Patents
Literature
363 results about "Pulsed DC" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulsed DC (PDC) or pulsating direct current is a periodic current which changes in value but never changes direction. Some authors use the term pulsed DC to describe a signal consisting of one or more rectangular ("flat-topped"), rather than sinusoidal, pulses.
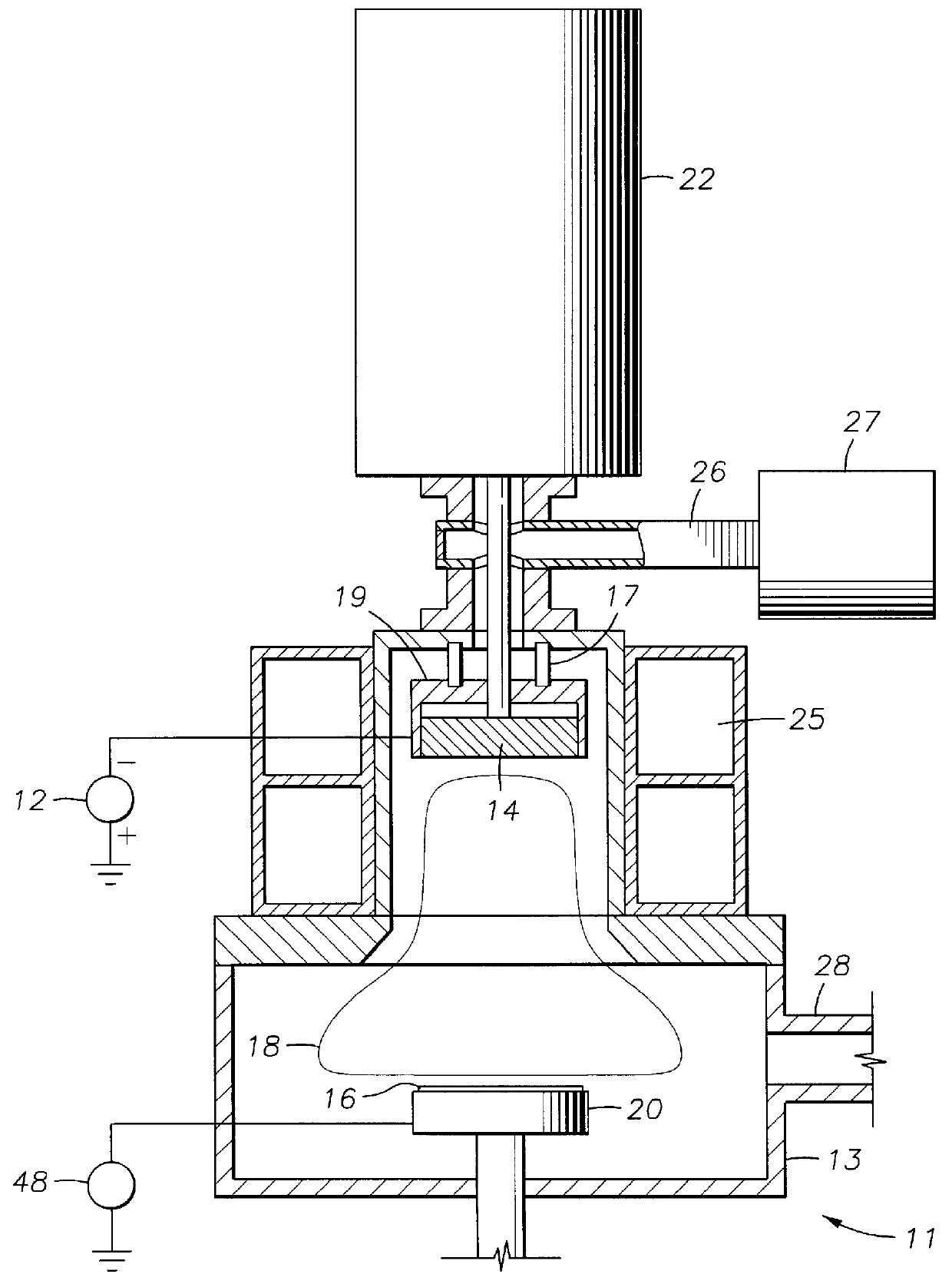
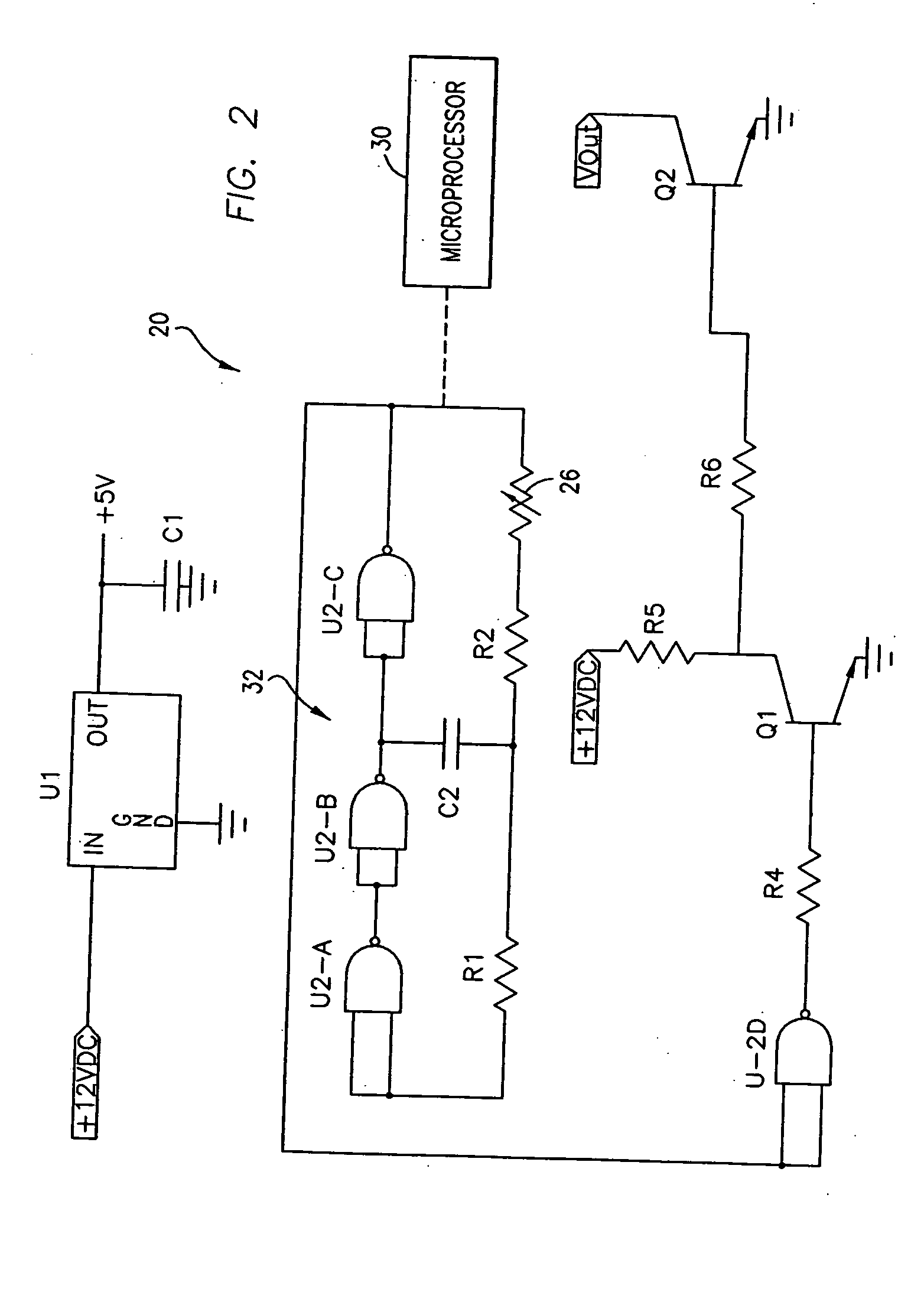
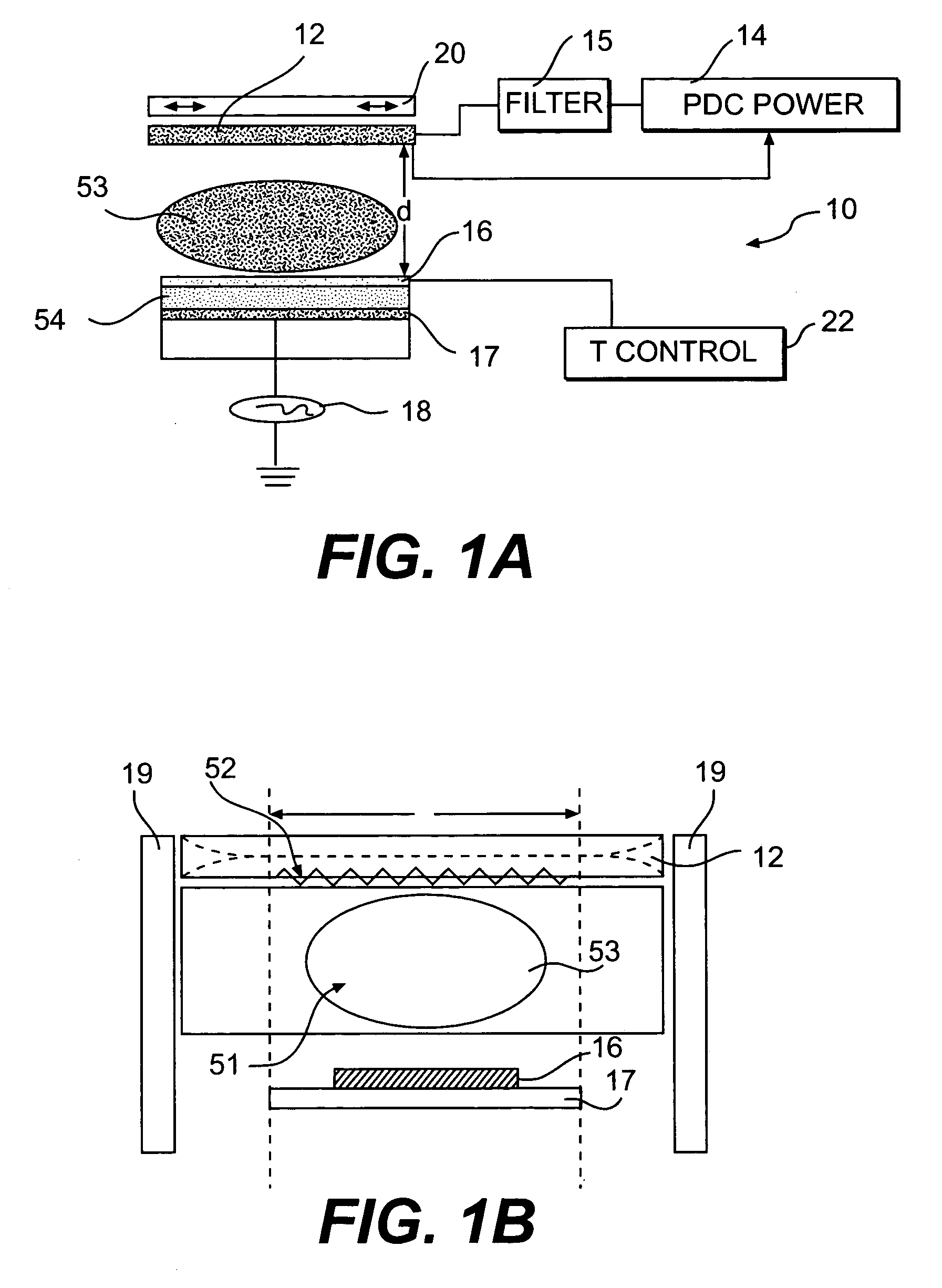
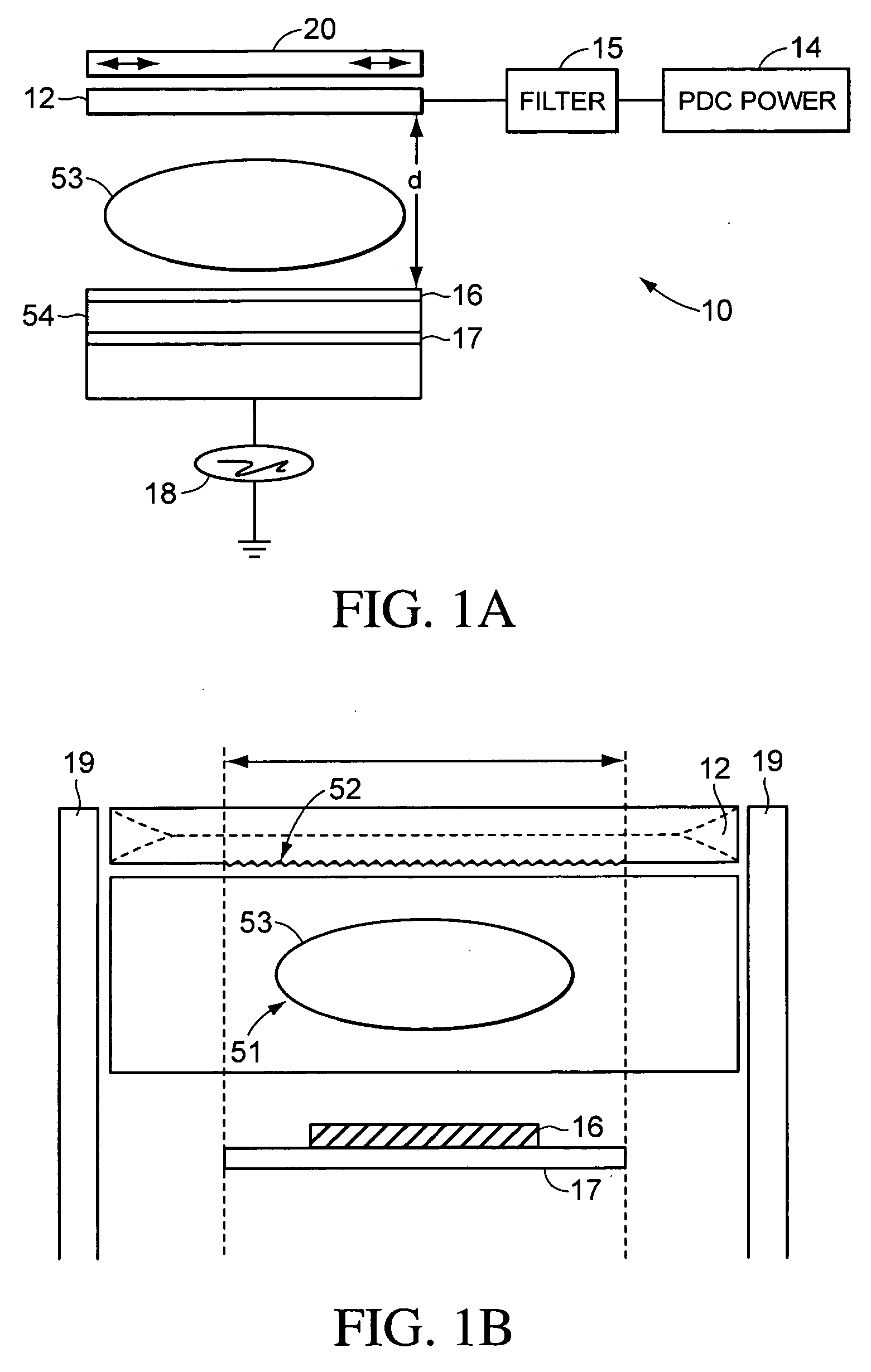
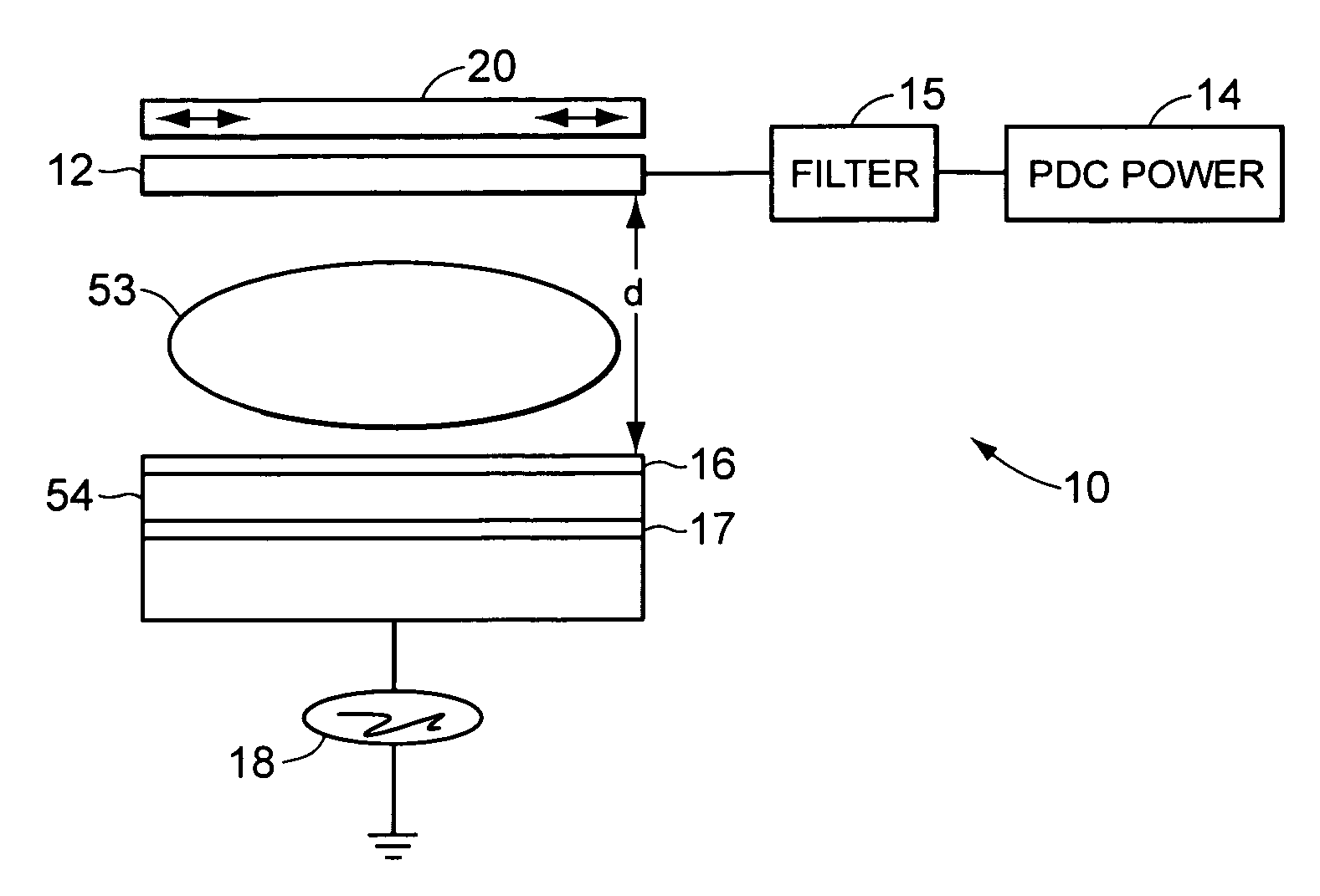
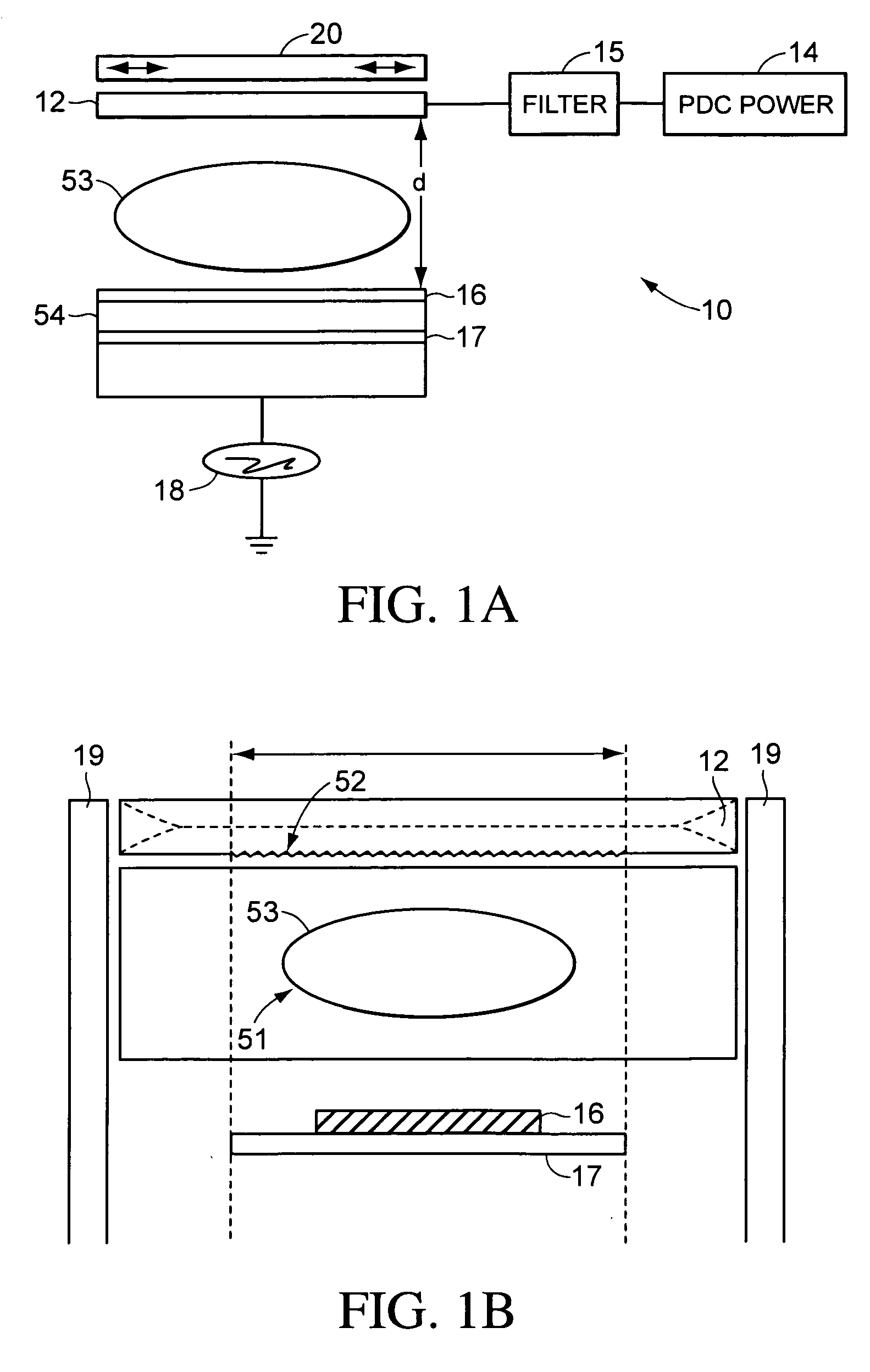
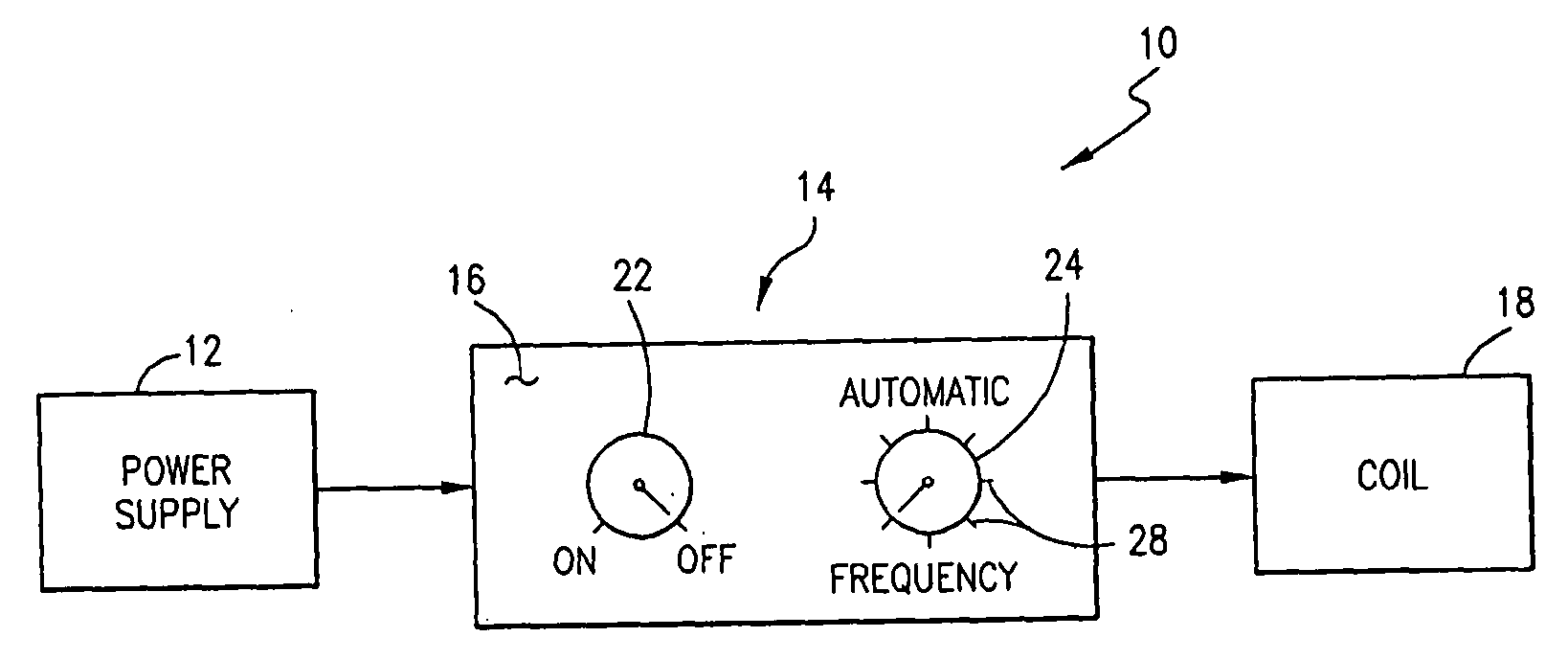
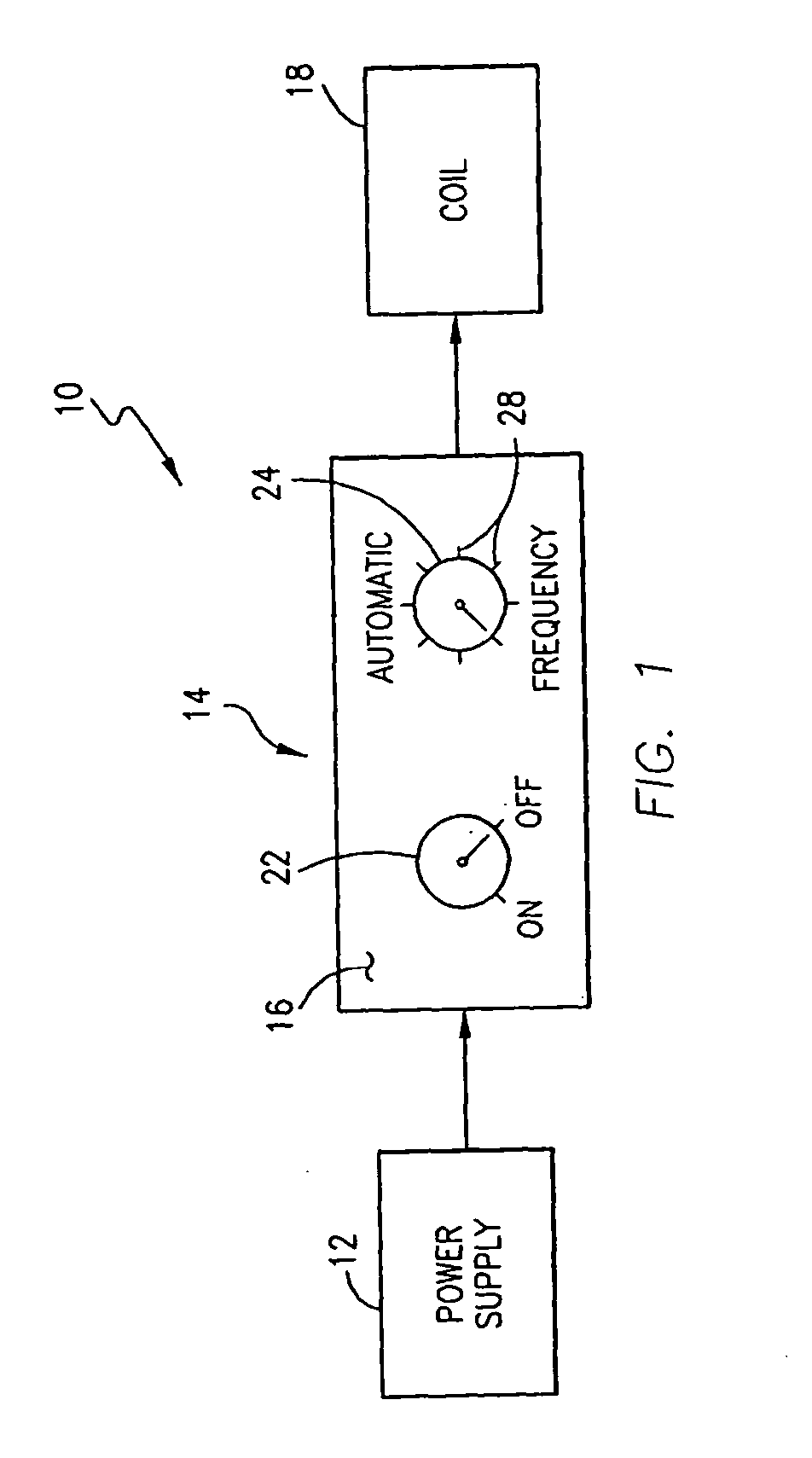
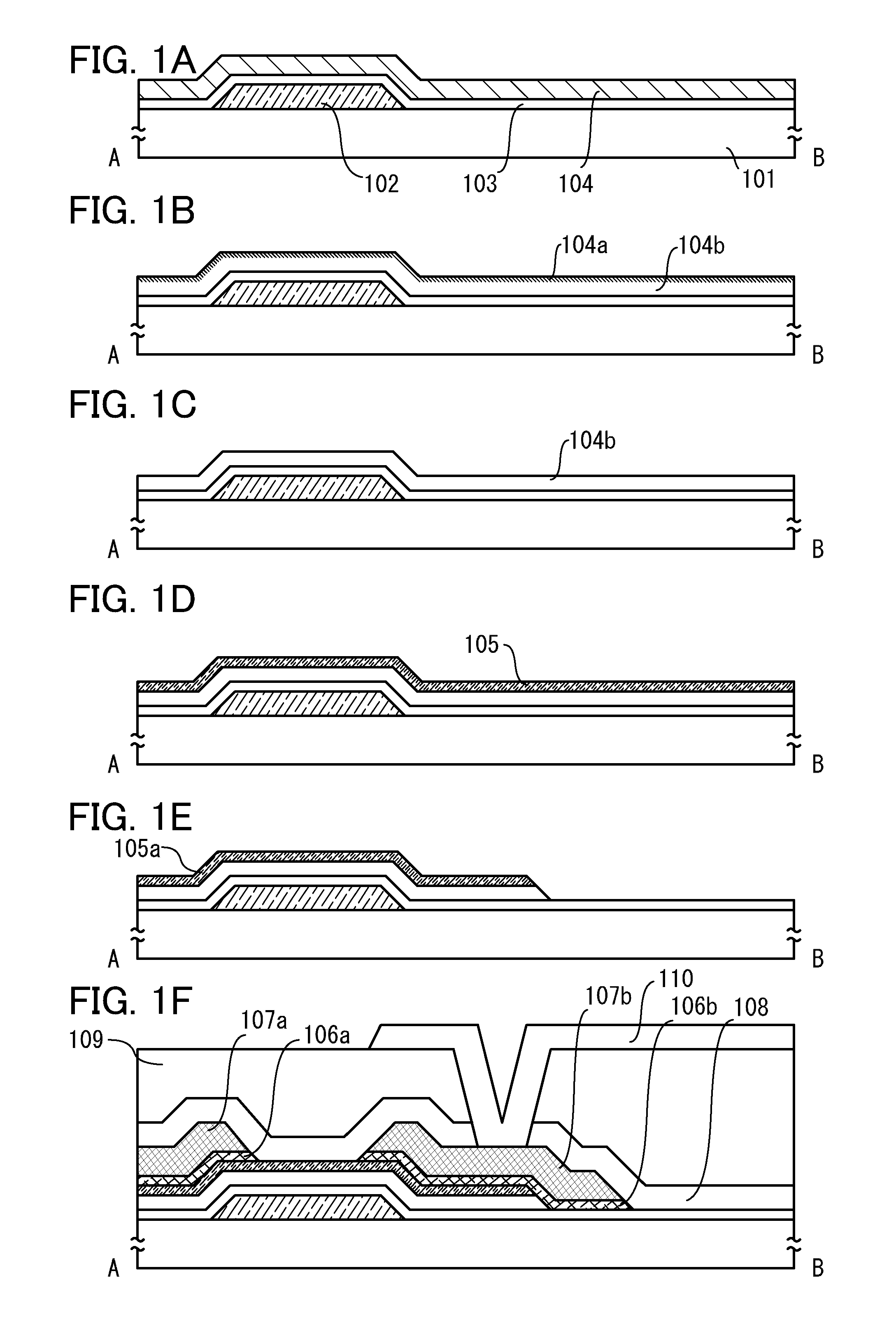
Use of pulsed-DC wafer bias for filling vias/trenches with metal in HDP physical vapor deposition
InactiveUS6051114AControl depositionPrevent openingCellsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceIon current
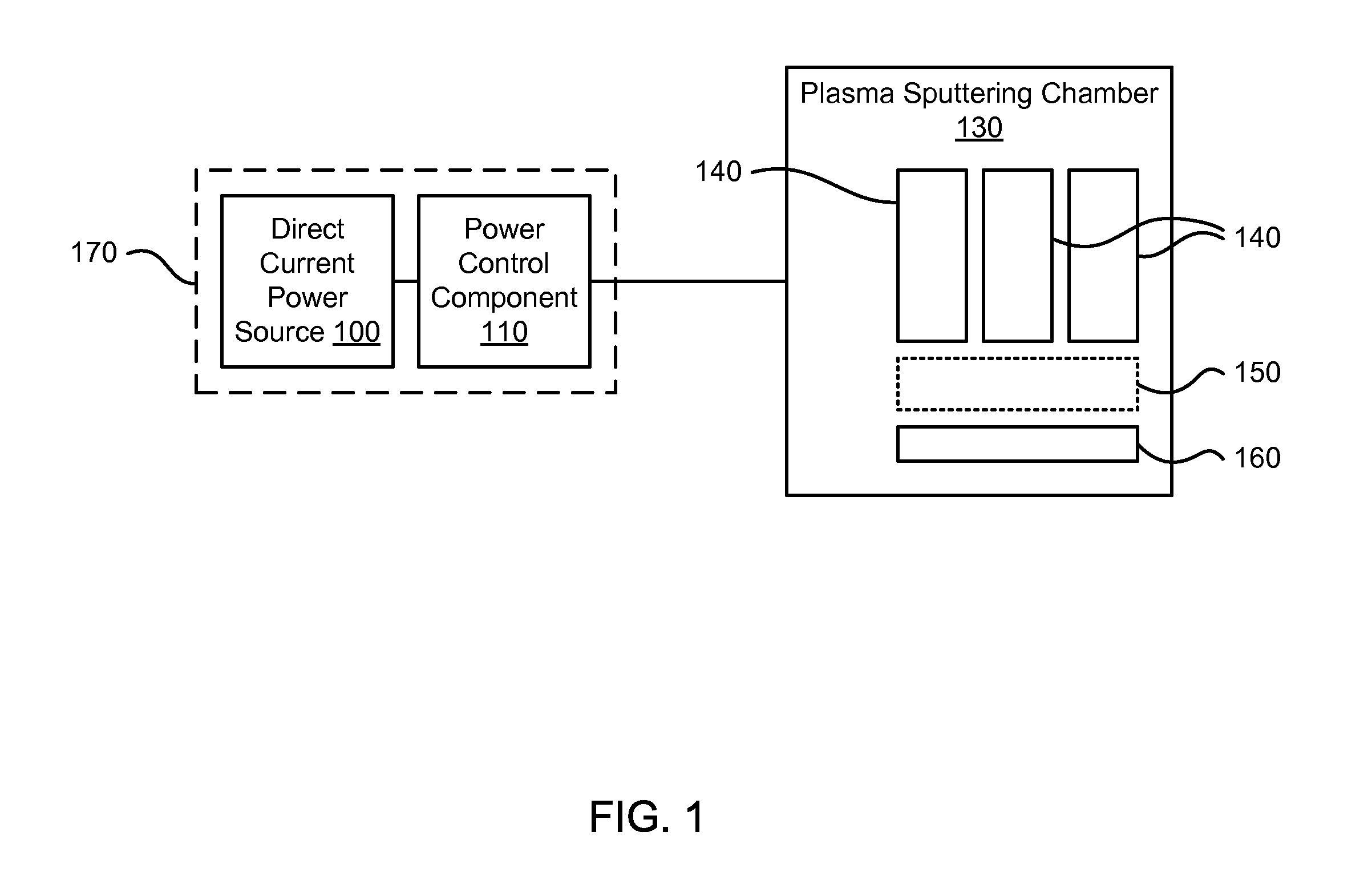
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for preferential PVD conductor fill in an integrated circuit structure. The present invention utilizes a high density plasma for sputter deposition of a conductive layer on a patterned substrate, and a pulsed DC power source capacitively coupled to the substrate to generate an ion current at the surface of the substrate. The ion current prevents sticking of the deposited material to the field areas of the patterned substrate, or etches deposited material from the field areas to eliminate crowning or cusping problems associated with deposition of a conductive material in a trench, hole or via formed on the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus for generating remote plasma
ActiveUS20100096367A1Eliminate chargeImprove film qualityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaPulsed DC
Provided is an apparatus for generating remote plasma, which can improve thin-film quality by preventing an arc at a bias electrode. The apparatus includes a radio frequency (RF) electrode installed inside an upper portion of a chamber, a bias electrode installed apart from the RF electrode, and including a plurality of through holes through which plasma passes, wherein a bias power is supplied to the bias electrode, a plasma generating unit formed between the RF electrode and the bias electrode, wherein a plasma gas is supplied to the plasma generating unit, and a ground electrode installed under and spaced apart from the bias electrode, and including plasma through holes corresponding to the through holes of the bias electrode, wherein a pulsed DC bias of a second voltage level, which has a first voltage level periodically, is applied to the bias electrode.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for the treatment of physical and mental disorders with low frequency, low flux density magnetic fields
ActiveUS20050182287A1Limited extentTreatment safetyElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMicrocontrollerPulsed DC
A method and apparatus for generating electromagnetic fields for healing. A device preferably includes a microcontroller and associated memory, a wire coil in electrical communication with a driving circuit that is controlled by the microcontroller in accordance with a program stored in the associated memory, wherein the driving circuit is effective to produce a pulsed DC output having a frequency in the range of about 0-45 Hz, more preferably in the range of 0.5-14.1 Hz and most preferably around 9.6 Hz. A user interface is provided for selecting one of a plurality of modes of operation and a port (e.g., a USB port) is provided to allow the program stored in the associated memory to be modified by way of a computer, memory card or the Internet. In another embodiment, the apparatus takes the form of a medallion that can be worn around a user's neck or strategically placed on a user's body or embedded in other user hardware such as a combat or racing helmet.
Owner:BECKER PAUL F
Dielectric barrier layer films
InactiveUS20050006768A1Improve performanceImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceGas phase
In accordance with the present invention, a dielectric barrier layer is presented. A barrier layer according to the present invention includes a densified amorphous dielectric layer deposited on a substrate by pulsed-DC, substrate biased physical vapor deposition, wherein the densified amorphous dielectric layer is a barrier layer. A method of forming a barrier layer according to the present inventions includes providing a substrate and depositing a highly densified, amorphous, dielectric material over the substrate in a pulsed-dc, biased, wide target physical vapor deposition process. Further, the process can include performing a soft-metal breath treatment on the substrate. Such barrier layers can be utilized as electrical layers, optical layers, immunological layers, or tribological layers.
Owner:DEMARAY
Plasma generator pulsed direct current supply in a bridge configuration
InactiveUS6222321B1Easy to controlIncrease depositionCellsElectric discharge tubesDc currentPulsed DC
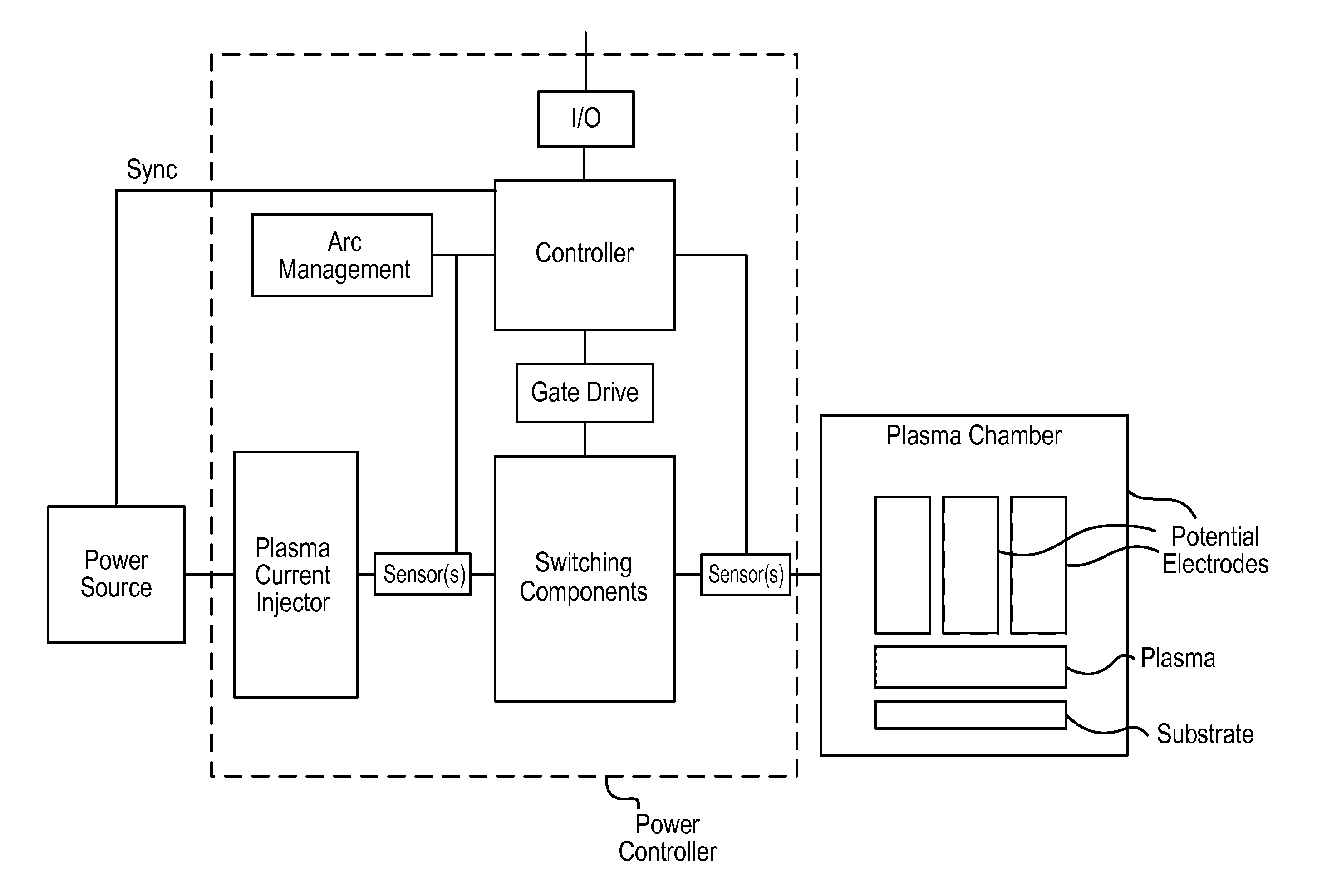
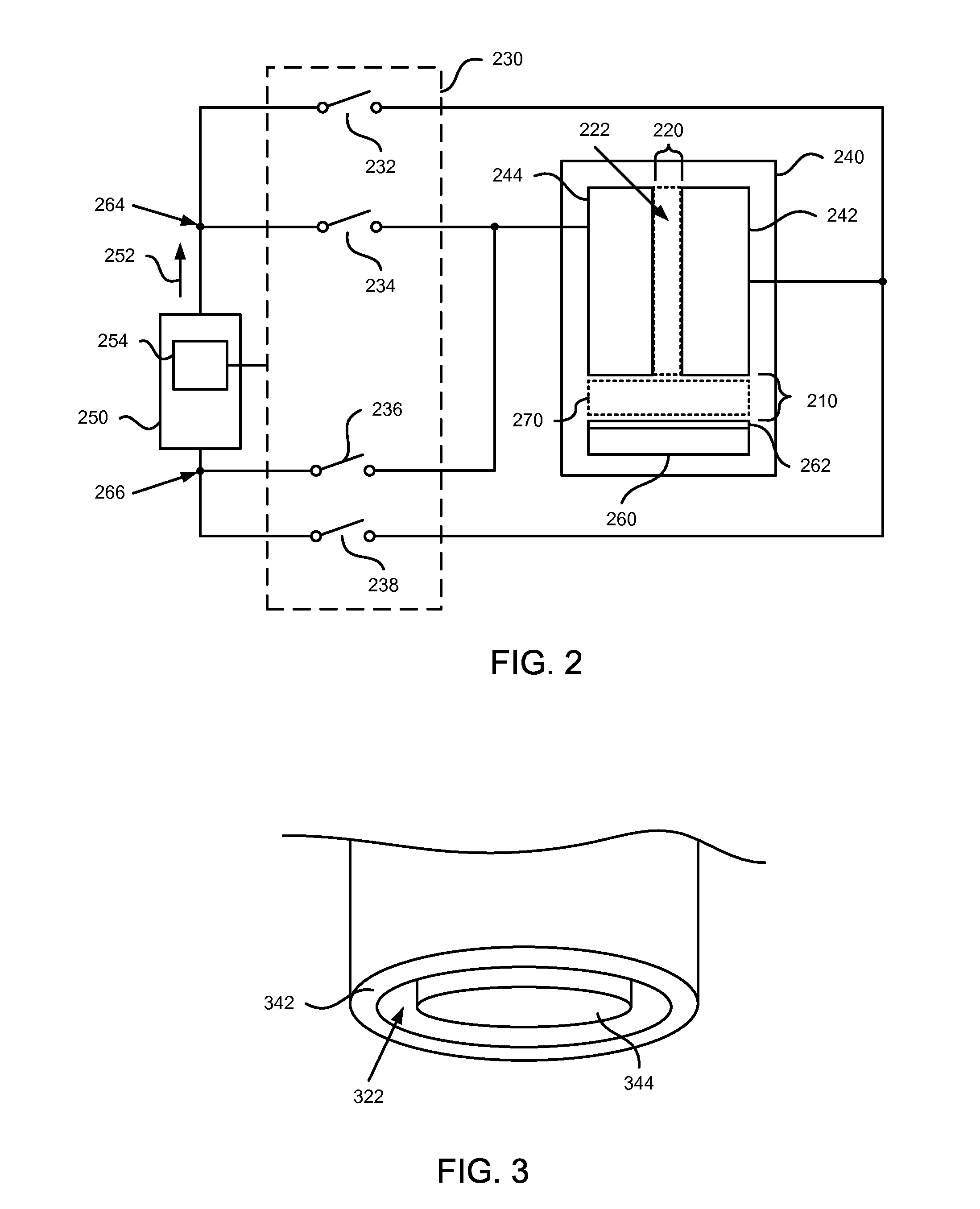
Current controlled power sources are disclosed that are capable of generating currents in low resistance, high temperature plasmas that are regulated to prevent the generation of excessive currents in the plasma. Current reversing switches are provided that control the flow of a direct current in a plasma chamber between various electrodes. Multiple power sources are provided in association with shunt switches for delivering a plurality of sources of direct current in various directions between electrodes in a plasma chamber. Inductive impedance can be provided in switch paths to cause a source of direct current to flow through a plasma chamber in various directions between electrodes.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Arrangement for generating extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation based on a gas discharge
InactiveUS6894298B2Stable generationProlong lifeOptical radiation measurementElectric lighting sourcesHigh energyPulsed DC
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for generating extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation, i.e., radiation of high-energy photons in the wavelength range from 11 to 14 nm, based on a gas discharge. The object of the invention, to find a novel possibility for generating EUV radiation in which an extended life of the system is achieved with stable generation of a dense, hot plasma column, is met according to the invention in that a preionization discharge is ignited between two parallel disk-shaped flat electrodes prior to the main discharge by a surface discharge along the superficies surface of a cylindrical insulator with a plasma column generated through the gas discharge with pulsed direct voltage, which preionization discharge carries out an ionization of the working gas in the discharge chamber by means of fast charged particles. The preionization discharge is triggered within a first electrode housing and the main discharge takes place between a narrowed output of the first electrode housing and a part of the second electrode housing close to the outlet opening of the discharge chamber. The plasma develops in a part of the second electrode housing covered by a tubular insulator and, as a result of the current-induced magnetic field, contracts to form a dense, hot plasma column, one end of which is located in the vicinity of the outlet opening of the second electrode housing.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Apparatus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS6441554B1Reduce discharge voltageReduce operating and installment cost and electricity consumptionElectric discharge tubesWater treatment compoundsDielectricElectrical conductor
Owner:SE PLASMA
Dielectric barrier layer films
InactiveUS20060071592A1Improve performanceImprove uniformityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesElectrical resistance and conductancePulsed DC
In accordance with the present invention, a dielectric barrier layer is presented. A barrier layer according to the present invention includes a densified amorphous dielectric layer deposited on a substrate by pulsed-DC, substrate biased physical vapor deposition, wherein the densified amorphous dielectric layer is a barrier layer. A method of forming a barrier layer according to the present inventions includes providing a substrate and depositing a highly densified, amorphous, dielectric material over the substrate in a pulsed-dc, biased, wide target physical vapor deposition process. Further, the process can include performing a soft-metal breath treatment on the substrate. Such barrier layers can be utilized as electrical layers, optical layers, immunological layers, or tribological layers.
Owner:DEMARAY
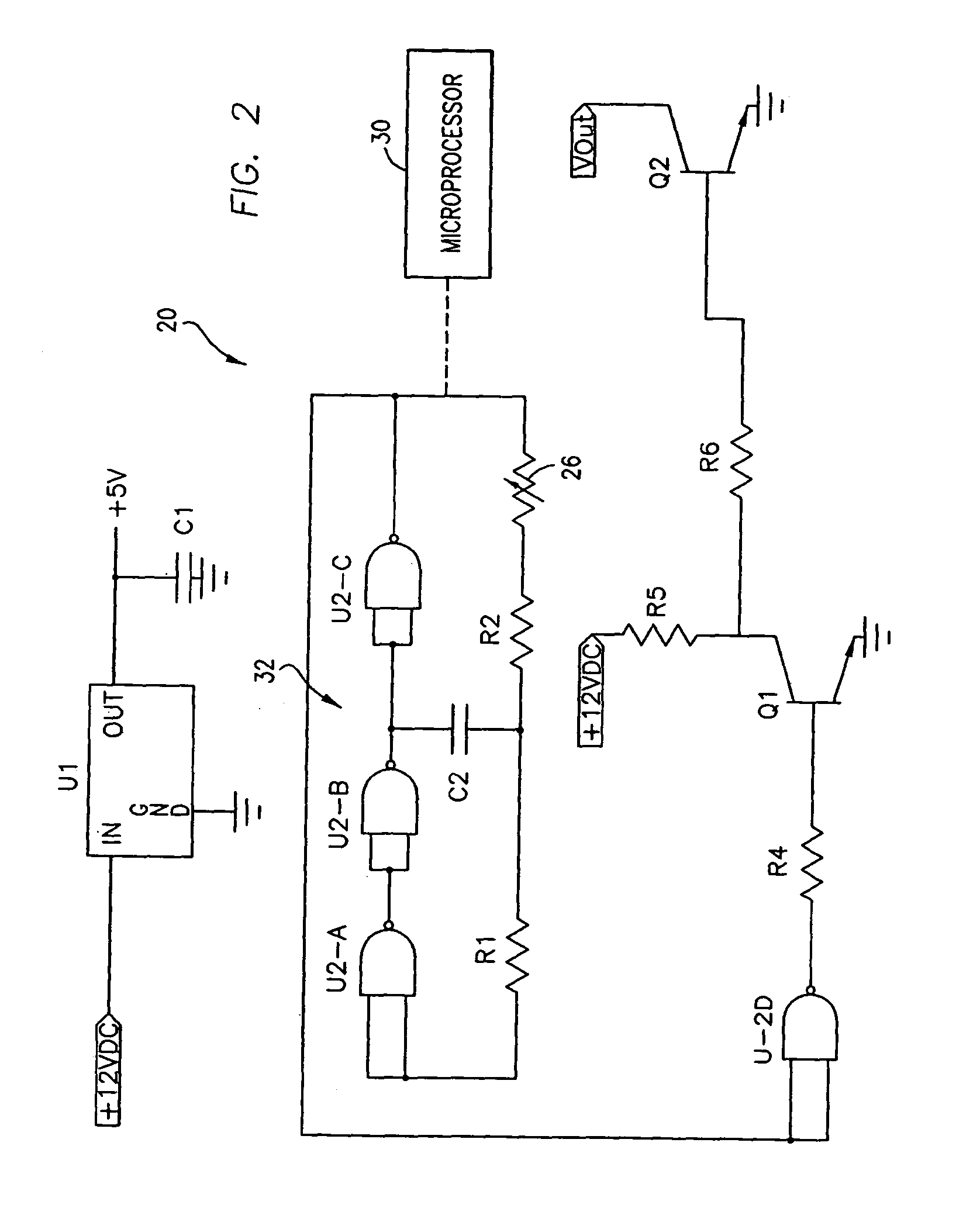
High peak power plasma pulsed supply with arc handling
InactiveUS6808607B2Efficient handling capabilityLimit currentCellsElectric discharge tubesVoltage pulseHigh peak
There is provided by this invention novel magnetron sputtering apparatus that is generally comprised of a pulsed dc power supply capable of delivering peak powers of 0.1 megaWatts to several megaWatts with a peak power density greater than 1 kW / cm2. The power supply has a pulsing circuit comprised of an energy storage capacitor and serially connected inductor with a switching means for disconnecting the pulsing circuit from the plasma and recycling the inductor energy back to the energy storage capacitor at the detection of an arc condition. The energy storage capacitor and the serially connected inductor provide an impedance match to the plasma, limits the current rate of rise and peak magnitude in the event of an arc, and shapes the voltage pulses to the plasma.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Energy conversion and storage films and devices by physical vapor deposition of titanium and titanium oxides and sub-oxides
High density oxide films are deposited by a pulsed-DC, biased, reactive sputtering process from a titanium containing target to form high quality titanium containing oxide films. A method of forming a titanium based layer or film according to the present invention includes depositing a layer of titanium containing oxide by pulsed-DC, biased reactive sputtering process on a substrate. In some embodiments, the layer is TiO2. In some embodiments, the layer is a sub-oxide of Titanium. In some embodiments, the layer is TixOy wherein x is between about 1 and about 4 and y is between about 1 and about 7. In some embodiments, the layer can be doped with one or more rare-earth ions. Such layers are useful in energy and charge storage, and energy conversion technologies.
Owner:DEMARAY
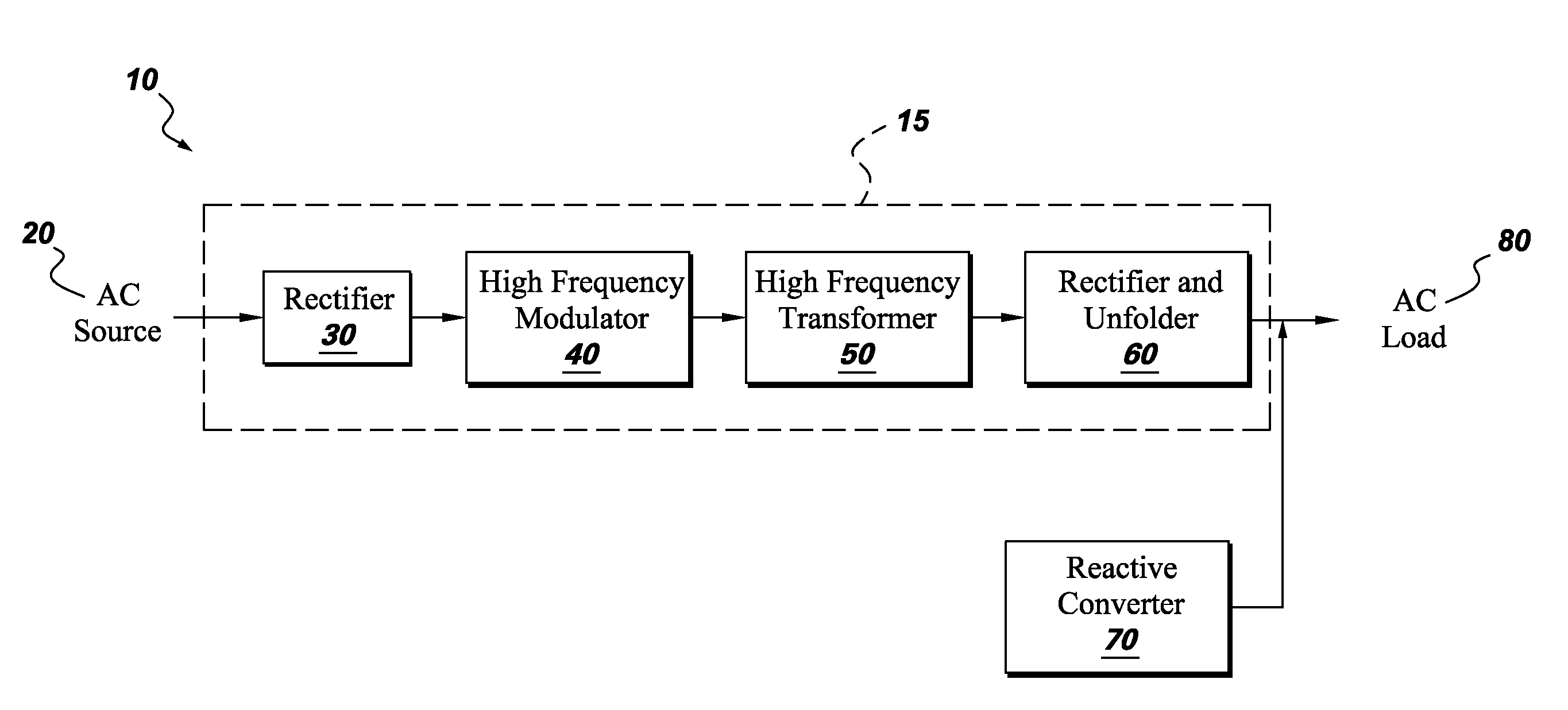
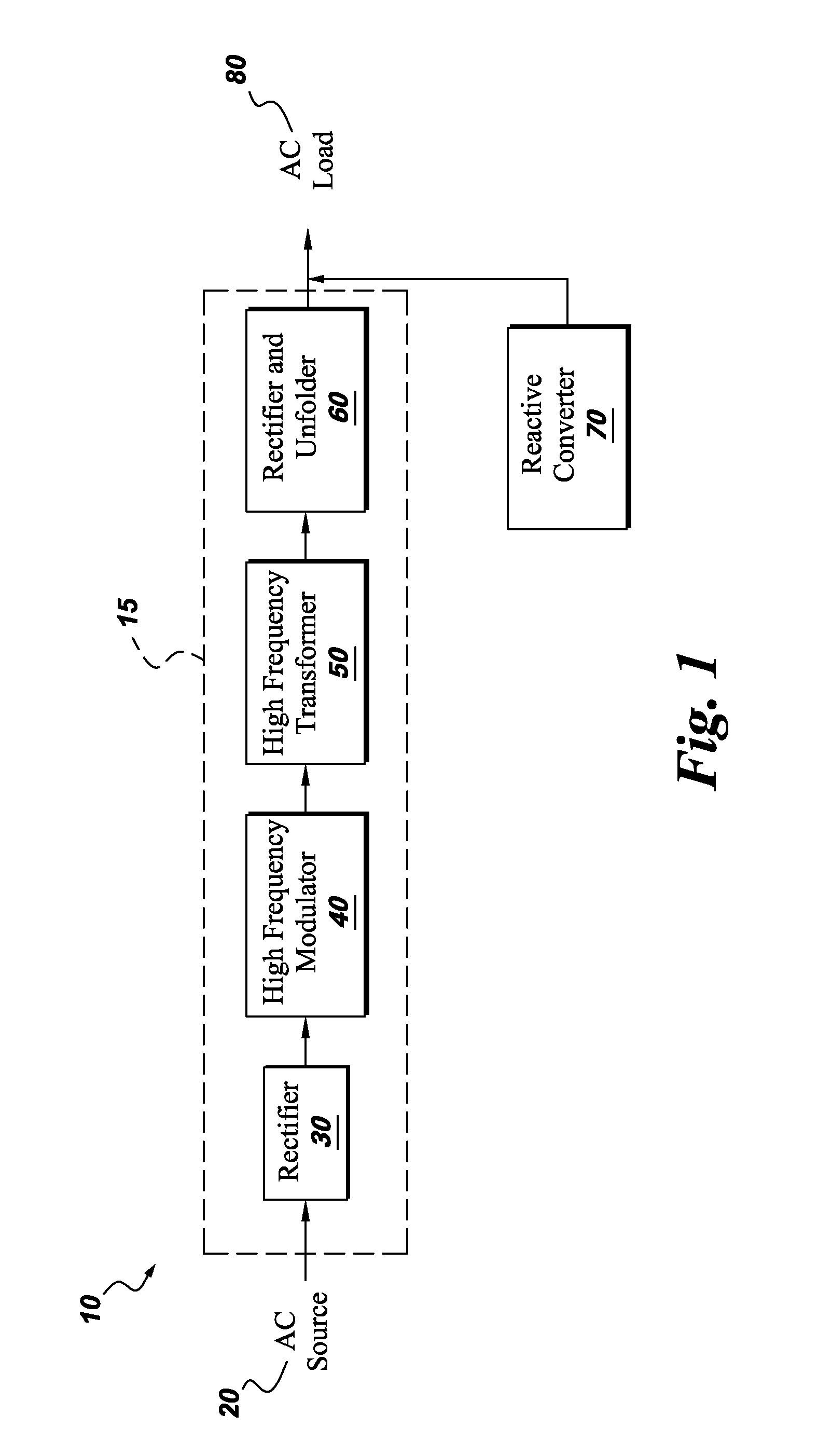
Ac-ac converter with high frequency link
An AC-AC Converter for an AC source which in one embodiment has a first rectifier section rectifying the AC source into a first pulsed DC link voltage signal and a high frequency modulating section coupled to the first pulsed DC link voltage signal and producing a high frequency AC voltage signal. A high frequency transformer is coupled to the high frequency AC voltage signal producing a transformed high frequency AC signal. There is a second rectifier section coupled to the transformed high frequency AC signal and producing a second pulsed DC voltage signal and an unfolder section coupled to the second pulsed DC voltage signal and producing an output AC signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
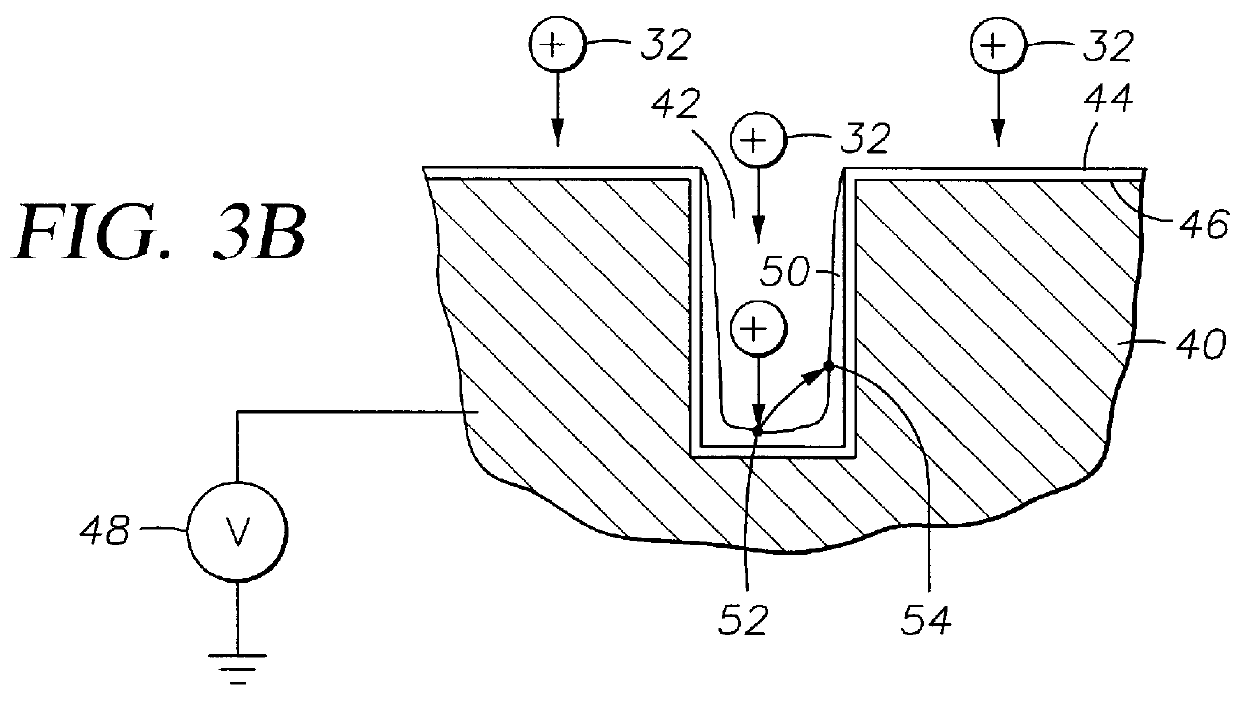
Biased pulse DC reactive sputtering of oxide films
Owner:DEMARAY
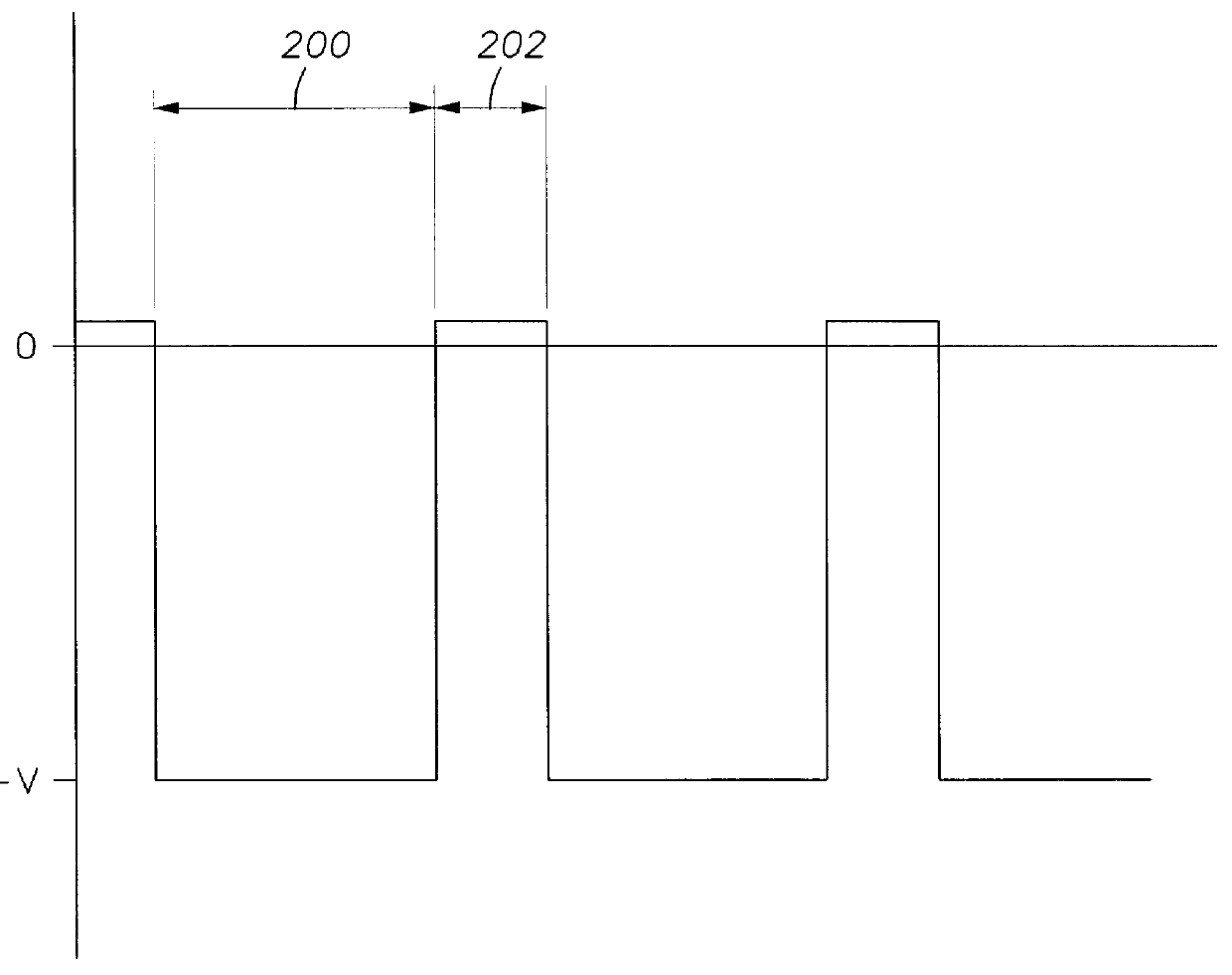
Methods and apparatus for applying periodic voltage using direct current
Methods and apparatus for applying pulsed DC power to a plasma processing chamber are disclosed. In some implementations, frequency of the applied power is varied to achieve desired processing effects such as deposition rate, arc rate, and film characteristics. In addition, a method and apparatus are disclosed that utilize a relatively high potential during a reverse-potential portion of a particular cycle to mitigate possible nodule formation on the target. The relative durations of the reverse-potential portion, a sputtering portion, and a recovery portion of the cycle are adjustable to effectuate desired processing effects.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
Biased pulse DC reactive sputtering of oxide films
A biased pulse DC reactor for sputtering of oxide films is presented. The biased pulse DC reactor couples pulsed DC at a particular frequency to the target through a filter which filters out the effects of a bias power applied to the substrate, protecting the pulsed DC power supply. Films deposited utilizing the reactor have controllable material properties such as the index of refraction. Optical components such as waveguide amplifiers and multiplexers can be fabricated using processes performed on a reactor according to the present inention.
Owner:DEMARAY
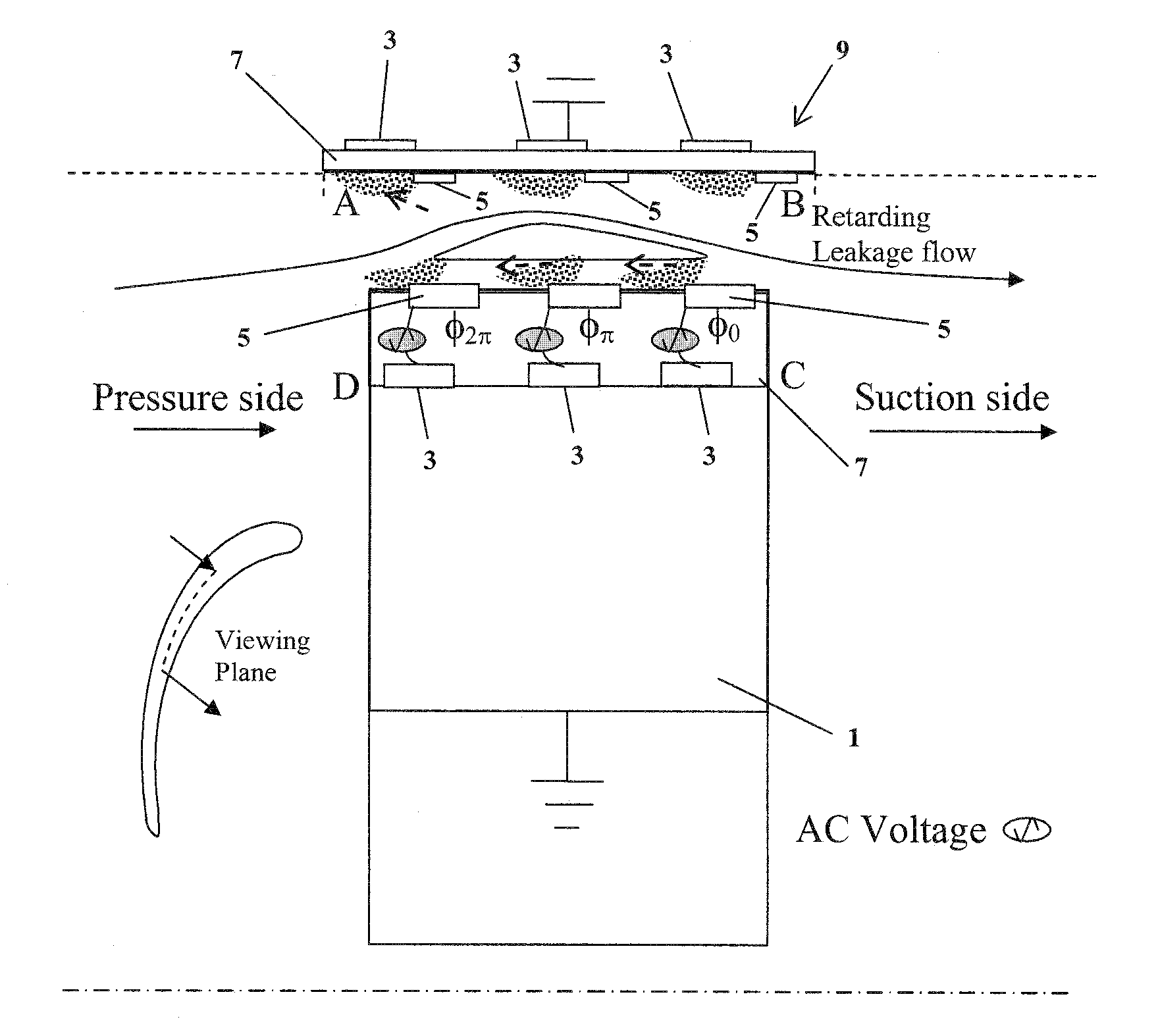
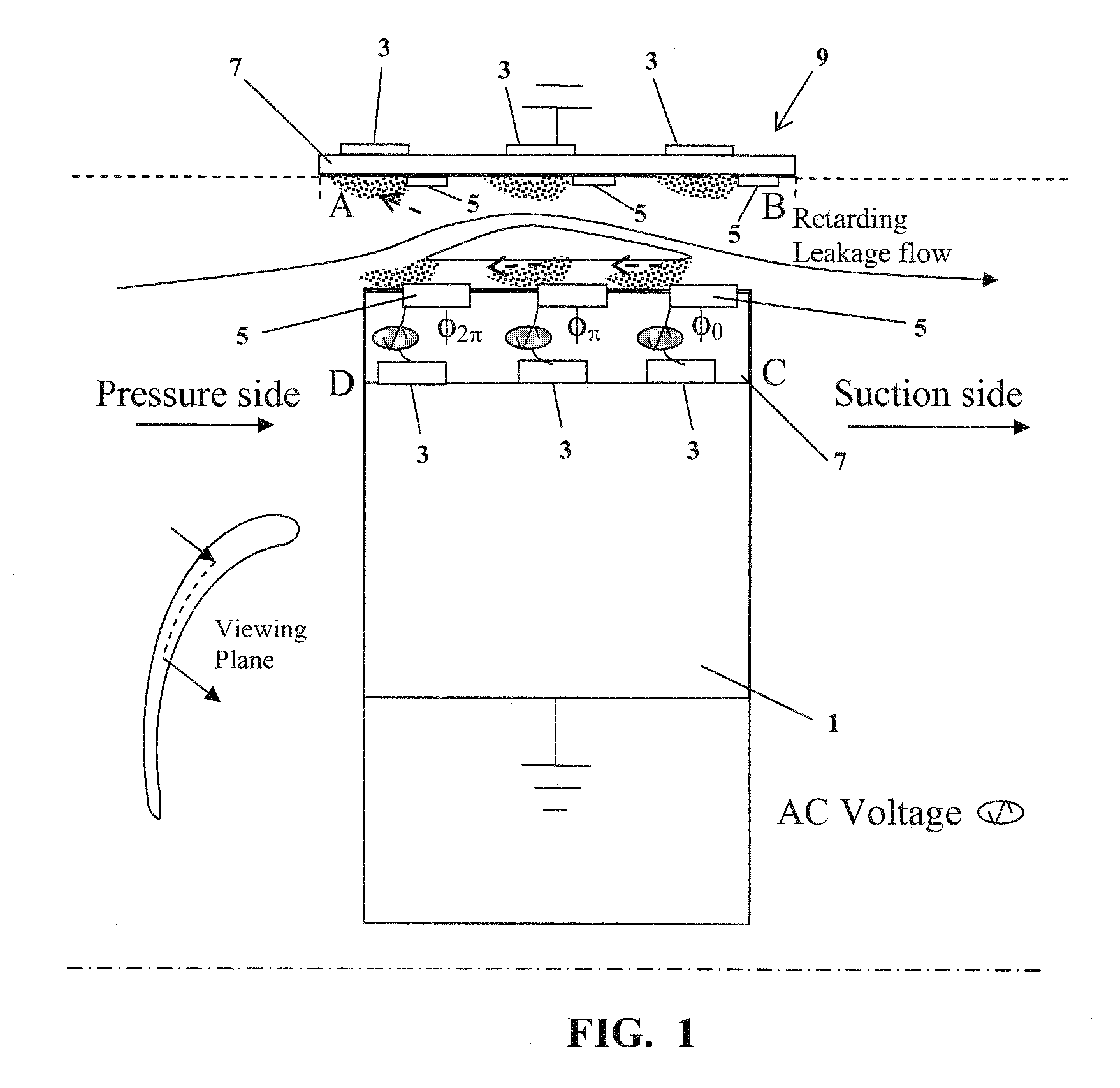
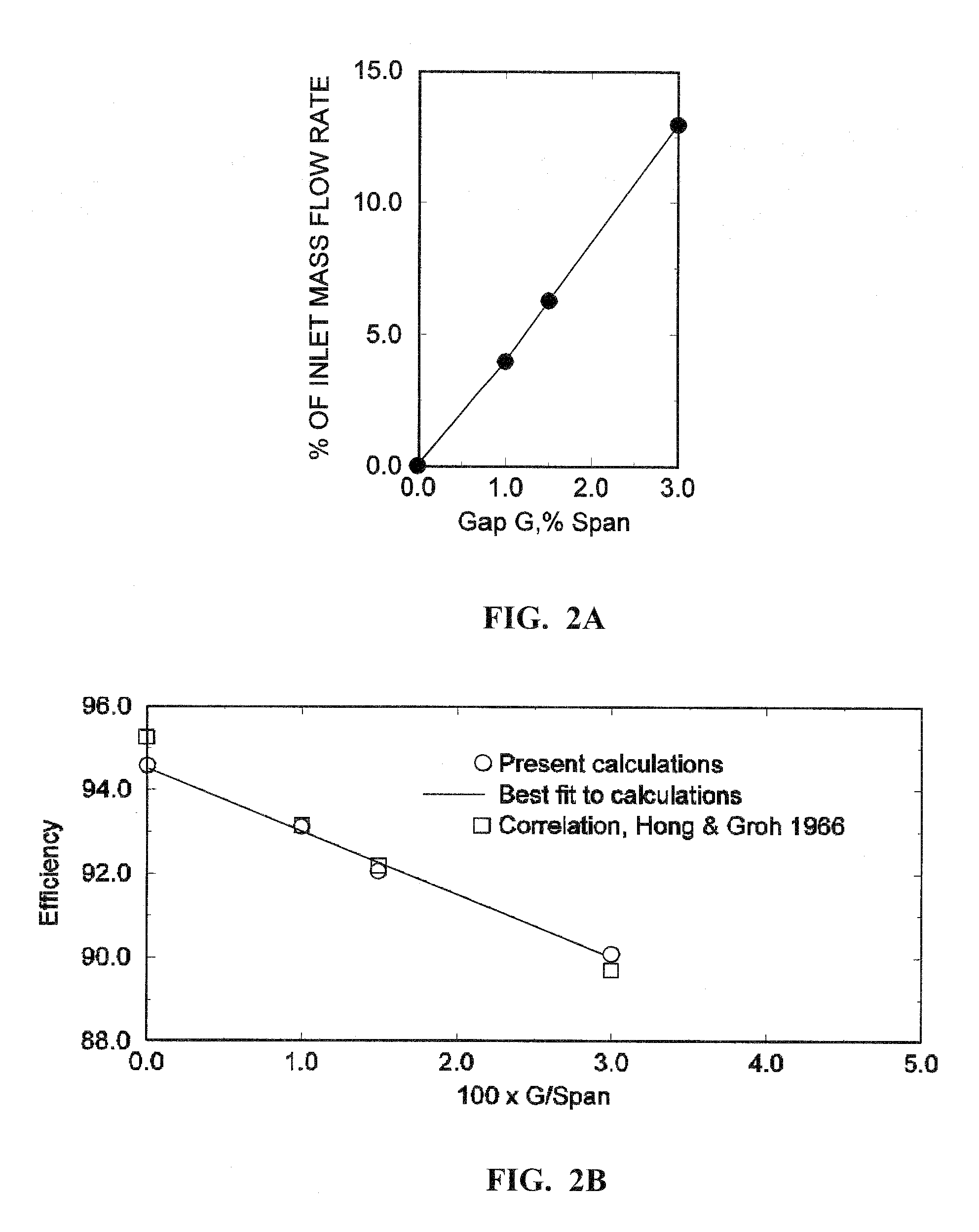
Electrodynamic Control of Blade Clearance Leakage Loss in Turbomachinery Applications
Electrodynamic control of fluid leakage loss is provided. Embodiments utilize electrohydrodynamic (EHD) principles to control and / or reduce leakage flow in turbomachinery. Electrodes can be used to provide a flow actuation mechanism inside the clearance gap for generating discharge. The electrodes can be positioned to have geometric asymmetry. Embodiments provide the electrodes on a turbine blade. The blade can have a DC power that can function as a square pulsed DC wave with the duty cycle equal to the blade passing frequency and the stator can be grounded. In an embodiment, the stator can have the actuator of the electrode-insulator assembly attached to the inside. In one embodiment, the actuators can be arranged just on the stator or casing. The phase and power supply to individual electrodes can be adapted as needed. In one embodiment, the phase can be lagged for accurate control of leakage flow. The control of the power supply to the electrodes can involve a closed control loop that monitors tip gap size.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Energy conversion and storage films and devices by physical vapor deposition of titanium and titanium oxides and sub-oxides
InactiveUS20040259305A1Vacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityRare earth ions
High density oxide films are deposited by a pulsed-DC, biased, reactive sputtering process from a titanium containing target to form high quality titanium containing oxide films. A method of forming a titanium based layer or film according to the present invention includes depositing a layer of titanium containing oxide by pulsed-DC, biased reactive sputtering process on a substrate. In some embodiments, the layer is TiO2. In some embodiments, the layer is a sub-oxide of Titanium. In some embodiments, the layer is TixOy wherein x is between about 1 and about 4 and y is between about 1 and about 7. In some embodiments, the layer can be doped with one or more rare-earth ions. Such layers are useful in energy and charge storage, and energy conversion technologies.
Owner:DEMARAY
Biased pulse DC reactive sputtering of oxide films
A biased pulse DC reactor for sputtering of oxide films is presented. The biased pulse DC reactor couples pulsed DC at a particular frequency to the target through a filter which filters out the effects of a bias power applied to the substrate, protecting the pulsed DC power supply. Films deposited utilizing the reactor have controllable material properties such as the index of refraction. Optical components such as waveguide amplifiers and multiplexers can be fabricated using processes performed on a reactor according to the present inention.
Owner:DEMARAY
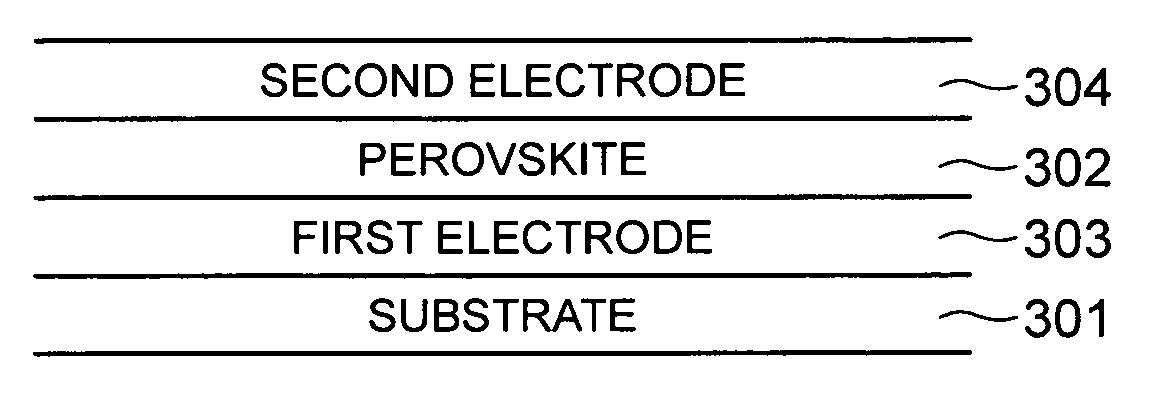
Deposition of perovskite and other compound ceramic films for dielectric applications
InactiveUS20070053139A1Increase capacitanceReduce the temperatureThin/thick film capacitorFixed capacitor dielectricHigh ratePulsed DC
In accordance with the present invention, deposition of perovskite material, for example barium strontium titanite (BST) film, by a pulsed-dc physical vapor deposition process or by an RF sputtering process is presented. Such a deposition can provide a high deposition rate deposition of a layer of perovskite. Some embodiments of the deposition address the need for high rate deposition of perovskite films, which can be utilized as a dielectric layer in capacitors, other energy storing devices and micro-electronic applications. Embodiments of the process according to the present invention can eliminate the high temperature (>700° C.) anneal step that is conventionally needed to crystallize the BST layer.
Owner:DEMARAY
Method for producing a grid structure, an optical element, an evanescence field sensor plate, microtitre plate and an optical communication engineering coupler as well as a device for monitoring a wavelength
InactiveUS6873764B2Improve accuracyLow effortCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGratingPulsed DC
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
Biased pulse DC reactive sputtering of oxide films
InactiveUS20050048802A1Electric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringWaveguide amplifier
A biased pulse DC reactor for sputtering of oxide films is presented. The biased pulse DC reactor couples pulsed DC at a particular frequency to the target through a filter which filters out the effects of a bias power applied to the substrate, protecting the pulsed DC power supply. Films deposited utilizing the reactor have controllable material properties such as the index of refraction. Optical components such as waveguide amplifiers and multiplexers can be fabricated using processes performed on a reactor according to the present inention.
Owner:DEMARAY
LED lighting array for a portable task light
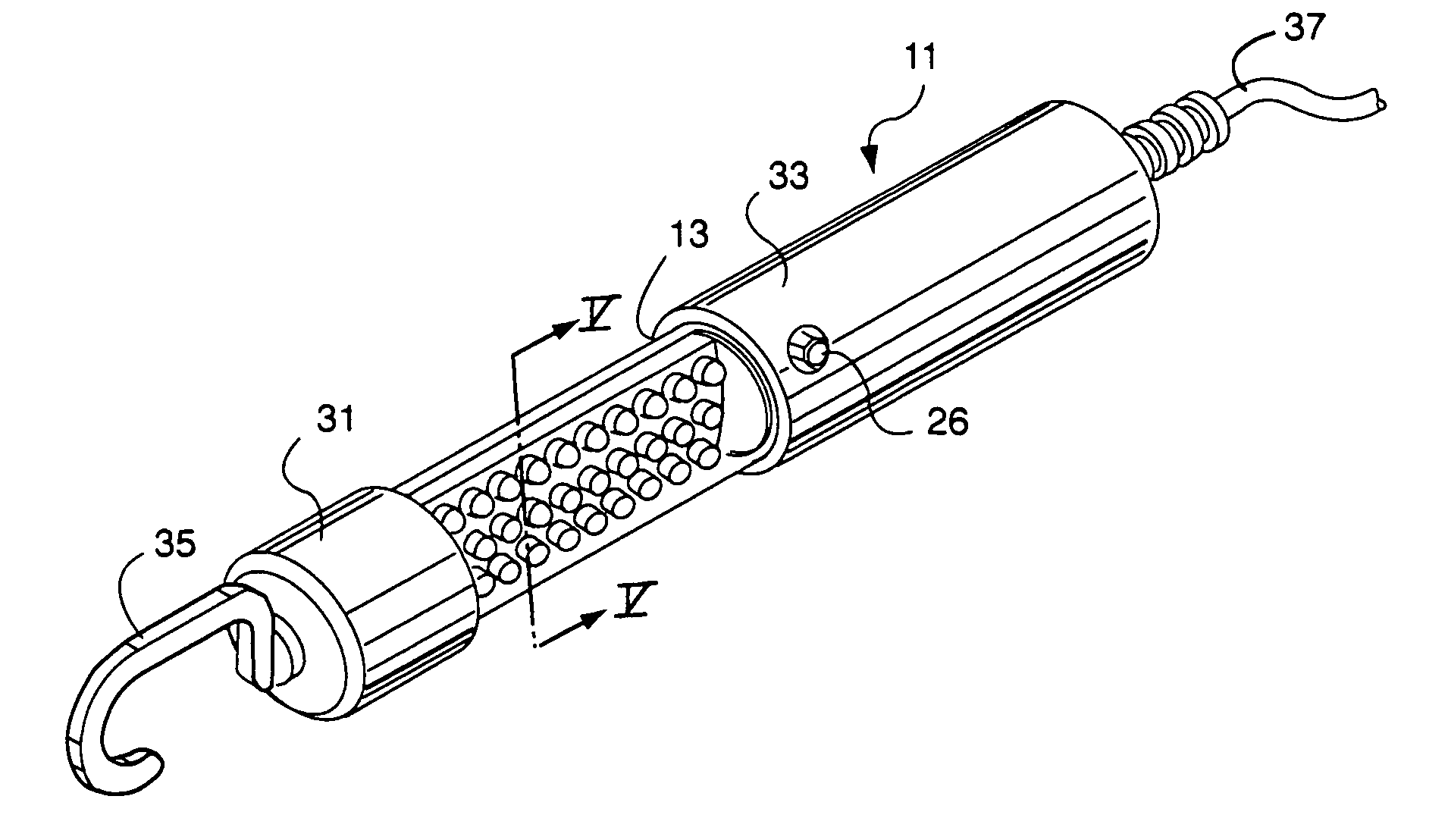
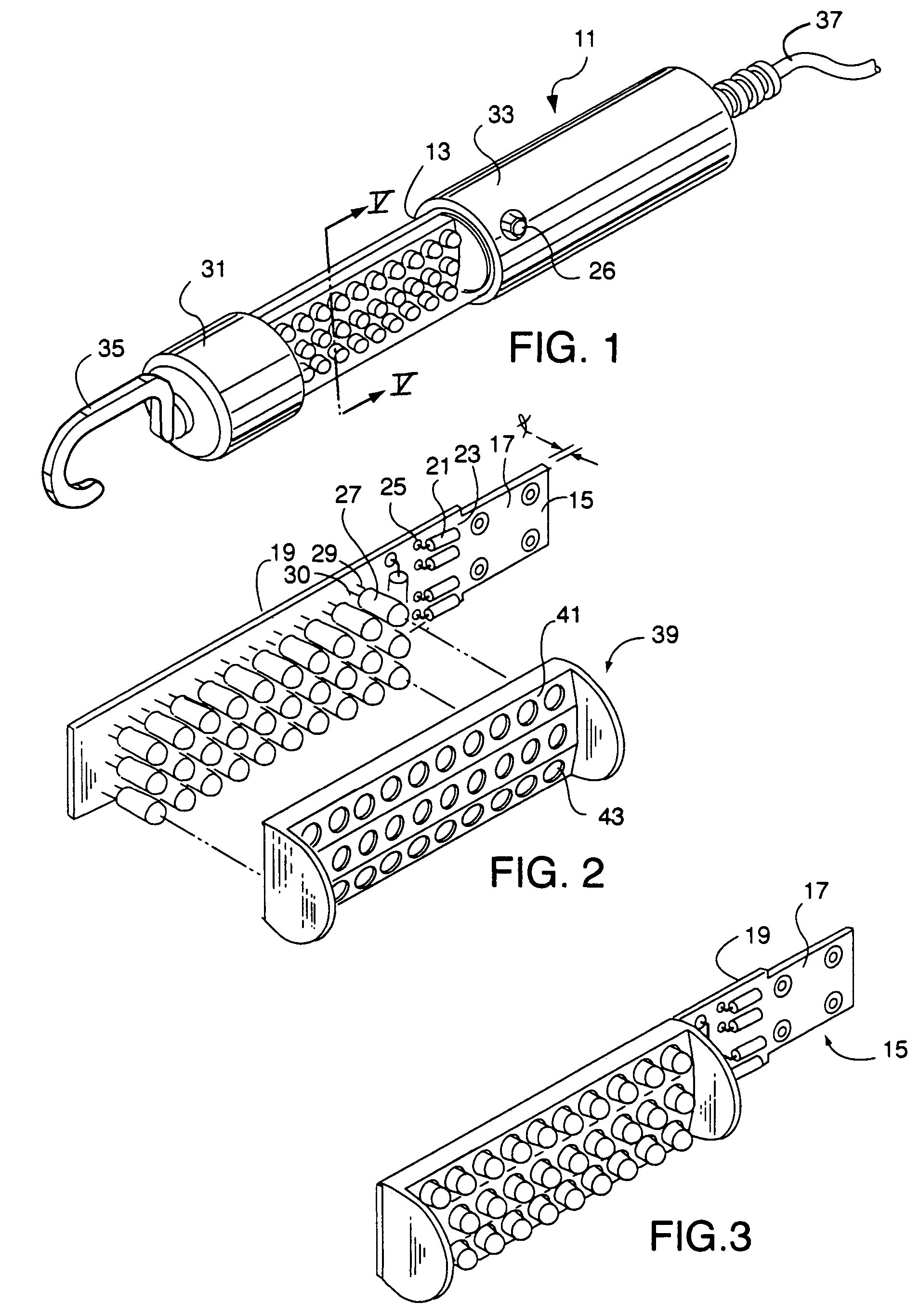
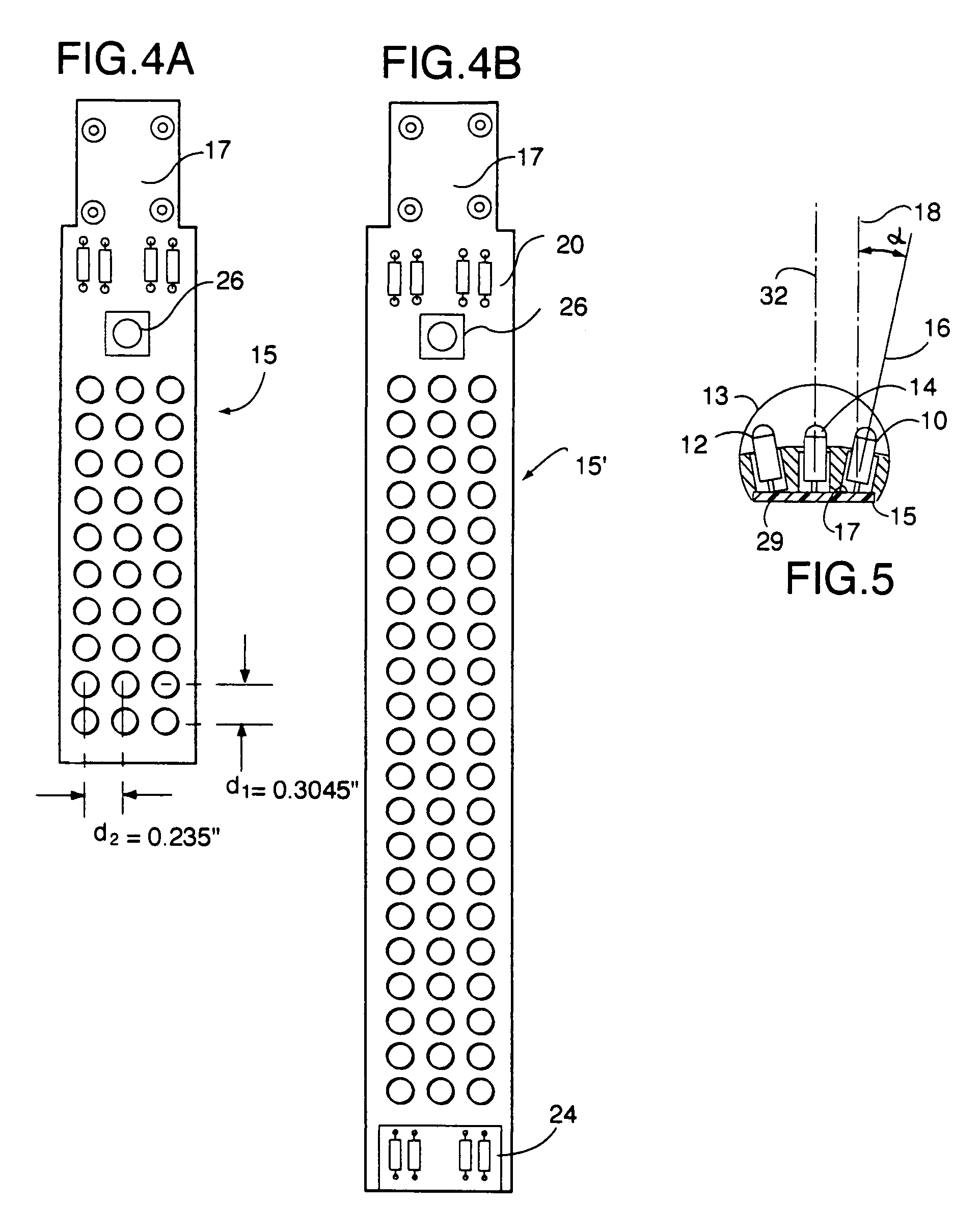
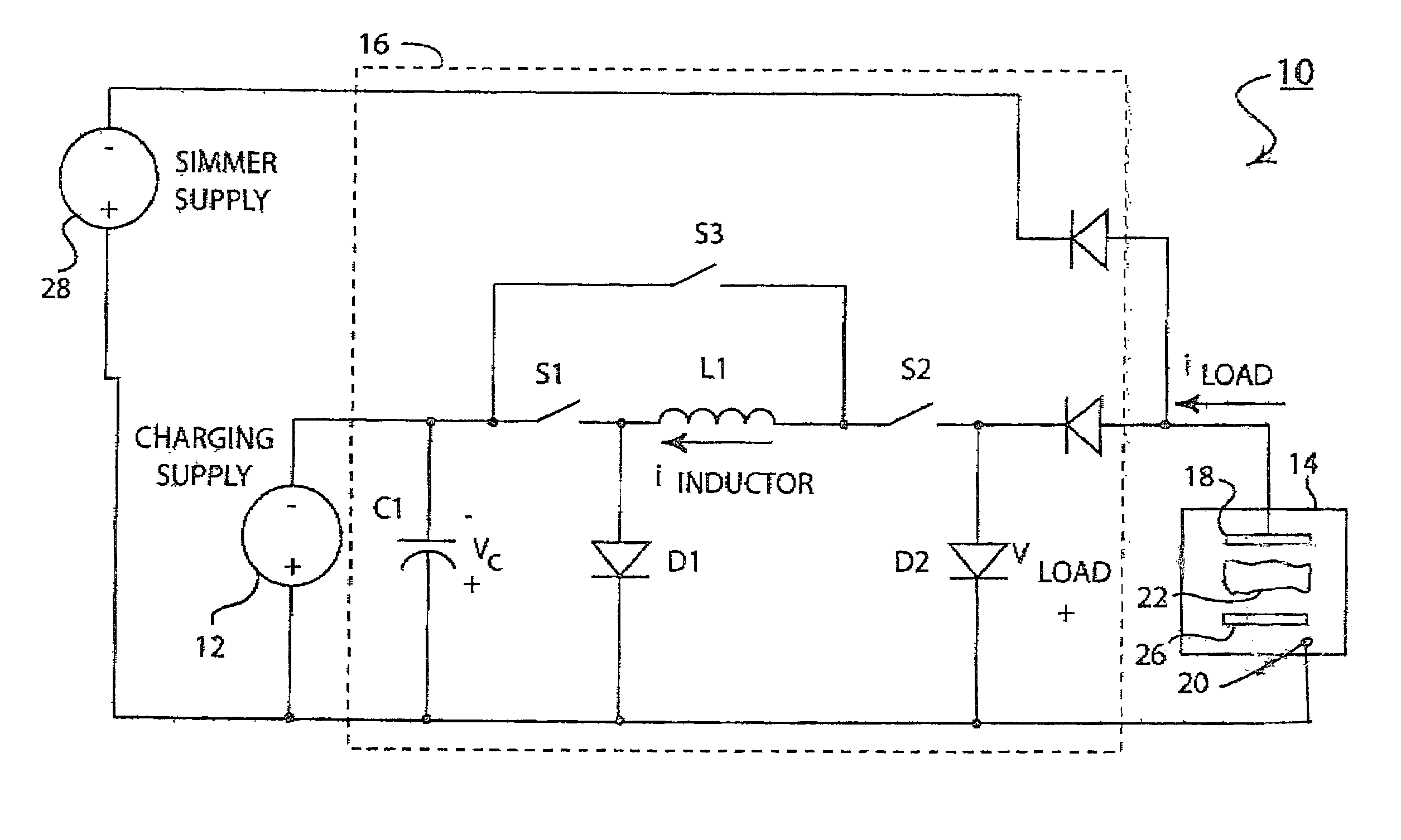
ActiveUS7334918B2Maximize LED intensityMaximizes disk flux efficiencyElectric lighting for hand-held usePlanar light sourcesElectricityPulsed DC
An LED lighting array is disclosed wherein a plurality of light emitting devices disposed in at least first and second columns are mounted on a planar mounting surface to form an emission plane. The emission axes of all the LEDs in a first column are parallel with each other and lie in a first plane. The emission axes of the LEDs in an adjacent, second column are also parallel, but a second plane containing the emission axes of the second column is disposed at a predetermined, non-zero angle with respect to the first plane. The non-zero angle is a function of the LED beam width and the distance to a lighting target. This configuration of the LEDs provides an optimum balance at a predetermined target distance between the size of the area illuminated and the brightness of the illumination of the target. In one aspect of the invention the LED lighting array includes at least first, second and third columns of LEDs. In another aspect of the invention an LED task light includes a transparent tube and an LED lighting array disposed within the tube. An electrical drive circuit associated with the mounting substrate within the tube provides pulsed direct current for driving the LED's.
Owner:BAYCO PRODS
High peak power plasma pulsed supply with arc handling
InactiveUS20040055881A1Efficient handling capabilityLimit currentCellsElectric discharge tubesVoltage pulsePulsed DC
There is provided by this invention novel magnetron sputtering apparatus that is generally comprised of a pulsed dc power supply capable of delivering peak powers of 0.1 megaWatts to several megaWatts with a peak power density greater than 1 kW / cm2. The power supply has a pulsing circuit comprised of an energy storage capacitor and serially connected inductor with a switching means for disconnecting the pulsing circuit from the plasma and recycling the inductor energy back to the energy storage capacitor at the detection of an arc condition. The energy storage capacitor and the serially connected inductor provide an impedance match to the plasma, limits the current rate of rise and peak magnitude in the event of an arc, and shapes the voltage pulses to the plasma.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY INDS
Appaaratus for generating low temperature plasma at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS20020063537A1Reduce discharge voltageReduce operating and installment cost and electricity consumptionWater treatment compoundsElectric discharge tubesDielectricElectrical conductor
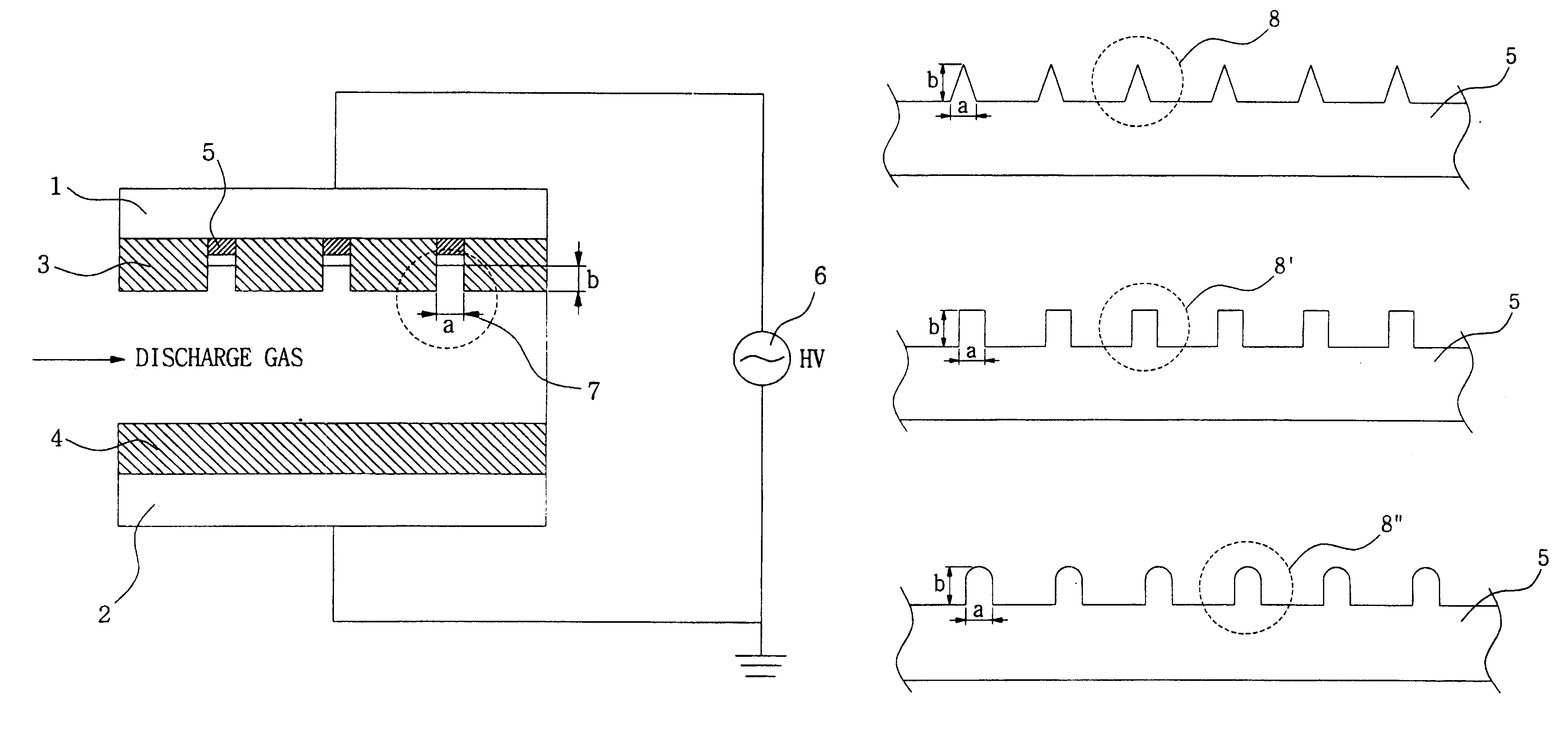
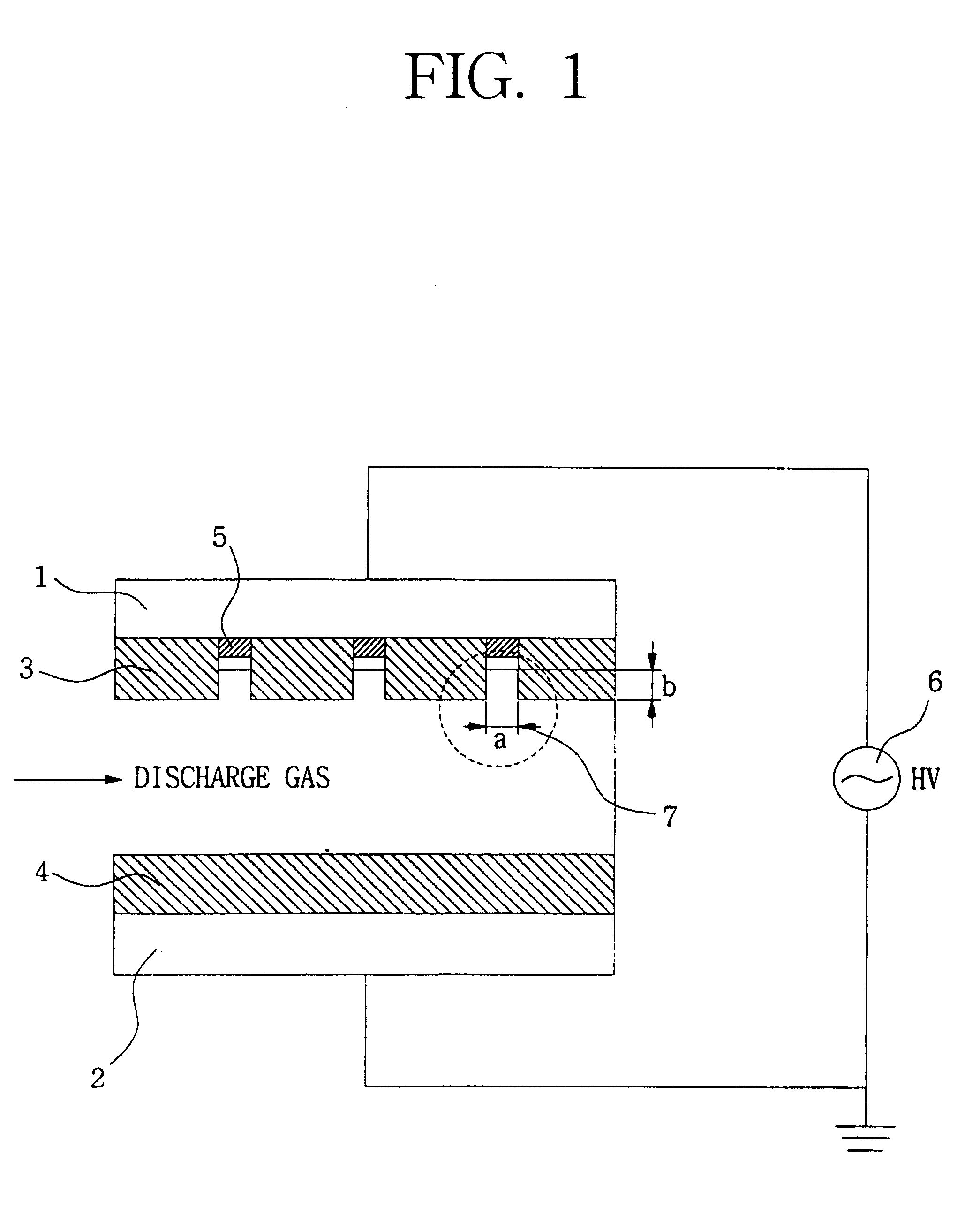
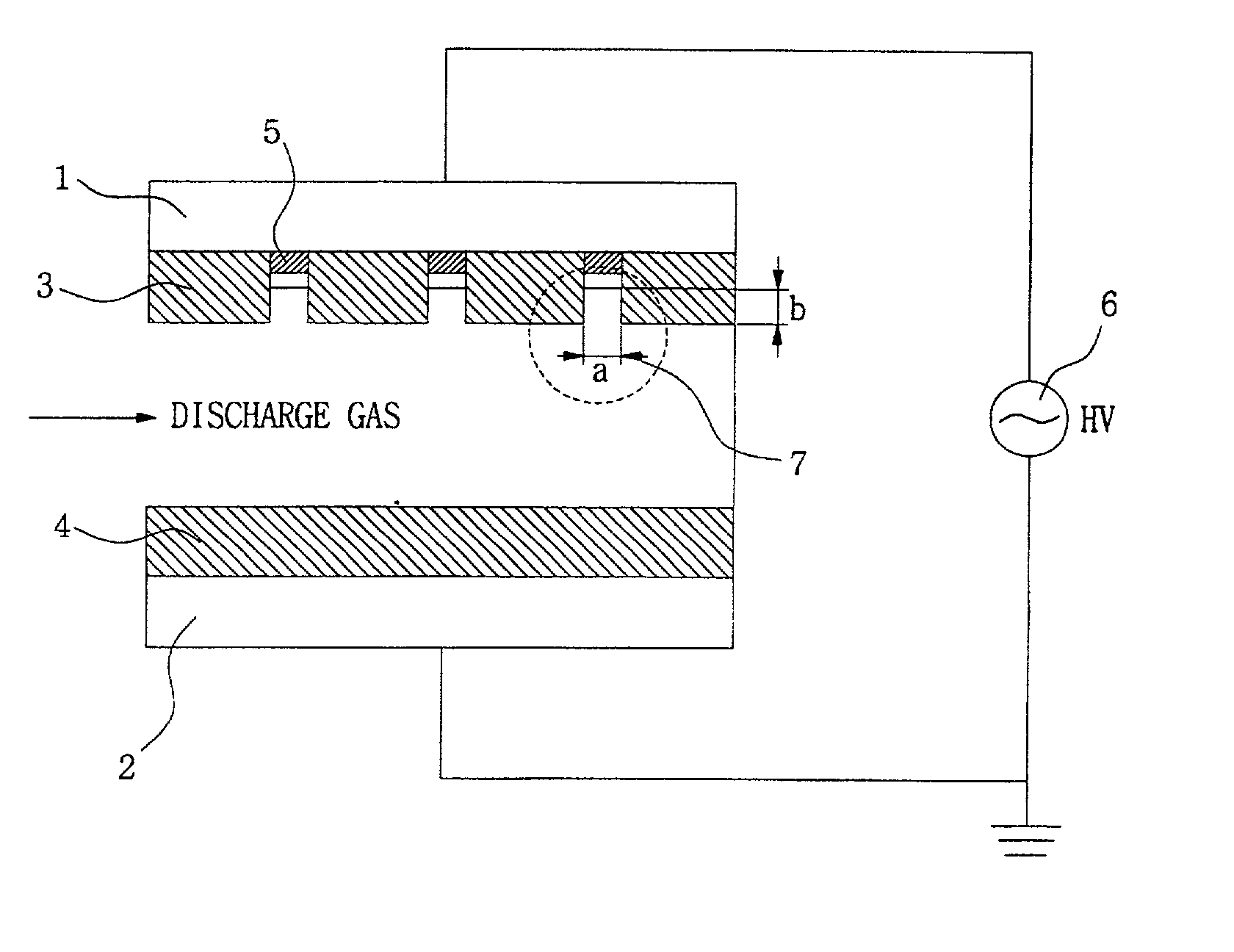
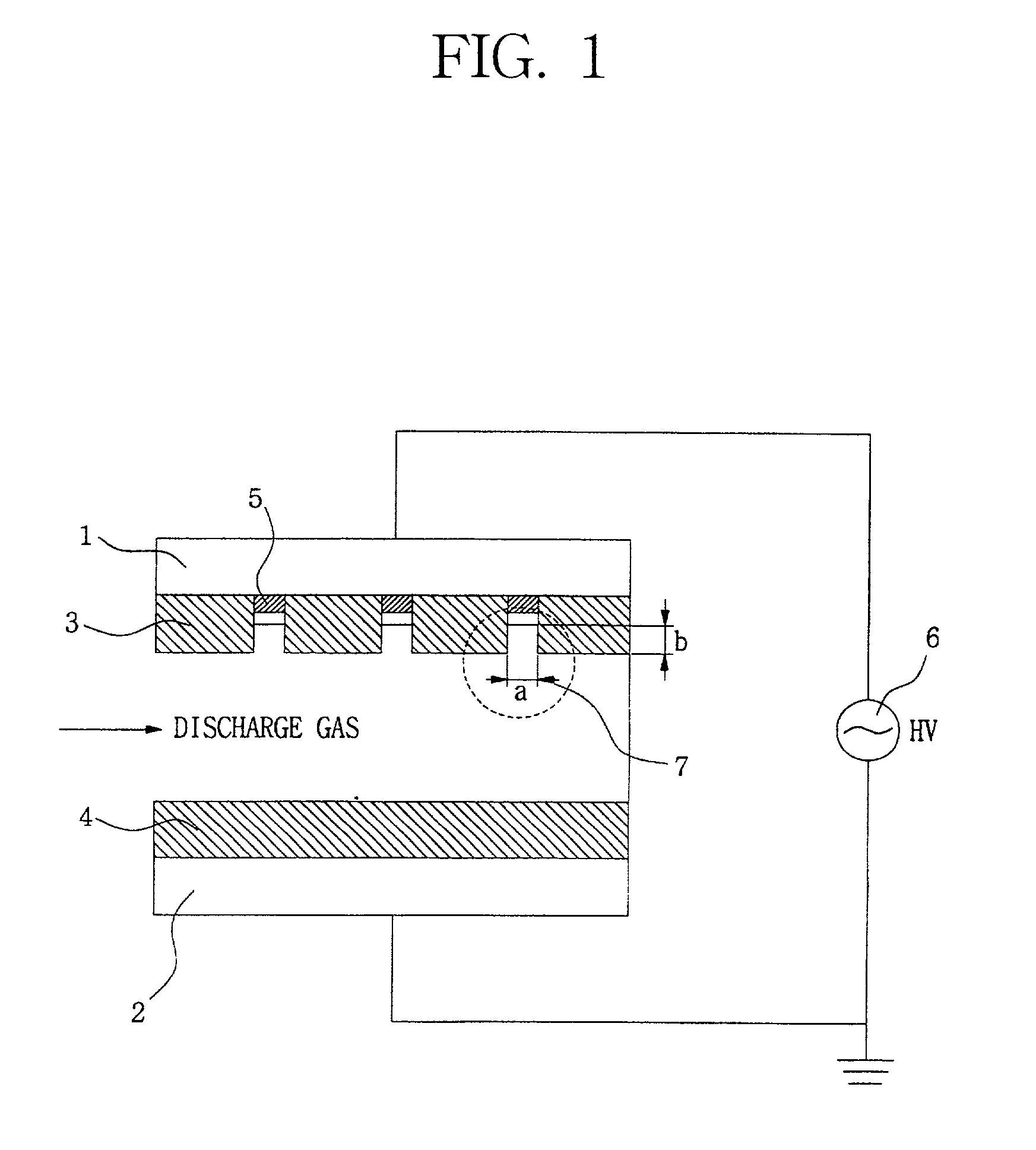
Disclosed is an apparatus for generating low-temp plasma at atmospheric pressure, comprising: a couple of electrodes facing each other at a distance, one of them being connected to a power supply, the other being grounded; a couple of dielectrics with a thickness of 25 mum-10 mm, positioned on the facing surfaces of the electrodes in such a way as to face each other, one of them having at least one discharge gap therein; and a conductor electrode having at least one tip positioned within the discharge gap, in which an electric field is applied at an intensity of 1-100 KV / cm through the power supply across the electrodes by use of a pulse direct current or an alternating current in a frequency bandwidth of 50 Hz-10 GHz while a reaction gas is fed between the electrodes, so as to induce a hollow cathode discharge, a capillary discharge or the high accumulation of charges from the discharge gap. With this structure, the apparatus prevents the conversion of the plasma to arcs and thus gives stable, low-temp plasma in a high density, and utilizes a broad bandwidth of frequencies in addition to being low in electricity consumption and being manufactured at a low cost. At low voltages, it can generate and maintain stable, low-temperature plasma over a large area. The plasma is suitable to form radicals of high energy and can be used for bonding, polishing, cleaning, thin films deposition, sterilization, ozone generation, printing, dyeing, etching, purification of water and air, complete combustion of fuels, manufacture of highly luminous lamps.
Owner:SE PLASMA
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and method of using same
ActiveUS20080207985A1Avoid problemsElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationPulsed DC
The present disclosure relates to an apparatus and associated methods to produce analgesia in a mammal by providing an electrical nerve stimulus utilizing a pulsed input of low level electrical current, wherein the level of current is measurable with the measurements utilized to at least adjust the strength of the current according to selected parameters. Additionally, the use of magnets to produce a magnetic field to further control chronic and acute pain. In exemplary implementations, the apparatus maintains continuous monitoring of the electrical characteristics of TENS at the site of input and output, and the electrical input can be modified during treatment to obtain desired electrical input. More particularly the disclosure relates to an electromagnetic apparatus incorporating pulsed direct current, two or more electrodes, and at least two dipole antennas wherein the dipole antenna circuits receive and analyze signal from the dipole antennas, using the information from signal analysis within the methods for producing analgesia in mammals. The strength of the current that the patient is receiving at the targeted site as the actual field is measured by the dipole antennas and adjustment is not dependent on subjective measurements to ascertain whether the proper amplitude, frequency and pulse duration are being applied.
Owner:WILSON SPENCE L
Method and apparatus for the treatment of physical and mental disorders with low frequency, low flux density magnetic fields
InactiveUS20100298624A1Limited extentTreatment safetyElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsMicrocontrollerPulsed DC
A method and apparatus for generating electromagnetic fields for healing. A device preferably includes a microcontroller and associated memory, a wire coil in electrical communication with a driving circuit that is controlled by the microcontroller in accordance with a program stored in the associated memory, wherein the driving circuit is effective to produce a pulsed DC output having a frequency in the range of about 0-45 Hz, more preferably in the range of 0.5-14.1 Hz and most preferably around 9.6 Hz. A user interface is provided for selecting one of a plurality of modes of operation and a port (e.g., a USB port) is provided to allow the program stored in the associated memory to be modified by way of a computer, memory card or the Internet. In another embodiment, the apparatus takes the form of a medallion that can be worn around a user's neck or strategically placed on a user's body or embedded in other user hardware such as a combat or racing helmet.
Owner:BECKER PAUL F
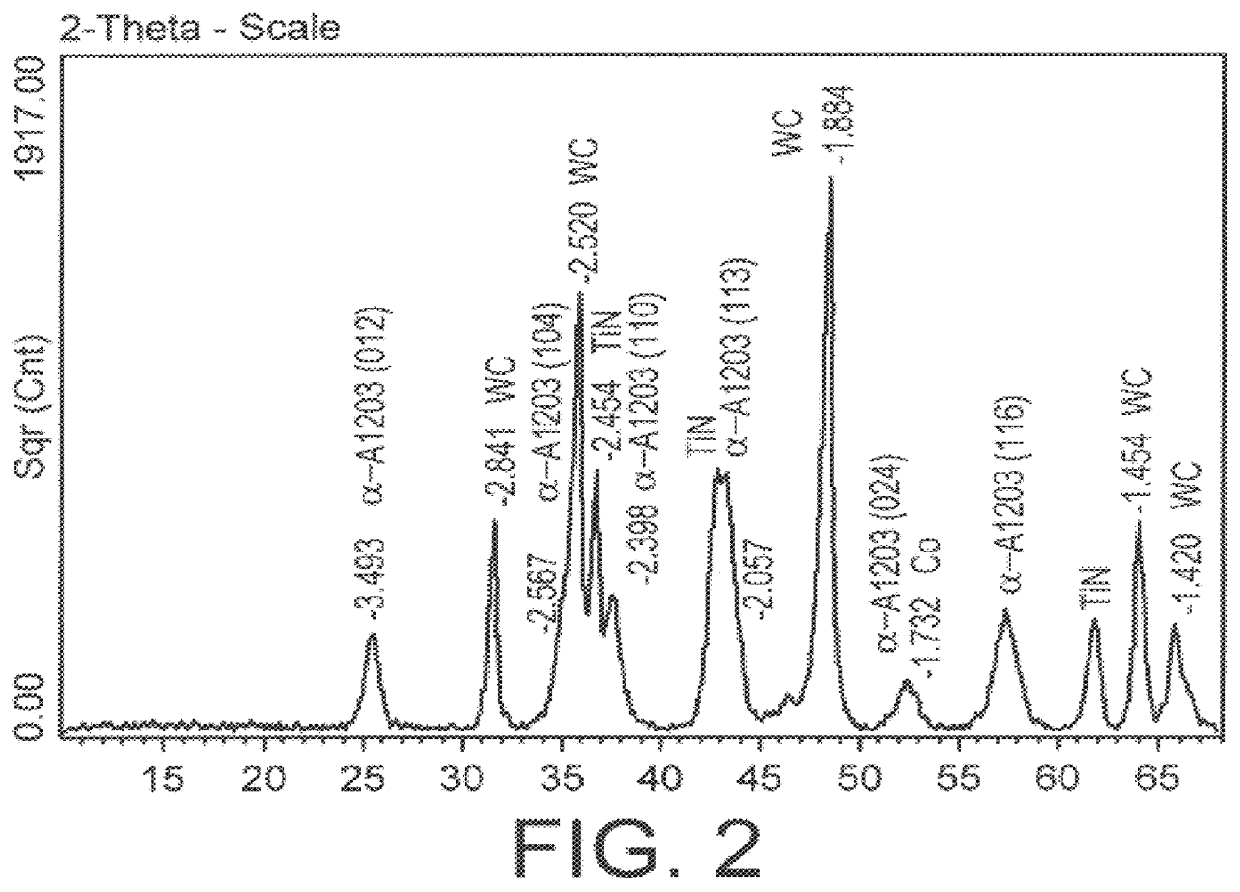
Method for depositing fine-grained alumina coatings on cutting tools
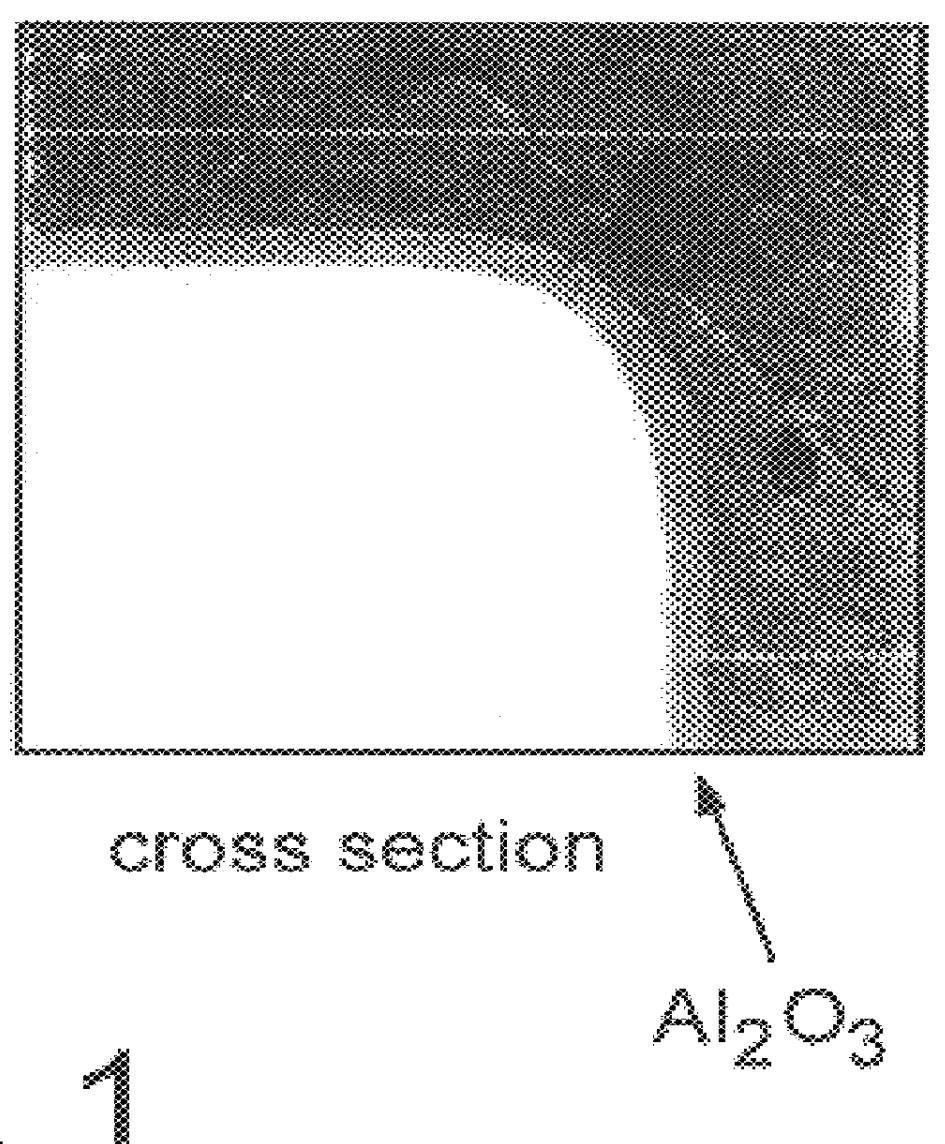
A method for depositing refractory alumina (A2O3) thin layers on cutting tools made of cemented carbide, cermet, ceramics or high speed steel is disclosed. The present method is a Plasma Activated Chemical Vapor Deposition (PACVD) process in which the plasma is produced by applying a bipolar pulsed DC voltage across two electrodes to which the tool substrates to be coated are fixtured and electrically connected. In contrast to prior art methods, built-up electrical charge on non-conducting surfaces is suppressed and hence, no arcing occurs on said surfaces. This will permit stable, long-term processing, With the present method, high-quality coatings of either single phase gamma-Al2O3 or of a mixture of gamma- and alpha-Al2O3 phases can be deposited on cutting tools at deposition temperatures as low as 500 DEG C. When coated cemented carbide tools according to the invention are used in the machining of steel or cast iron, several important improvements to prior art produced Al2O3-coated tools have been observed.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Methods and apparatus for applying periodic voltage using direct current
Methods and apparatus for applying pulsed DC power to a plasma processing chamber are disclosed. In some implementations, frequency of the applied power is varied to achieve desired processing effects such as deposition rate, arc rate, and film characteristics. In addition, a method and apparatus are disclosed that utilize a relatively high potential during a reverse-potential portion of a particular cycle to mitigate possible nodule formation on the target. The relative durations of the reverse-potential portion, a sputtering portion, and a recovery portion of the cycle are adjustable to effectuate desired processing effects.
Owner:AES GLOBAL HLDG PTE LTD
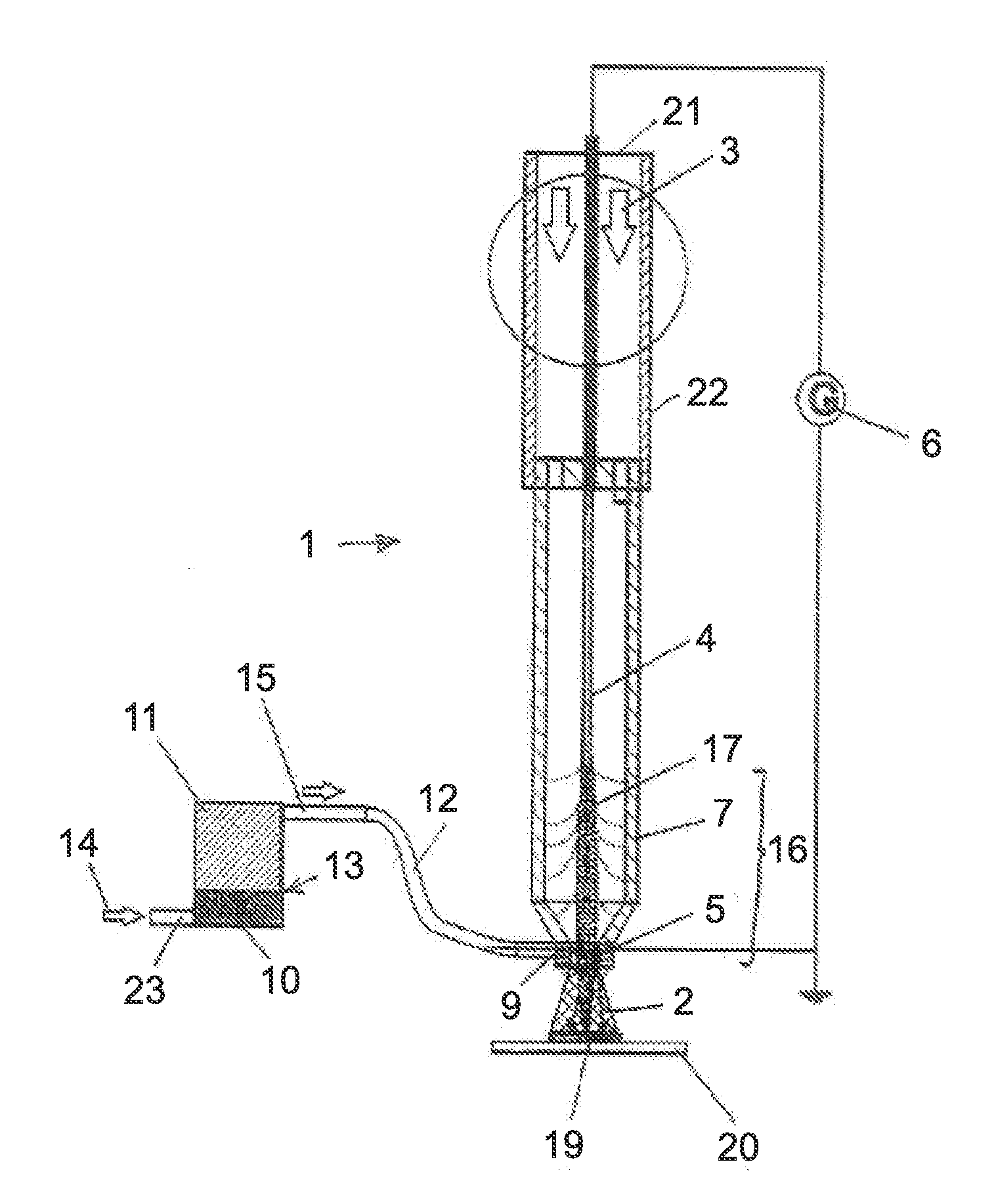
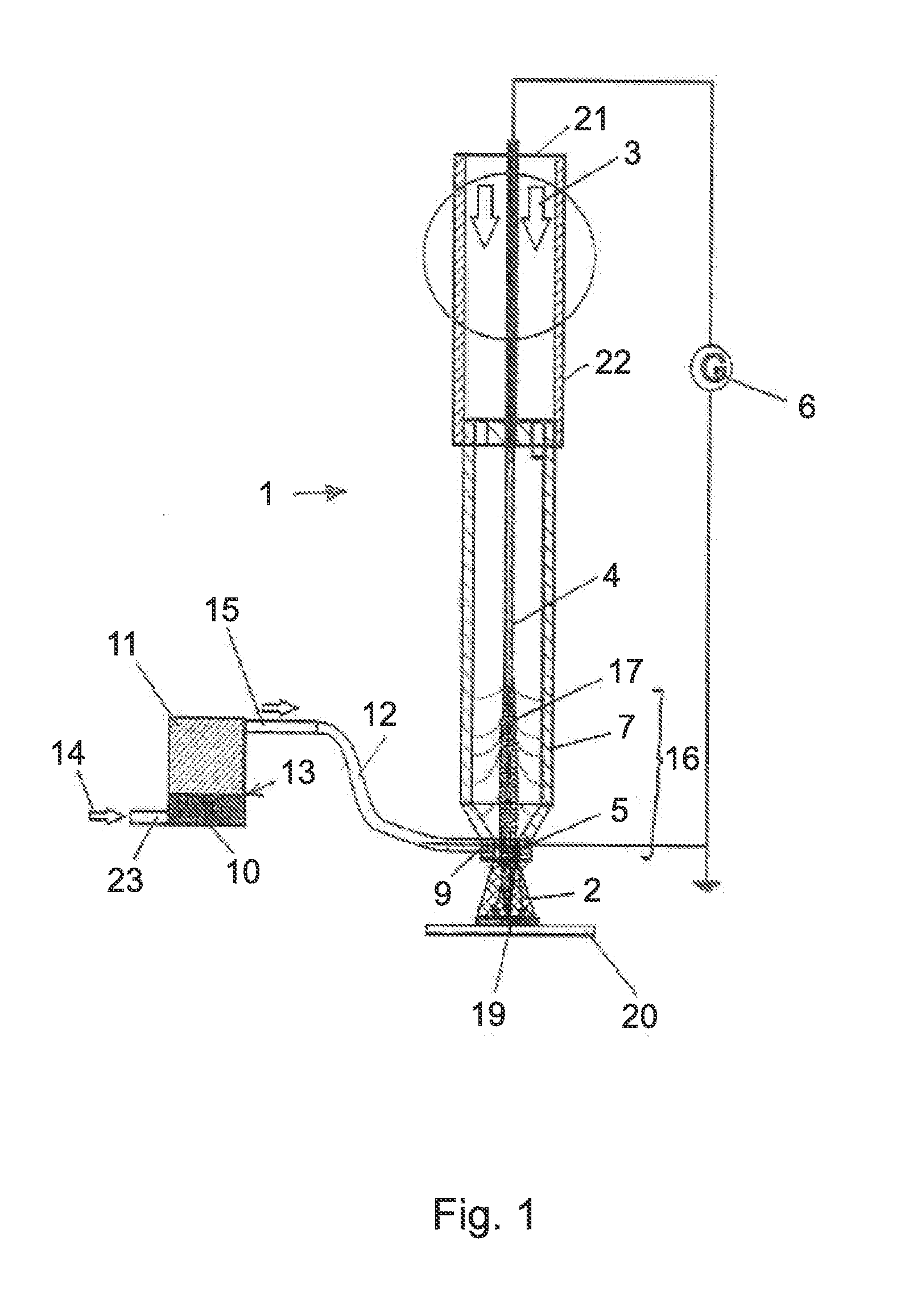
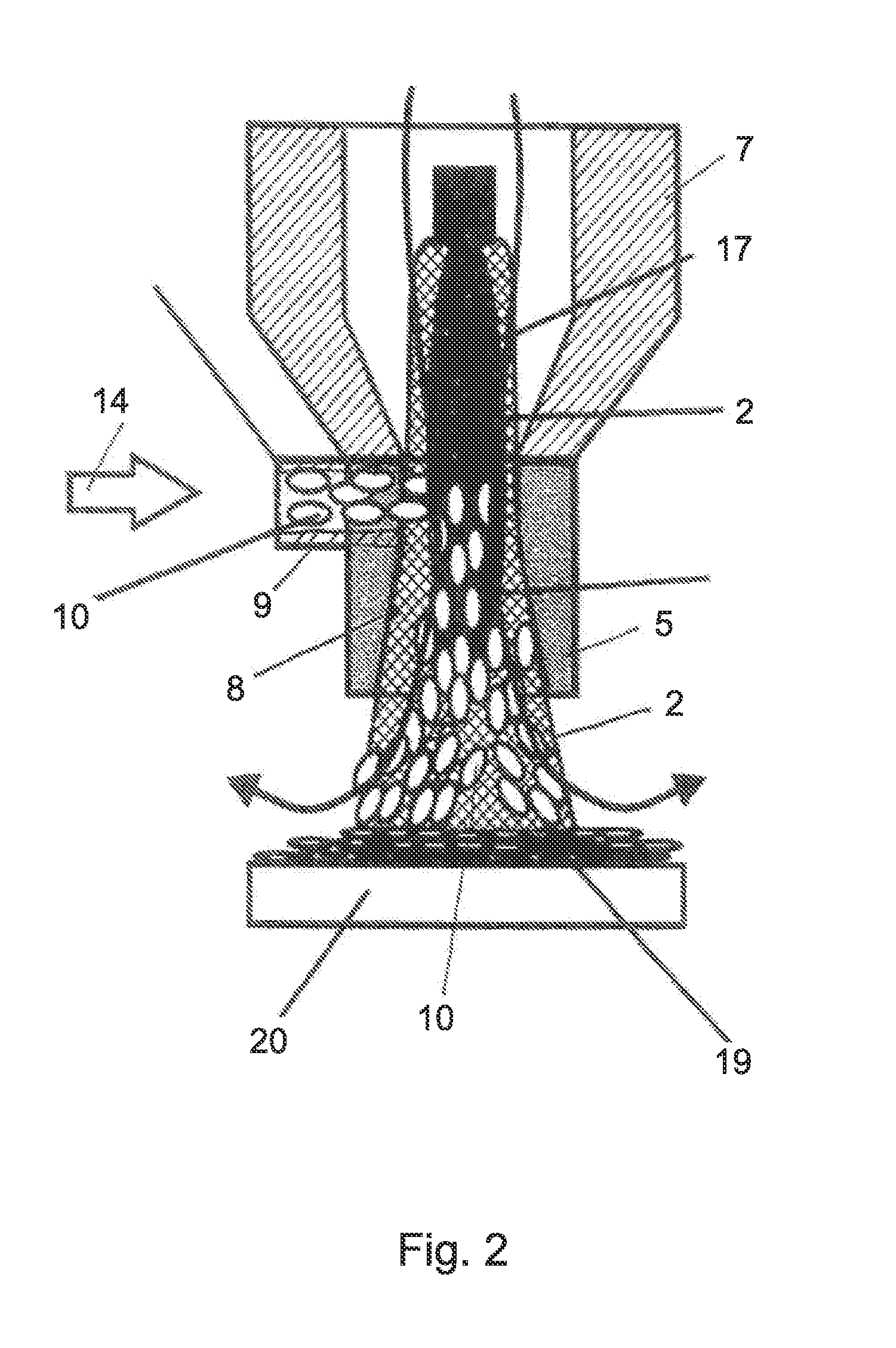
Coat as well as method and device for coating
The invention relates to a method and a device for applying a coating to a substrate, where a plasma jet of a low-temperature plasma is produced by conducting a working gas through an excitation zone. The plasma jet is directed at the substrate, and plate-shaped particles having an average thickness between 10 and 50,000 nanometers and a shape factor in a value range from 10 to 2000 are fed into the plasma jet. The plate-shaped particles are fed into the plasma jet by means of a carrier gas. The plasma jet is produced by exciting the working gas by means of an alternating voltage or a pulsed direct voltage.
Owner:ECKART GMBH & CO KG +1
Electronic device, manufacturing method of electronic device, and sputtering target
InactiveUS20120049183A1Easy to evaporateHigh heating temperatureCellsSolid-state devicesProduction rateSputtering
A film formation is performed using a target in which a material which is volatilized more easily than gallium when heated at 400° C. to 700° C., such as zinc, is added to gallium oxide by a sputtering method with high mass-productivity which can be applied to a large-area substrate, such as a DC sputtering method or a pulsed DC sputtering method. This film is heated at 400° C. to 700° C., whereby the added material is segregated in the vicinity of a surface of the film. Another portion of the film has a decreased concentration of the added material and a sufficiently high insulating property; therefore, it can be used for a gate insulator of a semiconductor device, or the like.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
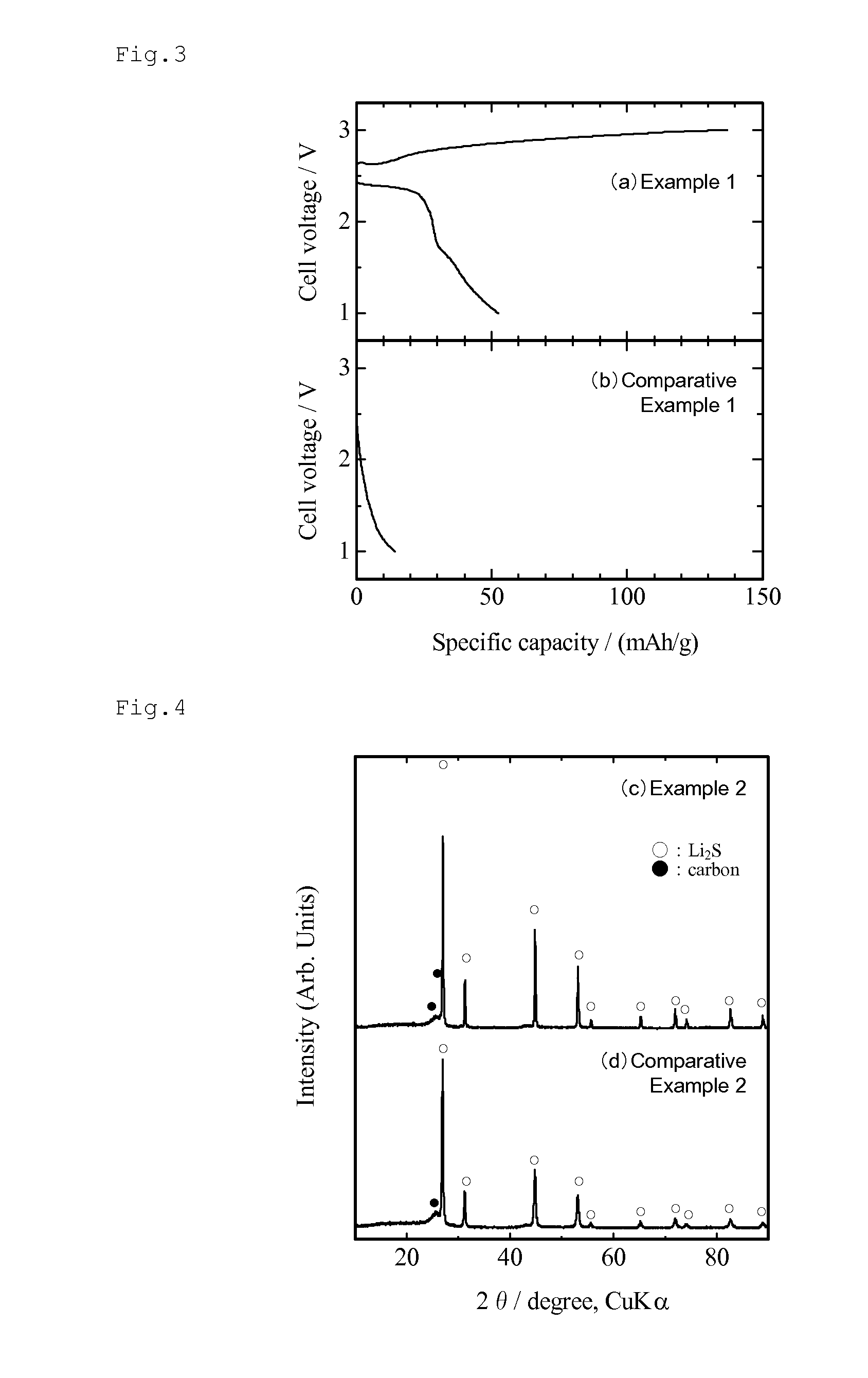
Lithium sulfide-carbon complex, process for producing the complex, and lithium ion secondary battery utilizing the complex
ActiveUS20110171537A1Improve electronic conductivityImprove conductivityElectrochemical processing of electrodesCarbon compoundsCarbon compositesPulsed DC
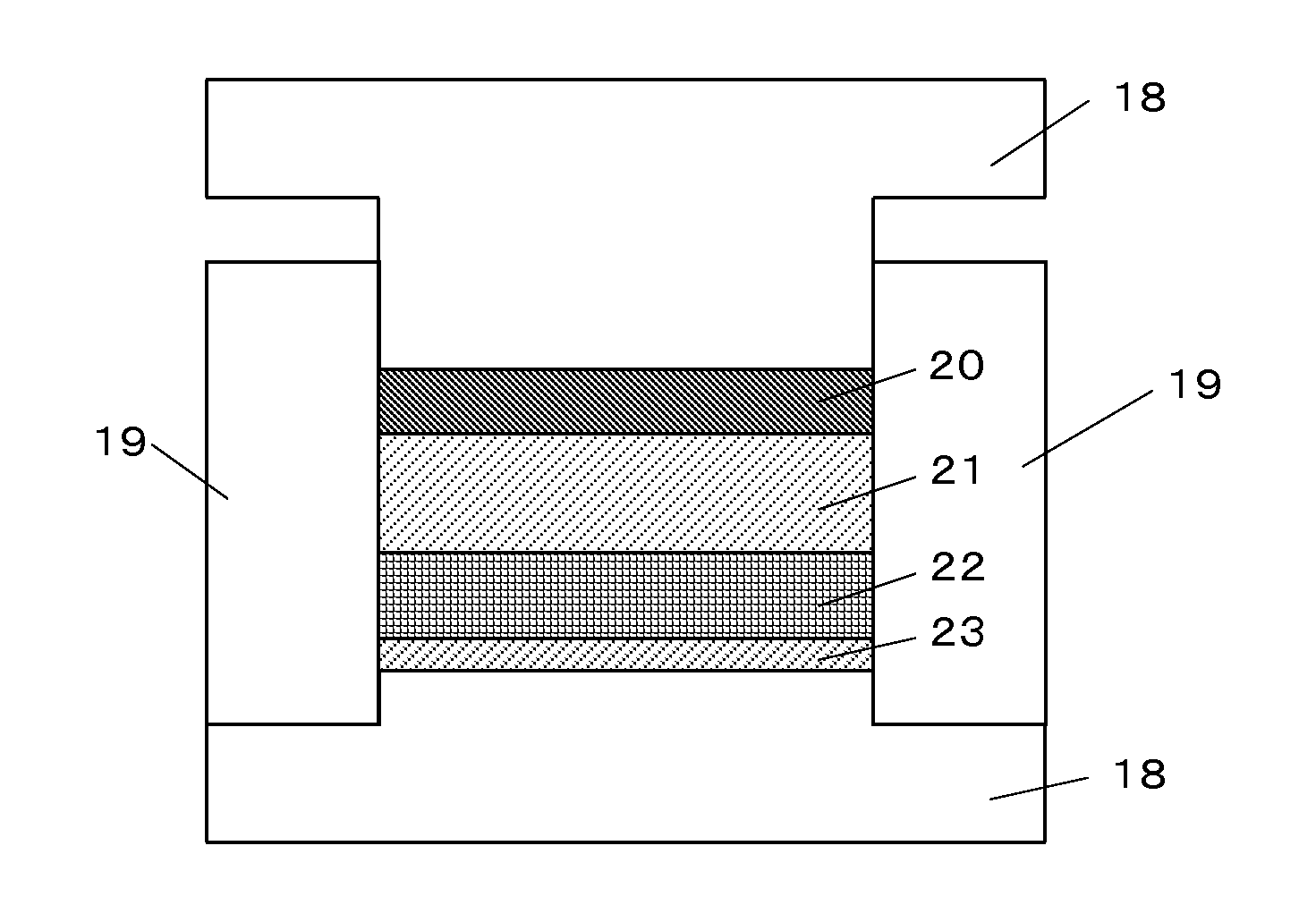
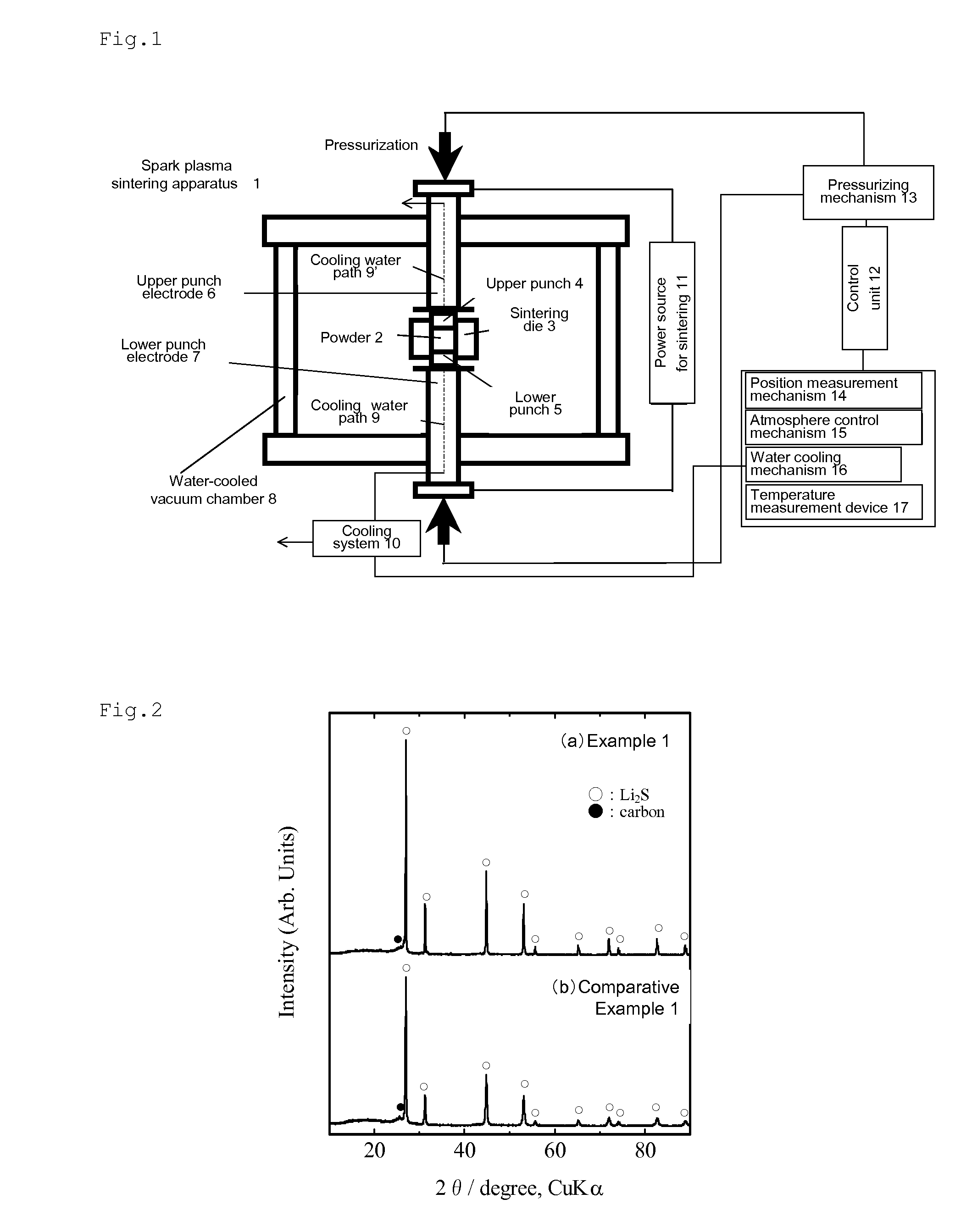
The present invention provides a process for producing a lithium sulfide-carbon composite, the process comprising placing a mixture of lithium sulfide and a carbon material having a specific surface area of 60 m2 / g or more in an electrically-conductive mold in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, and applying a pulsed direct current to the mold while pressurizing the mixture in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, thereby subjecting the lithium sulfide and the carbon material to heating reaction; and a lithium sulfide-carbon composite obtained by this process, the composite having a carbon content of 15 to 70 weight %, and a tap density of 0.4 g / cm3 or more when the carbon content is 30 weight % or more, or a tap density of 0.5 g / cm3 or more when the carbon content is less than 30 weight %. The present invention can improve the electronic conductivity of lithium sulfide, which is expected to be put into practical use as a high-capacity positive electrode active material, so as to further enhance the performance of lithium sulfide as a positive electrode active material for lithium ion secondary batteries.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com