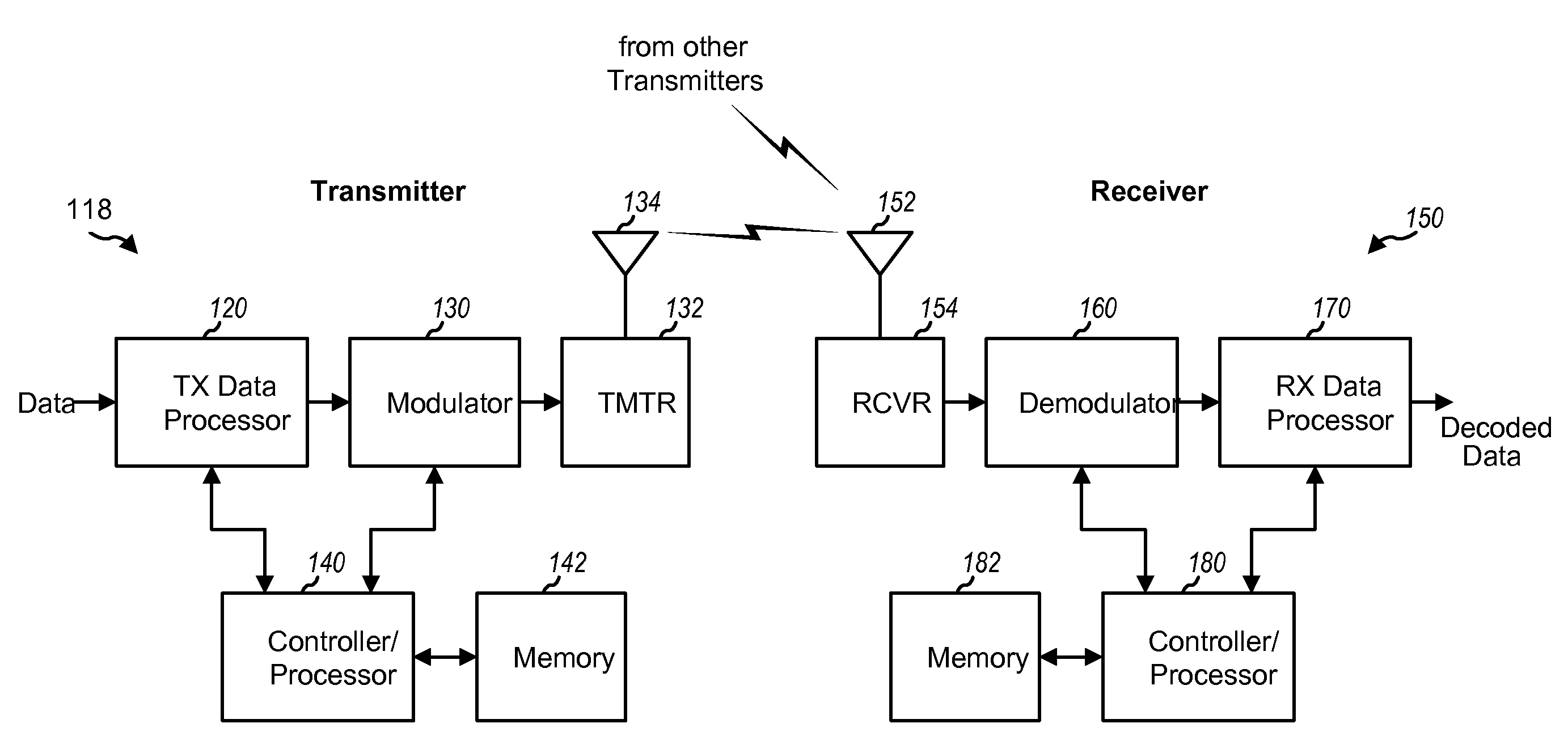
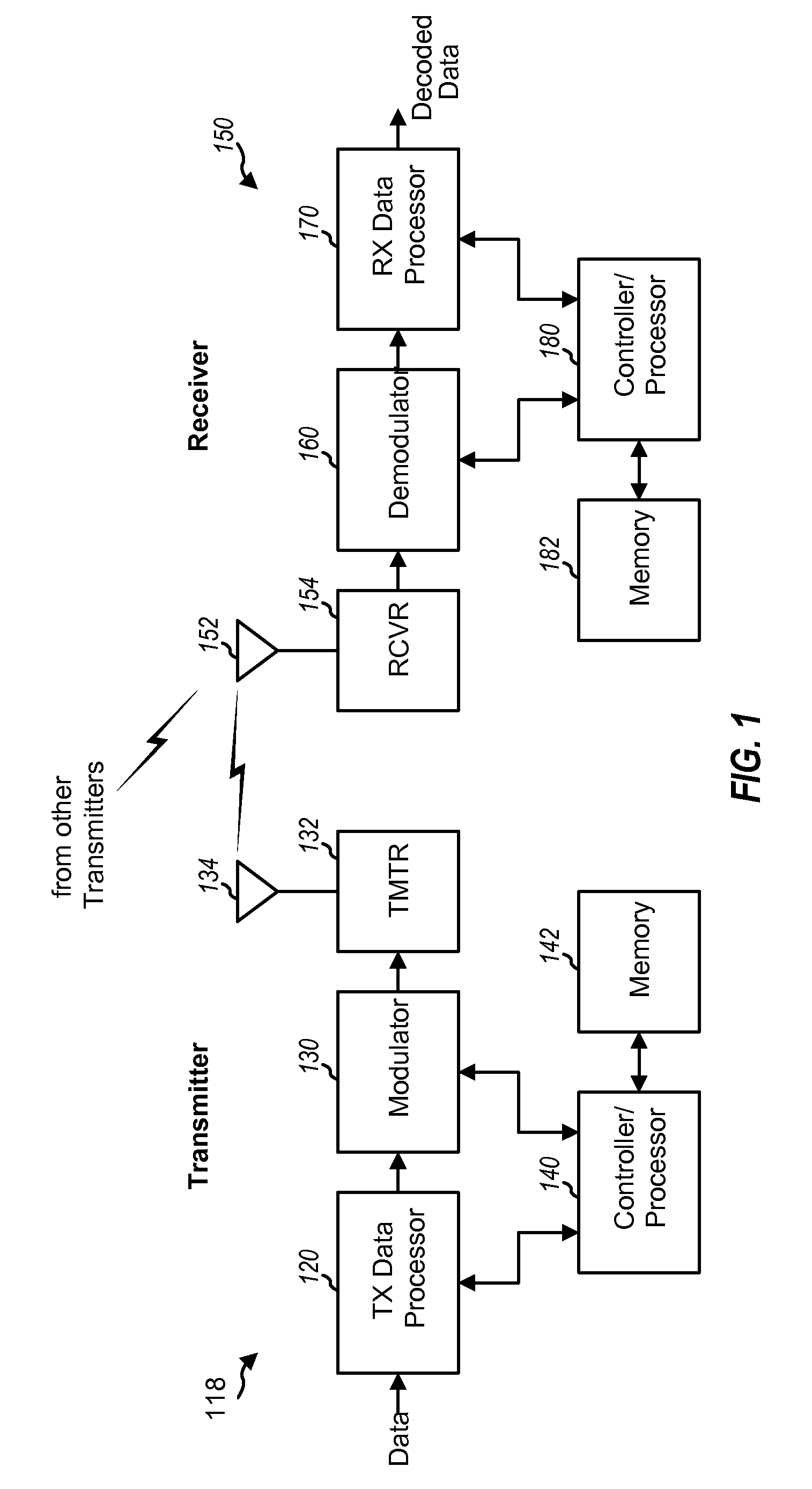
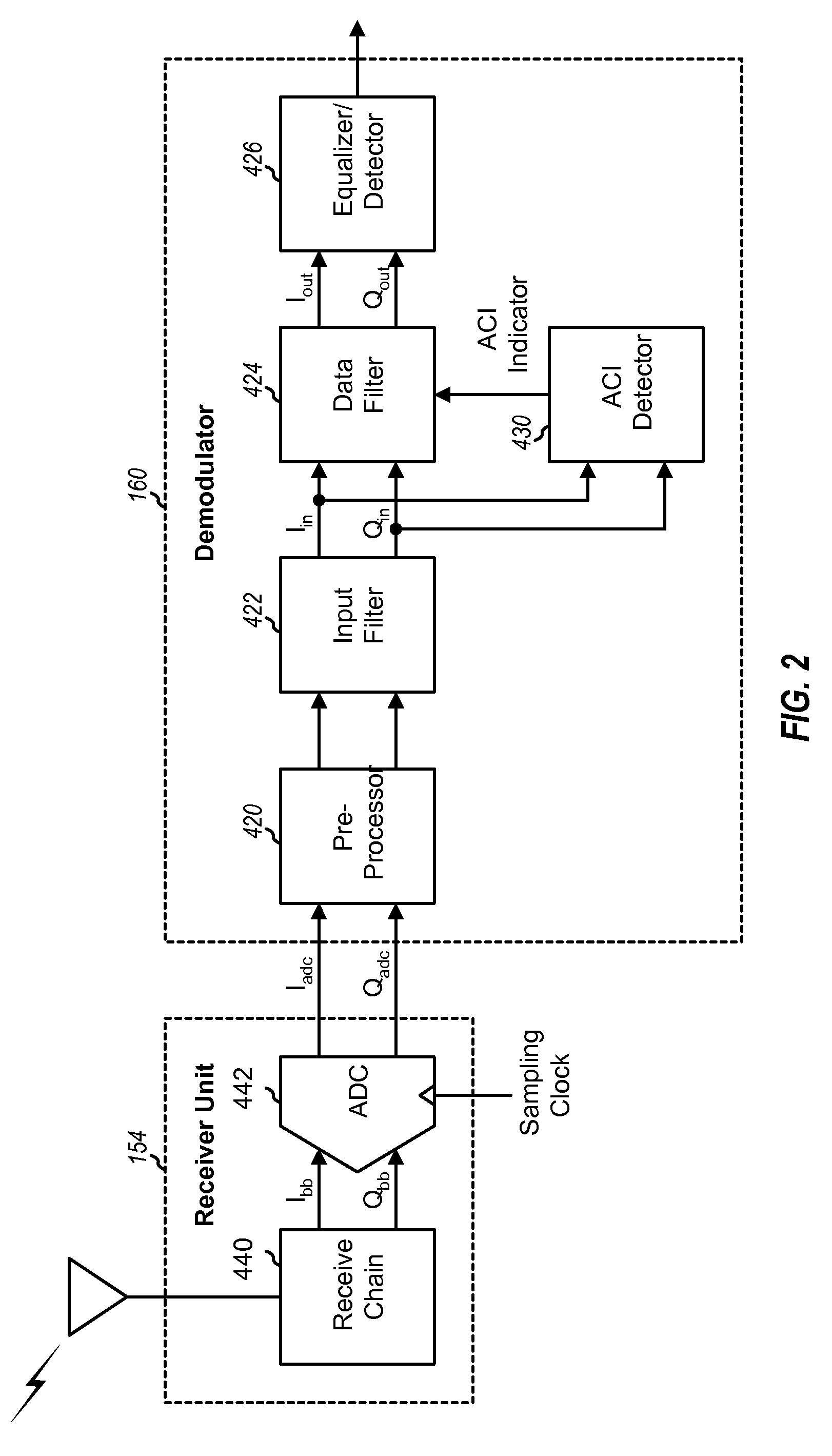
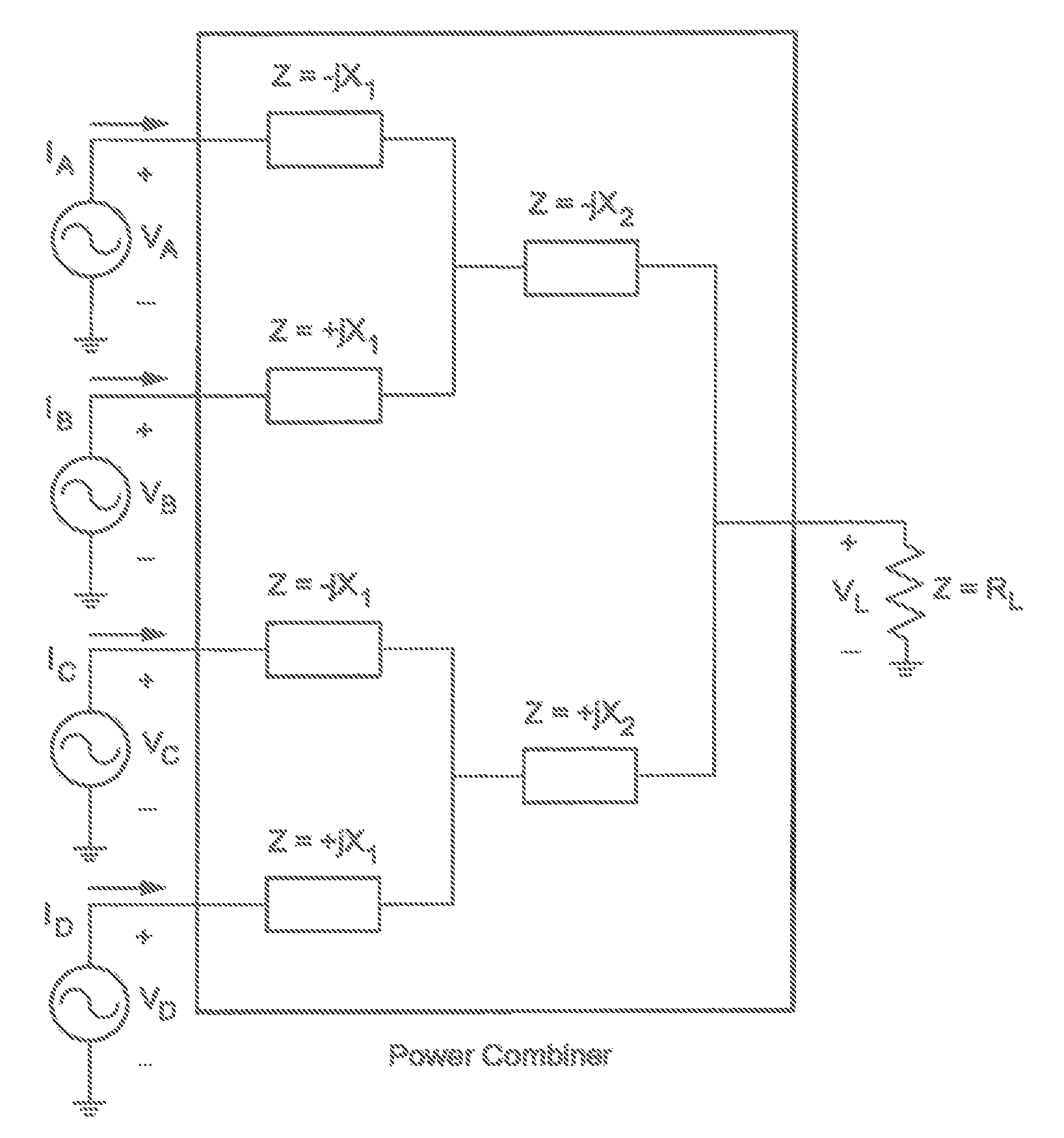
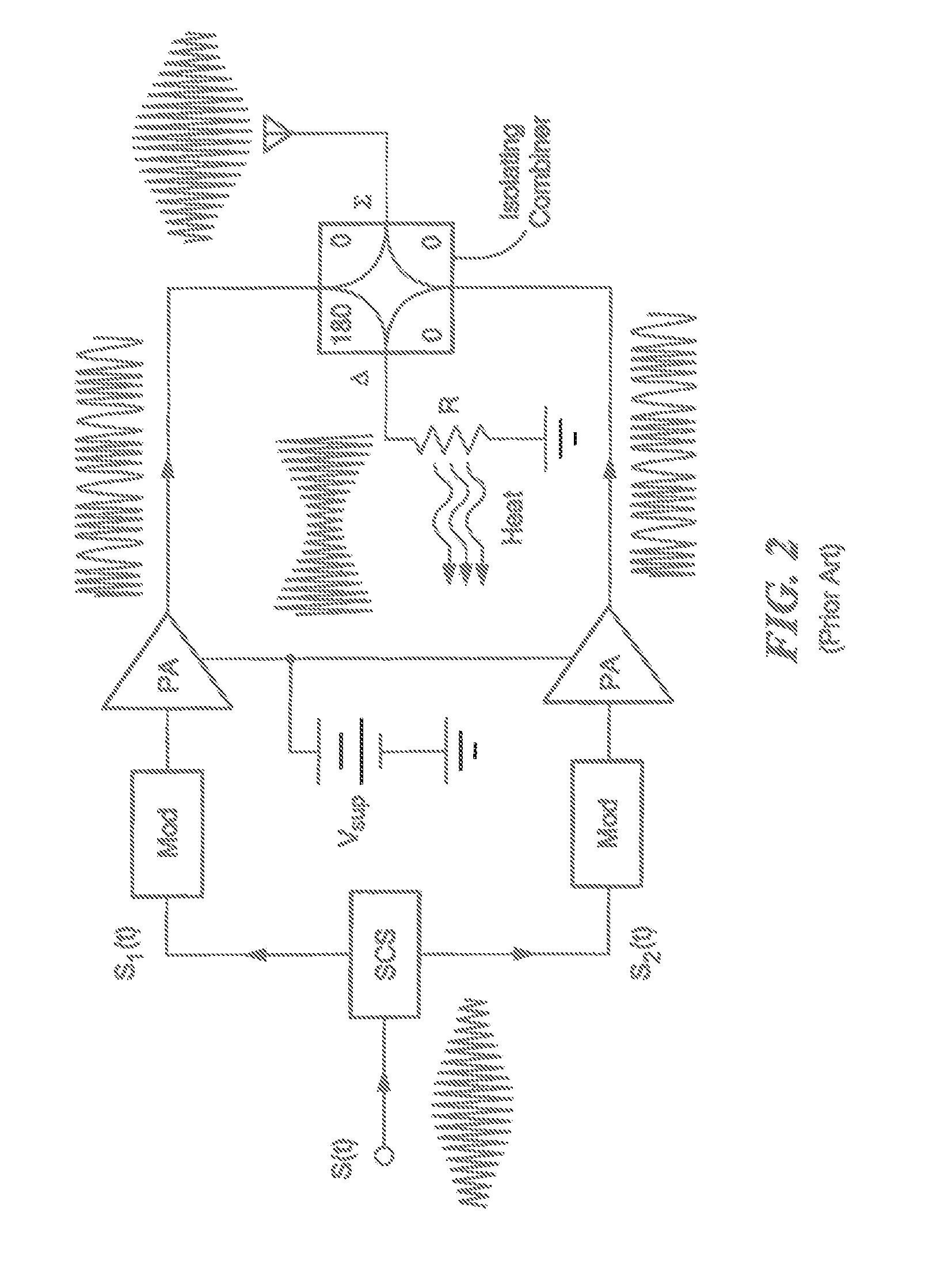Patents
Literature
534 results about "Broad bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bandwidth is a broad term defined as the bit-rate measure of the transmission capacity over a network communication system. Bandwidth is also described as the carrying capacity of a channel or the data transfer speed of that channel. However, broadly defined, bandwidth is the capacity of a network.
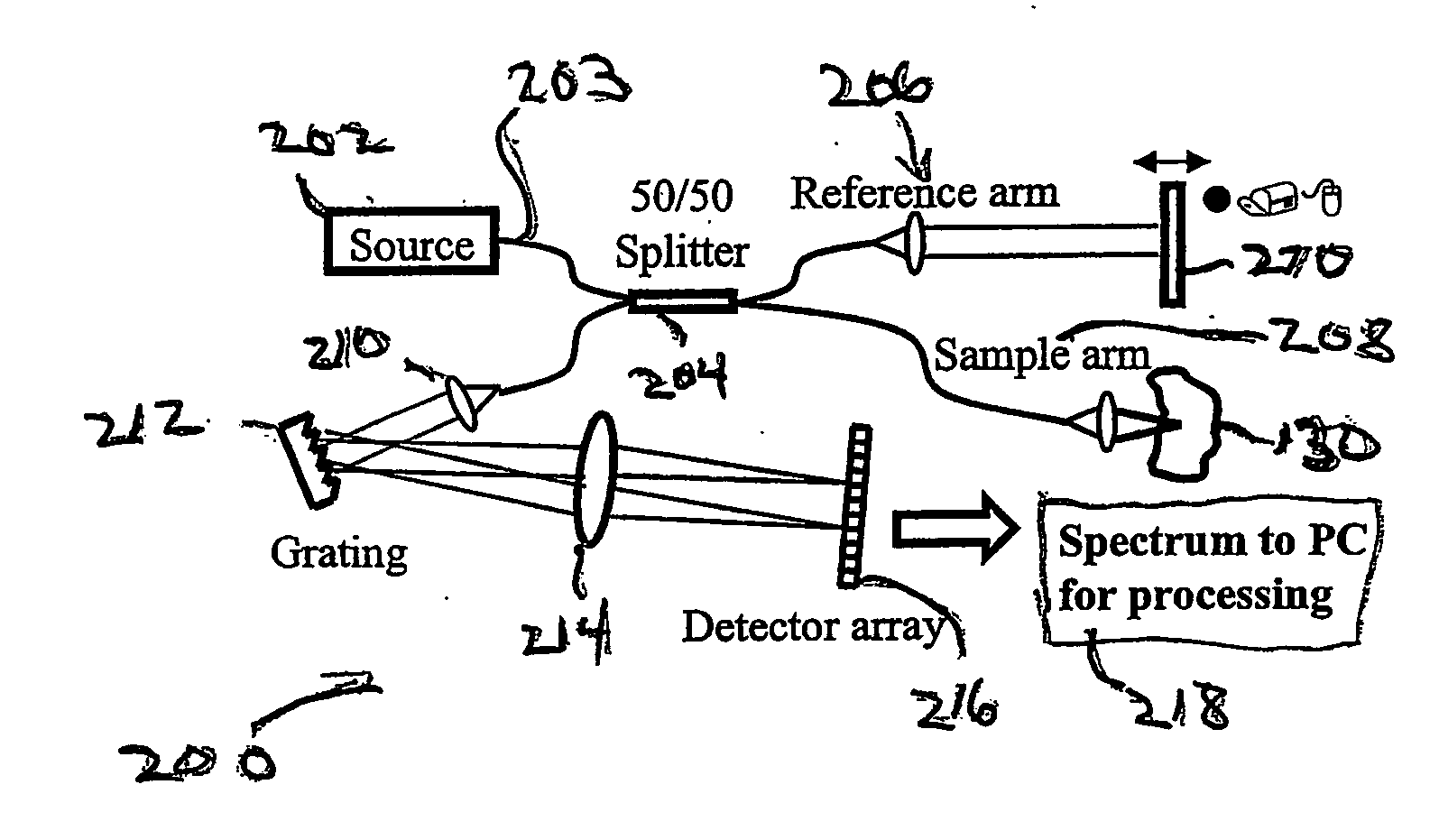
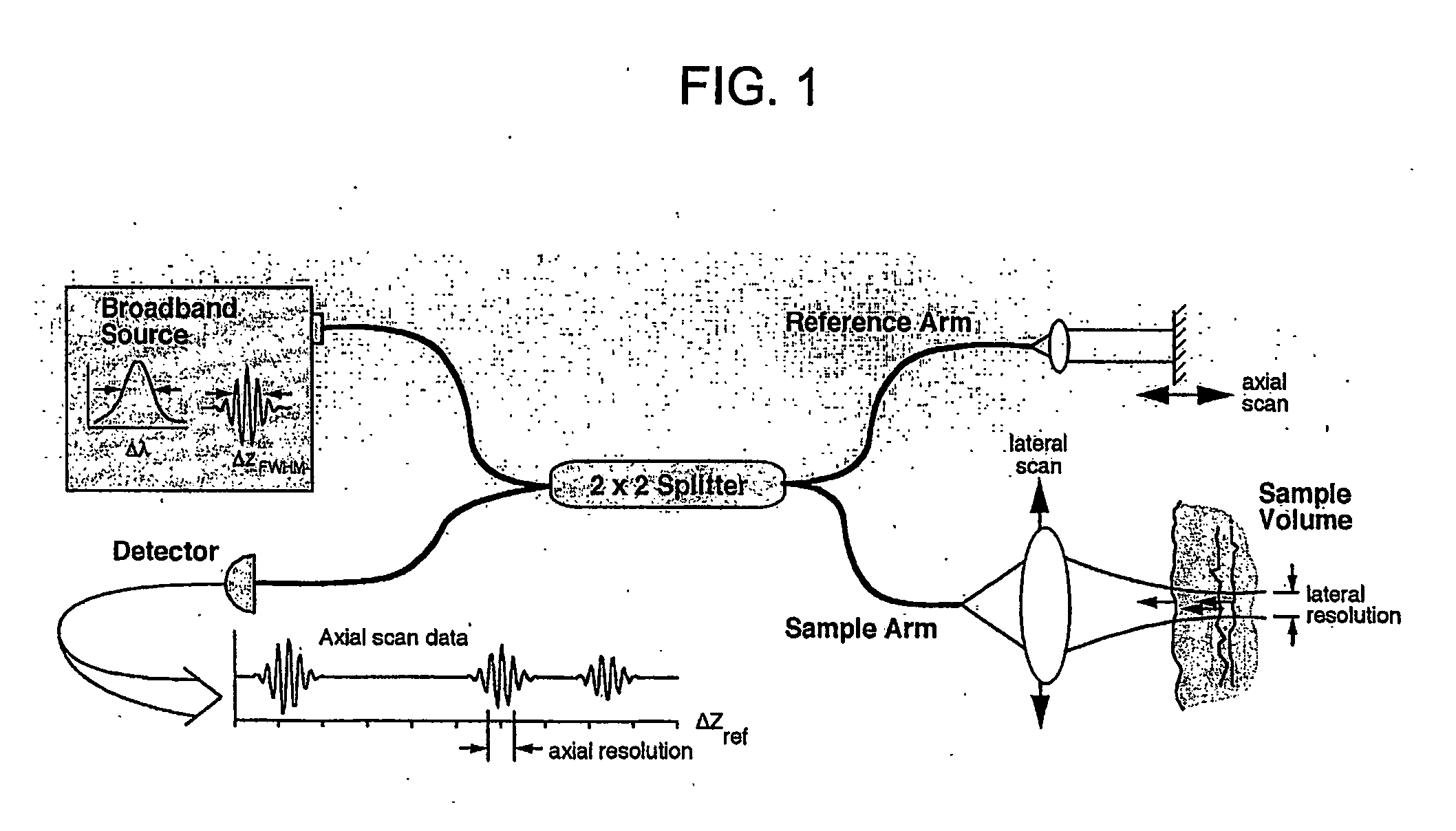
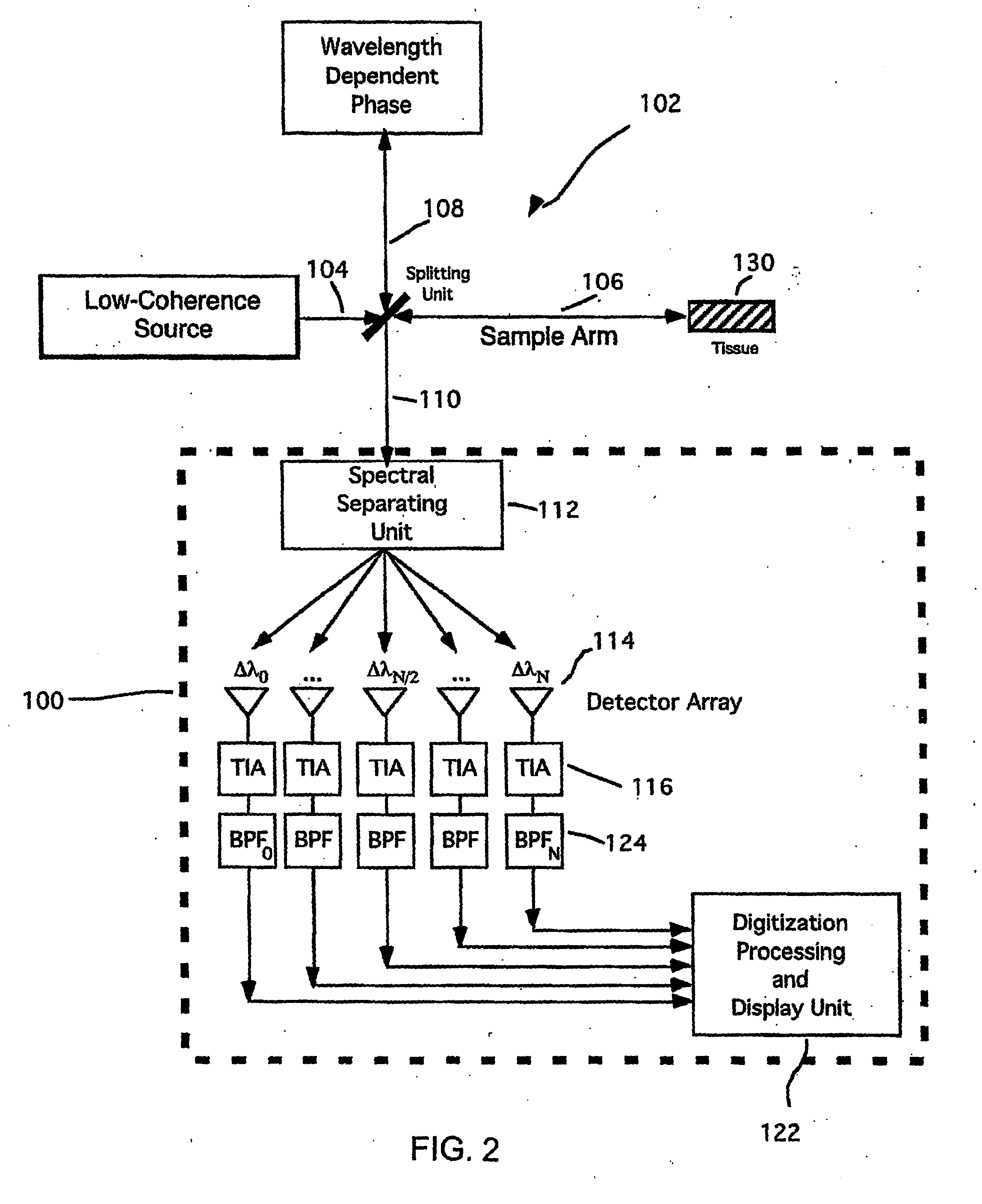
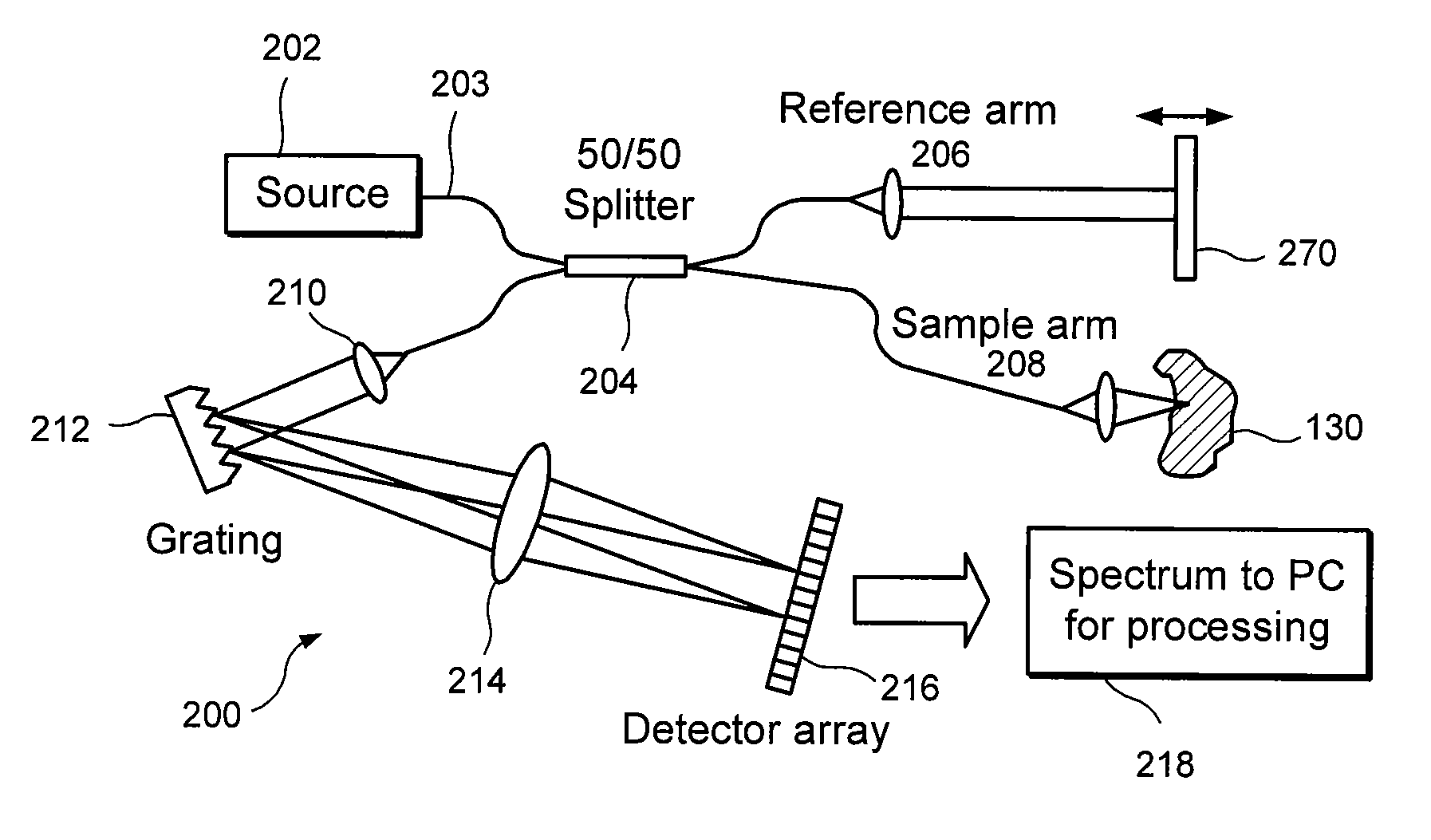
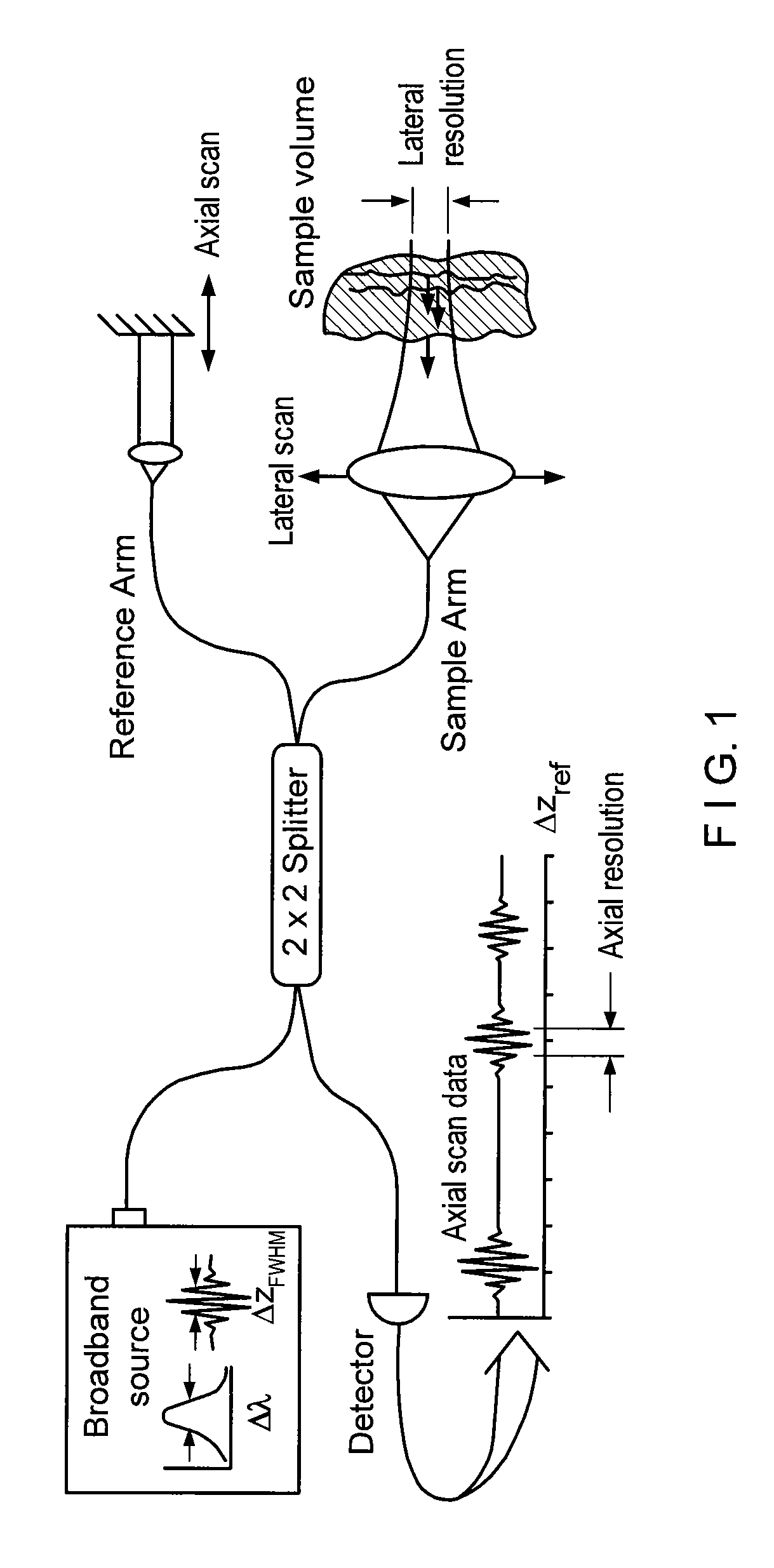
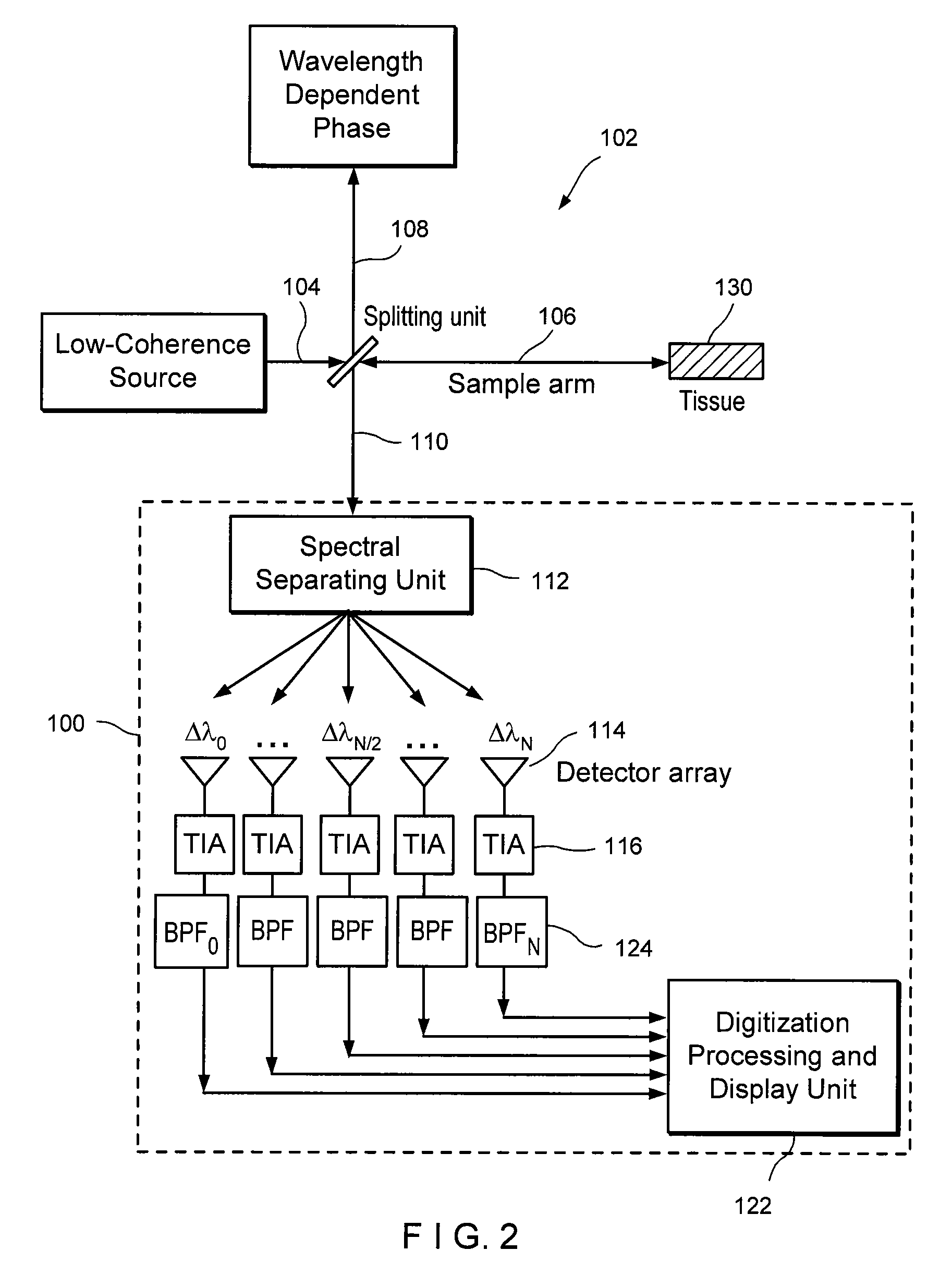
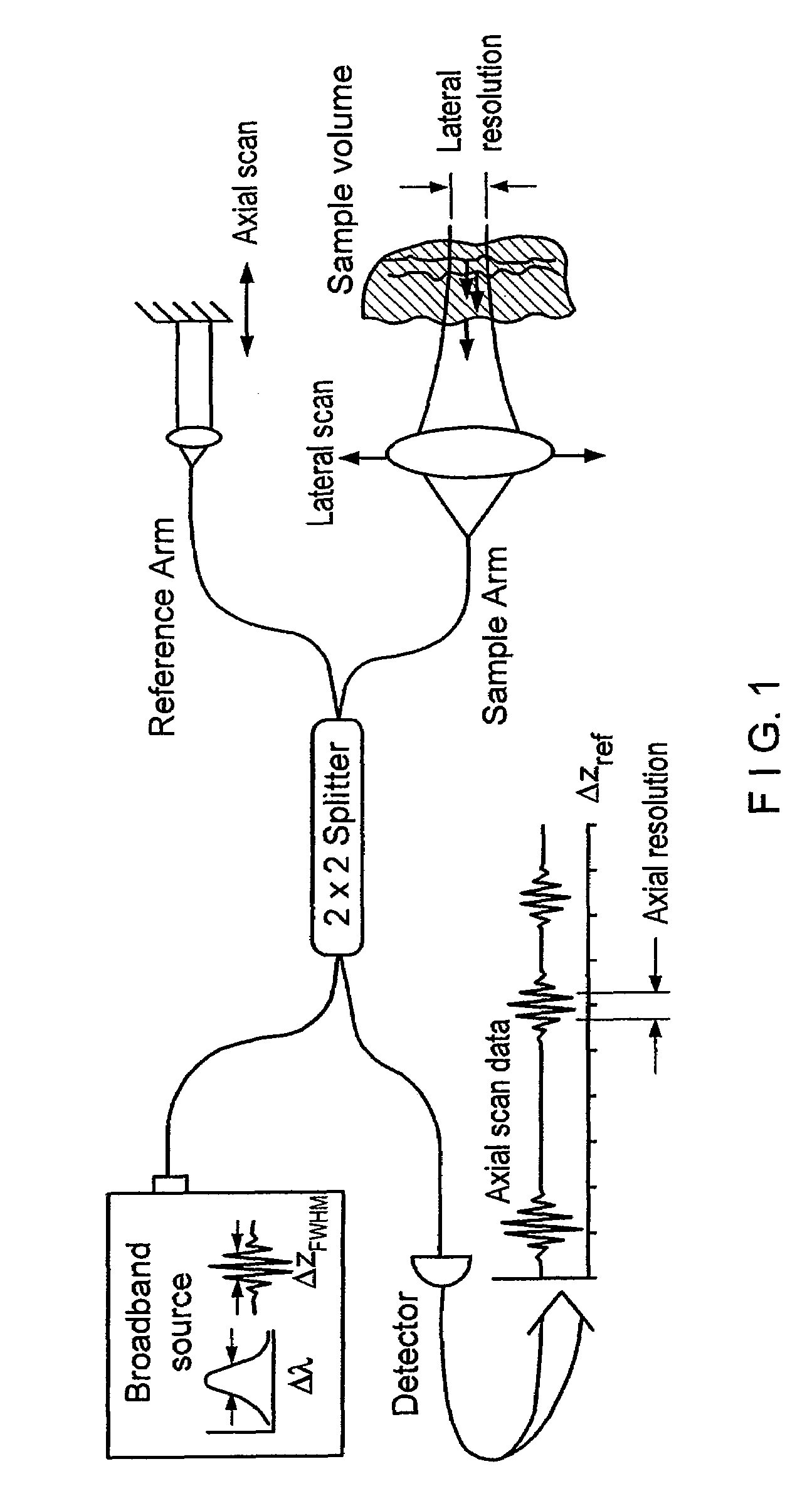
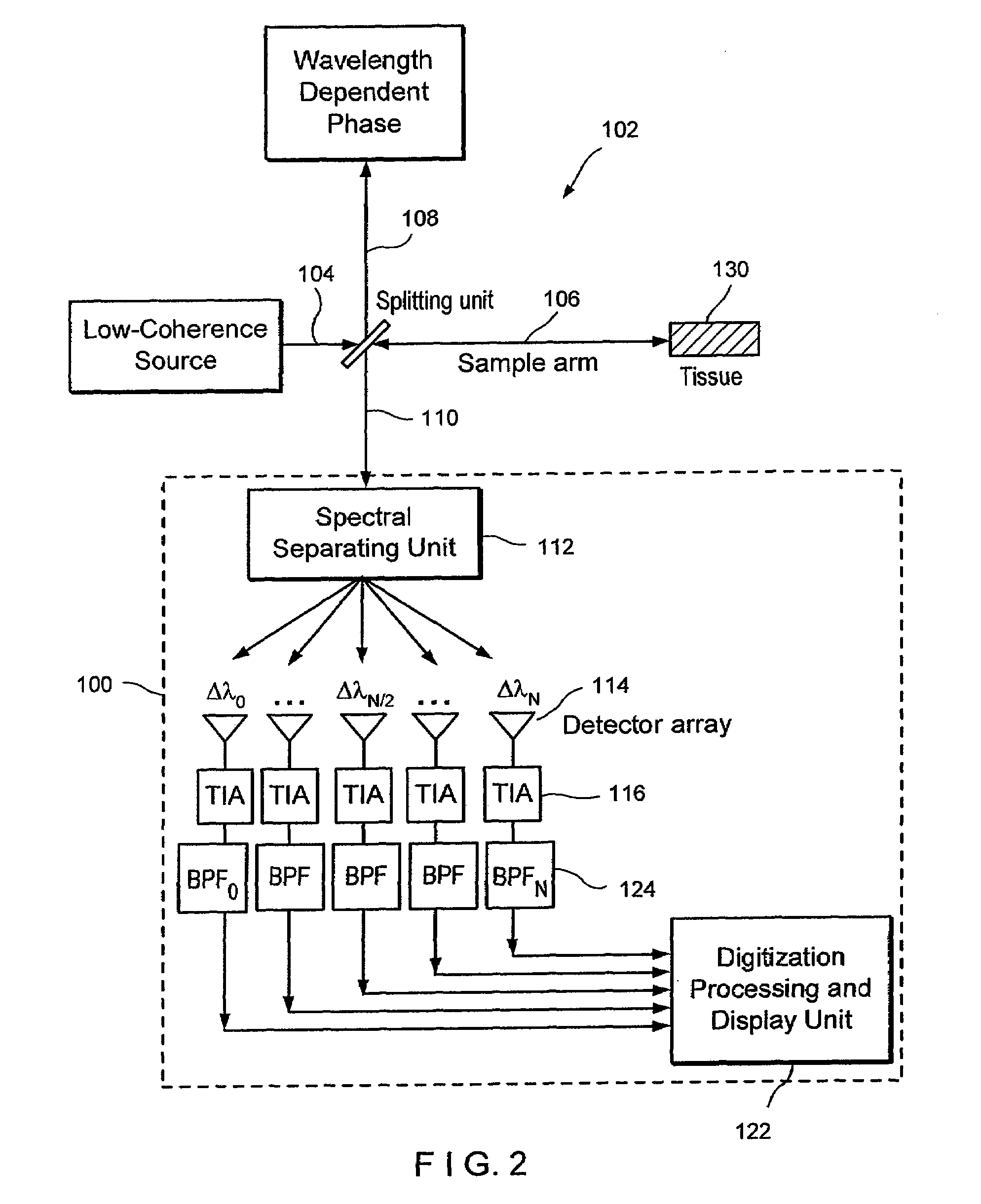
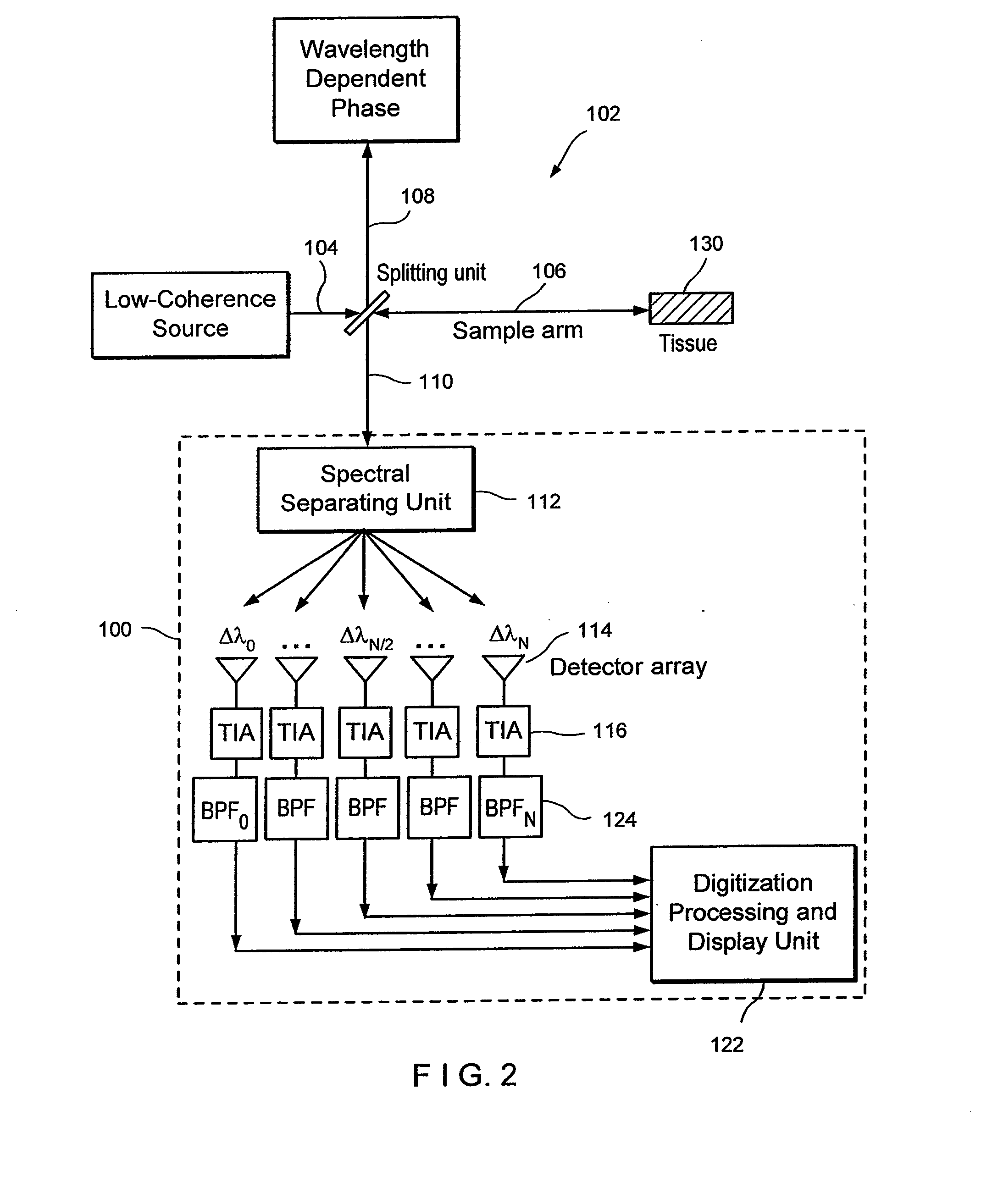
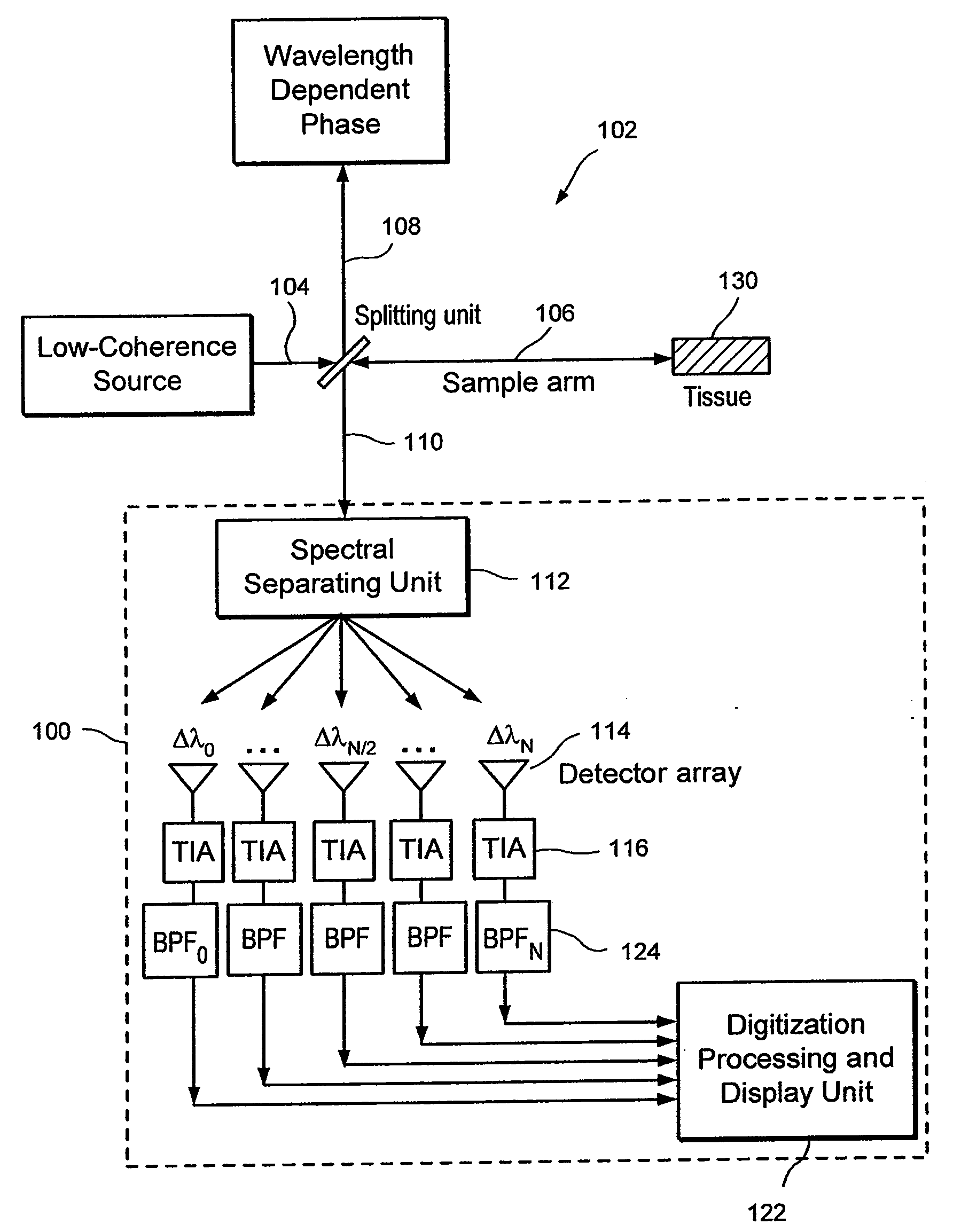
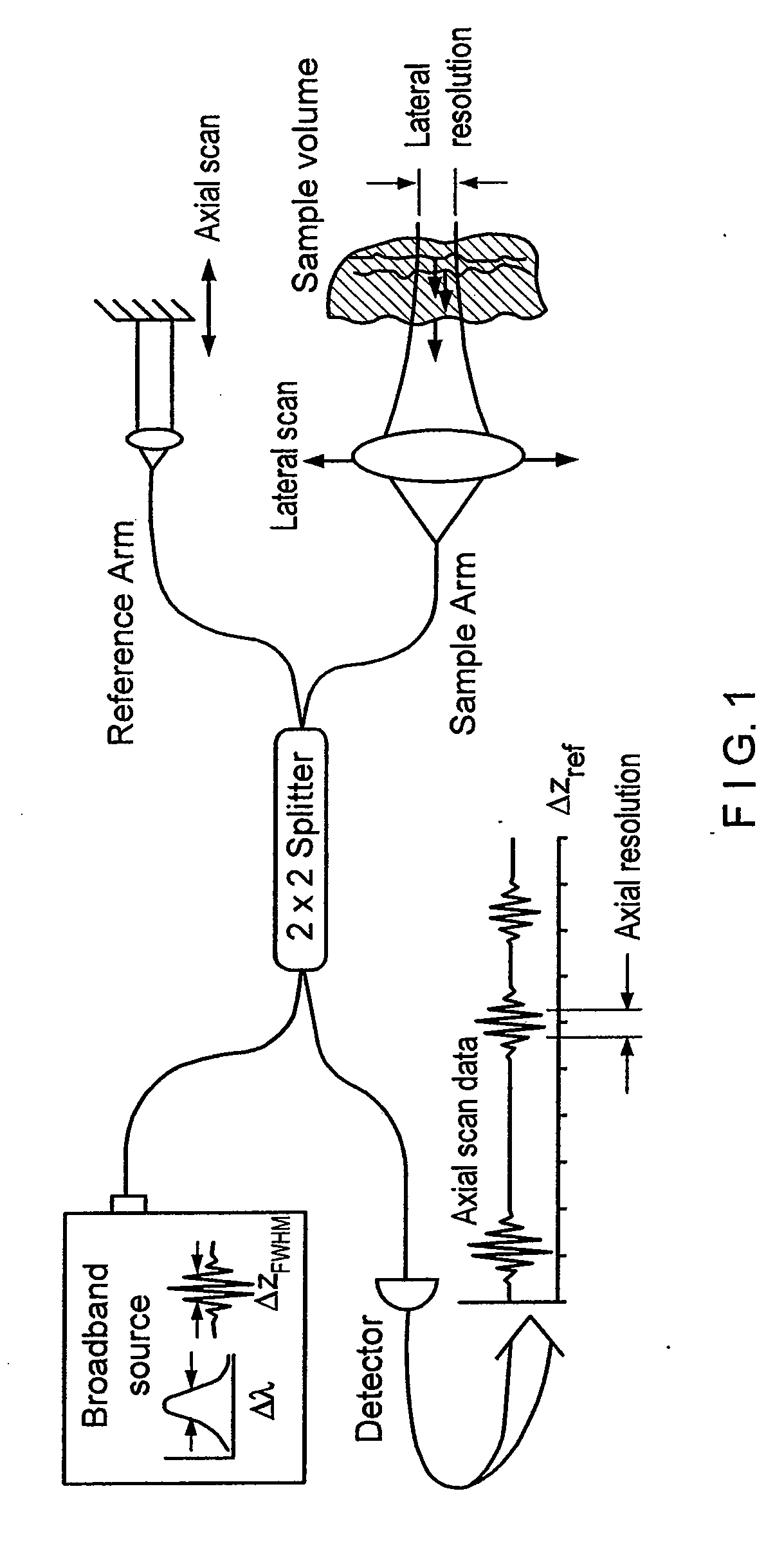
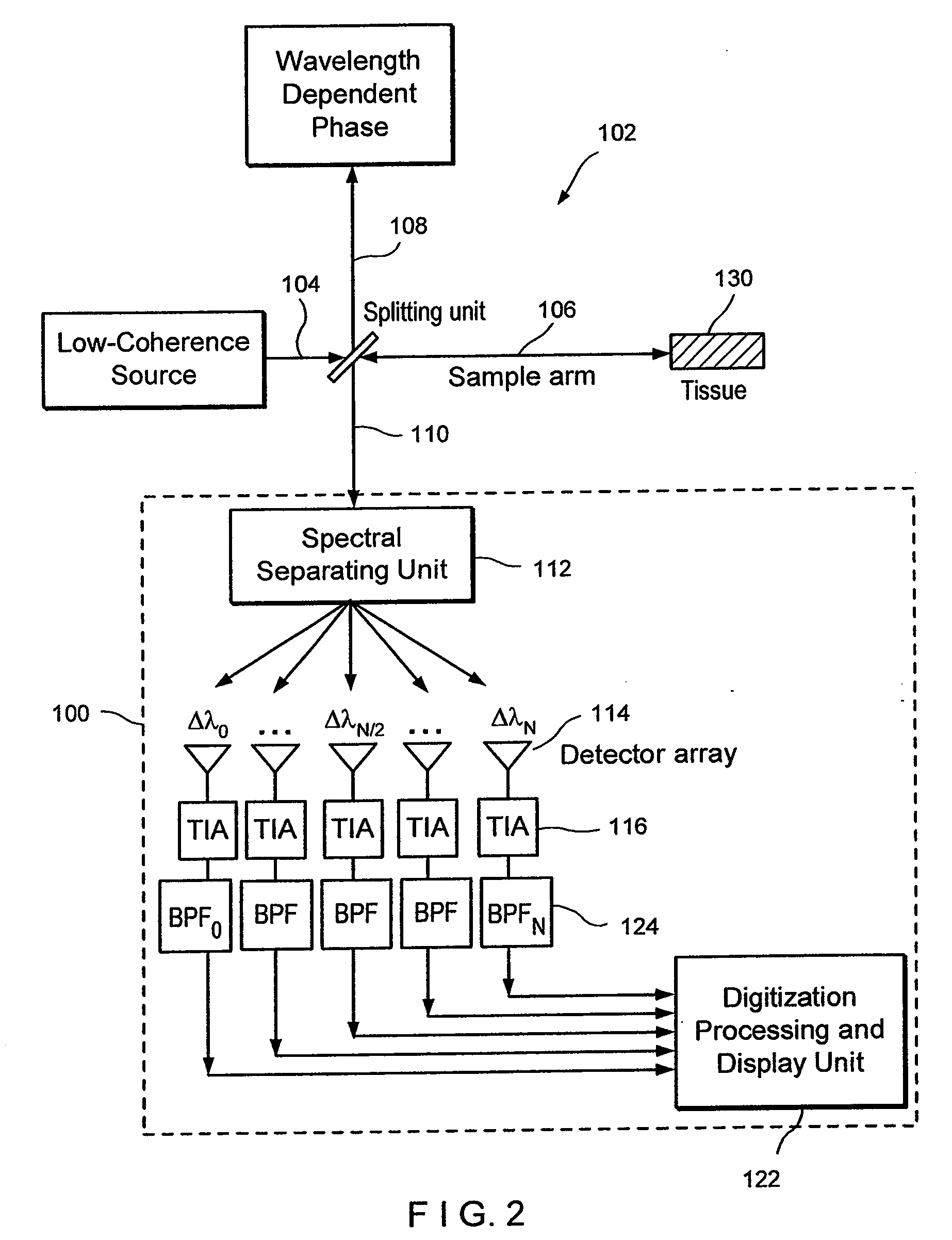
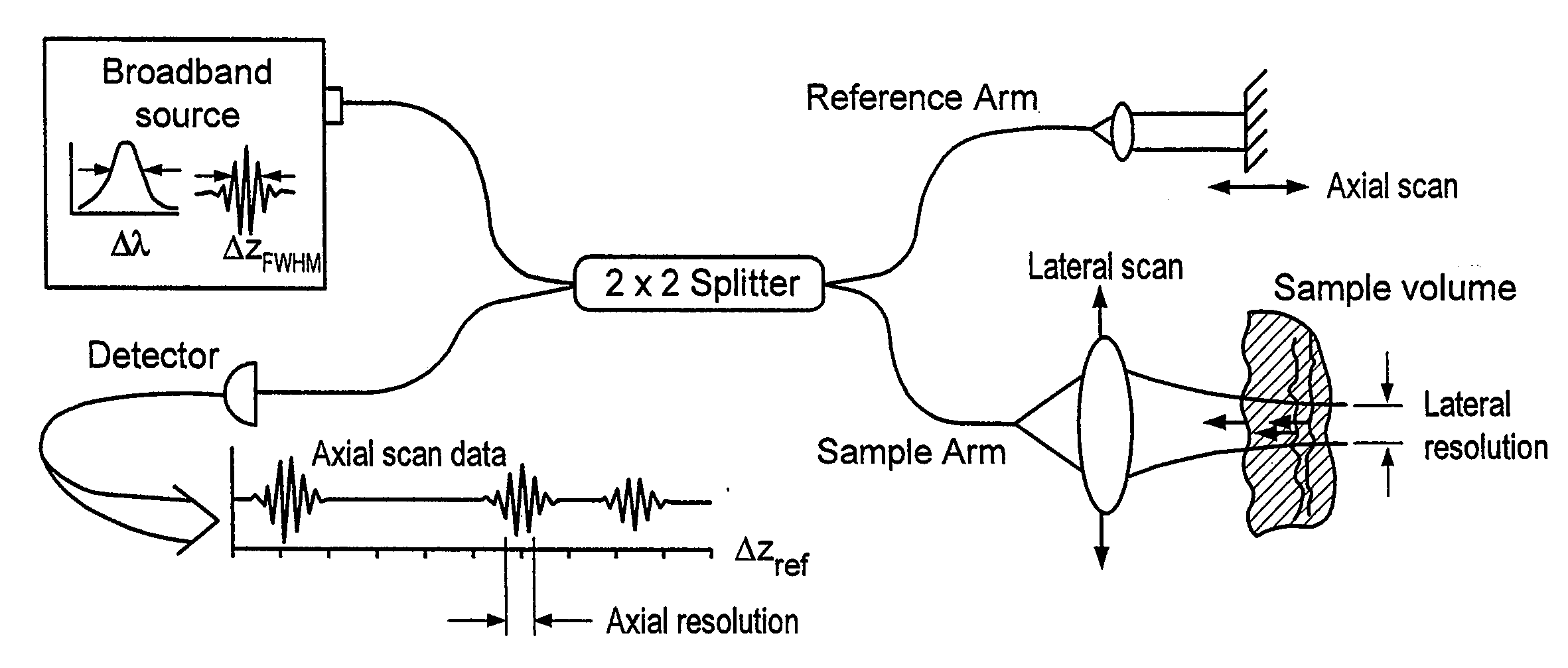
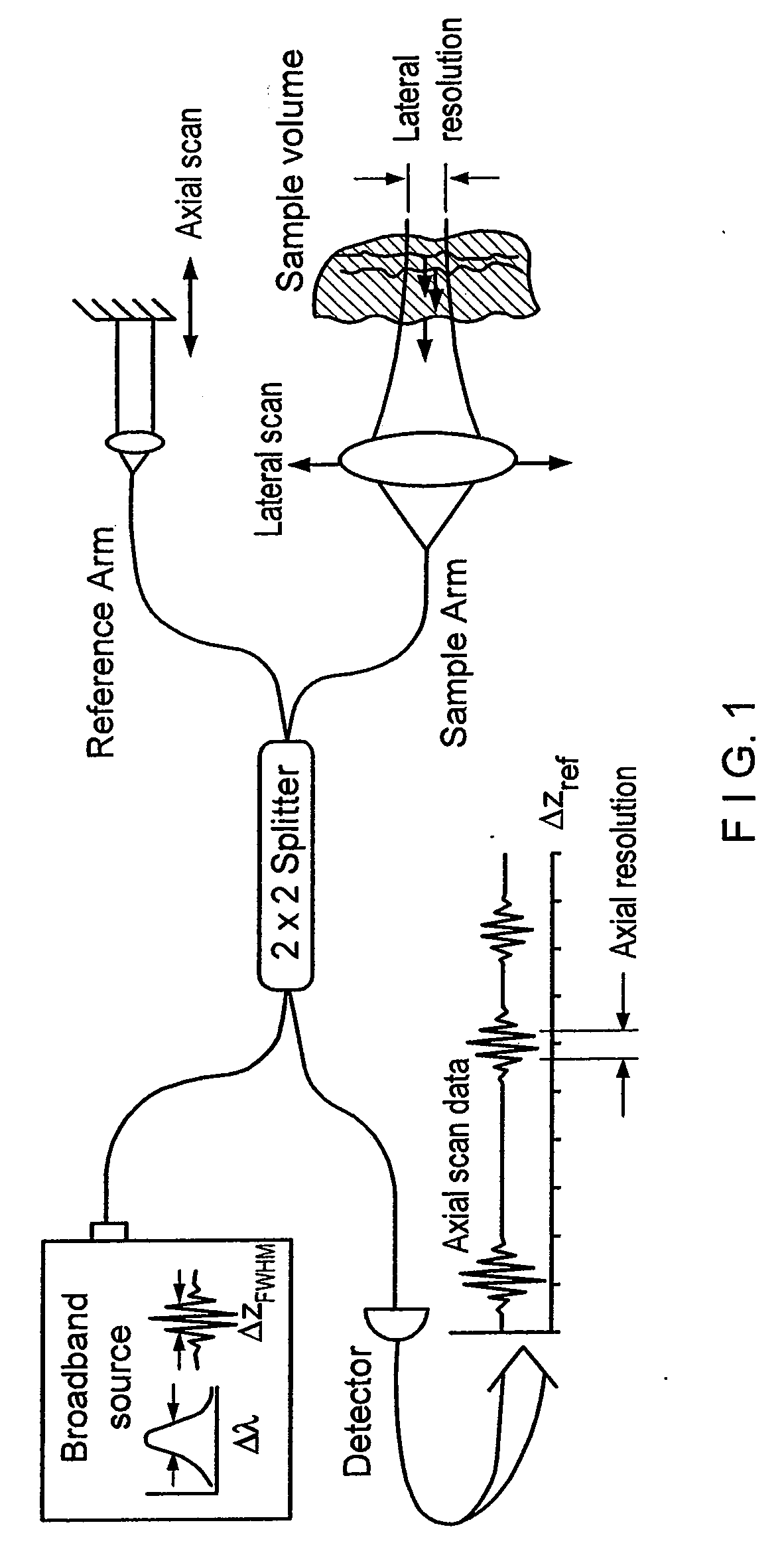
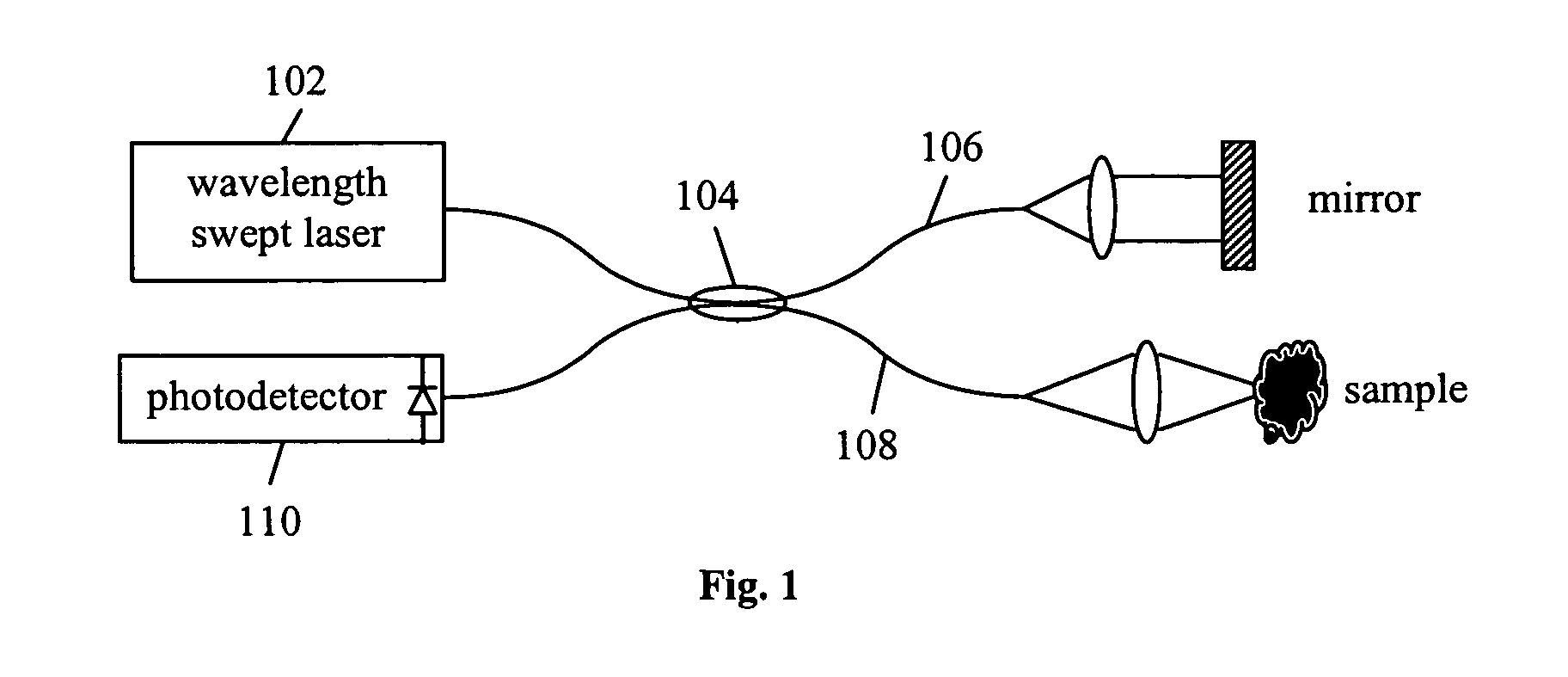
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
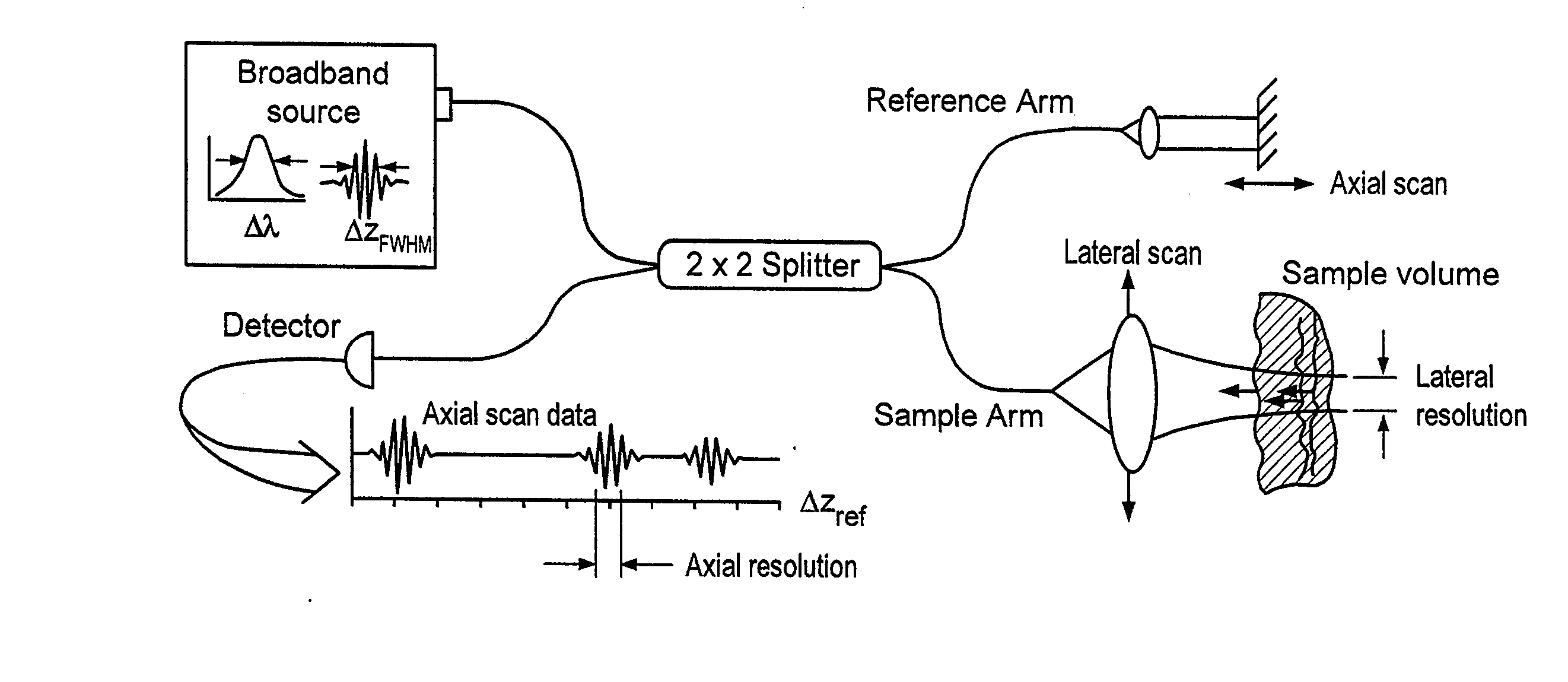
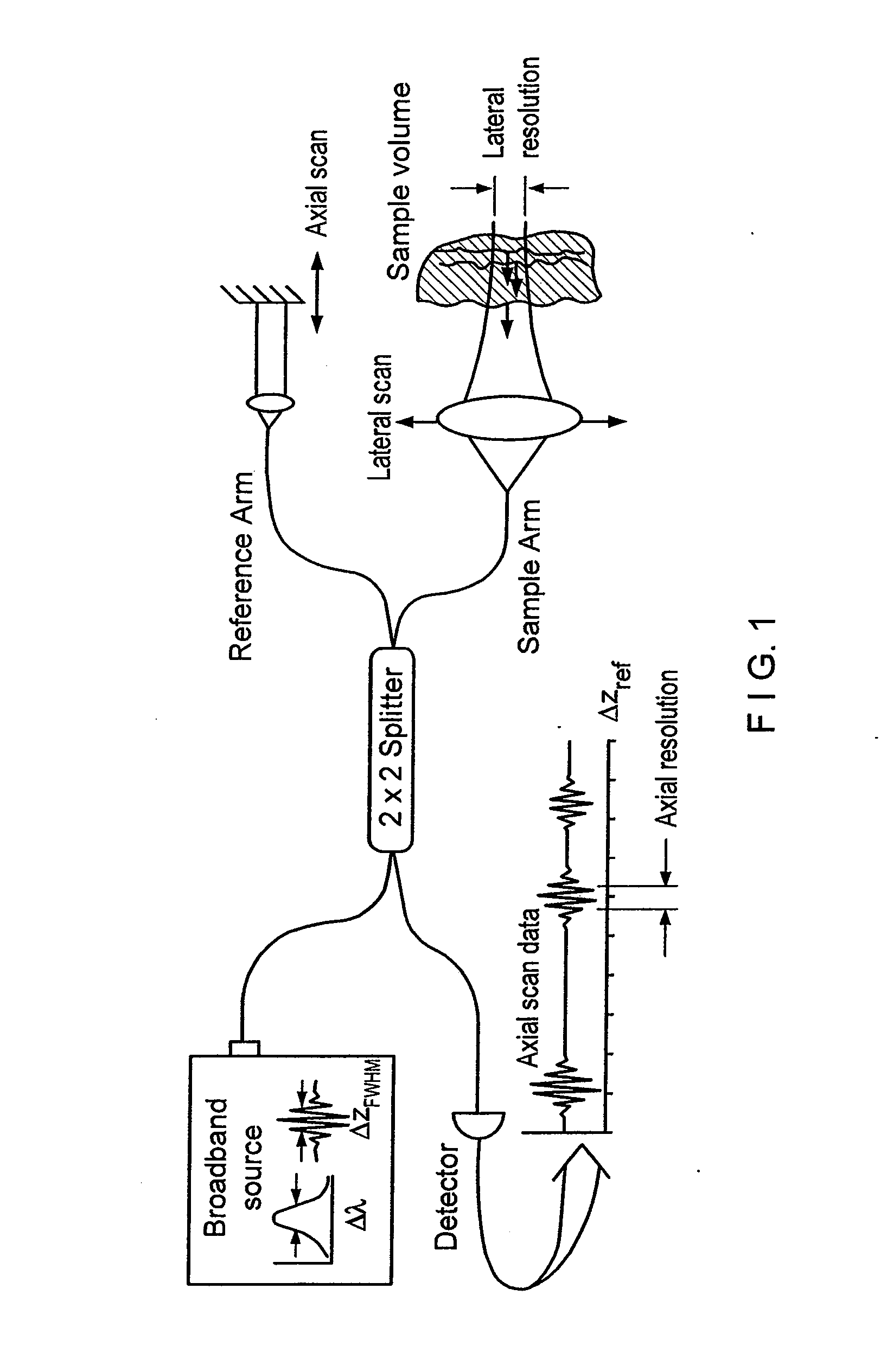
InactiveUS20050018201A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7355716B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
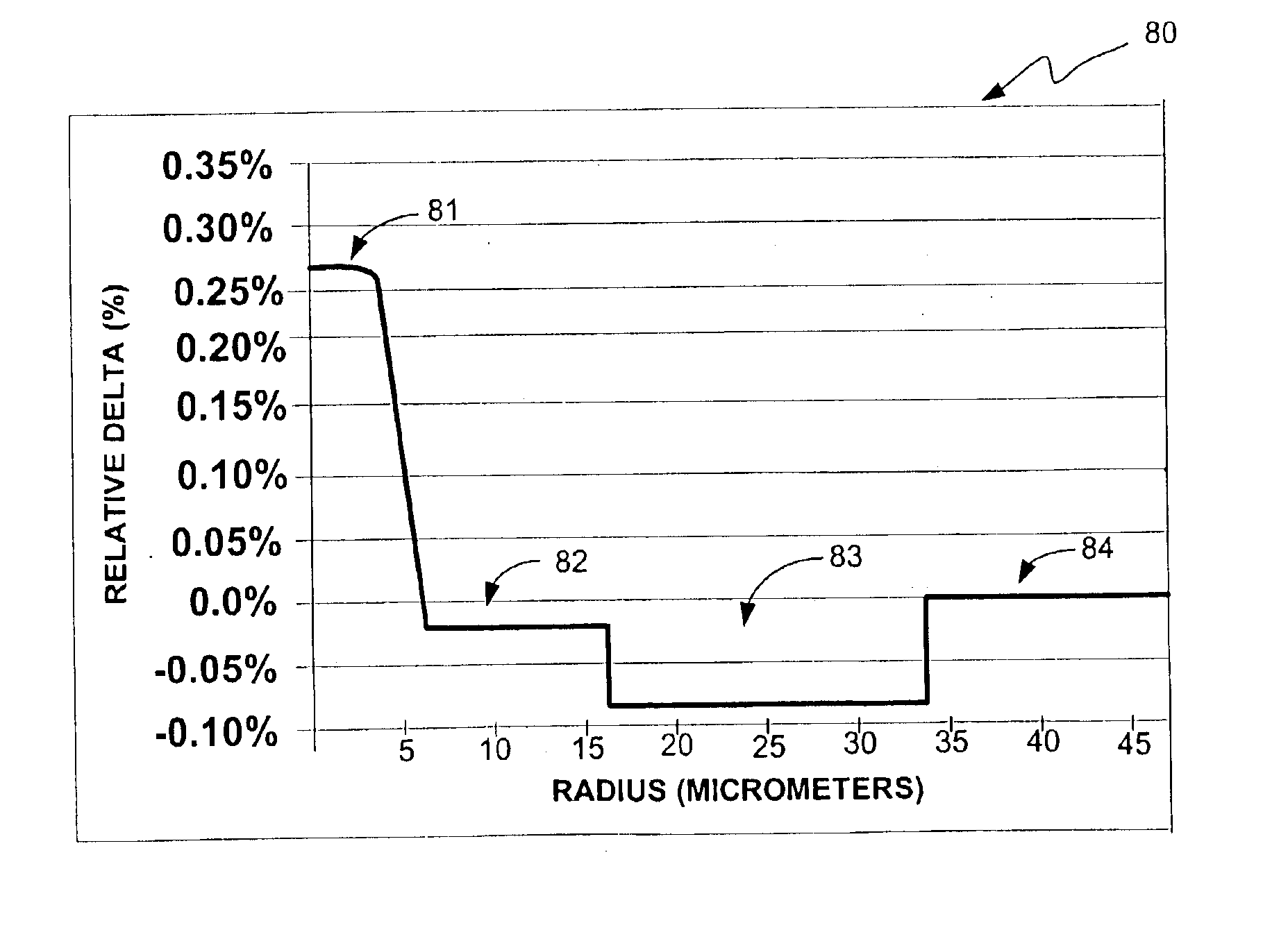
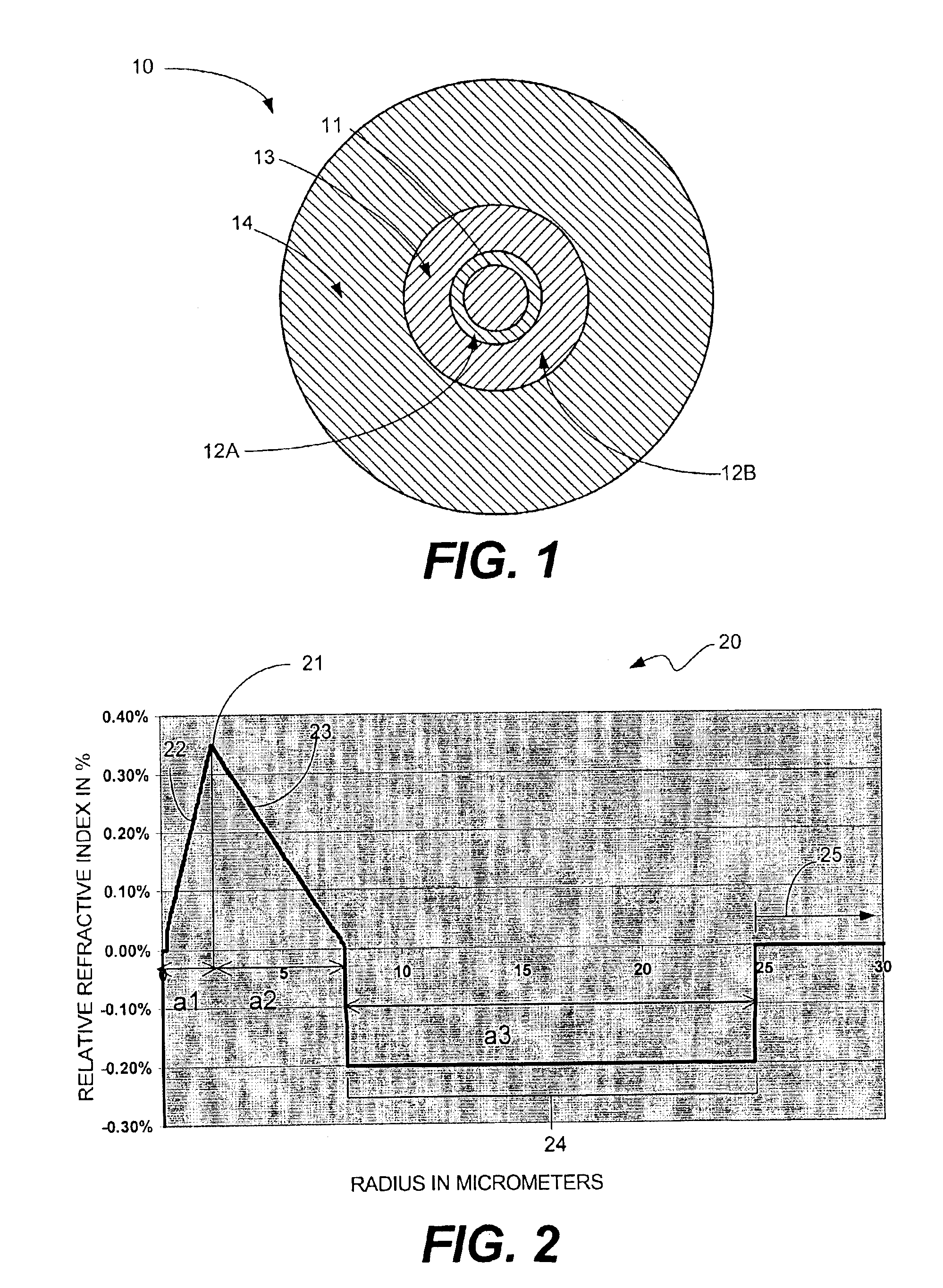
Super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber and communication system incorporating the same
ActiveUS6904218B2Increase the effective areaLow cutoff wavelengthOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberUltrasound attenuation
A super-large-effective-area (SLA) optical fiber that is suitable for communicating over a wide wavelength range and that, because of its large effective area, suppresses nonlinear effects that typically result from interaction between signal channels. The effective area, Aeff, of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is equal to or greater than approximately 80 μm2 at a wavelength window around 1310 nm. The cutoff wavelength of the SLA fiber of the present invention preferably is less than 1310 nm. Thus, the SLA fiber of the present invention has a very large effective area and a very low cutoff wavelength. In accordance with the present invention, a variety of SLA fibers are provided that all have very large effective areas and desirable transmission properties. The large effective areas of the SLA fibers of the present invention enable nonlinear effects to be suppressed, as well as Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in analog transmission. The large effective areas also enable attenuation to be reduced. The result of suppressing nonlinear effects and reducing attenuation enable signals to be transmitted over long distances and over a broad bandwidth.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Gap-mode waveguide
ActiveUS8952678B2Low dispersionMultiple-port networksResistance/reactance/impedenceUltrasound attenuationWaveguide
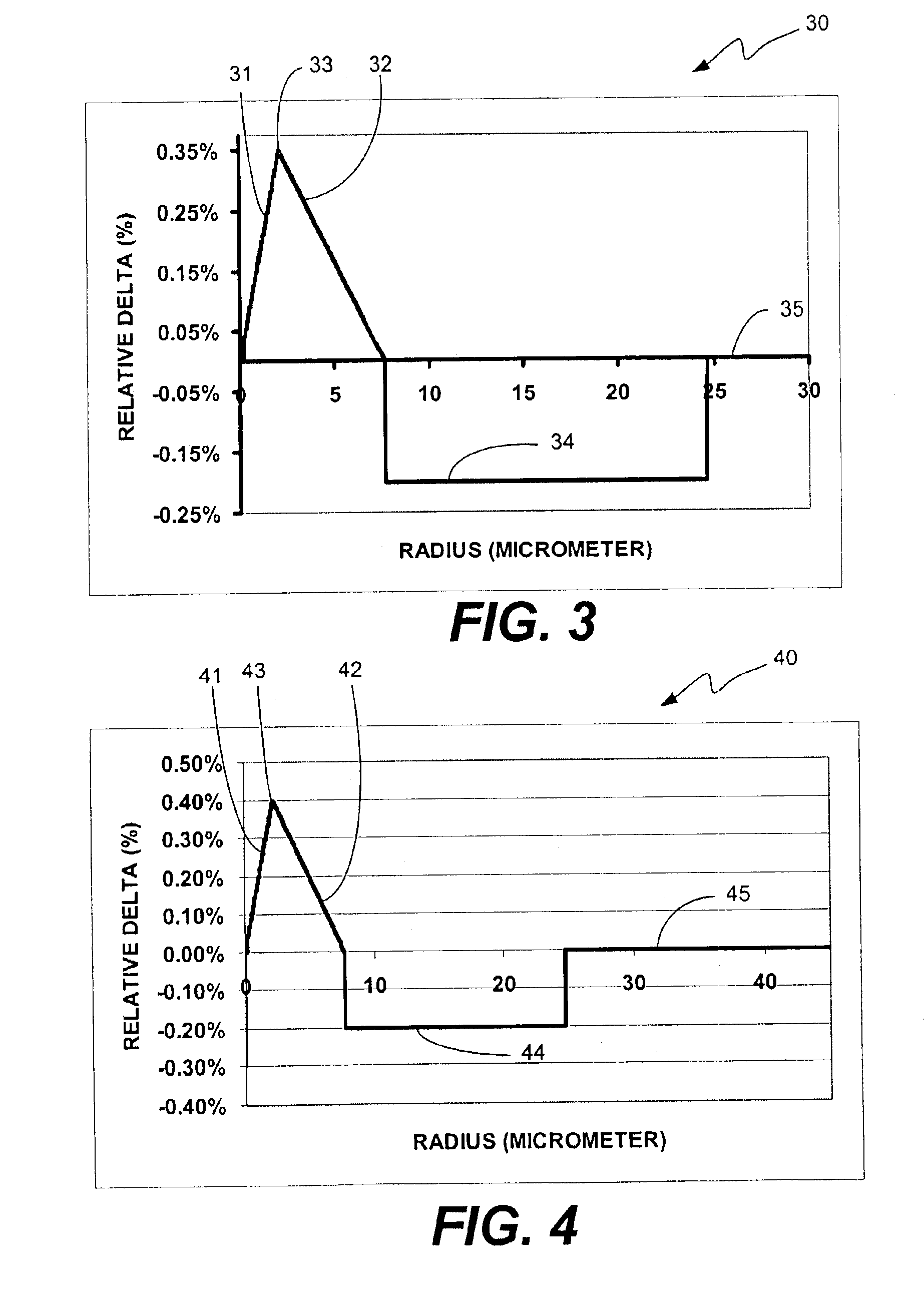
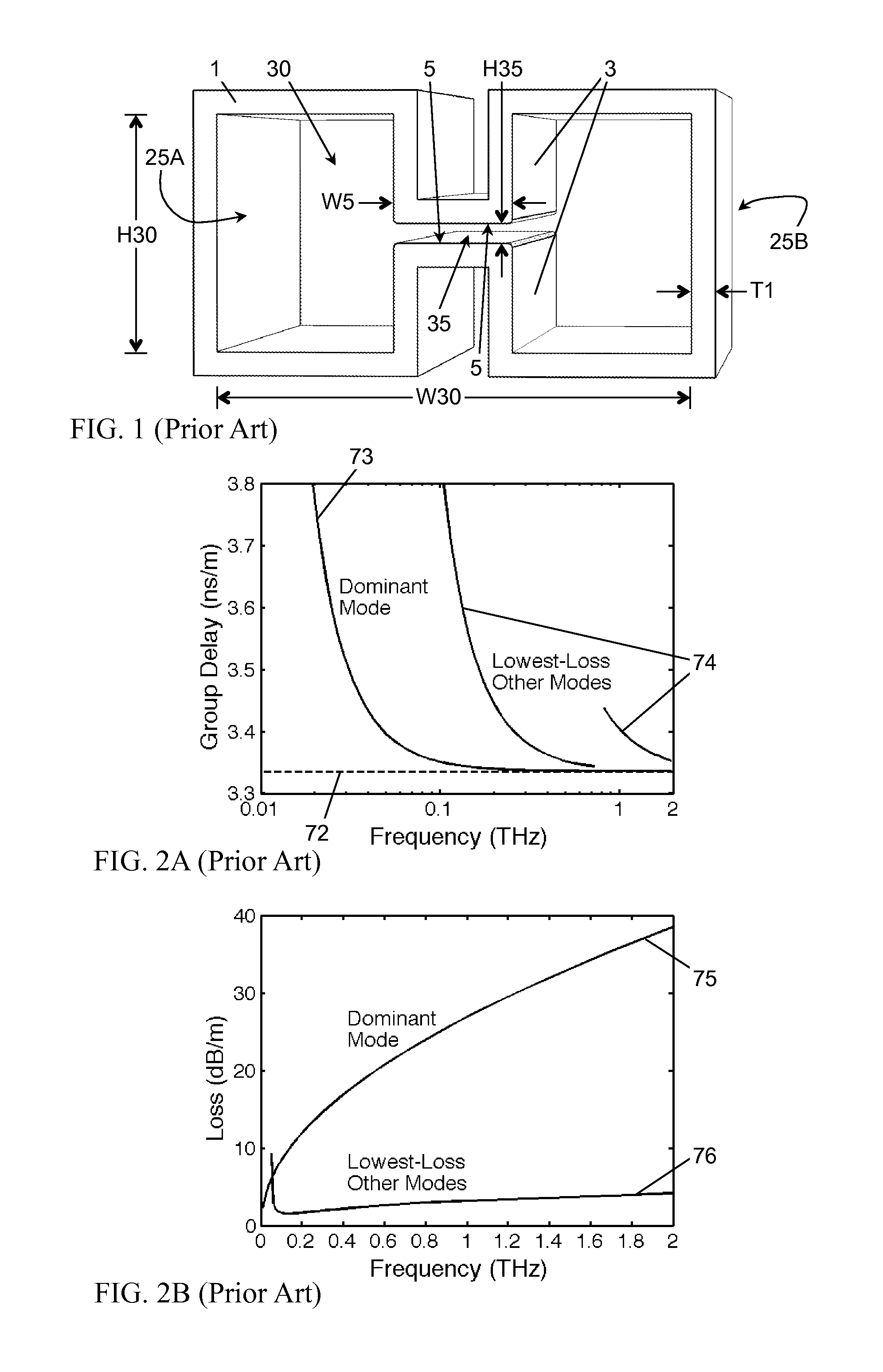
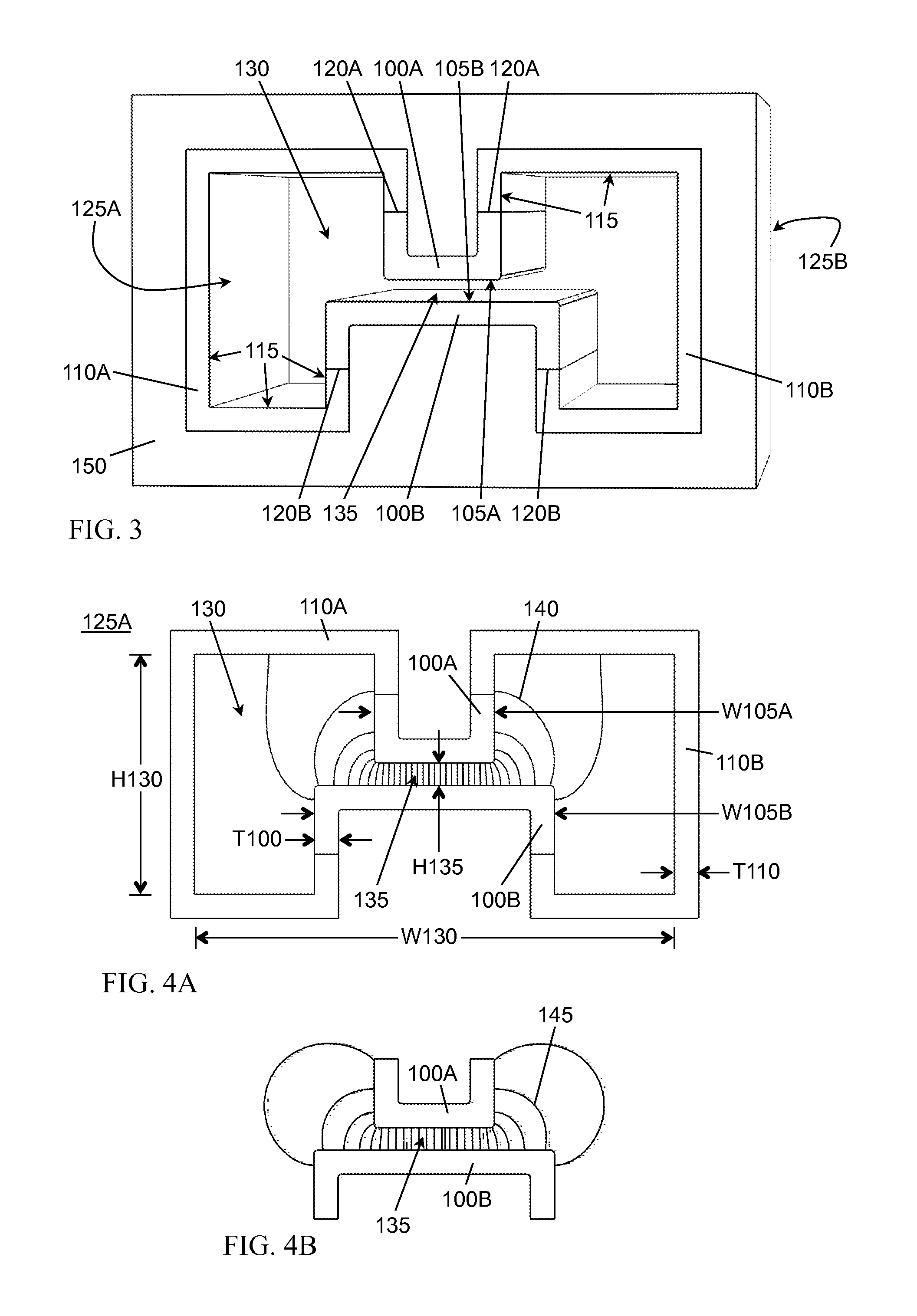
In a gap-mode waveguide embodiment, an interior gap in a tubular waveguide principally condenses a dominant gap mode near the interior gap, and an absorber dissipates electromagnetic energy away from the gap mode. In this manner, the gap mode may dissipate relatively little power in the absorber compared to other modes and propagate with lesser attenuation than all other modes. A gap mode launched into a gap-mode waveguide may provide for low-loss, low-dispersion propagation of signals over a bandwidth including a multimode range of the waveguide. Gap-mode waveguide embodiments of various forms may be used to build guided-wave circuits covering broad bandwidths extending to terahertz frequencies.
Owner:GIBONEY KIRK S
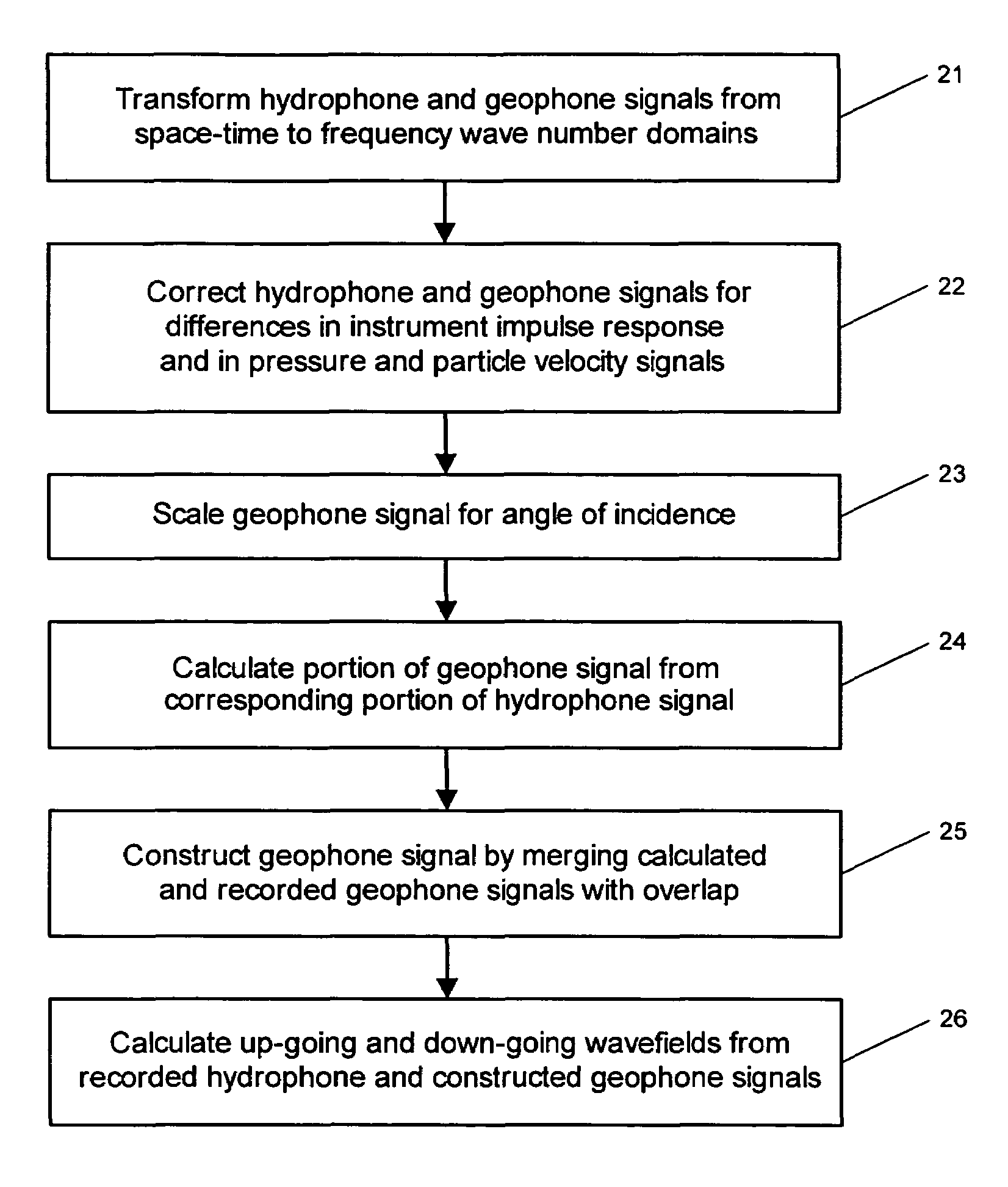
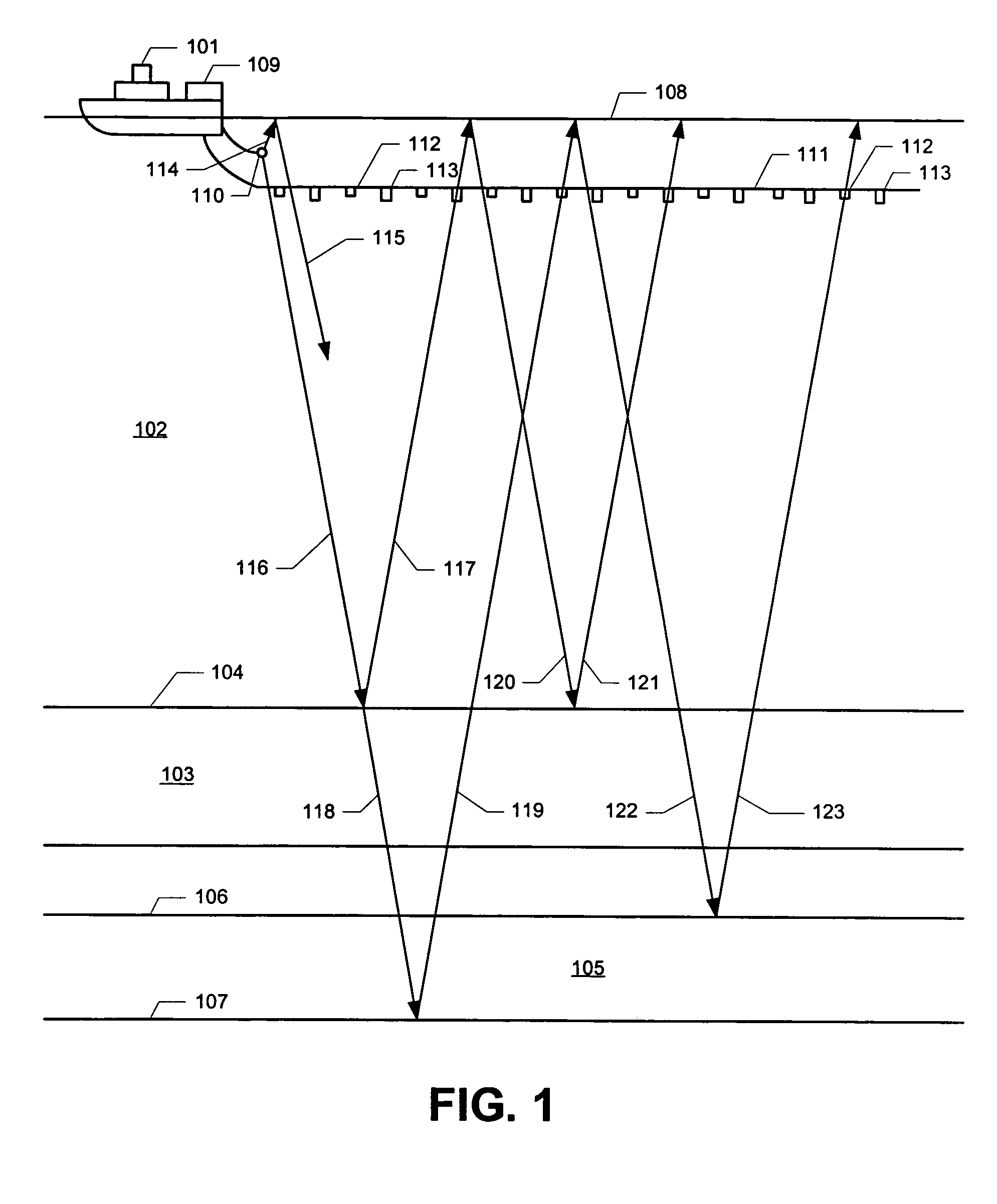
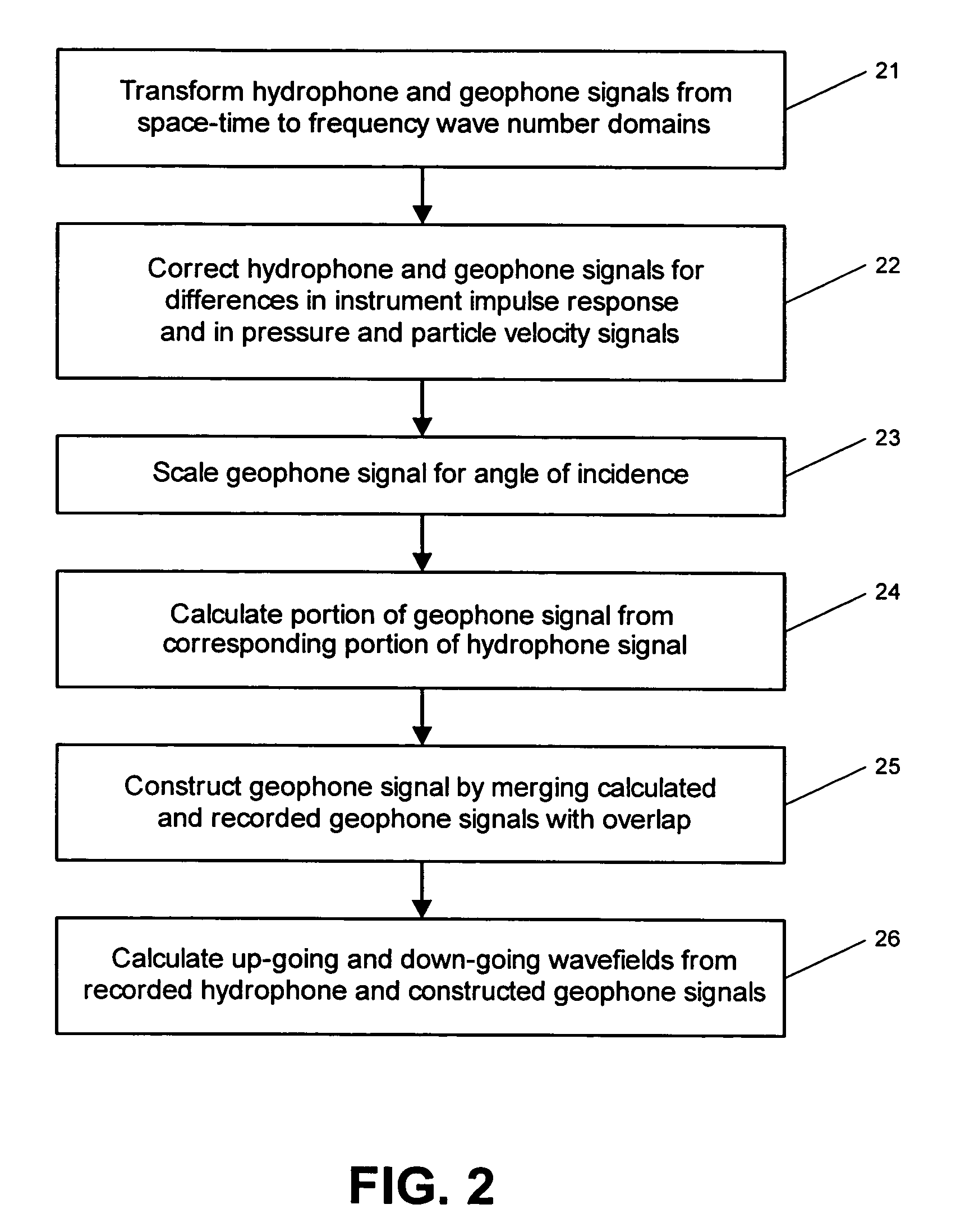
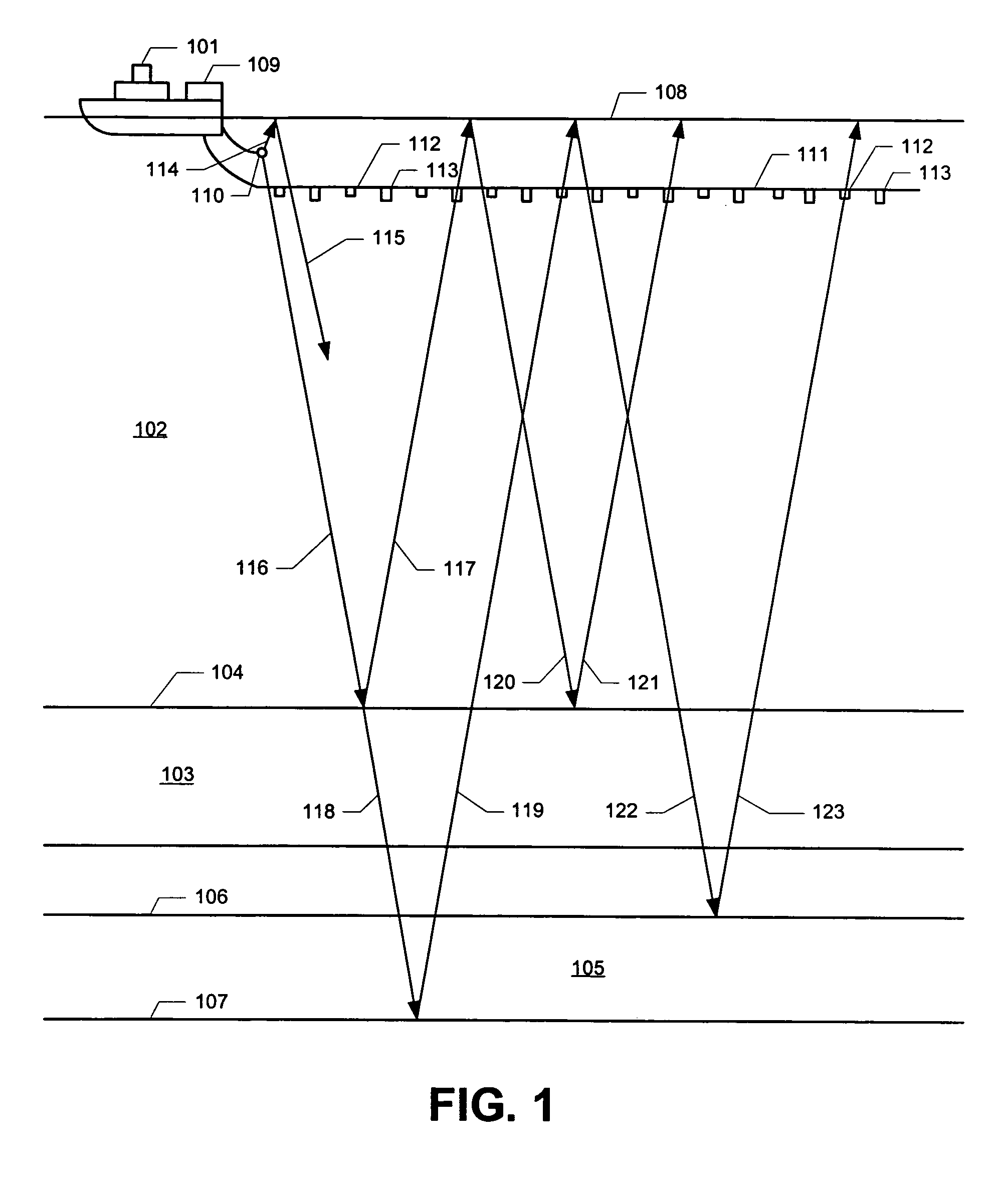
System for combining signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors in marine seismic streamers
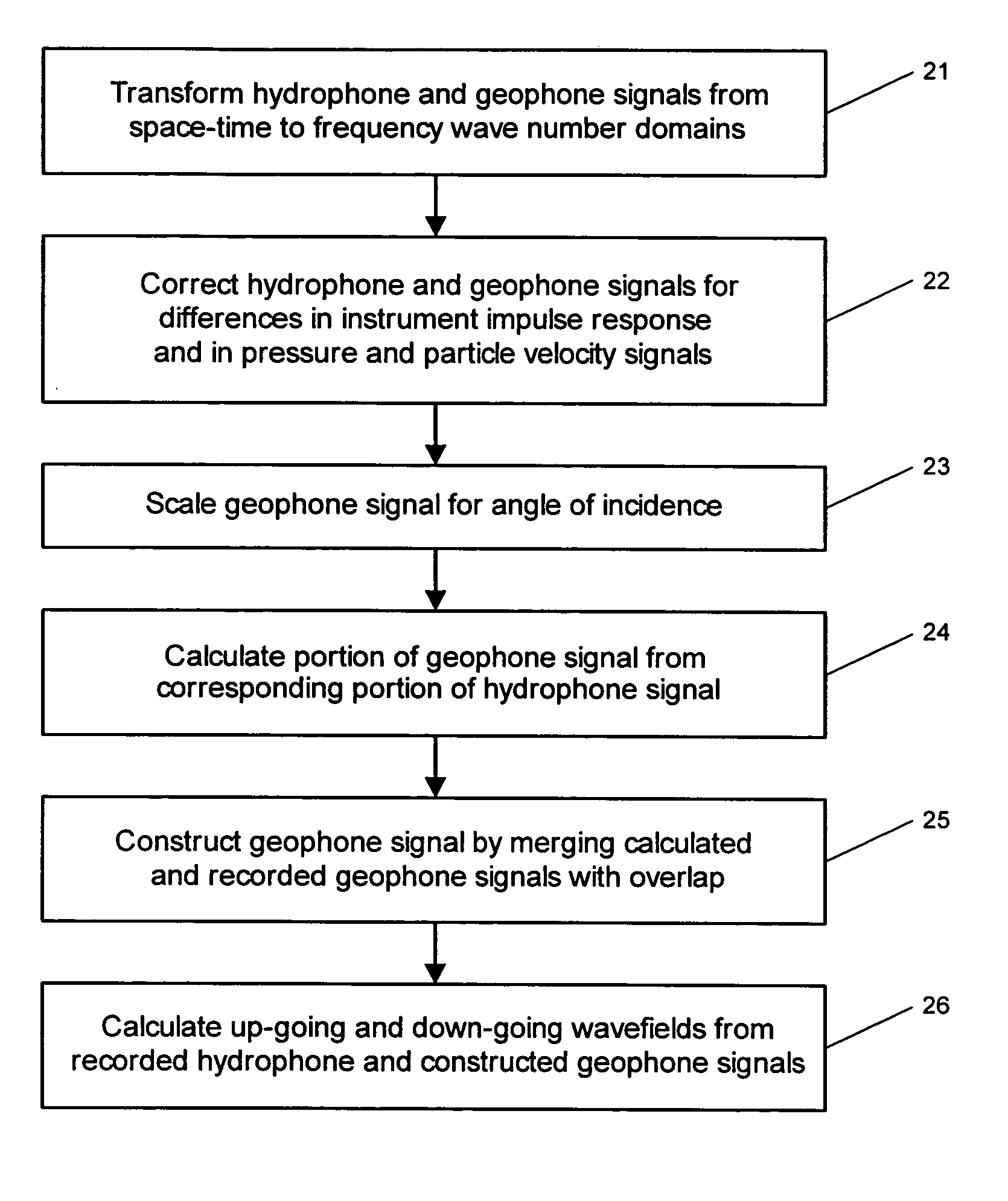
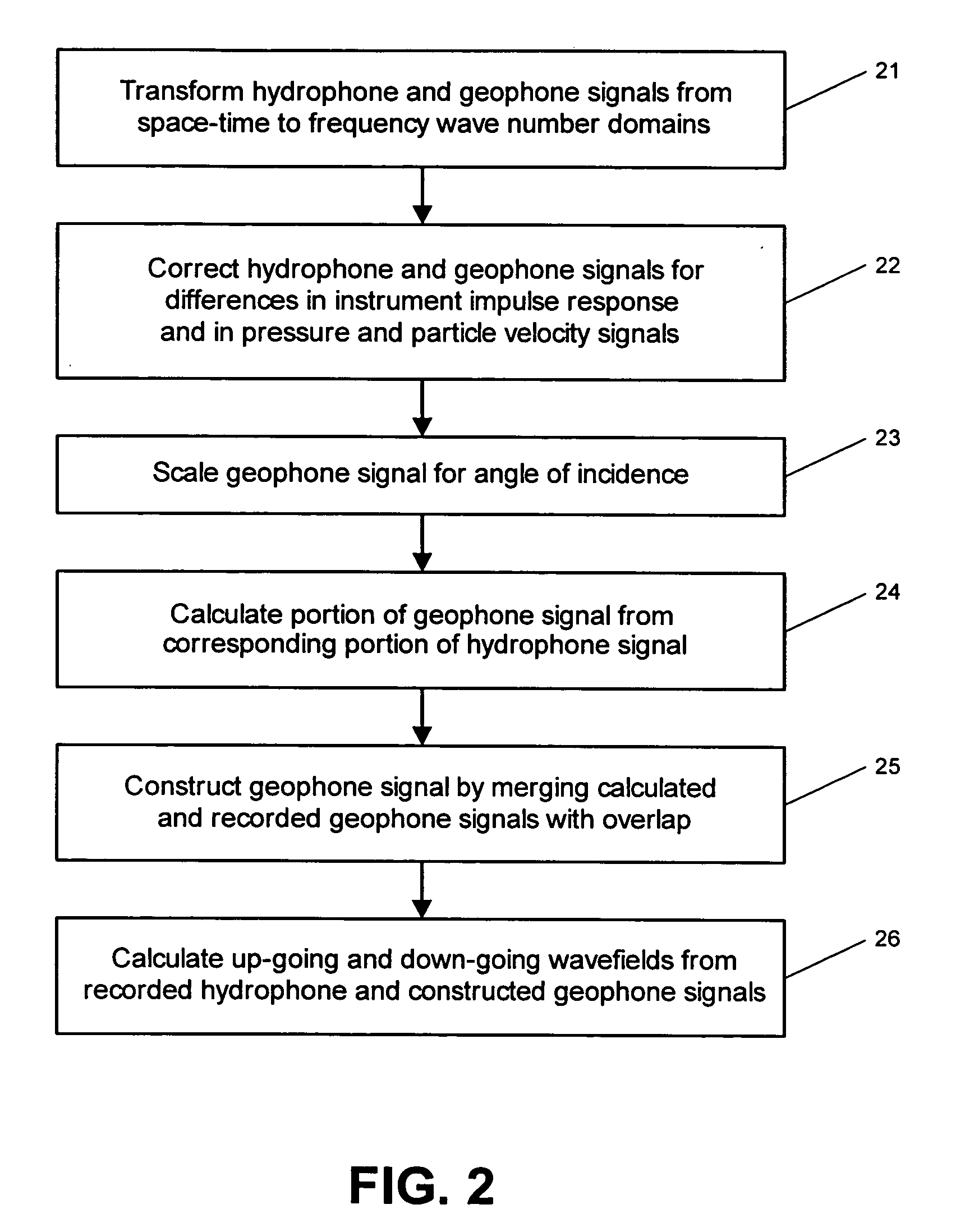
Signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors located in marine seismic streamers are combined to generate pressure sensor data and particle motion data with substantially the same broad bandwidth. The noisy low frequency part of the motion signals are calculated from the recorded pressure signals and merged with the non-noisy motion signals. The two broad bandwidth data sets can then be combined to calculate the full up- and down-going wavefields.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7643153B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
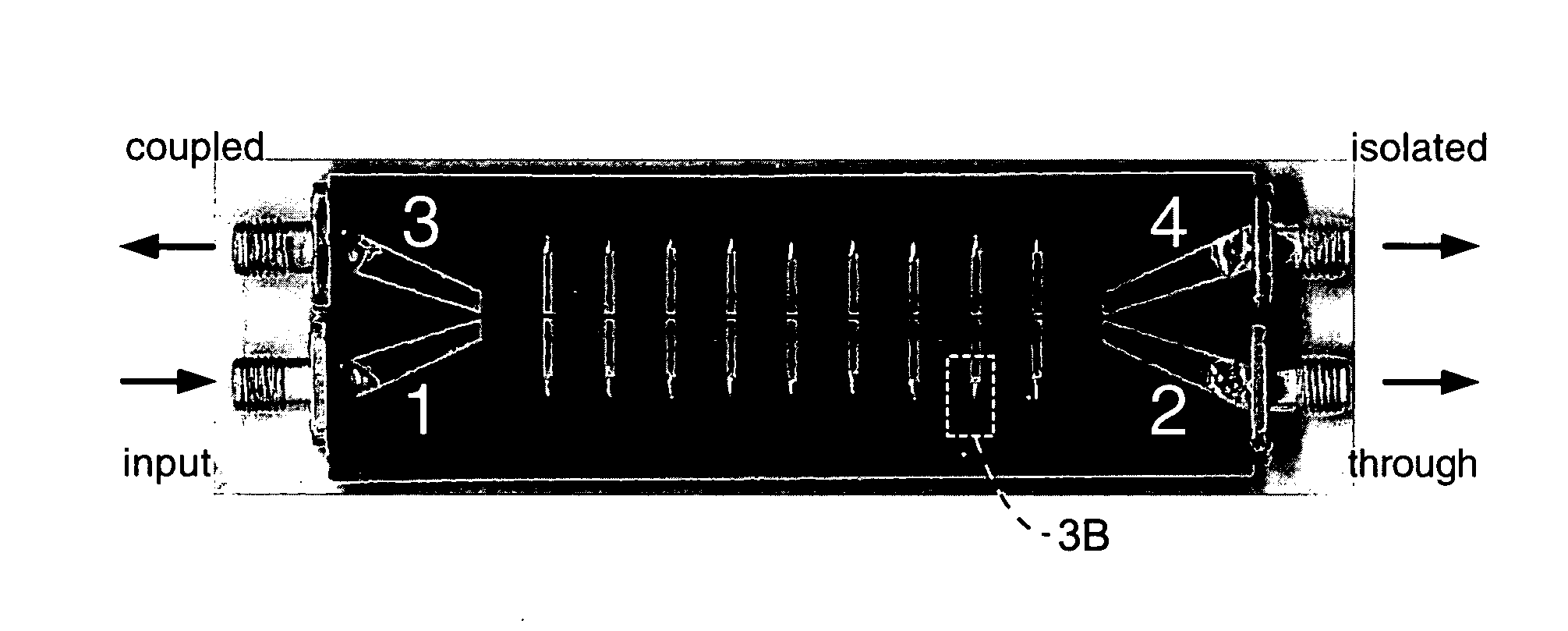
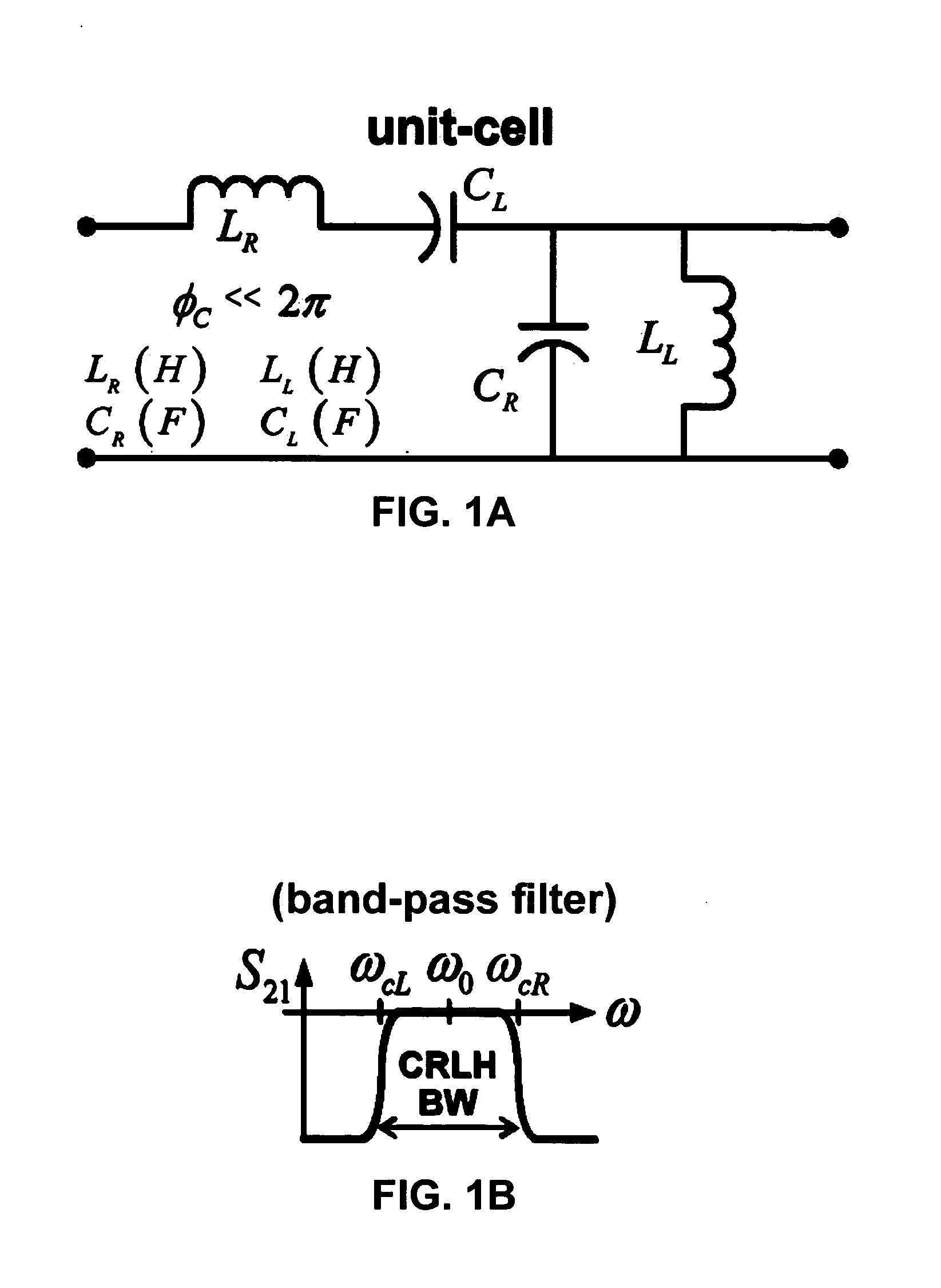
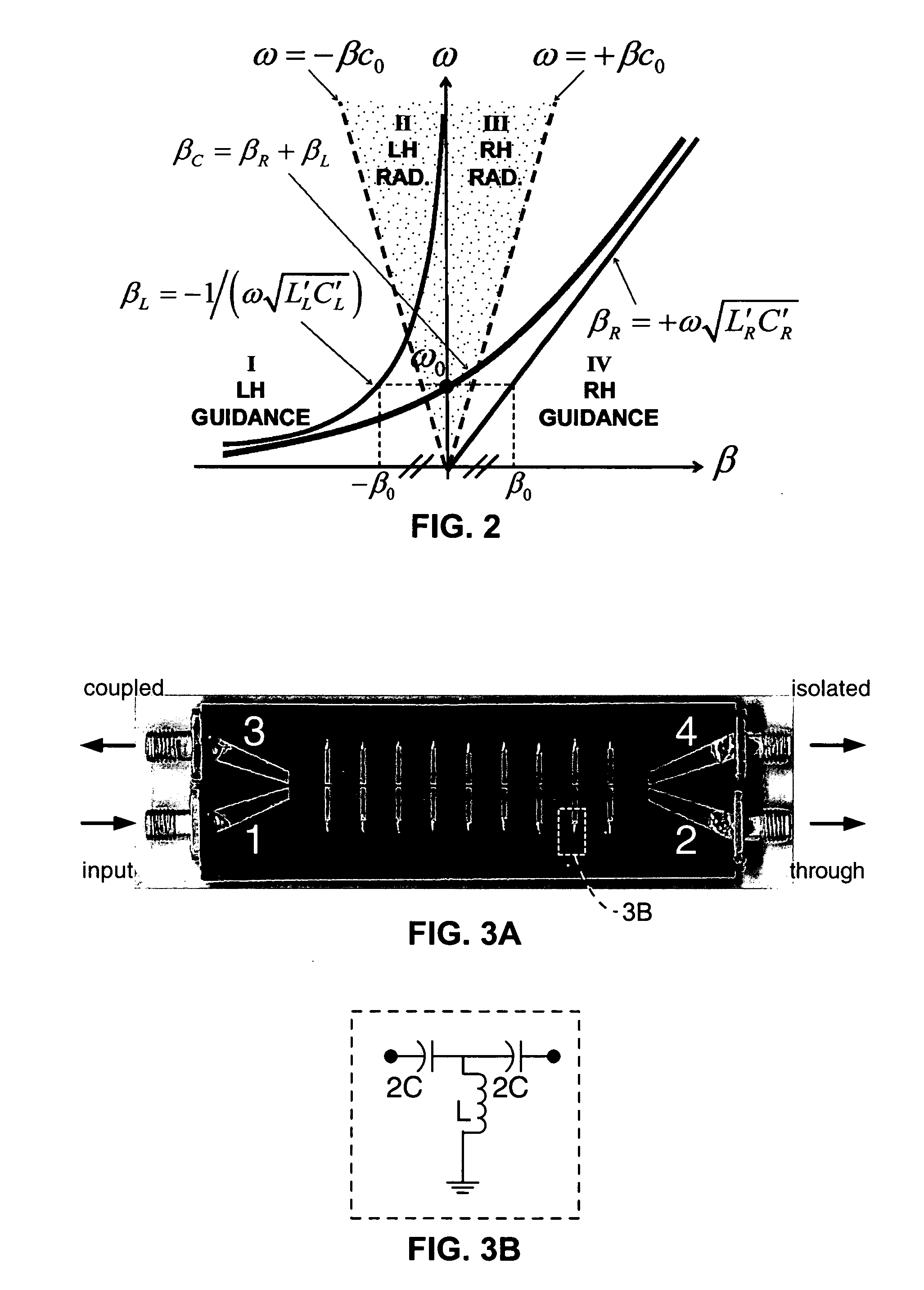
Composite right/left handed (CRLH) couplers
ActiveUS20050253667A1Reduce device sizeHigh bandwidthTransmissionCoupling devicesLoose couplingDecreased size
High-frequency couplers and coupling techniques are described utilizing artificial composite right / left-handed transmission line (CRLH-TL). Three specific forms of couplers are described; (1) a coupled-line backward coupler is described with arbitrary tight / loose coupling and broad bandwidth; (2) a compact enhanced-bandwidth hybrid ring coupler is described with increased bandwidth and decreased size; and (3) a dual-band branch-line coupler that is not limited to a harmonic relation between the bands. These variations are preferably implemented in a microstrip fabrication process and may use lumped-element components. The couplers and coupling techniques are directed at increasing the utility while decreasing the size of high-frequency couplers, and are suitable for use with separate coupler or couplers integrated within integrated devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tunable Dielectric Resonator Circuit
A dielectric resonator circuit is provided that is tunable over a broad frequency range and / or a broad bandwidth range. The center frequency is made tunable over a broad range by use of a dielectric tuning plug that is positioned in a through hole within the resonator. The bandwidth is made tunable over a broad range by tilting the resonators relative to the enclosure to increase the effective height of the cavity as seen by the resonator.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
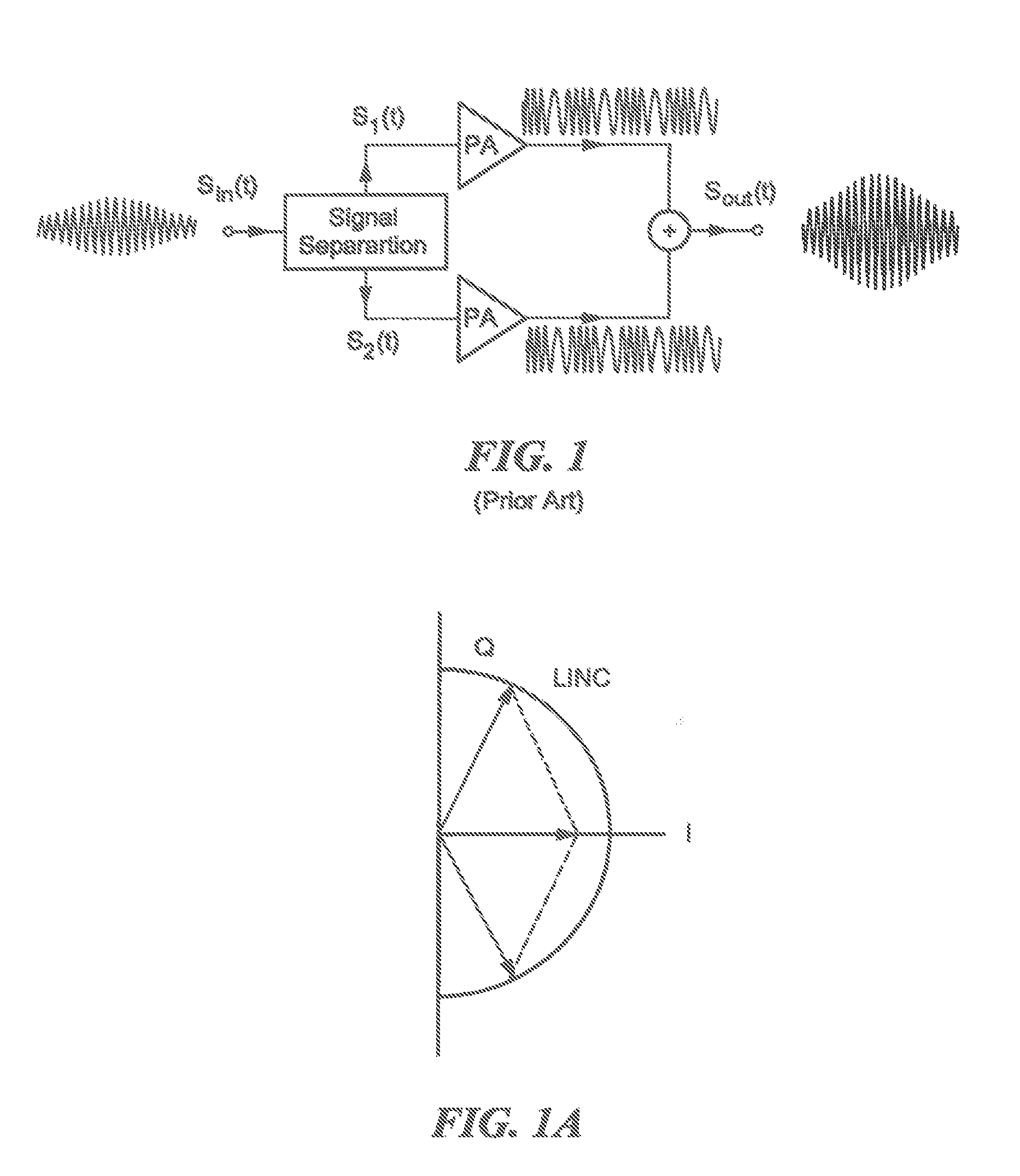
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
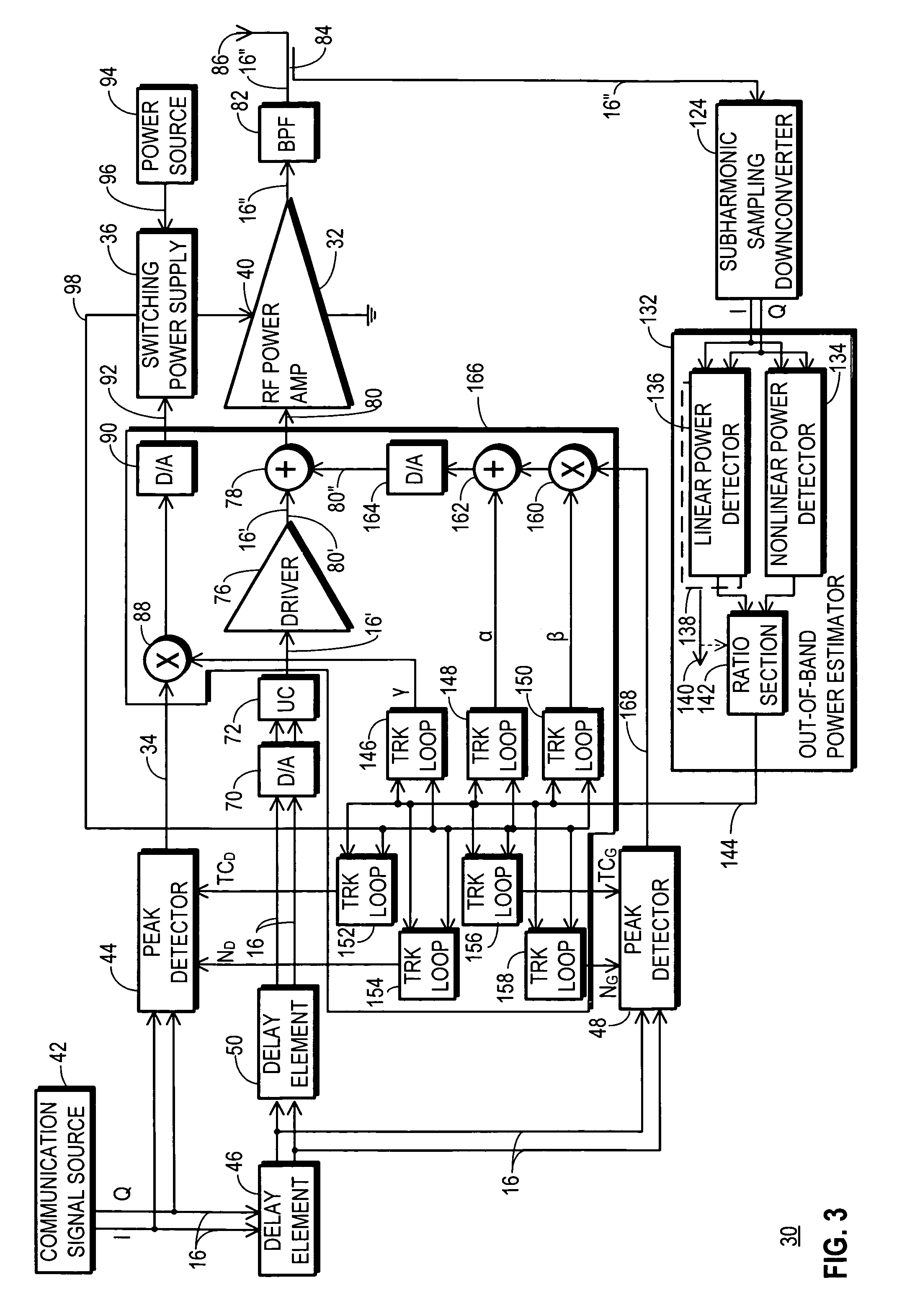
InactiveUS20070281635A1More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueWide band
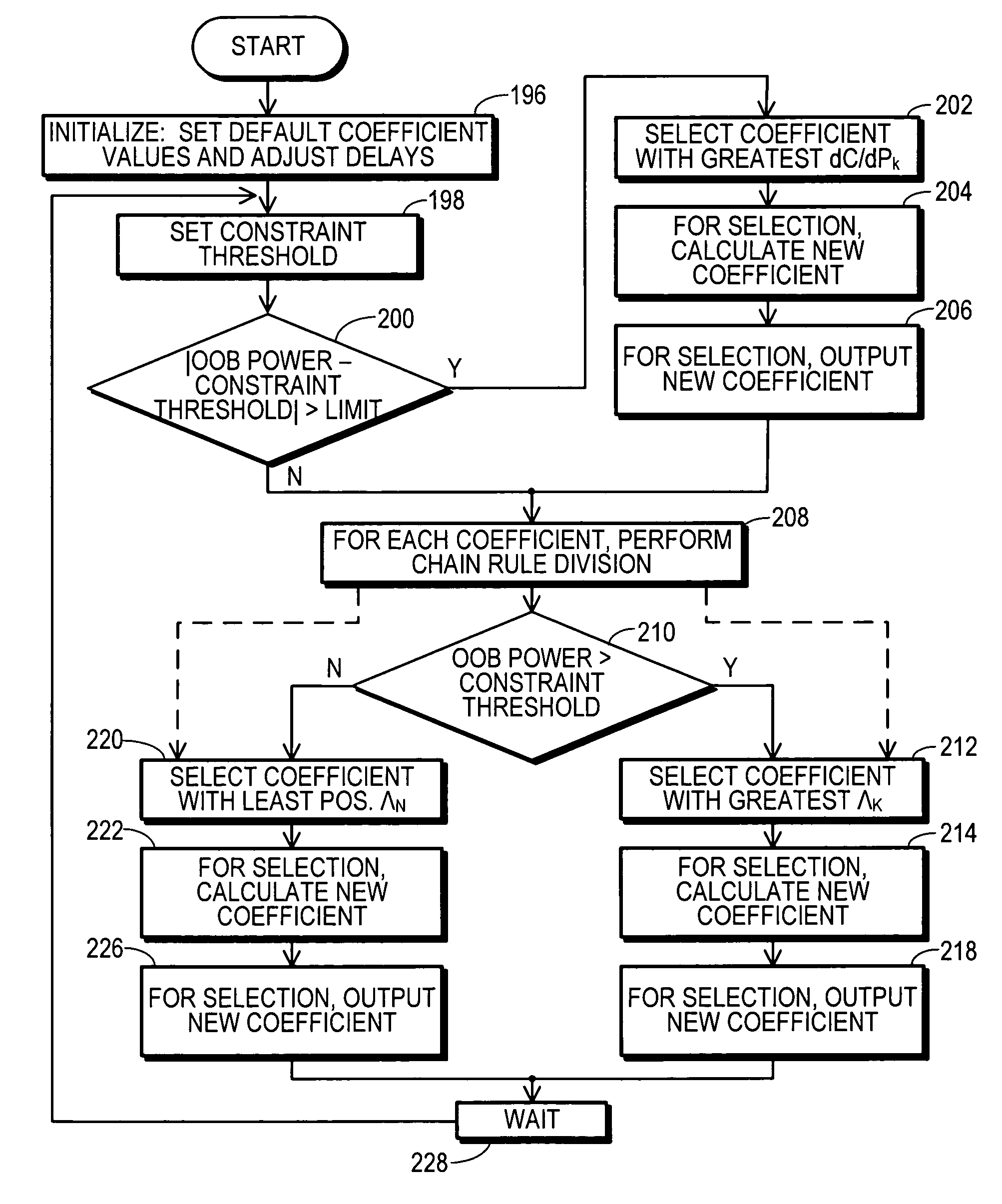
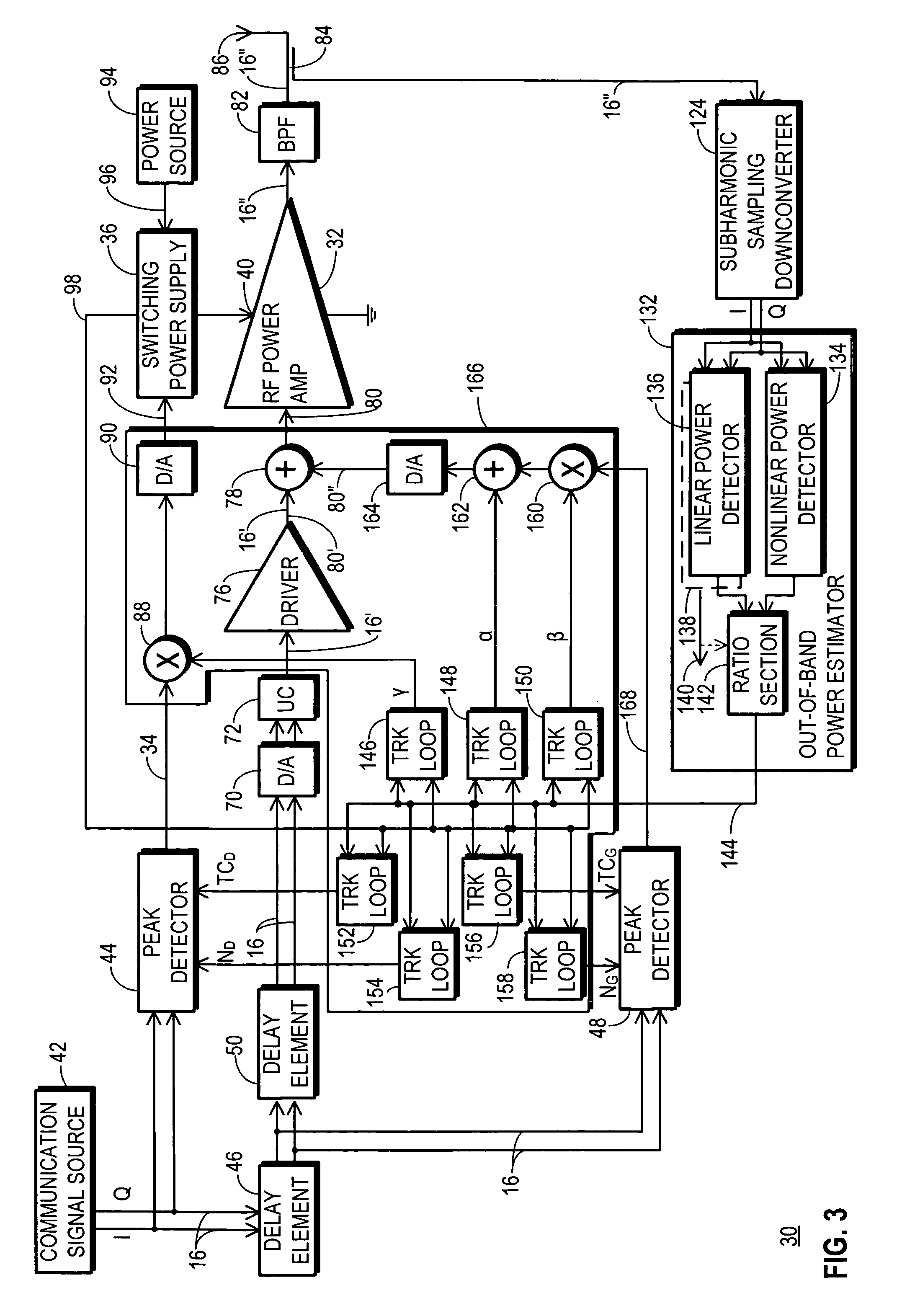
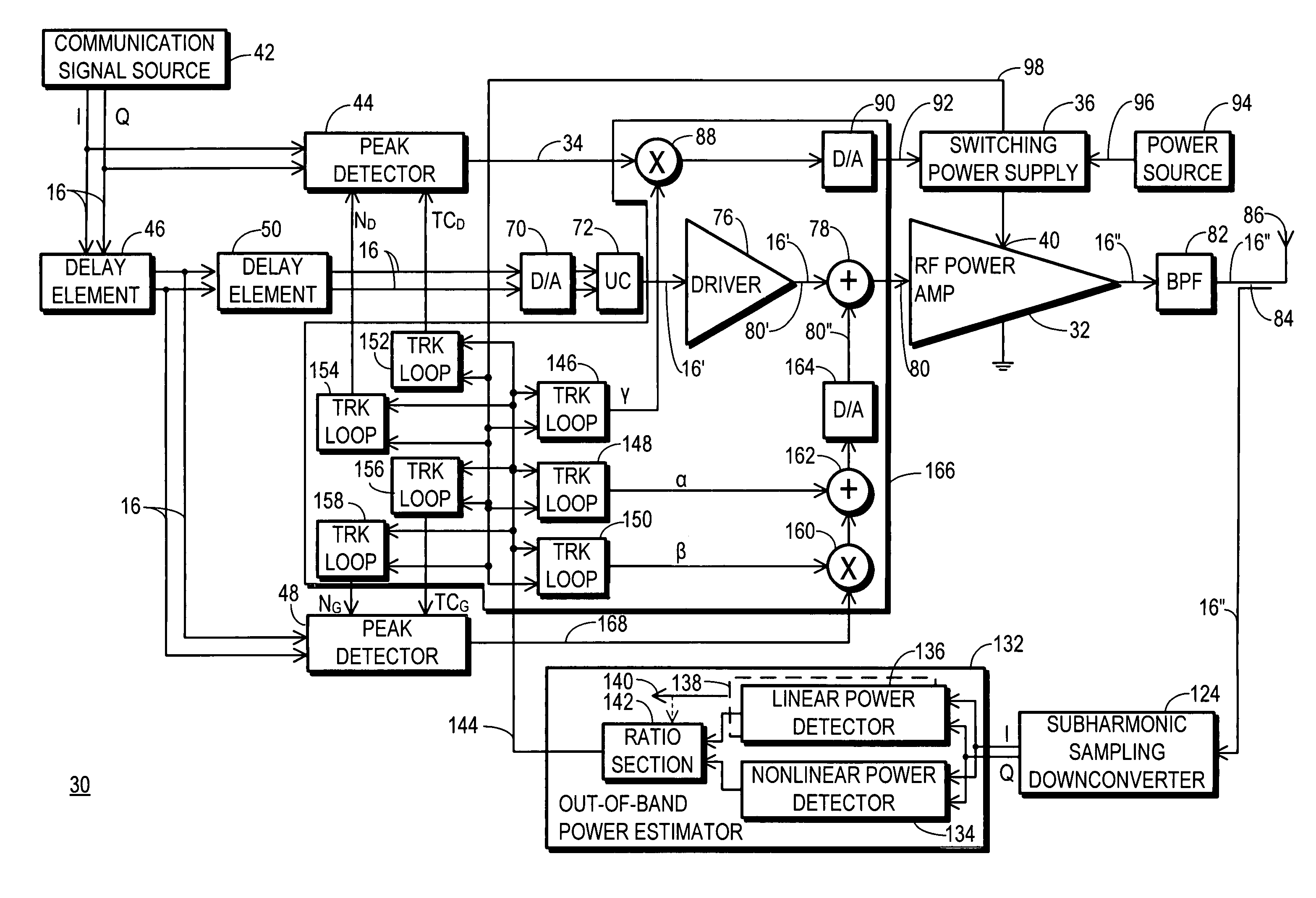
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
System for combining signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors in marine seismic streamers
Signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors located in marine seismic streamers are combined to generate pressure sensor data and particle motion data with substantially the same broad bandwidth. The noisy low frequency part of the motion signals are calculated from the recorded pressure signals and merged with the non-noisy motion signals. The two broad bandwidth data sets can then be combined to calculate the full up- and down-going wavefields.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
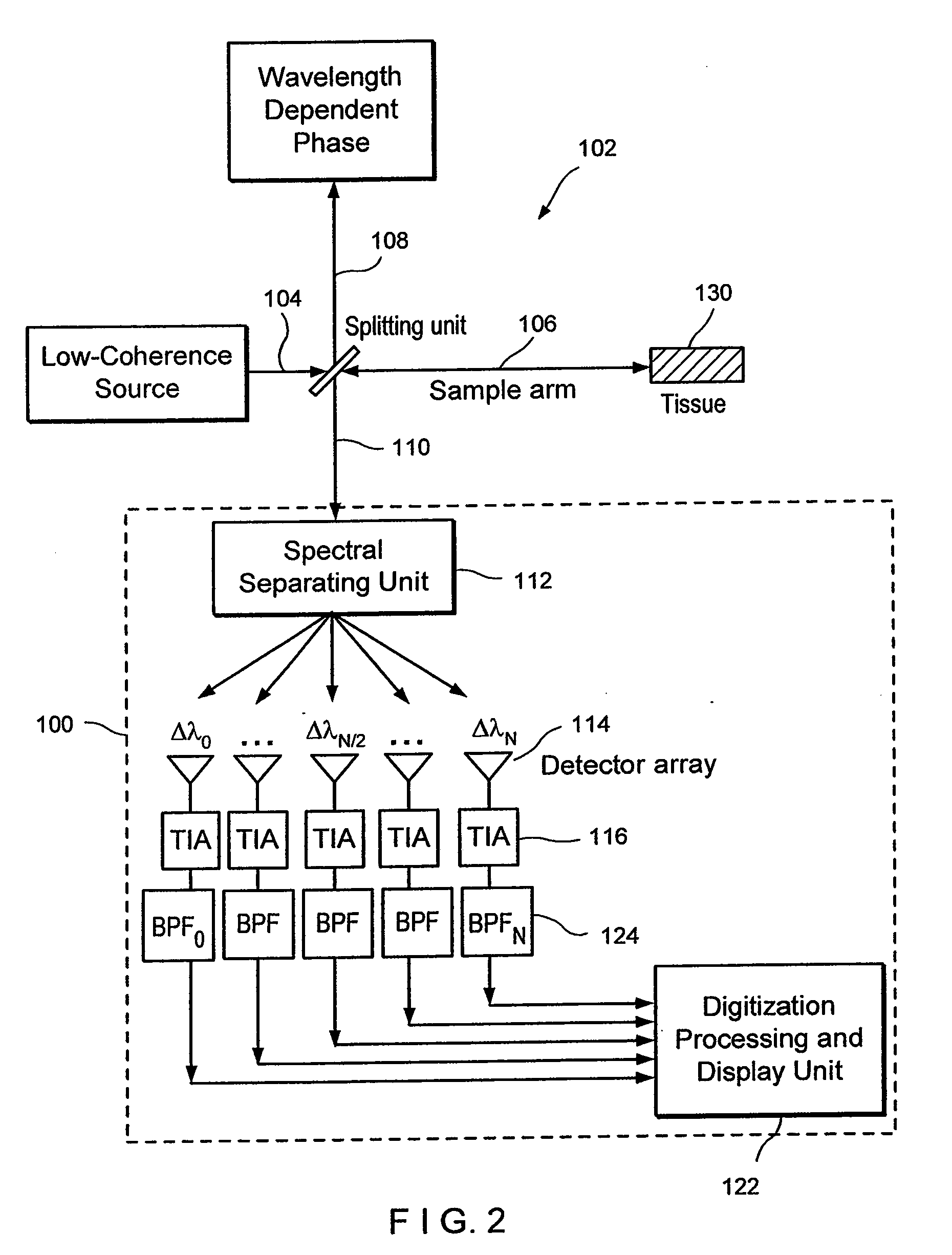
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080094637A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
ActiveUS20080094613A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080097709A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Electrostatic membranes for sensors, ultrasonic transducers incorporating such membranes, and manufacturing methods therefor
ActiveUS20060116585A1Maximize energy conversionEfficiently and effectively implementUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical vibrations separationUltrasonic sensorTransducer
A micro-machined ultrasonic transducer substrate for immersion operation is formed by a particular arrangement of a plurality of micro-machined membranes that are supported on a silicon substrate. The membranes, together with the substrate, form surface microcavities that are vacuum sealed to provide electrostatic cells. The cells can operate at high frequency and can cover a broader bandwidth in comparison with conventional piezoelectric bulk transducers.
Owner:VERMON
Package Design for Producing White Light With Short-Wavelength Leds and Down-Conversion Materials
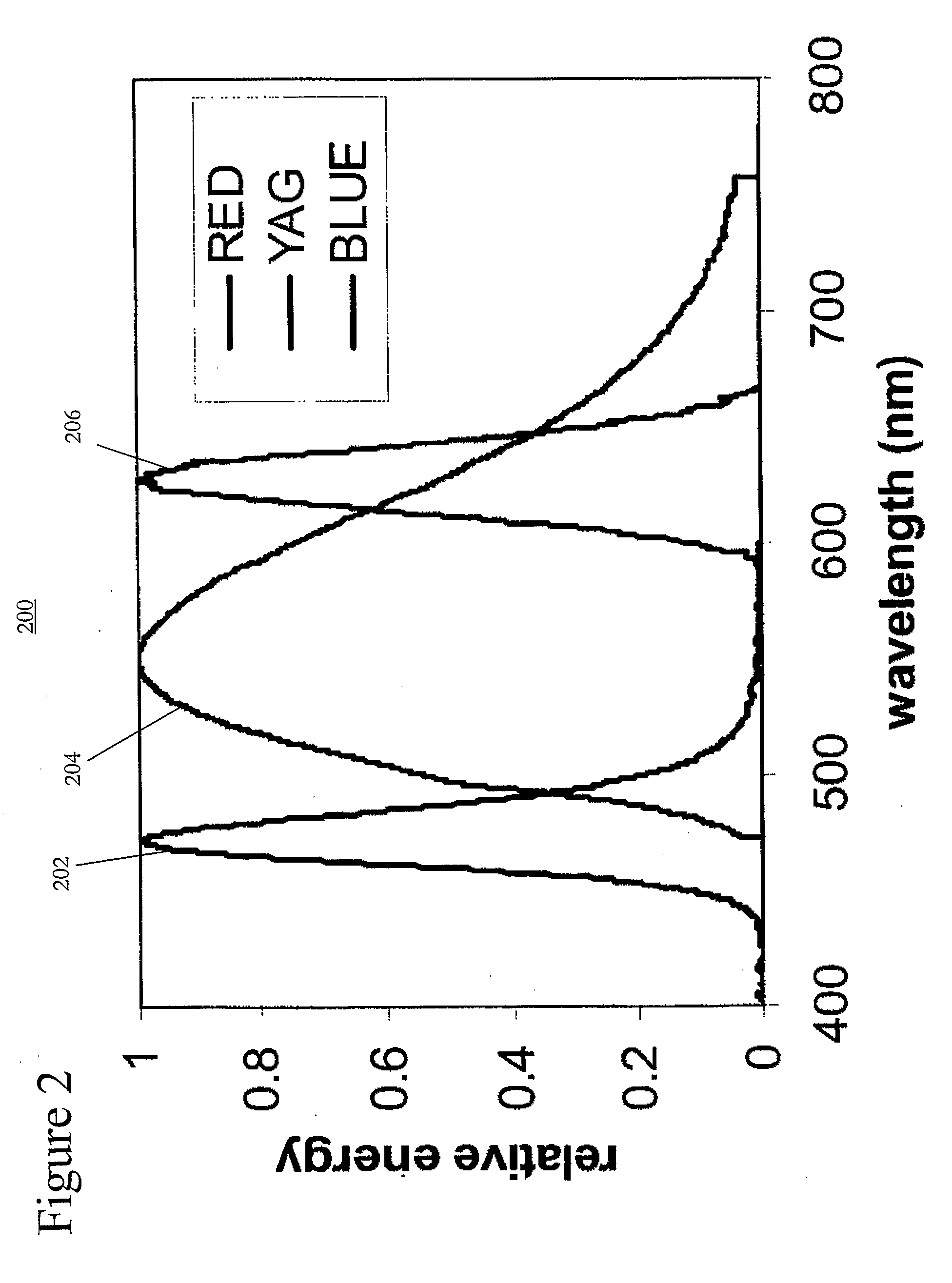
A broad bandwidth light source including: a solid state light emitting device that generates short wavelength light; and quantum dot material and phosphor material that are each irradiated by some of the short wavelength light. The short wavelength light has a spectrum with a first peak wavelength shorter than about 500 nm. The quantum dot material absorbs some of the short wavelength light and reemits it as long wavelength light having a spectrum with a second peak wavelength longer than about 600 nm. The phosphor material absorbs some of the short wavelength light and reemits it as mid wavelength light having a spectrum with a peak wavelength between the first and second peak wavelength. The light source is configured such that some of each light (short, mid, and long wavelength) is emitted coincidently as a light having a chromaticity value near the blackbody locus and a color rendering index greater than 80.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
System and method for providing a compact, flat, microwave lens with wide angular field of regard and wideband operation
PendingUS20180183152A1High instantaneous bandwidthLow overall depthAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDesign optimisation/simulationInterference (communication)Engineering
A system designs a thin and relatively flat microwave focusing lens that can produce multiple simultaneous beams, using readily-available isotropic dielectric materials, and having a gradient-index (GRIN) profile. The design optimizes the lens to achieve beam scanning and / or multiple beams over a wide field of regard (FOR) with broad bandwidth and a very short focal length compared with conventional lenses. The lens can be used individually or as an element in a more complex antenna having multiple lenses in various orientations that are independently switched, selected and / or excited simultaneously as elements in a phased array. The antenna terminal incorporates such lens into an array of lenses along with one or more feeds to produce single or multiple beams covering a broad field of regard for such applications as satellite communications on-the-move, cellular, broadband point-point or point-multipoint and other terrestrial or satellite communications systems. The lens and array design support multiple simultaneous independently steerable beams as well as null placement for interference cancellation.
Owner:ALL SPACE NETWORKS LTD
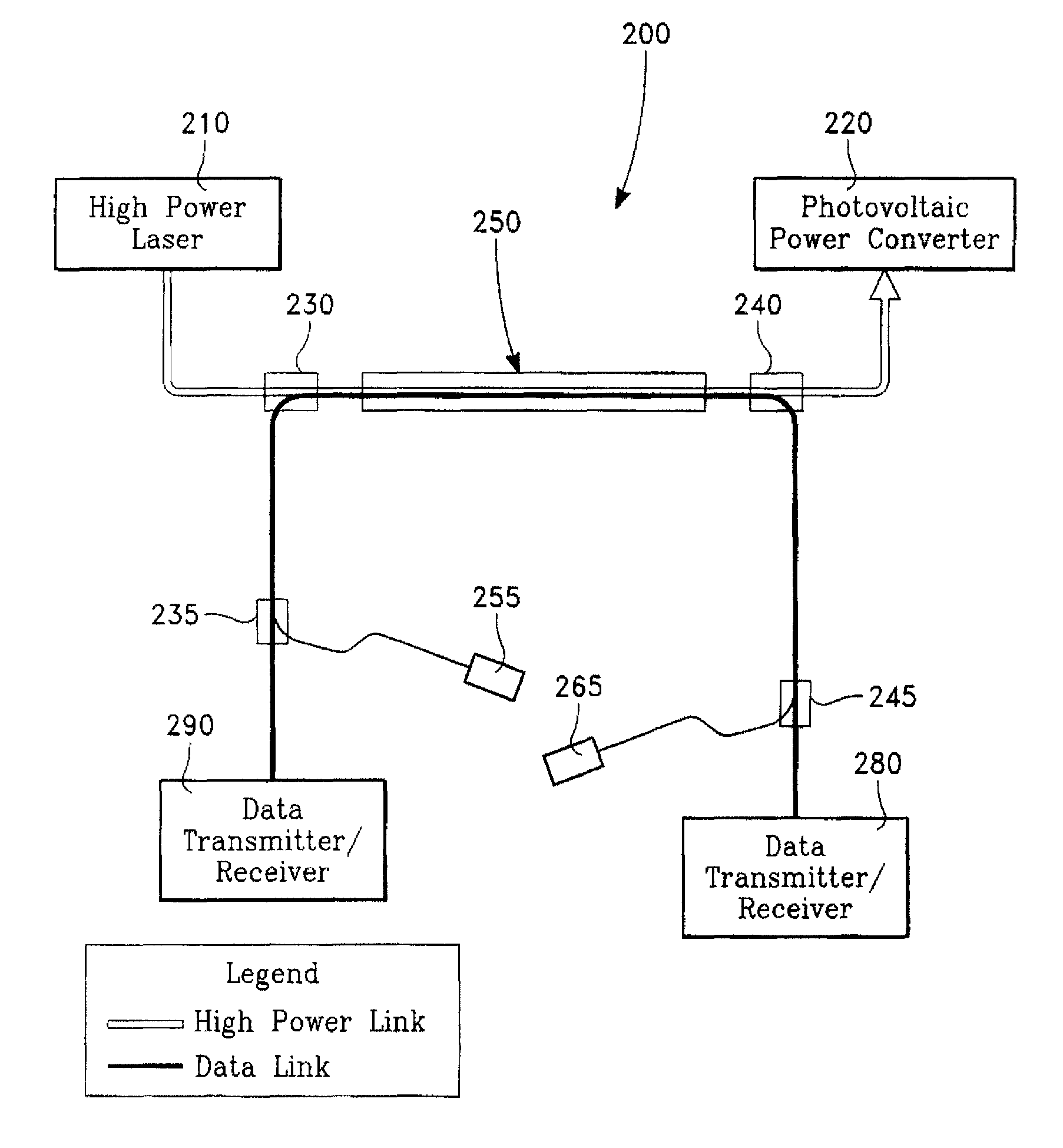
Single fiber optical links for simultaneous data and power transmission
ActiveUS7941022B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingElectromagnetic transmissionWavelength selectivityOptical power
Owner:HRL LAB
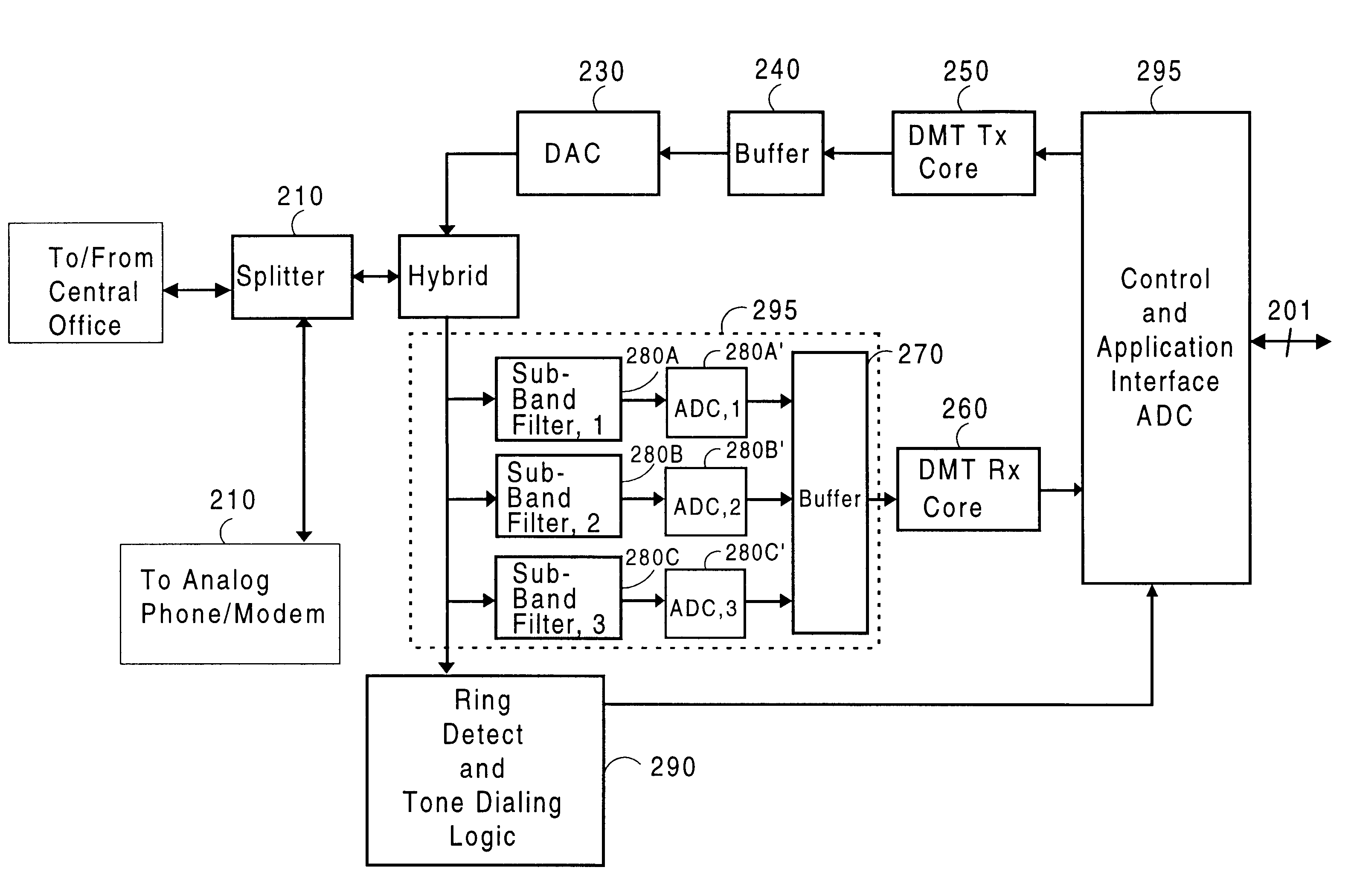
Multiple low speed sigma-delta analog front ends for full implementation of high-speed data link protocol
InactiveUS6442195B1Reduce quantization noiseReduce shapingTelephonic communicationSignal channelsModularityIntegrated circuit
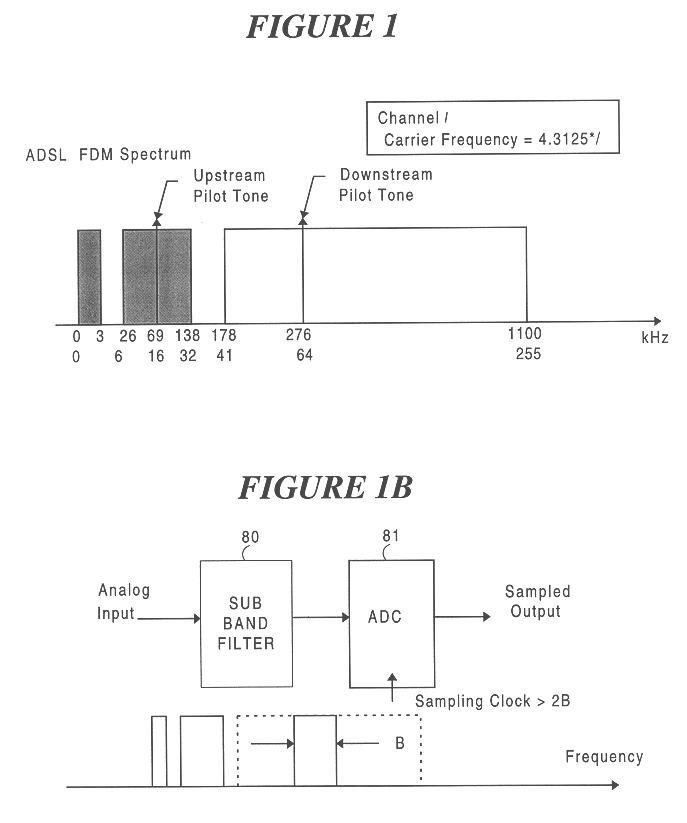
An analog front end (AFE) circuit used in a high-speed communications system is presented that includes multiple stages each including a bandpass filter, base band modulator, low pass filter and Sigma-Delta modulator. Each stage processes a fractional portion of the total frequency of a wide bandwidth analog signal. The number of such AFE stages is configurable in parallel to process the entire bandwidth of the received signal. The AFEs can be incorporated in a single integrated circuit or similar suitable manner so as to be modular, and easily replaceable / upgradeable. To achieve minimum quantization noise and reduce manufacturing costs, the Sigma-Delta modulators in each AFE are made to have identical characteristics. Because the wideband signal is broken down into smaller frequency portions, the sampling rate, and thus the complexity and cost associated with the AFEs, is reduced significantly. In a preferred embodiment, a number of such AFEs are used in an ADSL modem for processing separate but roughly equal portions of the wideband ADSL signal containing data carrying DMT sub-channels. The separated portions are re-combined in a DMT receiver logic circuit to reconstruct the original data stream.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP +1
RF transmitter with variably biased RF power amplifier and method therefor
InactiveUS7570931B2More powerSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationResonant long antennasPeak valueEngineering
An RF transmitter (30) includes an RF power amplifier (32) for which the power input bias voltage (40) and signal input bias voltage (80) are controlled within feedback loops. A peak detector (44) generates a lowered-spectrum, peak-tracking signal (34) that follows the largest amplitude peaks of a wide bandwidth communication signal (16) but exhibits a lower bandwidth. This signal (34) is scaled in response to the operation of a drain bias tracking loop (146) then used to control a switching power supply (36) that generates the power input bias voltage. The tracking loop (146) is responsive to out-of-band power detected in a portion of the amplified RF communication signal (16″). A ratio of out-of-band power (128) to in-band power (126) is manipulated in the tracking loop (146) so that the power input bias voltage is modulated in a way that holds the out-of-band power at a desired predetermined level.
Owner:CRESTCOM INC
Package design for producing white light with short-wavelength LEDS and down-conversion materials
A broad bandwidth light source including: a solid state light emitting device that generates short wavelength light; and quantum dot material and phosphor material that are each irradiated by some of the short wavelength light. The short wavelength light has a spectrum with a first peak wavelength shorter than about 500 nm. The quantum dot material absorbs some of the short wavelength light and reemits it as long wavelength light having a spectrum with a second peak wavelength longer than about 600 nm. The phosphor material absorbs some of the short wavelength light and reemits it as mid wavelength light having a spectrum with a peak wavelength between the first and second peak wavelength. The light source is configured such that some of each light (short, mid, and long wavelength) is emitted coincidentally as a light having a chromaticity value near the blackbody locus and a color rendering index greater than 80.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
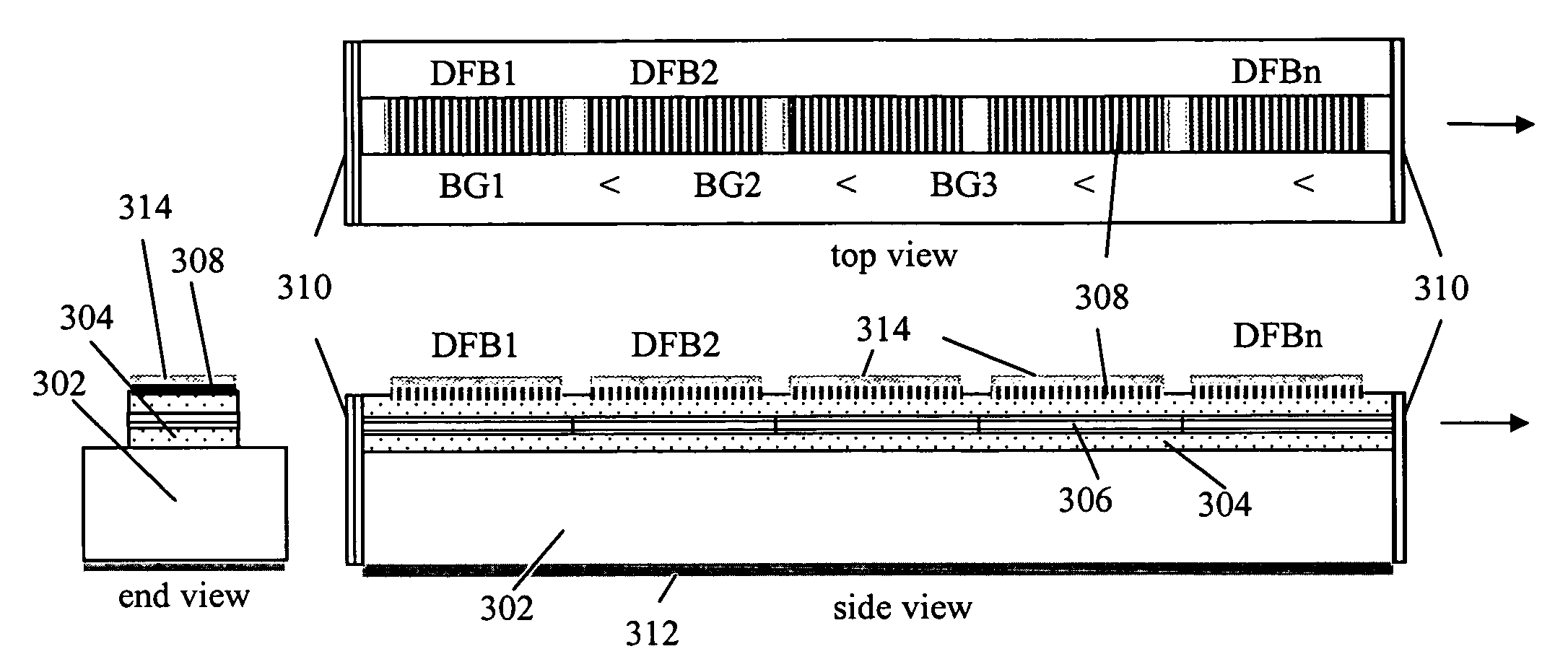
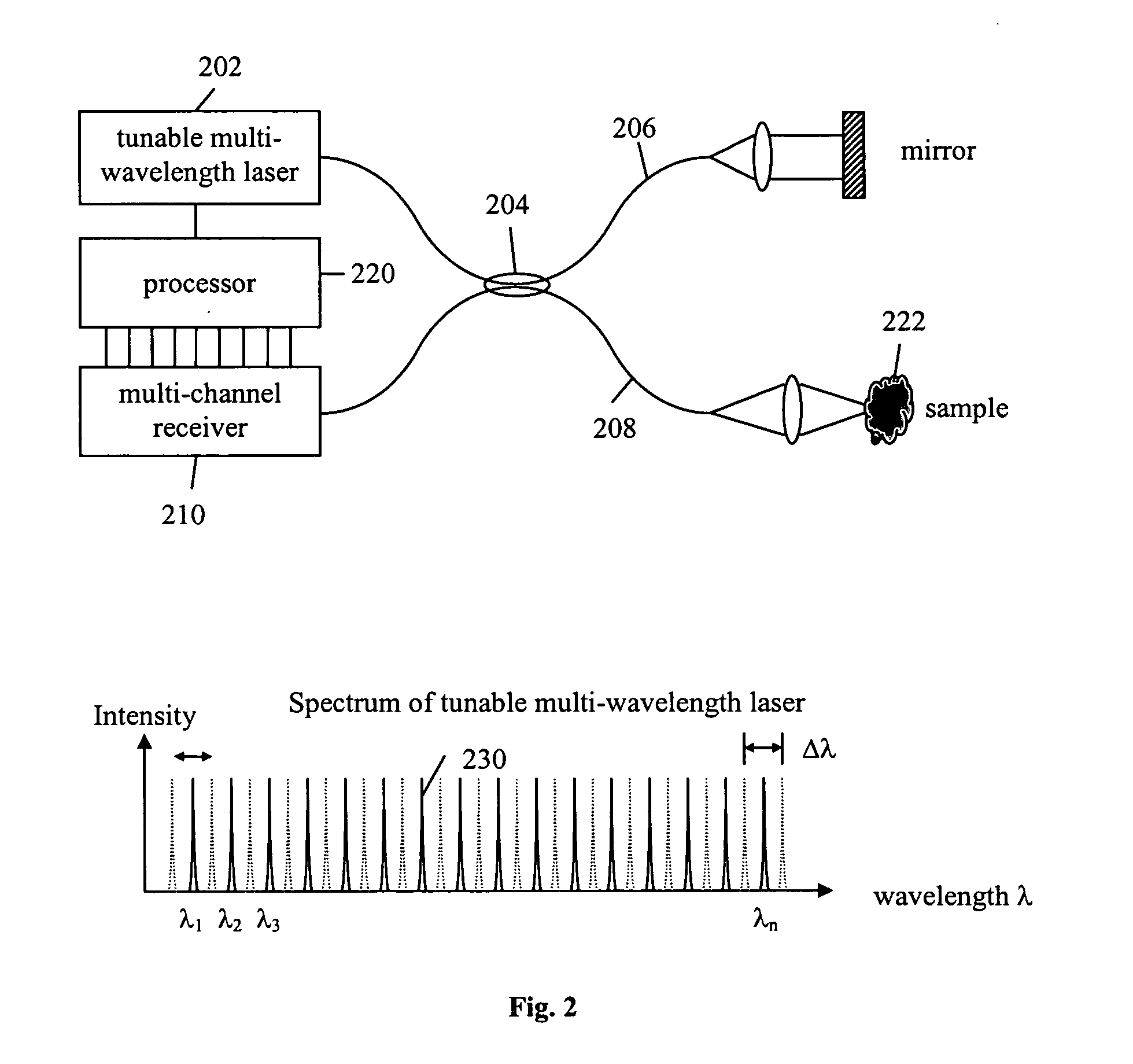
Light source for swept source optical coherence tomography based on cascaded distributed feedback lasers with engineered band gaps
ActiveUS20080037608A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDistributed feedback laserGrating
The present invention is a tunable semiconductor laser for swept source optical coherence tomography, comprising a semiconductor substrate; a waveguide on top of said substrate with multiple sections of different band gap engineered multiple quantum wells (MQWs); a multiple of distributed feedback (DFB) gratings corresponding to each said band gap engineered MWQs, each DFB having a different Bragg grating period; and anti-reflection (AR) coating deposited on at least the laser emission facet of the laser to suppress the resonance of Fabry-Perot cavity modes. Each DFB MQWs section can be activated and tuned to lase across a fraction of the overall bandwidth as is achievable for a single DFB laser and all sections can be sequentially activated and tuned so as to collectively cover a broad bandwidth, or simultaneously activated and tuned to enable a tunable multi-wavelength laser. The laser hence can emit either a single lasing wavelength or a multiple of lasing wavelengths and is very suitable for swept-source OCT applications.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Semiconductor nanocrystal probes for biological applications and process for making and using such probes
InactiveUS20030099968A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectromagnetic radiationSemiconductor nanocrystals
A semiconductor nanocrystal compound is described which is capable of linking to one or more affinity molecules. The compound comprises (1) one or more semiconductor nanocrystals capable of, in response to exposure to a first energy, providing a second energy, and (2) one or more linking agents, having a first portion linked to the one or more semiconductor nanocrystals and a second portion capable of linking to one or more affinity molecules. One or more of these semiconductor nanocrystal compounds are linked to one or more affinity molecules to form a semiconductor nanocrystal probe capable of bonding with one or more detectable substances in a material being analyzed, and capable of, in response to exposure to a first energy, providing a second energy. In one embodiment, the probe is capable of emitting electromagnetic radiation in a narrow wavelength band and / or absorbing, scattering, or diffracting energy when excited by an electromagnetic radiation source (of narrow or broad bandwidth) or a particle beam. The probe is stable to repeated exposure to energy in the presence of oxygen and / or other radicals. Treatment of a material with the semiconductor nanocrystal probe, and subsequent exposure of this treated material to a first energy, to determine the presence of the detectable substance within the material bonded to the probe, will excite the semiconductor nanocrystal in the probe bonded to the detectable substance, causing the probe to provide a second energy signifying the presence, in the material, of the detectable substance bonded to the semiconductor nanocrystal probe. In one embodiment, the semiconductor nanocrystals in the probe are excitable over a broad bandwidth of energy, and emit electromagnetic radiation over a narrow bandwidth, making it possible to use a single energy source to simultaneously excite a plurality of such probes, each emitting electromagnetic radiation of a differing wavelength band to simultaneously analyze for a plurality of detectable substances in a material being analyzed. Also described are processes for respectively making the semiconductor nanocrystal compound and the semiconductor nanocrystal probe. Processes are also described for treating materials with the probe, for example, to determine the presence of a detectable substance in the material bonded to the probe.
Owner:WEISS SHIMON +2
Method and Apparatus For Transmitting a Signal Within a Predetermined Spectral Mask
The present patent application comprises a transmitting method and apparatus 240. A signal source 241 provides an input signal to a low-pass filter 242 which filters the input signal to produce a filtered signal. The filter 242 is selectively operable in a first mode in which the input signal is filtered within a narrower bandwidth; and in a second mode in which the input signal is filtered within a broader bandwidth. The filtered signal is output to a modulator 243 which modulates the filtered signal to produce a modulated signal. The modulated signal is output to a transmitter 244 which transmits the modulated signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Multiway Lossless Power Combining and Outphasing Incorporating Transmission Lines
ActiveUS20130241625A1Reduce lossesSmall output powerHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsLinear amplificationLinearity
A power combining and outphasing system and related techniques for simultaneously providing both wide-bandwidth linear amplification and high average efficiency is described. Providing linear amplification encompasses the ability to dynamically control an RF output power level over a wide range while still operating over a wide frequency bandwidth. The system and techniques described herein also operate to maintain high efficiency across a wide range of output power levels, such that a high average efficiency can be achieved for highly modulated output waveforms.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Laser Material Processing System
ActiveUS20090188901A1Wide bandwidthImprove laser pulse performanceLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Electrostatic membranes for sensors, ultrasonic transducers incorporating such membranes, and manufacturing methods therefor
ActiveUS20080184549A1Maximize energy conversionEfficiently and effectively implementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltrasonic sensorTransducer
Owner:VERMON
Laser based frequency standards and their applications
InactiveUS7809222B2Increase powerReduced Power RequirementsLaser detailsCoupling light guidesFiberMode locked fiber laser
Frequency standards based on mode-locked fiber lasers, fiber amplifiers and fiber-based ultra-broad bandwidth light sources, and applications of the same.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
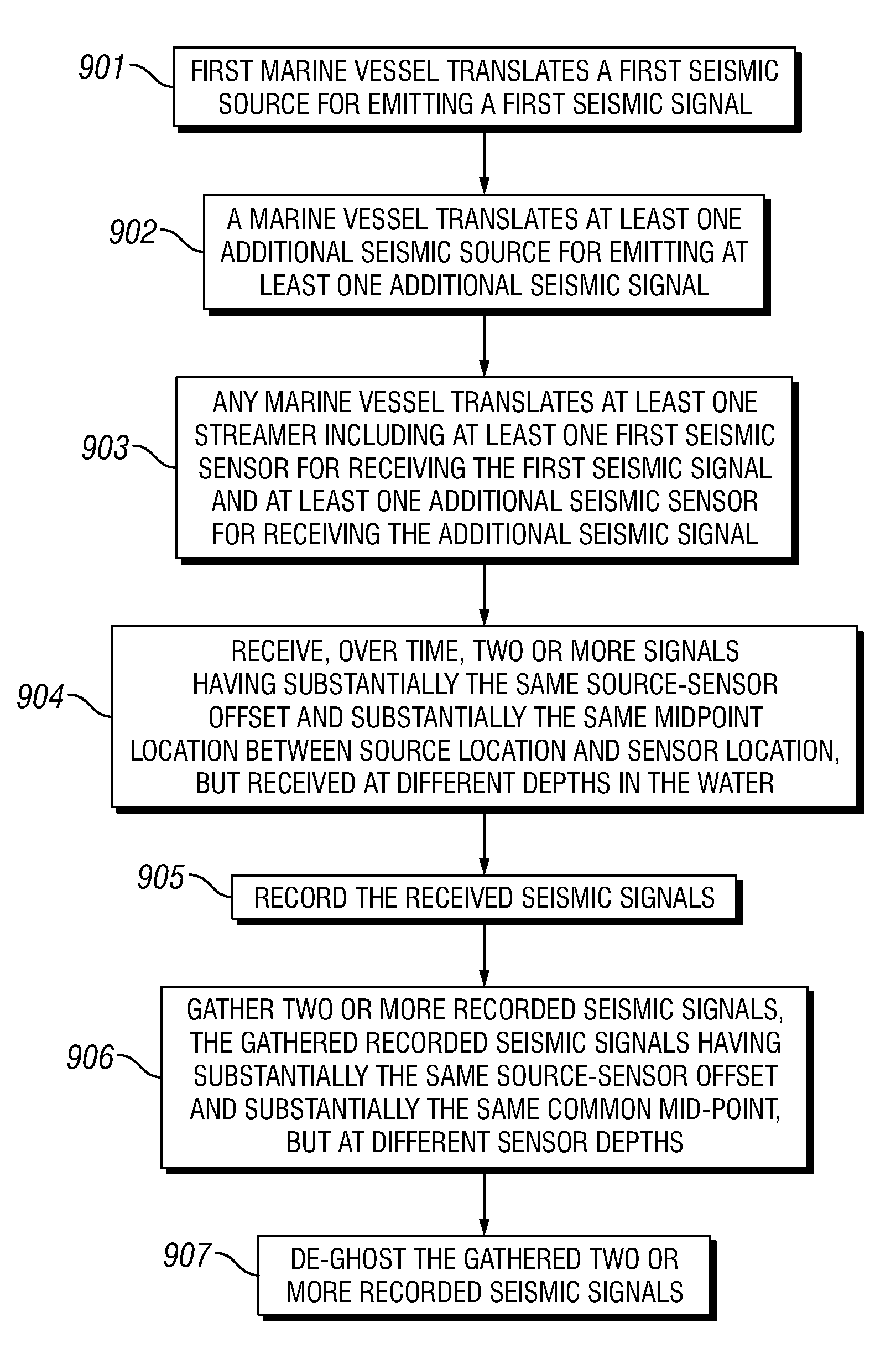
Acquisition and Processing of Multi-Source Broadband Marine Seismic Data
A method and a system of acquiring and processing multi-source broadband marine seismic data in such a way that at least a part of said acquired data is partially or fully de-ghosted on the receiver side and then partially or fully re-assembled to a pre-stack dataset. At least one non-uniformly horizontal streamer is towed and at least two seismic sources emit seismic signals at spaced apart positions. Further presented is a method of processing marine seismic data by using the thus resulting notch diversity in these two (or more) seismic records to de-ghost the dataset, gathering two or more recorded seismic signals having substantially the same source-sensor offset and substantially the same common mid-point at different sensor depths, the sensor depths at least different enough to enable identification of seismic signals originating from ghosting. The gather is de-ghosted, thus obtaining seismic data with significantly broader bandwidth.
Owner:CGG SERVICES NORWAY
Heterodyning time resolution boosting method and system
InactiveUS20060061770A1Increase temporal resolutionHigh resolutionOptical measurementsInterferometersImage resolutionThree-phase
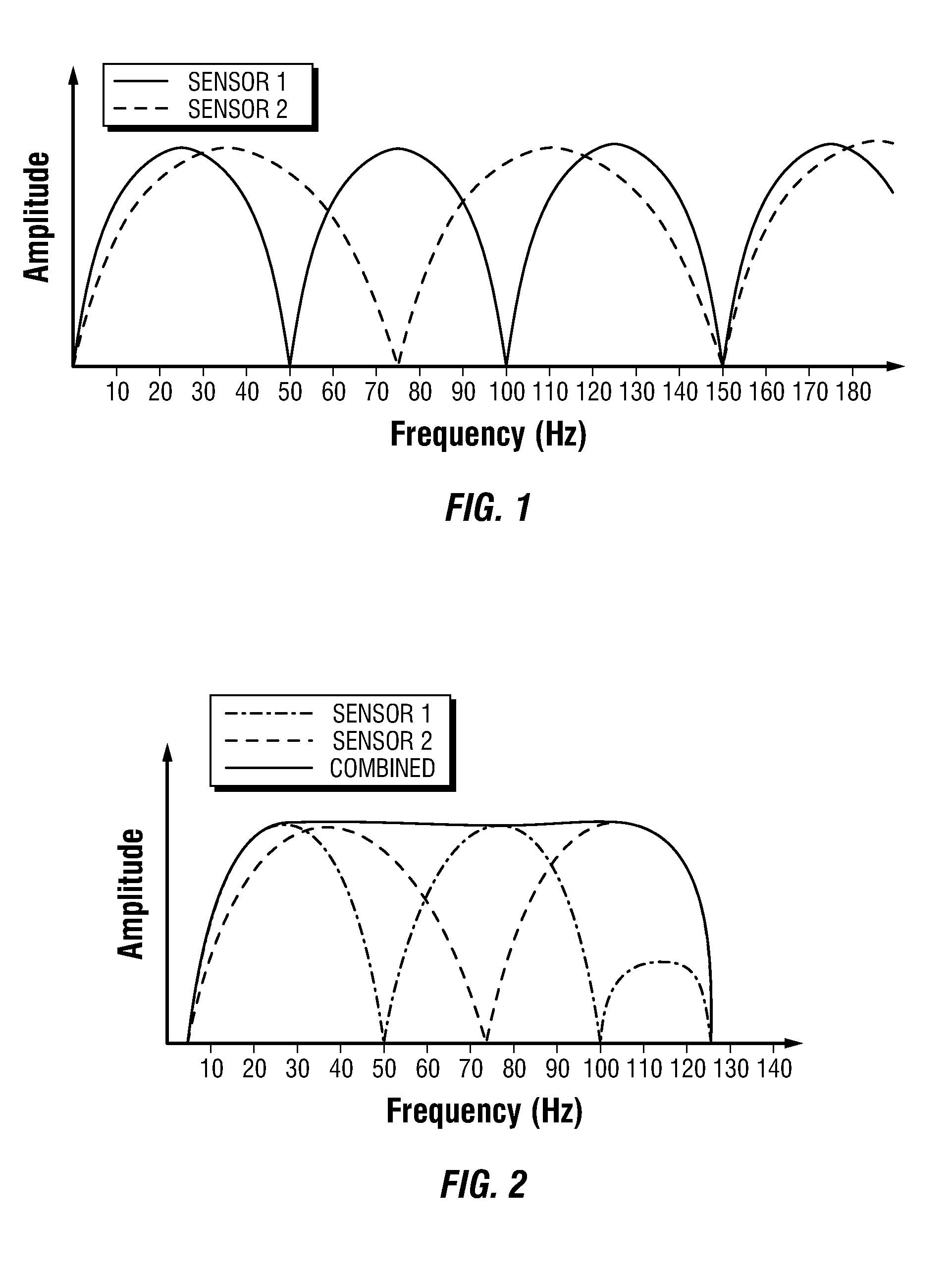
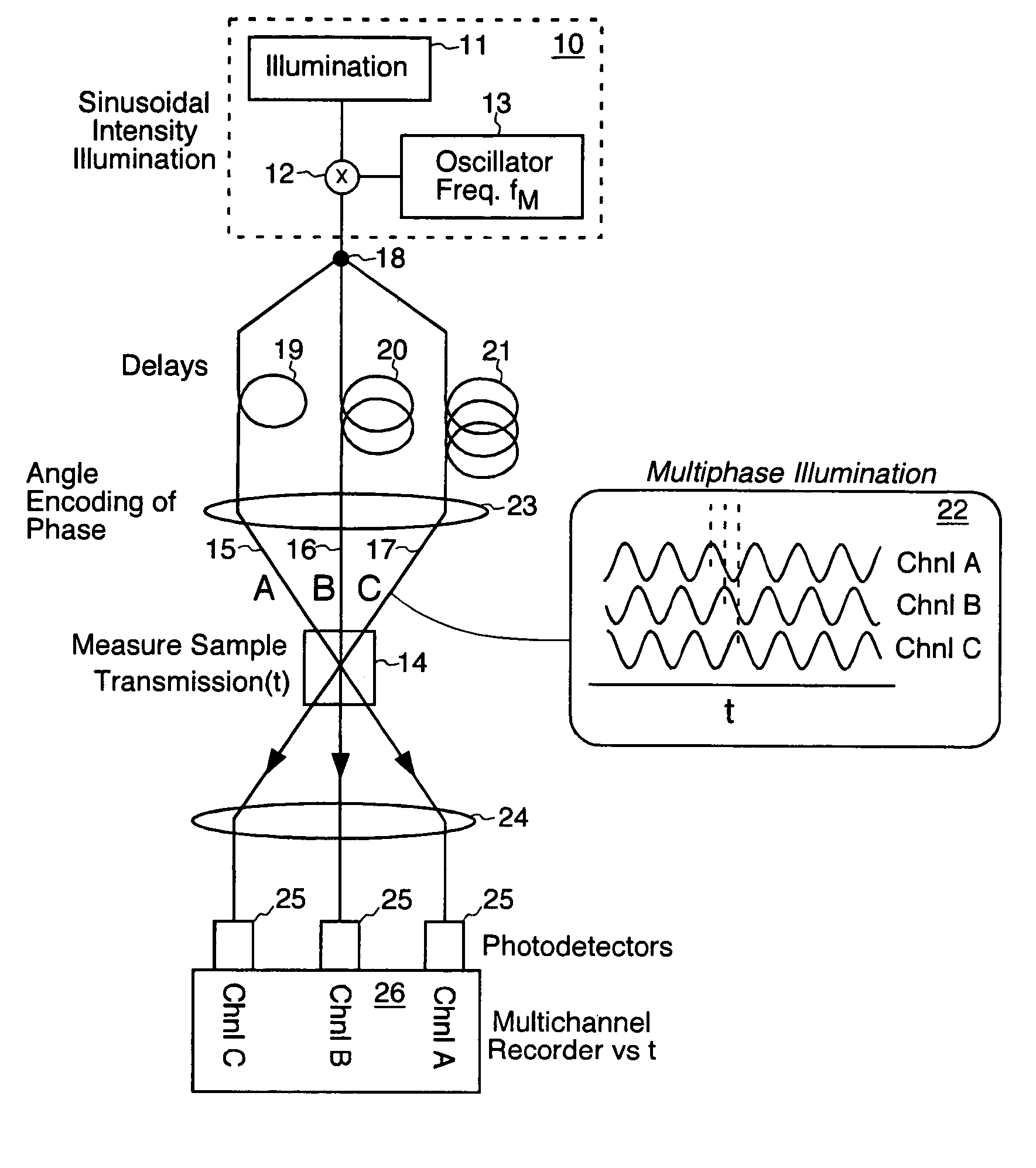
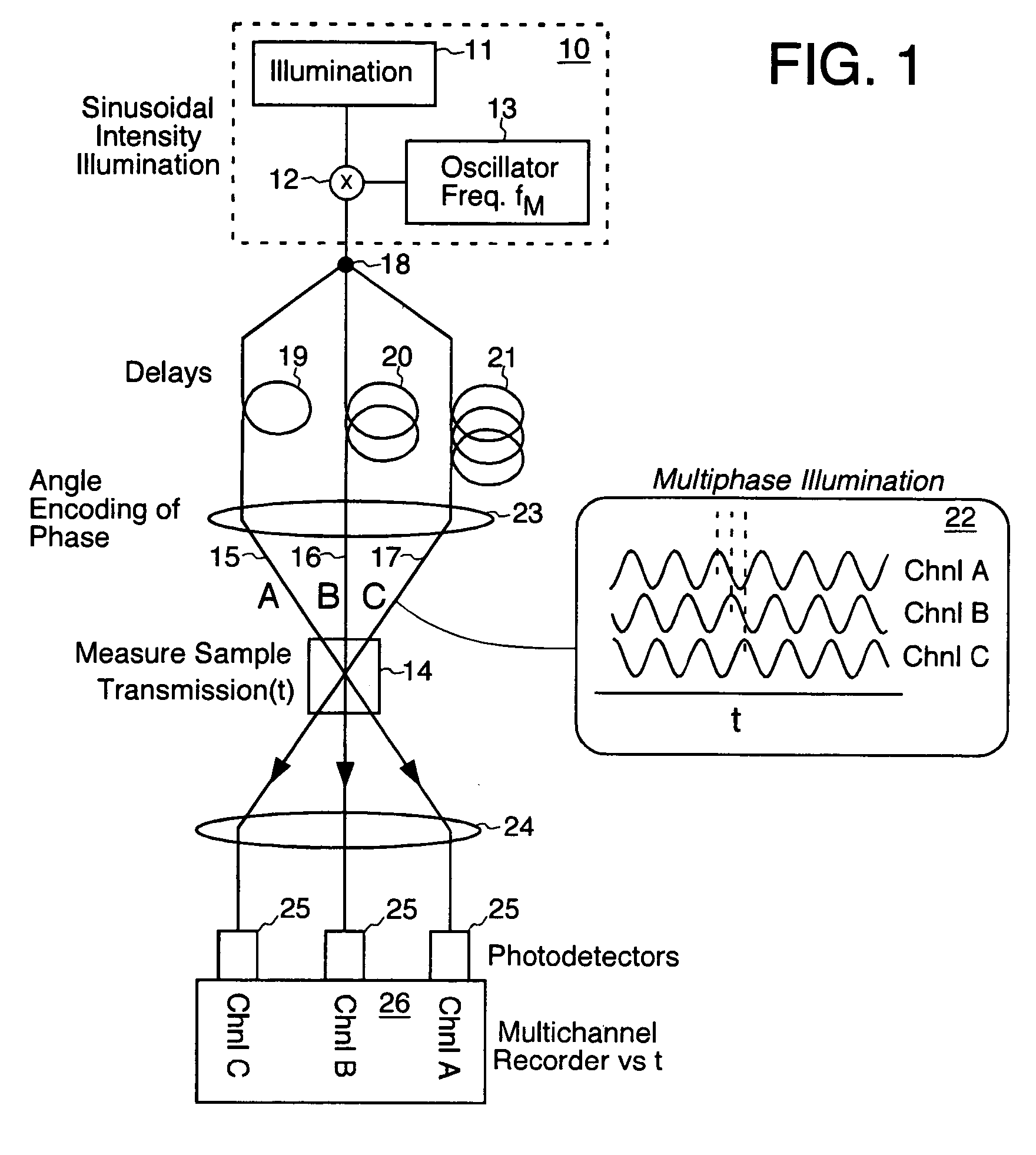
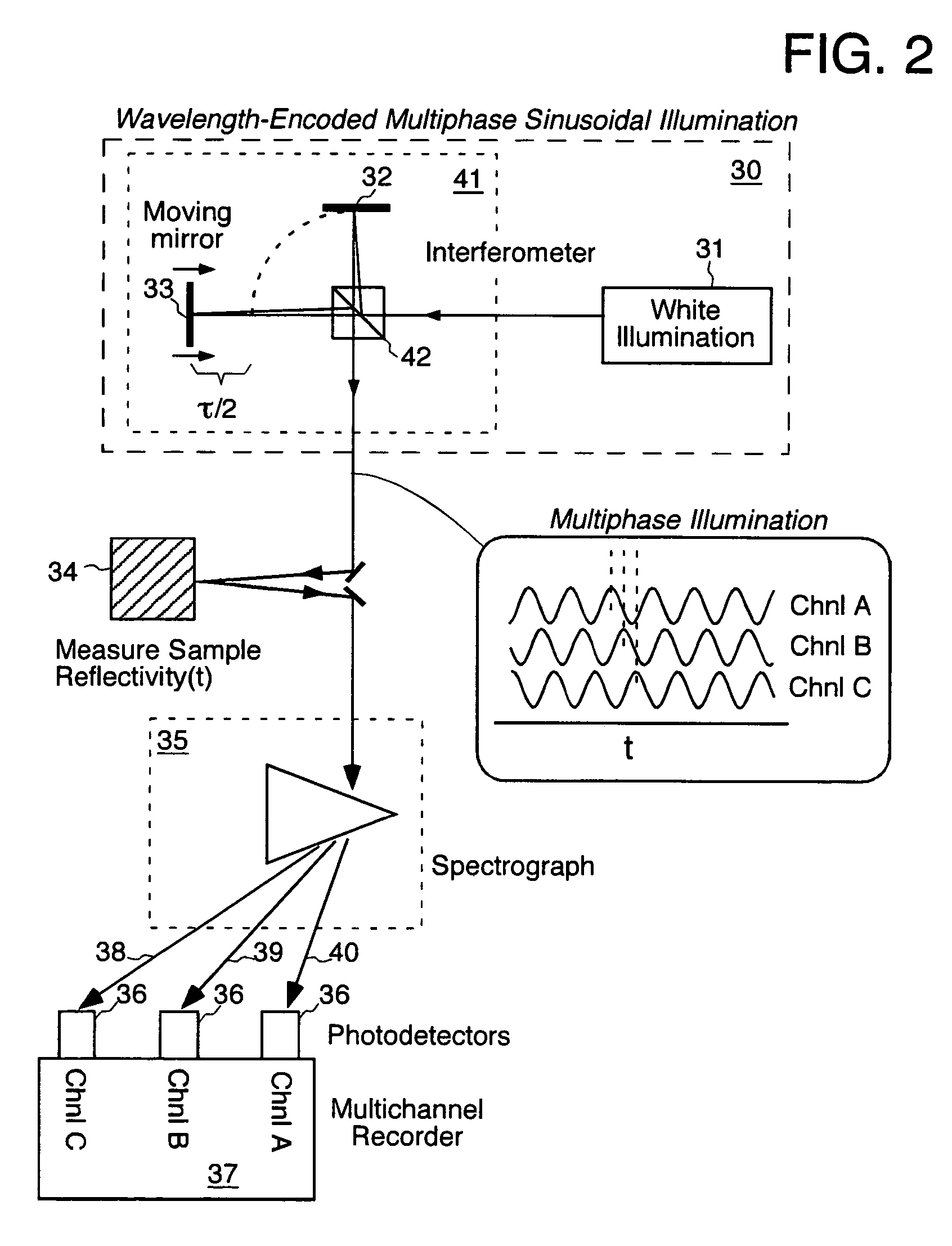
A method for enhancing the temporal resolving power of an optical signal recording system such as a streak camera or photodetector by sinusoidally modulating the illumination or light signal at a high frequency, approximately at the ordinary limit of the photodetector's capability. The high frequency information of the input signal is thus optically heterodyned down to lower frequencies to form beats, which are more easily resolved and detected. During data analysis the heterodyning is reversed in the beats to recover the original high frequencies. When this is added to the ordinary signal component, which is contained in the same recorded data, the composite signal can have an effective frequency response which is several times wider than the detector used without heterodyning. Hence the temporal resolving power has been effectively increased while maintaining the same record length. Multiple modulation frequencies can be employed to further increase the net frequency response of the instrument. The modulation is performed in at least three phases, recorded in distinct channels encoded by wavelength, angle, position or polarization, so that during data analysis the beat and ordinary signal components can be unambiguously separated even for wide bandwidth signals. A phase stepping algorithm is described for separating the beat component from the ordinary component in spite of unknown or irregular phase steps and modulation visibility values. This algorithm is also independently useful for analyzing interferograms or other phase-stepped interferometer related data taken with irregular or unknown phase steps, as commonly found in industrial vibration environments.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Broadband polarized antenna including magnetodielectric material, isoimpedance loading, and associated methods
ActiveUS20070188397A1Loop antennas with ferromagnetic coreProtective material radiating elementsMiniaturizationBandwidth limitation
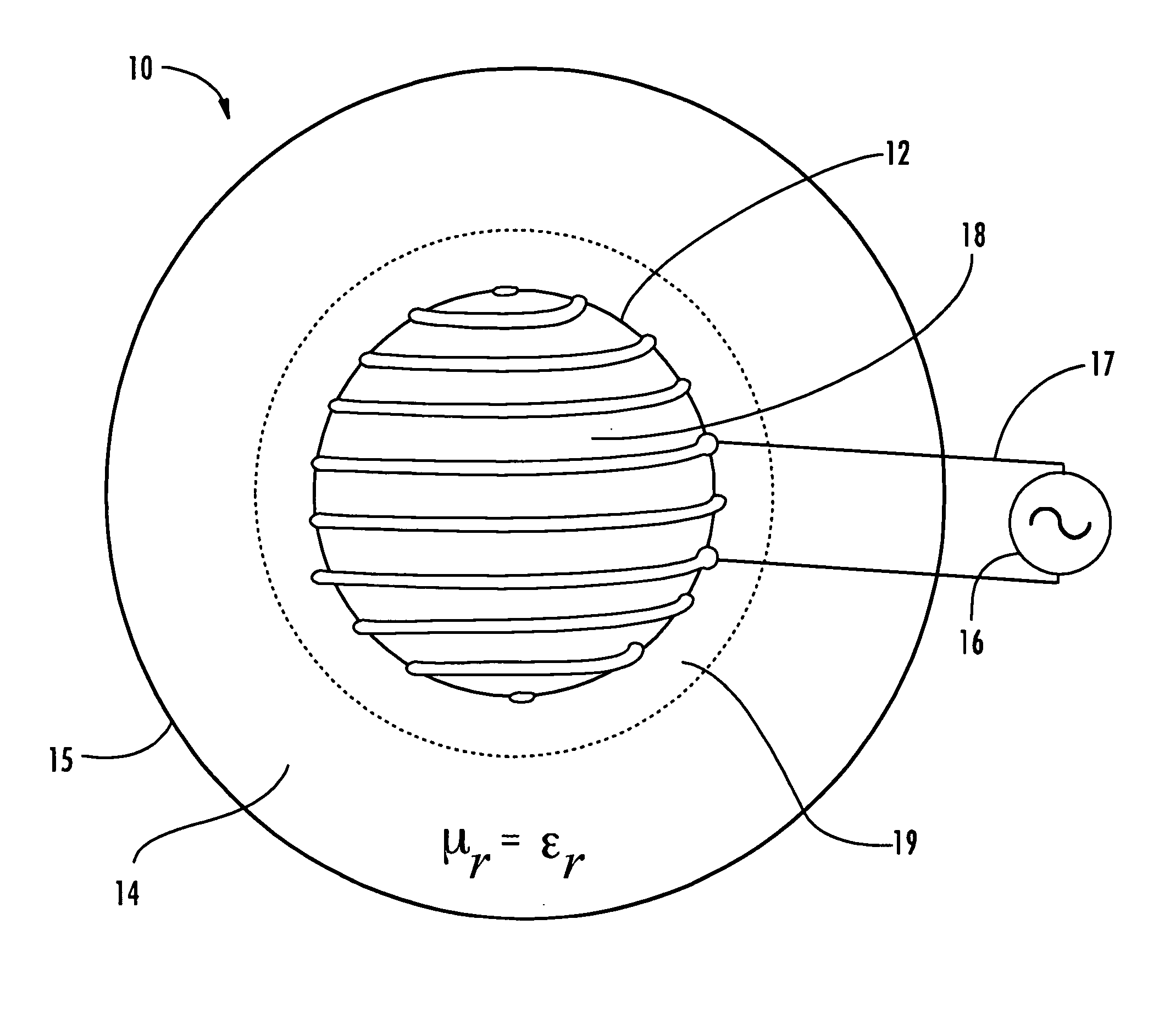
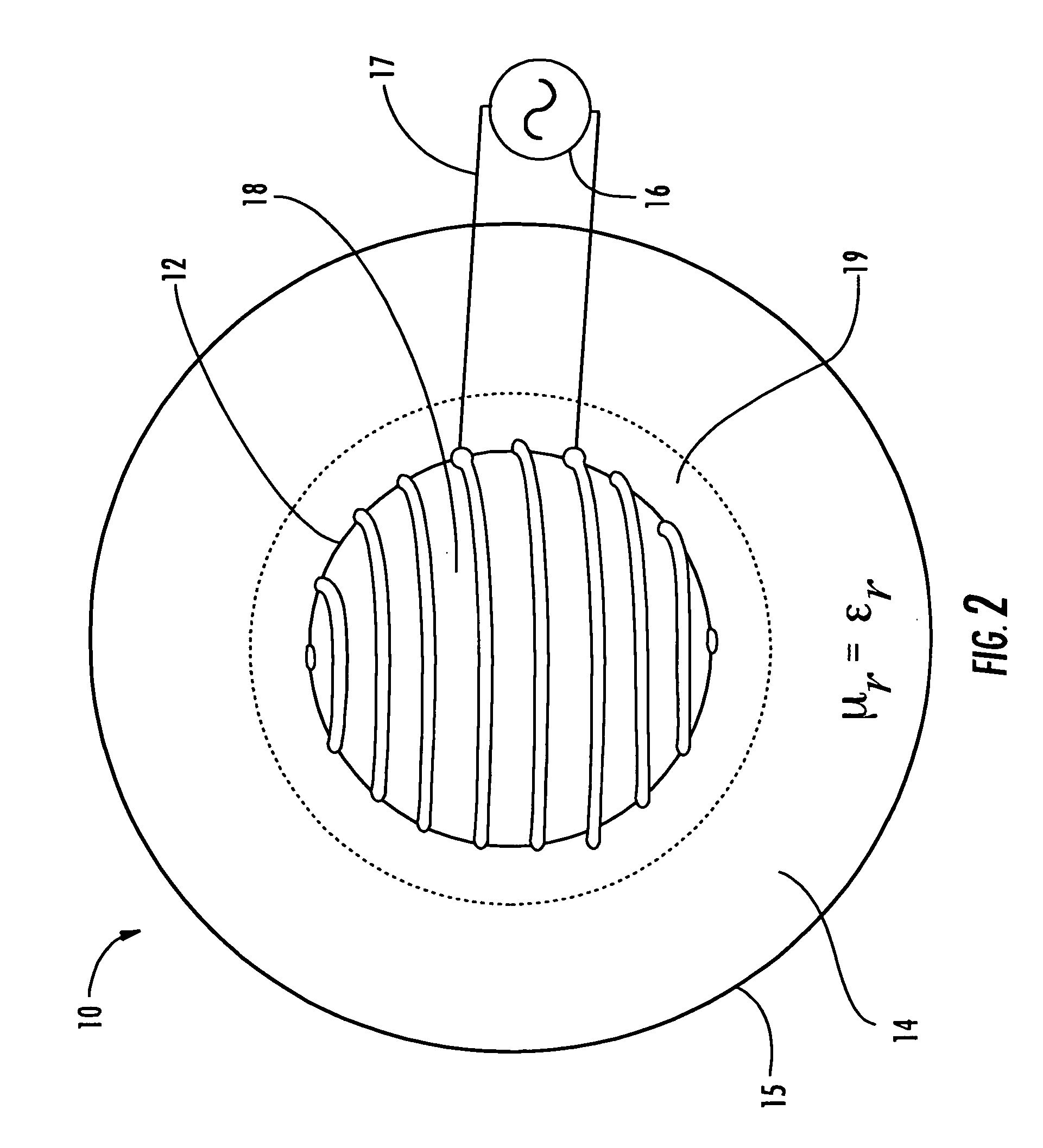
The broadband small antenna has equal magnetic electric proportions, circular polarization, and an isoimpedance magnetodielectric (μr≡εr) shell for controlled wave expansion. The shell is a radome without bandwidth limitation, with reflectionless boundary conditions to free space, providing loading and broad bandwidth antenna size miniaturization. The system is spherically structured based upon size, quality (Q) and bandwidth.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com