Patents
Literature
209 results about "Human anatomy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
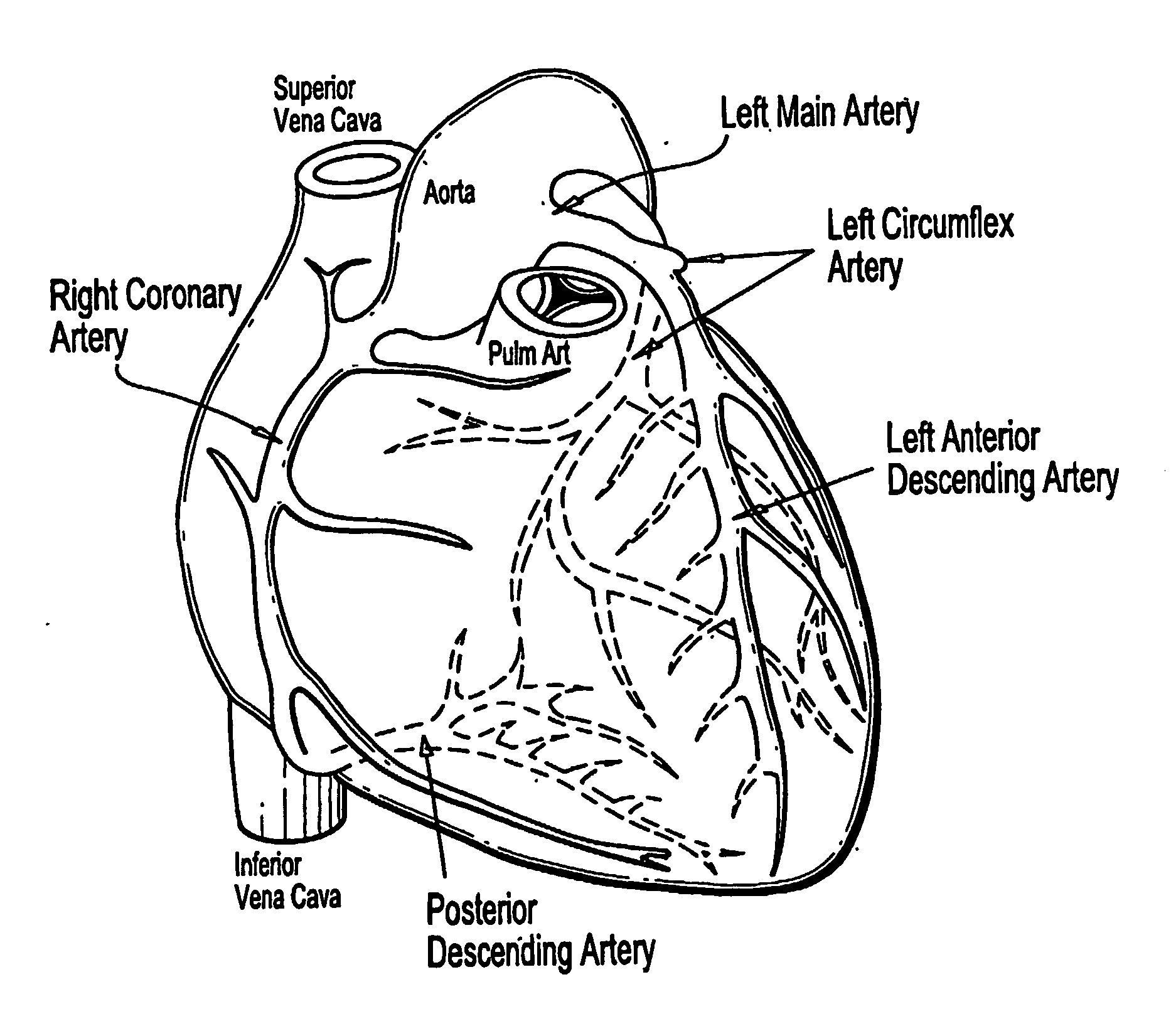
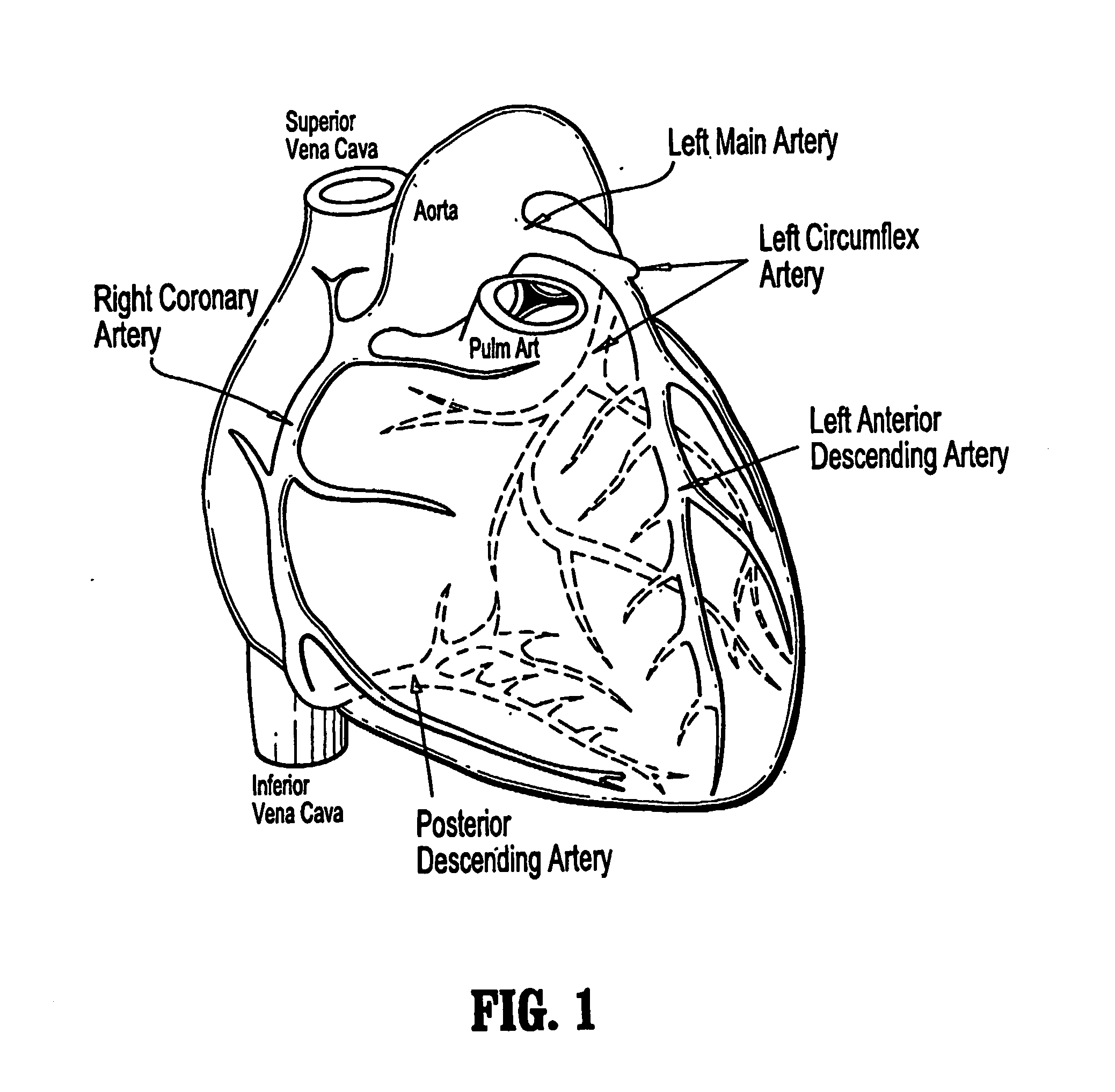
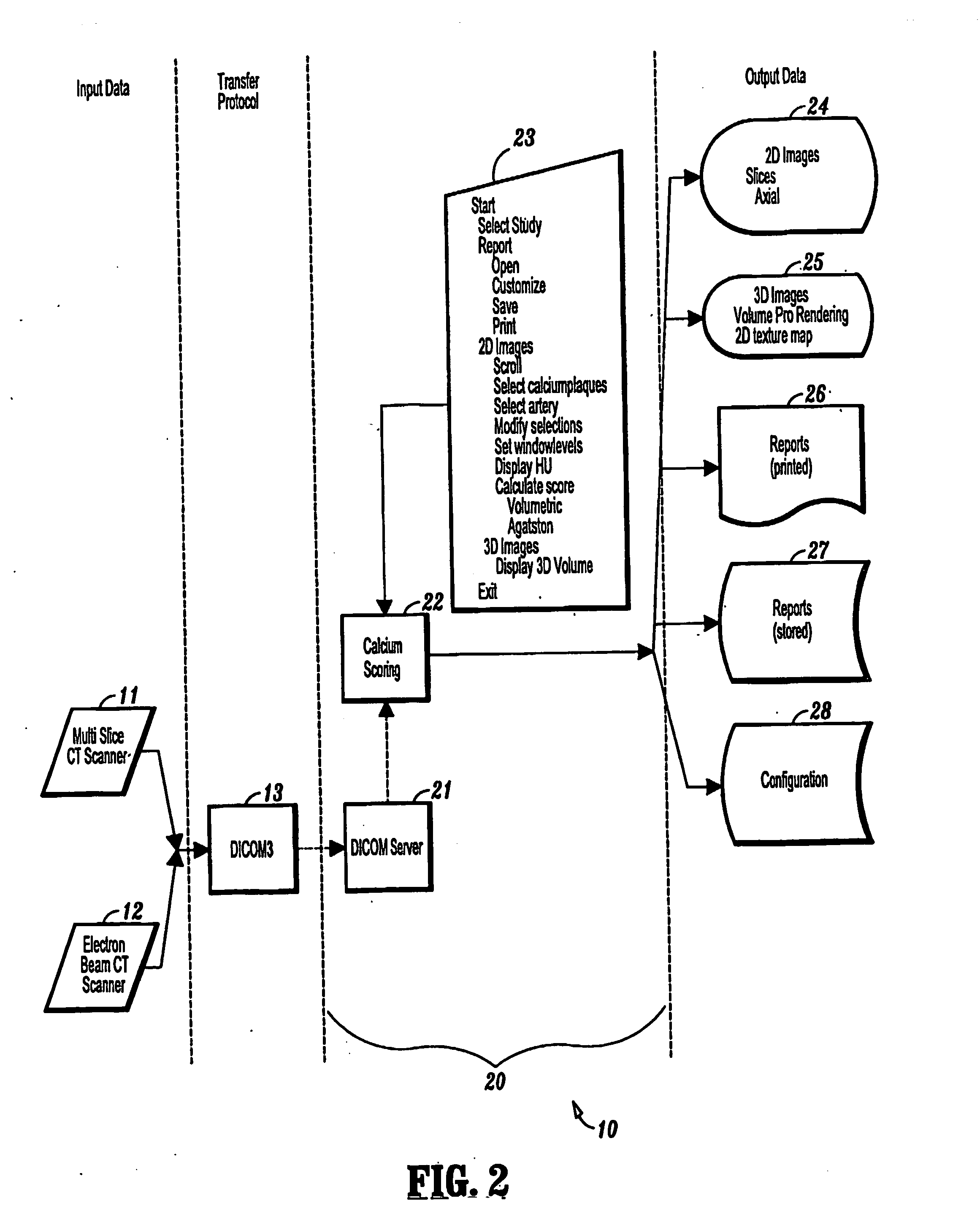
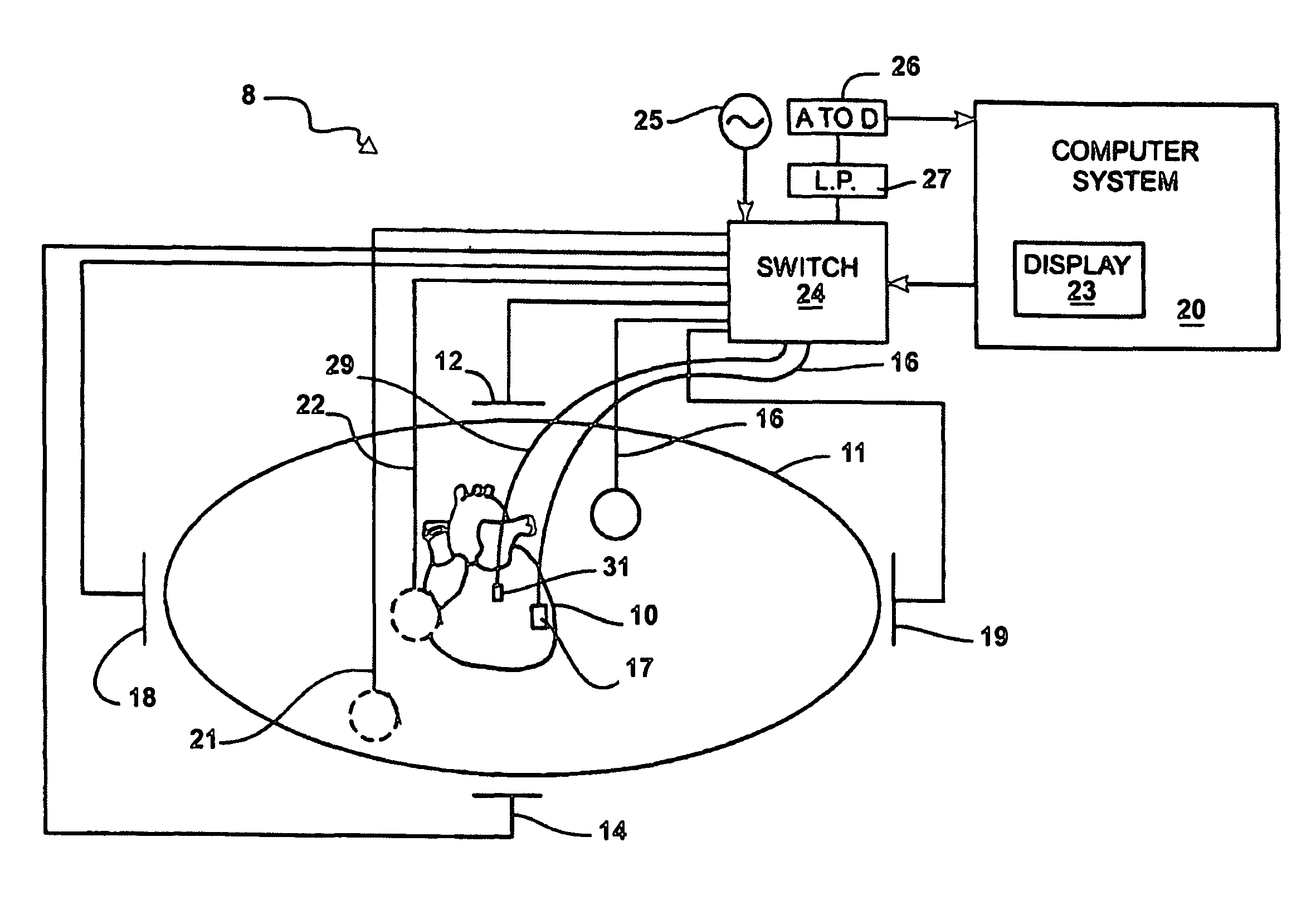
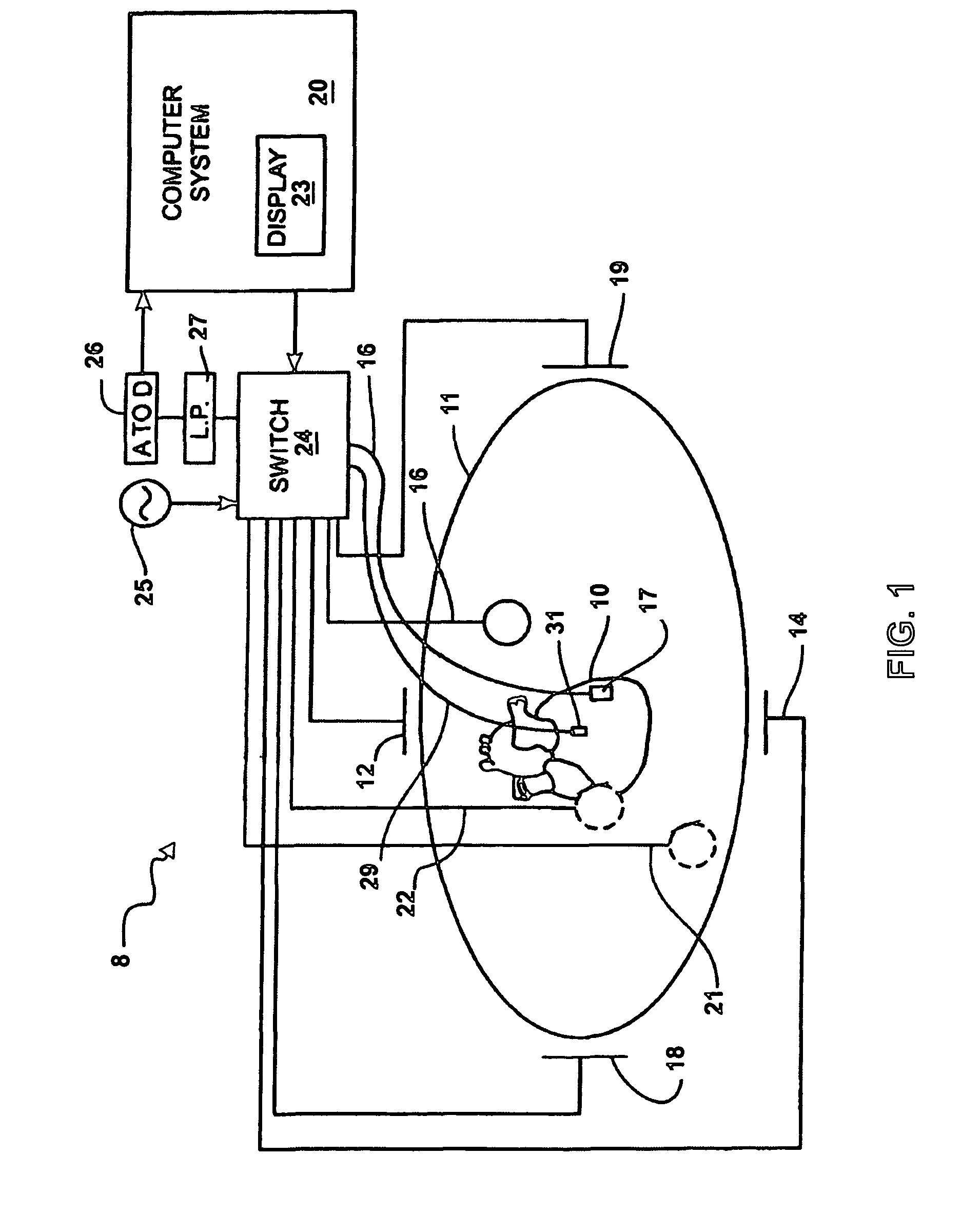
Imaging system and methods for cardiac analysis
InactiveUS20110206247A1Efficiently and accurately detect and viewLess tediousImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsHuman anatomy
Imaging systems and methods for viewing medical images of human anatomy and, in particular, to a 3-dimensional imaging system that allows a user to efficiently and accurately detect and view coronary artery calcification as displayed graphically on a computer screen. In one aspect, a method for displaying medical images comprises obtaining an image dataset comprising anatomical image data (step 50), automatically grouping connected components in the image data to form groups of connected components (steps 50-57), and displaying the groups of connected components are distinguishable in the displayed image (58-59). The image dataset may comprise a volume data set and the groups of connected components comprise regions of neighboring voxels that share a similar property. The image dataset may comprise a 2-dimensional data set and the groups of connected components comprise regions of neighboring pixels that share a similar property. Different groups of connected components may be displayed in different colors and / or different opacities or certain groups may not be displayed at all.
Owner:VIATRONIX
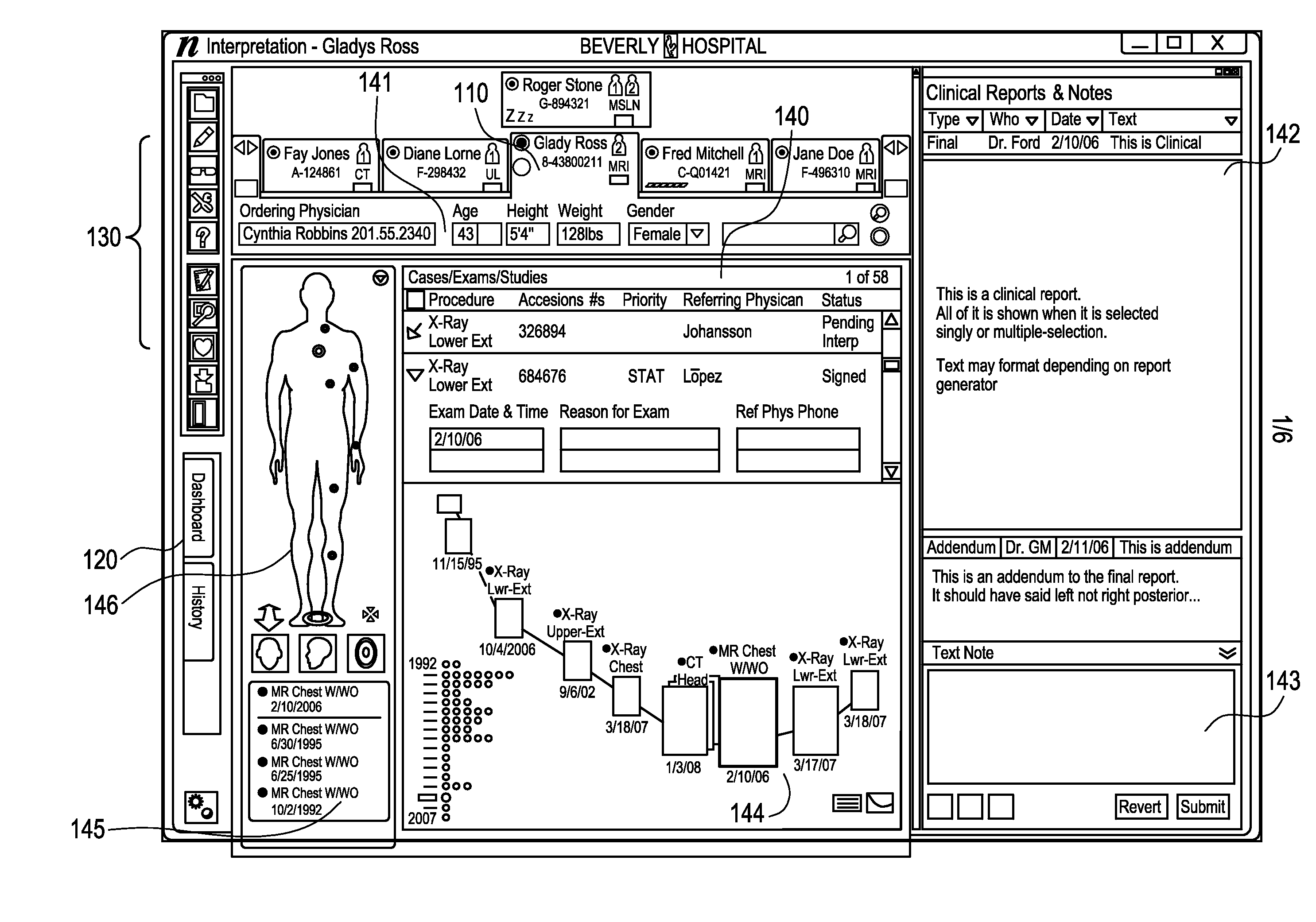
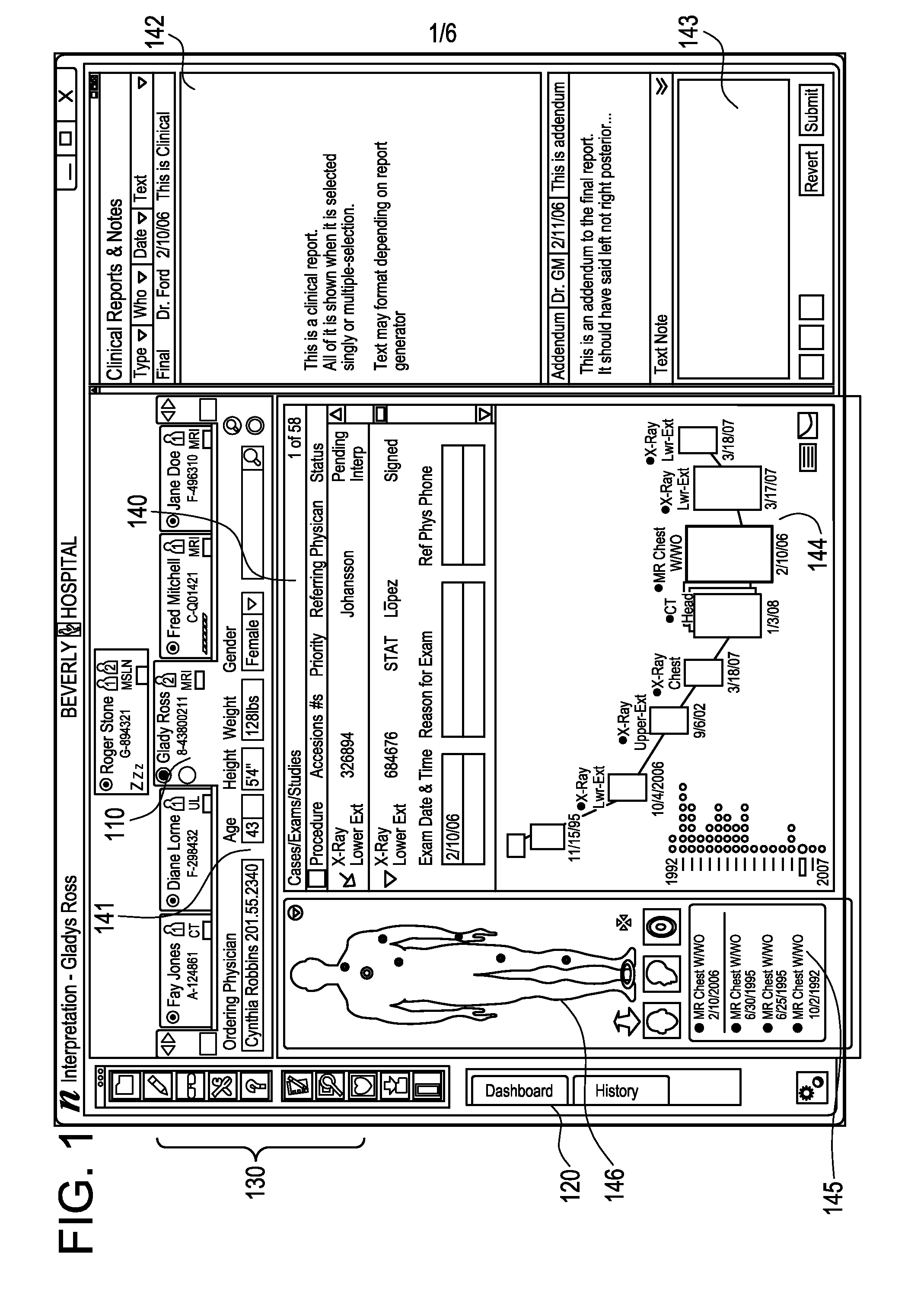
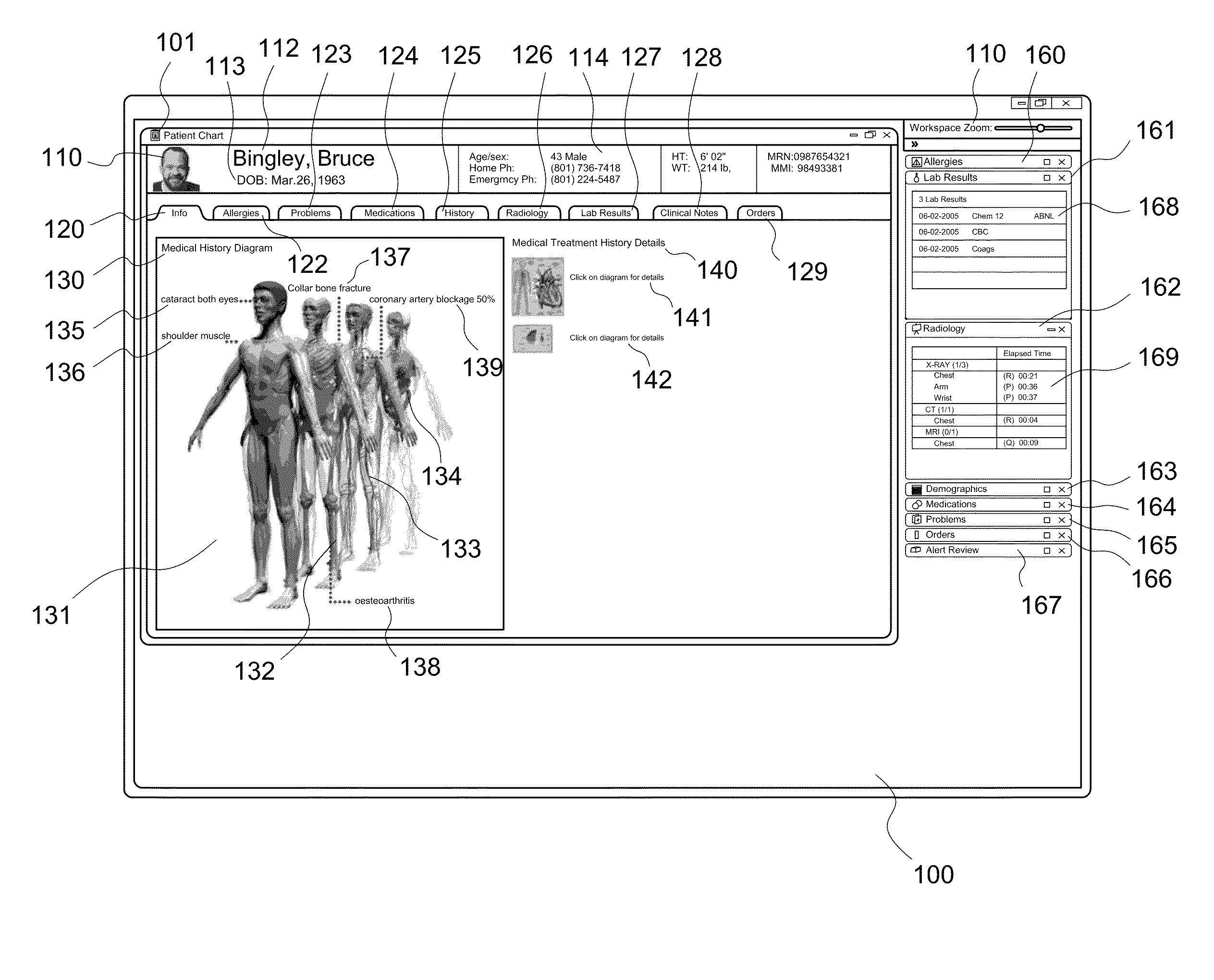
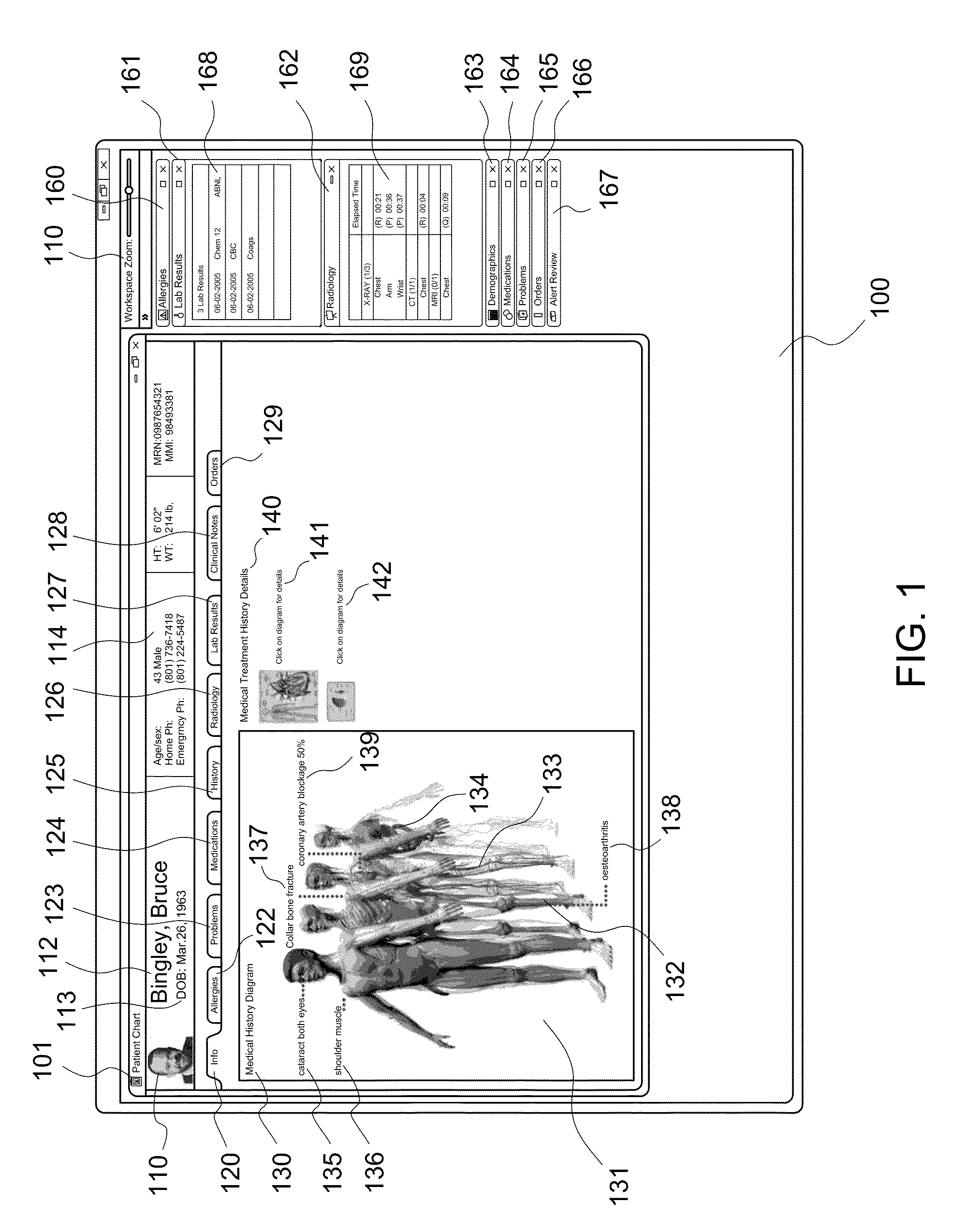
Electronic health record timeline and the human figure
ActiveUS20090192823A1Improve user interactionMedical report generationPatient personal data managementGraphicsHuman anatomy
A patient information interface system presents an aggregated, graphical view of patient anatomy and history. The system includes a graphical representation of at least a portion of a human anatomy including one or more indicators, aggregated from a plurality of clinical information sources and located at anatomical locations on the representation, that correspond to clinical events that have occurred in connection with a patient. The system also includes an electronic health record timeline of clinical events for the patient. The timeline includes the same one or more indicators that are displayed on the graphical representation corresponding to clinical events that have occurred in connection with a patient. A selection or change of an indicator on one of the graphical representation or the electronic health record timeline triggers a corresponding selection or change of the indicator on the other of the graphical representation or the electronic health record timeline.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Registration of human anatomy integrated for electromagnetic localization
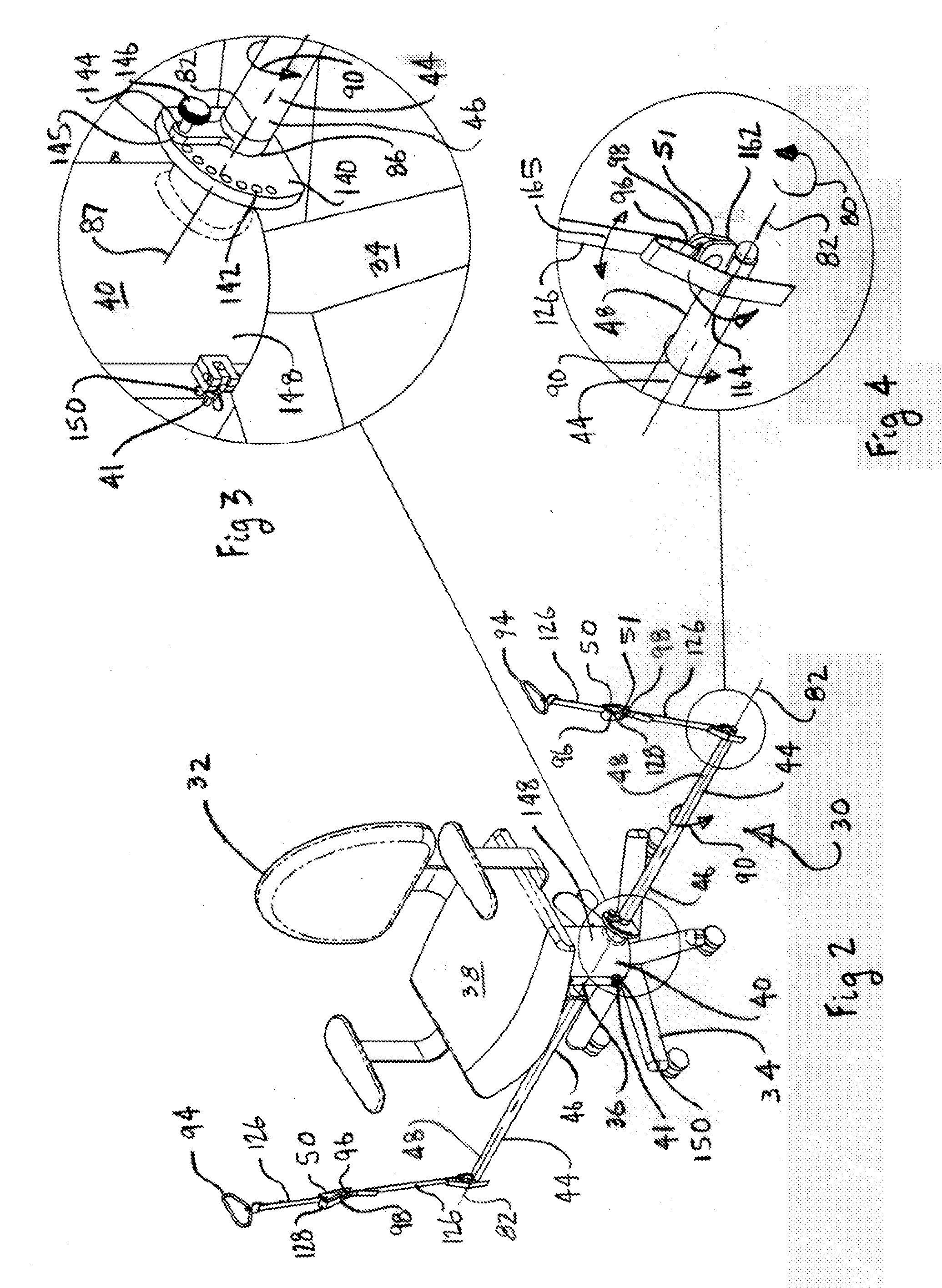
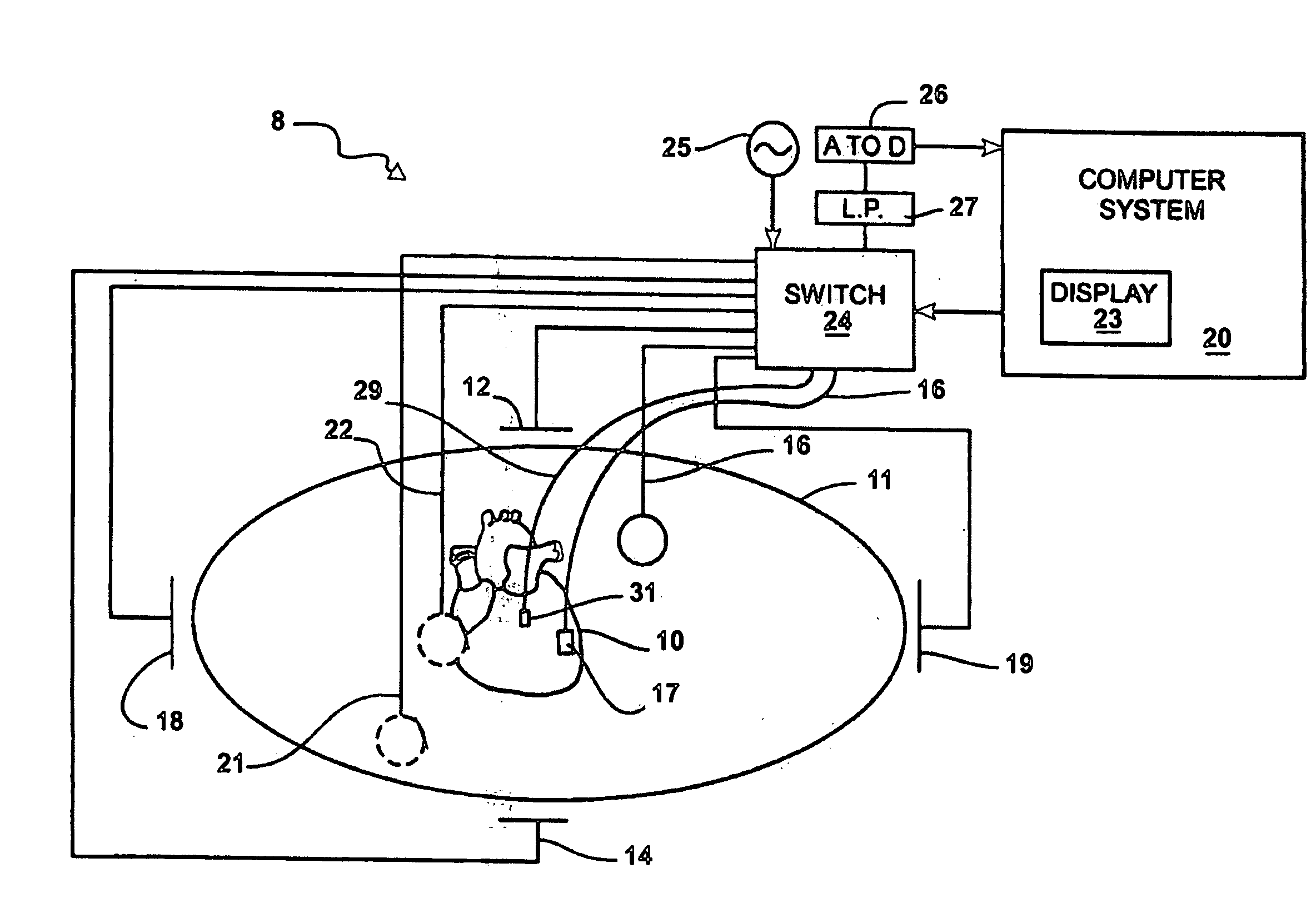
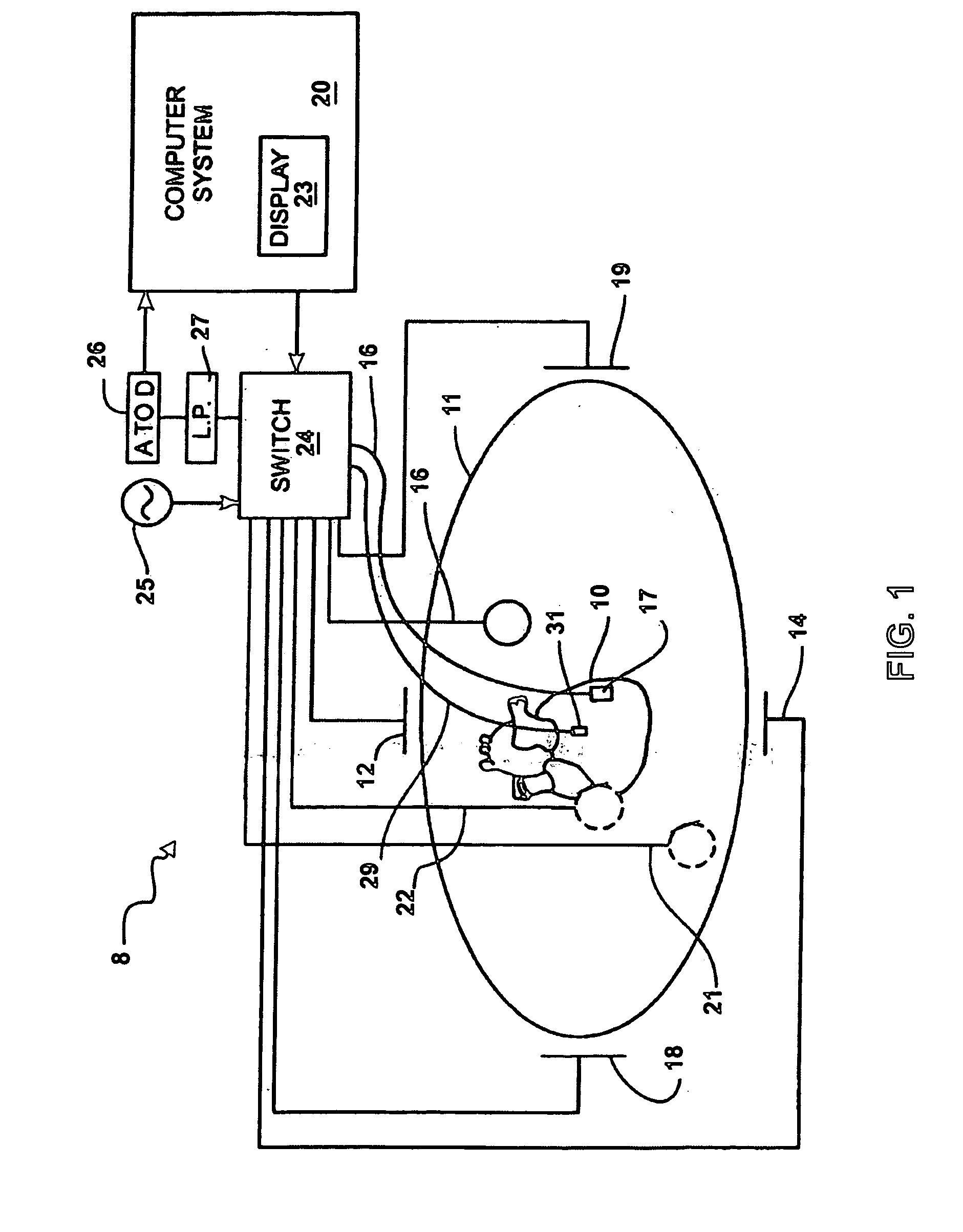
A method for use during a procedure on a body. The method generates a display representing relative positions of two structures during the procedure. The method comprises the steps of storing an image data set in memory, the image data set representing the position of the body based on scans taken of the body prior to the procedure; reading the image data set stored in the memory, the image data set having a plurality of data points in known relation to a plurality of reference points for at least one of the two structures; placing one or more magnetic field sensors in known relation to the reference points of the two structures; generating a magnetic field; detecting the magnetic field with the magnetic field sensors; ascertaining the locations of the sensors based upon the magnetic field detected by the sensors and processing the locations of the sensors to generate a displaced image data set representing the relative position of the two structures during the procedure; and generating a display based on the displaced image data set illustrating the relative position of the two structures during the procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
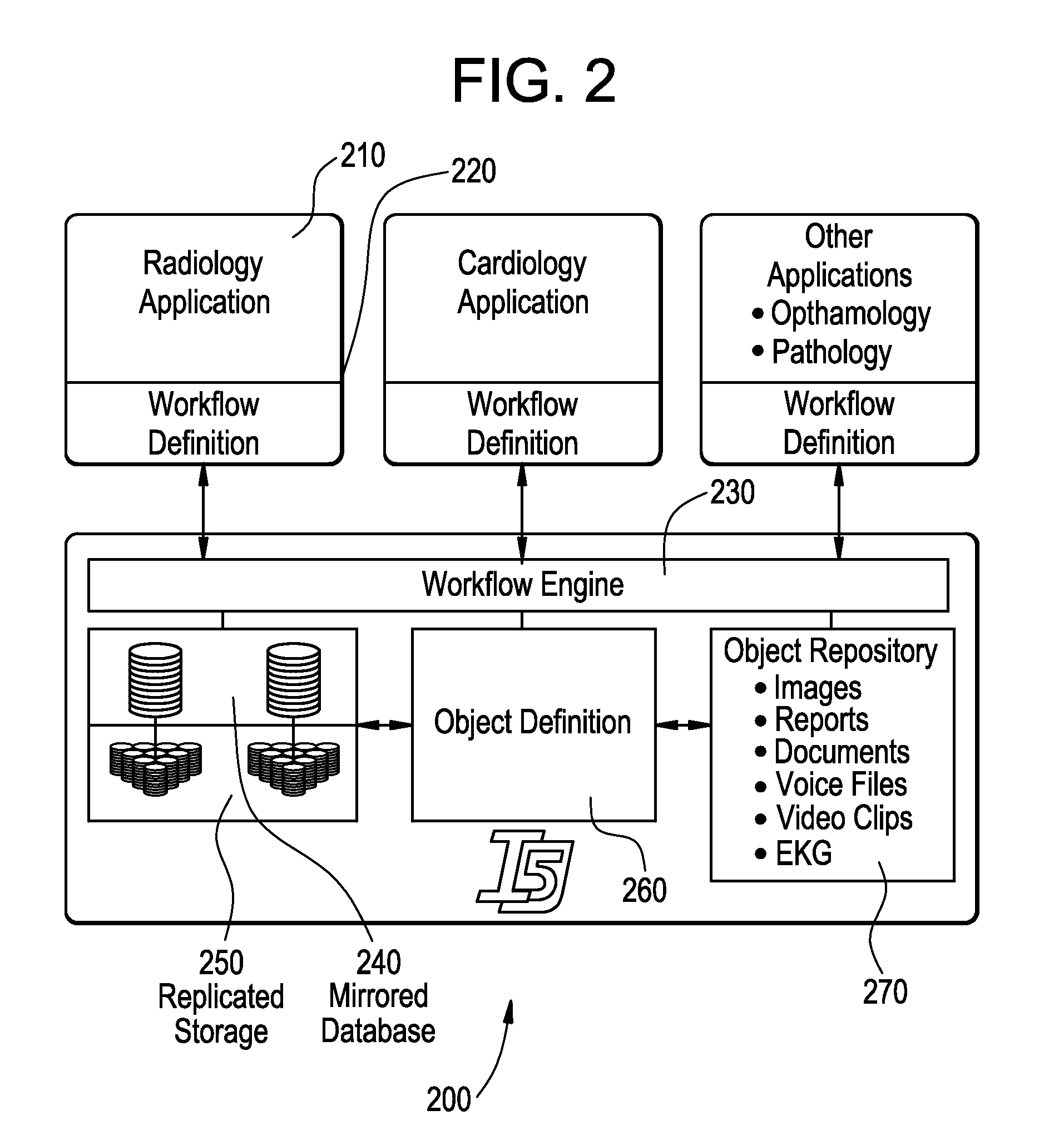
System and method for complex geometry modeling of anatomy using multiple surface models
ActiveUS7988639B2Accurate modelingImprove abilitiesElectrocardiographyCatheterComputational scienceHuman anatomy
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for creating a complex model of the human anatomy. The anatomy may be modeled using multiple geometries. Generally, a plurality of line-of-sight models may be combined into a composite model. Multiple clouds of points may be used to create surface models which may then be merged into a common volume. The resulting composite model may include portions that are not within a line of sight of a mean center point of the composite model. The surface models may be modeled using polygons, including for example, triangles. Disclosed herein are also ways in which electrophysiology data and / or other information may be mapped from a measurement point to a point on the composite model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
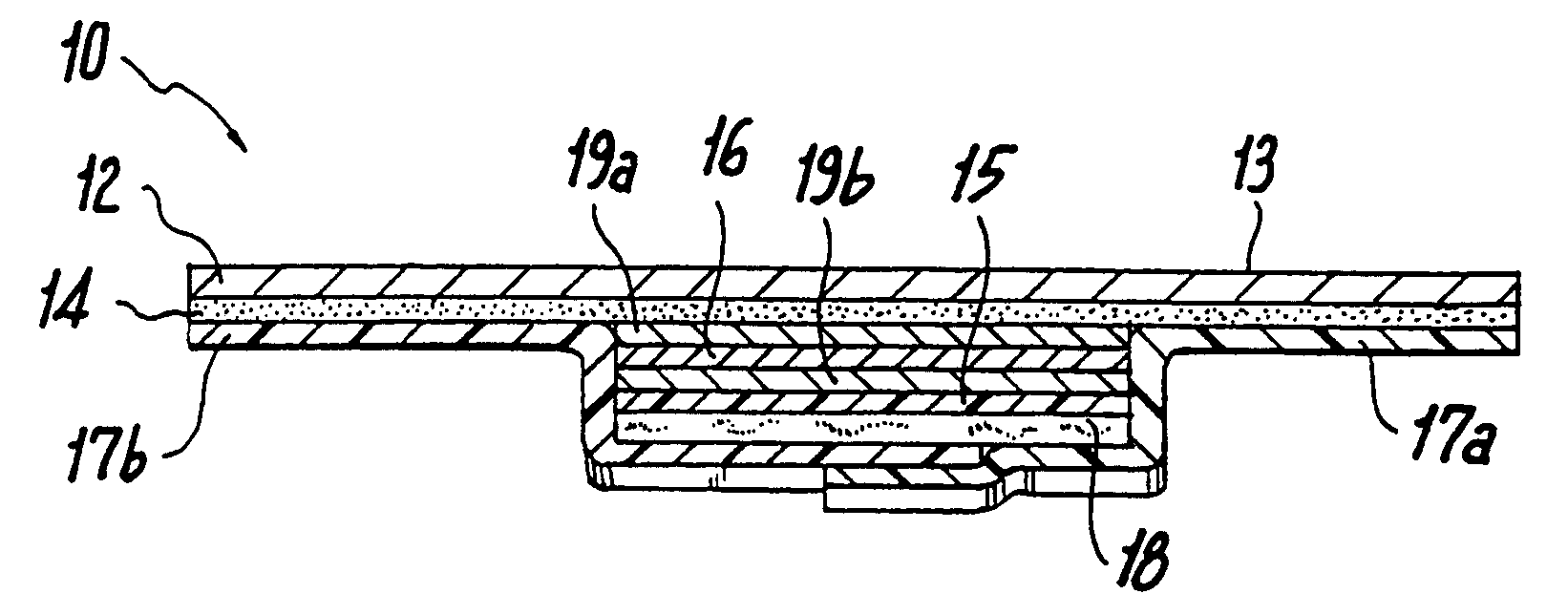
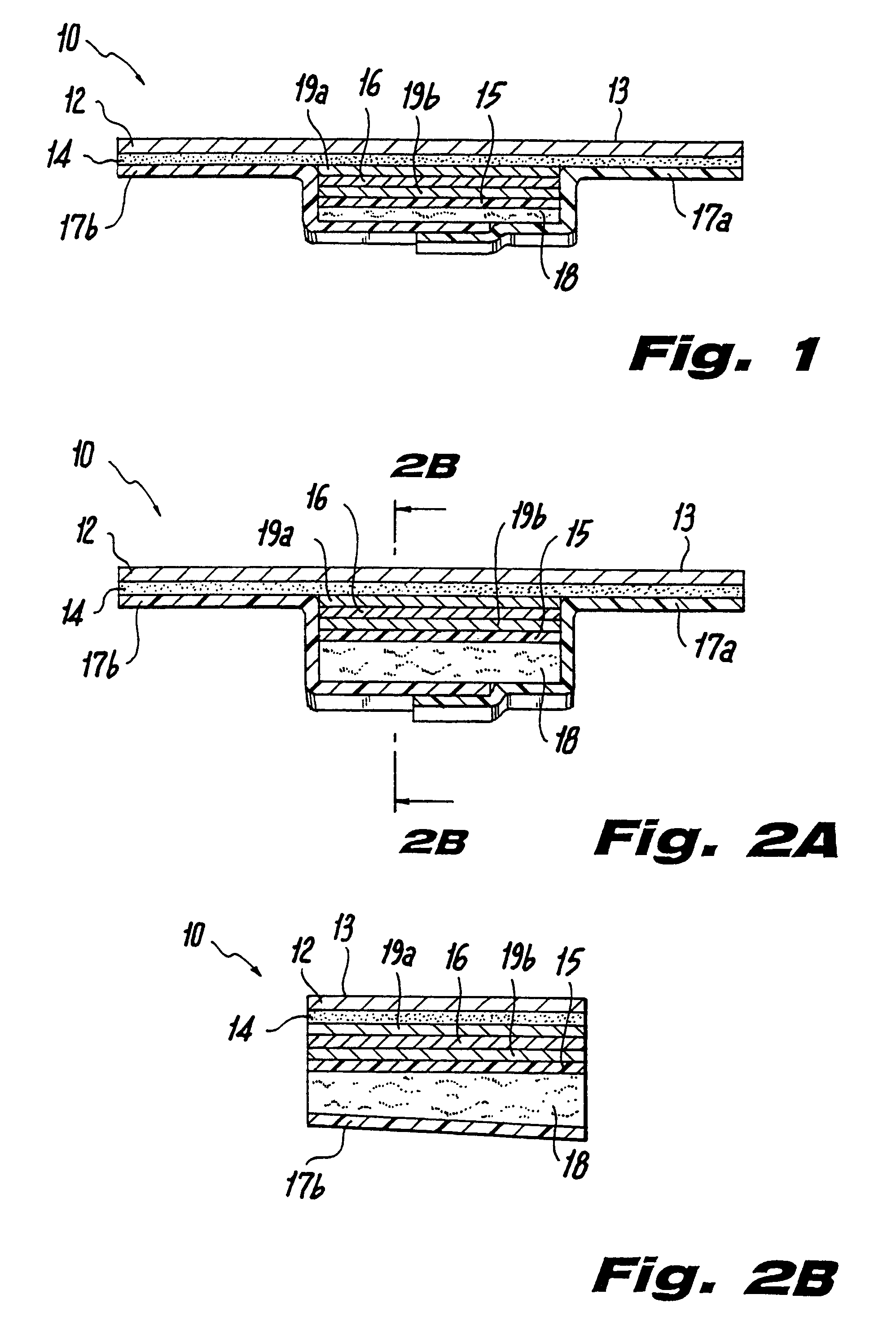
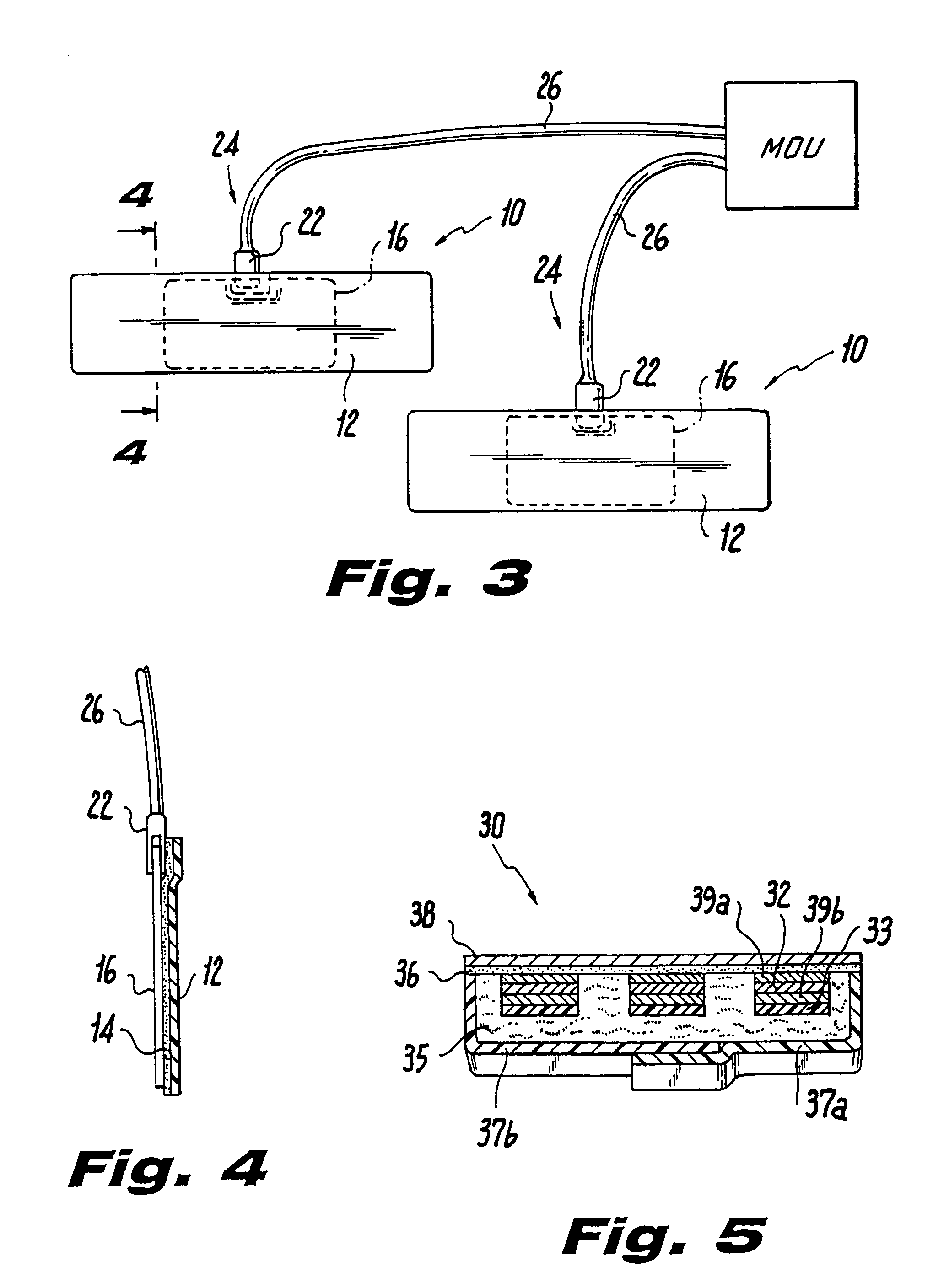
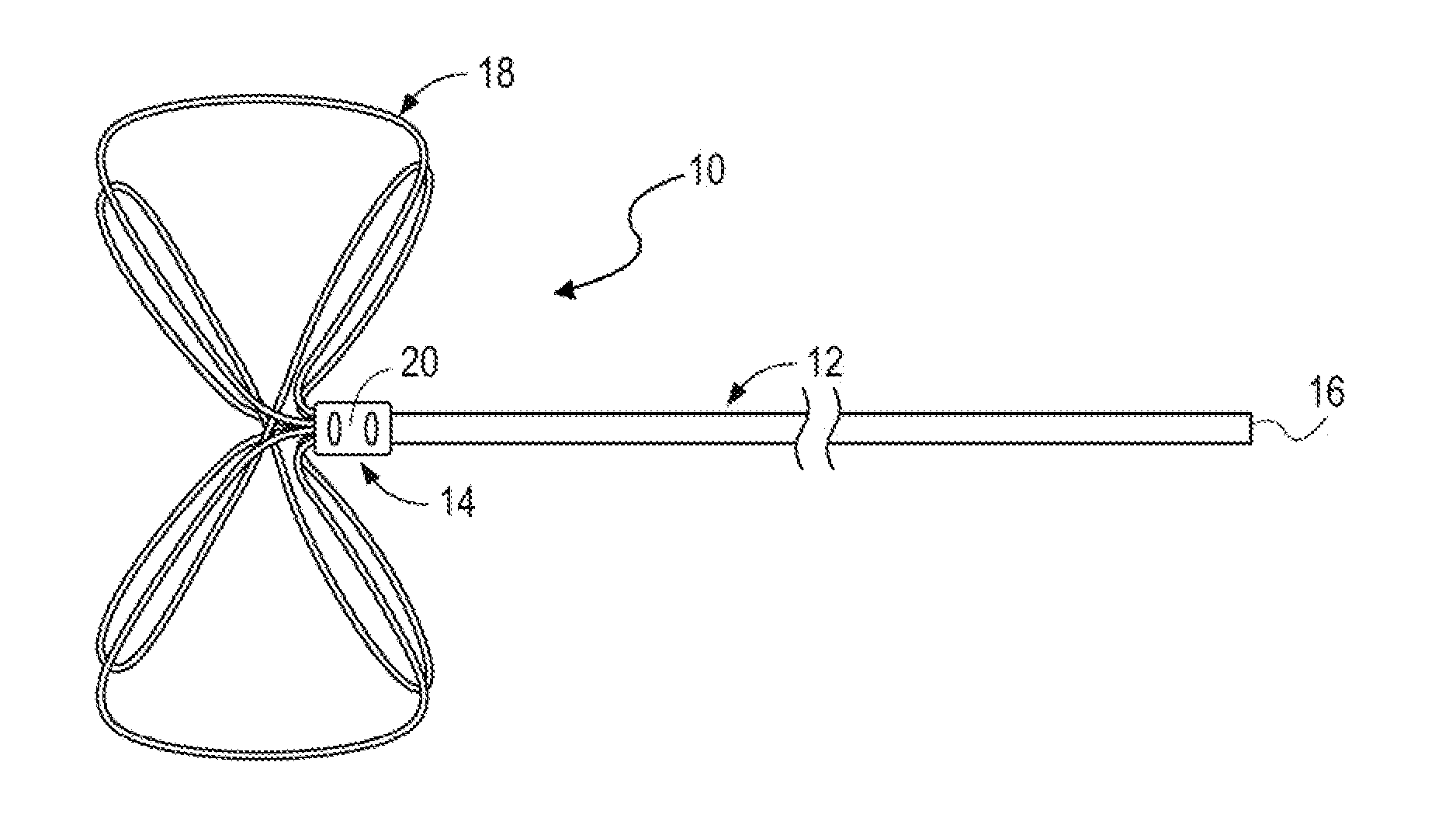
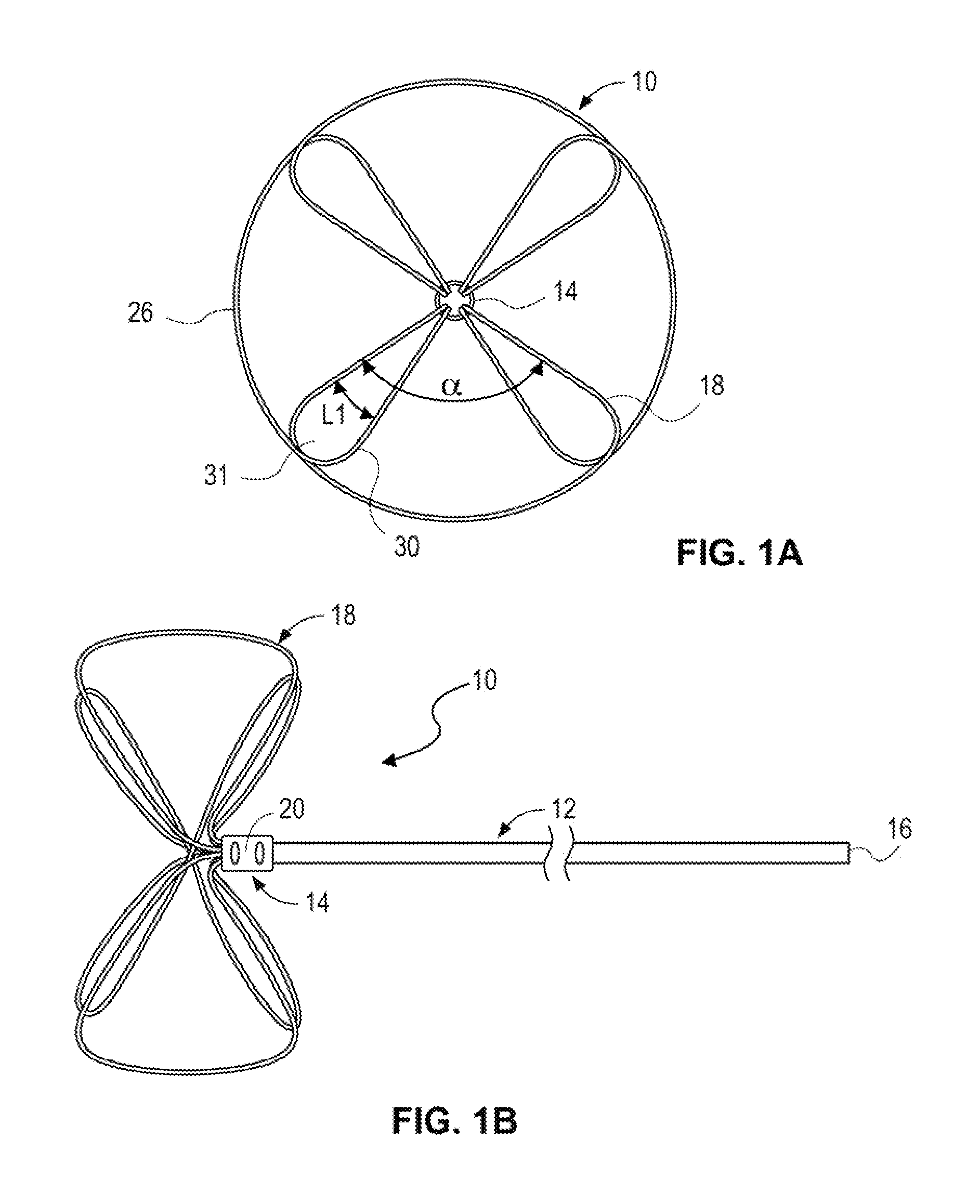
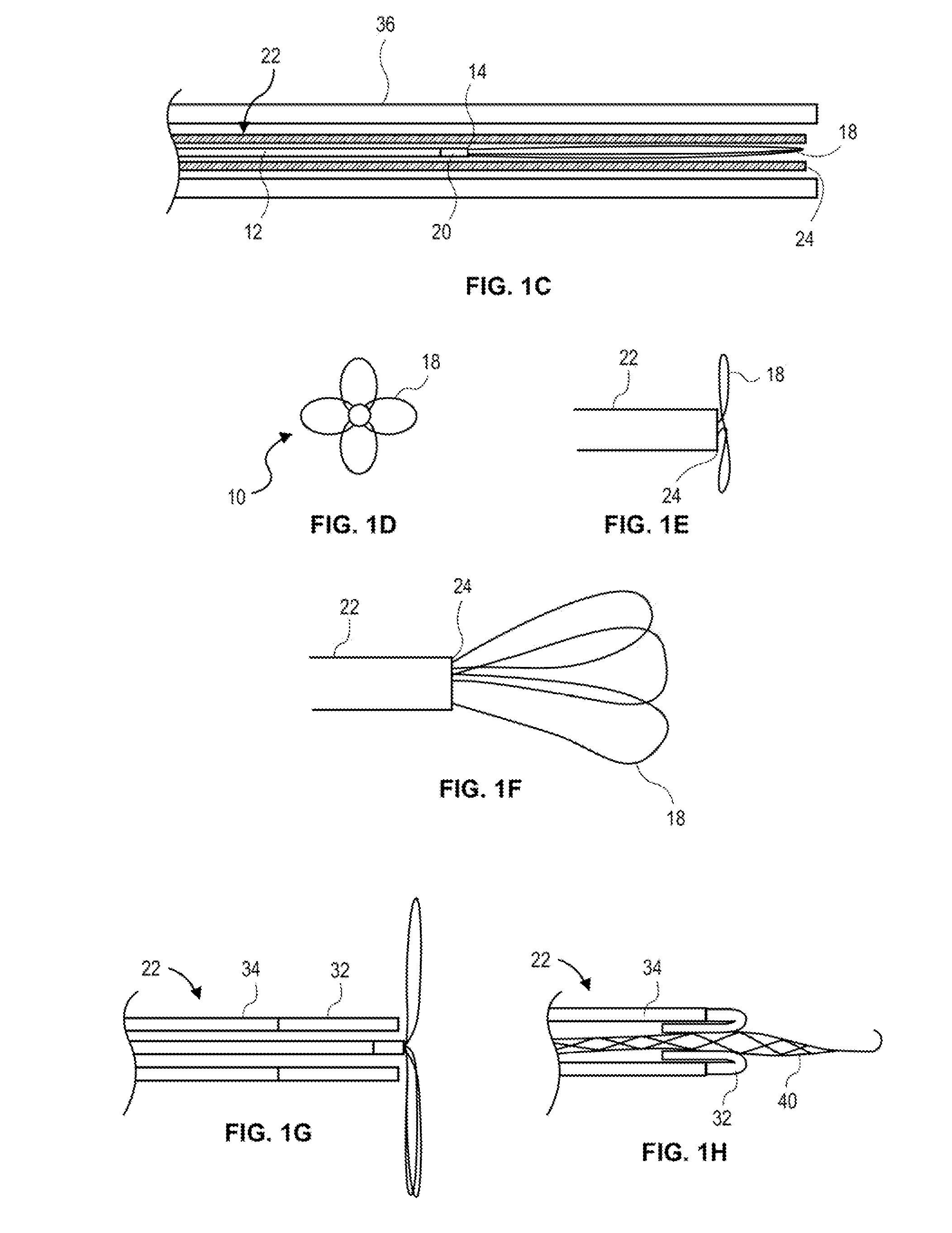
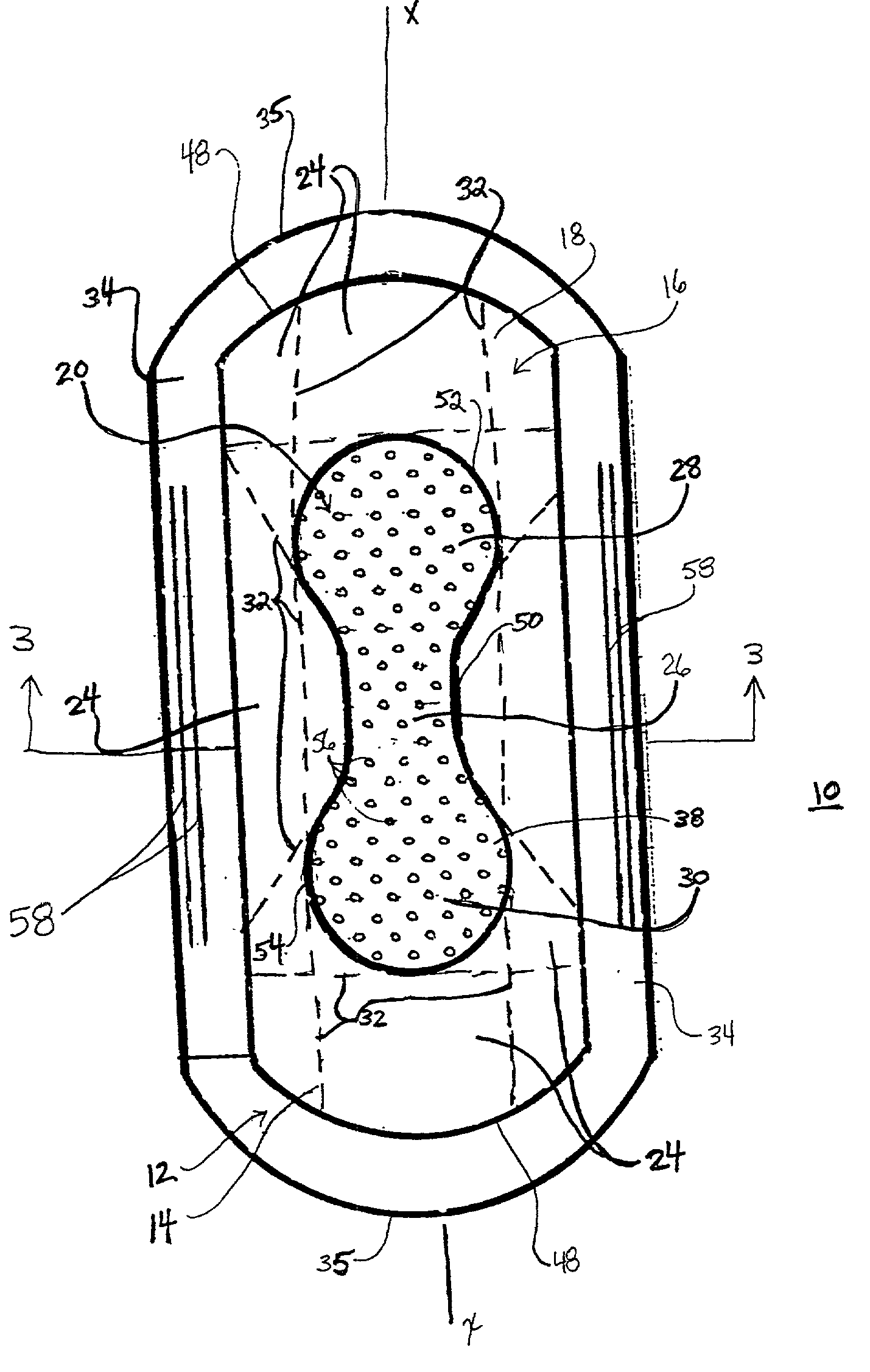
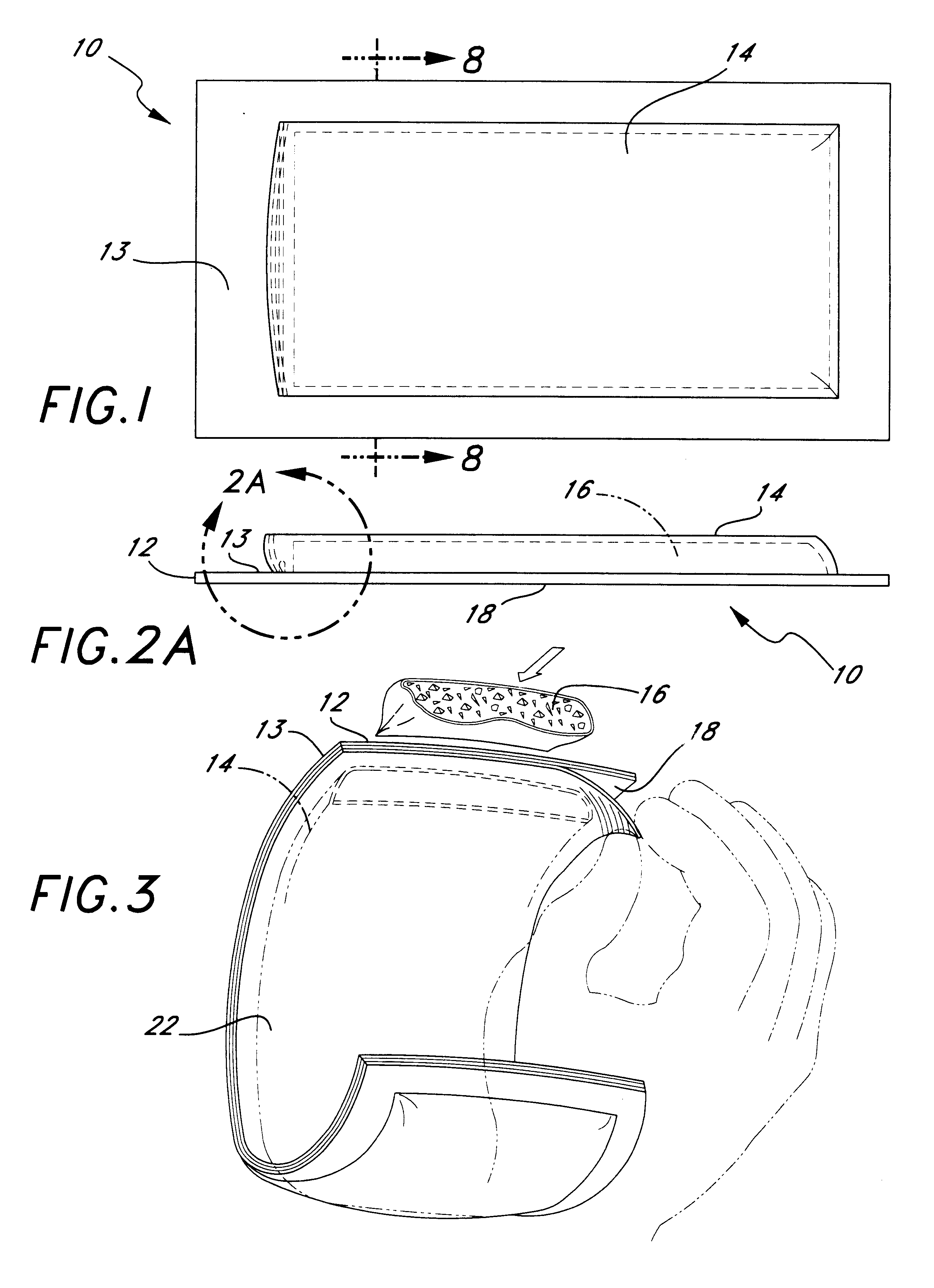
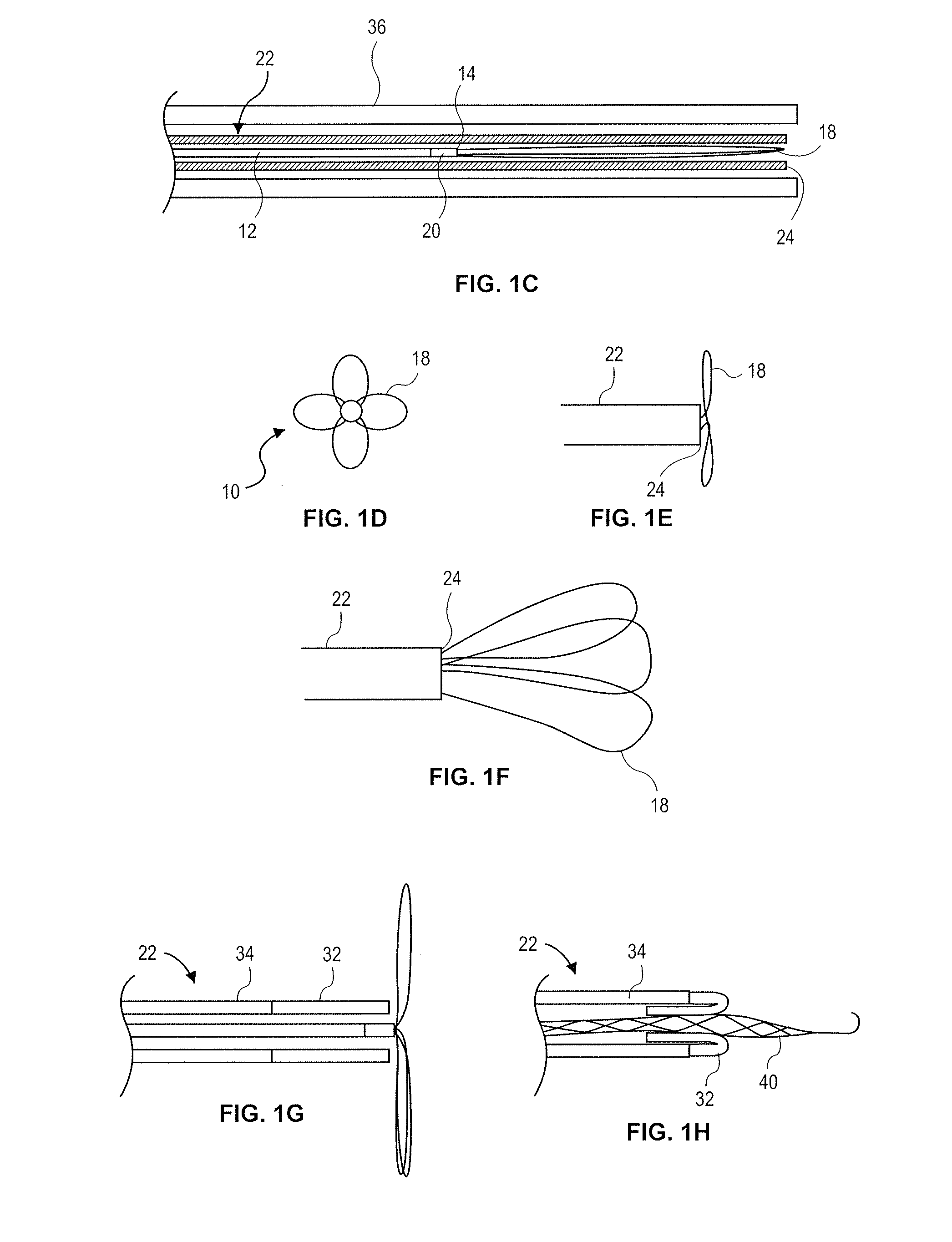
Ultrasound bandages
Ultrasound bandages (10) and ultrasound transducer array bandages are provided herein to accelerate the healing of wounds by positioning the ultrasound bandages (10) and ultrasound transducer array bandages adjacent to a wound and generating ultrasonic pulses. The ultrasound bandages (10) generally include (a) a backing layer (12), (b) an adhesive layer (14) applied to, and substantially coextensive with the backing layer (12), and (c) a transducer material (16) disposed on at least a portion of the adhesive layer (14). The ultrasound transducer array bandages generally include (a) a backing layer (13), (b) an adhesive layer applied to, and substantially coextensive with, the backing layer, and (c) an array comprising a plurality of transducer materials arranged in adjacent relation to define spaces therebetween, the array being disposed on at least a portion of the adhesive layer. The resulting ultrasound bandages (10) and ultrasound transducer array bandages allows for medical therapeutic applications as promoting the healing of wounds such as abrasions, lacerations, incisions and ulcers at any section or multiple sections of the human anatomy with the ultrasound bandages (10) and ultrasound transducer array bandages being conveniently discarded after each application and a new bandage then being applied for the next application.
Owner:EXOGEN
High torsion delivery catheter element
A jointed system for delivering a medical device to a target location within a human anatomy, comprising: a first segment that is a hollow cylinder, wherein a first flange and a second flange are attached to the distal end and extend distally away from the first segment; a second segment that is a hollow cylinder and has a proximal end and a distal end, wherein a third flange and a fourth flange are attached to the proximal end and extend proximally away from the second segment; a connector element having four cylindrical lugs extending radially away from a central point, wherein each lug passes, respectively, through a circular hole, and further wherein the connector element defines at least two separate openings extending in a direction from the distal end of the first segment to the proximal end of the second segment.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Radiation phantom
InactiveUS20050077459A1Low production costLessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHuman anatomyMedicine
A real, physical radiation phantom for simulating a portion of a human being includes a body portion providing an analytic outer shape of the phantom, the outer shape being similar to a shape of at least a portion of the human being, the body portion having a first physical characteristic of a first value similar to a second value of the first physical characteristic corresponding to human soft tissue, and at least one internal component disposed in the body, the internal component having an analytic shape approximating an internal portion of human anatomy and having a third value of the first physical characteristic different from the first value.
Owner:ENGLER MARK J +1
Systems and methods for determining the scale of human anatomy from images
Systems and methods are disclosed for generating a scaled reconstruction for a consumer product. One method includes receiving digital input comprising a calibration target and an object; defining a three-dimensional coordinate system; positioning the calibration target in the three-dimensional coordinate system; based on the digital input, aligning the object to the calibration target in the three-dimensional coordinate system; and generating a scaled reconstruction of the object based on the alignment of the object to the calibration target in the three-dimensional coordinate system.
Owner:BIS
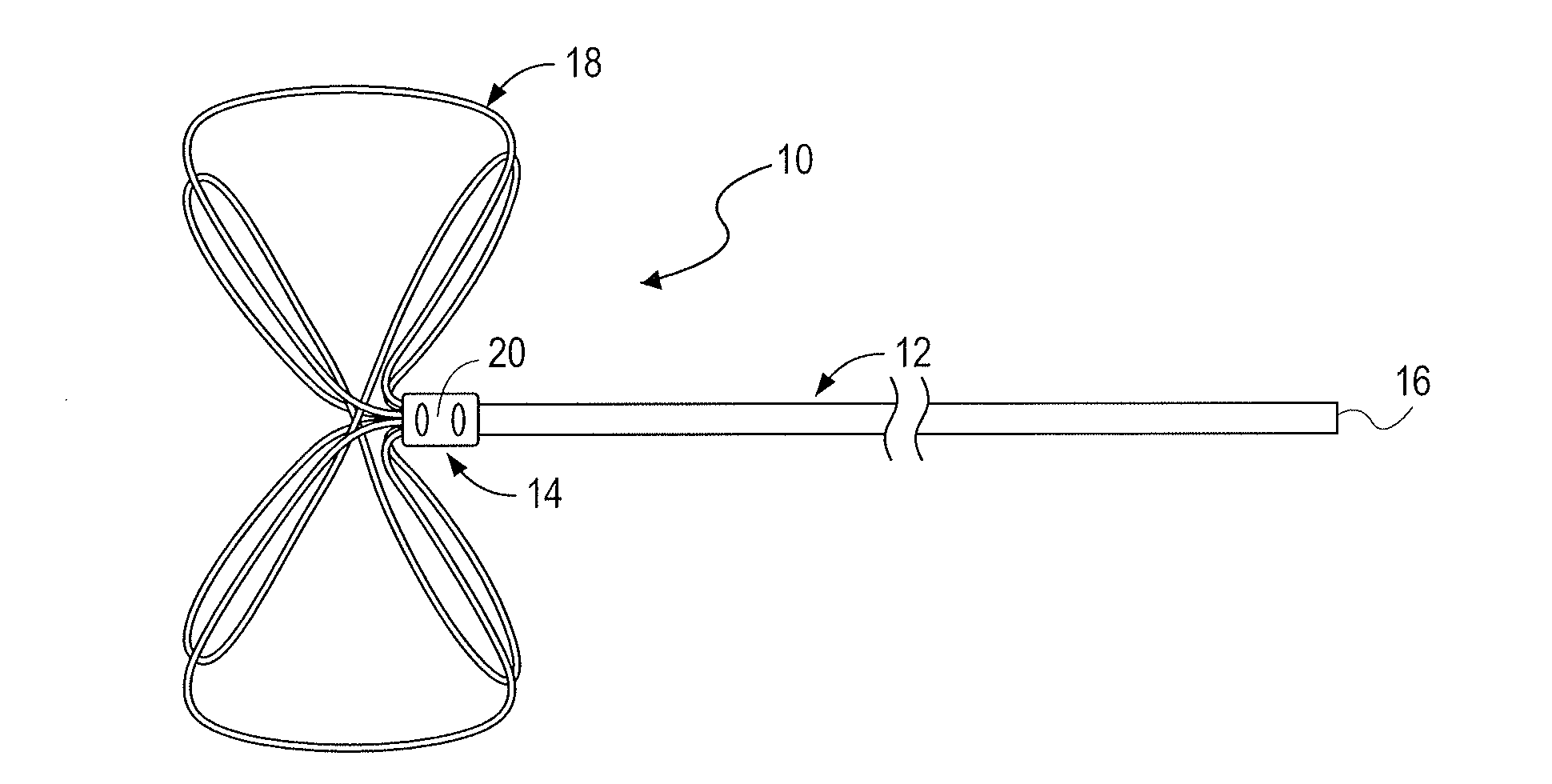
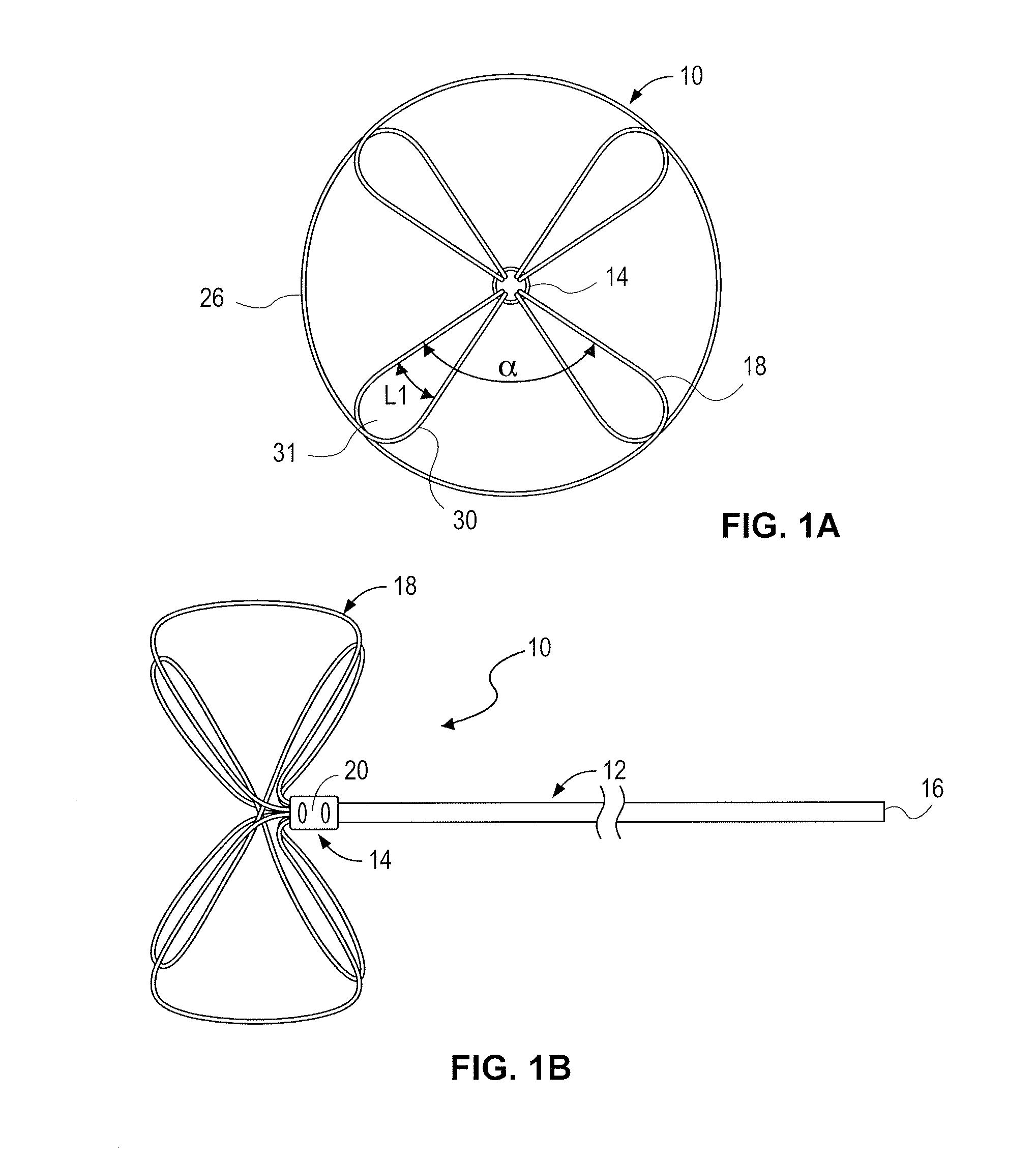
Retrieval snare device and method
The present invention relates generally to devices and methods for retrieving or manipulating objects within a lumen. More specifically, embodiments of the invention relate to devices and methods for retrieving or manipulating medical devices from a body lumen. One embodiment of the present invention provides a novel and improved retrieval snare and method of fabricating and using the same. The snare includes a snare wire, having a distal end and a proximal end, for use in the human anatomy, such as but not limited to blood vessels, pulmonary airways, reproductive anatomy, gastrointestinal anatomy, and organs such as the kidneys or lungs. The device enables a user to capture a foreign object located within the human anatomy, grasp said object in a controlled manner, and retrieve and remove said object from the human anatomy.
Owner:CRUX BIOMEDICAL
Multiple layer absorbent article
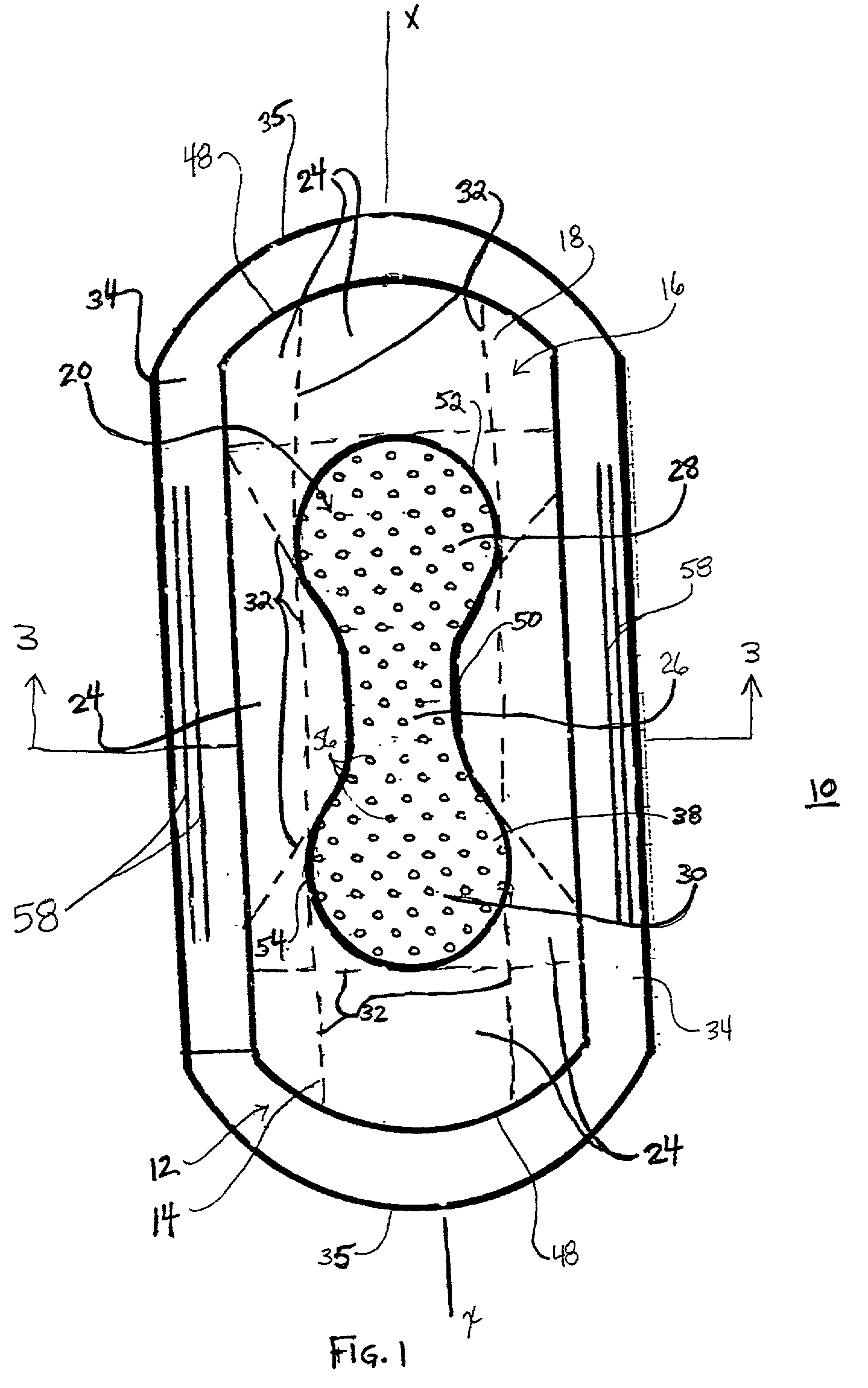
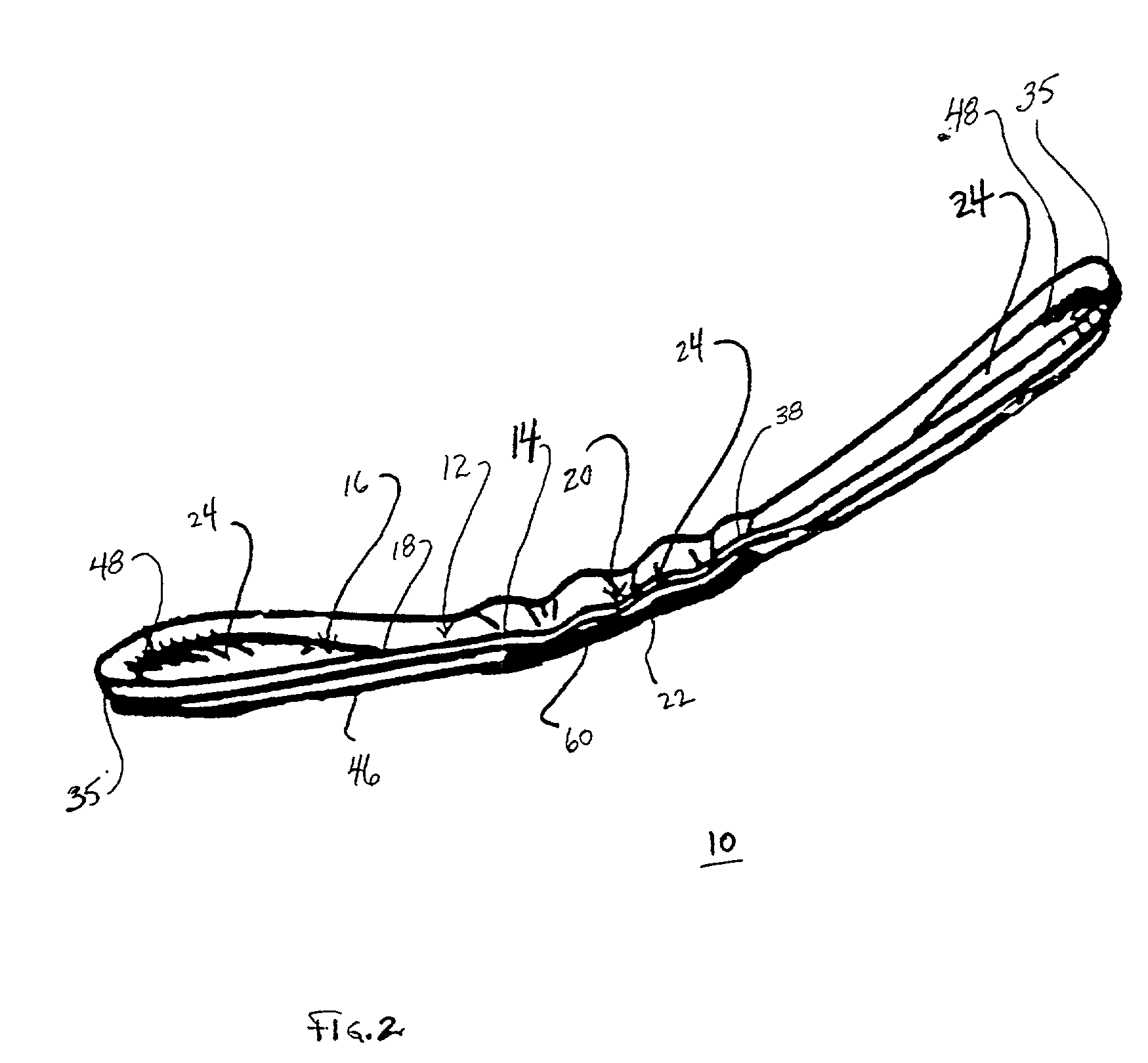
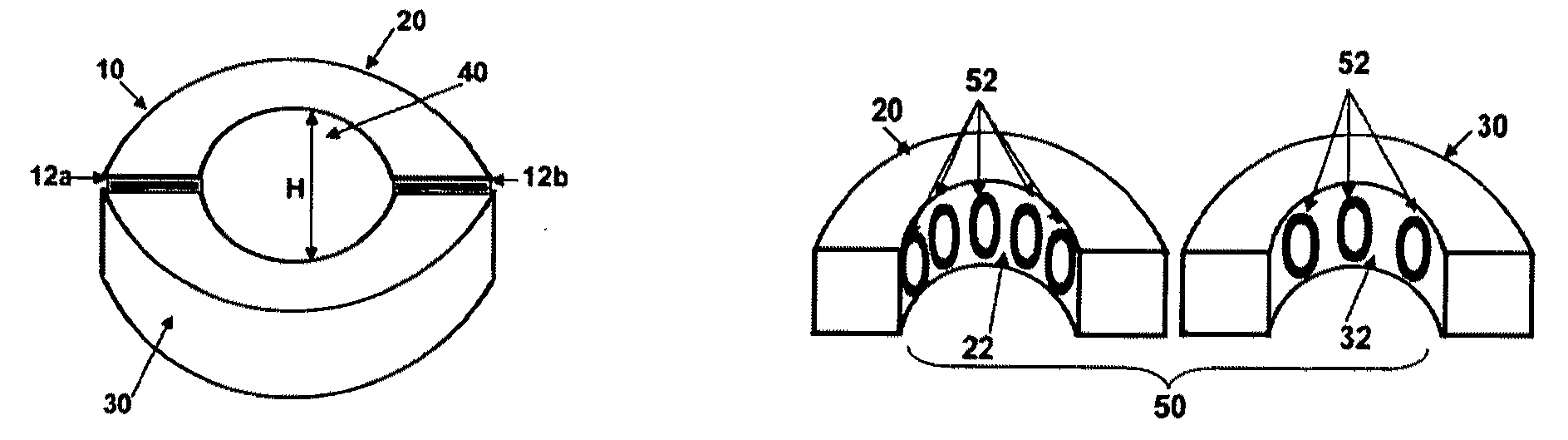
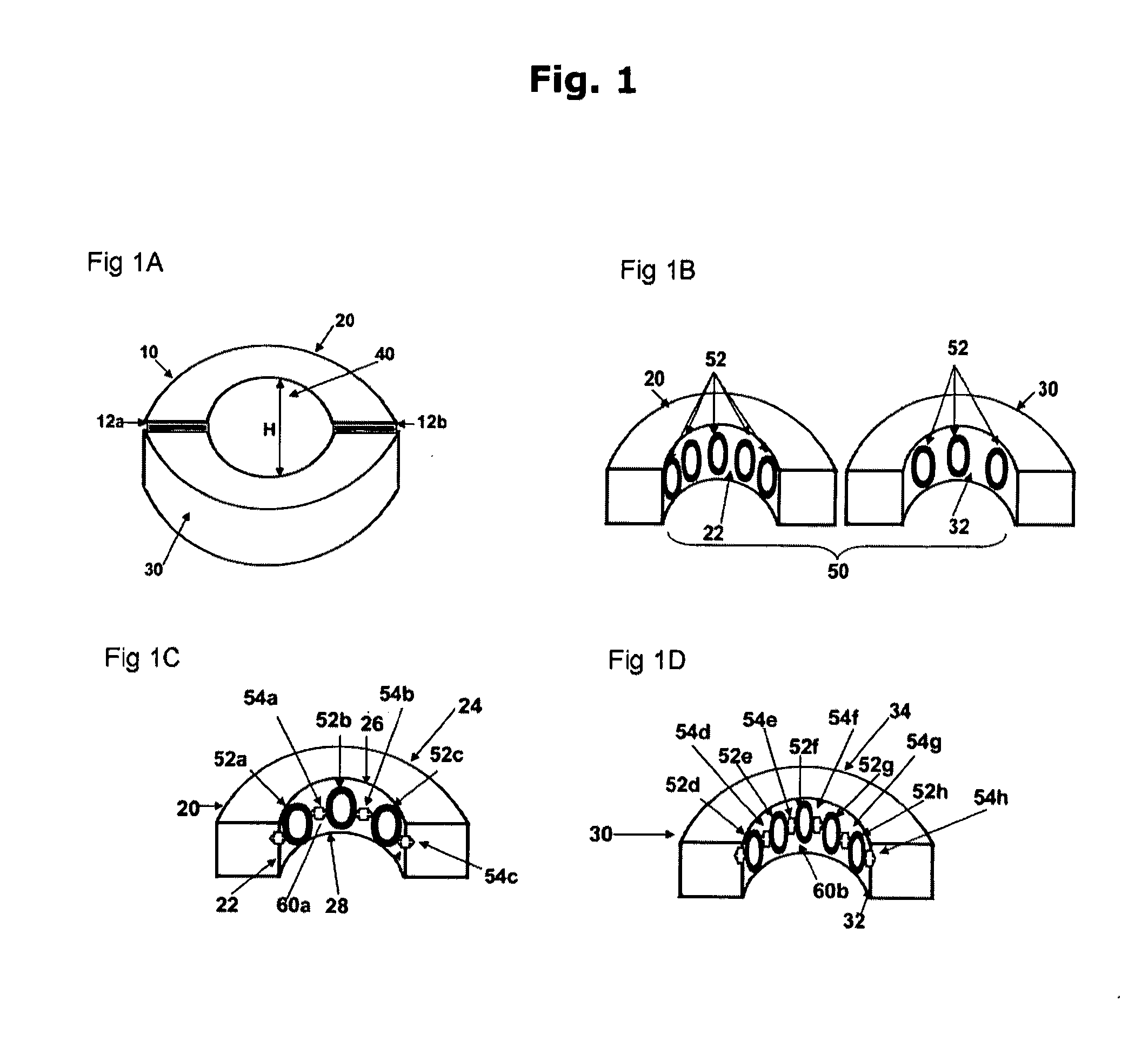
ActiveUS20030225383A1Stiffer in structural stabilityEasy to bendSanitary towelsBaby linensHuman anatomyFiber
An absorbent article is provided including a fluid permeable body facing surface and an absorbent core having a body facing side. An absorbent pledget is adhered to the body facing side of the absorbent core and is disposed between the absorbent core and the body facing surface. The pledget has a greater structural stiffness and a reduced surface area relative to the absorbent core. The pledget is configured to fit a human anatomy. In another alternate embodiment, the absorbent article has a fluid permeable coverstock configured to engage a body surface and defining longitudinal sides. The coverstock includes a bi-component fiber having a polypropylene inner core and a polyethylene outer sheath. An absorbent core of the absorbent article has a body facing side, an opposing side and extends longitudinally along the absorbent article. The absorbent core has arcuate outer ends and includes wood pulp and superabsorbent polymer materials. An hourglass shaped absorbent pledget is disposed between the absorbent core and the coverstock. The pledget includes airlaid material adhered to the body facing side of the absorbent core. The pledget further includes a three dimensional apertured acquisition film mounted to the airlaid material which engages the coverstock. The pledget has a greater structural stiffness and reduced surface area relative to the absorbent core. The absorbent core is configured to fold about the hourglass shape of the pledget and resist undesired deformity of the absorbent article. The coverstock includes adhesive coated elastic members disposed adjacent the longitudinal sides. The longitudinal sides are folded about a polylaminate backsheet to enclose the absorbent core and pledget.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY RETAIL SERVICES
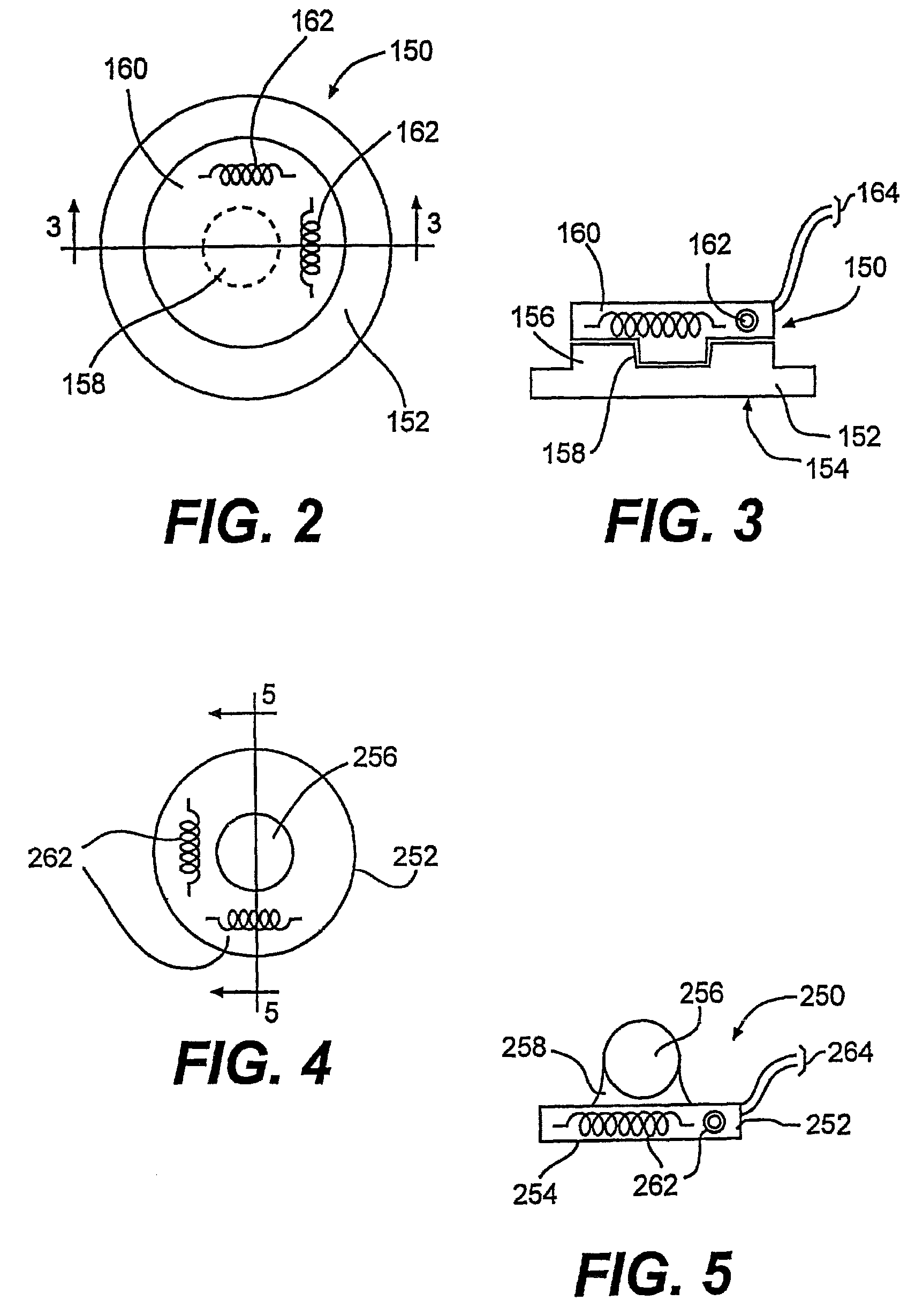
Transceiver apparatus, system and methodology for superior In-Vivo imaging of human anatomy
ActiveUS20120112748A1Maximize efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRHuman anatomyDisease
The inventive subject matter as a whole is an improved transceiver apparatus and system for diagnostic evaluations of living subject, human or animal; and is particularly effective as a clinical tool for the spectroscopic scanning or magnetic resonance imaging of humans suspected of being afflicted with a particular disease, disorder, or pathology. The improved transceiver apparatus is used as an essential component in a computer controlled system suitable for magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”), or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (“MRS”), and / or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (“MRSI”); and the present improvement of these electromagnetic signaling systems will provide far more accurate and precise visual images and accumulated data for the clinician or surgeon, as well as serve as a basis upon which to make a diagnosis and decide upon a mode of therapeutic treatment for that individual.
Owner:HETHERINGTON HOBY P +2
Trauma training simulator with event-based gesture detection and instrument-motion tracking
Surgical trauma training simulator system including replaceable trauma module structured to mimic a portion of human anatomy and, in particular, a prosthetic anatomical structure containing a periorbital structure that includes an eye-lid and an eye globe in cooperation with a drive mechanism. The system is structured to provide, in operation, an event-driven surgical gesture recognition-based tracking of the simulation of the surgical procedure by the trainee and, in absence of expert trainer, provide visual feedback comparing the tracked simulation with correct sequence of steps of such procedure.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
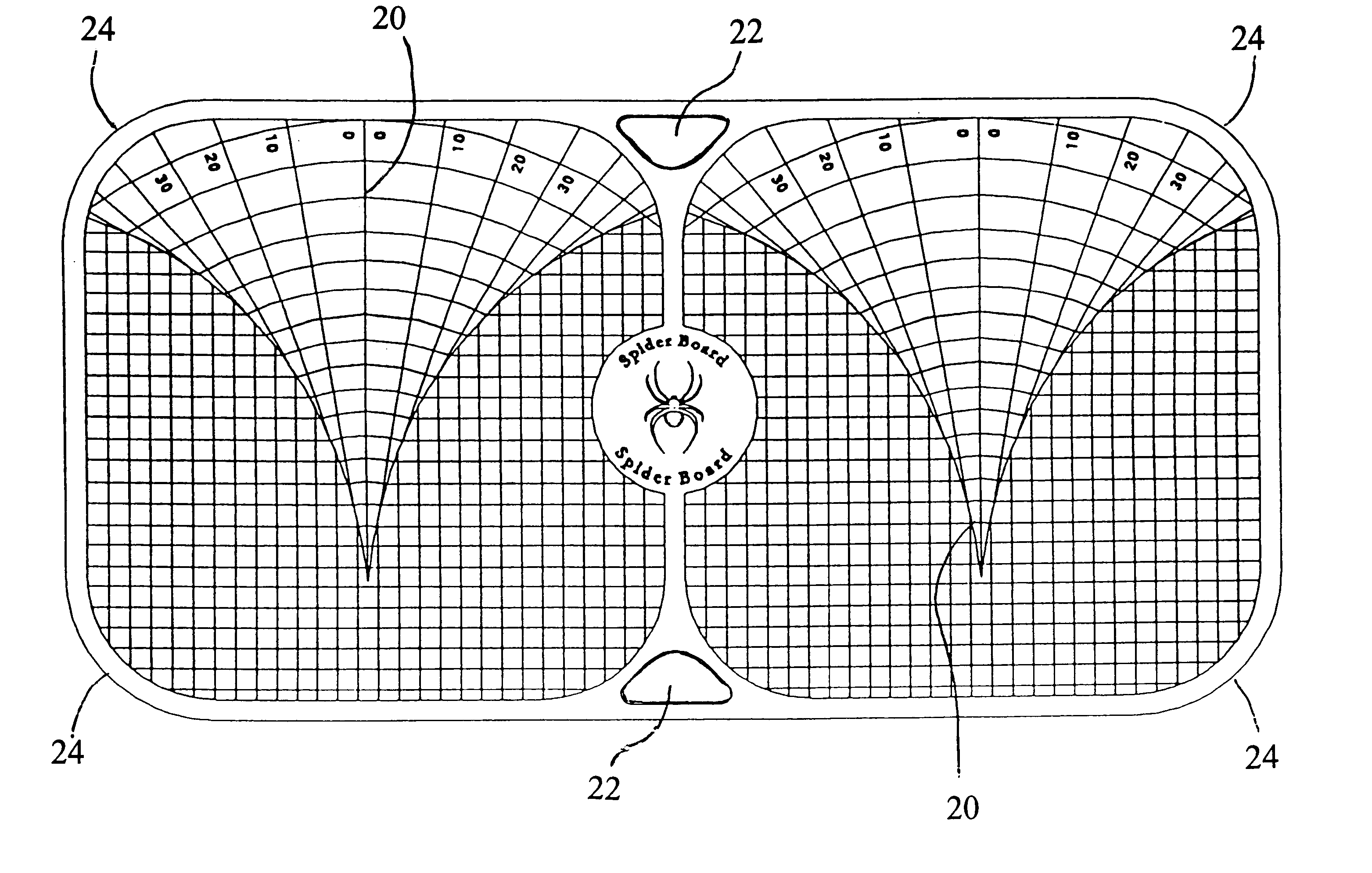
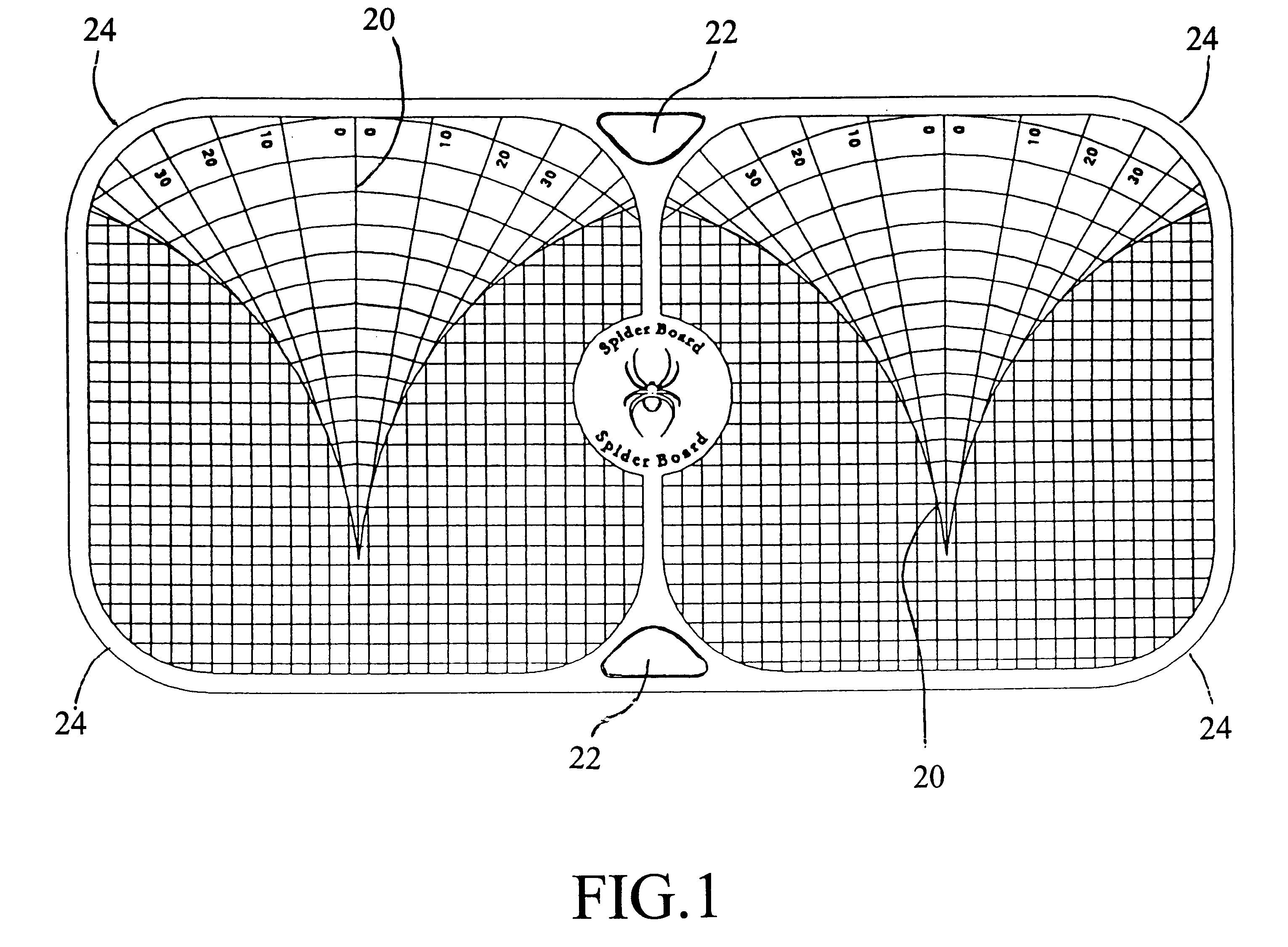
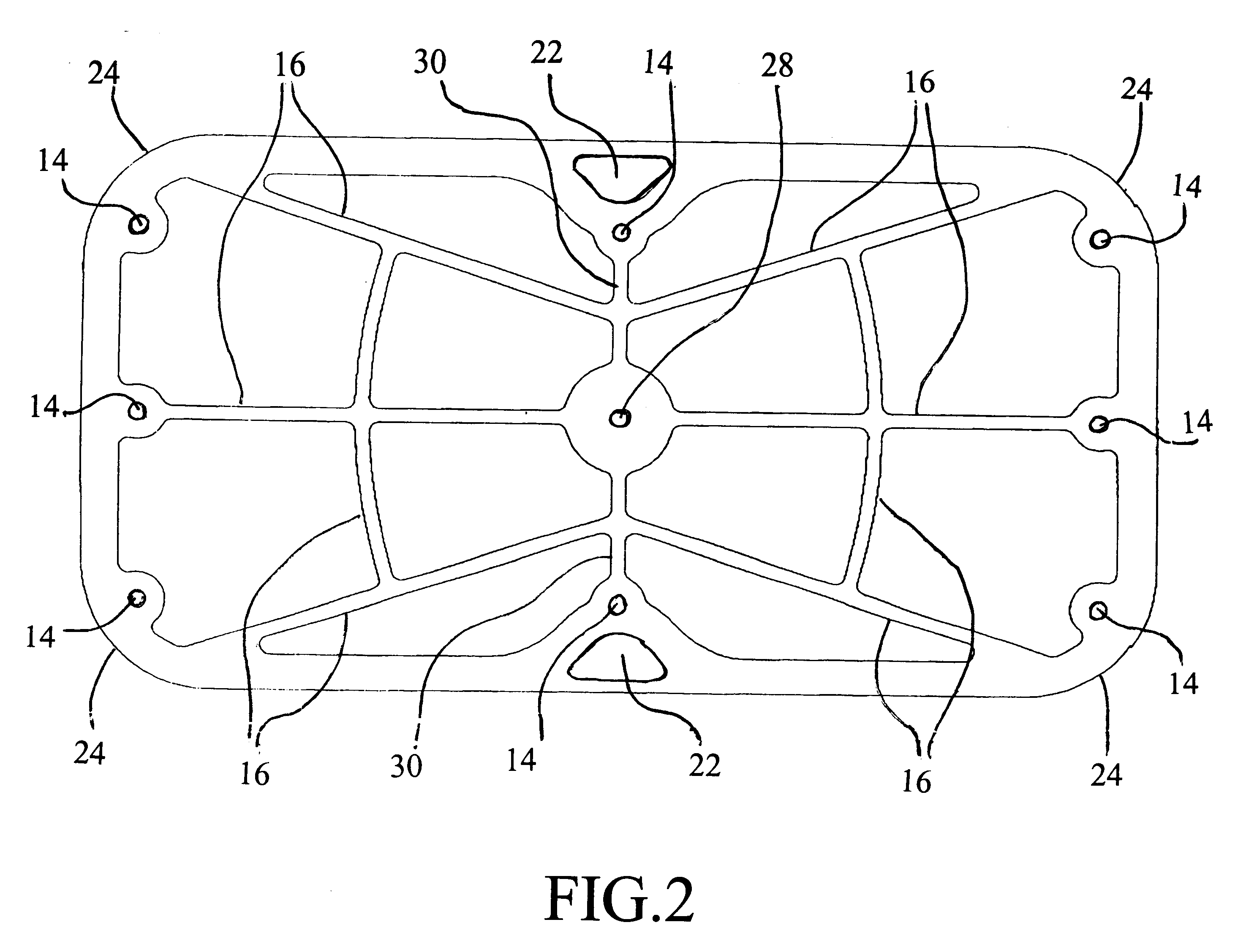
Tri-planar controller motion rehabilitation and exercise platform
A rehabilitation and exercise device for facilitating and limiting motion and biomechanical forces along the horizontal and vertical axes in the saggital, frontal, and transverse planes of the human anatomy. The device consists of an elongated, substantially flat platform with somewhat rounded corners (24). The platform is made of a rigid material to prevent fracturing and bending and is further supported on the bottom surface by central support spines (30) and peripheral support spines (16). The platform provides a decreased slip top surface (10) by utilizing a recessed grid (20). The bottom surface of the platform (12) is configured with a larger diameter central platform attachment extension (28) and smaller diameter peripheral platform attachment extensions (32) which have internal recesses (14) configured at a predetermined set of points to accommodate rigid, somewhat rounded pegs (18) of varying shape and diameter. The peg attachments are secured to the bottom surface of the platform with a peg attachment insert screw (34) which rotates into a heilcoil (26) located in the internal recess. The platform allows specific facilitation or limitation of motion and biomechanical forces along the horizontal and vertical axes depending on the placement of human anatomy on the top surface (10) and peg size and placement on the bottom surface (12) of the platform.
Owner:FOLLETT MICHAEL R +1
Thermal treatment system
An improved device for attaching thermal dressings-using essentially any type of source of heat or cold employs a novel adhesive that permits firm attachment of the dressing to essentially any portion of the human anatomy with no need for wrapping around the limb or other anatomical region. The adhesive is sufficiently weak that the dressing can be peeled from the skin-even in the presence of body hair-with no pain. The adhesive, a hypoallergenic hydrophilic gel, is thick and soft and adheres by molding itself to the skin surface, and into and around hair shafts. The material contains essentially no elastomers and does not grip hair or pull strongly on hairs when the dressing is removed. When the gel becomes dehydrated, it loses most, if not all, of its adhesive properties. The gel is sufficiently crosslinked so as to resist dissolution by additional water.
Owner:STI MEDICAL PRODS
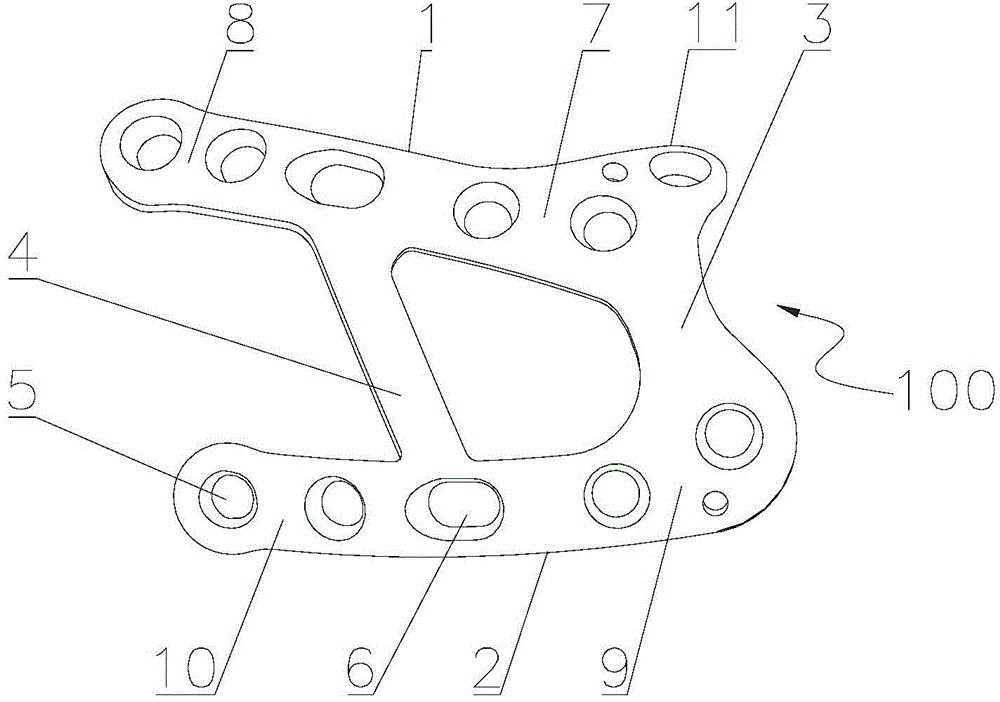
Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate
The invention relates to the field of medical devices, in particular a Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate. The fusion plate comprises a first tarsometatarsal joint plate, a second tarsometatarsal joint plate and a first transition plate for connecting the first tarsometatarsal joint plate and second tarsometatarsal joint plate; and the fusion plate provided with a plurality of fixing holes for fixing the fusion plate on a first metatarsal bone, an inner cuneiform bone, a second metatarsal bone and an intermediate cuneiform bone. The Lisfrance joint injury fusion plate has dissection-type design; in an operation, the fusion plate is not required to be pre-bent, the operation time is saved, and the bending influence on the plate strength; the close-end fixing holes of the first tarsometatarsal joint plate and the second tarsometatarsal joint plate have strong holding force for the inner cuneiform bone and the intermediate cuneiform bone; the curvature of human anatomy of Asian people is fully taken in to consideration of the design of the plates and bolts; and the fusion of multiple joint surfaces is conductive to arch anatomy reconstruction, excellent stability for joint fusion is provided, and the fixing effect of the fusion plate is further improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU WASTON MEDICAL APPLIANCE CO LTD
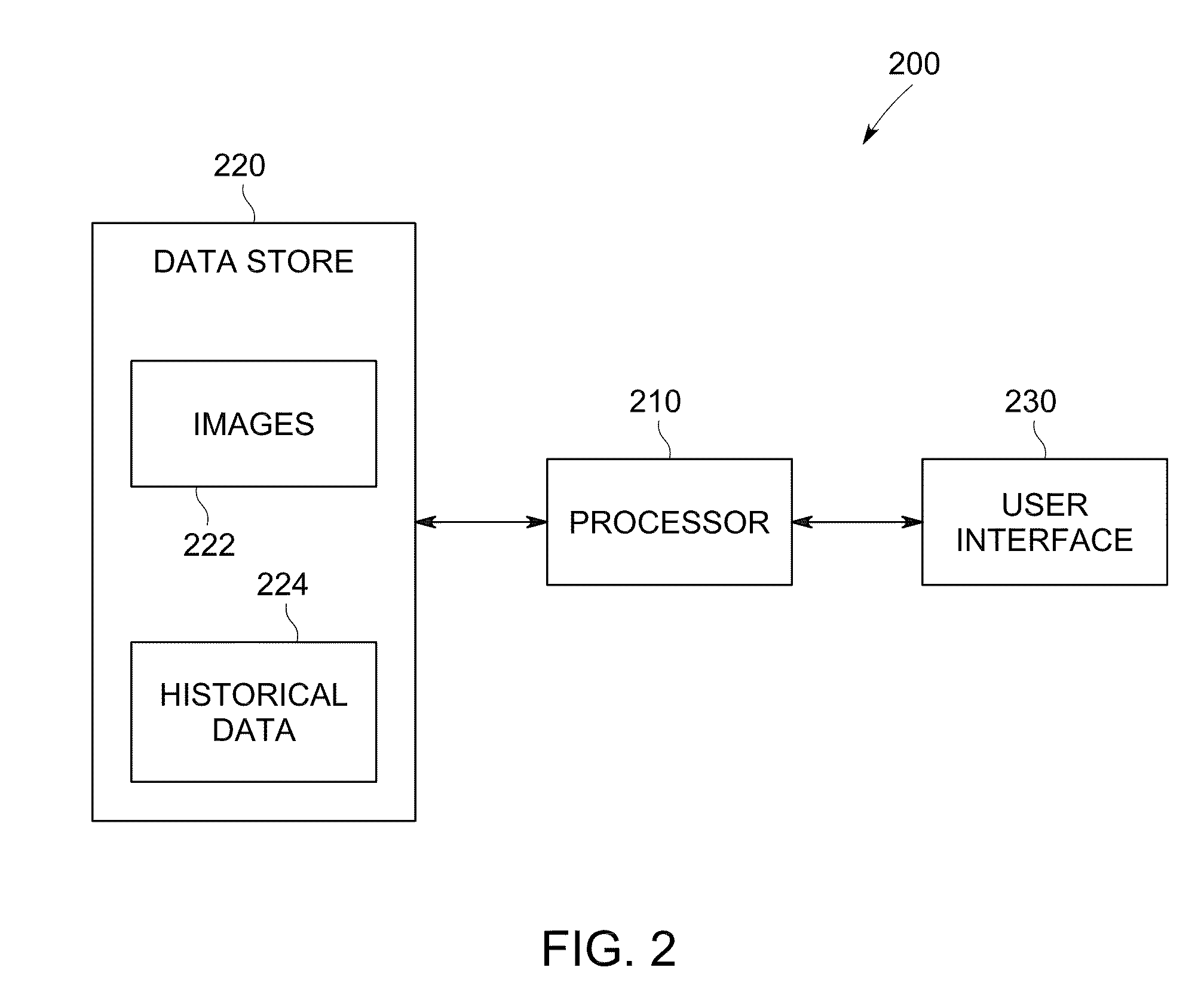
Systems and methods for a seamless visual presentation of a patient's integrated health information
InactiveUS20110161854A1Improve user interactionMedical imagesSpecial data processing applicationsHuman anatomyVisual presentation
Systems and methods provide visual presentation of clinical evidence to a user in association with a patient's anatomy. In certain examples, a patient information interface system to present an aggregated, graphical view of patient anatomy and history includes a data store to include images and patient history information and a processor to implement a user interface to accept user input. The processor provides a plurality of graphical representations of a human anatomy. Each graphical anatomy representation is to provide a view of a body system. Each graphical anatomy representation is to include one or more indicators corresponding to clinical events that have occurred in connection with a patient in the body system and are viewable through the graphical anatomy representation. Each of the one or more indicators is to be located at an anatomical location on the graphical representation affected by the clinical event corresponding to the indicator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Retrieval snare device and method
The present invention relates generally to devices and methods for retrieving or manipulating objects within a lumen. More specifically, embodiments of the invention relate to devices and methods for retrieving or manipulating medical devices from a body lumen. One embodiment of the present invention provides a novel and improved retrieval snare and method of fabricating and using the same. The snare includes a snare wire, having a distal end and a proximal end, for use in the human anatomy, such as but not limited to blood vessels, pulmonary airways, reproductive anatomy, gastrointestinal anatomy, and organs such as the kidneys or lungs. The device enables a user to capture a foreign object located within the human anatomy, grasp said object in a controlled manner, and retrieve and remove said object from the human anatomy.
Owner:CRUX BIOMEDICAL
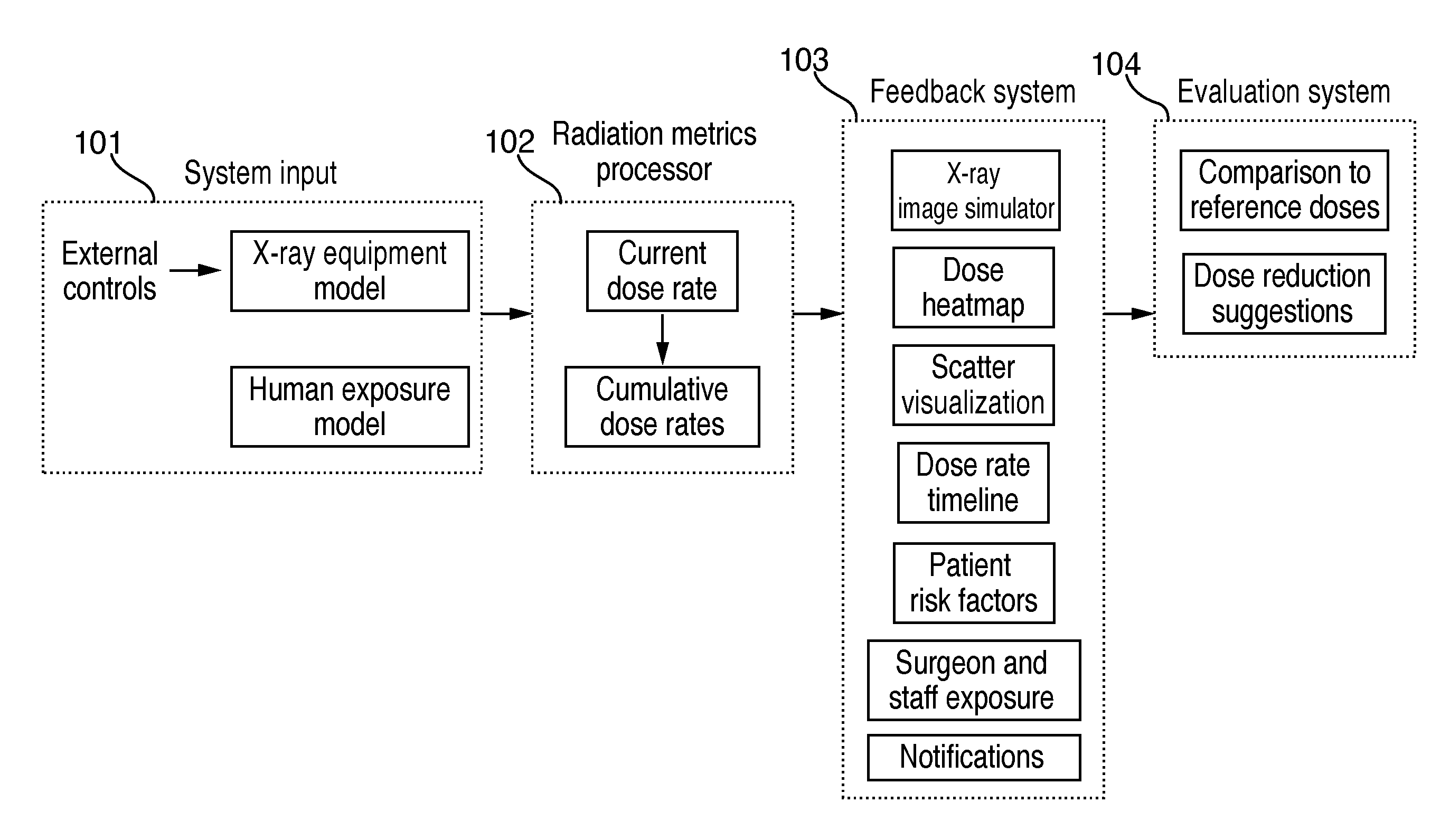
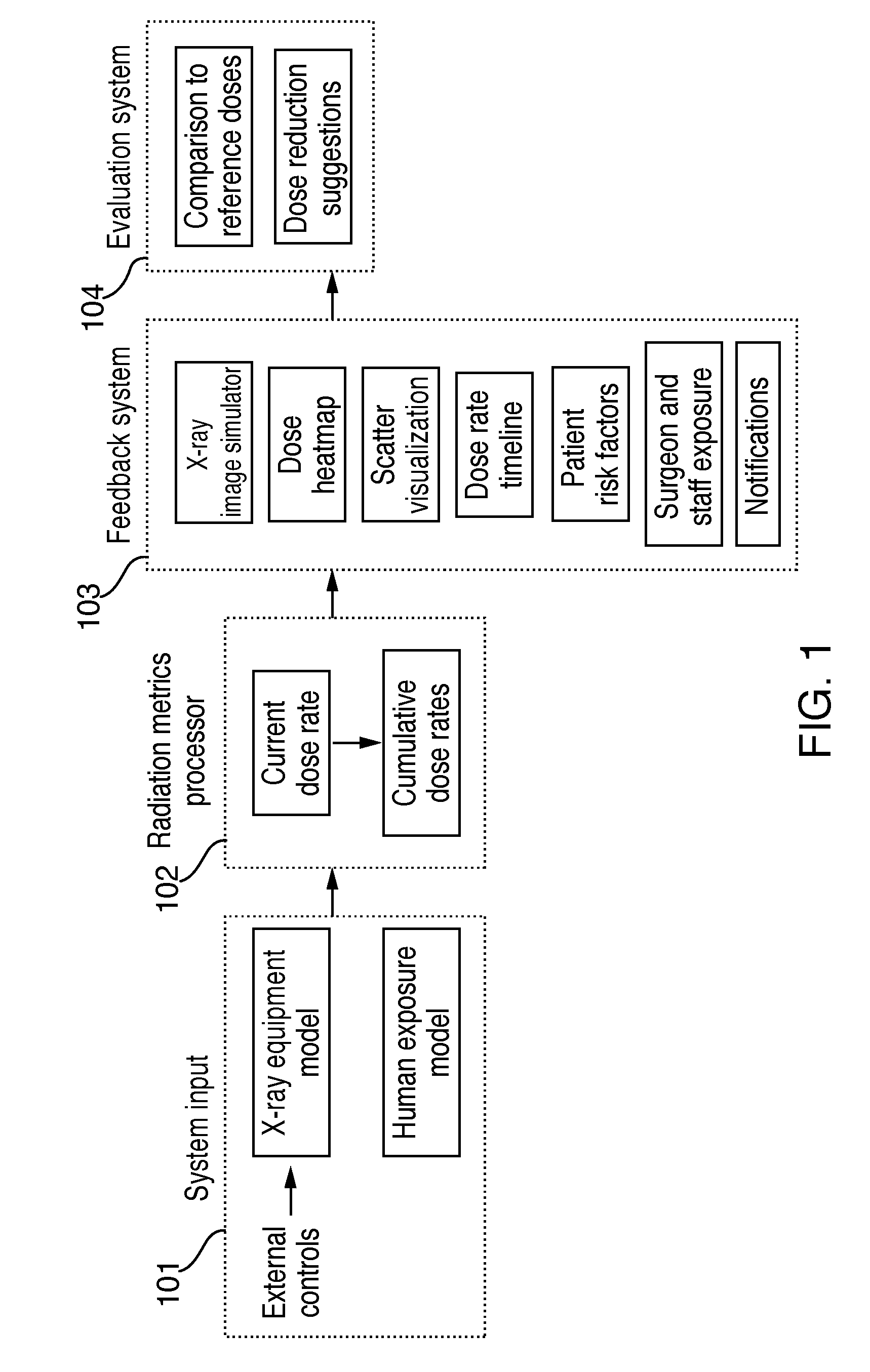
Systems and methods for simulation-based radiation estimation and protection for medical procedures
Systems and methods for determining radiation exposure during an x-ray guided medical procedure are disclosed. In some embodiments, the system includes an x-ray equipment model that simulates the emission of radiation from x-ray equipment during the x-ray guided medical procedure, a human exposure model that simulates one or more human anatomies during the x-ray guided medical procedure, a radiation metric processor that calculates at least one radiation exposure metric, and a feedback system for outputting information based on the at least one radiation exposure metric. The radiation metric processor calculates radiation exposure metrics based on input parameters that correspond to operating settings as well as the location and structure of one or more human anatomies.
Owner:MENTICE
System and method for identification of fingerprints and mapping of blood vessels in a finger
InactiveUS20110007951A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsHuman anatomyTopography
In accordance with an embodiment of the invention, there is provided an apparatus for characterizing and identifying a human. The apparatus comprises a light imaging device that images topography of a surface of a portion of human anatomy, and an infrared imaging device that images infrared radiation of the same portion of human anatomy. The light imaging device and the infrared imaging device are rotatable about at least one axis, each of the at least one axis extending through the portion of the anatomy.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
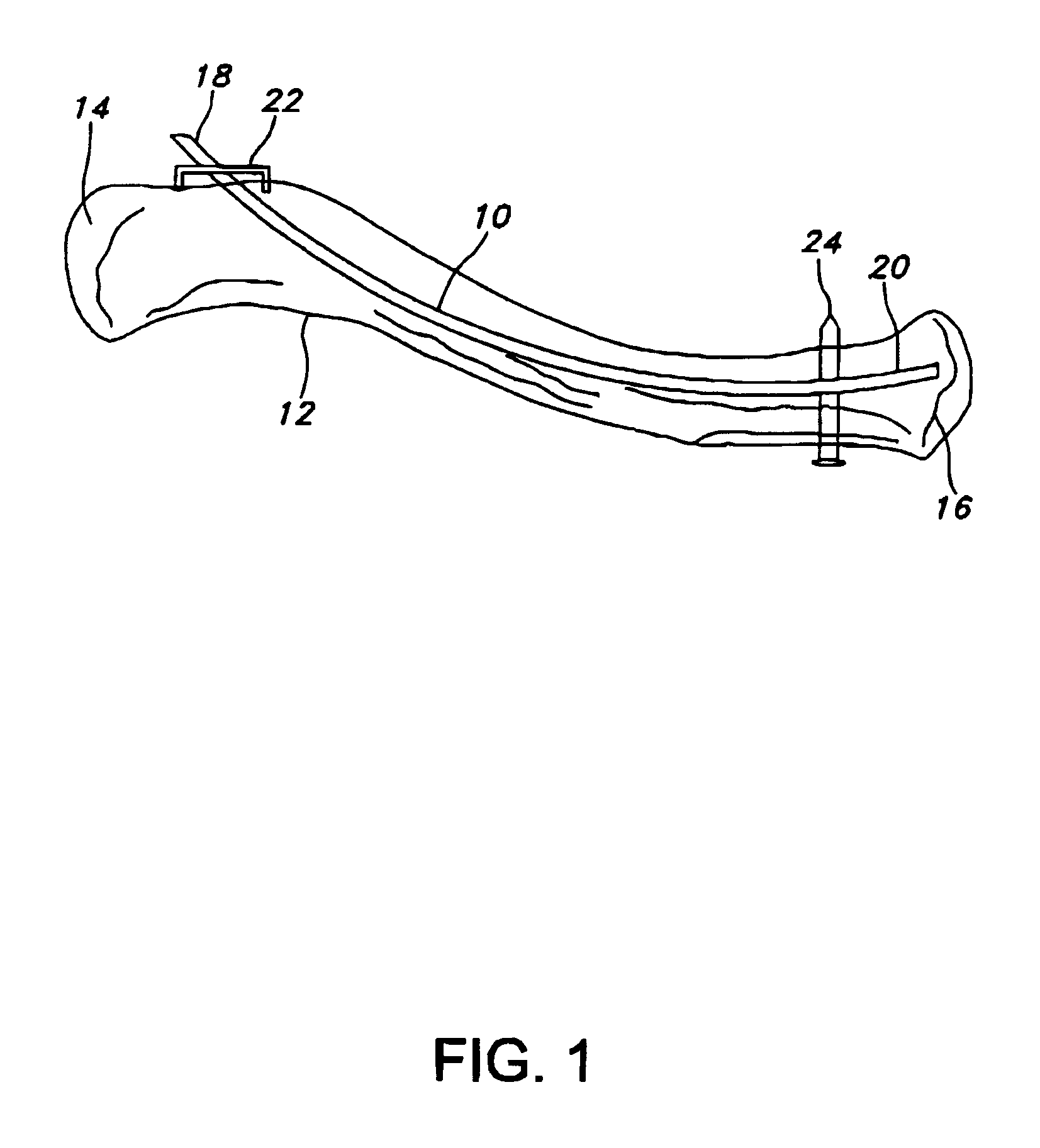
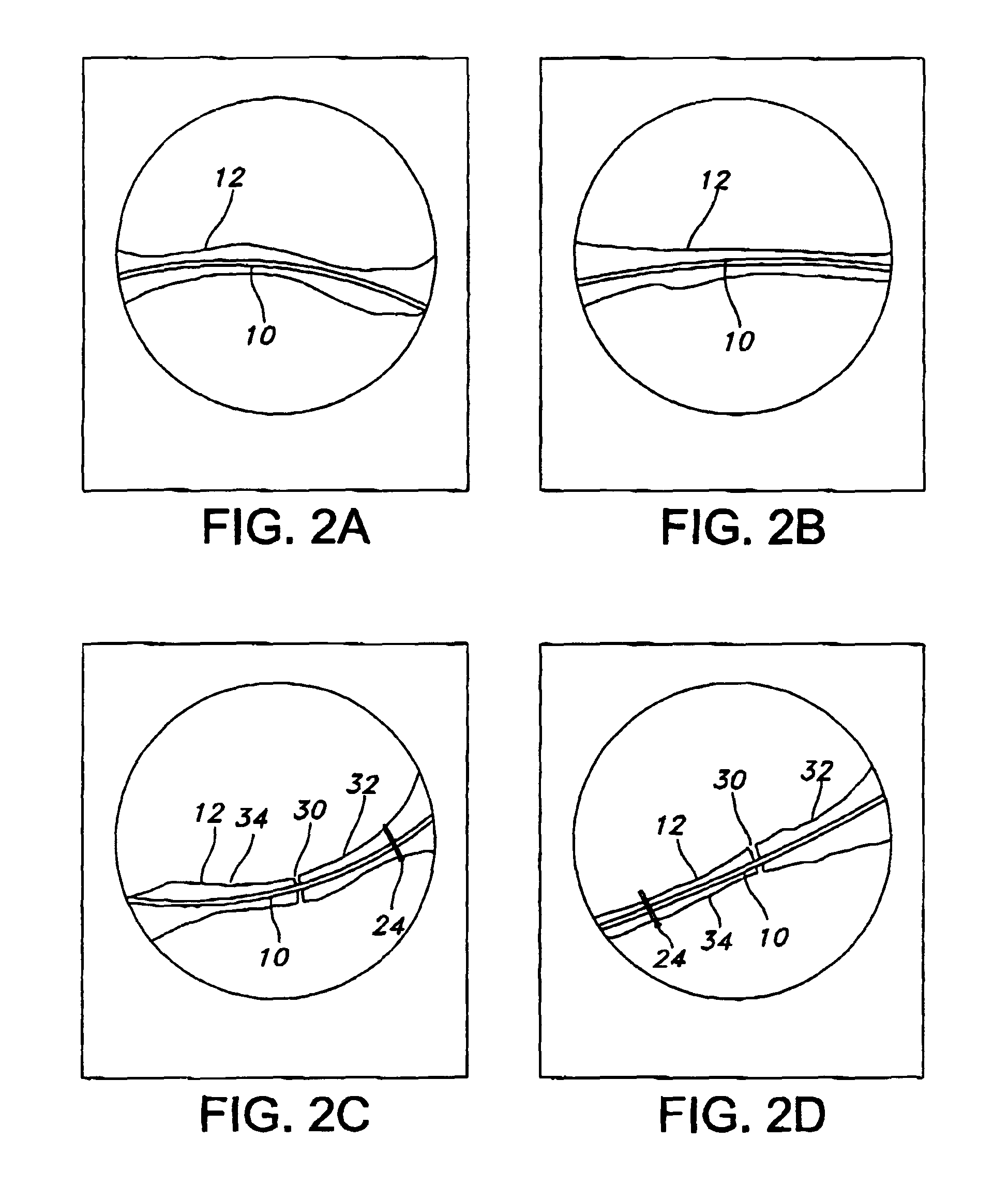
Pre-curved intramedullary clavicle nail and method of using same
ActiveUS9510878B2Reduce riskRestoring alignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsHuman anatomyDermatology
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
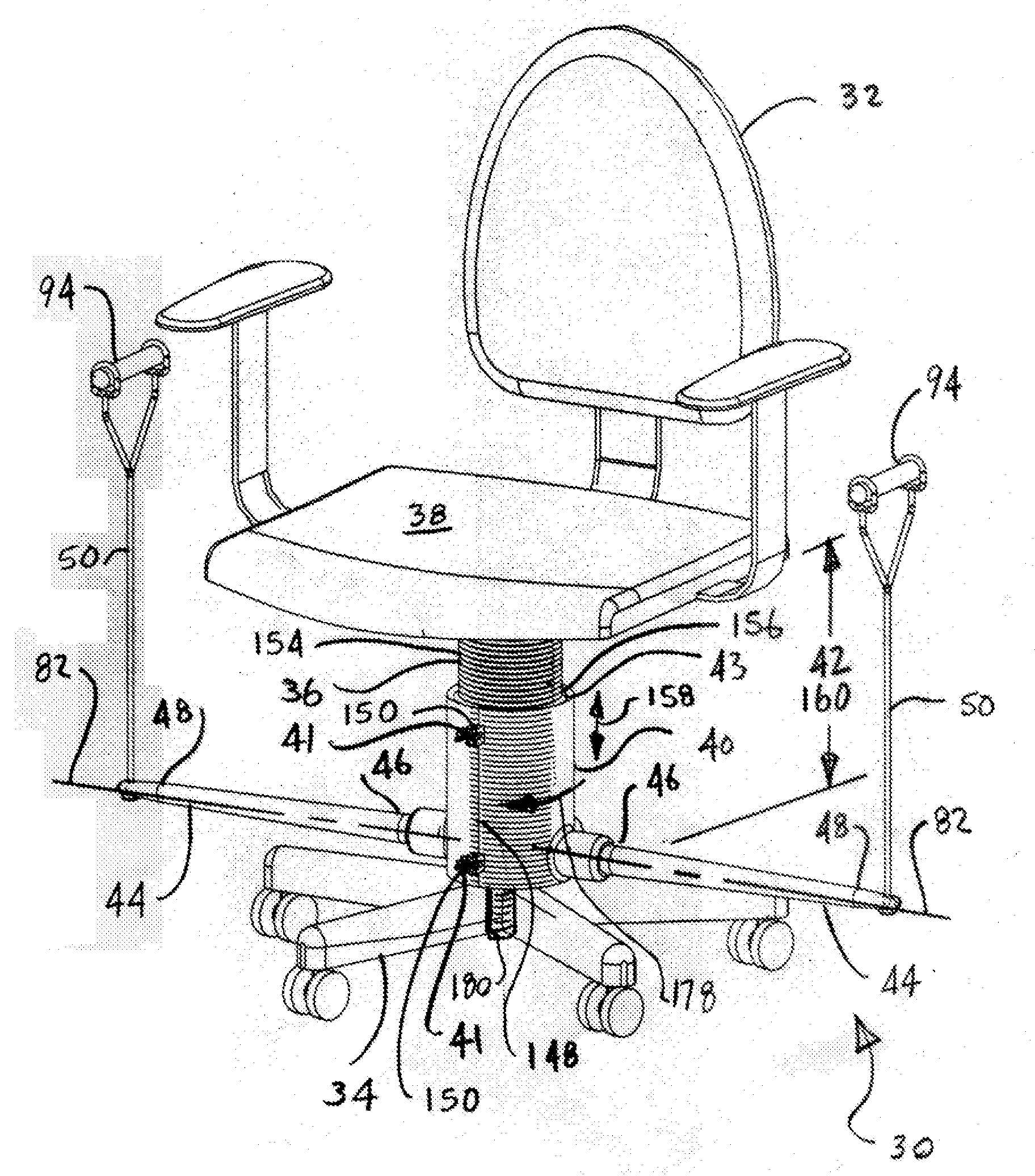
Exercise Apparatus
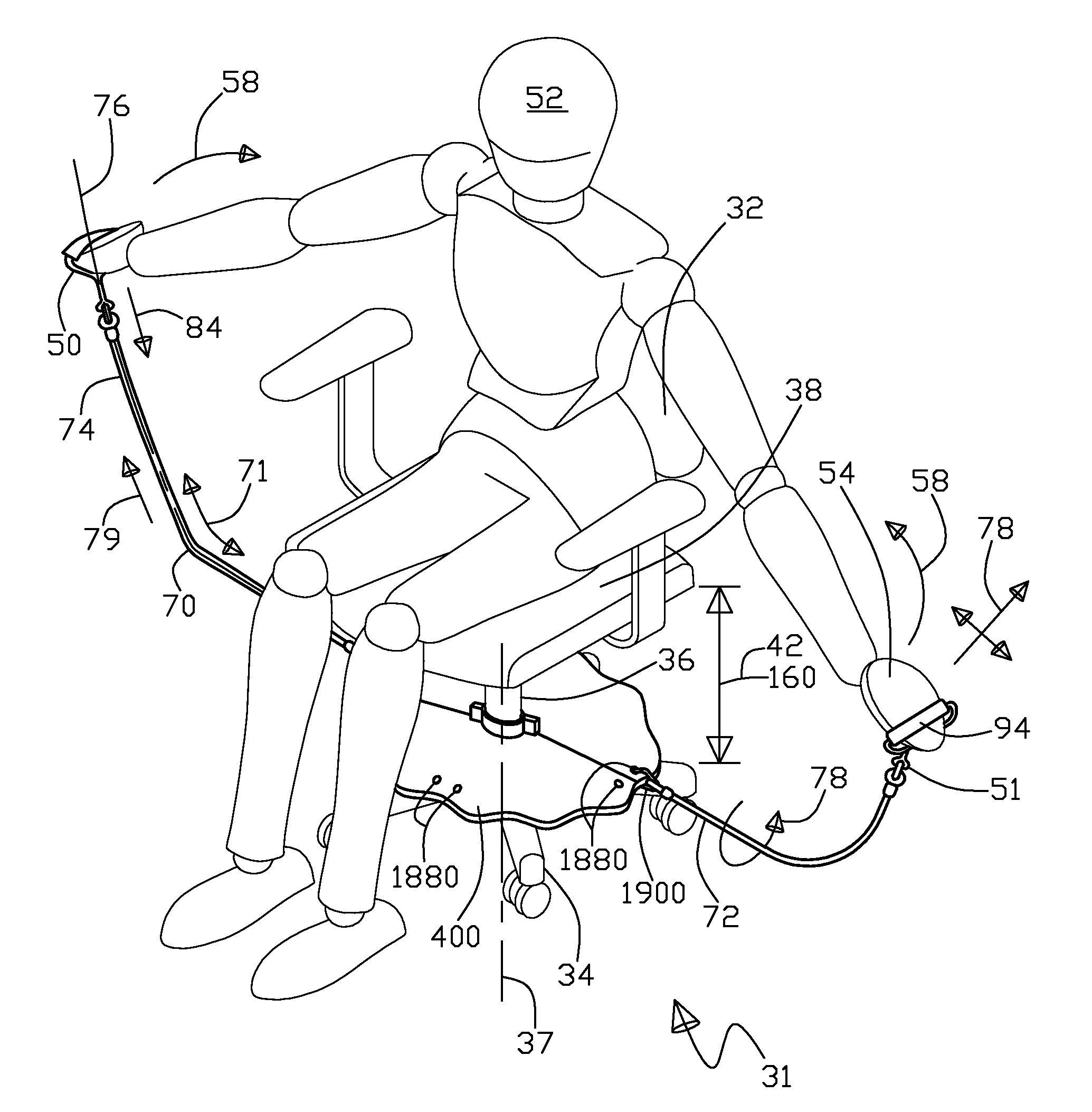
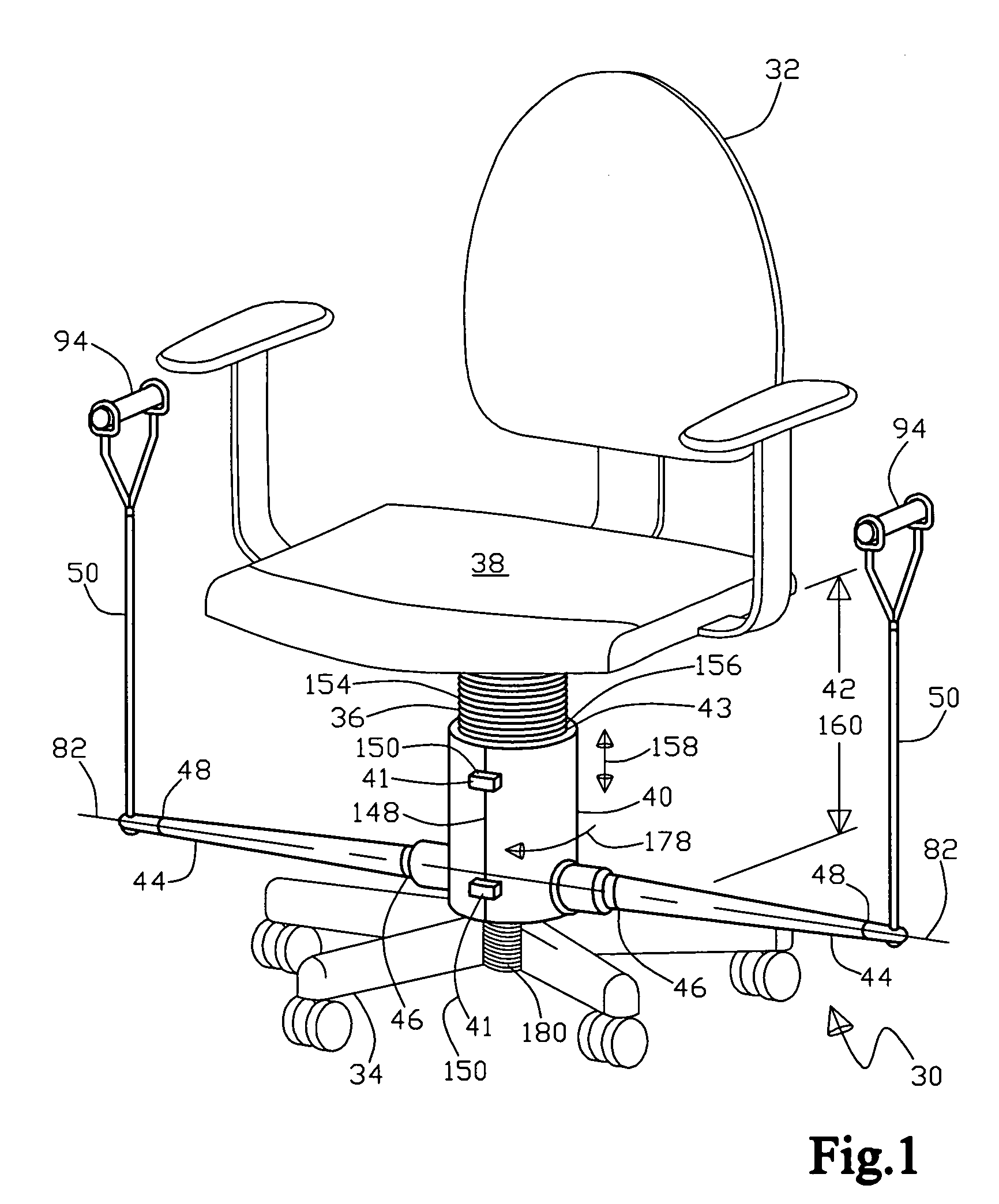
InactiveUS20080039301A1Easy to understandResilient force resistorsSpace saving gamesHuman anatomyElectrical resistance and conductance
An exercise apparatus is for use with a chair, the chair having a base, a pedestal, and a seat, with the exercise apparatus including a support structure that is adapted to removably attach to the chair pedestal, the support structure is also substantially adjustably interposed between the chair base and the chair seat. Also included in the exercise apparatus is a resilient rod having a first end portion and a second end portion, the rod first end portion is adjacent to the support structure in a cantilevered configuration with the rod second end portion free. Further included in the exercise apparatus is an attachment element adjacent to the rod second end, wherein the attachment element is adapted to removably engage to a portion of human anatomy for the purpose of exercise by omni directional flexing of the rod along its length causing a resistive force at the attachment element.
Owner:HALBRIDGE ADAM
System and method for complex geometry modeling of anatomy using multiple surface models
ActiveUS20070270705A1Accurate modelingImprove abilitiesElectrocardiographyCatheterComputational scienceHuman anatomy
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for creating a complex model of the human anatomy. The anatomy may be modeled using multiple geometries. Generally, a plurality of line-of-sight models may be combined into a composite model. Multiple clouds of points may be used to create surface models which may then be merged into a common volume. The resulting composite model may include portions that are not within a line of sight of a mean center point of the composite model. The surface models may be modeled using polygons, including for example, triangles. Disclosed herein are also ways in which electrophysiology data and / or other information may be mapped from a measurement point to a point on the composite model.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
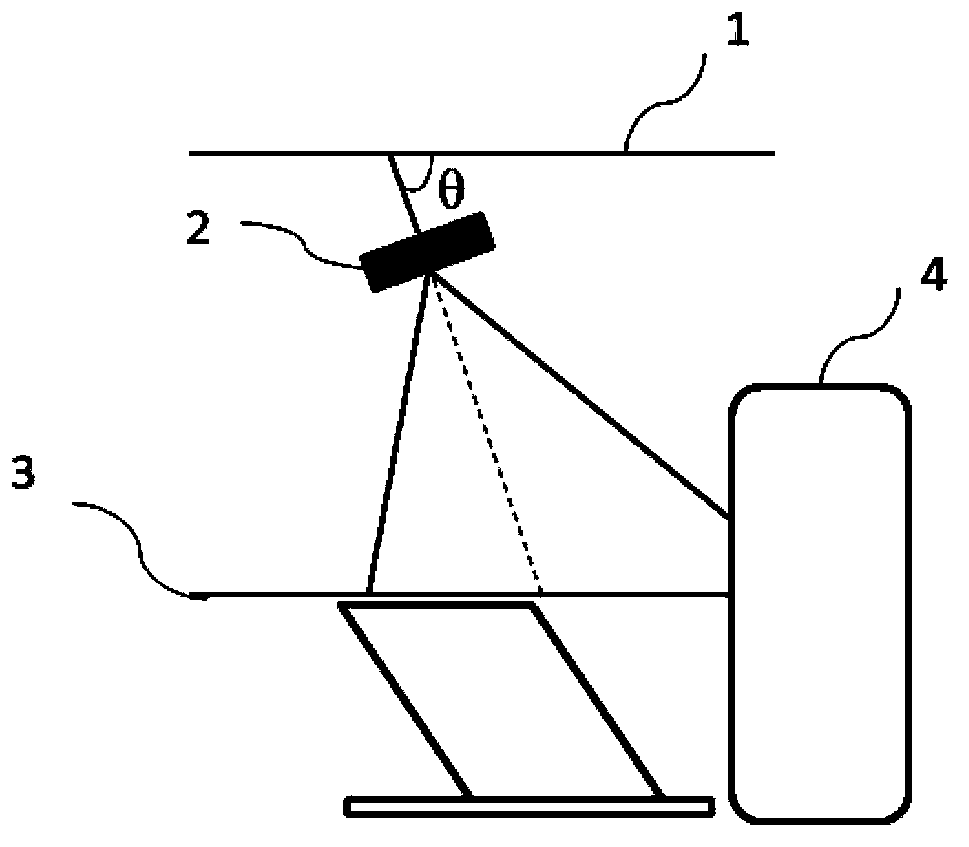
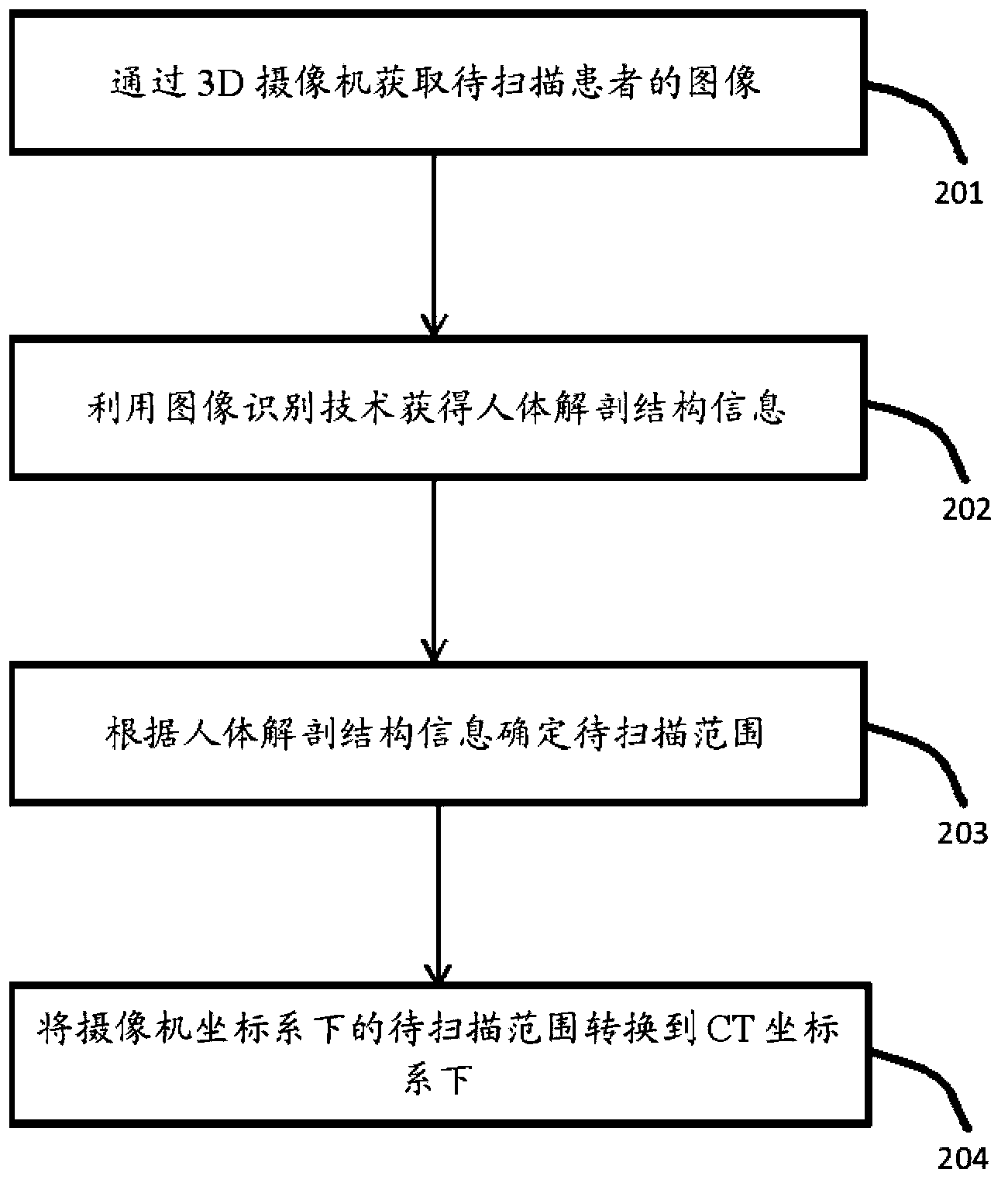
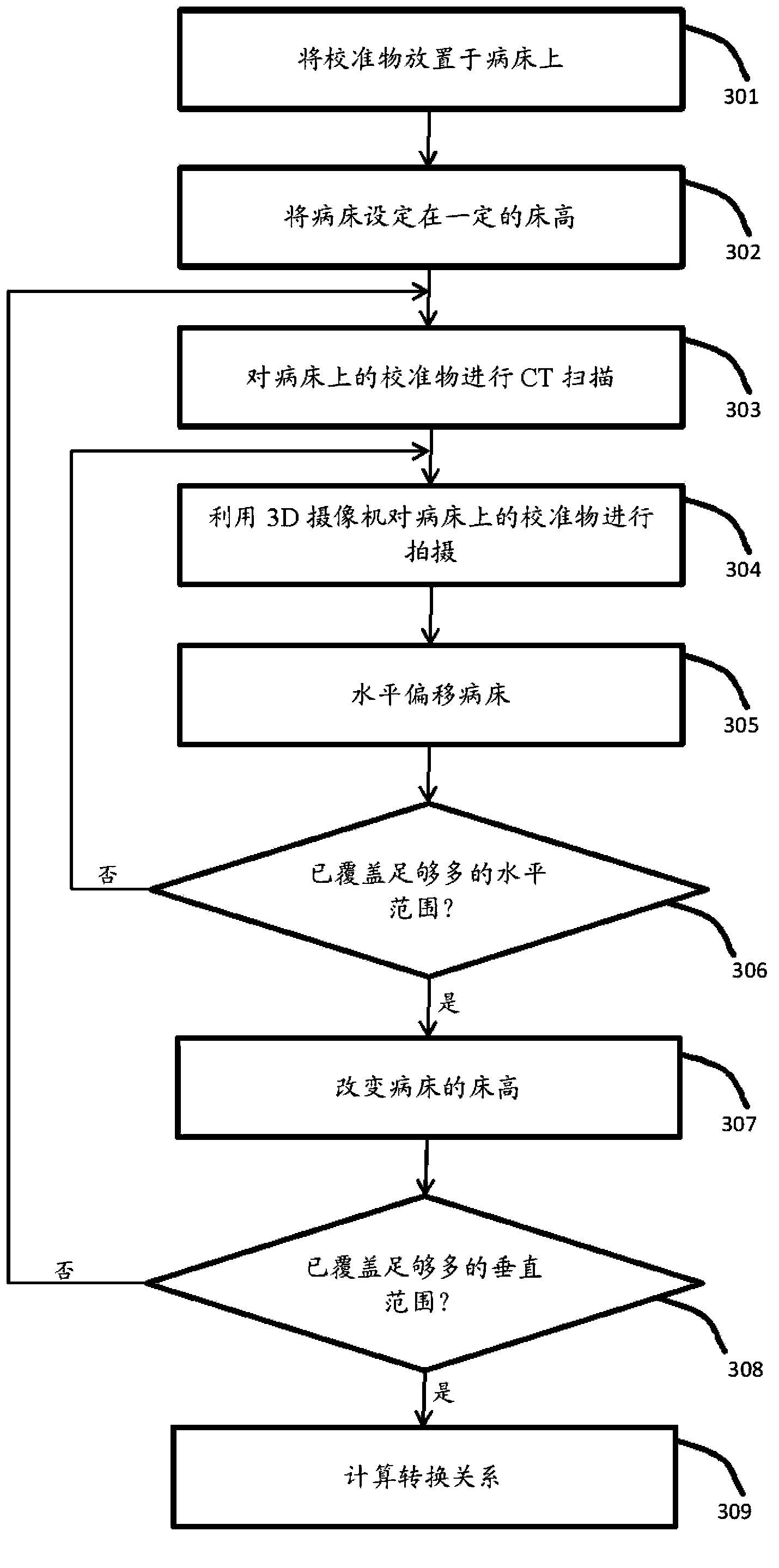
CT system, CT system scanning positioning method and CT system calibration method
ActiveCN104224212AHigh precisionReduce scan timeComputerised tomographsTomographyHuman anatomyComputed tomography
The invention relates to a CT system, a CT system scanning positioning method and a CT system calibration method. The CT system comprises a hospital bed, CT scanning and imaging equipment, a 3D video camera and a processing unit. The hospital bed is used for supporting a patient to be scanned on the hospital bed. The CT scanning and imaging equipment is used for conducting CT scanning and imaging on the patient to be scanned. The 3D video camera is used for shooting a 3D image of the patient to be scanned on the hospital bed. The processing unit is used for acquiring human anatomy structural information of the patient to be scanned according to the 3D image shot by the 3D video camera so as to determine the range to be scanned and for converting the range to be scanned of the 3D video camera under a space coordinate system to the range to be scanned of the CT scanning and imaging equipment under a space coordinate system. The CT scanning and imaging equipment conducts scanning and imaging on the patient to be scanned according to the converted range to be scanned of the CT scanning and imaging equipment under the space coordinate system. By means of the CT system, the CT system scanning positioning method and the CT system calibration method, the precision of the scanned range can be improved, scanning time is shortened, and radiation dosage is lowered.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Protective anatomical pads and methods of making
InactiveUS20110056004A1Minimal weightMinimal bulkWood working apparatusEye treatmentHuman anatomyBiomedical engineering
A protective padded garment includes one or more pads conforming to three-dimensional coordinate data representing the anatomical body part to be protected. The pads are designed from three-dimensional scanned images of the human anatomy and molded in situ with the garment to be worn.
Owner:SHOCK DOCTOR
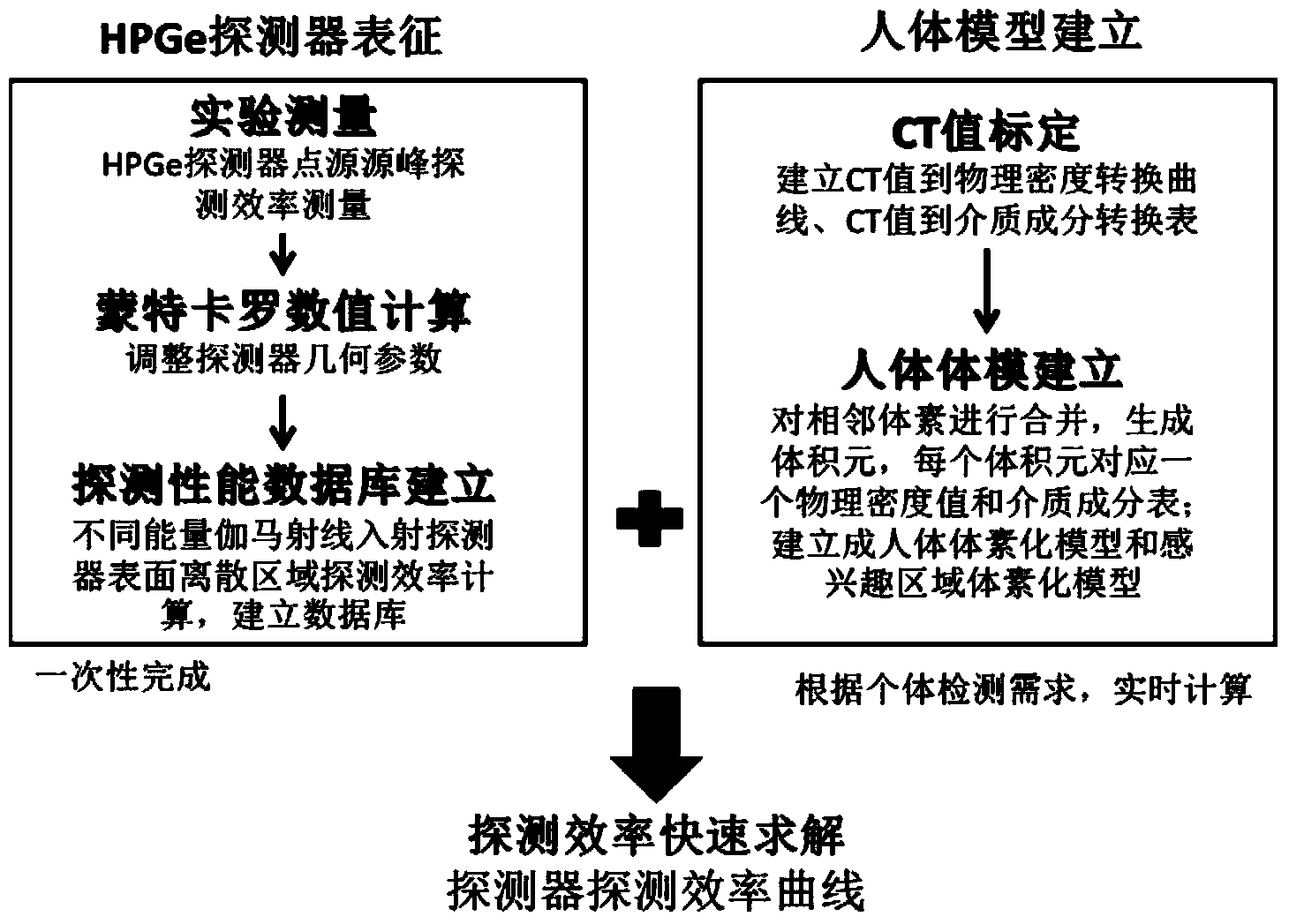
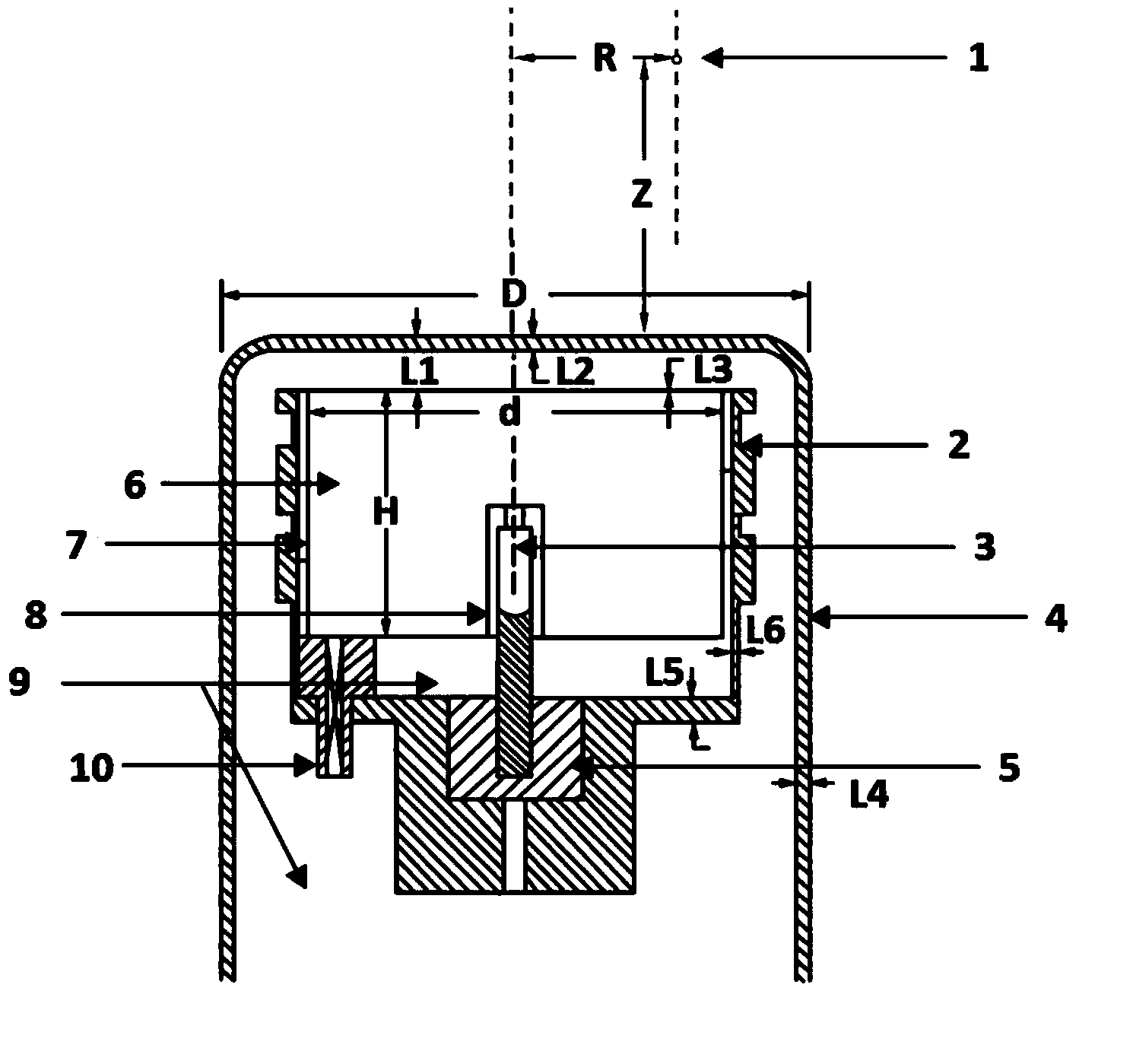
Method for determining detection efficiency of internal exposure HPGe detector based on CT data
ActiveCN104267425AHigh precisionMeet the time requirementRadiation intensity measurementHuman anatomyVoxel
The invention relates to a method for determining the detection efficiency of an internal exposure HPGe detector based on CT data. Based on different energy gamma ray full-energy peak detection efficiency measuring data, Monte Carlo particle transport numerical values are adopted for computing, so that geometrical parameters of a detector sensitive area are adjusted, and the geometrical parameters of the detector sensitive area are obtained; the Monte Carlo particle transport numerical values are adopted for computing, so that the corresponding differential detection efficiency distribution of different energy gamma rays on the surfaces of the detector in different discrete areas and different discrete angle phase spaces is solved; based on CT medical image data of a human body to be detected, a voxel model of human anatomy structural features and a voxel model of an interesting organ or area are established, and the interesting organ or area serves as a source area; an exponential decay formula is used for solving the direct-through gamma ray share from a source area voxel to a surface element on the surface of the detector, and established differential detection efficiency distribution data are used for obtaining the detector full-energy peak detection efficiency specific to the source area through the multiple integral.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multimodality bionic body model
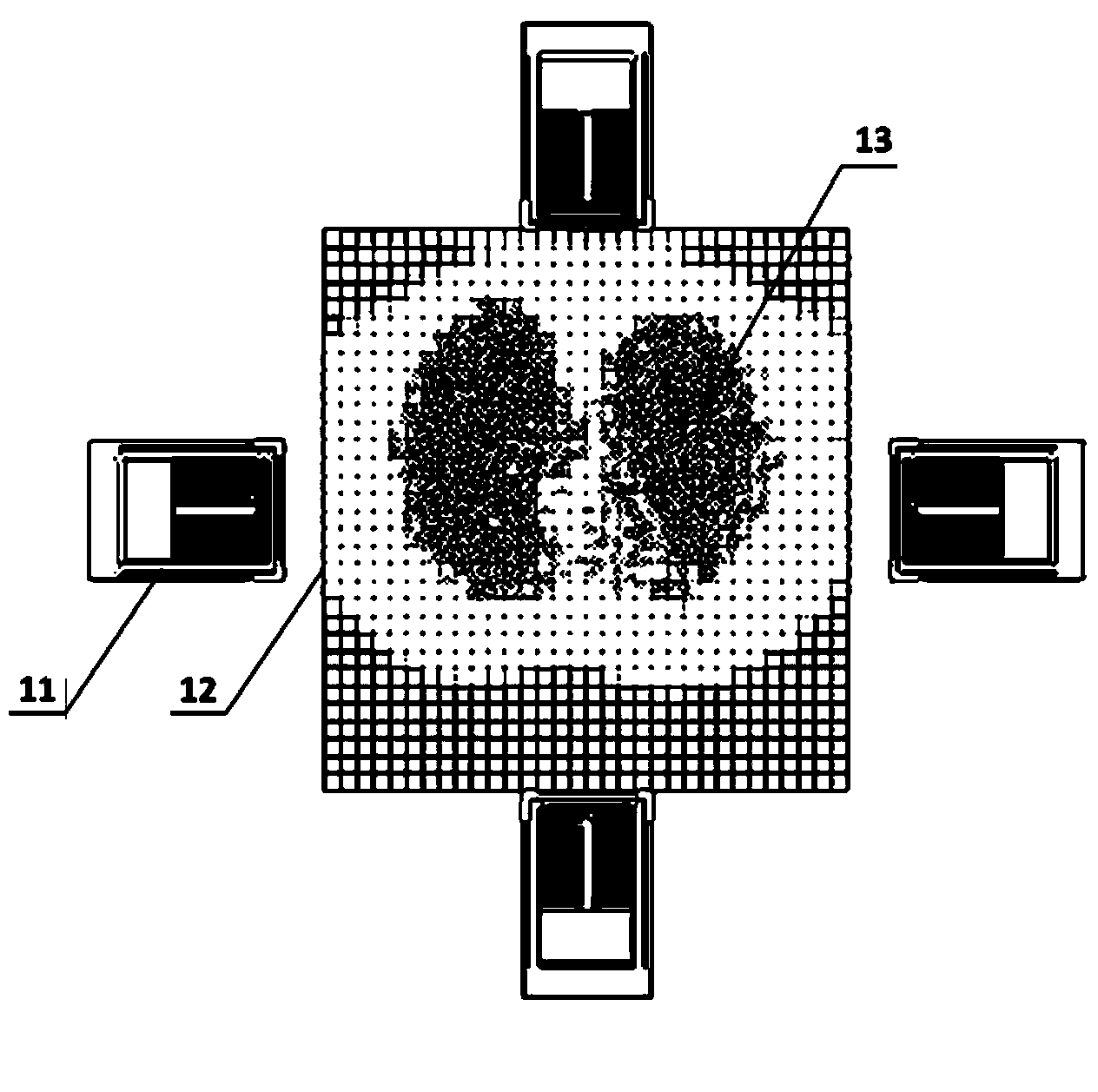
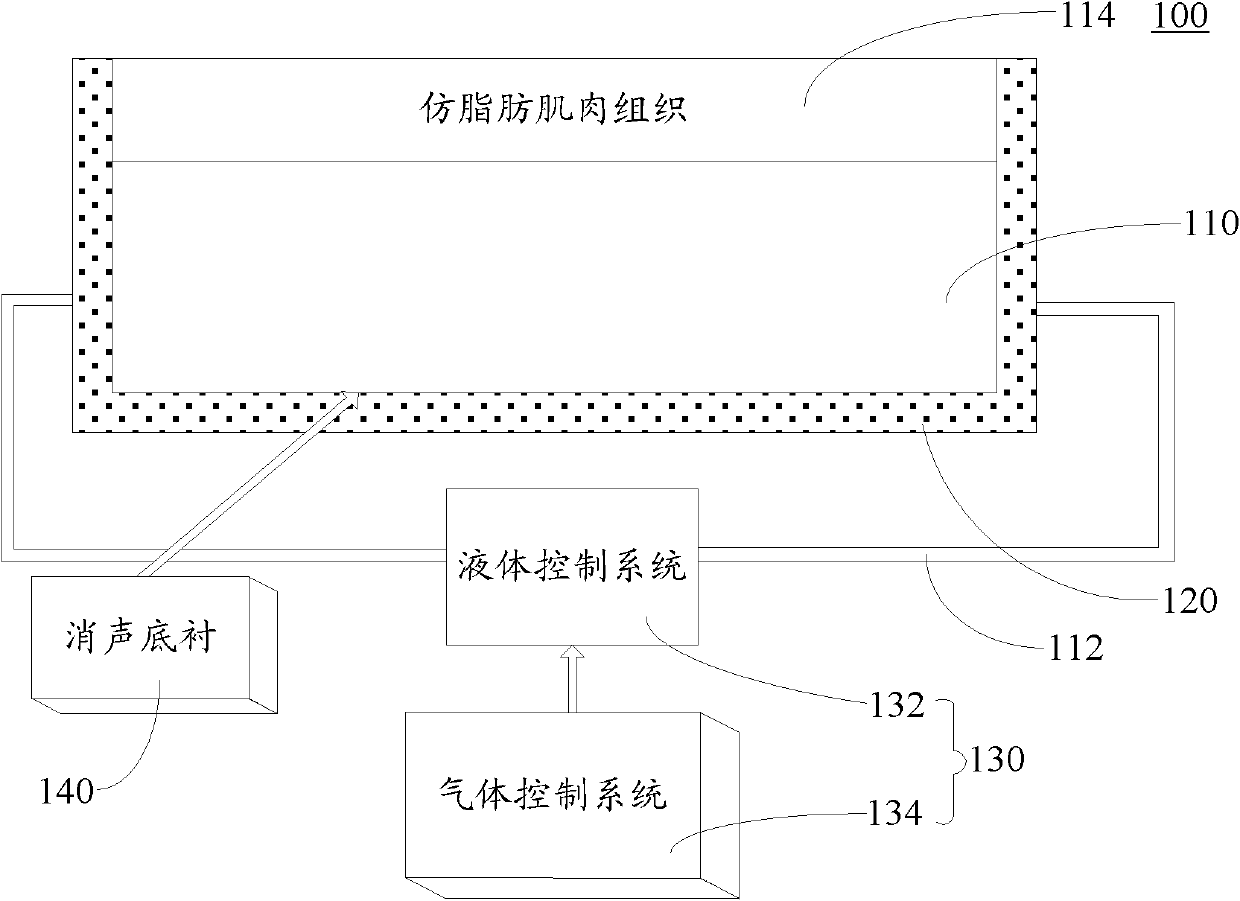
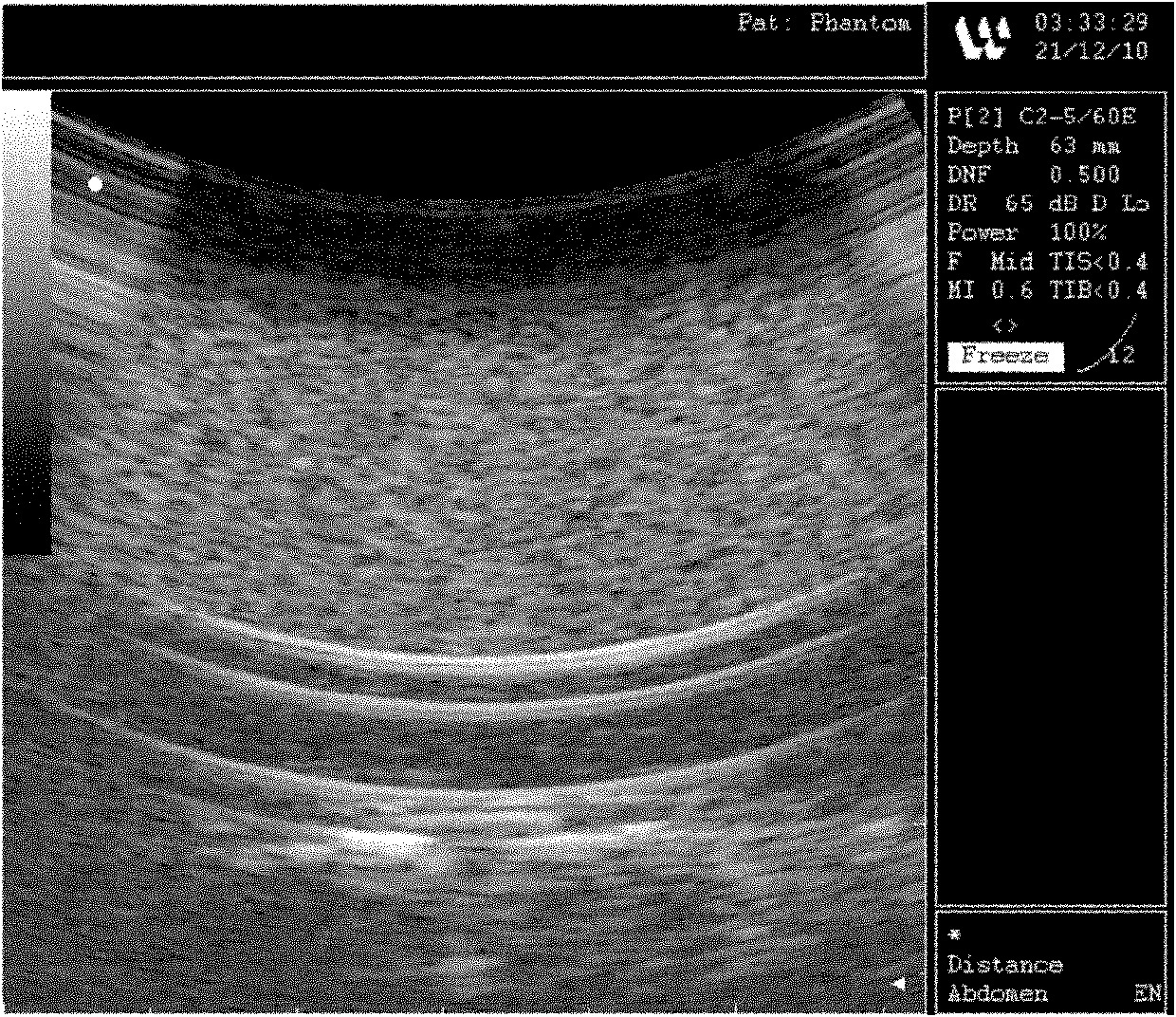
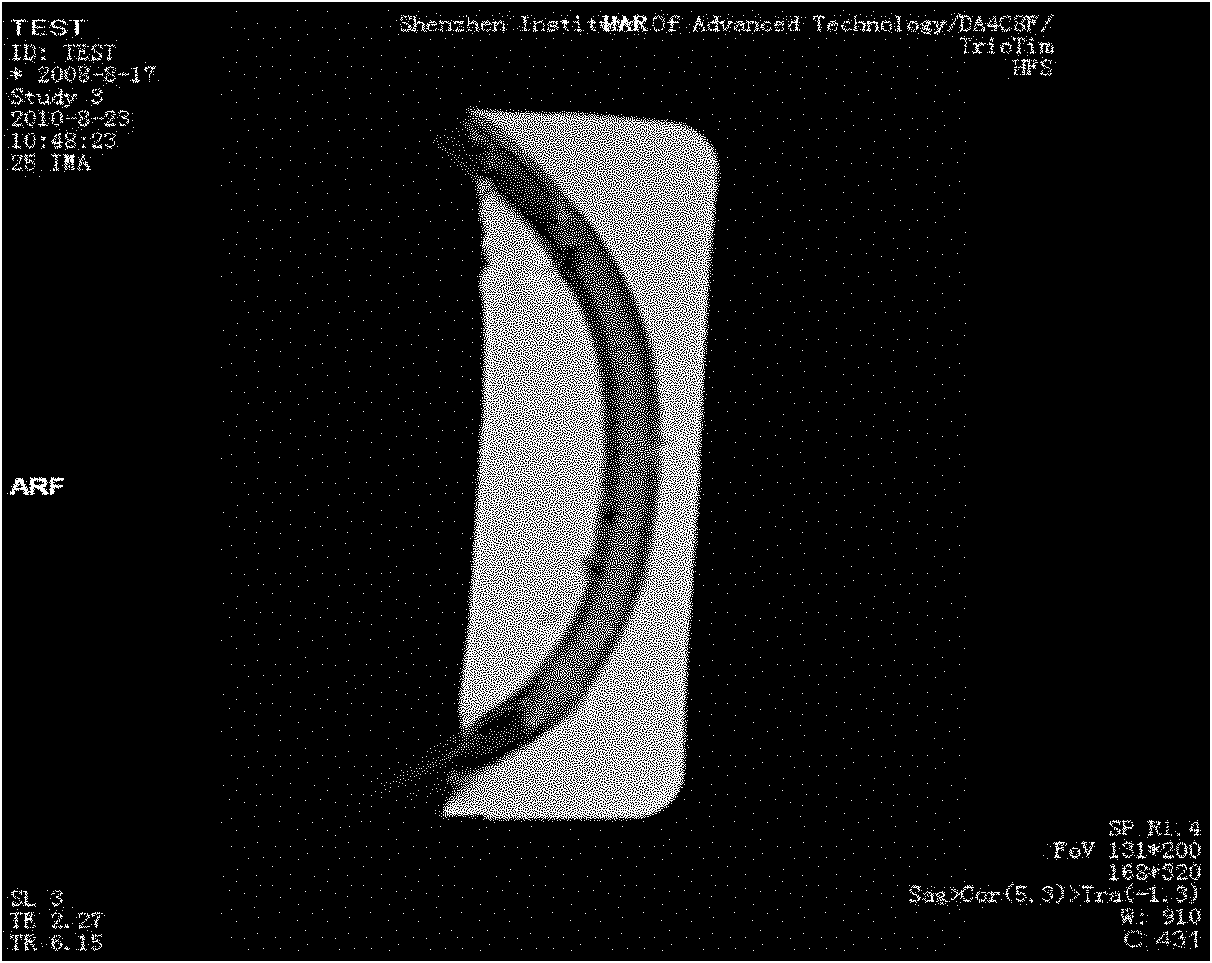
ActiveCN102568287ASimple structureAchieve realistic simulationEducational modelsHuman anatomyFluid control
The invention relates to a multimodality bionic body model applied to ultrasonic or nuclear magnetic resonance detection. The multimodality bionic body model comprises a tissue organ body model, a fixed base and a fluid control system, wherein the tissue organ body model comprises a plurality of body model units imitating human body tissue organs, the plurality of body model units are fixed on the fixed base conforming human anatomy structure according to the tissue organ positions of the human anatomy structure, the tissue organ body model and the fixed base are prepared from a non-metal material, the tissue organ body model is composed of an ultrasonic and nuclear-magnetic bionic material, and the fluid control system is used for analog control of the blood circulation and respiratory movement of the human body. The multimodality bionic body model integrates the body model units imitating a plurality of main tissue organs on a human body trunk position, and is simple in structure; and the body model units are fixed on the fixed base by adopting the anatomic position relation, so as to achieve the actual imitation effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
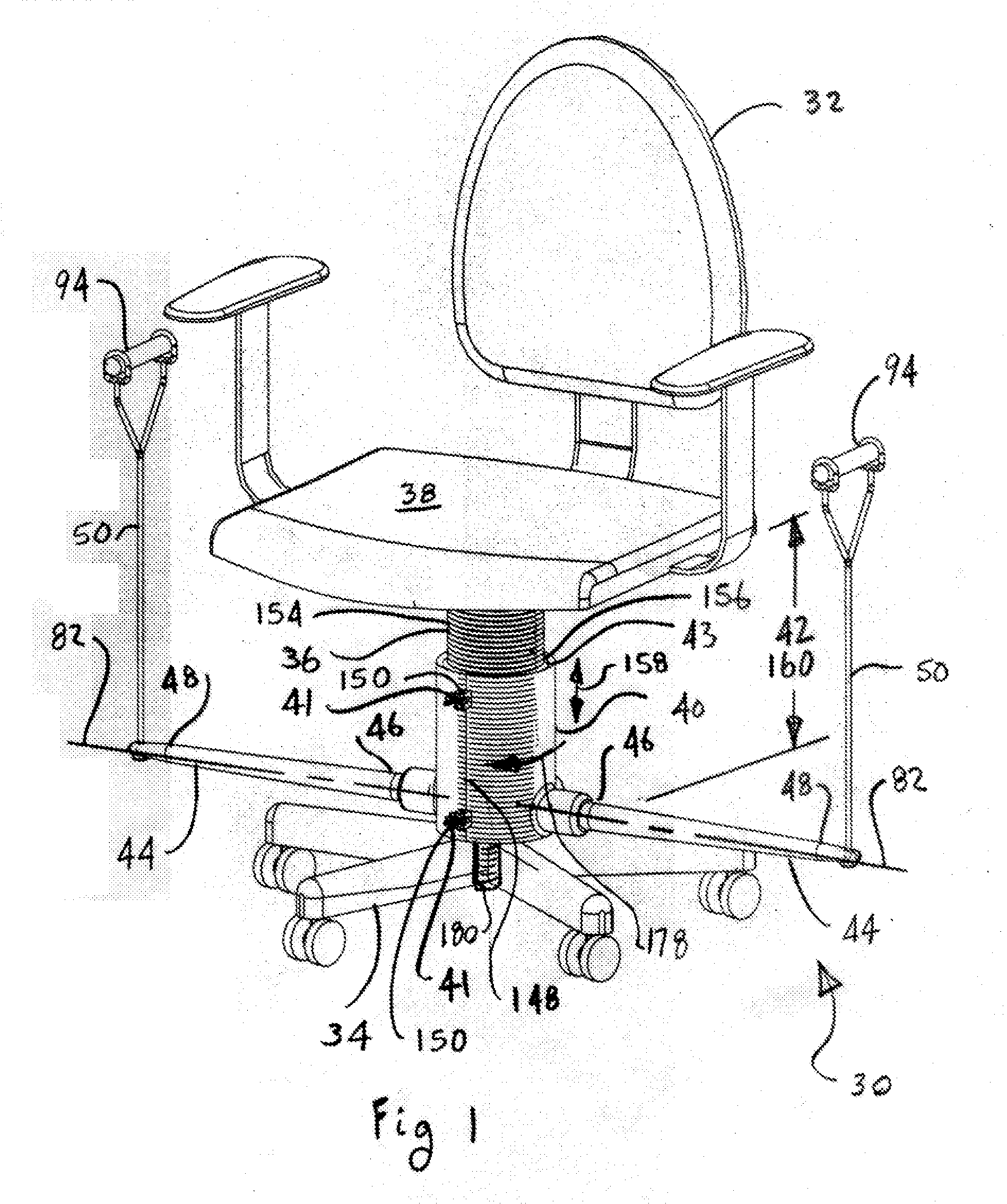
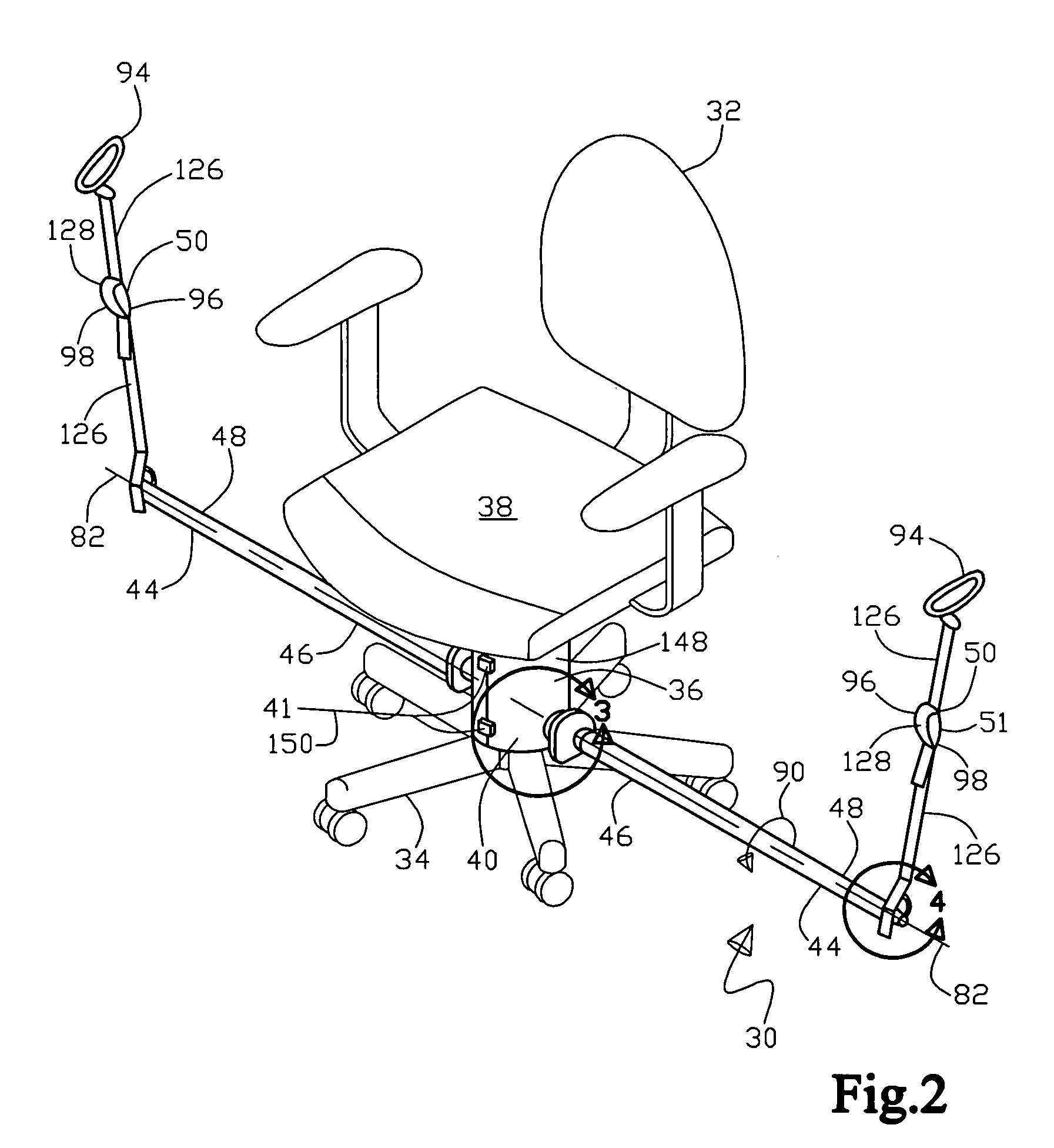
Exercise apparatus
An exercise apparatus for use with a chair, the chair having a base, a pedestal, and a seat, the exercise apparatus includes a support assembly adapted to removably attach to the pedestal, an elongate resilient member having a proximal end portion and a distal end portion with the proximal end portion being adjacent to the support assembly. Further, on the distal end portion is an attachment element, wherein the attachment element is adapted to removably engage to a portion of human anatomy for the purpose of exercise by extending of the elongate resilient member by moving the attachment element away from the support assembly causing a resistive force at the attachment element. Wherein, operationally the elongate resilient member has substantially free omni-directional movement by not contacting the seat when being used for exercise.
Owner:HALBRIDGE ADAM
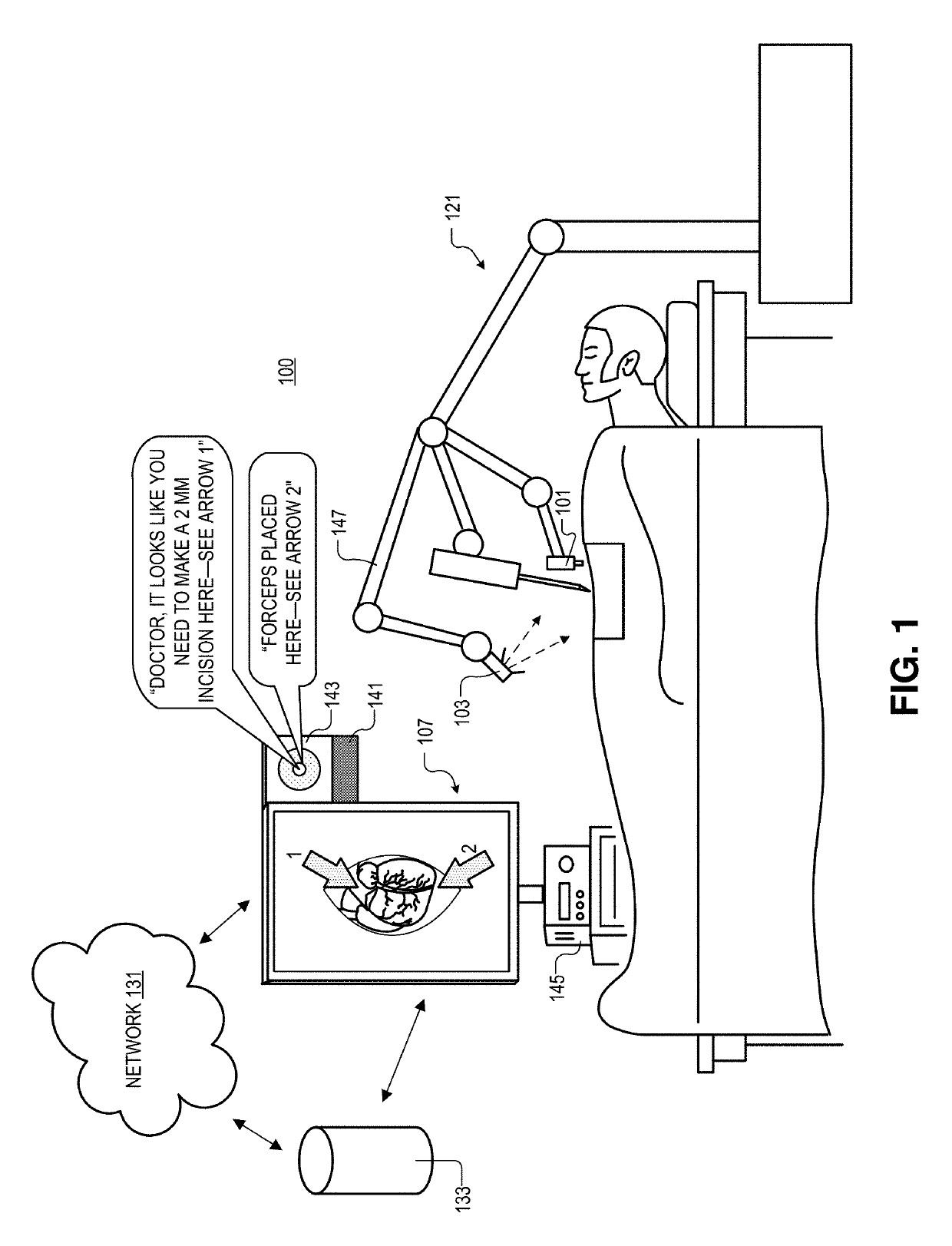
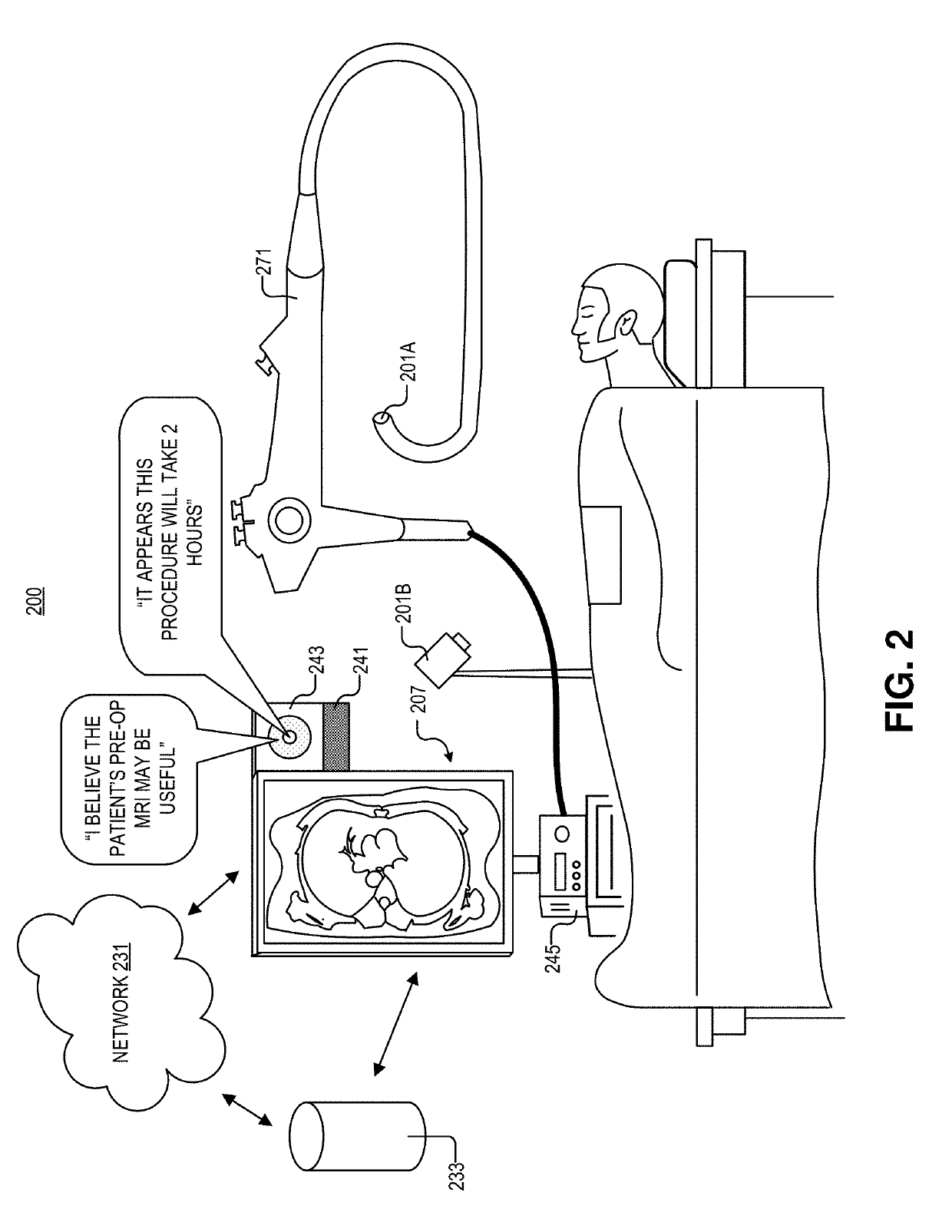
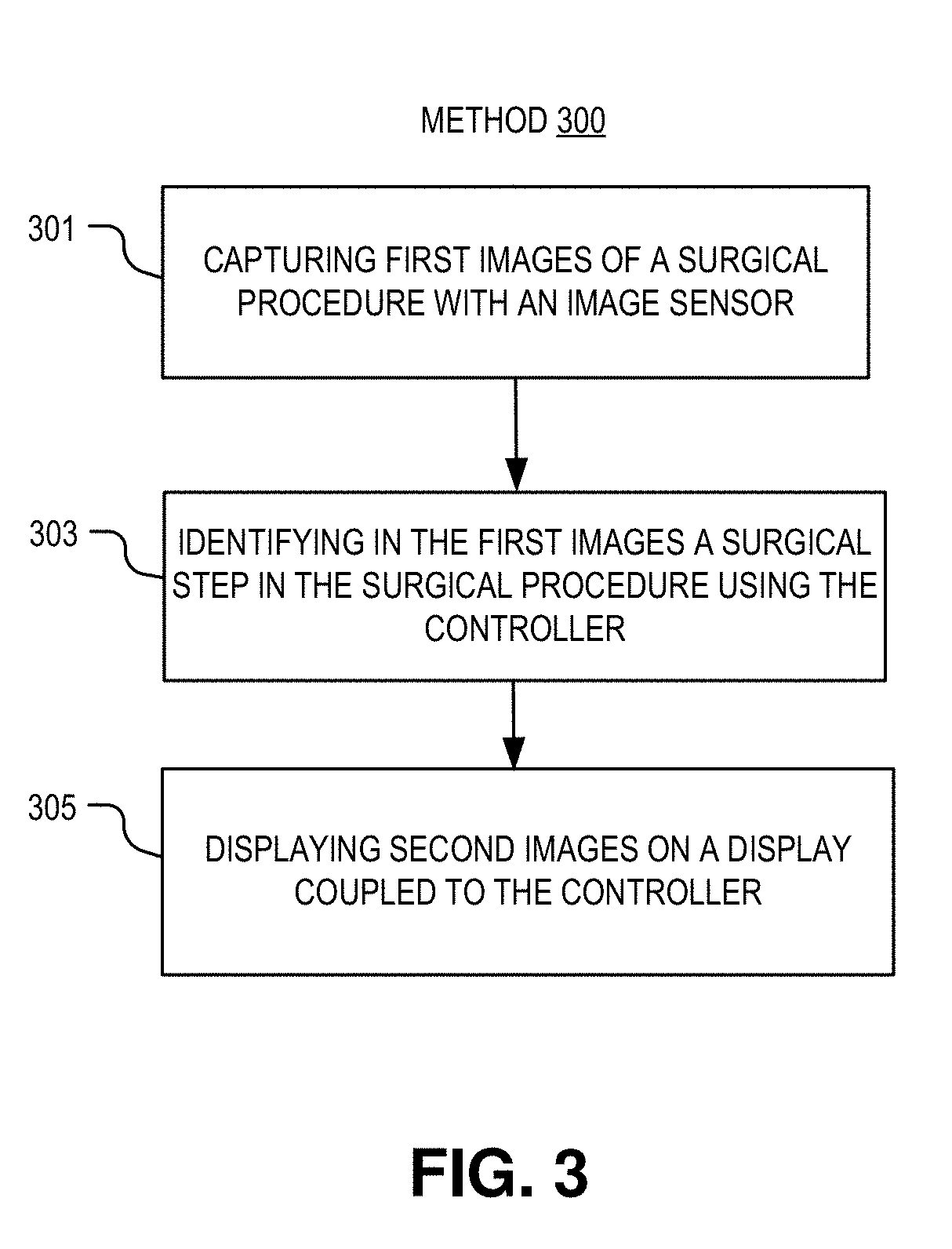
Step-based system for providing surgical intraoperative cues
A system for robot-assisted surgery includes an image sensor and a display. The system further includes a controller coupled to the image sensor and the display, where the controller includes logic that when executed by the controller causes the system to perform operations. The operations may include acquiring first images of a surgical procedure with the image sensor, and analyzing the first images with the controller to identify a surgical step in the surgical procedure. The operations may further include displaying second images on the display in response to identifying the surgical step; the second images may include at least one of a diagram of human anatomy, a preoperative image, an intraoperative image, or an annotated image of one of the first images.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
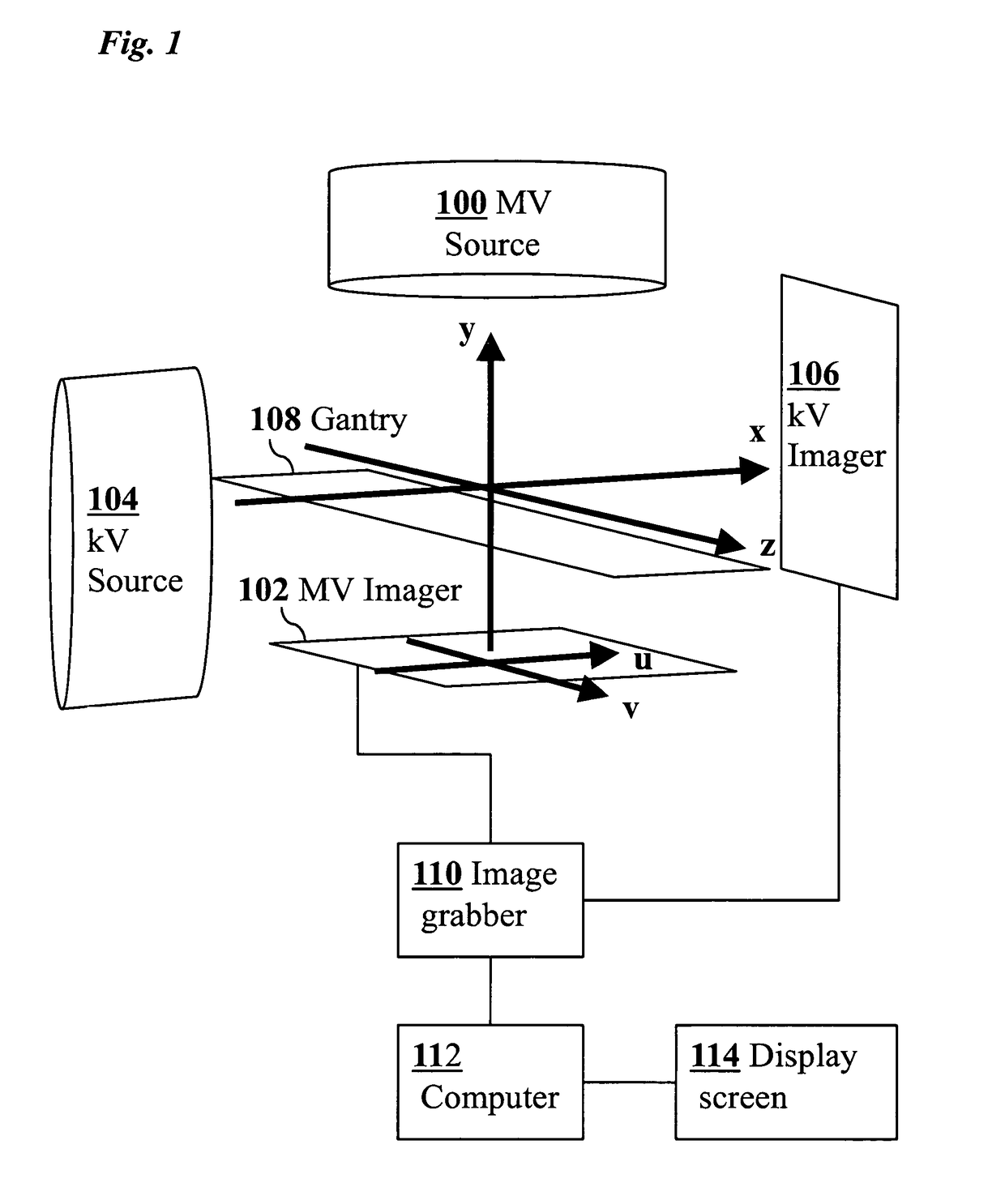
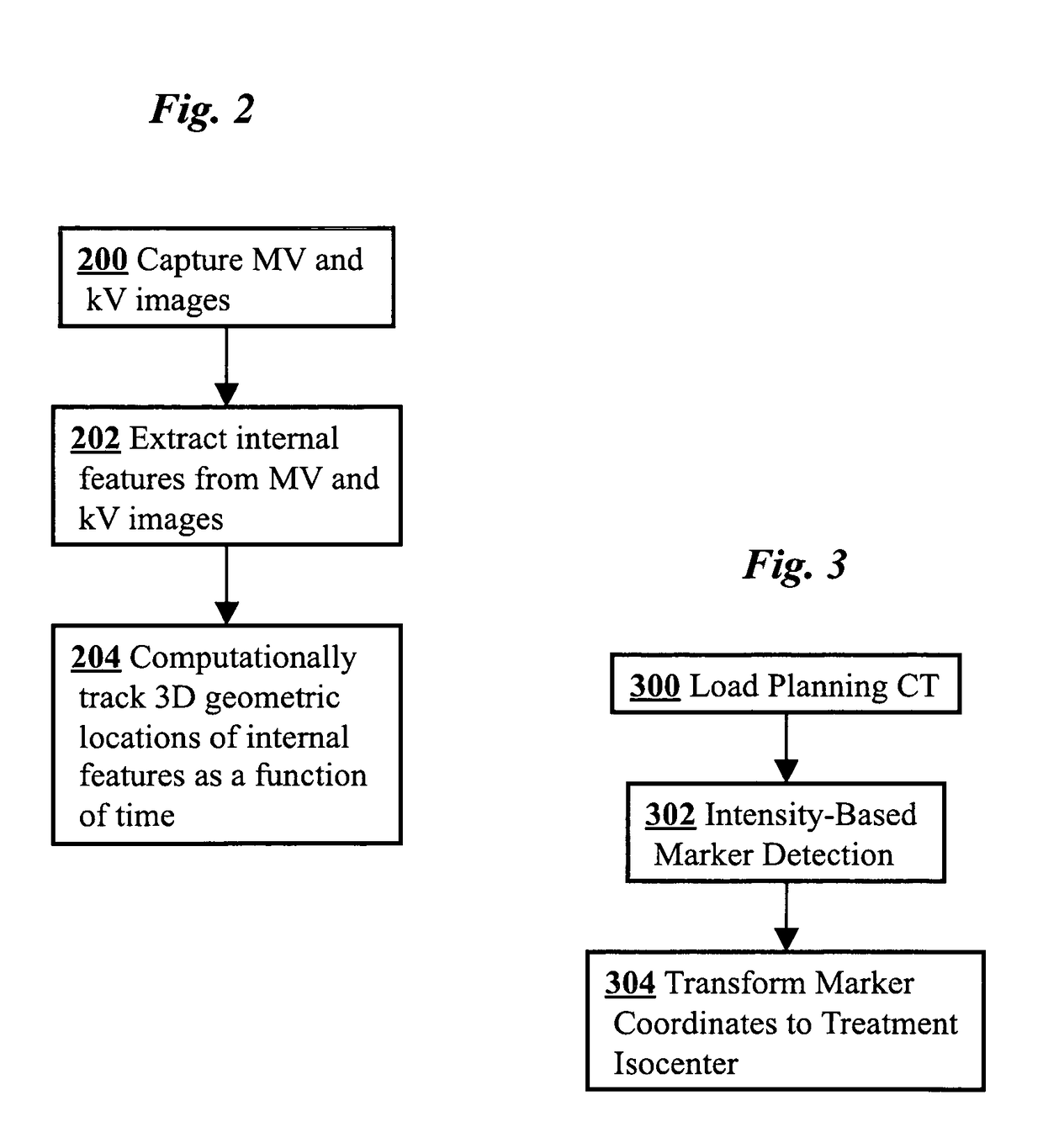
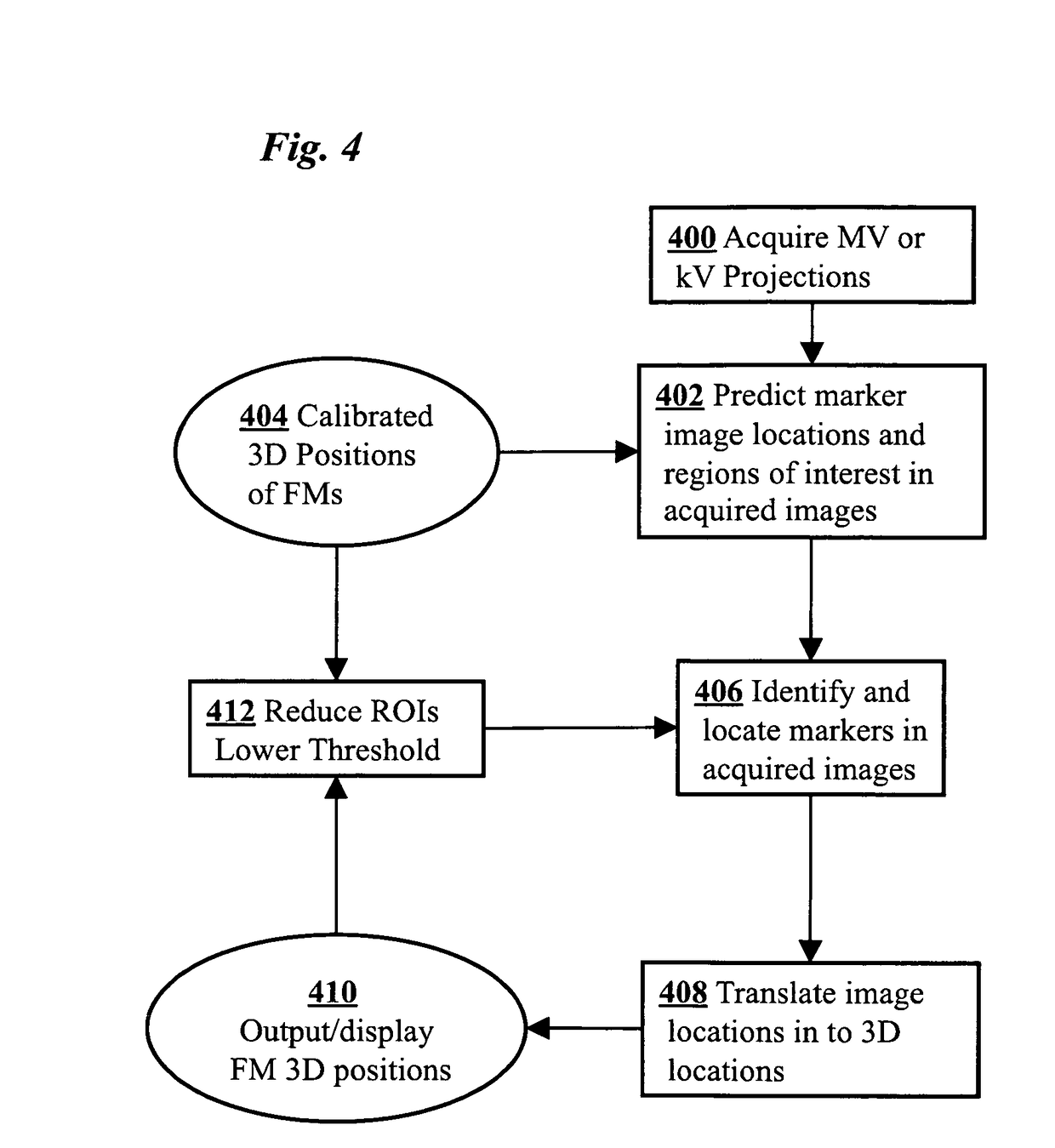
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS8121368B2Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
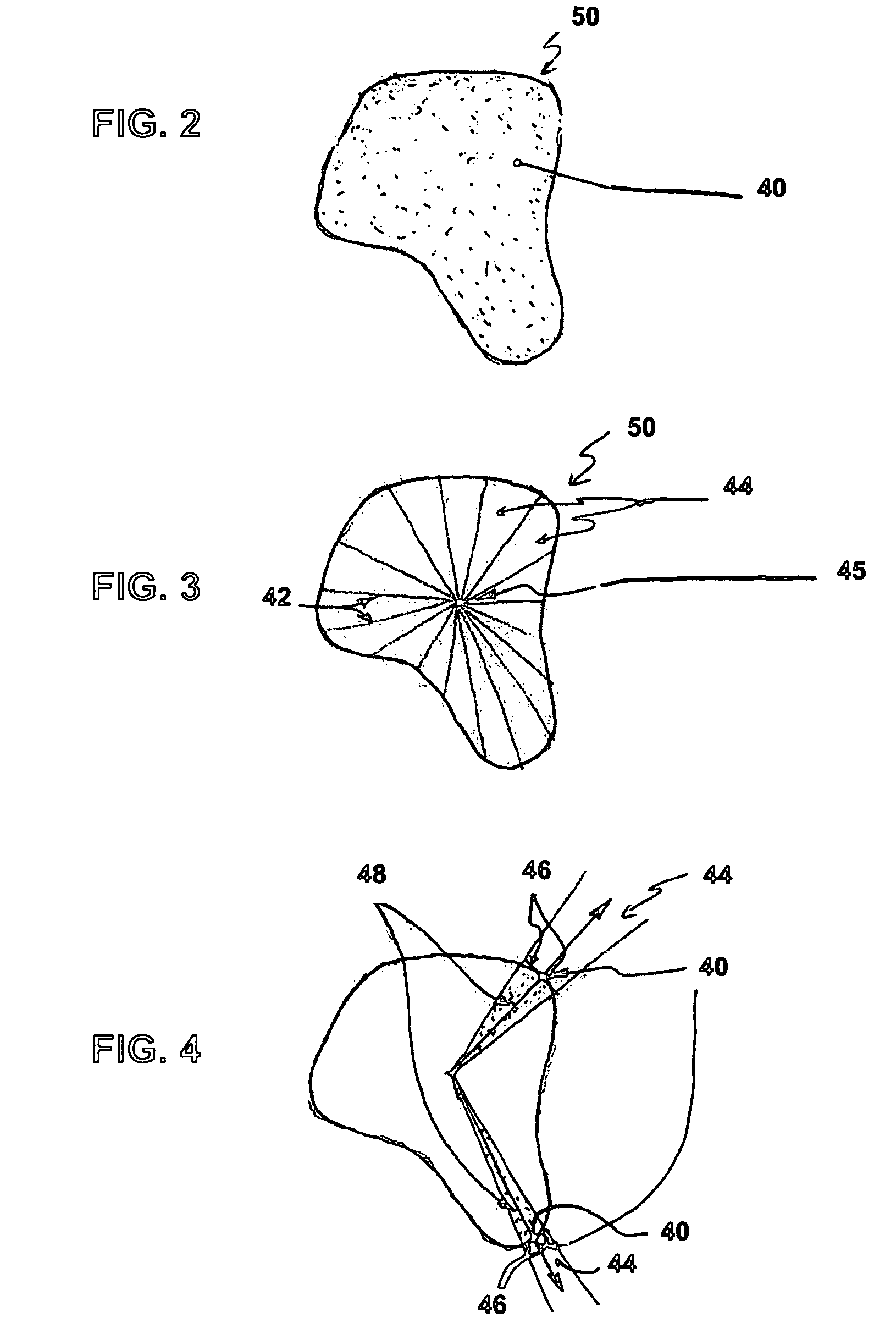
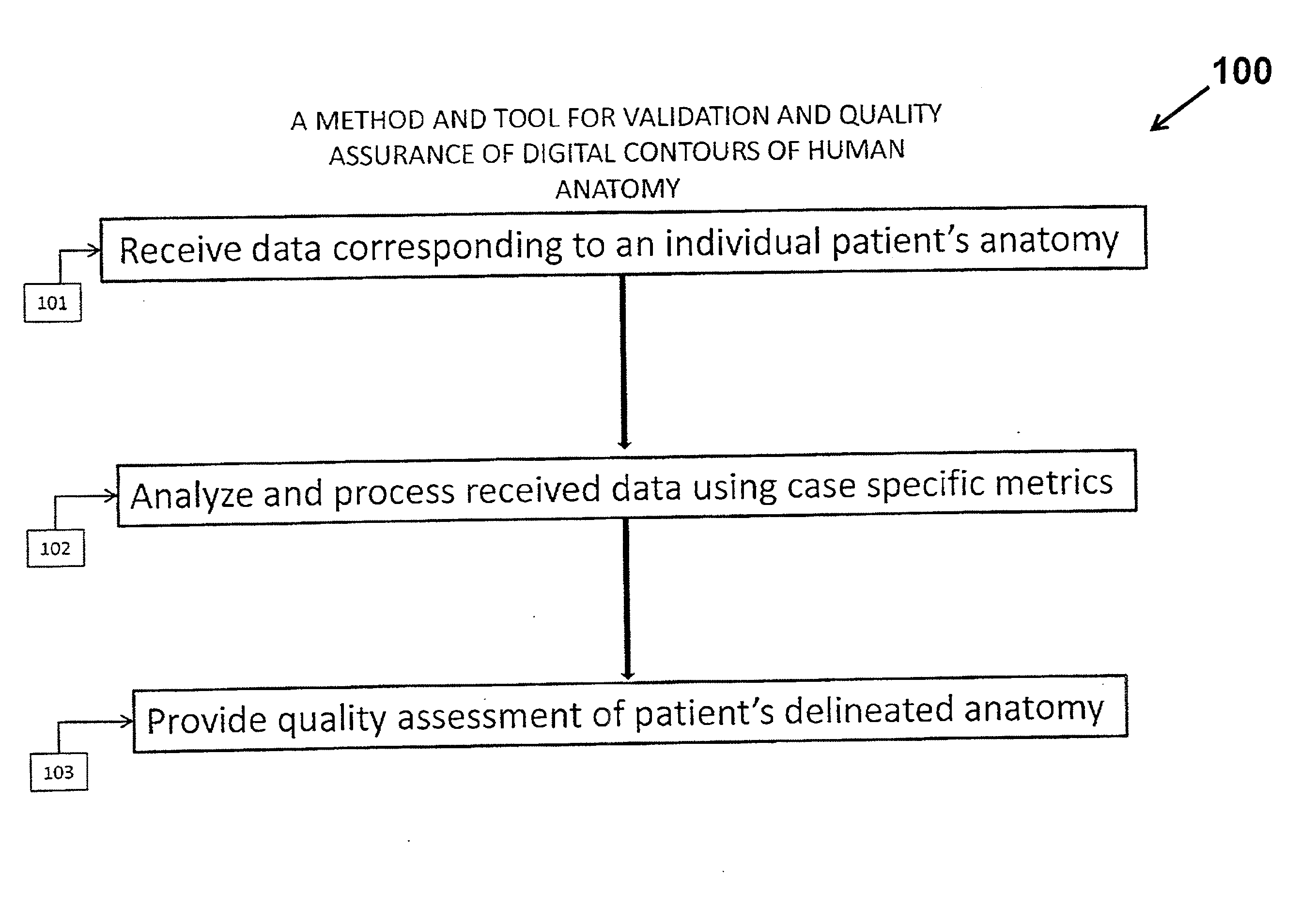
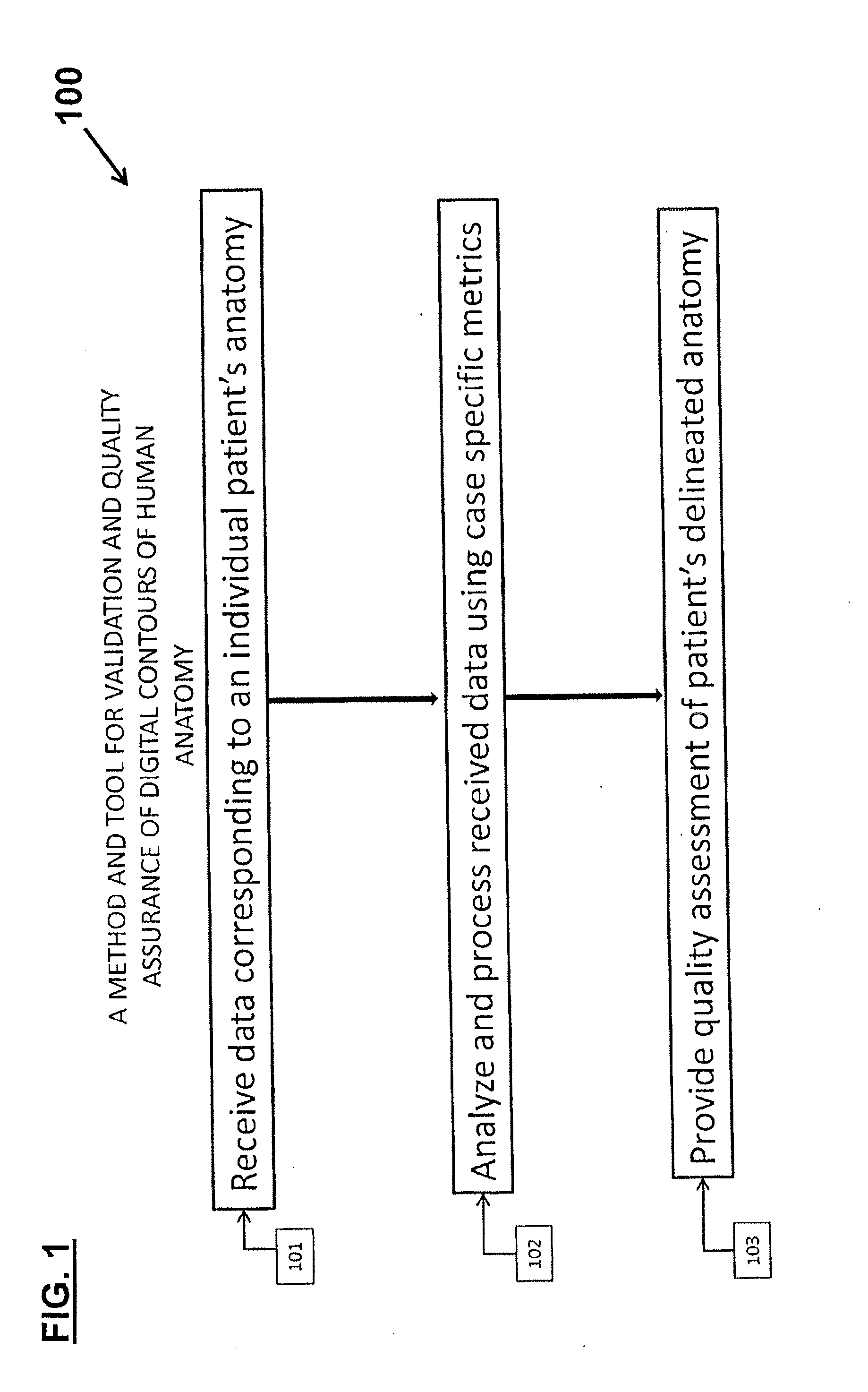
System and Method for the Validation and Quality Assurance of Computerized Contours of Human Anatomy
A system and method for validating the accuracy of delineated contours in computerized imaging using statistical data for generating assessment criterion that define acceptable tolerances for delineated contours, with the statistical data being conditionally updated and / or refined between individual processes for validating delineated contours to thereby adjust the tolerances defined by the assessment criterion in the stored statistical data, such that the stored statistical data is more closely representative of a target population. In an alternative embodiment, a system and method for validating the accuracy of delineated contours in computerized imaging using machine learning for assessing delineated contours, with the machine learning training data being used to generate geometric attributes, and the geometric attributes used to construct intra- and interstructural geometric attribute distribution models to automatically detect contouring errors. The present invention may be used to facilitate, as one example, radiation therapy.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com