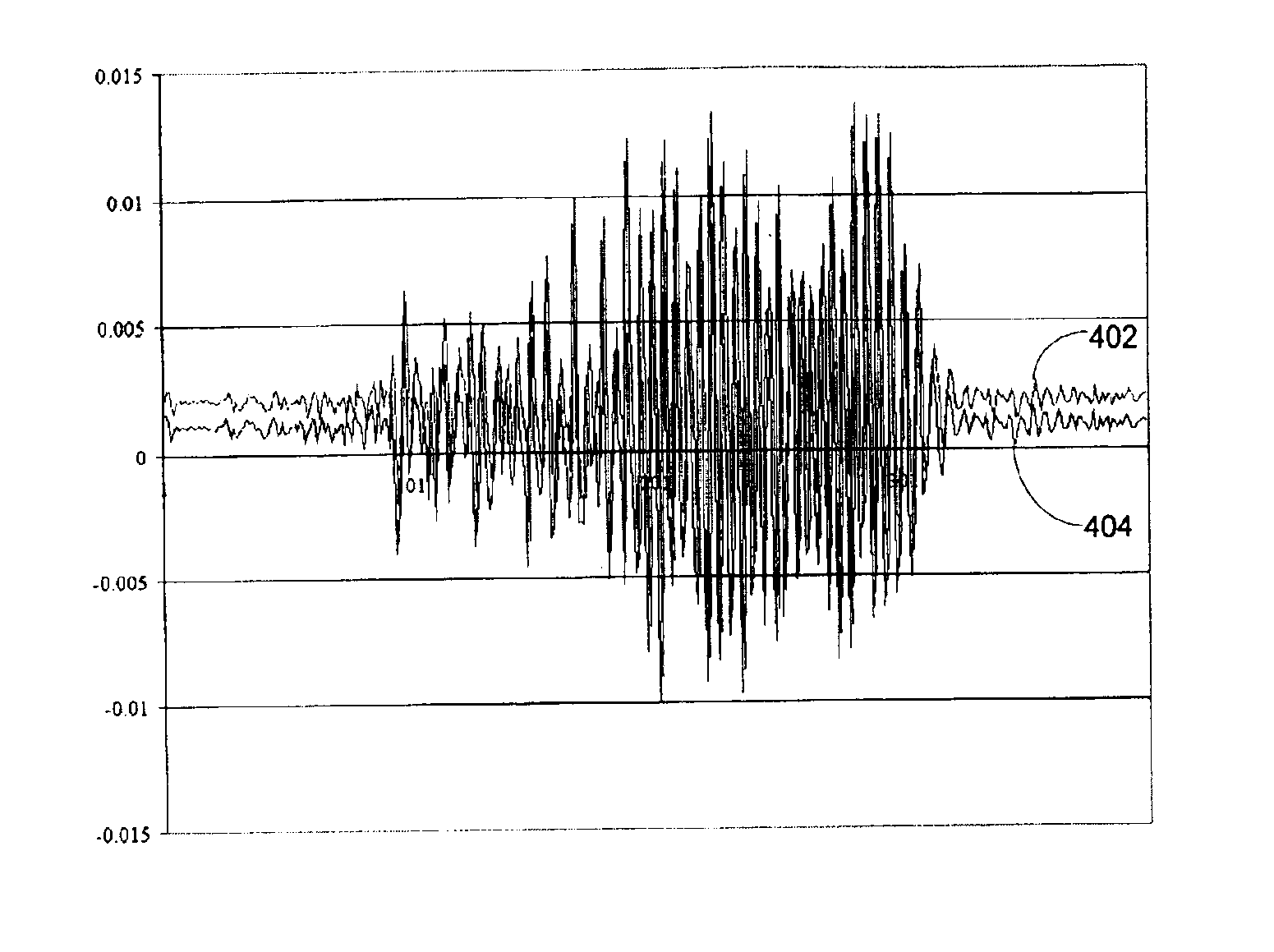
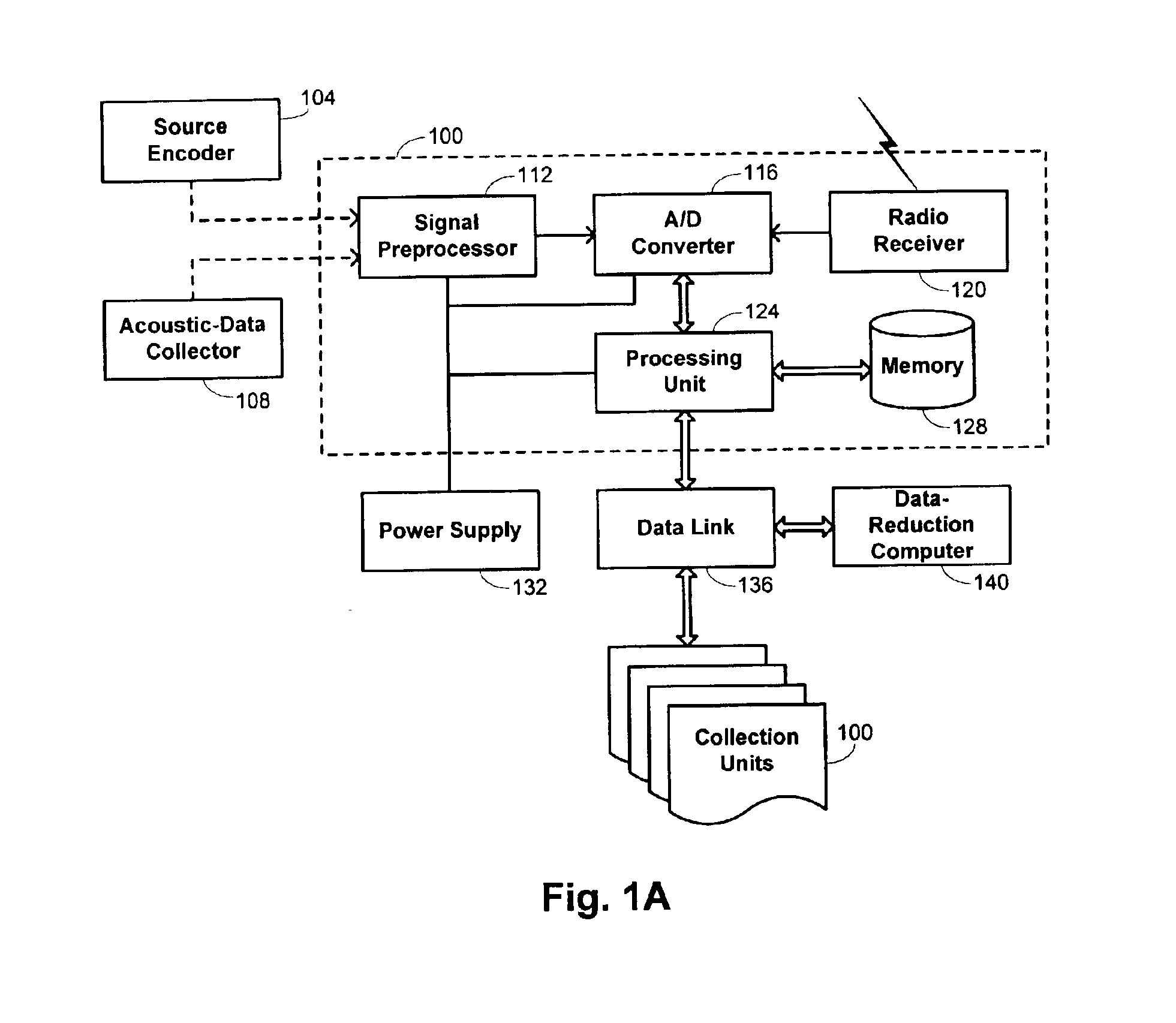
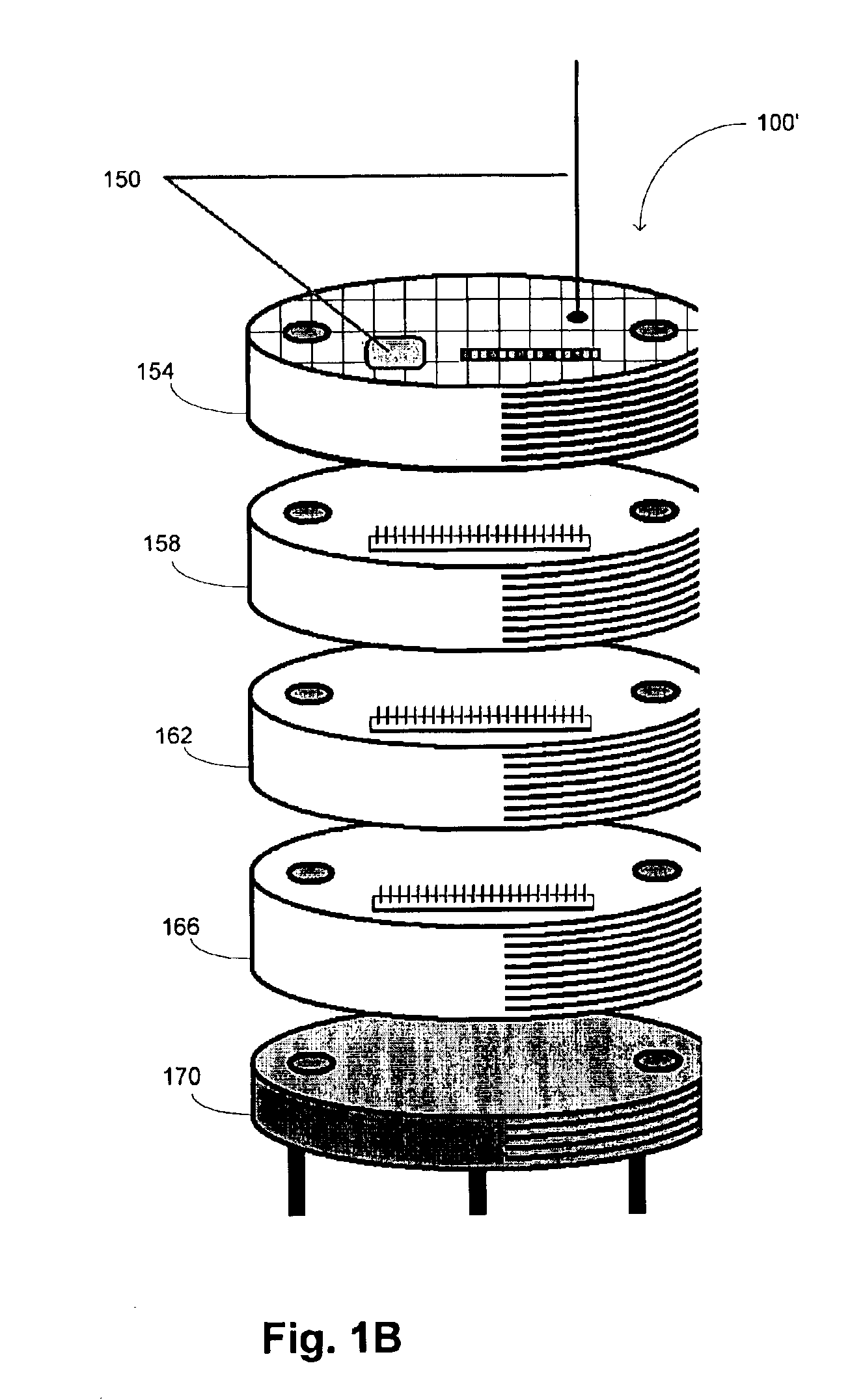
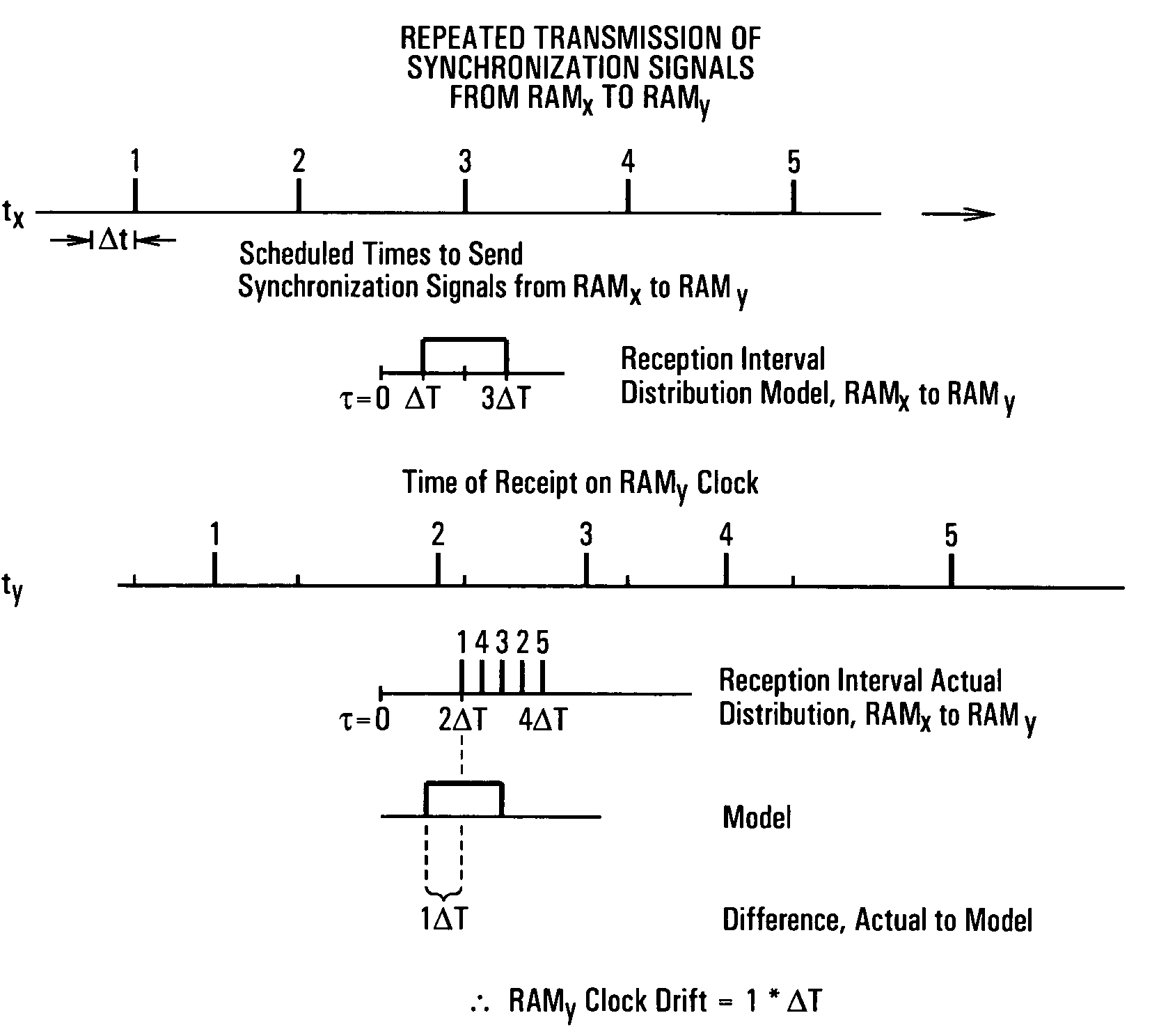
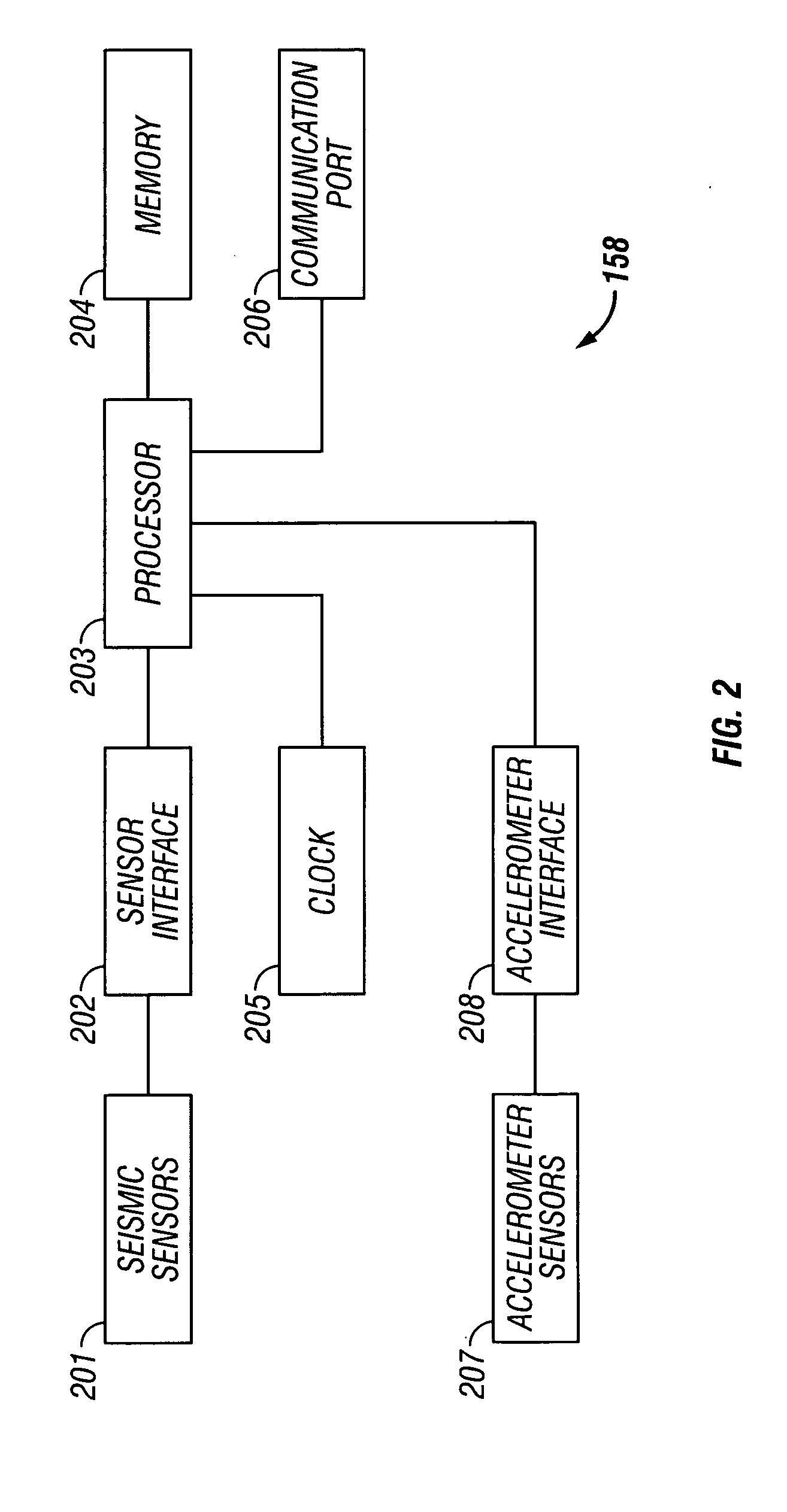
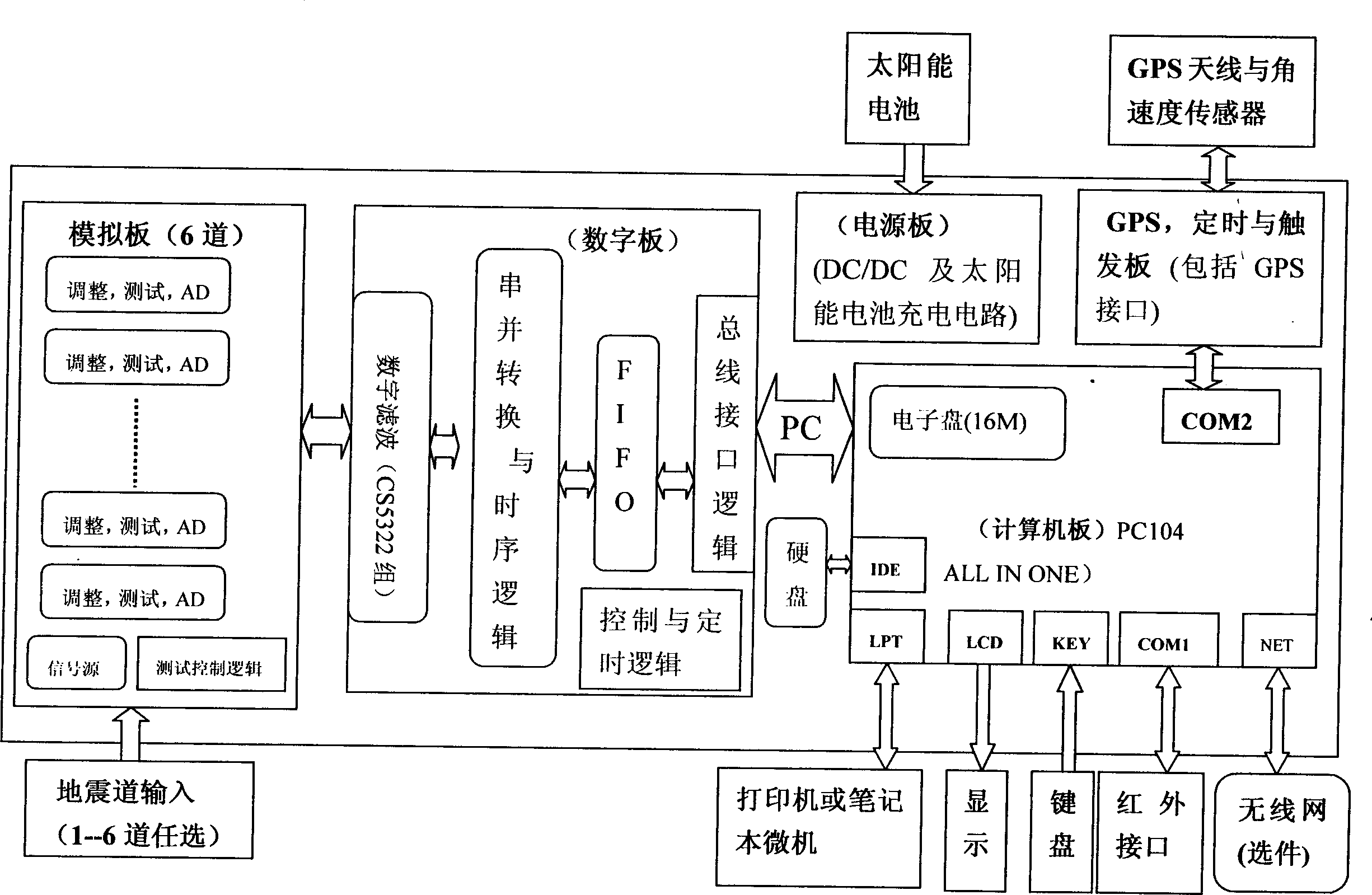
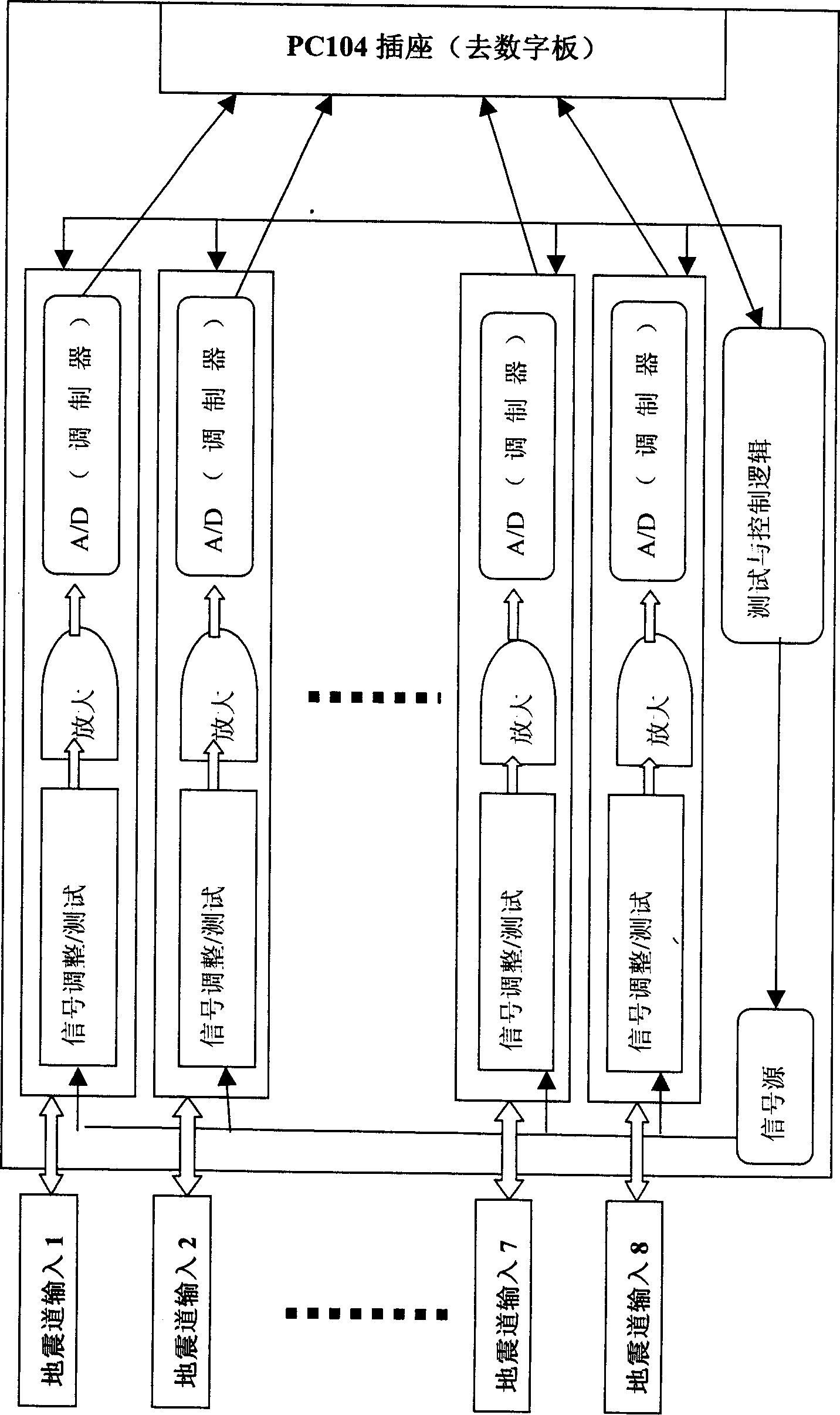
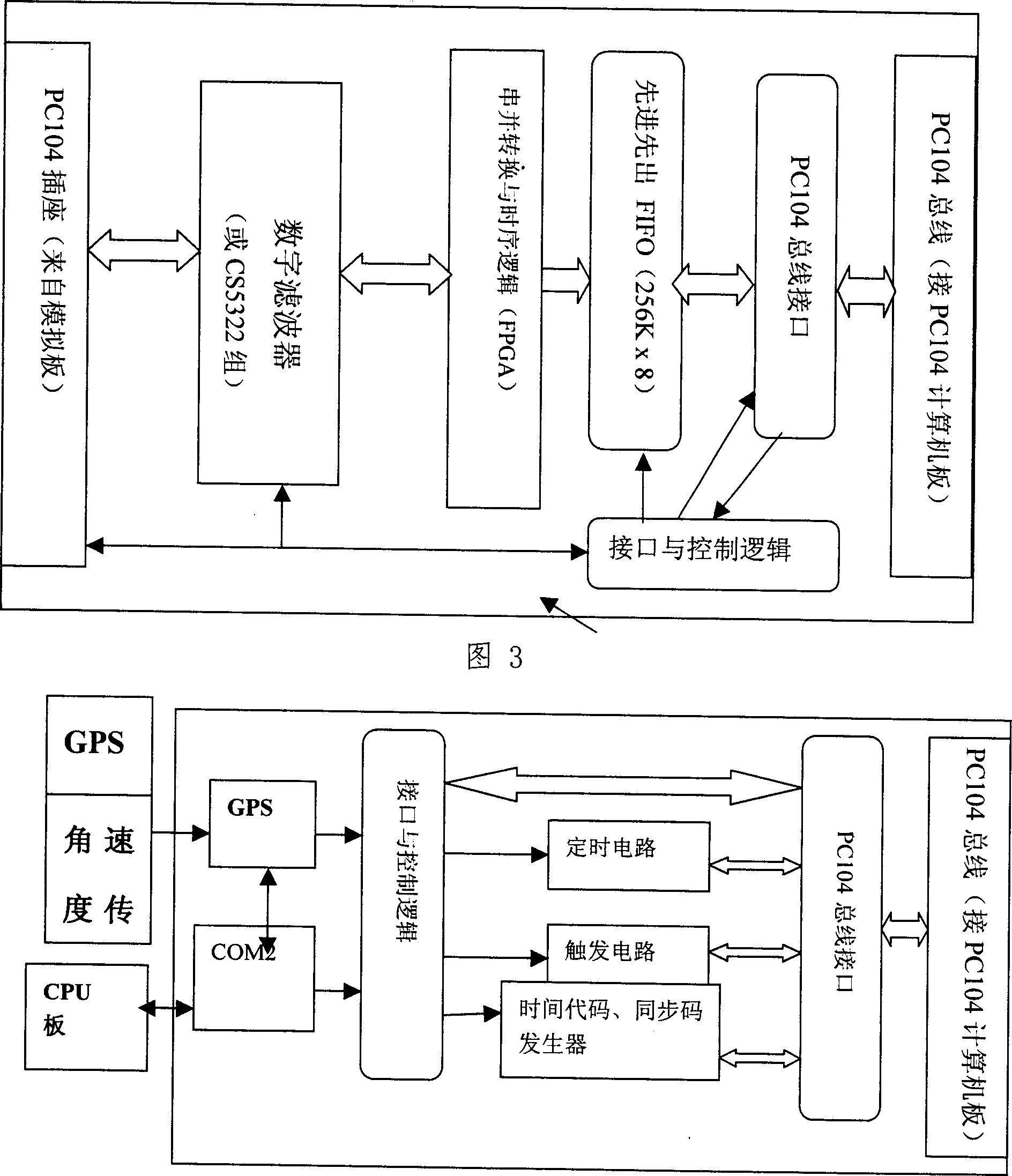
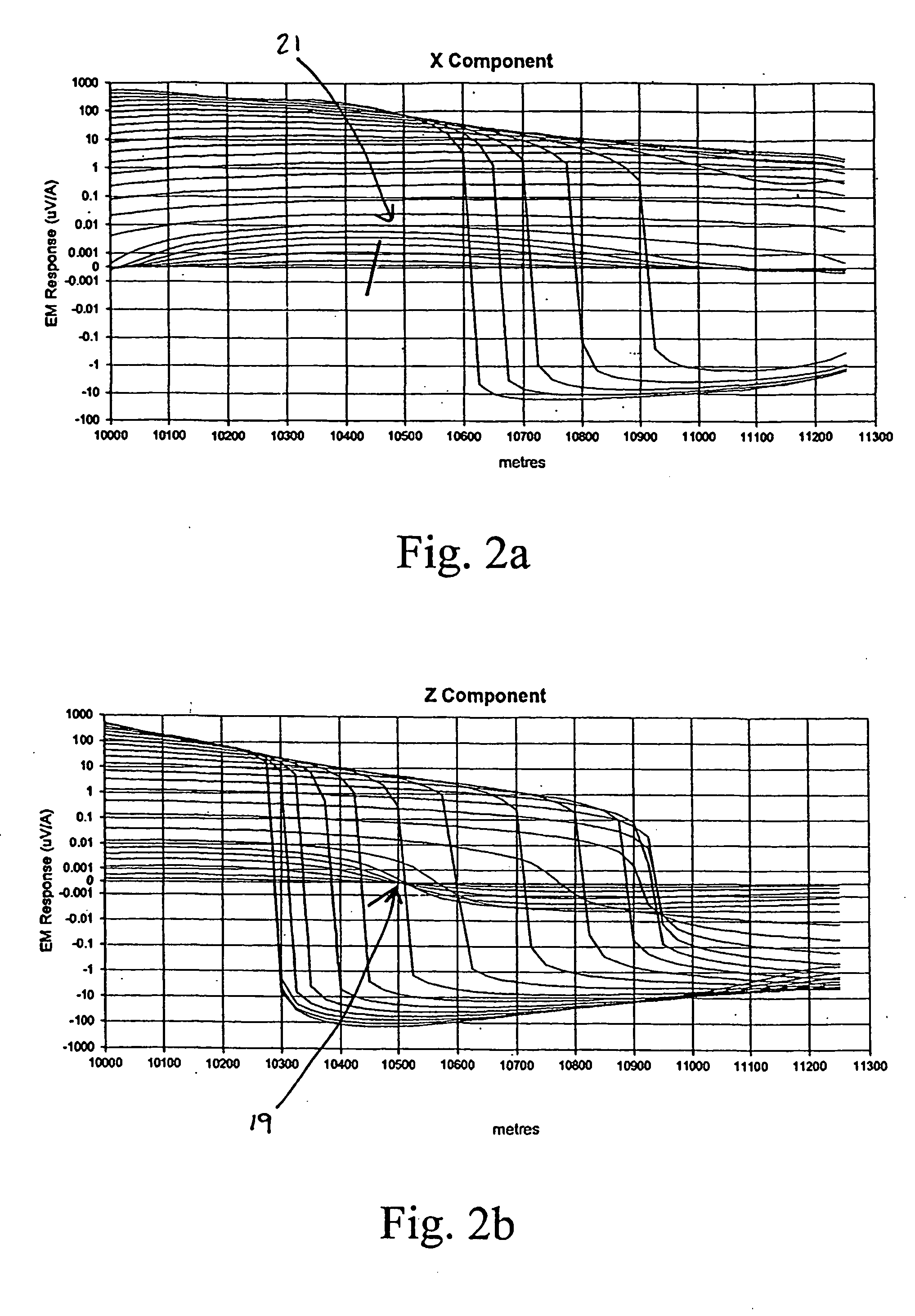
Patents
Literature
545results about "Seismic signal recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
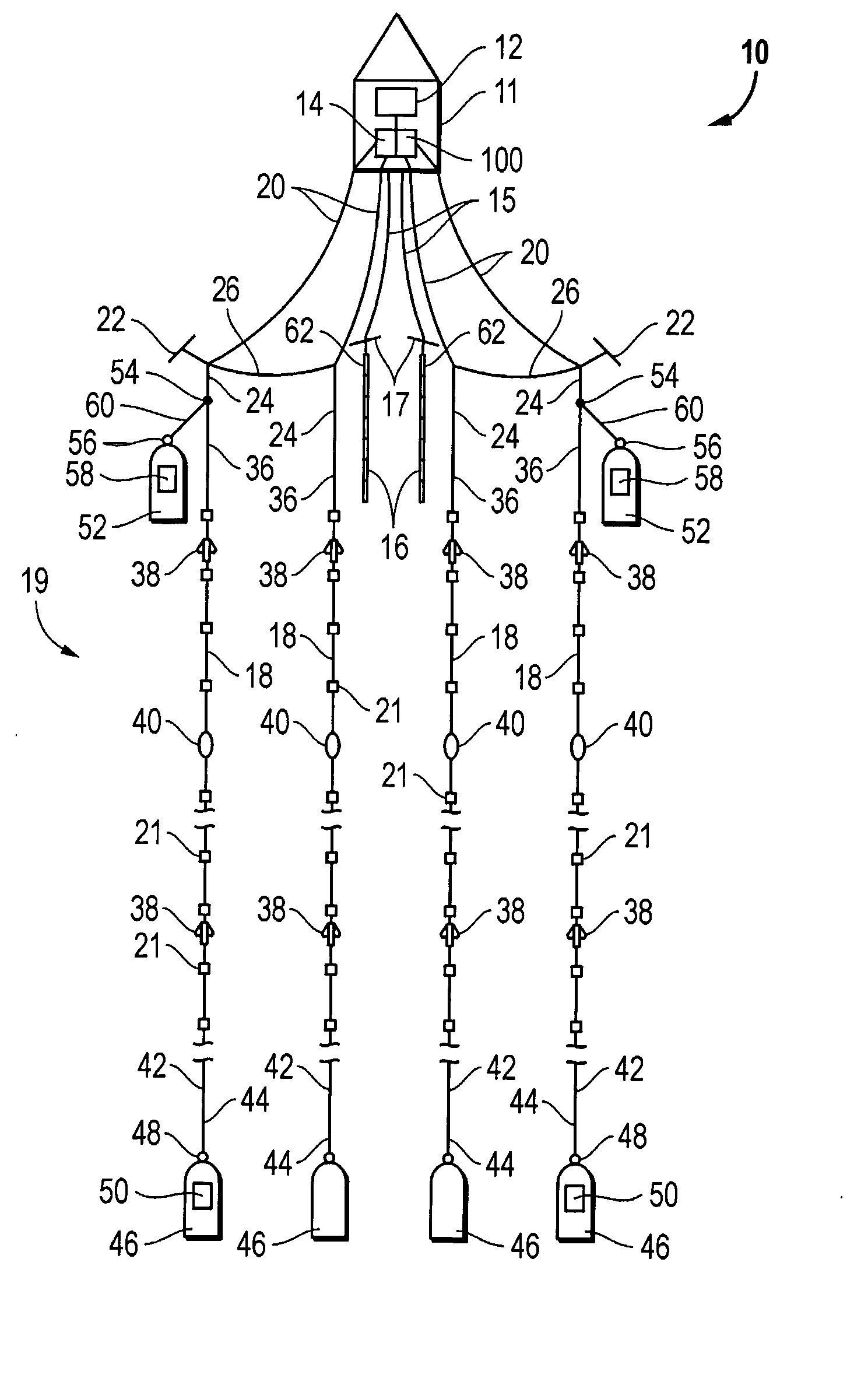
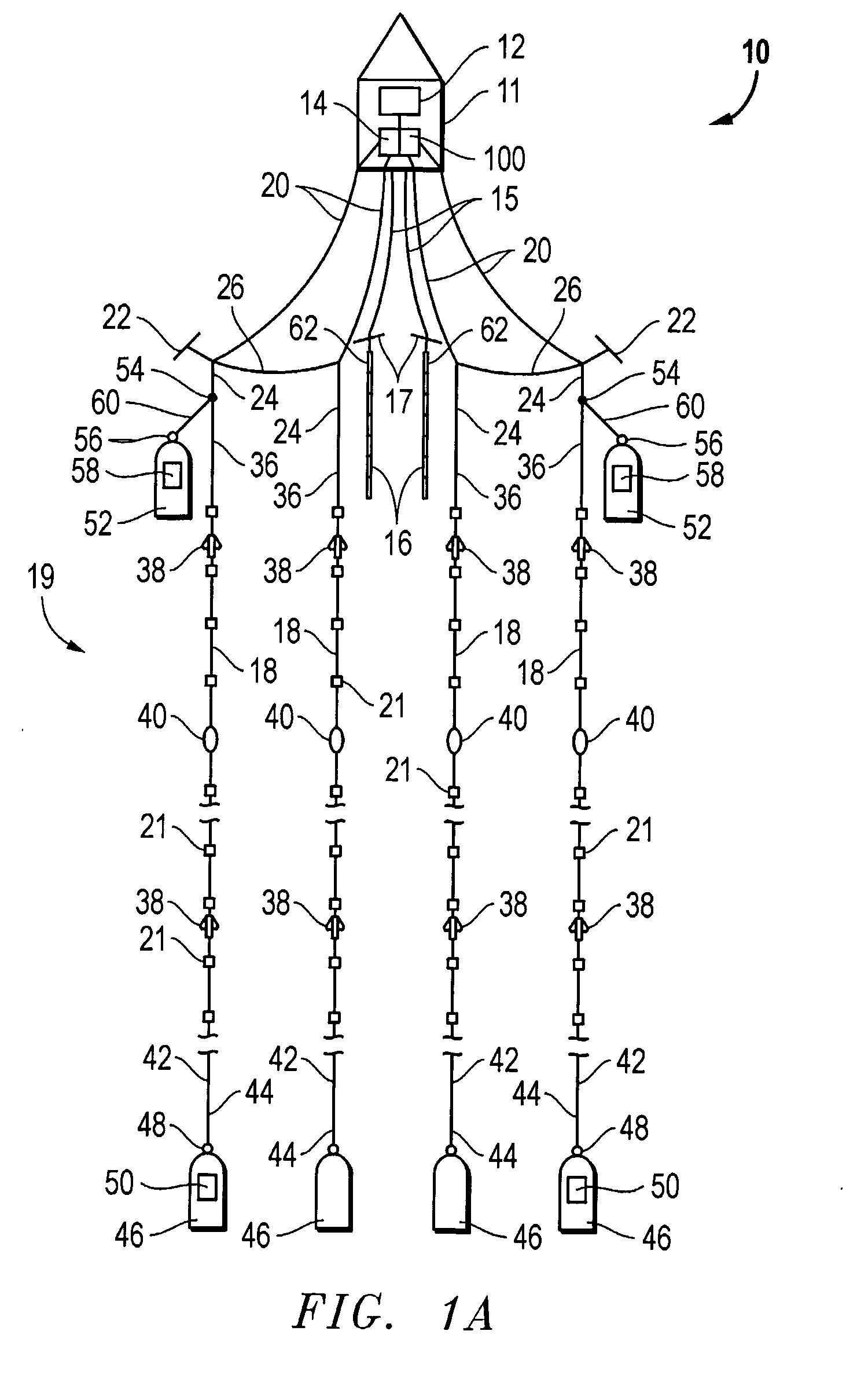
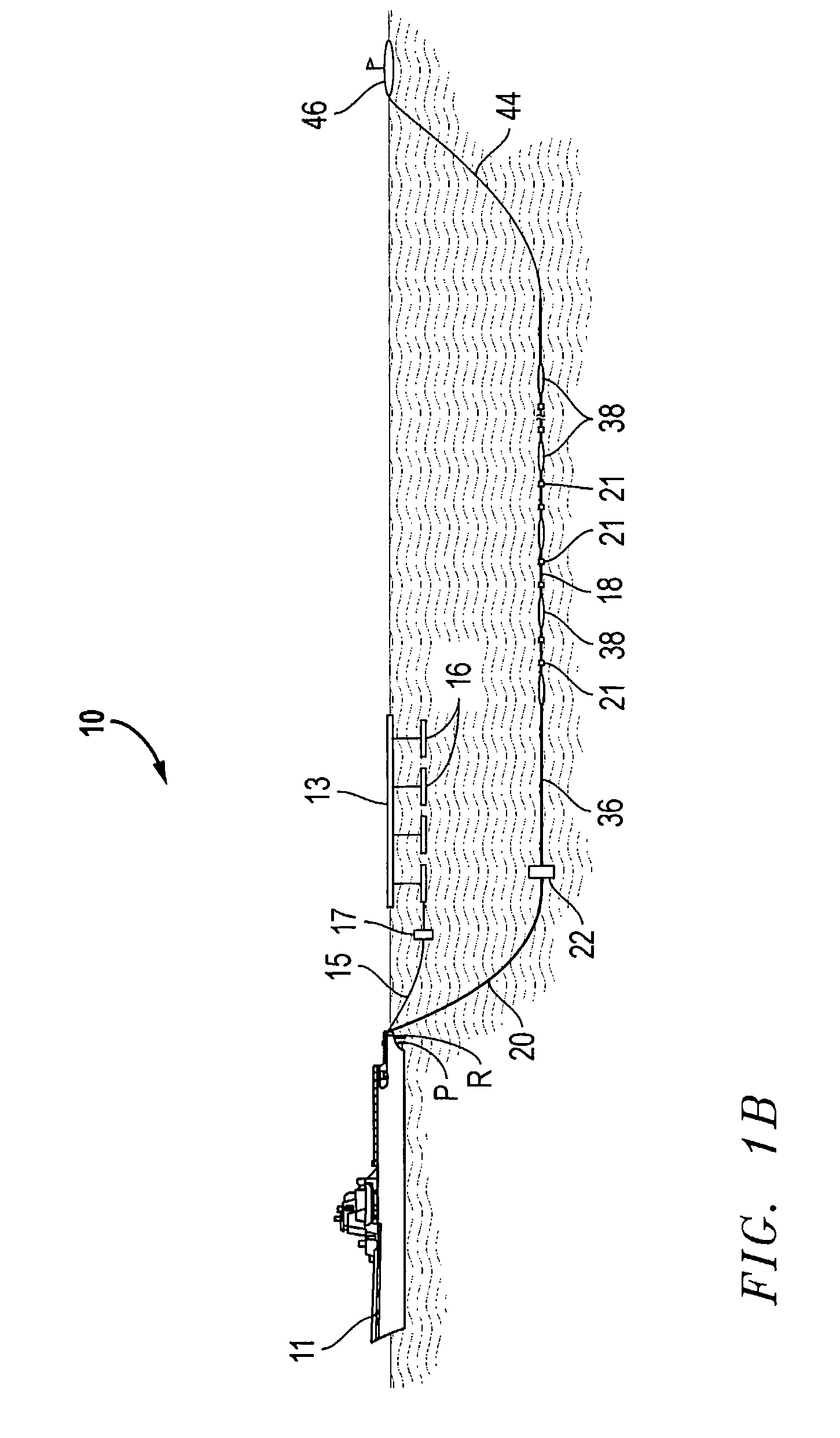
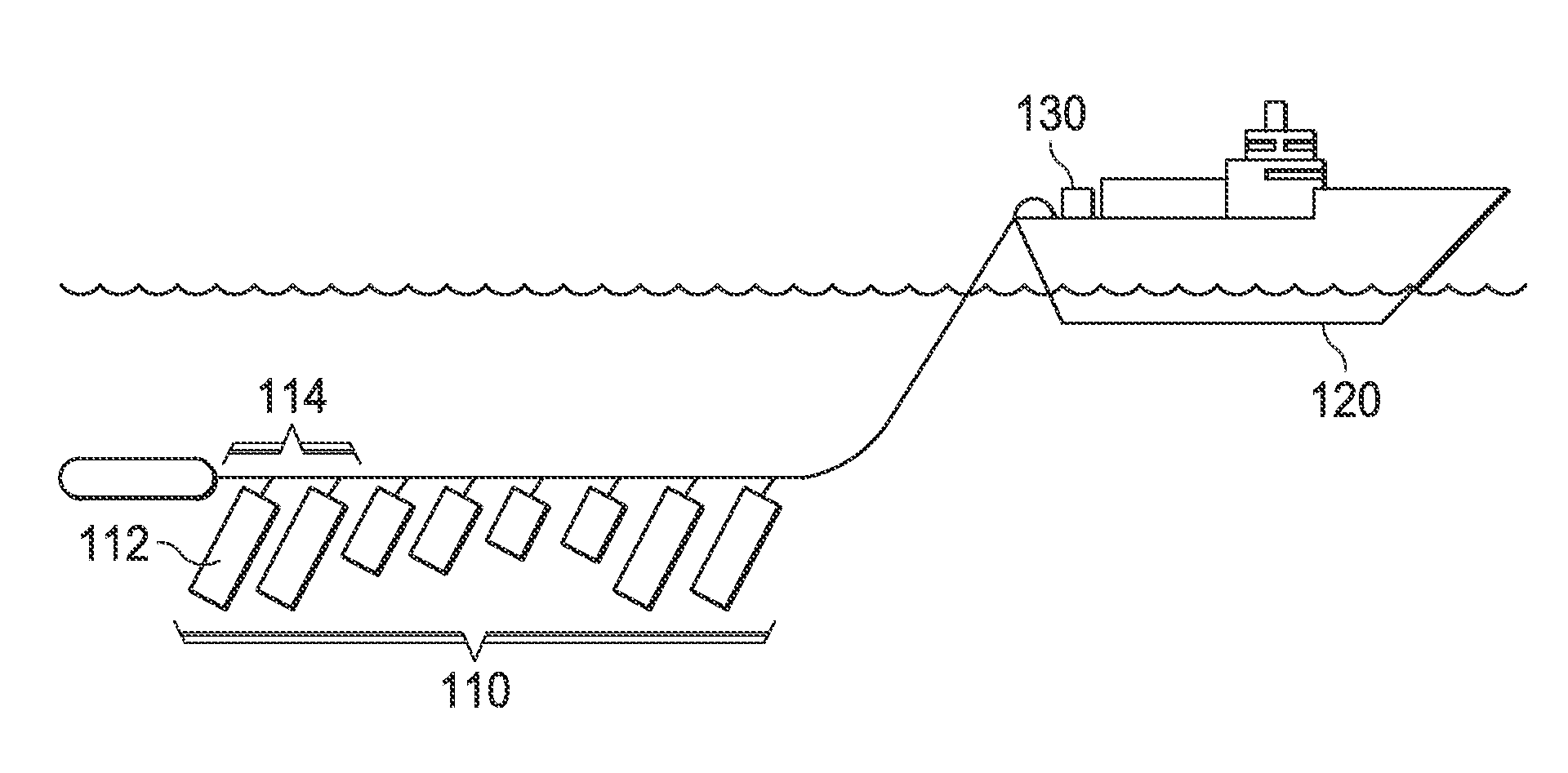
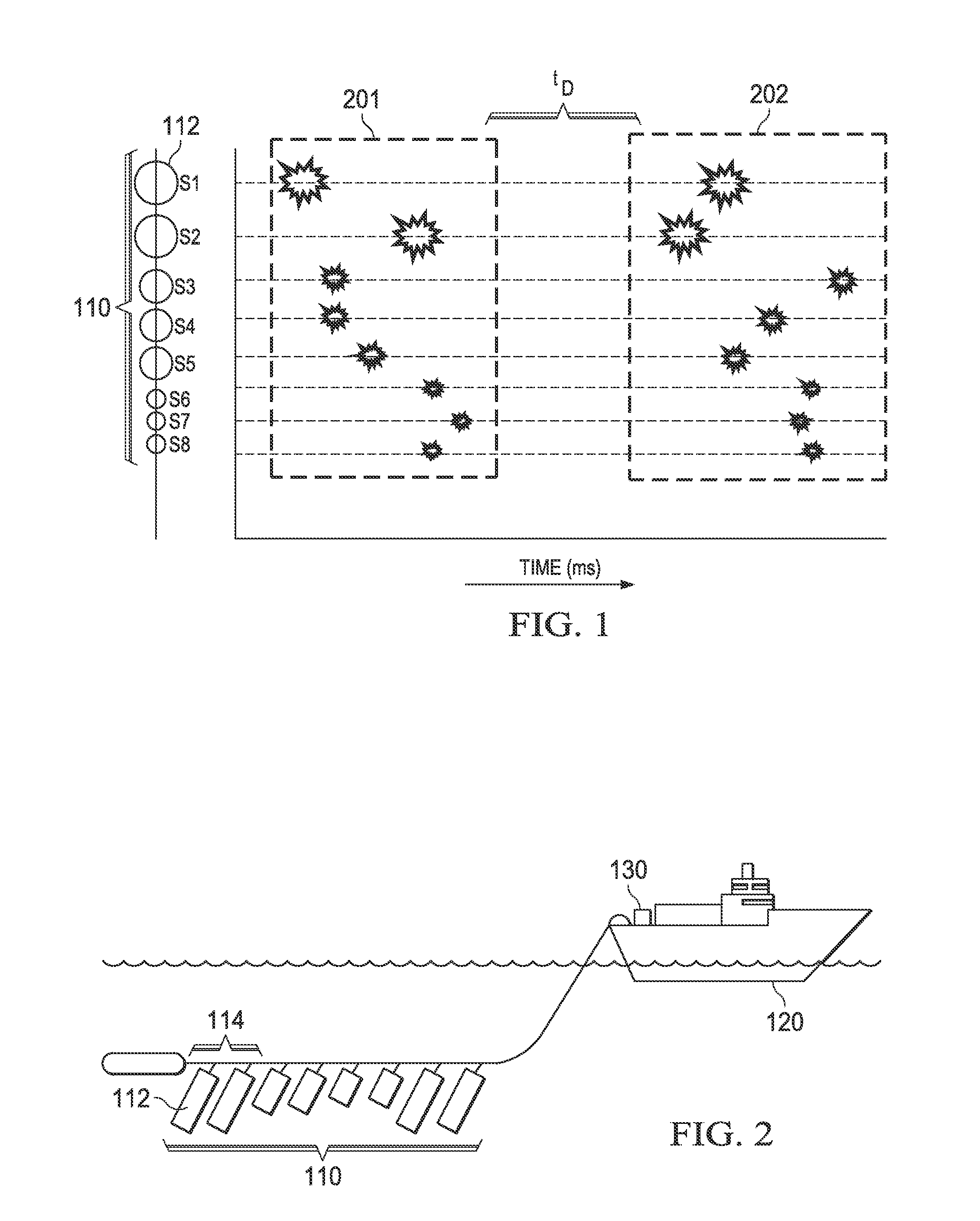
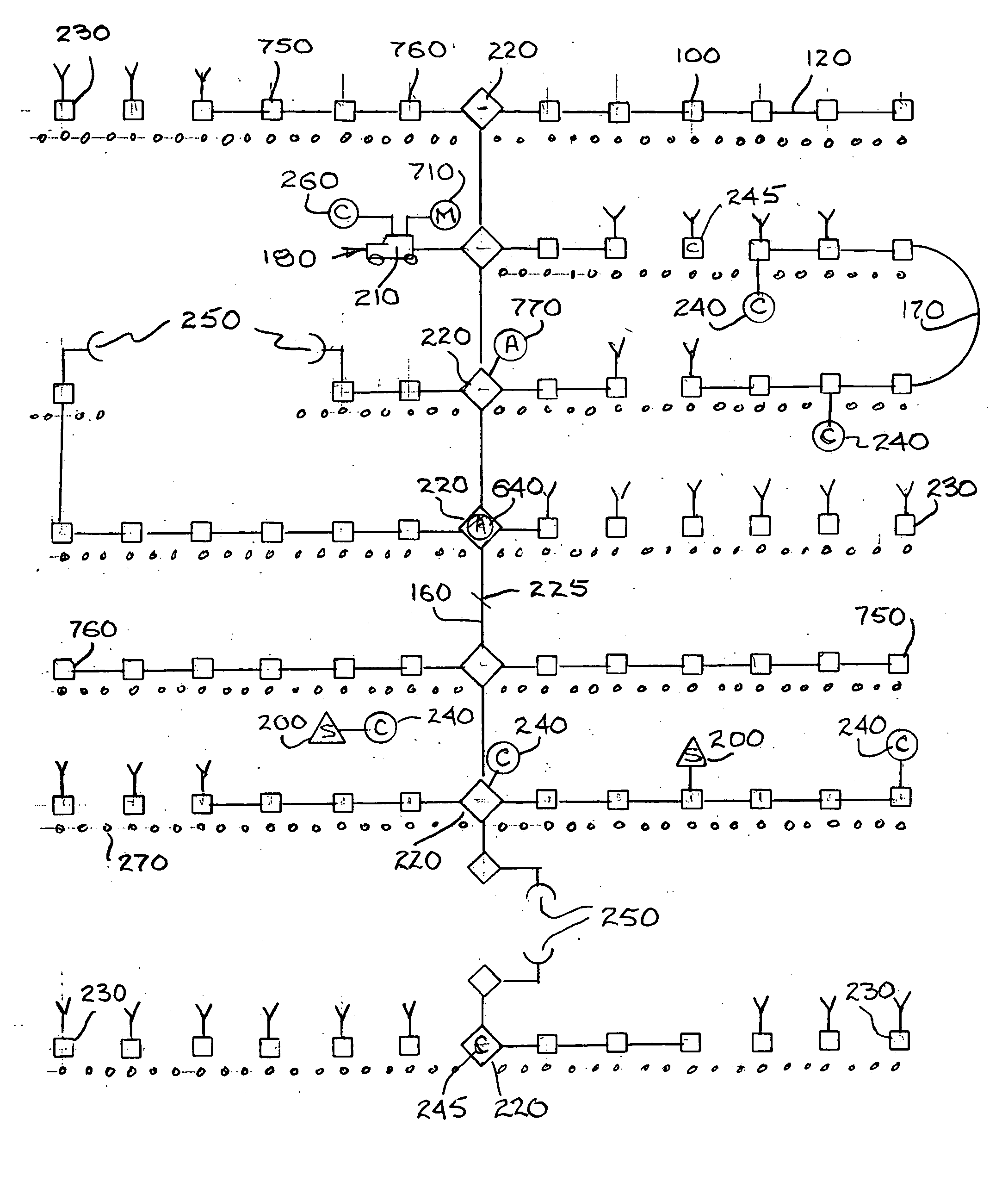
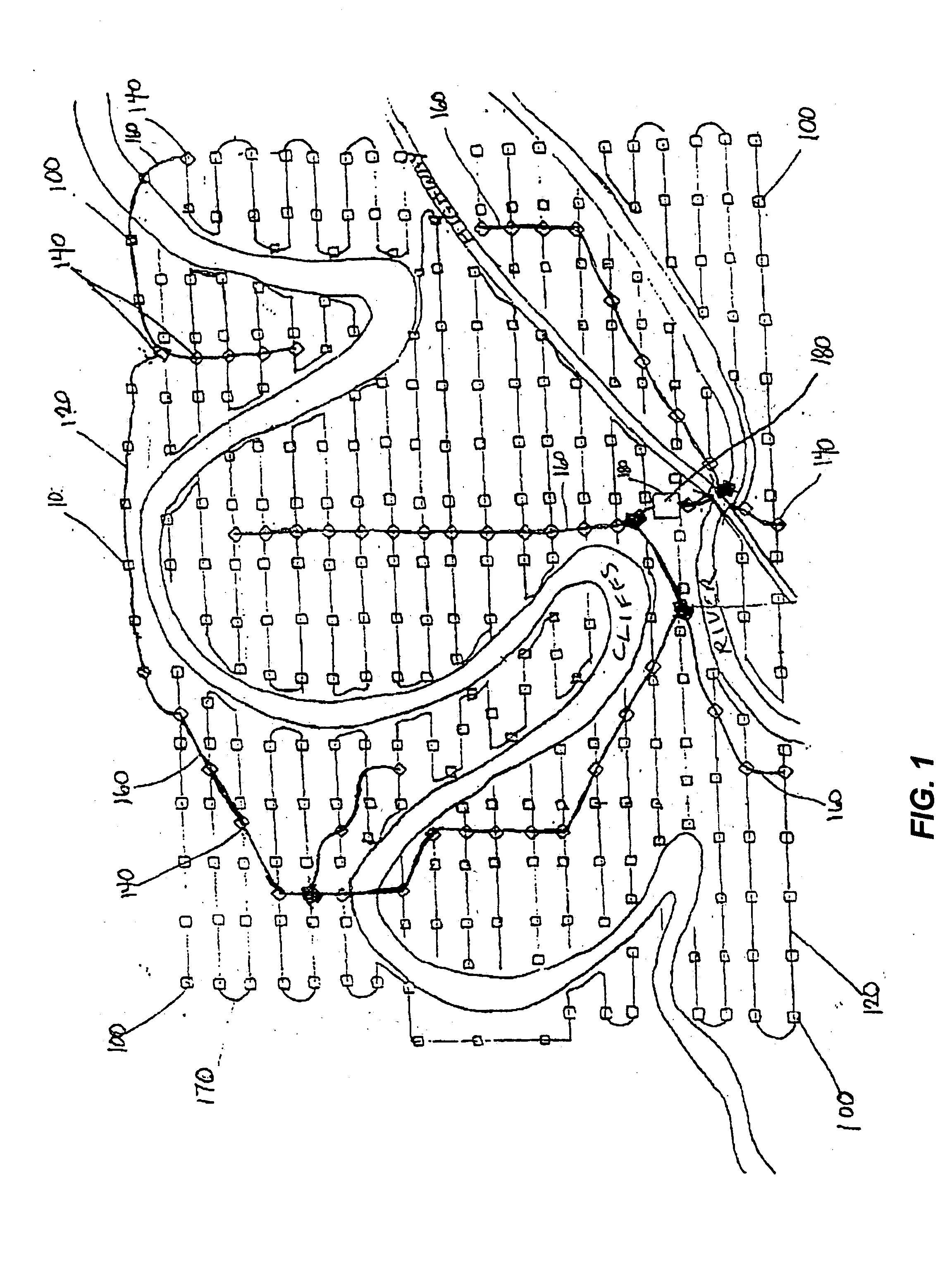
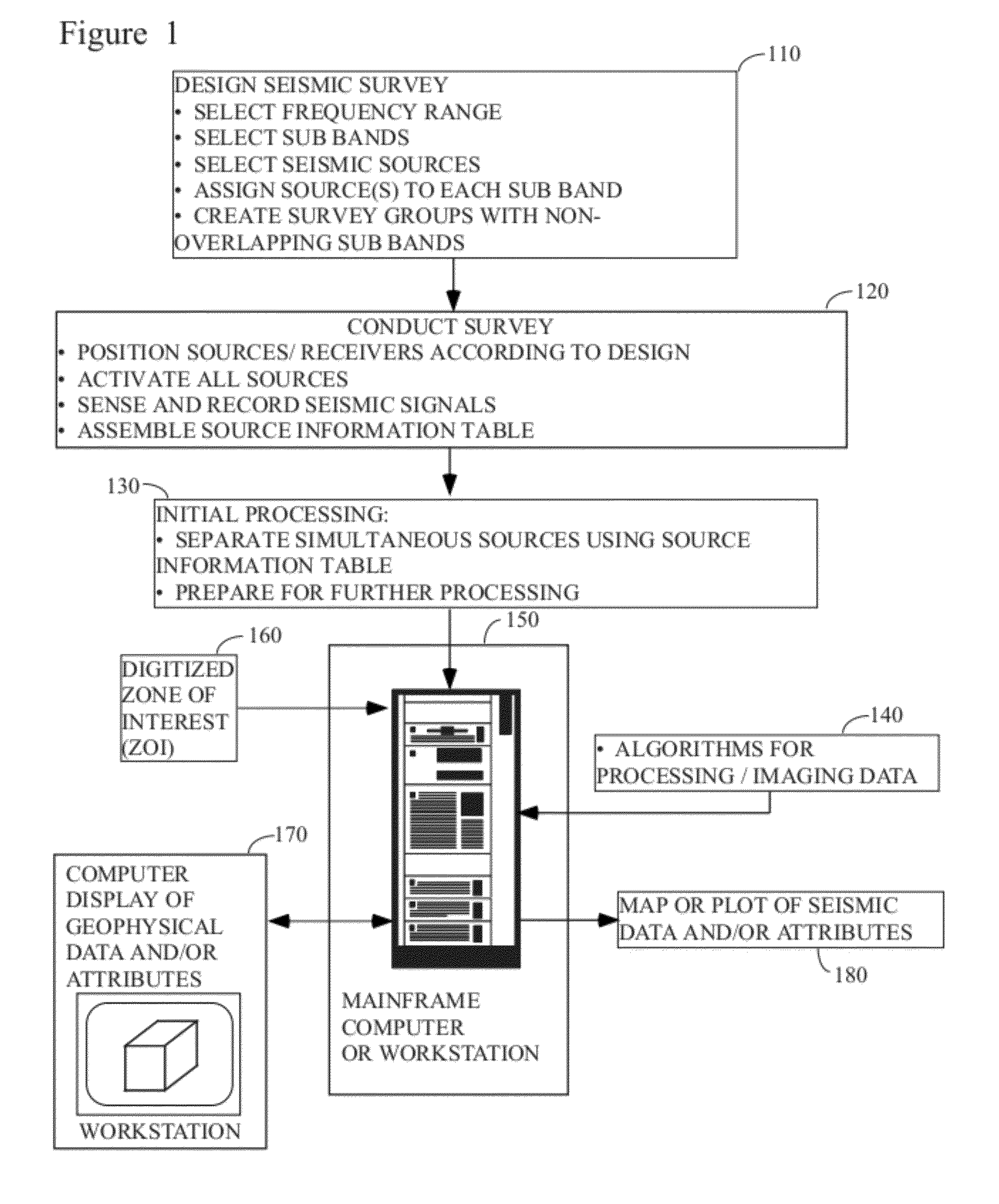
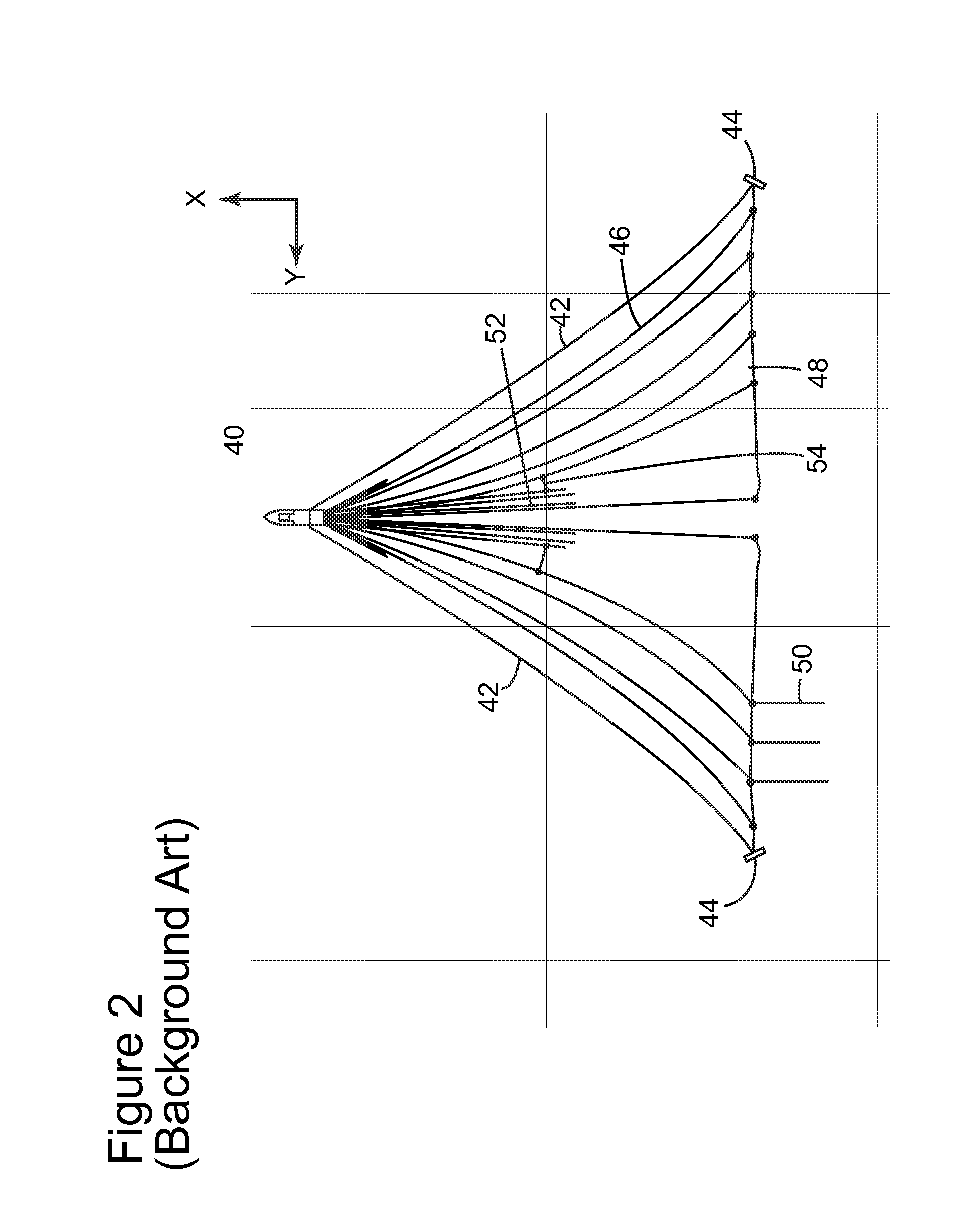
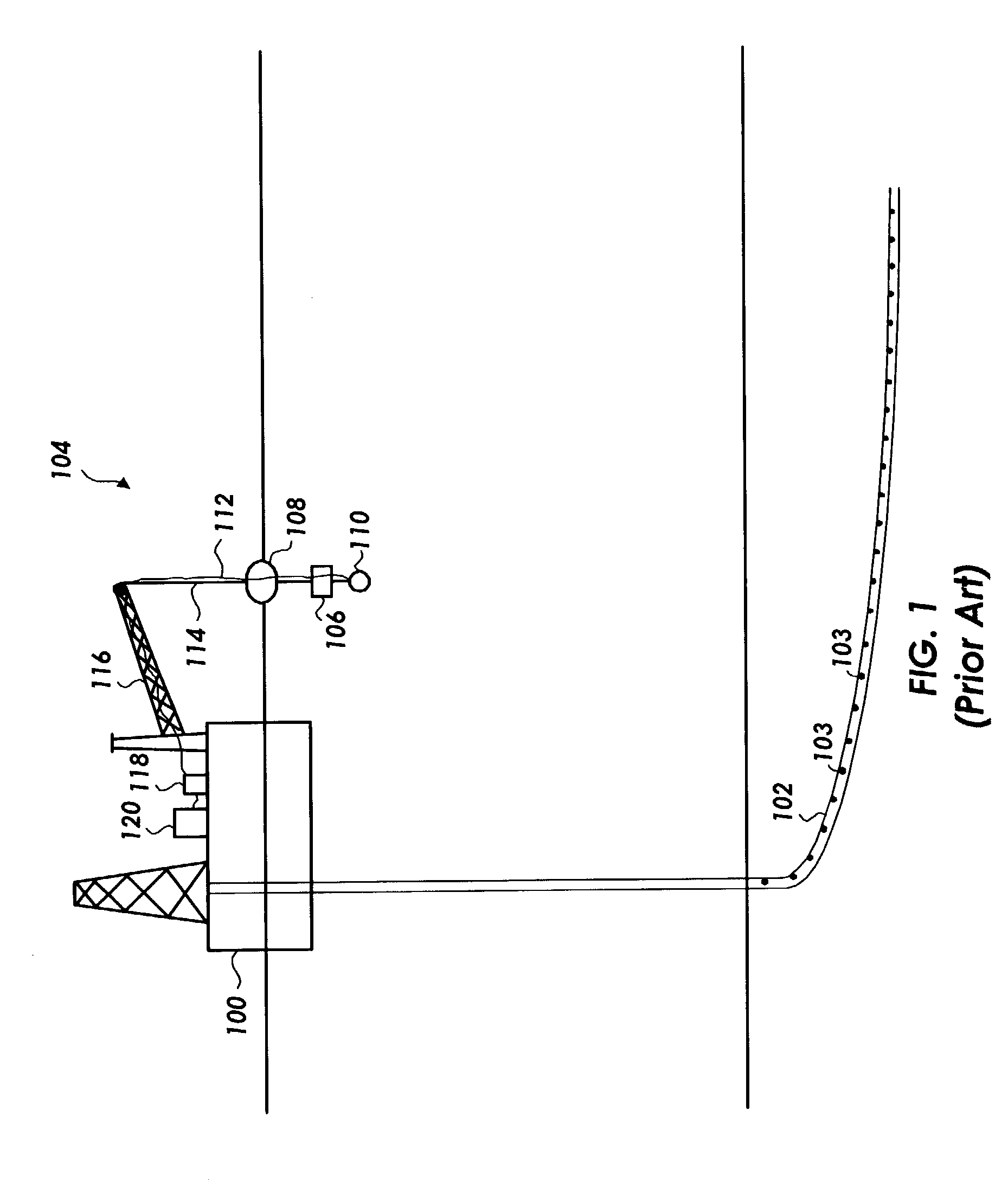
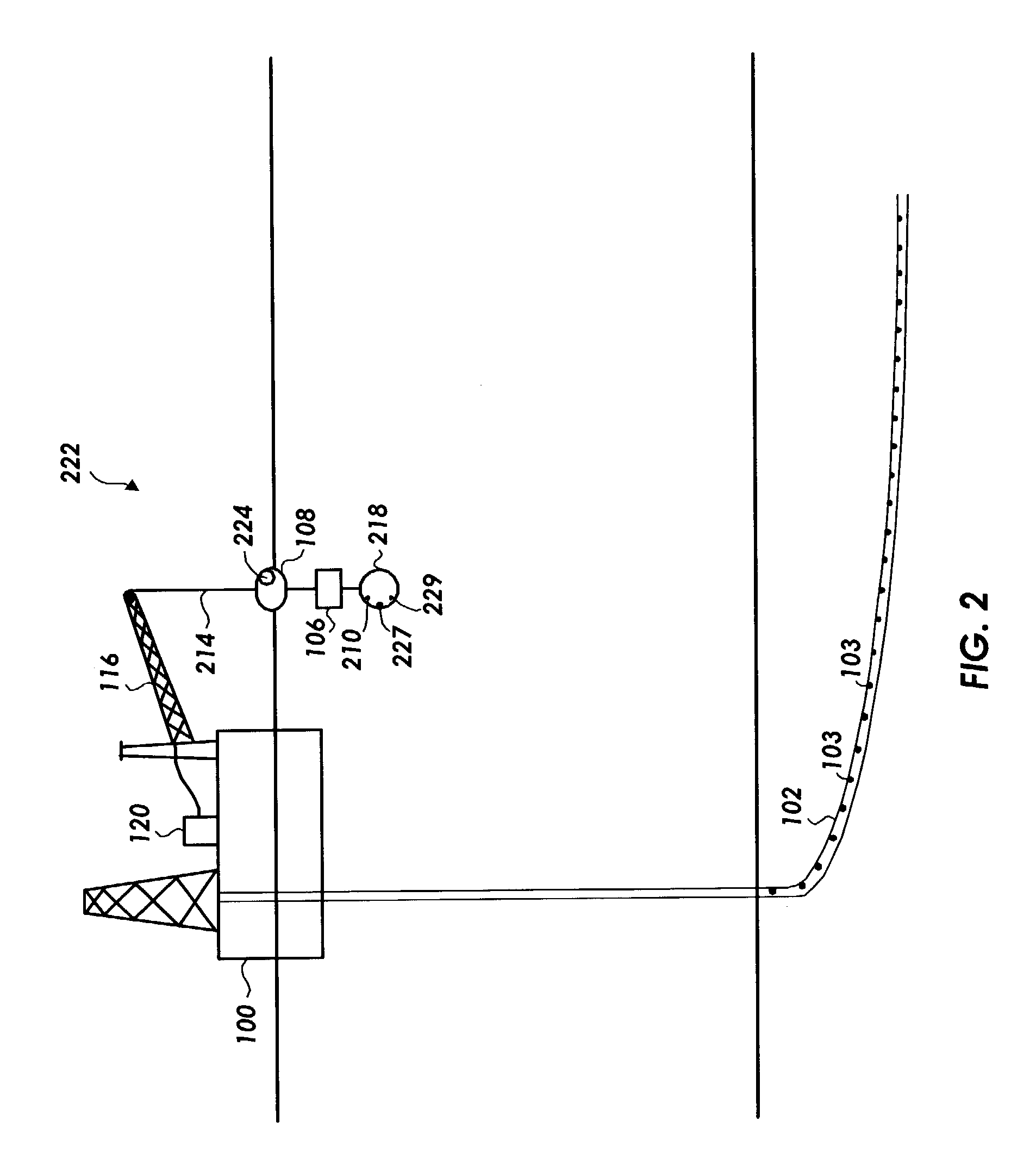
Marine seismic survey method and system
ActiveUS20090141587A1Reduce non-productive timeSeismic signal recordingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyEnvironmental data
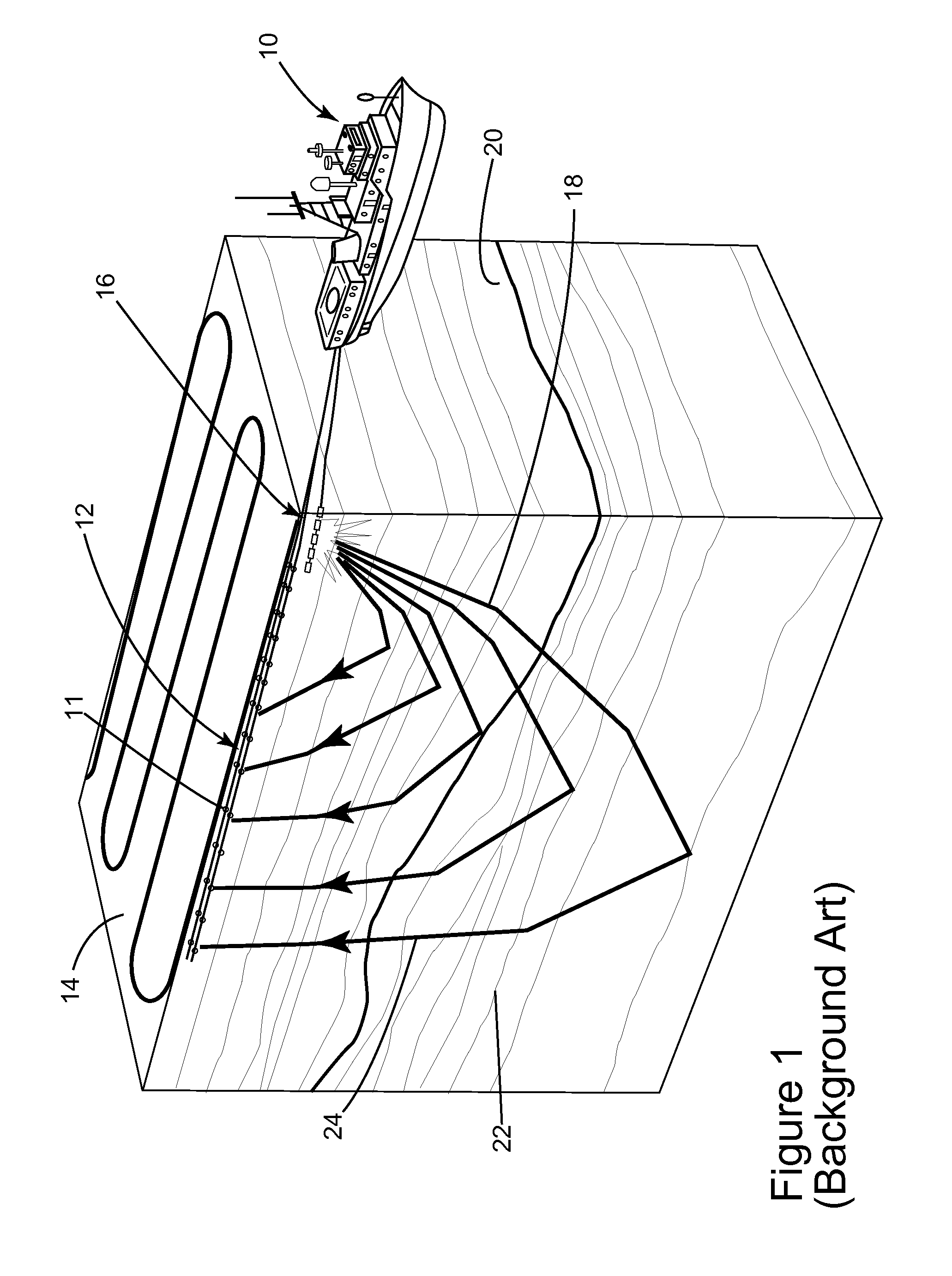
An inventive method provides for control of a seismic survey spread while conducting a seismic survey, the spread having a vessel, a plurality of spread control elements, a plurality of navigation nodes, and a plurality of sources and receivers. The method includes the step of collecting input data, including navigation data for the navigation nodes, operating states from sensors associated with the spread control elements, environmental data for the survey, and survey design data. The positions of the sources and receivers are estimated using the navigation data, the operating states, and the environmental data. Optimum tracks for the sources and receivers are determined using the position estimates and a portion of the input data that includes at least the survey design data. Drive commands are calculated for at least two of the spread control elements using the determined optimum tracks. The inventive method is complemented by an inventive system.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
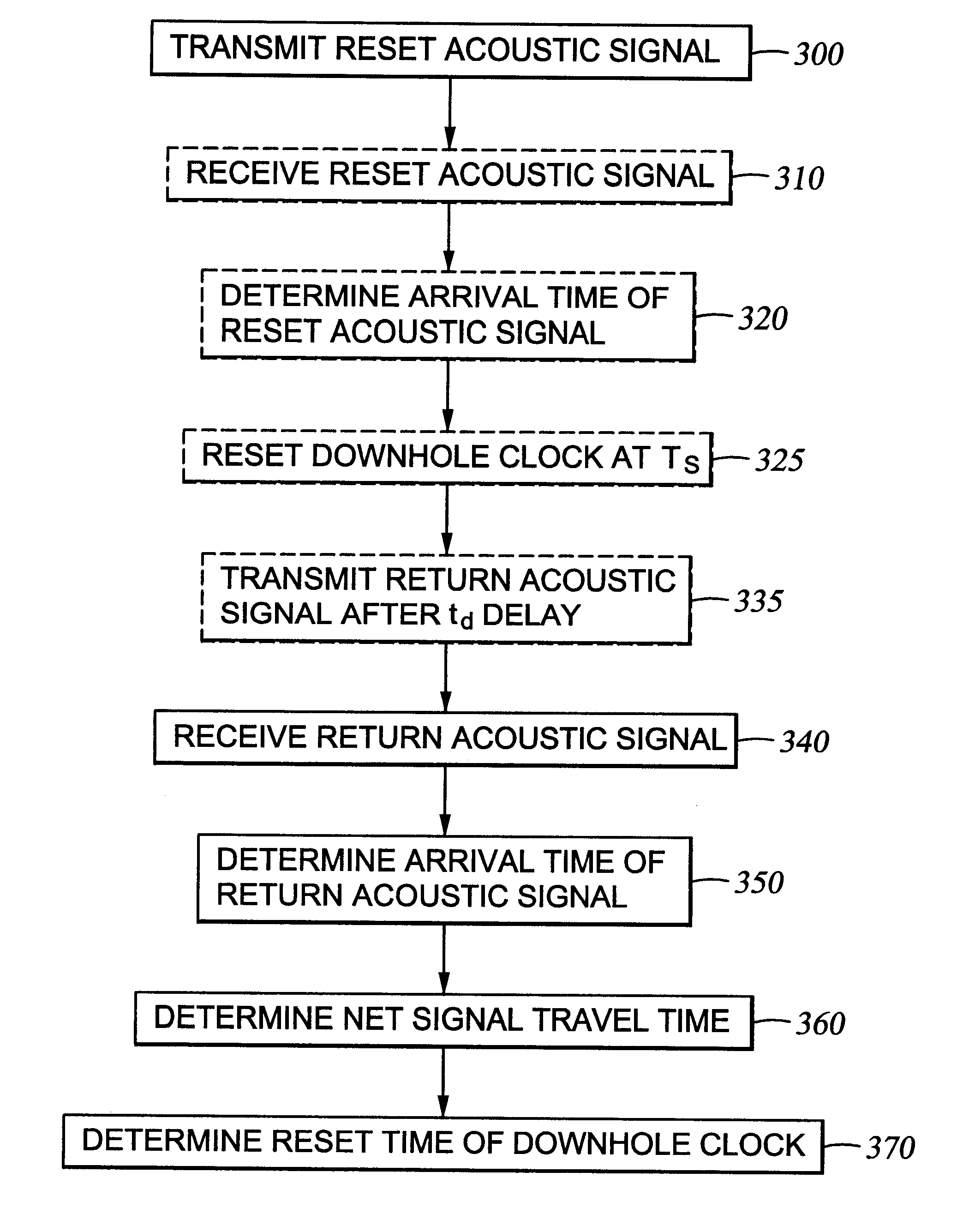
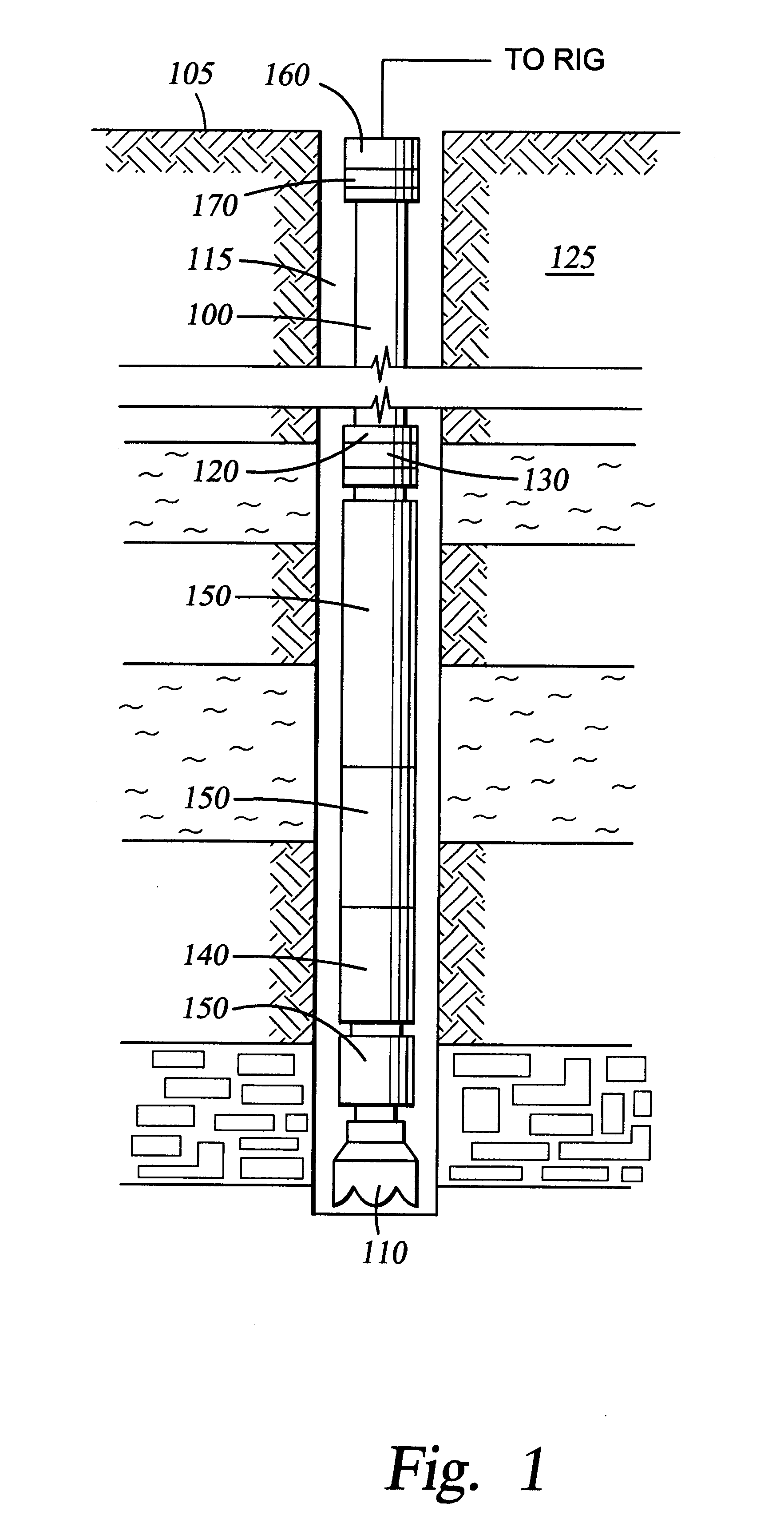
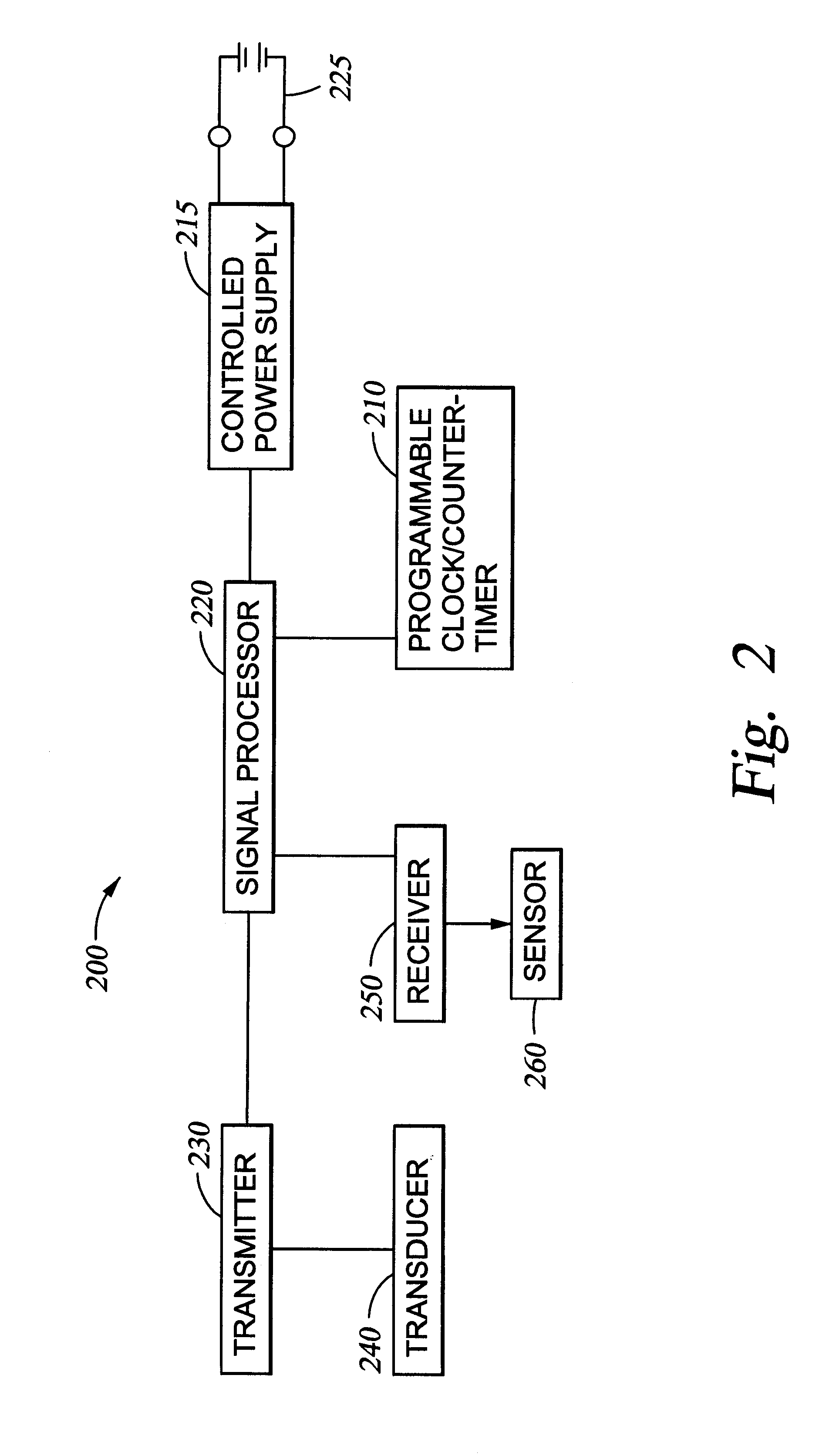
Method for compensating for remote clock offset
A system is disclosed for synchronizing a clock in a well containing a drill string with a clock located near the surface of the well. The system includes devices for transmitting and receiving a pair of acoustic signals between locations associated with each clock and processing those signals. The system determines the time of arrival of each acoustic signal by analyzing the shape of a function of the acoustic signal chosen from a group of functions suitable to determine a clock offset with millisecond accuracy.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Seismic acquisition method and system
ActiveUS20120147701A1Reduce impactReduce outputSeismic data acquisitionSeismic energy generationImaging qualityBiological activation
The maximum output of a seismic source array may be reduced by activating the individual seismic sources within these seismic source array in a pattern that is extended in time rather than by the presently employed conventional simultaneous activation of a large number of individual seismic sources. Methods are disclosed which take data shot with patterned sources and may use a sparse inversion method to create data with the about same image quality as that of conventional sources. In this manner the output of the maximum impulse of a seismic source array may be reduced by an amplitude factor of about 10 in the examples shown here, corresponding to a reduction of about 20 dB while maintaining virtually the same seismic image quality. The disclosed methods may be used in combination with any simultaneous sourcing technique. In addition, the disclosed methods may be used with a plurality of source arrays.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
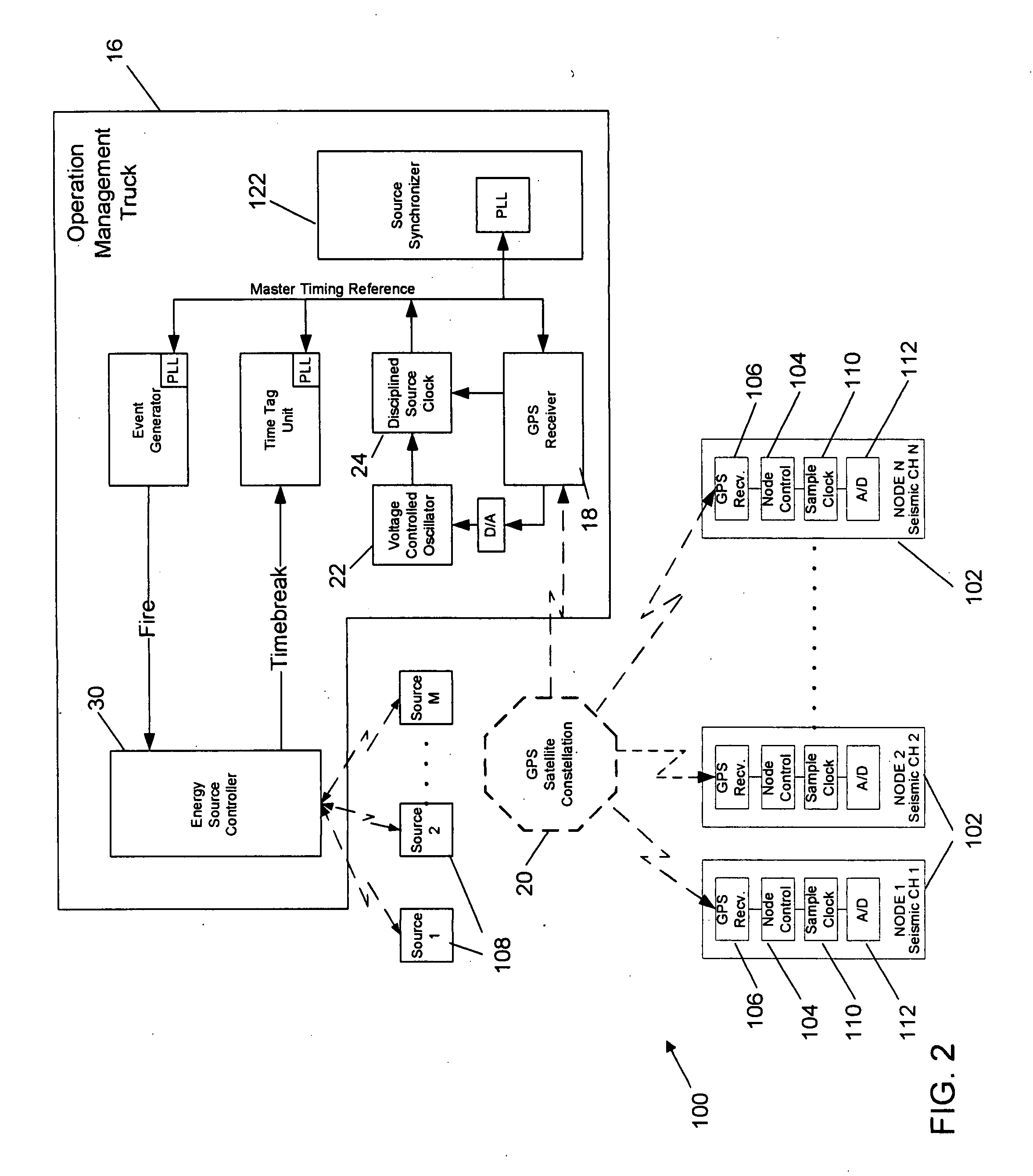
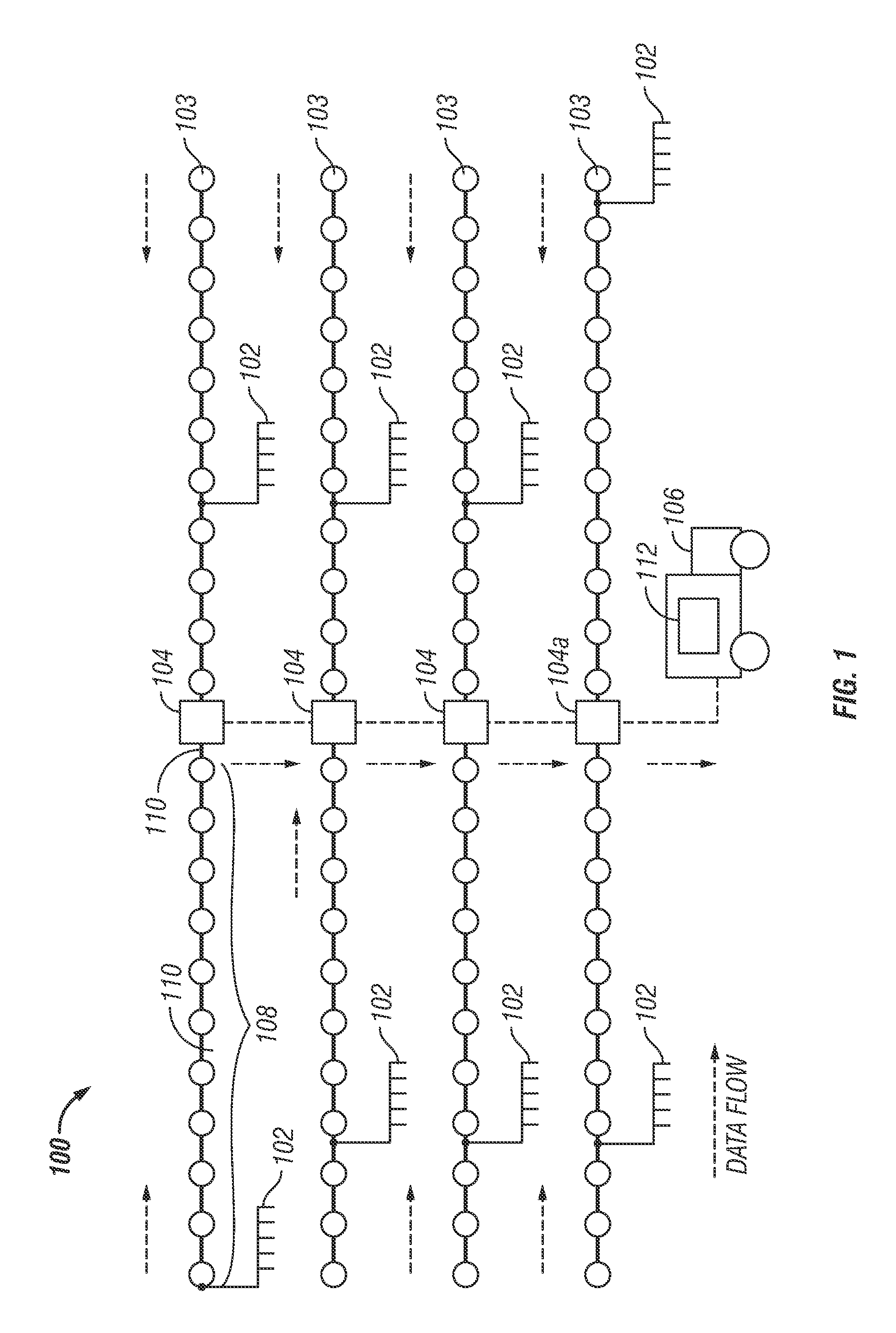
Synchronization and positioning of seismic data acquisition systems
InactiveUS20050047275A1Good synchronizationLess transmission delaySeismic signal receiversSeismic signal transmissionData acquisitionGlobal positioning system receiver
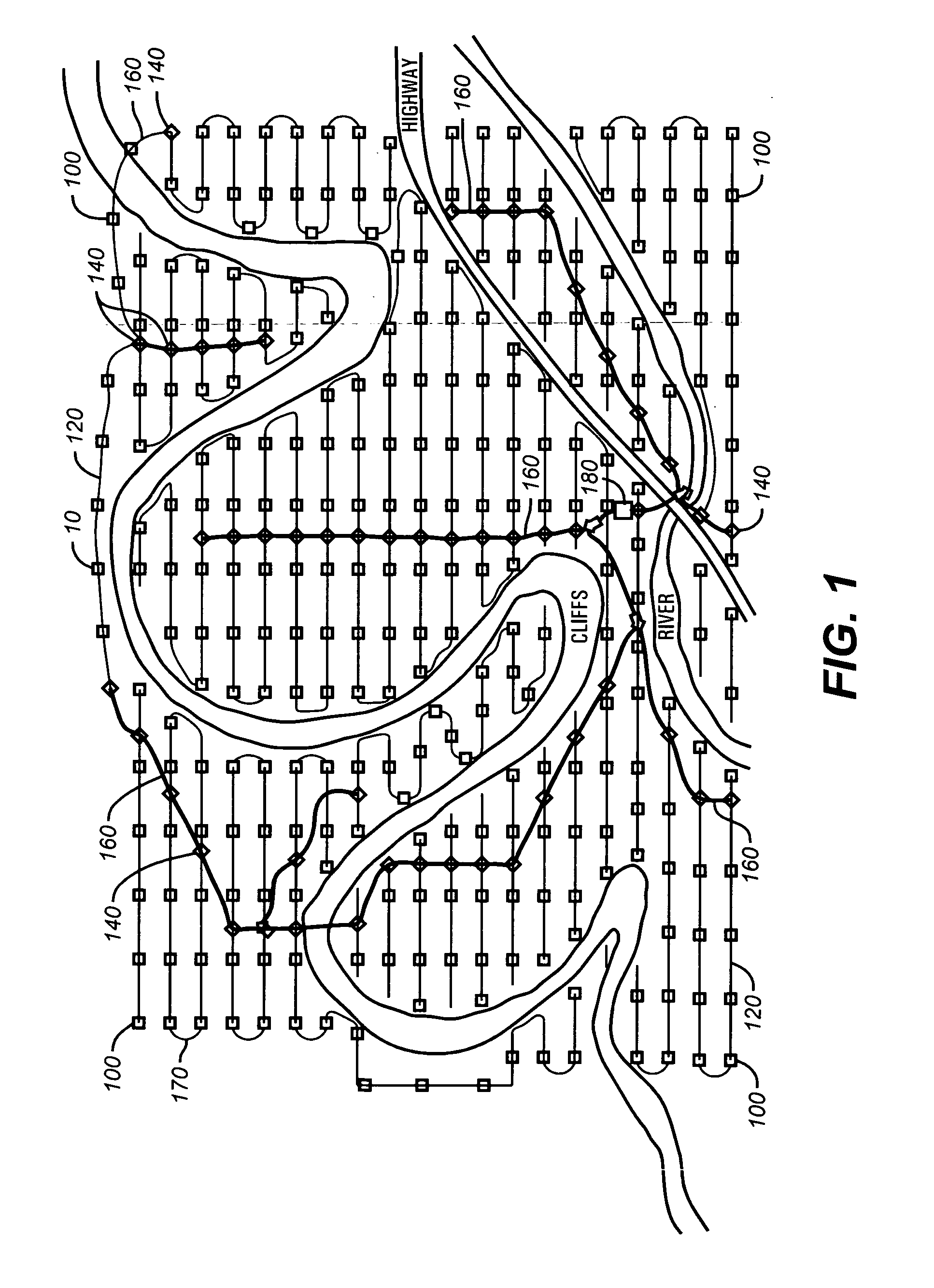
A network distributed seismic data acquisition system comprises seismic receivers, connected to remote acquisition modules, receiver lines, line tap units, base lines, central recording system and a seismic source event generation unit. Global positioning system receivers of full or partial capability are combined with some of these modules and units and a master global positioning receiver aids the distributed receivers. The global positioning receivers may be used to synchronize high precision clocks as well as to provide positioning information. A master clock is designated and one or more high precision clocks is added to the network to correct for timing uncertainty associated with propagation of commands through the network. Seismic receivers and seismic sources are thereby synchronized with greater accuracy than otherwise possible, thus enabling an improvement in subsurface geologic imaging.
Owner:GEO X SYST
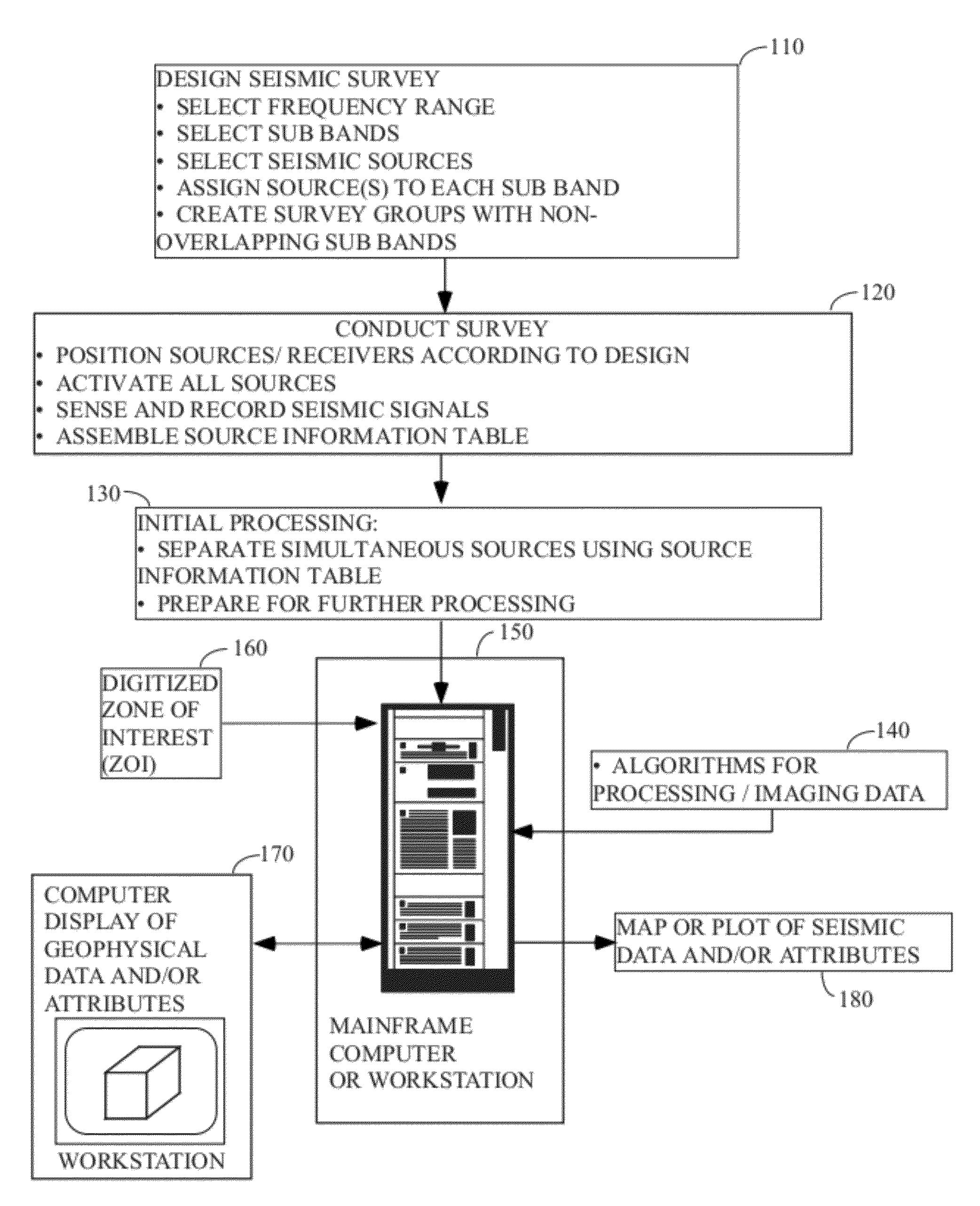
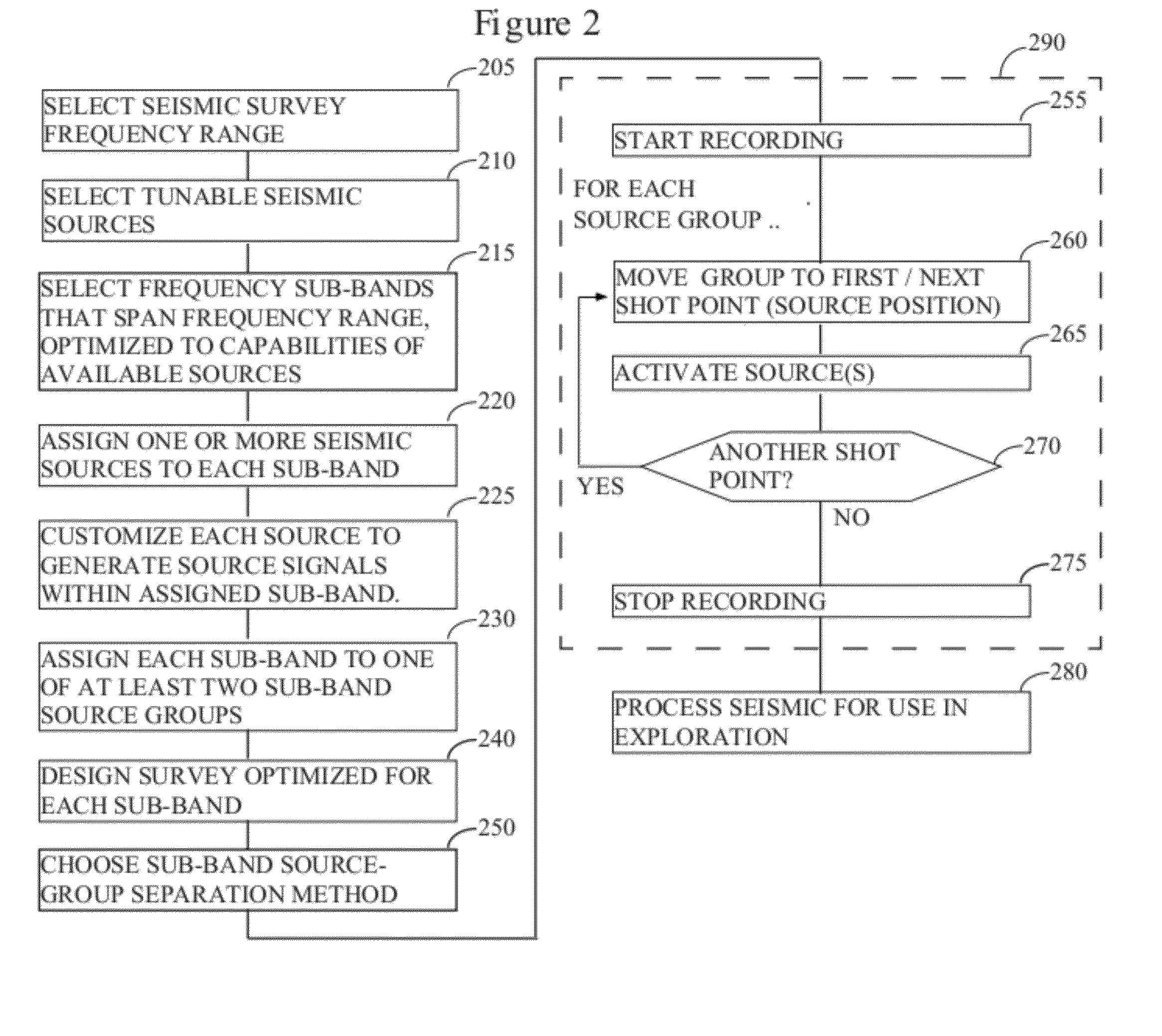
Distance- and frequency-separated swept-frequency seismic sources
InactiveUS20120147699A1Enhance simultaneous source separationEasy to separateSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal recordingBandpass filteringFrequency separation
There is provided a method of seismic acquisition that utilizes a bank of restricted-bandwidth swept-frequency sub-band sources as a seismic source. Each seismic source will cover a restricted sub-band of frequencies, with all the sources taken together covering the full frequency range. Adjacent frequency bands may partially overlap, but non-adjacent frequency bands should not. The sources may be divided into two or more groups, with no sources covering adjacent frequency bands being placed in the same group. The sources within a group can then be separated by bandpass filtering or by conventional simultaneous source-separation techniques. The source groups may be operated simultaneously but separated in space, and the individual sources themselves may each operate independently, on a sweep schedule customized for that particular source.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
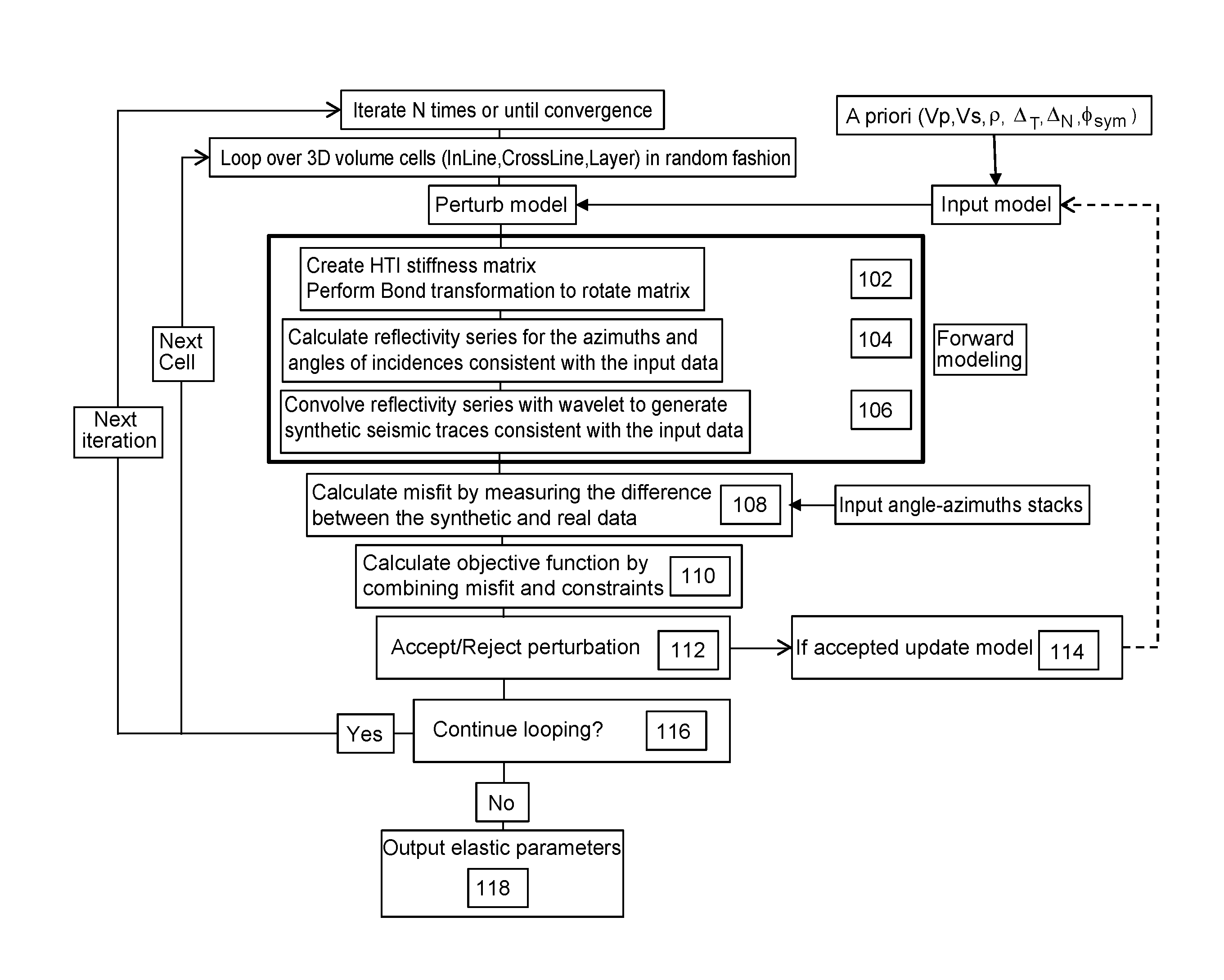
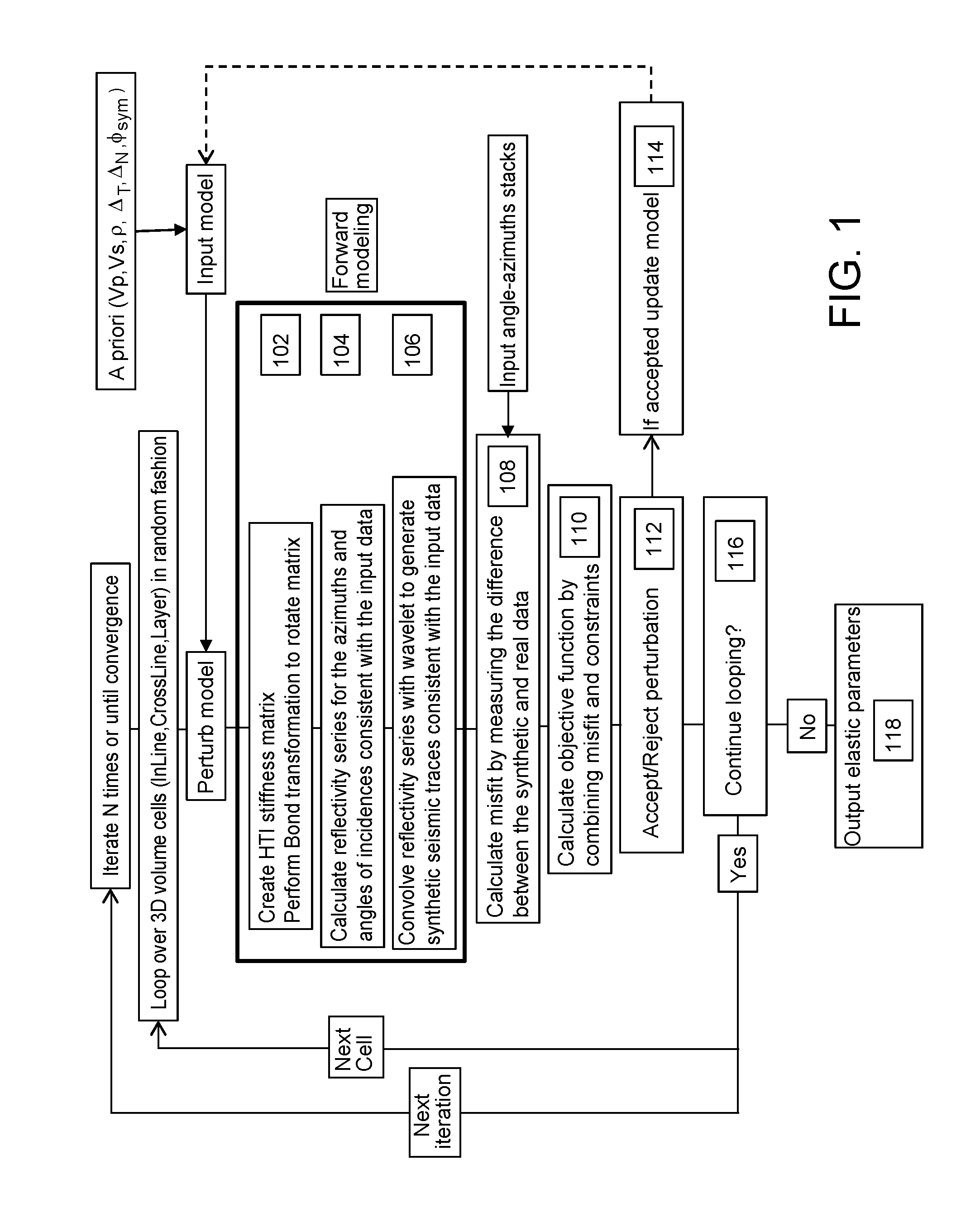
Methods and systems for performing azimuthal simultaneous elastic inversion
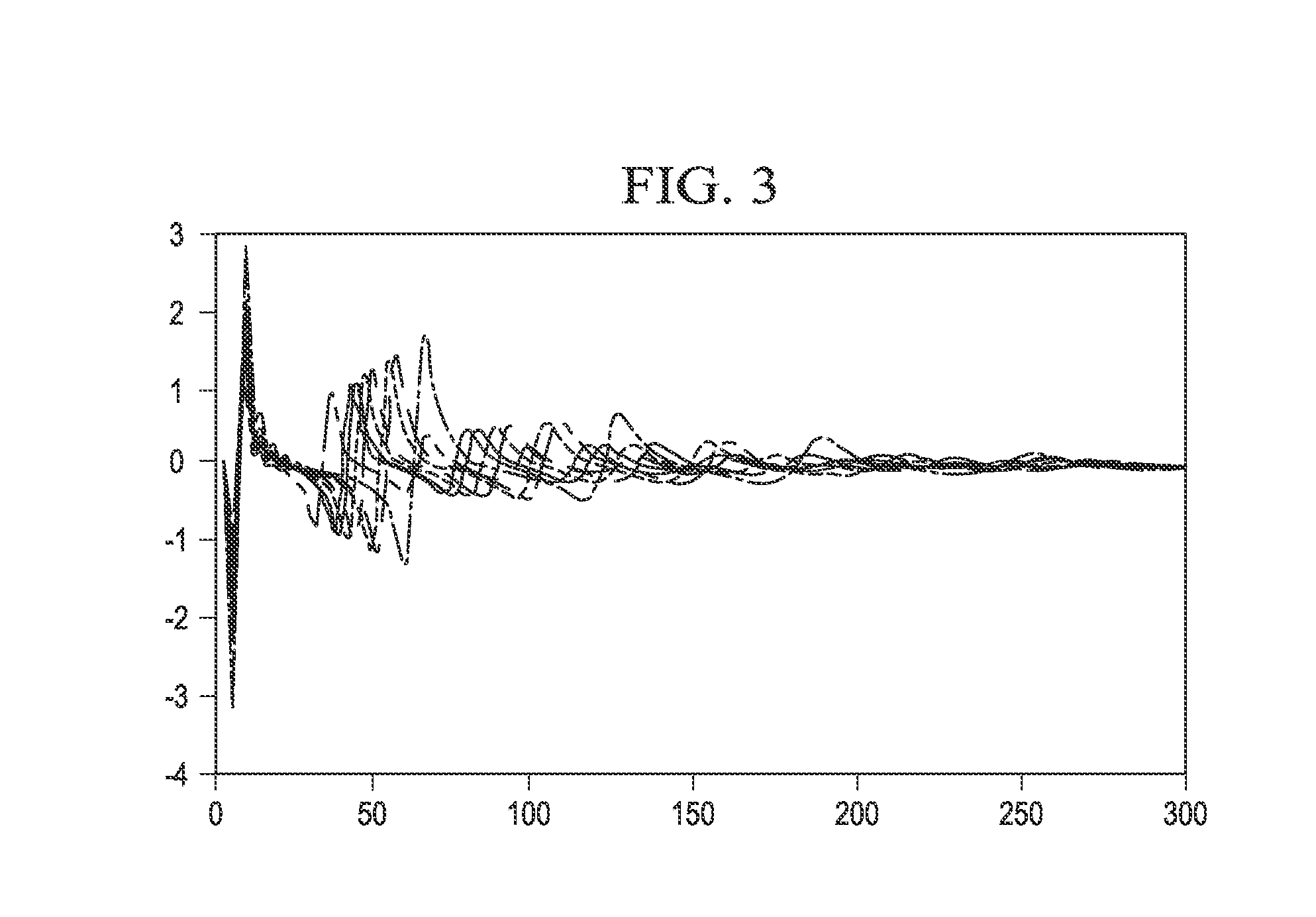
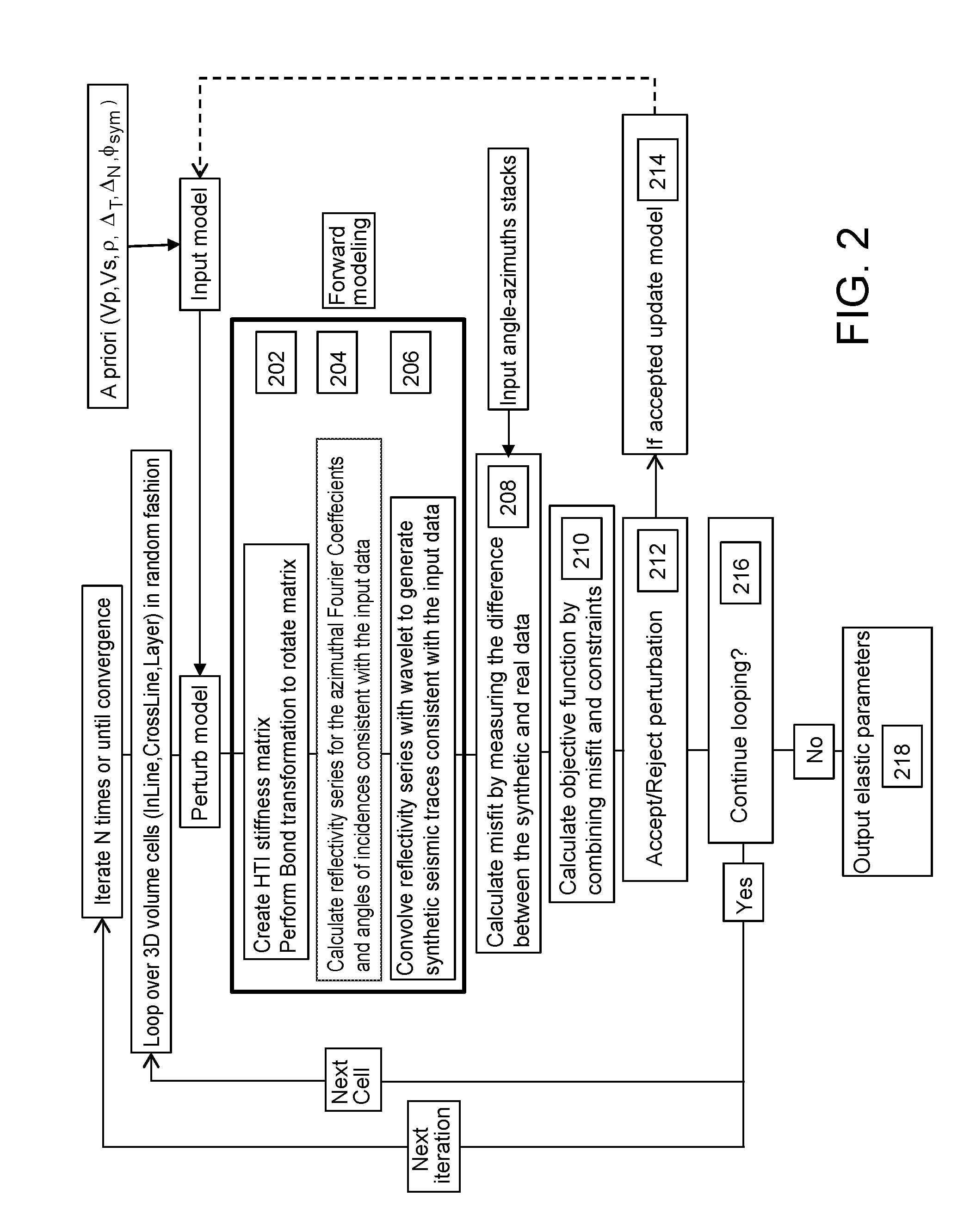
ActiveUS20110222370A1Improve stabilityReduce and constrain solution spaceSeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingImproved methodSeismic trace
An improved method for analyzing seismic data to obtain elastic attributes is disclosed. In one embodiment, a reflectivity series is determined for at least one seismic trace of seismic data obtained for a subterranean formation, where the reflectivity series includes anisotropy properties of a formation. One or more synthetic seismic traces are obtained by convolving the reflectivity series with a source wavelet. The one or more synthetic seismic traces are inverted to obtain elastic parameters estimates. According to one aspect, the data inputs are angle-azimuth stacks. According to another aspect, the data inputs are azimuthal Fourier coefficients, un, vn.
Owner:CGG SERVICES U S
Data offload and charging systems and methods
InactiveUS20050246137A1Batteries circuit arrangementsError detection/correctionTelecommunications linkData acquisition
Apparatus and methods are provided for simultaneously retrieving data from multiple data acquisition units and for recharging such data acquisition units. The data offload and charging unit comprises a frame that defines stations for holding the data acquisition units and a host computer. A combined power and communications port at each such station is adapted to interface with one of the data acquisition units such that power may flow from the data offload and charger unit to that data acquisition unit and data may flow from that data acquisition unit to the host computer substantially simultaneously. Communications links are provided between the host computer and each combined power and communications port.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
Methods and systems for acquiring seismic data
InactiveUS6934219B2Simple methodNew typeSeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingGeolocationGeophysics
Methods and systems are provided for acquiring seismic data. Data are collected representing acoustic signals received from the Earth at distinct geographic locations. Data representing an ambient signal at the distinct geographic locations are also collected. For each of the geographic locations, a known time dependence of the ambient signal is correlated with a time dependence of the collected acoustic-signal data to define time-correlated acoustic signal data. The collected acoustic-signal data for the distinct geographic locations are synchronized from the time-correlated acoustic-signal data.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
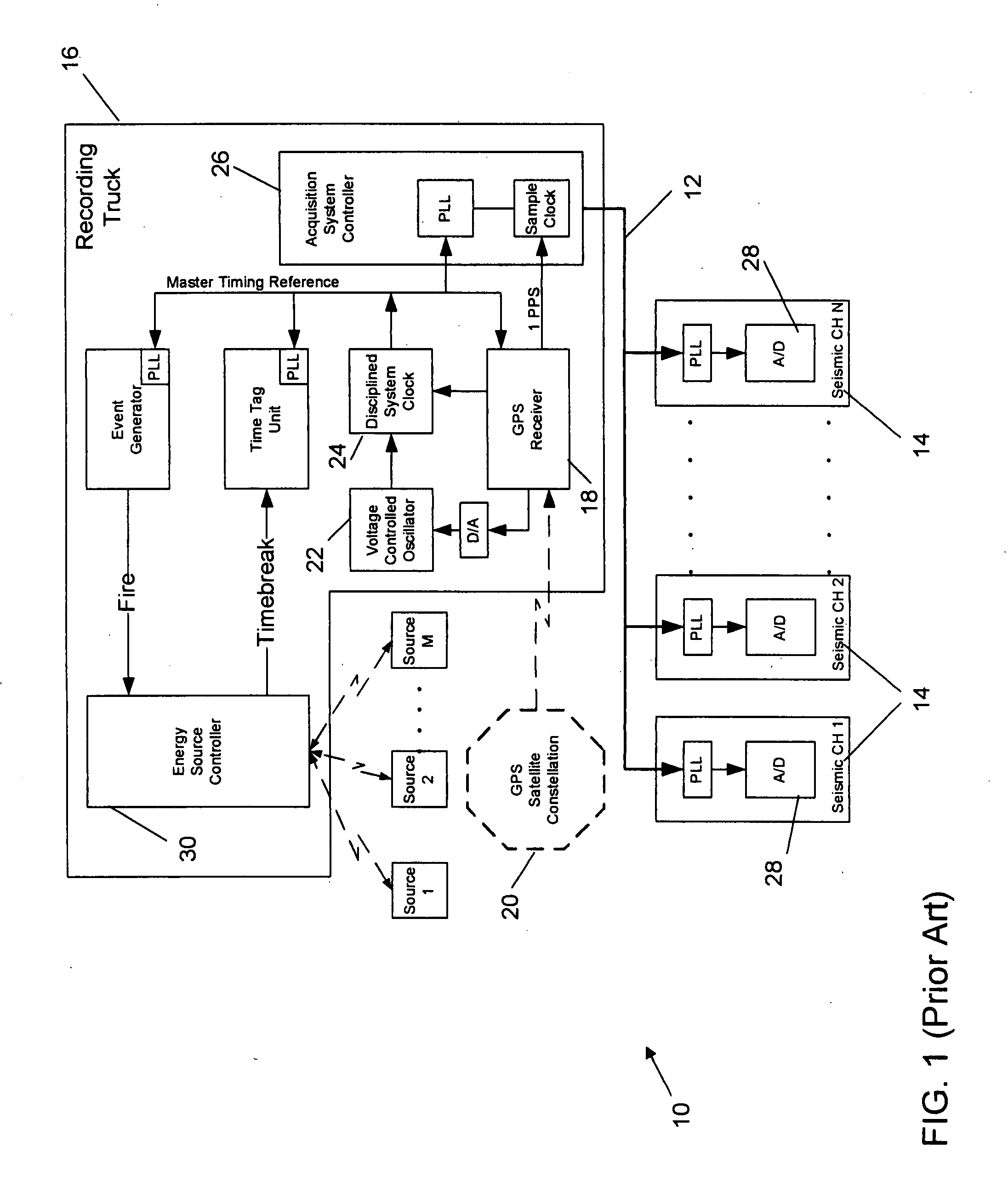
Synchronization of seismic data acquisition systems
ActiveUS7269095B2Good synchronizationLess transmission delaySeismic signal transmissionSeismic signal recordingTime errorData acquisition
A network distributed seismic data acquisition system comprises seismic receivers connected to remote acquisition modules, receiver lines, line tap units, base lines, a central recording system and a seismic source event generation unit synchronized to a master clock. One or more high precision clocks is added to the network to correct for timing uncertainty associated with propagation of commands through the network. Seismic receivers and seismic sources are thereby synchronized with greater accuracy than otherwise possible. Timing errors that interfere with the processing of the seismic recordings are greatly reduced, thus enabling an improvement in subsurface geologic imaging.
Owner:INOVA SYST CORP
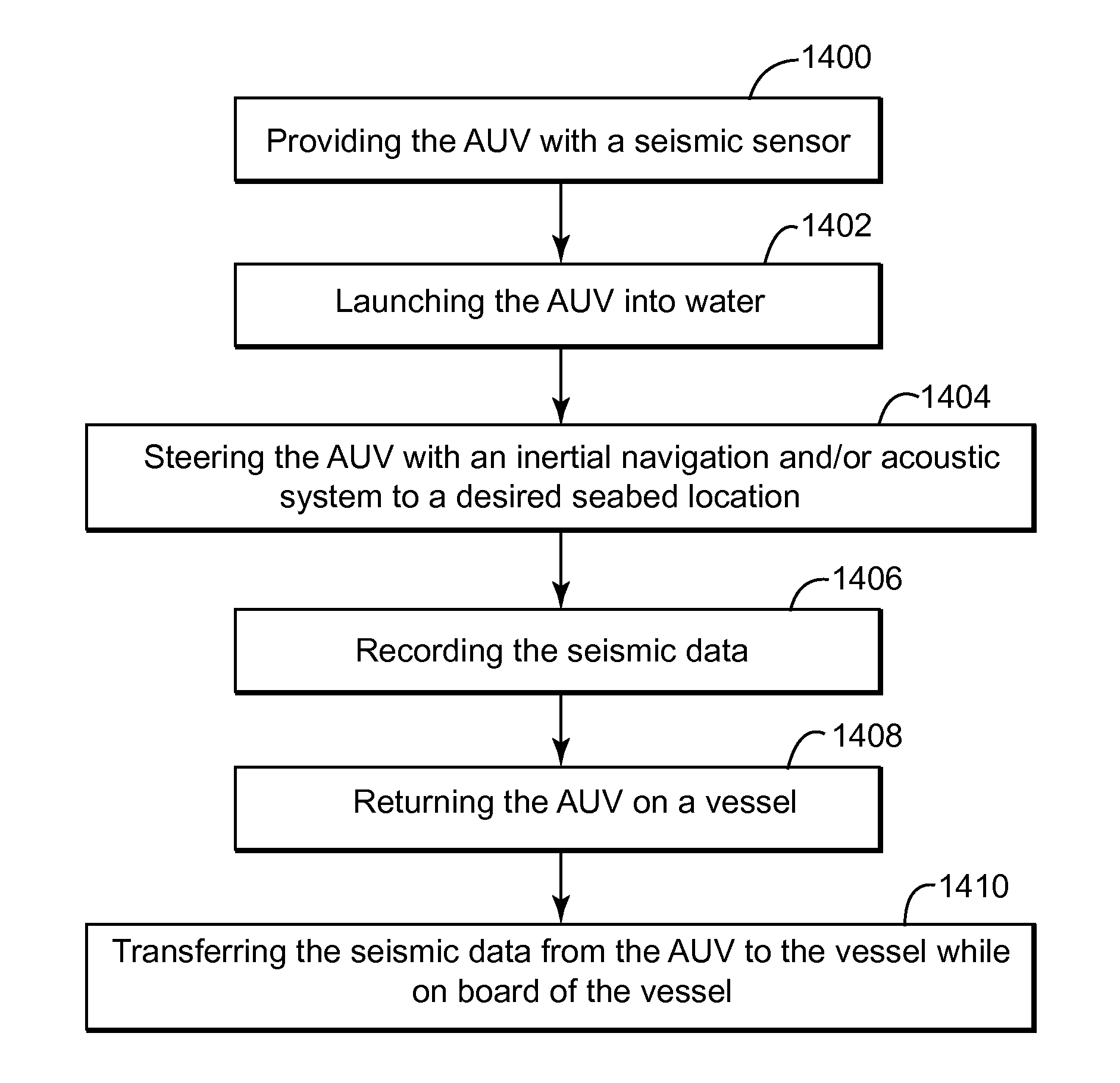
Autonomous underwater vehicle for marine seismic surveys
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) for recording seismic signals during a marine seismic survey. The AUV includes a body having a flush shape; an intake water element located on the body and configured to take in water; at least one propulsion nozzle located on the body and configured to eject the water from the intake water element for actuating the AUV; at least one guidance nozzle located on the body and configured to eject water to change a traveling direction of the AUV; and a seismic payload located on the body of the AUV and configured to record seismic signals.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
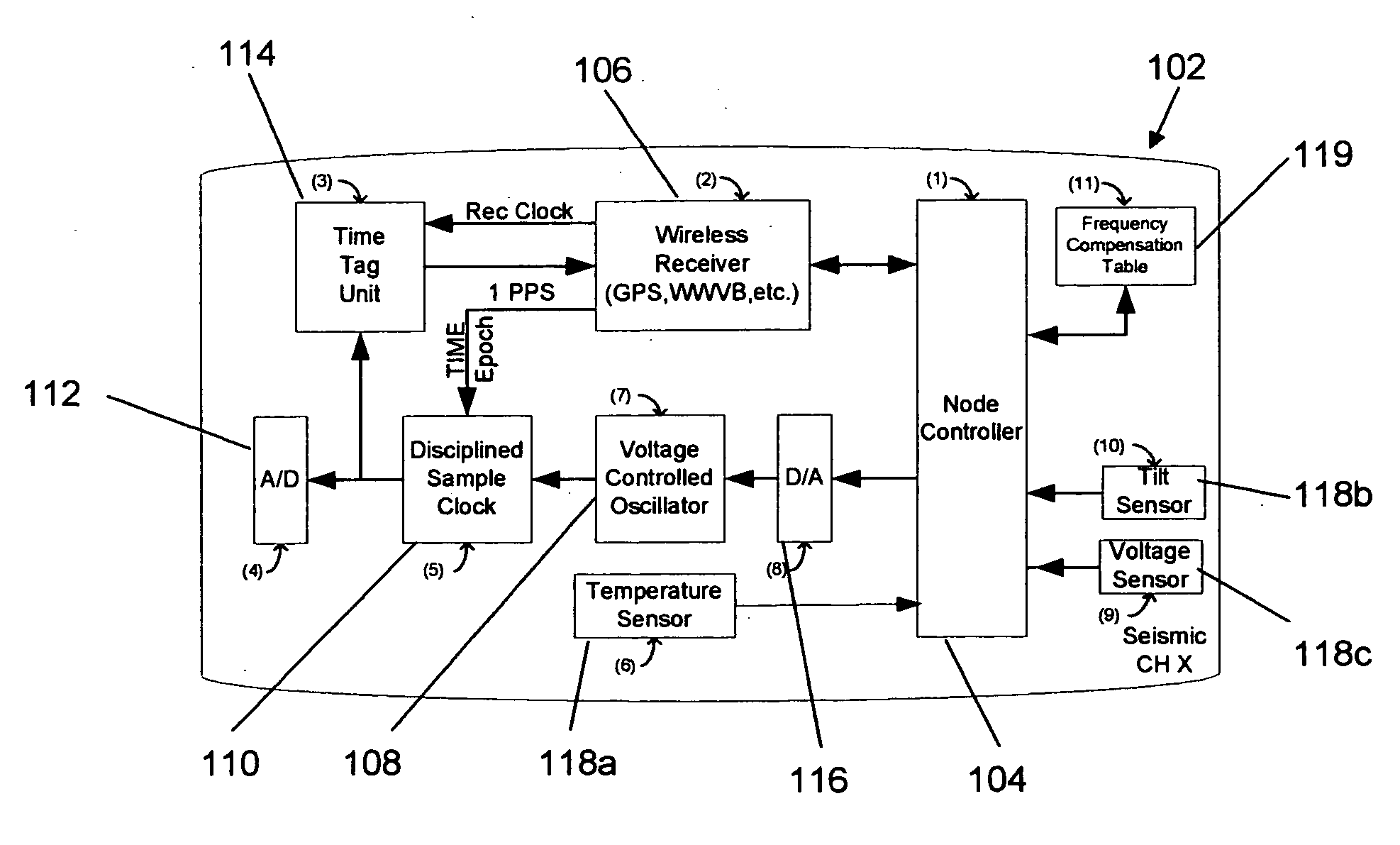
Method and apparatus for correcting the timing function in a nodal seismic data acquisition unit
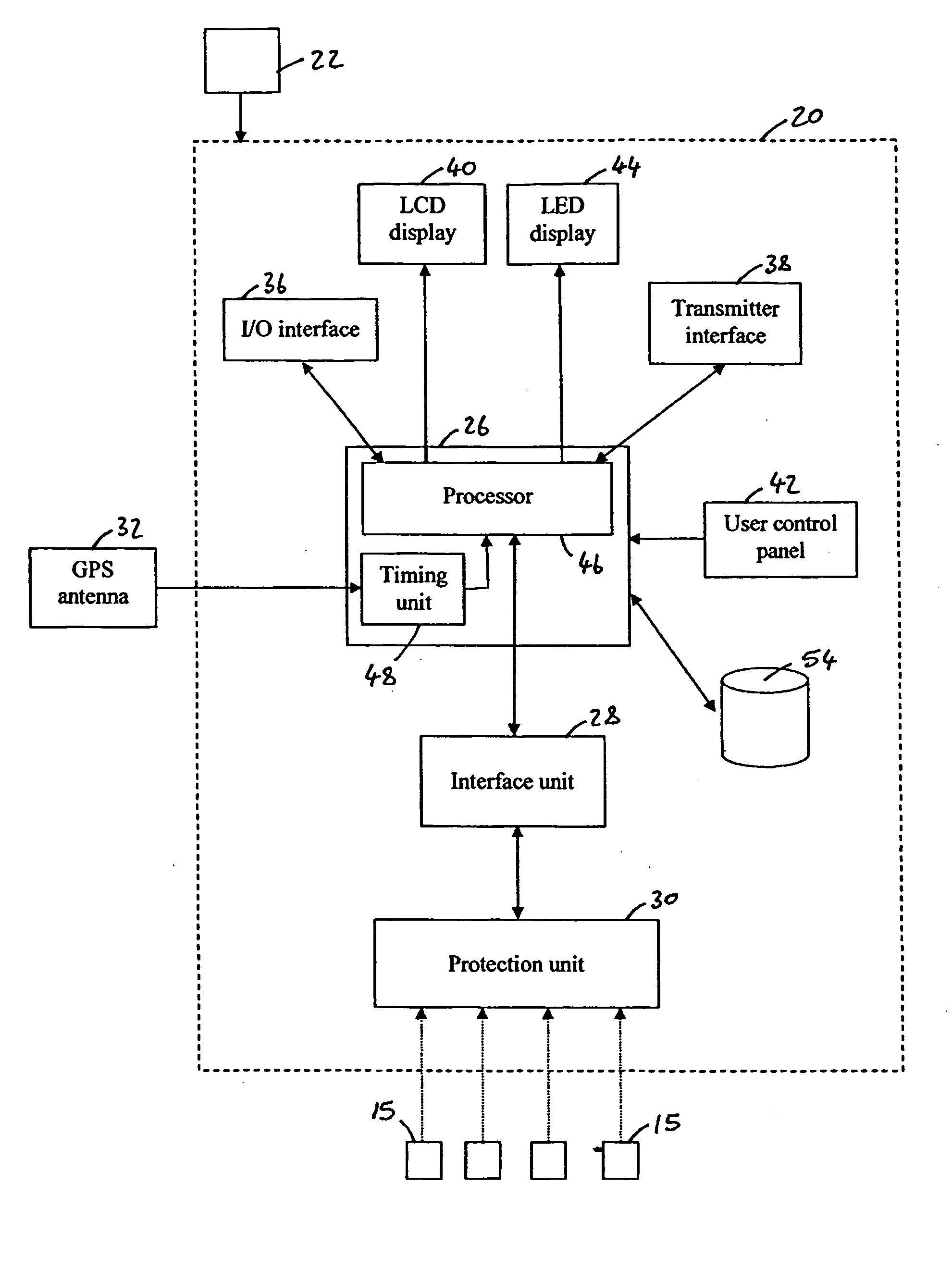
ActiveUS20090080290A1Minimize distortionReduce the valueSeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingData acquisitionAnalog-to-digital converter
A wireless seismic data acquisition unit with a wireless receiver providing access to a common remote time reference shared by a plurality of wireless seismic data acquisition units in a seismic system. The receiver is capable of replicating local version of remote time epoch to which a seismic sensor analog-to-digital converter is synchronized. The receiver is capable of replicating local version of remote common time reference for the purpose of time stamping local node events. The receiver is capable of being placed in a low power, non-operational state over periods of time during which the seismic data acquisition unit continues to record seismic data, thus conserving unit battery power. The system implements a method to correct the local time clock based on intermittent access to the common remote time reference. The method corrects the local time clock via a voltage controlled oscillator to account for environmentally induced timing errors. The invention further provides for a more stable method of correcting drift in the local time clock.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
Method and apparatus for land based seismic data acquisition
ActiveUS7561493B2Minimize the possibilityEliminate needSeismic signal receiversSeismic signal recordingGeophoneLand based
A seismic exploration method and unit comprised of continuous recording, self-contained wireless seismometer units or pods. The self-contained unit may include a tilt meter, a compass and a mechanically gimbaled clock platform. Upon retrieval, seismic data recorded by the unit can be extracted and the unit can be charged, tested, re-synchronized, and operation can be re-initiated without the need to open the unit's case. The unit may include an additional geophone to mechanically vibrate the unit to gauge the degree of coupling between the unit and the earth. The unit may correct seismic data for the effects of crystal aging arising from the clock. Deployment location of the unit may be determined tracking linear and angular acceleration from an initial position. The unit may utilize multiple geophones angularly oriented to one another in order to redundantly measure seismic activity in a particular plane.
Owner:MAGSEIS FF LLC
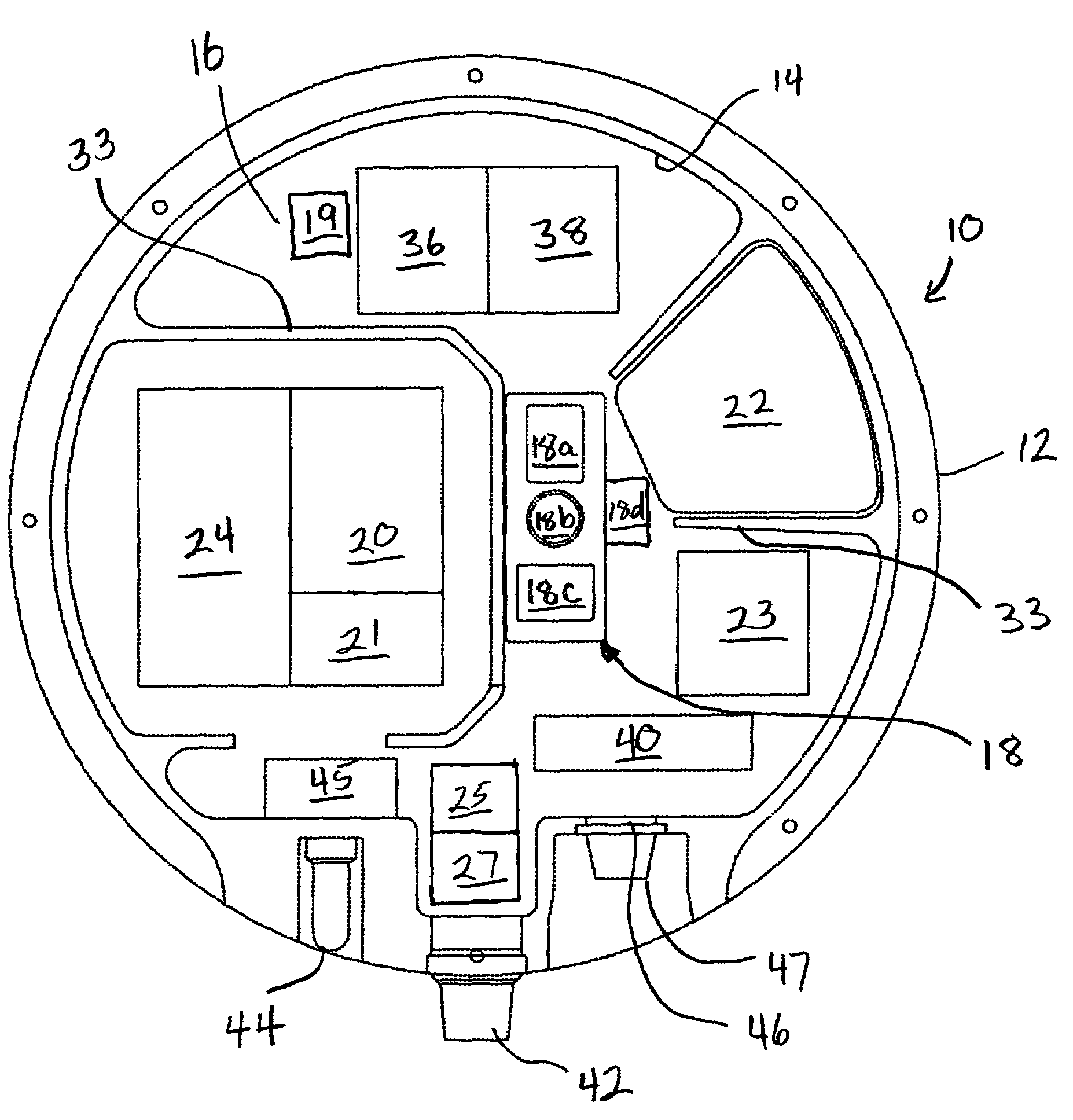
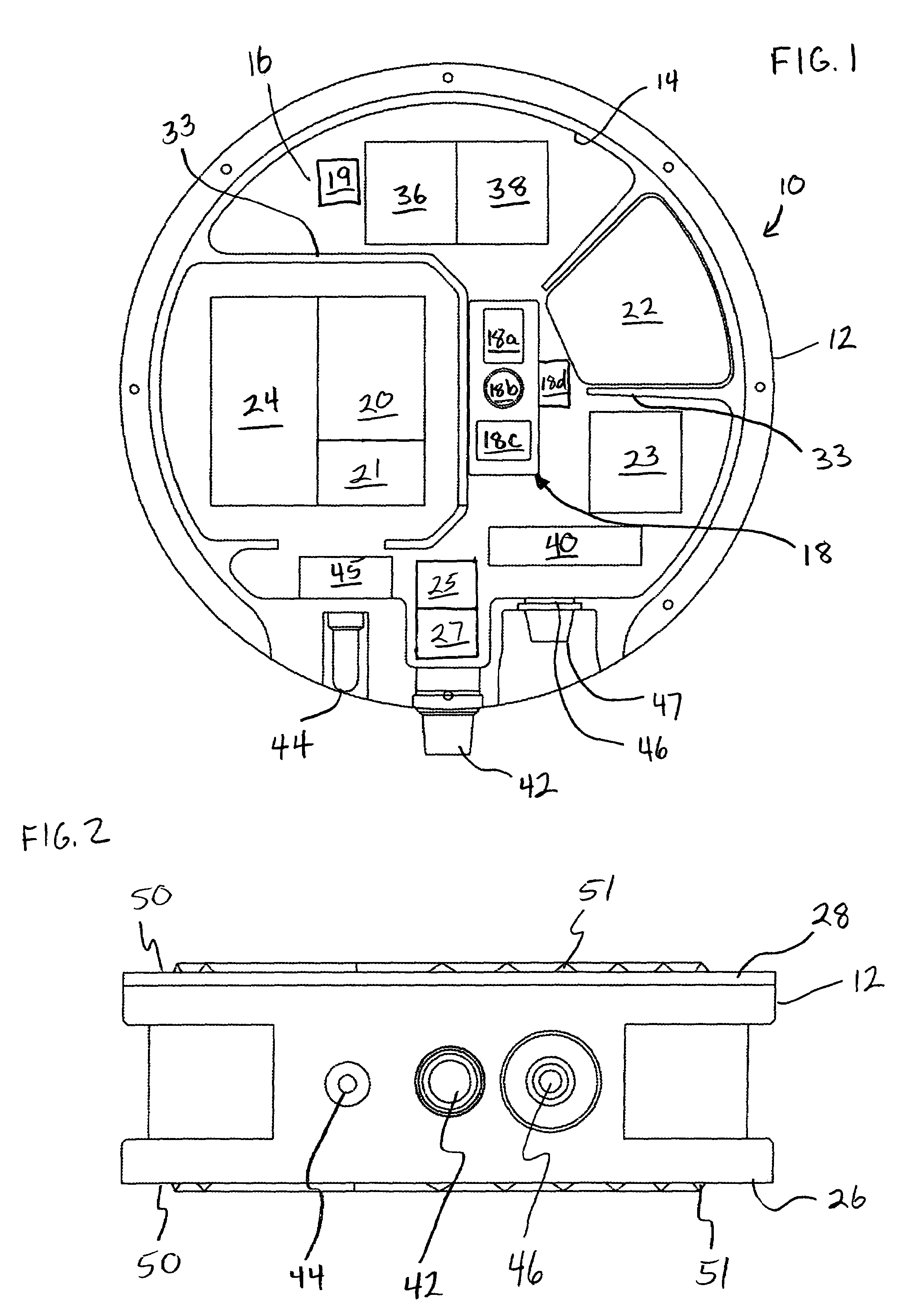
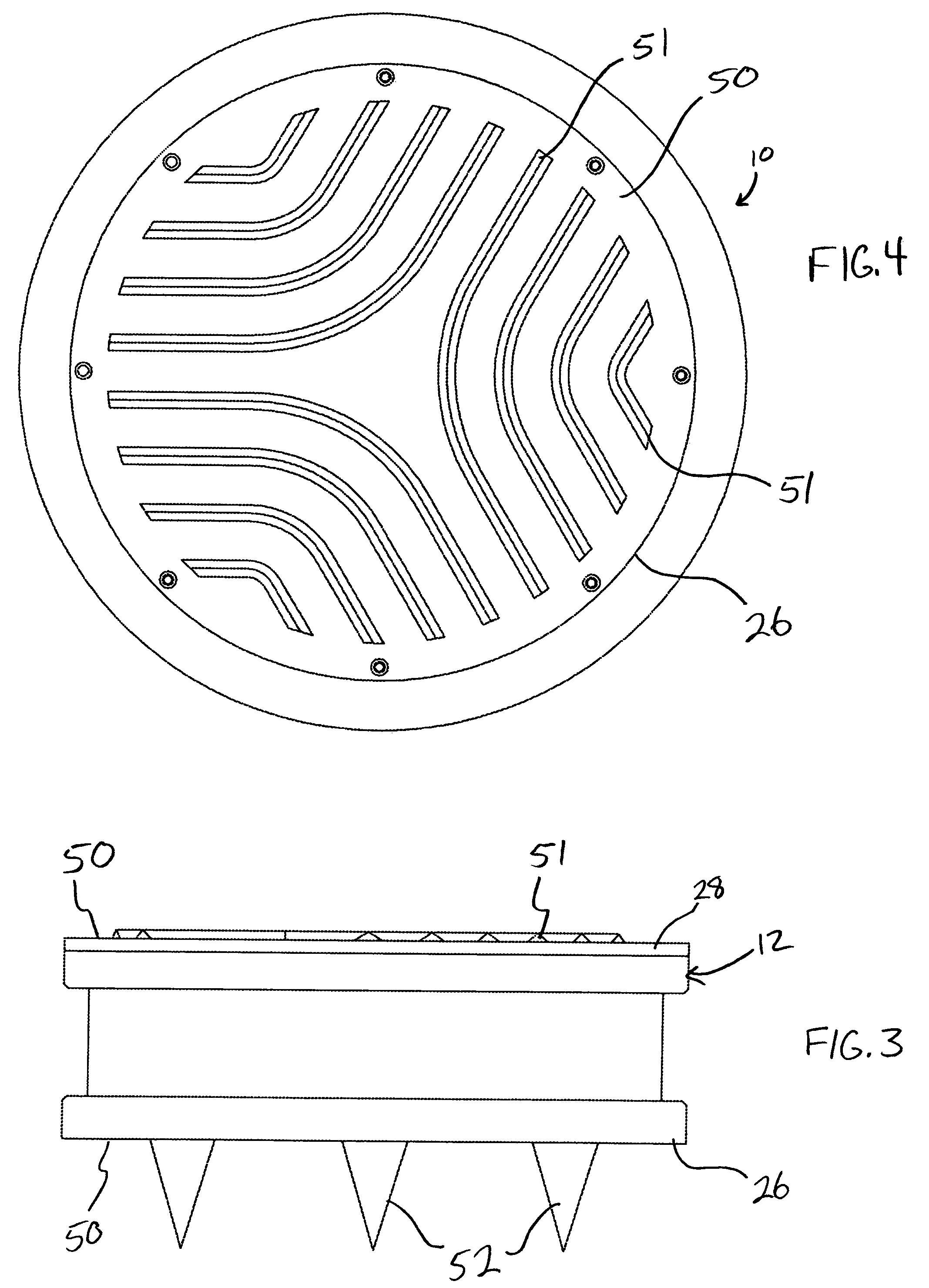
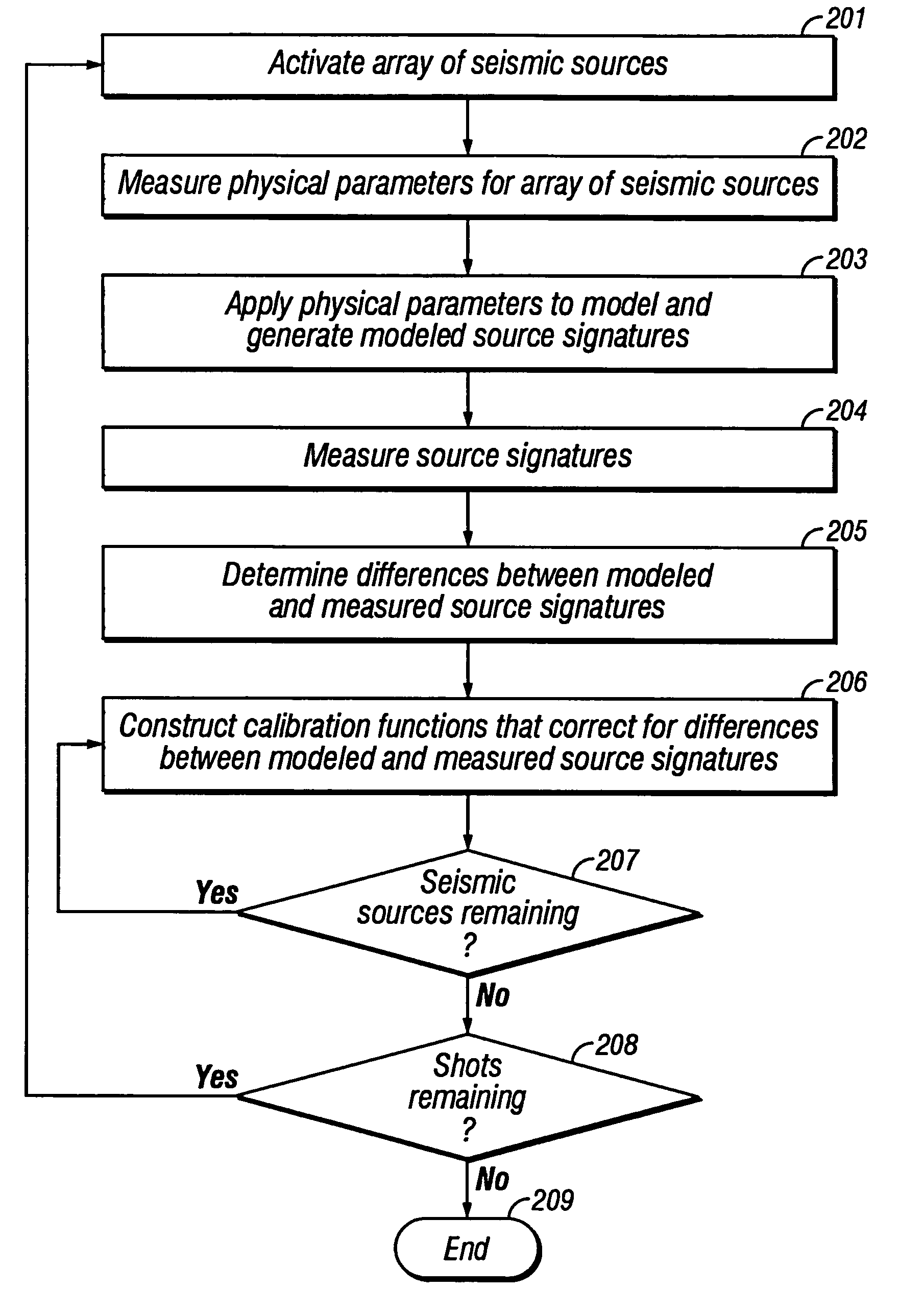
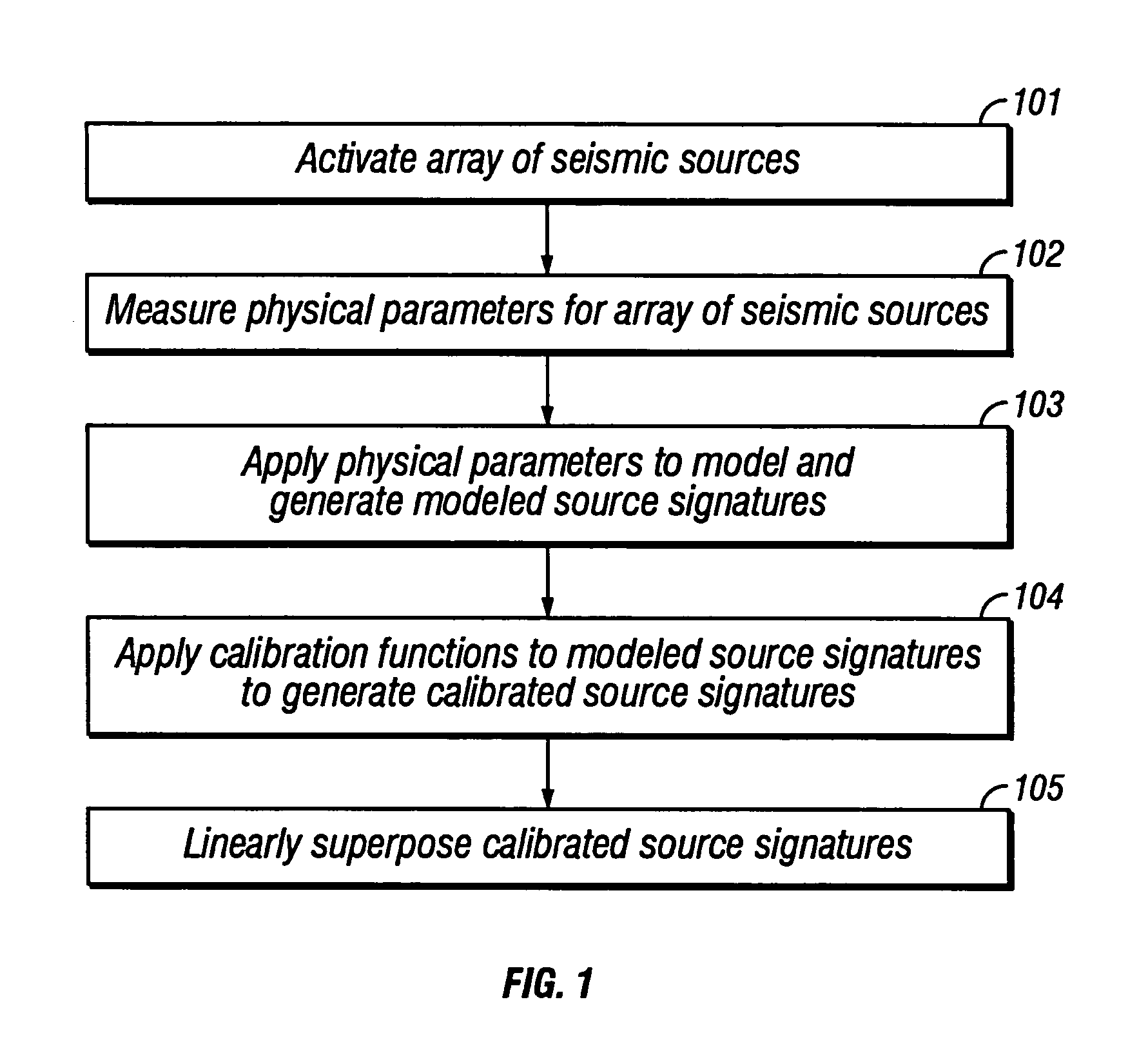
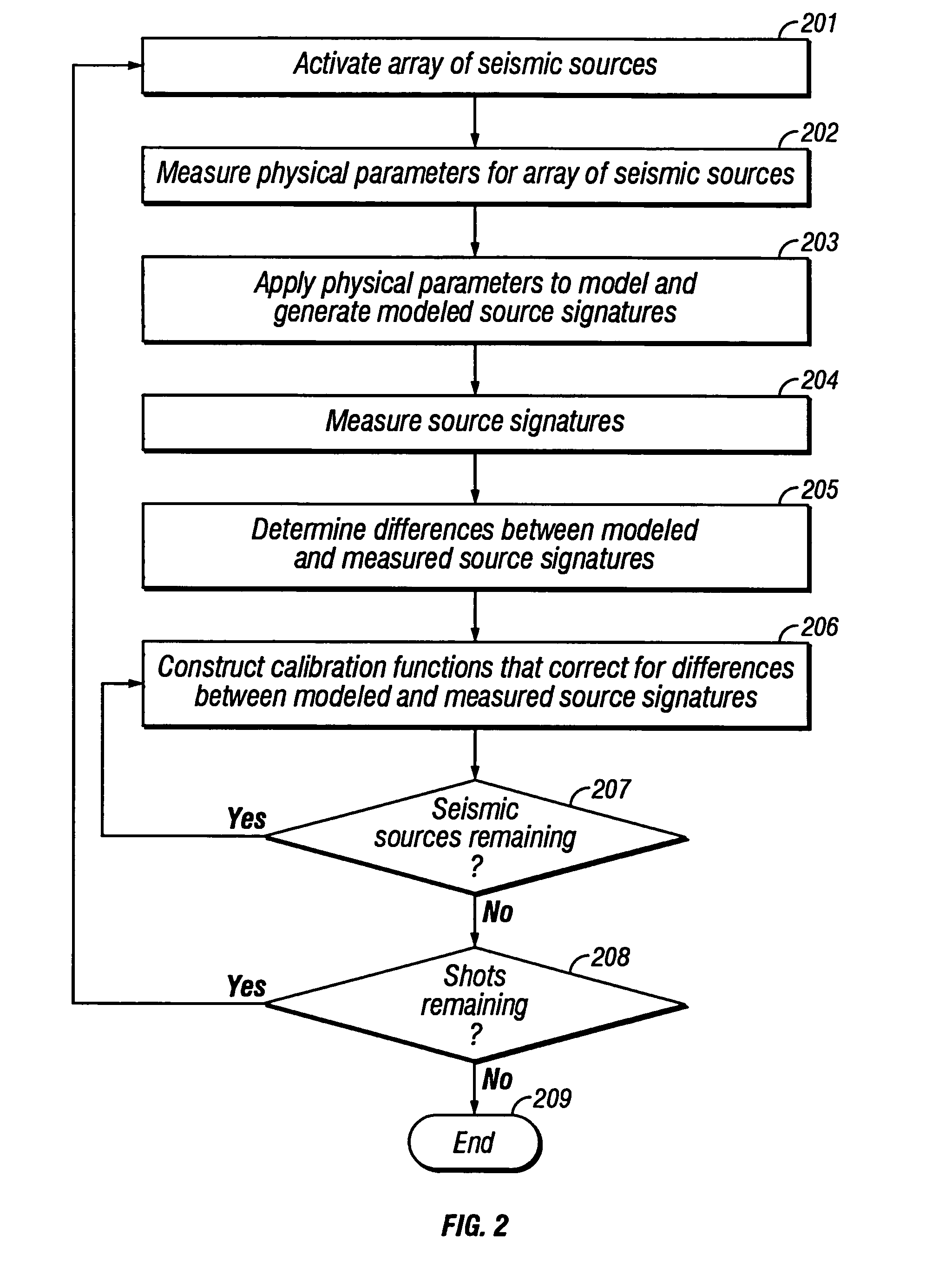
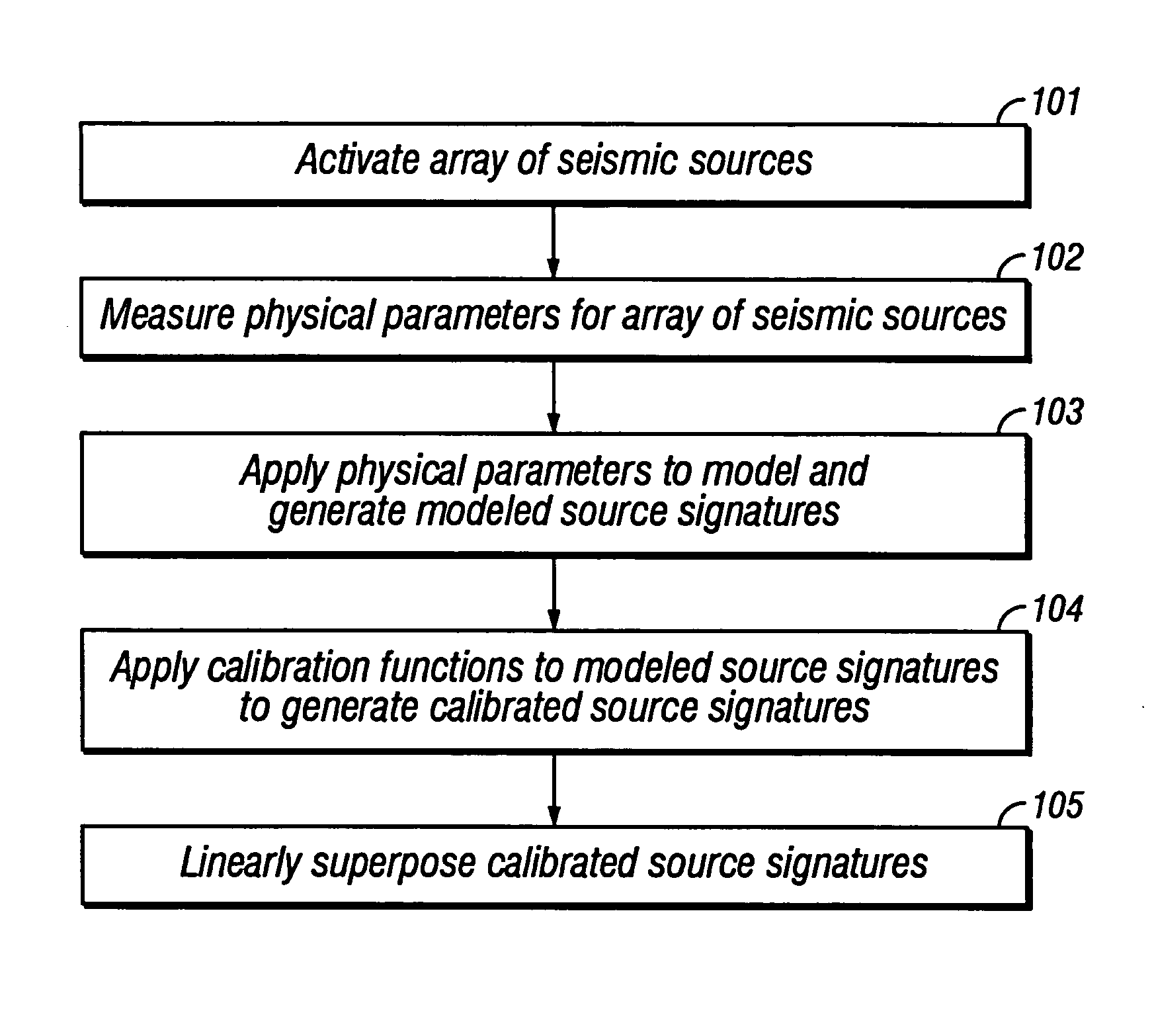
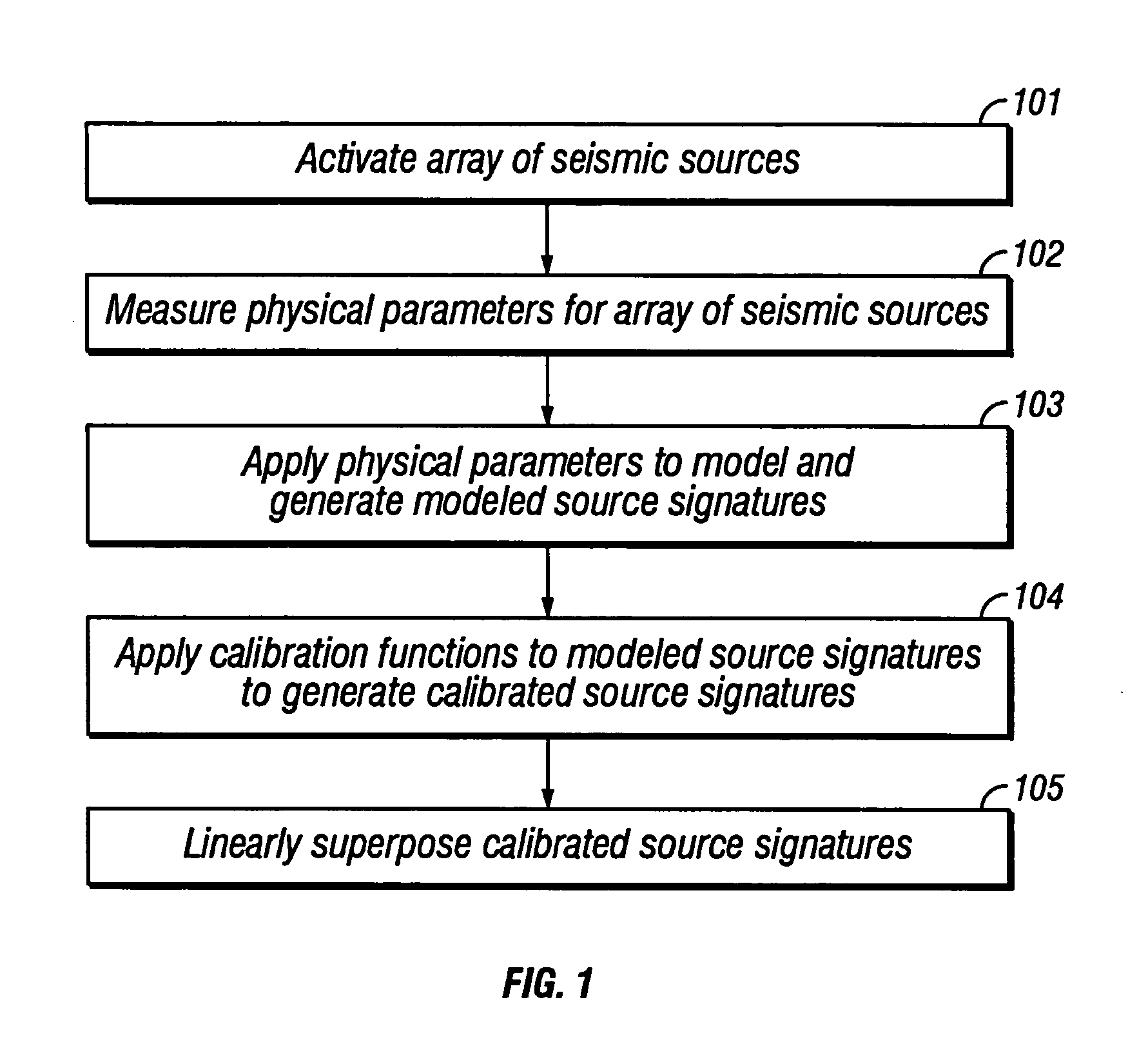
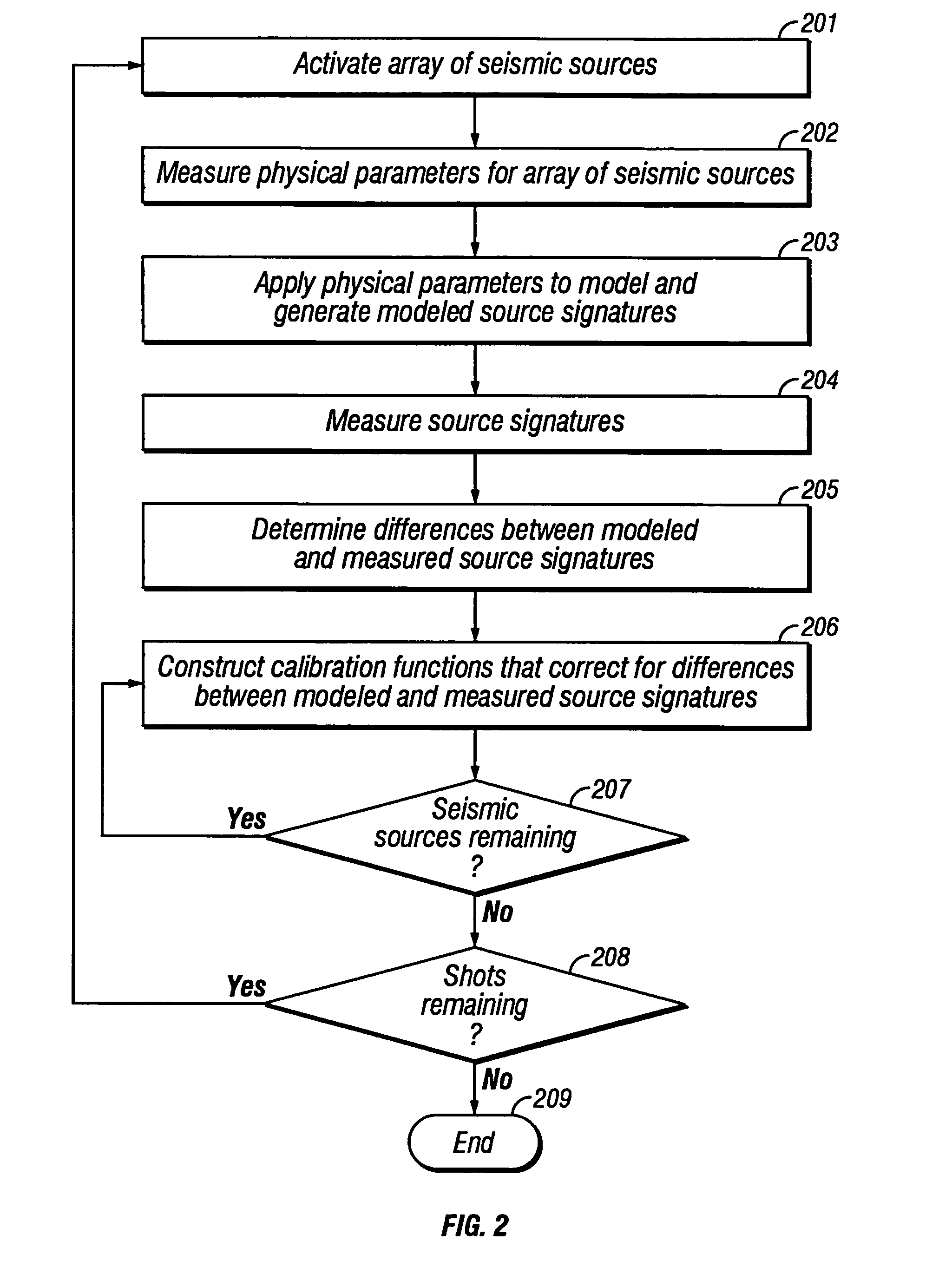
Method of seismic source monitoring using modeled source signatures with calibration functions
Owner:PGS EXPLORATION US
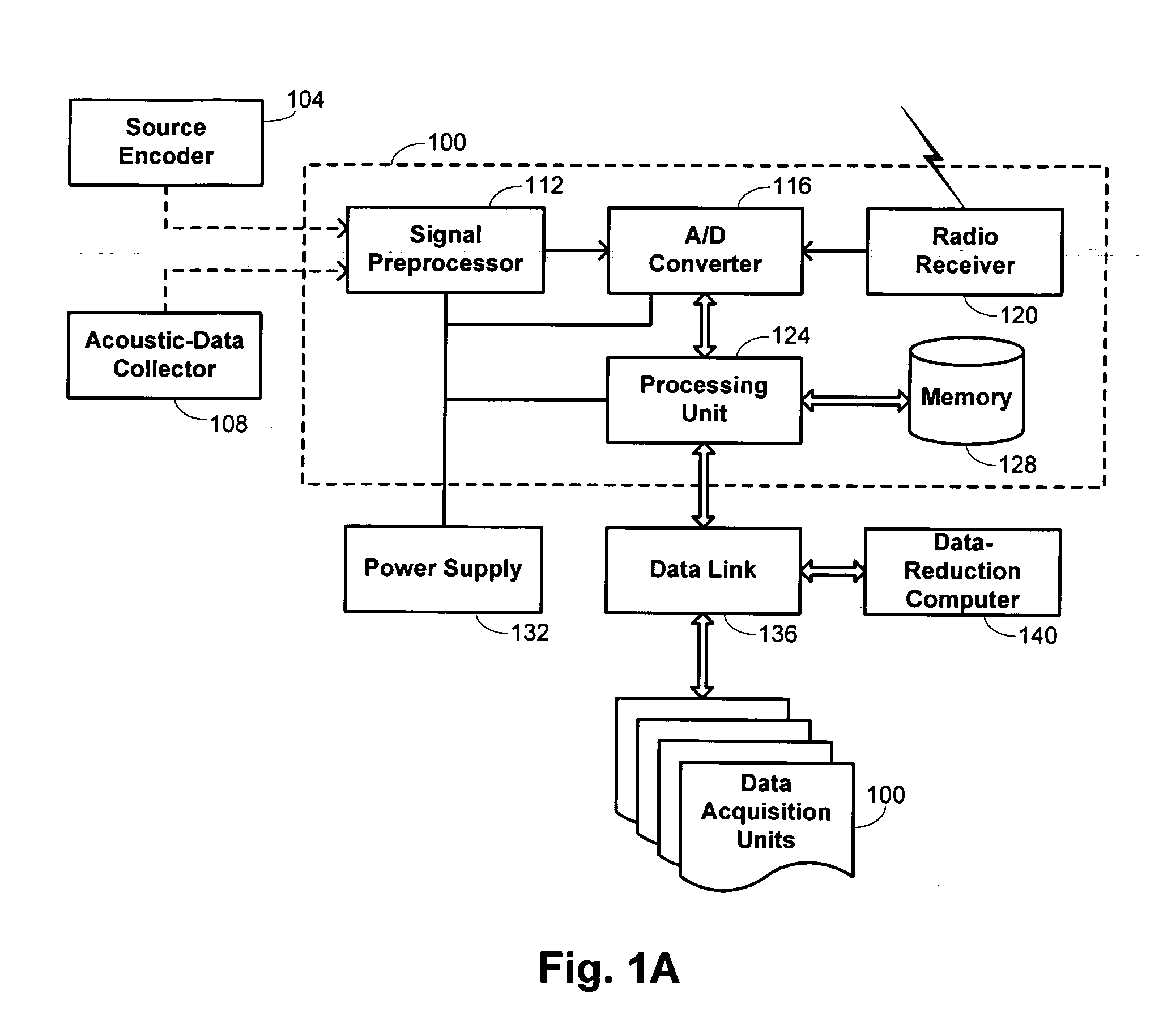
Methods and systems for acquiring and processing seismic data
InactiveUS20060009911A1Seismic data acquisitionSeismic signal recordingData acquisitionTime dependency
Methods and systems are provided for acquiring seismic data. An ambient electromagnetic signal having a known time dependence is transmitted for propagation within a survey area. The ambient electromagnetic signal is received at distinct geographic locations with independently operating data acquisition units positioned at the distinct locations. Data representing acoustic signals received from the Earth at the distinct geographic locations are collected with the data acquisition units. The collected acoustic signals for the distinct geographic locations are synchronized by correlating the known time dependence of the propagated electromagnetic signal with time dependencies of the collected acoustic signals.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
Method of seismic source monitoring using modeled source signatures with calibration functions
Owner:PGS EXPLORATION US
Non-uniform sampling to extend dynamic range of interferometric sensors
ActiveUS20090122319A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAcceleration measurementInterferometric sensorEngineering
Methods and apparatus for interrogating optical sensors with high slew rates using non-uniform sampling are provided. The transmission of optical signals in a non-uniform pattern is employed to allow for demodulation of fringe rates exceeding the commonly understood Nyquist frequency limit given as one half of the mean sampling frequency. By monitoring the time dependent fringe frequency and assuming that the fringe frequency has a limited bandwidth, only a limited bandwidth smaller than the Nyquist bandwidth around the instantaneous fringe frequency needs to be reconstructed at any time.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Immersible seismic emission device and implementation method
InactiveUS6175809B1Eliminate the effects ofCarry-out quicklySeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingCommunications systemThermal energy storage
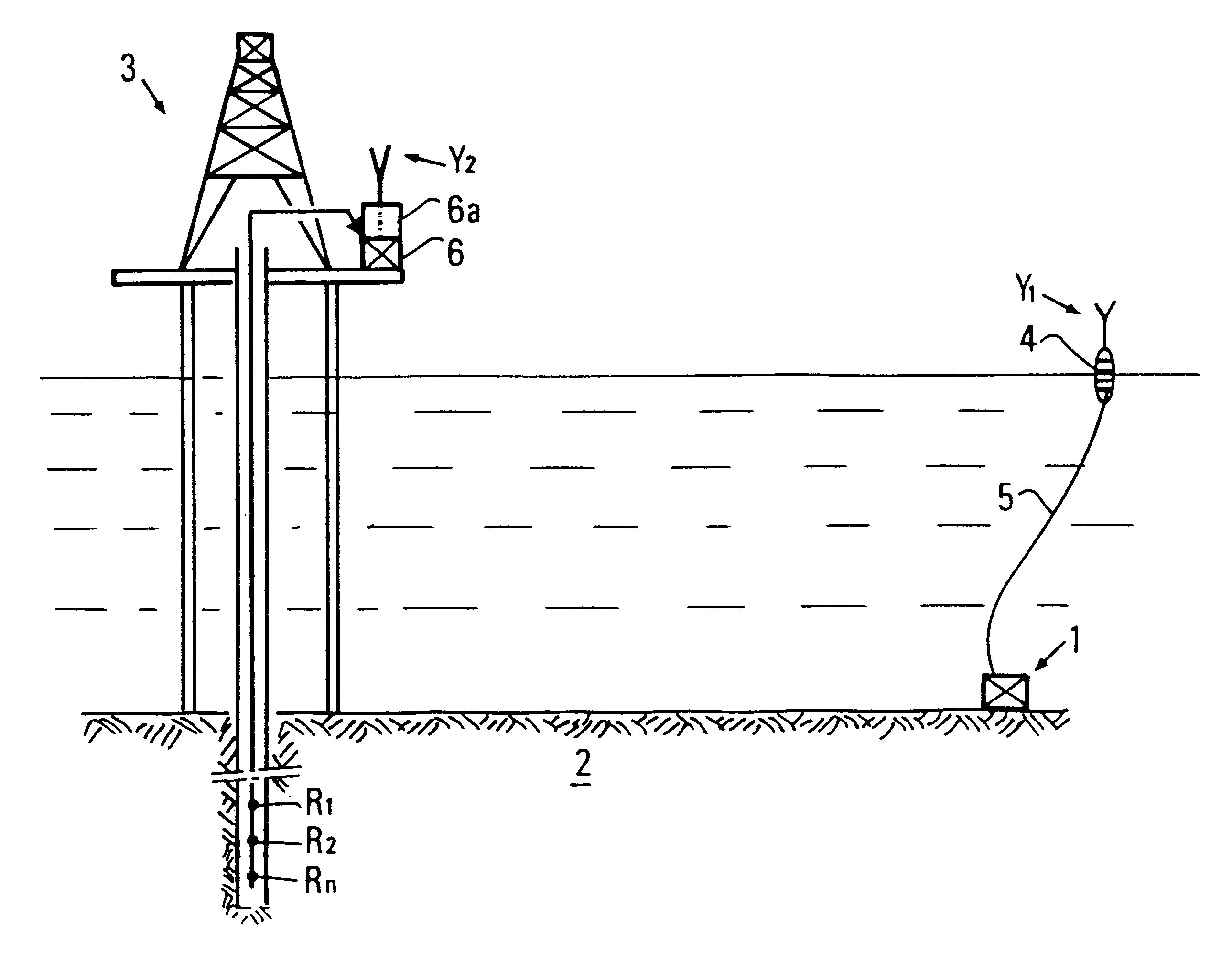
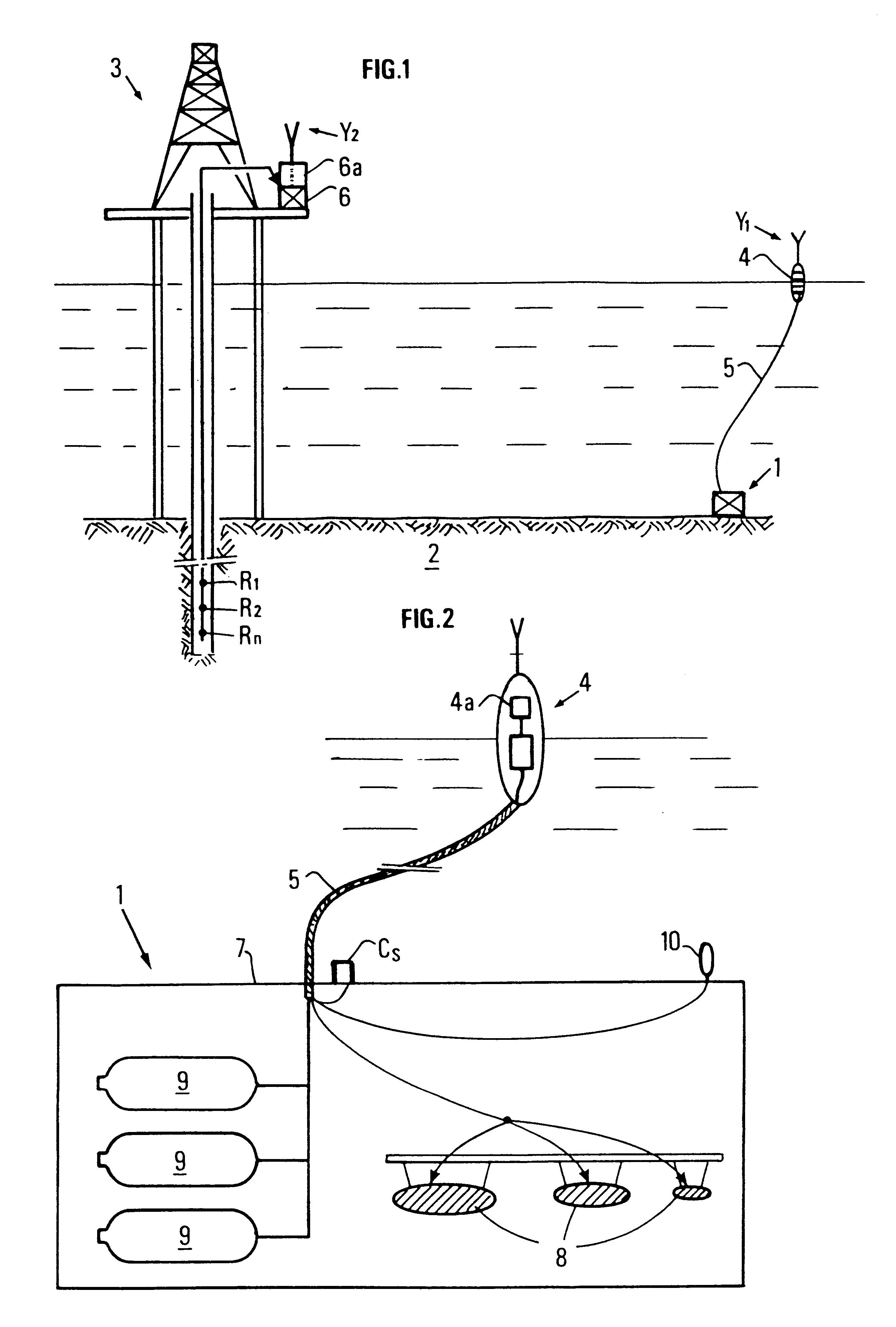
The invention is a seismic emission device designed to be immersed at the bottom of a water body (sea, lake, etc.), and method of implementation. The device comprises at least one (and preferably several) self-contained emission units (1) immersible at the bottom of a water body, combining at least one or more seismic wave sources (8), such as air guns for example, suited to be placed in contact with the body, local energy storage (9) which supplies the device a multifunction connection cable (5) connecting each self-contained emission unit to a surface relay unit (4), a communication system (4a, 6a, Y) providing communication with a central control station (6) located for example on a drilling or production platform (3). VSP repetitive exploration operations can be carried out in a well by activating successively the various emission units and by acquiring the signals picked up by receivers R1-n placed in a well for example and coupled with the formation. The device can be used for oil prospecting.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Use of pattern recognition in a measurement of formation transit time for seismic checkshots
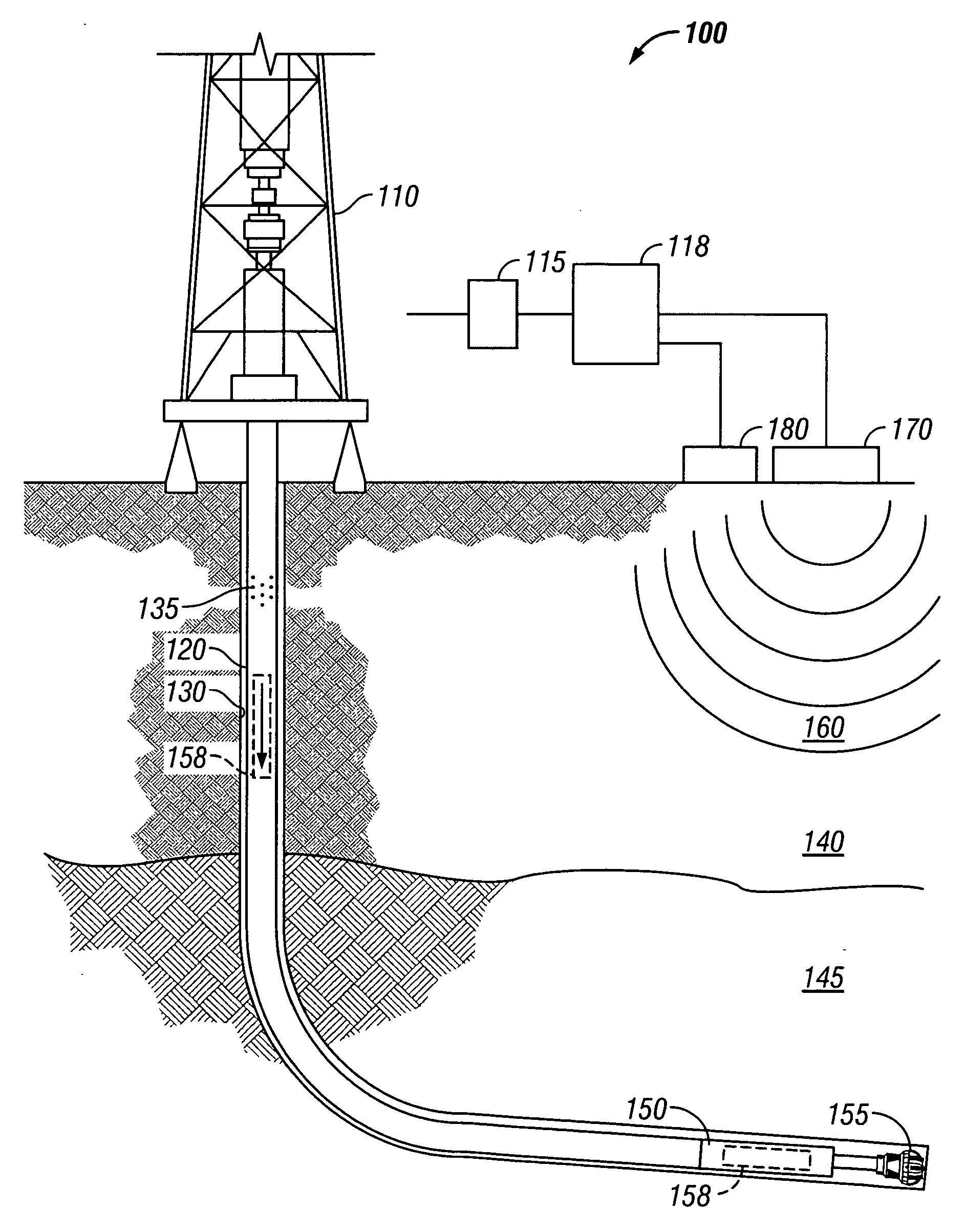
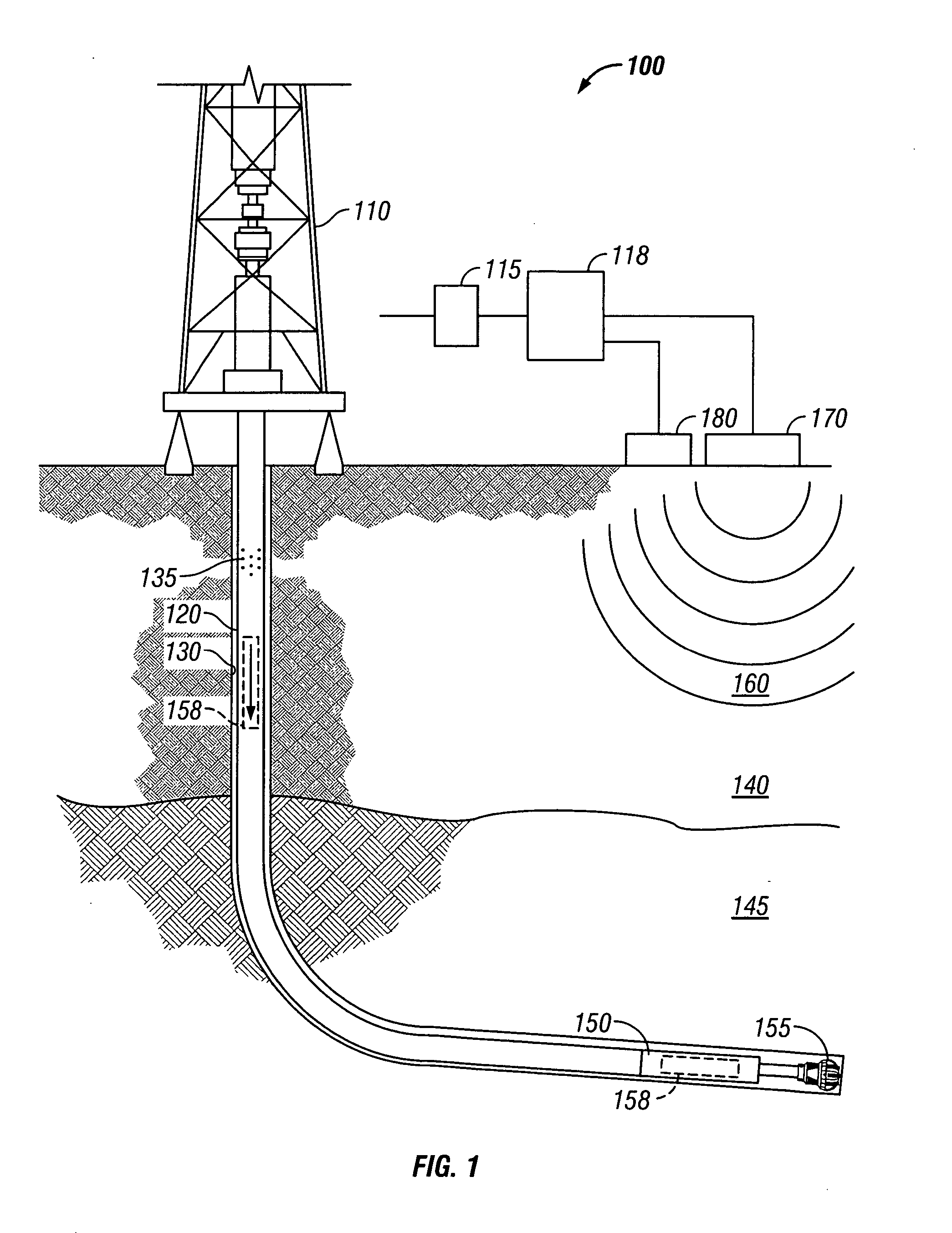
A method and system is provided for acquiring seismic data while conducting drill string operations in a wellbore. A seismic receiver is conveyed in a drill string to a location of interest; coded seismic signals are generated by a seismic source near a surface location; the coded seismic signals are detected with at least one sensor in the seismic receiver at least one location of interest in the wellbore as the drill string is operated in the wellbore; an arrival time of the detected seismic signal is computed in the seismic receiver; and the detected seismic signals or computed arrival times are stored in the seismic receiver or transferred to the surface.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
GPS satellite time service telemetering seismograph
InactiveCN1417593AReduce weightReduce volumeSeismic energy generationSeismic signal recordingDetonationData collecting
A GPS satellite time service telemetering seismograph is used in natural seismic measurements; synchronous data measurement and record; and synchronous timing detonation, and consists of two parts including data collecting and processing unit and timing start and blowing unit. The present invention can realize unattended and fully automatic functions and may be used to meet the requirement of exploration in complex area and for complex construction method. It has completely new seismograph structure without host computer, master cable and communication station.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Autonomous Seismic Data Acquisition Unit
InactiveUS20080049550A1Pulse automatic controlSeismic signal recordingData acquisitionAcquisition rate
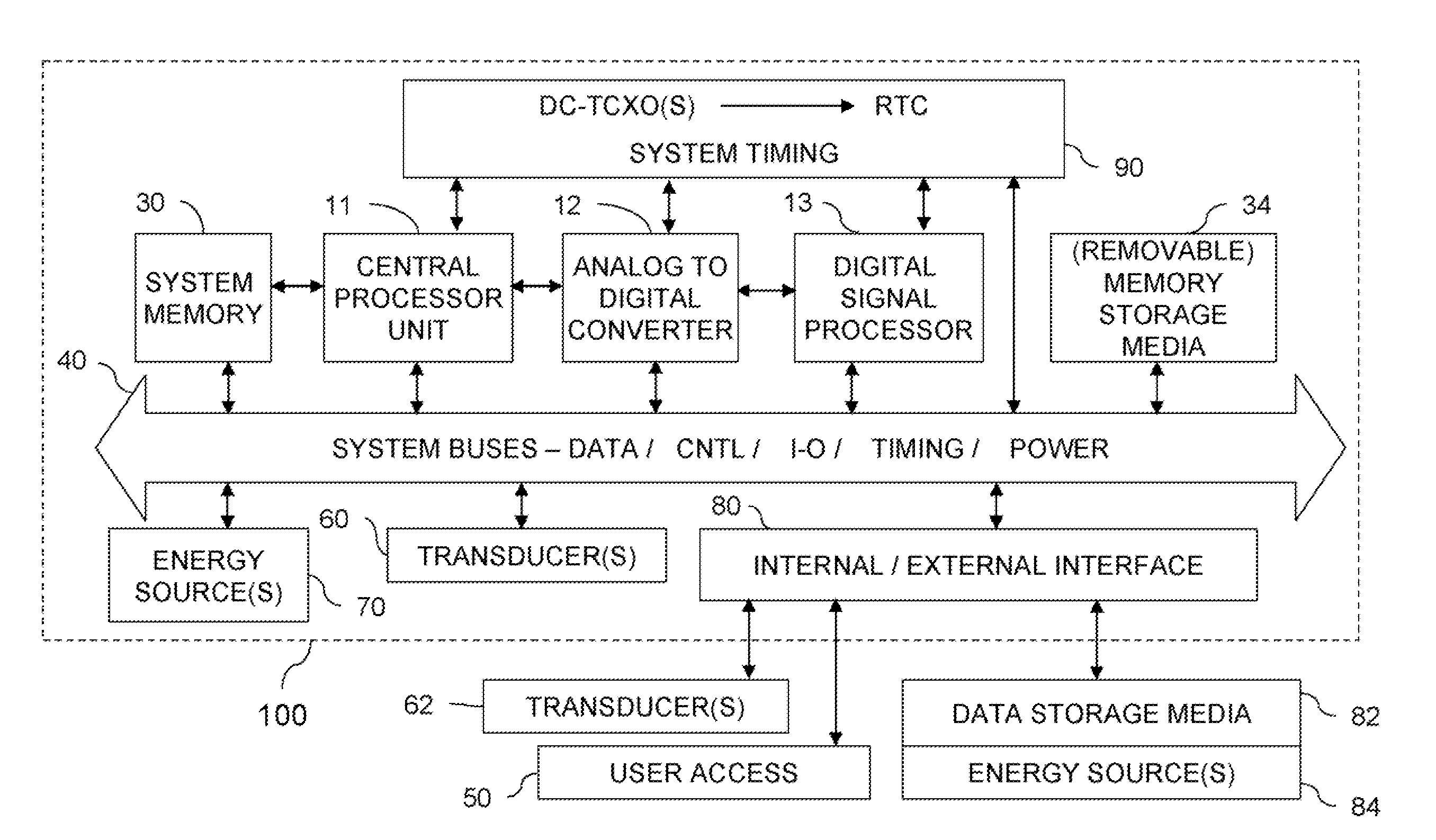
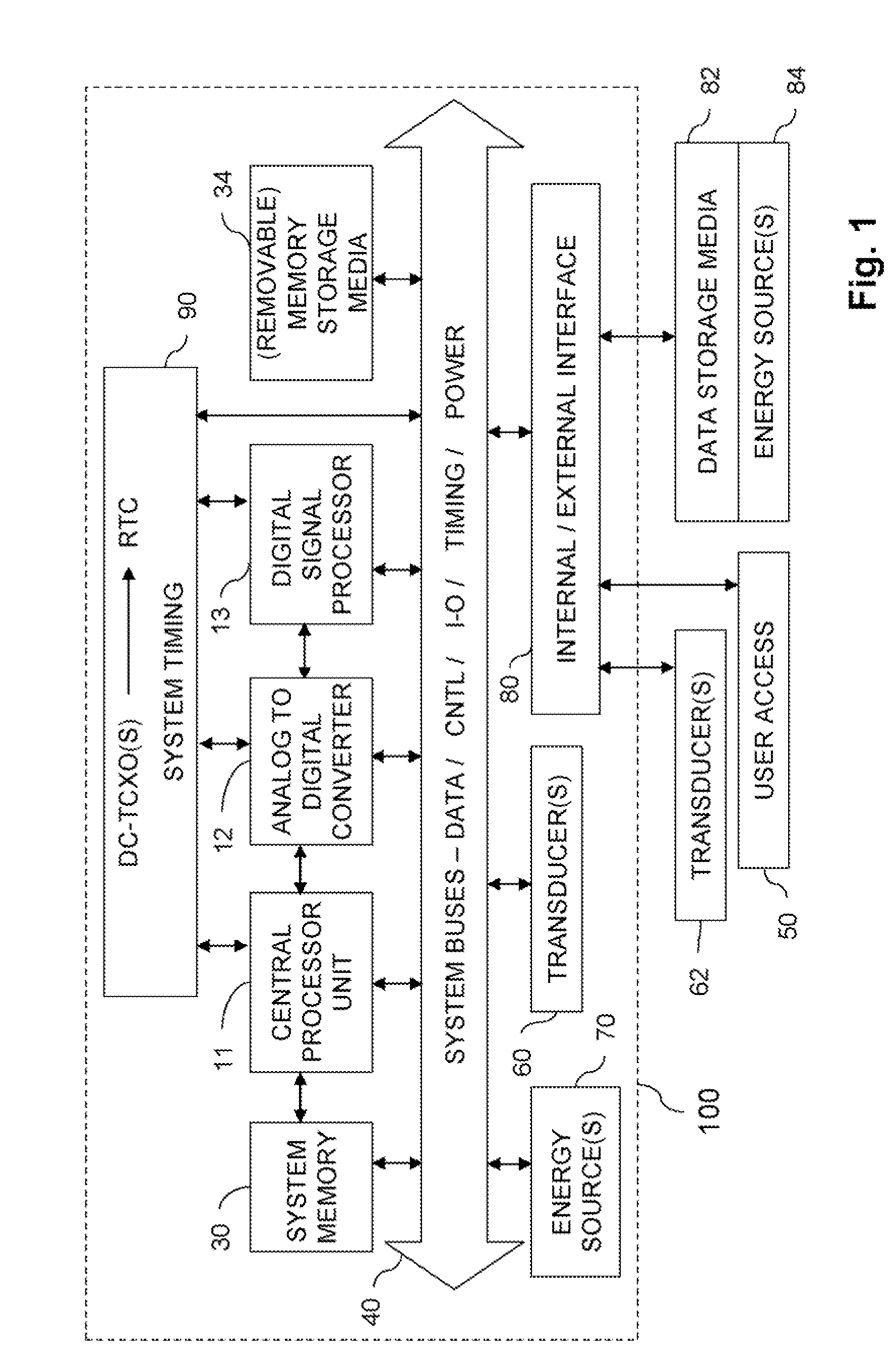
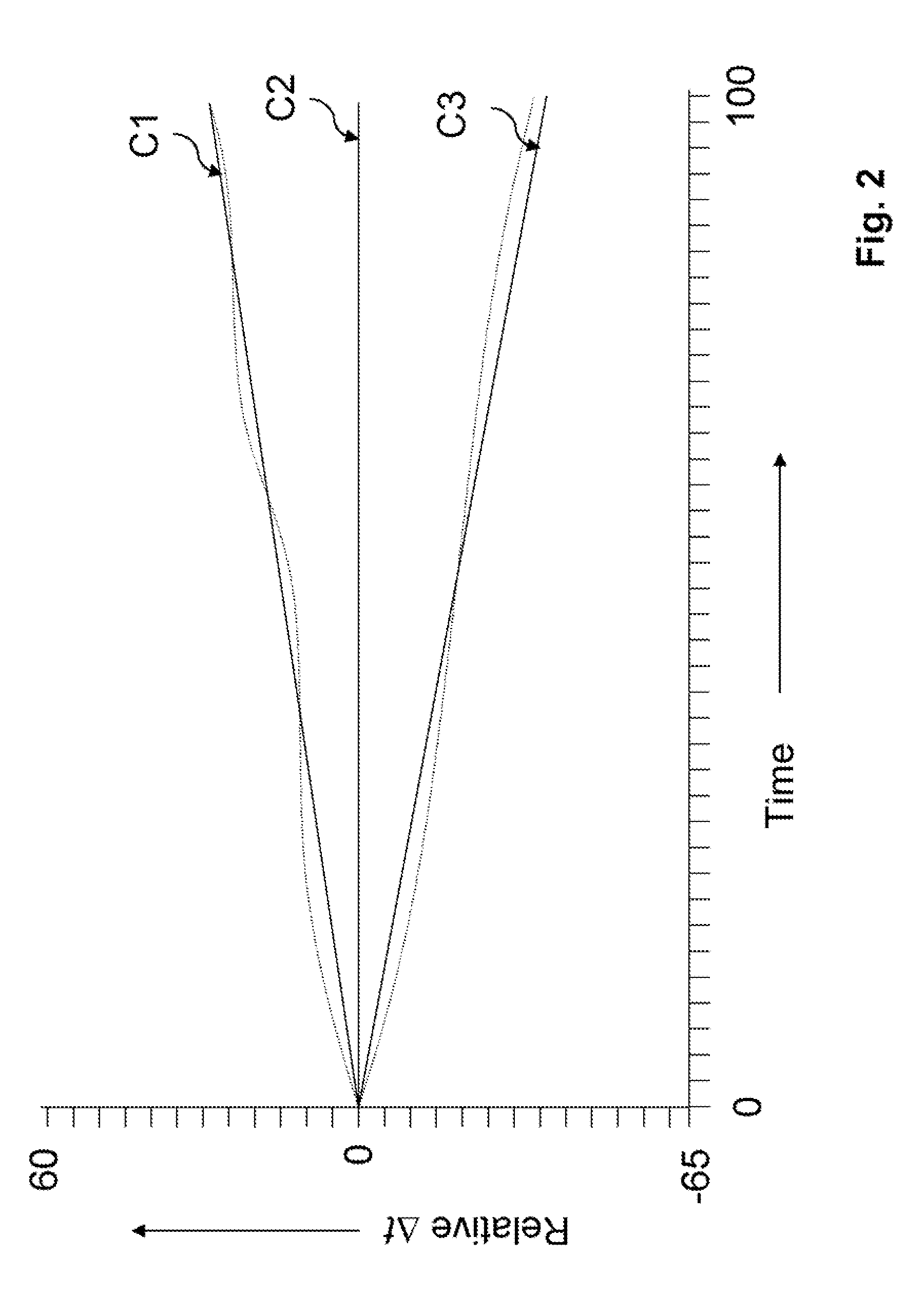
A method, apparatus and system for acquiring land seismic data includes acquiring seismic data with a first autonomous seismic data acquisition unit and a second autonomous seismic data acquisition unit wherein each acquisition unit comprises a plurality of digitally controlled temperature-compensated crystal oscillators. Oscillator-based timing signals are acquired that are associated with the plurality of digitally controlled temperature-compensated crystal oscillators and a time correction is determined to apply to the seismic data acquired with the first autonomous seismic data acquisition unit. The time correction is determined using the oscillator-based timing signals from the first and second autonomous seismic data acquisition units.
Owner:GEOPHYSICAL TECH +1
Methods and apparatus of source control for borehole seismic
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus and Method for Integrating Survey Parameters Into a Header
A method, apparatus and system for acquiring seismic data is disclosed that in one aspect receives a seismic signal detected by at least one sensor in response to a seismic energy signal generated by a source at a selected location at a data acquisition unit in data that is in data communication with the sensor, receives at least one parameter of the source and / or receiver at the data acquisition unit; and generates a data block at the data acquisition unit having data representative of the received seismic signal and a header that contains data representative of the at least one parameter of the source and / or receiver. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:INOVA
Synchronization and positioning of seismic data acquisition systems
InactiveUS20080189044A1Good synchronizationIncrease profitBeacon systemsSeismic signal transmissionData acquisitionGlobal positioning system receiver
A network distributed seismic data acquisition system comprises seismic receivers, connected to remote acquisition modules, receiver lines, line tap units, base lines, central recording system and a seismic source event generation unit. Global positioning system receivers of full or partial capability are combined with some of these modules and units and a master global positioning receiver aids the distributed receivers. The global positioning receivers may be used to synchronize high precision clocks as well as to provide positioning information. A master clock is designated and one or more high precision clocks is added to the network to correct for timing uncertainty associated with propagation of commands through the network. Seismic receivers and seismic sources are thereby synchronized with greater accuracy than otherwise possible, thus enabling an improvement in subsurface geologic imaging.
Owner:GEO X SYST
Autonomous underwater vehicle for marine seismic surveys
An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) for recording seismic signals during a marine seismic survey. The AUV includes a body having a flush shape; an intake water element located on the body and configured to take in water; at least one propulsion nozzle located on the body and configured to eject the water from the intake water element for actuating the AUV; at least one guidance nozzle located on the body and configured to eject water to change a traveling direction of the AUV; and a seismic payload located on the body of the AUV and configured to record seismic signals.
Owner:SEABED GEOSOLUTIONS
Stabilizing remote clocks in a network
InactiveUS20080170469A1Improve oscillator stabilityIncrease amplitudeSeismic signal transmissionSeismic signal recordingWide areaClock rate
Owner:ARAM SYST
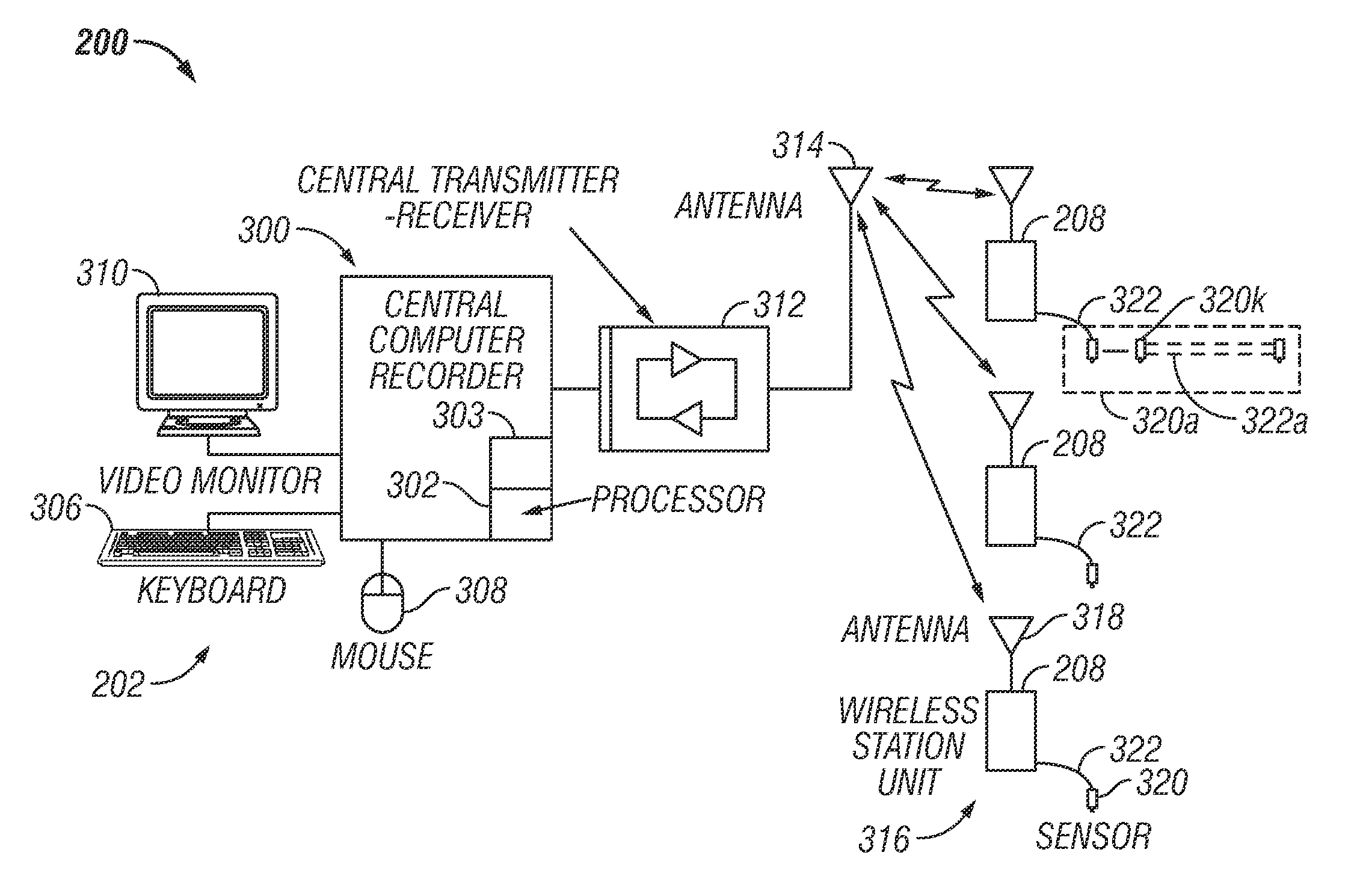
Data acquisition unit, system and method for geophysical data
InactiveUS20050177310A1Easy transferReduce noiseSatellite radio beaconingSeismic signal recordingData acquisitionComputer science
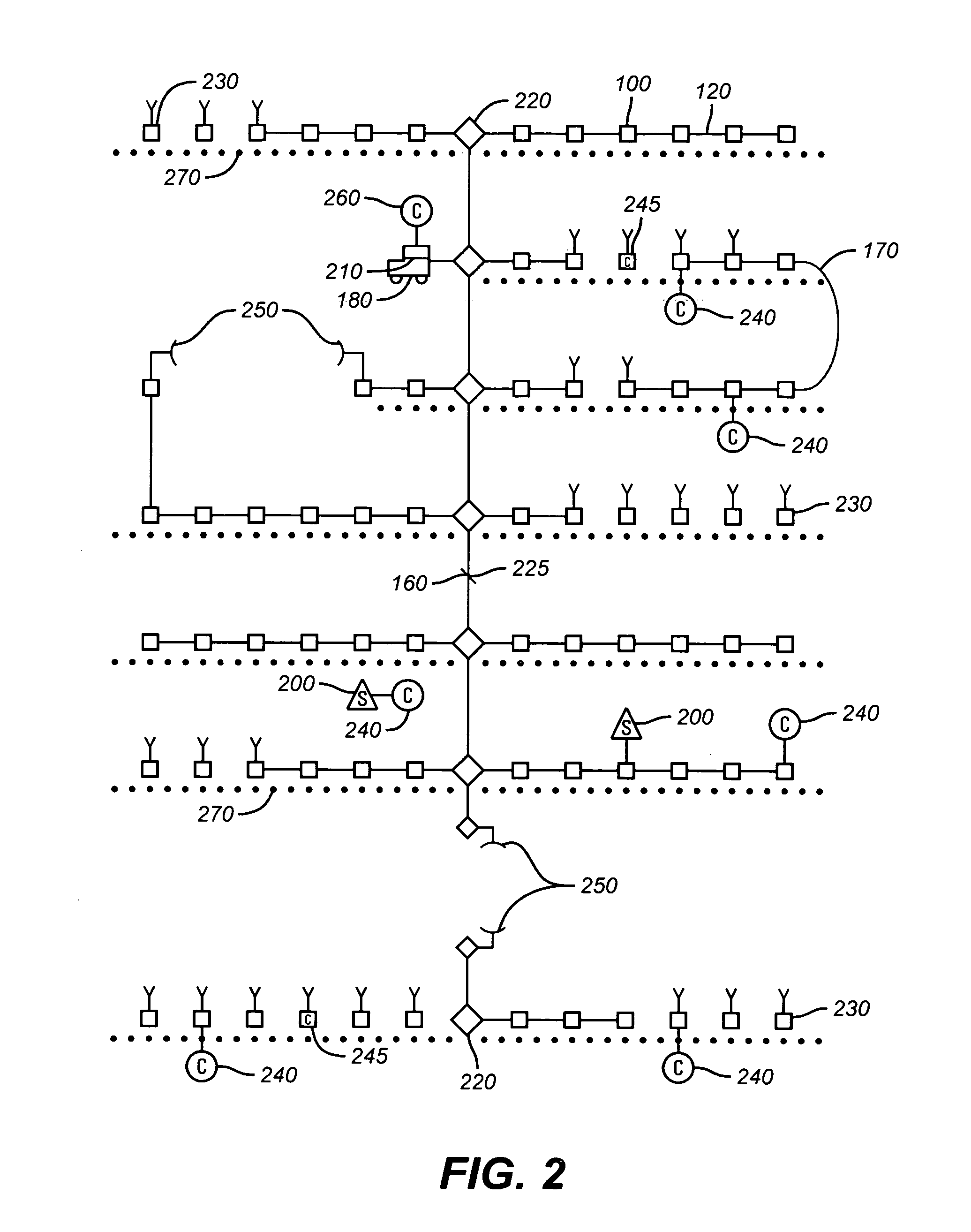
A data acquisition system for gathering geophysical data, a corresponding method, and a data acquisition unit for use with the system and method are disclosed. The system (10) comprises a plurality of data acquisition units (14) for gathering geophysical data, each data acquisition unit (14) being connectable to at least one sensor (15) and being arranged, during use, to gather geophysical data from the at least one sensor (15). Each data acquisition unit (14) comprises time referencing means (48) arranged to generate time reference data usable to control the time at which samples of geophysical data are taken. The system (10) further comprises means for calculating spatial derivatives between samples associated with adjacent sensors (15) connected during use to the data acquisition units (14).
Owner:WMC RESOURCES LTD
Practical autonomous seismic recorder implementation and use
ActiveUS20110019502A1Less energyImprove accuracySeismic signal receiversSeismic signal recordingGeophysicsHigh resolution
Seismic systems and methods are provided to synchronize both source and receiver data using inexpensive timers and / or low energy timers to obtain high resolution seismic data.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
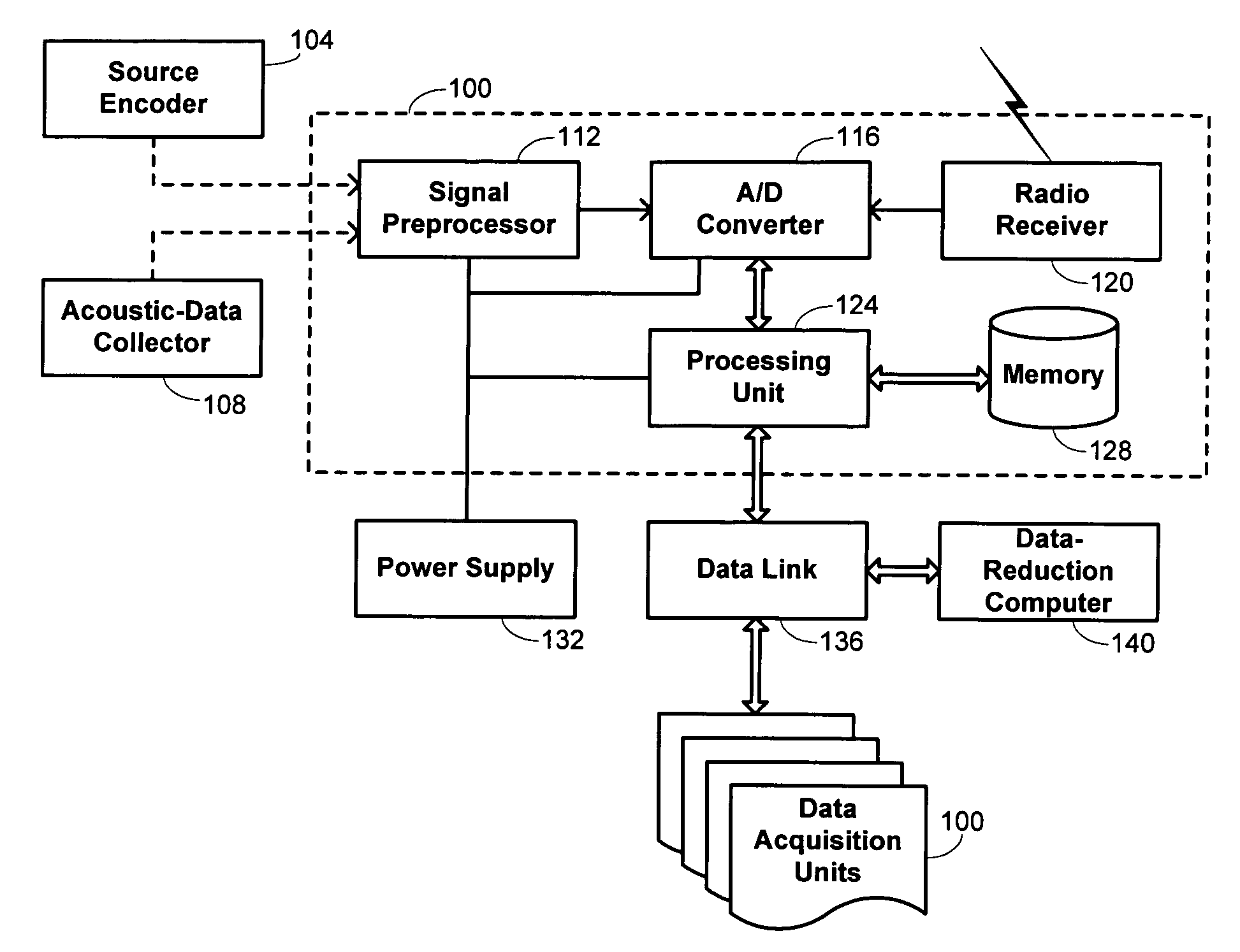
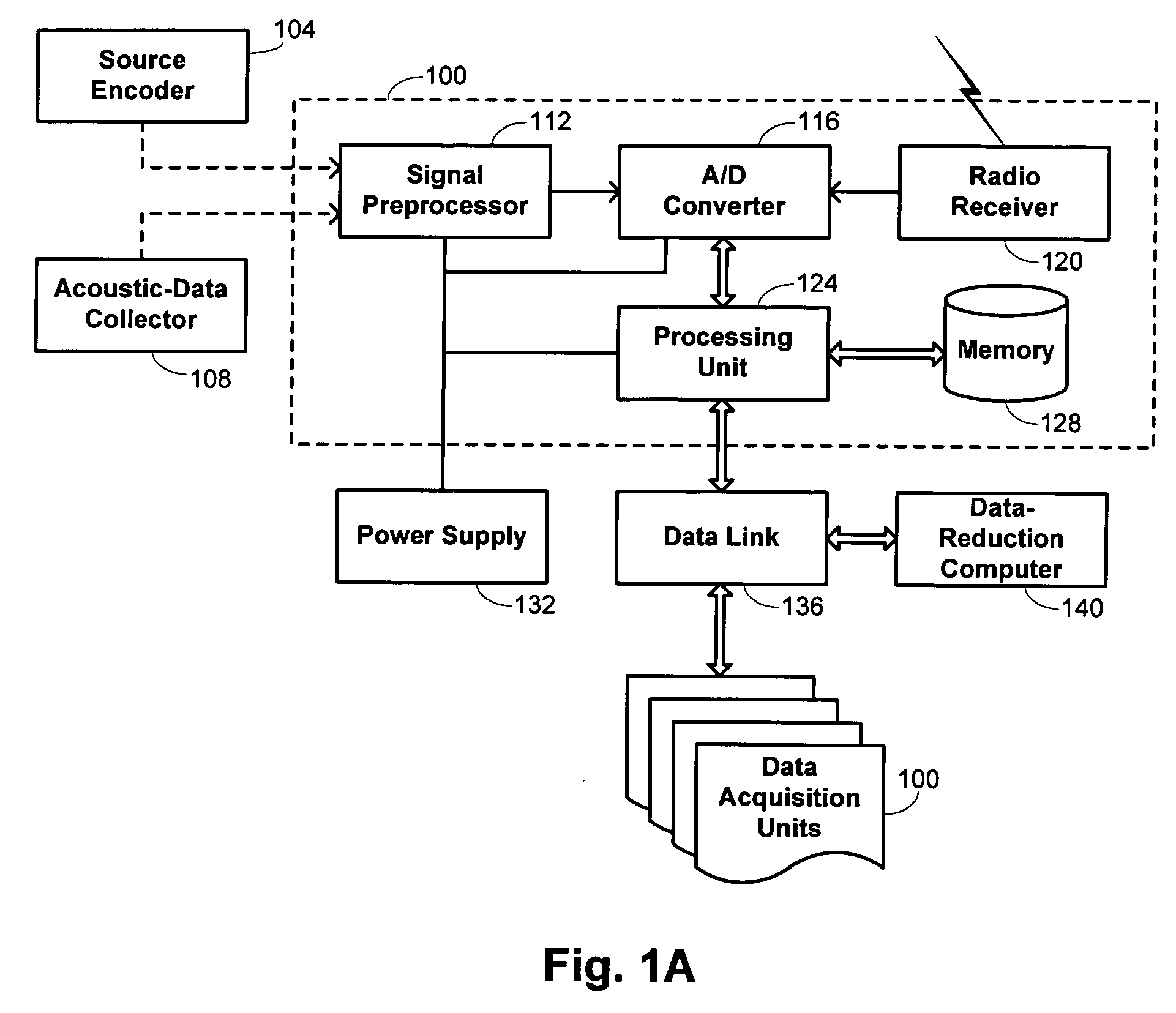
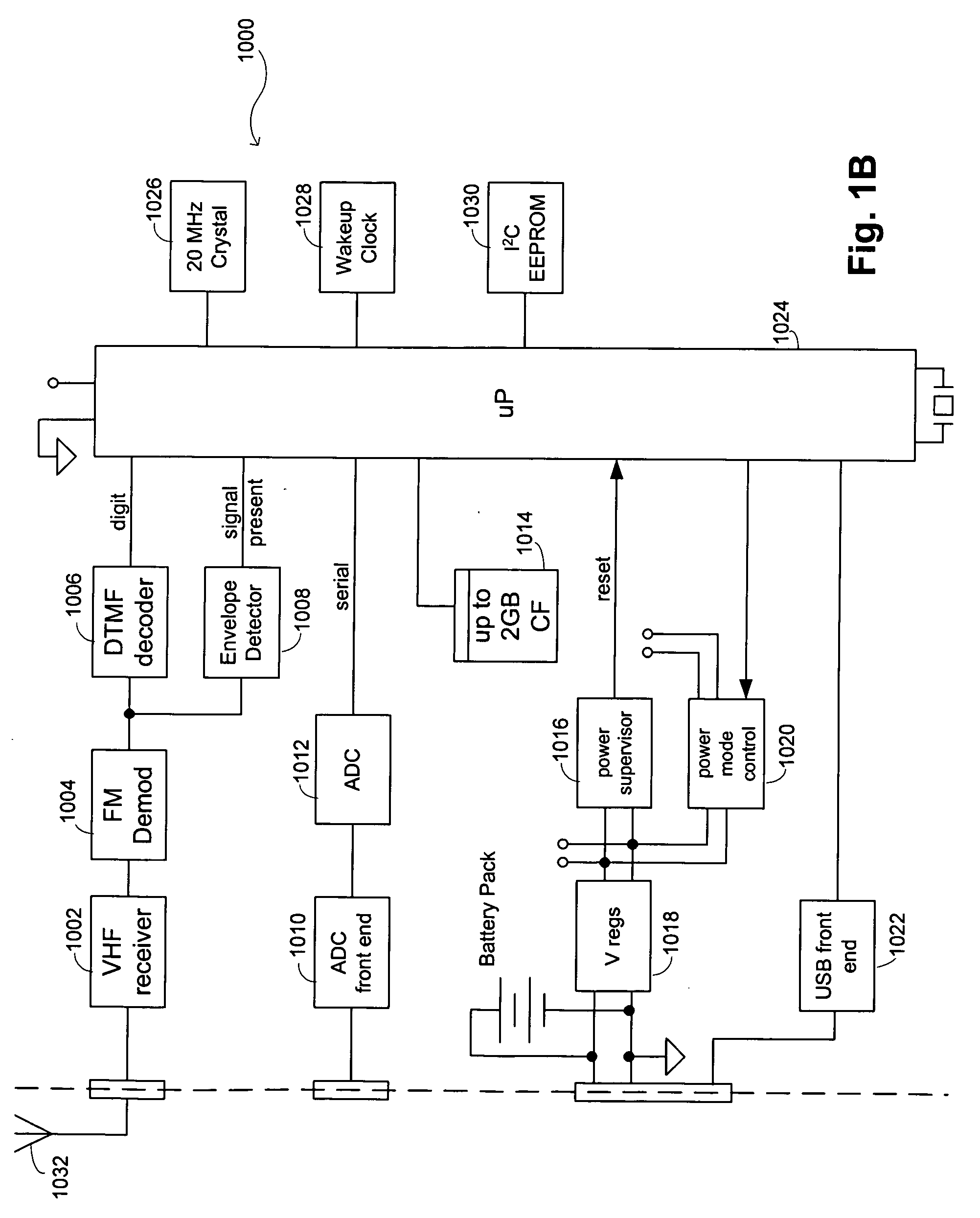
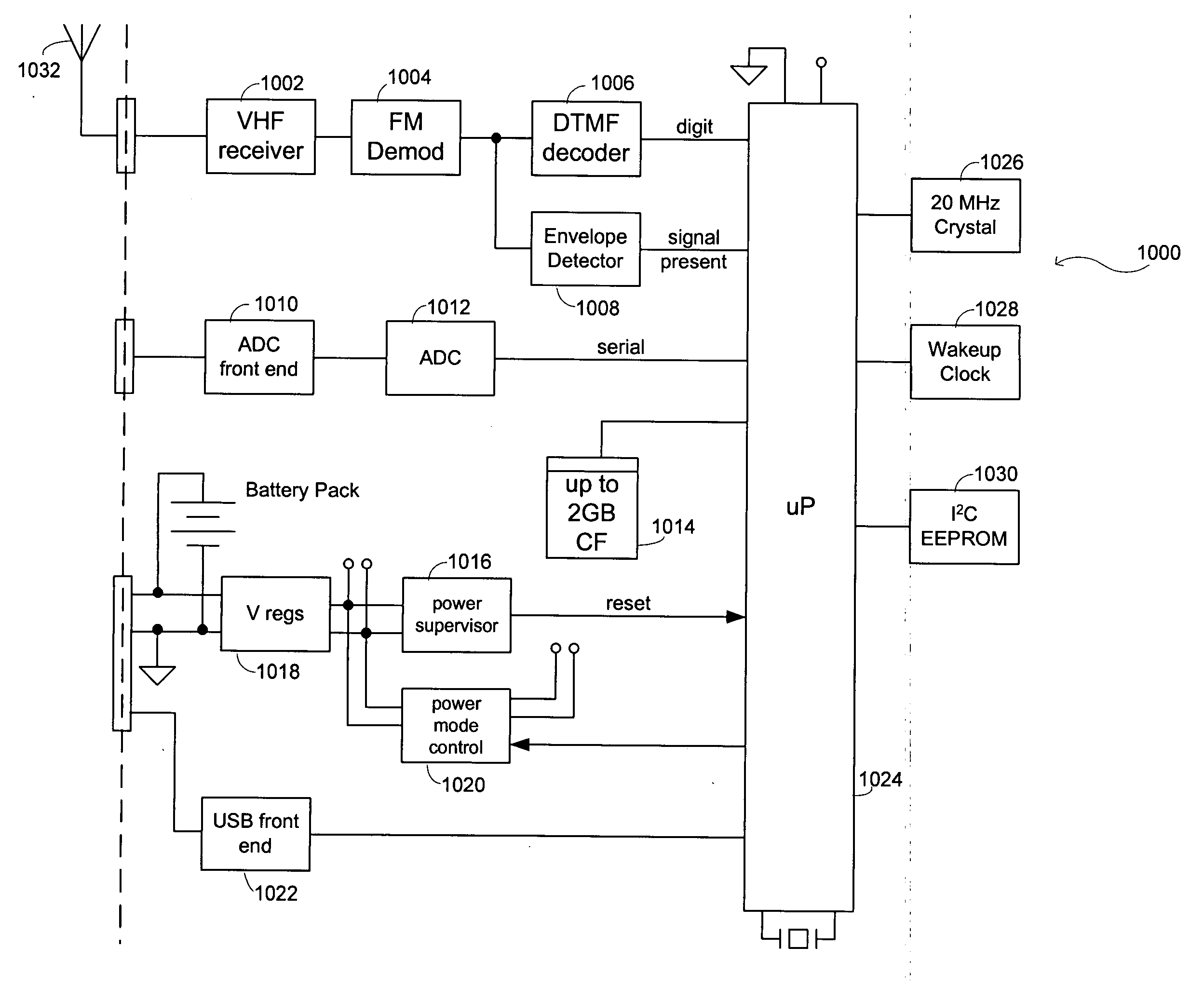
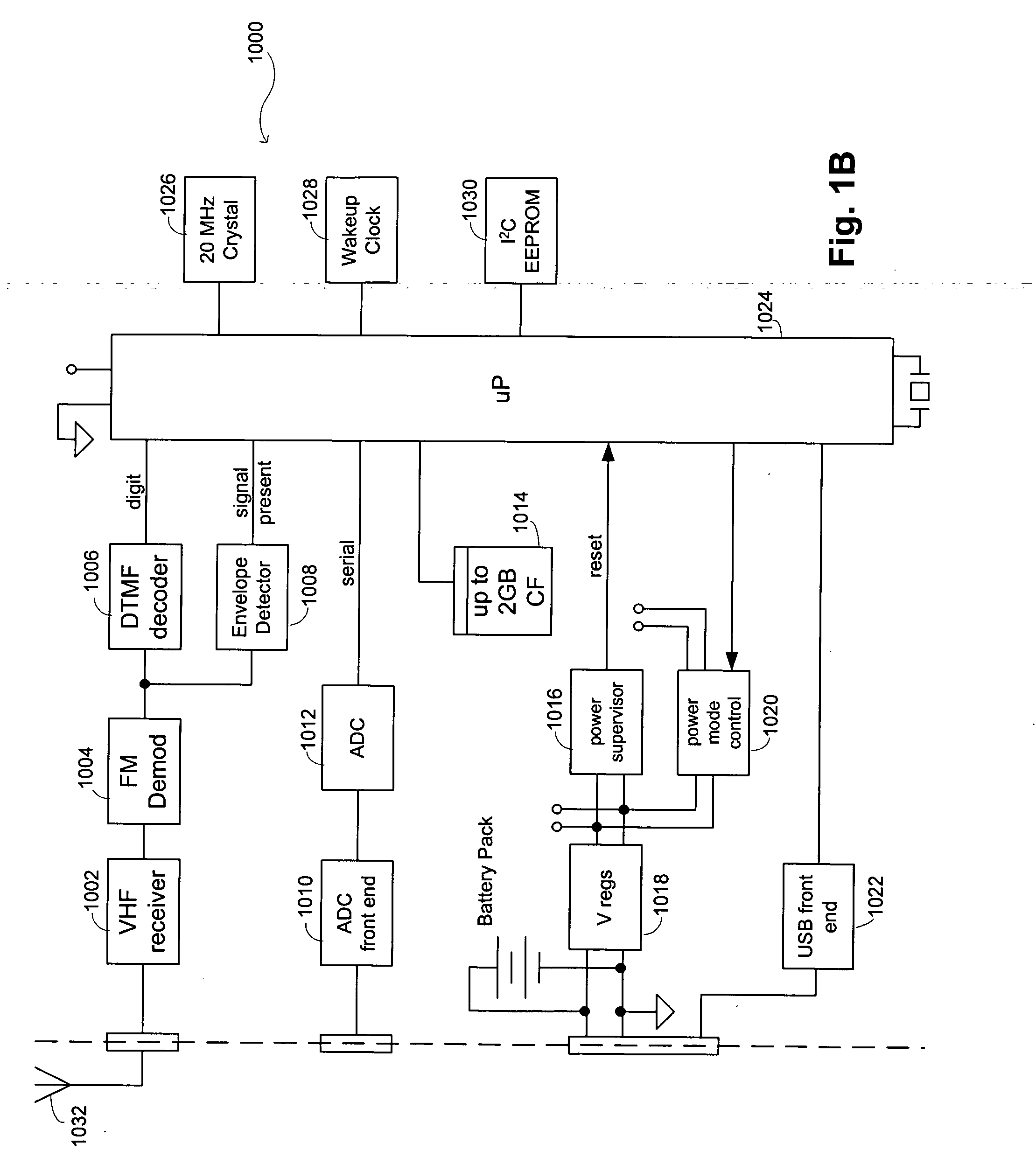
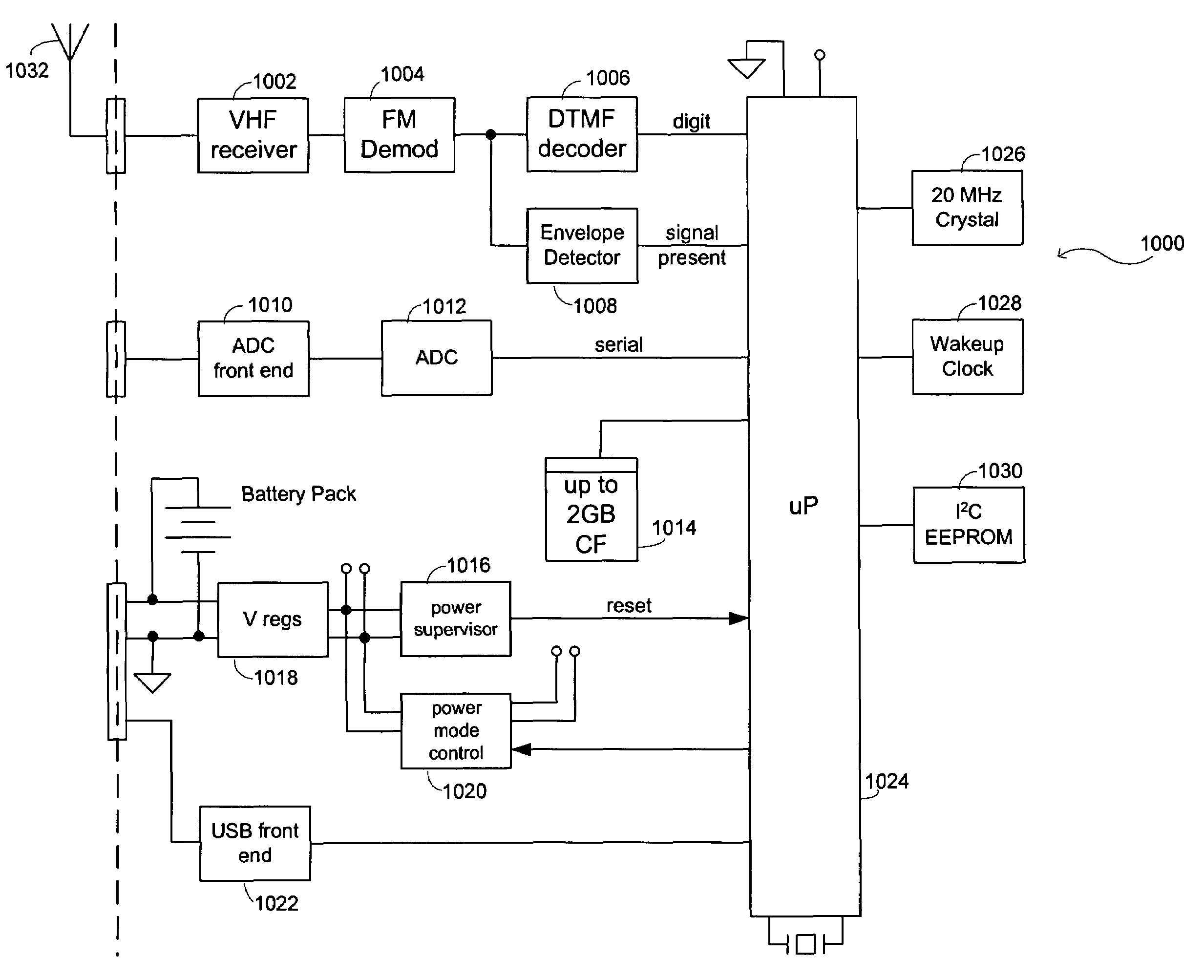
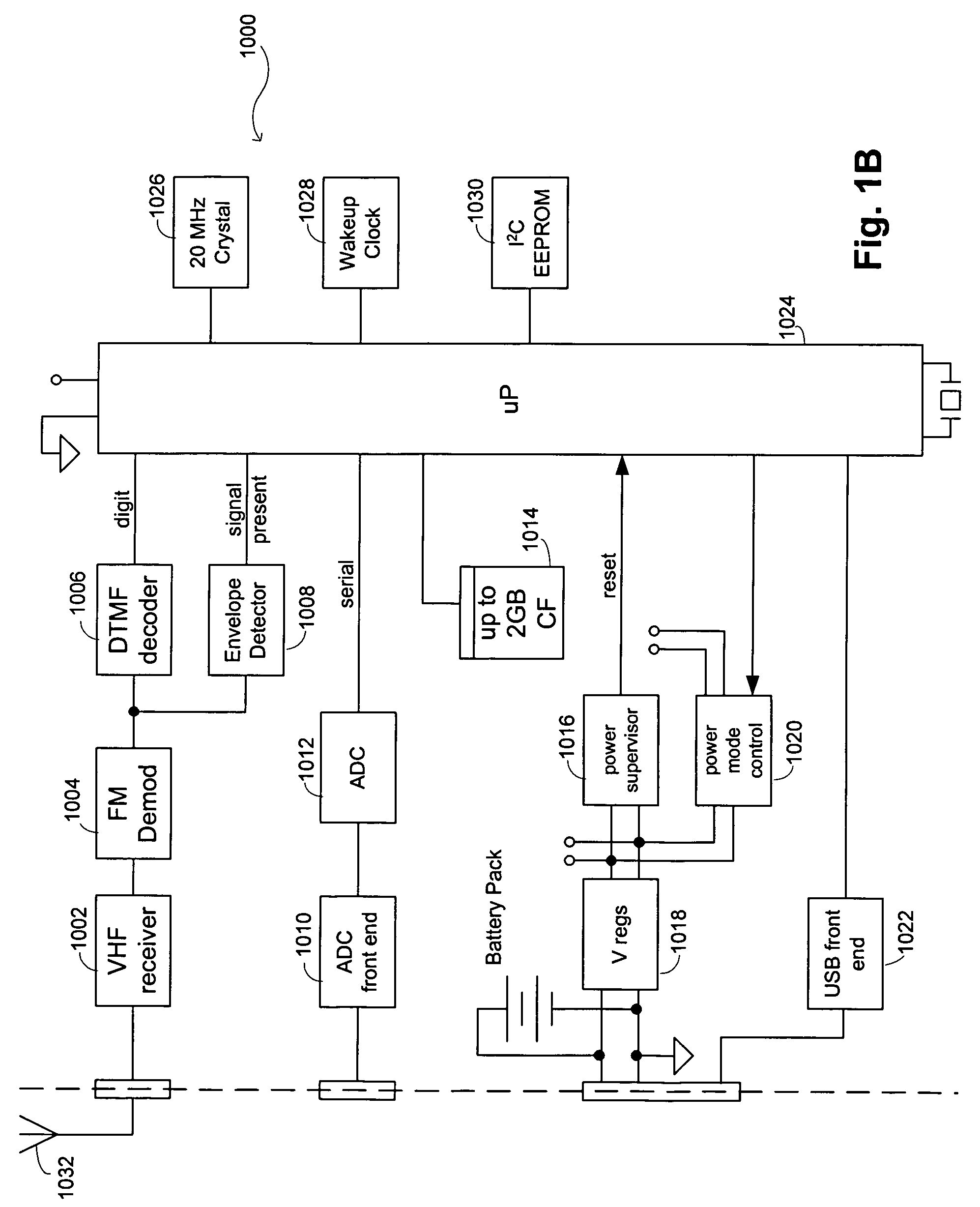
Seismic-data acquisition methods and apparatus
A self-contained data acquisition unit is provided for acquiring seismic data. The unit has a microprocessor and an antenna adapted to receive an electromagnetic signal. A decoder is connected with the microprocessor and adapted to convert received electromagnetic signals to dual-tone multiple-frequency (“DTMF”) digits. A geophone interface is provided with a geophone for collecting acoustic data incident on the geophone. A memory is connected with the geophone interface for storing a representation of the collected acoustic data and for storing a representation of a reference electromagnetic signal to be used in synchronizing acoustic data collected by other data acquisition units. A battery power source is connected with the microprocessor.
Owner:ASCEND GEO
System for measuring a time offset and method of measuring a time offset
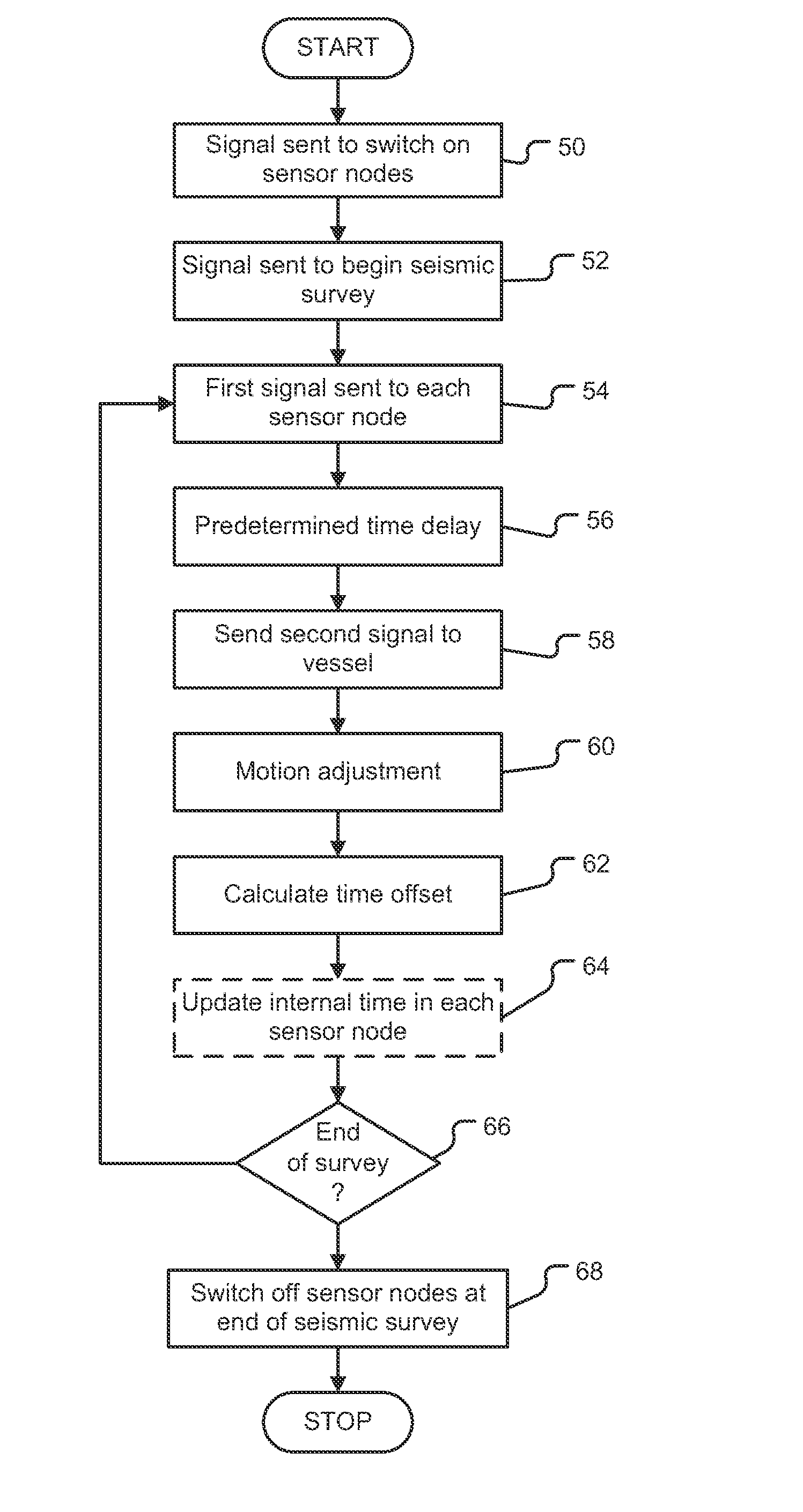
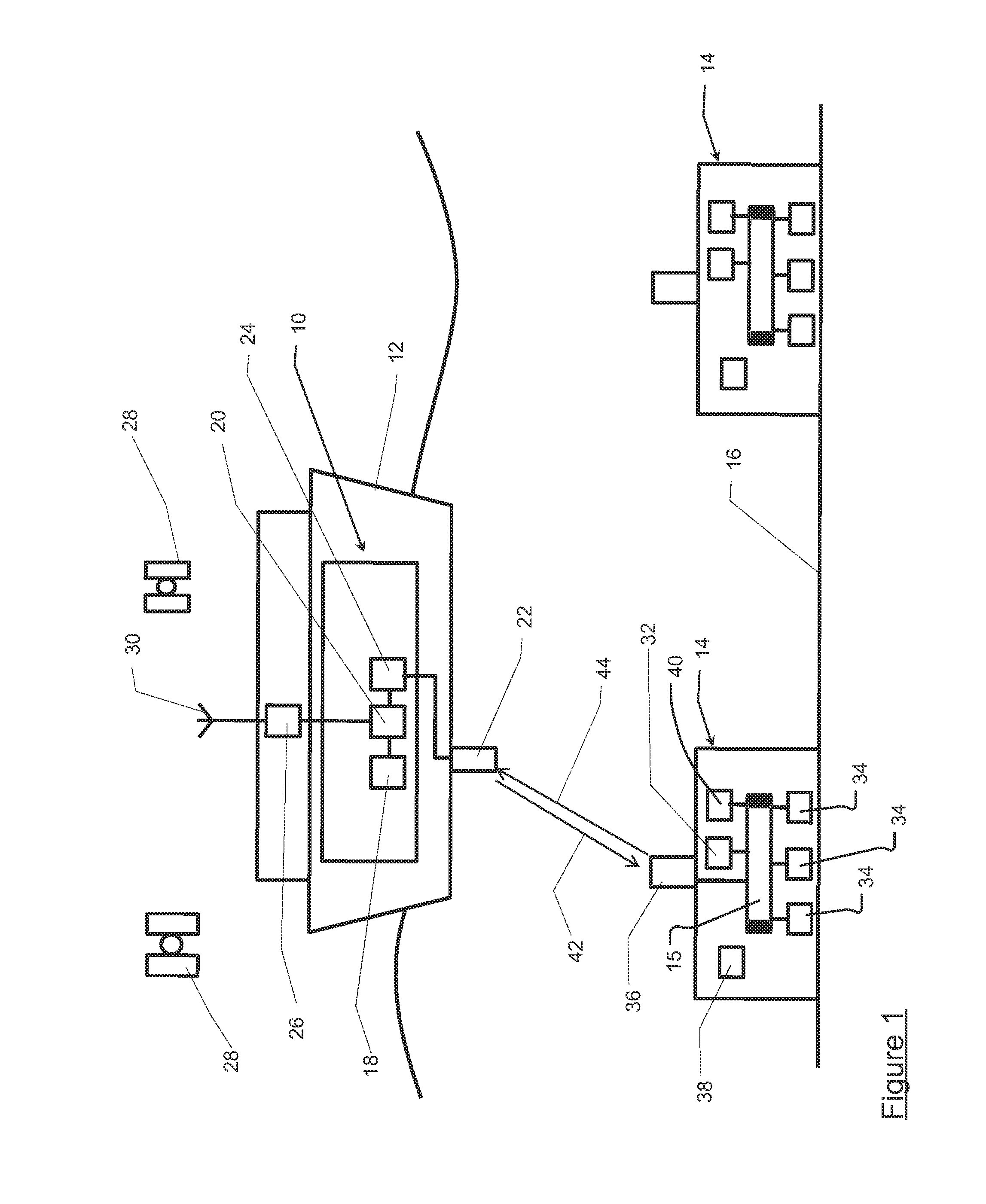
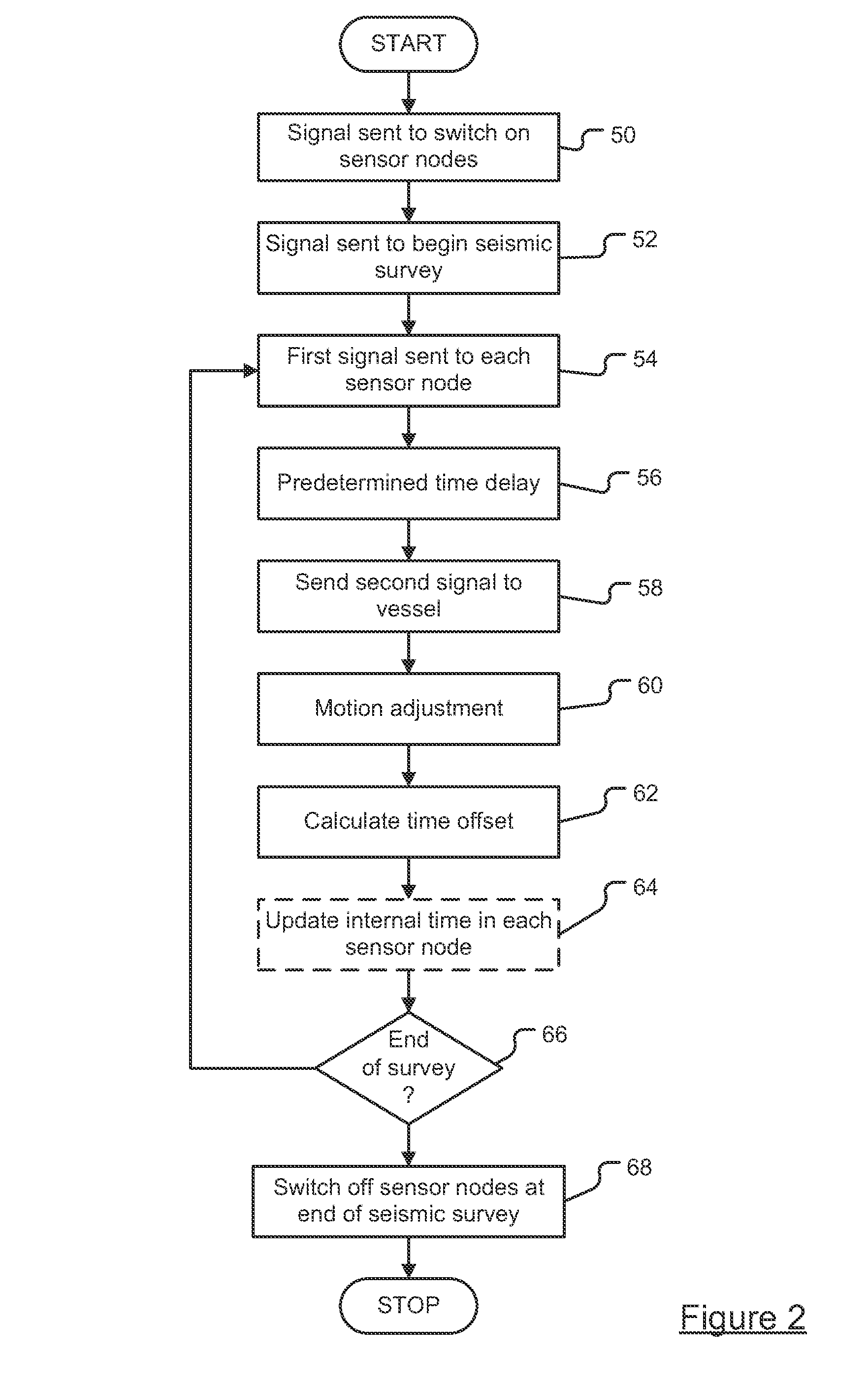
ActiveUS20120294112A1Improve convenienceImprove energy efficiencySonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionSeismic signal transmissionTransceiverTime delays
A system and method measures the time offsets of a plurality of acoustic sensor nodes relative to a reference time. The system includes an acoustic transceiver arranged to transmit a first signal to each acoustic sensor node and a processing resource arranged to record the transmission time of the first signal relative to the reference time. The acoustic sensor nodes receive the first signal and transmit a return second signal to the acoustic transceiver after a predetermined time delay, the second signal including the current acoustic sensor node internal time. The acoustic transceiver receives the second signal, and the processing resource records the time at which the second signal was received relative to the reference time and records also the combined time of flight of the first and second signal. From this data the time offset between the sensor node internal time and the reference time is calculated.
Owner:SONARDYNE INT LTD
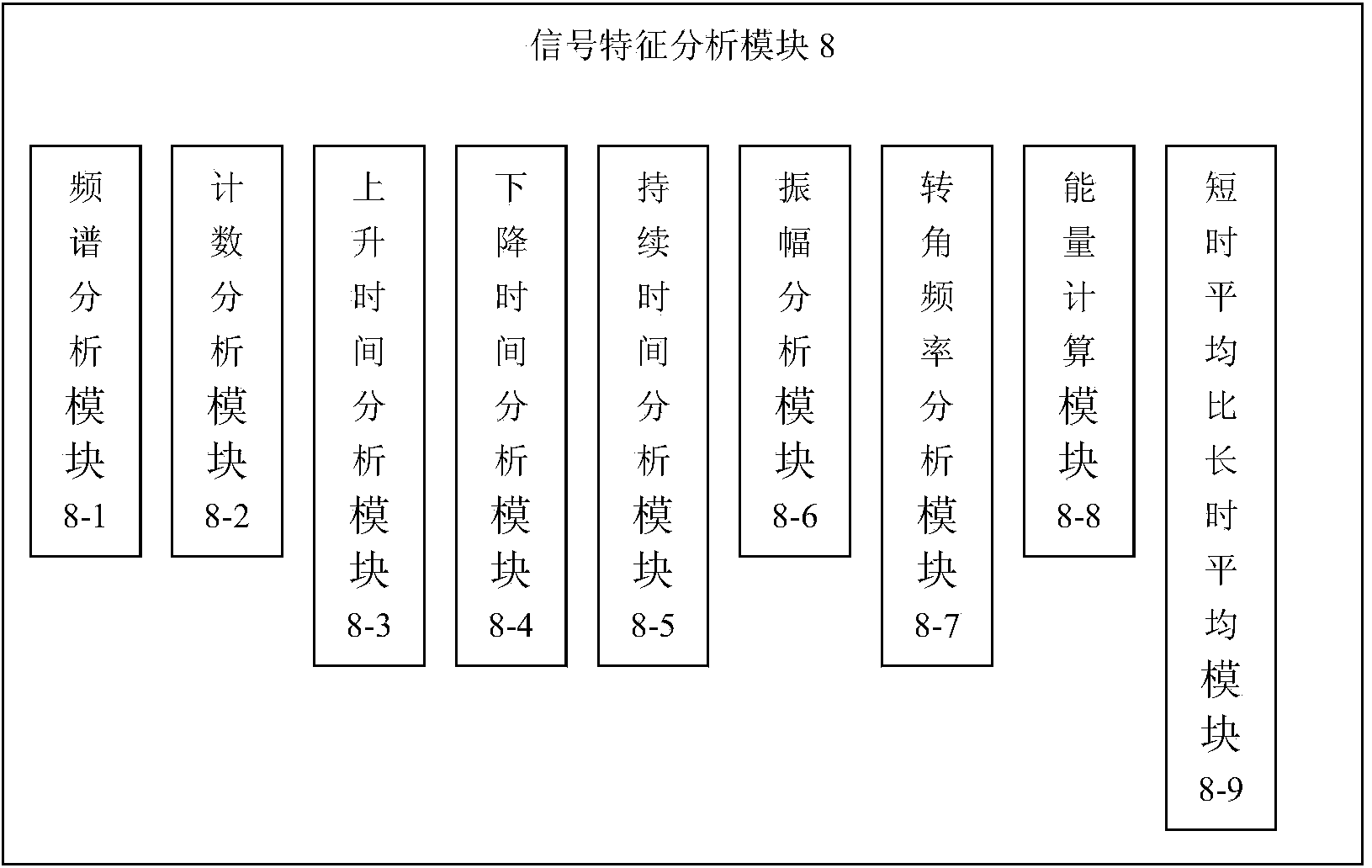
Multifunctional comprehensive integrated high-precision intelligent micro-seismic monitoring system
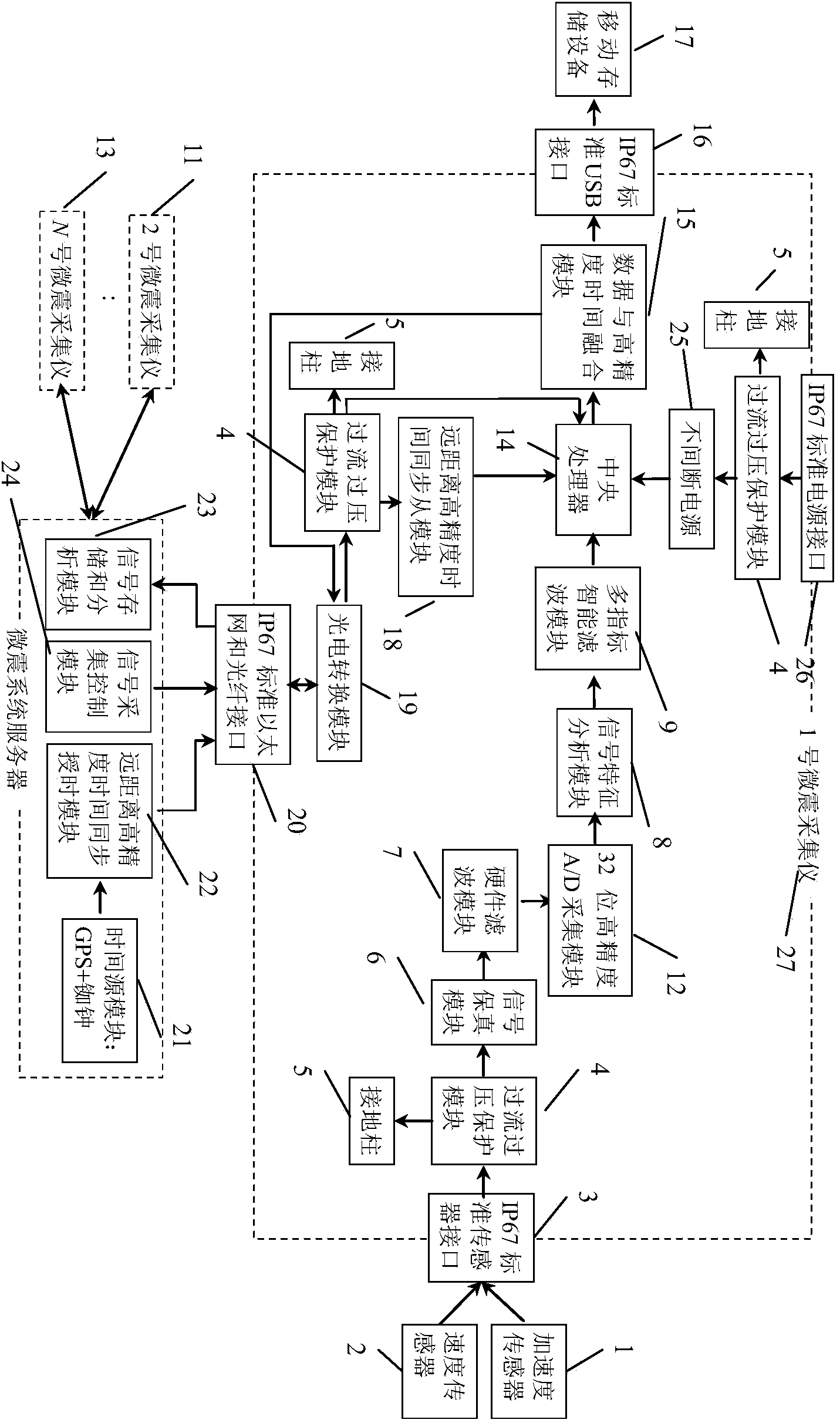
ActiveCN104062677AImprove time synchronization accuracyAchieve coordinationSeismic signal recordingNoise levelMonitoring system
The invention discloses a multifunctional comprehensive integrated high-precision intelligent micro-seismic monitoring system, and the system mainly comprises a micro-seismic collector and a micro-seismic system server. The micro-seismic collector mainly comprises a signal hardware filter module, an AD collection module, a signal characteristic analysis module, and a multi-index intelligent filter module, and a data and high-precision time fusion module. The micro-seismic collector is mainly used for signal filtering, analysis, collection and transmission. The micro-seismic system server comprises a signal collection control module, a signal storage and analysis module, and a time module. The micro-seismic system server is mainly used for achieving the functions of parameter setting, signal analysis and time synchronization. The system provided by the invention improves the precision of time synchronization, can meet the demands of an on-site high-precision test, can record micro-seismic data continuously and effectively, can enable noise to be kept under a lower level, can carry out the setting of intelligent filtering and waveform collection according to the actual needs, achieves the stable transmission, storage and processing of data, and guarantees the quick analysis of disasters and warning for disasters.
Owner:INST OF ROCK & SOIL MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com