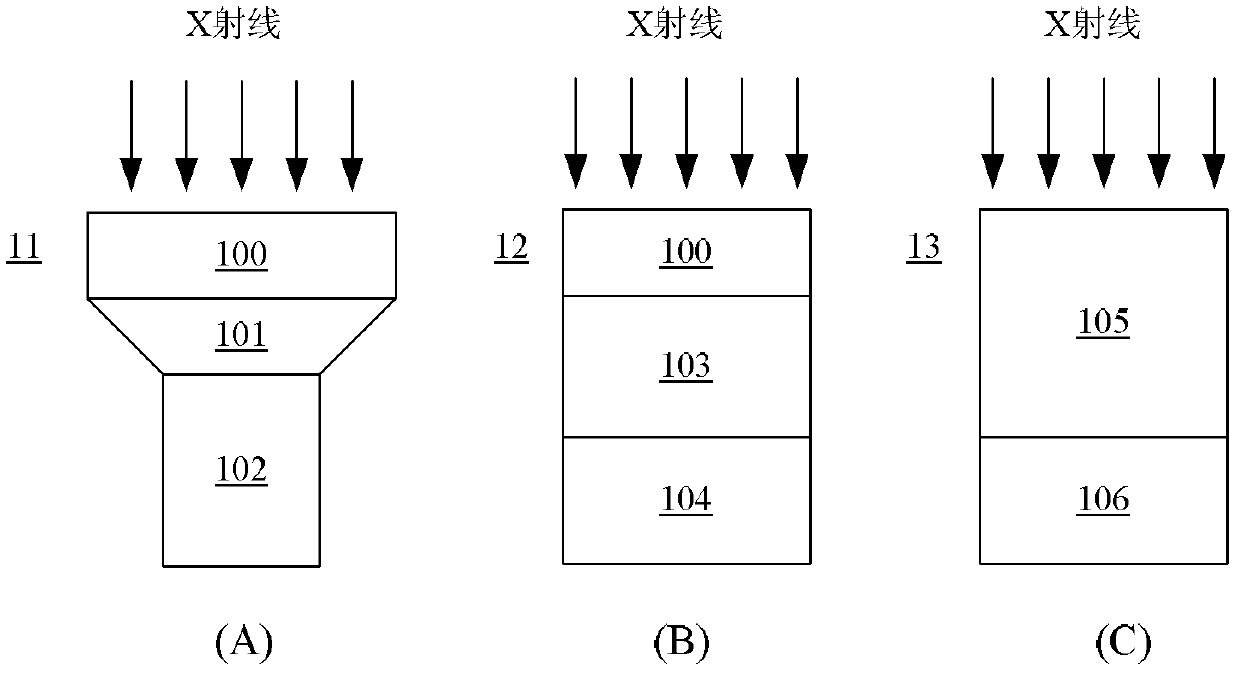
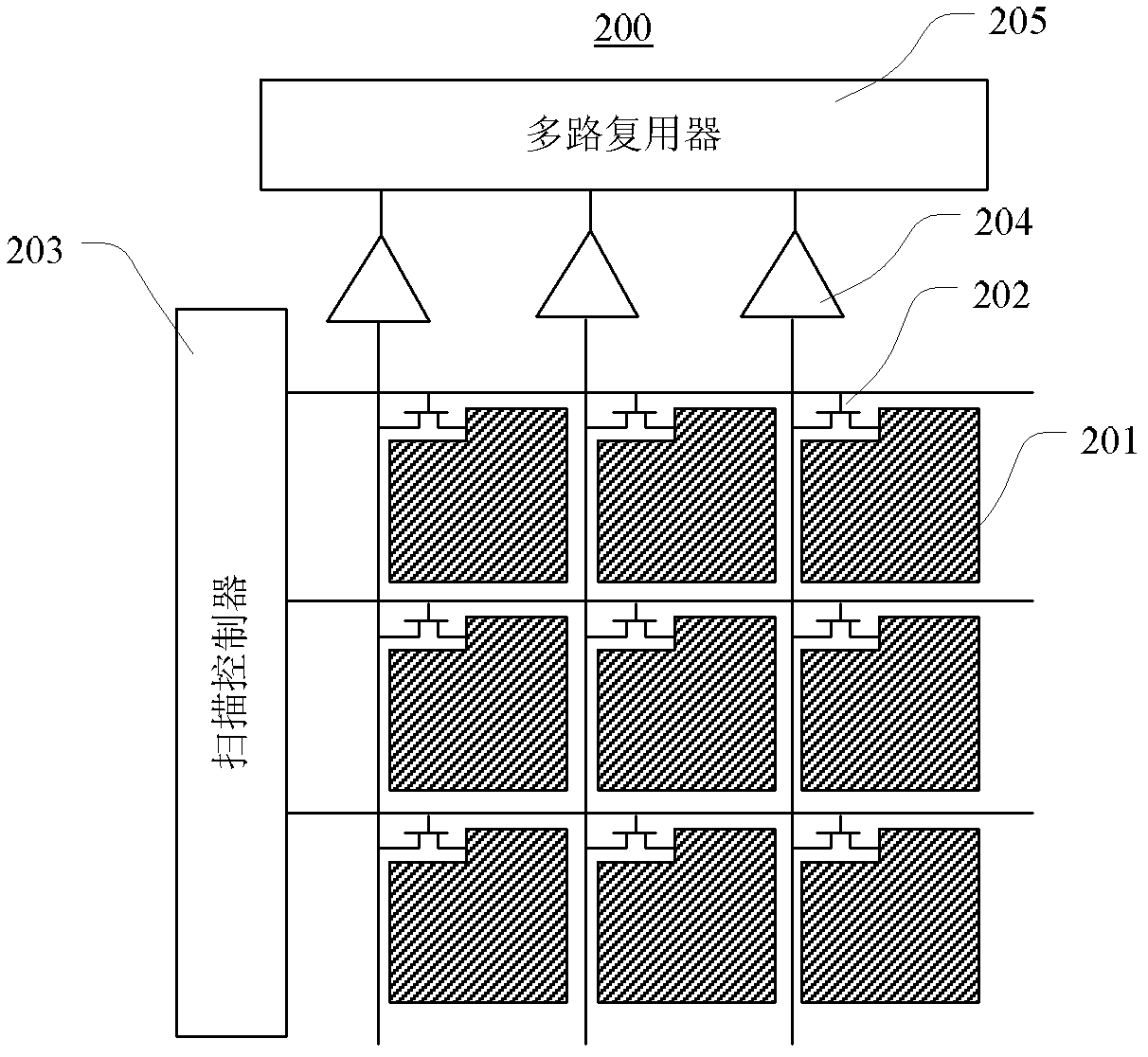
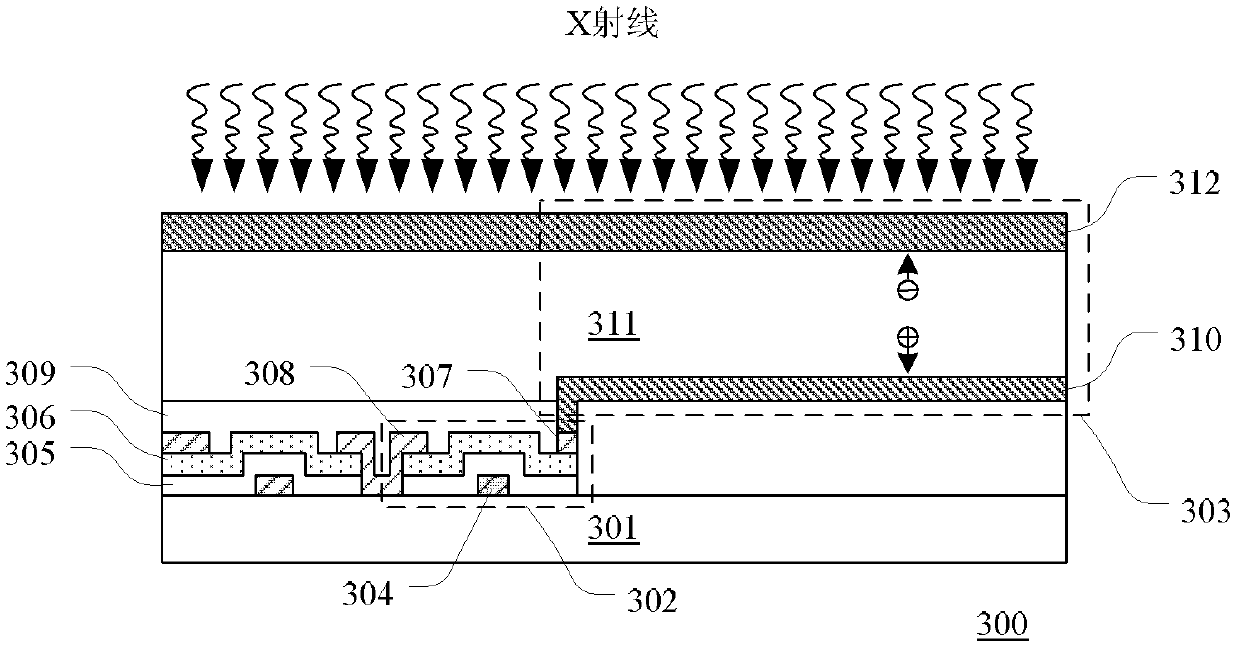
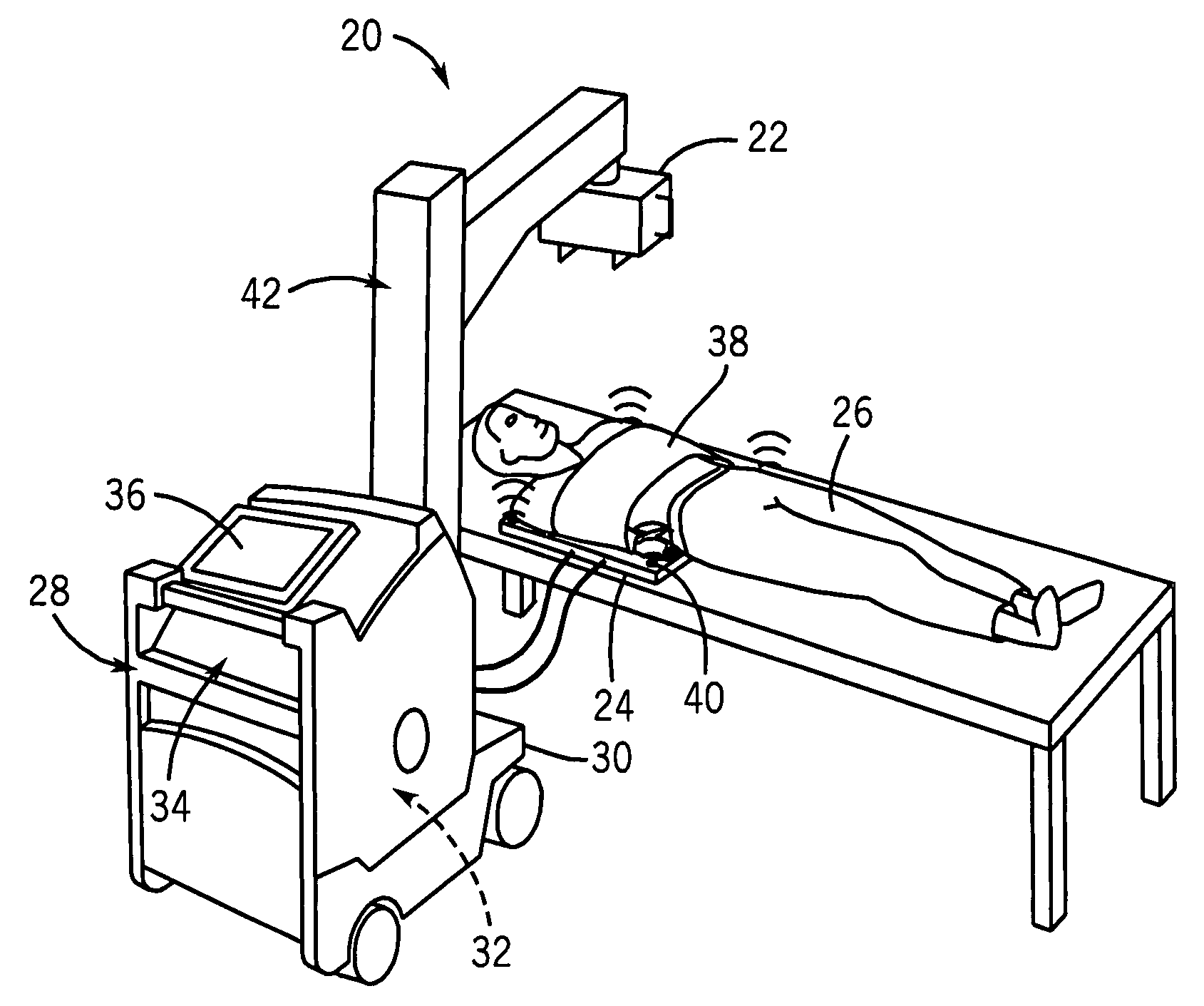
Patents
Literature
848 results about "Flat panel detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
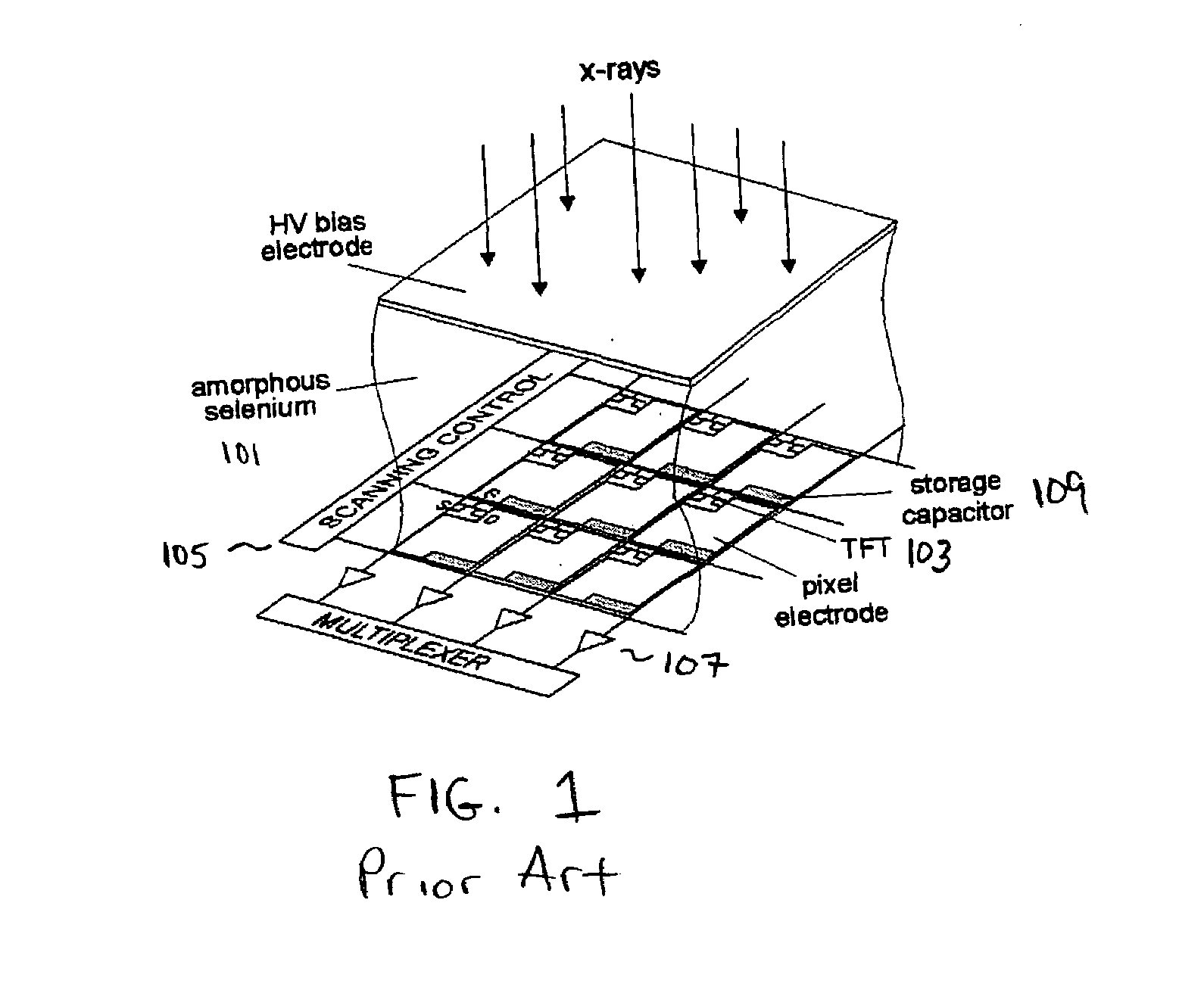
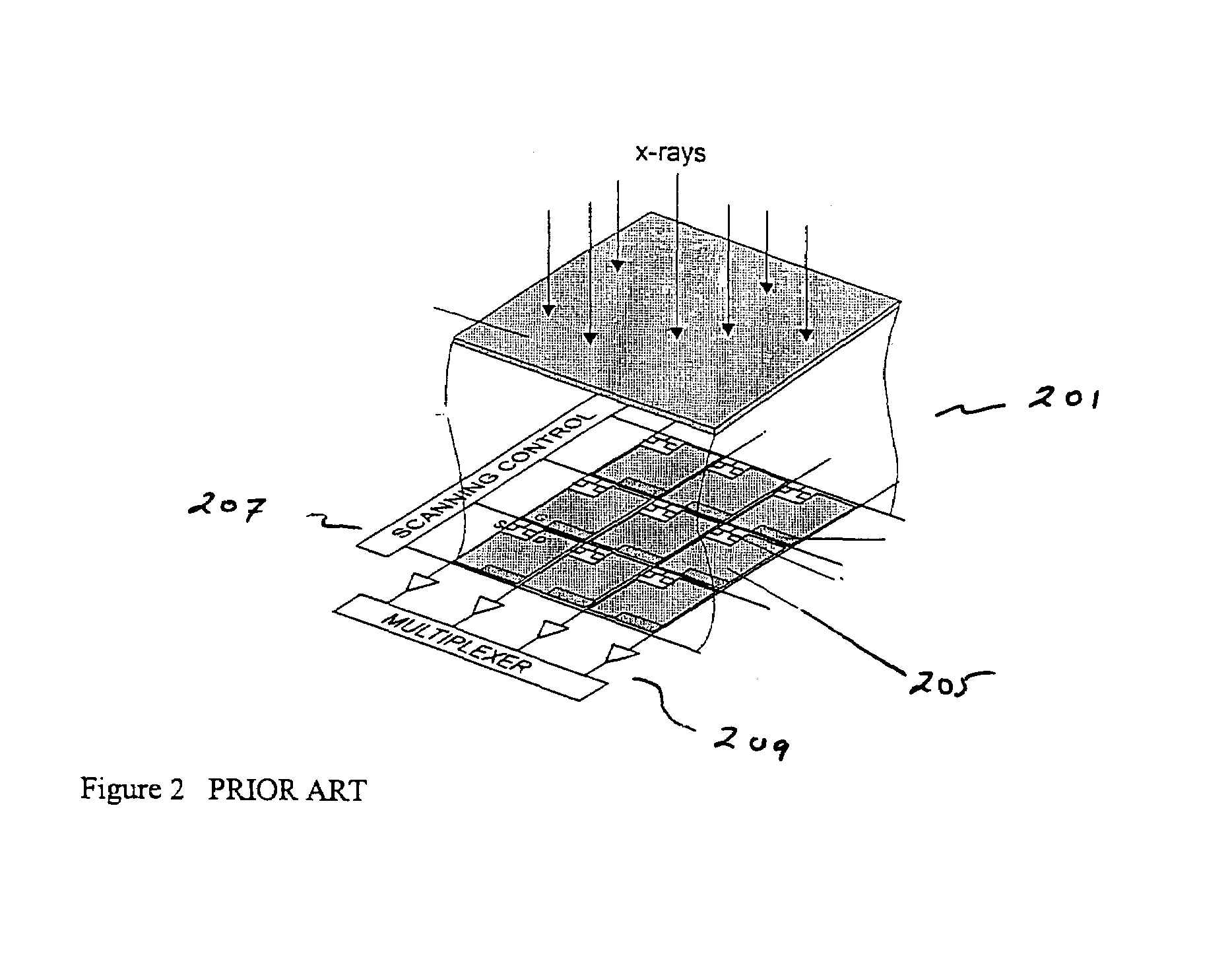
Flat-panel detectors are a class of solid-state x-ray digital radiography devices similar in principle to the image sensors used in digital photography and video. They are used in both projectional radiography and as an alternative to x-ray image intensifiers (IIs) in fluoroscopy equipment.
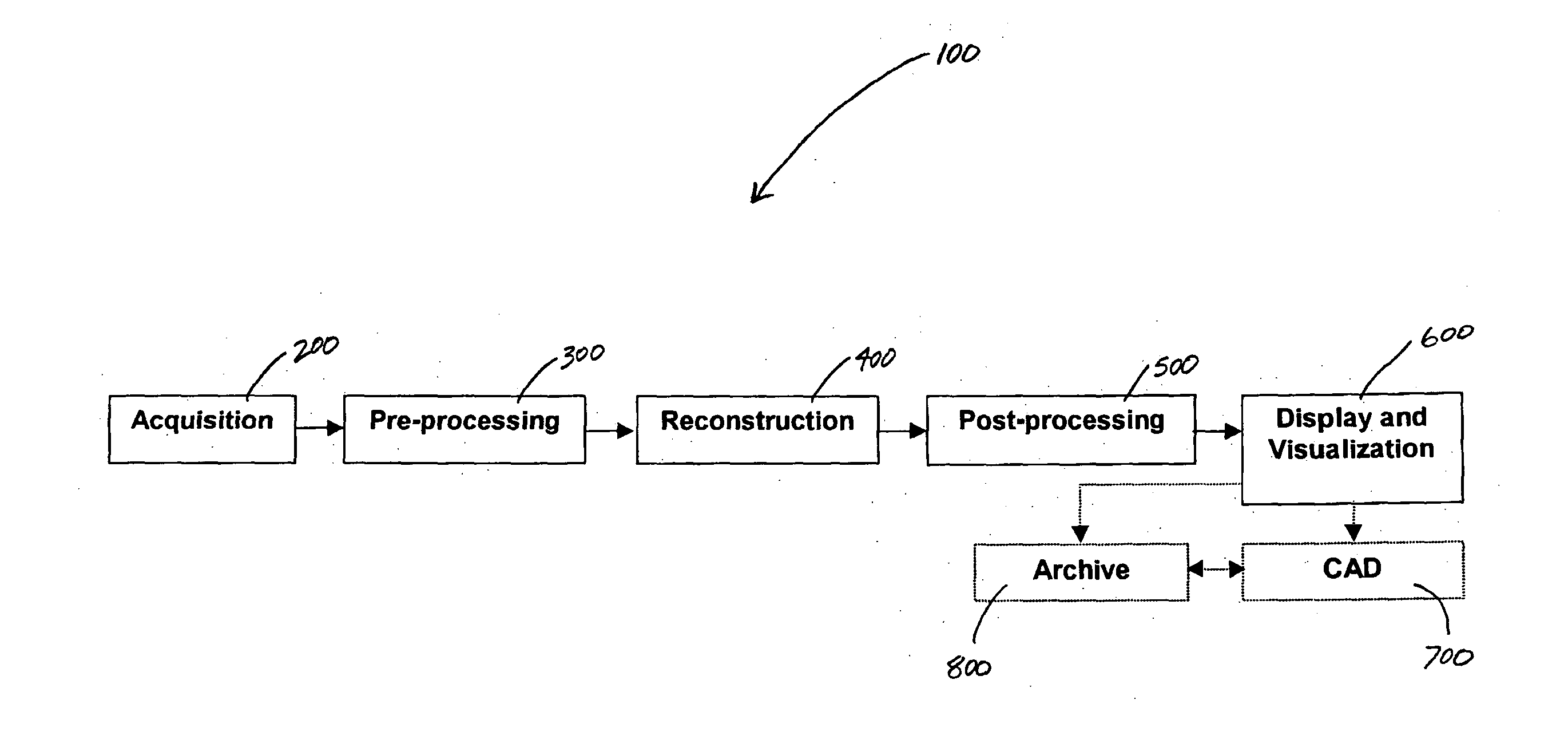
Systems and methods for imaging large field-of-view objects
InactiveUS7108421B2Quantity minimizationAvoiding corrupted and resulting artifacts in image reconstructionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingBeam sourceX-ray
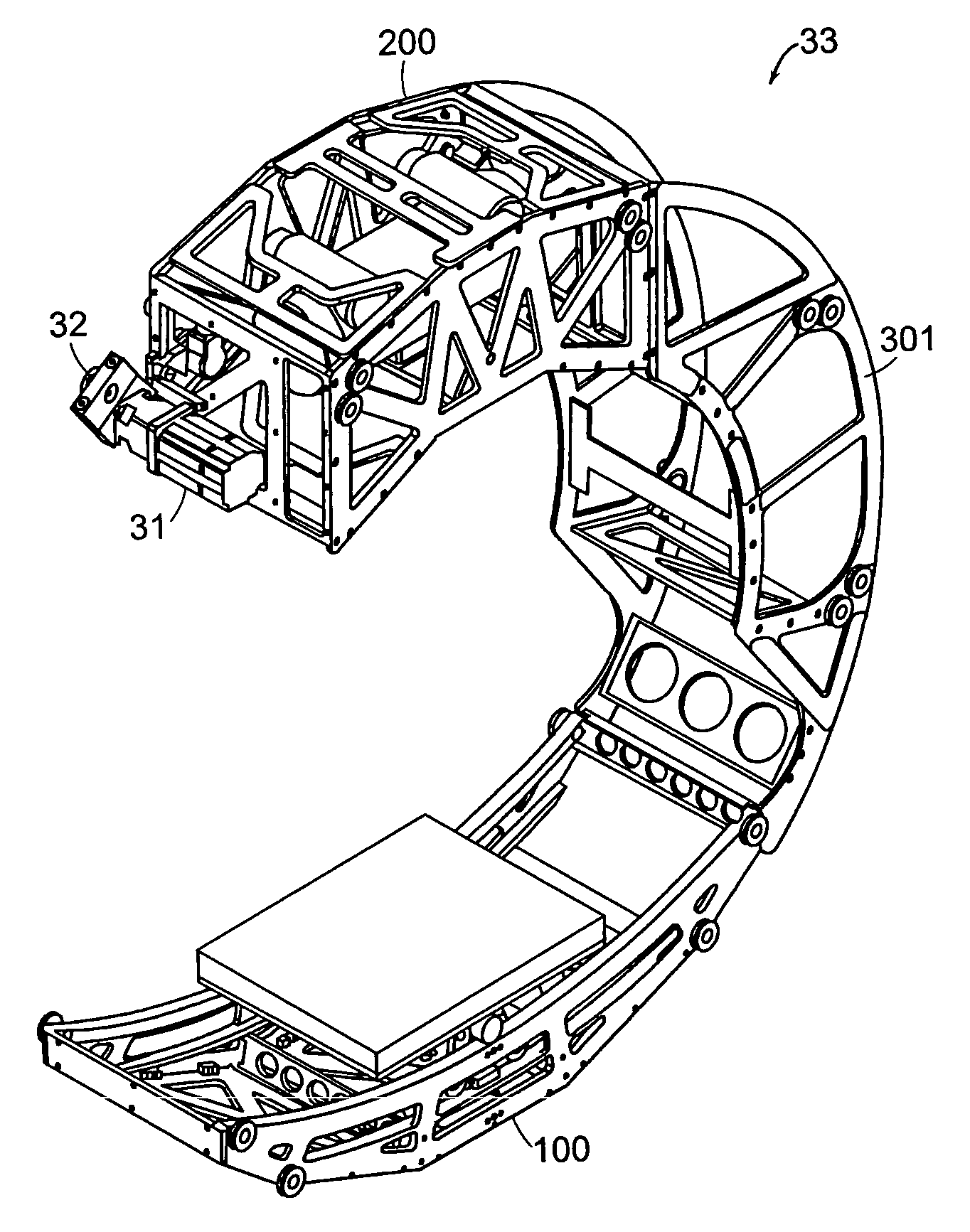
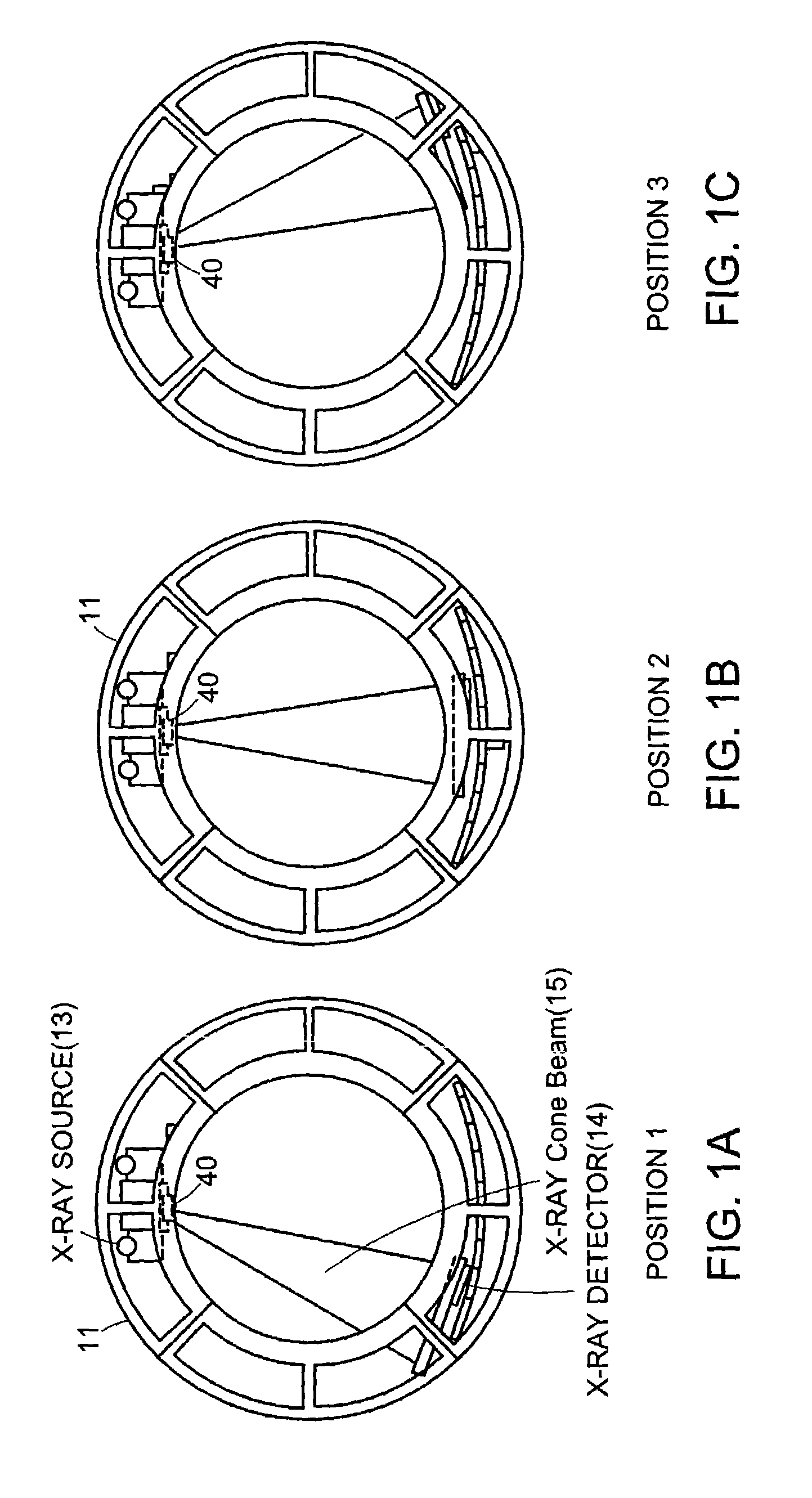
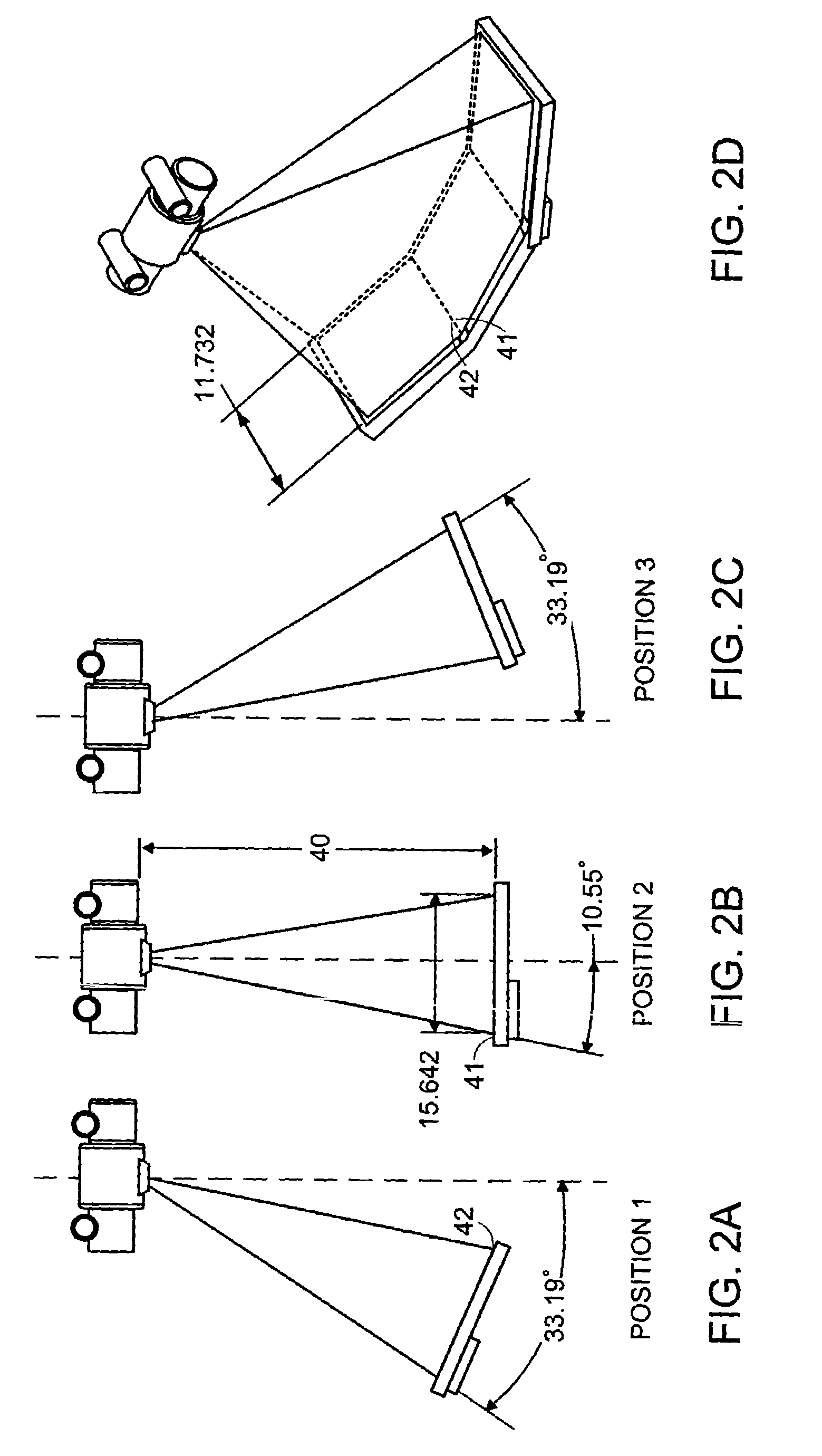
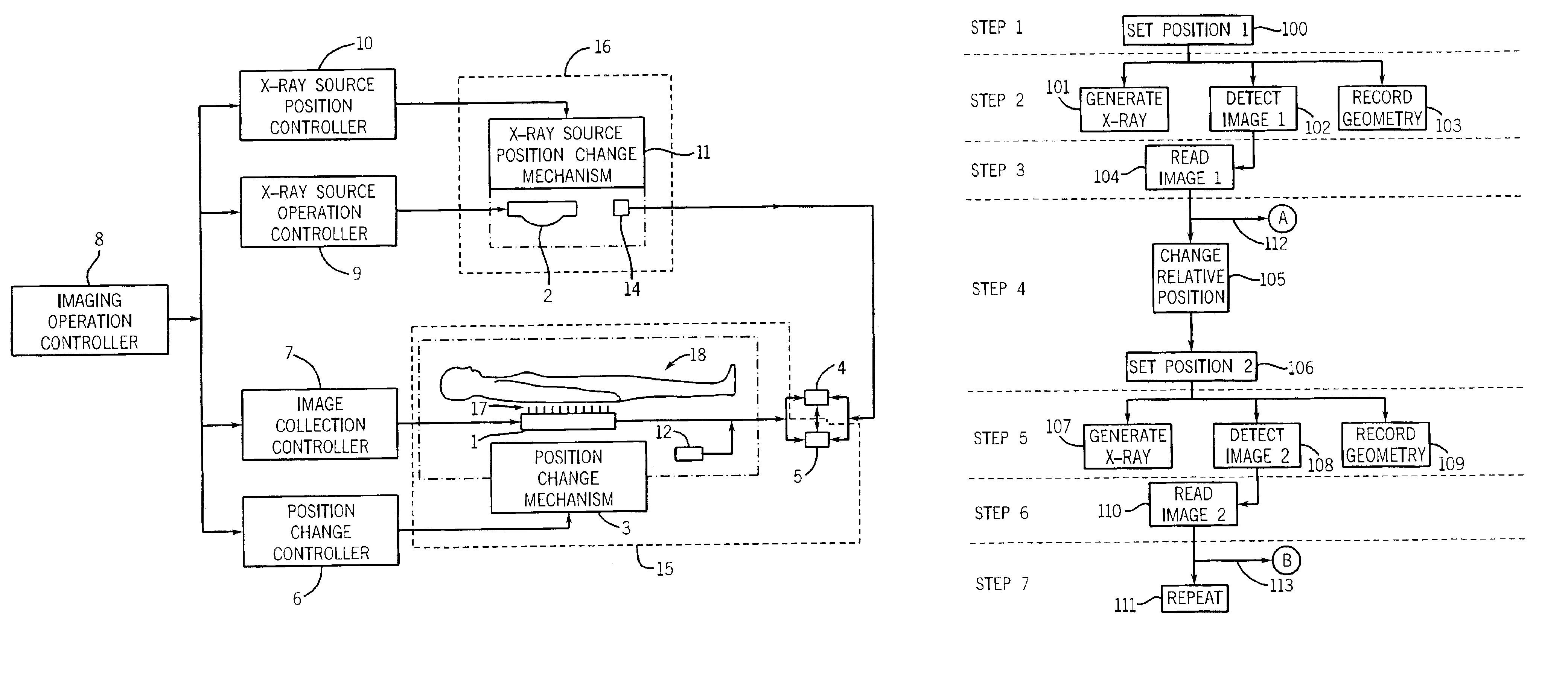
An imaging apparatus and related method comprising a source that projects a beam of radiation in a first trajectory; a detector located a distance from the source and positioned to receive the beam of radiation in the first trajectory; an imaging area between the source and the detector, the radiation beam from the source passing through a portion of the imaging area before it is received at the detector; a detector positioner that translates the detector to a second position in a first direction that is substantially normal to the first trajectory; and a beam positioner that alters the trajectory of the radiation beam to direct the beam onto the detector located at the second position. The radiation source can be an x-ray cone-beam source, and the detector can be a two-dimensional flat-panel detector array. The invention can be used to image objects larger than the field-of-view of the detector by translating the detector array to multiple positions, and obtaining images at each position, resulting in an effectively large field-of-view using only a single detector array having a relatively small size. A beam positioner permits the trajectory of the beam to follow the path of the translating detector, which permits safer and more efficient dose utilization, as generally only the region of the target object that is within the field-of-view of the detector at any given time will be exposed to potentially harmful radiation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
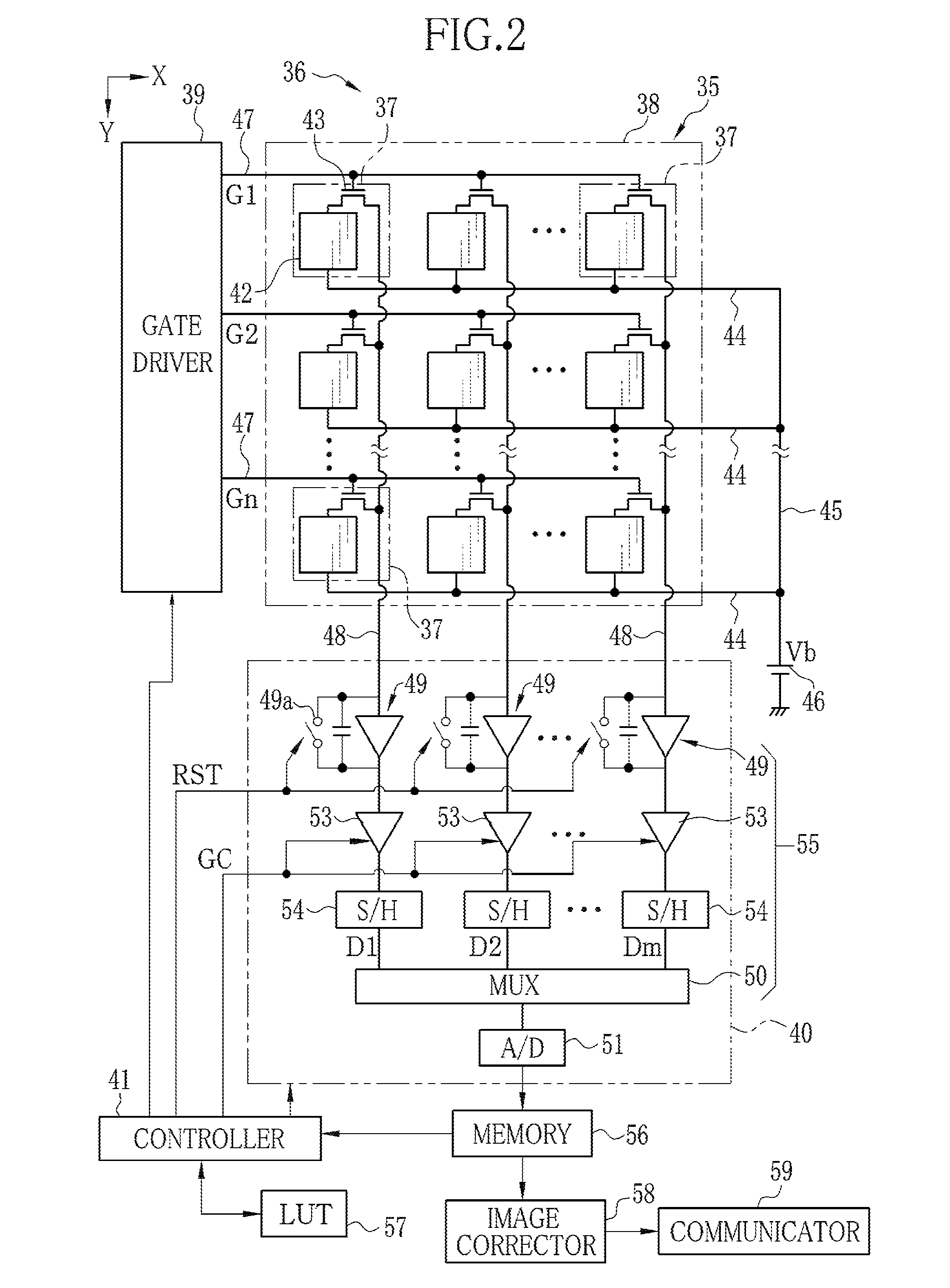
Flat-panel detector with avalanche gain
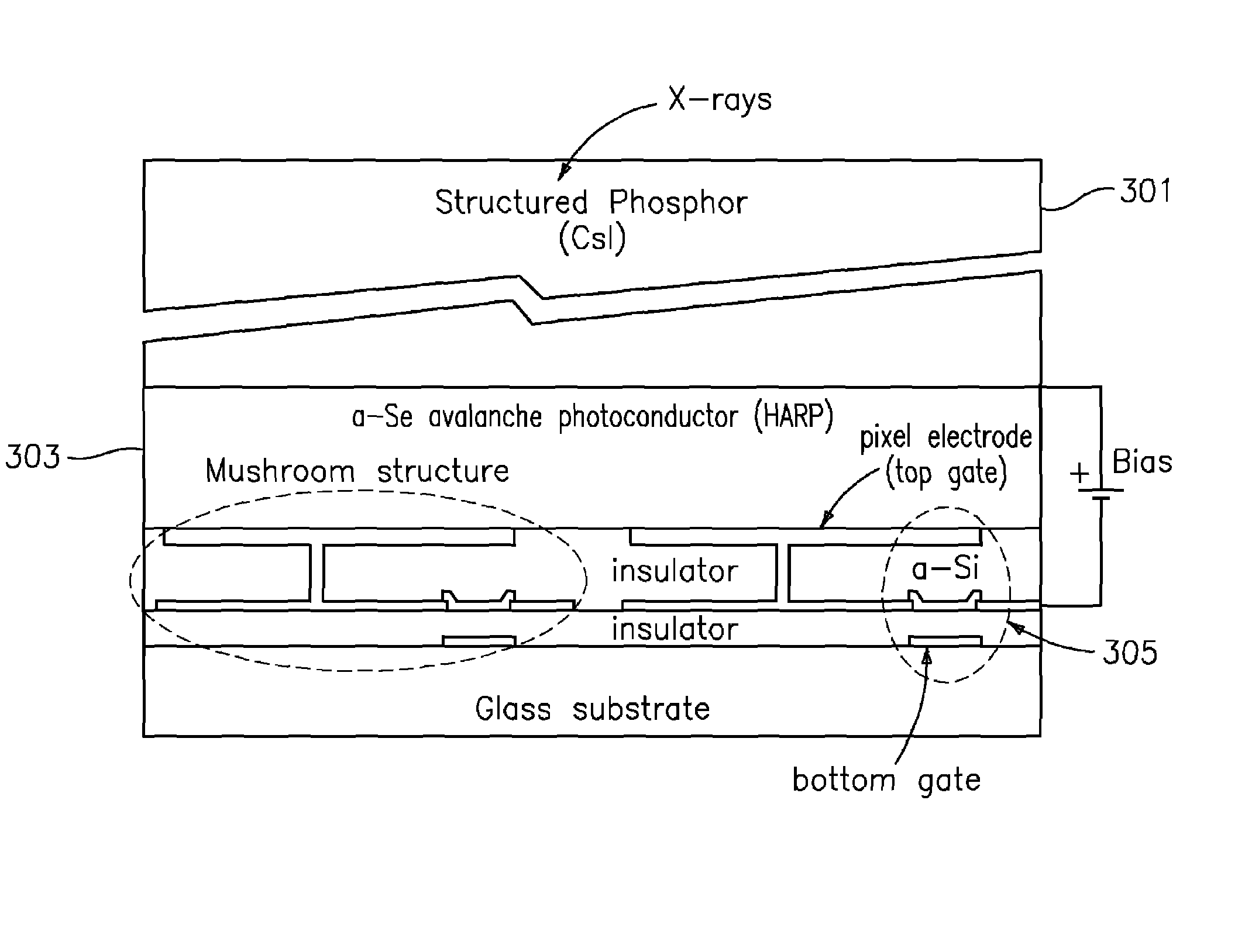
ActiveUS7323692B2Improve image qualityReduce doseSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFlat panel detectorAudio power amplifier
The present invention is an indirect AMFPI wherein a phosphor such as a structured cesium iodide (CsI) is used to convert x-ray energy to optical photons or a charge, which is then detected by a two-dimensional array of either thin-film transistors (TFTs) such as an amorphous a-Se TFTs or a photodiode array. A scanning control circuit generates pulses to turn on the TFTs one row at a time, and thus the charge in the individual arrays is transferred from the TFT to one or more external charge-sensitive amplifiers. The charge-sensitive amplifiers are shared by all the pixels in the same column. The two-dimensional array can be read in real time.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
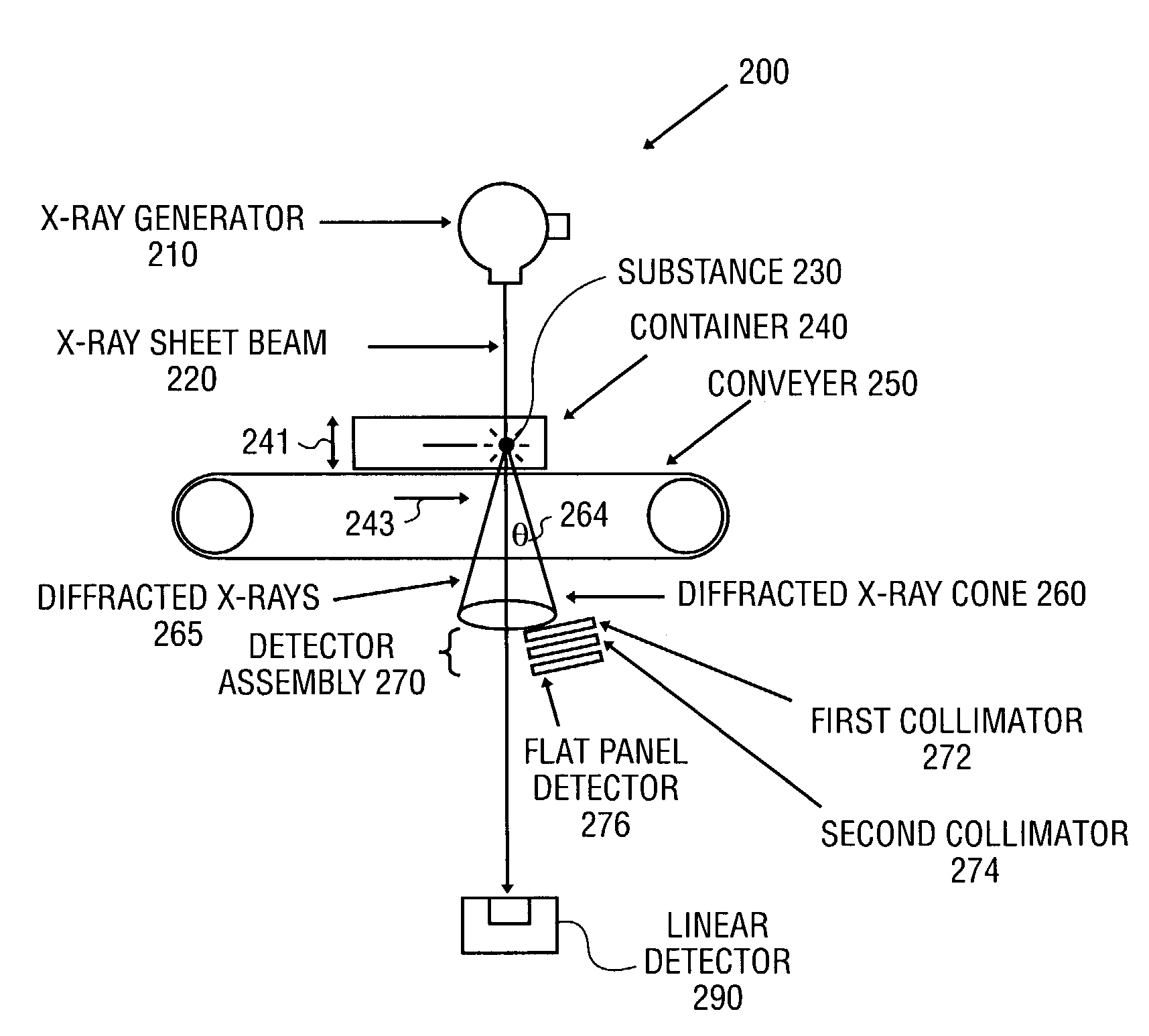
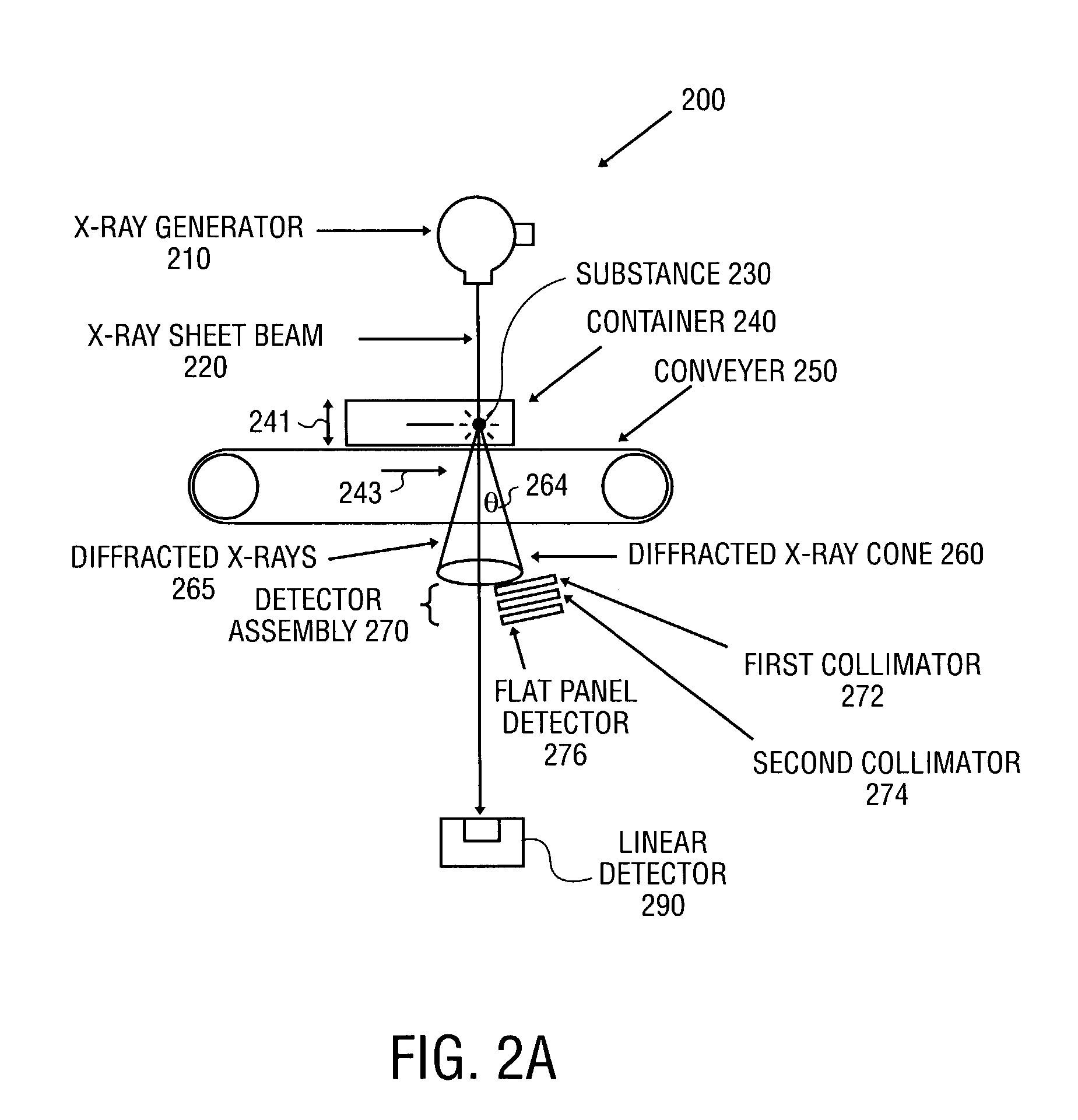
X-ray diffraction-based scanning system
InactiveUS7065175B2X-ray tube electrodesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoft x rayFlat panel detector
An x-ray diffraction-based scanning method and system are described. The method includes screening for a particular substance in a container at a transportation center using a flat panel detector having a photoconductor x-ray conversion layer to detect x-rays diffracted by a particular substance in the container. The diffracted x-rays may be characterized in different ways, for examples, by wavelength dispersive diffraction and energy dispersive diffraction.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
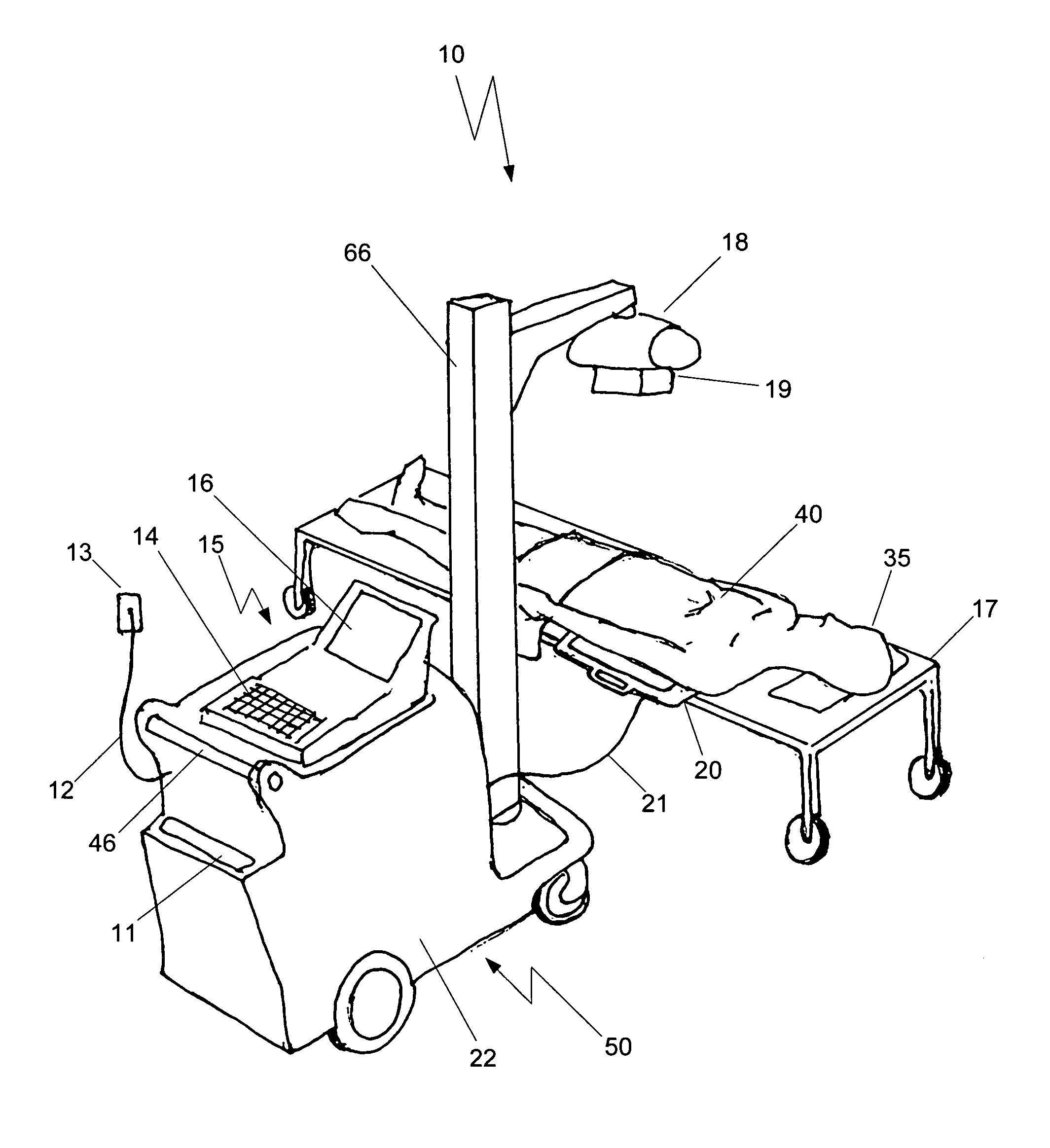
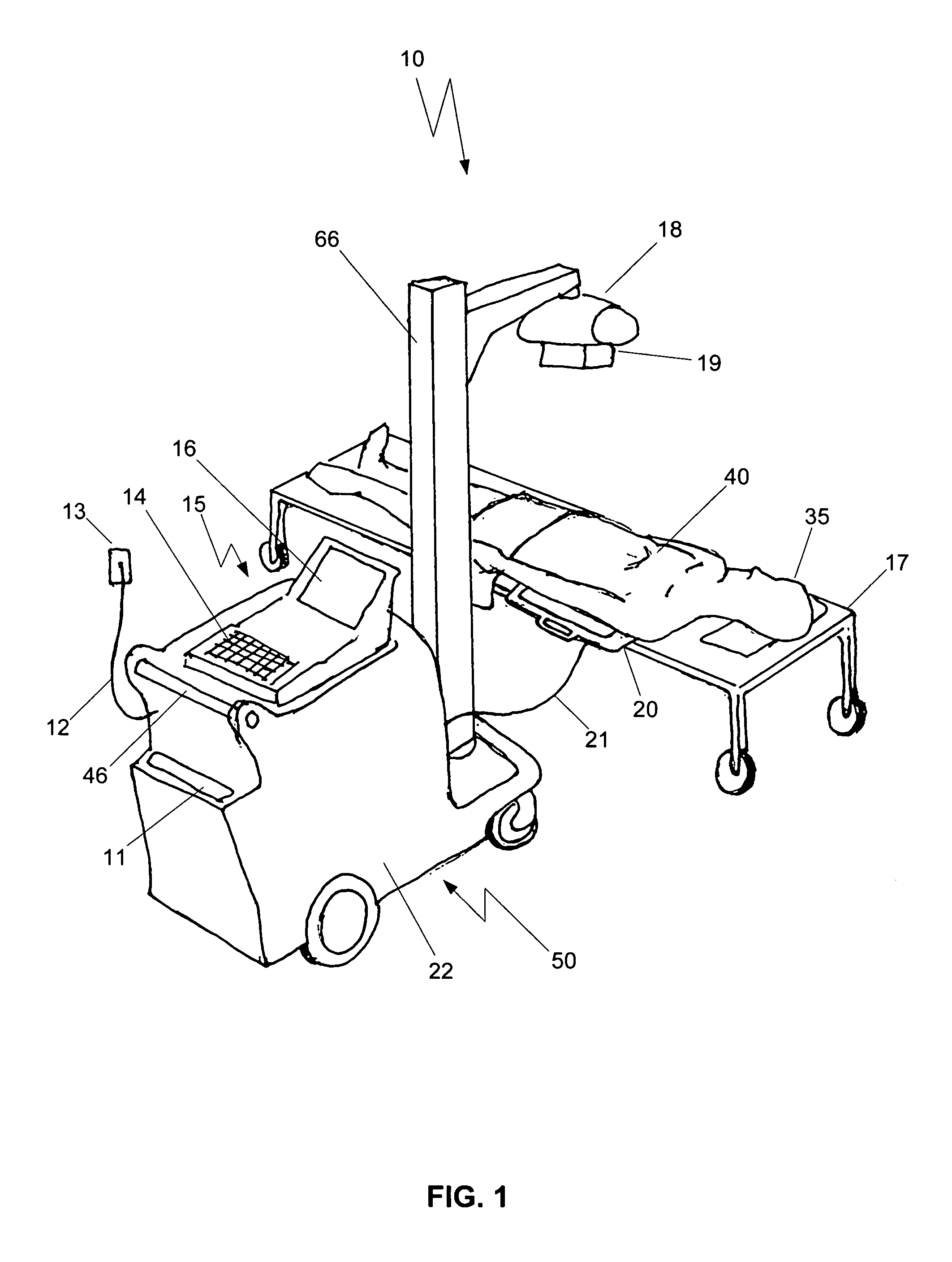
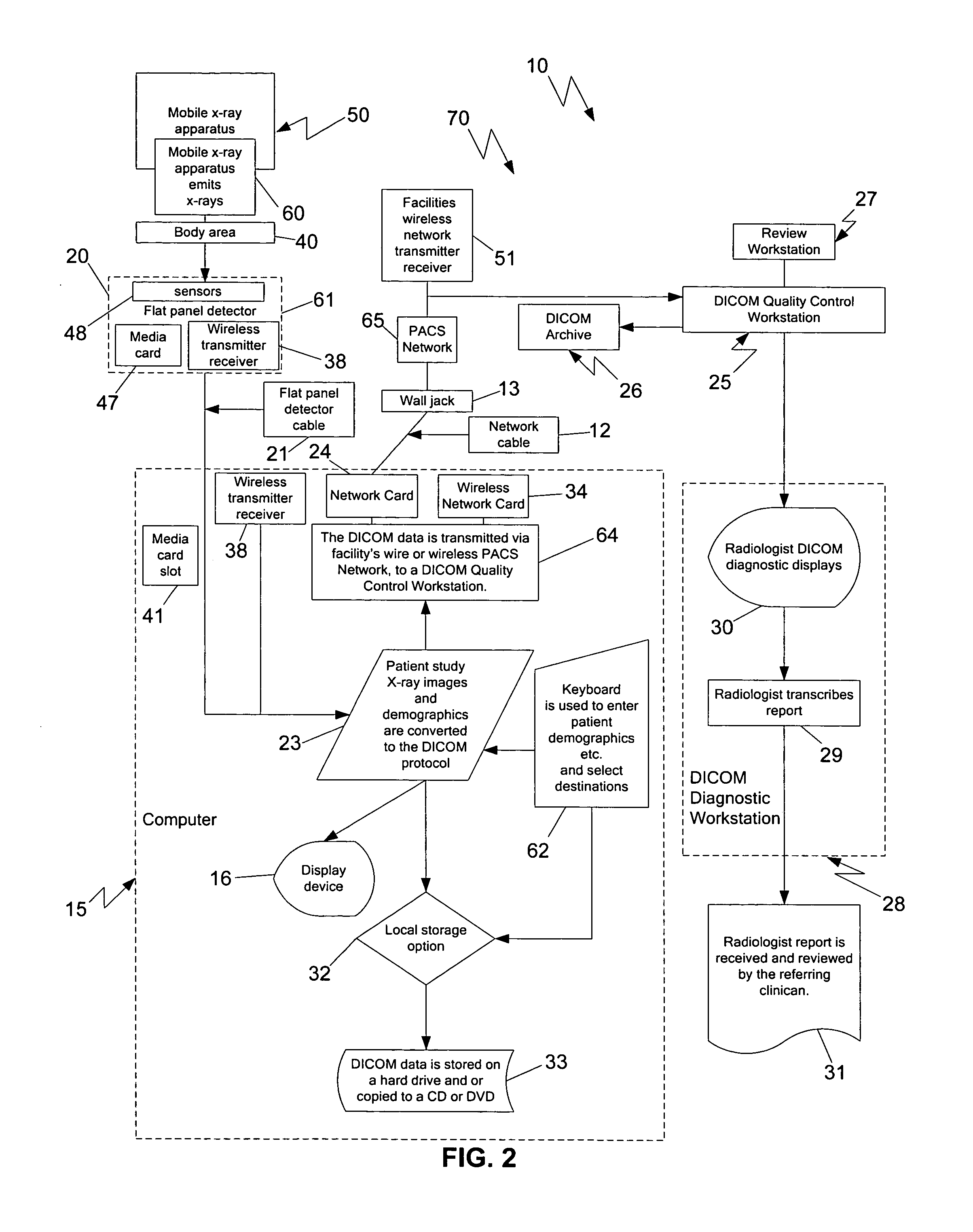
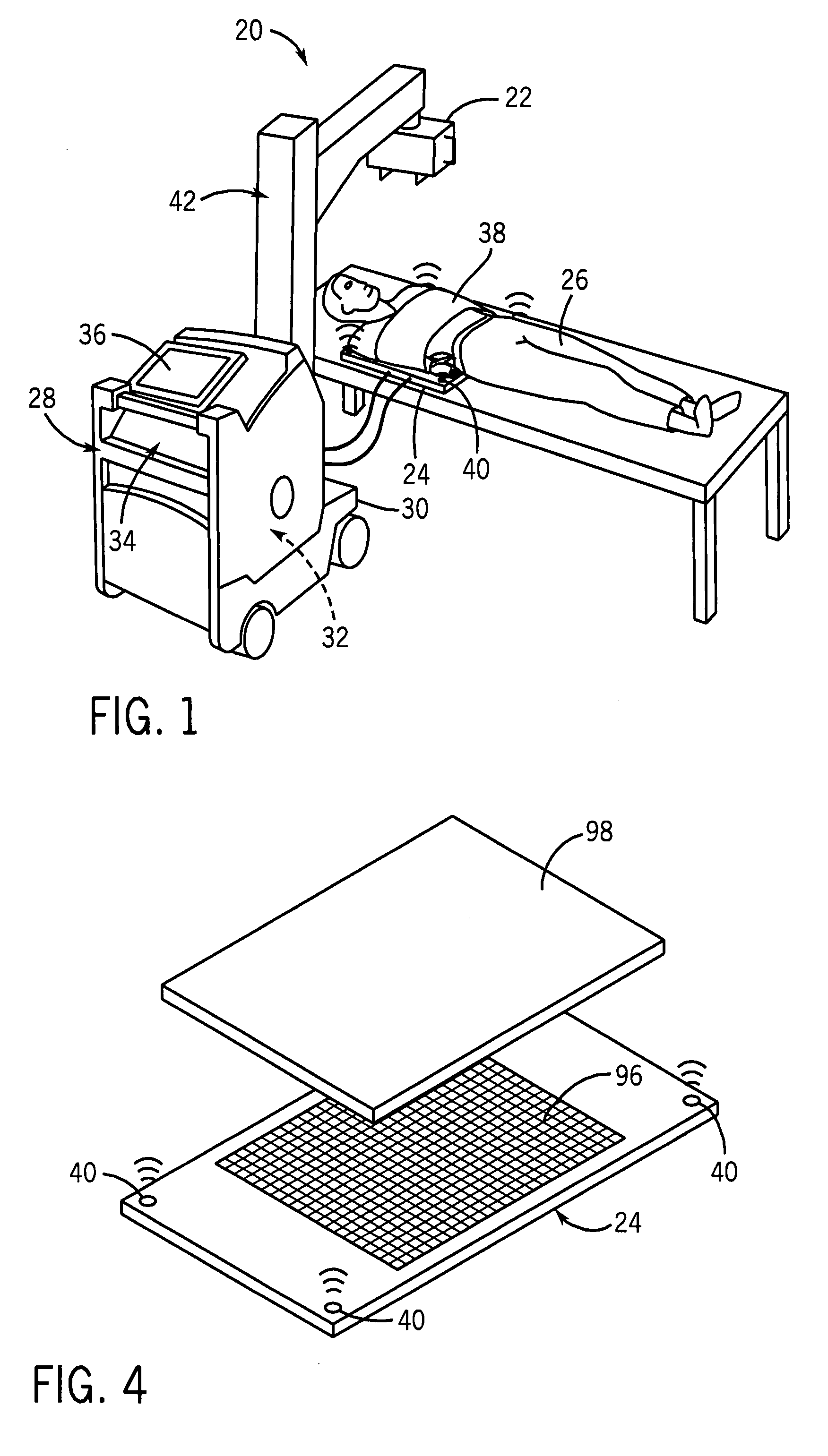
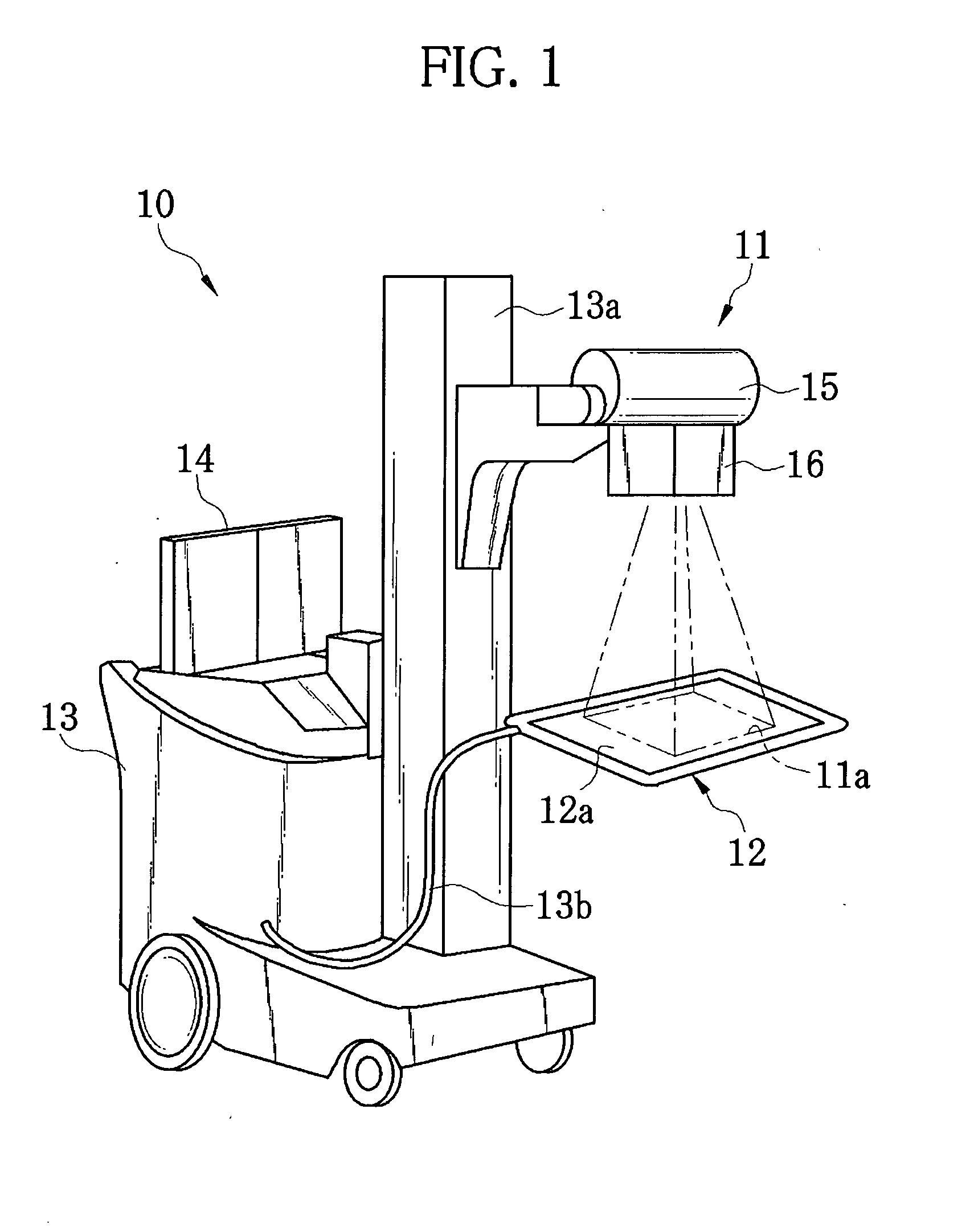
Mobile digital radiography x-ray apparatus and system
A mobile x-ray apparatus for generating a digital x-ray image and transmitting it to a remote site, includes: (a) a first computer; (b) a flat panel detector in communication with the first computer; and (c) an x-ray cart assembly removably supporting the first computer, which includes a cart with a battery charger and an x-ray machine in communication with the flat panel detector; wherein the mobile x-ray apparatus includes an x-ray tube extendible from the cart, and a mechanism for framing a target body area of a patient. Also included herein is a method of generating a digital x-ray image and forwarding it to a remote site using the mobile x-ray apparatus.
Owner:BROOKS JACK JEROME
Imaging chain for digital tomosynthesis on a flat panel detector
A method of creating and displaying images resulting from digital tomosynthesis performed on a subject using a flat panel detector is disclosed. The method includes the step of acquiring a series of x-ray images of the subject, where each x-ray image is acquired at different angles relative to the subject. The method also includes the steps of applying a first set of corrective measures to the series of images, reconstructing the series of images into a series of slices through the subject, and applying a second set of corrective measures to the slices. The method further includes the step of displaying the images or slices according to at least one of a plurality of display options.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
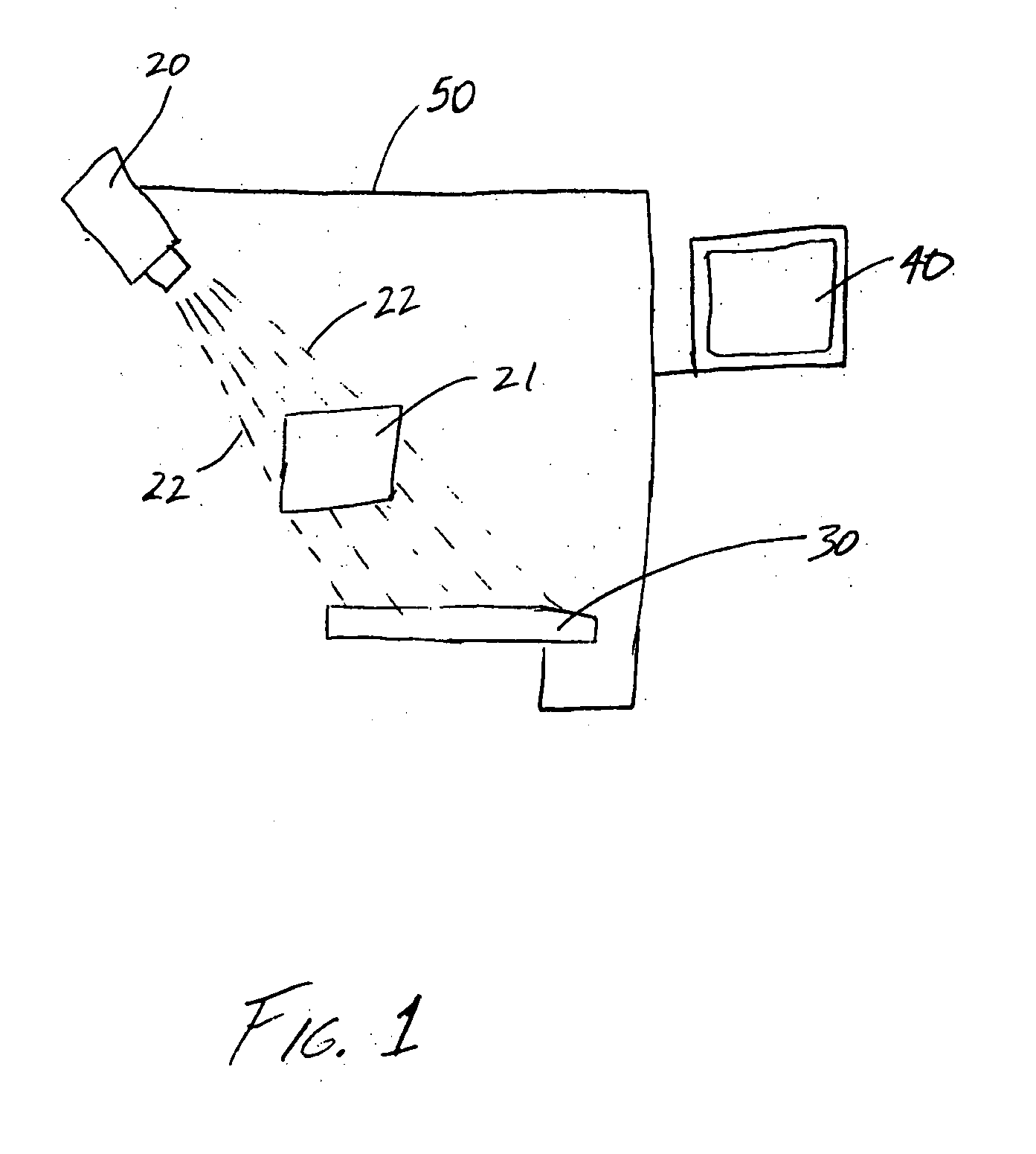
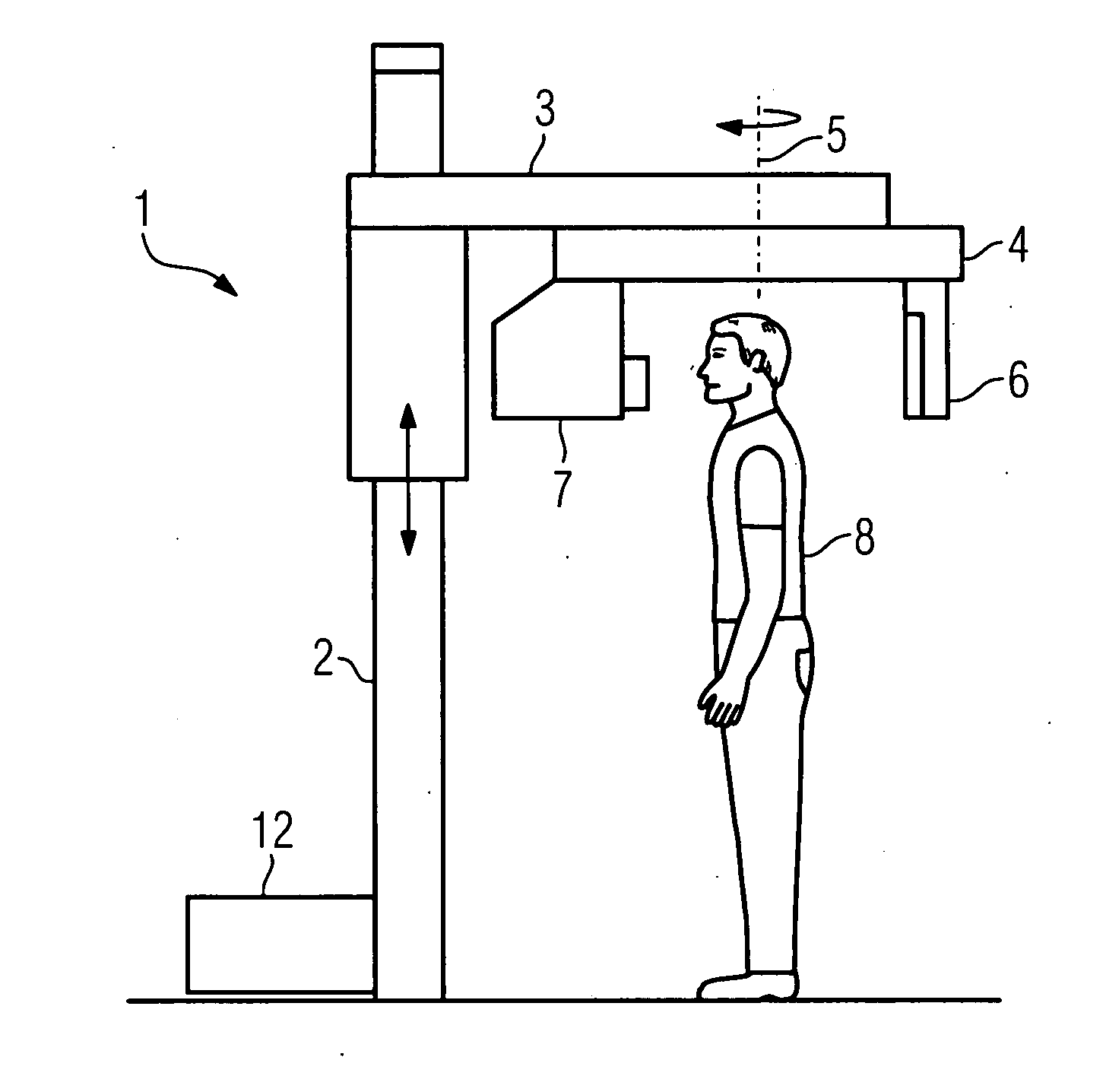
X-ray diagnostic device
InactiveUS20070269001A1Improve representationCharacter and pattern recognitionRadiation diagnostics for dentistryX-rayBlood vessel
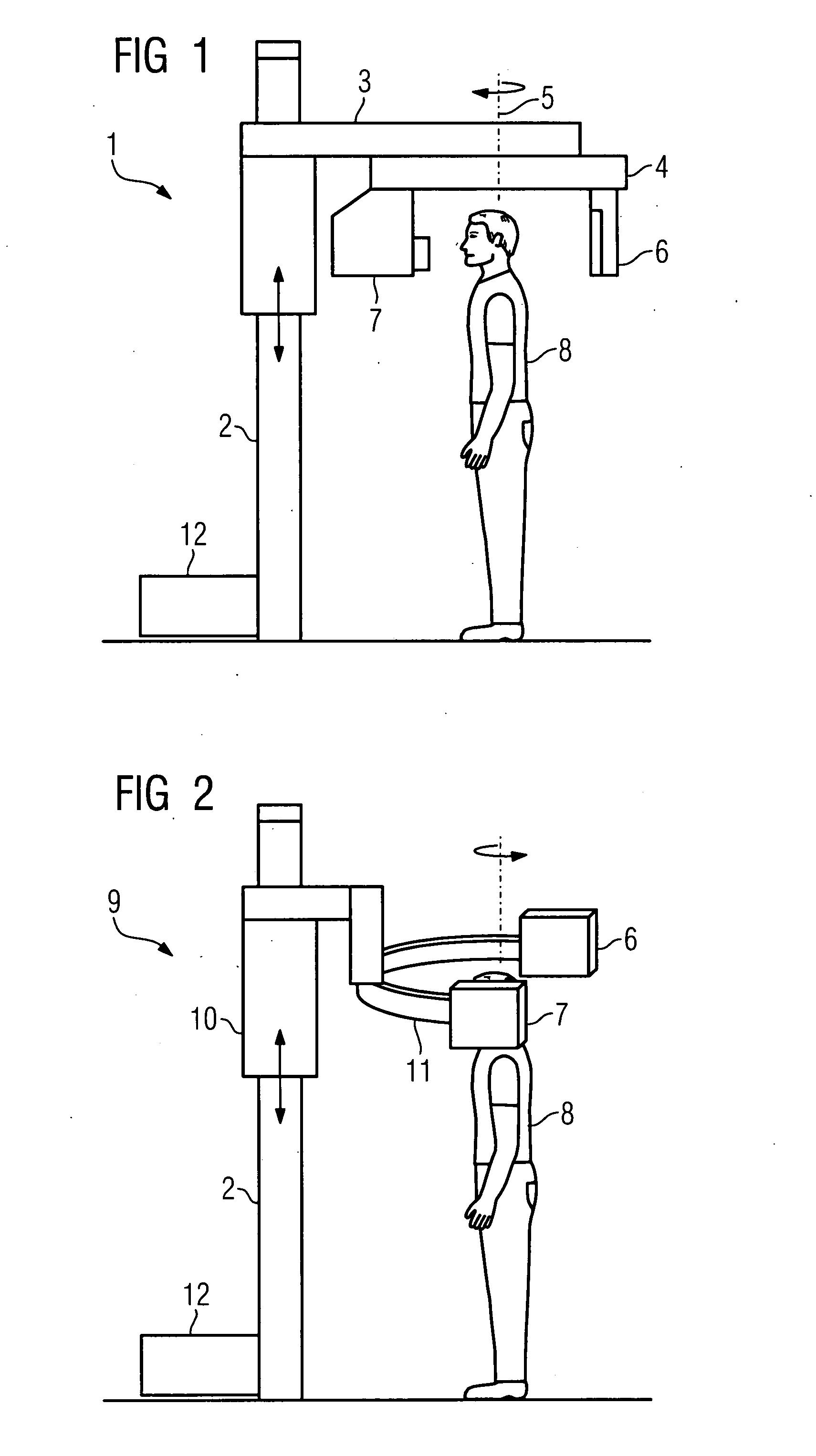
There is described an X-ray diagnostic device for performing cephalometric, dental or orthopedic examinations on a patient who is seated or standing. The X-ray diagnostic device comprises an X-ray emitter and an image detector embodied as a flat-panel detector that are arranged situated opposite each other on an orbitally moveable mount. The X-ray diagnostic device further comprises means for adjusting the height of the X-ray emitter and the image detector, a digital image system for recording a projection image using rotation angiography, a device for image processing for reconstructing the projection image into a 3D volume image; and a device for correcting physical effects or artifacts for representing soft tissue in the projection image and in the 3D volume image reconstructed therefrom.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range
InactiveUS6868138B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayFlat panel detector
A method, processor and computed tomography (CT) machine for generating images utilizing high and low sensitivity data collected from a flat panel detector having an extended dynamic range. Hardware modifications for extending the dynamic range include grouping pixel rows and pixel columns into clusters of two. The sensitivity of the rows / columns is modified by positioning optical masks that have different transparencies for different rows / columns. Software modifications for extending the dynamic range include taking two correlated exposure scan measurements at each angle and combining the two data sets into one scan prior to image reconstruction. This method uses a spatially varying pixel exposure method where several adjacent pixels are clustered and each cluster has a different sensitivity. The signals of these clusters are combined to form one image effectively producing an increased dynamic range. The flat panel imager may be an a-Si:H based flat panel detector for use in X-ray imaging, including cone beam computer tomography (CBCT).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
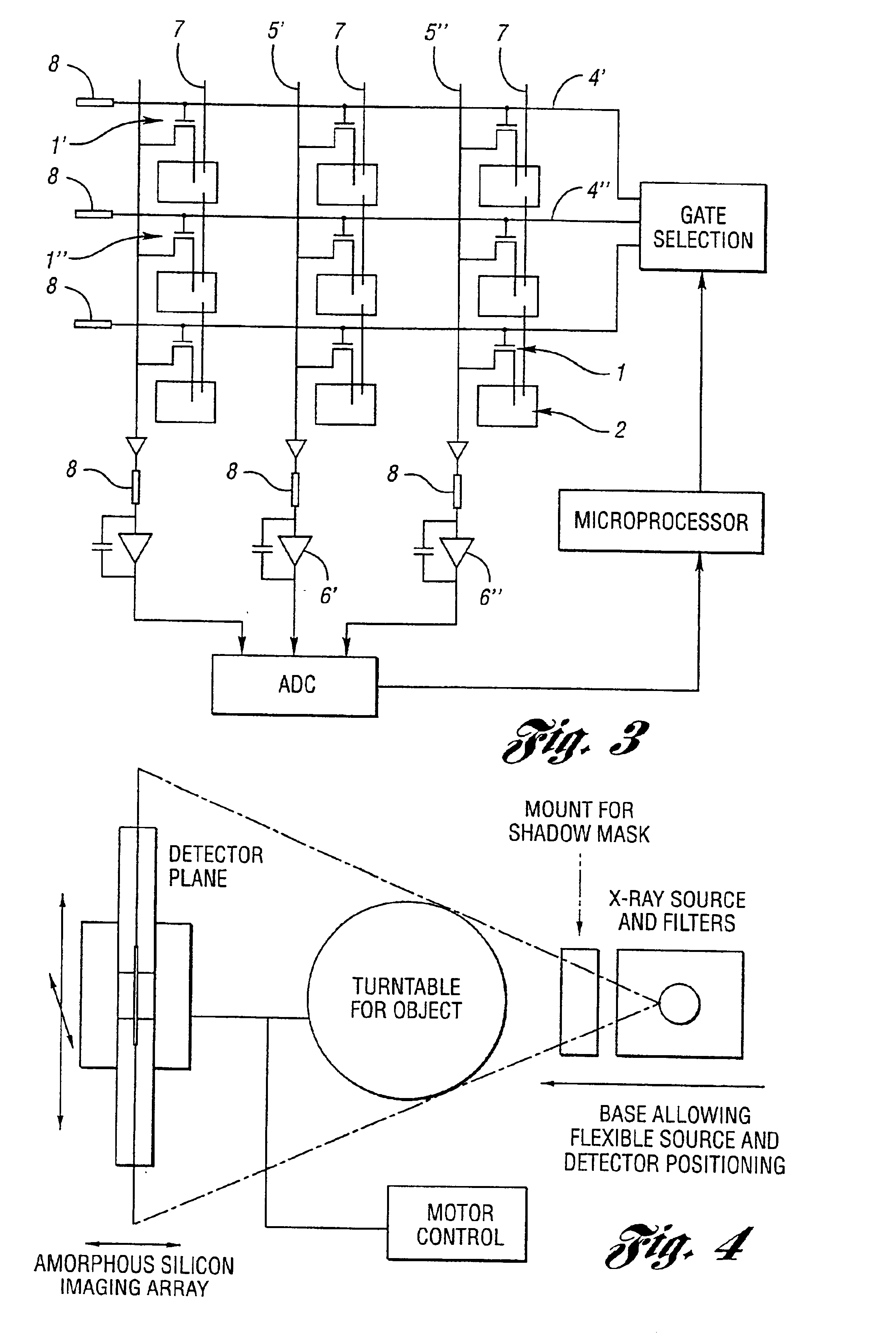
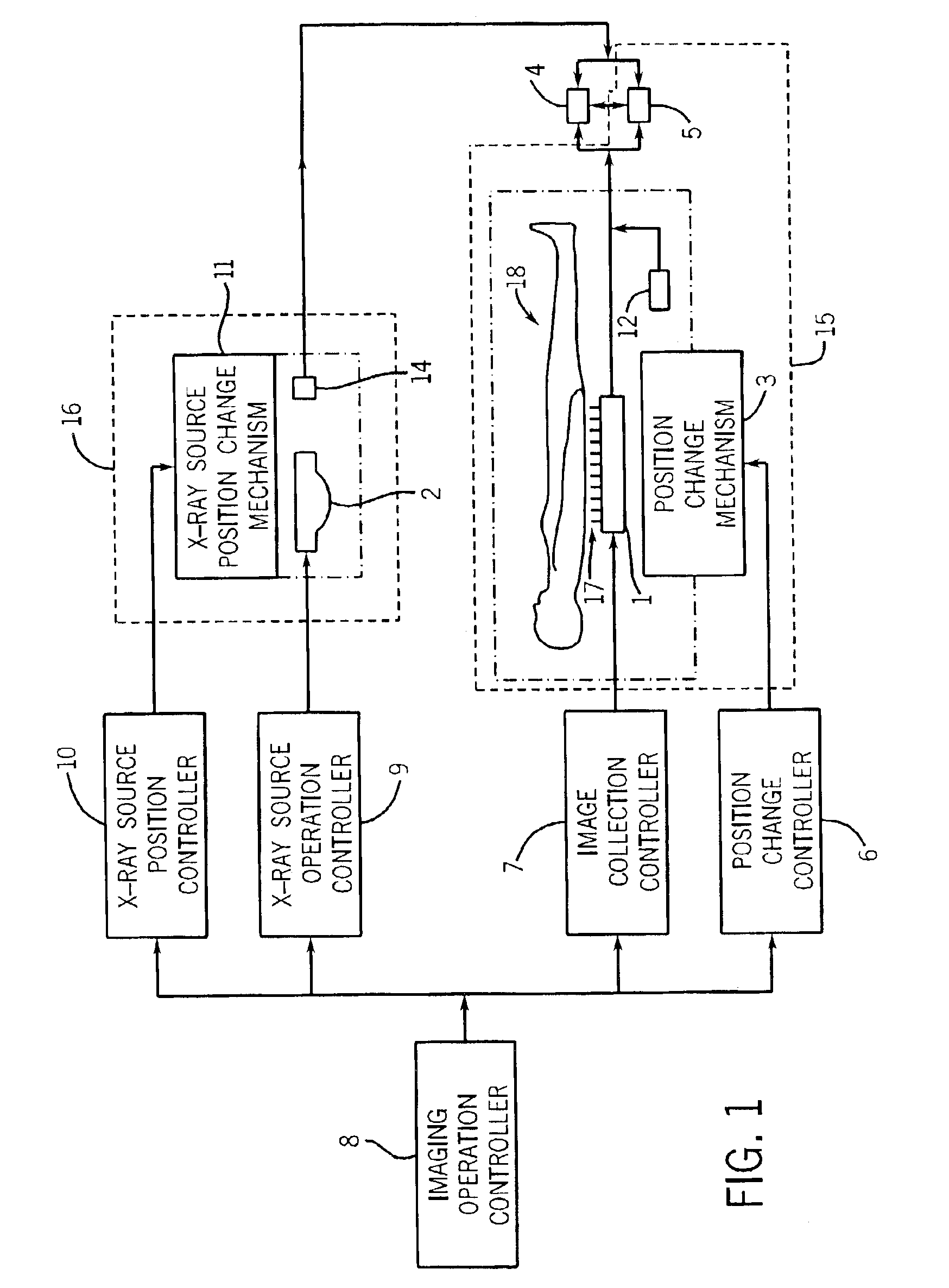
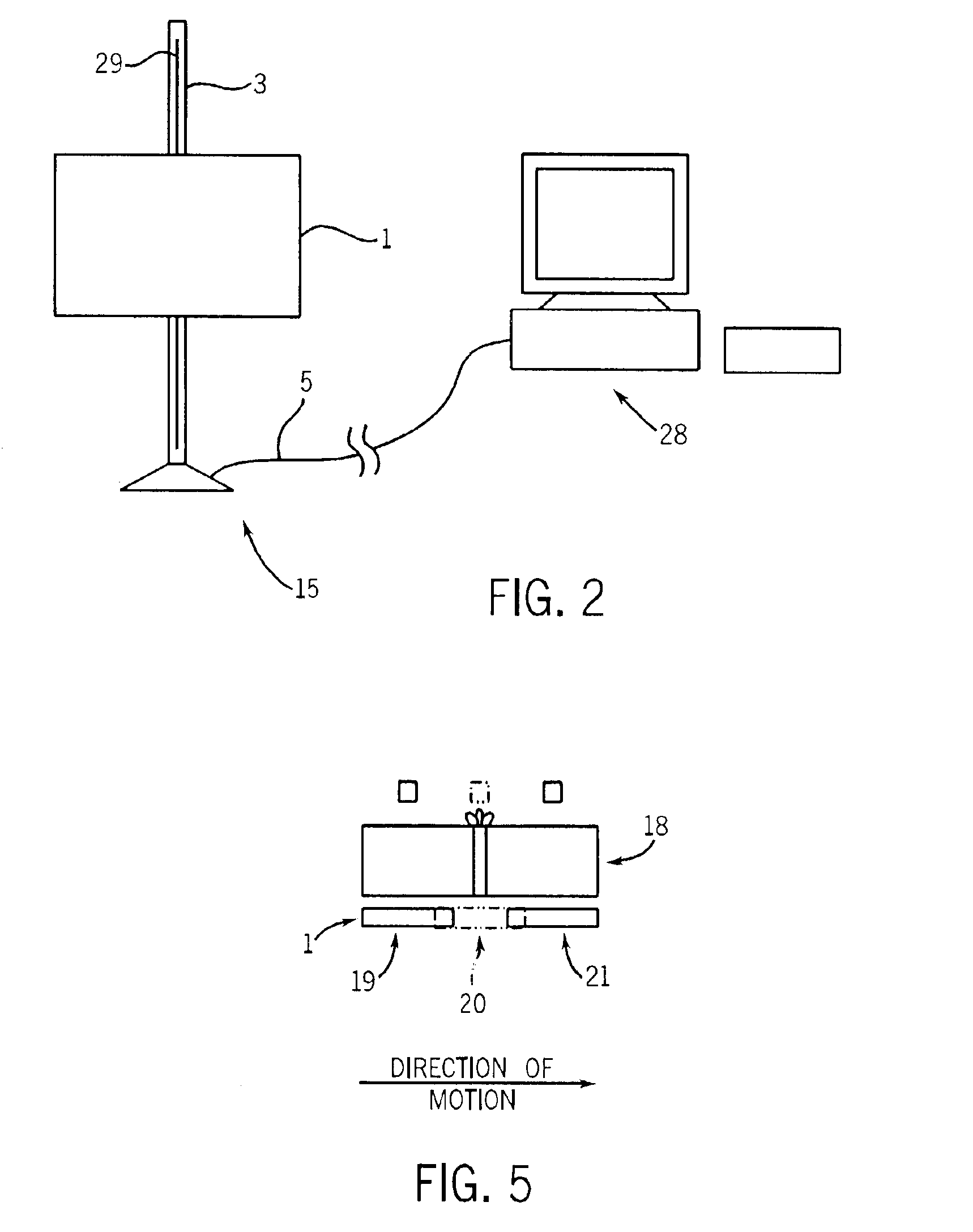
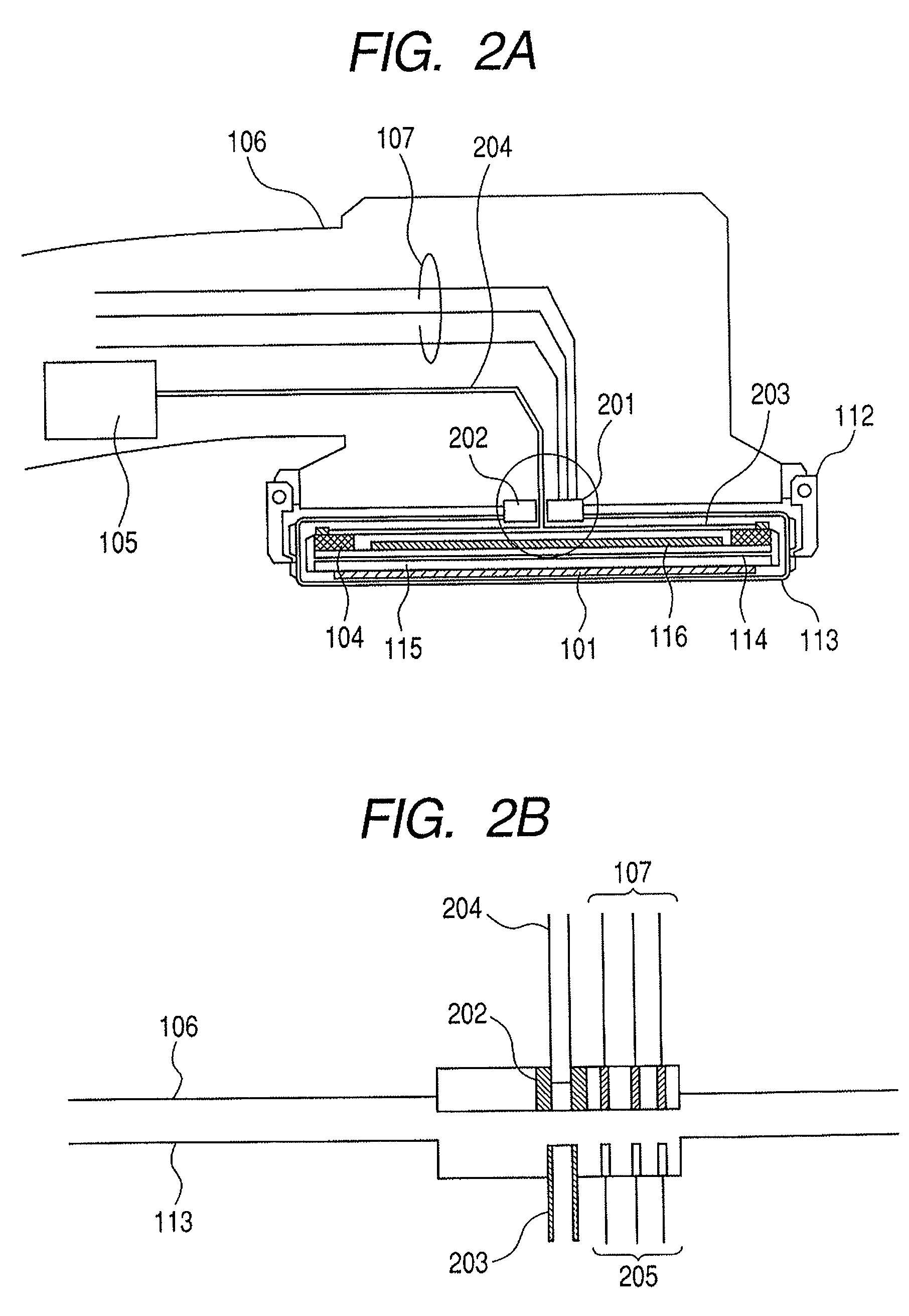
Image pasting using geometry measurement and a flat-panel detector
InactiveUS6944265B2Promote sportsX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationFlat panel detectorMeasurement device
A device for use in image pasting is described. The device includes a digital x-ray detector capable of automatic digital imaging without the use of an image intensifier; the detector preferably being a flat-panel detector. Additionally, an image pasting system using a solid-state detector is described. The system can connect the detected images to a display via a network (such as a WAN, a LAN, or the internet). Further, an image geometry measurement device for use in pasting x-ray images is disclosed. The geometry measurement device helps determine the relative position of two images to be used in image pasting. This information can be used alone, or in connection with an image pasting algorithm. Still further, methods of forming composite images are disclosed using a flat-panel detector and using the geometry of the images. The disclosed devices and systems can be integrated with other digital image pasting technology.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Noninvasive radiotherapy system for robot
ActiveCN103143124AReduce treatment errorAchieve regulationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyNumerical controlMedical equipment
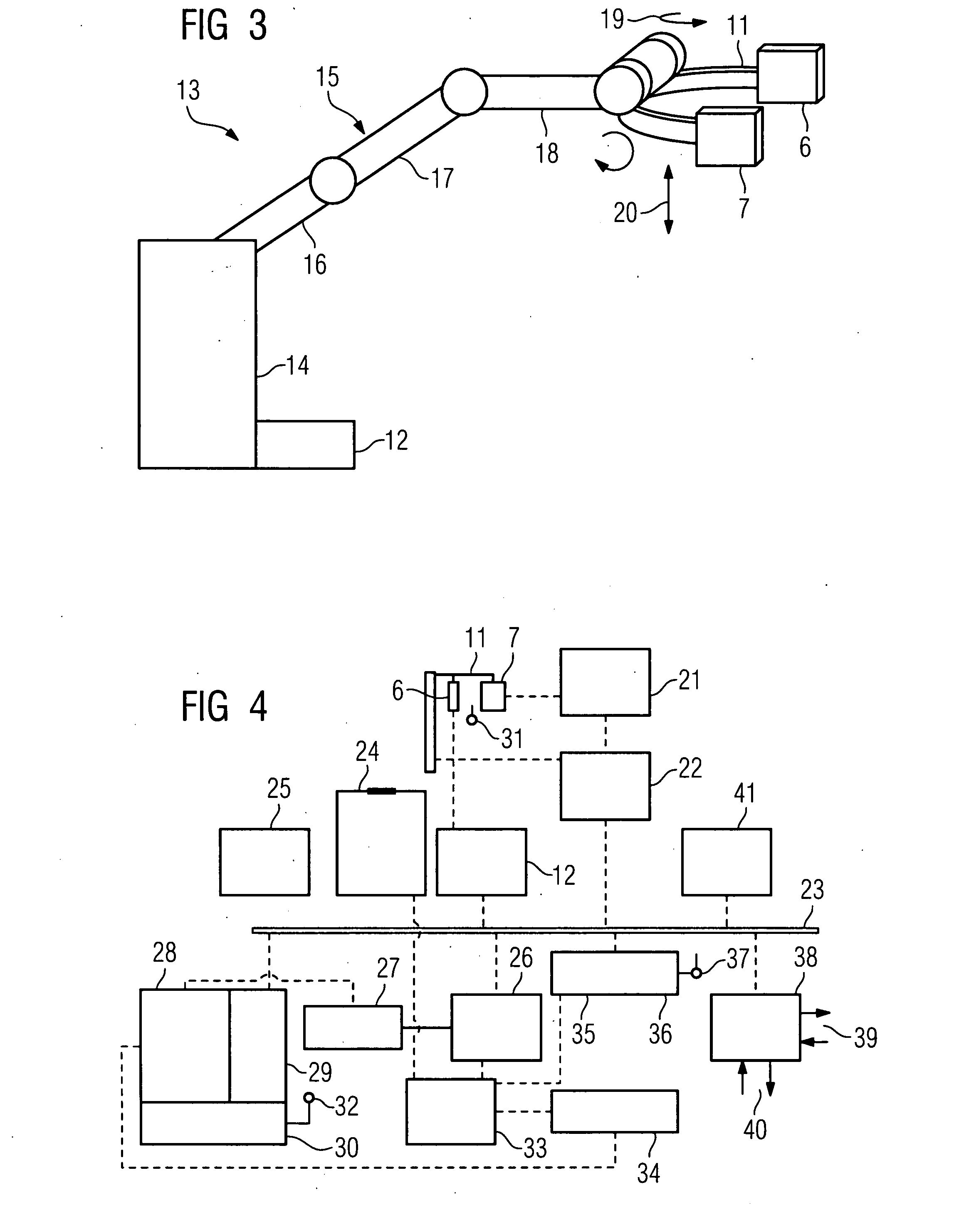
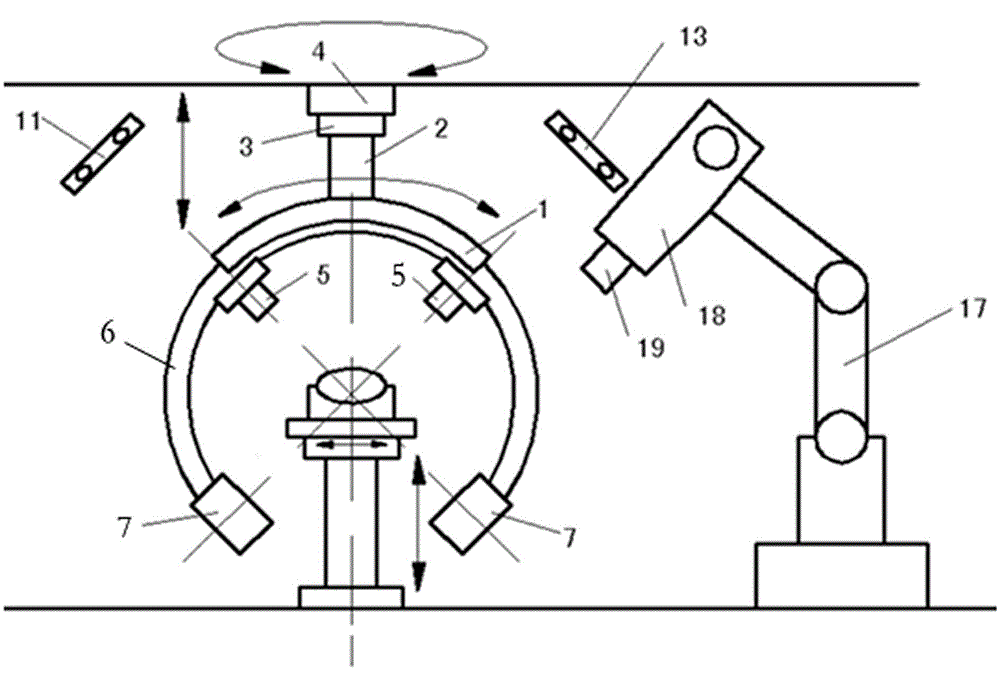
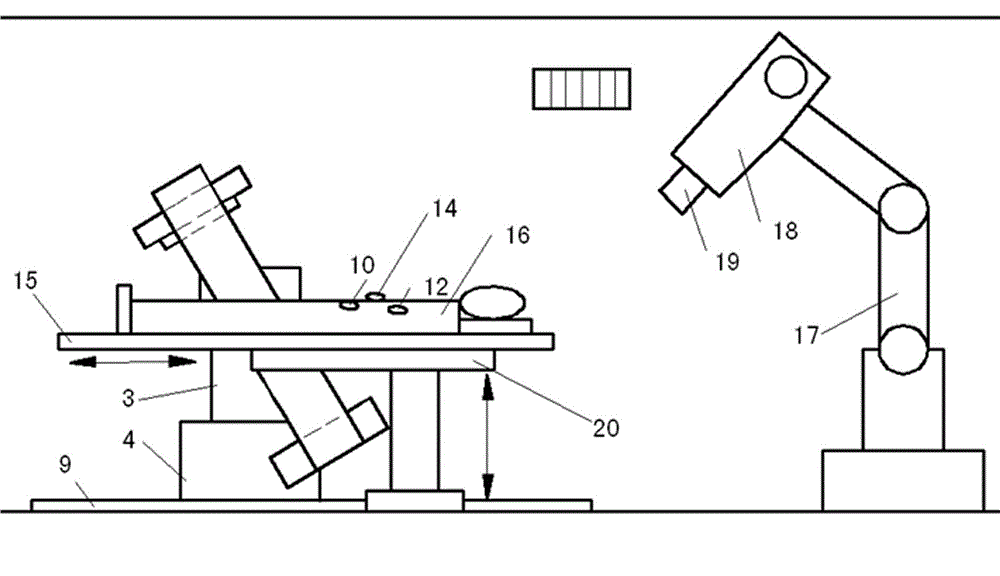
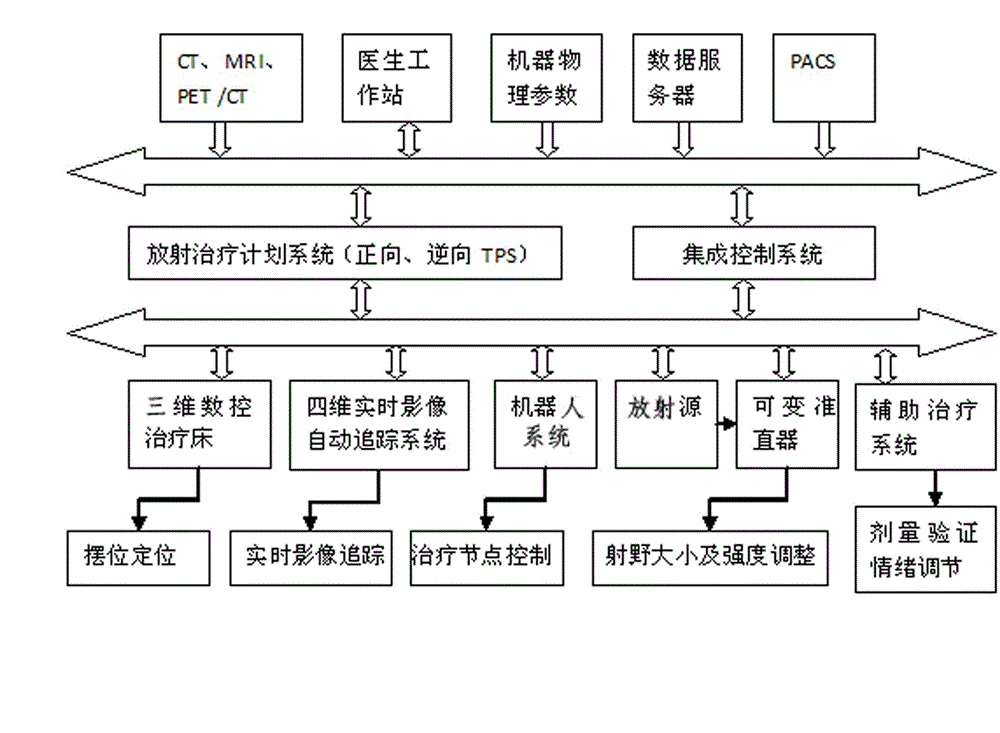
The invention relates to a noninvasive radiotherapy system for a robot, and belongs to the medical equipment field. The noninvasive radiotherapy system for the robot consists of seven modules, i.e. a radiotherapy planning system, a three-dimensional numerical-control therapy bed, an automatic tracking system for a four-dimensional real-time image, a robot system, a radioactive source, an adjuvant therapy system and an integrated control system, wherein the automatic tracking system for the four-dimensional real-time image consists of a six-freedom-of-degree G-shaped arm real-time image system and an intelligent tracking system; the six-freedom-of-degree G-shaped arm real-time image system is formed by successively connecting a G-shaped arm, a G-shaped arm sliding rail, a G-shaped arm spindle, a G-shaped arm pitch shaft and a G-shaped arm sliding seat; an X ray source and an X ray dynamic flat panel detector are formed into one group, and two groups are correspondingly installed on the G-shaped arm; and the G-shaped arm sliding seat is installed in a rail (9). According to the noninvasive radiotherapy system for the robot, which is disclosed by the invention, the defects of unmatched projection time, time waste and low therapy precision in the prior art are overcome, the precise therapy of the whole body tumor can be carried out, and the cardiovascular disease therapy and the noninvasive regulation of the renal nerve disease can be carried out.
Owner:RADIATION THERAPY MEDICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
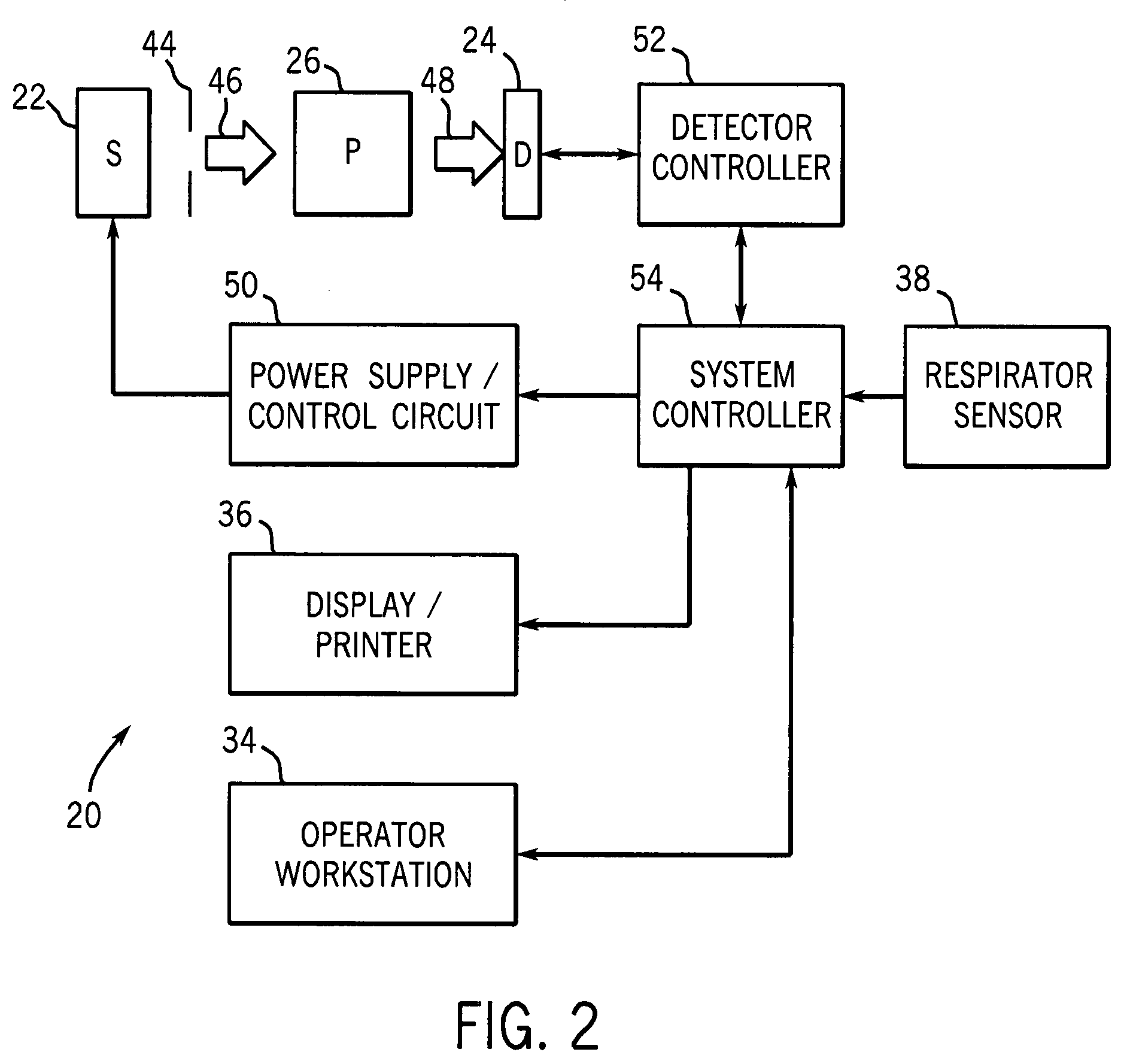
Radiation imaging apparatus, apparatus control method, and computer-readable storage medium storing program for executing control
ActiveUS20080011958A1Reduce dosageSuppress feverTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFlat panel detectorRadiation imaging
To provide a radiation imaging apparatus which is capable of both connecting state radiographing for radiographing with a C arm connected and non-connecting state radiographing for radiographing with the C arm disconnected, and is convenient and obtains high quality images, the apparatus includes: a flat panel detector; a holding unit for holding at least the flat panel detector;and a control unit for controlling the flat panel detector. With the configuration, the flat panel detector can be connected to and disconnected from the holding unit; connecting state radiographing can be performed with the flat panel detector connected to the holding unit, and non-connecting state radiographing can be performed with the flat panel detector disconnected from the holding unit; the control unit controls the flat panel detector such that a heat generation quantity of the flat panel detector during the non-connecting state radiographing can be lower than a heat generation quantity of the flat panel detector during the connecting state radiographing.
Owner:CANON KK
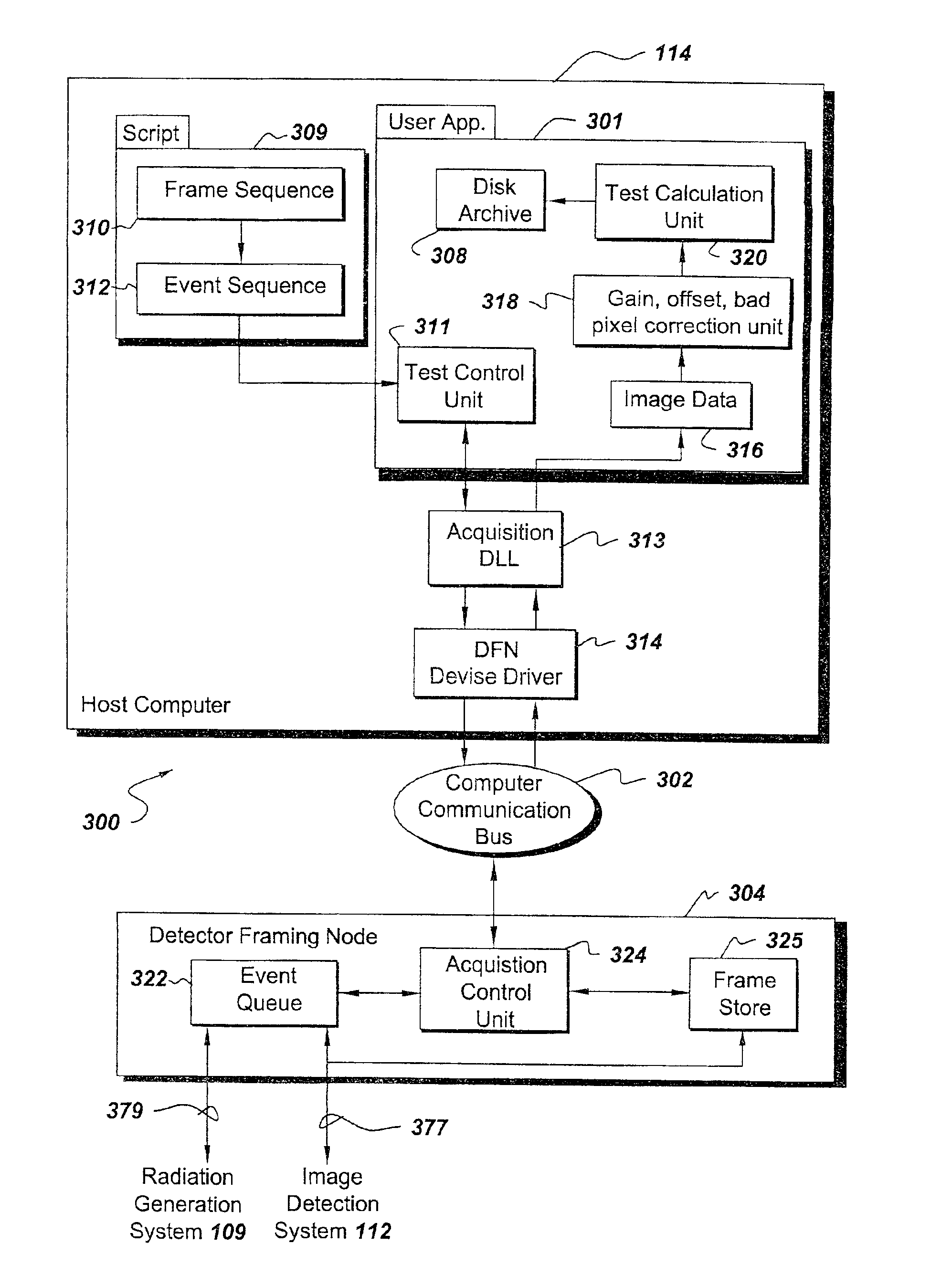
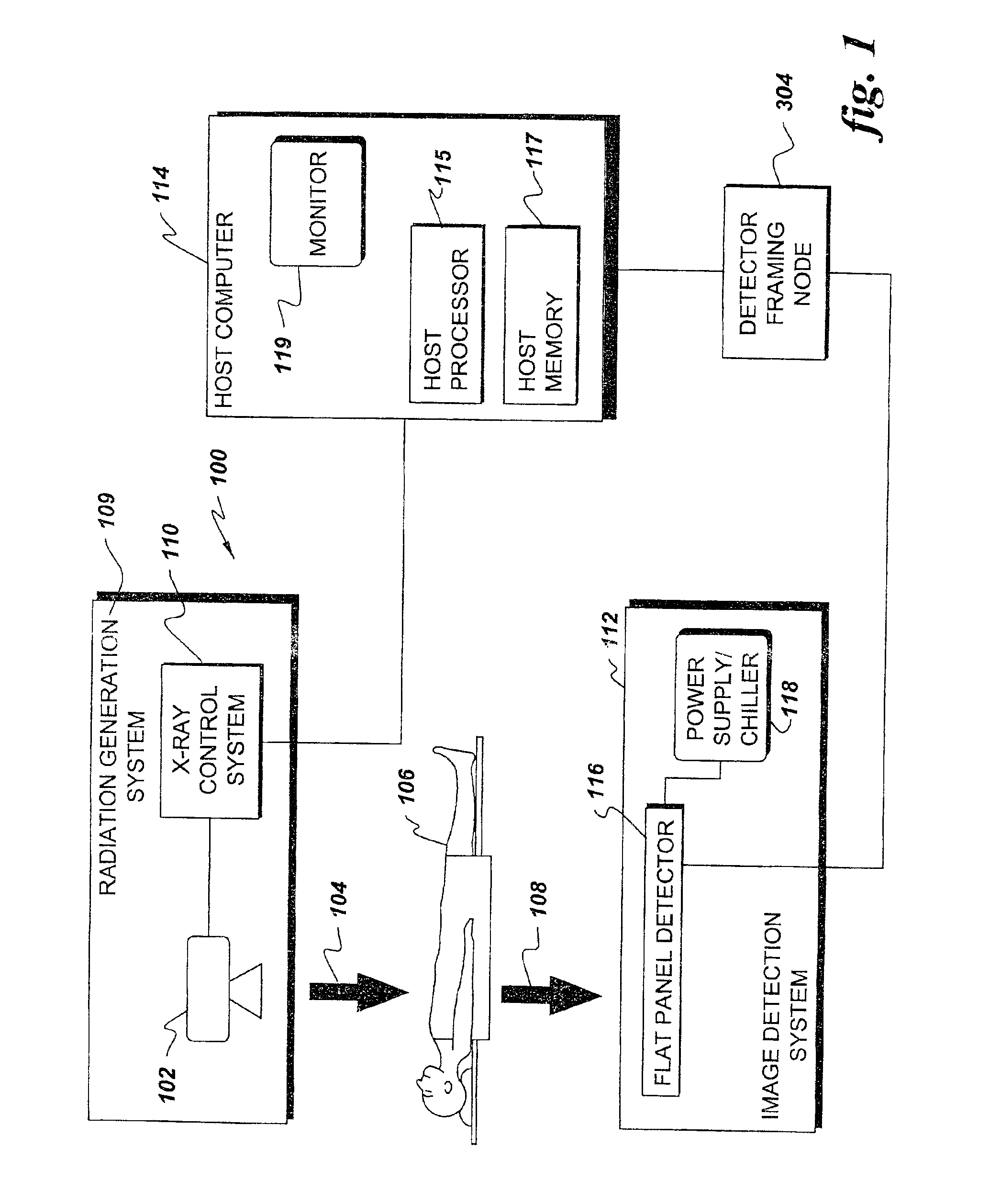
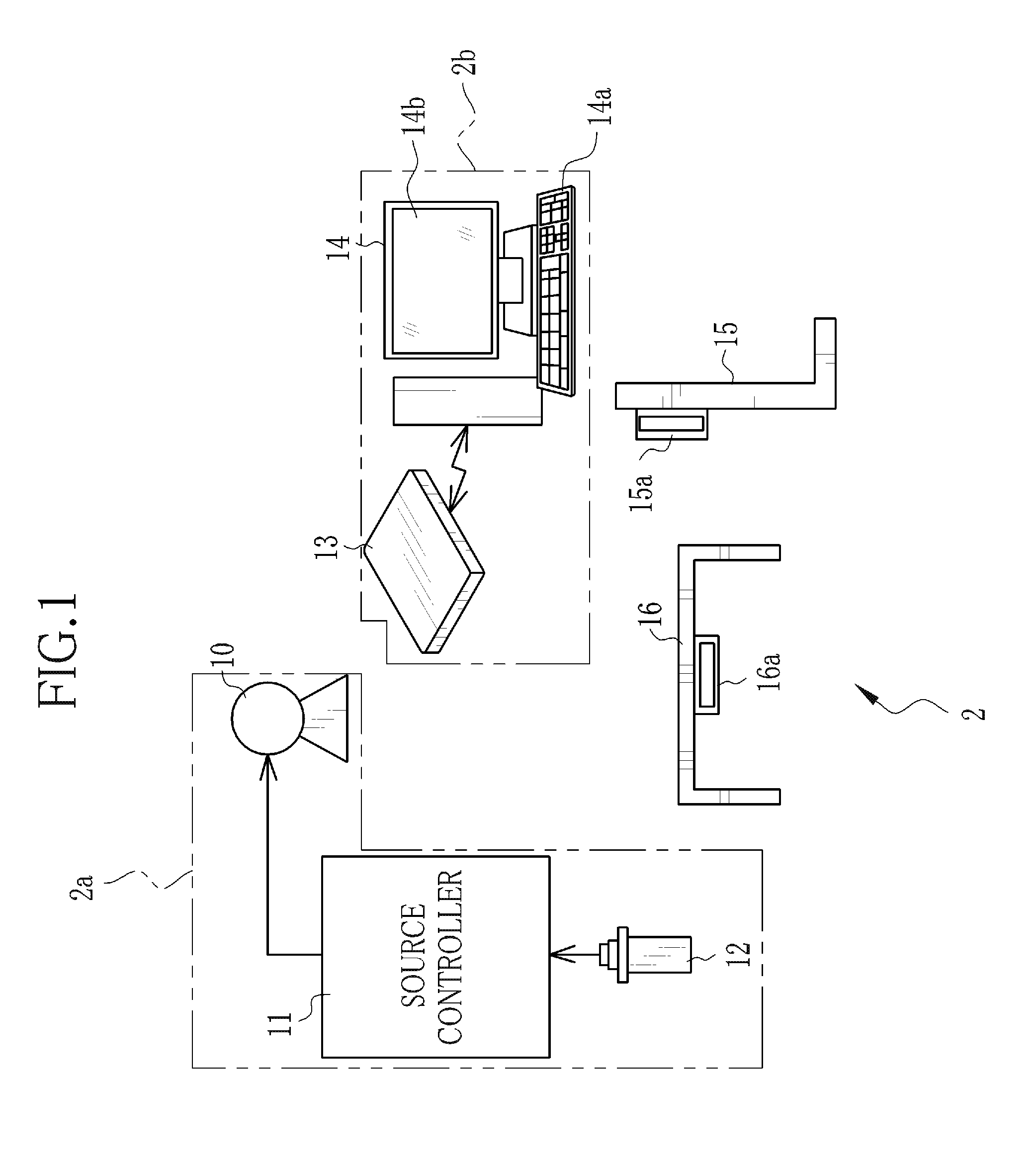
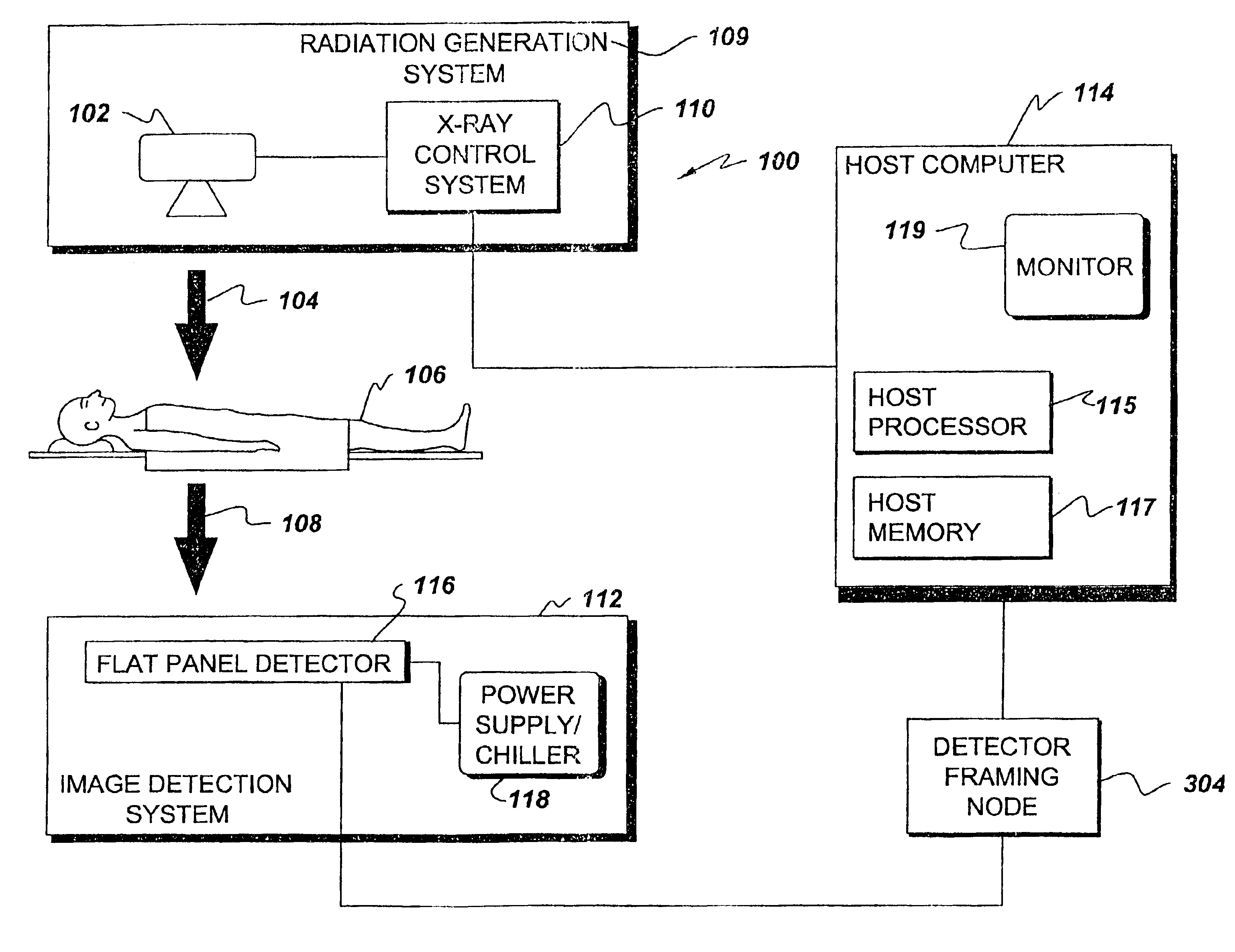
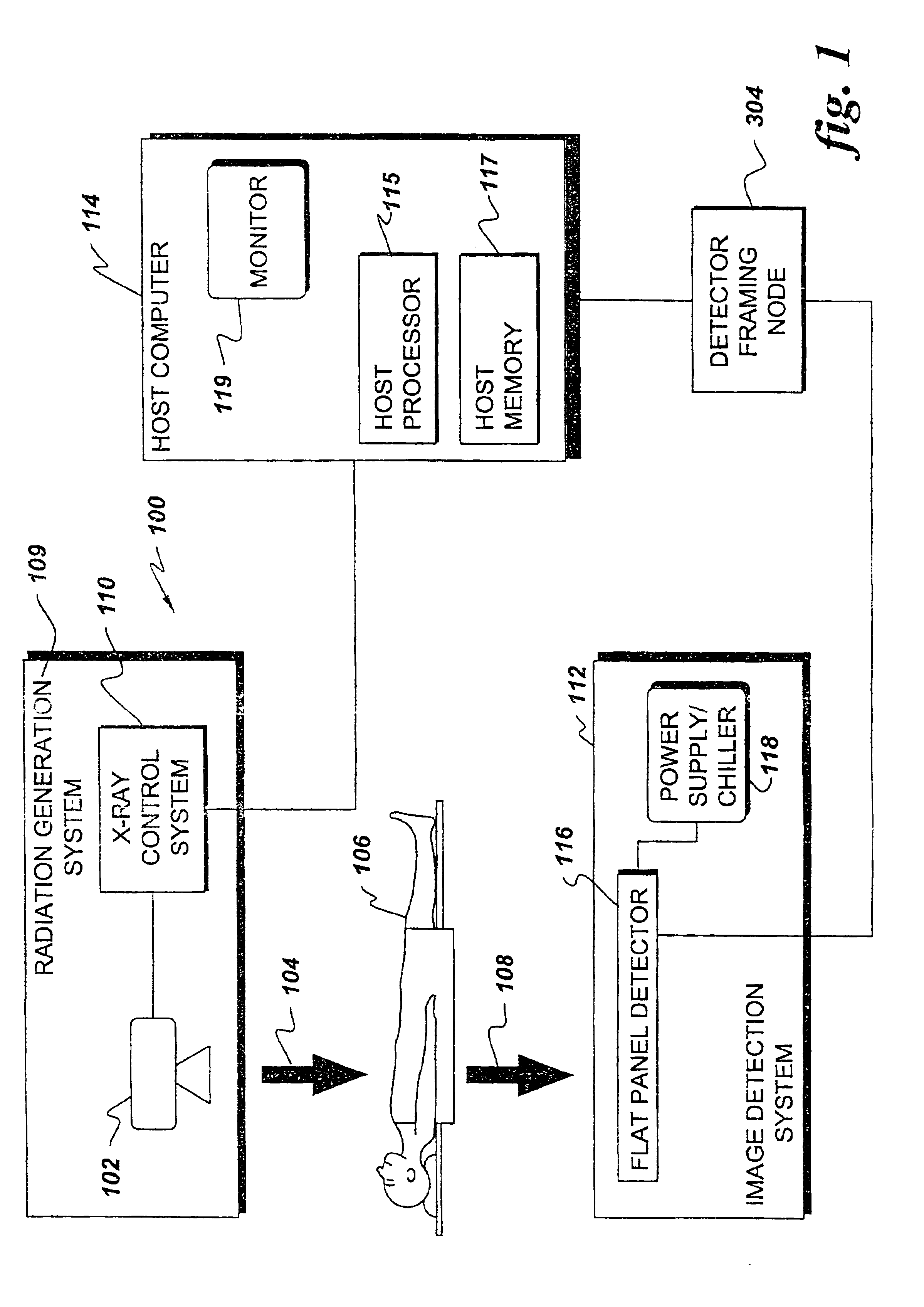
Imaging system including detector framing node
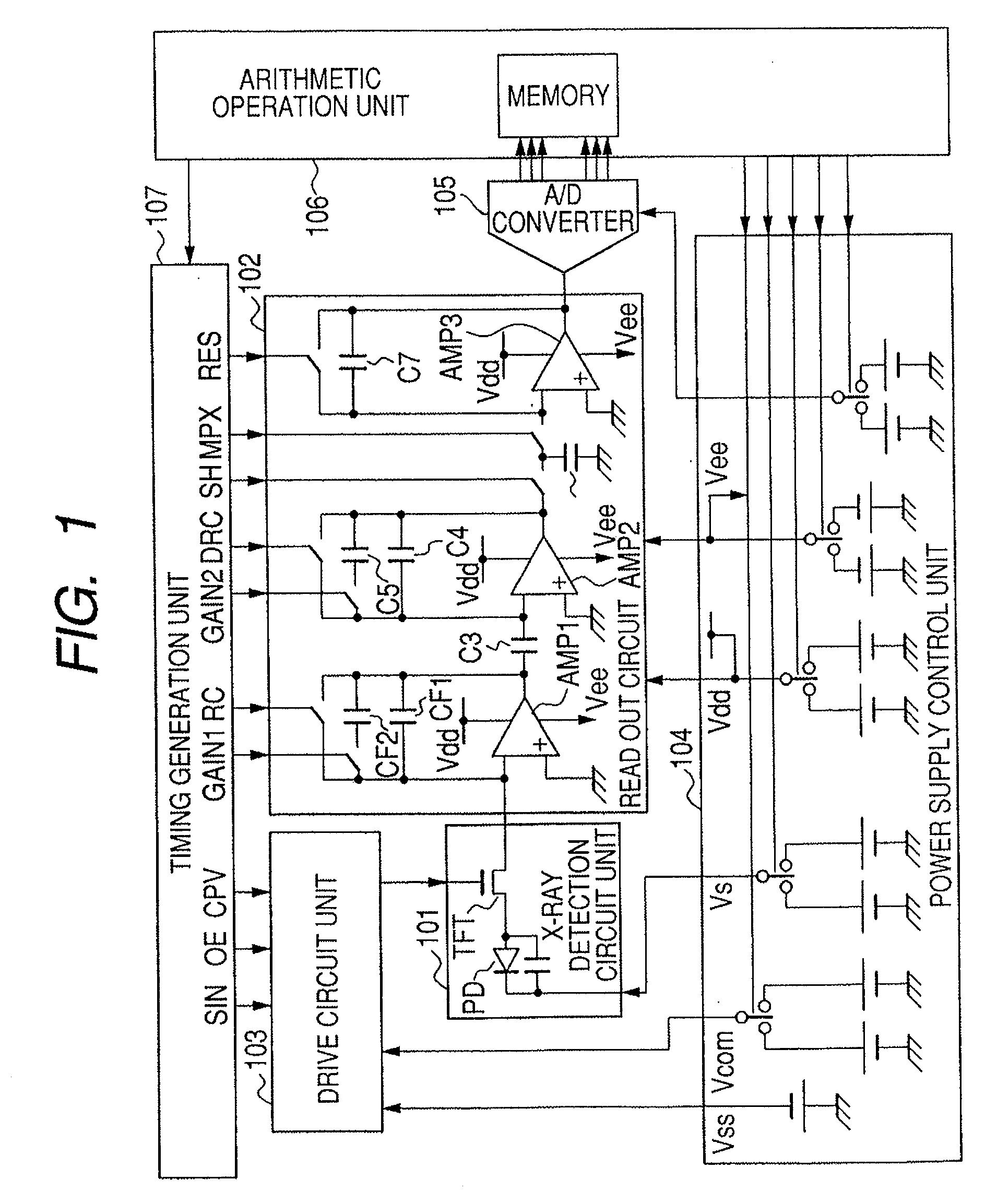
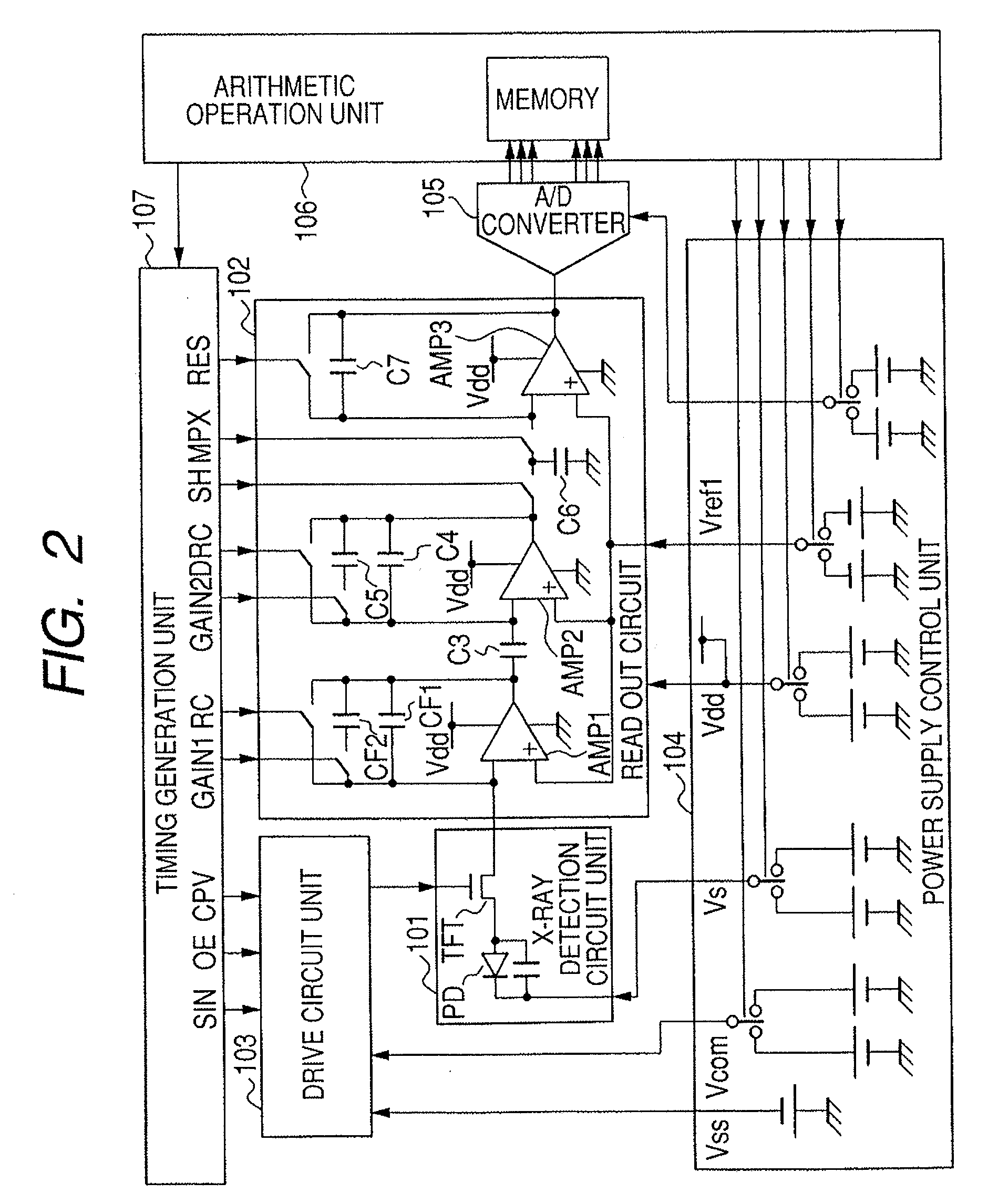
An imaging system includes a programmable detector framing node controlling generation of radiation and controlling radioscopic image detection. Radioscopic image data is acquired and communicated independently of a host computer operating system. The detector framing node controls events in real time according to an event instruction sequence and communicates received radioscopic image data to host memory through a computer communication bus. Image data is received from a selected flat panel detector of a plurality of different flat panel detectors. The image data is selectively reordered according to parameters of the selected flat panel detector before communication to host memory.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
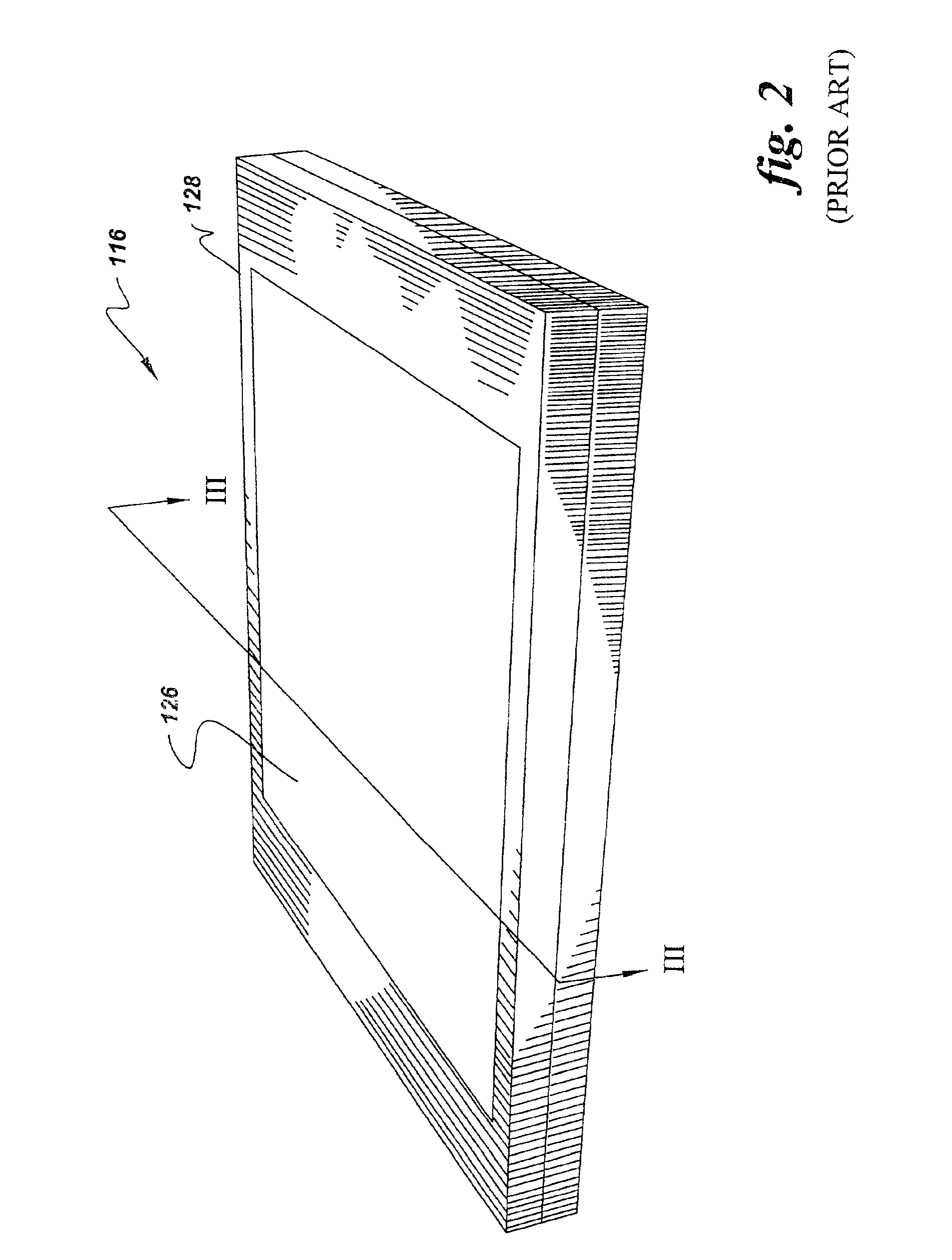
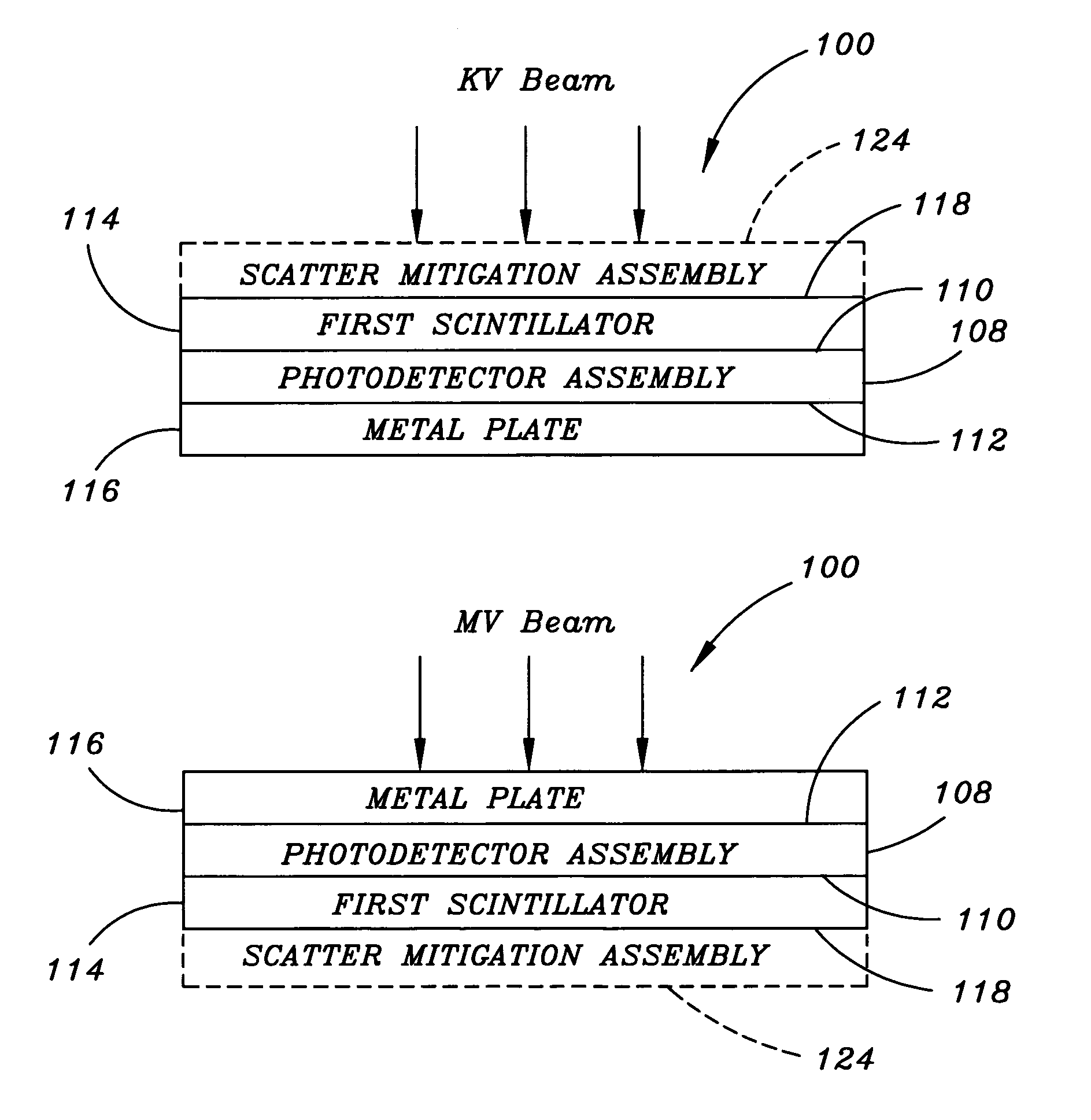
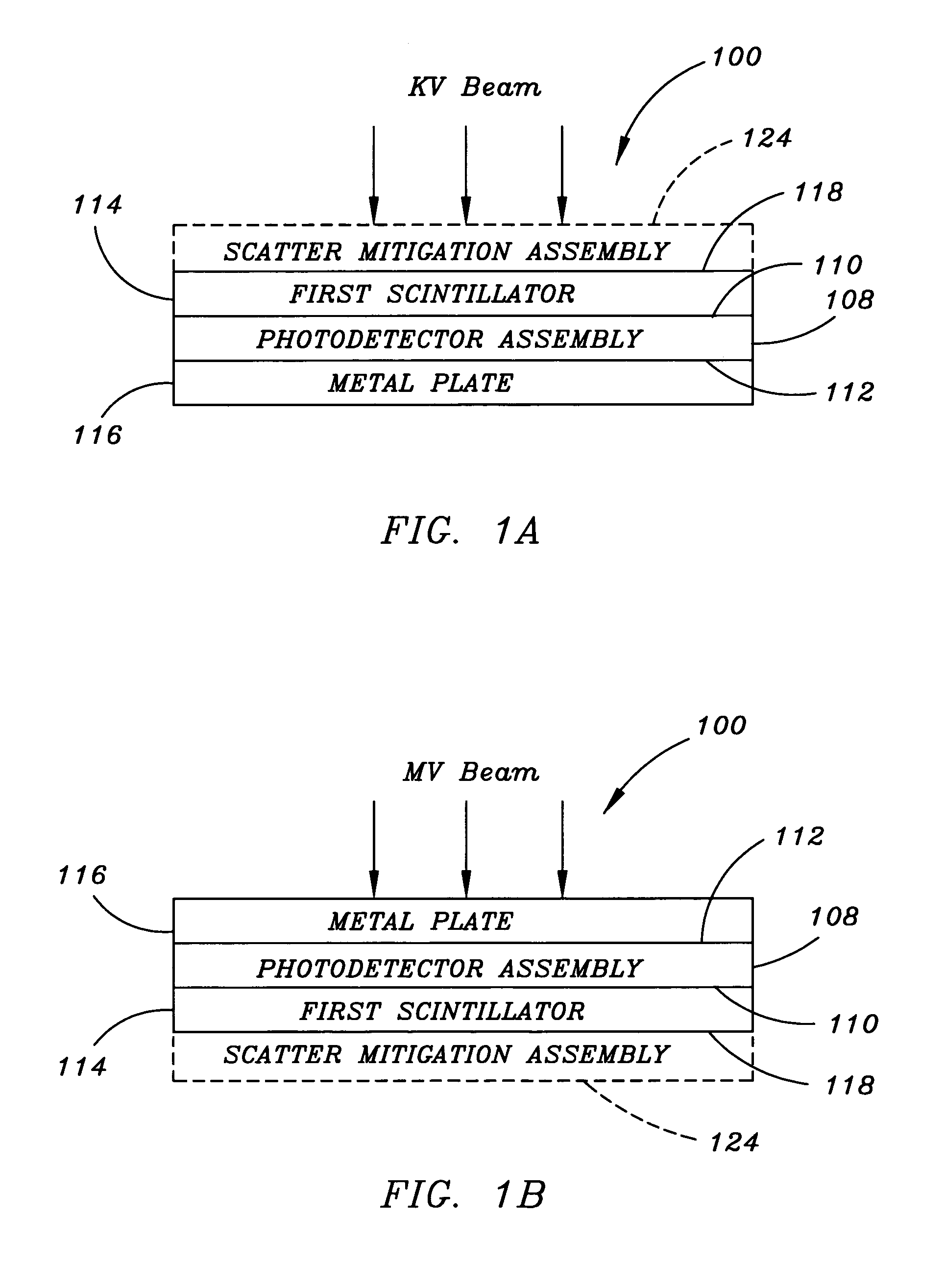
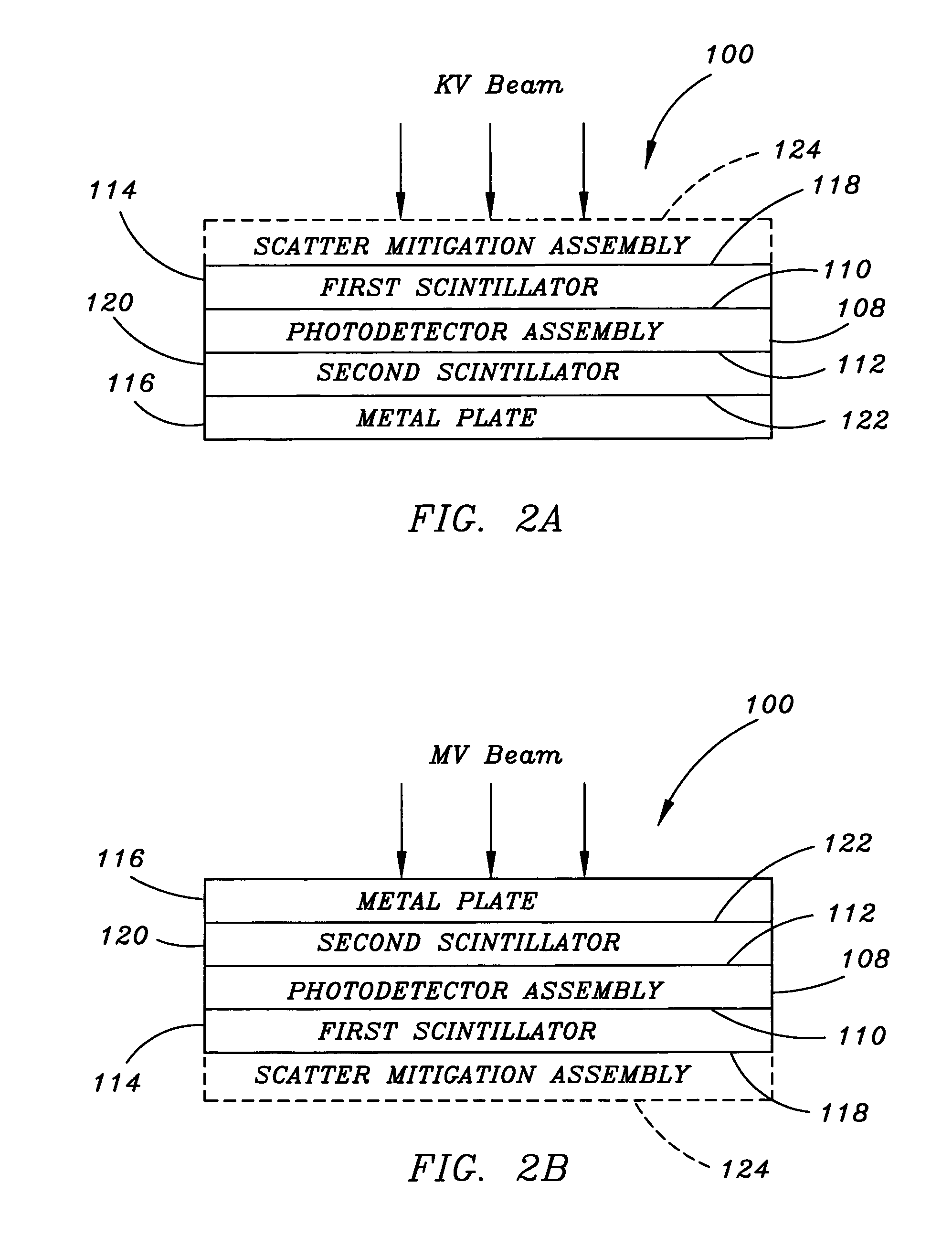
Flat panel detector with KV/MV integration
InactiveUS7263165B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansFlat panel detectorPhotovoltaic detectors
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
X-ray flat panel detector and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103296035AImprove image qualityReduce manufacturing costRadiation controlled devicesFlat panel detectorImaging quality
The invention provides an X-ray flat panel detector and a manufacturing method thereof. The X-ray flat panel detector comprises a plurality of pixel units which are arranged according to matrixes. Each pixel unit comprises a sensor and a pixel reading circuit both of which are integrated on an insulating substrate. Each pixel reading unit comprises at least one thin film transistor which is located below a top electrode of each sensor, and at least one thin film transistor from the thin film transistors is connected with the corresponding sensor. According to the X-ray flat panel detector, the sensors can be integrated with the complex pixel reading circuits so that improved image quality and lowered production cost can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image acquisition and processing chain for dual-energy radiography using a portable flat panel detector
ActiveUS7627084B2Improve acquisitionImprove rendering capabilitiesRadiation/particle handlingTomographyHigh energyDual energy
A mobile dual-energy X-ray imaging system is presented. The mobile dual-energy X-ray imaging system is a digital X-ray system that is designed both to acquire original image data and to process the image data to produce an image for viewing. The system has an X-ray source and a portable flat-panel digital X-ray detector. The system is operable to produce a high energy image and low energy image, which may be decomposed to produce a soft tissue image and a bone image for further analysis of the desired anatomy. The system is disposed on a carrier to facilitate transport. The imaging system has an alignment system for facilitating alignment of the flat-panel digital detector with the X-ray source. The imaging system also comprises an anti-scatter grid and an anti-scatter grid registration system for removing artifacts of the anti-scatter grid from images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
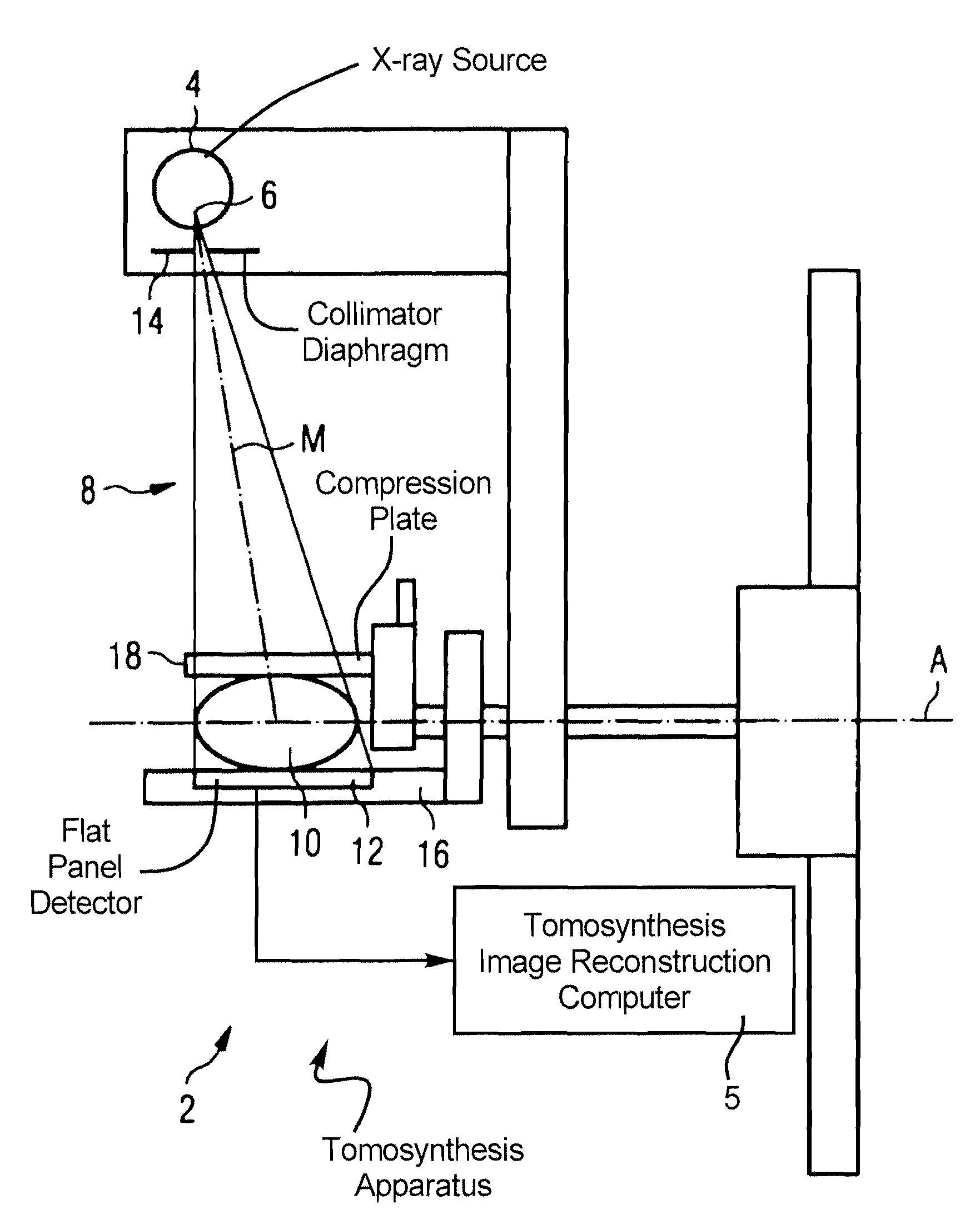
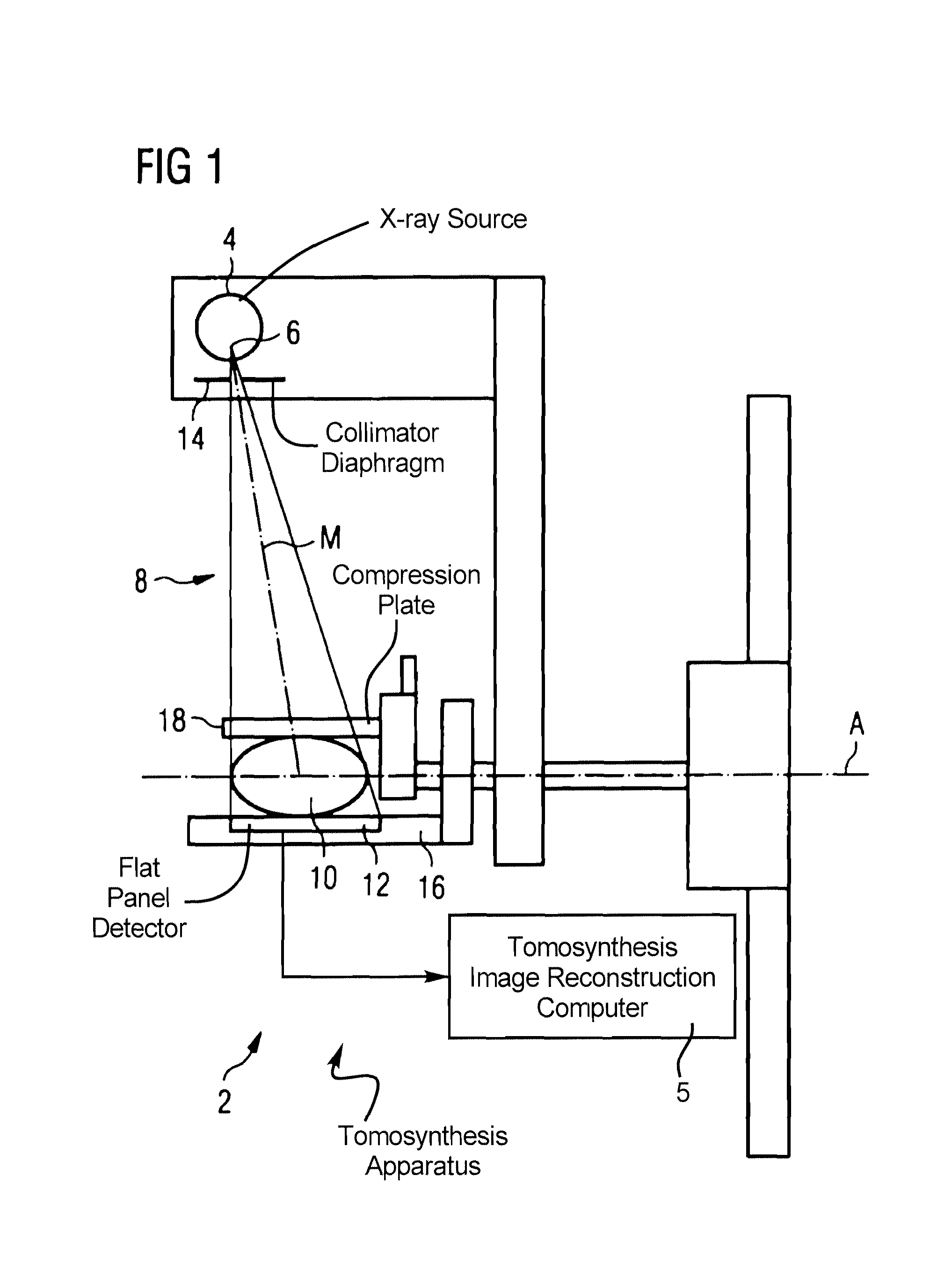
Tomosynthesis apparatus and method to operate a tomosynthesis apparatus
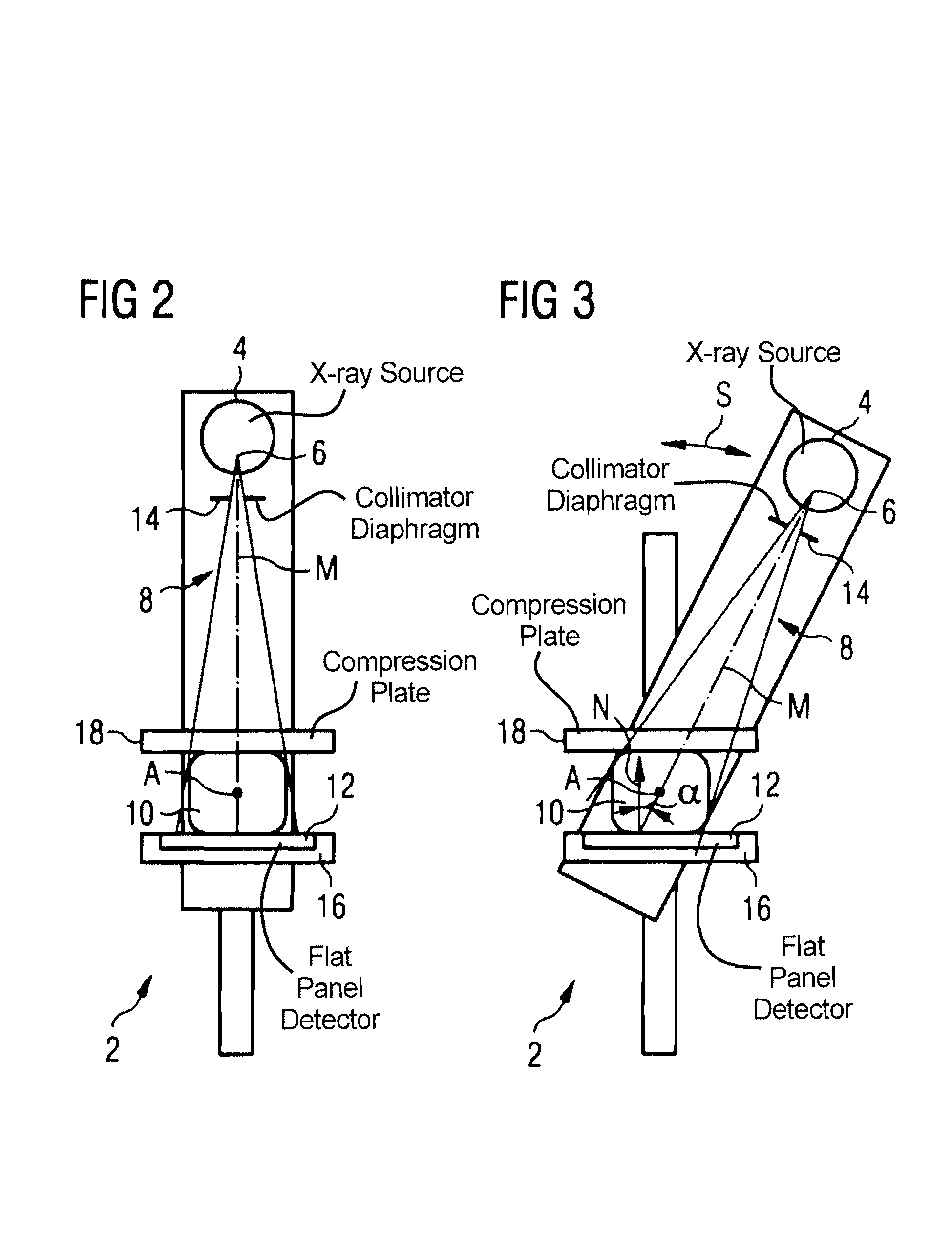
ActiveUS8031834B2Increase exposureEasy to shapeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisFlat panel detector
A tomosynthesis apparatus has an x-ray source that generates an x-ray beam emanating from a focus, which is received by a flat panel detector. To set a tomosynthesis angle, the position of the central axis of the x-ray beam of the x-ray source is variable. A collimator diaphragm has a diaphragm aperture that limits the expansion of the x-ray beam at the location of the flat panel detector. The collimator diaphragm is arranged in the beam path between the focus and the flat panel detector. The shape and size of the diaphragm aperture are dynamically varied (adjusted) dependent on the changing tomosynthesis angle, such that the expansion of the x-ray beam at the location of the flat panel detector always essentially corresponds to the detector dimensions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
X-ray diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS20050078793A1Eliminate artifactsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFlat panel detectorX-ray
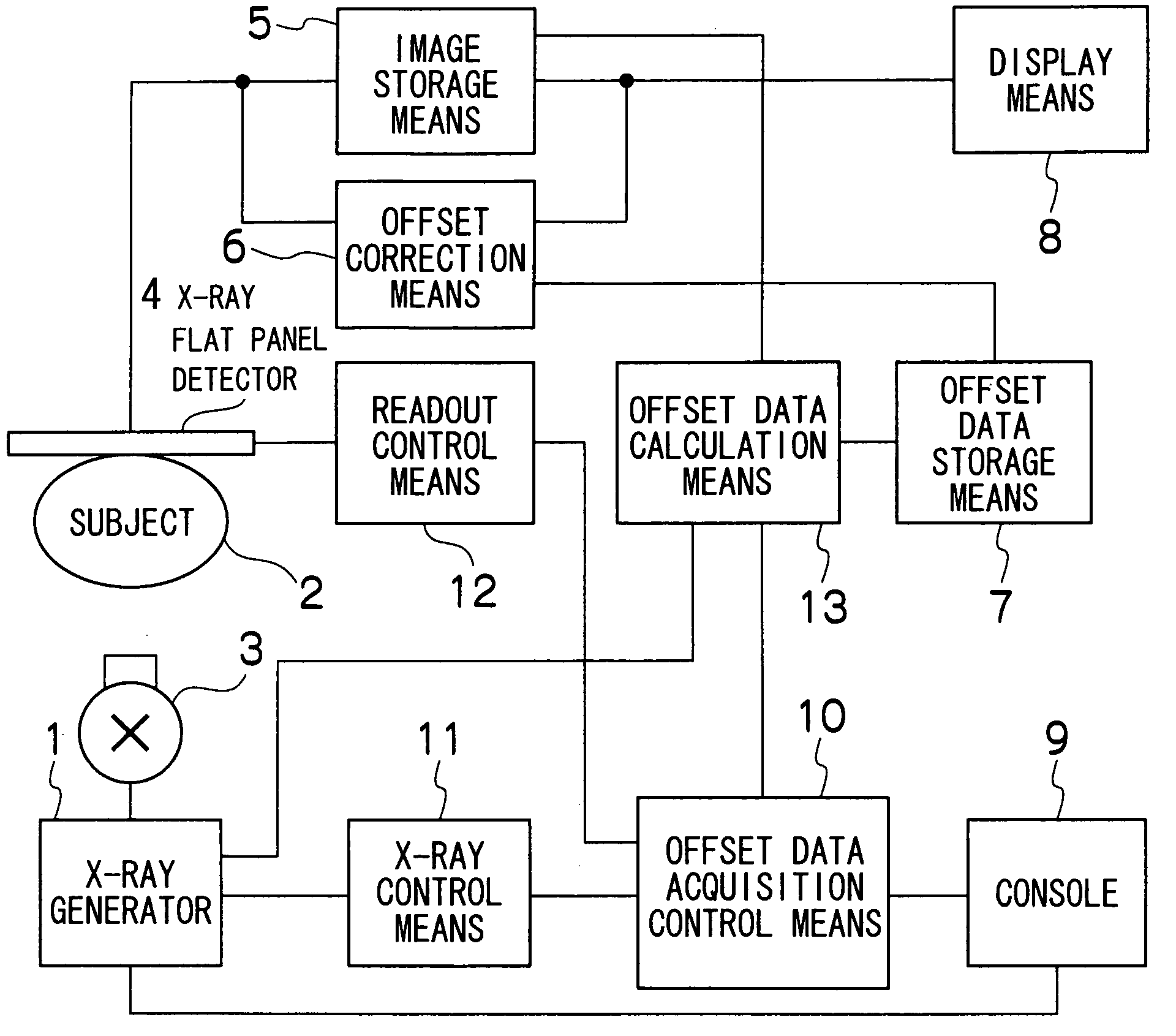
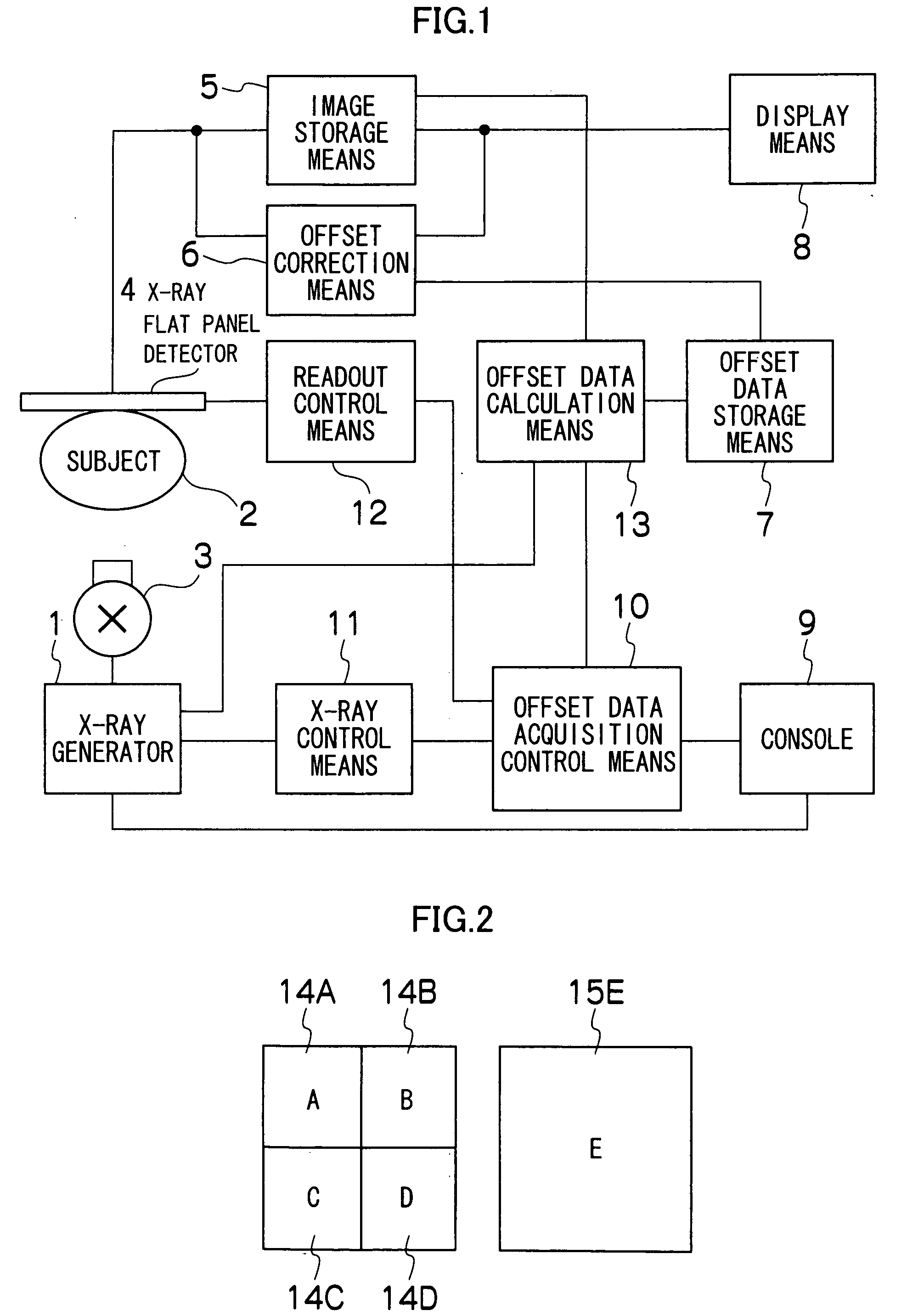
Offset data calculation means has a normal offset data calculation function for calculating offset data based on data obtained from an X-ray flat panel detector while no X-ray is incident in each of the modes, i.e., an entire region fluoroscopy mode, a partial region fluoroscopy mode, imaging mode, etc. and storing the data in offset data storage means, and additionally has a function for updating, upon calculation of new offset data in any of the modes, another mode offset data stored in the offset data storage means based on the new offset data calculated. Thus, from offset data acquired in any of the plurality of modes, it is possible to obtain the latest offset data in all the modes.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
X-ray flat panel detection device
The invention relates to an X-ray flat panel detector. The X-ray flat panel detector comprises a thin film transistor substrate, a photoelectric sensing layer which is electrically connected with the thin film transistor substrate, a flickering layer and a reflecting layer, wherein the photoelectric sensing layer comprises multiple photoelectric sensing elements and multiple light absorption elements, the light absorption elements are arranged in gaps between the photoelectric sensing elements, the flickering layer is located on the photoelectric sensing layer, and the reflecting layer is arranged on the flickering layer.
Owner:INNOCOM TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
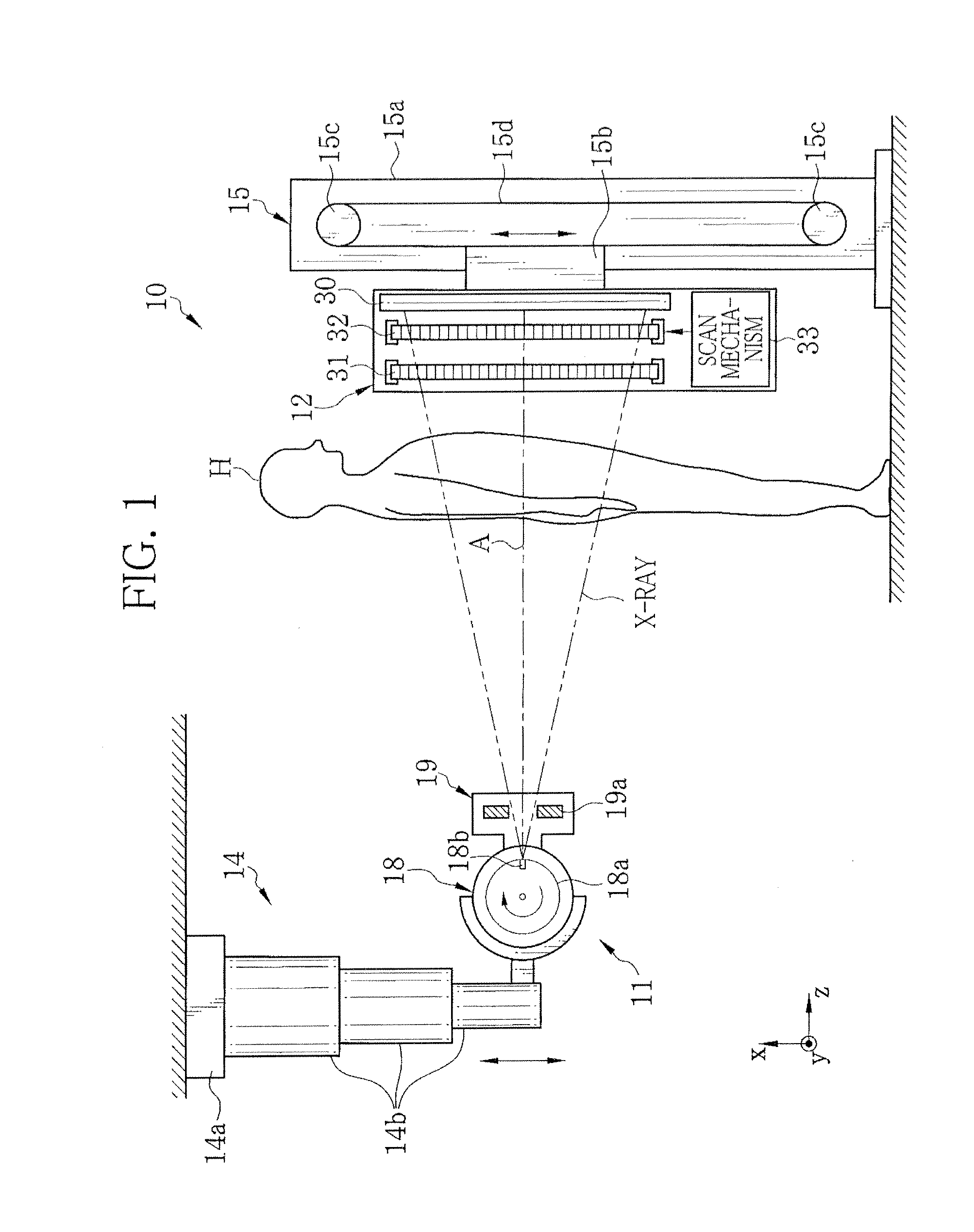
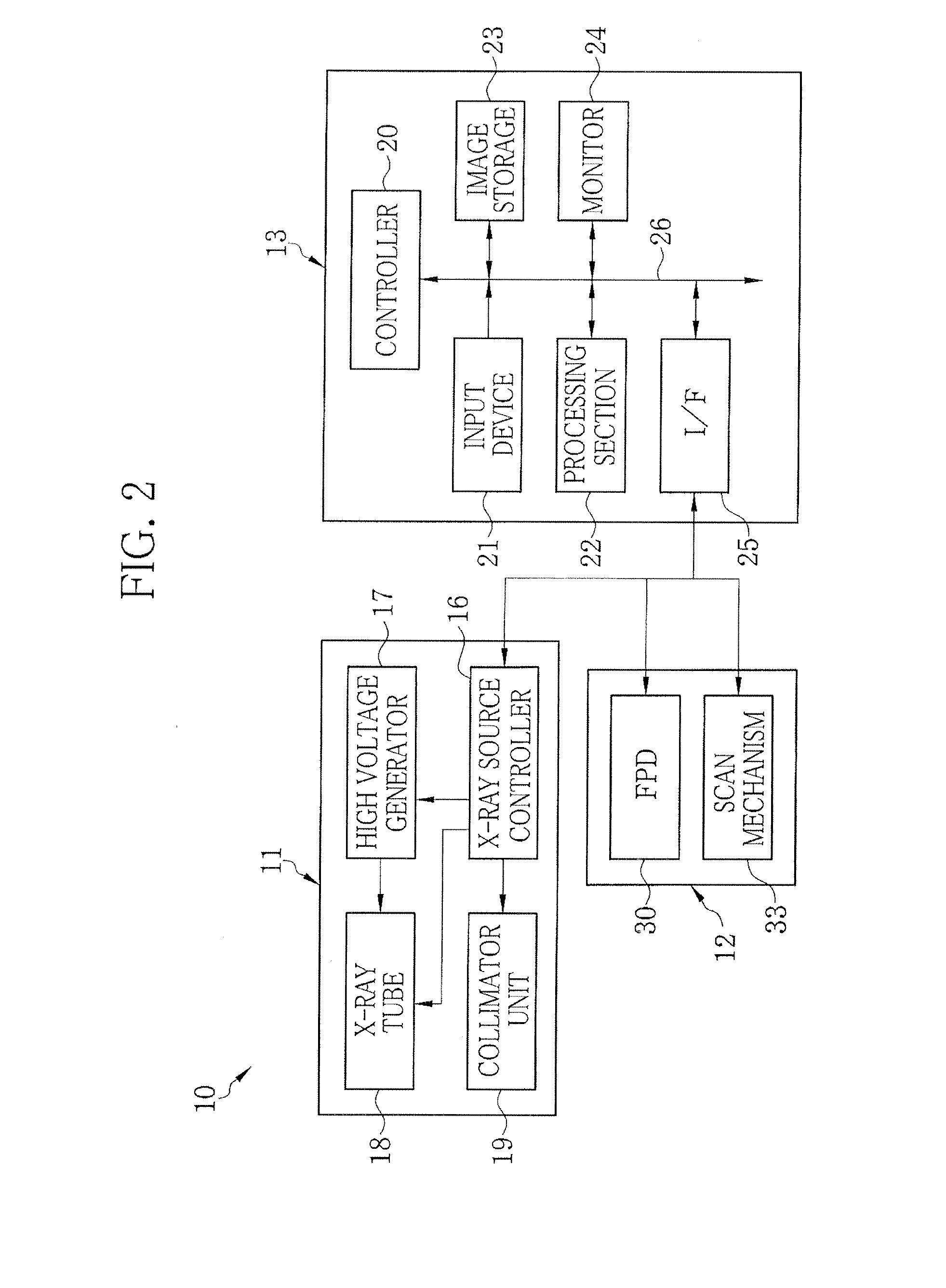
Radiation imaging system
InactiveUS20120288056A1Good phase contrast imageEnhance the imageImaging devicesX-ray/infra-red processesFlat panel detectorGrating
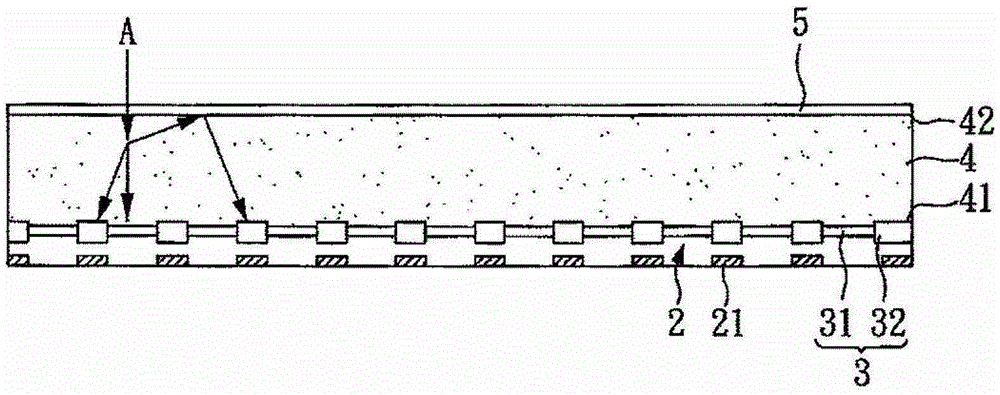
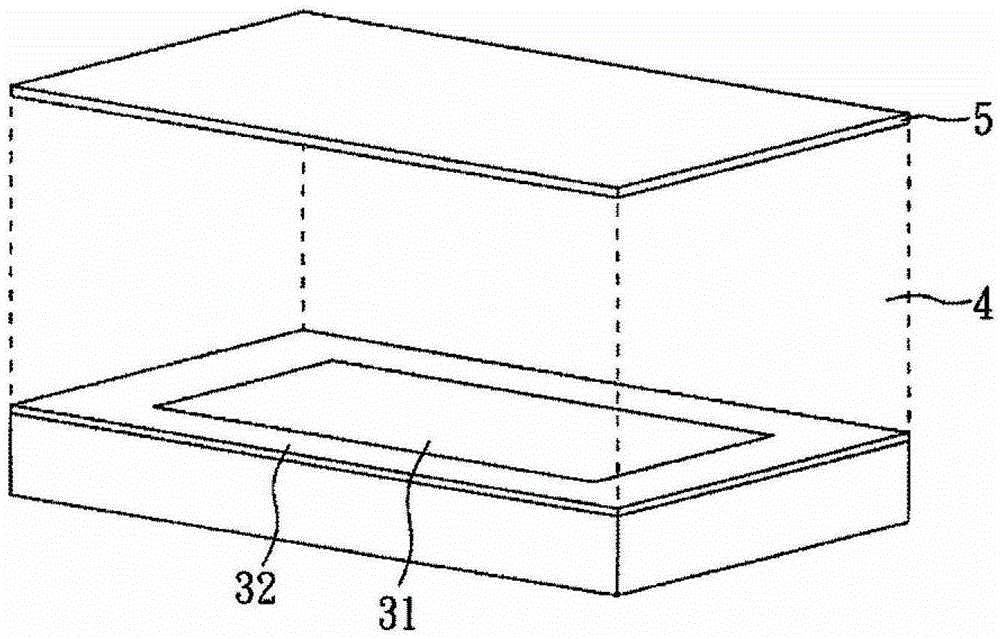
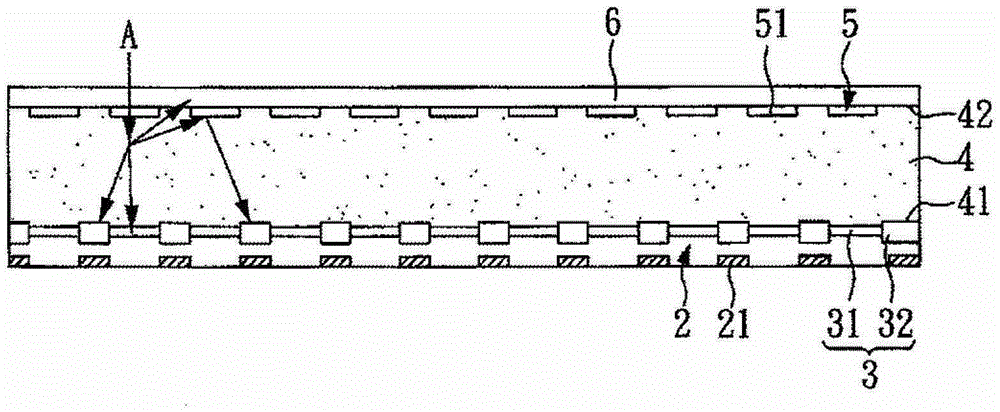
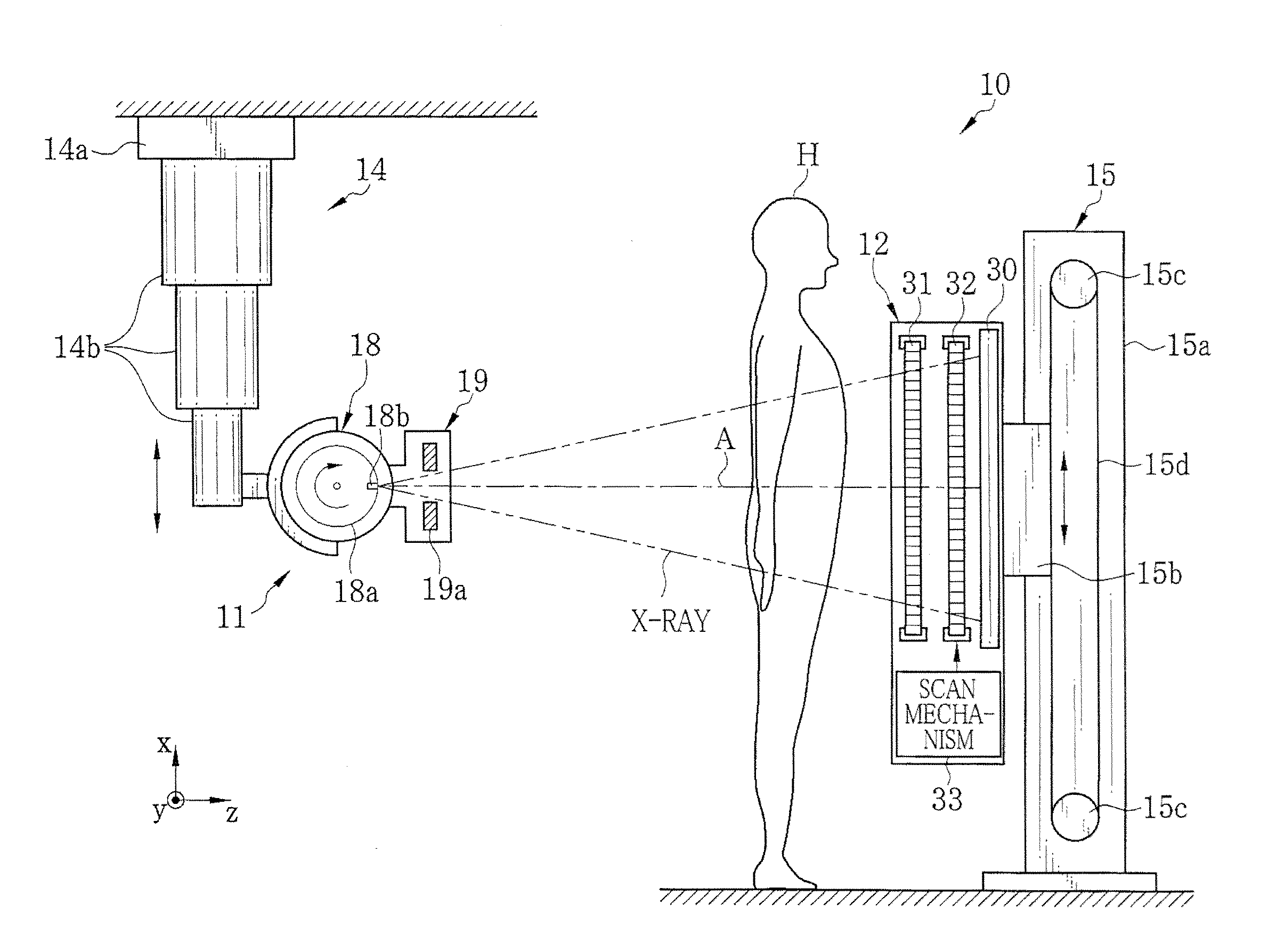
An X-ray imaging system is provided with an X-ray source (11), first and second absorption gratings (31, 32), and a flat panel detector (FPD) (30), and obtains a phase contrast image of an object H by performing imaging while moving the second absorption grating (32) in x direction relative to the first absorption grating (31). The following mathematical expression is satisfied where p1′ denotes a period of a first pattern image at a position of the second absorption grating (32), and p2′ denotes a substantial grating pitch of the second absorption grating (32), and DX denotes a dimension, in the x-direction, of an X-ray imaging area of each pixel of the FPD (30). Here, “n” denotes a positive integer.DX≠n×(p1′×p2′) / |p1′−p2′|
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiation imaging apparatus
ActiveUS7629587B2Increase the number ofRadiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis by optical meansFlat panel detectorRadiation imaging
A single flat panel detector provides radiation images which can correspond with various radiographic modes. In a radiation imaging apparatus including a flat panel detector which derives a radiation image according to incident radiation, a holding unit which holds the flat panel detector and a connecting mechanism capable of performing a connecting and a disconnecting between the holding unit and the flat panel detector, the flat panel detector can be controlled so that the maximum number of radiation images that the flat panel detector can derive when the flat panel detector is disengaged from the holding unit is smaller than the maximum number of radiation images that the flat panel detector can derive when the flat panel detector is held by the holding unit.
Owner:CANON KK
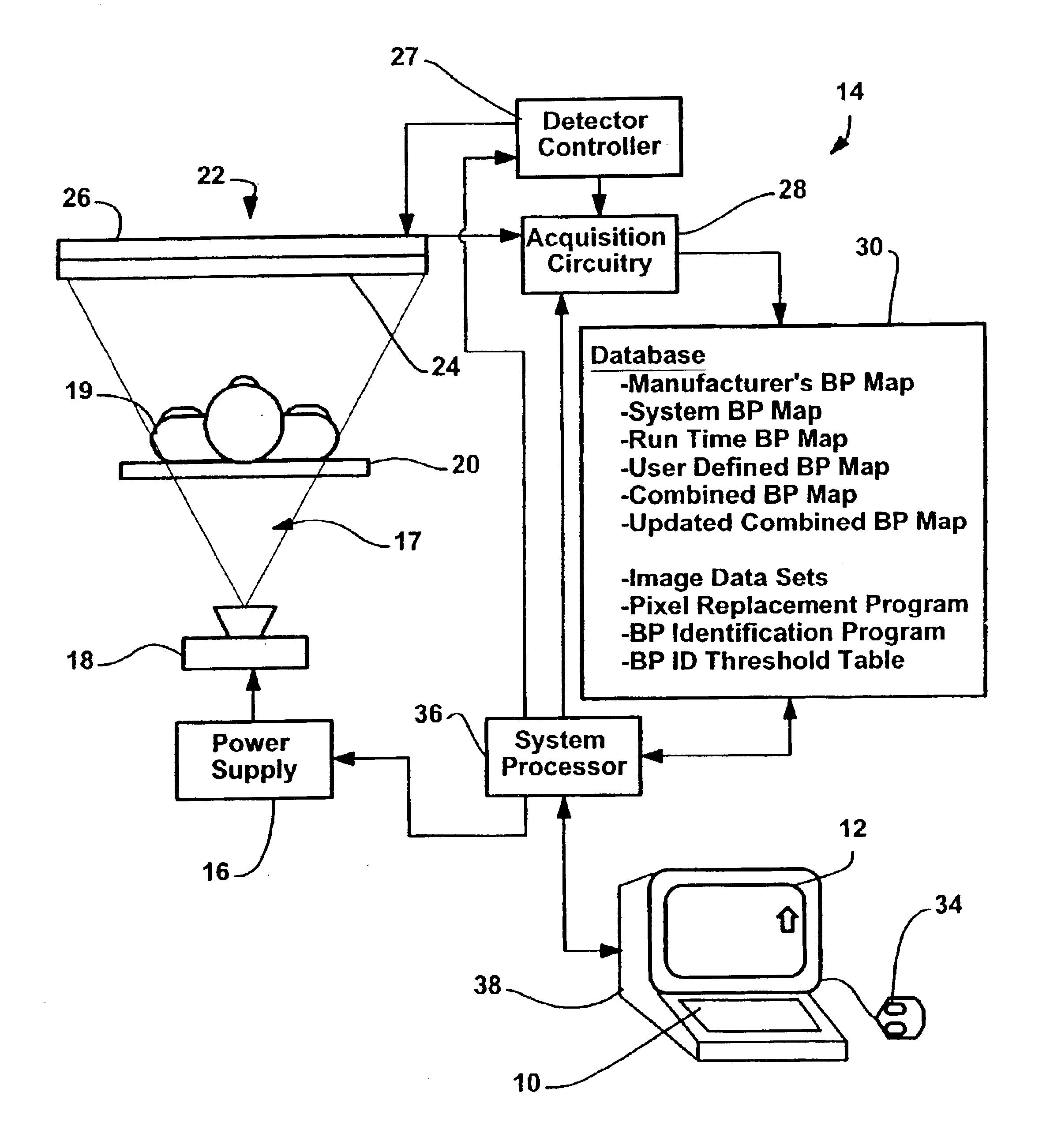
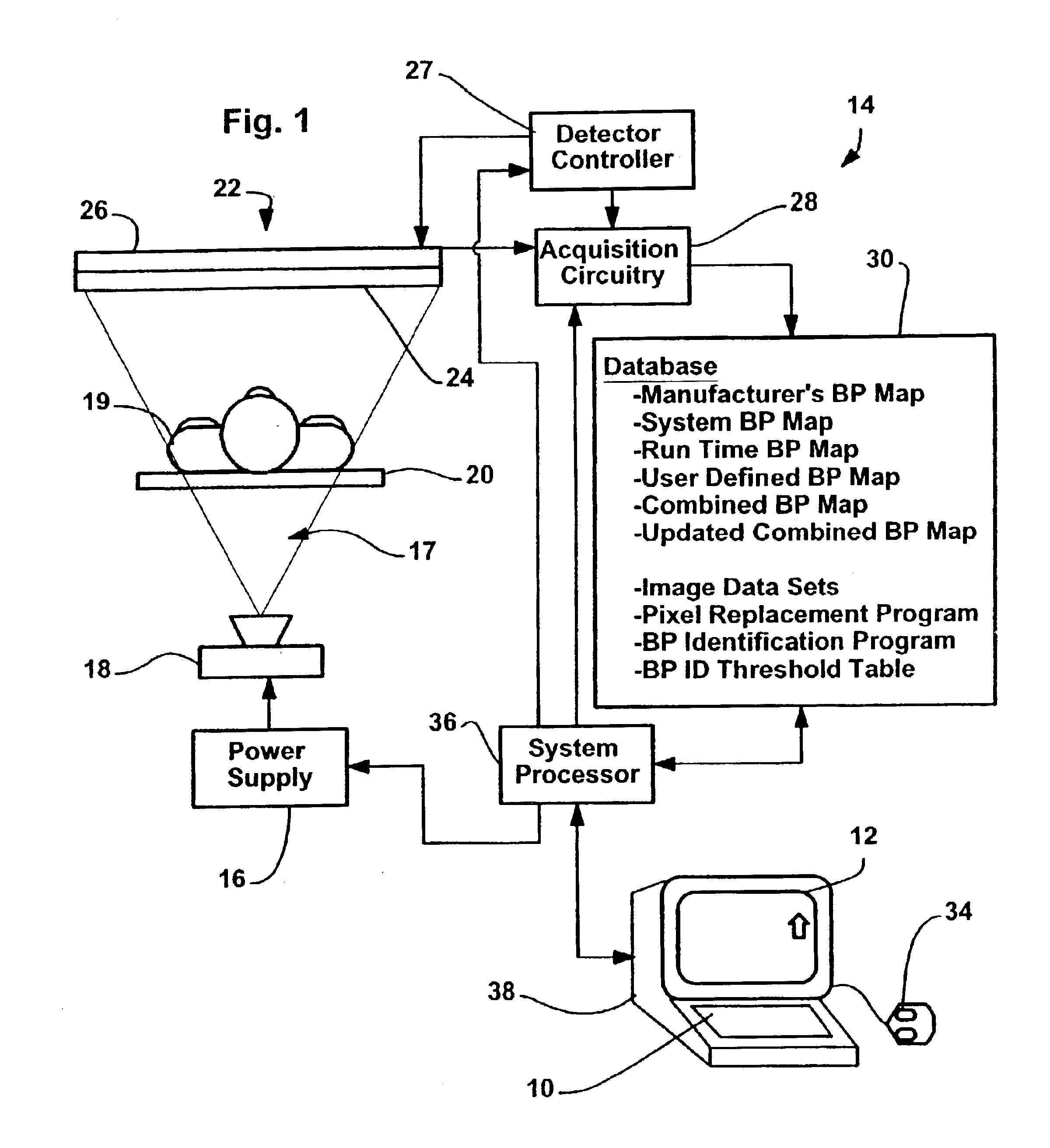
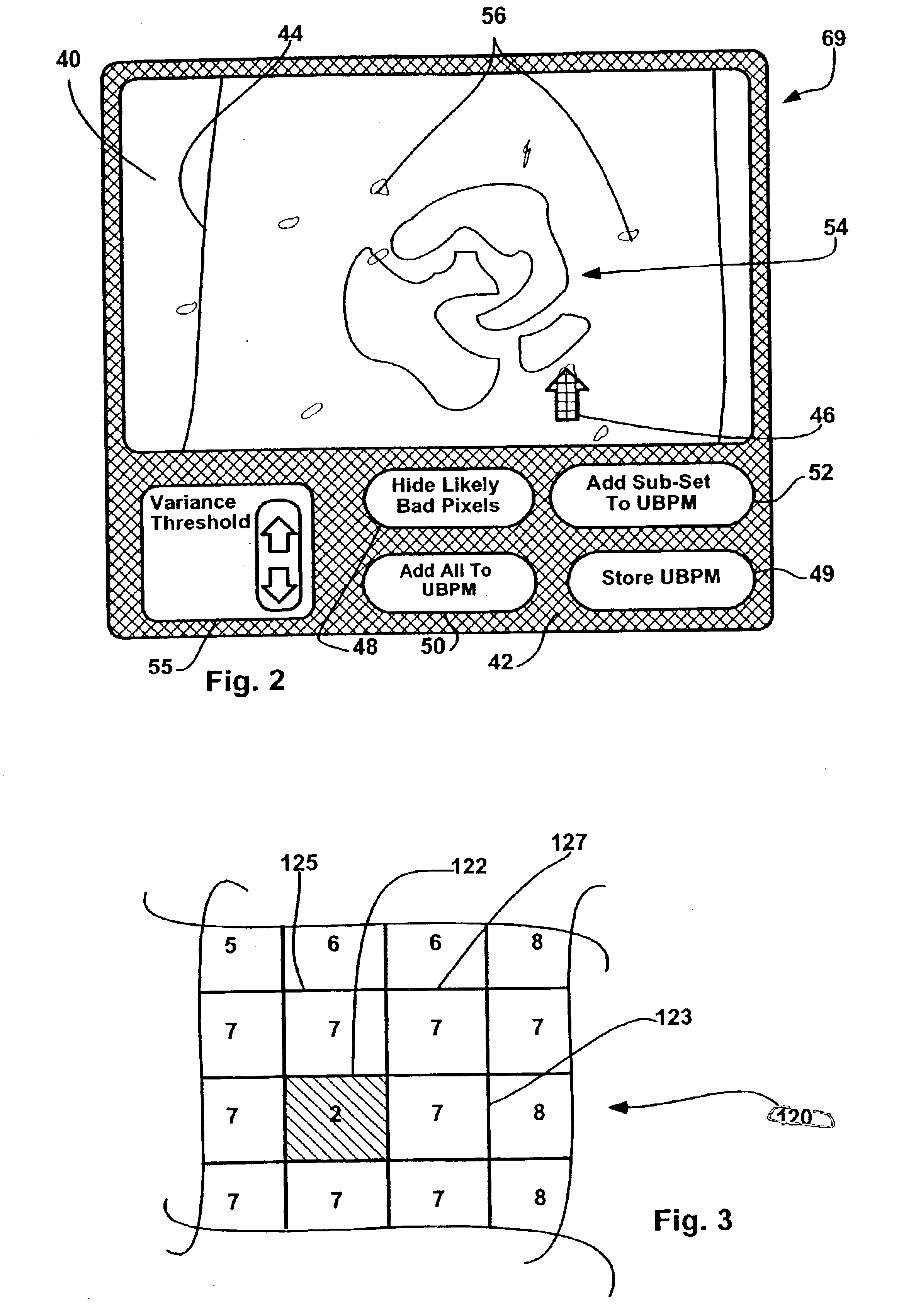
Method and apparatus for identifying composite defective pixel map
InactiveUS6919568B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsFlat panel detectorComputer vision
An apparatus for use with a detector system including a solid state flat panel detector and an image processor, the detector including a plurality of pixels, each pixel generating an initial intensity signal, the initial signals together defining an initial image, the processor storing an initial bad pixel map that includes a known bad pixel set, after signals are generated, the processor automatically using intensity signals corresponding to other than the bad pixel set to generate replacement intensity signals for each of the bad pixel set pixels thereby generating a corrected image, the apparatus for identifying additional bad pixels, the apparatus comprising a processor that, after the image data is collected, examines at least one of the initial image and the corrected image to identify a likely additional bad pixel set including pixels that have unexpected values and an interface for indicating the likely bad set to a system user.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
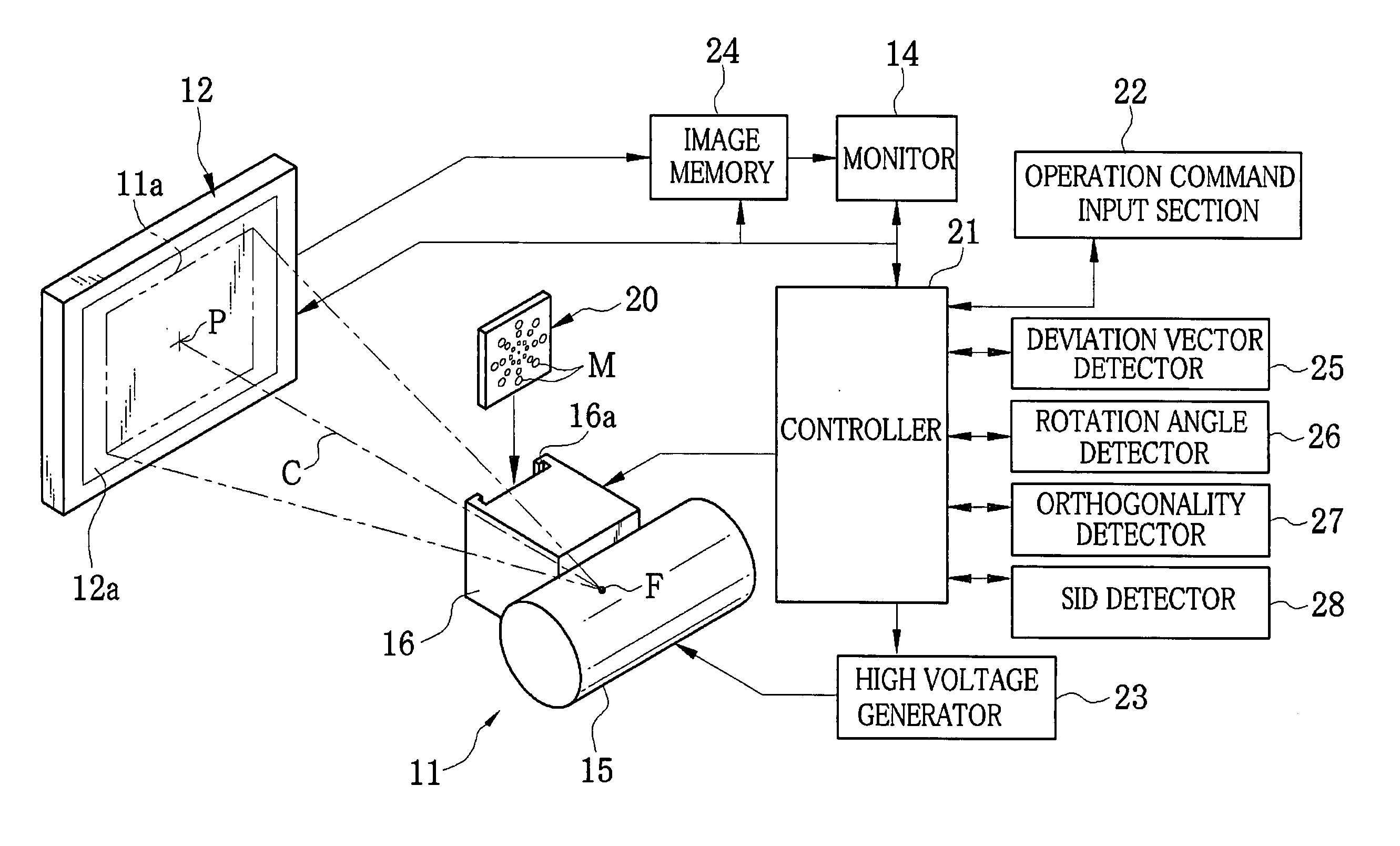
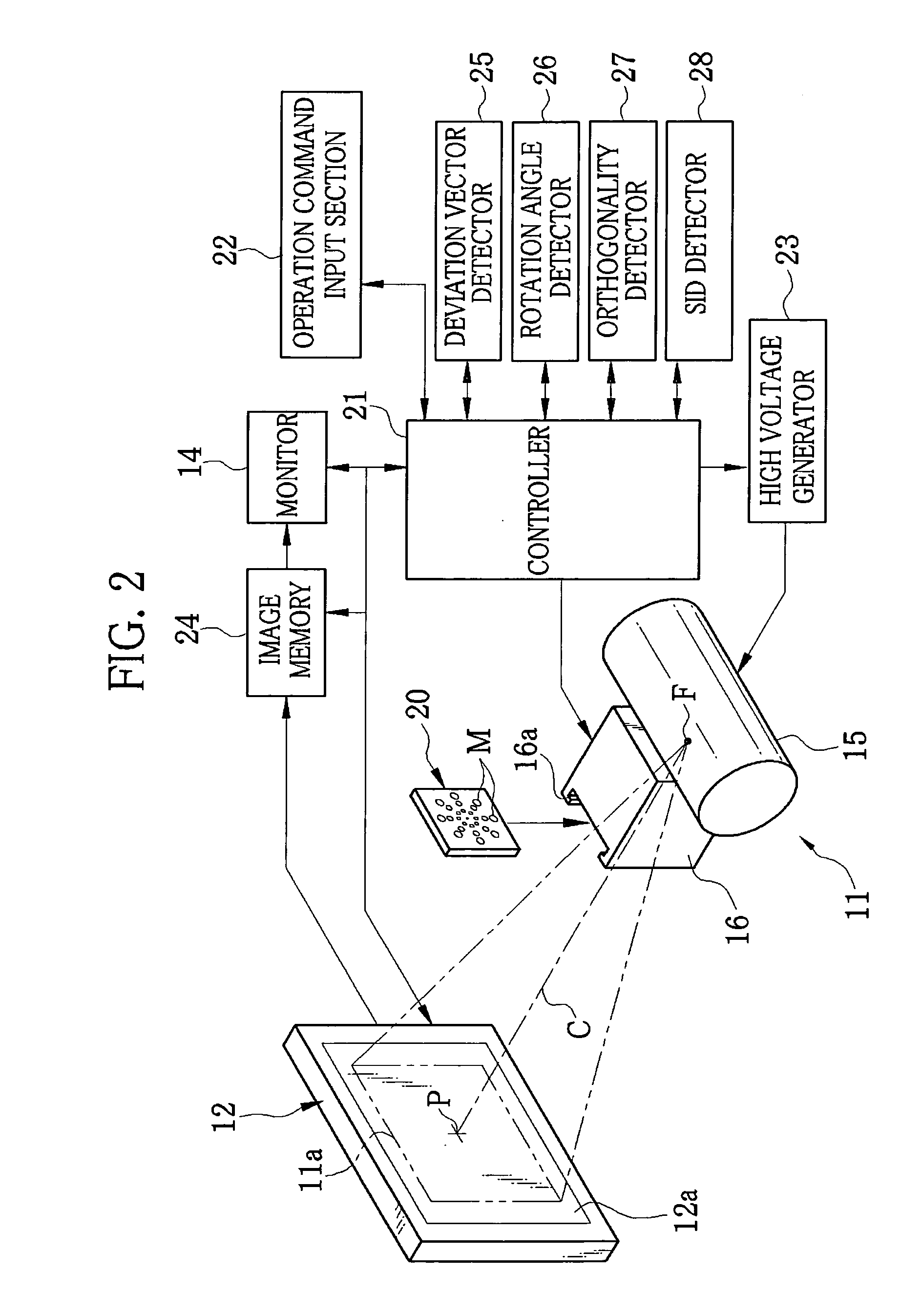
X-ray imaging device, method for detecting deviation of flat panel detector, and program for the same
ActiveUS20110013752A1Detect deviation amountAccurate detectionRadiation beam directing meansInstrumentsDeviation vectorFlat panel detector
An X-ray imaging device includes an X-ray generator, a filter plate detachably attached to an X-ray outlet of the X-ray generator, and a FPD. The filter plate has a plurality of circular markers of different sizes. The smallest marker is disposed at the center of the filter plate. The other markers are disposed on lines radiating from the smallest marker in increasing order of size and at regular intervals. An X-ray radiation beam passes through the markers and patient's body, and is incident upon an imaging surface of the FPD. The FPD produces a preliminary radiographic image from the incident X-ray radiation beam. A deviation vector detector chooses adjoining two marker images of different sizes from the preliminary radiographic image, and identifies to which markers the marker images correspond based on a size ratio. Then, the deviation vector detector determines the center of an X-ray field.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiographic image detector and controlling method therefor
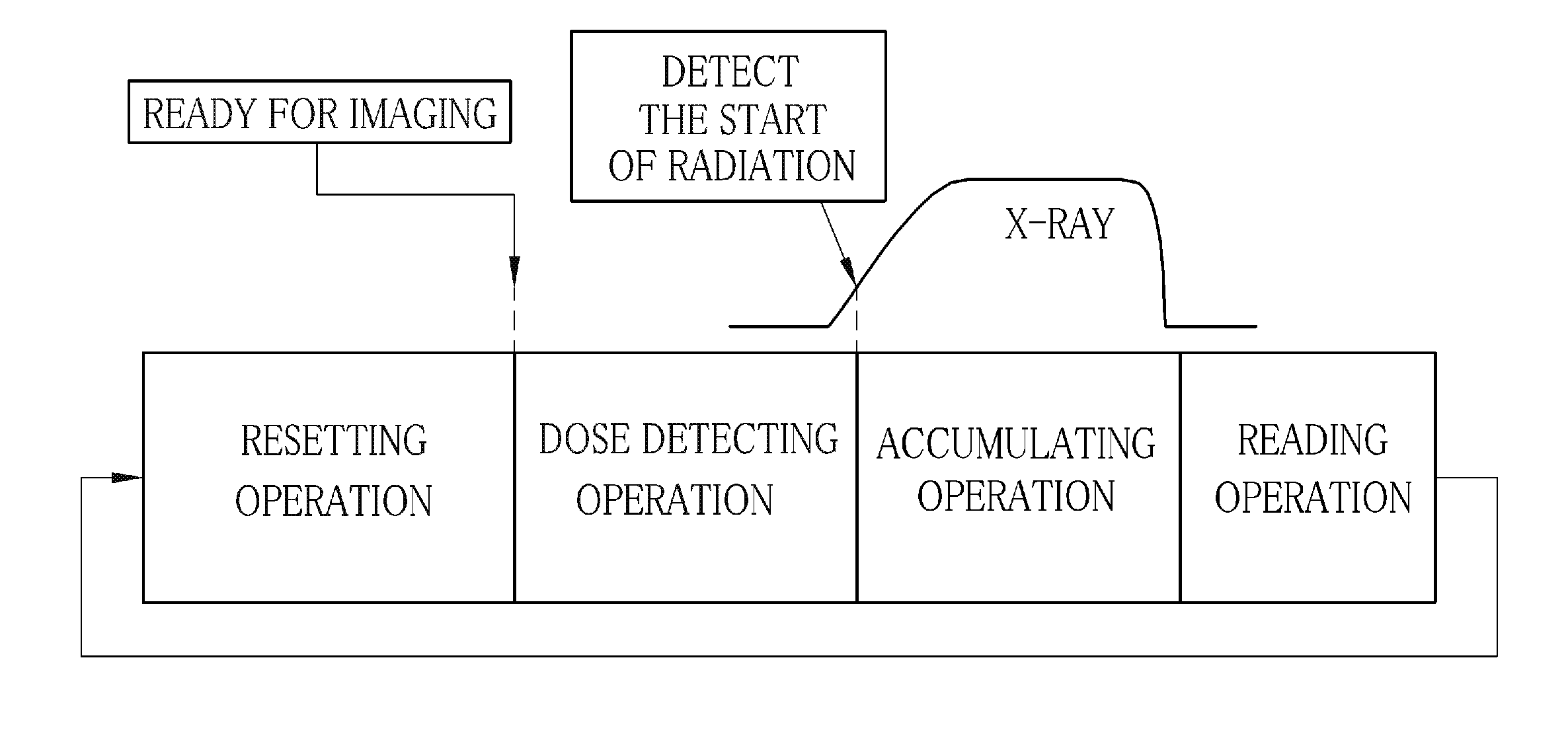
ActiveUS20130136234A1Television system detailsX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentFlat panel detectorSignal processing circuits
A flat panel detector has pixels for obtaining image signals and detective pixels for detecting the amount of incident x-rays. A signal processing circuit is of a pipeline-type, wherein first and second buffer memories are connected to the output of an A / D converter. In a dose detecting operation, the signal processing circuit repeats primary cycles alternately with secondary cycles of a shorter length than the primary cycles. In the primary cycle, a dose detection signal based on electric charges from the detective pixels is input in the first buffer memory and, simultaneously, a dummy signal is output from the second buffer memory. In secondary cycle, the dose detection signal is output from the first buffer memory and, simultaneously, a second dummy signal is input in the second buffer memory. On the basis of the dose detection signals, a start-of-radiation detector detects the start of x-ray radiation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Indirect programming of detector framing node
InactiveUS6904124B2Television system detailsRadiation/particle handlingFlat panel detectorOperational system
A real time imaging system includes a programmable detector framing node controlling generation of radiation and controlling radioscopic image detection. Radioscopic image data is acquired and communicated by the detector framing node independently of a host computer operating system. The detector framing node controls events in real time according to an event instruction sequence and communicates the received radioscopic image data to host memory through a computer communication bus. The image data is received from a selected flat panel detector of a plurality of different flat panel detectors. The detector framing node is programmable by way of a pair of JTAG loops. The JTAG loops receive programming instructions from the host computer and from a pair of JTAG ports.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
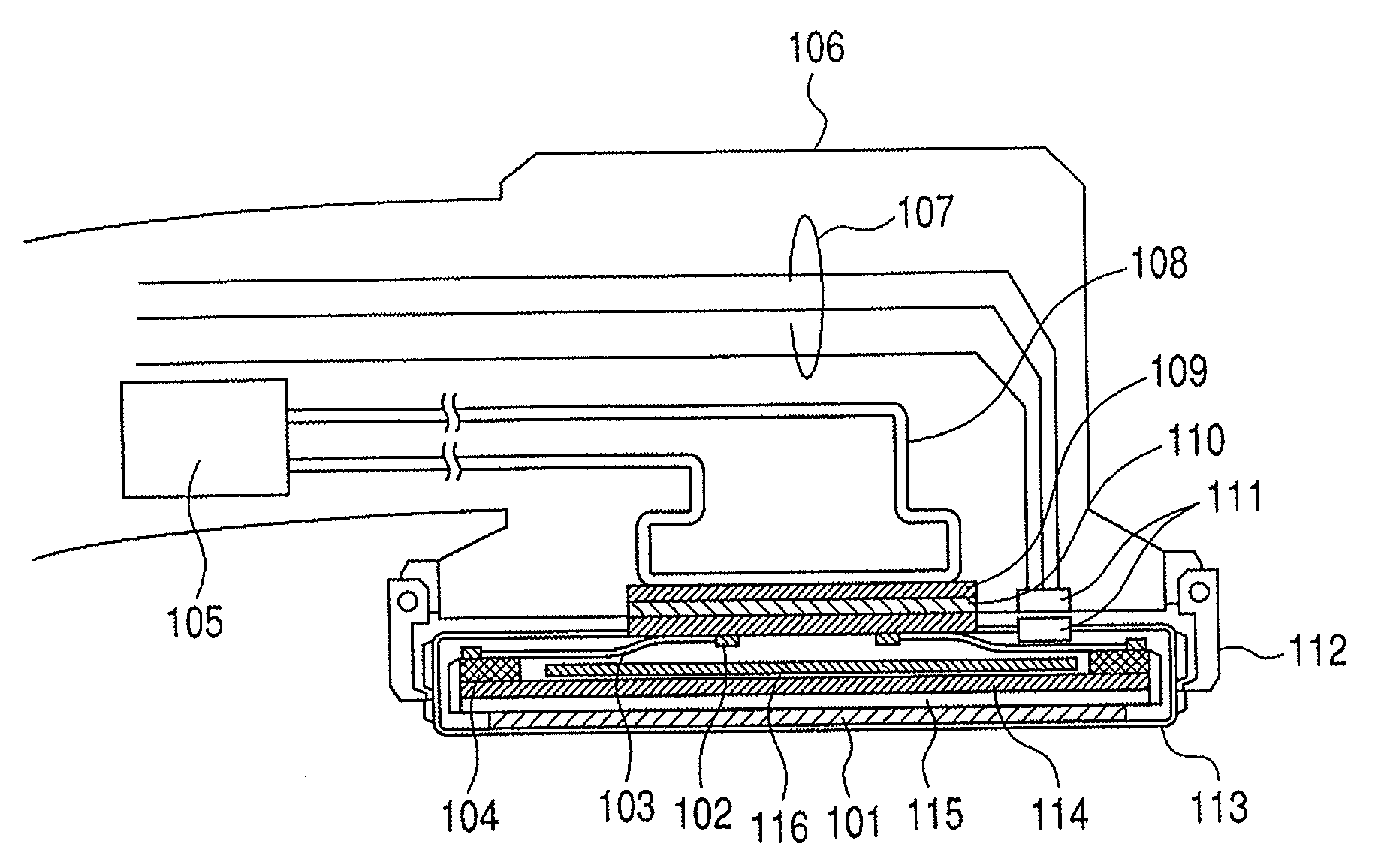
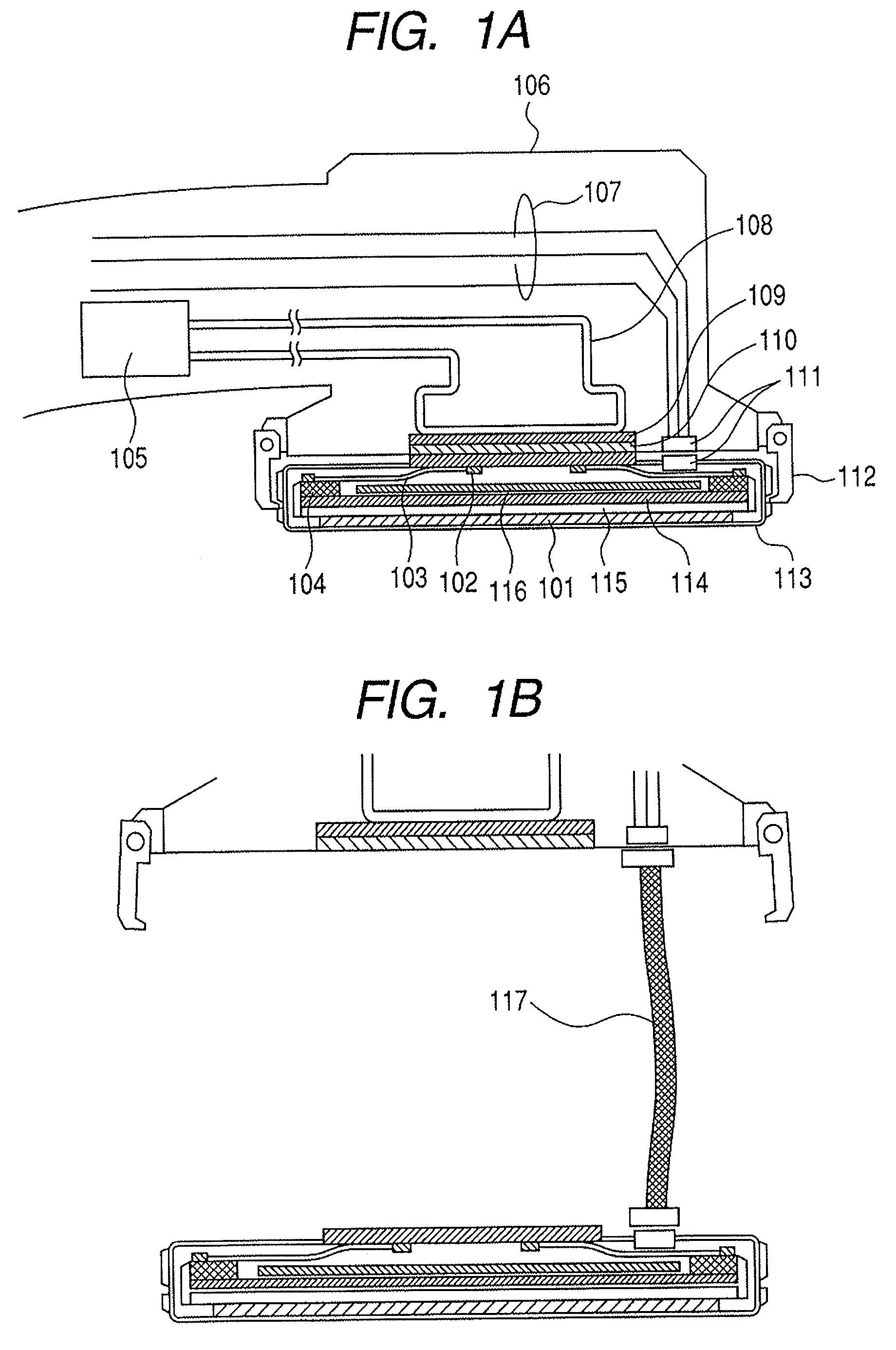
Dental fluoroscopic imaging system
ActiveUS20110150185A1X-ray/infra-red processesRadiation diagnostics for dentistryFluorescenceDental examination
The dental fluoroscopic imaging system includes a flat panel detector comprised by a gamma-rays or x-rays converter, a plate, a collector, a processing unit and a transmitter suitable for 2D intraoral / extraoral and 3D extraoral dental fluoroscopy. The x-ray converter contains a material capable of transforming the low dose gamma rays or x-rays beam received from an emitter after going through the dental examination area into electrical signals or a light image consequent with the radiographed image. The plate transmits the electric signals or light image to a collector which amplifies it and sends it to a processing unit and then to transmitter designed to transfer digital images sequentially to a host computer and software which can acquire, process, transform, record, freeze and enhance 2D and 3D images of video frame rates. Two dimensional images are obtained while using a C-arm / U-arm configuration while 3D images are obtained while using the O-arm configuration.
Owner:REAL TIME IMAGING TECH
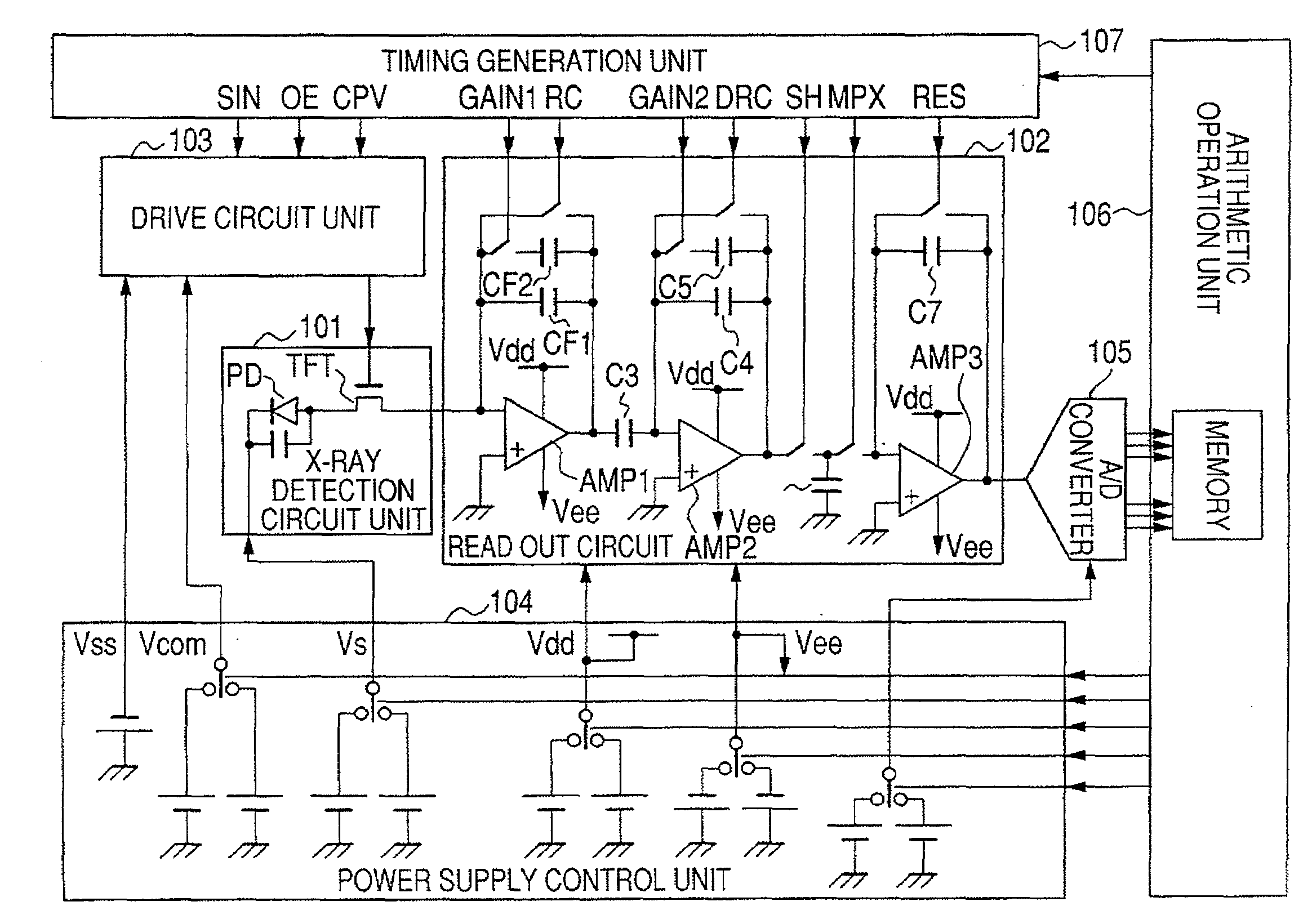
Methods for improving image quality of image detectors, and systems therefor
InactiveUS20090129659A1Quick and efficient verificationEliminate artifactsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsFlat panel detectorImaging quality
The present invention relates to methods and systems for improving image quality of imaging devices such as image detectors, and preferably of flat panel detectors such as amorphous silicon flat panel detectors, for example used in radiotherapy. The invention also relates to the improving of life span of used or aged detectors.
Owner:DEUTMANN HEINZ
Radiographic image detector and gain setting method for radiographic image detector
In a radiography system, after a radiation dose, signal charges are accumulated in sensor pixels in an imaging area of a flat panel detector corresponding to the dosed amounts of radioactive rays on the pixels. The signal charges are read out from the pixels and converted into voltage signals representative of density levels of respective pixels of a radiographic image. Before reading the signal charges, a dose profile representative of distribution of the dosed amounts of radioactive rays is measured by leak currents from the pixels or bias currents through bias lines for applying a bias voltage to the pixels. Based on the contrast or difference between the maximum value and the minimum value in the dose profile, a gain of amplifiers for the voltage signals is determined such that the gain increases with decreasing contrast.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
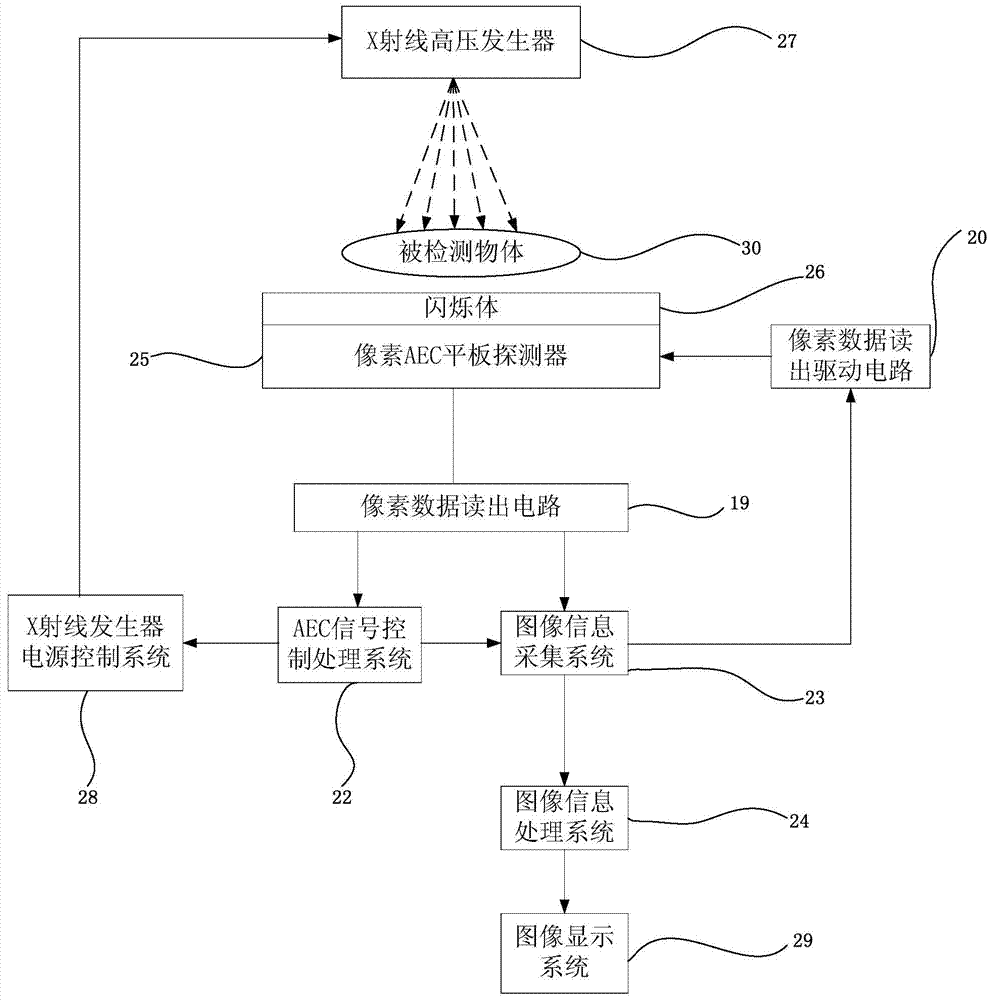
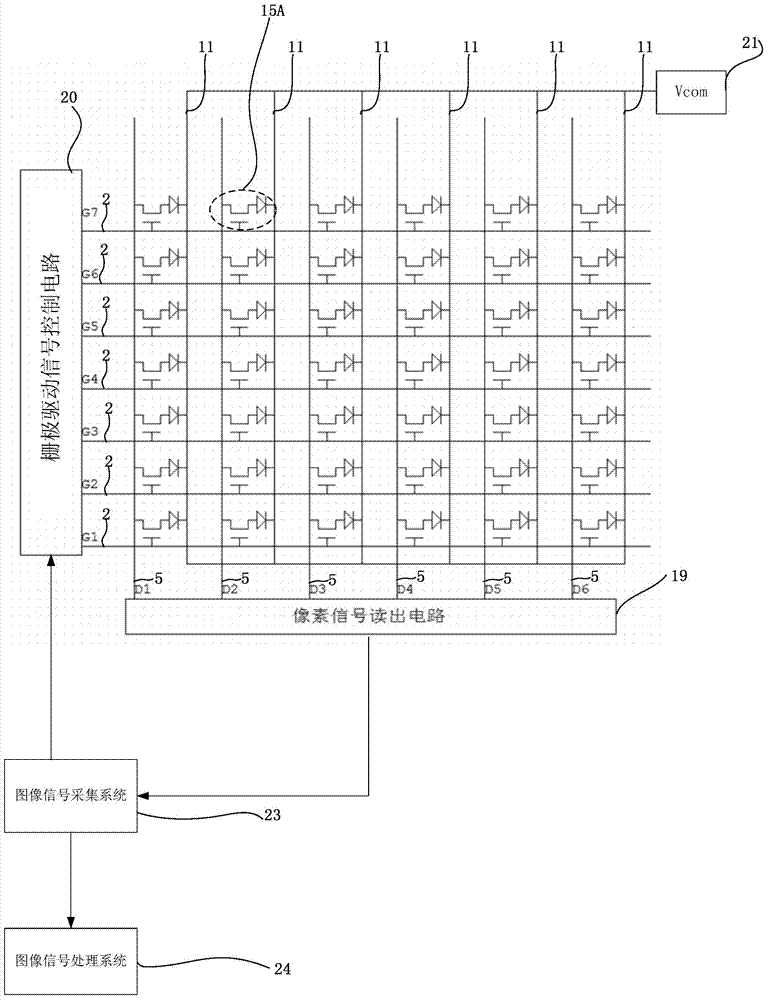
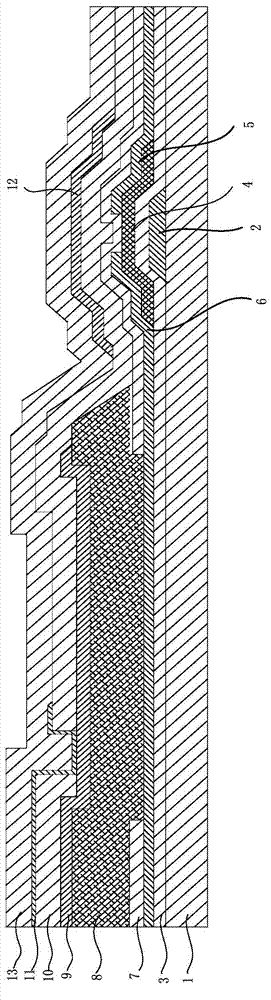
Pixel AEC flat panel detector
ActiveCN104124256AWill not change the semiconductor process technologyEasy to implementRadiation controlled devicesRadiation diagnosticsInformation processingAutomatic control
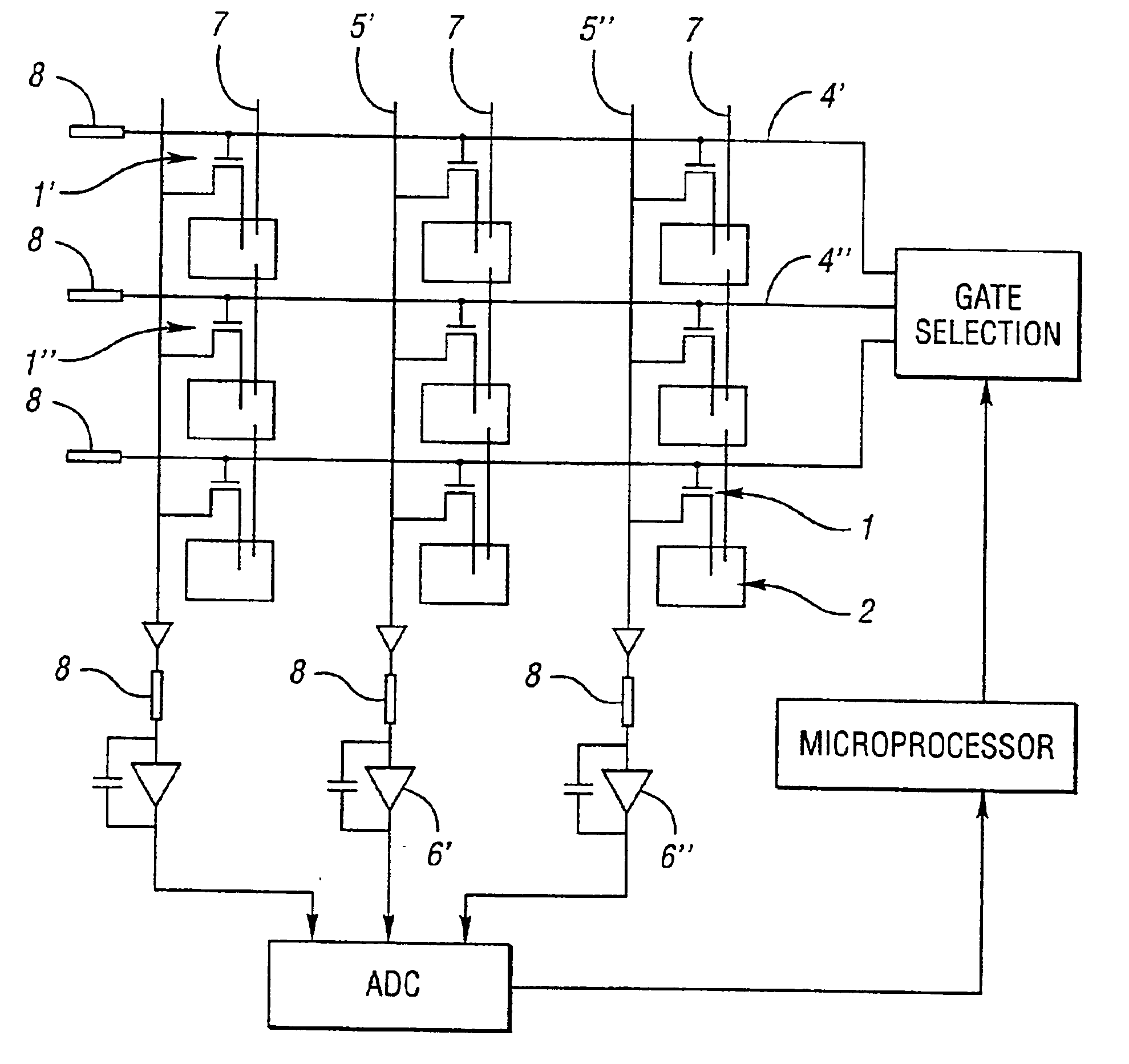
The invention provides a pixel AEC flat panel detector. The pixel AEC flat panel detector comprises a pixel array, a gate drive signal control circuit, a normal pixel signal reading circuit, an AEC signal control processing system, an image information acquisition system and an image information processing system, wherein the pixel array comprises a plurality of normal pixel units and a plurality of AEC pixel units, wherein the plurality of normal pixel units form an array, the plurality of AEC pixel units are distributed in the array by means of replacing normal pixels in the array, each of the normal pixel units is composed of a thin film transistor switch and a photodiode, and each of the AEC pixel units is composed of a photodiode. The pixel AEC flat panel detector provided by the invention is capable of accurately detecting an exposure starting time, automatically controlling an exposure ending time, and automatically controlling an exposure dose. The pixel AEC flat panel detector provided by the invention is simple in structure and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI IRAY TECH
Method for inversing patient target region dosage in radiation therapy
InactiveCN101209367AHigh precisionTroubleshooting Accurate ExecutionImage data processing detailsRadiation diagnosticsFlat panel detectorImage resolution
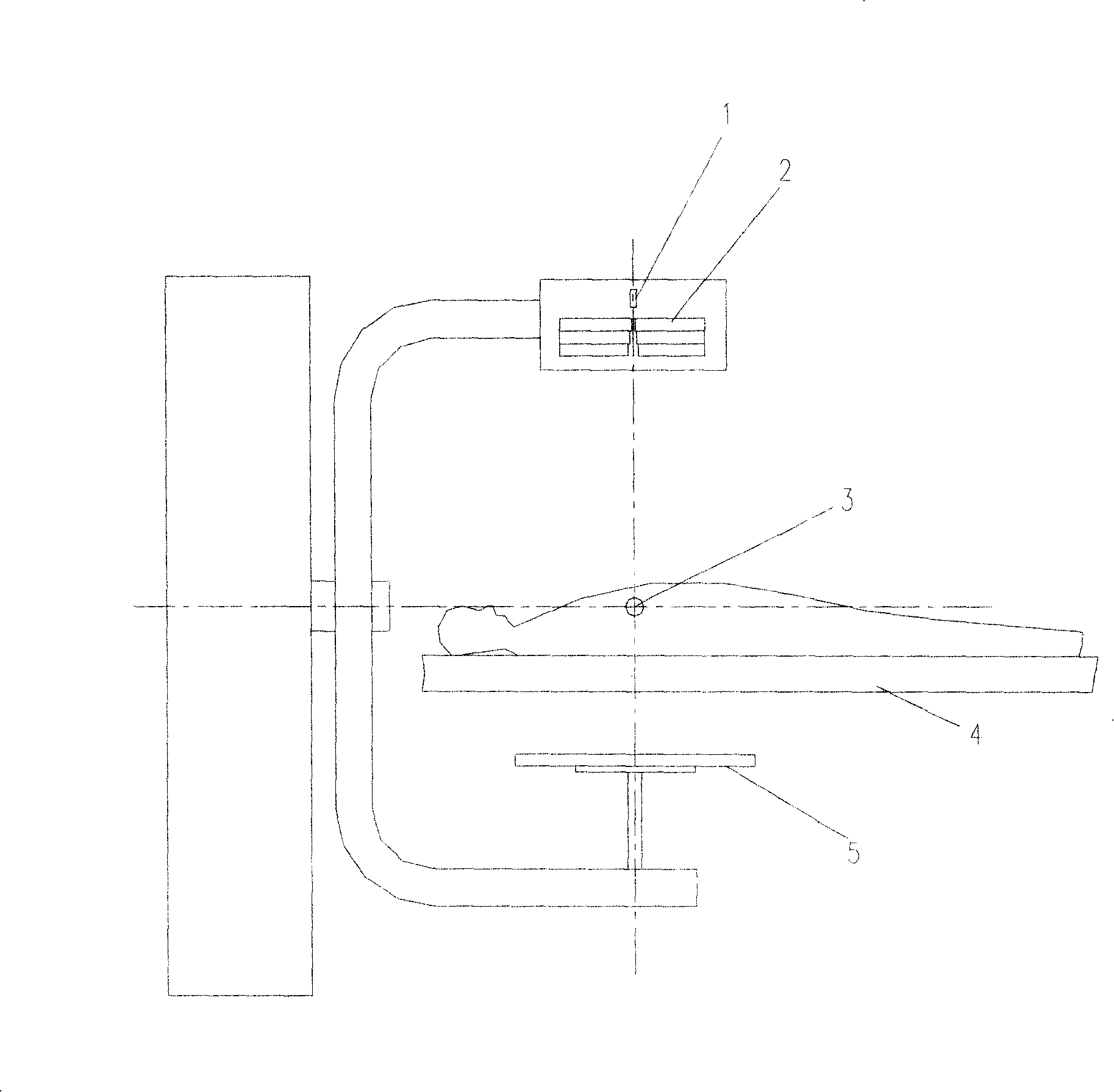
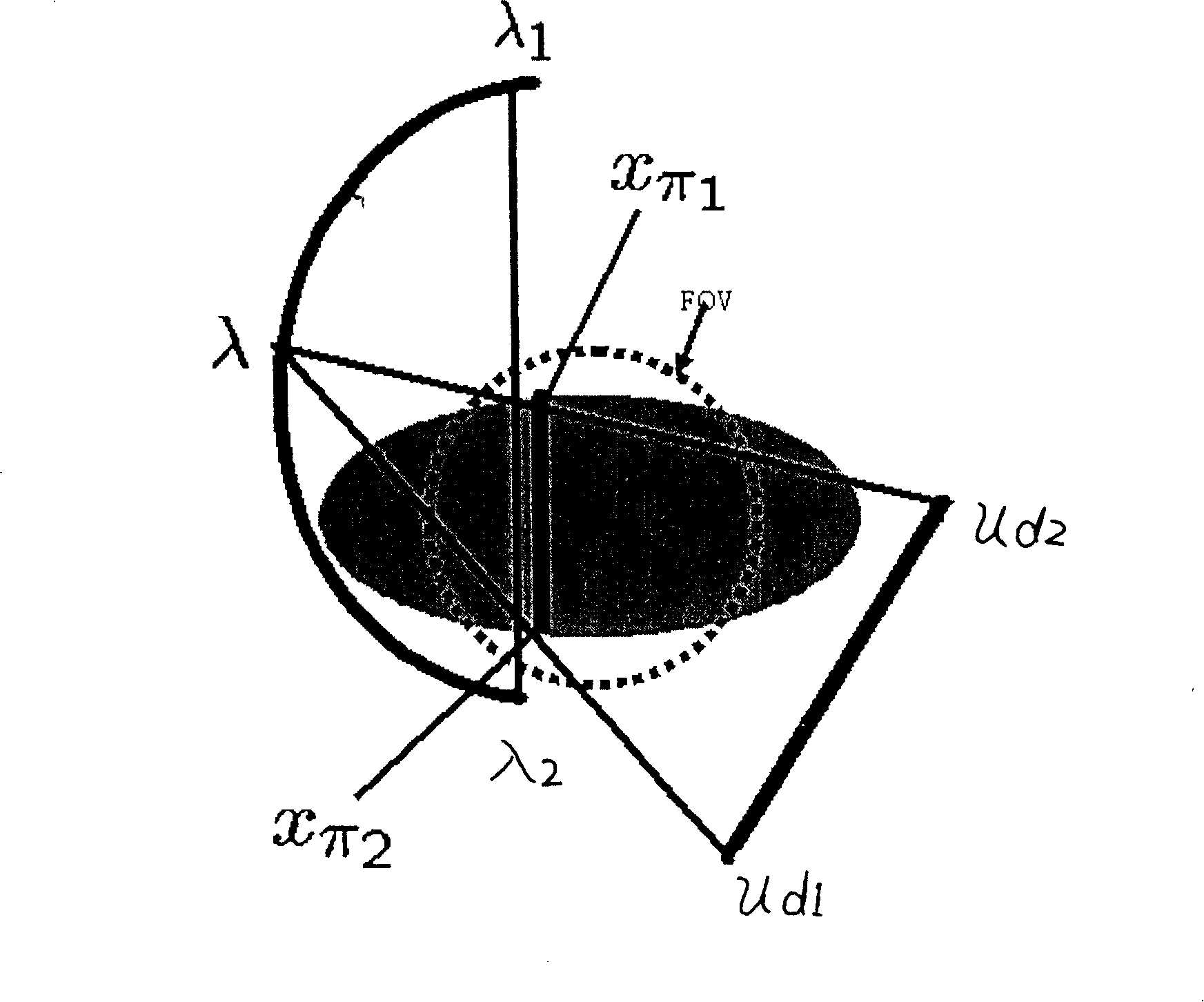
The invention discloses a method of dose reversal of the target of a patient in radiotherapy, the method makes use of a light source and a flat panel detector to carry out the rotary scanning around the target of the patient, so as to obtain the data of the target image of the patient and the dose data which penetrates the target of the patient; the invention applies a virtual PI line reconstruction algorithm to carry out the reconstruction and processing, and the treatment is carried out by adjusting the position of the patient and the input dose distribution data according to the processing results. As the invention adopts a true three-dimensional image reconstruction algorithm which is based on the flat panel detector, the spatial resolution of the true three-dimensional image is isotropic, the invention does not need interpolation, and can directly realize the processing of the image on the three-dimensional space, thus greatly improving the imaging precision and solving the problem that the imaging is not precise due to the interpolation error during the integration process into a quasi three-dimensional image of the existing radiotherapy, which can further affect the accurate implementation of the treatment plan of focus.
Owner:SHEN ZHEN HYPER TECH SHENZHEN +1
Radiation imaging system
InactiveCN102740775AChange in intensityGood phase contrast imagesImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionFlat panel detectorGrating
An X-ray imaging system is provided with an X-ray source (11), first and second absorption gratings (31, 32), and a flat panel detector (FPD) (30), and obtains a phase contrast image of an object H by performing imaging while moving the second absorption grating (32) in x direction relative to the first absorption grating (31). The following mathematical expression is satisfied where p1' denotes a period of a first pattern image at a position of the second absorption grating (32), and p2' denotes a substantial grating pitch of the second absorption grating (32), and DX denotes a dimension, in the x-direction, of an X-ray imaging area of each pixel of the FPD (30). Here, "n" denotes a positive integer. DX is not equal to n x (p1' x p2') / |p1' - p2'|
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Deposition substrate and scintillator panel
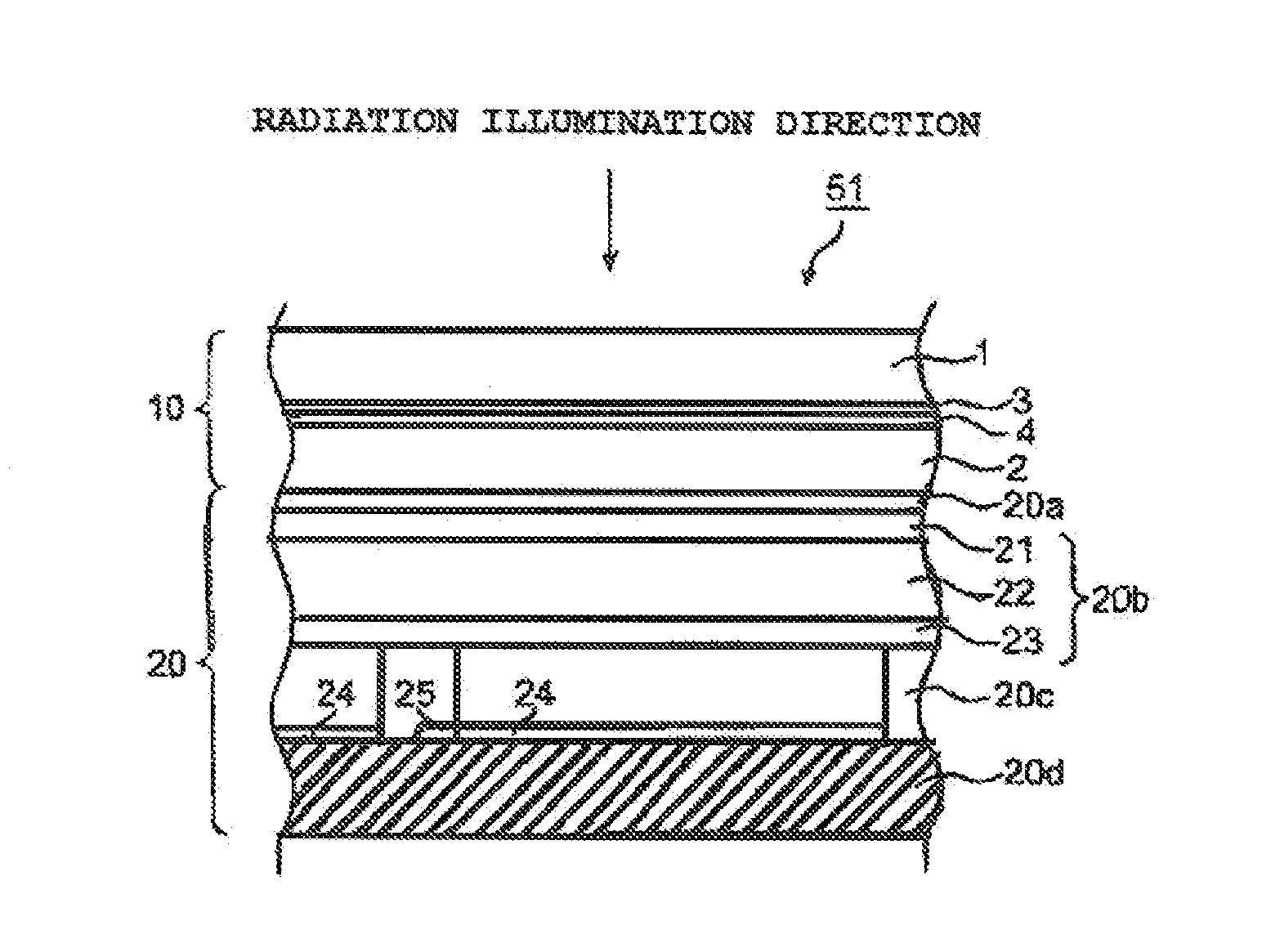
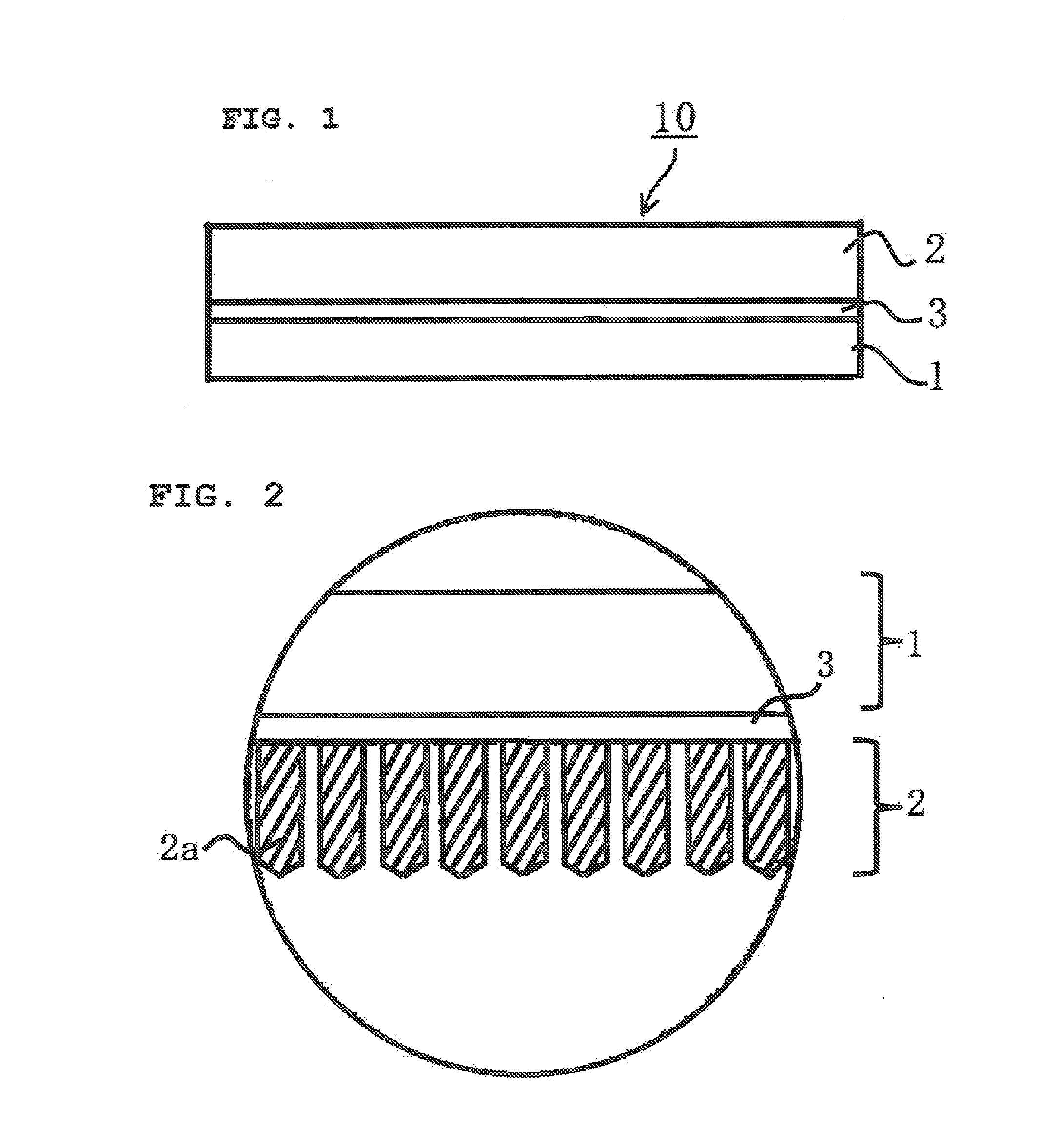
ActiveUS20140239196A1Excellent cuttabilityUniform Image QualityDiffusing elementsPhotometryIn planeFlat panel detector
An object of the invention is to provide scintillator panels which can give radiographic images such as X-ray images with excellent sharpness and excellent uniformity of sharpness, which realize devices such as flat panel detectors having uniform image quality characteristics in the light-receiving plane, and which exhibit excellent cuttability, excellent sharpness and excellent in-plane uniformity of sharpness. A scintillator panel of the invention includes a support, a reflective layer on the support, and a scintillator layer formed on the reflective layer by deposition. The reflective layer includes light-scattering particles and a binder resin. A specific region of the reflective layer is defined by a resin or includes light-scattering particles having a specific area average particle diameter, or the reflective layer has a specific arithmetic average roughness.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com