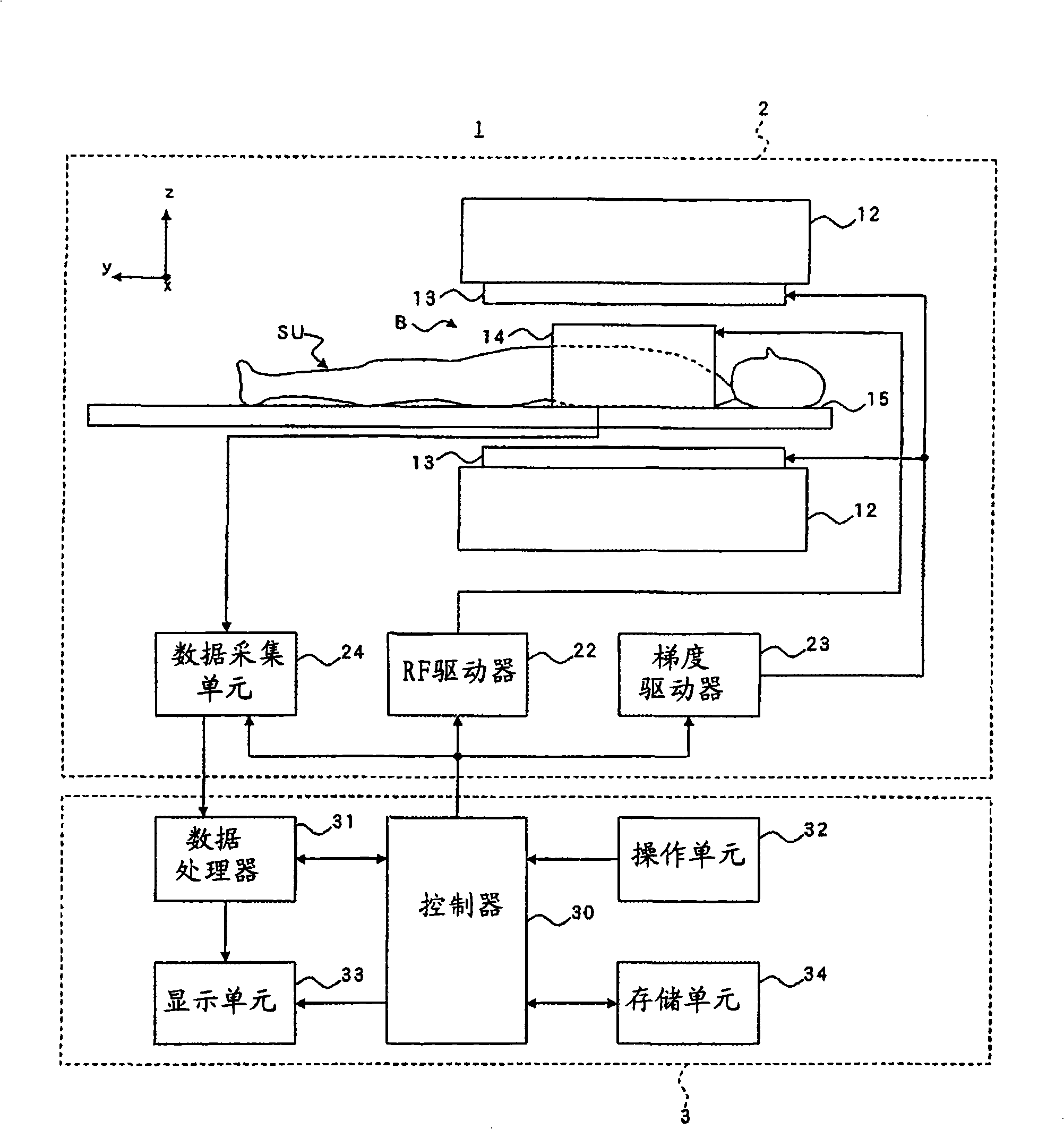
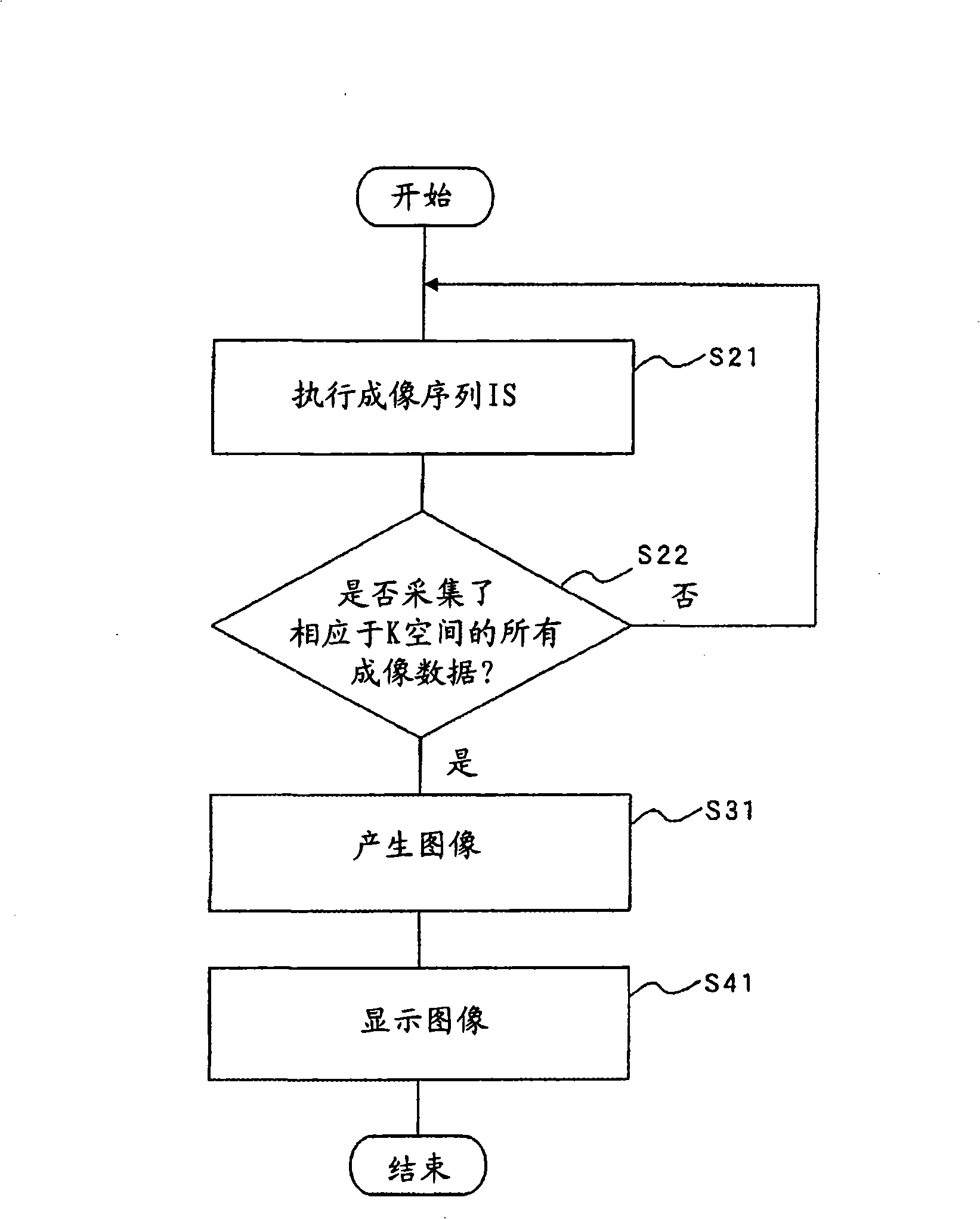
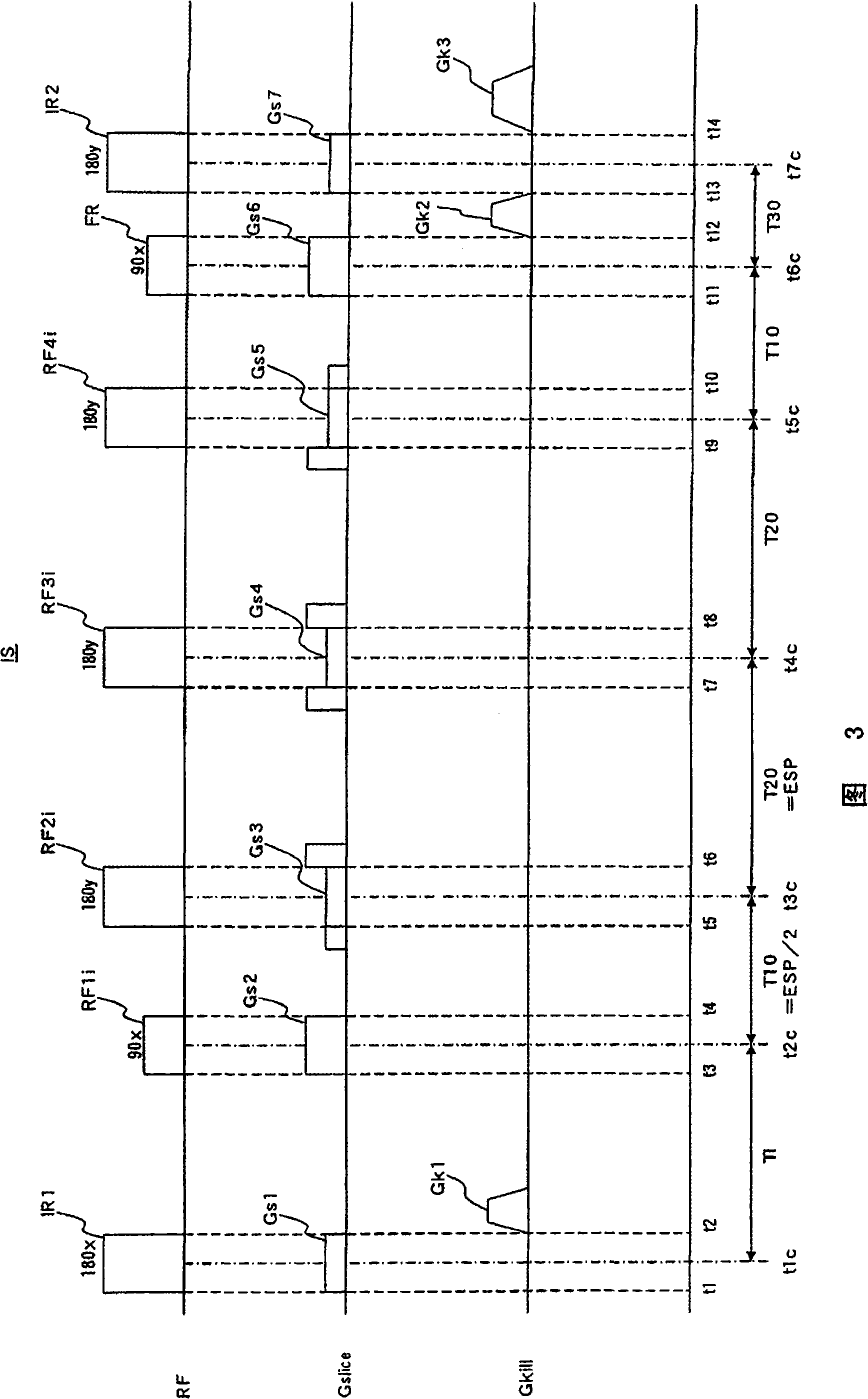
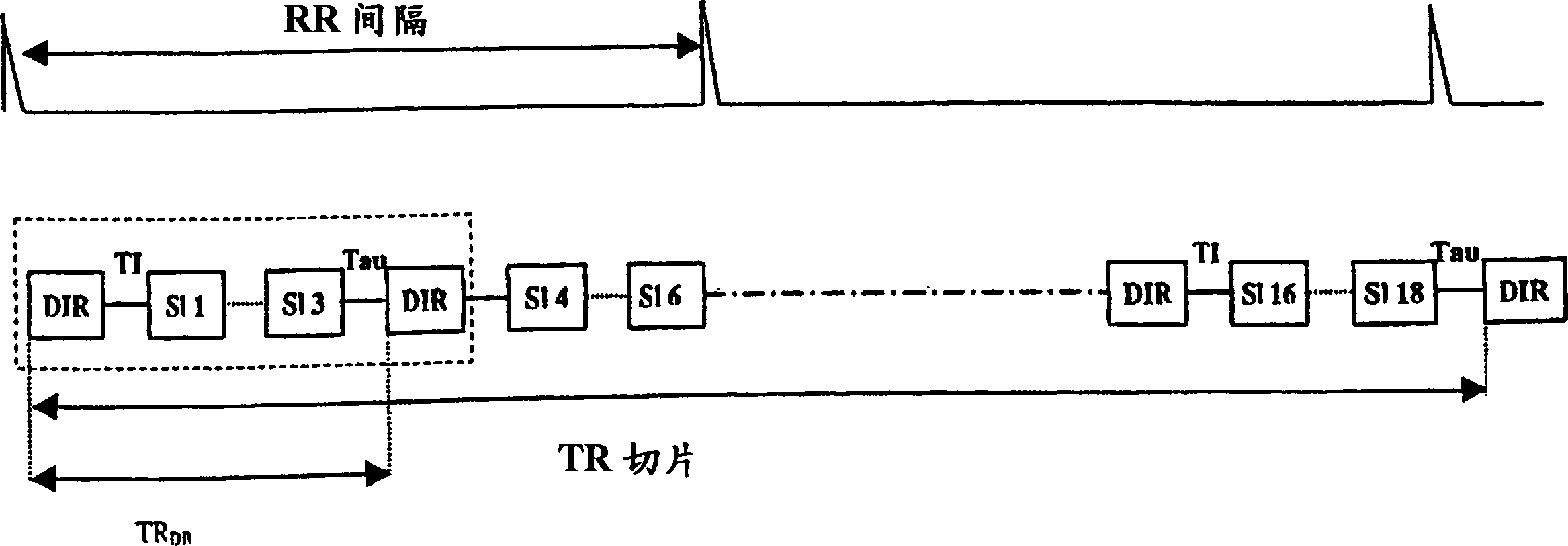
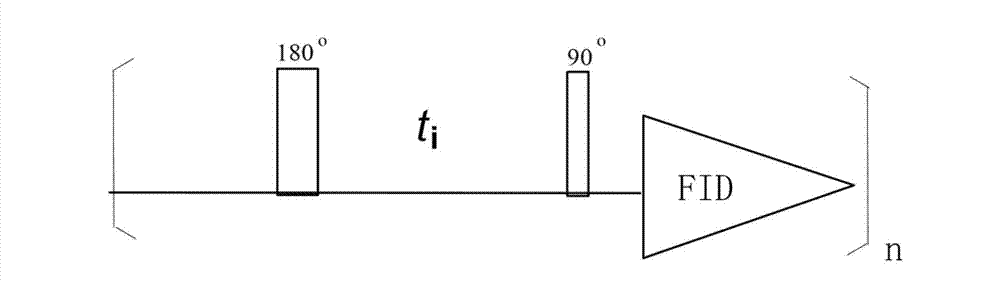
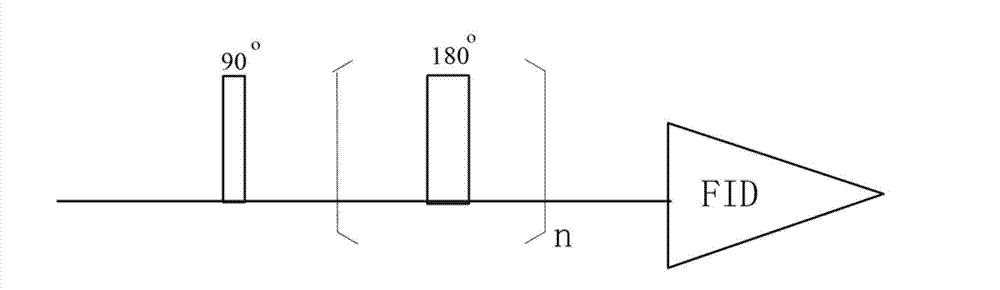
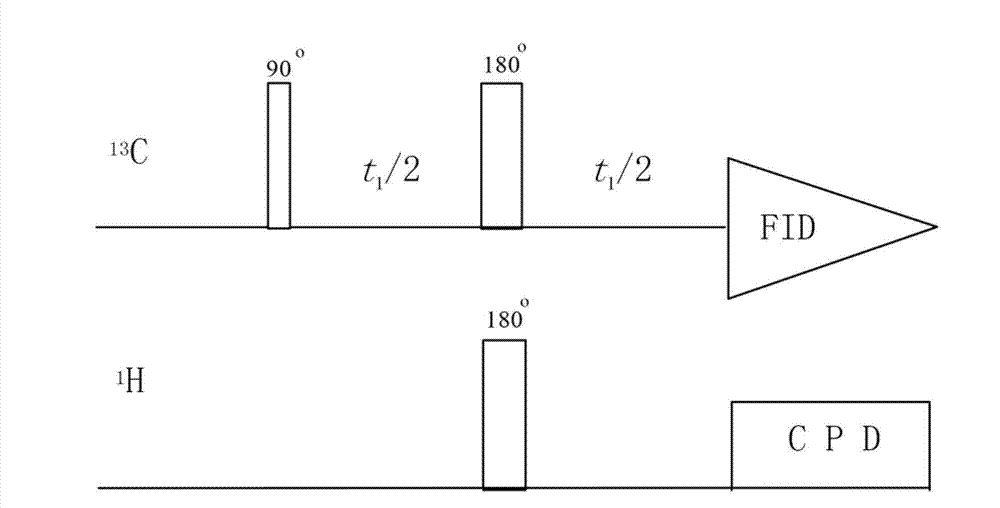
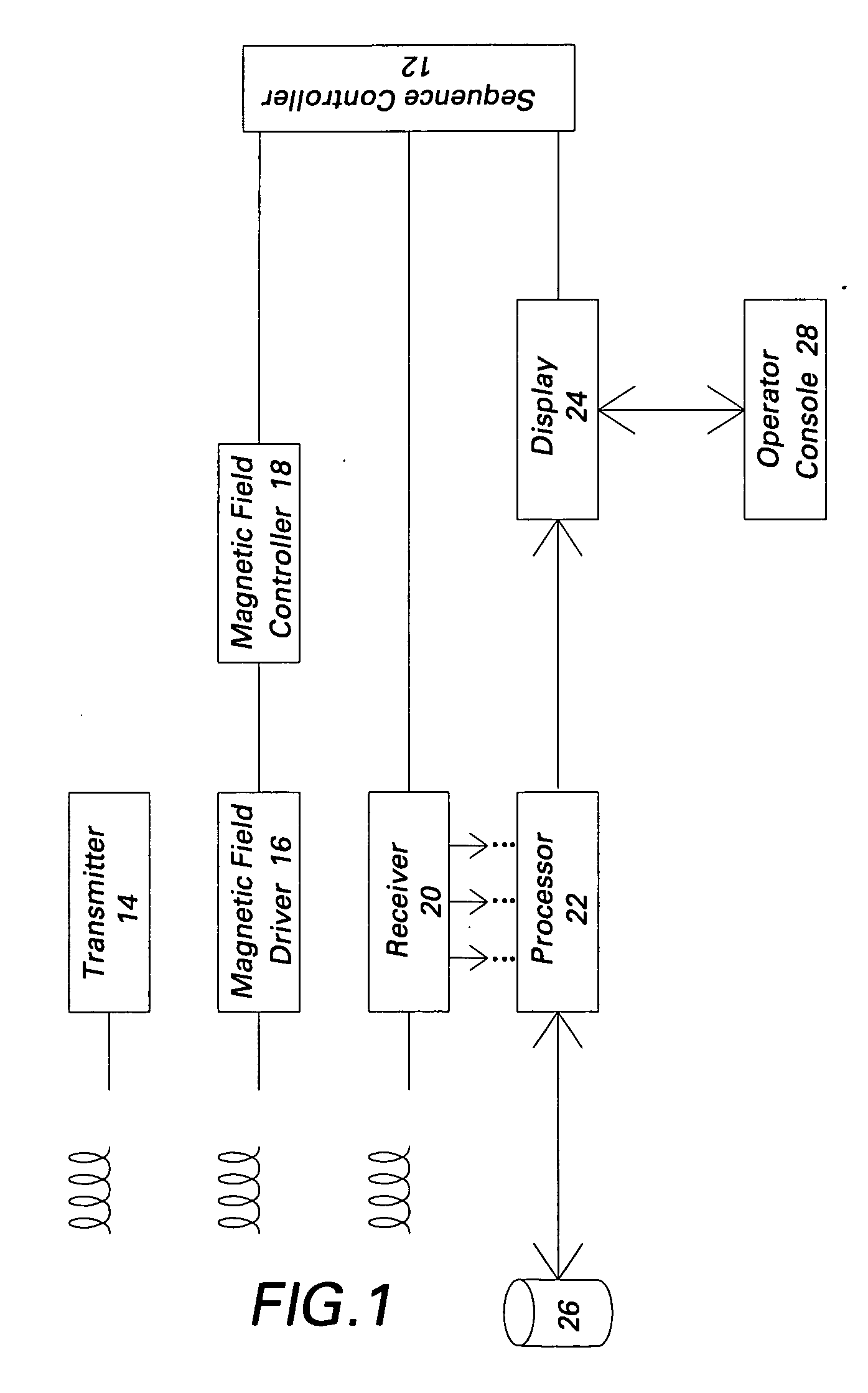
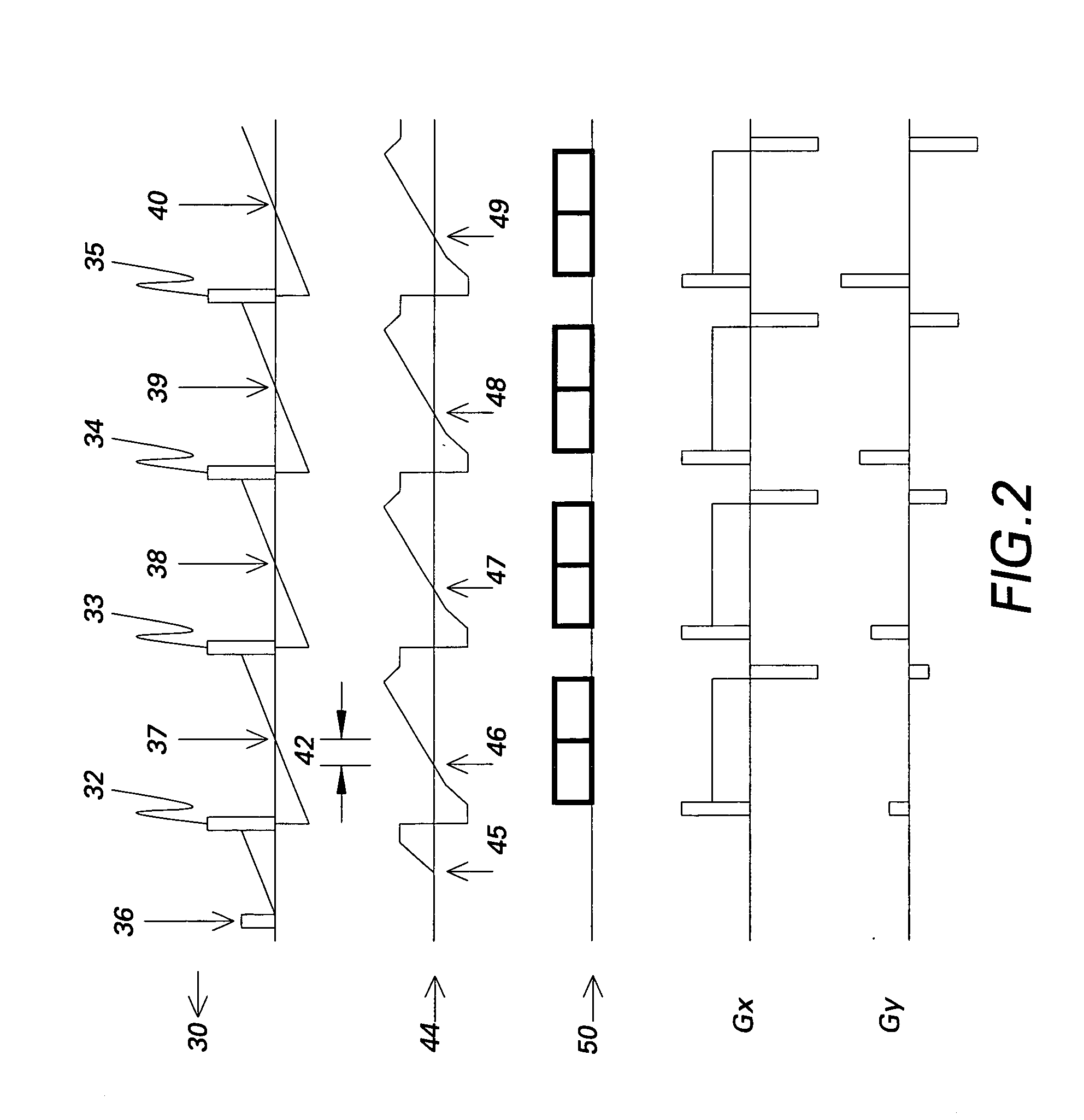
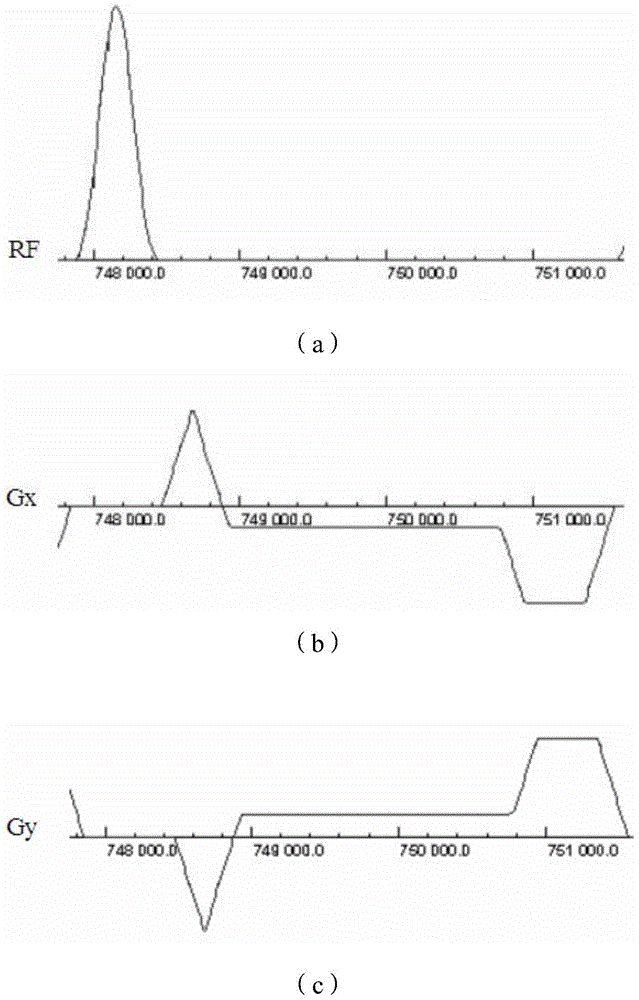
Patents
Literature
92 results about "Inversion recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
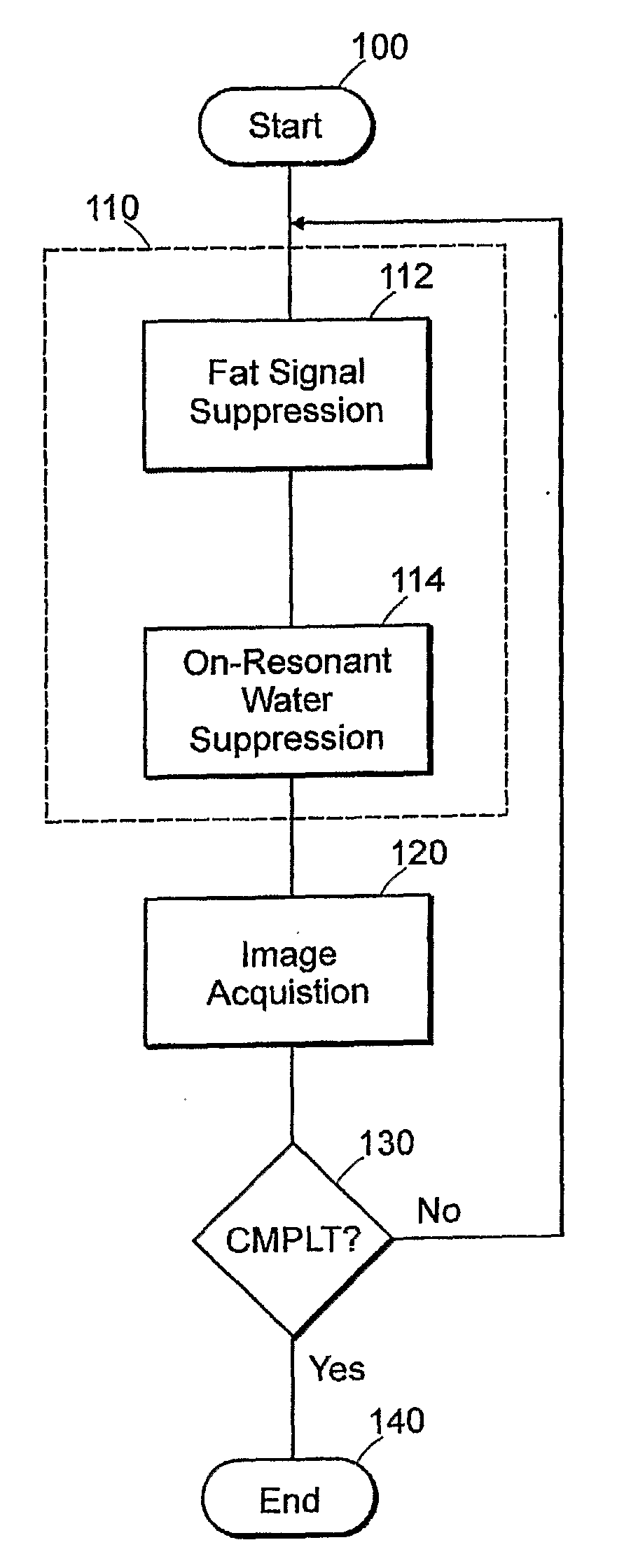
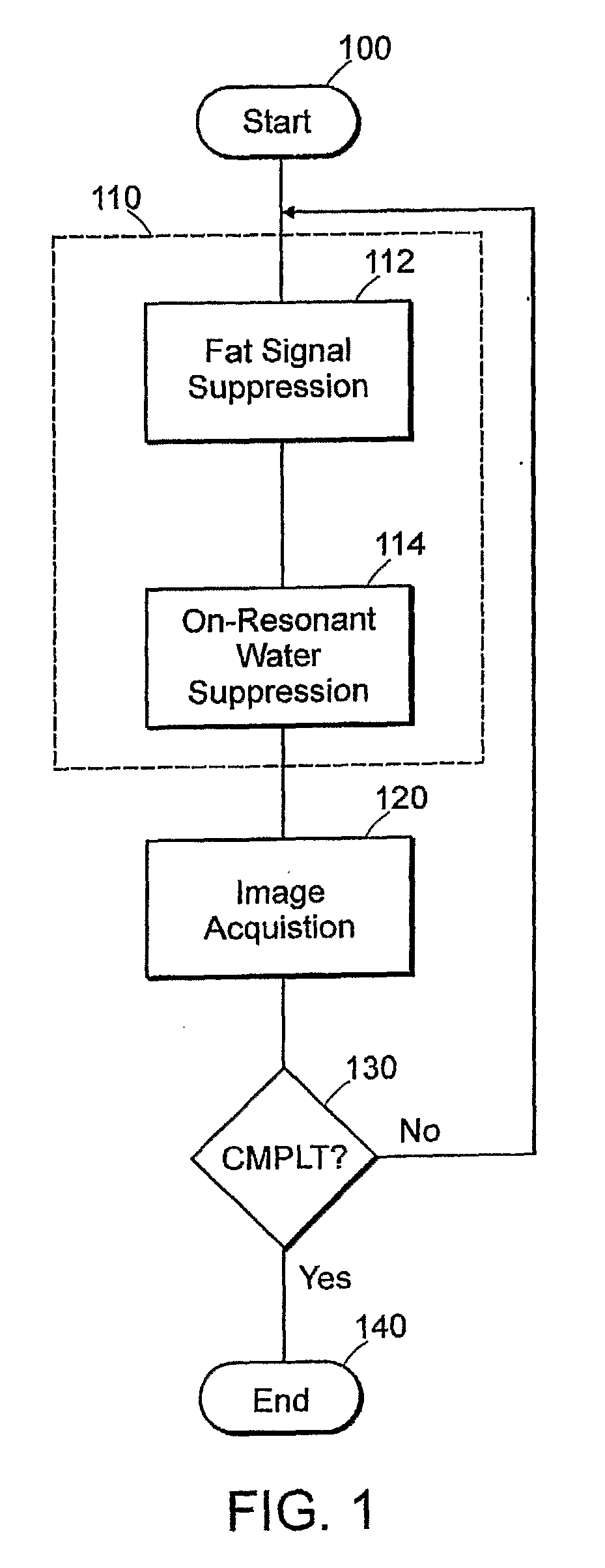
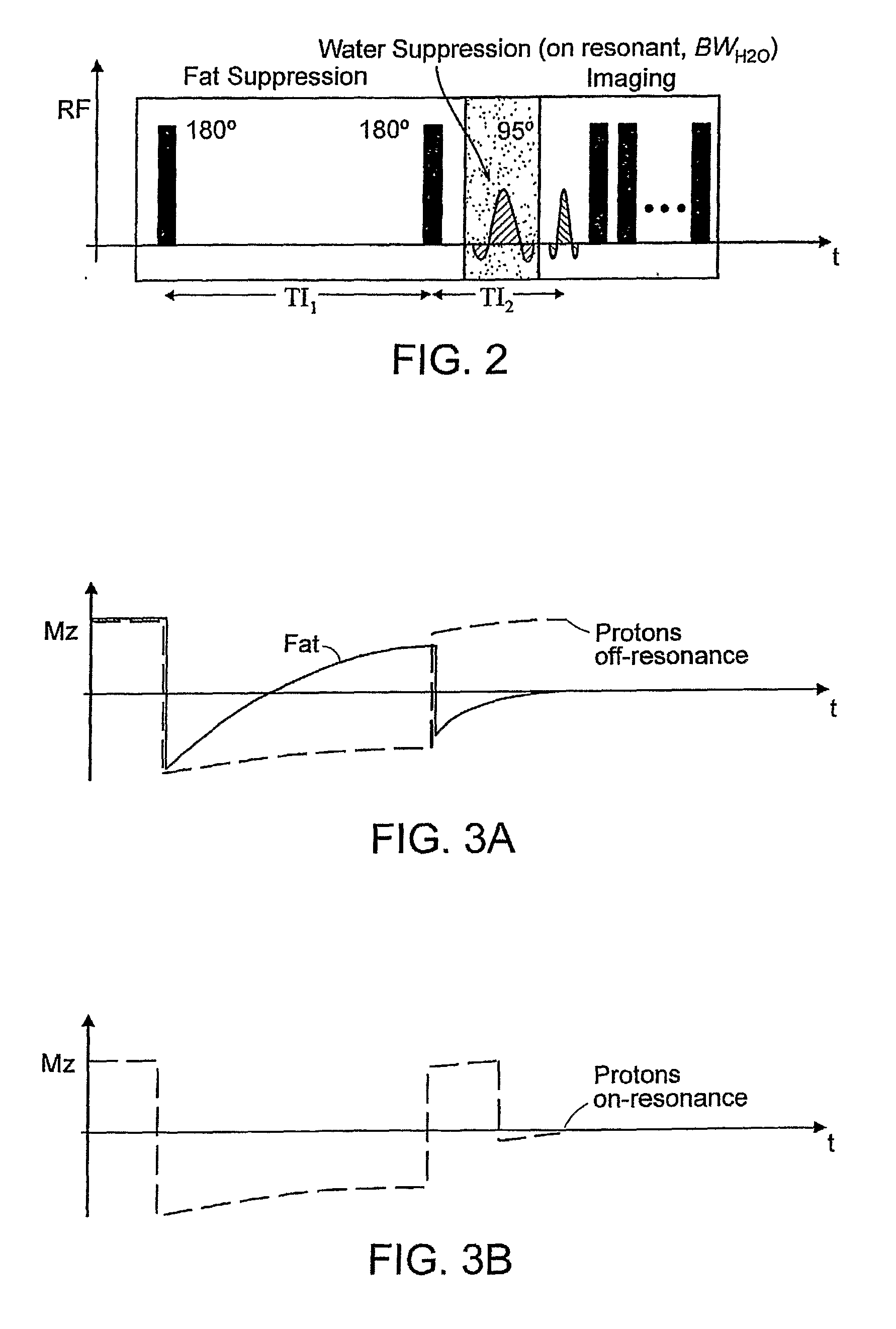
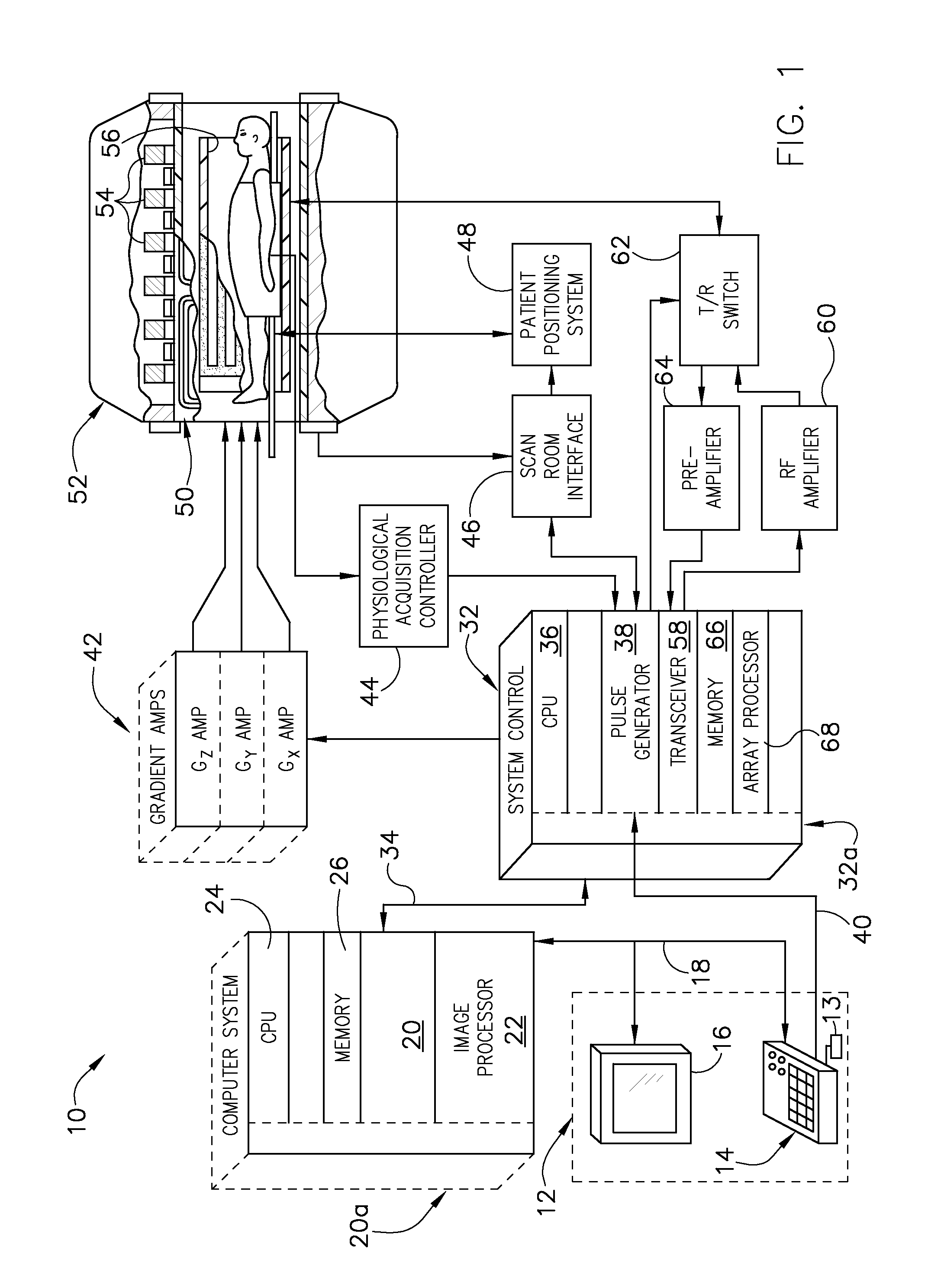
Method for magnetic resonance imaging using inversion recovery with on-resonant water suppression including mri systems and software embodying same
ActiveUS20090027051A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilityInversion recovery
Featured are methods for magnetic resonance imaging of a volume, such a volume having susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches therein. Such a method includes selectively visualizing one of susceptibility-generating objects or interfaces having susceptibility mismatches as hyperintense signals, where such visualizing includes controlling variable imaging parameters so as to control a geometric extent of a signal enhancing effect, m more particular aspects of the present invention, such selectively visualizing includes attenuating or essentially suppressing signals from fat and / or water, namely on-resonant water protons, so as to thereby enhance a signal(s) associated with magnetic susceptibility gradient(s). Also featured are MRI systems, apparatuses and / or applications programs for execution on a computer system controlling the MRI data acquisition process embodying such methods.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
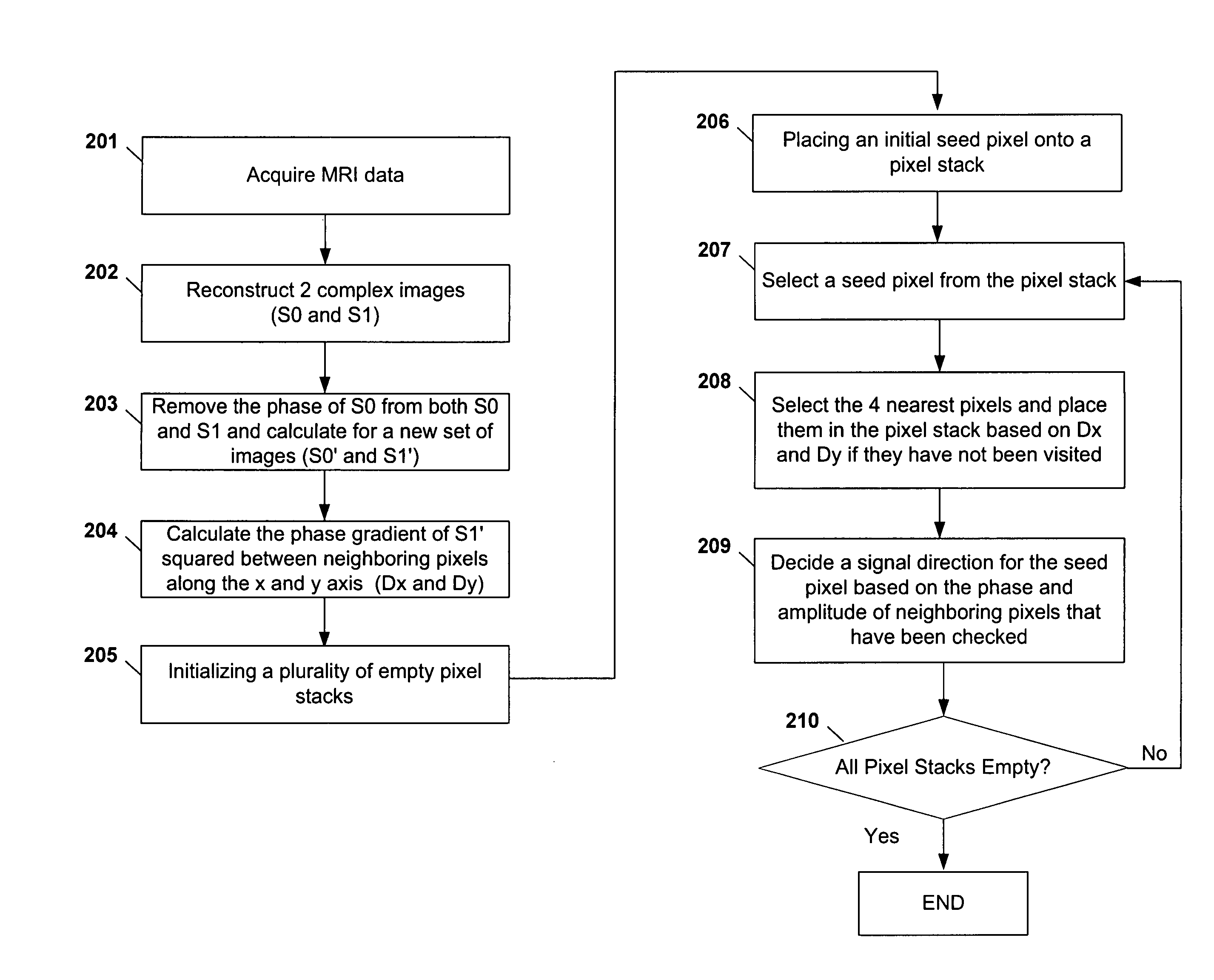
Method and apparatus for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20050165296A1Maintain consistencyAccurate identificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionInversion recovery
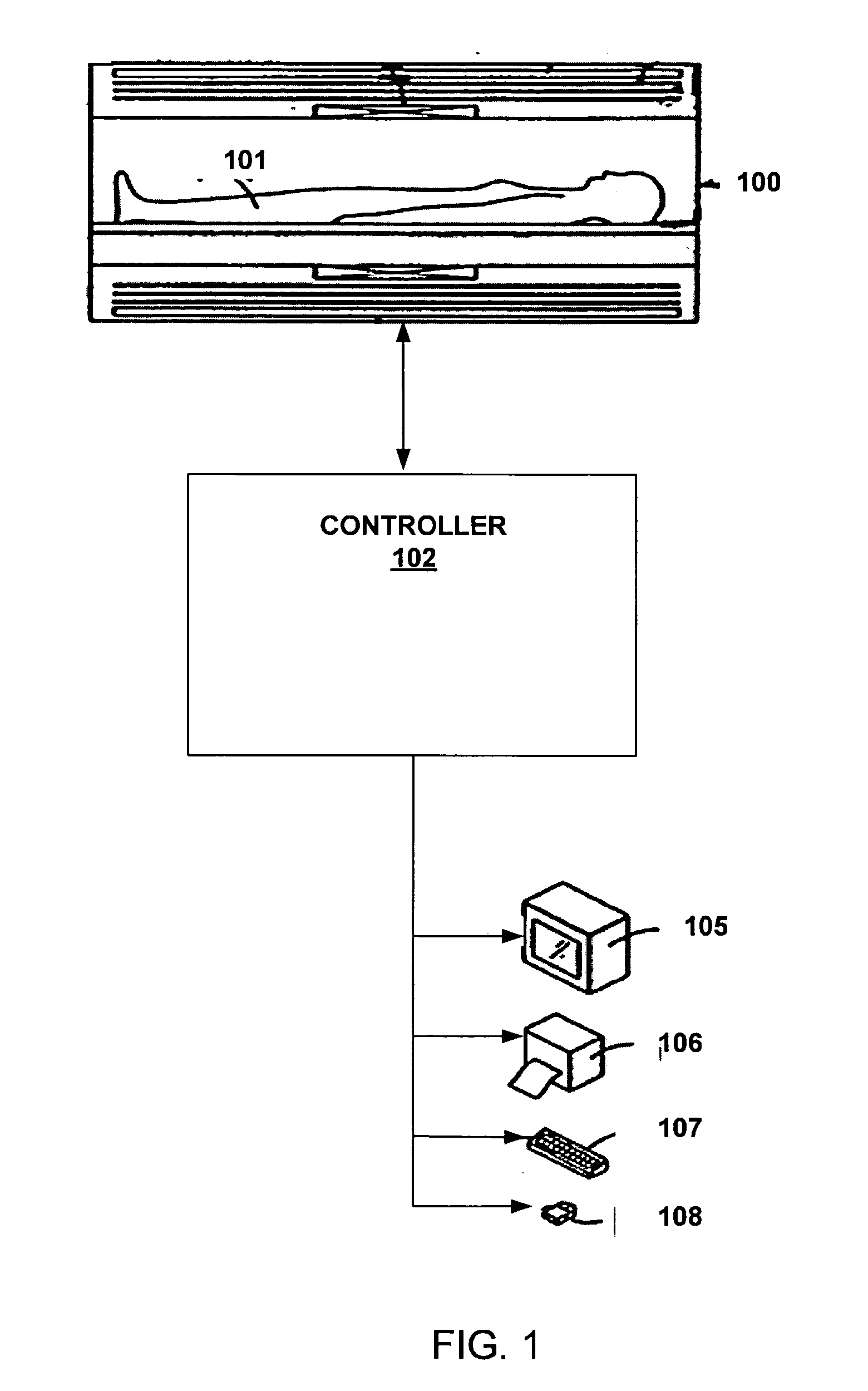
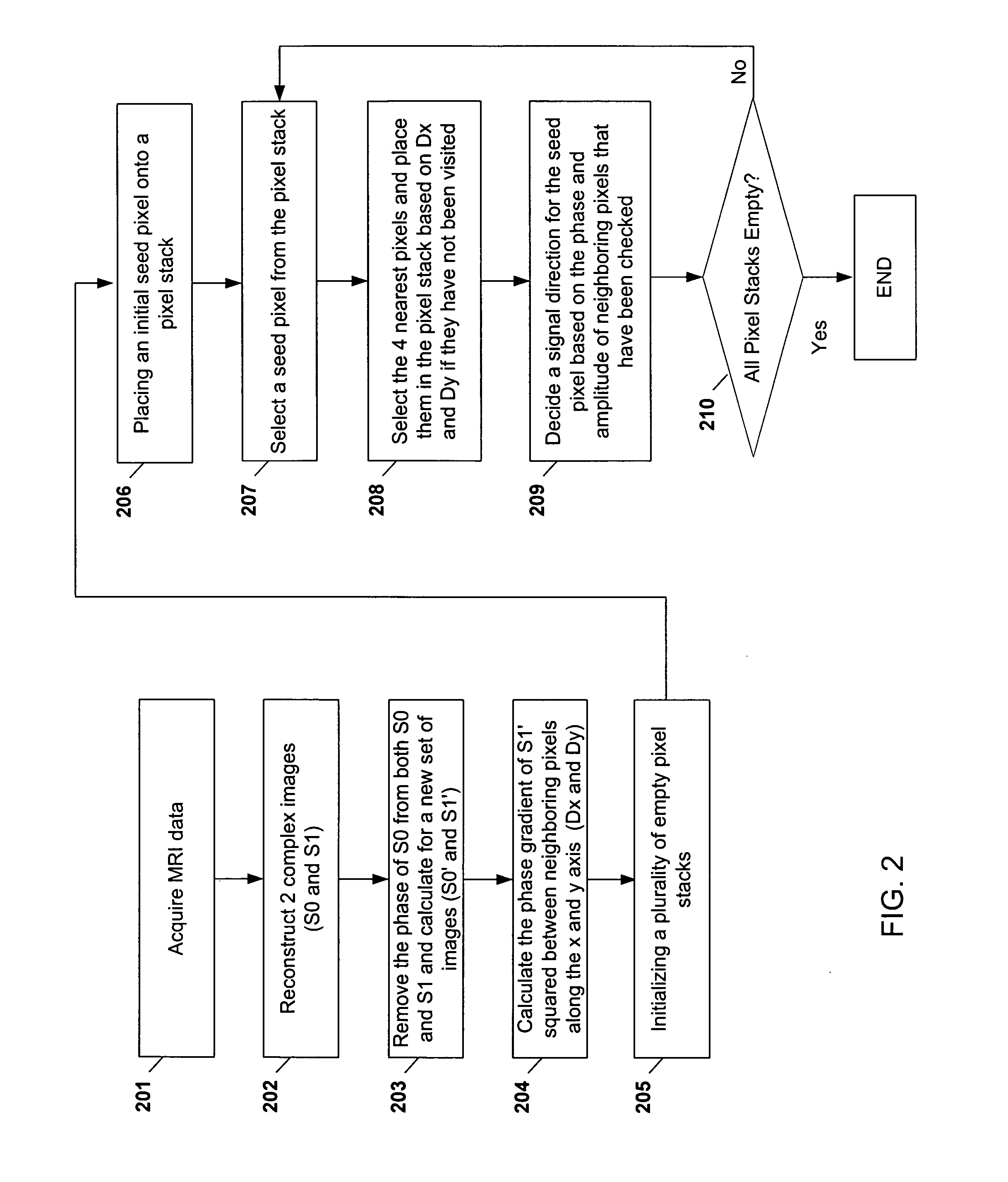
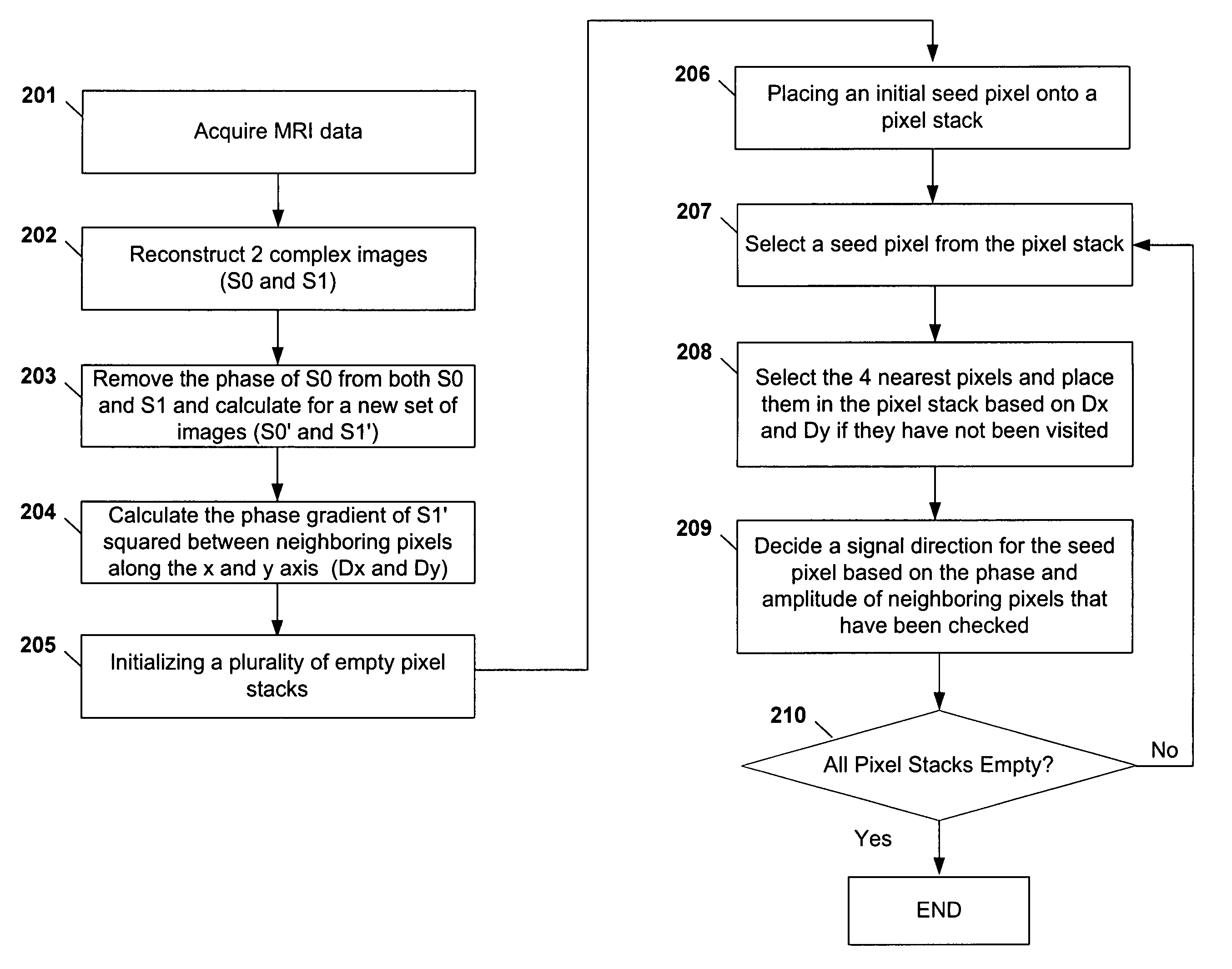
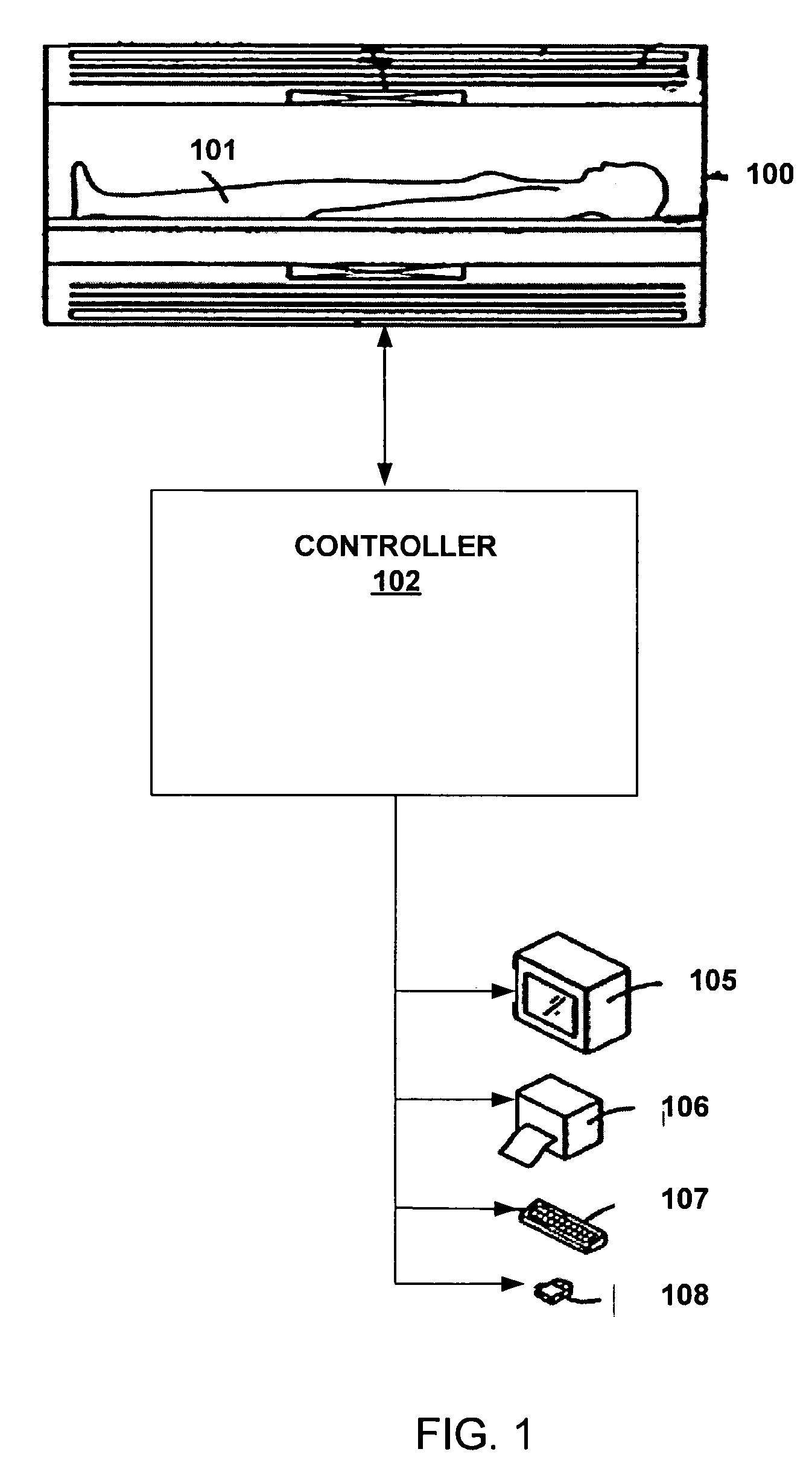
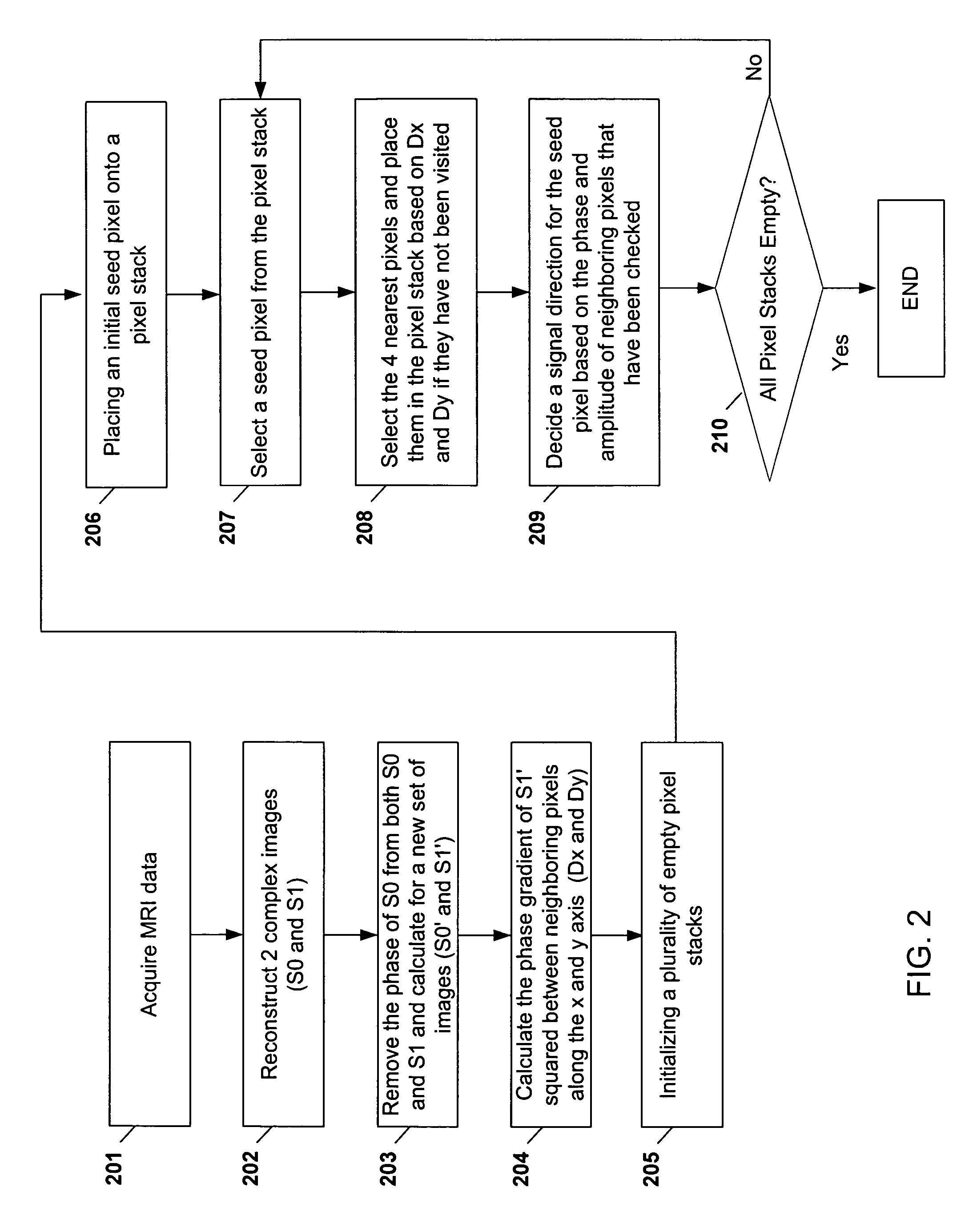
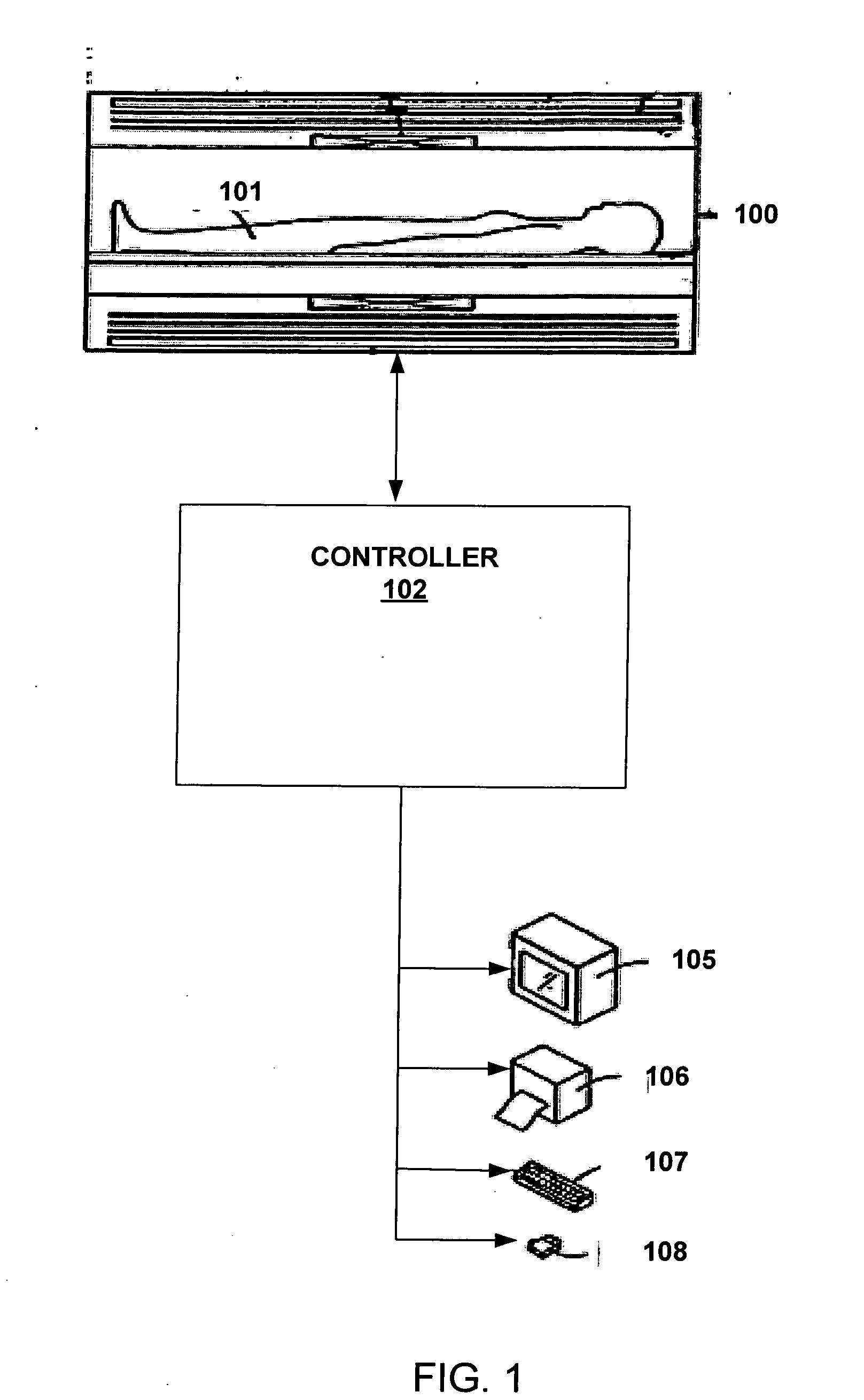
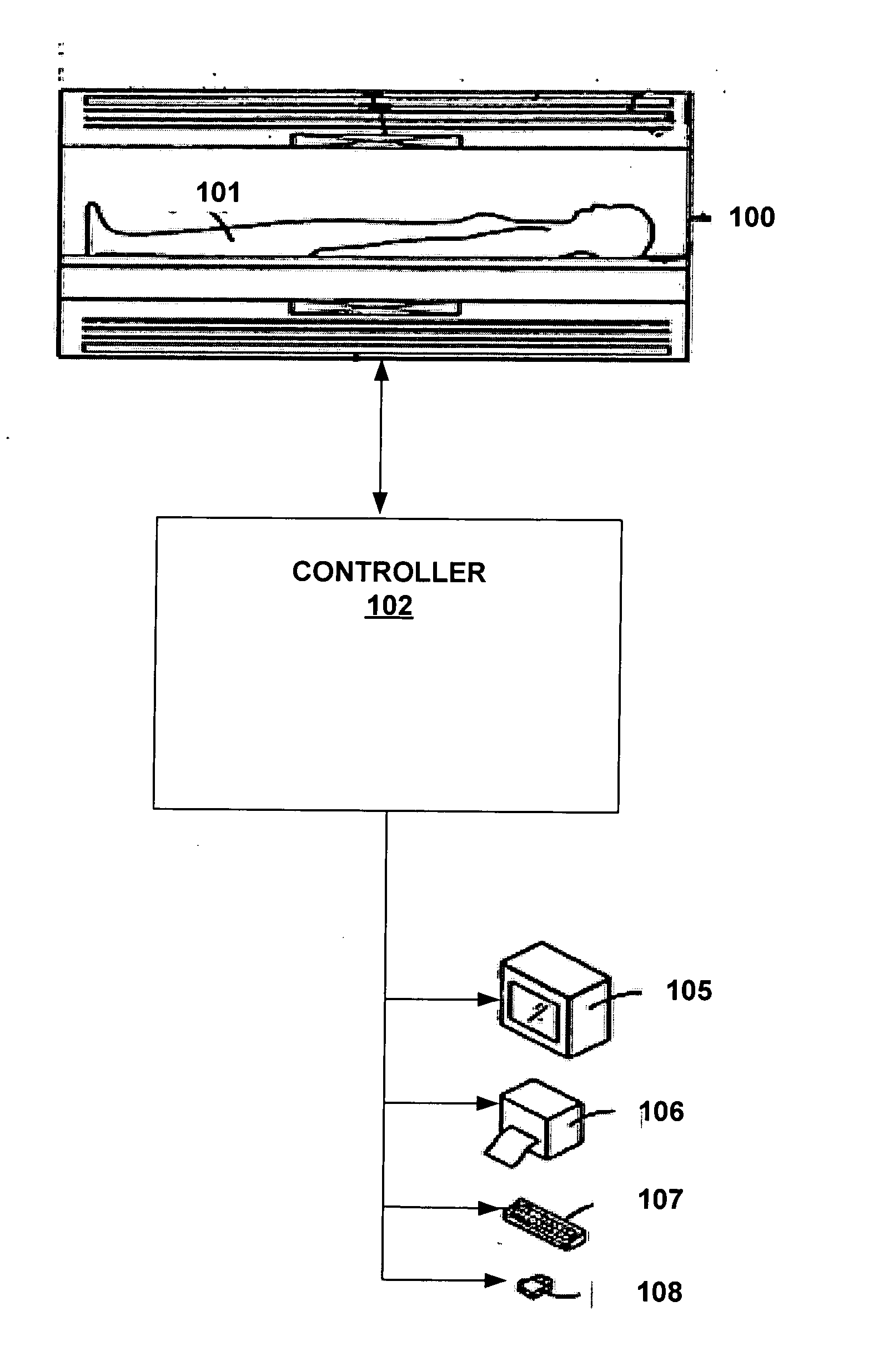
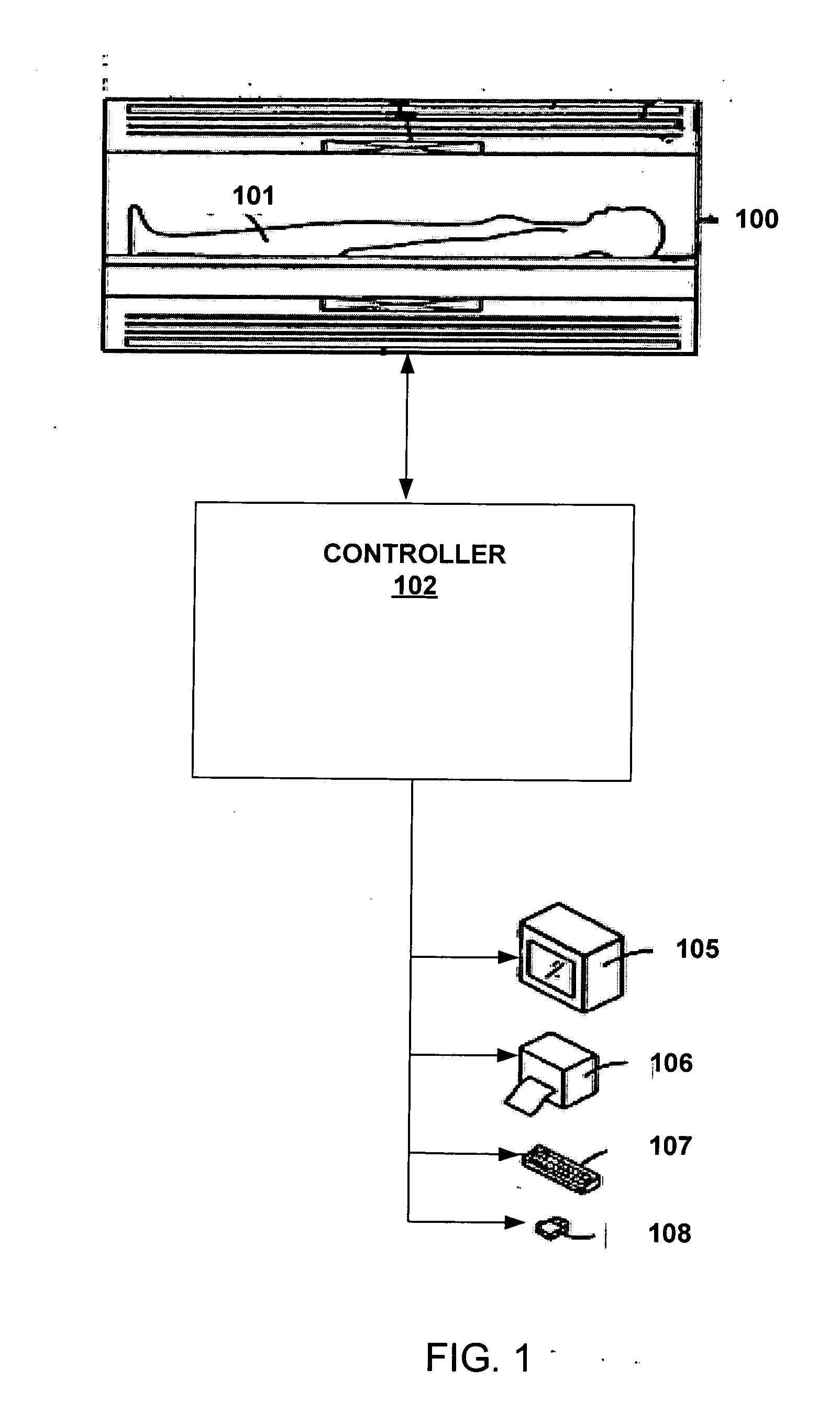
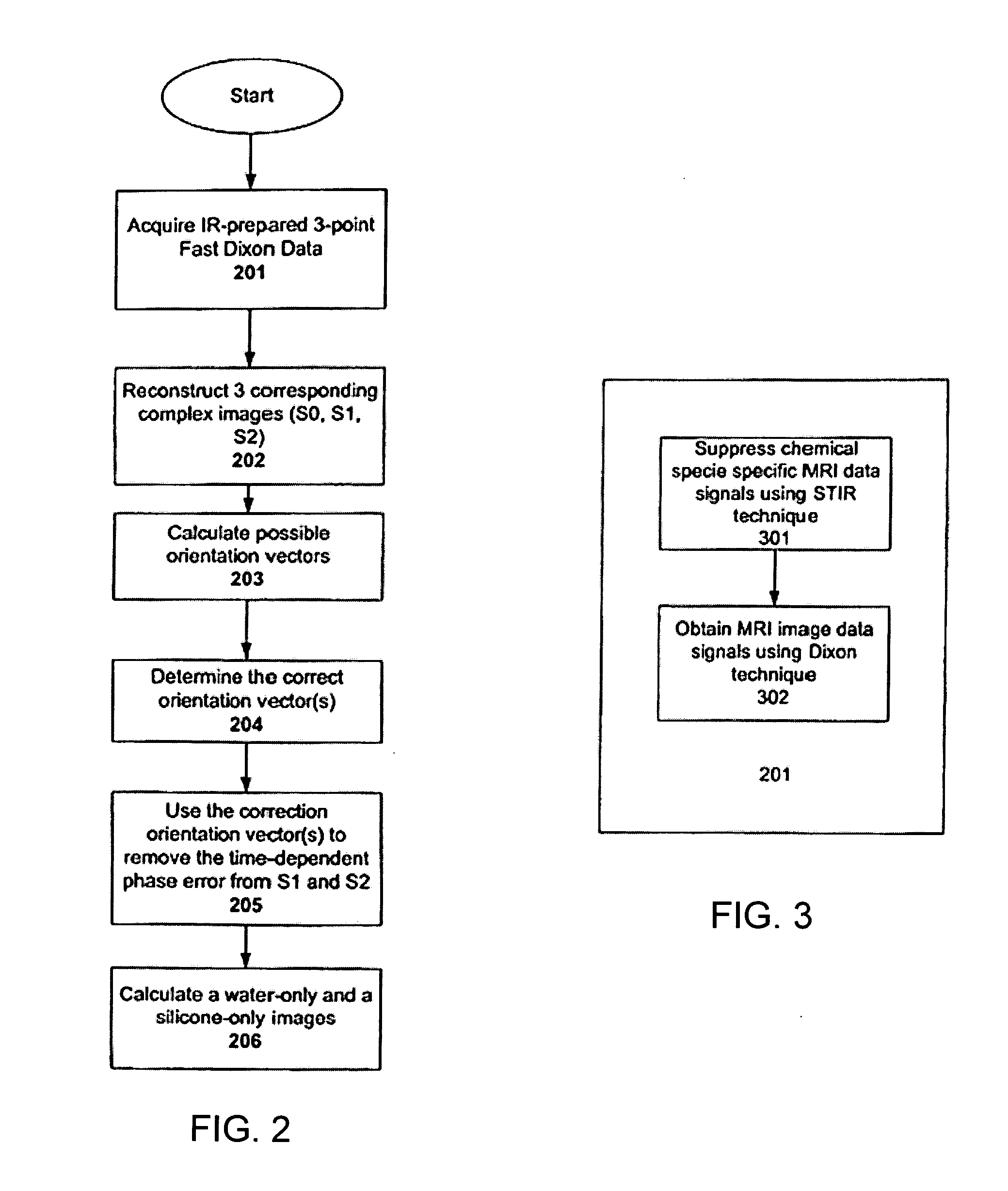
Systems and methods are described for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging using an efficient and robust phase correction algorithm. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals, such as two-point Dixon data, one-point Dixon data, or inversion recovery prepared data. The method further includes implementing a phase-correction algorithm, that may use phase gradients between the neighboring pixels of an image. At each step of the region growing, the method uses both the amplitude and phase of pixels surrounding a seed pixel to determine the correct orientation of the signal for the seed pixel. The method also includes using correlative information between images from different coils to ensure coil-to-coil consistency, and using correlative information between two neighboring slices to ensure slice-to-slice consistency. A system includes a MRI scanner to obtain the data signals, a controller to reconstruct the images from the data signals and implement the phase-correction algorithm, and an output device to display phase sensitive MR images such as fat-only images and / or water-only images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and apparatus for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7227359B2Maintain consistencyAccurate identificationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase correctionInversion recovery
Systems and methods are described for phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging using an efficient and robust phase correction algorithm. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals, such as two-point Dixon data, one-point Dixon data, or inversion recovery prepared data. The method further includes implementing a phase-correction algorithm, that may use phase gradients between the neighboring pixels of an image. At each step of the region growing, the method uses both the amplitude and phase of pixels surrounding a seed pixel to determine the correct orientation of the signal for the seed pixel. The method also includes using correlative information between images from different coils to ensure coil-to-coil consistency, and using correlative information between two neighboring slices to ensure slice-to-slice consistency. A system includes a MRI scanner to obtain the data signals, a controller to reconstruct the images from the data signals and implement the phase-correction algorithm, and an output device to display phase sensitive MR images such as fat-only images and / or water-only images.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method and system of MR imaging with simultaneous fat suppression and T1 inversion recovery contrast
ActiveUS7323871B2Suppressing signalImprove lesionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionInversion recovery
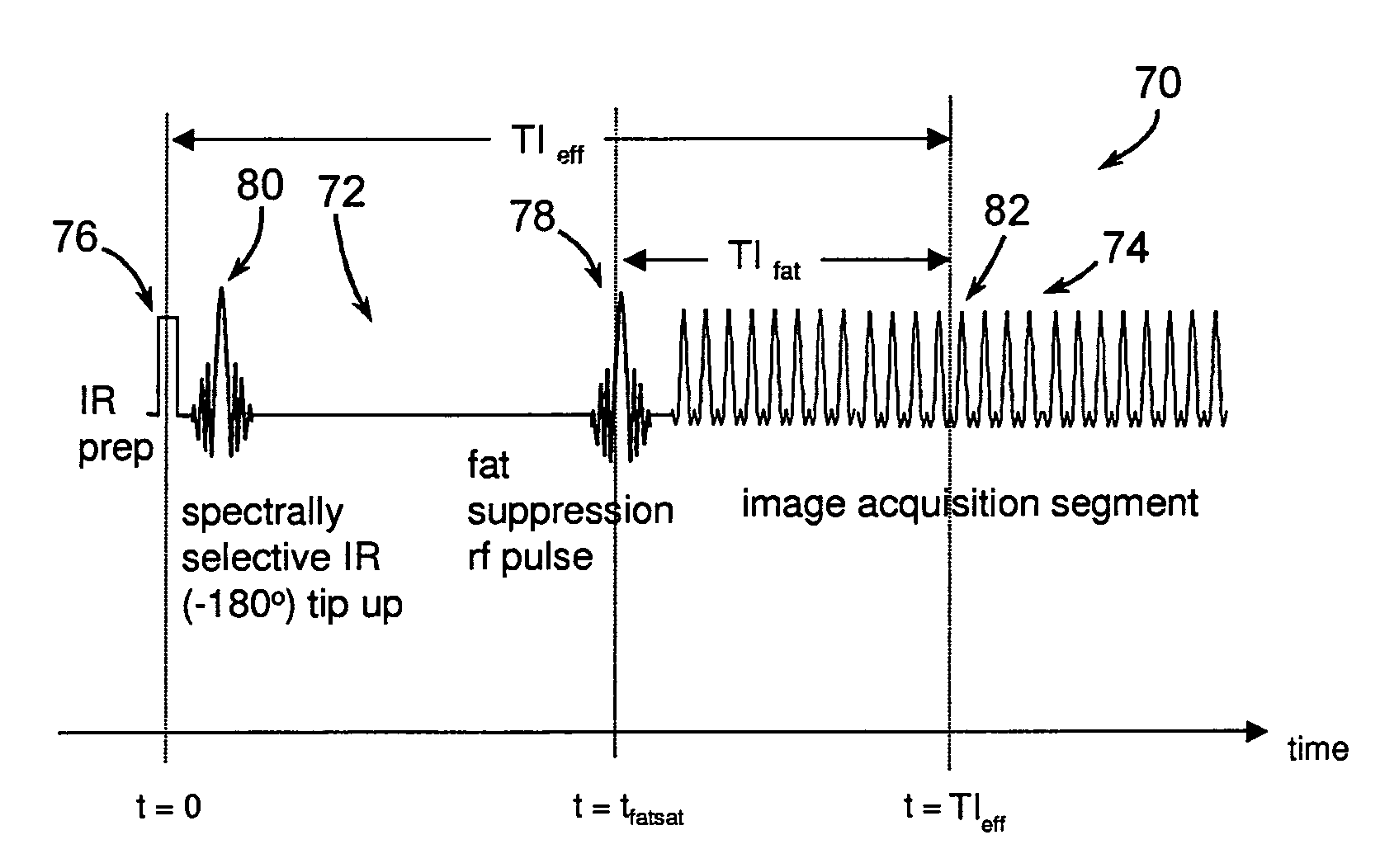
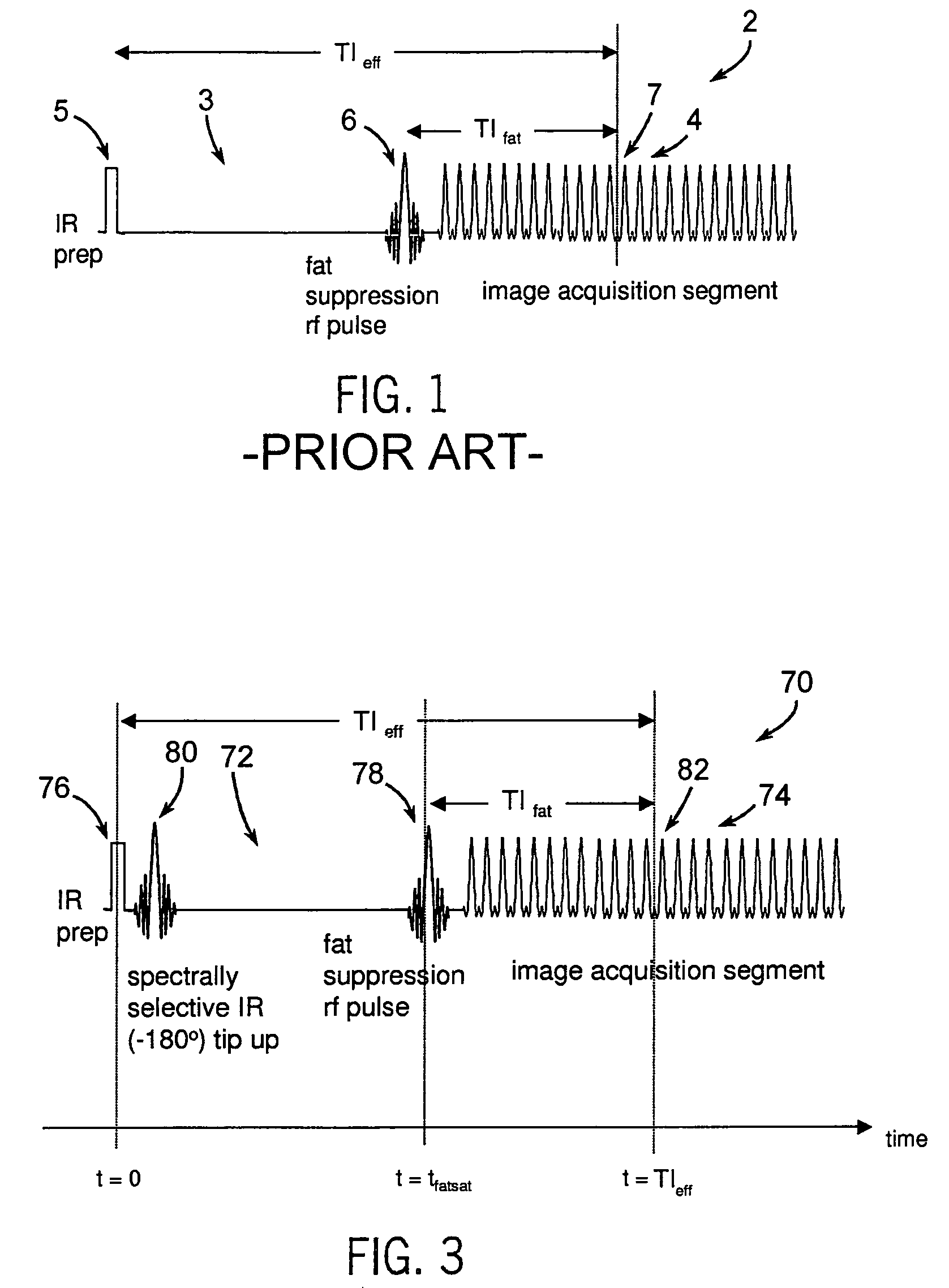
A method and system for fat suppression with T1-weighted imaging includes a pulse sequence generally constructed to have a non-spectrally selective IR pulse that is played out immediately before a spectrally selective IR tip-up pulse. Thereafter, a fat suppression RF pulse is played out followed by the acquisition of fat-suppressed MR data. The pulse sequence maintains T1 contrast by not perturbing the non-fat signals from the IR preparation. The pulse sequence also ensures that the blood pool signal is homogeneously suppressed from the non-spectrally selective IR RF pulse. The pulse sequence also allows for increased fat suppression and provides flexibility for adjustment of the degree of fat suppression without affecting the view acquisition order for an image acquisition segment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
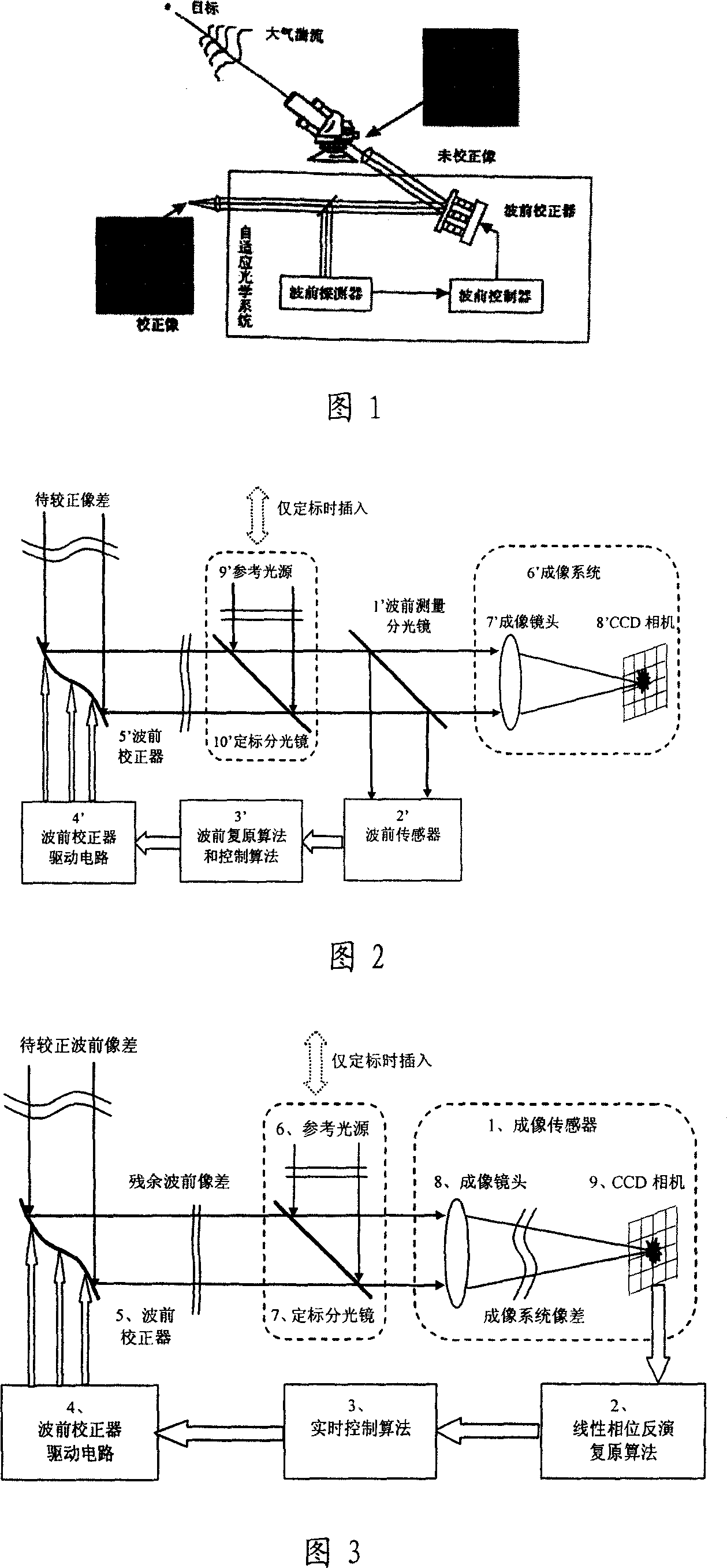
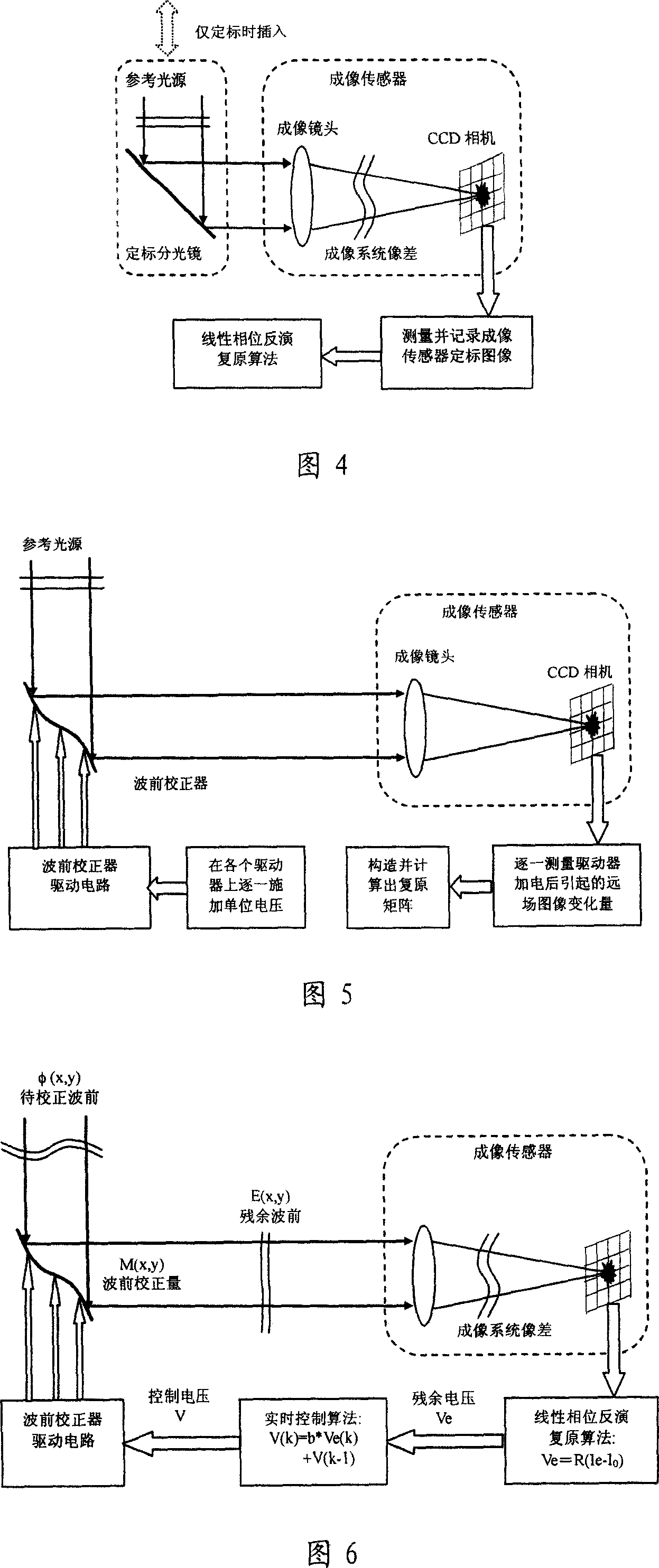
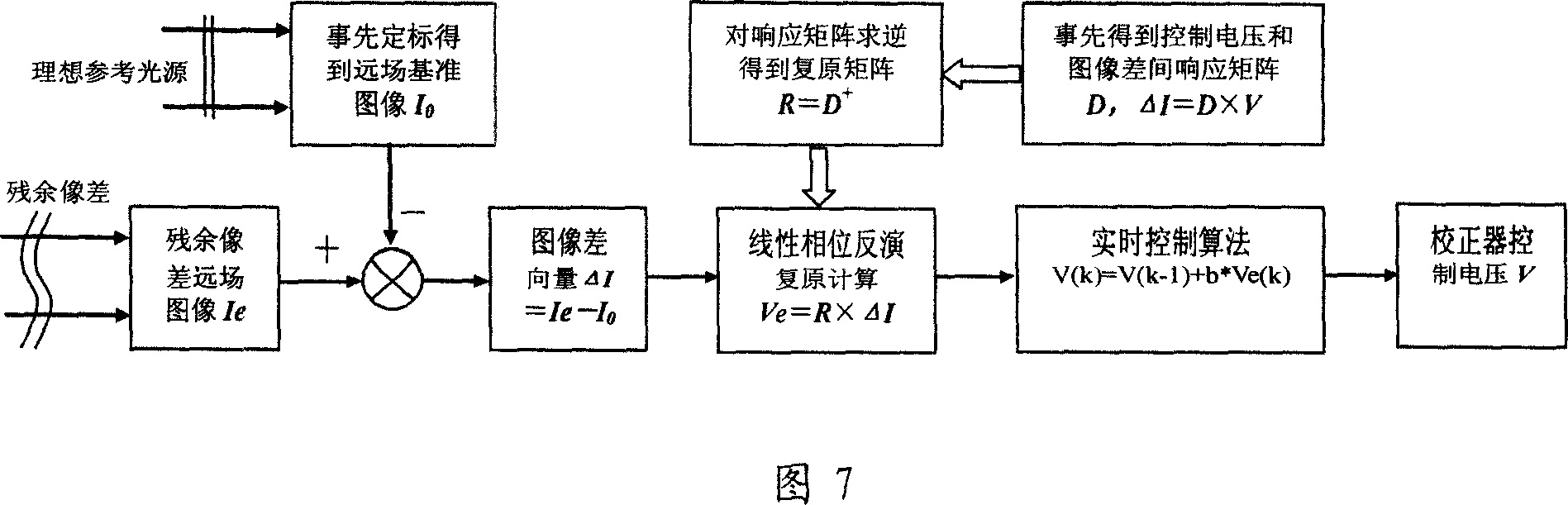
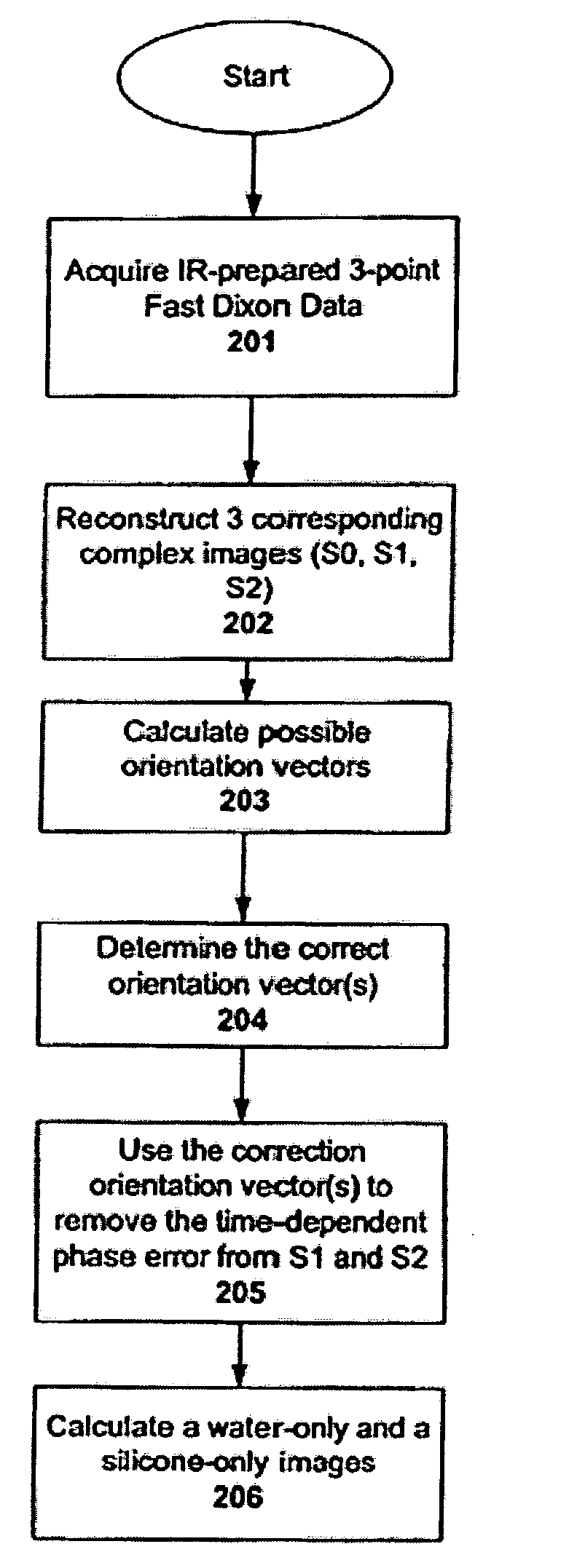
Self-adaptive optical system based on linear phase inversion restoration technology
InactiveCN101013195ASimple structureImprove light energy utilizationOptical measurementsOptical elementsInversion recoveryTime control
It is an adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique, comprising the imaging sensor, the linear phase inversion recovery algorithm, the real-time control algorithm, the wave-front correction and drive circuit, and the reference light source. During the system running, the imaging sensor measures the residual aberration far-field image after the compensation of the wave-front correction device, and subtracting with the benchmark image to obtain the image difference vector. In advance, using the reference light source to calibrate the imaging sensor to obtain the benchmark image, and according to the corresponding relations between the wave-front correction device and the imaging sensor, obtaining the recovery matrix between the image difference vector and control voltage. Multiply the image difference vector and the recovery matrix to obtain the corresponding control voltage of the residual wave-front, and use real-time control algorithms, such as proportional integral, to obtain the control voltage of the wave-front correction device, making the wave-front aberration to be corrected. Compared the adaptive optics system based on the linear phase inversion recovery technique and the conventional adaptive optical technology, it has simple structure, high optical energy efficiency, and other advantages.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and apparatuses for fast chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20060094952A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryChemical species
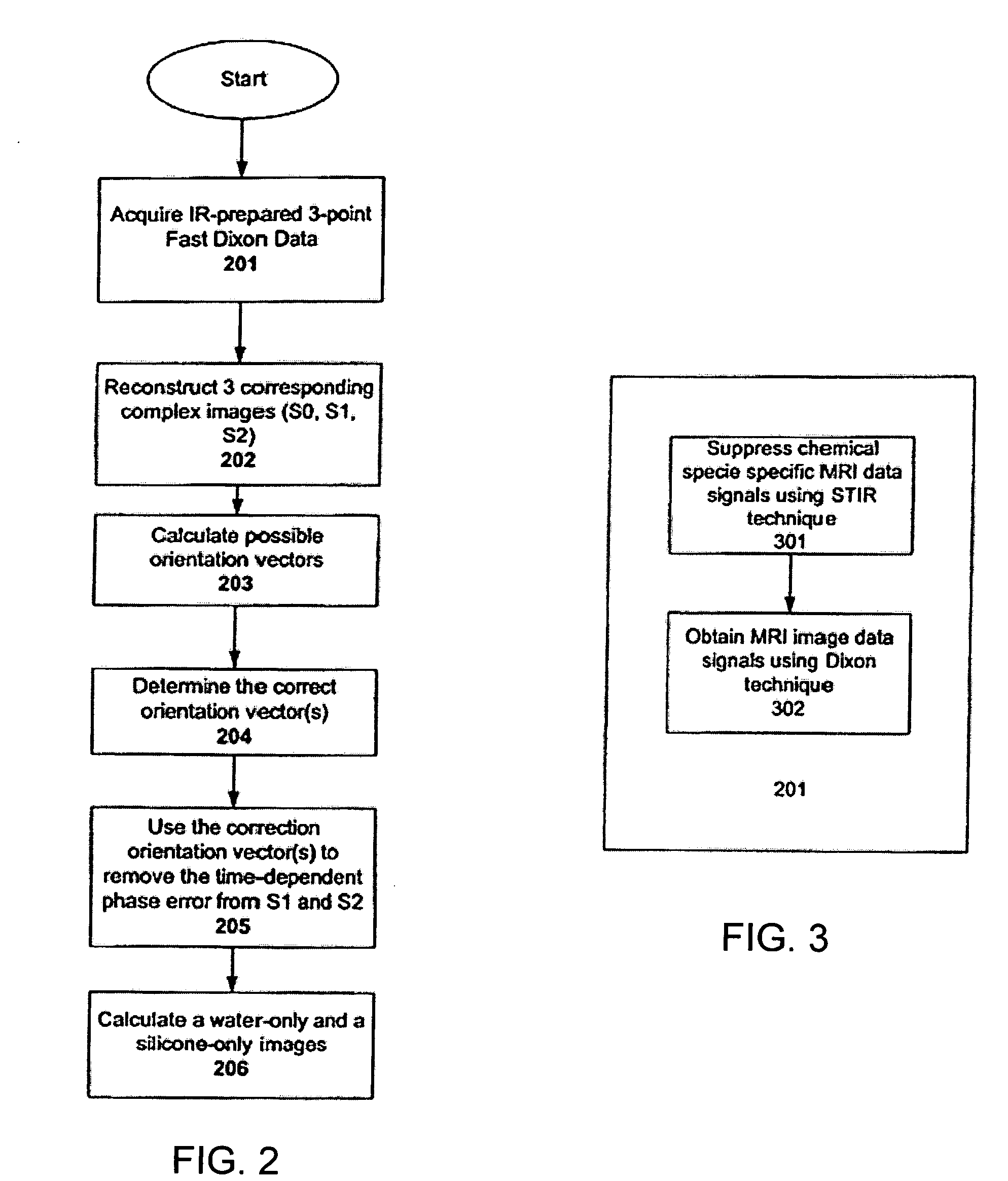
Systems and methods are described for chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of multiple chemical species. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image. An apparatus includes a MRI scanner for obtaining images, a controller configured to provide input to the scanner to acquire images using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques to produce a plurality of MRI data signals, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image, and an output device to display the resulting image.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods and apparatuses for fast chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging
Systems and methods are described for chemical shift magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of multiple chemical species. A method includes obtaining a plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image. An apparatus includes a MRI scanner for obtaining images, a controller configured to provide input to the scanner to acquire images using a Dixon technique in combination with partially parallel imaging techniques and / or inversion recovery techniques to produce a plurality of MRI data signals, and processing the plurality of MRI data signals using a Dixon reconstruction technique to create a chemical specific shift image, and an output device to display the resulting image.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
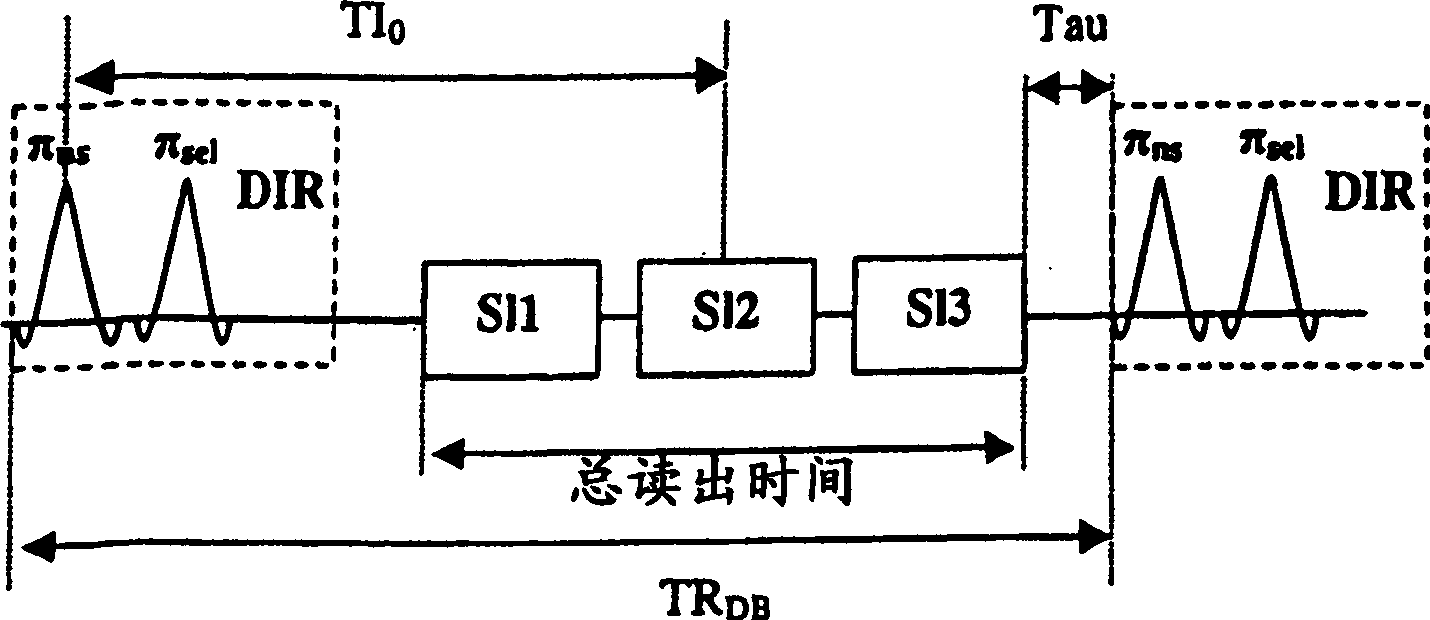
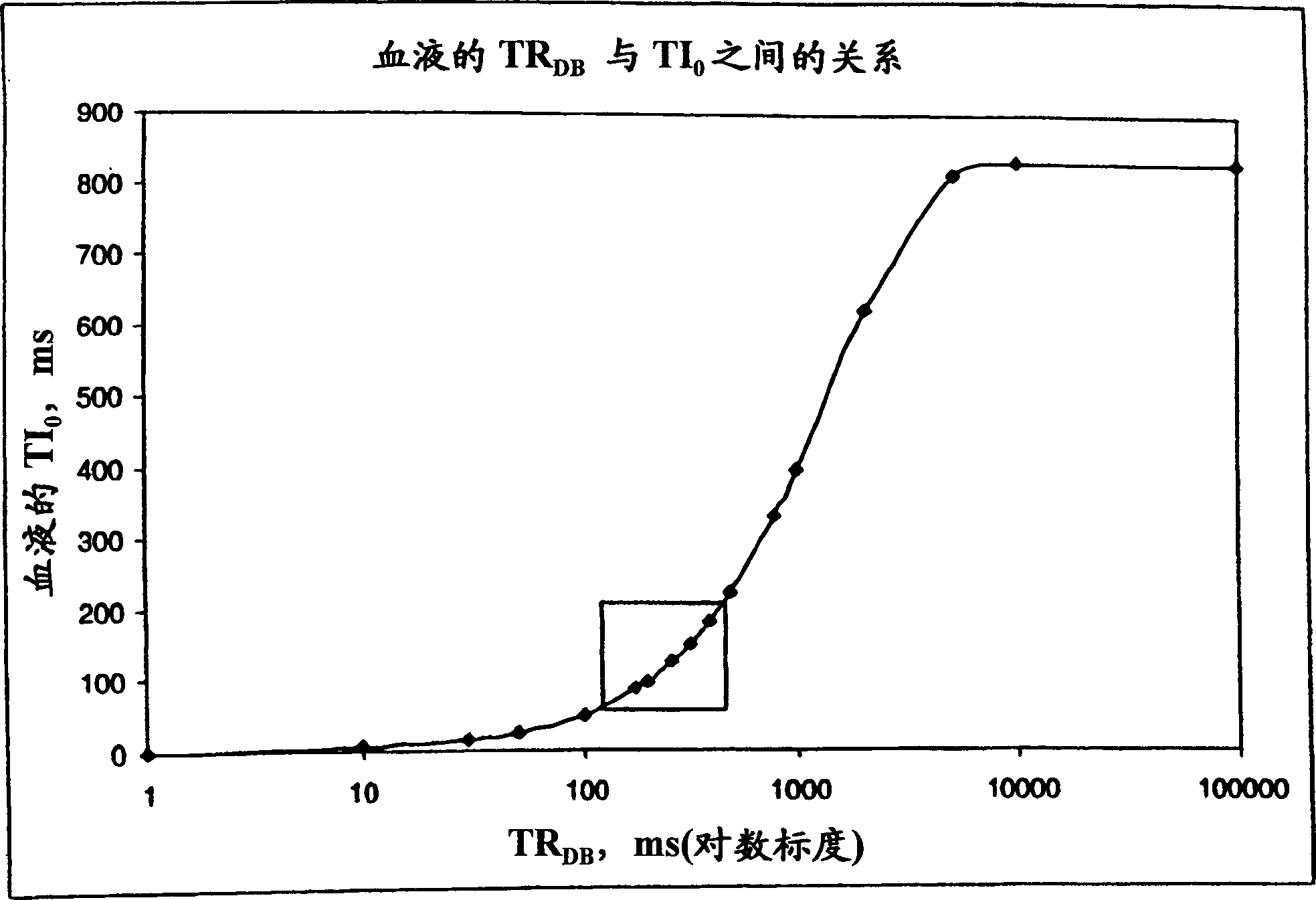
Rapid multislice black blood double-inversion recovery technique for blood vessel imaging
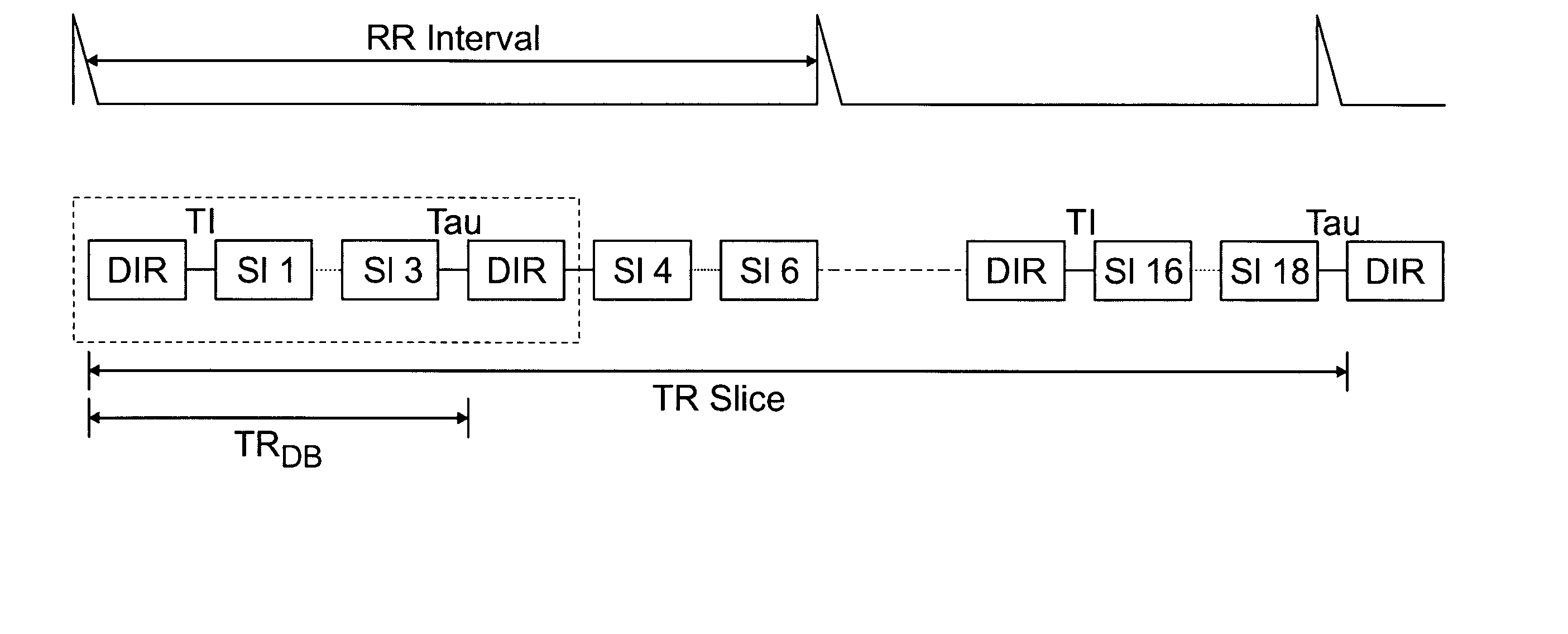
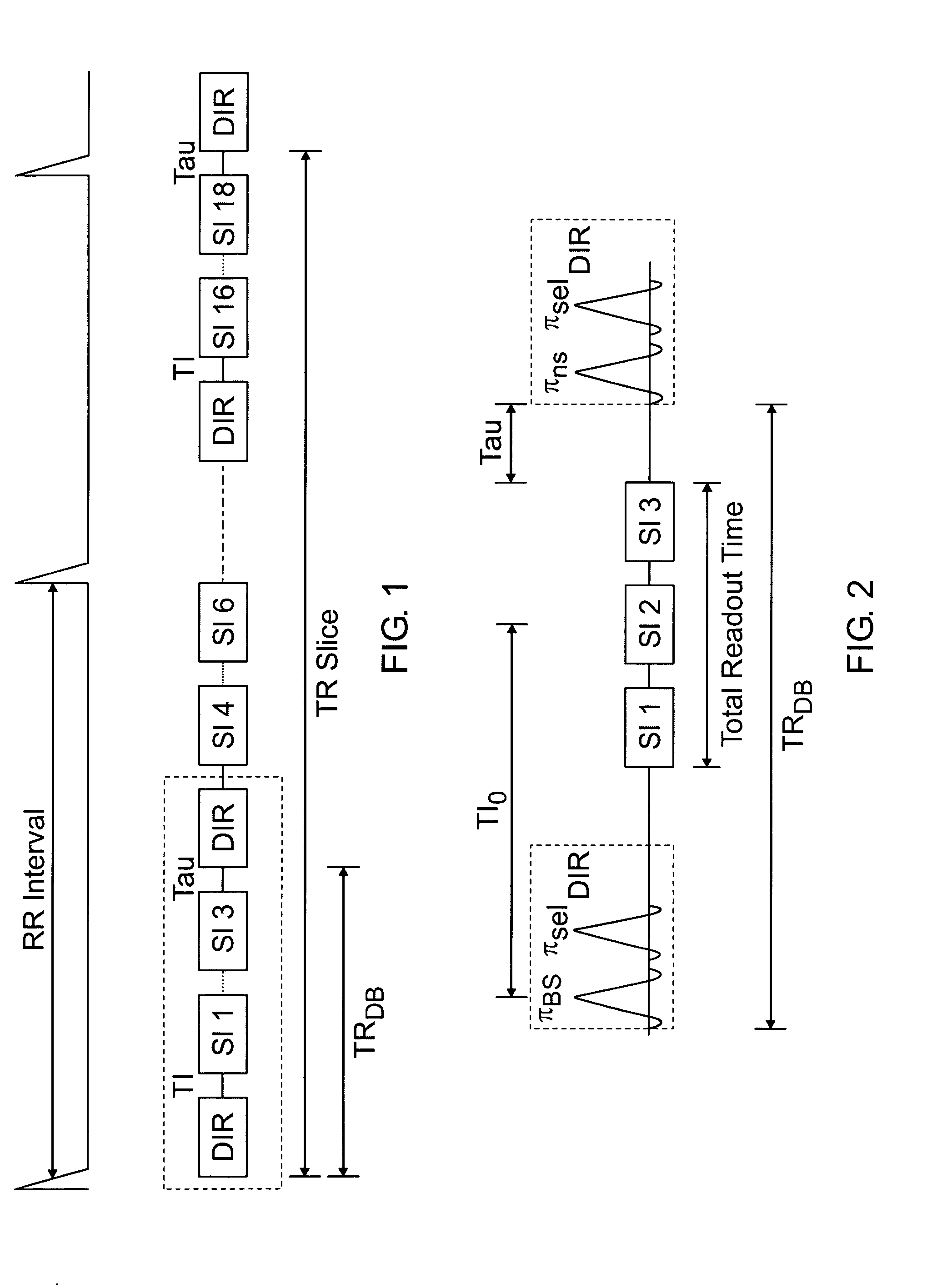
ActiveUS20050010104A1Fast image acquisitionAcceptable image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlack bloodRR interval
DIR imaging of blood vessels by administering a series of DIR preparation pulse modules at a repetition interval short enough that at least two DIR preparation pulse modules generally occur within each RR interval, and by acquiring image data for a plurality of slices following each DIR module.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
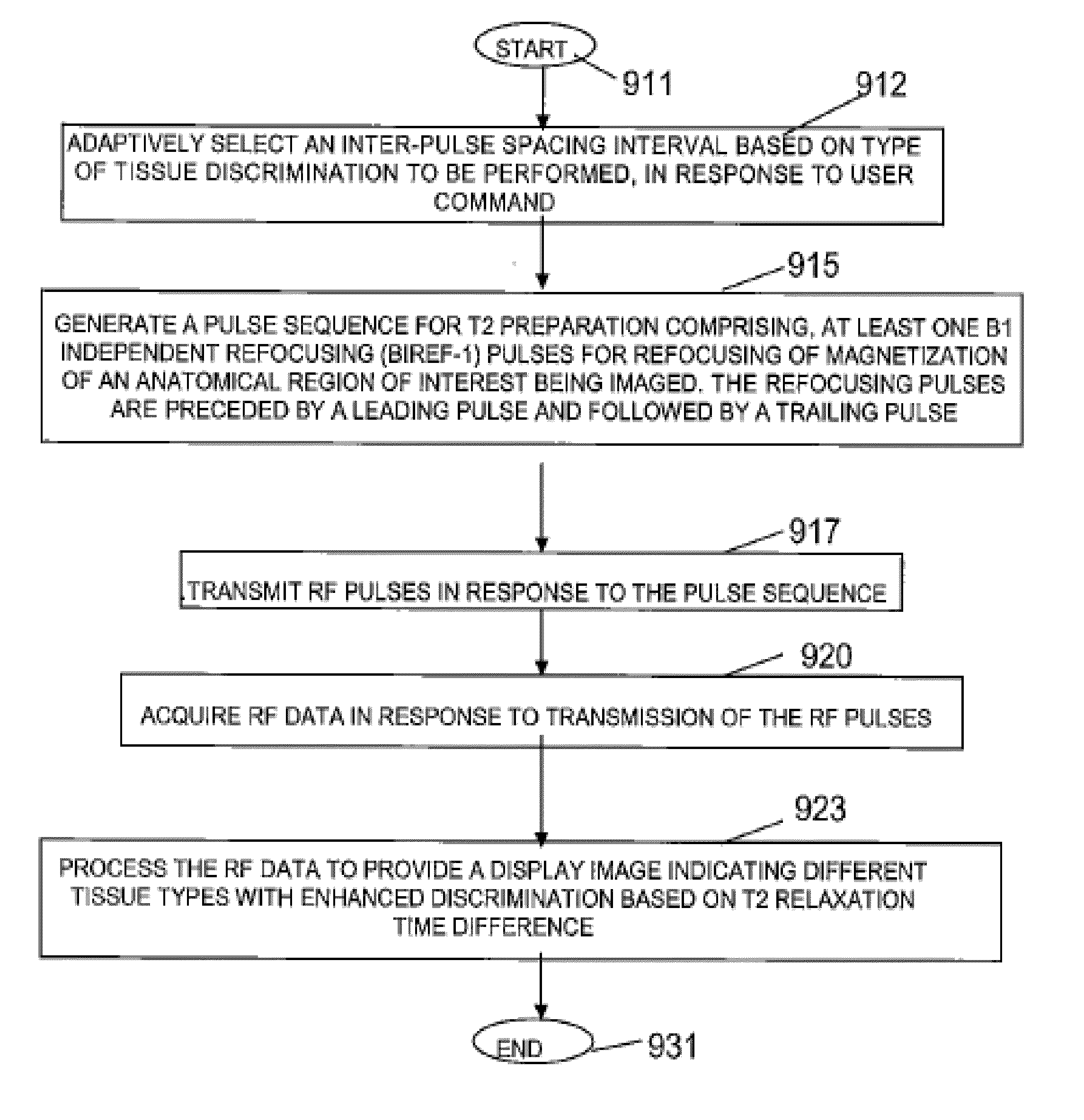
MR Imaging System for Discriminating Between Imaged Tissue Types
ActiveUS20120194186A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionInversion recoveryMagnetization
A system provides B1- and B0-insensitive, blood flow and motion-robust T2-preparation and T2-preparation combined with inversion recovery. An MR imaging system discriminates between imaged tissue types based on transverse relaxation time (T2) or transverse relaxation time combined with longitudinal recovery time (T1). A signal generator generates a pulse sequence for T2 preparation or combined T2-preparation with inversion recovery comprising one or more B1 independent refocusing (BIREF-1) pulses for refocusing of magnetization of an anatomical region of interest being imaged, and different combinations of adiabatic or non-adiabatic tip-down and flip-back pulses. Multiple RF coils transmit RF pulses in response to the pulse sequence and acquire RF data in response to transmission of the RF pulses. A processing system processes the RF data to provide a display image indicating different tissue types with enhanced discrimination based on T2 relaxation time difference or combined T2 and T1 time difference.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Single-stage decoder for raptor codes
A system and method for recovering erased symbols in a wireless communication is provided. The system and method includes a receiver configured to receive encoded data transmissions. The receiver includes a single stage decoder configured to perform a decoding operation. The single stage decoder also is configured to determine a symbol erasure rate, the symbol erasure rate defined by a number of erased symbols. The single stage decoder further is configured to generate a recovery matrix based on the symbol erasure rate and invert the recovery matrix. Thereafter, the single stage decoder recovers the erased symbols based on a function of the inverted recovery matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement
ActiveCN104161517ASolve the scan time is too longReduce usageDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryPhase sensitive
The invention discloses an imaging method for MRI contrast enhancement. Optimized inversion pulses are utilized to replace inversion pulses of a conventional inversion recovery sequence in MRI and to restore delay time, under the precise control of the optimized pluses, spin of different tissue will be evolved towards the trend of maximization of longitudinal magnetic moment differences, and the maximum longitudinal magnetic moment difference is obtained at the end moment of the pluses; on that basis, 90-degree excitation read pluses are applied to enable the maximized magnetic moment difference among the tissue to be turned over to a transverse plane, gradient echo signals are collected to form k spatial data, and the purpose of contrast enhancement among the tissue can be finally achieved through improvement on a phase sensitive image reconstruction method. According to the imaging method, the problem of too long scanning time of the conventional inversion recovery sequence is solved, the advantages of flexibility of optimized pulse waveforms and flexibility of the phase sensitive image reconstruction method are fully utilized, use of expensive magnetic resonance contrast media can be avoided, and the imaging method is superior to an existing MRI contrast enhancement method both in performance and in cost.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
System for Automated Parameter Setting in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveUS20100268066A1Easy to operateImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setInversion recovery
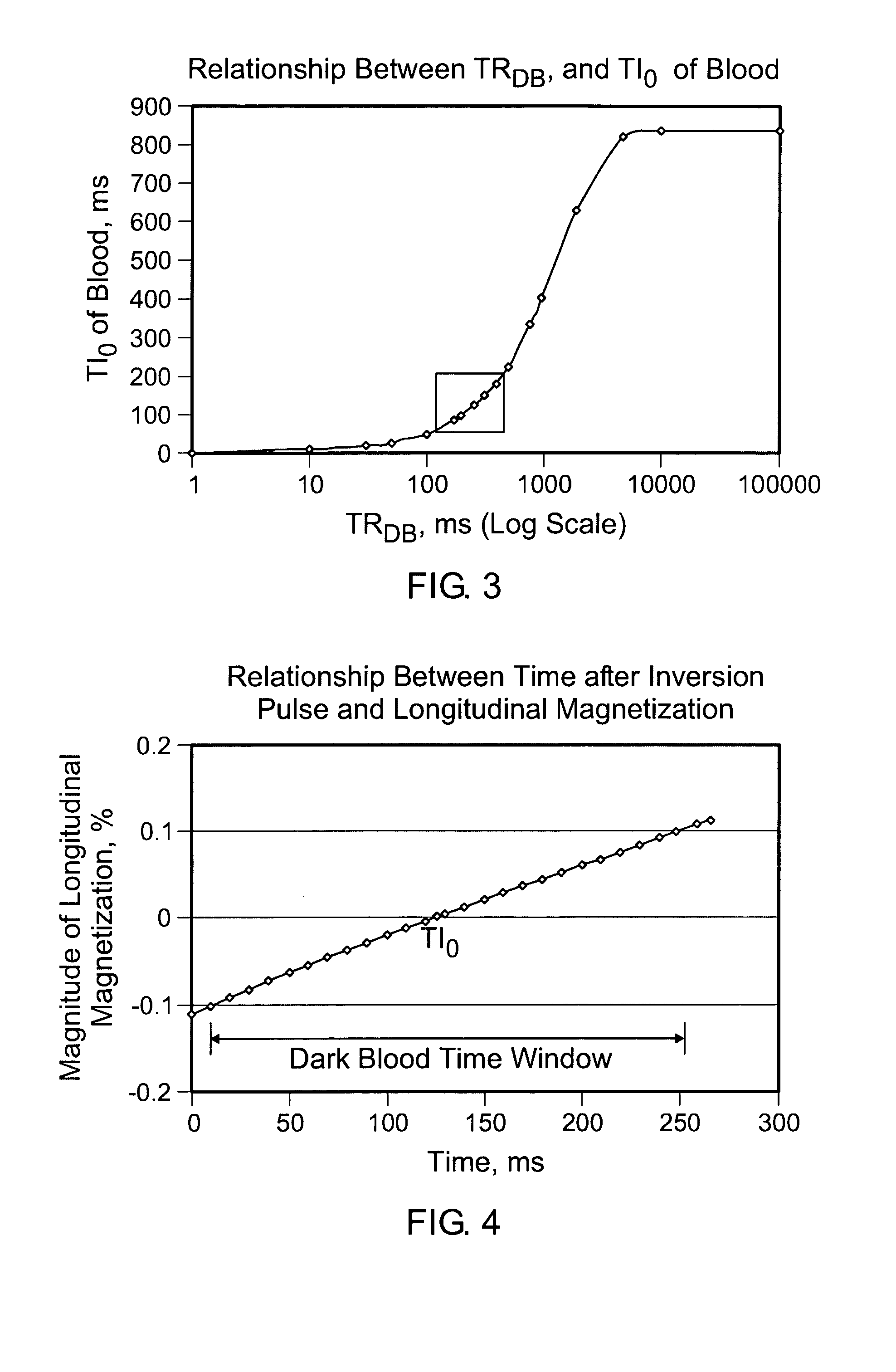
A system automatically calculates optimal protocol parameters for dark-blood (DB) preparation and inversion recovery. The system automatically determines pulse sequence timing parameters for MR imaging with blood related signal suppression. The system comprises an acquisition processor for acquiring data indicating a patient heart rate. A pulse timing processor automatically determines an acquisition time of an image data set readout, relative to a blood signal suppression related magnetization preparation pulse sequence, by calculating the acquisition time in response to inputs including, (a) the acquired patient heart rate, (b) data indicating a type of image contrast of the pulse sequence employed and (c) data indicating whether an anatomical signal suppression related magnetization preparation pulse sequence used has a slice selective, or non-slice selective, data acquisition readout.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveCN101259018ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryImaging quality
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging apparatue and magnetic resonance imaging method. With the objective of generating an imaging area including fluid with desired image quality at a subject and enhancing image quality, a first inversion recovery pulse is transmitted so as to invert spins in a second subject region which includes a first subject region used as the imaging area and is broader than the first subject region, before execution of a pulse sequence corresponding to an FSE method at every TR in an imaging sequence. After the execution of the pulse sequence corresponding to the FSE method, a second refocus pulse is transmitted so as to cause spins in a third subject region including the first subject region and wider than the first subject region to reconverge. A fast recovery pulse is transmitted to selectively recover spins in the first subject region. Thereafter, a second inversion recovery pulse is transmitted so as to invert the spins in the second subject region.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Rapid multislice black blood double-inversion recovery technique for blood vessel imaging
InactiveCN1575748ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBlack bloodInversion recovery
DIR imaging of blood vessels by administering a series of DIR preparation pulse modules at a repetition interval short enough that at least two DIR preparation pulse modules generally occur within each RR interval, and by acquiring image data for a plurality of slices following each DIR module.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20080136411A1Easily improving image qualityImproving Imaging EfficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryImaging quality
With the objective of generating an imaging area including fluid with desired image quality at a subject and enhancing image quality, a first inversion recovery pulse is transmitted so as to invert spins in a second subject region which includes a first subject region used as the imaging area and is broader than the first subject region, before execution of a pulse sequence corresponding to an FSE method at every TR in an imaging sequence. After the execution of the pulse sequence corresponding to the FSE method, a second refocus pulse is transmitted so as to cause spins in a third subject region including the first subject region and wider than the first subject region to reconverge. A fast recovery pulse is transmitted to selectively recover spins in the first subject region. Thereafter, a second inversion recovery pulse is transmitted so as to invert the spins in the second subject region.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Simulated Post-Contrast T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
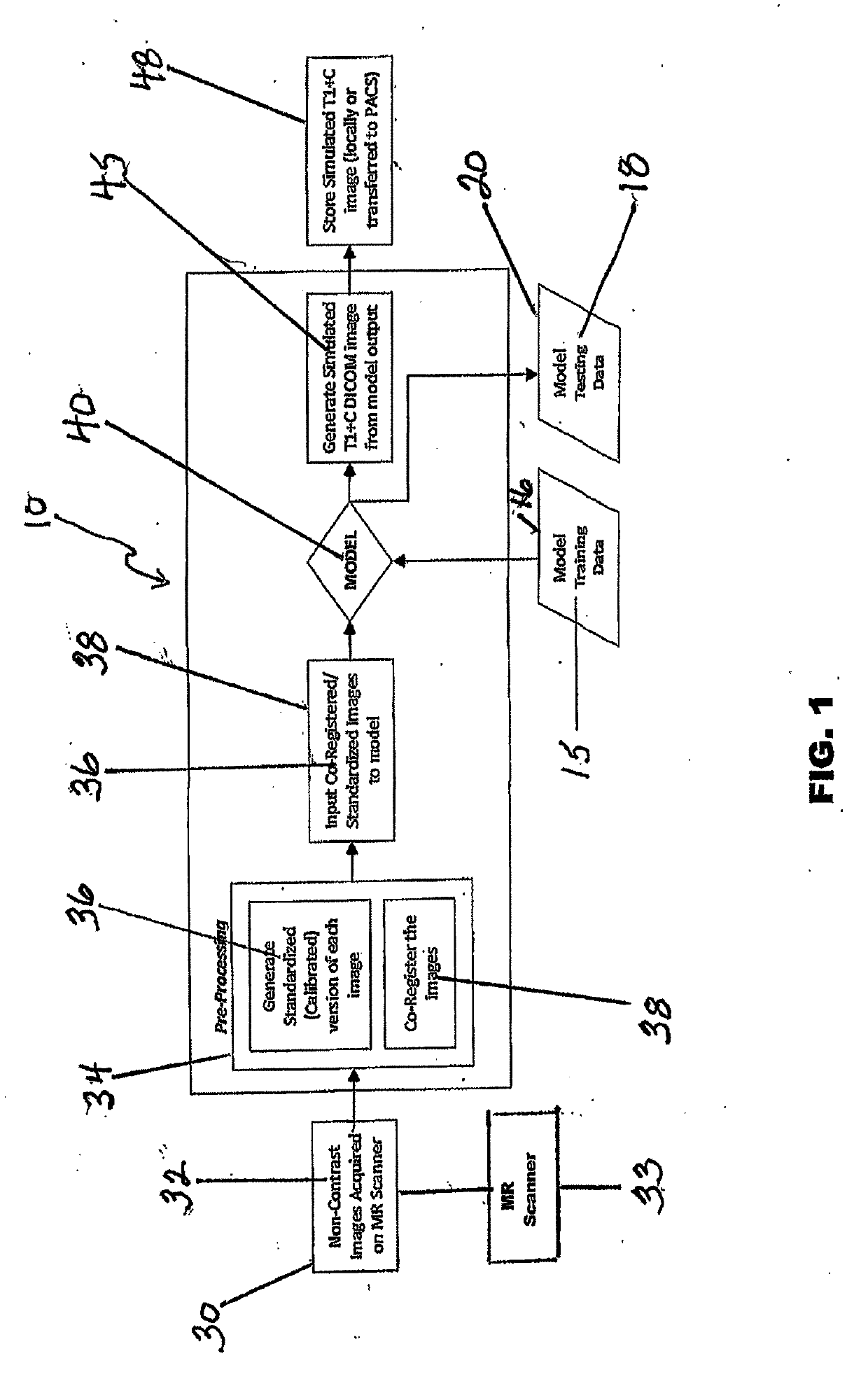
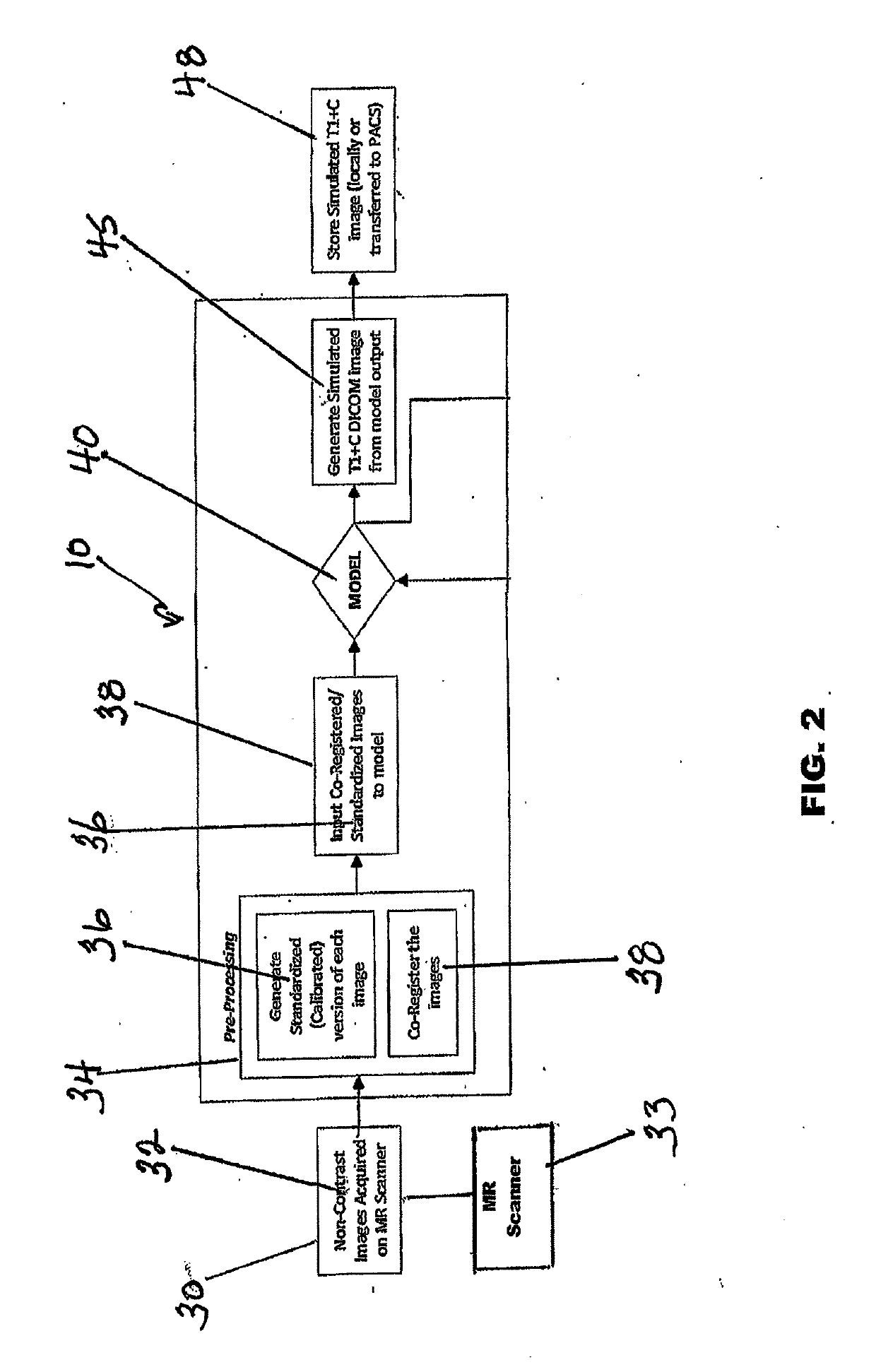
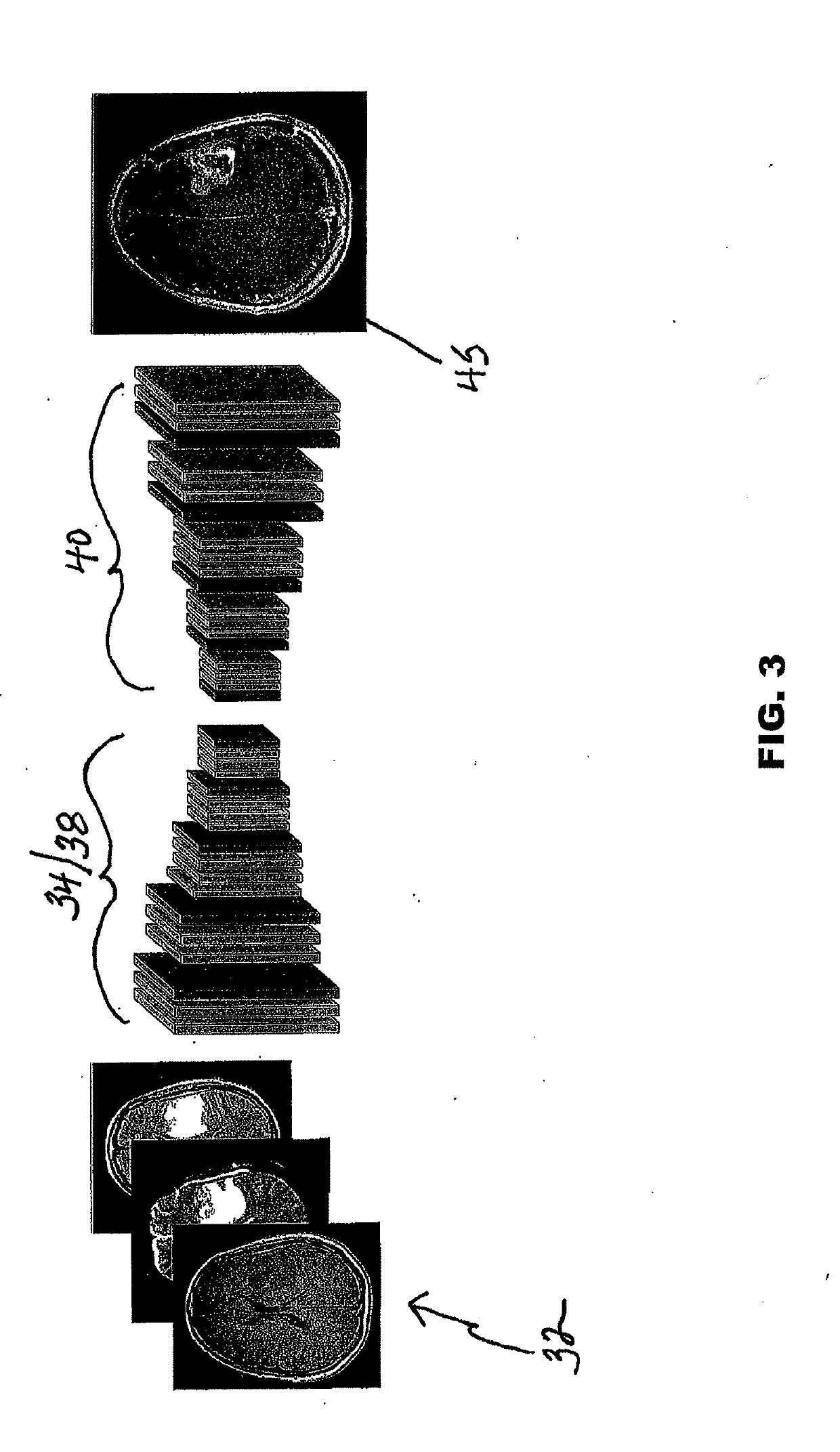
ActiveUS20190122348A1Eliminates common operationalEliminate errorsMedical simulationImage enhancementDiffusionInversion recovery
A system and method for generating simulated post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images without the use of exogenous contrast material based upon patient-specific non-contrast MR images using machine learning / artificial intelligence techniques to train the system to generate post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance images based upon retrospectively collected non-contrast MR images of various sequence types including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, FLAIR (Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery), and / or DWI (Diffusion-Weighted Imaging).
Owner:IMAGING BIOMETRICS
Nuclear-magnetic-resonance-technology-based method for detecting transformer oil ageing state parameters
ActiveCN103091345AGood linear relationshipAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceInversion recovery
The invention discloses a nuclear-magnetic-resonance-technology-based method for detecting transformer oil ageing state parameters. The ageing state parameters comprise oil sample viscosity, oil sample density, oil sample furfural content, oil sample resistance and the like. The method comprises the following steps: performing nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum analysis on a solution gas-containing transformer oil sample and detecting the parameters, wherein the oil sample viscosity eta is measured through the formula shown in the abstract, T1 and T2 respectively refer to longitudinal / transverse relaxation time of the oil sample, T1 is measured by an inversion recovery method, T2 is measured by a CPMG method, the oil sample density and the other parameters are measured by measuring the content of CHn functional groups in the oil sample by utilizing a two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy nuclear magnetic resonance analysis method according to a relation model between the content of functional groups and the oil sample density and other parameters; and n in the CHn is equal to 0, 1, 2 and 3. The method has the advantages of few sample quantity, simple and direct sampling process, high analysis speed, high analysis accuracy and the like.
Owner:STATE GRID HUNAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD MAINTENANCE CO +2
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system
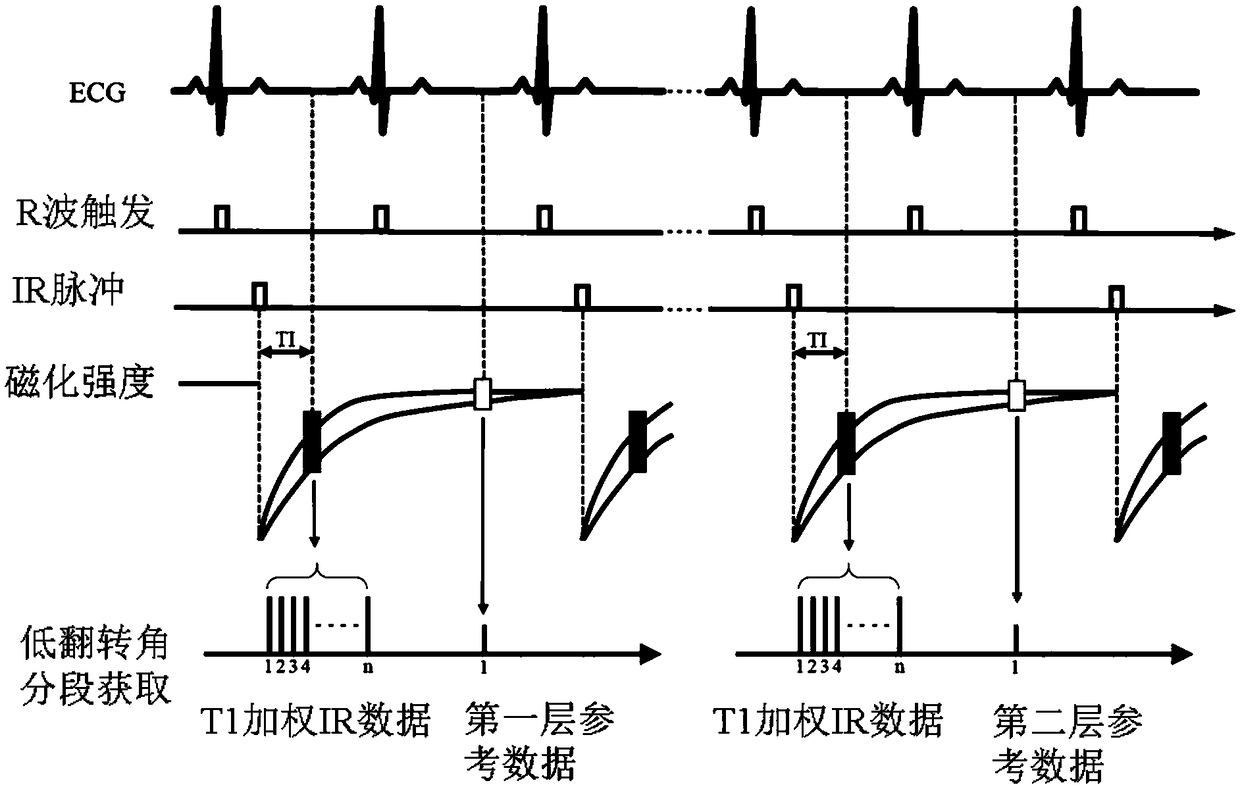
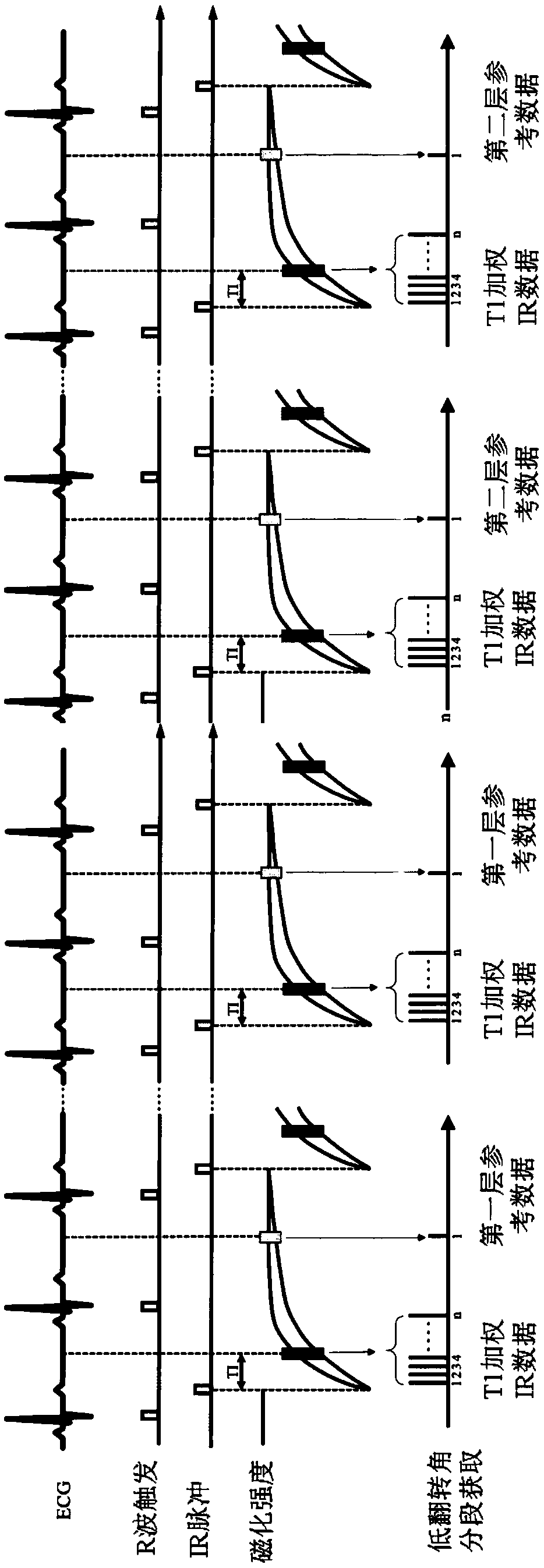
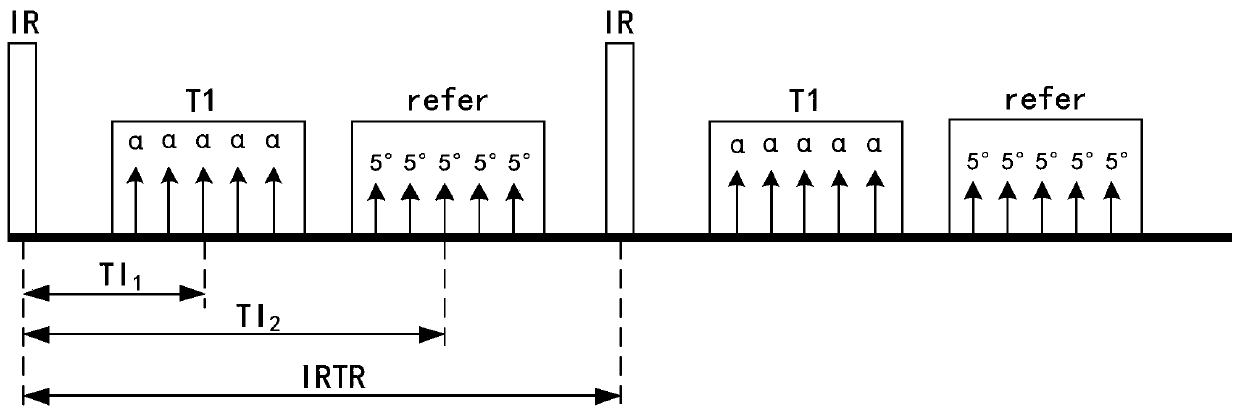
ActiveCN109507622AReduce the number of acquisitionsImprove data collection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryImaging quality
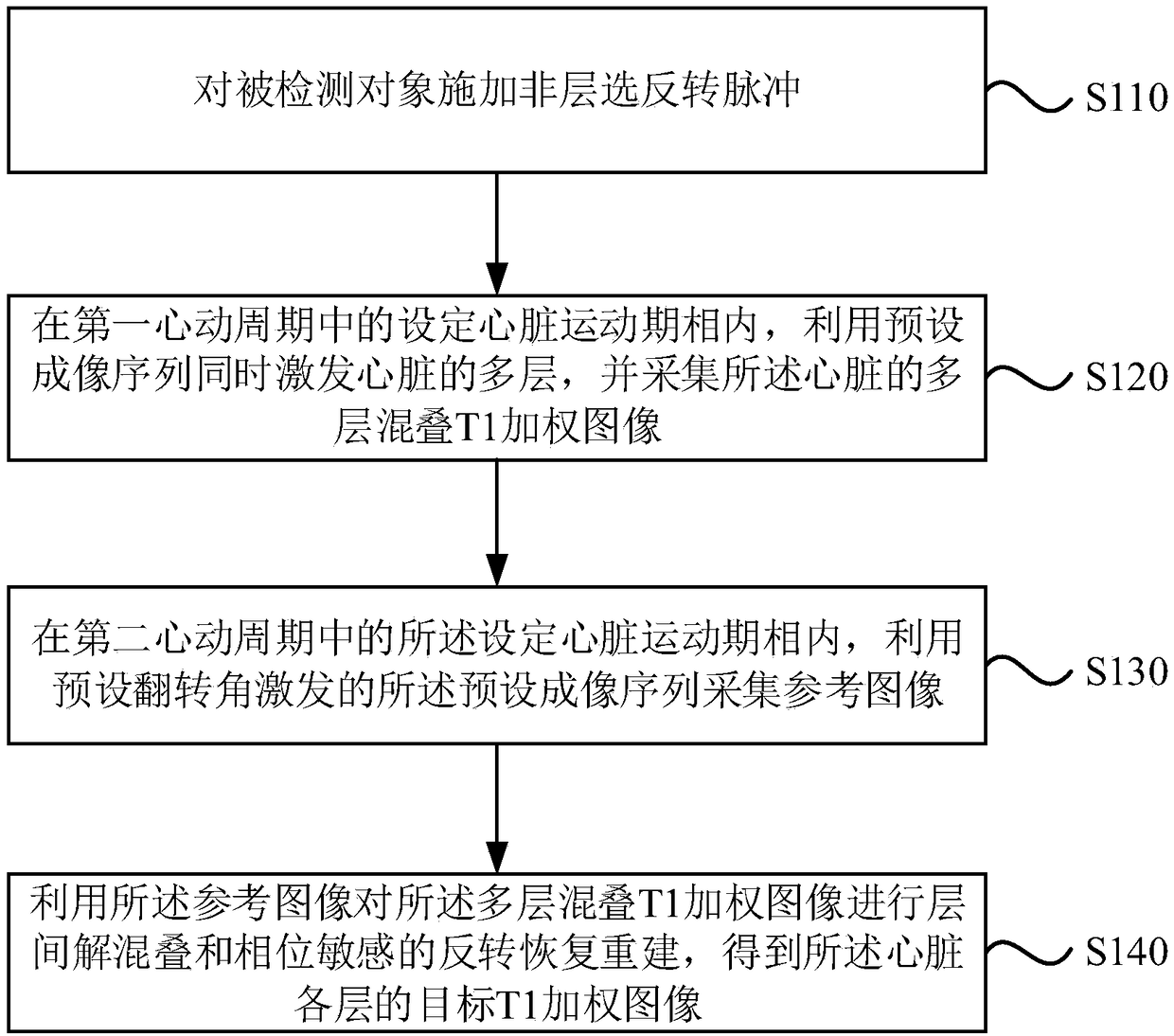
Embodiments of the invention disclose a magnetic resonance imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: applying non-layering inverse pulses to a detected object; simultaneously stimulating multiple layers of a heart by using a preset imaging sequence in a set heart movement phase in a first heartbeat period, and acquiring a multilayer aliasing T1 weighted image of the heart; acquiring a reference image by using a preset imaging sequence stimulated by a preset overturning angle in a set heart movement phase in a second heartbeat period, wherein the first heartbeat period and the second heartbeat period correspond to a same breath-holding and are two adjacent heartbeat periods, and the reference image corresponds to one layer of the multiple layers; and performing the interlayer de-aliasing and phase-sensitive reverse restoration re-establishment for the multilayer aliasing T1 weighted image by using the reference image to obtain a target T1 weighted image of each layer of the heart. By virtue of the technical scheme, on the premise of ensuring the image quality, the magnetic resonance data acquisition efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Magnetic resonance angiography method, device and equipment
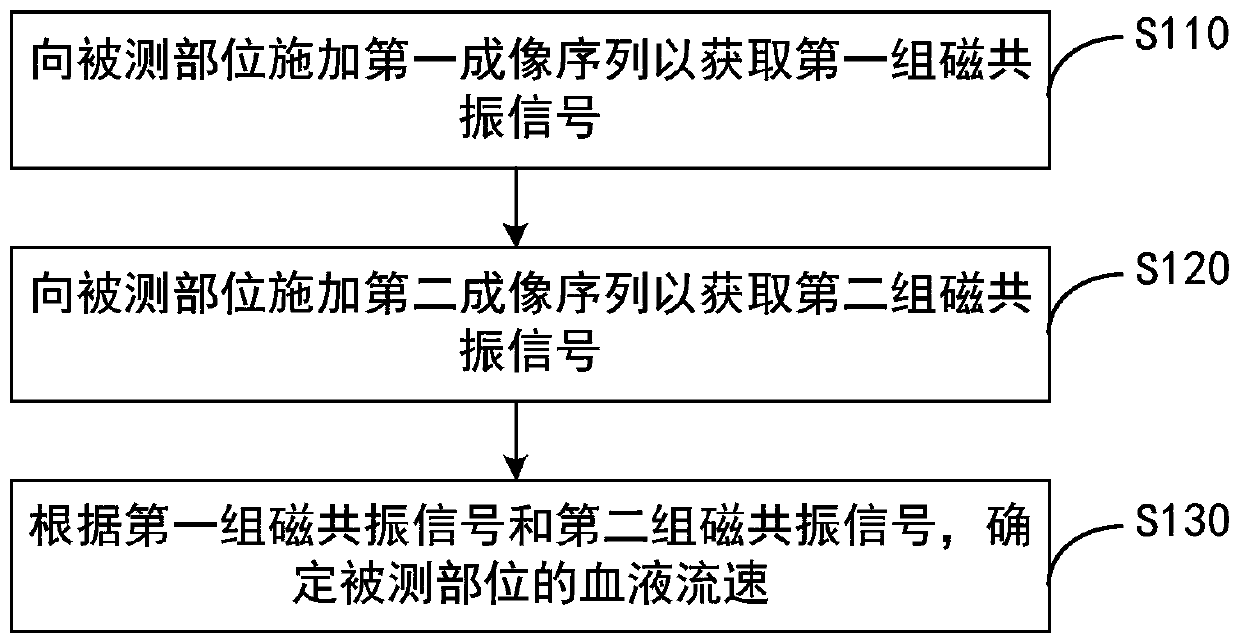
ActiveCN111265206AImproving Imaging EfficiencySolving the problem of multiple repeated MRI scansDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryRadio frequency
The embodiment of the invention discloses a magnetic resonance angiography method, a device and equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: a first imaging sequence is applied to a measured part to obtain a first set of magnetic resonance signals, wherein the measured part comprises blood flow, the first imaging sequence comprises a first inversion recovery radio frequency pulse anda first gradient pulse, and the first gradient pulse is used for inhibiting phase information of the blood flow; a second imaging sequence is applied to the measured part to obtain a second set of magnetic resonance signals, wherein the second imaging sequence comprises a second inversion recovery radio frequency pulse and a second gradient pulse, and the second gradient pulse is used for obtaining phase information of the blood flow; and the blood flow velocity of the measured part is determined according to the first set of magnetic resonance signals and the second set of magnetic resonancesignals. According to the embodiment of the invention, the imaging sequence is improved, so that the problem that magnetic resonance scanning needs to be repeated for multiple times is solved, and themagnetic resonance angiography efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System and methods for active suppression of superior tagging in flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery
InactiveUS20100164496A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionInversion recoverySaturation pulse
Apparatuses, systems, and methods for suppression of venous artifacts from superior tagging in flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery. The systems may include an image capture device and a controller. The controller may be configured to cause the image capture device to perform a labeling experiment, capture a first image of a slice of body tissue, perform a control experiment, and capture a second image of the slice of body tissue. The systems may be configured to perform a ninety (90) degree RF saturation pulse directed to a portion of body tissue that is superior to the first slice of body tissue imaged during at least one of the labeling experiment and / or the control experiment, and to apply a spoiler gradient subsequent to the saturation pulse during at least one of the labeling experiment and / or the control experiment.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
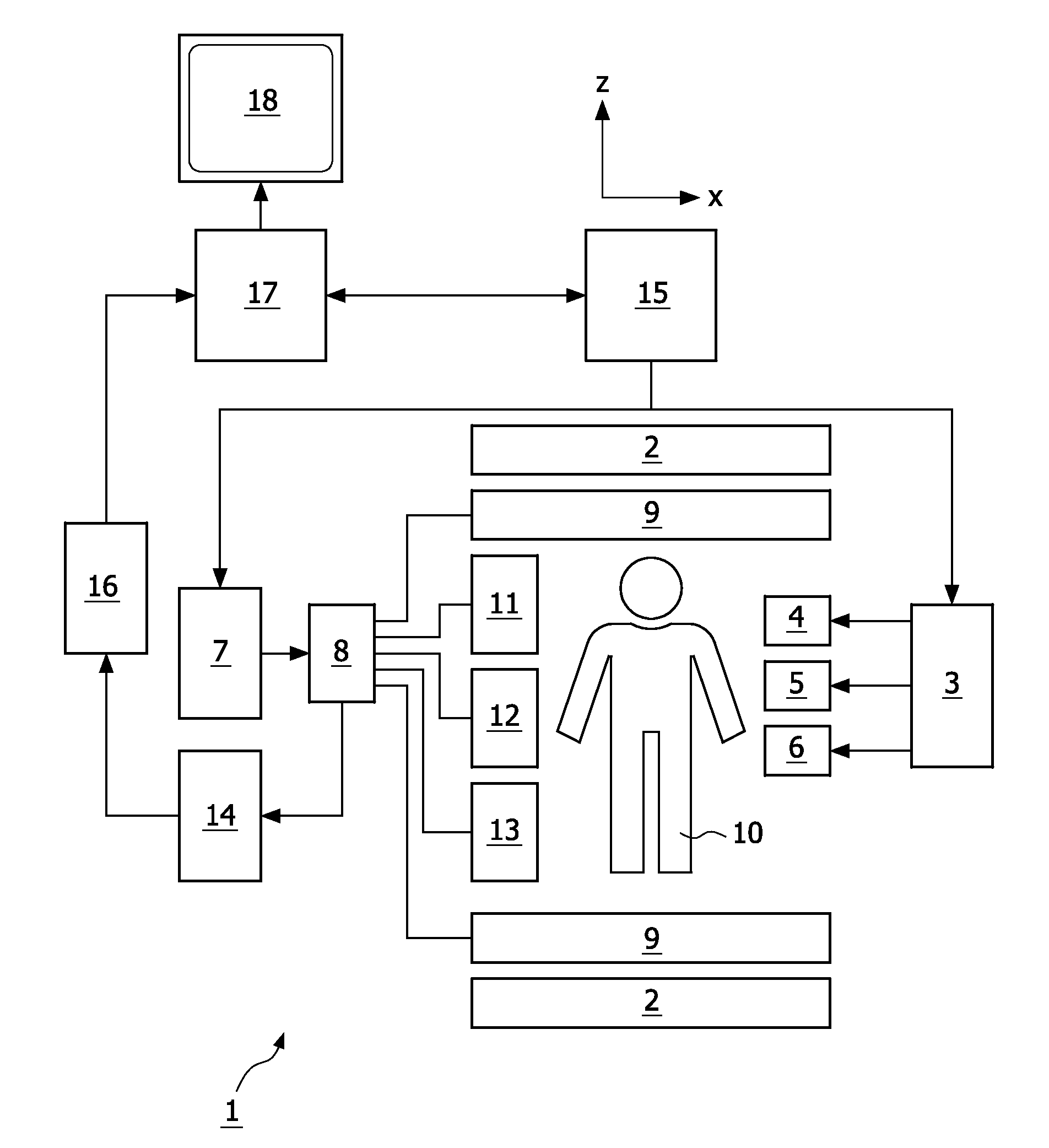
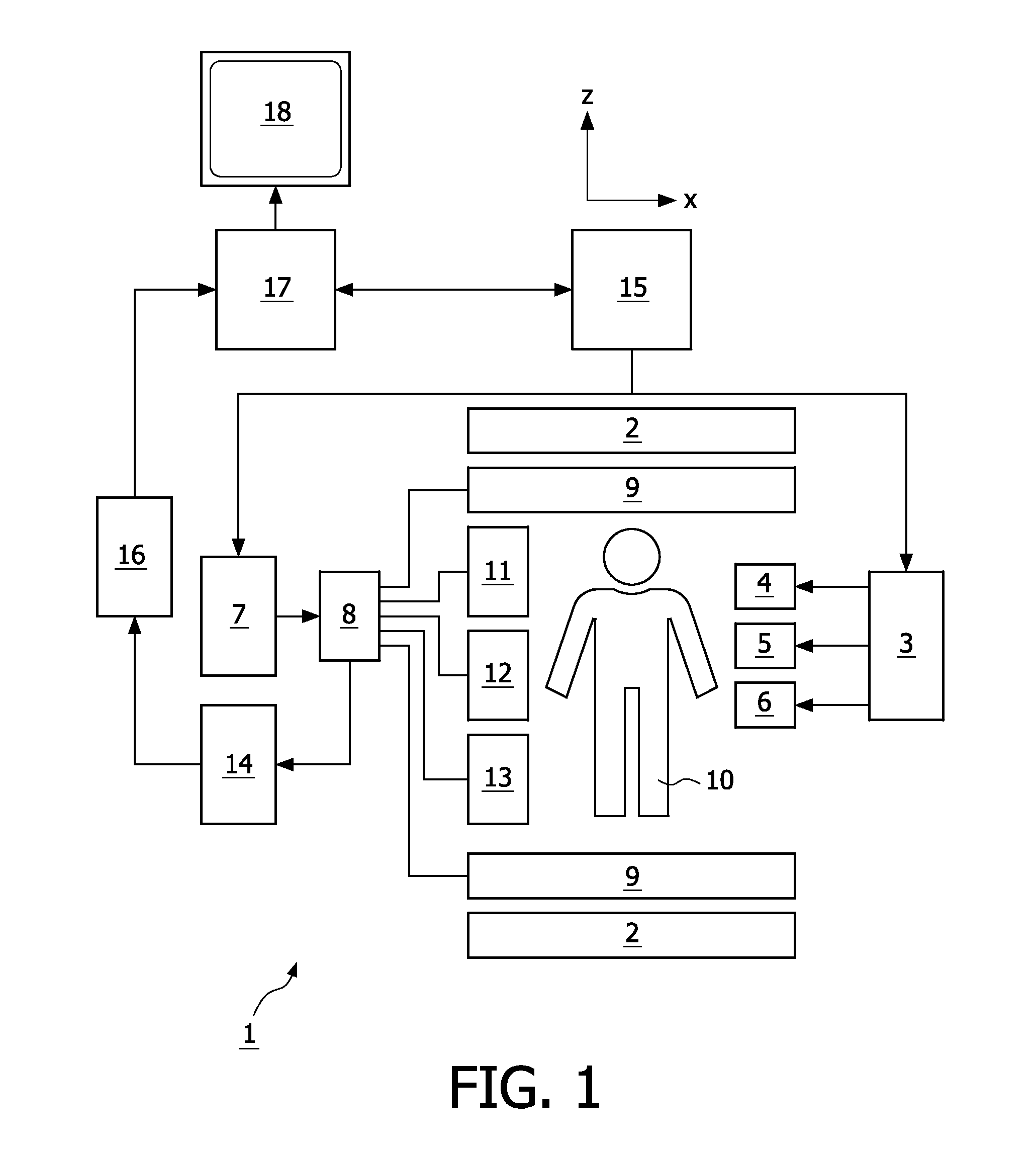
Magnetic resonance imaging system and method
InactiveUS20060074291A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringBlack bloodInversion recovery
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system using a double inversion recovery (DIR) imaging pulse sequence for acquiring black-blood images for obtaining a first level of nulling of a blood signal from acquired imaging slices is provided. The MRI system comprises an image processor configured changing a respective time order of the imaging slices at a selected point or points during the pulse sequence to obtain a second level of nulling of the residual blood signal from the imaging slices.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Myocardium T1 quantifying method and device
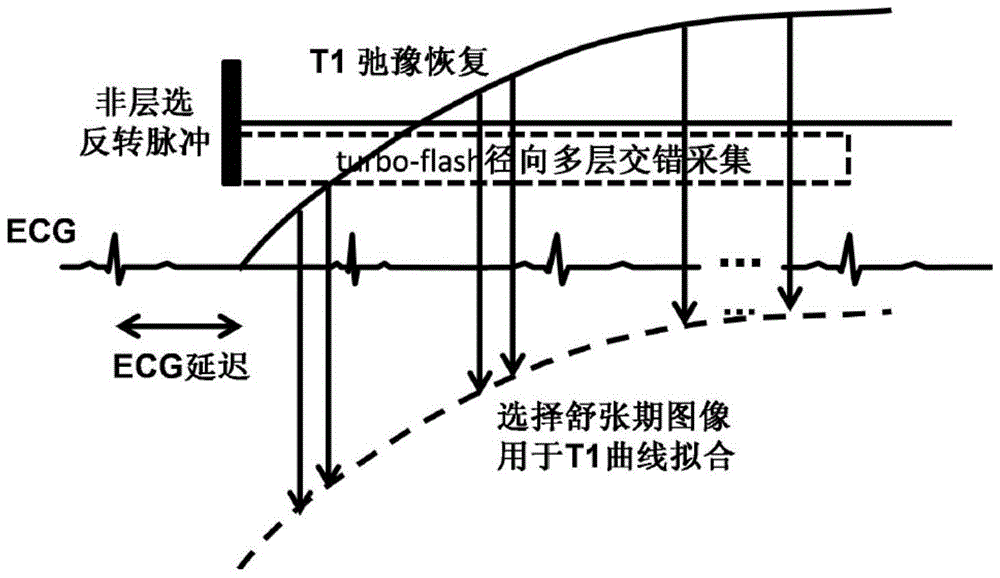
ActiveCN105662413AWaste less timeClear timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryCardiac muscle
The invention discloses a myocardium T1 quantifying method. The method includes the steps that after electrocardiograph gating trigger delay, non-layer-selection inversion pulses are applied; real-time interlaced collection of at least two layers of images is carried out with a fast spoiled gradient echo low-angle shot sequence of a radial sampling trajectory, and the inversion recovery process of signals is captured; a sampling line in diastole is selected to serve as a K space center line; with the selected sampling line as the center, the sampling line is symmetrically selected to carry out image reconstruction according to the size of a reconstruction window; a T1 quantifying graph is fitted with restructured images. The invention further discloses a device based on the method. By means of the method and the device, multiple layers of T1 quantifying images can be collected in one time of breathholding, the whole heart can be covered in two or three times of breathholding, and thus time waste and patient discomfort caused by breathholding are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Dynamic myocardium activity detection method and system
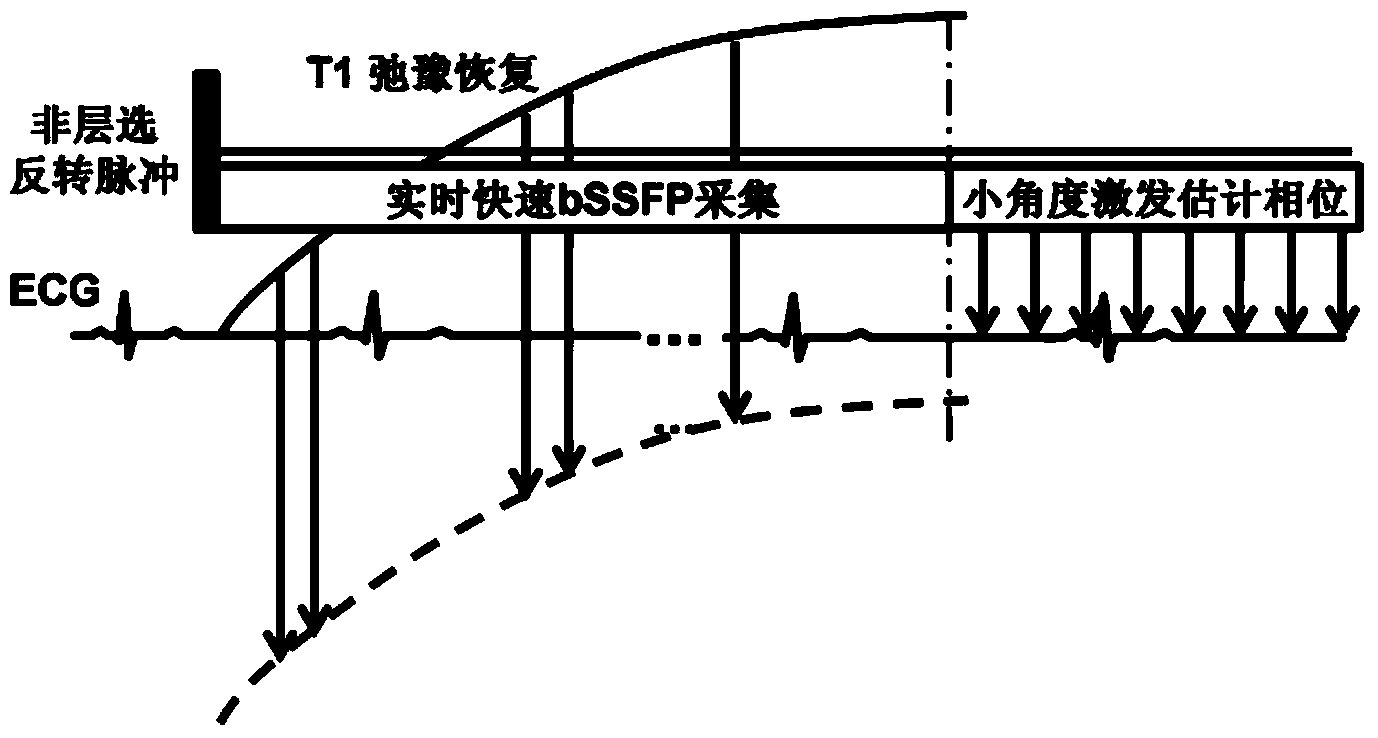
ActiveCN104013405AEfficient determinationImprove collection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInversion recoveryCine mri
The invention discloses a dynamic myocardium activity detection method. The dynamic myocardium activity detection method comprises the steps that a non-layer-selection inversion pulse is applied on a detected object; a balanced steady-state free procession is used for carrying out real-time sampling on the inversion recovery process of signals in the whole cardiac cycle including a diastole period and a systole period, and a set of heart cine-MRI images; a small-angle excitation balanced steady-state free procession within a preset range is used for collecting a reference image; phase sensitivity inversion recovery reconstruction is carried out on the collected heart cine-MRI images through the reference image. By the adoption of the dynamic myocardium activity detection method, the collection efficiency and imaging efficiency can be improved, and the dynamic myocardium activity is effectively measured. The invention further provides a dynamic myocardium activity detection system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
System for Cardiac MR & MR Cine Imaging Using Parallel Image Processing
ActiveUS20130116545A1Improves temporalImproves spatial image resolutionElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsInversion recoveryData set
A system for cardiac MR imaging receives a heart rate signal representing heart electrical activity. The system, over multiple successive heart cycles, uses multiple MR imaging RF coils in gradient echo imaging a patient heart, synchronized with the heart rate signal and uses an inversion recovery pulse for inverting myocardium tissue MR signal for an individual heart cycle, to acquire, within multiple individual successive portions of an individual heart cycle, corresponding successive multiple patient heart images. An individual image of an individual heart cycle portion is derived from multiple heart image representative data sets comprising a reduced set of k-space data elements acquired using corresponding multiple coils of the RF imaging coils. An image generator generates an MR image of an individual heart cycle portion using the multiple heart image representative data sets comprising the reduced set of k-space data elements.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System for automated parameter setting in cardiac magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS9014783B2Easy to operateImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryData set
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Image segmentation method, image segmentation apparatus and electronic device
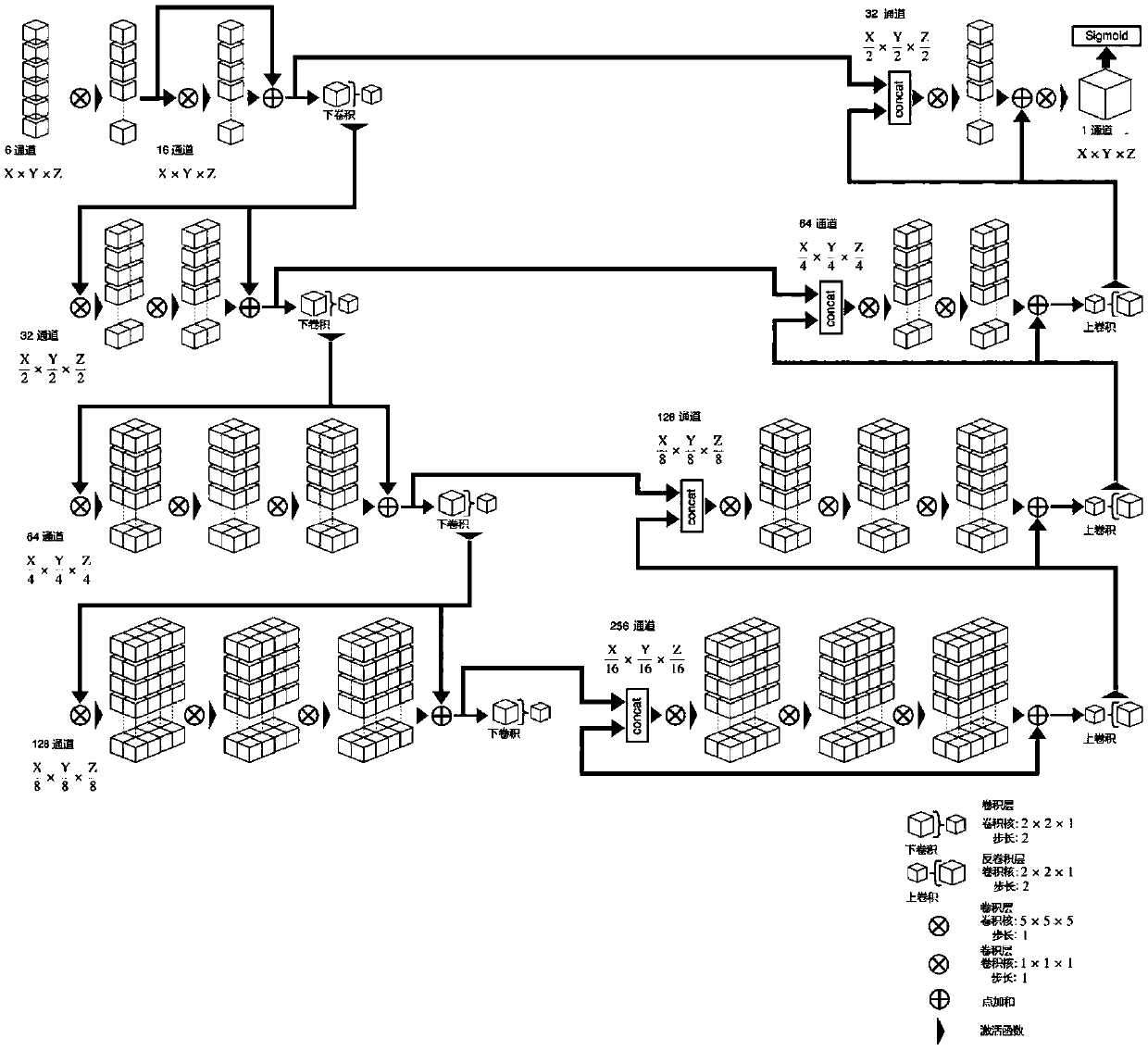
ActiveCN108765447AAccurate divisionAccurately Segment AtlasesImage enhancementImage analysisParenchymaInversion recovery
The invention provides an image segmentation method, an image segmentation apparatus and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image and a T1 weighted magnetic resonance image of a to-be-tested individual; based on the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, determining a cerebrospinalfluid segmentation graph; inputting the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image to a neural network model, thereby obtaining a lateral ventricle segmentation graph; on the basis of the cerebrospinal fluid segmentation graph and the lateral ventricle segmentation graph, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based o the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image; and by utilizing a spatial conversion relationship between the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image and the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based on the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image. According to the technical scheme, a cerebrospinal fluid part and a non-cerebrospinal fluid part can be moreaccurately divided, so that the more accurate brain parenchyma segmentation graphs can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN BRAINNOW MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for detecting and classifying atherosclerotic plaque hemorrhage
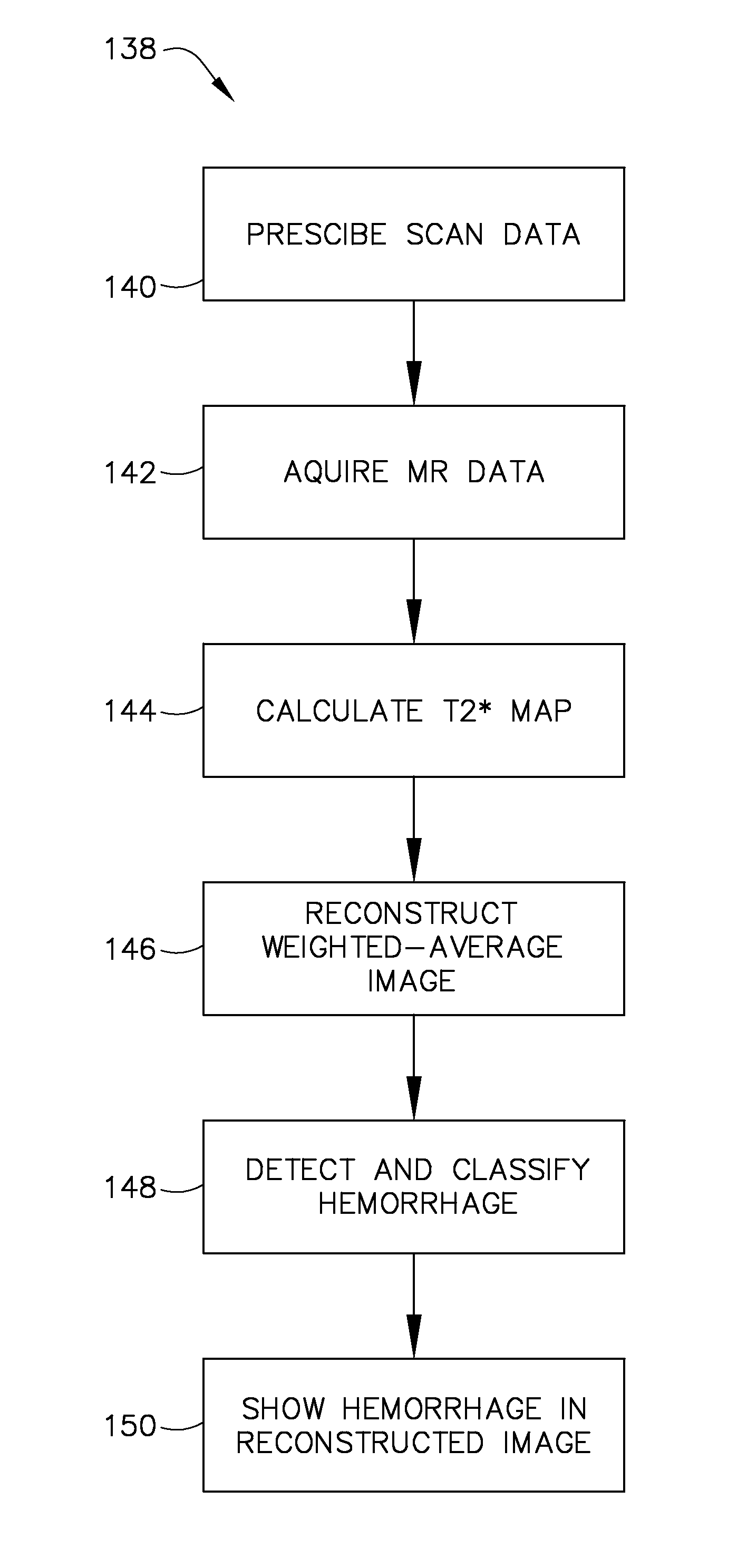
A system and method for detecting atherosclerotic plaque hemorrhage includes a controller programmed to apply a non-selective inversion recovery RF pulse to a region of interest, apply a plurality of encoding sequences to the region of interest to cause generation of a plurality of echoes during application of each encoding sequence. The controller is further programmed to acquire three dimensional MR data from the region of interest during generation of each of the plurality of echoes, identify a hemorrhage based on the three dimensional MR data, characterize a type of the hemorrhage, and reconstruct an image based on the three dimensional MR data, the image comprising the characterized hemorrhage.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV +1
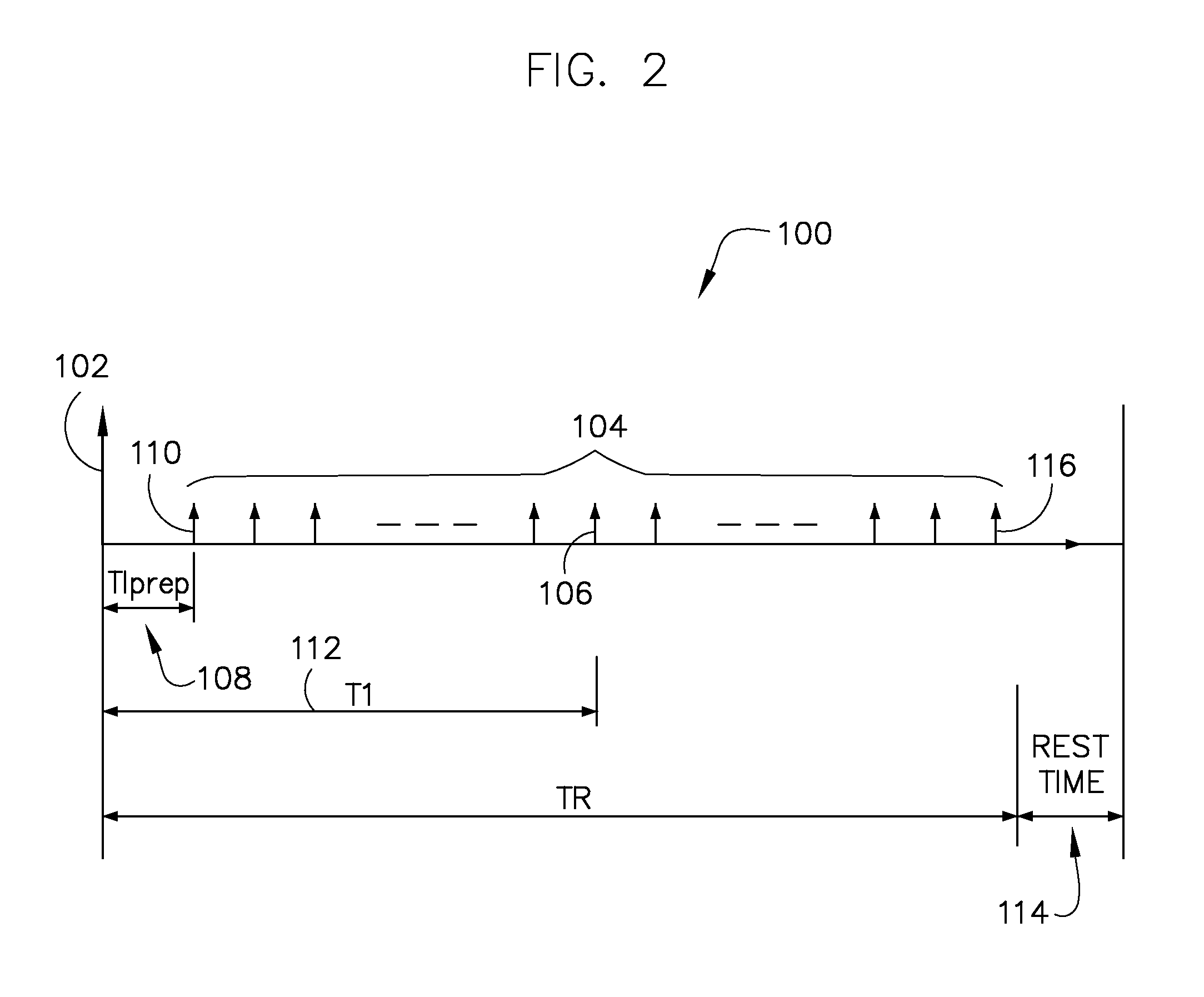
Dual-contrast mr imaging using fluid-attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR)
InactiveUS20120046539A1Reduce the differenceIncrease relaxation timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDelayed periodsData set
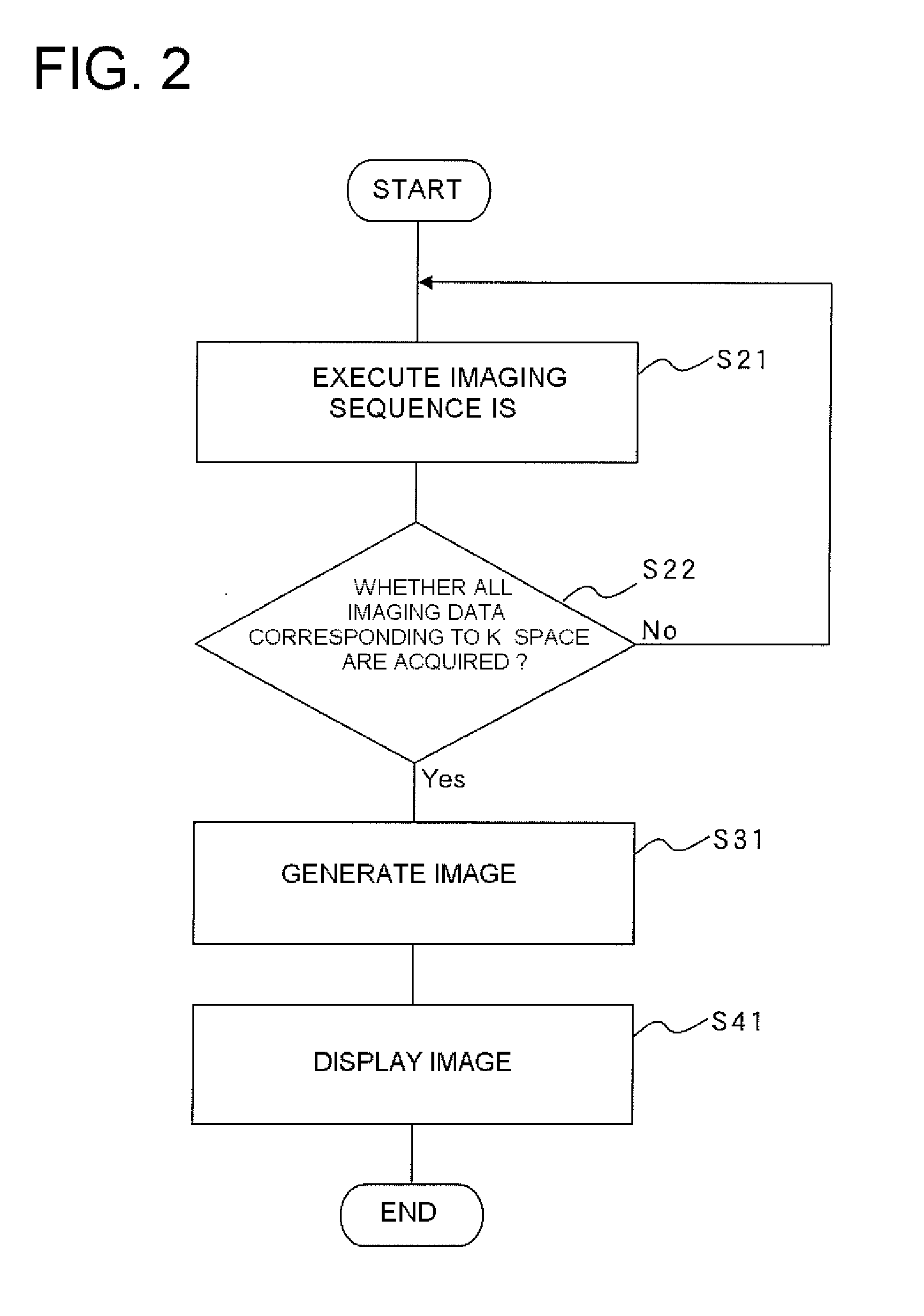
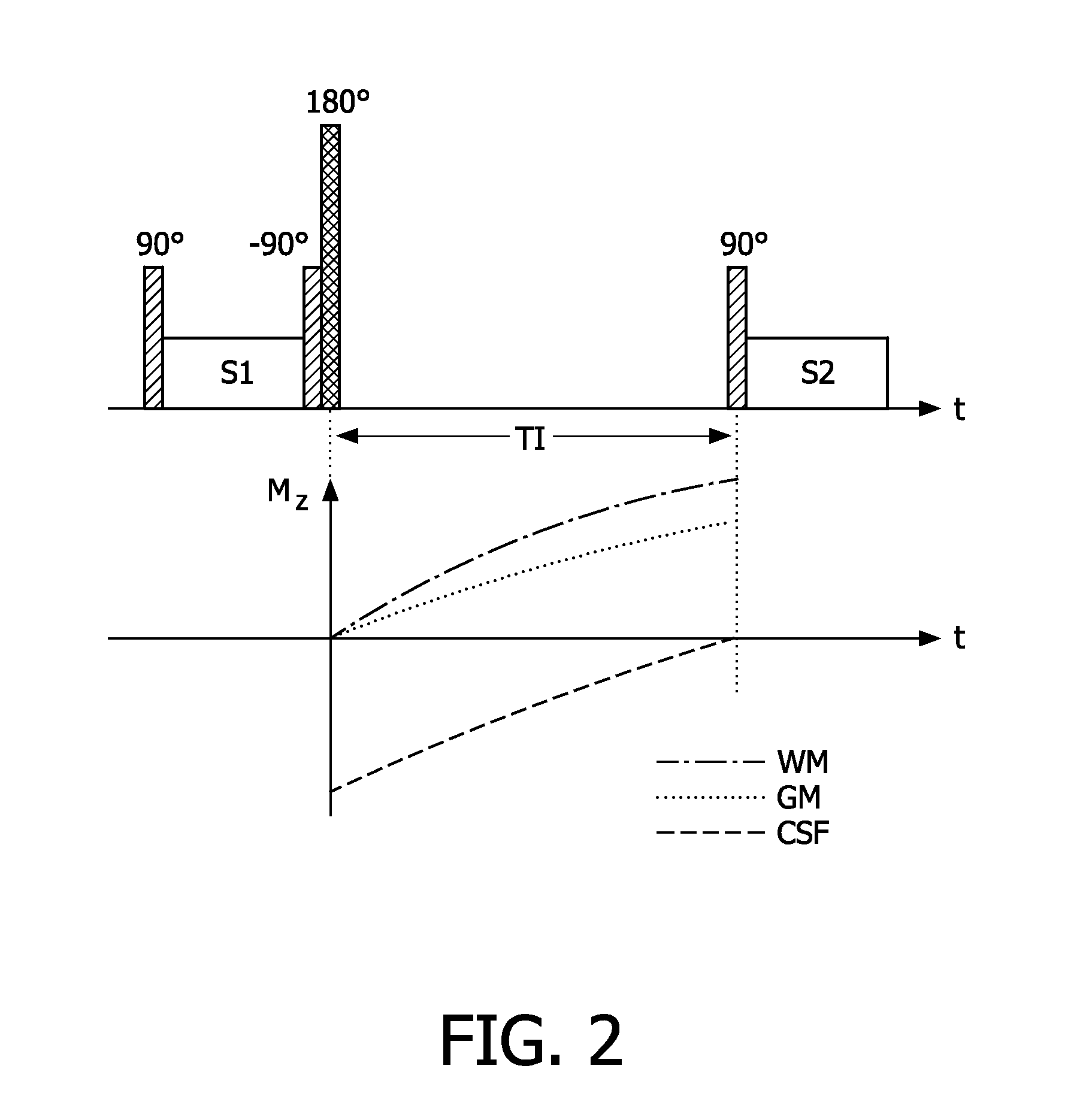
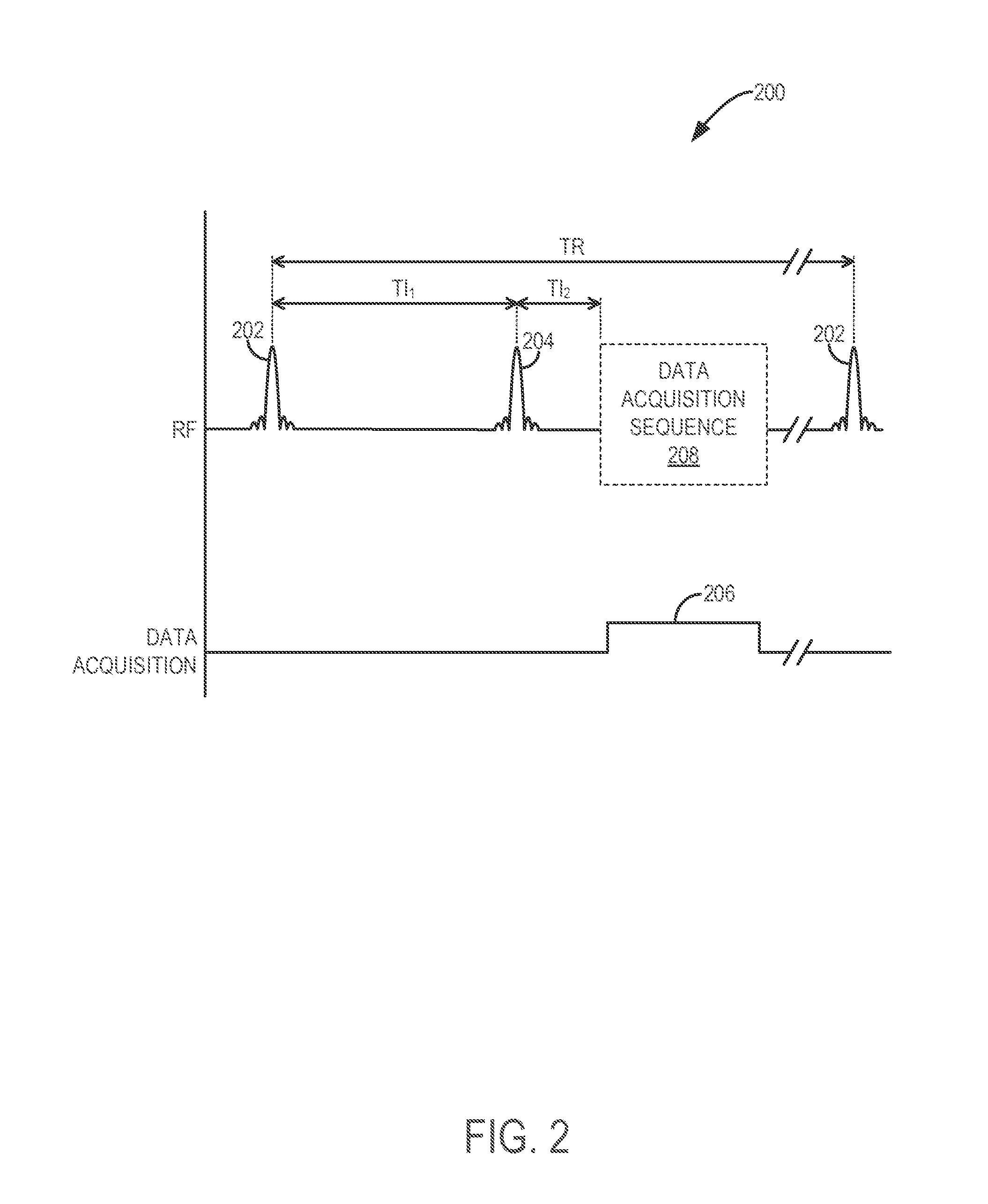
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) of a patient placed in an examination volume of an MR device (1). The acquisition of high-resolution three-dimensional FLAIR images as well as T2-weighted images at high main magnetic field strength (>3 Tesla) results in unacceptable long scan times. The present invention contemplates a new and improved MR imaging method which overcomes this problem. The method of the invention comprises the steps of subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a first imaging sequence (S1) for acquiring a first signal data set; immediately subsequent to the first imaging sequence (S1) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an inversion RF pulse that inverses longitudinal magnetization within the portion; after an inversion delay period (TI) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a second imaging sequence (S2) for acquiring a second signal data set; reconstructing first and second MR images from the first and second signal data sets respectively.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Magnetic resonance imaging system and method
ActiveUS20100134107A1Improve accuracyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionInversion recoveryPulse sequence
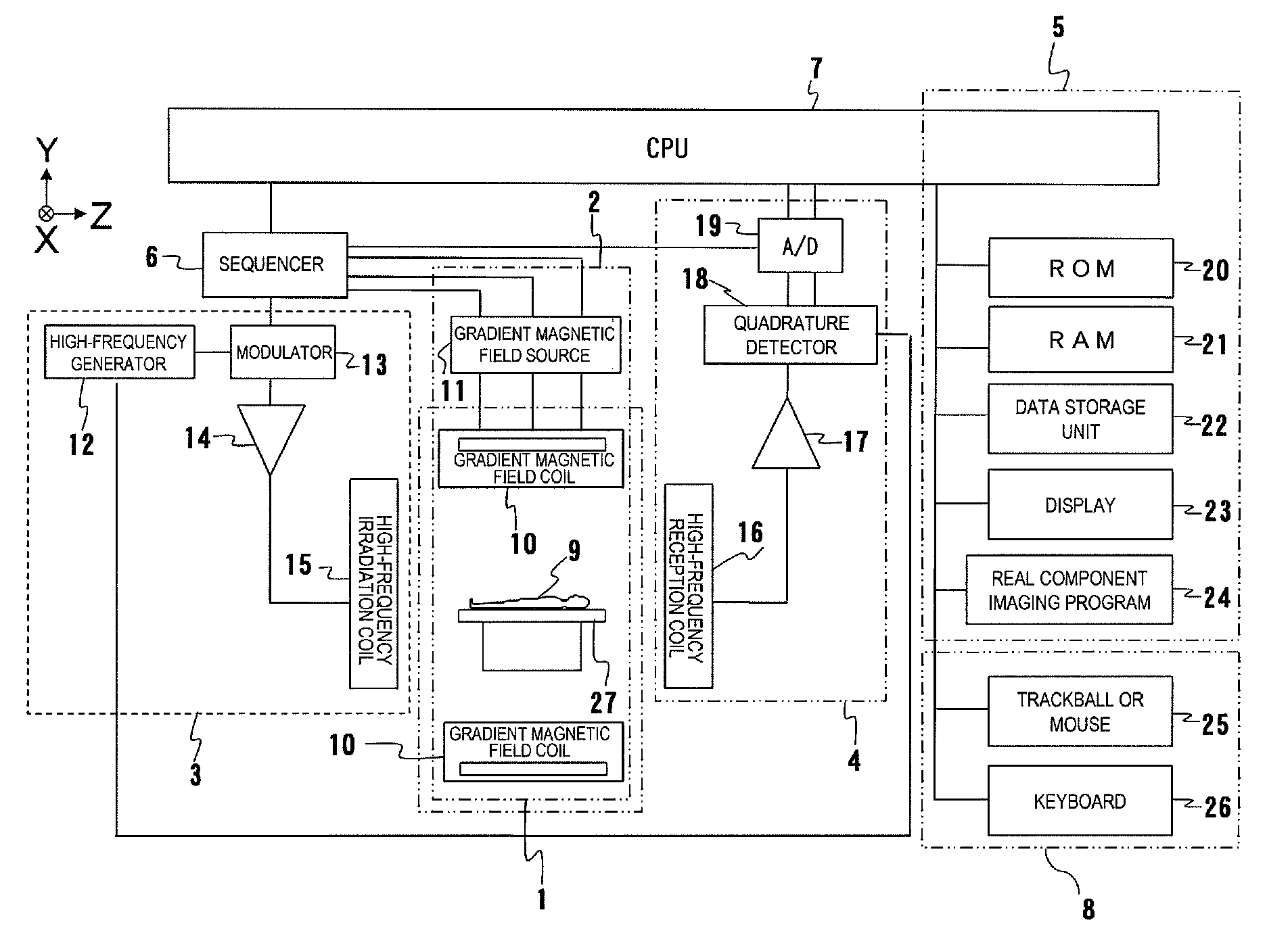
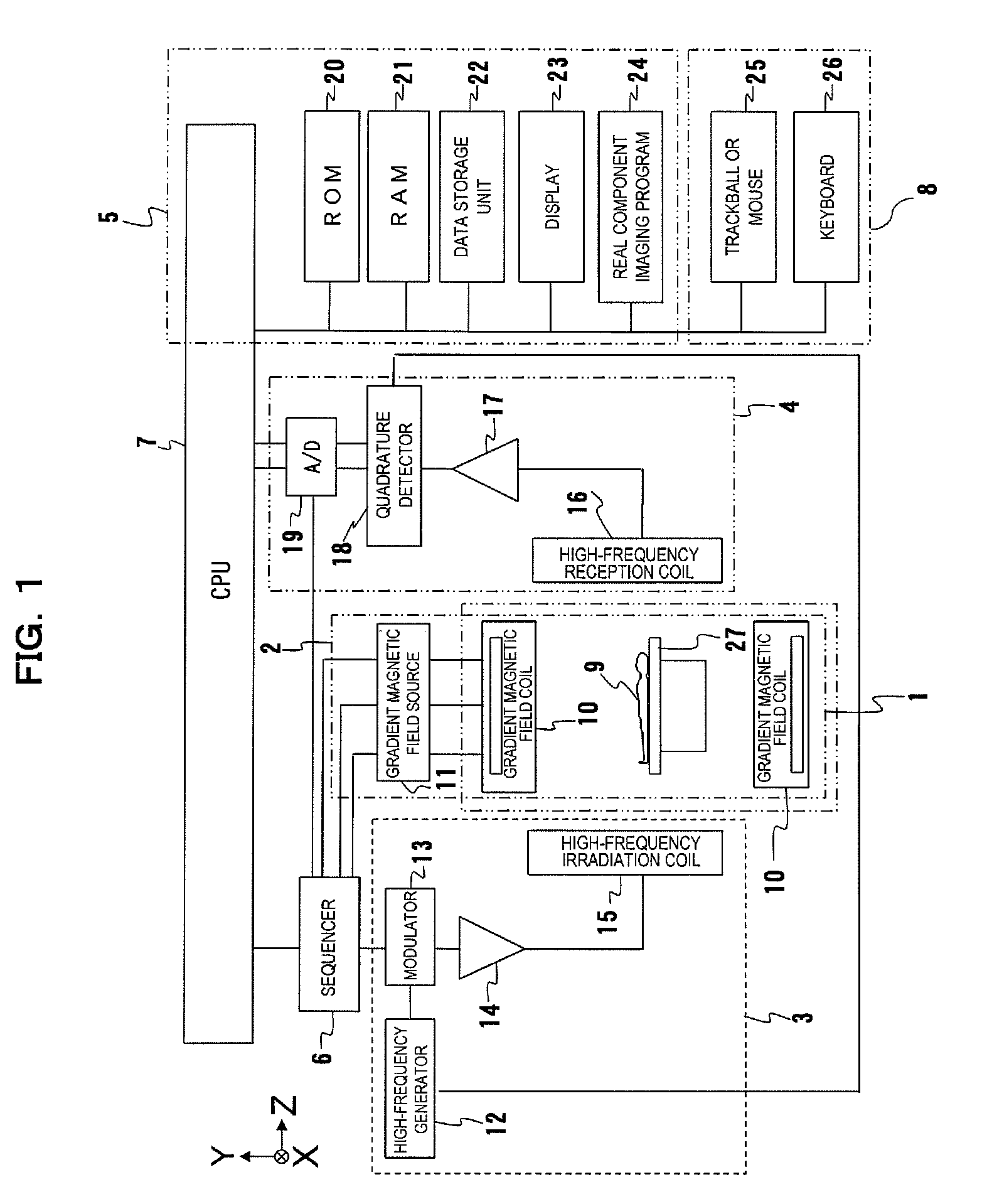
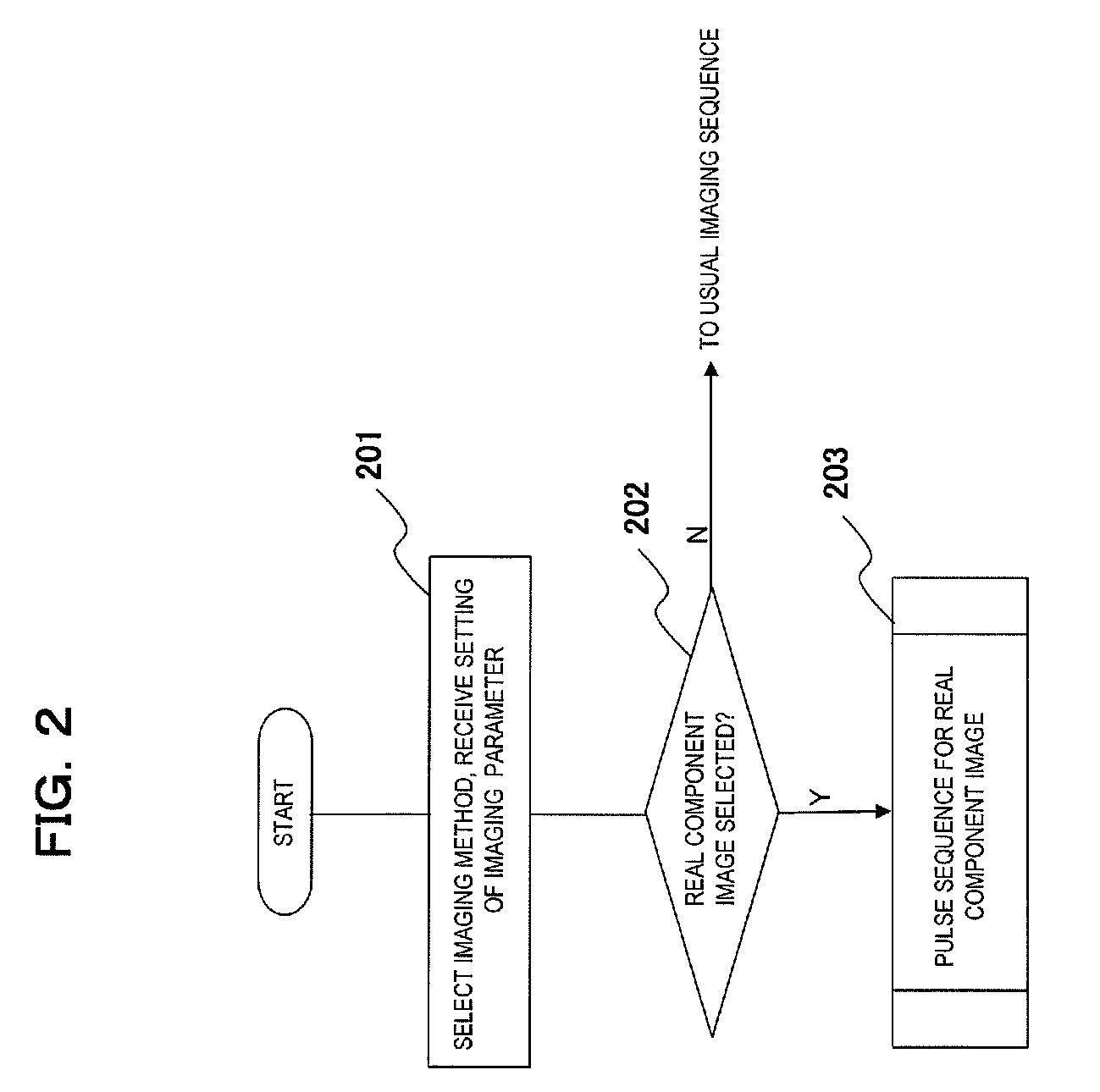
A magnetic resonance imaging system is characterized in that a control unit executes, as pulse sequences, a first sequence for obtaining data of a predetermined 2-dimensional region in a k-space and a second sequence for obtaining data required for reconstruction of an image by irradiating an object to be examined with an inversion recovery pulse and corrects the phase of the data obtained by the second sequence with the data of the 2-dimensional region obtained by the first sequence, and in that a signal processing unit reconstructs a real component image with corrected data.Upon execution of the first sequence, the control unit obtains the data of the predetermined 2-dimensional region in the k-space while varying a phase encoding amount.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
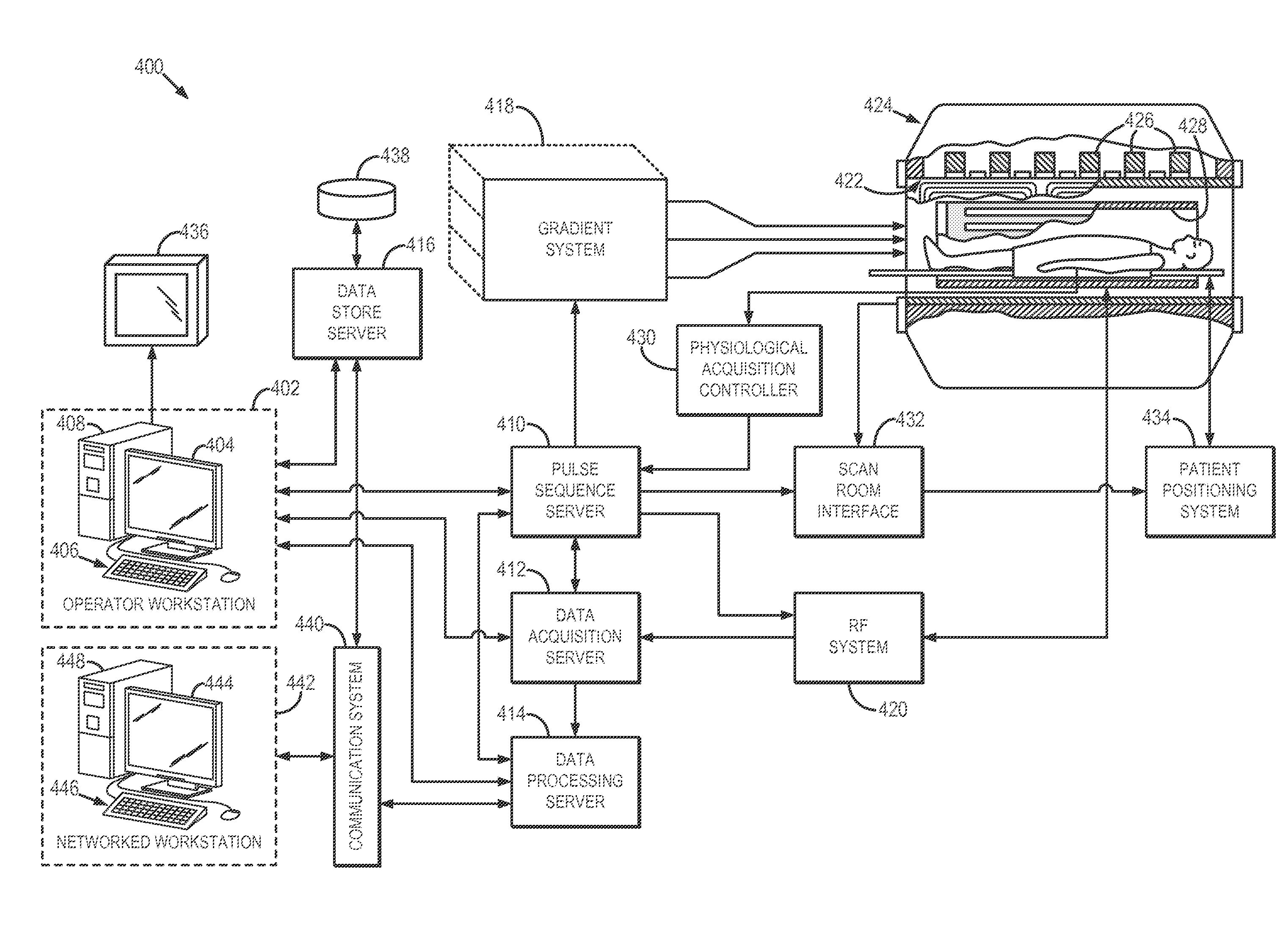
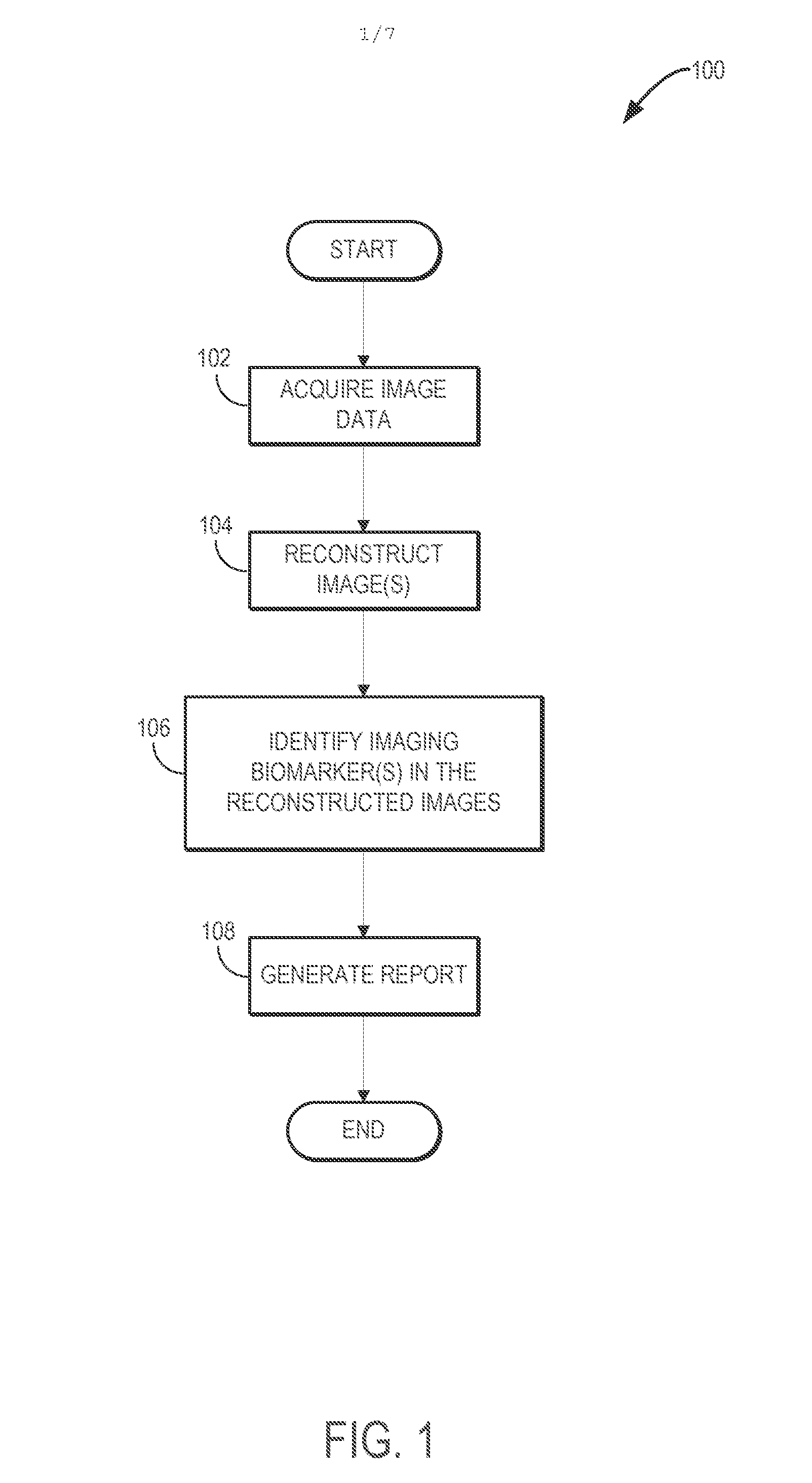
Systems and methods for producing imaging biomarkers indicative of a neurological disease state using gray matter suppressions via double inversion-recovery magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160220168A1Medical imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryPulse sequence
Systems and methods related to imaging biomarkers for determining neurological disease states of a subject are provided. In one embodiment, a method for producing an image indicative of a neurological disease using a magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) system is provided. The method includes directing the MRI system to perform a double inversion-recovery (“DIR”) pulse sequence to generate data where signals from gray matter and cerebral spinal fluid are substantially suppressed. The method also includes analyzing the DIR images, reconstructed from the acquired data, to identify cortical and white matter lesions. This includes identifying imaging biomarkers based on visual signatures of brain tissue, including white matter tissue. In some aspects, diffusion-weighted data may also be obtained using the MRI system. Diffusion-weighted data may be used in a tractography process to determine connectivities, or connectivity patterns between the identified lesions, including cortical lesions, to determine neurological disease states of the subject.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com