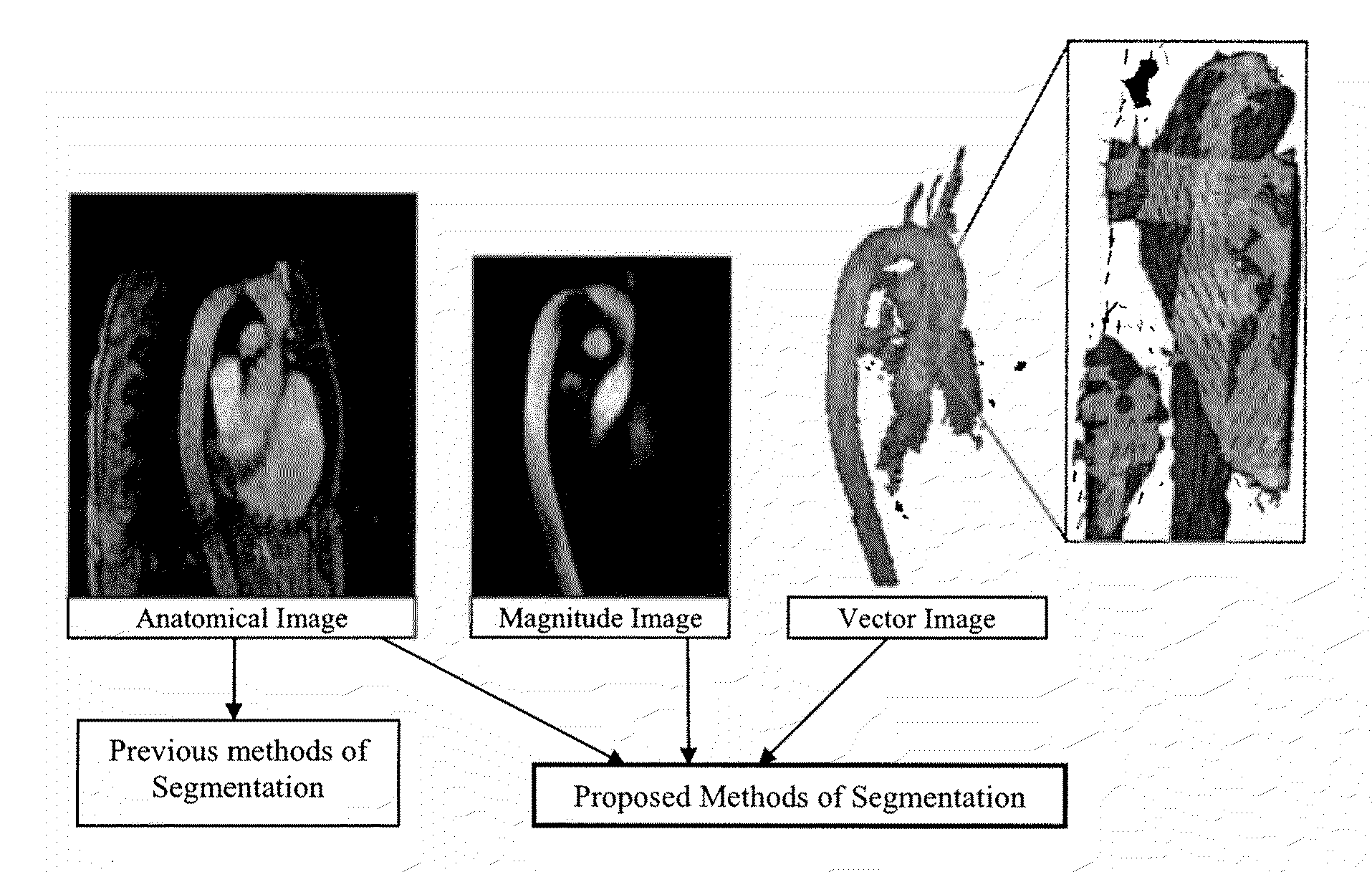
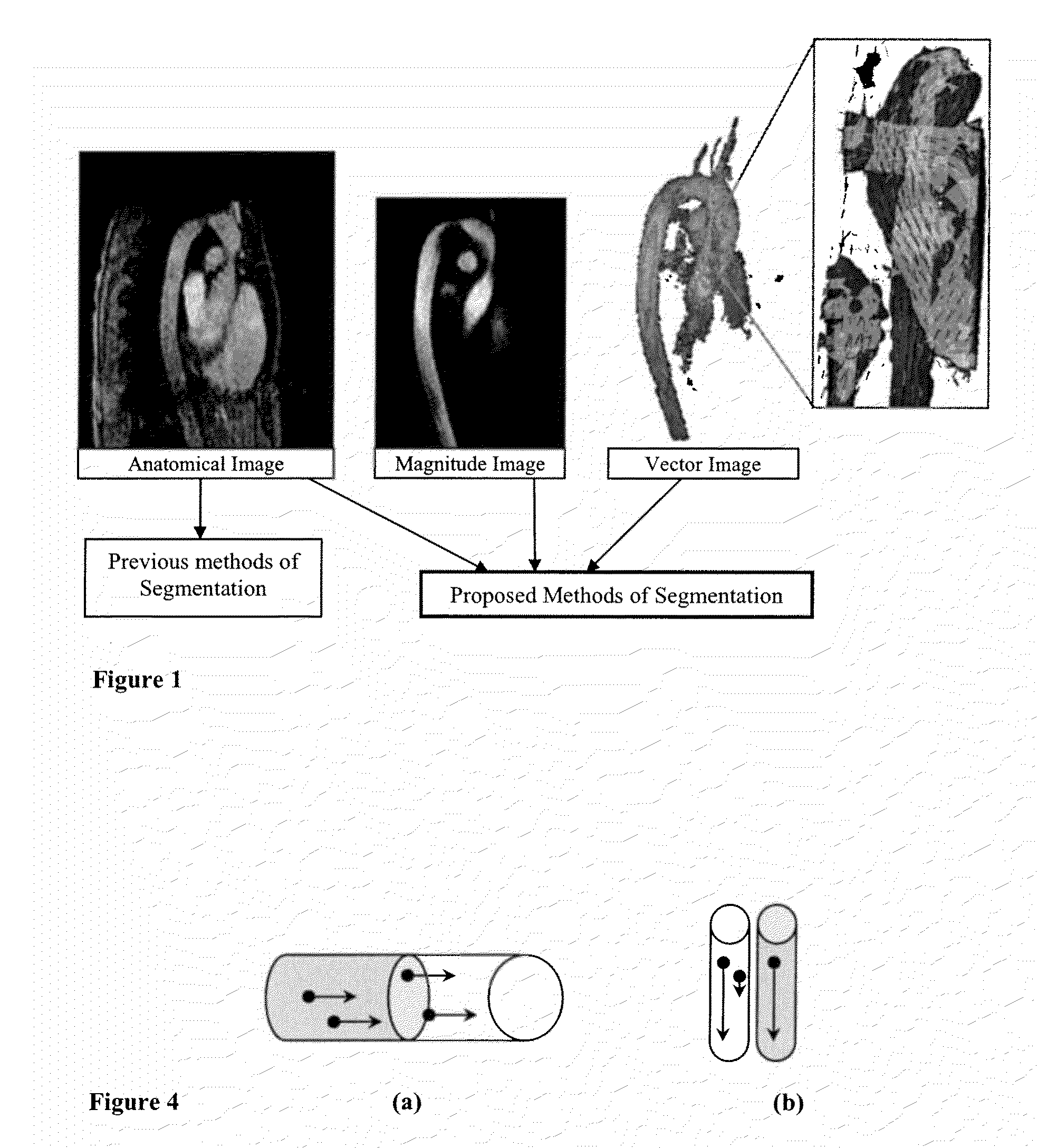
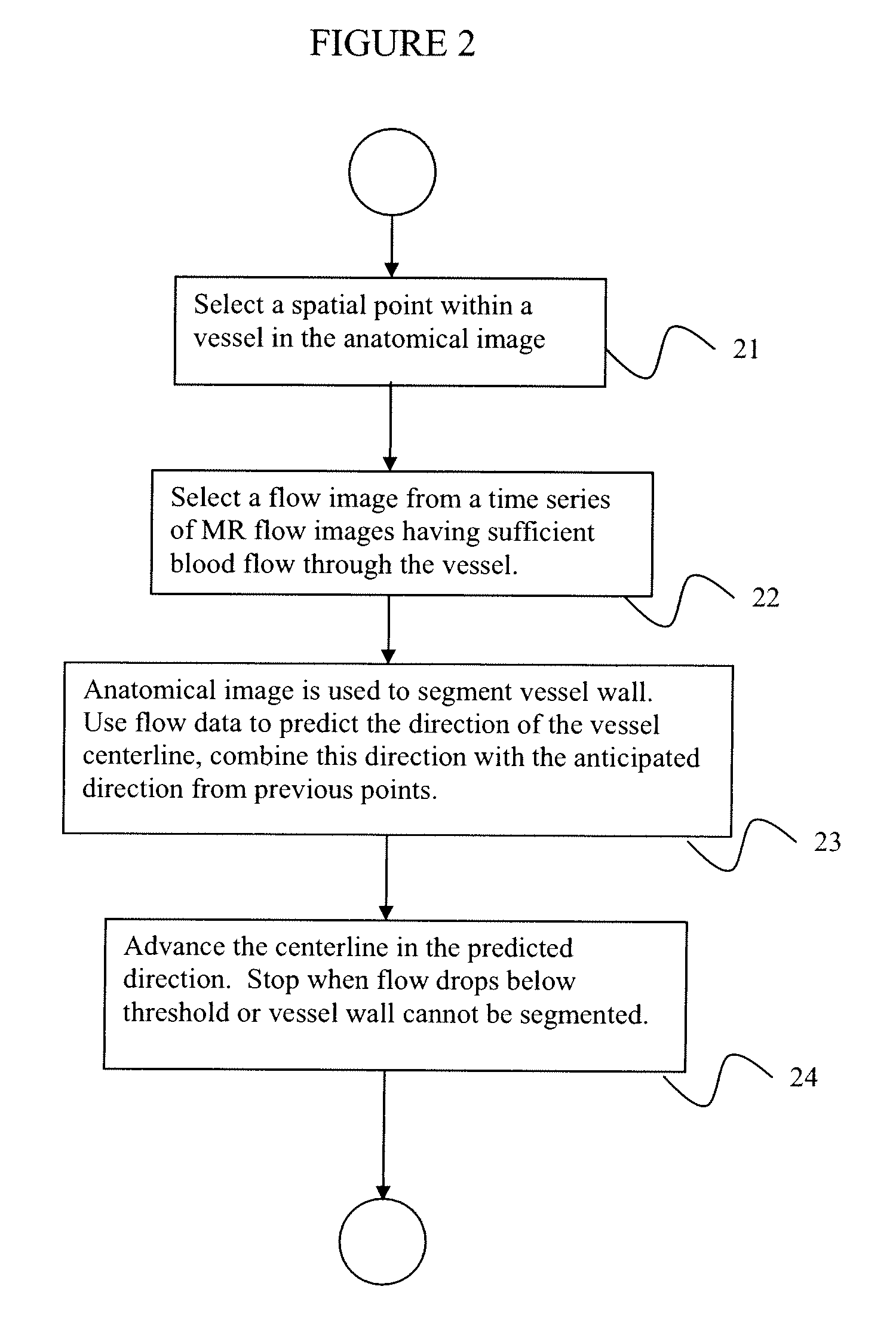
InactiveUS20100014739A1Improve segmentationOptimalImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusion methodsVector field
Methods for vessel segmentation and tracking using 7D MRI flow image data incorporate information from the velocity field and the magnitude. A vessel tracking methods selects a time containing sufficient blood flow through a vessel, uses the magnitude image to determine the vessel boundary and uses the velocity image to define the vessel direction. A method for segmenting tubular and circular objects segments the objects into separate vessels and then uses the velocity data to reunite the objects, where touching components are evaluated by the velocity field where they are connected. If vectors point towards the other component, the two components are reconnected. An advection-diffusion method based on fluid dynamics performs a fluid dynamics simulation with image forces according to the Navier-Stokes equations. With the 7D data, the vector field is available from the flow data, from the time point at which maximal flow occurs in the vessel of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
People counting method based on video flowing image processing
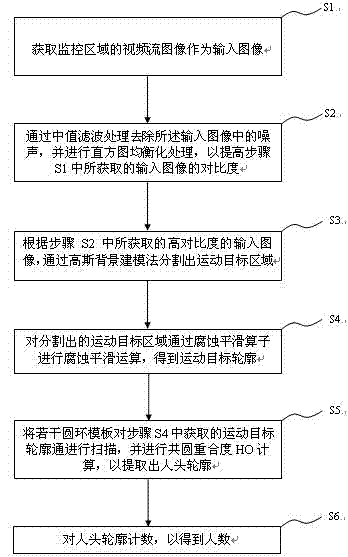
InactiveCN102831472AImprove statistical efficiencyImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingSmoothing operator
The invention provides a people counting method based on video flowing image processing. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, acquiring a video flowing image of a monitoring region to be used as an input image; S2, removing noises in the input image by using median filter processing, and carrying out histogram equalization processing to improve the contrast of the input image obtained in the step S1; S3, segmenting a motion target region through using a Gaussian background modeling method according to the input image (obtained in the step S2) with the high contrast; S4, carrying out erosion smoothing operation on the segmented motion target region through an erosion smoothing operator to obtain a motion target outline; S5, scanning the motion target outline obtained in the step S4 by using a plurality of ring modules, carrying out concyclic overlap ratio HO calculation to extract human head outlines; and S6, counting the human head outlines to obtain the number of people. By using people counting method based on the video flowing image processing, the efficiency and the accuracy degree of counting the number of the people in real time in a public area are effectively improved.
Owner:ABD SMART EYE ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com