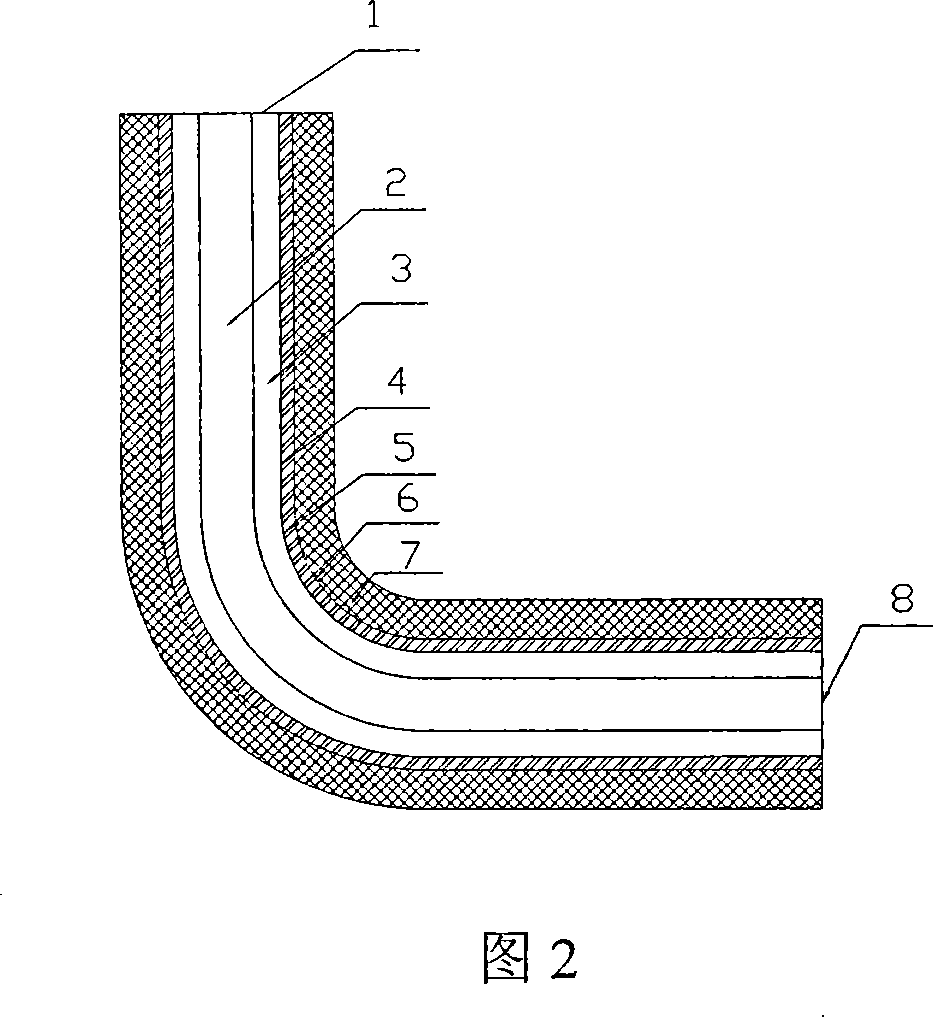
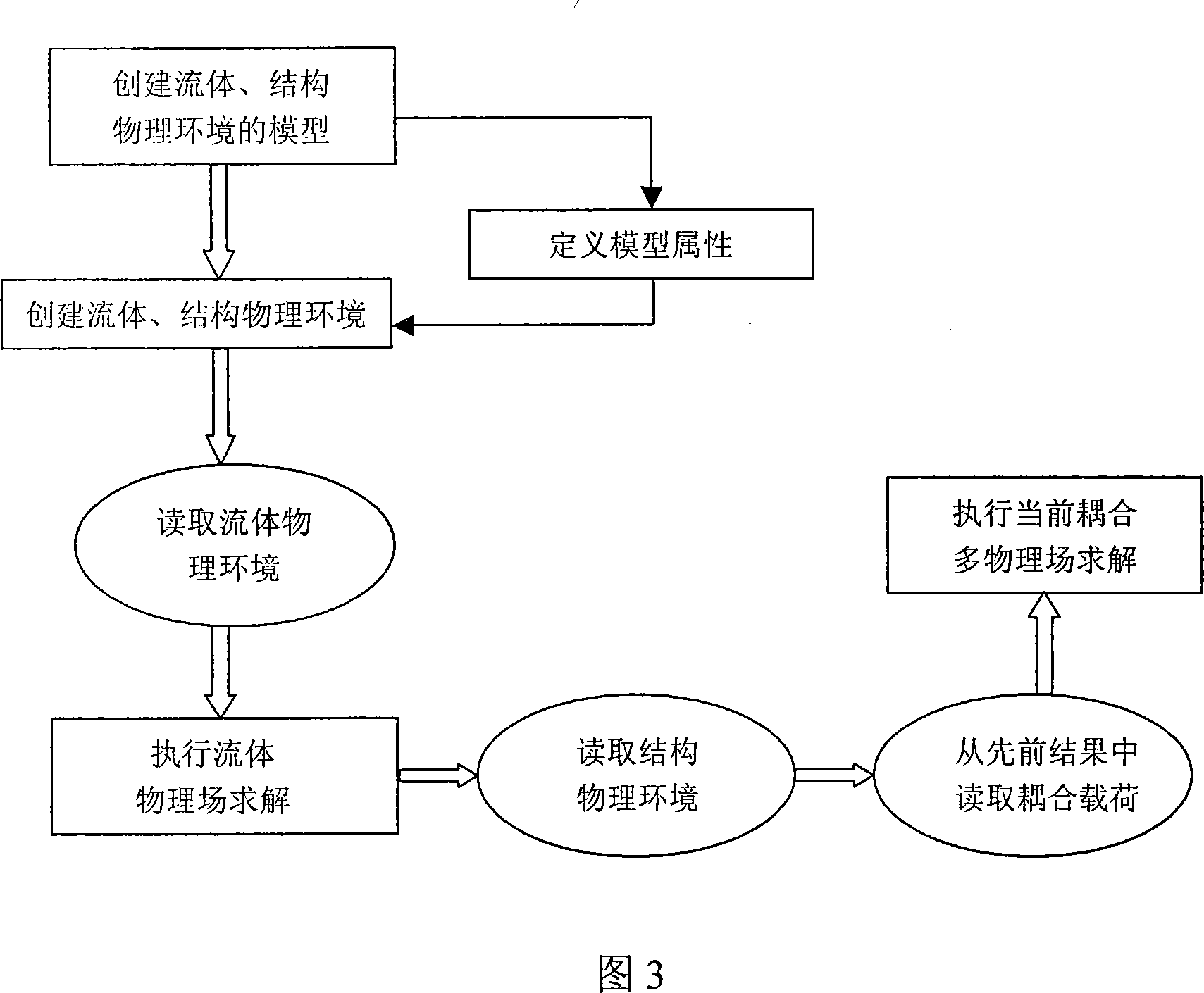
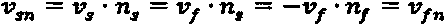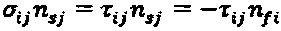Patents
Literature
302 results about "Fluid–structure interaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluid–structure interaction (FSI) is the interaction of some movable or deformable structure with an internal or surrounding fluid flow. Fluid–structure interactions can be stable or oscillatory. In oscillatory interactions, the strain induced in the solid structure causes it to move such that the source of strain is reduced, and the structure returns to its former state only for the process to repeat.
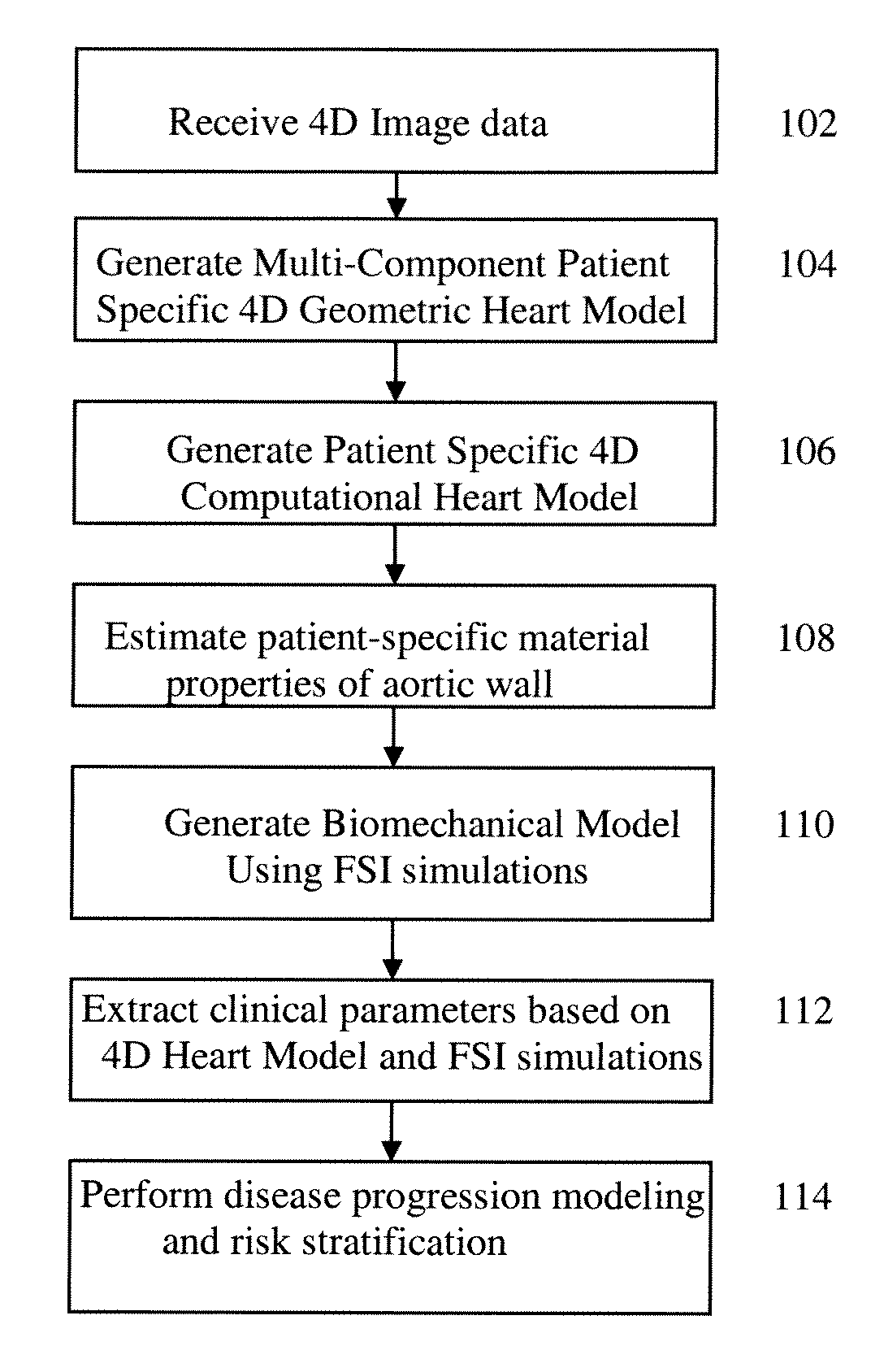
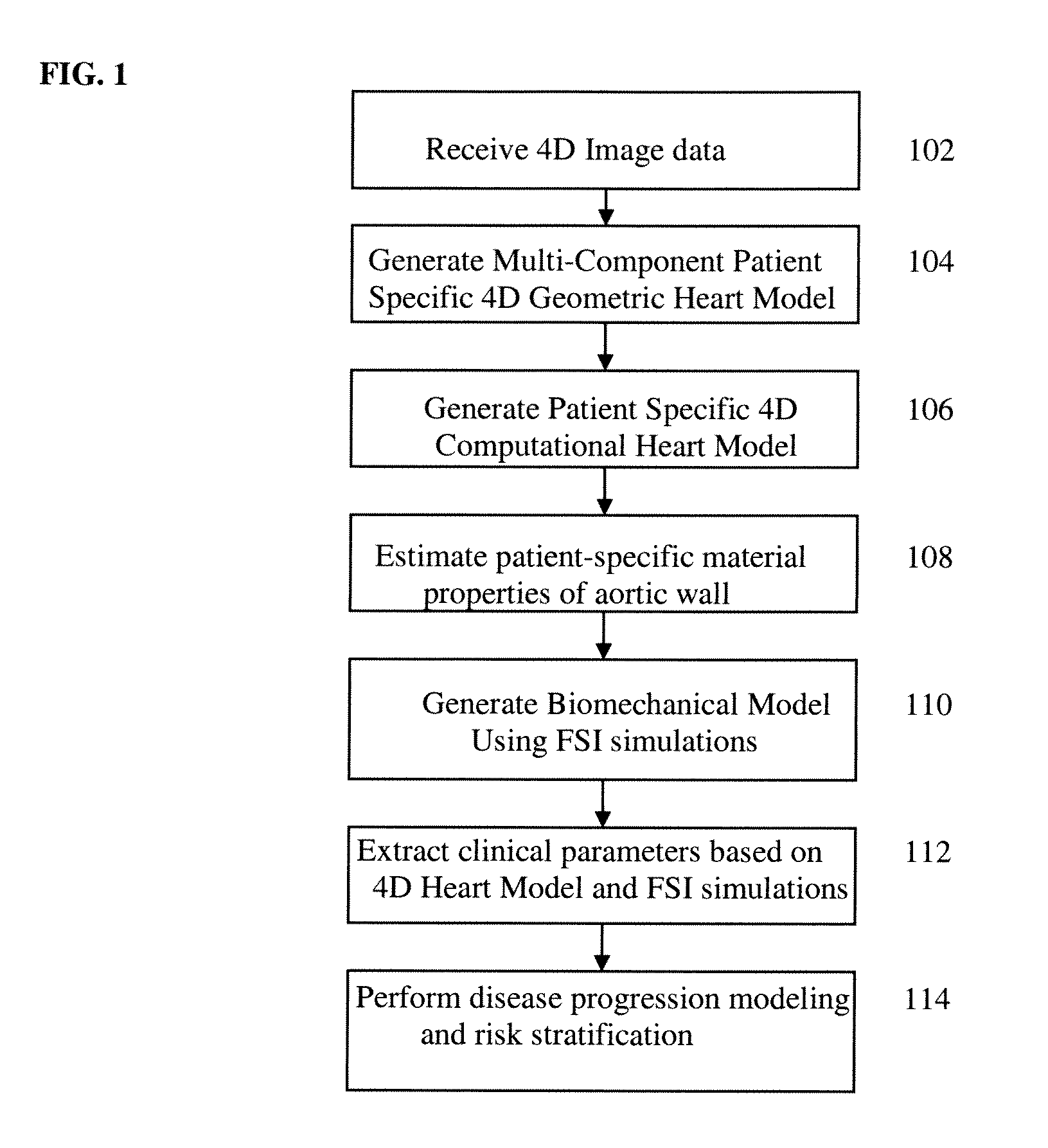
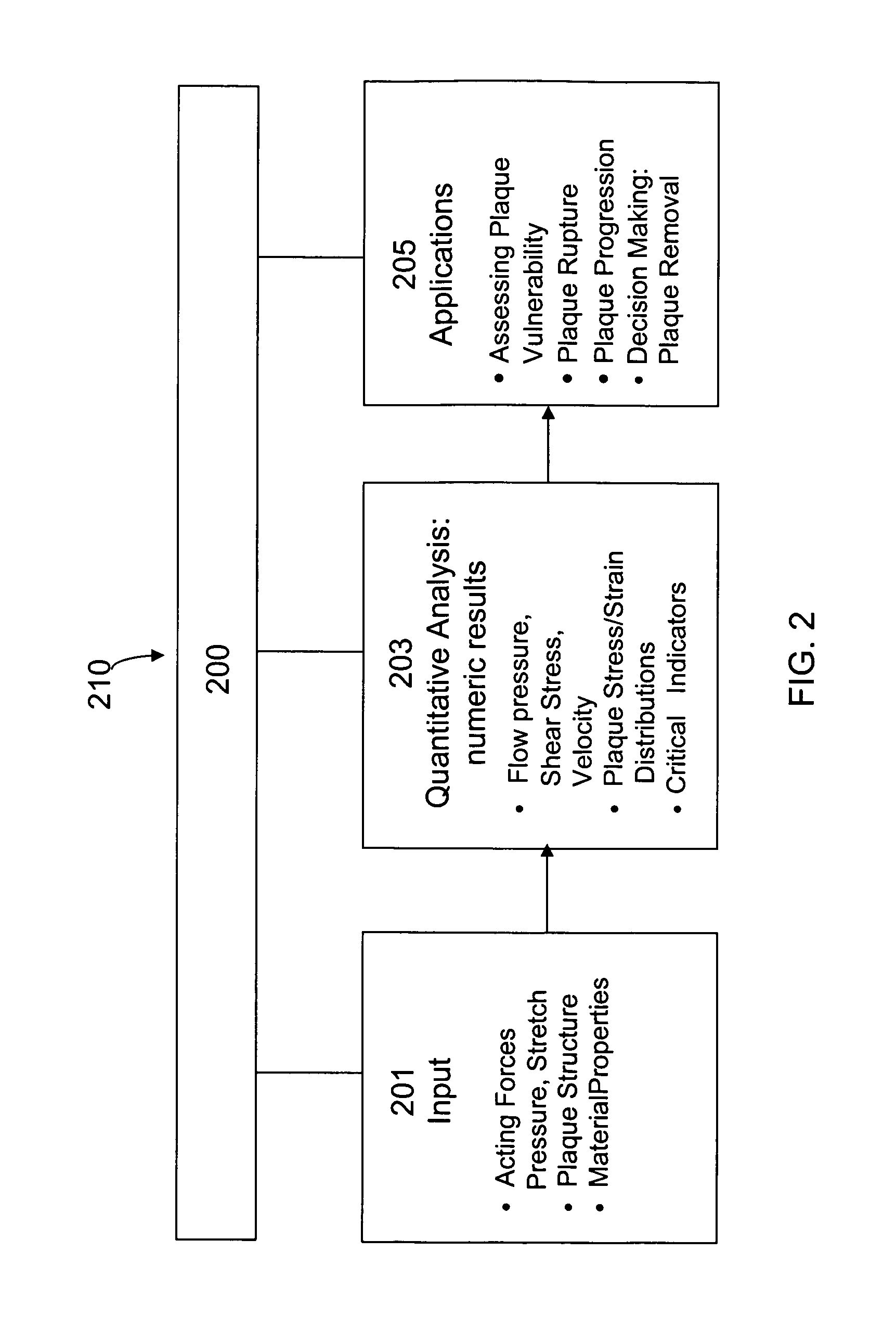
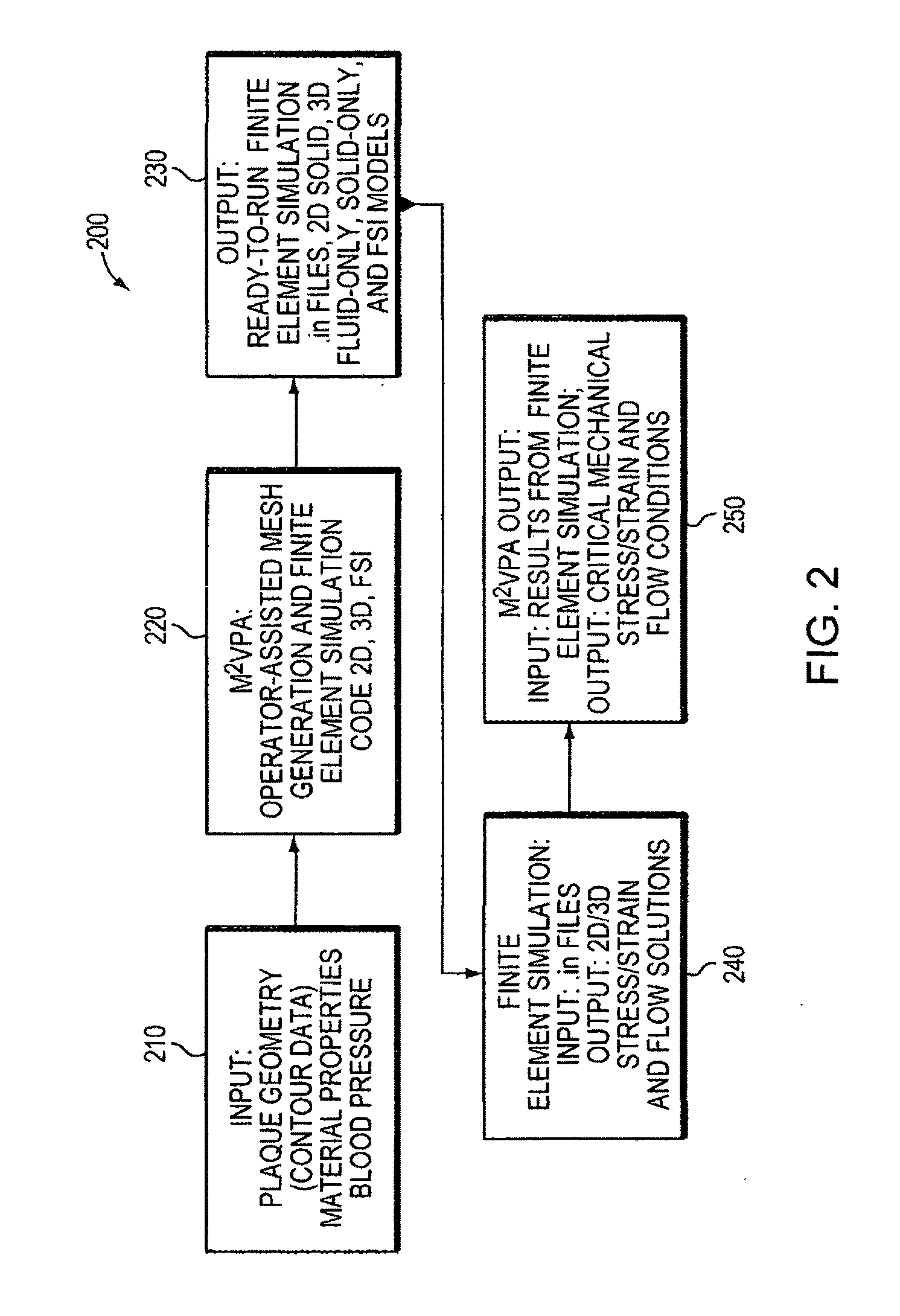
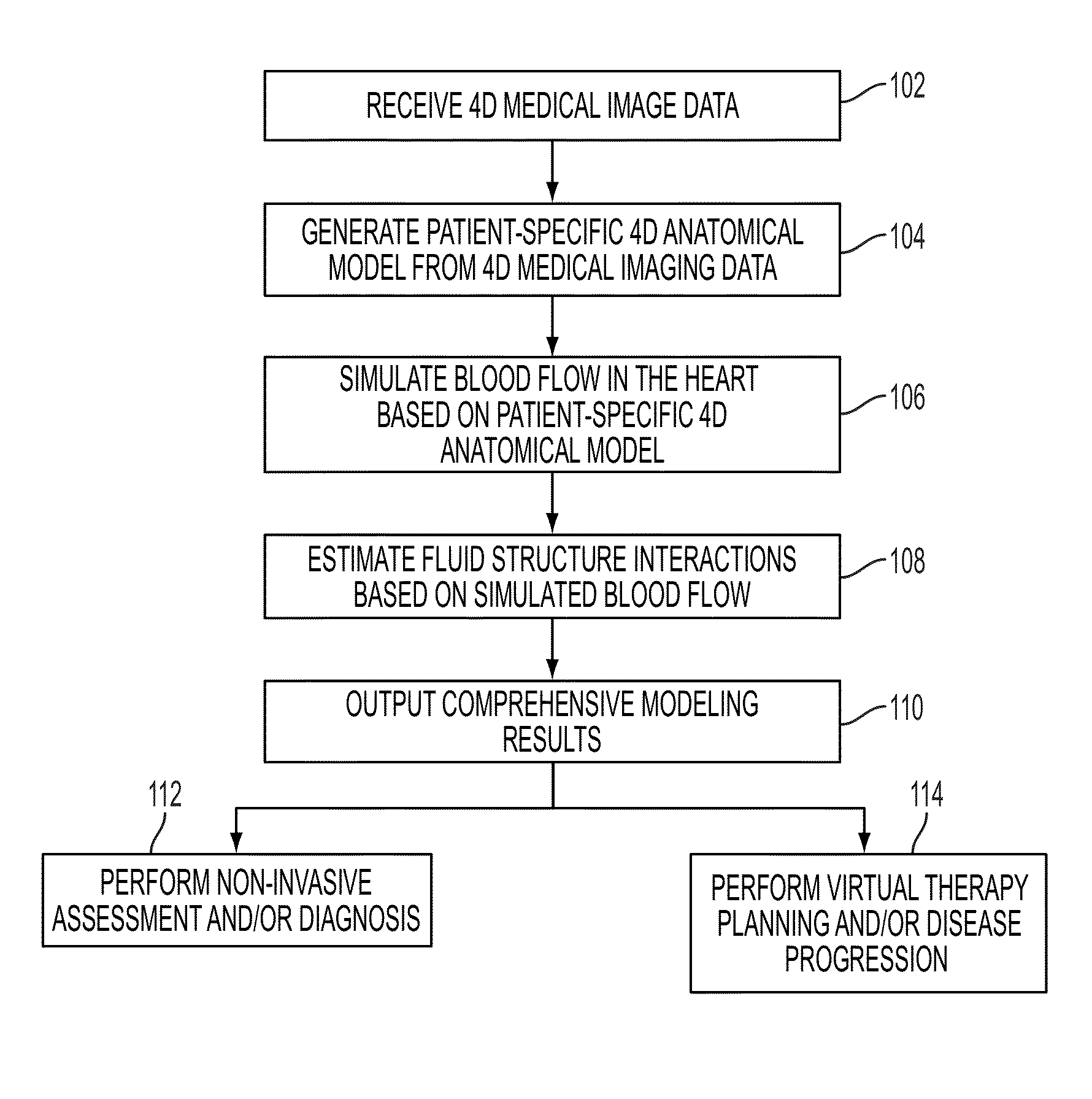
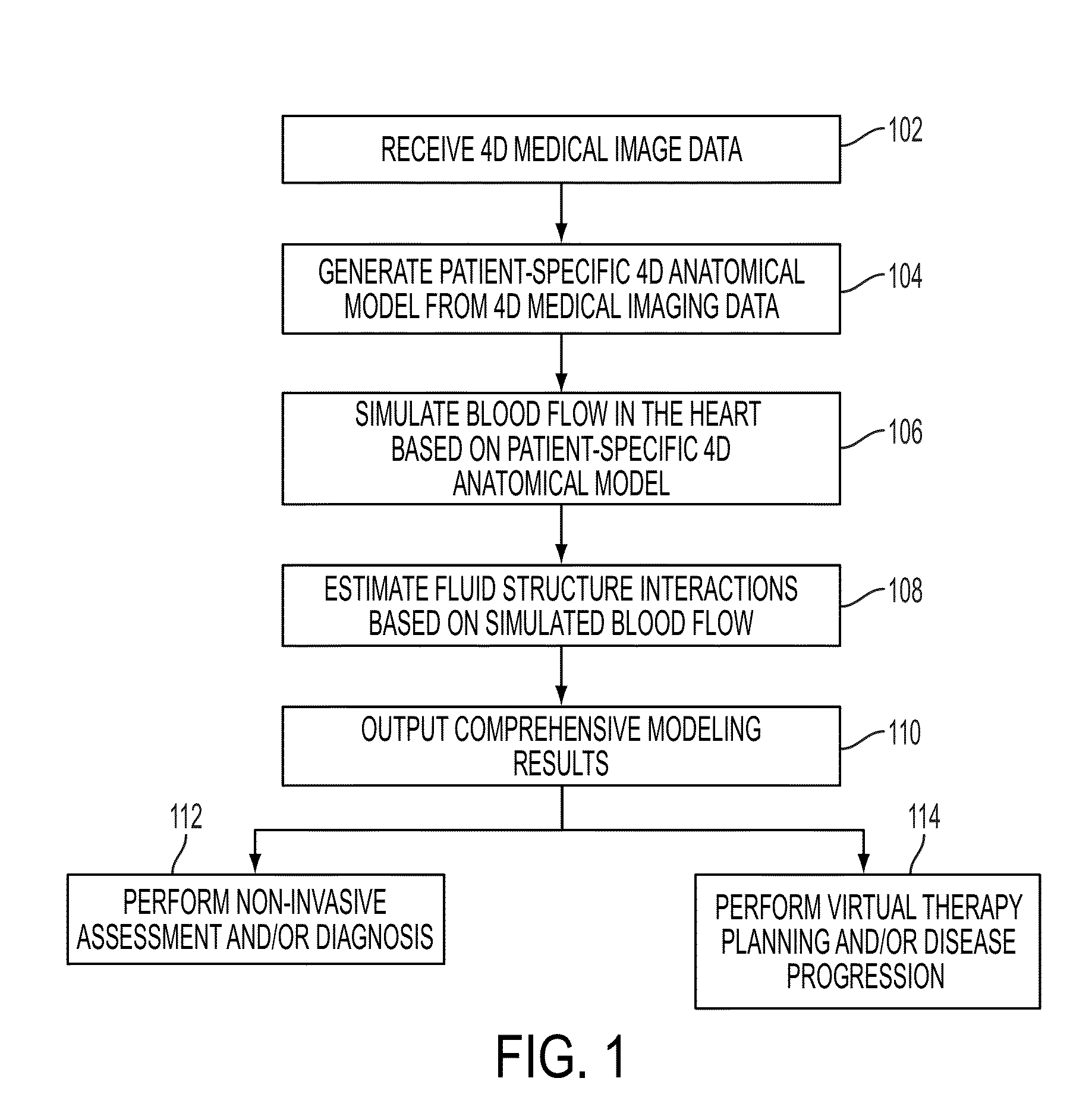
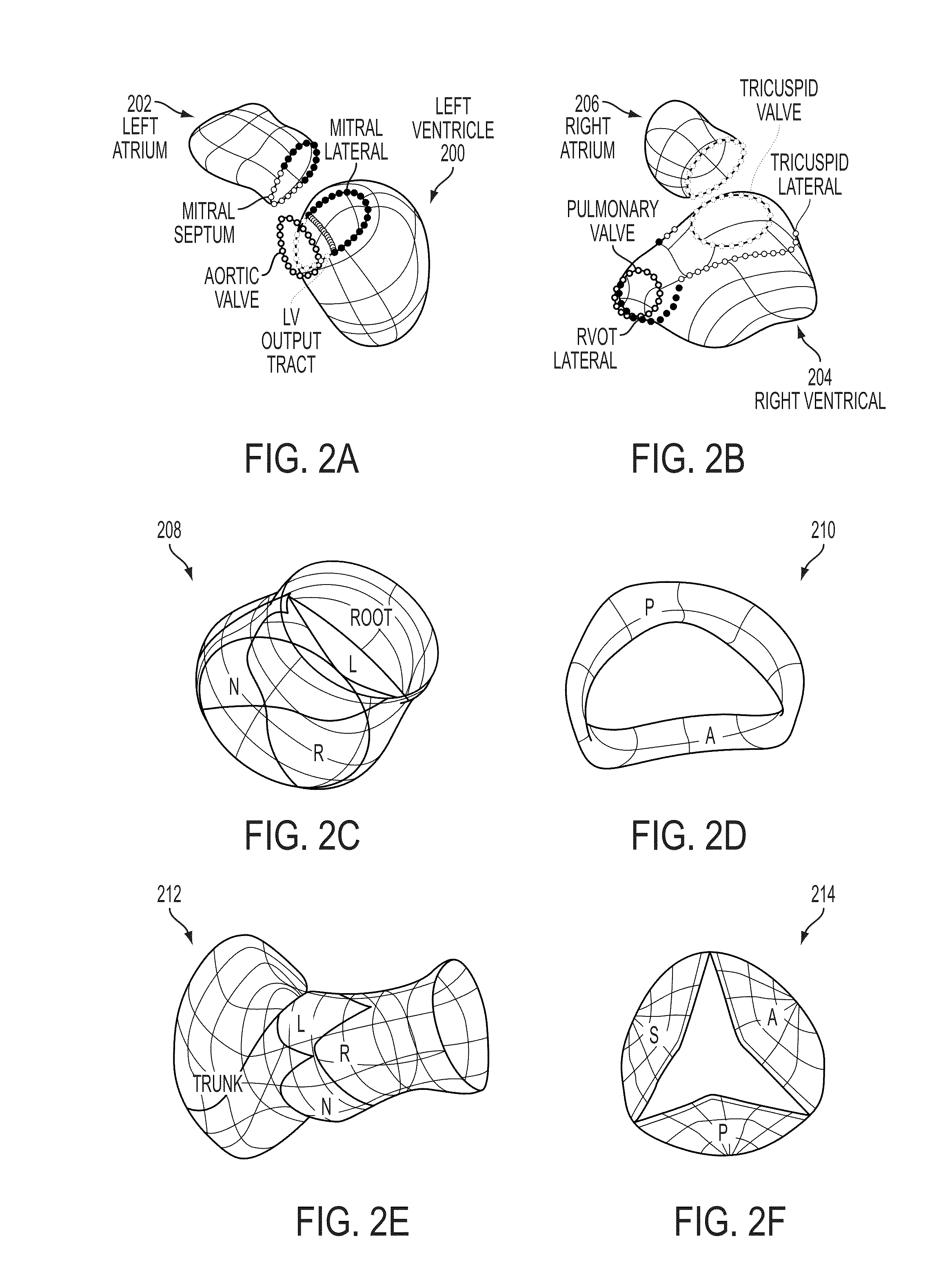
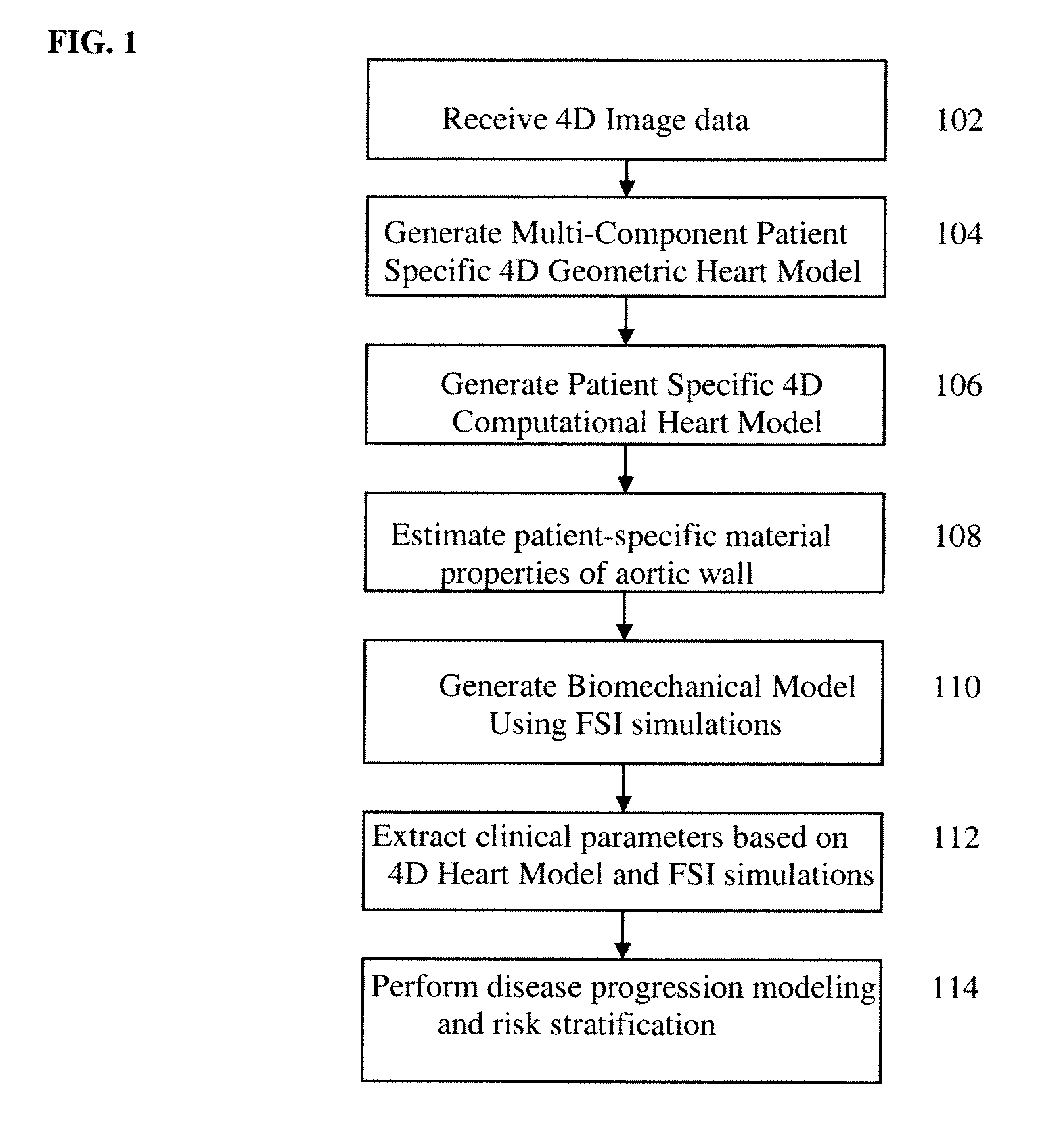
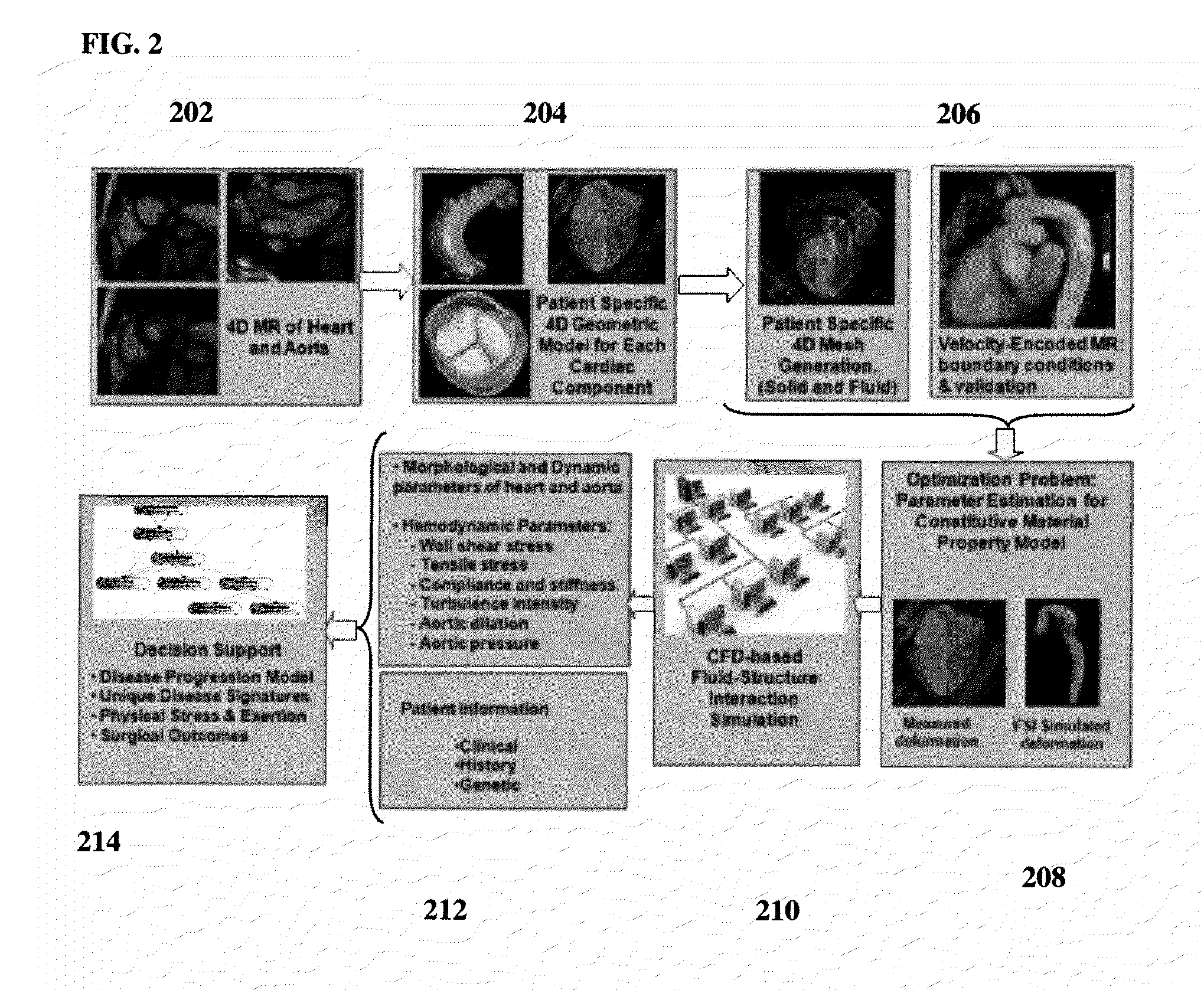
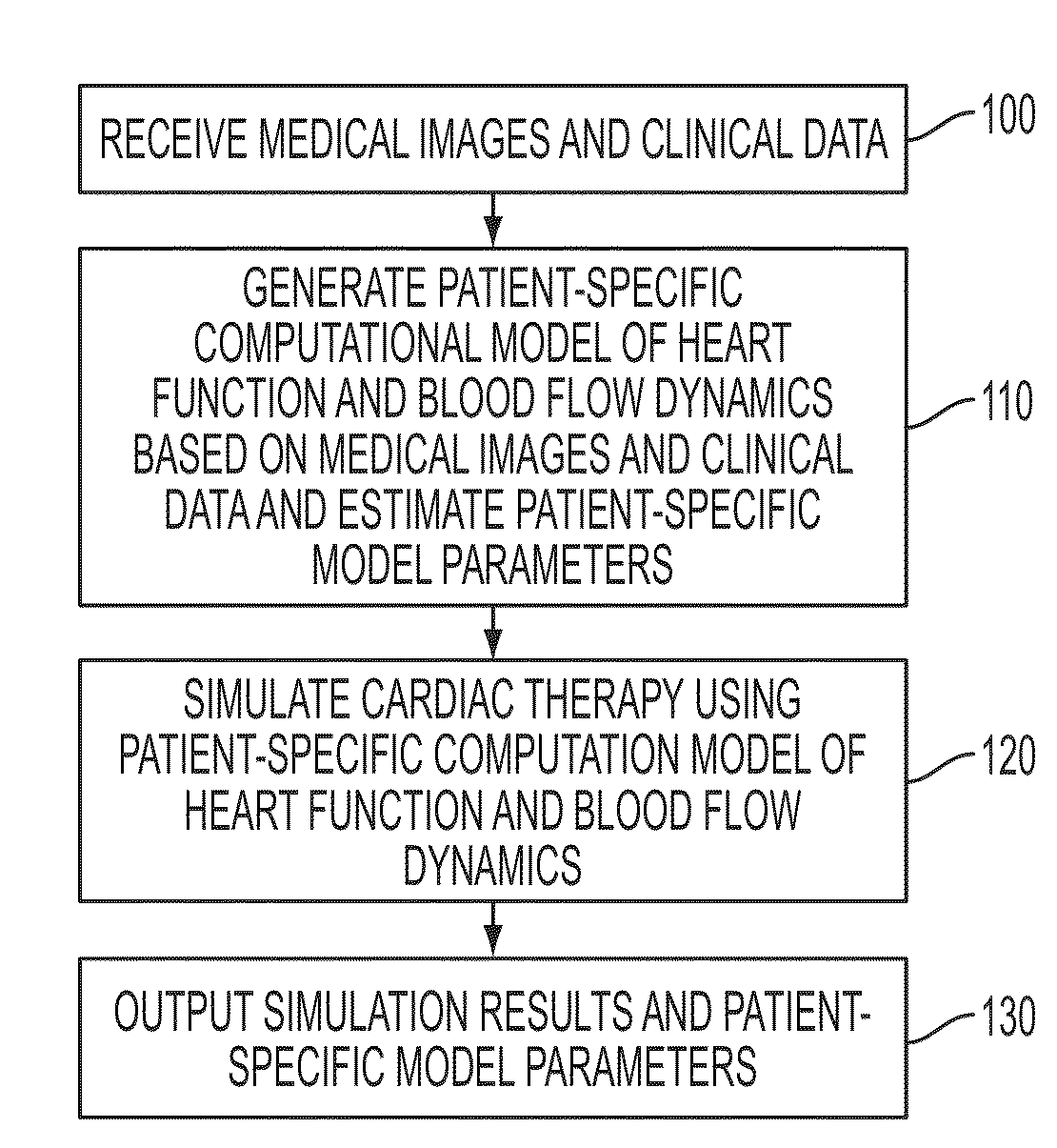
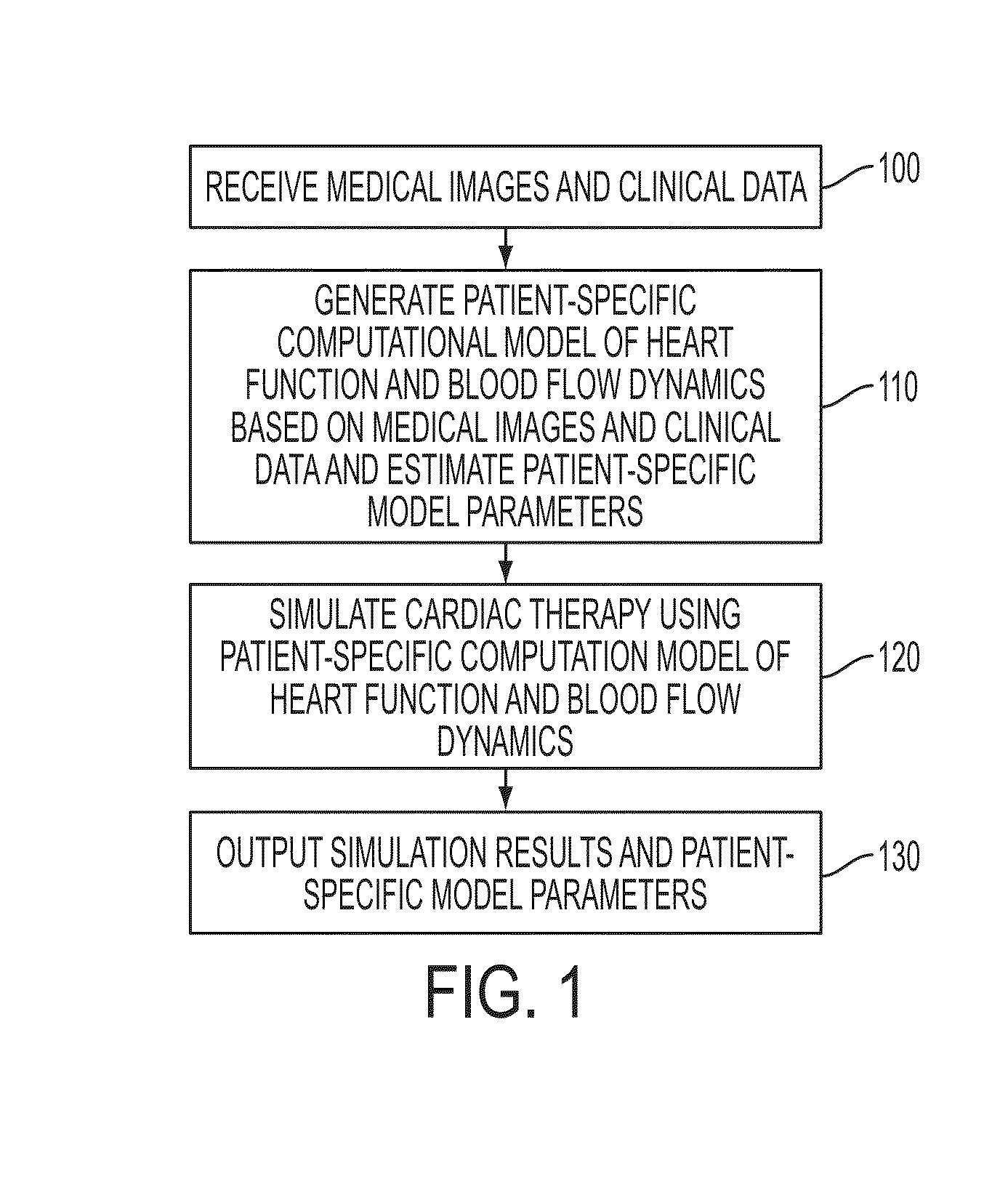
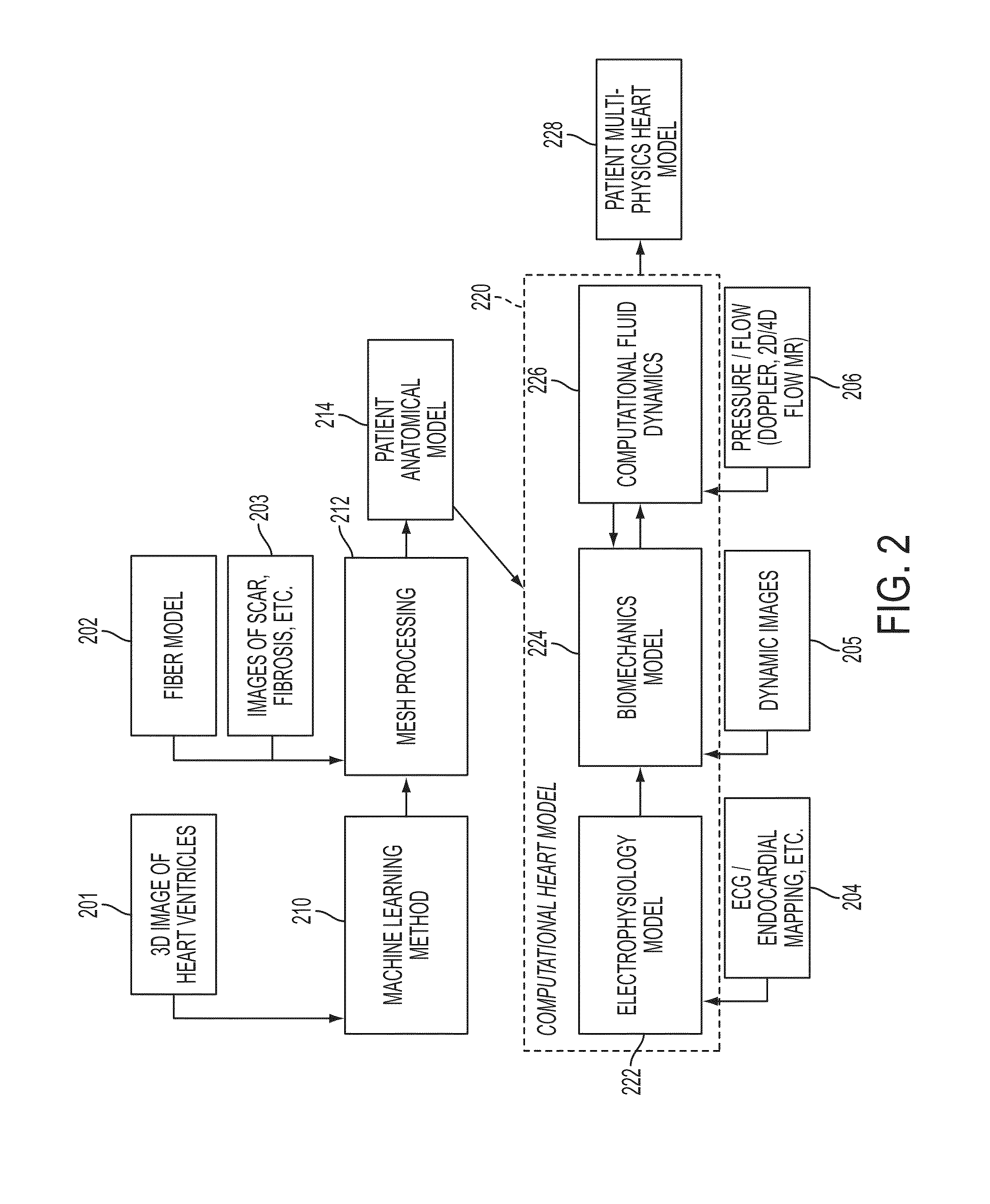
Method and System for Computational Modeling of the Aorta and Heart
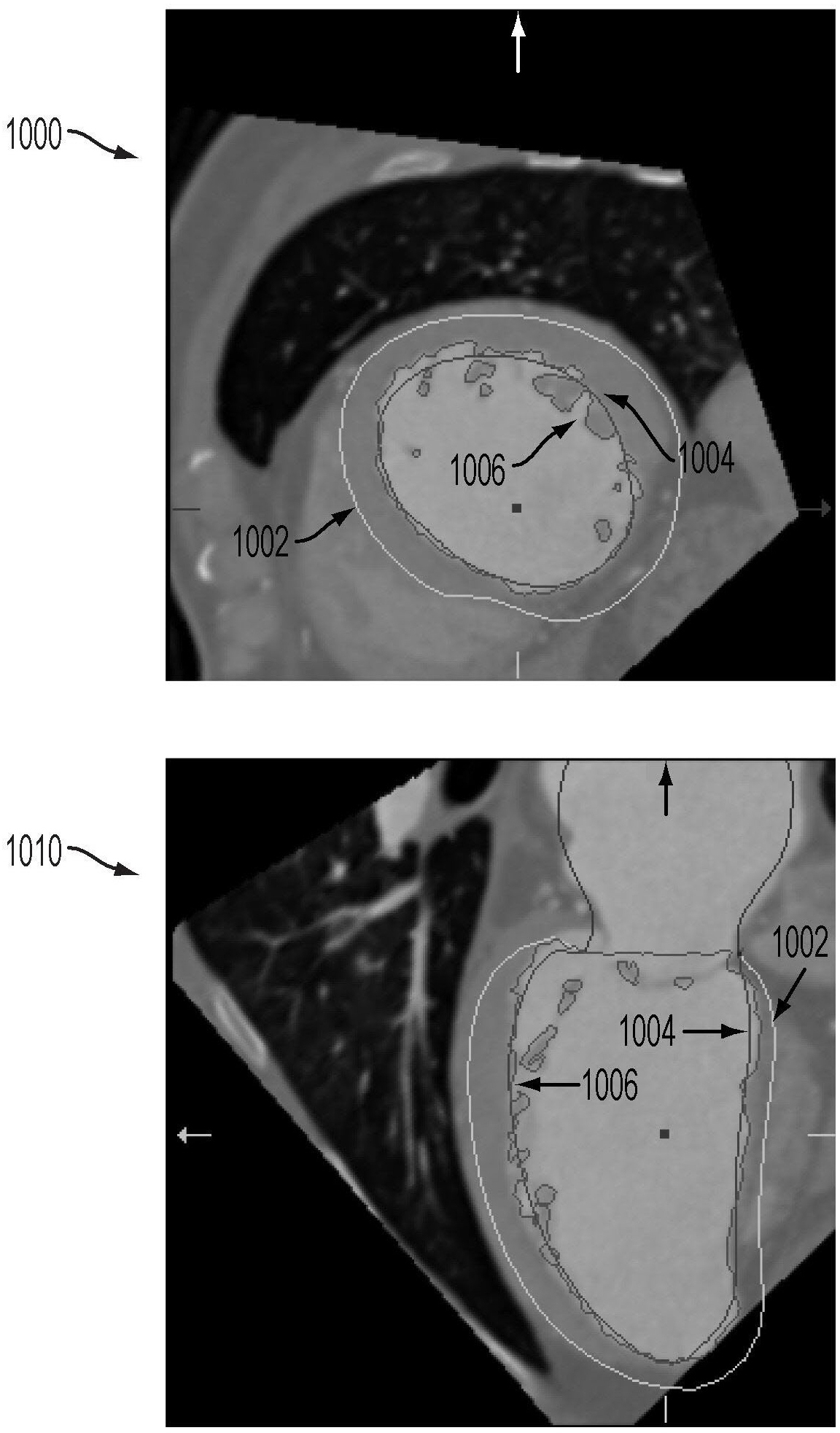
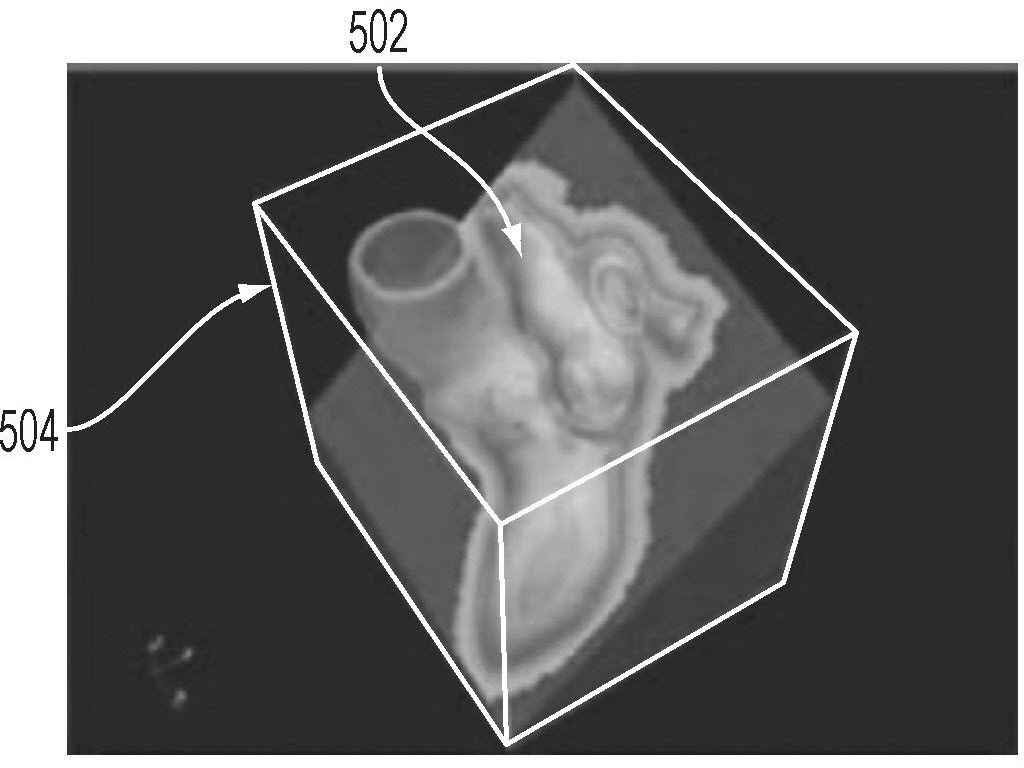
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
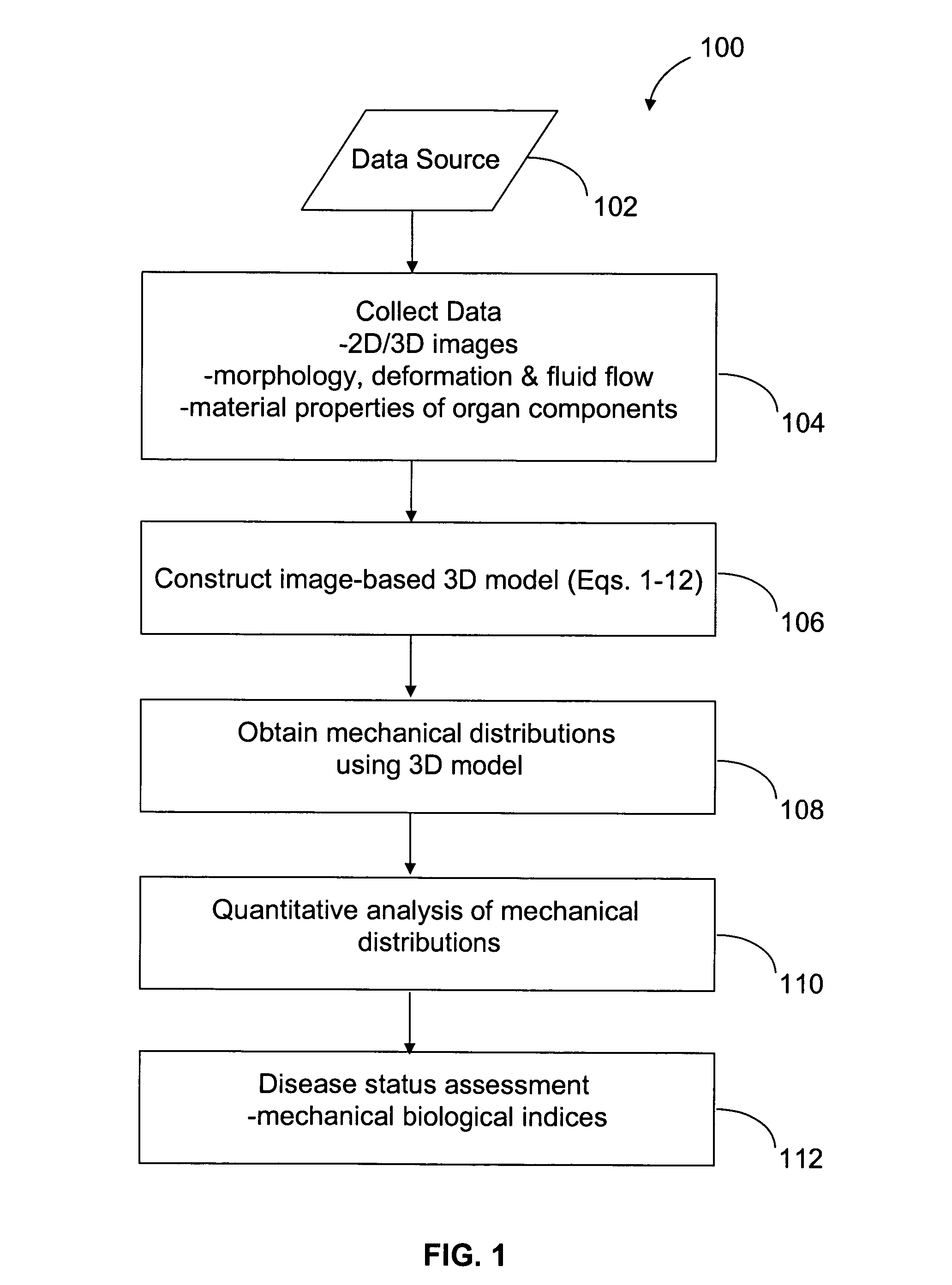
Image-based computational mechanical analysis and indexing for cardiovascular diseases
ActiveUS7751984B2Accurate modelingMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesOrgan ModelMedicine
A method and a computer system, for providing an assessment for disease status of a disease, such as a cardiovascular disease, employ construction of image-based 3D computational model of an organ representative of the disease status; computationally obtaining a certain mechanical distribution using the 3D-organ model; and computational, quantitative analysis of the mechanical distribution to provide an assessment for disease status of a disease. The image-based 3D computational model includes a fluid-structure interaction and multiple components within the organ.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
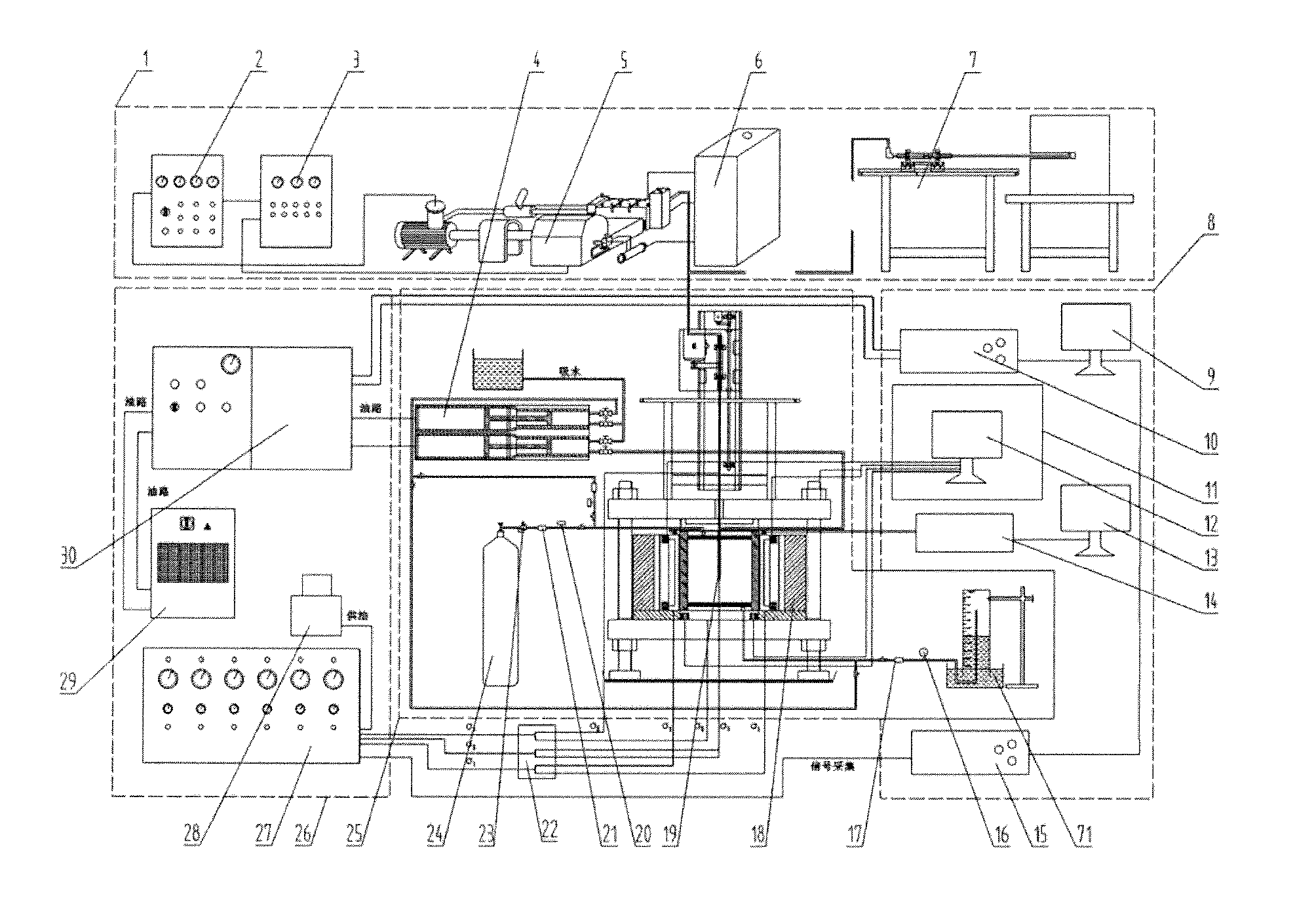
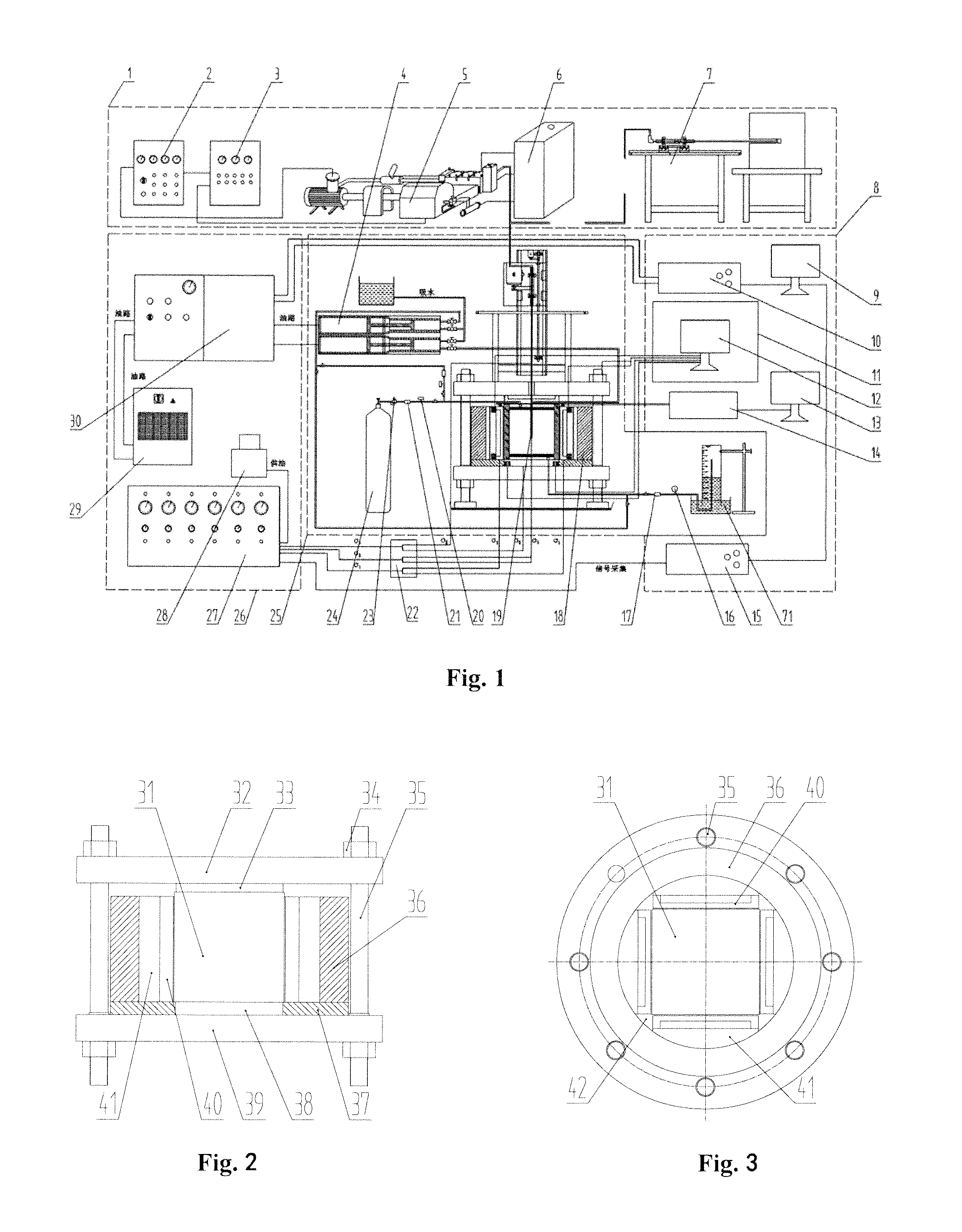
Integrated experimental system of hydrofracturing, water jet slotting, seepage and gas displacement under true triaxial stress
ActiveUS20170003263A1Good effectImprove securityEarth material testingMultiple fluid pressure valves simultaneous measurementMonitoring systemHydraulic fracturing
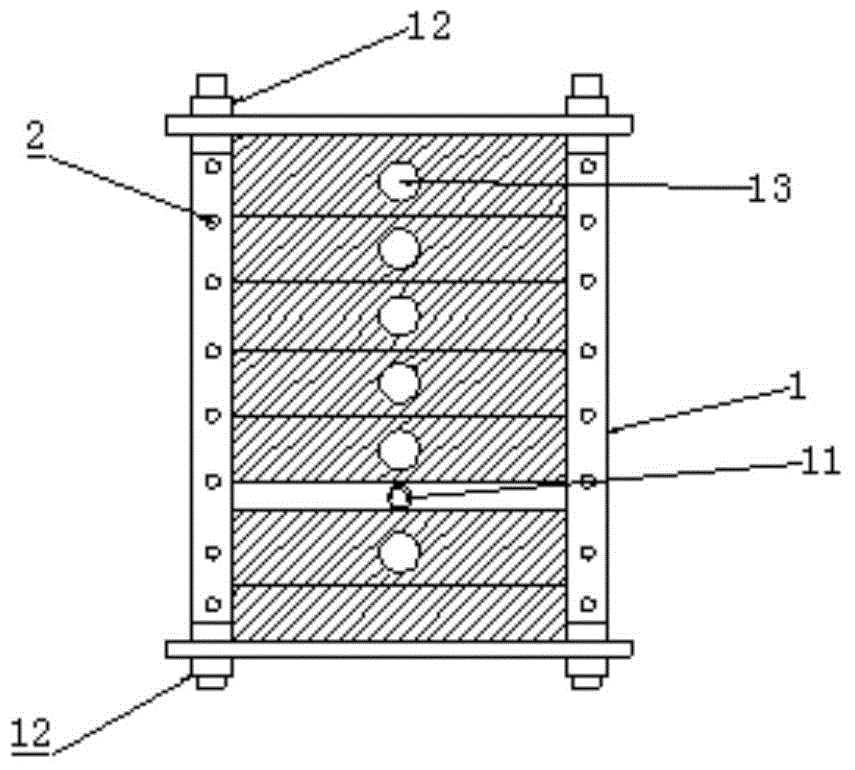
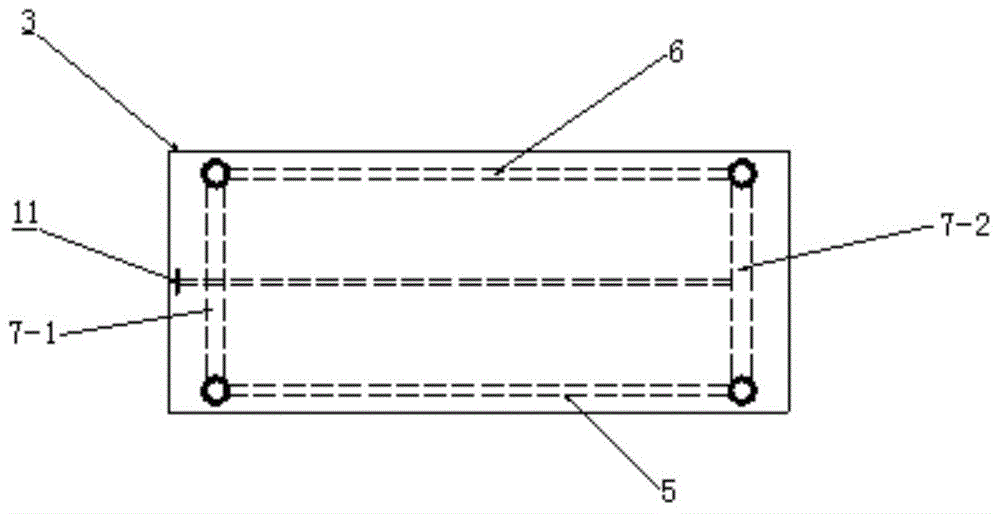
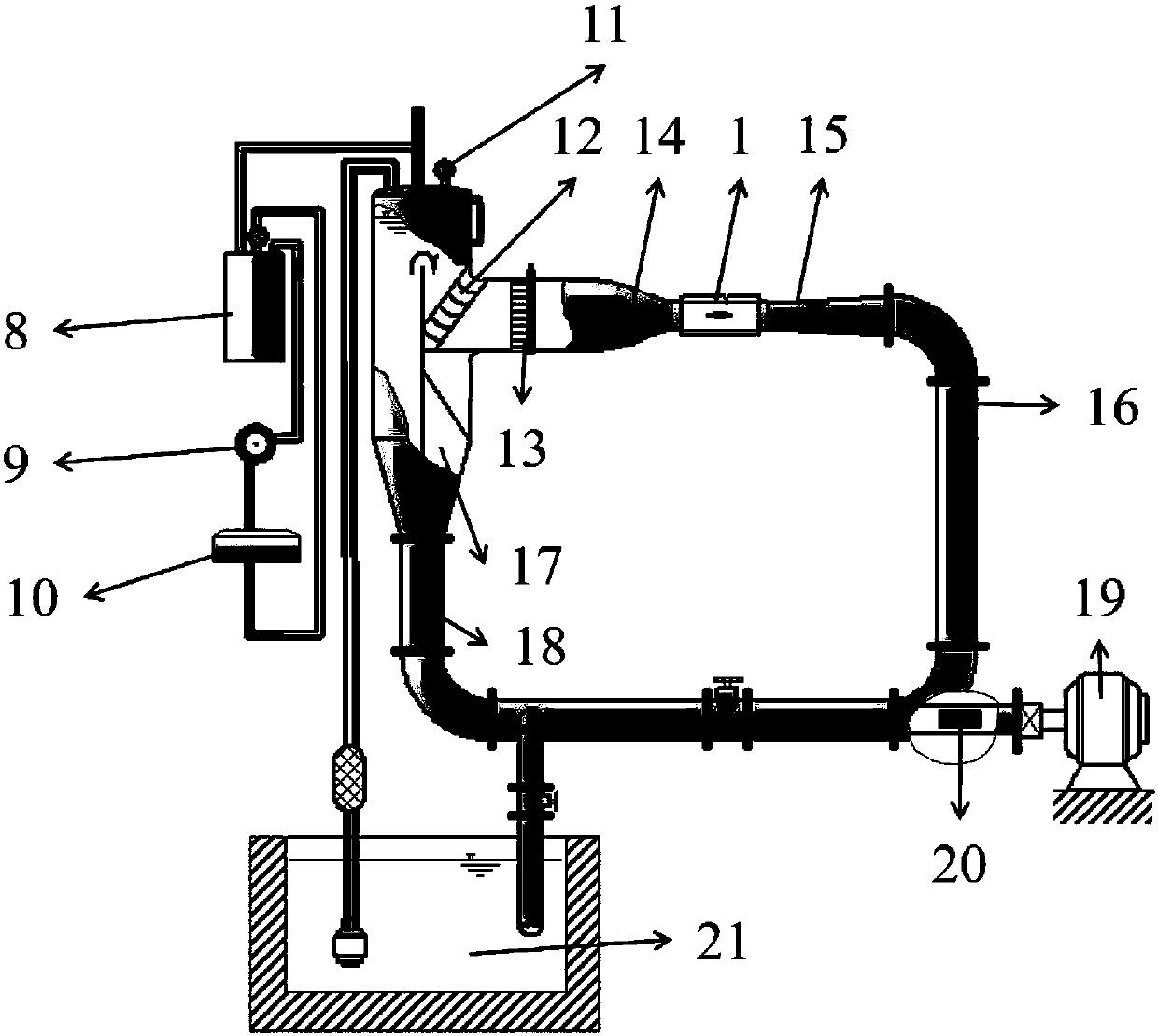
This invention relates to the coal mining field, specifically, to an integrated experimental system of hydrofracturing, water jet slotting, seepage and gas displacement under true triaxial stress. This invention consists of true triaxial stress loading experimental framework, a loading system and a monitoring system. Under true triaxial stress, experiments can be conducted with sample size as large as of 500 mm×500 mm×500 mm. The hydrofracturing experiment can be controlled by as many as 5 independent boreholes at the same time. The borehole water pressure in hydraulic fracturing can reach 63 MPa. Experiments of seepage and fluid-structure interaction with high seepage pressure can be achieved with sample dimension as large as 400 mm×400 mm×400 mm. Mine-used experimental bench of high pressure pump with rated flow of 70 L / min and maximum water pressure of 70 MPa can be used to drill borehole and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method and System for Advanced Measurements Computation and Therapy Planning from Medical Data and Images Using a Multi-Physics Fluid-Solid Heart Model
ActiveUS20130197884A1Exact reproductionMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputational modelPatient data
Method and system for computation of advanced heart measurements from medical images and data; and therapy planning using a patient-specific multi-physics fluid-solid heart model is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image patient data. A patient-specific computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and patient-specific clinical data. The computational model includes biomechanics, electrophysiology and hemodynamics. To generate the patient-specific computational heart model, initial patient-specific parameters of an electrophysiology model, initial patient-specific parameters of a biomechanics model, and initial patient-specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) boundary conditions are marginally estimated. A coupled fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulation is performed using the initial patient-specific parameters, and the initial patient-specific parameters are refined based on the coupled FSI simulation. The estimated model parameters then constitute new advanced measurements that can be used for decision making.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
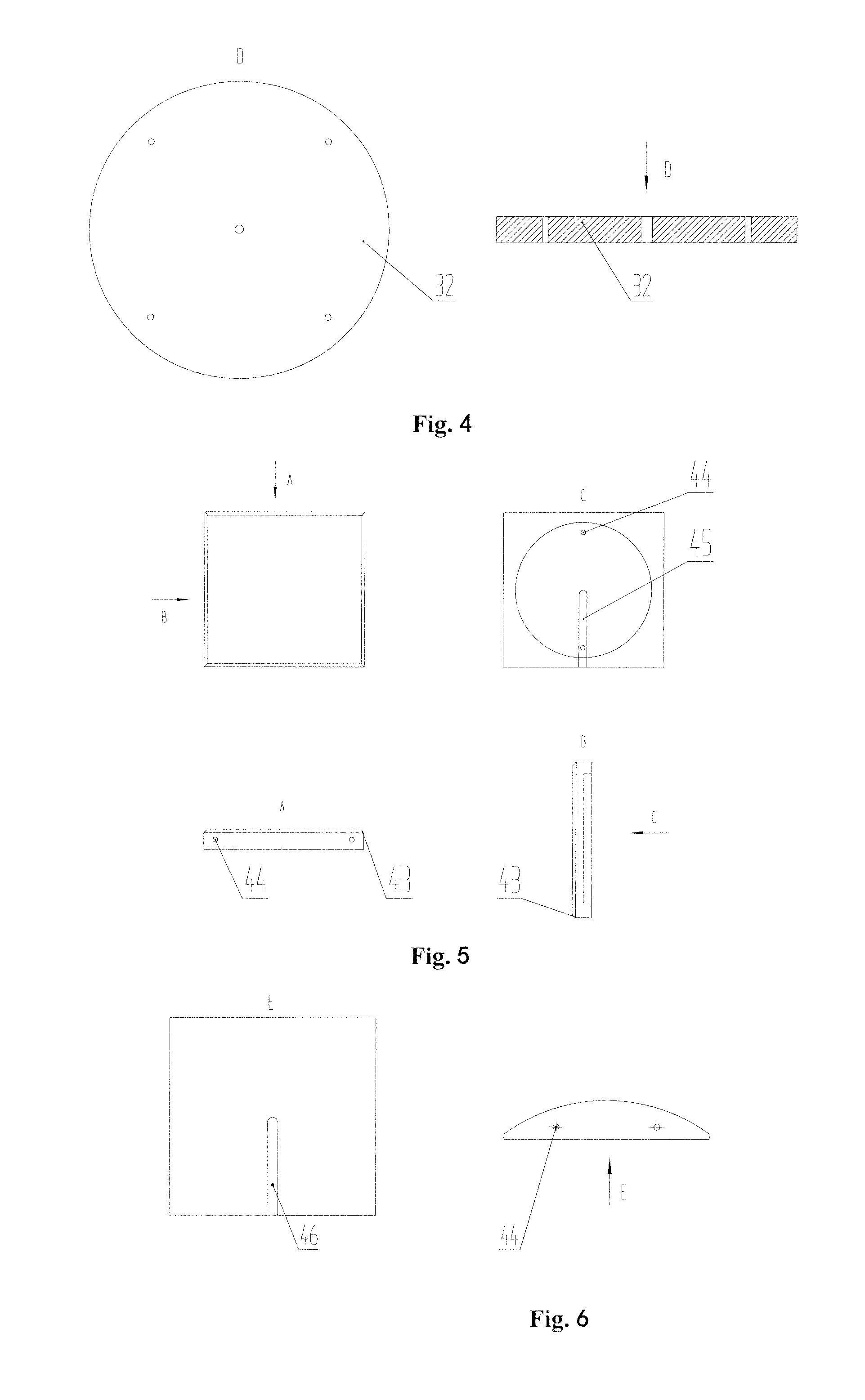
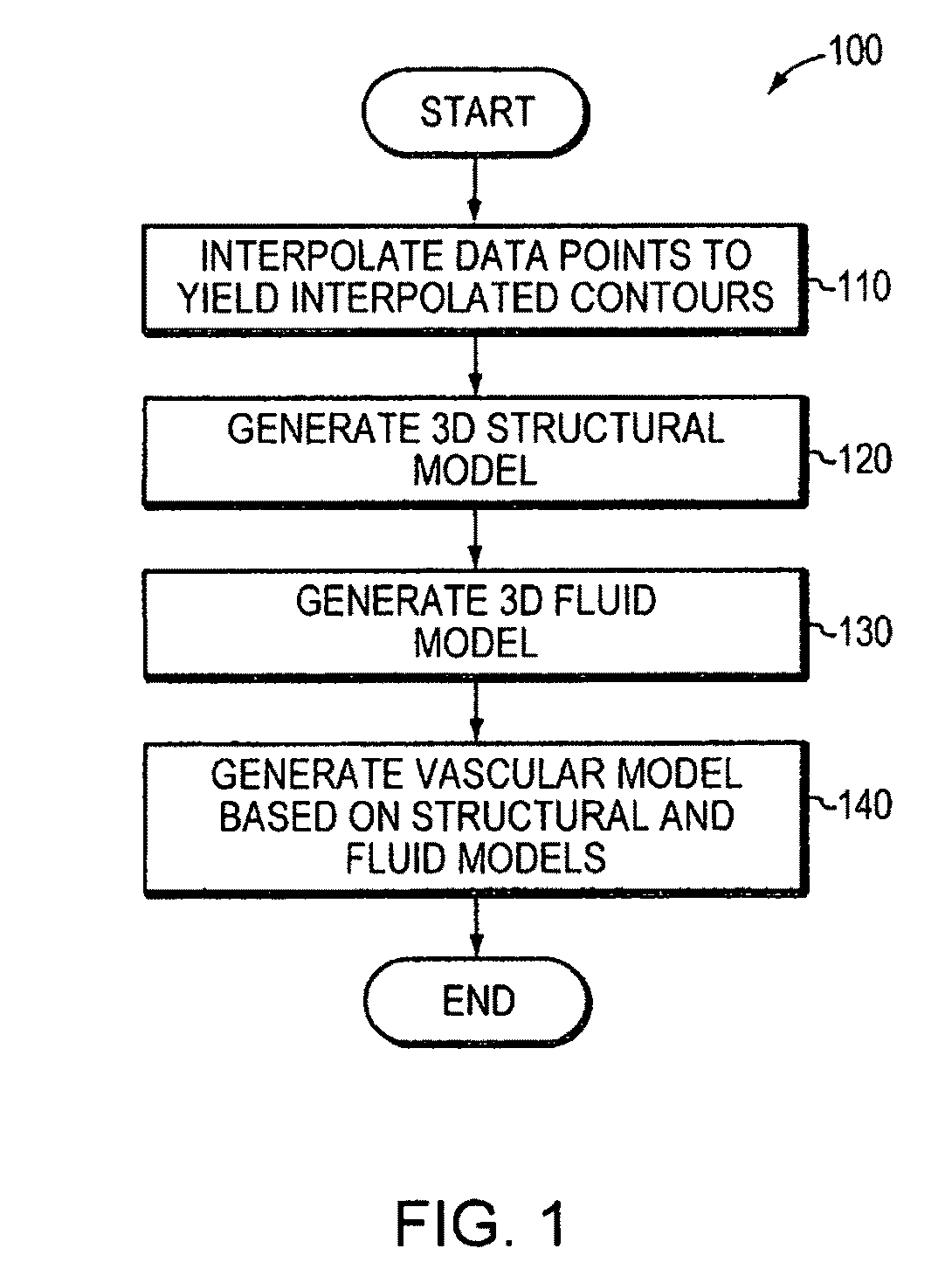
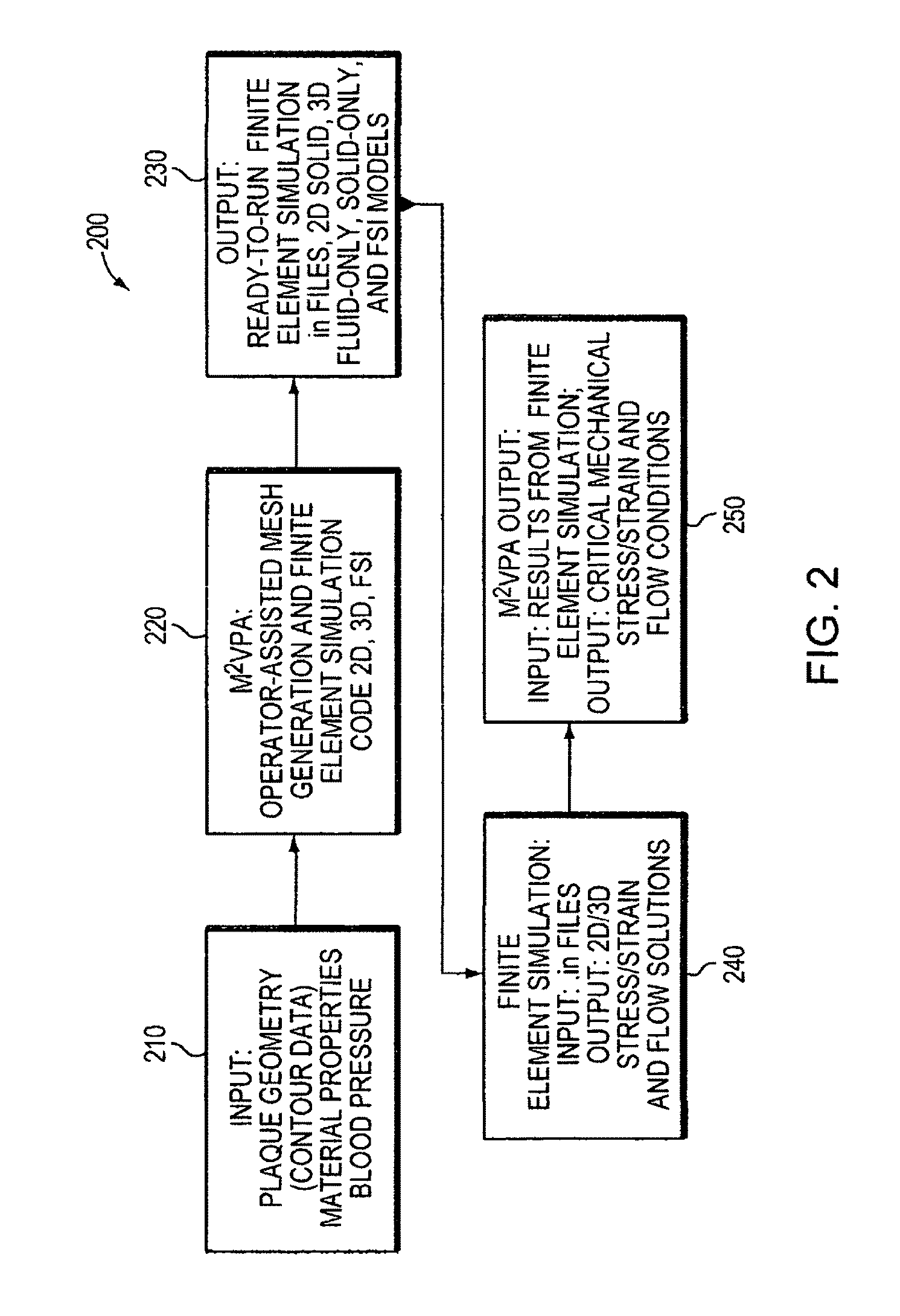
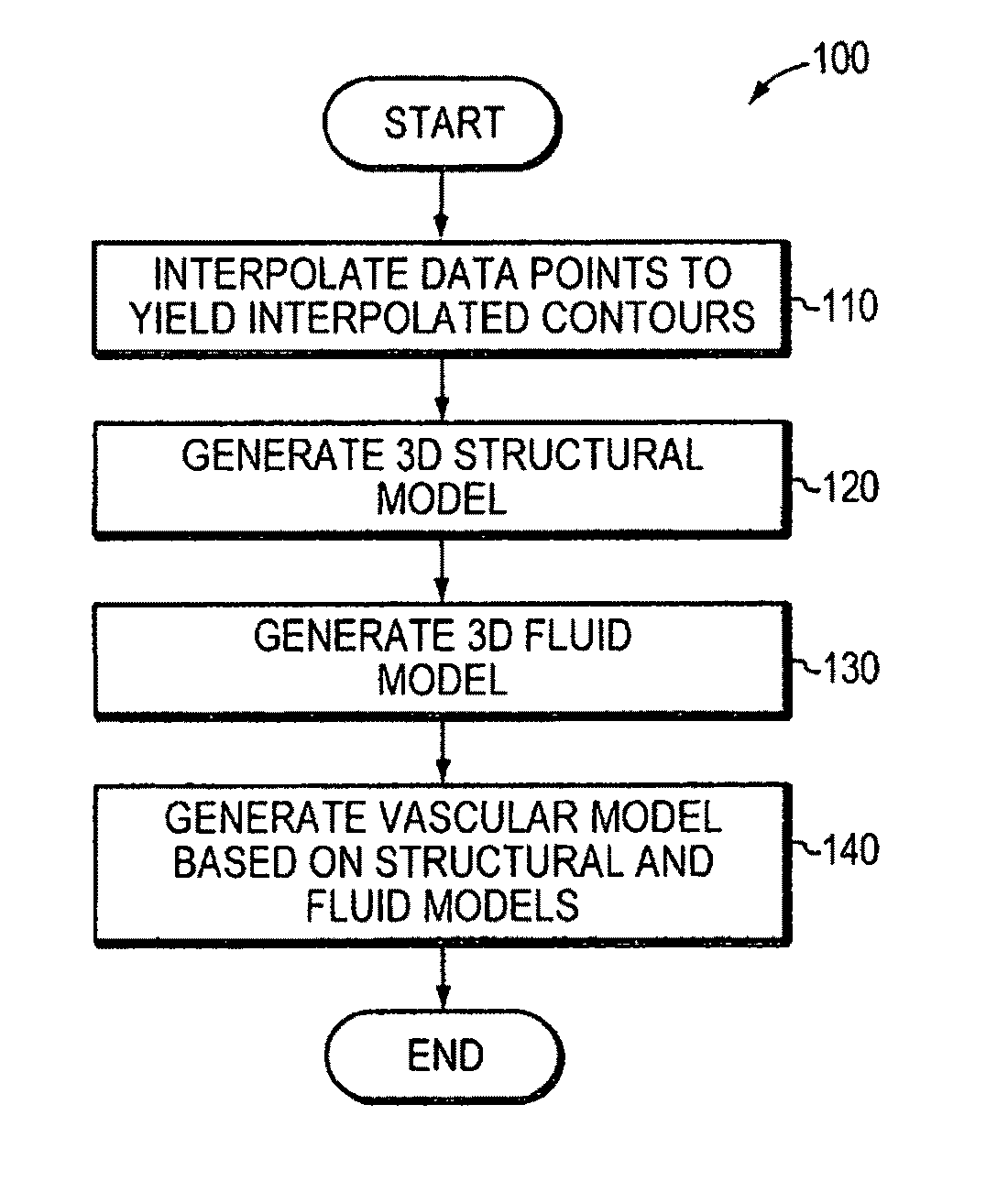
Automatic vascular model generation based on fluid-structure interactions (FSI)
ActiveUS8554490B2Automatically and accurately modelCatheterCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiologyComputerized system
A computer system and method are disclosed for automatically generating a vascular model of a blood vessel to support, for example, identification of mechanical factors corresponding to the blood vessel. The method includes interpolating data points corresponding to a contour of the blood vessel; generating a structural model representing three-dimensional structural characteristics of the blood vessel based on interpolated contours; generating a fluid model representing three-dimensional characteristics of fluid flow within the vessel; and generating a vascular model based on the structural model and the fluid model. The method may also include performing a mechanical analysis of the vascular model to identify a mechanical factor associated with the vessel, for example, a factor associated with a potential plaque rupture within the vessel. Embodiments of the invention are applicable to the diagnosis, assessment, or treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Multifunctional true triaxial flow solid coupling test system
ActiveCN102735548AReveal deformationRevealing intensityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPermeability/surface area analysisCouplingEngineering
The invention discloses a multifunctional true triaxial flow solid coupling test system which comprises a frame (100) and a pressure chamber (200) capable of arranging a coal rock sample, wherein the frame (100) comprises a support (1); the support (1) is fixedly connected with a frame (2), and a pressurizing system and a sensing system which are independent are arranged in each of X, Y and Z directions of the pressure chamber. Therefore, according to the multifunctional true triaxial flow solid coupling test system, a real work condition can be really simulated, and a theoretical basis is provided for solving on-site problems.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Automatic vascular model generation based on fluid-structure interactions (FSI)
ActiveUS20110295579A1Facilitate decision-makingAutomatically and accurately modelCatheterCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiologyComputerized system
A computer system and method are disclosed for automatically generating a vascular model of a blood vessel to support, for example, identification of mechanical factors corresponding to the blood vessel. The method includes interpolating data points corresponding to a contour of the blood vessel; generating a structural model representing three-dimensional structural characteristics of the blood vessel based on interpolated contours; generating a fluid model representing three-dimensional characteristics of fluid flow within the vessel; and generating a vascular model based on the structural model and the fluid model. The method may also include performing a mechanical analysis of the vascular model to identify a mechanical factor associated with the vessel, for example, a factor associated with a potential plaque rupture within the vessel. Embodiments of the invention are applicable to the diagnosis, assessment, or treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
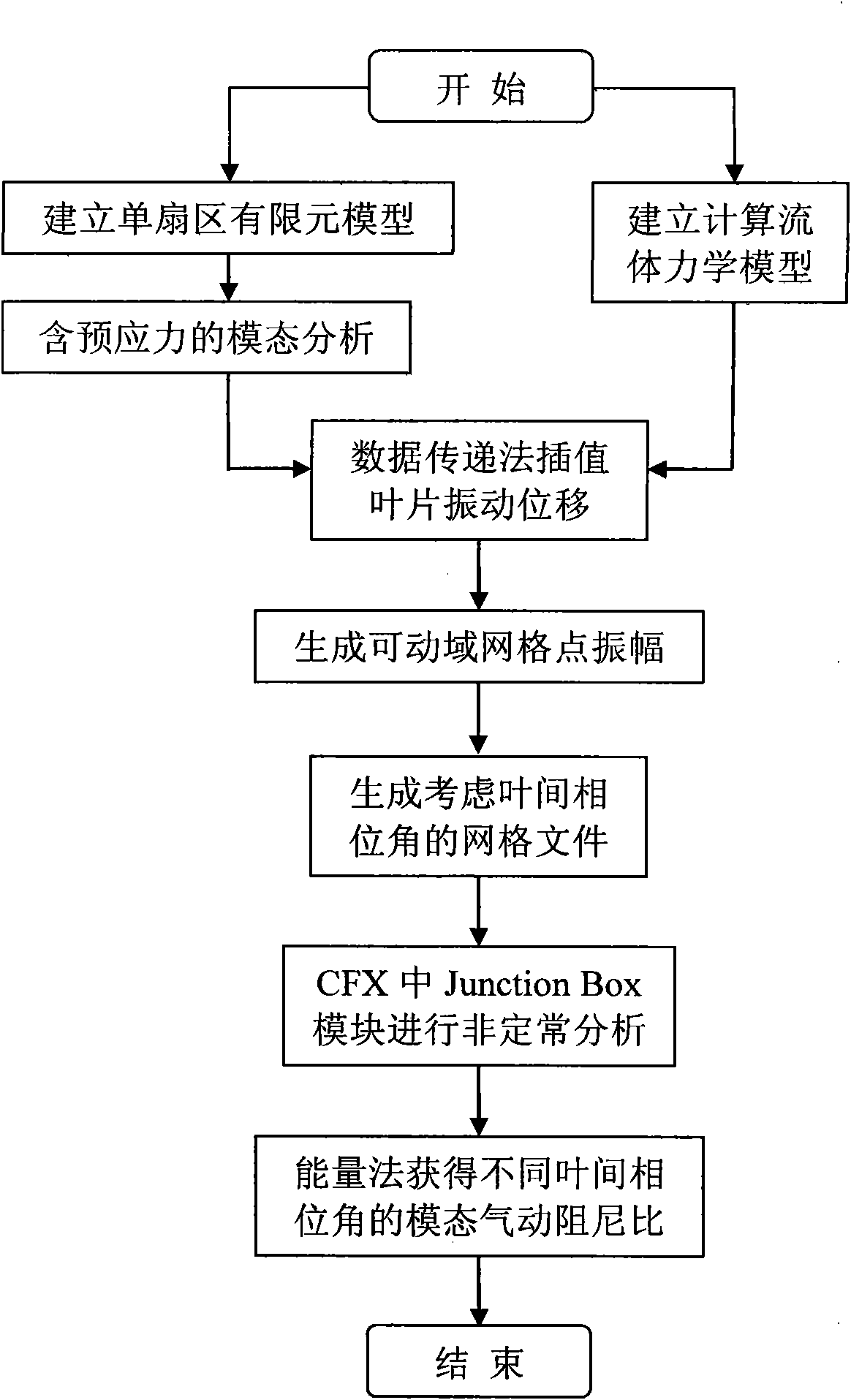
Aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles
InactiveCN101882177AReduce computing costCoupling calculation simplificationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelPredictive methods
The invention relates to an aeroelastic stability fluid-structure interaction prediction method of turbo-machine changed interblade phase angles, which predicts the aeroelastic stability of a turbo-machine through the modal pneumatic damping ratio of different interblade phase angles by adopting an energy method. The method adopts the modal analysis containing prestress on established single-sector finite element models, realizes the vibration displacement transfer on the fluid-structure interaction interface through a data transfer method, adopts the dynamic mesh technology for obtaining mesh files taking the interblade phase angles into consideration, is used for unsteady computation fluid mechanic analysis of Junction Box modules in CFX, further obtains the modal pneumatic damping ratio of each interblade phase angle, and is used for predicting the aeroelastic stability. The method based on the fluid-structure interaction fully utilizes the cutting edge technology of the computational structural mechanics and the computation fluid mechanics, ensures the computation precision in each sub system, and improves the computation efficiency through the division of a fixed region and a movable region. The invention has good practical value and wide application prospects in the technical field of turbo-machine simulation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
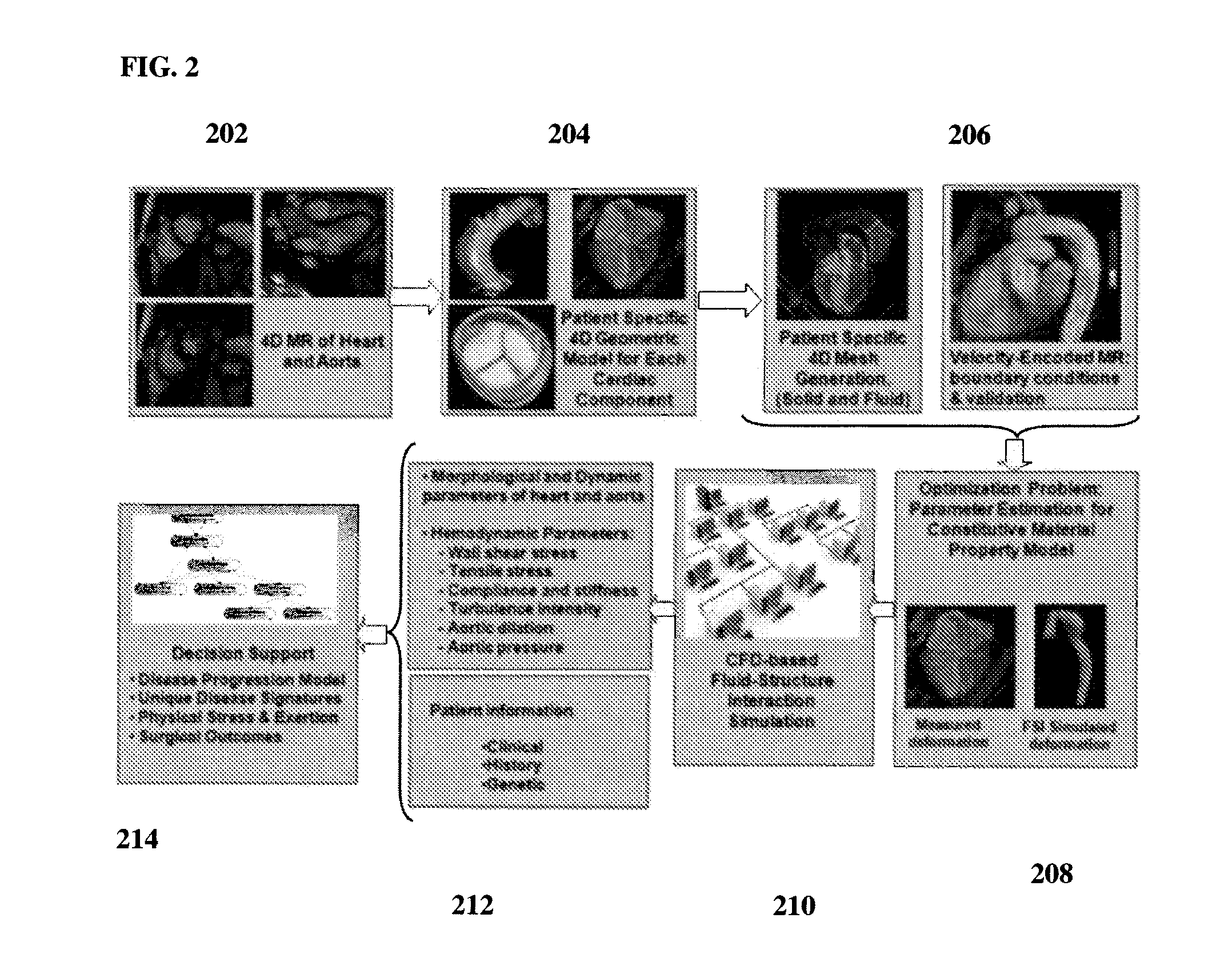
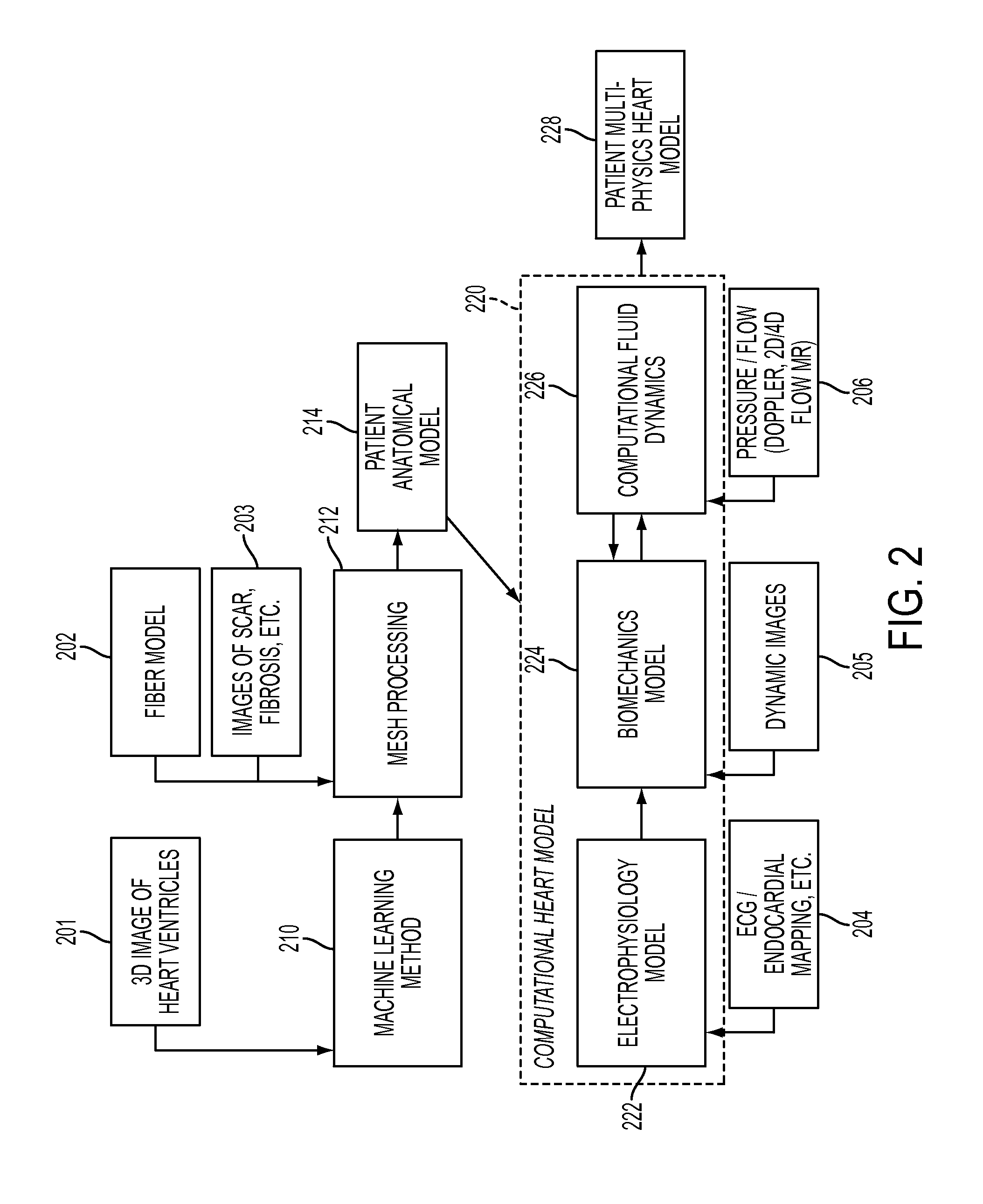
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveUS8682626B2Medical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesAnatomical structuresEntire heart
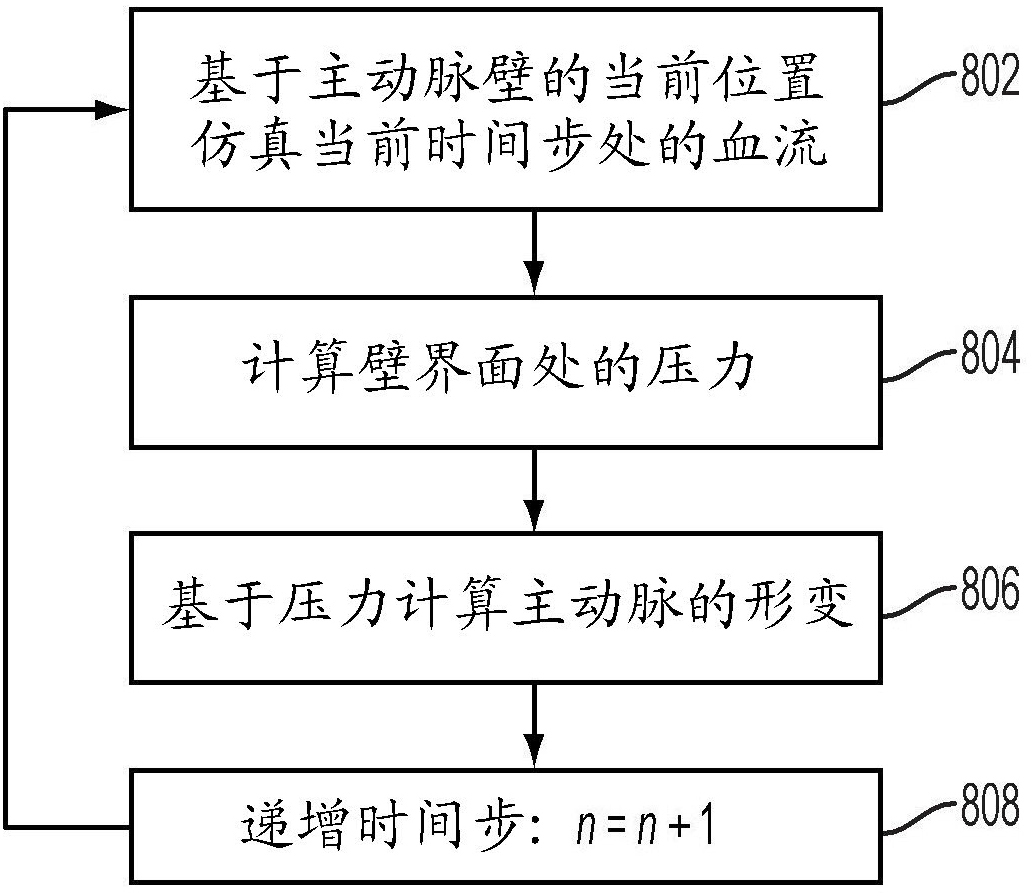
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
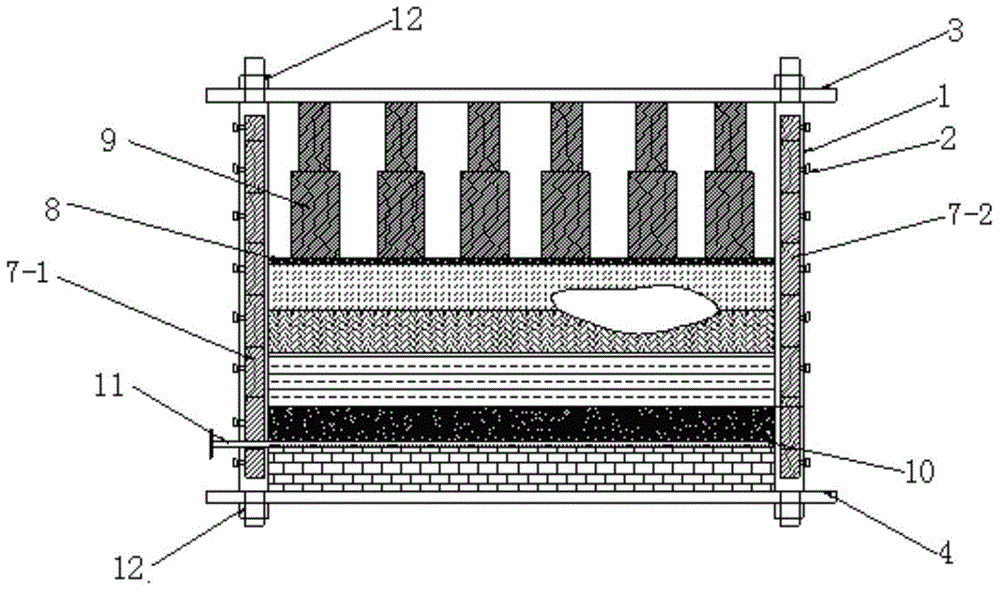
Fluid-solid coupled similar simulation experimental platform
InactiveCN104568706ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisDirect observationEngineering
The invention discloses a fluid-solid coupled similar simulation experimental platform which comprises a box body top plate, a box body bottom plate, a front baffle, a rear baffle, a left lateral insertion plate and a right lateral insertion plate, wherein the box body bottom plate, the front baffle, the rear baffle, the left lateral insertion plate, the right lateral insertion plate and the box body top plate form a closed box body structure of the experimental platform; a transmission bar is arranged in the box body structure and is positioned above the box body bottom plate; a mining steel plate is arranged above the transmission bar and is movably connected with the transmission bar; a coal layer is laid on the mining steel plate; a simulated rock stratum is arranged above the coal layer; a data monitoring system is arranged in the simulated rock stratum; a pressure-bearing steel plate covers the top of the simulated rock stratum; and a hydraulic jack is arranged between the pressure-bearing steel plate and the box body top plate. The experimental platform disclosed by the invention is simple in structure and low in manufacturing cost, a research worker can directly observe and record the movement and deformation conditions of overlying rock and the water permeability condition in the rock stratum cracks under the mining action, and the influence of coal mining on permeability rules of surface water and karstic water is analyzed.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for comprehensive patient-specific modeling of the heart
ActiveCN102346811ADescription of measurement accuracySpecial data processing applicationsTreatment optionsEntire heart
A method and system for patient-specific modeling of the whole heart anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction from 4D medical image data is disclosed. The anatomy and dynamics of the heart are determined by estimating patient-specific parameters of a physiological model of the heart from the 4D medical image data for a patient. The patient-specific anatomy and dynamics are used as input to a 3D Navier-Stokes solver that derives realistic hemodynamics, constrained by the local anatomy, along the entire heart cycle. Fluid structure interactions are determined iteratively over the heart cycle by simulating the blood flow at a given time step and calculating the deformation of the heart structure based on the simulated blood flow, such that the deformation of the heart structure is used in the simulation of the blood flow at the next time step. The comprehensive patient-specific model of the heart representing anatomy, dynamics, hemodynamics, and fluid structure interaction can be used for non-invasive assessment and diagnosis of the heart, as well as virtual therapy planning and cardiovascular disease management. Parameters of the comprehensive patient-specific model are changed or perturbed to simulate various conditions or treatment options, and then the patient specific model is recalculated to predict the effect of the conditions or treatment options.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
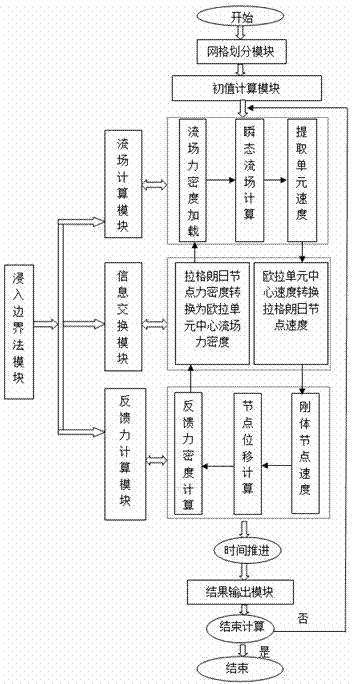
Immersing boundary flow field calculation method based on fluid/solid interface consistency
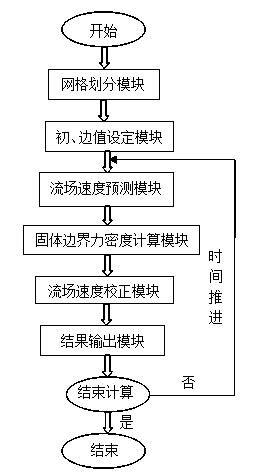
ActiveCN103970989AReduce usageSave computing resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingComputer module
The invention relates to an immersing boundary flow field calculation method based on fluid / solid interface consistency and belongs to the technical field of computational fluid mechanics and liquid / solid coupling simulation. The method comprises the steps that A, a grid division module is called, and two grids including a flow field region and a solid boundary region are adopted; B, a flow field calculation model is called, and a predicted value of the flow field region is obtained; C, a solid boundary force density calculation model is called, and the density of force acting on a solid boundary is obtained; D, a flow field velocity correction module is called, a correction value of the flow field region is obtained, and the flow field velocity is updated; E, a result output module is called, the force acting on the solid boundary and flow field information are output to a file and are read and displayed on a backstage; F, whether calculation is ended is judged. According to the method, use of the dynamic mesh technique is avoided, and a large number of computing resources are saved; the defects that when a traditional immersing boundary method is used, an interpolation algorithm is complex in the velocity solving process in a near wall region, and the intensity of the acting force on the solid boundary can not be calculated easily are overcome.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for computational modeling of the aorta and heart
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
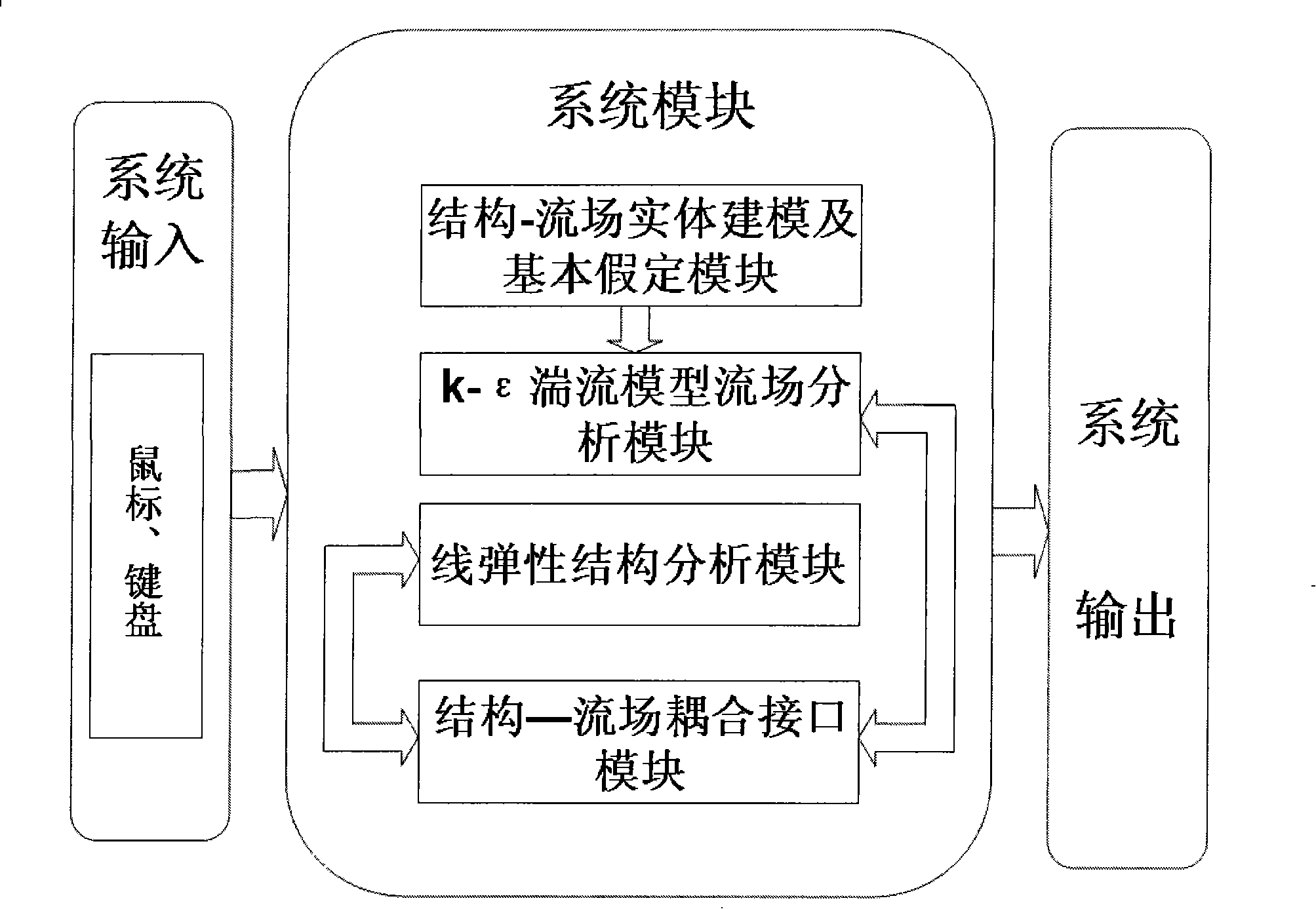
Flex wing minisize aerial craft fluid-solid coupling numerical value emulation method
InactiveCN101236573AReduce developmentSpeed up the R&D processSpecial data processing applications3D modellingStructure analysisFlight vehicle
The invention belongs to the flex-wing miniature aircraft auxiliary design technical field. The invention is characterized in that: the following modules which are respectively a structure-flow field entity modeling and basic assumption module, a k-epsilon turbulent flow model flow field analysis module, a linear elastic structure analysis module and a structure-flow field coupling interface module are set in a computer, wherein, the structure-flow field entity modeling and basic assumption module is provided with flexible wings and a three-dimensional model in a circumferential flow field; the k-epsilon turbulent flow model flow field analysis module is used for obtaining distribution pressure on a fluid-solid coupling surface of the flow field under different flight conditions; the linear elastic structure analysis module obtains displacement and speed of flex-wing structure meshes; the structure-flow field coupling interface module obtains deformation of the meshes of the flow field from the obtained displacement of the flex-wing structure meshes, and the deformation is taken as an input condition of the k-epsilon turbulent flow model flow field analysis module and then outputted; distribution pressure on wing surfaces of the flexible wings is obtained according to the distribution pressure of the flow field and taken as an input condition of the linear elastic structure analysis module and then outputted. The flex-wing miniature aircraft has the advantages that: higher accuracy than two dimensional analysis is guaranteed and simultaneously the efficiency of simulation calculation can be improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for predicting fluid-solid coupled characteristic value of elastic hydrofoil
InactiveCN104298869AIncrease credibilityImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsImpellerMechanical models
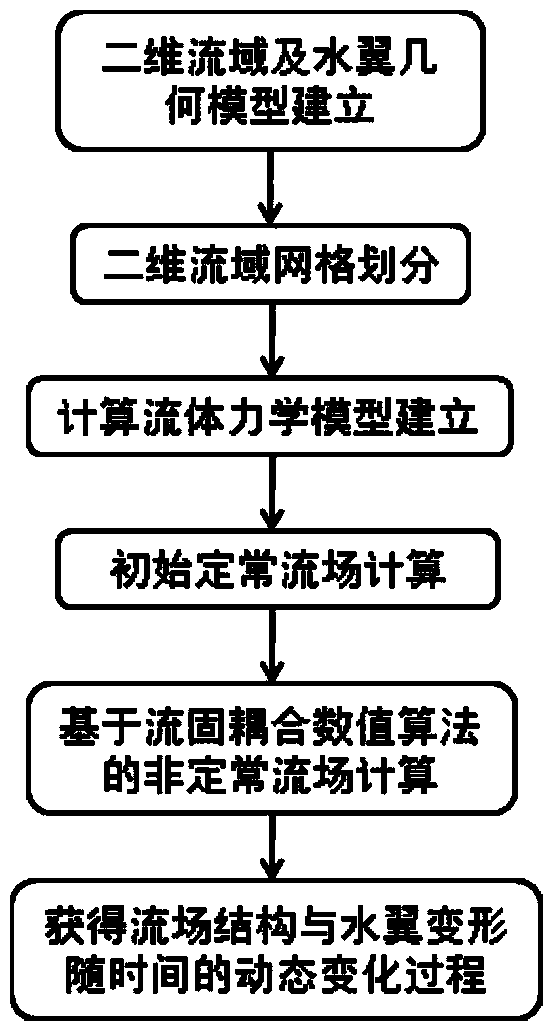
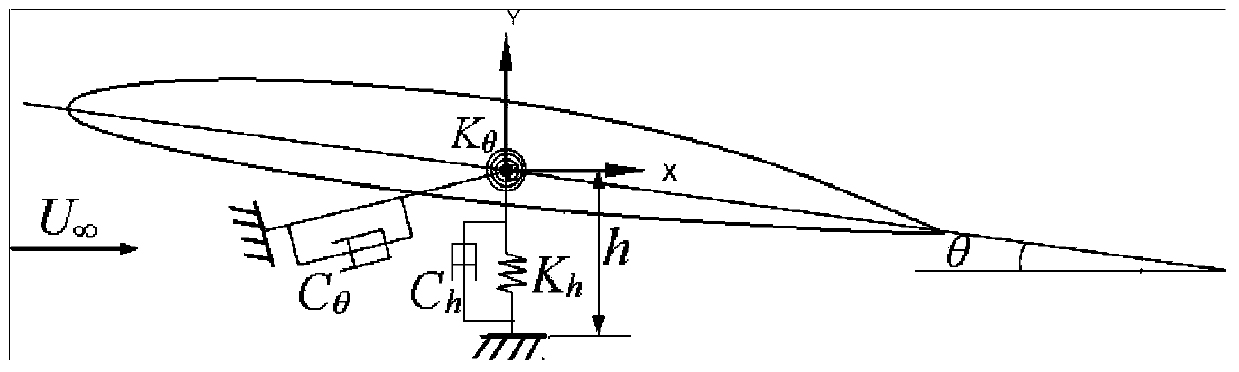
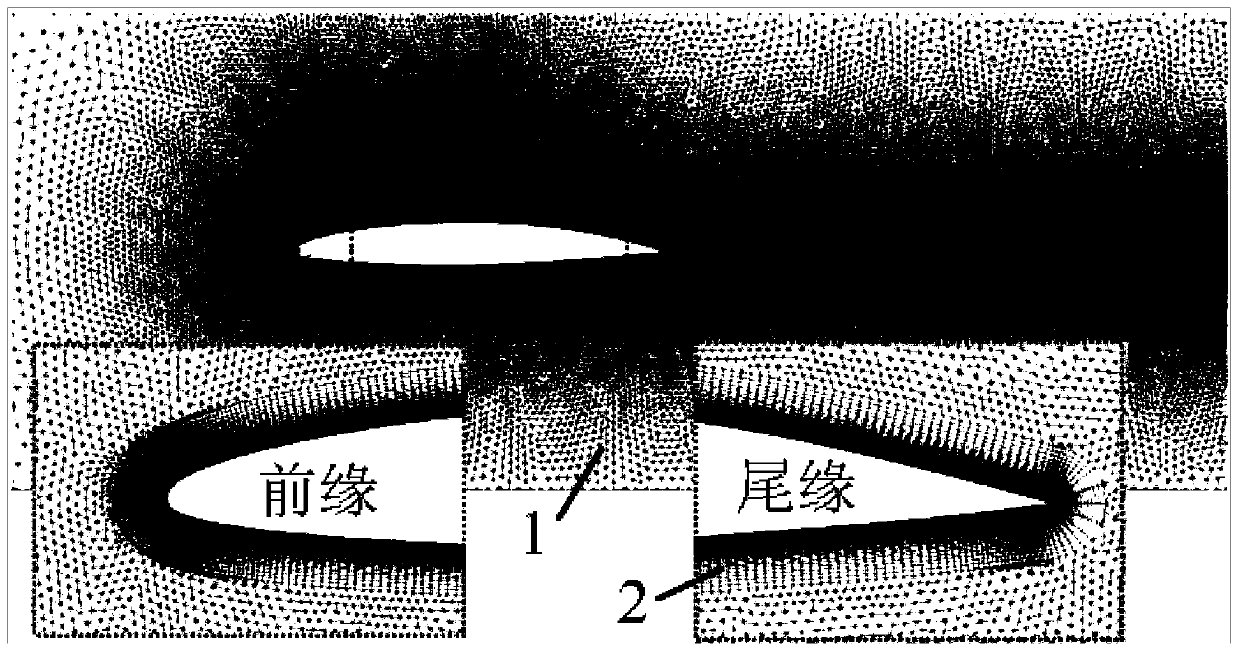
The invention relates to a method for predicting a fluid-solid coupled characteristic value of an elastic hydrofoil and belongs to the technical field of turbomachinery simulation. The method comprises the steps of establishing a two-dimensional drainage basin-hydrofoil geometric model, dividing the gridding of a two-dimensional drainage basin, establishing a computational fluid mechanical model, calculating an initial steady flow field value and an unsteady flow field fluid-solid coupled value, and then performing after-processing on the calculation results to obtain the dynamic change process of the deformation of the flow field structure and the hydrofoil with time. The method for predicting the fluid-solid coupled characteristic value of the elastic hydrofoil has the advantages that the influence of an added mass effect on flowing is taken into account so that the stability of value calculation and the reliability of a numerical prediction result are improved, quick high-accuracy numerical prediction on an oscillation phenomenon induced by flowing around the elastic hydrofoil can be realized, and the flexibility of selection of numerical computation methods can be enhanced by virtue of secondary development of computational fluid mechanical software in combination with an embedded fluid-solid coupled algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Unsteady cavitation flow-excited vibration multi-field synchronous measurement system for water tunnel experiment
InactiveCN107907296ASimultaneous measurement is preciseSynchronous Analysis FeaturesHydrodynamic testingPhysical fieldMulti field
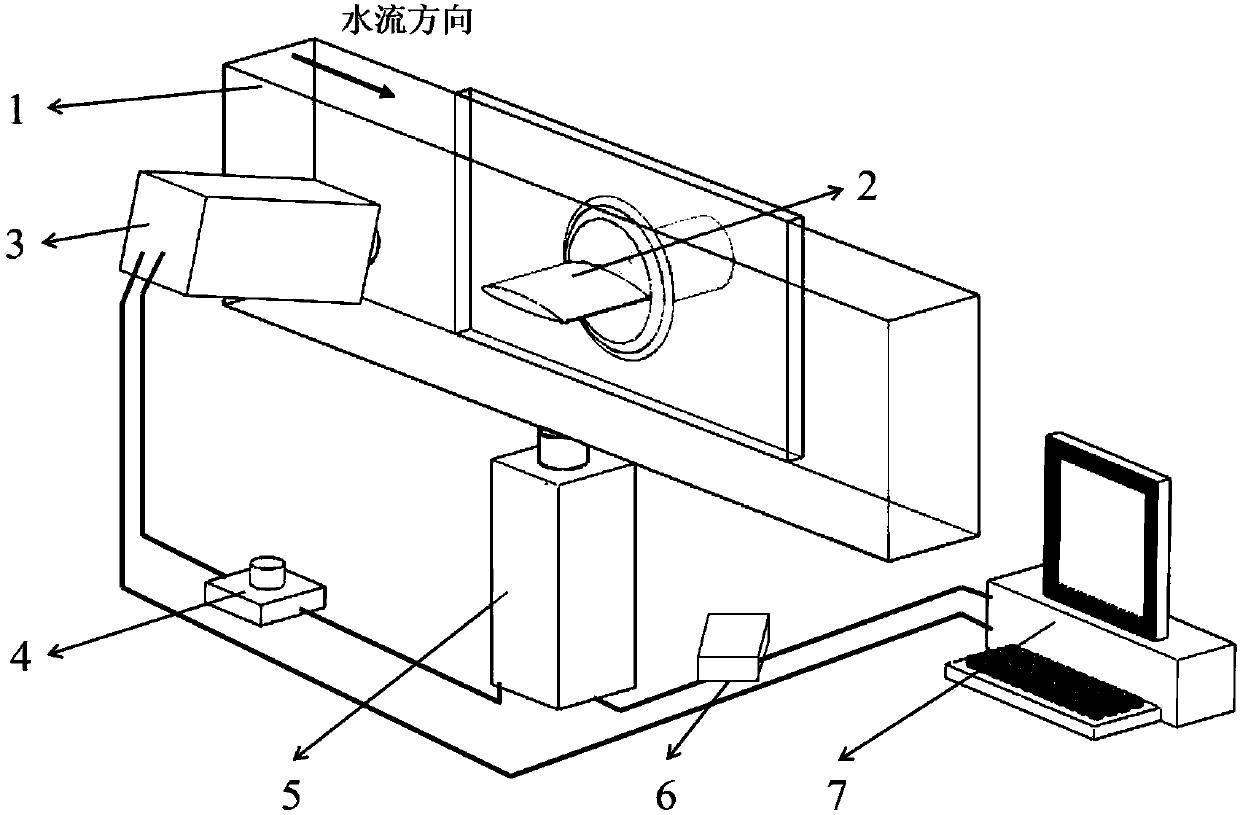
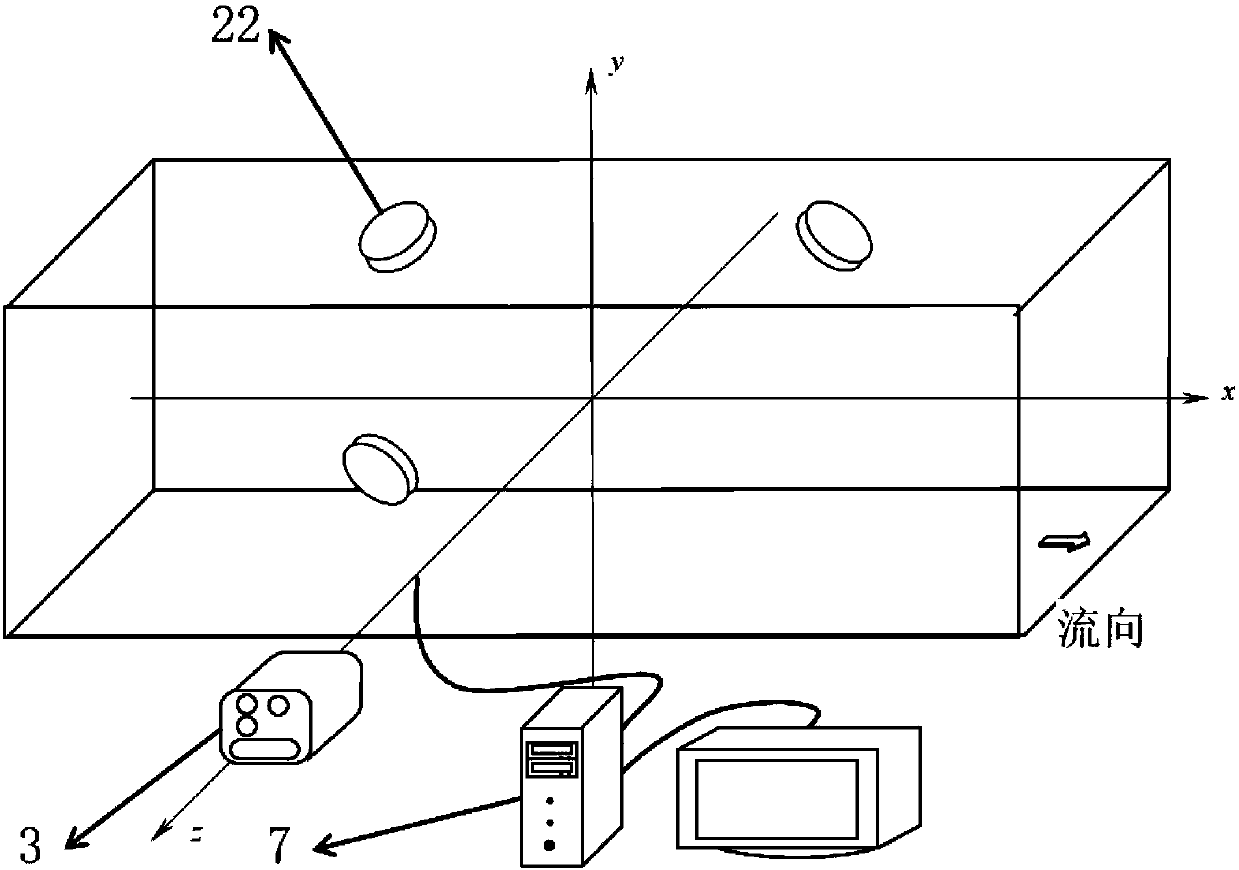
The invention relates to an unsteady cavitation flow-excited vibration multi-field synchronous measurement system for a water tunnel experiment and belongs to the ship and underwater vehicle engineering and water conservancy and hydropower engineering technology field. The system is composed of an experimental section, an experimental model, a high-speed camera, a synchronous trigger switch, a laser Doppler vibration meter, a data acquisition instrument, a data processing system / computer and display assembly and a light source. According to the system of the invention, rising edge voltage signals are generated through the synchronous trigger switch, trigger signals are controlled by using the voltage signals, and therefore, the signal acquisition starting instructions of the high-speed camera and the laser Doppler vibration meter are controlled quantitatively and precisely, and the quantitative and accurate synchronous measurement of an unsteady cavitation flow field and a structure field can be realized; and data obtained through multi-physical field synchronous acquisition are subjected to preprocessing, time-domain analysis, frequency-domain analysis and time-frequency analysis,and therefore, reliable analysis experimental data can be provided for the study of fluid-structure interaction characteristics.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Explosion Simulation in Finite Element Analysis
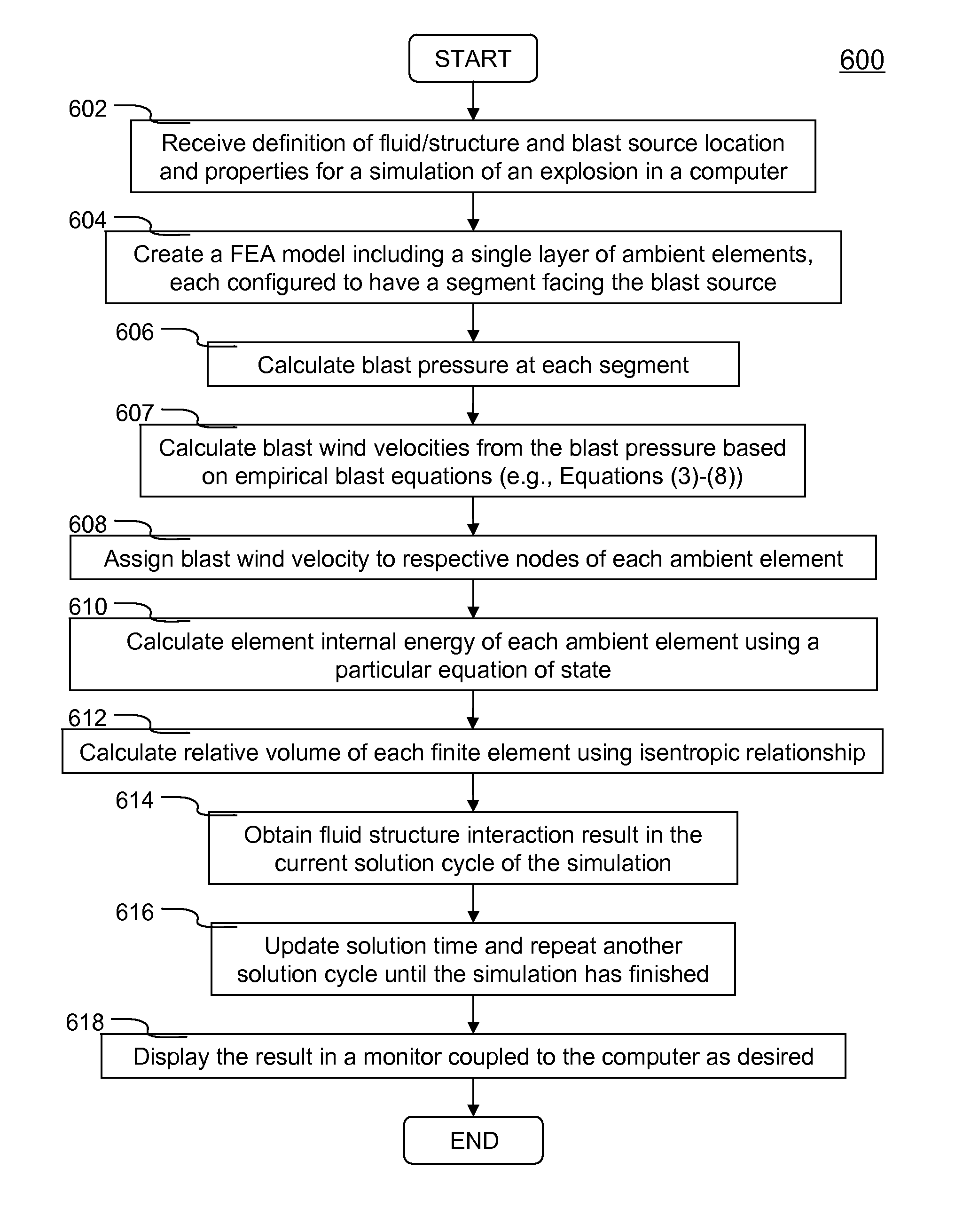
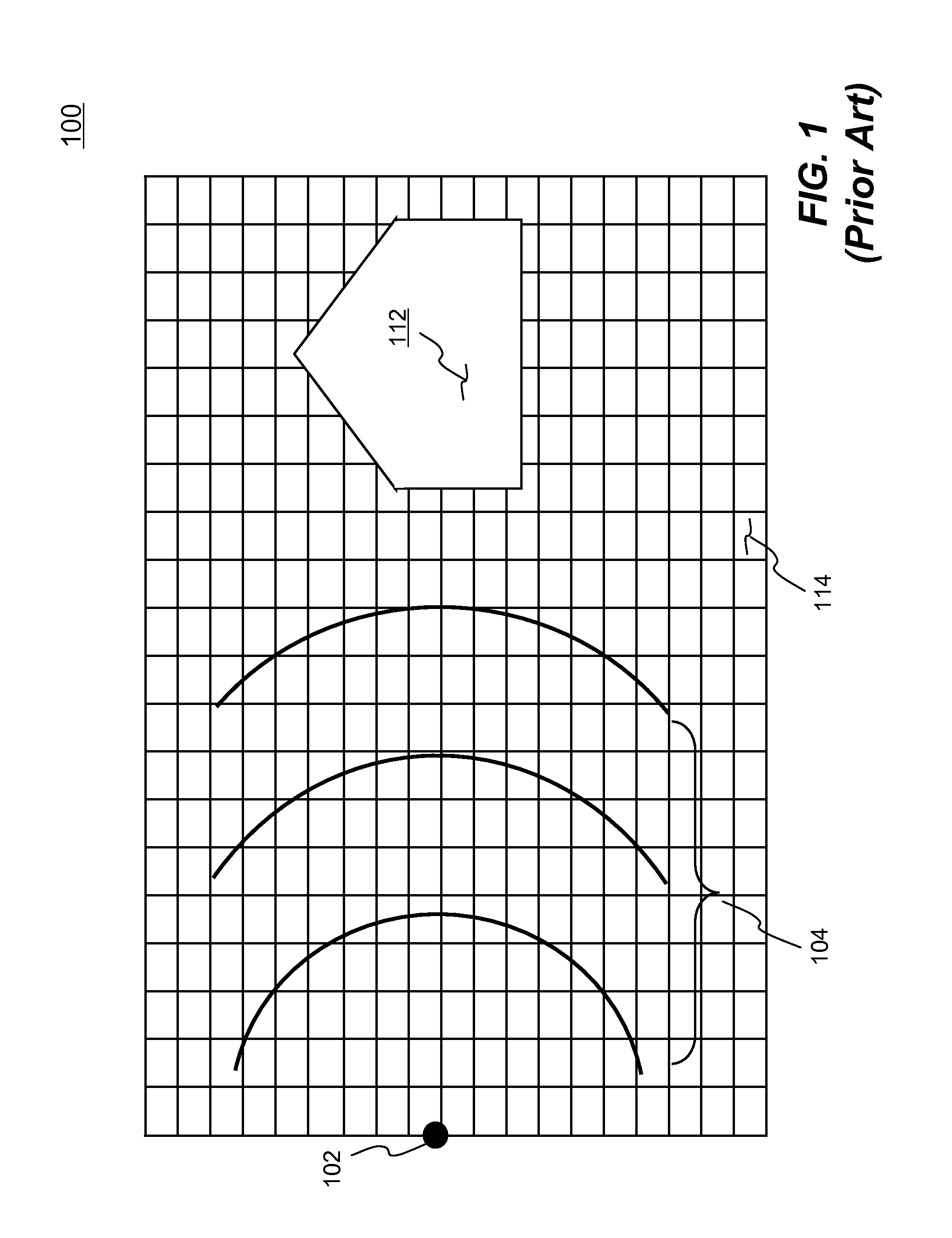
ActiveUS20100256957A1Reduce computing timeImprove userComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationProduction rateElement analysis
Systems and methods of simulating an explosion in time-marching finite element analysis are disclosed in the present invention. According to one aspect, a method is configured for increasing user (e.g., engineer or scientist) productivity by reducing computation time of simulating fluid-structure interaction due to an explosion. The method comprises a creation of a finite element analysis model that includes structure, surrounding fluid, a blast source of the explosion and a single layer of ambient elements each having a segment representing a boundary of the fluid facing the blast source. Each ambient element is associated with a particular finite element representing the fluid at the boundary. The ambient elements are configured to be situated between the blast source and the structure such that the simulation can be carried on a set of boundary conditions specified thereon. The boundary conditions comprise a set of nodal velocities that are determined from the empirical formula (e.g., Friedlander equation).
Owner:ANSYS
Bidirectional fluid-solid-heat coupling calculating method of water-lubricated rubber bearing
InactiveCN107506562AHigh solution accuracyReduce the number of iterationsGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCouplingMechanical models
The invention discloses a bidirectional fluid-solid-heat coupling calculating method of a water-lubricated rubber bearing, comprising the following steps of setting basic assumption of a solution process according to the special structure and practical operating condition of the water-lubricated rubber bearing and combined with heat transfer characteristics of the water-lubricated rubber bearing; determining fluid, solid and temperature field coupling boundary conditions of the water-lubricated rubber bearing; building fluid domain and solid domain solution models, including mathematical models and mechanical models, of the water-lubricated rubber bearing,; meshing the fluid domain and solid domain of the water-lubricated rubber bearing by means of a finite element software platform and professional meshing software; building differential control equations of the fluid domain, solid domain and heat transfer characteristics of the water-lubricated rubber bearing; and building a fluid-solid-heat coupling model of the water-lubricated rubber bearing, solving the fluid-solid-heat coupling model by using a numerical method, and obtaining deformation conditions of the fluid domain, solid domain and temperature field. The method is effectively suitable for three-field coupling solution of the water-lubricated rubber bearing, solution precision is high, and the number of iterations is low.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for advanced measurements computation and therapy planning from medical data and images using a multi-physics fluid-solid heart model
ActiveUS9129053B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical simulationComputational modelModel parameters
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
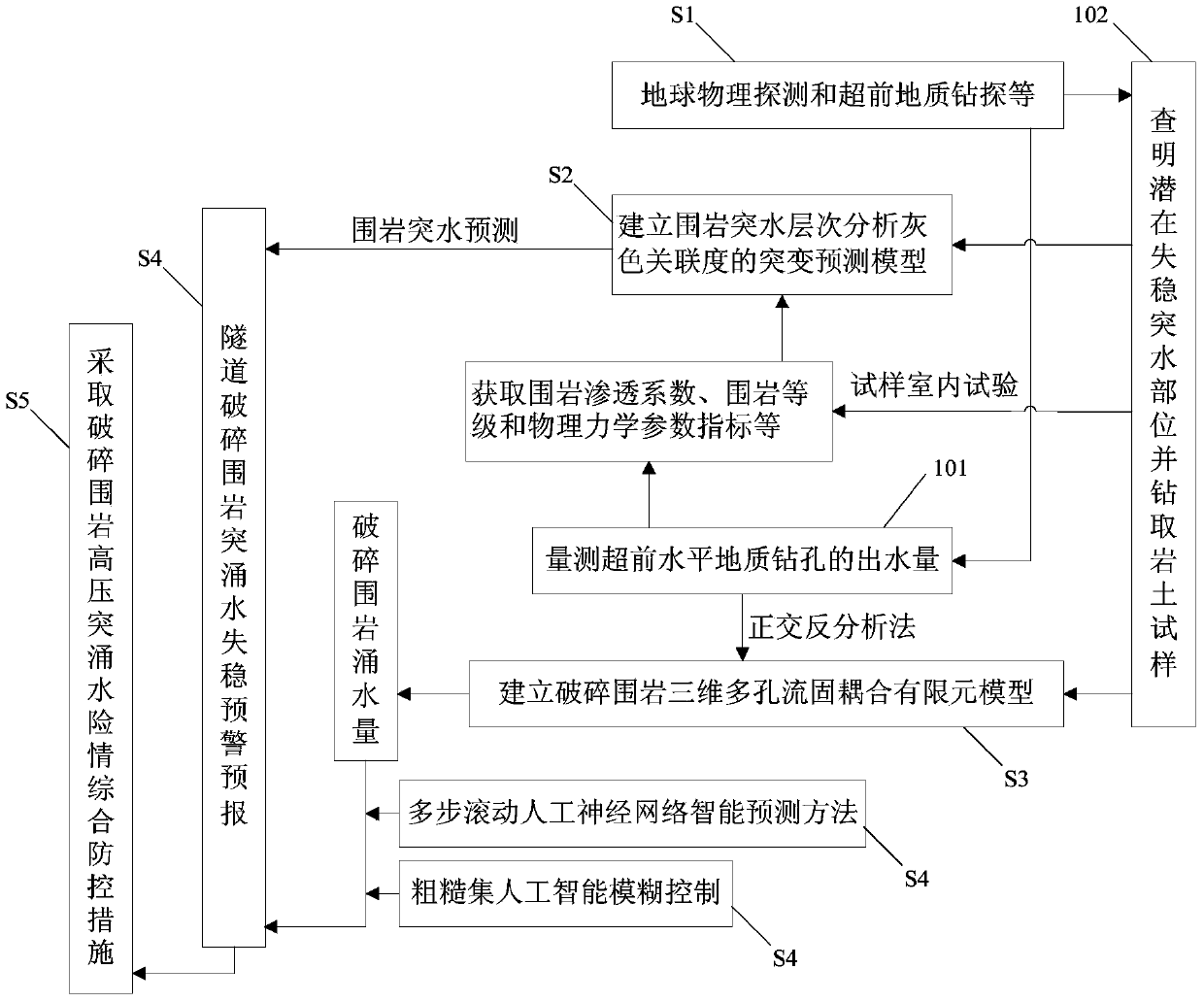
Method for water inrush prediction and seepage control for underwater-tunnel broken surrounding rocks
InactiveCN104179514ARealize surrounding rock water inrush predictionImprove rational designUnderground chambersTunnel liningElement modelInstability
The invention relates to a method for water inrush prediction and seepage control for underwater-tunnel broken surrounding rocks. The method includes the steps of S1), exploring by adopting a geophysical exploration and advanced-level geological drilling method and performing tests; S2), establishing a saltation prediction model of analytic hierarchy grey correlation of water inrush of the surrounding rocks by adopting an analytic hierarchy grey correlation method; S3), establishing a three-dimensional porous continuous medium fluid-structure coupled finite element model of the underwater-tunnel broken surrounding rocks by adopting an orthogonal back-analysis method; S4), performing dynamic prediction and seepage control on water inflow of the broken surrounding rocks and performing intelligent fuzzy logic control and instability early-warning forecast on high-pressure water inrush of the broken surrounding rocks; S5), adopting comprehensive prevention and control measures. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that instability of water inrush of the underwater-tunnel broken surrounding rocks under high water pressure can be predicted and subjected to economical, reasonable, safe and reliable comprehensive seepage control.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Evaluation method for unconventional reservoir volume transformation multi-pore media productivity contribution
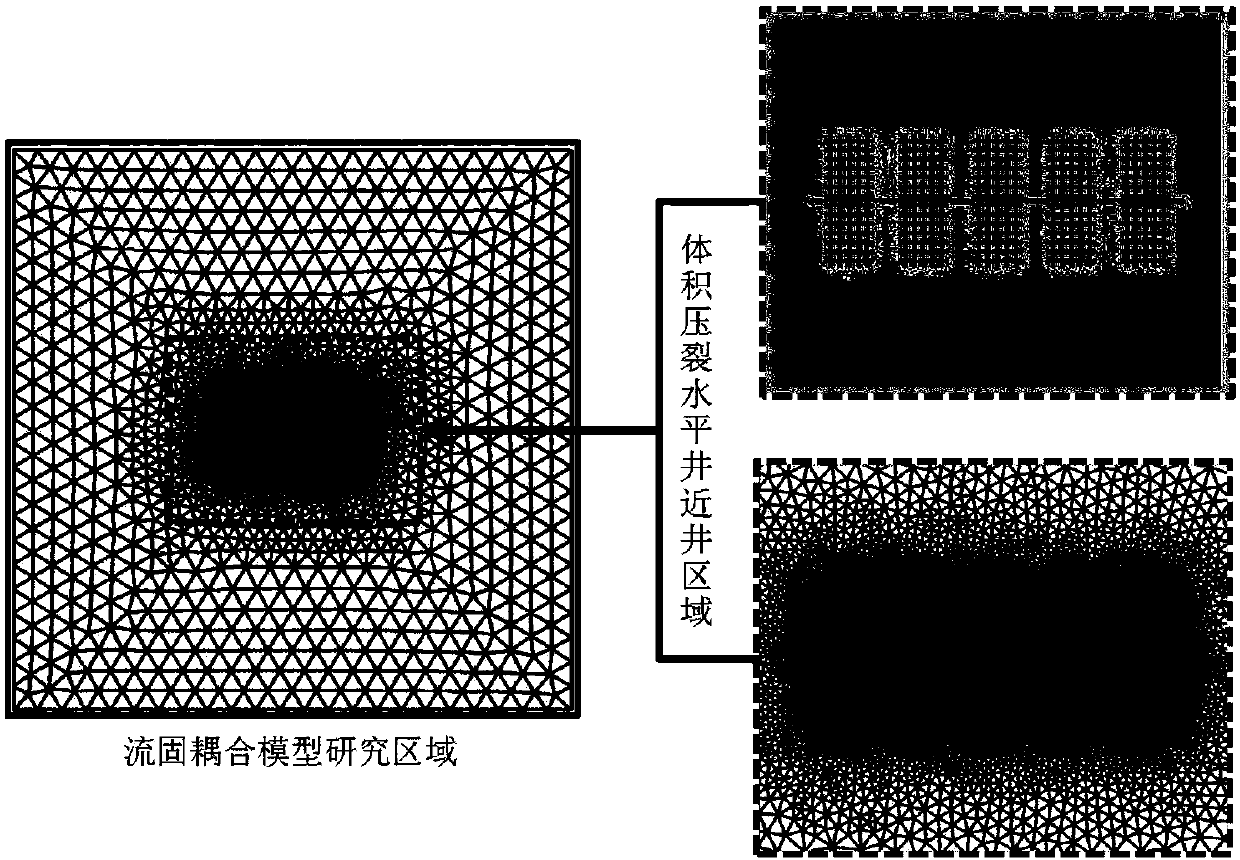
ActiveCN108266185AFind out the problem of dynamic energy changeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelPartial differential equation
The invention discloses an evaluation method for unconventional reservoir volume transformation multi-pore media productivity contribution. The evaluation method comprises the following steps that firstly, based on the principle of effective stress and flow characteristics of a transformation zone, and a fluid-solid coupling mathematical model of interaction between a geotechnical deformation field (stress field) and a fluid flow field (seepage field) of the unconventional reservoirs is established; then a perfectly coupled method solution of the seepage field and the stress field is realizedby solving a fluid-solid perfectly coupled system of partial differential equations in a general formula mode; and finally, fluid-solid coupling interactions under different combinations of pore mediaare simulated, and the contribution ratio of three systems of base materials, natural cracks and grid cracks to the cumulative production of a volume transformation well is obtained. A set of evaluation method for unconventional reservoir volume transformation multi-pore media productivity contribution is established eventually. The evaluation method for unconventional reservoir volume transforming multi-pore media productivity contribution has the advantages that the model factor consideration is comprehensive, the evaluation method is simple and results are quantifiable, an oil and gas field can be guided timely to be subjected to development measure adjustment and comprehensive management, and a theoretical basis and technical support are provided to the unconventional reservoir to realize economic recovery.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
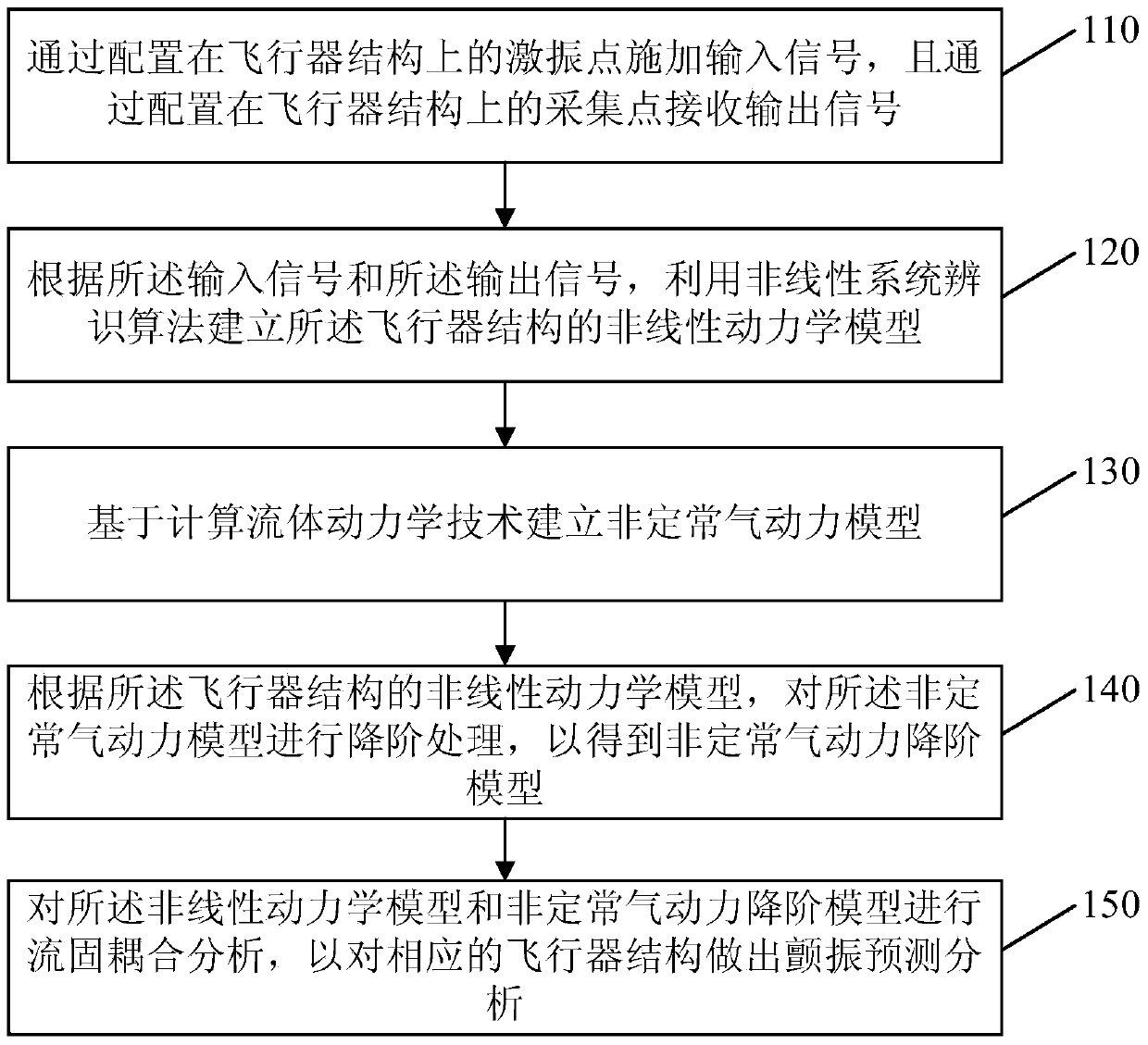
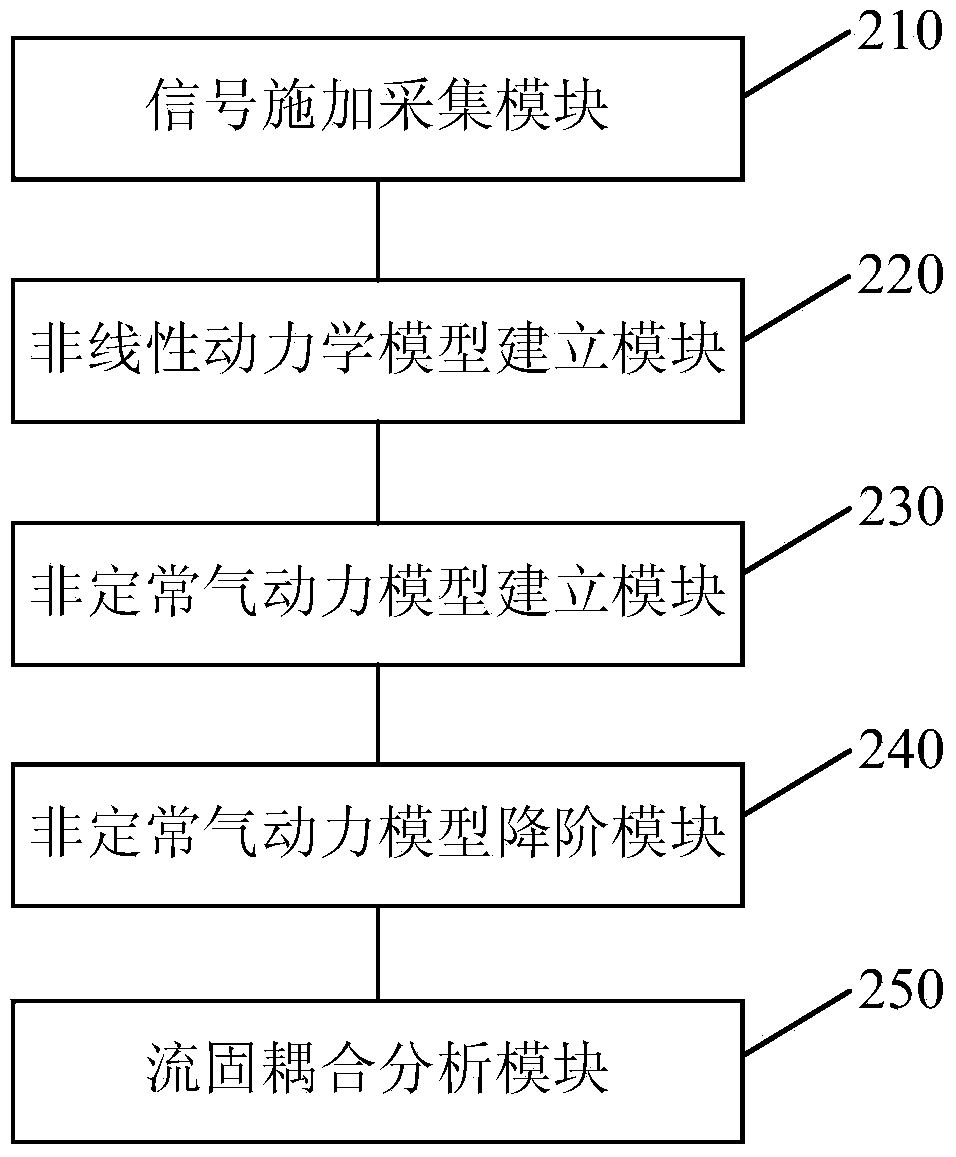
Aircraft flutter prediction and analysis method and device
ActiveCN104182560AImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsRecognition algorithmSimulation
The invention discloses an aircraft flutter prediction and analysis method and device. The method comprises the following steps: applying an input signal through an exciting point on an aircraft structure, and receiving an output signal through a collection point which is configured on the aircraft structure; establishing a nonlinear kinetic model of the aircraft structure by utilizing a nonlinear system recognition algorithm according to the input signal and the output signal; establishing an unsteady aerodynamic model on the basis of the calculation fluid kinetic technology; performing reduced order for the unsteady aerodynamic model according to the nonlinear kinetic model of the aircraft structure to obtain a reduced order model; performing the fluid-structure interaction analysis on the nonlinear kinetic model and the reduced order model so as to make the flutter prediction and analysis on the corresponding aircraft structure. Since the nonlinear kinetic model of the aircraft structure is acquired by performing the test according to the real aircraft structure, the accuracy in flutter prediction and analysis can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING AERONAUTIC SCI & TECH RES INST OF COMAC +1
Immersed boundary force feedback method based on right body and fluid coupling effect prediction
InactiveCN103778326AReduce usageSave computing resourcesSpecial data processing applicationsTransient stateFluid coupling
The invention relates to an immersed boundary force feedback method based on right body and fluid coupling effect prediction, and belongs to the technical field of the computational fluid mechanics and fluid-solid coupling simulation of the computational fluid mechanics. The method includes the steps that 1, grids are called for dividing modules, and two sets of grids including a fluid field region and a rigid body region are adopted; 2, an initial value calculation module is called to obtain initial value conditions calculated with a stable fluid field of the fluid field region serving as a fluid field transient state ; 3, an immersed boundary method module is called, a whole physical system composed of rigid bodies and fluid fields advances in time, and the following three sub-modules of the fluid field calculation module, the information exchange module and the feedback force calculation module are set in the immersed boundary method module; 4, a result output module is called, force exerted on the rigid bodies and fluid field information are output to a file to be read and displayed by a background; 5 whether calculation ends or not is judged. According to the method, the moving-grid technology is prevented from being used, and therefore a large number of calculation resources are saved; the defects that deformation energy of the rigid bodies is zero, and the acting force density of solid bodies cannot be calculated easily are overcome.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
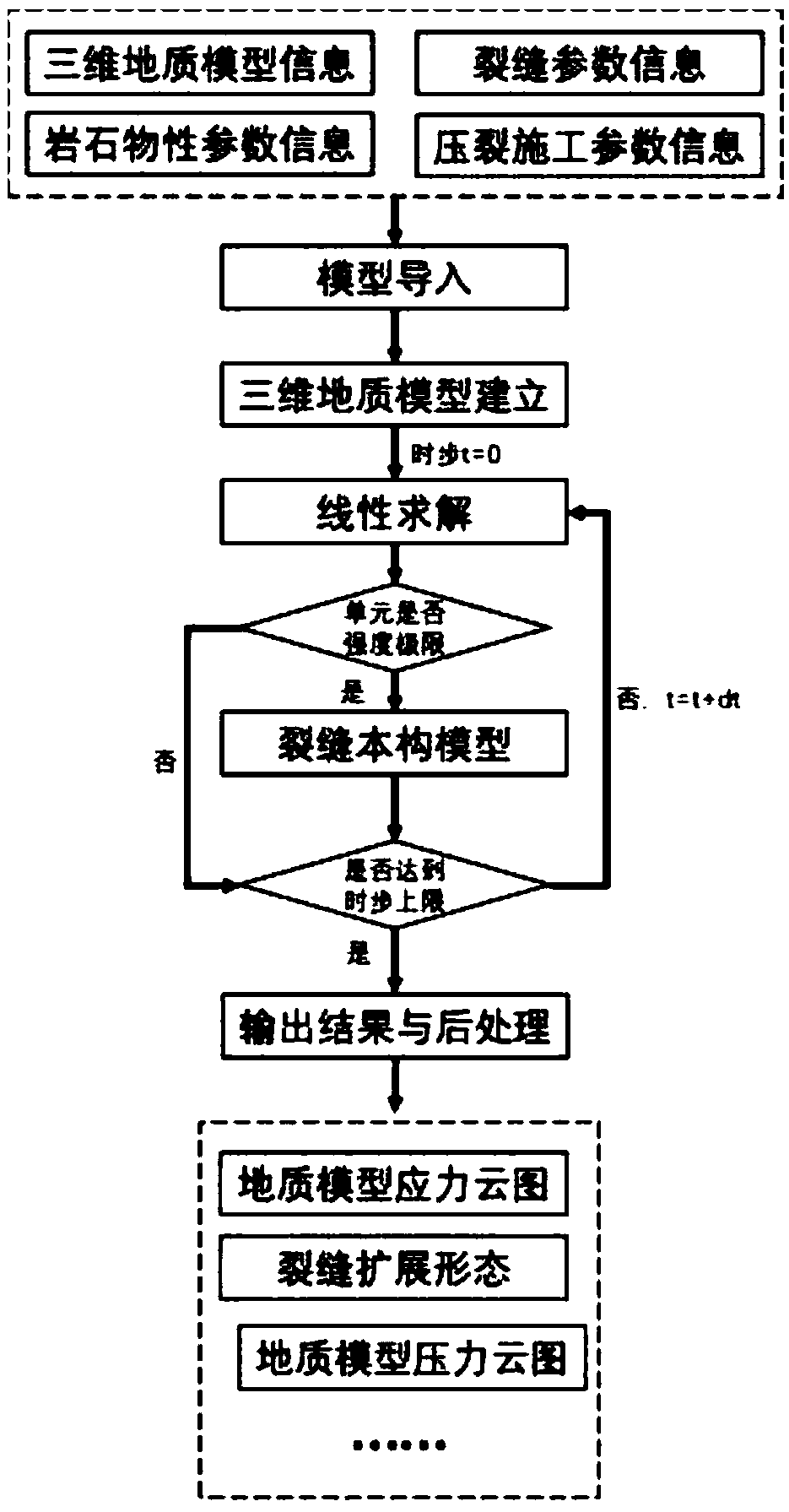
A simulation method of single fracture propagation based on quasi-continuous geomechanical model
ActiveCN109241588AImprove reliabilityEasy to set upDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress strengthHydraulic fracturing
The invention discloses a simulation method of single propagation expansion based on a quasi-continuous geomechanical model, which comprises the following steps: acquiring geological parameters, including three-dimensional geological information and rock physical property information; Correcting petrophysical information; Establishing three-dimensional geological model of stratum; establishing FEMfluid-solid coupling model; obtaining the pressure field, displacement field, stress field and strain field of the three-dimensional geological model by solving the fluid-solid coupling equations ofthe finite element method; judging whether cracks are produced or not according to the stress strength criterion; obtaining The fracture width, permeability matrix and flexibility matrix, and then calculating the influence of fracture on pressure field and displacement field. The simulation of single fracture propagation based on quasi-continuous geomechanical model is realized. The invention hasthe advantages of quick solution, high accuracy and good reliability, and effectively solves the problem of dynamic display of fractures in the process of hydraulic fracturing simulation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements
InactiveCN103699715ASolve problems that are difficult to directly coupleEasy to implement in parallelSpecial data processing applicationsSmoothed-particle hydrodynamicsElement model
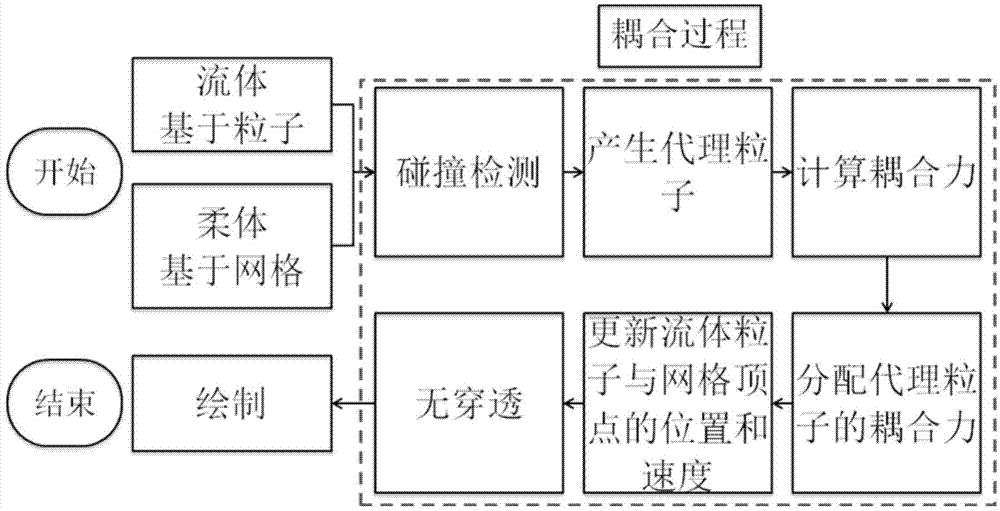
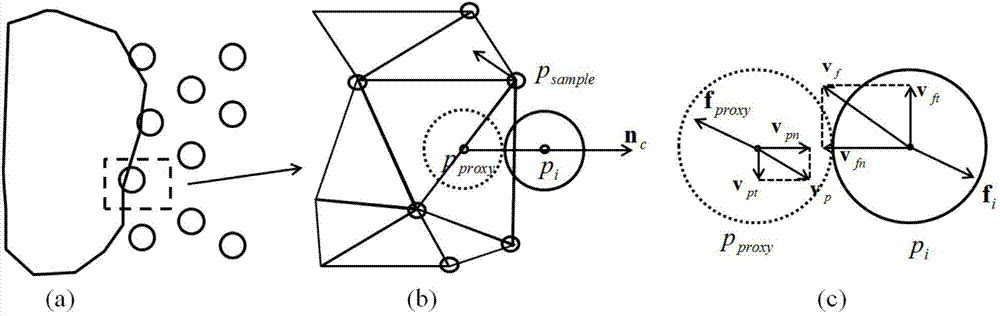
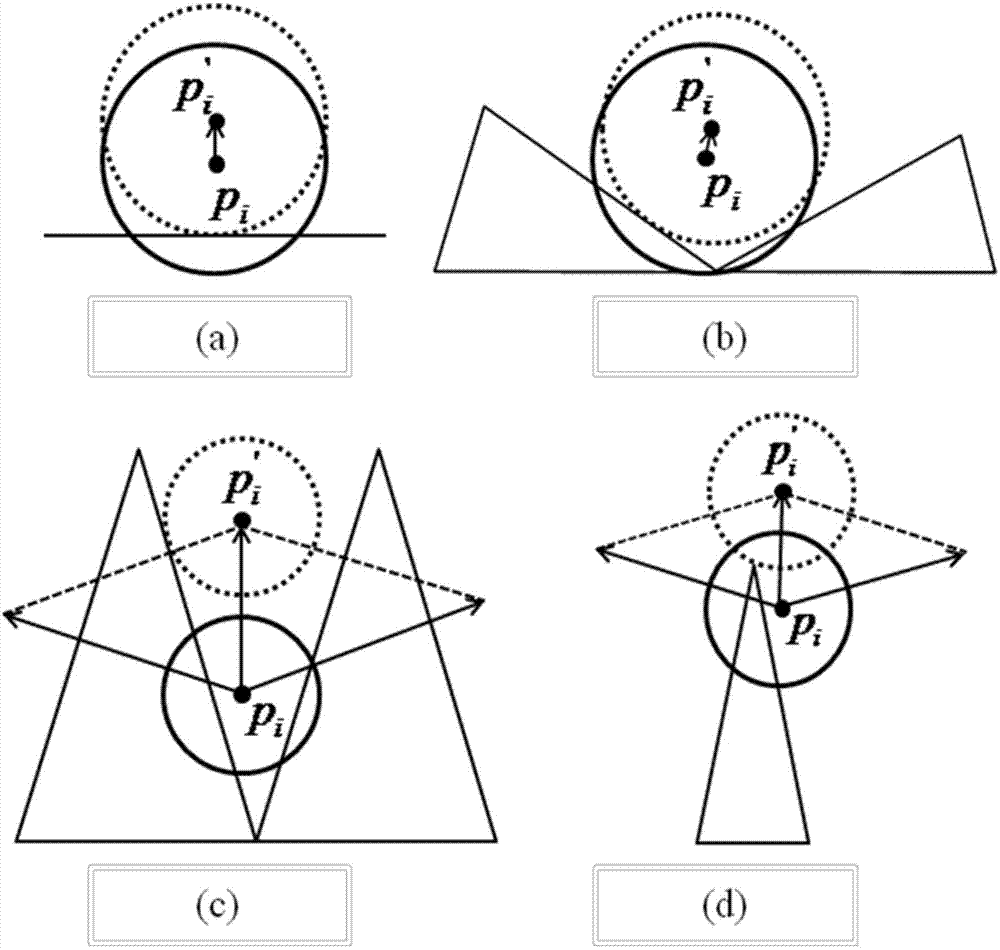
The invention provides a fluid-solid coupling method based on smoothed-particle hydrodynamics (SPH) and nonlinear finite elements. The method comprises the following six steps: at a collision detection stage, detecting collision information of fluid particles with a finite element network; at an agent particle generation stage, generating collision agent particles presenting a finite element model according to the collision information for processing the collision between a fluid and a solid; at a coupling force calculation stage, calculating force generated by collision between agent particles and fluid particles according to the position and speed relations of the agent particles and the fluid particles; at a coupling force allocation stage, controlling the position relation of the agent particles and the finite element model and allocating the coupling force to a finite element stress model; at a position and speed updating stage, driving the position and speed update of the finite element model and a fluid particle model according to the calculated coupling force; at a non-penetration modification stage, modifying penetration fluid particles according to an updated position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
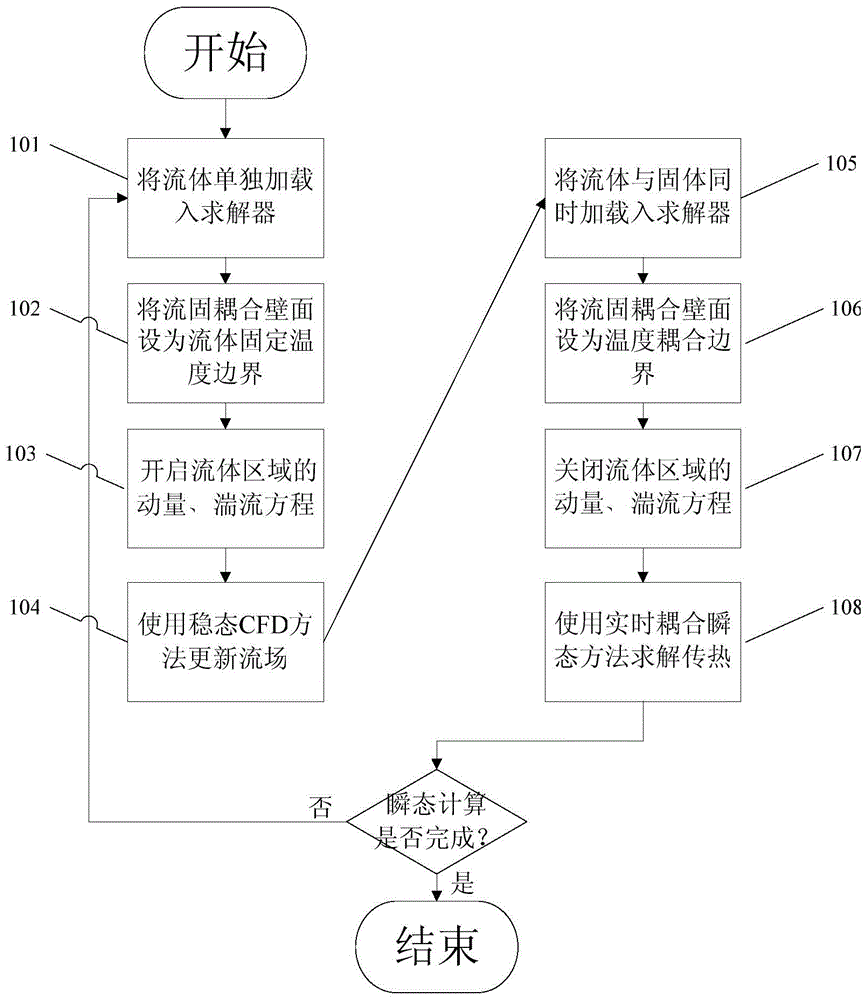
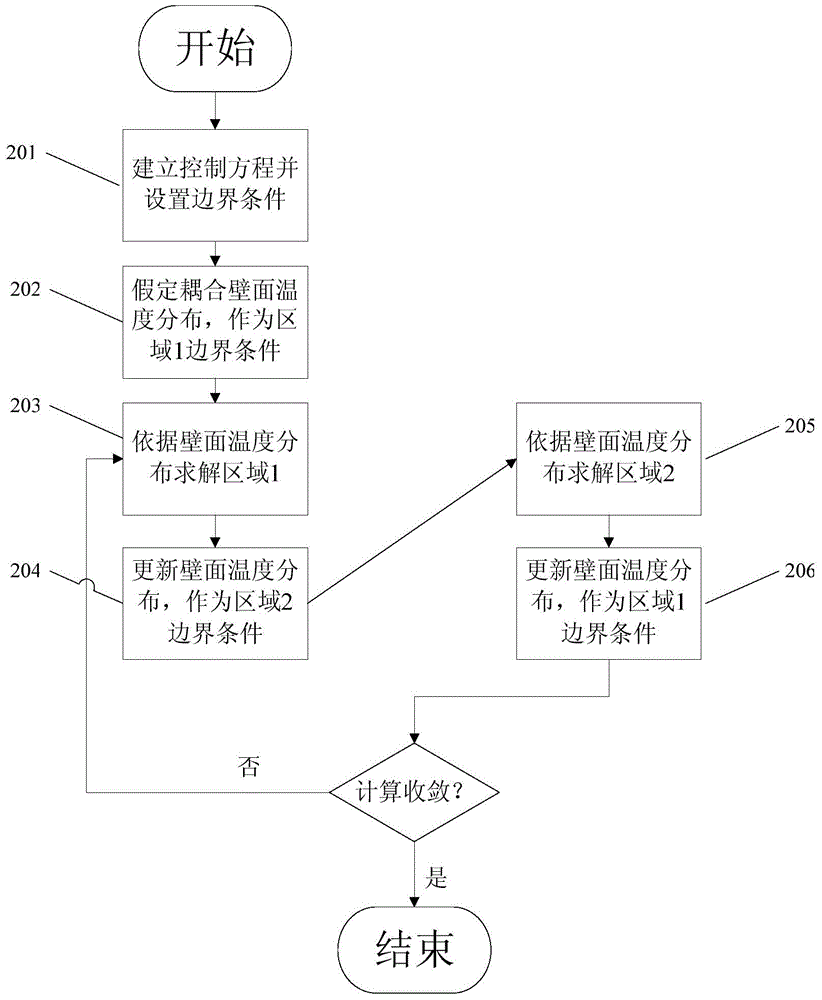
Loose coupling modeling method for fluid-solid coupling heat transfer
The invention provides a loose coupling modeling method for fluid-solid coupling heat transfer. The loose coupling modeling method is characterized in that the transient change process of a flow filed is ignored, and the global transient heat transfer process is assumed to be performed in a quasi-stable-state flow field. The method comprises the specific calculation procedures that 1, the flow field is updated, wherein only fluid is taken as a solving object, the fluid-solid coupling wall surface is set as a fixed temperature boundary of the fluid, and the flow field is solved through a stable-state CFD algorithm; 2, transient heat transfer is calculated, wherein the fluid and solid are both taken as the solving object, the fluid-solid coupling wall surface is set as a heat transfer coupling boundary, a momentum equation and a turbulent flow equation of the fluid are closed, and transient heat transfer is calculated until the flow field is updated for the next time and / or calculation stops; 3, the first step and the second step are repeated, wherein flow field updating and transient heat transfer calculating are alternately performed until the time arrives at the transient heat transfer termination moment. For the forced-convection heat transfer process of air in a pipe, by comparing the modeling method with a tight coupling calculation result of Fluent commercial software, the absolute error is 1 K or below, the calculation efficiency is improved by one order of magnitude, and the engineering calculation requirement is met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Fluid-solid coupling analysis based erosion destruction invalidation quantitative forecast method
InactiveCN101059417AQuantitative prediction of erosion damage failurePredict failure hazardWeather/light/corrosion resistanceInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceCharacter analysisTectorial membrane
The invention discloses an abrasion destroy failure quantitative prediction method, based on flow-solid couple analysis, comprising abrasion product protective film character analysis and failure prediction analysis under flow function. Based on the real condition of tube, via flow mechanics similar theory, the invention finds the standard, test condition and flow medium of object tube, via electrochemical test method, processes instant character test of abrasion destroy, builds flow-solid couple model to set characteristic parameter values of abrasion product protective film, uses finite element analysis software to process flow-solid couple simulation, combined with test, corrects the characteristic parameter values of the abrasion product protective film, based on real tube system typical tube, processes flow-solid couple simulation, to realize abrasion destroy failure quantitative prediction of tube system, which can accurately predict the failure points of whole tube system, to support the safe protection technique of pressure tube system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Reverse twist designing method of pre-deformation influence of moving blades of marine combustion engine gas compressor
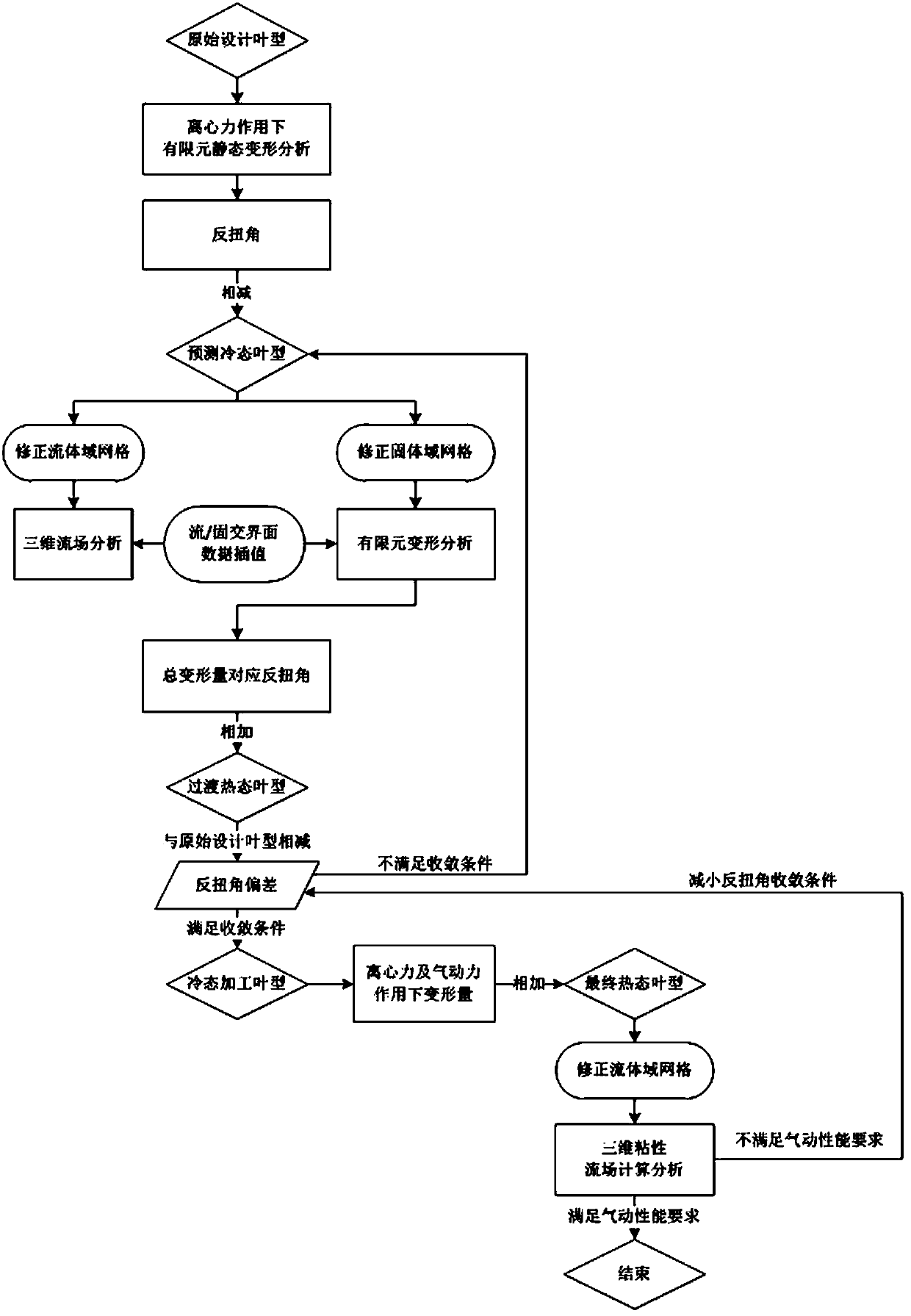
InactiveCN108710746AAchieve seamless connectionImprove the efficiency of anti-torsion designGeometric CADSustainable transportationGas compressorEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of gas turbines, in particular to a reverse twist designing method of pre-deformation influence of moving blades of a marine combustion engine gas compressor. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out nonlinear static analysis on original pneumatic designed blade forms under a centrifugal force action so as to acquire initial prediction cold-state blade forms; then carrying out repeated iteration on fluid-solid coupling solution to acquire final transitional heat-state blade forms and corresponding cold-state processing blade forms; carrying out three-dimensional viscous flow field analysis solution on the whole working conditions of the whole gas compressor according to the final heat-state blade forms of the cold-state processingblade forms under different working conditions, and verifying a reverse twist design result. By using twist twist angle numerical values as a convergence condition, based on that, a reverse twist design process of the moving blades of the marine combustion engine gas compressor is built, and the pneumatic performance checking result of the whole gas compressor as a final judgement evidence of thereverse twist design, so that seamless connection between the reverse twist design and gas compressor engineering design is realized, the reverse twist design efficiency is improved, and the reverse twist designing method has an important engineering application values.
Owner:HARBIN GUANGHAN GAS TURBINE
Fluid-structure coupled numerical simulation method and program for fluid-structure coupled numerical simulation storage device
InactiveUS20070129919A1Simple procedureSmall loadFlow propertiesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsPressure balanceComputer science
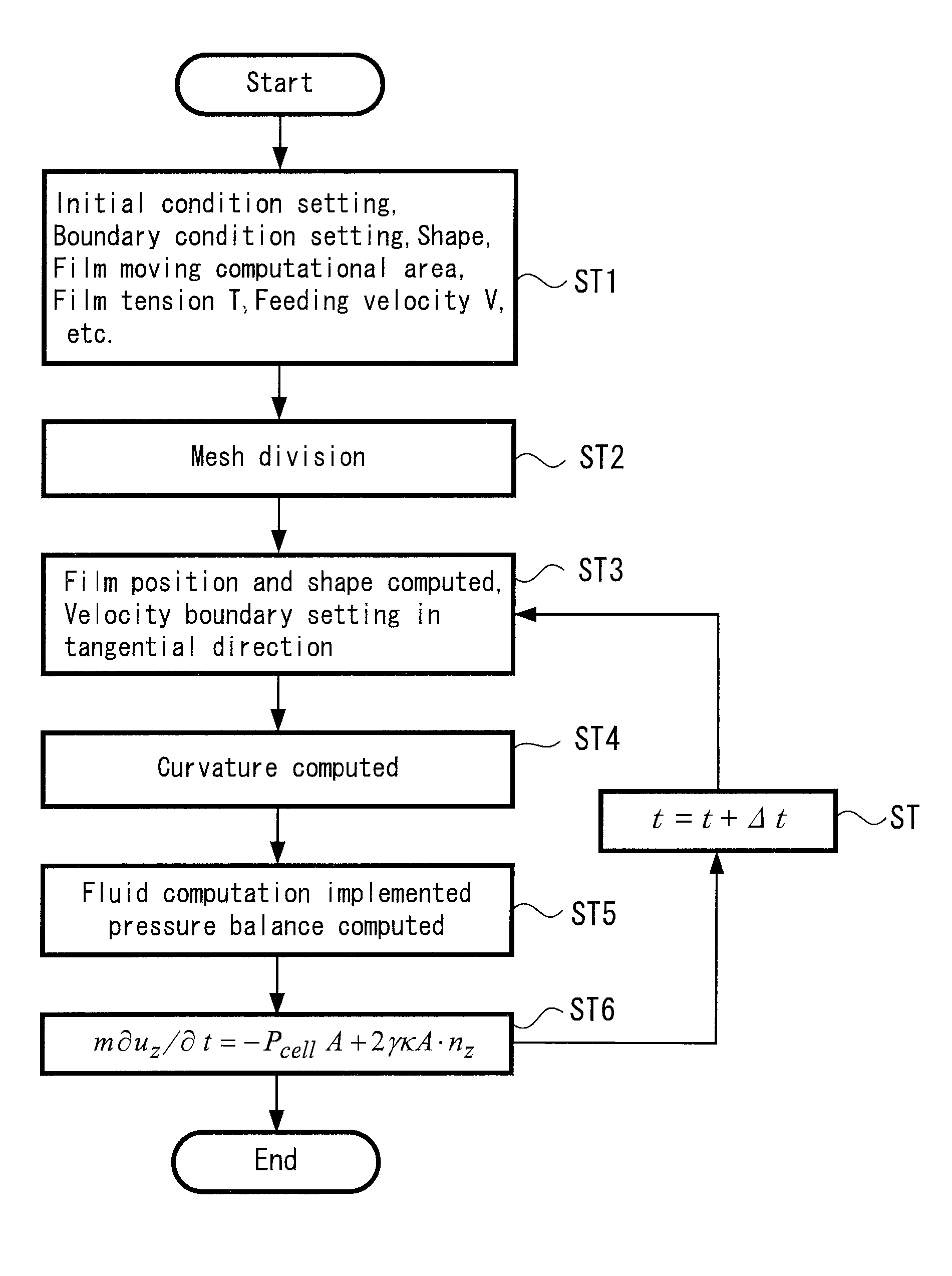
A fluid-structure coupled numerical simulation method is provided. The method uses a finite volume method employing an orthogonal mesh and a computer and memory setting a solid area based on a solid rate inside a mesh and at a tangent position to each mesh, including the steps of: setting initial and boundary conditions of a moving film structure; setting a velocity boundary in the tangent direction of the film structure by computing a position and shape thereof; and computing a curvature thereof. The method further includes the step of computing a pressure balance based on a balance between a pressure obtained from a fluid computation and a repulsive force obtained from the tension and curvature of the film structure to implement processing of a mutually-coupled phenomenon. A shift amount of the film surface for each time of said computing steps is simulated using the same program.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multiple fluid-solid coupling calculation method for tail bearing-rotor system
InactiveCN106383930ASimulation is accurateSolve the problem of low calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPropellerEngineering
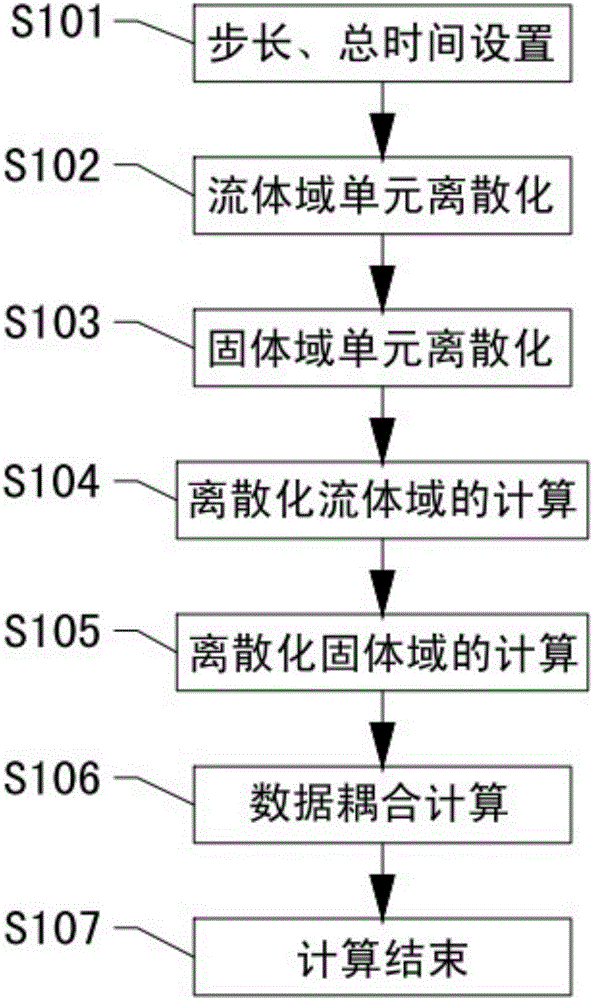
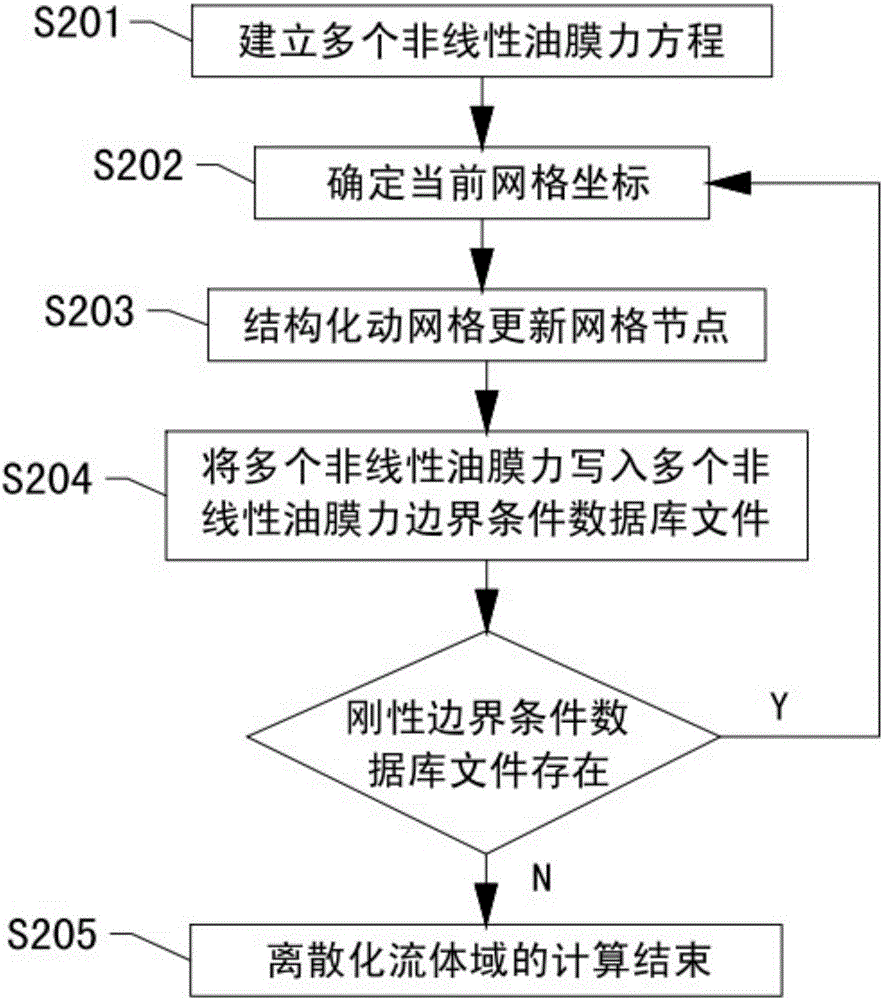
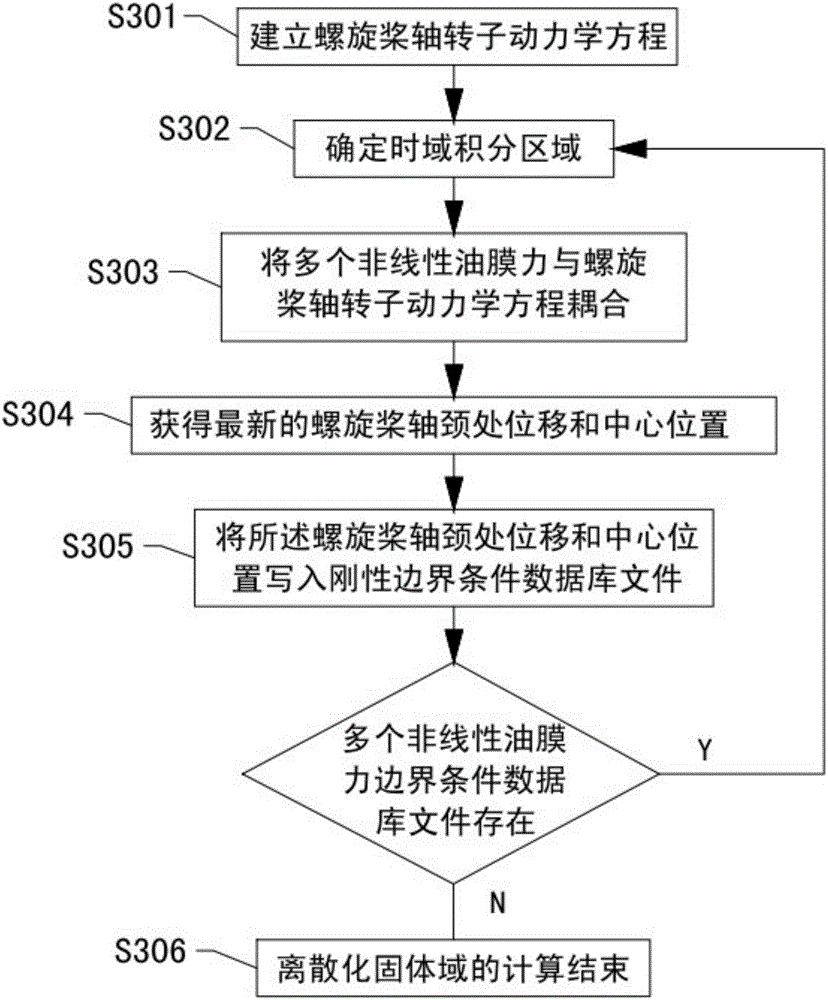
The invention discloses a multiple fluid-solid coupling calculation method for a tail bearing-rotor system, and belongs to the technical field of fluid-solid coupling of ocean platforms. The method involves a plurality of tail bearings and a propeller shaft, and comprises the steps of setting a step length of unit time and total calculation time, discretizing a fluid domain unit, discretizing a solid domain unit, calculating a discretized fluid domain, calculating a discretized solid domain, performing data coupling calculation, and ending the calculation. According to the multiple fluid-solid coupling calculation method for the tail bearing-rotor system, accurate simulation of a working process of the tail bearing and rotor system is realized, and the problem of low fluid domain calculation precision caused by excessively large mesh distortion in application of an existing dynamic mesh technique to spatial regions occupied by the tail bearings to perform numerical simulation is solved; and multiple fluid-solid coupling calculation is realized, the defects of coupling calculation of a symmetric bearing-rotor system are overcome, and multiple coupling effects, between vibration and lubrication, of the propeller shaft and the tail bearings can be accurately simulated.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com