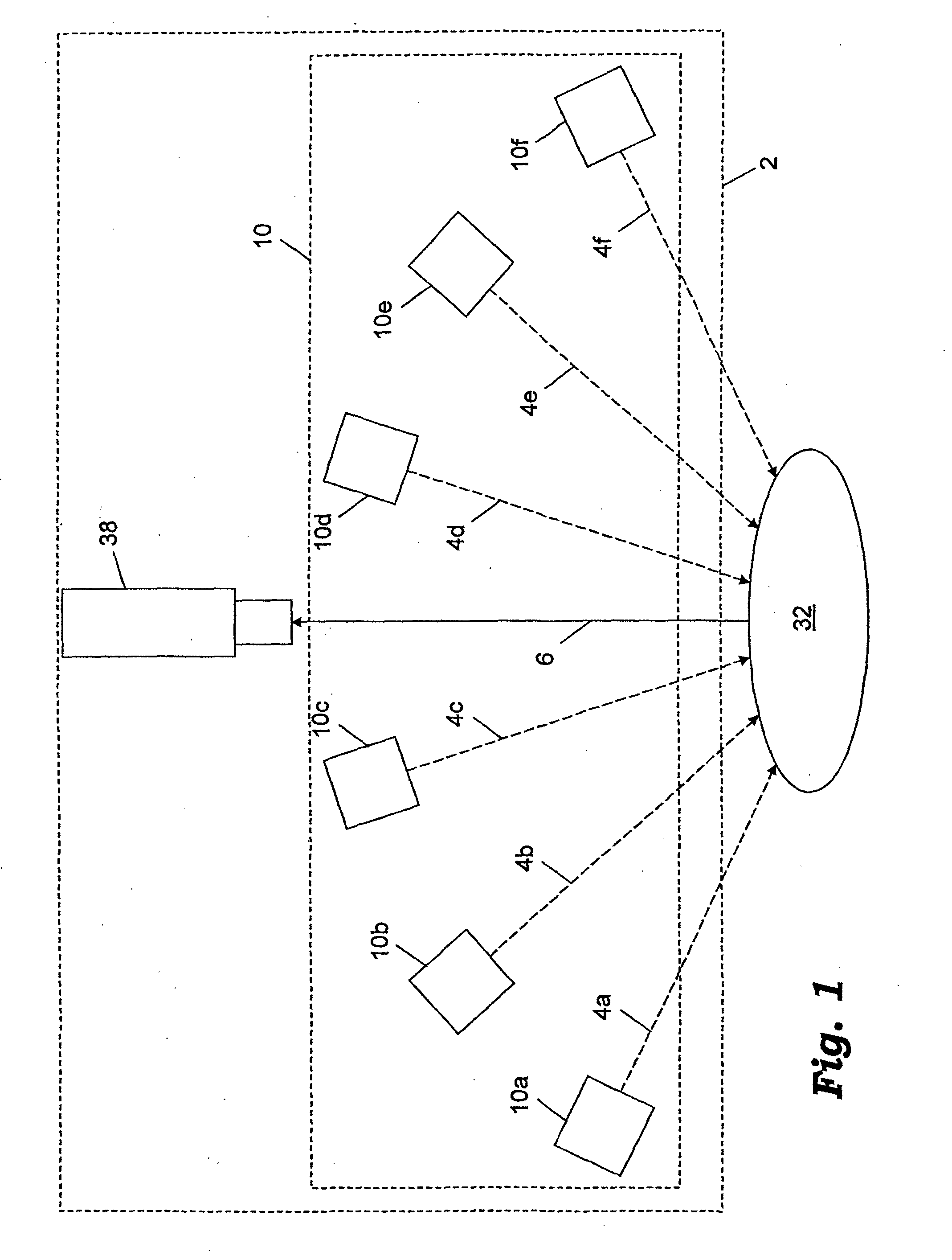
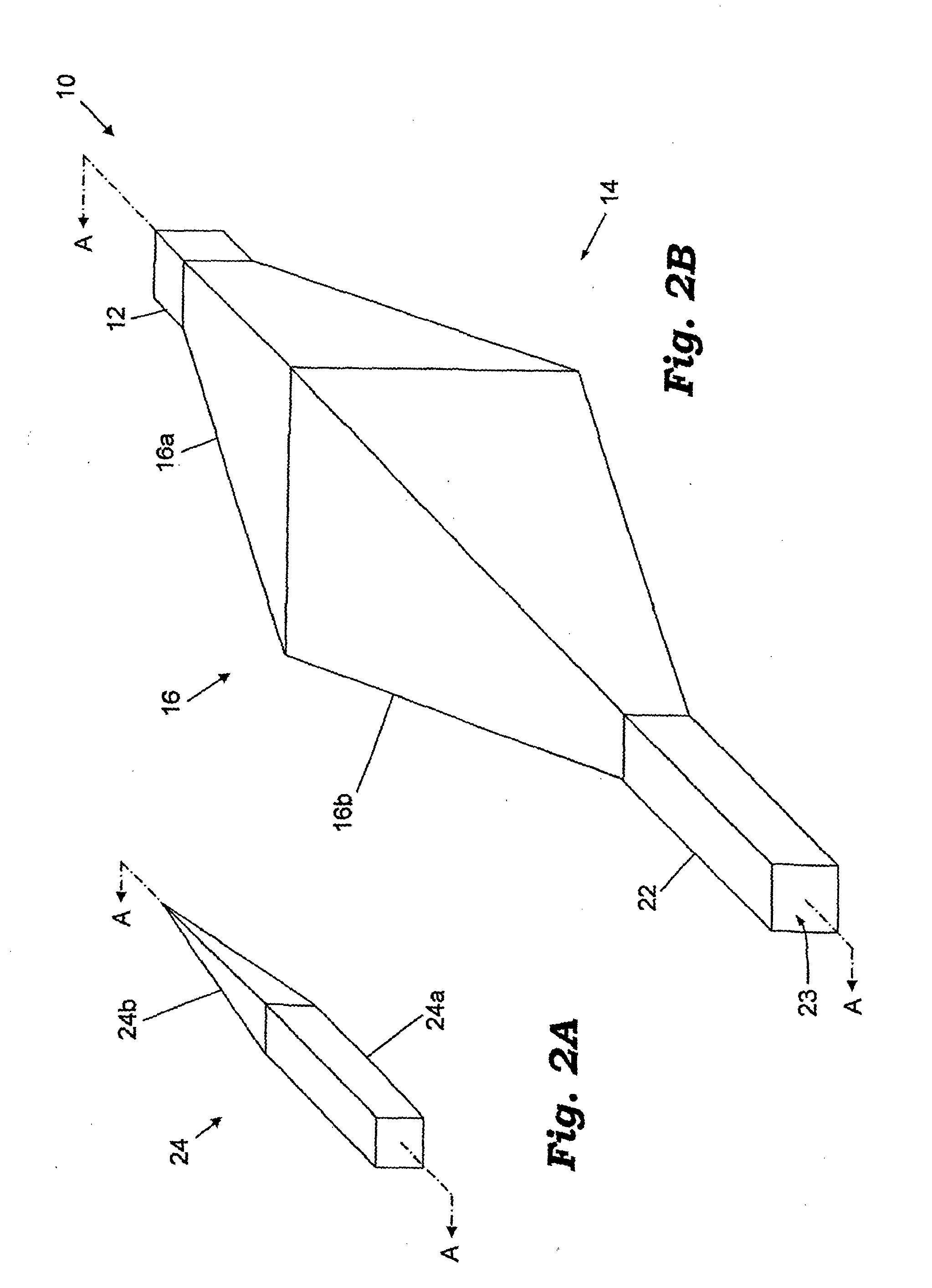
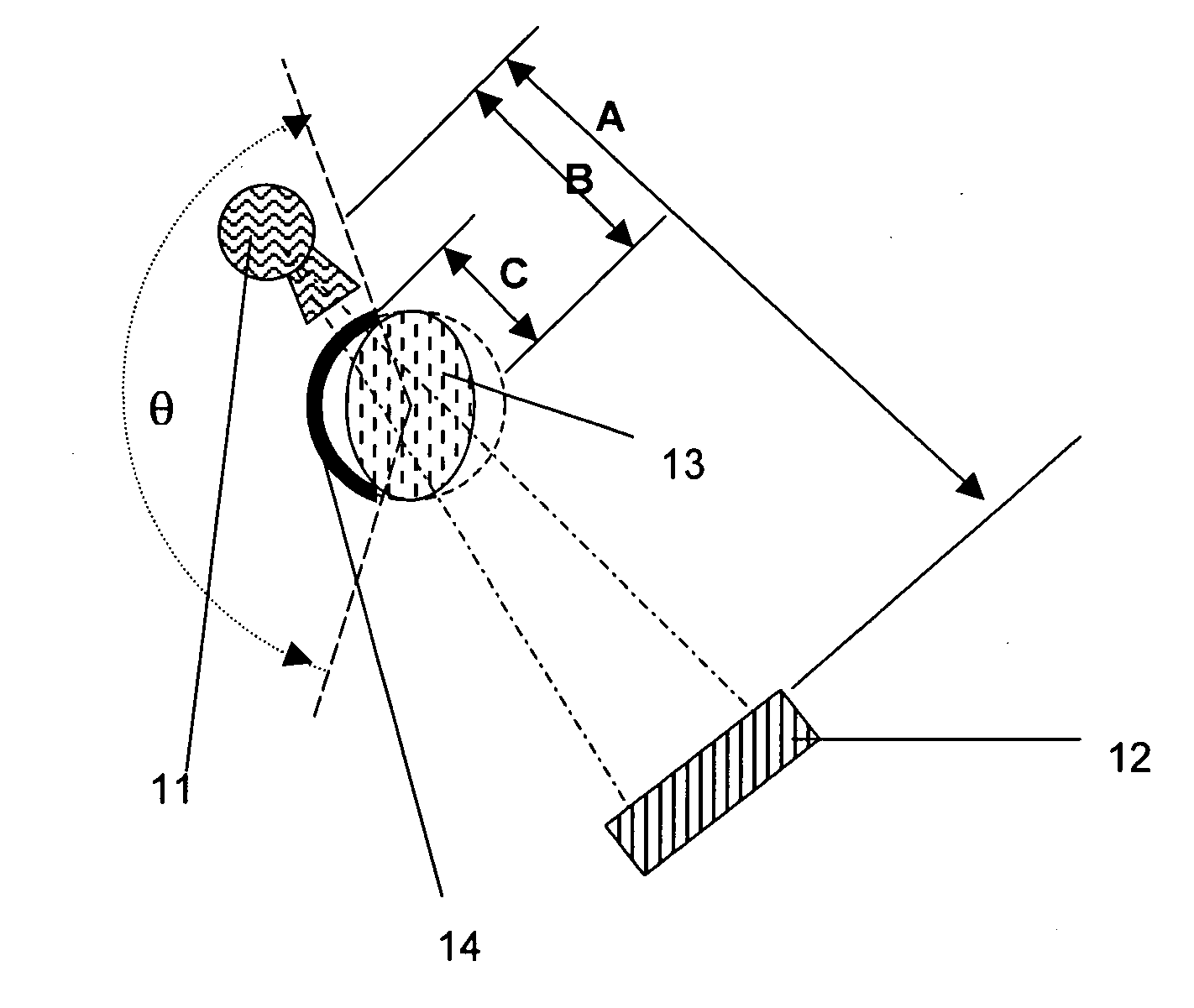
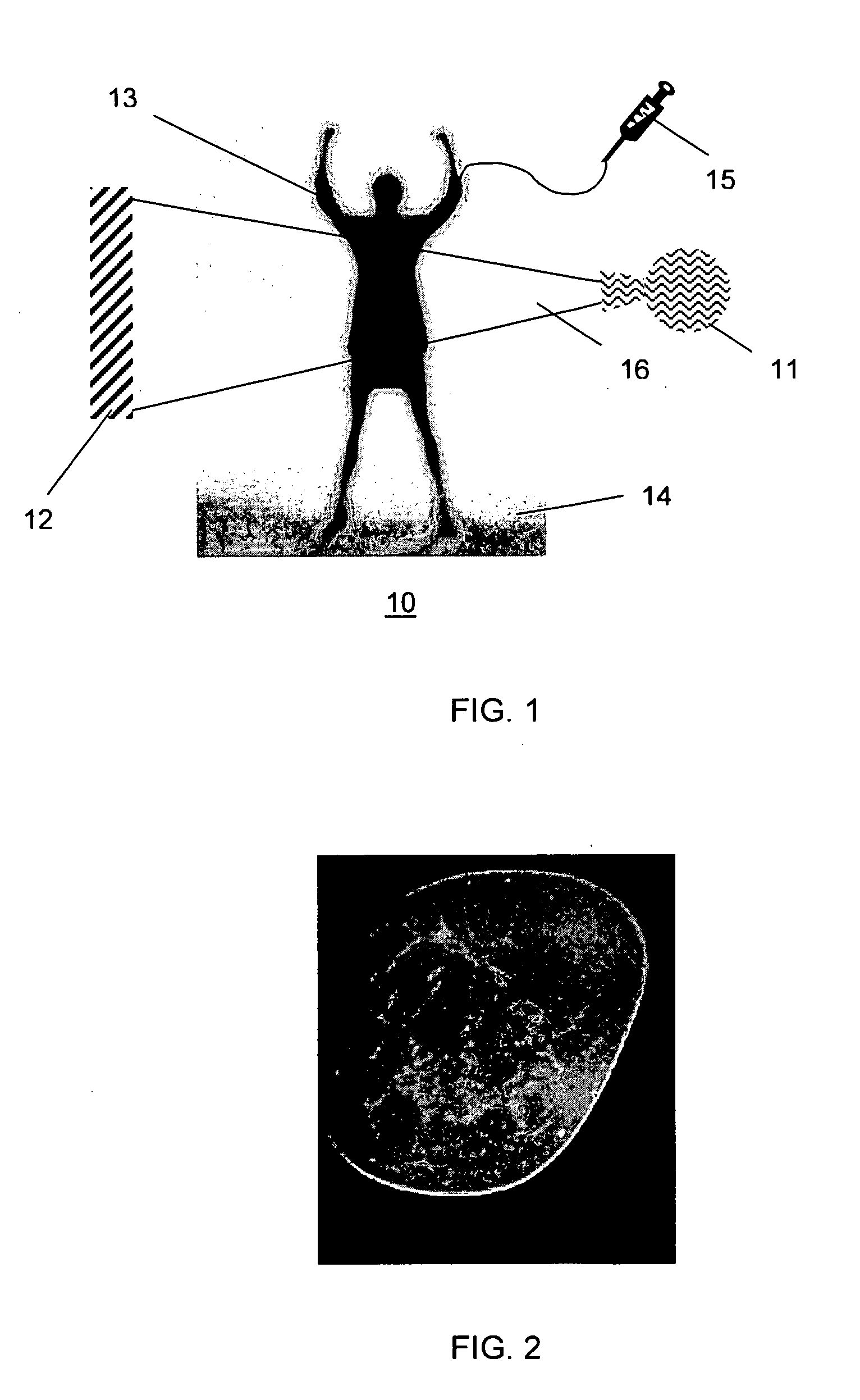
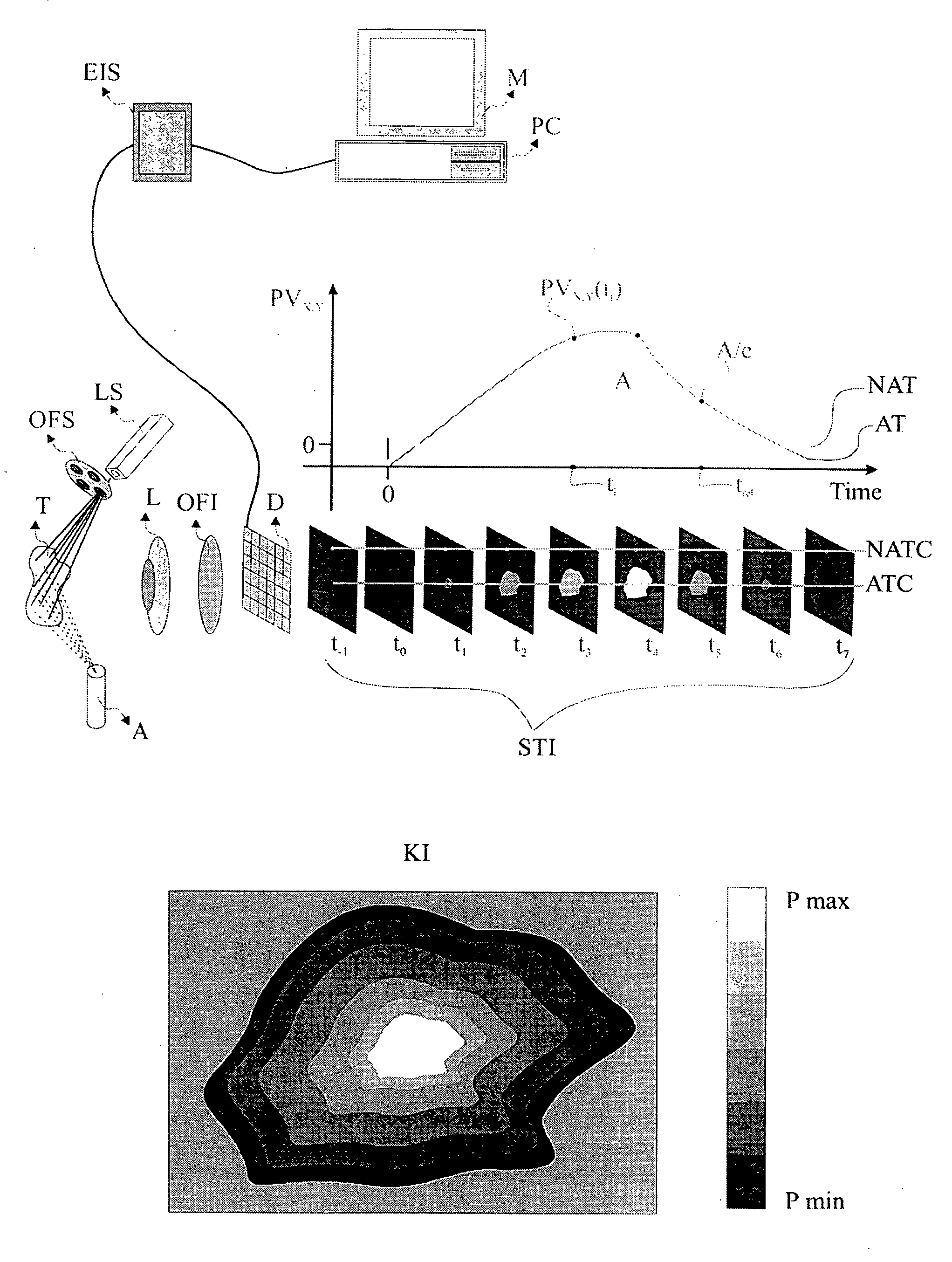
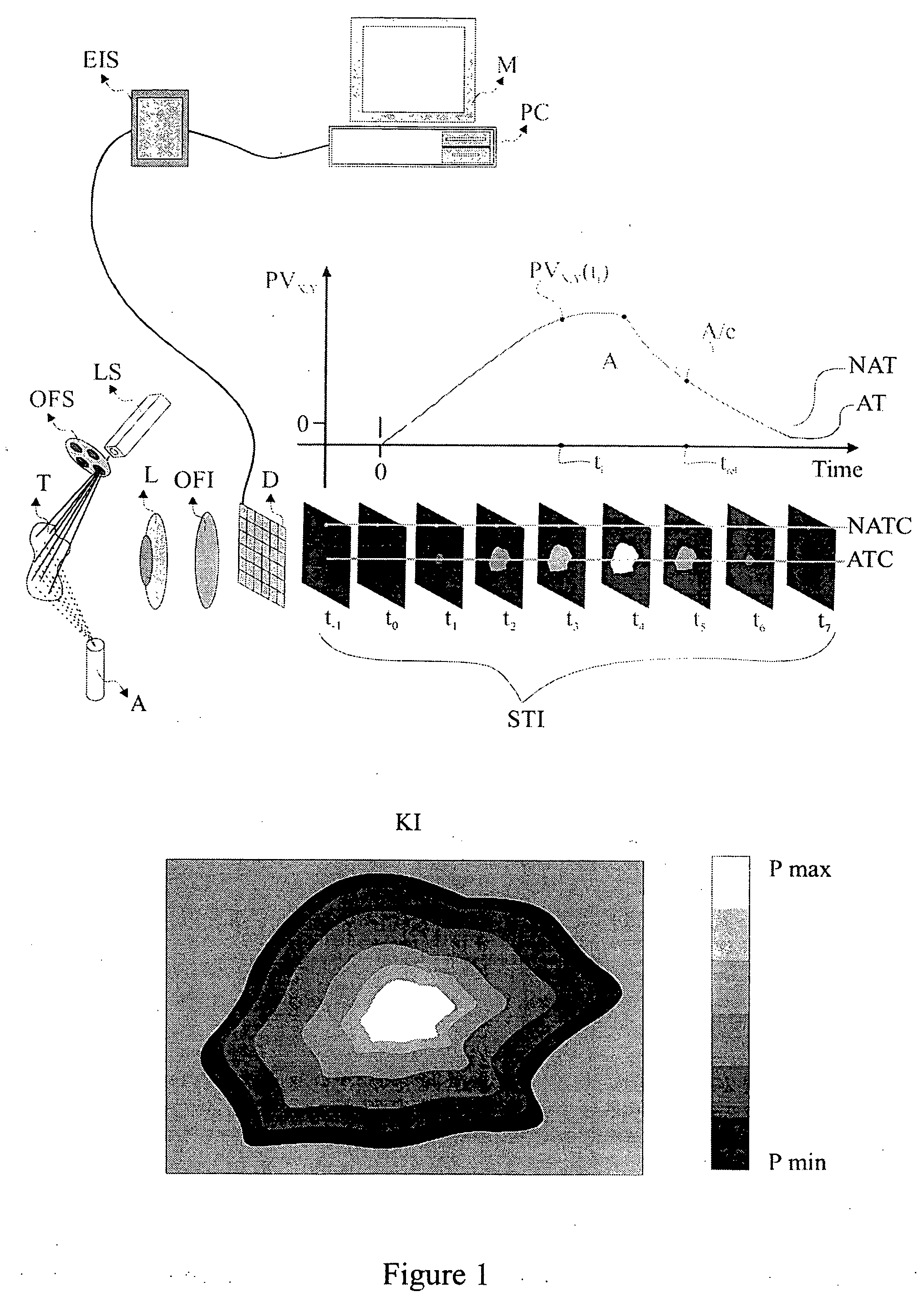
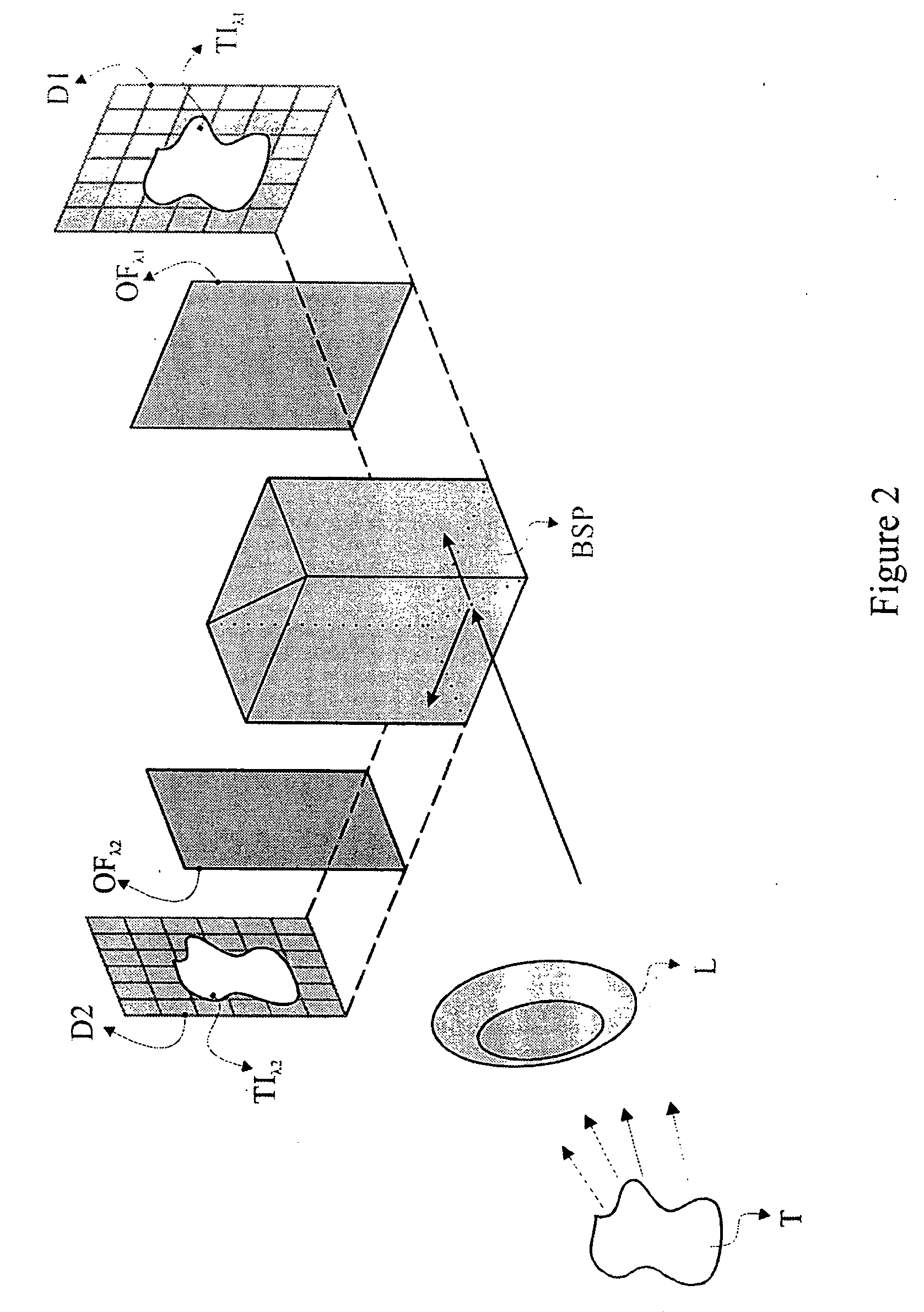
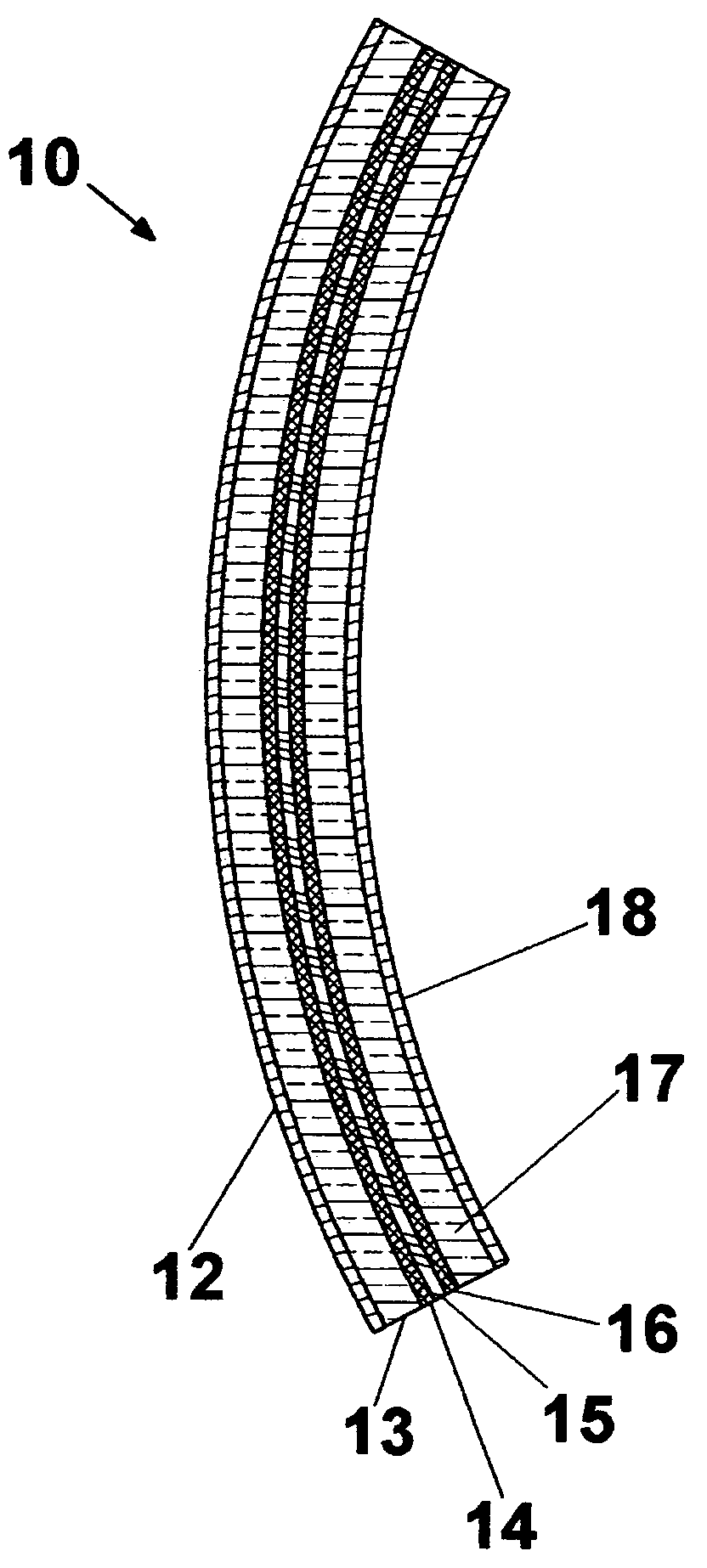
Patents
Literature
1395 results about "Contrast enhancement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What is Contrast Enhancement. 1. An image processing technique in which the contrast of the image, or the difference in color and light between parts of it, is touched up in order to improve its perception by human eye.
Contrast-enhanced ocular imaging
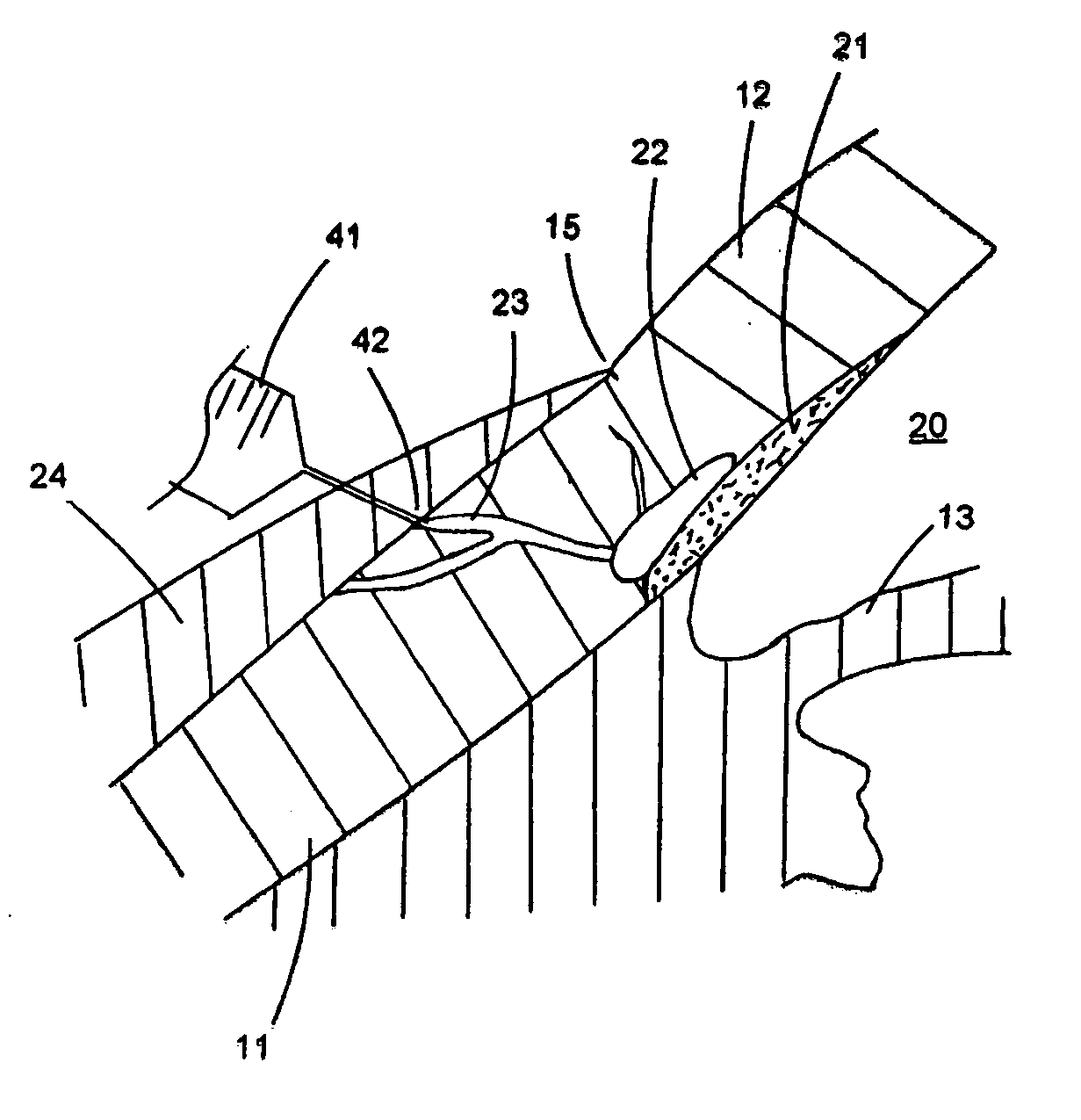
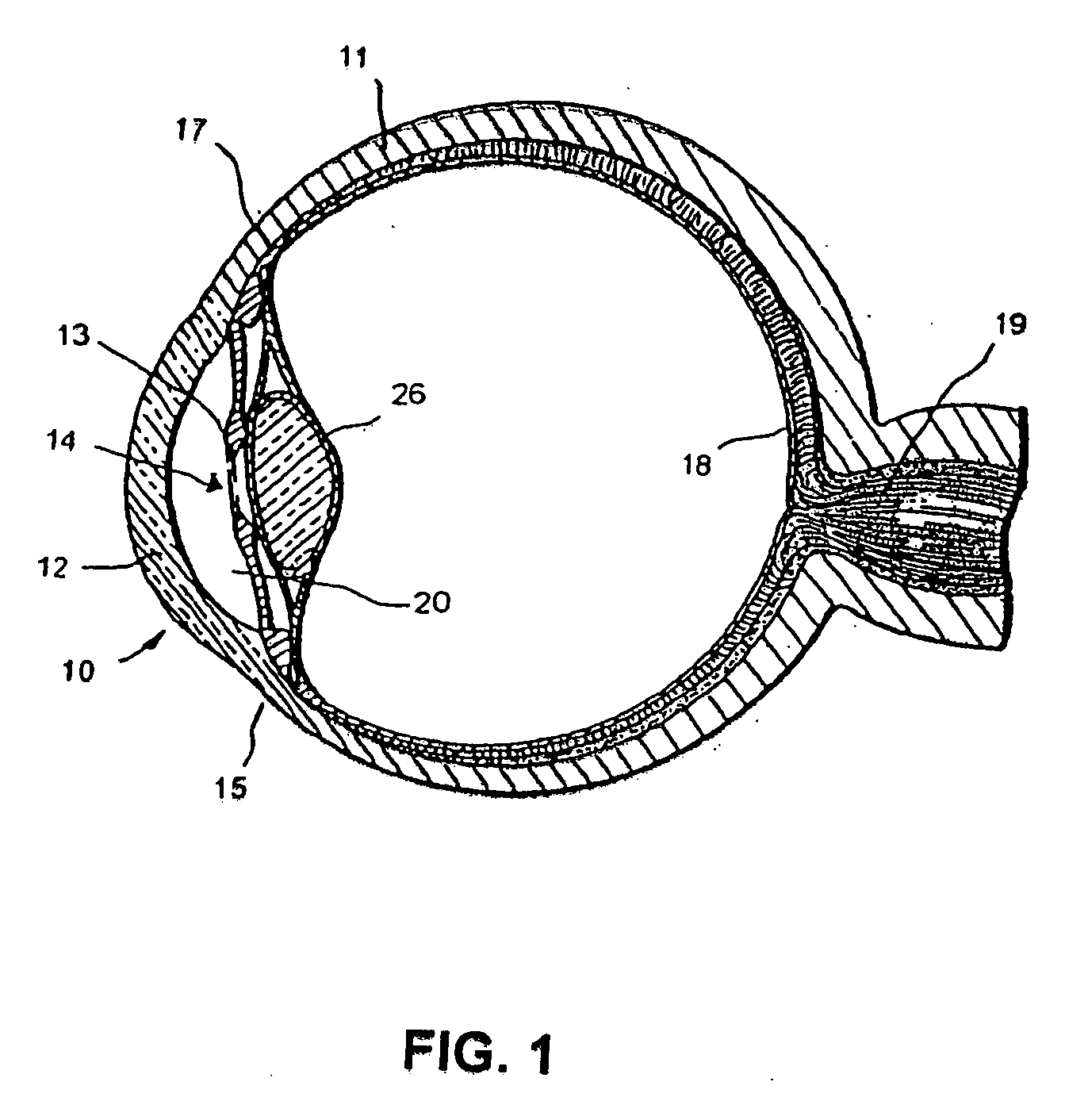
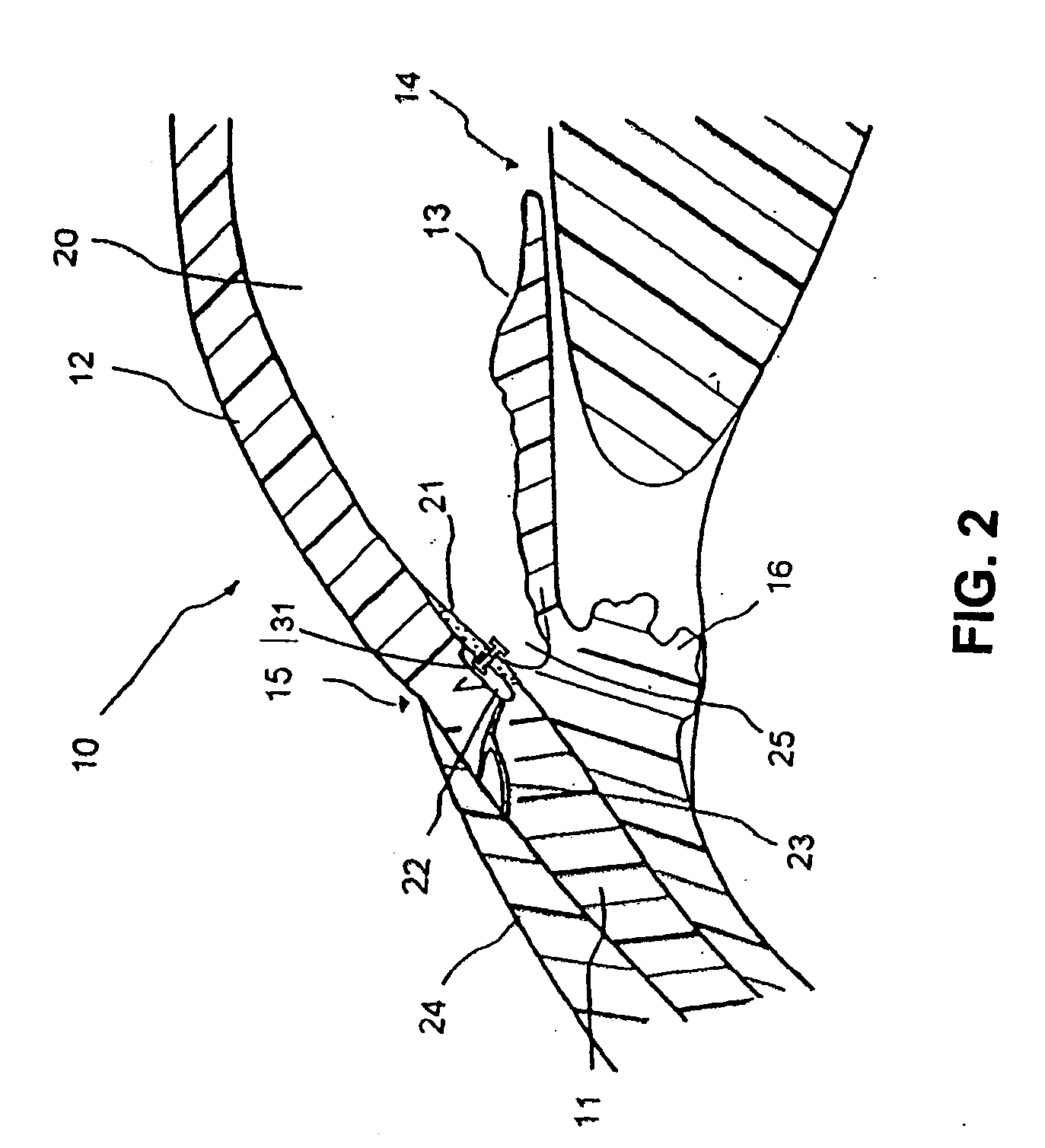
The invention relates generally to medical devices and methods for ocular imaging and, more particularly, to devices and methods for increasing contrast in an eye in which an imaging contrast agent is introduced into an aqueous humor outflow channel. For example, in one embodiment, the outflow channel may be Schlemm's Canal, or in another embodiment, the outflow channel may be an episcleral vein. Also disclosed are methods for implanting a trabecular stent via an ab extemo procedure with assistance of enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to restore a part or all of the normal physiological function of directing aqueous outflow for maintaining a normal intraocular pressure in an eye.
Owner:GLAUKOS CORP
Systems, methods, apparatus, and computer program products for spectral contrast enhancement
Systems, methods, and apparatus for spectral contrast enhancement of speech signals, based on information from a noise reference that is derived by a spatially selective processing filter from a multichannel sensed audio signal, are disclosed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC +1
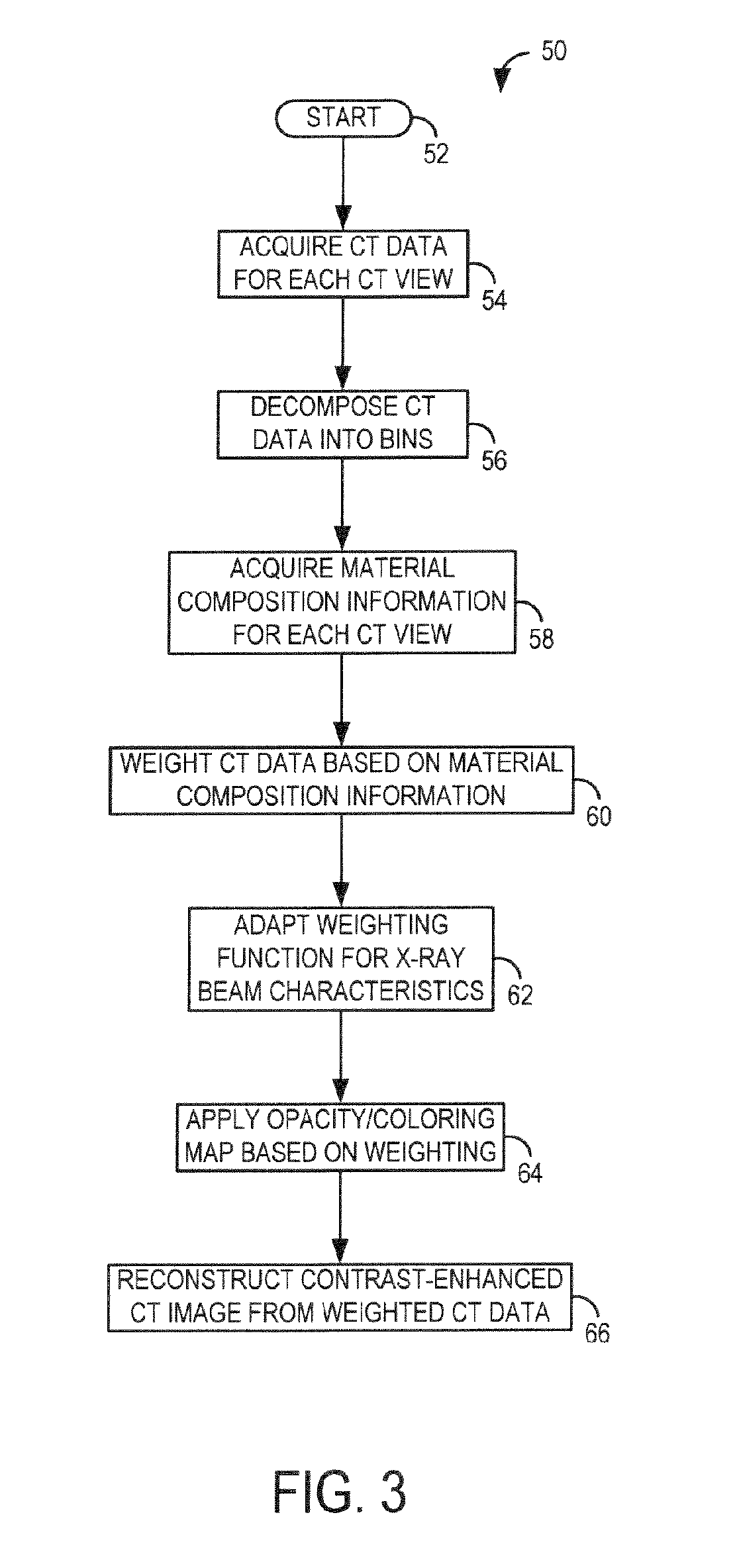
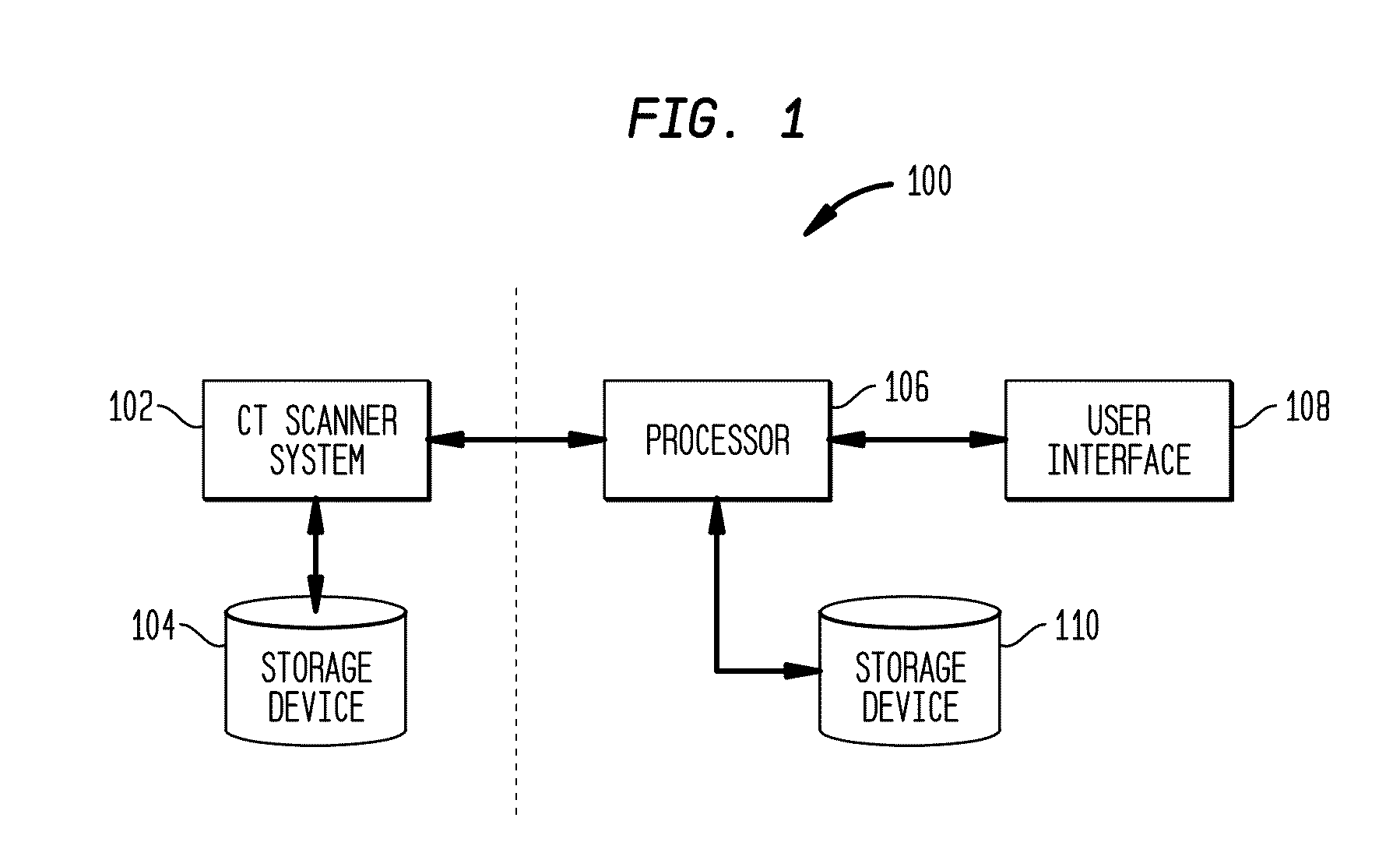
System and method for acquisition and reconstruction of contrast-enhanced, artifact-reduced CT images
ActiveUS20060109949A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationView basedPhoton
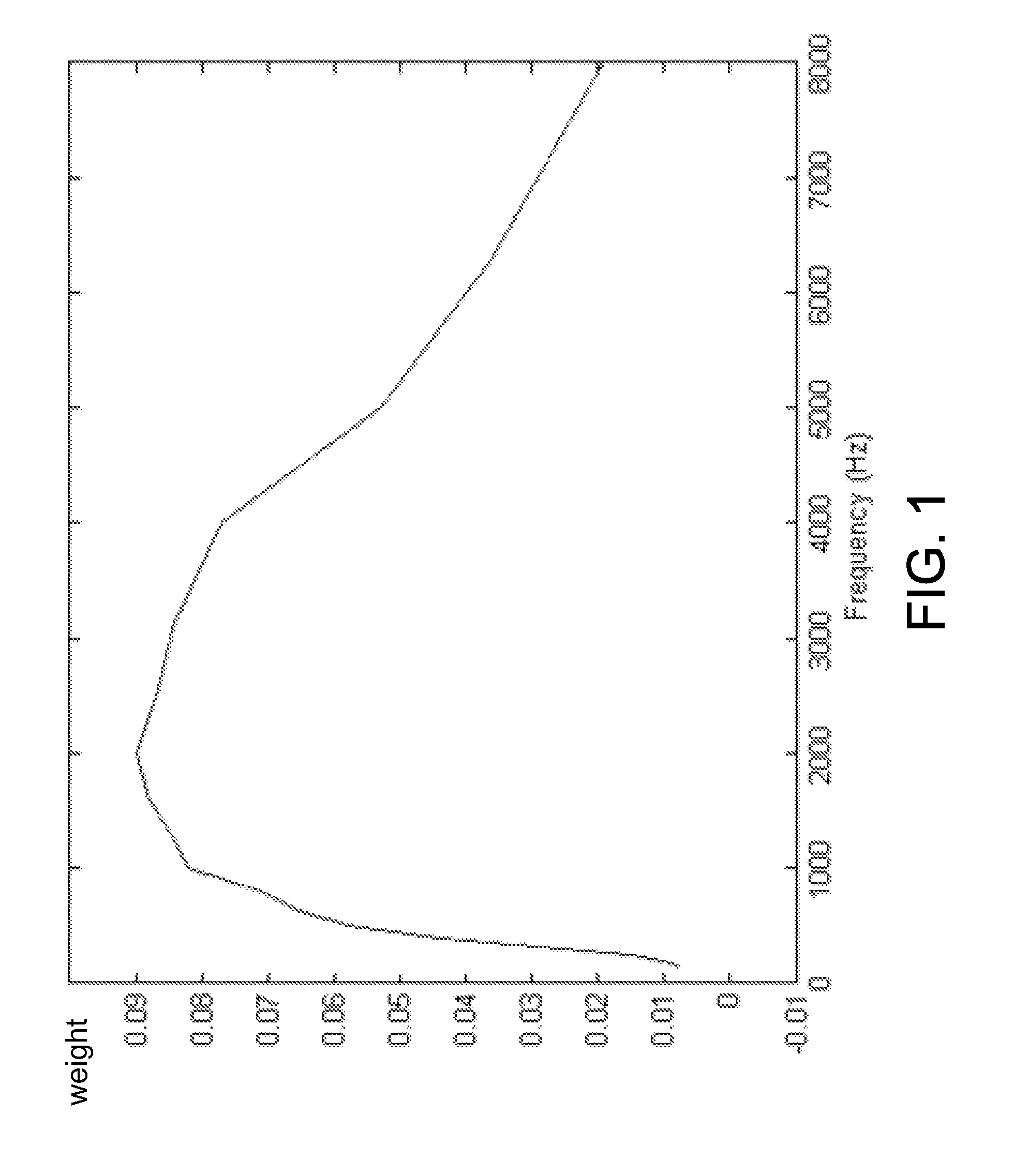
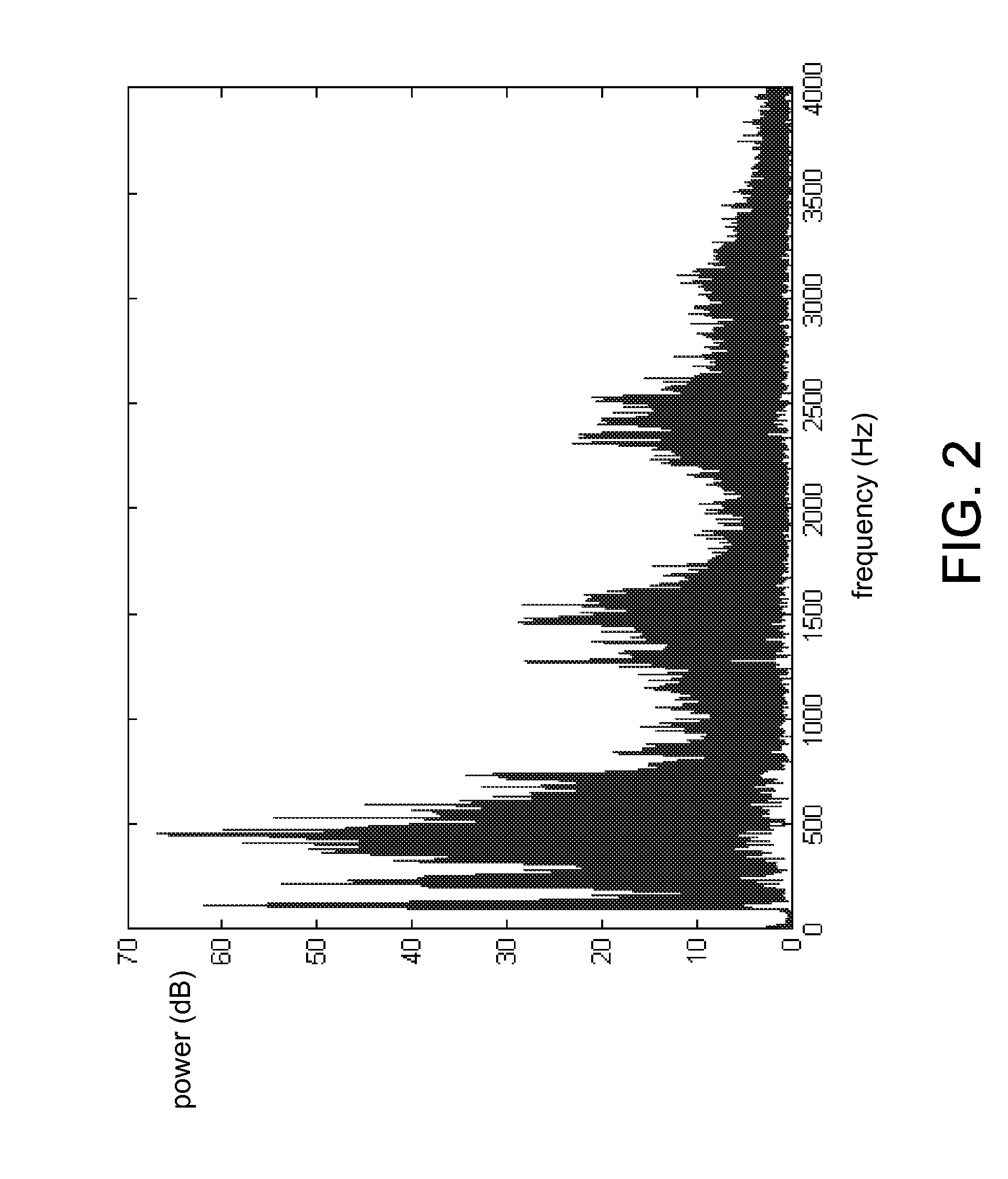
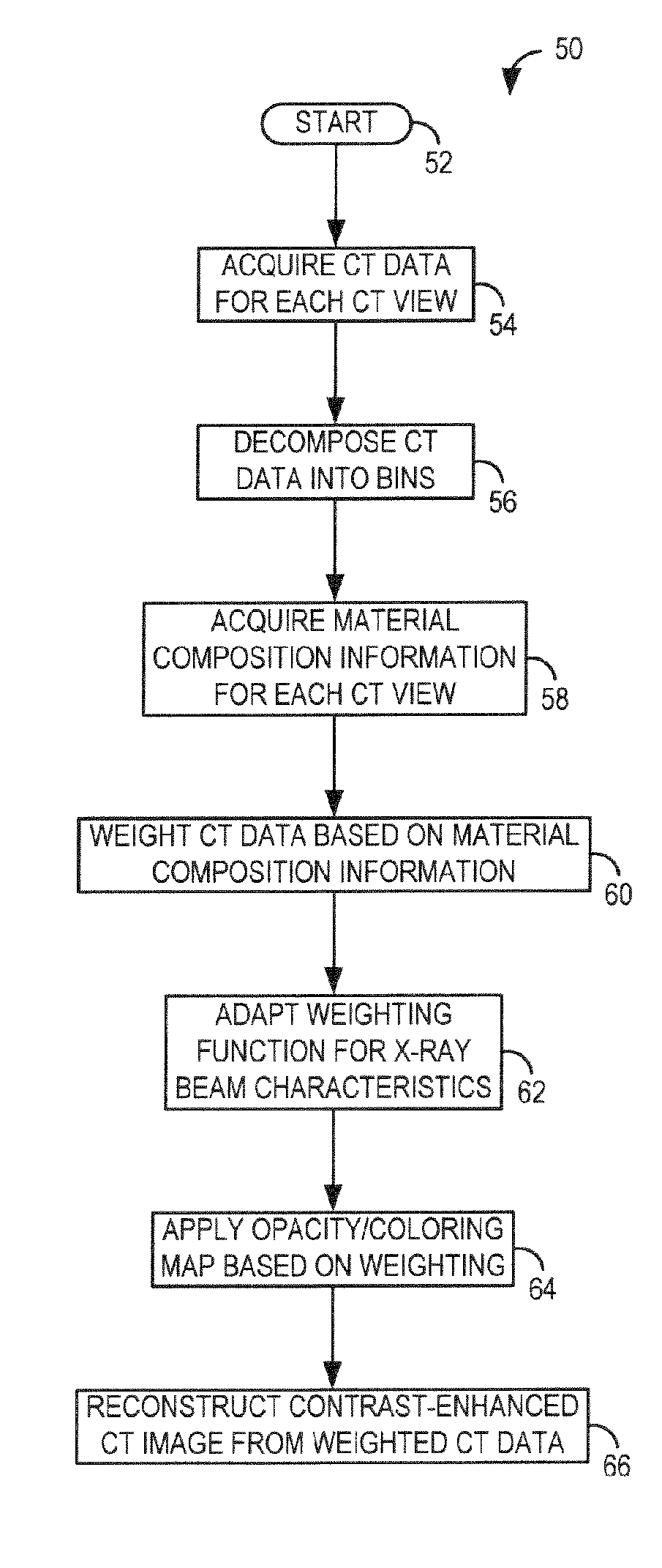
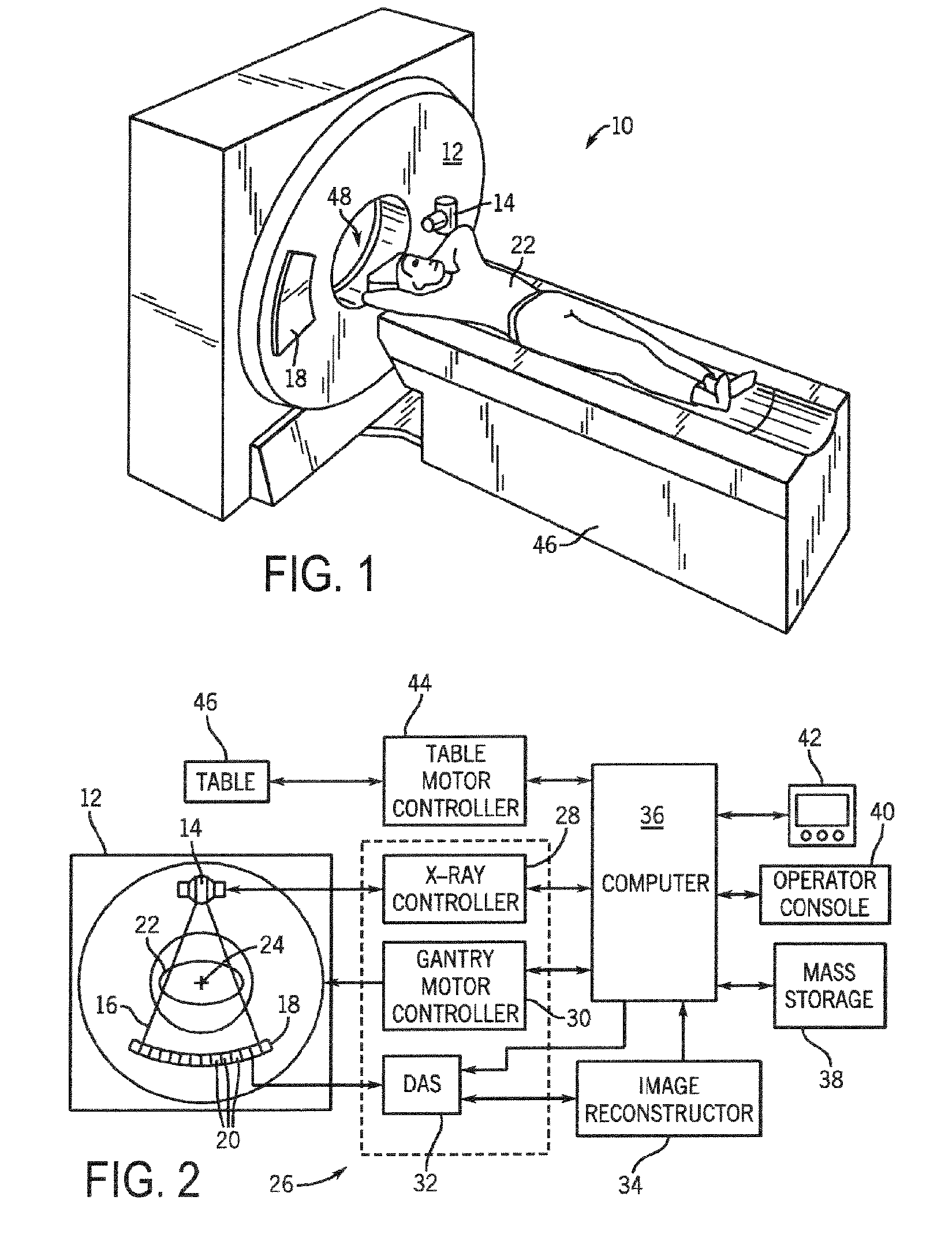
A system and method are disclosed for reconstructing contrast-enhanced CT images that are substantially free of beam-hardening artifacts. An imaging system includes a radiation source configured to project radiation toward an object to be scanned and an energy discriminating detector assembly having a plurality of detector elements and configured to detect radiation emitted by the radiation source and attenuated by the object to be scanned. The imaging system also includes computer programmed to count a number of photons detected by each detector element and associate an energy value to each counted photon and determine a material composition of a CT view from the number of photons counted and the energy value associated with each counted photon. The computer is also programmed to apply a weighting to the CT view based on the material composition of the CT view and reconstruct an image with differential weighting based on the weighting of the CT view.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Color translating UV microscope
A color translating UV microscope for research and clinical applications involving imaging of living or dynamic samples in real time and providing several novel techniques for image creation, optical sectioning, dynamic motion tracking and contrast enhancement comprises a light source emitting UV light, and visible and IR light if desired. This light is directed to the condenser via a means of selecting monochromatic, bandpass, shortpass, longpass or notch limited light. The condenser can be a brightfield, darkfield, phase contrast or DIC. The slide is mounted in a stage capable of high speed movements in the X, Y and Z dimensions. The microscope uses broadband, narrowband or monochromat optimized objectives to direct the image of the sample to an image intensifier or UV sensitive video system. When an image intensifier is used it is either followed by a video camera, or in the simple version, by a synchronized set of filters which translate the image to a color image and deliver it to an eyepiece for viewing by the microscopist. Between the objective and the image intensifier there can be a selection of static or dynamic switchable filters. The video camera, if used, produces an image which is digitized by an image capture board in a computer. The image is then reassembled by an overlay process called color translation and the computer uses a combination of feedback from the information in the image and operator control to perform various tasks such as optical sectioning and three dimensional reconstruction, coordination of the monochromater while collecting multiple images sets called image planes, tracking dynamic sample elements in three space, control of the environment of the slide including electric, magnetic, acoustic, temperature, pressure and light levels, color filters and optics, control for microscope mode switching between transmitted, reflected, fluorescent, Raman, scanning, confocal, area limited, autofluorescent, acousto-optical and other modes.
Owner:RICHARDSON TECH
Brightness and contrast enhancement of direct view emissive displays
InactiveUS20050007000A1Increase brightnessIncrease the amount of lightIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensTotal internal reflectionDisplay device
Emissive displays can include a plurality of independently operable light emitters that emit light through one or more transmissive layers. The emissive displays further include elements disposed between the light emitters and the transmissive layers to frustrate total internal reflections that can occur at one or more of the interfaces created by the transmissive layers, such as at an interface between the light emitter and a transmissive layer or at an interface between a transmissive layer and air. By frustrating total internal reflections, the brightness of the emissive display can be enhanced. Elements for frustrating total internal reflections include volume diffusers, surface diffusers, microstructures, and combinations of these or other suitable elements.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
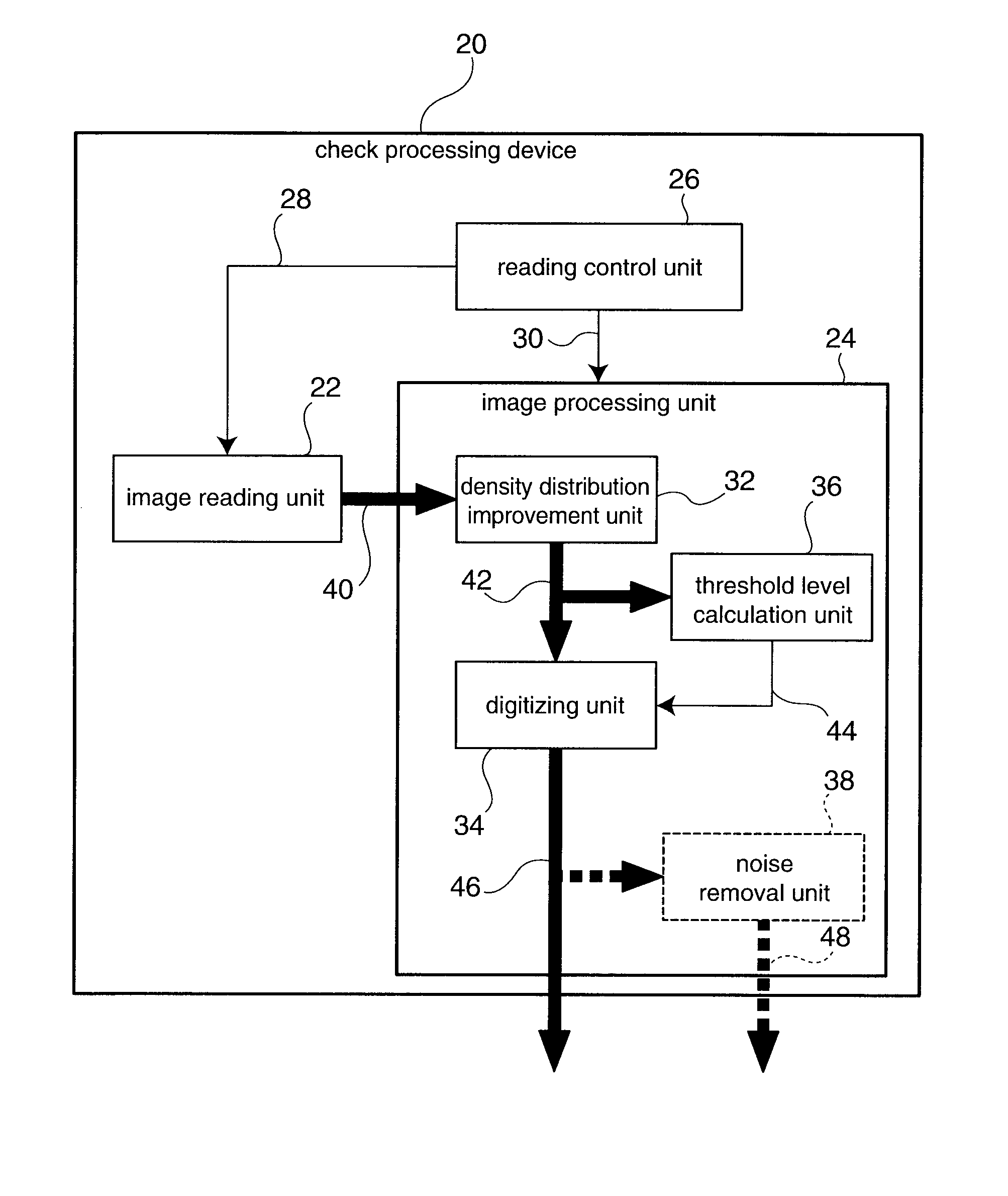
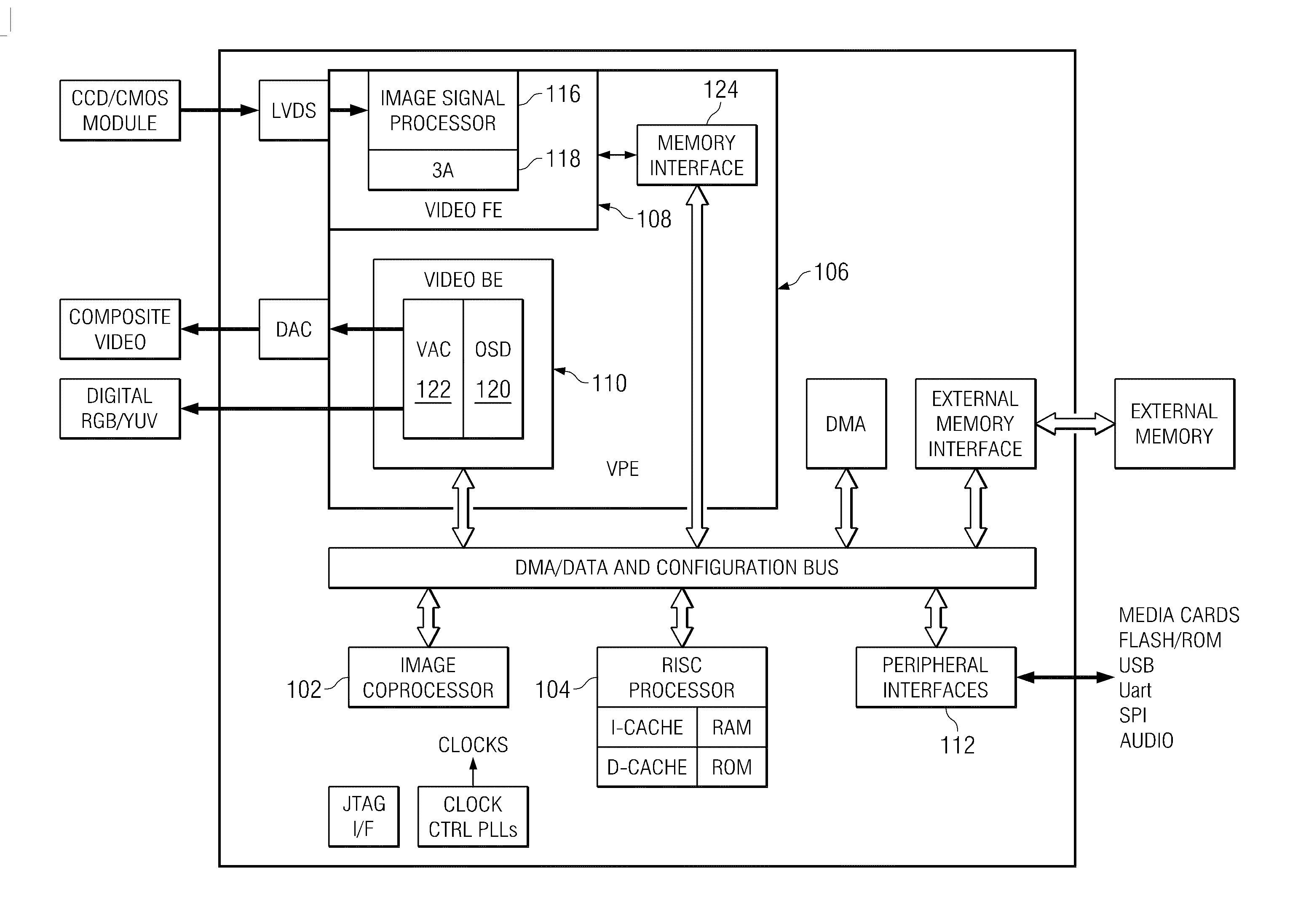
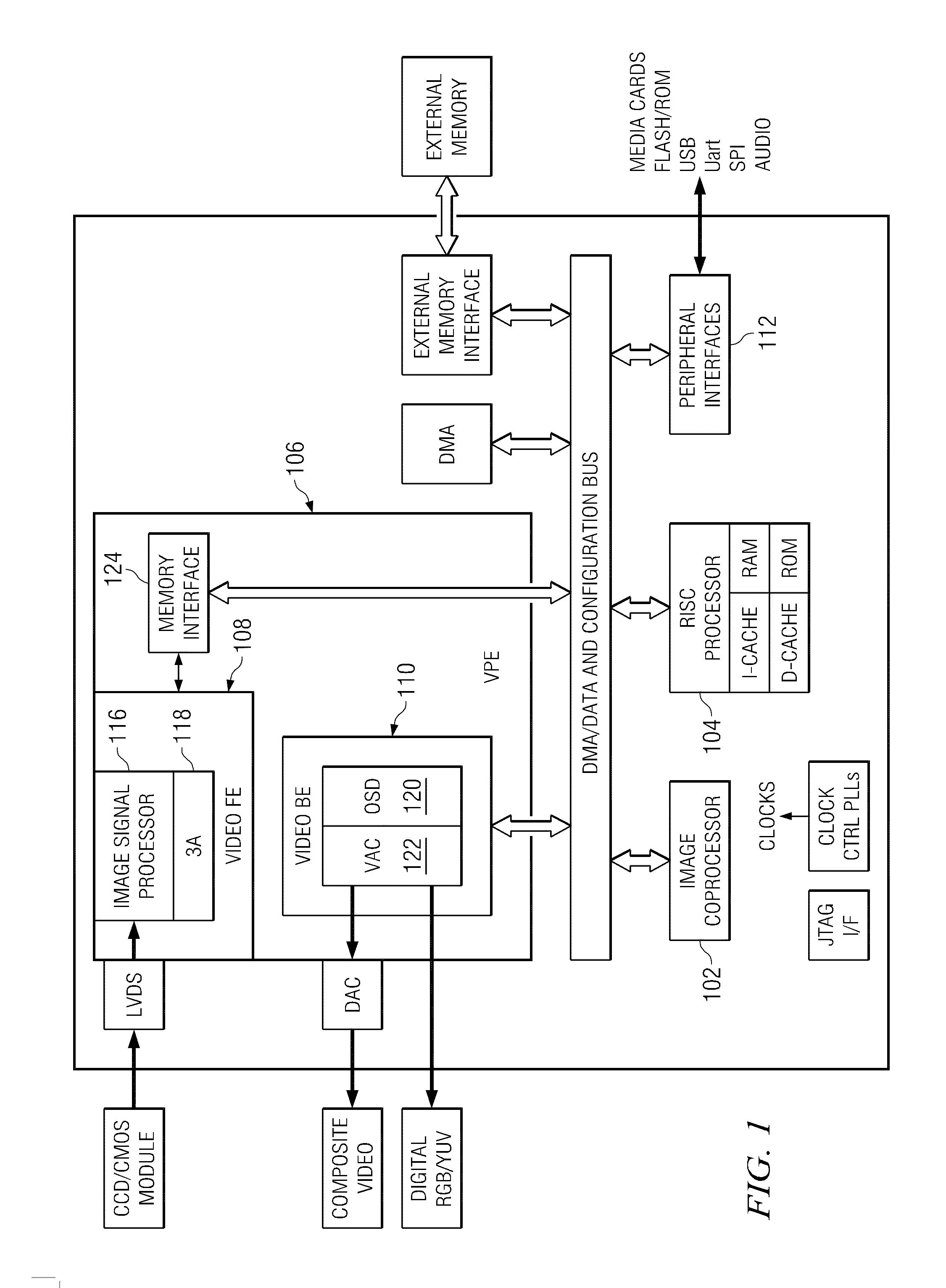
Image Processing Apparatus And Image Processing Method
InactiveUS20070019243A1Improve accuracyImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingDensity distribution
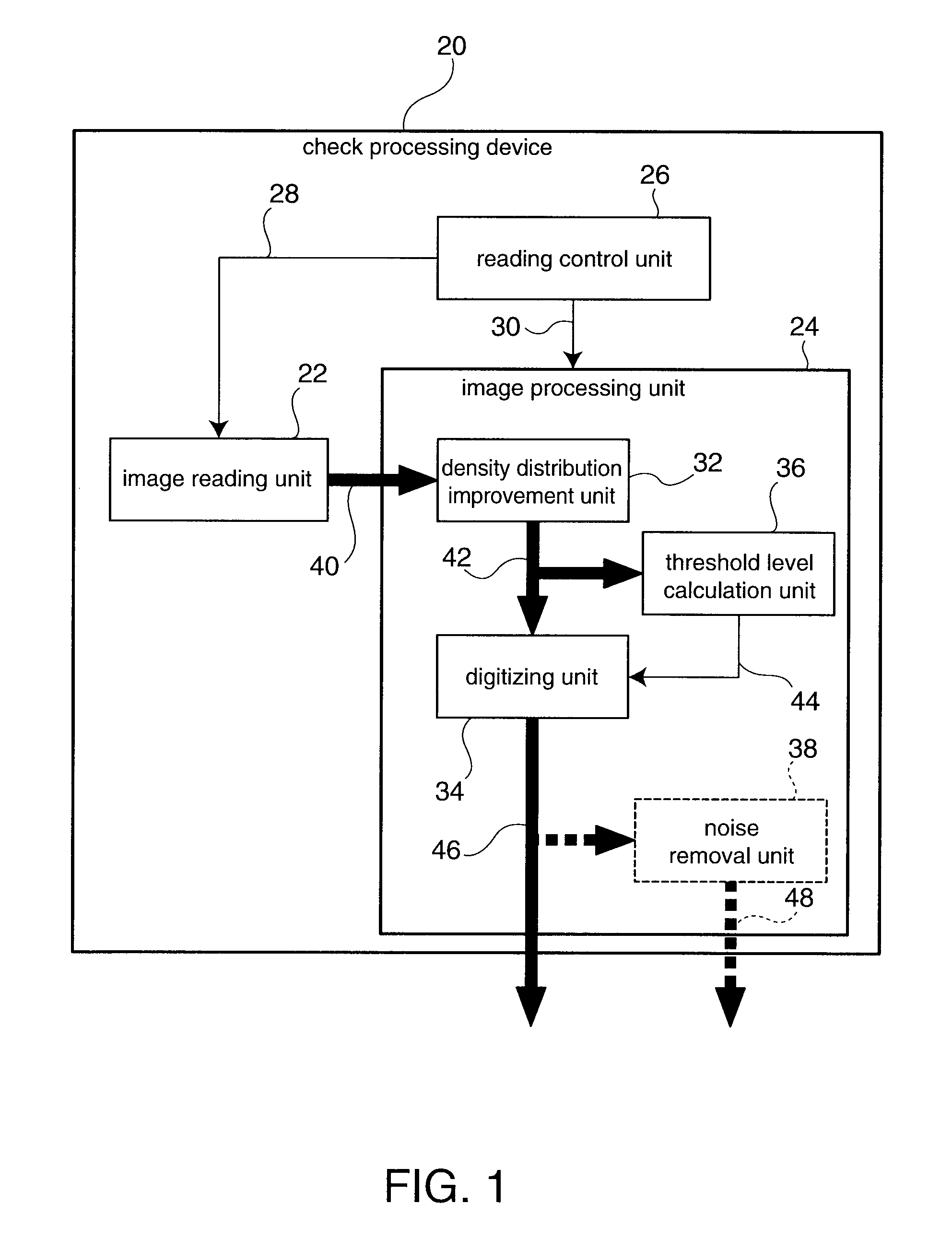
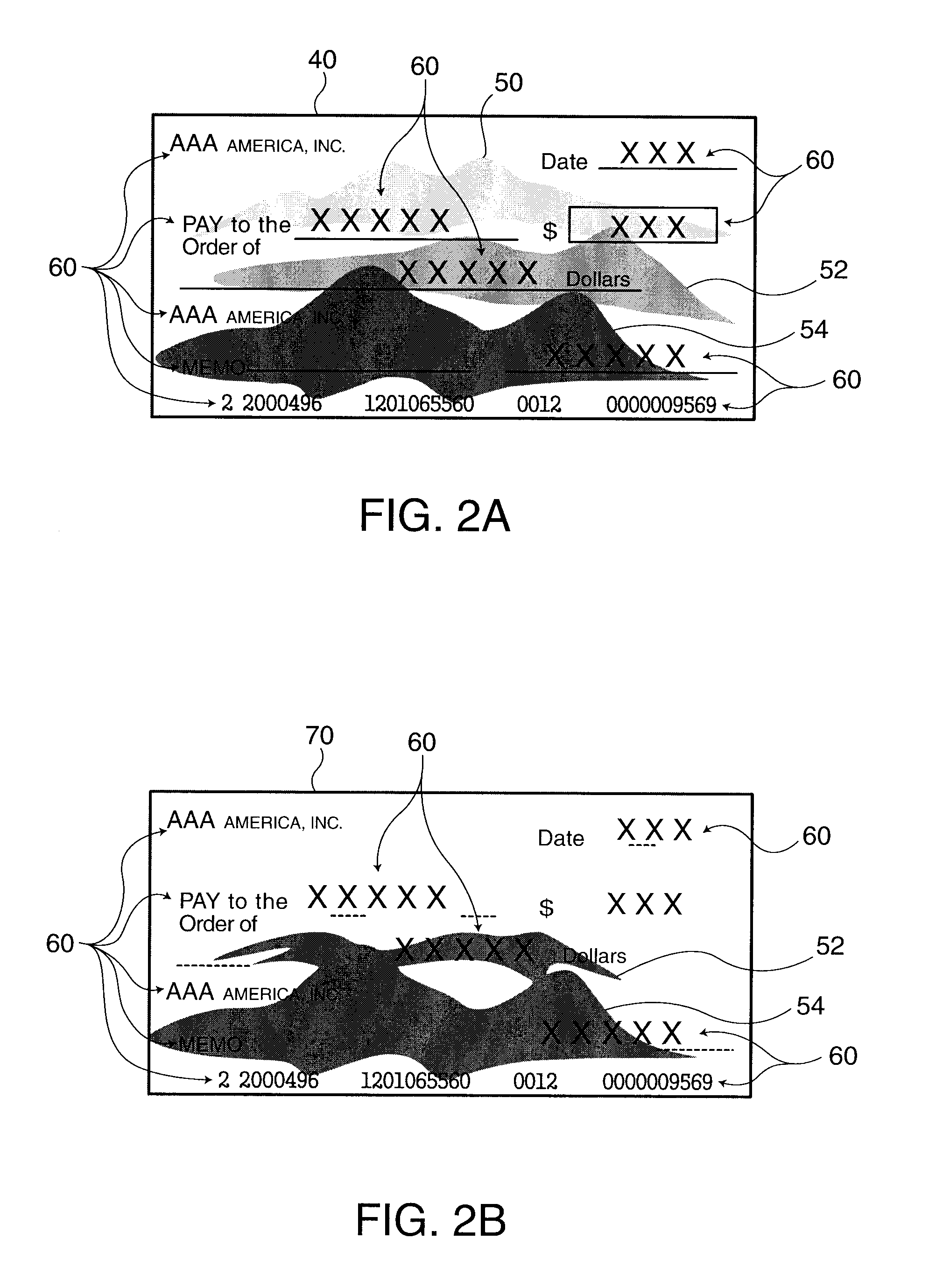
Background images are removed and only the desired payment information is extracted from a grayscale image of a check or similar financial instrument. A density distribution improvement process applied to grayscale raw image data 40 acquired by scanning a check corrects the density distribution of the raw image data 40 to separate the density range of the desired payment information from the density range of the background image. Image sharpening or contrast enhancement can be used as the density distribution improvement method. A threshold level 44 for clearly separating the payment information from the background image is then calculated from the characteristics of the density distribution of the grayscale improved image data 42 acquired by the density distribution improvement process. Histograms of the density distributions are used to determine the characteristics of the density distribution. The improved image data 42 is then converted to binary image data 46 using the threshold level 44. Most of the background image is white and most of the desired payment information is black in the binary image data 46.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
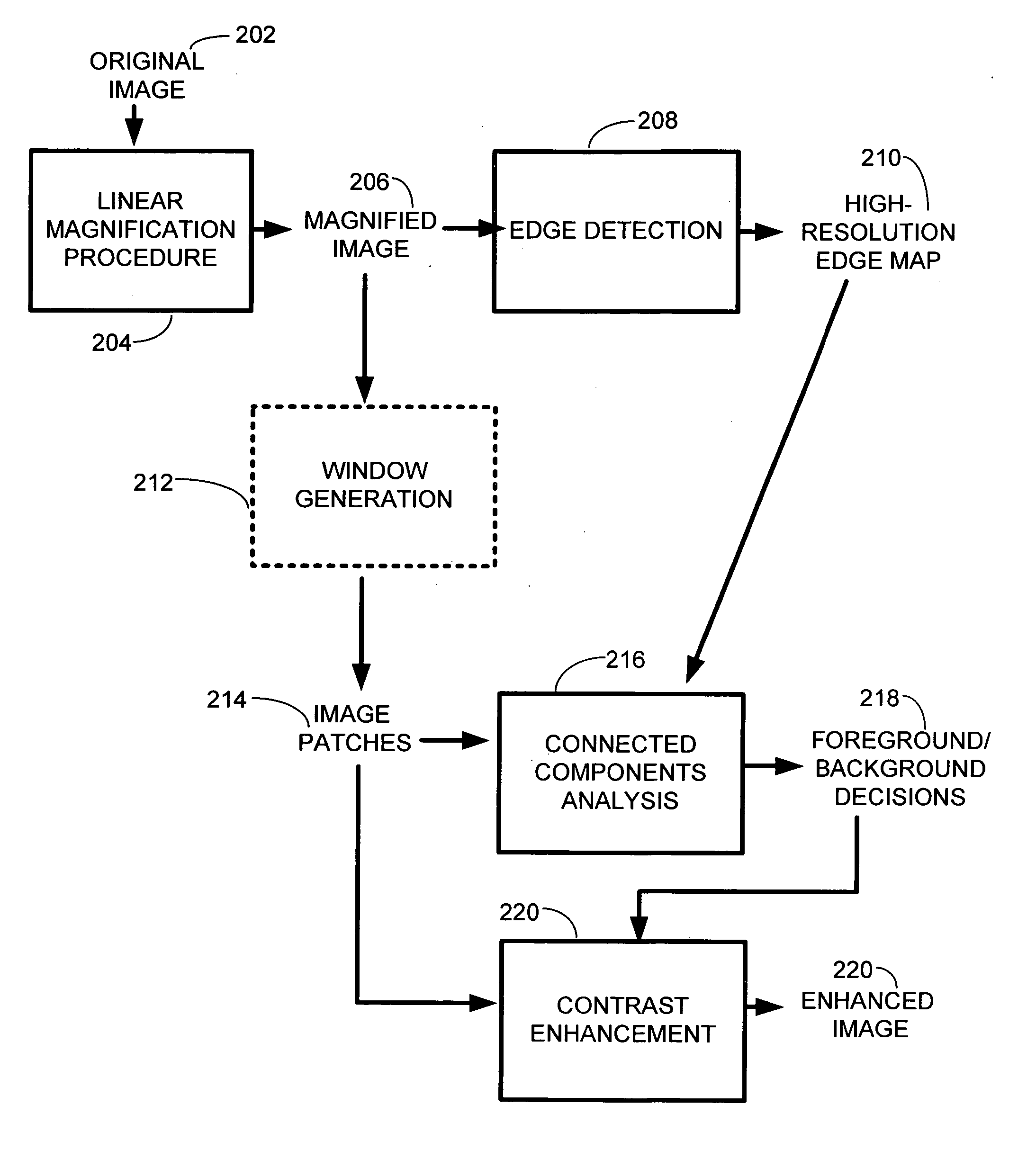
Image superresolution through edge extraction and contrast enhancement
InactiveUS20060290950A1Remove jaggednessAccurate descriptionImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage resolutionEdge extraction
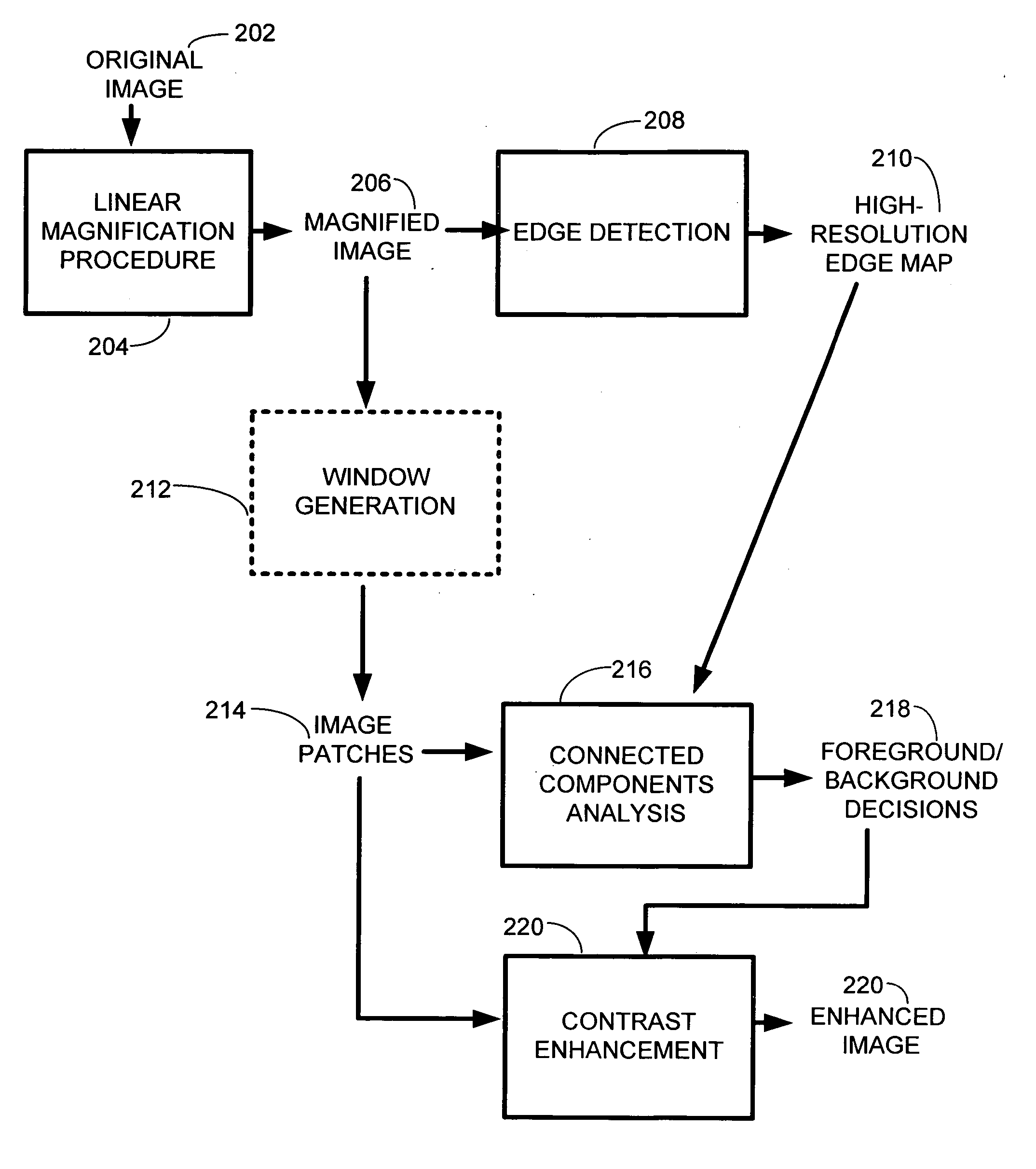
A technique for generating high-resolution bitmaps from low-resolution bitmaps. A low-resolution bitmap is magnified to form a magnified image. Edge detection is performed on the magnified image to find high contrast edges. A plurality of image patches of the magnified image are generated. These images patches are analyzed by performing connected components analysis on each of them using the high contrast edges to produce a plurality of foreground and background decisions determining whether a portion of an image patch is a background or a foreground region. Then the contrast of one or more pixels in each of the plurality of image patches is enhanced based on the foreground and background decisions. Finally, the system and method of the invention combines the luminance of the enhanced output pixels with the color values generated by the magnification algorithm. This produces a high-resolution bitmap from the contrast-enhanced pixels.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
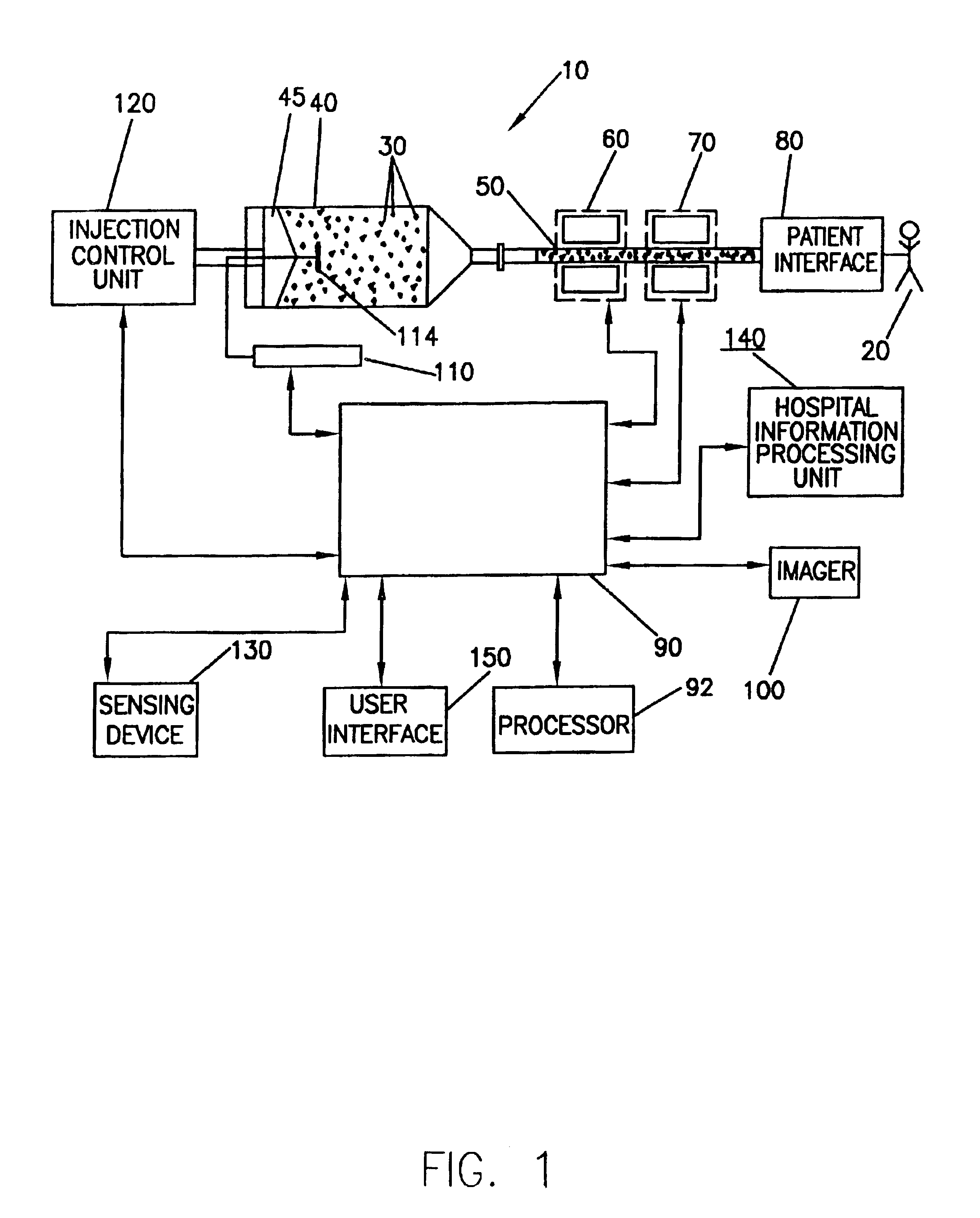
Data communication and control for medical imaging systems
InactiveUS6970735B2Raise the intensity levelDrug and medicationsMedical devicesCommunication interfaceContrast enhancement
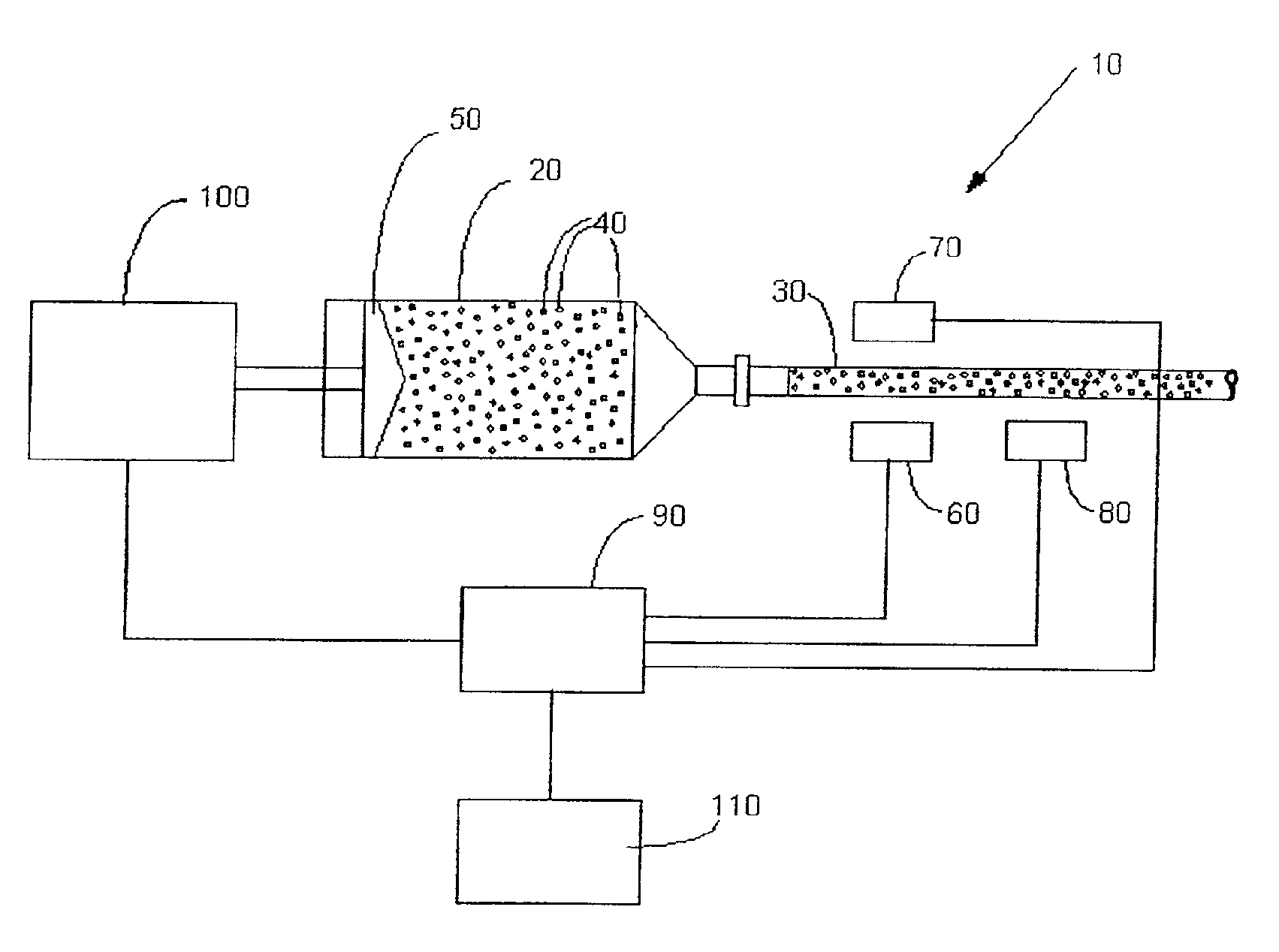
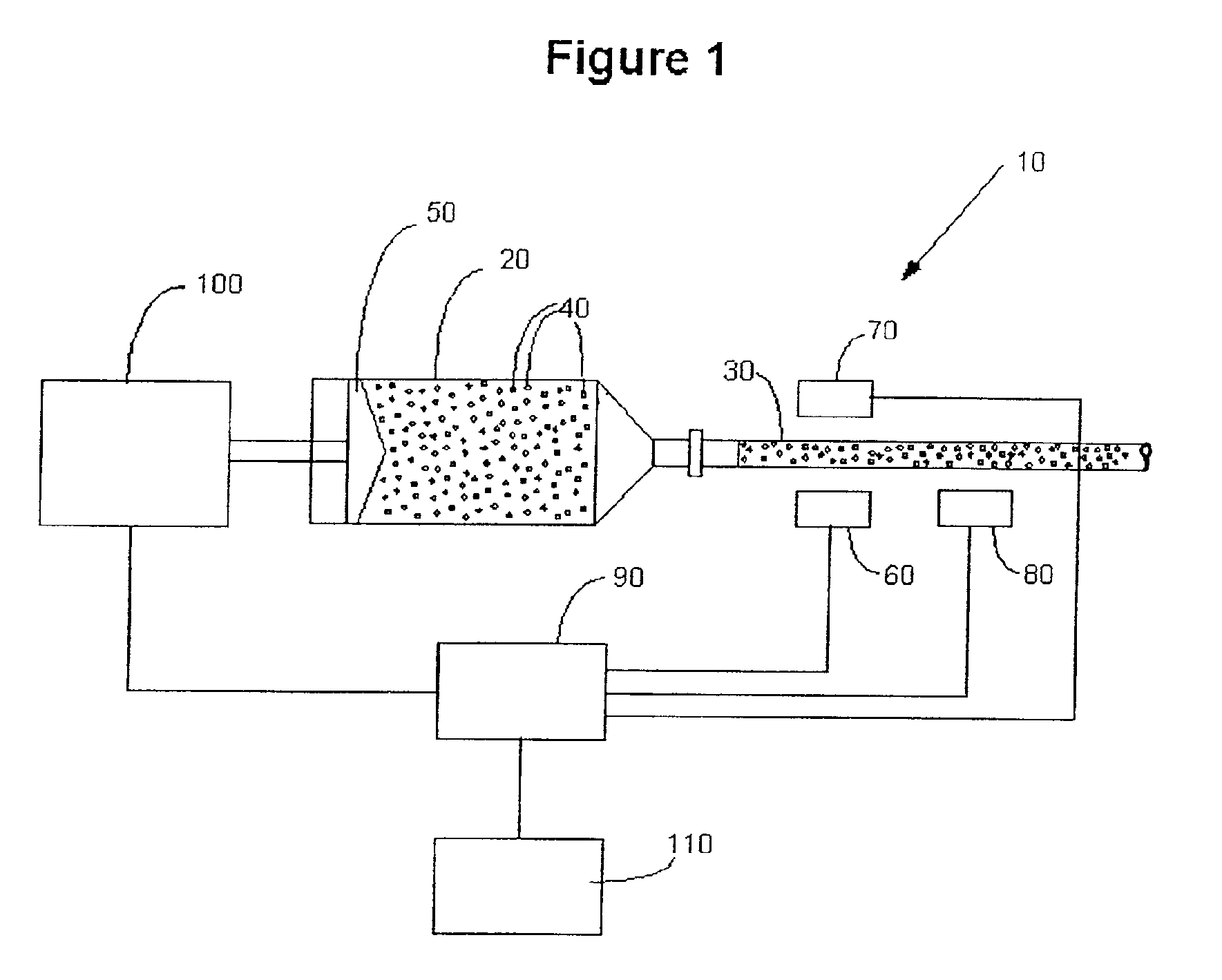
A system for producing a contrast-enhanced medical image of a patient includes a source of a contrast or enhancement medium, a pressurizing unit in fluid connection with the source of contrast or enhancement medium, an energy source operable to apply energy to a region of the patient, an imaging unit providing a visual display of an internal view of the patient based upon a signal resulting from the energy applied to the region of the patient, and a control unit. In an embodiment, the signal is affected by a condition of the contrast or enhancement medium in the patient. To control the procedures, the control unit adjusts the condition of the contrast or enhancement medium in the patient based upon the signal. A communication interface preferably enables information between an injector subsystem and an imaging subsystem.
Owner:BAJER MEDIKAL KEHA INK
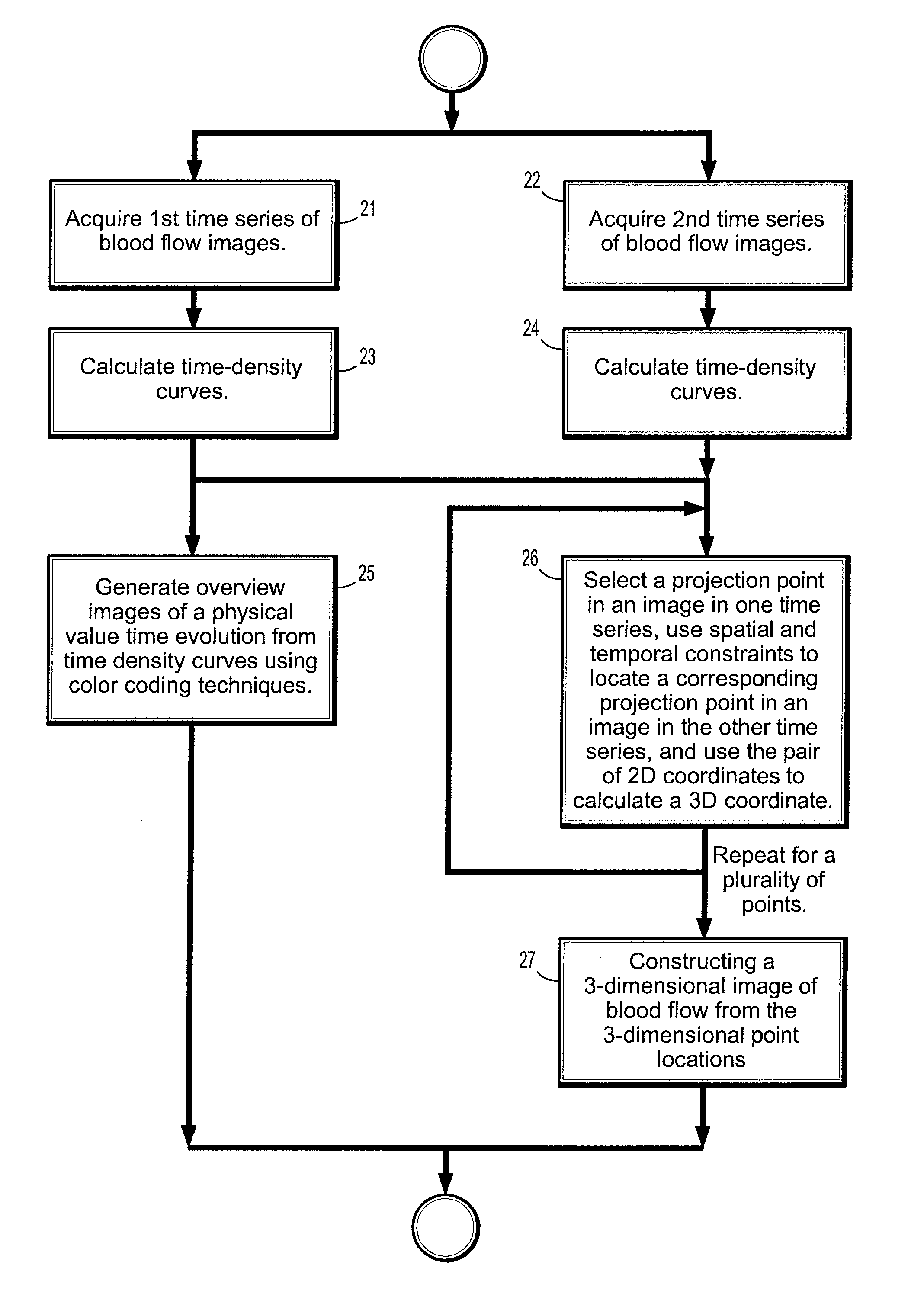
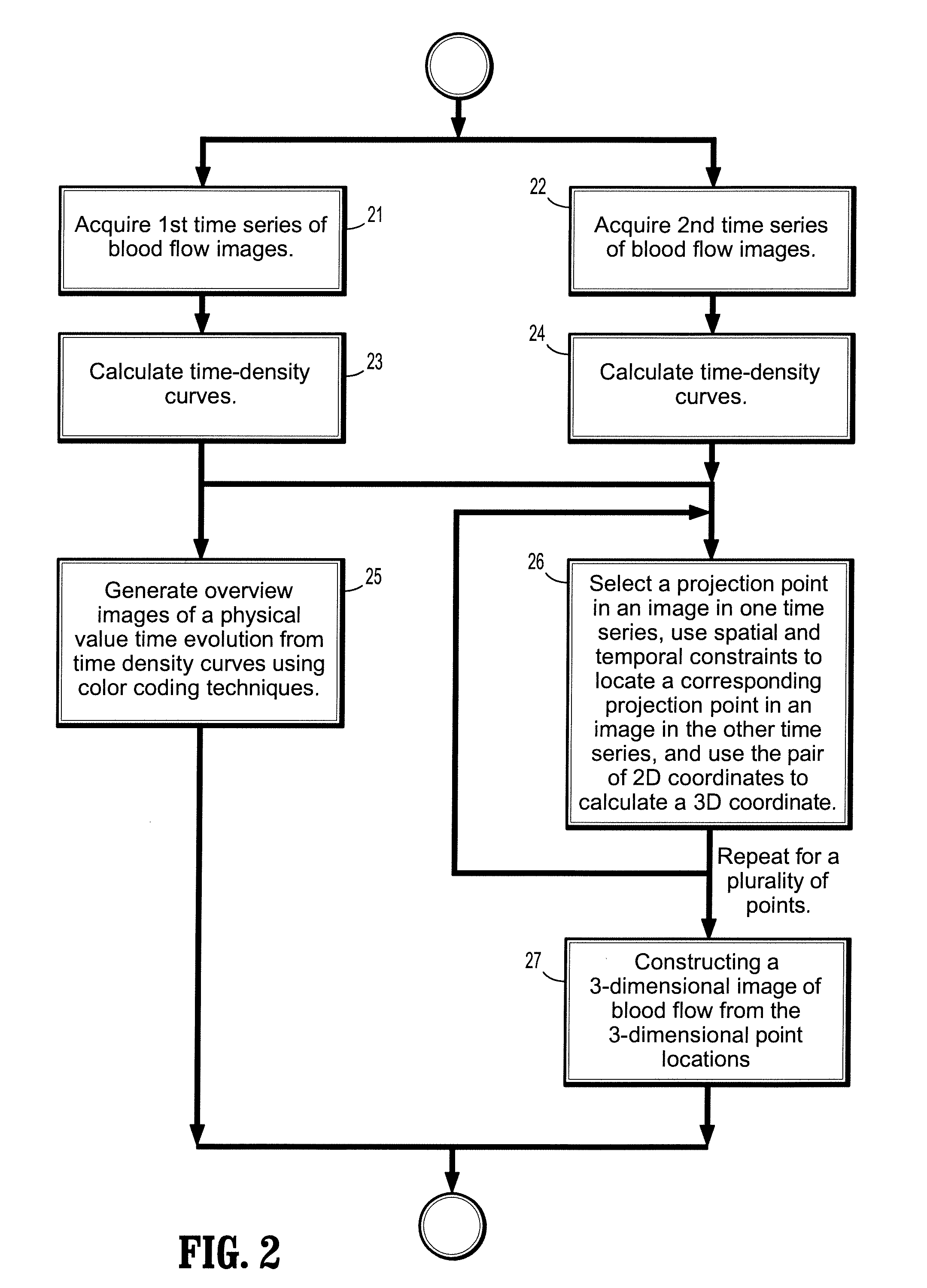
System and method for two-dimensional visualization of temporal phenomena and three dimensional vessel reconstruction
A method for visualizing temporal phenomena and constructing 3D views from a series of medical images includes providing a first time series of digital images of contrast-enhanced blood flow in a patient, each acquired from a same viewing point with a known epipolar geometry, each said image comprising a plurality of intensities associated with an N-dimensional grid of points, calculating one or more time-density curves from said first time series of digital images, each curve indicative of how the intensity at corresponding points in successive images changes over time, and generating one or more overview images from said time density curves using a color coding technique, wherein said each overview image depict how a physical property value changes from said blood flow at selected corresponding points in said first time series of images.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
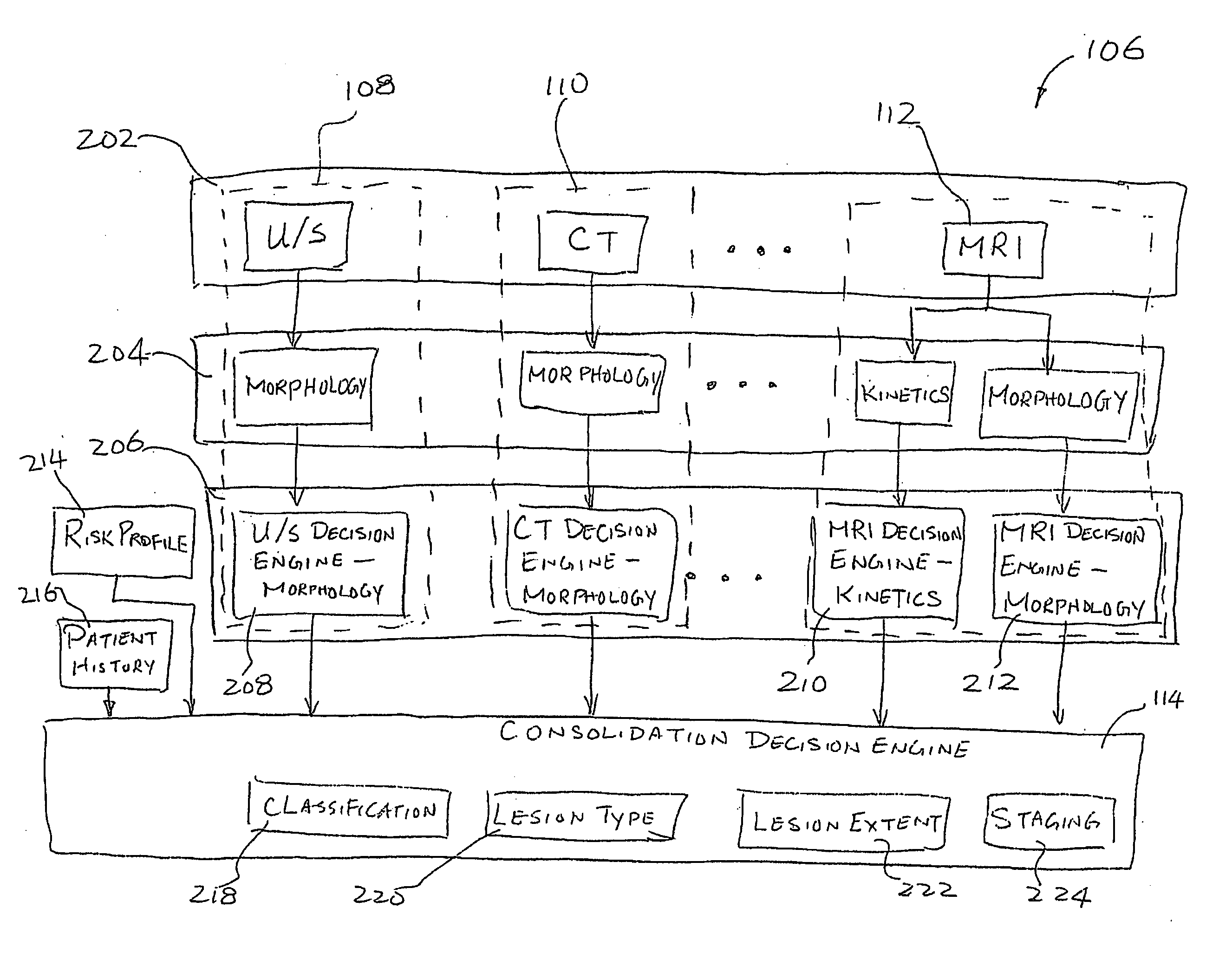
Method and system of computer-aided quantitative and qualitative analysis of medical images
ActiveUS20070133852A1Improve discriminationImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputer-aided
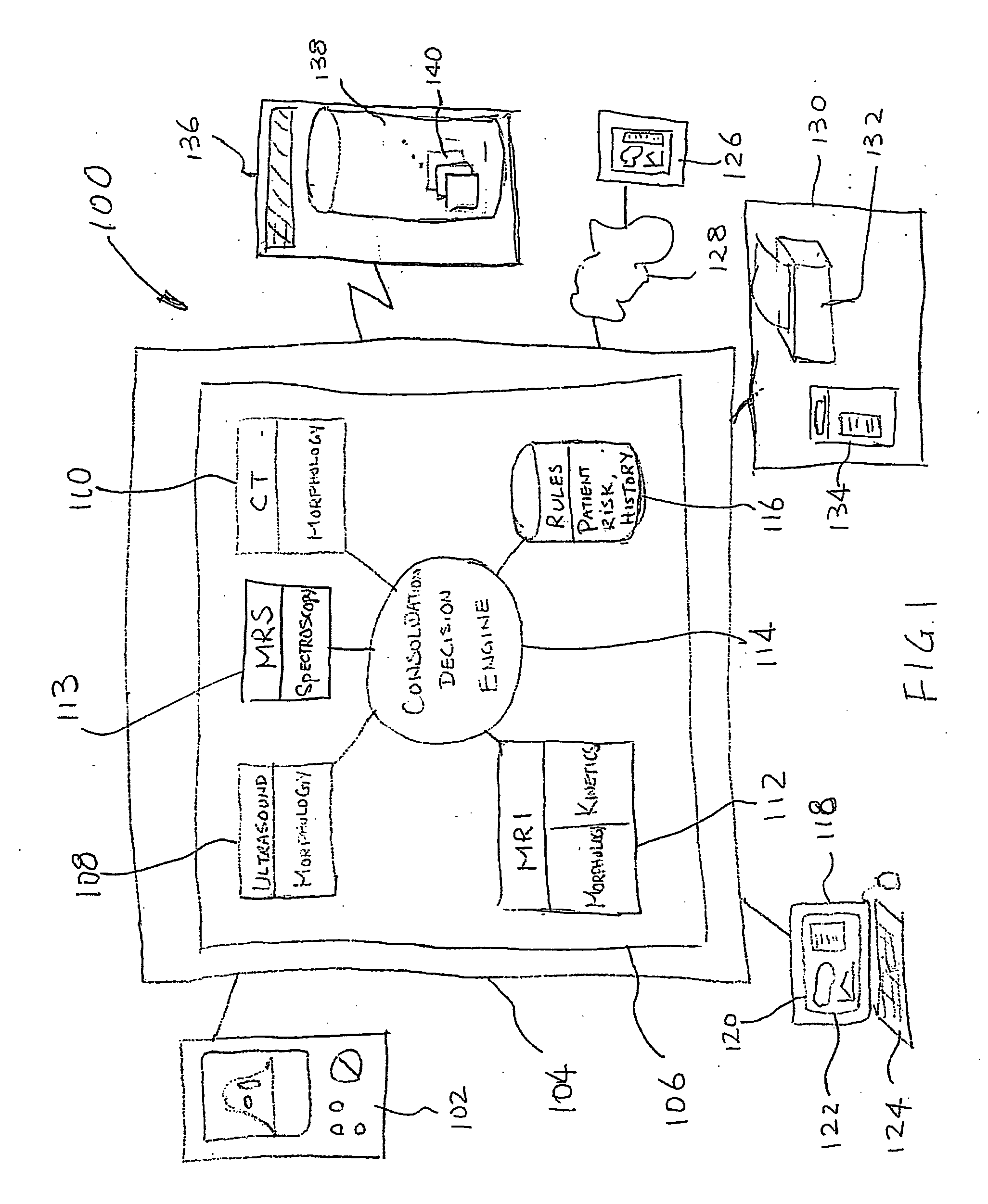
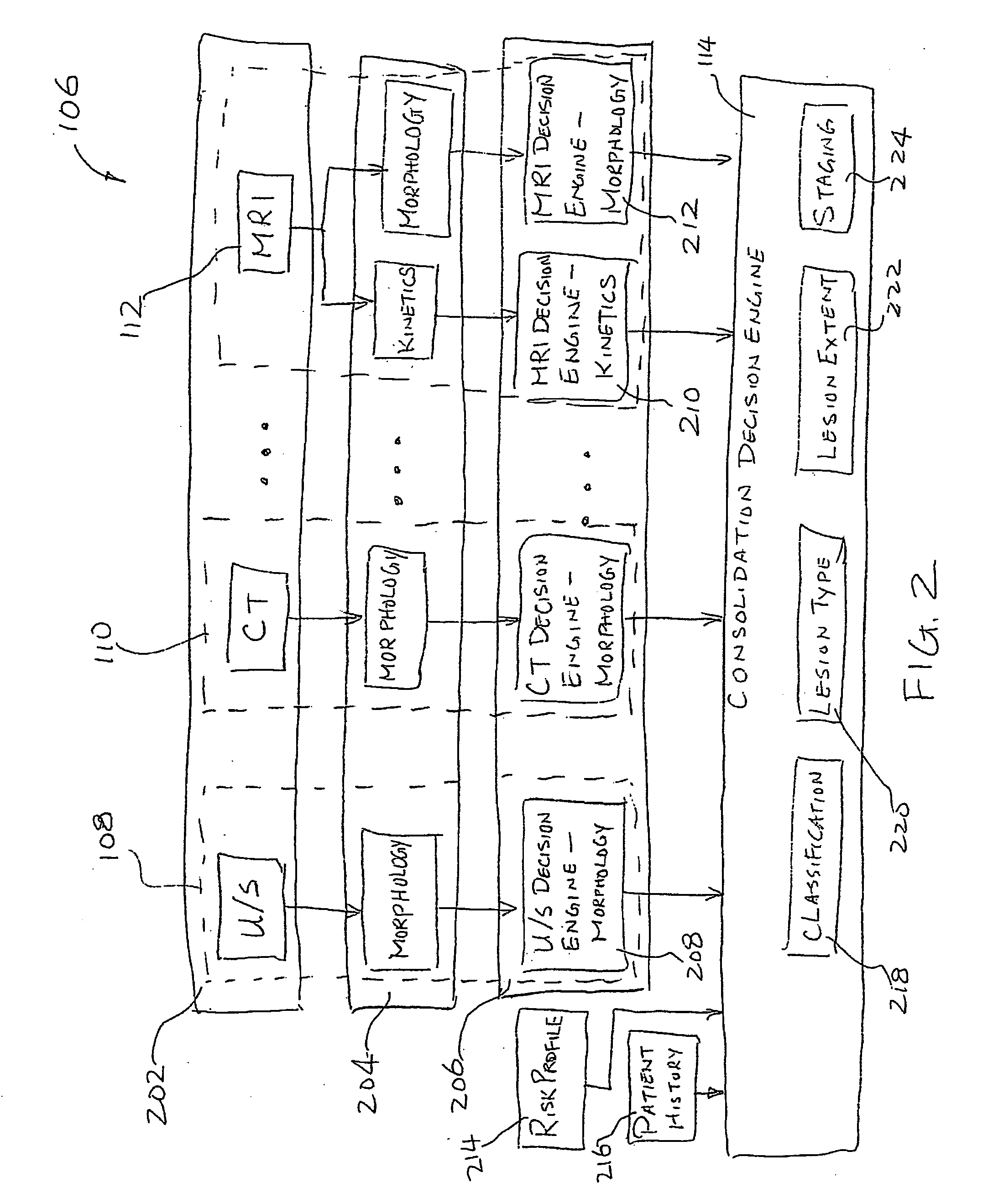
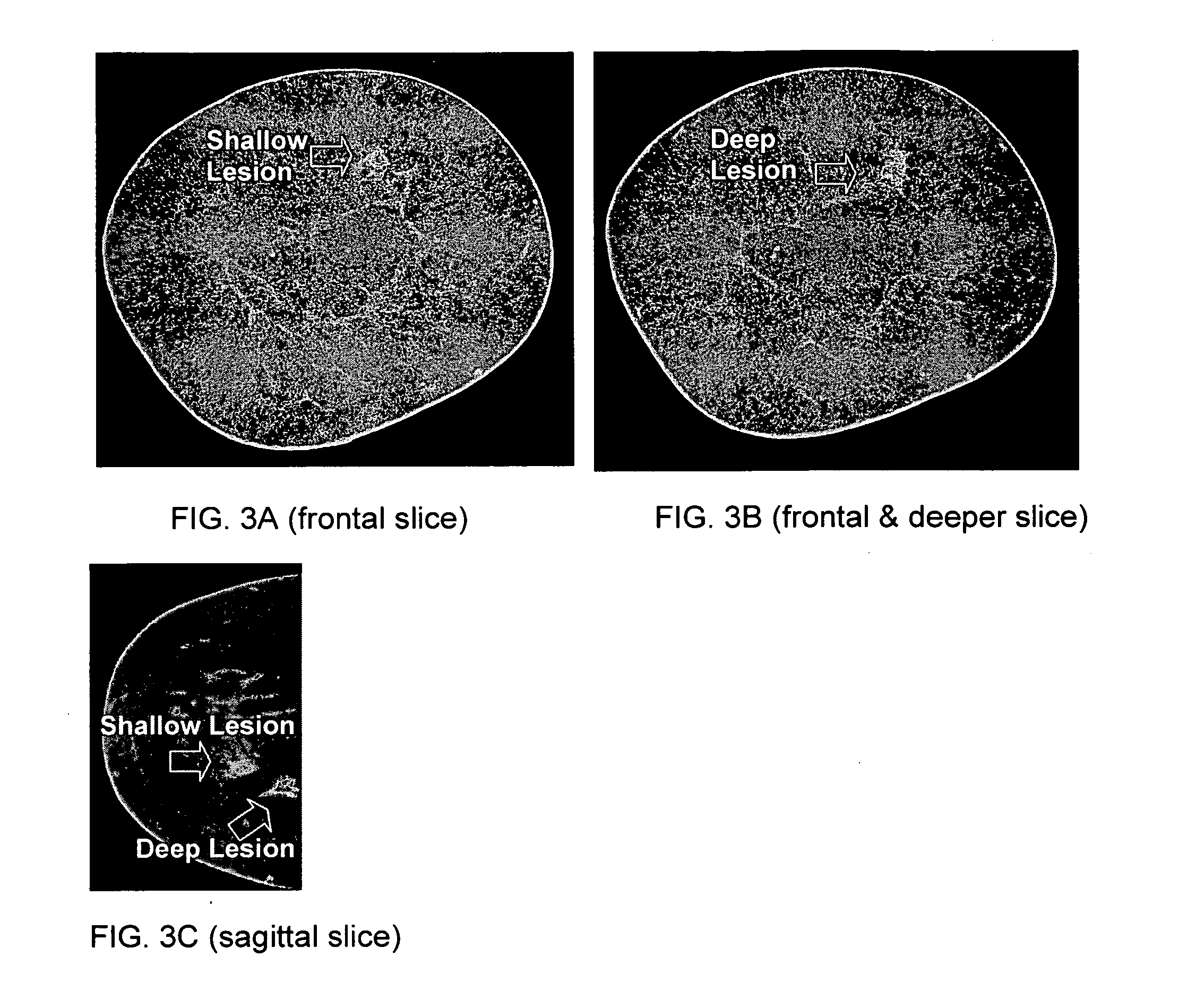
A system and method of computer aided analysis of medical images and detection of malignant lesions is described. Medical images obtained from multiple modalities are analyzed. Morphological features as well as temporal, i.e., kinetics features, are combined to compute a consolidated assessment of a possible lesion detected in the medical images. The system includes at least one kinetics module, which is capable of extracting kinetics features from a time sequence of MRI images or MRS data taken after administering a contrast enhancement agent to a patient. The consolidated assessment is presented to a user for confirmation or modification.
Owner:SALIENT IMAGING +1
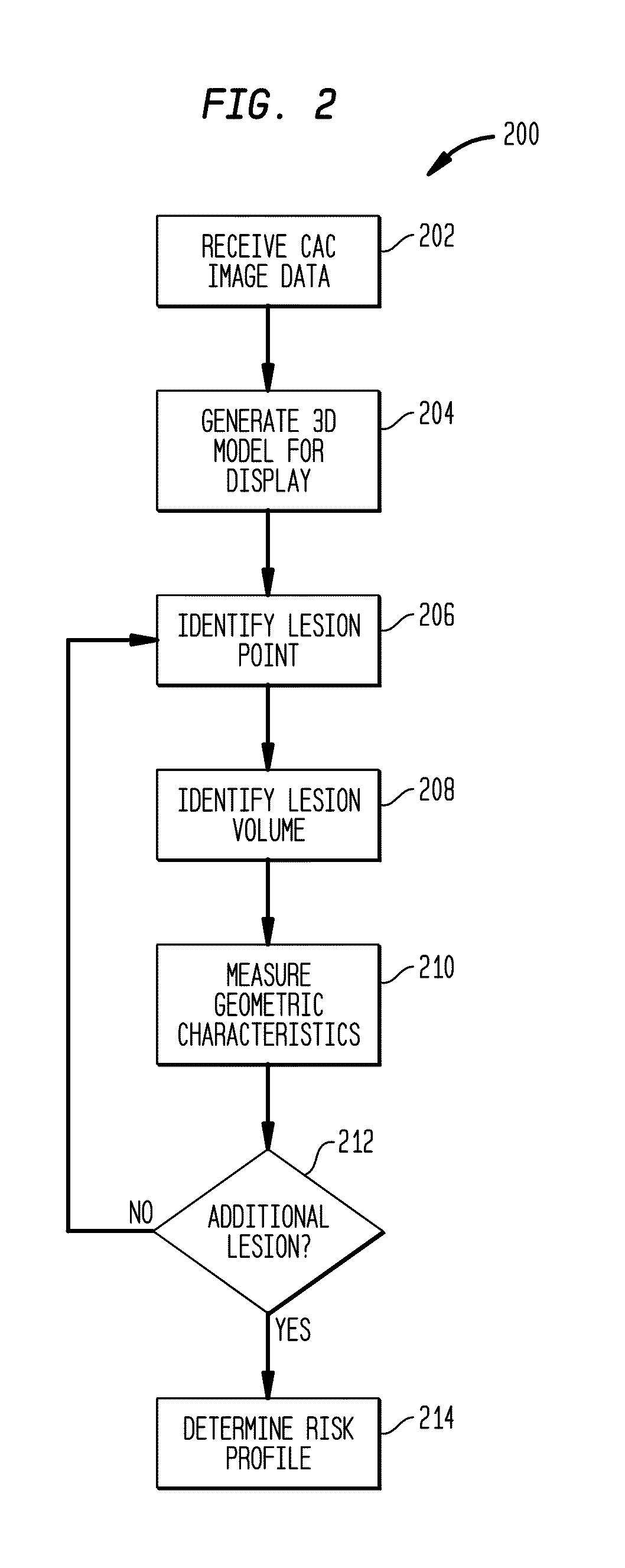
System and method for lesion-specific coronary artery calcium quantification
ActiveUS20100156898A1Predict in advanceImprove assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyContrast enhancement
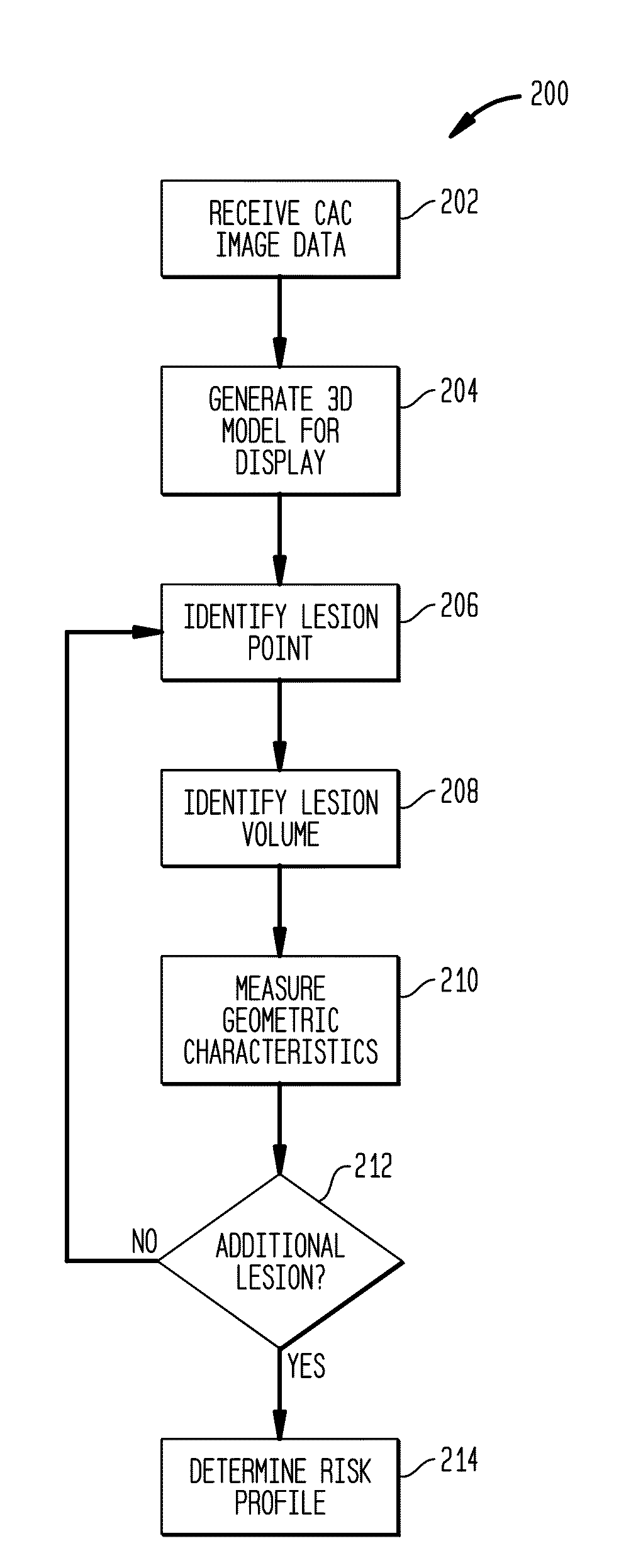
Methods and systems utilizing the data provided by a non-contrast-enhanced CAC scan that is left unused by the “whole-heart” Agatston or volume scores. Agatston and volume scores summarize overall coronary calcium burden, but do not show the number of vessels involved, the geographic distribution of the lesions, the size and shape of the individual lesions and the distance of the lesions from the coronary ostium. The methods and systems described herein extract and use the enhanced information provided by 3-D CAC scan data and significantly increases its clinical predictive value by providing vessel and lesion specific CAC scores which are superior to the whole-heart Agatston and volume scores in predicting obstructive Coronary artery disease (CAD).
Owner:VOROS SZILARD +1
Video contrast enhancement through partial histogram equalization
Methods and apparatus for video contrast enhancement are disclosed. A pixel level threshold is set for an input video frame in a video sequence. For pixel levels in the input video frame that are below the threshold, an adaptive contrast-enhancing function is applied. For other pixel levels, a scene-stable mapping function is applied.This contrast enhancement method can improve the contrast in darker areas of a scene depicted in the video sequence, without destroying the intended light levels for a scene or causing temporal brightness fluctuations in the enhanced video sequence.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
Methods and systems for contrast enhancement
InactiveUS20100278423A1Increase contrastEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisGray levelContrast enhancement
Methods for contrast enhancement of digital images are provided. A method of adaptive histogram equalization is provided that determines weighting factors for discriminating between sub-regions of a digital image to be more enhanced or less enhanced. Another method for content adaptive local histogram equalization is provided that uses a mapping function in which the dynamic range is not changed by the transformation. A third method for contrast enhancement is provided that includes dividing a digital image into a plurality of regions of pixels, and for each region in the plurality of regions, determining a threshold gray level for the region, generating a mapping curve for the region based on the threshold gray level, and applying the generated mapping curve to each pixel in the region to enhance contrast.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System And Method For Projection of Subsurface Structure Onto An Object's Surface
InactiveUS20100177184A1Increase contrastOvercome disadvantagesTelevision system detailsImage enhancementVisibilityContrast enhancement
An imaging system and method illuminates body tissue with infrared light to enhance visibility of a vascular structure, and generates an image of the body tissue and the subcutaneous blood vessels based on reflected infrared light. The system includes an infrared illumination source for generating the infrared light and a structure for diffusing the infrared light. The system further includes an imaging device for receiving the infrared light reflected from the body tissue and for generating an enhanced image of the body tissue based on the reflected infrared light. The enhanced image is produced by contrast enhancement techniques involving applications of an unsharp mask. The system further includes a project a projector for receiving an output signal from the imaging device and for projecting the enhanced image onto the body tissue.
Owner:CHRISTIE MEDICAL HLDG
Contrast-enhanced cone beam X-ray imaging, evaluation, monitoring and treatment delivery
ActiveUS20070269000A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelData set
A method of imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using X-ray cone beam computed tomography or cone beam digital tomography comprises the step of introducing an effective amount of a contrast agent to the uncompressed region of interest. A system for imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or cone beam digital tomography (CBDT) comprises an X-ray source transmitting an X-ray to the uncompressed region of interest, an image acquisition system acquiring a plurality of two-dimensional projection images data for a CBCT or CBDT data set with at least one of the projection images acquired in 35 milliseconds or less, and a processor generating a three-dimensional computed tomography image data set resolving voxels with dimensions of 0.4 mm or less in at least two orthogonal directions.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +2
Robust static and moving object detection system via attentional mechanisms
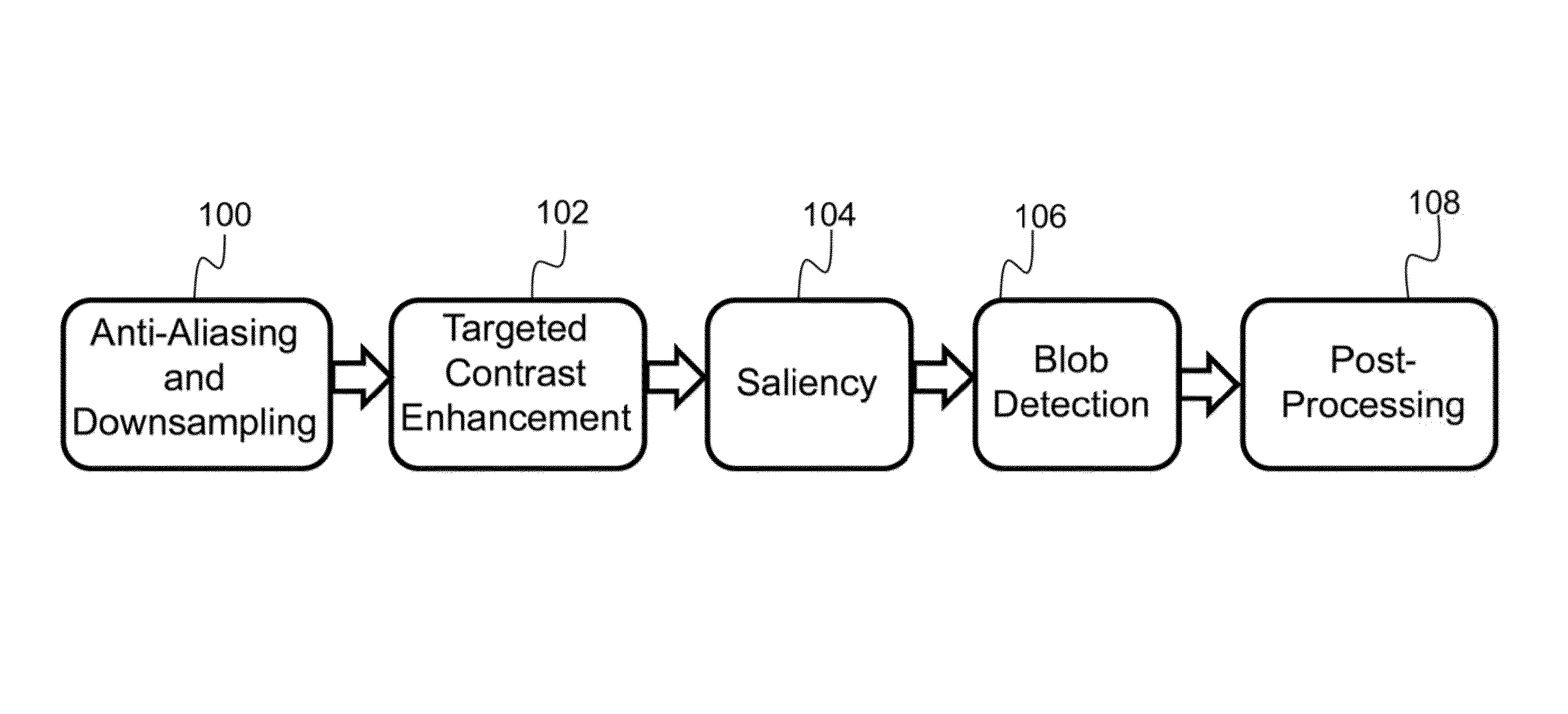
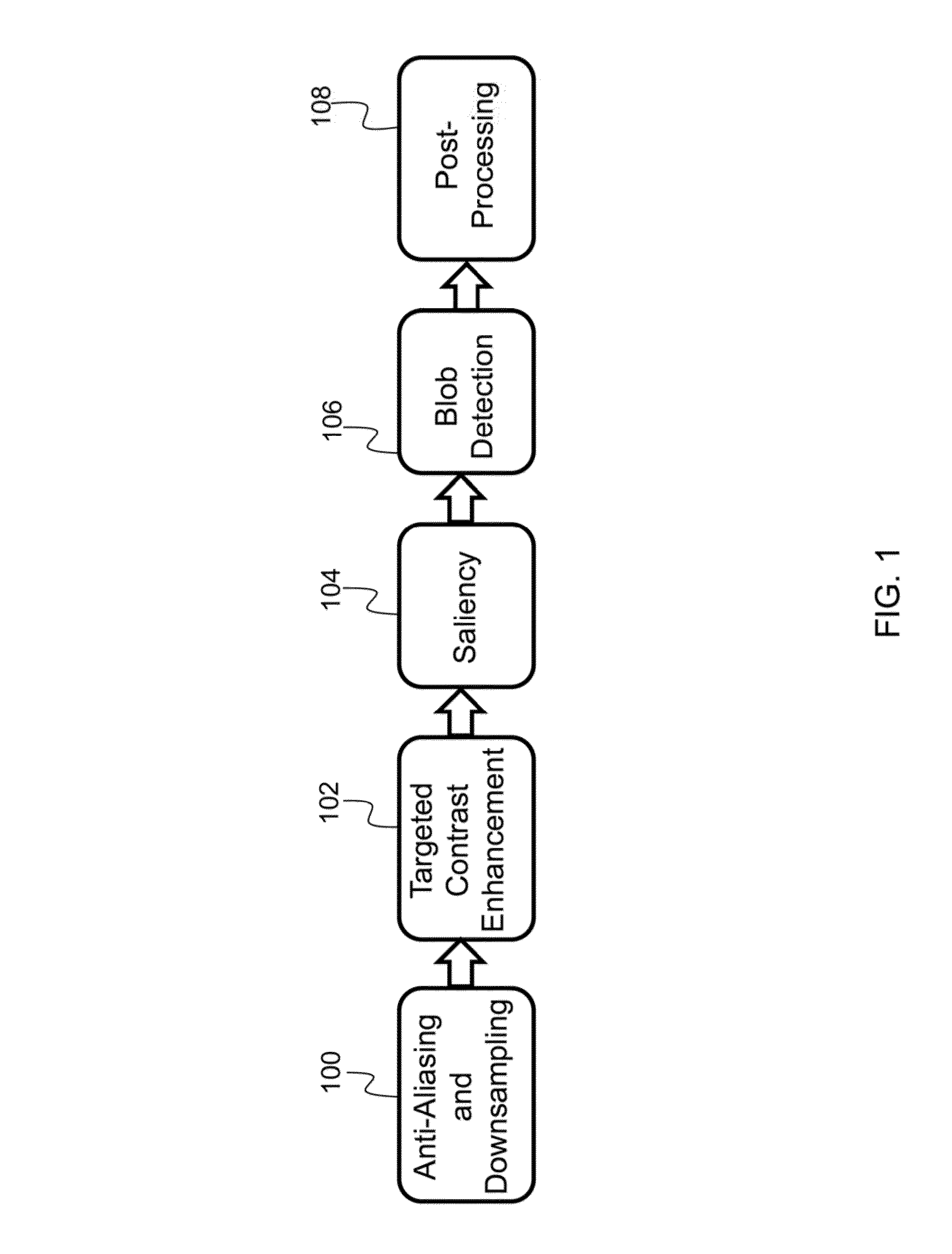
Described, is a system for object detection via multi-scale attentional mechanisms. The system receives a multi-band image as input. Anti-aliasing and downsampling processes are performed to reduce the size of the multi-band image. Targeted contrast enhancement is performed on the multi-band image to enhance a target color of interest. A response map for each target color of interest is generated, and each response map is independently processed to generate a saliency map. The saliency map is converted into a set of detections representing potential objects of interest, wherein each detection is associated with parameters, such as position parameters, size parameters, an orientation parameter, and a score parameter. A post-processing step is applied to filter out false alarm detections in the set of detections, resulting in a final set of detections. Finally, the final set of detections and their associated parameters representing objects of interest is output.
Owner:HRL LAB
Apparatus and method for controlling contrast enhanced imaging procedures
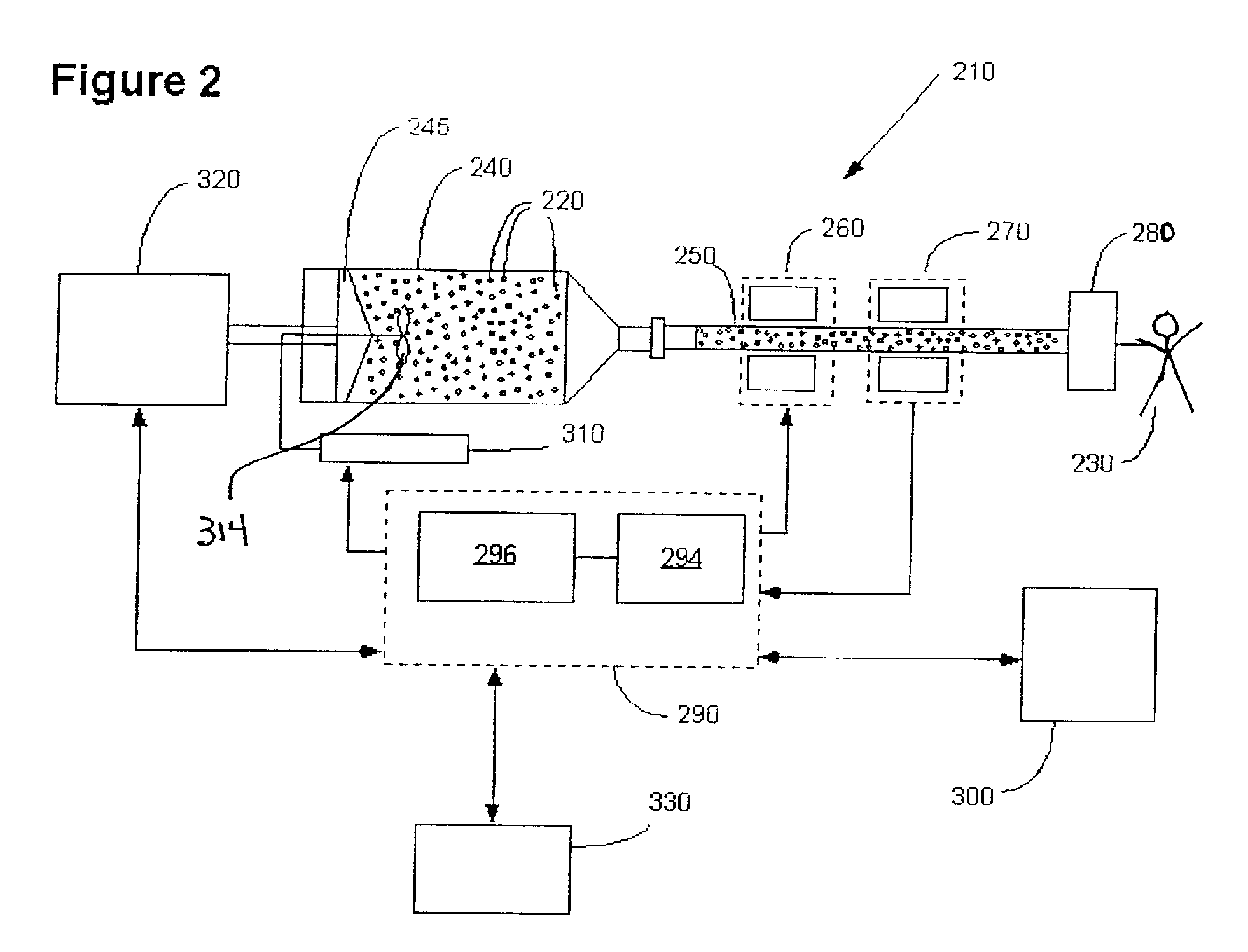
InactiveUS6939302B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPressure infusionContrast enhancementDelivery system
A system for delivery of a medium having ultrasound contrast enhancement agents therein to a patient includes a pressurizing device for pressurizing the medium, a fluid path connecting the pressurizing device to the patient and a concentration sensor in communication with the fluid path. The concentration of the contrast enhancement agents is measured by the concentration sensor during injection of the medium into the patient to assist in controlling the delivery system and / or an imaging procedure.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
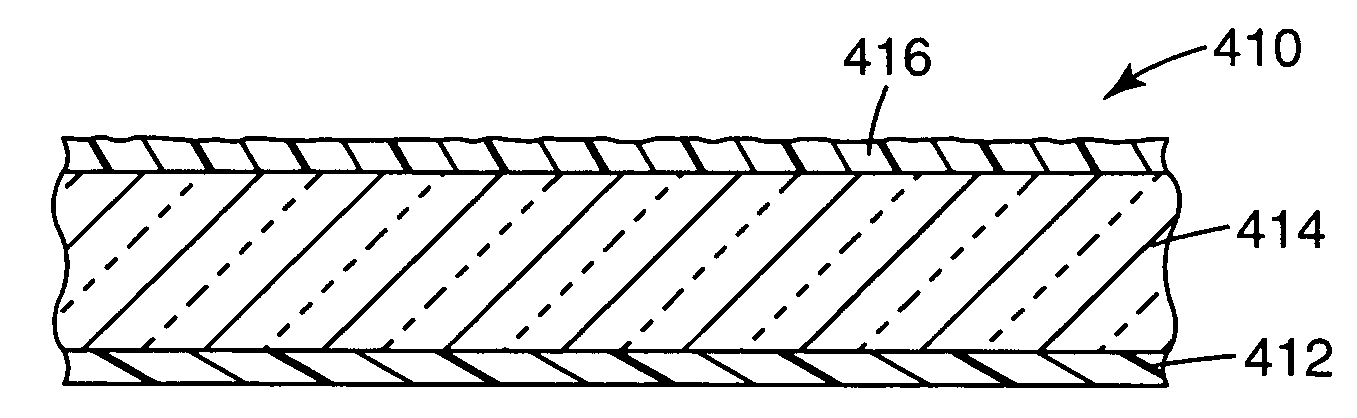
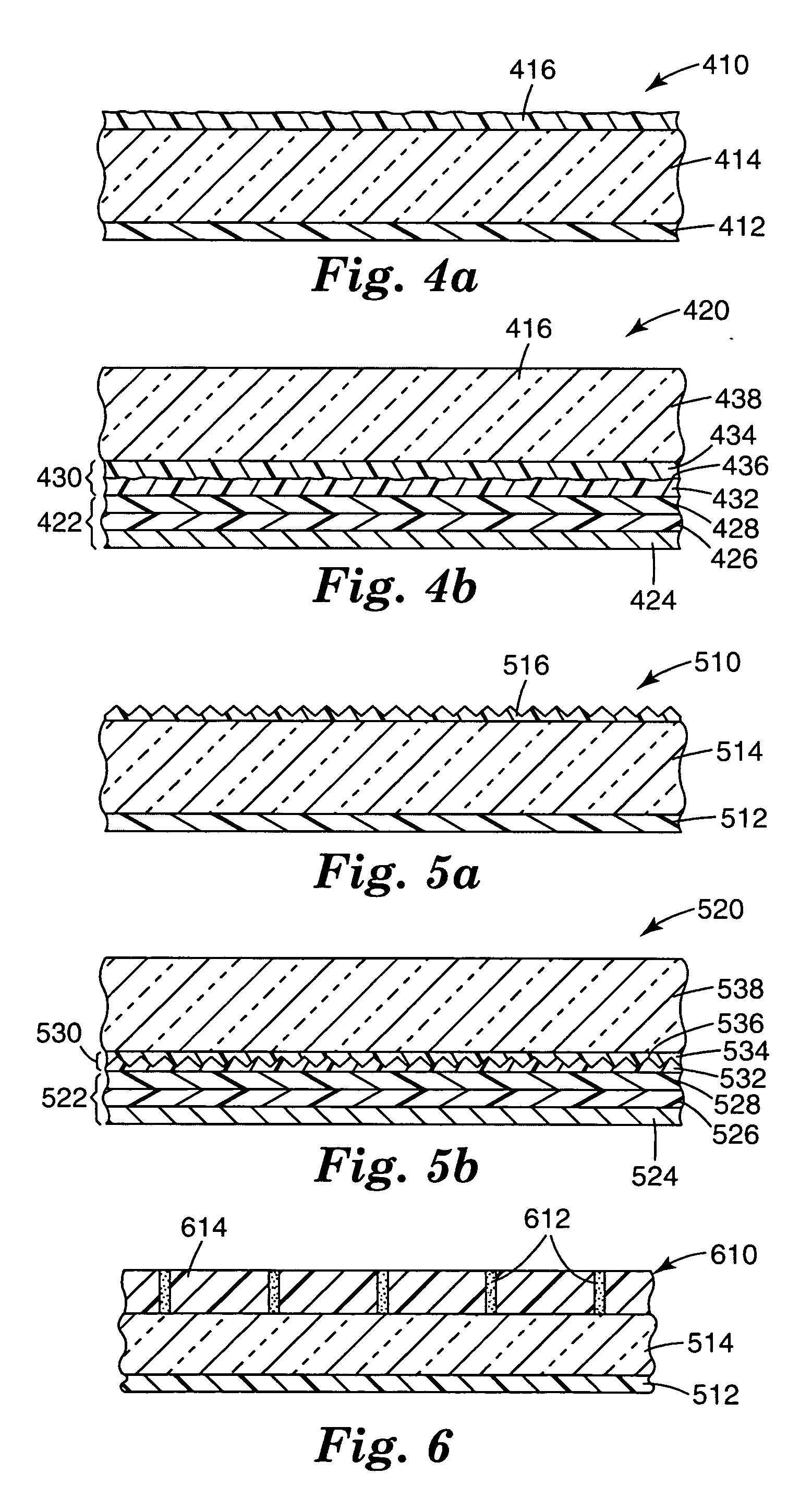
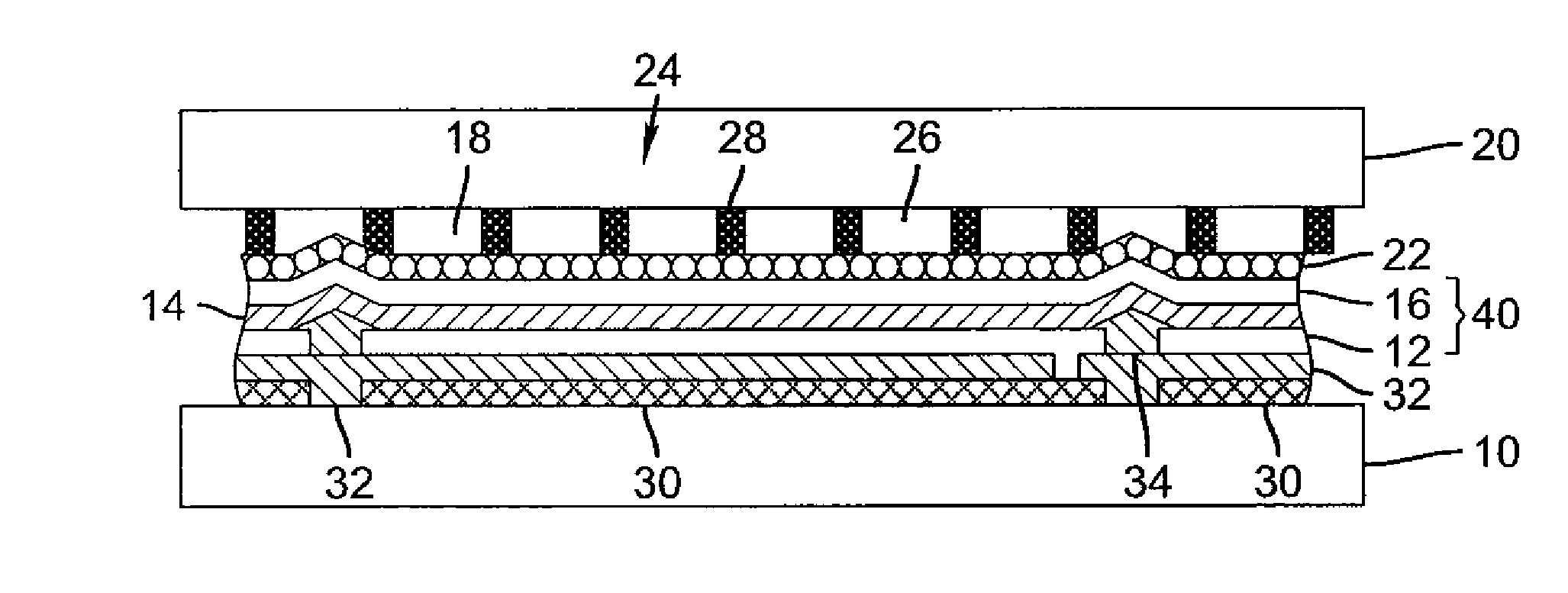
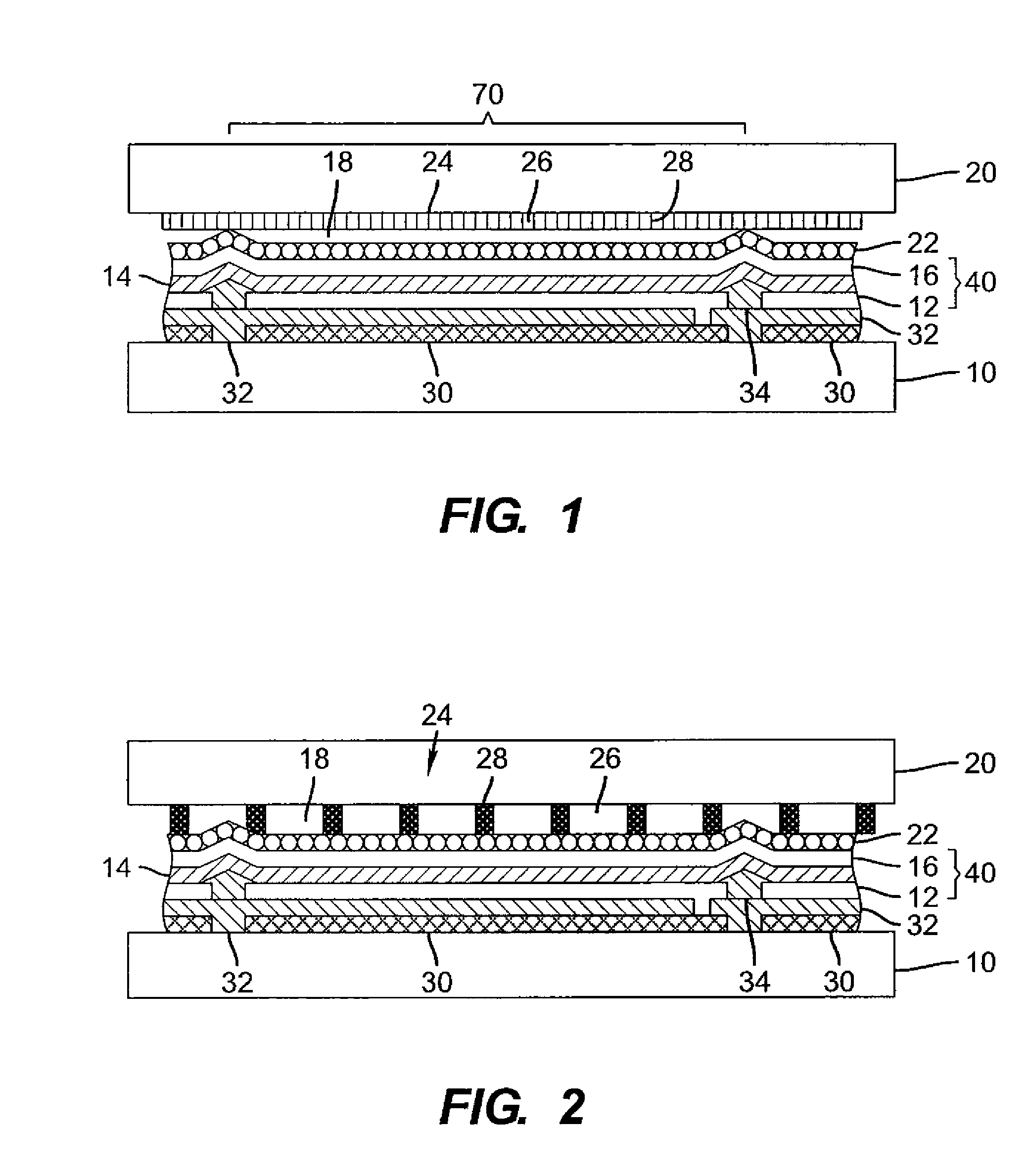
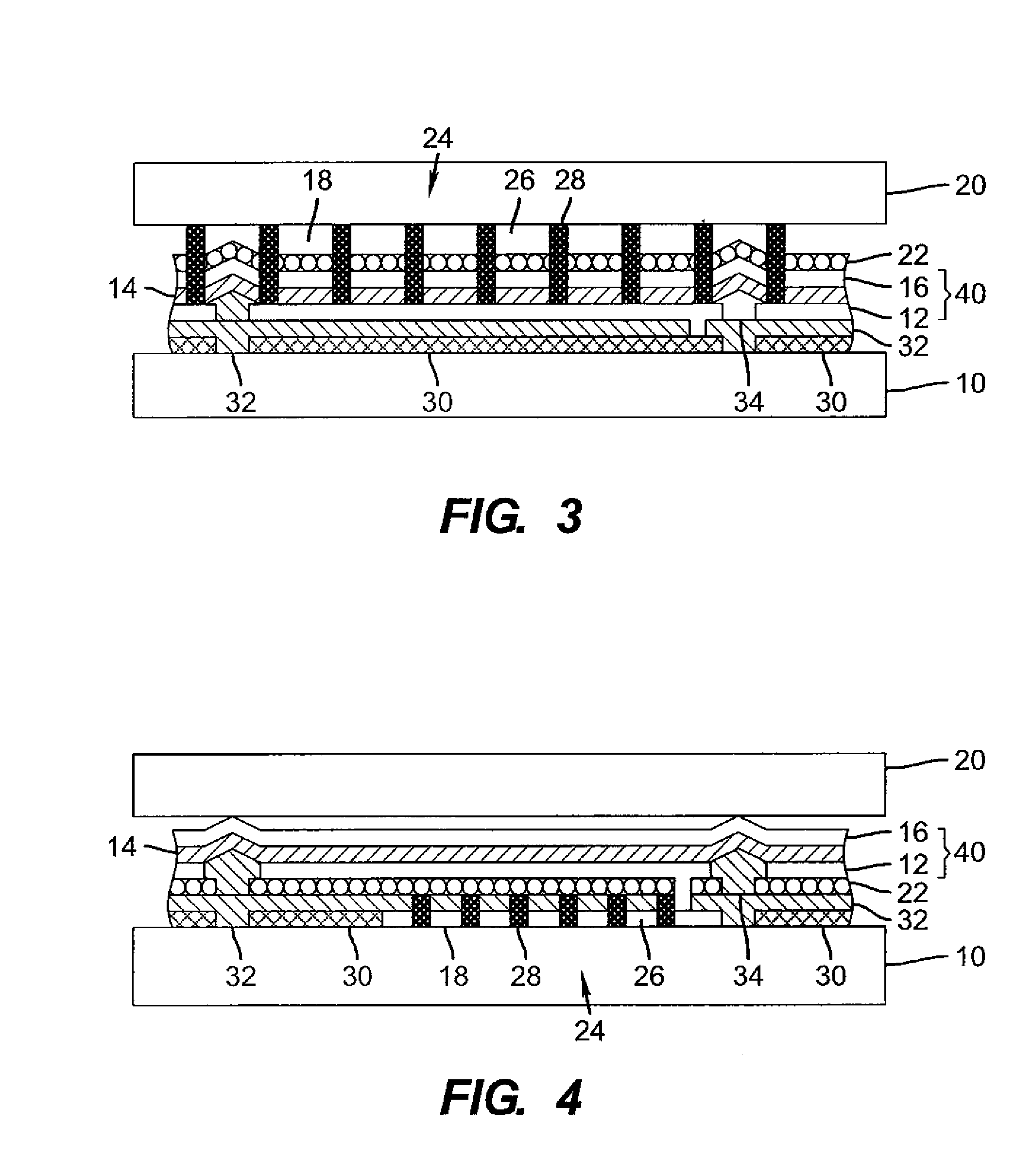
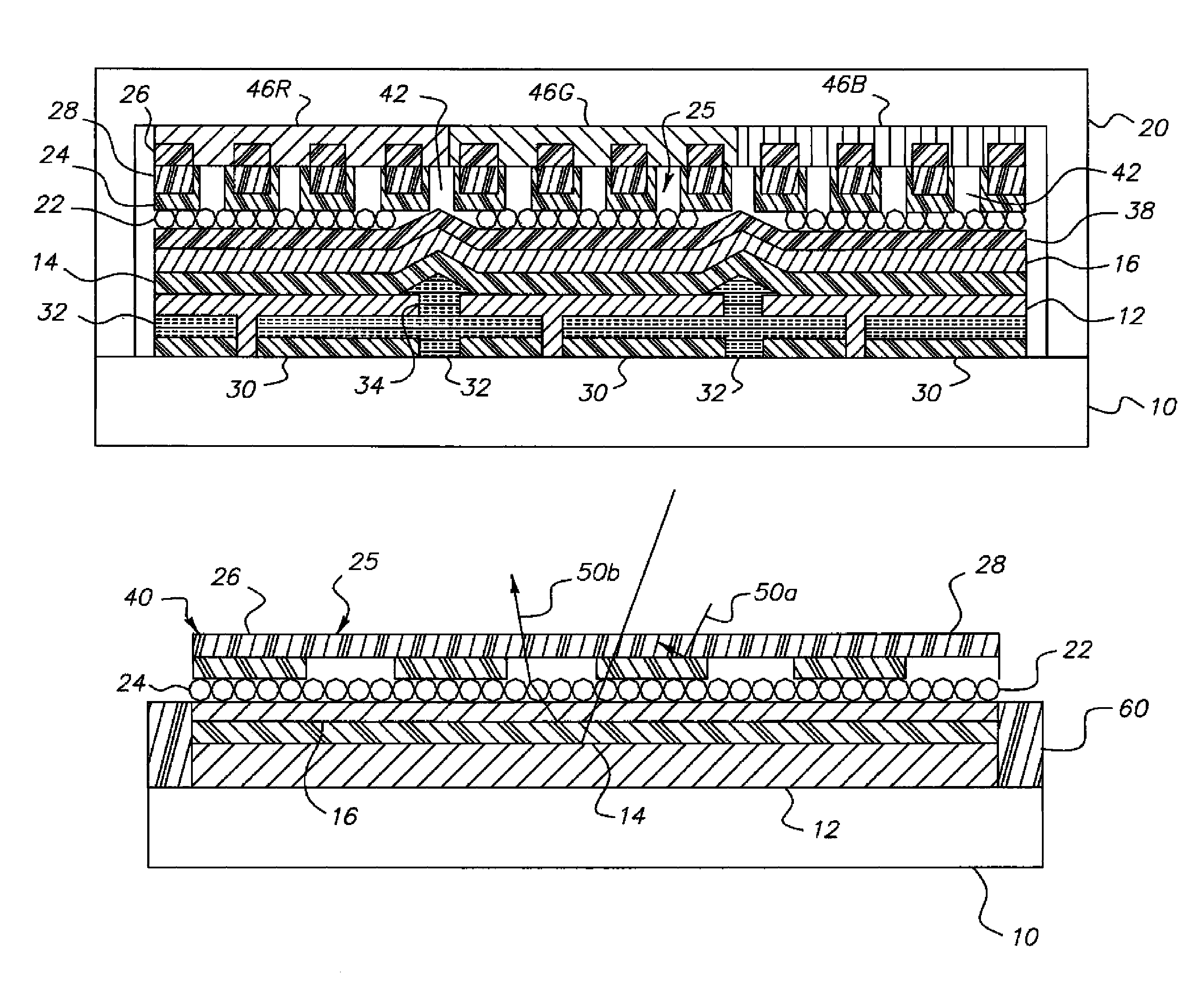
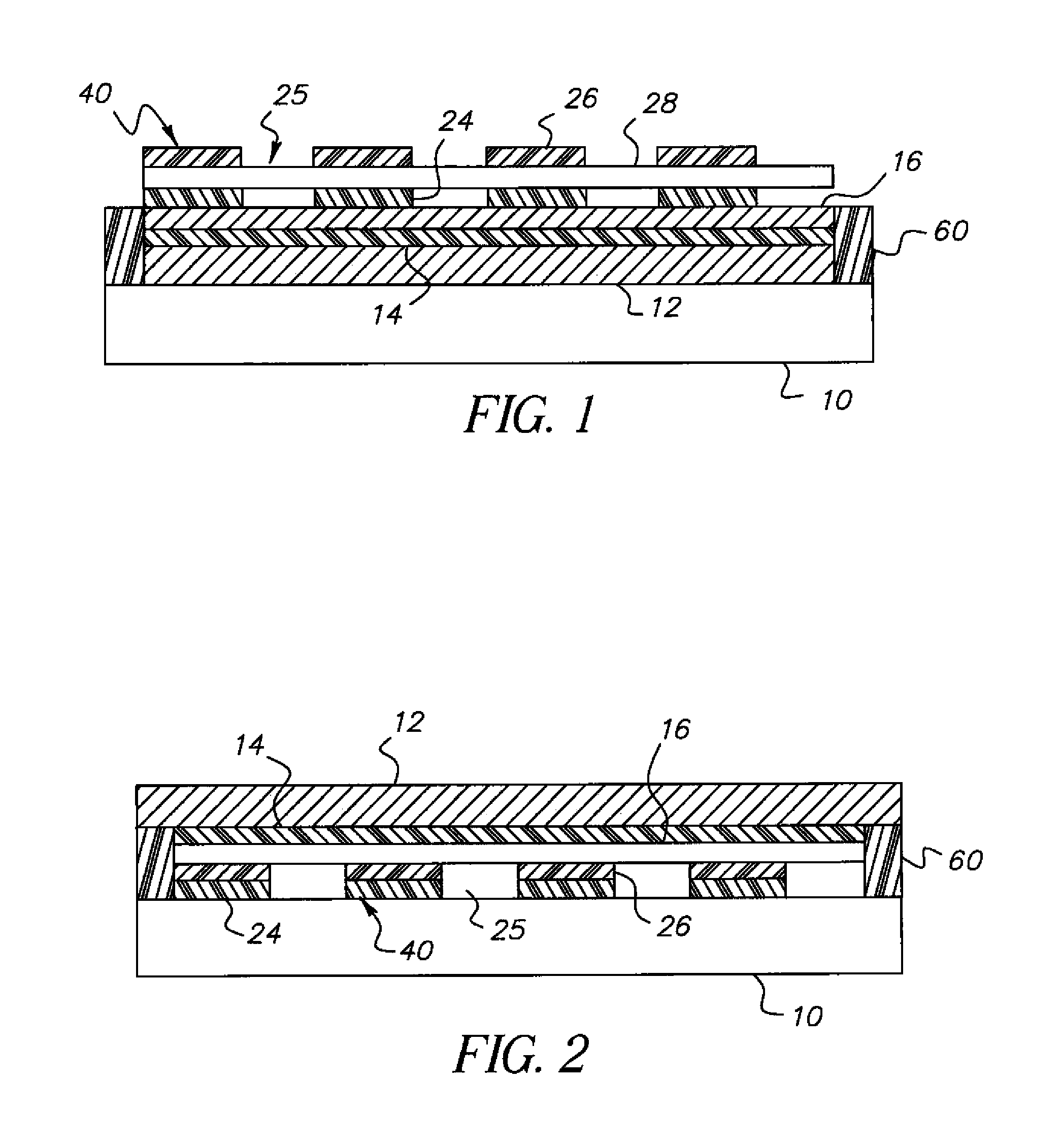
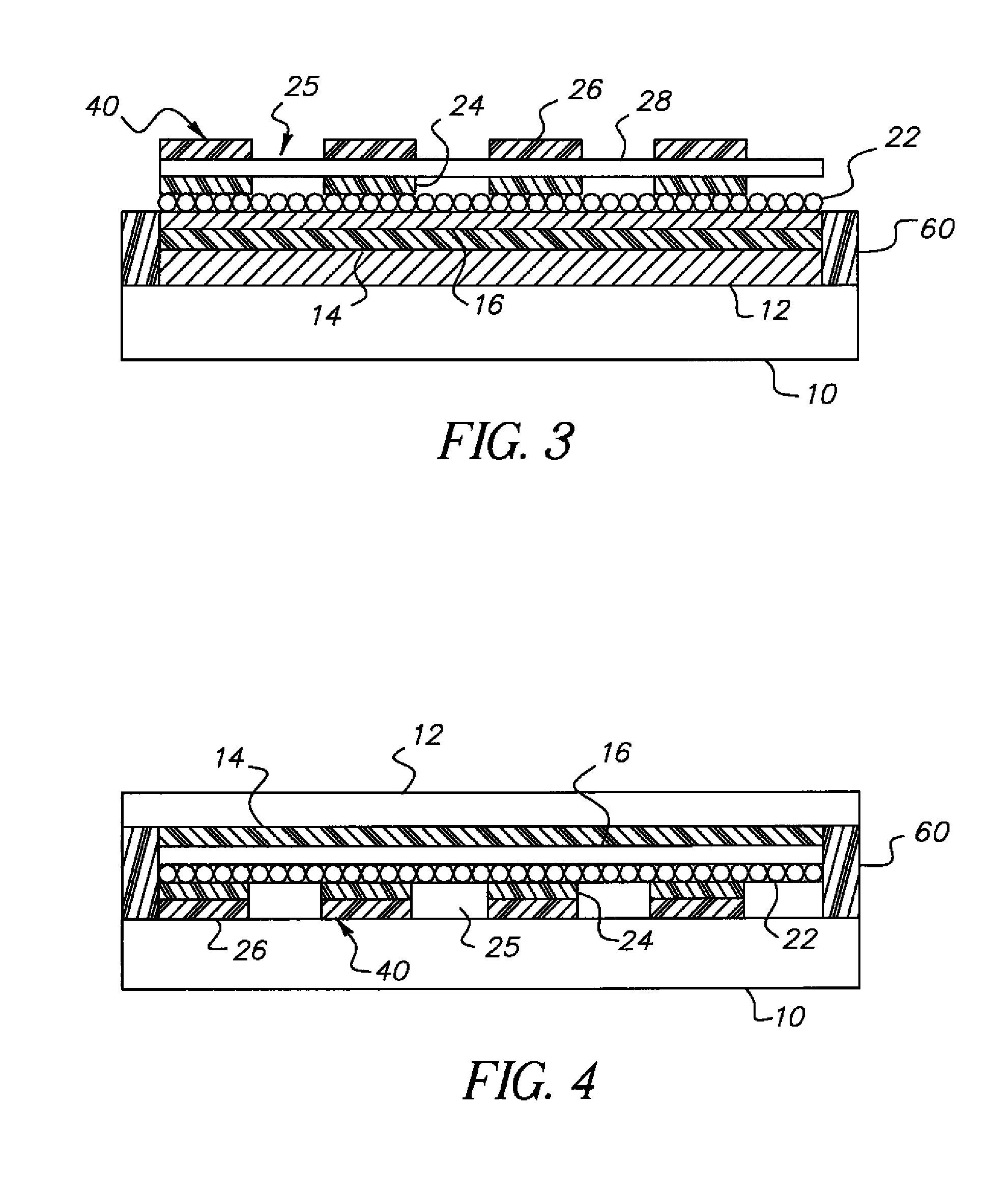
OLED device having improved output and contrast with light-scattering layer and contrast-enhancement layer
ActiveUS7466075B2Incadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensRefractive indexContrast enhancement
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, with an OLED formed on a substrate having a first and second electrodes and one or more light-emitting organic material layers formed between the electrodes, the organic material layer(s) having a first optical index and at least one of the electrodes patterned to define light-emitting areas; a cover formed over the OLED. The cover or substrate is transparent and has a second optical index and the light is emitted through the transparent cover or substrate; a light-scattering layer formed between the cover and substrate for scattering light; a low-index element having an optical index lower than the first and second optical indices formed between the scattering layer and the transparent cover or substrate; and a contrast-enhancement layer having a plurality of alternating light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions formed in the layer located between the light-scattering layer and the transparent substrate or cover through which light is emitted, wherein a plurality of light-absorbing portions and light-transmissive portions are located in each light-emitting area.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Electroluminescent device having improved contrast
InactiveUS20080237611A1Improved ambient contrastDecreasing light emissionMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesQuantum dotContrast enhancement
A method for increasing ambient light contrast ratio within an electroluminescent device, including: a reflective electrode and a transparent electrode having an EL unit formed there-between. The EL unit includes a light-emitting layer containing quantum dots. Additionally, the method includes locating a contrast enhancement element on a side of the transparent electrode opposite the EL unit. The contrast enhancement element includes a patterned reflective layer and a patterned light-absorbing layer whose patterns define one or more transparent openings, so that light emitted by the light-emitting layer passes through the one or more transparent openings. The patterned reflective layer is located between the patterned light absorbing layer and the transparent electrode.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
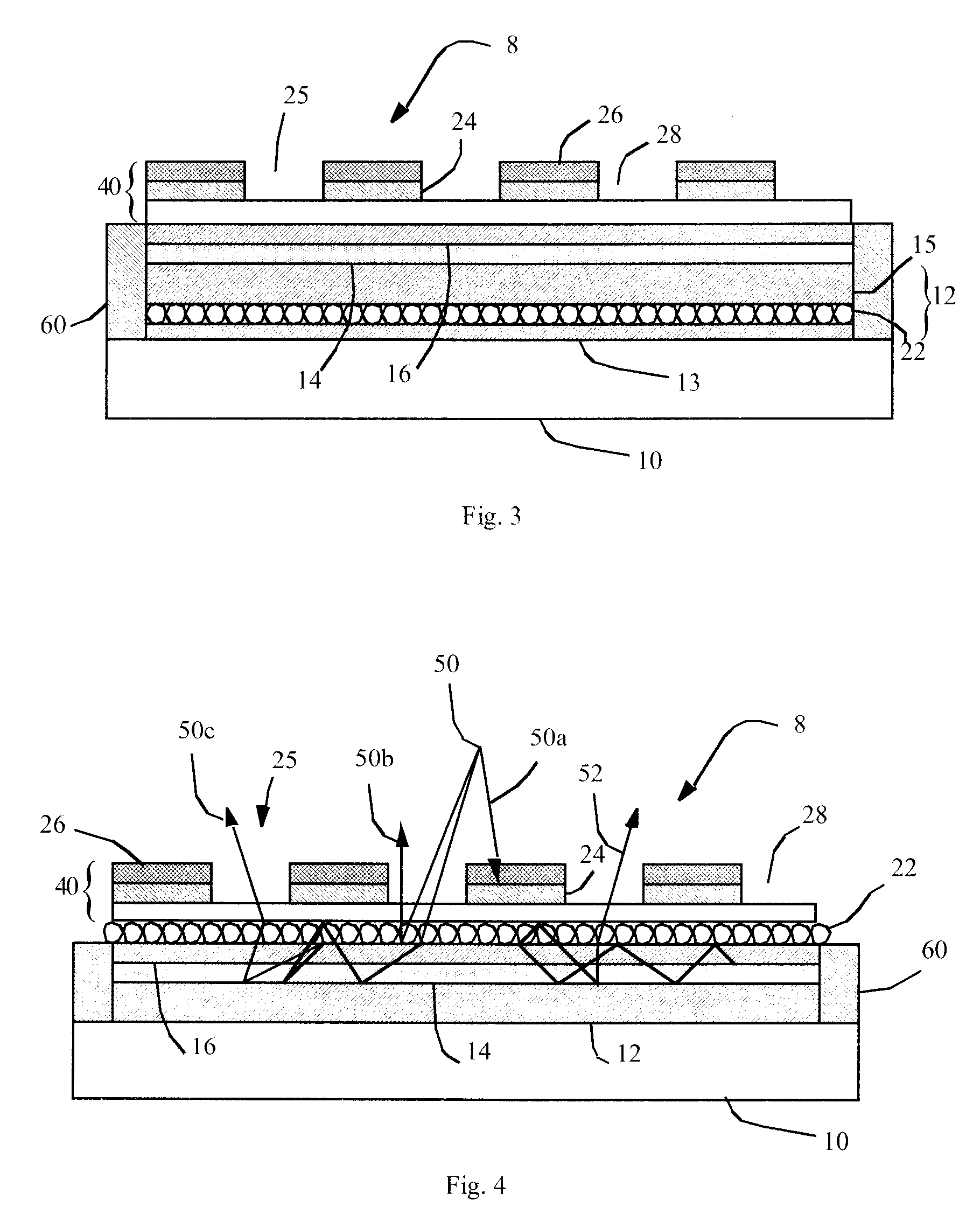
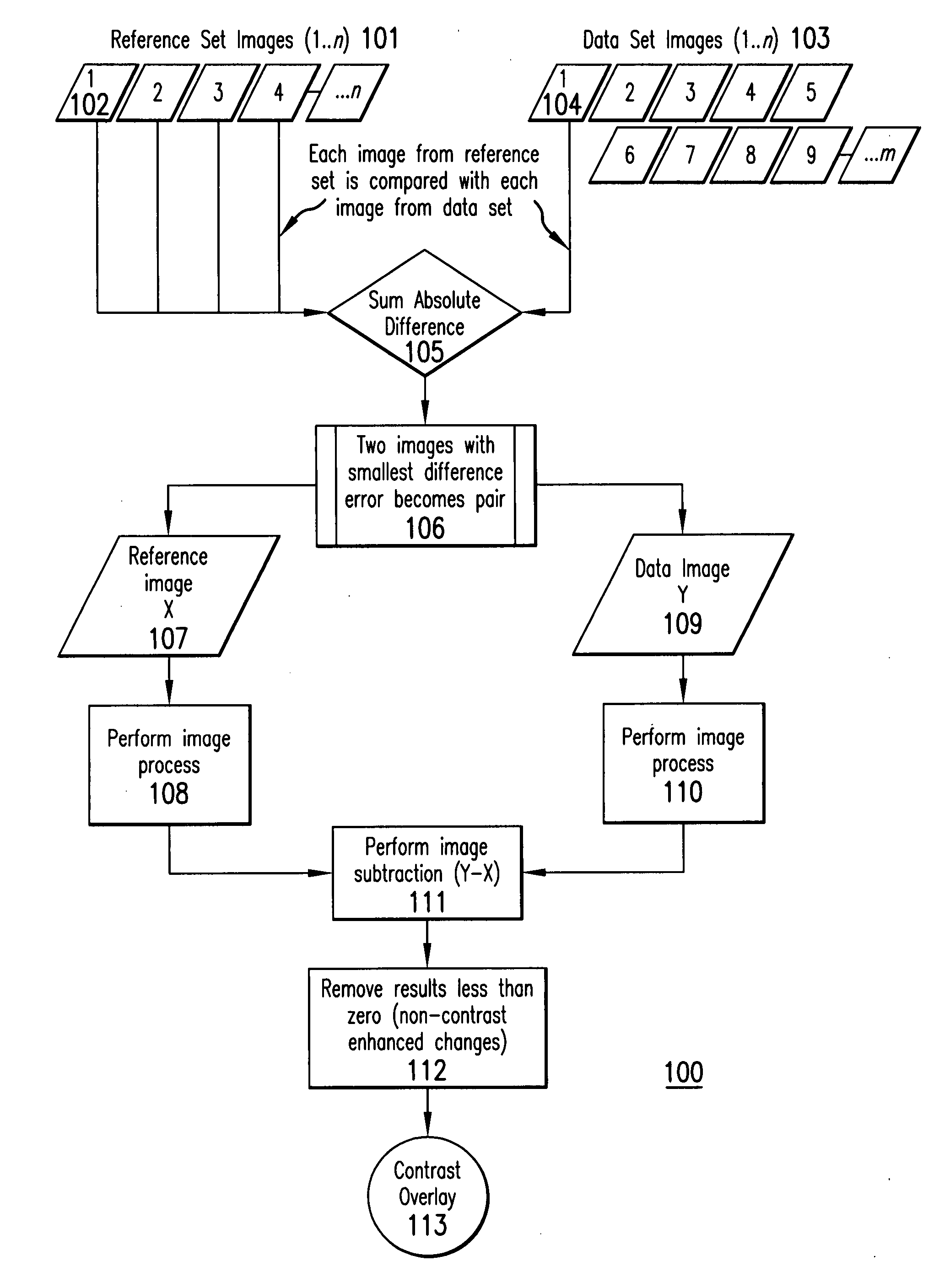
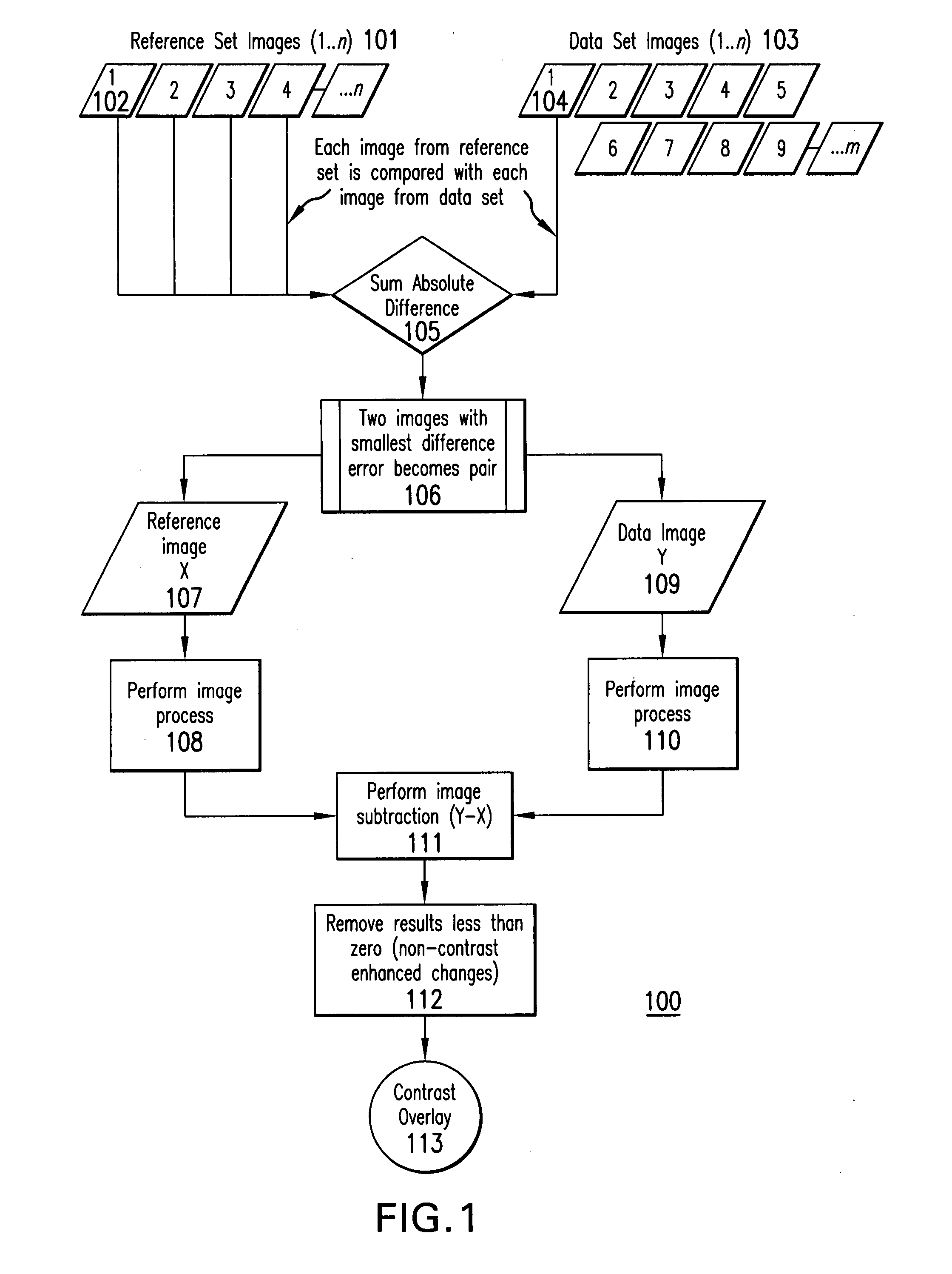
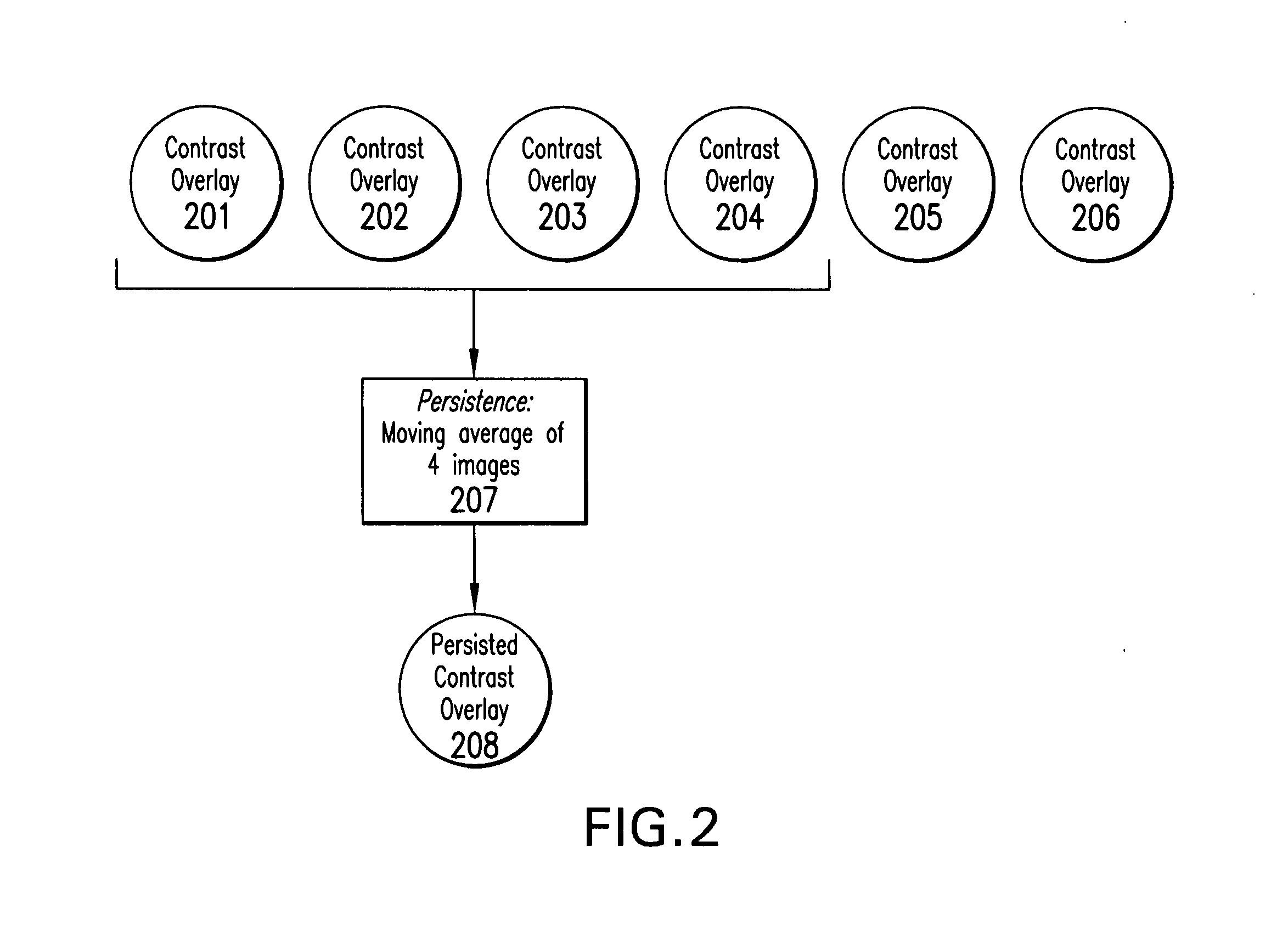
Overlay image contrast enhancement
ActiveUS20070238954A1Enhance the imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImage contrastReference image
A method of creating an image difference overlay comprises identifying a loop of reference images of a subject and identifying a loop of data images of the subject. The loop of image data can be identified after an event, such as the administration of contrast agent to the subject. A reference loop image frame is compared to one or more data loop image frames and the reference loop frame is associated with a data loop image frame which closely resembles the data loop image frame. Each of the associated frames can then be processed and used to create an image difference overlay frame.
Owner:FUJIFILM SONOSITE
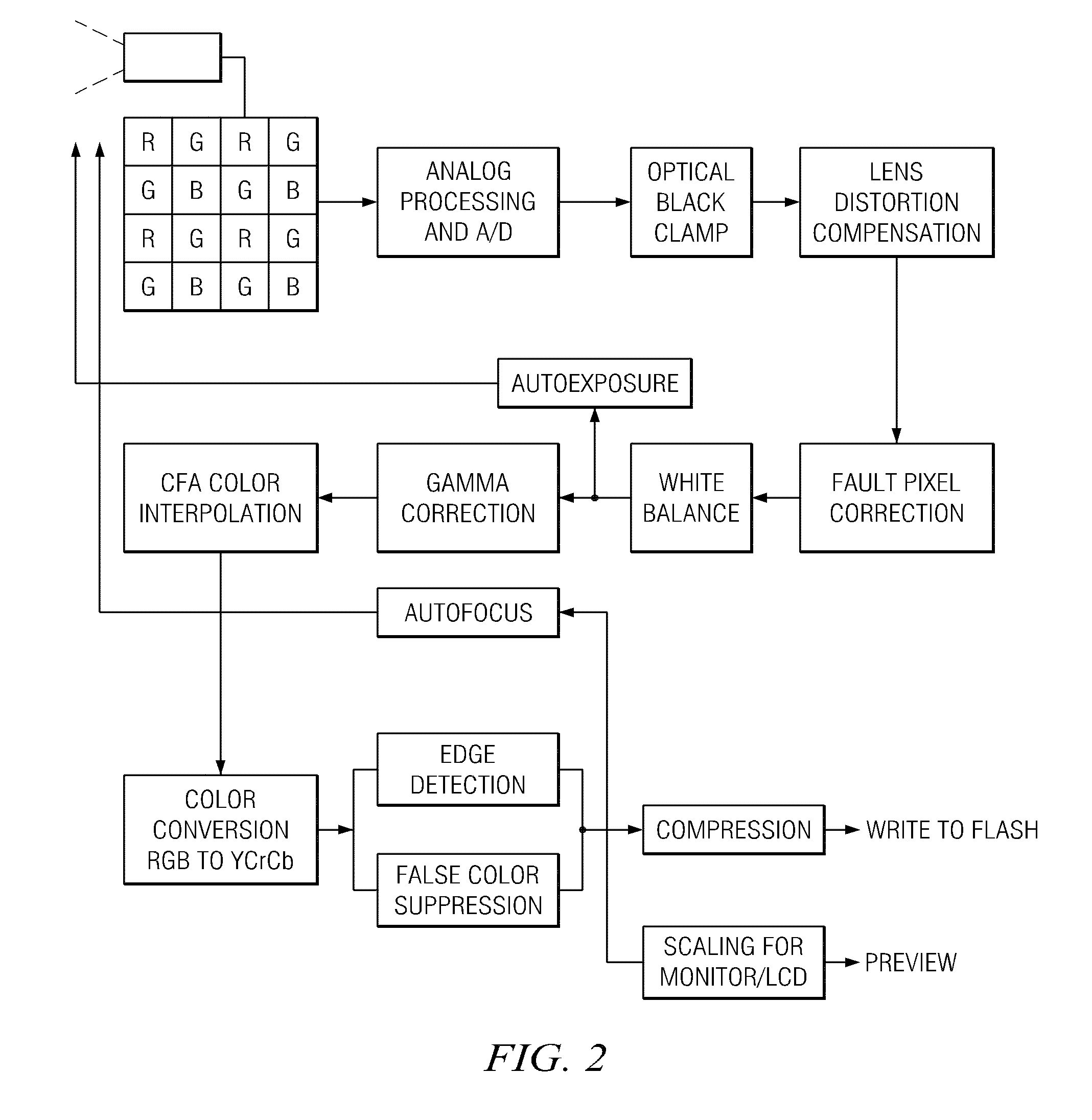
Large depth-of-field imaging system and iris recogniton system
InactiveUS20100110275A1High transfer functionTelevision system detailsImage analysisDepth of fieldDigital image processing
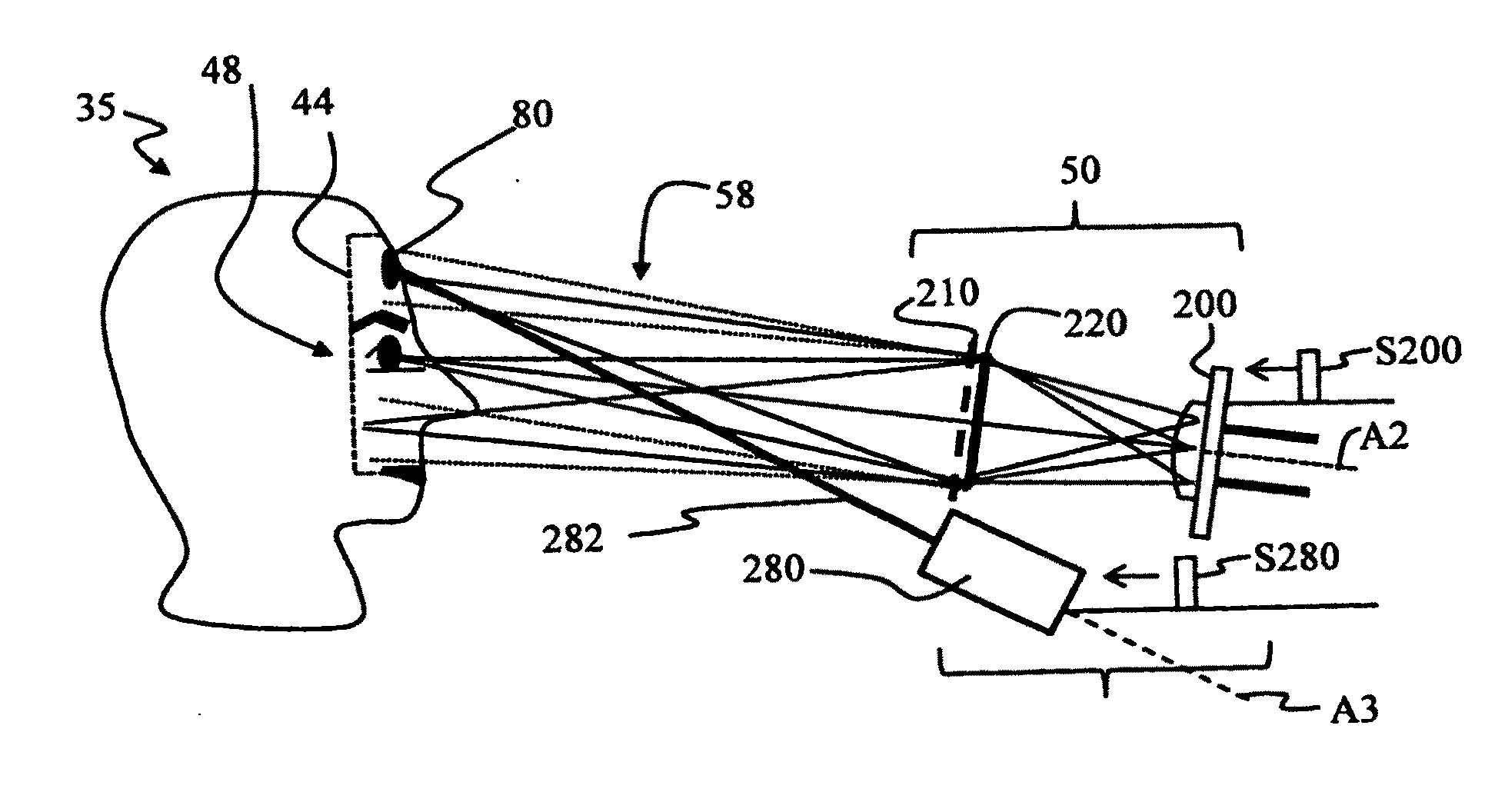
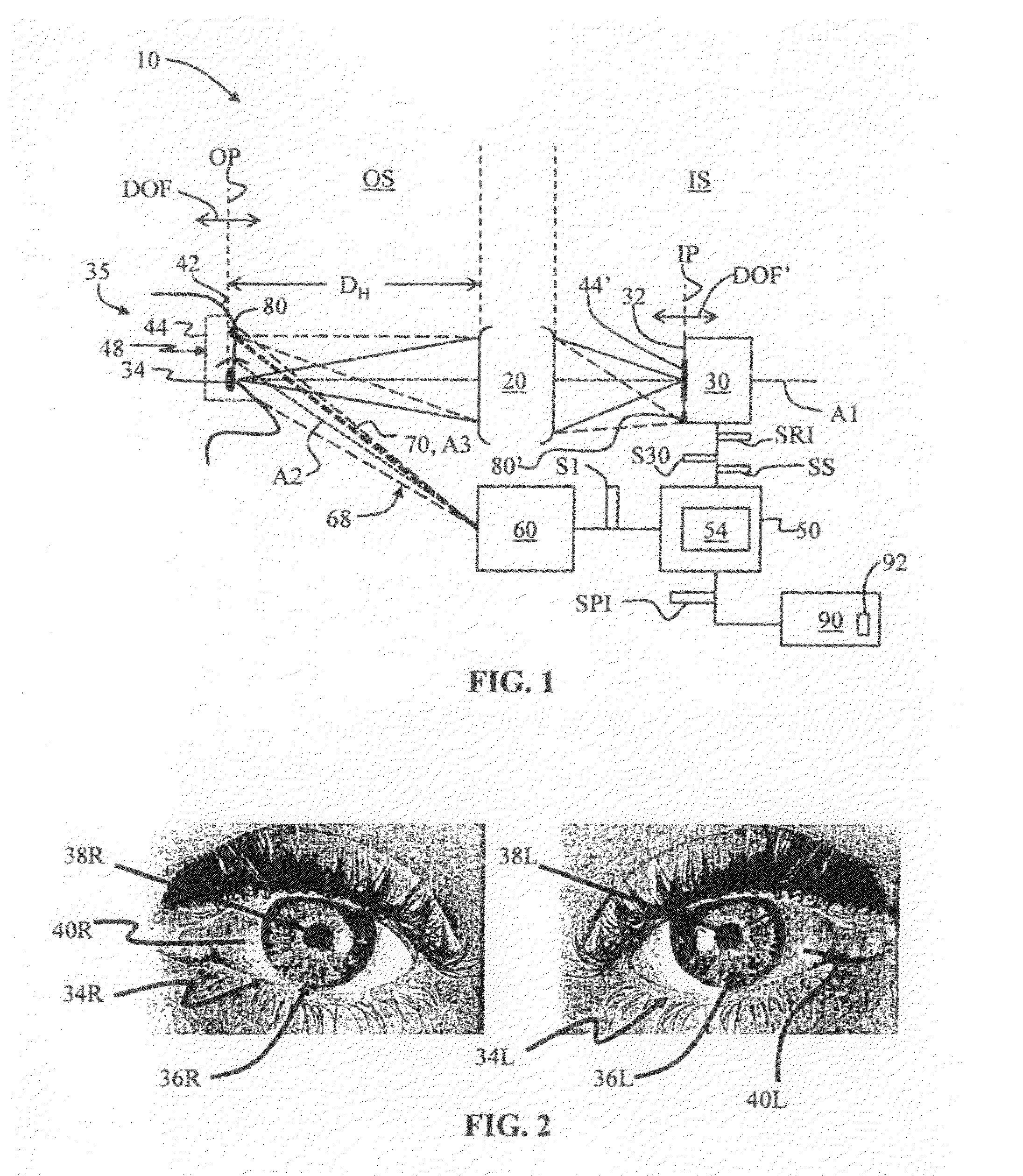
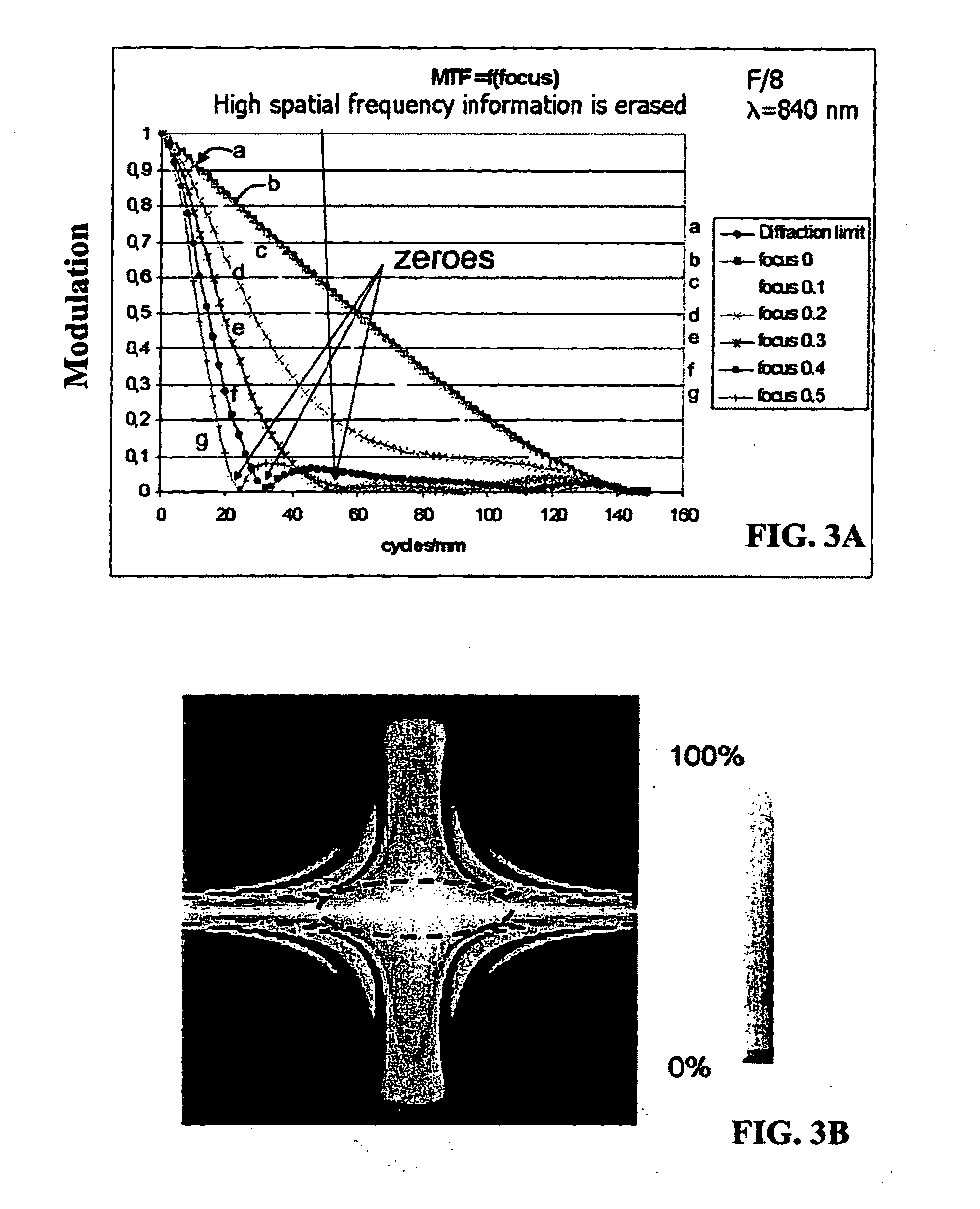
(A2) An extended depth of field (DOF) imaging system (10) is disclosed that has a corresponding extended depth of focus (DOF′) by virtue of its optical system (20) having a select amount of spherical aberration. The imaging system has an image processing unit (54) adapted to process the raw images and perform contrast enhancement to form processed images. The image processing includes restoring the defocused modulation transfer functions (MTFs) using a gain function (G) and the amount of defocus. The imaging system can include an illumination system (60) that illuminates the object being imaged to establish a distance (DH) between the optical system and the object, where distance DH is used in the restoring of the MTF. An iris-recognition (I-R) system based on the enhanced DOF imaging system is also disclosed.; Optical system embodiments for use in the DOF imaging system that can provide select amounts of spherical aberration—and thus select increases in DOF—without increasing the adverse impact of other aberrations on image formation are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBAL BIONIC OPTICS PTY LTD
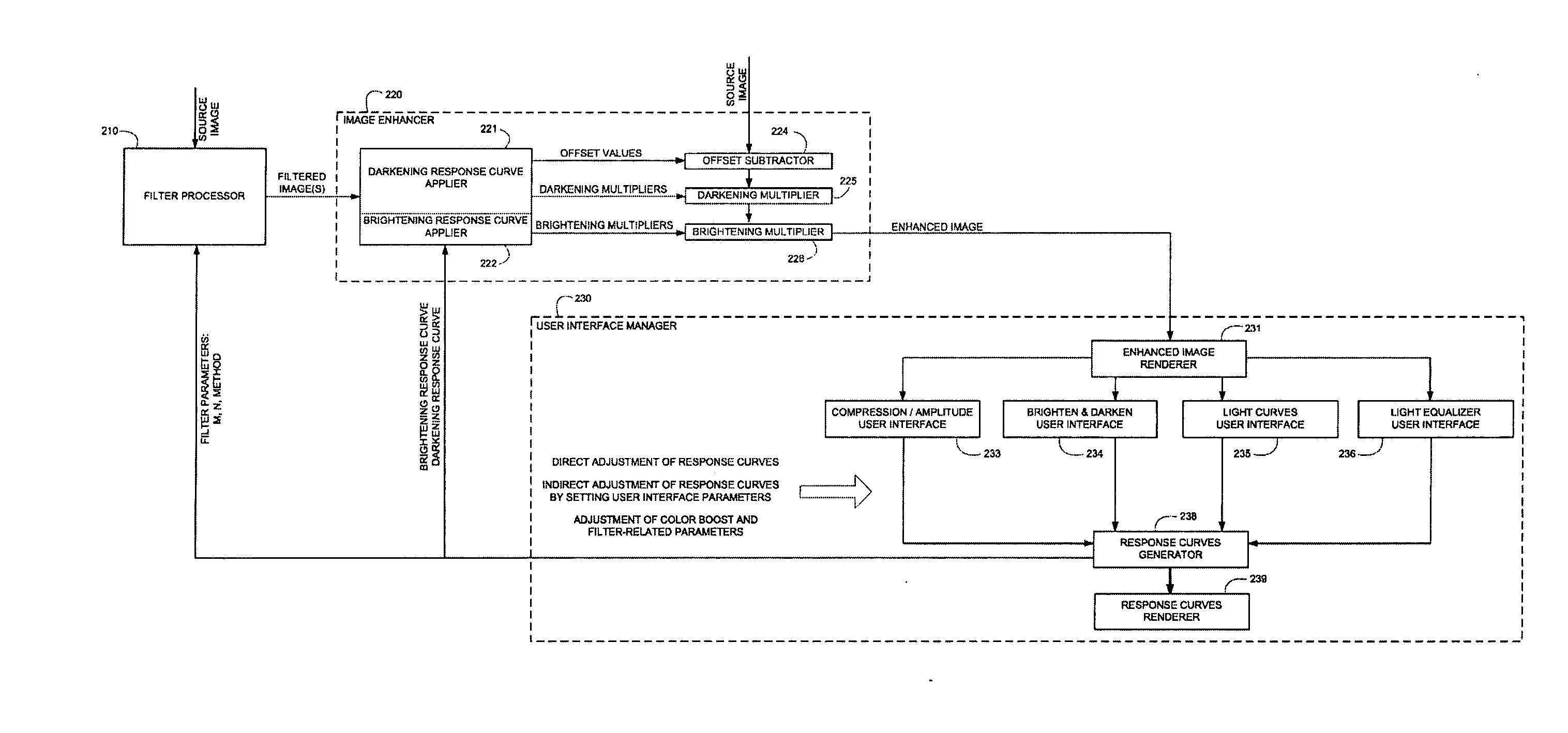
Color correcting contrast enhancement of displays
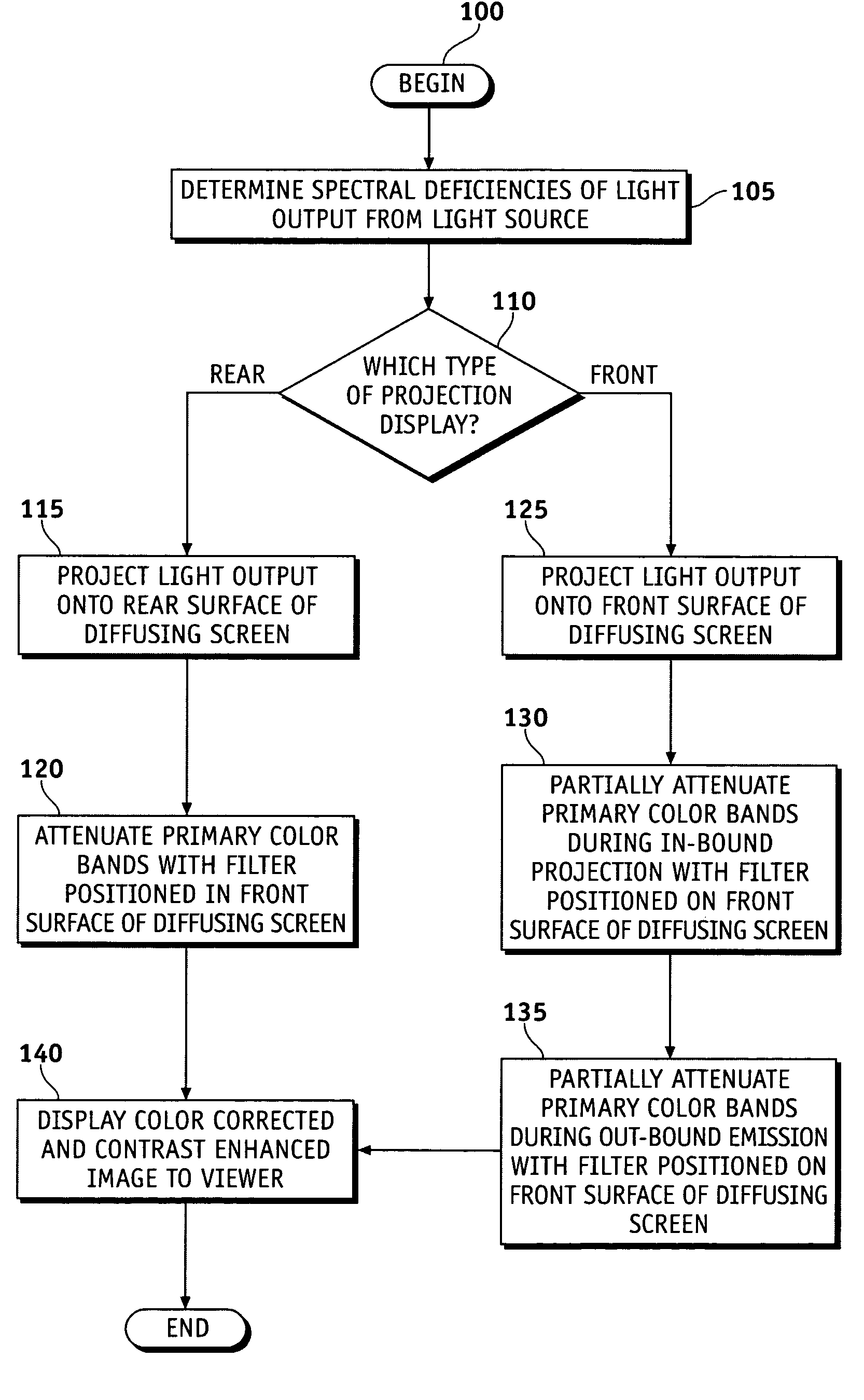
Methods and apparatus are provided for color correction and contrast enhancement of projection displays. A visual display system includes a projector having a light source with a fixed spectral output, a display screen receiving the output of the projector and emitting a diffused output, and a color correction contrast enhancement filter positioned between the diffusing screen and a viewer. The filter differentially attenuates primary colors of the emission from the diffusing screen. The method includes projecting a light output from a light source having a fixed spectral output onto a diffusing screen, and attenuating primary colors of the emission from the diffusing screen with a light filter positioned adjacent to the diffusing screen.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for seismic feature extraction
InactiveUS20060122780A1Easy to useSignificant comprehensive benefitsSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionImaging processing
A method and apparatus for seismic image processing is disclosed. A preferred embodiment aids in the identification of subterranean faults, which are significant in hydrocarbon exploration. The method includes steps of: a) reading a three dimensional seismic data volume; b) computing the three-dimensional orientation of the subsurface; c) subdividing the original volume into small data volumes that are rotated at a predetermined set of dips and azimuths related to those of the subsurface orientation; volumes formed in step c; e) performing a 3-D contrast enhancement operation in each of the small volumes; f) filtering the result of the contrast enhancement with selected 3-D filters at the predetermined set of dips and azimuths; g) skeletonizing the results of the filtering operation; h) separating the individual fault surfaces, and i) labelling the individual fault surfaces for further interpretation and exploration.
Owner:GEOENERGY
Cell scaffold matrices with image contrast agents
The invention is directed to methods and compositions for monitoring remodeling of an artificial tissue construct using image or contrast enhancing agents. The invention allows the growth, development, and remodeling of the artificial tissue to be monitored.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
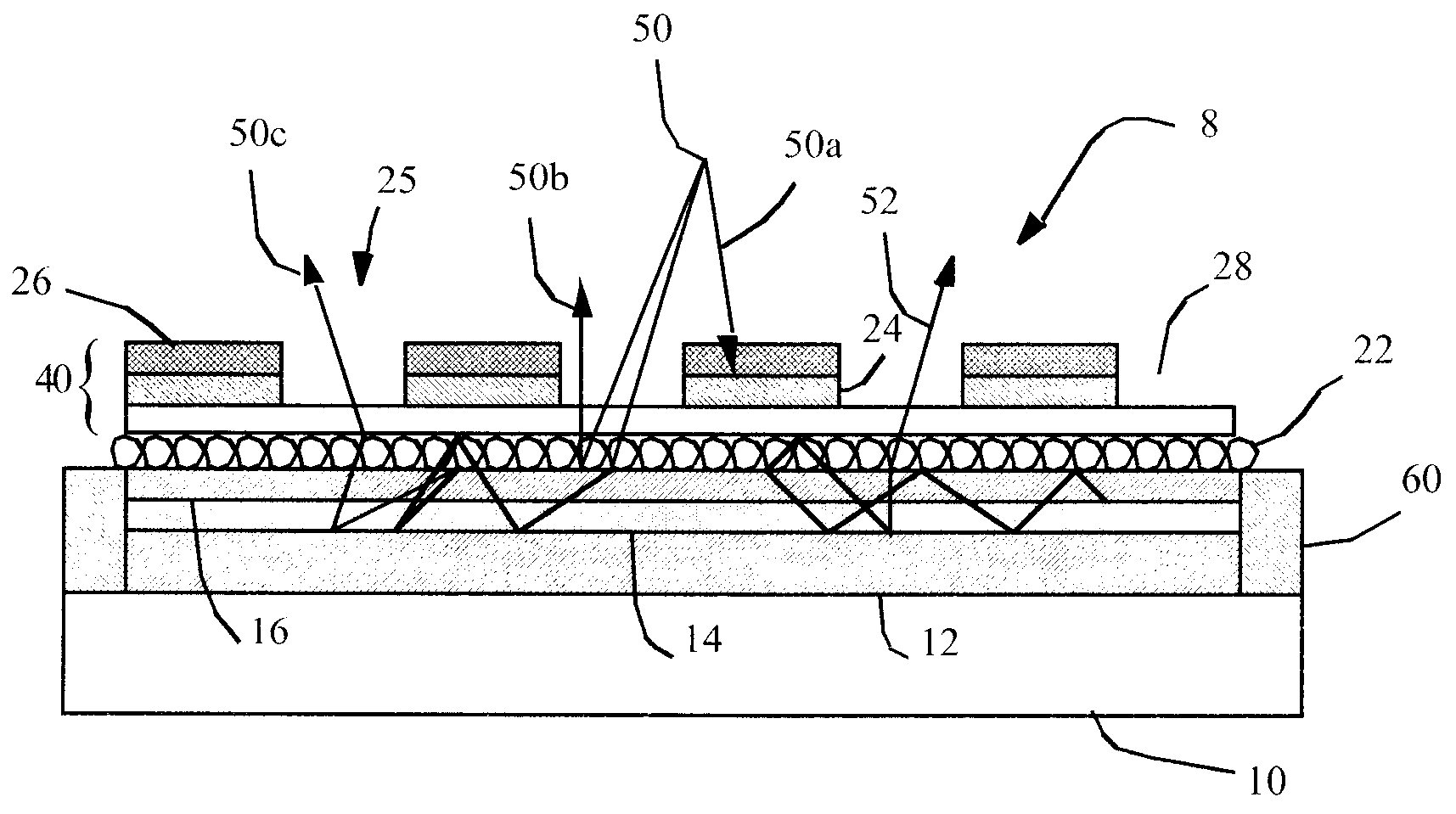
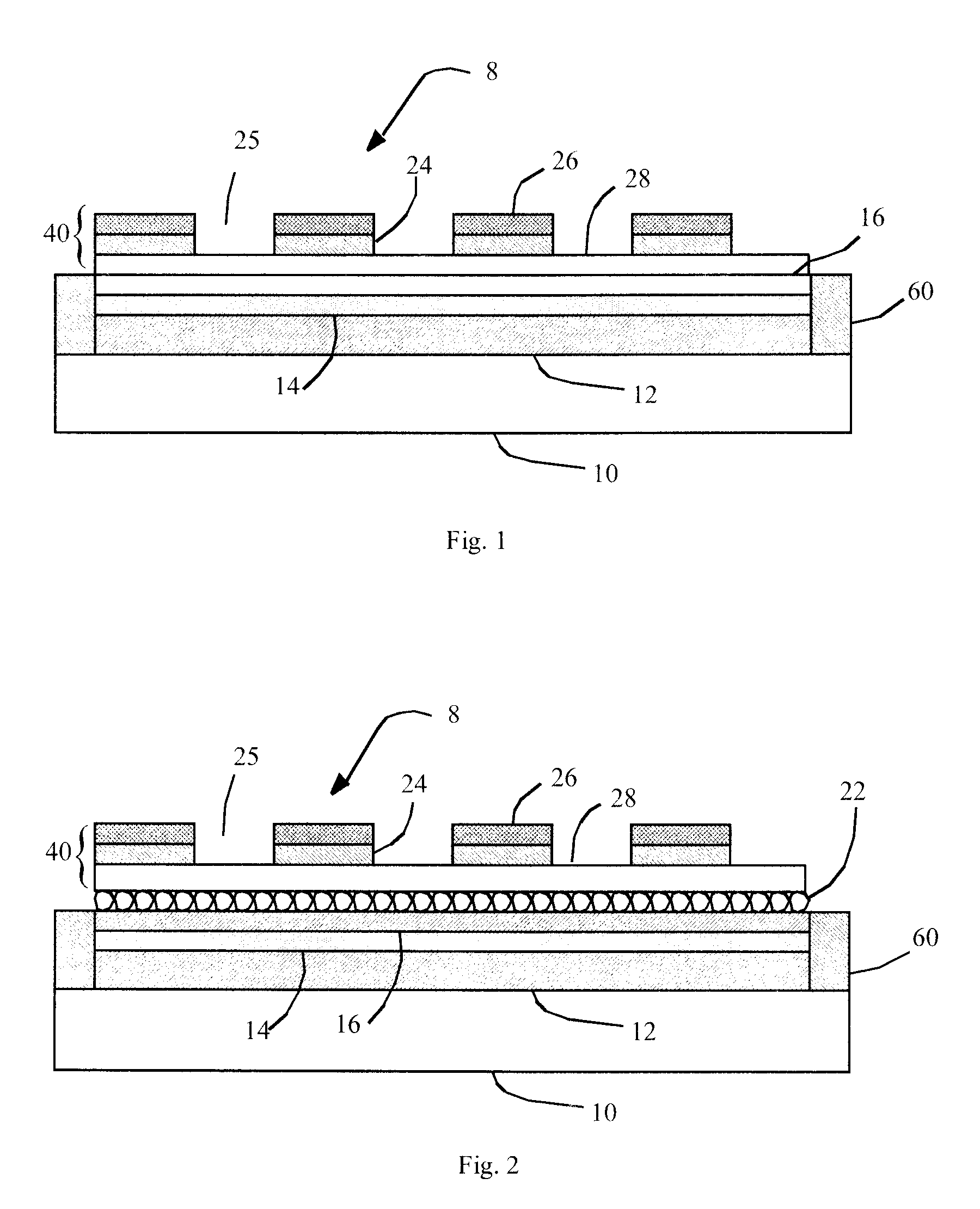
OLED device having improved contrast
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, comprises: a first electrode and a second transparent electrode having one or more organic layers formed there-between, at least one organic layer being light-emitting; and a contrast enhancement element formed on a side of the second transparent electrode opposite the organic layers, wherein the contrast enhancement element comprises a patterned reflective layer for reflecting emitted light and a corresponding light-absorbing layer for absorbing ambient light, wherein the reflective layer is located between the light-absorbing layer and the second transparent electrode and wherein the corresponding layers form one or more transparent openings through the reflective and light-absorbing layers so that light emitted by the light-emitting organic layer passes through the transparent openings.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
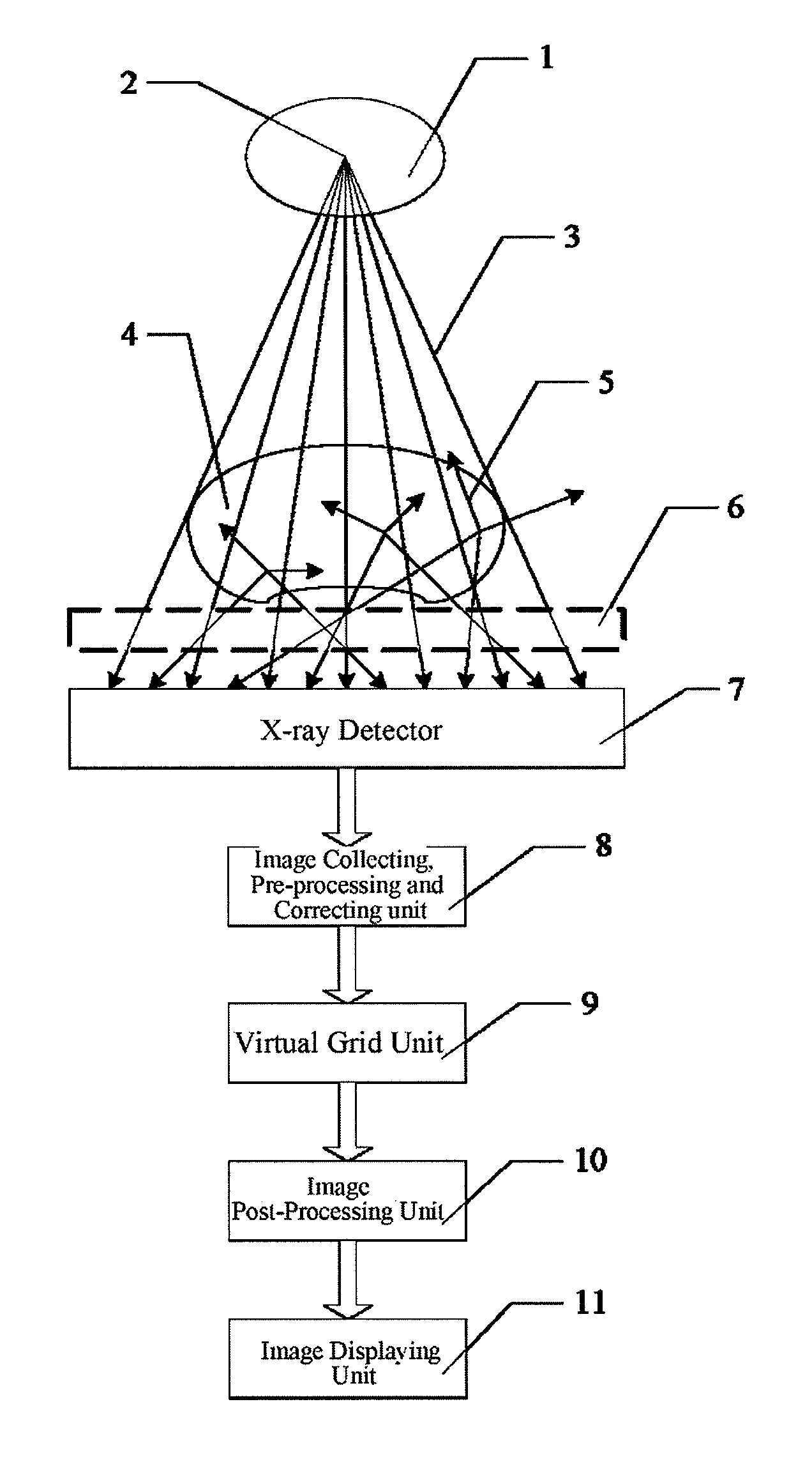
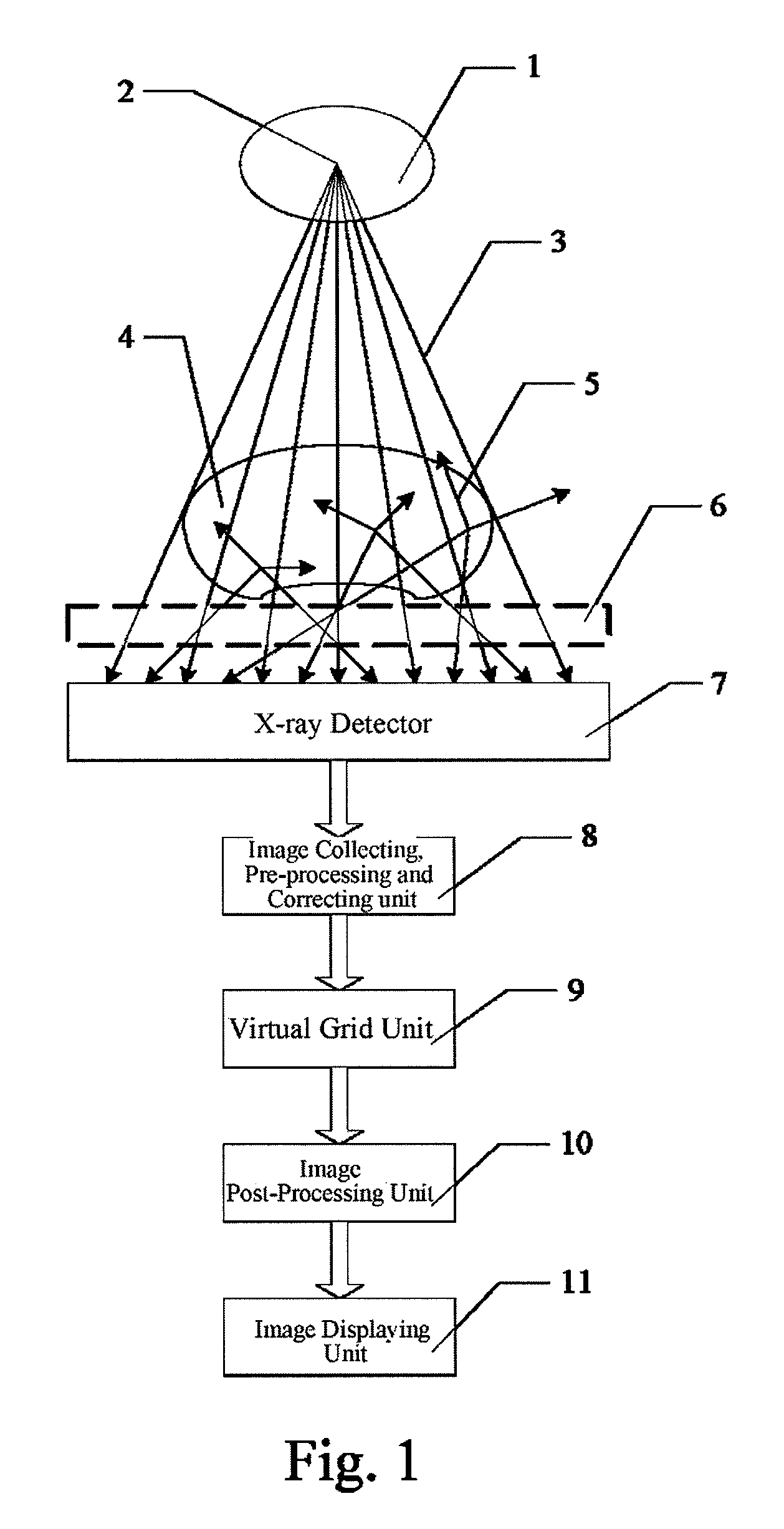
Virtual grid imaging method and system for eliminating scattered radiation effect
InactiveUS8064676B2Eliminate the effects ofComponent can be removedImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandHigh energy
Owner:BEIJING SINOPHARM HUNDRIC MEDLINE INFO TECH
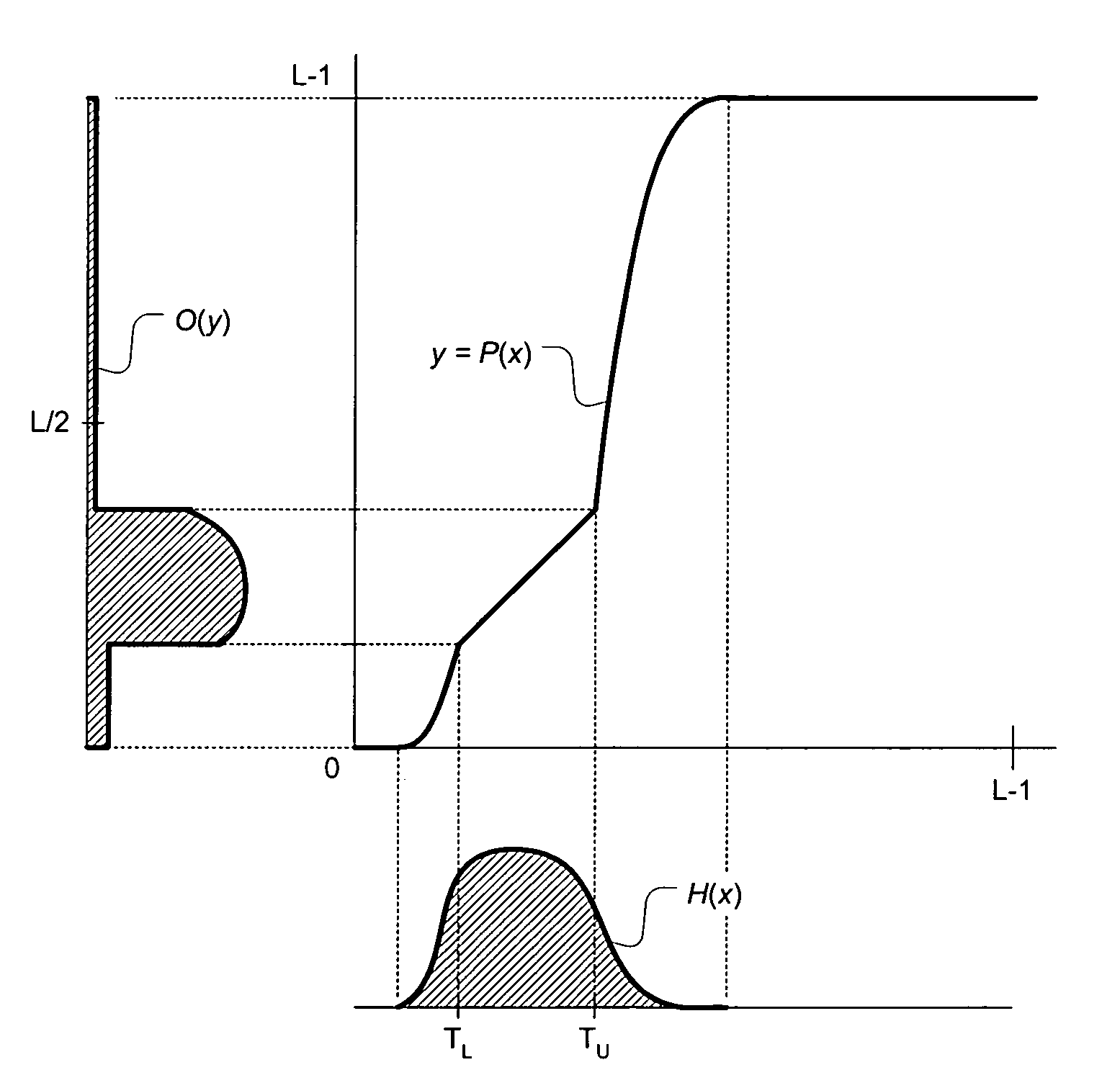
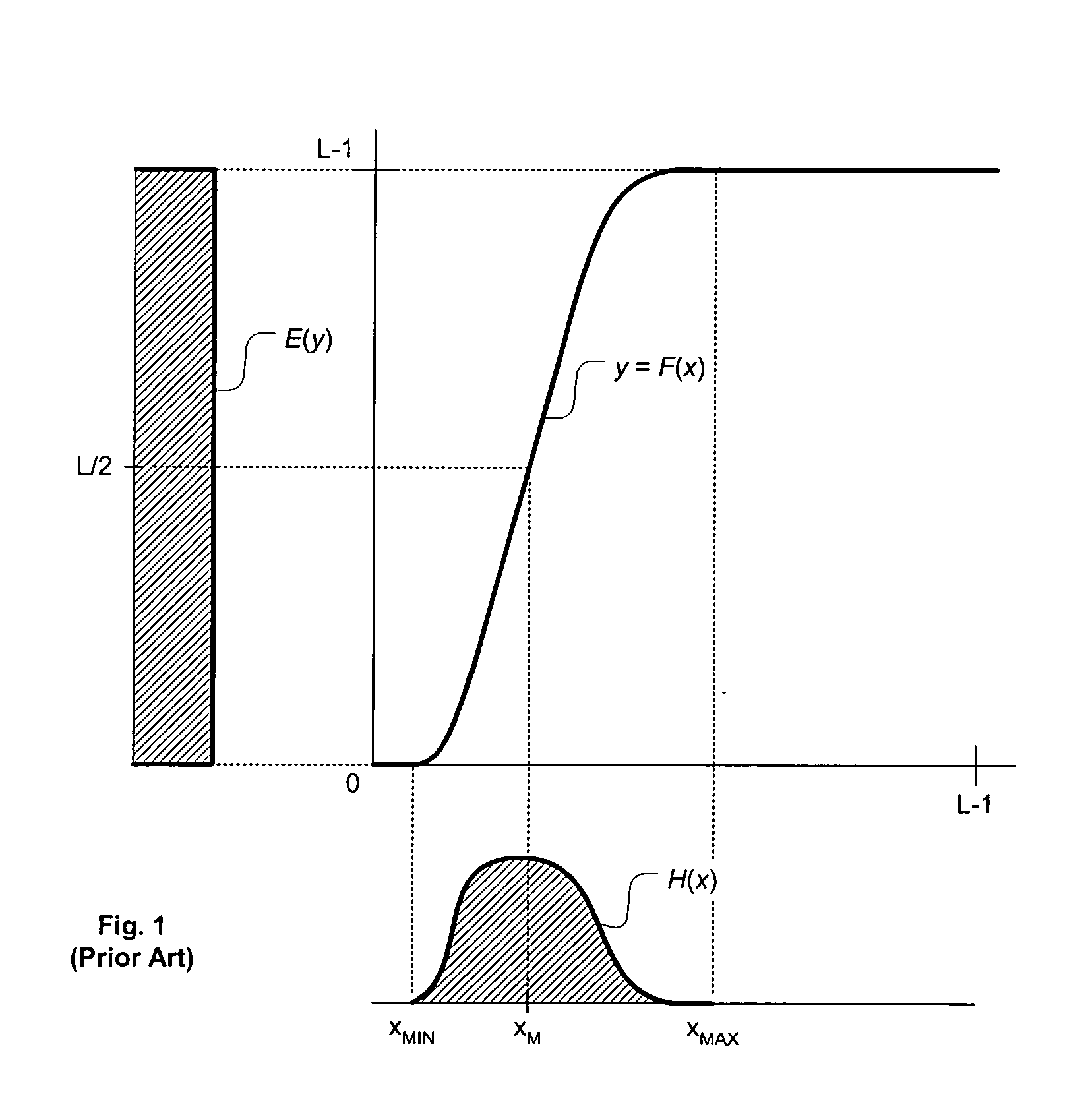
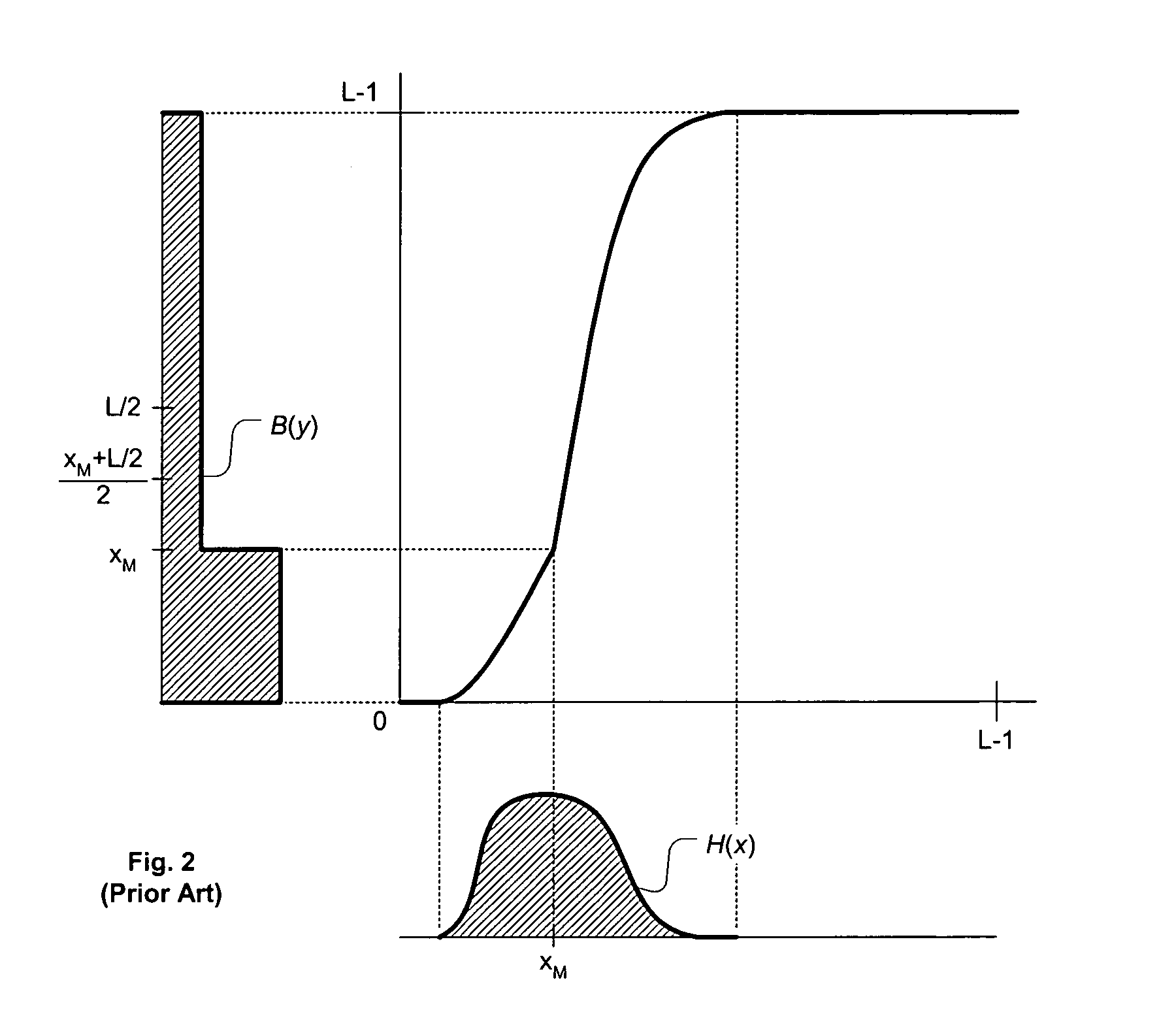
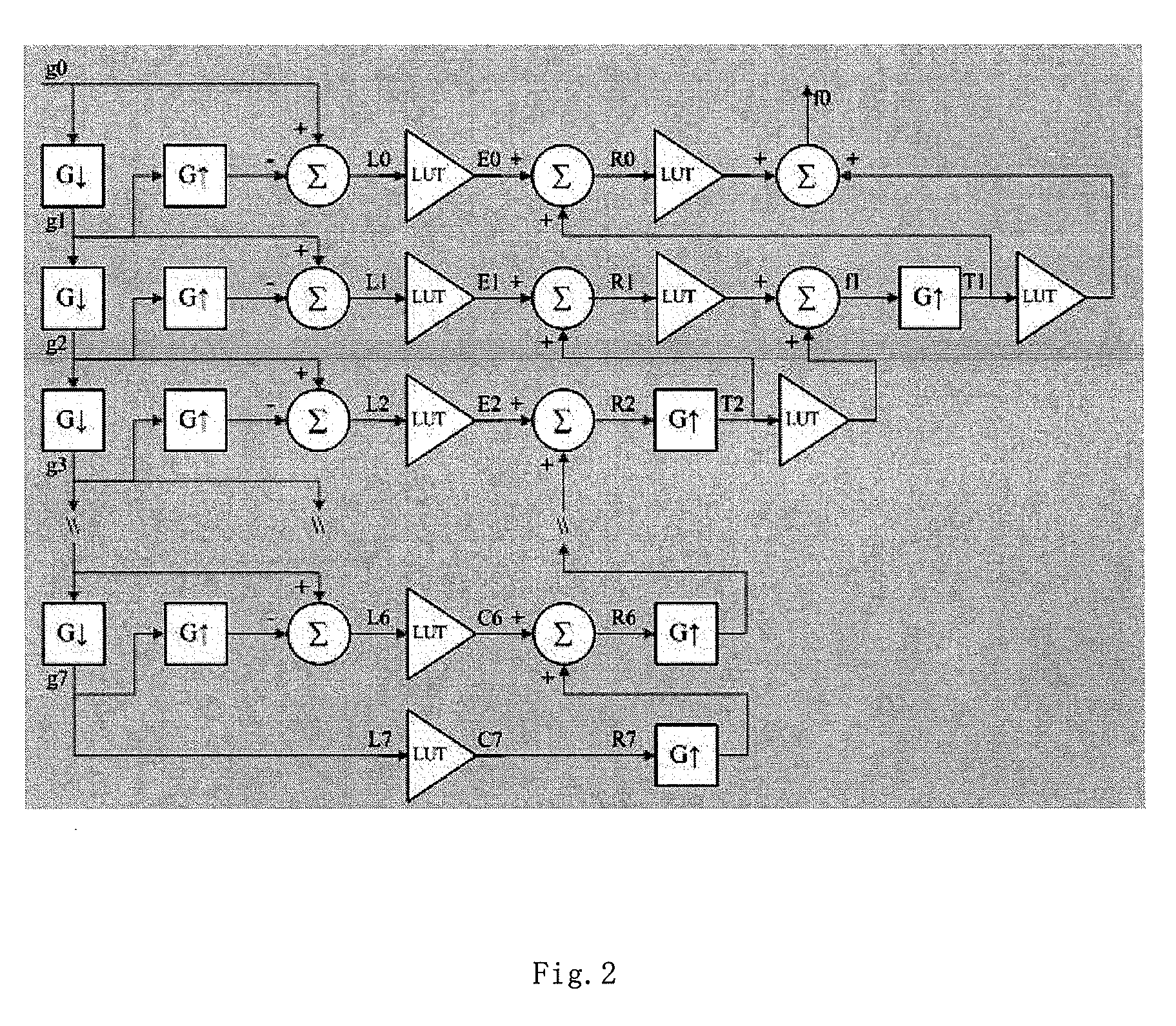
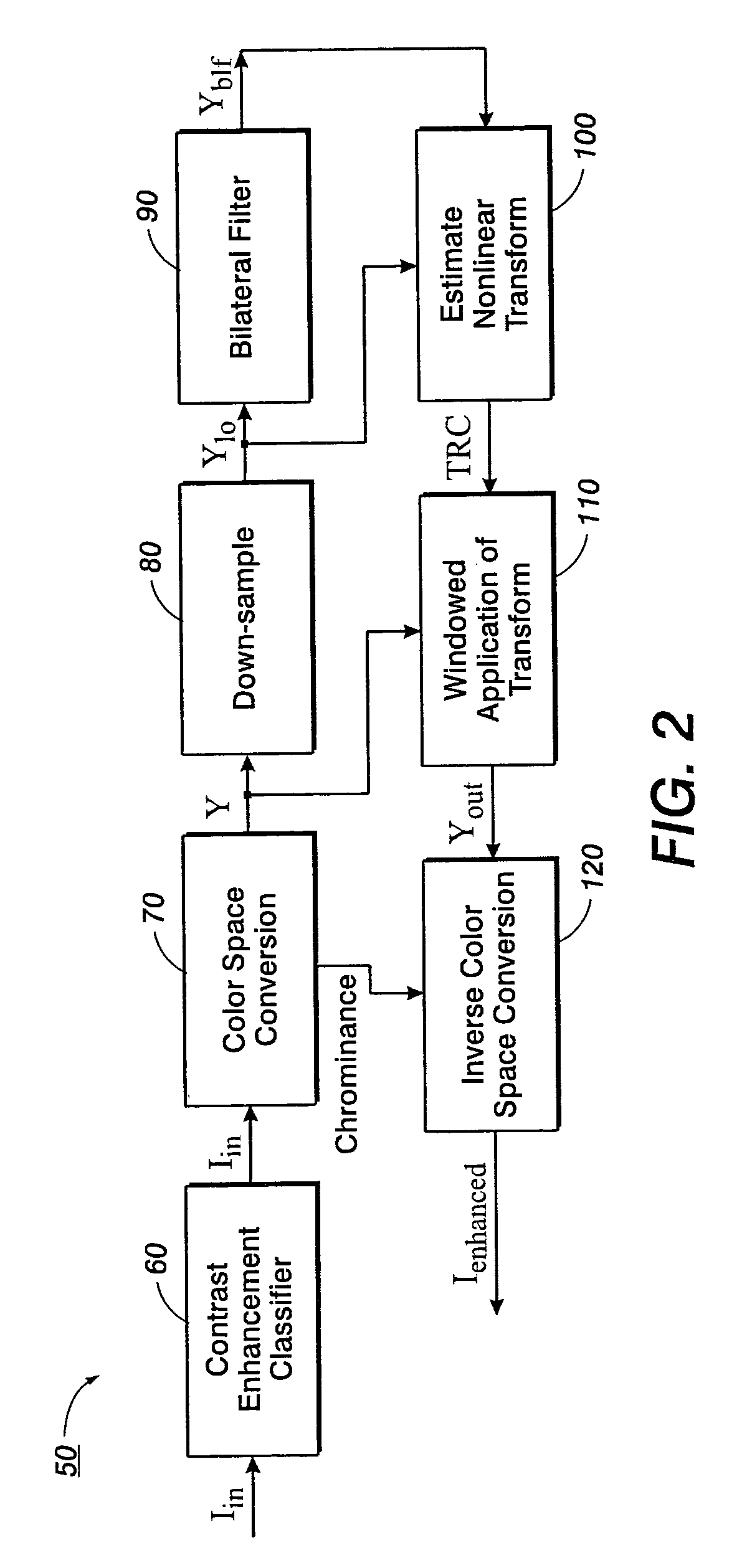
Contrast enhancement of images
A method and system for contrast enhancement of an input image that utilizes luminance values of pixels of the input image to derive transforms. The method down-samples and partitions an image into sub-images whereby transforms are generated for selected sub-images. The selected sub-image transforms are used to generate an output transform which is applied to the input image for local contrast enhancement of the image. Furthermore, a decision method as to whether or not the input image is to receive local contrast enhancement wherein darkness features of the input image are compared to threshold values and combined into an expression which results in the determination.
Owner:XEROX CORP
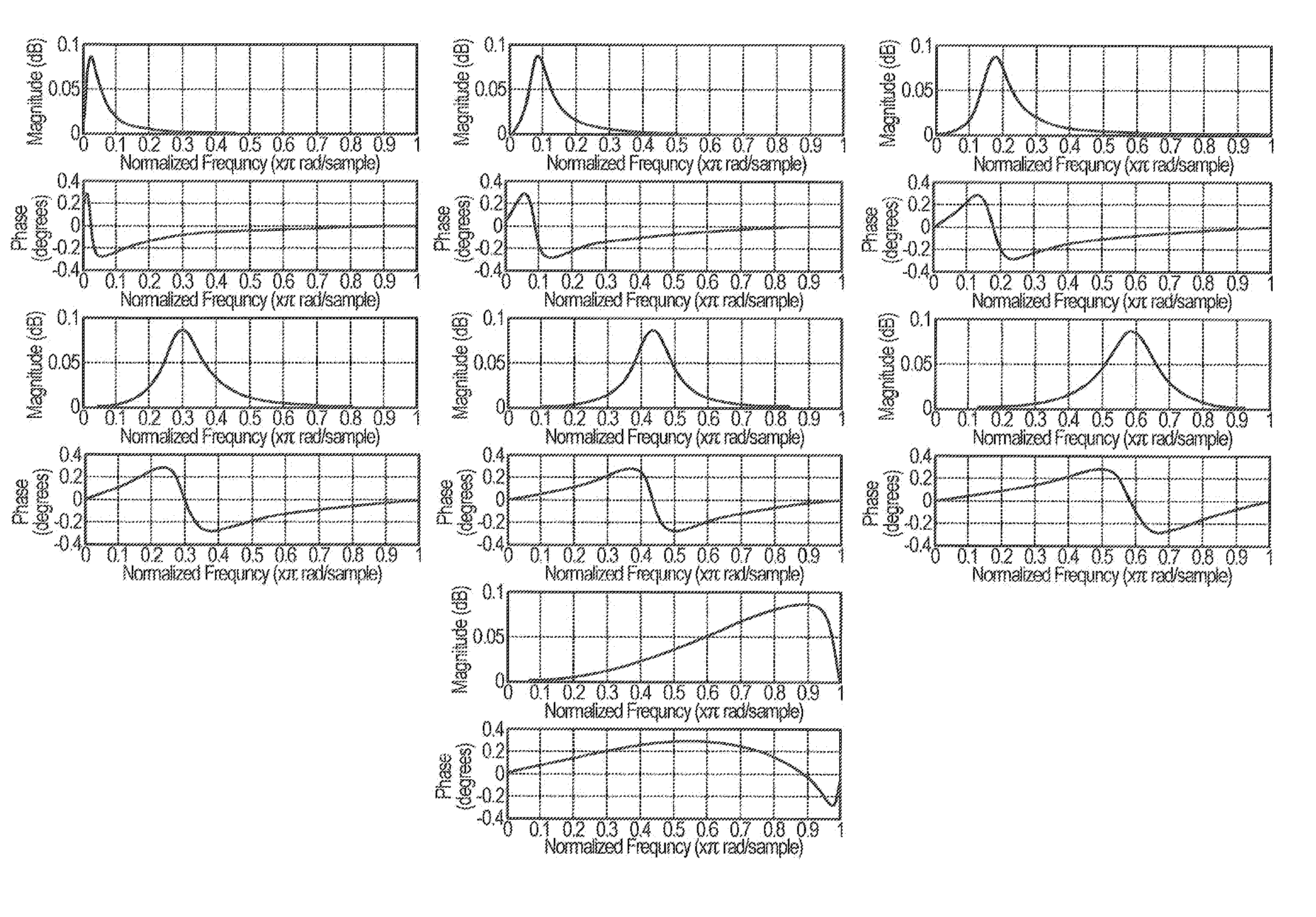
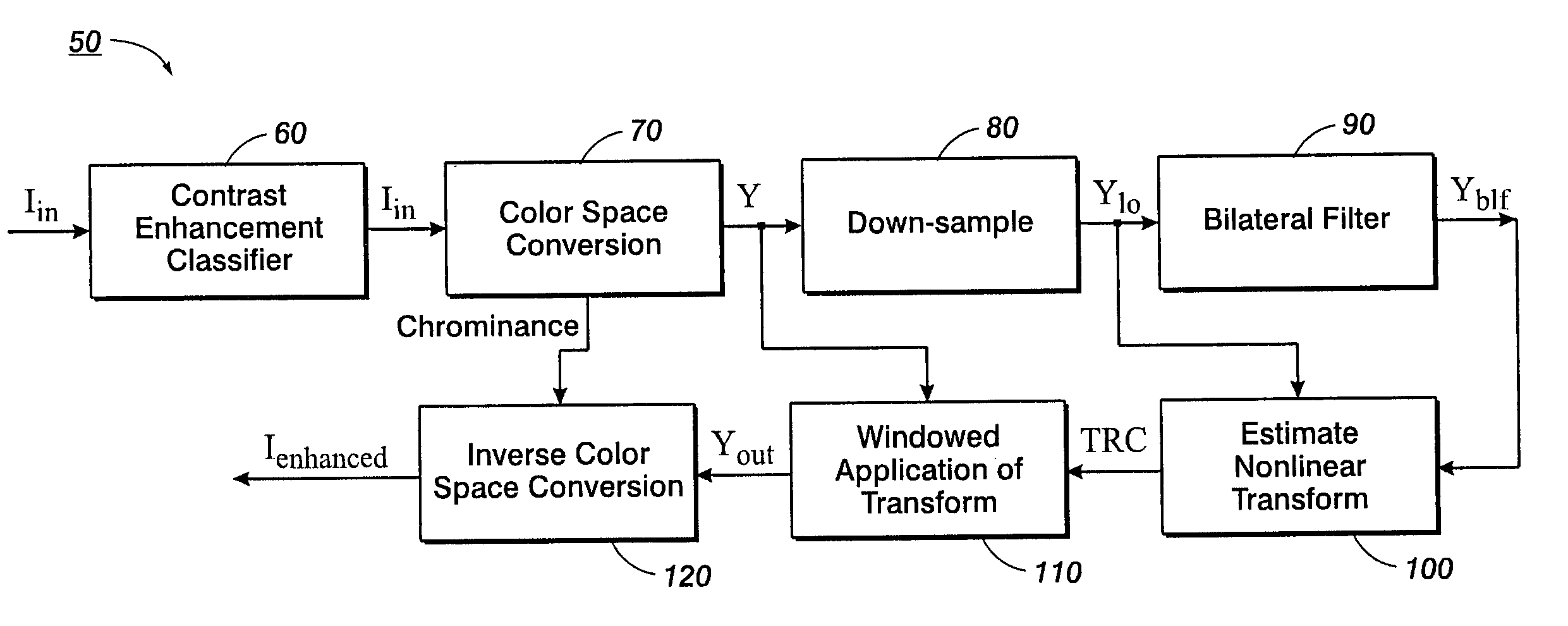
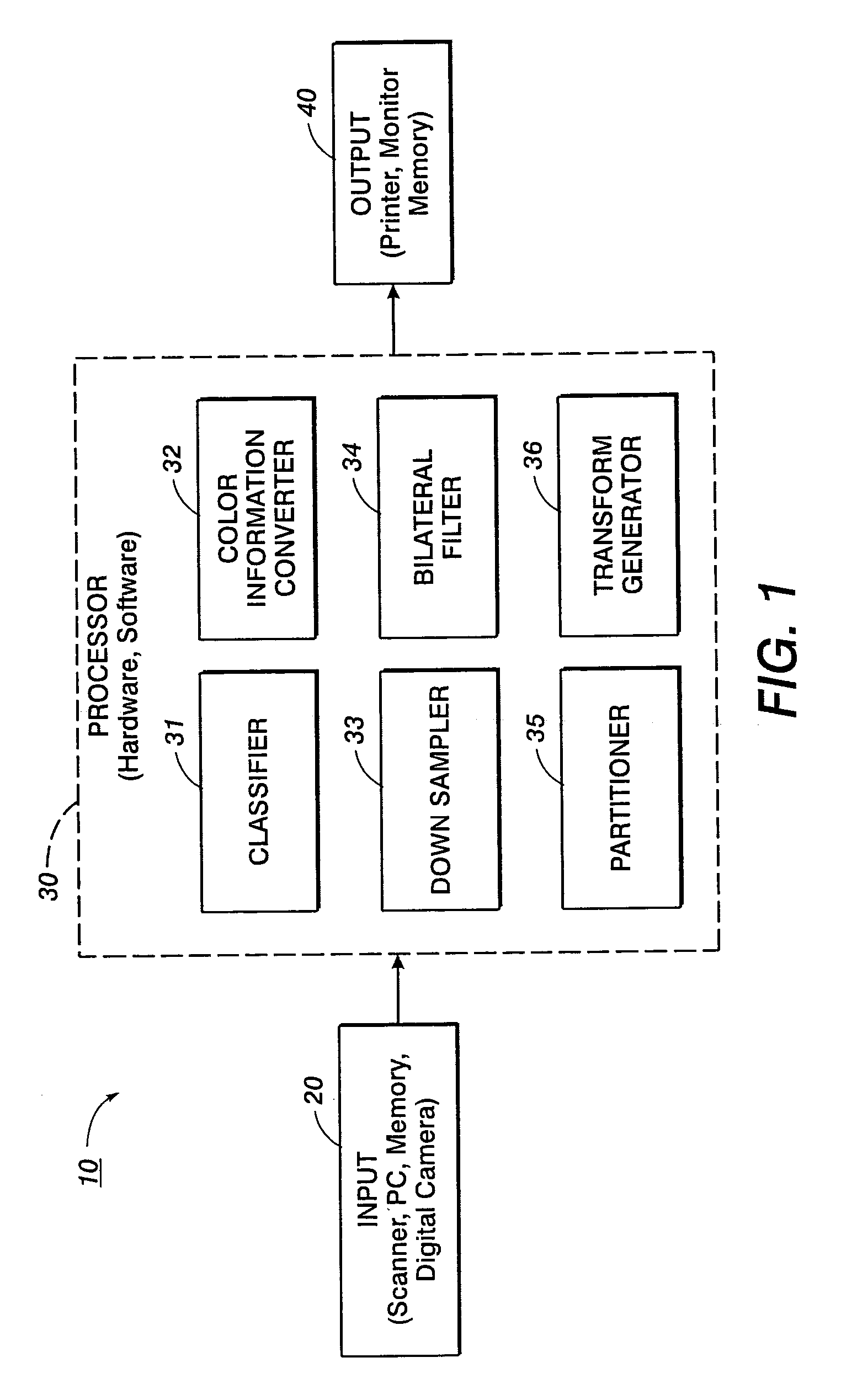
Image contrast enhancement
ActiveUS20070036456A1Easy to adjustAccurate fine-tuningTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage contrastContrast enhancement
Owner:ACD SYST INT
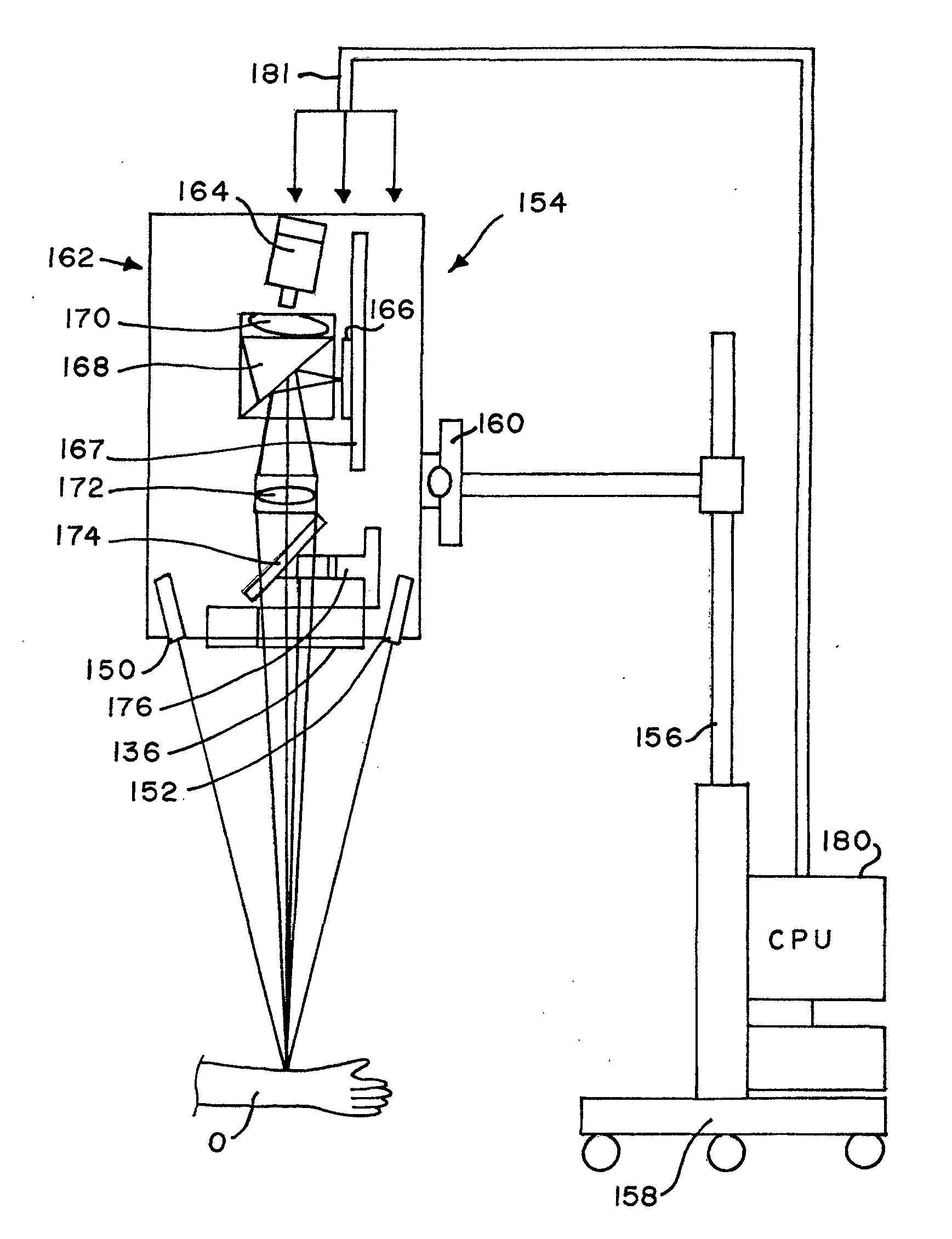
Method and system for characterization and mapping of tissue lesions
InactiveUS20050090751A1Evaluation of the accuracy in selectingGood choiceBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesSpectral bandsNon invasive
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for the in vivo, non-invasive, early detection of alterations and mapping of the grade of these alterations, caused in the biochemical and / or in the functional characteristics of epithelial tissues during the development of tissue atypias, dysplasias, neoplasias and cancers. The method is based, at least in part, on the simultaneous measurement of the spatial, temporal and spectral alterations in the characteristics of the light that is re-emitted from the tissue under examination, as a result of a combined tissue excitation with light and special chemical agents. The topical or systematic administration of these agents result in an evanescent contrast enhancement between normal and abnormal areas of tissue. The apparatus enables the capturing of temporally successive imaging in one or more spectral bands simultaneously. Based on the measured data, the characteristic curves that express the agent-tissue interaction kinetics, as well as numerical parameters derived from these data, are determined in any spatial point of the examined area. Mapping and characterization of the lesion, are based on these parameters.
Owner:KREOS CAPITAL V UK LTD
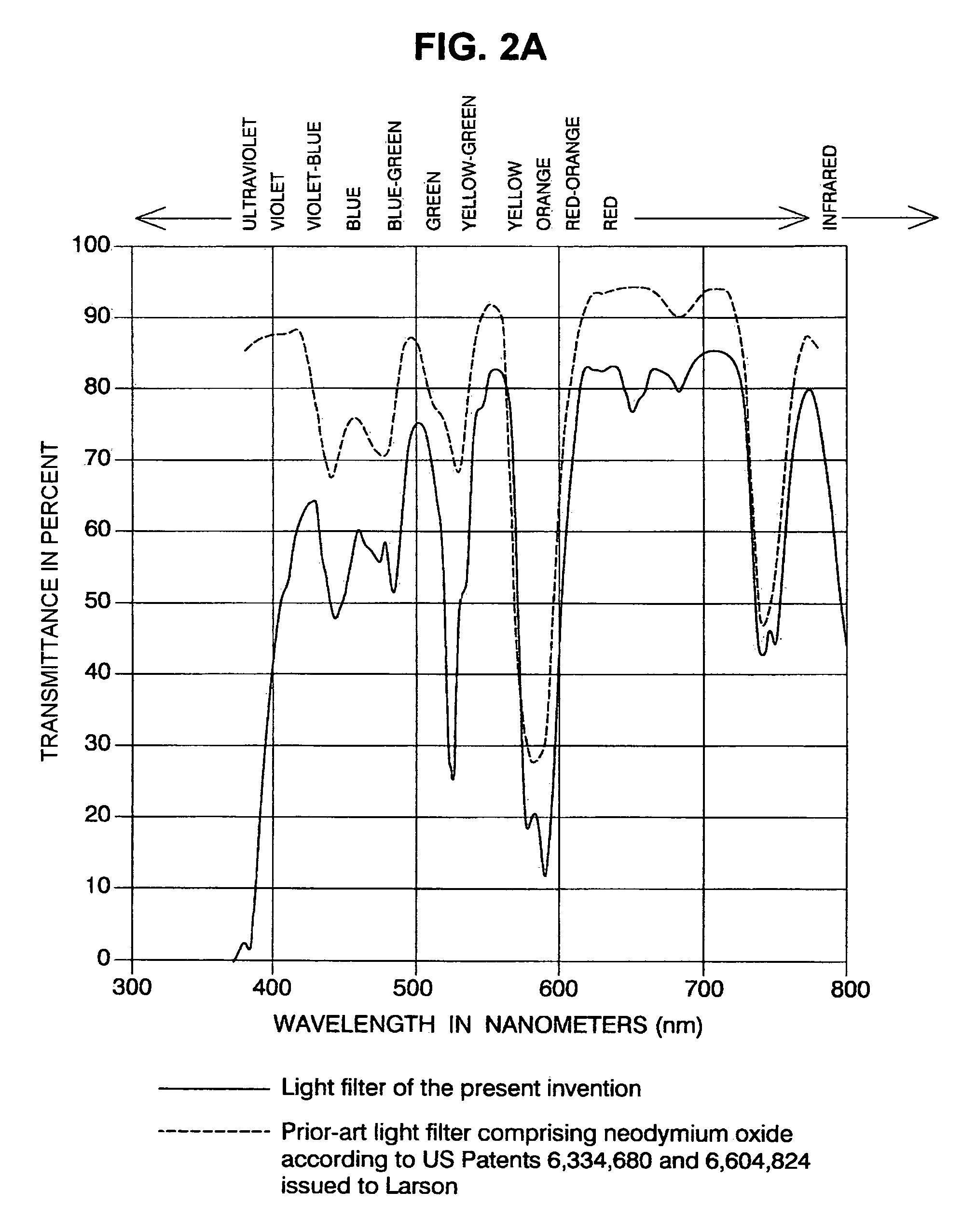
Polarized contrast enhancing sunglass lens
InactiveUS7597441B1Promotes accurate color perceptionHigh light transmittanceSpectales/gogglesOptical partsUv spectrumUltraviolet
The invention is a polarized sunglass lens that utilizes a multiband contrast enhancer comprised of three rare-earth oxides to provide relatively high peak transmittance in portions of the red and green spectrum, relatively lower transmittance for the blue spectrum, and very low transmittance for the UV spectrum. The lens provides enhanced perception of colors, heightened contrast, and improved visual acuity. The inclusion of vanadium pentoxide in the lens provides attenuation of the UV spectrum, thus protecting the user's eyes and the internal layers and colorants from UV-induced damage. The front lens element can be either the multiband contrast enhancer or a photochromic lens element.
Owner:FARWIG MICHAEL J
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com