Patents
Literature
1770 results about "Compute tomography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Computed tomography. n. Abbr. Tomography in which computer analysis of a series of x-ray scans made of a bodily structure or tissue is used to construct a three-dimensional image of that structure. The technique is used in diagnostic studies of internal bodily structures, as in the detection of tumors or brain aneurysms.
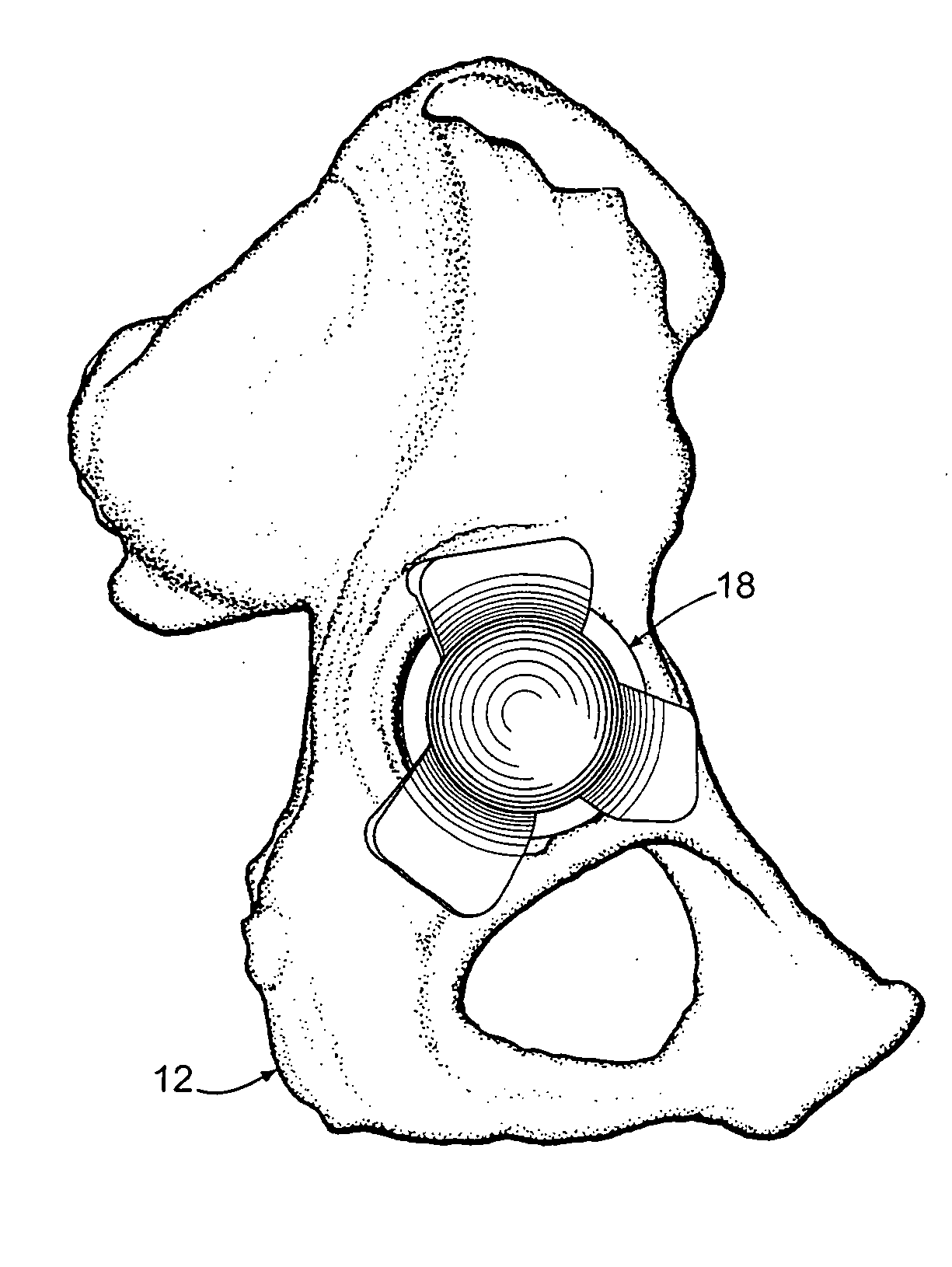
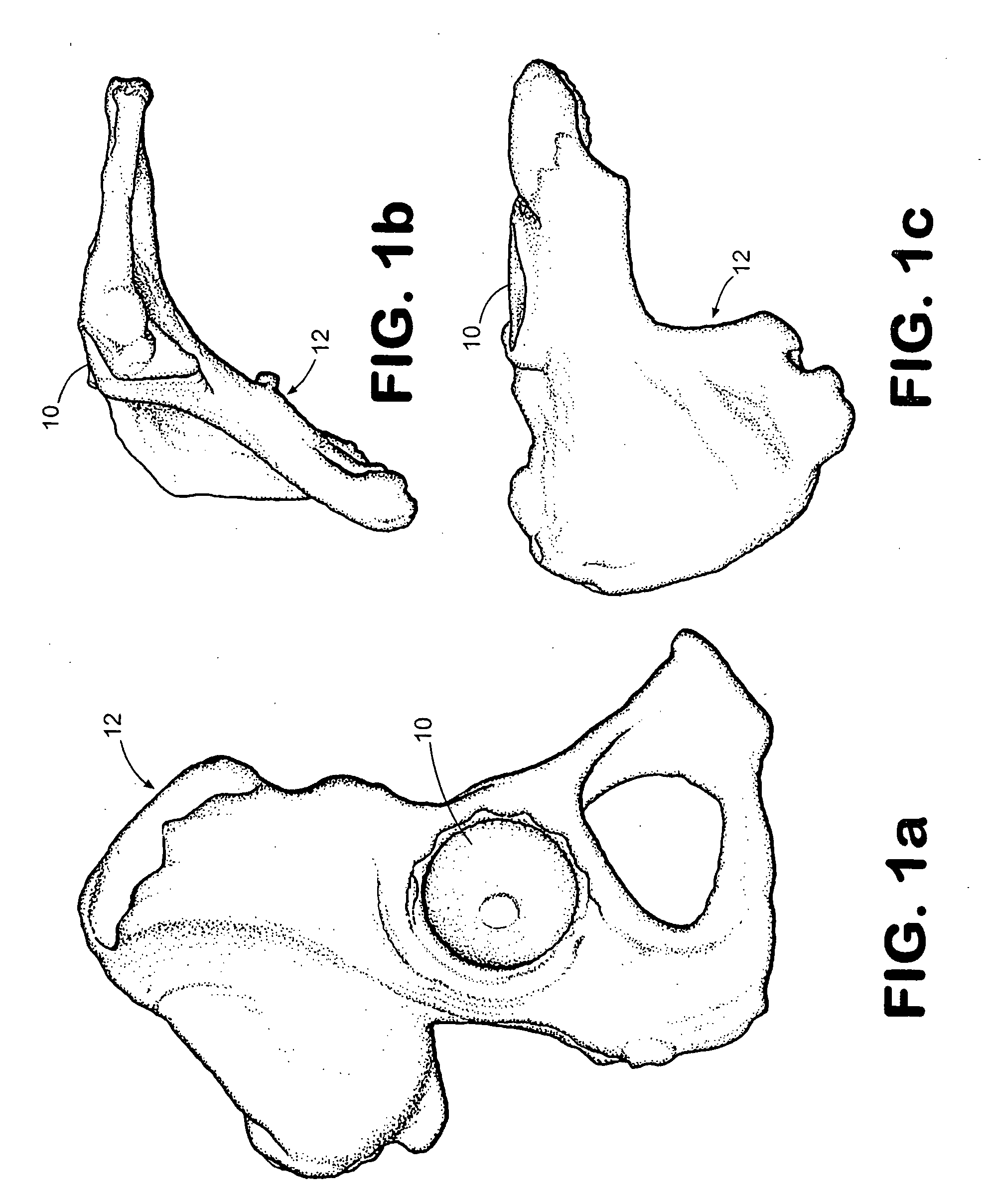
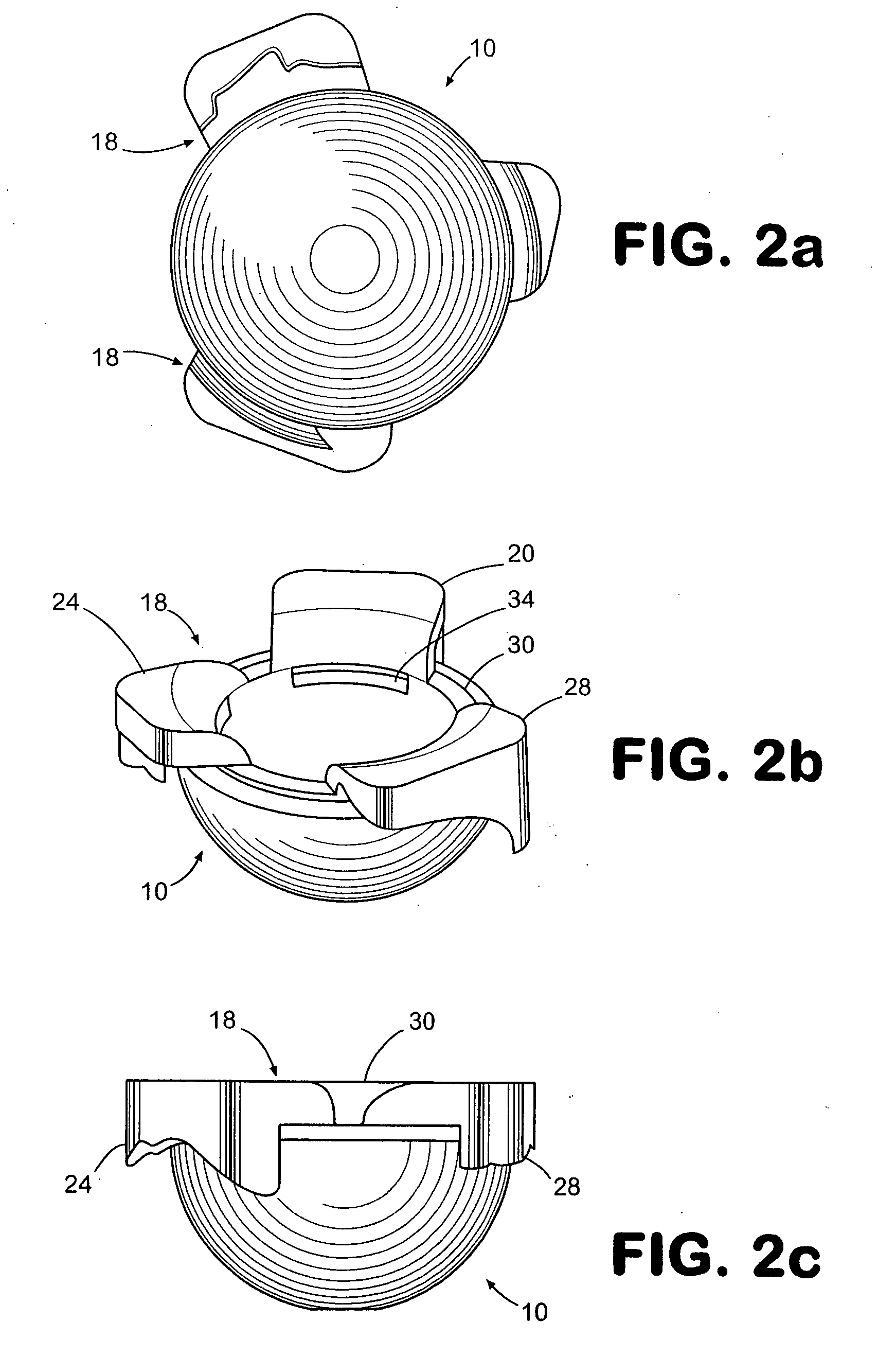
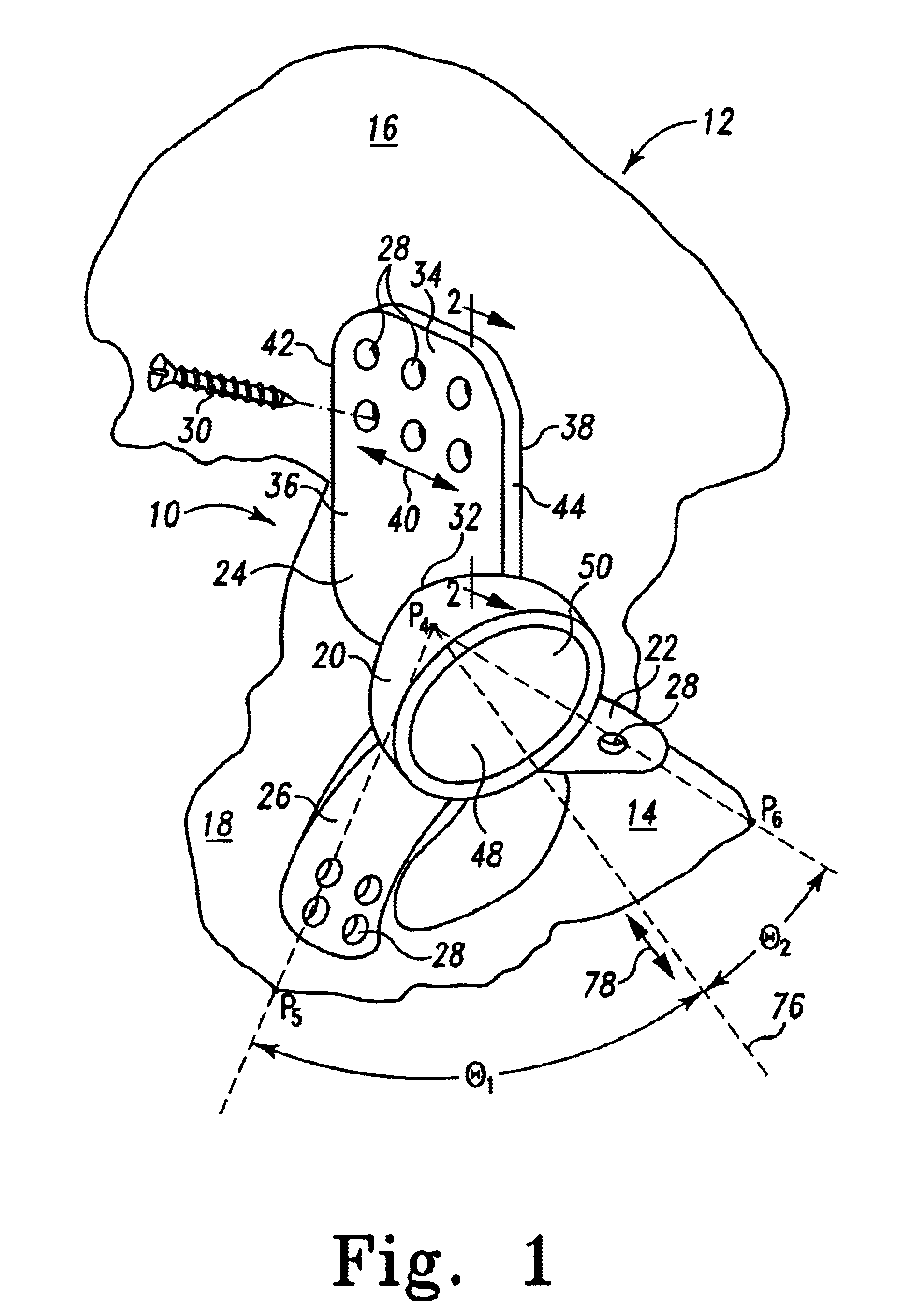
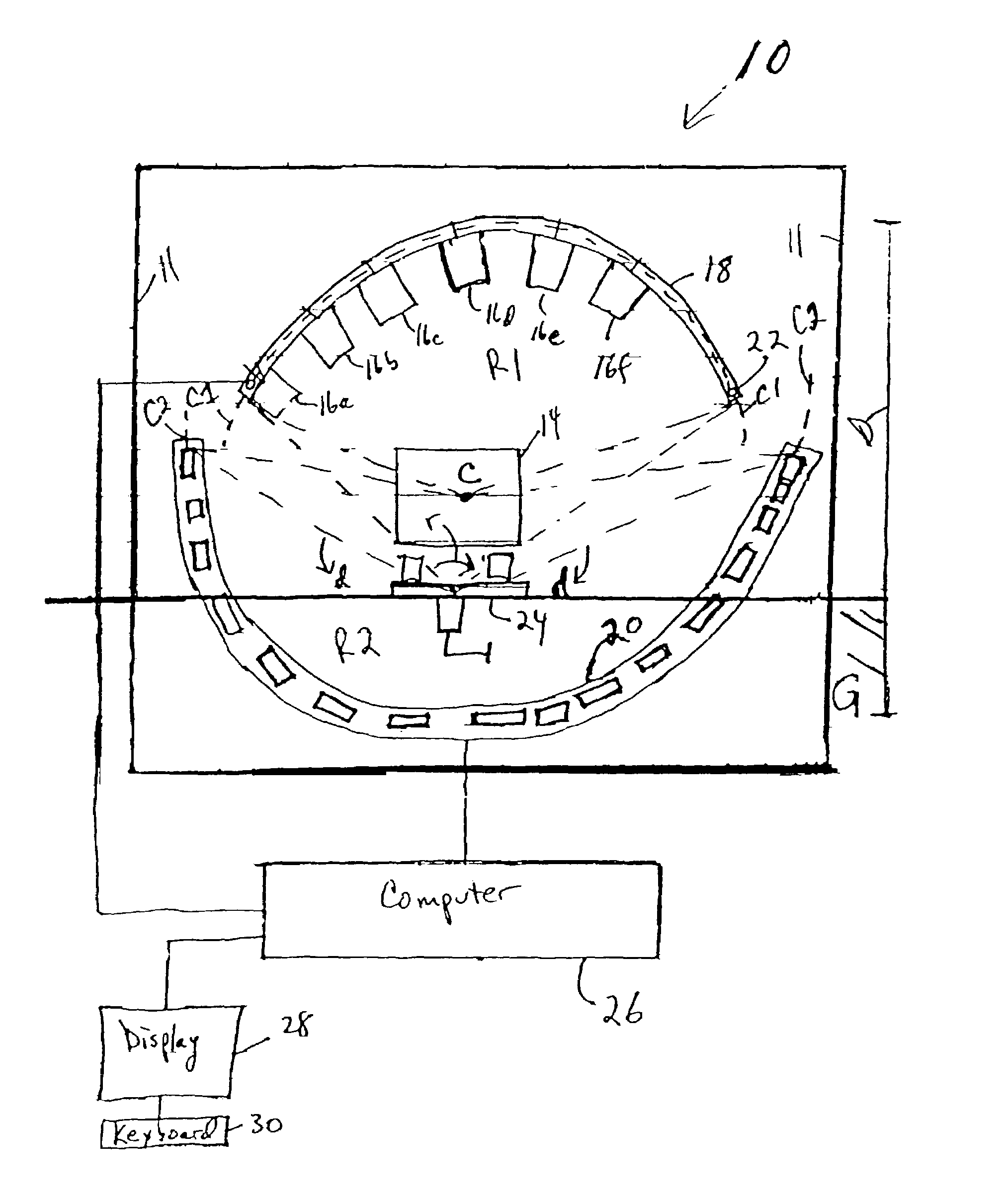
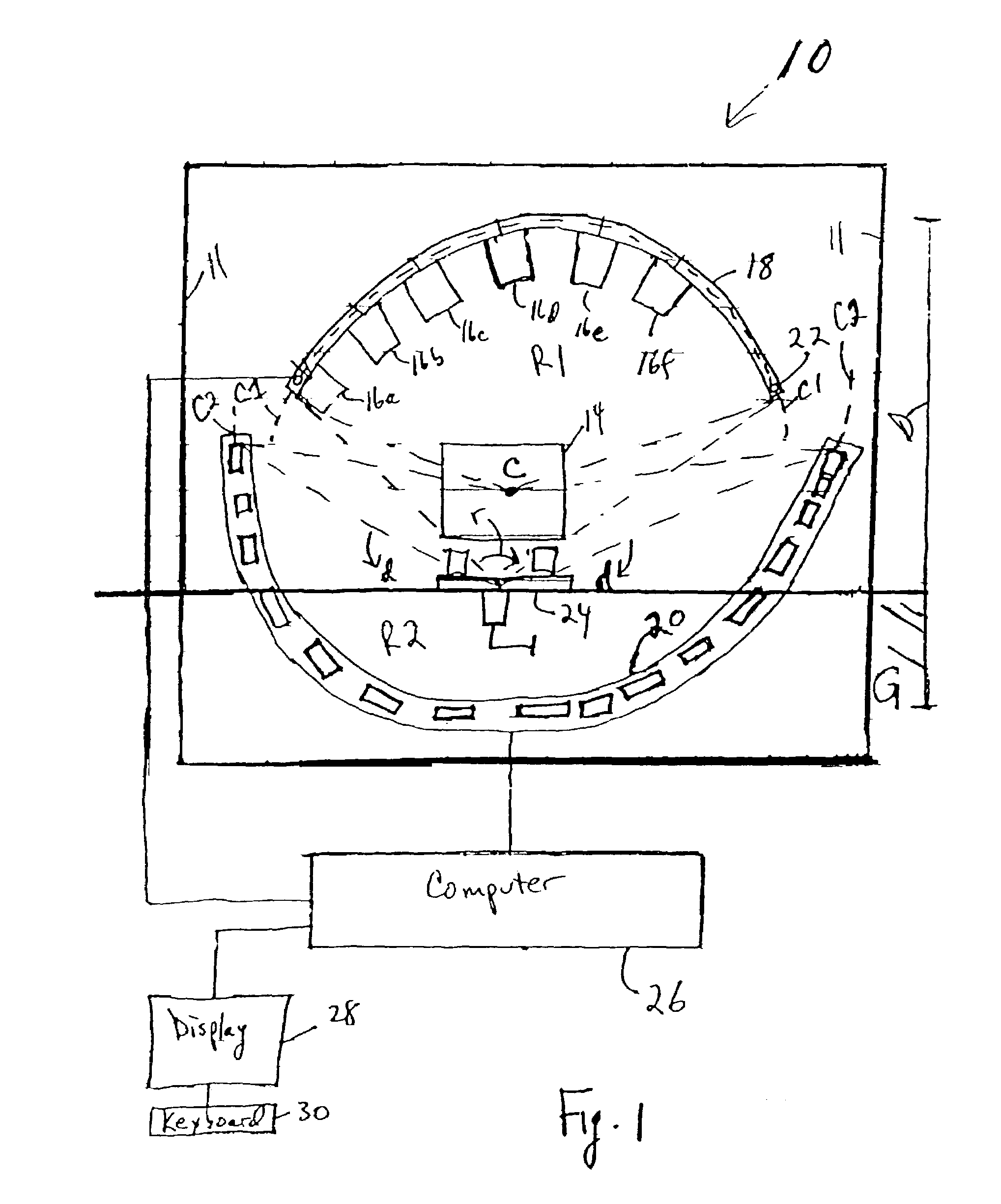
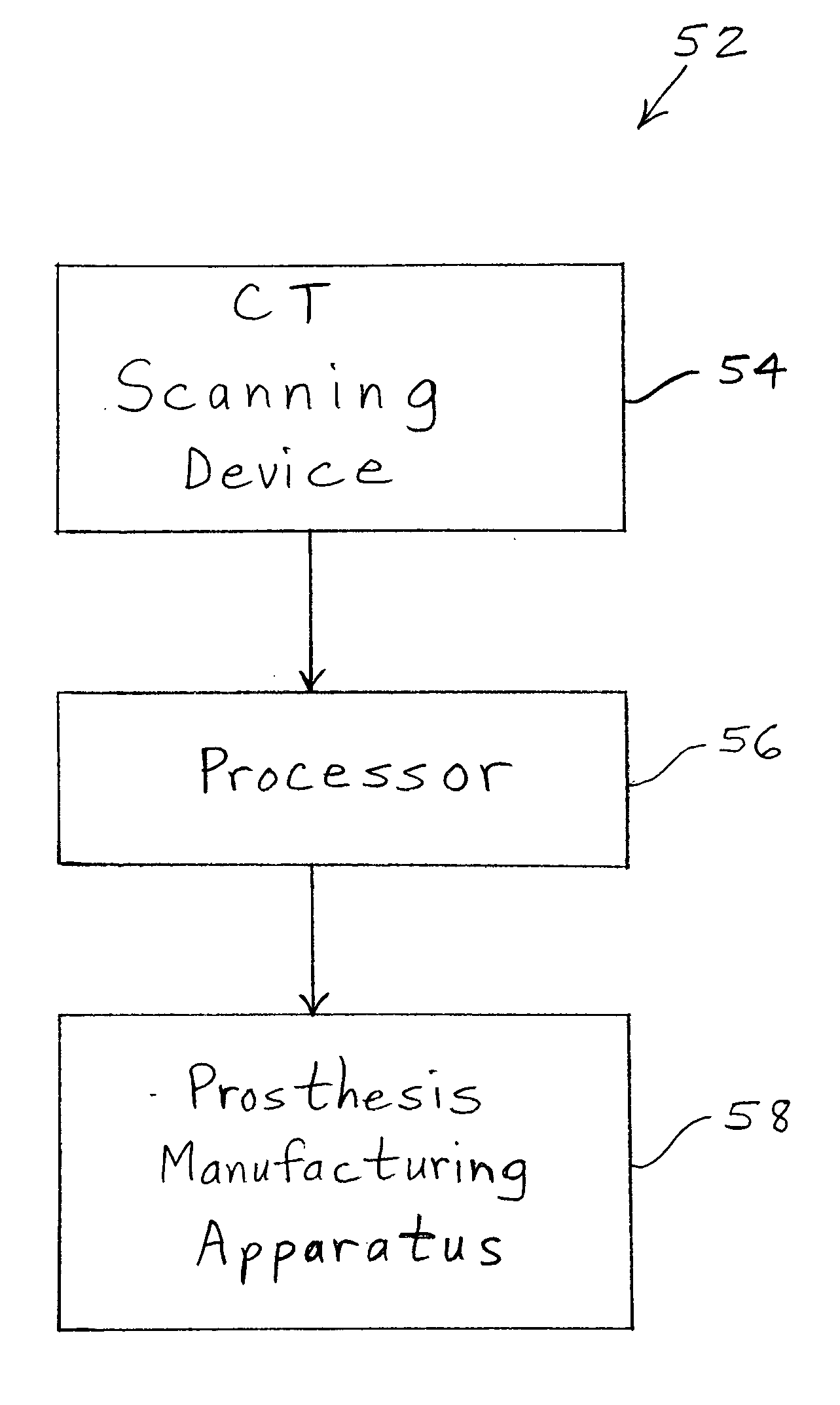
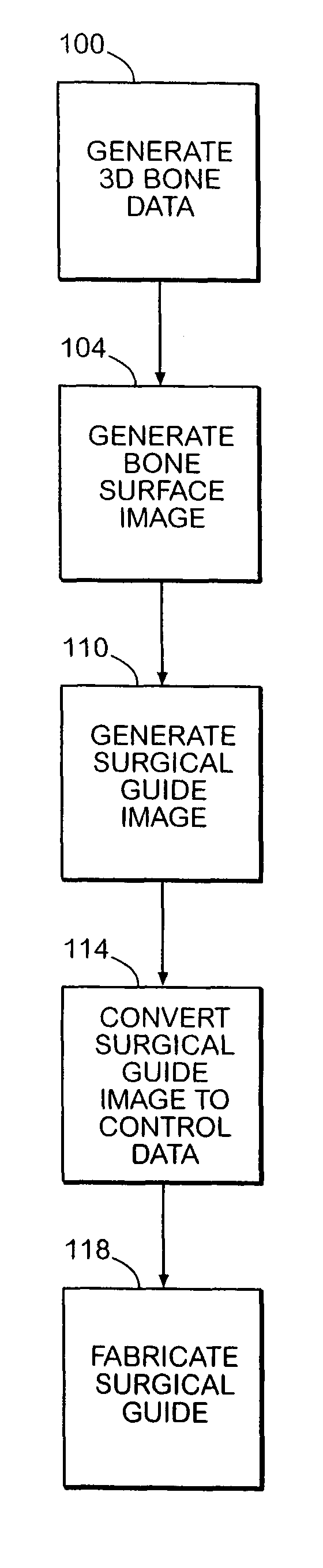
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS20050148843A1Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationJoint implantsMedicineControl data
A method and system may be used to design and control the manufacture of a surgical guide for implanting a prosthetic component. The system includes a bone surface image generator, a surgical guide image generator, and a surgical guide image converter. The bone surface image generator receives three dimensional bone anatomical data for a patient's bone and generates a bone surface image. The surgical guide image generator generates a surgical guide image from the bone surface image and an image of a prosthesis imposed on the bone surface image. The supporting structure of the generated surgical guide image conforms to the surface features of the three dimensional bone surface image. The surgical guide image is converted by surgical guide image converter into control data for operating a machine to form a surgical guide that corresponds to the surgical guide image.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
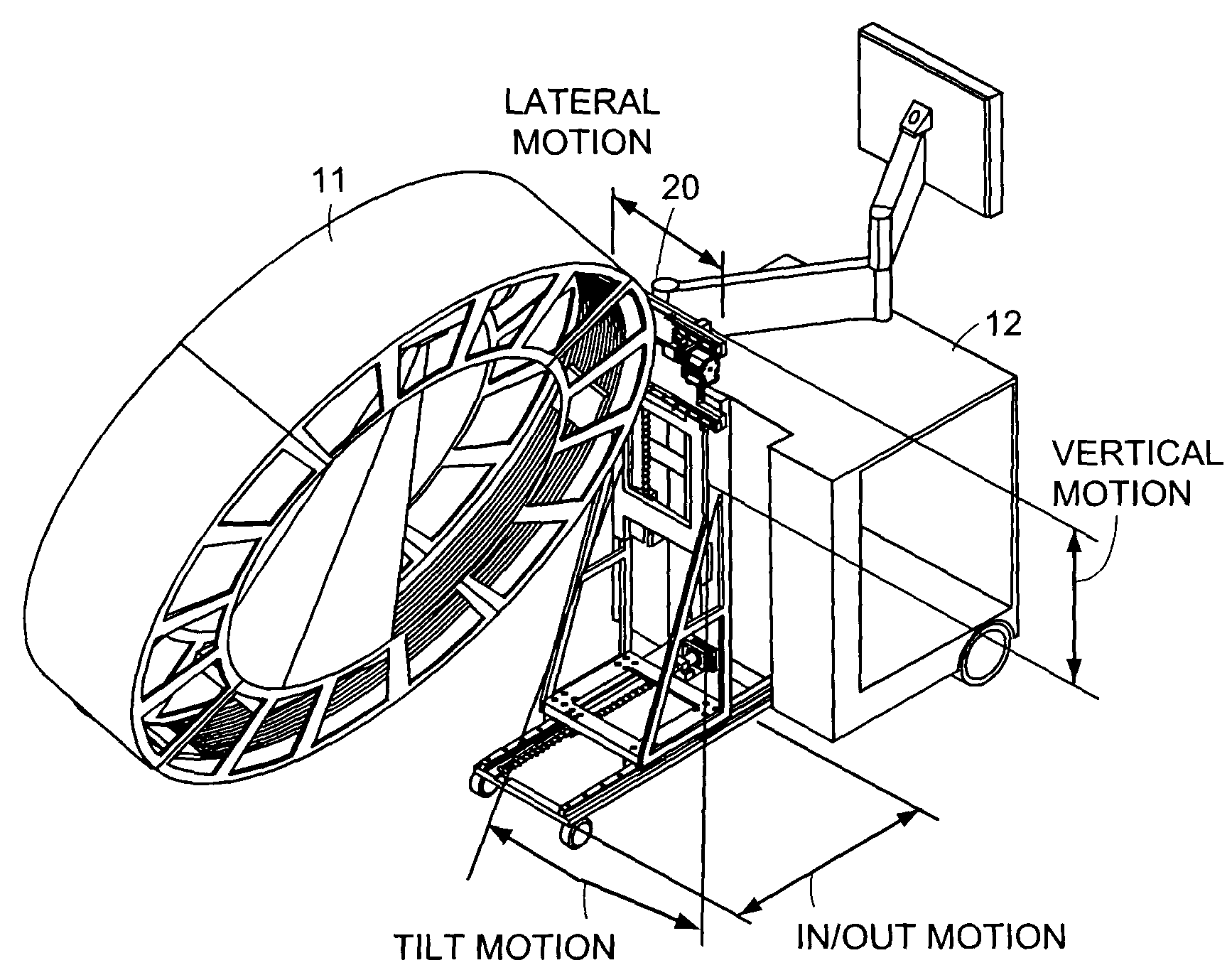
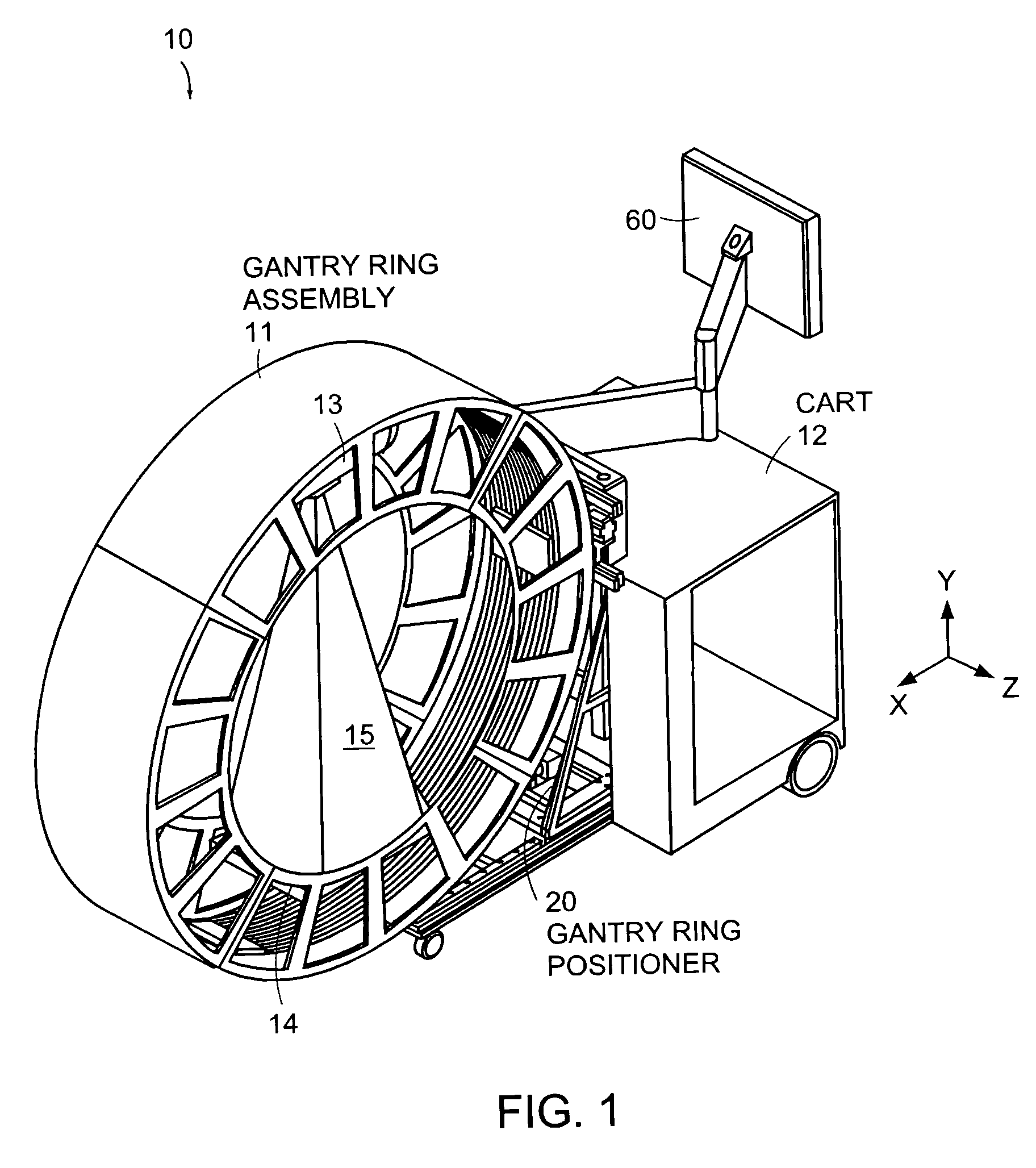
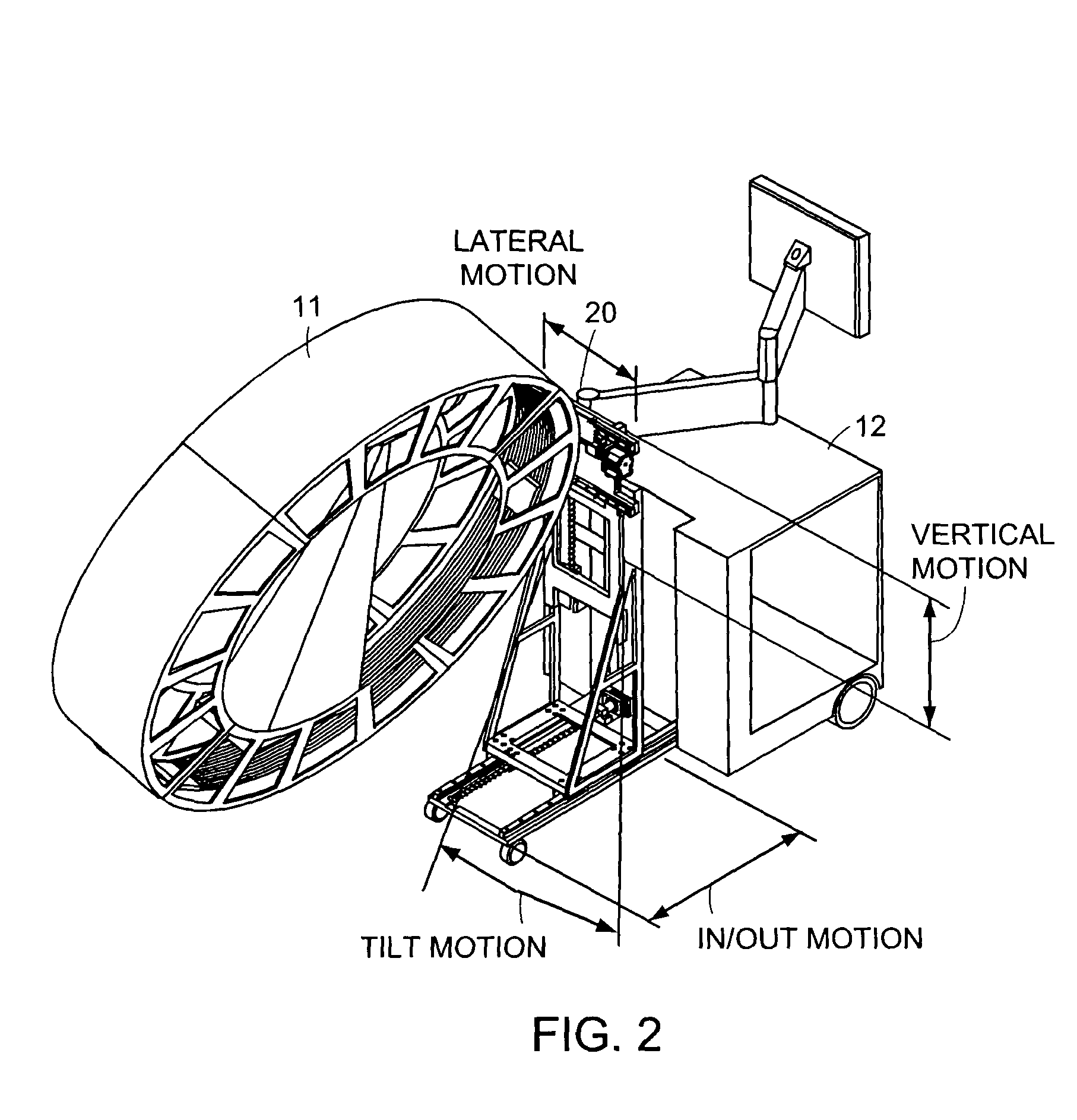
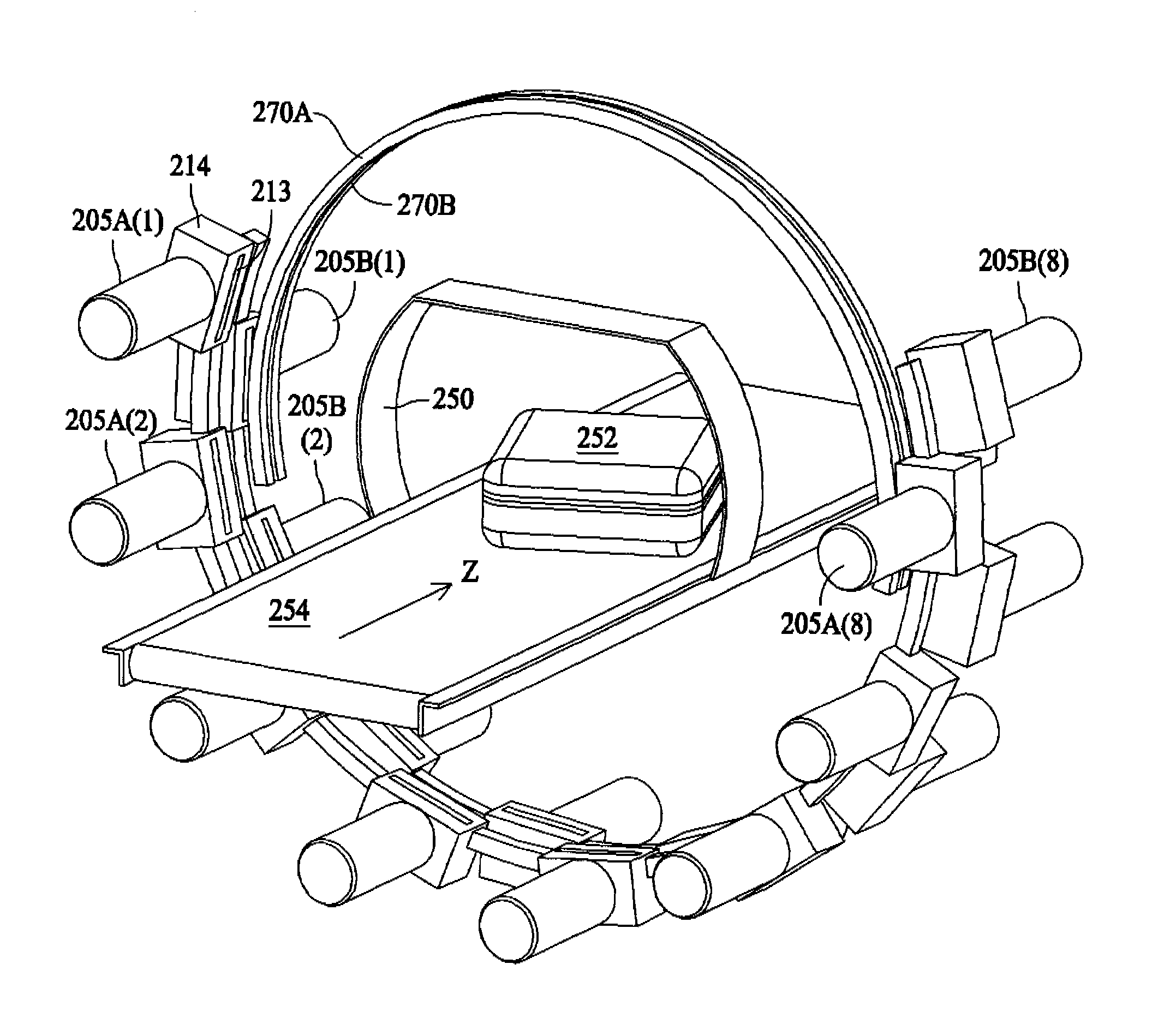
Cantilevered gantry apparatus for x-ray imaging
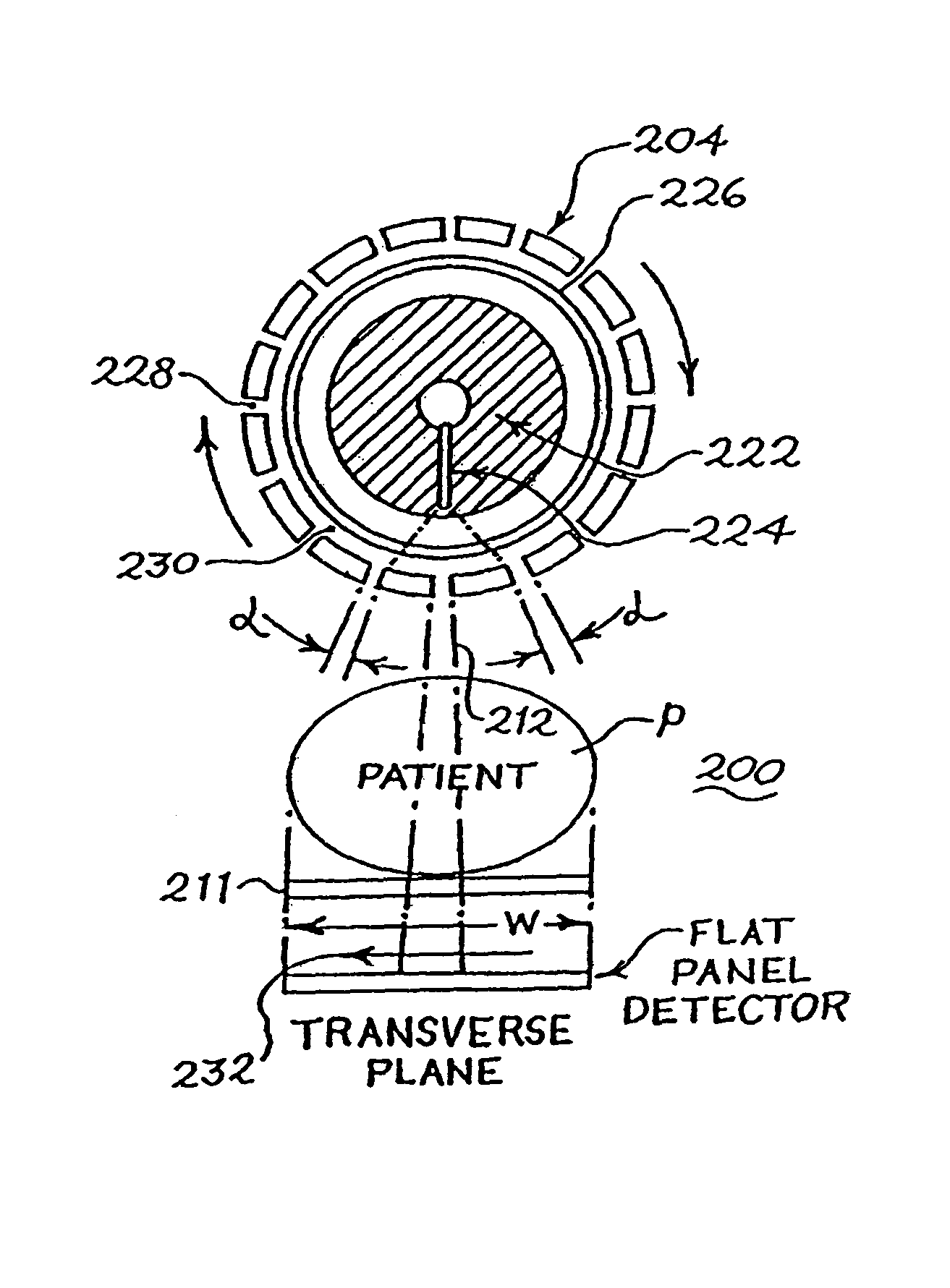
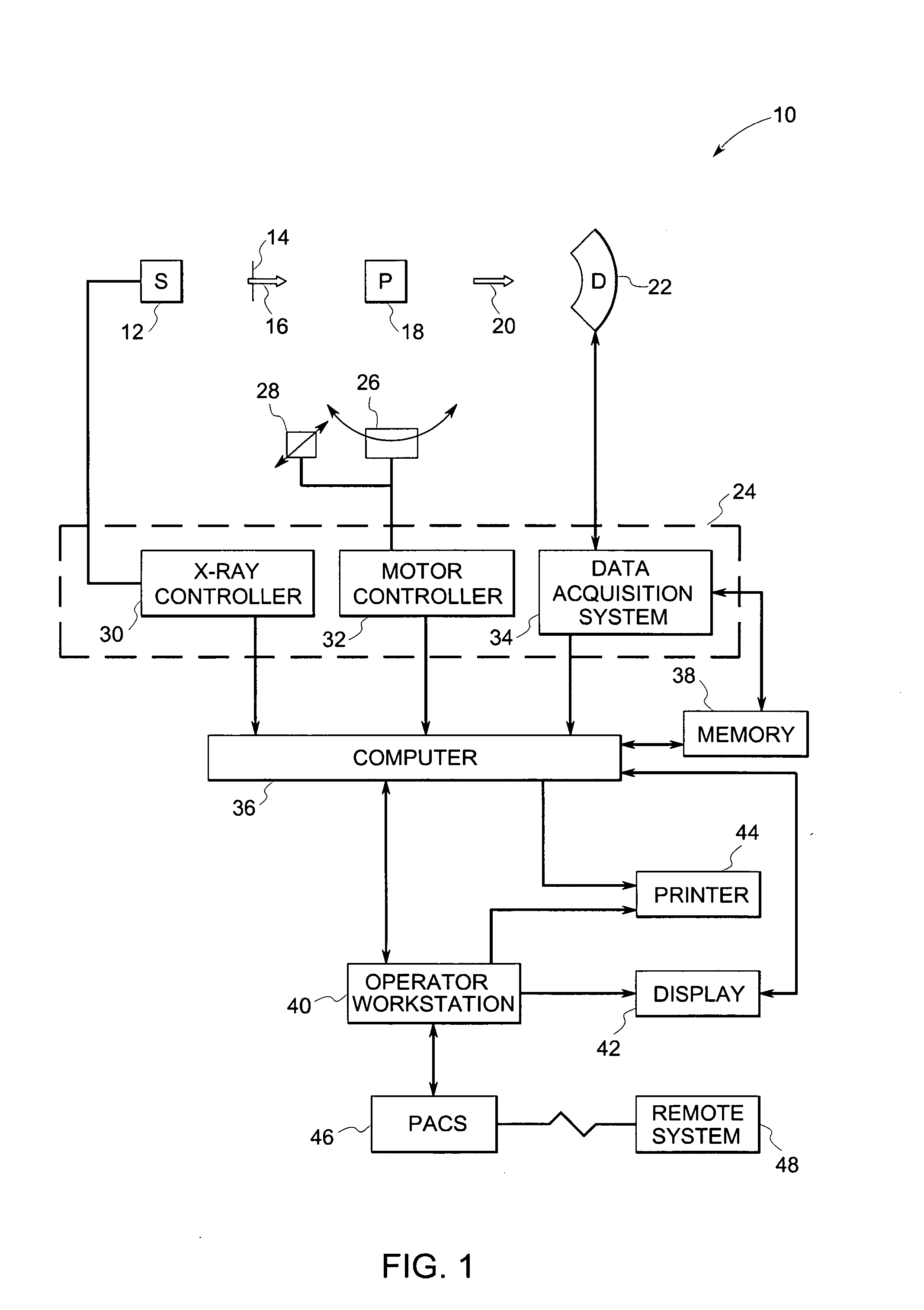
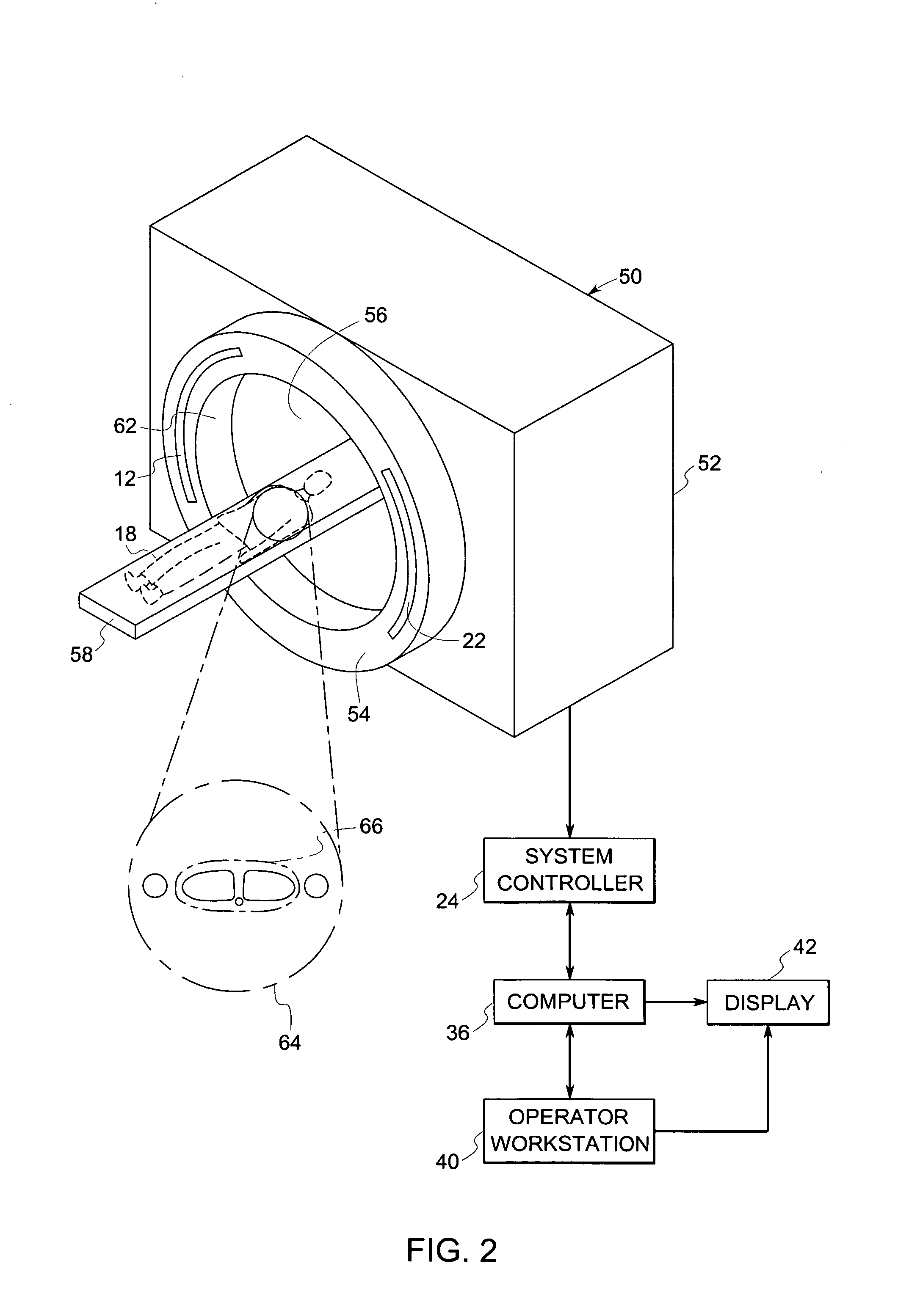
An x-ray scanning imaging apparatus with a rotatably fixed generally O-shaped gantry ring, which is connected on one end of the ring to support structure, such as a mobile cart, ceiling, floor, wall, or patient table, in a cantilevered fashion. The circular gantry housing remains rotatably fixed and carries an x-ray image-scanning device that can be rotated inside the gantry around the object being imaged either continuously or in a step-wise fashion. The ring can be connected rigidly to the support, or can be connected to the support via a ring positioning unit that is able to translate or tilt the gantry relative to the support on one or more axes. Multiple other embodiments exist in which the gantry housing is connected on one end only to the floor, wall, or ceiling. The x-ray device is particularly useful for two-dimensional multi-planar x-ray imaging and / or three-dimensional computed tomography (CT) imaging applications
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
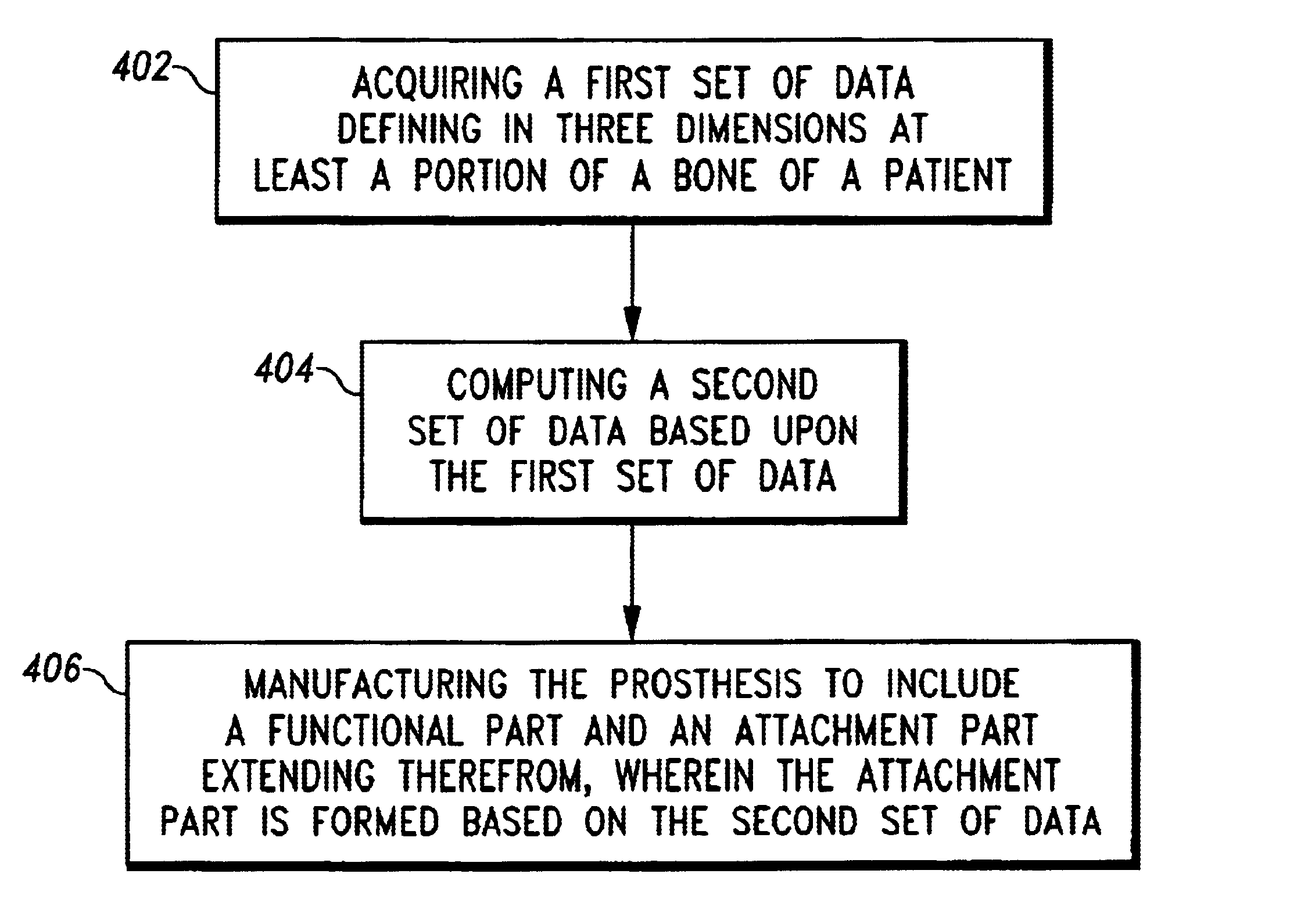
Customized prosthesis and method of designing and manufacturing a customized prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
InactiveUS6944518B2Uniform thicknessFast preparationMedical simulationProgramme controlProsthesisComputing tomography
A method of making an acetabular prosthesis includes acquiring a first set of data defining in three dimensions at least a portion of a bone of a patient. A second set of data is computed based upon the first set of data. The prosthesis is manufactured to include an acetabular cup and an attachment part extending therefrom. The manufacturing step includes the step of forming the attachment part based on the second set of data.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
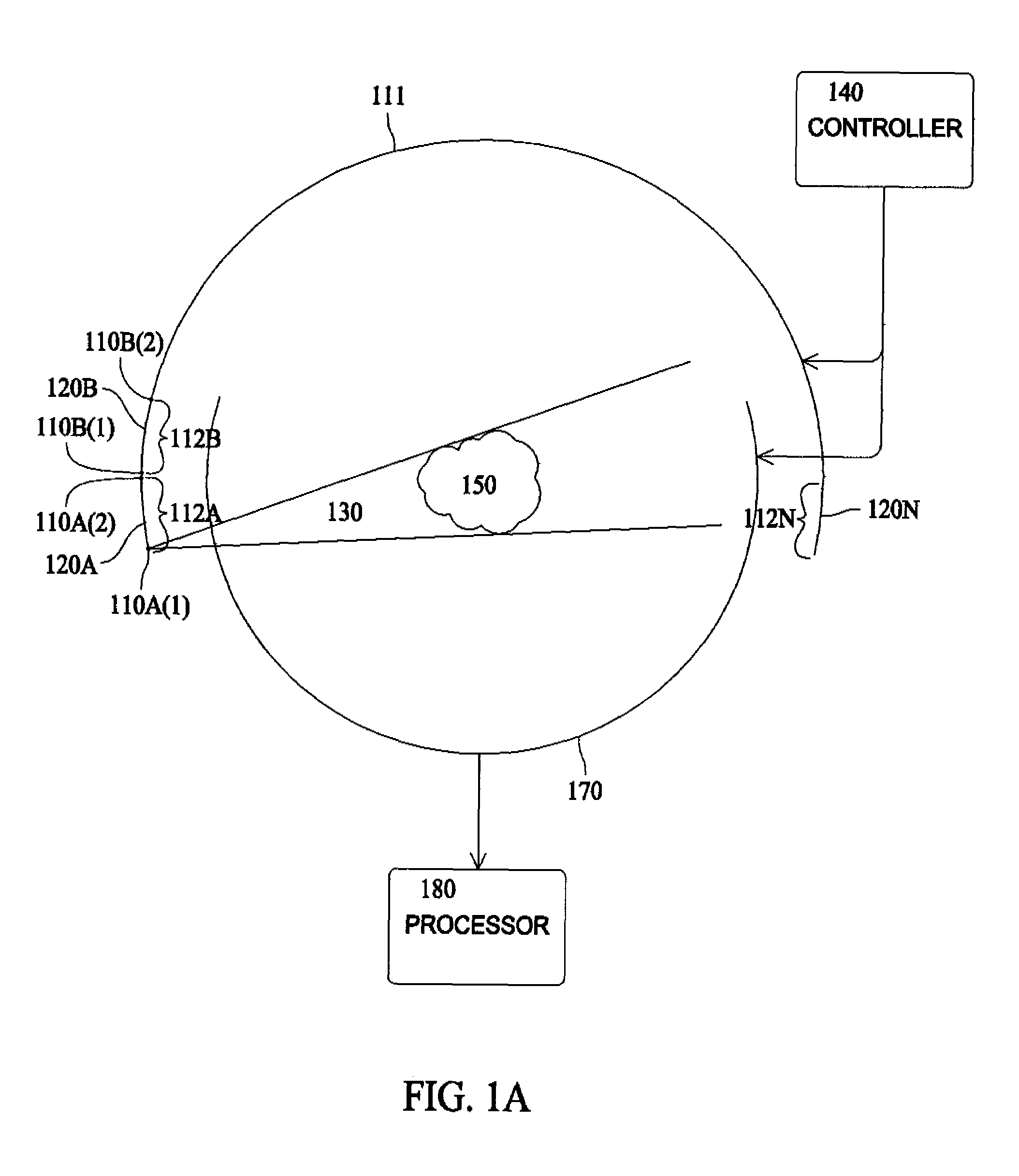
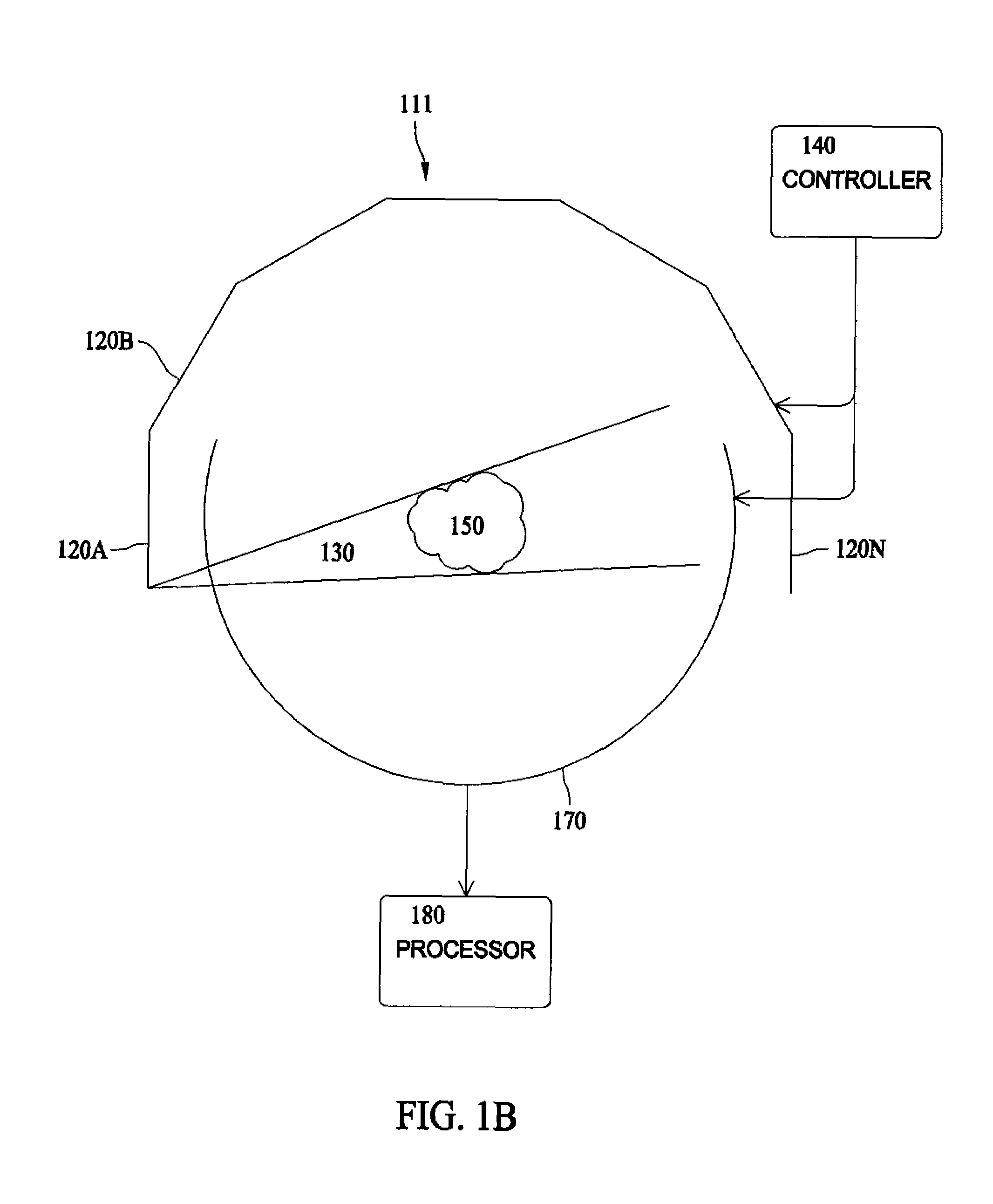
Apparatus and method for reconstruction of volumetric images in a divergent scanning computed tomography system
ActiveUS7106825B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDetector arrayComputing tomography
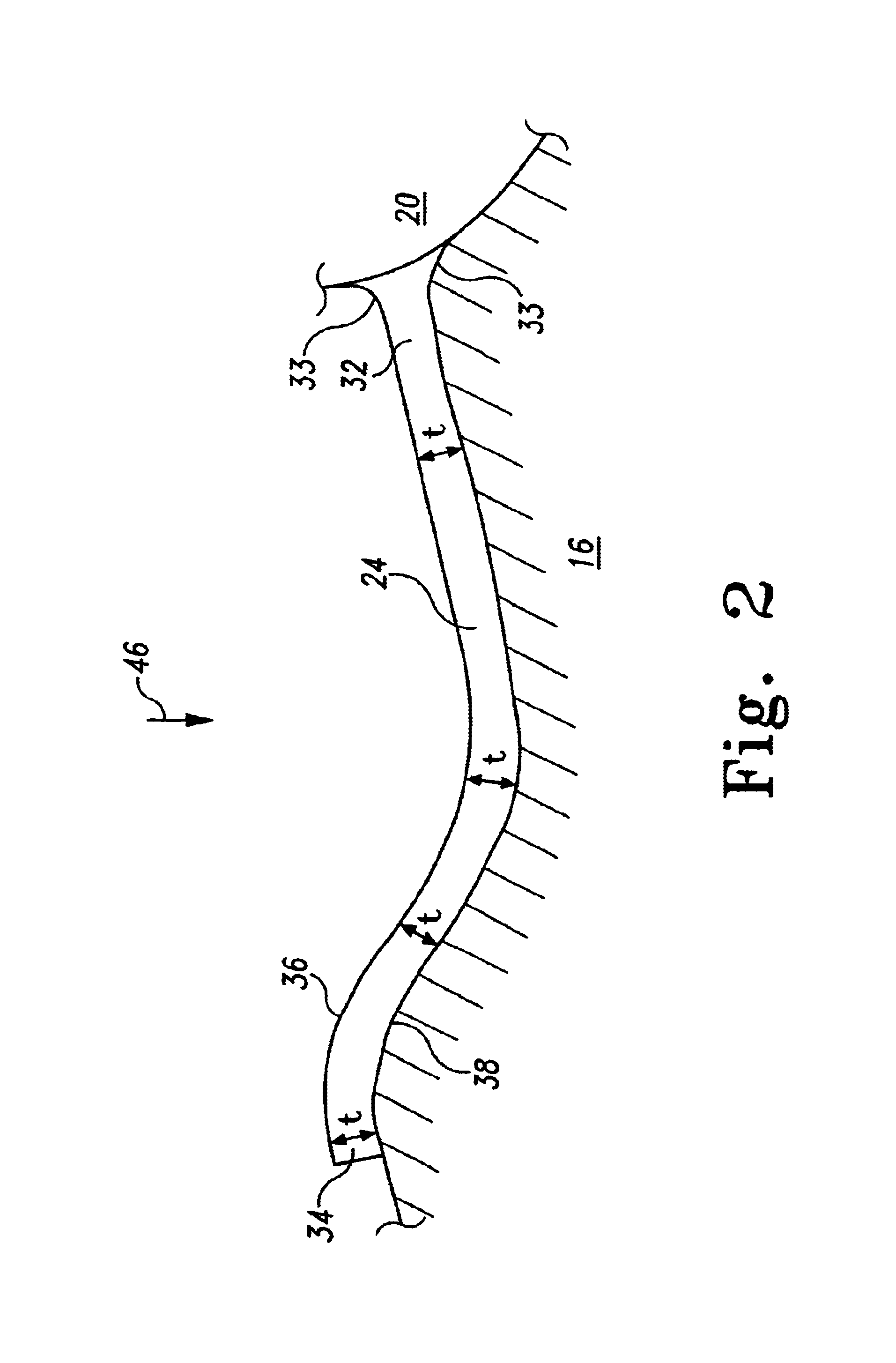
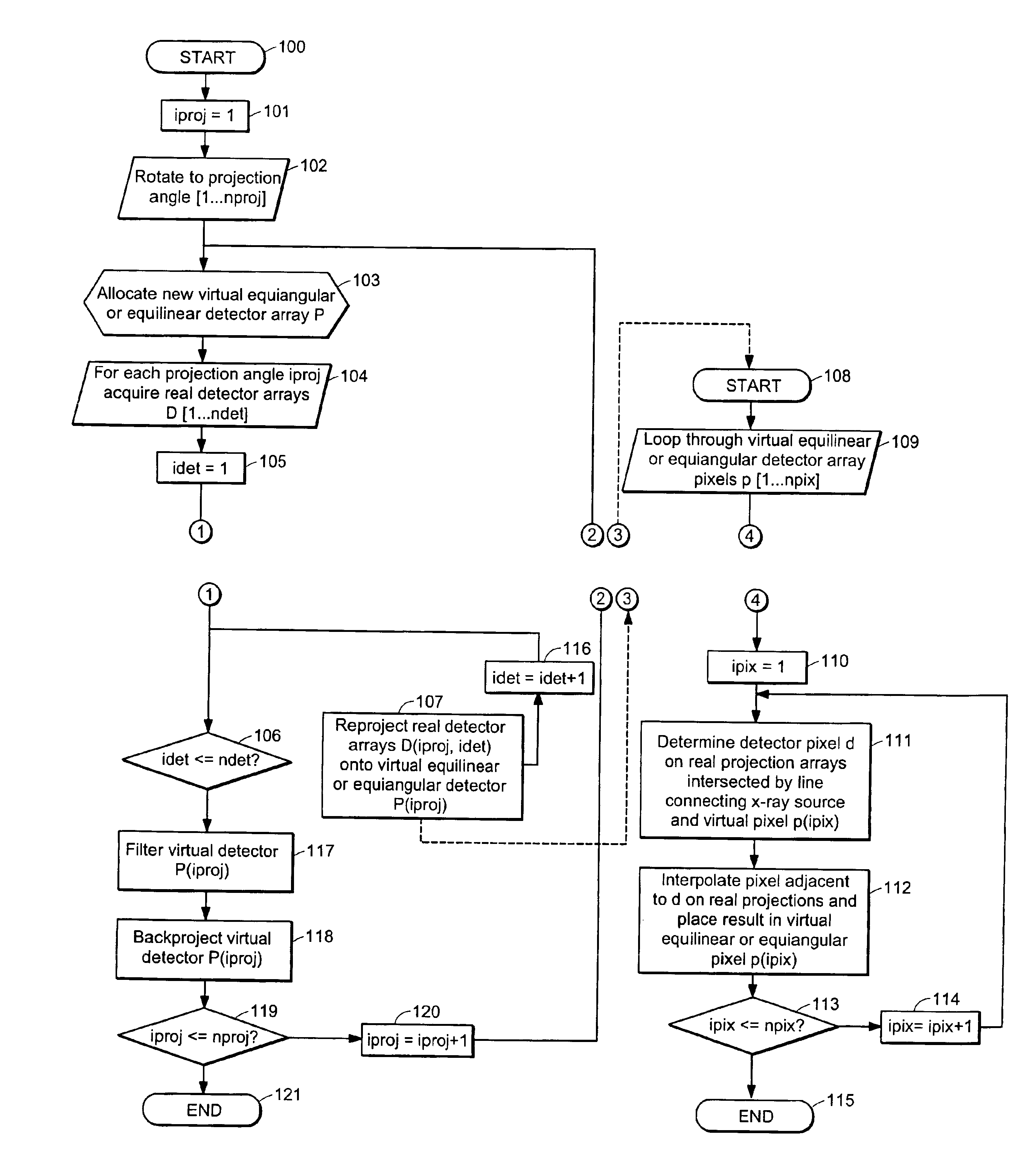
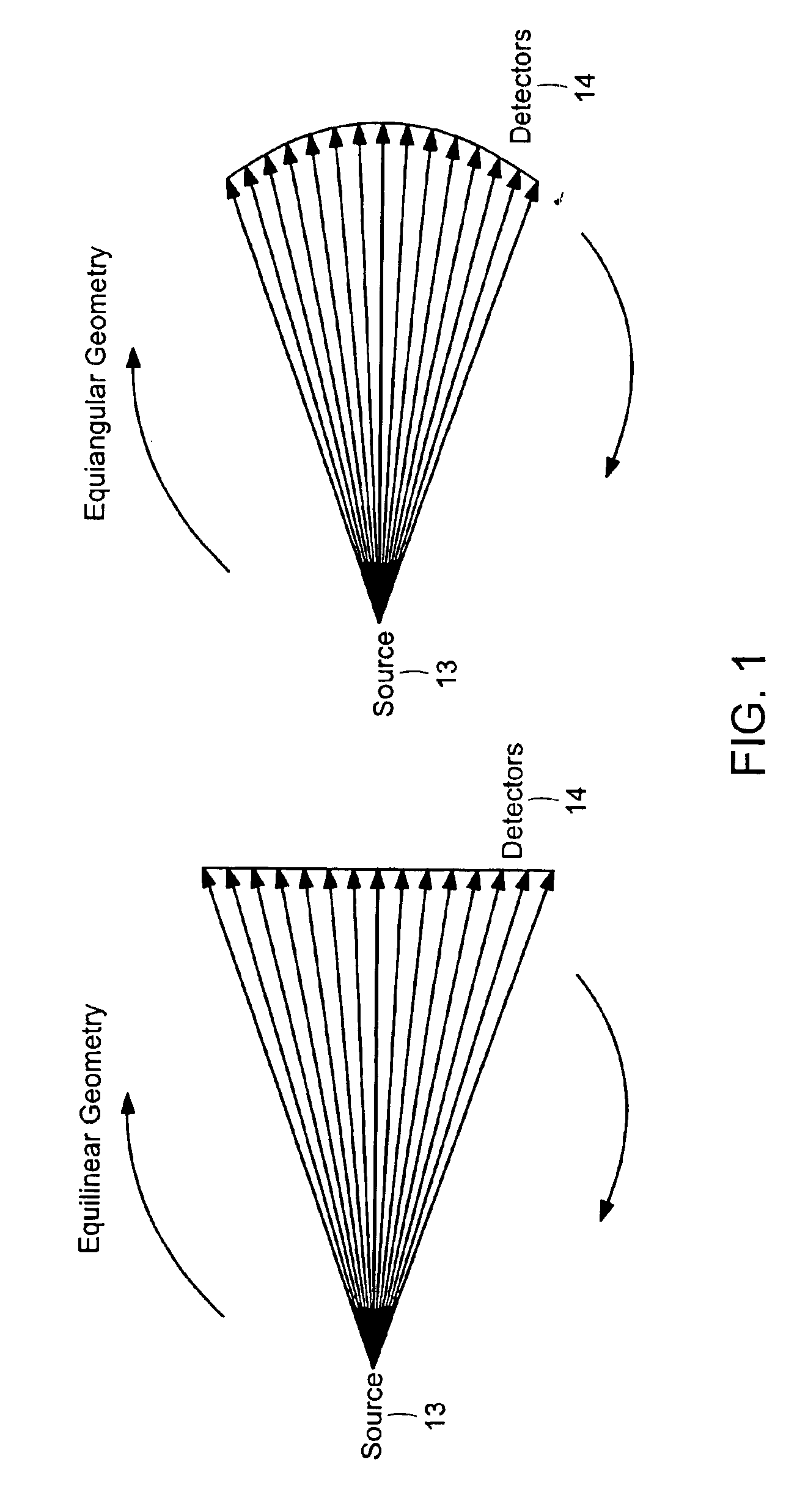
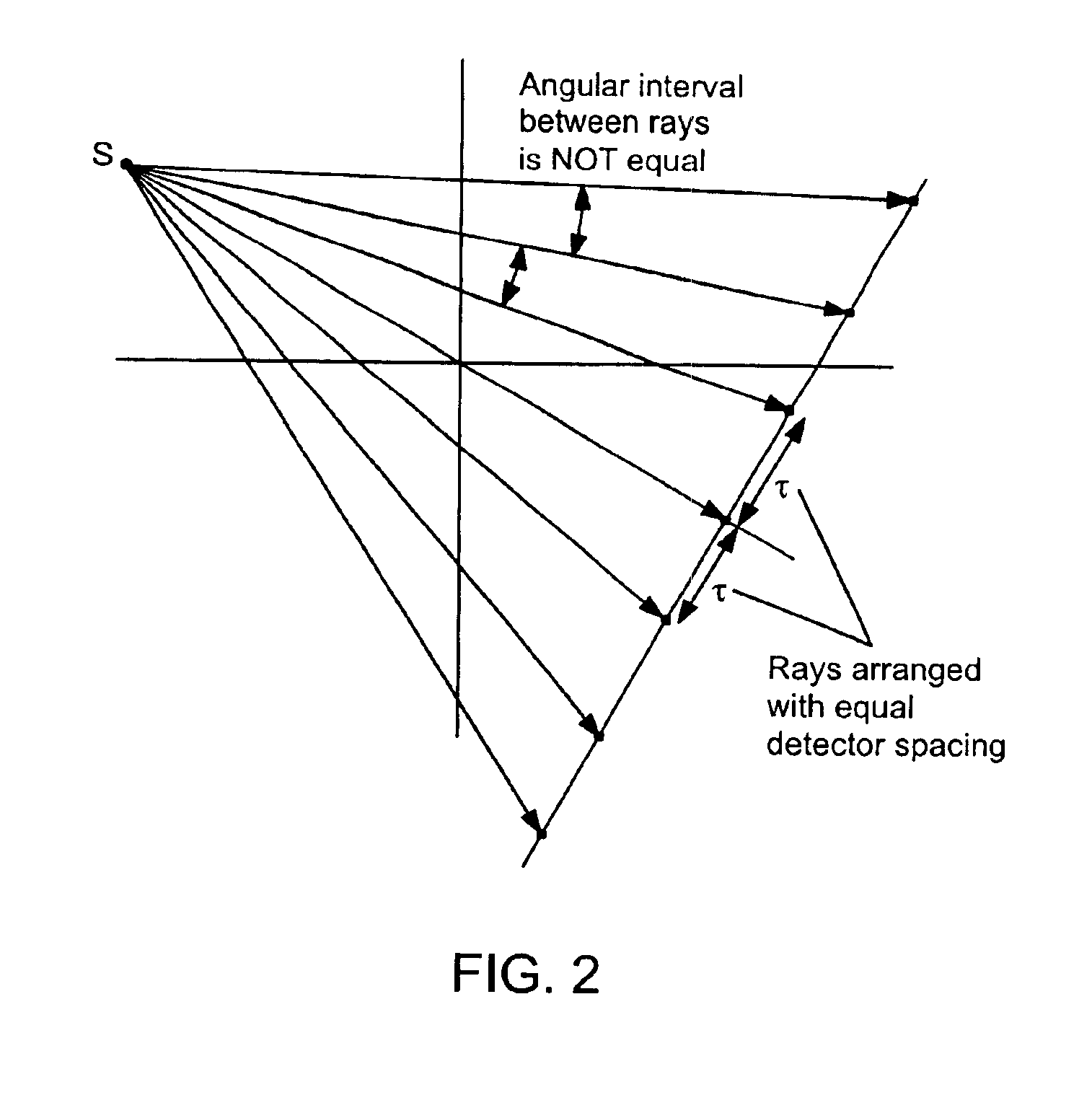
An apparatus and method for reconstructing image data for a region are described. A radiation source and multiple one-dimensional linear or two-dimensional planar area detector arrays located on opposed sides of a region angled generally along a circle centered at the radiation source are used to generate scan data for the region from a plurality of diverging radiation beams, i.e., a fan beam or cone beam. Individual pixels on the discreet detector arrays from the scan data for the region are reprojected onto a new single virtual detector array along a continuous equiangular arc or cylinder or equilinear line or plane prior to filtering and backprojecting to reconstruct the image data.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
Radiation scanning of objects for contraband
InactiveUS7103137B2Radiation/particle handlingX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentX-rayDetector array
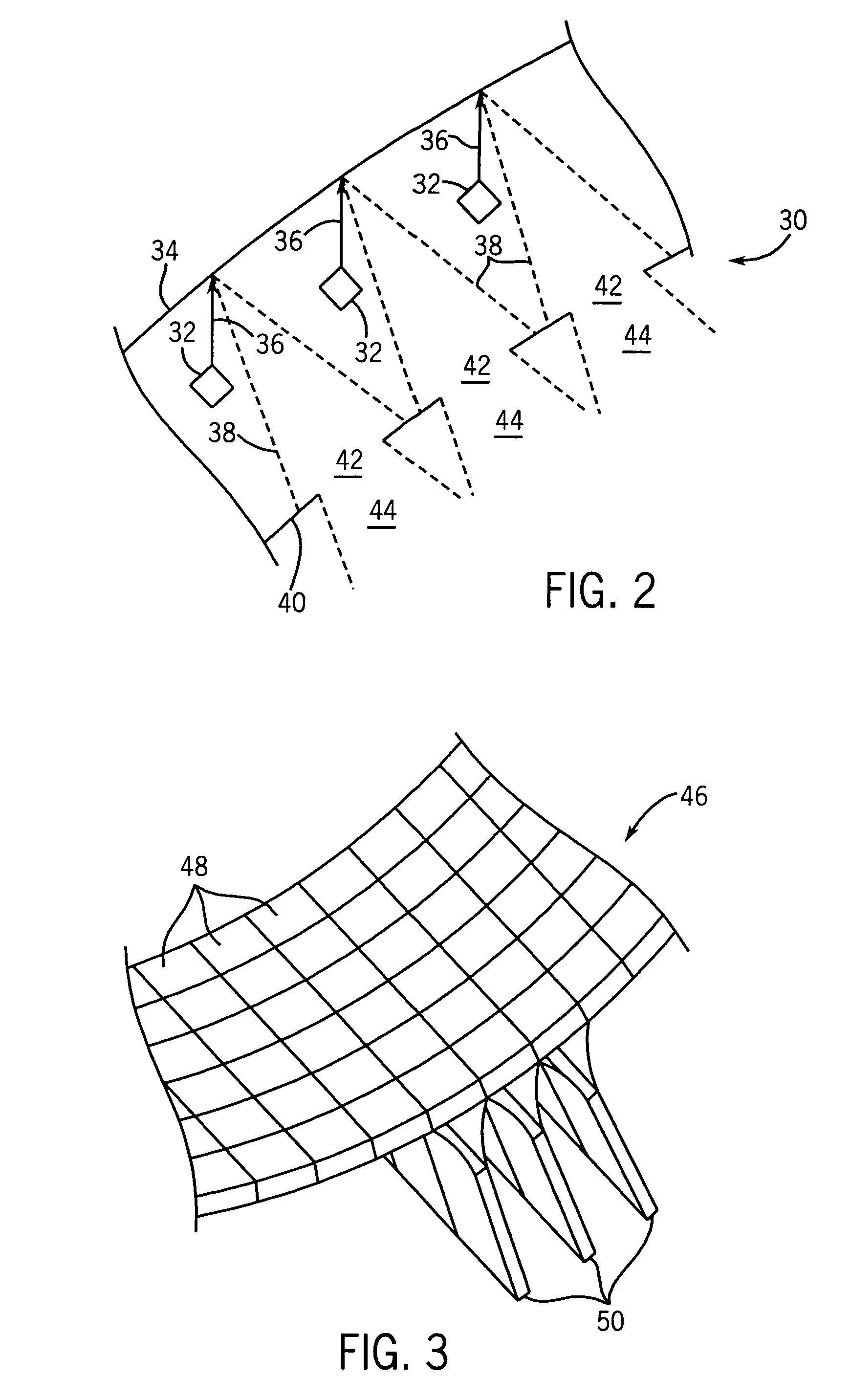
A scanning unit for identifying contraband within objects, such as cargo containers and luggage, moving through the unit along a first path comprises at least one source of a beam of radiation movable across a second path that is transverse to the first path and extends partially around the first path. A stationary detector transverse to the first path also extends partially around the first path, positioned to detect radiation transmitted through the object during scanning. In one example, a plurality of movable X-ray sources are supported by a semi-circular rail perpendicular to the first path and the detector, which may be a detector array is also semi-circular and perpendicular to the path. A fan beam may also be used. Radiographic images may be obtained and / or computed tomography (“CT”) images may be reconstructed. The images may be analyzed for contraband. Methods of scanning objects are also disclosed.
Owner:VAREX IMAGING CORP
Customized prosthesis and method of designing and manufacturing a customized prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS20050065628A1Uniform thicknessFast preparationProgramme controlMedical simulationProsthesisComputing tomography
A method of making an acetabular prosthesis includes acquiring a first set of data defining in three dimensions at least a portion of a bone of a patient. A second set of data is computed based upon the first set of data. The prosthesis is manufactured to include an acetabular cup and an attachment part extending therefrom. The manufacturing step includes the step of forming the attachment part based on the second set of data.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
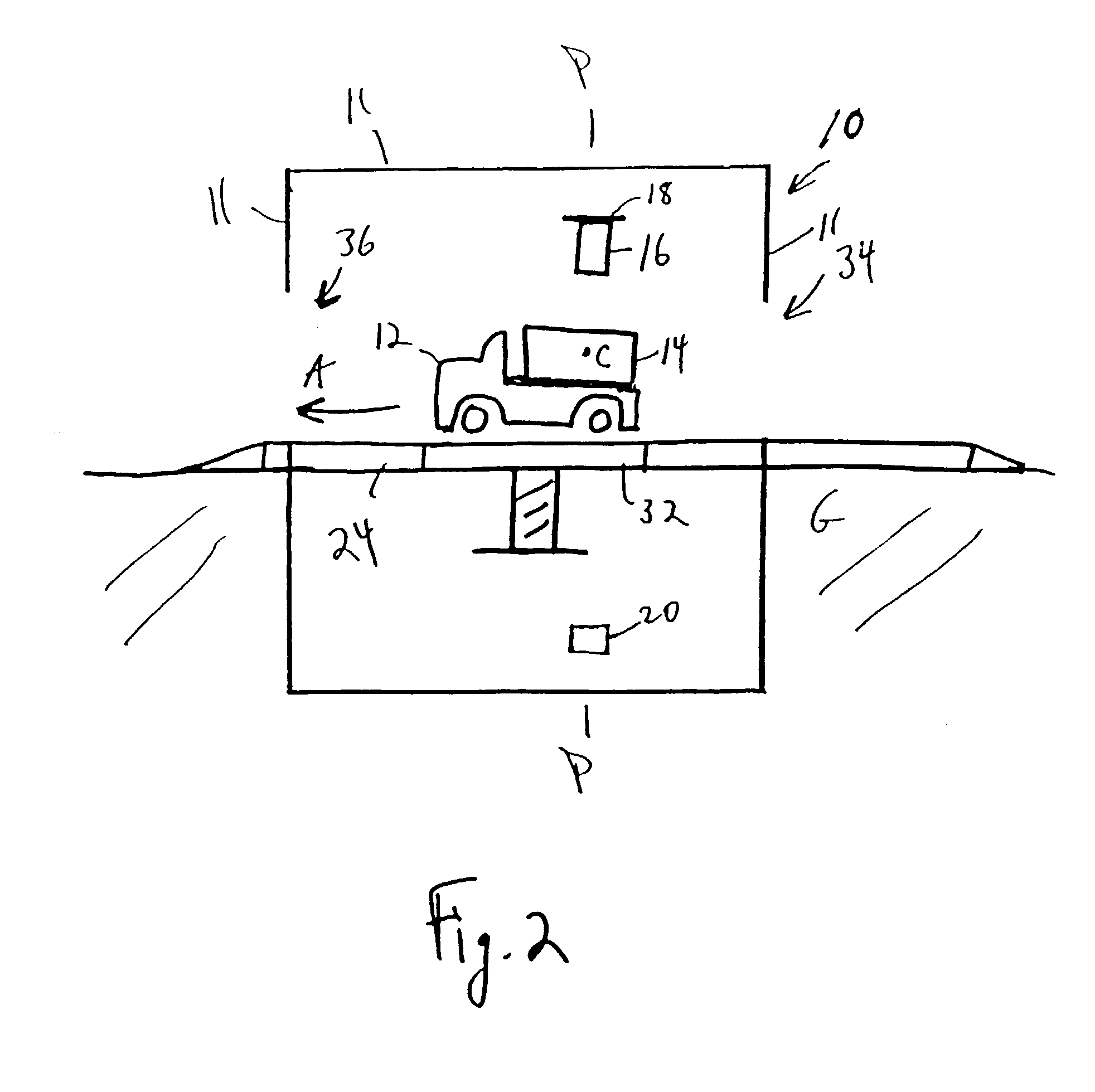
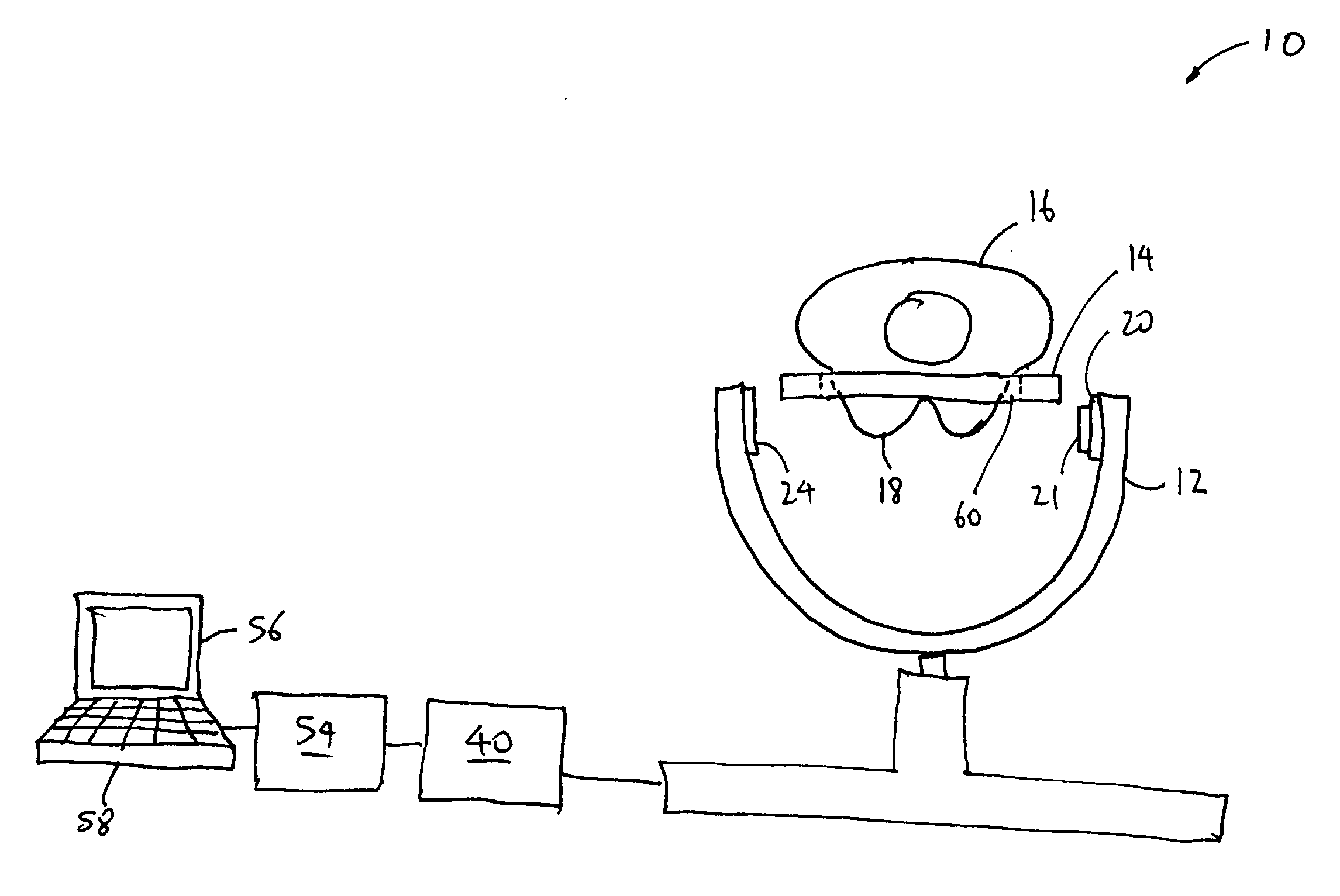
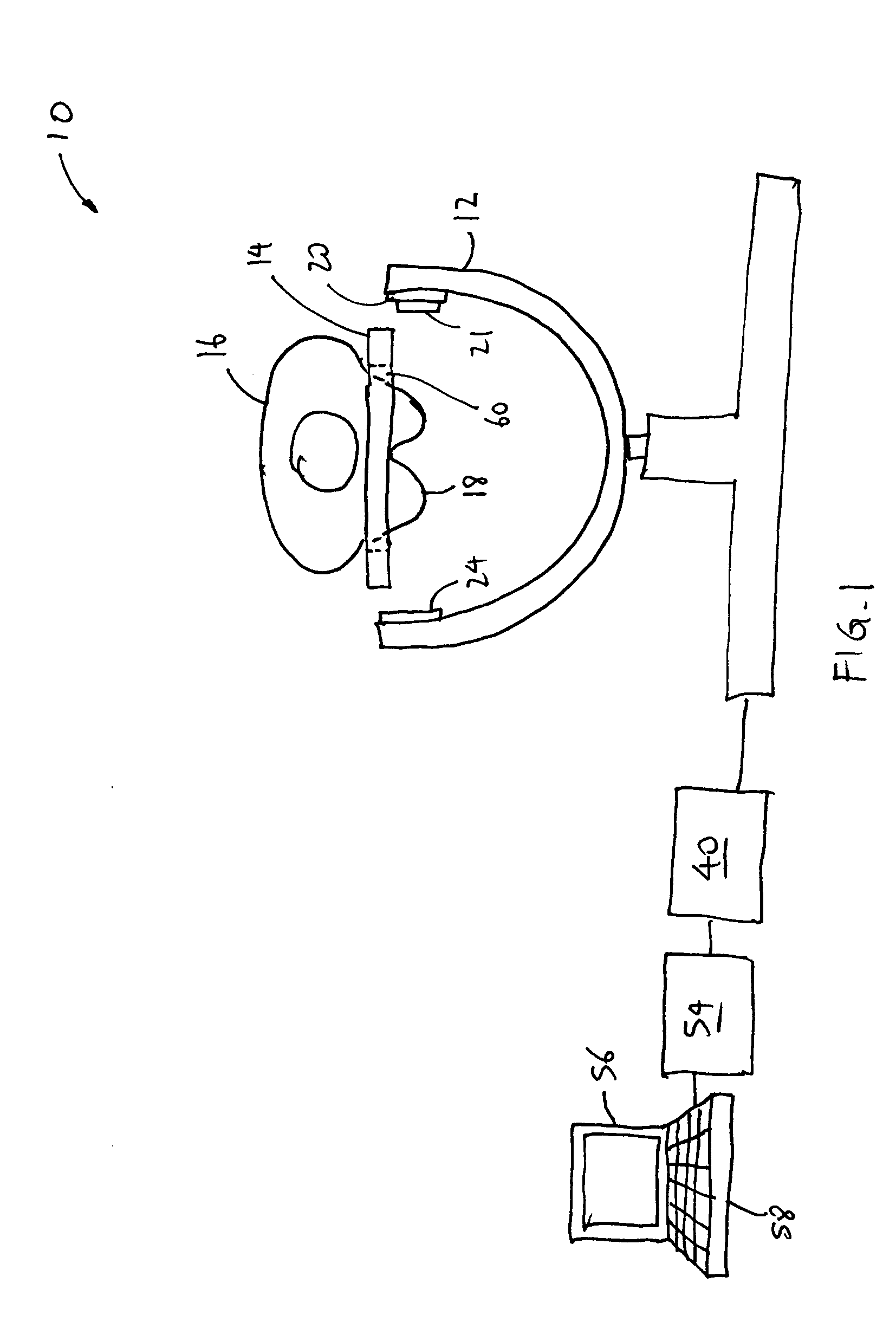
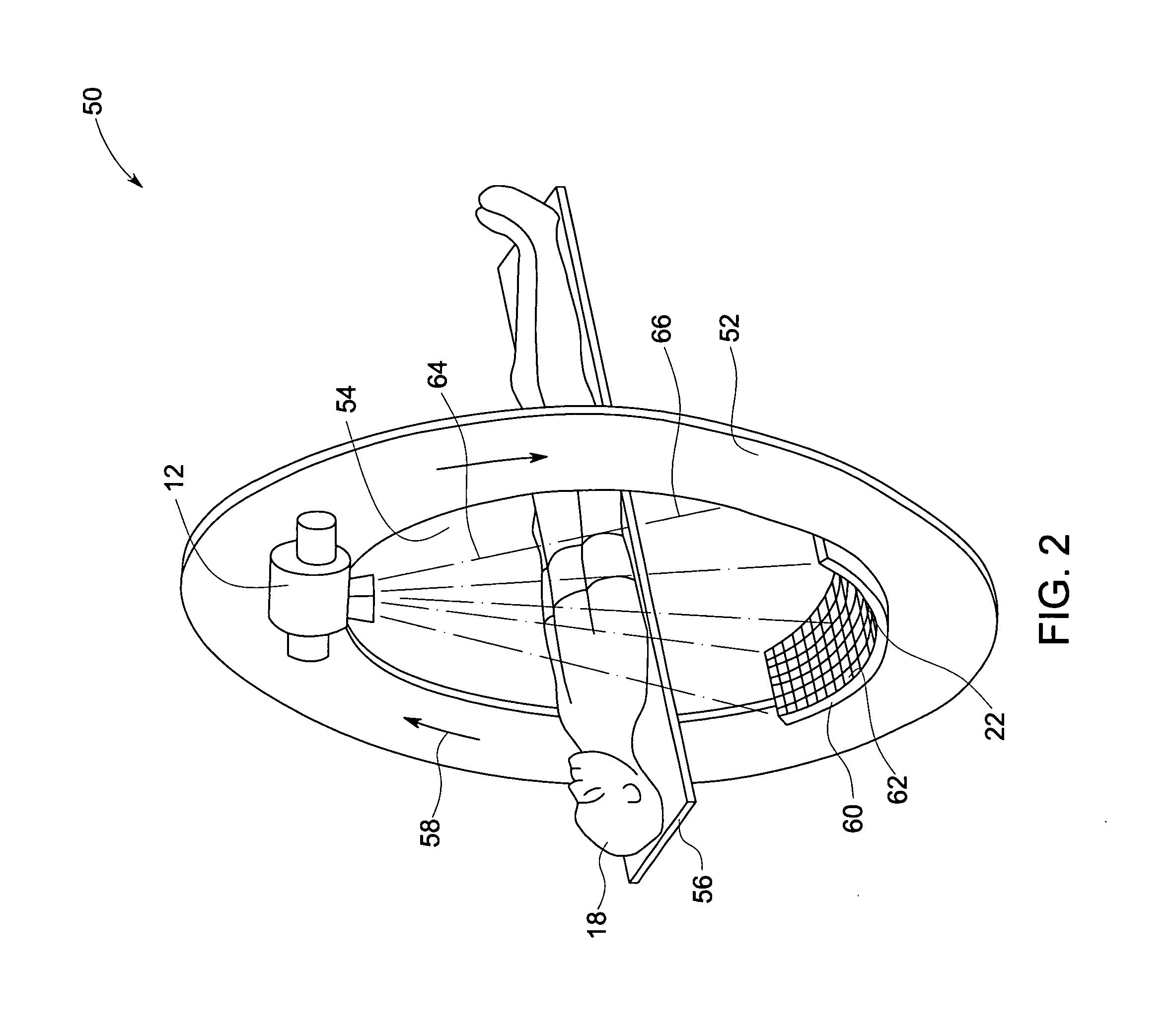
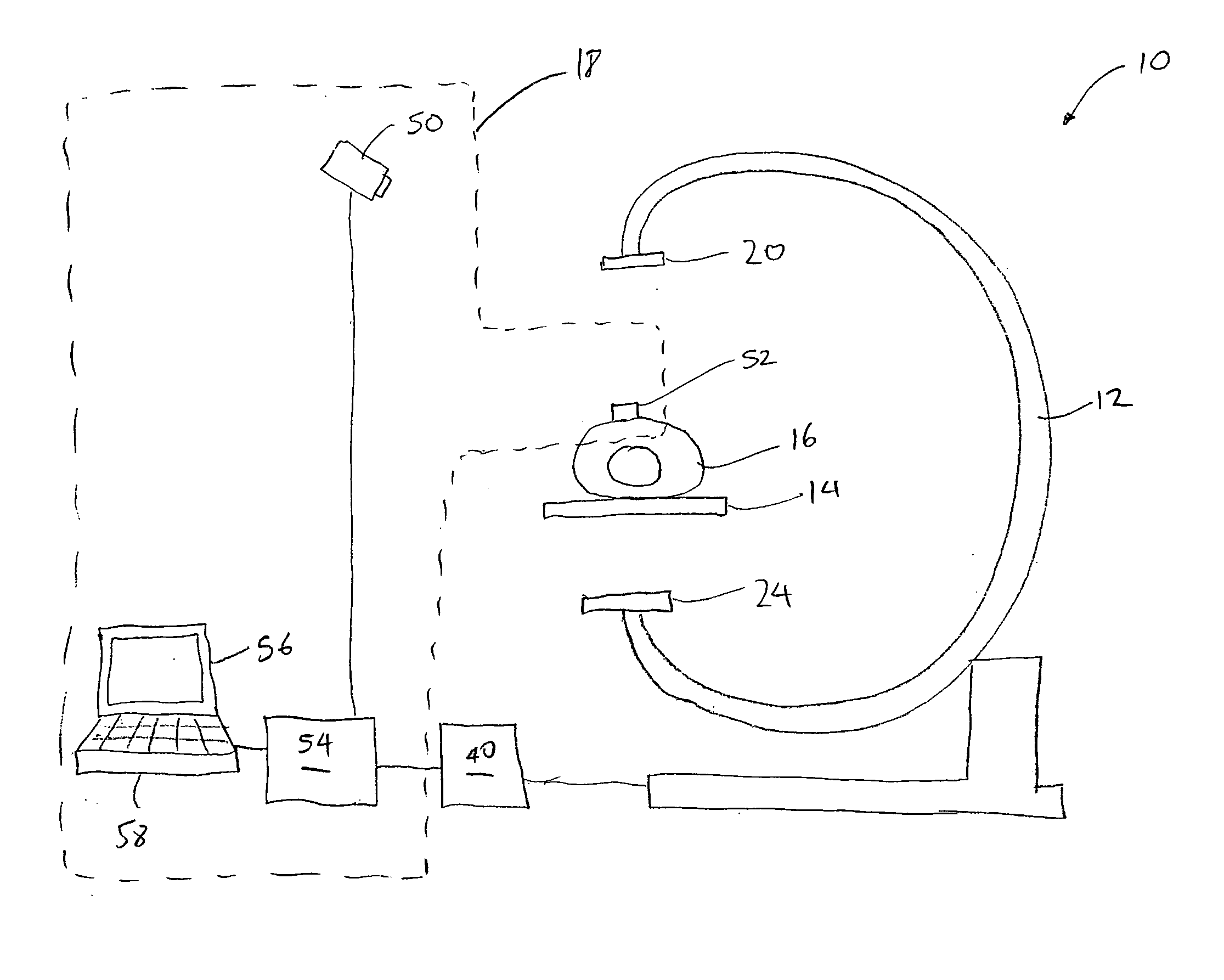
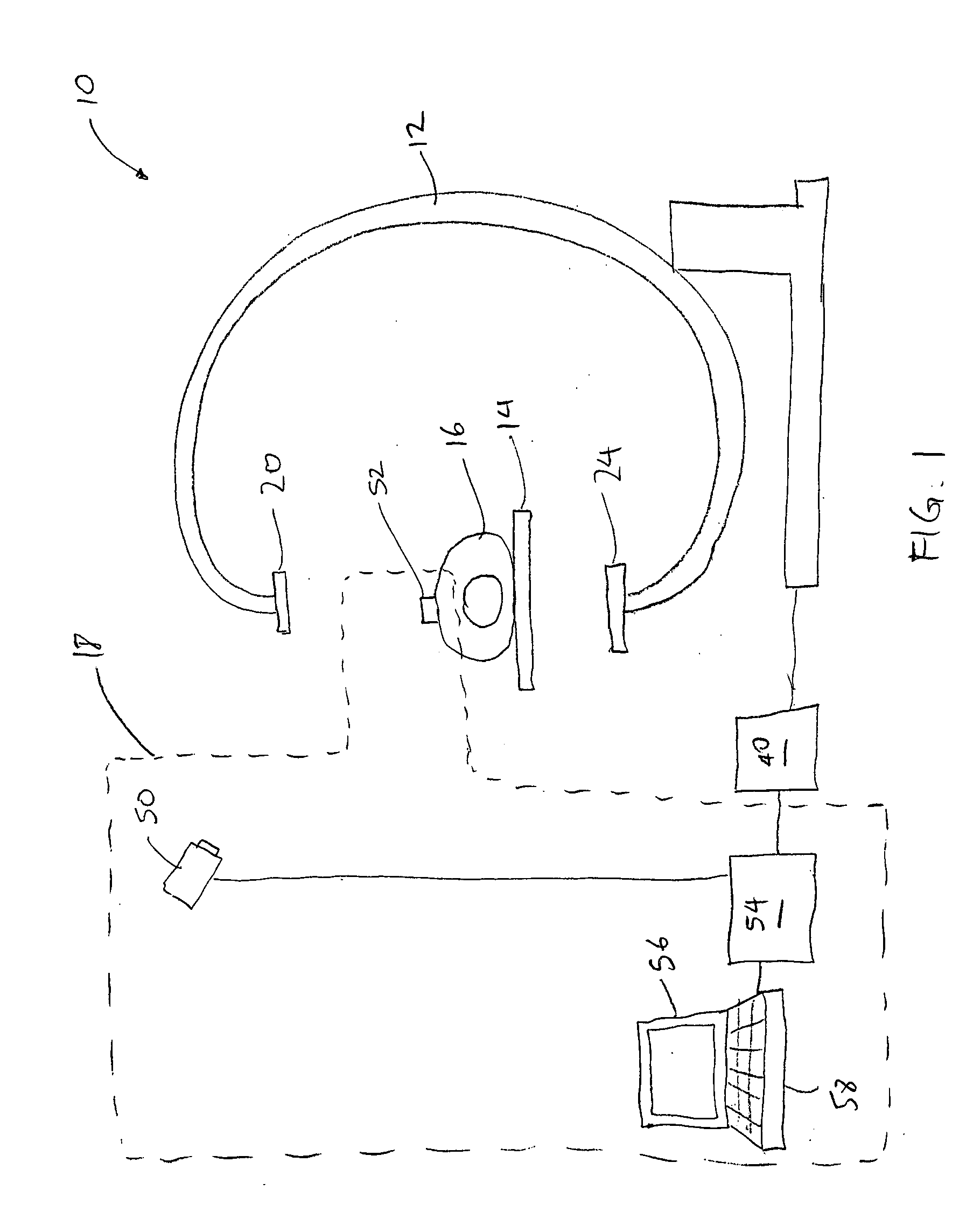
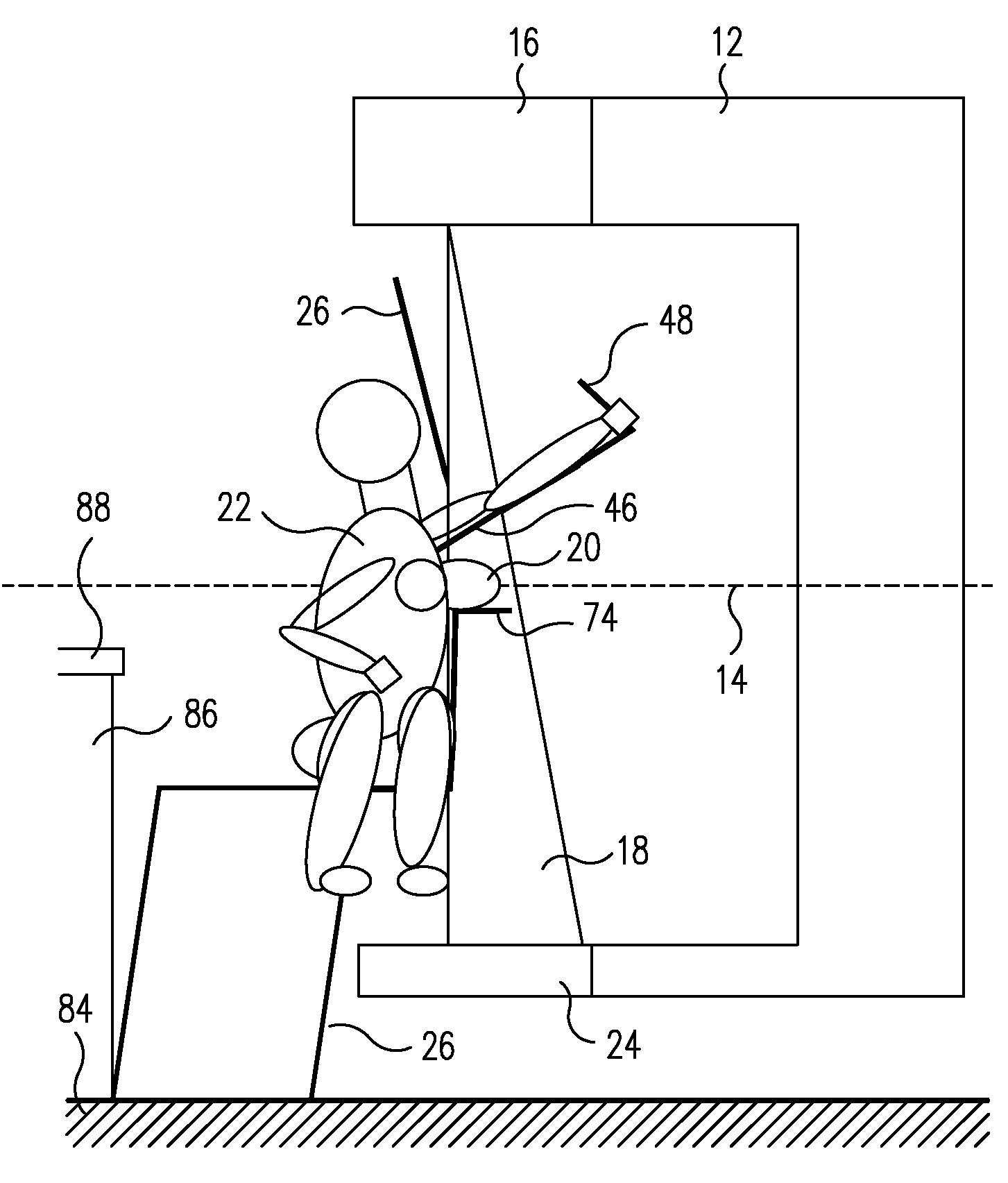
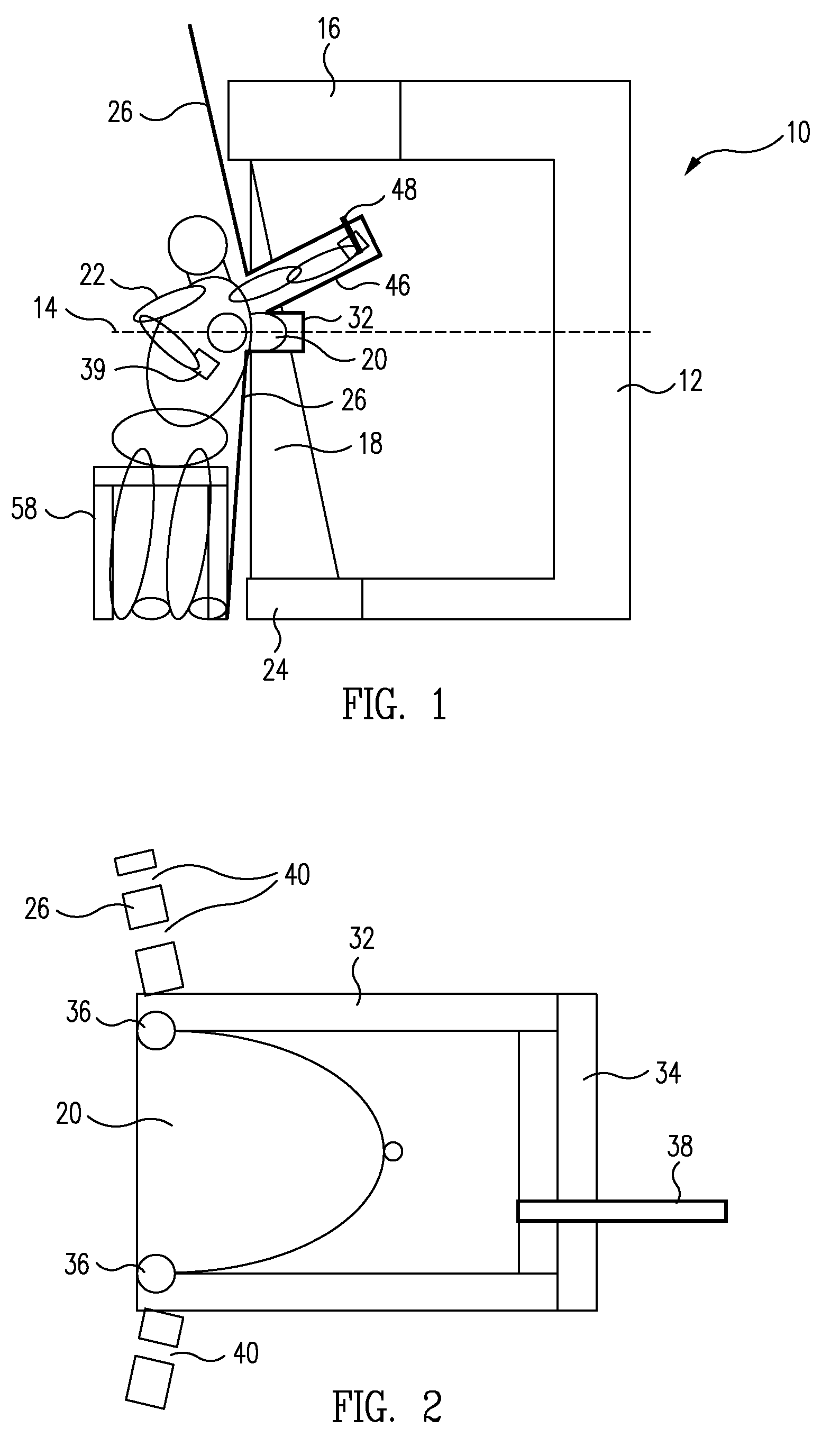
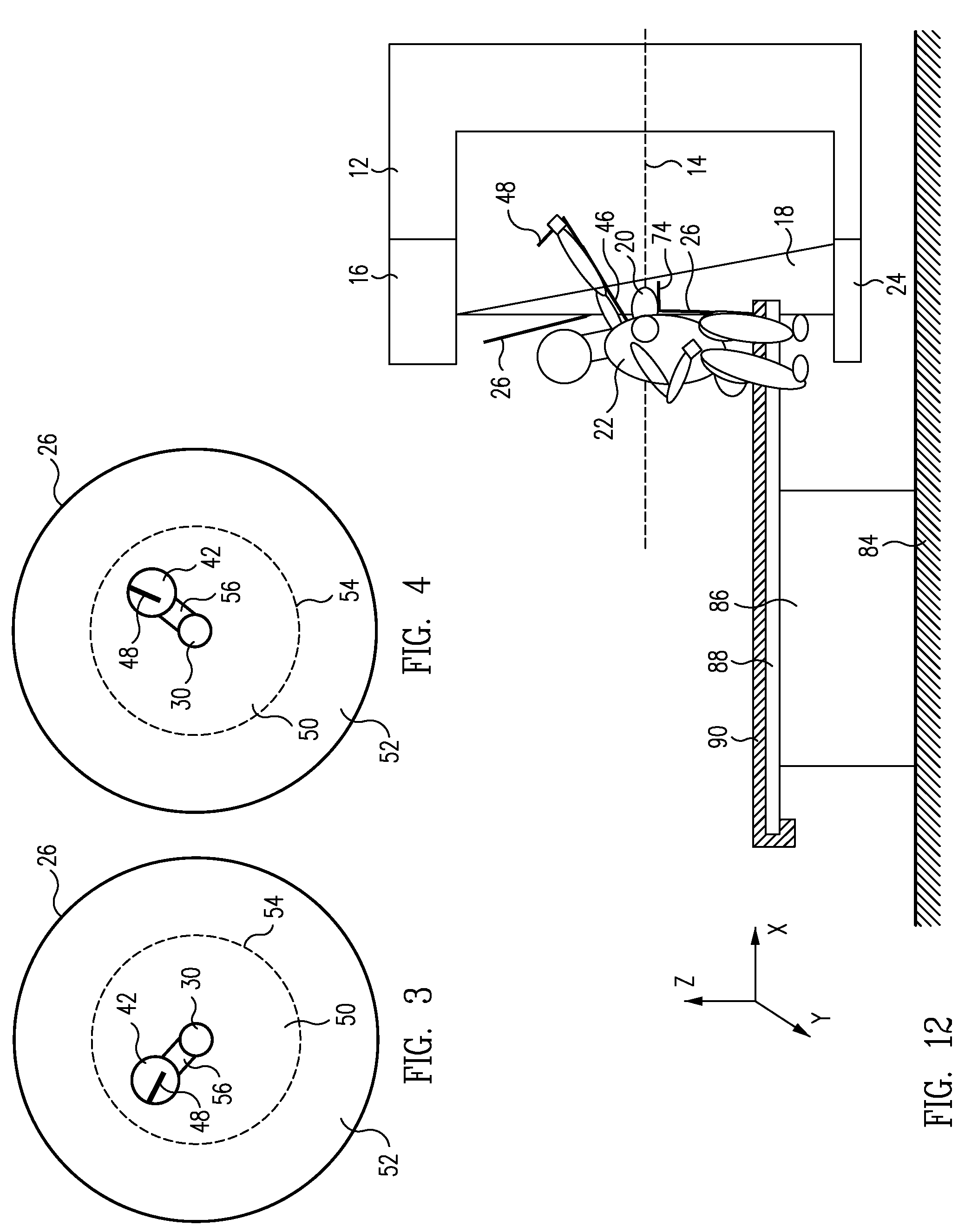
System and method for imaging and treatment of tumorous tissue in breasts using computed tomography and radiotherapy
InactiveUS20060262898A1Preventing formation of vacuumInhibition formationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMuscle tissueTumour tissue
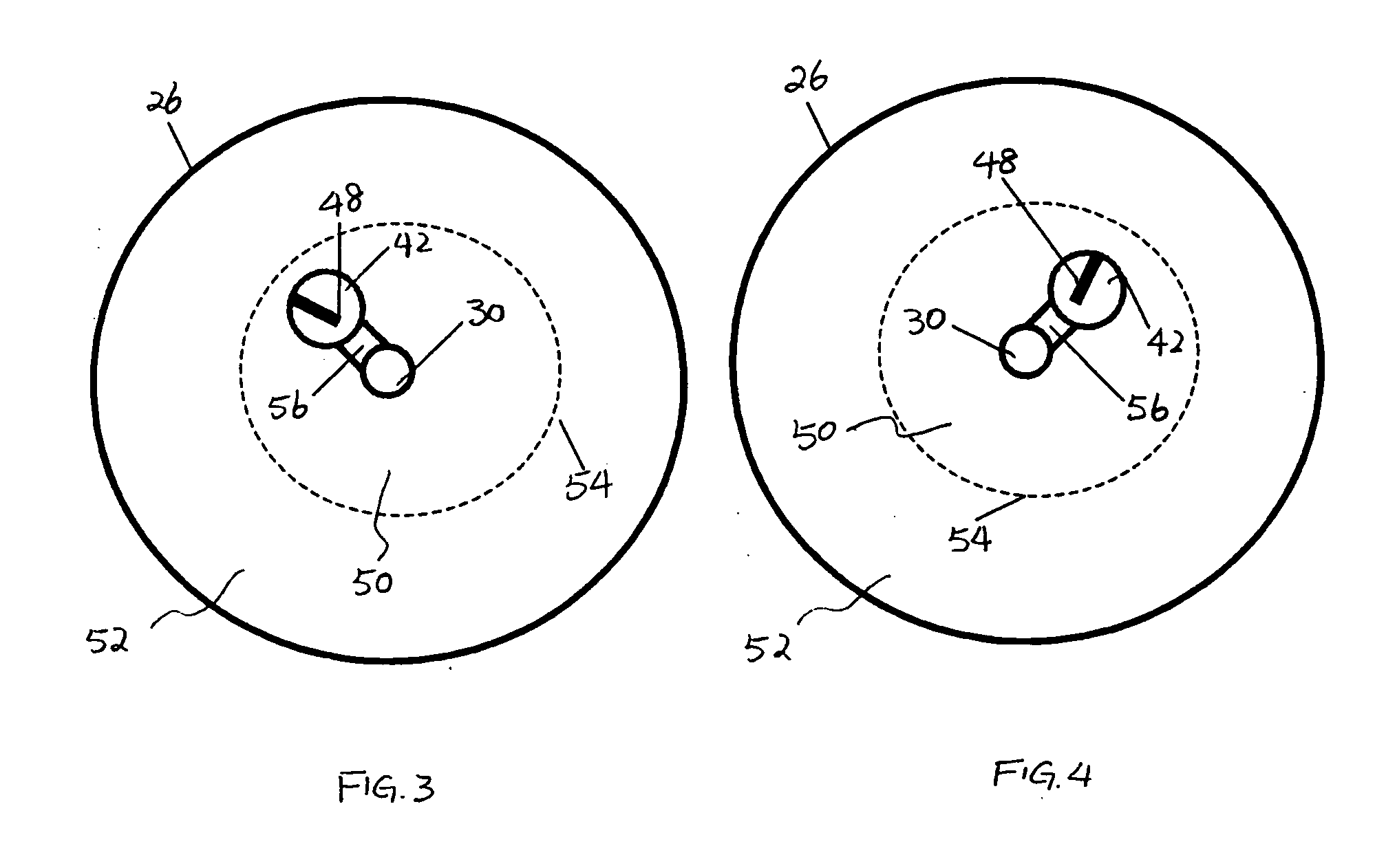
The present invention provides a system 10 for irradiating a breast 20 of a patient 22. The system 10 comprises a gantry 12 rotatable about a horizontal axis 14 and comprising a radiation source 16 for generating a radiation beam 18 and a detector 24 spaced from the radiation source 16, and a barrier 26 disposed between the patient 22 and the gantry 12. The barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow a breast 20 passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18. In some embodiments, the barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow both the breast 20 and the tissue leading from the breast to axilla and the muscle tissue of the adjacent chest wall passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Multi-parameter X-ray computed tomography
ActiveUS8121249B2Eliminate crosstalkIncrease sampling rateRadiation/particle handlingTomographyData setX-ray
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
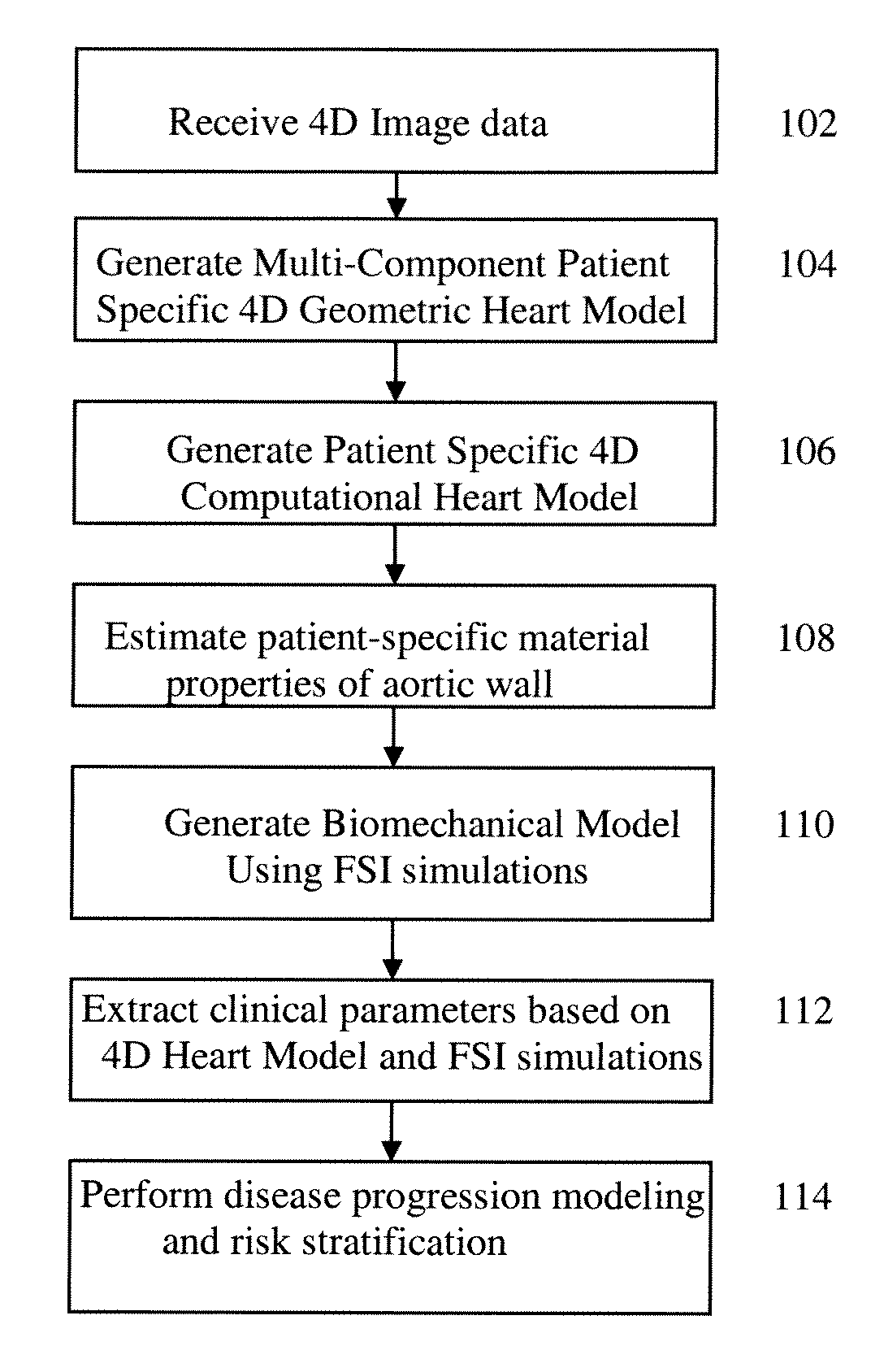
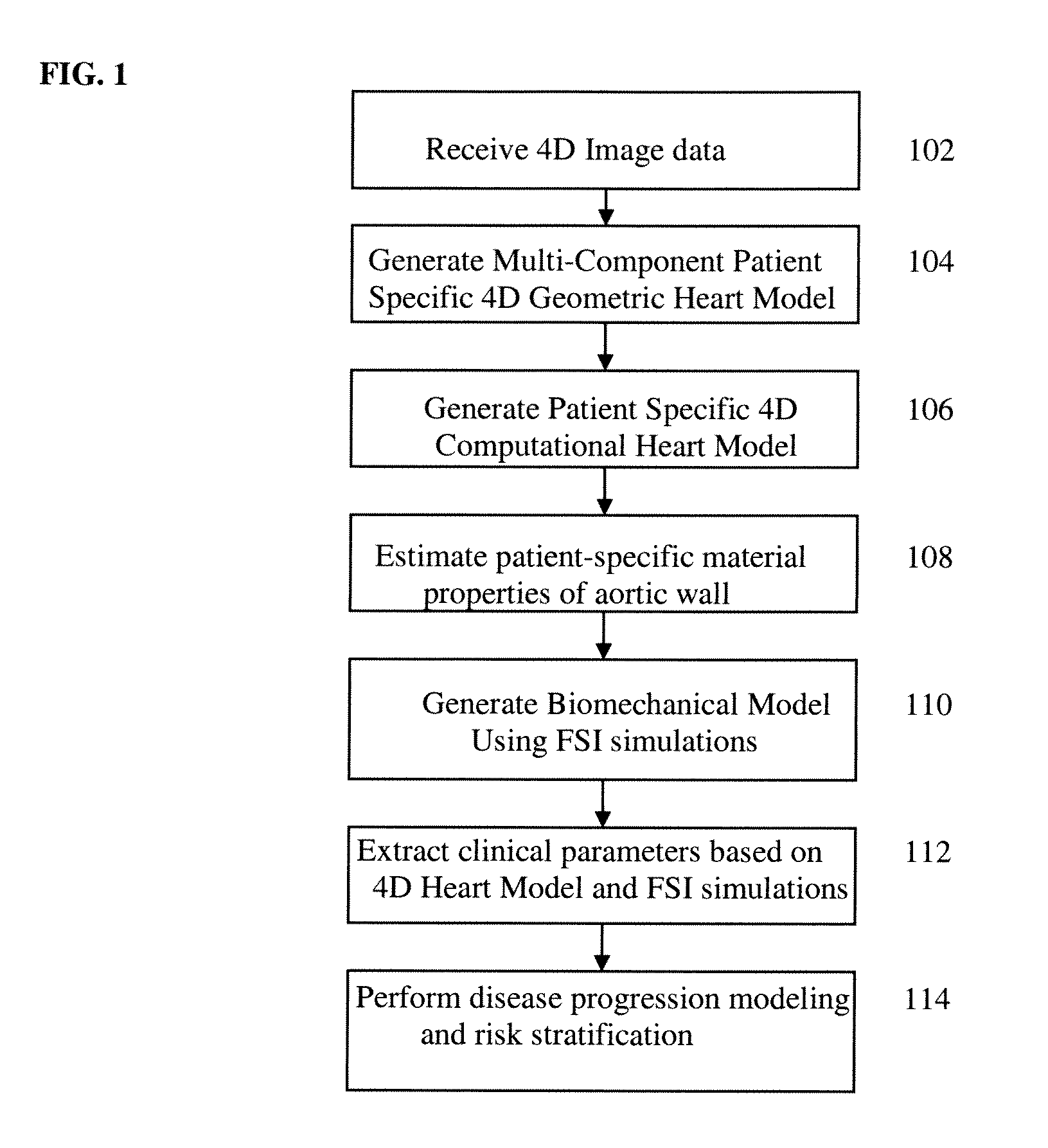
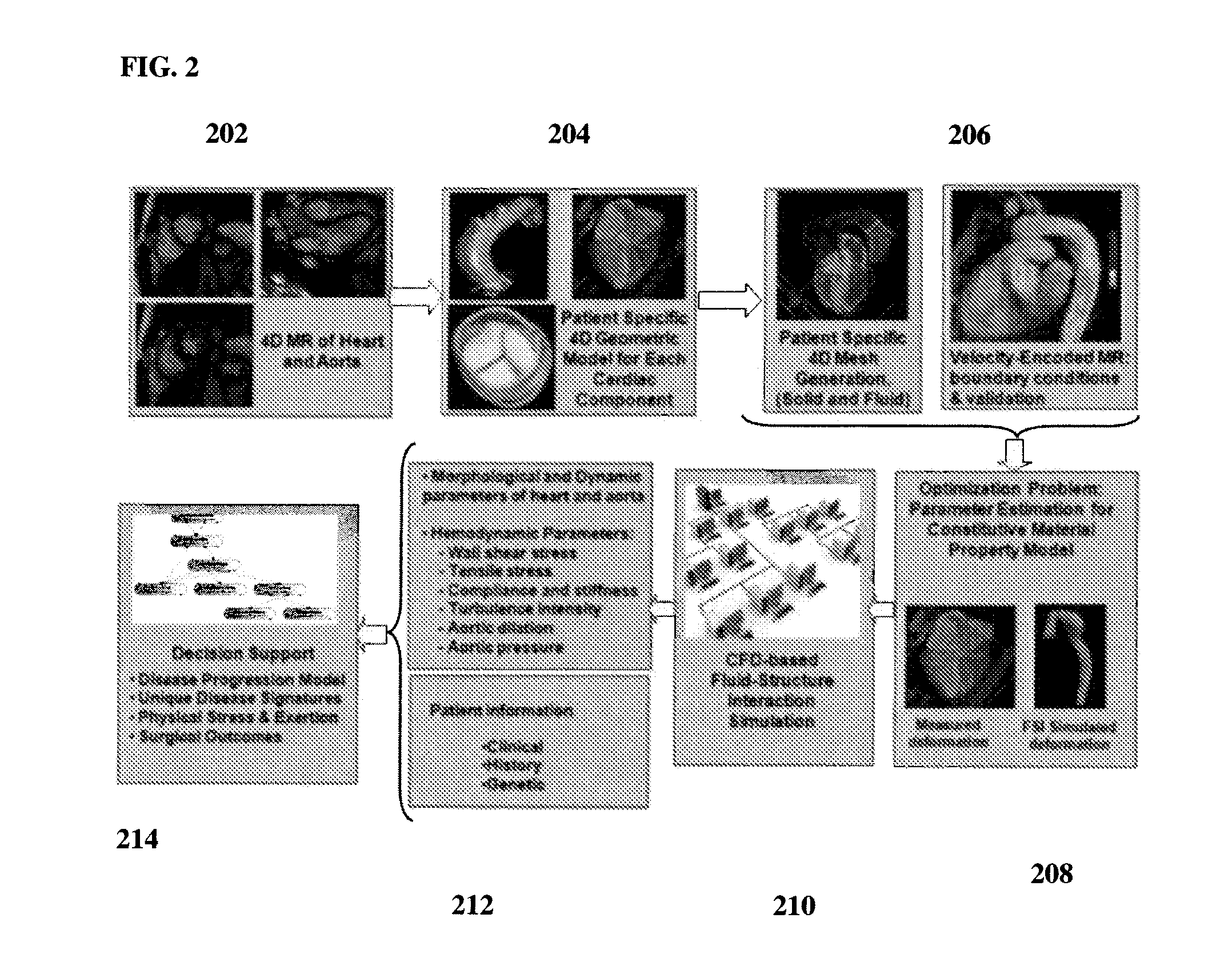
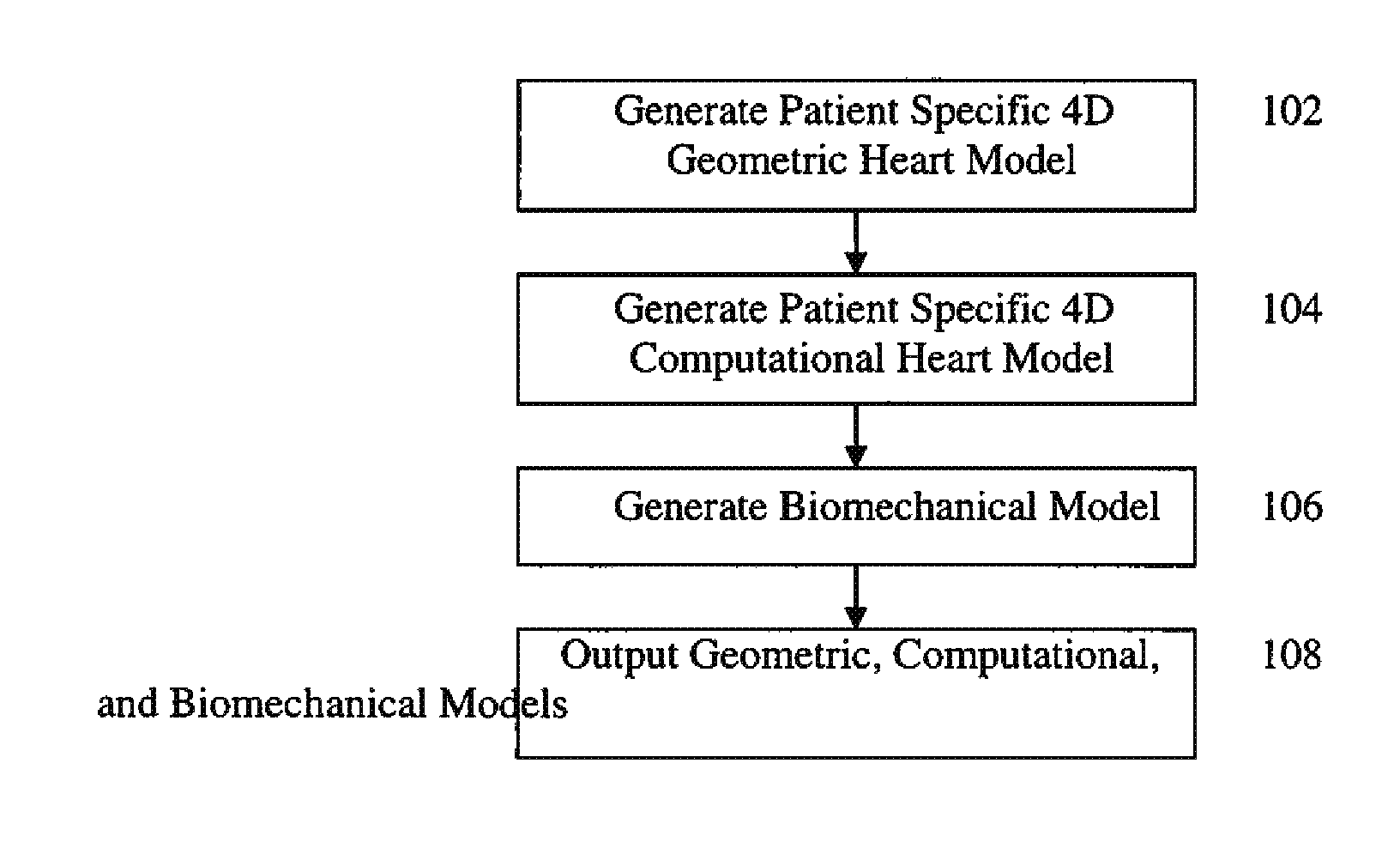
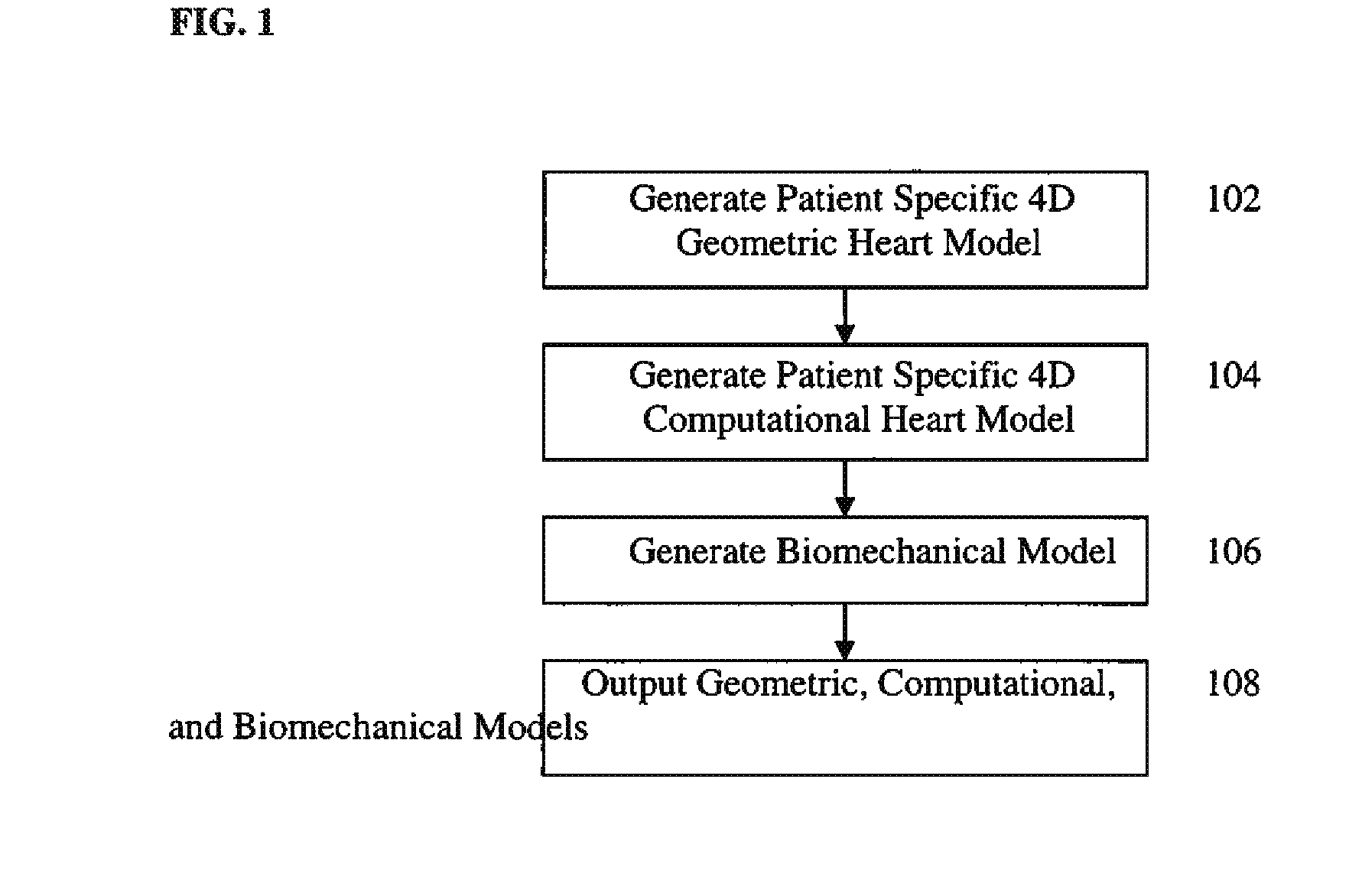
Method and System for Computational Modeling of the Aorta and Heart
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for functional imaging using contrast-enhanced multiple-energy computed tomography
ActiveUS20050084060A1Characteristic is differentRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsFunctional imagingComputing tomography
A method of generating images of a portion of a body includes introducing a contrast agent into the body, generating a first set of image data using radiation at a first energy level after the contrast agent is introduced into the body, generating a second set of image data using radiation at a second energy level after the contrast agent is introduced into the body, and creating a volumetric composite image using the first and the second sets of image data.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
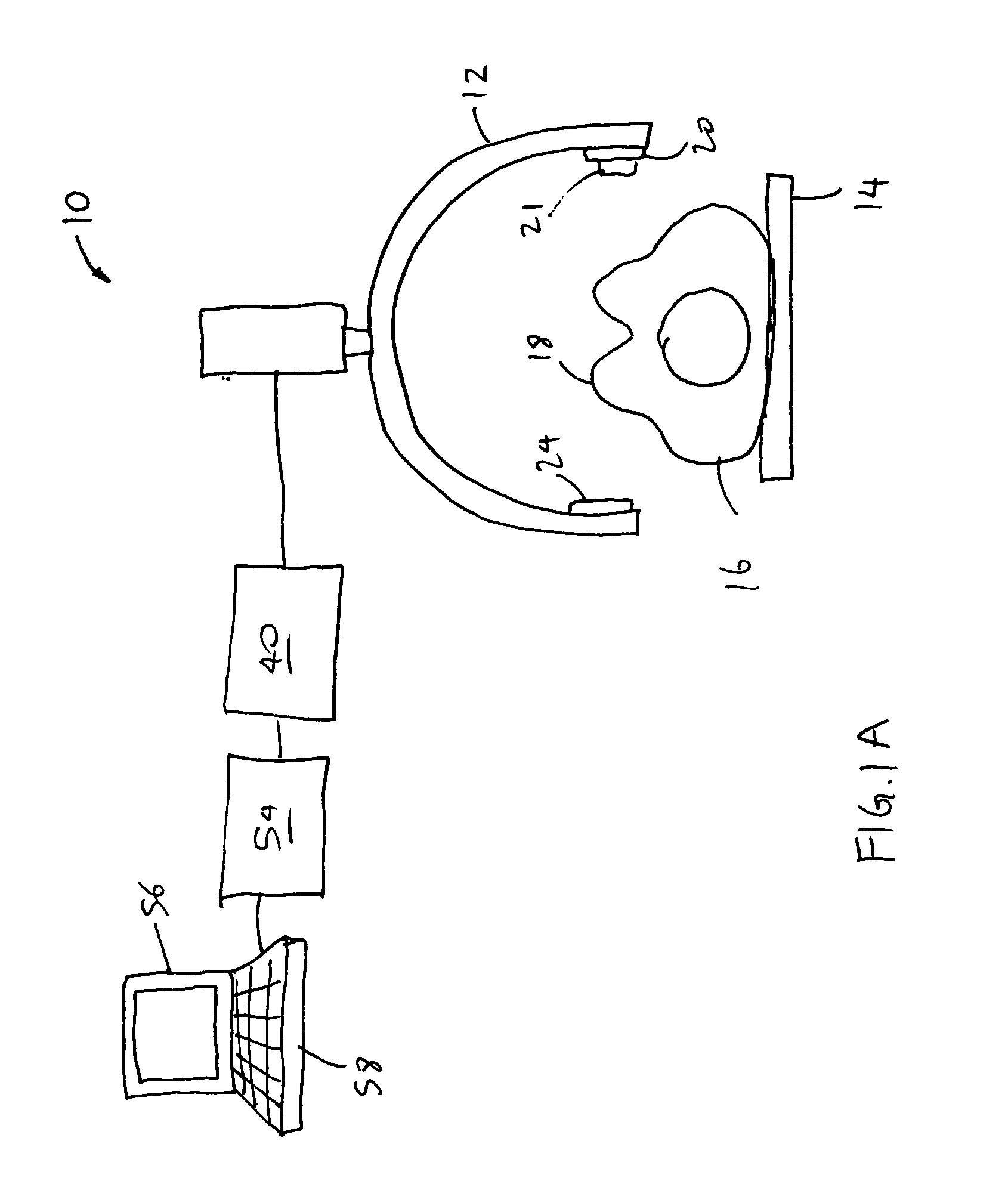
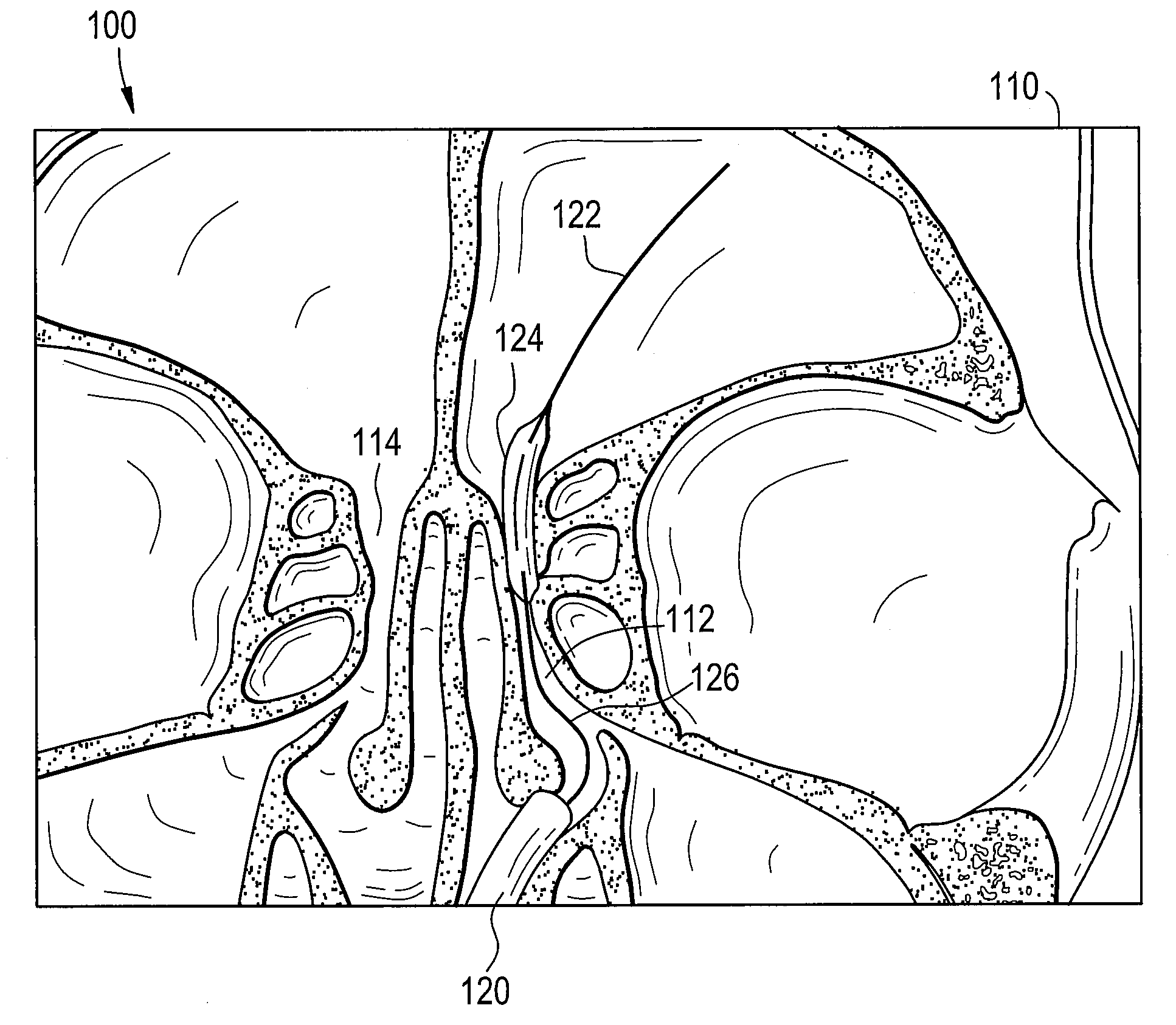
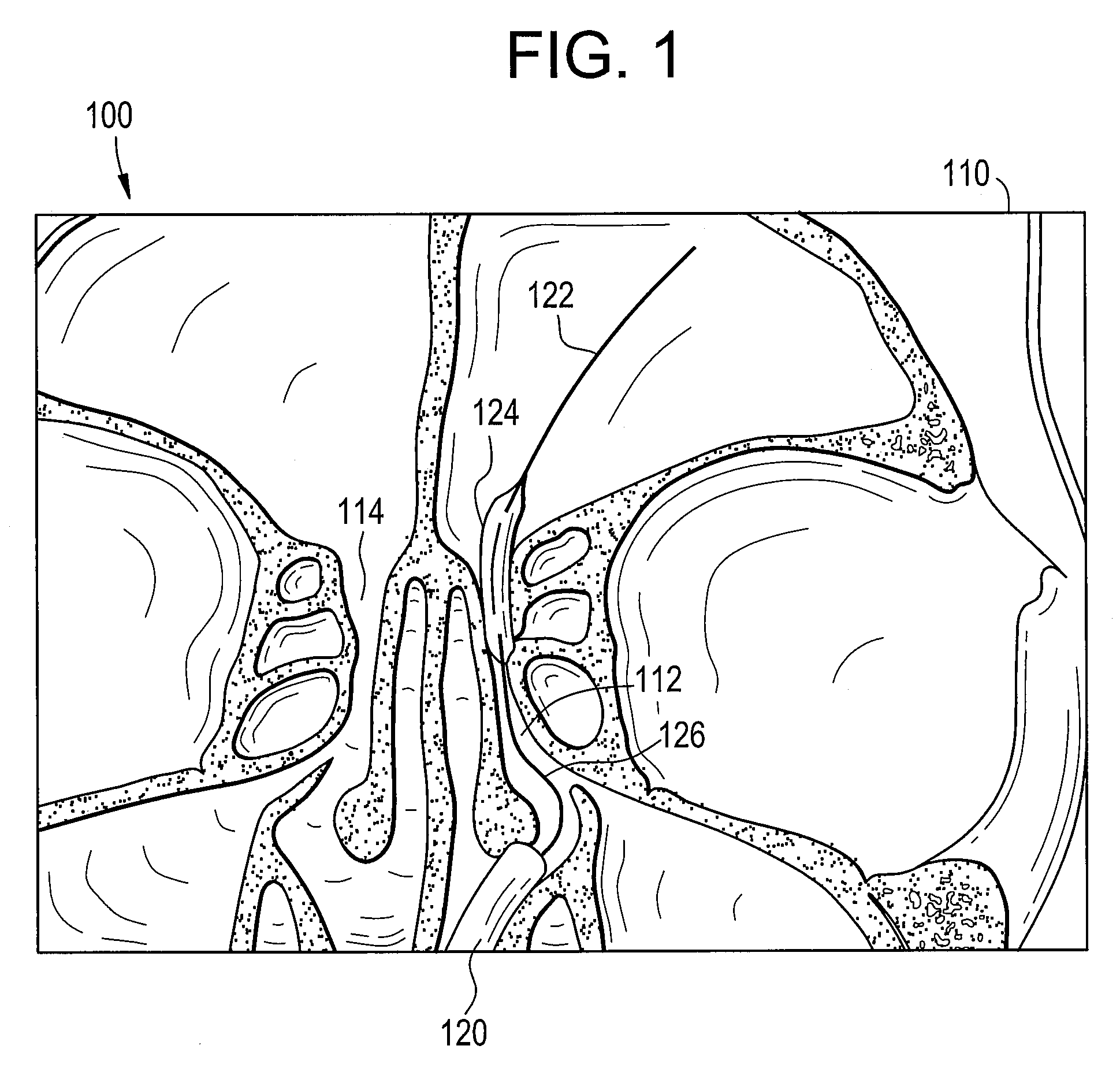
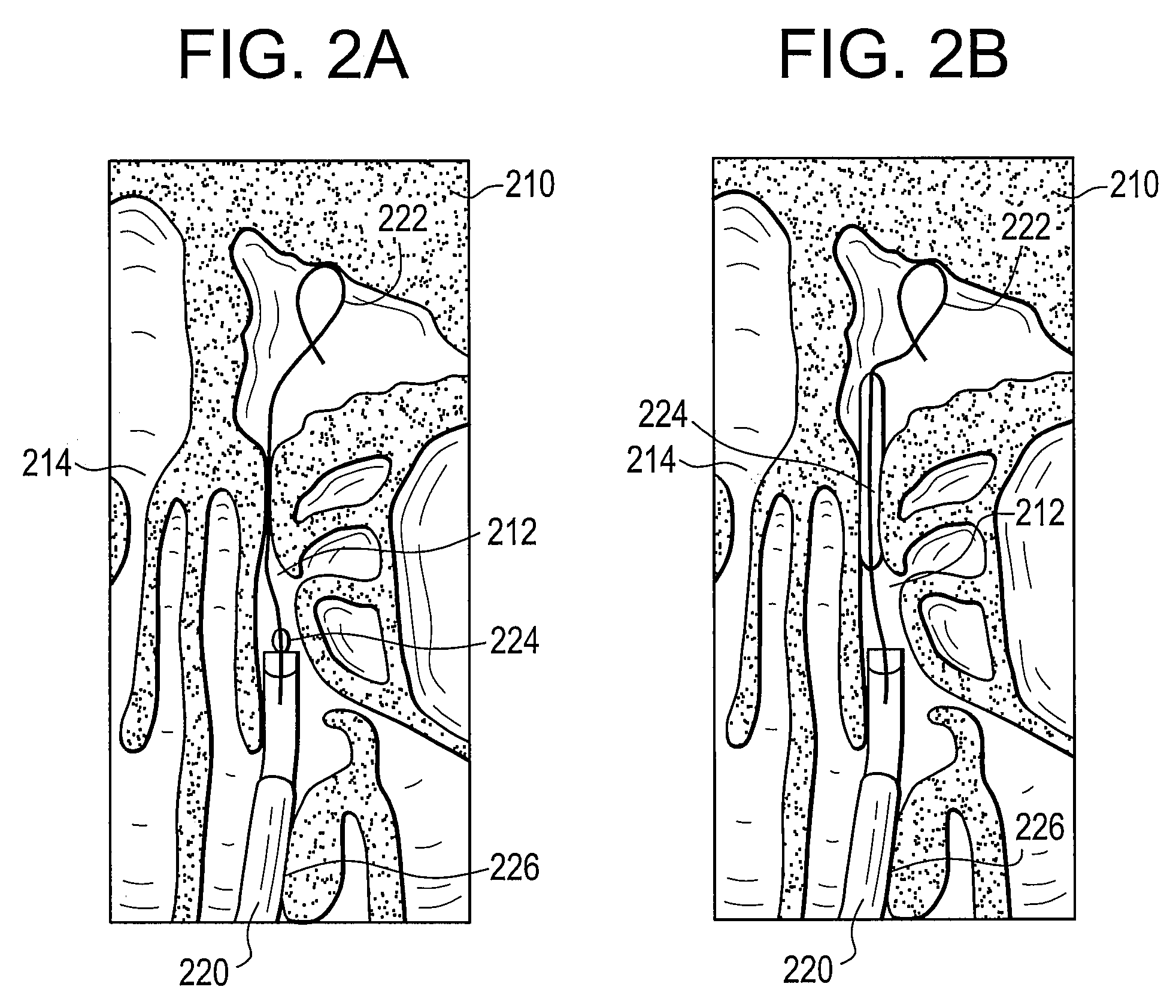
System and Method for Use of Fluoroscope and Computed Tomography Registration for Sinuplasty Navigation
InactiveUS20090080737A1Improved medical device navigationStentsSurgeryMethod of imagesIonising radiation exposure
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods of improved medical device navigation. Certain embodiments include acquiring a first image of a patient anatomy, a second image of patient anatomy, and creating a registered image based on the first and second images. Certain preferred embodiments teach systems and methods of automated image registration without the use of fiducial markers, headsets, or manual registration. Thus the embodiments teach a simplified method of image registration that allows a medical device to be navigated within a patient anatomy. Furthermore, the embodiments teach navigating a medical device in a patient anatomy with reduced exposure to ionizing radiation. Additionally, the improved systems and methods of image registration provide for improved accuracy of the registered images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Computed tomographic scanner using rastered x-ray tubes
ActiveUS7233644B1Reduce coolingReduced Power RequirementsRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusComputing tomographyComputed tomography scanner
A high speed computed tomography x-ray scanner using a plurality of x-ray generators. Each x-ray generator is scanned along a source path that is a segment of the scanner's source path such that each point in the source path is scanned by at least one tube. X-ray generators and detectors can be arranged in different scan planes depending on the available hardware so that a complete and near planar scan of a moving object can be assembled and reconstructed into an image of the object.
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
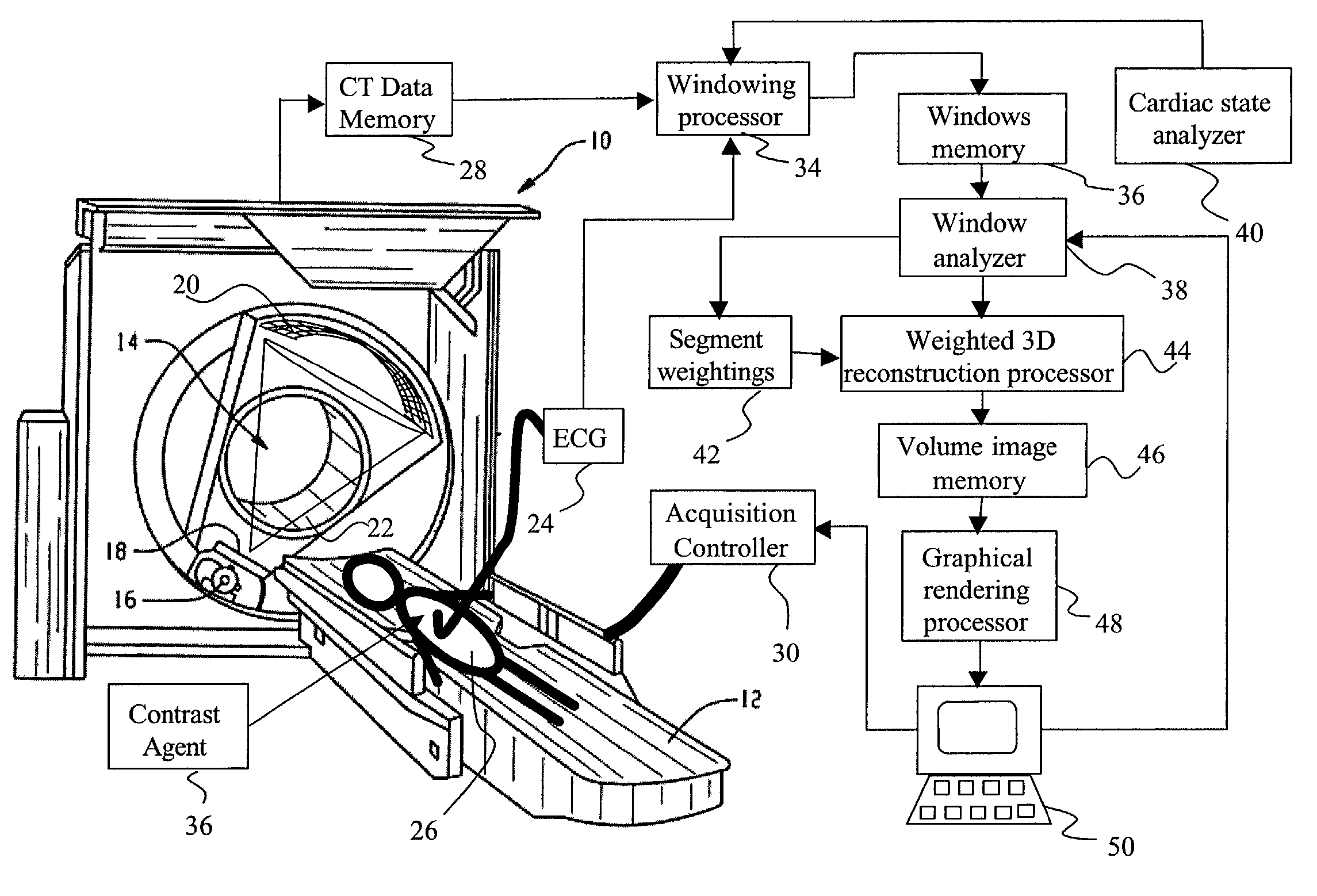
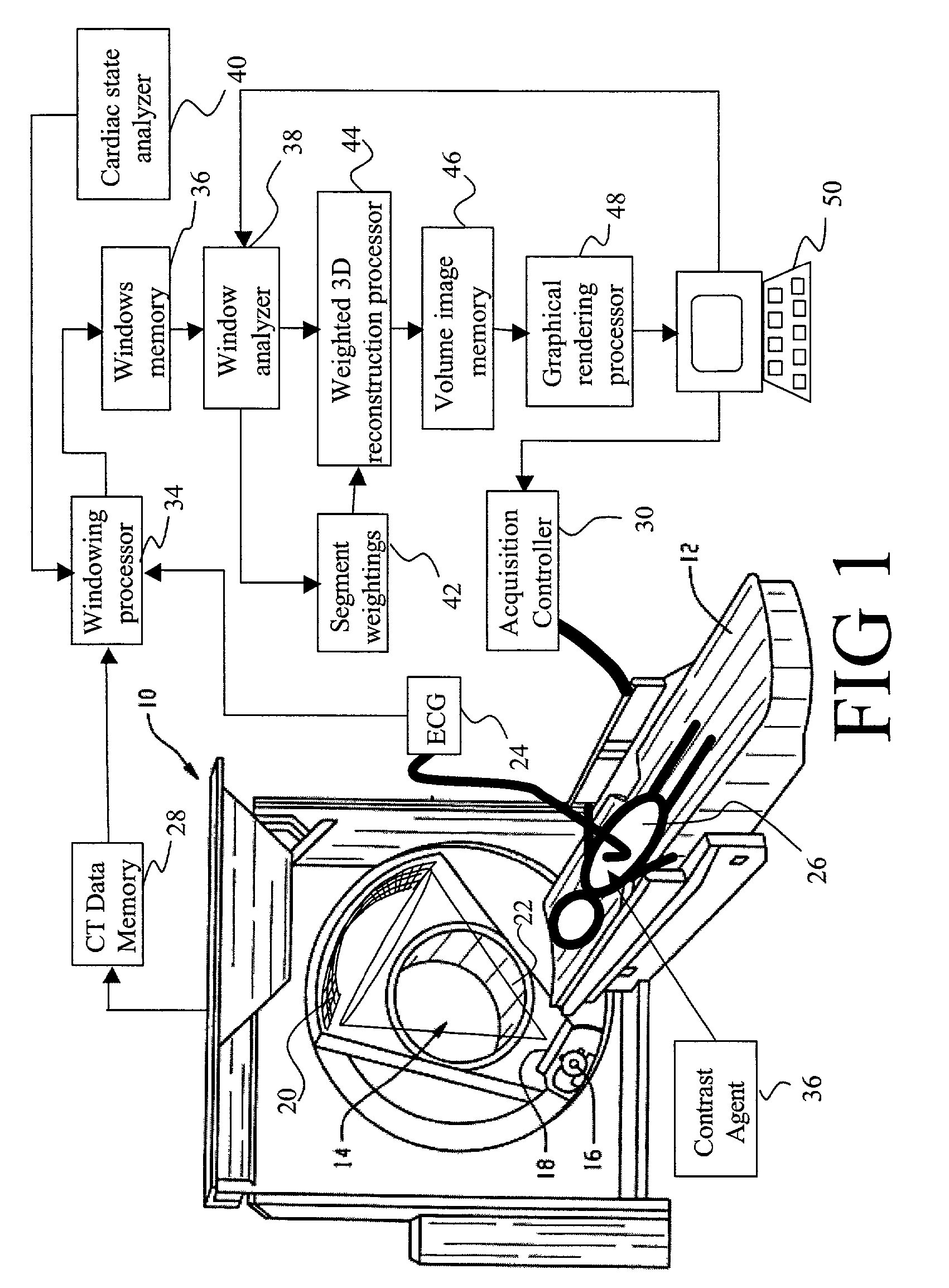
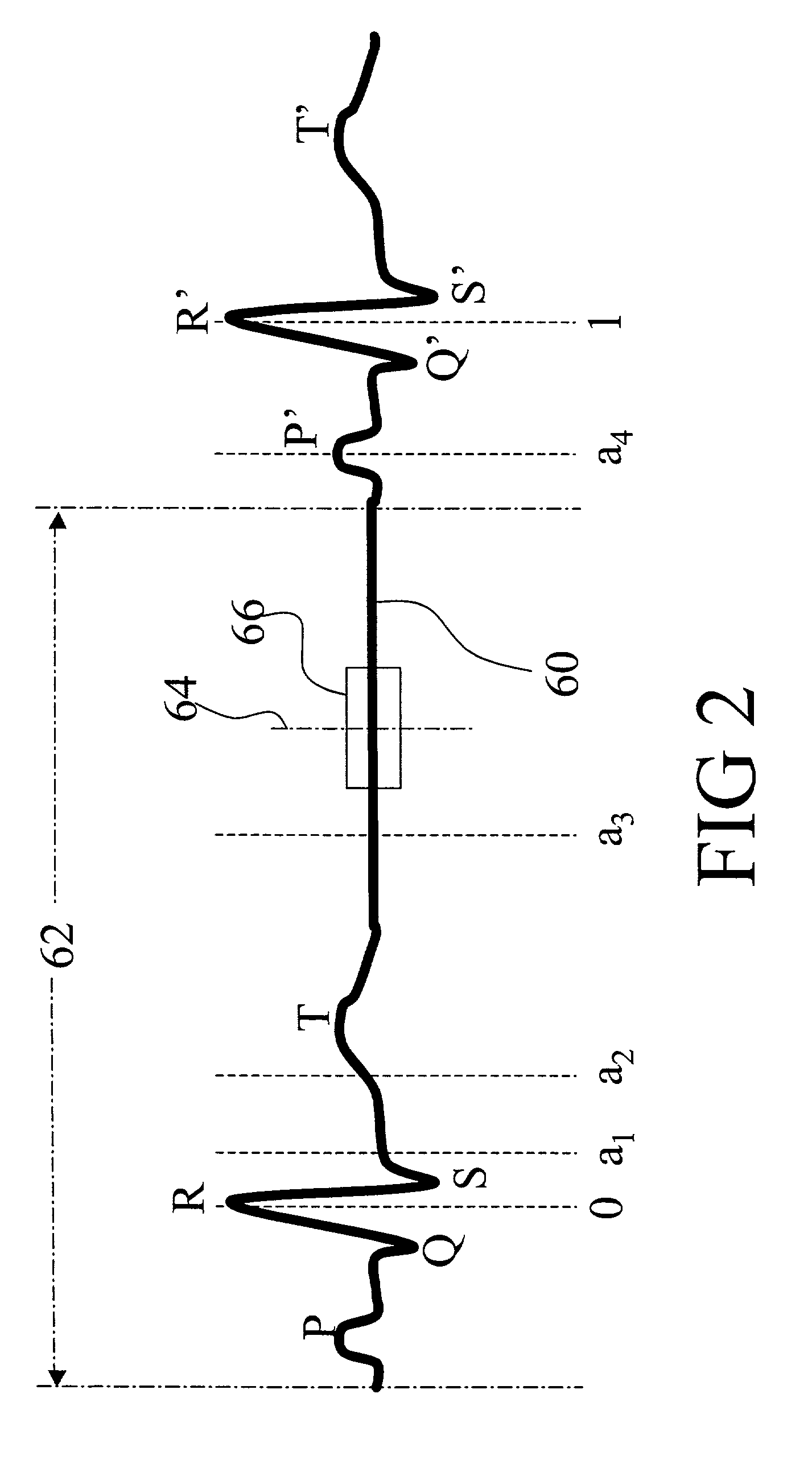
Dynamic computed tomography imaging using positional state modeling
InactiveUS7058440B2Improves temporalImprove spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData segmentData set
An apparatus for computed tomography (CT) imaging of a cyclically moving organ includes a positional state monitor (24, 40) that monitors a positional state of the cyclically moving organ such as the heart. A cone-beam CT scanner (10) acquires image data at least within a plurality of time windows. Each time window is centered about an occurrence of a selected positional state of the organ. A window analyzer (38) selects a data segment within each time window such that the data segments combine to form a complete data set covering a selected angular range. A reconstruction processor (44) reconstructs the selected data segments into an image representation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
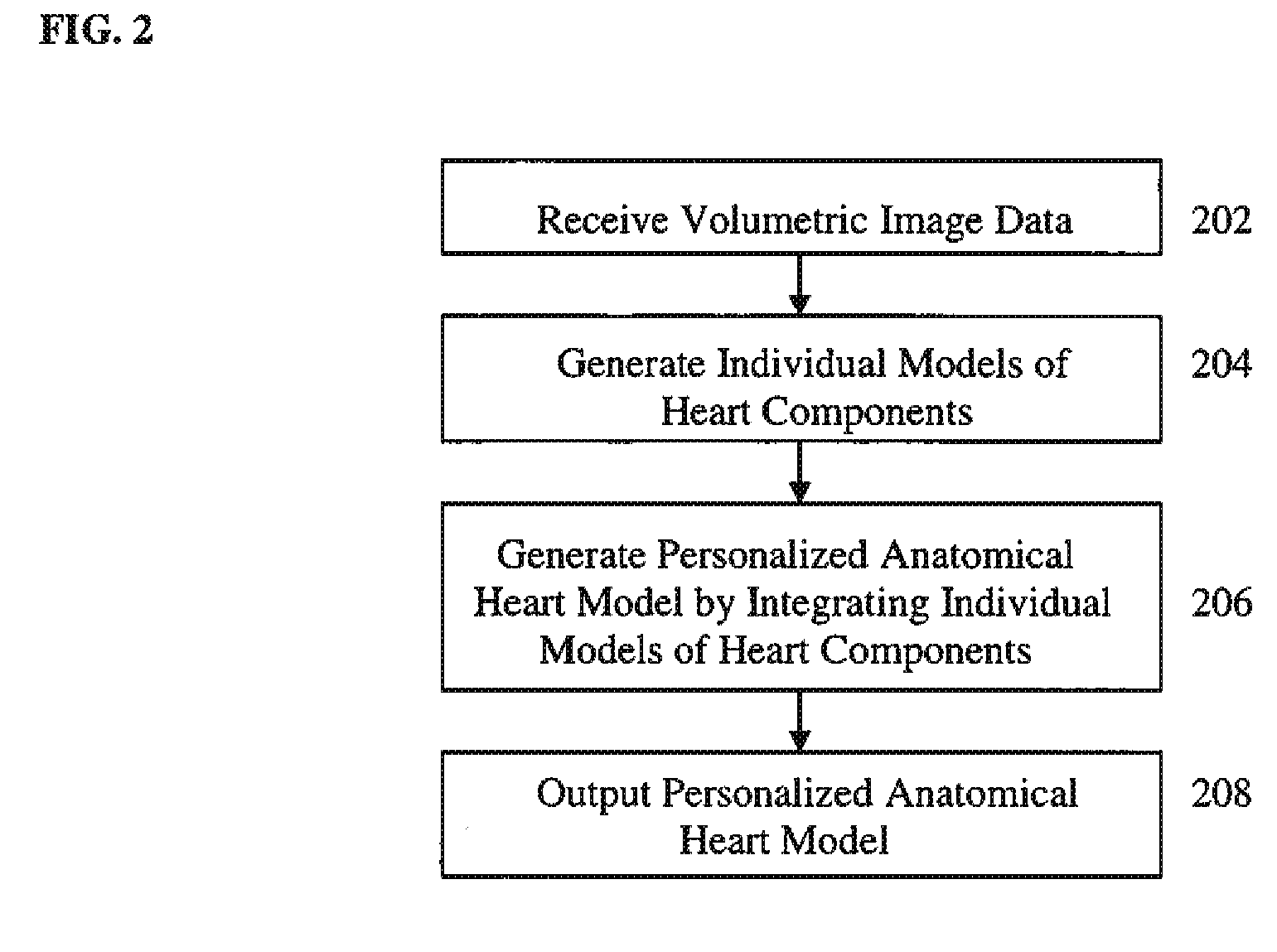
Method and System for Generating a Personalized Anatomical Heart Model
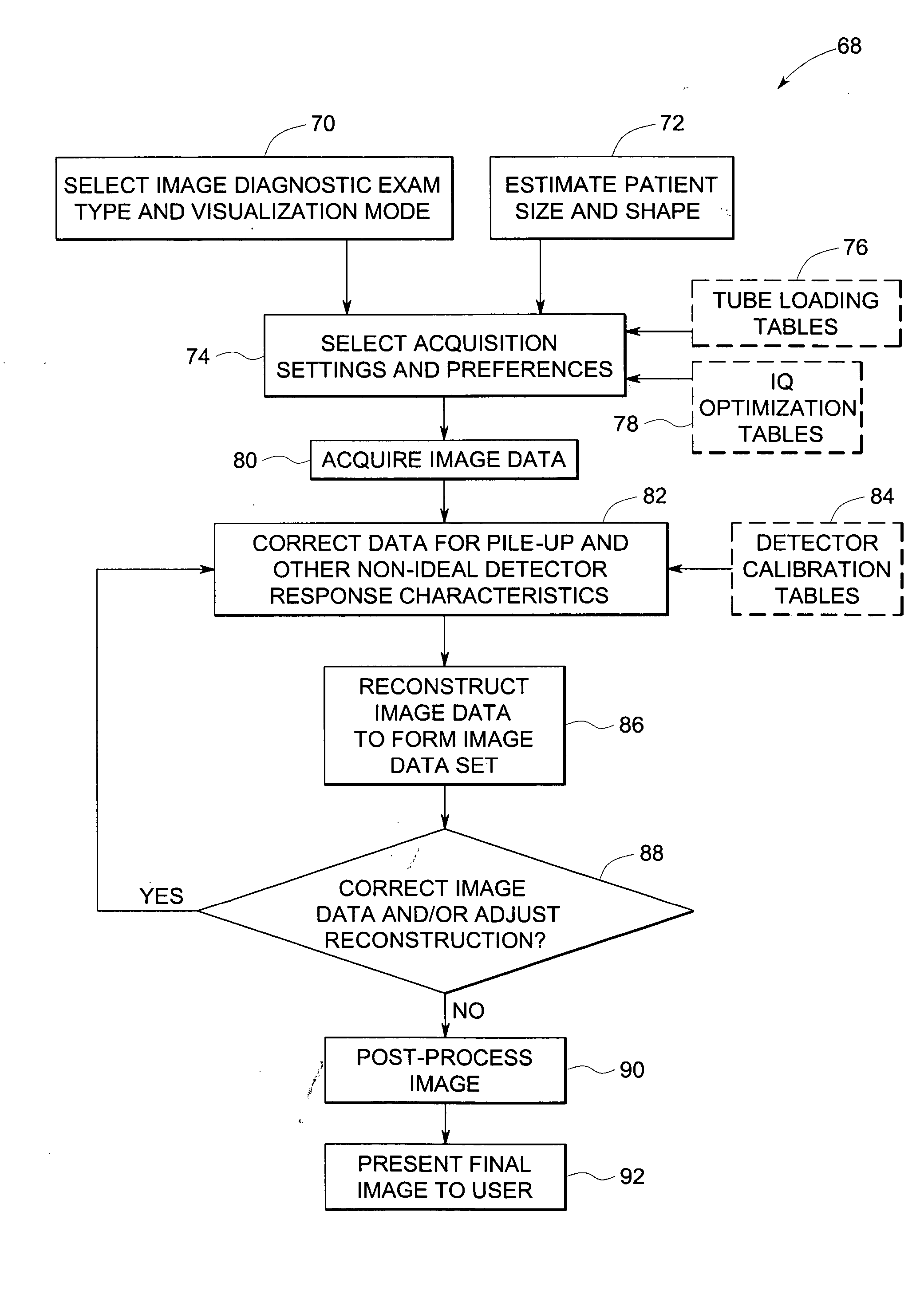
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. Volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT) or echocardiography image data, of a patient's cardiac region is received. Individual models for multiple heart components, such as the left ventricle (LV) endocardium, LV epicardium, right ventricle (RV), left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), mitral valve, aortic valve, aorta, and pulmonary trunk, are estimated in said volumetric cardiac image data. A patient specific anatomical heart model is generated by integrating the individual models for each of the heart components.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for volumemetric navigation supporting radiological reading in medical imaging systems
InactiveUS20050065424A1Local control/monitoringCharacter and pattern recognitionData setImaging data
A method and system for three-dimensional (3D) volumetric navigation supporting radiological readings in two-dimensional (2D) medical image display systems. Reformatted 3D medical image data such as magnetic resonance (MR) data is linked to raw and formatted 2D image data such as computed tomography (CT) data. An automatic synchronized navigation through entire linked 3D and 2D data sets is provided.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Adaptable energy discriminating computed tomography system
InactiveUS20070076842A1Improve image qualityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedicineImaging quality
A method of enhancing image quality and providing tissue composition information by analysis of energy discrimination data, the method comprising determining a radiation dosage at one or more energy spectrum levels based on patient parameters and user selected parameters. Computer-readable medium and systems that afford functionality of the type defined by this method are also contemplated in conjunction with the present technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method of designing and manufacturing customized instrumentation for accurate implantation of prosthesis by utilizing computed tomography data
ActiveUS8175683B2Quickly and accurately attachesPrecise positioningPerson identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionProsthesisControl data
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Apparatus and method for hybrid computed tomography imaging
InactiveUS20070205367A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingData setEnergy integration
A system is presented. The system includes a plurality of energy integrating detector elements configured to acquire energy integrating data. Further, the system includes a plurality of energy discriminating detector elements configured to acquire energy discriminating data, where the plurality of energy integrating detector elements and the plurality of energy discriminating detector elements are arranged in a spatial relationship to form a hybrid detector, and where the plurality of energy integrating detector elements and the plurality of energy discriminating detector elements are configured to obtain respective sets of energy integrating data and energy discriminating data for use in generating an image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
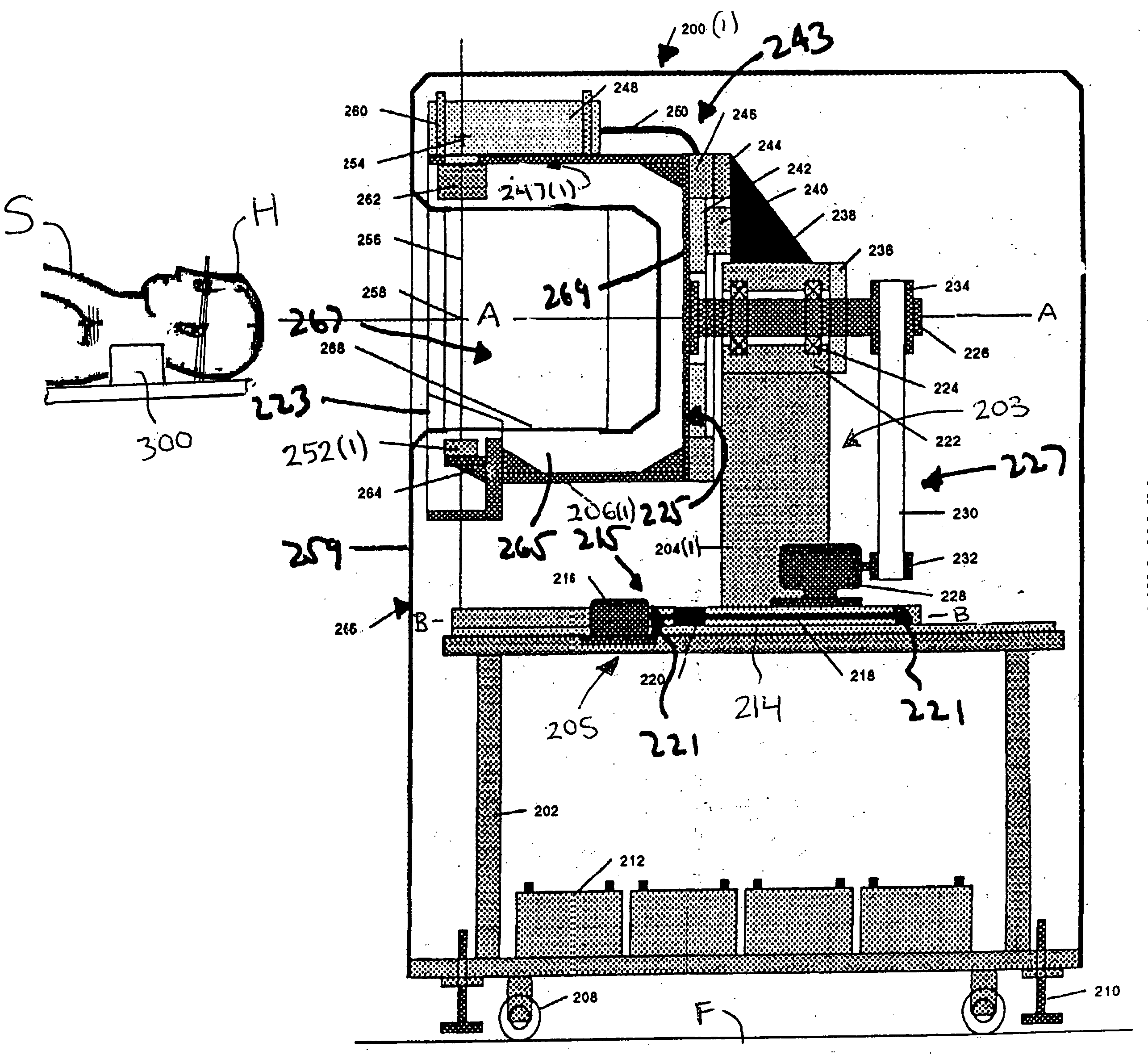
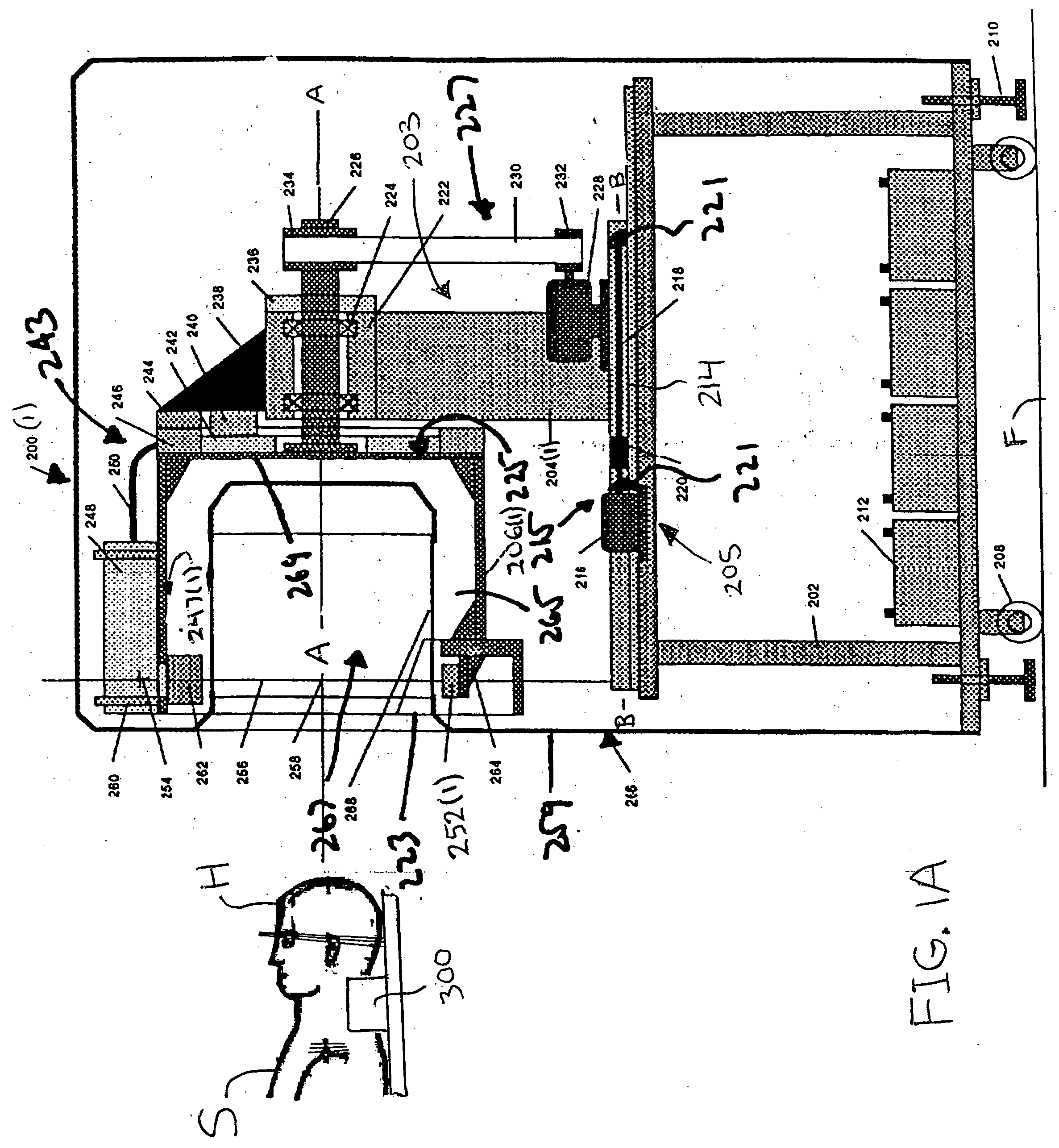
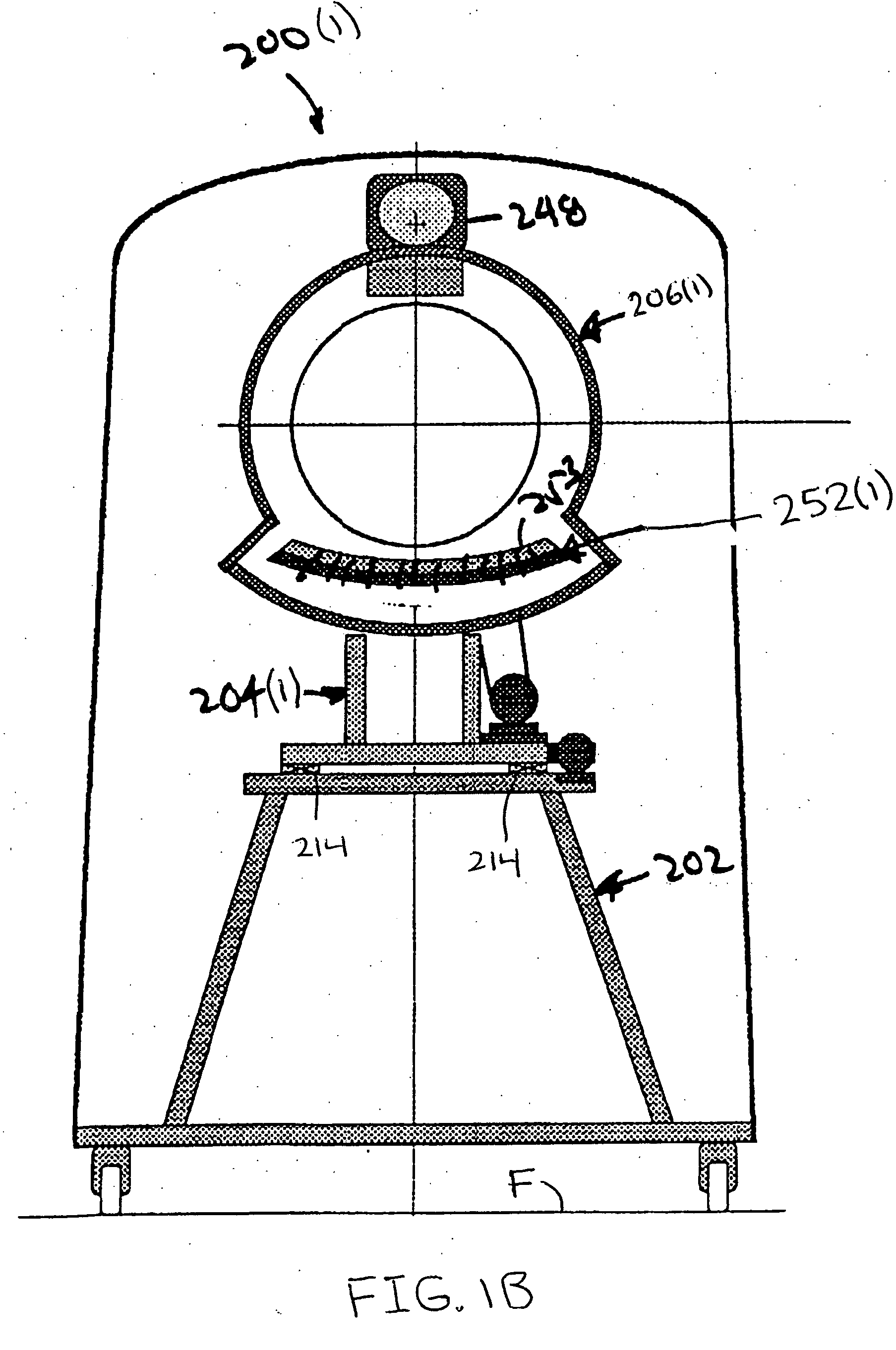
Portable computed tomography scanner and methods thereof
InactiveUS20050135560A1Less riskAddressing slow performanceRadiation diagnosis data transmissionX-ray apparatusX-rayEngineering
A computed tomography scanner includes a base system and a rotor system. The rotor system has an axle that is rotationally mounted to the base system. At least one x-ray source is mounted to the rotor system. A power interface system at least partially disposed about the axle couples power to the x-ray source. The power interface may include a slip ring assembly or a cable assembly that winds and unwinds about the axle as the rotor system rotates.
Owner:BRAIN SAVING TECH
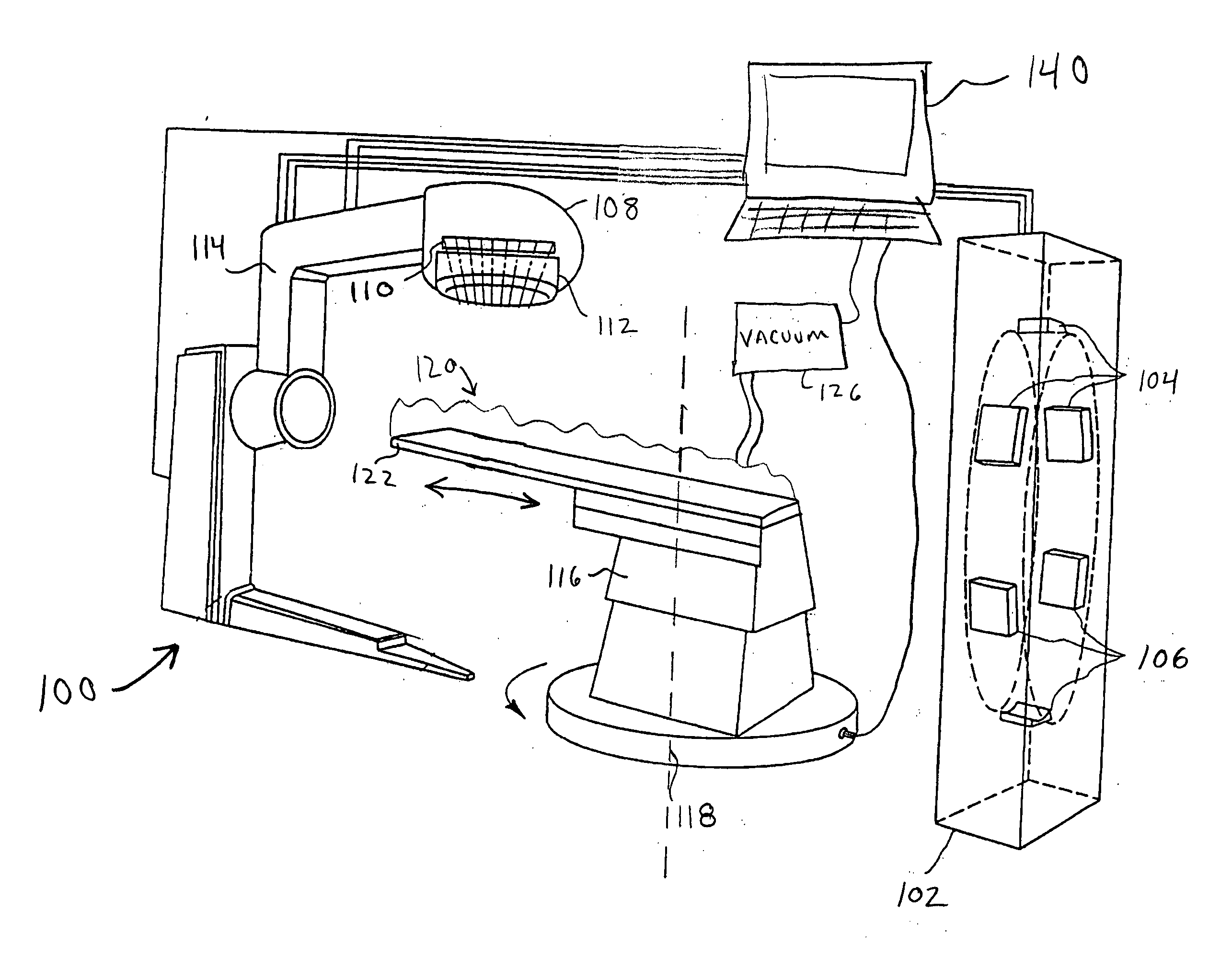
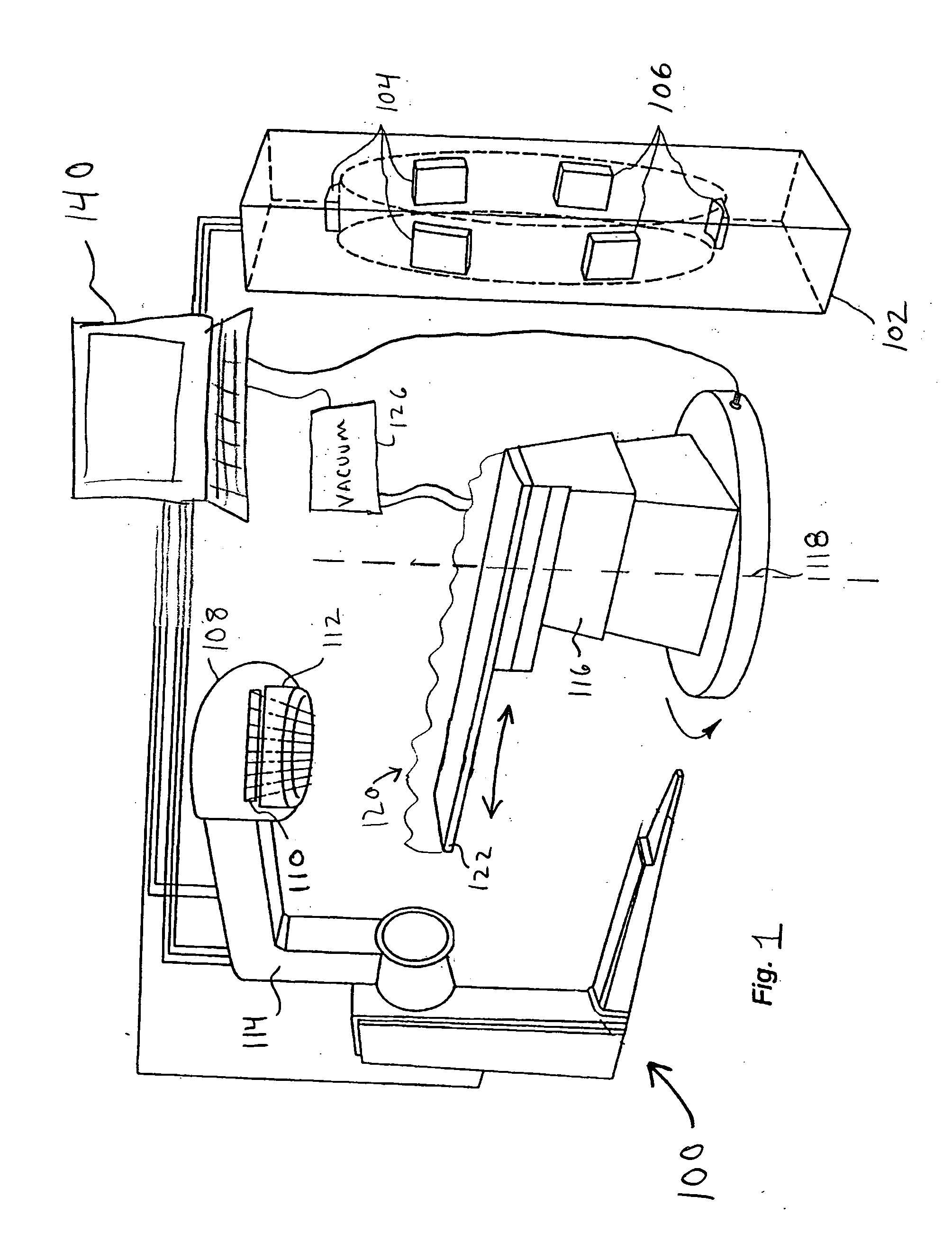
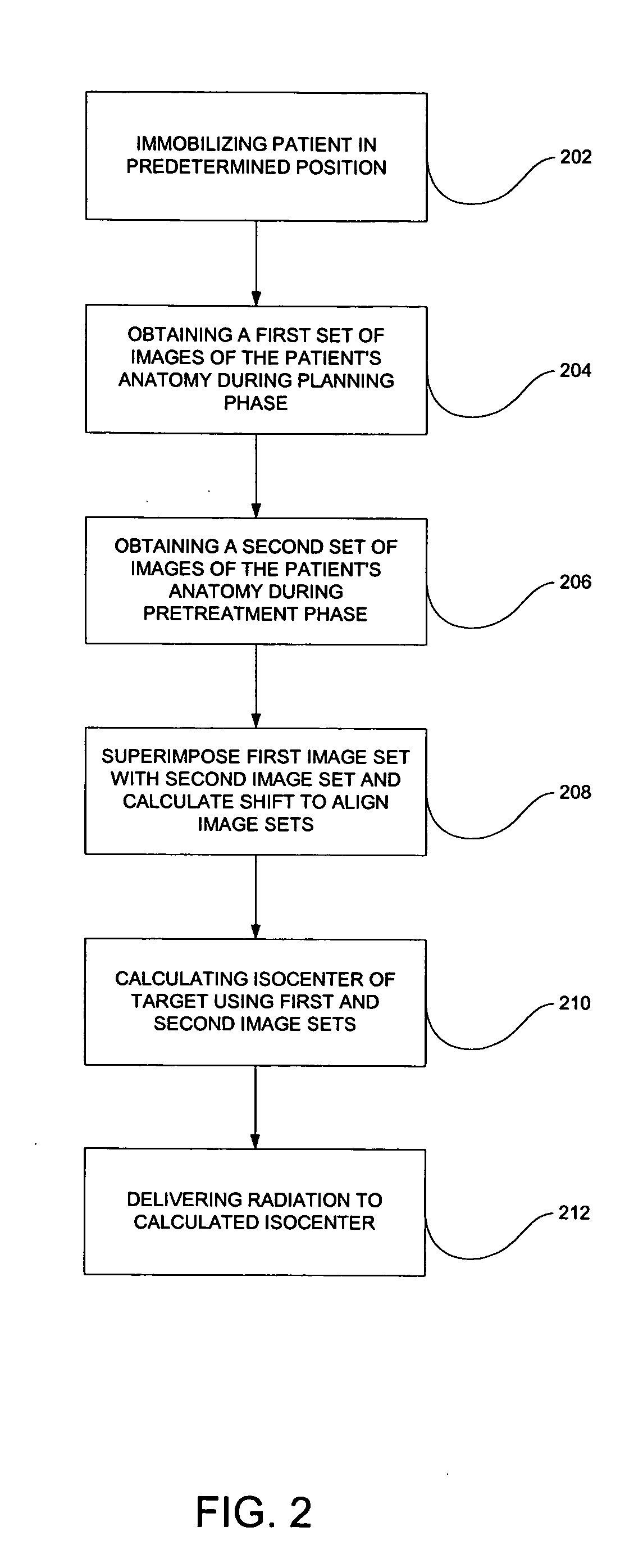
Near simultaneous computed tomography image-guided stereotactic radiotherapy
InactiveUS20050080332A1Minimize body motionHighly accurate dose of radiationSurgical instrument detailsComputerised tomographsStereotactic radiotherapyTomography
A targeting system for administering radiation to a patient and methods therefor are provided. The targeting system includes a stereotactic frame system for immobilizing the patient; an imaging scanner for acquiring images of a patient's anatomy, wherein at least one image is acquired during a planning phase, and at least one image is acquired during a pretreatment phase; a processor for fusing the planning image to the pretreatment image and for determining a shift, for example, translation and rotation, between the images to locate a predetermined portion of the patient's anatomy; and a radiation source for delivery of radiation to the predetermined portion of the patient's anatomy.
Owner:INTEGRA RADIONICS INC
Breathing synchronized computed tomography image acquisition
ActiveUS20050201509A1Efficient collectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputing tomographyComputer science
A method for collecting computed tomography (CT) image data includes determining a number of intervals N into which a respiratory cycle is to be divided, determining a number of respiratory cycles M to be covered in one gantry rotation, and rotating a gantry to collect at least M×N sets of CT image data of at least a portion of a patient, wherein each set of the CT image data corresponds to a phase of a respiratory cycle.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
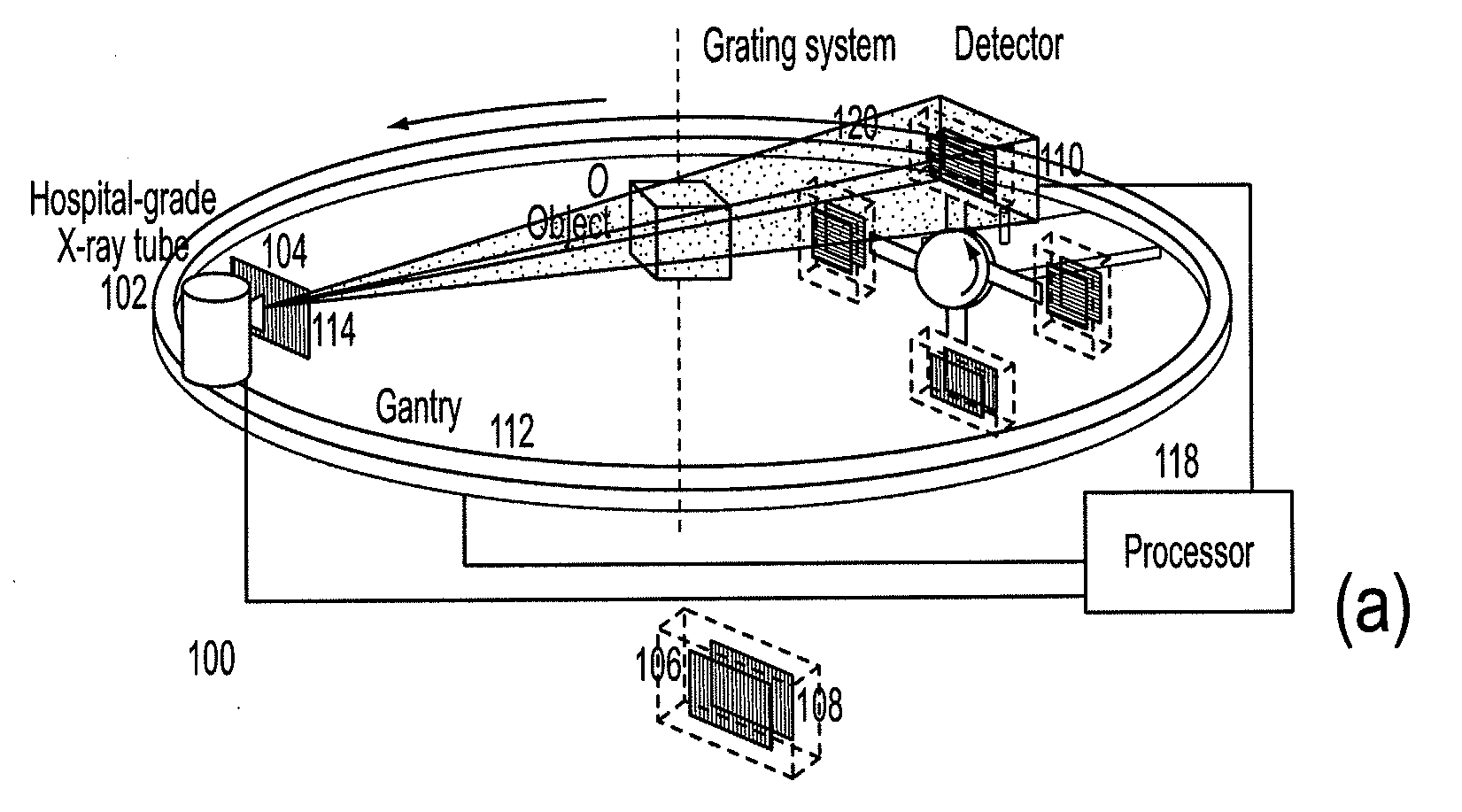
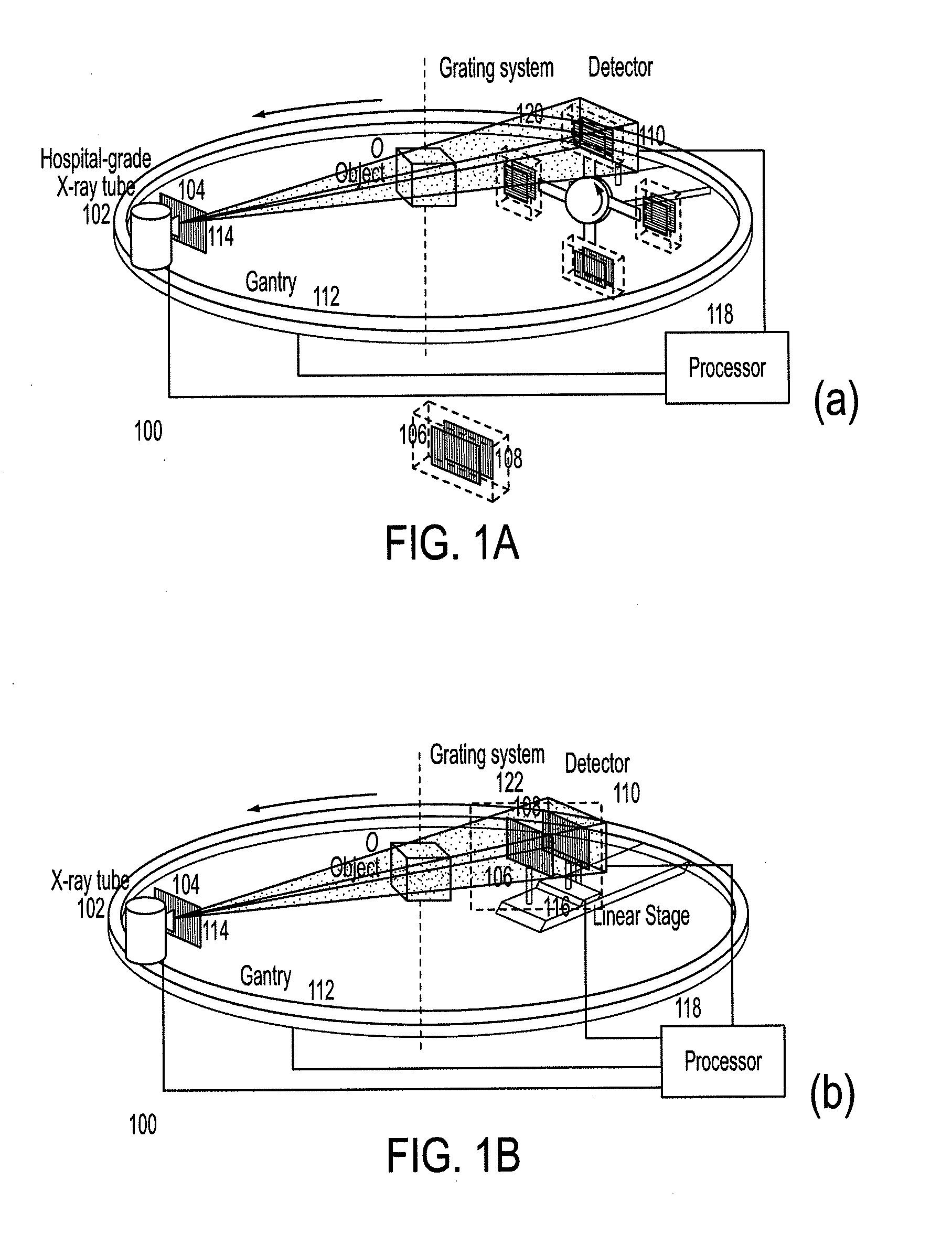
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
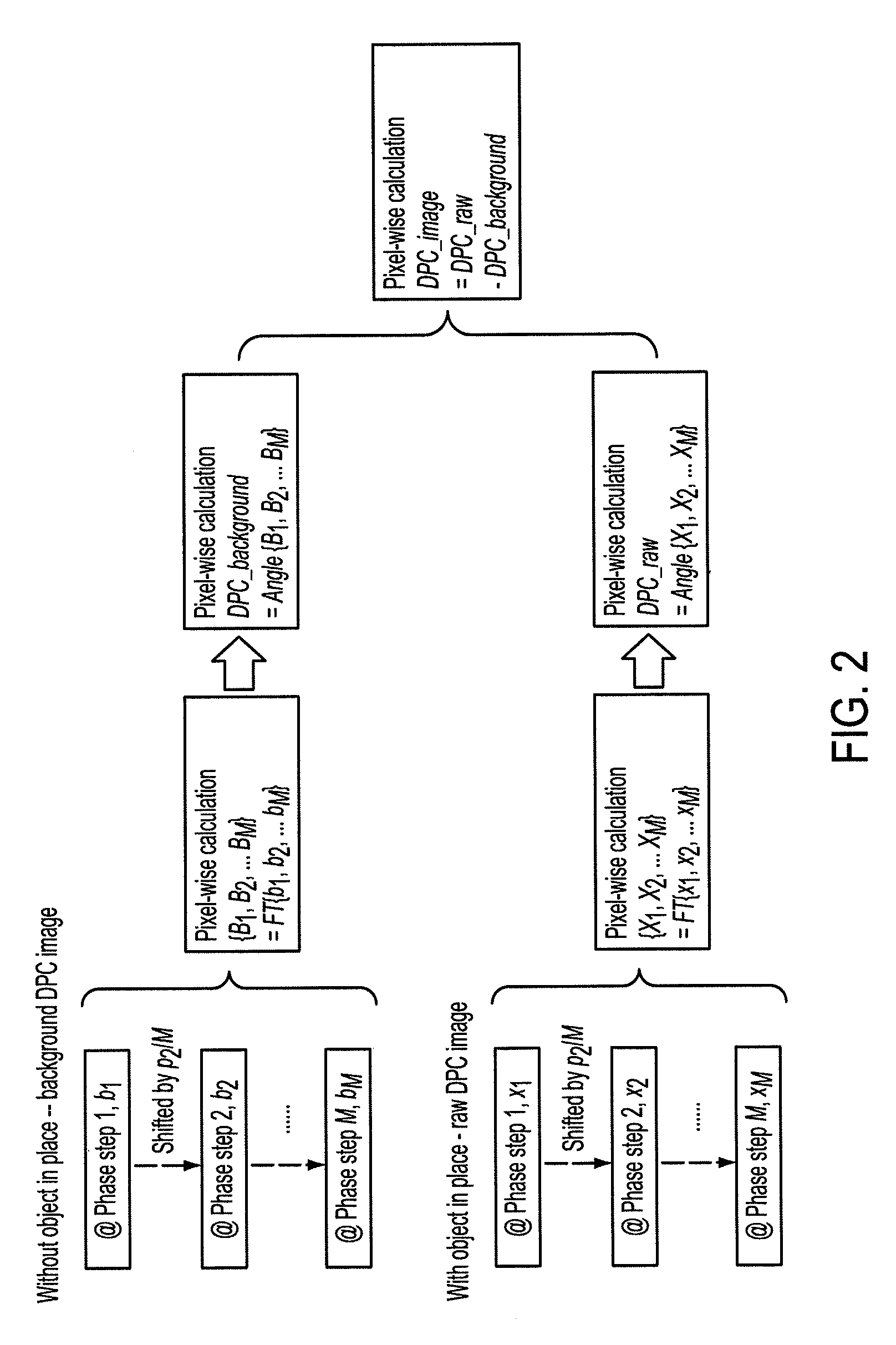
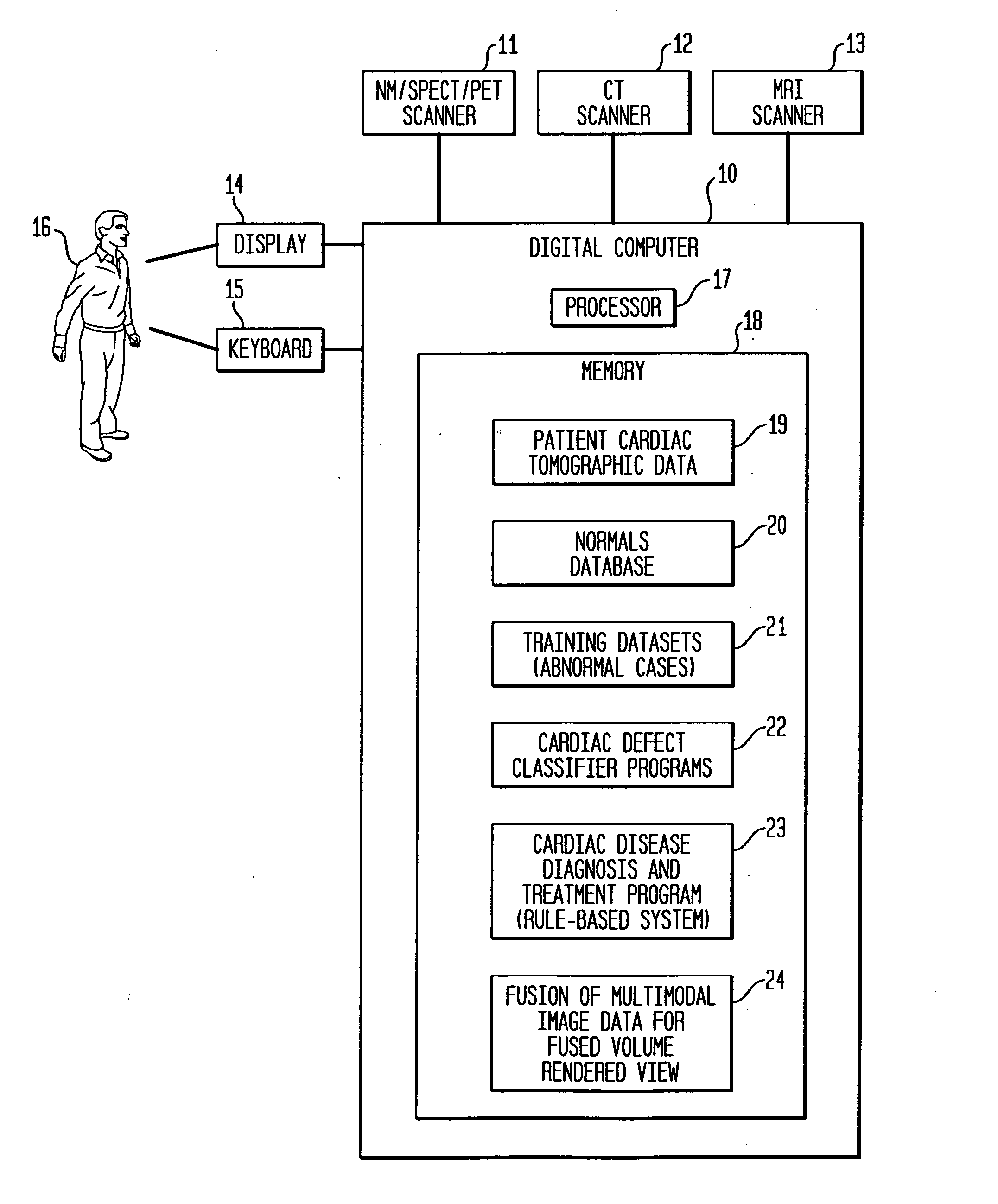
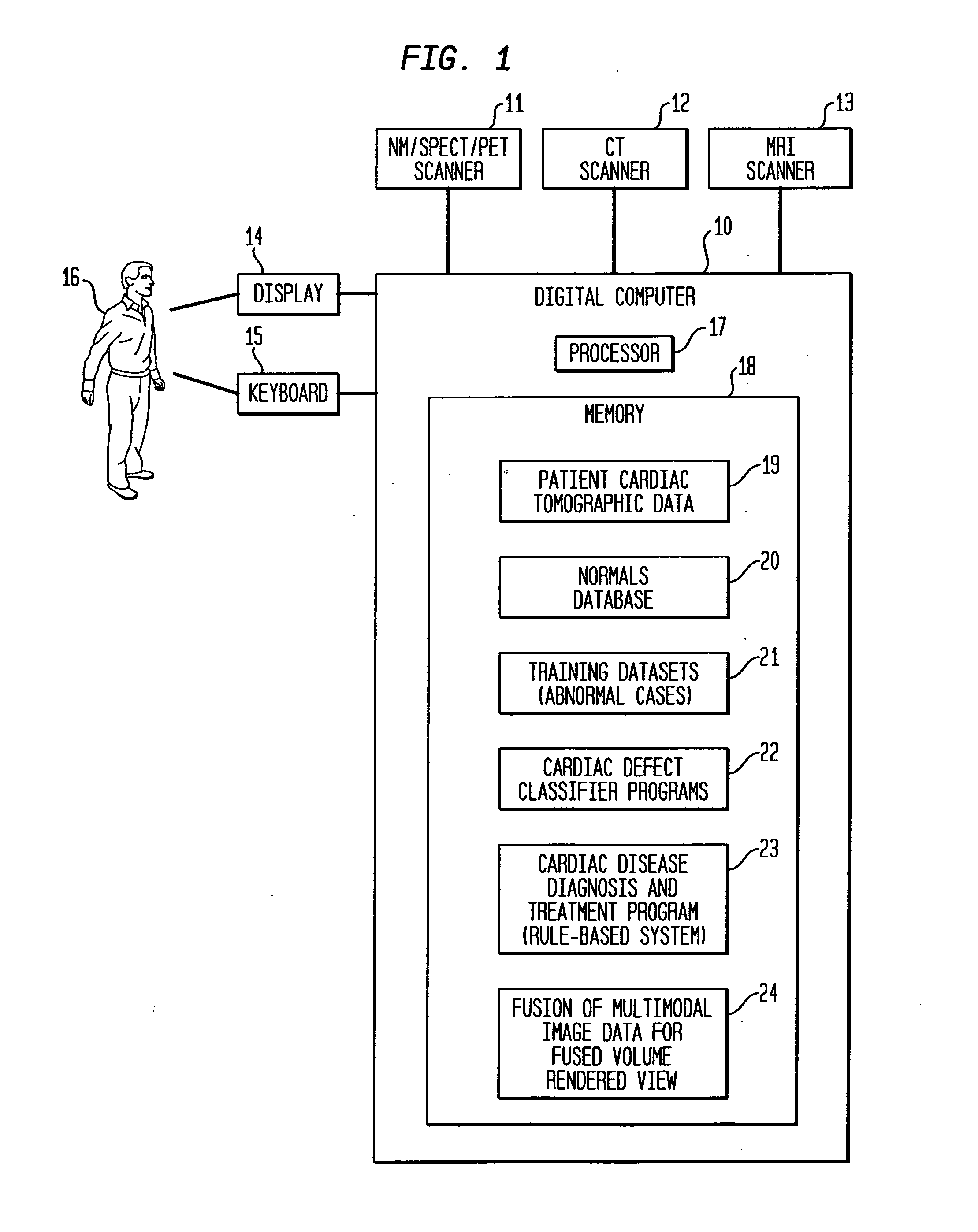
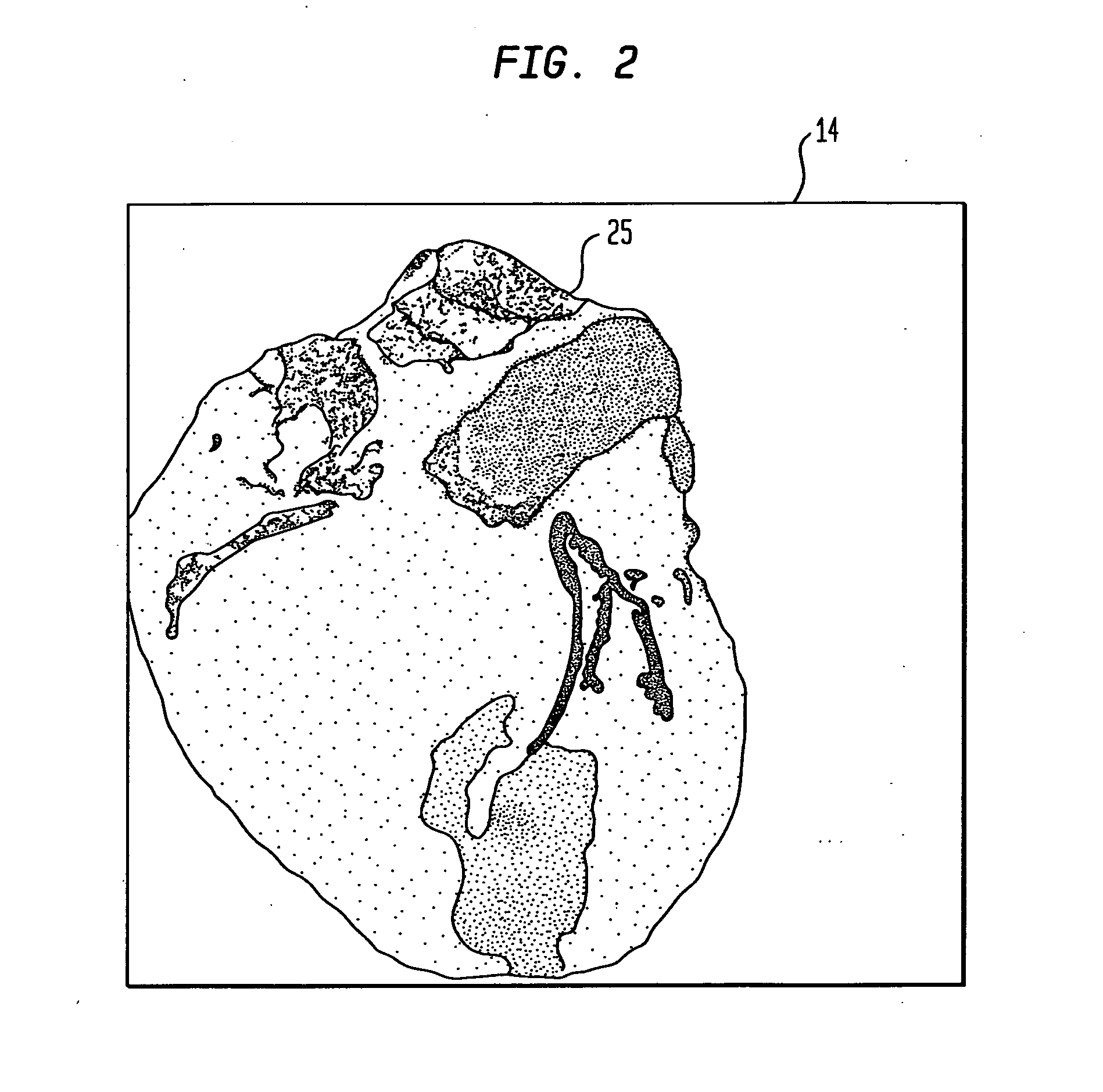
Dedicated display for processing and analyzing multi-modality cardiac data
For diagnosis and treatment of cardiac disease, images of the heart muscle and coronary vessels are captured using different medical imaging modalities; e.g., single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), electron-beam X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or ultrasound (US). For visualizing the multi-modal image data, the data is presented using a technique of volume rendering, which allows users to visually analyze both functional and anatomical cardiac data simultaneously. The display is also capable of showing additional information related to the heart muscle, such as coronary vessels. Users can interactively control the viewing angle based on the spatial distribution of the quantified cardiac phenomena or atherosclerotic lesions.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
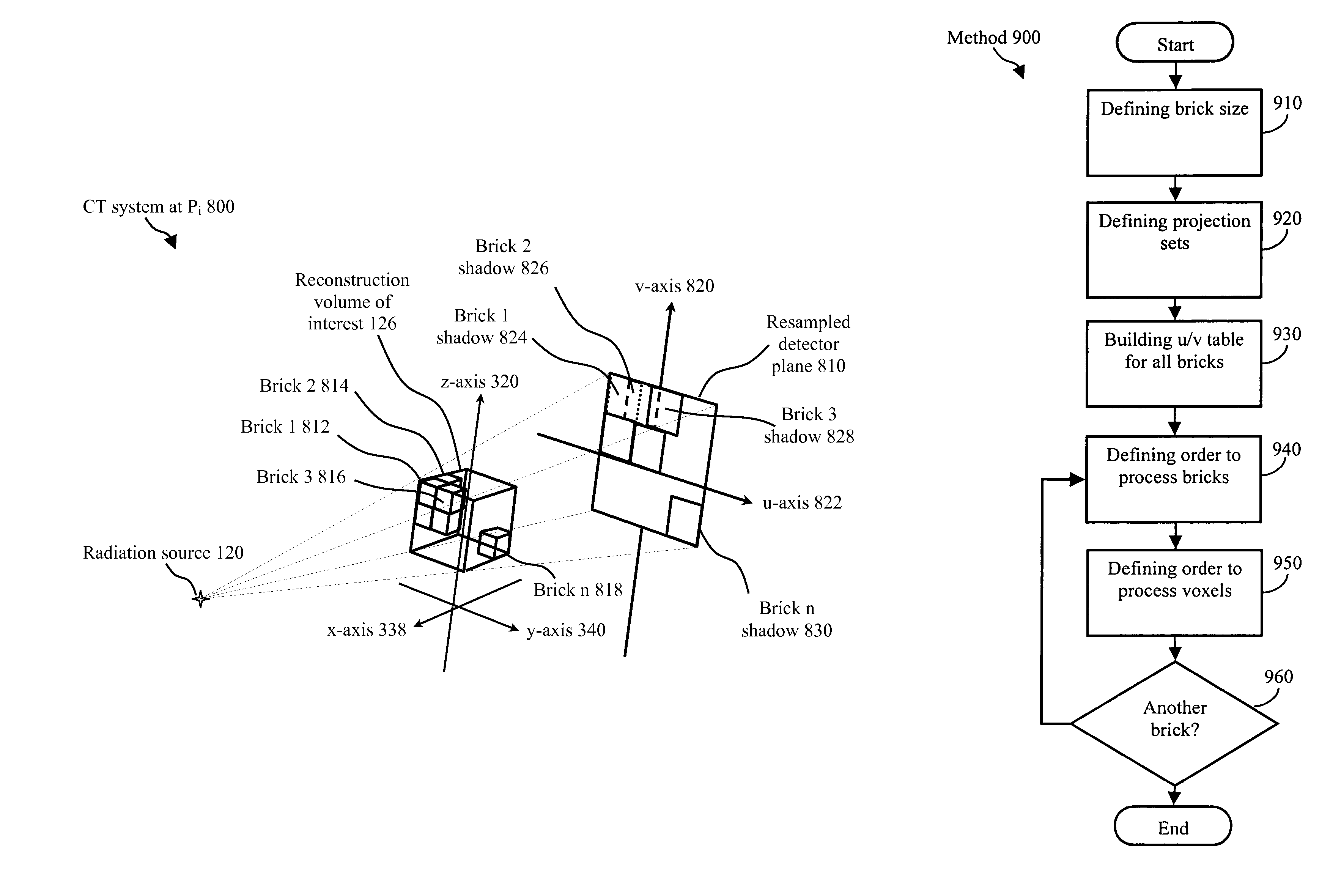
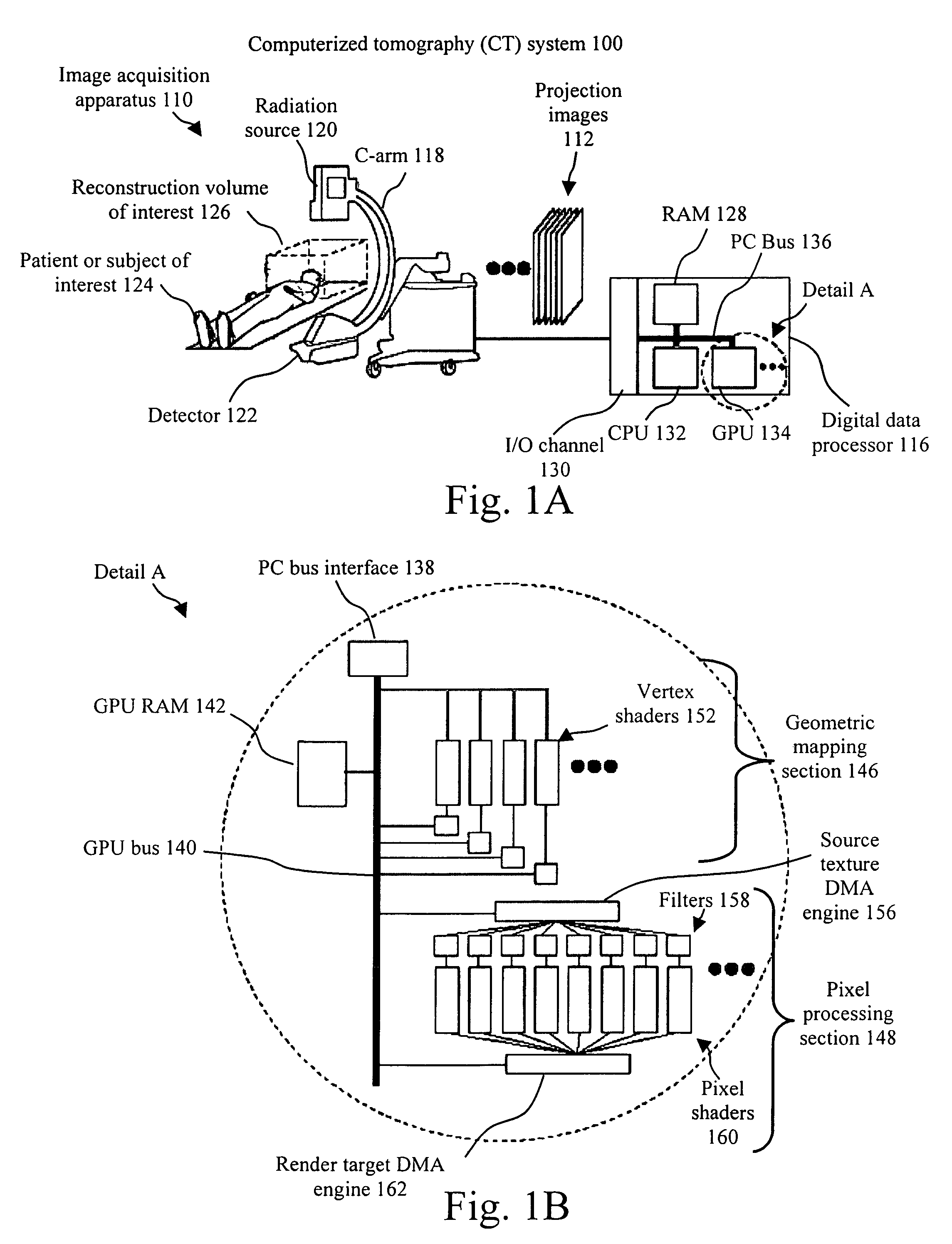
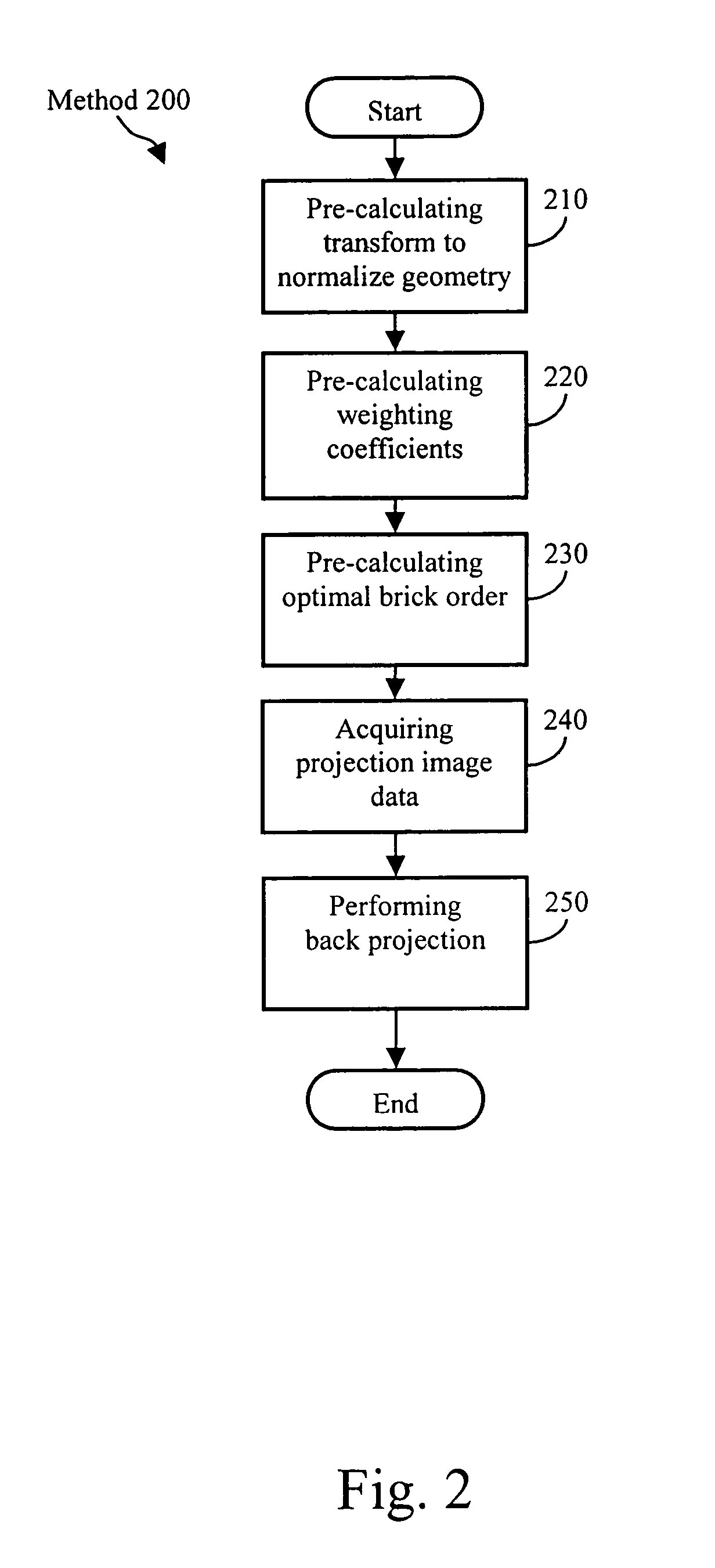
Method of reconstructing computed tomography (CT) volumes suitable for execution on commodity central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processors, and apparatus operating in accord with those methods (rotational X-ray on GPUs)
ActiveUS7778392B1Reduce in quantityShorten the timeReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationVoxelWeight coefficient
The invention provides in one aspect methods and apparatus for use with C-arm and other CT systems, e.g., with non-rigid geometries. In such systems, by way of example, calibration can be performed to determine the exact position of the x-ray source and the exact orientation of the detector where each projection measurement is made. Next, a weighting coefficient can be determined for the voxels in each plane of a reconstruction volume at every possible projection. Finally, the order in which to process the voxels during image reconstruction can be determined. Following an actual CT scan procedure in which scans are obtained of a volume to be constructed, a system according to these and related aspects of the invention can use an optimal, pre-calculated processing method, while utilizing offsets and weighting coefficients determined during calibration, for performing backprojection image reconstruction.
Owner:PME IP
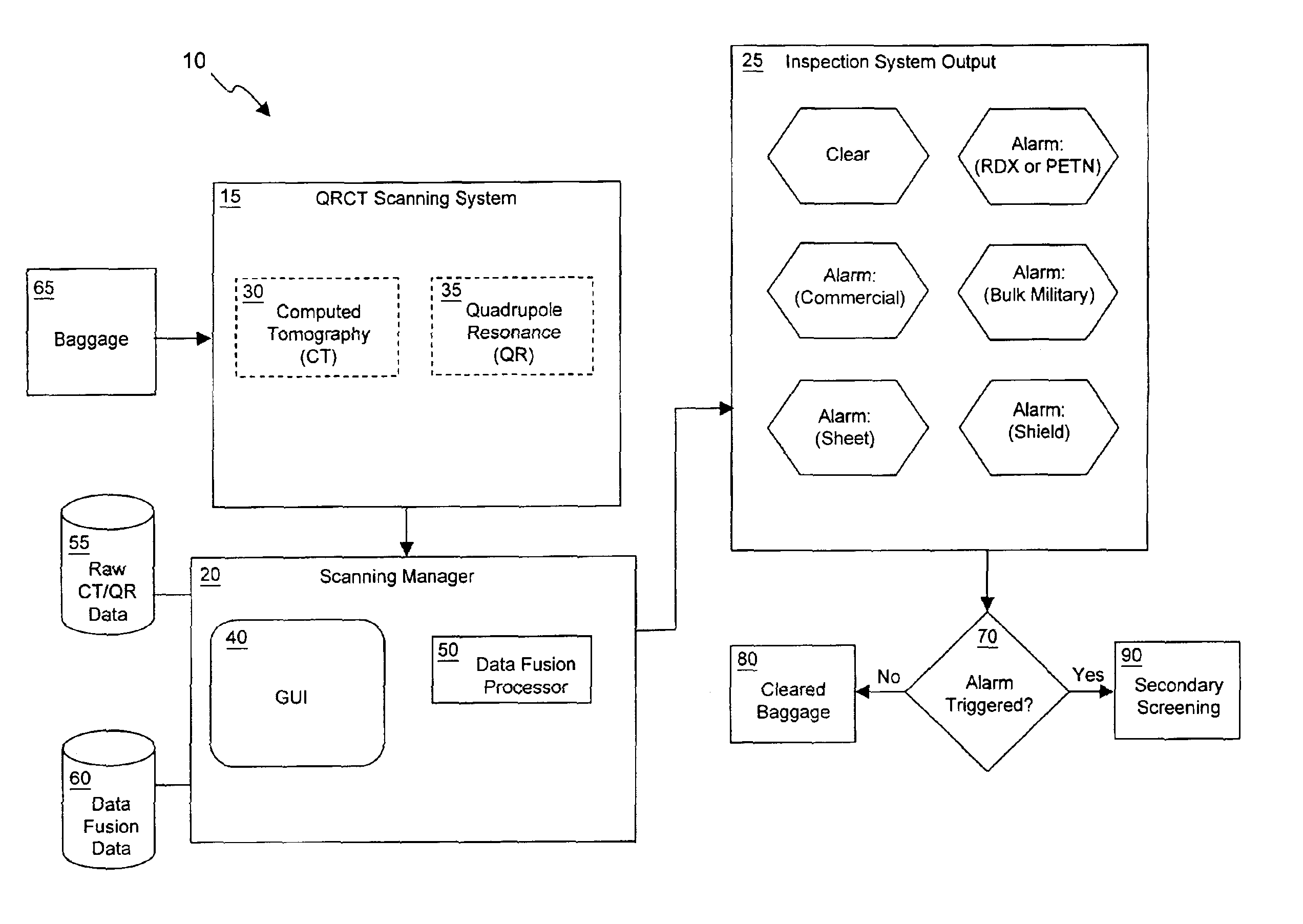
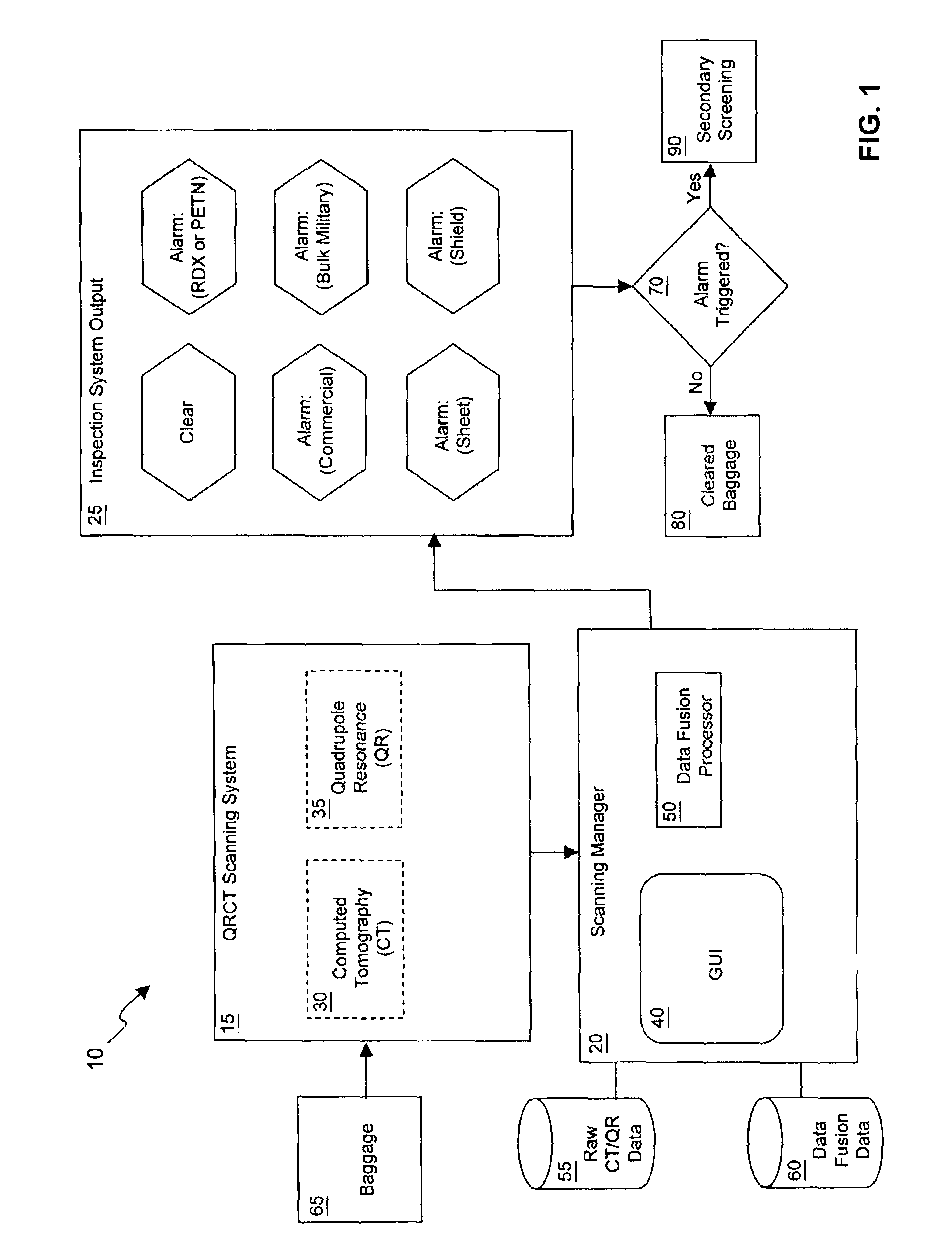
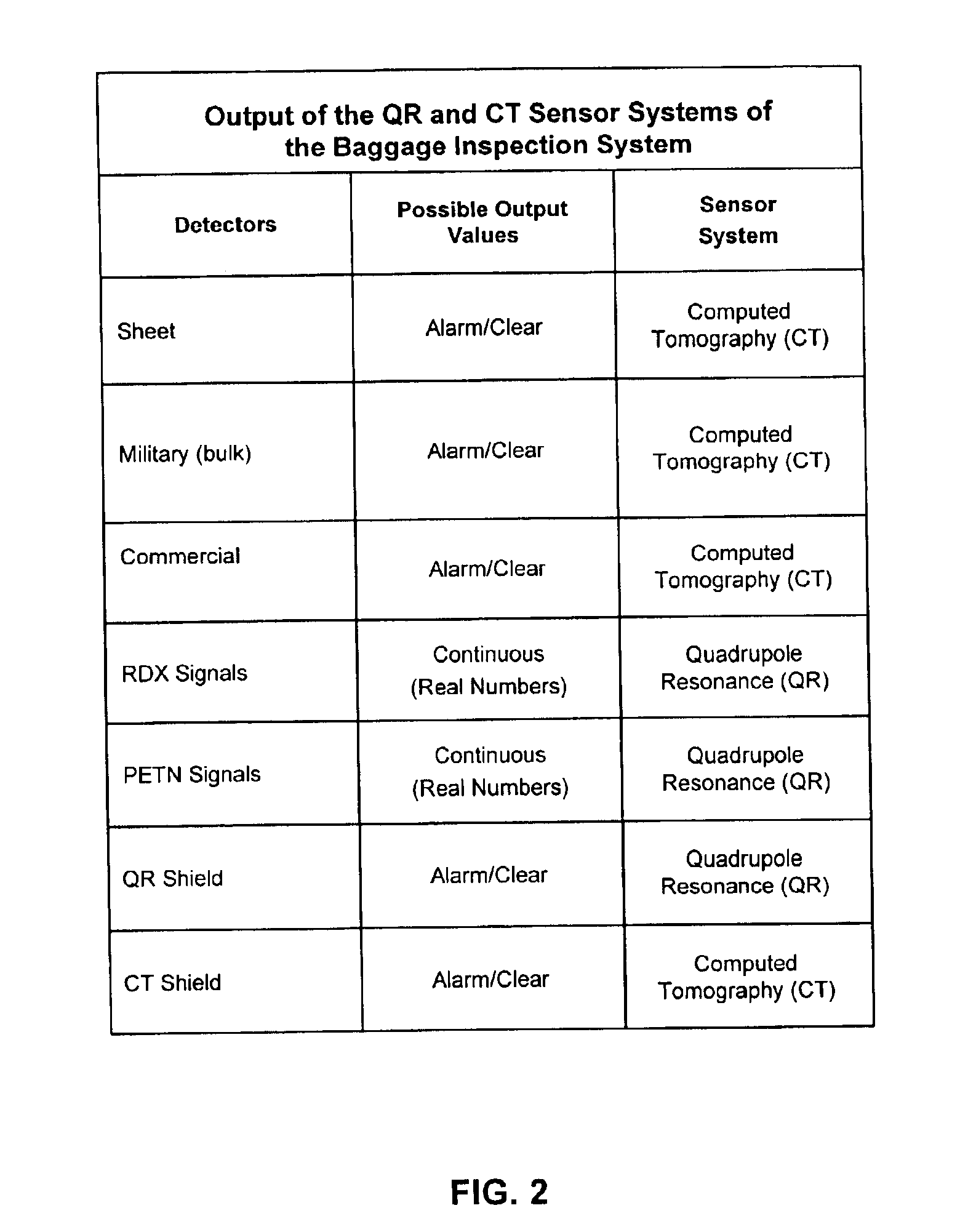
Explosives detection system using computed tomography (CT) and quadrupole resonance (QR) sensors
InactiveUS6922460B2Material analysis by transmitting radiationDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceResonanceEngineering
An explosives detection system which includes computed tomography (CT) and quadrupole resonance (QR) sensors for identifying particular explosive compounds present in passenger baggage. The CT sensor may be configured to automatically identify the presence or absence of bulk military, commercial, and sheet explosives during CT scanning of the baggage. Similarly, the QR sensor may be configured to responsively generate RDX and PETN signals during QR scanning of the passenger baggage. Using any of a variety of inspection protocols, the explosives detection system may generate an output alarm based upon data obtained from the CT and QR sensors.
Owner:QUANTUM MAGNETICS
Stationary computed tomography system and method
ActiveUS7280631B2Improve data qualityImprove integrityRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsDistributed sourceX-ray
Configurations for stationary imaging systems are provided. The configurations may include combinations of various types of distributed sources of X-ray radiation, which generally include addressable emitter elements which may be triggered for emission in desired sequences and combinations. The sources may be ring-like, partial ring-like, or line-like (typically along a Z-axis), and so forth. Combinations of these are envisaged. Corresponding detectors may also be full ring detectors or partial ring detectors associated with the sources to provide sufficient coverage of imaging volumes and to provide the desired mathematical completeness of the collected data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and systems for the rapid detection of concealed objects
InactiveUS20050104603A1Reduce frequencyTrue natureAntenna arraysResistance/reactance/impedenceX-rayComputing tomography
The present invention provides for an improved scanning process having microwave arrays comprised of microwave transmitters in radiographic alignment with microwave receivers. The microwave array emits controllably directed microwave radiation toward an object under inspection. The object under inspection absorbs radiation in a manner dependent upon its metal content. The microwave radiation absorption can be used to generate a measurement of metal content. The measurement, in turn, can be used to calculate at least a portion of the volume and shape of the object under inspection. The measurement can be compared to a plurality of predefined threats. The microwave screening system can be used in combination with other screening technologies, such as NQR-based screening, X-ray transmission based screening, X-ray scattered based screening, or Computed Tomography based screening.
Owner:RAPISCAN SYST INC (US)
System and Method for Imaging and Treatment of Tumorous Tissue in Breasts Using Computed Tomography and Radiotherapy
InactiveUS20080317202A1Inhibition formationMinimize exposureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTumour tissueMuscle tissue
The present invention provides a system 10 for irradiating a breast 20 of a patient 22. The system 10 comprises a gantry 12 rotatable about a horizontal axis 14 and comprising a radiation source 16 for generating a radiation beam 18 and a detector 24 spaced from the radiation source 16, and a barrier 26 disposed between the patient 22 and the gantry 12. The barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow a breast 20 passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18. In some embodiments, the barrier 26 is provided with an opening 30 adapted to allow both the breast 20 and the tissue leading from the breast to axilla and the muscle tissue of the adjacent chest wall passing therethrough to be exposed to the radiation beam 18.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
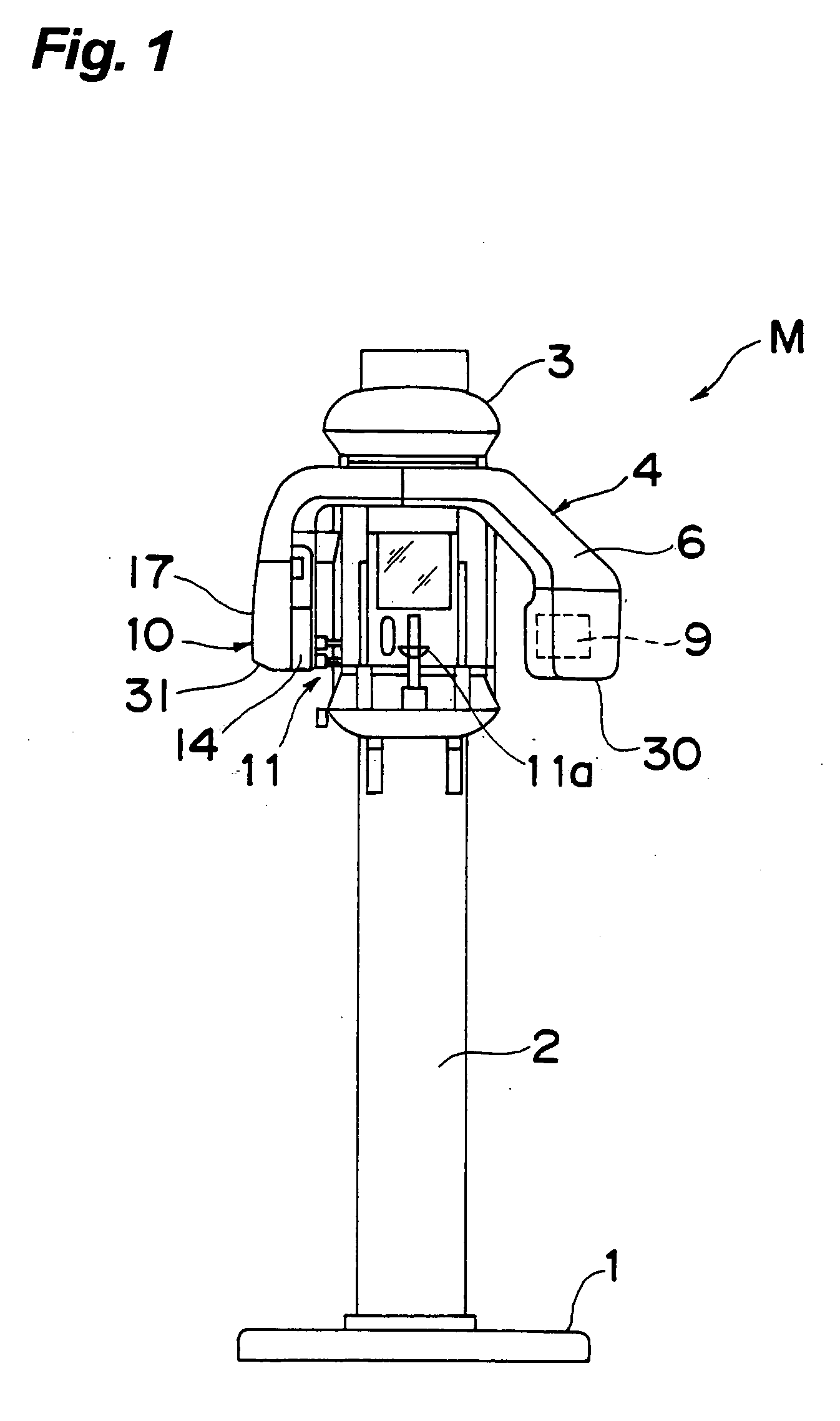
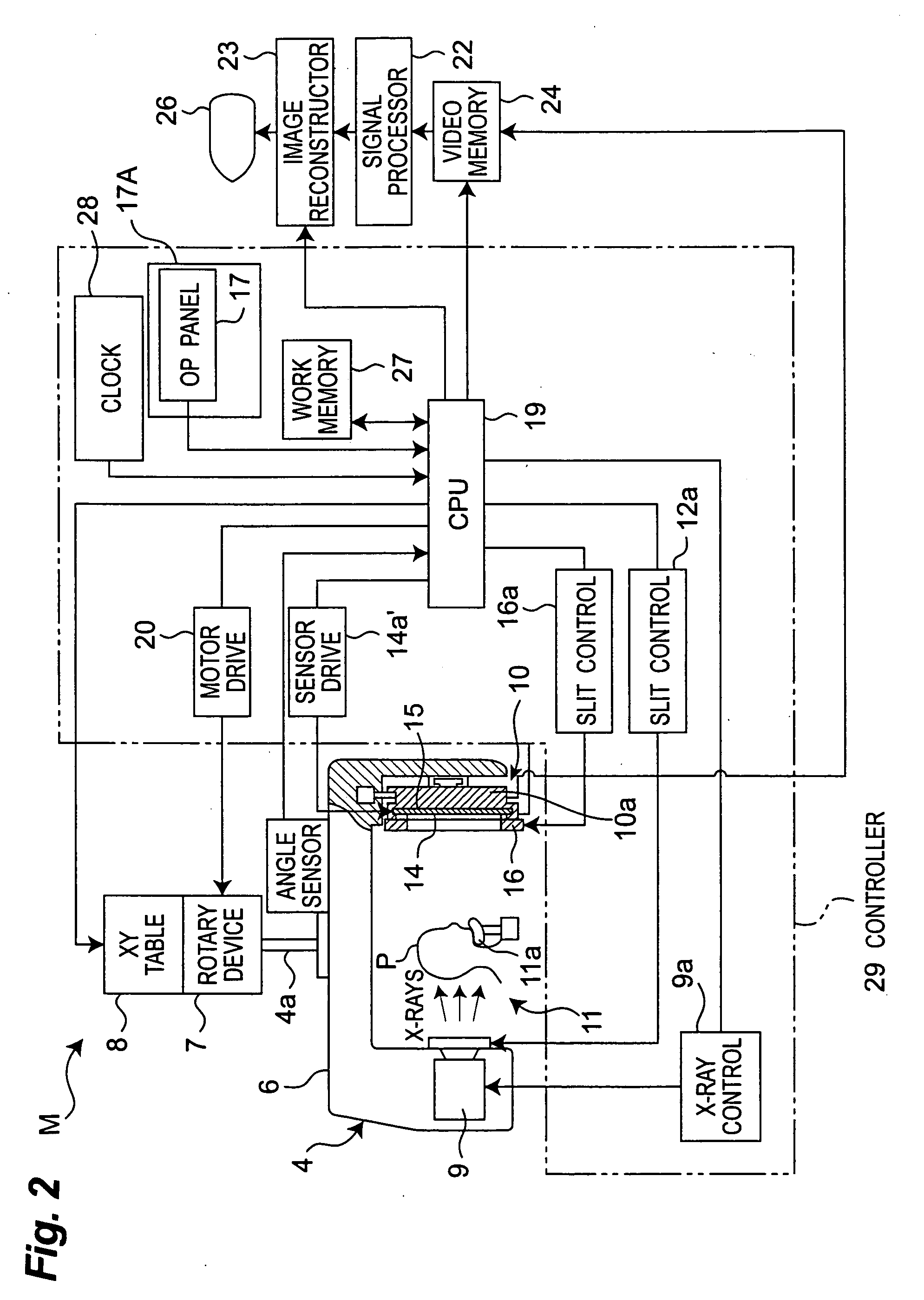
Medical Digital X-Ray Imaging Apparatus and Medical Digital X-Ray Sensor
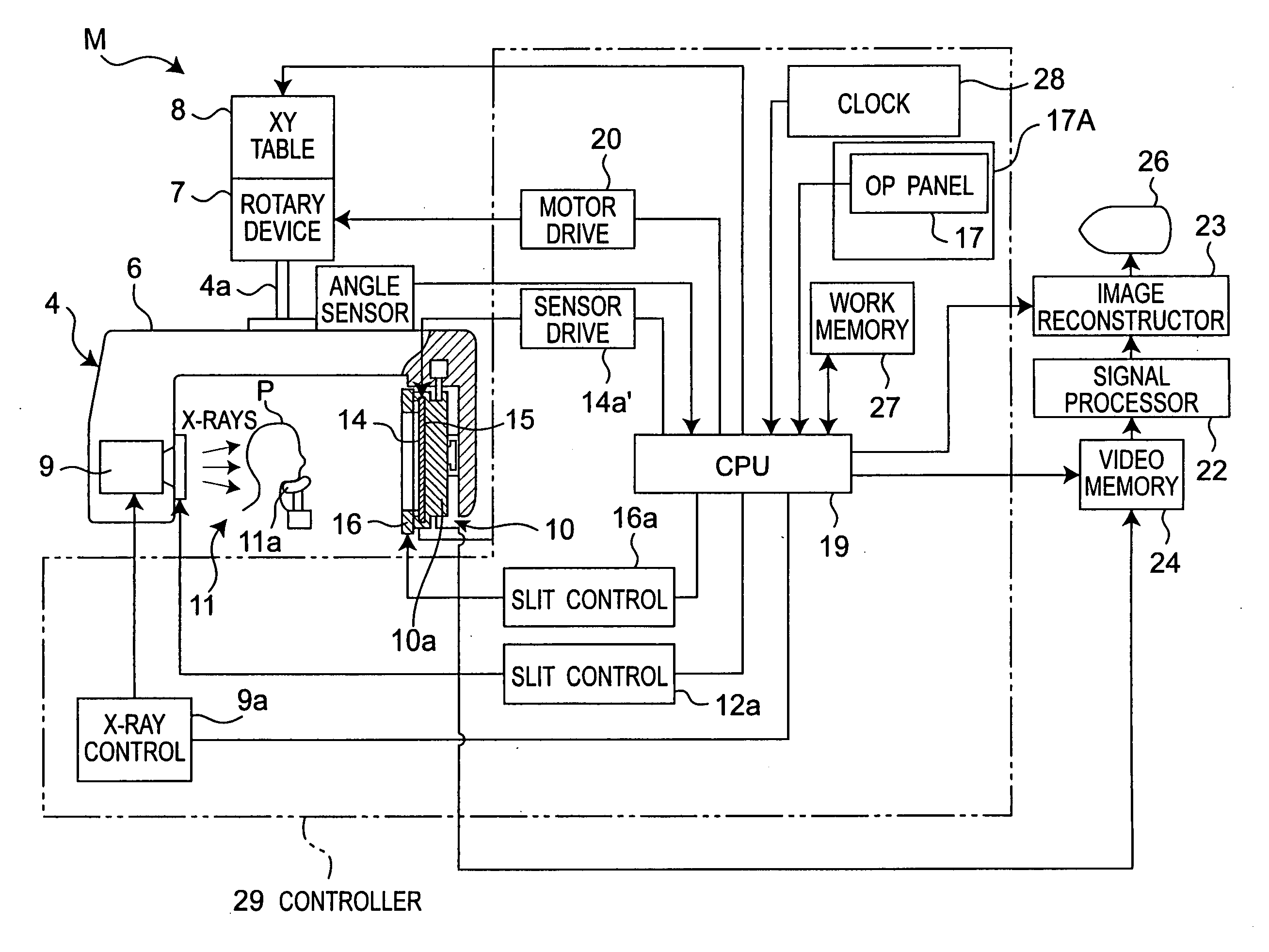
ActiveUS20090168966A1Increase data capacityMany timesTomographyDiaphragms for radiation diagnosticsX-rayComputing tomography
In a medical digital X-ray imaging apparatus having a plurality of imaging modes including computed tomography mode, a supporter supports an X-ray source and a digital X-ray sensor having a two-dimensional detection plane for detecting X-rays, while interposing an object between them. An image reconstructor acquires data from the digital X-ray sensor and reconstructs an image based on the acquired data. An operator selects one of a first imaging mode and a second imaging mode. The second imaging mode has an irradiation field different from the first imaging mode and has an area to be read in the digital X-ray sensor smaller than that in the first imaging mode.
Owner:MORITA MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com