Patents
Literature
67 results about "3d tracking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
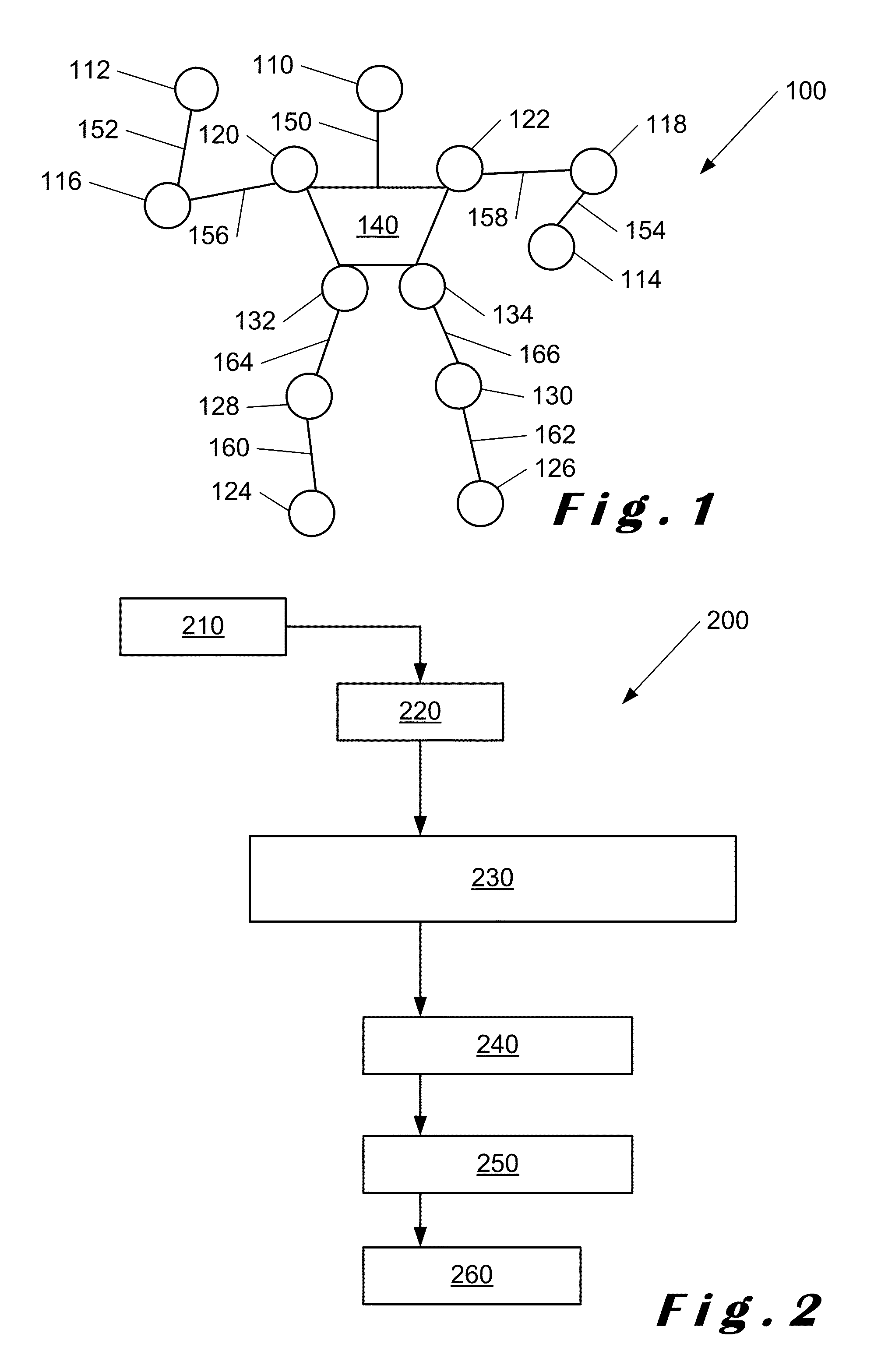
Monocular tracking of 3D human motion with a coordinated mixture of factor analyzers
ActiveUS7450736B2Efficiently and accurately trackingSmall sizeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOffline learningMultiple hypothesis tracking
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Monocular tracking of 3D human motion with a coordinated mixture of factor analyzers
ActiveUS20070104351A1Efficiently and accurately trackingSmall sizeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionOffline learningMultiple hypothesis tracking
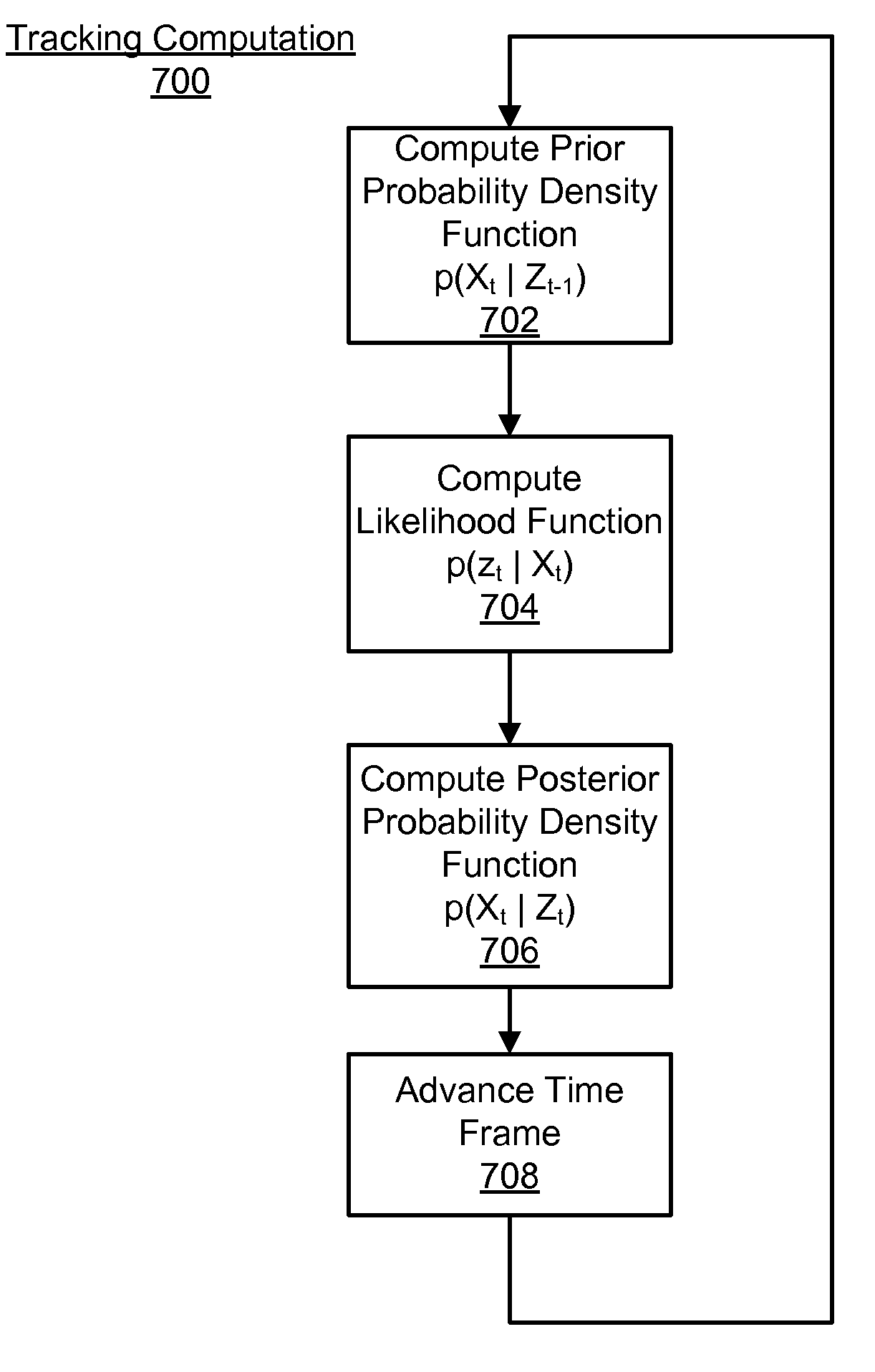
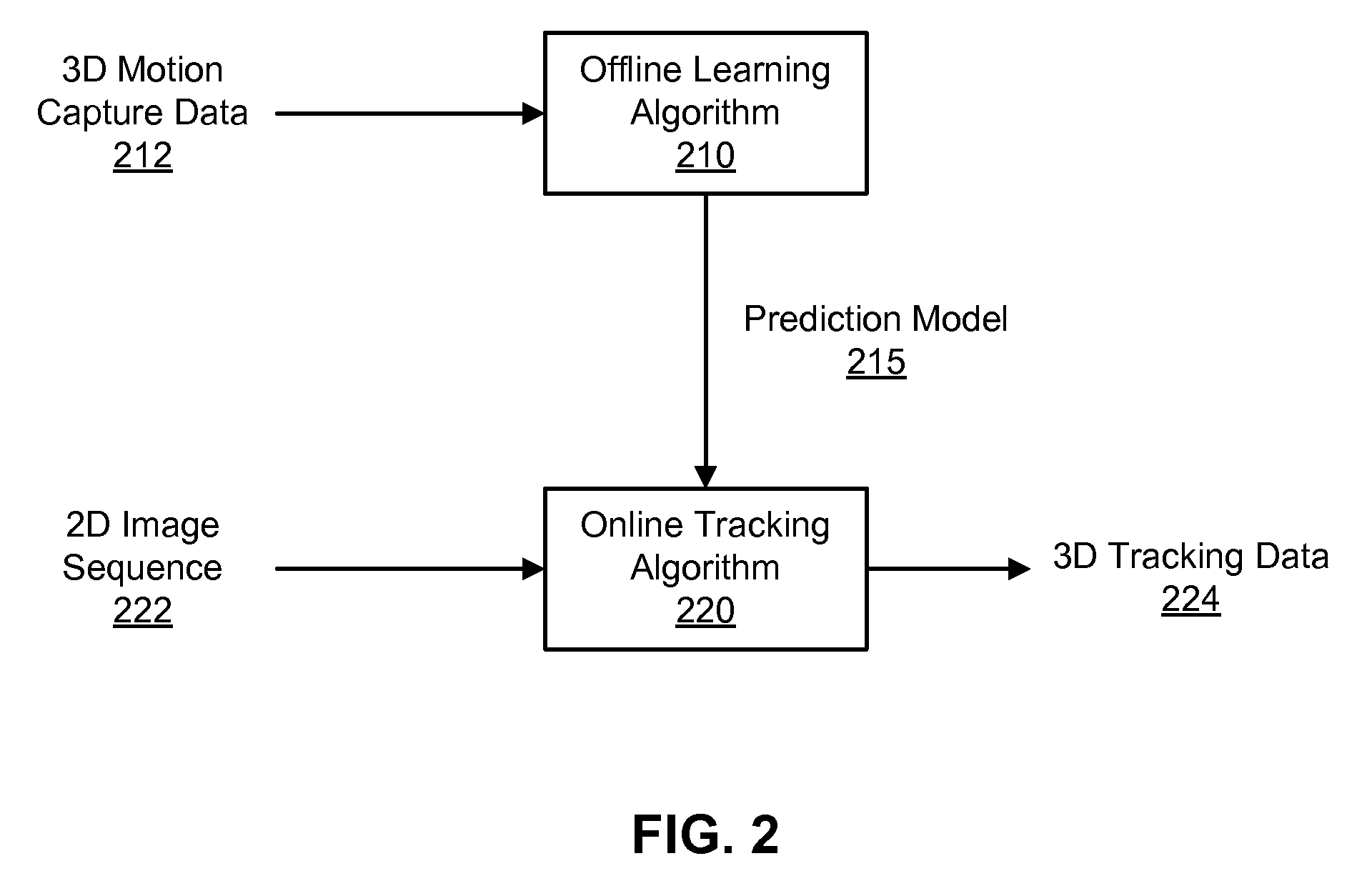
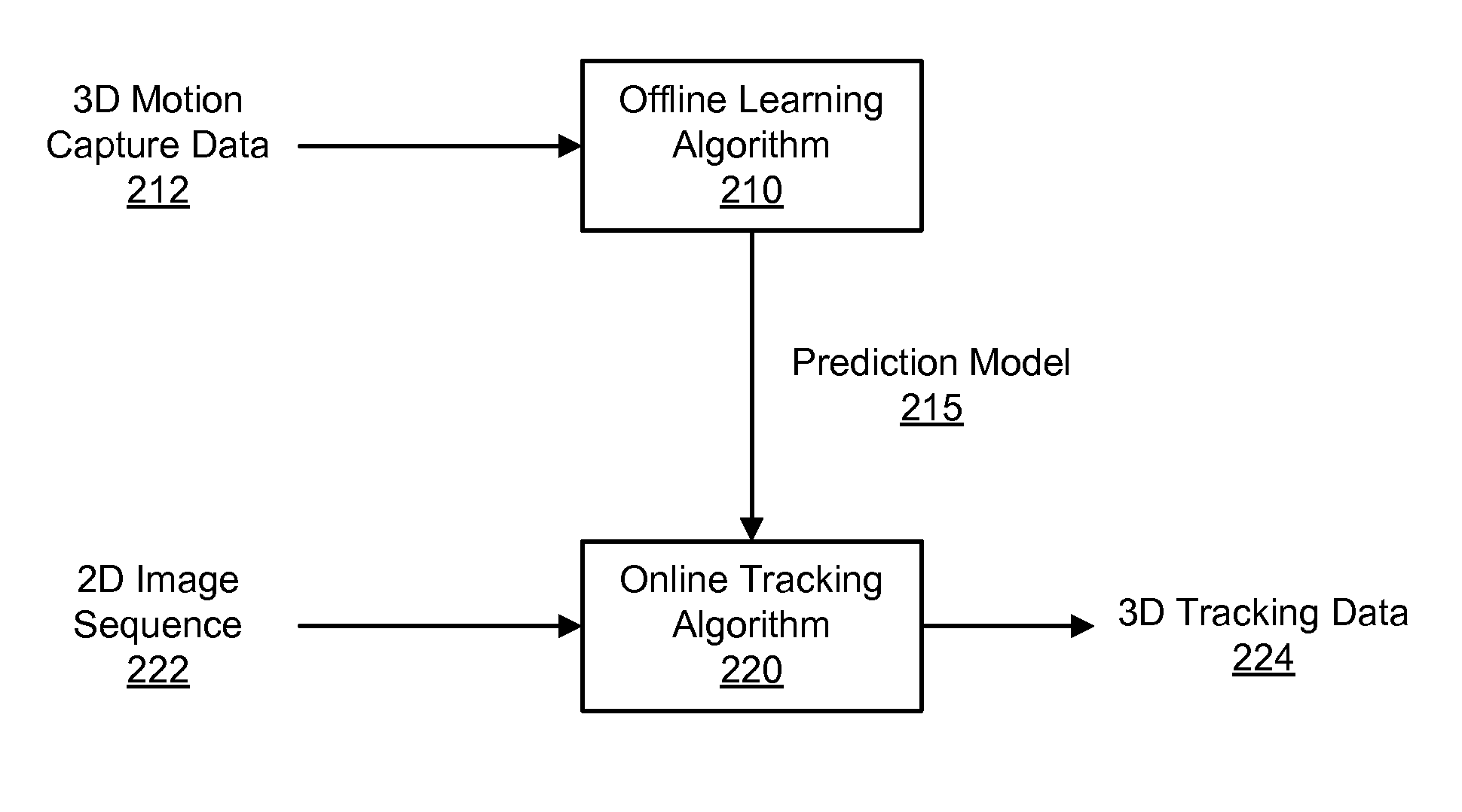
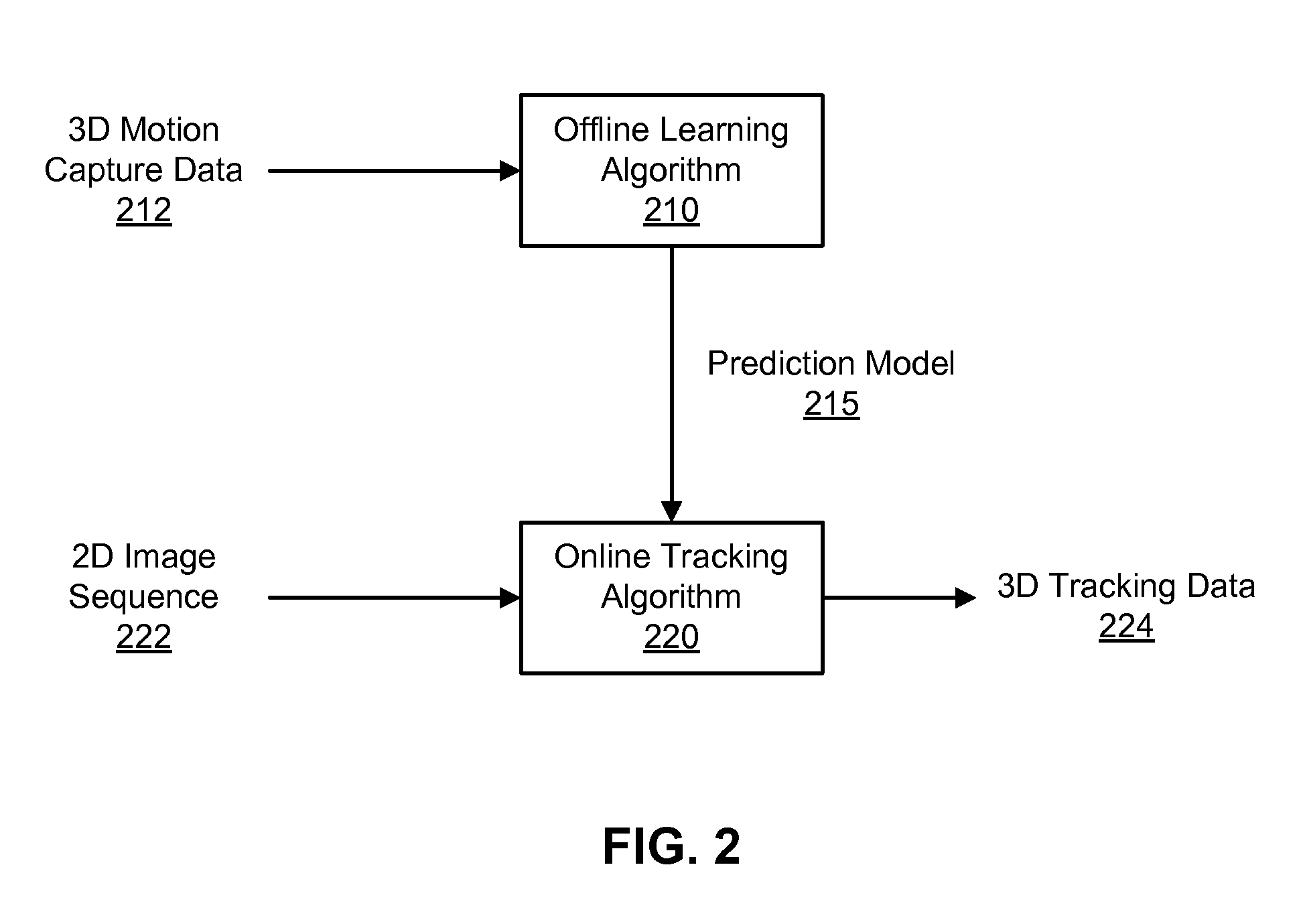
Disclosed is a method and system for efficiently and accurately tracking three-dimensional (3D) human motion from a two-dimensional (2D) video sequence, even when self-occlusion, motion blur and large limb movements occur. In an offline learning stage, 3D motion capture data is acquired and a prediction model is generated based on the learned motions. A mixture of factor analyzers acts as local dimensionality reducers. Clusters of factor analyzers formed within a globally coordinated low-dimensional space makes it possible to perform multiple hypothesis tracking based on the distribution modes. In the online tracking stage, 3D tracking is performed without requiring any special equipment, clothing, or markers. Instead, motion is tracked in the dimensionality reduced state based on a monocular video sequence.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
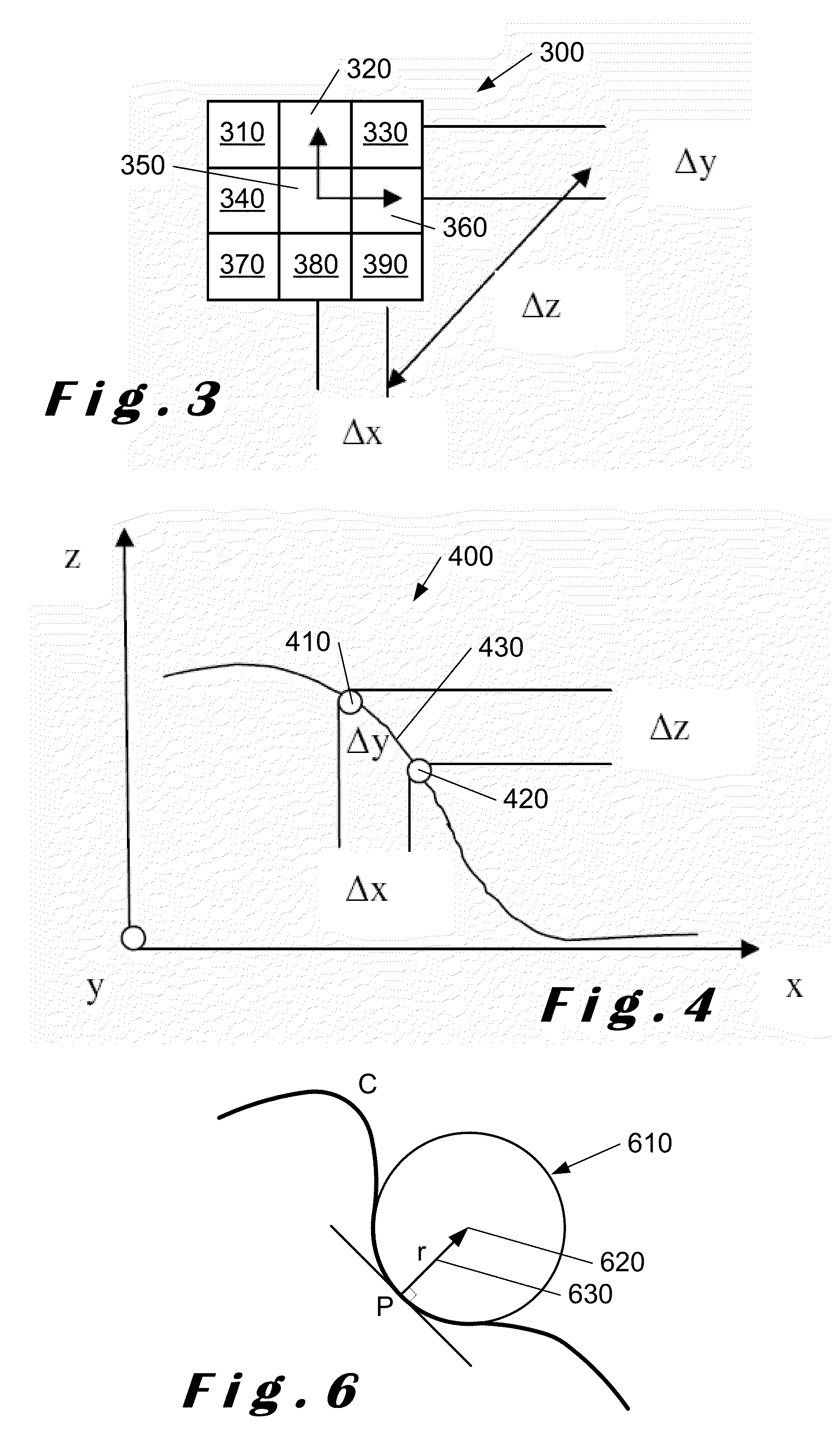
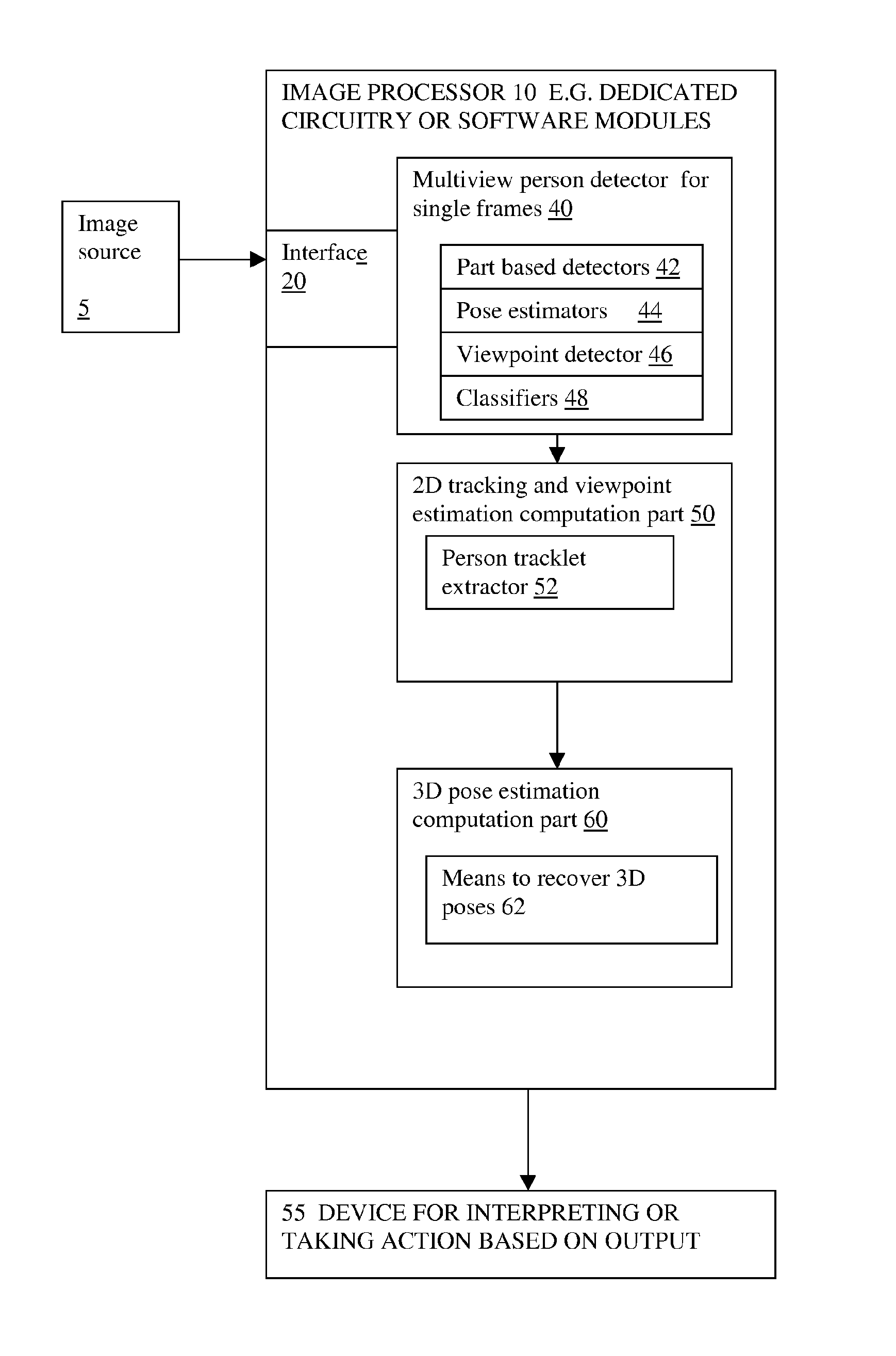
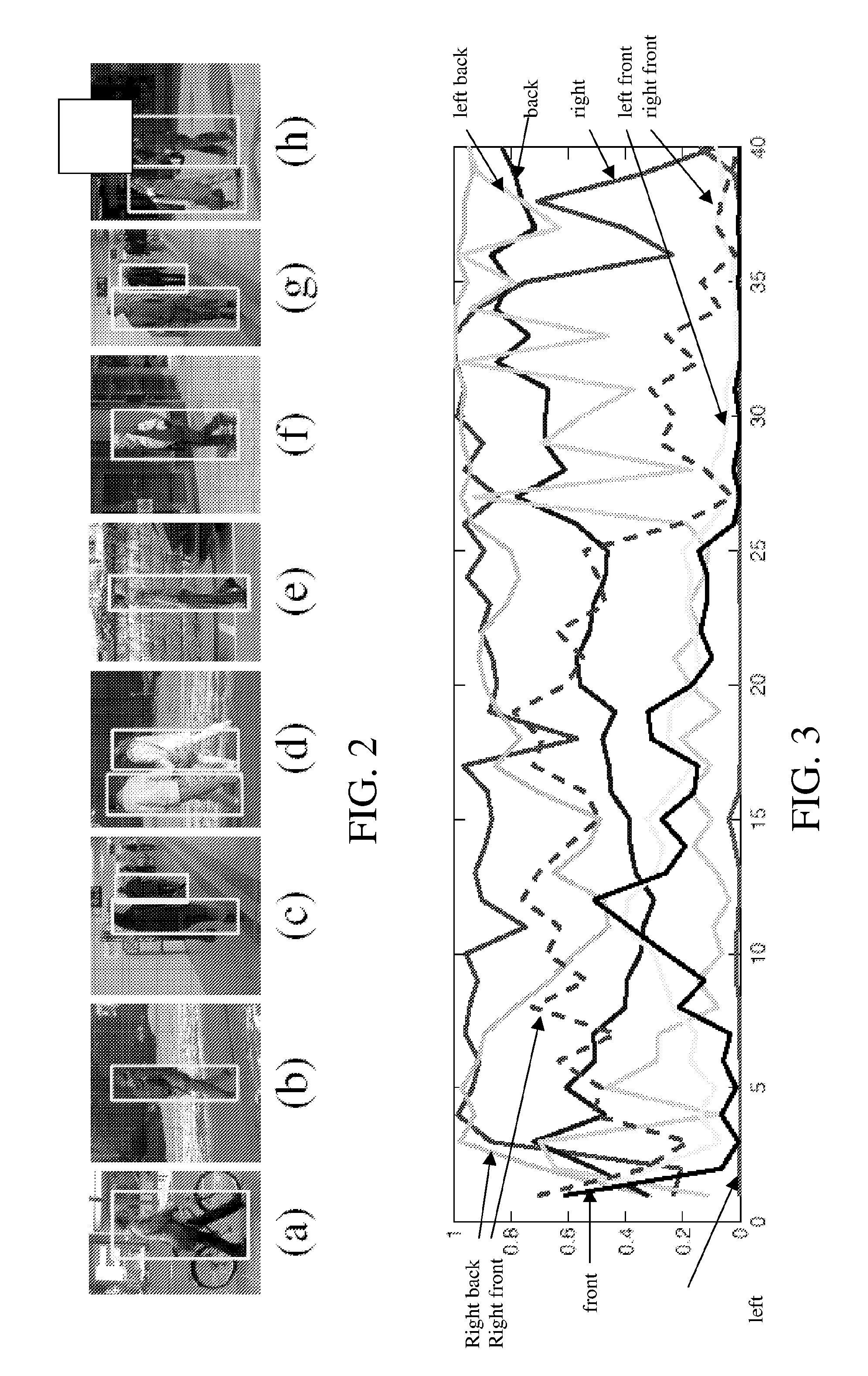
Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection
InactiveUS20130142390A1Low applicabilityReduce in quantityImage enhancementImage analysisThree stageBayesian formulation
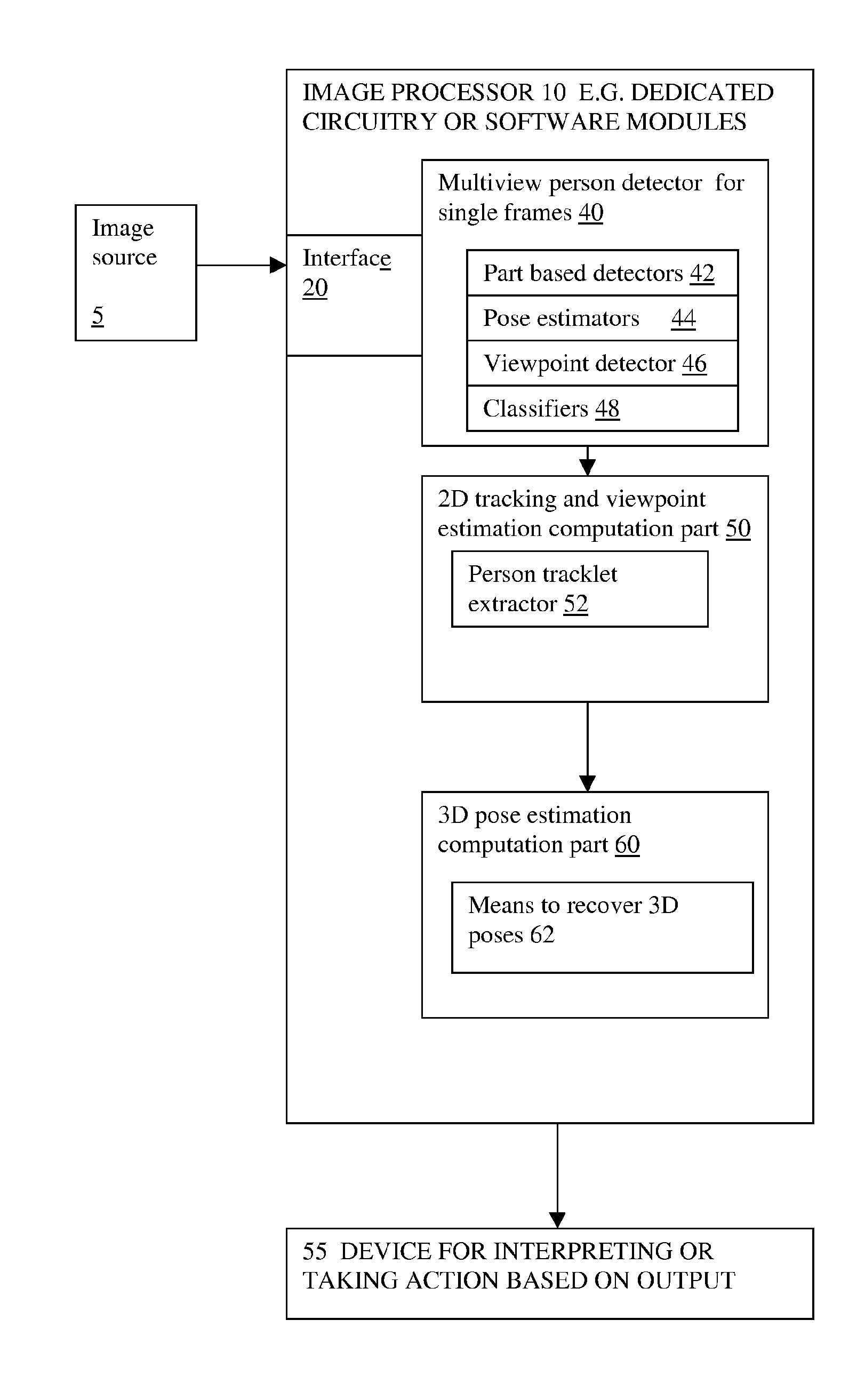
Methods and apparatus are described for monocular 3D human pose estimation and tracking, which are able to recover poses of people in realistic street conditions captured using a monocular, potentially moving camera. Embodiments of the present invention provide a three-stage process involving estimating (10, 60, 110) a 3D pose of each of the multiple objects using an output of 2D tracking-by detection (50) and 2D viewpoint estimation (46). The present invention provides a sound Bayesian formulation to address the above problems. The present invention can provide articulated 3D tracking in realistic street conditions.The present invention provides methods and apparatus for people detection and 2D pose estimation combined with a dynamic motion prior. The present invention provides not only 2D pose estimation for people in side views, it goes beyond this by estimating poses in 3D from multiple viewpoints. The estimation of poses is done in monocular images, and does not require stereo images. Also the present invention does not require detection of characteristic poses of people.
Owner:TECH UNIV DARMSTADT +1
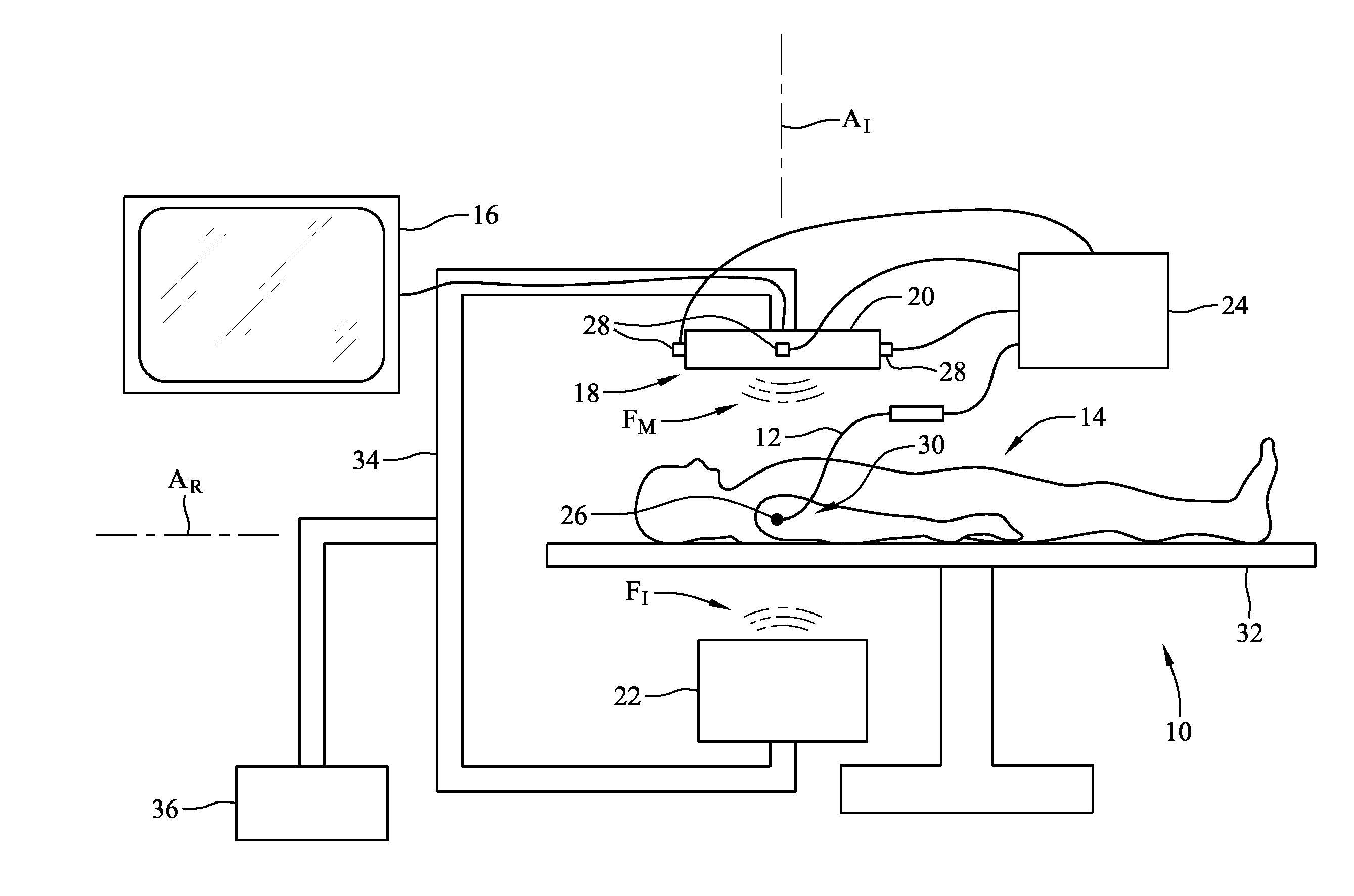
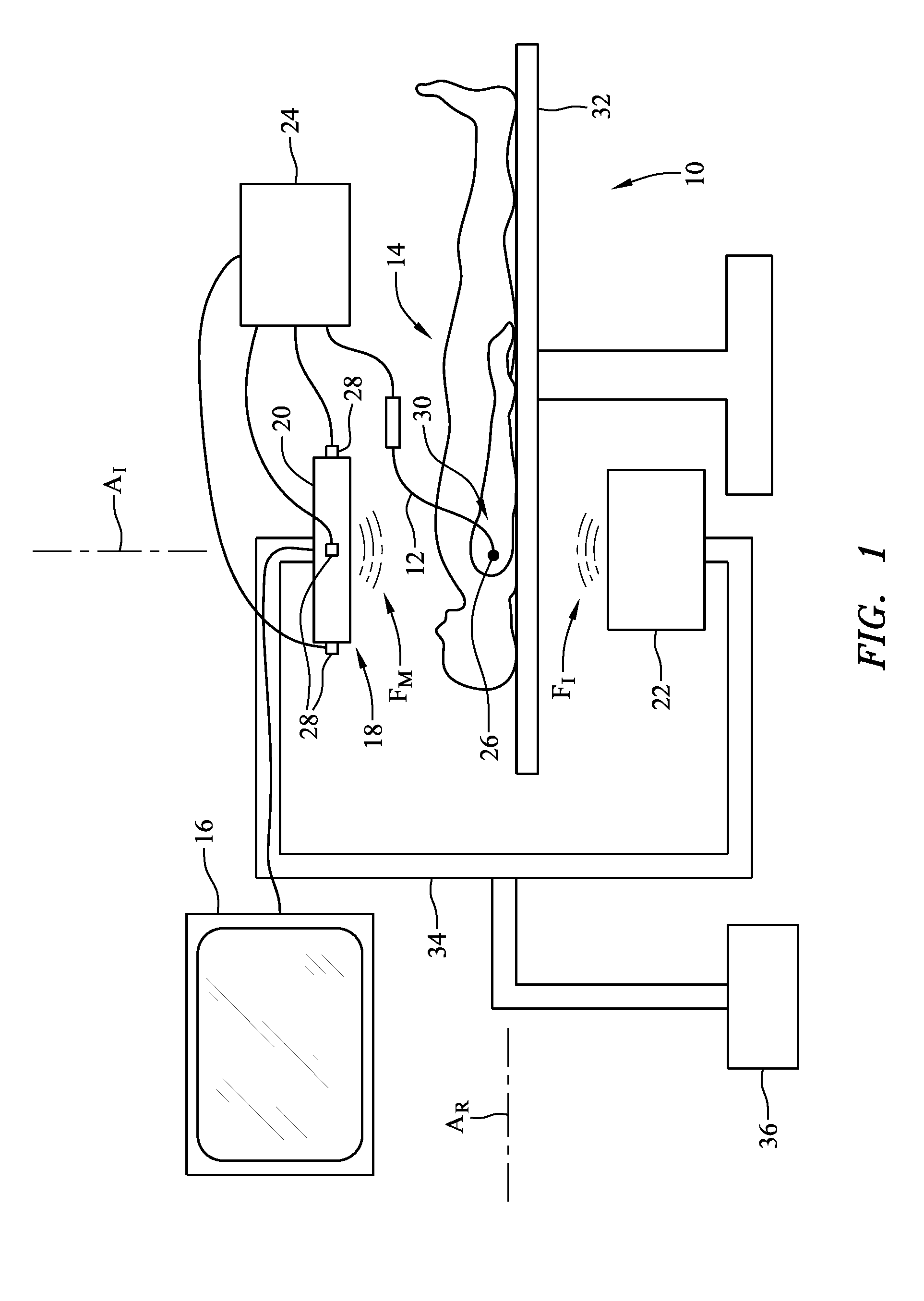
System and method for augmented reality inspection and data visualization
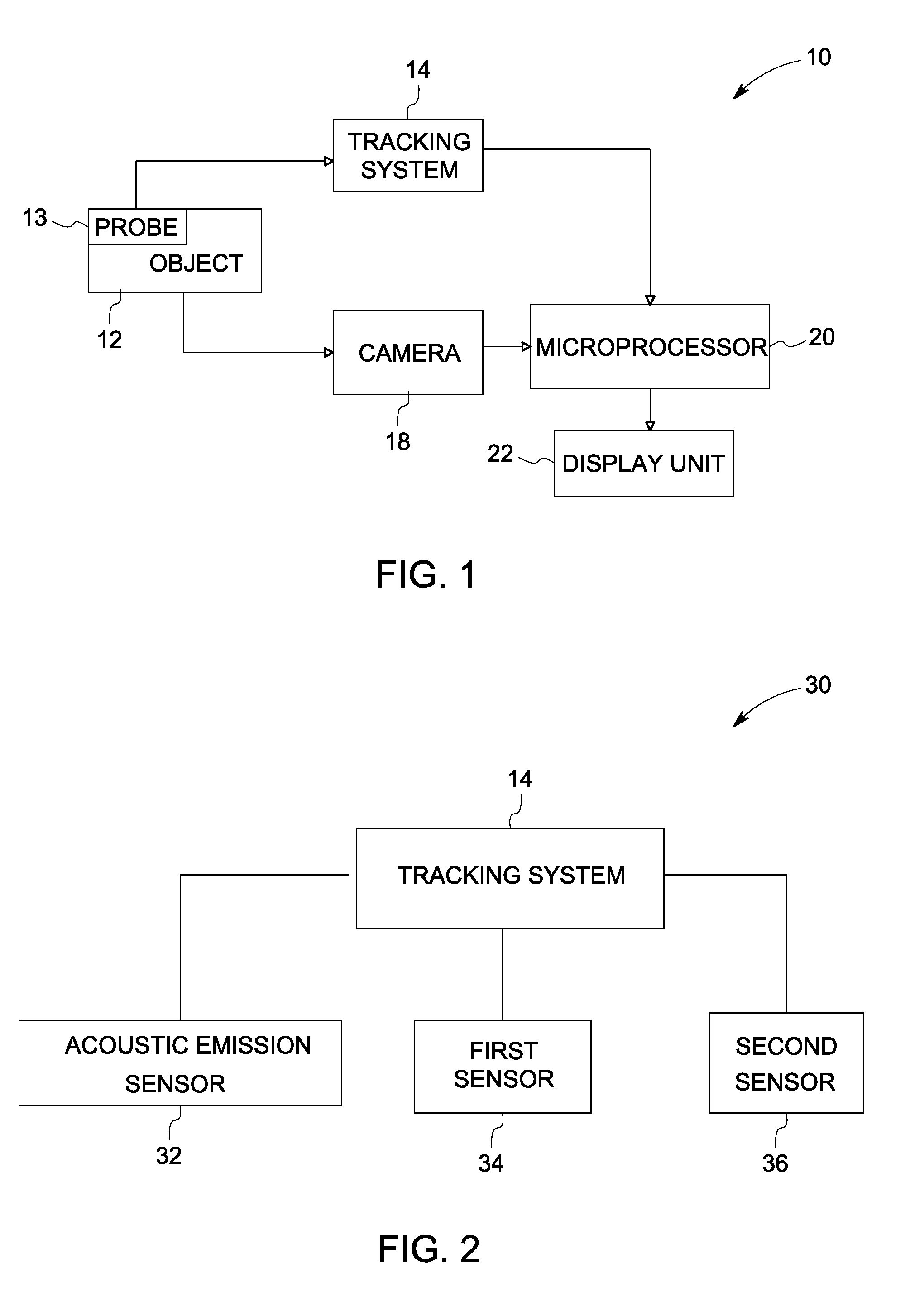
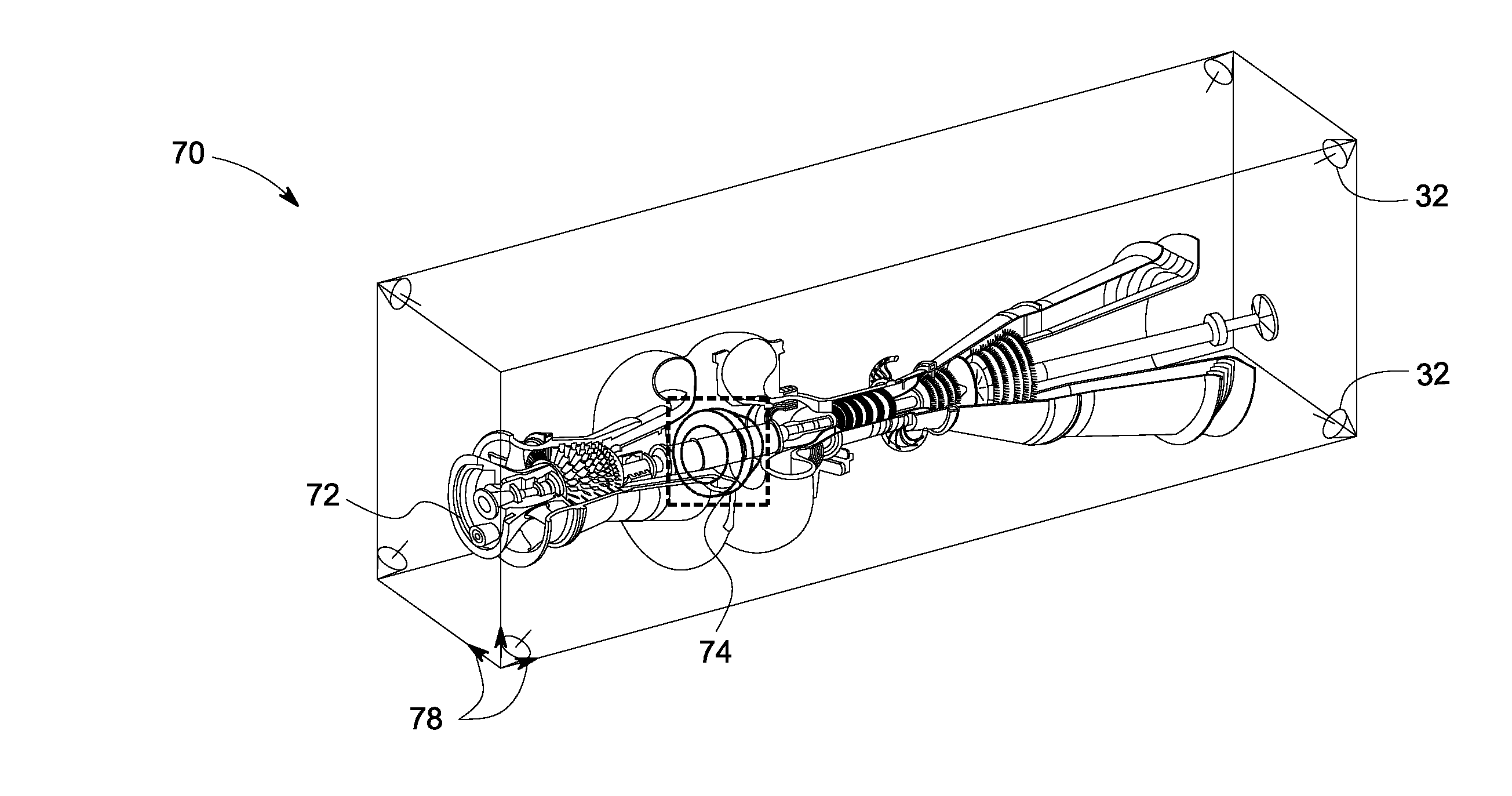
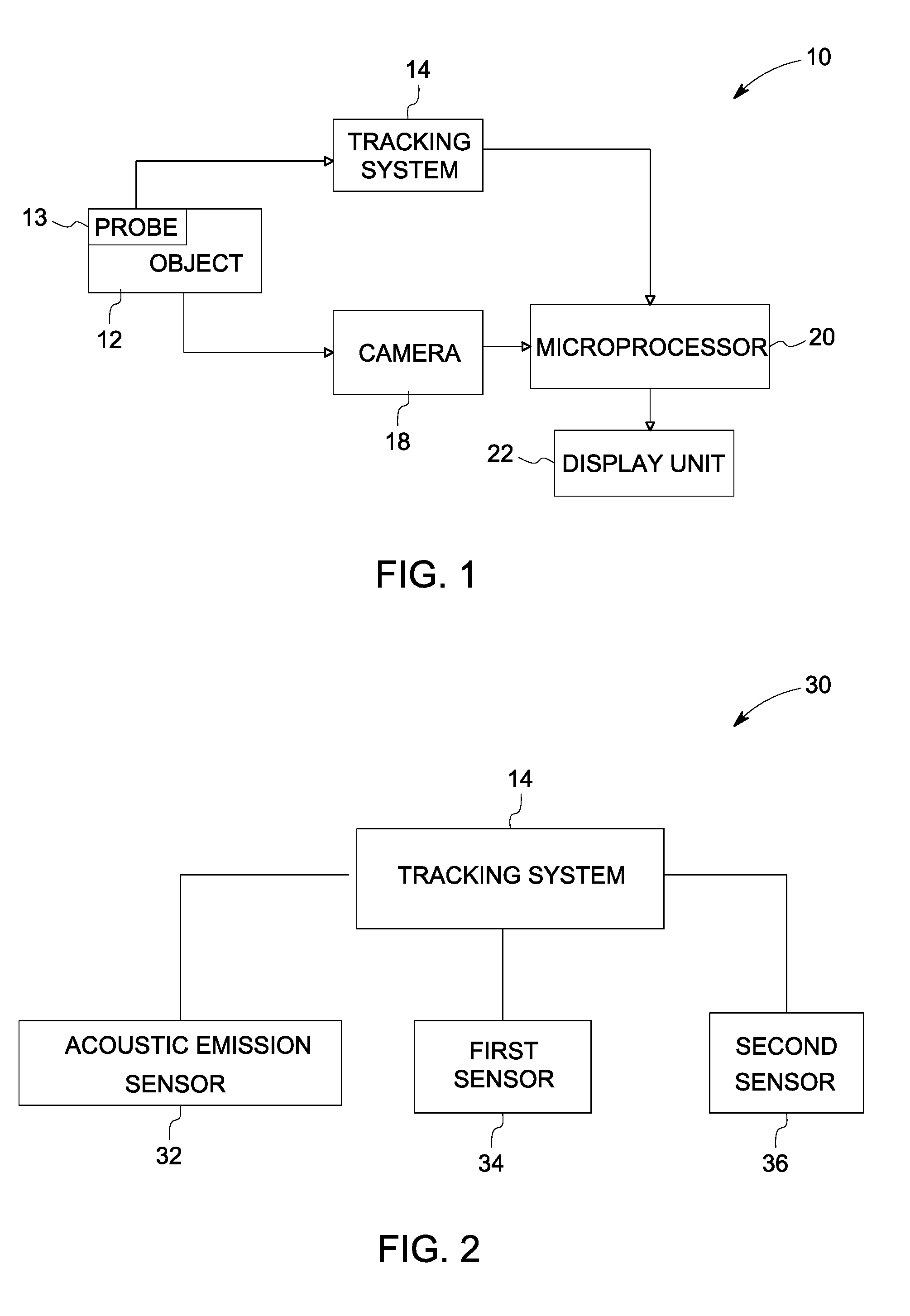
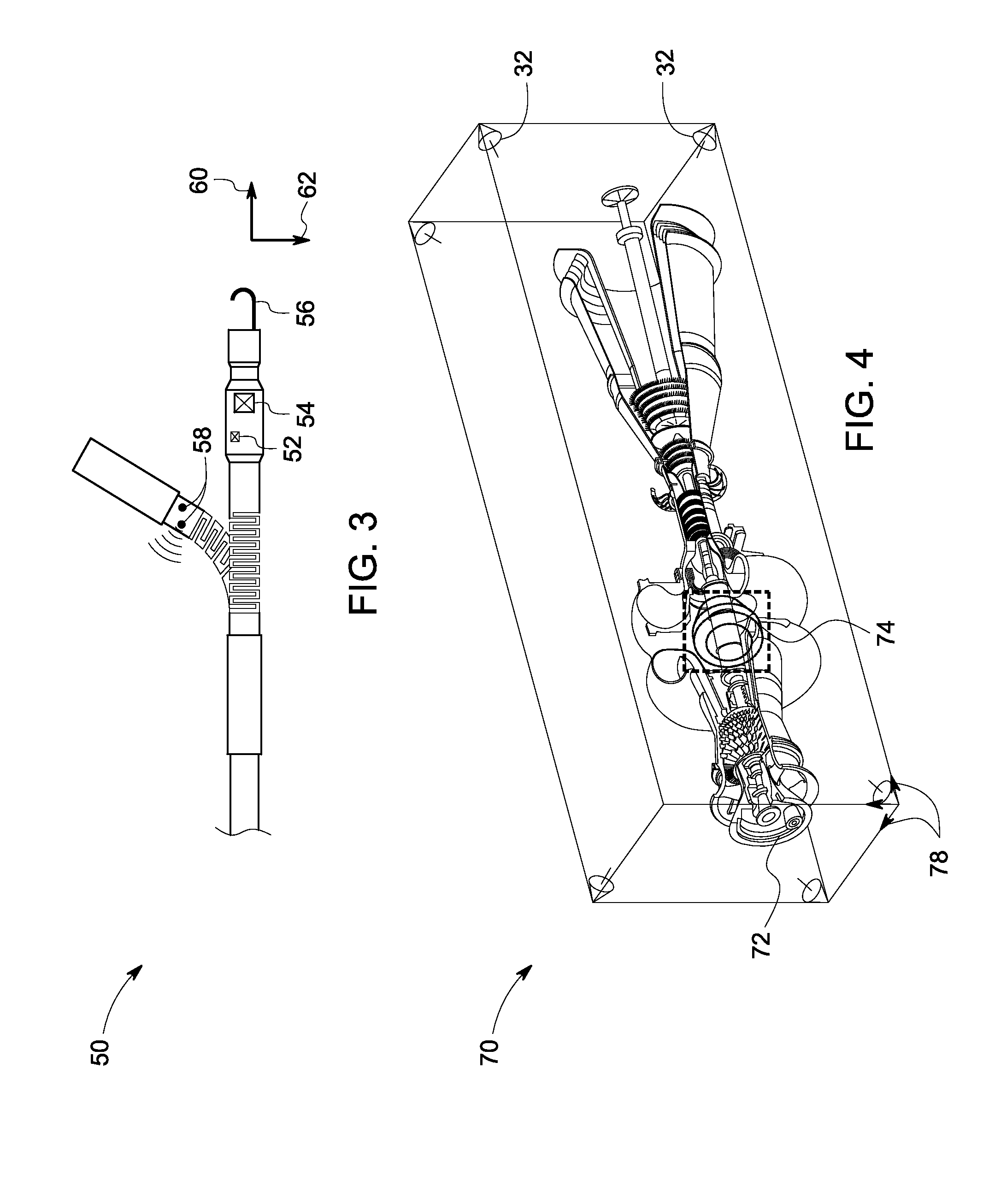
ActiveUS20090154293A1Vibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingObject basedAcoustic emission
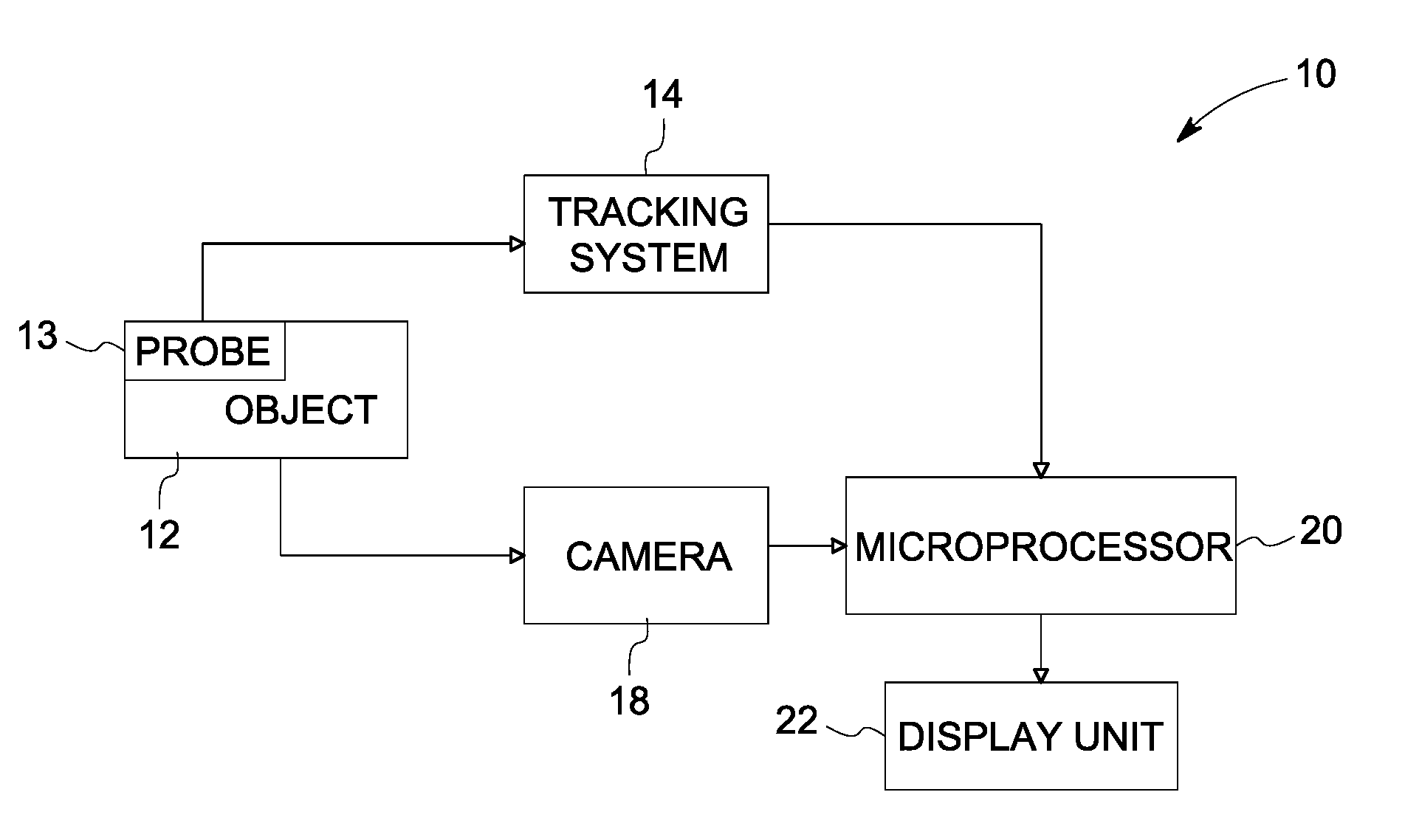
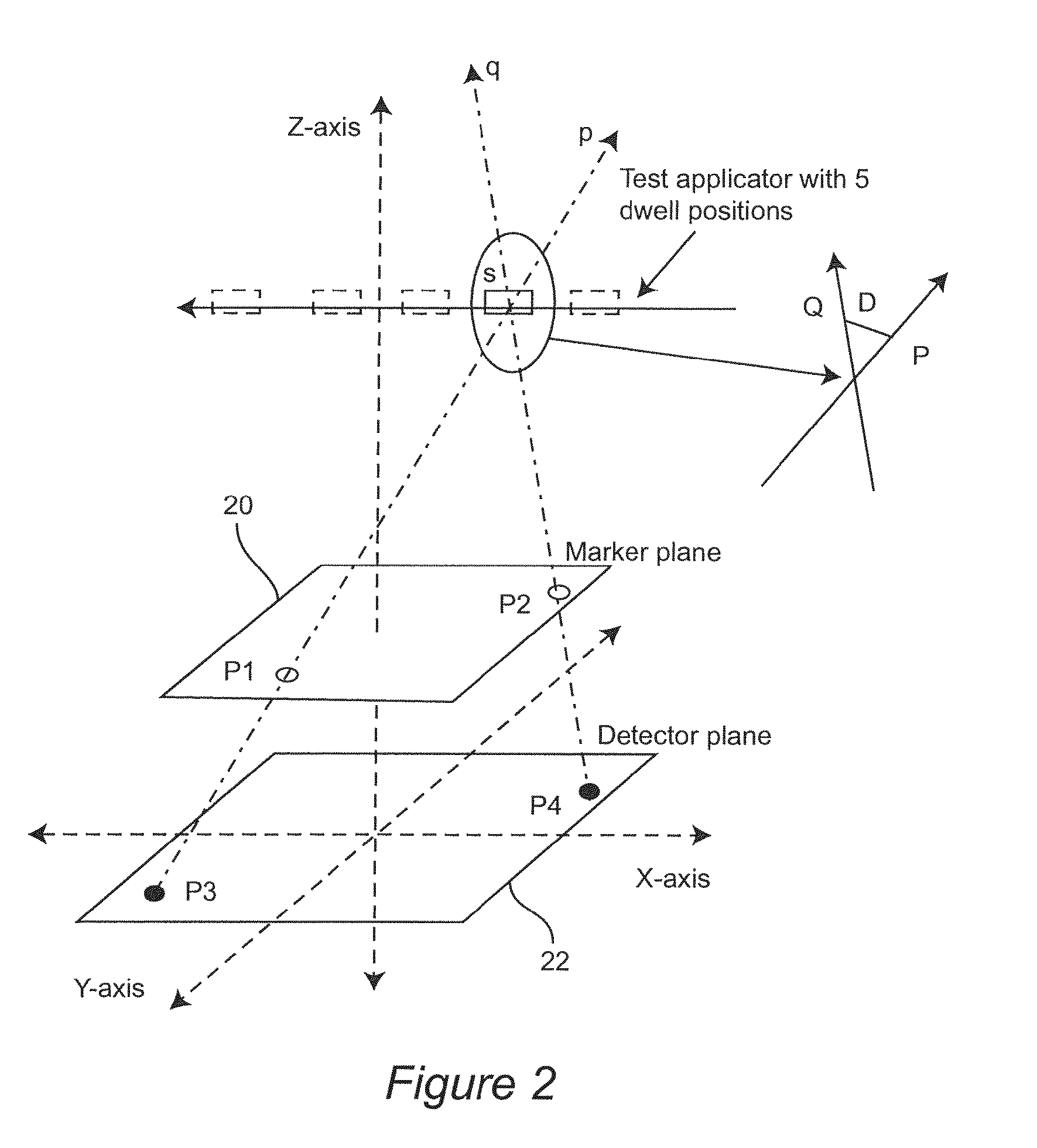
A 3D tracking system is provided. The 3D tracking system includes at least one acoustic emission sensor disposed around an object. The acoustic emission sensor is configured to identify location of a probe inserted into the object based upon time of arrival of an acoustic signature emitted from a location on or near the probe. The 3D tracking system also includes a first sensor configured to detect an elevation of the probe. The 3D tracking system further includes a second sensor configured to detect an azimuth of the probe.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
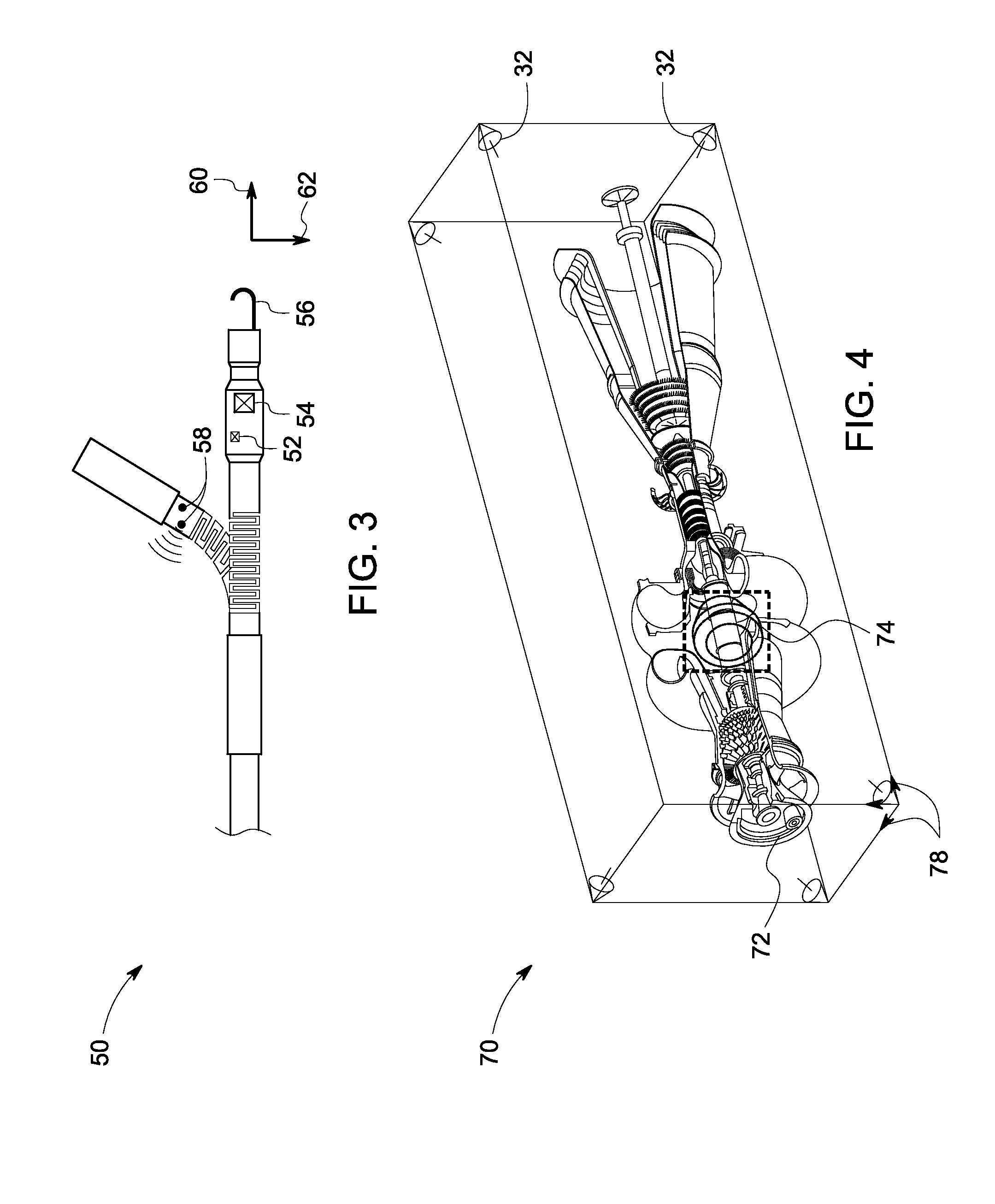
Bracket for mounting at least one position detecting sensor on an ultrasonic probe
A bracket for use on an ultrasound transducer to releasably mount at least one 3D tracking sensor on the transducer. Each sensor has a pair of axially aligned pins projecting outward from its body. The bracket includes at least one socket having a pair of spaced-apart wall portions, each of which includes a slot arranged to receive a respective one of the pins of the sensor when the sensor is in a first position. From this position the sensor's body can be rotated to a second position, whereupon the spaced apart wall portions releasably engage (snap-fit about) a portion of the body of the sensor to deter the accidental displacement of the sensor with respect to the transducer.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
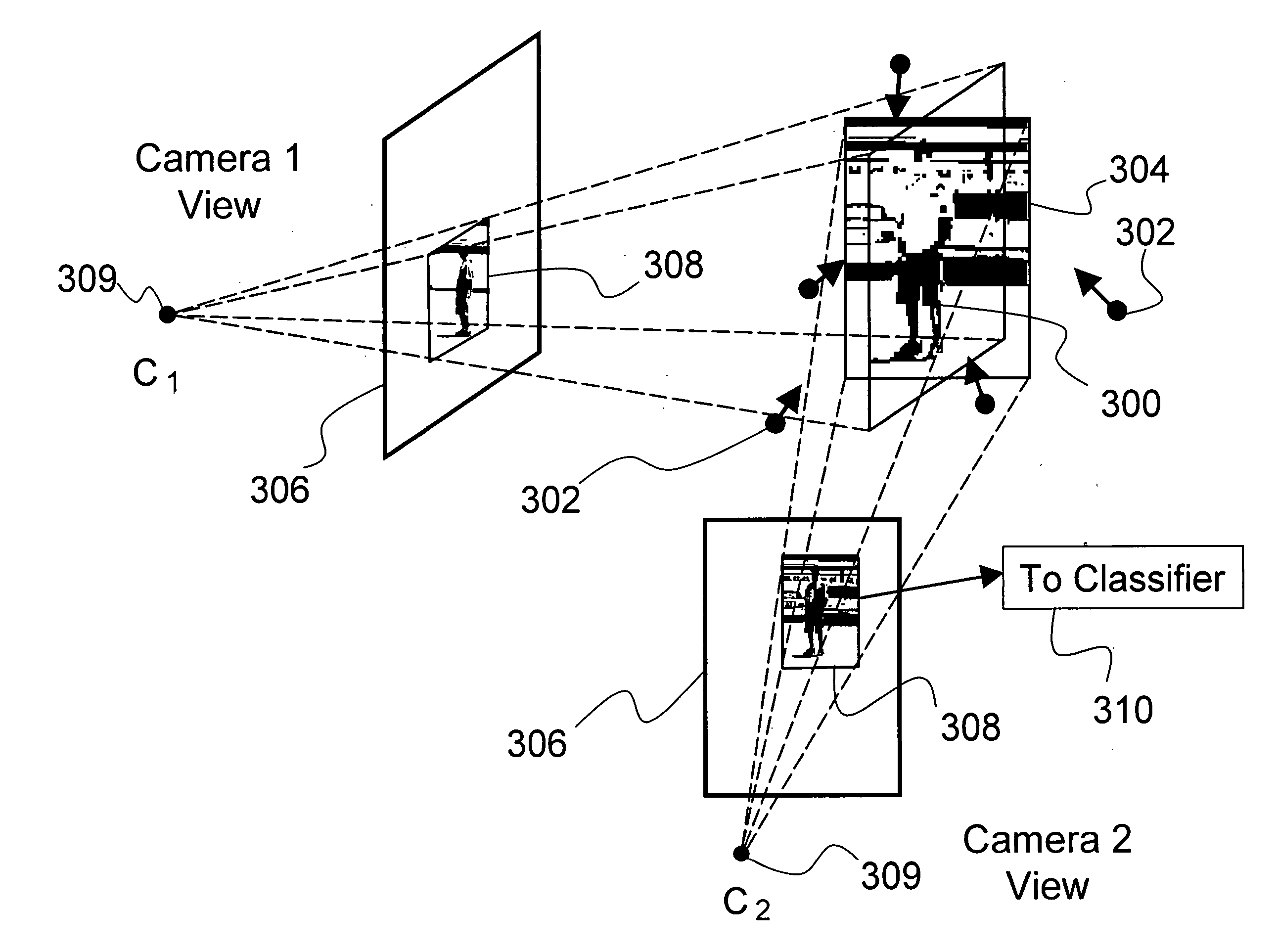
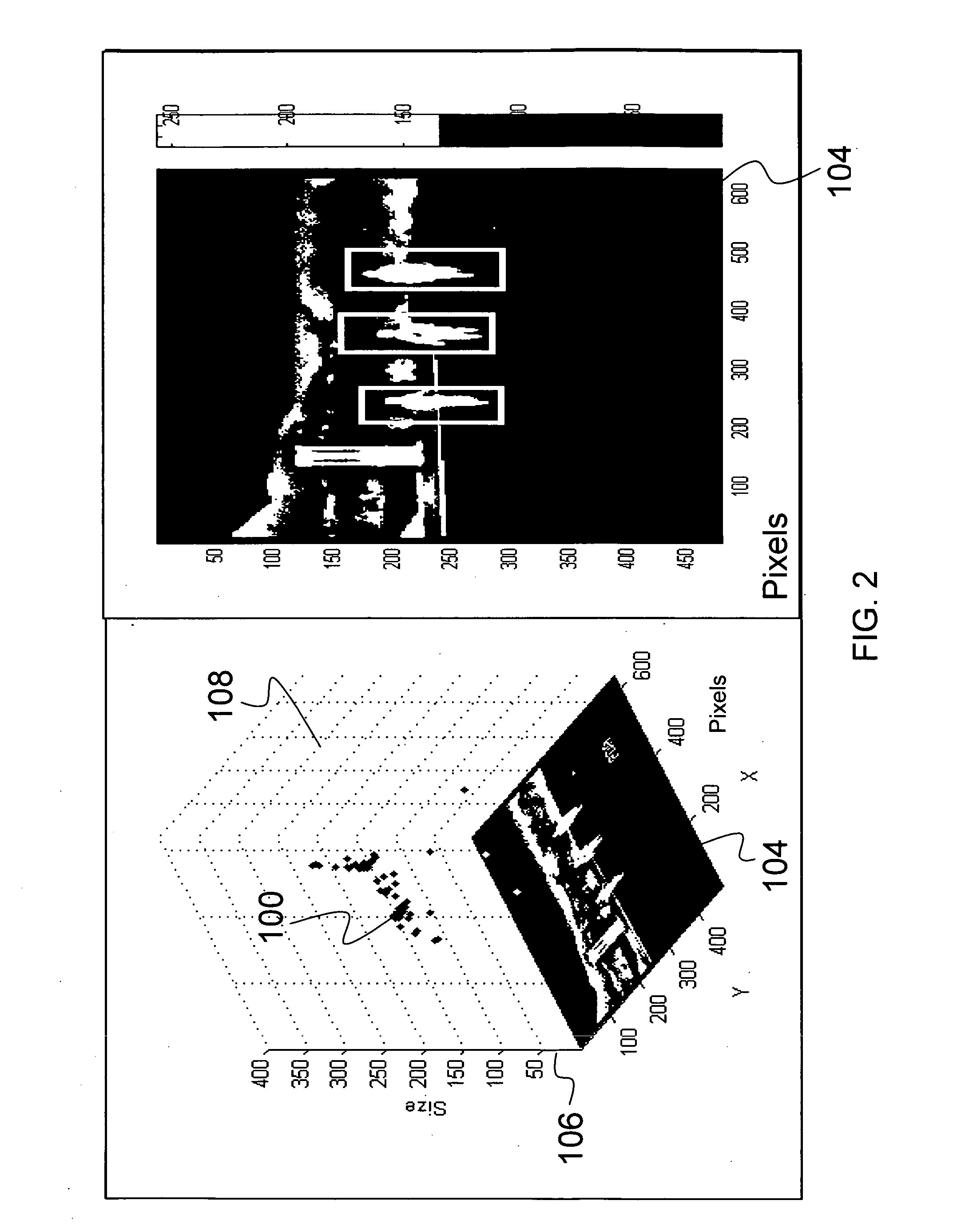
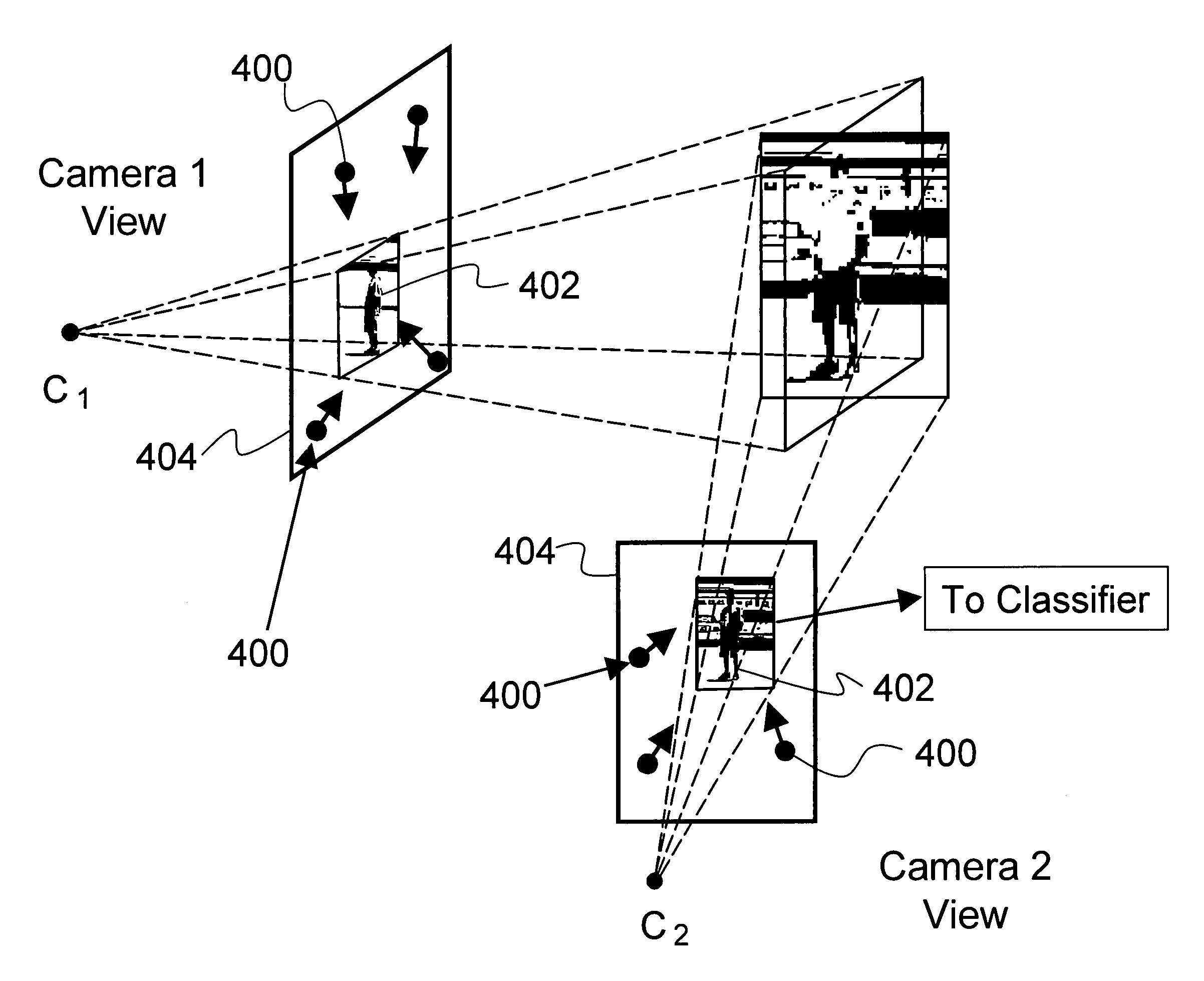
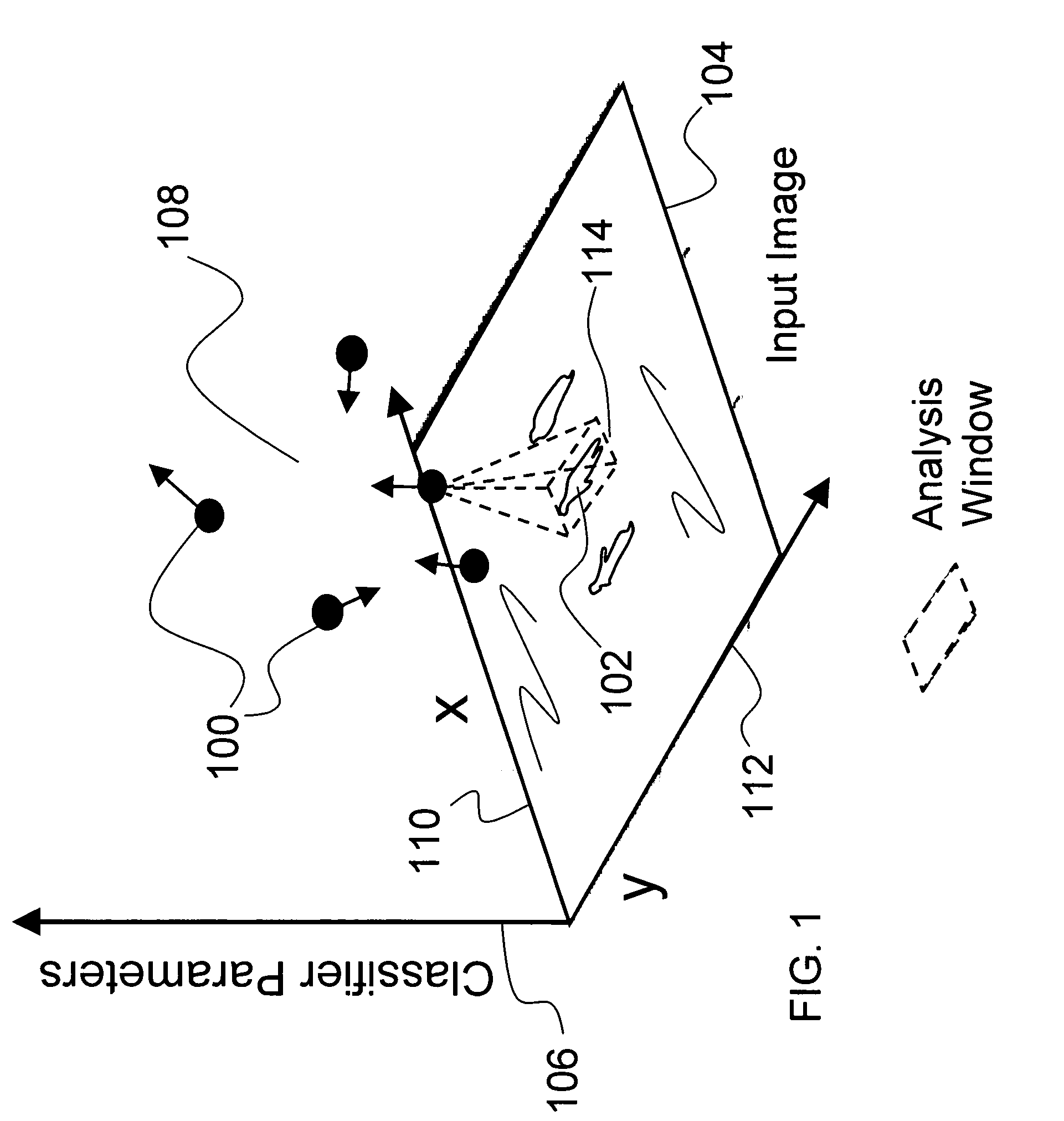
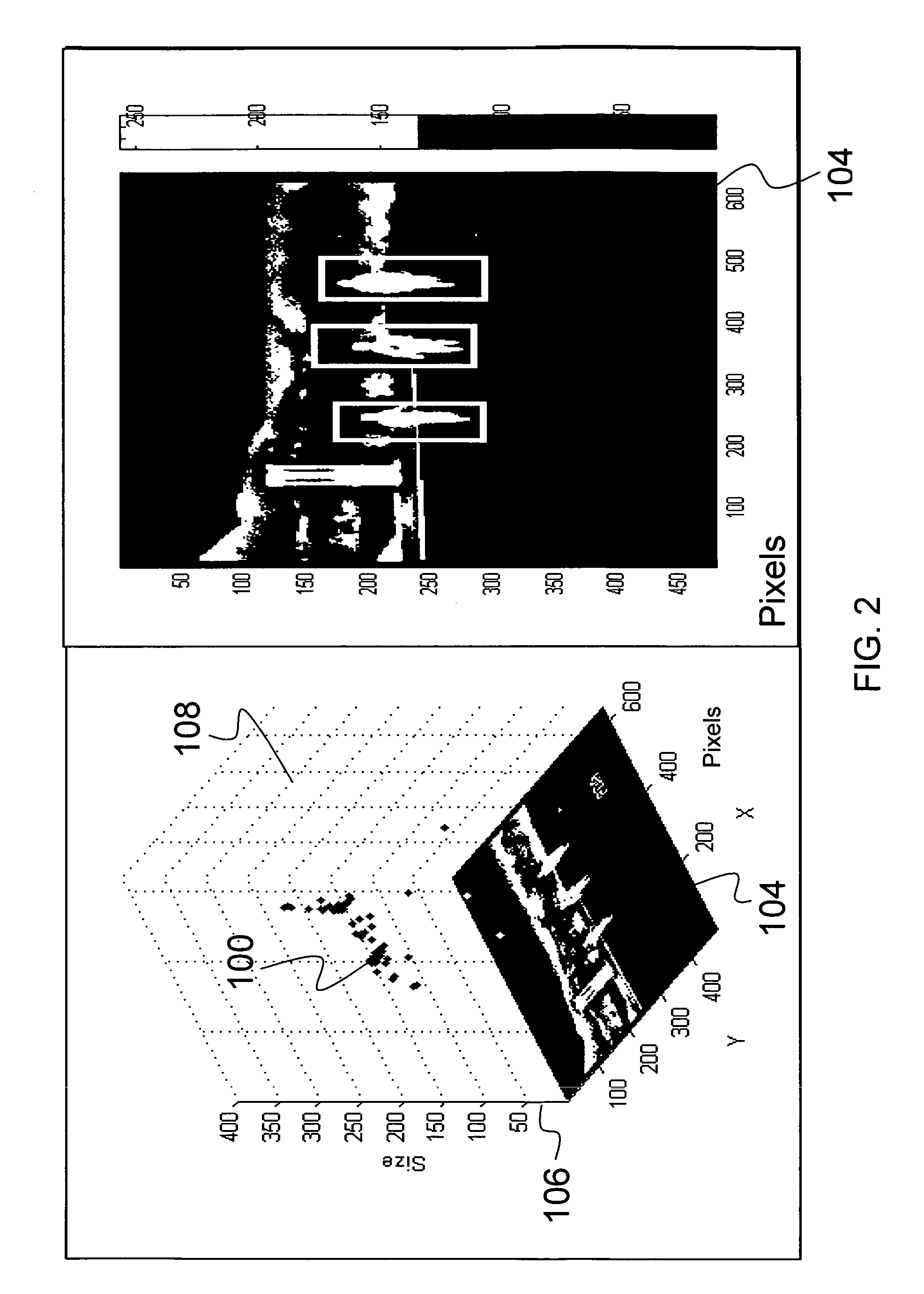
Multi-view cognitive swarm for object recognition and 3D tracking
An object recognition system is described that incorporates swarming classifiers. The swarming classifiers comprise a plurality of software agents configured to operate as a cooperative swarm to classify an object in a domain as seen from multiple view points. Each agent is a complete classifier and is assigned an initial velocity vector to explore a solution space for object solutions. Each agent is configured to perform an iteration, the iteration being a search in the solution space for a potential solution optima where each agent keeps track of its coordinates in multi-dimensional space that are associated with an observed best solution (pbest) that the agent has identified, and a global best solution (gbest) where the gbest is used to store the best location among all agents. Each velocity vector changes towards pbest and gbest, allowing the cooperative swarm to concentrate on the vicinity of the object and classify the object.
Owner:HRL LAB
Multi-view cognitive swarm for object recognition and 3D tracking
An object recognition system is described that incorporates swarming classifiers. The swarming classifiers comprise a plurality of software agents configured to operate as a cooperative swarm to classify an object in a domain as seen from multiple view points. Each agent is a complete classifier and is assigned an initial velocity vector to explore a solution space for object solutions. Each agent is configured to perform an iteration, the iteration being a search in the solution space for a potential solution optima where each agent keeps track of its coordinates in multi-dimensional space that are associated with an observed best solution (pbest) that the agent has identified, and a global best solution (gbest) where the gbest is used to store the best location among all agents. Each velocity vector changes towards pbest and gbest, allowing the cooperative swarm to concentrate on the vicinity of the object and classify the object.
Owner:HRL LAB
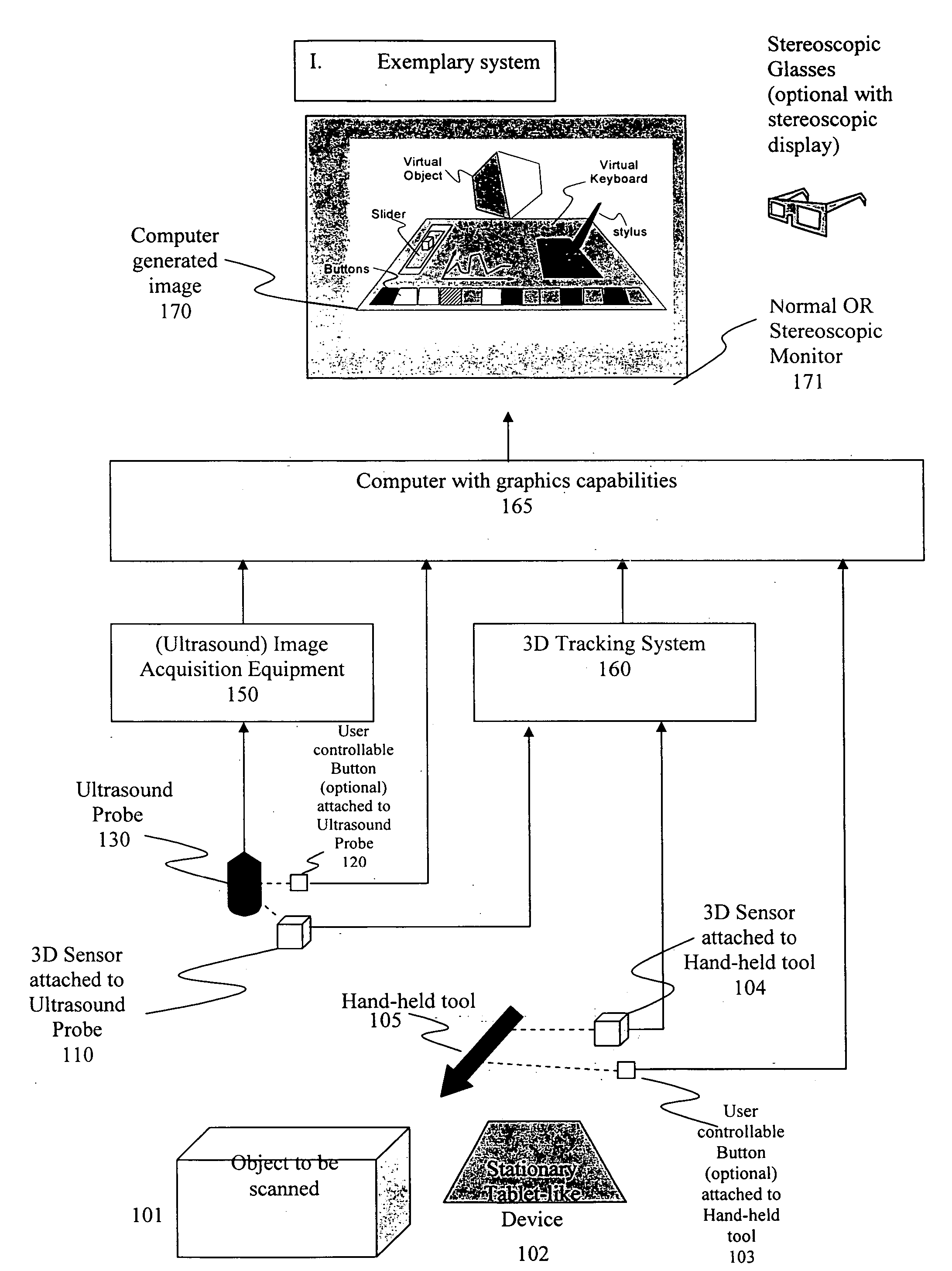
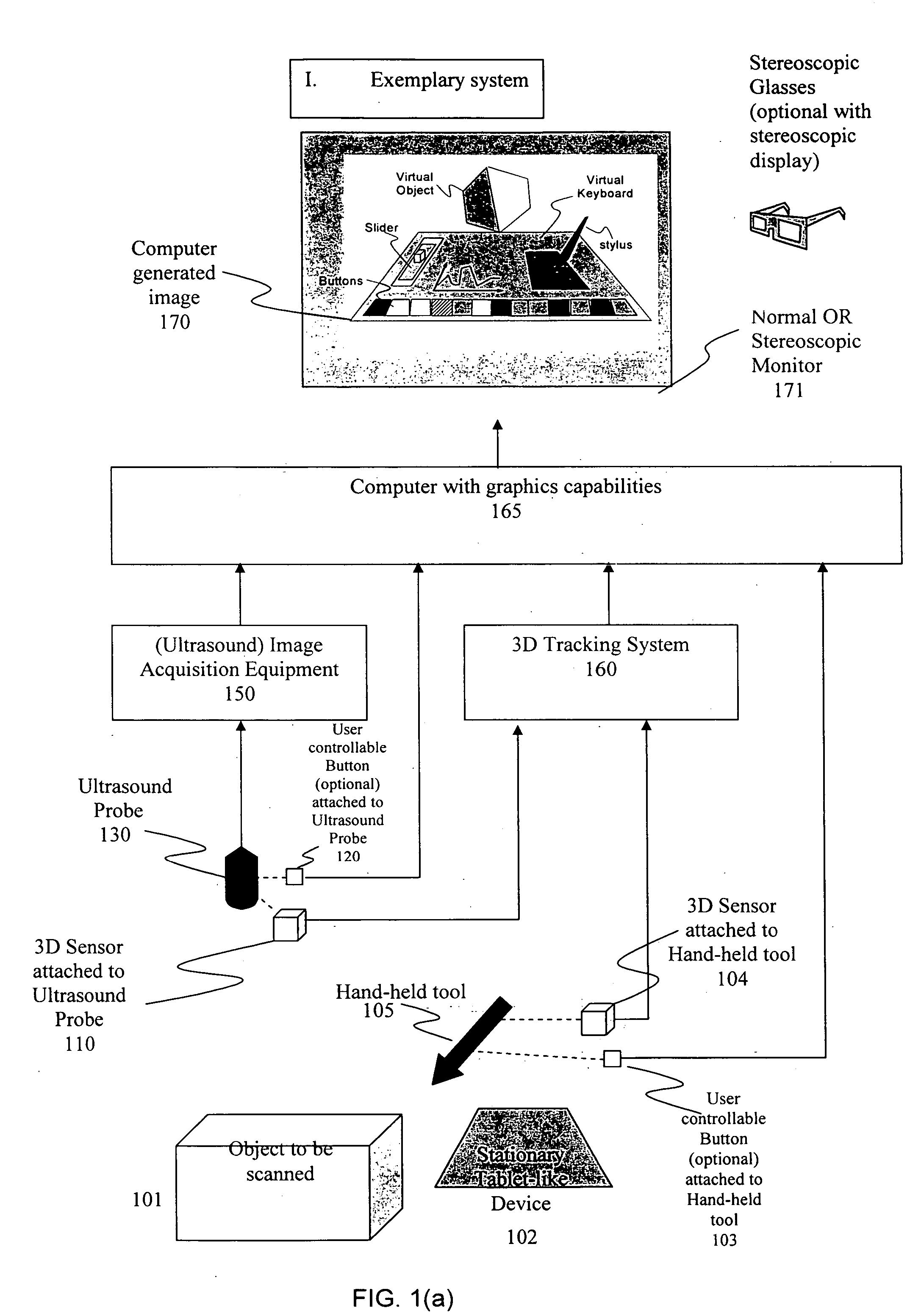
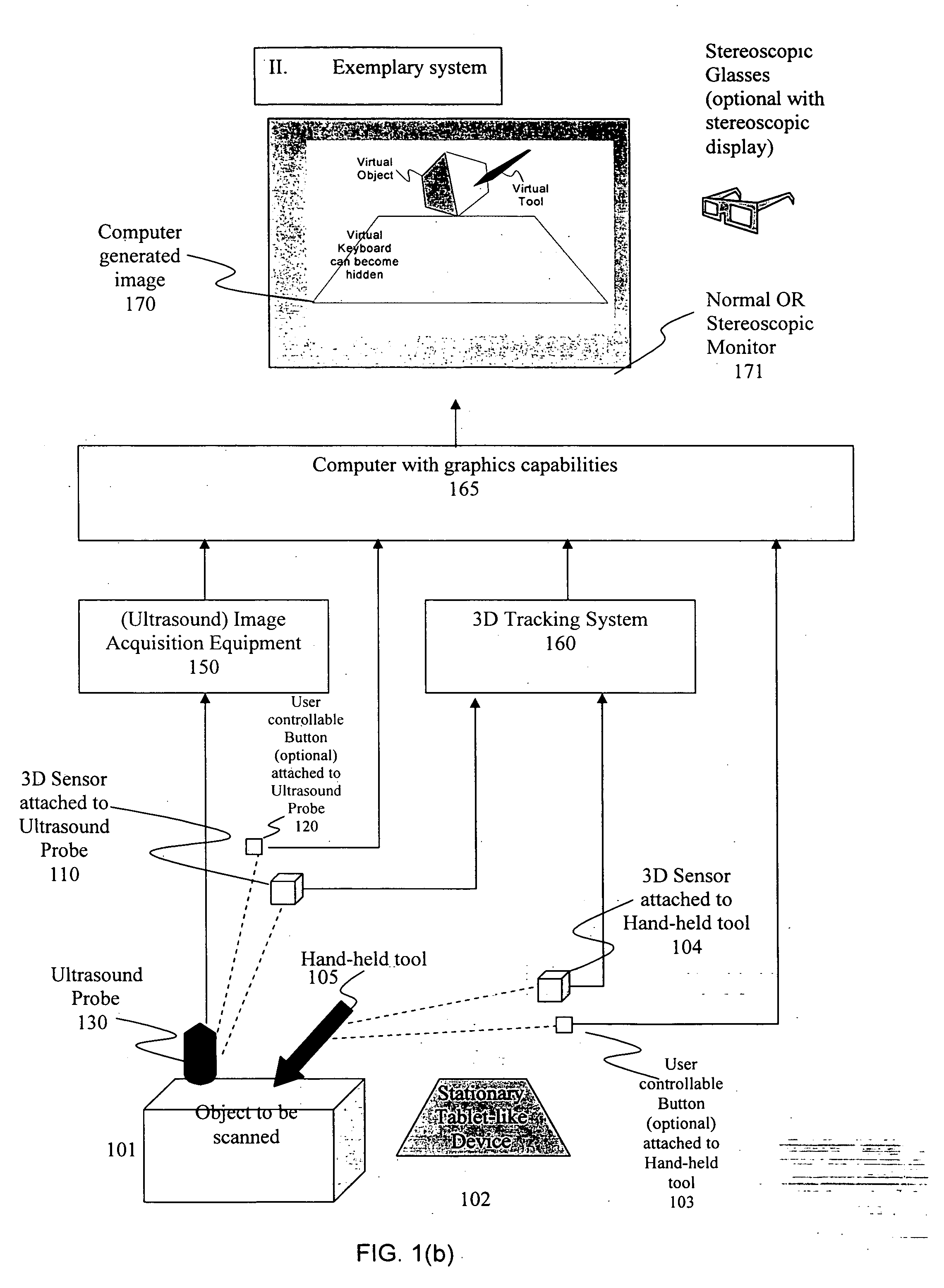
System and method for a virtual interface for ultrasound scanners
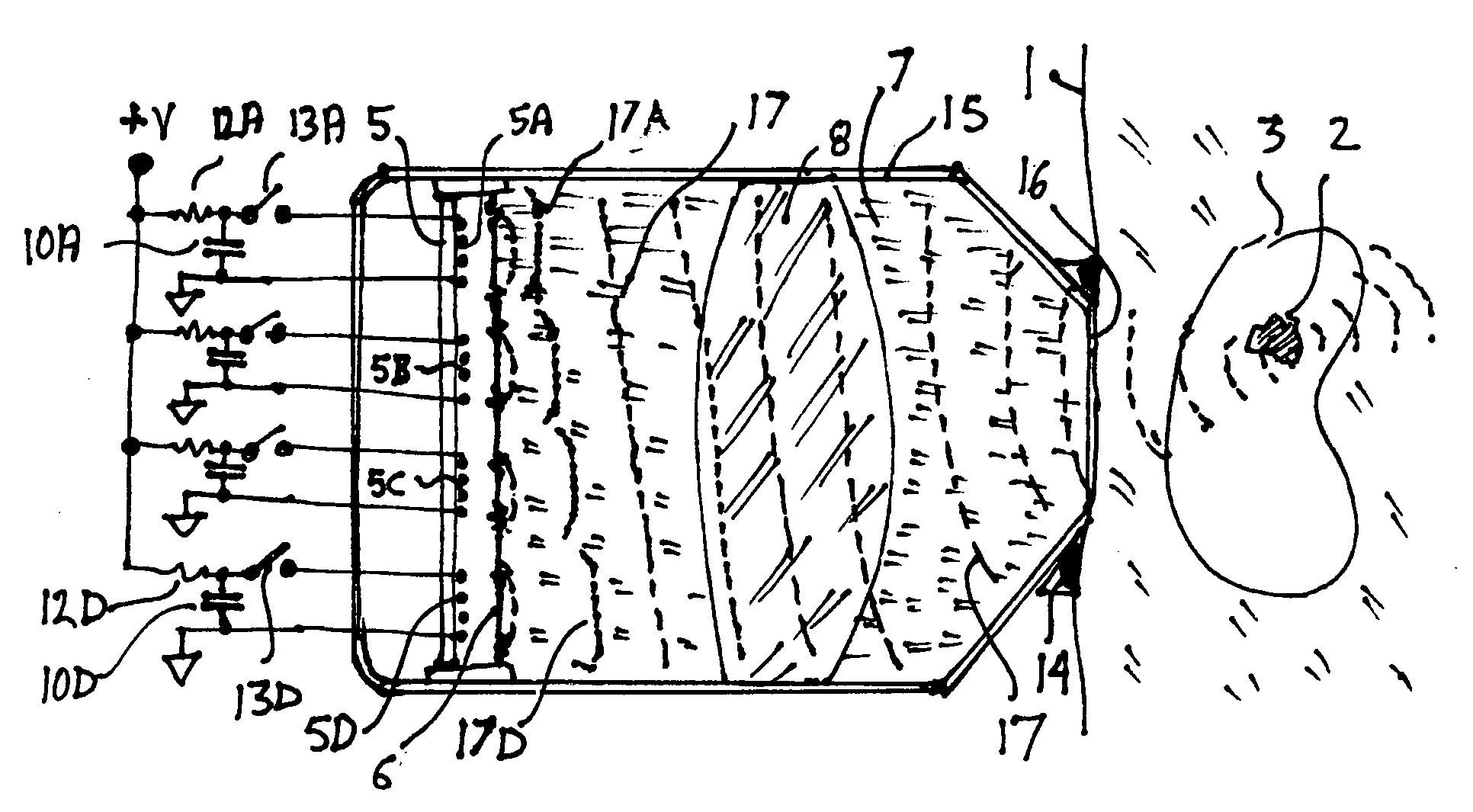
A virtual control system for substantially real-time imaging machines, such as, for example, ultrasound, is presented. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a virtual control system comprises a physical interface communicably connected to a scanner / imager, such as, for example, an ultrasound machine. The scanner / imager has, or is communicably connected to, a processor that controls the display of, and user interaction with, a virtual control interface. In operation, a user can interact with the virtual control interface by physically interacting with the physical interface. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention the physical interface can comprise a handheld tool and a stationary tablet-like device. In exemplary embodiments according to the present invention the control system can further include a 3D tracking device that can track both an ultrasound probe as well as a handheld physical interface tool. In such exemplary embodiments a user can control scan and display functions of the ultrasound machine by moving a handheld tool relative to the stationary tablet, and can perform 3D interactive display and image processing operations on a displayed 3D image by manipulating the handheld tool within a defined 3D space. Alternatively, all control functions, those associated with scan and display control as well as those associated with 3D interactive display and image processing can be mapped to manipulations of the handheld tool in a defined 3D space.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Using a moving imaging system to monitor anatomical position as a function of time
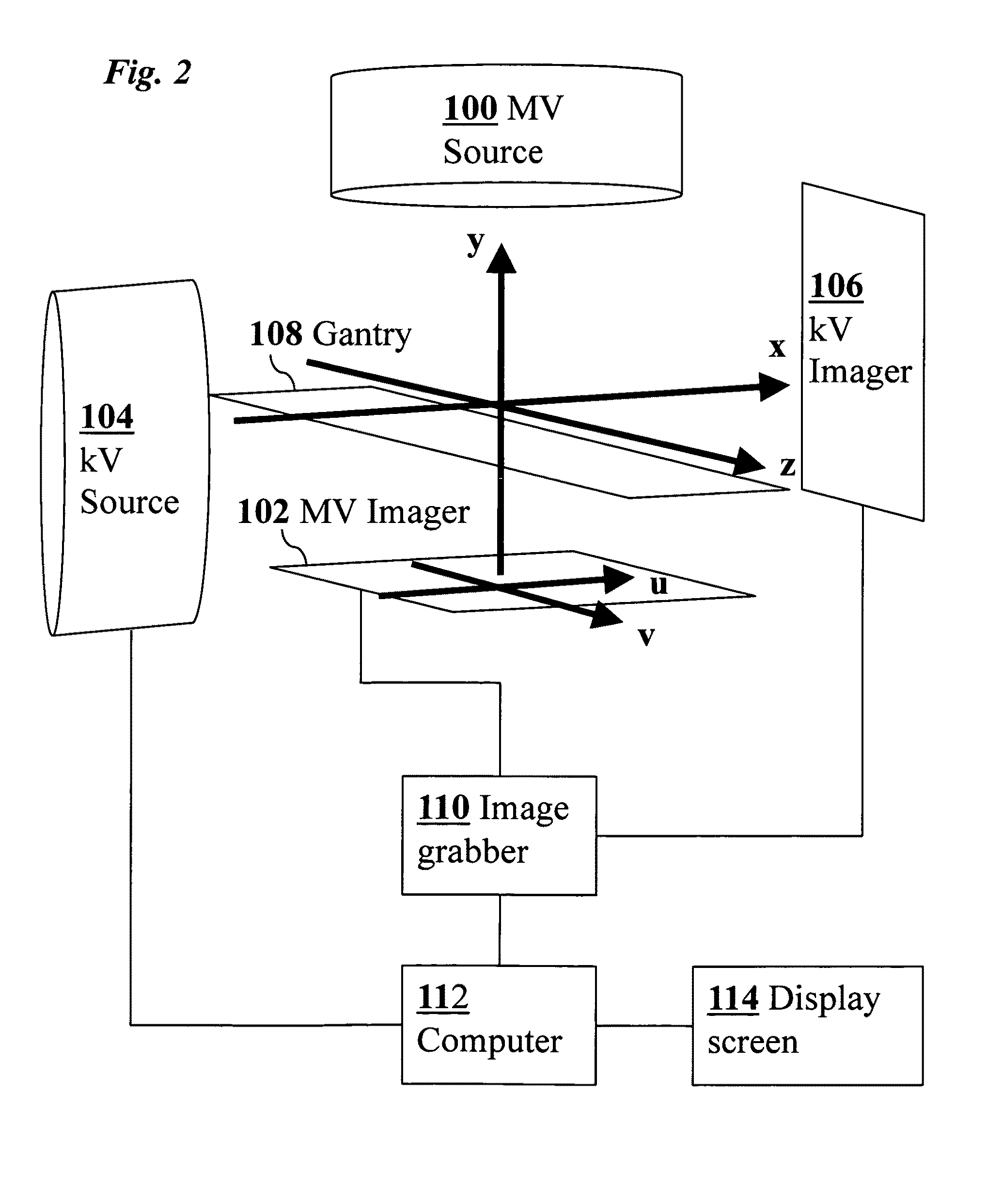
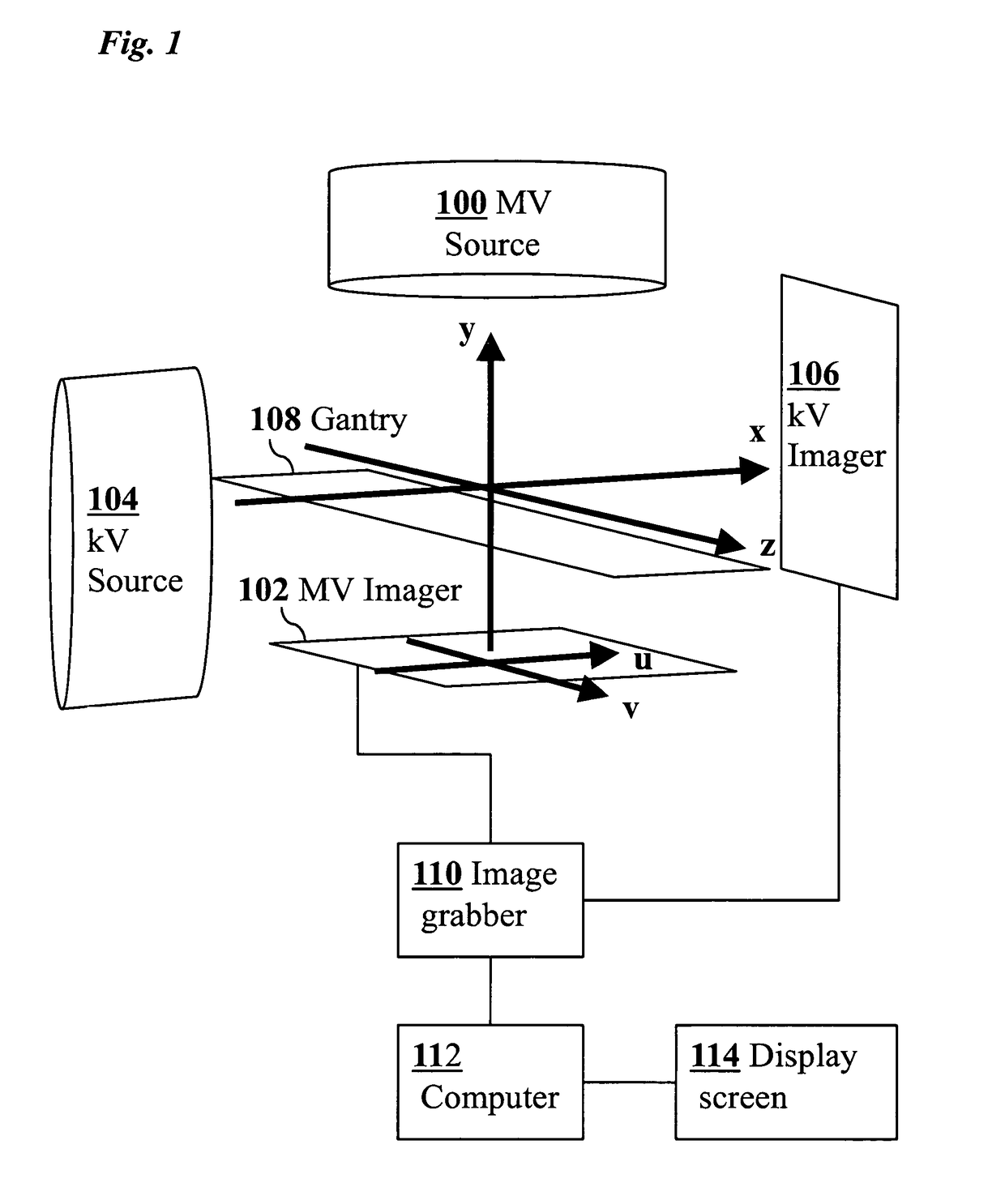
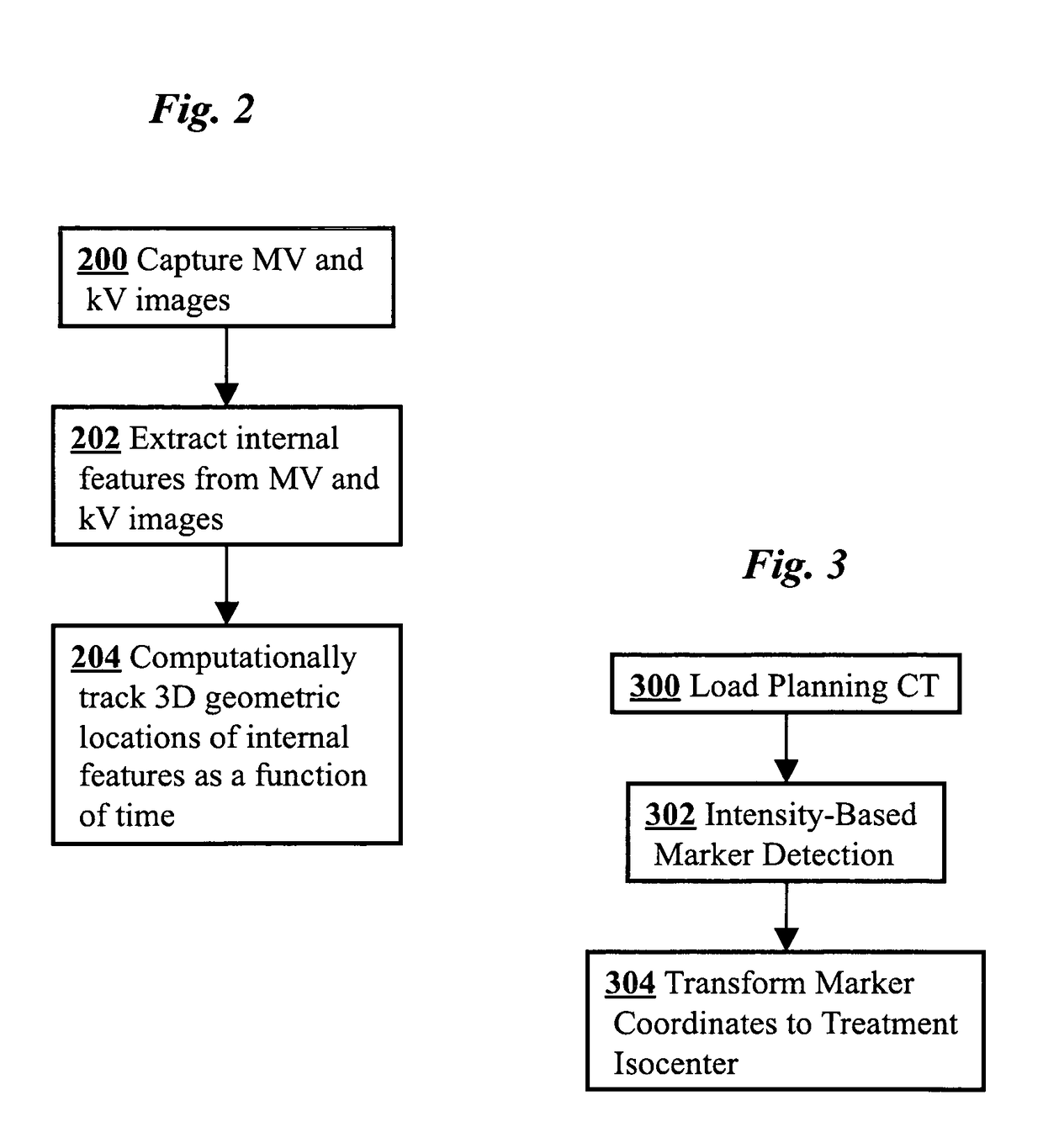
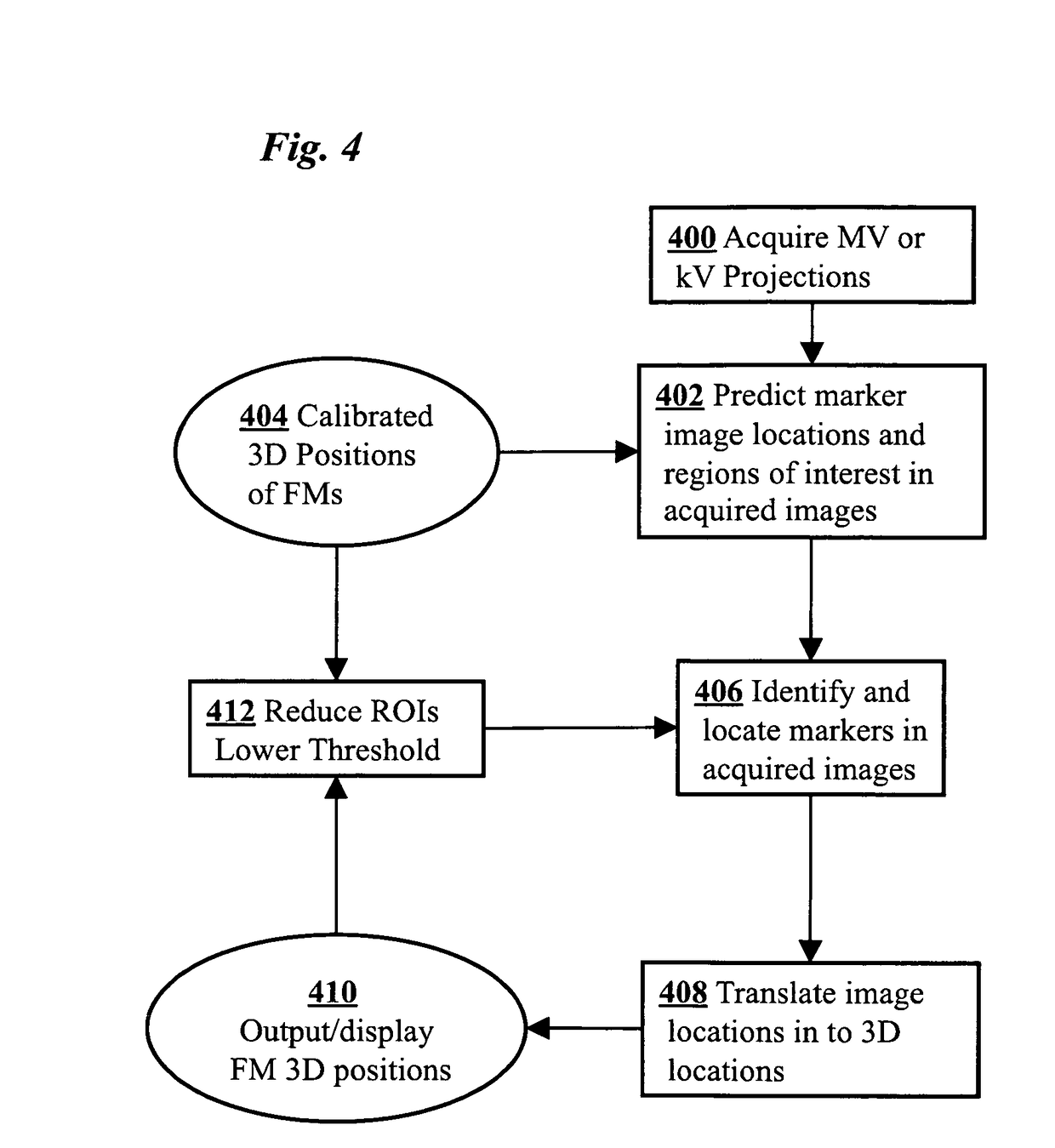
InactiveUS20100316259A1Increase doseReduce adverse effectsImage enhancementImage analysis3d trackingRadiation therapy
Real-time 3D tracking of anatomical positions during radiation therapy uses acquired image data from an MV treatment beam as it is rotated around the patient during arc radiotherapy treatment. The acquired image data and associated angular positions are computationally combined during the arc radiotherapy treatment to estimate in real time 3D positions of anatomical features of the patient, e.g., combining present image data and prior image data at earlier times. Supplementary image data from a kV imaging system may be acquired on an as-needed basis if MV position estimates indicate movement exceeding a predetermined threshold, and the supplementary kV image data combined with the acquired MV image data to improve an accuracy of the estimated 3D positions.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
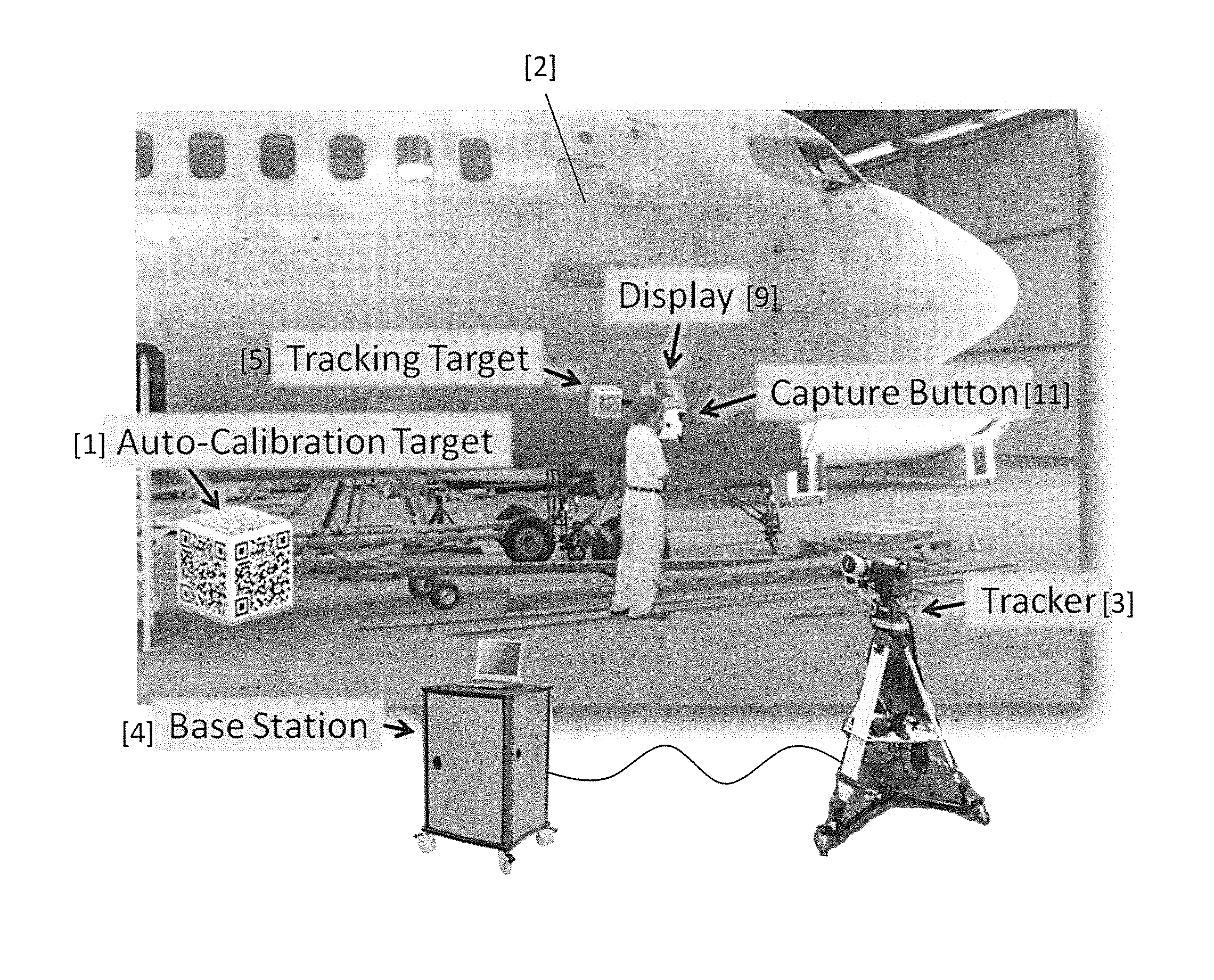
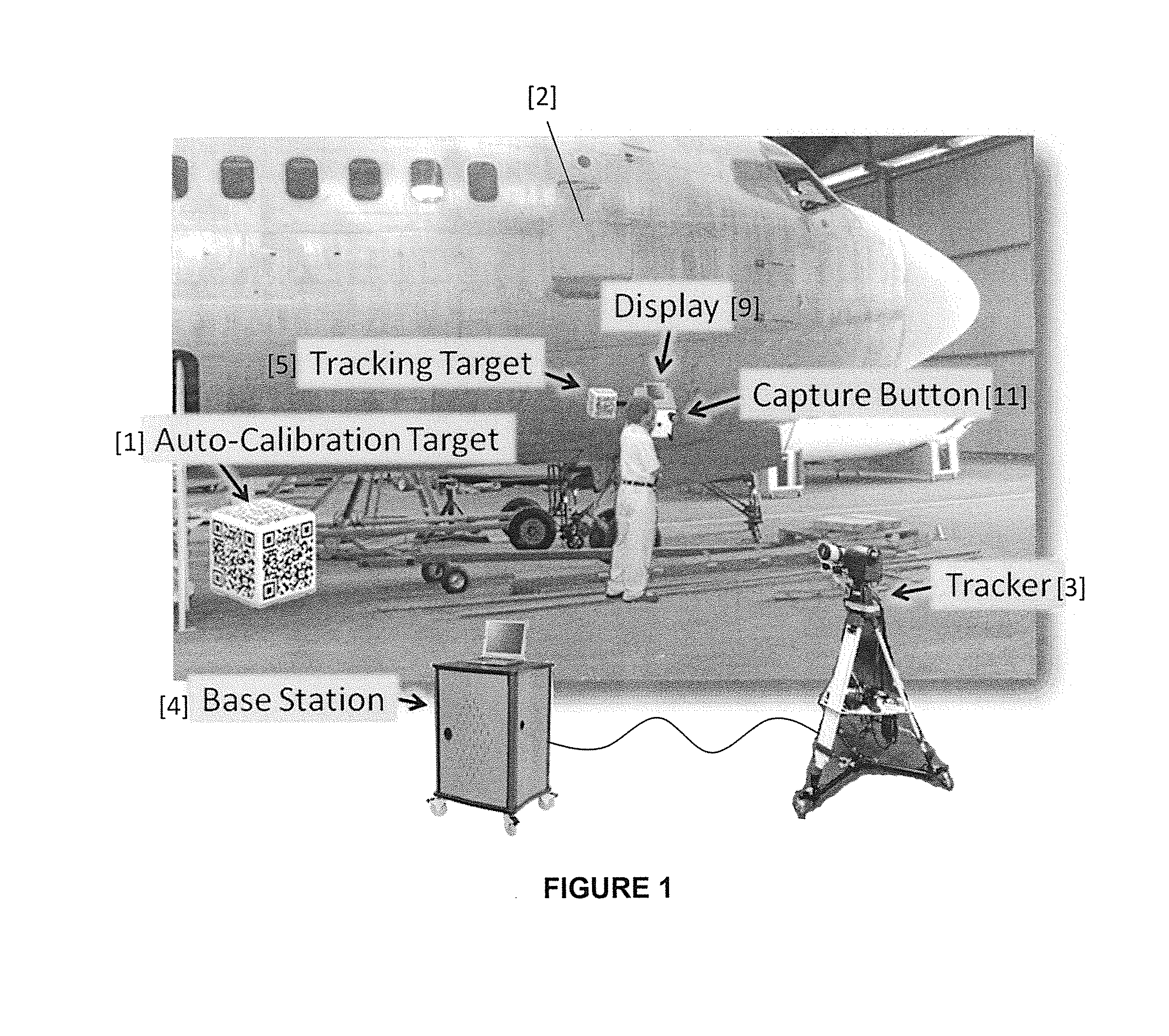
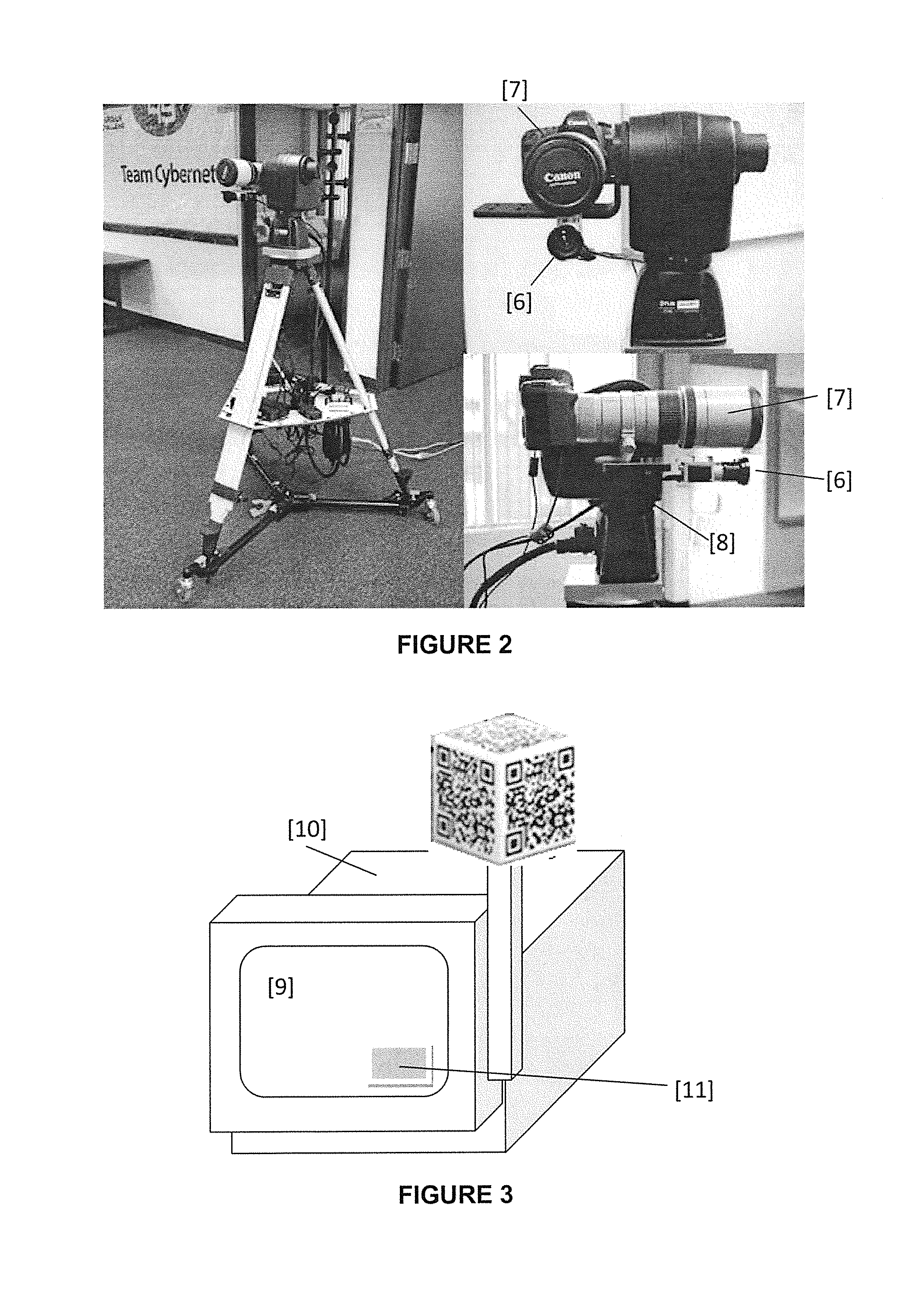
Method and apparatus for camera-based 3D flaw tracking system
Systems and methods facilitate long-range, accurate fiducial tracking using a mixture of pan-tilt and camera devices enabling generalized 3D tracking of fiducials with the automatic mapping of flaw data to component models within standard CAD packages. The invention is suitable to many various tracking applications, particularly large inspection sites such as aircraft surfaces which require vast coverage with a medium-degree of accuracy. A method of surface inspection comprises the steps of moving a fiducial target over a surface under inspection, and tracking the fiducial as it is moved by capturing and storing the coordinates of the fiducial in a database for subsequent retrieval. Machine vision is used to acquire surface inspection data associated with the coordinates of the fiducial as it is moved. The inspection data is integrated into a CAD model, enabling the use of finite element analysis (FEA) to determine or predict flaw and material behavior over time.
Owner:CYBERNET SYST
System and method for augmented reality inspection and data visualization
A 3D tracking system is provided. The 3D tracking system includes at least one acoustic emission sensor disposed around an object. The acoustic emission sensor is configured to identify location of a probe inserted into the object based upon time of arrival of an acoustic signature emitted from a location on or near the probe. The 3D tracking system also includes a first sensor configured to detect an elevation of the probe. The 3D tracking system further includes a second sensor configured to detect an azimuth of the probe.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE TECH INT LLC
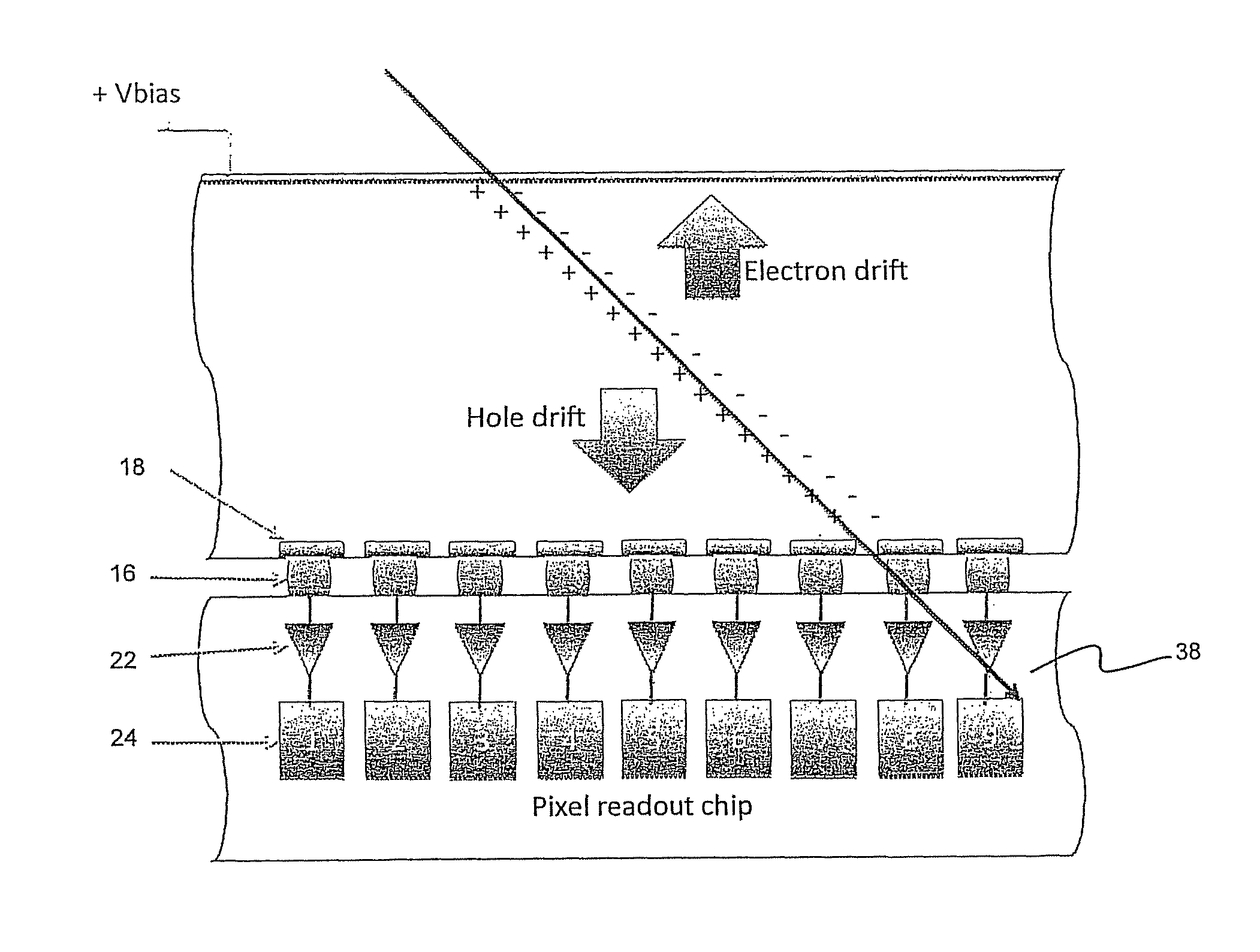
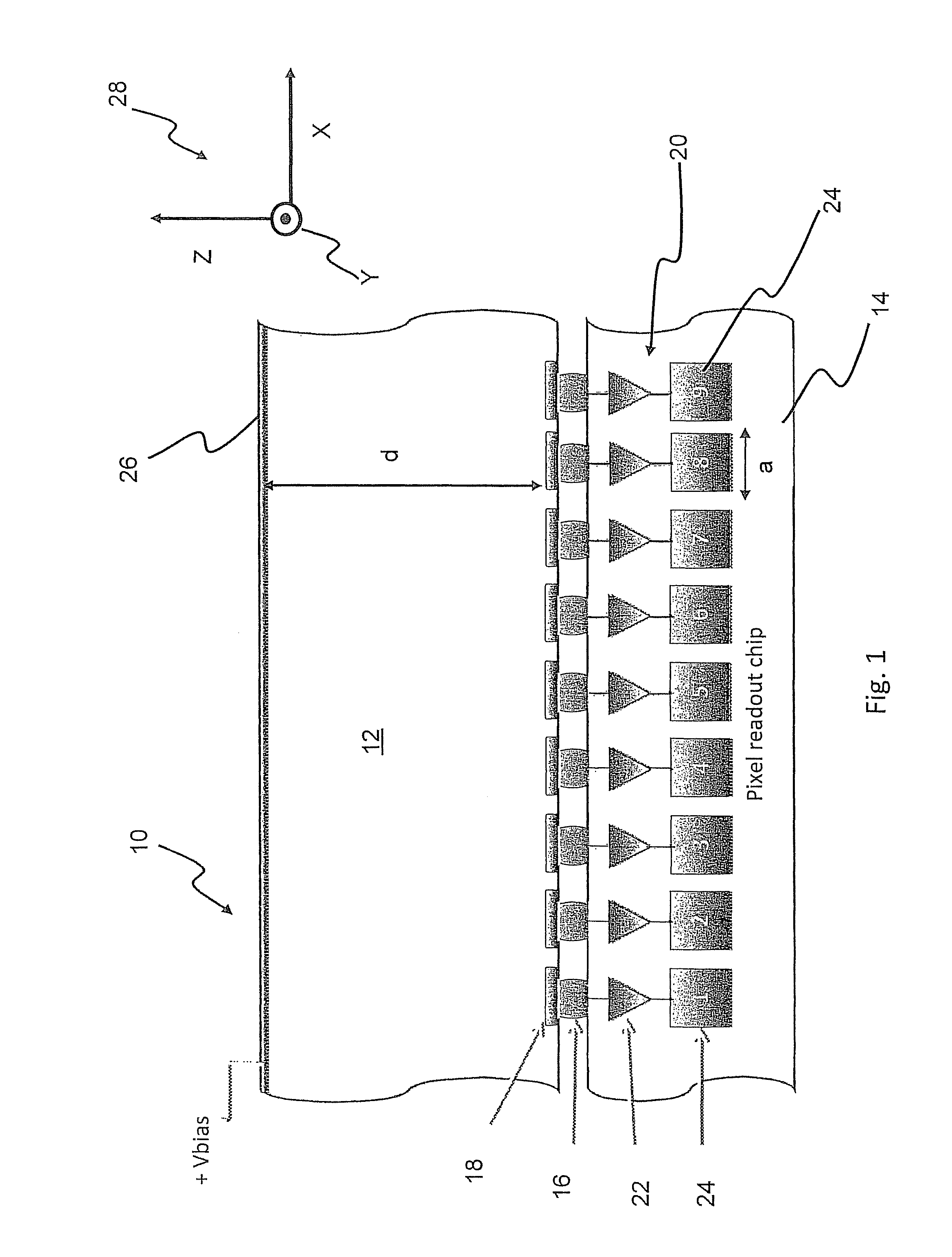
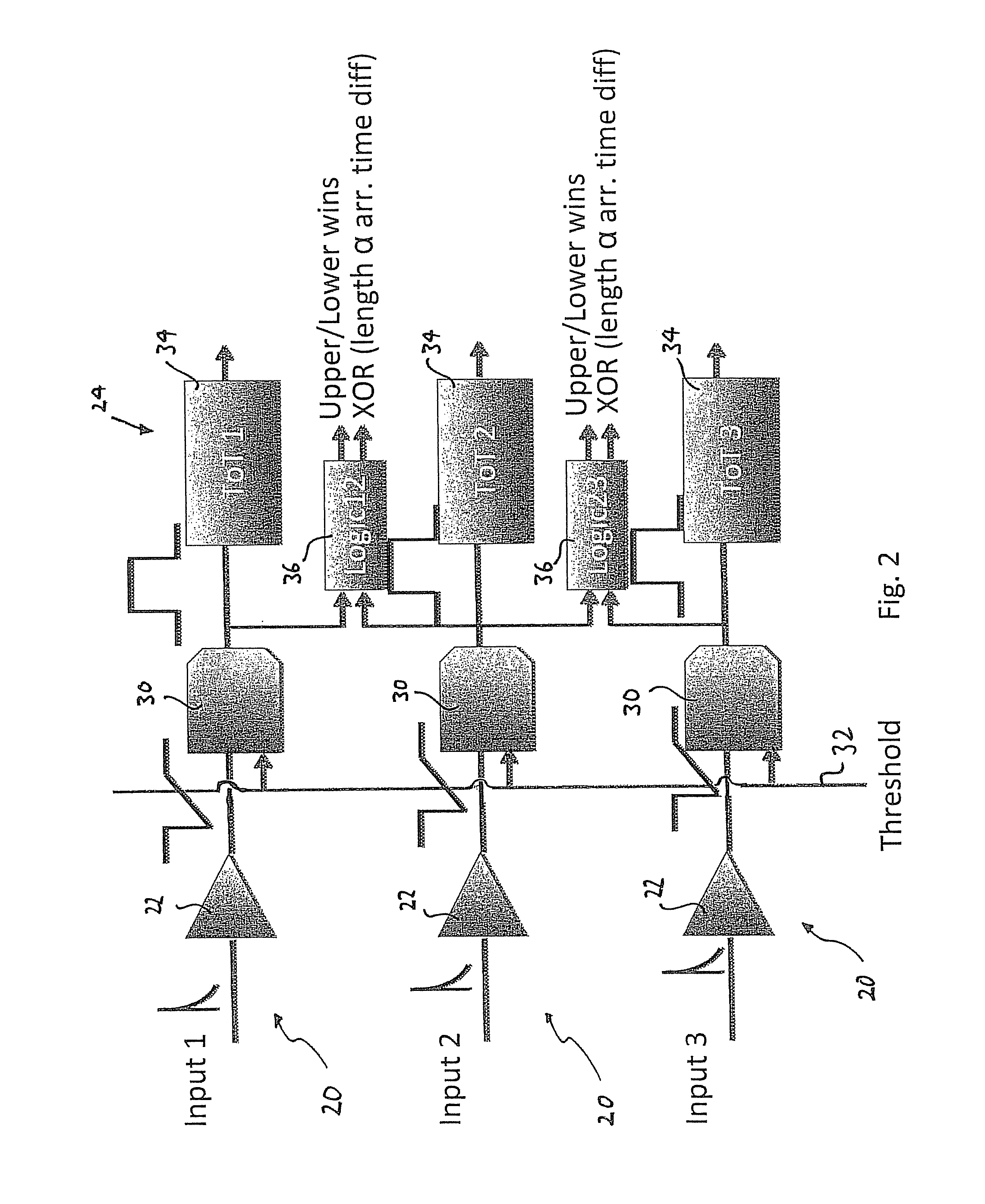
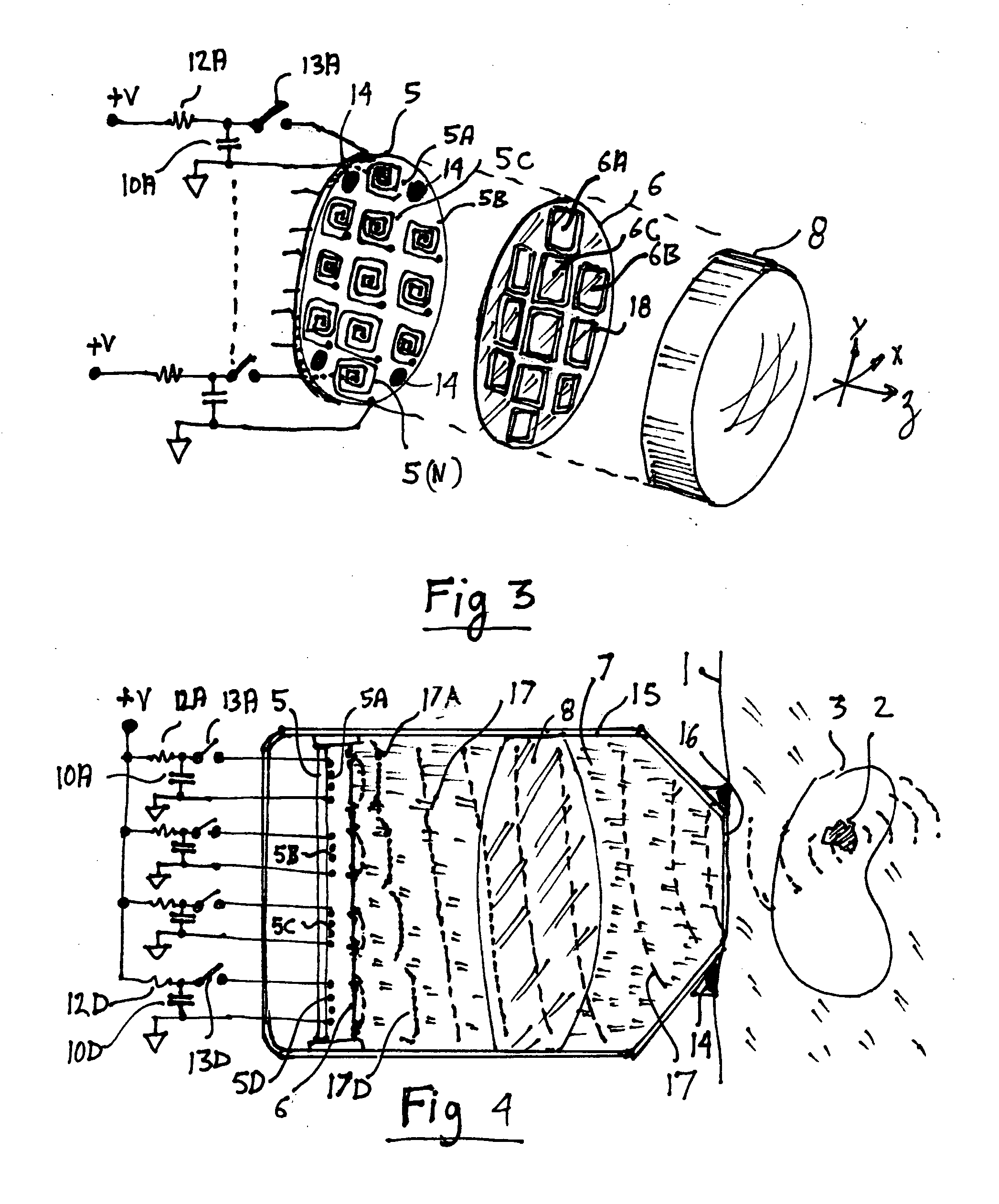
Single layer 3D tracking semiconductor detector
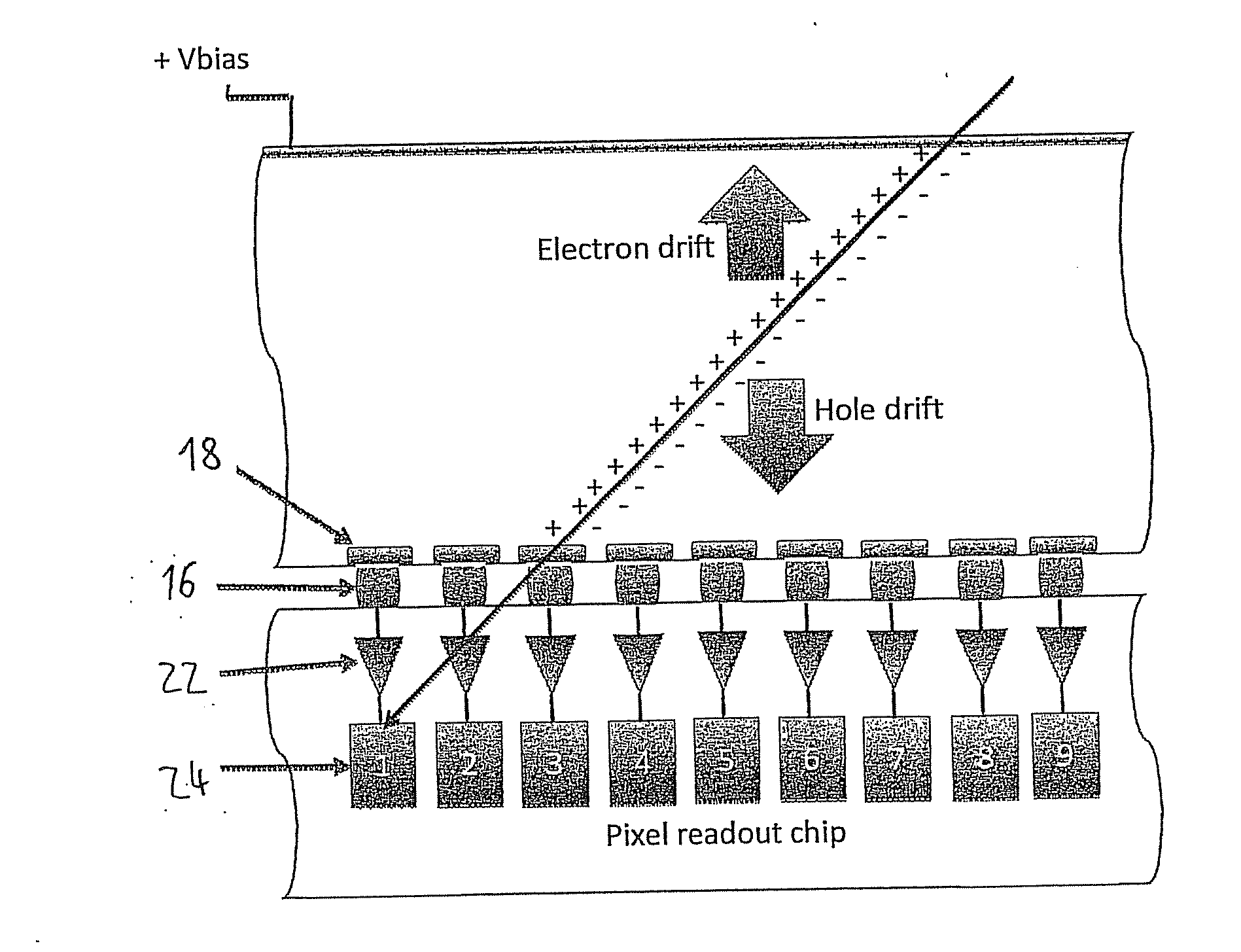
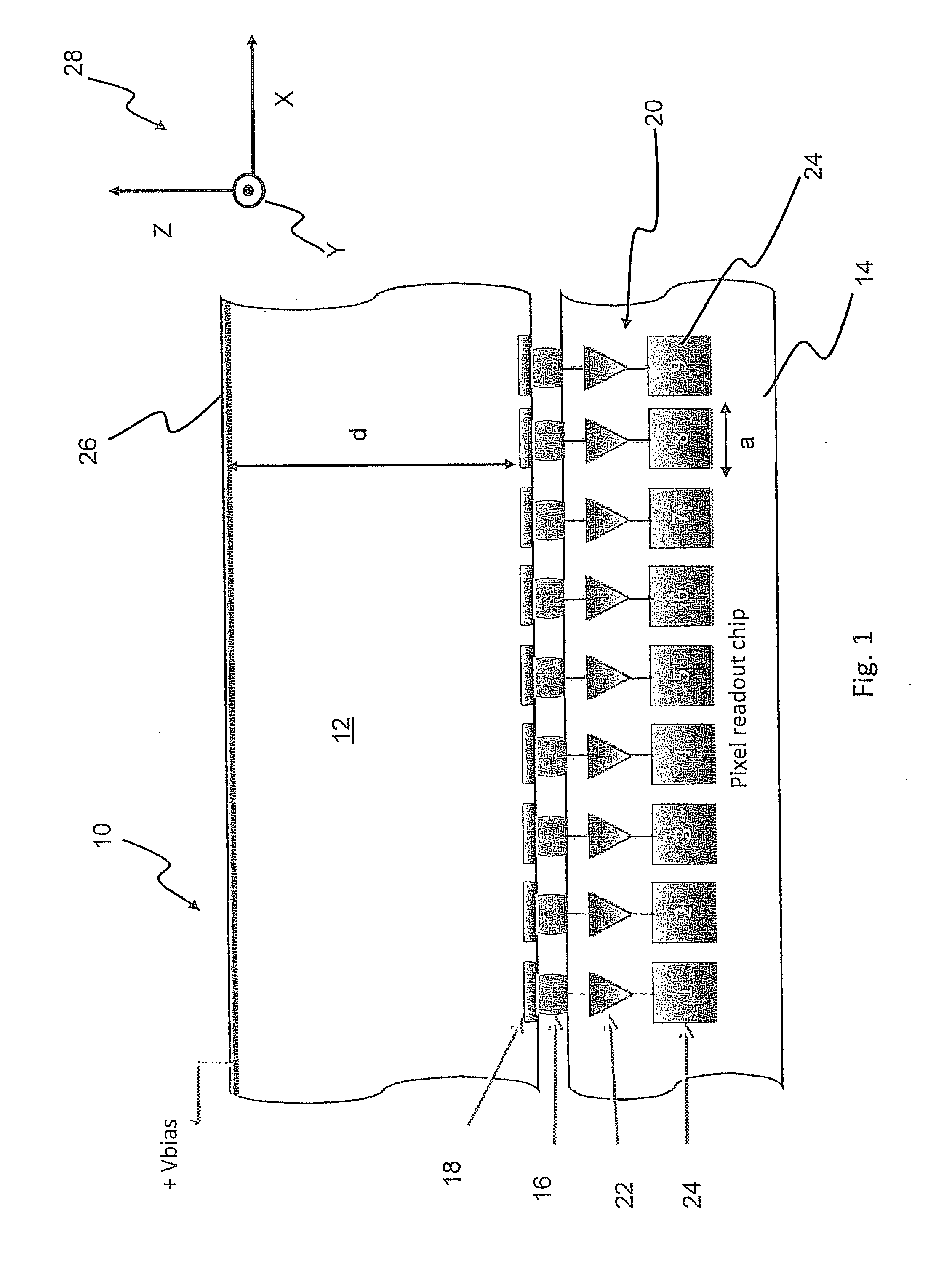
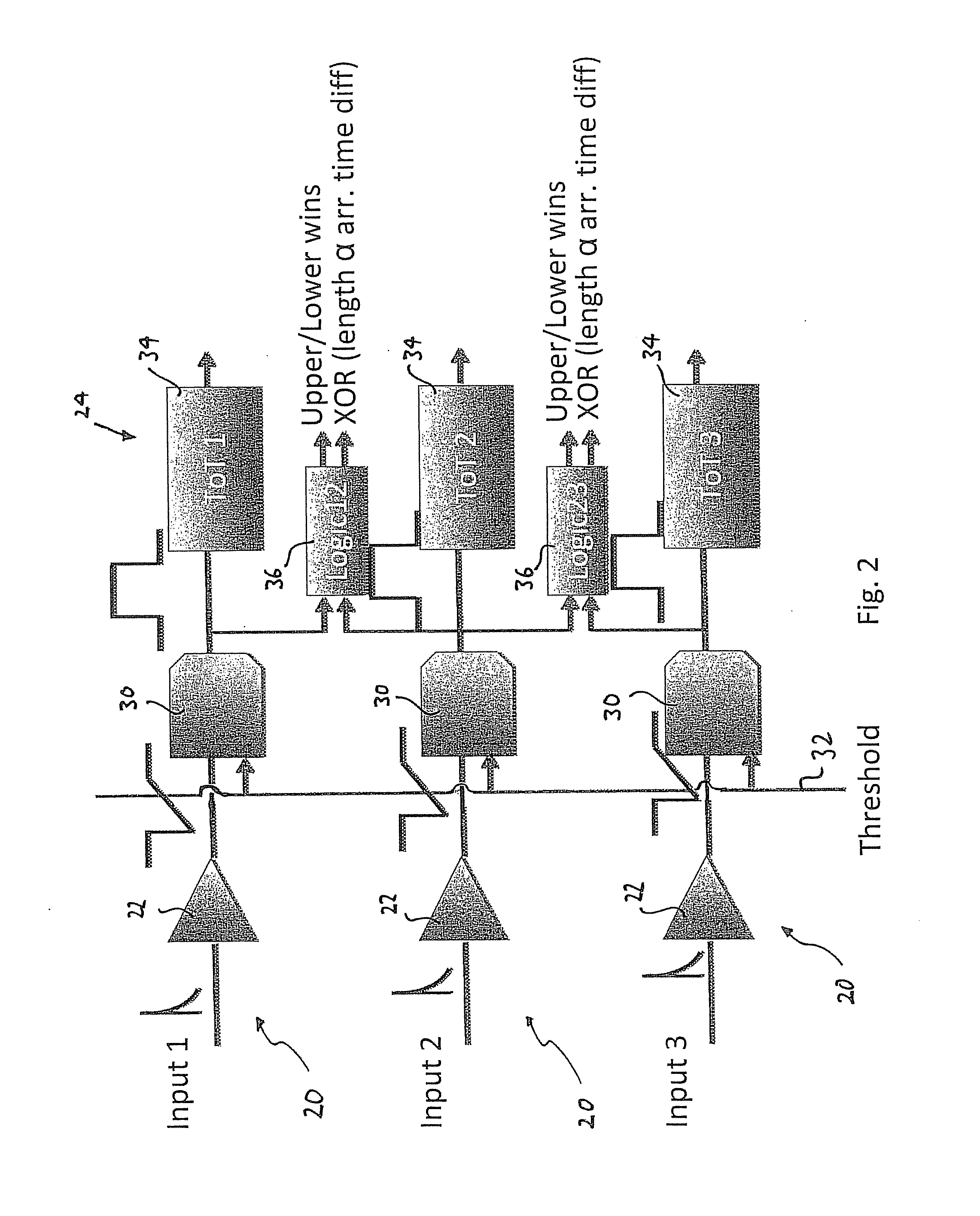
ActiveUS9297912B2Three-dimensional reconstruction more straightforwardModerate power consumptionSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devices3d trackingSemiconductor sensor
The present invention relates to a pixel detector (10), comprising a semiconductor sensor layer (12), in which charges can be generated upon interaction with particles to be detected. The semiconductor layer defines an X-Y-plane and has a thickness extending in Z-direction. The detector further comprises a read-out electronics layer (14) connected to said semiconductor layer (12), said read-out electronics layer (14) comprising an array of read-out circuits (20) for detecting signals indicative of charges generated in a corresponding volume of said semiconductor sensor layer (12). The neighboring read-out circuits (20) are connected by a relative timing circuit configured to determine time difference information between signals detected at said neighboring read-out circuits (20). The time difference information is indicative of a difference in the Z-components of the locations of charge generations in the corresponding neighboring sensor volumes caused by a particle trajectory that is inclined with respect to the X-Y-plane.
Owner:CZECH TECH UNIV IN PRAGUE
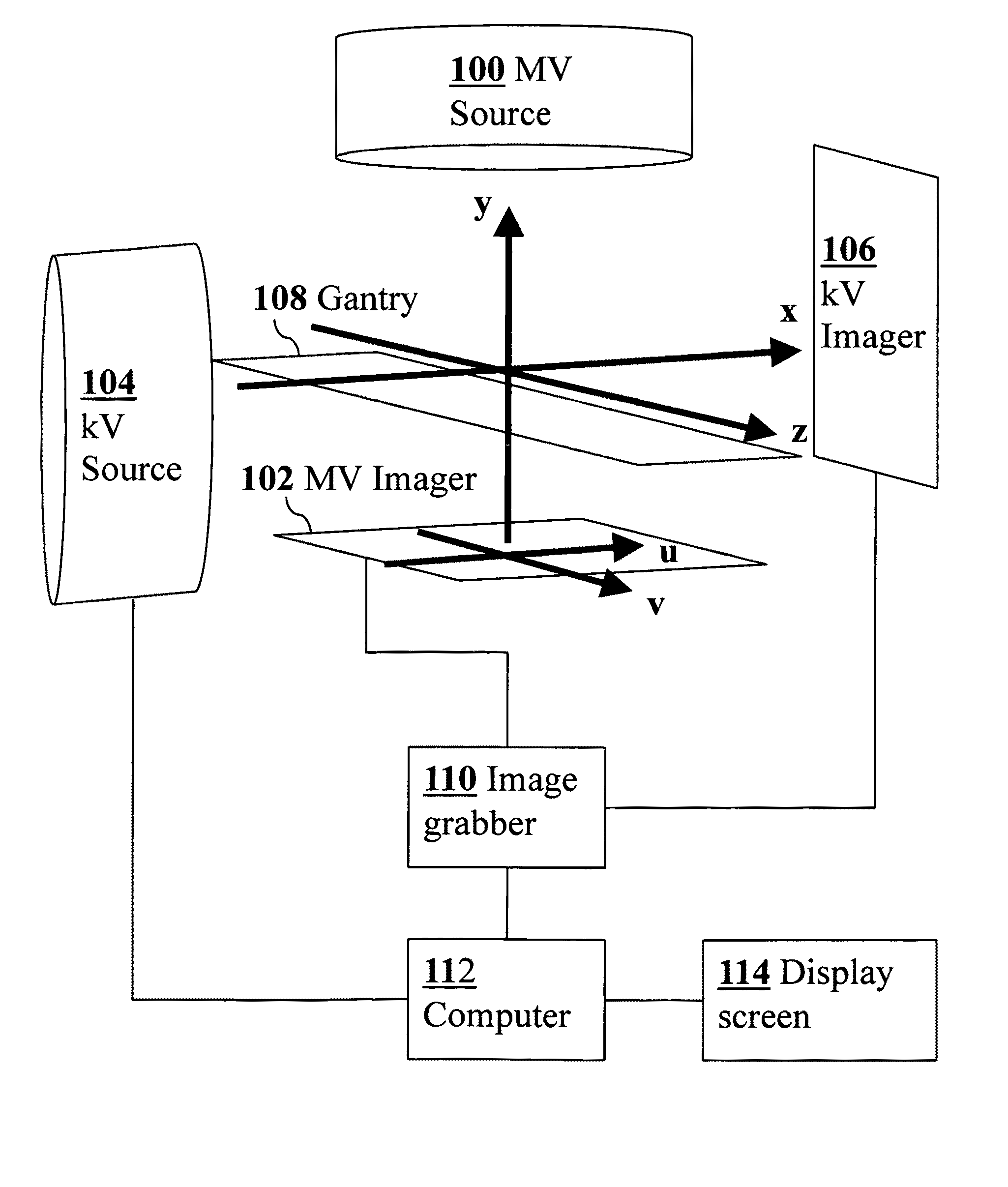
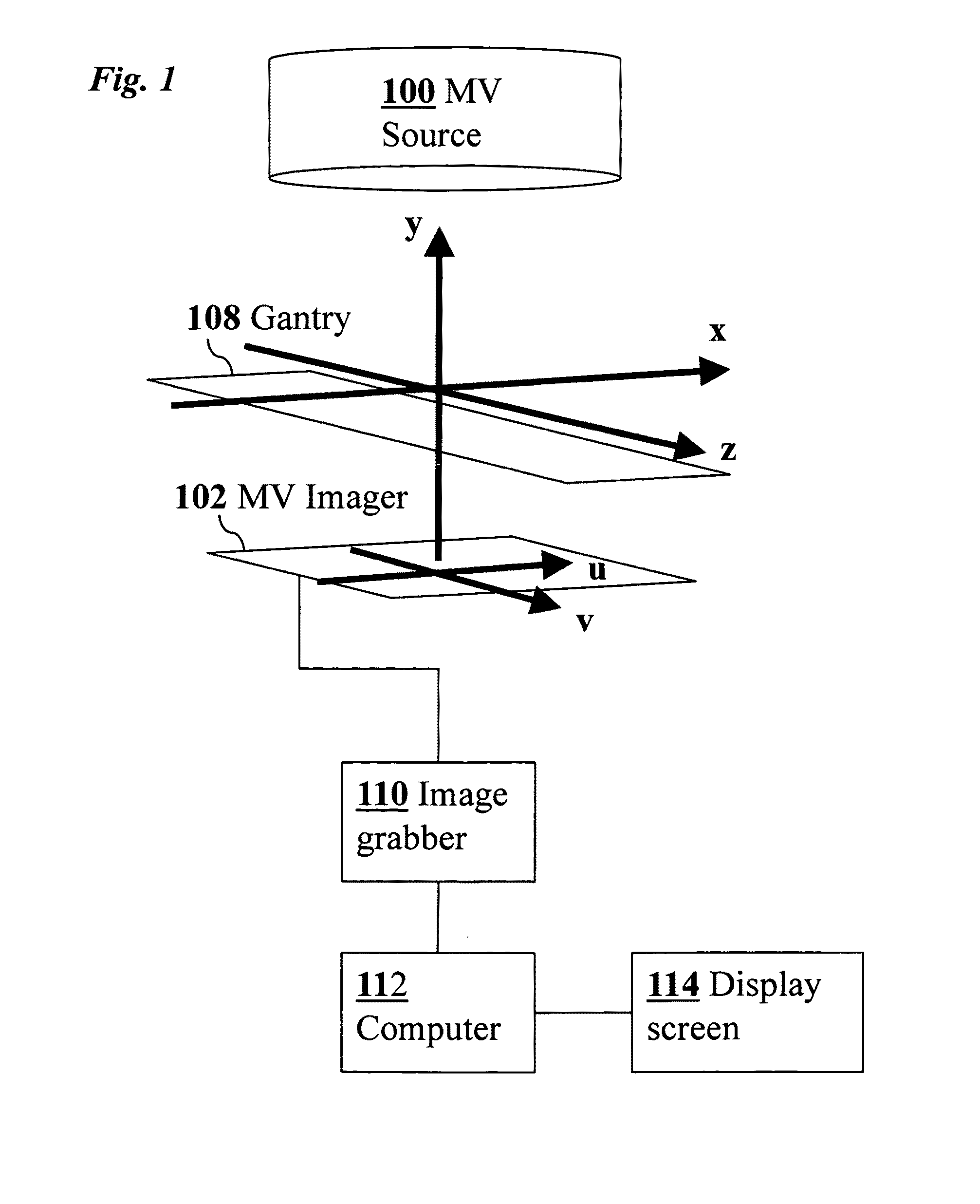
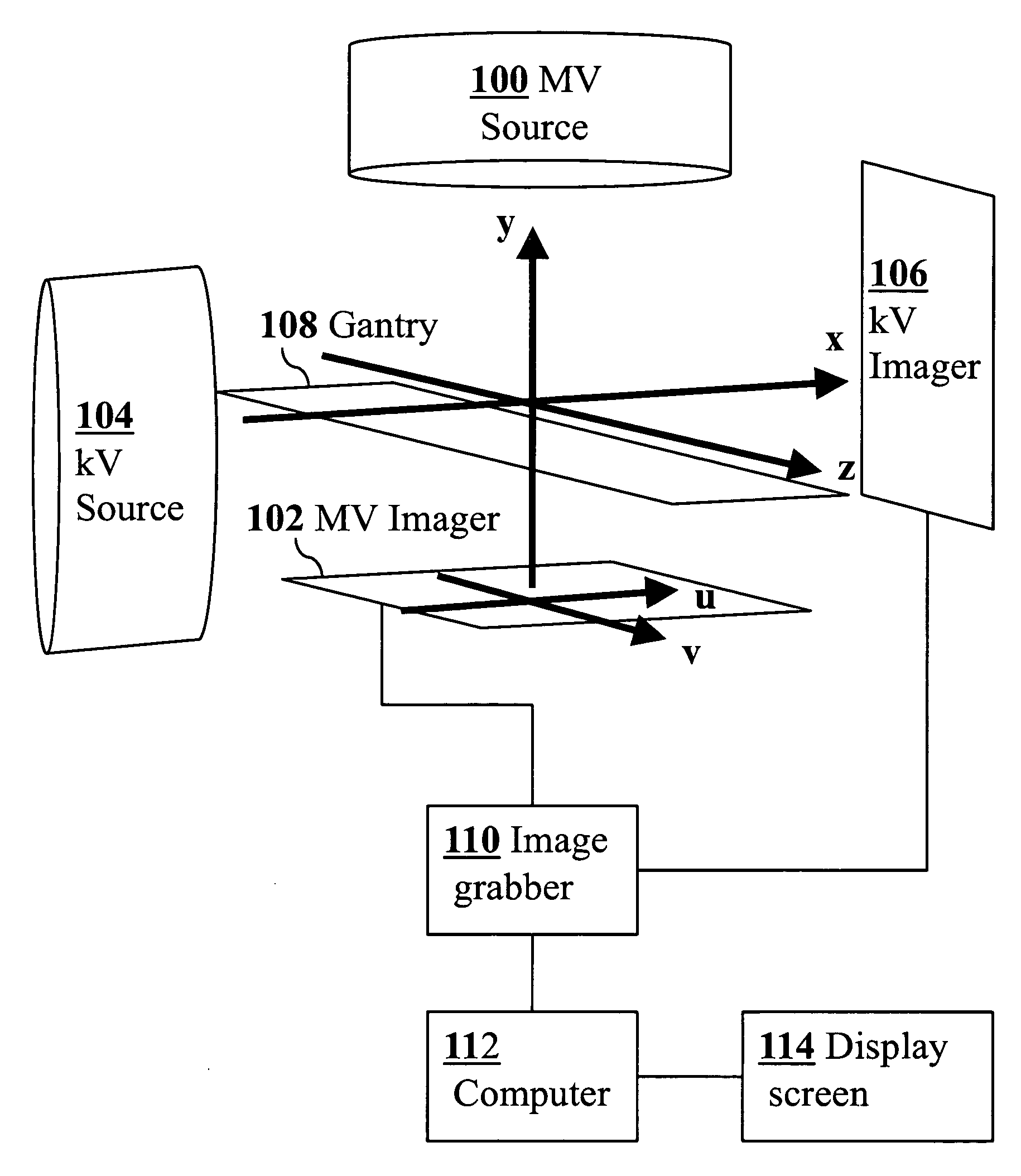
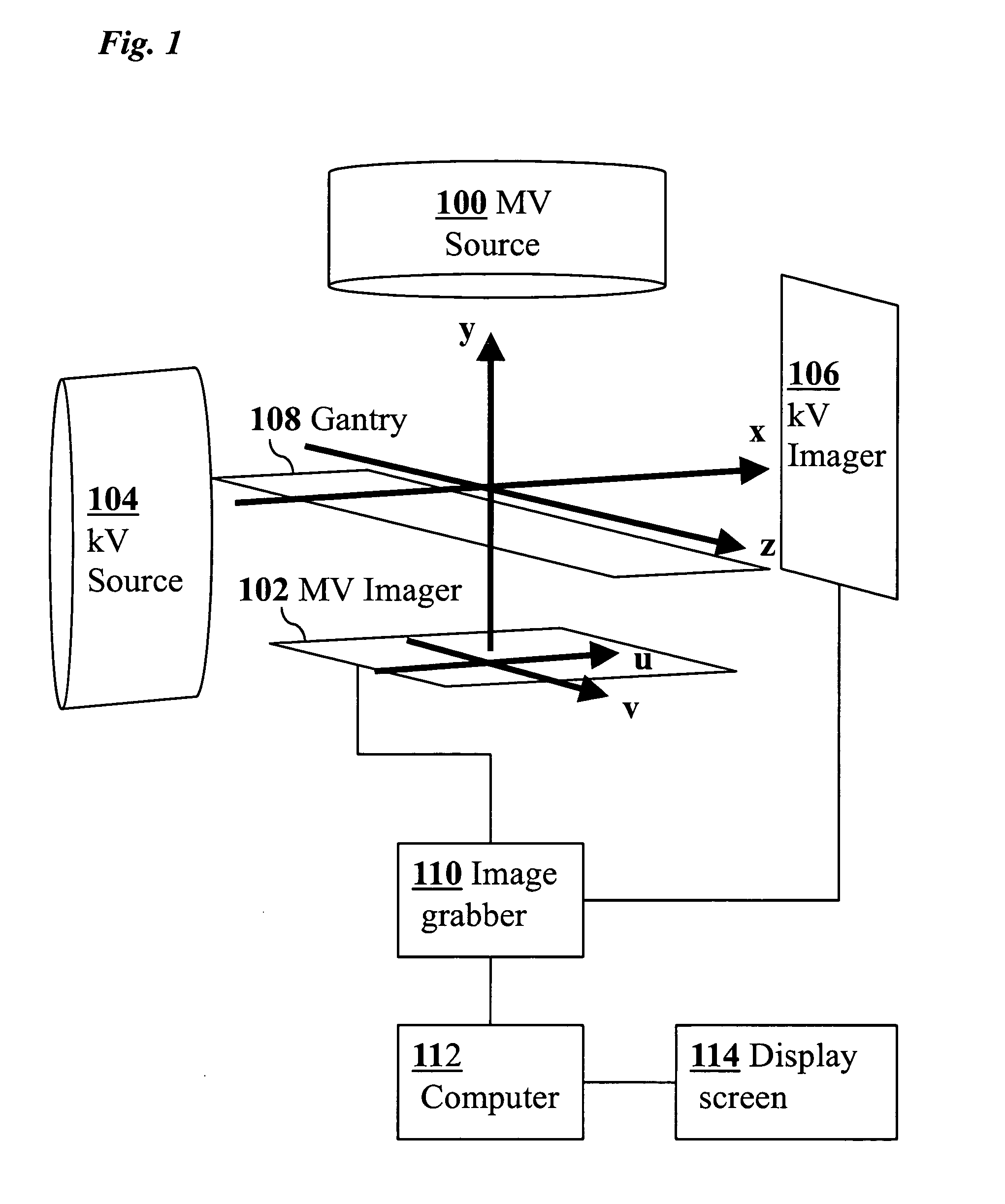
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS8121368B2Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Bracket for mounting at least one position detecting sensor on an ultrasonic probe
A bracket for use on an ultrasound transducer to releasably mount at least one 3D tracking sensor on the transducer. Each sensor has a pair of axially aligned pins projecting outward from its body. The bracket includes at least one socket having a pair of spaced-apart wall portions, each of which includes a slot arranged to receive a respective one of the pins of the sensor when the sensor is in a first position. From this position the sensor's body can be rotated to a second position, whereupon the spaced apart wall portions releasably engage (snap-fit about) a portion of the body of the sensor to deter the accidental displacement of the sensor with respect to the transducer.
Owner:CIVCO MEDICAL INSTR CO
3D real-time tracking of human anatomy using combined kV and MV imaging
ActiveUS20090208074A1Reduce radiationOvercome disadvantagesImage enhancementImage analysisHuman anatomy3d tracking
A medical imaging-based system and method uses both kV and MV images captured during a treatment period for organ motion tracking. 3D geometric locations of internal features are computationally tracked as a function of time from internal features, such as natural biological features or implanted fiducials, which are computationally extracted from the captured kV and MV images. A partial information method allows 3D tracking to be maintained in the event that imaging information is temporarily not available.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
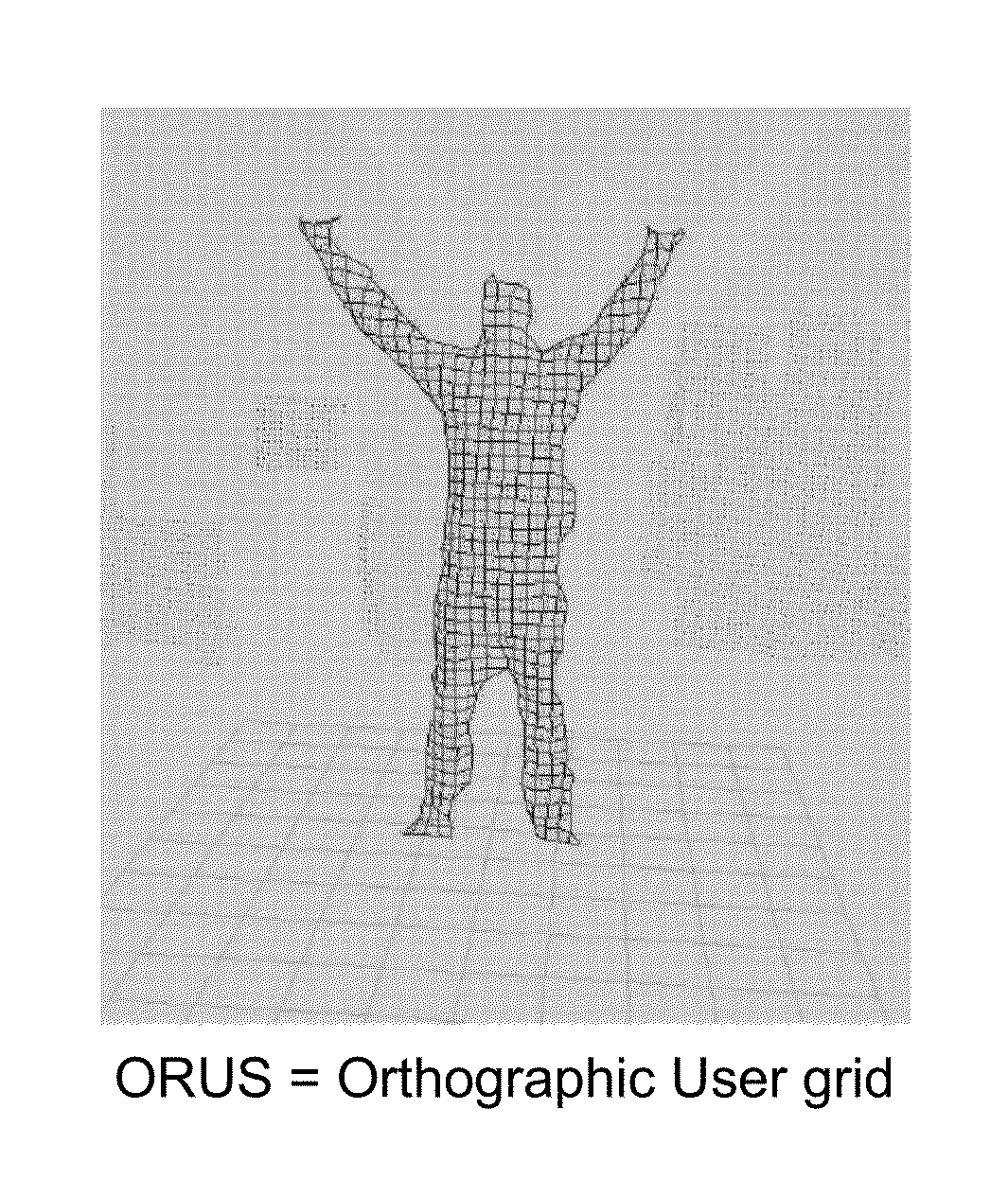
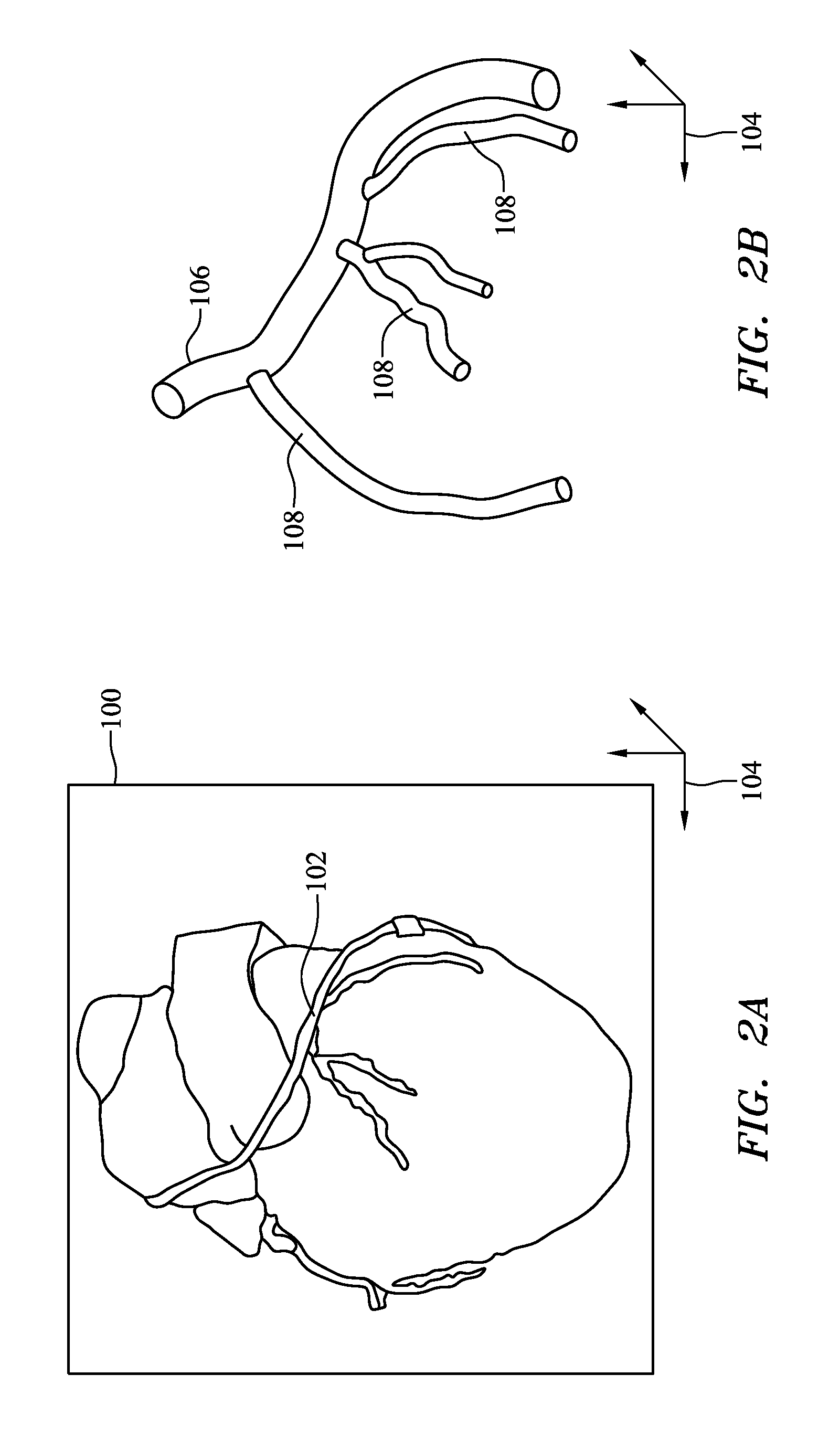
Three-dimensional object modeling fitting and tracking
ActiveUS9317741B2Efficient and robustEffective trackingImage enhancementImage analysisPoint cloudAmbiguity
Described herein is a method and system for marker-less three-dimensional modelling, fitting and tracking of a skeletal representation of an object in a three-dimensional point cloud. In particular, it concerns the tracking of a human user skeletal representation with respect to time. The method comprises inputting a three-dimensional point cloud derived from a depth map; predetermining a set of control points representing the skeleton of the user, determining a start-up skeleton pose, obtaining an orthographic representation of the user 3D point cloud projected onto a grid by sampling the 3D point cloud with a predetermined static size, determining a set of curvature centers points approximating central axes of main parts of the user, determining the torso plane, and refining and / or defining the principal direction of the body. The method comprises then the step of performing iterative local and global fittings of the set of control points onto the user 3D point cloud and the associated data such as the curvature center points, using topological and geometric constraints so that to track skeleton posture along the time. Stabilizing the skeleton pose; resolving ambiguities; and providing a suitable output are then the last steps of a preferred embodiment of the invention.
Owner:SOFTKINETIC SOFTWARE
Monocular 3D pose estimation and tracking by detection
InactiveUS8958600B2Reduce in quantityRepresentation flexibleImage enhancementImage analysisThree stageBayesian formulation
Methods and apparatus are described for monocular 3D human pose estimation and tracking, which are able to recover poses of people in realistic street conditions captured using a monocular, potentially moving camera. Embodiments of the present invention provide a three-stage process involving estimating (10, 60, 110) a 3D pose of each of the multiple objects using an output of 2D tracking-by detection (50) and 2D viewpoint estimation (46). The present invention provides a sound Bayesian formulation to address the above problems. The present invention can provide articulated 3D tracking in realistic street conditions.The present invention provides methods and apparatus for people detection and 2D pose estimation combined with a dynamic motion prior. The present invention provides not only 2D pose estimation for people in side views, it goes beyond this by estimating poses in 3D from multiple viewpoints. The estimation of poses is done in monocular images, and does not require stereo images. Also the present invention does not require detection of characteristic poses of people.
Owner:TECH UNIV DARMSTADT +1
Single layer 3D tracking semiconductor detector
ActiveUS20140332691A1Moderate power consumptionRobust and simple and affordable meanMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devices3d trackingSemiconductor sensor
The present invention relates to a pixel detector (10), comprising a semiconductor sensor layer (12), in which charges can be generated upon interaction with particles to be detected. The semiconductor layer defines an X-Y-plane and has a thickness extending in Z-direction. The detector further comprises a read-out electronics layer (14) connected to said semiconductor layer (12), said read-out electronics layer (14) comprising an array of read-out circuits (20) for detecting signals indicative of charges generated in a corresponding volume of said semiconductor sensor layer (12). The neighbouring read-out circuits (20) are connected by a relative timing circuit configured to determine time difference information between signals detected at said neighbouring read-out circuits (20). The time difference information is indicative of a difference in the Z-components of the locations of charge generations in the corresponding neighbouring sensor volumes caused by a particle trajectory that is inclined with respect to the X-Y-plane.
Owner:CZECH TECH UNIV IN PRAGUE
Lithotripsy system with automatic 3D tracking
A lithotripsy system capable of 3D tracking monitors the acoustic reflection from the stone in order to focus the shock wave on the stone regardless of shock wave displacement or stone movement. The tracking and focusing is based on a phased array concept, allowing the lithotripsy head to remain stationary and well coupled to the body. An alternate shock wave steering is based on refraction by a variable liquid wedge.
Owner:IKOMED TECH
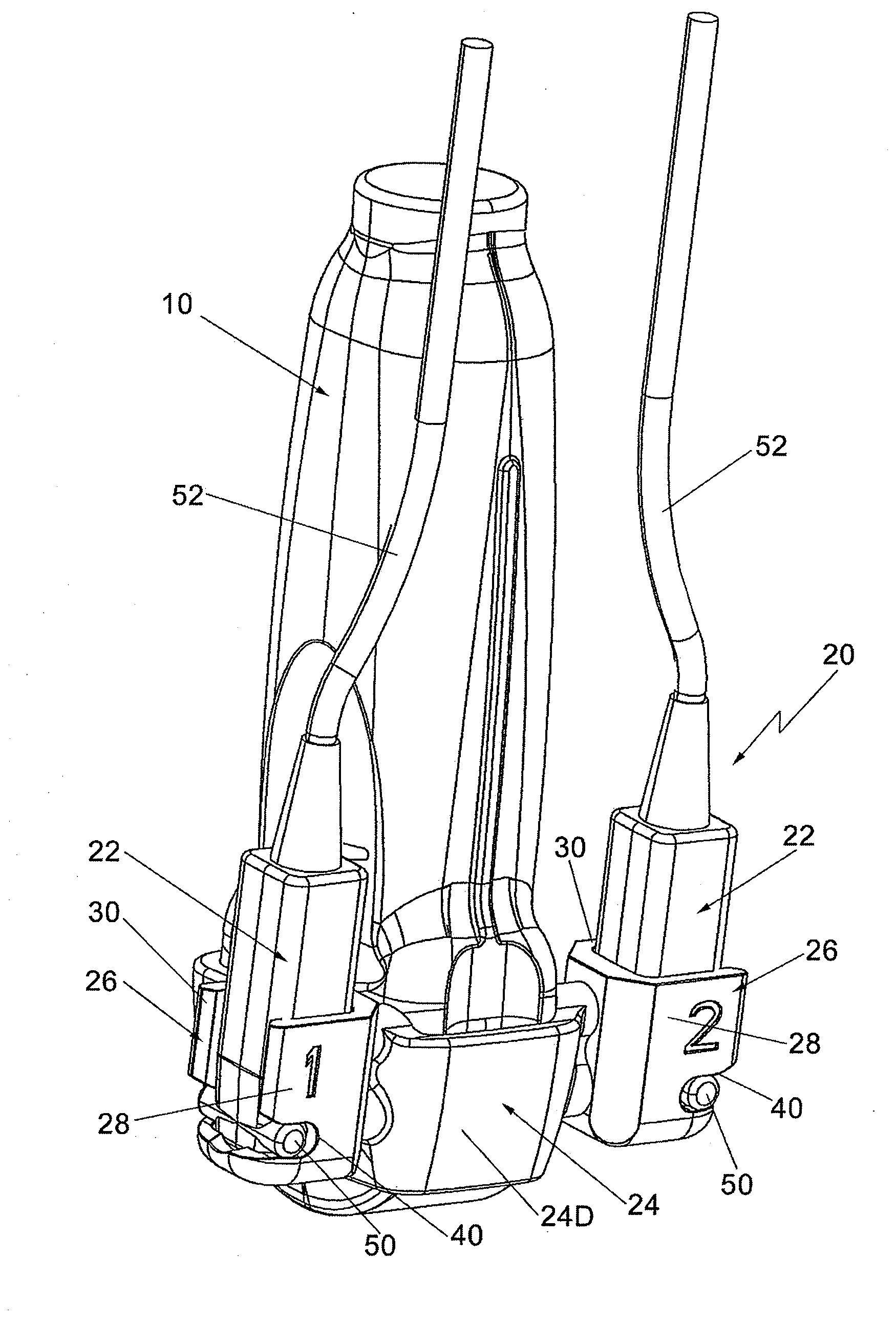
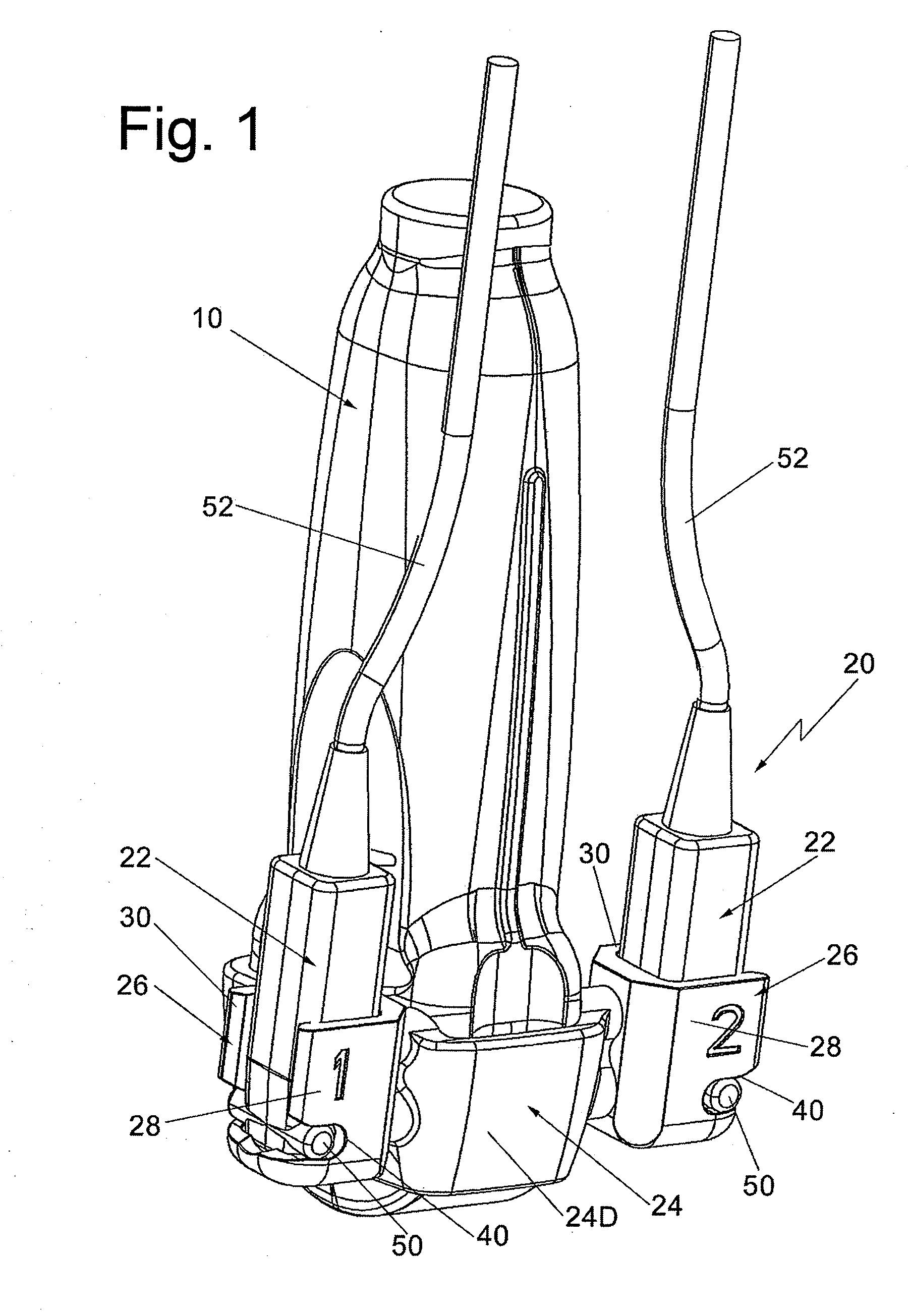
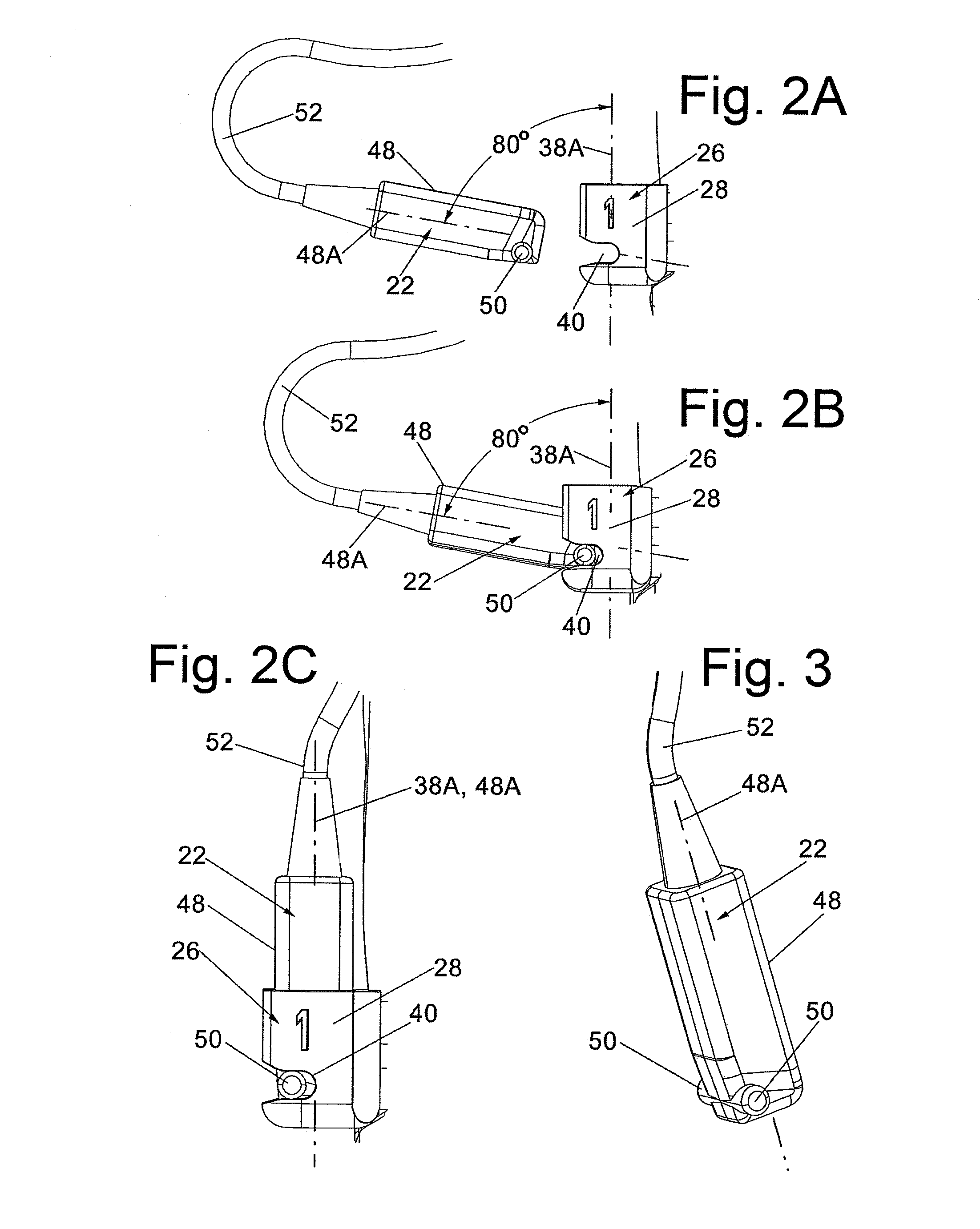
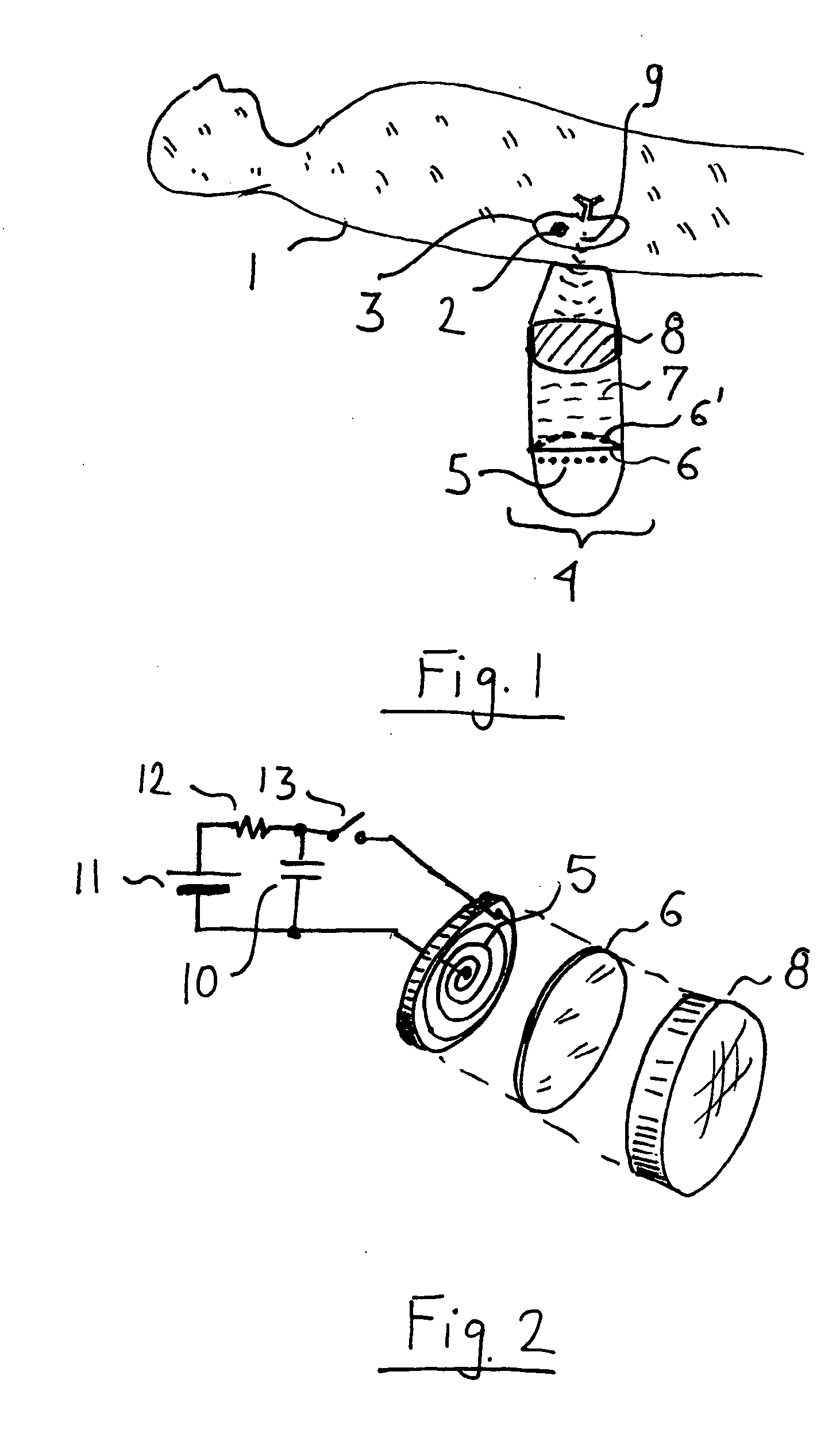
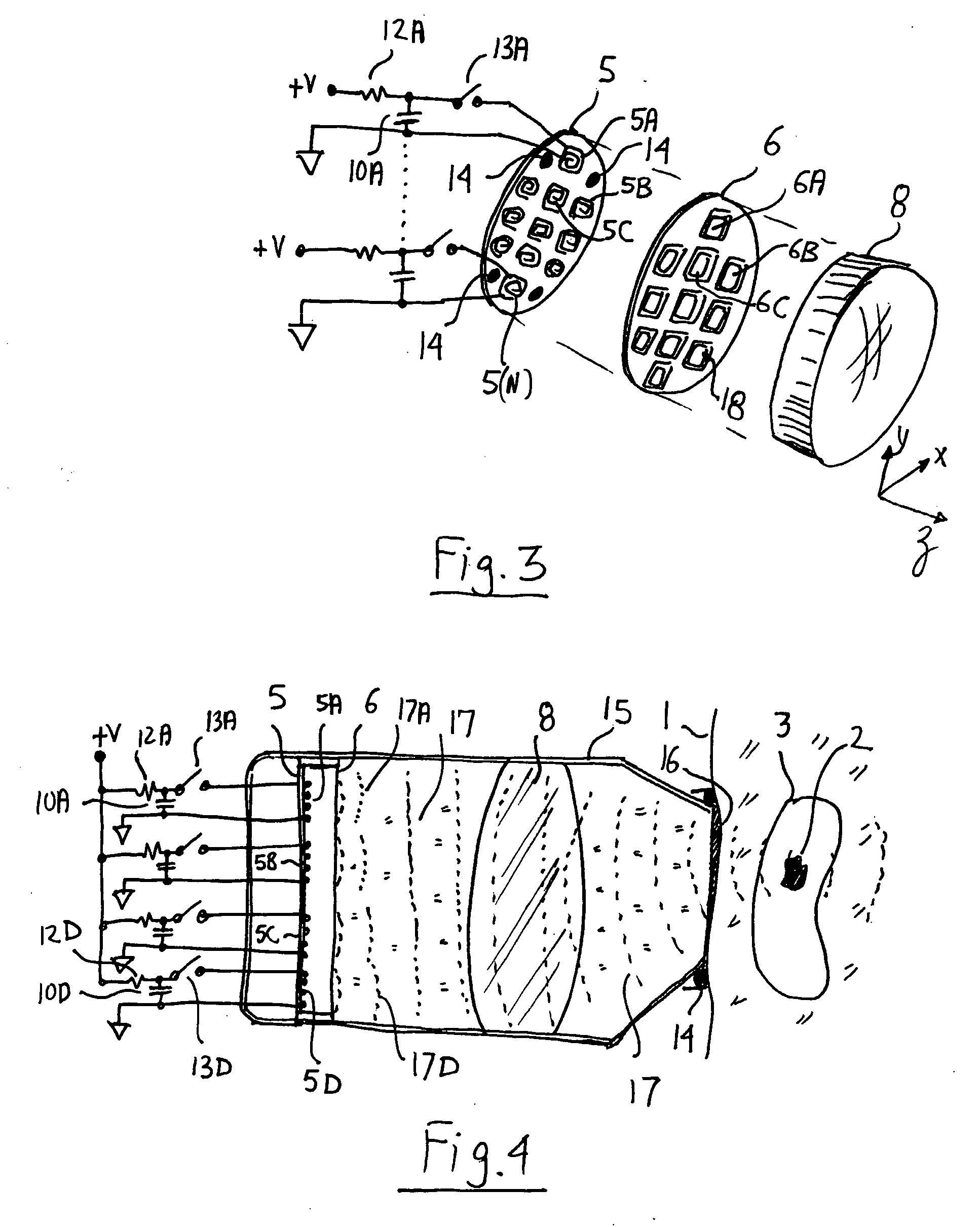
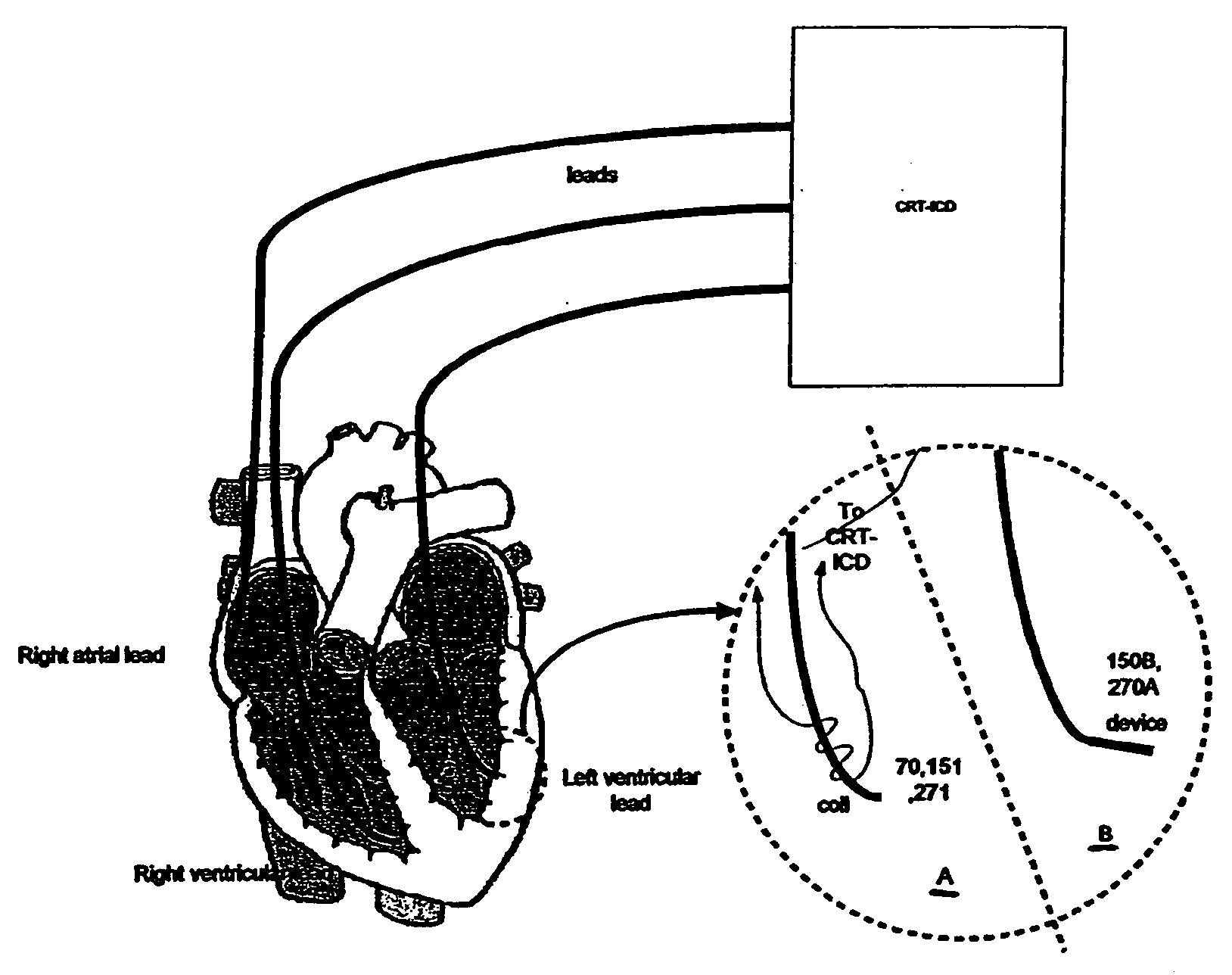
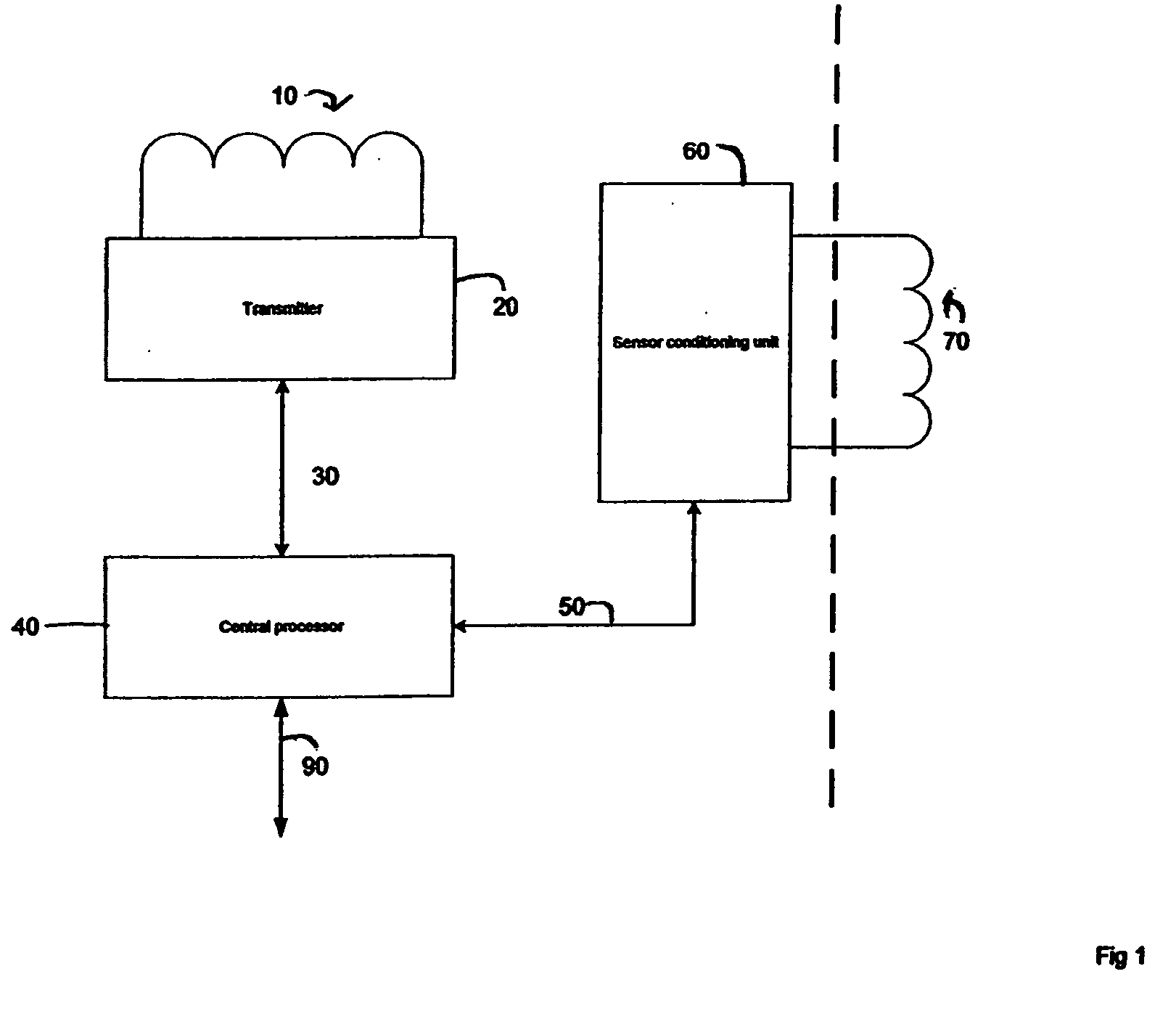
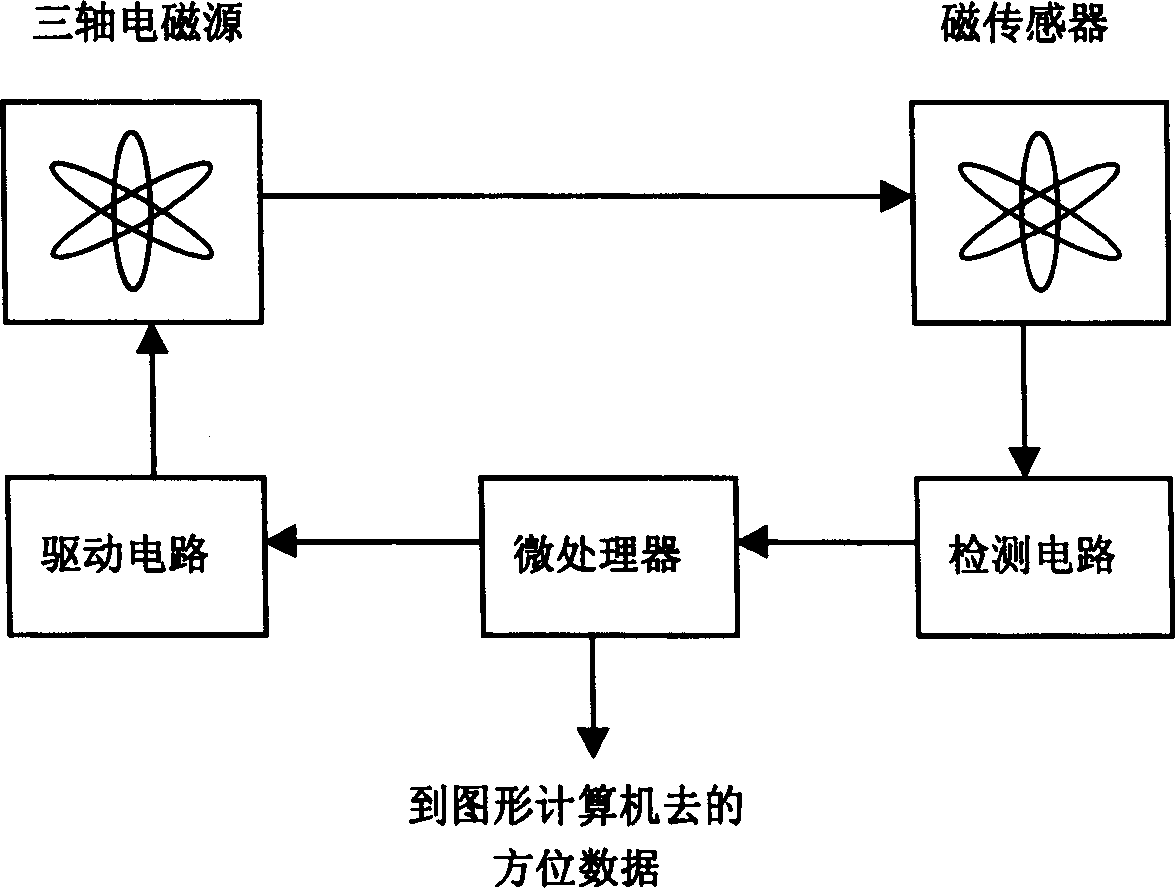
Lead Tracking Of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) And Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Devices
InactiveUS20090105779A1Eliminate fragile wiringImprove reliabilityTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical navigation systemsHome environment3d tracking
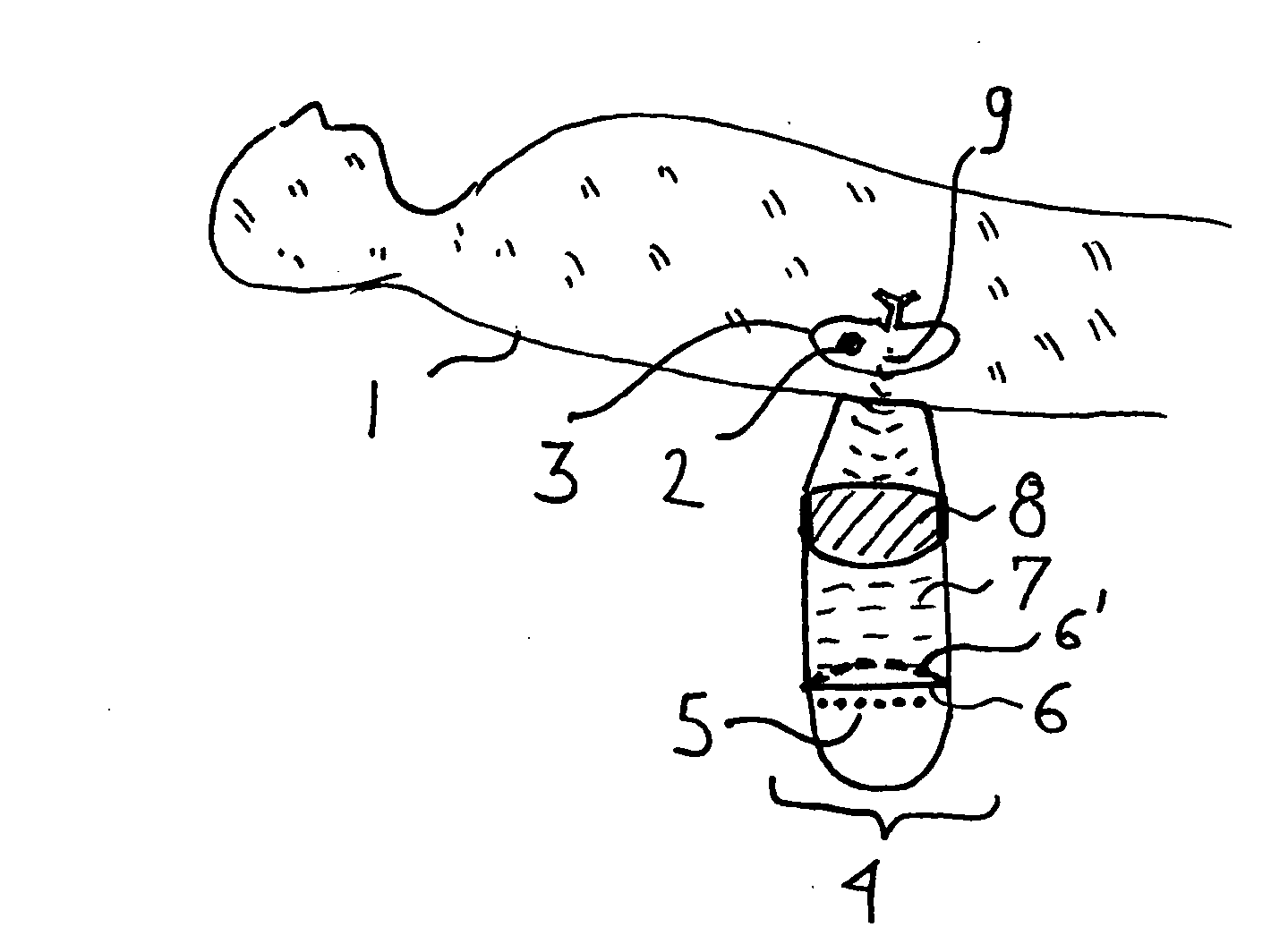
Lead Tracking of Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Devices improve upon the process of implantation of ICD-CRT devices, placing their leads, and improving the information fed back to the device and / or clinician. Tracking of the placement of the leads during implantation is accomplished along with monitoring the leads once implanted. Benefits include reducing the risk and complication rate, simplifying implantation procedure, and enabling the extraction of vital data not previously available. Leads are tracked to at least minimize the need to use fluoroscopy. Three dimensional tracking (10) is employed to facilitate obtaining of data that allows the surgeon to better visualize lead insertion and placement. Placement of the leads during a procedure requires use of an external tracking component along with means and method for tracking the implantable leads. Transmitting antennas (10, 110) are provided, equal in number to the number of degrees of freedom of tracking required. A link (50) between the sensor (70) and the computation unit (40) can be wired or wireless. Once leads are implanted, heart wall motion must be monitored via the tracking of the leads within a clinical or home environment. Such tracking of the leads may be accomplished in real time.
Owner:ASCENSION TECH
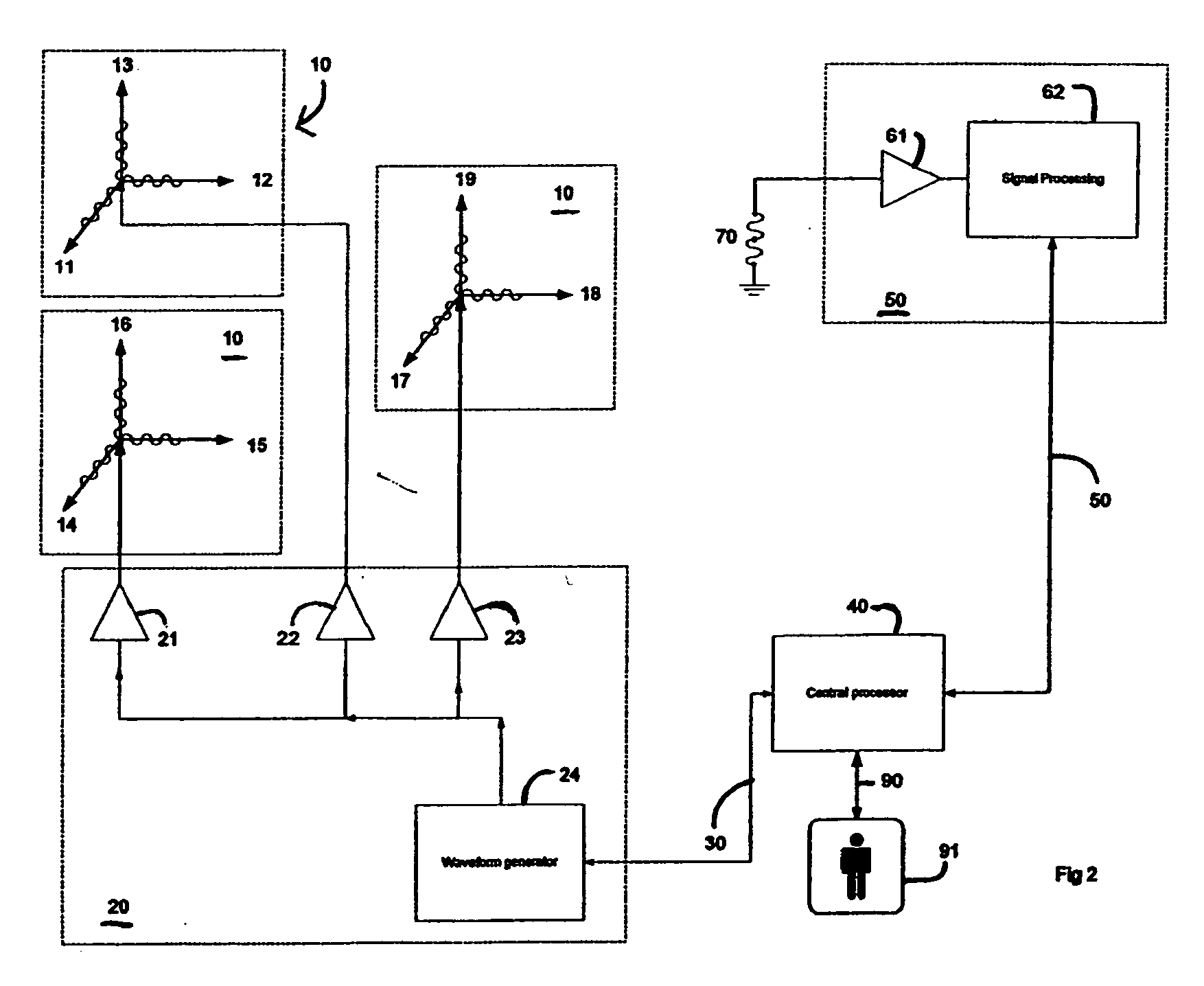
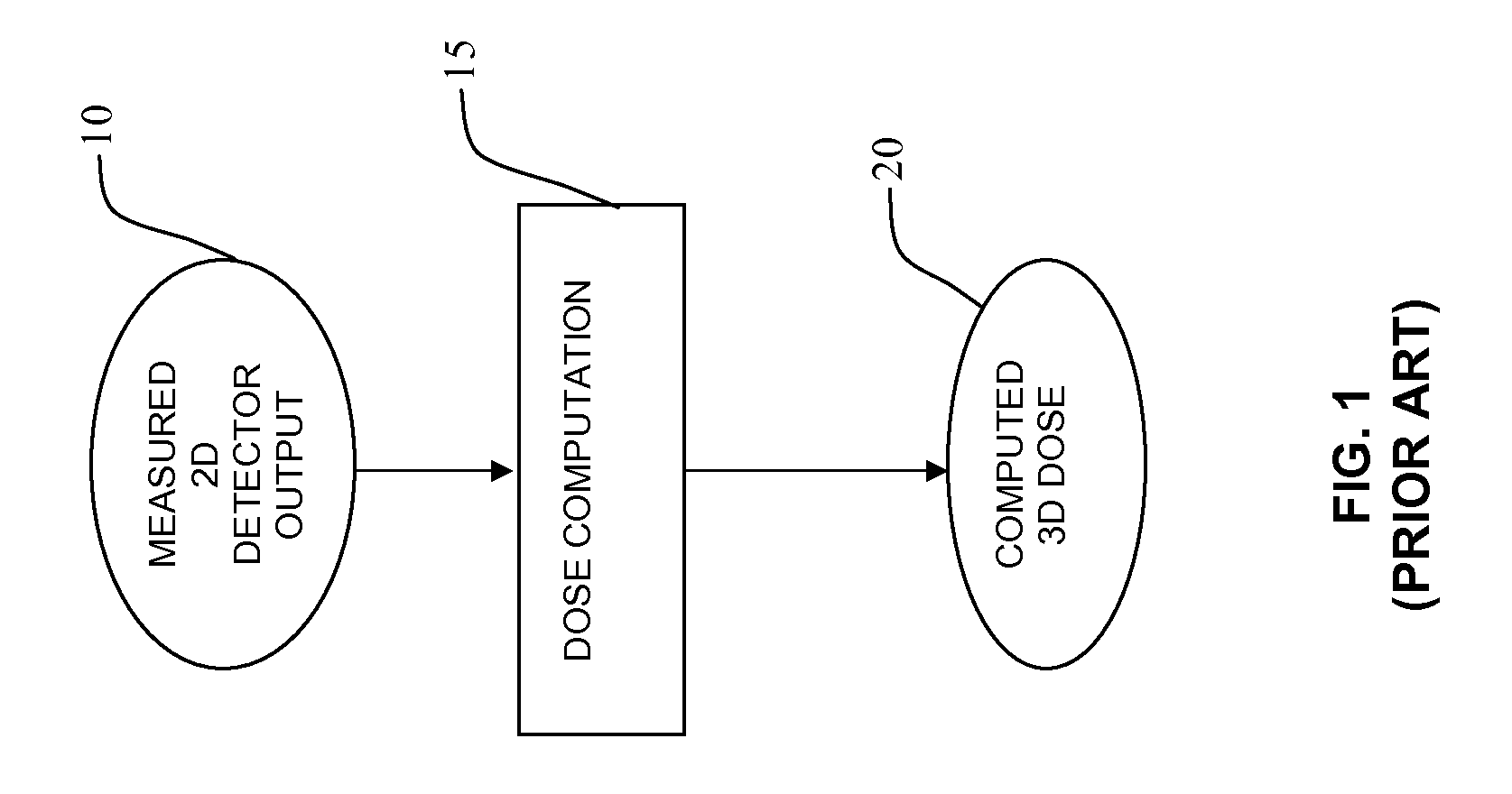
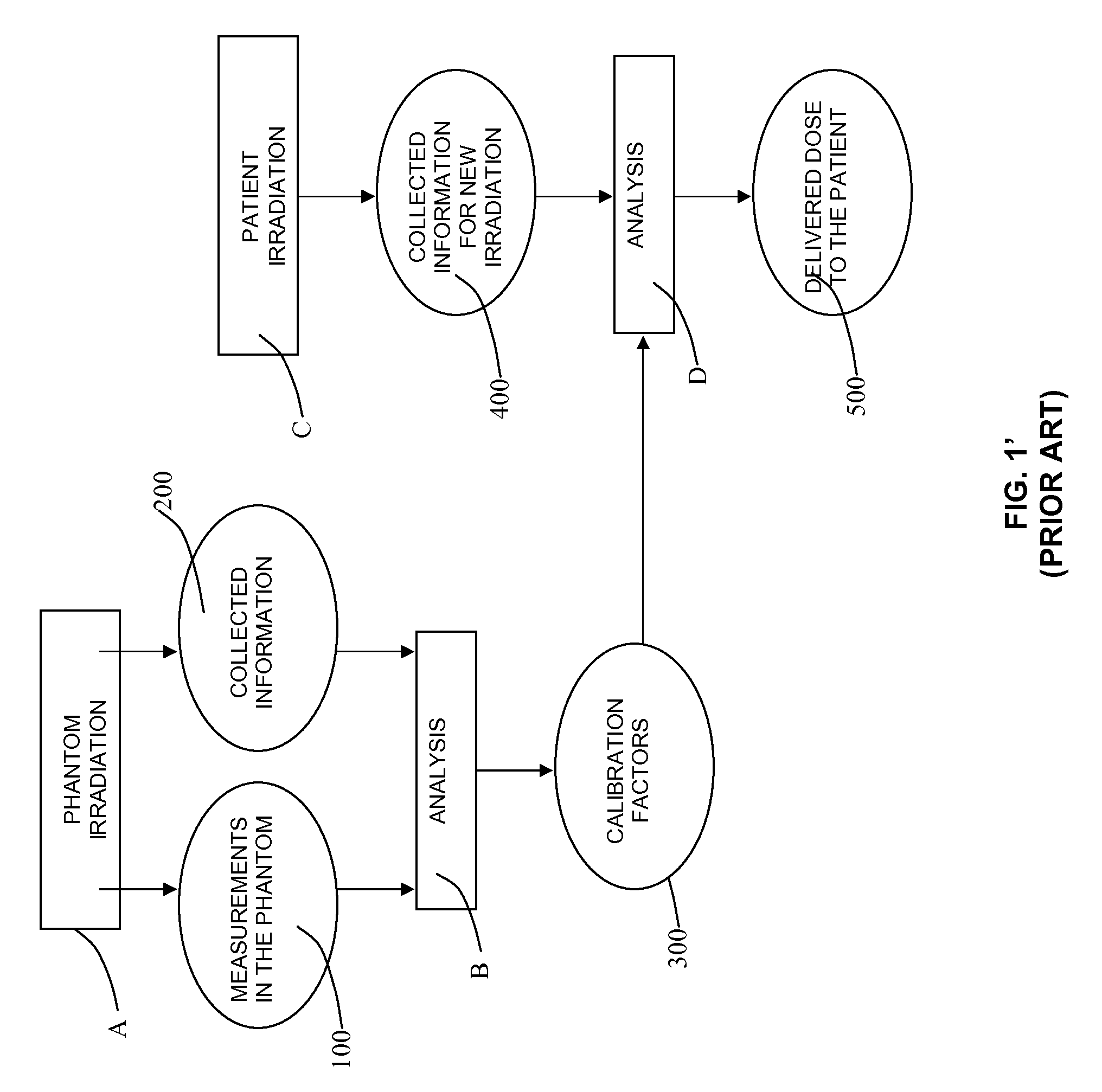
Device and method for 3D dose tracking in radiation therapy
The present invention relates to a device and method for verification of the quality of a radiation beam in conformal radiation therapy, and in particular for IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) applications. The actual 3D dose distribution in the patient is tracked during the course of the entire treatment by reconstructing the photon fluences from measured 2D detector responses during irradiation in conjunction with updated patient images.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
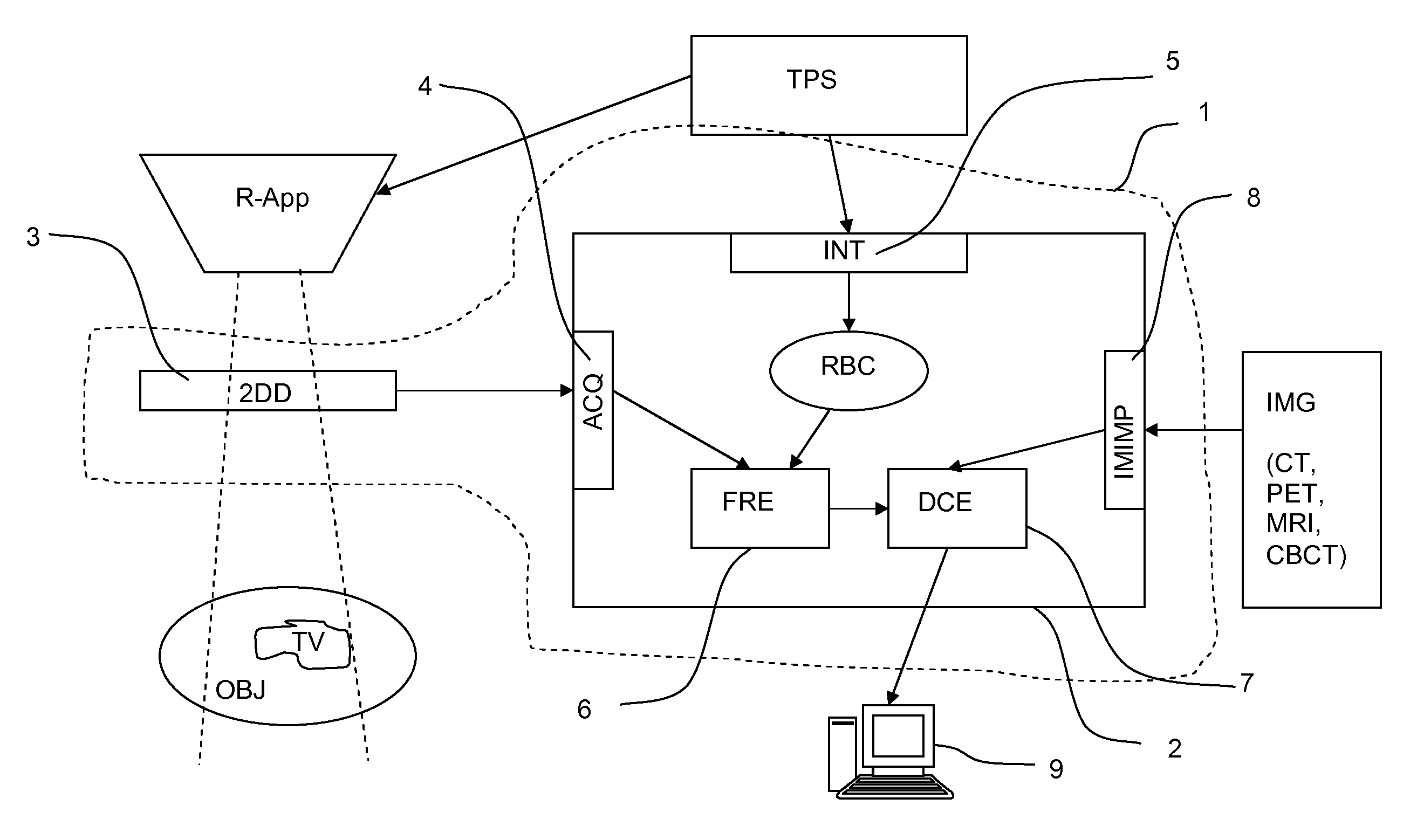
Tracking-based 3D model enhancement
A method for enhancing a three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of an object comprises obtaining a signal indicative of a static 3D reconstruction of an object disposed in a tracking space, co-registering the 3D reconstruction to the 3D tracking space, collecting enhancement data from a tracked tool disposed in the 3D tracking space, and adding real-time features of the object to the static 3D reconstruction using the enhancement data. A system for enhancing data obtained by a medical system includes an electronic control unit configured to receive a first signal for a static 3D reconstruction of an organ, co-register the static 3D reconstruction to a 3D tracking space for a tracked tool, receive a second signal for enhancement data generated by the tracked tool operating within a region of interest of the organ, and add real-time features of the area of interest to the static 3D reconstruction using the enhancement data.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
3D tracking and measurement method of moving objects by 2D code
The present invention relates to the field of the optical 3D contour measuring technology. Two video cameras are used to collect the image of some objects and the two CCD cameras are in some certain distance, the 3D measurement is performed based on double-eye stereo visual principle. The measured object is marked with the geographic shapes in different color and in specific range order so that matching point can be found out in the images the two CCD cameras obtain. The position of some point in the 3D space is calculated according to the parallex of a matching point in two images. It can beused to track moving human body and has wide application in 3D motion picture production, selection and training of athlete, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Lithotripsy system with automatic 3D tracking
InactiveUS20090275832A1Enhanced couplingOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryShock wave3d tracking
A lithotripsy system capable of 3D tracking monitors the acoustic reflection from the stone in order to focus the shock wave on the stone regardless of shock wave displacement or stone movement. The tracking and focusing is based on a phased array concept, allowing the lithotripsy head to remain stationary and well coupled to the body.
Owner:GELBART DANIEL +1
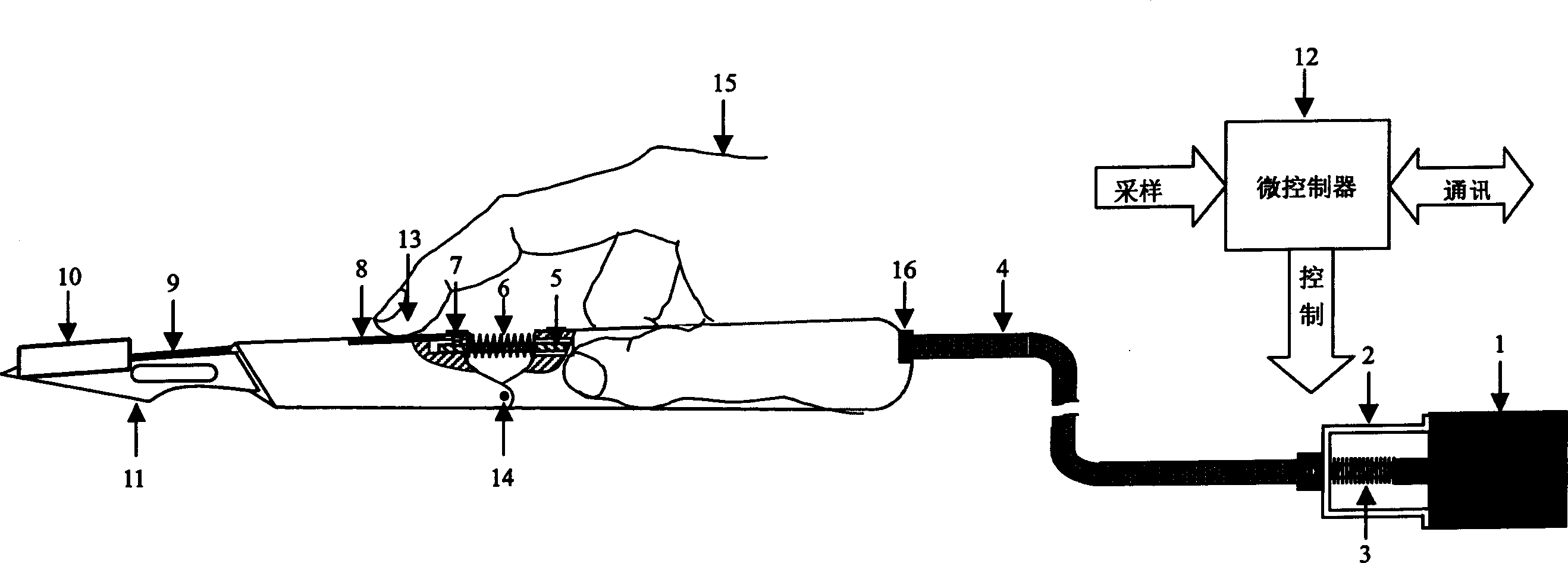
Analog scalpel unit
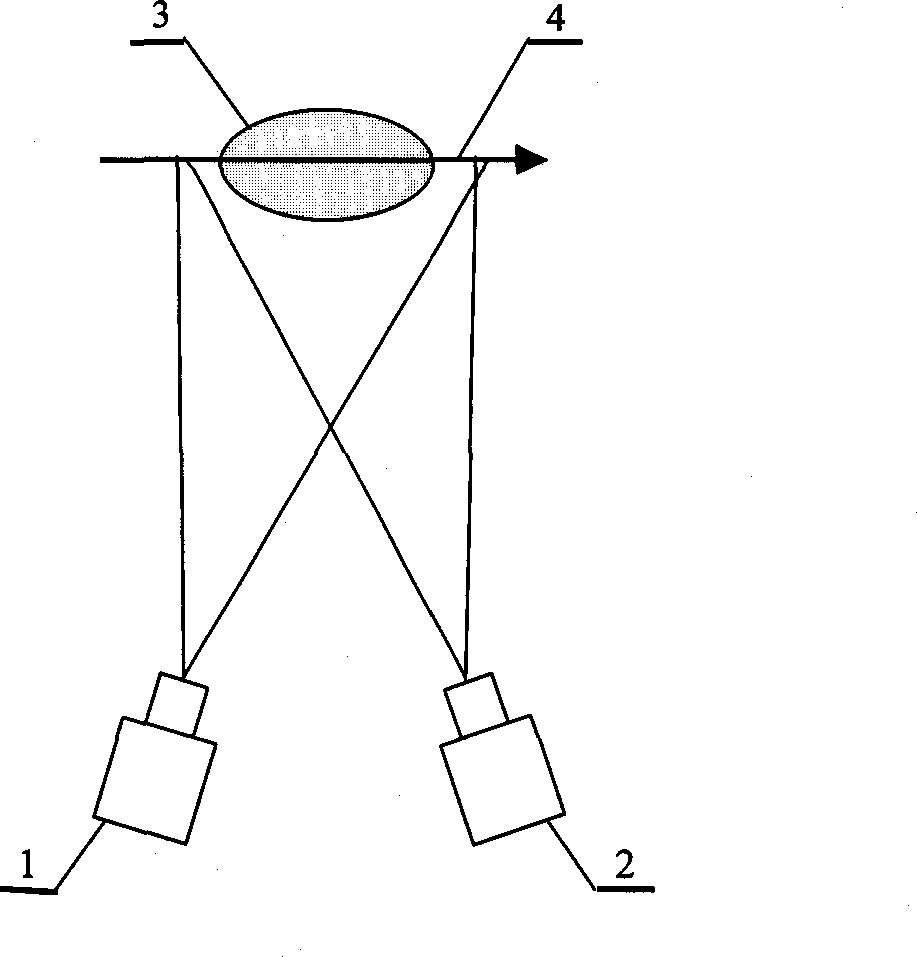
The virtual scalpel unit includes micro controller, scalpel, force transferring device connecting the scalpel and proportional electromagnet for transmitting the drive force from the proportional electromagnet, repositioning spring connected across the force transferring device, force sensor on the scalpel handle for detecting the upward force of the scalpel, and 3D tracking device for detecting the position and posture of the scalpel. The 3D tracking device and the force feeding back mechanism are small and light and has no influence on the action of the operator. The present invention maybe used in virtual operation.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
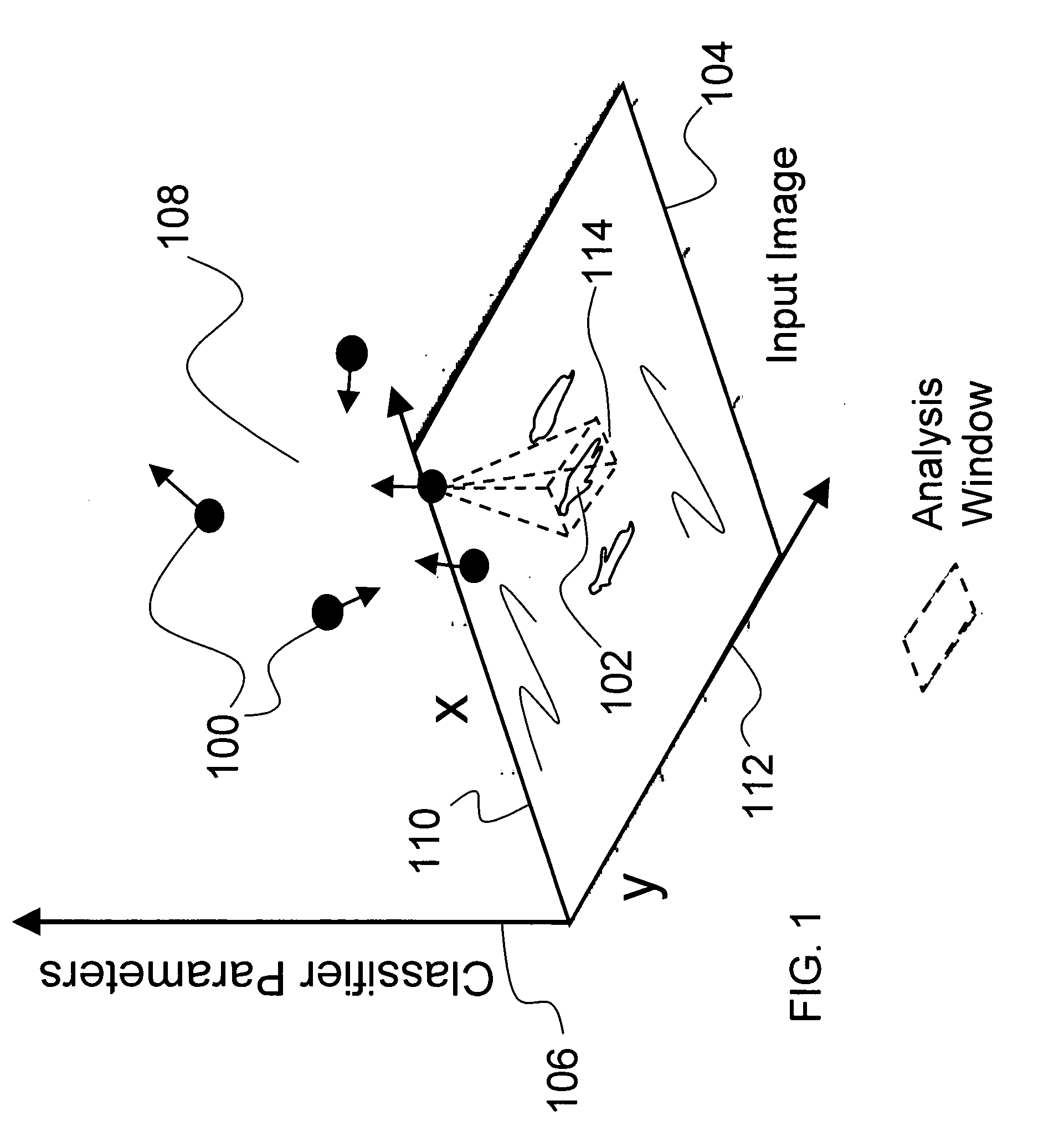
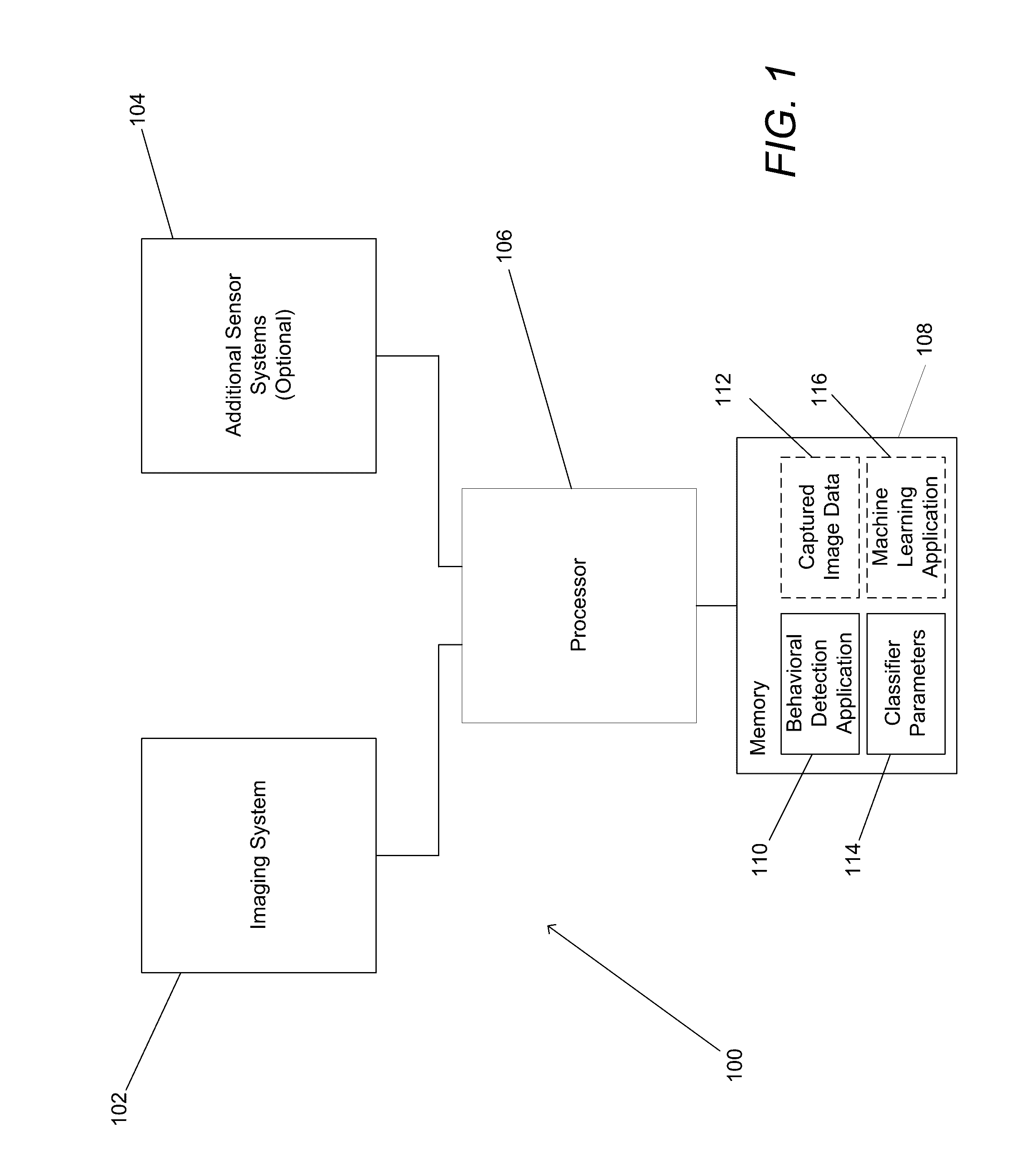
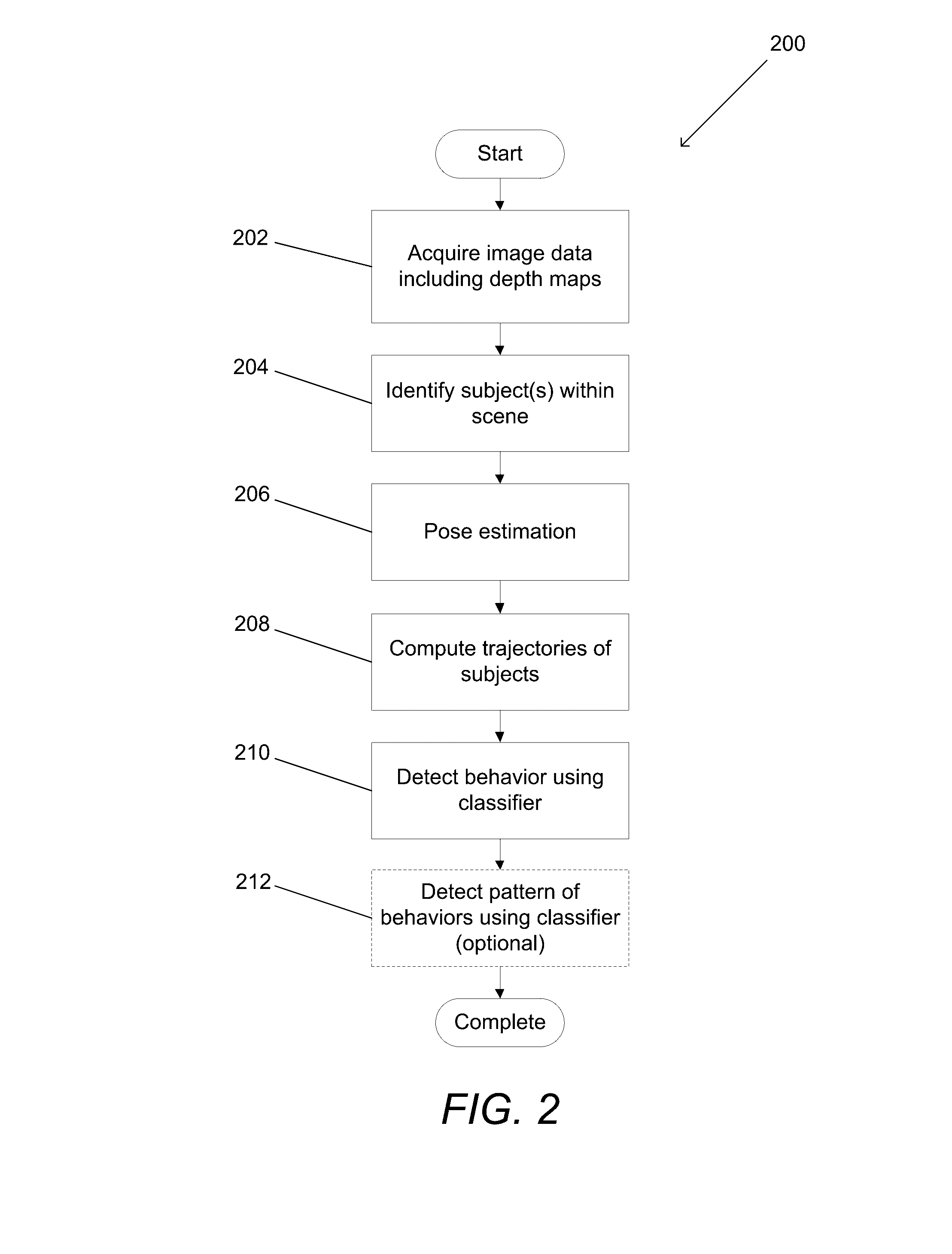
Systems and Methods for Behavior Detection Using 3D Tracking and Machine Learning
Systems and methods for performing behavioral detection using three-dimensional tracking and machine learning in accordance with various embodiments of the invention are disclosed. One embodiment of the invention involves a the classification application that directs a microprocessor to: identify at least a primary subject interacting with a secondary subject within a sequence of frames of image data including depth information; determine poses of the subjects; extract a set of parameters describing the poses and movement of at least the primary and secondary subjects; and detect a social behavior performed by at least the primary subject and involving at least the second subject using a classifier trained to discriminate between a plurality of social behaviors based upon the set of parameters describing poses and movement.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
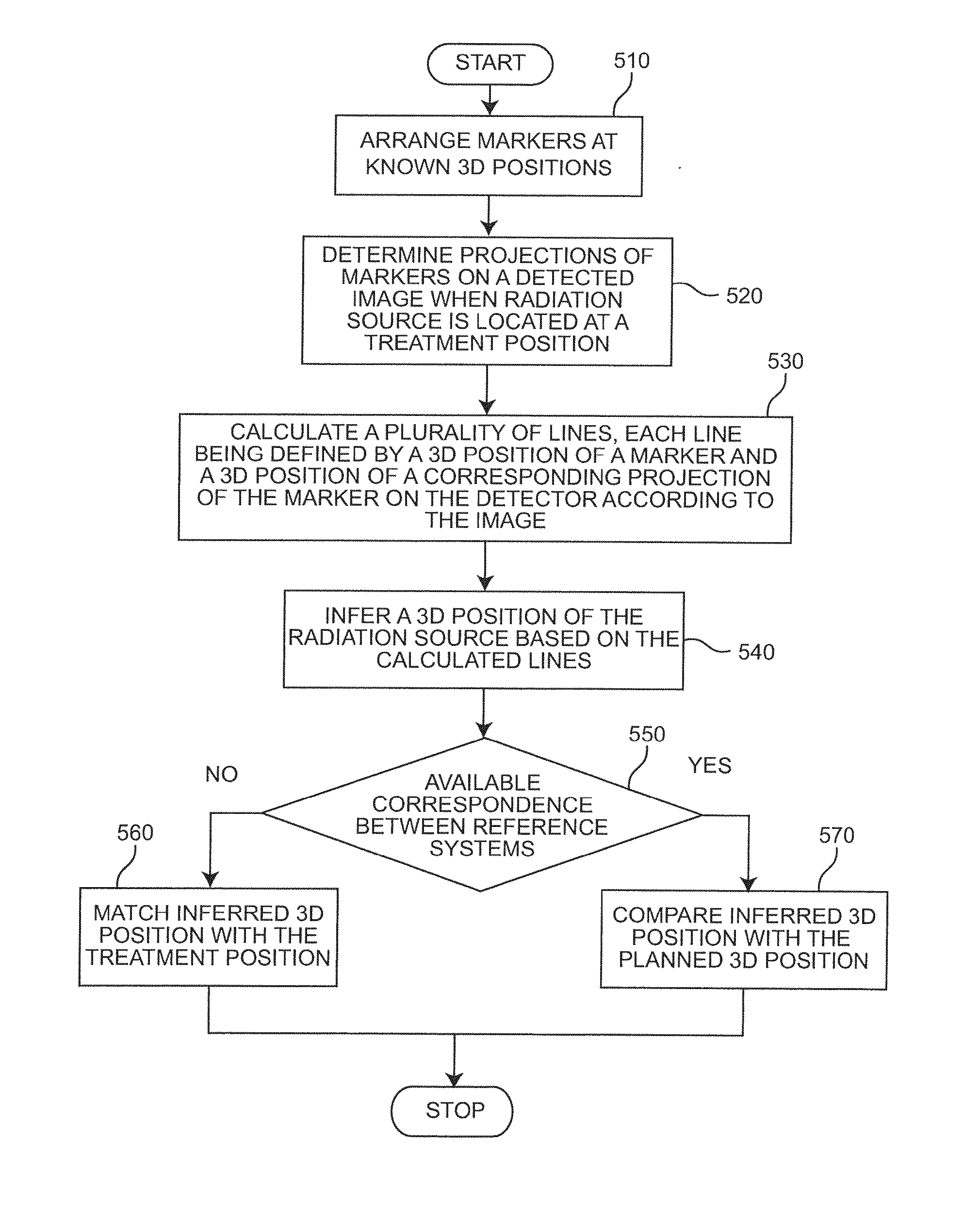
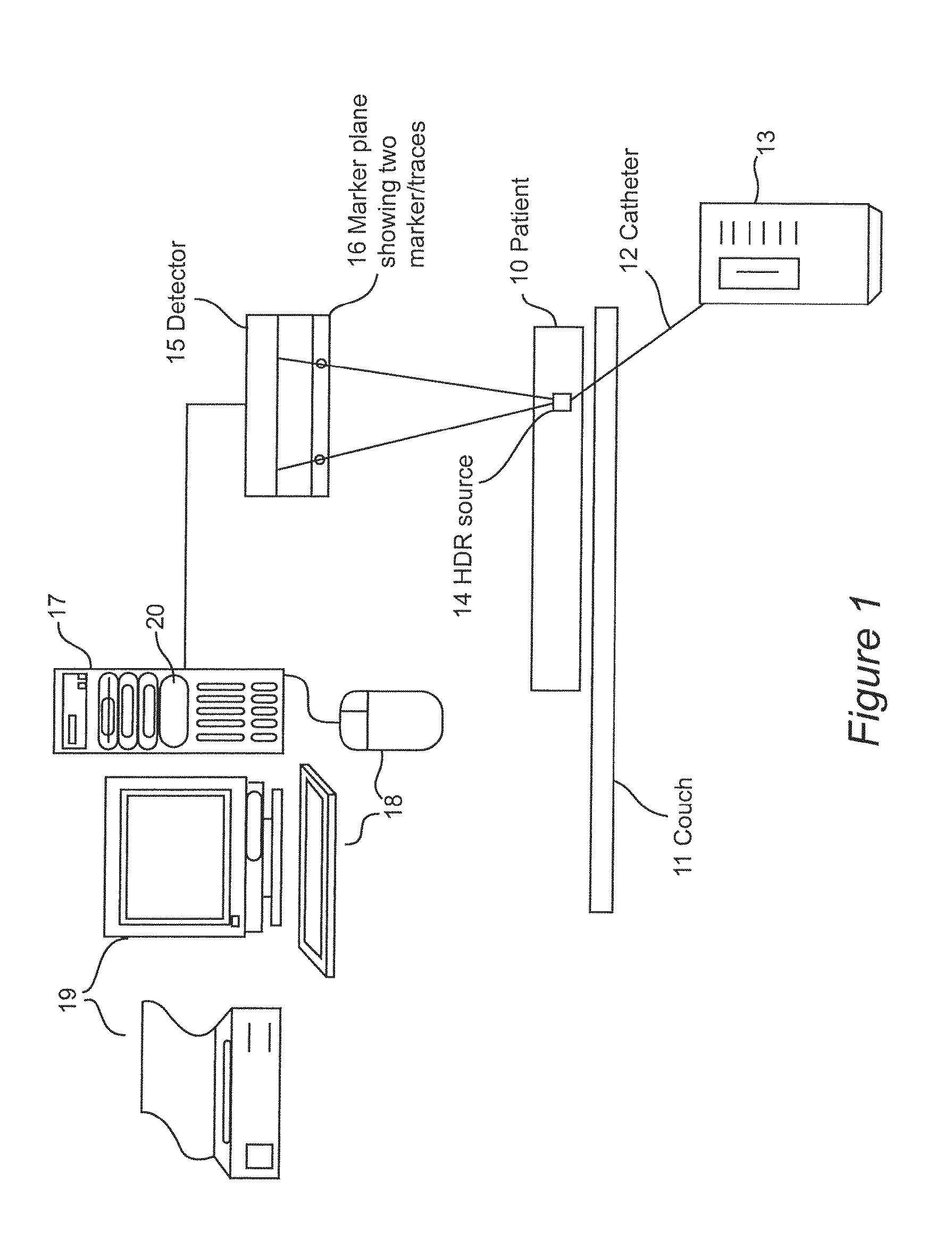
3D Tracking of an HDR Source Using a Flat Panel Detector
ActiveUS20120277570A1Error freeShort timeImage enhancementImage analysisFlat panel detectorHigh doses
A method and apparatus are used to compare in real-time an intended radiation treatment plan with a delivered plan. Markers are arranged, on a subject receiving radiation, at three-dimensional (3D) positions between a two dimensional radiation detector and a radiation source and are used to reconstruct the actual position of a high dose rate (HDR) source in three-dimensional (3D) space. The detected position is compared with the intended radiation path of the treatment plan. Adjustments can be made to the treatment plan if the detected position and the intended path do not correspond.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Device tracking using longitudinal encoding
A method for reconstructing 3D shape of a longitudinal device using an optical fiber with optical shape sensing (OSS) properties, e.g. Bragg gratings. By attaching the optical fiber to the longitudinal device, such that the optical fiber follows its 3D shape upon bending, known OSS techniques can be applied to reconstruct 3D shape of the optical fiber, and thus also the longitudinal device, e.g. a medical catheter. E.g. the optical fiber, e.g. placed in a guide wire, can be inserted in a lumen of the longitudinal device. Hereby, one OSS system can be used for 3D tracking a plurality of non-shape sensed catheters or other longitudinal devices. In case the longitudinal device is longer than the optical fiber, the position and shape of the remaining part of the longitudinal device may be estimated and visualized to a user, e.g. based on a known length of the longitudinal device, and based on an orientation of an end point of the optical fiber, e.g. using knowledge about the stiffness or other properties of the longitudinal device.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
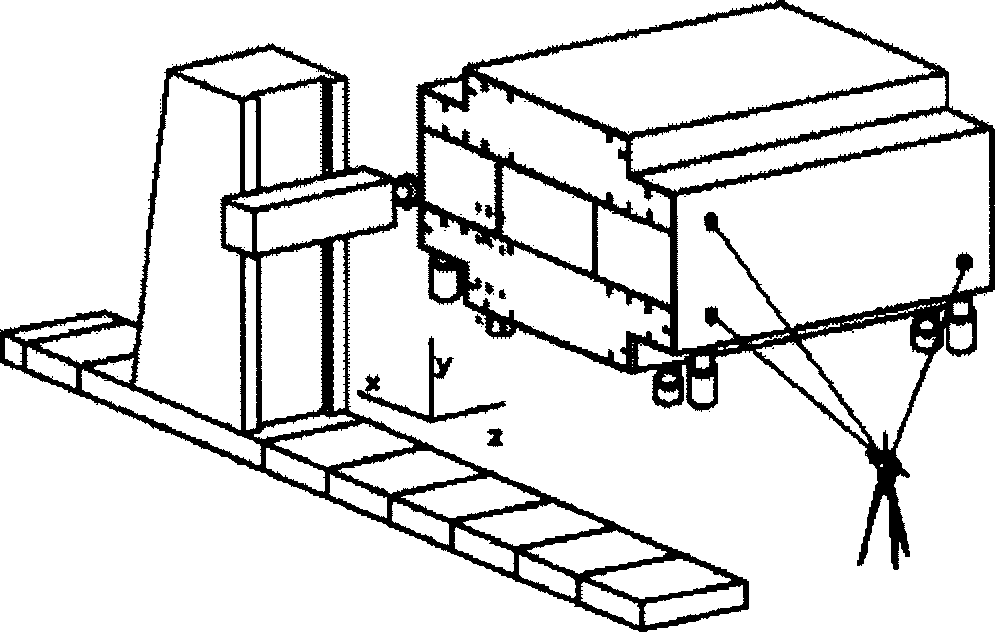
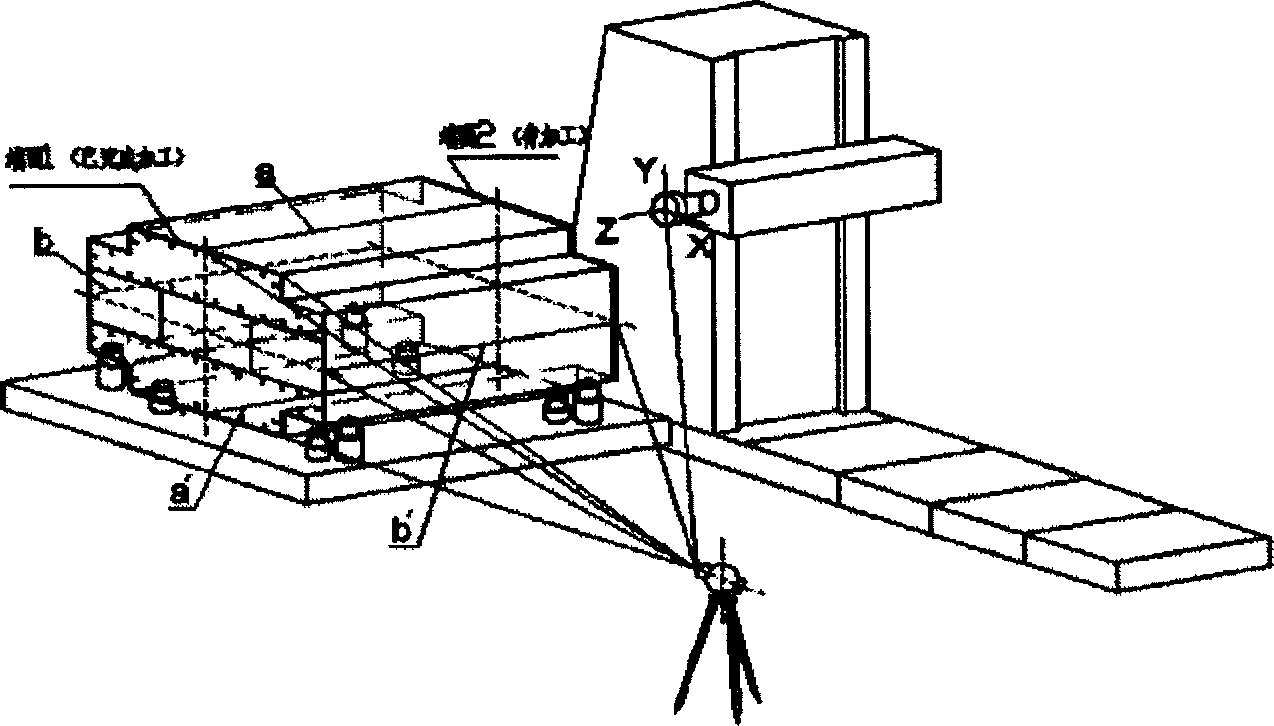
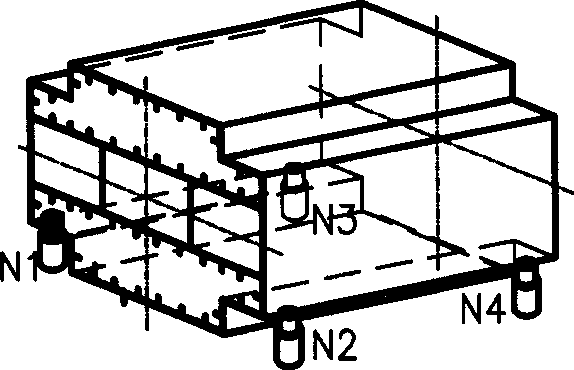
Machining alignment and location method of cable tower segment
InactiveCN1868668AImprove efficiencySatisfy processabilityMeasurement/indication equipmentsPositioning apparatus3d trackingEngineering
A centering and locating method for machining the end face of the segment of steel cable tower includes such steps as using numeral controlled hydraulic locating system to support said segment and locate it to a machining position, centering the first end face by using 3D tracking measurer to measure machine and 3 laser markers for determining the position relation between machine and workpiece and regulating and locking the position of workpiece, centering the second end face by transporting the segment to machining position, creating the coordinate system of machine, measuring and processing the machined first end face, and checking its position in said coordinate system.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY BAOJI BRIDGE GRP
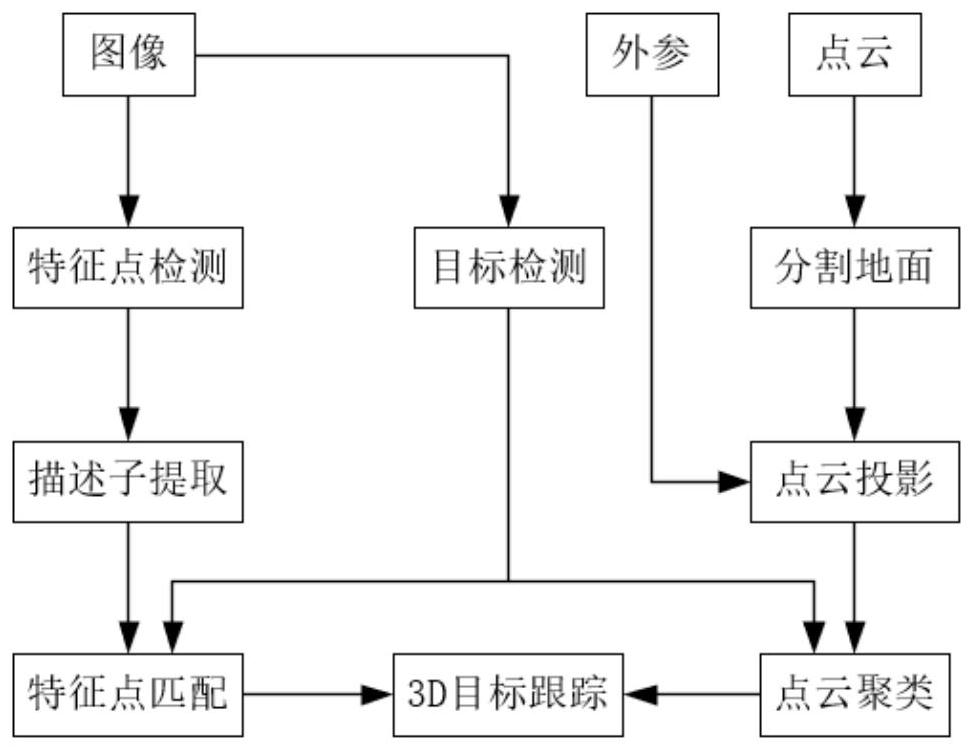
3D target detection and tracking method based on camera and laser radar
The invention discloses a 3D target detection and tracking method based on a camera and a laser radar. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing target detection on an image acquired by a camera to obtain a 2D detection frame and assign a number; meanwhile, carrying out feature point detection, descriptor extraction and feature point matching on the image; then, performing ground segmentation on the point cloud data, and projecting the non-ground point cloud into a corresponding image according to the external parameters of the laser radar and the camera; then, screening and clustering the point clouds according to the 2D detection frame in the image to obtain an object 3D detection frame; and finally, according to the matched feature points, performing matching association on the detection frames of the front and rear frames of images, and replacing numbers to realize 3D tracking of the object. According to the method, the advantages of the laser radar and the camera data are fully fused, the defects that the laser radar classification capability is weak and the camera lacks depth information are overcome, 3D target tracking of the object is realized, and the method can be used for unmanned 3D target detection and tracking tasks.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com