Patents
Literature
2310results about "Seismology for water-covered areas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
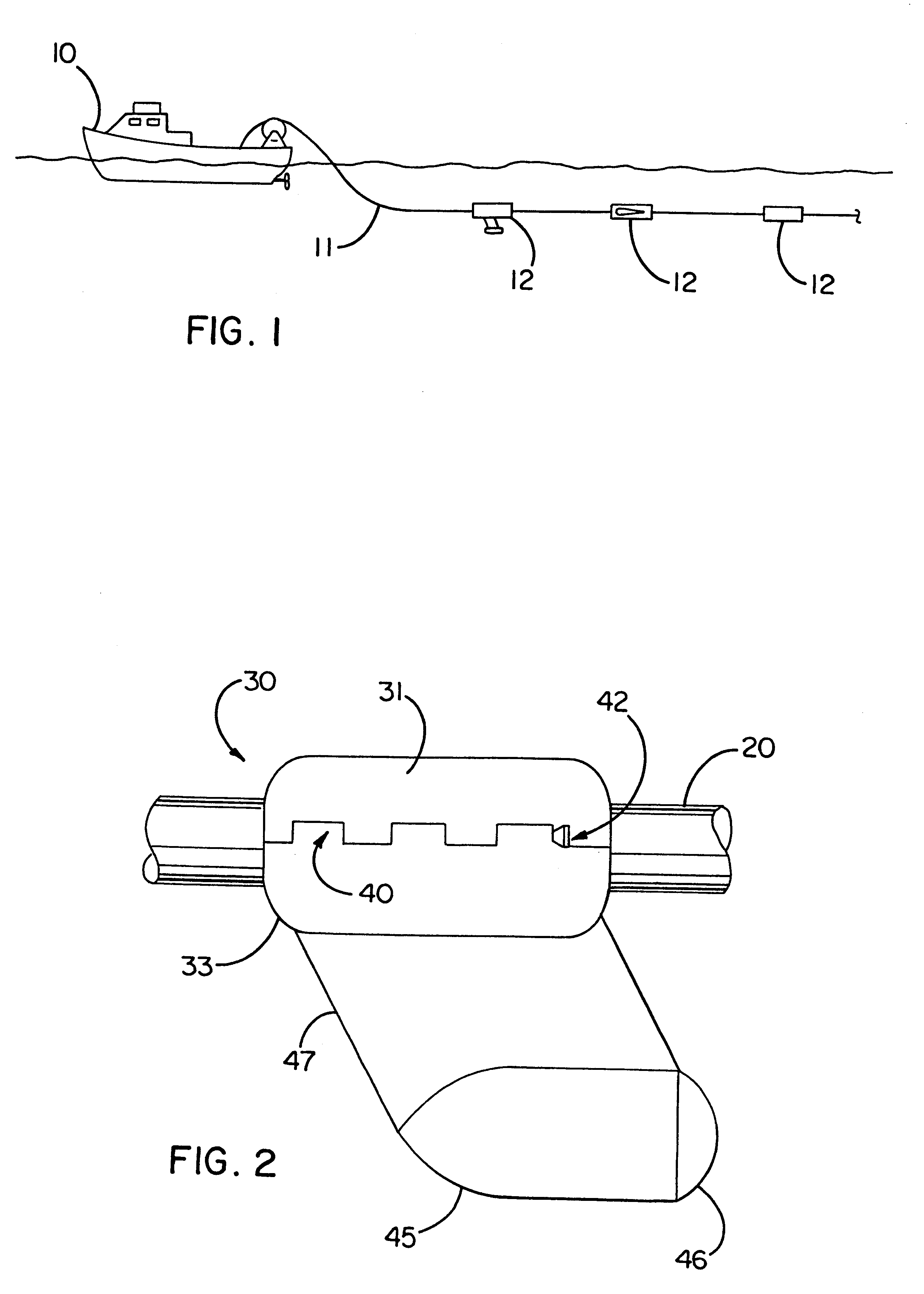
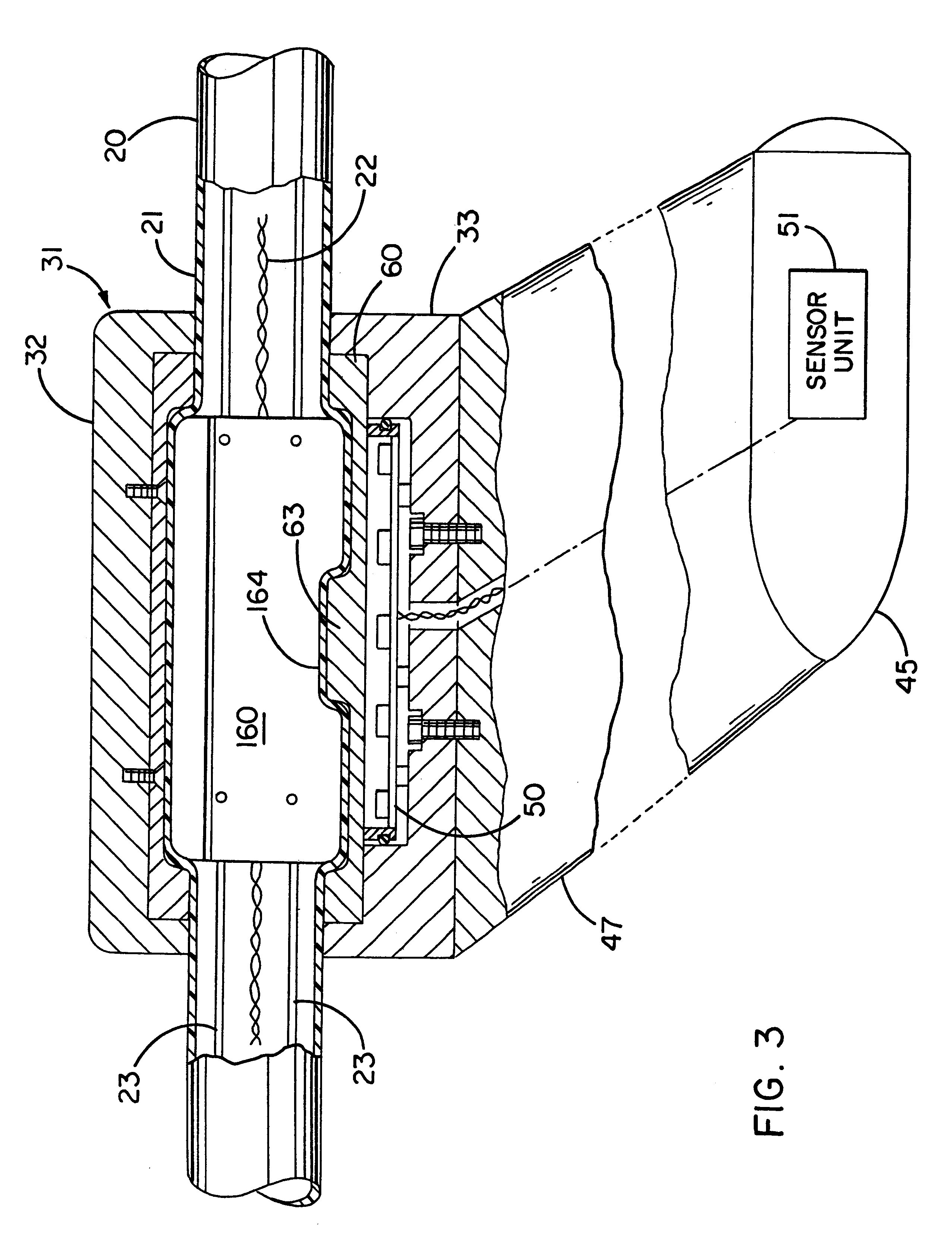
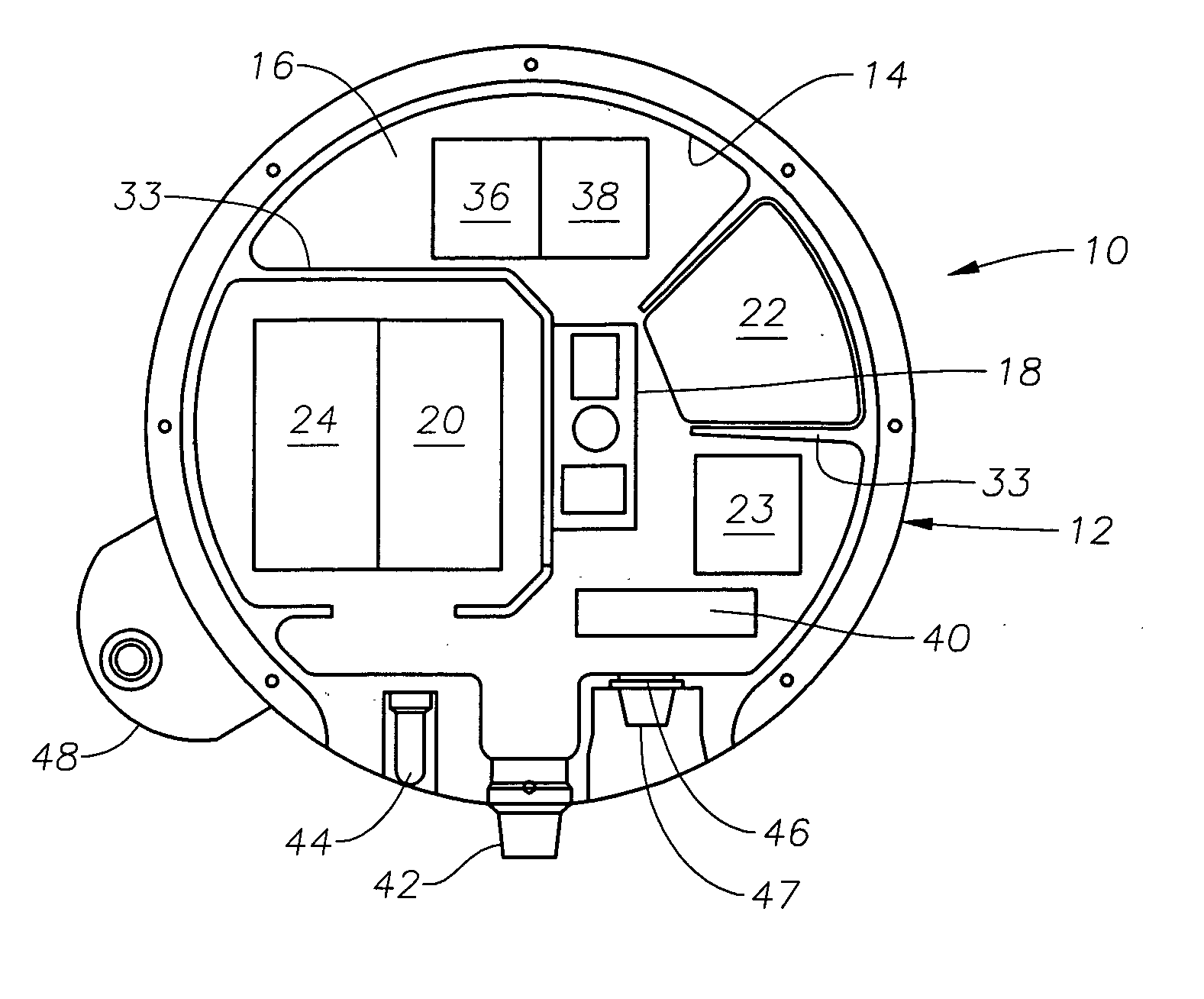
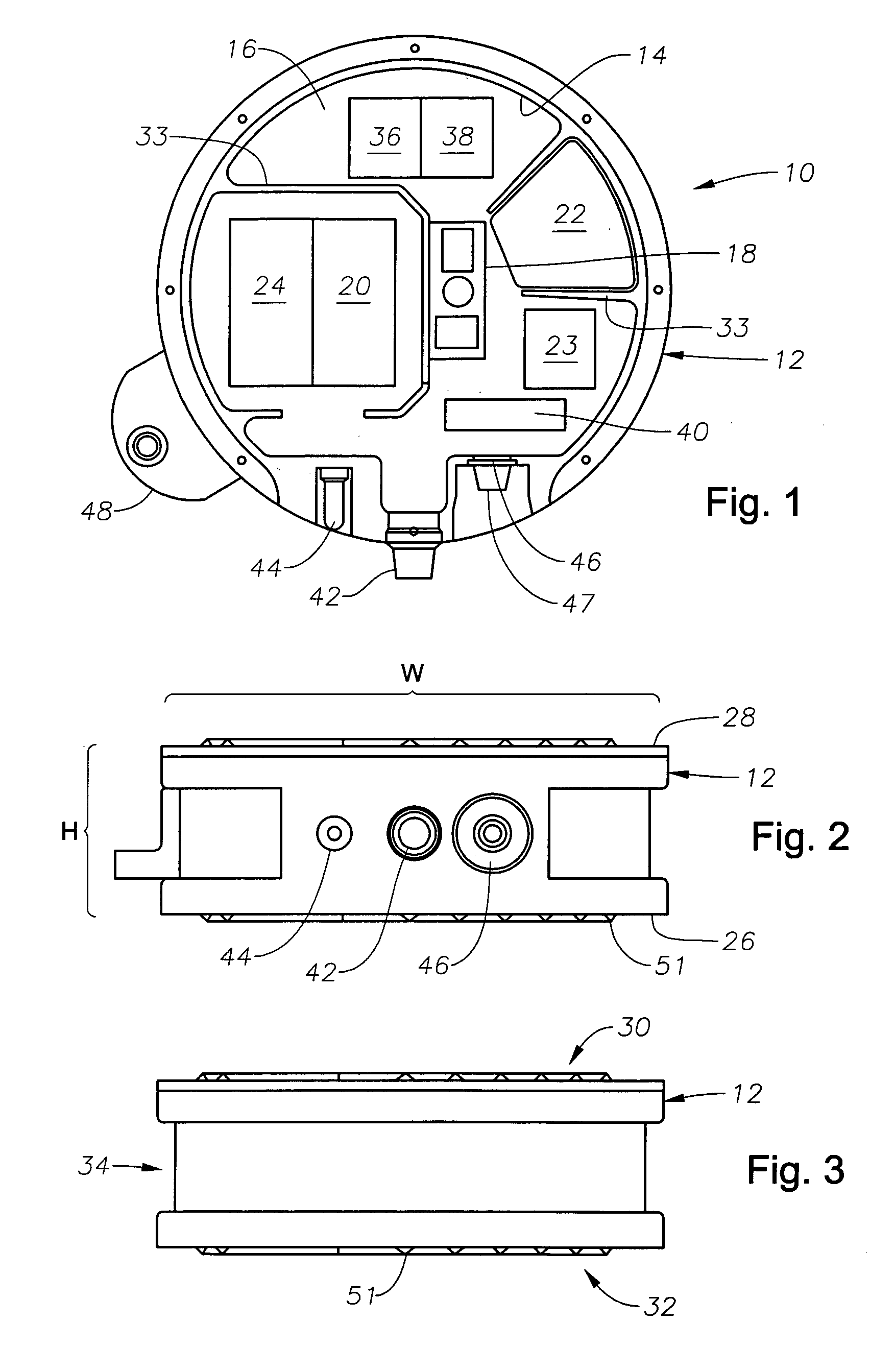
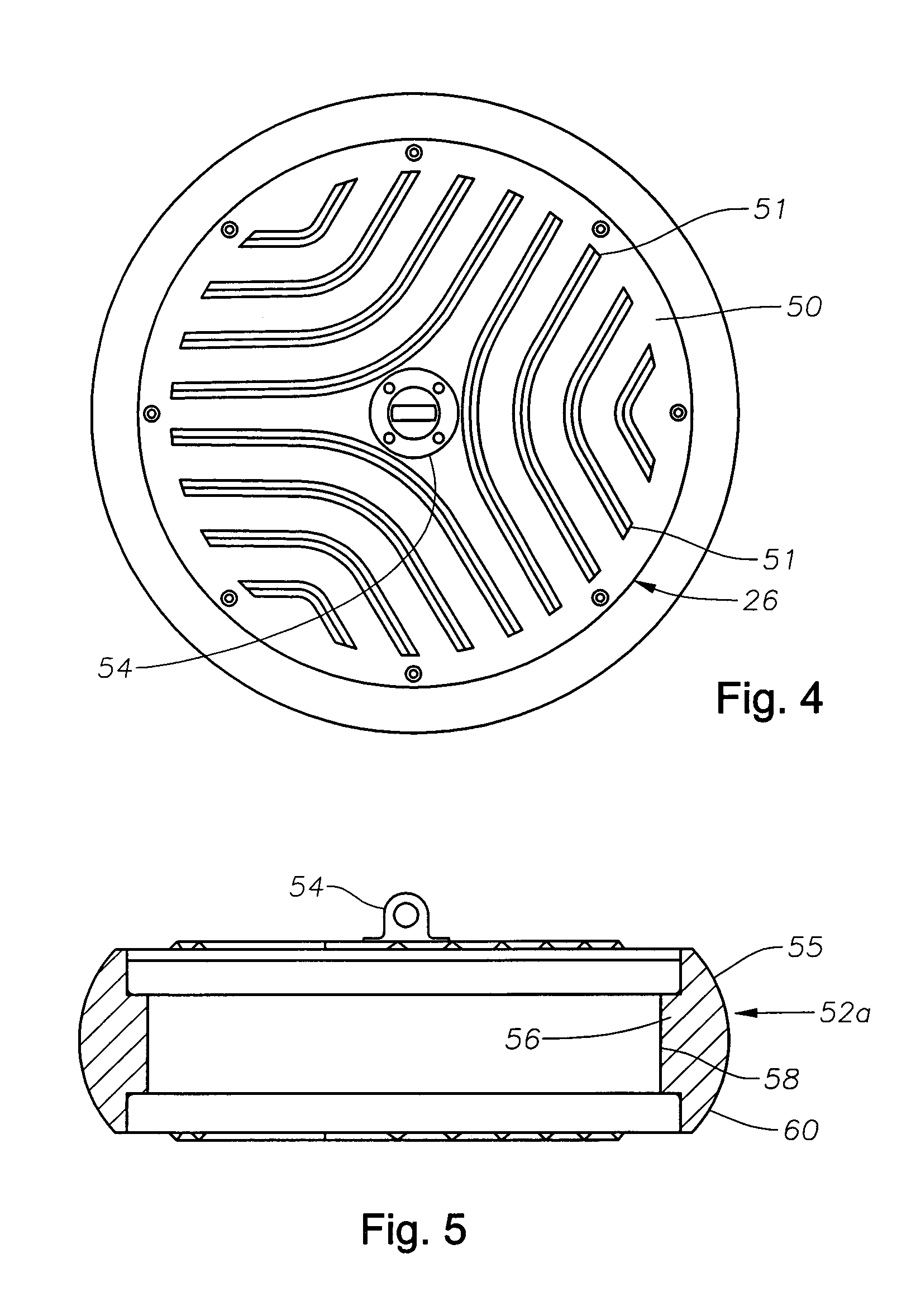
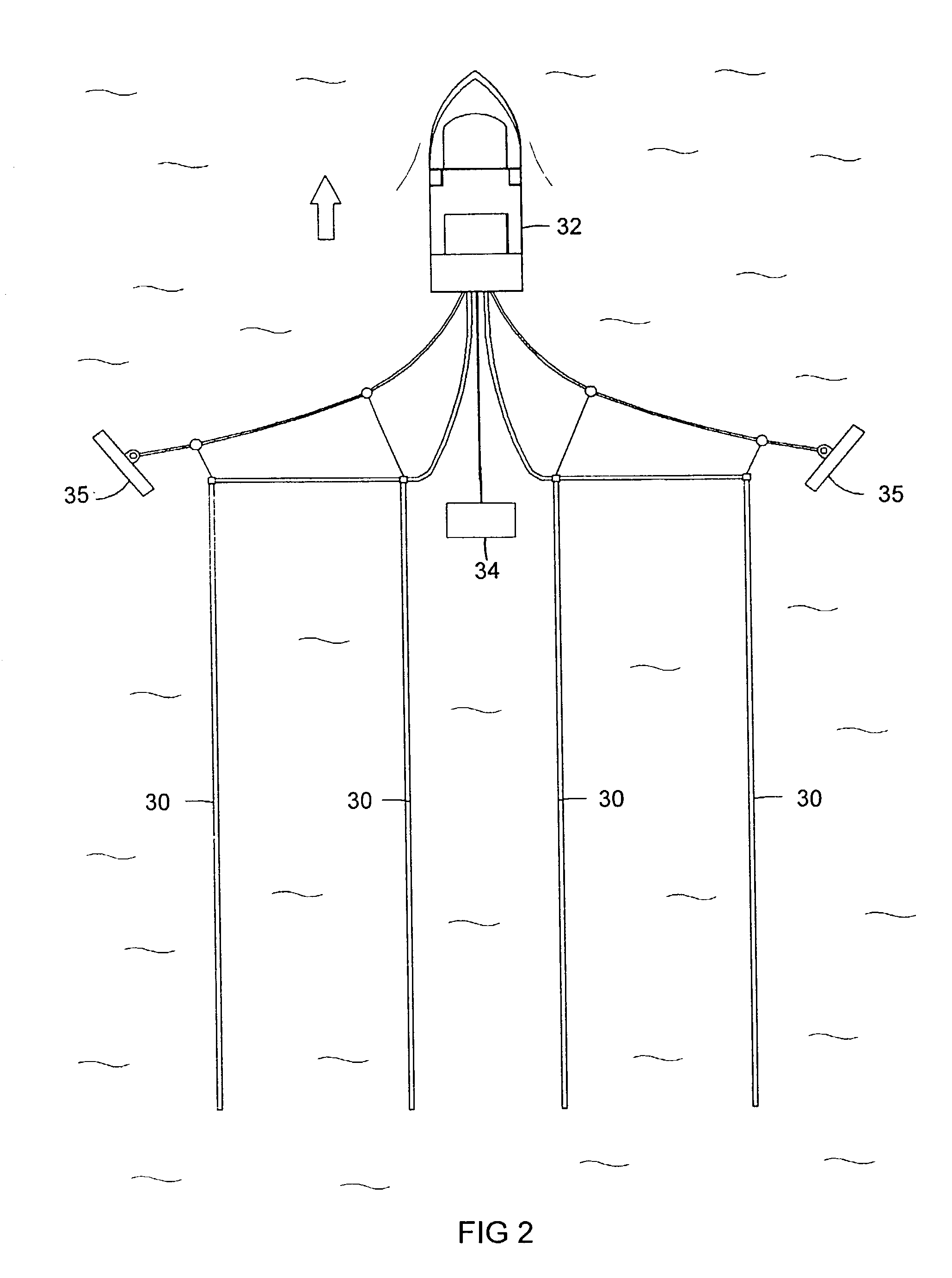
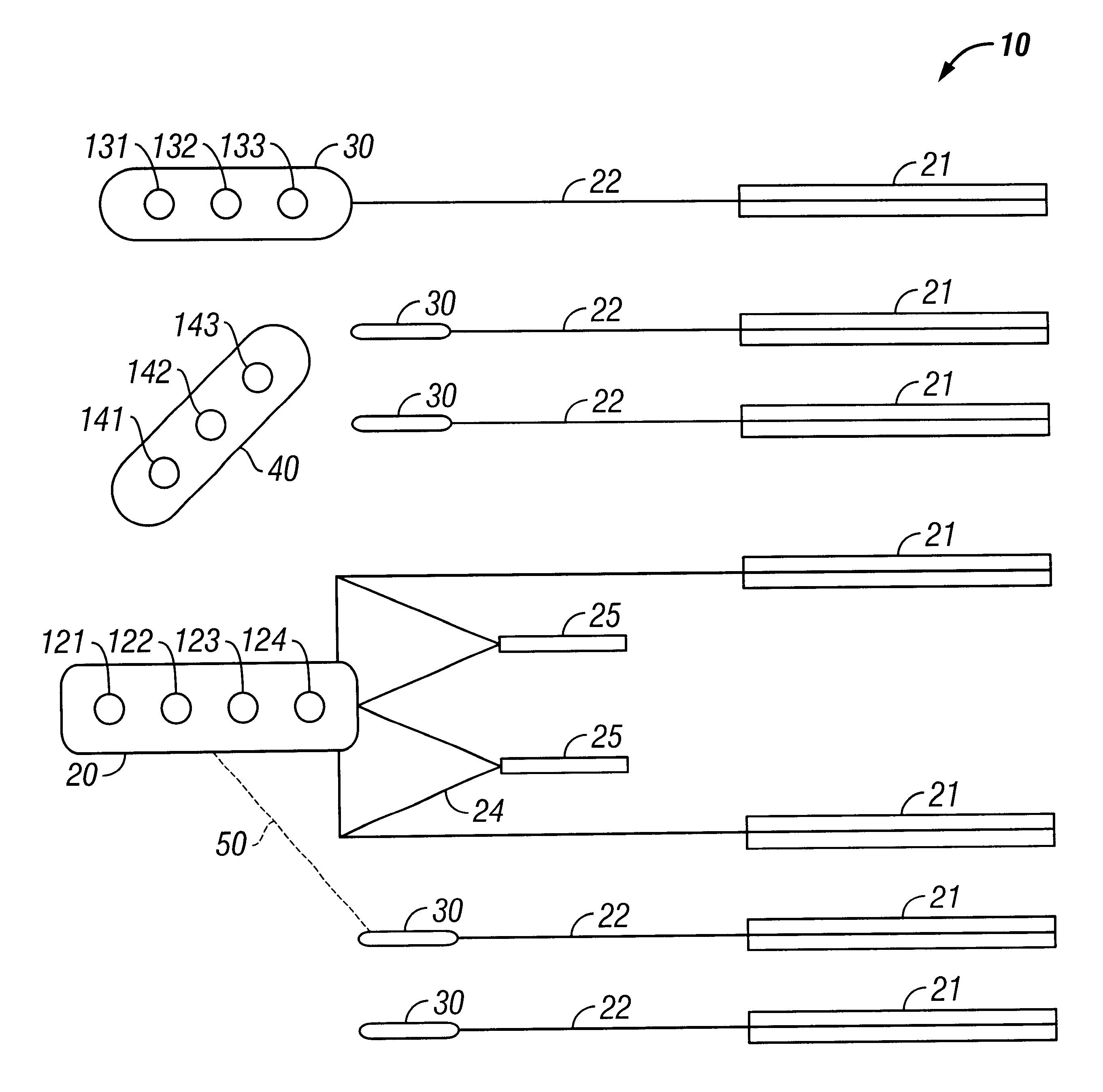
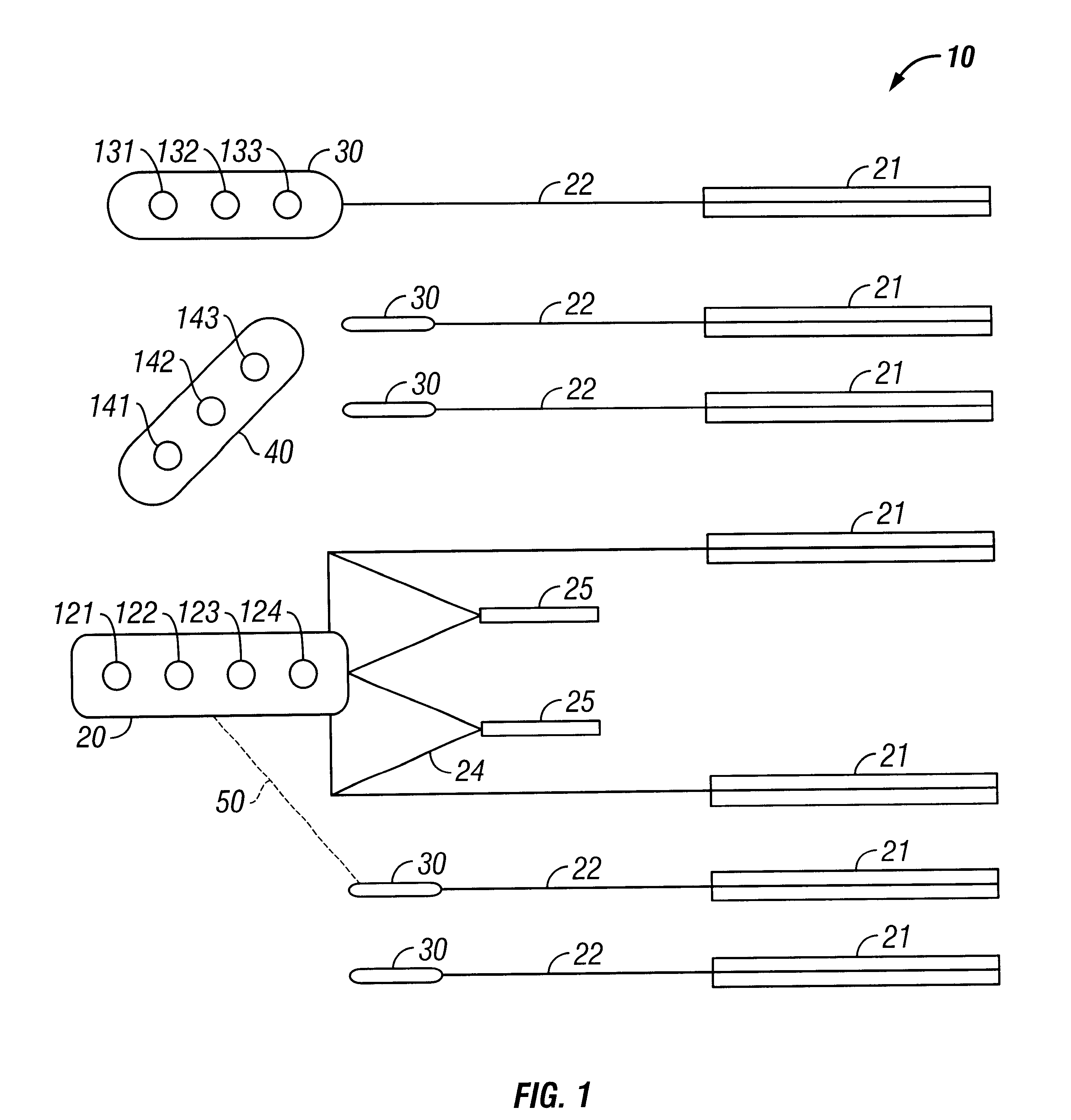
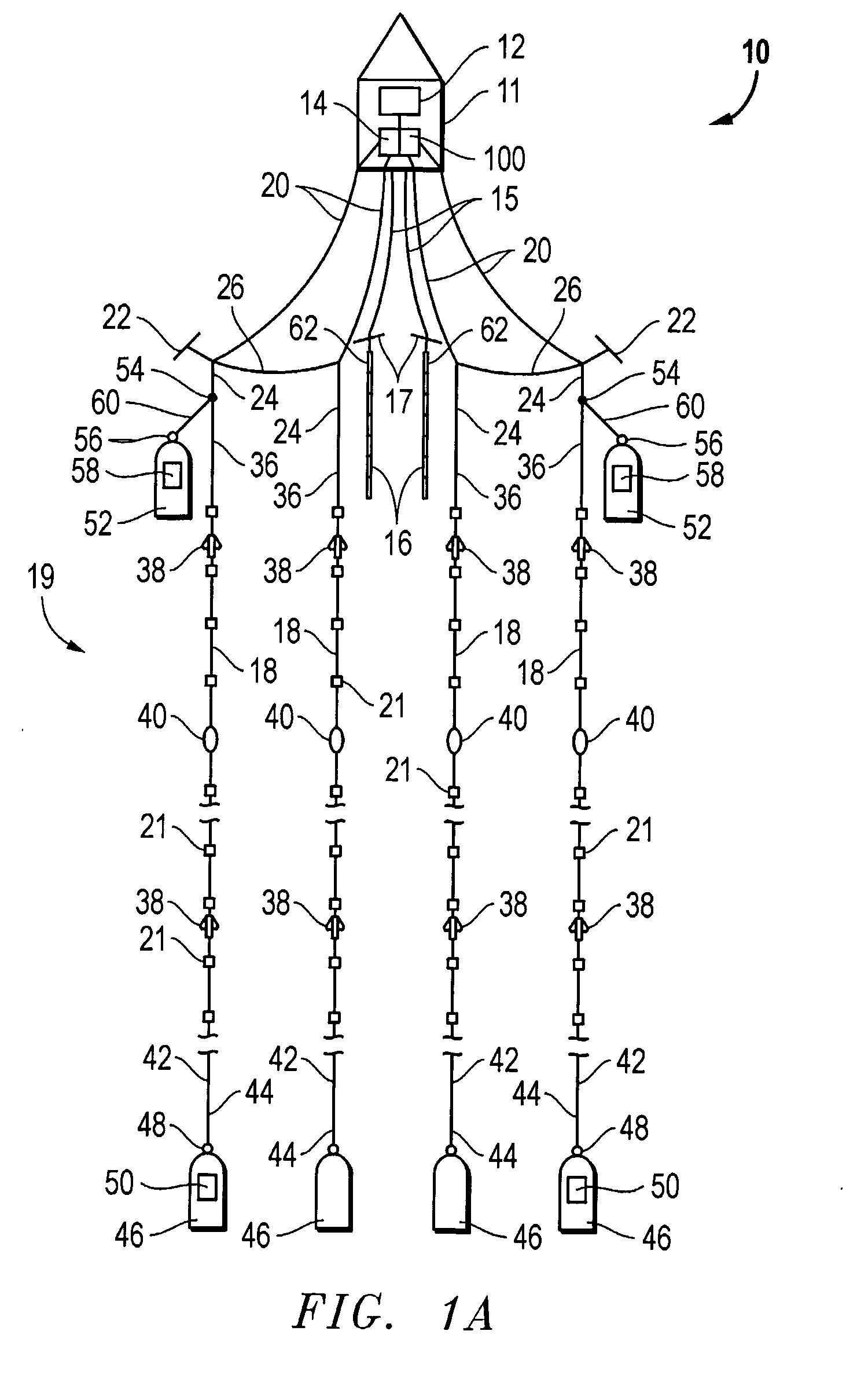
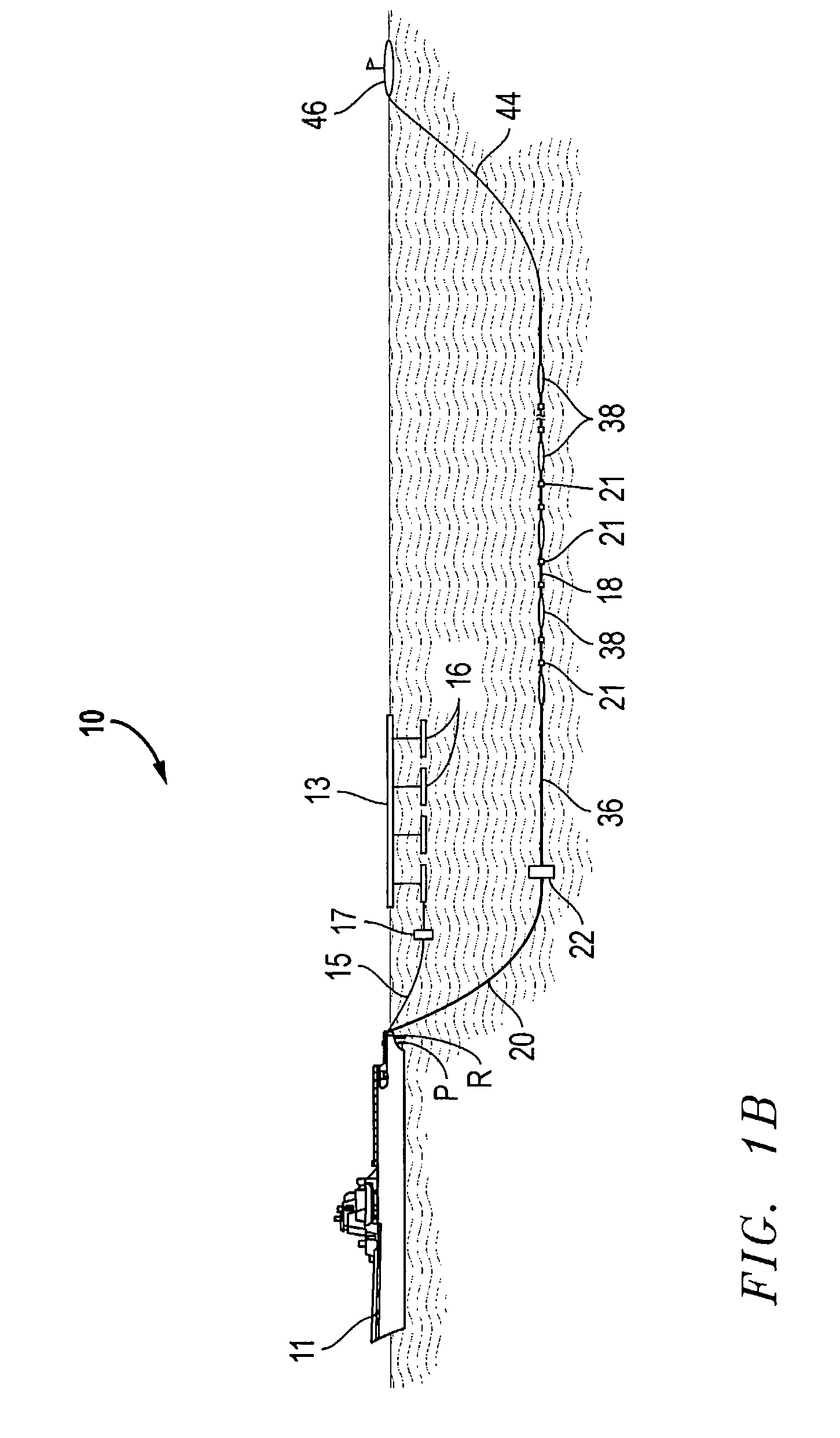
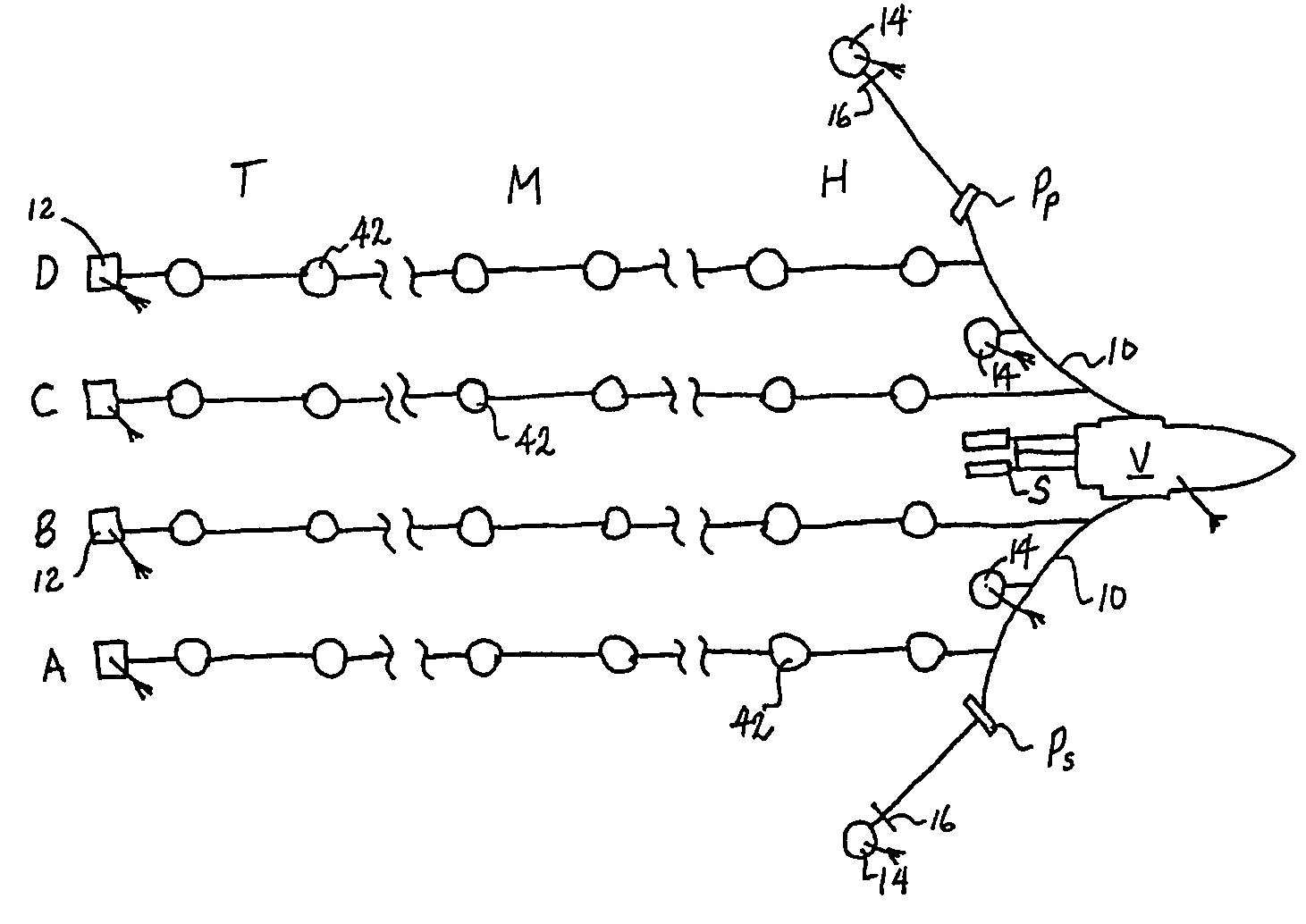
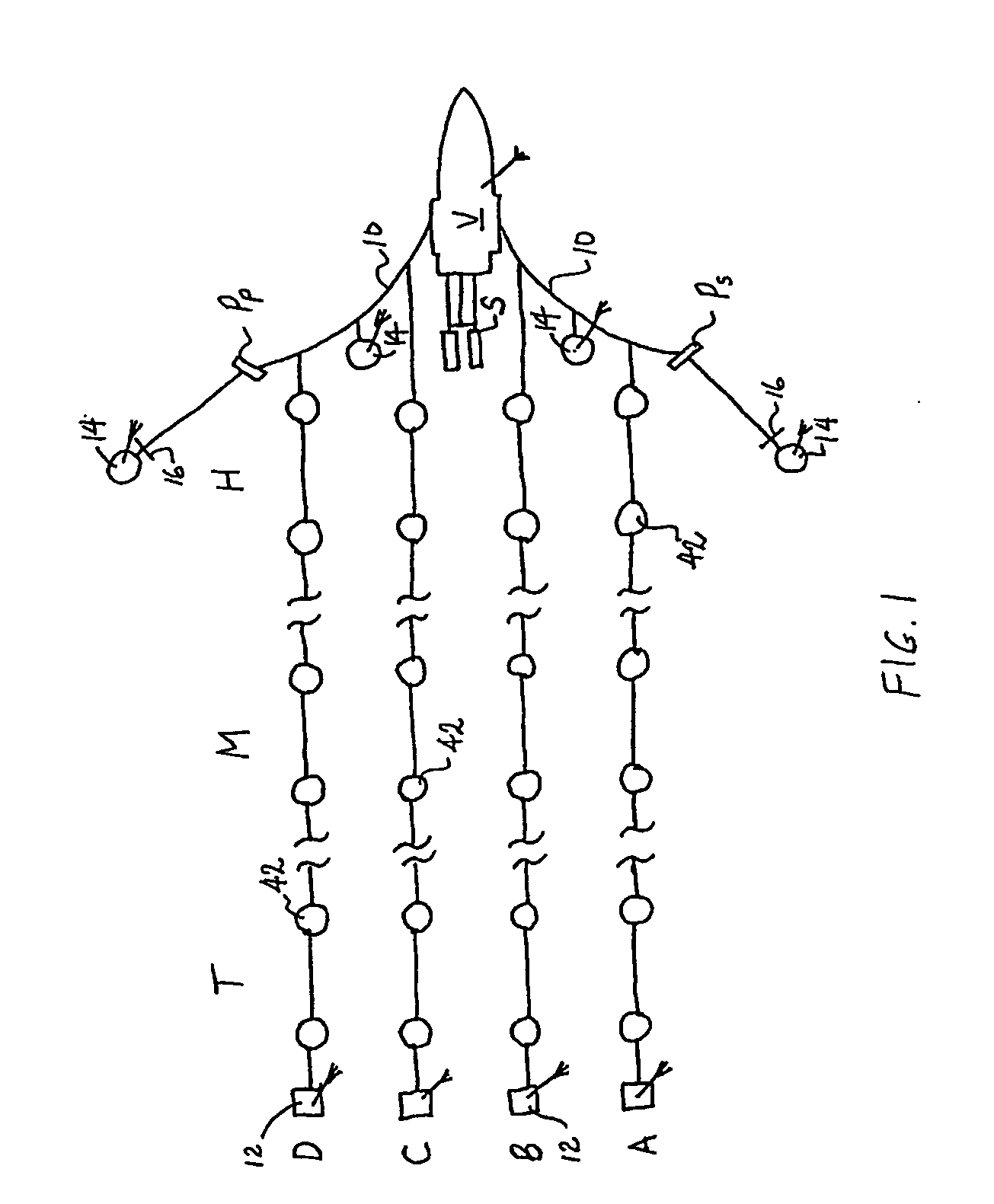
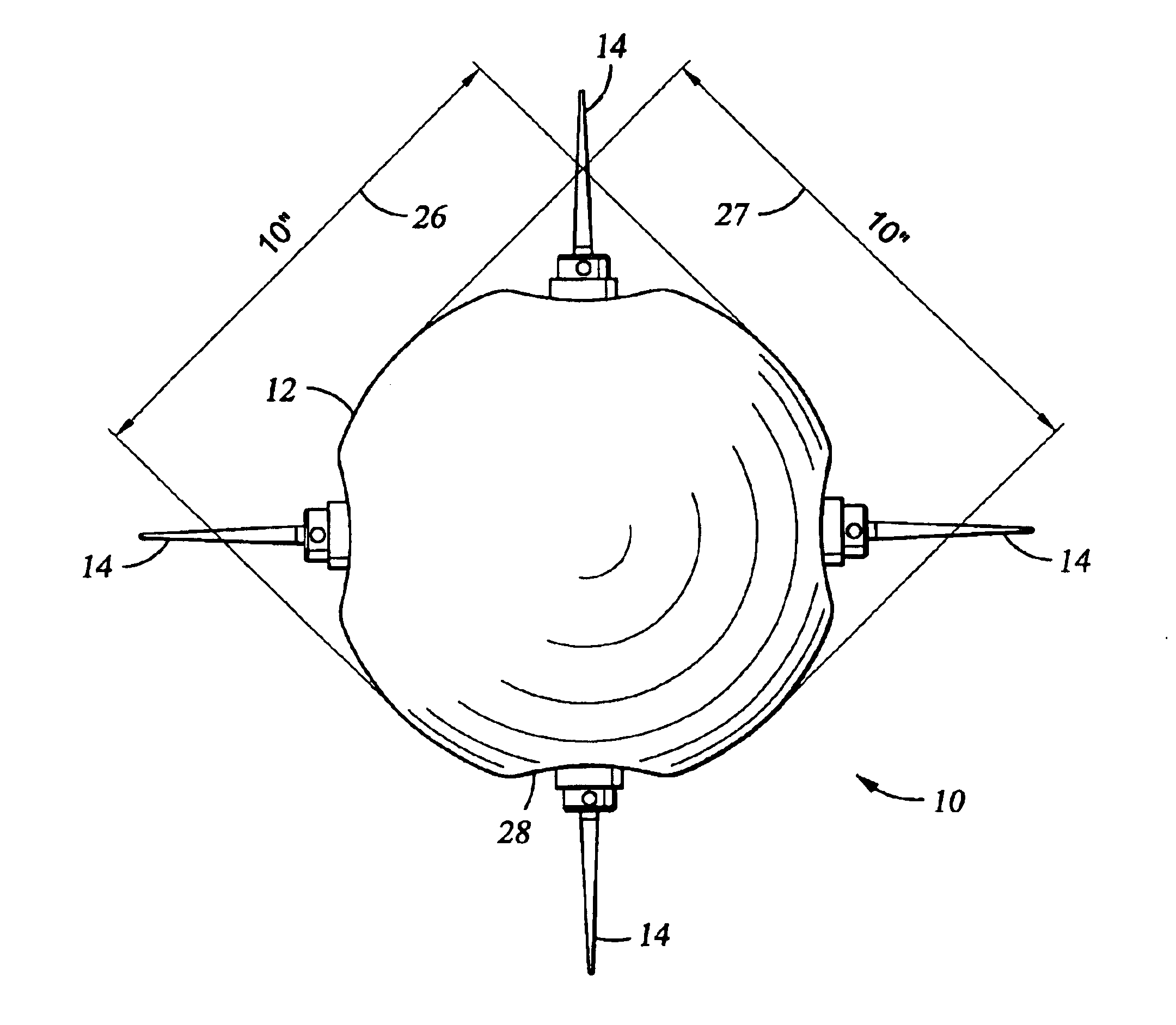
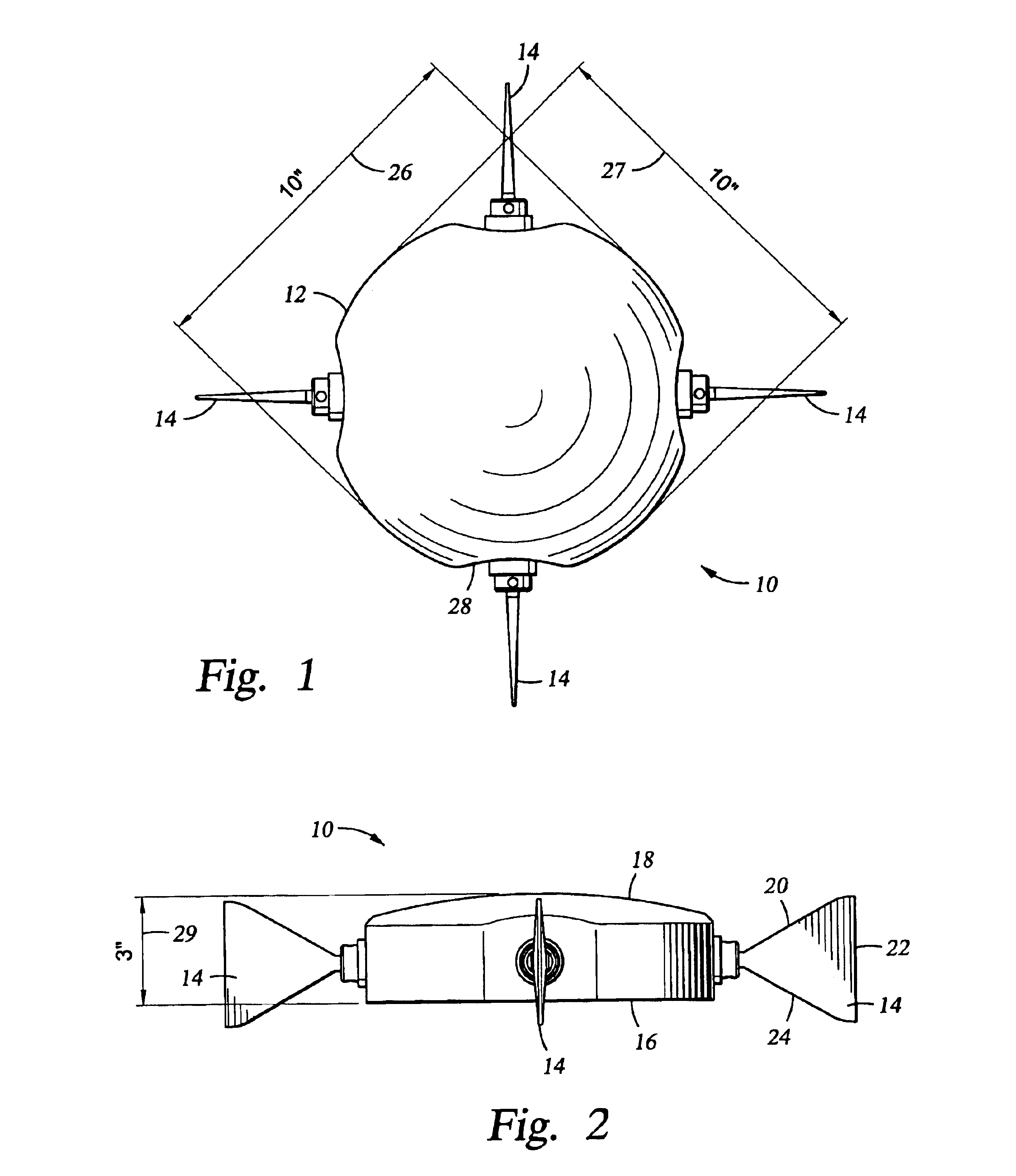
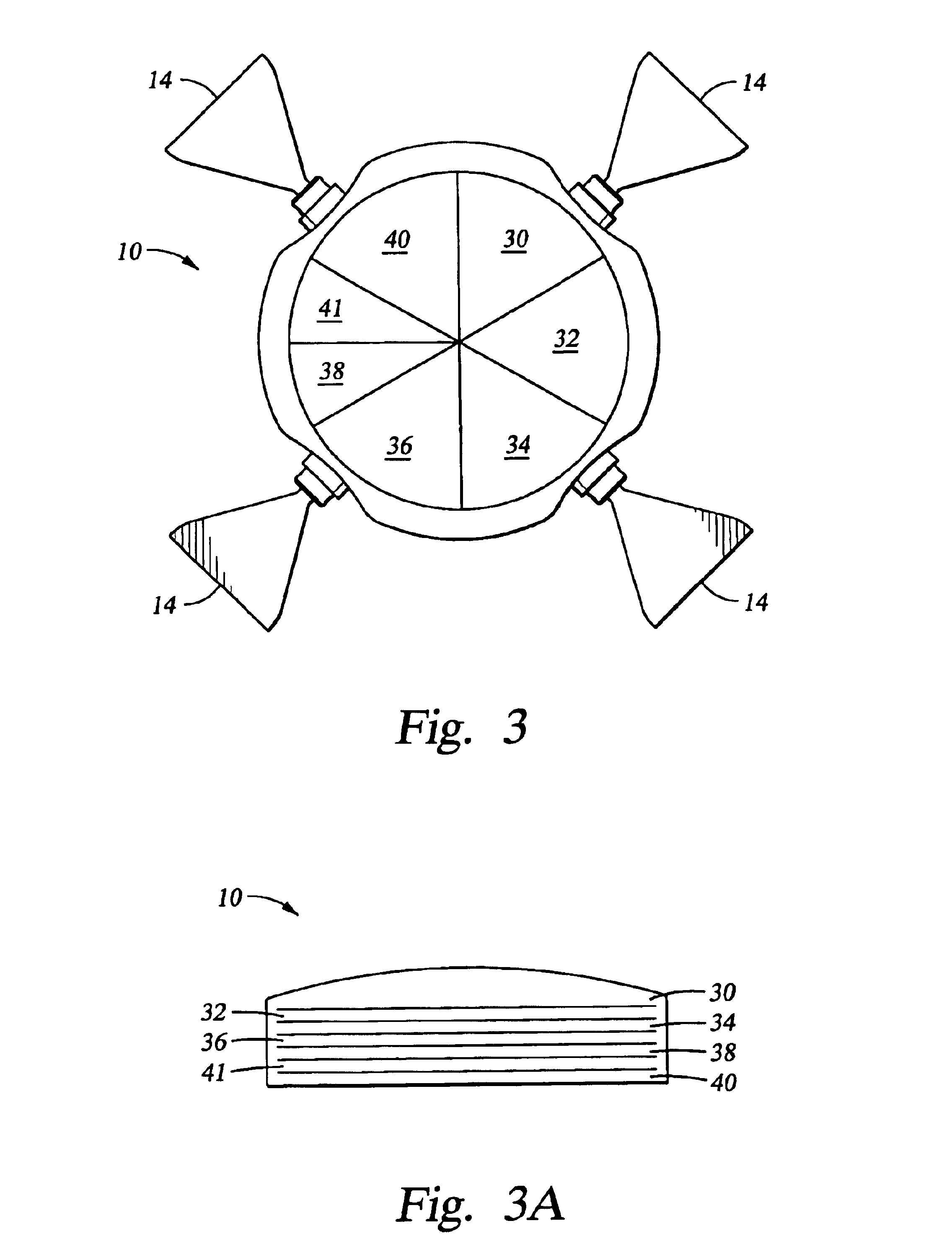
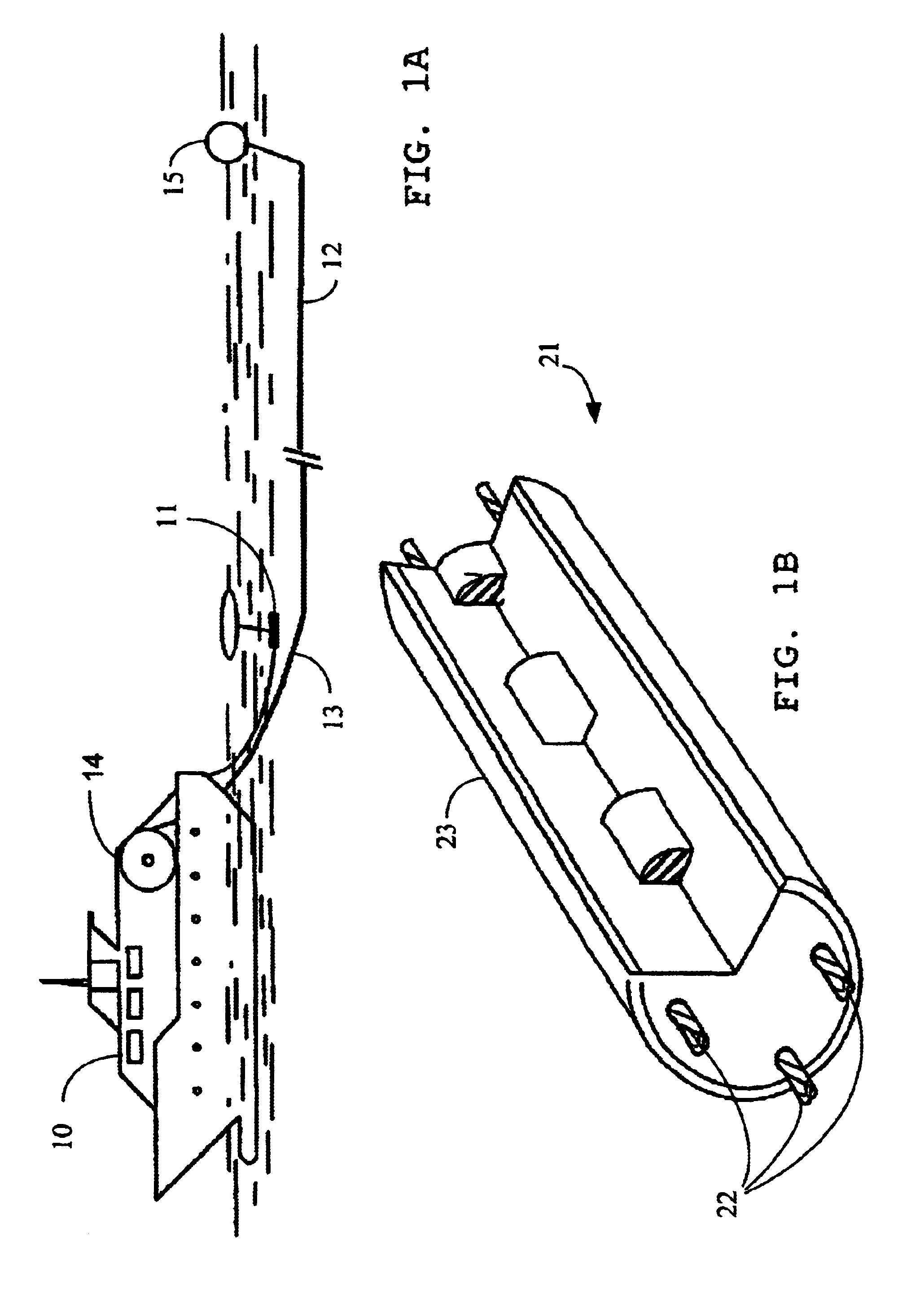
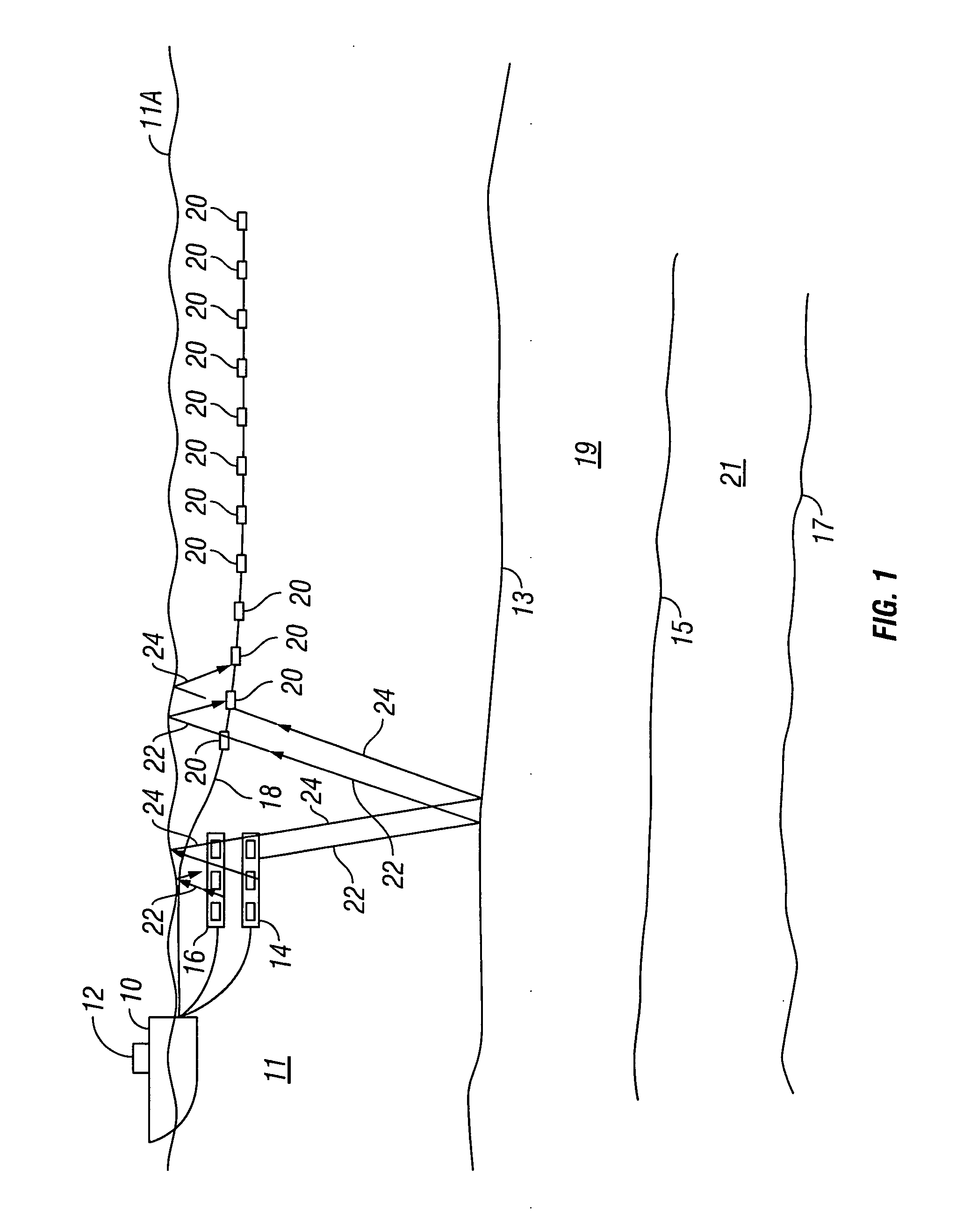
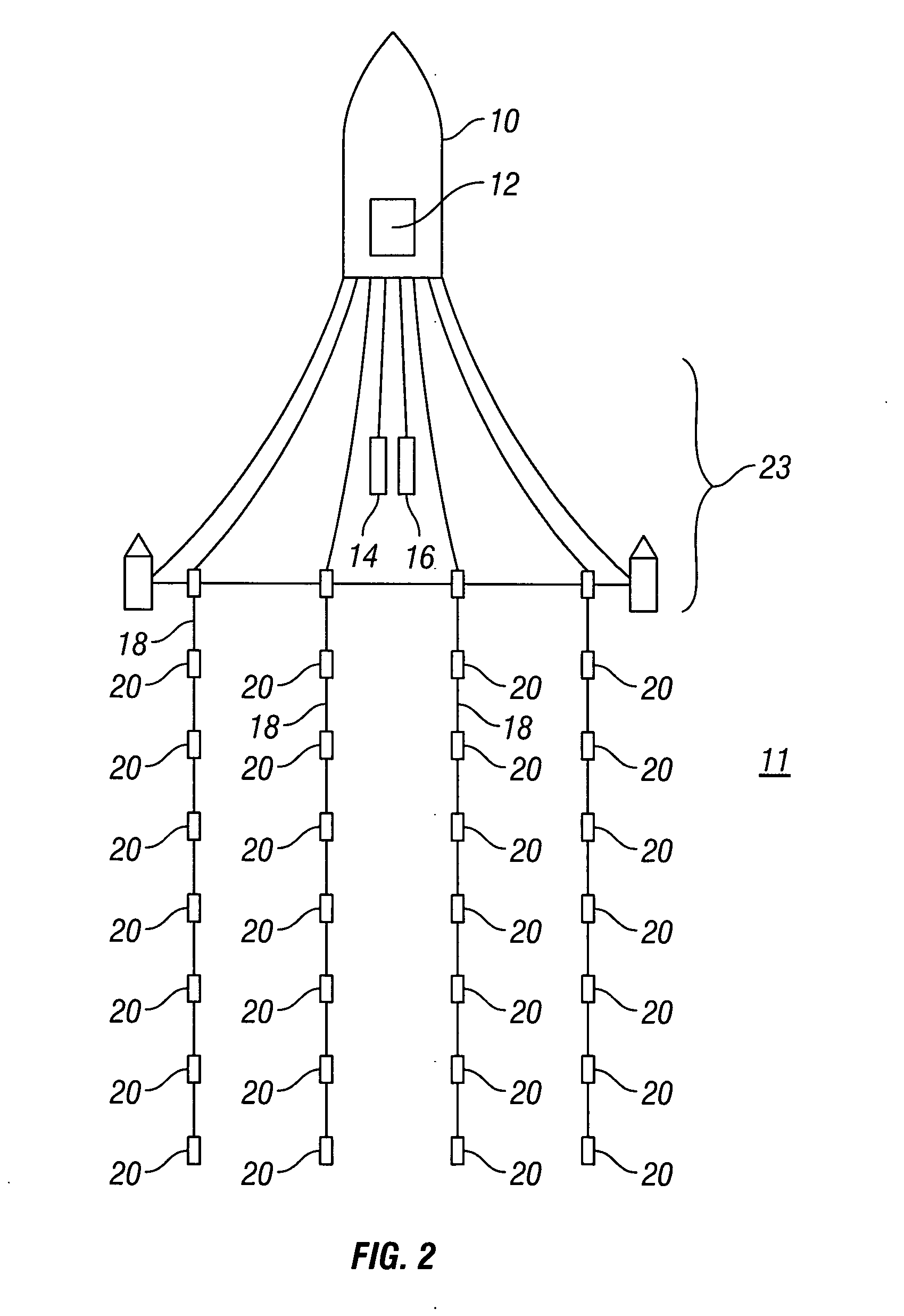
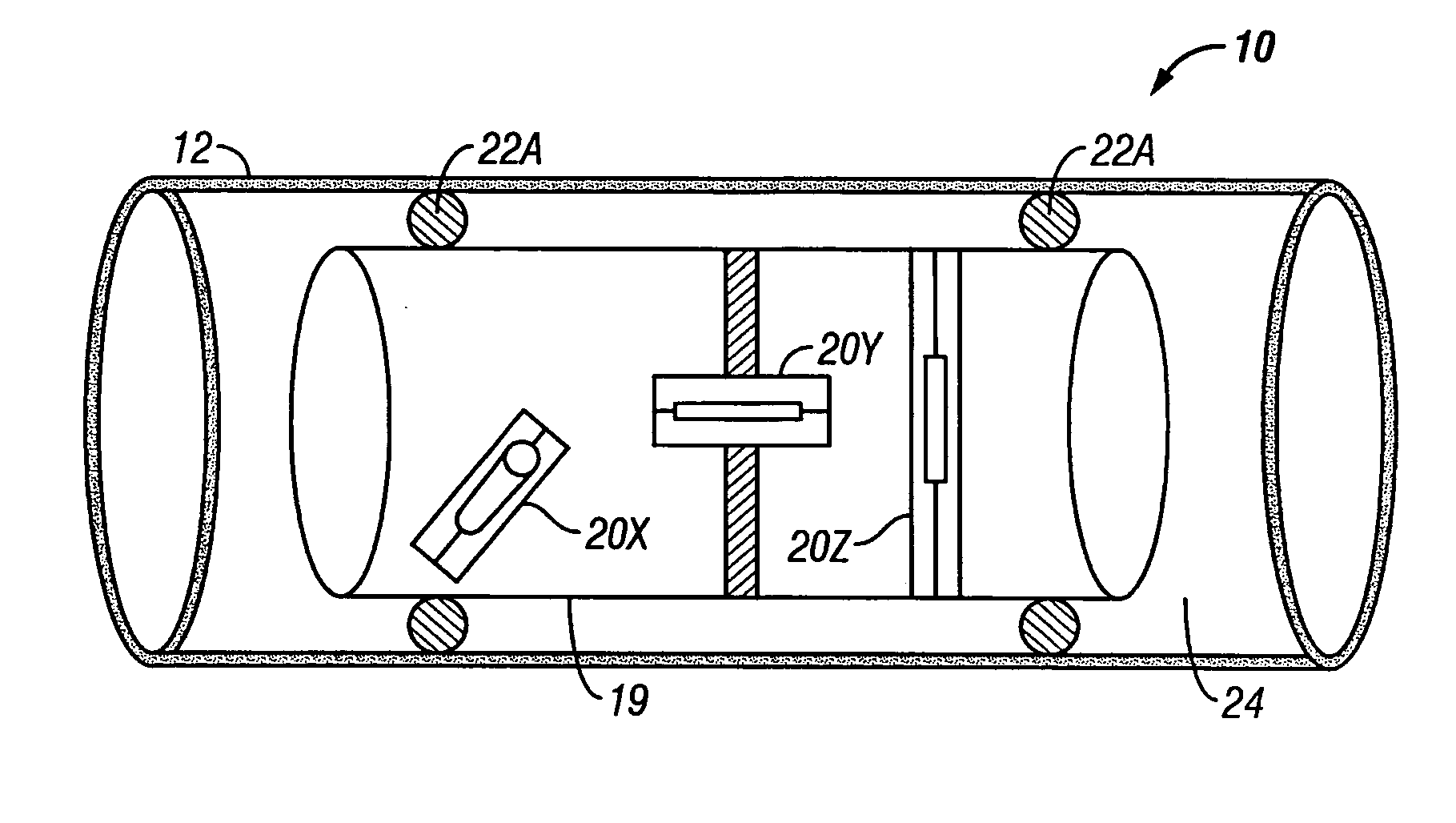
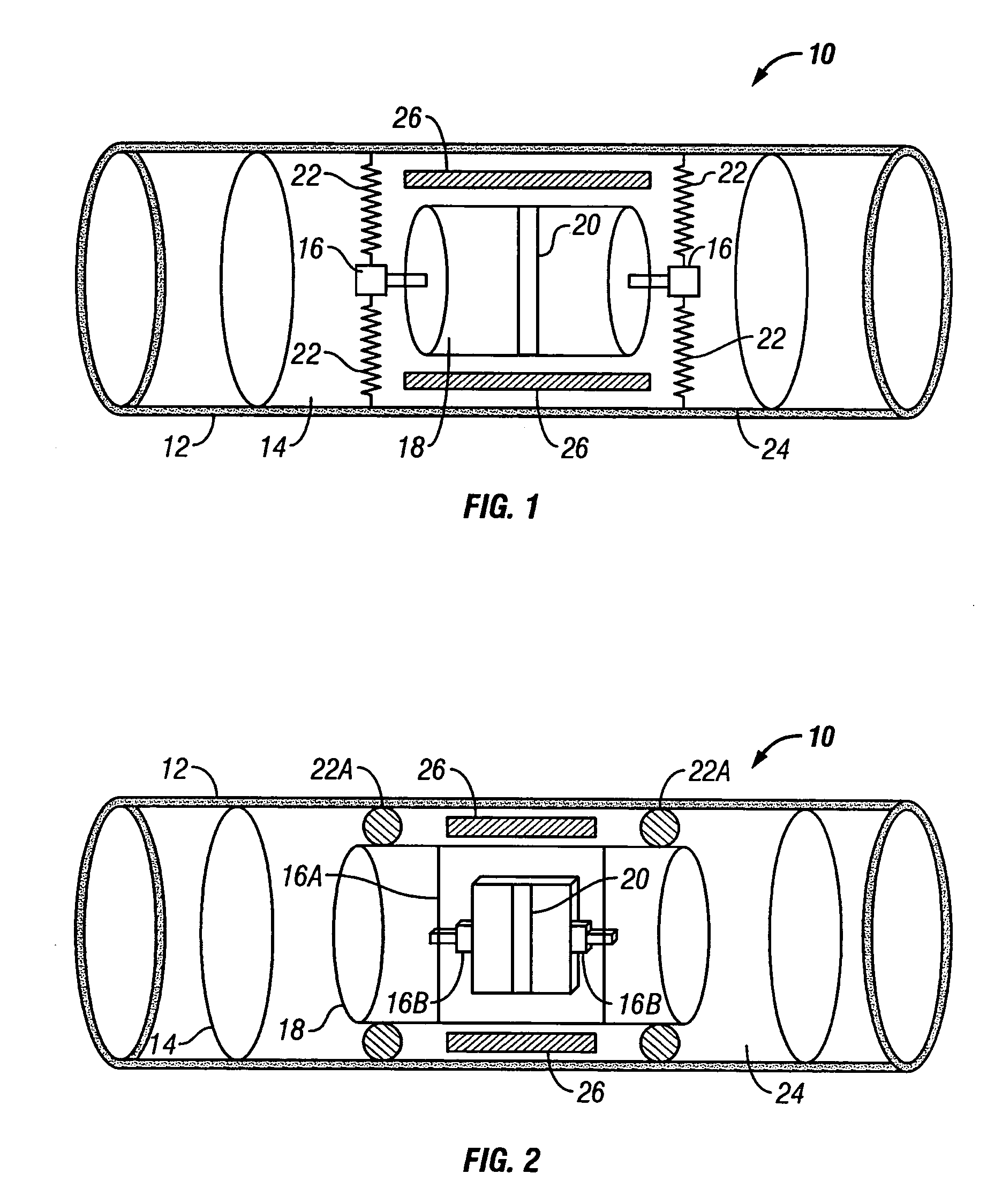
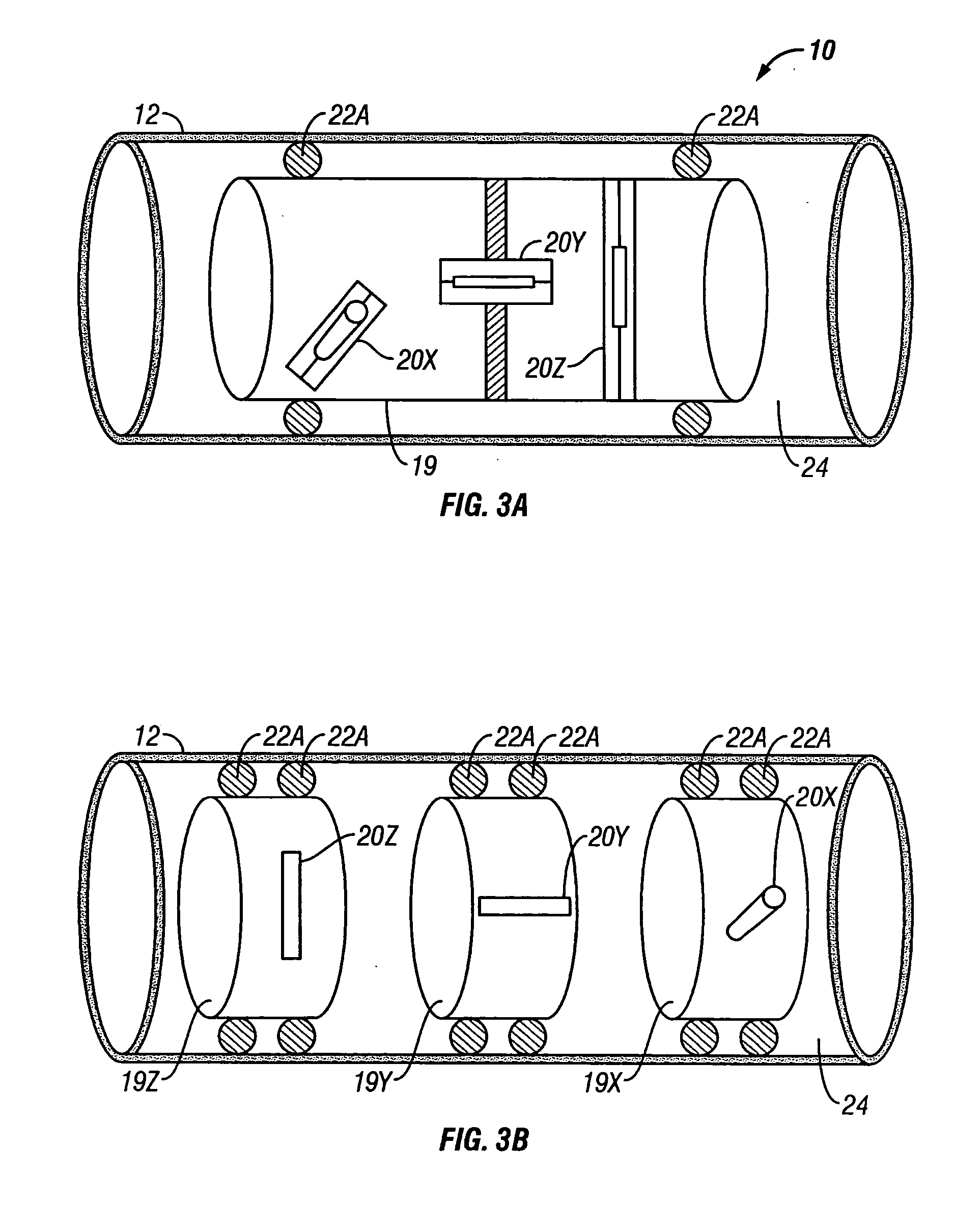
Apparatus and methods for multicomponent marine geophysical data gathering
InactiveUS7239577B2Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFloating cablesGeophoneCubic metre per second
In one embodiment the invention comprises a particle velocity sensor that includes a housing with a geophone mounted in the housing. A fluid that substantially surrounds the geophone is included within the housing. The particle velocity sensor has an acoustic impedance within the range of about 750,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m3) to about 3,000,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m3). In another embodiment the invention comprises method of geophysical exploration in which a seismic signal is generated in a body of water and detected with a plurality of co-located particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors positioned within a seismic cable. The output signal of either or both of the particle velocity sensors or the pressure gradient sensors is modified to substantially equalize the output signals from the particle velocity sensors and the pressure gradient sensors. The output signals from particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors are then combined.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
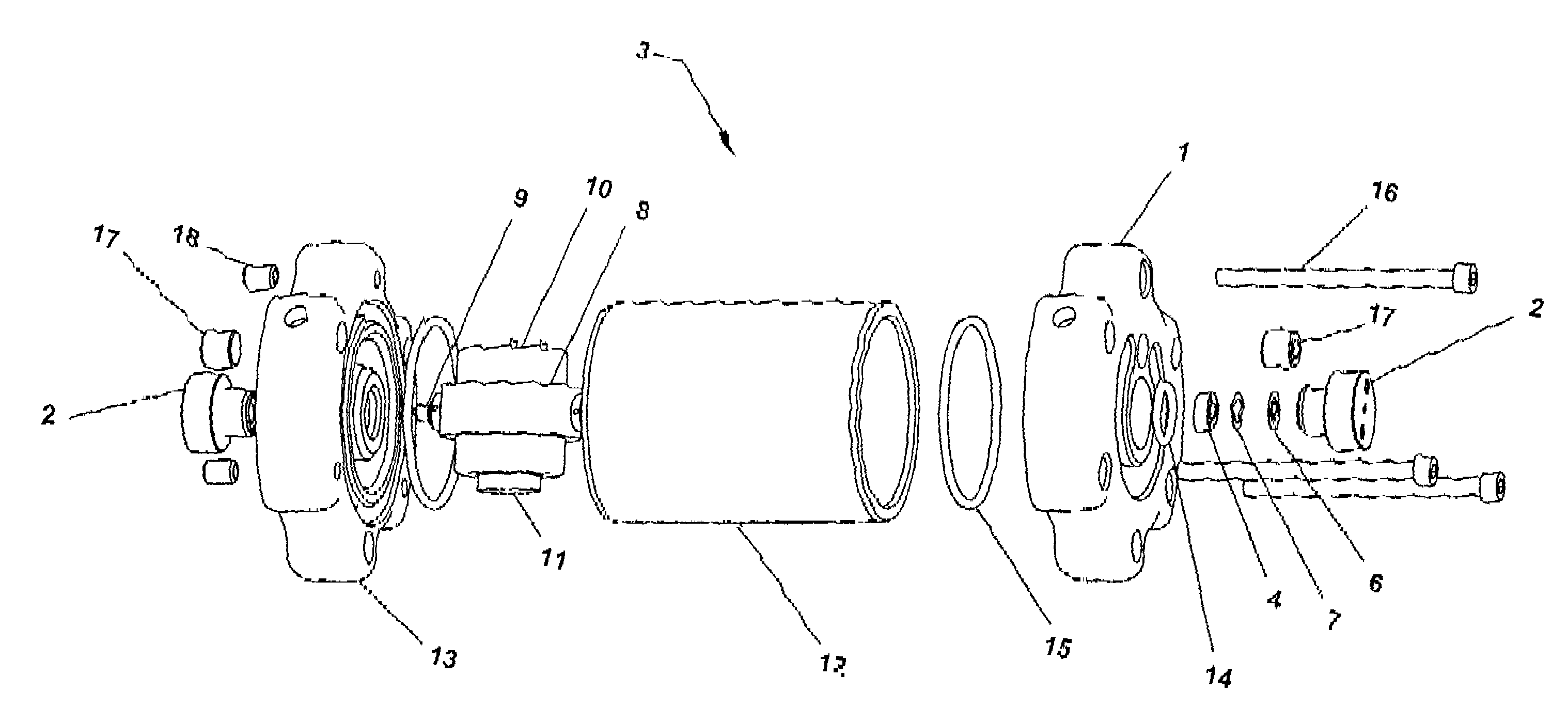
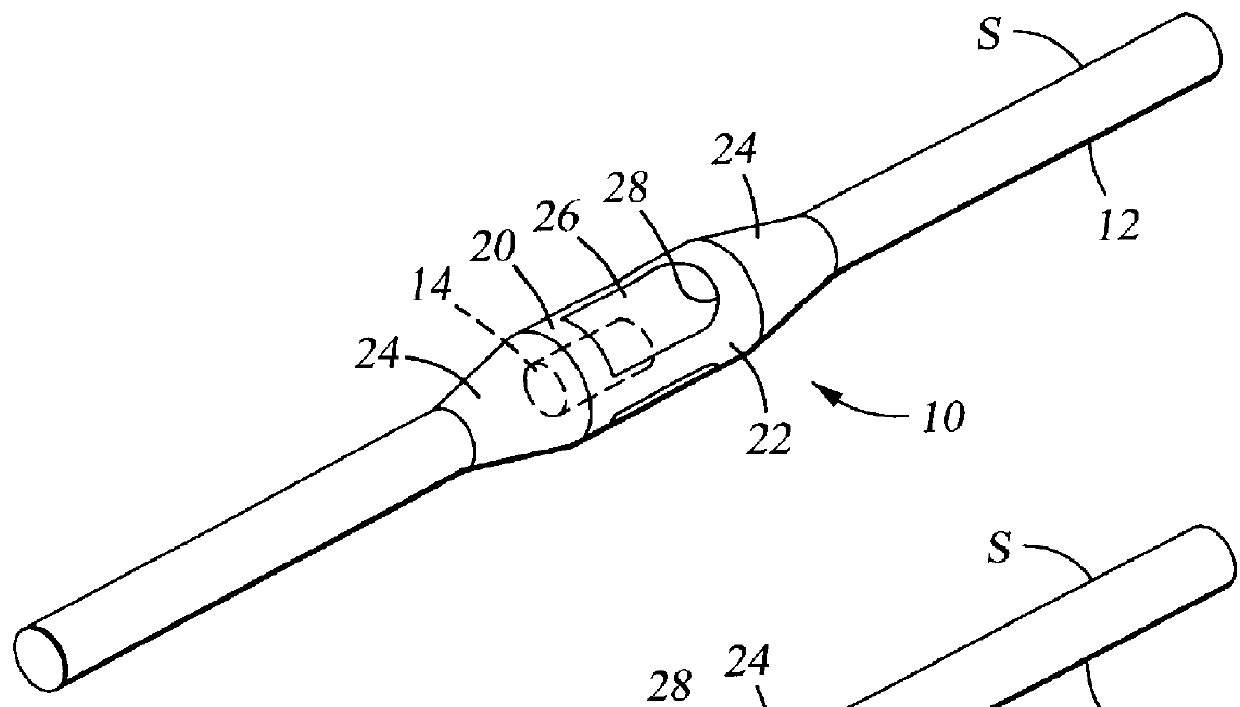
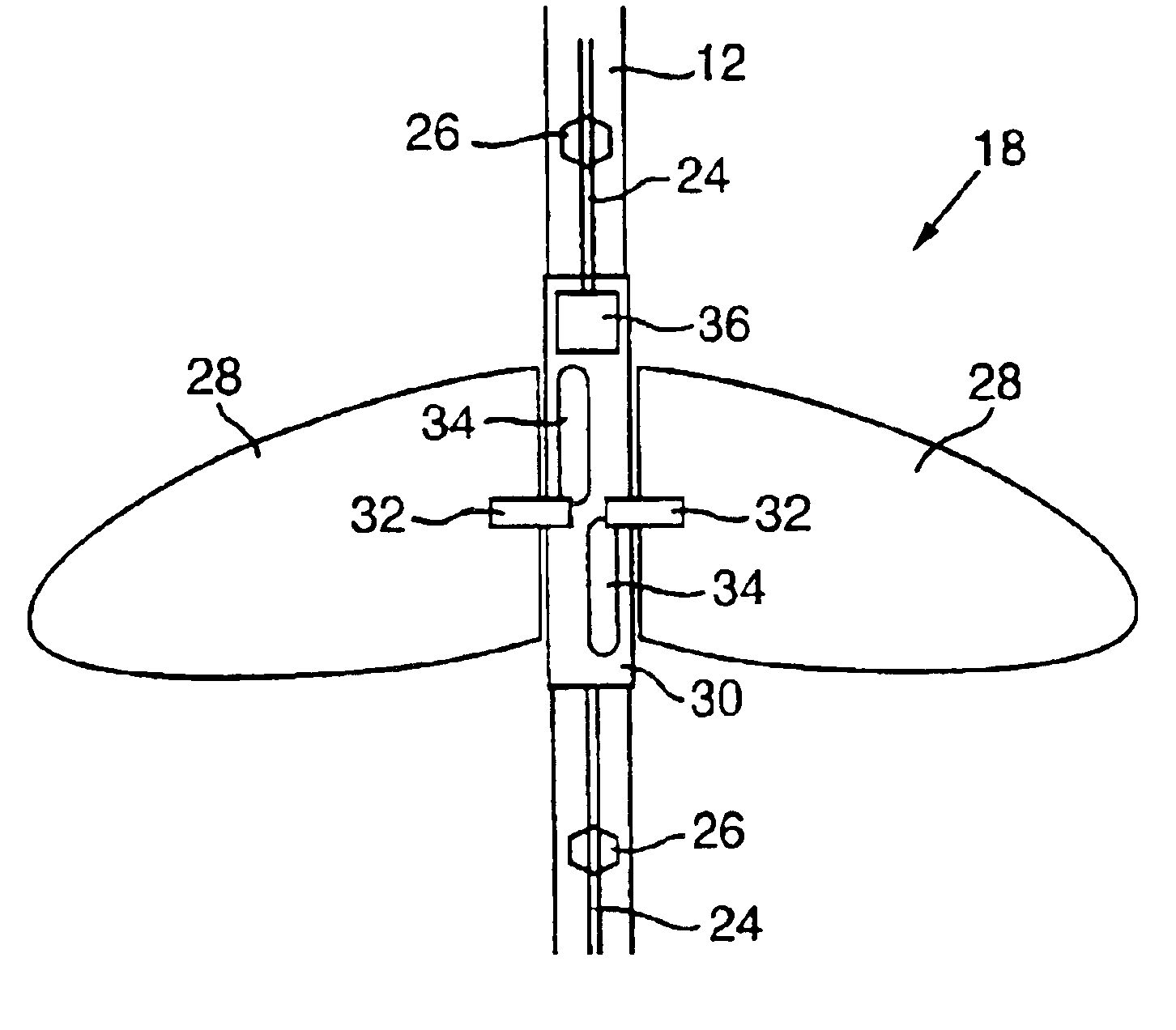
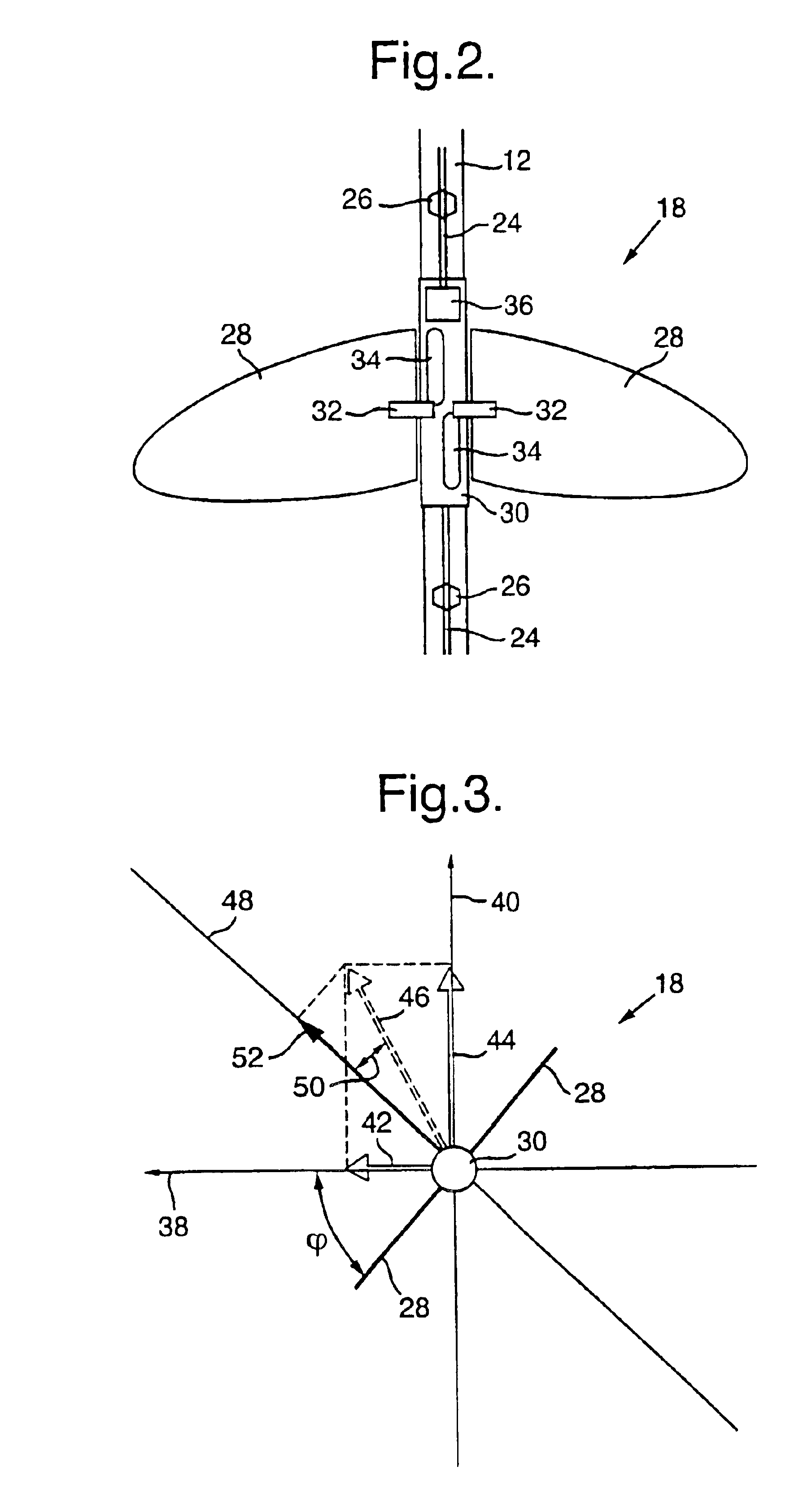
Devices for controlling the position of an underwater cable
A device for controlling the position of an underwater cable comprises a body, first and second actuators, and a pair of wings. The body is stationarily mountable to the underwater cable and the first and second actuators are disposed in the body. Each wing has an axis of rotation and the wings are coupled to the first and second actuators to control the depth and the horizontal position of the underwater cable in the water.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
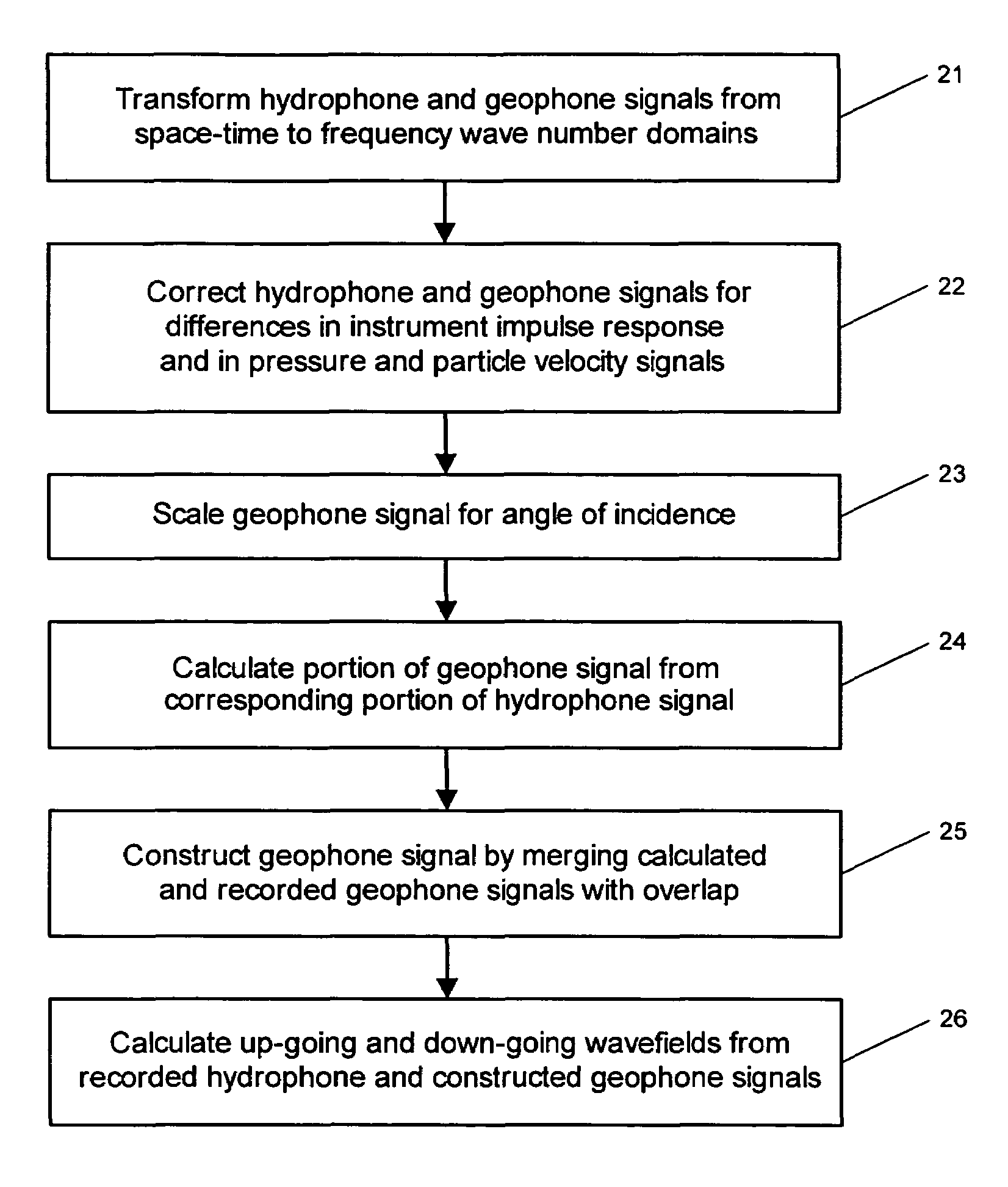
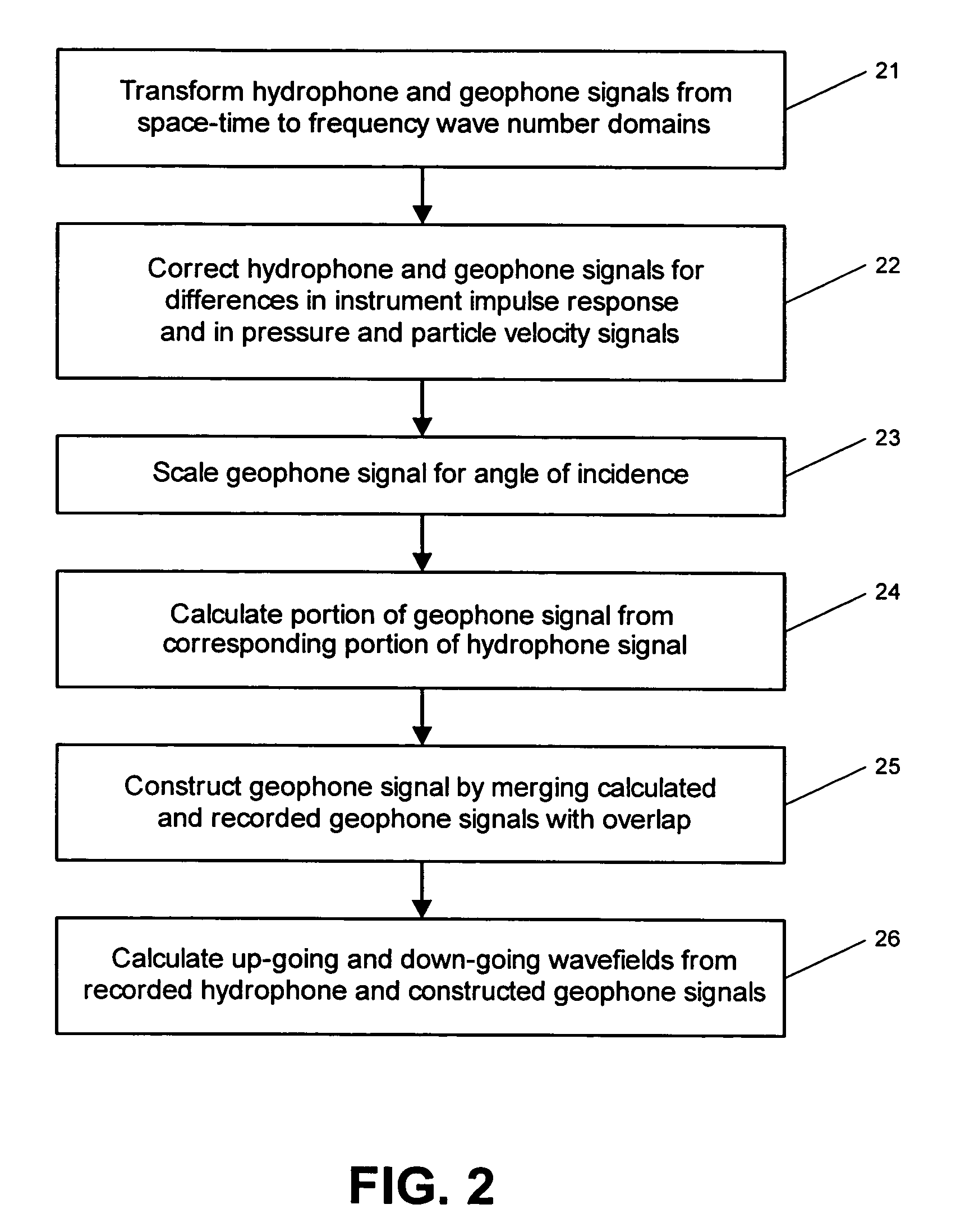
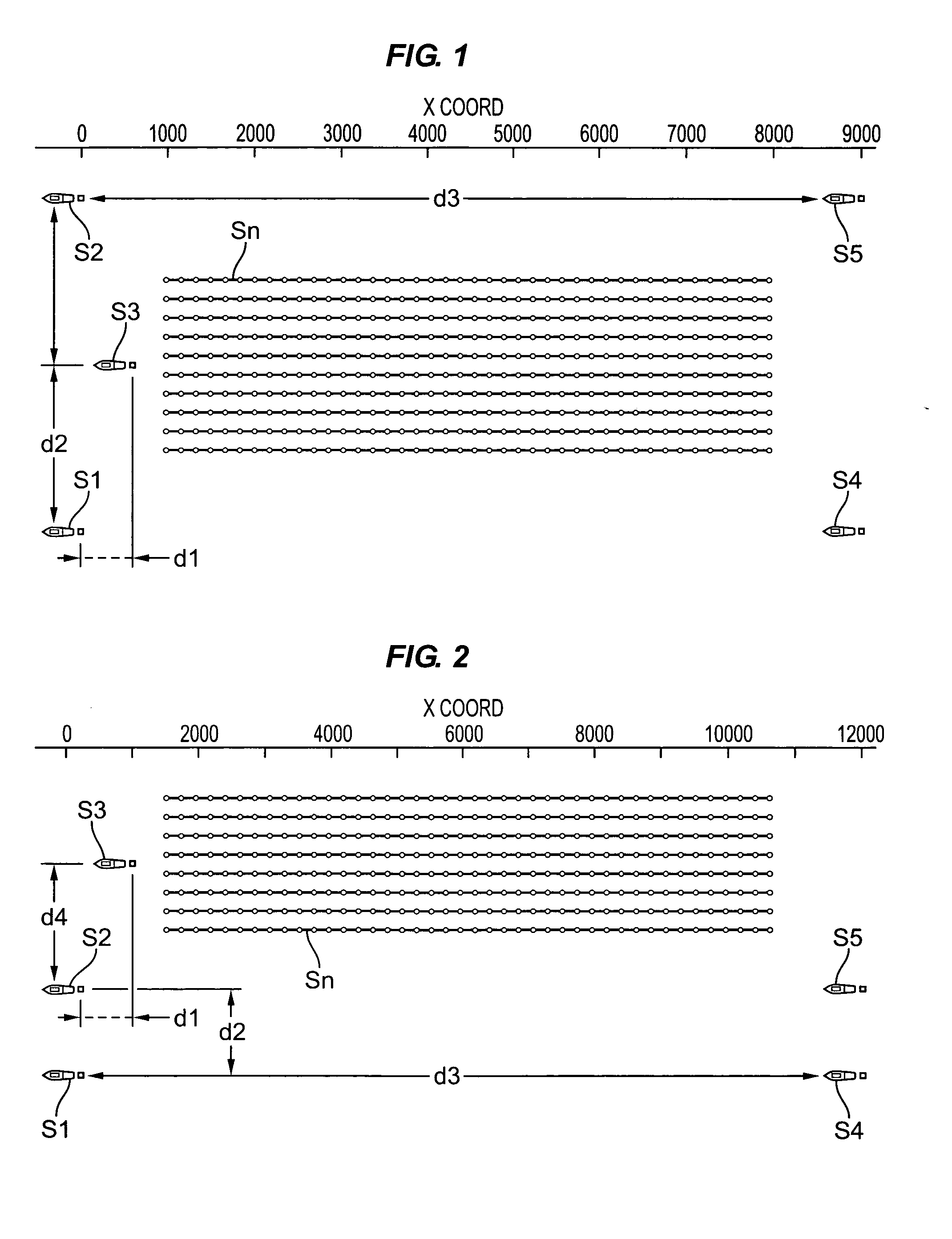
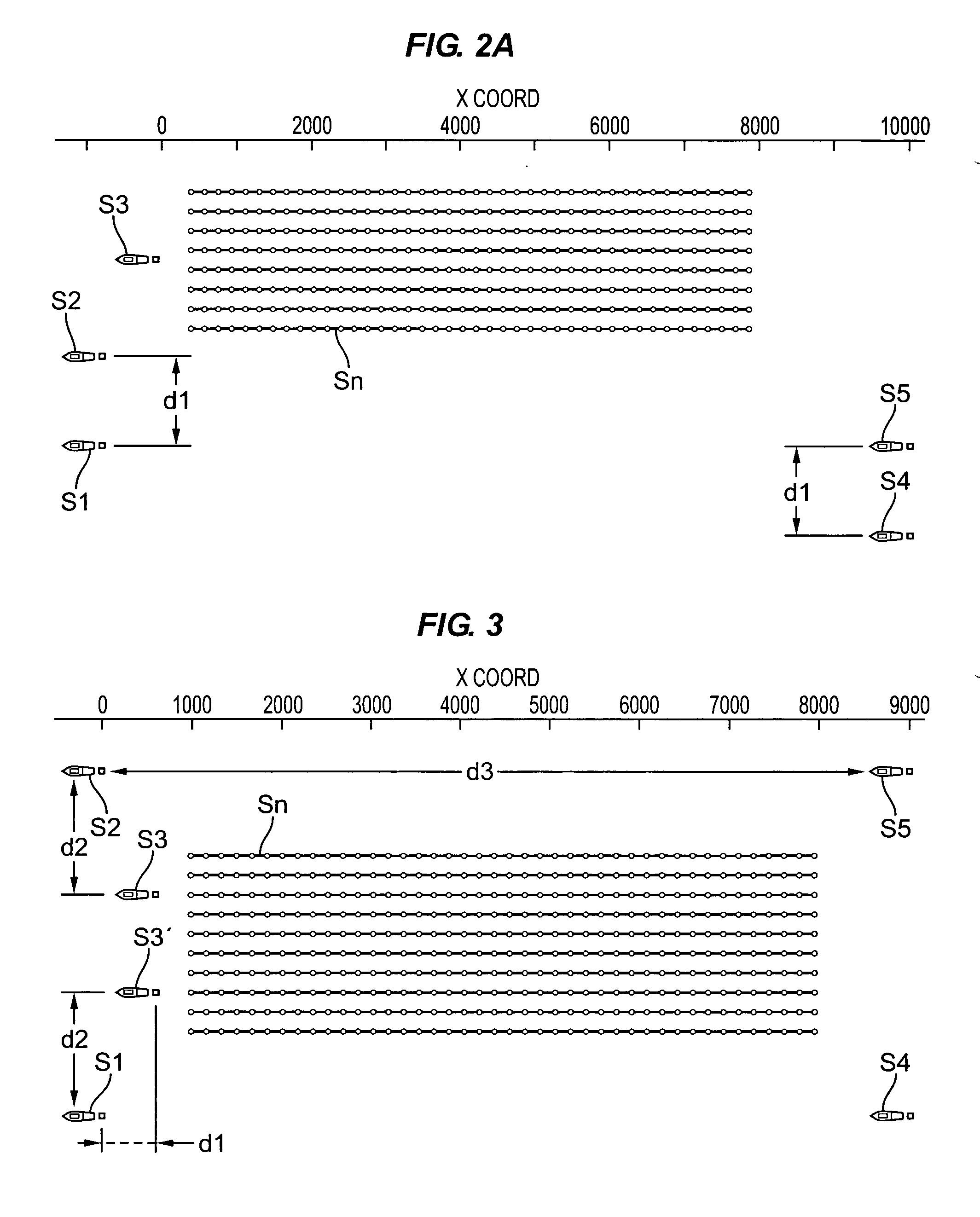
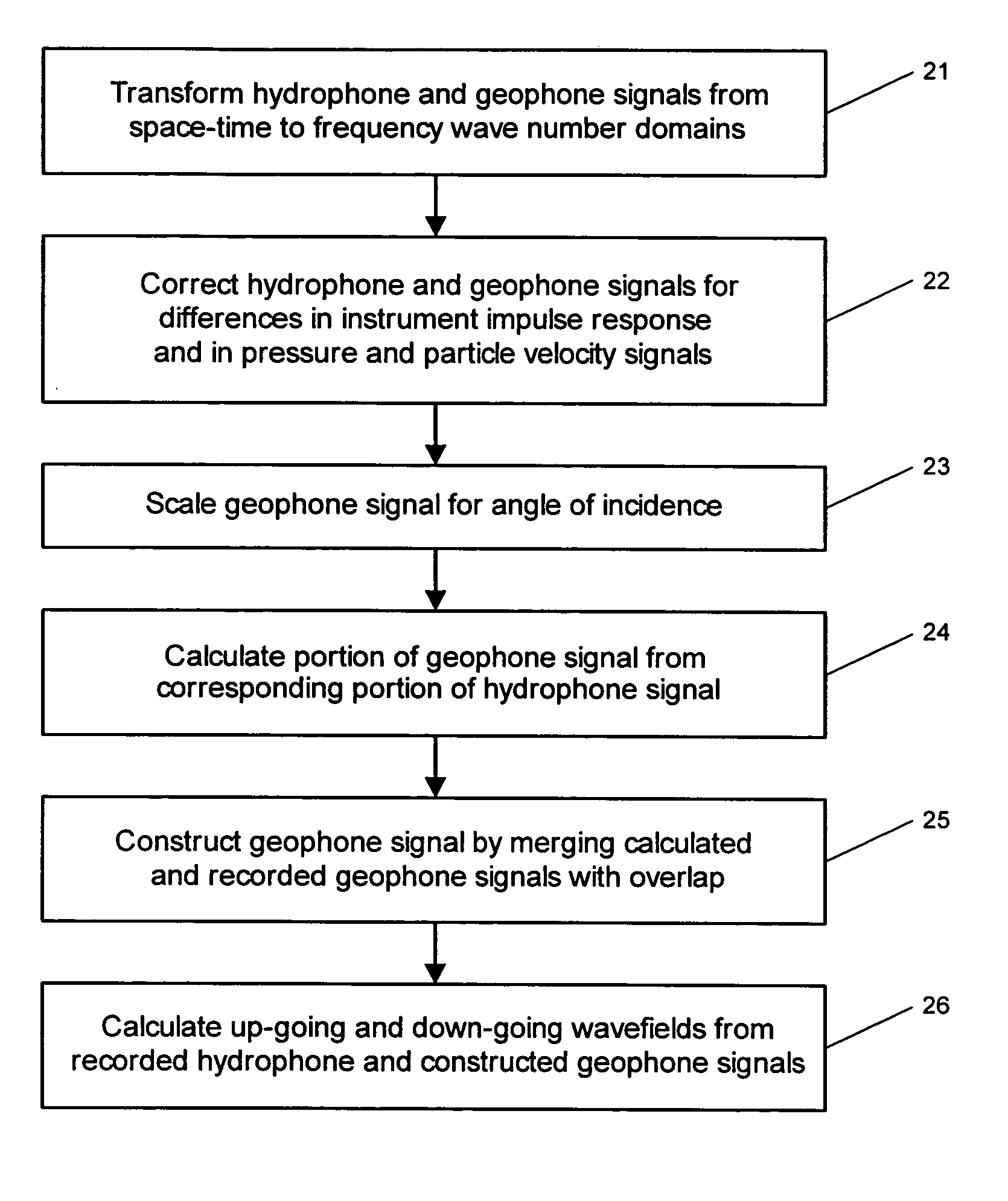
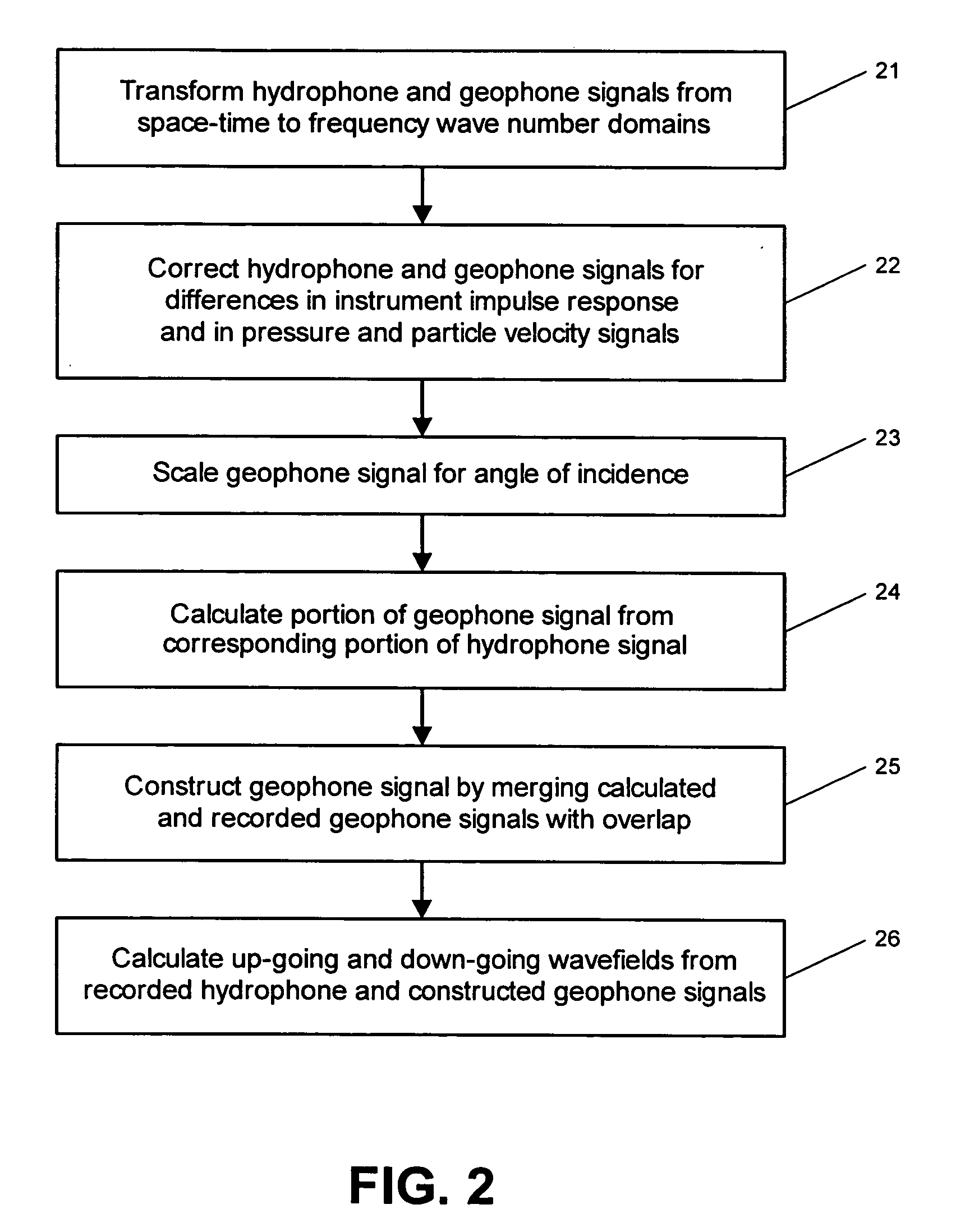
System for combining signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors in marine seismic streamers
Signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors located in marine seismic streamers are combined to generate pressure sensor data and particle motion data with substantially the same broad bandwidth. The noisy low frequency part of the motion signals are calculated from the recorded pressure signals and merged with the non-noisy motion signals. The two broad bandwidth data sets can then be combined to calculate the full up- and down-going wavefields.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Apparatus, systems and methods for seabed data acquisition
ActiveUS20080144442A1Reduce errorsThe effect is accurateSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismic signal transmissionOcean bottomData acquisition
Seabed sensor units, systems including same, and methods for acquiring seabed data are described, one seabed sensor unit comprising a base, the base containing at least one sensor able to detect a seismic signal, electronics comprising a clock and one or more electronic components enabling the sensor to communicate seismic data to one or more memory modules, and a local autonomous power source. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Method and apparatus for seismic data acquisition
InactiveUS20050052951A1Avoid entrapmentMinimize the possibilityTransducer detailsSeismic signal receiversOcean bottomRubidium
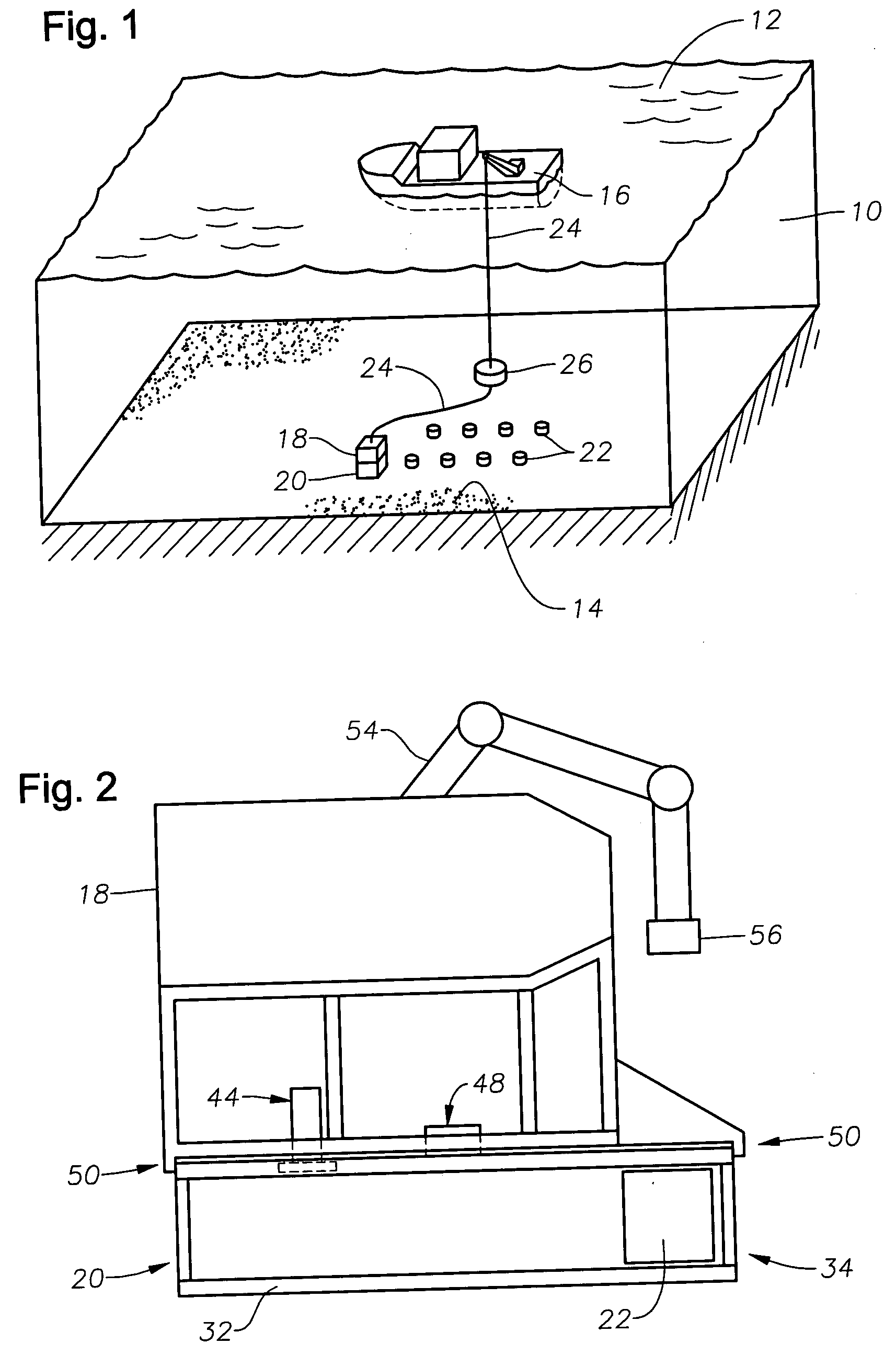
A marine seismic exploration method and system comprised of continuous recording, self-contained ocean bottom pods characterized by low profile casings. An external bumper is provided to promote ocean bottom coupling and prevent fishing net entrapment. Pods are tethered together with flexible, non-rigid, non-conducting cable used to control pod deployment. Pods are deployed and retrieved from a boat deck configured to have a storage system and a handling system to attach pods to cable on-the-fly. The storage system is a juke box configuration of slots wherein individual pods are randomly stored in the slots to permit data extraction, charging, testing and synchronizing without opening the pods. A pod may include an inertial navigation system to determine ocean floor location and a rubidium clock for timing. The system includes mathematical gimballing. The cable may include shear couplings designed to automatically shear apart if a certain level of cable tension is reached.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Method and apparatus for deployment of ocean bottom seismometers
ActiveUS20060159524A1Effective movementEasy to deploySeismic signal receiversBuoysOcean bottom seismometerOrbit
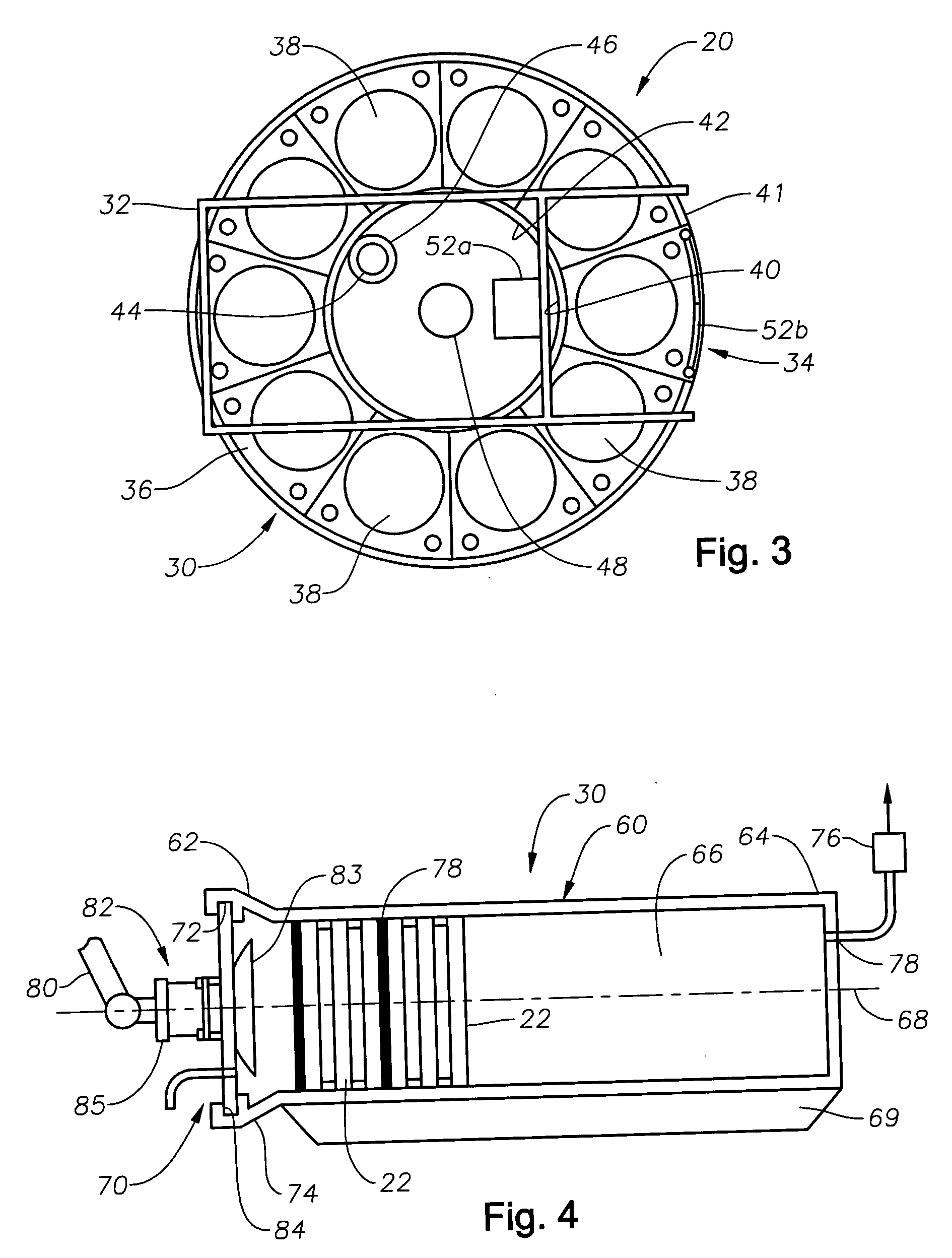
A method and apparatus for deployment and retrieval of ocean bottom seismic receivers. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a carrier containing a plurality of receivers attached to a remotely operated vehicle (ROV). The carrier comprises a frame in which is mounted a structure for seating and releasing said receivers. The structure may comprise a movable carousel or a movable conveyor or fixed parallel rails or a barrel. In the case of the barrel, the receivers are axially stacked therein. The structure is disposed to deliver said receivers to a discharge port on said frame, where the receivers are removable from said carrier. The apparatus includes a discharge mechanism for removing said receivers from said carrier. In another embodiment, the method comprises the steps of loading a carrier with a plurality of receivers, attaching said carrier to an ROV, utilizing said ROV to transport the carrier from a surface vessel to a position adjacent the seabed and thereafter utilizing said ROV to remove receivers from said carrier and place the receivers on the seabed. In yet another embodiment, an ROV adjacent the seabed engages a deployment line extending from the vessel. The deployment line is used to guide receivers attached thereto down to the ROV for “on-time” delivery and placement on the seabed.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Apparatus and methods for multicomponent marine geophysical data gathering
InactiveUS20040042341A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFloating cablesGeophoneCubic metre per second
In one embodiment the invention comprises a particle velocity sensor that includes a housing with a geophone mounted in the housing. A fluid that substantially surrounds the geophone is included within the housing. The particle velocity sensor has an acoustic impedance within the range of about 750,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m<3>) to about 3,000,000 Newton seconds per cubic meter (Ns / m<3>). In another embodiment the invention comprises method of geophysical exploration in which a seismic signal is generated in a body of water and detected with a plurality of co-located particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors positioned within a seismic cable. The output signal of either or both of the particle velocity sensors or the pressure gradient sensors is modified to substantially equalize the output signals from the particle velocity sensors and the pressure gradient sensors. The output signals from particle velocity sensors and pressure gradient sensors are then combined.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
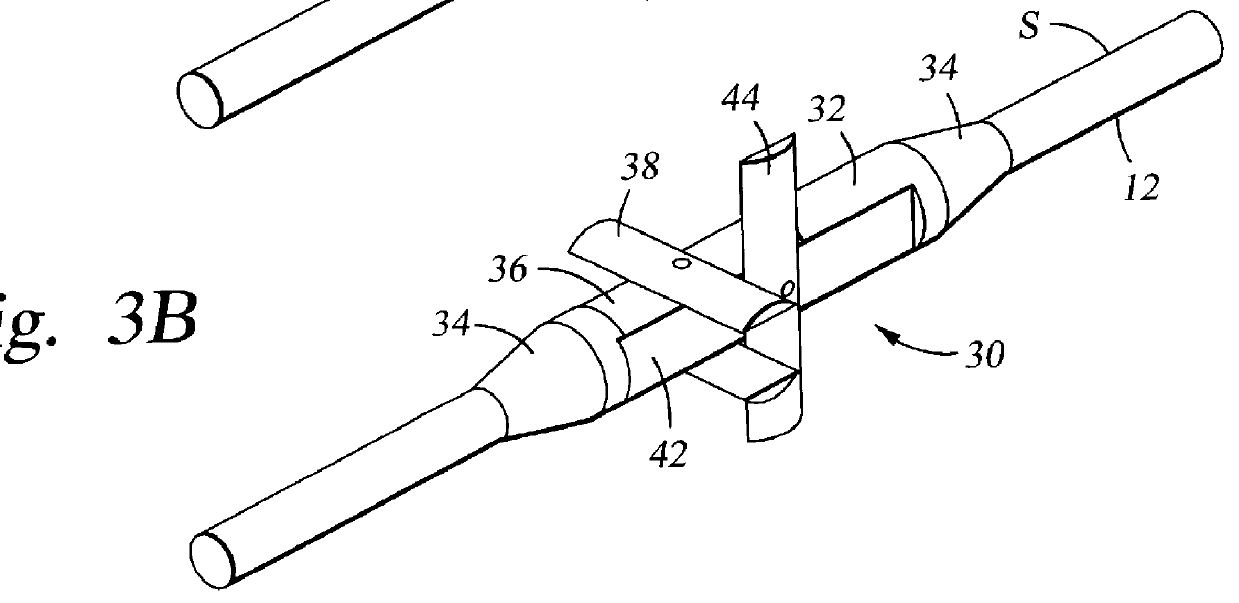
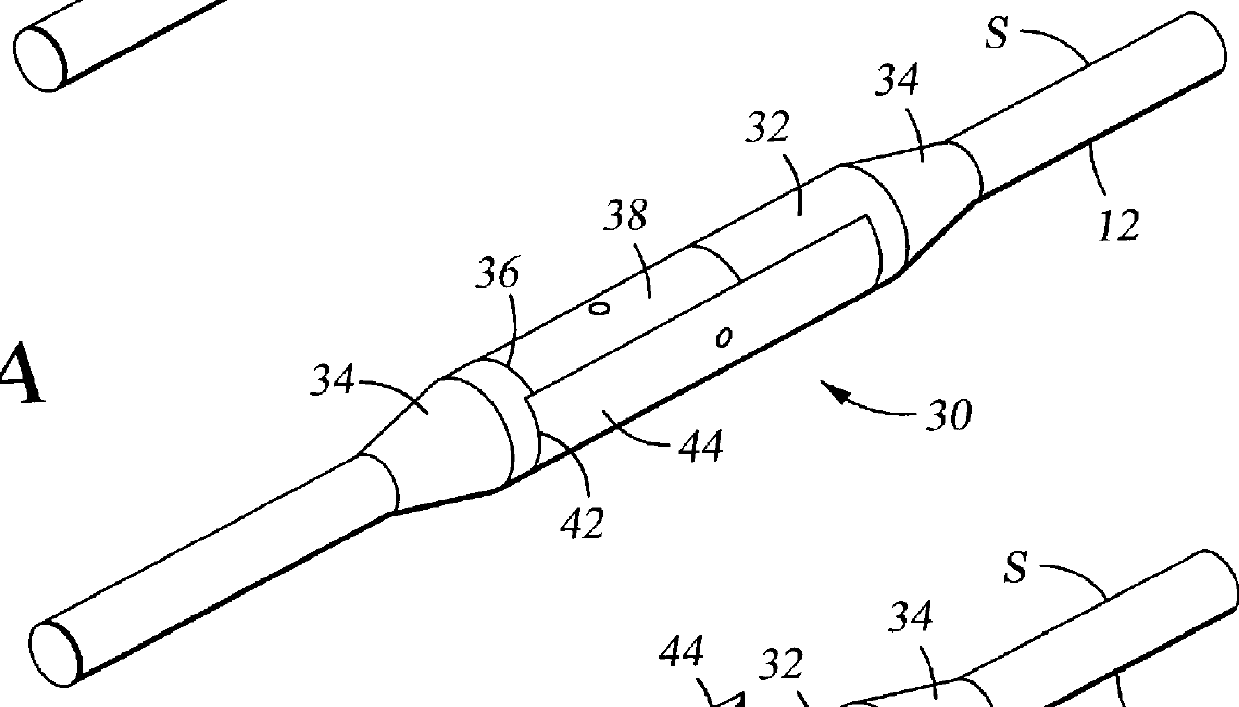
Seismic streamer position control module
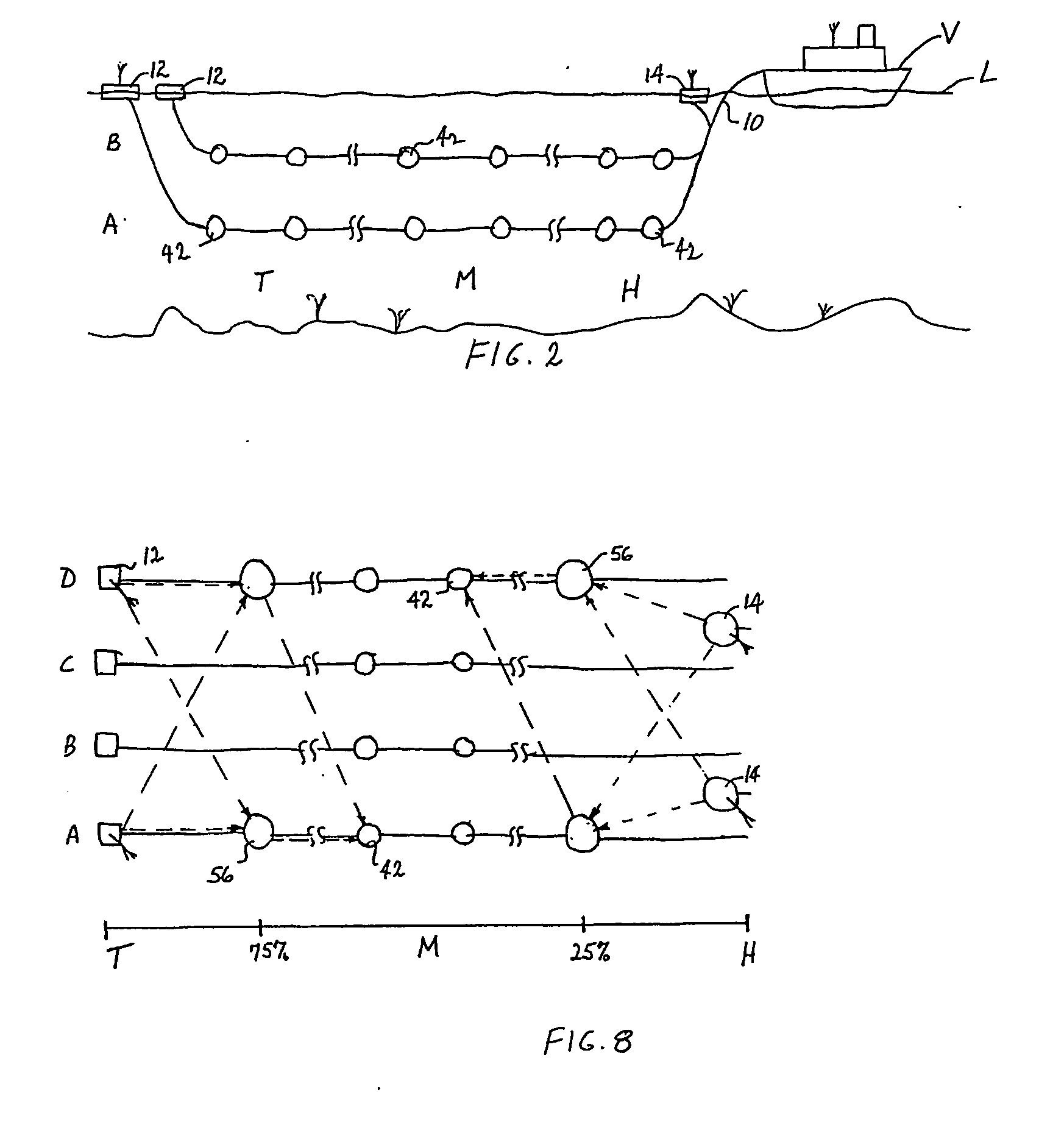
InactiveUS6011752AAvoid tanglesPrevent and minimize damageDefensive equipmentTowing/pushing equipmentEngineeringPosition control
A seismic streamer position control module has been invented having a body with a first end and a second end and a bore therethrough from the first end to the second end for receiving a seismic streamer therethrough, at least one control surface, and at least one recess in which is initially disposed the at least one control surface, the at least one control surface movably connected to the body for movement from and into the at least one recess and for movement, when extended from the body, for attitude adjustment. In one aspect the seismic streamer position control module body has tapered ends.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
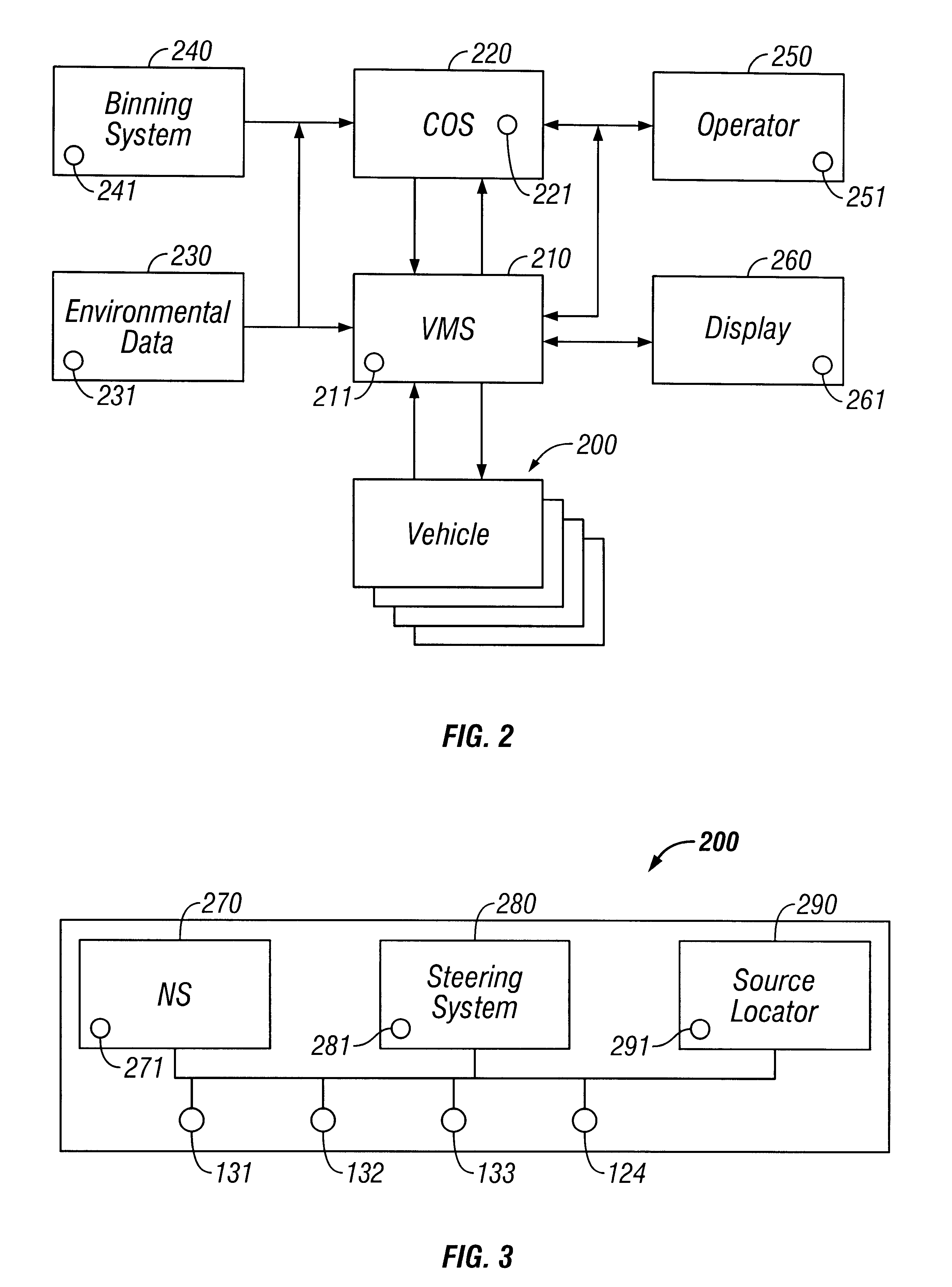
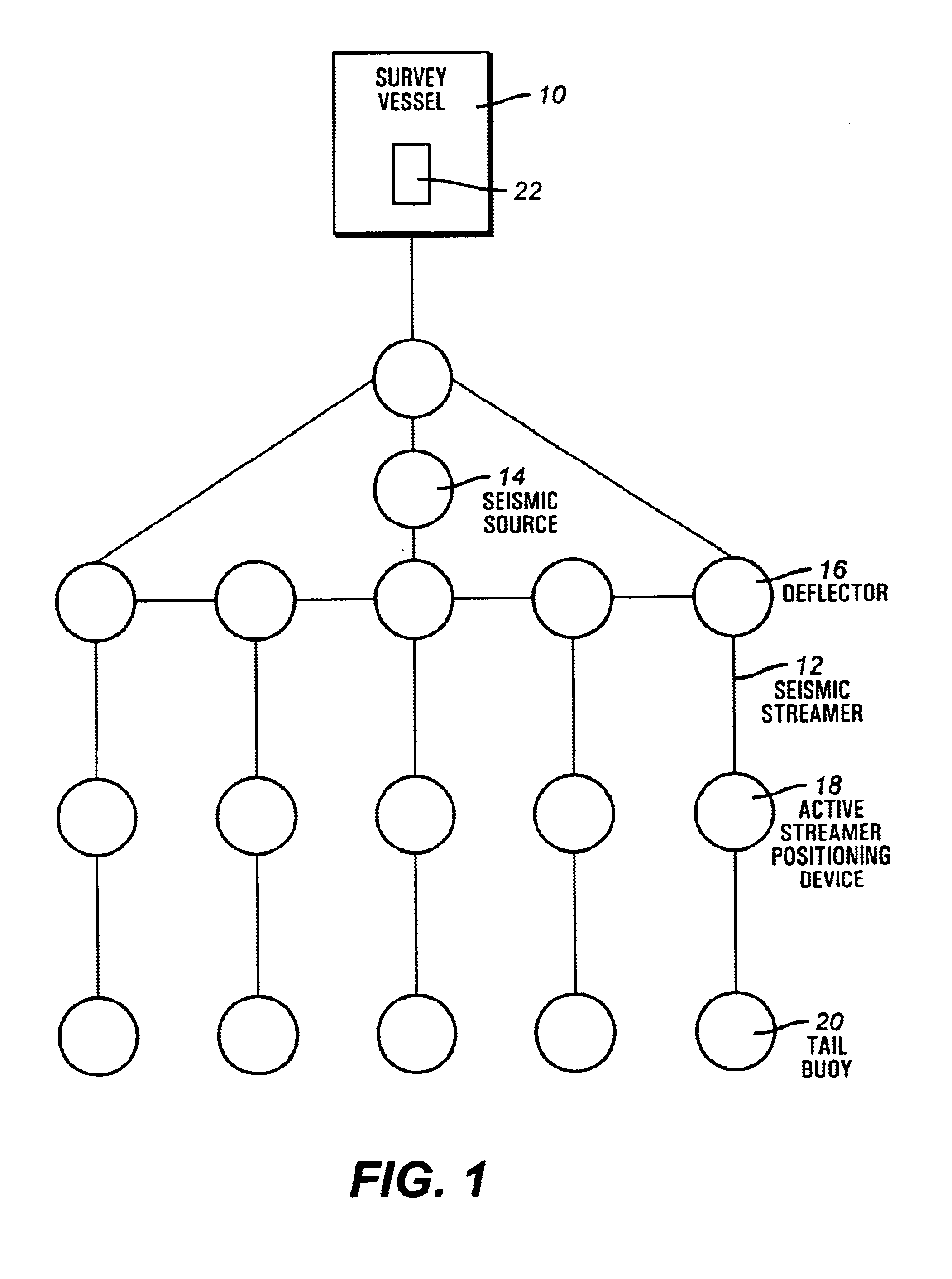
Method and apparatus for controlling and optimizing seismic data acquisition
InactiveUS6590831B1Towing/pushing equipmentSeismic signal processingMarine engineeringData acquisition
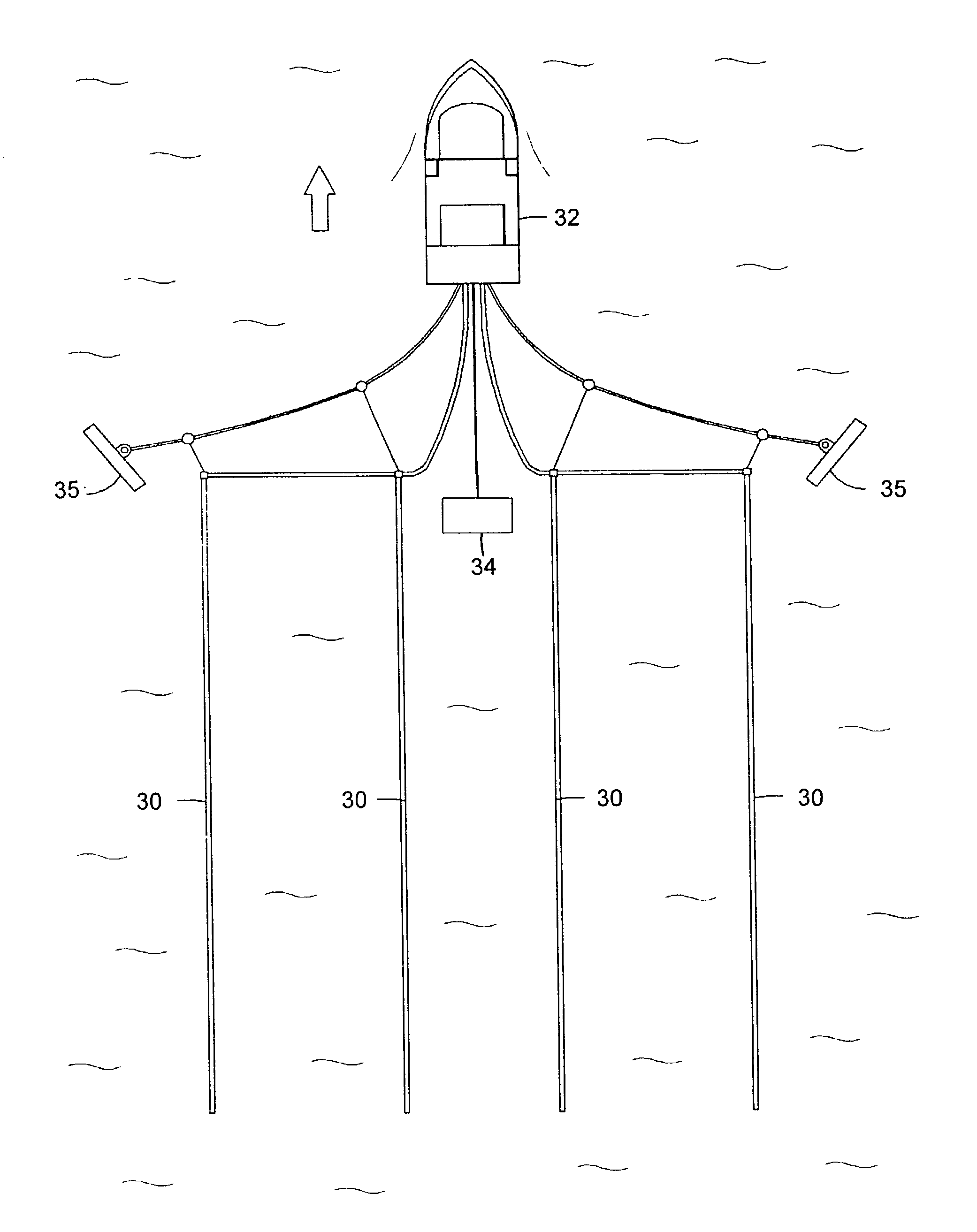
A system and method for coordinating the operation of multiple manned, remotely operated or autonomous marine vessels engaged in marine seismic data acquisition to direct cooperating vessels from one point to the next while minimizing deviations in the desired spatial configuration of assets, risk to vessels and seismic assets, and personnel and to obtain optimal midpoint coverage by evaluating inputs from subsystems providing positioning information for cooperating vessels, prospect coverage, vessel capabilities, environmental information, and navigation hazards.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC +1
Marine seismic survey method and system
ActiveUS20090141587A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEnvironmental data
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Control system for positioning of marine seismic streamers
InactiveUS6932017B1Reduce needEasy to controlDefensive equipmentTowing/pushing equipmentSeismic surveyControl system
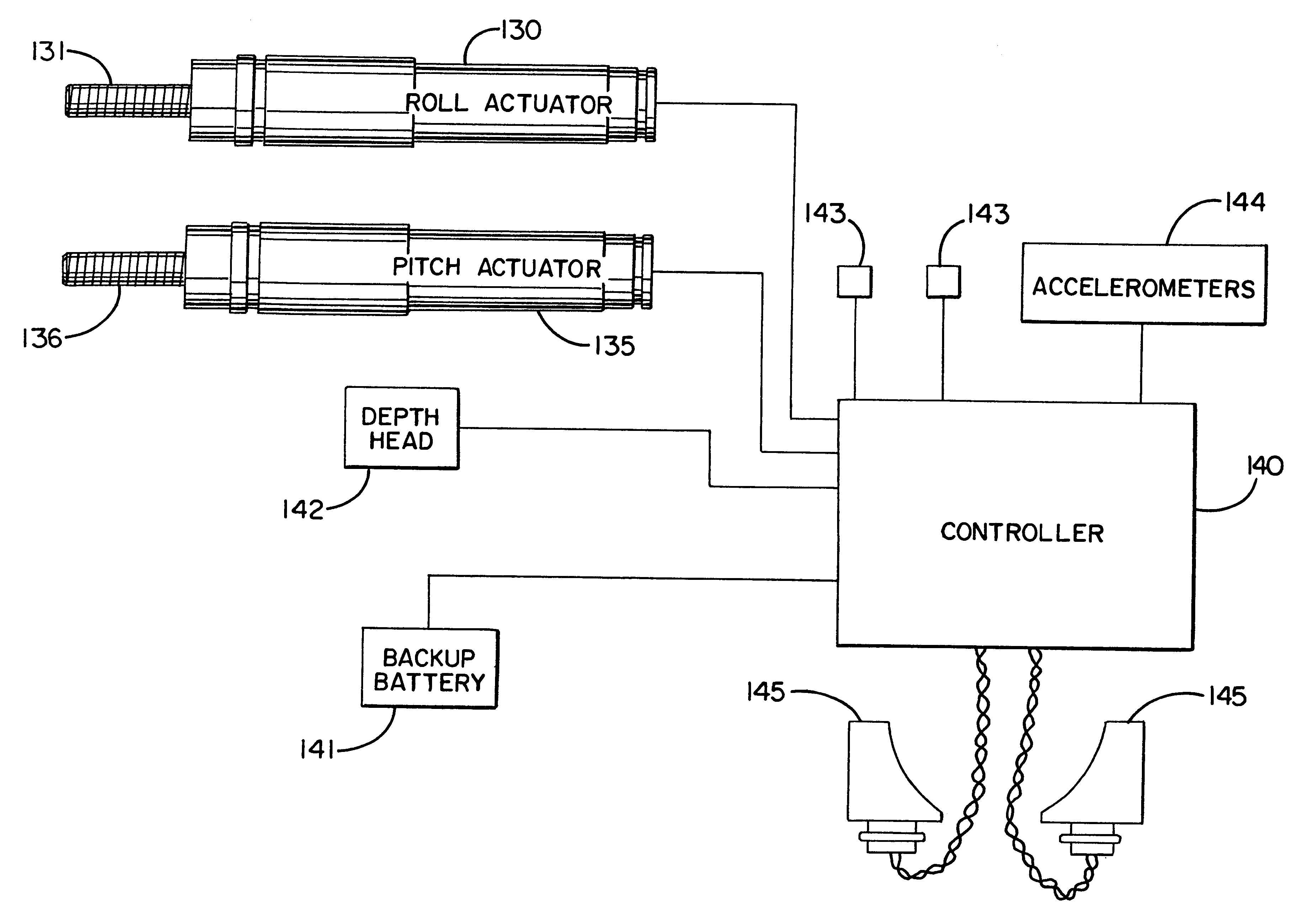
A method of controlling a streamer positioning device (18) configured to be attached to a marine seismic streamer (12) and towed by seismic survey vessel (10) and having a wing and a wing motor for changing the orientation of the wing. The method includes the steps of: obtaining an estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, calculating a desired change in the orientation of the wing using the estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, and actuating the wing motor to produce the desired change in the orientation of the wing. The invention also involves an apparatus for controlling a streamer positioning device including means for obtaining an estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, means for calculating a desired change in the orientation of the wing using the estimated velocity of the streamer positioning device, and means for actuating the wing motor to produce the desired change in the orientation of the wing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method and system for acquiring marine seismic data using multiple seismic sources
InactiveUS6906981B2Easy to foldIncrease the lengthSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationSeismic surveySurveyor
A method for seismic surveying is disclosed which includes towing a first seismic energy source and at least one seismic sensor system. A second seismic energy source is towed at a selected distance from the first source. The first seismic energy source and the second seismic energy source are actuated in a plurality of firing sequences. Each of the firing sequences includes firing of the first source, waiting a selected time firing the second source and recording signals generated by the seismic sensor system. The selected time between firing the first source and the second source is varied between successive ones of the firing sequences. The firing times of the first and second source are indexed so as to enable separate identification of seismic events originating from the first source and seismic events originating from the second source in detected seismic signals.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
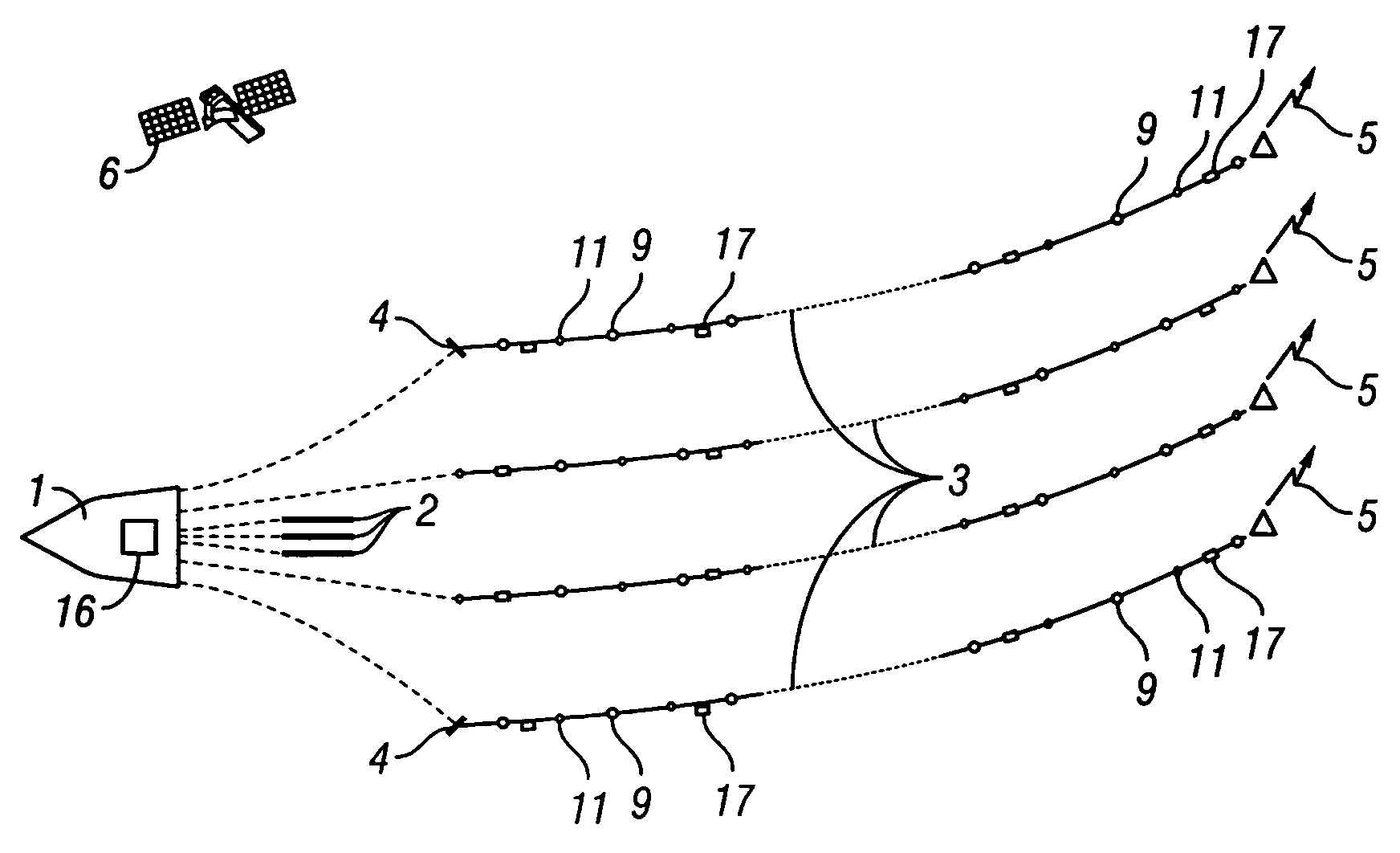
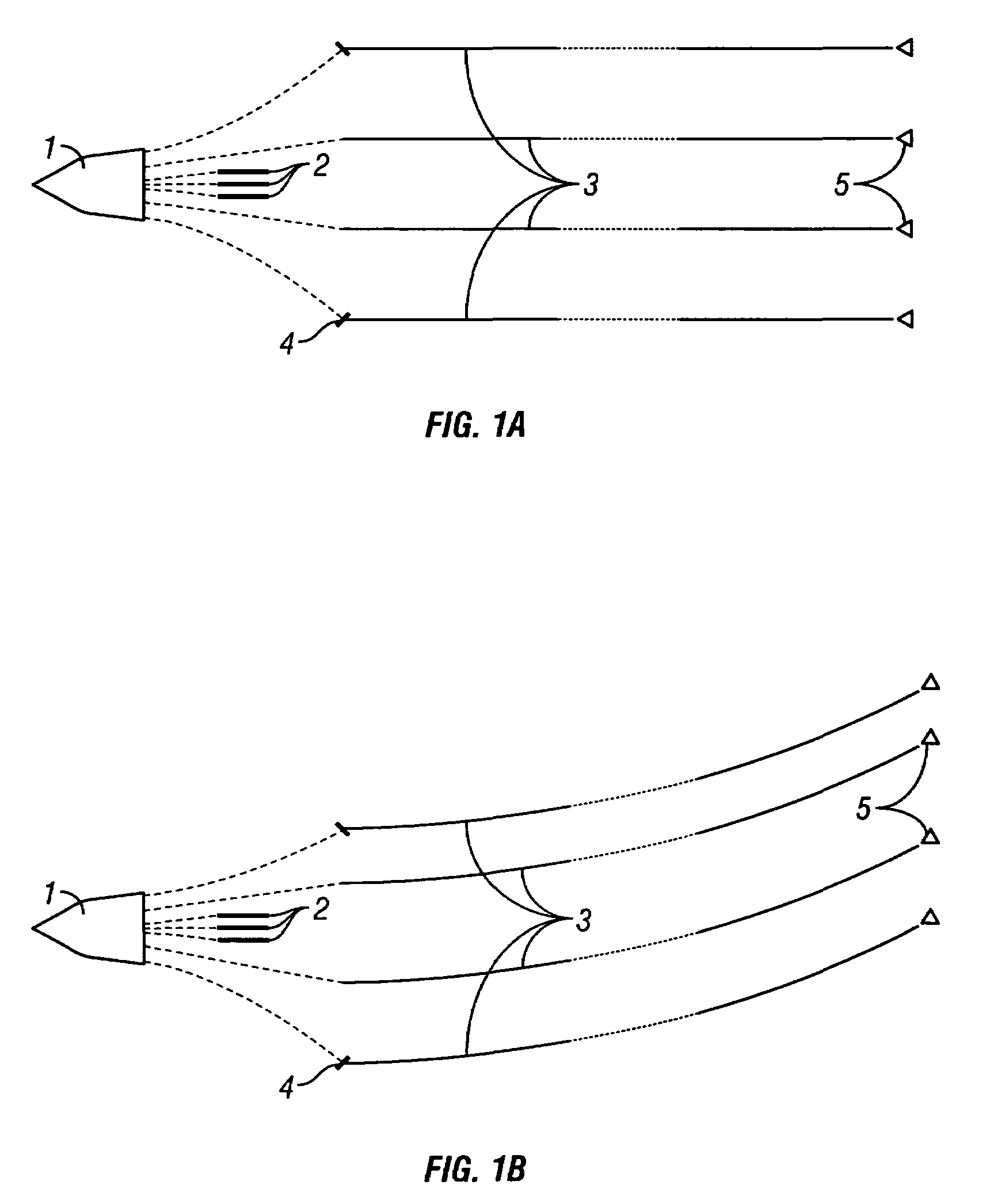
Active separation tracking and positioning system for towed seismic arrays
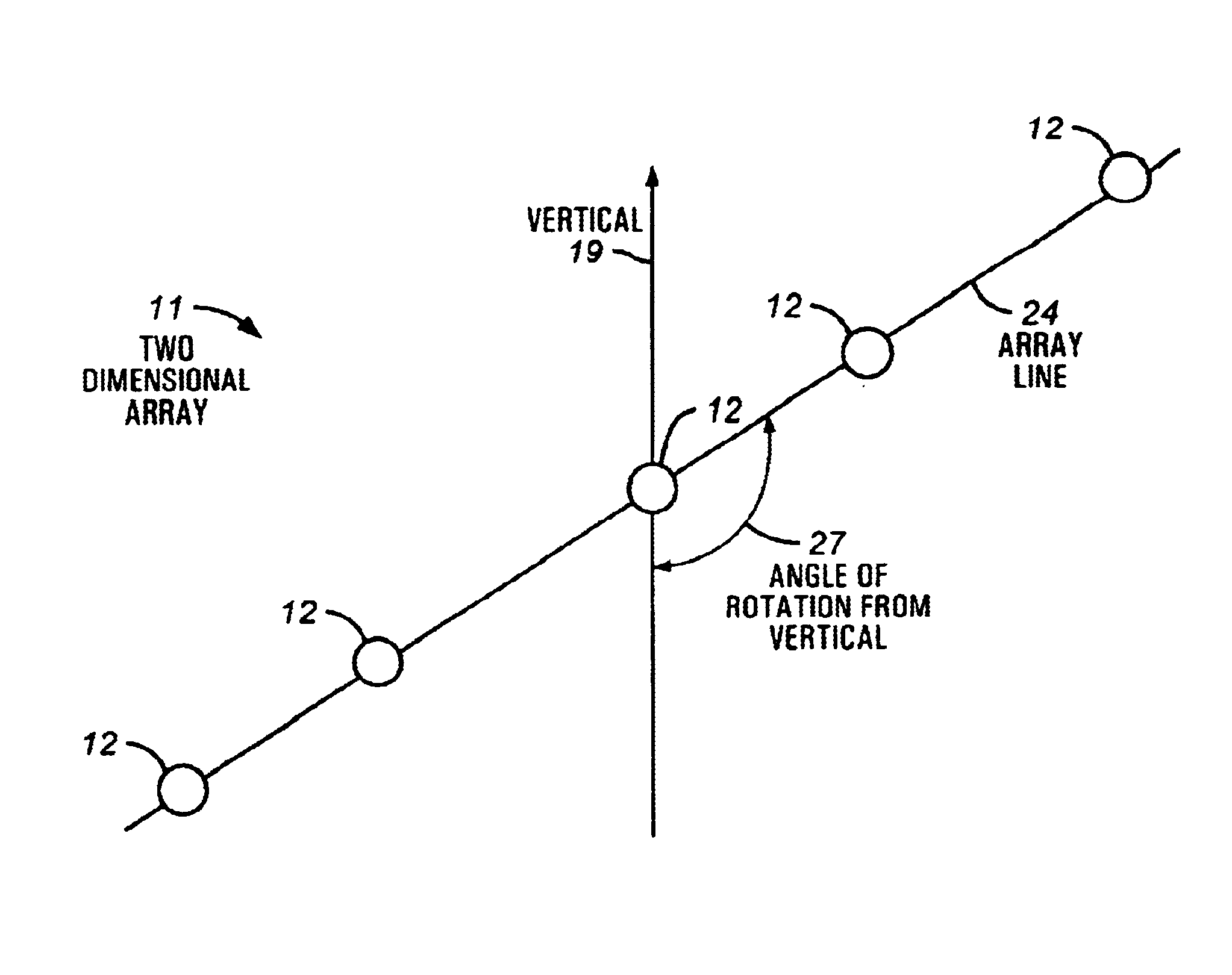
InactiveUS6691038B2Facilitate detachment and removalMaintain positionSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasArray data structureControl system
A method and apparatus comprising an active control system for a towed seismic streamer array that enables any relative positional control of any number of towed seismic streamers. The streamer positions are controlled horizontally and vertically using active control units positioned within the seismic array. The three component (x, y, z) position of each streamer element, relative to the vessel and relative to each other is controlled, tracked and stored during a seismic data acquisition run. The present invention enables a seismic array to be maneuvered as the towing vessel maintains course, enables maintenance of specific array position and geometry in the presence of variable environmental factors and facilitates four-dimensional seismic data acquisition by sensing and storing the position of the array and each array element with respect to time.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
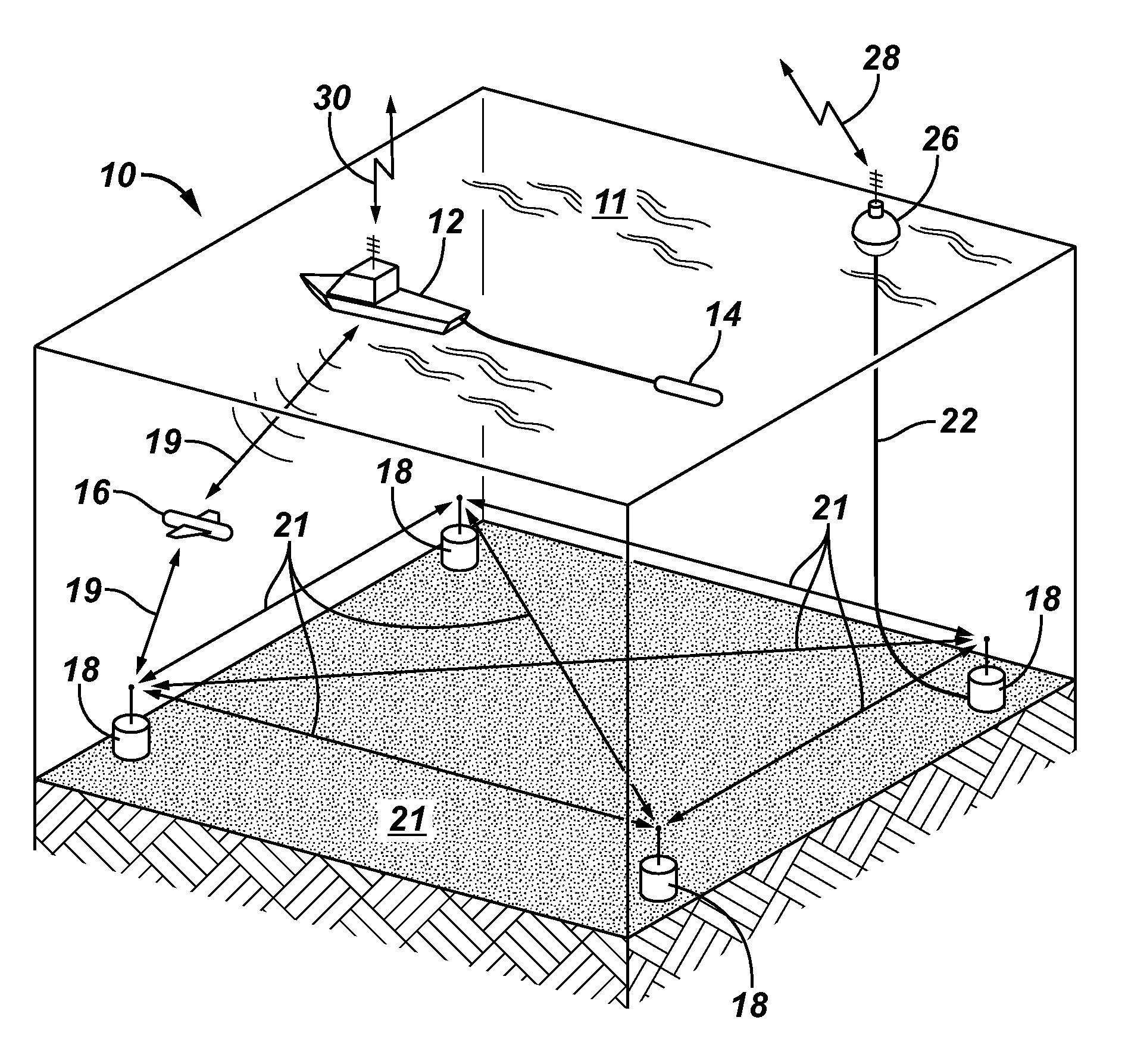
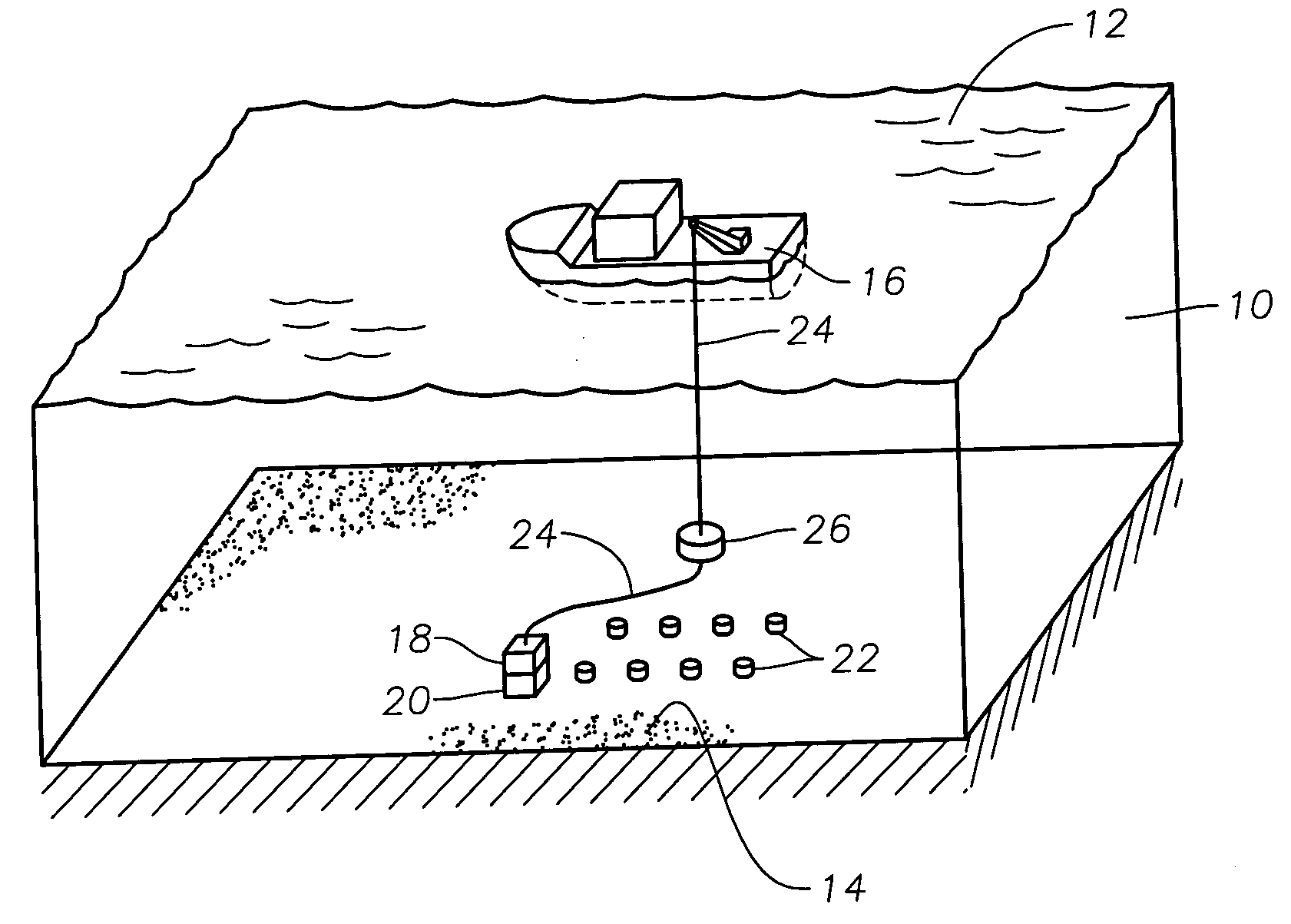
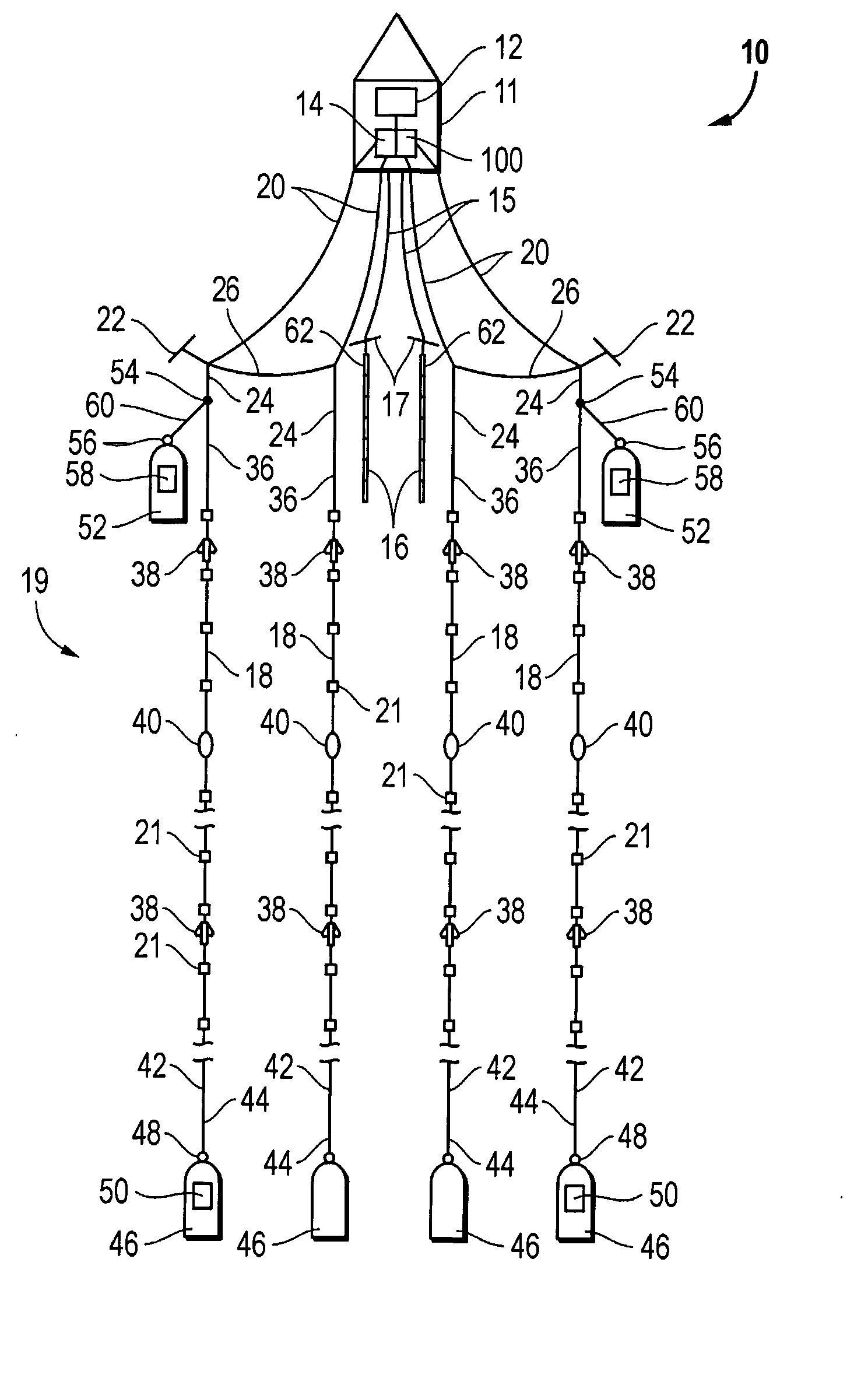
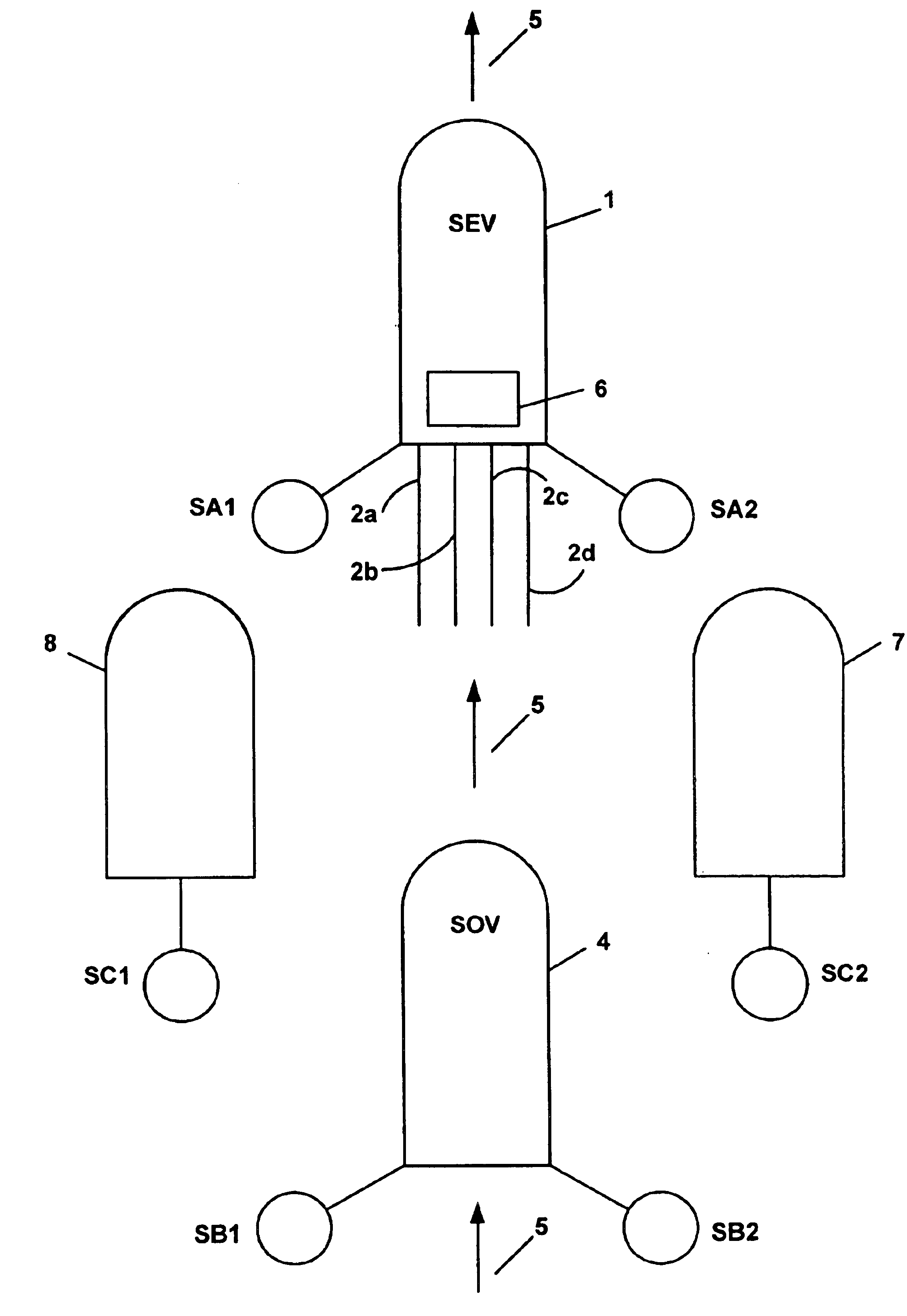
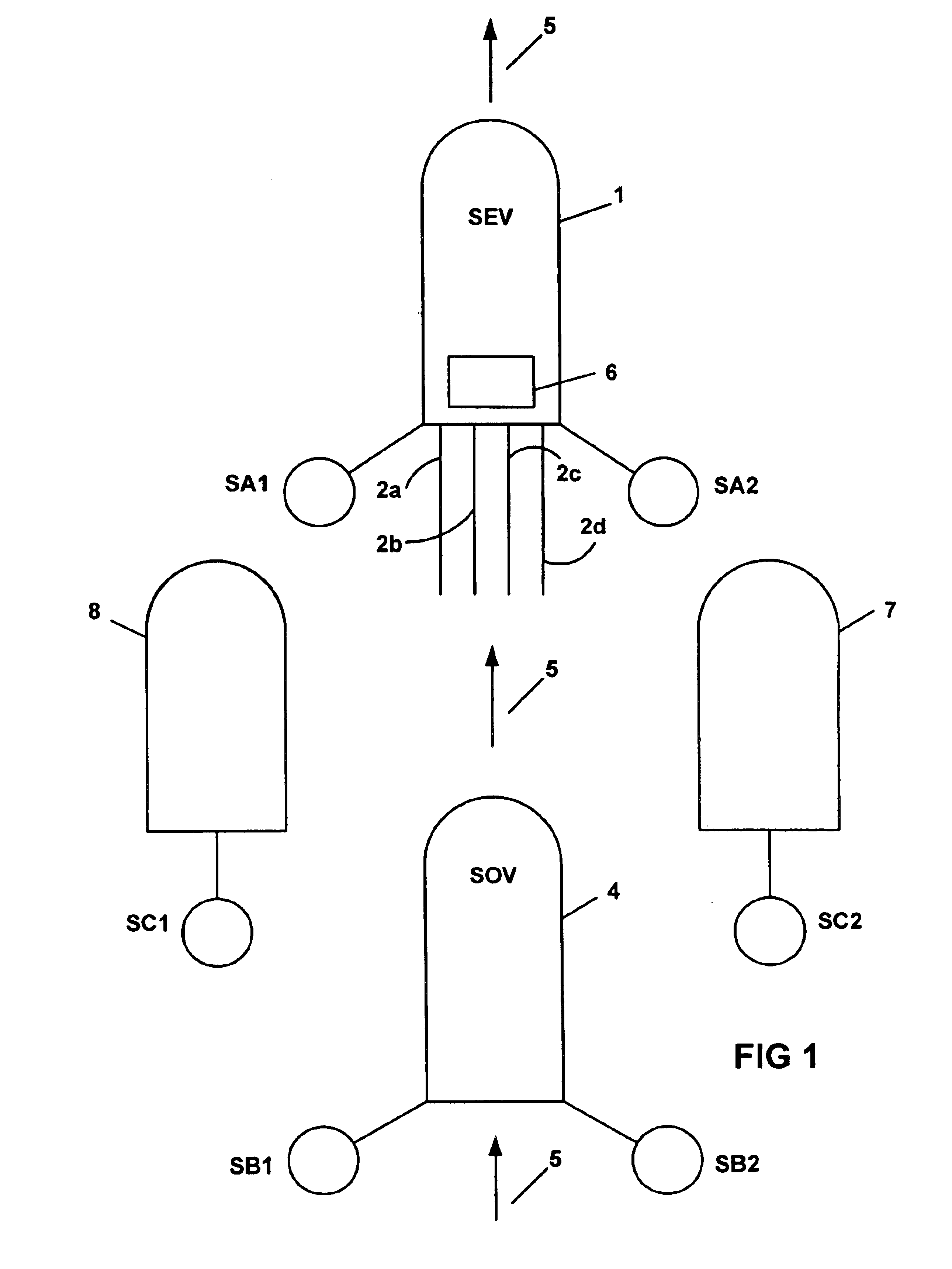
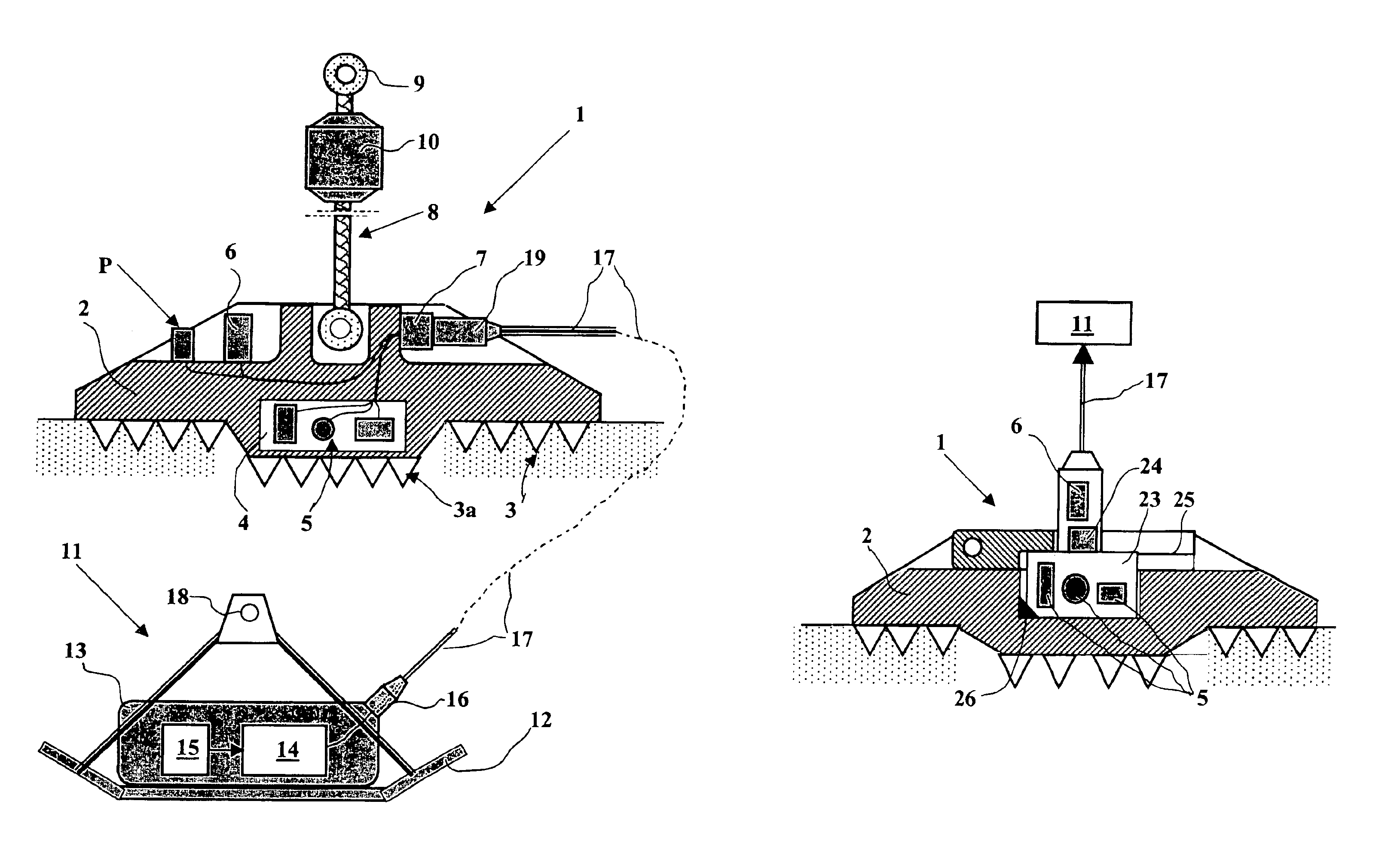
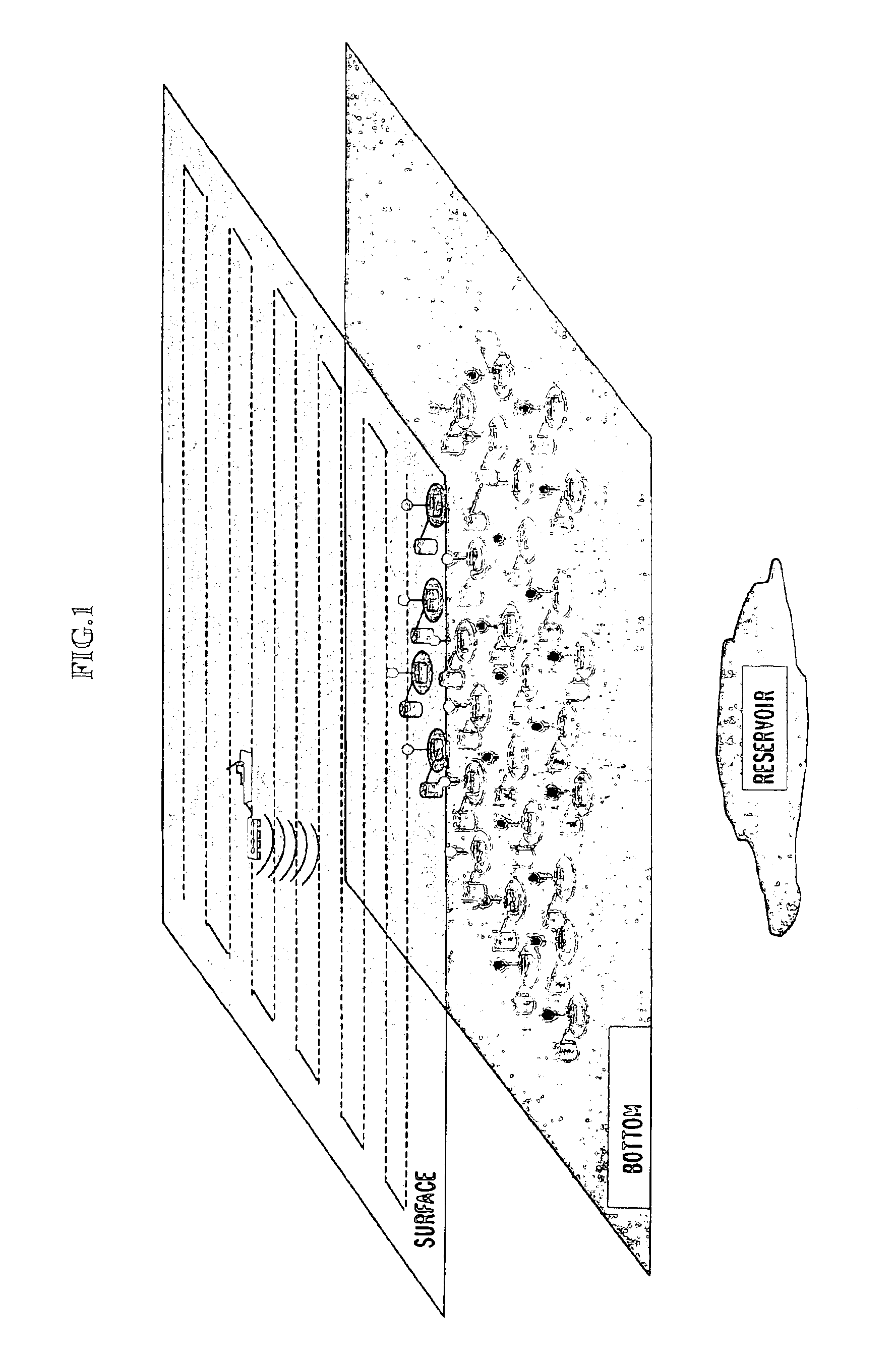
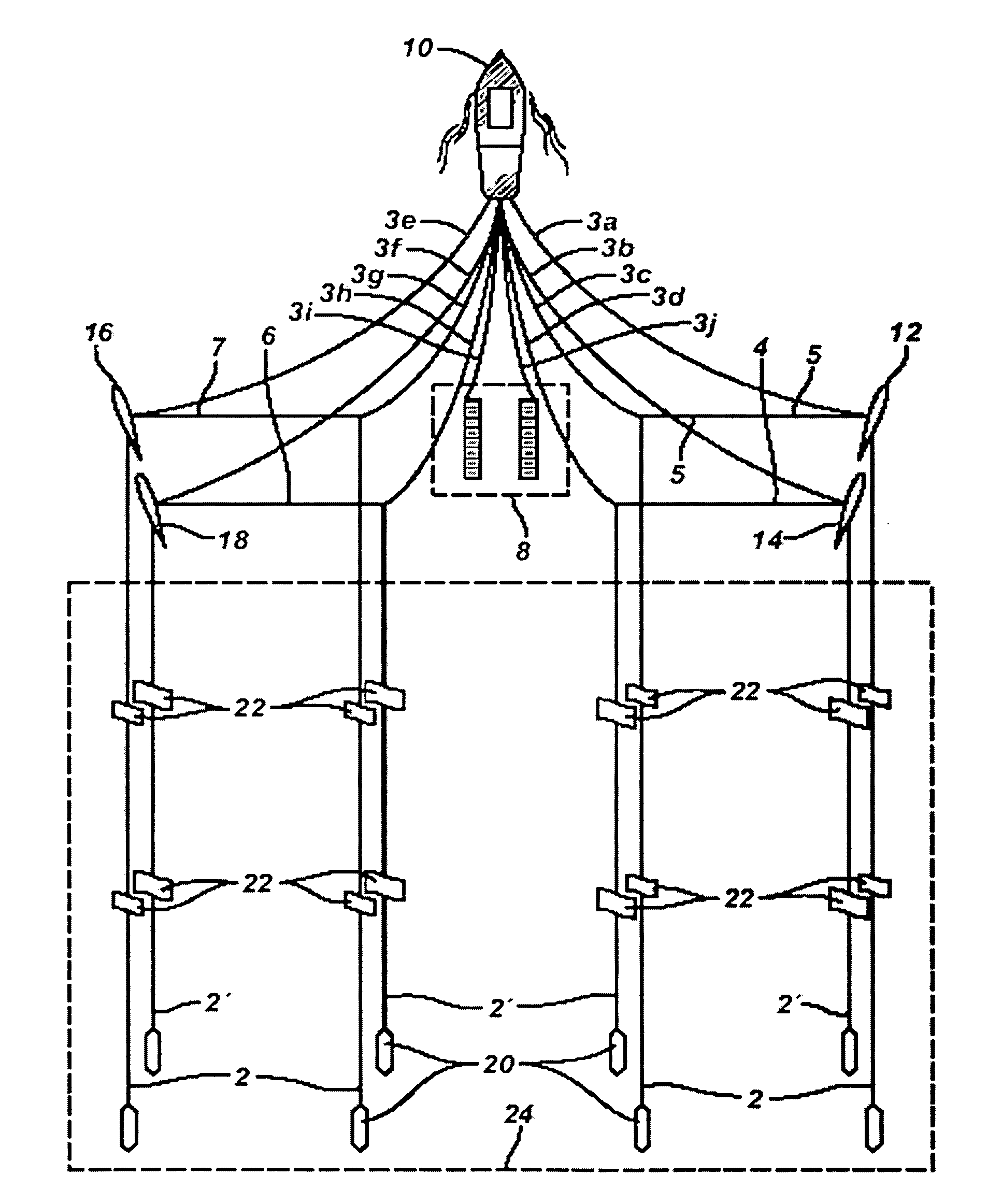
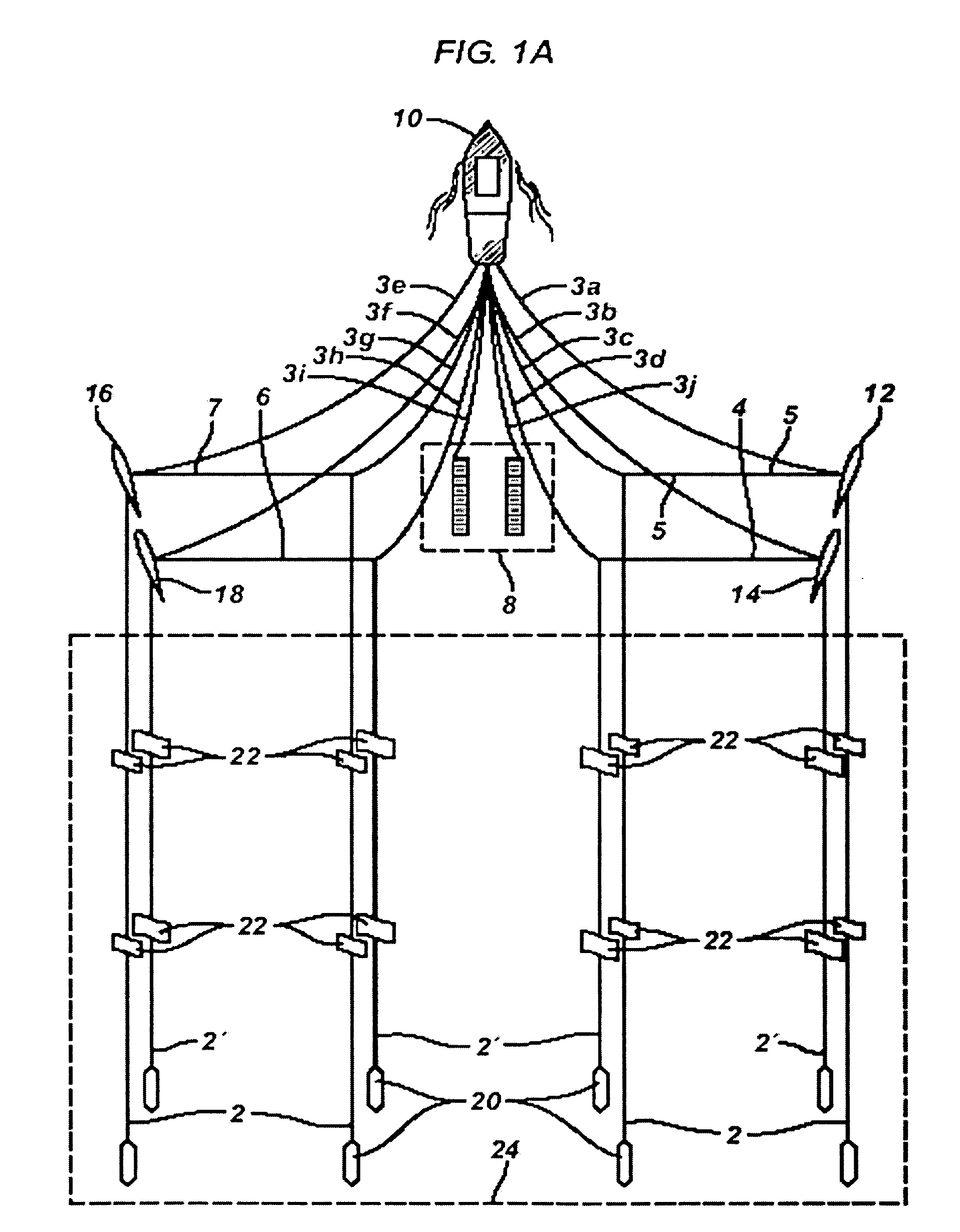
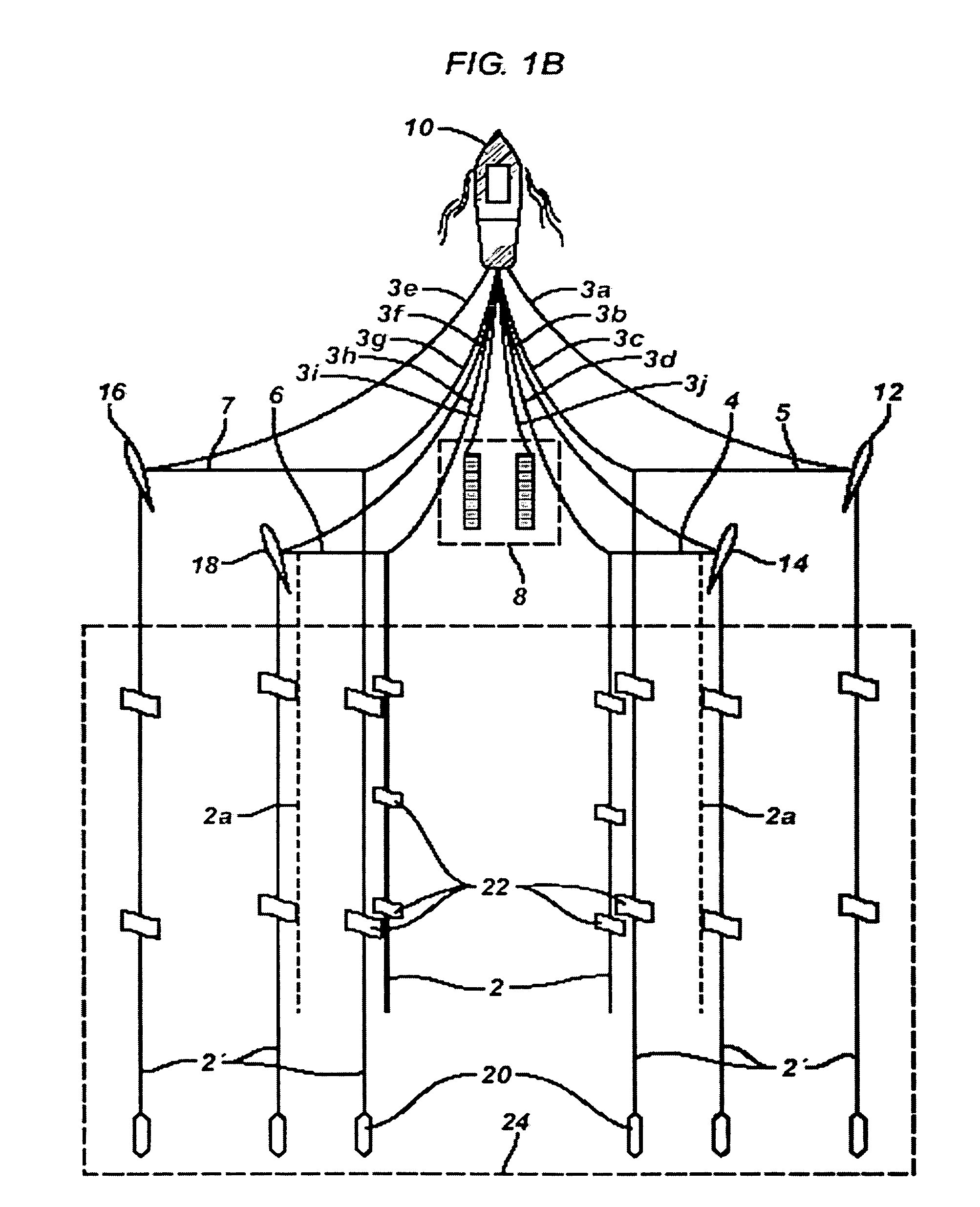
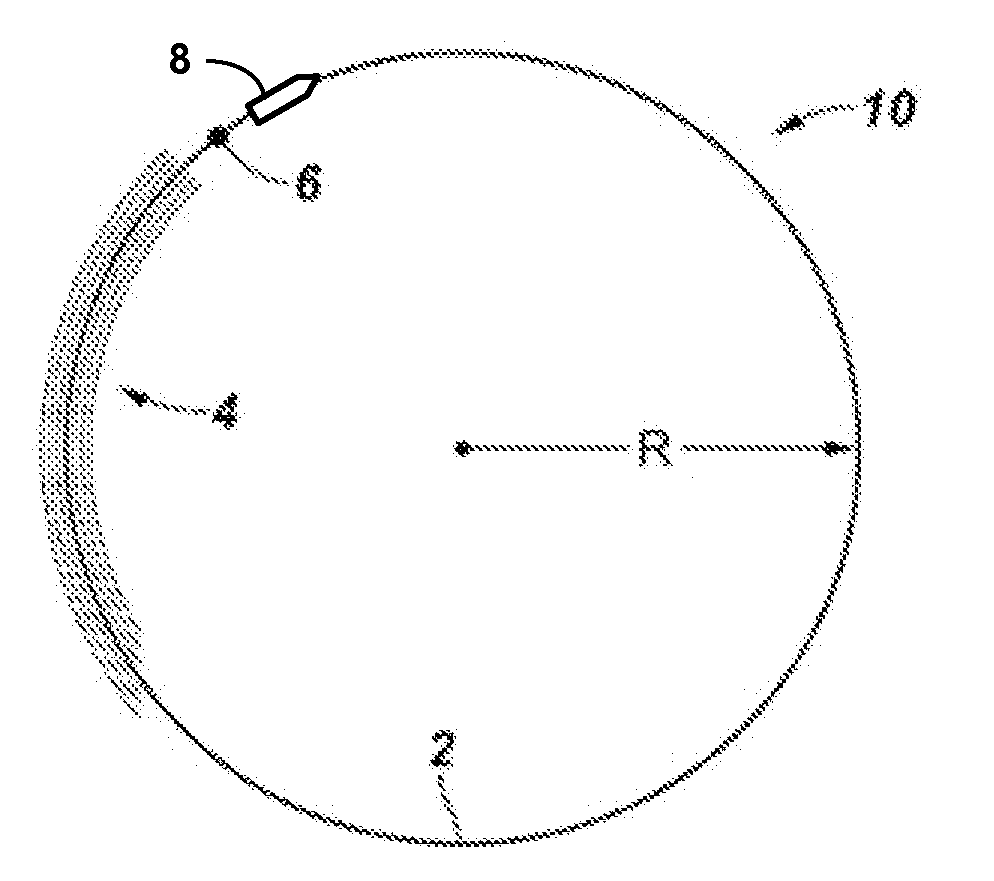
Acquisition method and device for seismic exploration of a geologic formation by permanent receivers set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS6932185B2Good flexibilityFine divisionSeismic energy generationSeismic signal receiversGeophoneHydrophone
A method and device for seismic exploration of a subsea geologic formation by pickups set on the sea bottom and intermittently connectable to active data acquisition stations (11) brought nearby. Permanent passive reception stations (1) comprising a heavy pedestal provided with housings for seismic pickups (geophones (6), hydrophone (7) which receive acoustic or seismic signals from the underlying formation are arranged at the bottom of the water body. When collection sessions for the signals received by the pickups are scheduled, mobile active acquisition stations (11) connected to permanent passive reception stations (1) are positioned at the bottom of the water body. The signals picked up are then recorded, for the time required to carry out at least one session of acquisition and recording of the acoustic or seismic signals received by the passive stations in response to the emission of seismic waves by one or more seismic sources. The mobile active acquisition stations (11) are thereafter recovered at the surface and the records acquired by each one are transferred to a central collection laboratory.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
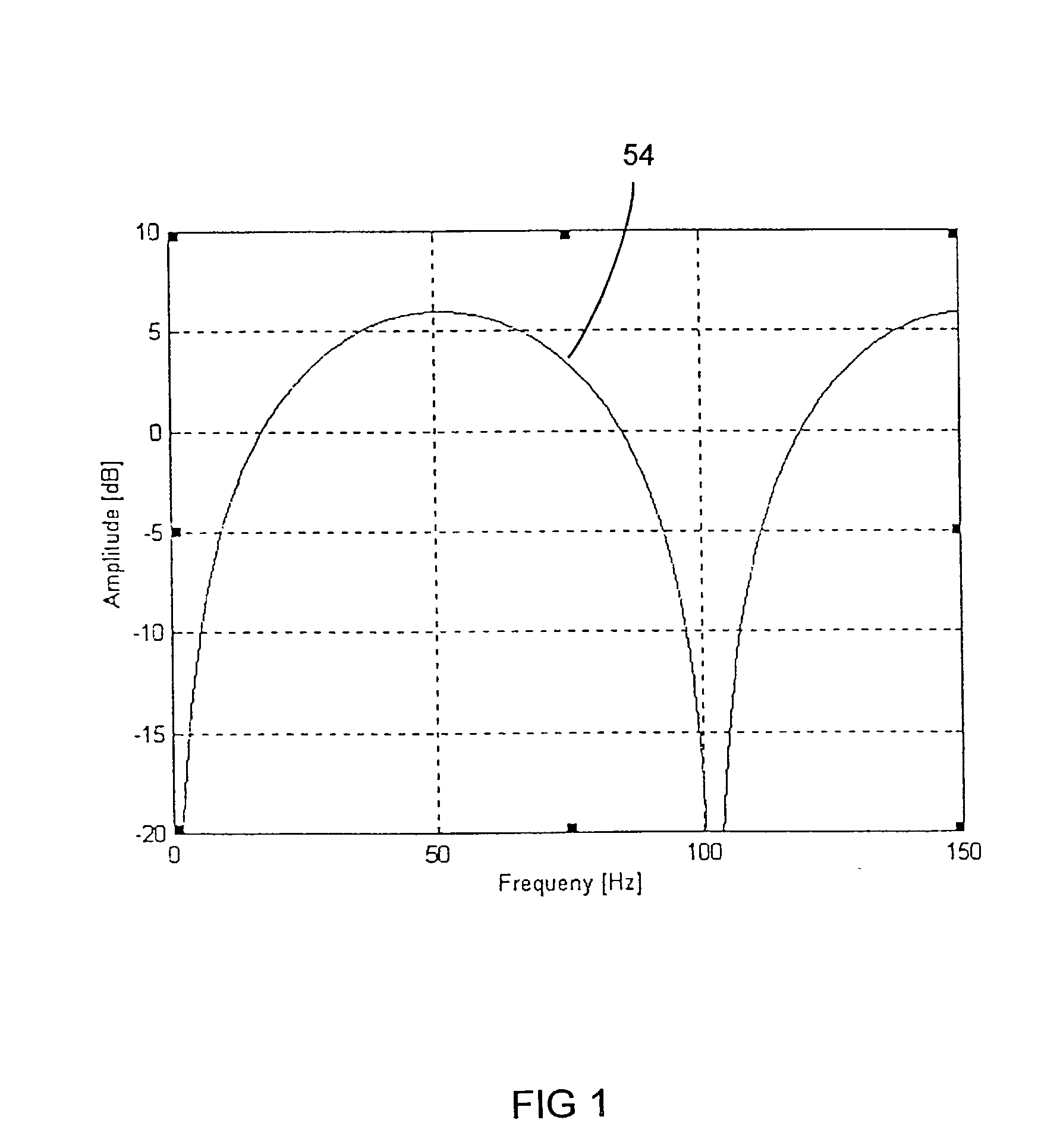
System and method for determining positions of towed marine seismic streamers
ActiveUS7376045B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationBroadbandEngineering
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
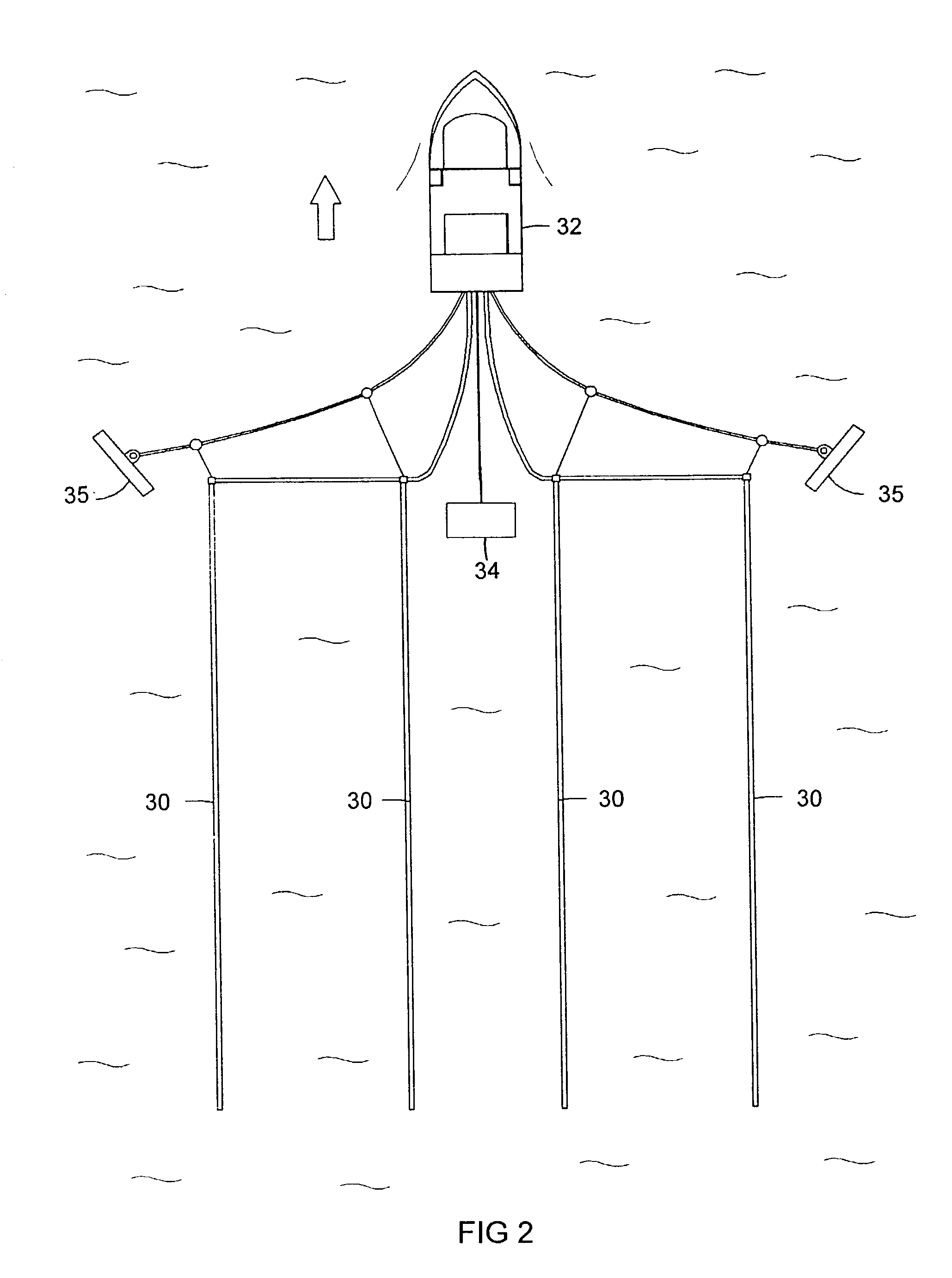
Marine seismic system with independently powered tow vehicles
The present invention discloses a marine seismic system with a control system and at least one powered (manned or unmanned) tow vehicle with at least one seismic apparatus or system attached thereto, the at least one powered tow vehicle for selectively towing under its own power the at least one seismic apparatus or system. In one aspect such towing is done in controlled conjunction with movement of one or more host vessels. In another aspect such a marine seismic system includes at least one service boat for servicing the at least one powered tow vehicle.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Gps-based underwater cable positioning system
ActiveUS20050180263A1Improve positioning geometryEnhanced signalBeacon systems using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesHydrophoneTransceiver
A GPS-based underwater cable positioning system for use in determining the shape and position of hydrophone streamers towed underwater behind survey vessels involved in marine seismic prospecting. The system includes a plurality of surface units towed behind the vessel. Each surface unit includes a GPS receiver to receive radio frequency GPS signals and to determine its positions. Each surface unit also has an acoustic transmitter to transmit an acoustic message signal representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water. Acoustic receiver units, attached spaced apart locations along one or more streamer cables, each include an acoustic receiver to receive the acoustic message signals from the surface units and to determine its position from the message signals. To augment the message signals from the surface units at locations distant from the surface units, acoustic transceiver units may be used. The acoustic transceiver units are attached to the streamer cables at ranges between the surface units and distant acoustic receiver units. The acoustic transceiver units each include an acoustic receiver that performs as the receivers in the acoustic receiver units and an acoustic transmitter to transmit acoustic message signals representing its position and an optional time stamp into the water to be received by the acoustic receiver units. In this way, the positions and shapes of towed streamer cables can be determined.
Owner:INPUT OUTPUT INC
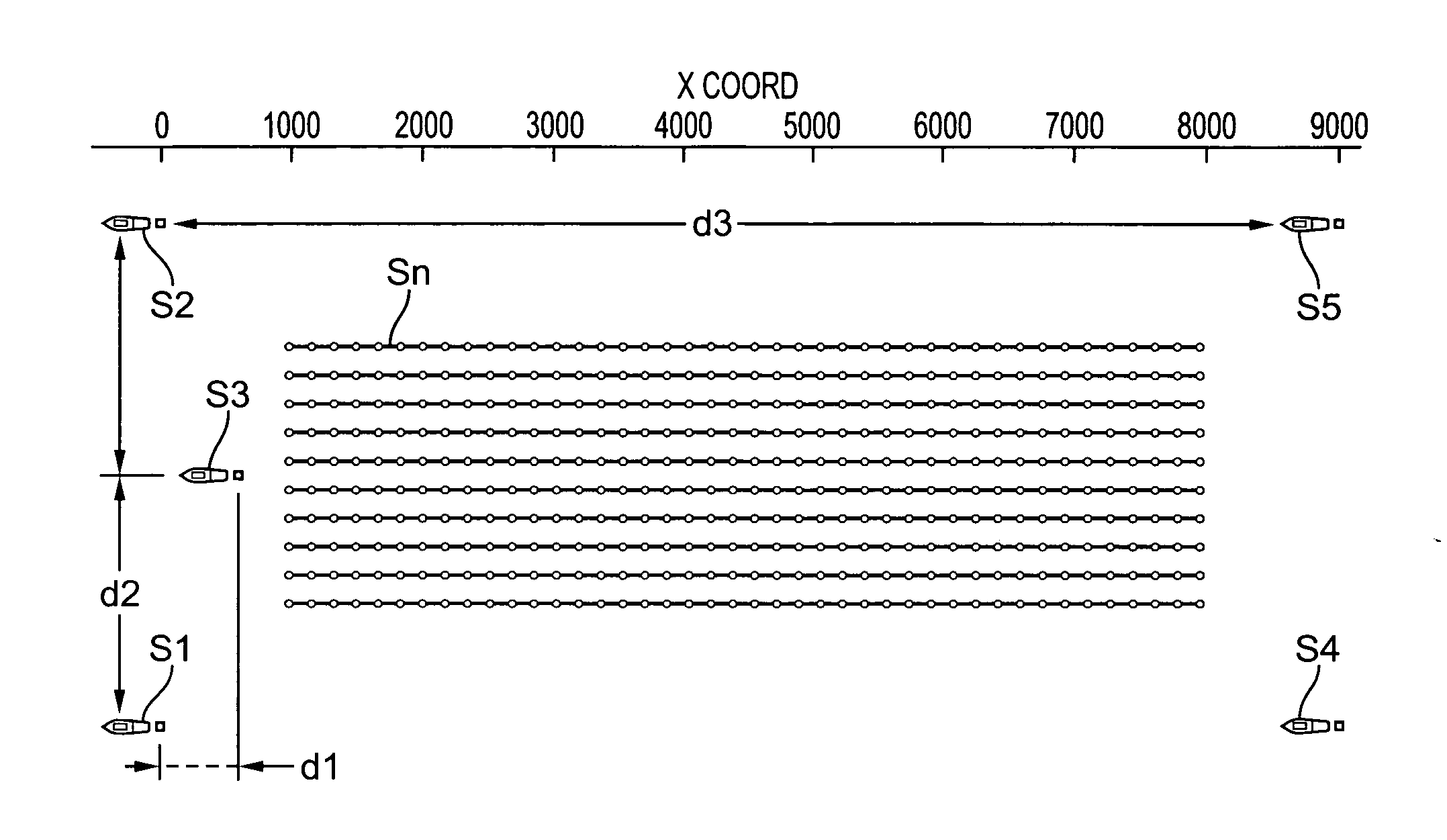
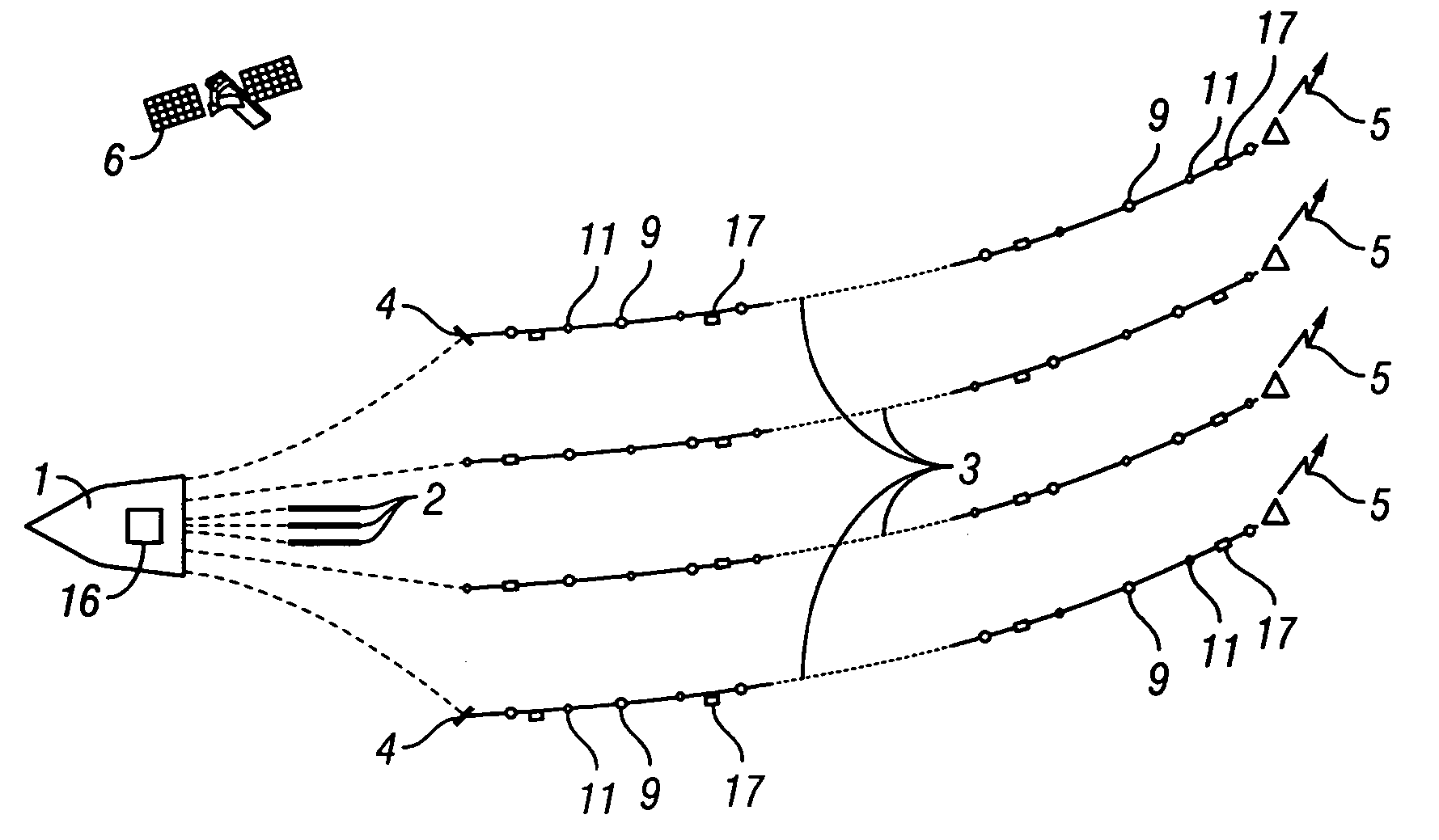
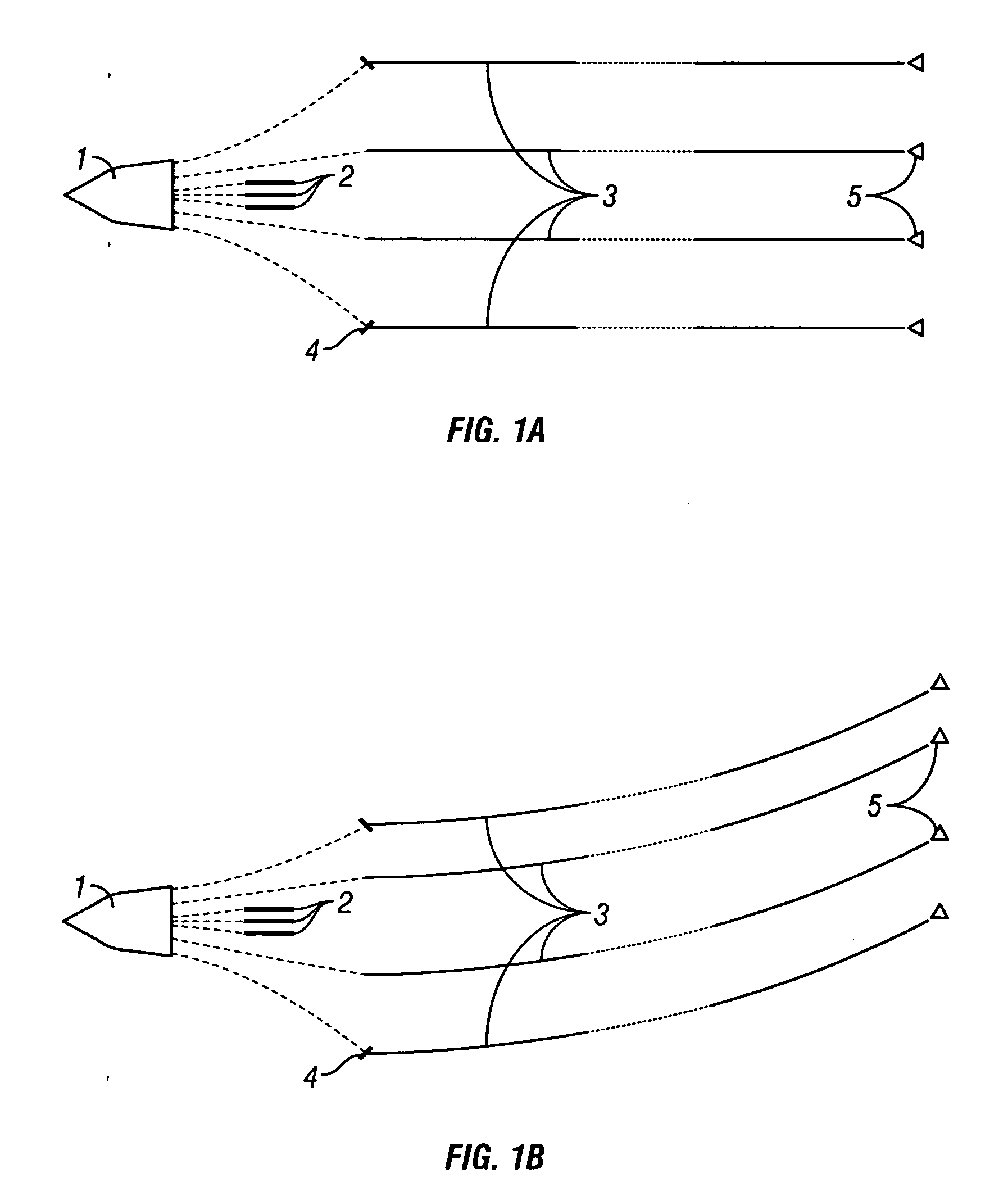
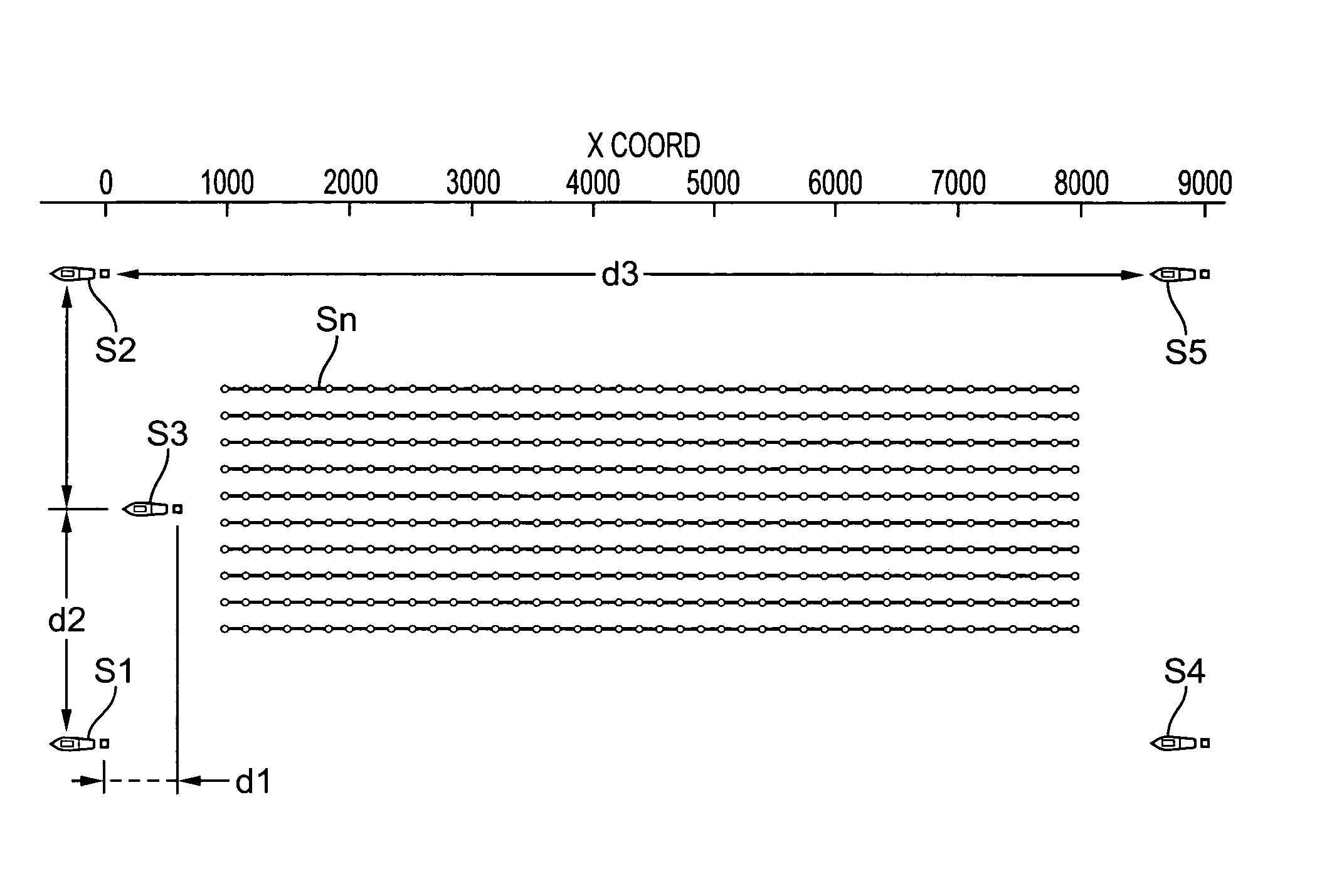
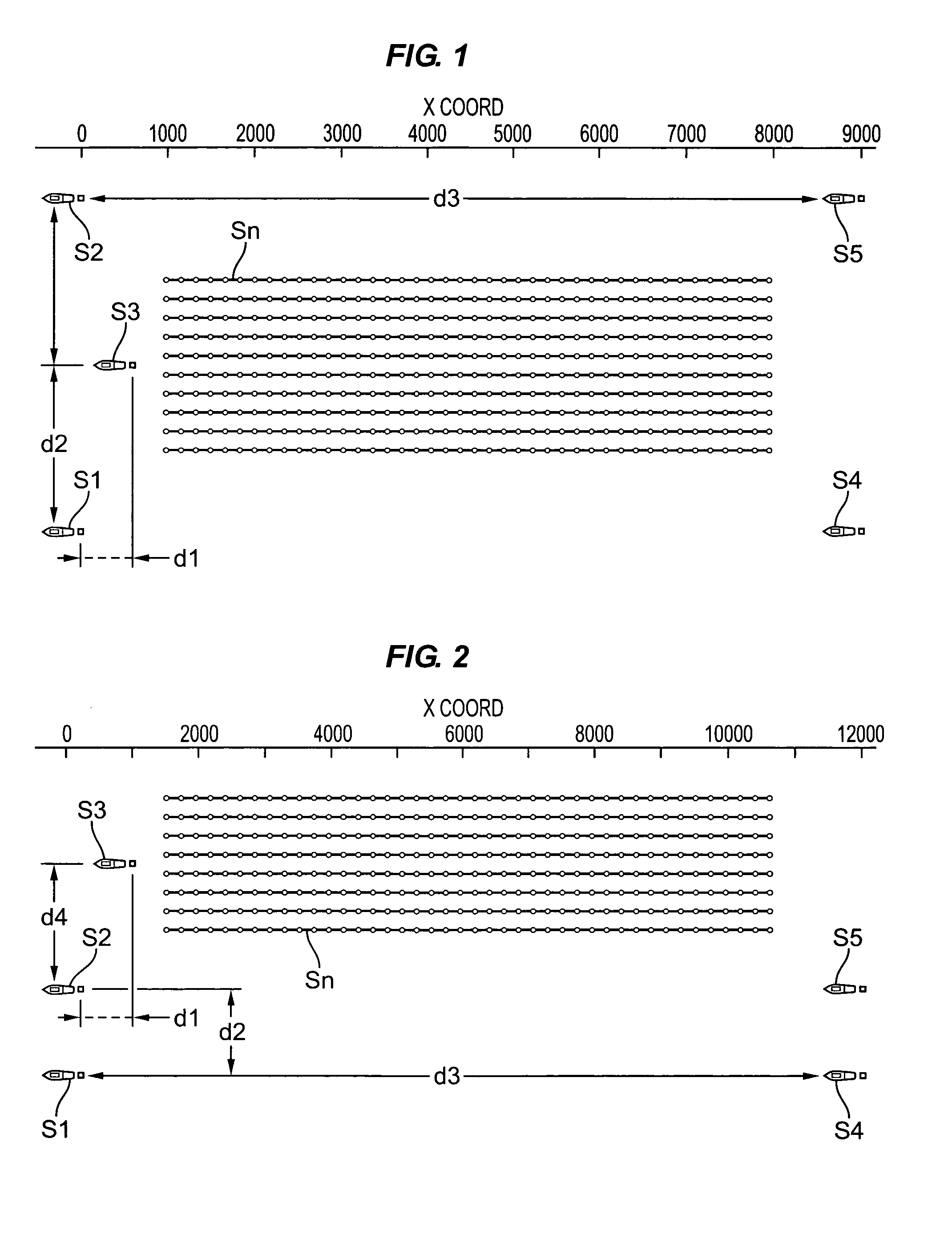
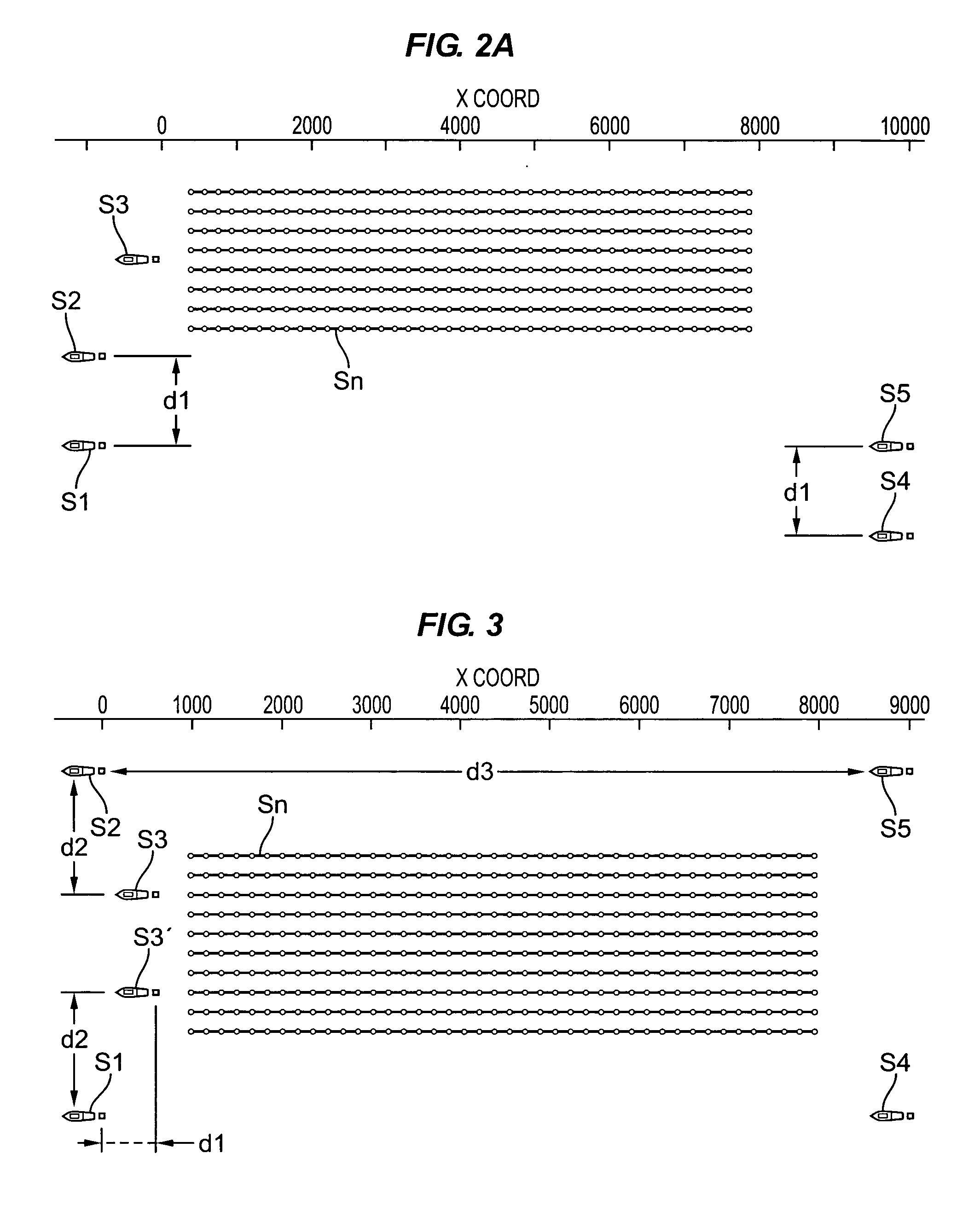
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer seismic surveys
ActiveUS20070165486A1Improved seismic imagingLess timeSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSurveyorSeismic survey
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer marine seismic data are described. One method and system comprises positioning a plurality of source-only tow vessels and one or more source-streamer tow vessels to acquire a wide- and / or full-azimuth seismic survey without need for the spread to repeat a path once traversed. Another method and system allows surveying a sub-sea geologic feature using a marine seismic spread, the spread smartly negotiating at least one turn during the surveying, and shooting and recording during the turn. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, allowing a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
System for combining signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors in marine seismic streamers
Signals of pressure sensors and particle motion sensors located in marine seismic streamers are combined to generate pressure sensor data and particle motion data with substantially the same broad bandwidth. The noisy low frequency part of the motion signals are calculated from the recorded pressure signals and merged with the non-noisy motion signals. The two broad bandwidth data sets can then be combined to calculate the full up- and down-going wavefields.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
Method and apparatus for an ocean bottom seismic acquisition technique
InactiveUS6951138B1Enhanced couplingImproved vector fidelityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersForce measurementOcean bottomSurface ocean
A seismometer having a hydrodynamically efficient shaped body containing a seismic sensor or source, having a propulsion unit located and a control unit for directional control of the propulsion unit for guiding the seismometer to and from an ocean floor. The seismometer can be deployed from a surface ship, helicopter or airplane. The seismometer or surface support vessel contains a navigation unit for directing the control unit to a desired location on the ocean bottom. The apparatus provides a storage device for storing seismic data sensed by the seismic sensor. The navigation system sends a responsive directional command to the apparatus based on the current location and the desired location. Upon arrival at the desired ocean bottom location, the propulsion system acts to couple the apparatus to the ocean floor. A flight control system manages a plurality of the seismometers during navigation to and from the a ocean bottom.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
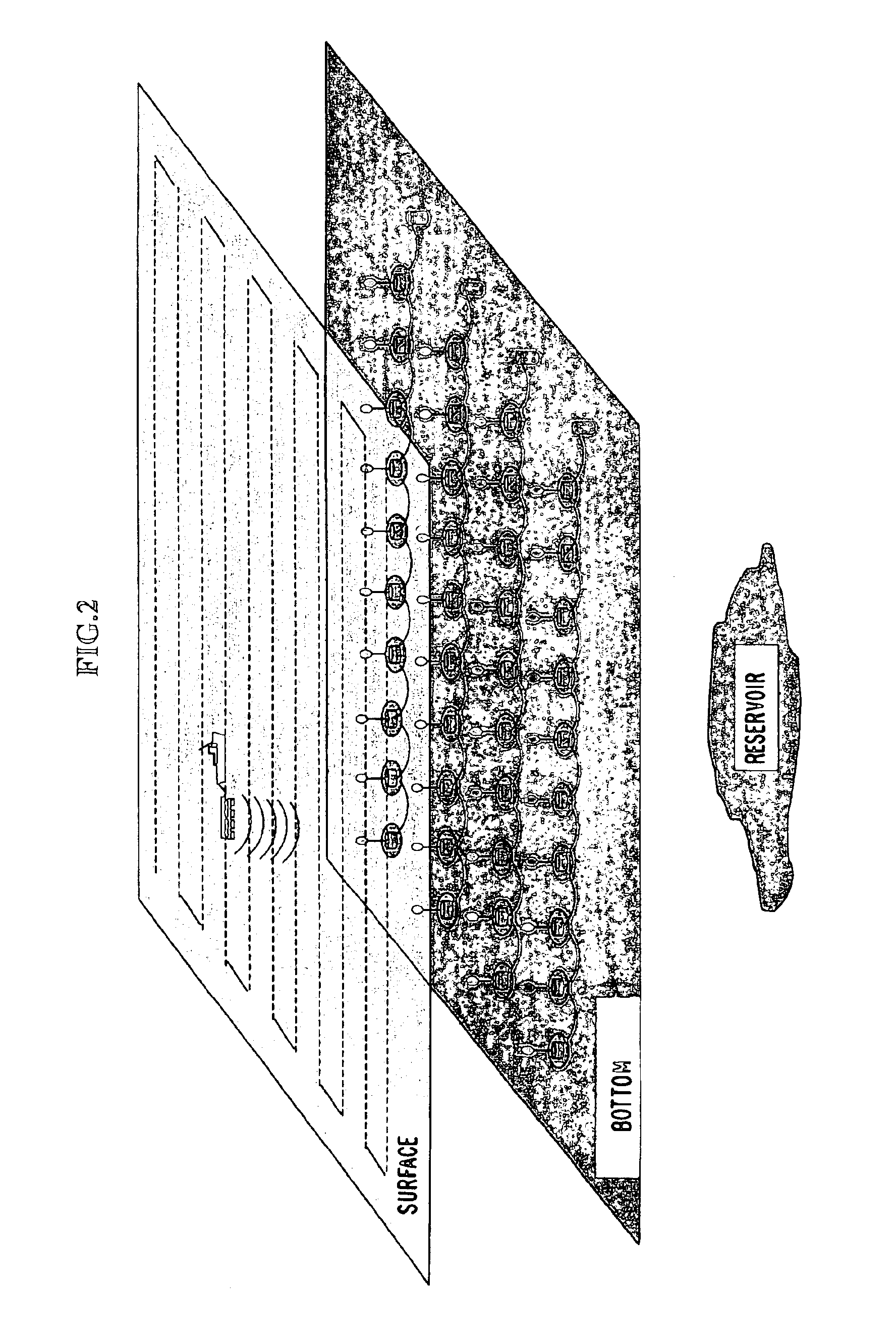
Seismic data acquisition system using acquisition stations set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS7016260B2Good synchronizationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsSystems designData acquisition
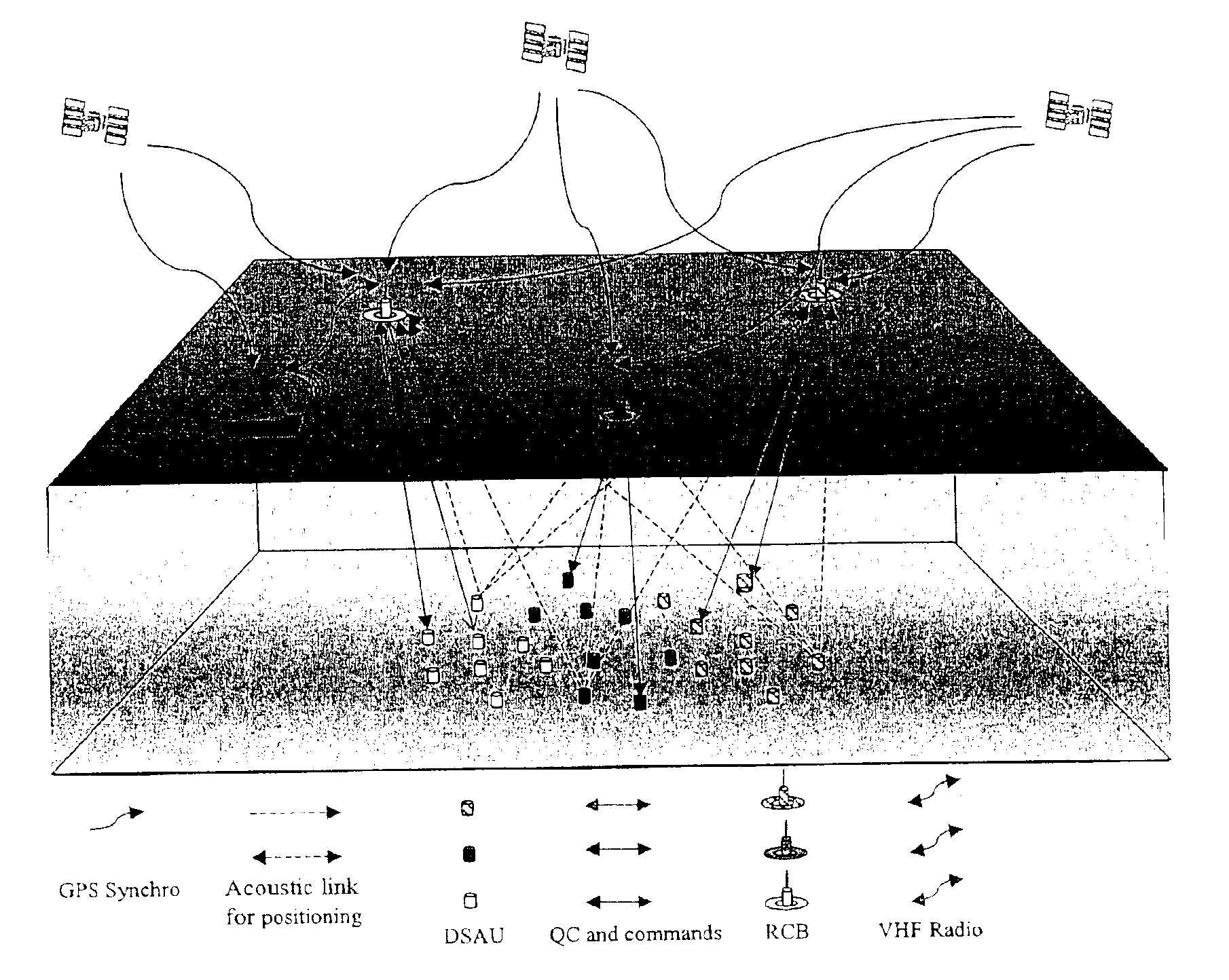
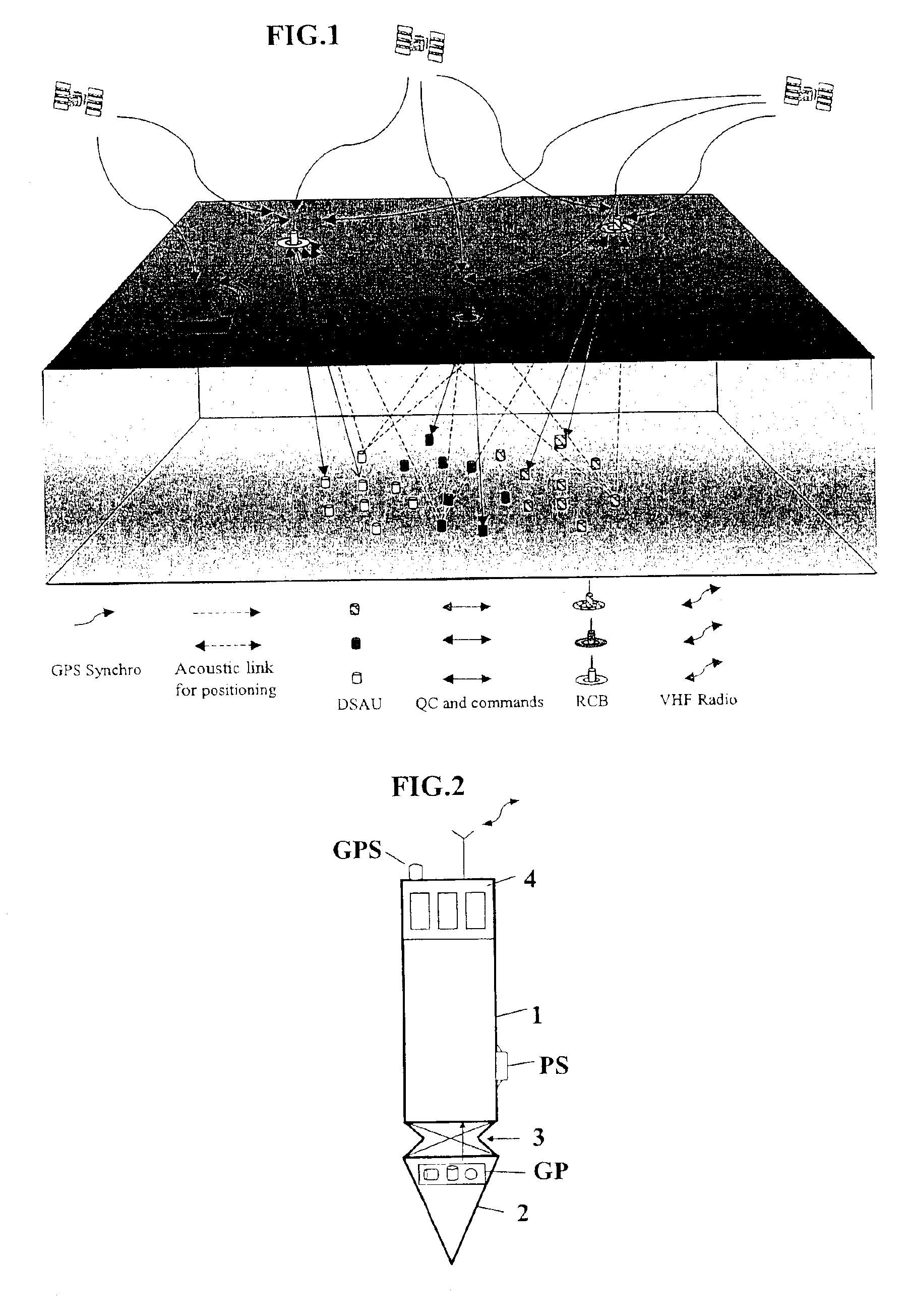
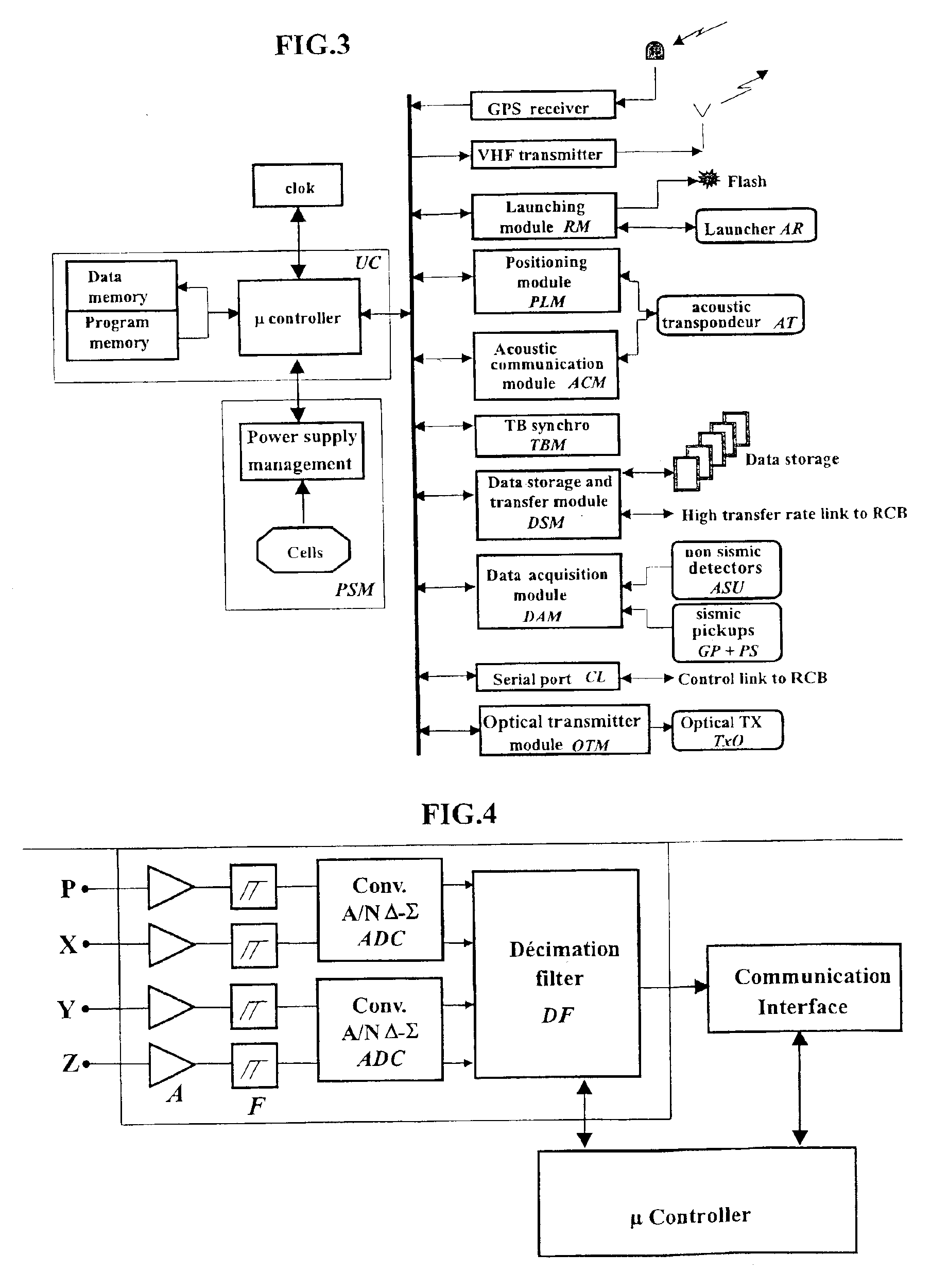
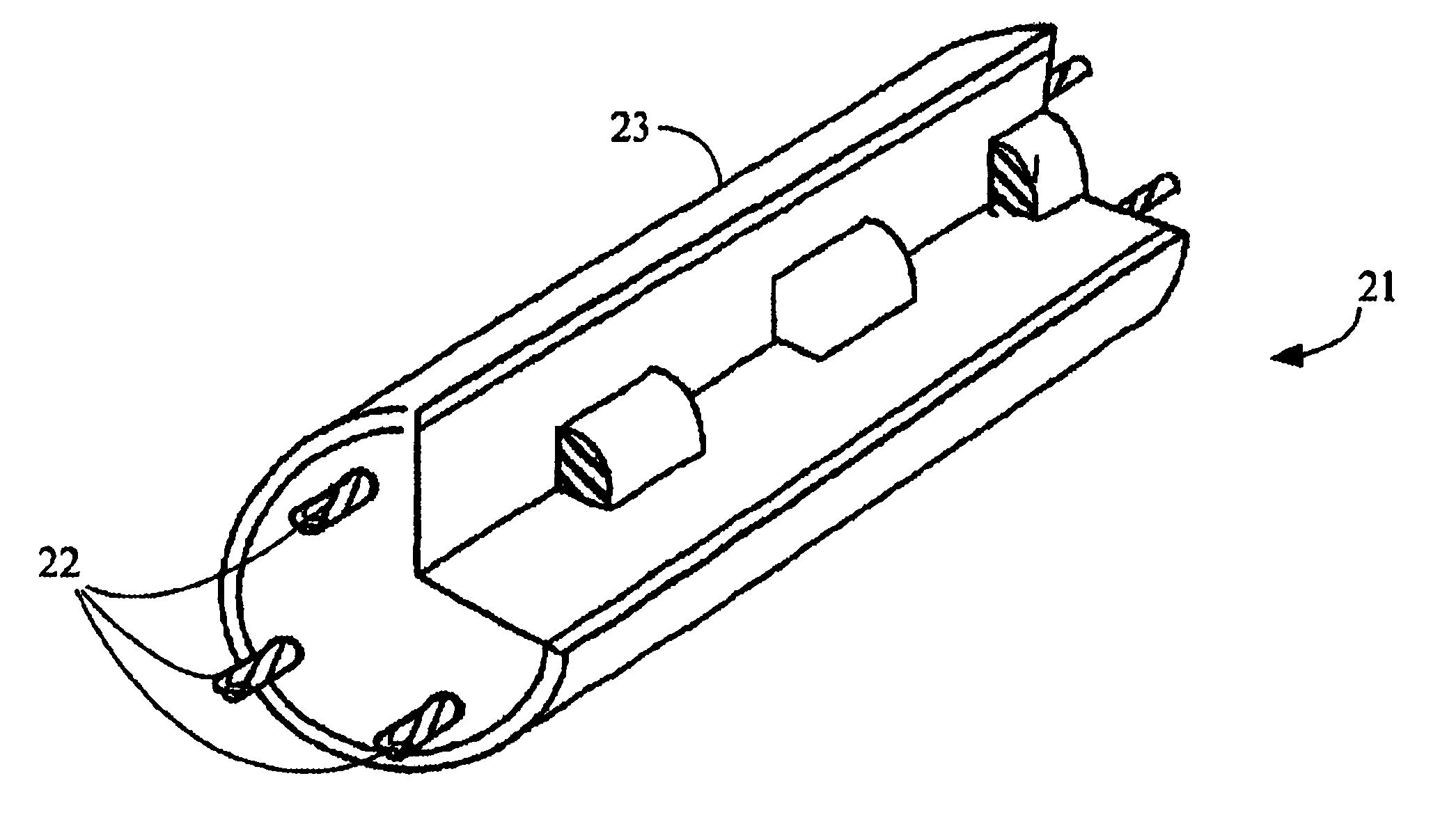
The invention is a system designed for acquisition of seismic data by means of acquisition stations set on water bottom of a water body. The system comprises acquisition stations (DSAU) combining a streamlined boom suited to penetrate the bottom and thus couple seismic receivers with the underlying formation, a sealed body for electronic data acquisition and communication modules. These acquisition stations (DSAU) are placed in the water and drop to the bottom under the effect of gravity. Relay buoys (RCB) are positioned at the surface, each with a GPS positioning module, a radio link with a central station (CCRU), on a ship for example, and modules providing acoustic communication with bottom acquisition stations (DSAU), which are used to determine the position of the stations in relation to the relay buoys and to exchange control data and seismic data (good running order data or possibly seismic traces acquired if the conditions lend themselves thereto) to provide seismic prospecting or monitoring of an underground formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Marine seismic acquisition system and method
InactiveUS6684160B1Reduce contentReduce noiseSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal processingHydrophoneSeismic survey
A method and system for performing a marine seismic survey is described, including towing at least one seismic streamer comprising a plurality of hydrophones distributed at average intervals of not more than 625 cm therealong in the water over the area to be surveyed; directing acoustic signals down through the water and into the earth beneath; receiving with the hydrophones seismic signals reflected from strata in the earth beneath the water; digitizing the output of each hydrophone separately; and filtering the output to reduce the noise present in the output and to generate a signal with a reduced noise content wherein the filtering process uses as further input the digitized output of at least one nearby hydrophone. The filtering is applied to single sensor recording prior to group-forming and thus able to detect and reduce coherent noise with a coherency length of 20 meters or less. It reduces noise such as streamer or bulge noise.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System and method for determining positions of towed marine seismic streamers
ActiveUS20070091719A1Reduce cross-correlationDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesMechanical vibrations separationEngineeringBroadband
A system comprises a plurality of acoustic transmitters, mounted inside the streamers, adapted to transmit broadband signals having low cross-correlation between the signals of different transmitters; a plurality of acoustic receivers, mounted inside the streamers, adapted to receive the signals from the transmitters; at least one processor adapted to cross-correlate the signals received at the receivers with copies of transmitter signals to determine identities of the transmitters of the received signals and to determine travel times of the received signals; and a main processor adapted to convert the travel times to distances between the identified transmitters and the receivers and to determine relative positions of the streamers from the distances.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
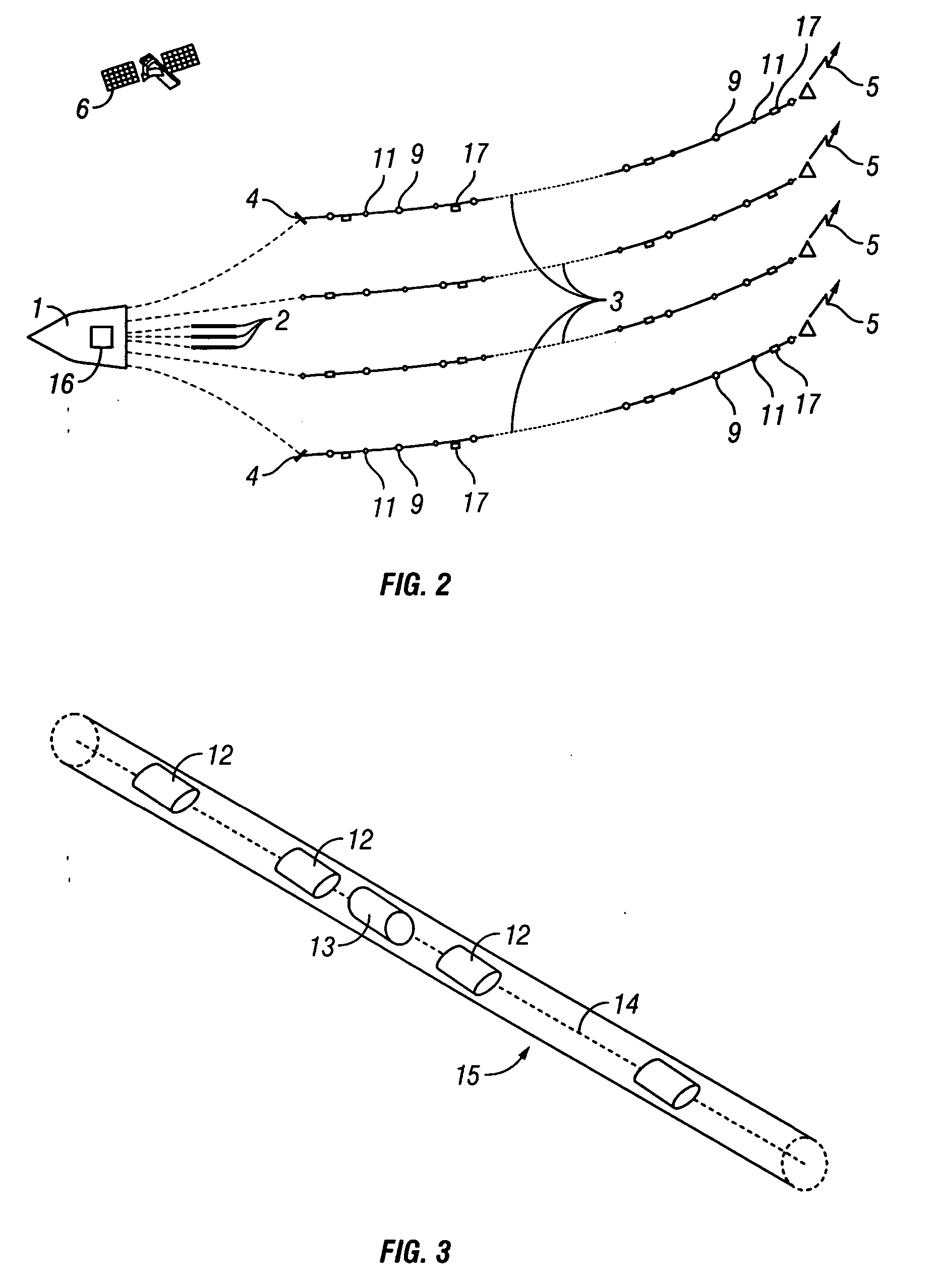
System and method for using time-distance characteristics in acquisition, processing, and imaging of t-CSEM data
InactiveUS20060203613A1Enhance the imageEasy to processSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasUltrasound attenuationTime of use
There is provided herein a system and method of acquiring, processing, and imaging transient Controlled Source ElectroMagnetic (t-CSEM) data in ways that are similar to those used for seismic data. In particular, the instant invention exploits the time-distance characteristics of t-CSEM data to permit the design and execution of t-CSEM surveys for optimal subsequent processing and imaging. The instant invention illustrates how to correct t-CSEM data traces for attenuation and dispersion, so that their characteristics are more like those of seismic data and can be processed using algorithms familiar to the seismic processor. The resulting t-CSEM images, particularly if combined with corresponding seismic images, may be used to infer the location of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
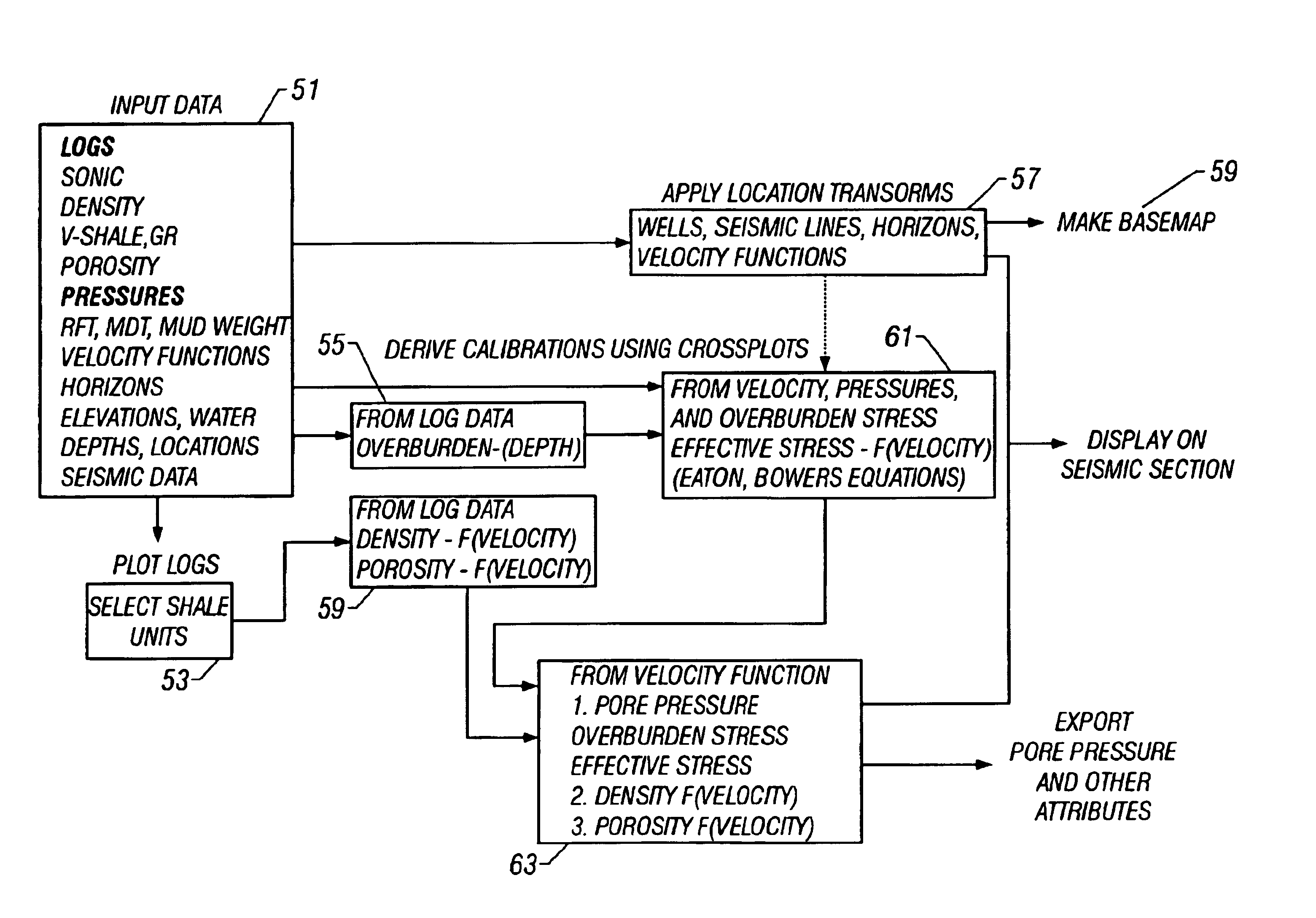
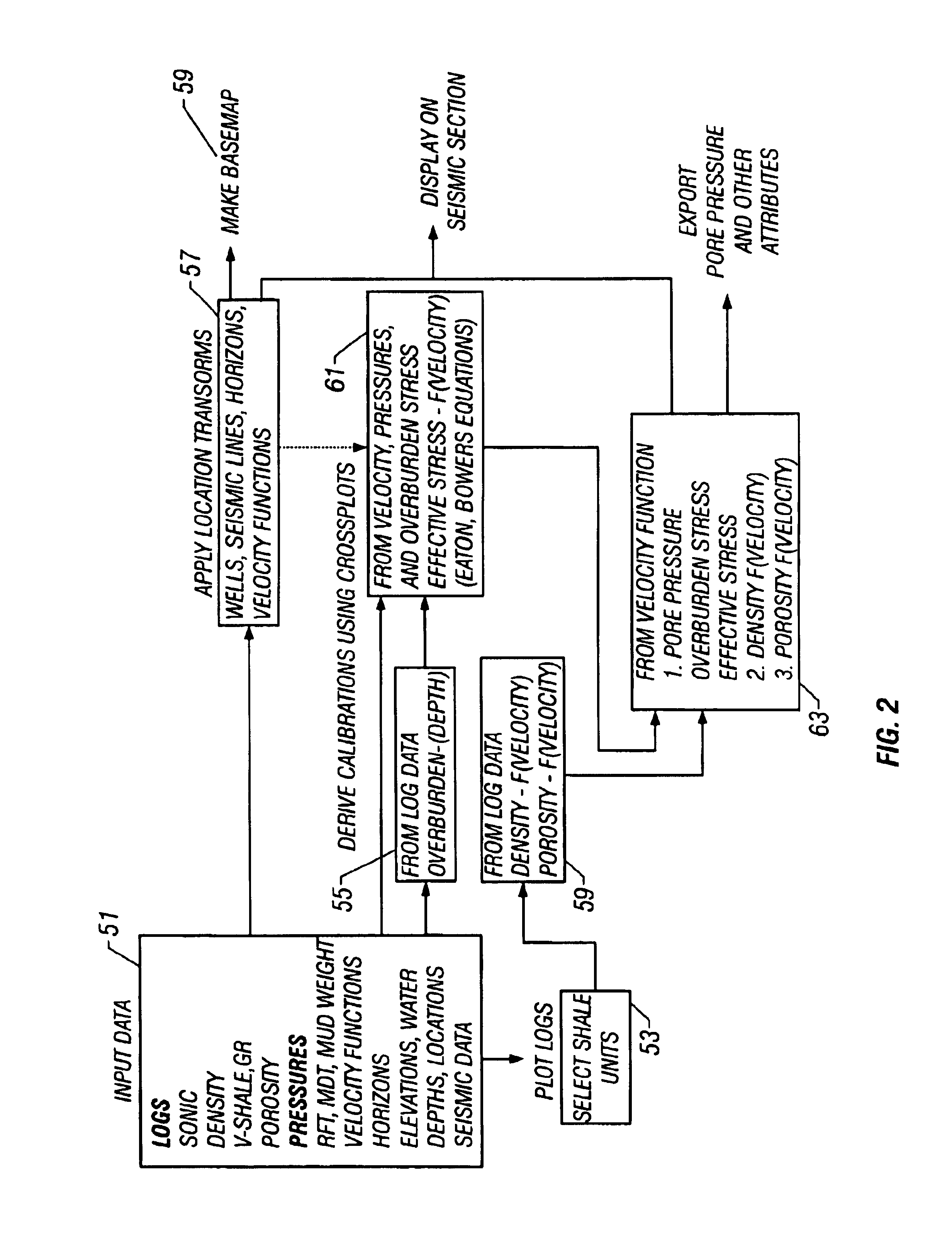
Method and process for prediction of subsurface fluid and rock pressures in the earth
A method of determination of fluid pressures in a subsurface region of the earth uses seismic velocities and calibrations relating the seismic velocities to the effective stress on the subsurface sediments. The seismic velocities may be keyed to defined seismic horizons and may be obtained from many methods, including velocity spectra, post-stack inversion, pre-stack inversion, VSP or tomography. Overburden stresses may be obtained from density logs, relations between density and velocity, or from inversion of potential fields data. The seismic data may be P-P, P-S, or S-S data. The calibrations may be predetermined or may be derived from well information including well logs and well pressure measurements. The calibrations may also include the effect of unloading. The determined pressures may be used in the analysis of fluid flow in reservoirs, basin and prospect modeling and in fault integrity analysis.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
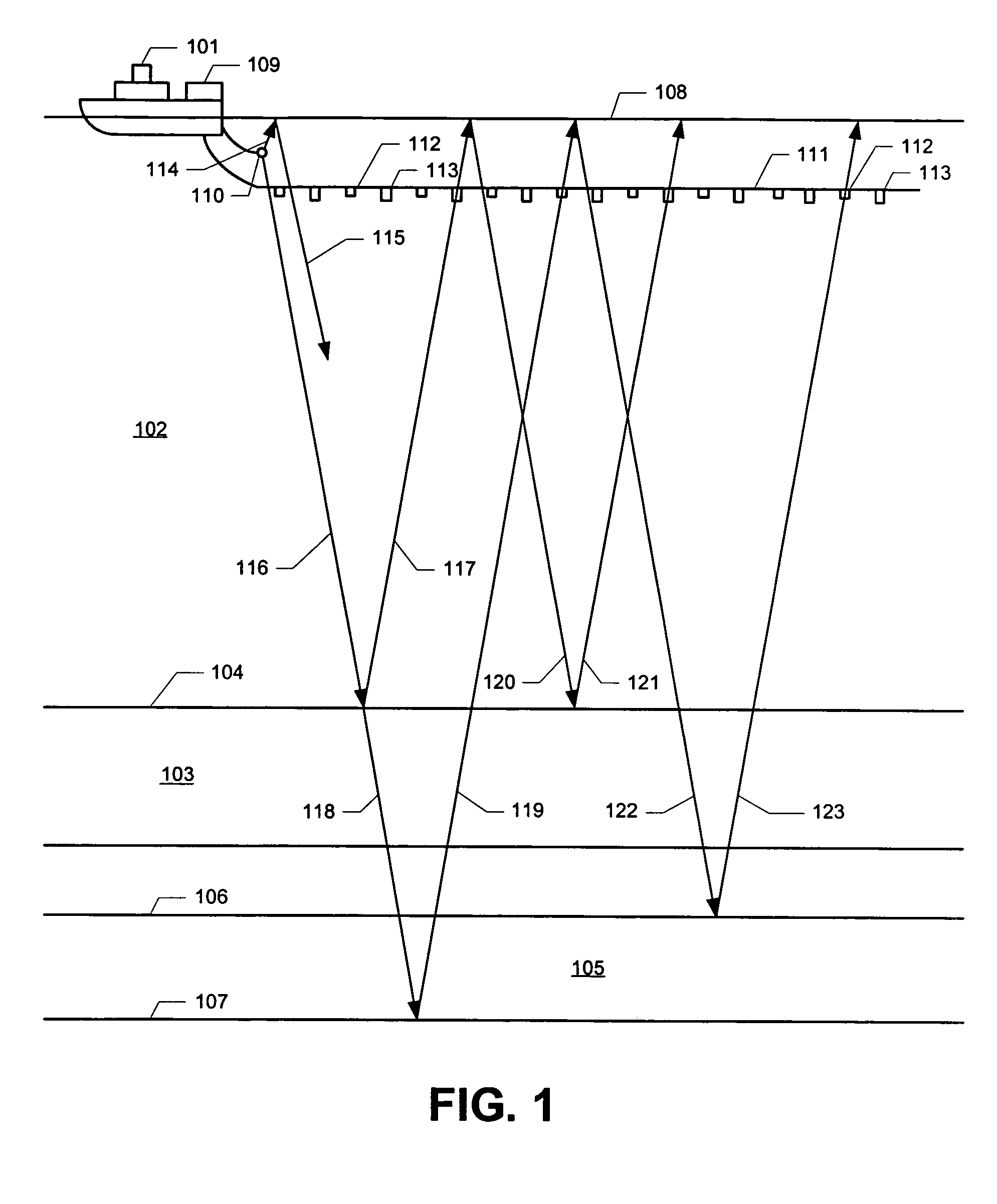
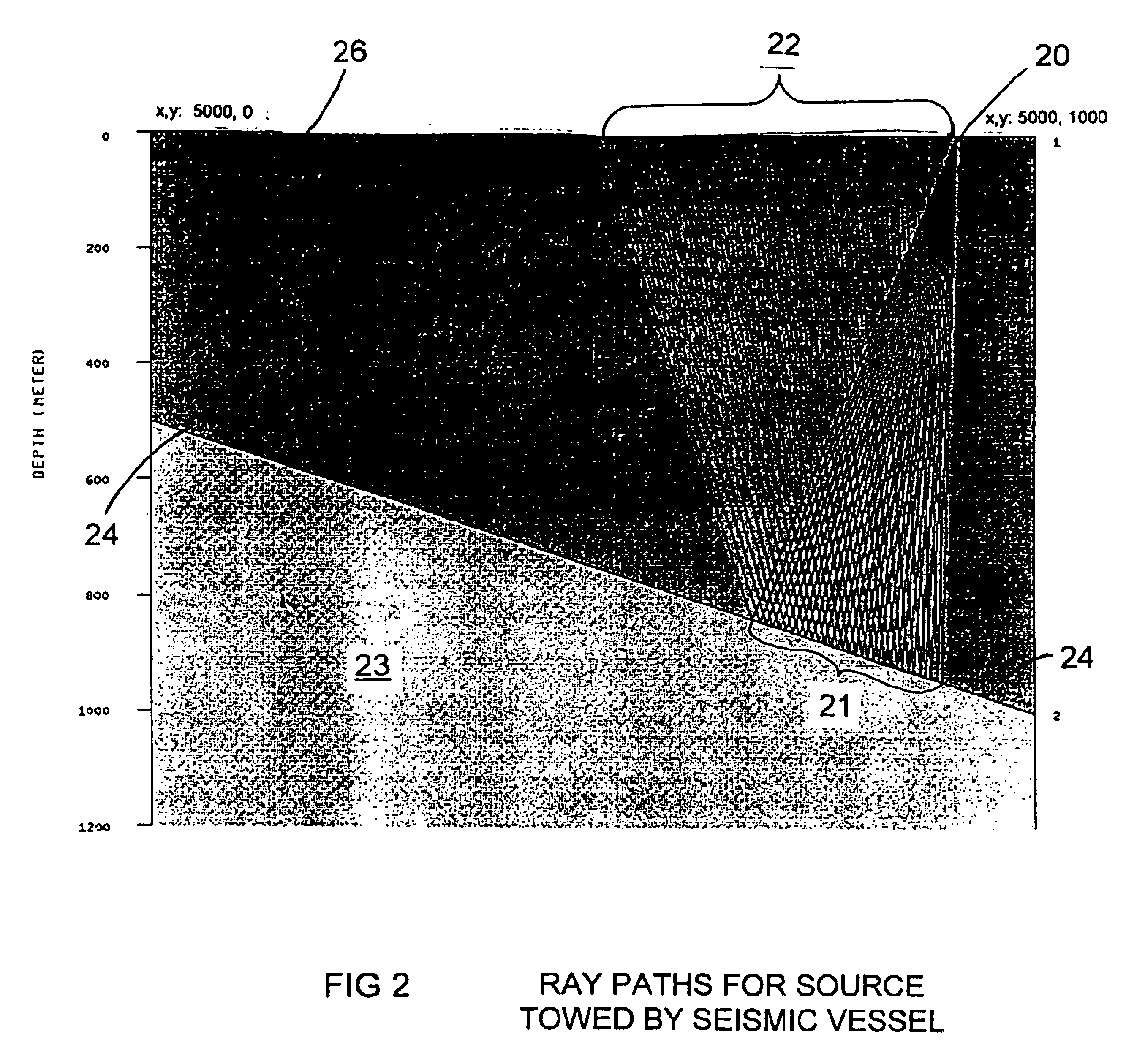
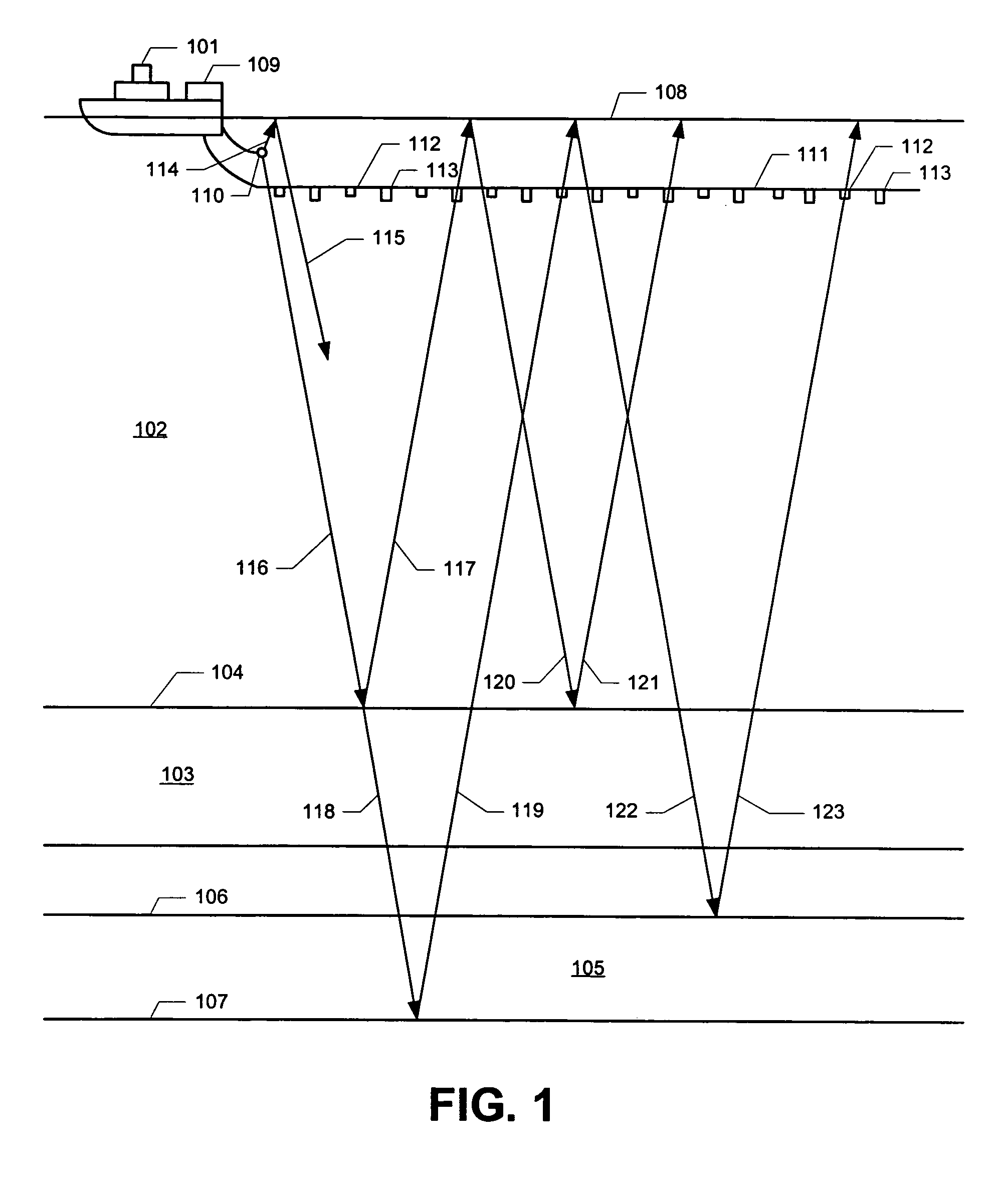
Method for aquiring and processing marine seismic data to extract and constructively use the up-going and down-going wave-fields emitted by the source(s)
InactiveUS20100008184A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSeismic signal processingSurface oceanPhase shifted
A method for acquisition and processing of marine seismic signals to extract up-going and down- going wave-fields from a seismic energy source includes deploying at least two marine seismic energy sources at different depths in a body of water. These seismic energy sources are actuated with known time delays that are varied from shot record to shot record. Seismic signals from sources deployed at different depths are recorded simultaneously. Seismic energy corresponding to each of the sources is extracted from the recorded seismic signals. Up-going and down-going wave-fields are extracted from the sources deployed at different depths using the extracted seismic energy therefrom. A method includes the separated up-going and down-going wave-fields are propagated to a water surface or a common reference, the up-going or the down-going wave-field is 180 degree phase shifted, and the signals from these modified up-going and down-going wave-fields are summed.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Apparatus and methods for seismic streamer positioning
InactiveUS20060227657A1Reduce signalingTowing/pushing equipmentSeismology for water-covered areasSubject matterEngineering
Systems and methods for positioning seismic streamers are disclosed that enable two or more streamers to be positioned in over / under configuration. One system comprises first and second pluralities of remotely controllable birds mounted on or inline in first and second streamers, the birds functioning to control position of the streamers relative to each other, to another pair of streamers, or to some reference. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer seismic surveys
ActiveUS7400552B2Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasOcean bottomSeismic survey
Methods and systems for efficiently acquiring towed streamer marine seismic data are described. One method and system comprises positioning a plurality of source-only tow vessels and one or more source-streamer tow vessels to acquire a wide- and / or full-azimuth seismic survey without need for the spread to repeat a path once traversed. Another method and system allows surveying a sub-sea geologic feature using a marine seismic spread, the spread smartly negotiating at least one turn during the surveying, and shooting and recording during the turn. This abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract, allowing a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Particle motion sensor for marine seismic sensor streamers
InactiveUS20050194201A1Seismic signal receiversSeismology for water-covered areasClassical mechanicsMotion sensors
A seismic sensor is disclosed which includes at least one particle motion sensor, and a sensor jacket adapted to be moved through a body of water. The particle motion sensor is suspended within the sensor jacket by at least one biasing device. In one embodiment, a mass of the sensor and a force rate of the biasing device are selected such that a resonant frequency of the sensor within the sensor jacket is within a predetermine range.
Owner:PGS AMERICA INC
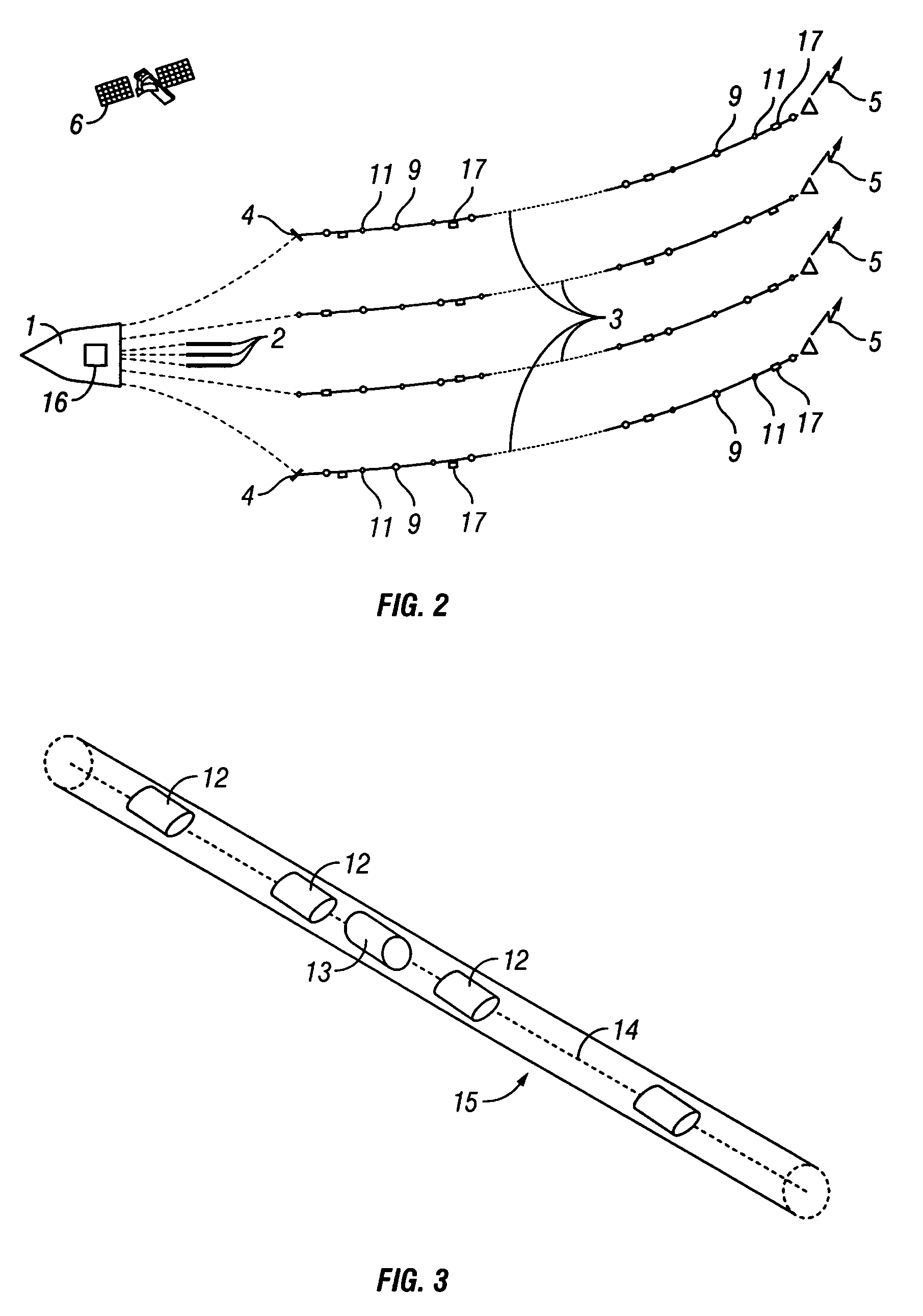
Methods for Efficiently Acquiring Wide-Azimuth Towed Streamer Seismic Data
A technique for use in marine seismic surveying includes a method and an apparatus. In one aspect, the method includes towing a seismic spread including a source multiple streamers on a generally curved advancing path, the streamers being actively steered. The source is fired and data is acquired on the curve. In other aspects, the method is performed with only a single vessel or the generally curved advancing path is a sincurve advancing path. The method may include a dual circular shoot in another aspect. And, in yet another aspect, the invention includes an apparatus comprised of a computing apparatus on board a tow vessel receiving positioning data from the marine seismic streamers. It is also programmed to: sail the tow vessel in a generally curved advancing path and actively steer the marine seismic streamers through the generally curved advancing path.
Owner:REFLECTION MARINE NORGE AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com