Patents
Literature
977 results about "Real time imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
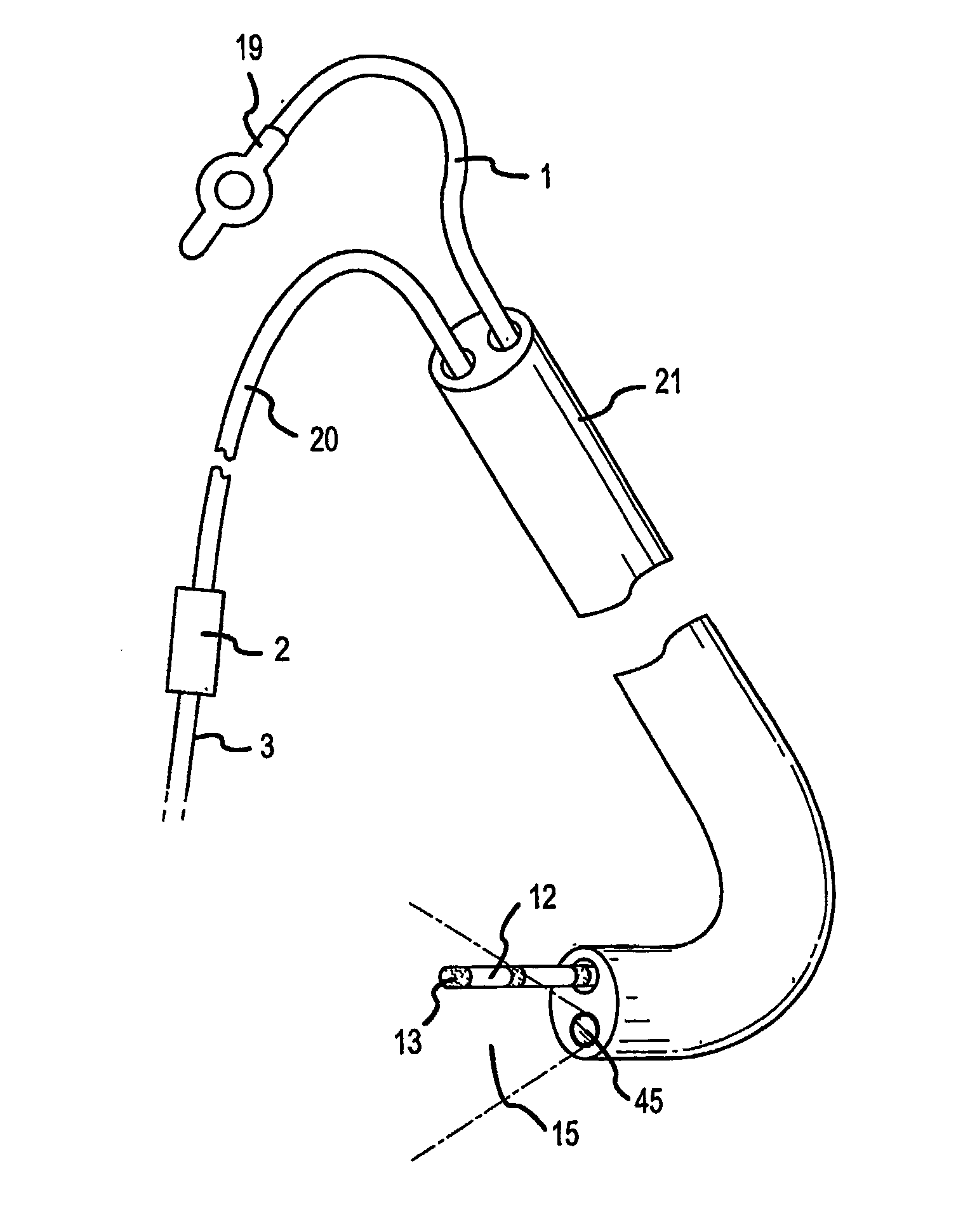
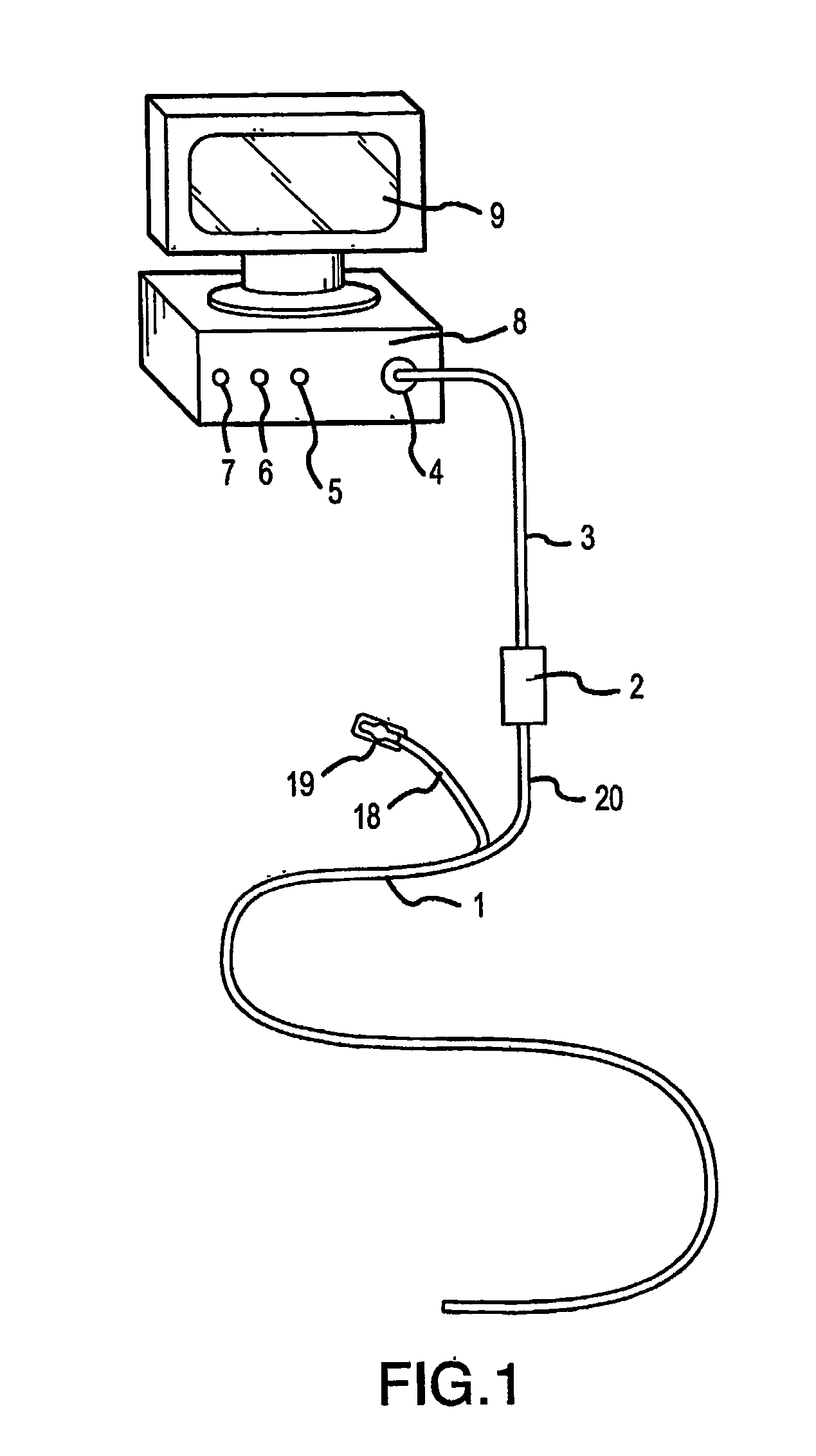
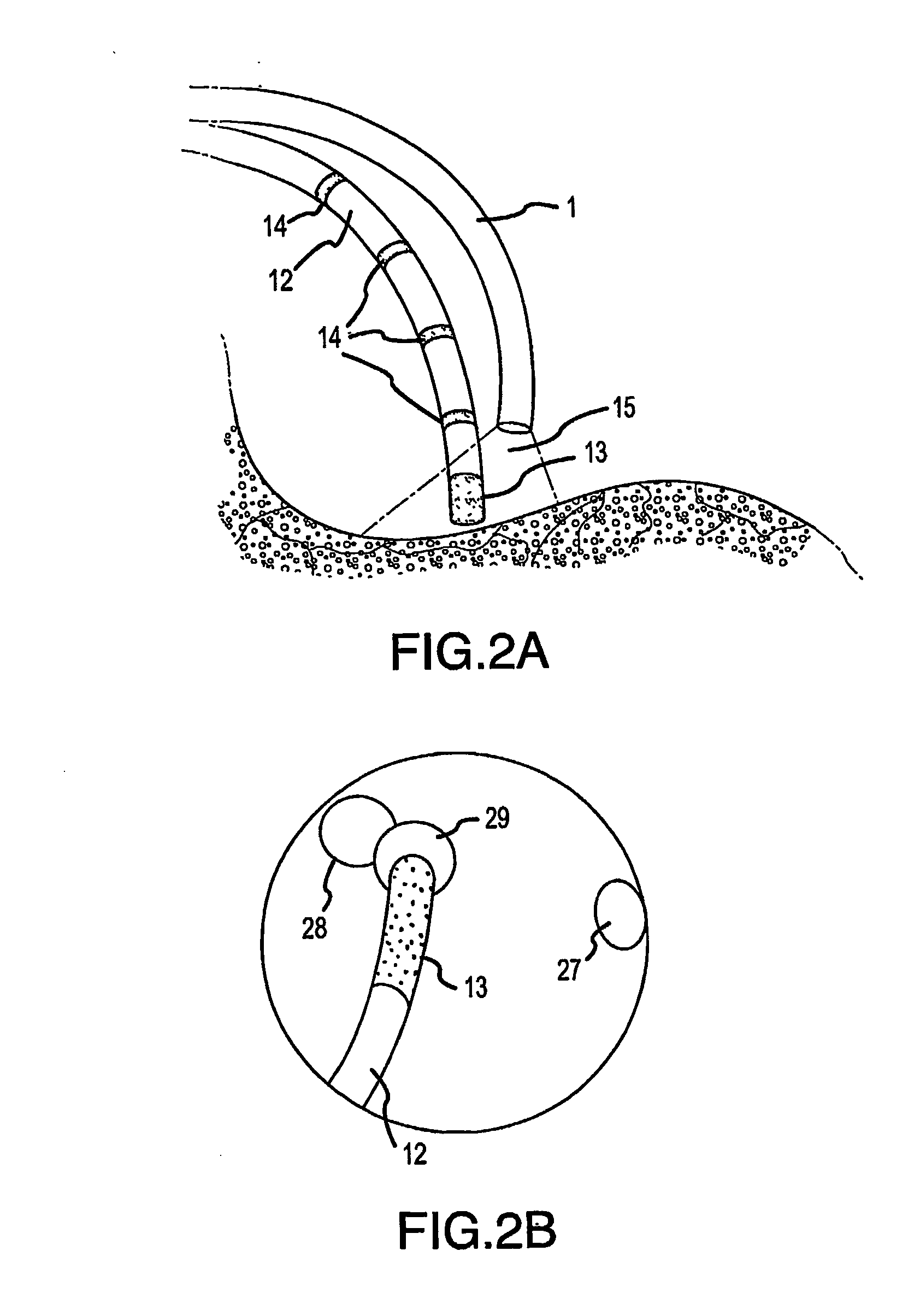
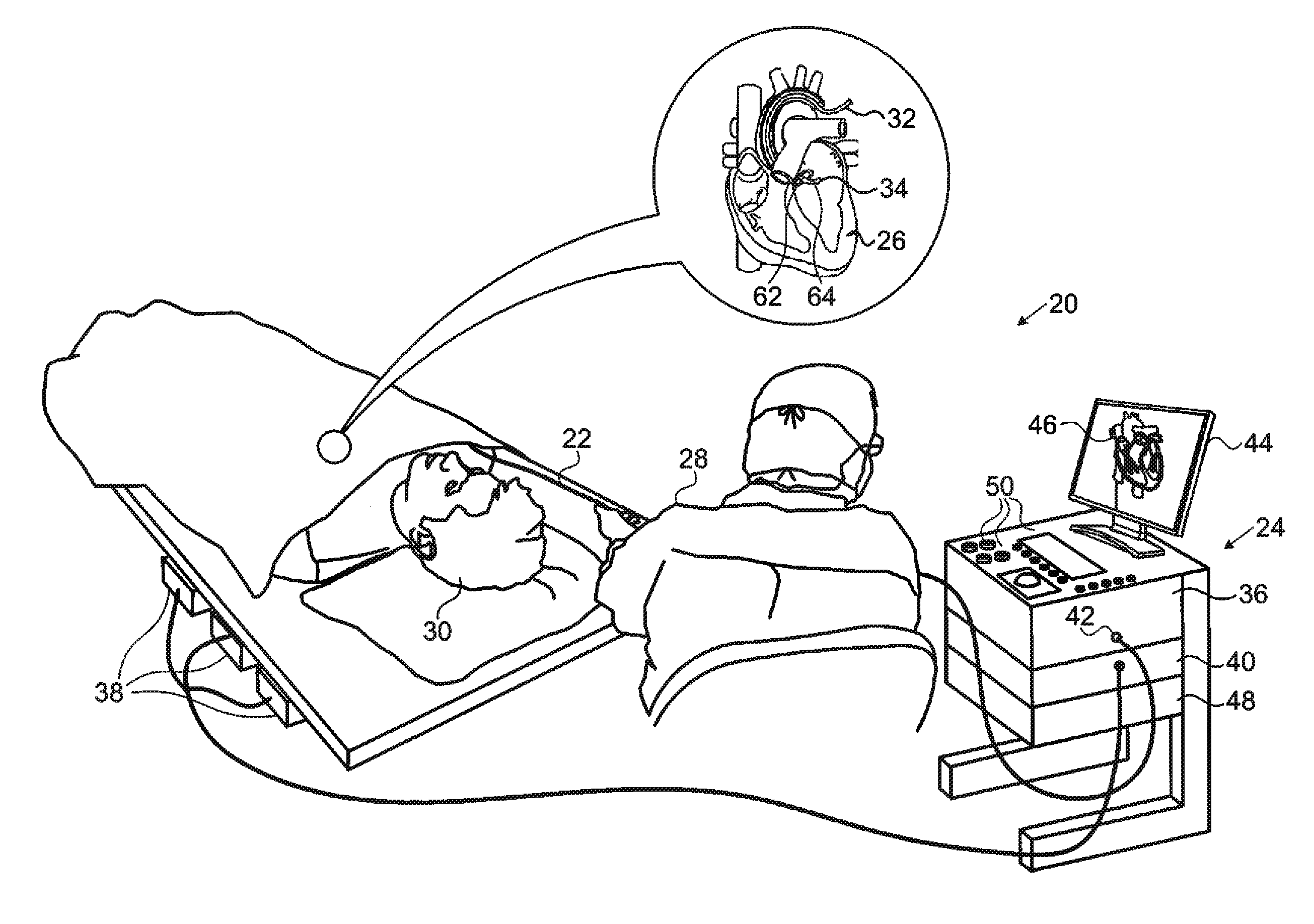
Direct, real-time imaging guidance of cardiac catheterization
Devices (1) and methods for accomplishing tasks within a body using infrared imaging are disclosed which, in connection with other known components, are useful in ablation, stitching and other operations, identification of sizes and composition of objects, and the creation of maps by taking multiple images at different positions or times.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
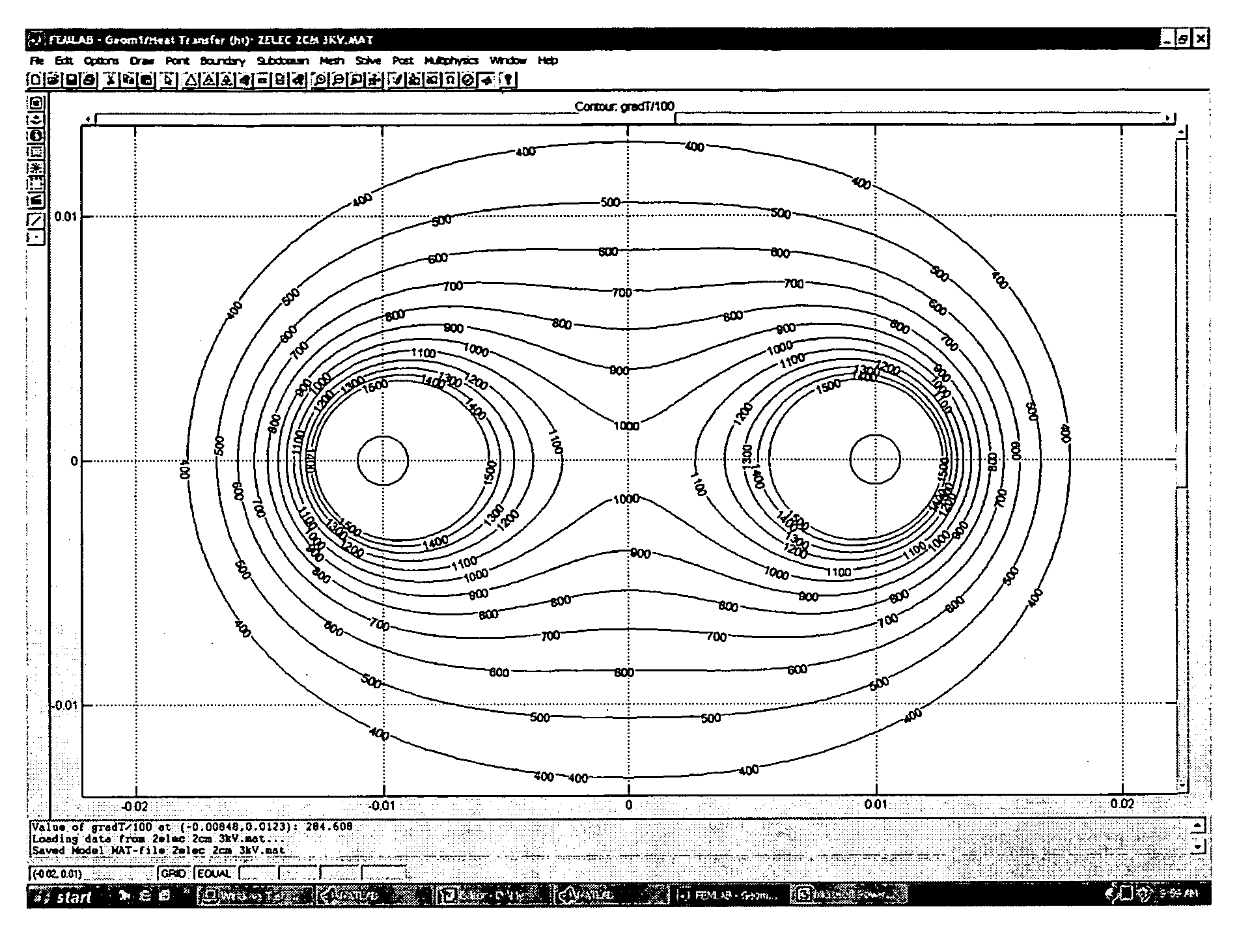
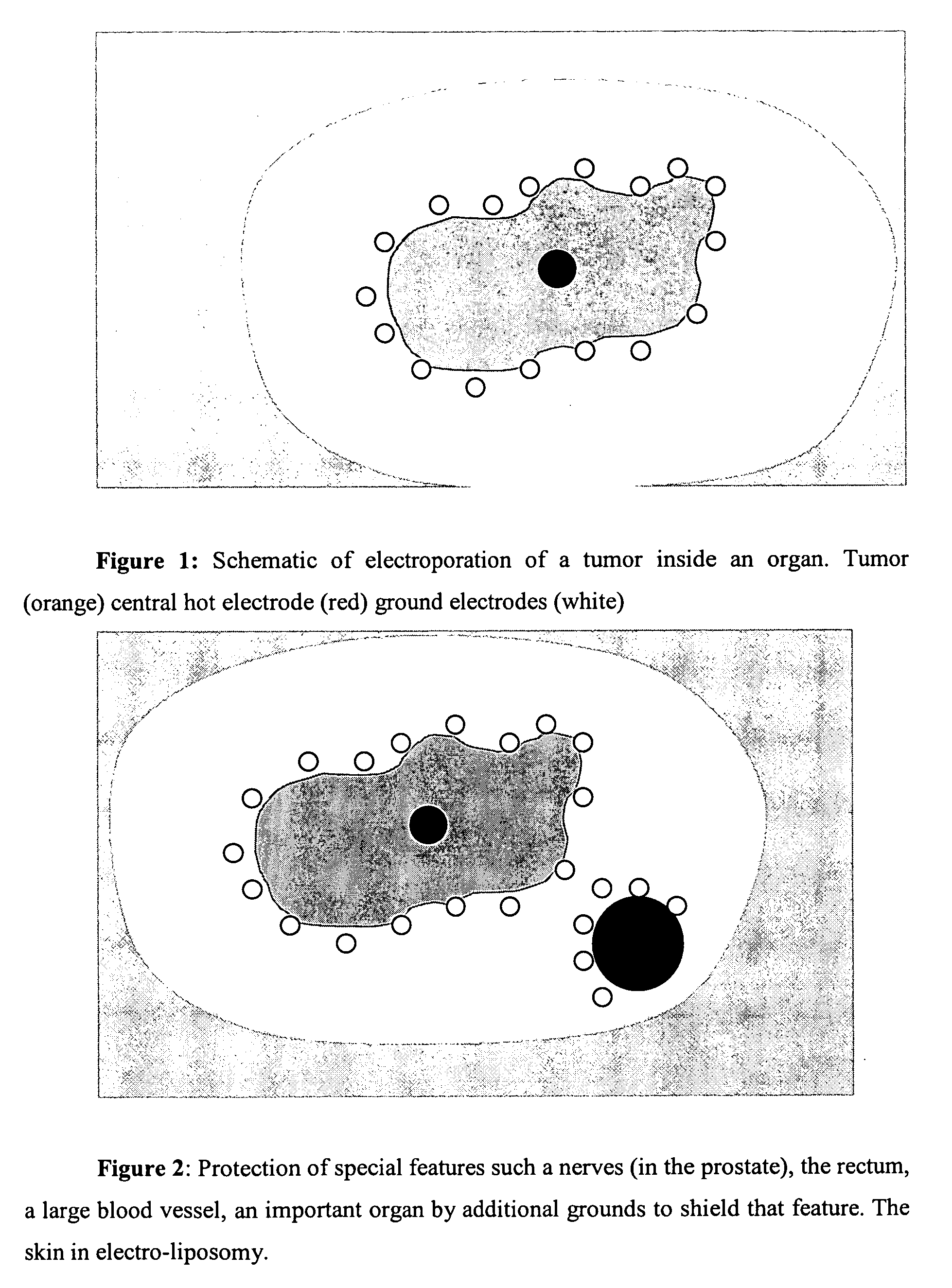
Electroporation controlled with real time imaging
InactiveUS20060264752A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMedical imagingIrreversible electroporation
A method and a system for producing the method are disclosed whereby irreversible electroporation pulses are produced across an area of target tissue. A medical imaging device is used to create an image of the irreversible electroporation in real time thereby making it possible to determine the area of electroporation and the extent of results obtained and to adjust the positioning of electrodes and / or the current as needed based on the image being viewed.
Owner:ONCOBIONIC +1
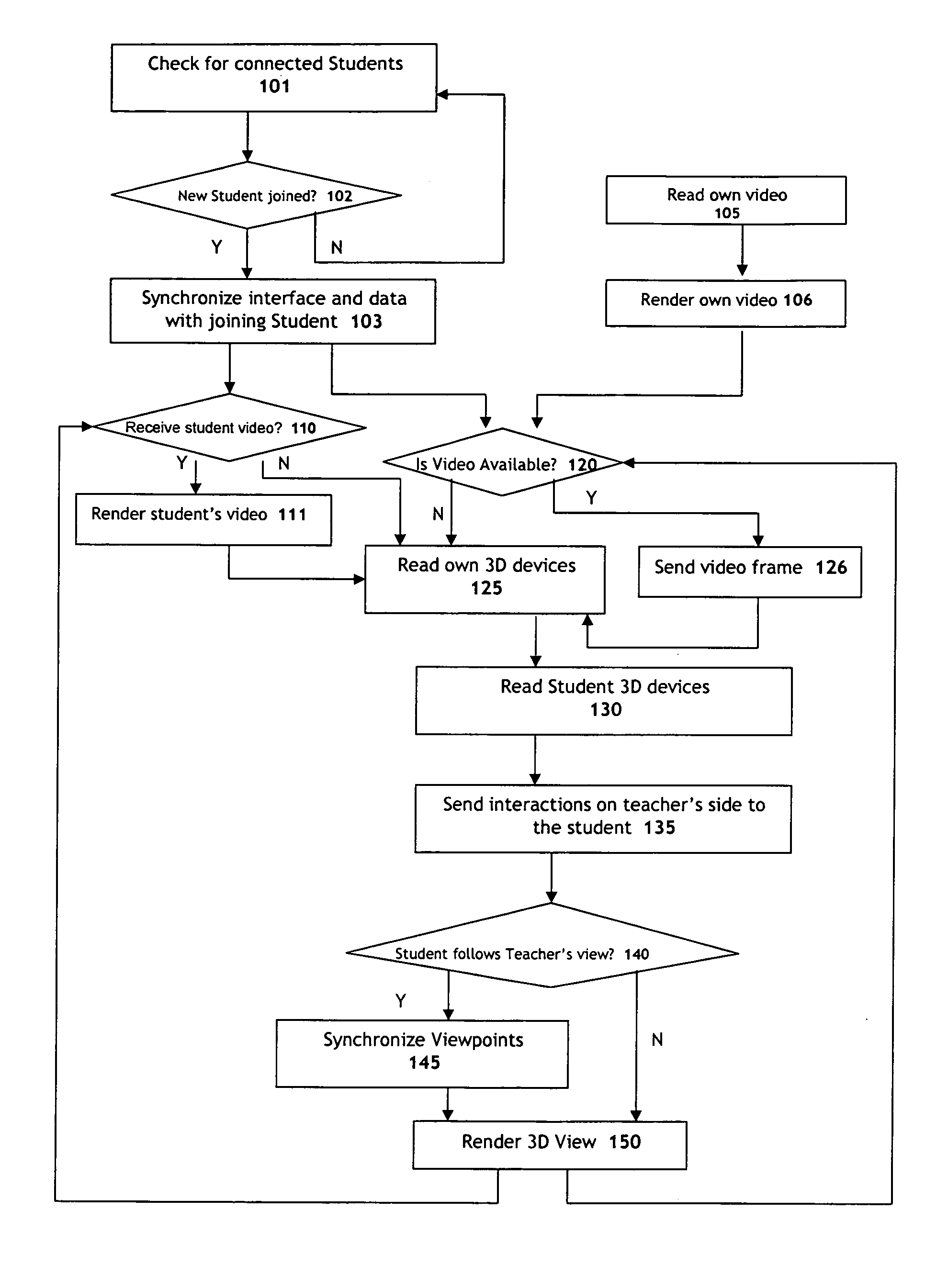
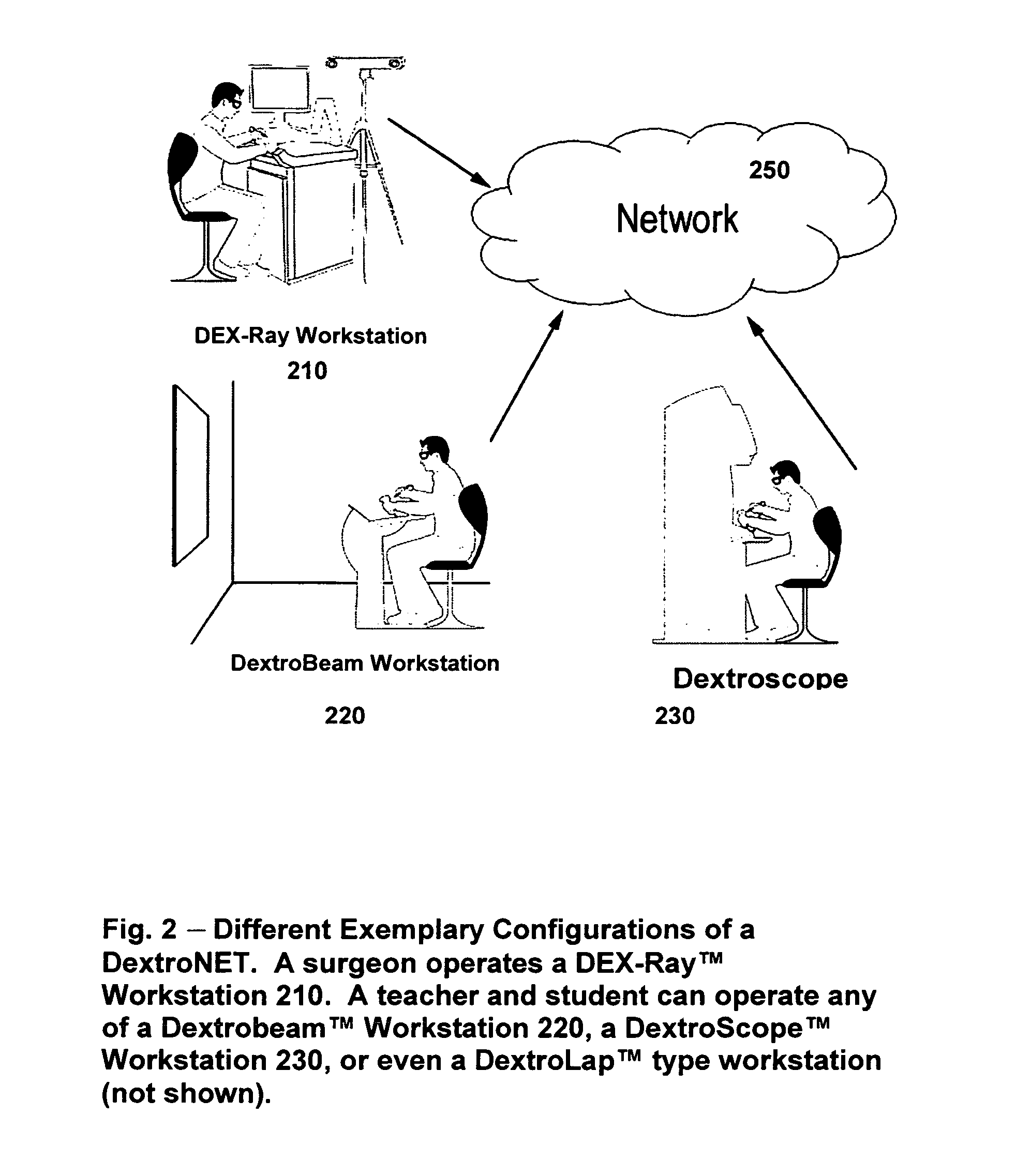
Systems and methods for collaborative interactive visualization of 3D data sets over a network ("DextroNet")
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Medical imaging systems
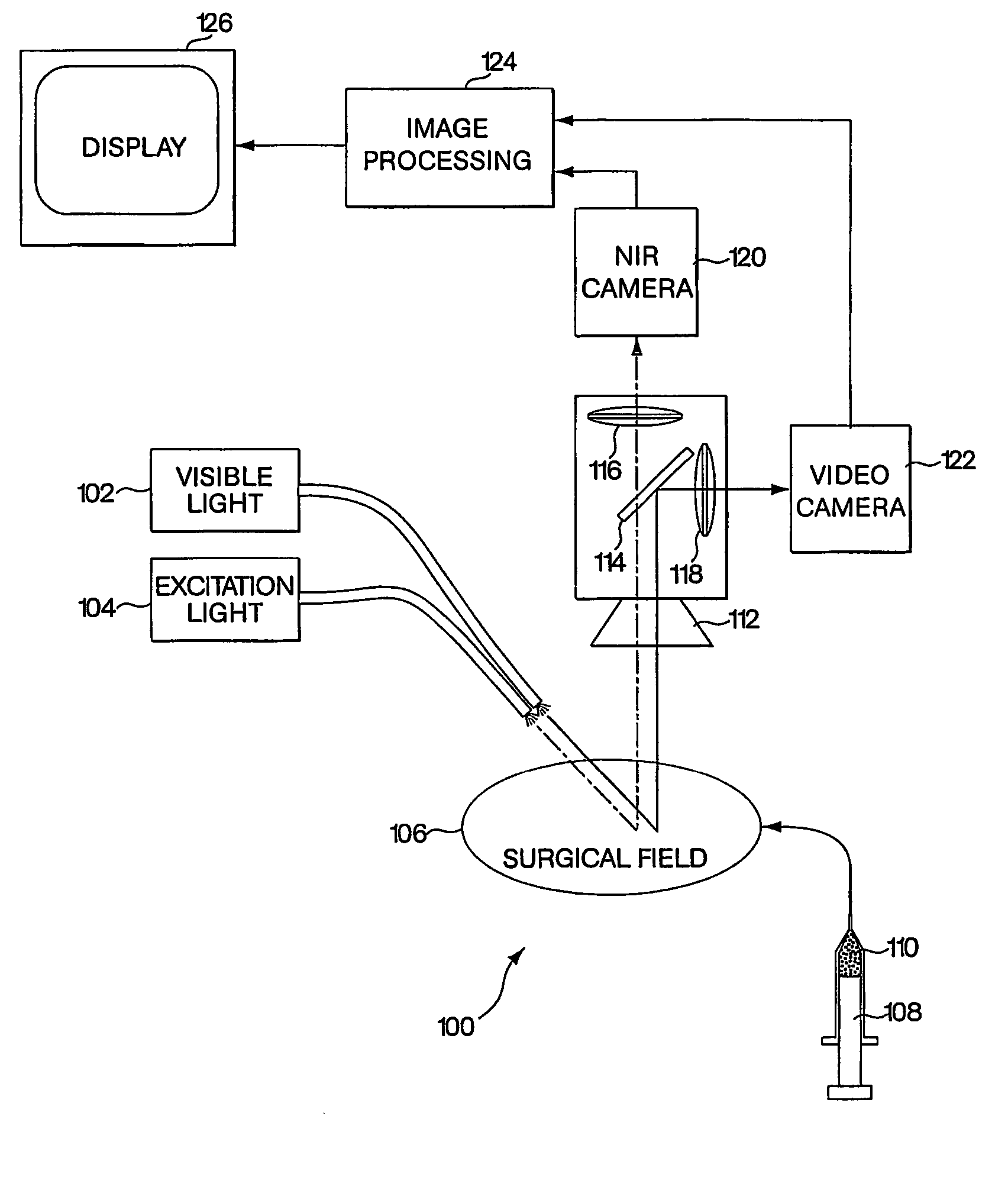
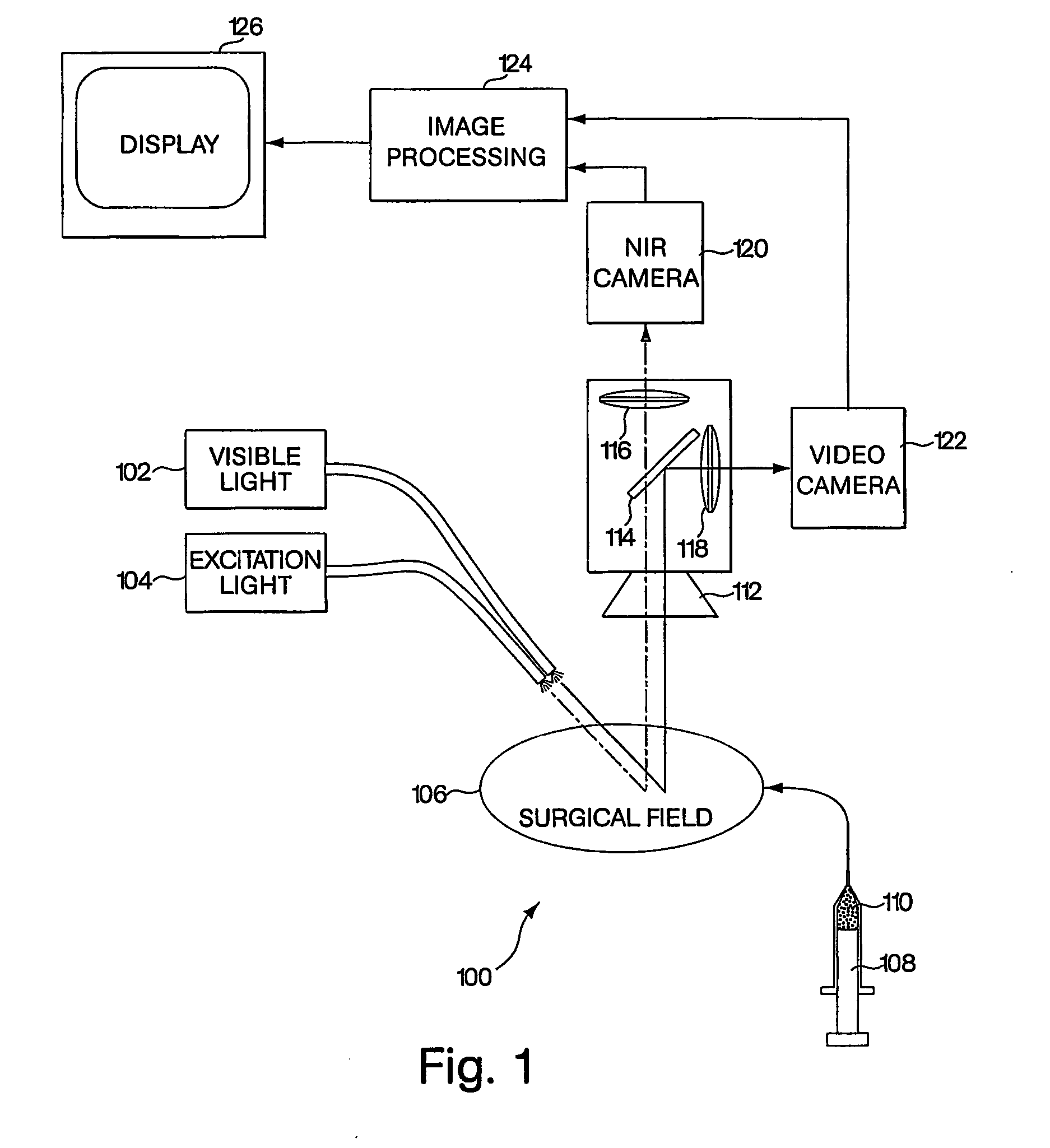
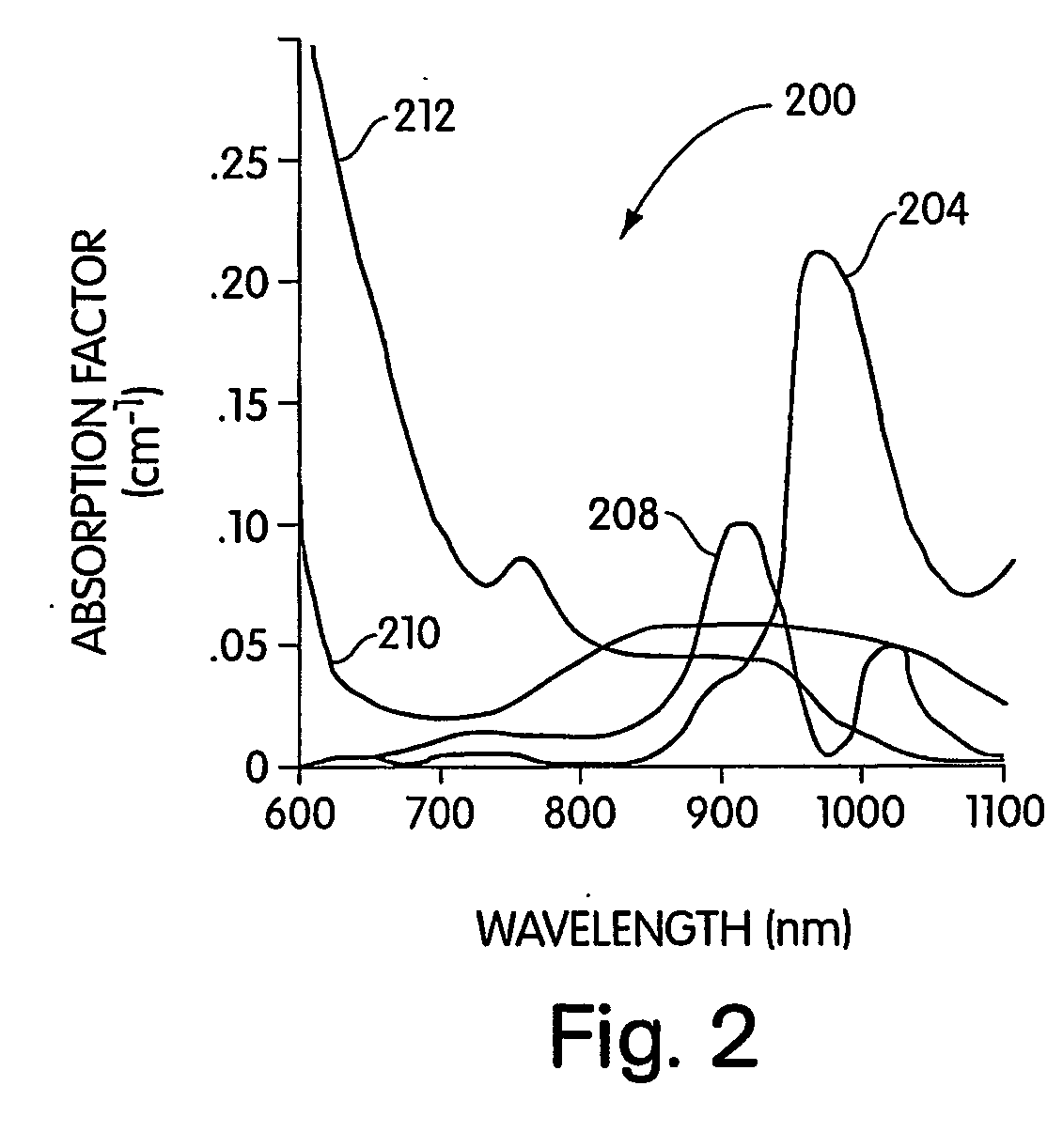
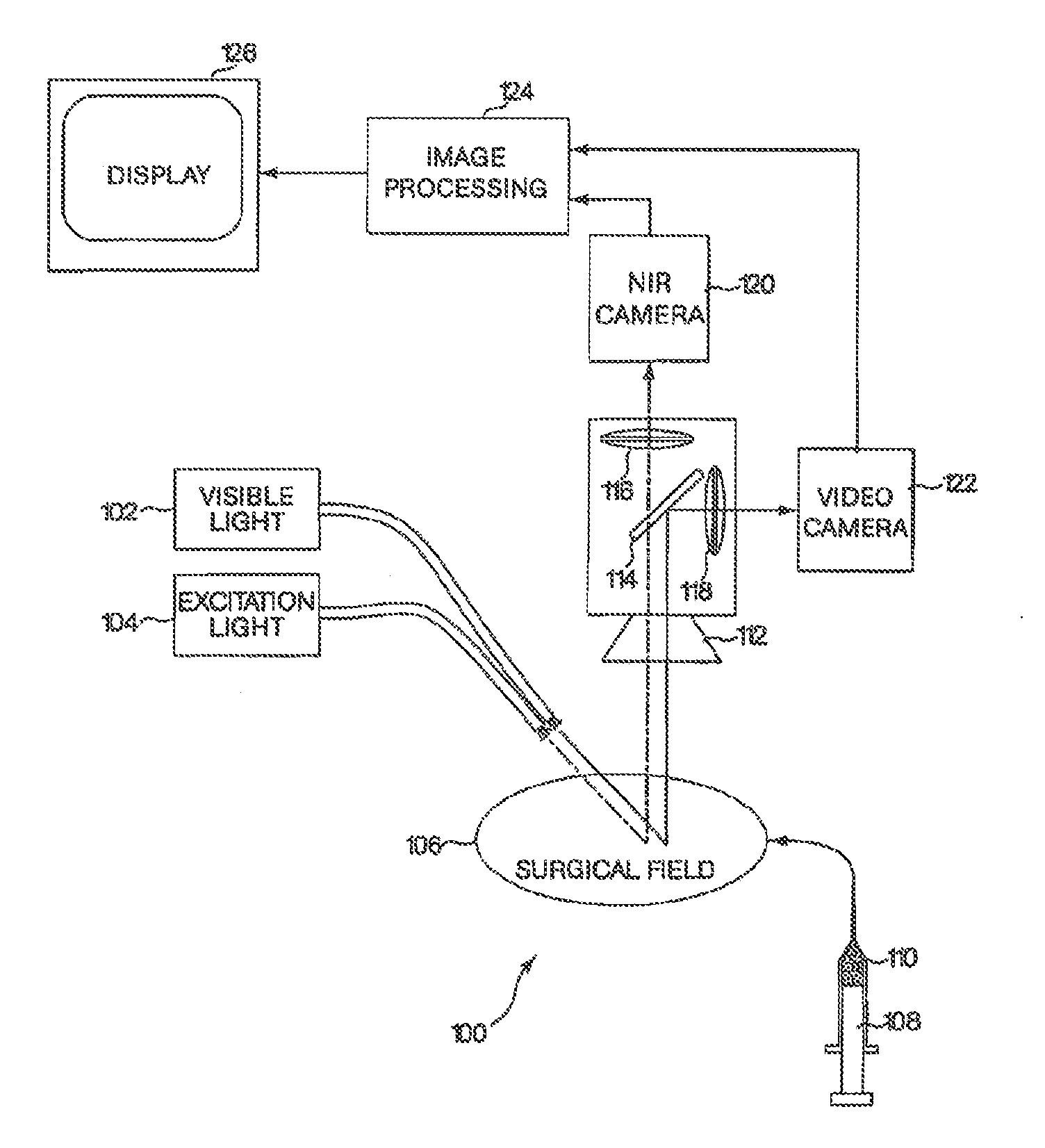
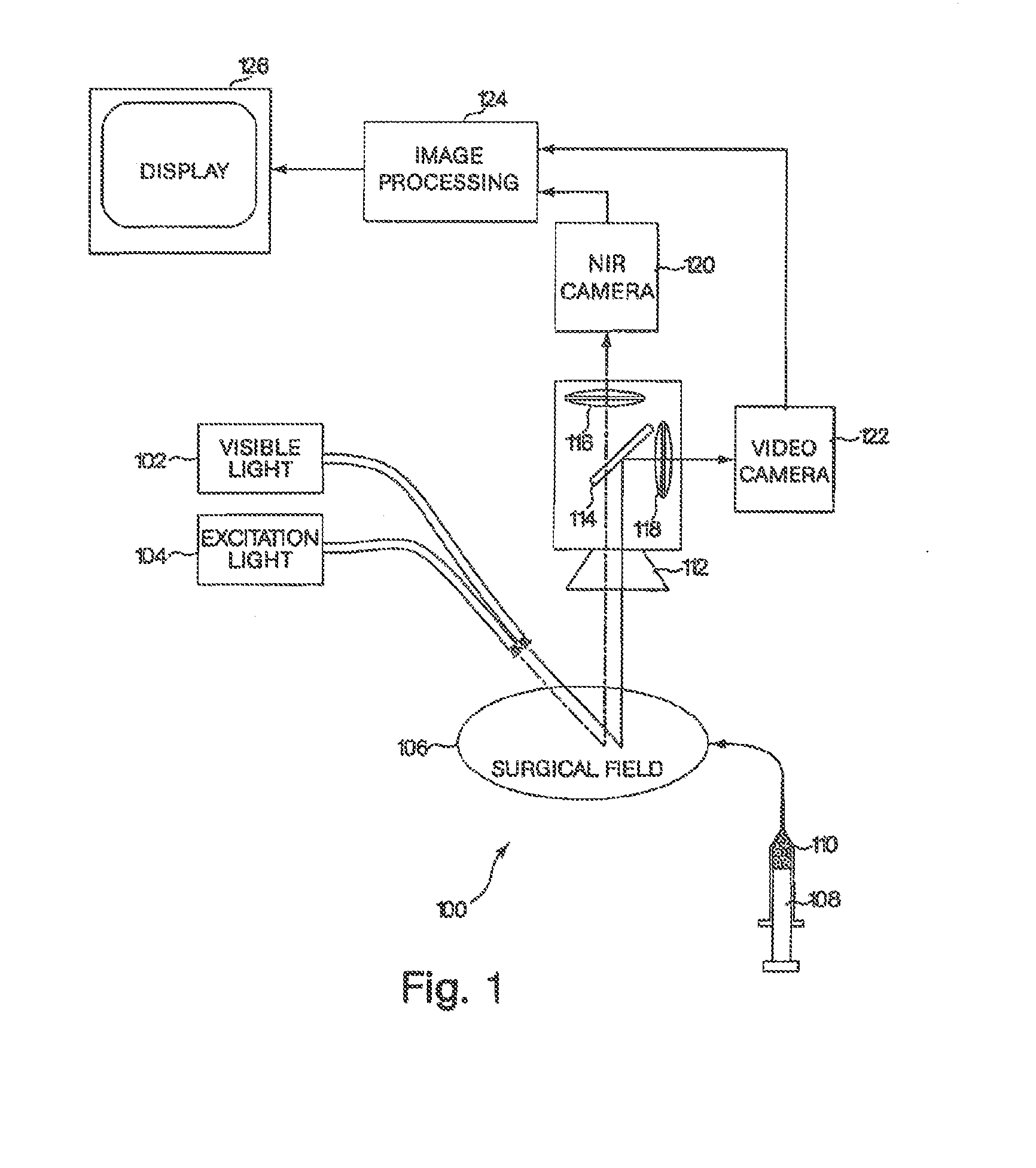
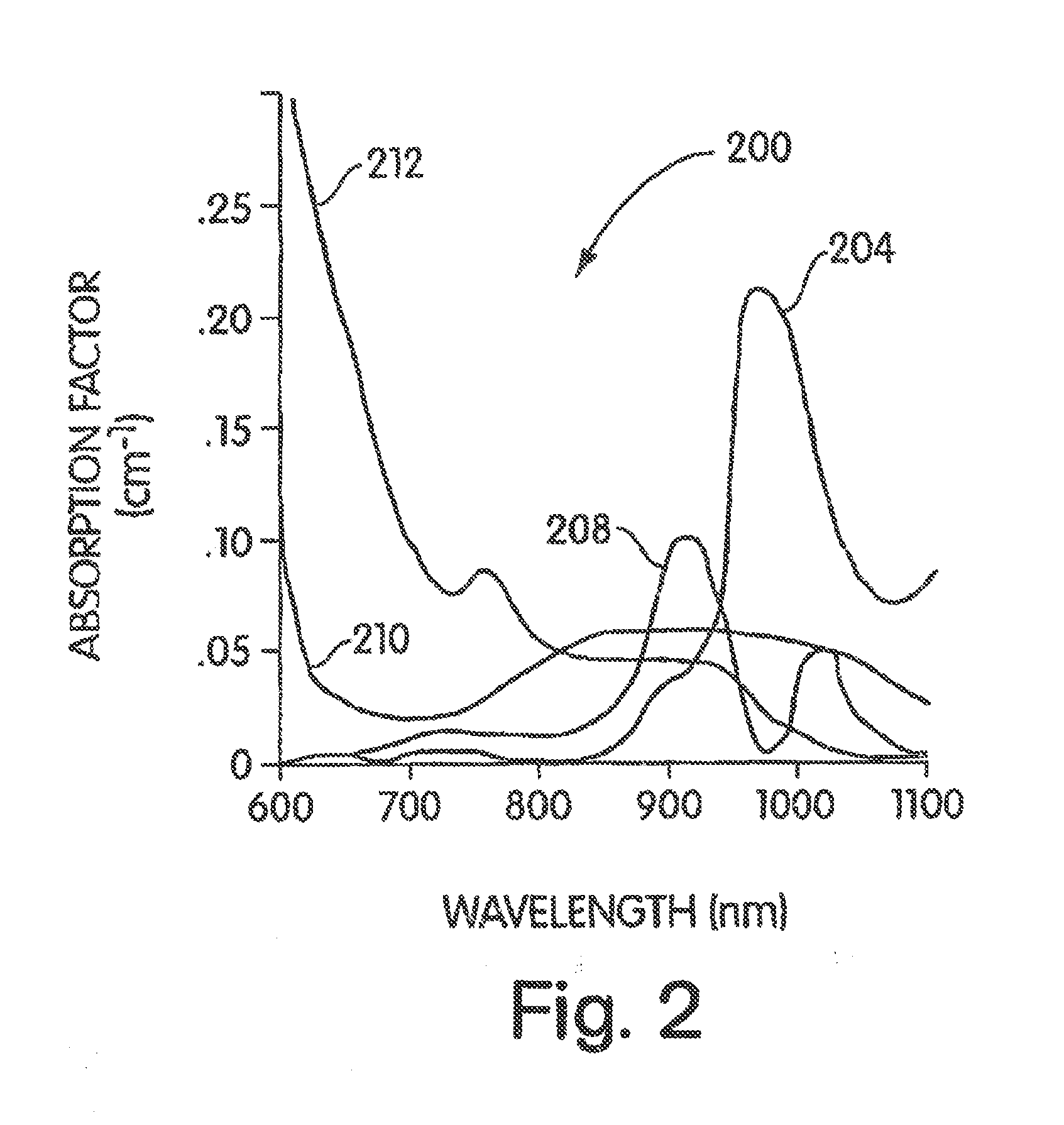
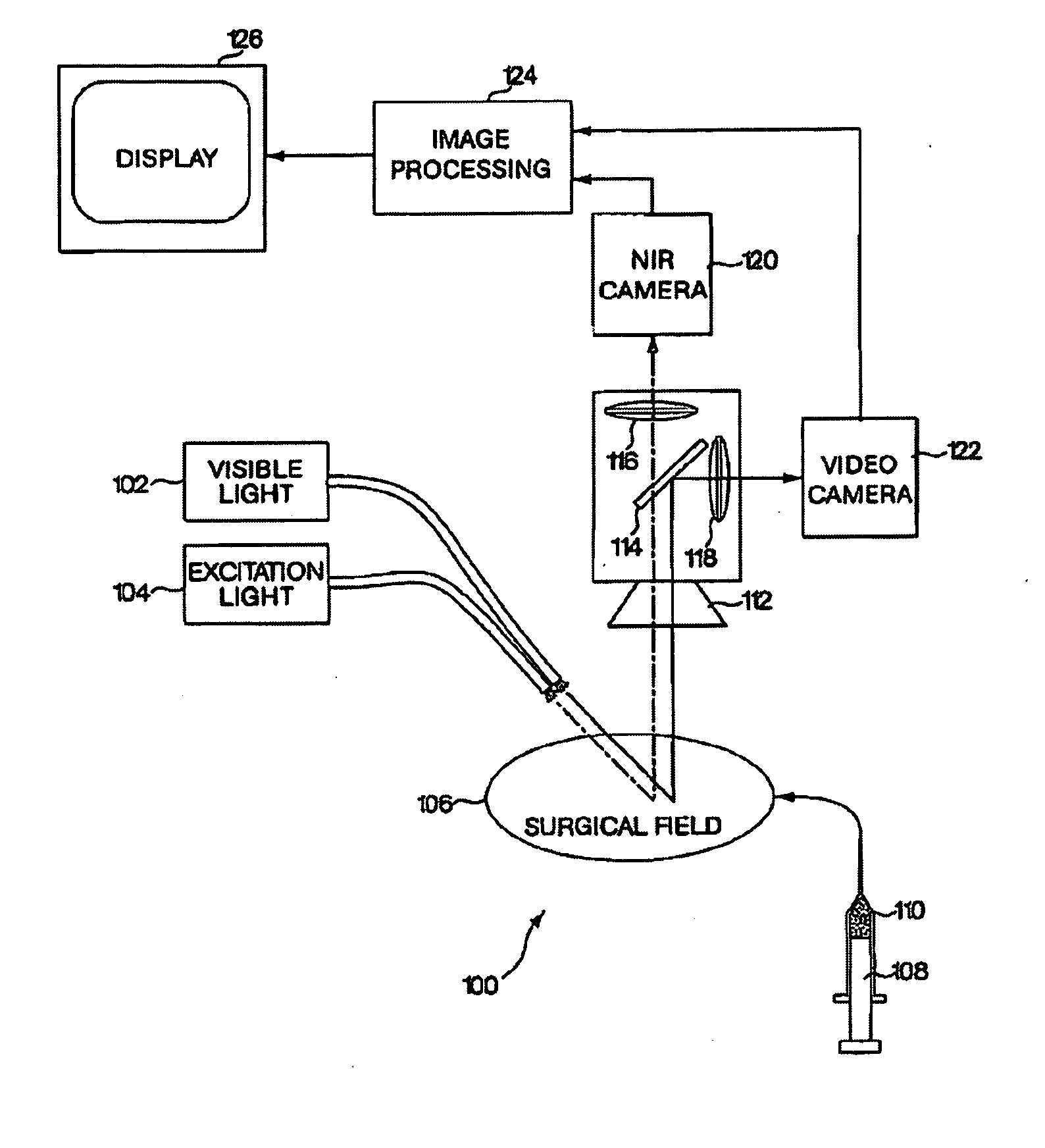
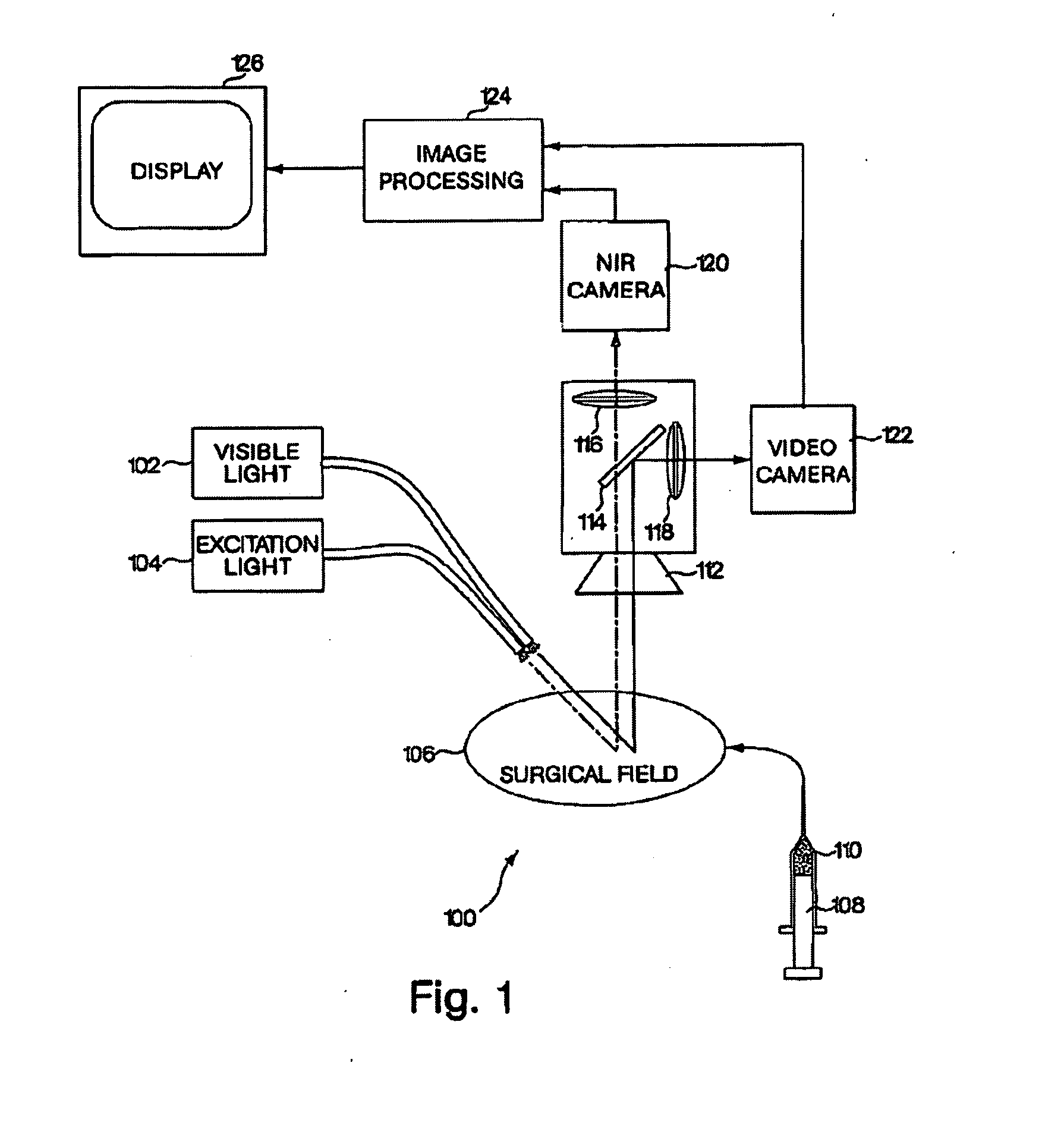
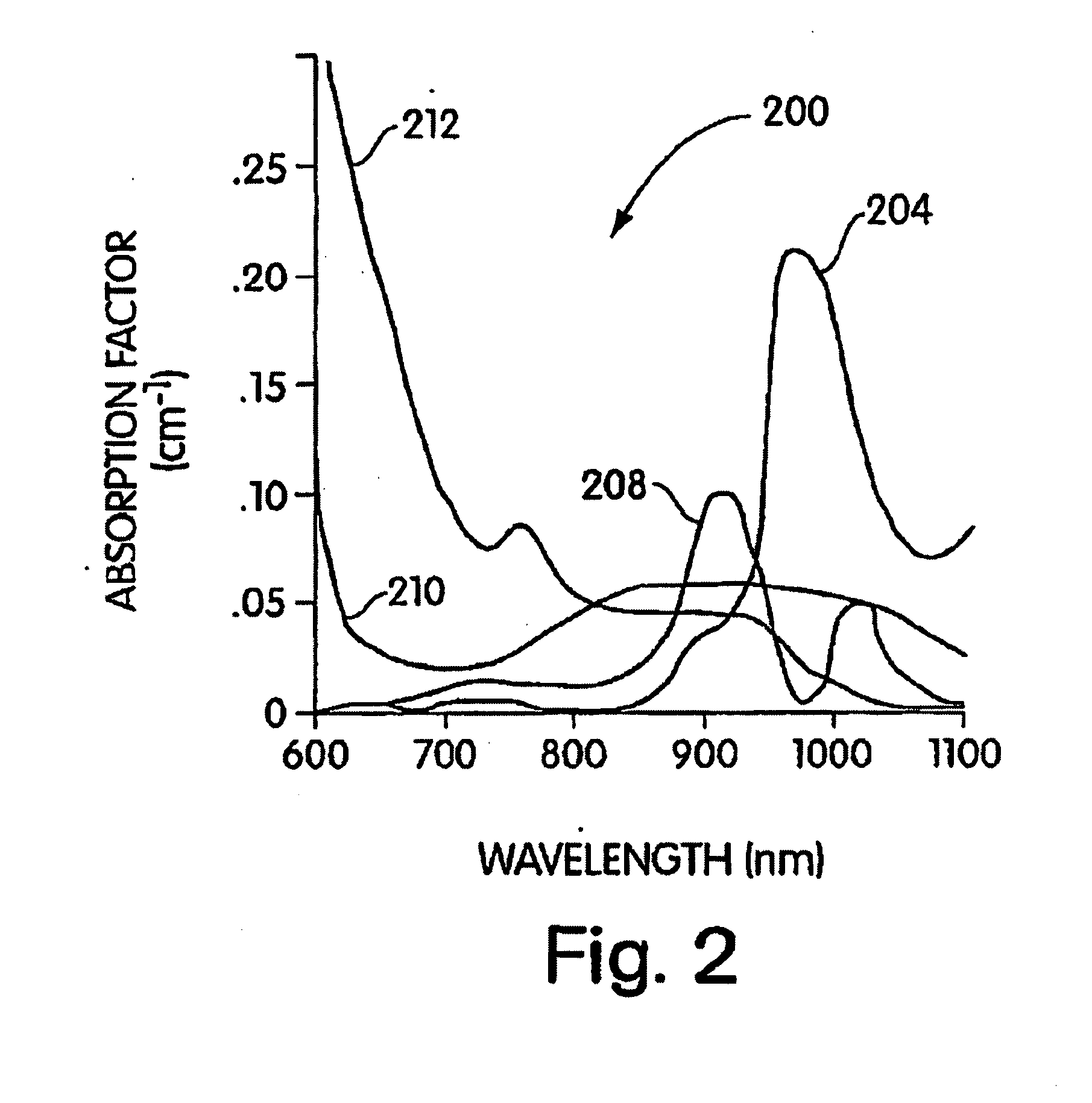
A medical imaging system provides simultaneous rendering of visible light and fluorescent images. The system may employ dyes in a small-molecule form that remains in a subject's blood stream for several minutes, allowing real-time imaging of the subject's circulatory system superimposed upon a conventional, visible light image of the subject. The system may also employ dyes or other fluorescent substances associated with antibodies, antibody fragments, or ligands that accumulate within a region of diagnostic significance. In one embodiment, the system provides an excitation light source to excite the fluorescent substance and a visible light source for general illumination within the same optical guide that is used to capture images. In another embodiment, the system is configured for use in open surgical procedures by providing an operating area that is closed to ambient light. More broadly, the systems described herein may be used in imaging applications where a visible light image may be usefully supplemented by an image formed from fluorescent emissions from a fluorescent substance that marks areas of functional interest.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
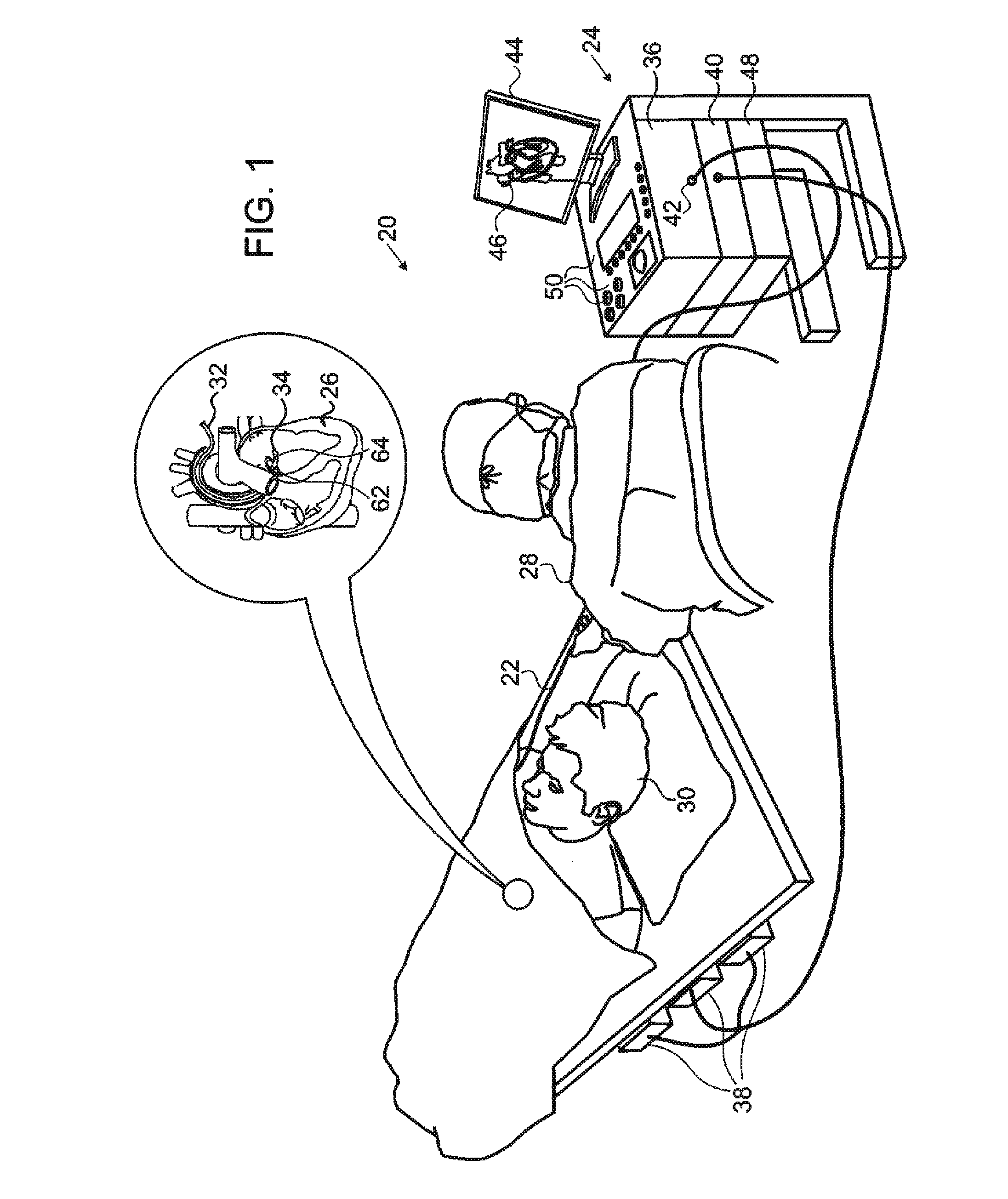
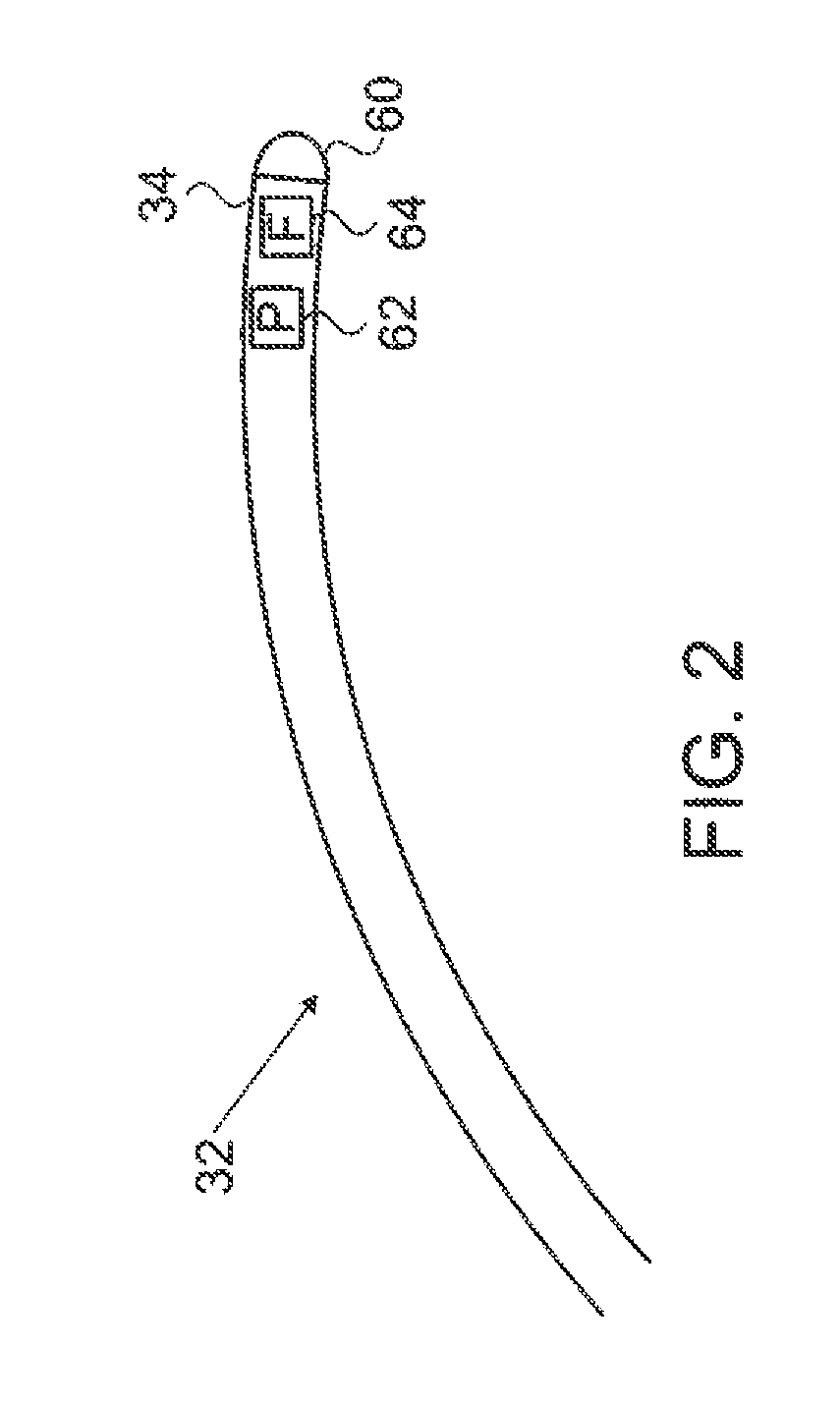
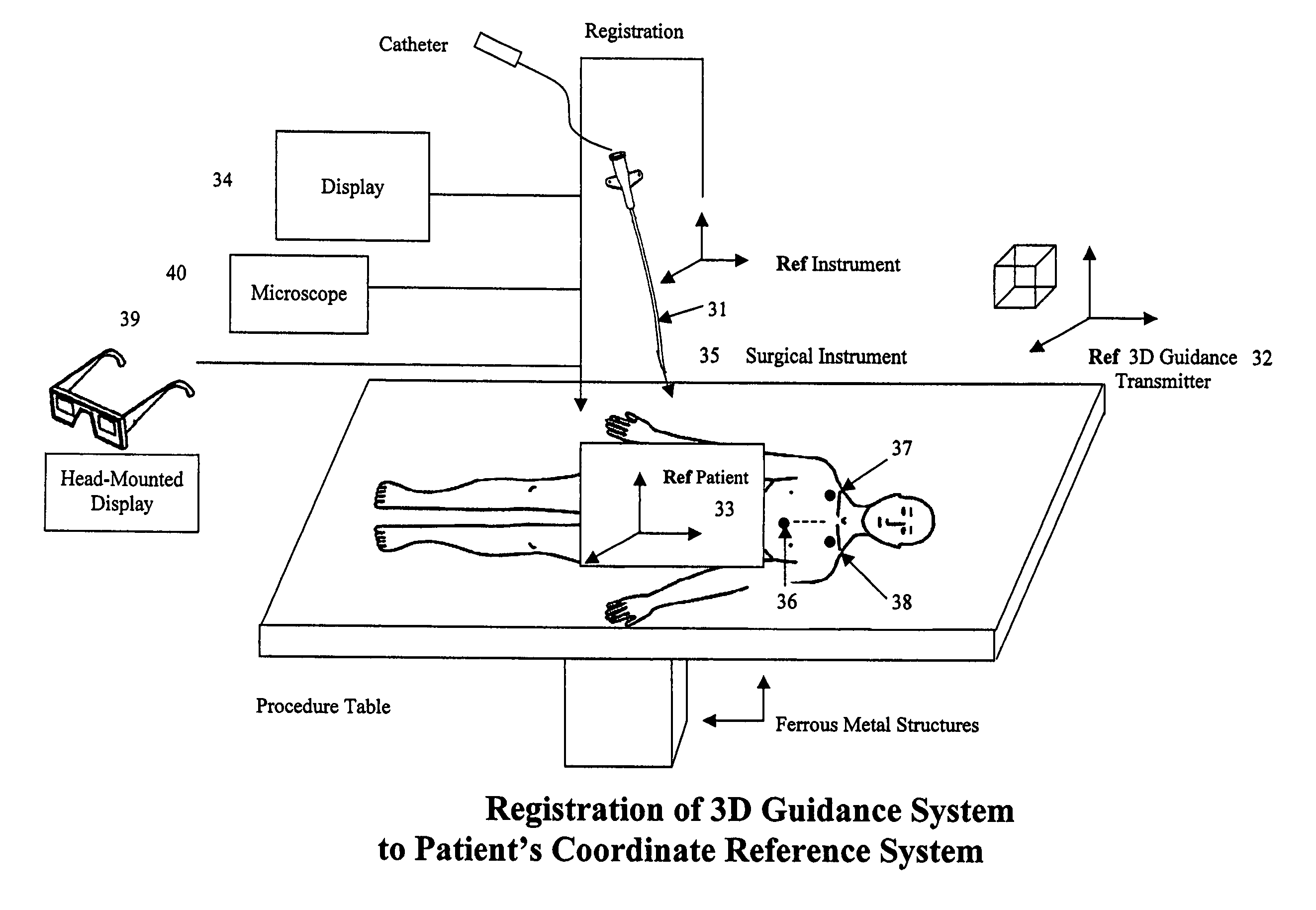
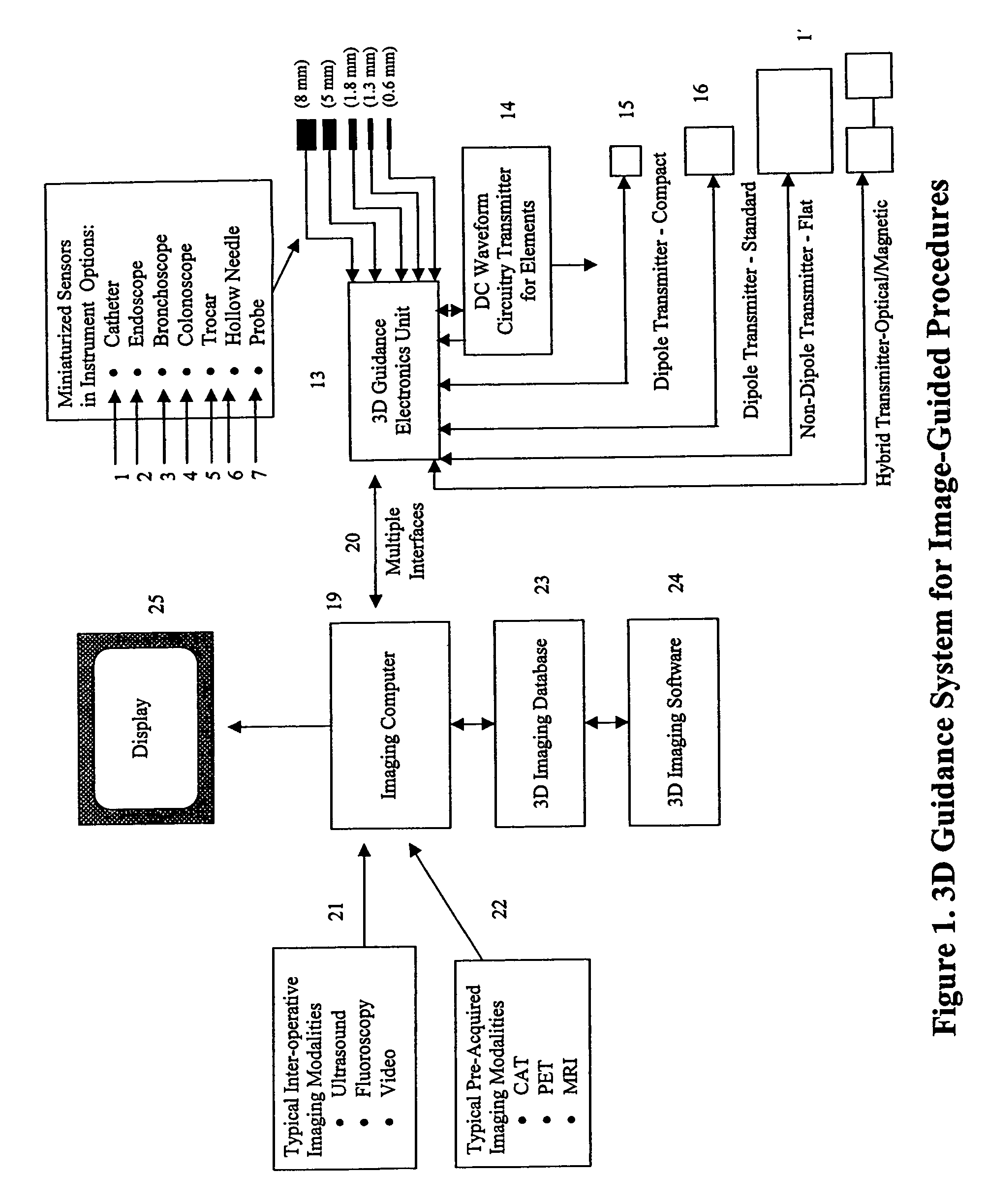
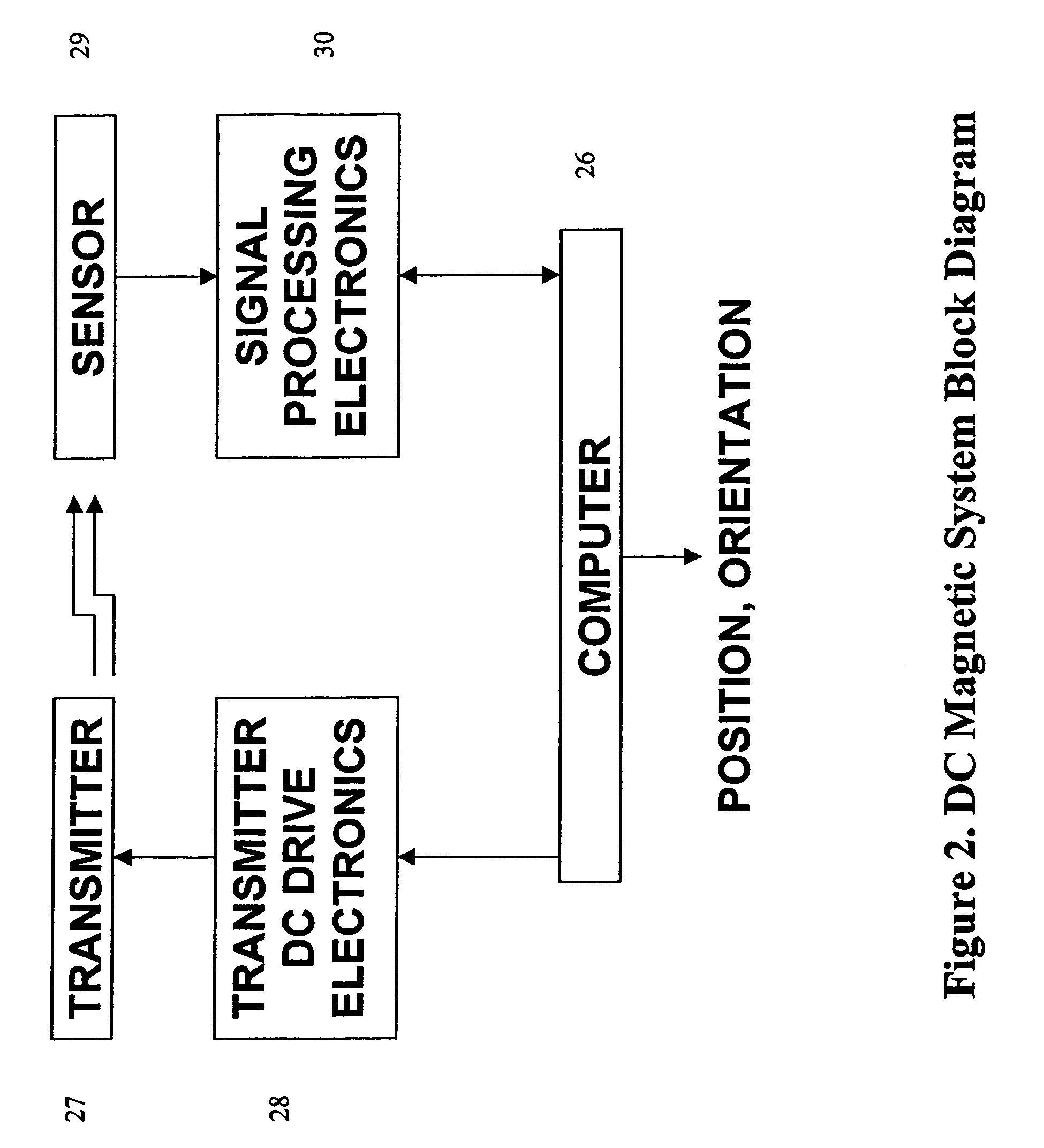
DC magnetic-based position and orientation monitoring system for tracking medical instruments
ActiveUS20070078334A1Overcome disposabilityOvercome cost issueDiagnostic recording/measuringSensors3d sensorEngineering
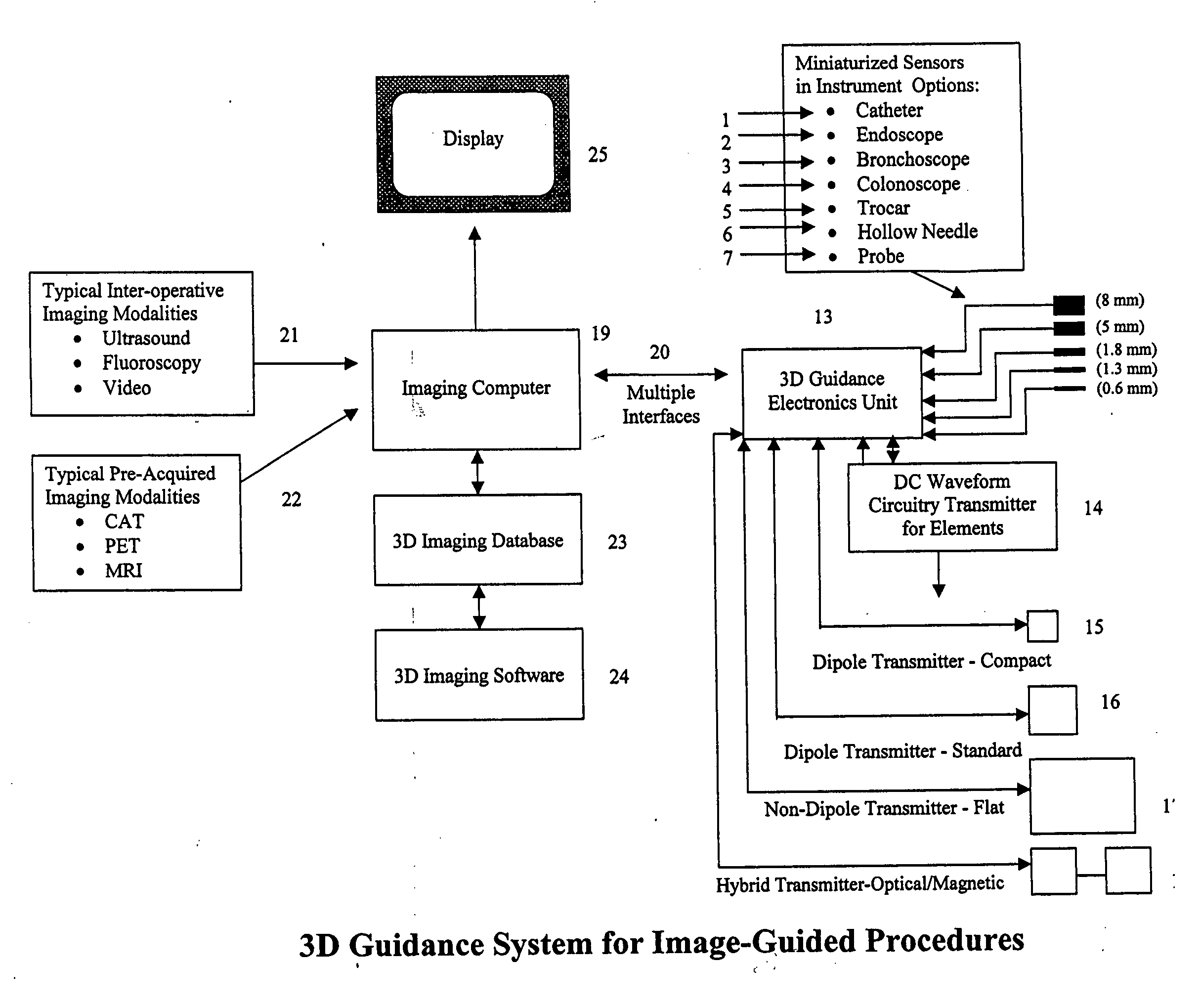
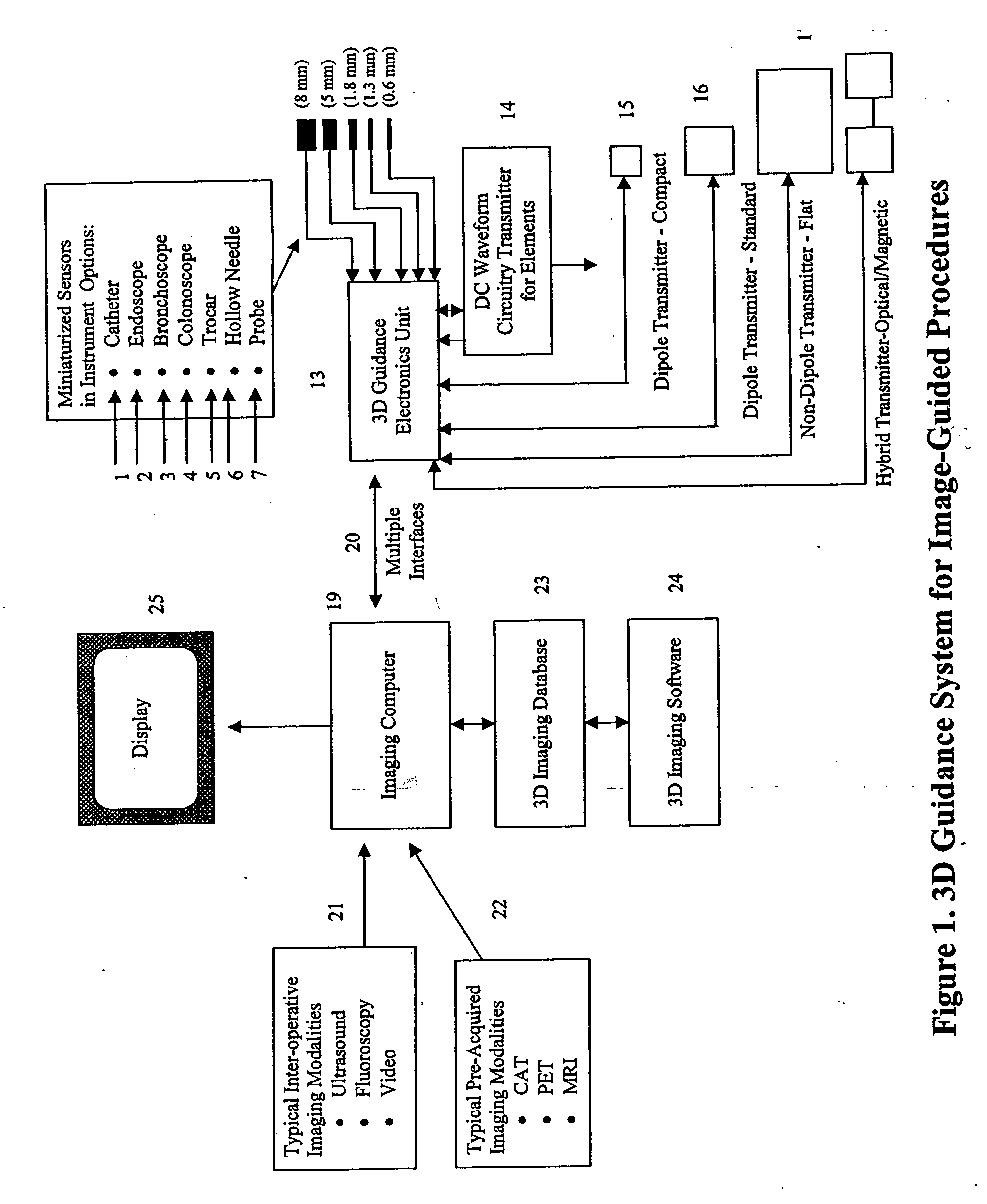
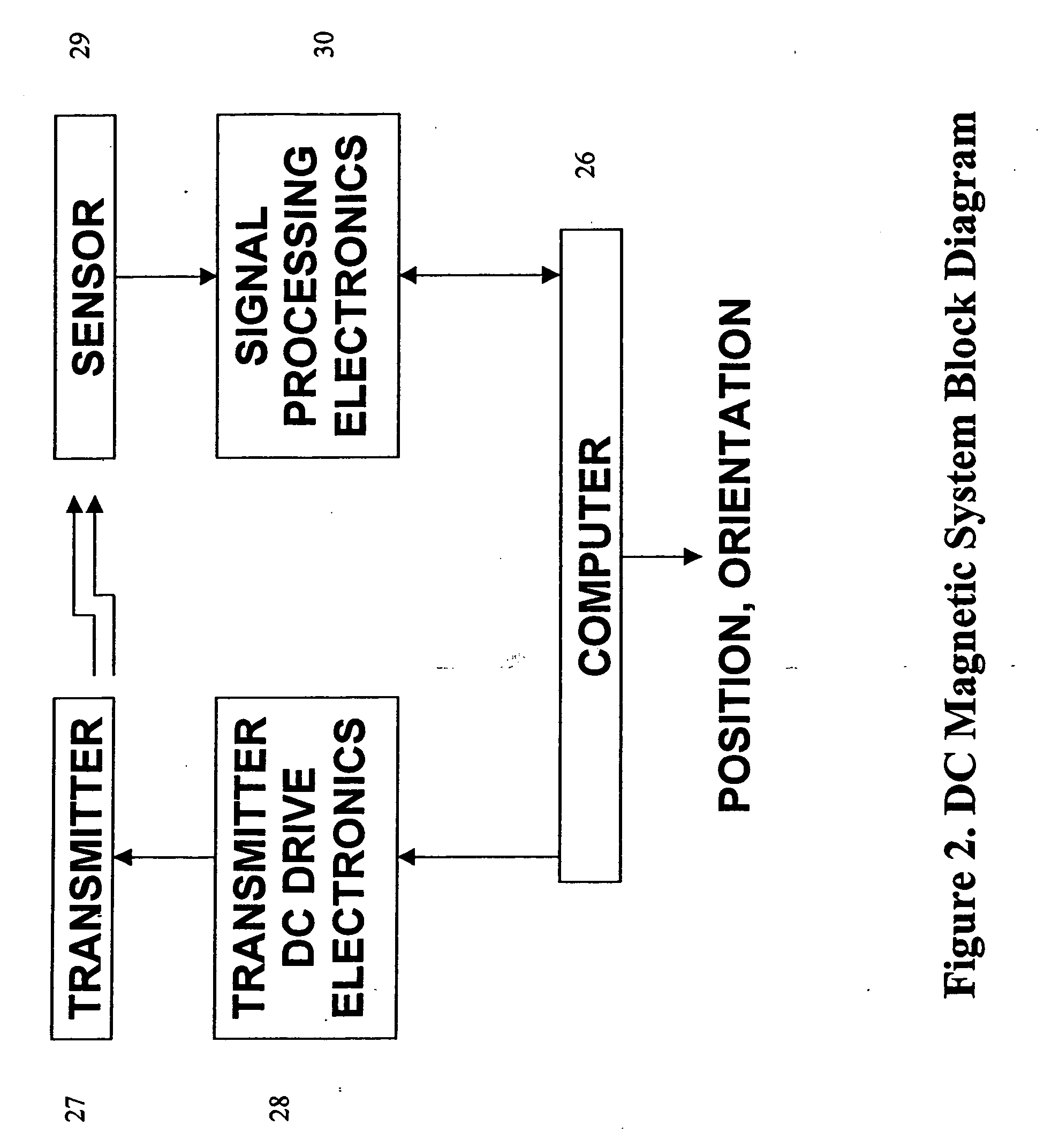
Miniaturized, five and six degrees-of-freedom magnetic sensors, responsive to pulsed DC magnetic fields waveforms generated by multiple transmitter options, provide an improved and cost-effective means of guiding medical instruments to targets inside the human body. The end result is achieved by integrating DC tracking, 3D reconstructions of pre-acquired patient scans and imaging software into a system enabling a physician to internally guide an instrument with real-time 3D vision for diagnostic and interventional purposes. The integration allows physicians to navigate within the human body by following 3D sensor tip locations superimposed on anatomical images reconstructed into 3D volumetric computer models. Sensor data can also be integrated with real-time imaging modalities, such as endoscopes, for intrabody navigation of instruments with instantaneous feedback through critical anatomy to locate and remove tissue. To meet stringent medical requirements, the system generates and senses pulsed DC magnetic fields embodied in an assemblage of miniaturized, disposable and reposable sensors functional with both dipole and co-planar transmitters.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Multi-channel medical imaging systems
A medical imaging system provides simultaneous rendering of visible light and fluorescent images. The system may employ dyes in a small-molecule form that remain in a subject's blood stream for several minutes, allowing real-time imaging of the subject's circulatory system superimposed upon a conventional, visible light image of the subject. The system may provide an excitation light source to excite the fluorescent substance and a visible light source for general illumination within the same optical guide used to capture images. The system may be configured for use in open surgical procedures by providing an operating area that is closed to ambient light. The systems described herein provide two or more diagnostic imaging channels for capture of multiple, concurrent diagnostic images and may be used where a visible light image may be usefully supplemented by two or more images that are independently marked for functional interest.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Methods and devices for generating a representation of a 3D scene at very high speed
ActiveUS20130300838A1High measurement accuracyReduce in quantityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning details3d imageDetector array
The present invention relates to a 3D landscape real-time imager. It also relates to methods for operating such an imager. Such an imager comprises: —at least one illuminating part which is designed to scan at least a portion of the landscape at a given range and having an ultra-short laser pulse source emitting at least one wavelength, and an optical rotating block, with a vertical axis of rotation, and controlled such that given packets of pulses are shaped in a pattern of rotating beams sent toward the said at least partial landscape; —at least one receiving part which comprises a set of SPAD detector arrays, each arranged along a vertical direction and rotating at a given speed in synchronism with the optical rotating block of the illuminating part, the detection data of the SPAD detector arrays being combined to acquire 3D imaging data of the said at least partial landscape in a central controller.
Owner:FASTREE3D
Image-guided delivery of therapeutic tools duing minimally invasive surgeries and interventions
InactiveUS20080221448A1Enhance the imageMinimally invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCapacitanceUltrasonic sensor
Imaged-guided therapy for minimally invasive surgeries and interventions is provided. An image-guided device includes an elongate tubular member, such as a catheter, an annular array of capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers (cMUTs) for real-time three-dimensional forward-looking acoustic imaging, and a therapeutic tool. The therapeutic tool is positioned inside an inner lumen of the elongate tubular member and can be a device for tissue ablation, such as a high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) device or a laser. The HIFU device is operable at high frequencies to have a sufficiently small focus spot, thus a high focal intensity. The imaging annular array is also operable at high frequencies for good acoustic imaging resolution. The high resolution forward-looking imaging array, in combination with the high frequency HIFU transducer, provides a single image-guided therapy device for precise tissue ablation and real-time imaging feedback.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
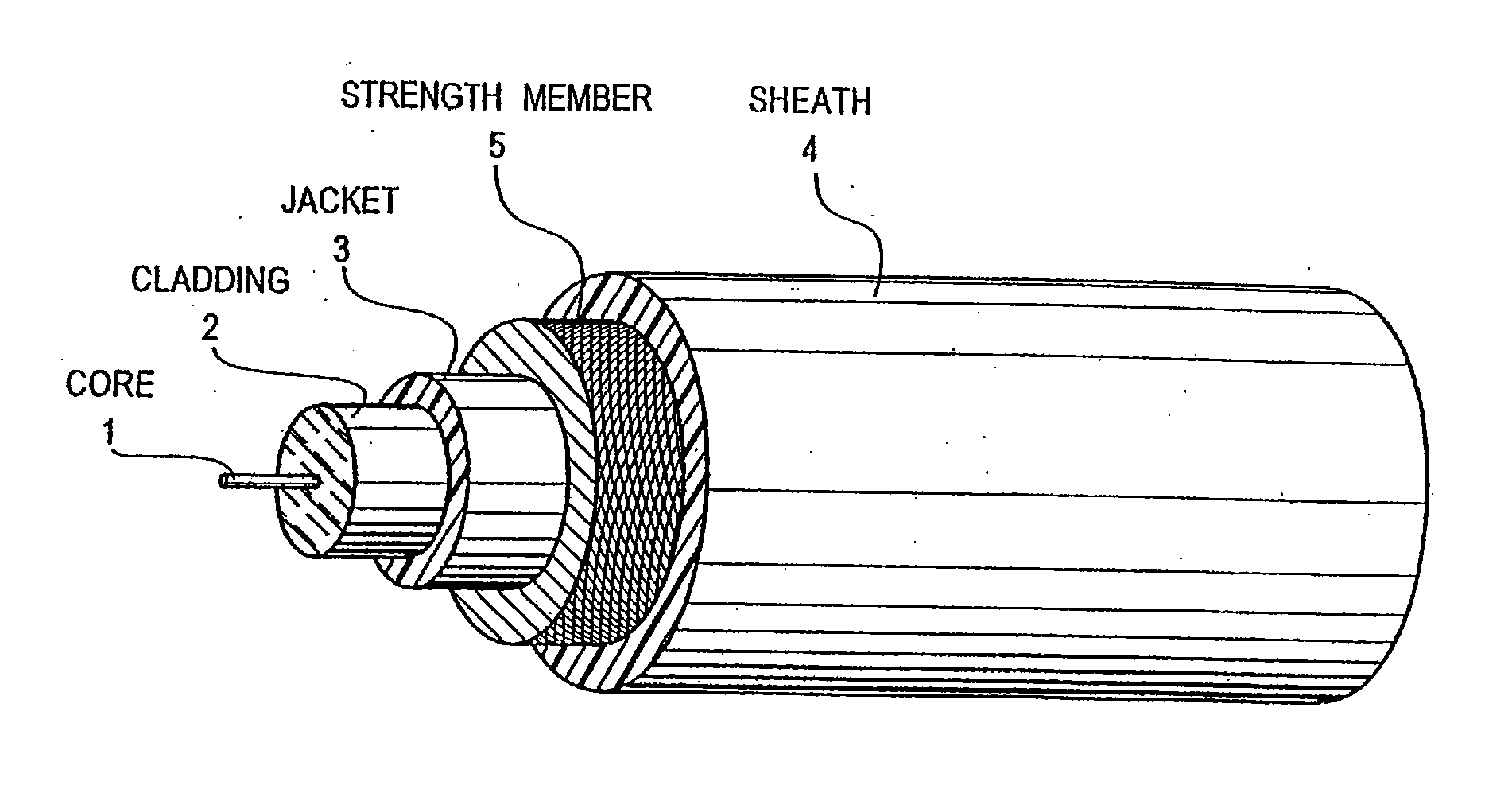
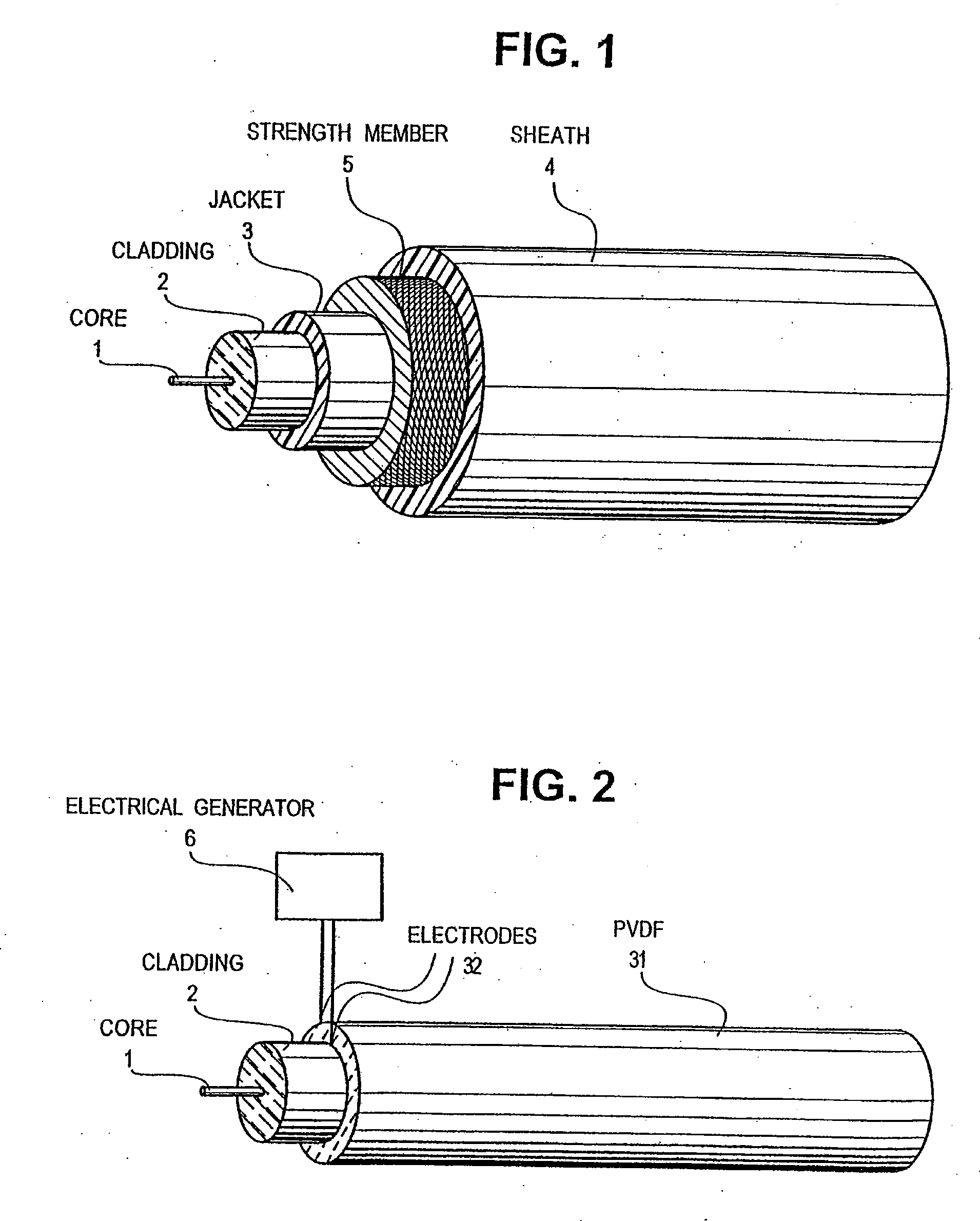
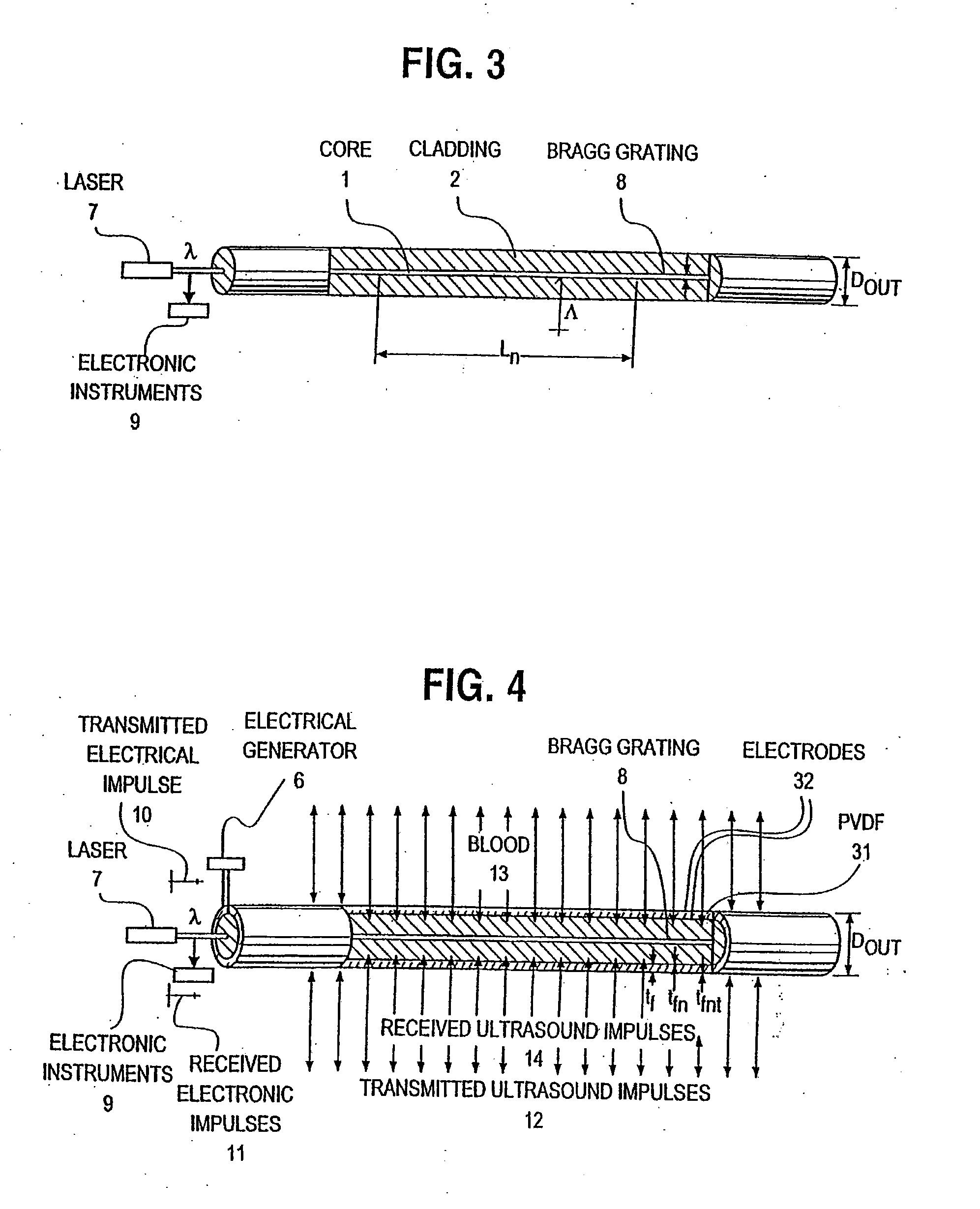
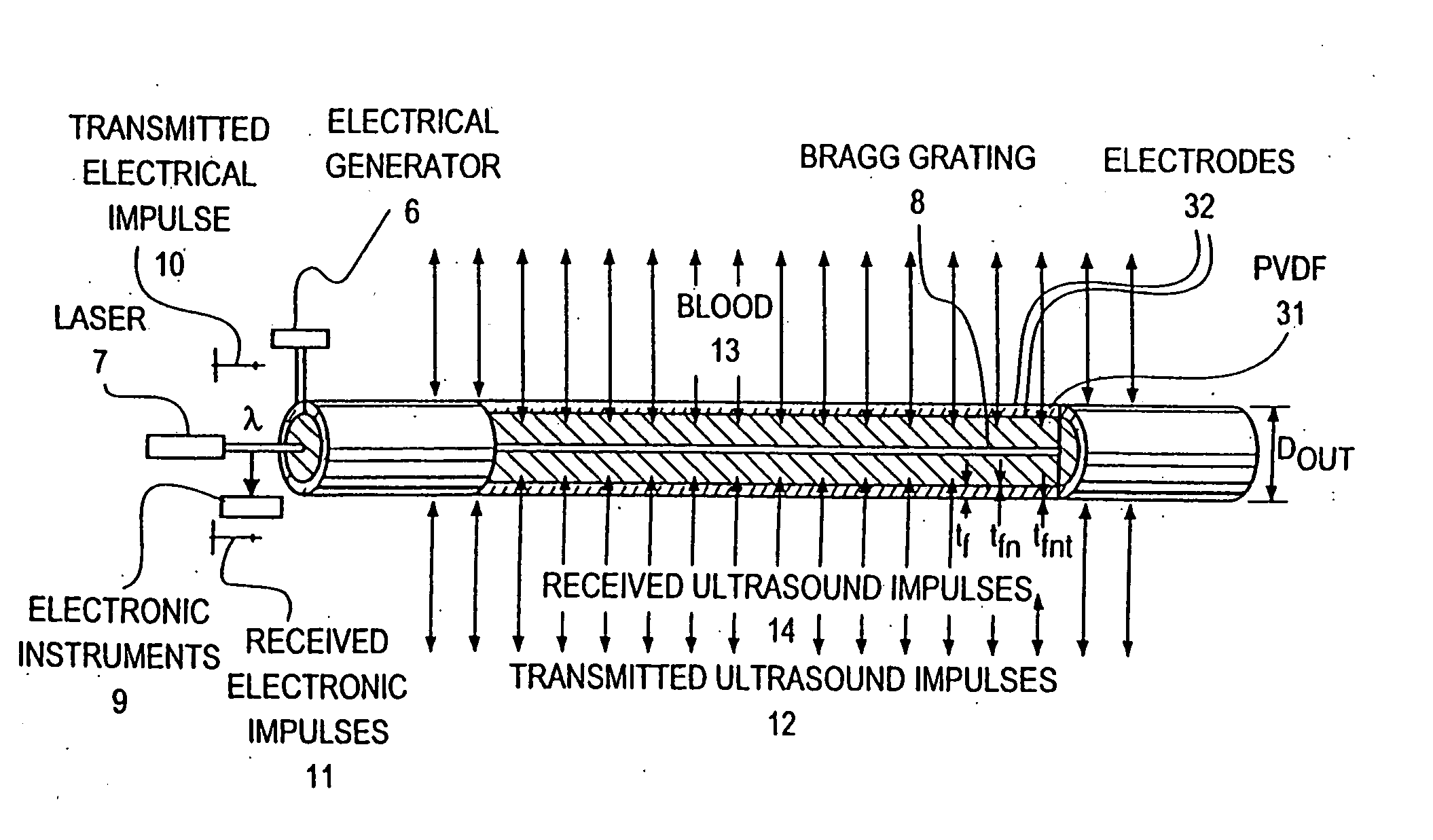
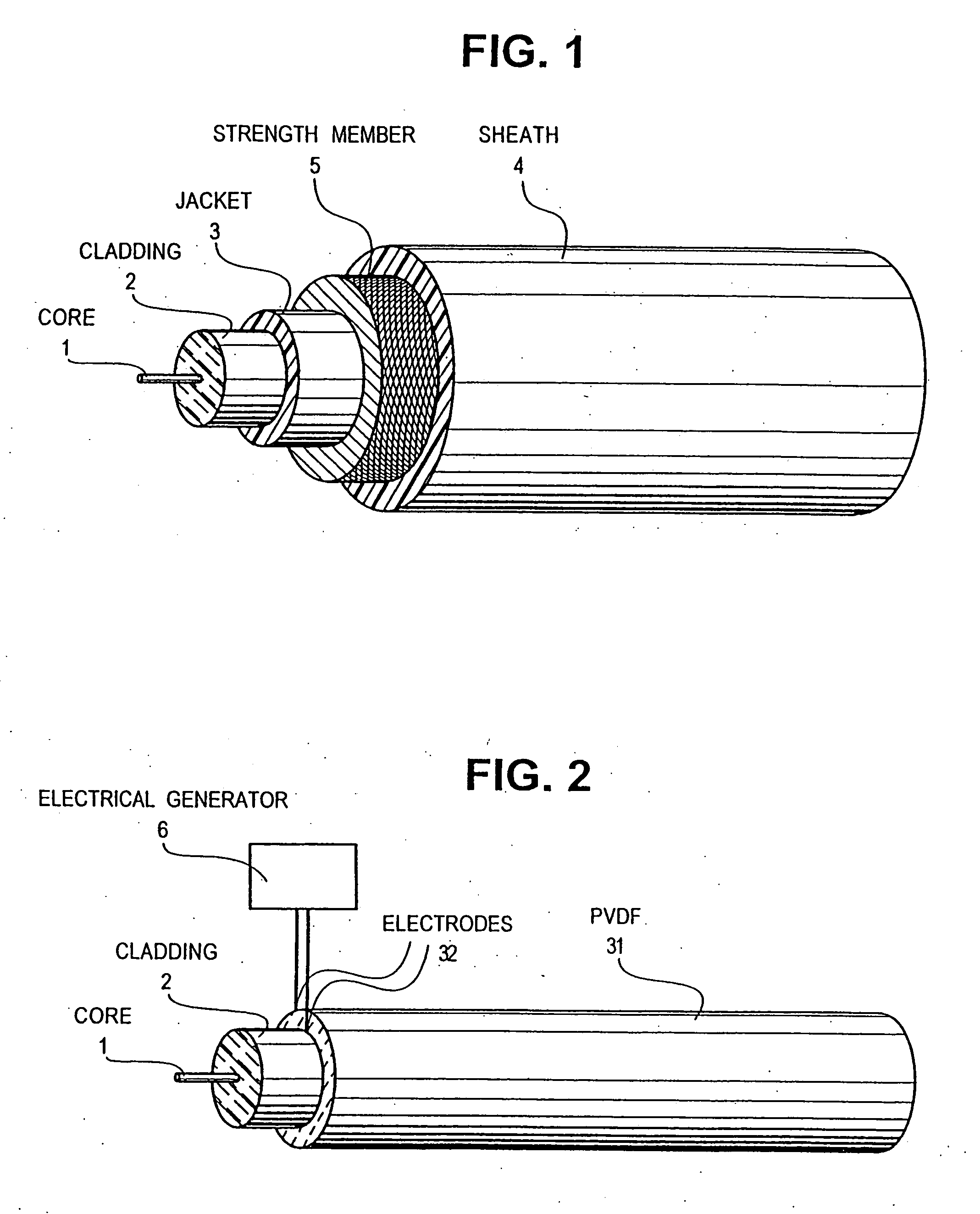
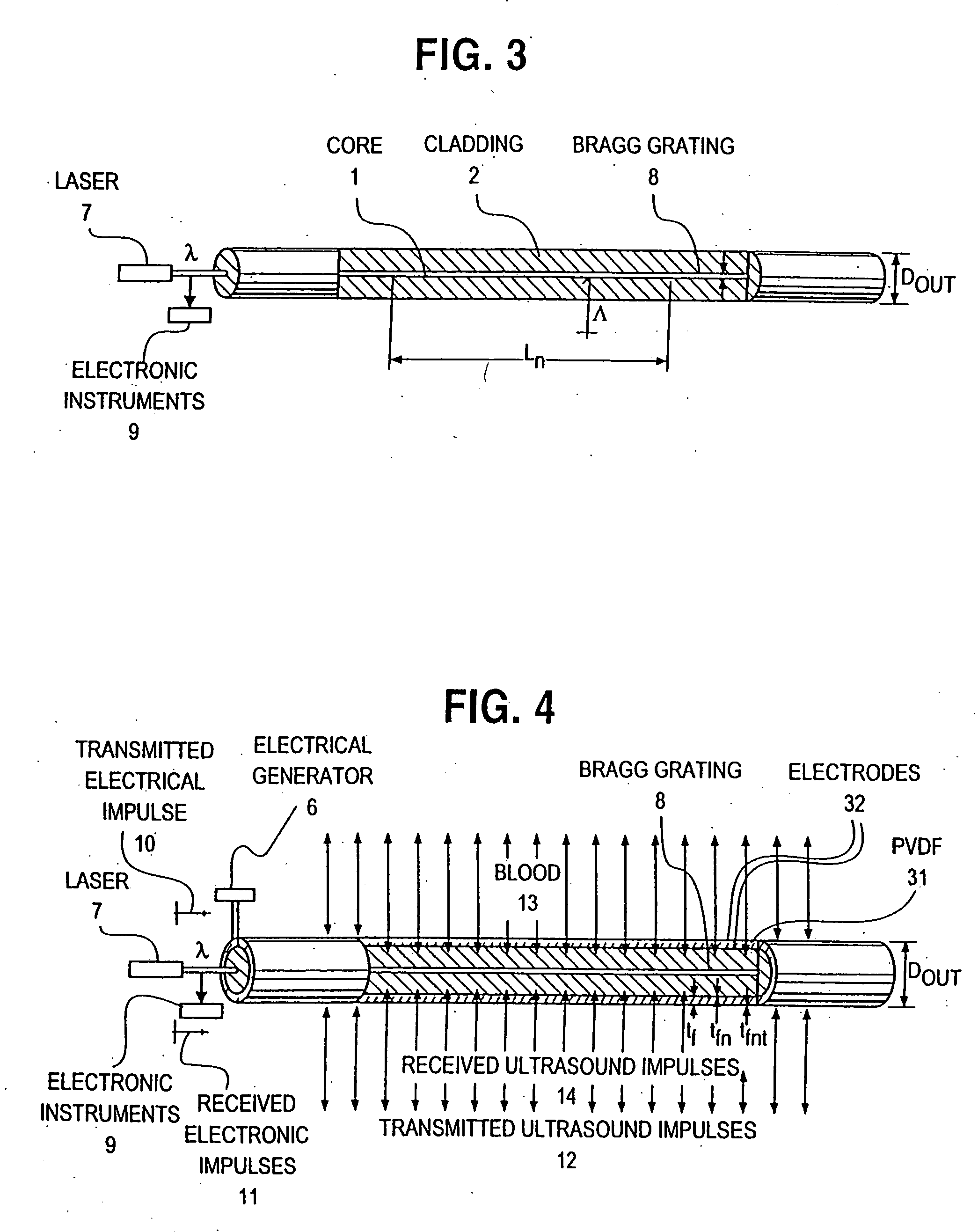
Optical-acoustic imaging device
InactiveUS20080119739A1Reduce radiation exposureShorten operation timeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGratingRadiation exposure
The present invention is a guide wire imaging device for vascular or non-vascular imaging utilizing optic acoustical methods, which device has a profile of less than 1 mm in diameter. The ultrasound imaging device of the invention comprises a single mode optical fiber with at least one Bragg grating, and a piezoelectric or piezo-ceramic jacket, which device may achieve omnidirectional (360°) imaging. The imaging guide wire of the invention can function as a guide wire for vascular interventions, can enable real time imaging during balloon inflation, and stent deployment, thus will provide clinical information that is not available when catheter-based imaging systems are used. The device of the invention may enable shortened total procedure times, including the fluoroscopy time, will also reduce radiation exposure to the patient and to the operator.
Owner:PHYZHON HEALTH INC
Tubular compliant mechanisms for ultrasonic imaging systems and intravascular interventional devices
InactiveUS20070167804A1Successfully penetrateSuccessfully recanalizeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterCompliant mechanismUltrasonic imaging
A micromanipulator comprising a tubular structure and a structural compliance mechanism that are formed from a tube made of an elastic and / or superelastic material. The micromanipulator is useful for intravascular interventional applications and particularly ultrasonic imaging when coupled with an ultrasound transducer. Also disclosed are medical devices for crossing vascular occlusions using radio-frequency energy or rotary cutting, preferably under the guidance of real-time imaging of the occlusion, as well as accompanying methods.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
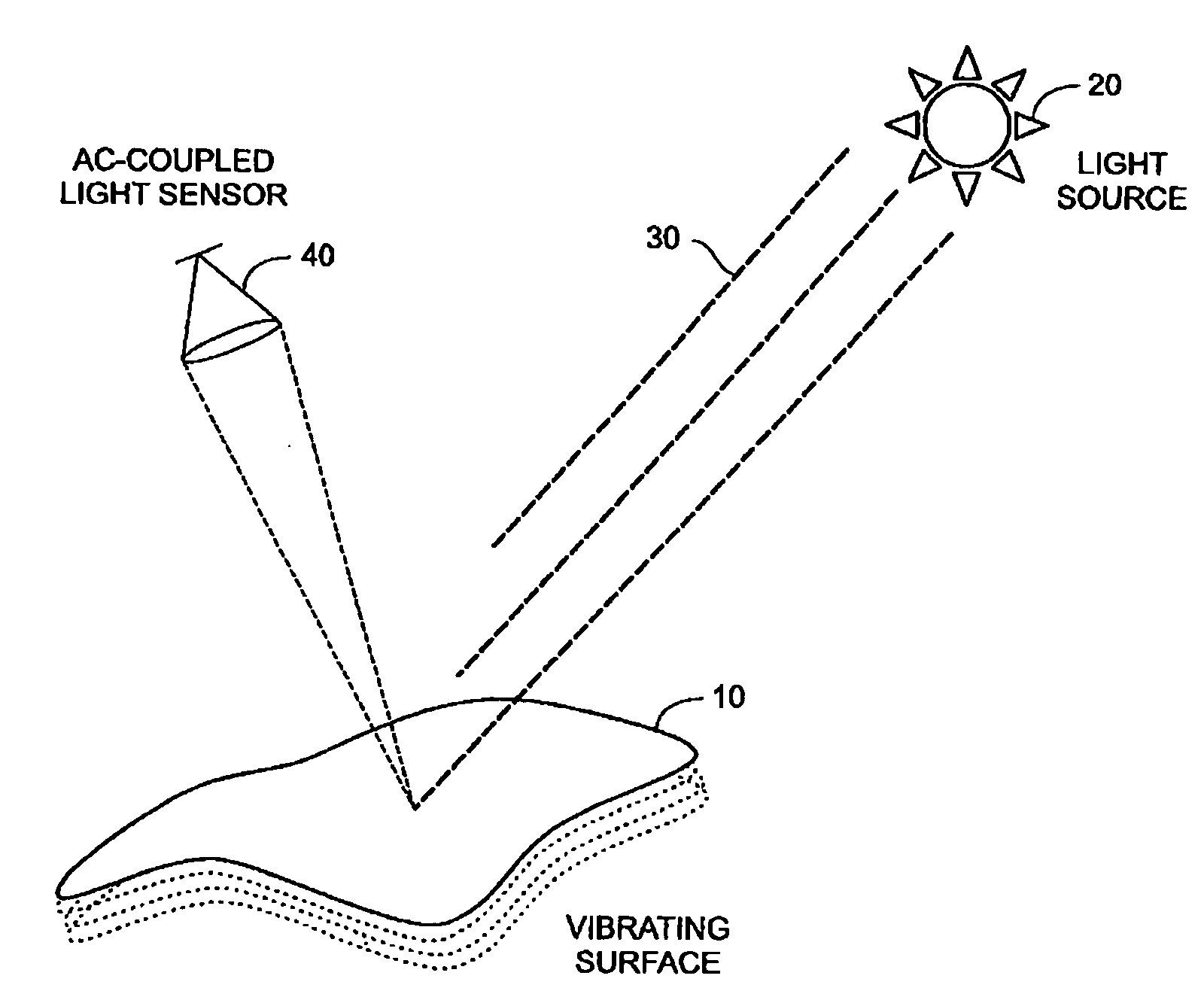
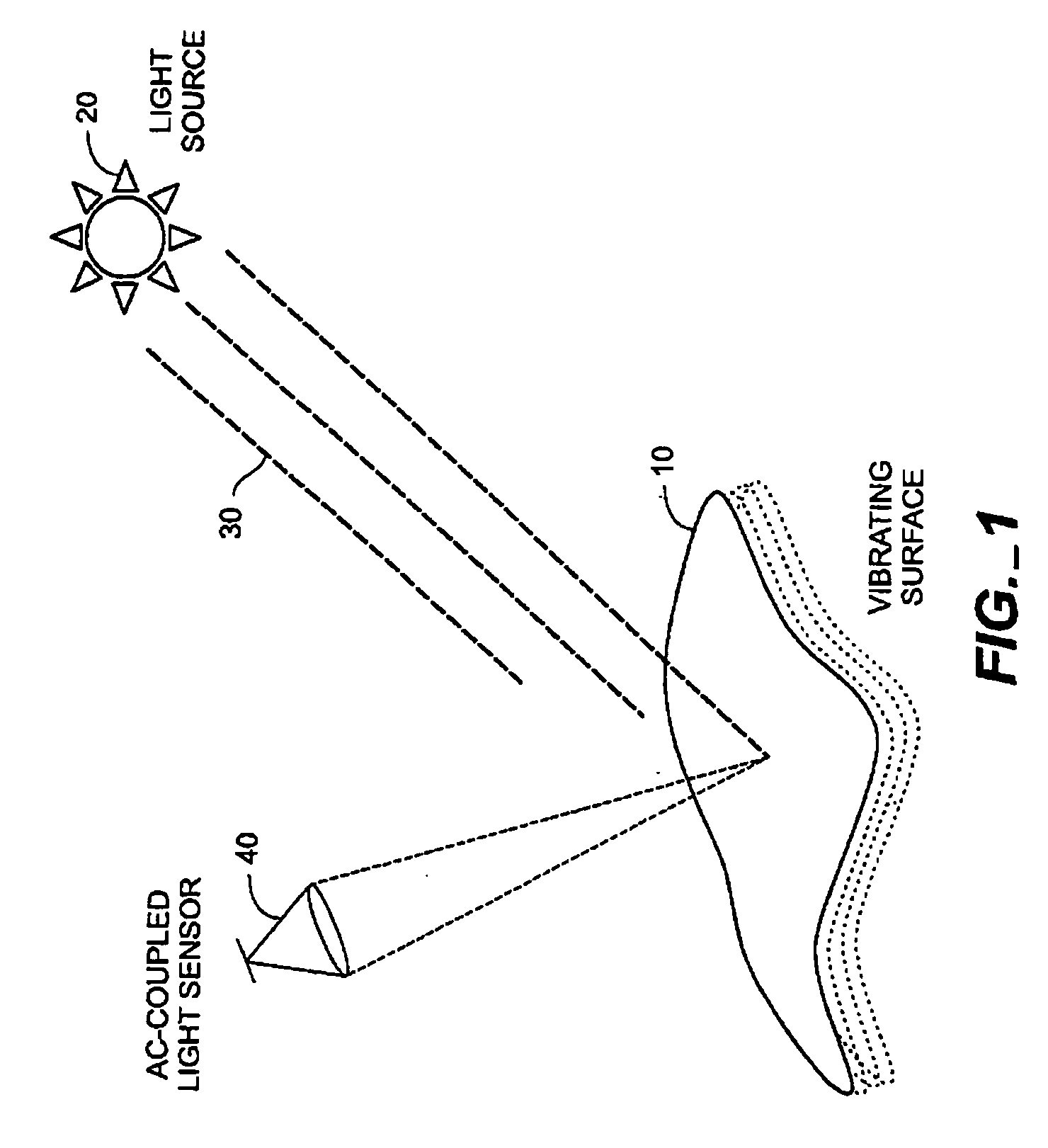
Method for detecting vibrations in a biological organism using real-time vibration imaging
InactiveUS20060209631A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis by observing immersed bodiesUltravioletDetector array
The present invention provides a method for detecting vibration information by receiving electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from a biological organism at a light amplitude modulation detector array to provide real-time imaging of the target object. The detected radiation may be visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, and / or of other desired frequency ranges. The detected radiation is preferably AC-coupled to isolate components relating to oscillations of the biological organism from components relating to ambient radiation, e.g. background sunlight. The isolated oscillations may then be digitized, stored, and subjected to processing such as a Fourier transform to generate outputs representative of frequencies of oscillation. This output can then be used for analysis of the target object.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
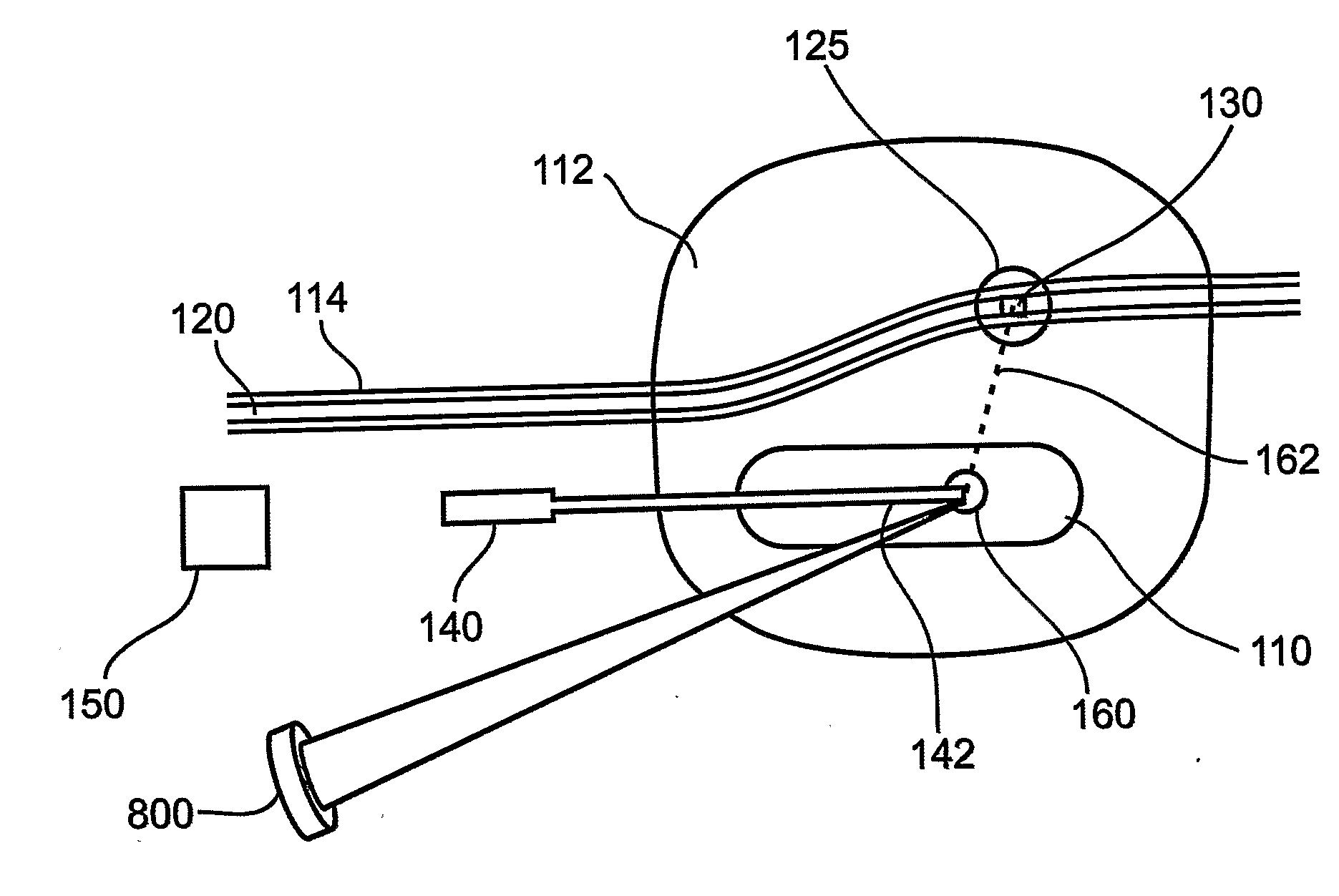
Apparatus for insertion of a medical device during a medical imaging process
ActiveUS20060241368A1Easy accessMaximize accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesMedical imagingMedical device
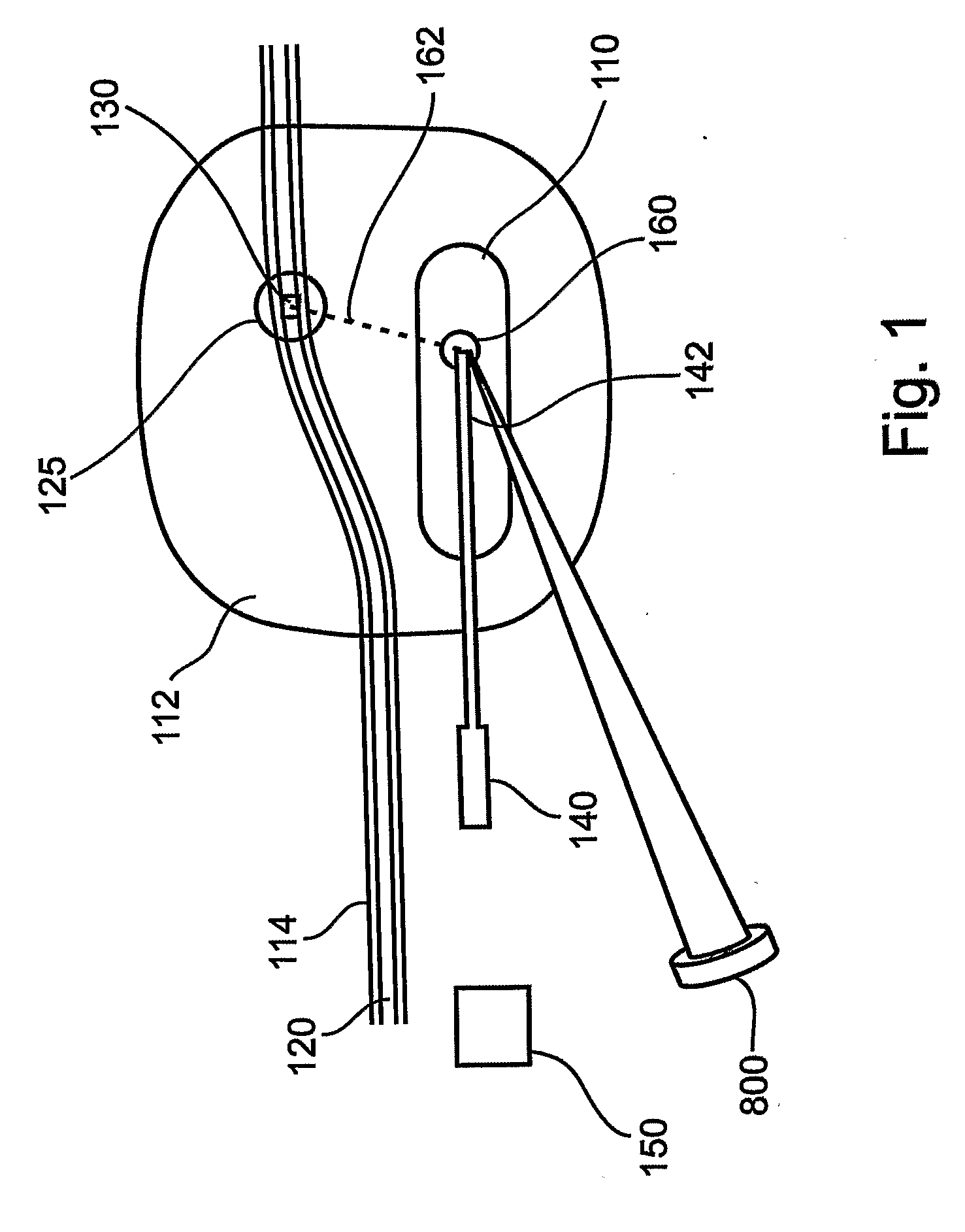
The end-effector (150) includes a sheath (152) and a medical device or needle carrier (154) that is disposed within the interior compartment (166) of the sheath. Aperture (162) is located in a portion of the sheath proximal a distal end of the sheath that is inserted into a natural or artificial cavity. This device is guided by a real-time imager.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Vision catheter
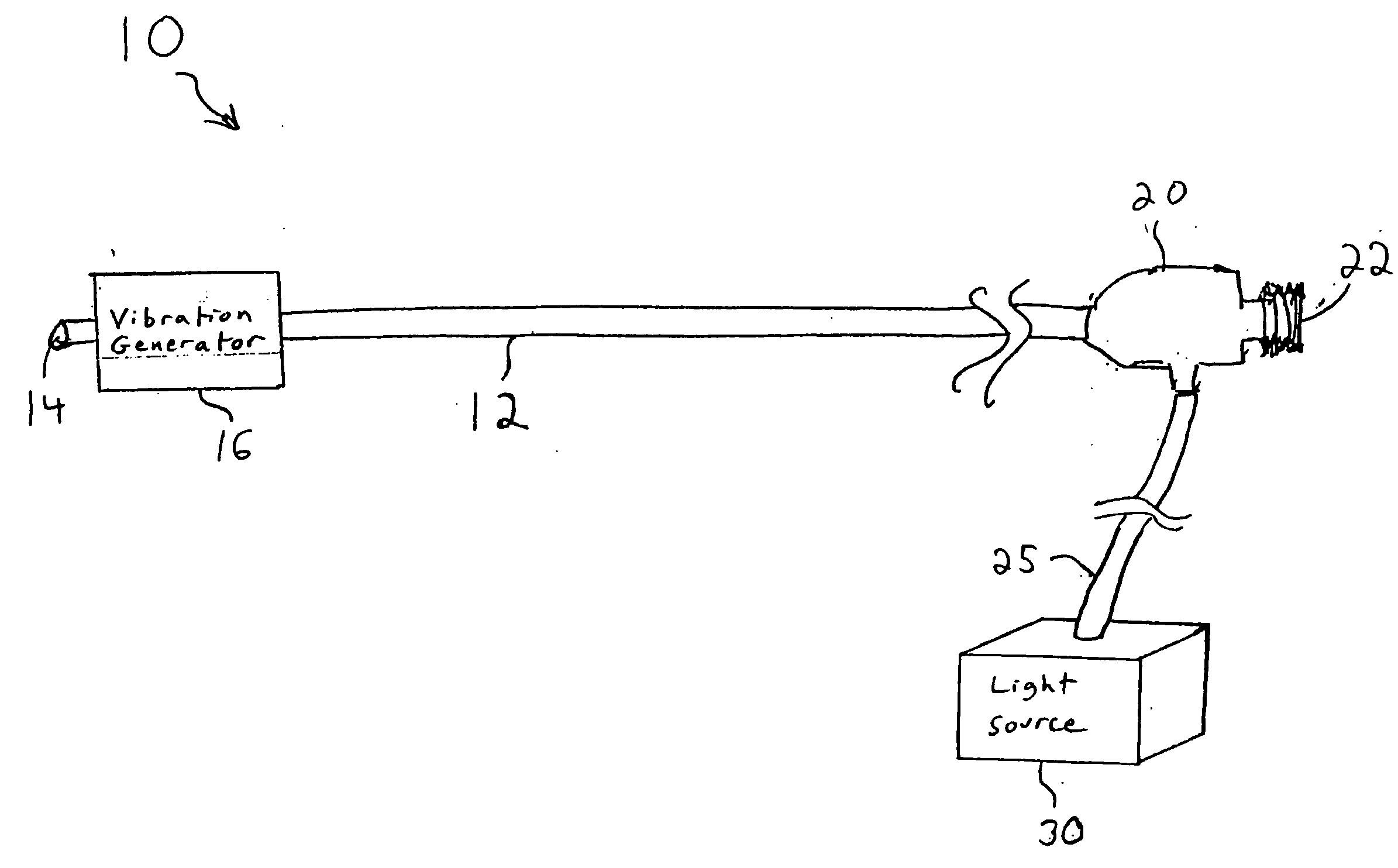
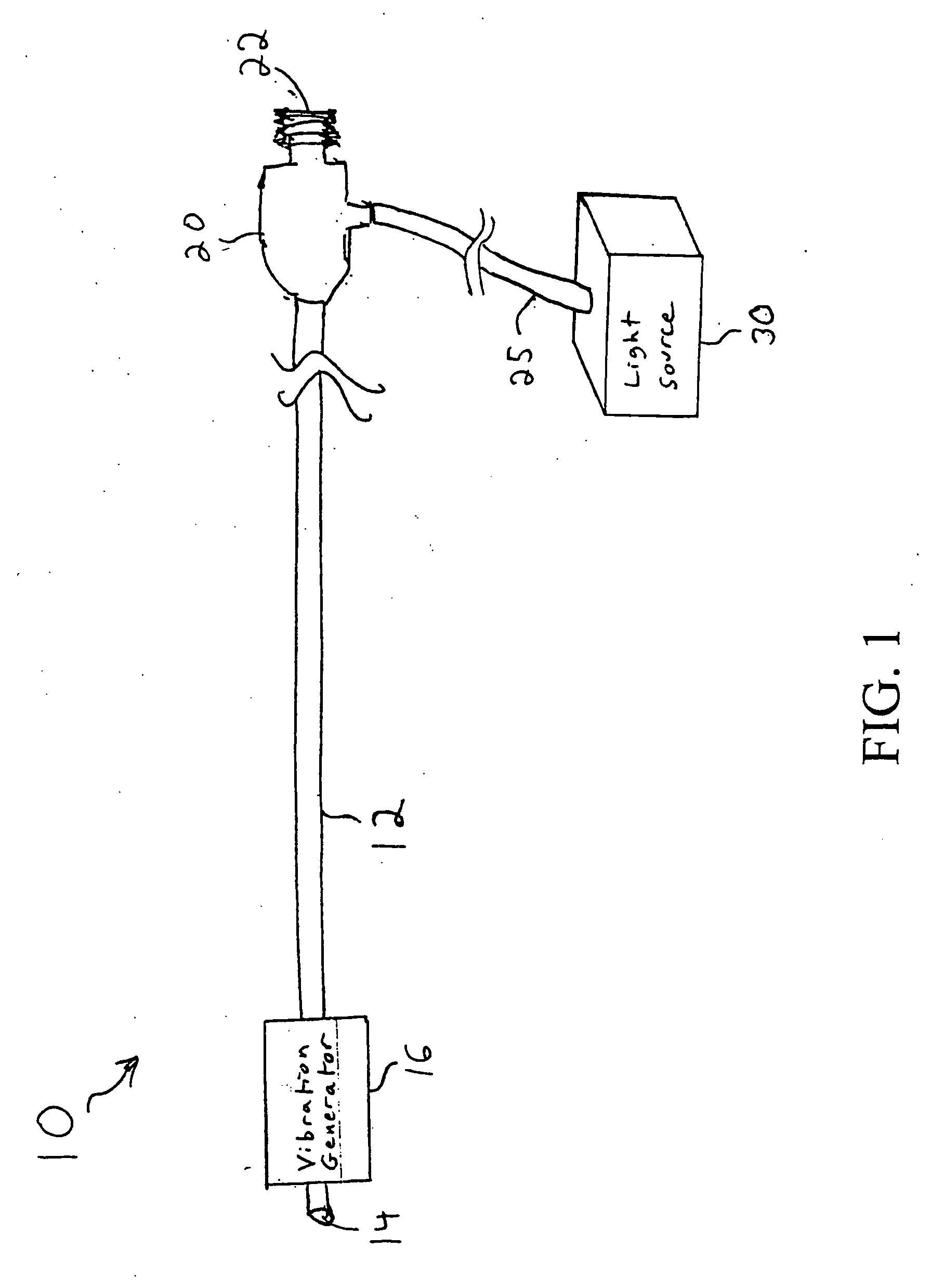
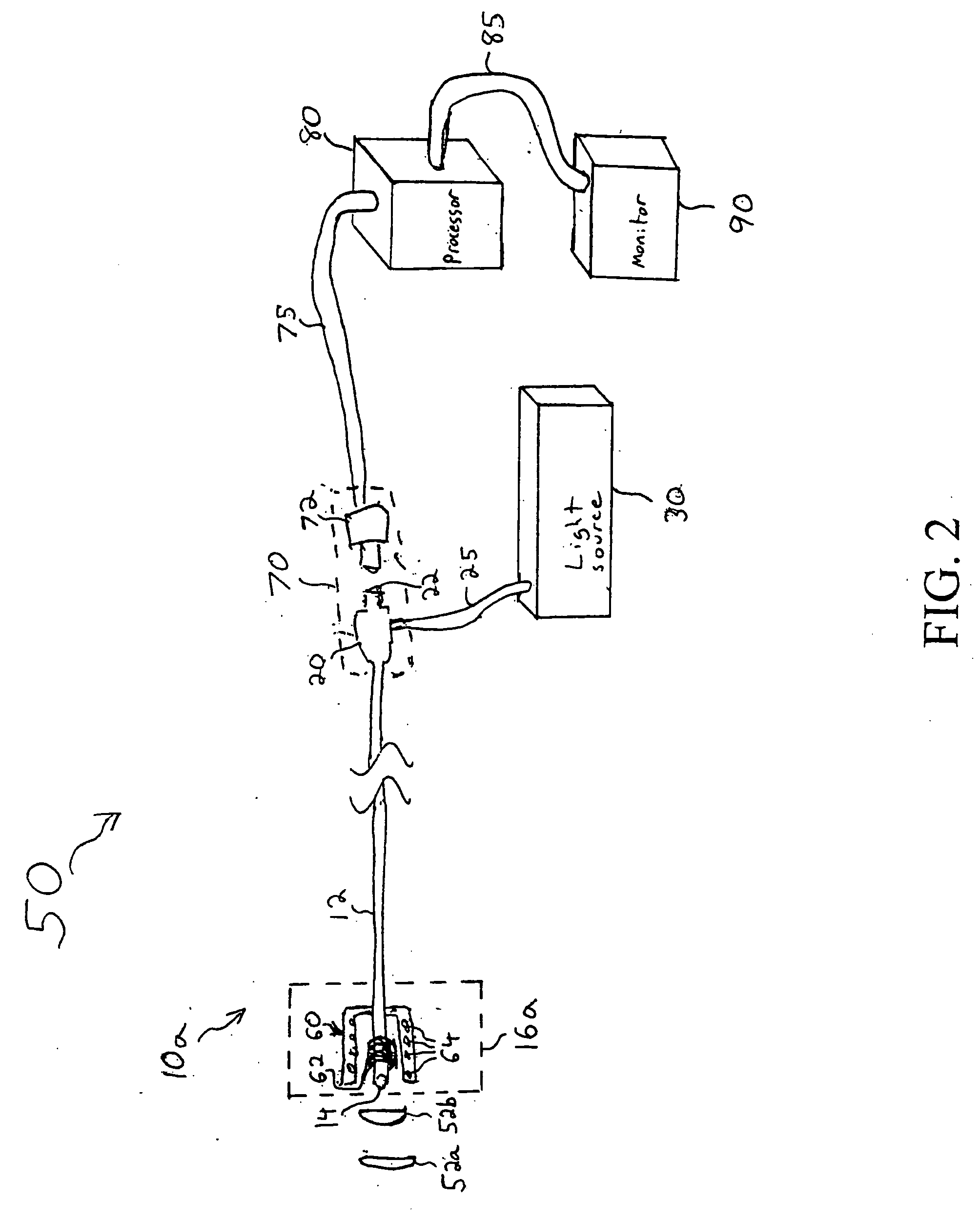
A catheter with a small optical fiber or bundle of fibers includes a scanning mechanism constructed with the use of any vibration capable component. Magnetic, piezoelectric or other mechanisms are used to vibrate the end of the fiber and thus create a scanning effect which extends the field of view. One or more lenses may be utilized, including a lens attached to the distal tip of the image fiber, or a lens attached to the distal tip of the catheter for creating an image plane which can be scanned by the fiber. In one embodiment, multiple light sources may be connected to the fiber for enabling the use of field sequential color techniques for real-time imaging, as well as real-time fluorescent imaging for disease detection. A photodetector assembly connected to the proximal end may contain both filtered and unfiltered detectors for use with both standard imaging and fluorescent imaging. The resulting vision catheter is relatively inexpensive and disposable.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
In-vivo calibration of contact force-sensing catheters using auto zero zones
A method for the in vivo re-calibration of a force sensing probe such as an electrophysiology catheter provides for the generation of an auto zero zone. The distal tip of the catheter or other probe is placed in a body cavity within the patient. Verification that there is no tissue contact is made using electrocardiogram (ECG) or impedance data, fluoroscopy or other real-time imaging data and / or an electro-anatomical mapping system. Once verification that there is no tissue contact is made, the system recalibrates the signal emanating from the force sensor setting it to correspond to a force reading of zero grams and this recalibrated baseline reading is used to generate and display force readings based on force sensor data.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
DC magnetic-based position and orientation monitoring system for tracking medical instruments
ActiveUS7835785B2Low costEasy to integrateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensors3d sensorDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Miniaturized, five and six degrees-of-freedom magnetic sensors, responsive to pulsed DC magnetic fields waveforms generated by multiple transmitter options, provide an improved and cost-effective means of guiding medical instruments to targets inside the human body. The end result is achieved by integrating DC tracking, 3D reconstructions of pre-acquired patient scans and imaging software into a system enabling a physician to internally guide an instrument with real-time 3D vision for diagnostic and interventional purposes. The integration allows physicians to navigate within the human body by following 3D sensor tip locations superimposed on anatomical images reconstructed into 3D volumetric computer models. Sensor data can also be integrated with real-time imaging modalities, such as endoscopes, for intrabody navigation of instruments with instantaneous feedback through critical anatomy to locate and remove tissue. To meet stringent medical requirements, the system generates and senses pulsed DC magnetic fields embodied in an assemblage of miniaturized, disposable and reposable sensors functional with both dipole and co-planar transmitters.
Owner:NORTHERN DIGITAL
Optical-acoustic imaging device
InactiveUS20040082844A1Shorten operation timeReduce radiation exposureMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementGratingRadiation exposure
The present invention is a guide wire imaging device for vascular or non-vascular imaging utilizing optic acoustical methods, which device has a profile of less than 1 mm in diameter. The ultrasound imaging device of the invention comprises a single mode optical fiber with at least one Bragg grating, and a piezoelectric or piezo-ceramic jacket, which device may achieve omnidirectional (360°) imaging. The imaging guide wire of the invention can function as a guide wire for vascular interventions, can enable real time imaging during balloon inflation, and stent deployment, thus will provide clinical information that is not available when catheter-based imaging systems are used. The device of the invention may enable shortened total procedure times, including the fluoroscopy time, will also reduce radiation exposure to the patient and to the operator.
Owner:PHYZHON HEALTH INC
Multi-channel medical imaging system
ActiveUS20100262017A1Luminescence/biological staining preparationNanoinformaticsFluorescenceBlood stream
A medical imaging system provides simultaneous rendering of visible light and fluorescent images. The system may employ dyes in a small-molecule form that remain in a subject's blood stream for several minutes, allowing real-time imaging of the subject's circulatory system superimposed upon a conventional, visible light image of the subject. The system may provide an excitation light source to excite the fluorescent substance and a visible light source for general illumination within the same optical guide used to capture images. The system may be configured for use in open surgical procedures by providing an operating area that is closed to ambient light. The systems described herein provide two or more diagnostic imaging channels for capture of multiple, concurrent diagnostic images and may be used where a visible light image may be usefully supplemented by two or more images that are independently marked for functional interest.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Convergent parameter instrument
InactiveUS20120078113A1Advanced technologyLow-cost and robust and portableMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringControl setImaging technique
The present invention relates to a convergent parameter instrument and method for performing real-time imaging using multiple imaging techniques. More particularly, the present invention relates to a handheld convergent parameter instrument providing some or preferably all of real-time imaging, including surface mapping, color imaging, perfusion imaging, thermal imaging, and near infrared spectroscopy, and including a common control set and a common display.
Owner:POINT OF CONTACT
Extra-oral digital panoramic dental x-ray imaging system
ActiveUS20080063139A1Sufficient speedFast readoutRadiation diagnostics for dentistryDigital imaging3d image
An extra-oral digital panoramic dental x-ray imaging system is disclosed for multi-layer panoramic and transverse X-ray imaging. The system includes an X-ray source and a digital imaging device capable of “real time” frame mode output. The source and imaging device are mounted in a mechanical manipulator defining the trajectory of a predetermined image layer. The imaging device communicates with a processor that generates a frames memory from which an image reconstruction mechanism composes the final images. For “real time” imaging, the frames memory is a fast data storage system such as RAM. The processing unit executes the reconstruction algorithms, allowing the system to selectively generate dental panoramic X-ray images, dental transverse x-ray images and dental tomosynthetic 3D images.
Owner:OY AJAT LTD
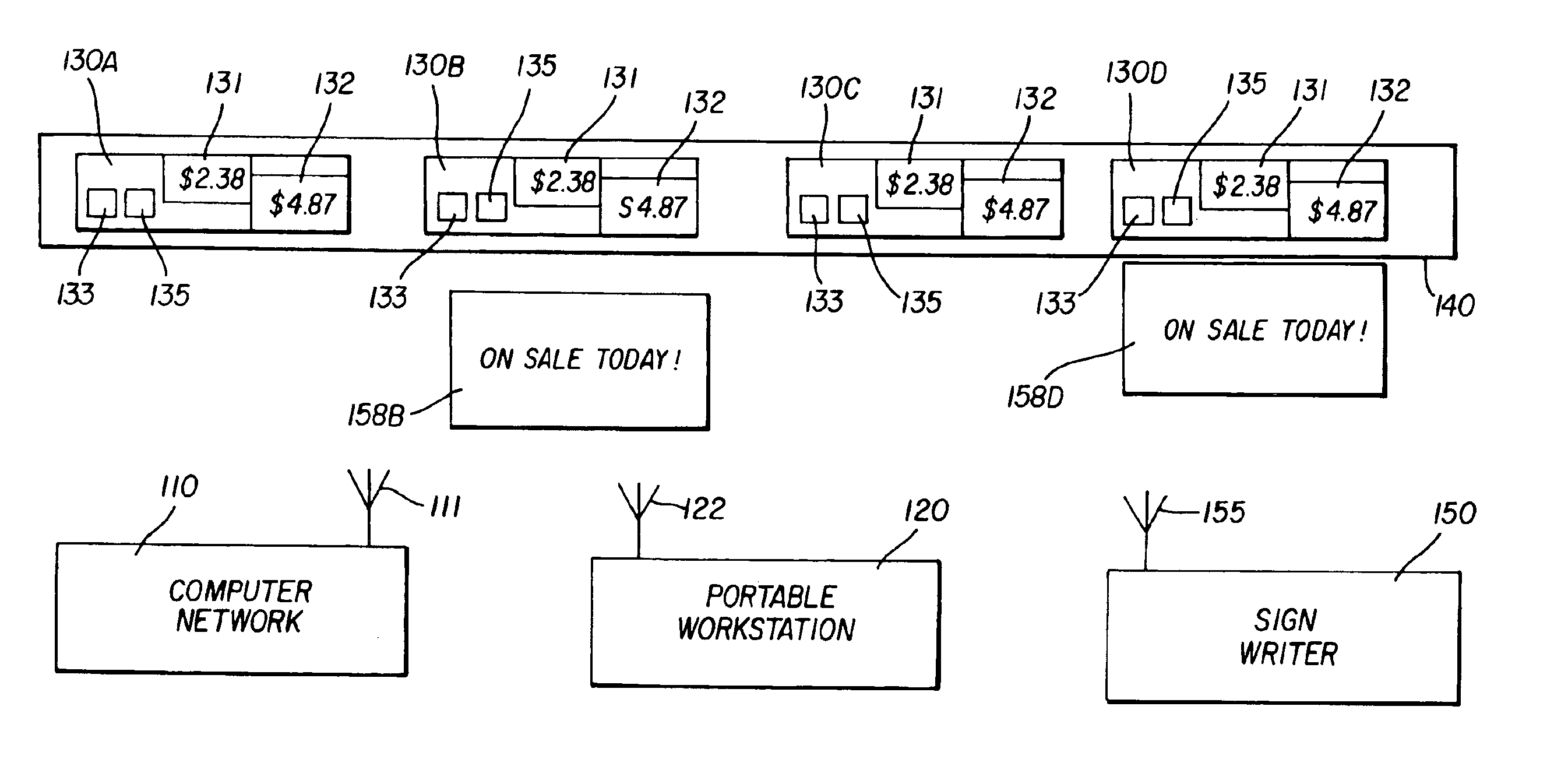
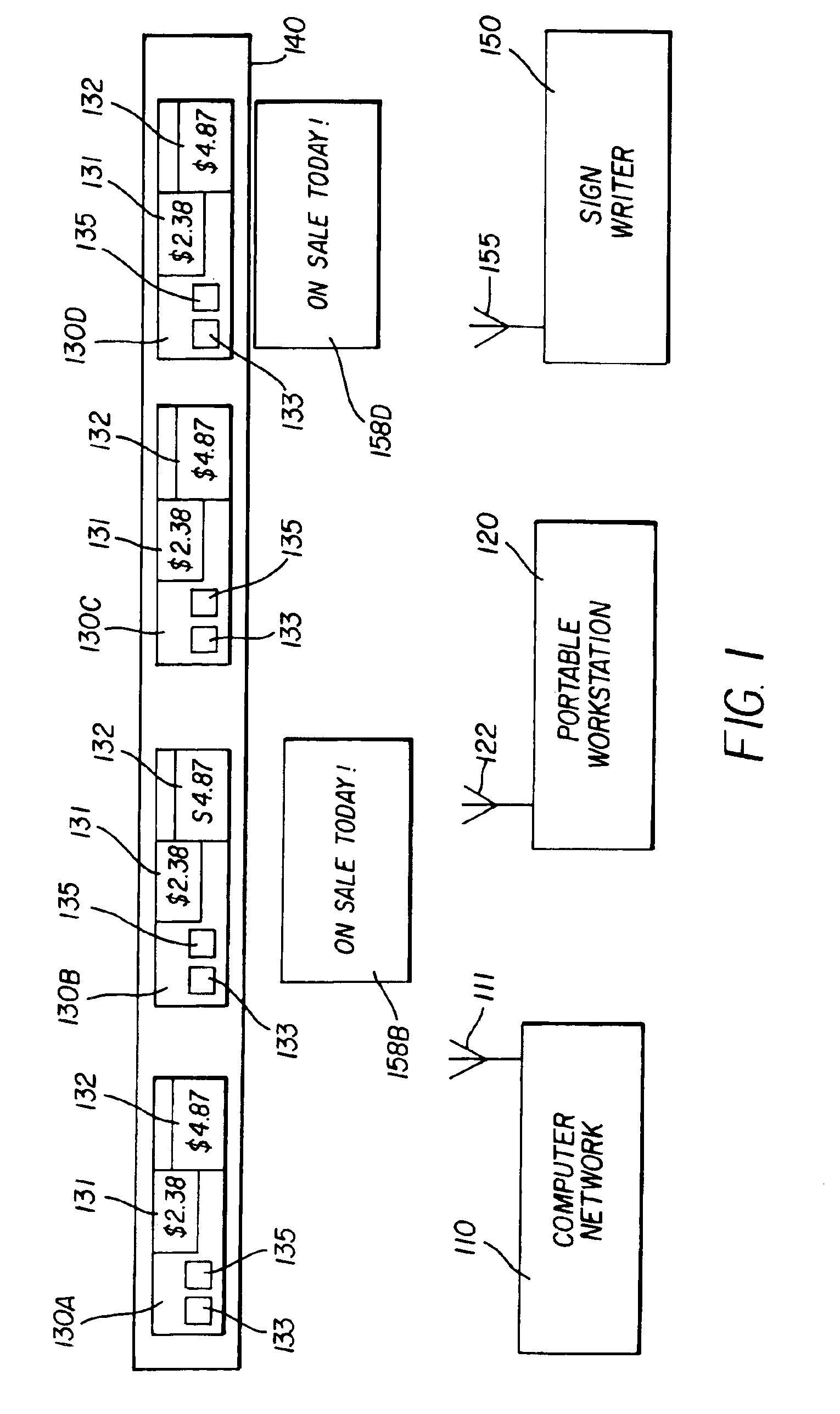
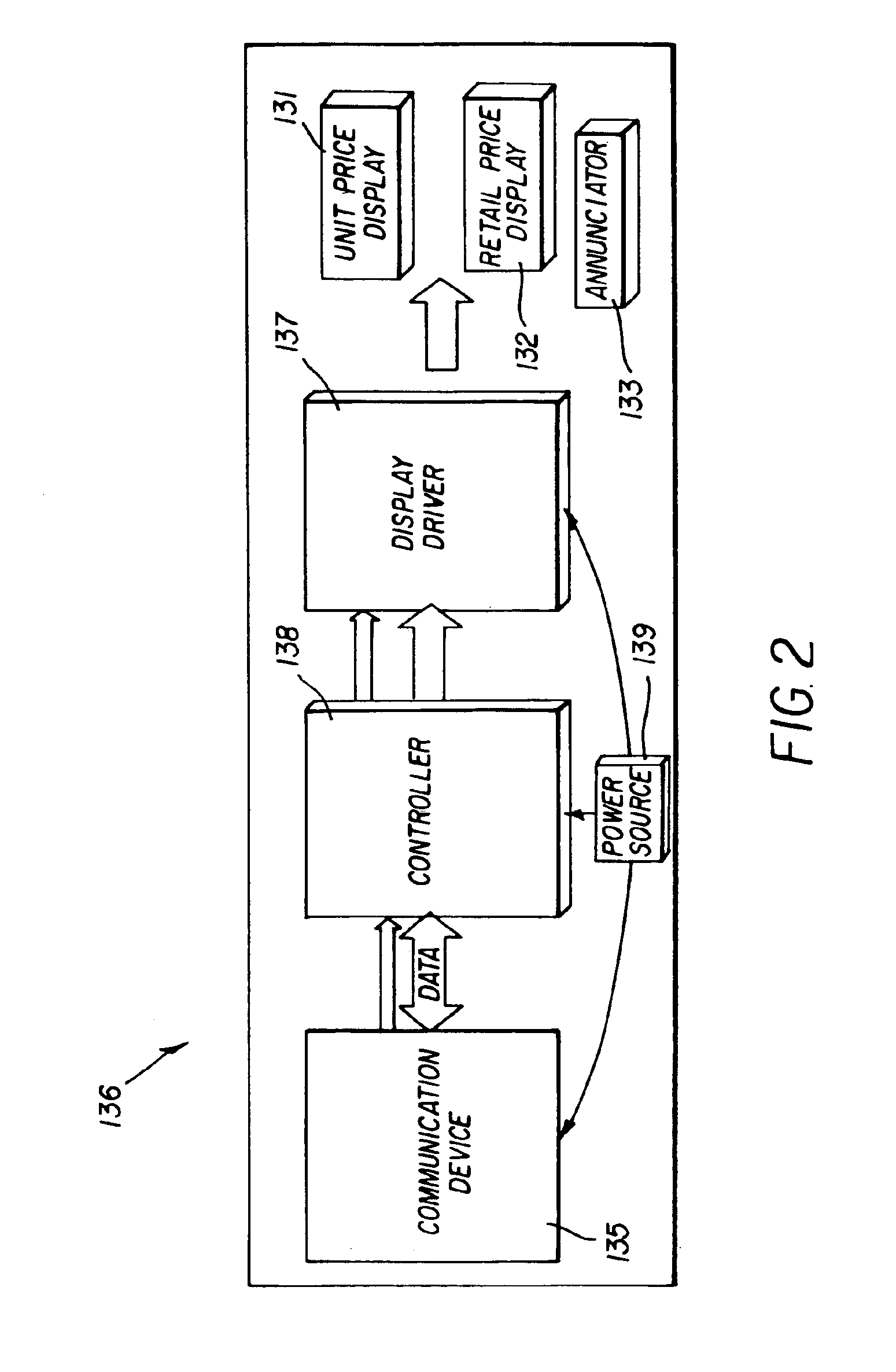
Retail signage management system
InactiveUS6897763B2Electric signal transmission systemsHand manipulated computer devicesWorkstationManagement system
A mobile retail signage management system includes a communication device capable of transmitting a specific location for which a corresponding sign needs to be positioned at the specific location; a portable workstation including a product database that associates product information with the specific location, wherein the product information includes display information for a corresponding sign positioned at the location. Moreover, the portable workstation communicates to the communication device as the portable workstation comes within the communication range of the communication device, wherein the communication range corresponds to the near vicinity of the portable workstation with respect to the communication device. A sign writer for imaging the corresponding sign in real-time, in the near vicinity of the specific location; and a computer network for updating the database are provided. Additionally a clerk is alerted that the corresponding sign needs to be imaged and positioned at the specific location.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Instrument guidance system for sinus surgery
ActiveUS20170231714A1Enhanced D perceptionImage enhancementImage analysisGuidance systemObject based
A method for generating an augmented reality image for supporting the adjustment of the position of a surgical instrument during sinus surgery comprising the steps of: selecting at least one of sinus cells, cavities and orifices of the sinus in a pre-operative image by marking them with at least one geometric primitive or tube shaped object; using real-time intra-operative imaging for displaying the operating field; determining the relative positions at least between the real-time imaging of the patient and the pre-operative image data; computing a virtual image corresponding to a real-time image comprising at least one marked geometric primitive or tube shaped object based on the determined relative positions; combining the virtual image and the real-time intraoperative image for visualization in an augmented reality image.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
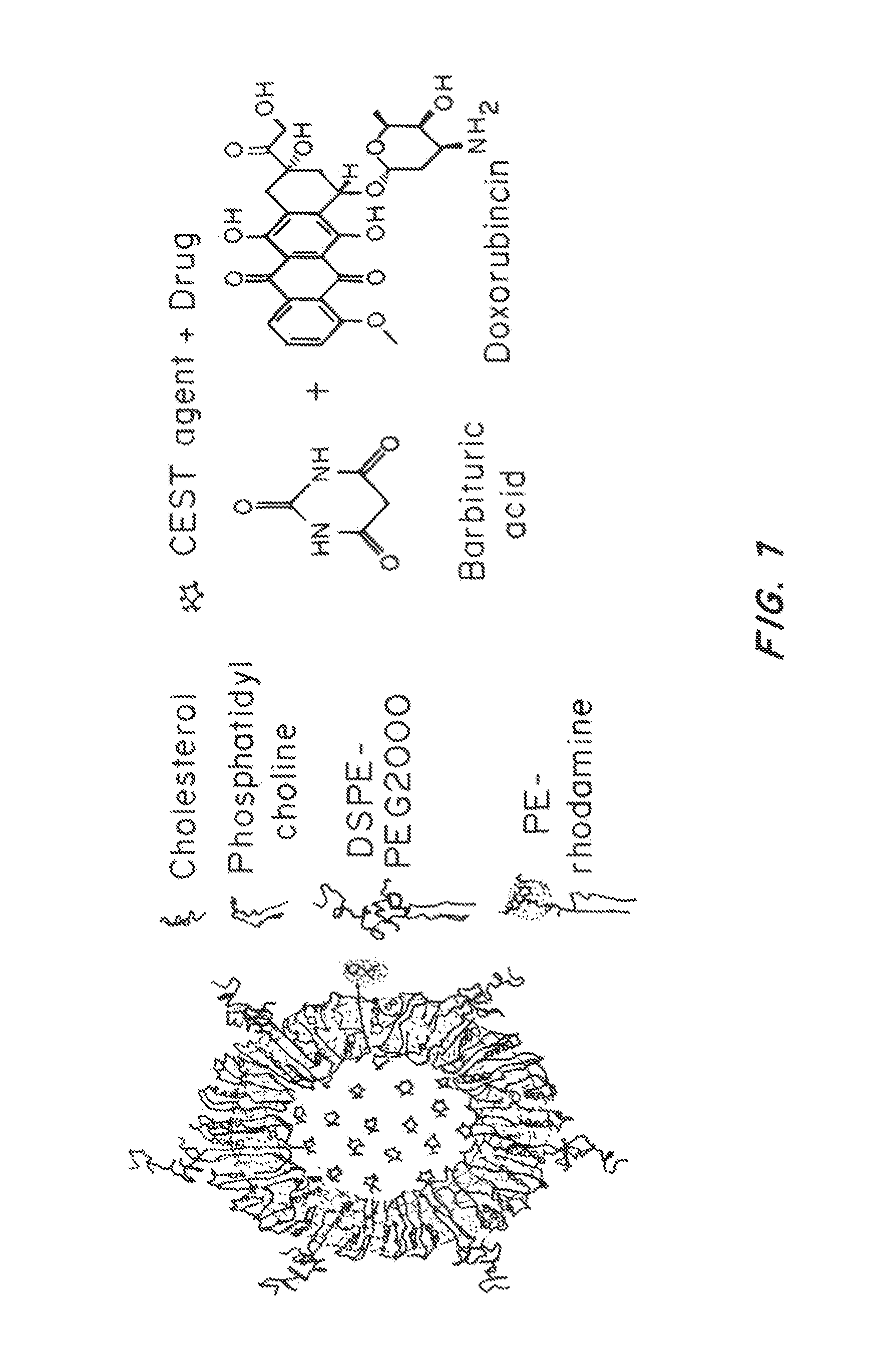
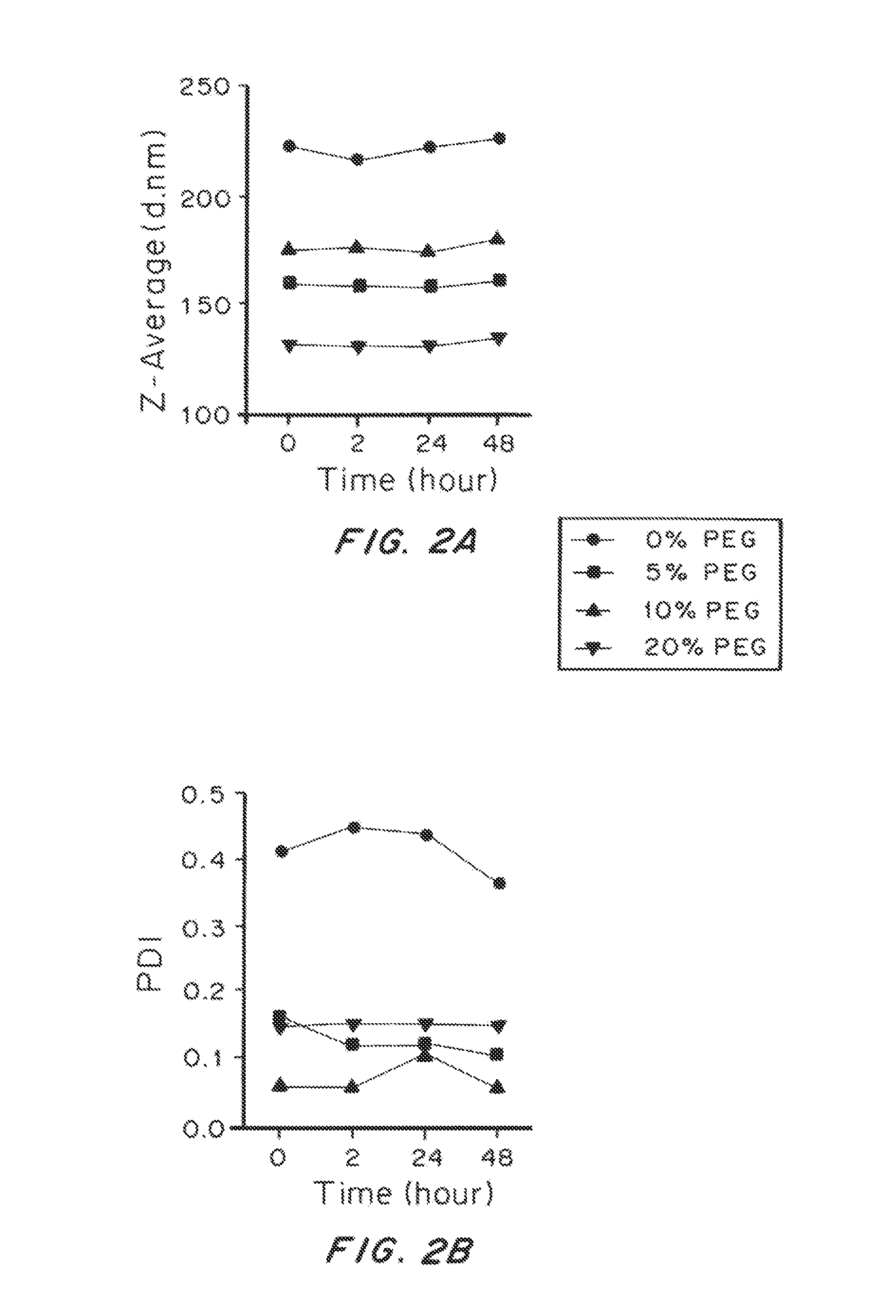
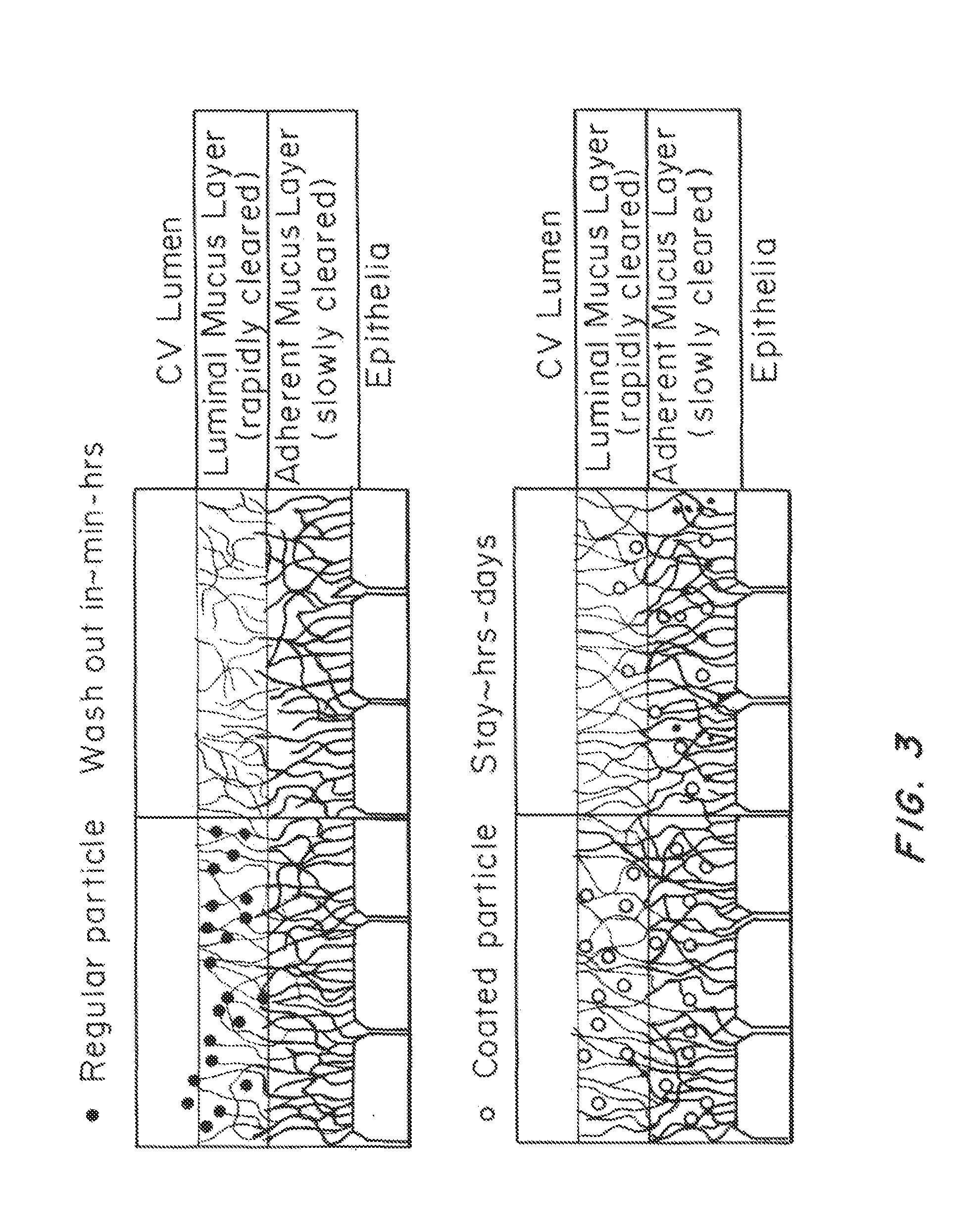
Lipid-Based Drug Carriers for Rapid Penetration Through Mucus Linings
Mucus-penetrating liposomal nanoparticles and methods of making and using thereof are described herein. The nanoparticles contain one or more lipids, one or more PEG-conjugated lipids, and optionally one or more additional materials that physically and / or chemically stabilize the particles. The nanoparticle have an average diameter of about 100 nm to about 300 nm, preferably from about 100 nm to about 250 nm, more preferably from about 100 nm to about 200 nm. The particles are mobile in mucus. The liposomes can further contain one or more therapeutic, prophylactic, and / or diagnostic agent to be delivered to a mucosal surface, such as the CV tract, the colon, the nose, the lungs, and / or the eyes. The liposomes can further contain one or more CEST agents to allow real time imaging of the particles in a live animal. The particles may also further contain an imaging agent, such as a fluorescent label.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Imaging-guided anesthesia injection systems and methods
InactiveUS20130041258A1Precise deliveryPatient benefitUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAutomatic syringesAnatomical structuresDisplay device
Devices and systems for injecting fluids, such as anesthetics, to or near nerve tissue or other targeted anatomical location are disclosed herein. A conduit is generally configured to place the fluid delivery module in fluid communication with a needle that is configured to be inserted into the patient's anatomy. One or more medicaments (e.g., anesthetics) and / or other materials contained within containers (e.g., vials) that are secured to the injection system can be selectively delivered into an anatomy through the needle. Nerve stimulation and / or imaging technologies (e.g., ultrasound) can be used to locate a targeted anatomical location. Aspiration can be used to confirm needle location. An overlay on the imaging display can include, in addition to real-time imaging data, data and other information relating to back pressure at or near the needle tip, volumes or other amounts of fluids delivered by and remaining within the system, stimulation level and / or the like.
Owner:CARTICEPT MEDICAL
Dental implantation system and method
Drilling of an implant shaft is carried out with a handpiece tool whose location and angular orientation with respect to a radiographic working guide is updated in real time with respect to the radiographic working guide and anatomical structures of the patient, free of viewing obstructions. Prior to the drilling, the radiographic working guide is fitted to a particular patient. Real-time imaging support is provided on a display of a computer, wherein the radiographic workpiece guide includes a plurality of fiducial markers that define a substantially planar reference surface of the radiographic workpiece guide. The radiographic workpiece guide also includes an alignment structure located a predetermined distance from a pilot hole proximate the work site. The image is updated based on an initial radiographic scan and updated position information from the handpiece tool as to location and angular orientation of the handpiece tool relative to the workpiece guide.
Owner:PRECISION THROUGH IMAGING
Subcutanous Blood Vessels Imaging System
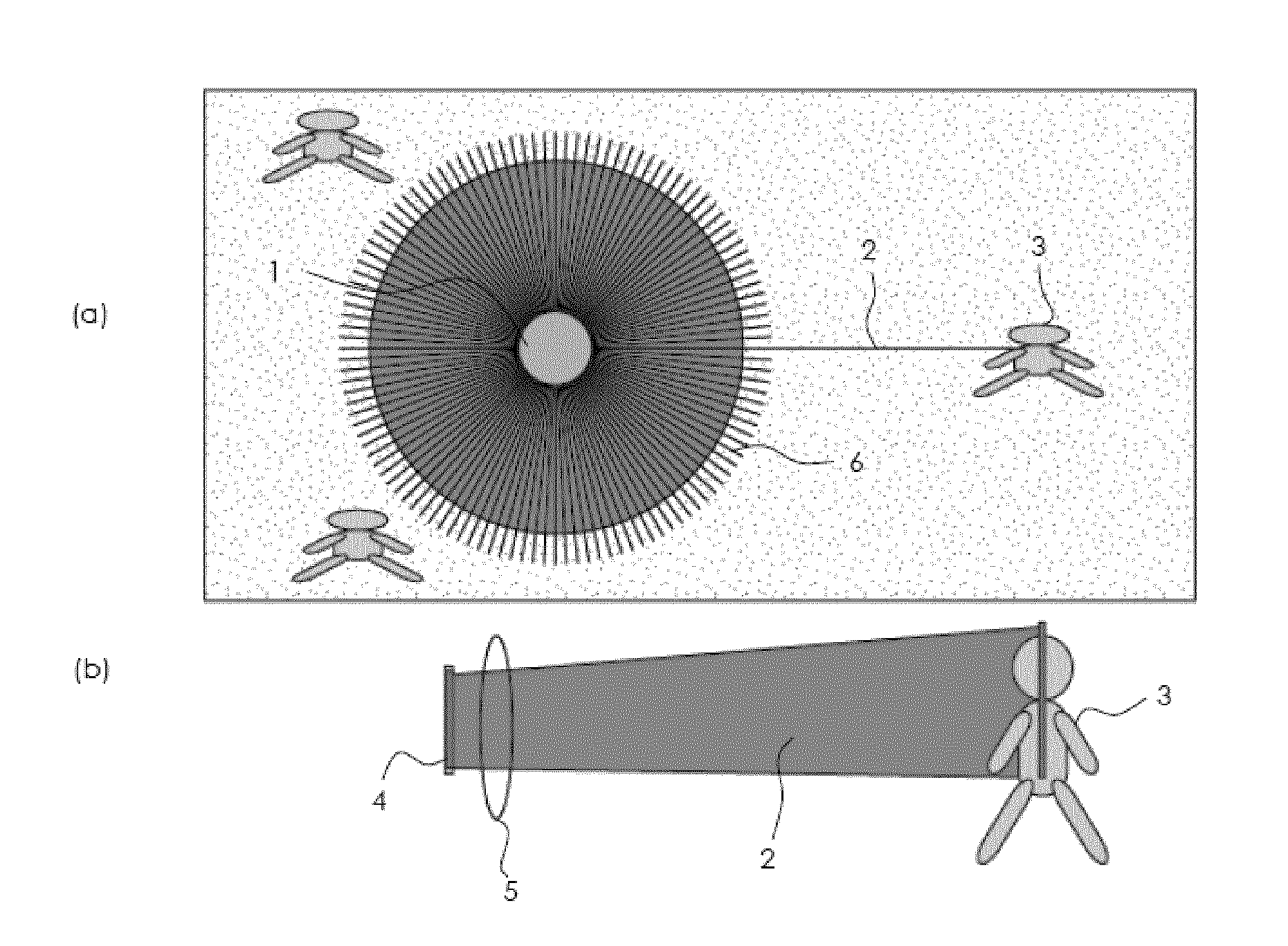
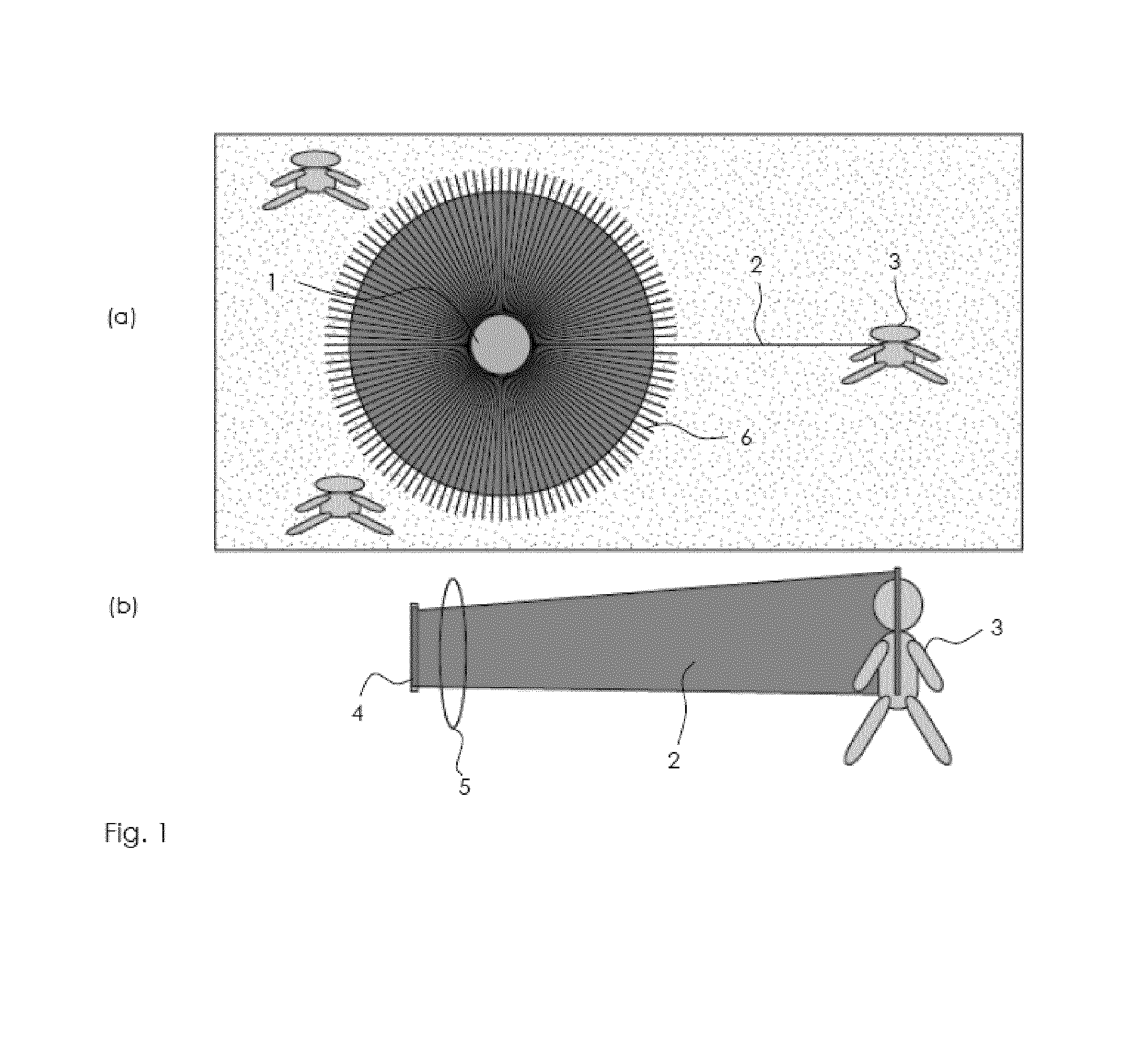
InactiveUS20090018414A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioClear presentationDiagnostics using lightSensorsAnatomical structuresVein
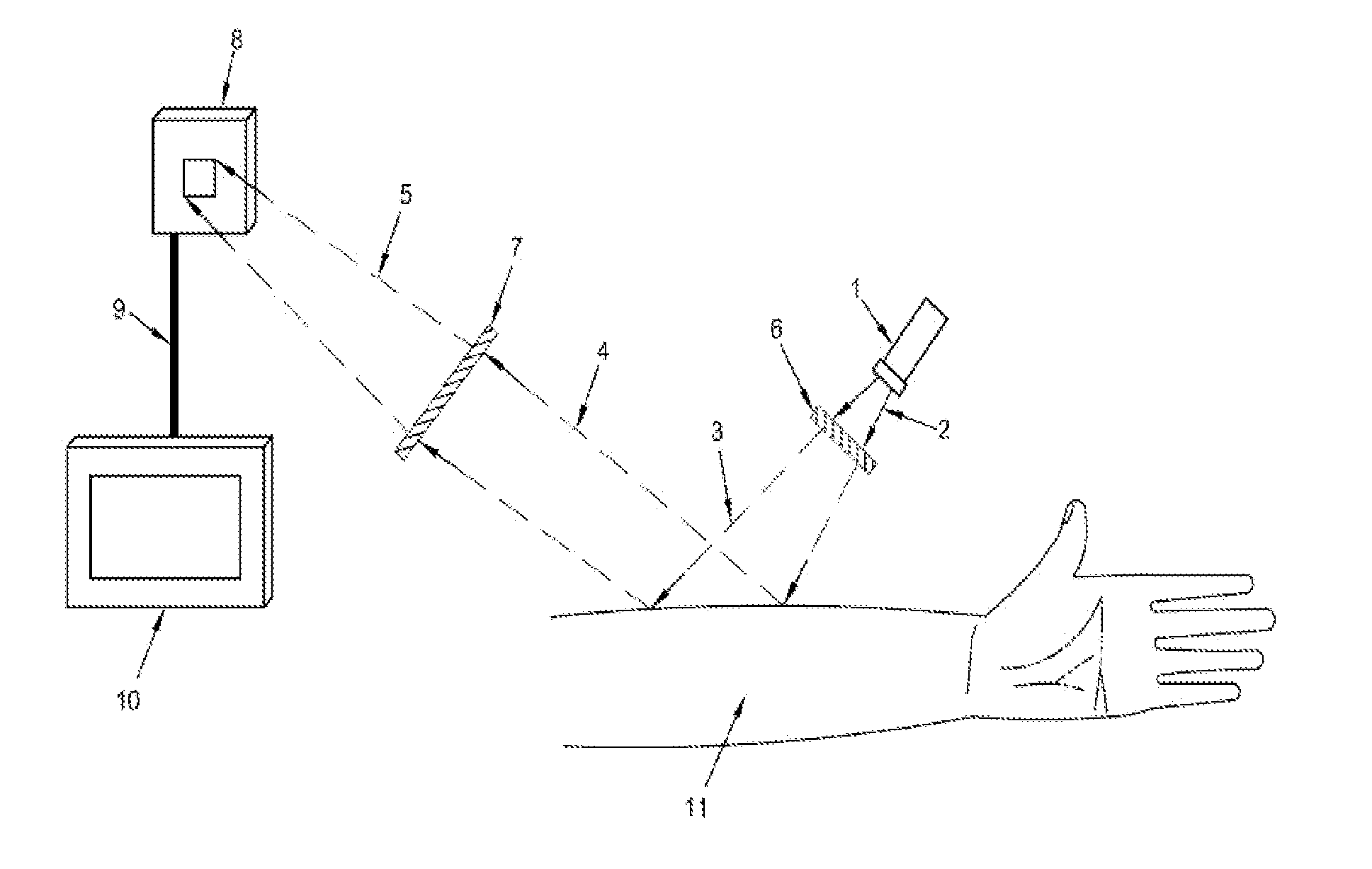
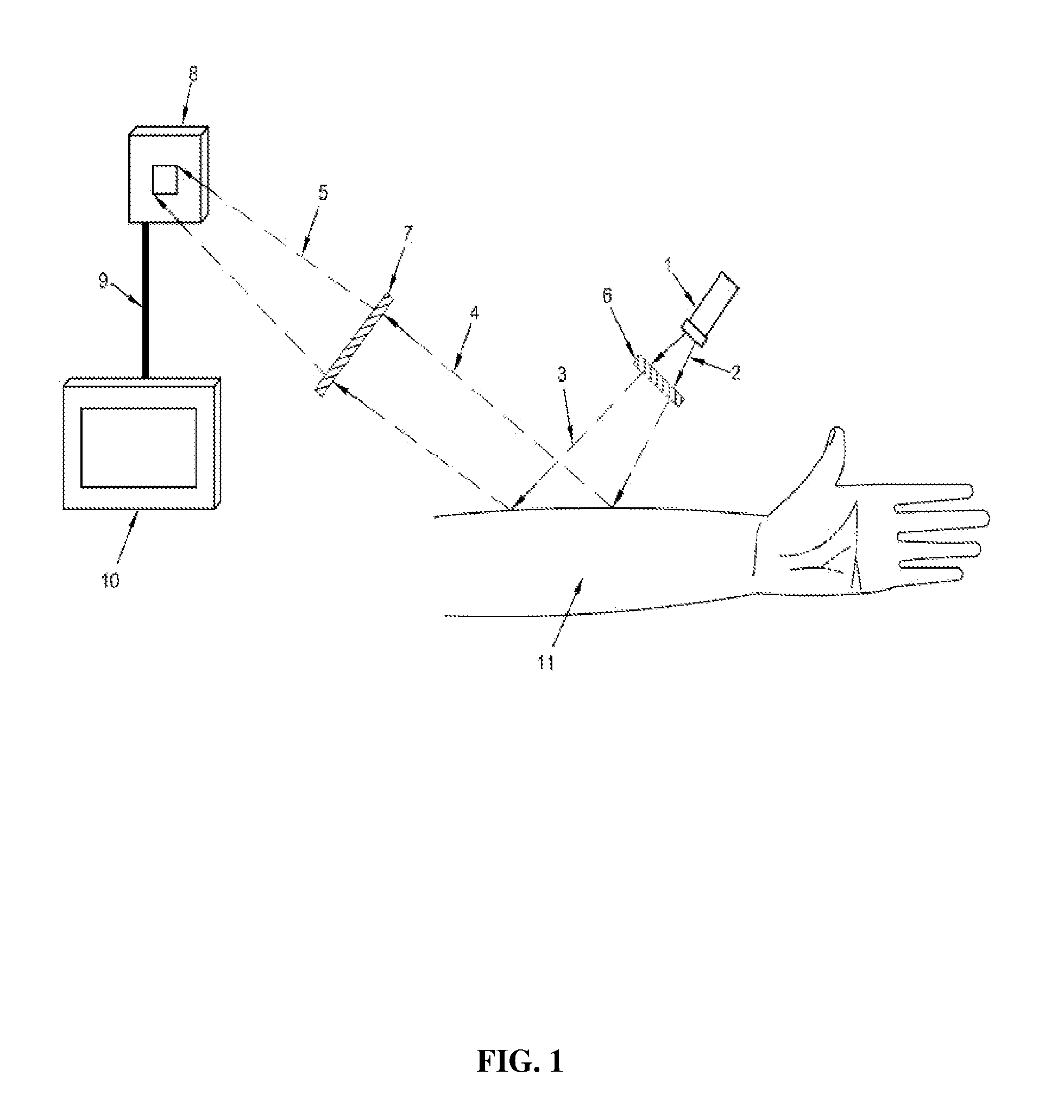
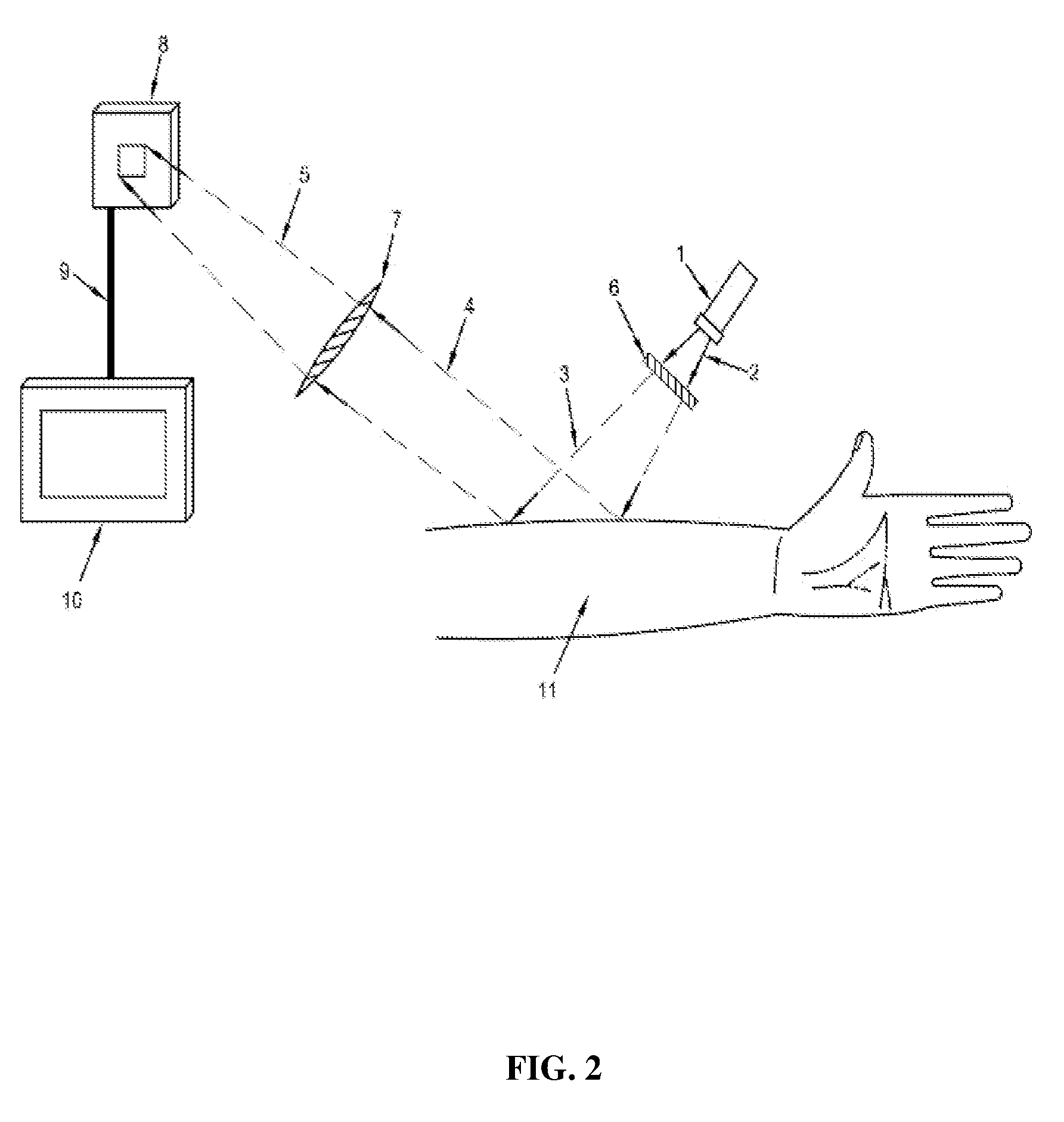
A real time imaging system is described which displays subcutaneous veins whereby facilitating diagnosis, inspection and easy intravenous access for administration of drugs. The imaging system comprises an infrared source (1), a pinhole focusing unit (7), an infrared Focal Plane Array (8), and a display unit (10). The infrared source (1) emits infrared light which penetrates and is subsequently scattered differently at different layers and depths of the anatomical structure (11) while substantially being absorbed by the blood vessels. Reflected light (4) from the anatomical structure (11) contains the imaging information of the subcutaneous blood vessels of the anatomical structure (11) which is then focused by said pinhole focusing unit (7) upon said infrared Focal Plane Array (8). The image captured by said infrared Focal Plane Array is then displayed on the display unit (10).
Owner:TOOFAN MEHRDAD
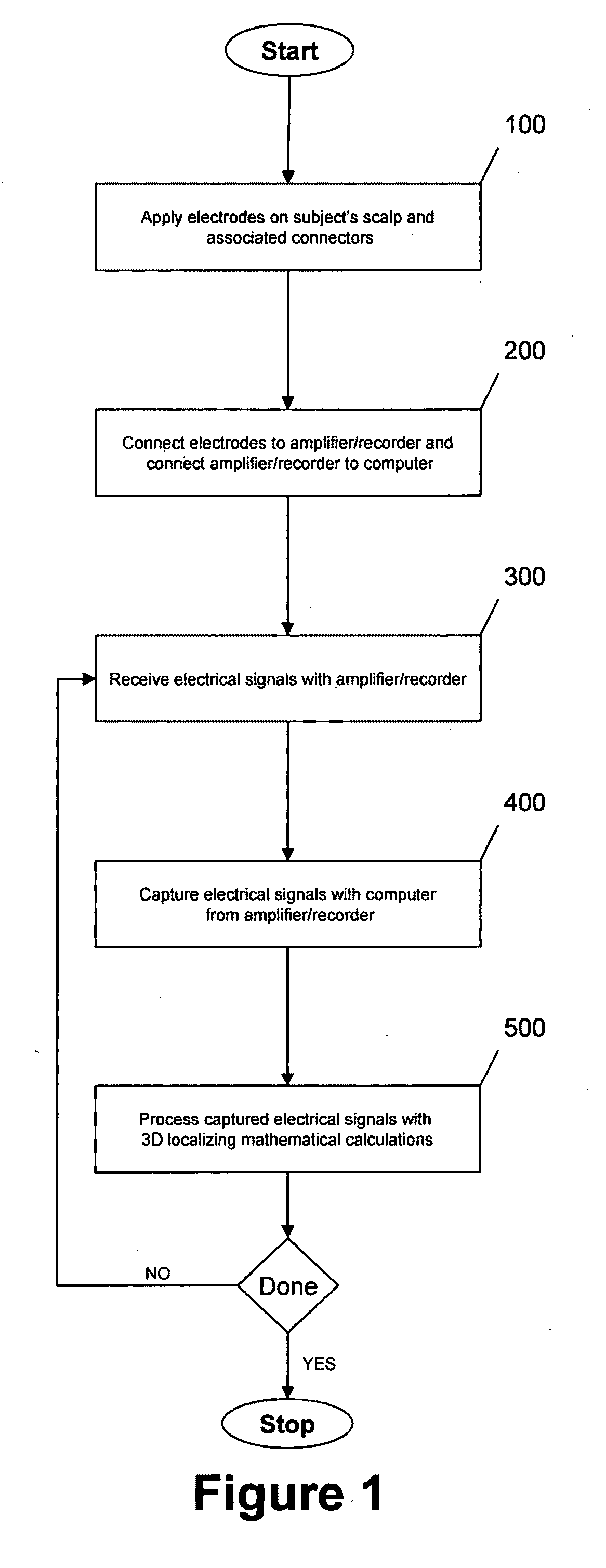
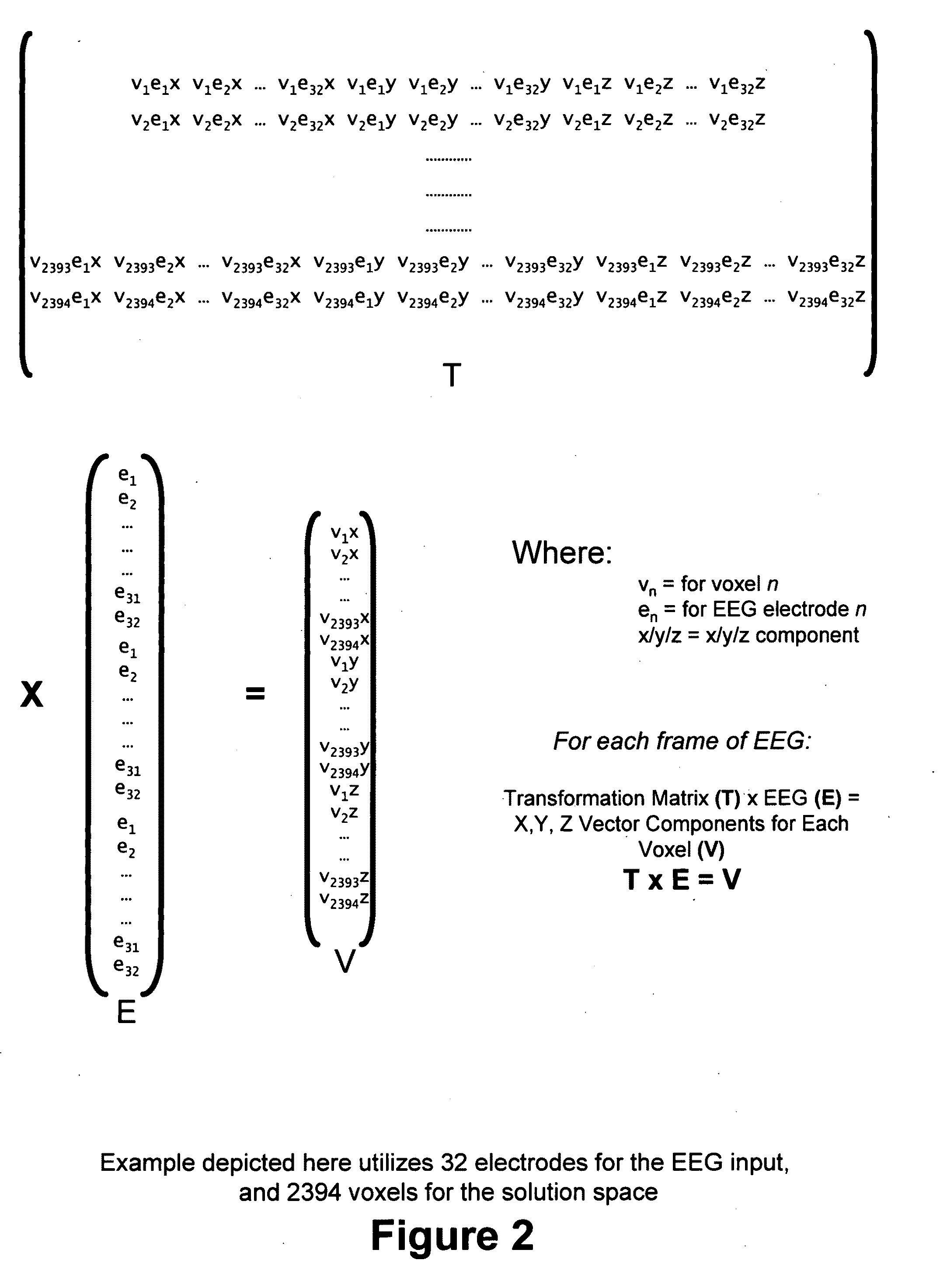
Three-dimensional localization, display, recording, and analysis of electrical activity in the cerebral cortex
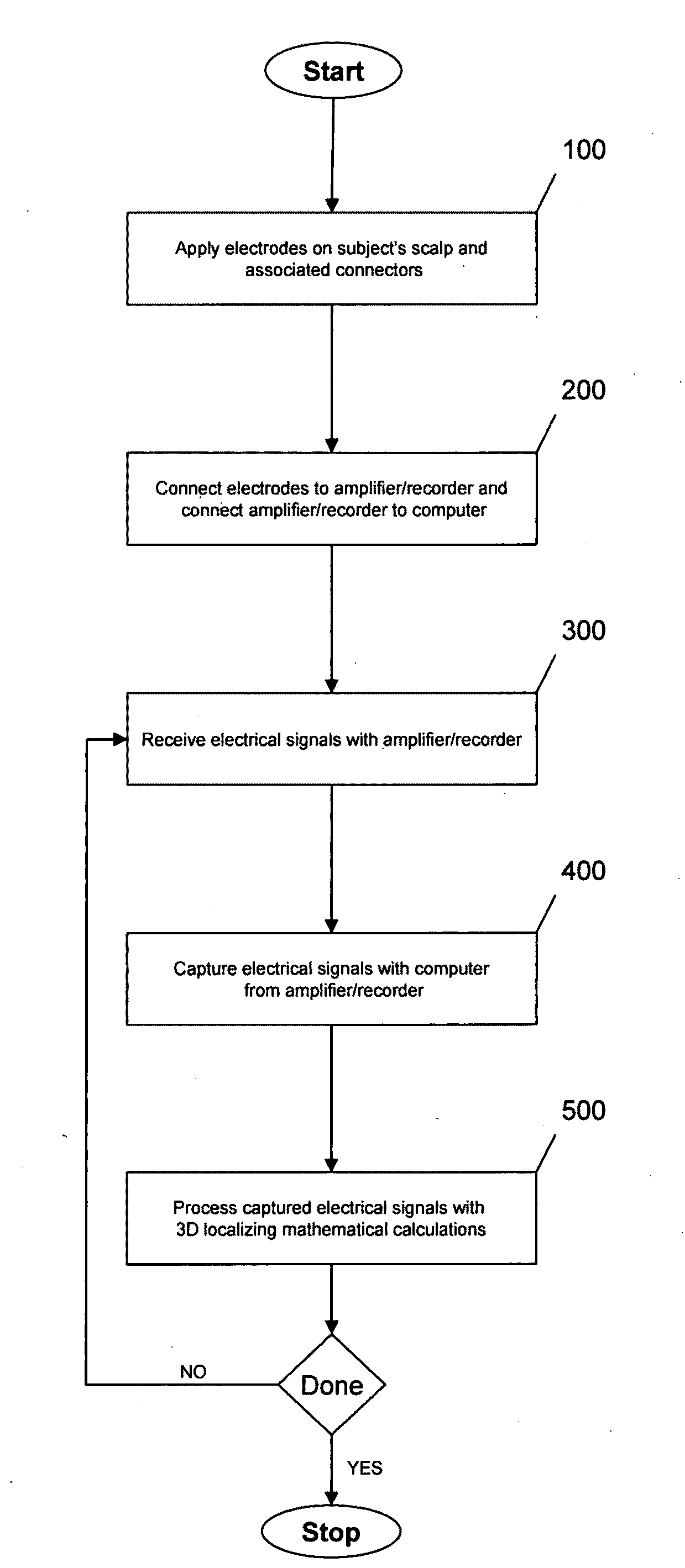
The present invention describes a method and apparatus to localize the electrical signals measured from a subject's scalp surface, preferably in near-real time, and to generate dynamic three-dimensional information of the electrical activity occurring within the cerebral cortex of the brain. In the preferred embodiment, it can produce images that can be immediately inspected and analyzed by an operator in near-real time, resulting in a powerful new cortical imaging modality, which we denote as Dynamic Electrocortical Imaging (DECI). The present invention involves the use of a computer, an electroencephalographic (EEG) amplifier, EEG electrodes, and custom software. It can measure healthy and diseased cortical events and states in both conscious and unconscious subjects. This is useful, as it allows for the diagnosis, monitoring and treatment of cortical disorders, while also furthering the understanding of the human brain and lending use to additional non-medical applications such as in entertainment, education, lie-detection and industry. The invention in one embodiment is implemented using software in conjunction with readily available EEG hardware. Furthermore, this same method can be applied to pre-existing data and when doing so, EEG hardware is not required. Having a practical near-real time 3D imaging system brings a far more accessible technology to doctors, researchers, individuals, and private clinics to better diagnose, monitor, treat and understand many of the conditions and abnormalities of the brain.
Owner:DOIDGE MARK S +1
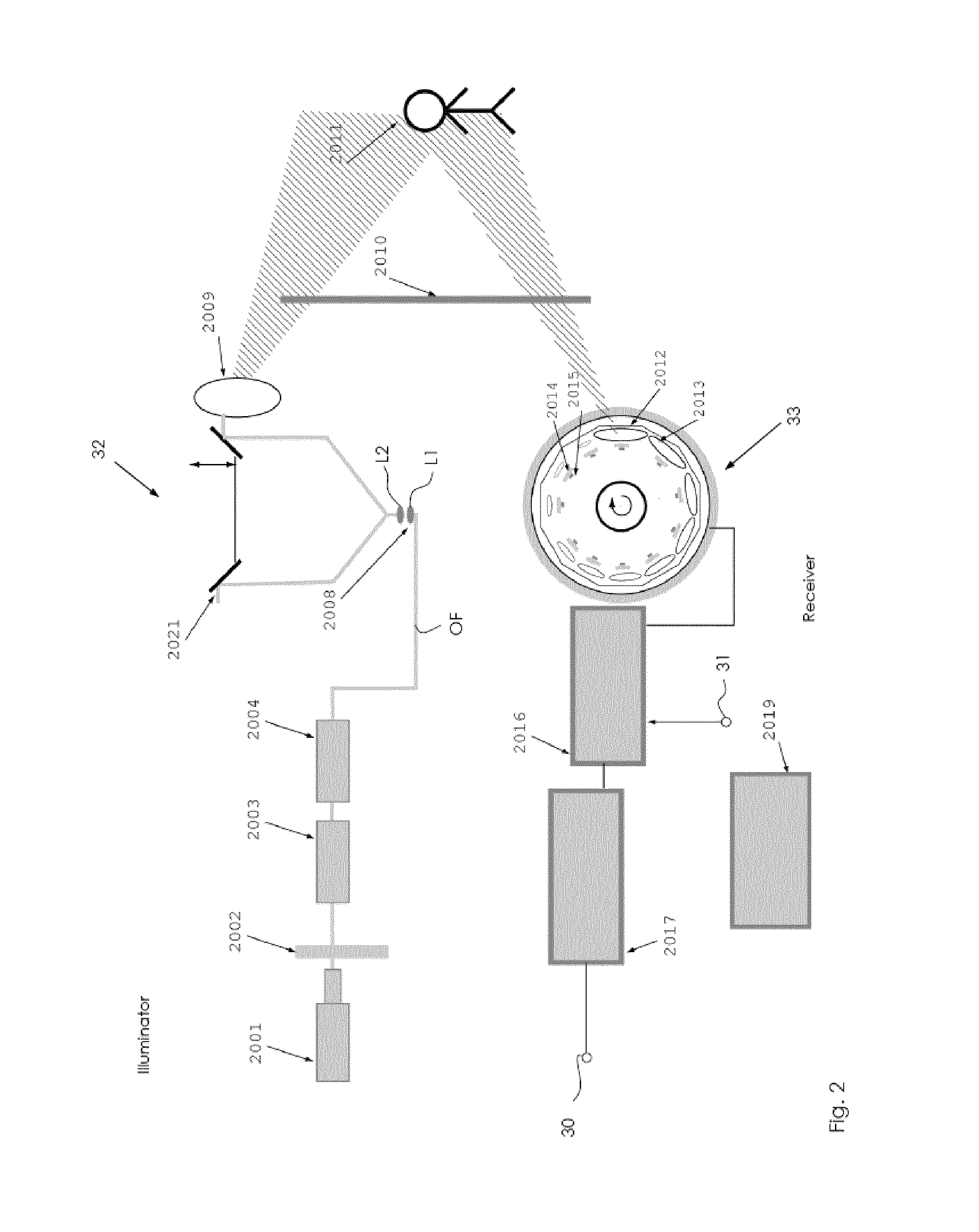
3D landscape real-time imager and corresponding imaging methods
ActiveUS20130300840A1Enhanced speed and distance and resolutionEfficient detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systems3d imageDetector array
A 3D landscape real-time imager, and method for operating such an imager, where the imager includes:at least one illuminating part which is designed to scan at least a portion of the landscape at a given range and having an ultra-short laser pulse source emitting at least one wavelength, and an optical rotating block, with a vertical axis of rotation, and controlled such that given packets of pulses are shaped in a pattern of rotating beams sent toward the at least partial landscape; andat least one receiving part which includes a set of SPAD detector arrays, each arranged along a vertical direction and rotating at a given speed in synchronism with the optical rotating block of the illuminating part, the detection data of the SPAD detector arrays being combined to acquire 3D imaging data of the at least partial landscape in a central controller.
Owner:FASTREE3D
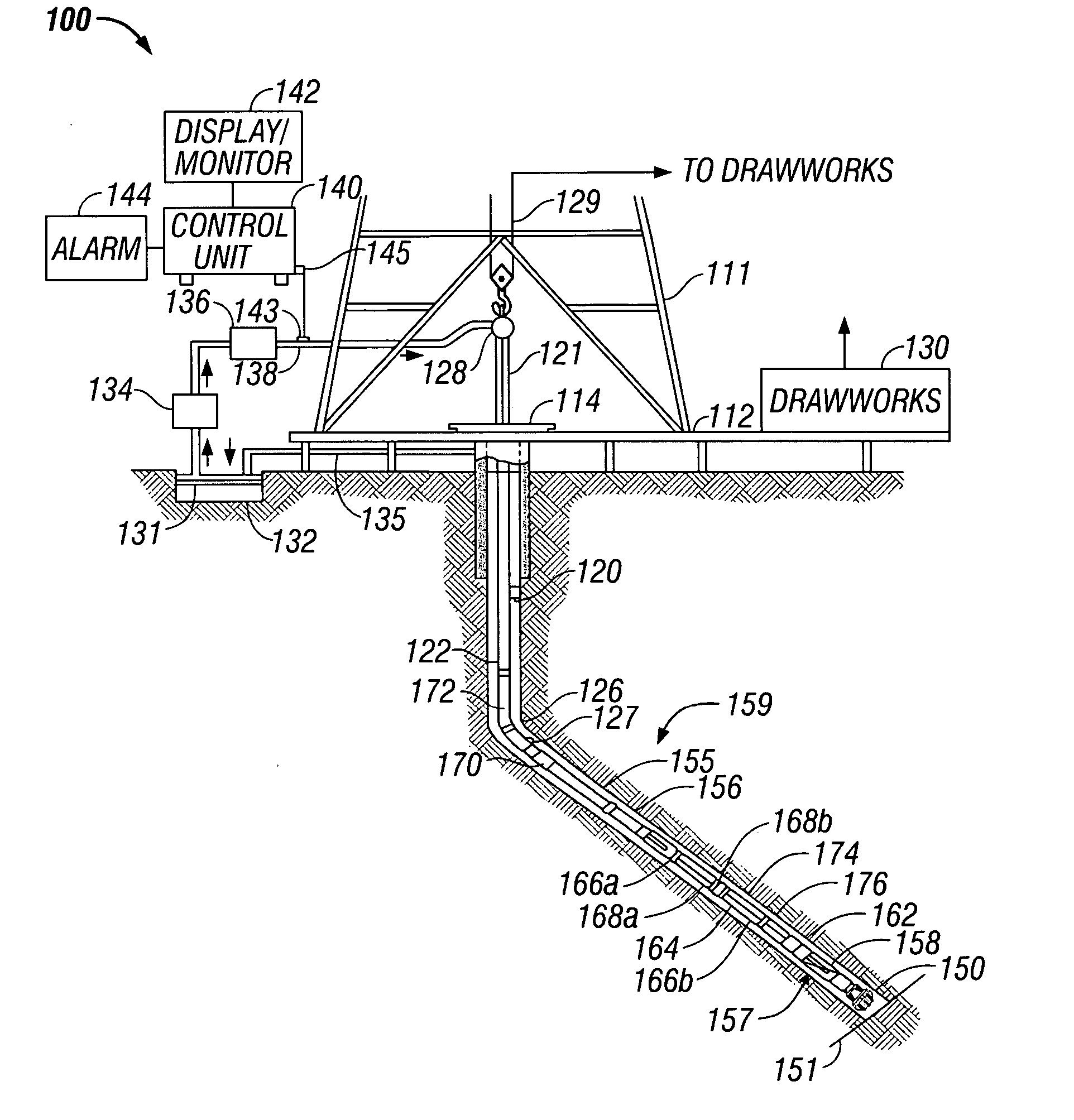
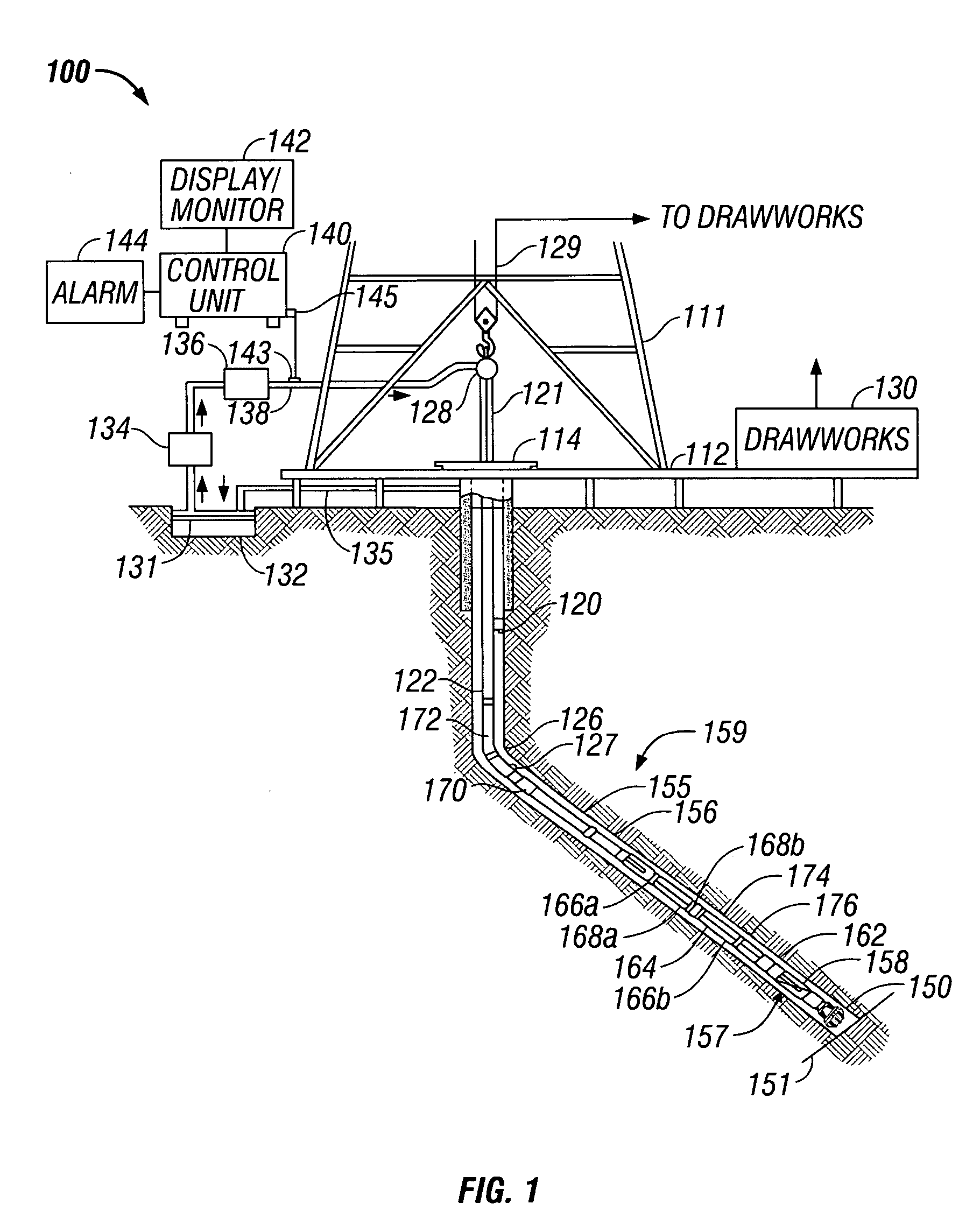
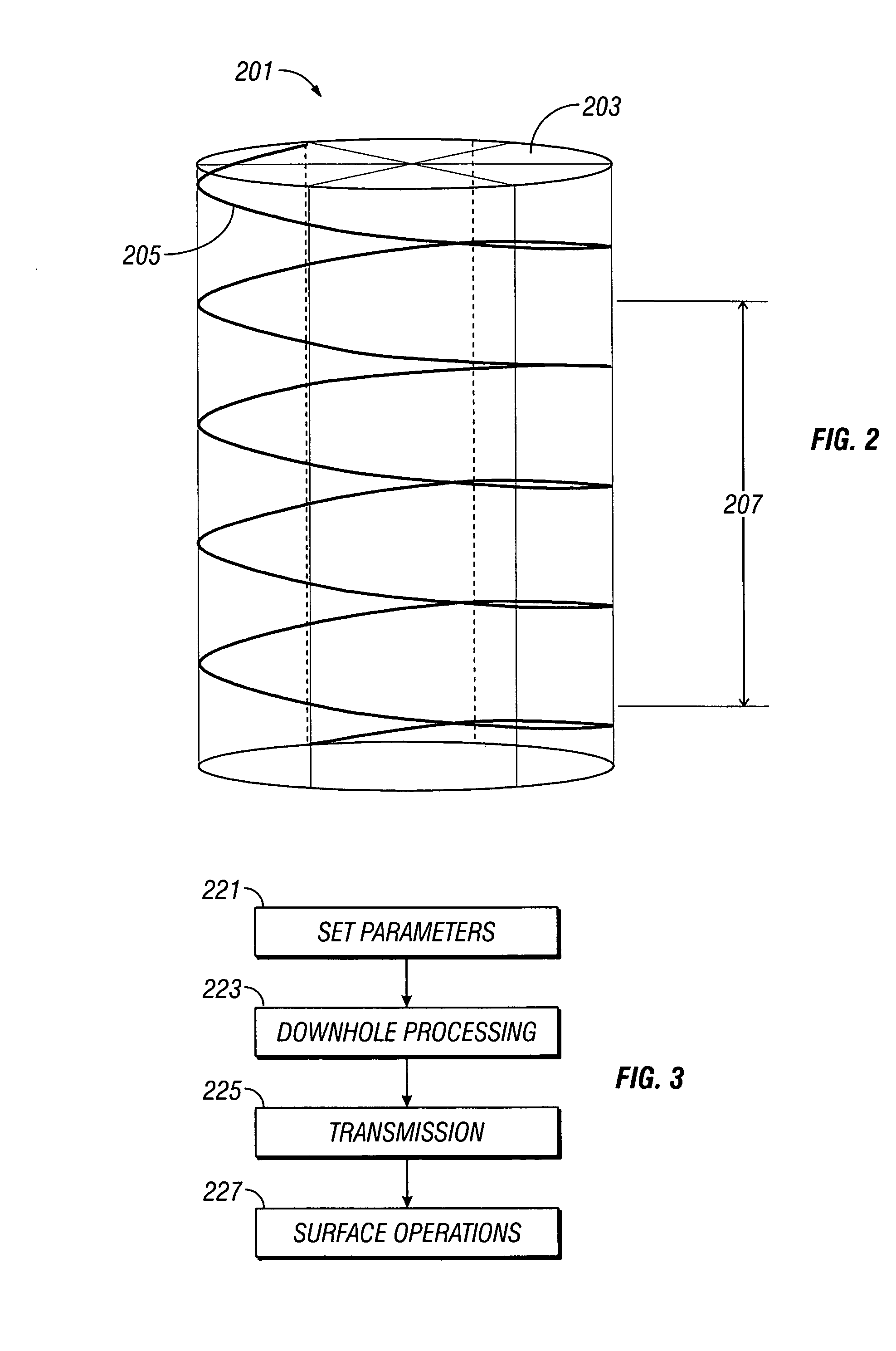
Real-time imaging while drilling
ActiveUS20070112521A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyAtmospheric sciencesFormation evaluation
Measurements made by a formation evaluation sensor downhole are processed to produce an image and a bitstream characterizing the image is transmitted uphole. The parameters used in the downhole processing are dynamically alterable.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
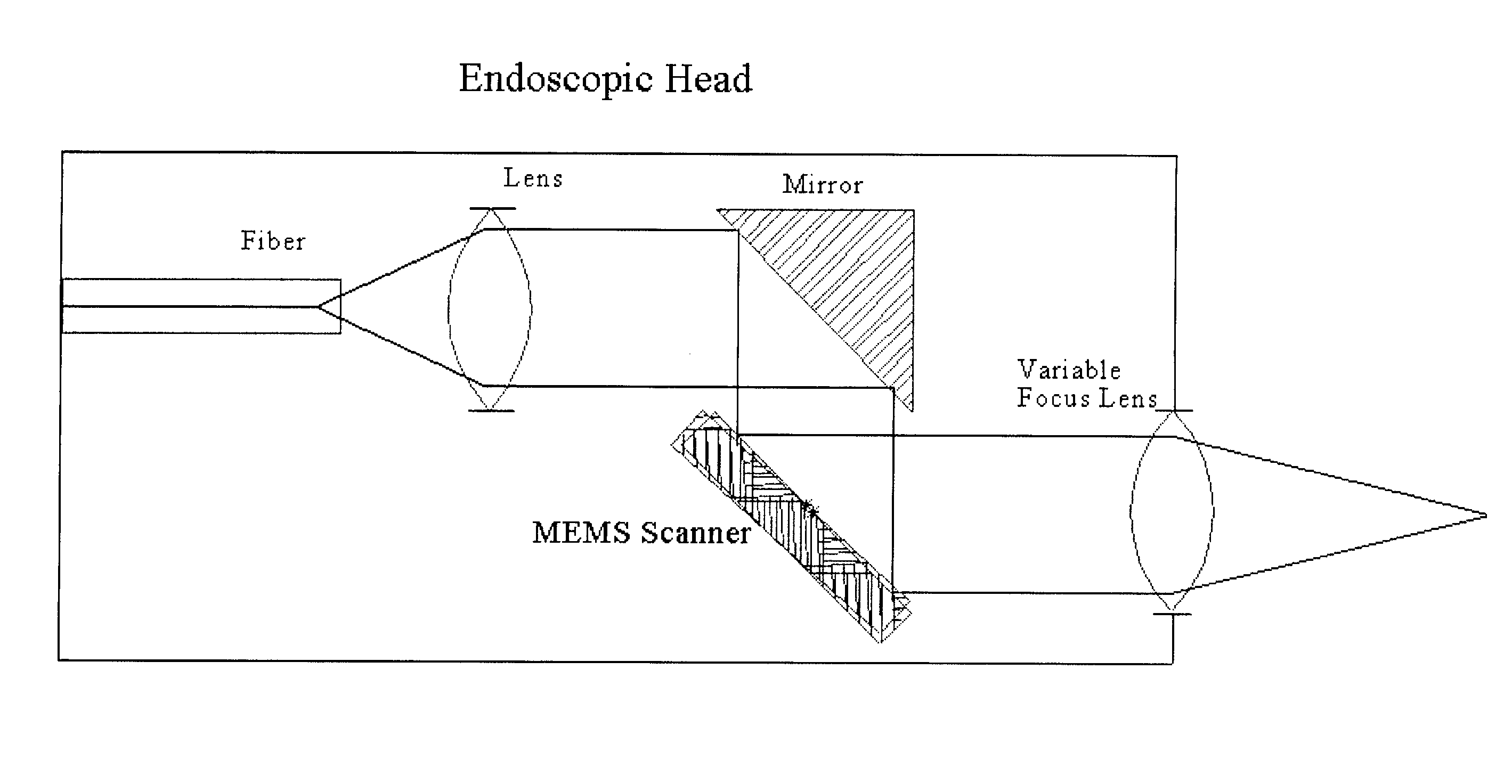
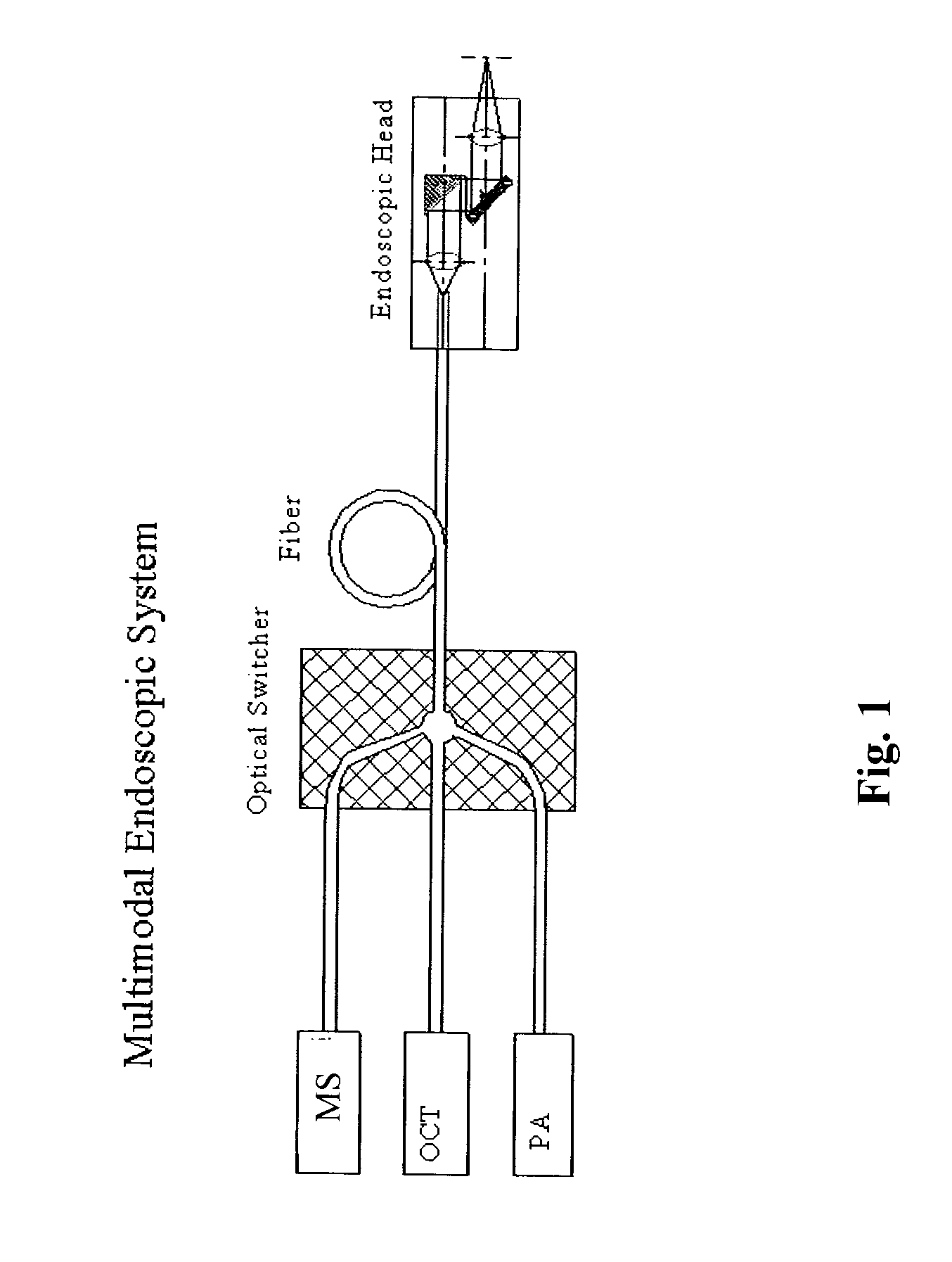
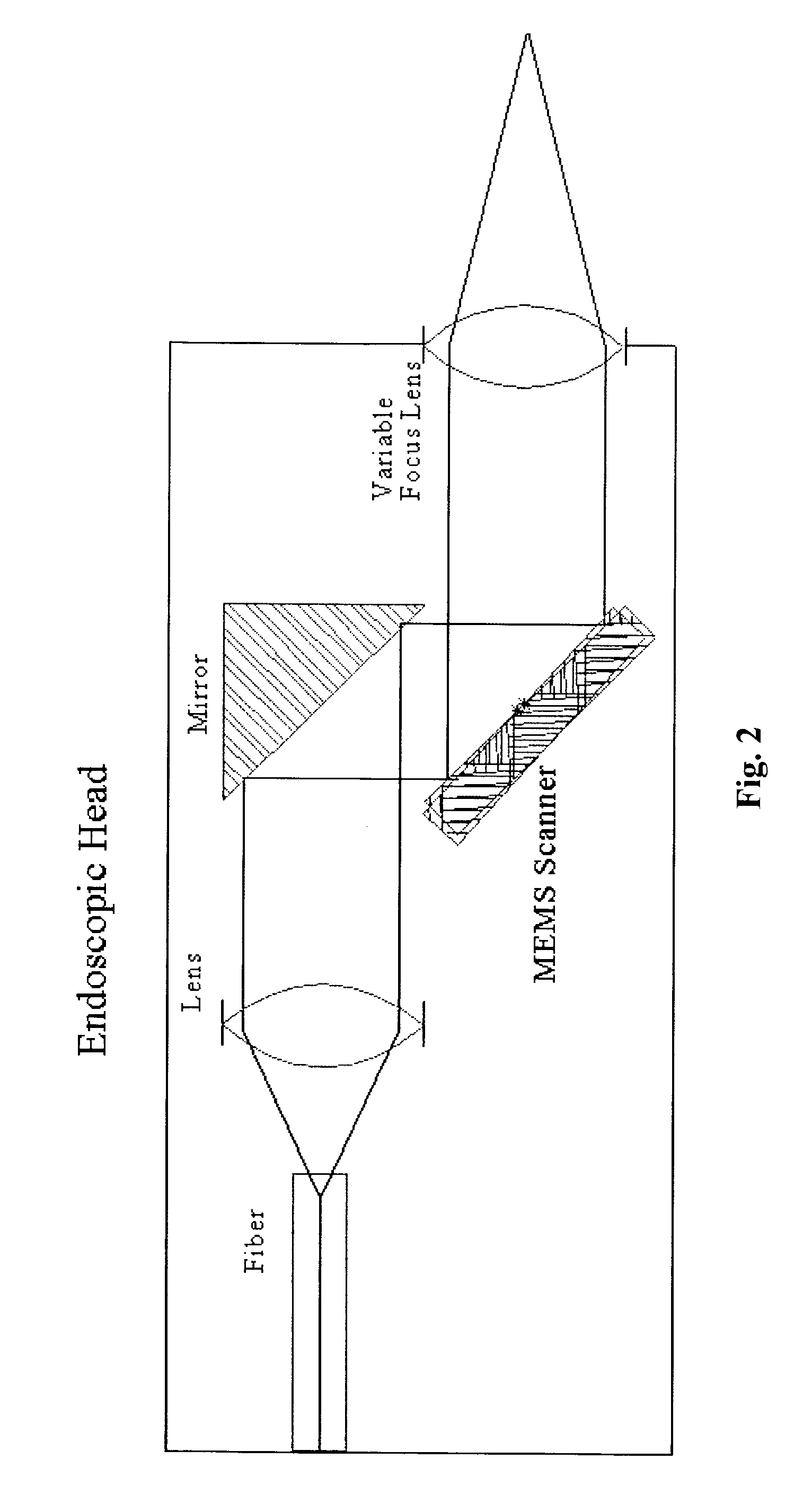
Multimodal depth-resolving endoscope
InactiveUS20110282192A1High rateDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndoscopesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityBeam scanning
A fiber-optic multimodal multi-spectral (MS), Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), photoacoustic (PA) endoscope with beam scanning by a two-dimensional Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) scanner present in the endoscopic head, combined in a synergetic way in a single endoscopic system. The PA, OCT and MS light sources are coupled to the endoscopic head through an optical switcher. Using a single optical endoscopic head and an electro-optical switch the endoscope of the invention is capable of sequential or parallel MS, OCT and PA imaging. The endoscope provides real-time imaging with a rate of 5 to 60 frames per second for each of the three imaging modalities.
Owner:AXELROD NOEL +2
Method and Apparatus for Positioning a Medical Instrument
InactiveUS20090118724A1Accurate directionUltrasound therapySurgical needlesSurgical departmentSaturation Biopsy
Presented are methods and apparatus for delivering a surgical instrument to a treatment site within the body of a subject, enabling accurate placement of surgical tools in areas not directly visible to a surgeon during a surgical procedure, while reducing or eliminating need for real-time imaging modalities to guide placement of those surgical tools. A treatment tool is guided to a treatment site by placing a guiding element at a reference site within a body of a subject, the reference site having a known spatial relationship to the treatment site, and utilizing a positioning tool to guide a treatment tool to a locus so positioned with respect to that guiding element that the spatial relationship between that guiding element and that locus is substantially similar to the spatial relationship known to exist between the reference site and the treatment site, thereby positioning the treatment tool substantially at the treatment site. Methods and apparatus for focusing energy at a treatment site, methods and apparatus for treatment of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia, and methods and apparatus for performing a saturation biopsy of an organ are also presented.
Owner:UC CARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com