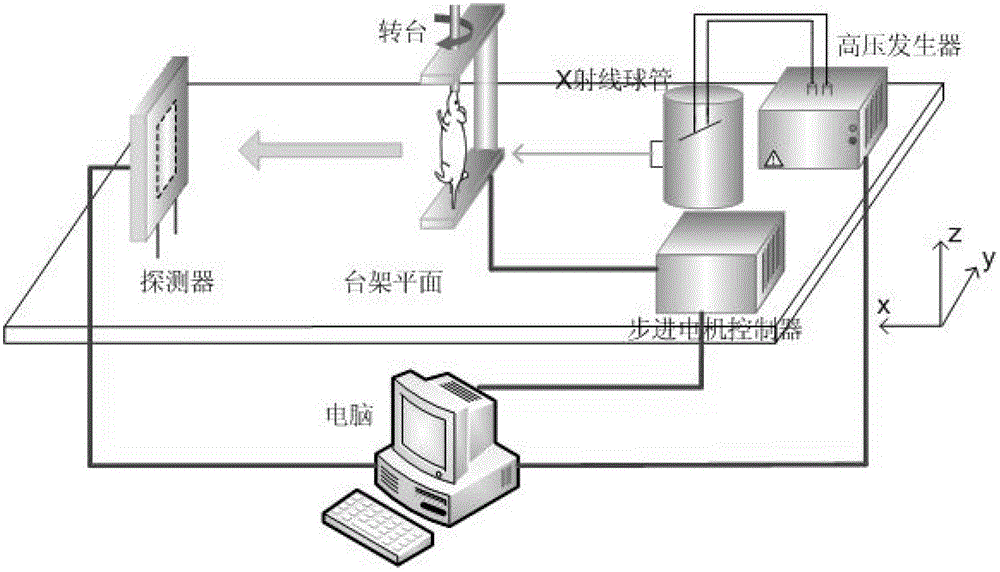
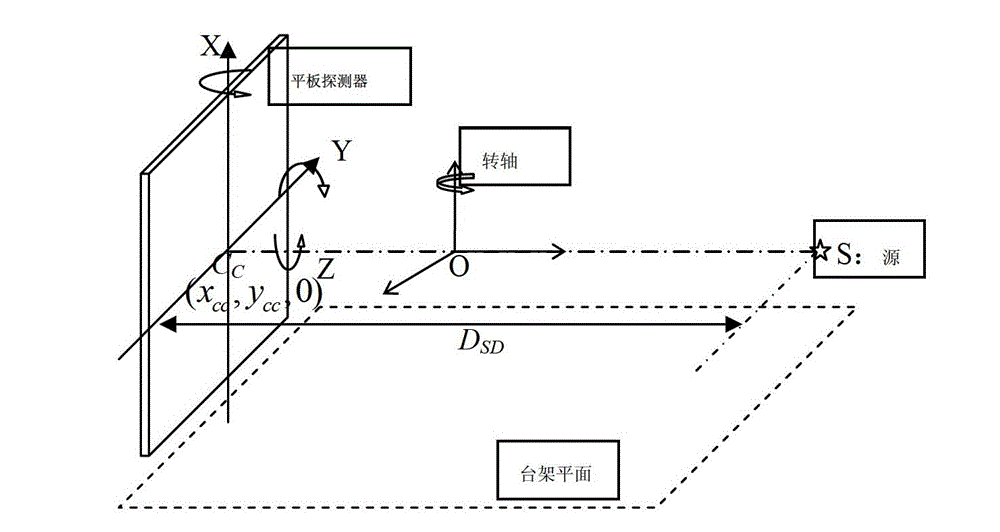
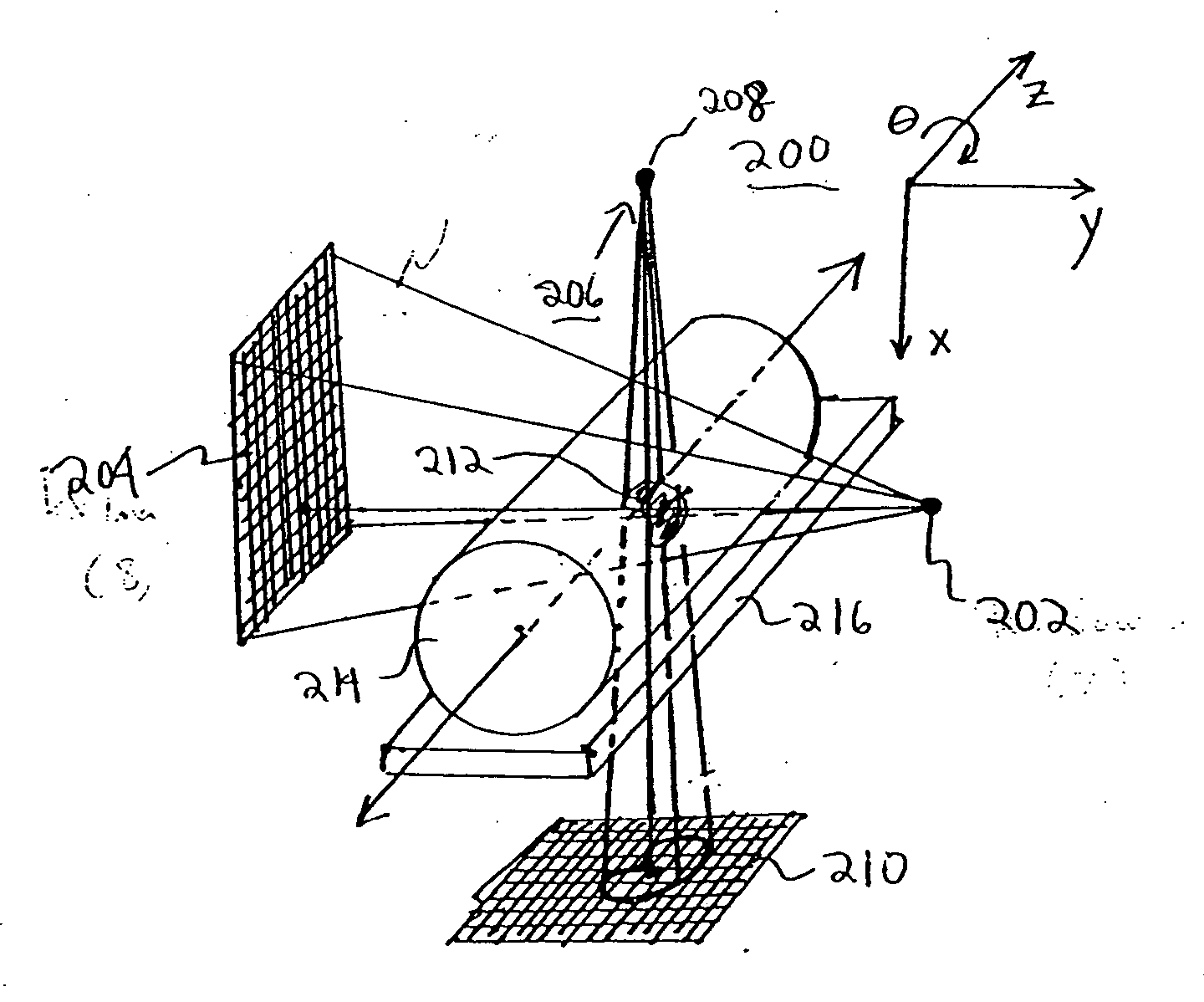
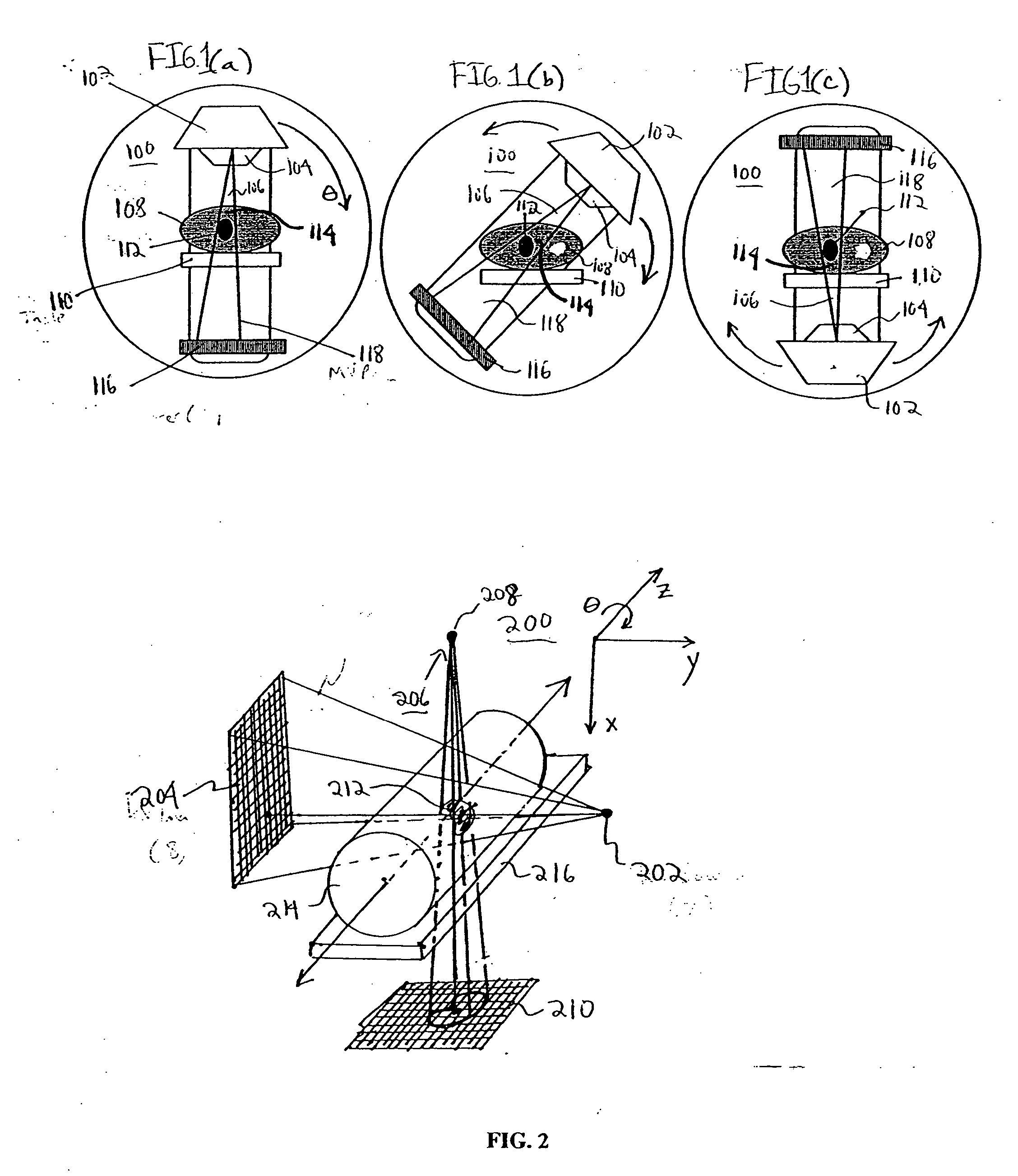
Patents
Literature
159 results about "Cone beam computed tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
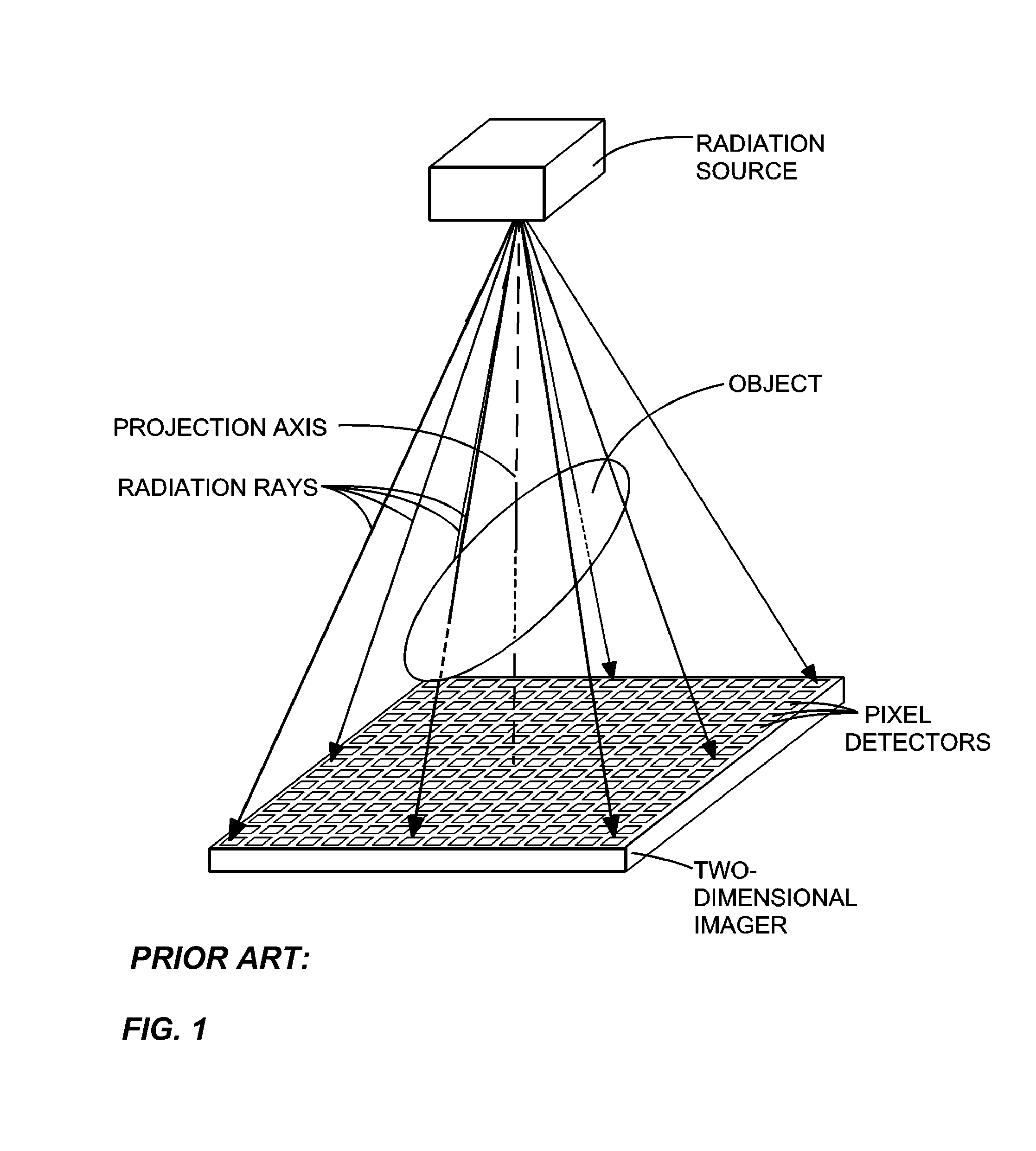
Cone beam computed tomography (or CBCT, also referred to as C-arm CT, cone beam volume CT, or flat panel CT) is a medical imaging technique consisting of X-ray computed tomography where the X-rays are divergent, forming a cone.
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
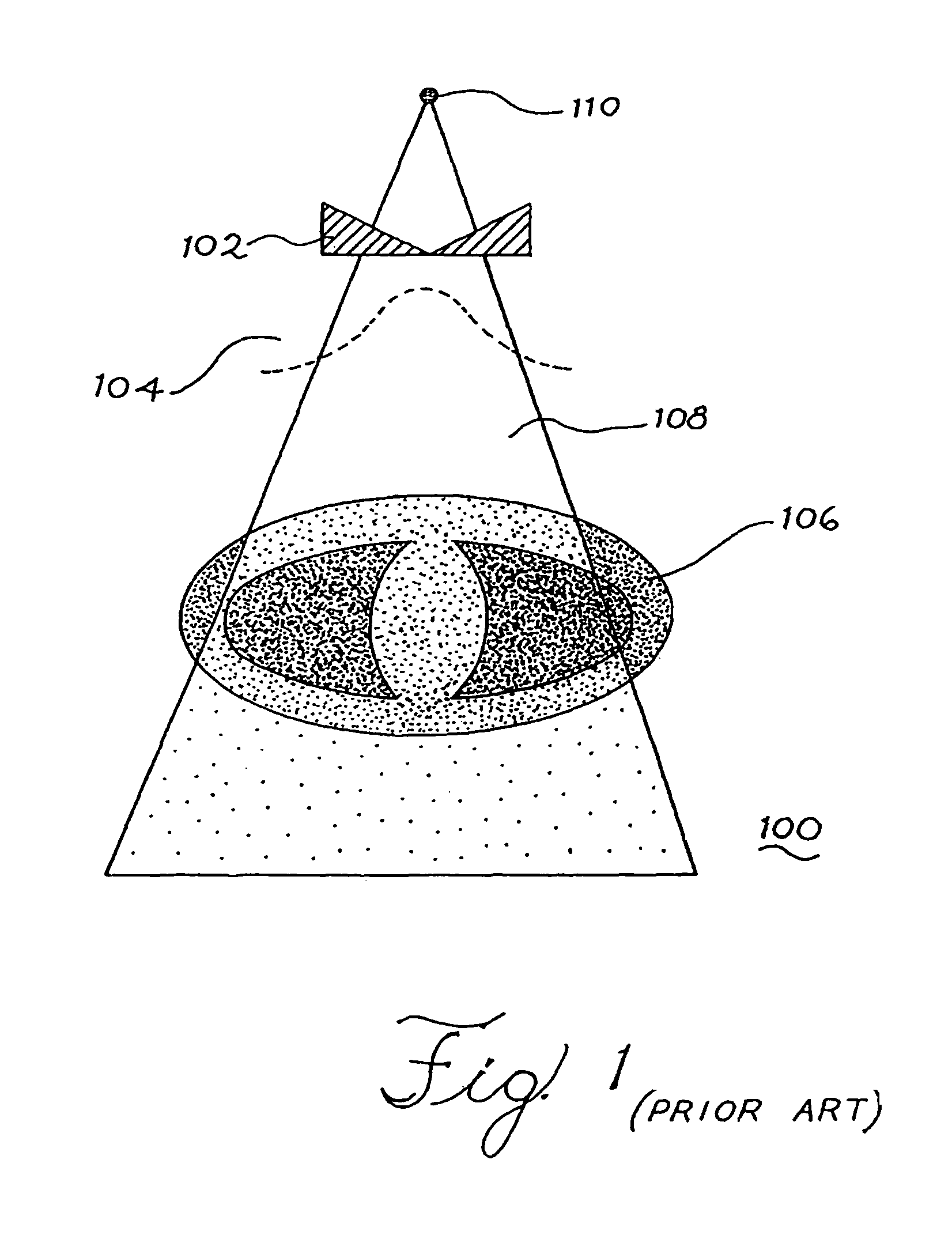
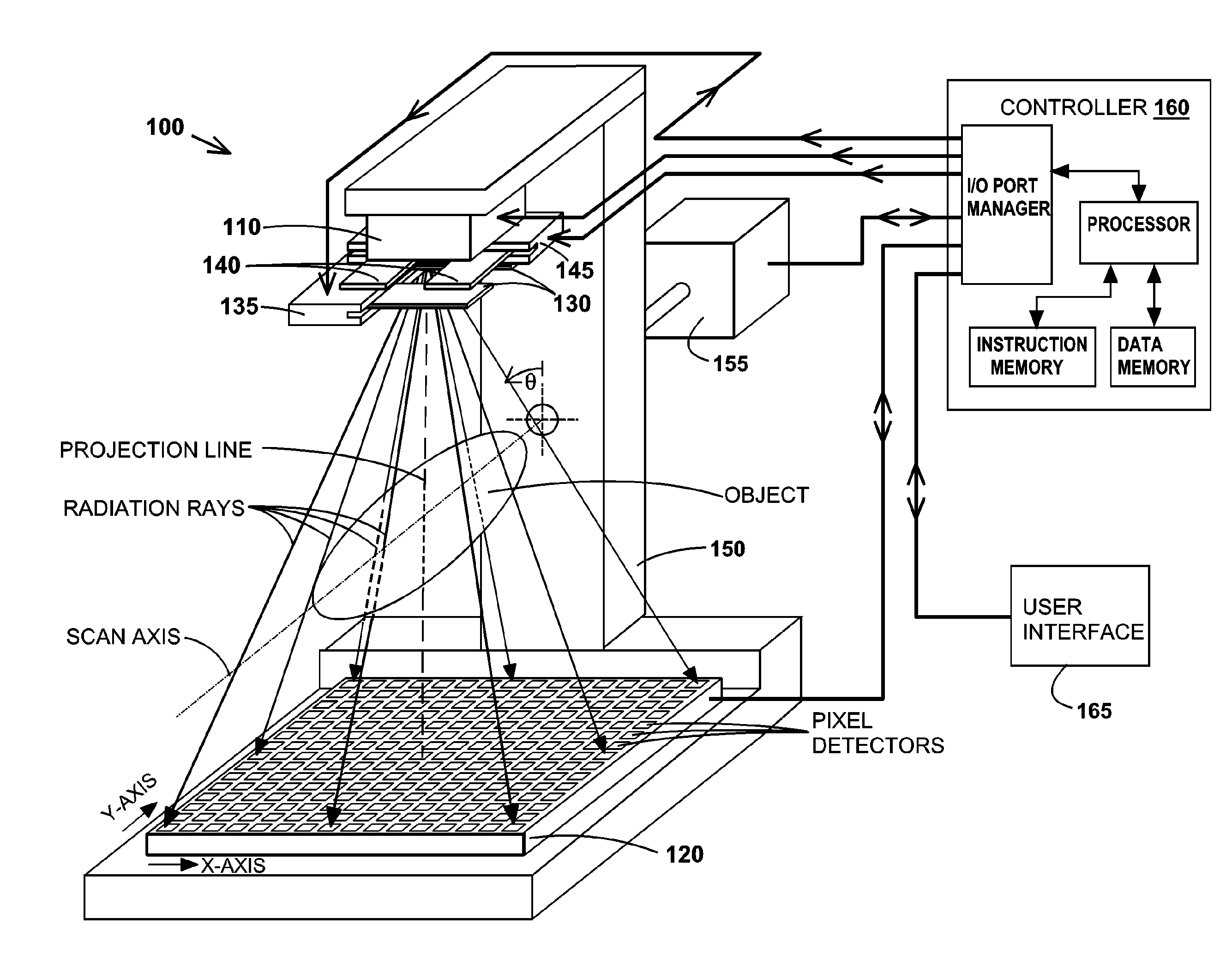
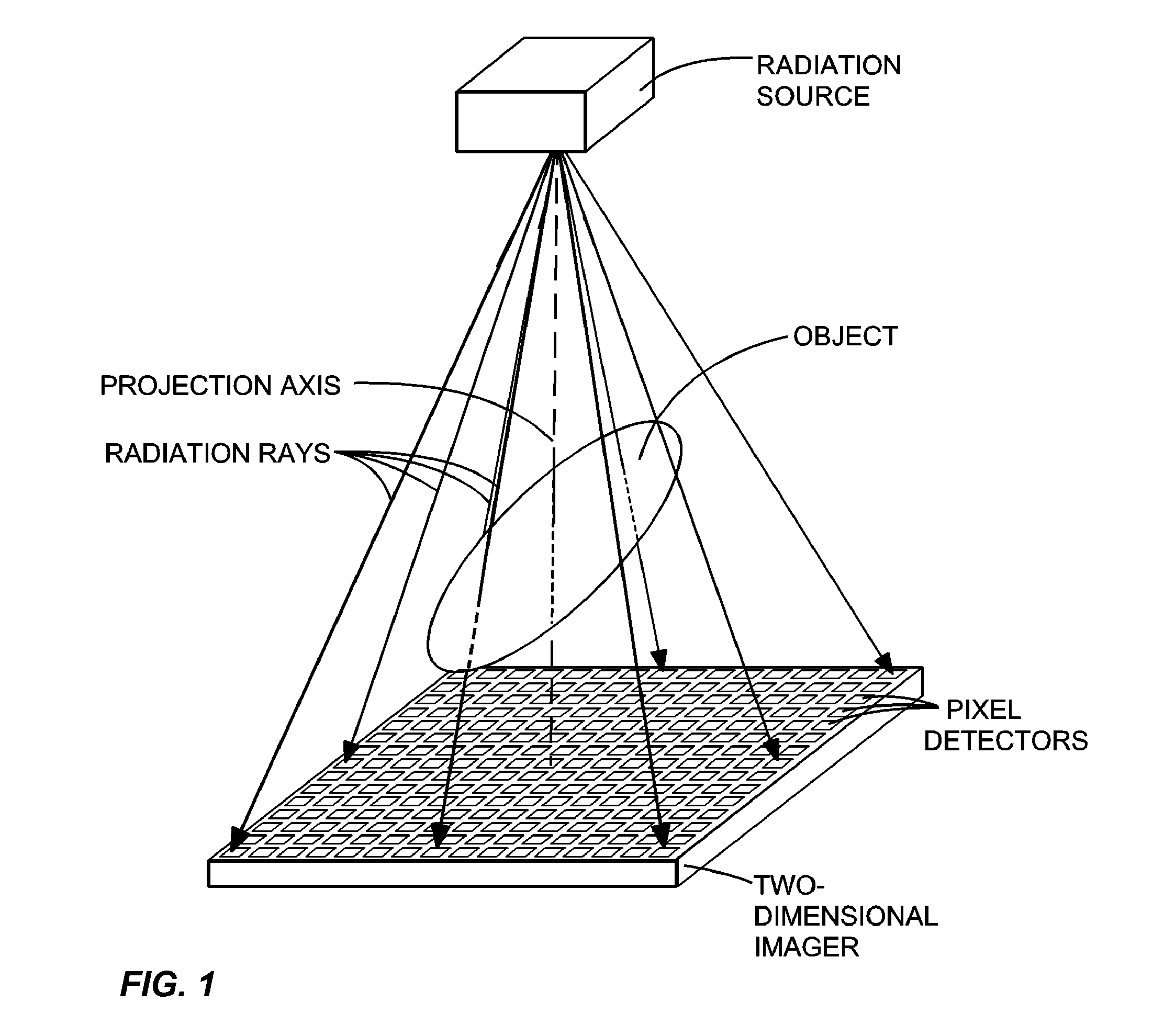
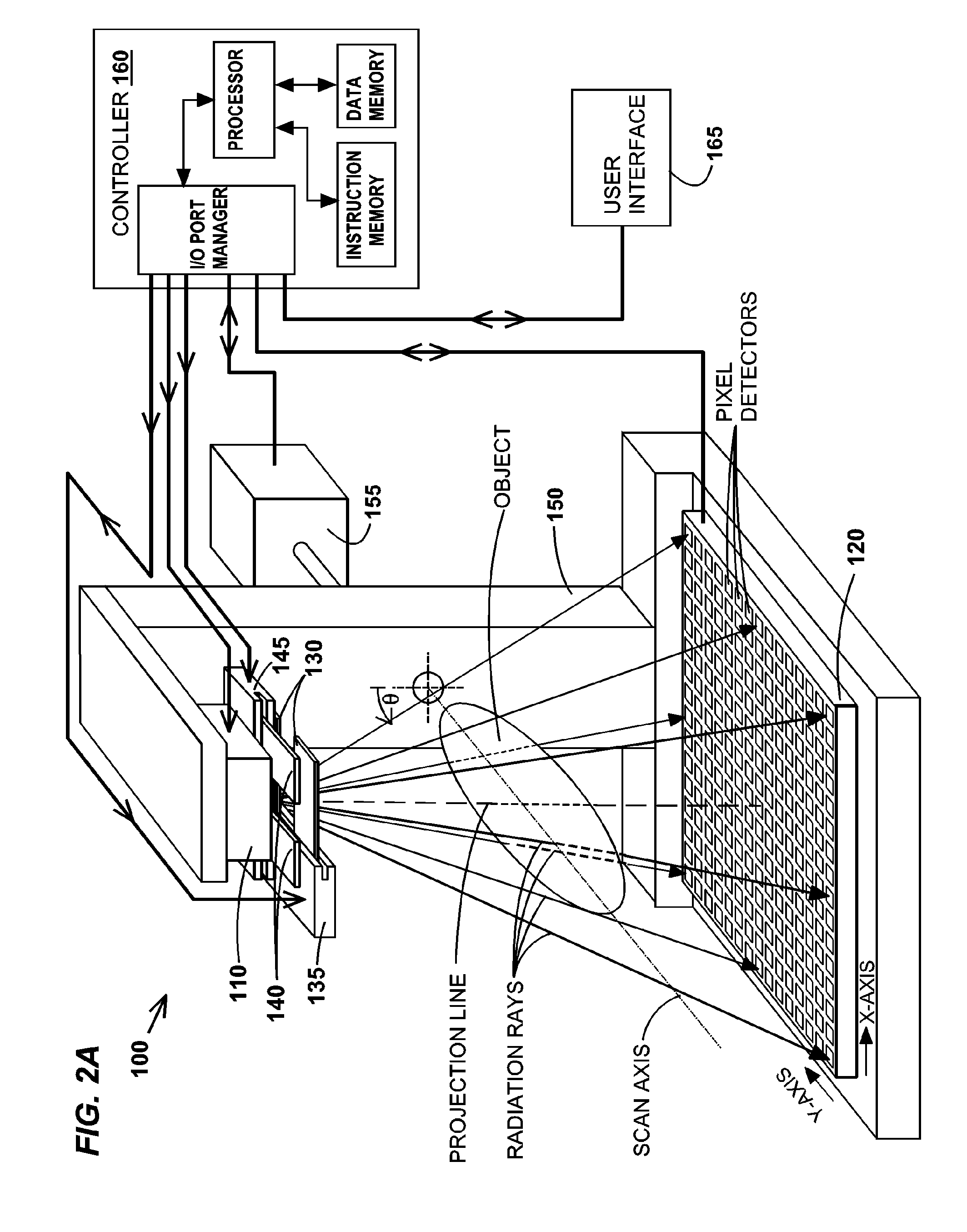
InactiveUS6842502B2Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
A radiation therapy system that includes a radiation source that moves about a path and directs a beam of radiation towards an object and a cone-beam computer tomography system. The cone-beam computer tomography system includes an x-ray source that emits an x-ray beam in a cone-beam form towards an object to be imaged and an amorphous silicon flat-panel imager receiving x-rays after they pass through the object, the imager providing an image of the object. A computer is connected to the radiation source and the cone beam computerized tomography system, wherein the computer receives the image of the object and based on the image sends a signal to the radiation source that controls the path of the radiation source.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
System, method and computer-accessible medium for providing a panoramic cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
InactiveUS20150213633A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageCone beam computed tomography
Exemplary devices, procedures and computer-readable mediums for providing a projection image associated with at least one target. The projection image can be formed from a plurality of locations of a source arrangement. At each source location, a plurality of panoramic projection images associated with a target can be acquired. At least two of the panoramic projection images can be obtained at view angles which are different from one another. These panoramic projection images can be stitched together or otherwise combined. A resulting image can then be generated using a computed tomography procedure based on the stitched or combined projection images that are generated at the plurality of location.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
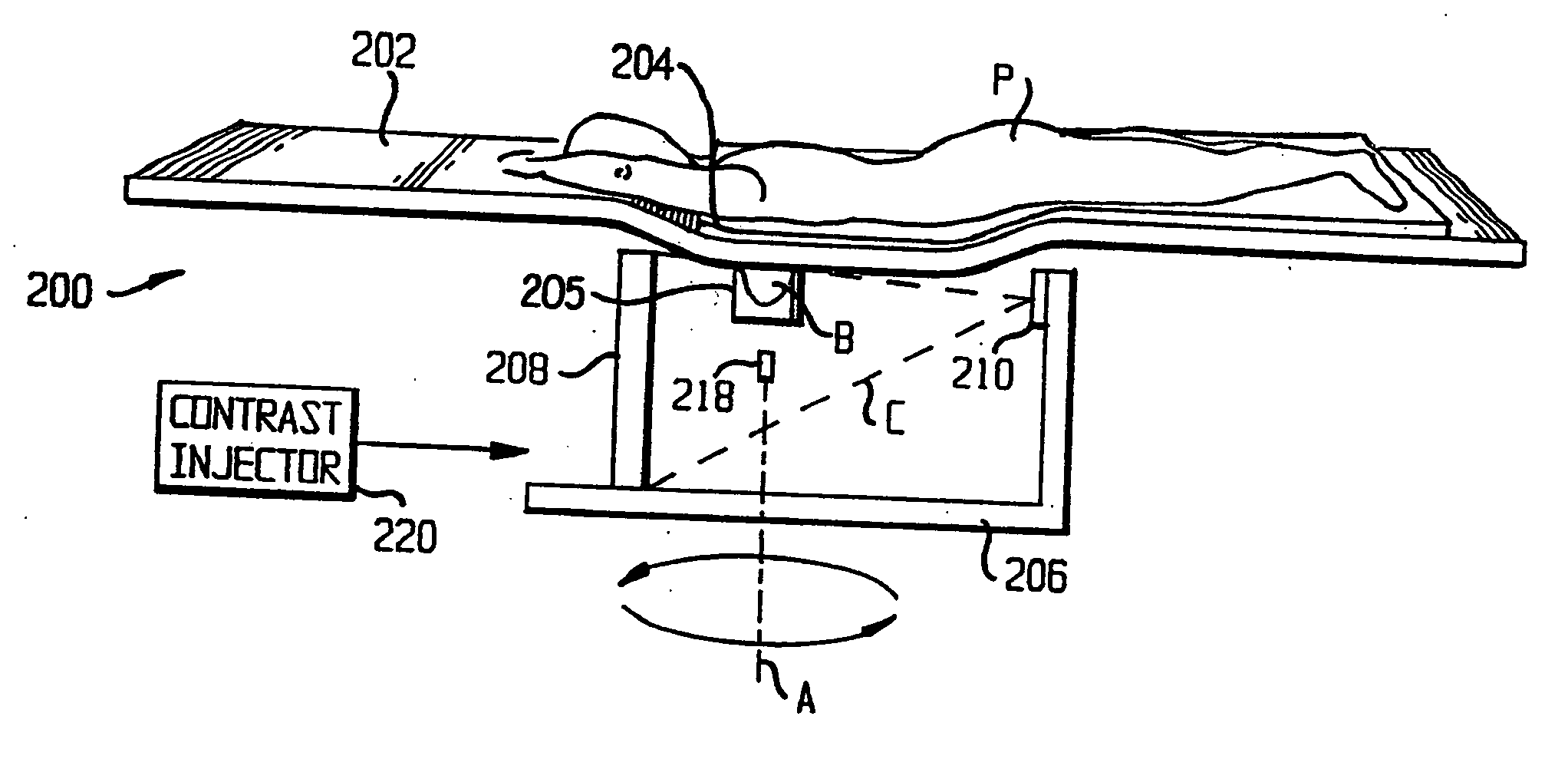
Contrast-enhanced cone beam X-ray imaging, evaluation, monitoring and treatment delivery
ActiveUS20070269000A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingVoxelData set
A method of imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using X-ray cone beam computed tomography or cone beam digital tomography comprises the step of introducing an effective amount of a contrast agent to the uncompressed region of interest. A system for imaging a patient's uncompressed region of interest using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) or cone beam digital tomography (CBDT) comprises an X-ray source transmitting an X-ray to the uncompressed region of interest, an image acquisition system acquiring a plurality of two-dimensional projection images data for a CBCT or CBDT data set with at least one of the projection images acquired in 35 milliseconds or less, and a processor generating a three-dimensional computed tomography image data set resolving voxels with dimensions of 0.4 mm or less in at least two orthogonal directions.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS +2
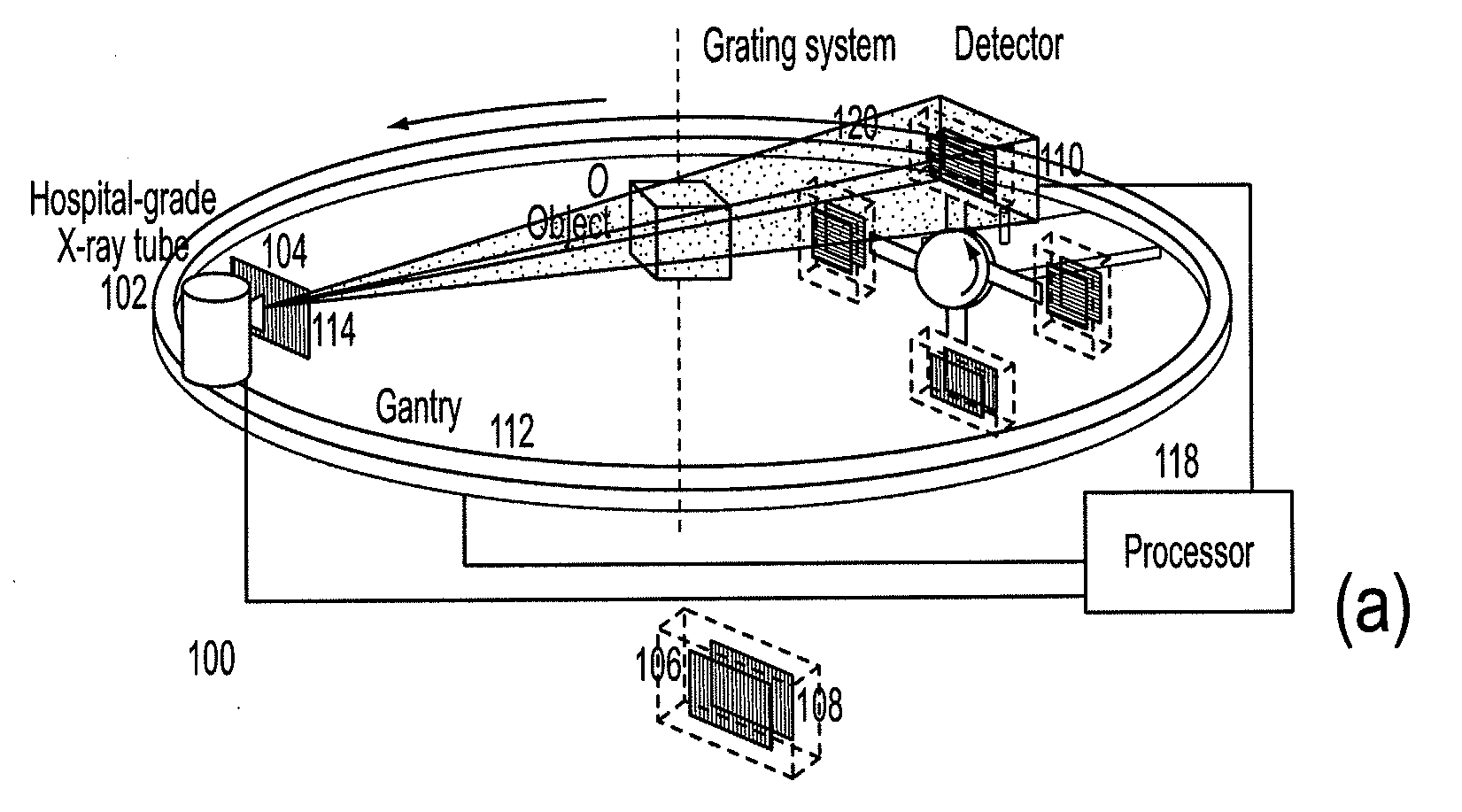
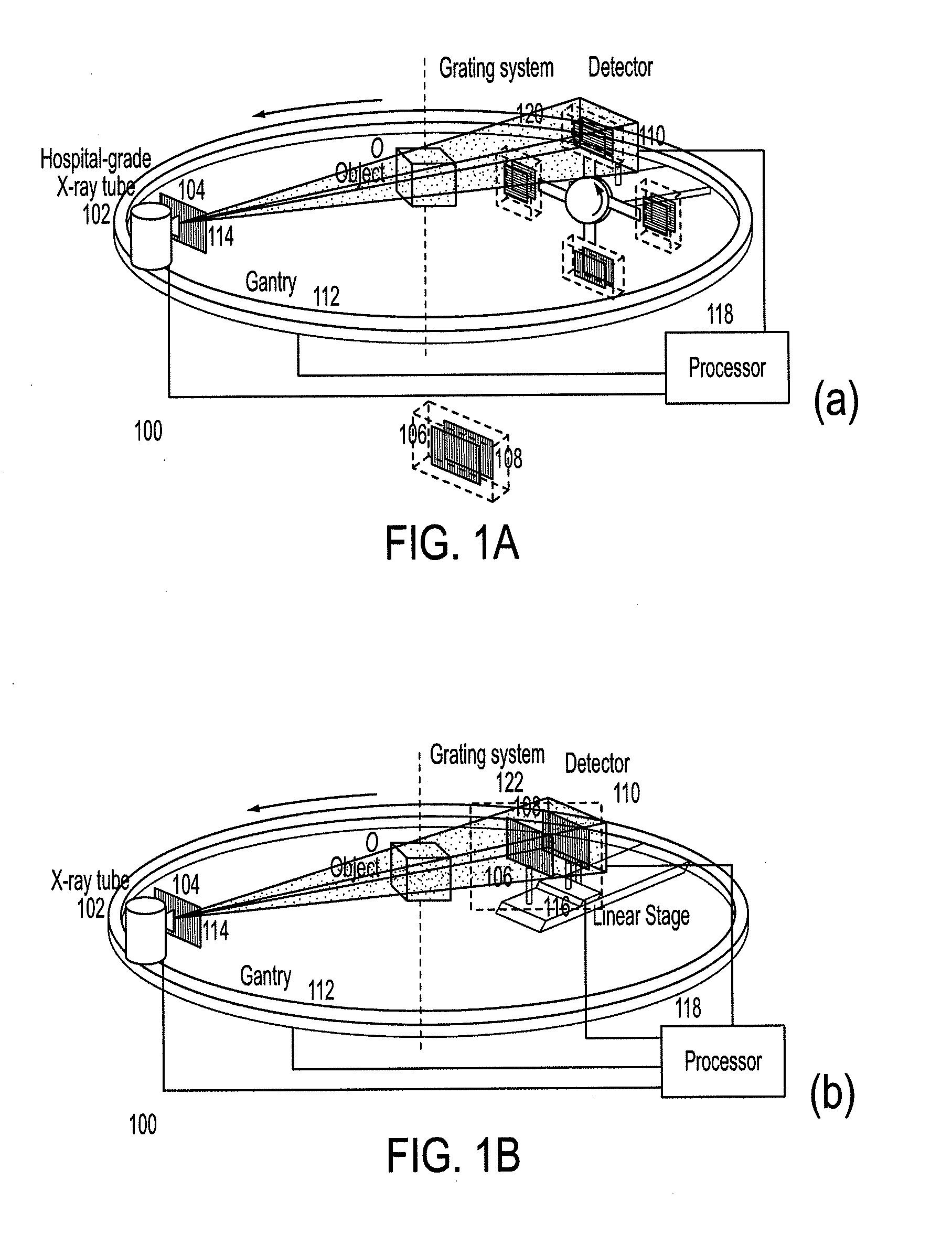
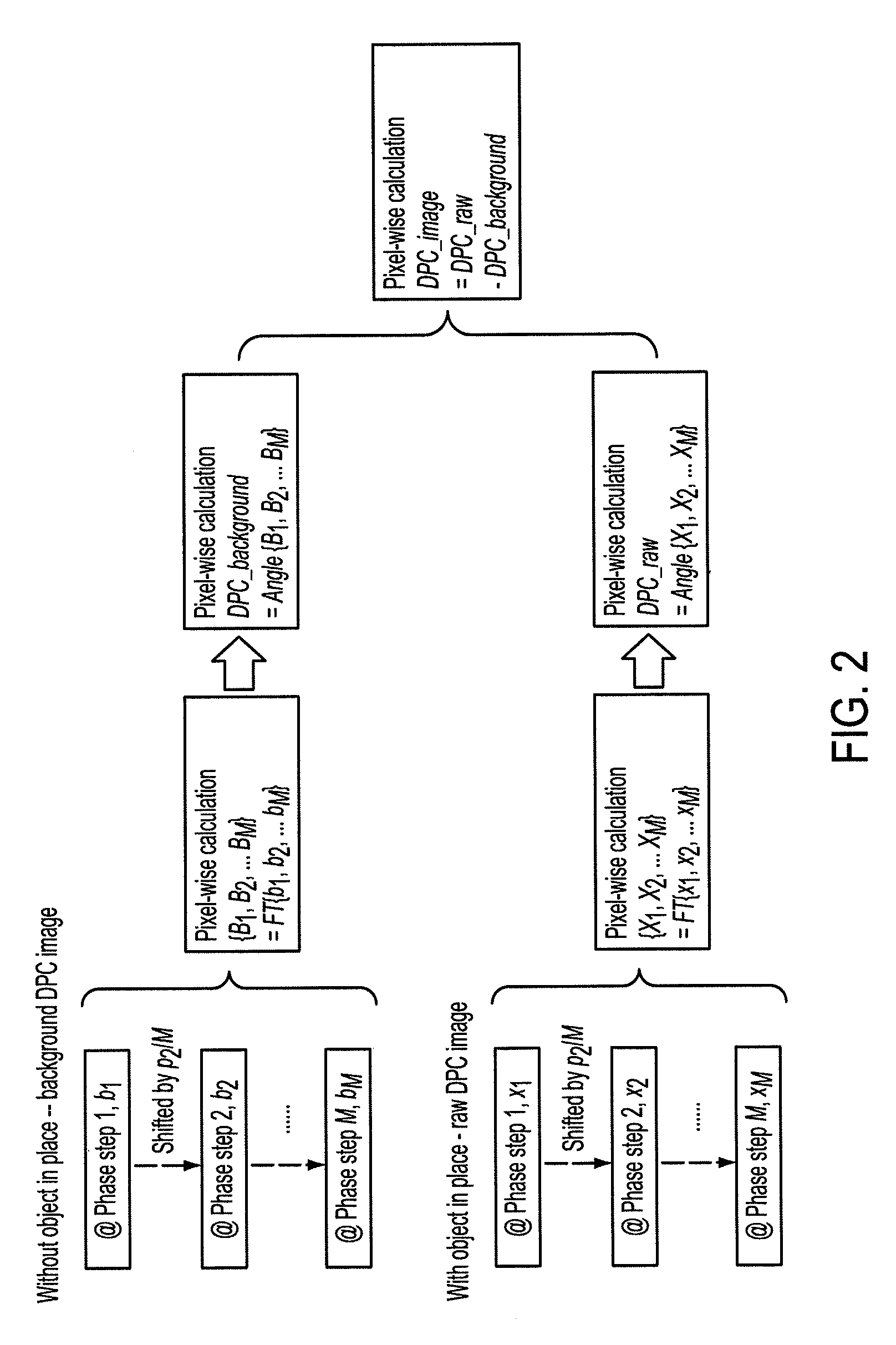
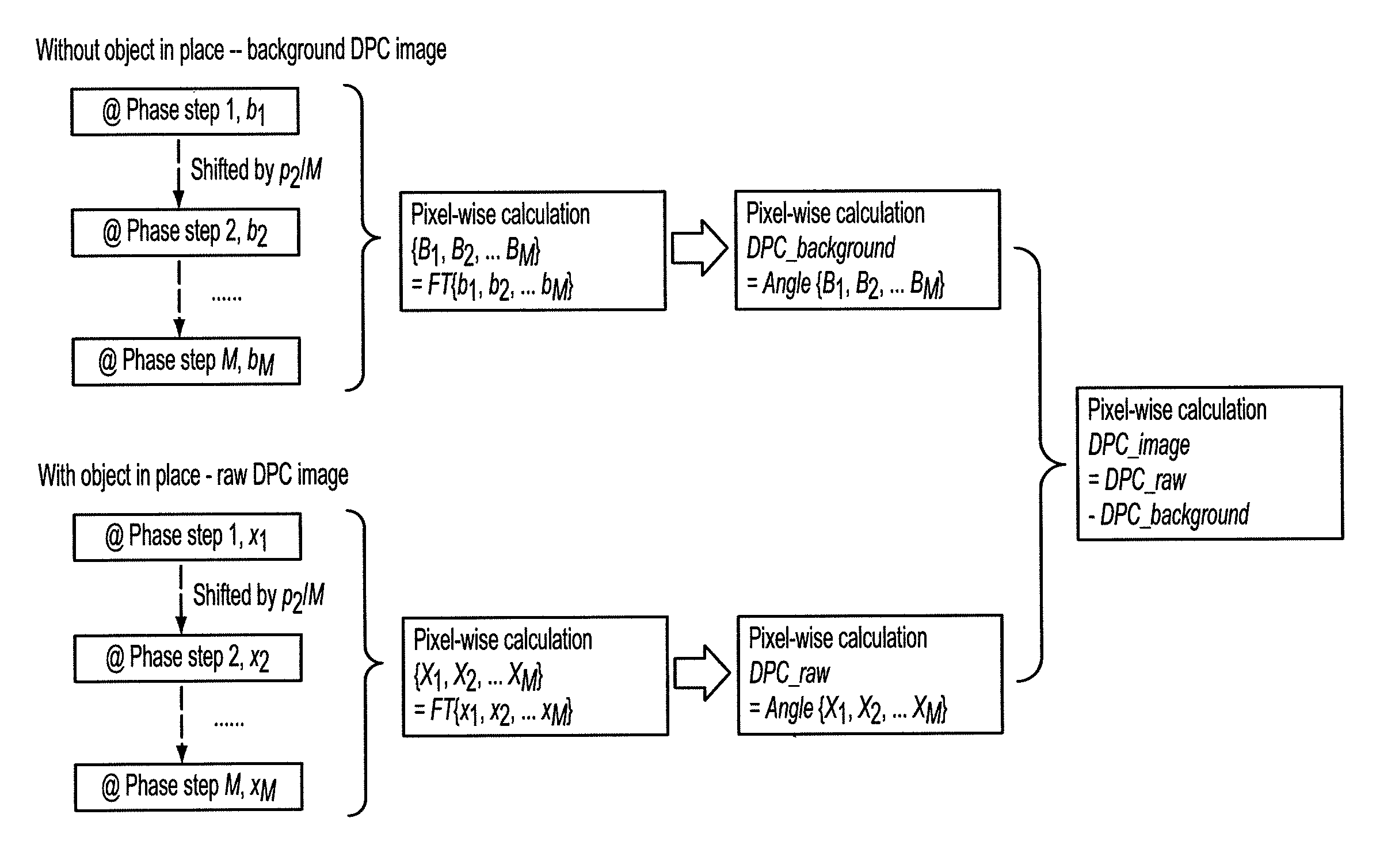
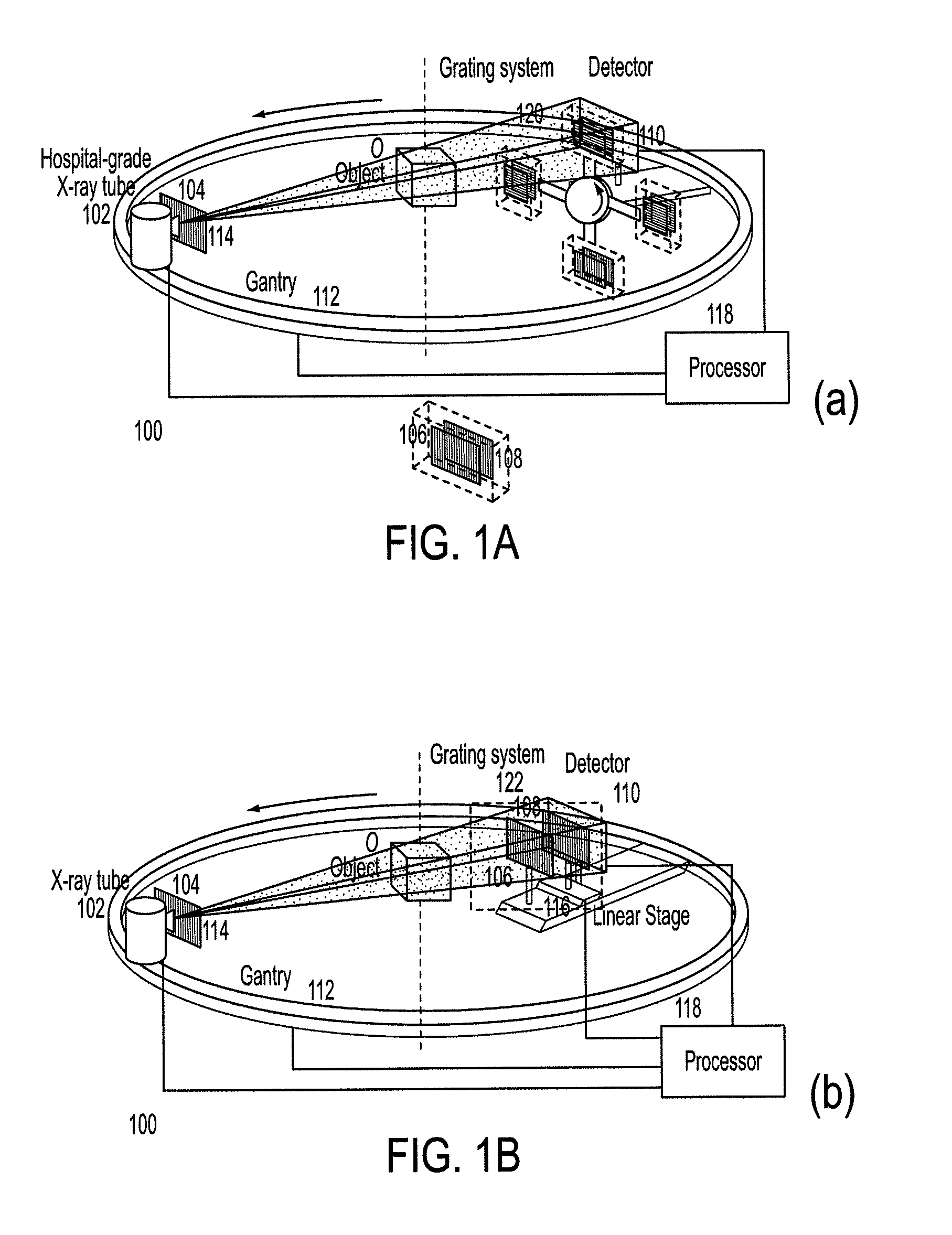
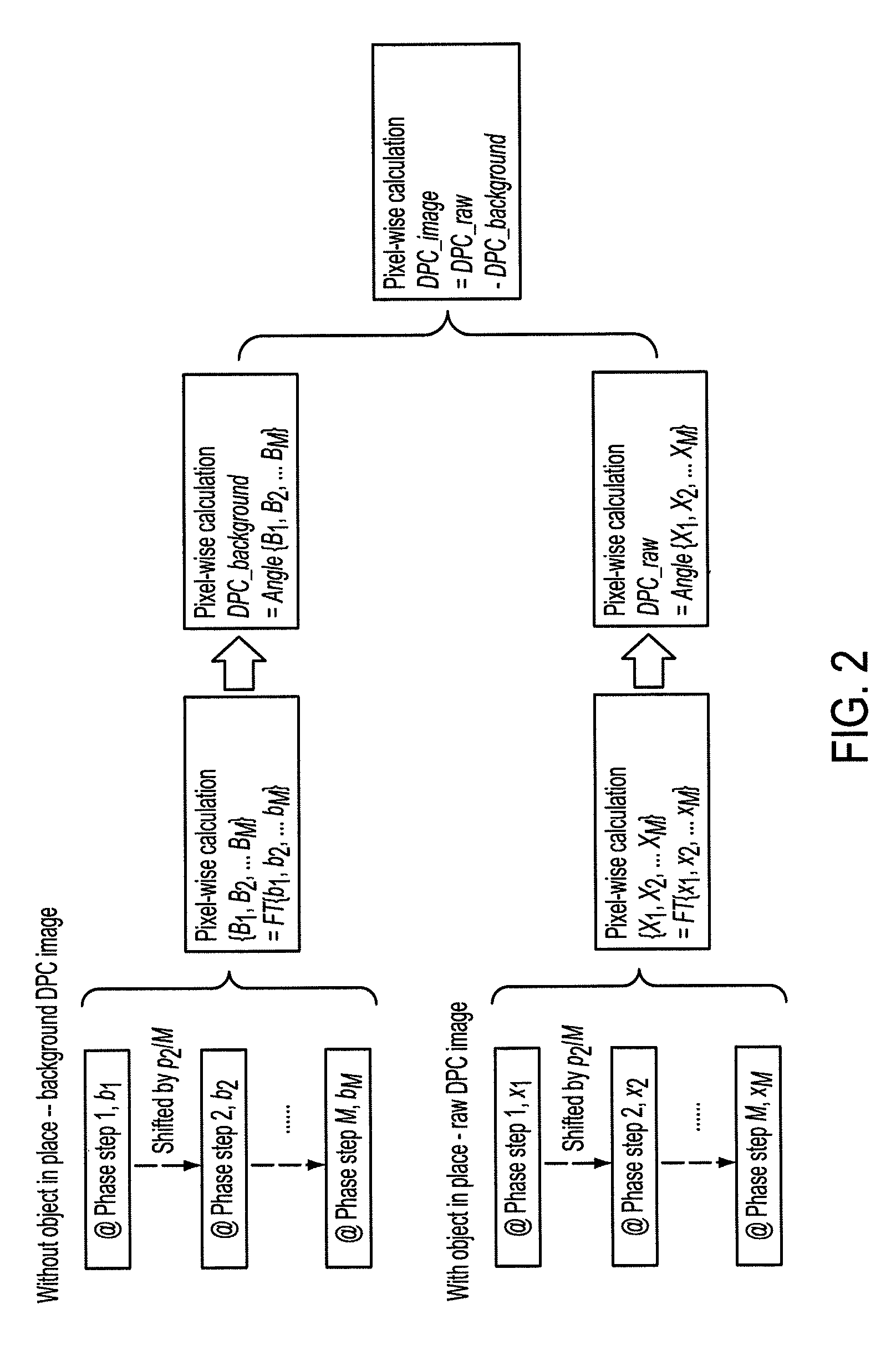
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Apparatus and method for cone beam computed tomography breast imaging
InactiveUS20060094950A1Promote quick completionGuaranteed continuous performanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsX-rayEntire breast
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
System and method for medical imaging
PendingUS20190000564A1Image enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityImaging modalities
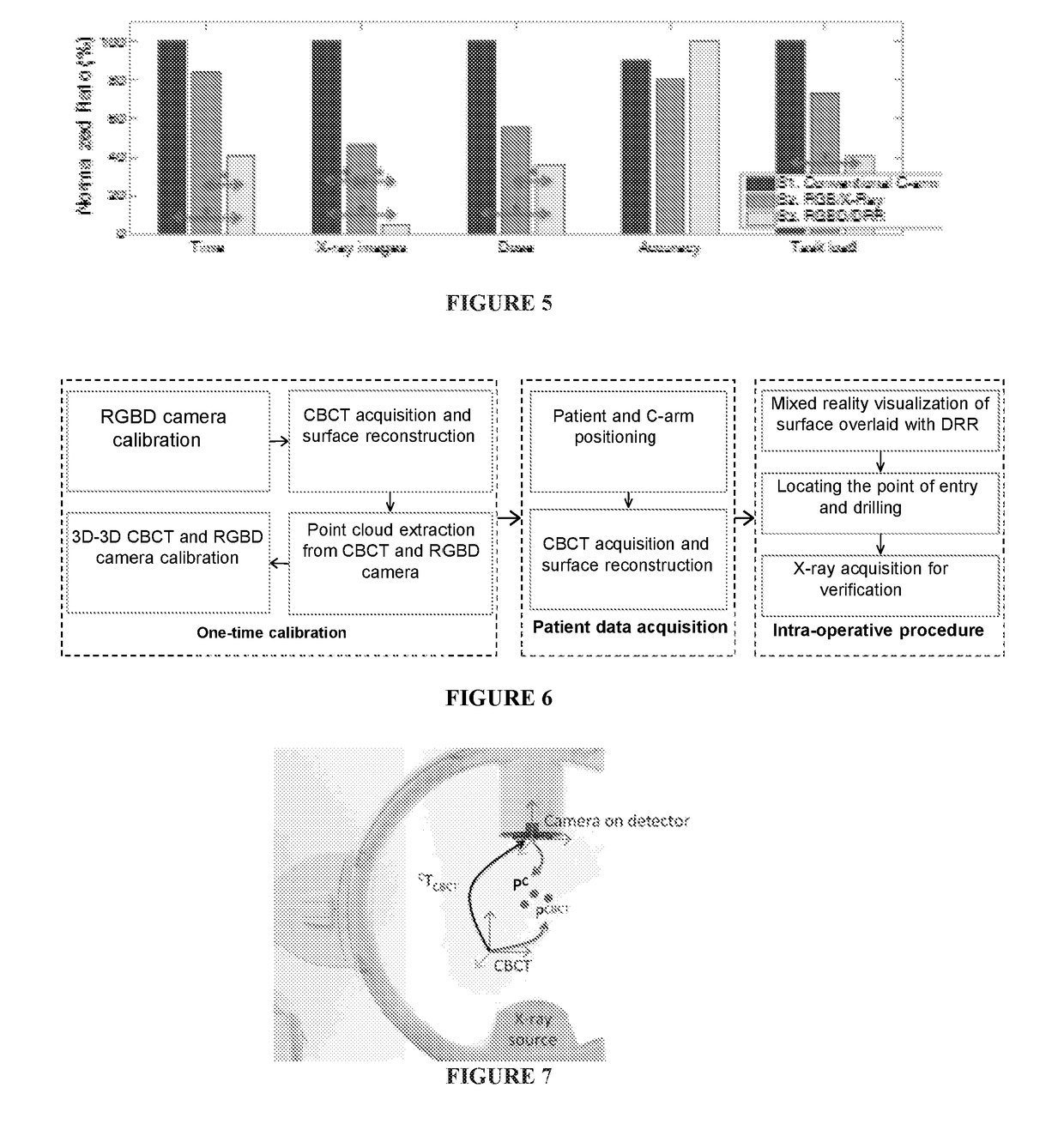
The present disclosure provides a system and method for generating medical images. The method utilizes a novel algorithm to co-register Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) volumes and additional imaging modalities, such as optical or RGB-D images.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Scatter correction methods
ActiveUS20120263360A1Reduce pollutionAccurate methodImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageImproved method
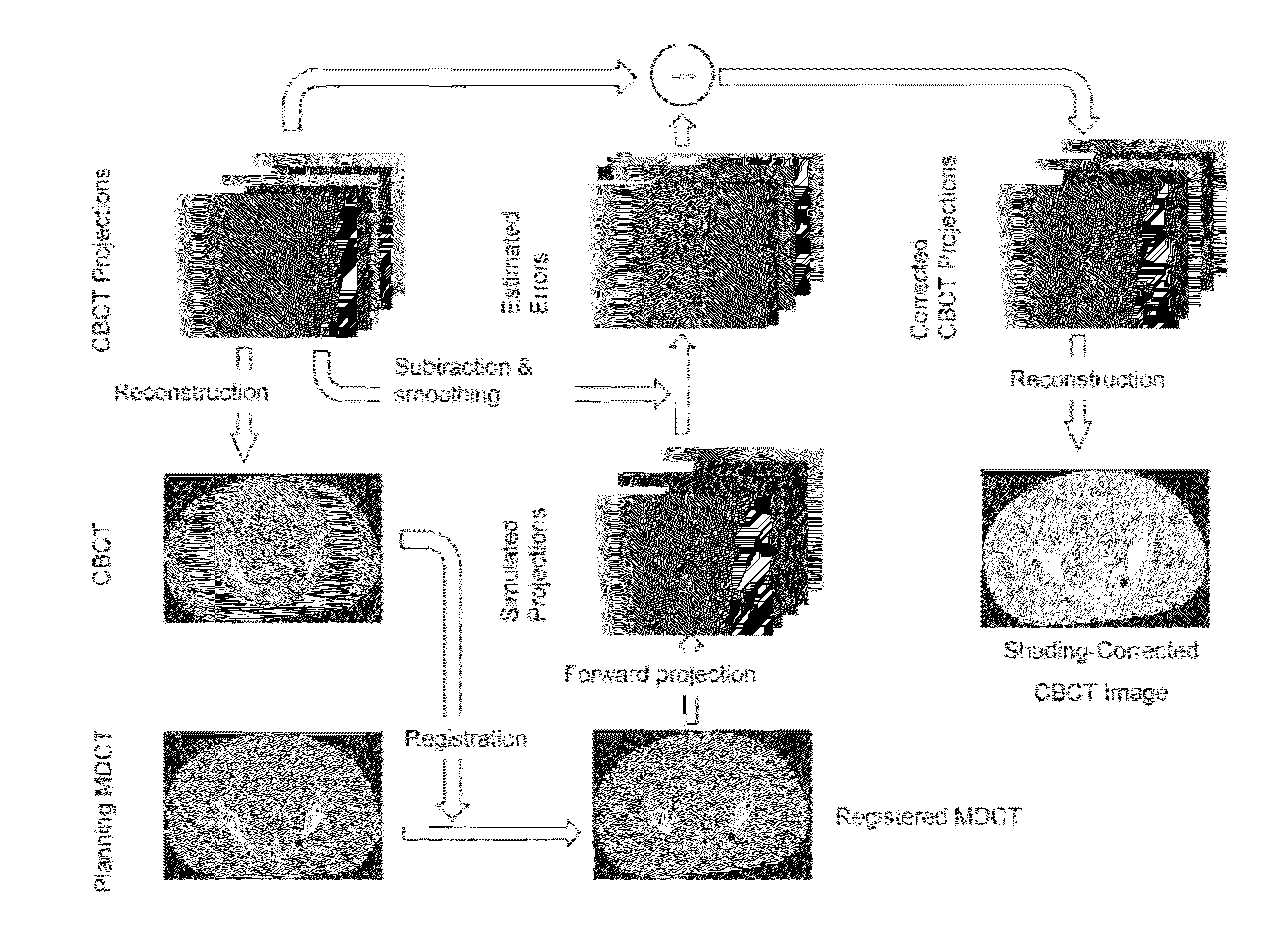
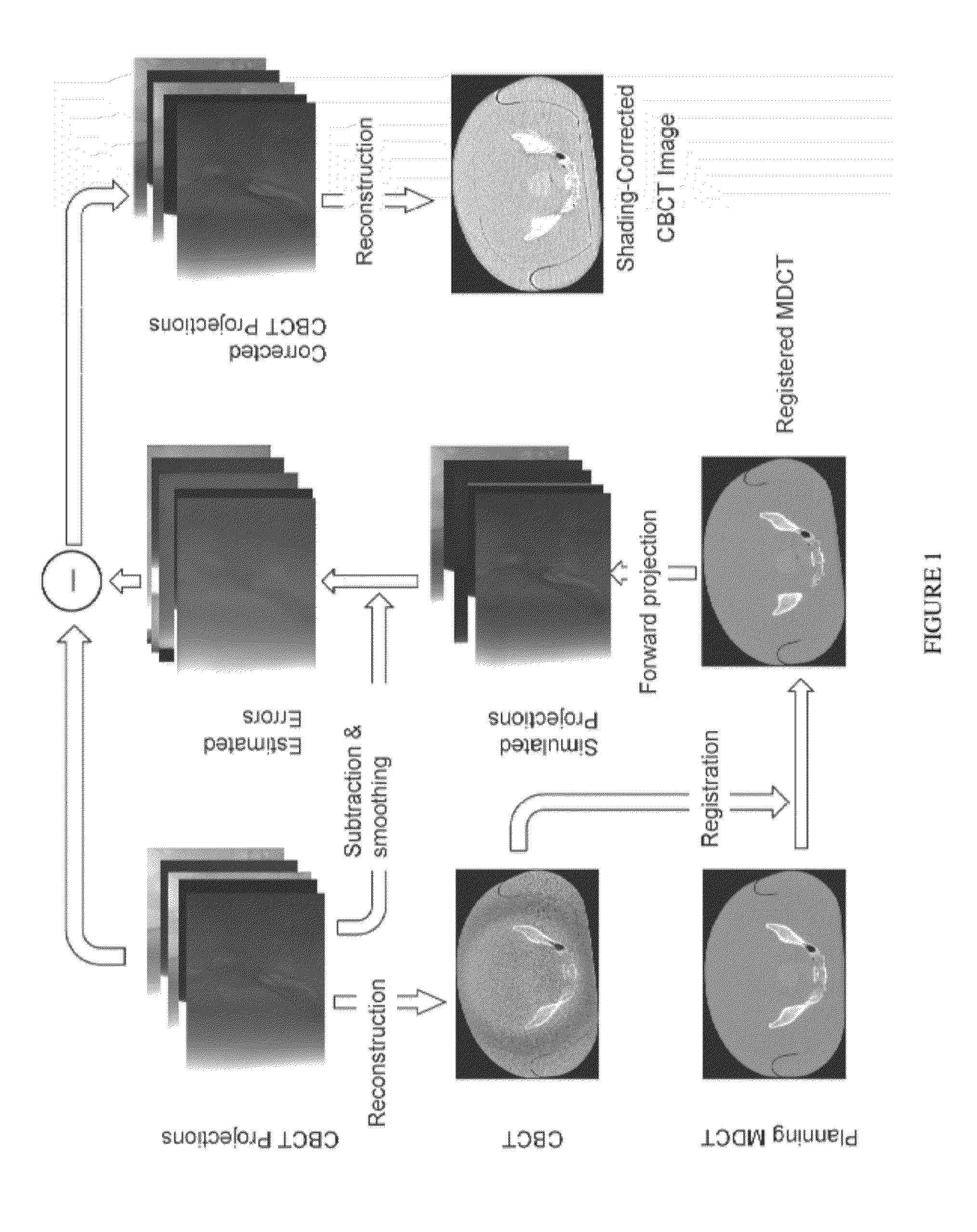
Described herein are improved methods for correcting cone beam computed tomography signals to reduce scatter contamination contained therein. Generally, the improved methods involve generating a plurality of two-dimensional projection images of a subject from a three-dimensional multi-detector computed tomography image of the subject. This is followed by subtracting the plurality of two-dimensional projection images from a plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images of the subject to produce a plurality of two-dimensional estimated error projections that comprise an estimated error in the plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images. The plurality of two-dimensional estimated error projection images are subtracted from the plurality of two-dimensional cone beam projection images to generate a plurality of two-dimensional corrected cone beam projection images. A three-dimensional corrected cone beam computed tomography image of the subject is then constructed from the plurality of two-dimensional corrected cone beam projection images.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
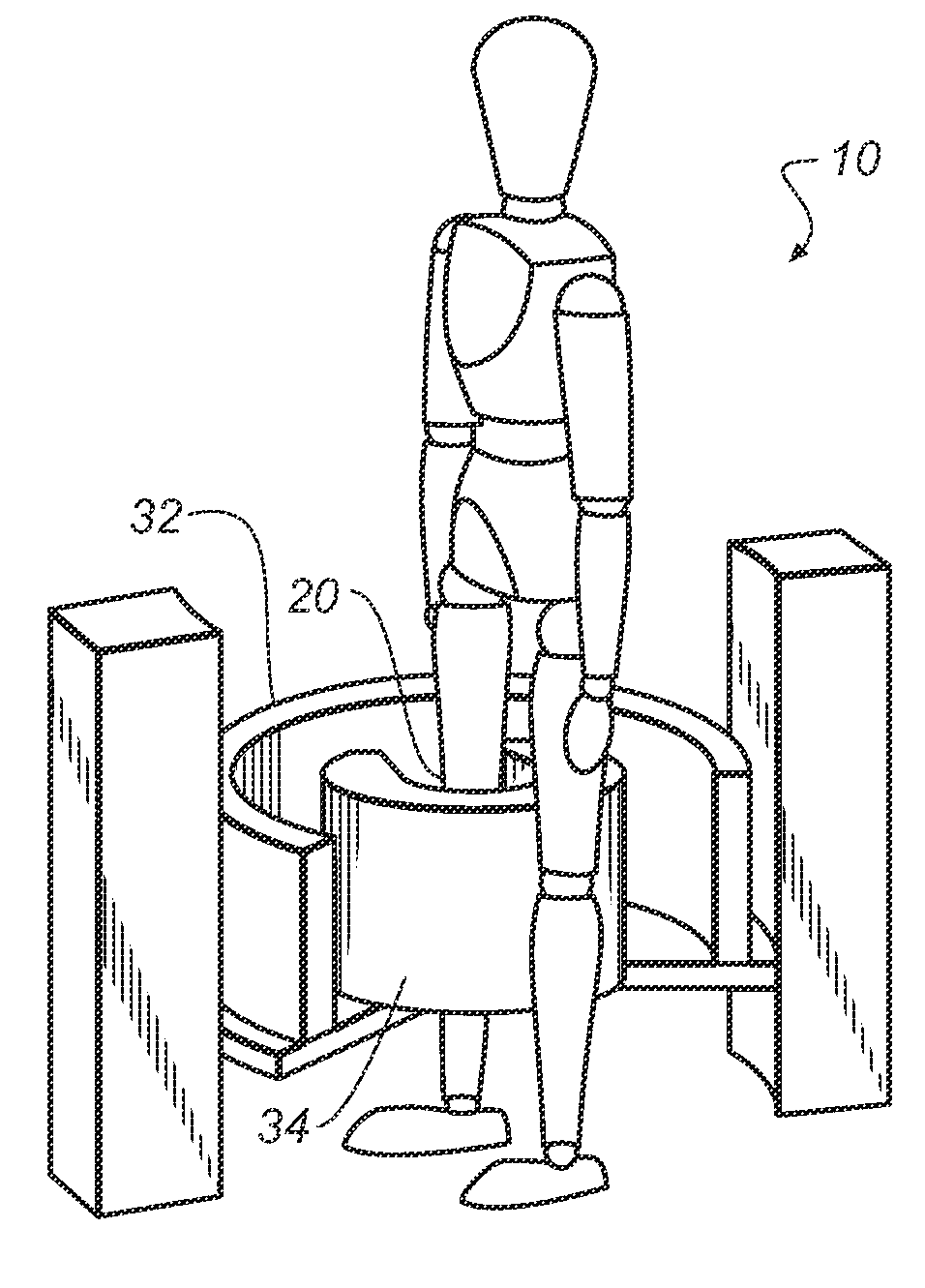
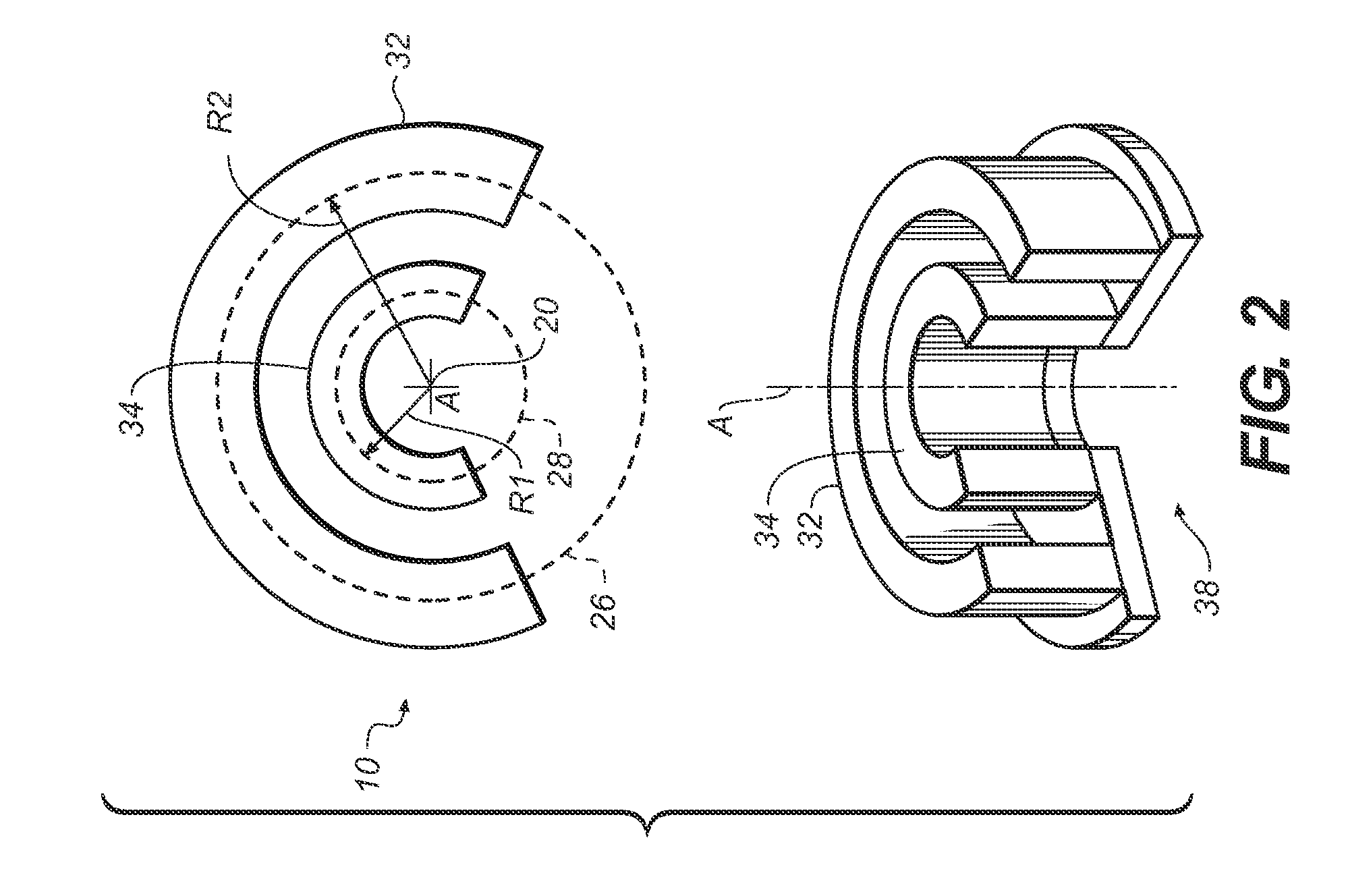
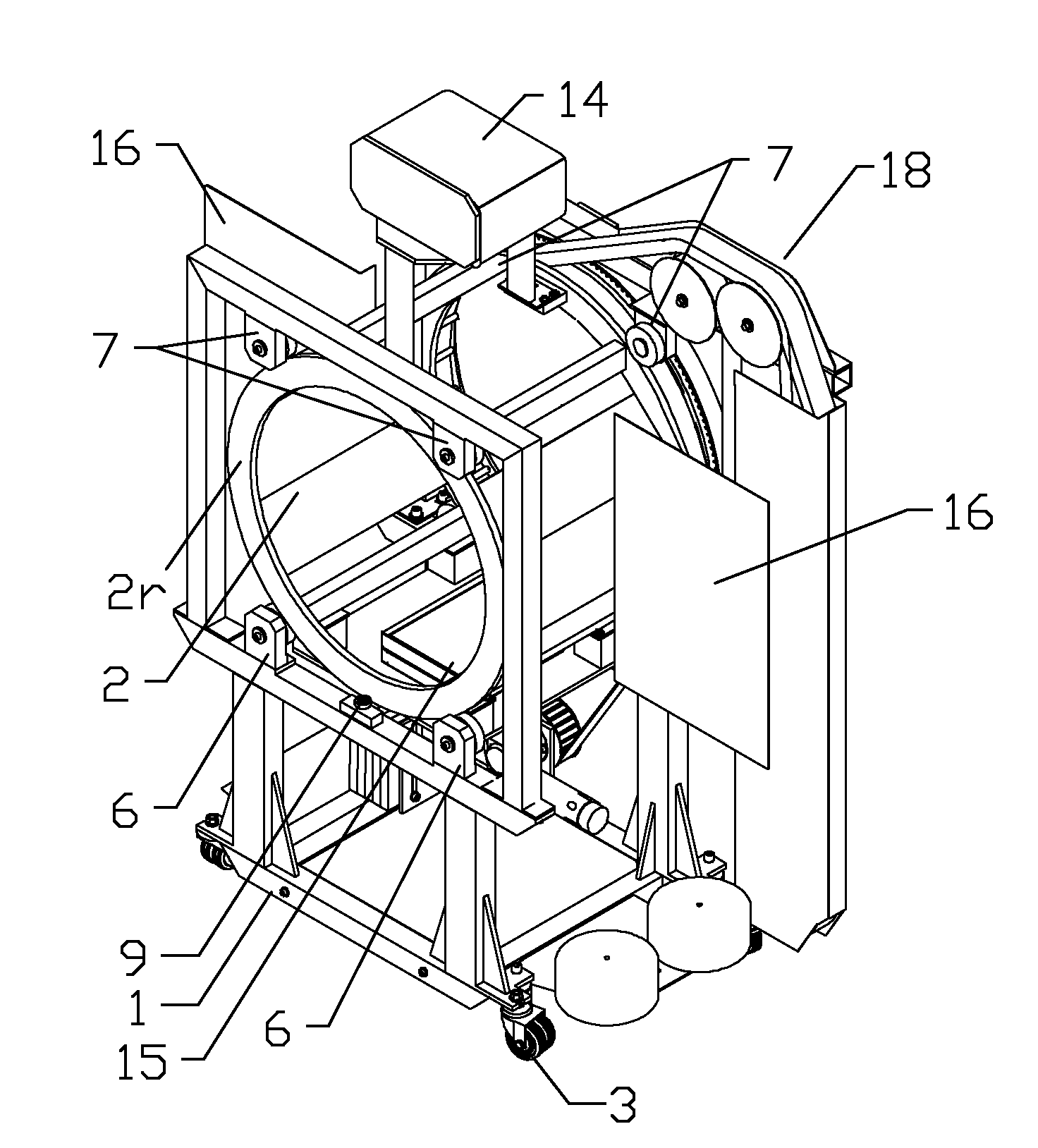
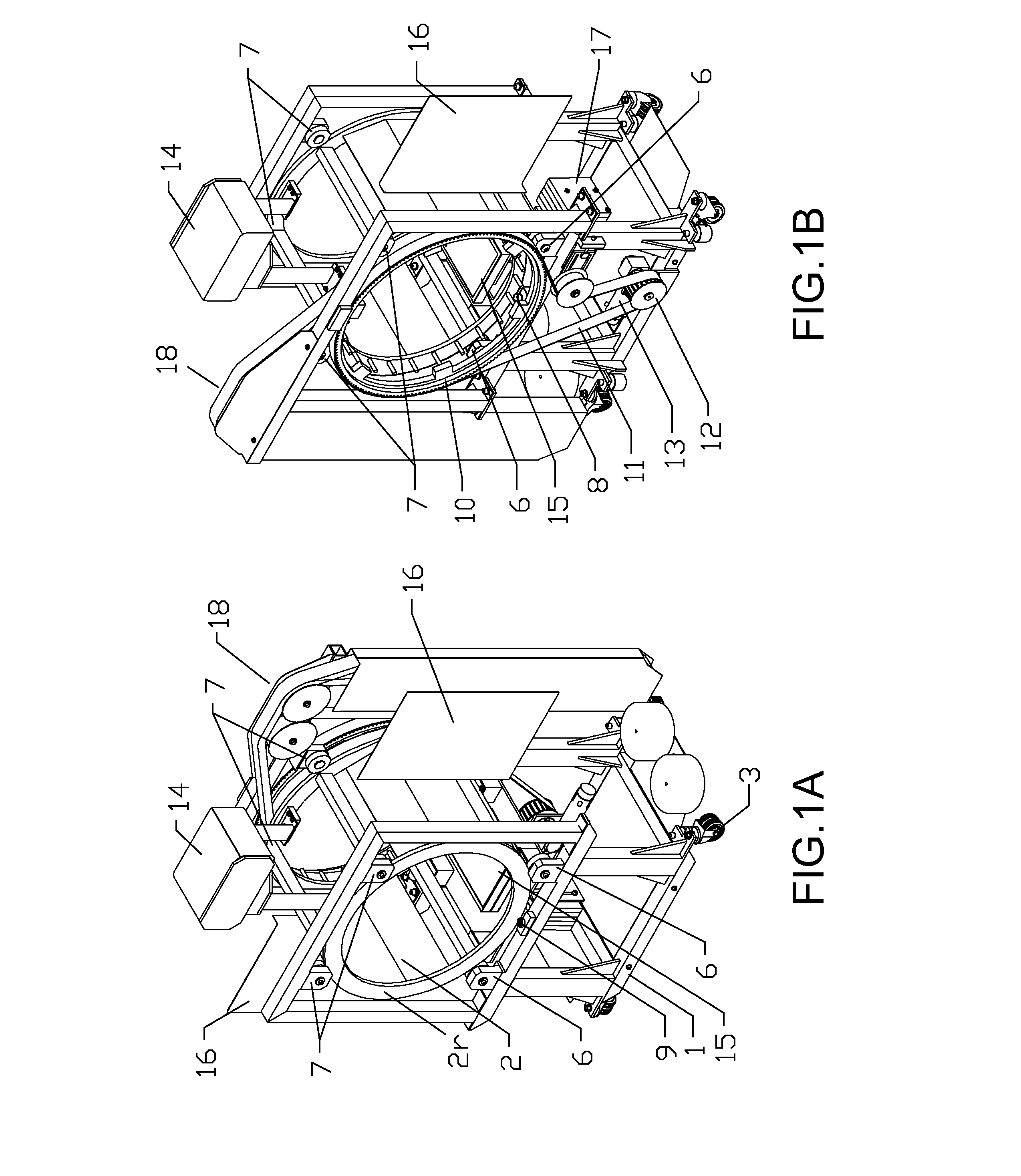
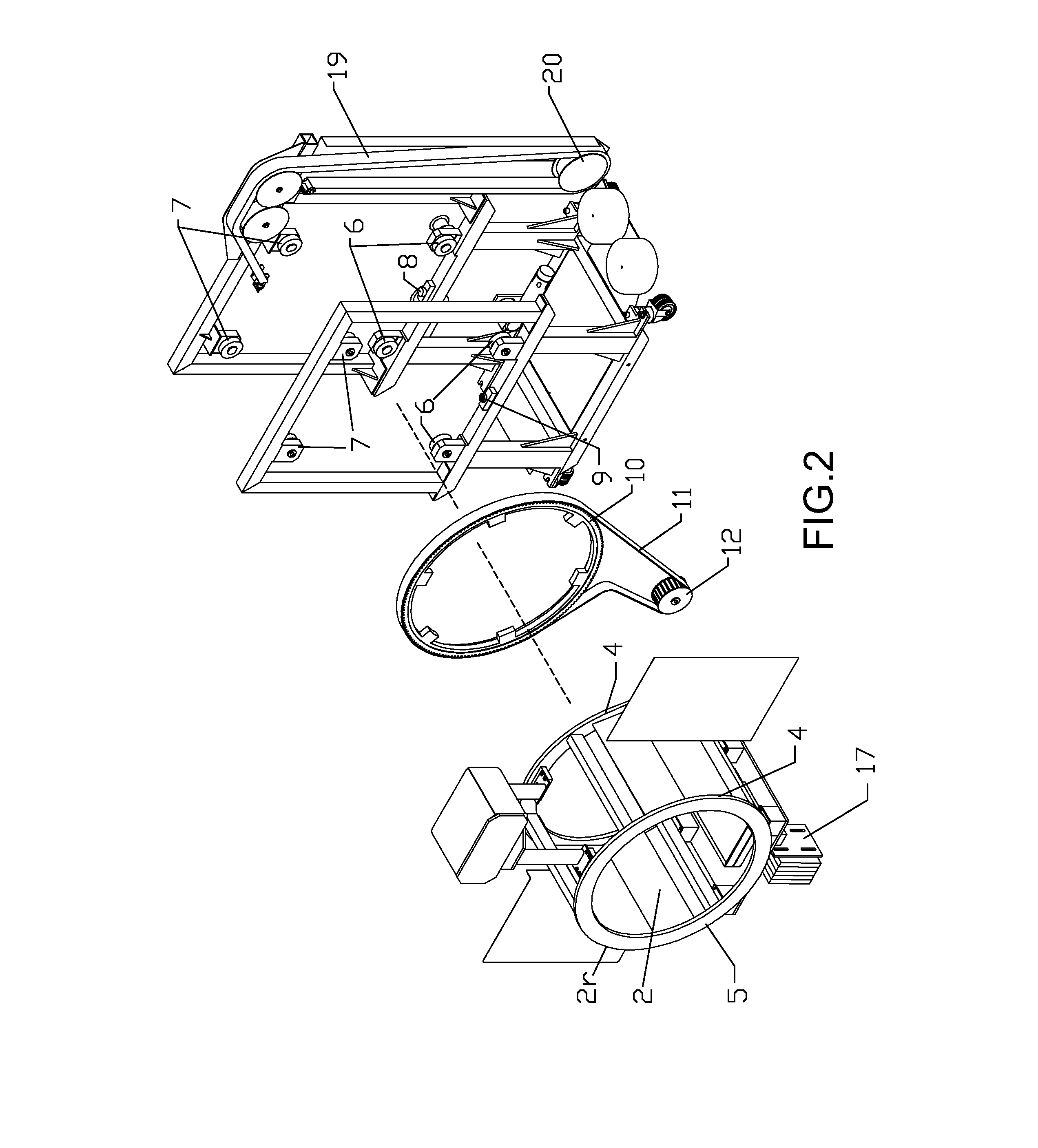
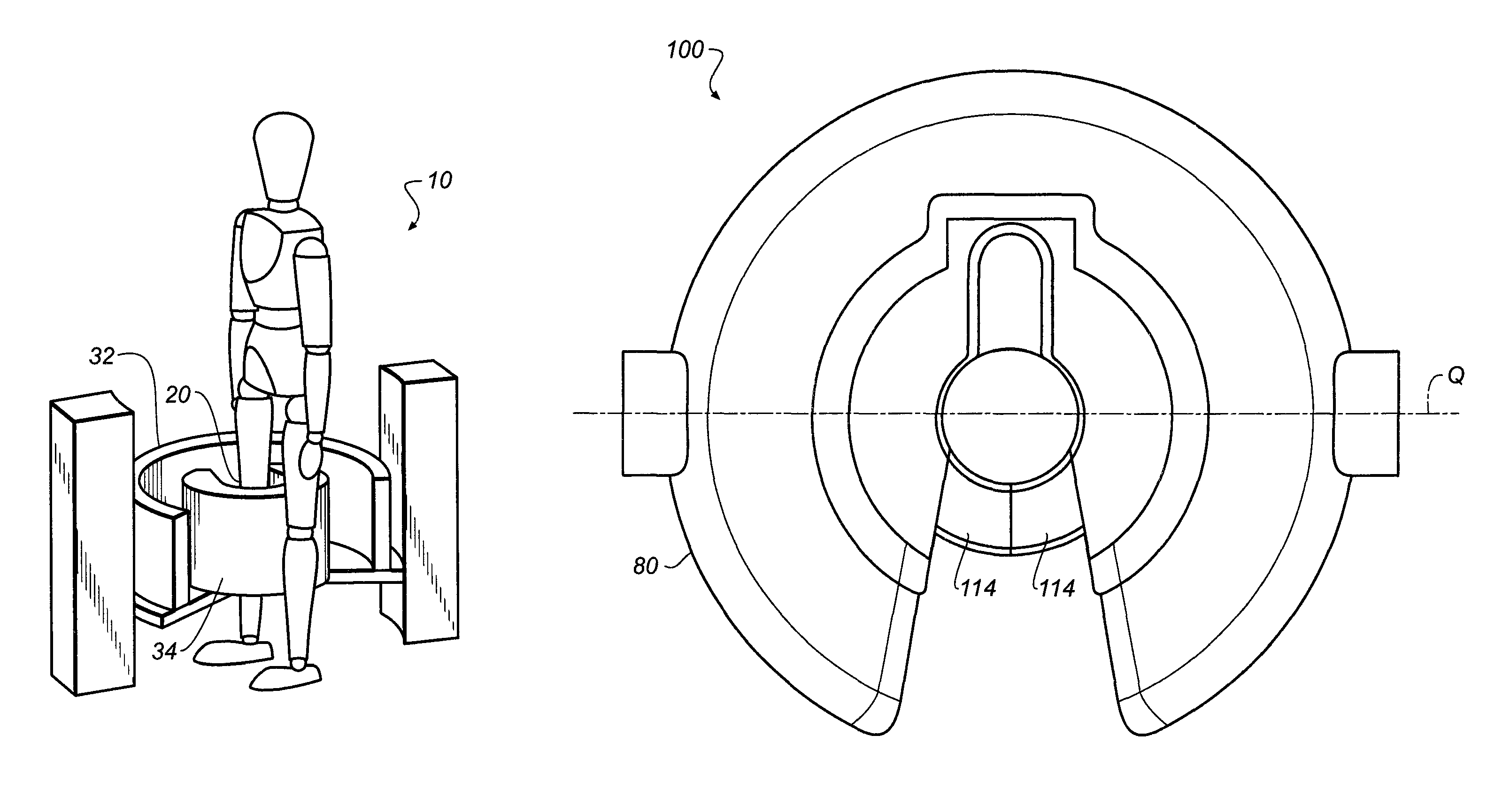
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20110228901A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomographyCone beam computed tomography
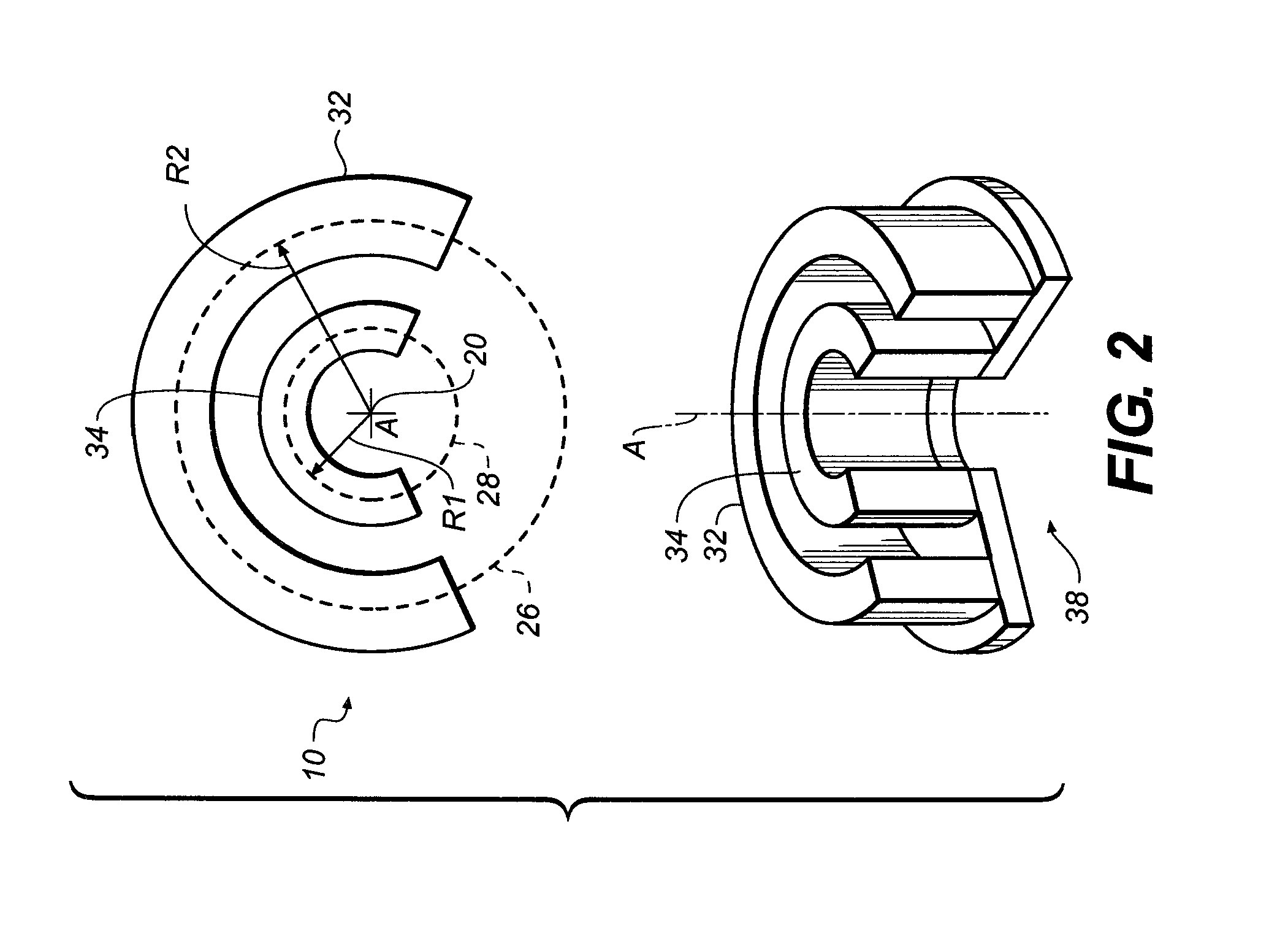
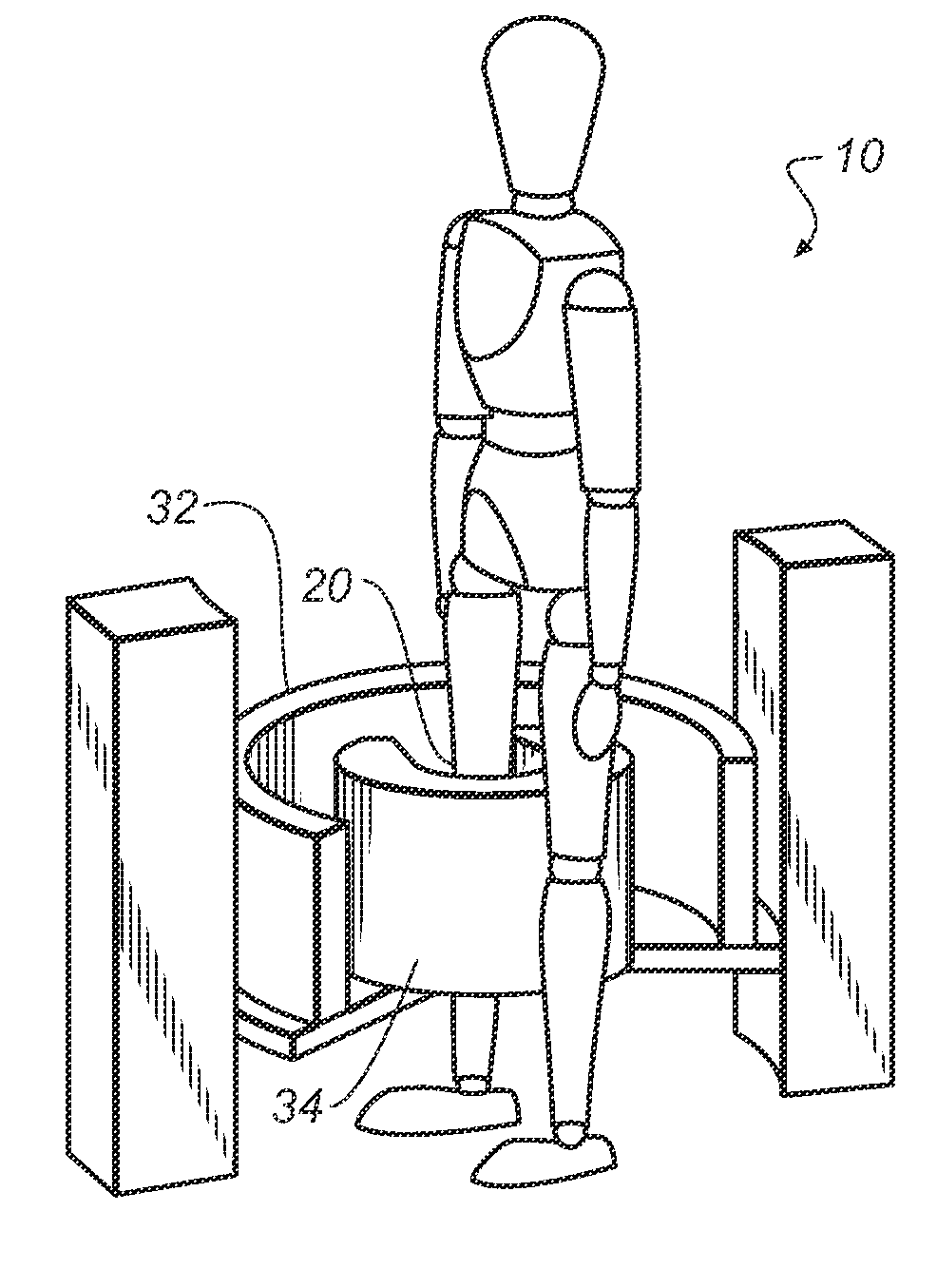
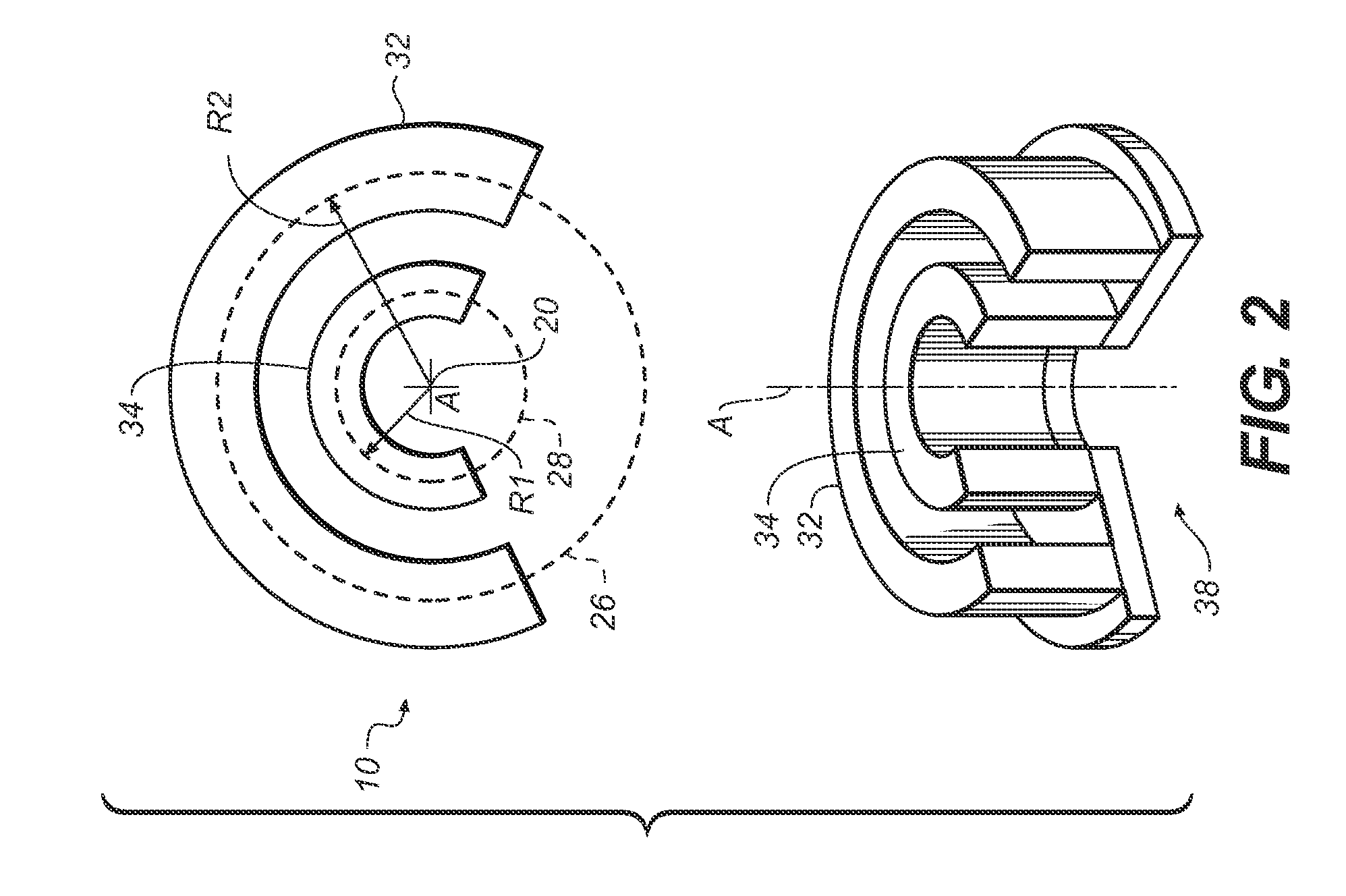
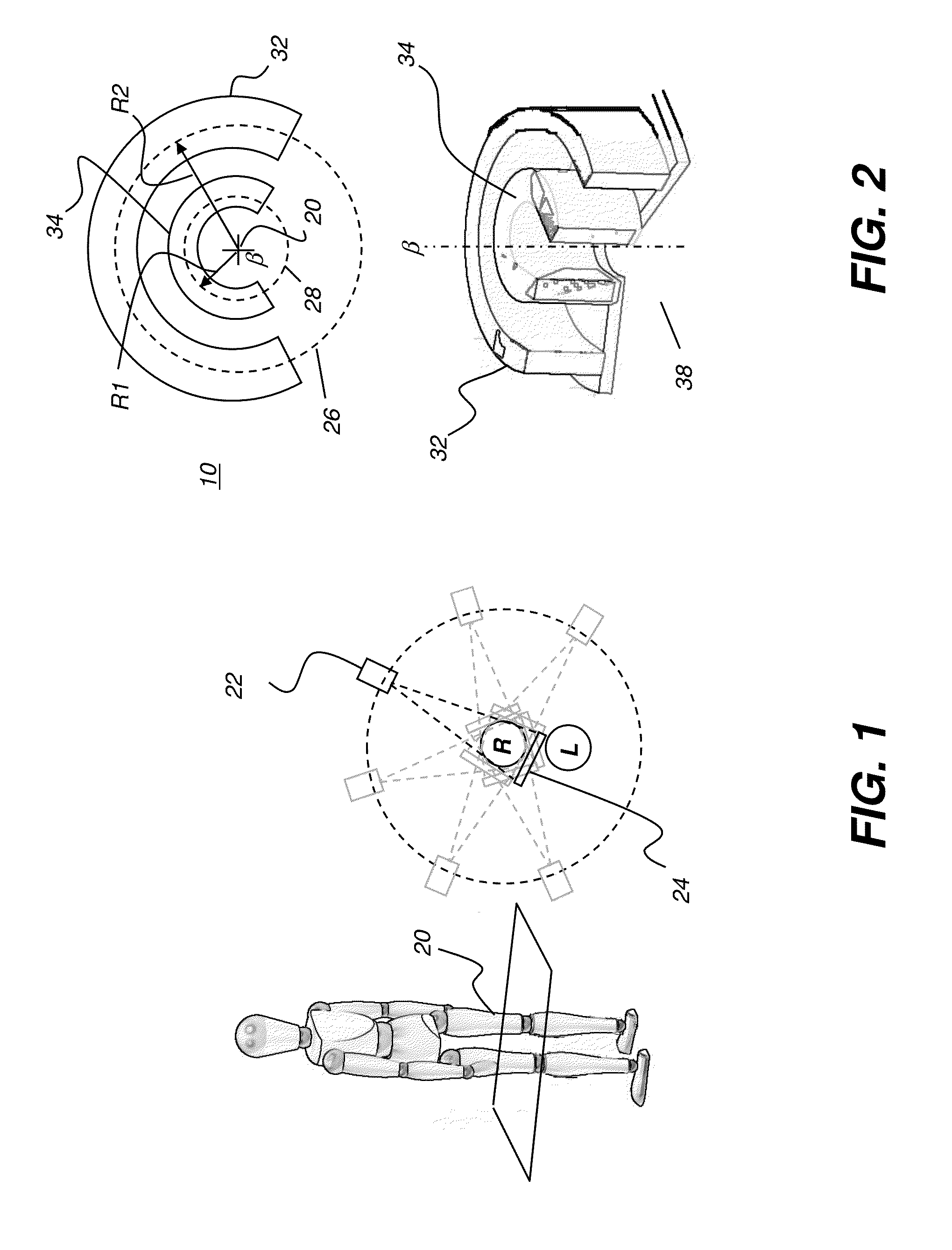
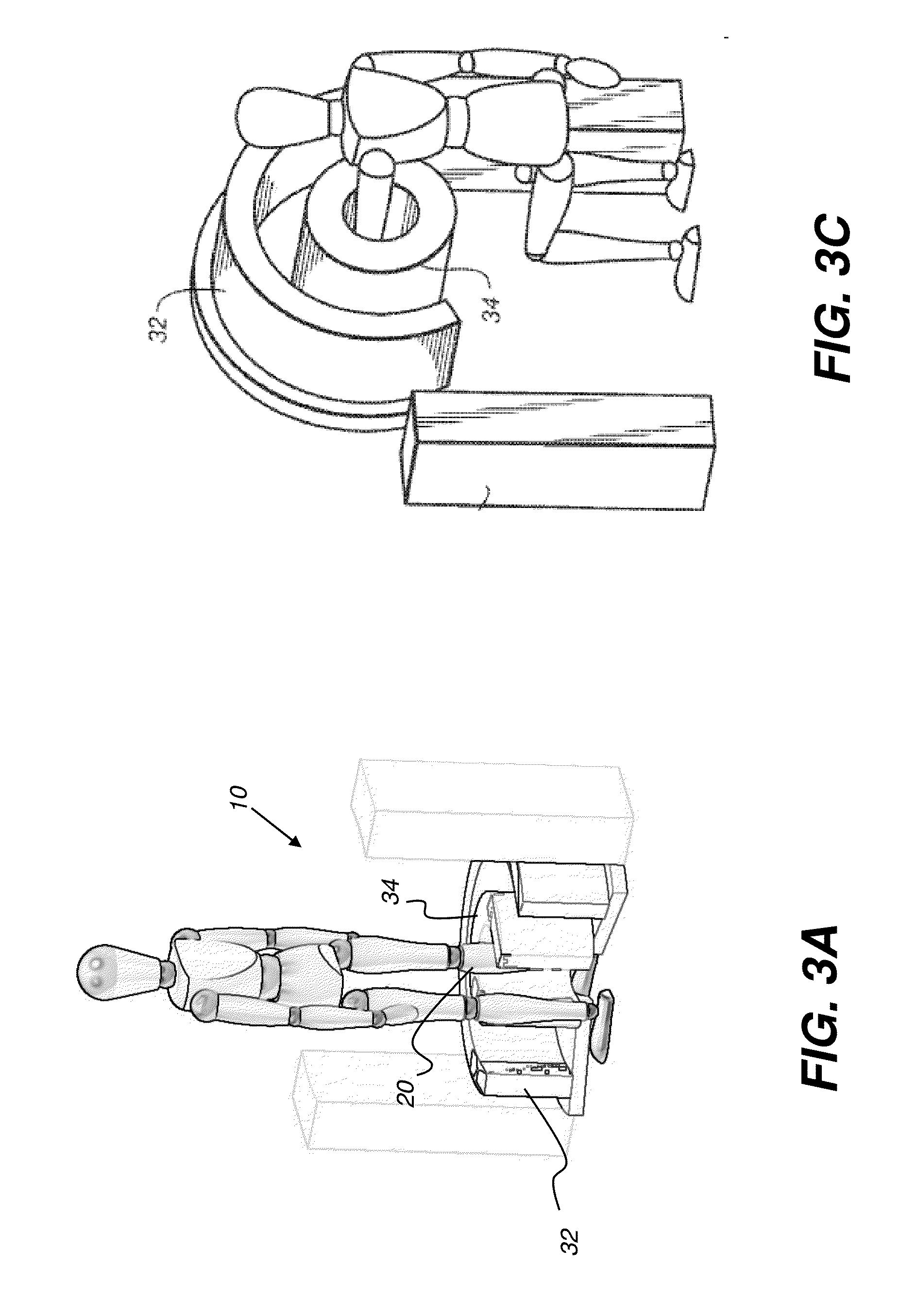
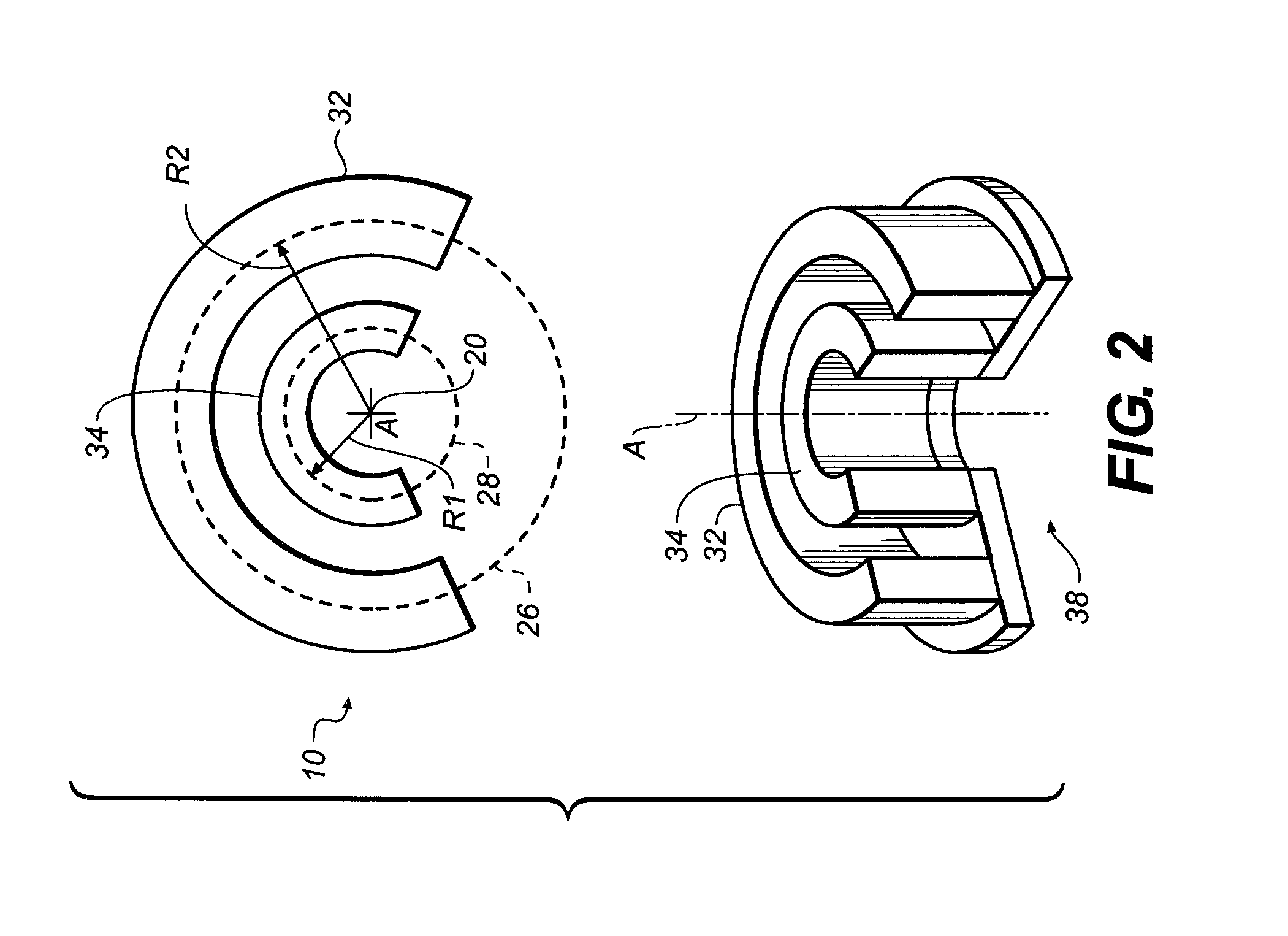
An apparatus for cone beam computed tomography of lower leg portions of a patient has a radiation source and a source transport actuable to move the source along an arcuate source path within a housing, from one side of a circumferential gap to the other and has a radius R2 about a center. A housing is provided for placement of the patient's foot. A digital radiation detector has a detector transport actuable to move the detector along an arcuate detector path within the housing, the detector path having a radius R1 about the center and concentric with the source path, wherein R1 is less than R2, and wherein the detector path extends from one side of the pedestal indent to the other. A gap closure apparatus is movable to a position that continues the detector path across the circumferential gap and encloses the detector path.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC +1
Dentition model generation method based on oral cavity scanning data and CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) data
ActiveCN105447908AMeet clinical requirementsCalculation speedImage enhancementImage analysisCone beam computed tomographyDentition
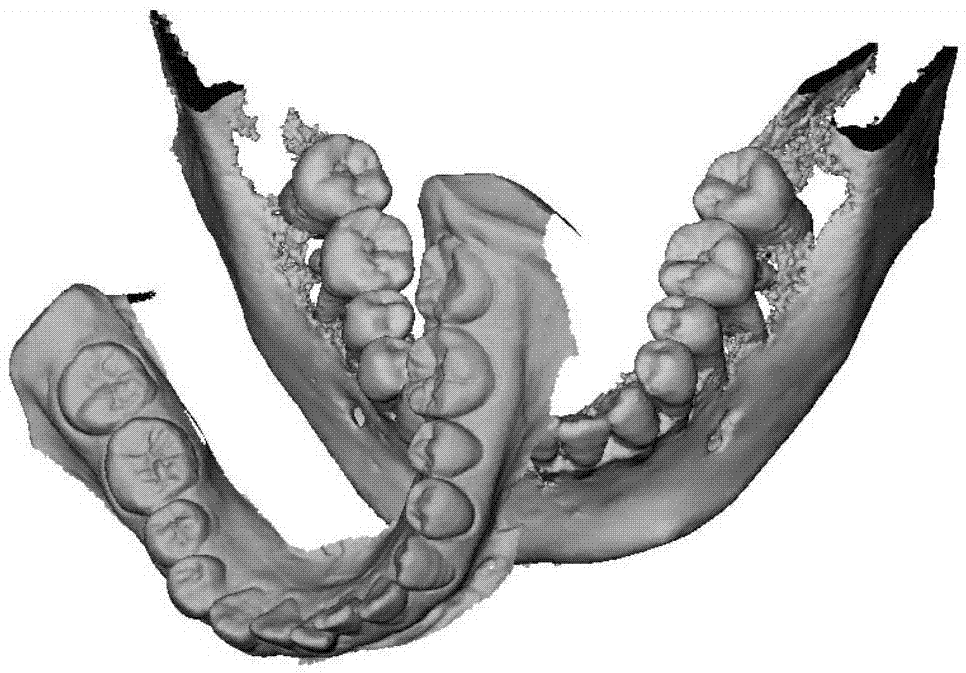
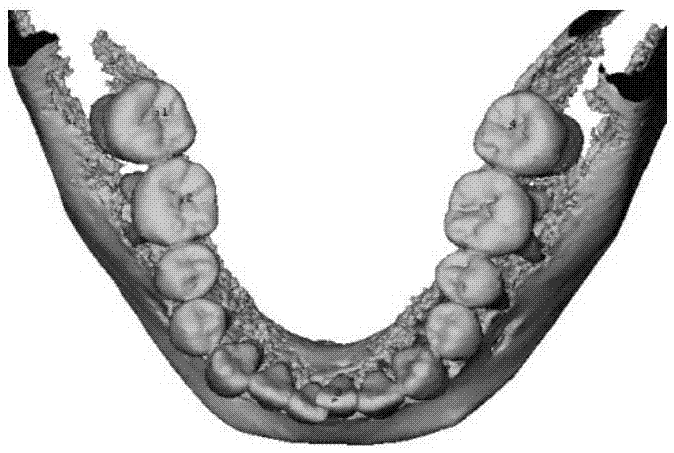
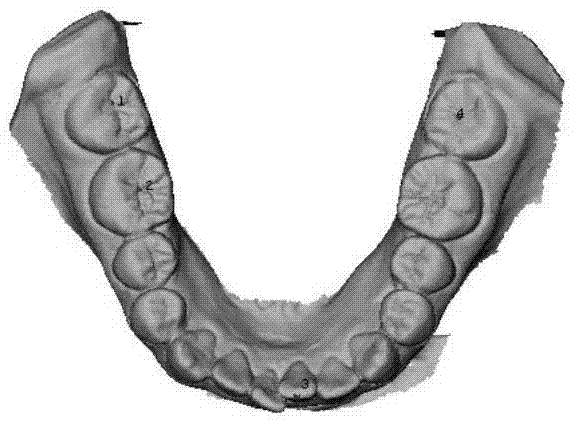
The present invention discloses a dentition model generation method based on oral cavity scanning data and CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) data. The method comprises: reading a three-dimensional multi-source data model of an oral cavity; setting and registering a fixed model and a floating model, wherein the fixed model is a triangular mesh model created by means of CBCT, and the floating model is a triangular mesh model of intraoral scanning; manually picking up feature point pairs of the models on the fixed model and the floating model, correcting the feature point pairs according to point cloud curvature of the models, moving feature points to a point with the largest curvature in a surrounding neighborhood, and performing preliminary registration on the feature point pairs by using a point-to-point ICP (Iterative Closest Point) algorithm; calculating a point cloud error of the models after preliminary registration, and by combination with medical parameter requirements, setting a parameter of precise registration; performing precise registration by using an optimized point-to-surface ICP algorithm; and fusing the CBCT data and intraoral scanning data after registration, and outputting tooth root and crown models after registration and fusion. Rapid and precise registration and fusion of data of different devices or data of different postures of patients are implemented.
Owner:山东山大华天软件有限公司
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20100278300A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation exposureImaging equipment
An apparatus for cone beam computed tomography of an extremity has a digital radiation detector and a first device to move the detector along a circular detector path extending so that the detector moves both at least partially around a first extremity of the patient and between the first extremity and a second, adjacent extremity. The detector path has radius R1 sufficient to position the extremity approximately centered in the detector path. There is a radiation source with a second device to move the source along a concentric circular source path having a radius R2 greater than radius R1, radius R2 sufficiently long to allow adequate radiation exposure of the first extremity for an image capture by the detector. A first circumferential gap in the source path allows the second extremity to be positioned in the first circumferential gap during image capture.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Geometrical parameter calibration method of X-ray cone beam computed tomography system
The invention discloses a geometrical parameter calibration method of an X-ray cone beam computed tomography system and belongs to the field of the X-ray cone beam computed tomography systems (a cone beam CT for short). By means of a camera calibration technique, a geometrical position relationship among an X-ray source, a panel detector and a rotary shaft in a cone beam CT system is reproduced, thereby geometrical parameters and errors of the cone beam CT can be directly solved, the geometrical parameter calibration method is a systematized measurement solving method, the cone beam CT can beabstracted to be a basic camera system model, and then a plurality of correlative geometrical parameters in the system can be simultaneously solved. Compared with prior calibration methods, the geometrical parameter calibration method has the advantages that the geometrical parameters are not required to be measured one by one, repeated adjustment for the parameters one by one is not required, thereby the complexity level of calibration measurement of the whole system is greatly simplified, and simultaneously the stability of the cone beam CT geometrical calibration is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cone beam computed tomography with a flat panel imager
InactiveUS20060050847A1Adequate visualizationReduce errorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayAmorphous silicon
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
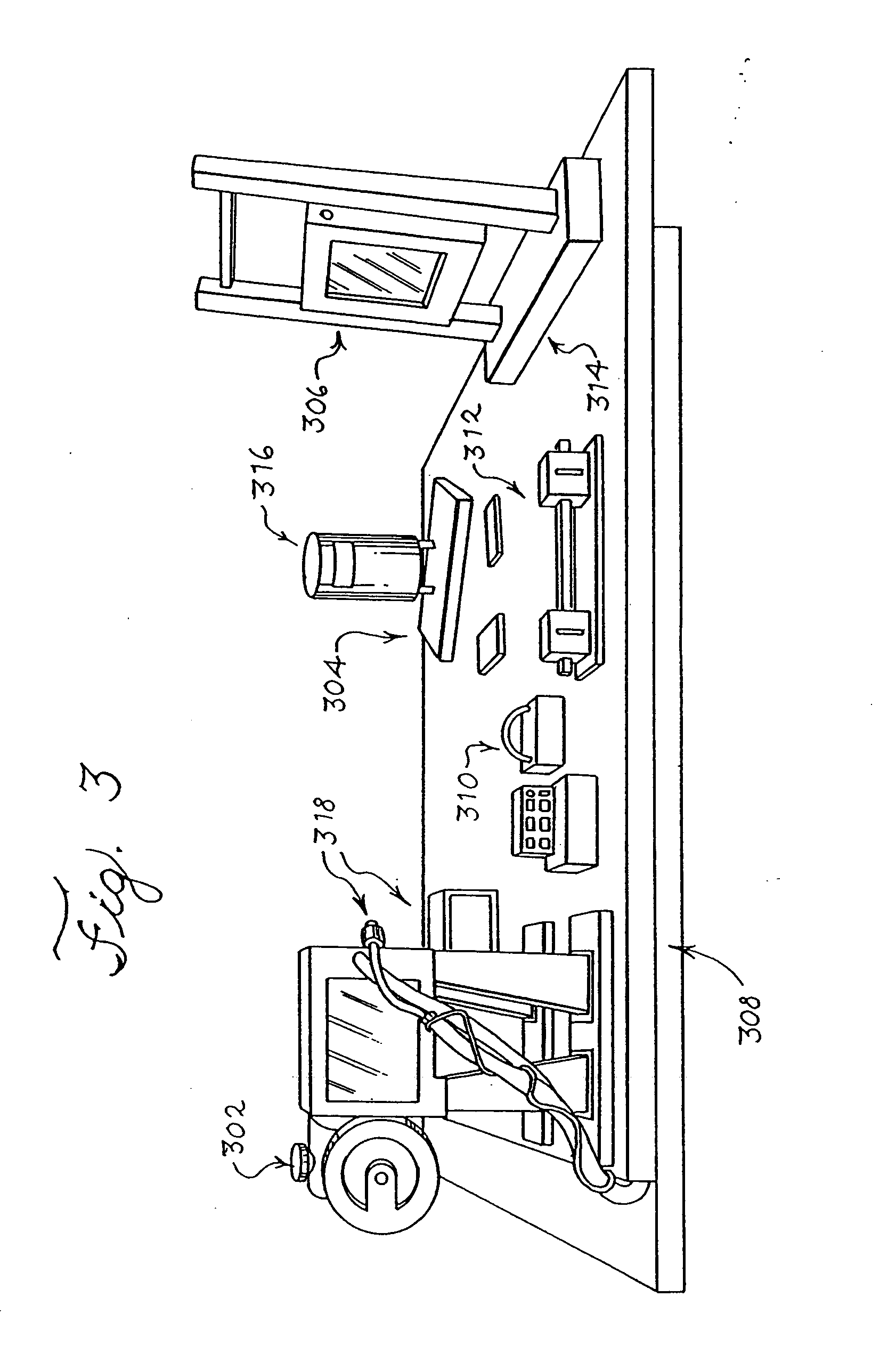
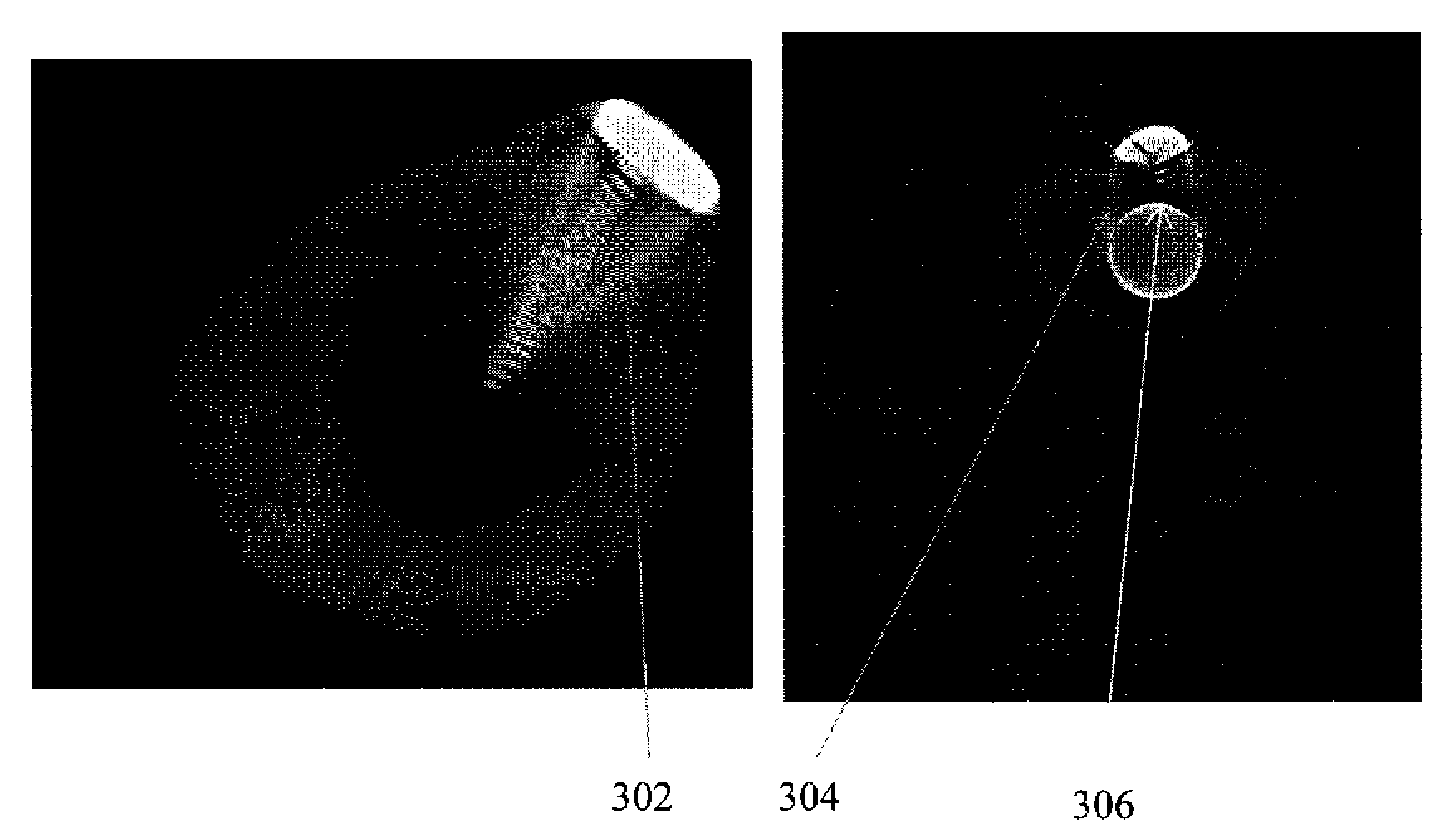
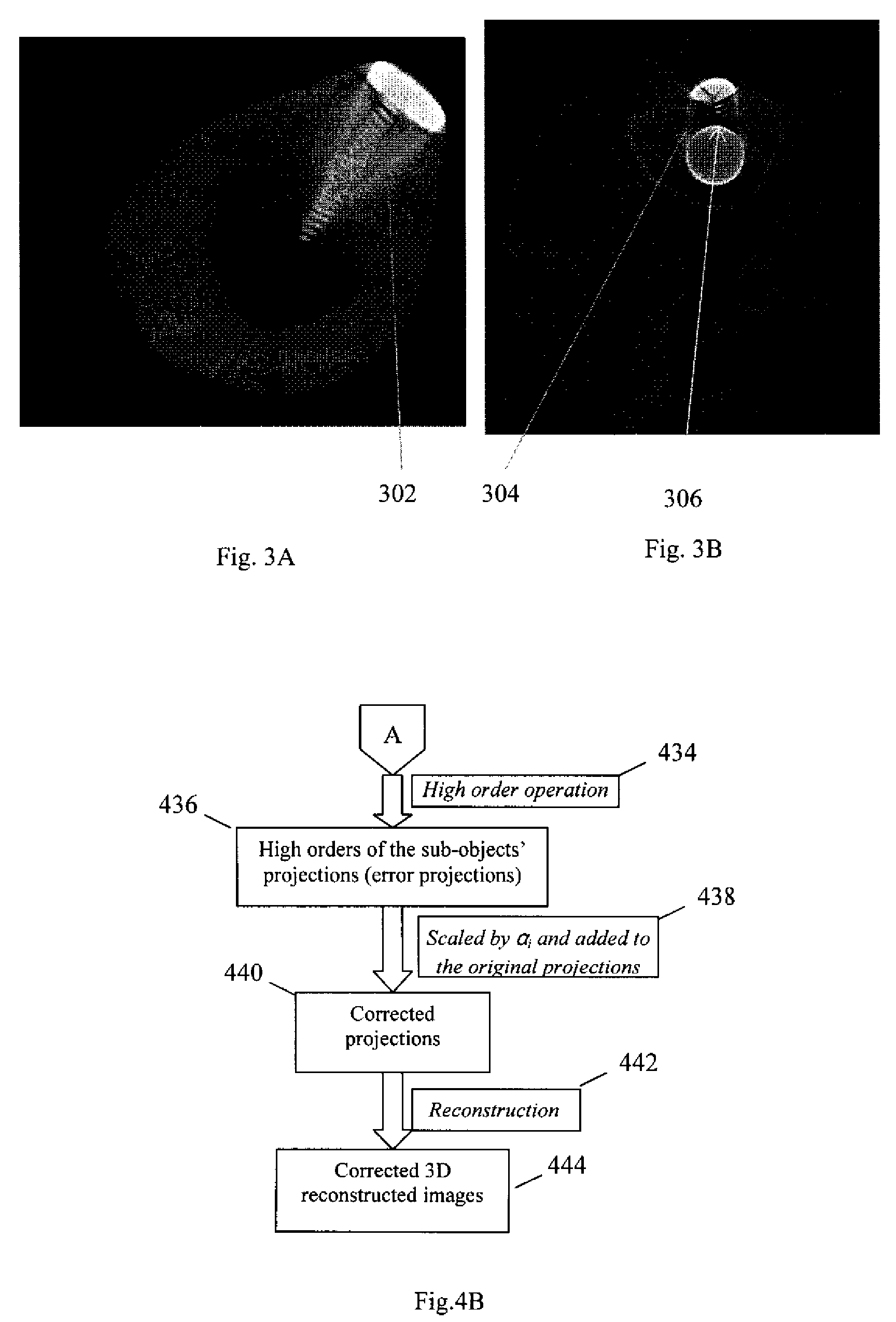
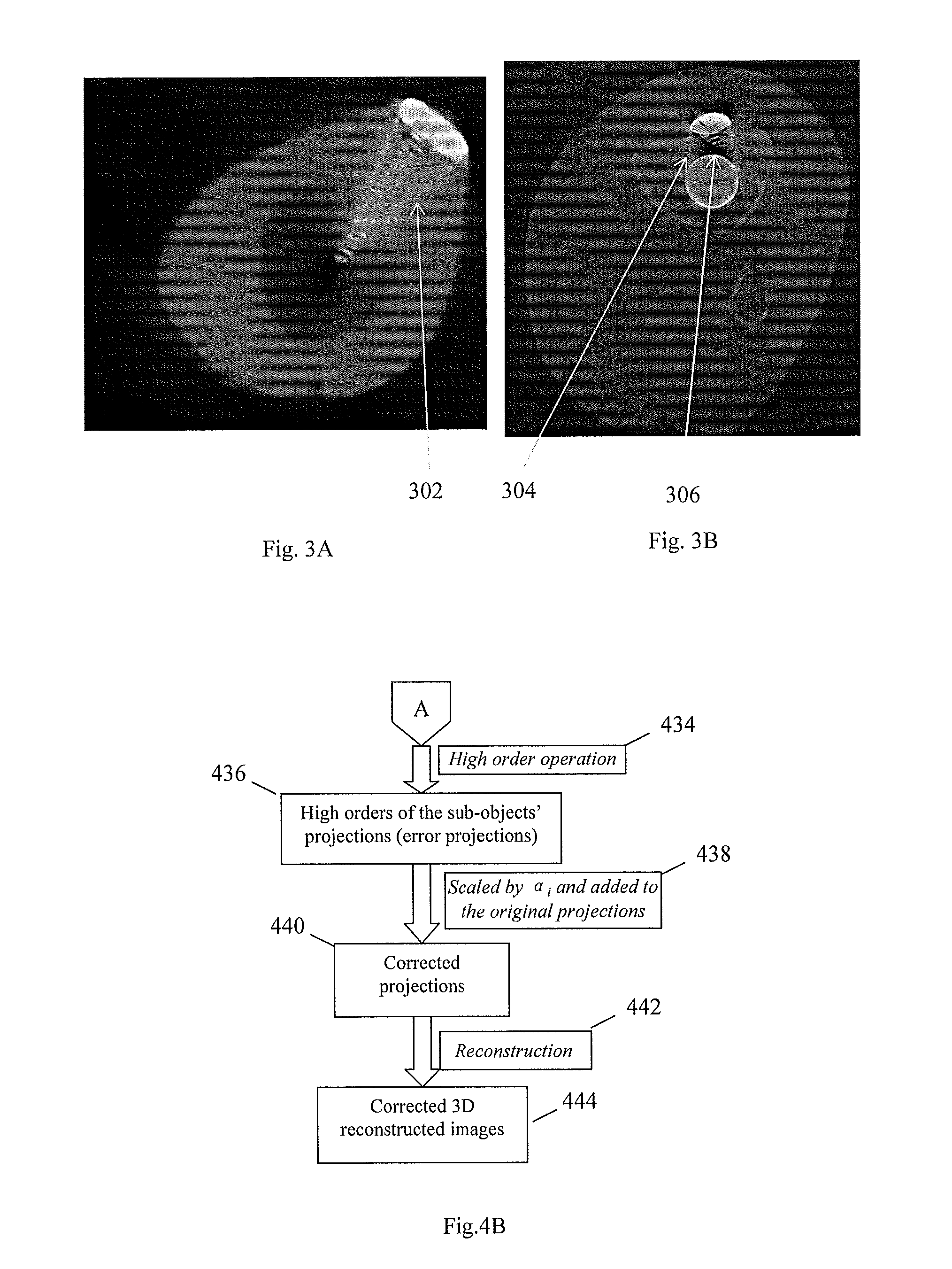
Method and apparatus for 3D metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam CT imaging
ActiveUS8023767B1Correction of artifactAccurate reconstruction imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS8348506B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation exposureCone beam computed tomography
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
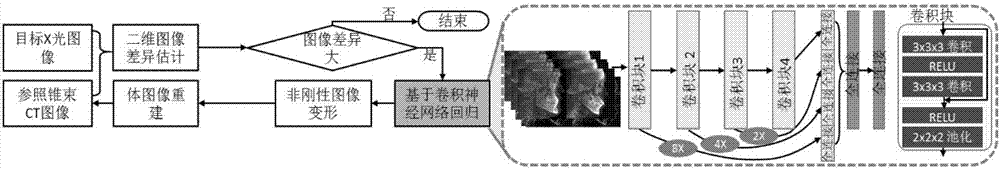
Cone-beam computed tomography image and X-ray image registration method
ActiveCN107507234AMeet the precision requirementsReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkX-ray
The invention discloses a cone-beam computed tomography image and X-ray image registration method; the method uses a regression model based on a mixing residual error convolution nerve network to build associations between two-dimension X-ray images and three dimensional cone-beam CT image non-rigid deformation parameters, and uses a mixing residual error convolution nerve network and deformation parameter iteration optimization method to realize reliable online two-dimension three dimensional image registration; the method comprises the following steps: extracting to obtain an image channel; training the regression model based on the mixing residual error convolution nerve network; carrying out two-dimension three dimensional non-rigid registration based on regression; iterating and optimizing deformation parameters; obtaining a final body image determined by the deformation parameters, and thus realizing two-dimension three dimensional image registration based on iteration regression. The method can realize reliable online two-dimension three dimensional image registration, can be applied to oral cavity clinics, and can evaluate treatments and analyze craniofacial growth according to two-dimension three dimensional image registrations.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
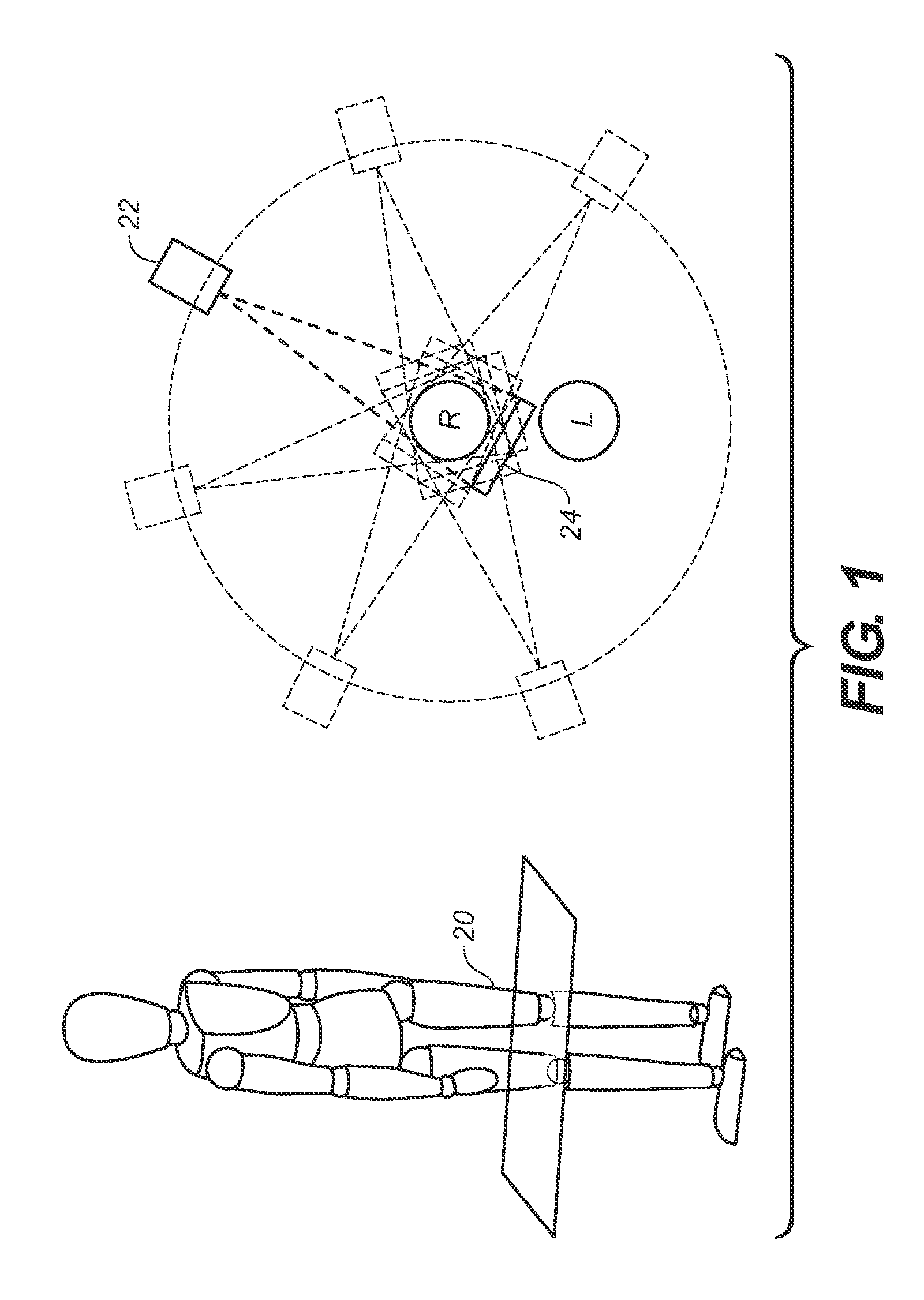
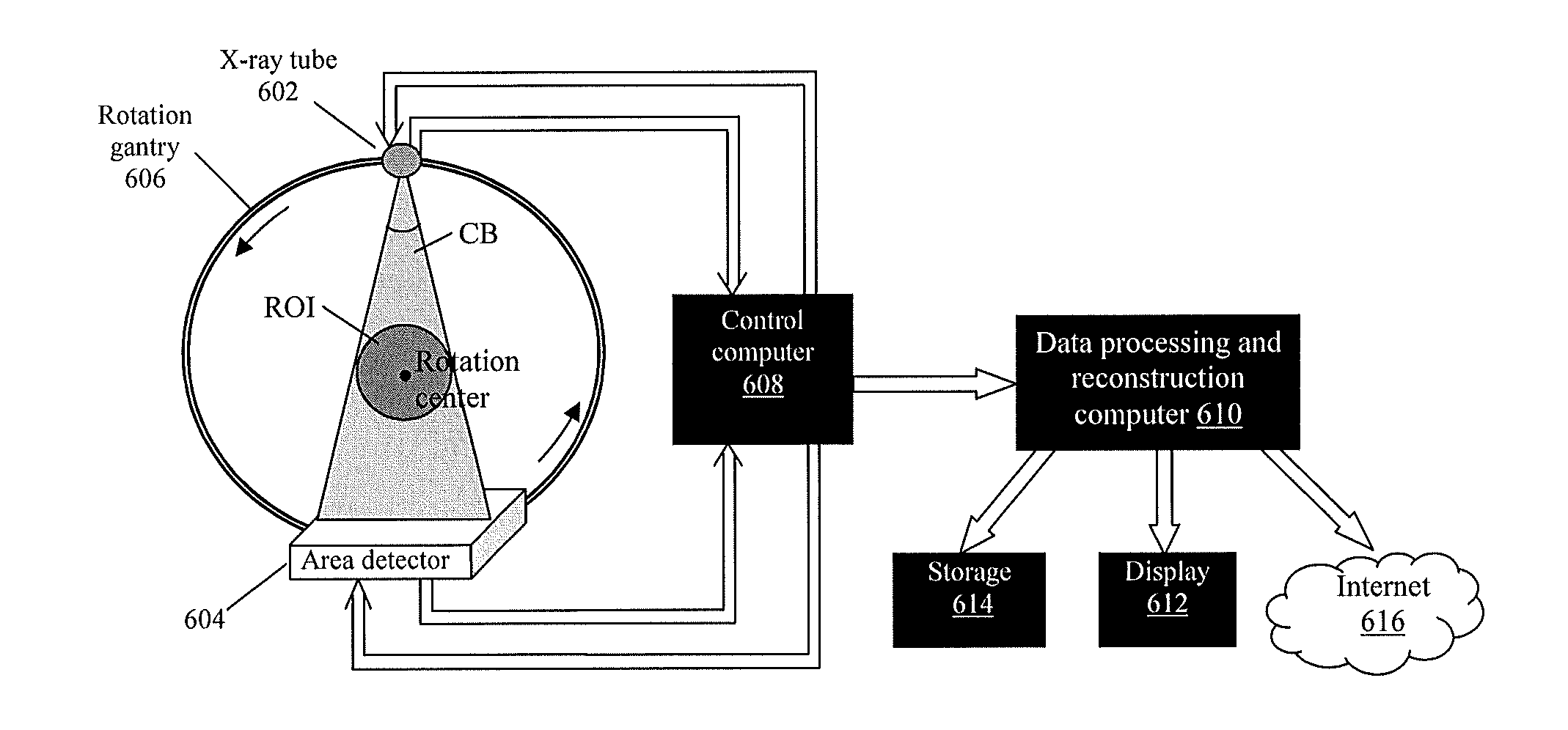
Methods and apparatus of cone beam ct imaging and image-guided procedures
ActiveCN101983033AReconstruction from projectionVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsThree degrees of freedomMulti axis
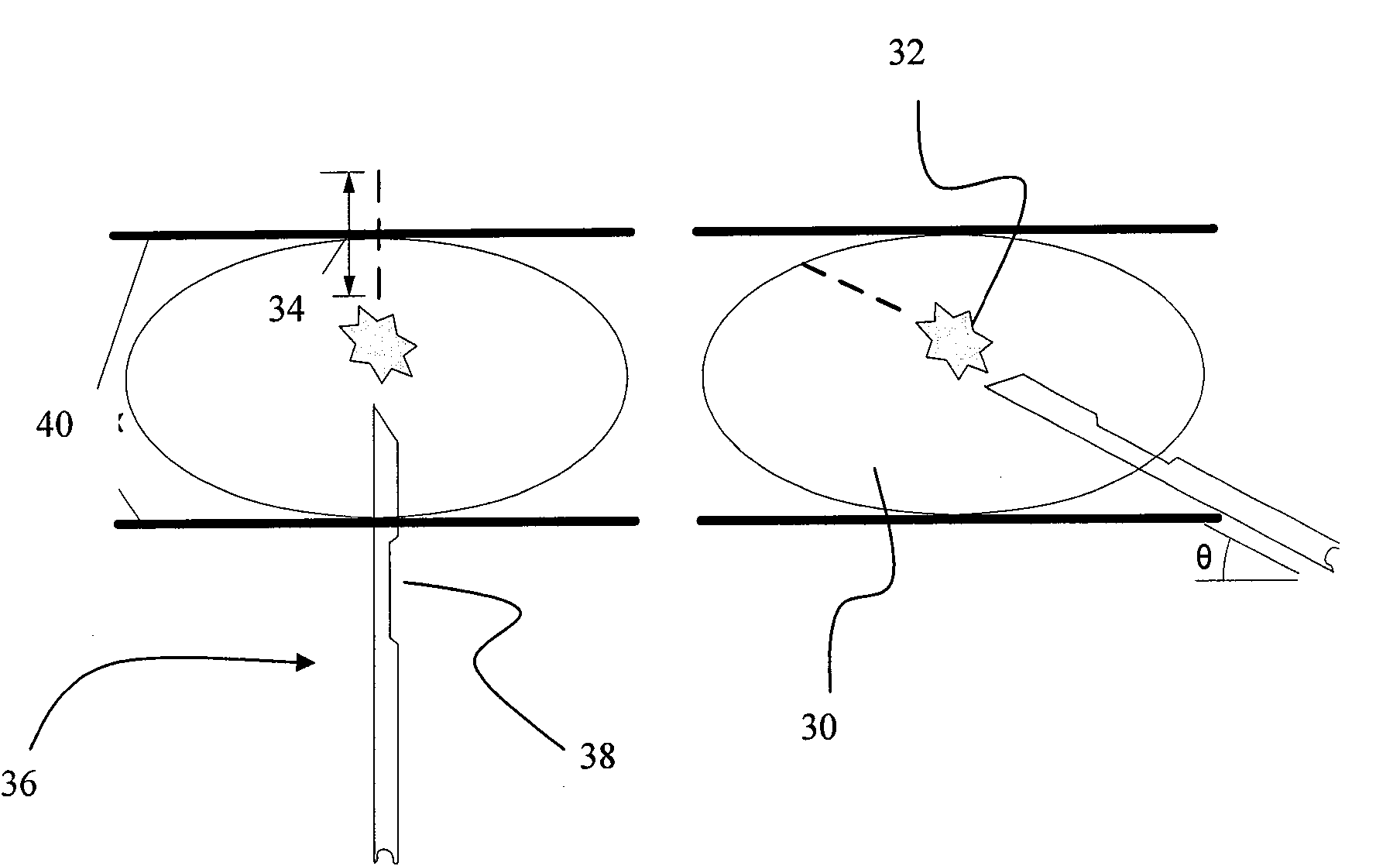
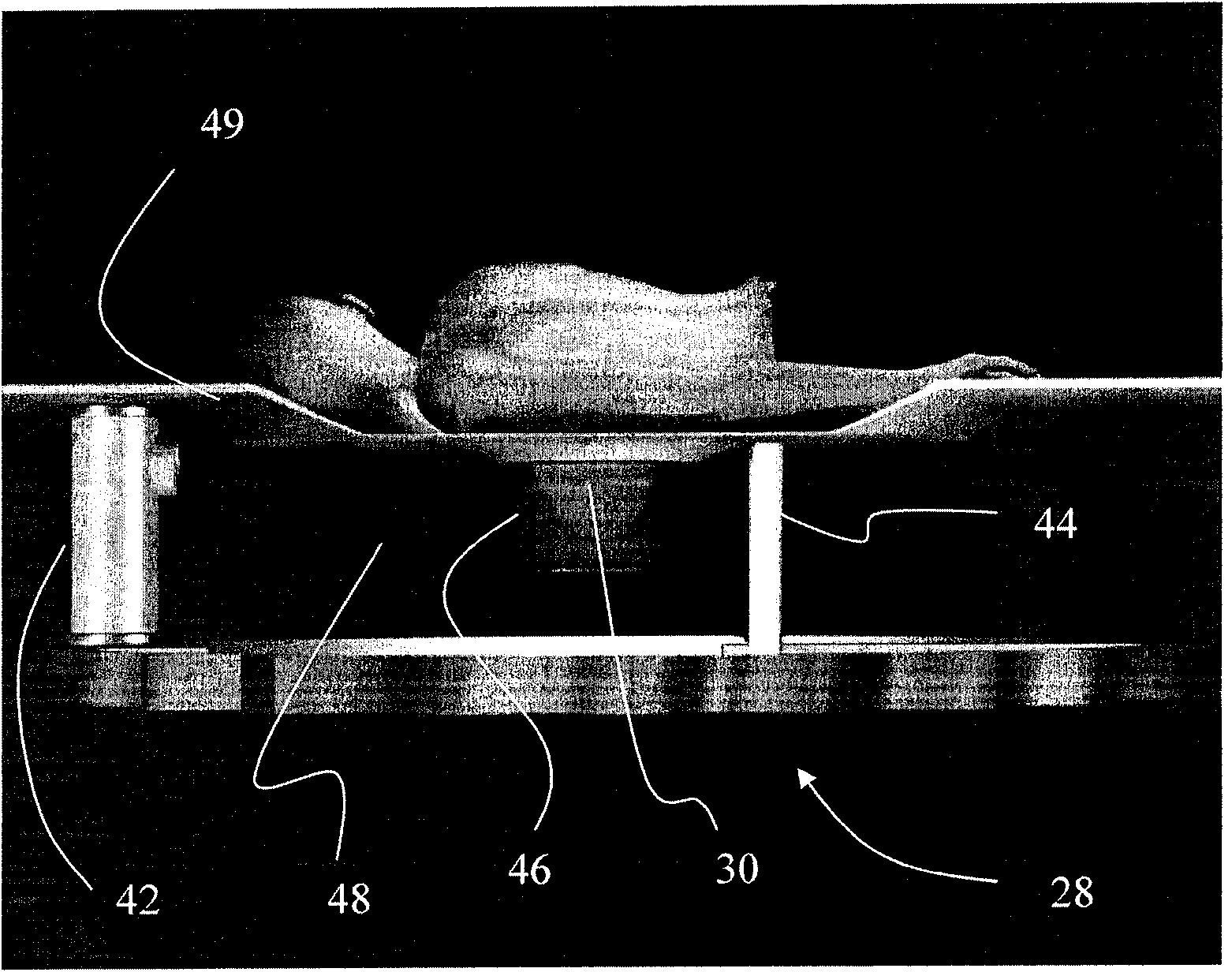
Disclosed are embodiments of methods of and systems for detecting and biopsying lesions with a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) system. The system comprises, in some embodiments, a CBCT device configured to output a cone beam CT image of at least a portion of a patient's breast and a multi-axis transport module, having at least three degrees of freedom and configured to position a biopsy needle within a 3D frame of reference based on inputs received from the cone beam CT device. The transport module can be configured to place the biopsy needle adjacent to, or within, a target of interest within the breast. Also disclosed are embodiments of methods of and systems for testing CBCT systems with phantoms.
Owner:CORNING LTD
Image denoising method based on projection sequential data similarity
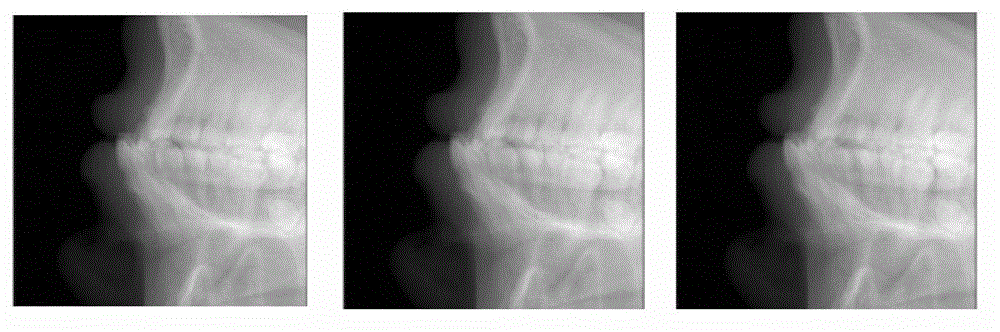
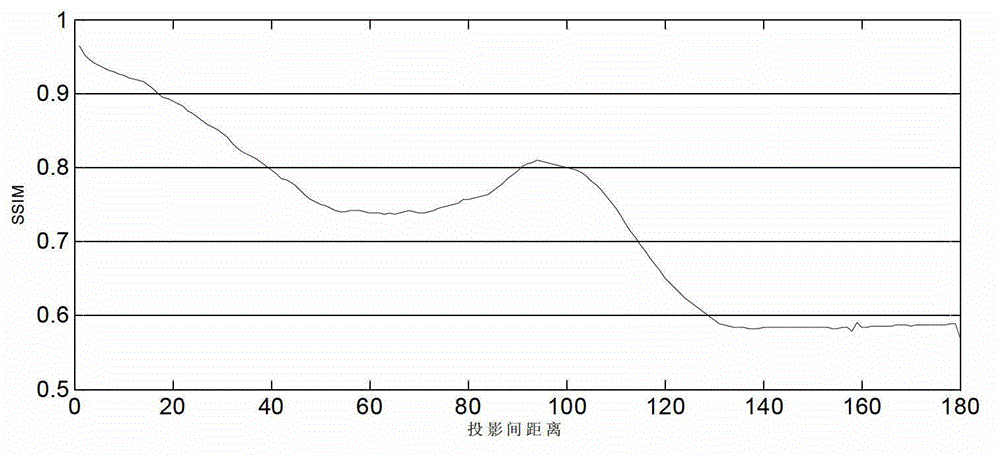
The invention provides an image denoising method specific to cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and relates to the technical field of radiation imaging. An area similar to the projection data is searched in adjacent projection data (similarity is calculated and determined through SSIM) specific to each pixel to be denoised and neighbourhood of the pixel in CBCT projection data according to data redundancy of the projection data, weighting average calculation is carried out on the pixel-to-be-denoised by utilizing the data in the similar areas so as to effectively reduce noises of the projection data, and three-dimensional reconstruction is preformed after denoising process is finished. The method is characterized by utilizing high similarity and data redundancy of the adjacent projection data. Compared with a traditional image denoising method, the image denoising method can achieve a better denoising effect, effectively improves the signal to noise ratio, and maintains image edge and detail information to the maximum extent. Meanwhile, the sequence image denoising concept is also applied to the filed of visible light imaging, such as the fields of denoising and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method and system for cone beam computed tomography high density object artifact reduction
ActiveUS20110206258A1Speed of computationCorrection capabilityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionHigh density
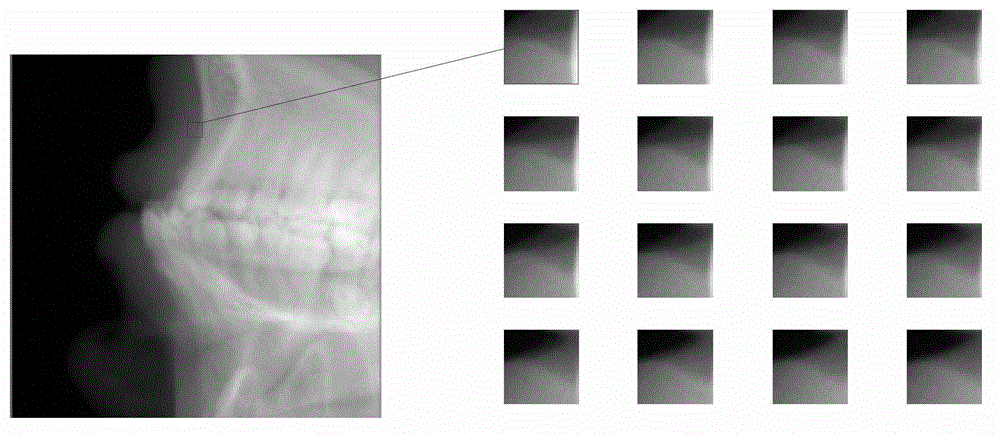
A method of providing a corrected reconstructed computed tomography image accesses image data for computed tomography images of a subject, identifying a subset of the computed tomography images that contain high density features. At least one high density feature is detected in each of the identified subset. The high density feature is classified and a compensation image is formed by distributing pixels representative of tissue over the classified high density feature. A difference sinogram is generated for each image in the identified subset of images by subtracting a first sinogram of the high density feature from a second sinogram of the original image. A resultant sinogram is generated for each image in the identified subset by adding a third sinogram generated according to the compensation image to the difference sinogram. The corrected reconstructed computed tomography image is formed according to the resultant sinogram generated for each image in the identified subset of images.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
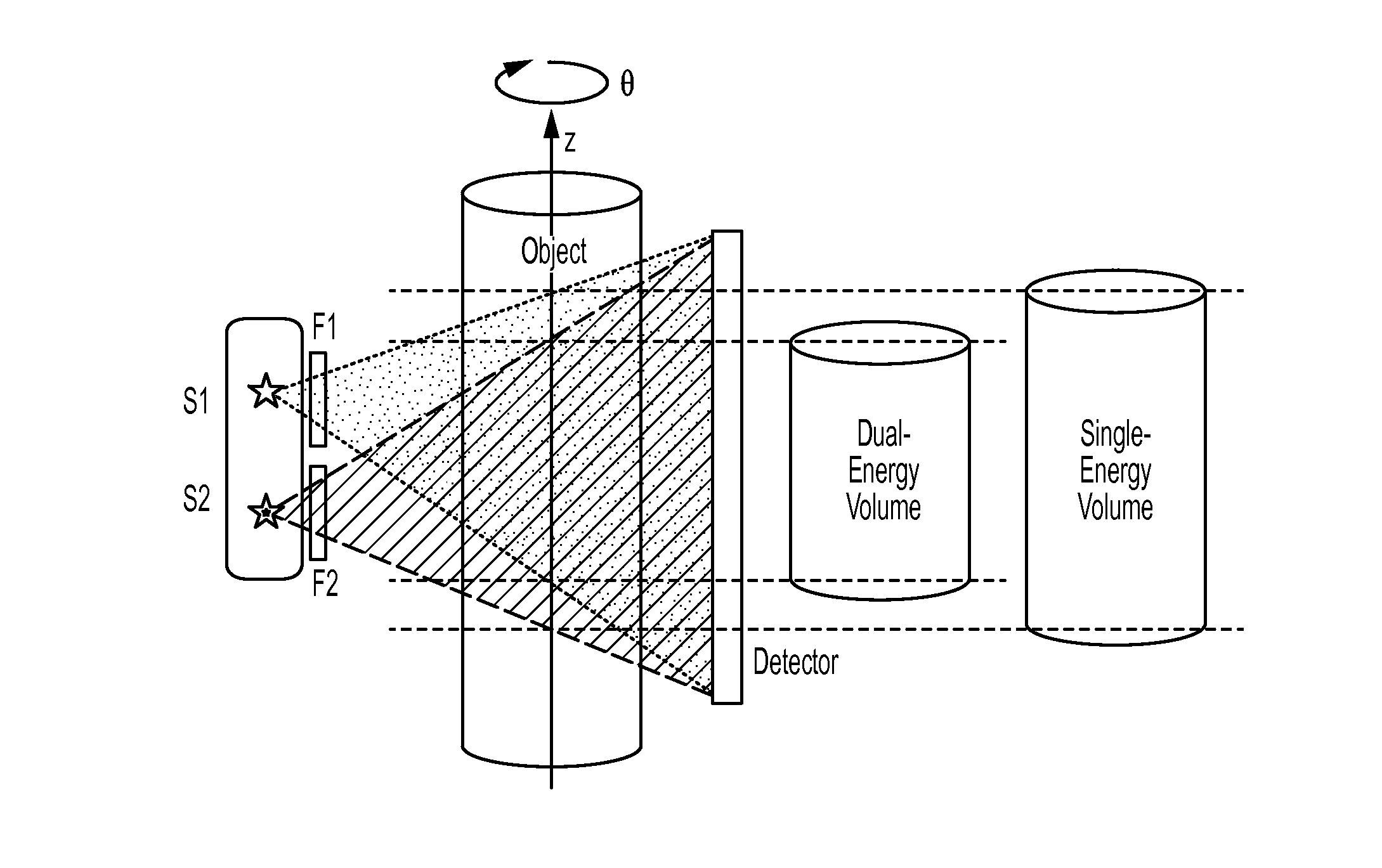
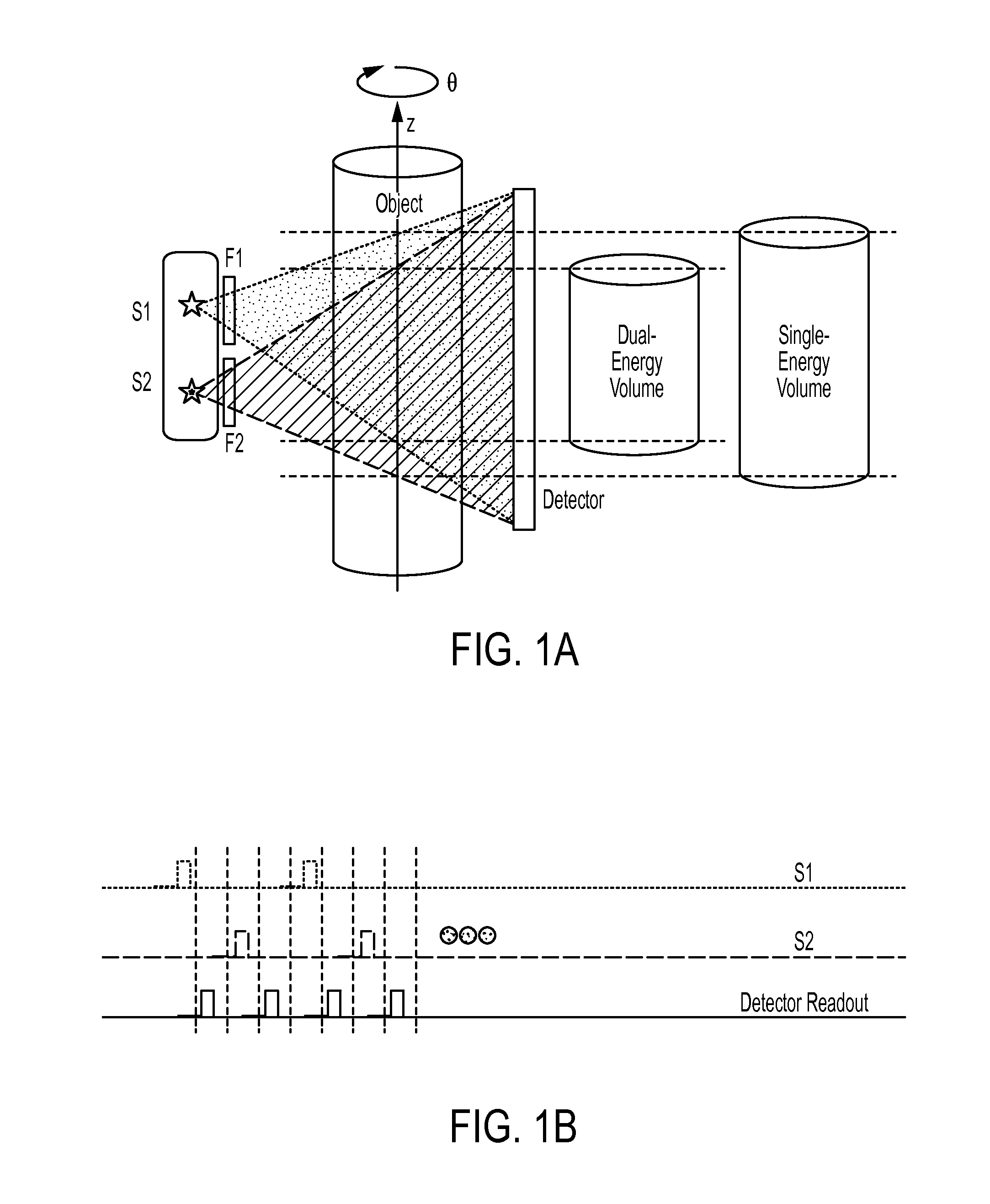
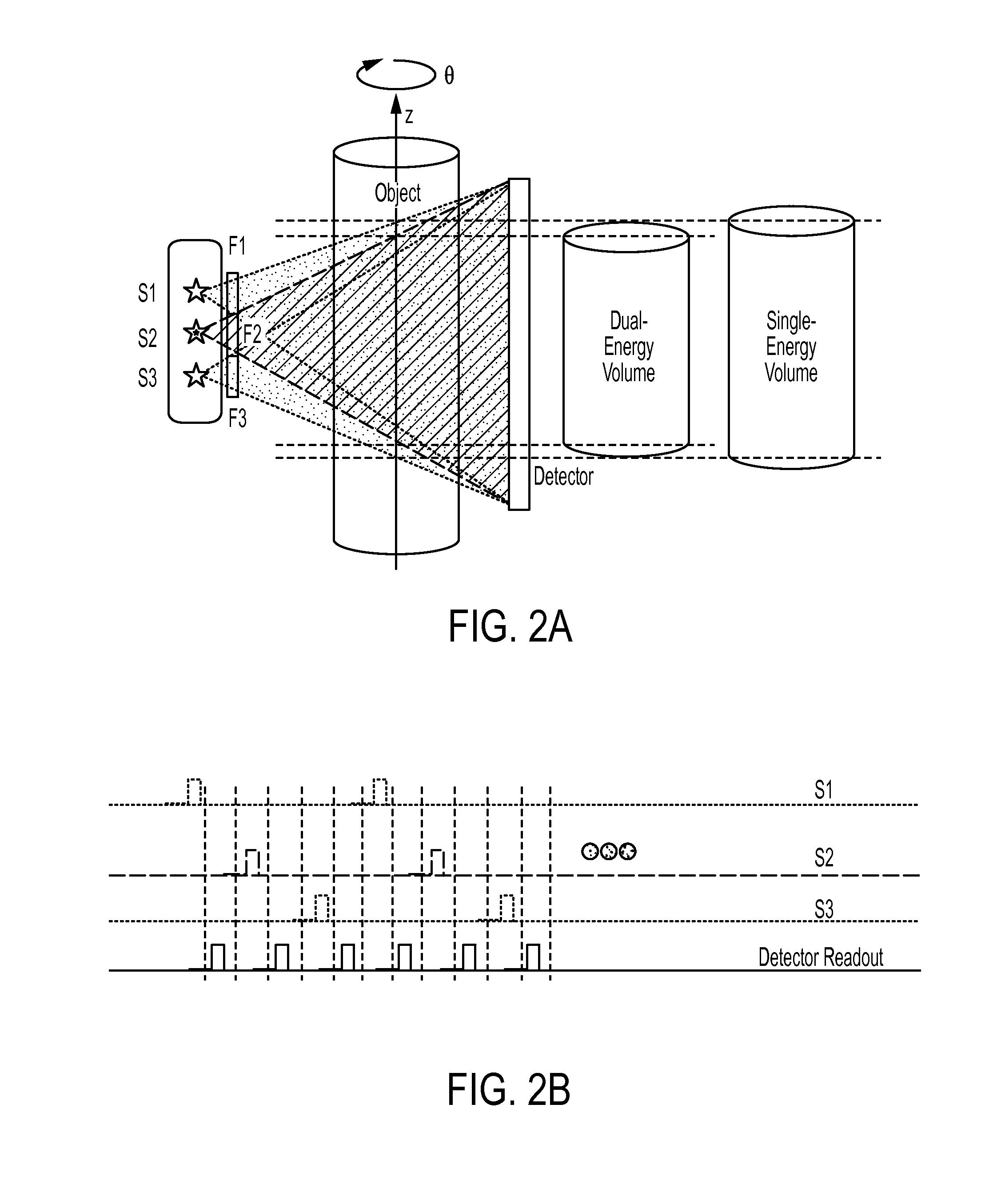
Dual-energy cone-beam computed tomography with a multiple source, single-detector configuration
The present invention is directed to a system and method for dual-energy (DE) or multiple-energy (spectral) cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using a configuration of multiple x-ray sources and a single detector. The x-ray sources are operated to produce x-ray spectra of different energies (peak kilovoltage (kVp) and / or filtration). Volumetric 3D image reconstruction and dual or triple energy 3D image decomposition can be executed using data from the CBCT scan. The invention allows for a variety of selections in energy and filtration associated with each source and the order of pulsing for each source (“firing pattern”). The motivation for distributing the sources along the z direction in CBCT includes extension of the longitudinal field of view and reduction of cone-beam artifacts.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC +1
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20140098930A1Room for improvementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation exposureCone beam computed tomography
An apparatus for cone beam computed tomography can include a support structure, a scanner assembly coupled to the support structure for controlled movement in at least x, y and z orientations, the scanner assembly can include a DR detector configured to move along at least a portion of a detector path that extends at least partially around a scan volume with a distance D1 that is sufficiently long to allow the scan volume to be positioned within the detector path; a radiation source configured to move along at least a portion of a source path outside the detector path, the source path having a distance D2 greater than the distance D1, the distance D2 being sufficiently long to allow adequate radiation exposure of the scan volume for an image capture by the detector; and a first gap in the detector path.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIV OF ROCHESTER
Methods, apparatus, and computer-program products for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography
ActiveUS8009794B2Reduce errorsImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersSources of errorTomography
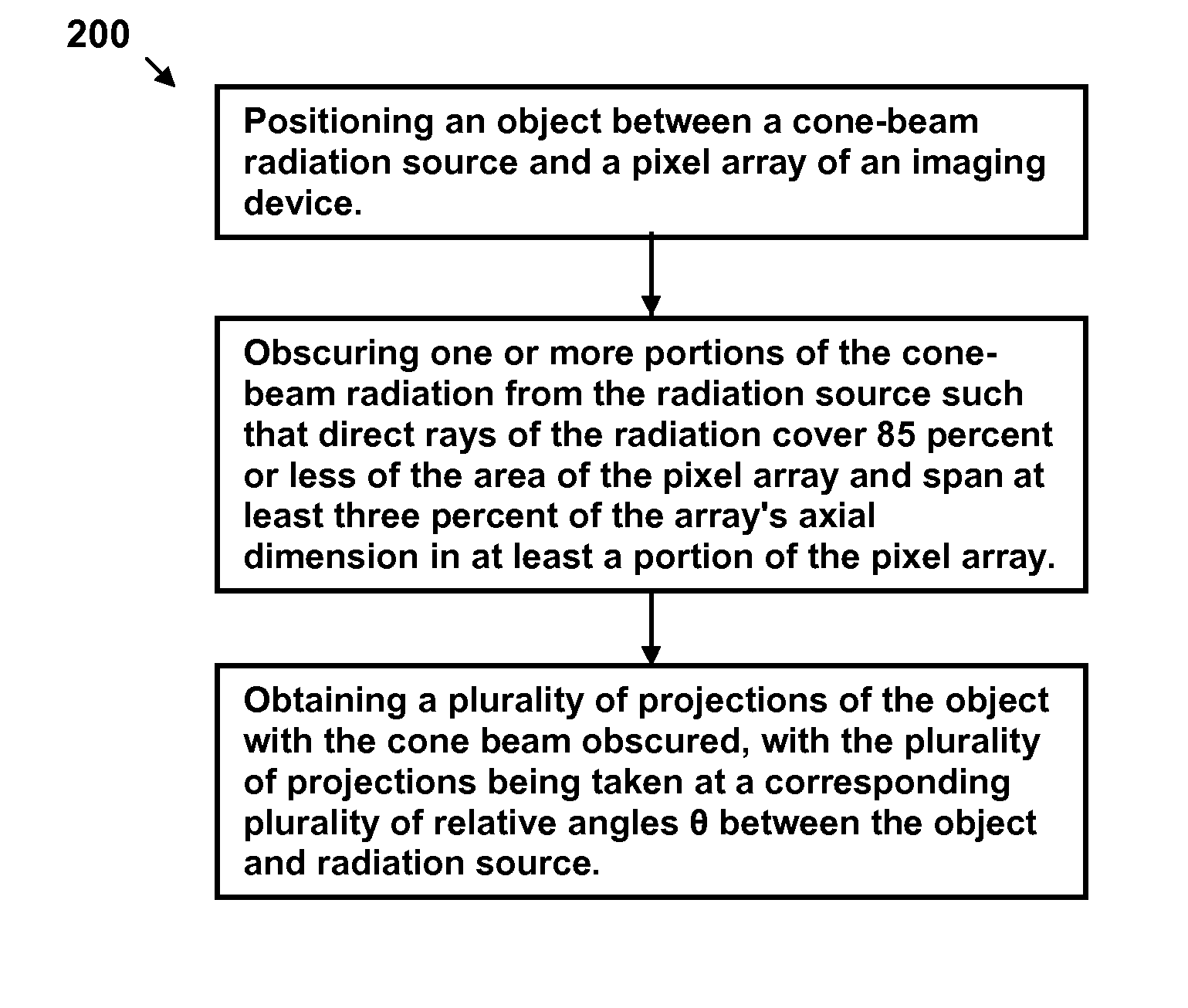
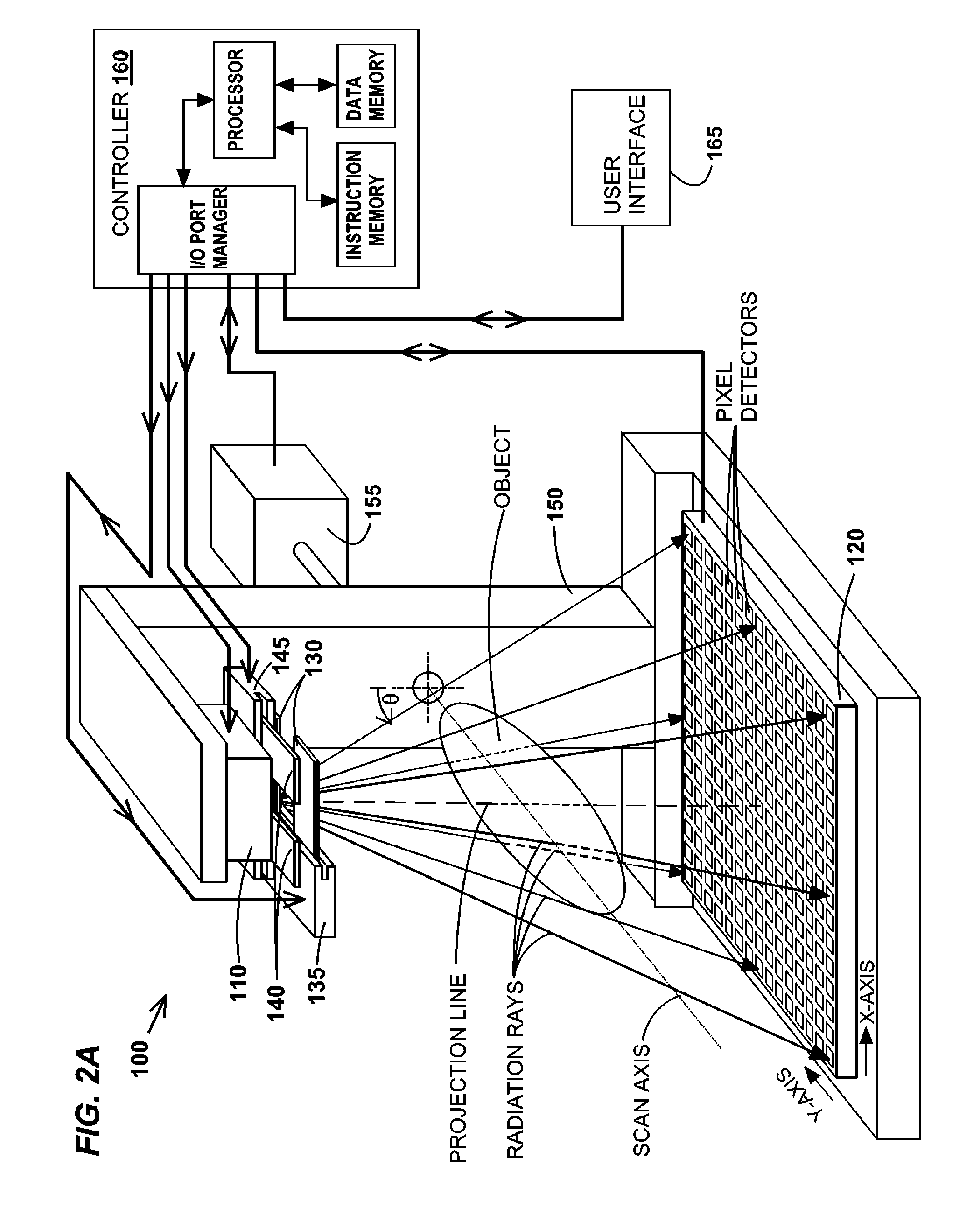
Disclosed are methods, systems, and computer-product programs for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) by obscuring portions of the radiation source so that the radiation only passes through the specific areas of the patient related to the regions-of-interest to the doctor. The obscuring action causes less radiation scattering to occur in the patient's body, thereby reducing a major source of error in the image accuracy caused by scattered radiation. Scattered radiation received by detector pixels that are obscured by direct-line of sight radiation may be used to estimate the scattered radiation in the un-obscured portion, which can be used to further increase the accuracy of the image.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
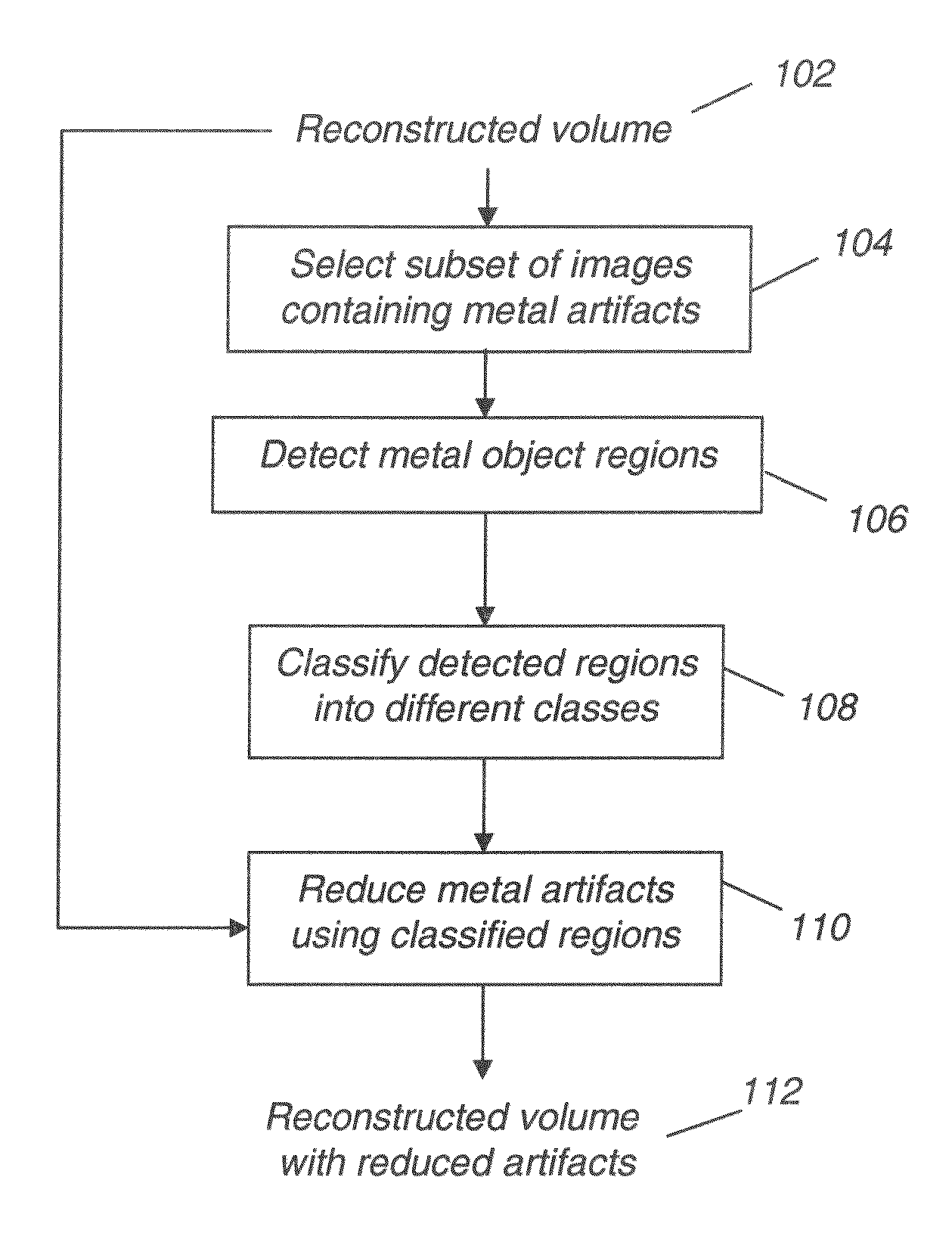
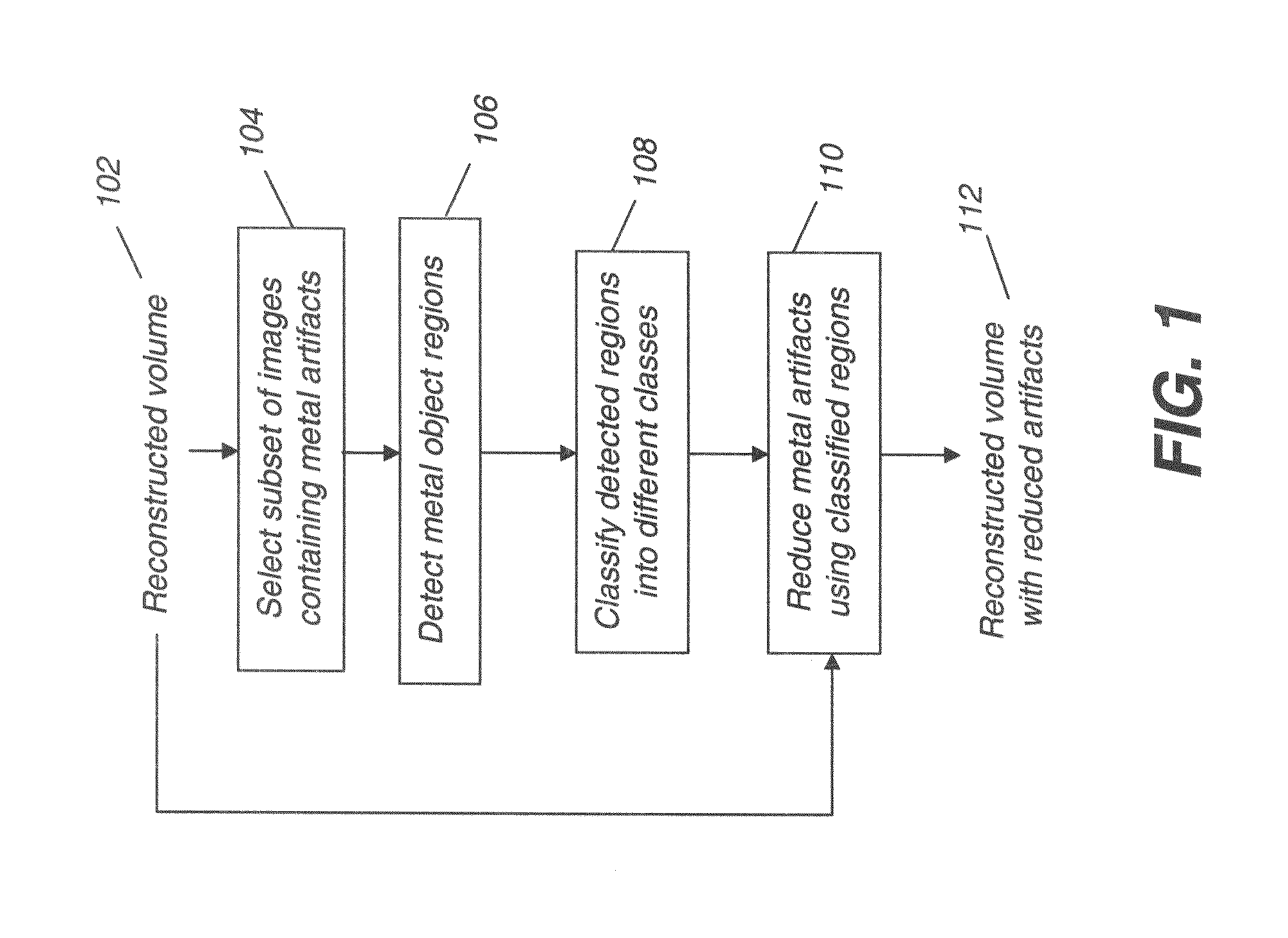
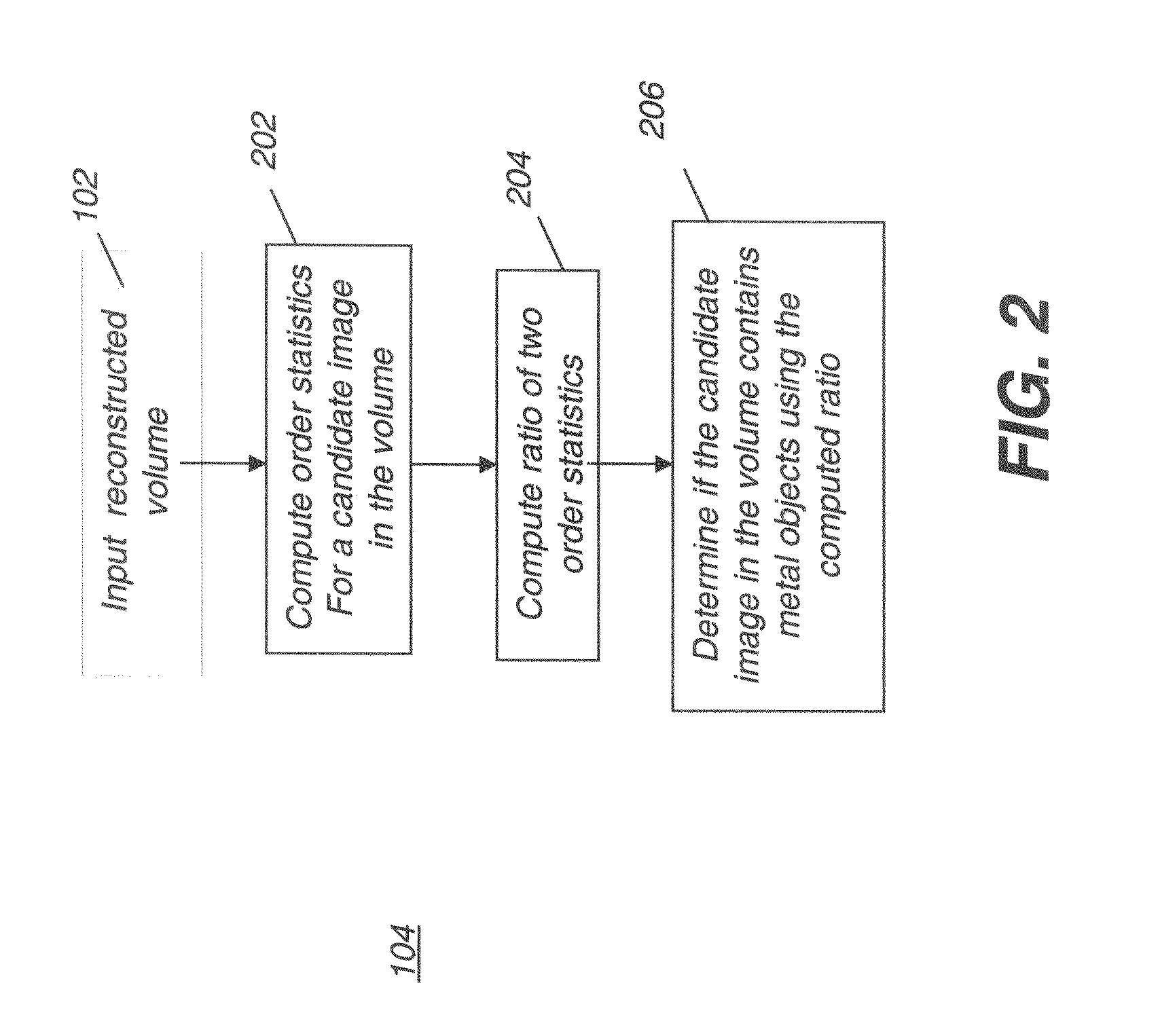
Methods and systems for cone-beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20170086758A1Minimize exposureCollisionComputerised tomographsTomographyTomographyCone beam computed tomography
Various methods and systems are provided for collision avoidance in cone-beam computed tomography (CT) systems. In one embodiment, a method for an imaging apparatus comprises calculating a likelihood of a collision between the imaging apparatus and a subject and / or its support based on a model of the subject, performing a scan of the subject responsive to the likelihood below a threshold, and not performing the scan otherwise. In this way, collisions between the patient and the imaging apparatus can be avoided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
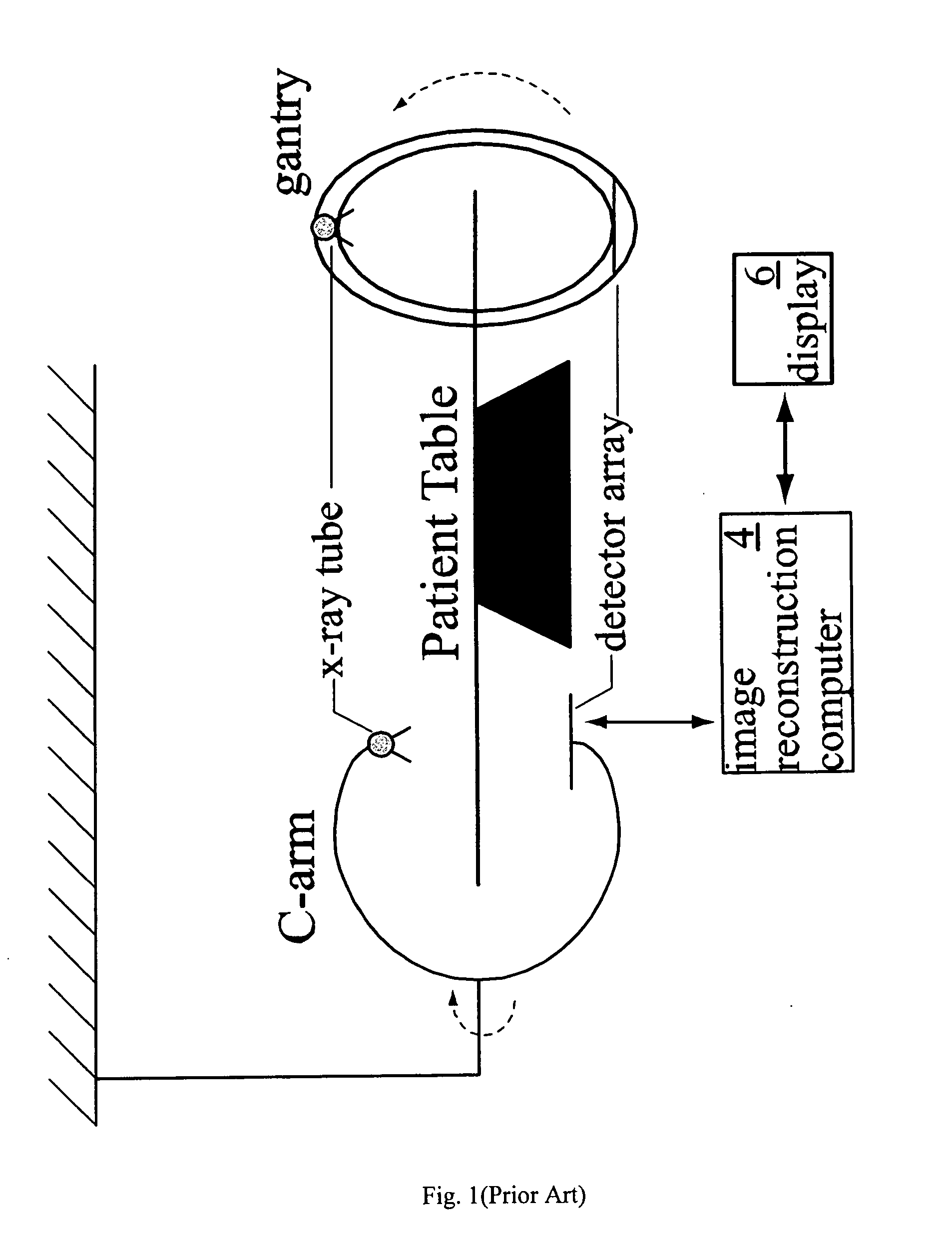
Efficient image reconstruction algorithm for the circle and line cone beam computed tomography
InactiveUS20060034417A1Create efficientlyReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBack projectionImage reconstruction algorithm
Methods, systems and processes for providing efficient, accurate and exact image reconstruction using portable and easy to use C-arm scanning devices and rotating gantries, and the like. The invention can provide exact convolution-based filtered back projection (FBP) image reconstruction by combining a curved scan of the object and a line scan of the object. The curved scan can be done before or after the line scan. The curved scan can be less than or greater than a full circle about an object being scanned.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for 3d metal and high-density artifact correction for cone-beam and fan-beam ct imaging
ActiveUS20120008845A1Accurate reconstruction imageHigh artifactImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactHigh density
A 3D metal artifacts correction technique corrects the streaking artifacts generated by titanium implants or other similar objects. A cone-beam computed tomography system is utilized to provide 3D images. A priori information (such as the shape information and the CT value) of high density sub-objects is acquired and used for later artifacts correction. An optimization process with iterations is applied to minimize the error and result in accurate reconstruction images of the object.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
System and method for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20130077737A1Easy accessRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsX-rayHorizontal axis
A cone beam computed tomography system with a horizontally disposed, cylindrical gantry and a method for its use are provided. The cylindrical gantry includes a rotatable cylindrical frame fixed to a support frame. A cone beam X-ray source and X-ray detector are mounted to the circumference of the cylindrical frame at diametrically opposed positions. The cylindrical frame is actuated to revolve the X-ray source-detector arrangement around a horizontal axis, thereby scanning a recumbent subject positioned in the aperture of the cylindrical frame.
Owner:QUEENSLAND RAIL LIMITED
Methods, Apparatus, and Computer-Program Products for Increasing Accuracy in Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20090190714A1Reduce errorsImproving Imaging AccuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHandling using diaphragms/collimetersComputer scienceCone beam computed tomography
Disclosed are methods, systems, and computer-product programs for increasing accuracy in cone-beam computed tomography.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS8210745B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCone beam computed tomographyRadiation
An apparatus for cone beam computed tomography of lower leg portions of a patient has a radiation source and a source transport actuable to move the source along an arcuate source path within a housing, from one side of a circumferential gap to the other and has a radius R2 about a center. A housing is provided for placement of the patient's foot. A digital radiation detector has a detector transport actuable to move the detector along an arcuate detector path within the housing, the detector path having a radius R1 about the center and concentric with the source path, wherein R1 is less than R2, and wherein the detector path extends from one side of the pedestal indent to the other. A gap closure apparatus is movable to a position that continues the detector path across the circumferential gap and encloses the detector path.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com