Patents
Literature
600results about How to "Accurate modeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
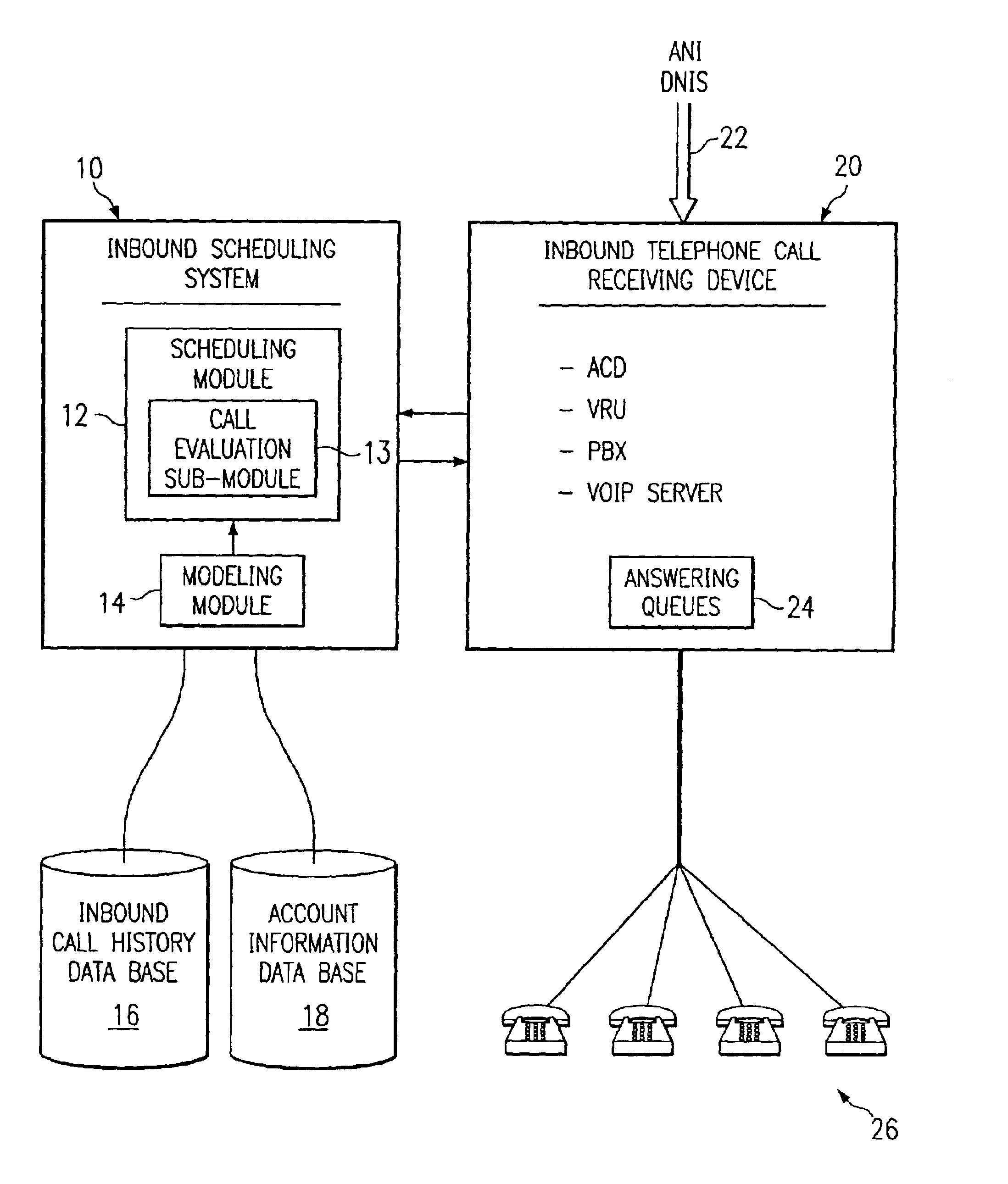
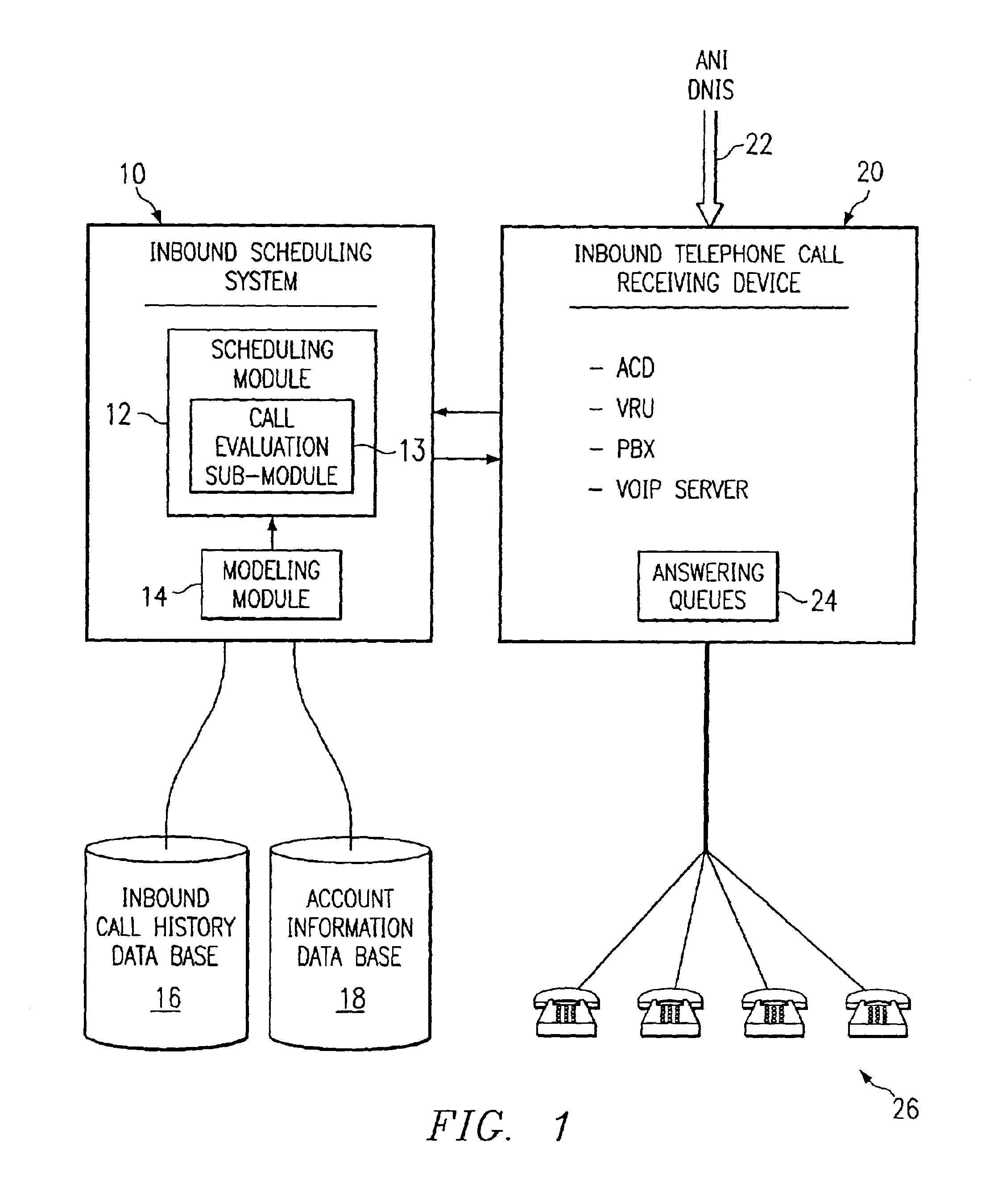
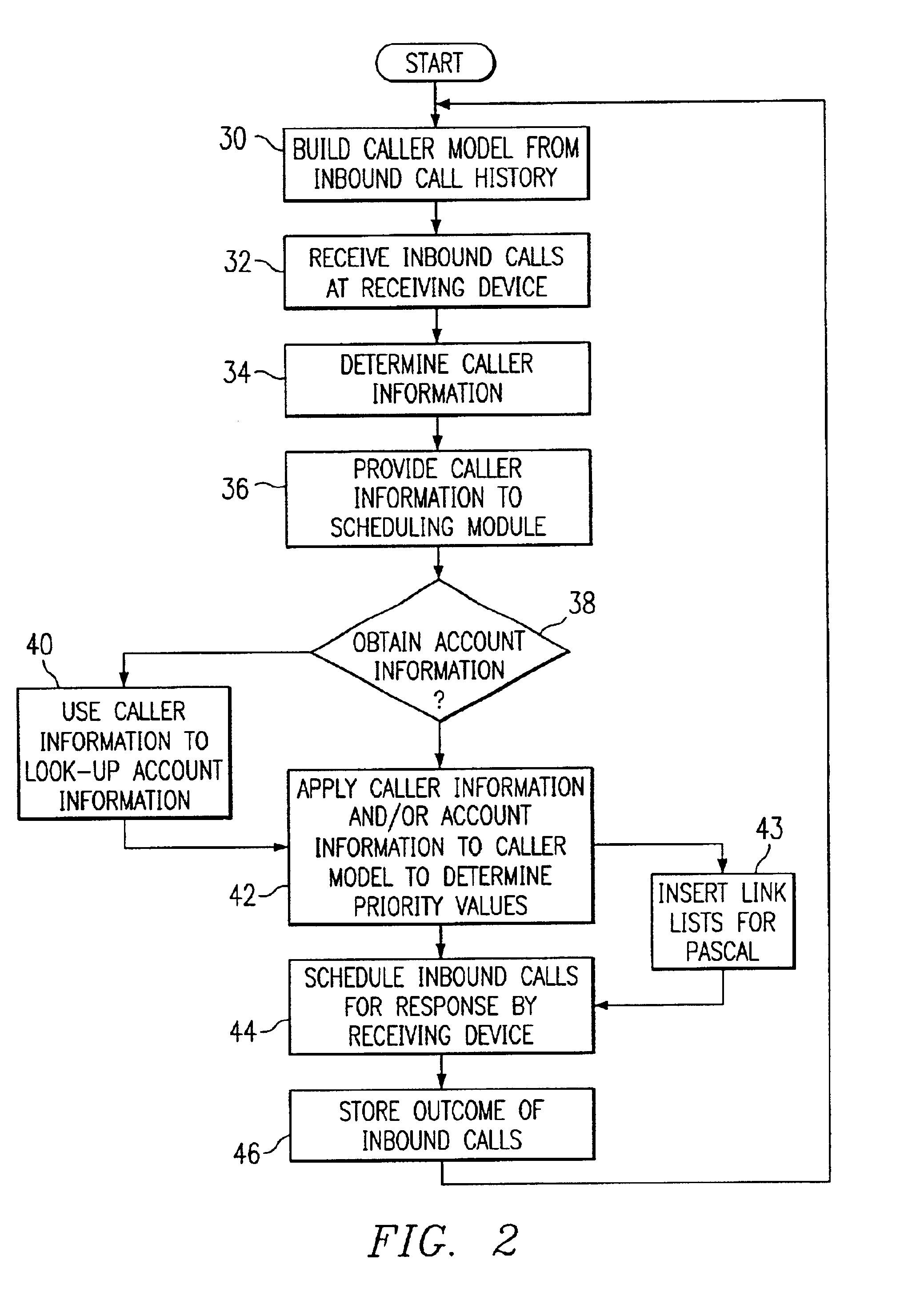
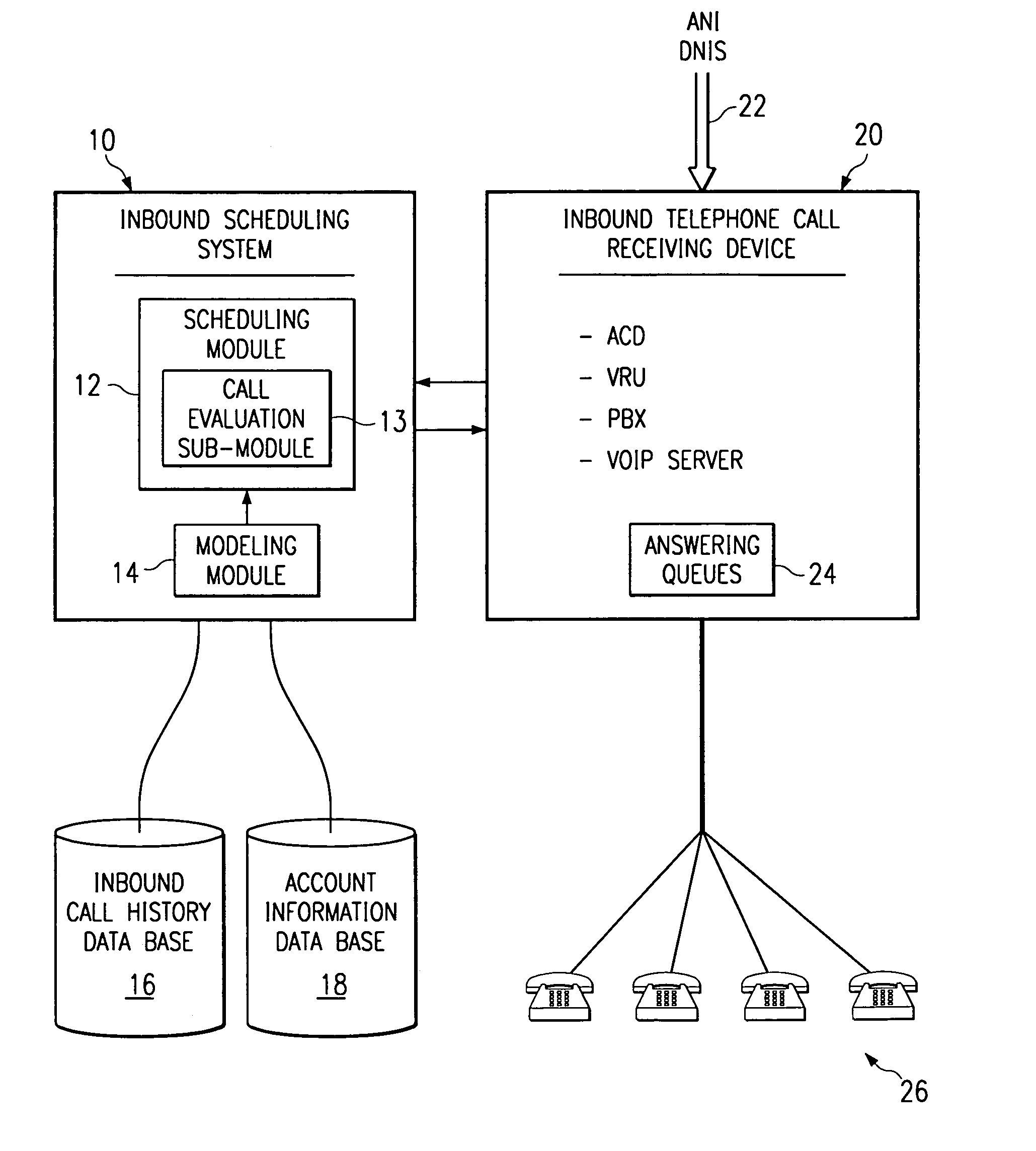
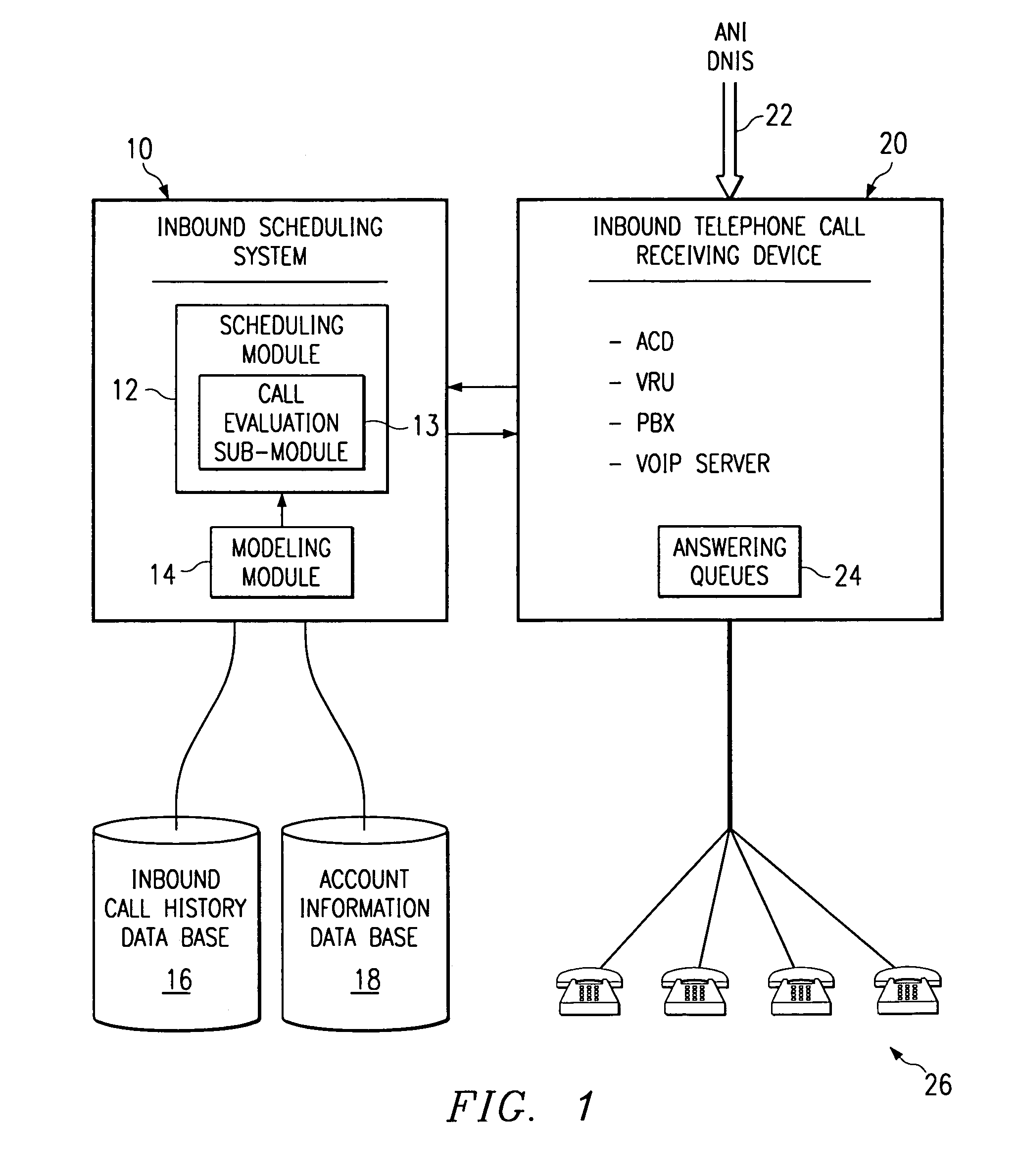
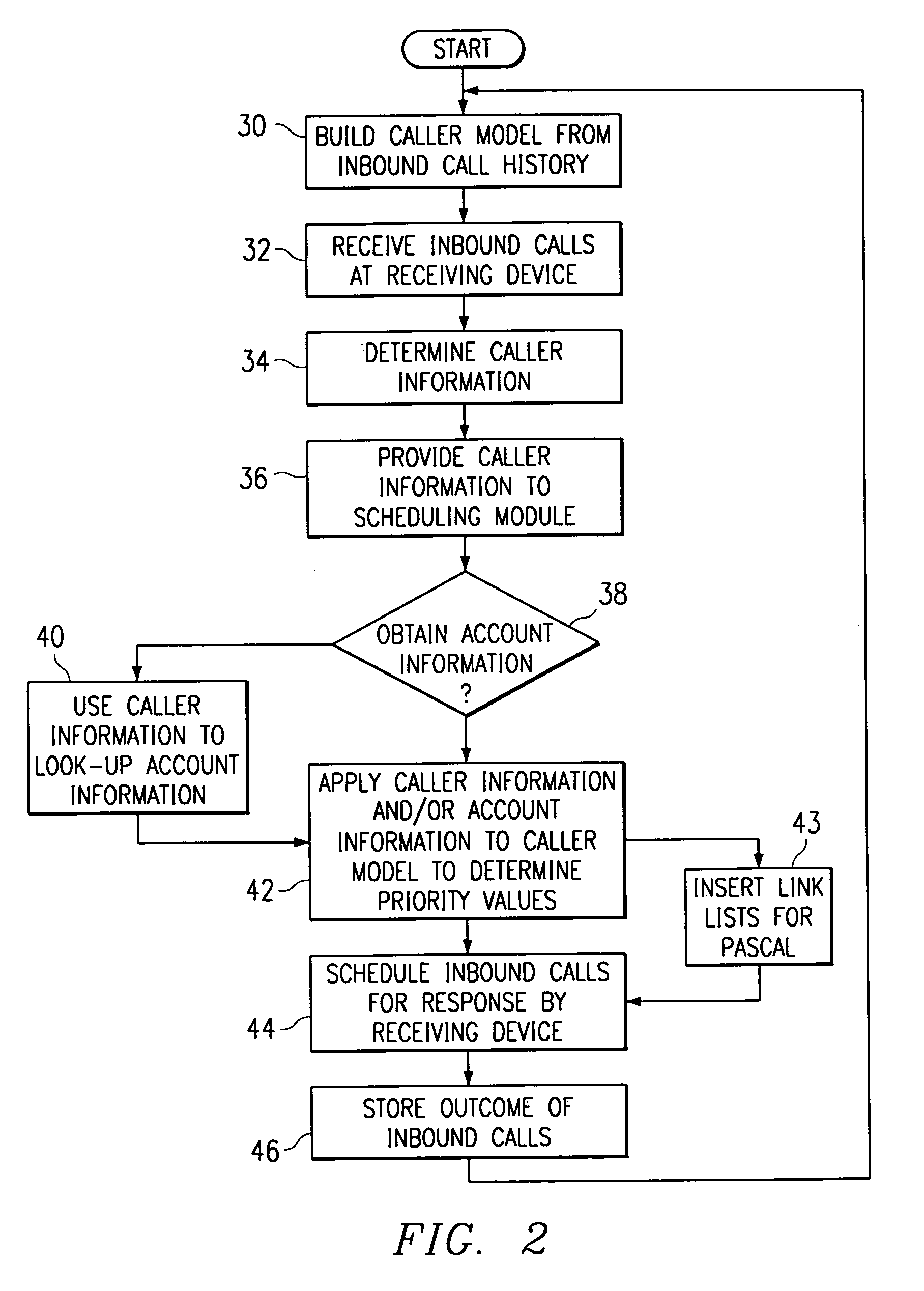
Method and system for self-service scheduling of inbound inquiries
InactiveUS6859529B2Accurate modelingMaximize useSpecial service for subscribersManual exchangesProduction rateRegression analysis
A method and system schedules inbound inquiries, such as inbound telephone calls, for response by agents in an order that is based in part on the forecasted outcome of the inbound inquiries. A scheduling module applies inquiry information to a model to forecast the outcome of an inbound inquiry. The forecasted outcome is used to set a priority value for ordering the inquiry. The priority value may be determined by solving a constrained optimization problem that seeks to maximize an objective function, such as maximizing an agent's productivity to produce sales or to minimize inbound call attrition. A modeling module generates models that forecast inquiry outcomes based on a history and inquiry information. Statistical analysis such as regression analysis determines the model with the outcome related to the nature of the inquiry. Operator wait time is regulated by forcing low priority and / or highly tolerant inbound inquiries to self service.
Method and system for scheduling inbound inquiries
InactiveUS6956941B1Accurate modelingMaximize useSpecial service for subscribersManual exchangesStatistical analysisRegression analysis
A method and system schedules inbound inquiries, such as inbound telephone calls, for response by agents in an order that is based in part on the forecasted outcome of the inbound inquiries. A scheduling module applies inquiry information to a model to forecast the outcome of an inbound inquiry. The forecasted outcome is used to set a priority value for ordering the inquiry. The priority value may be determined by solving a constrained optimization problem that seeks to maximize an objective function, such as maximizing an agent's productivity to produce sales or to minimize inbound call attrition. The inbound call may be placed on a virtual hold or be responded to on a real-time basis based on the inbound inquiry's priority value. A modeling module generates models that forecast inquiry outcomes based on a history and inquiry information. Statistical analysis such as regression analysis determines the model with the outcome related to the nature of the inquiry. Forecasted outcomes are based on the goal of the inbound calls and include factors such as probability an inbound caller will hang up, probability that an inbound caller will alter a business relationship based on hold time, probability that an inbound caller will make a purchase, and the relative probable reward of responding to an inbound call.
Owner:UNWIRED BROADBAND INC
Force effects for object types in a graphical user interface
InactiveUS7168042B2Avoid conflictGood flexibilityProgramme controlInput/output for user-computer interactionGraphical user interfaceApplication software
Force effects for a graphical user interface of a computer are provided based on user preference information, which indicates the types of graphical objects in the graphical user interface which are to have force effects associated with them, and at least one particular force effect assigned to each of those types of graphical objects. An output of a force sensation by a haptic feedback device to the user is based on those assigned force effects and occurs when a displayed cursor controlled by a user interacts with a graphical object having one of the types. An architecture for a host computer allowing multi-tasking application programs to interface with a feedback device is also disclosed.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
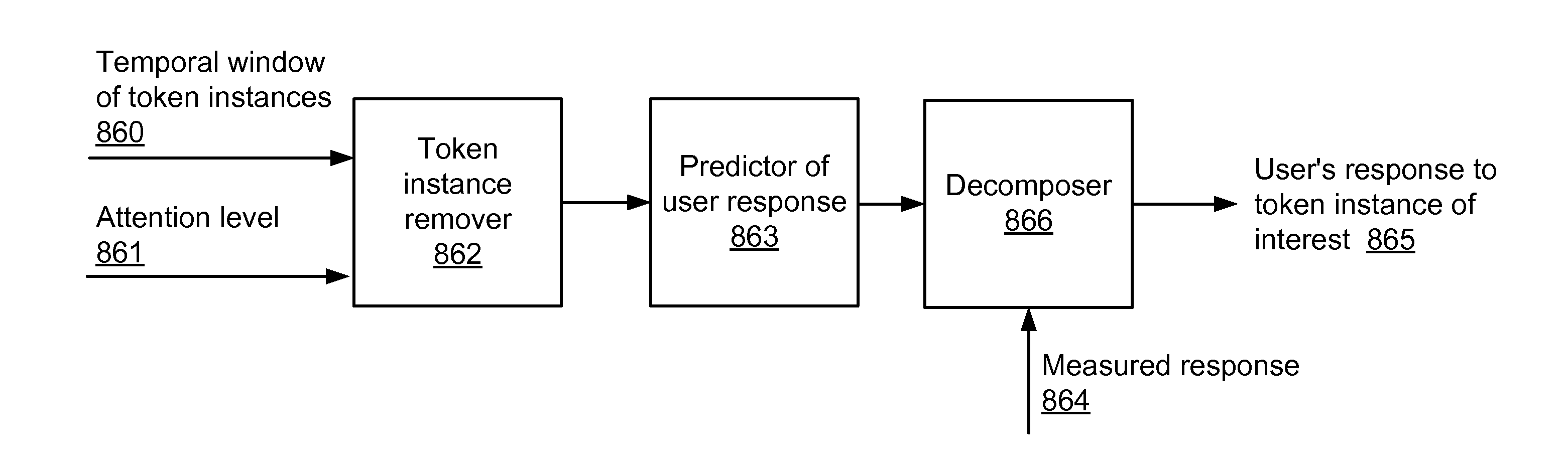
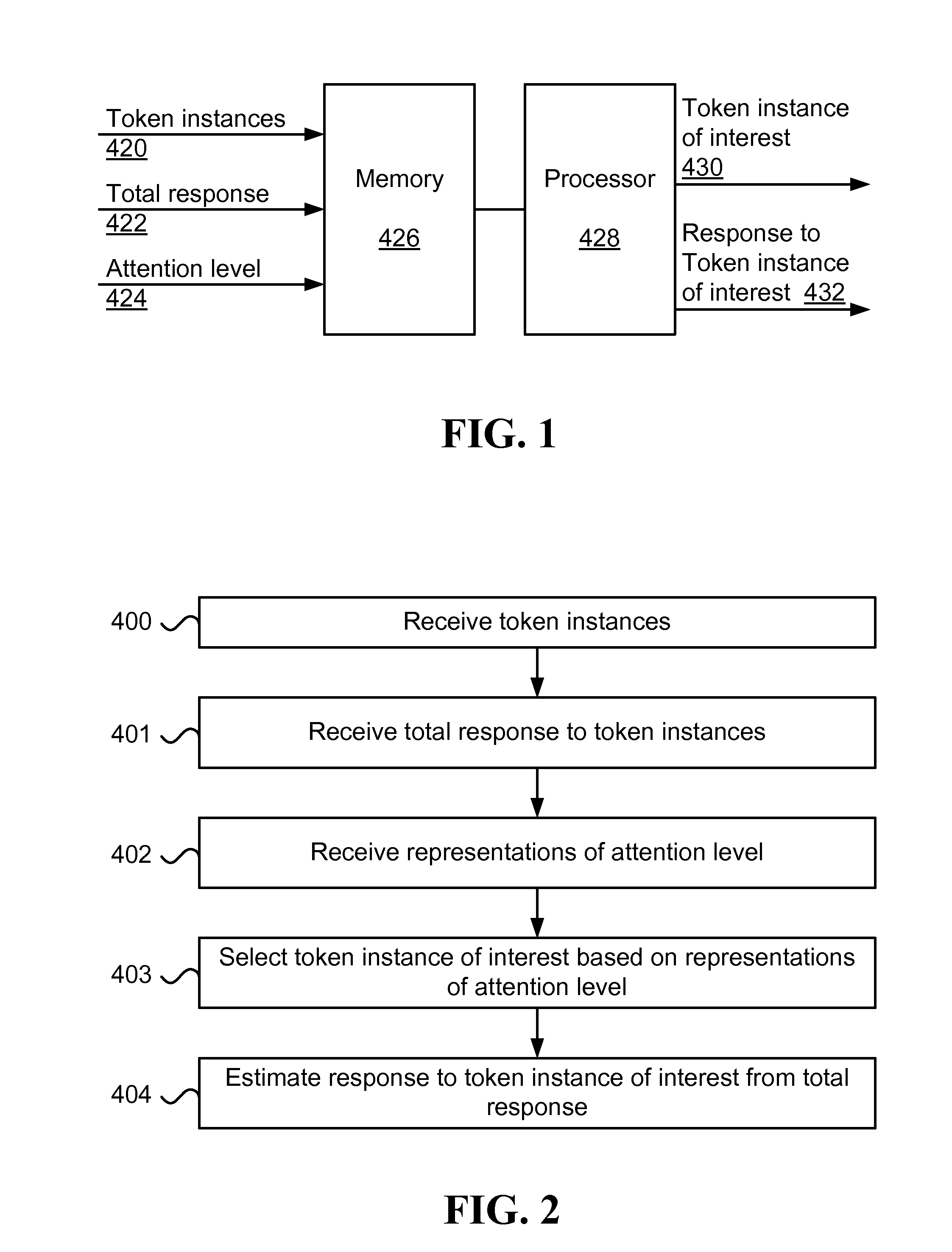
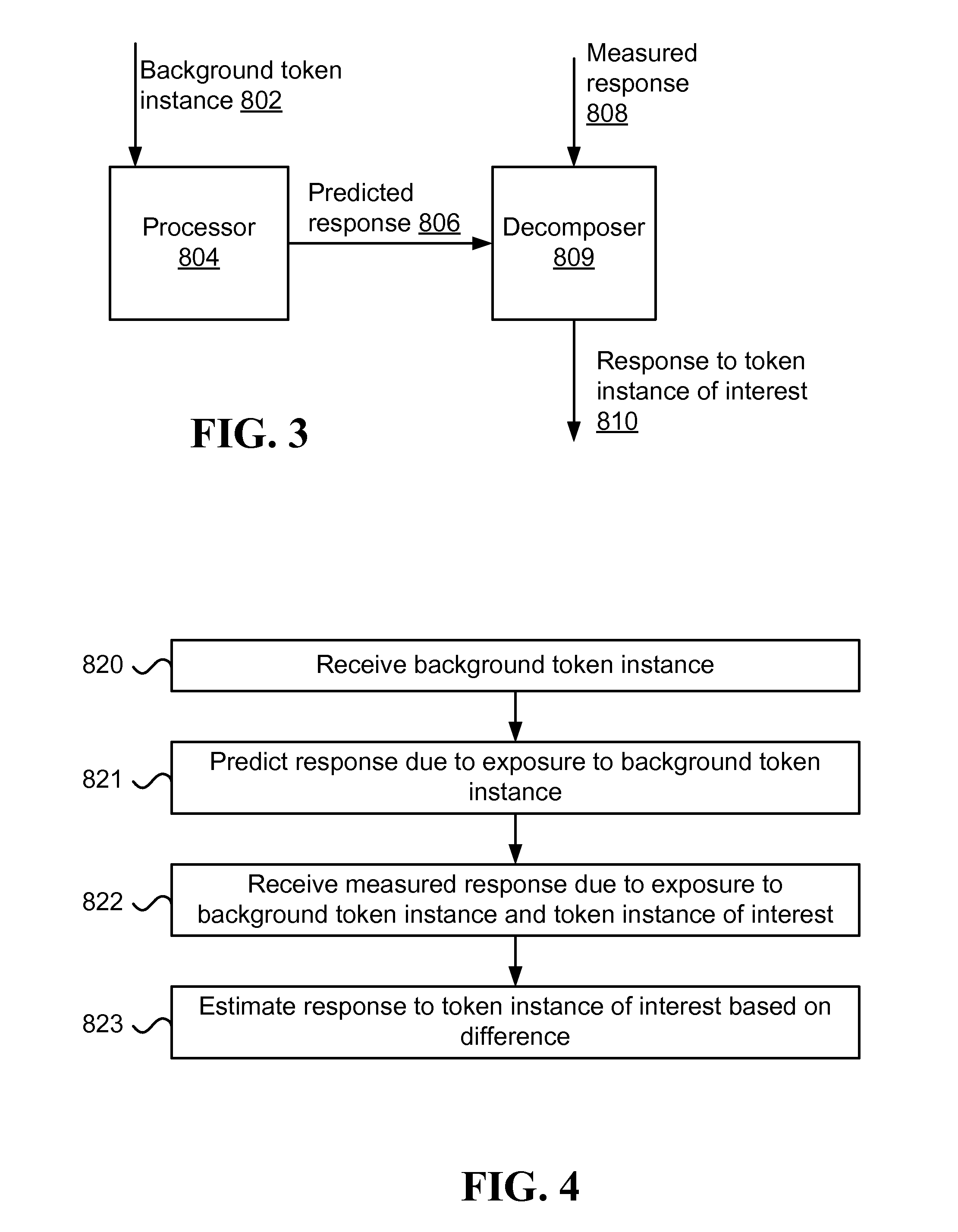
Method and system for estimating response to token instance of interest
ActiveUS20130103624A1Accurate modelingDigital computer detailsMedical automated diagnosisTheoretical computer scienceAlgorithm
Estimating a response to a token instance of interest, including the steps of: receiving token instances to which a user was exposed, receiving a total response of the user to the token instances; receiving attention levels of the user in the token instances; selecting the token instance of interest from among the token instances based on the attention level; and estimating the response to the token instance of interest from the total response.
Owner:AFFECTOMATICS
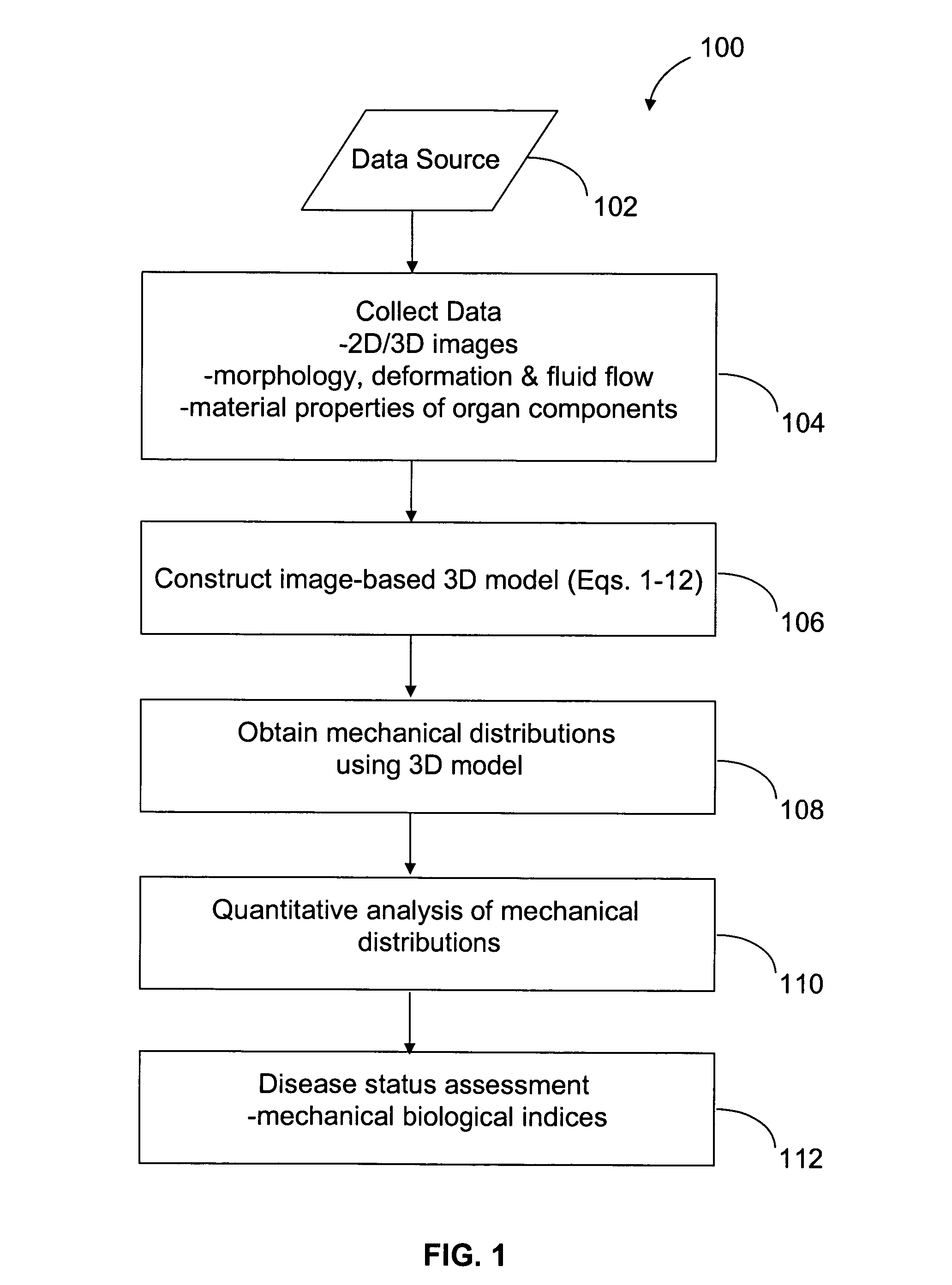
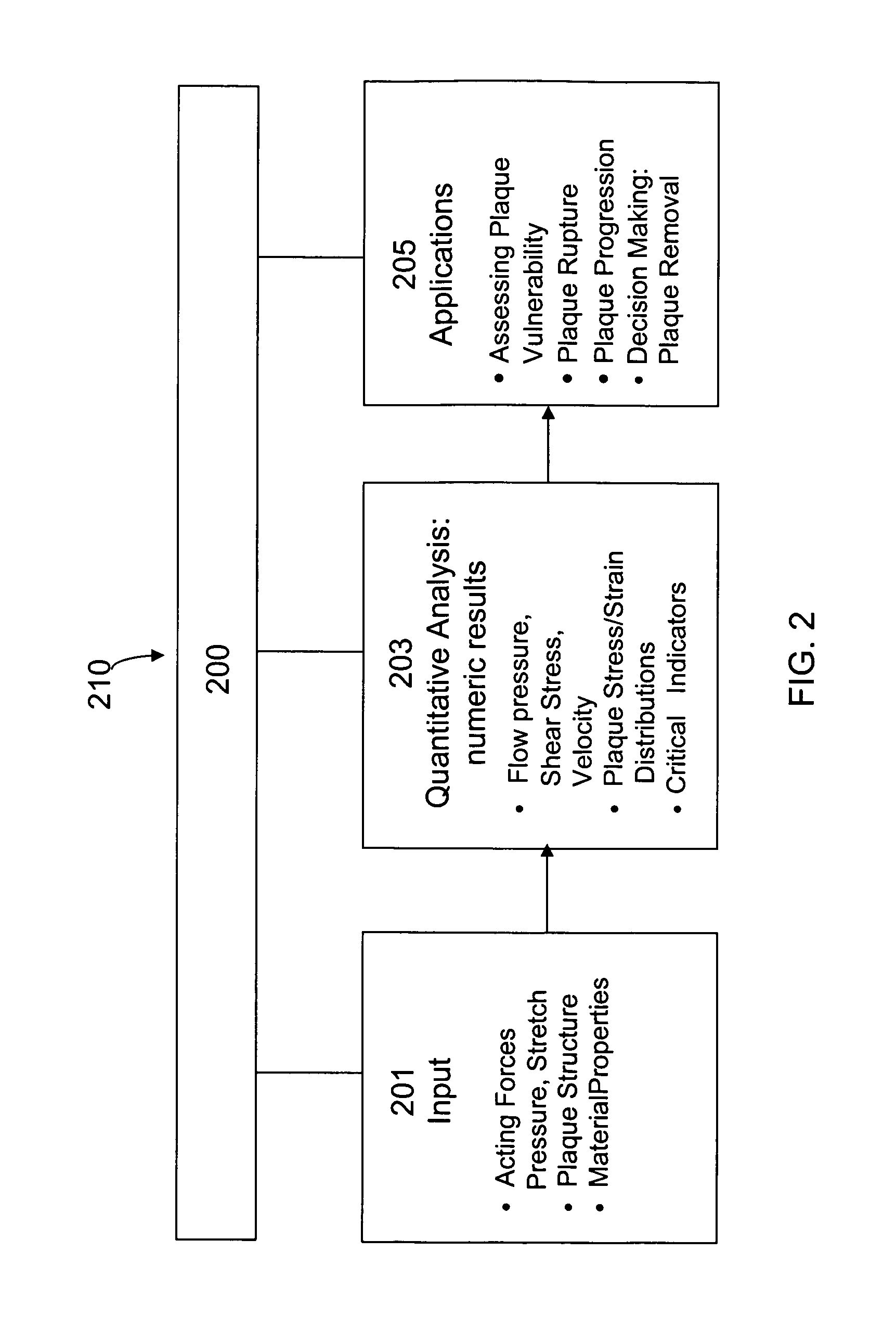
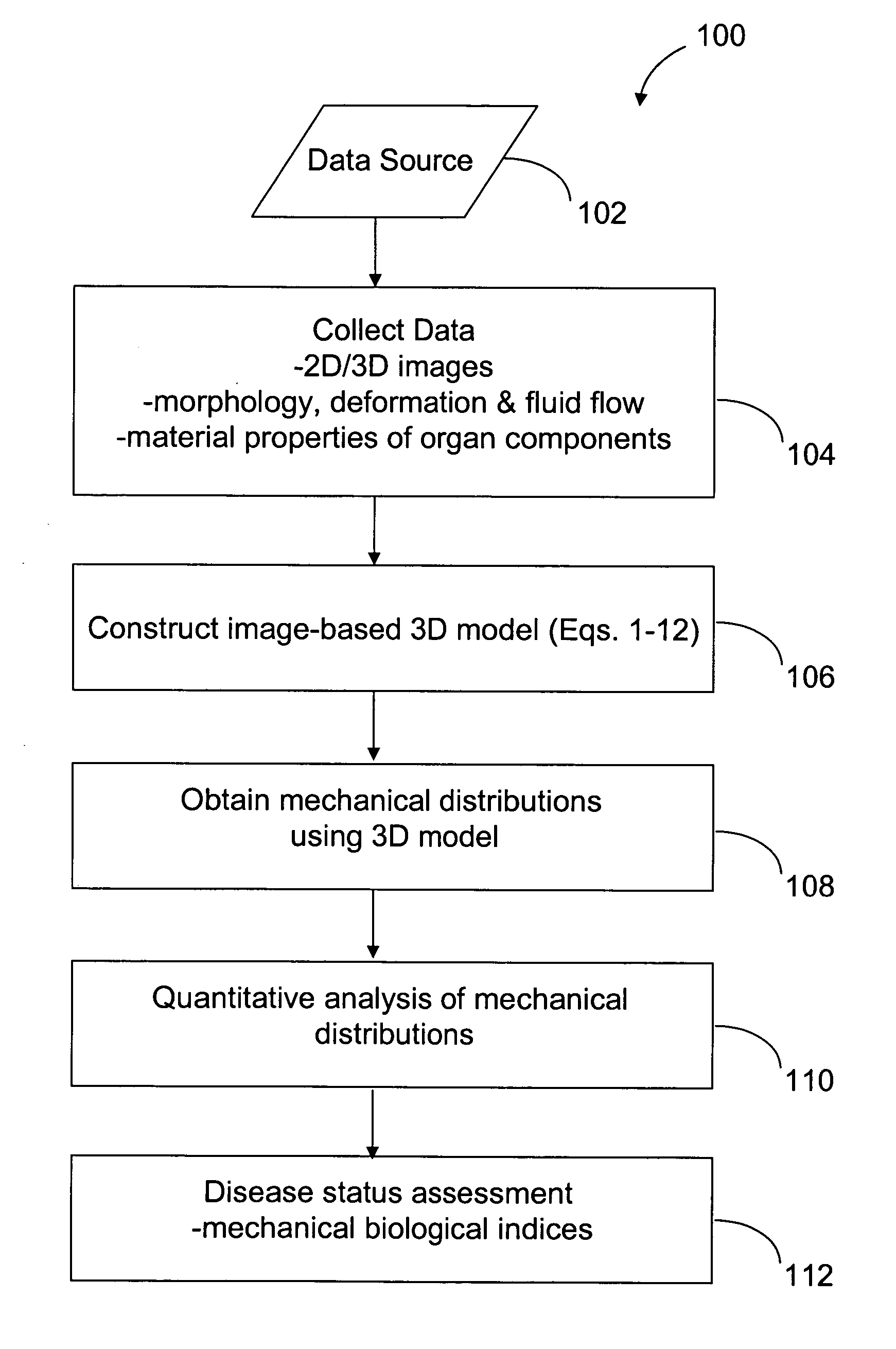
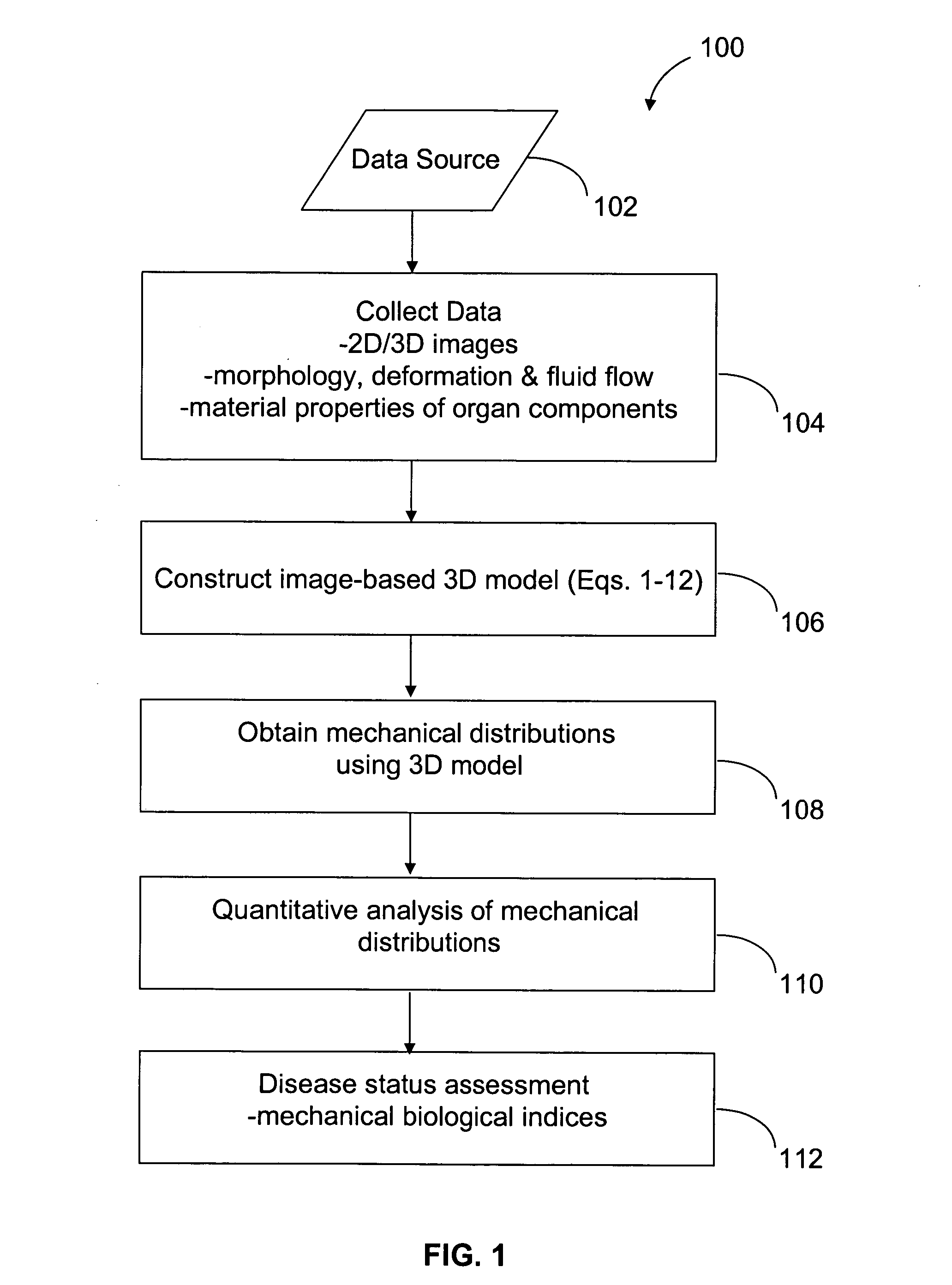
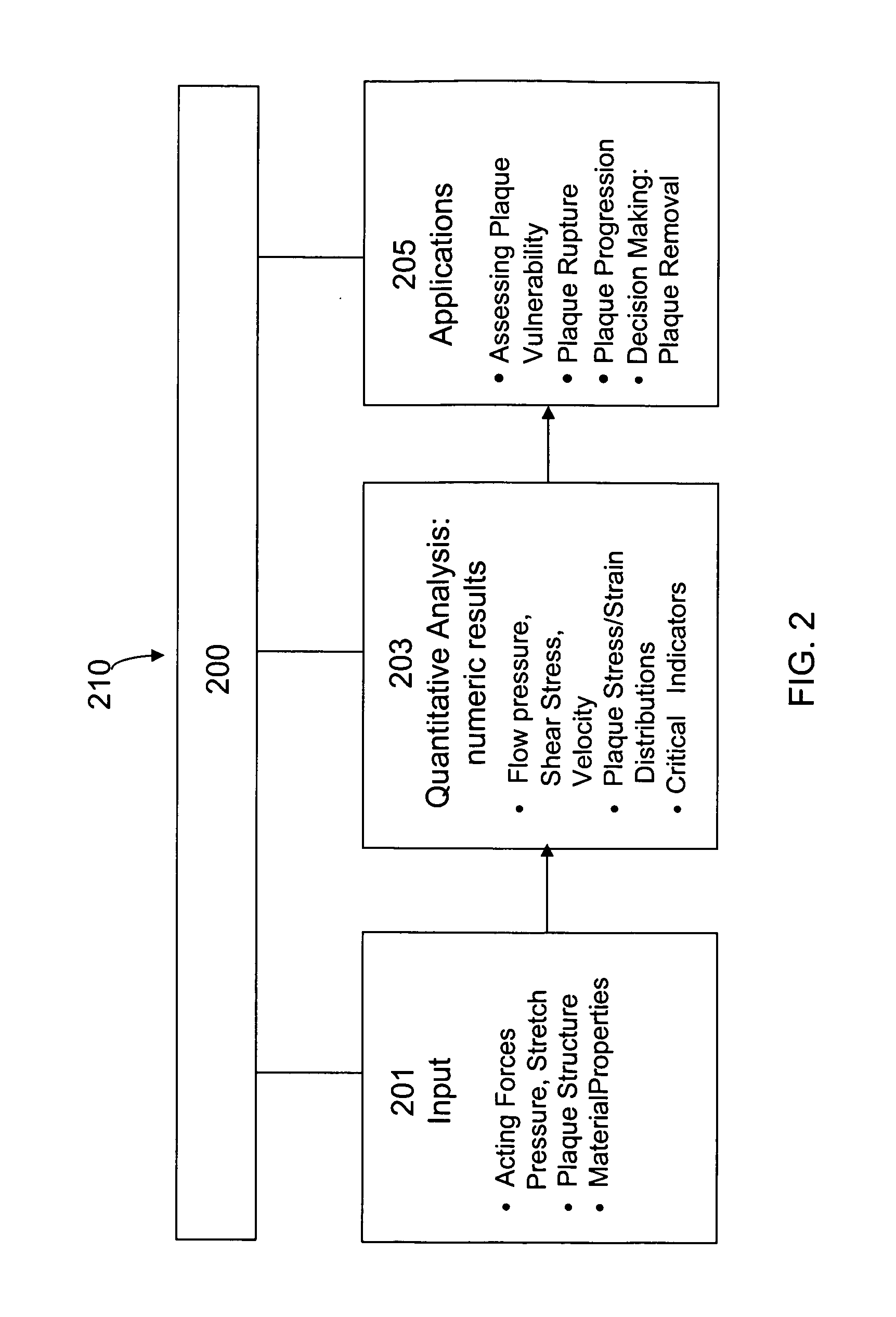
Image-based computational mechanical analysis and indexing for cardiovascular diseases
ActiveUS7751984B2Accurate modelingMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesOrgan ModelMedicine
A method and a computer system, for providing an assessment for disease status of a disease, such as a cardiovascular disease, employ construction of image-based 3D computational model of an organ representative of the disease status; computationally obtaining a certain mechanical distribution using the 3D-organ model; and computational, quantitative analysis of the mechanical distribution to provide an assessment for disease status of a disease. The image-based 3D computational model includes a fluid-structure interaction and multiple components within the organ.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
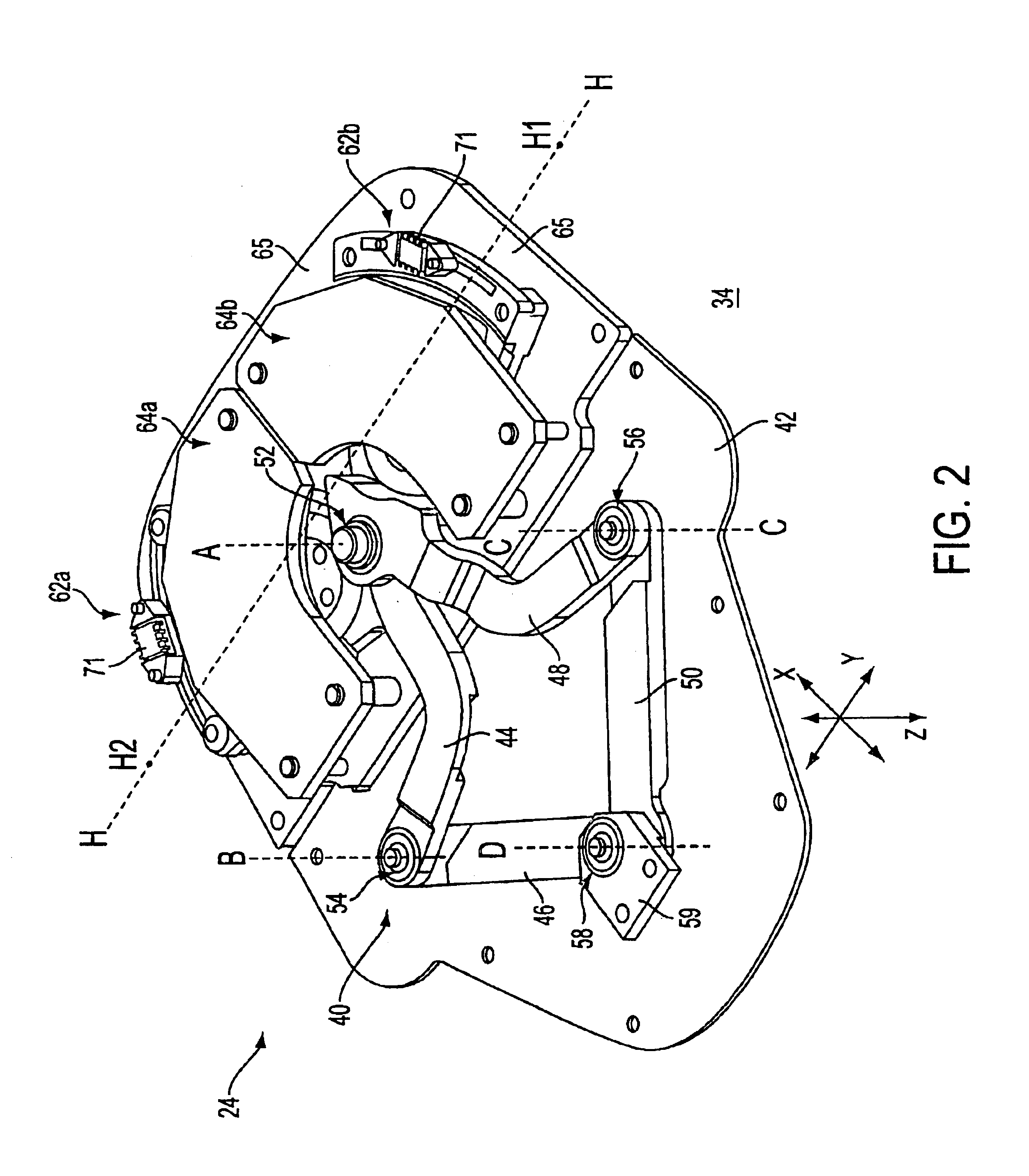
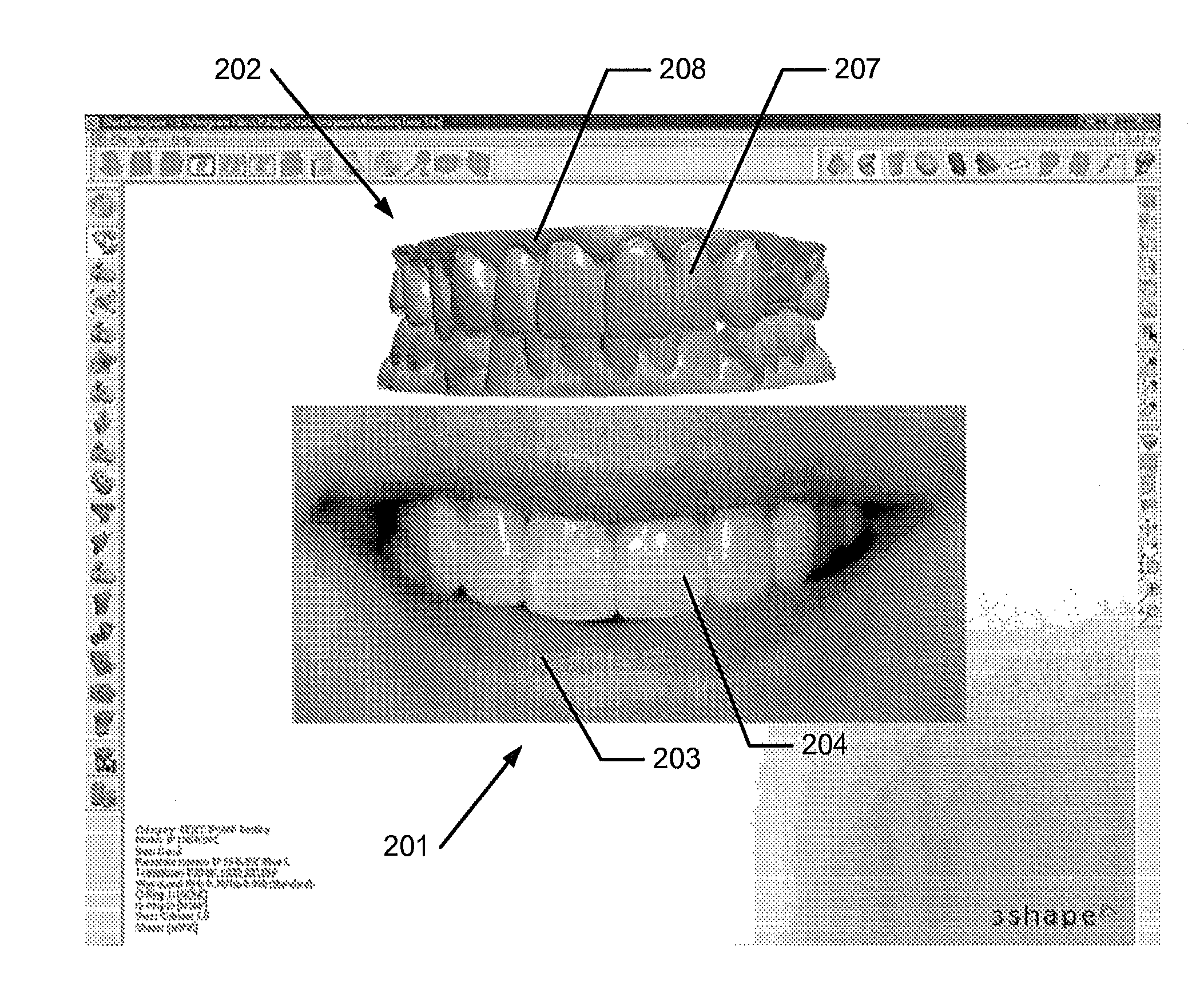
2d image arrangement
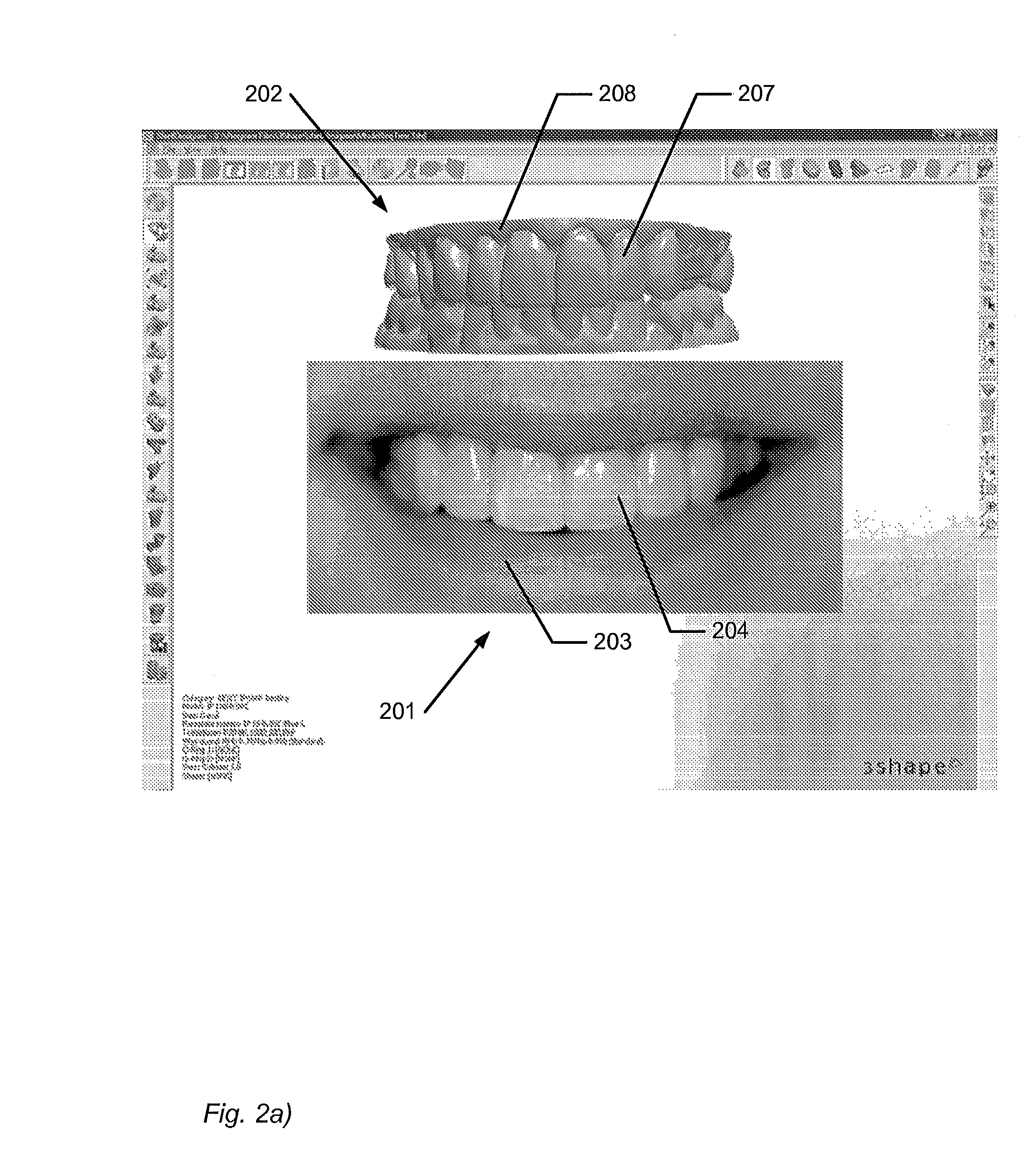
ActiveUS20130218530A1Good for comparisonDetection is slightImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed is a method of designing a dental restoration for a patient, wherein the method includes providing one or more 2D images, where at least one 2D image includes at least one facial feature; providing a 3D virtual model of at least part of the patient's oral cavity; arranging at least one of the one or more 2D images relative to the 3D virtual model in a virtual 3D space such that the 2D image and the 3D virtual model are aligned when viewed from a viewpoint, whereby the 3D virtual model and the 2D image are both visualized in the 3D space; and modeling a restoration on the 3D virtual model, where the restoration is designed to fit the facial feature of the at least one 2D image.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
System and method for complex geometry modeling of anatomy using multiple surface models
ActiveUS7988639B2Accurate modelingImprove abilitiesElectrocardiographyCatheterComputational scienceHuman anatomy
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for creating a complex model of the human anatomy. The anatomy may be modeled using multiple geometries. Generally, a plurality of line-of-sight models may be combined into a composite model. Multiple clouds of points may be used to create surface models which may then be merged into a common volume. The resulting composite model may include portions that are not within a line of sight of a mean center point of the composite model. The surface models may be modeled using polygons, including for example, triangles. Disclosed herein are also ways in which electrophysiology data and / or other information may be mapped from a measurement point to a point on the composite model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
2D image arrangement
ActiveUS9336336B2Accurate modelingGood for comparisonImpression capsAdditive manufacturing apparatusViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed is a method of designing a dental restoration for a patient, wherein the method includes providing one or more 2D images, where at least one 2D image includes at least one facial feature; providing a 3D virtual model of at least part of the patient's oral cavity; arranging at least one of the one or more 2D images relative to the 3D virtual model in a virtual 3D space such that the 2D image and the 3D virtual model are aligned when viewed from a viewpoint, whereby the 3D virtual model and the 2D image are both visualized in the 3D space; and modeling a restoration on the 3D virtual model, where the restoration is designed to fit the facial feature of the at least one 2D image.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Image-based computational mechanical analysis and indexing for cardiovascular diseases
ActiveUS20060149522A1Accurate modelingMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesMultiple componentComputational model
A method and a computer system, for providing an assessment for disease status of a disease, such as a cardiovascular disease, employ construction of image-based 3D computational model of an organ representative of the disease status; computationally obtaining a certain mechanical distribution using the 3D-organ model; and computational, quantitative analysis of the mechanical distribution to provide an assessment for disease status of a disease. The image-based 3D computational model includes a fluid-structure interaction and multiple components within the organ.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Method for non-intrusive load monitoring using a hybrid systems state estimation approach
ActiveUS20110144819A1Few false positiveImprove accuracyLevel controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusHybrid systemMathematical model
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Hand-held self-referenced apparatus for three-dimensional scanning
ActiveUS20100134598A1Improve accuracyAccurate modelingCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing record carriersHand held3d scanning
A method and hand-held scanning apparatus for three-dimensional scanning of an object is described. The hand-held self-referenced scanning apparatus has a light source for illuminating retro-reflective markers, the retro-reflective markers being provided at fixed positions on or around the object, a photogrammetric high-resolution camera, a pattern projector for providing a projected pattern on a surface of the object; at least a pair of basic cameras, the basic camera cooperating with light sources, the projected pattern and at least a portion of the retro-reflective markers being apparent on the 2D images, a frame for holding all components in position within the hand-held apparatus, the frame having a handle, the frame allowing support and free movement of the scanning apparatus by a user.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
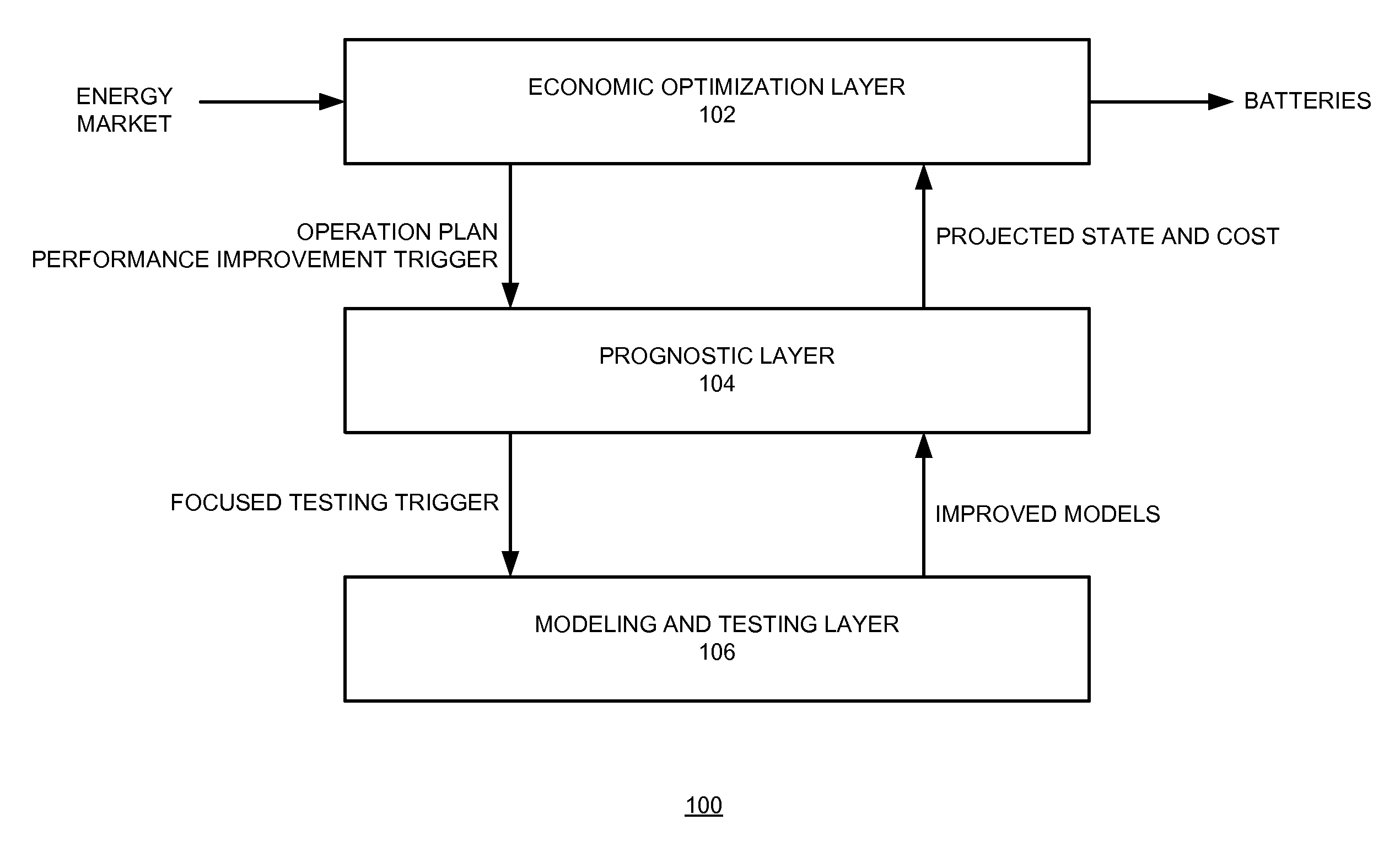
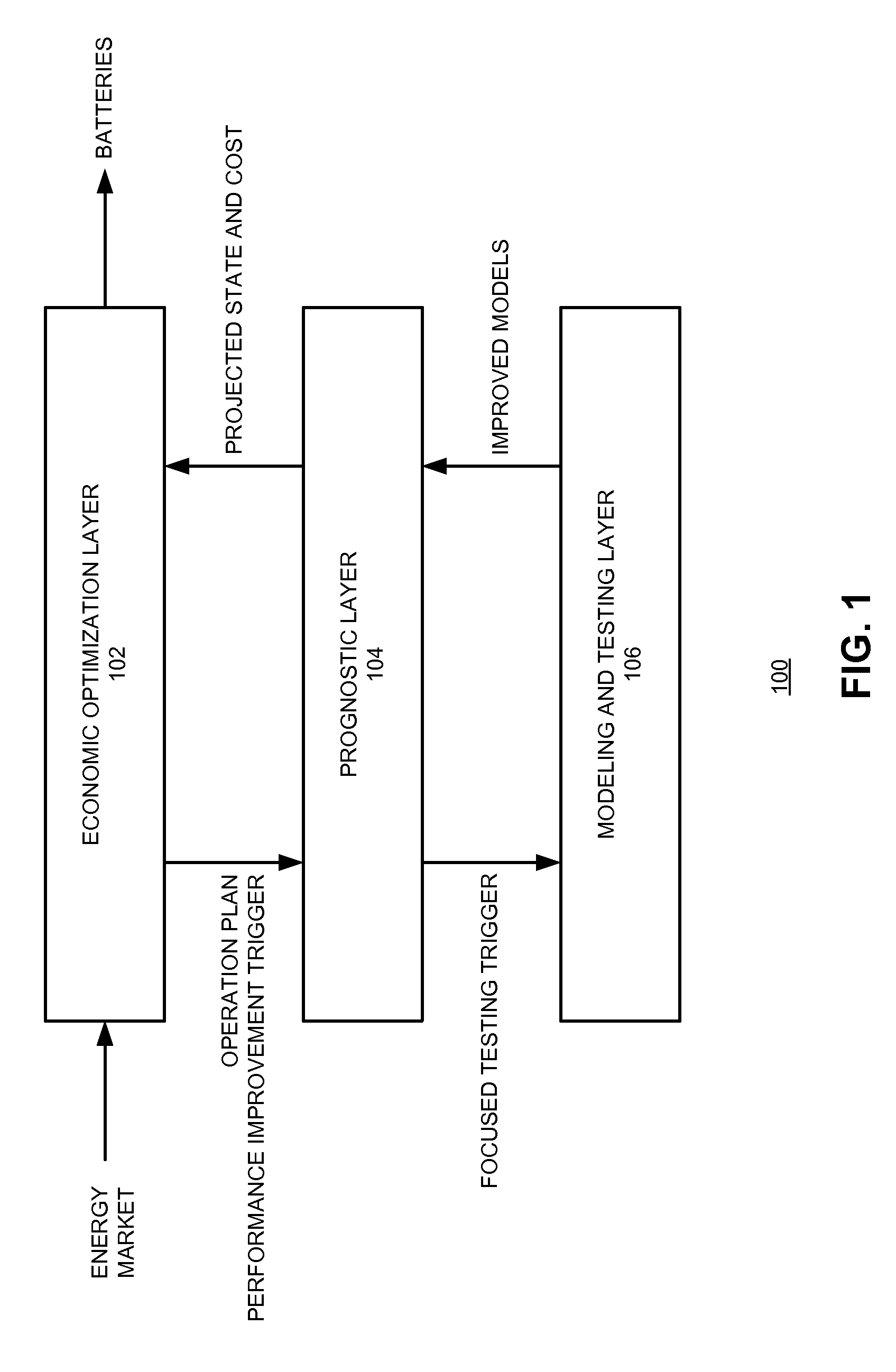
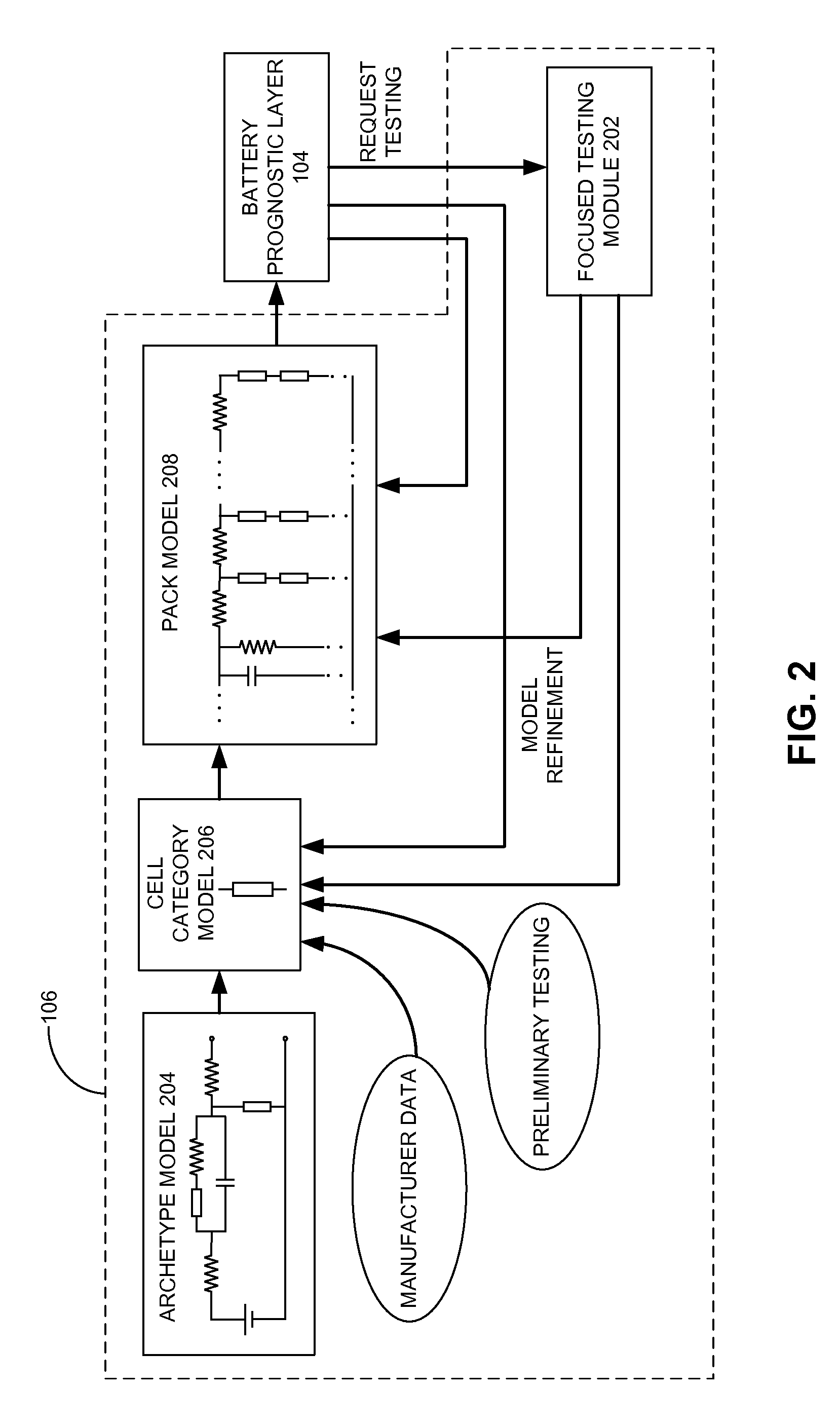
Strategic modeling for economic optimization of grid-tied energy assets
ActiveUS20150127425A1Accurate modelingFuture prognosticForecastingAc network load balancingControl systemEngineering
One embodiment of the present invention provides an energy-asset control system for utilizing an energy asset to provide one of more modes of operation services. The system includes an economic optimizer configured to identify at least one mode of operation opportunity based on current and / or future market conditions; a prognostics module configured to perform a prognostic analysis associated with the mode of operation opportunity for the energy asset using an existing model, and determine a confidence level associated with the prognostic analysis; and an operation controller. The economic optimizer is further to configured to, in response to the prognostics module determining the confidence level exceeding a predetermined threshold, determine an expected profit of the mode of operation opportunity based on outcomes of the prognostic analysis; and optimize, over a predetermined time period, a usage of the energy asset based on the expected profit of the mode of operation opportunity.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Apparatus for imaging and treating a breast
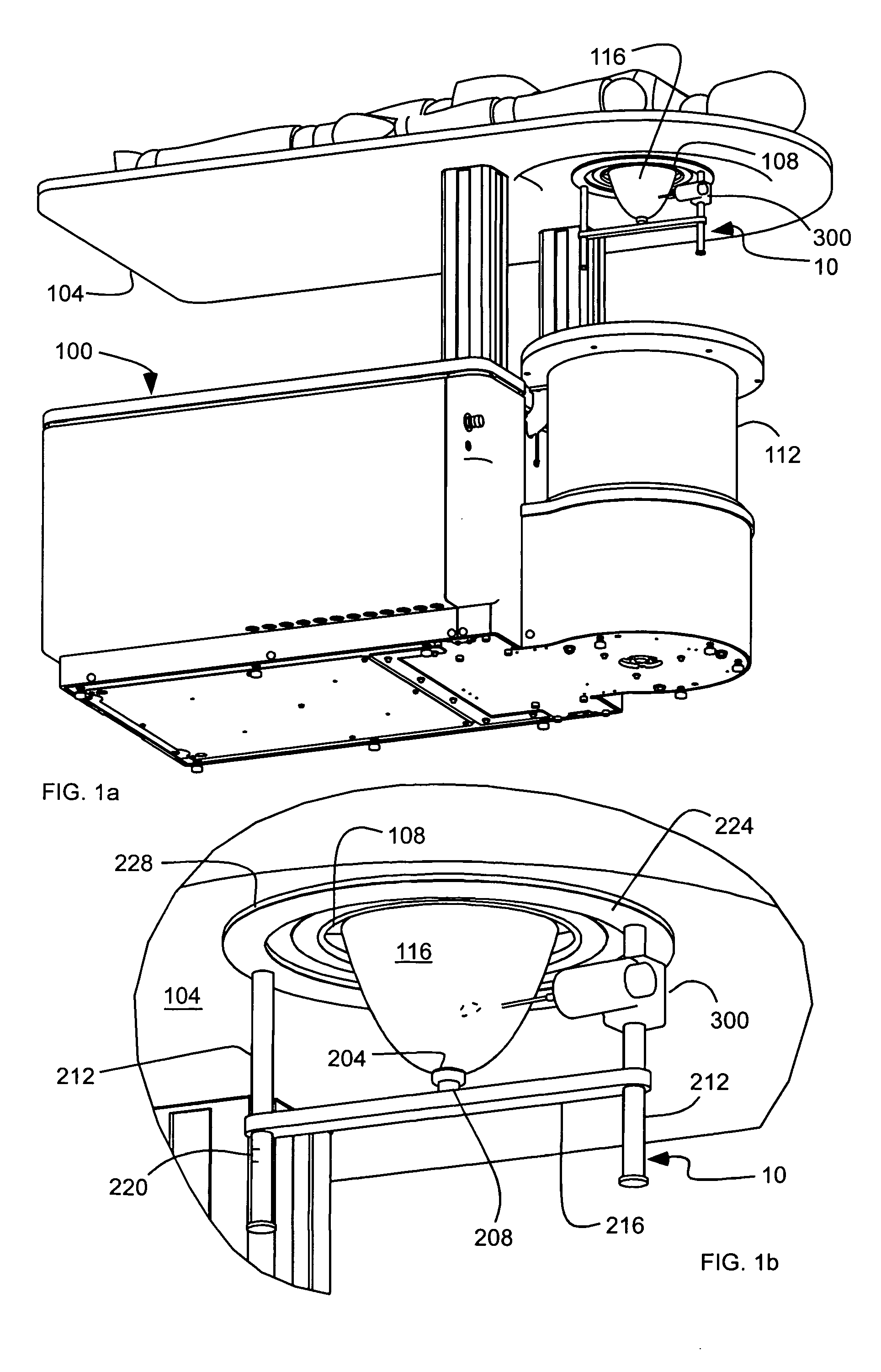
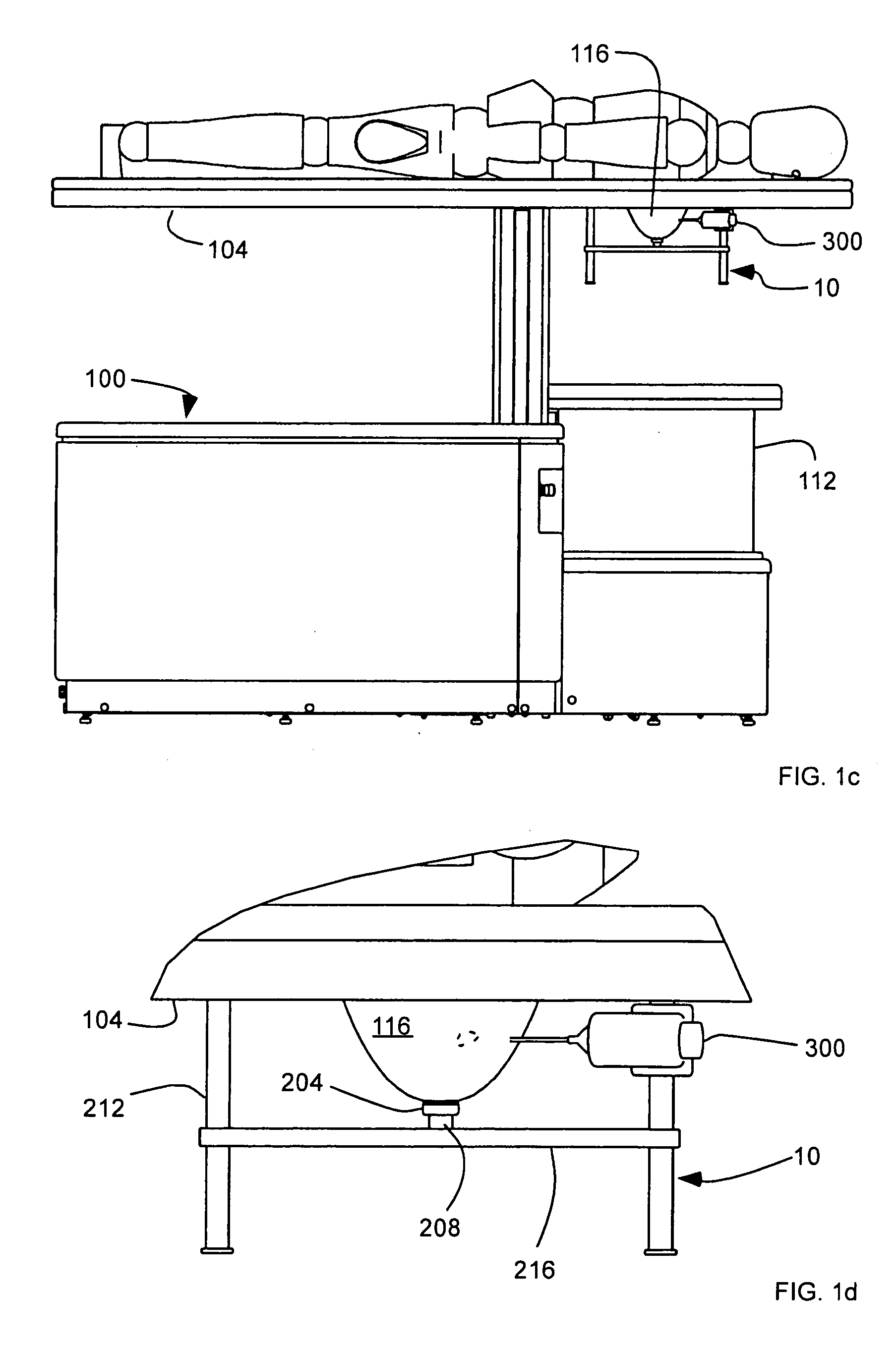
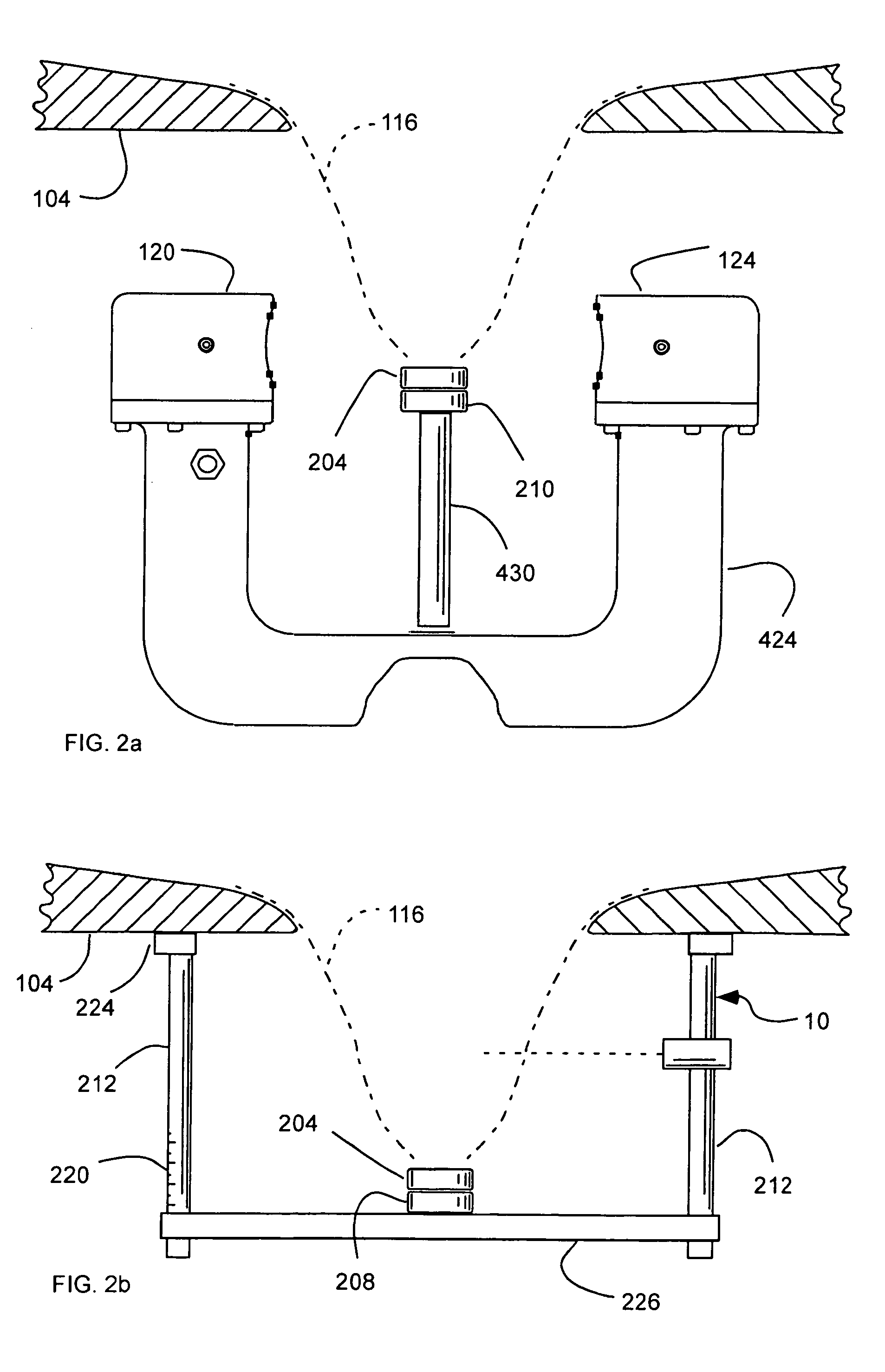
InactiveUS20060009693A1Convenient treatmentAccurate modelingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringUltrasound
A system for imaging and treating a breast of a patient includes a table configured to receive the patient thereon, having an aperture formed therein configured to receive the breast of the patient pendent therethrough and positionable over a bath configured to contain a medium. Means for transmitting and receiving ultrasound signals is disposed in the bath. A frame is disposable out of the bath, and includes means for securing the breast to the frame to substantially maintain a position and a shape of the breast out of the bath as in the bath.
Owner:TECHNISCAN
Training model for endoscopic vessel harvesting
A leg model, designed to teach endoscopic saphenous vein harvesting, is provided that accurately models the anatomy of the saphenous vein in the human thigh, and closely approximates the subcutaneous tissues in a human. The subcutaneous tissue is formulated and manufactured such that the saphenous vein adheres to the subcutaneous tissue to simulate the adhesion in a human leg. The model includes a reusable base and a replaceable single use insert. The base is size and configured to receive the insert. The tray can include a slit located at a point along its length that permits the ends of the tray to rotate about the slit so that the ends can be bent with respect to one another.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
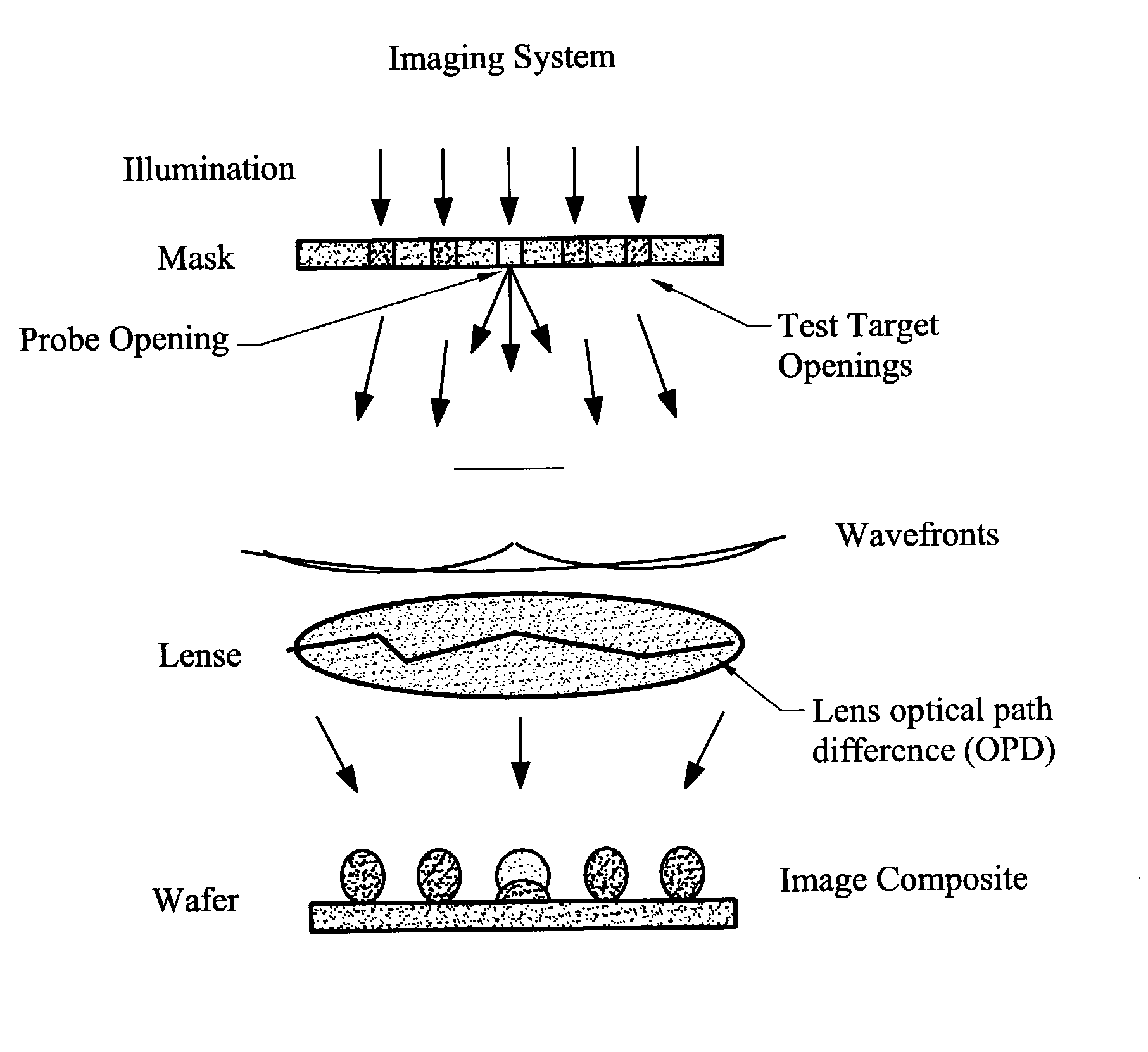
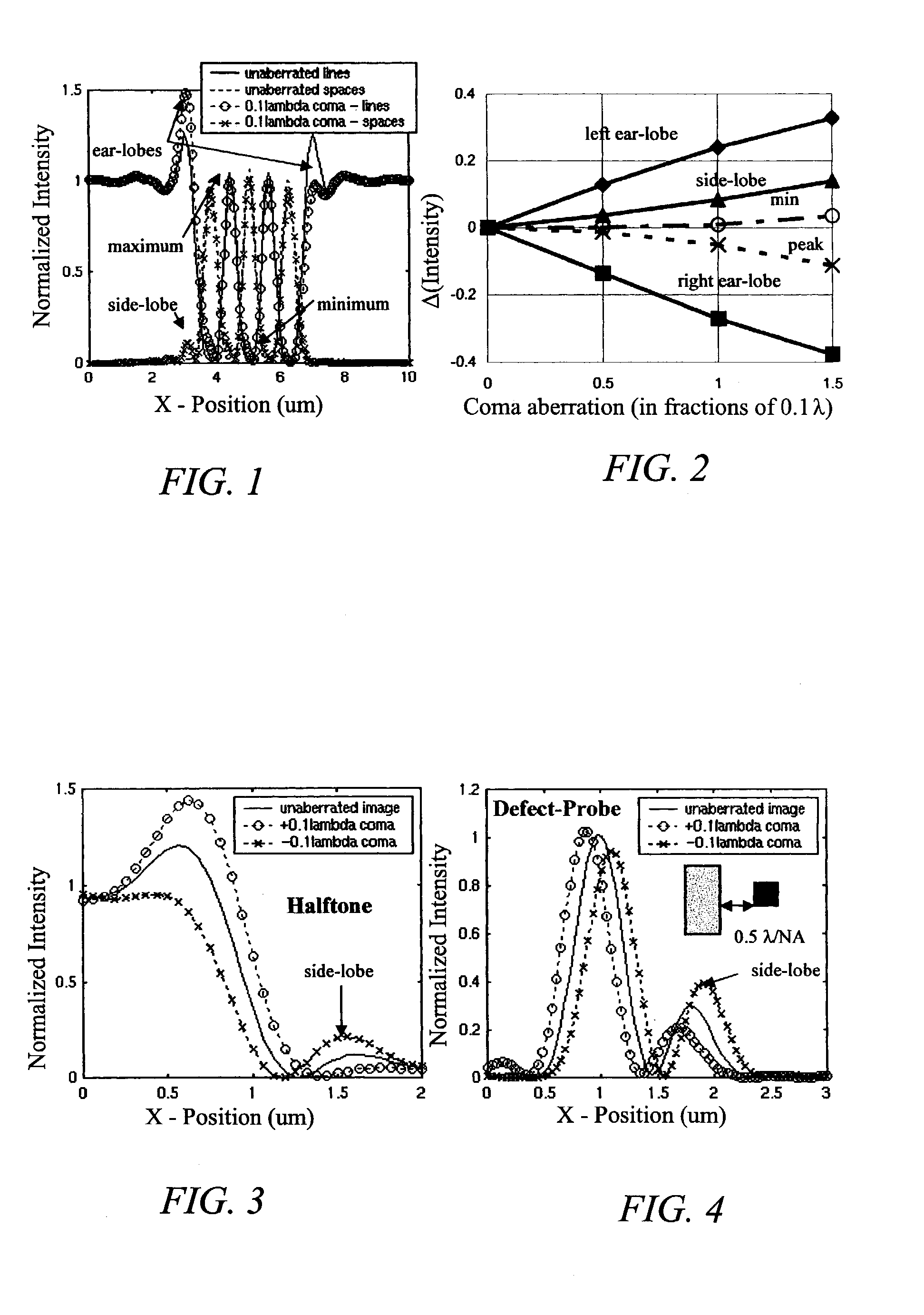
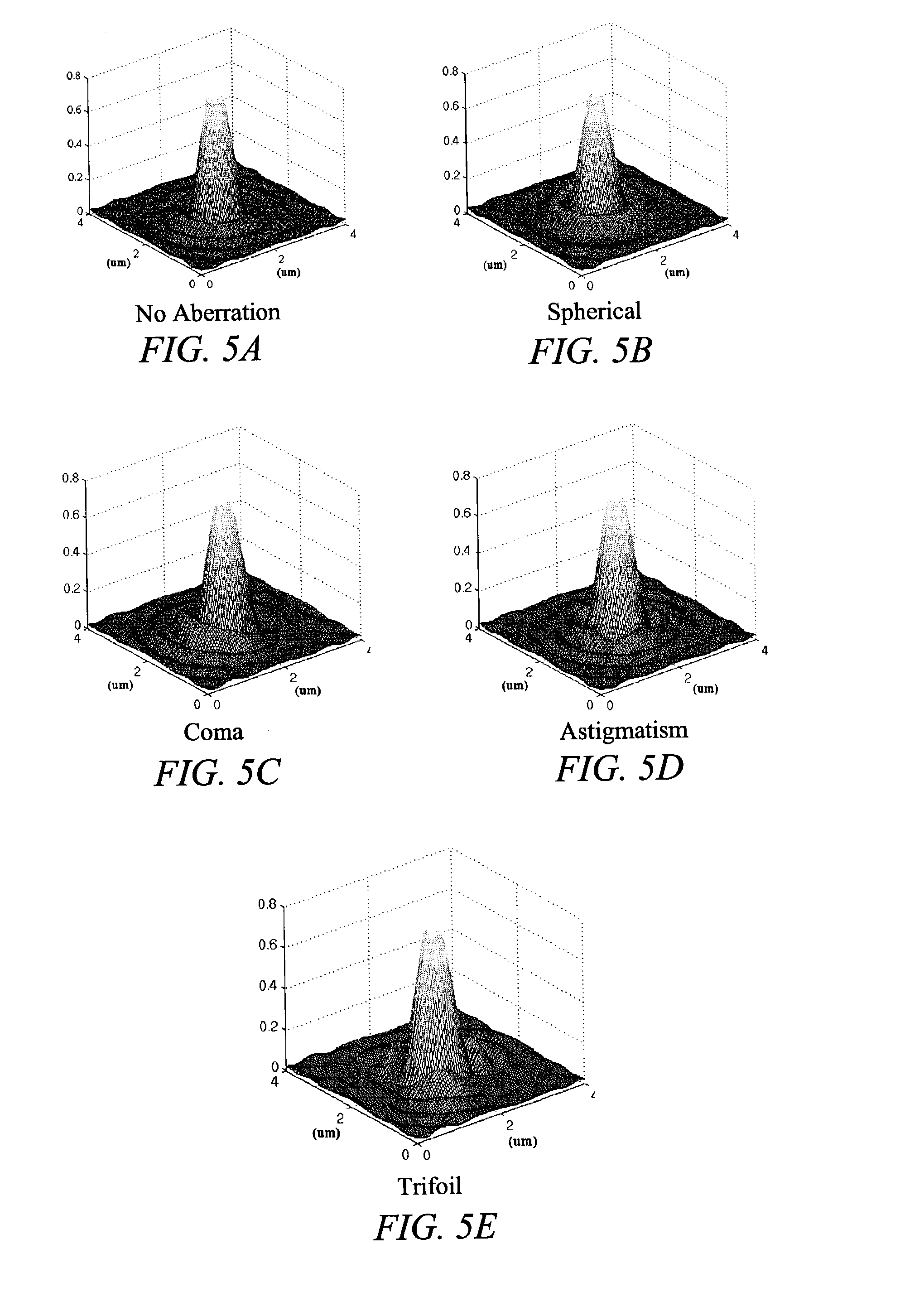
Characterizing aberrations in an imaging lens and applications to visual testing and integrated circuit mask analysis
InactiveUS7030997B2Quick fixAccurate modelingEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansCamera lensVisual test
Aberrations in a lens and lens system are identified by projecting an optical beam through a mask having an opening (probe) and a surrounding open geometry (pattern) and through the lens to an image plane. Lens aberrations are identified from the combined intensity of the beam in the image plane. In one embodiment the pattern is a plurality of rings concentric with the probe. Spillover between the probe and the geometry becomes intermixed in passing through the lens and alters the light intensity in the image plane. Vision of a patient can be tested by providing a plurality of probe openings and surrounding geometries that are illuminated. The patient then compares the images for brighter and darker probes as a measure of pupil aberrations. Areas in an integrated circuit mask layout impacted by aberrations in projection printing can be identified by sequentially comparing an aberration function to a mask layout, which can then be used to modify the mask layout.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
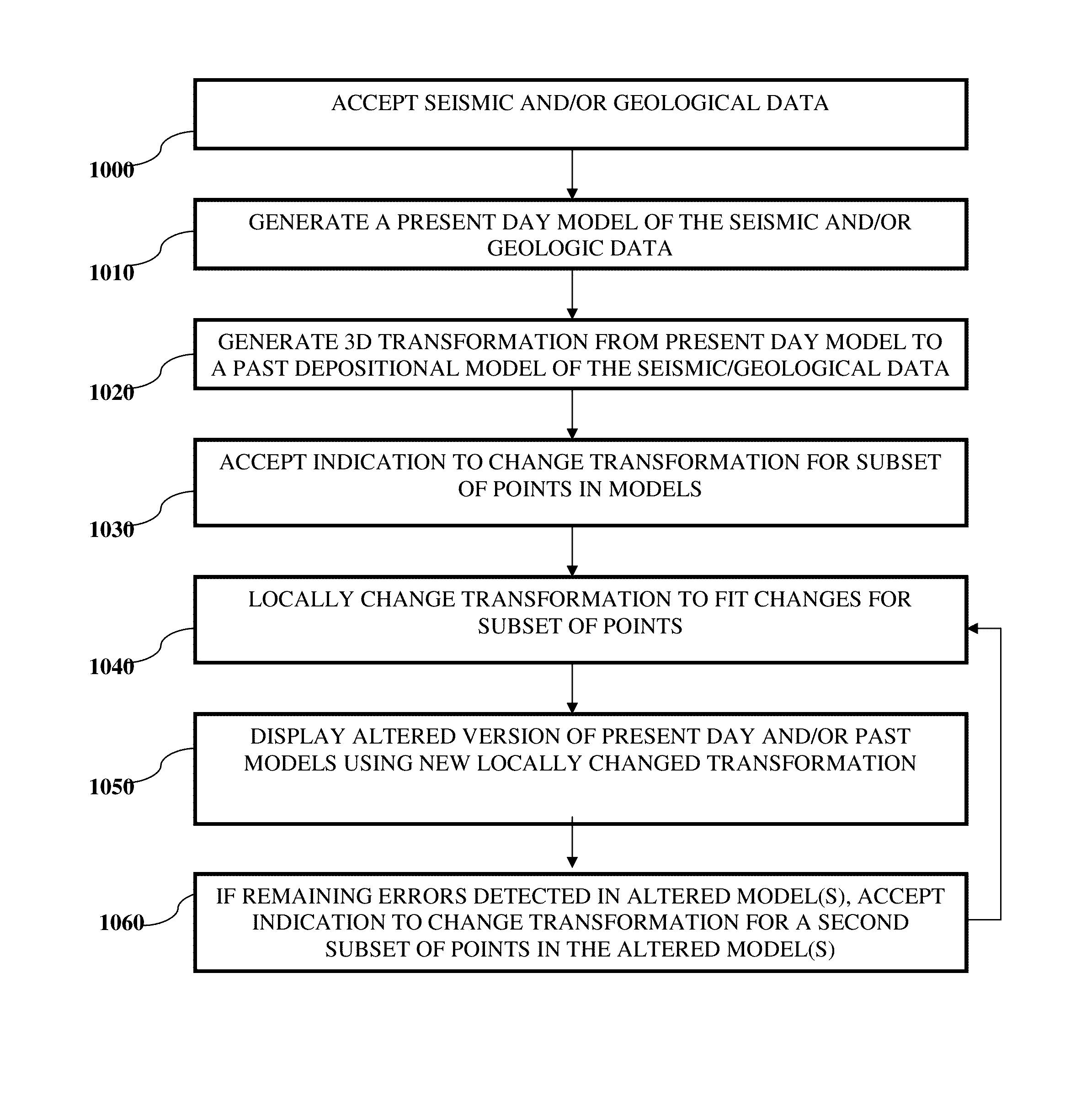
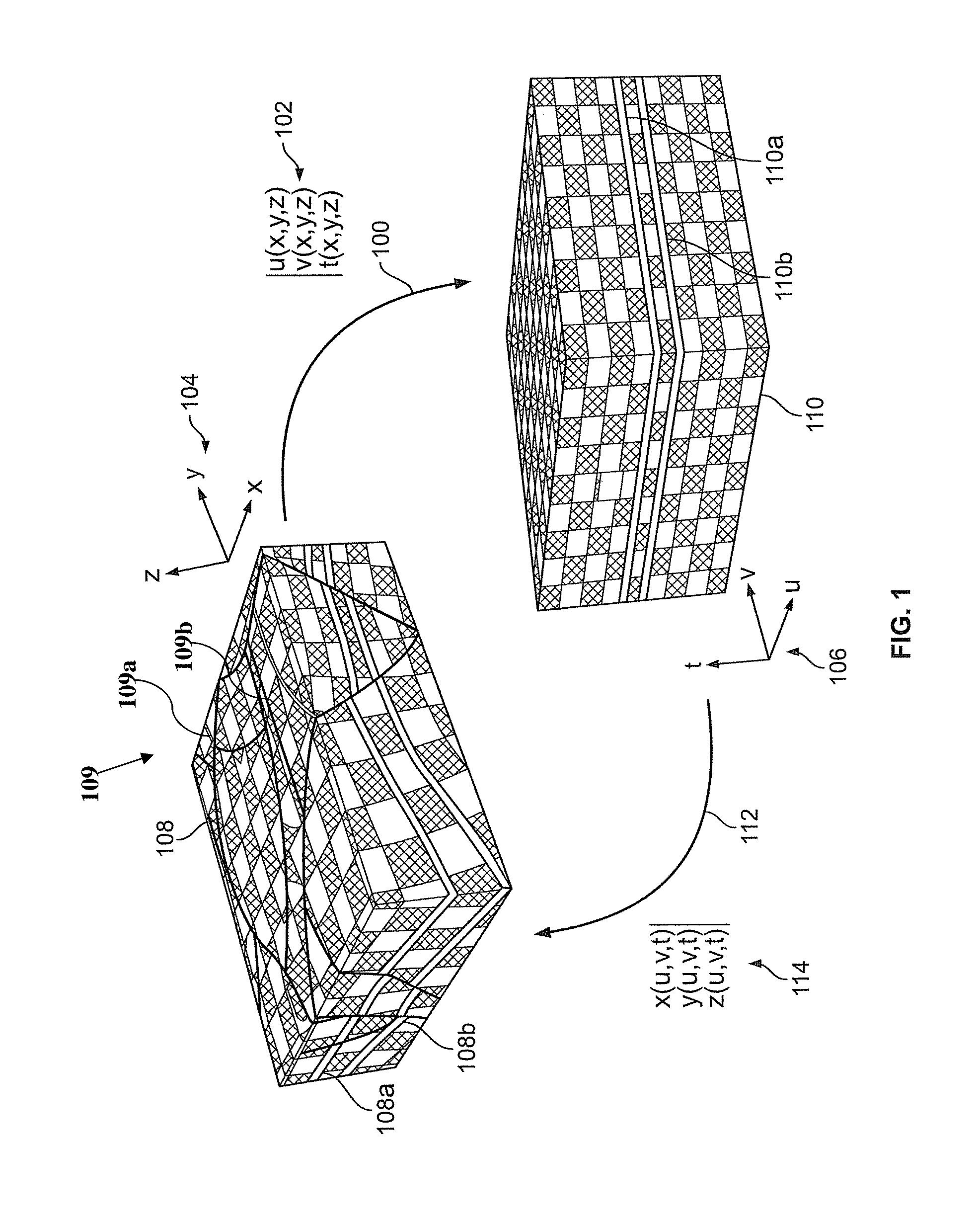
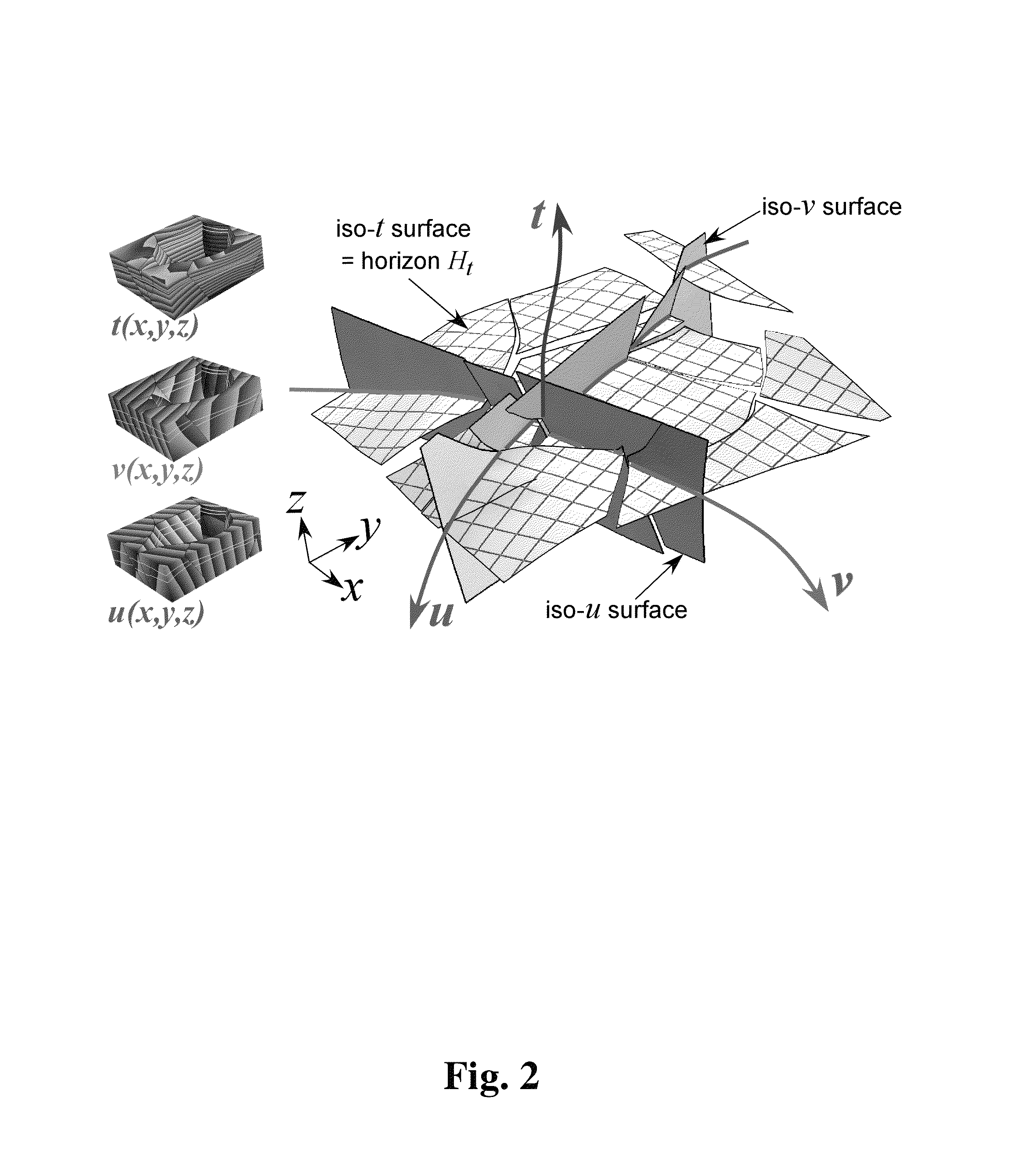
Systems and methods for coordinated editing of seismic data in dual model
A system and method may model physical geological structures. Seismic and geologic data may be accepted. A three-dimensional (3D) transformation may be generated between a 3D present day model having points representing present locations of the physical geological structures and a 3D past depositional model having points representing locations where the physical geological structures were originally deposited. An indication may be accepted to locally change the 3D transformation for a subset of sampling points in a first model of the models. The 3D transformation may be locally changed to fit the updated subset of sampling points. A locally altered or updated version of the first model and, e.g., second model, may be displayed where local changes to the first model are defined by the locally changed 3D transformation. The transformation may also be used to extract geobodies in the past depositional model.
Owner:ASPEN PARADIGM HLDG LLC
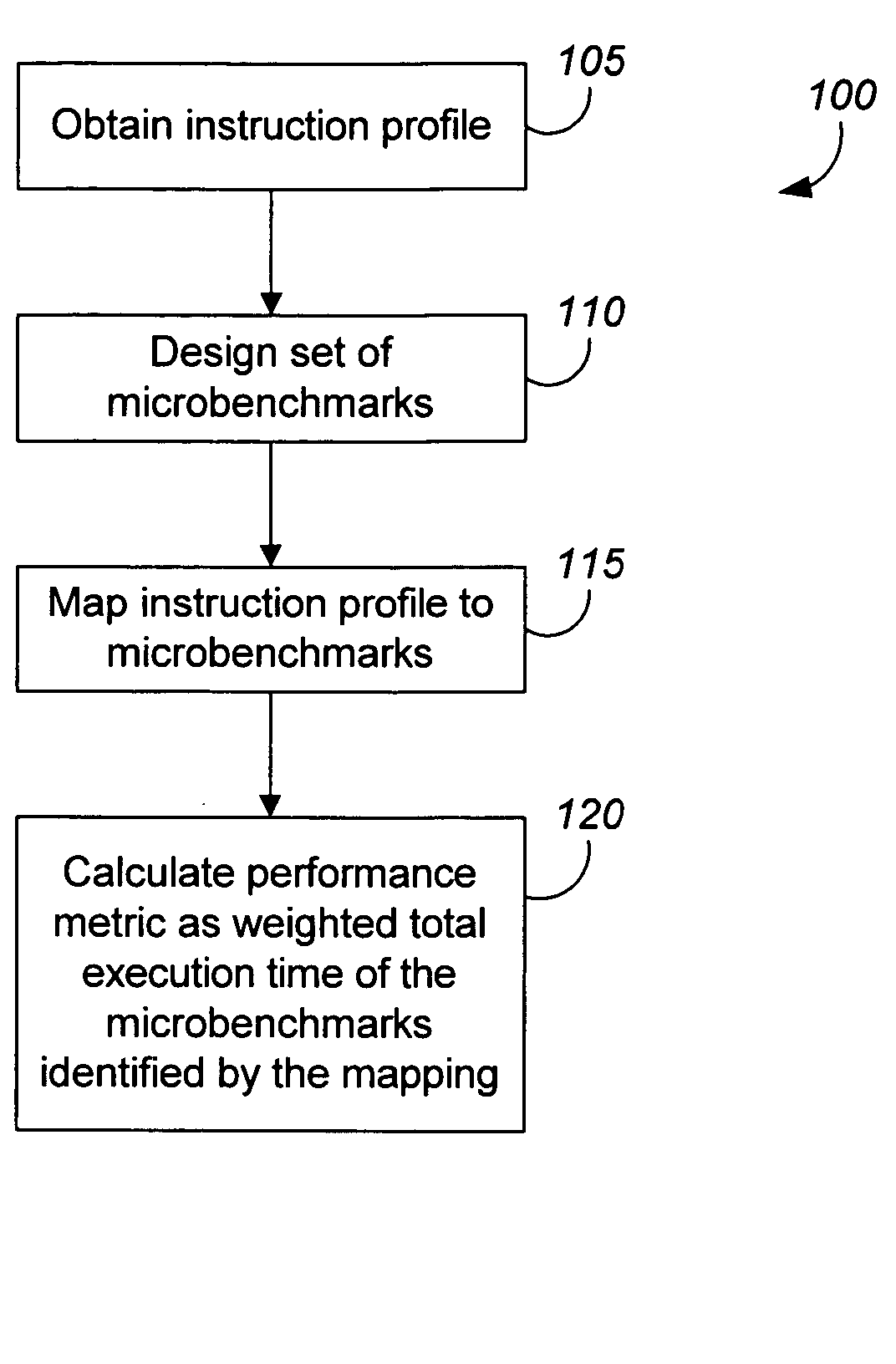
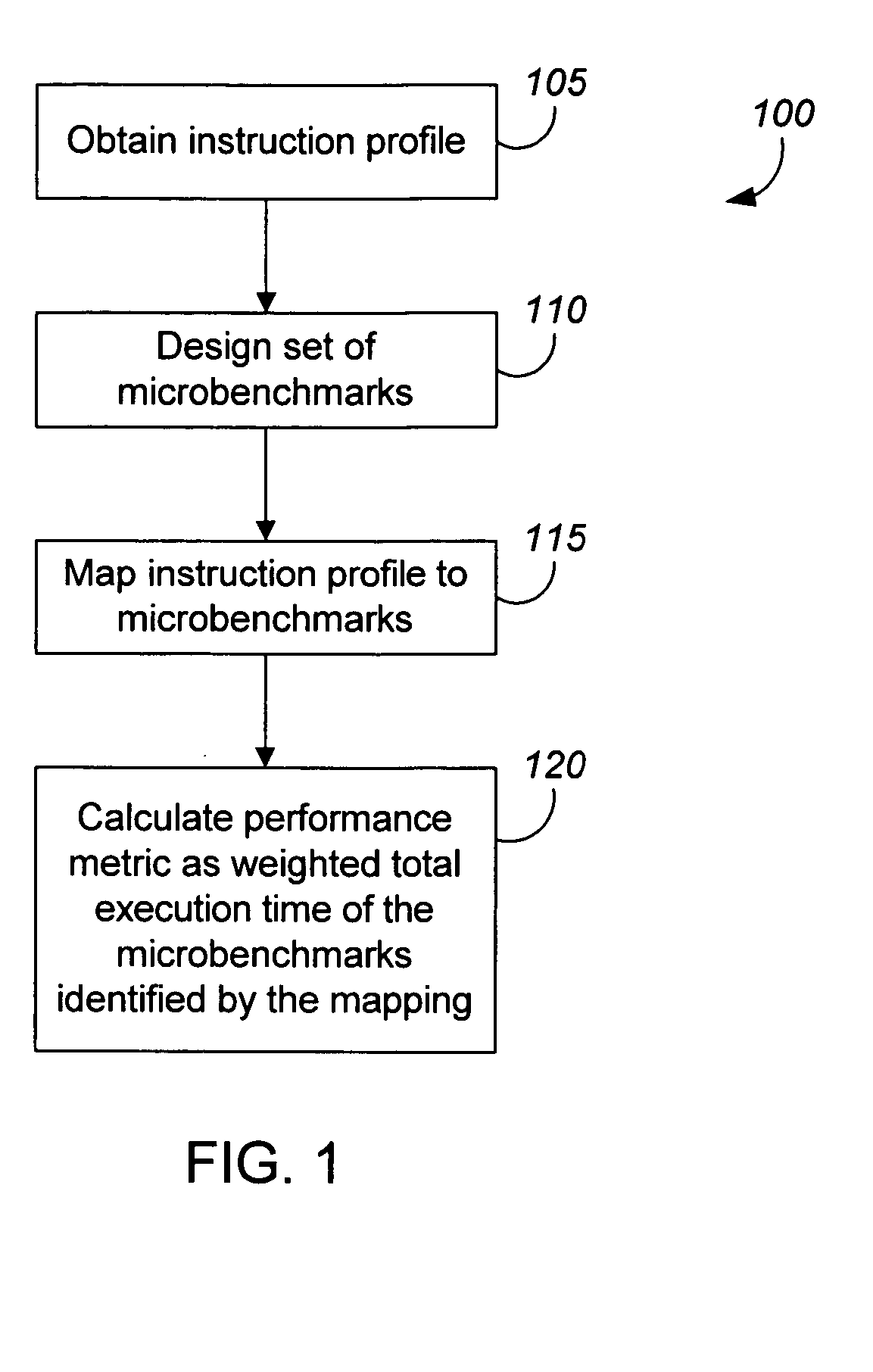
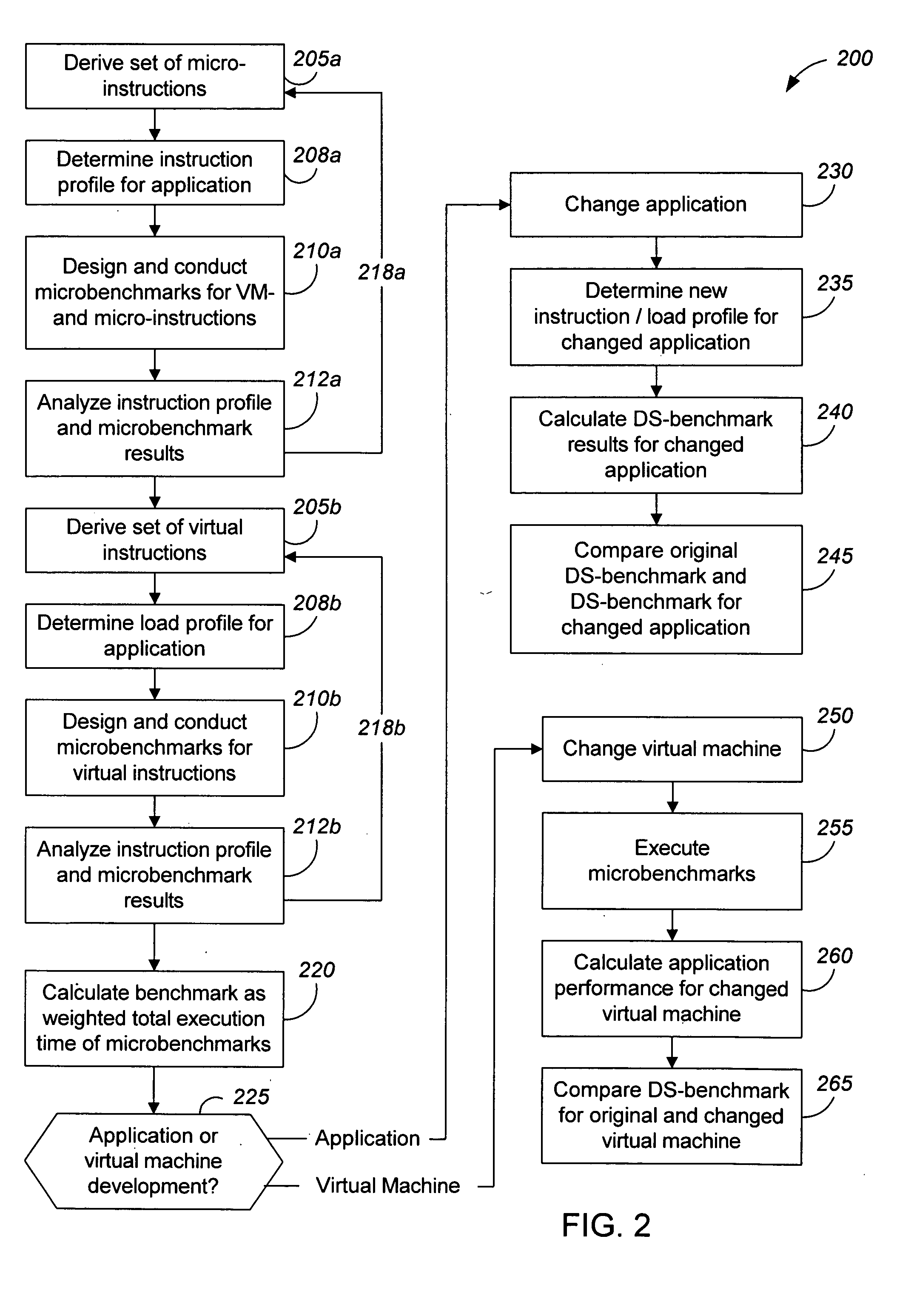
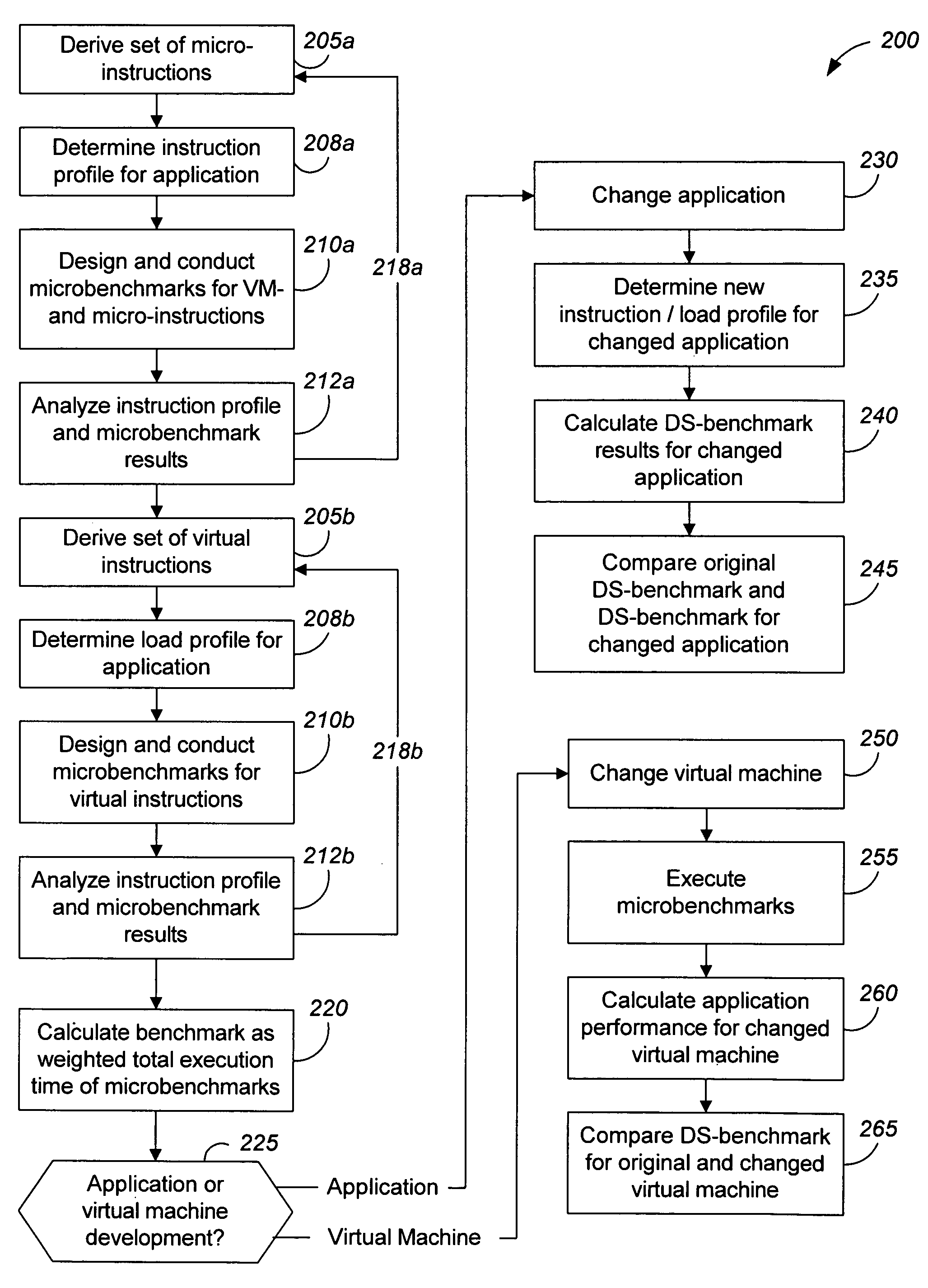
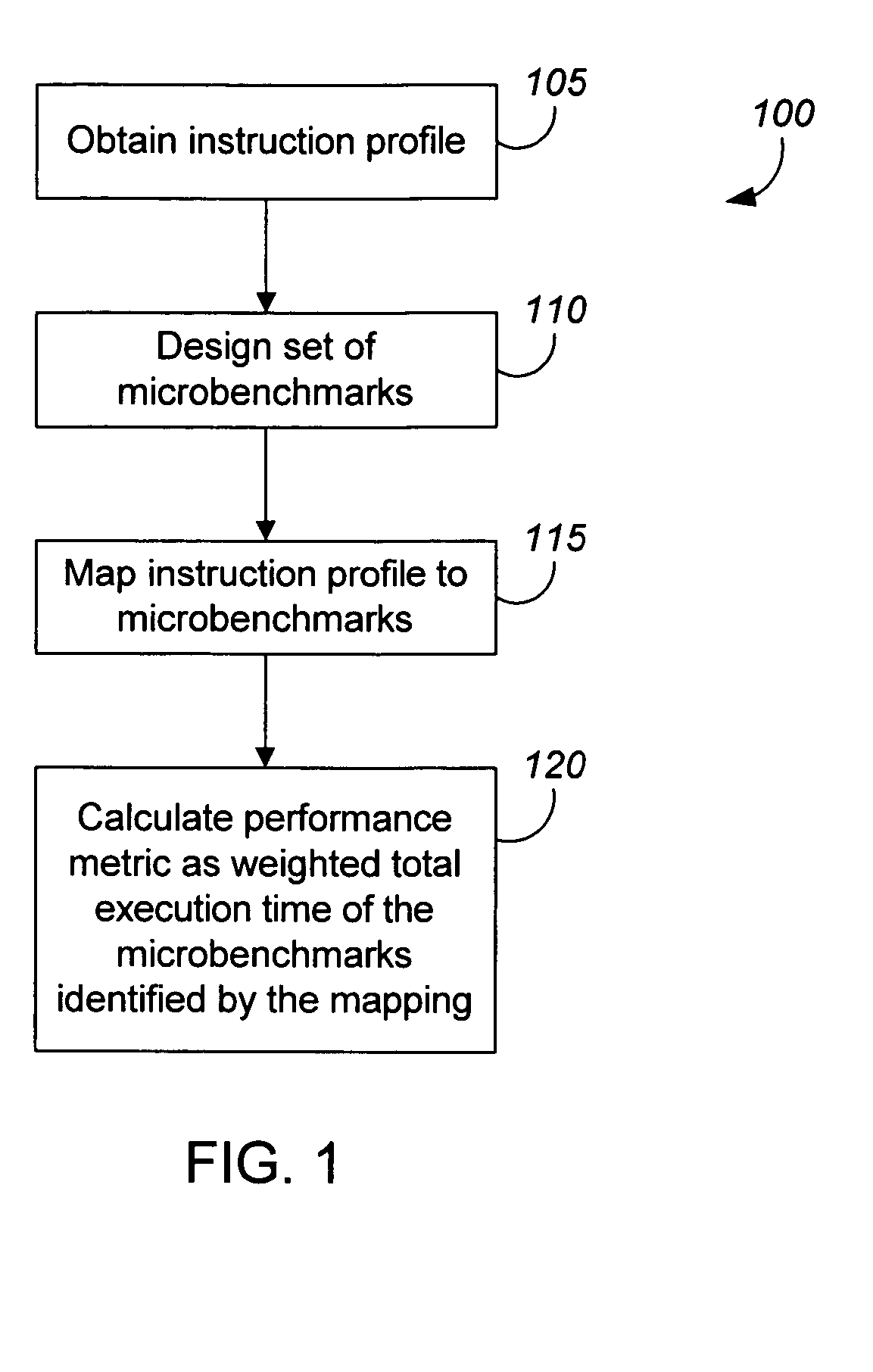
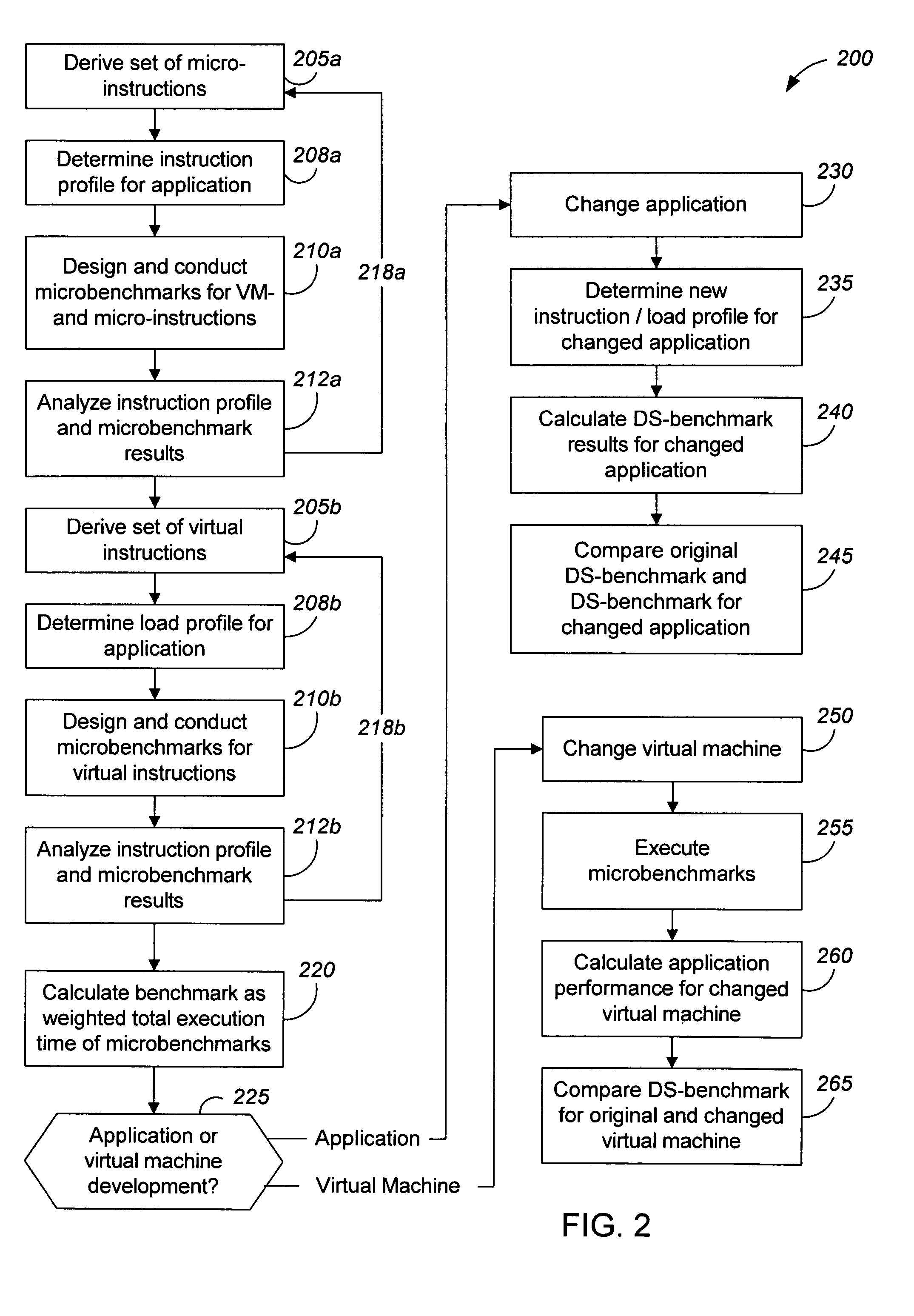
Measuring software system performance using benchmarks
ActiveUS20050120341A1Debug performanceDevelopment cost be very expensiveError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsVirtual machineWorkload
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for measuring the performance of aspects of a complex data processing system. In one aspect, a method uses a dynamic synthetic benchmark to provide performance information for a program application running on a virtual machine. The benchmark in one implementation uses a load profile that includes information about instructions that make up the application, their call frequencies, and their workloads. Microbenchmarks of individual virtual machine instructions provide performance information about the virtual machine that is used with the load profile to synthesize a performance benchmark for the application.
Owner:SAP AG
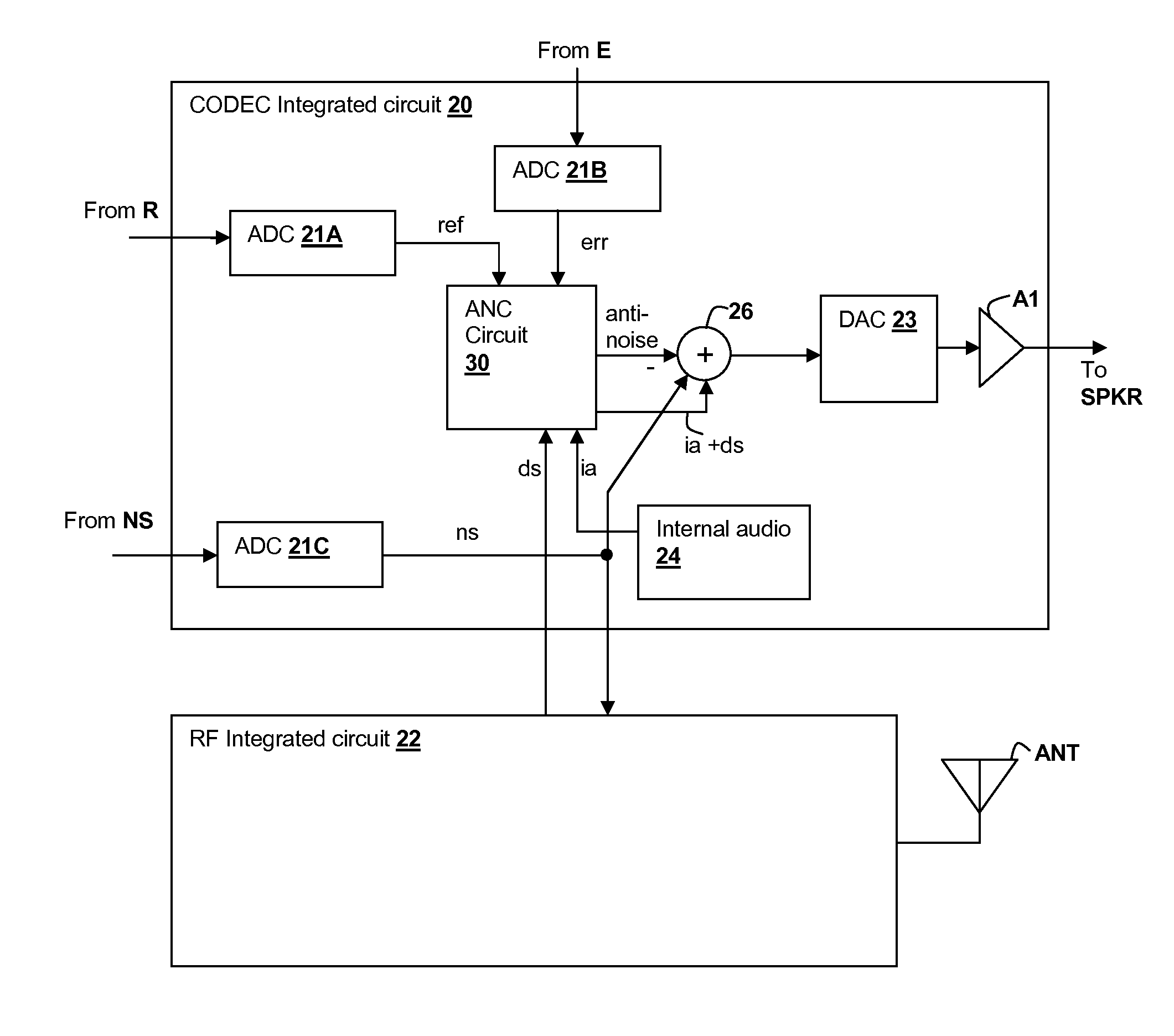
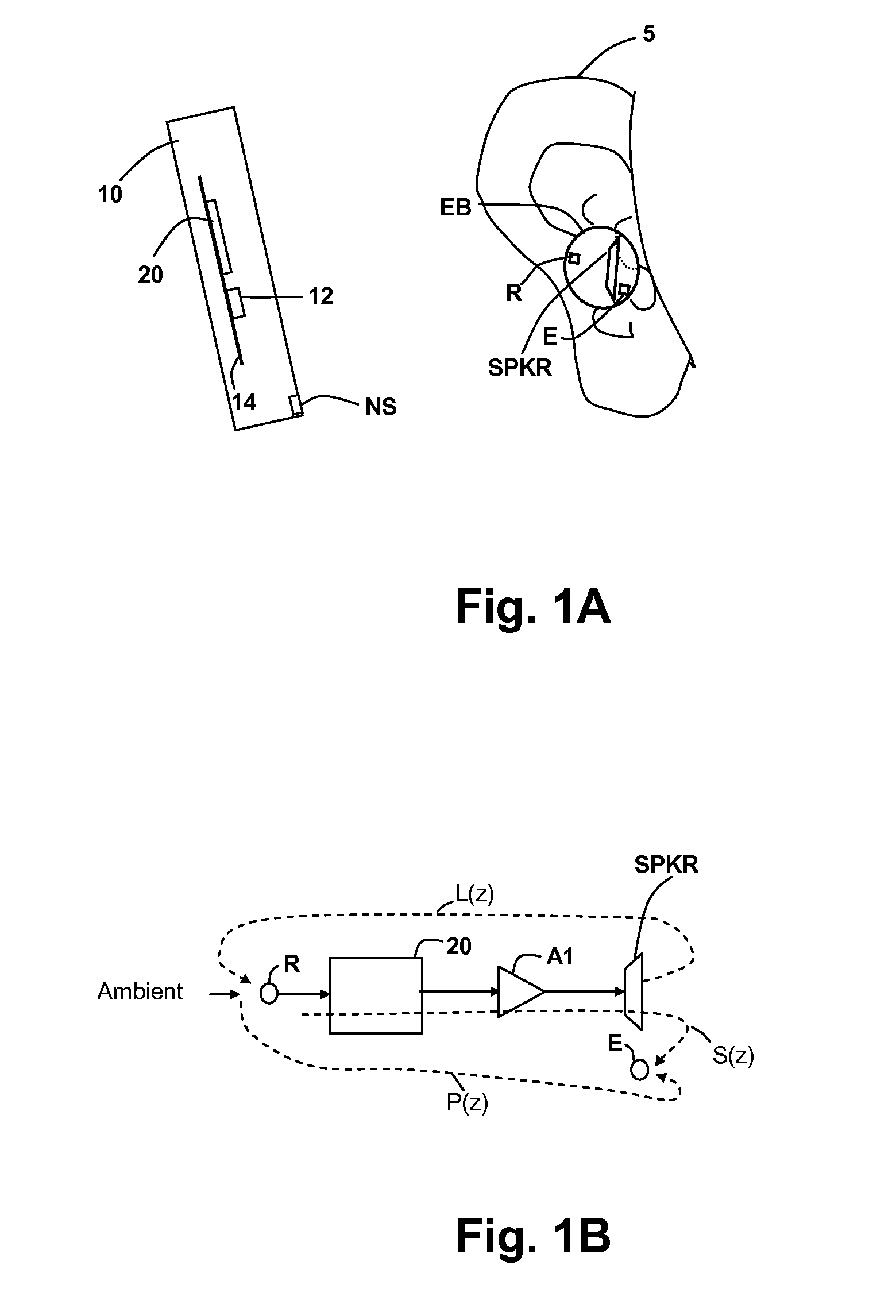
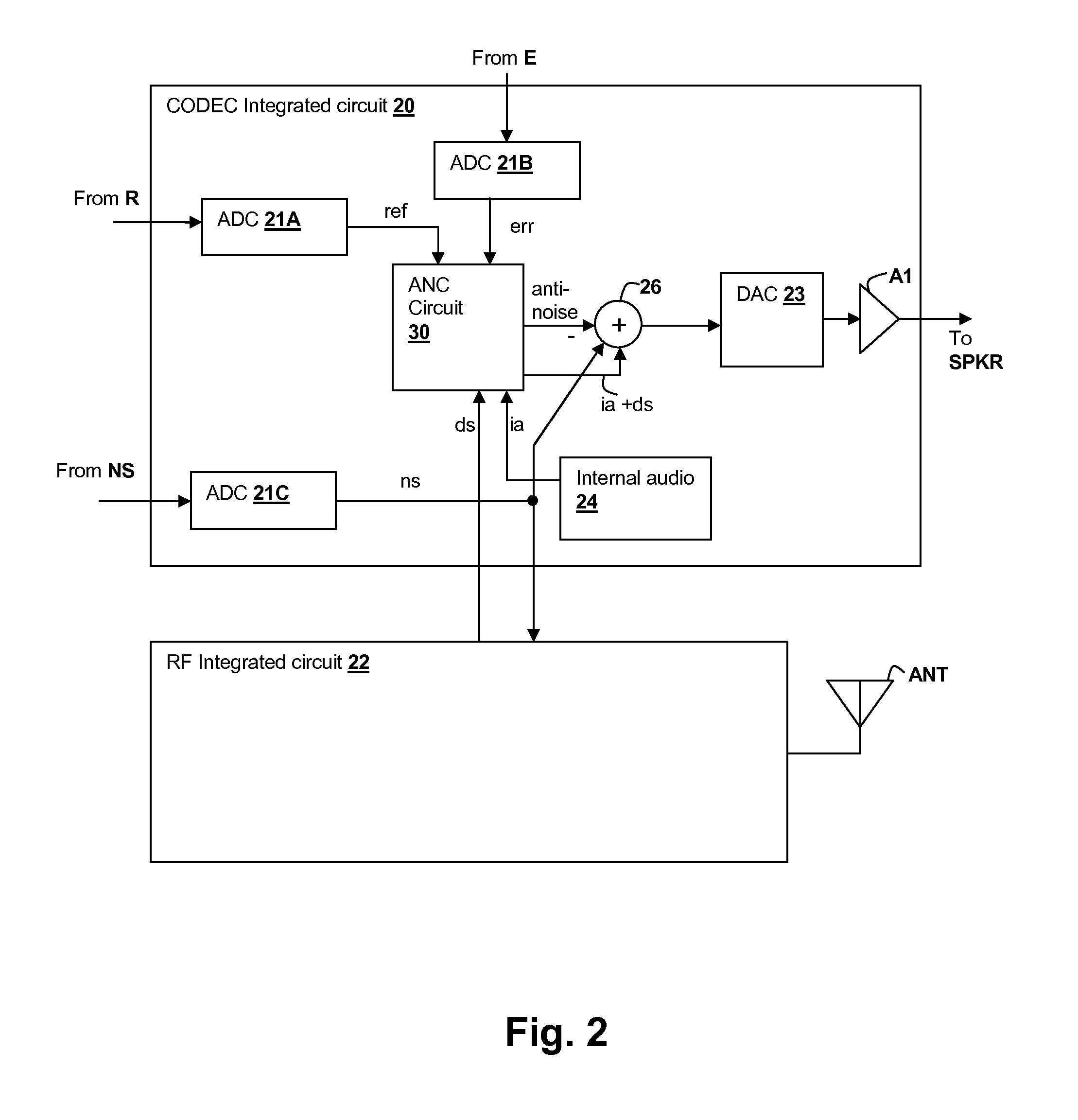
Error-signal content controlled adaptation of secondary and leakage path models in noise-canceling personal audio devices
ActiveUS20130301849A1Maximal cancellationComponent can be removedEar treatmentSound producing devicesAdaptive filterTransducer
A personal audio device, such as a wireless telephone, generates an anti-noise signal from a microphone signal and injects the anti-noise signal into the speaker or other transducer output to cause cancellation of ambient audio sounds. The microphone measures the ambient environment, but also contains a component due to the transducer acoustic output. An adaptive filter is used to estimate the electro-acoustical path from the noise-canceling circuit through the transducer to the at least one microphone so that source audio can be removed from the microphone signal. A determination of the relative amount of the ambient sounds present in the microphone signal versus the amount of the transducer output of the source audio present in the microphone signal is made to determine whether to update the adaptive response.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
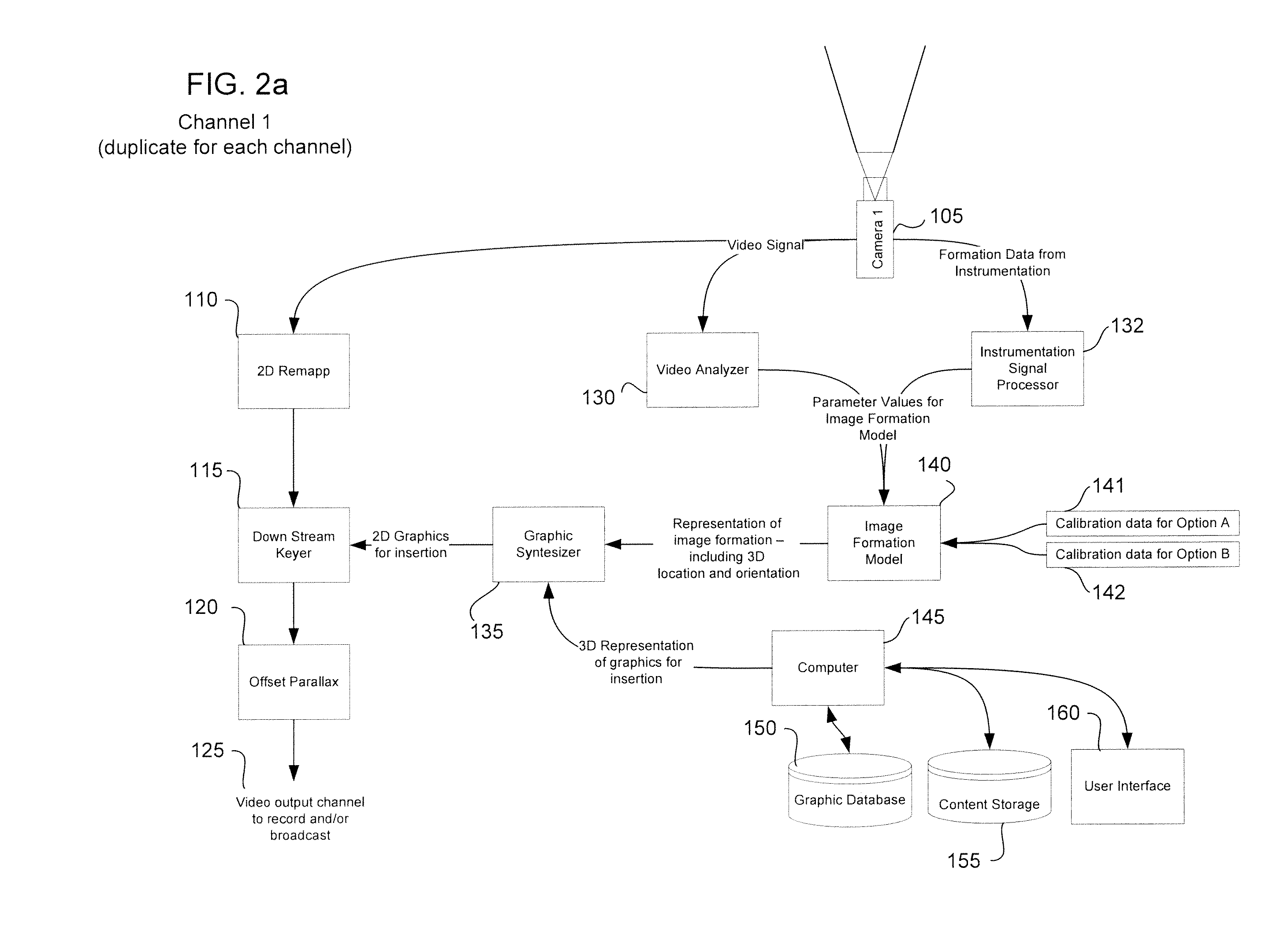
3D Graphic Insertion For Live Action Stereoscopic Video
ActiveUS20120002014A1Accurate modelingImage data processingSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoGraphics
Systems and methods for the insertion of graphics into stereoscopic live action 3D video using image models taking into account positional data from the stereoscopic camera rig.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
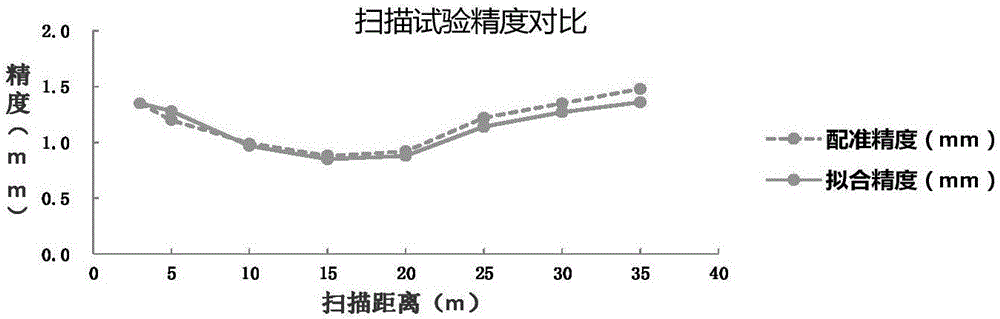
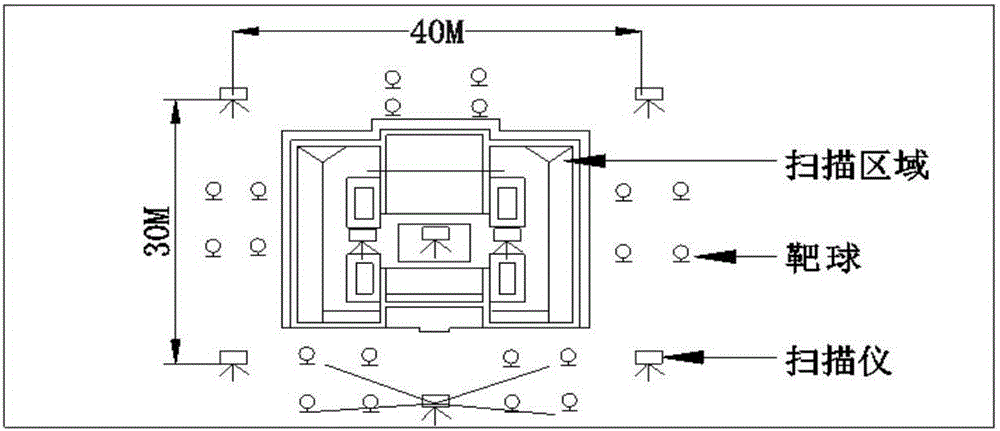
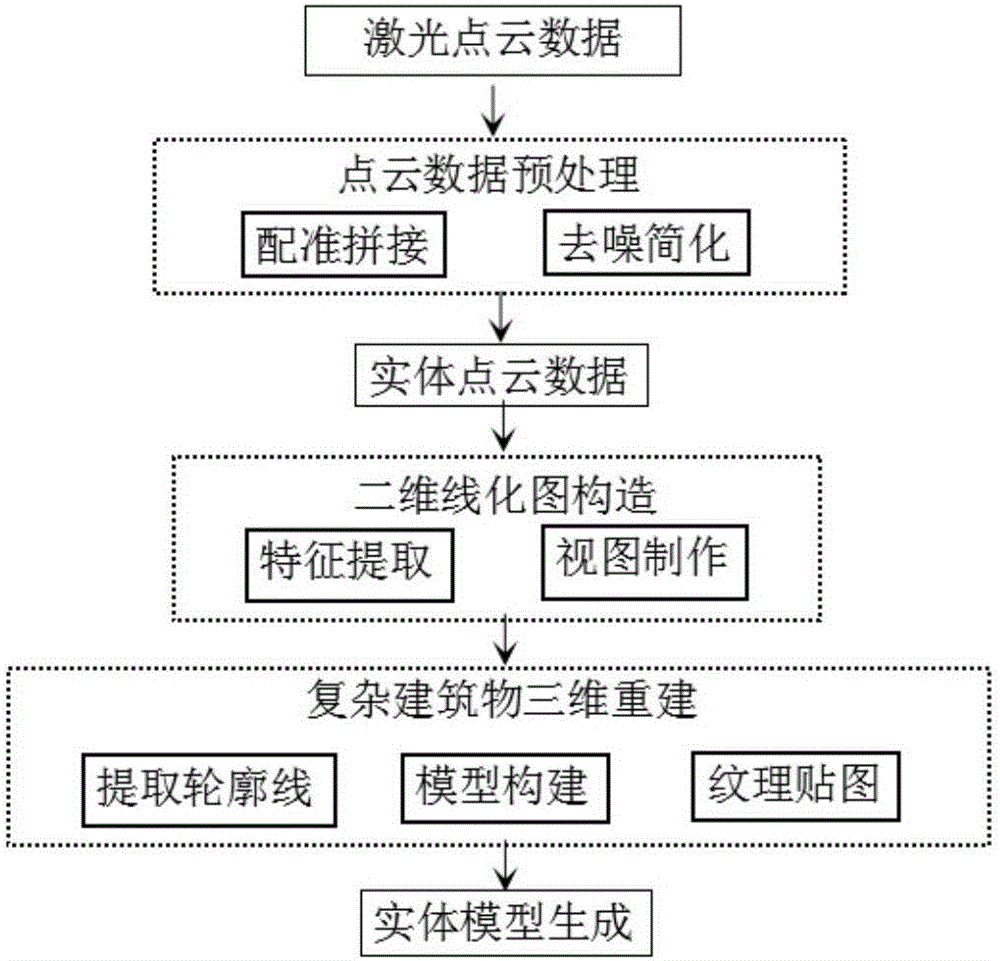
Complex building three-dimensional modeling method based on point cloud data
ActiveCN106600690AOvercome limitationsFast 3D ModelingImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsPoint cloudLaser scanning
The invention discloses a complex building three-dimensional modeling method based on point cloud data. The method includes the following steps: step one, scanning a building by laser and obtaining complete laser point cloud data of the surface of the building; step two, constructing a two-dimensional line map of the building; and step three, reconstructing a three-dimensional entity model. The modeling method avoids restrictions of a conventional modeling method, and can construct a building three-dimensional model in a quick, accurate and highly efficient manner.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV OF TECH
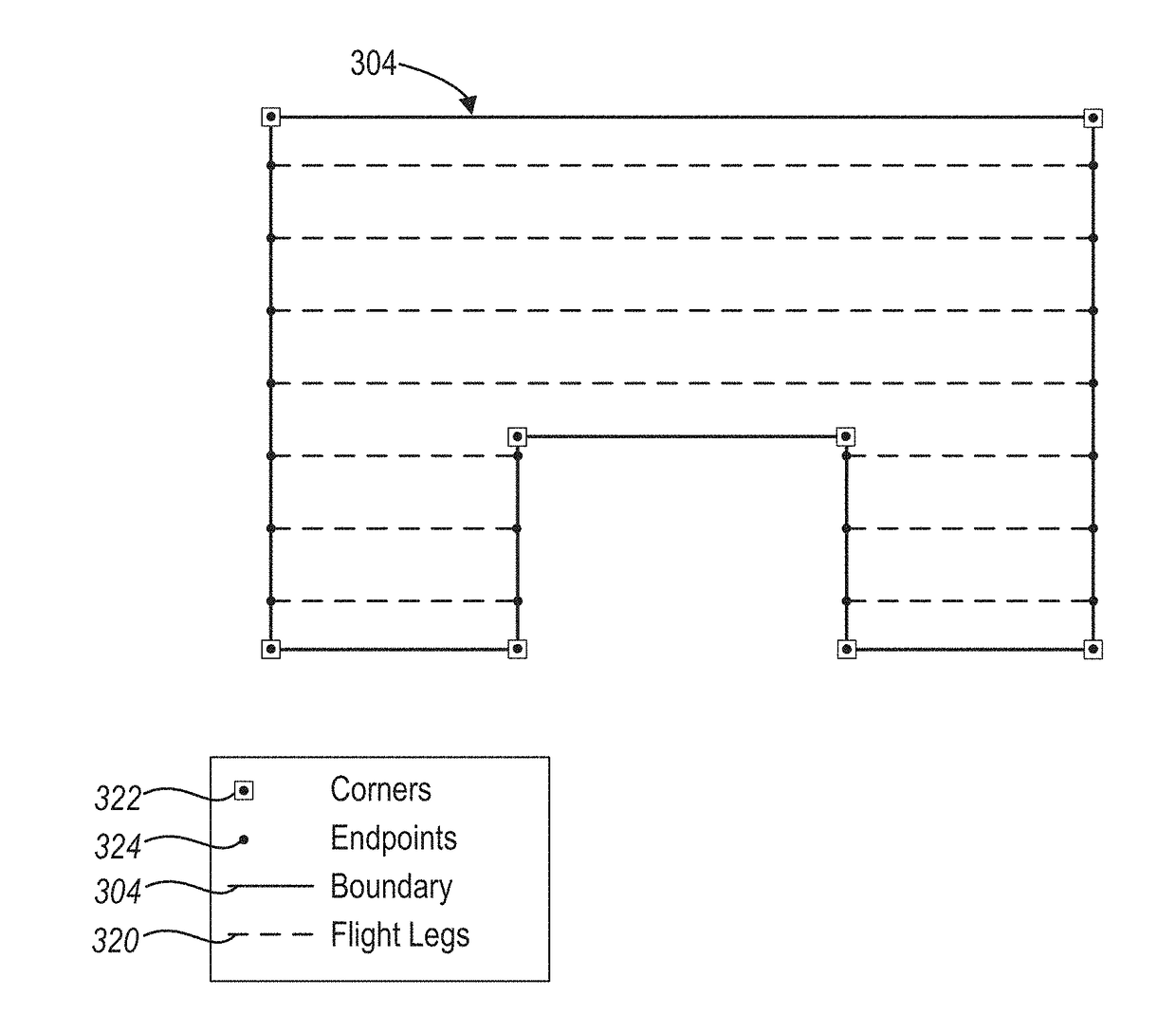
Generating a mission plan for capturing aerial images with an unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveUS20170337824A1Accurate modelingQuick buildUnmanned aerial vehiclesPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviationUncrewed vehicle
Systems and methods are disclosed for generating a digital flight path within complex mission boundaries. In particular, in one or more embodiments, systems and methods generate flight legs that traverse a target site within mission boundaries. Moreover, one or more embodiments include systems and methods that utilize linking algorithms to connect the generated flight legs into a flight path. Moreover, one or more embodiments include systems and methods that generate a mission plan based on the flight path. In one or more embodiments, the generated mission plan enables a UAV to traverse a flight area within mission boundaries and capture aerial images with regard to the target site. Furthermore, in one or more embodiments, systems and methods capture digital aerial images of vertical surfaces of a structure by generating a reference surface and flight legs corresponding to the reference surface.
Owner:SKYCATCH
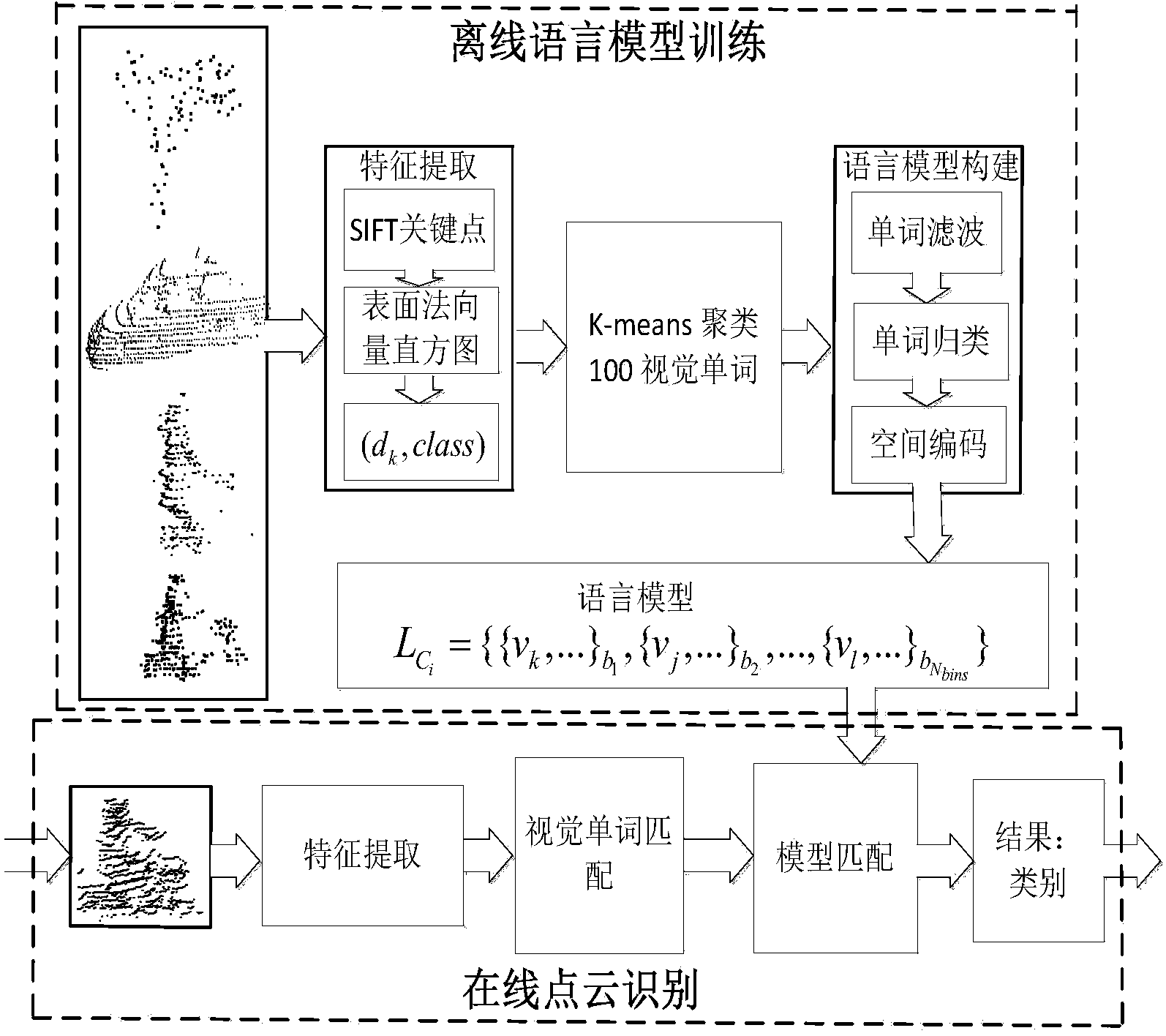
Method for identifying objects in 3D point cloud data
ActiveCN104298971AFeatures are stable and reliableAccurate modelingCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudCrucial point
The invention discloses a method for identifying objects in 3D point cloud data. 2D SIFT features are extended to a 3D scene, SIFT key points and a surface normal vector histogram are combined to achieve scale-invariant local feature extraction of 3D depth data, and the features are stable and reliable. A provided language model overcomes the shortcoming that a traditional visual word bag model is not accurate and is easily influenced by noise when using local features to describe global features, and the accuracy of target global feature description based on the local features is greatly improved. By means of the method, the model is accurate, and identification effect is accurate and reliable. The method can be applied to target identification in all outdoor complicated or simple scenes.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
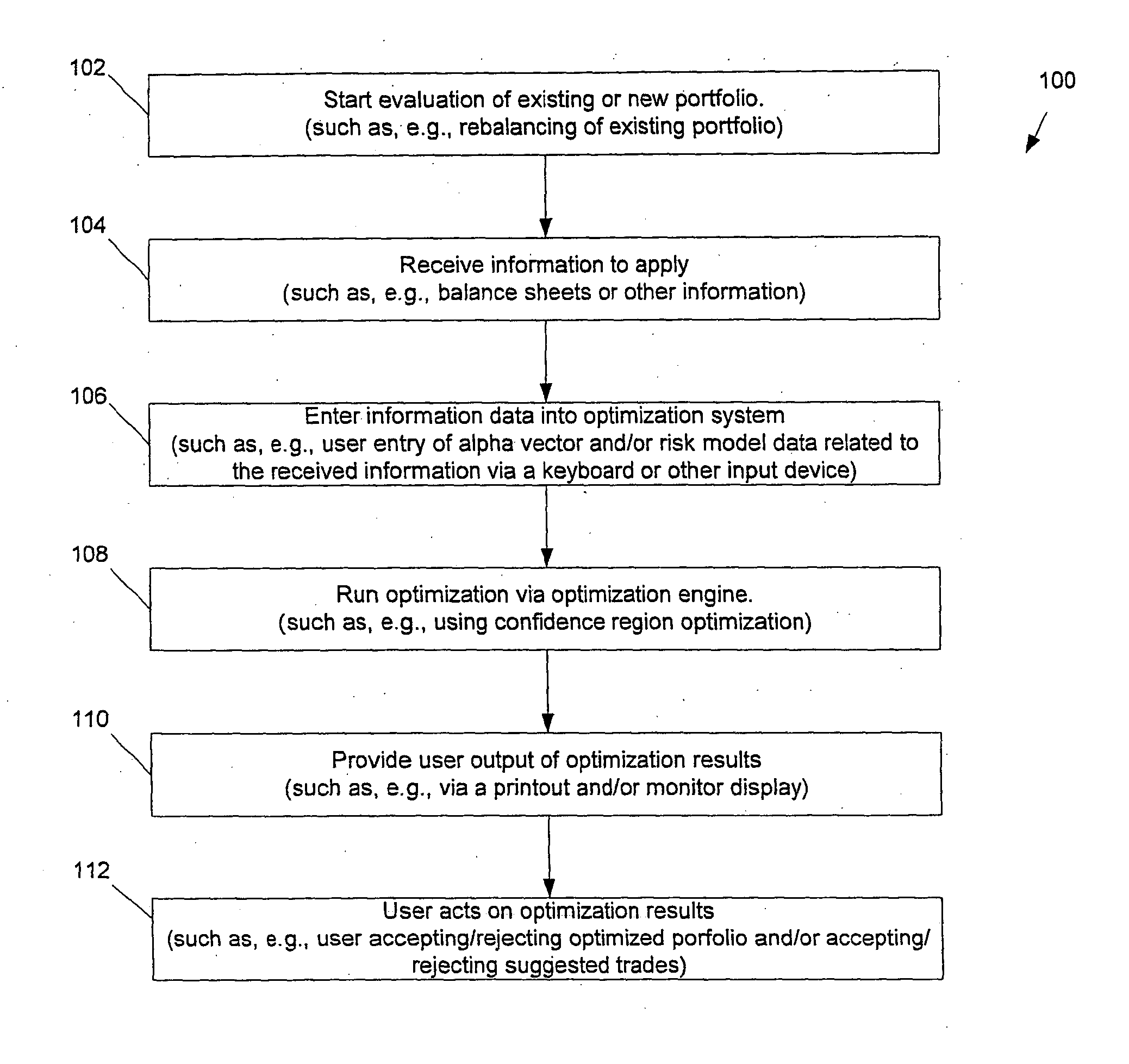
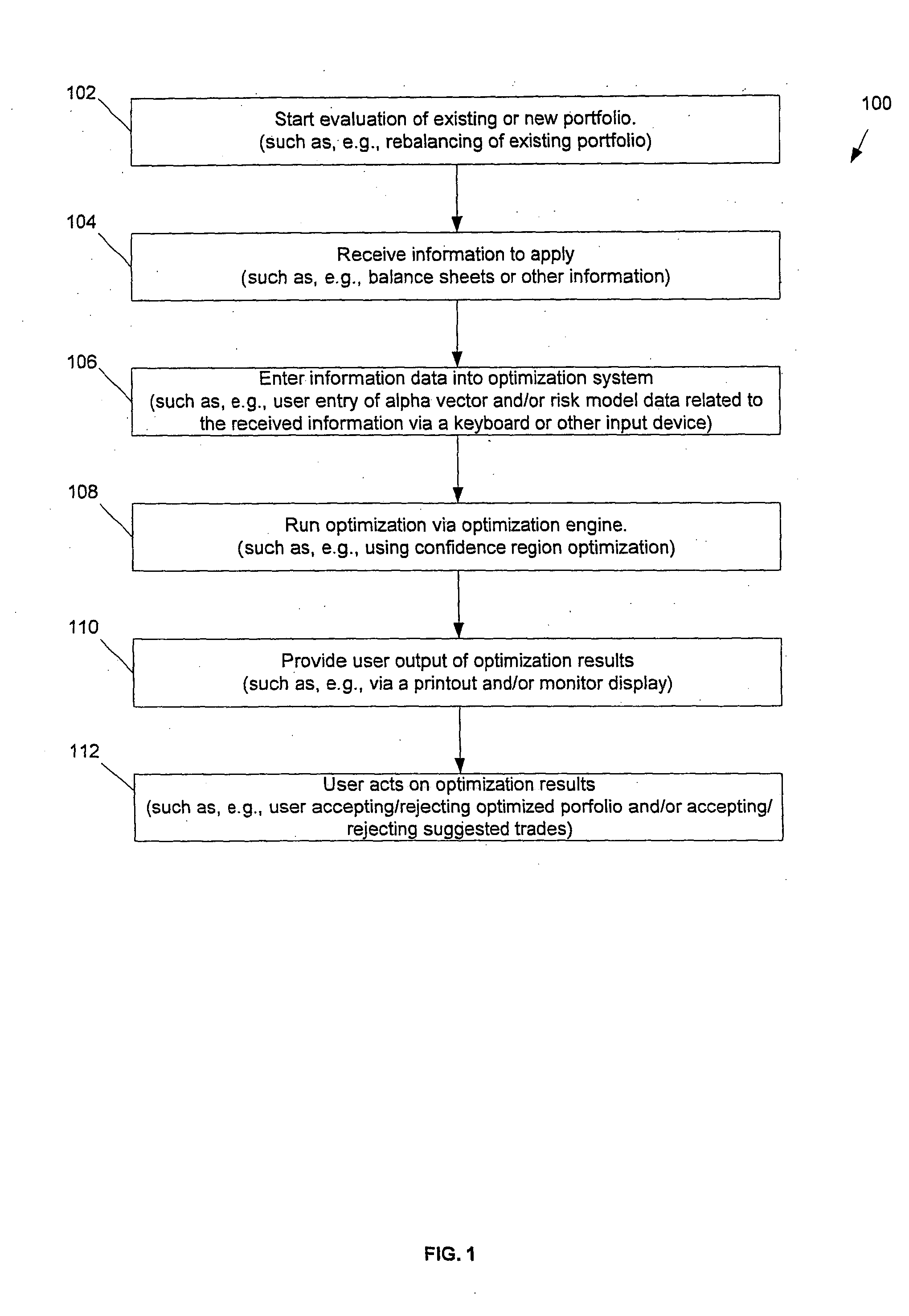
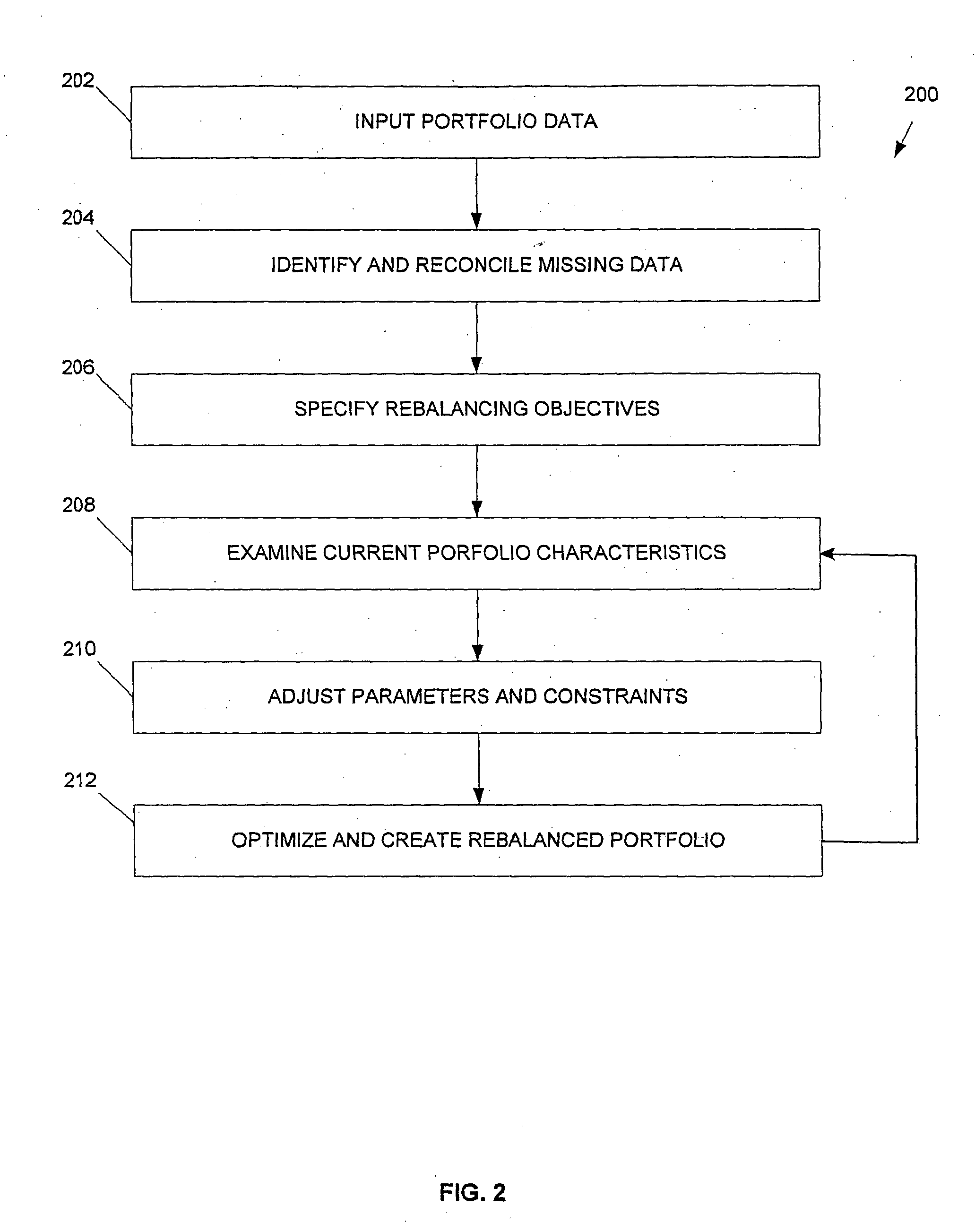
Investment portfolio optimization system, method and computer program product
ActiveUS20040181479A1Increase in sizeThe result is accurateFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmConfidence region
The preferred embodiments provide improved systems, methods and products for the optimization of a portfolio and / or multi-portfolios of assets, such as stocks. In some preferred embodiments, new methodology can be employed wherein a confidence region for a mean-varience efficiency set is utilized. In some preferred embodiments, new methodology can be employed for improved computation of a reward-to-variability ratio or Sharpe Ratio. In some preferred embodiments, new methodology can be employed for multiportfolio optimization. In some preferred embodiments, a portfolio optimization engine or module can be adapted to implement one or more of these new methodologies, along with any other desired methodologies.
Owner:ITG SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS INC
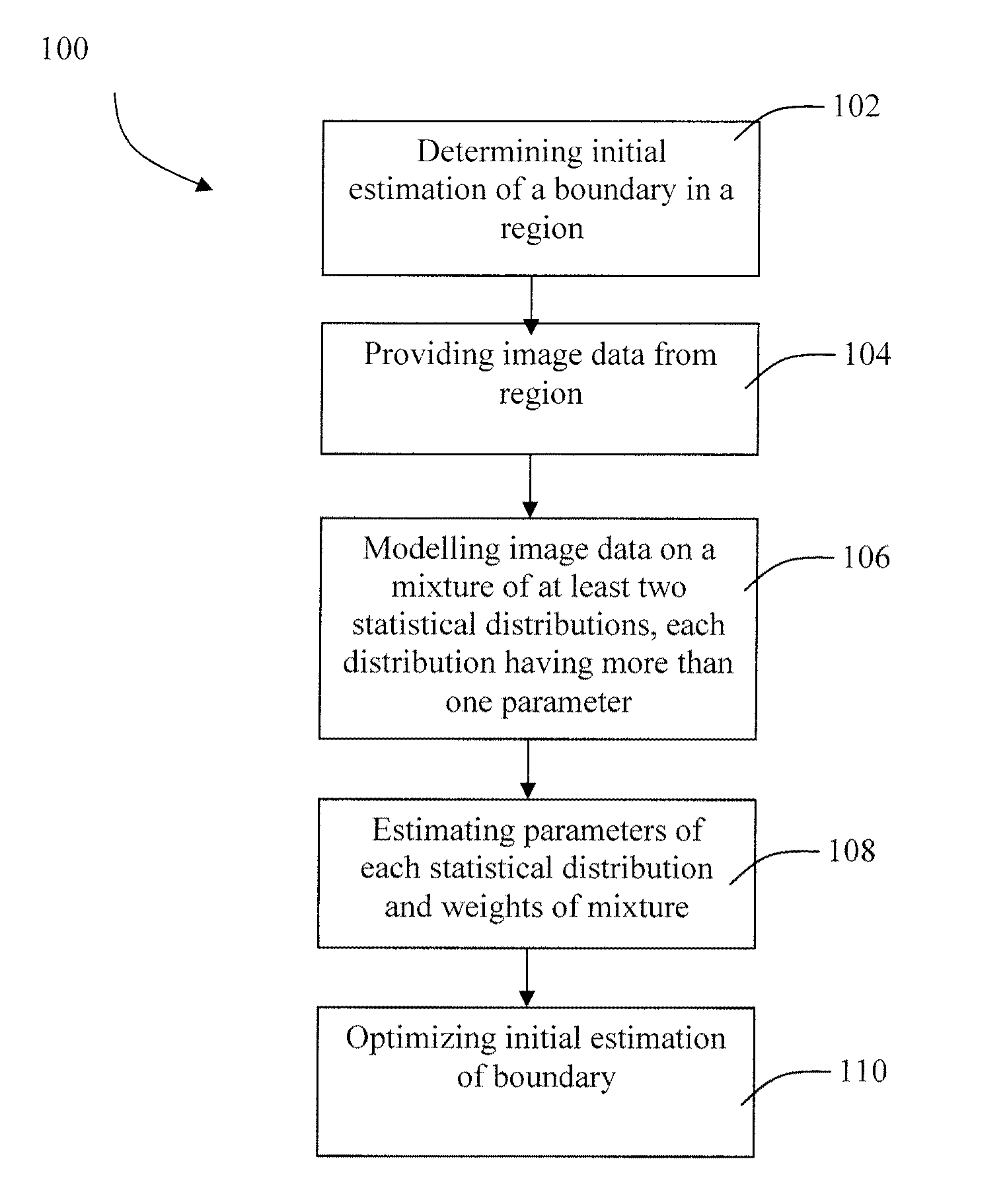
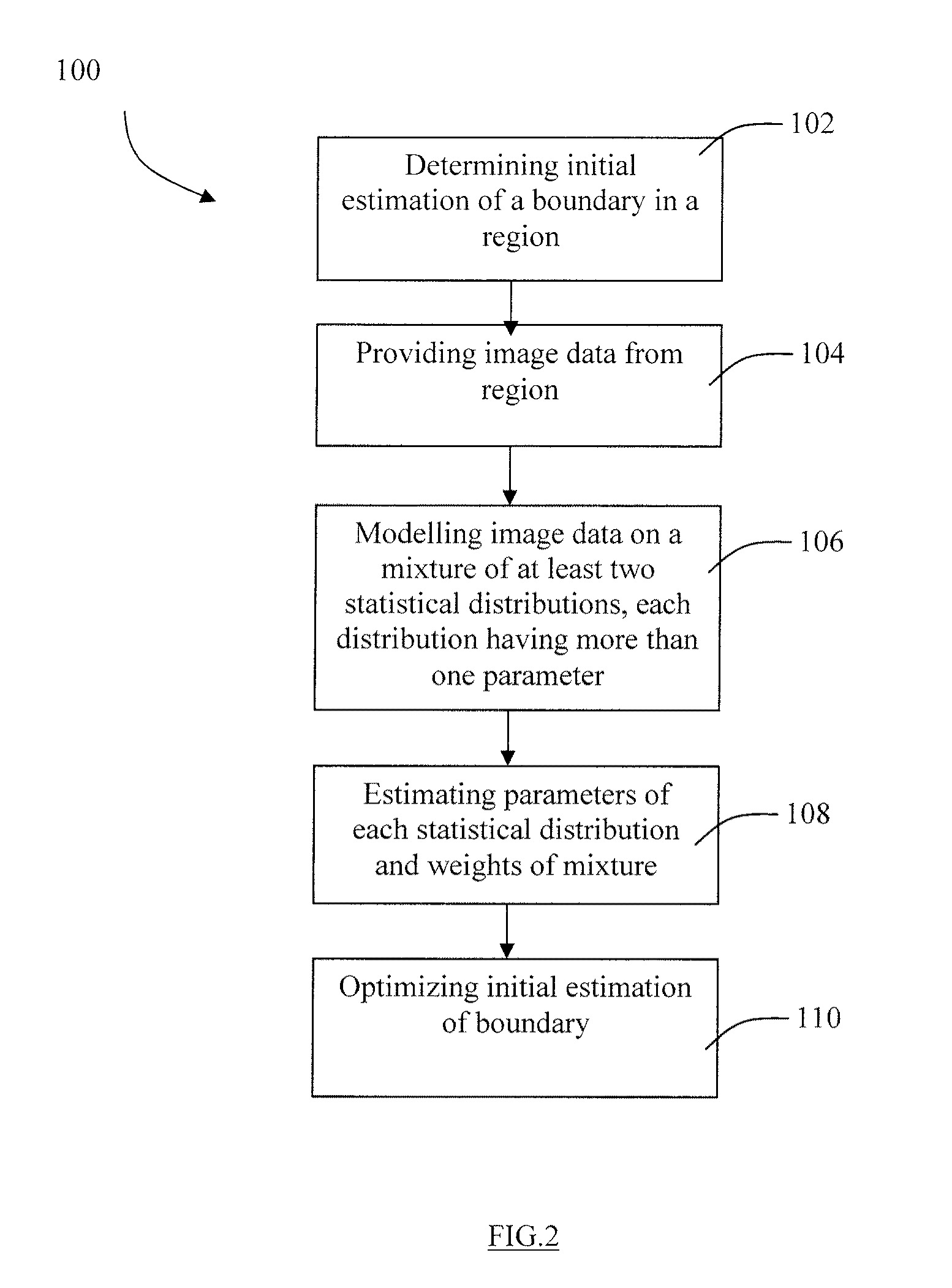
Image segmentation
InactiveUS20100081931A1Cheap and quick and efficient and consistent segmentation of imageSegmented more quicklyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementEstimated WeightPattern recognition
A method for segmenting an image comprising: determining an initial estimation of a boundary between at least two components in a region of an image to be segmented; providing image data from the region of the image to be segmented, the image data representing gray level values of a plurality of image elements of the components; modelling the image data on a mixture of at least two statistical distributions, each statistical distribution having more than one parameter, and each component being associated with certain weights of the statistical distributions in the mixture; estimating the parameters of the statistical distributions in the mixture; for each component, estimating the weights of the statistical distributions in the mixture based on the estimated parameters and the image data of each image element; and optimizing the initial estimation of the boundary between the components based on the estimated parameters and estimated weights.
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL +1
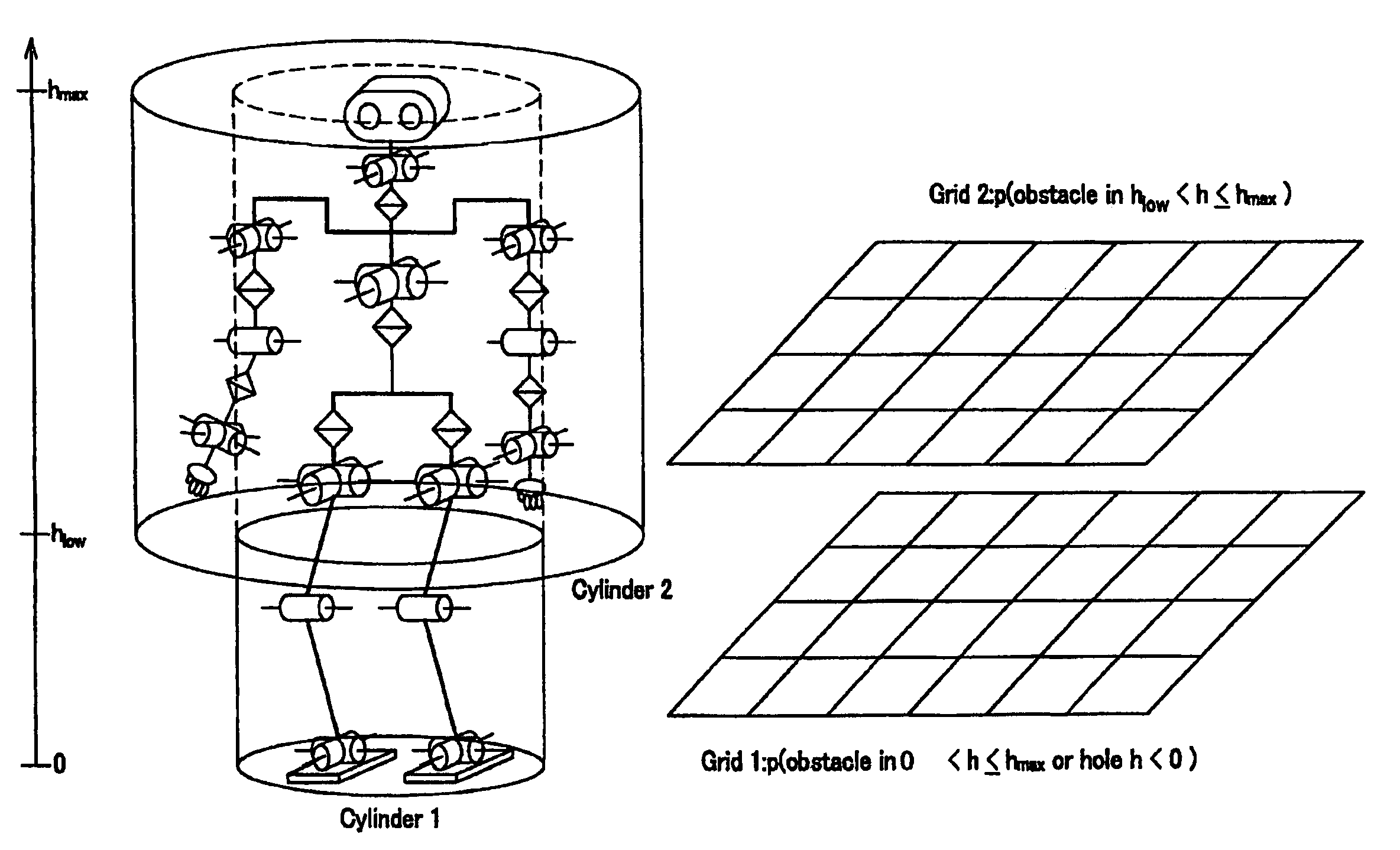
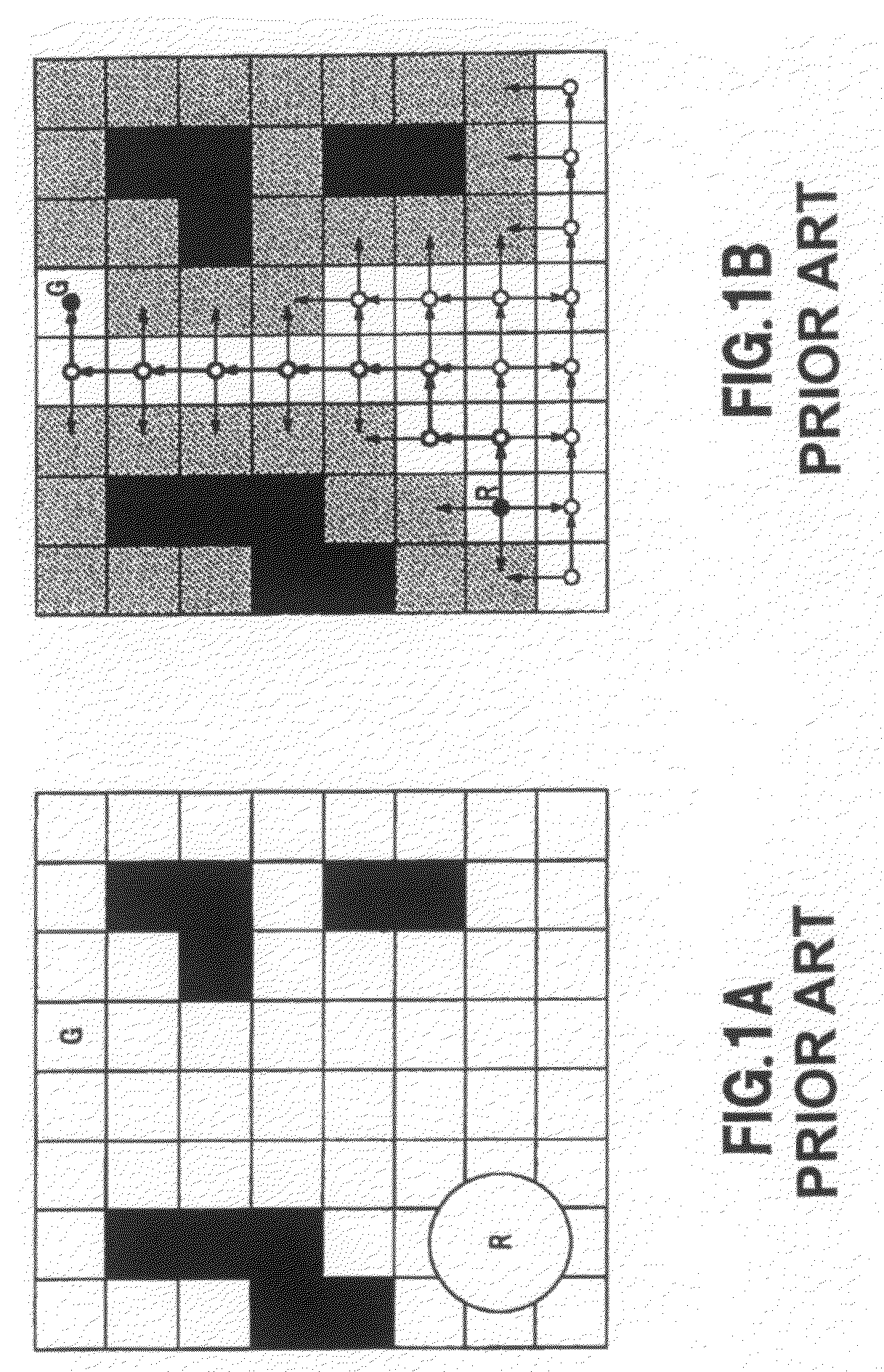
Obstacle avoiding apparatus, obstacle avoiding method, obstacle avoiding program, and mobile robot apparatus
InactiveUS7769491B2Accurate modelingHighly precise moving routeComputer controlSimulator controlEngineeringRoute planning
The present invention provides an obstacle avoiding apparatus, an obstacle avoiding method, an obstacle avoiding program, and a mobile robot apparatus that can accurately model a robot apparatus and plan a highly precise moving route for the robot apparatus that avoids obstacles. The obstacle avoiding apparatus, to be used for a mobile robot apparatus to avoid obstacles, includes an obstacle environment map drawing section that divides the range of height from the reference surface for the mobile robot apparatus to move thereon to the height of the mobile robot apparatus into a plurality of layers corresponding to predetermined respective ranges of height and draws obstacle environment maps, each showing the condition of being occupied by one or more than one obstacles existing in the corresponding layer, and a route planning section that plans a route for the robot apparatus to move along according to an enlarged environment map prepared by enlarging the area occupied by the obstacle or obstacles in the obstacle environment maps as a function of the cross sectional profile of the mobile robot apparatus in each of the layers.
Owner:SONY CORP
Measuring software system performance using benchmarks
ActiveUS7546598B2Accurate modelingLow costError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsData processing systemSoftware system
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for measuring the performance of aspects of a complex data processing system. In one aspect, a method uses a dynamic synthetic benchmark to provide performance information for a program application running on a virtual machine. The benchmark in one implementation uses a load profile that includes information about instructions that make up the application, their call frequencies, and their workloads. Microbenchmarks of individual virtual machine instructions provide performance information about the virtual machine that is used with the load profile to synthesize a performance benchmark for the application.
Owner:SAP AG
Automated generation of local grid refinement at hydraulic fractures for simulation of tight gas reservoirs
ActiveUS20130073268A1Reasonable computational complexityLow costComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationHorizontal wellsHydraulic fracturing
A computer system and method of automatically generating a Local Grid Refinement (LGR) gridded model of a gas reservoir. A geologic file includes information identifying the locations of one or more wells according to root grid cells within a volume of the earth to be modeled. User inputs specify the number of hydraulic fractures from each well, and such parameters as the fracture length, etc. User inputs also specify the number of “splits” of the root grid cells containing hydraulic fractures; those root grid cells are then split into finer resolution grid cells of increasing width within the root grid cells containing the fractures. For horizontal wells, user inputs indicate the number of splits of root grid cells containing the lateral portions of the wellbore. Non-orthogonal and complex fractures are processed by a“nested” LGR approach. Geologic properties are assigned to each grid cell, with a tensorial adjustment included for non-orthogonal fractures, and the resulting model is available for simulation.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
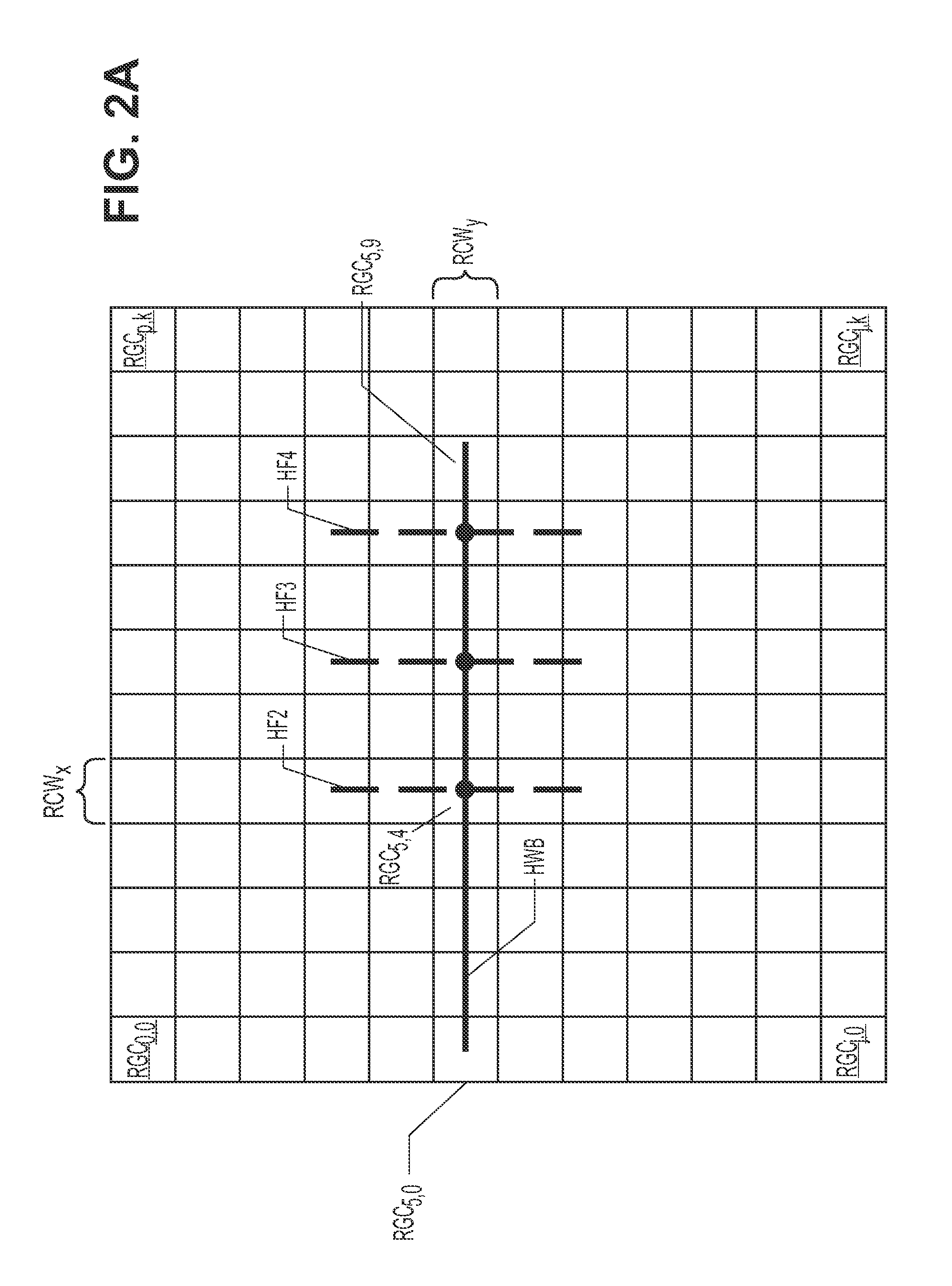
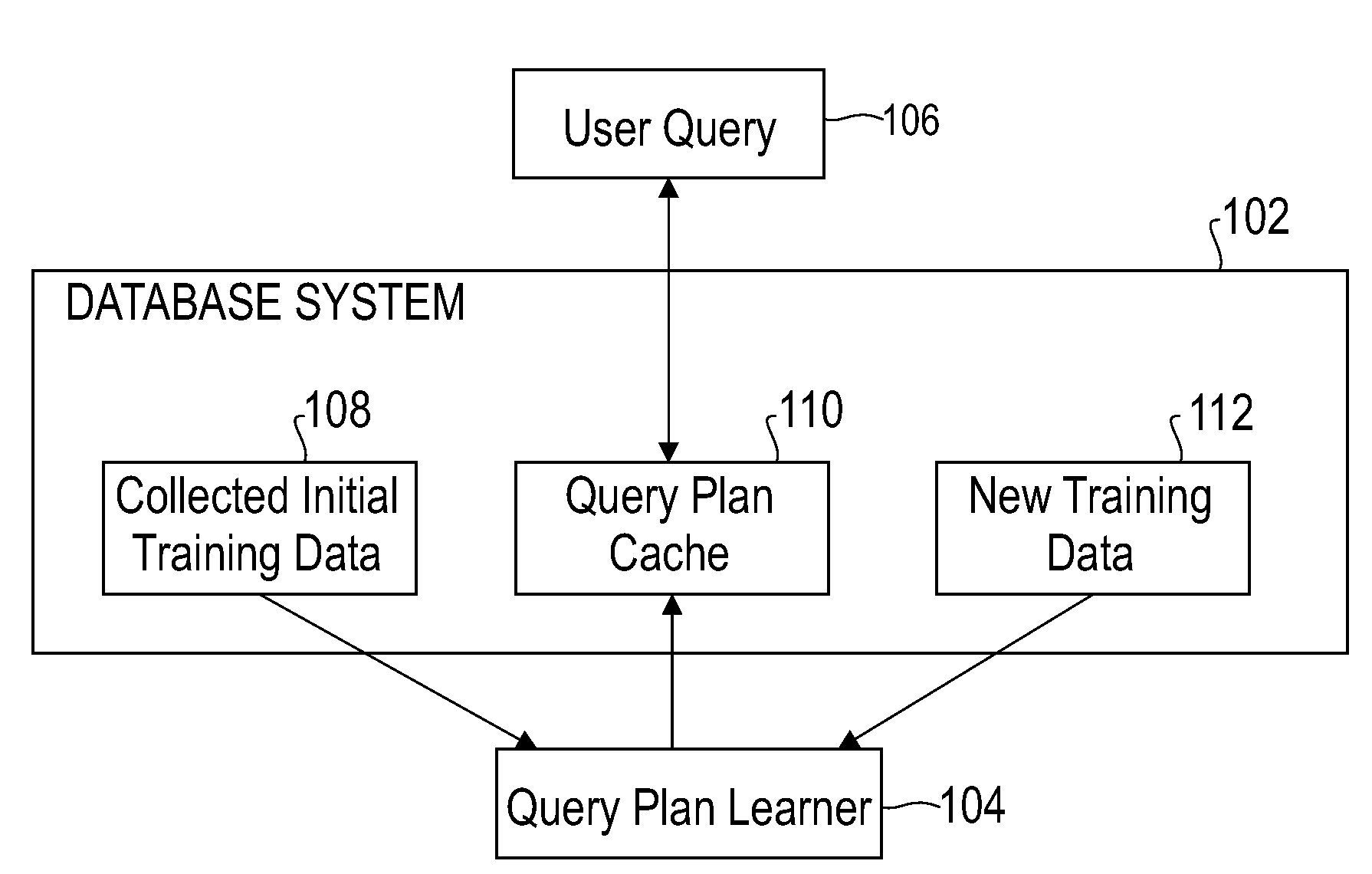
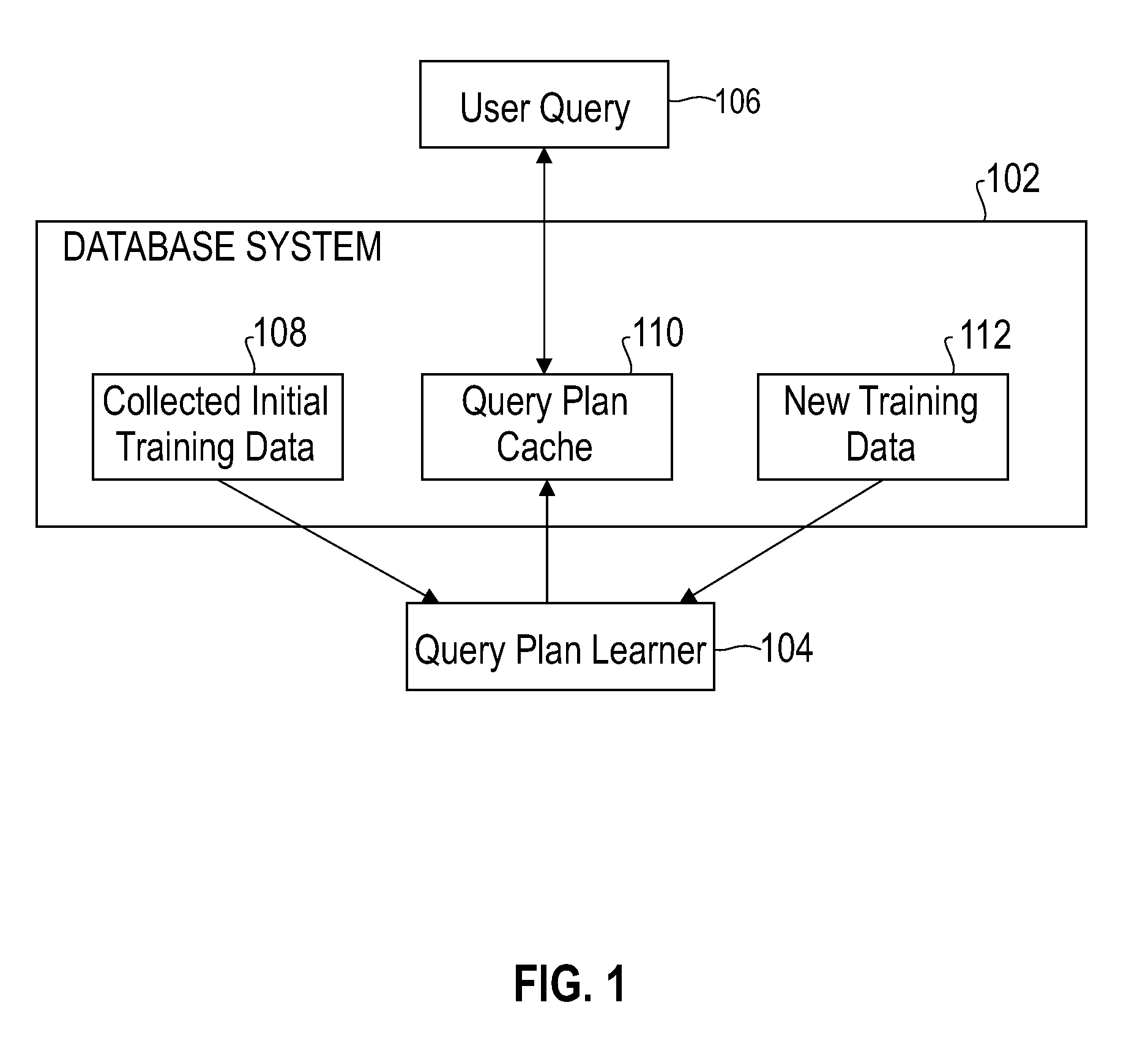
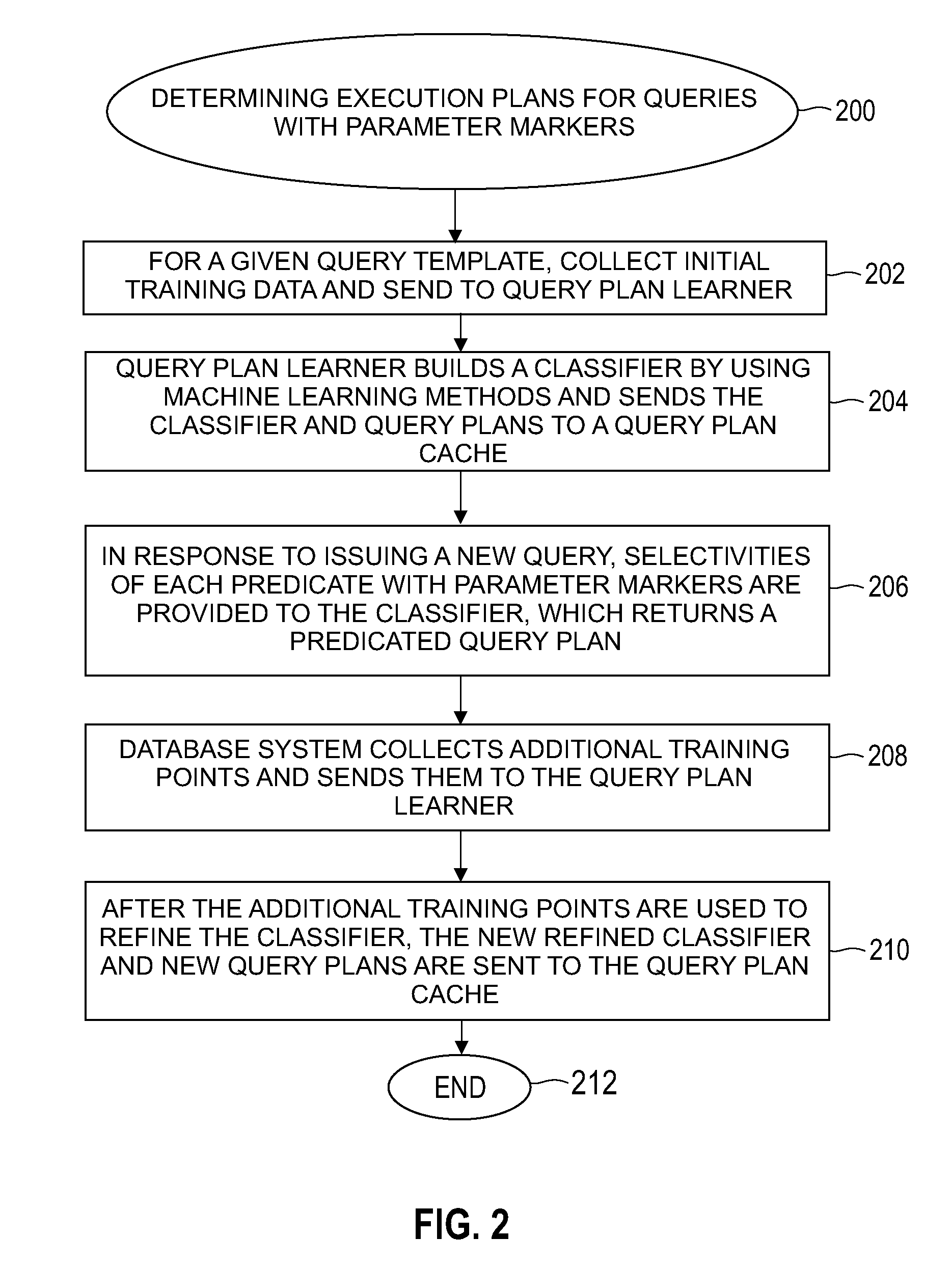
Automatically and adaptively determining execution plans for queries with parameter markers
InactiveUS20080222093A1Accurate modelingImprove forecast accuracyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsExecution planProgram planning
A method and system for automatically and adaptively determining query execution plans for parametric queries. A first classifier trained by an initial set of training points is generated. A query workload and / or database statistics are dynamically updated. A new set of training points is collected off-line. Using the new set of training points, the first classifier is modified into a second classifier. A database query is received at a runtime subsequent to the off-line phase. The query includes predicates having parameter markers bound to actual values. The predicates are associated with selectivities. A mapping of the selectivities into a plan determines the query execution plan. The determined query execution plan is included in an augmented set of training points, where the augmented set includes the initial set and the new set.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and apparatus for automatically identifying animal species from their vocalizations
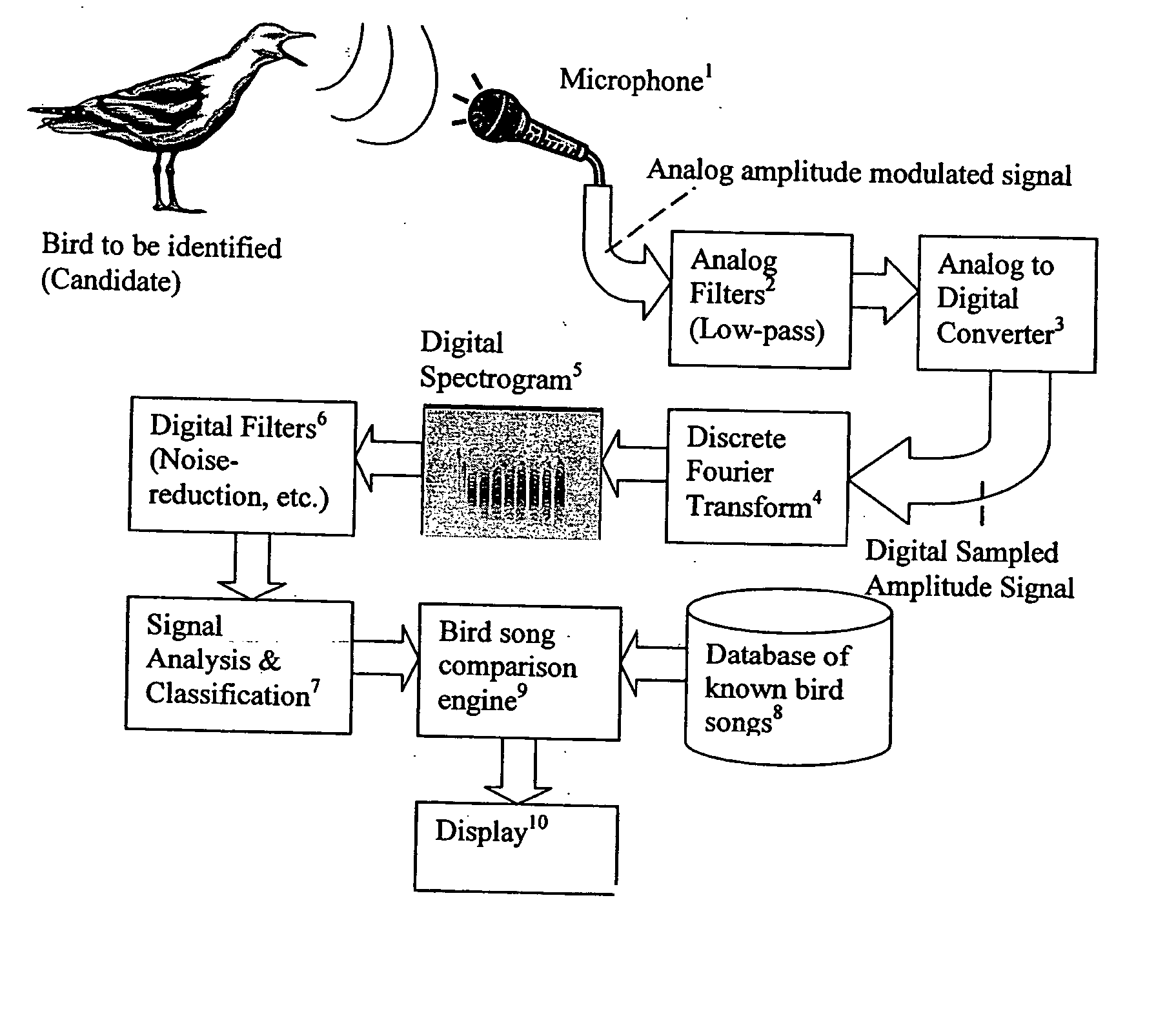
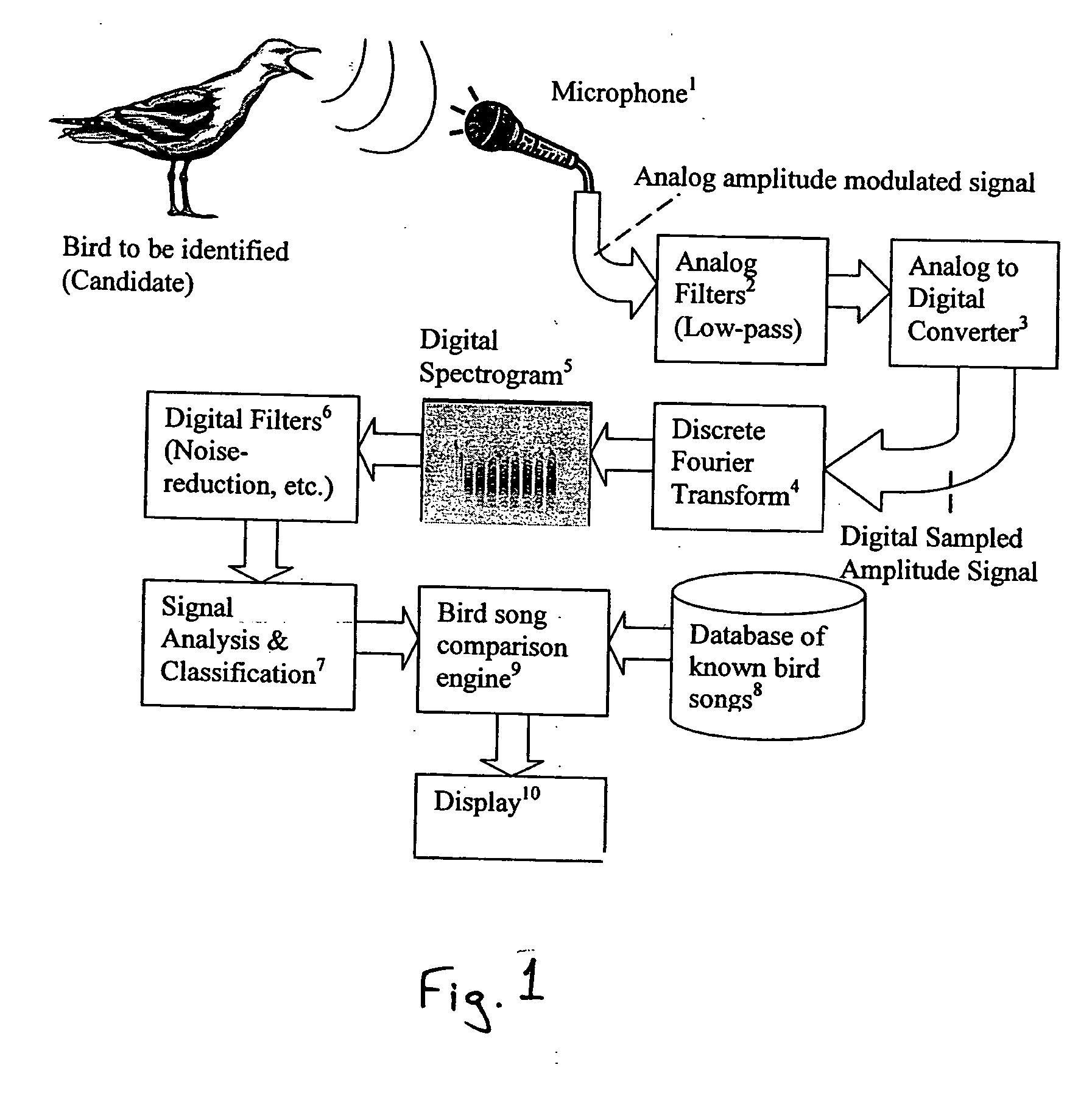
ActiveUS20050049877A1Accurate modelingReduce the impact of noiseAvicultureSpeech recognitionPhraseHide markov model
Relatively powerful hand-held computing devices, Digital Signal Processors, Audio signal processing technology, voice recognition technology, expert systems, Hidden Markov Models, and / or neural networks are employed in a device capable of real-time automated species identification by listening to bird vocalizations in the field, analyzing their waveforms, and comparing these waveforms against known reference samples. An apparatus for identifying animal species from their vocalizations, comprises a source of digital signal representative of at least one animal candidate vocalization; a feature extractor that receives the digital signal, recognizes notes therein and extracts phrases including plural notes and that produces a parametric representation of the extracted phrases; and a comparison engine that receives the parametric representation of at least one of the digital signal and the extracted phrases, and produces an output signal representing information about the animal candidate based on a likely match between the animal candidate vocalization and known animal vocalizations. A computer-implemented method of identifying animal species, comprises: obtaining a digital signal representing a vocalization by a candidate animal; transforming the digital signal into a parametric representation thereof; extracting from the parametric representation a sequence of notes defining a phrase; comparing the phrase to phrases known to be produced by a plurality of possible animal species; and identifying a most likely match for the vocalization by the candidate animal based upon the comparison. The comparison engine or comparison function may use Hidden Markov Models, expert systems and / or neural networks.
Owner:WILDLIFE ACOUSTICS
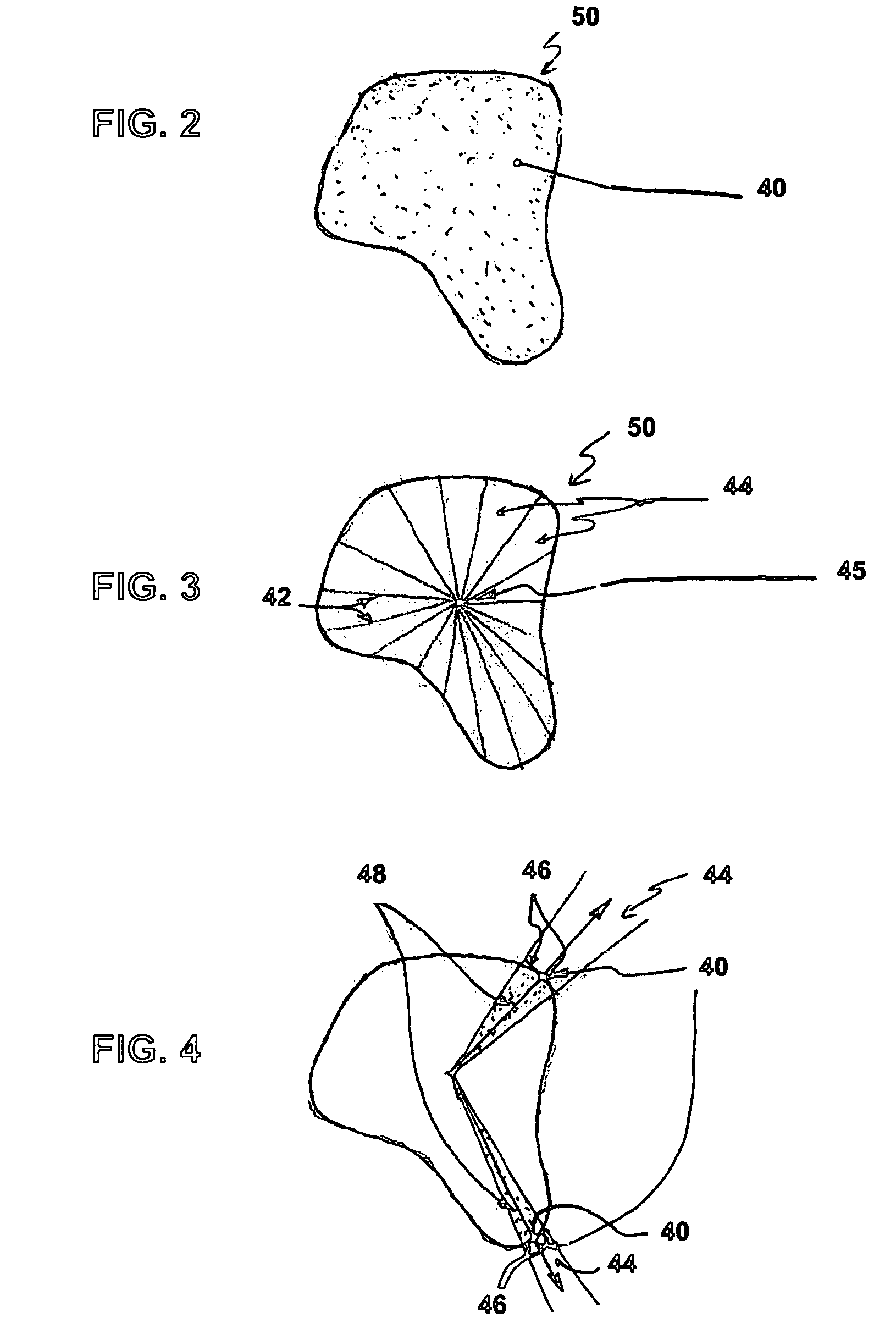
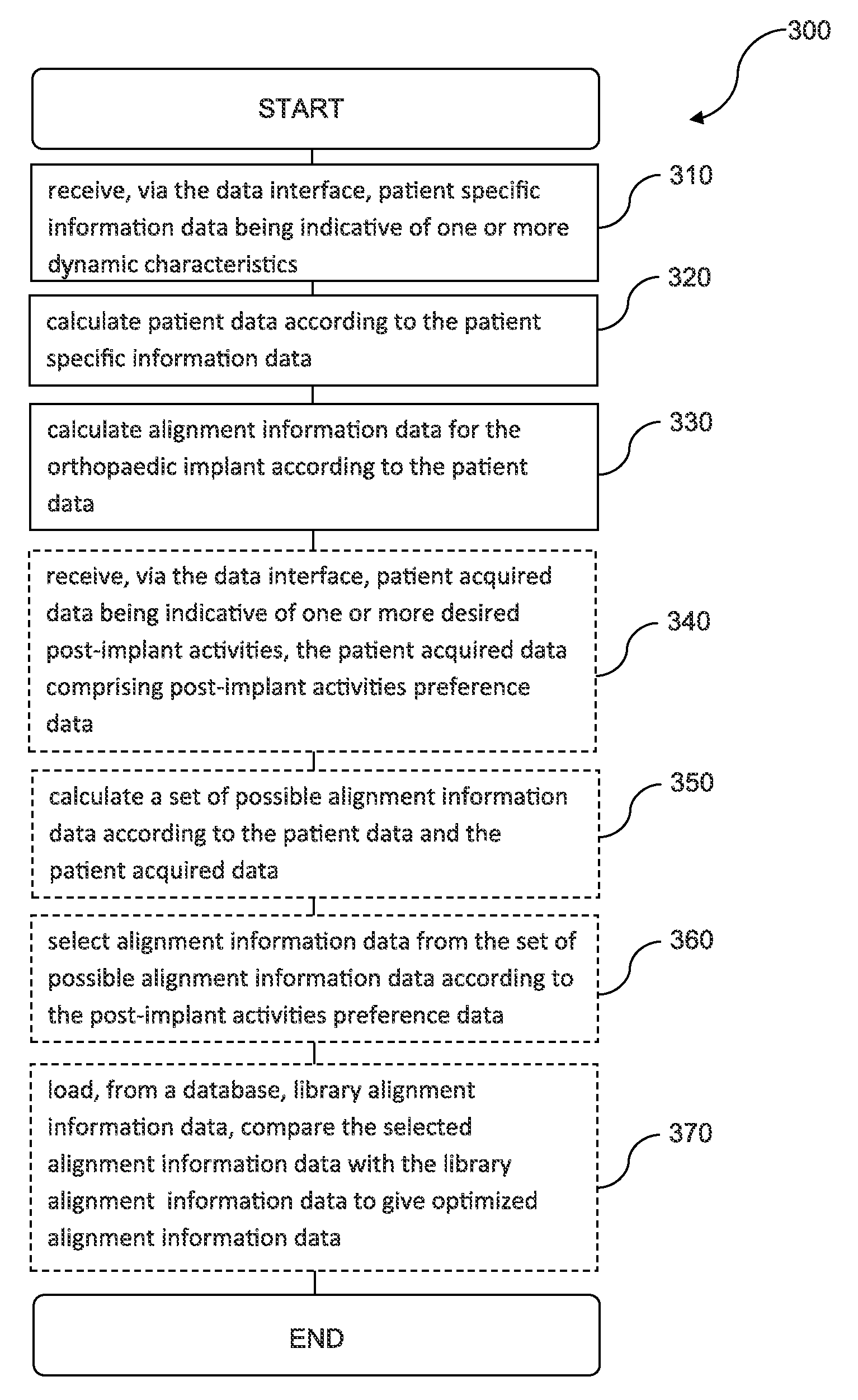
Computer-implemented method, a computing device and a computer readable storage medium for providing alignment information data for the alignment of an orthopaedic implant for a joint of a patient
ActiveUS8983813B2Precise alignmentAccurate modelingSuture equipmentsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPatient dataSurgical implant
The present disclosure relates to a computer-implemented method, a computing device, and a computer readable storage medium, for providing alignment information data for the alignment of an orthopaedic implant for a joint of a patient. The computer-implemented method comprises the steps of being responsive to patient specific information data for deriving patient data, where the patient specific information data is indicative of one or more dynamic characteristics, and being responsive to the patient data for providing the alignment information data for the alignment of the orthopaedic implant.
Owner:CORIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com