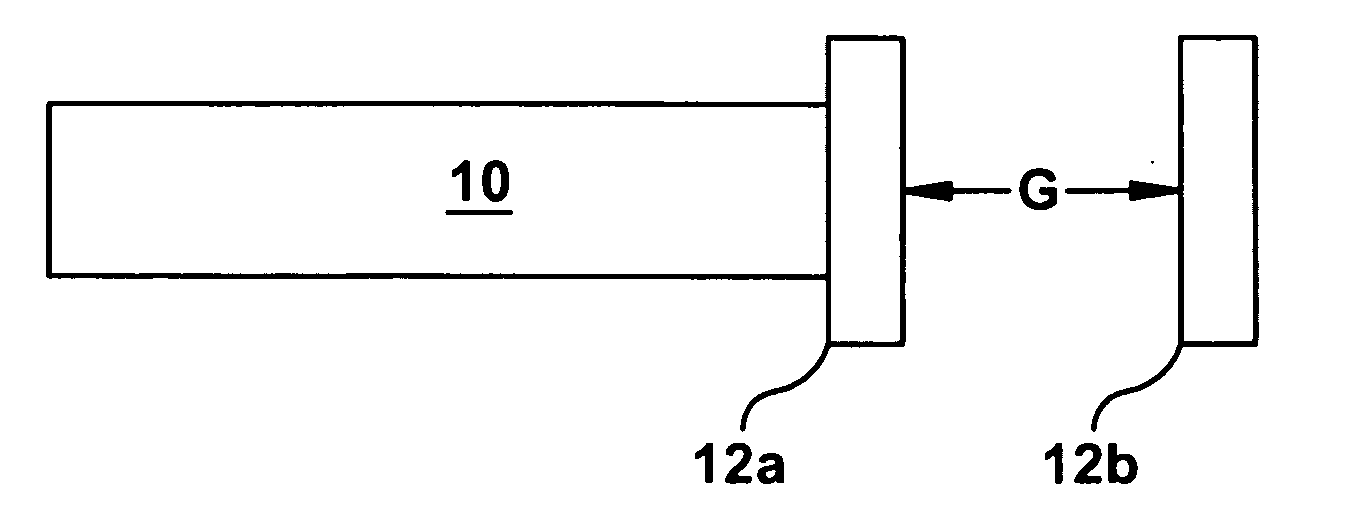
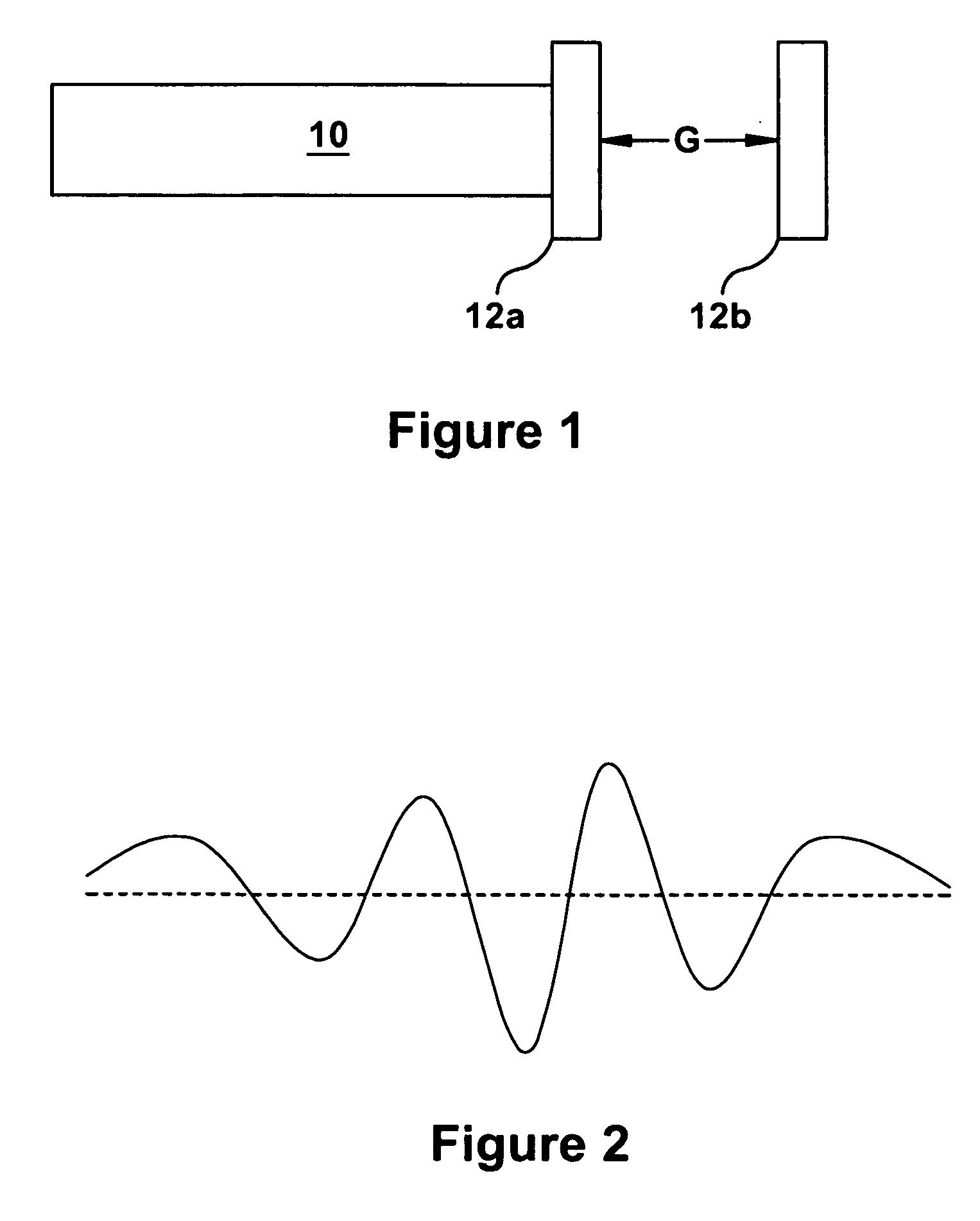
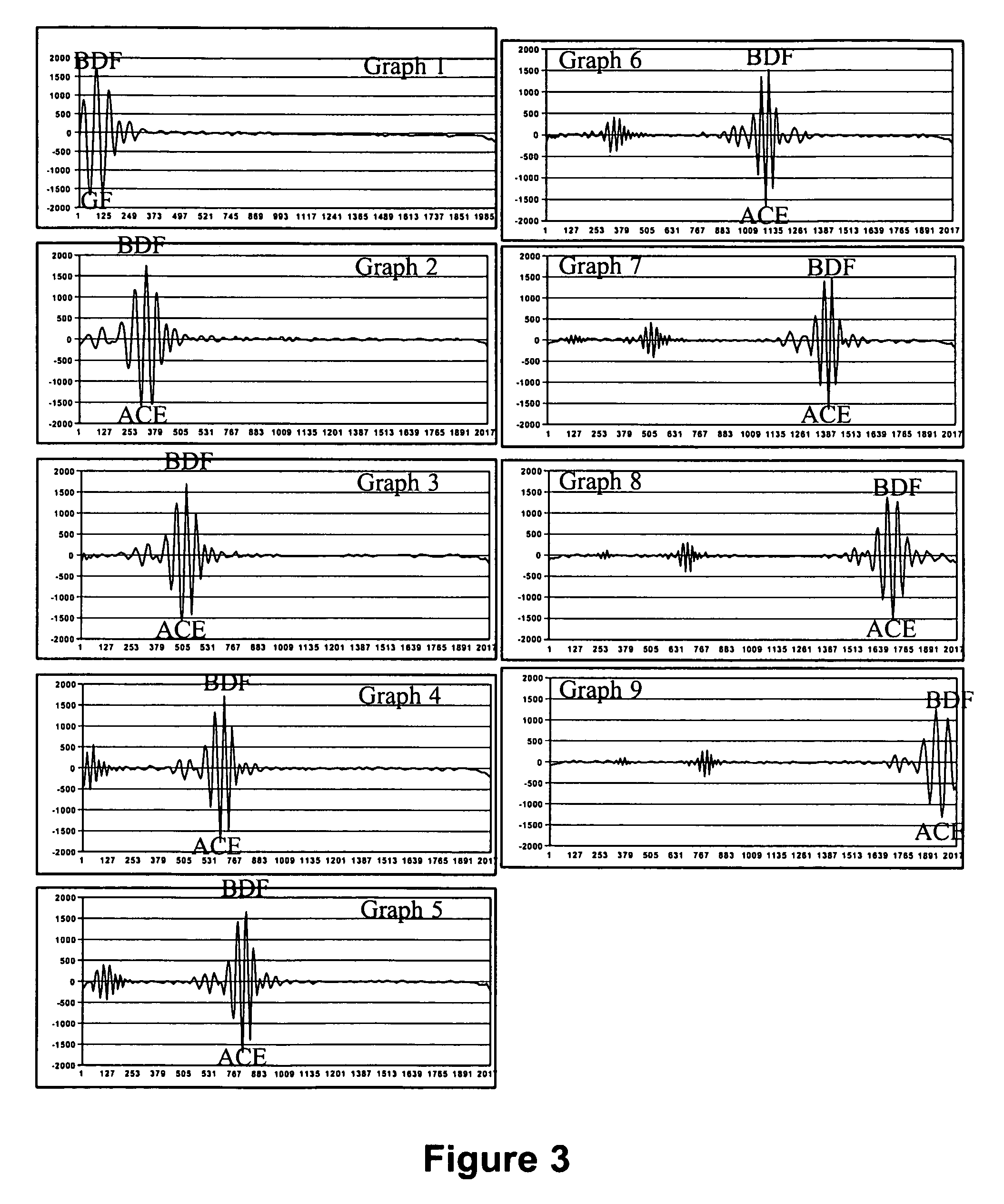
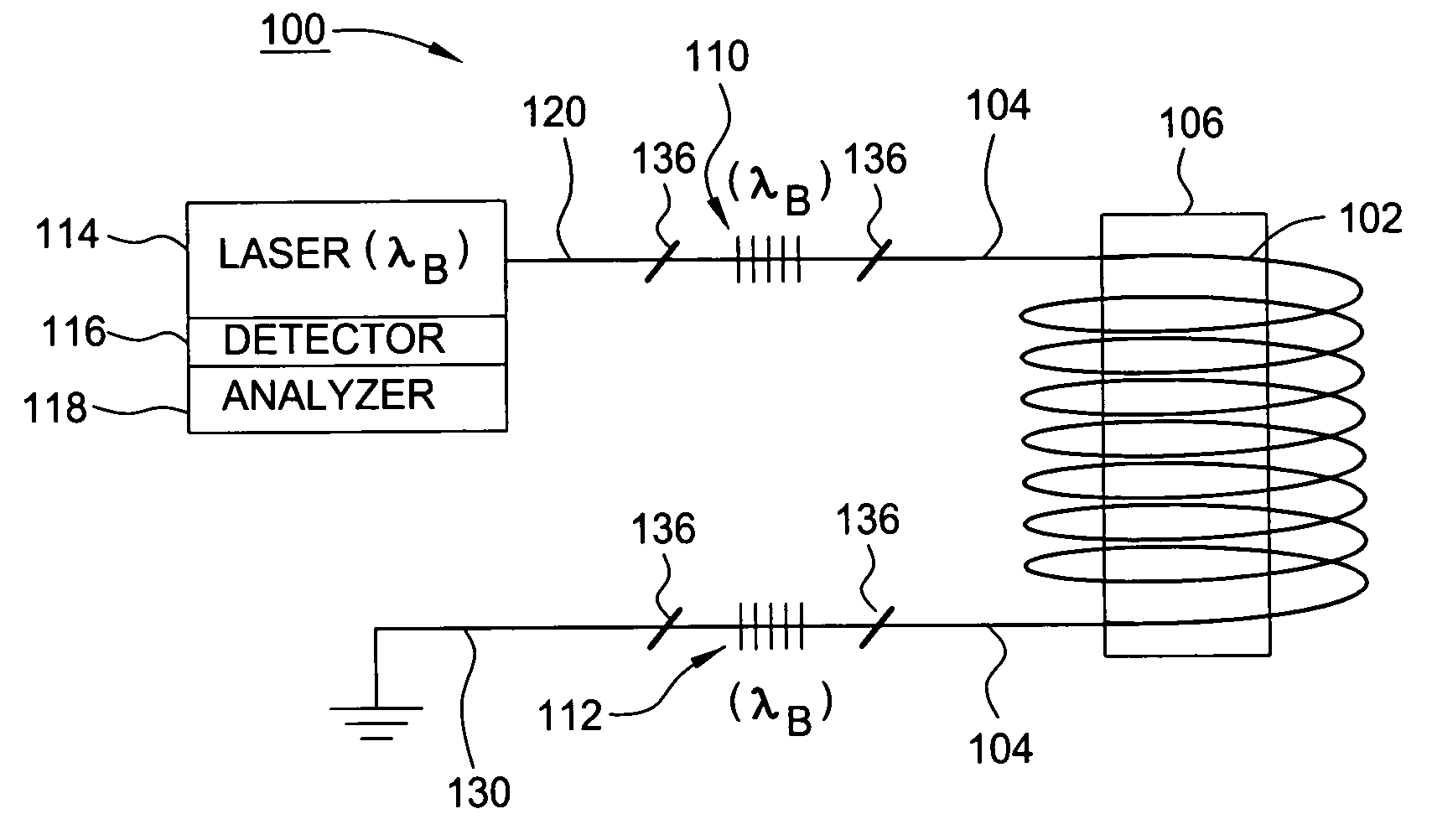
Patents
Literature
102 results about "Interferometric sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
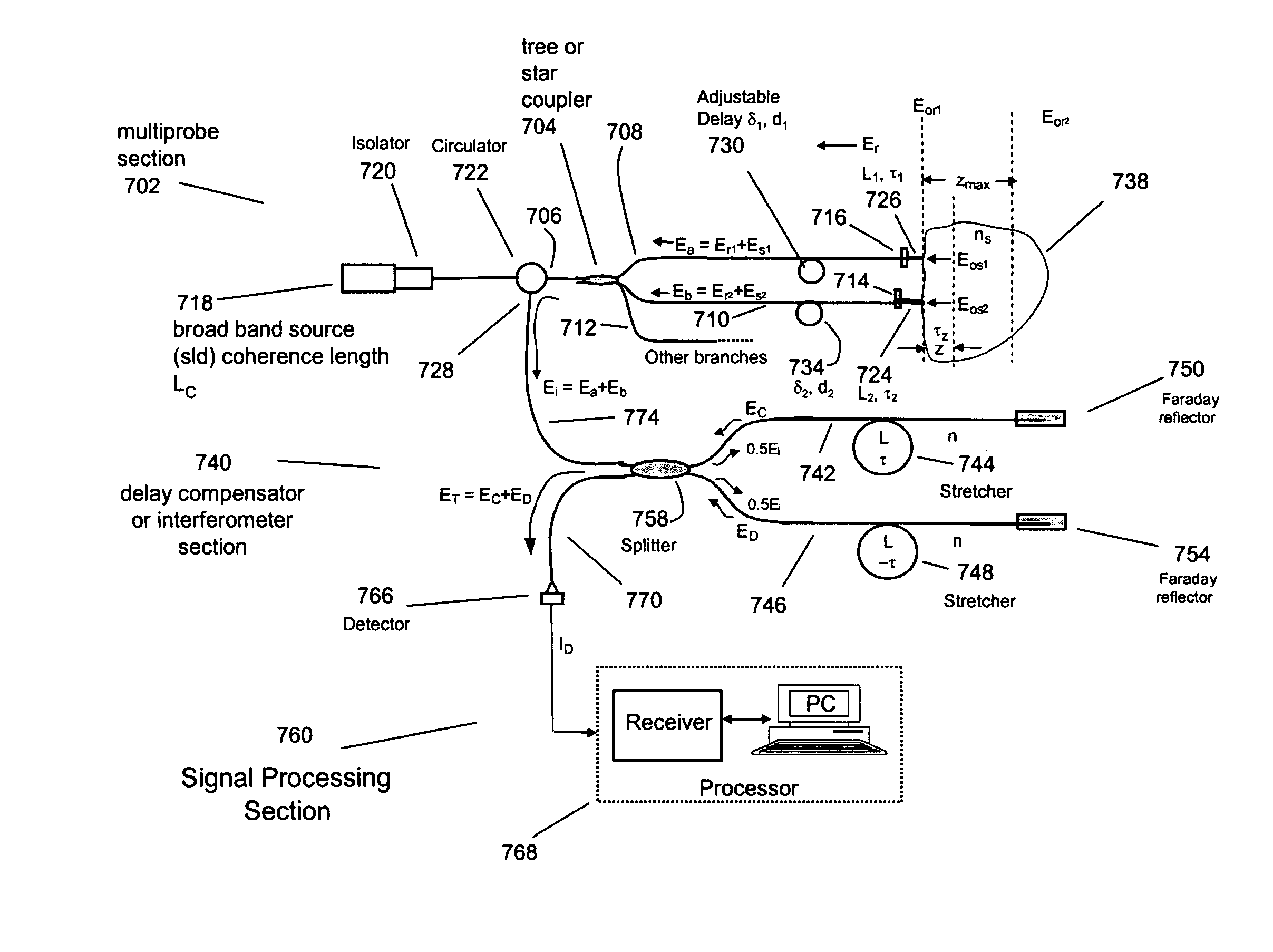
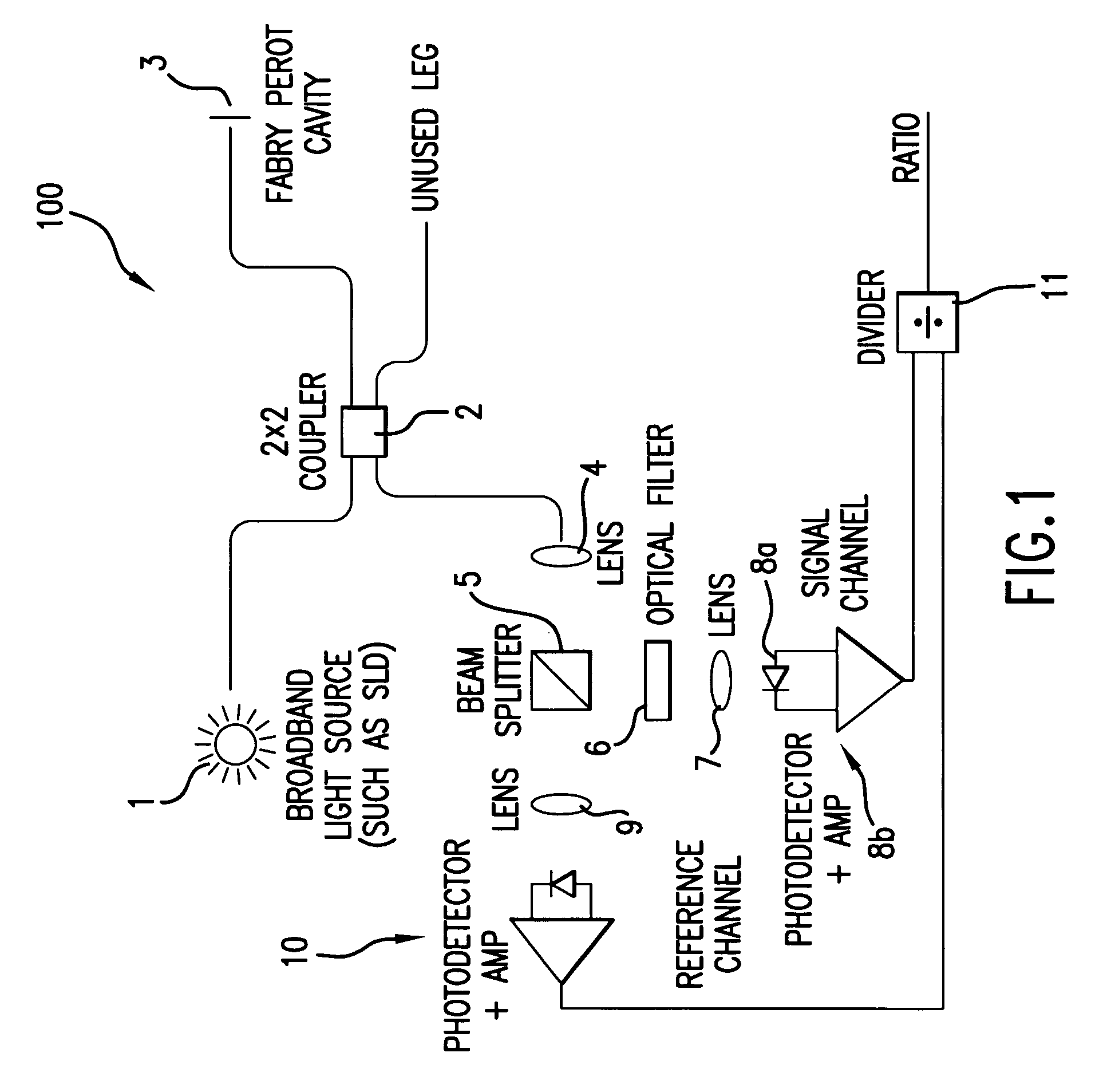
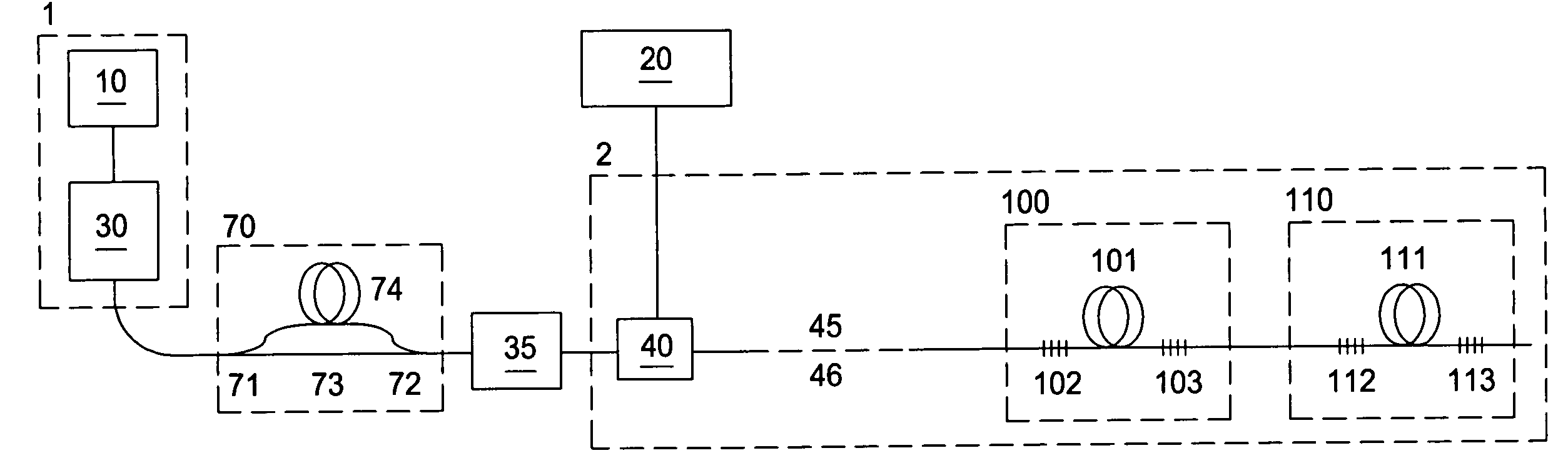
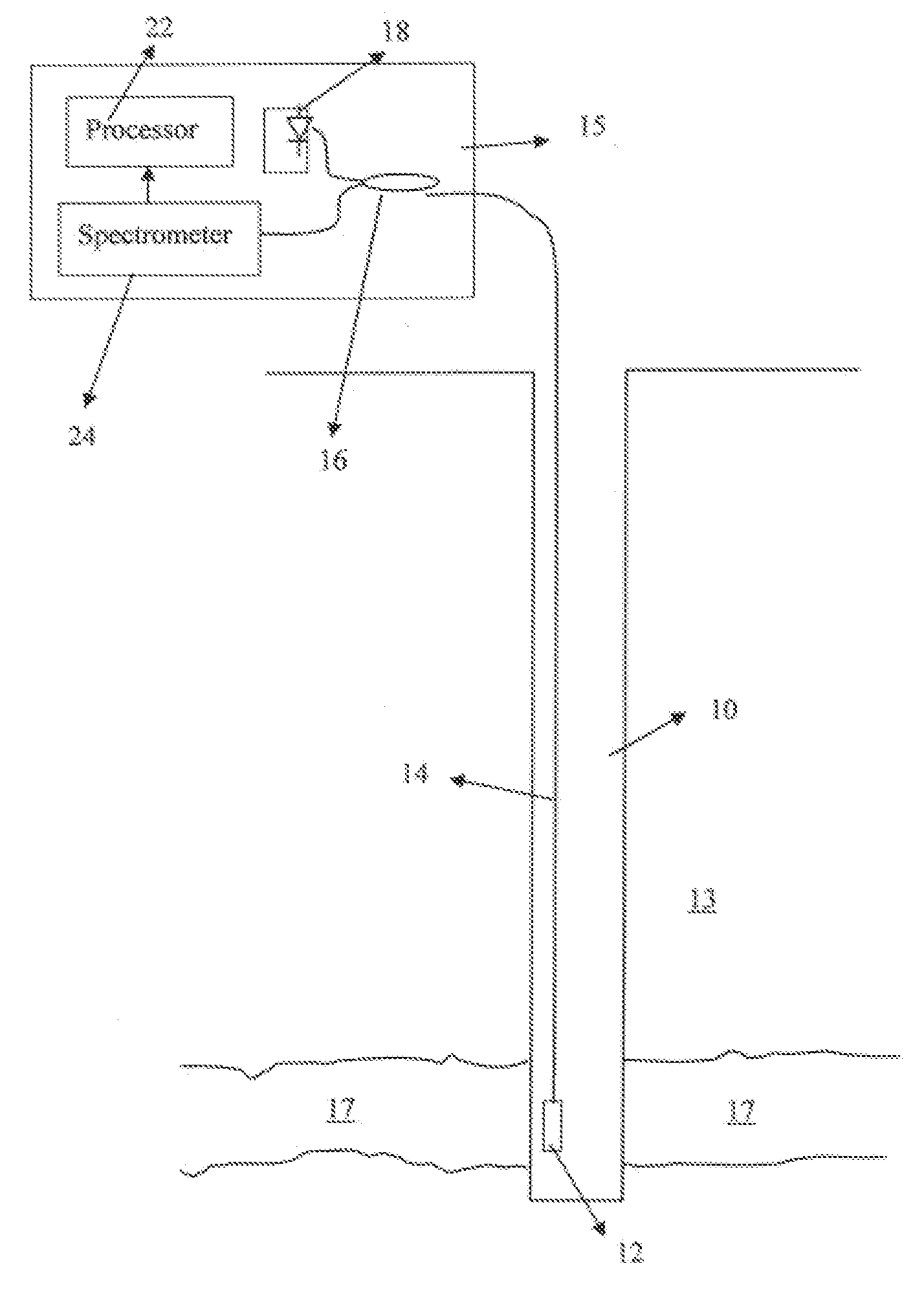
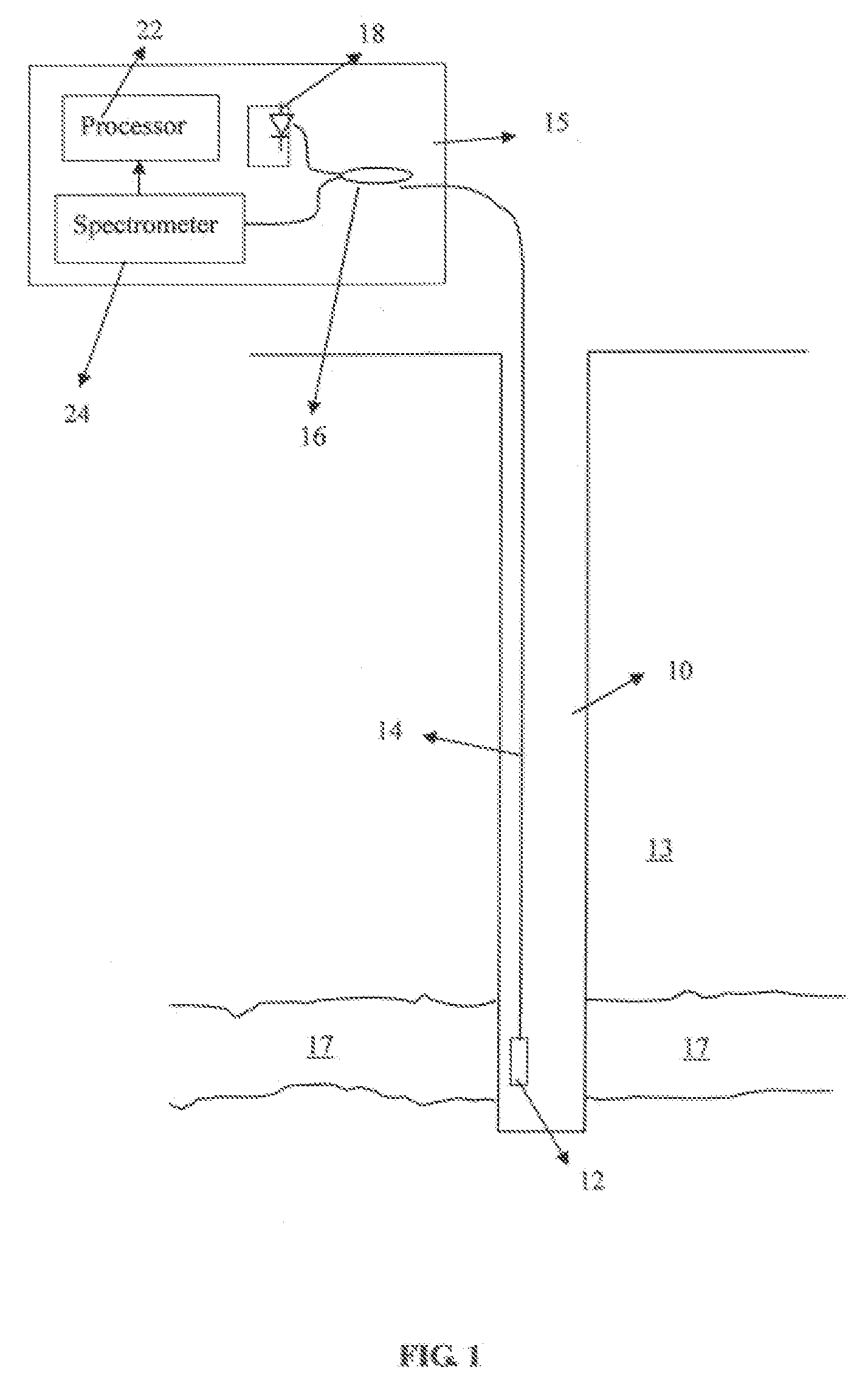
Single trace multi-channel low coherence interferometric sensor
InactiveUS20060103850A1Shorten the timeQuick identificationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringInterferometric sensorBorescope
Interferometers and autocorrelator based sensors are disclosed that are configured to have multiple sample arms which can be scanned and the backscattered low coherence source light from a sample resolved in a single sweep of one or more variable delays of the sensor. Borescopes and catheters capable of scanning multiple sections or areas of materials and tissues using these sensors are described.
Owner:MEDEIKON
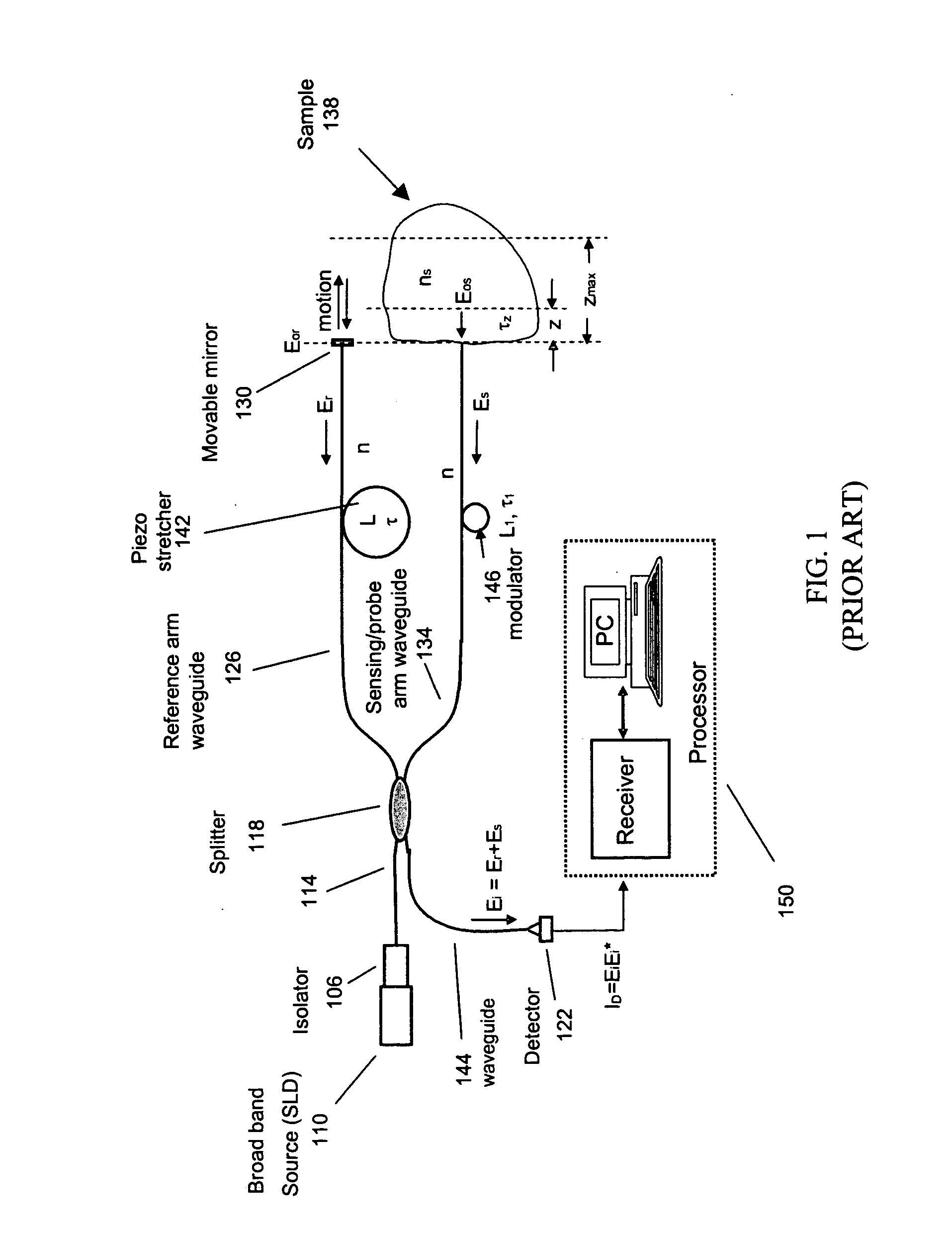
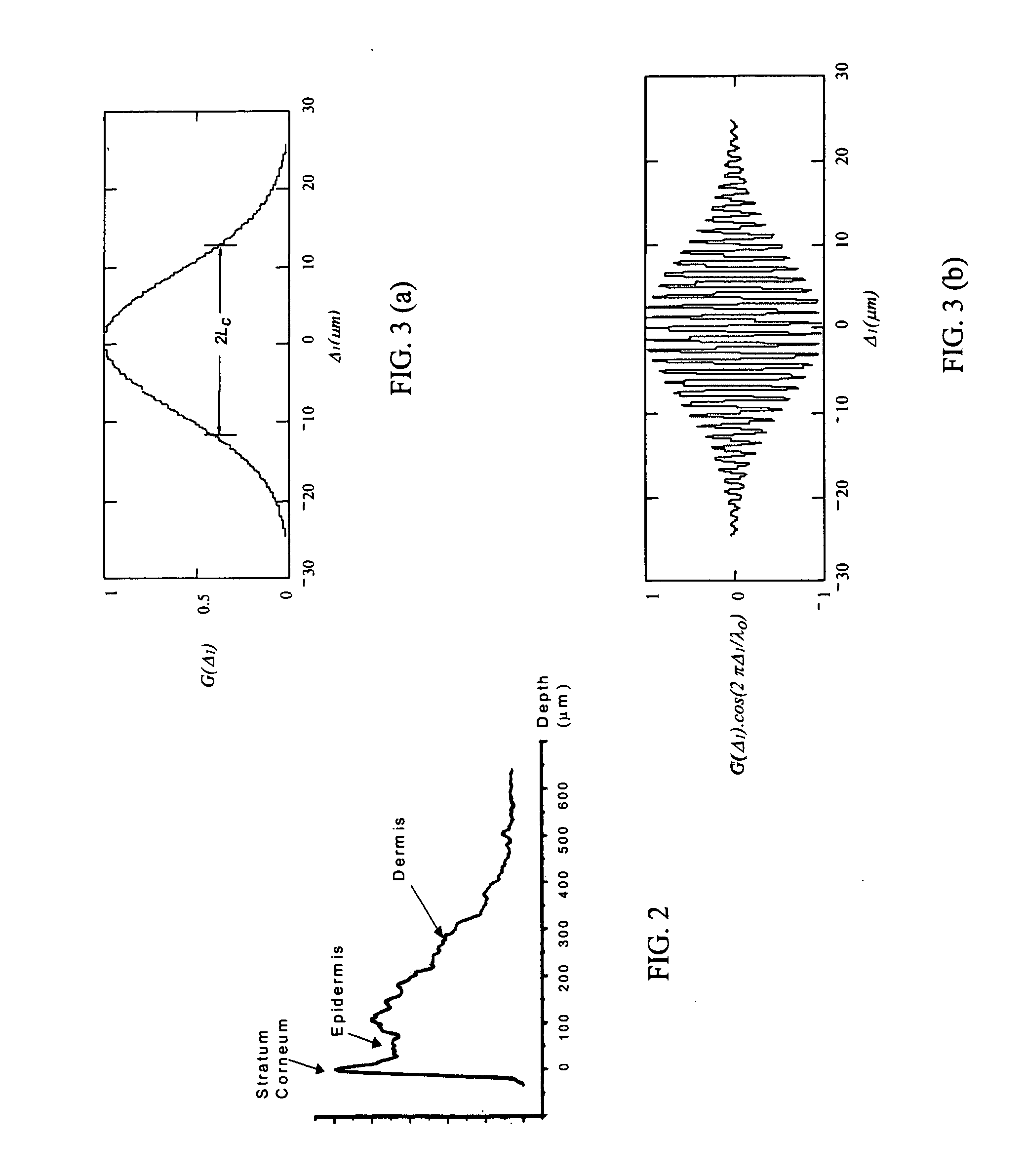
Interferometric sensor for characterizing materials
ActiveUS20050190372A1Fast and inexpensiveRobust designScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberInterferometric sensor
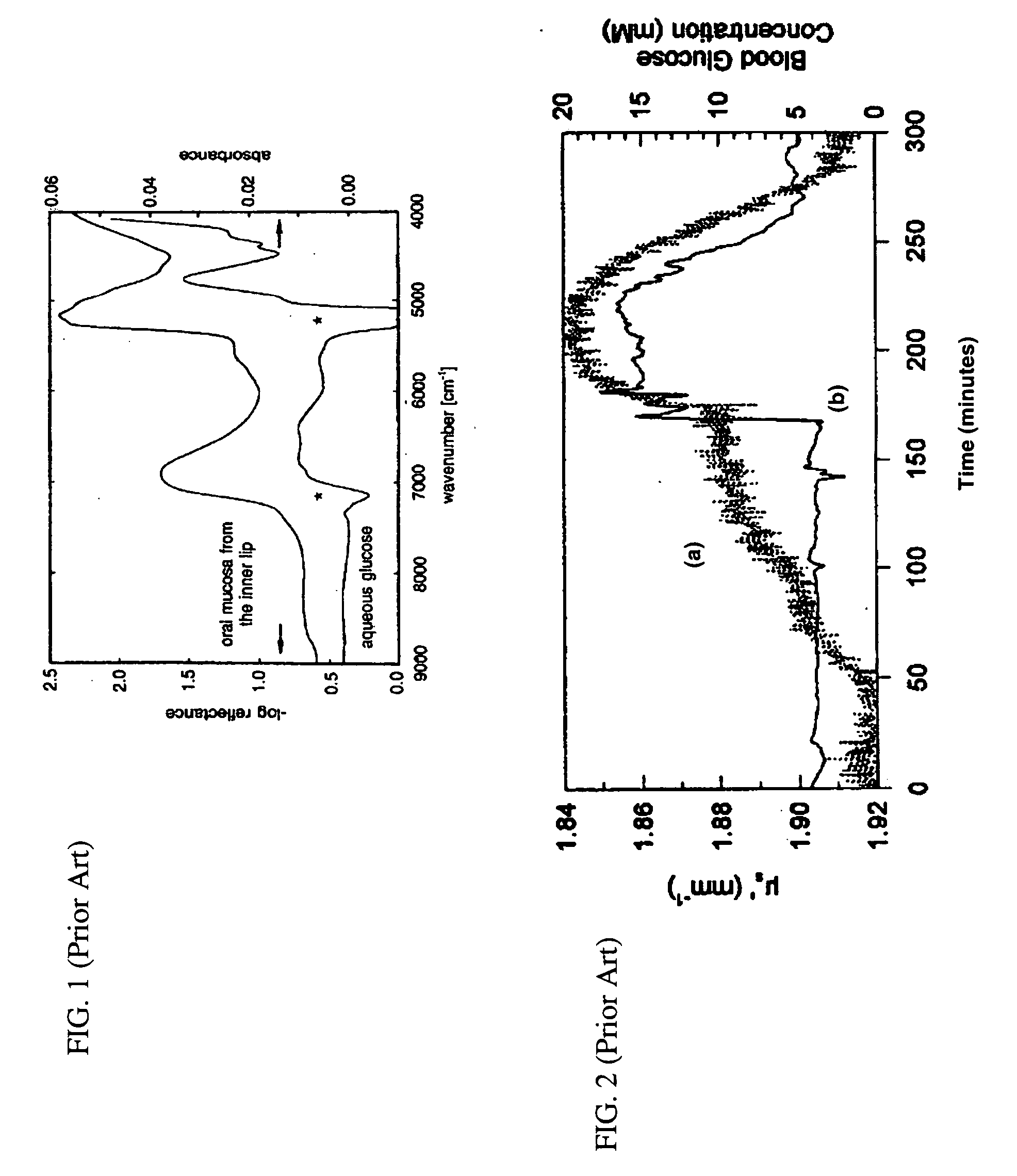
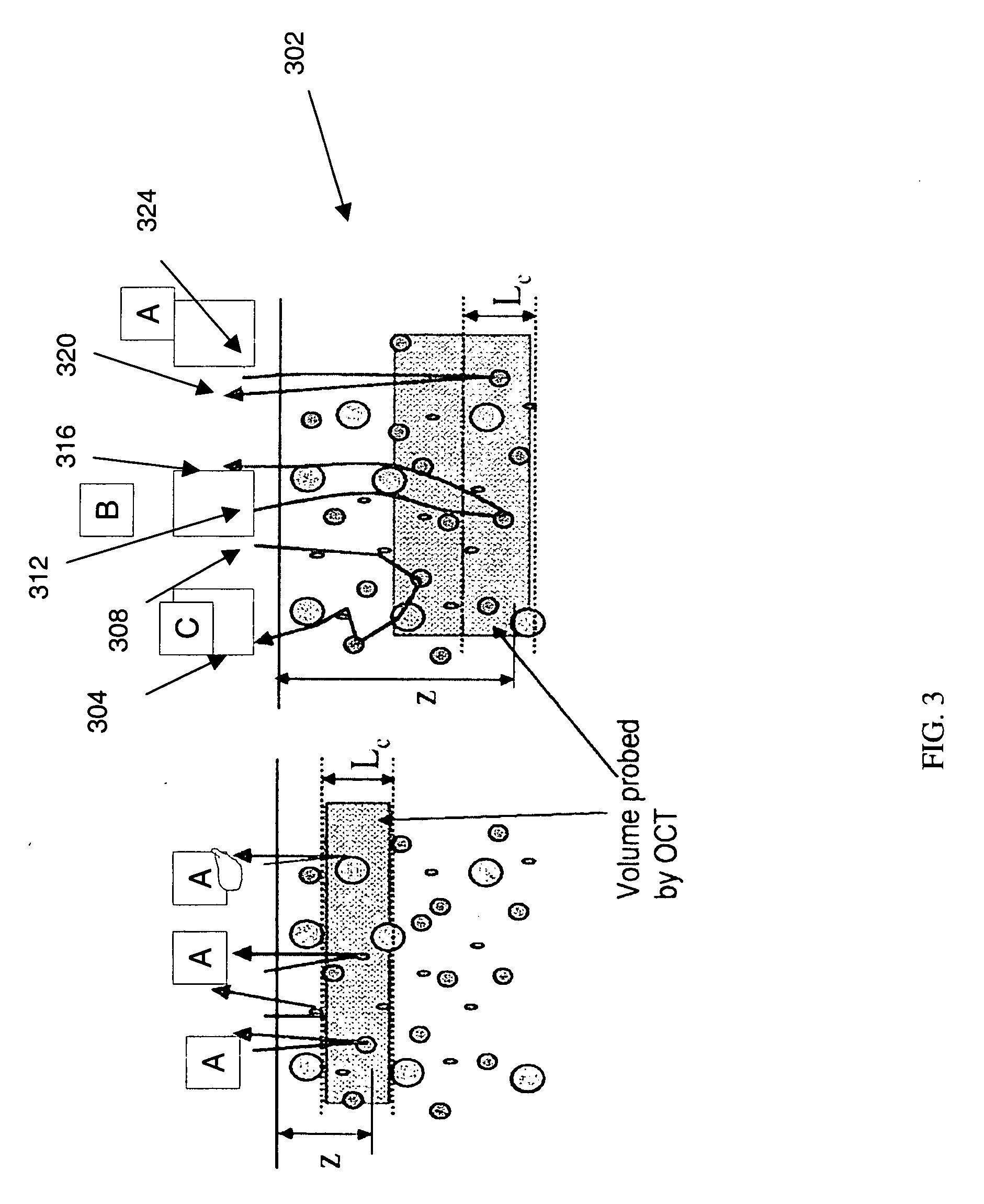
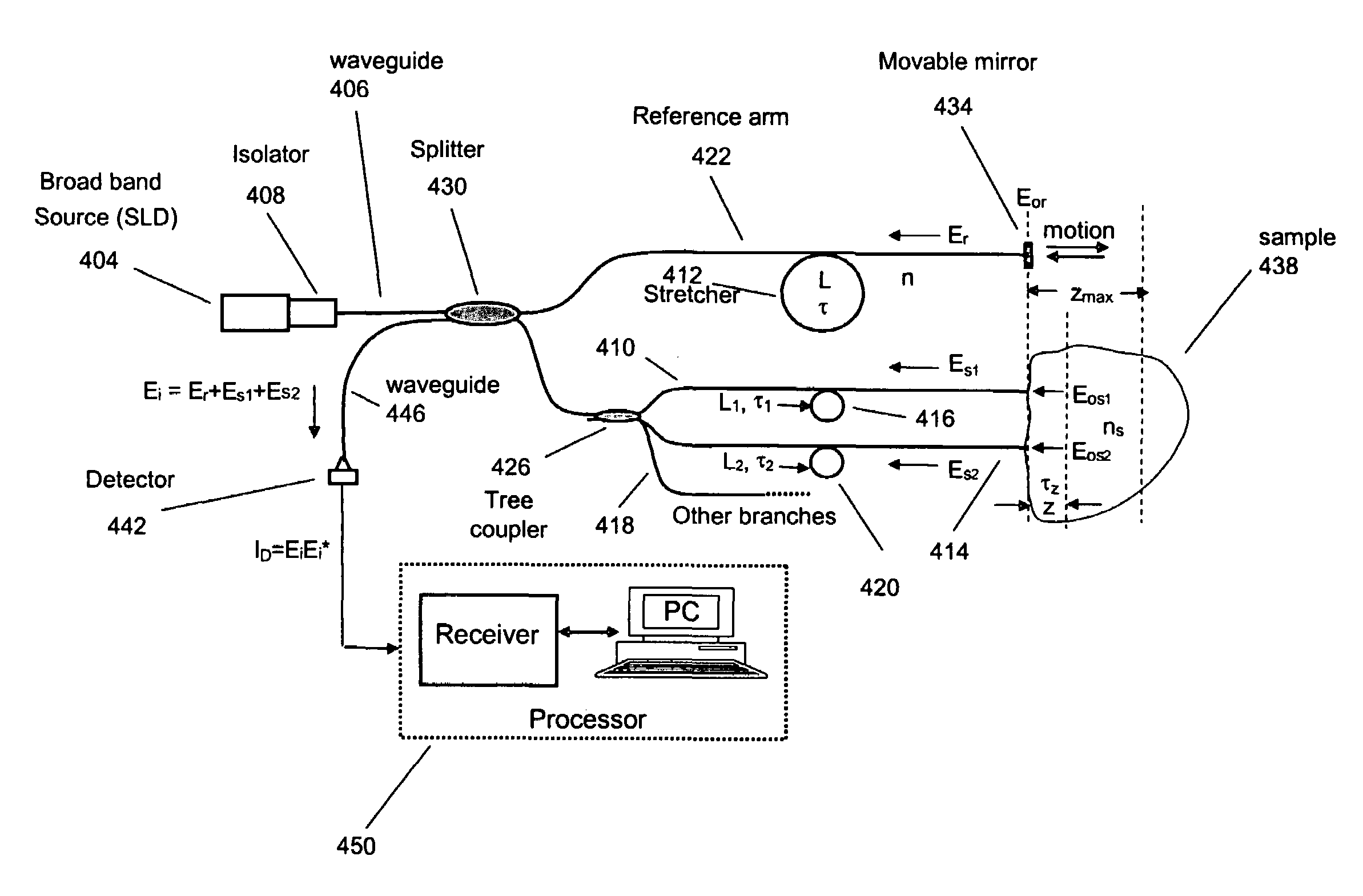
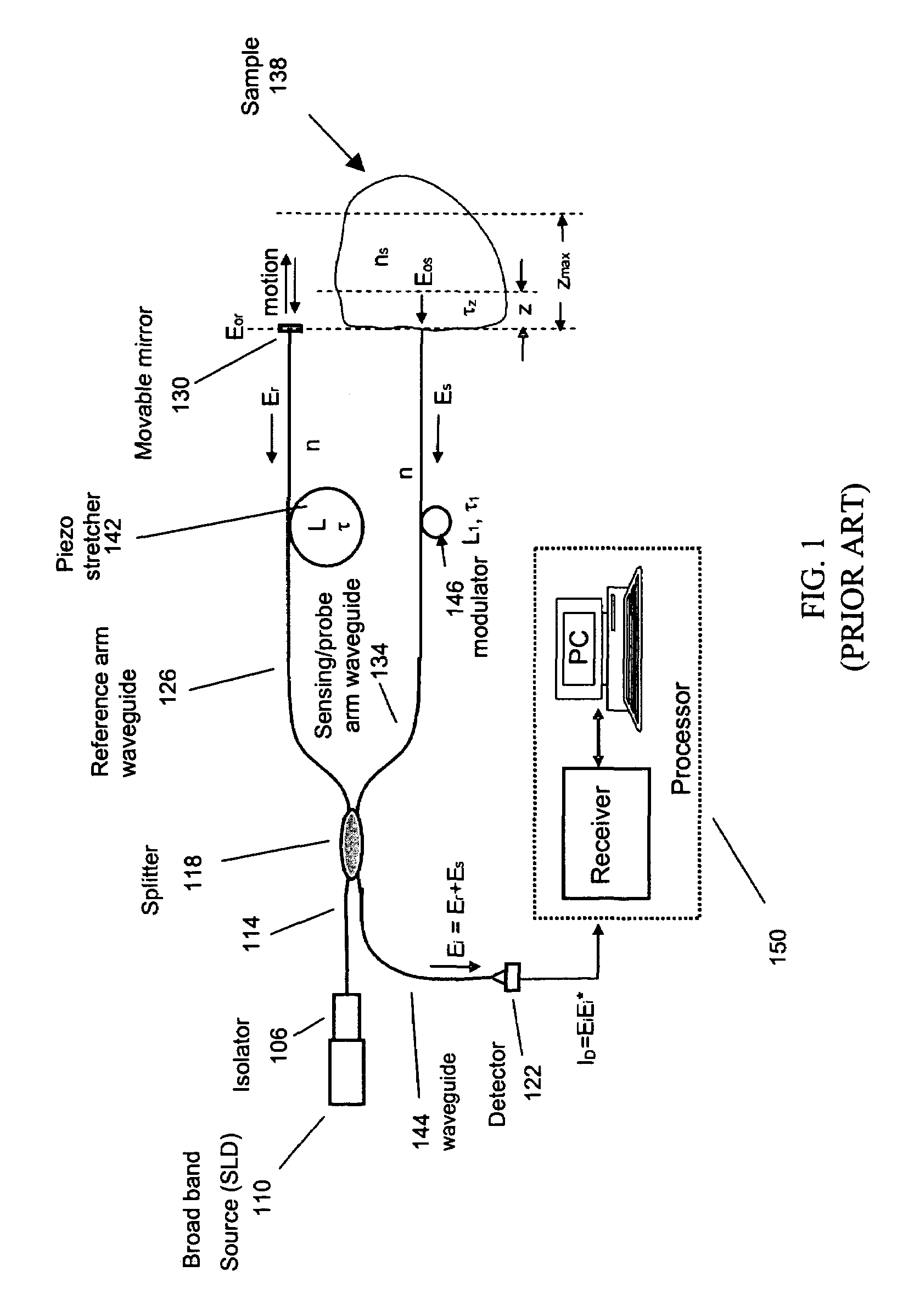
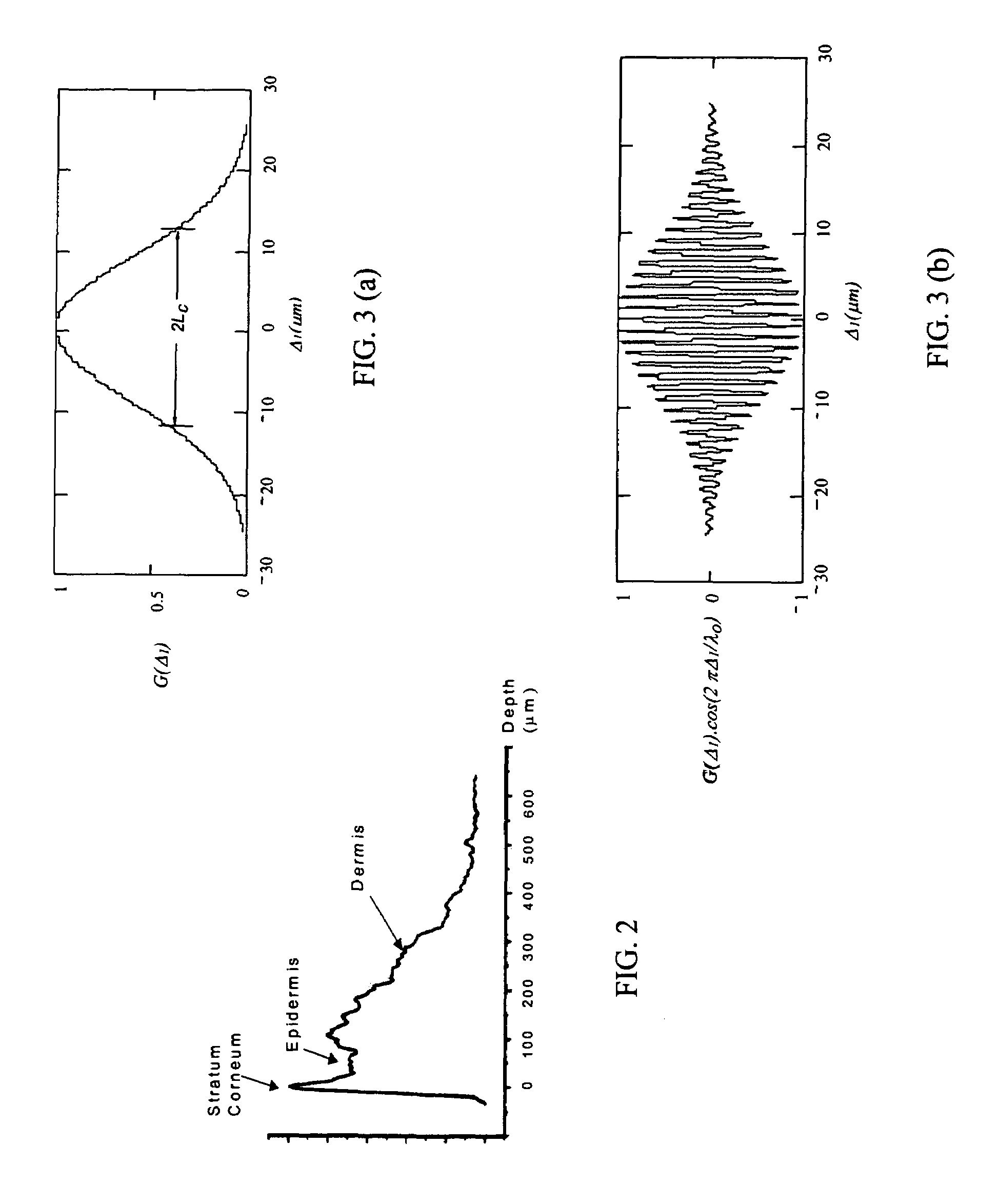
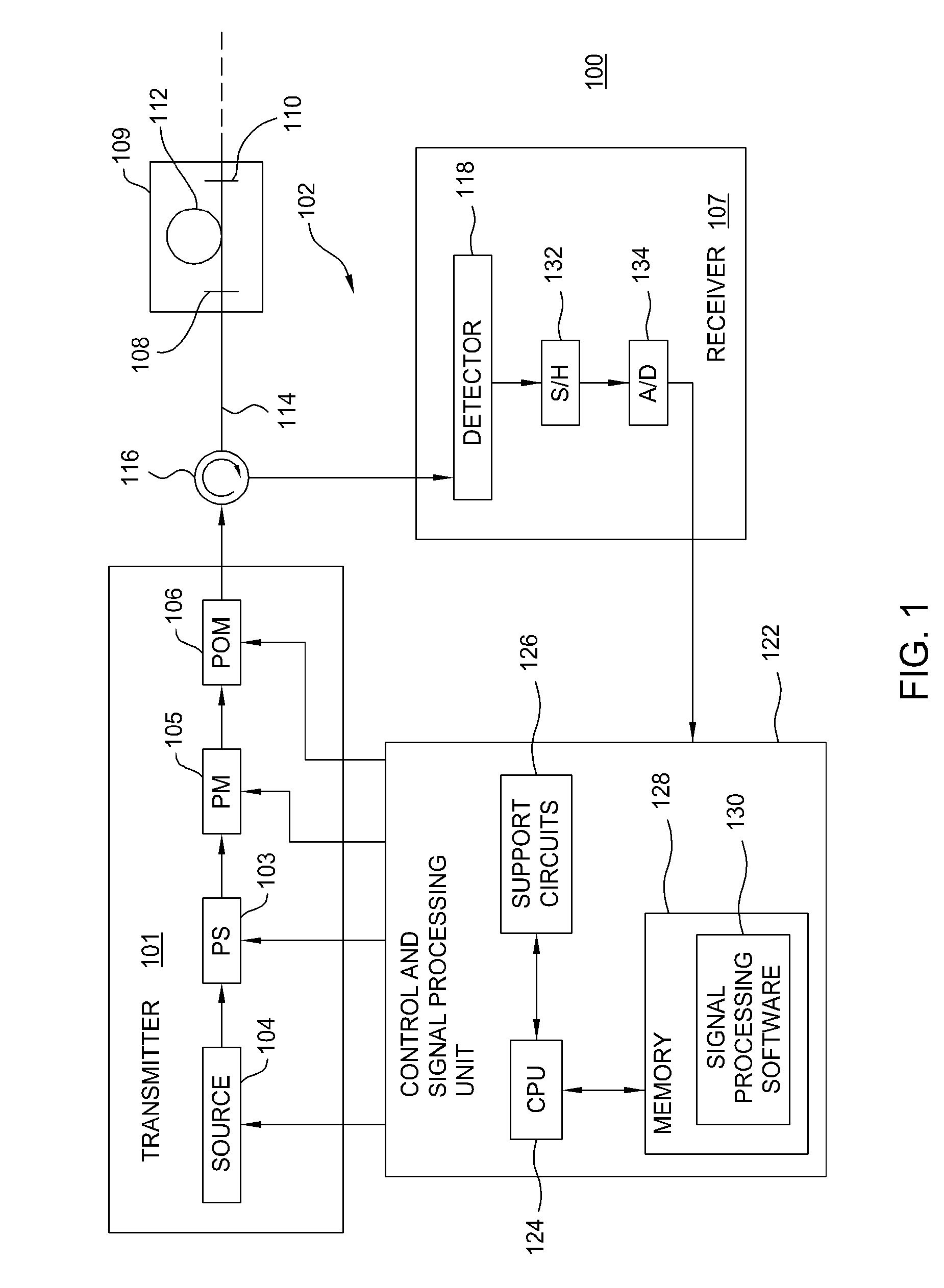
An integrated optical sensor, using low coherence interferometry, is capable of determining analyte concentration in a material sample based on absorption, scattering and polarization. The sensor includes one or more light collectors, with each collector having a separation distance from the region where the sample is illuminated by the source. The light backscattered from the sample is combined with reference arm light at the same optical path length for each light collector. The intensity of interference may be correlated with the concentration of an analyte in the material, for example the glucose concentration in a turbid medium like skin. The sensor operation can be based on fiber optics technology, integrated optics, or a combination of these. The operation is such that the spectrally resolved scattering and absorption coefficients can be measured simultaneously. In addition, the operation of the sensor can be synchronized with other sensors, for example temperature, pressure, or heartrate.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA
Single trace multi-channel low coherence interferometric sensor
Interferometers and autocorrelator based sensors are disclosed that are configured to have multiple sample arms which can be scanned and the backscattered low coherence source light from a sample resolved in a single sweep of one or more variable delays of the sensor. Borescopes and catheters capable of scanning multiple sections or areas of materials and tissues using these sensors are described.
Owner:MEDEIKON
Interferometric MOEMS Sensor
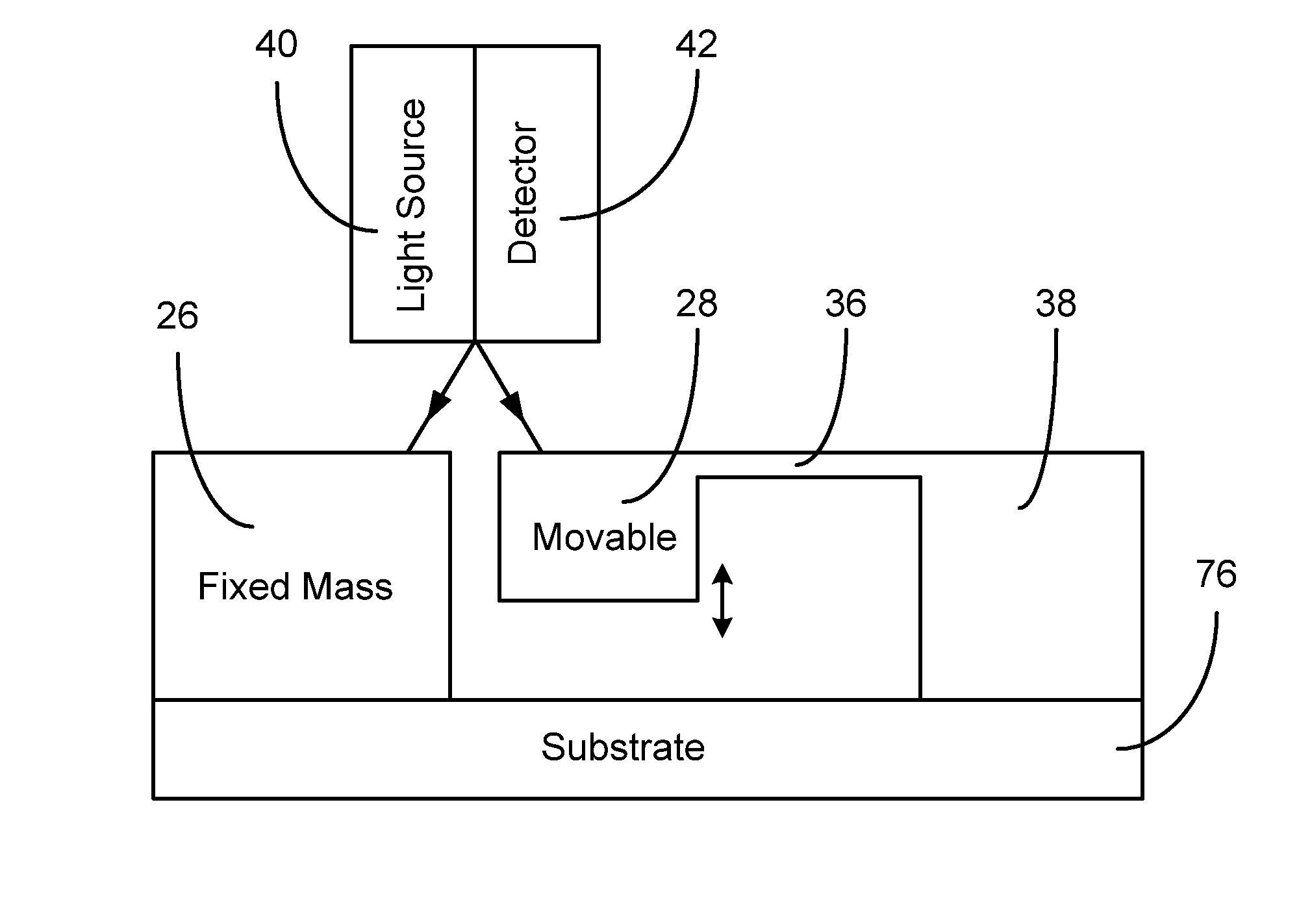
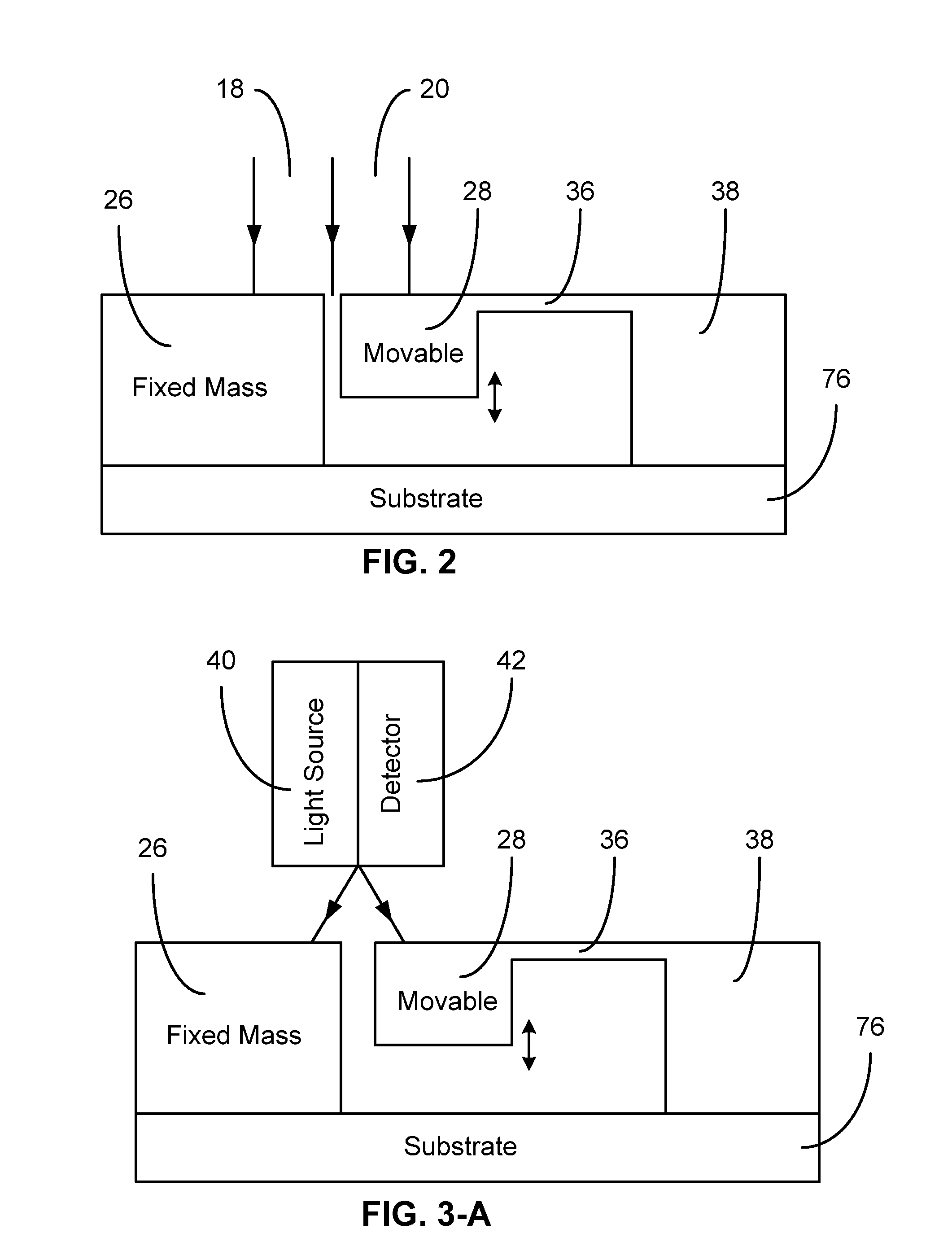
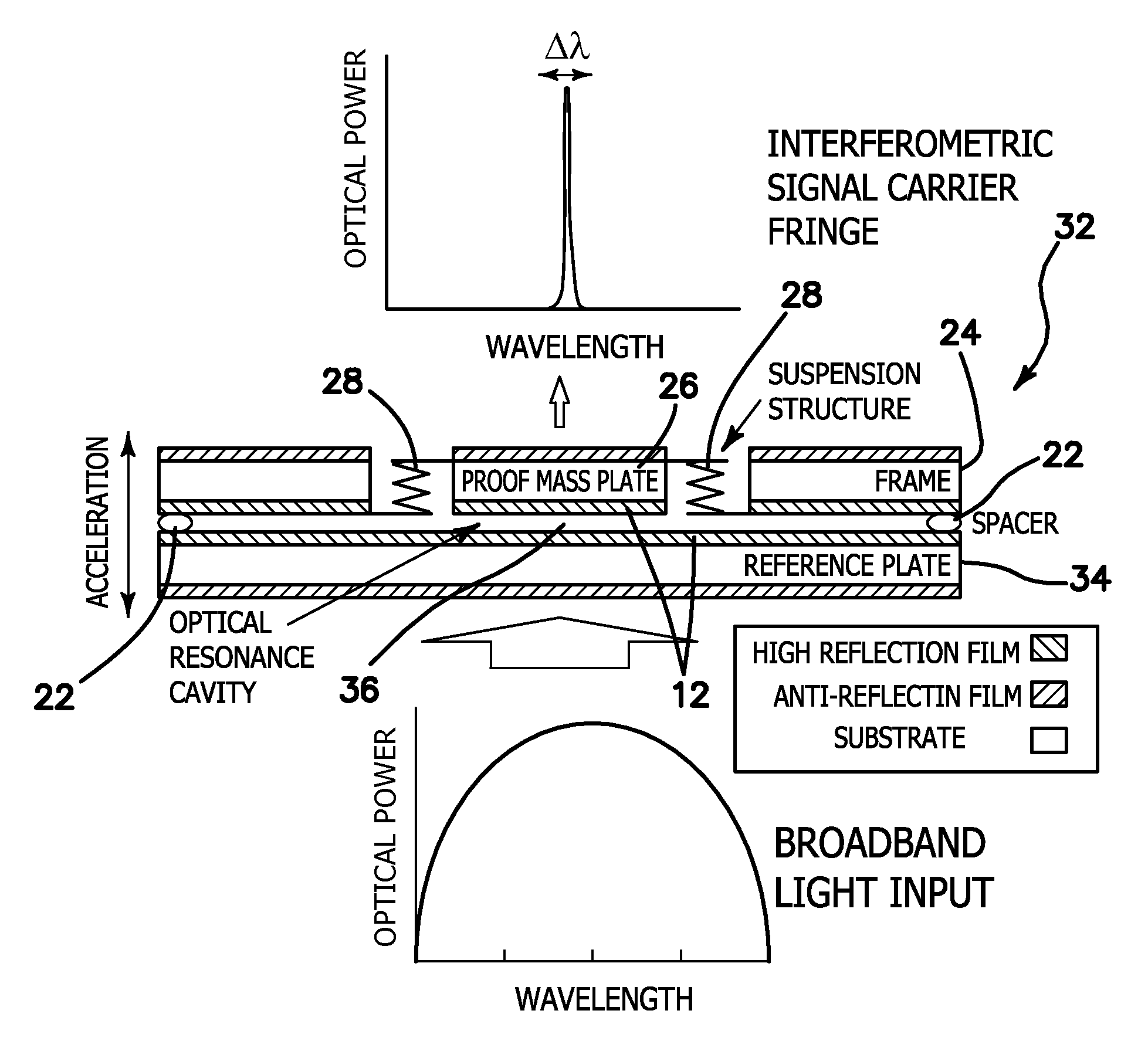
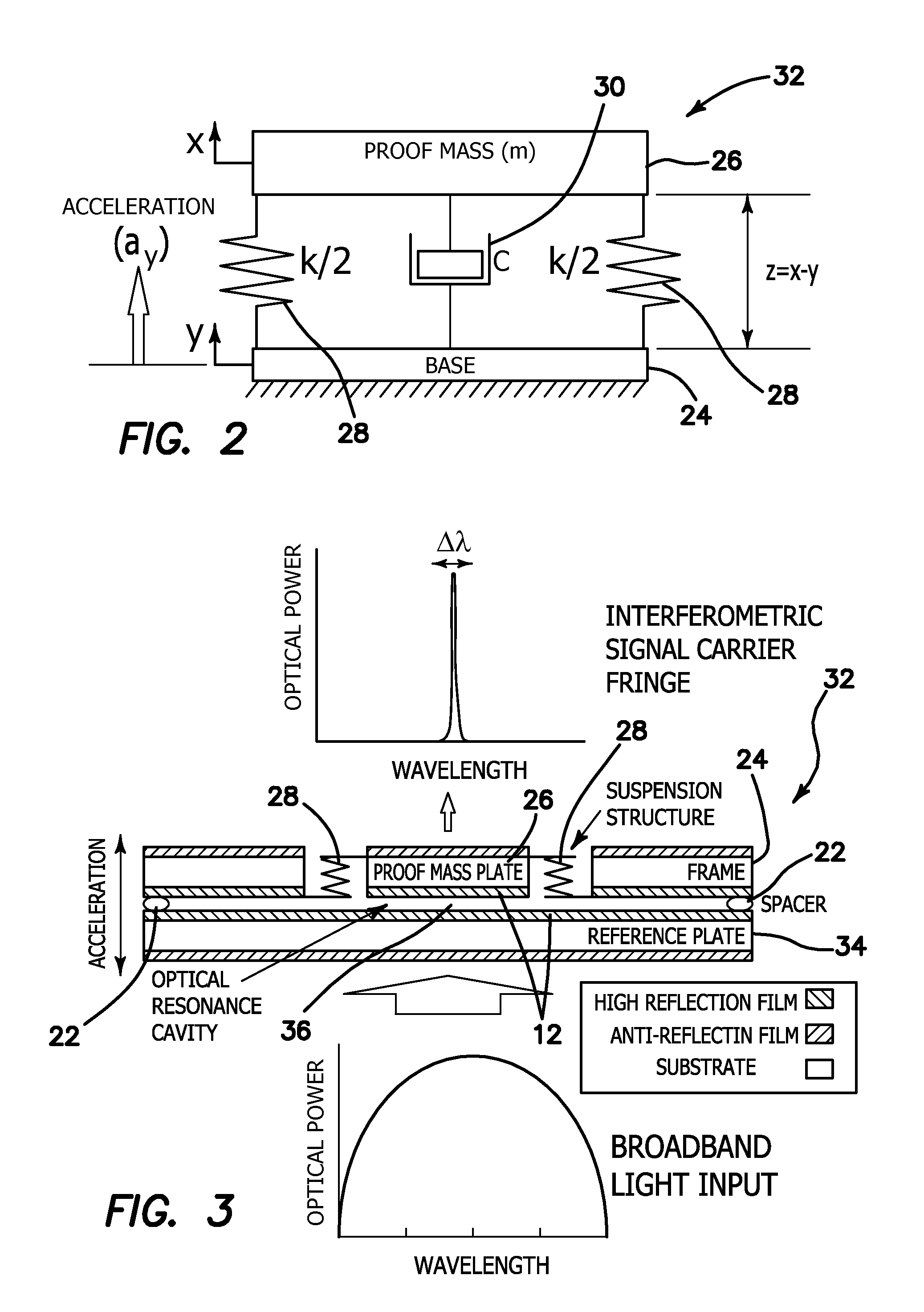
InactiveUS20060192974A1Small and simple structureEasy to manufactureAcceleration measurement using interia forcesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsInterferometric sensorLight beam
The present invention relates to an optical interferometric apparatus and method for measuring acceleration, pressure, and pressure of fluids during flow using micro-opto-electro-mechanical-systems (MOEMS). The high-sensitivity and high-resolution apparatus includes a movable mass, a stationary mass, a light source, and a photo detector. The light source emits a beam which is converted into two beam portions after impinging onto the movable and stationary masses. Interference between the beam portions are used to measure acceleration or pressure. The MOEMS structure may be integrated with a photo detector or planar waveguide. Differential amplification can be realized by employing two similar detecting structures.
Owner:LI CHIAN CHIU
Active coherence reduction for interferometer interrogation
ActiveUS20050078316A1Broadened optical spectrumEvenly distributedUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyControl mannerInterferometric sensor
Methods and apparatus for reducing the coherence of an optical signal that is used to interrogate optical interferometric sensors are disclosed. The optical field phasor of the interrogation source is modulated in a controlled manner to produce a broadened optical source power spectrum at the output of the source unit. The output from the source unit is launched into an optical sensor network, comprising a multiple of optical pathways from its input to the detection unit, where pairs of optical pathways form sensor interferometers. A compensating interferometer with delay difference similar to the sensor delay difference may be arranged in a serially coupled manner with the optical sensor network, either before or after the network. The optical output power from the source unit may either be continuous or pulsed with a pulse duration similar to the sensor delay. The coherence modulation may be performed through direct modulation of the source or through external modulation of the light with piezoelectric ring modulator, a Lithium niobate phase or intensity modulator, or an acoustooptic modulator.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Non-uniform sampling to extend dynamic range of interferometric sensors
ActiveUS20090122319A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAcceleration measurementInterferometric sensorEngineering
Methods and apparatus for interrogating optical sensors with high slew rates using non-uniform sampling are provided. The transmission of optical signals in a non-uniform pattern is employed to allow for demodulation of fringe rates exceeding the commonly understood Nyquist frequency limit given as one half of the mean sampling frequency. By monitoring the time dependent fringe frequency and assuming that the fringe frequency has a limited bandwidth, only a limited bandwidth smaller than the Nyquist bandwidth around the instantaneous fringe frequency needs to be reconstructed at any time.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Interferometric sensor for characterizing materials
ActiveUS7307734B2Measure of healthAcceptable signal to noise ratio (SNR)Scattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberAnalyte
An integrated optical sensor, using low coherence interferometry, is capable of determining analyte concentration in a material sample based on absorption, scattering and polarization. The sensor includes one or more light collectors, with each collector having a separation distance from the region where the sample is illuminated by the source. The light backscattered from the sample is combined with reference arm light at the same optical path length for each light collector. The intensity of interference may be correlated with the concentration of an analyte in the material, for example the glucose concentration in a turbid medium like skin. The sensor operation can be based on fiber optics technology, integrated optics, or a combination of these. The operation is such that the spectrally resolved scattering and absorption coefficients can be measured simultaneously. In addition, the operation of the sensor can be synchronized with other sensors, for example temperature, pressure, or heartrate.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA
Method and apparatus for providing polarization insensitive signal processing for interferometric sensors
A method and apparatus that uses specific source modulation and detectors to detect a response that carries information about a system response matrix associated with each sensor in a interferometric sensor array and extracting a sensor response in a manner that eliminates polarization-induced signal fading and that is insensitive to lead fiber birefringence fluctuations.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
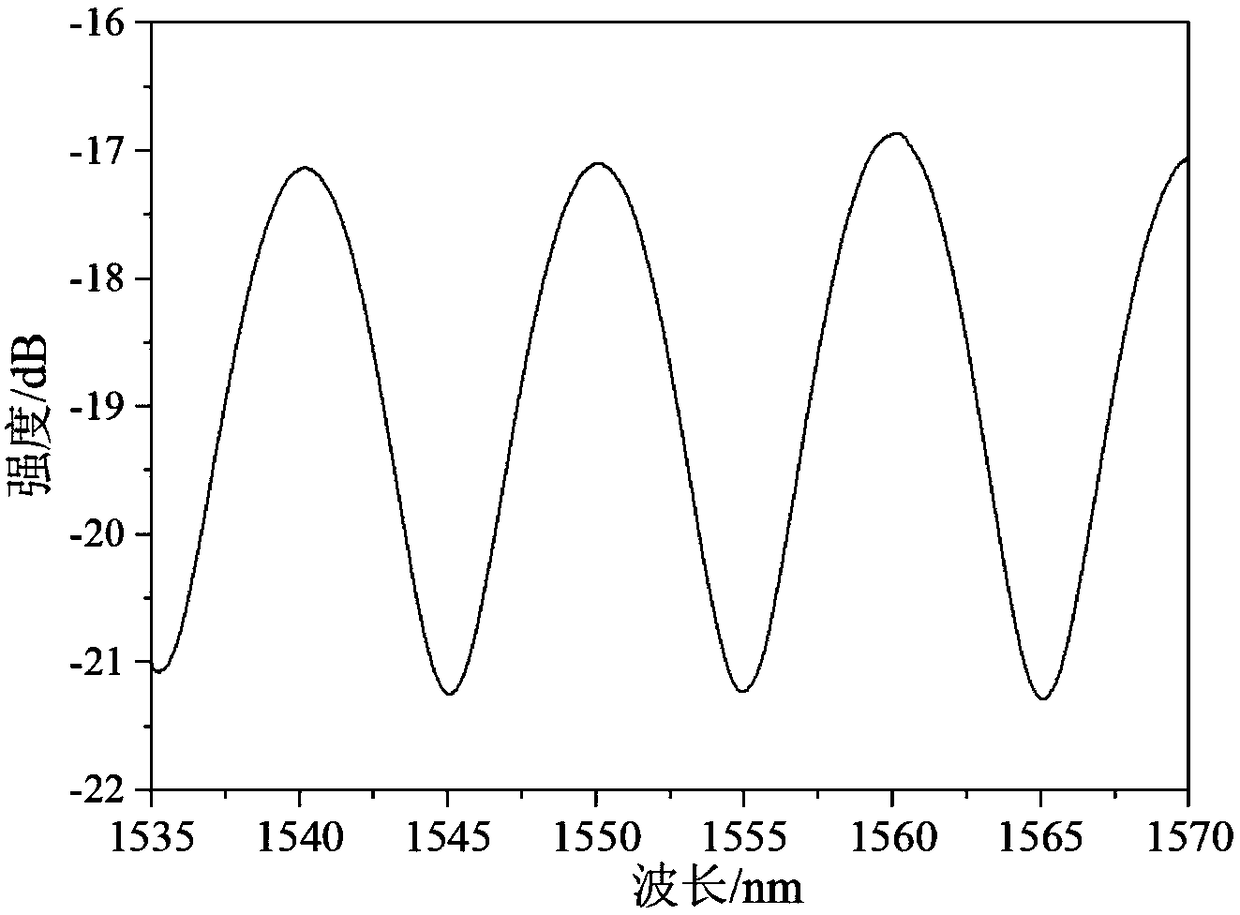
Quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102374874ALow costHigh degree of miniaturizationConverting sensor output opticallyHigh volume manufacturingInterferometric sensor
The invention discloses a quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor which comprises a single-mode optical fiber, a quartz capillary tube, a reflective optical fiber and a protective film, wherein the reflective optical fiber is a single-mode optical fiber or a multimode optical fiber, the two ends of the quartz capillary tube are respectively connected with one end of the single-mode optical fiber and one end of the reflective optical fiber by way of welding, and the hollow part of the quartz capillary tube is taken as the interferometric cavity of the interferometric sensor. In the interferometric sensor disclosed by the invention, a quartz capillary tube is adopted without plating a film, therefore, the cost for manufacturing the Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor is reduced, and the high contrast of the fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor can be realized. The invention also discloses a method for manufacturing the sensor. The quartz capillary tube embedded all-silica fiber Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of low cost, simple processing method, high miniaturization degree and good mechanical stability, and is convenient for production on large scale; and the practicability of the interferometric sensor is easy to realize, and the interferometric sensor has a potential practical value and a broad market in the field of interferometric sensors.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor, manufacturing method and air pressure detecting method
ActiveCN103994851AImprove applicabilitySmall creepFluid pressure measurement by optical meansResonanceEngineering
The invention provides a resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor which comprises a sensor body and a through hole penetrating through the sensor body. One end of the through hole is provided with a graphene thin film for sensing the to-be-detected air pressure in an attached mode, and the other end of the through hole is provided with transmission optical fibers which penetrate through the through hole and are matched with the through hole. According to the resonant type Fabry-Perot optical fiber sensor, the air pressure of gas is calculated in the mode that graphene thin film resonant frequency changes are caused by damp of the gas to the graphene thin film, so that a closed Fabry-Perot cavity is not needed, and the manufacturing difficulty is reduced; the the original measurement thin film deformation quantity is replaced by resonance to further conduct air pressure measurement, and thin film material creeping caused by repeated film deformation is effectively reduced; digital frequency signals after probe laser detection are output after the sensor conducts detection, and result analysis can be conveniently carried out compared with light wave signals of an interferometric sensor. Stimulation and detection are carried out through the single transmission optical fibers, and long-distance air pressure measurement can be achieved, and the applicability of the sensor is greatly improved.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST
A Fabry-Perot interference sensor based on solid-core photonic crystal fiber and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN102261924ASimple structureSmall sizeCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallyThermal dilatationInterferometric sensor
The invention provides a Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor based on a photonic crystal fiber and a manufacturing method thereof. The sensor is composed of a conventional communication single-mode fiber and a solid photonic crystal fiber, wherein the conventional communication single-mode fiber and the solid photonic crystal fiber are welded by using a certain welding method. Because air holes ona cladding of the photonic crystal fiber collapse, an air cavity (namely, an F-P cavity) is formed between the two fibers, and the two end faces (namely, the front and rear surfaces of the air cavity) of the photonic crystal fiber and the single-mode fiber are two reflecting surfaces of the F-P cavity. The solid photonic crystal fiber is made of a single material, and does not cause the mismatching of thermal expansion coefficients of materials in the process of temperature variation, thereby ensuring that the influence of temperature variation on the interferometric sensor is small; in the manufacturing process, only a fiber cutting and welding process is used, therefore, the preparation process is simple; by using the sensor, high-fineness and high-contrast interference fringes can be obtained, therefore, the sensor has a great application potential in large-capacity and quasi-distributed sensing systems; and the sensor is in an all-fiber structure, and has the advantages of small volume, good robustness and low cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
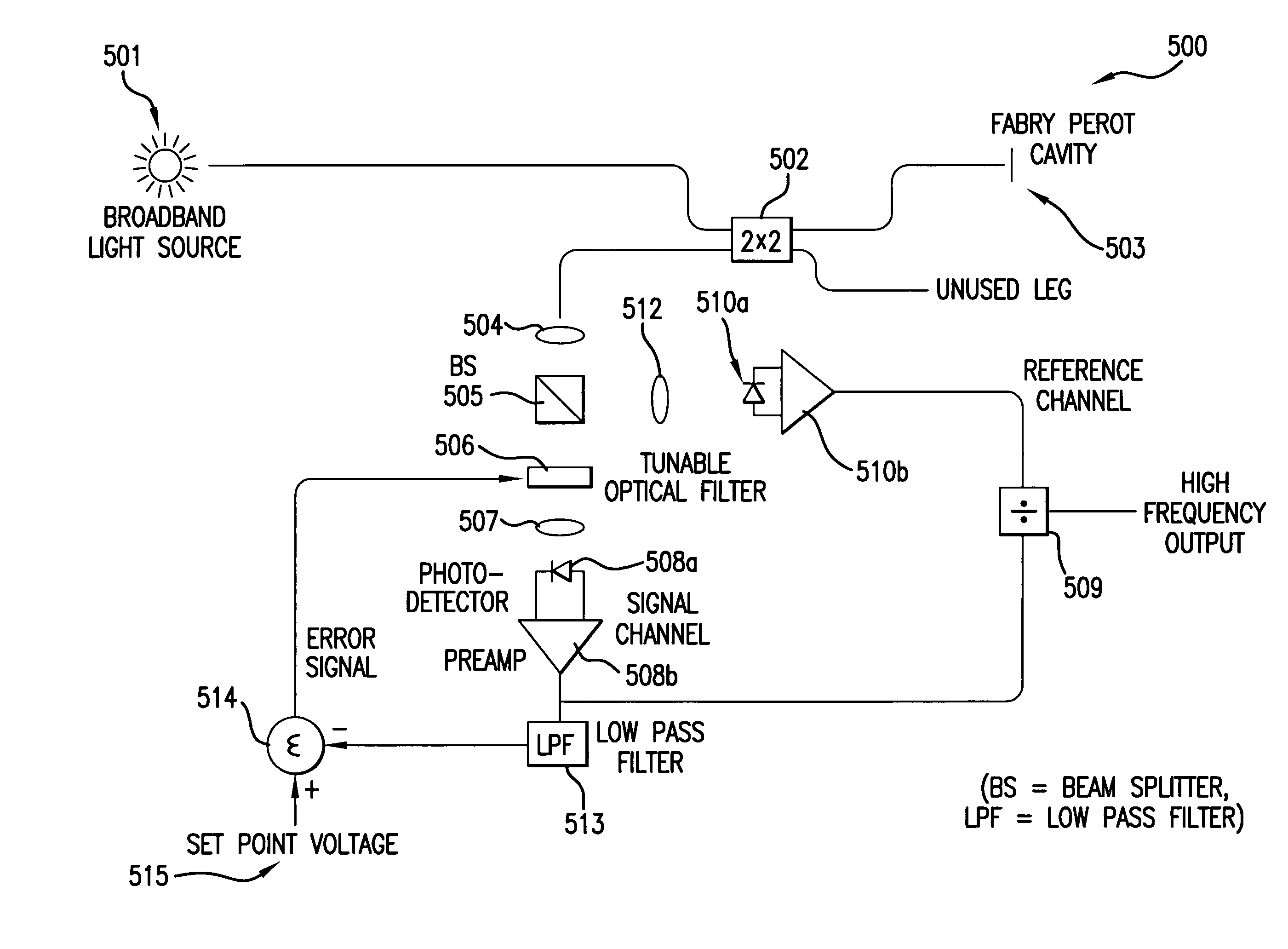
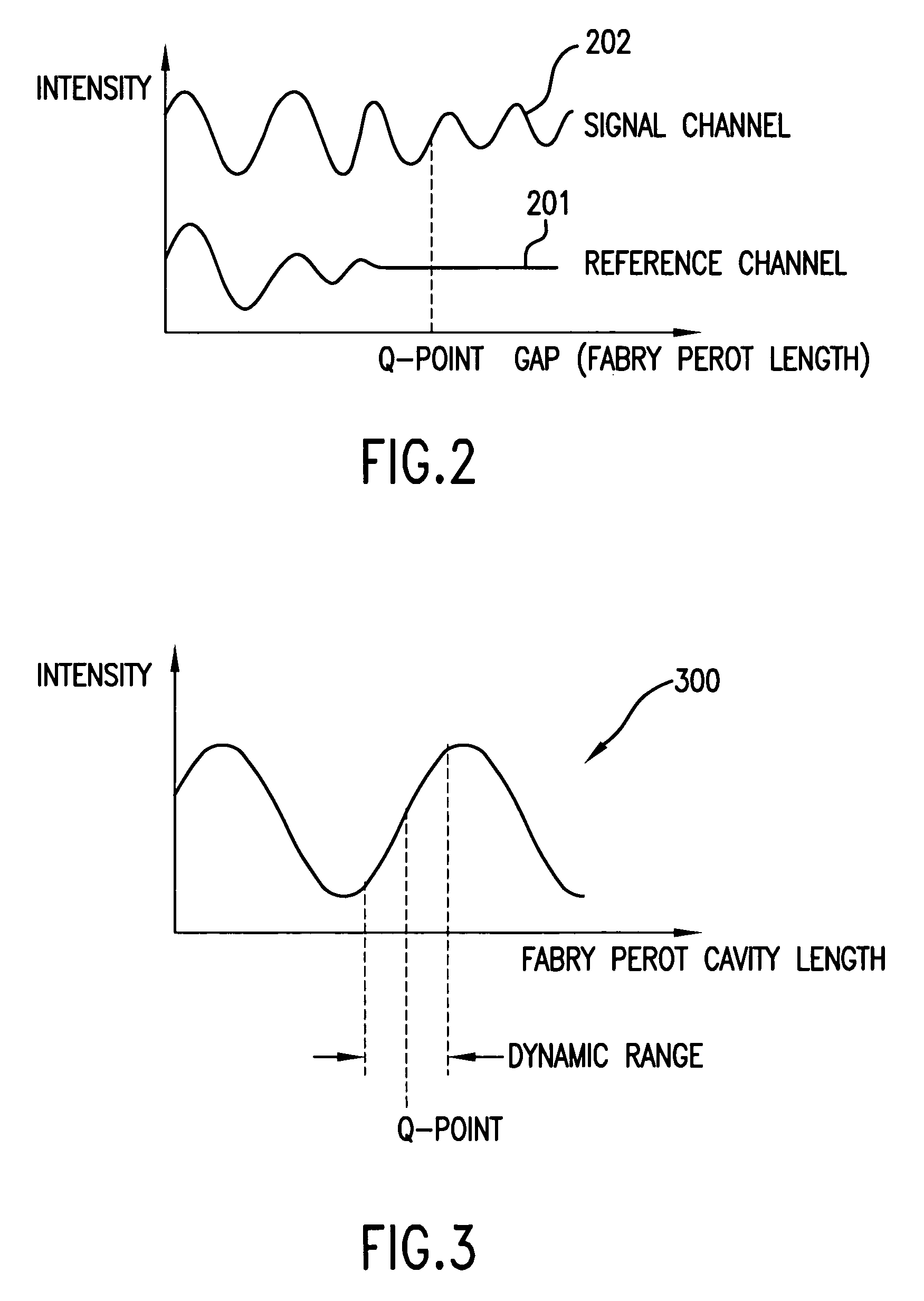
Active Q-point stabilization for linear interferometric sensors
InactiveUS7016047B2Using optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyBandpass filteringElectricity
A linear interferometric sensor system in which the light output from the interferometric sensor is optically bandpass filtered before conversion to an electrical signal by an adjustable band-pass filtering device and the center wavelength of the adjustable band-pass filtering device is controlled by a feedback circuit responsive to the steady state component of the electrical signal corresponding to the filtered sensor return. In a preferred embodiment, the adjustable band-pass filtering device is an electrically tunable optical filter. The invention is particularly useful in self calibrating interferometric / intensity-based sensor configuration, but can be used with other linear interferometric sensor configurations.
Owner:PRIME PHOTONICS LC
Single wafer fabrication process for wavelength dependent reflectance for linear optical serialization of accelerometers
ActiveUS20100046002A1Easy to manufactureHigh resolutionAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMultiplexingAccelerometer
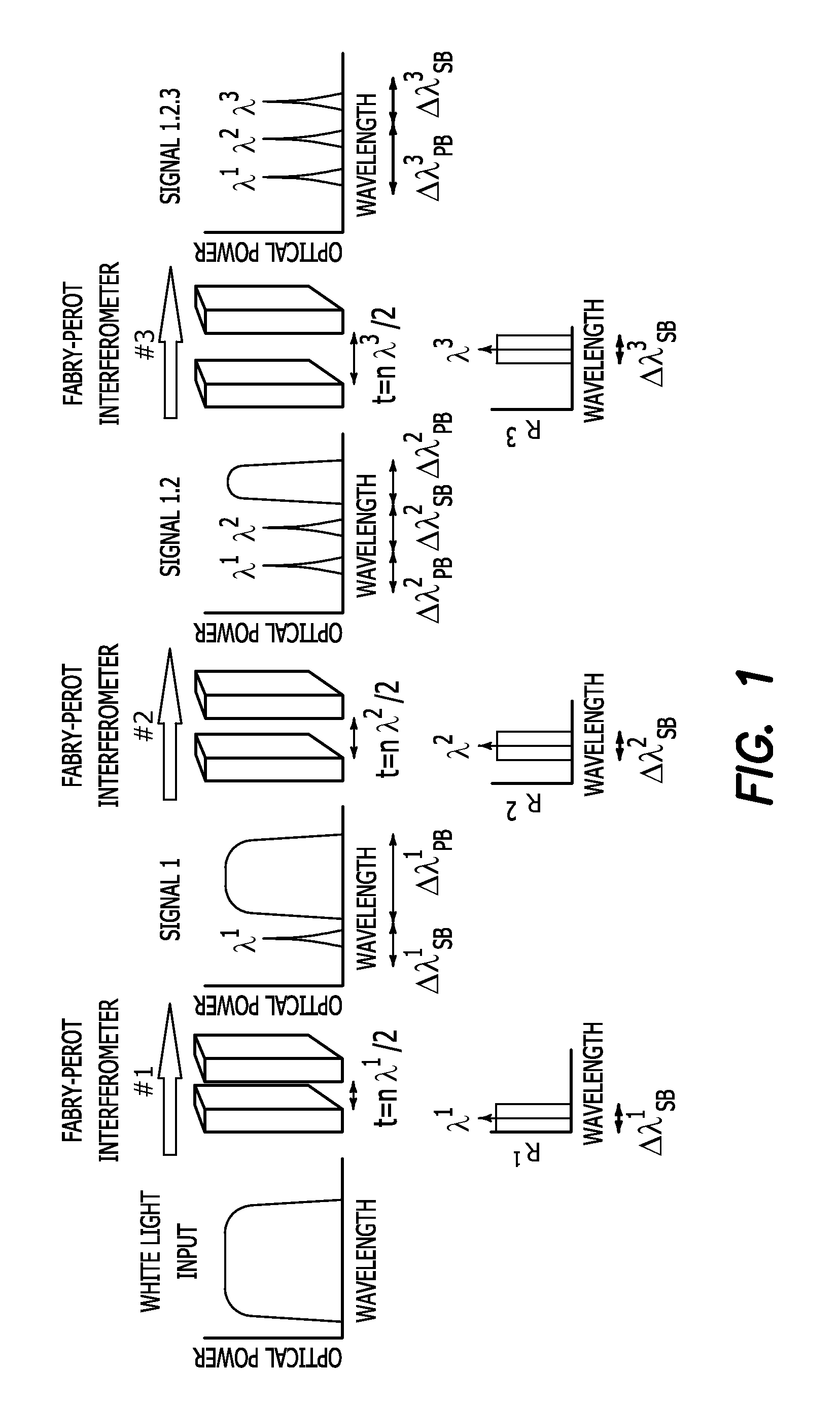
A plurality of Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors are optically coupled in series with each other to form an ordered optical series. Each Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor has a unique signalband and a passband. Each Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor has its unique signalband within the passbands of all of the next higher ordered Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors in the optical series so that a corresponding unique fringe signal from each of the Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors is a multiplexed output from the optical series.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
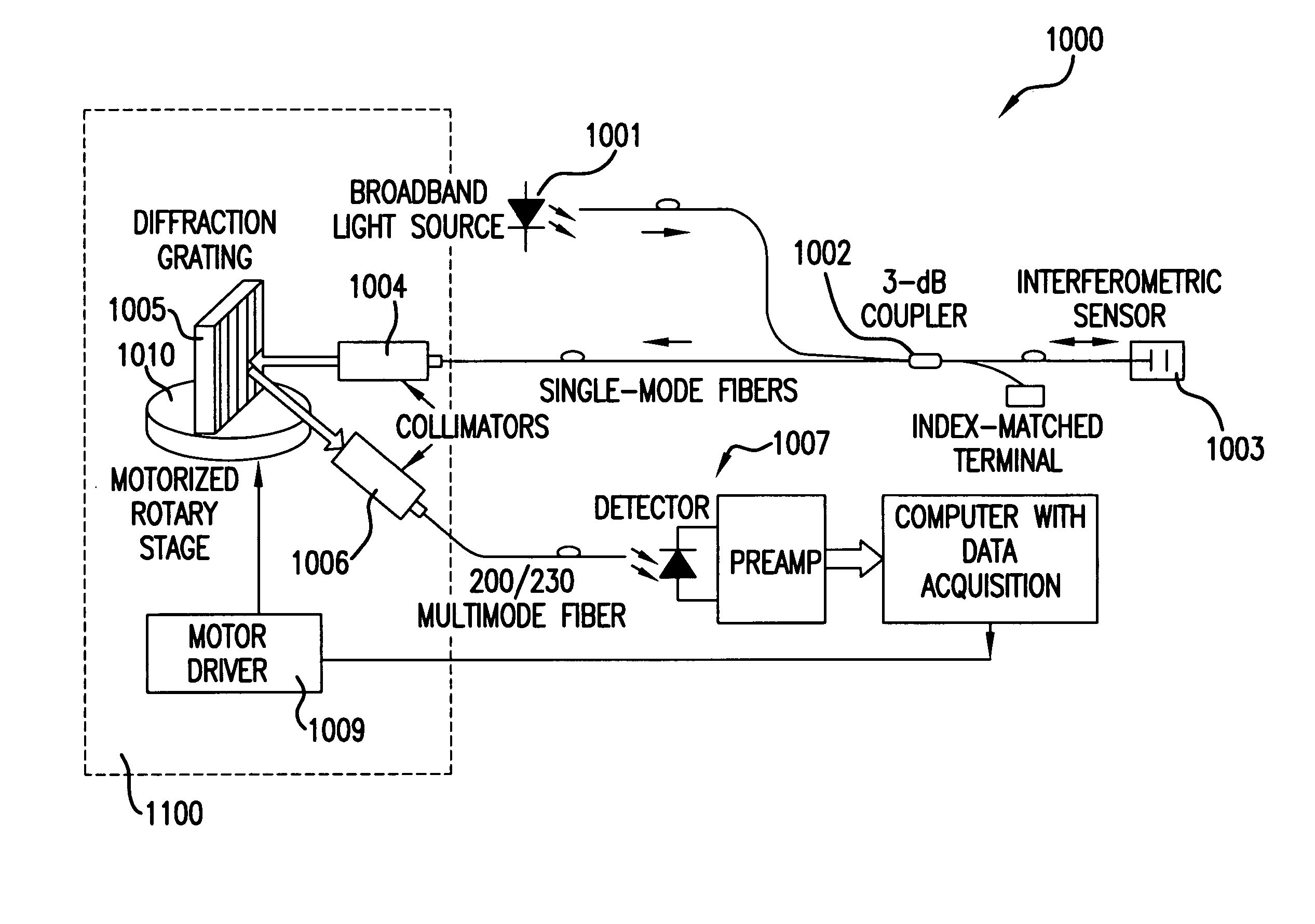
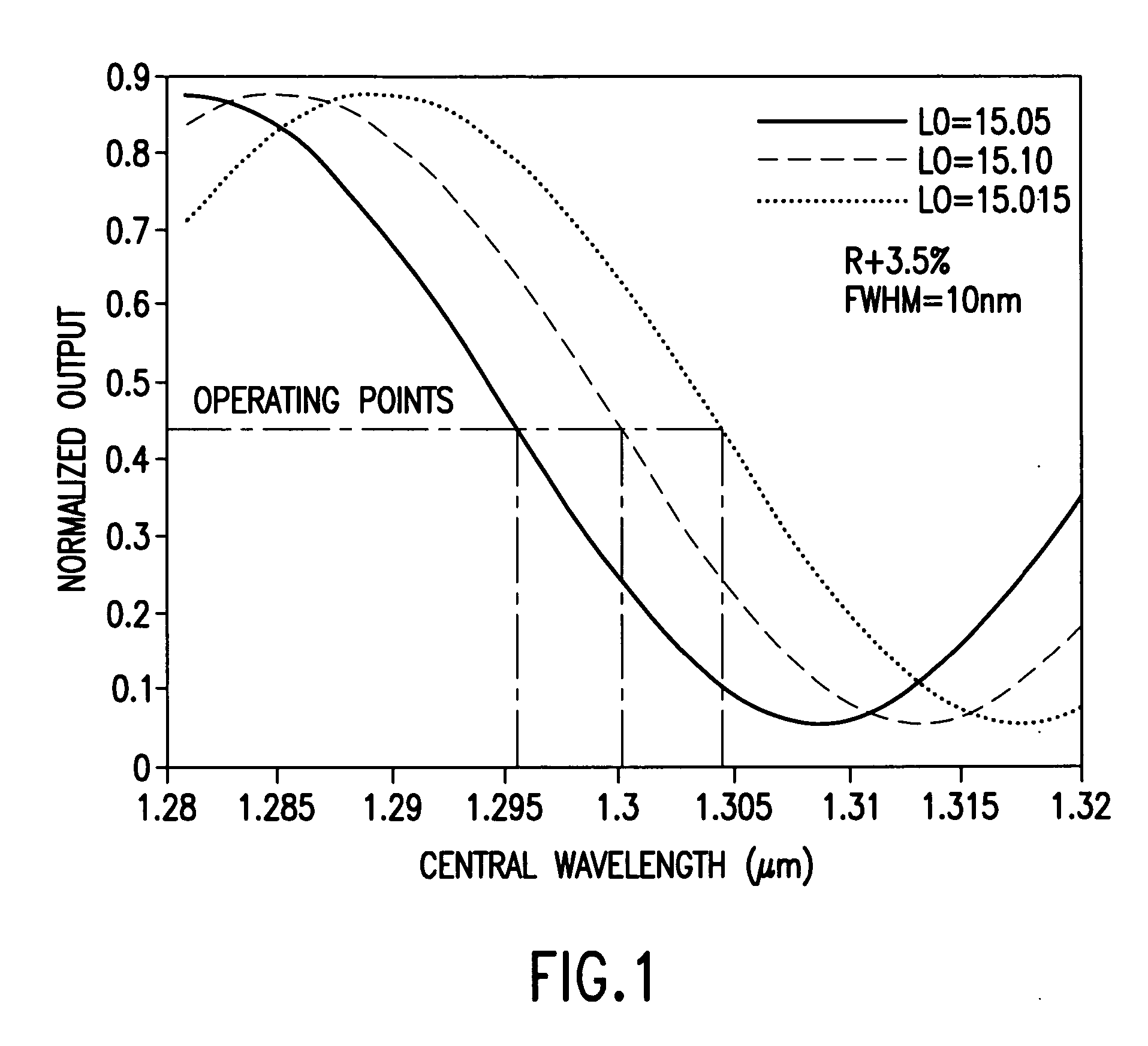
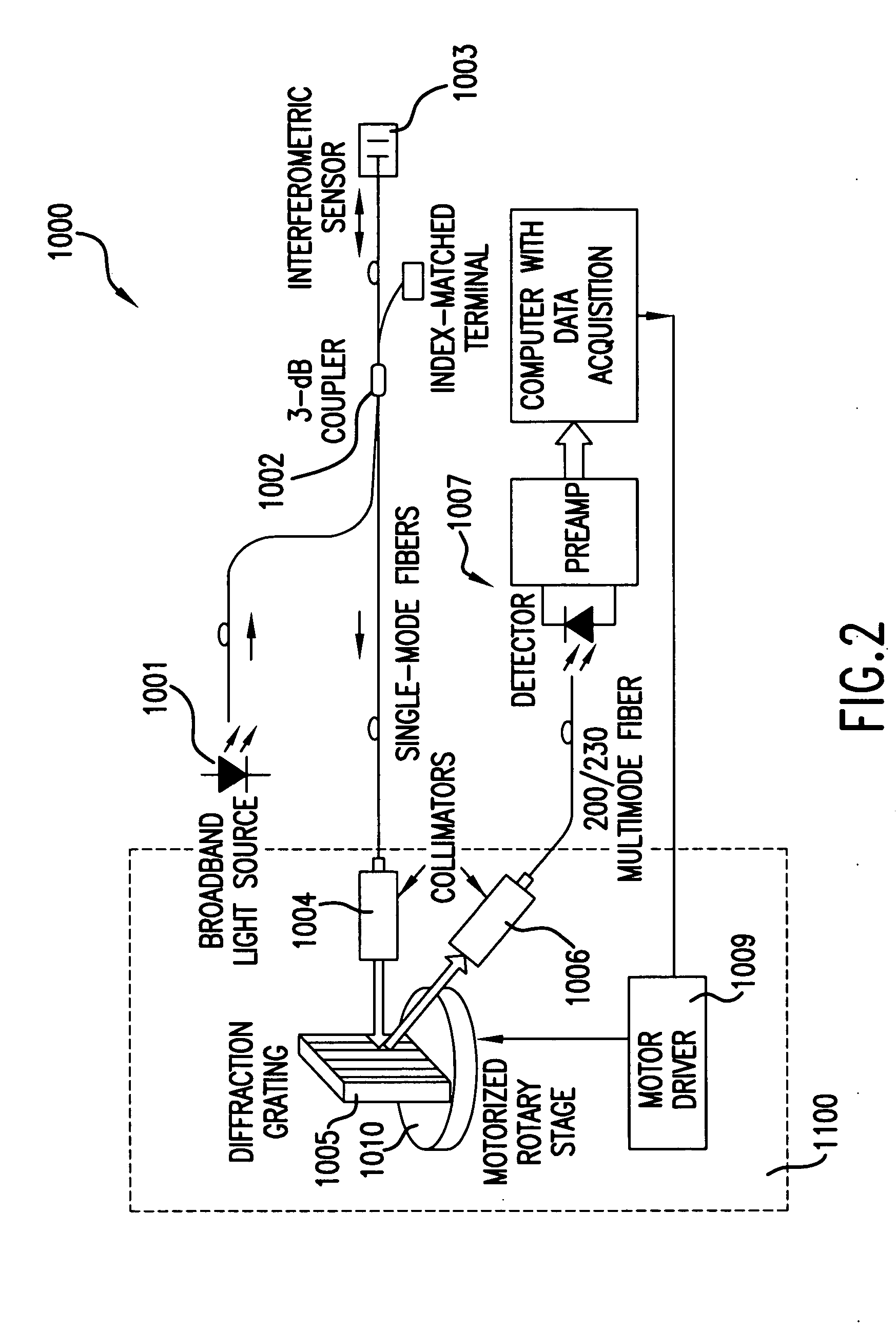
Q-point stabilization for linear interferometric sensors using tunable diffraction grating
A linear interferometric sensor system in which the light output from the interferometric sensor is optically bandpass filtered before conversion to an electrical signal by an adjustable diffraction grating and the center wavelength of the adjustable diffraction grating is controlled by a feedback circuit responsive to the steady state component of the electrical signal corresponding to the filtered sensor return. The adjustable may comprise a diffraction grating a diffraction grating mounted on a motor driven rotary stage. The invention is particularly useful in self calibrating interferometric / intensity-based sensor configuration, but is also applicable in a wide variety of linear interferometric sensor configurations.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method and apparatus for providing polarization insensitive signal processing for interferometric sensors
ActiveUS7081959B2Using optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyInterferometric sensorBirefringent fiber
A method and apparatus that uses specific source modulation and detectors to detect a response that carries information about a system response matrix associated with each sensor in a interferometric sensor array and extracting a sensor response in a manner that eliminates polarization-induced signal fading and that is insensitive to lead fiber birefringence fluctuations.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Internal fiber integration type miniature Michelson interferometric sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101614601AEasy to makeLow costThermometers using physical/chemical changesCoupling light guidesInterferometric sensorElectromagnetic interference
The invention discloses an internal fiber integration type miniature Michelson interferometric sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The sensor comprises two single mode fibers with different external diameters and the same core diameters; the single mode fiber with small external diameter is fusion-jointed on the single mode fiber with large external diameter by axis dislocation; the core parts of the two single mode fibers are overlapped; the uncovered part of the end face of the core of the single mode fiber with large external diameter is the reflecting surface of a reference arm; the core end of the exposed end of the single mode fiber with small external diameter is the reflecting surface of a measuring arm; the cores of the two fibers are made of SiO2. The sensor has the beneficial technical effects of simple manufacturing, low cost, small volume, good electromagnetic interference resistance, good high temperature resistance and good electric insulativity.
Owner:SICHUAN GUANGSHENG IOT TECH CO LTD
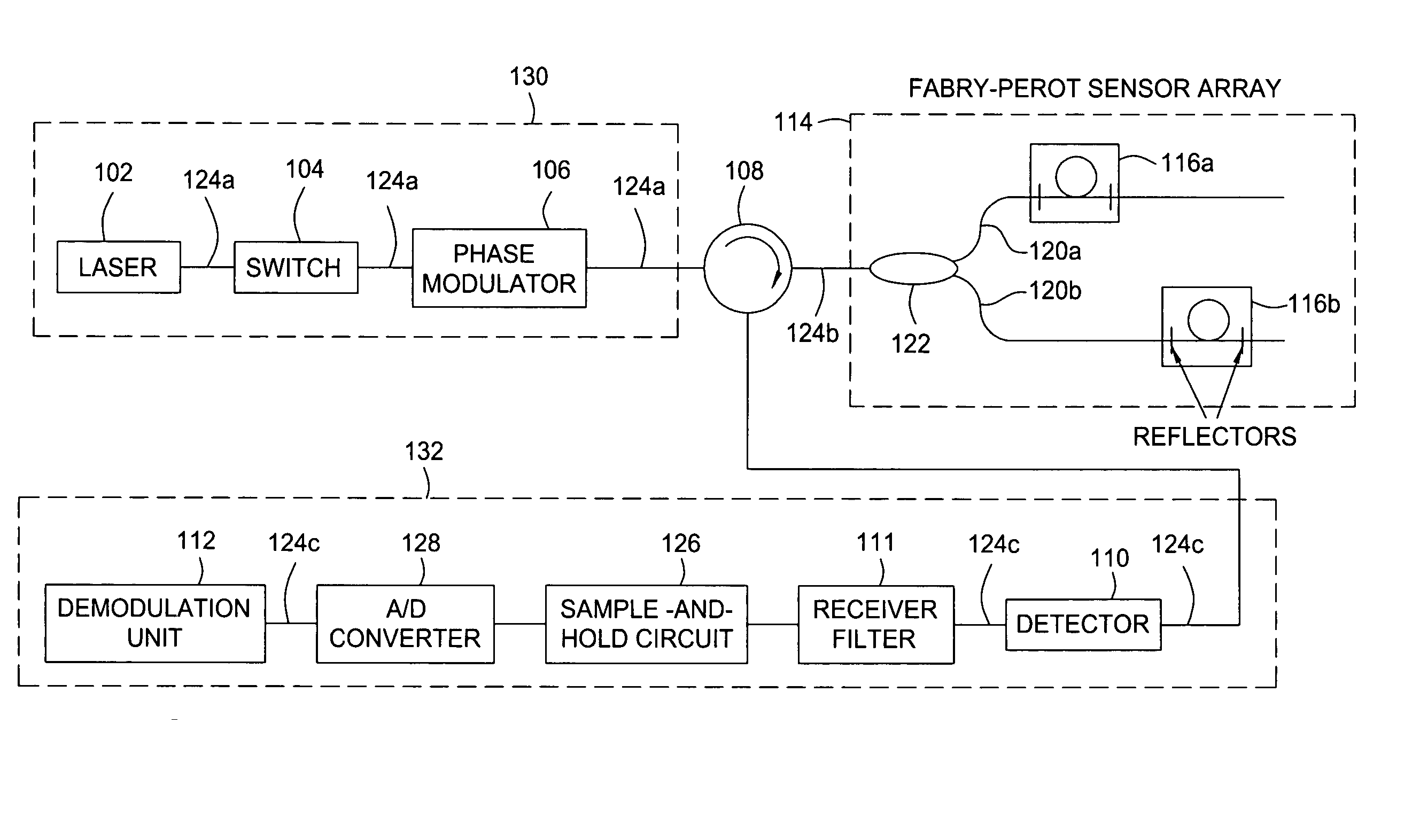
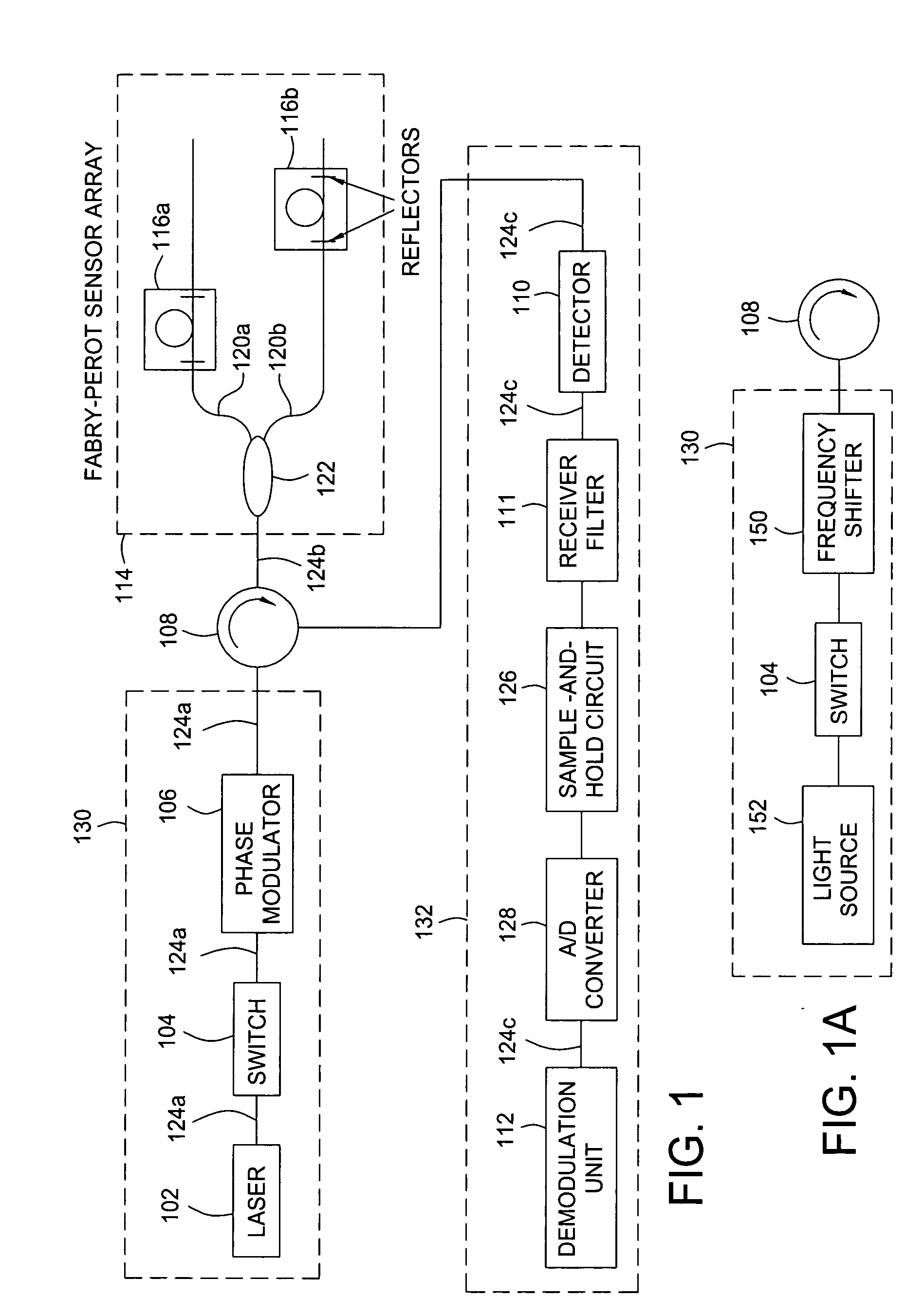
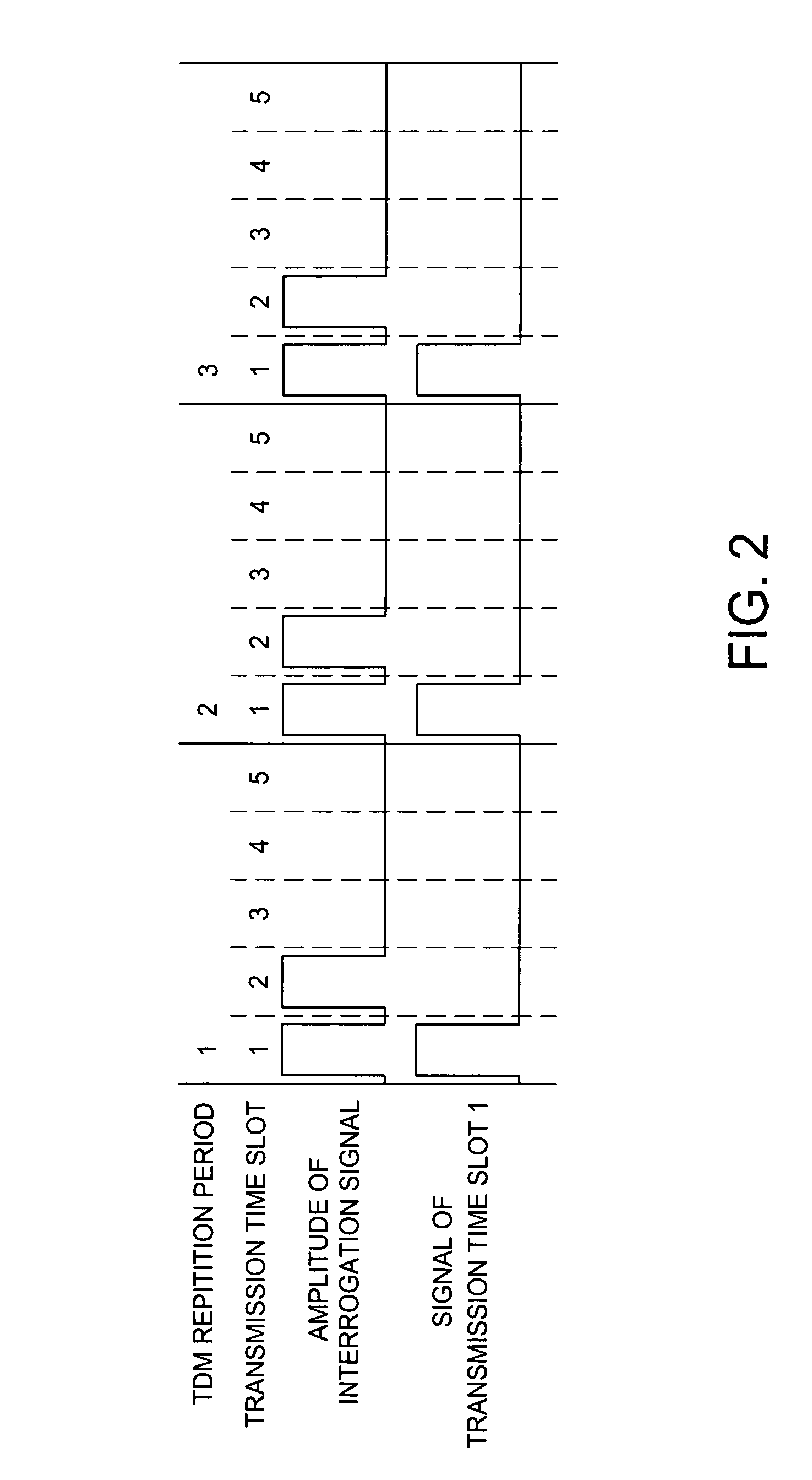
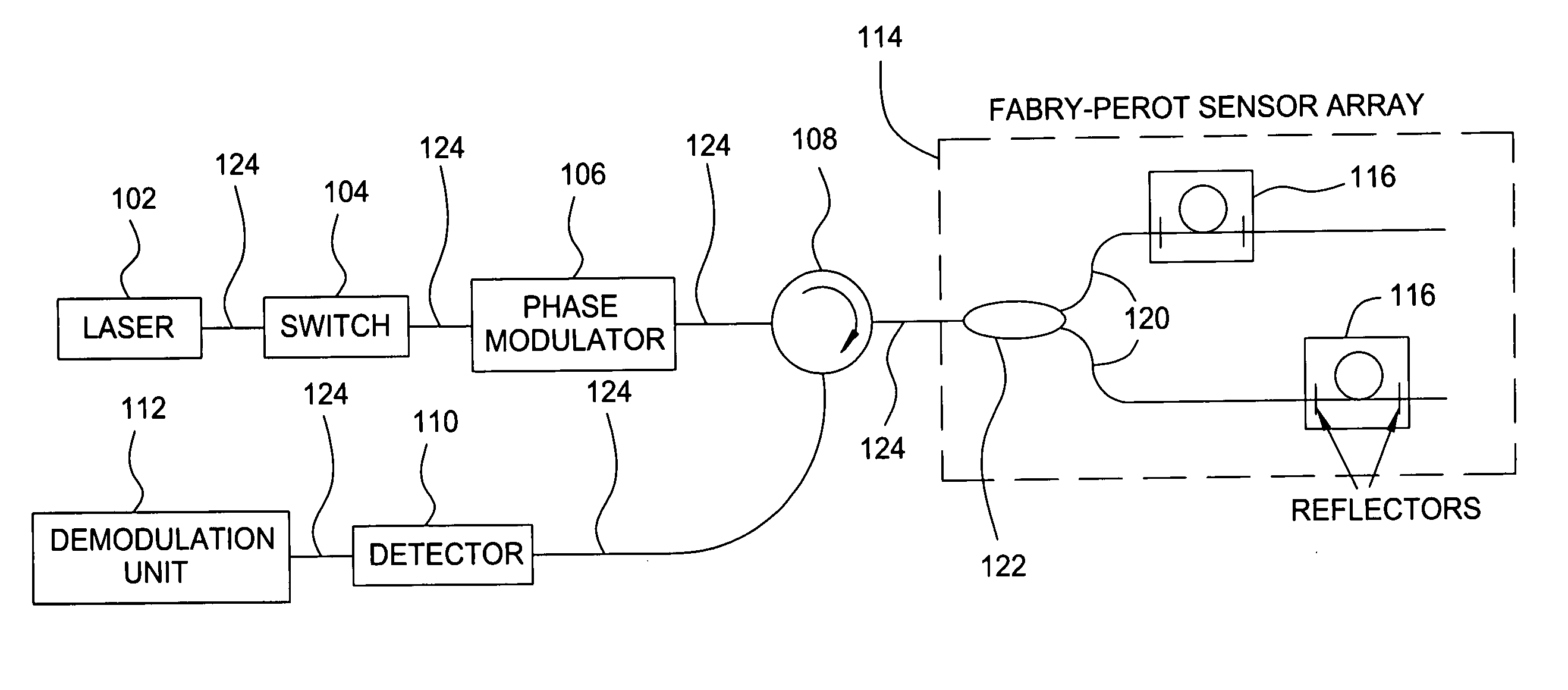
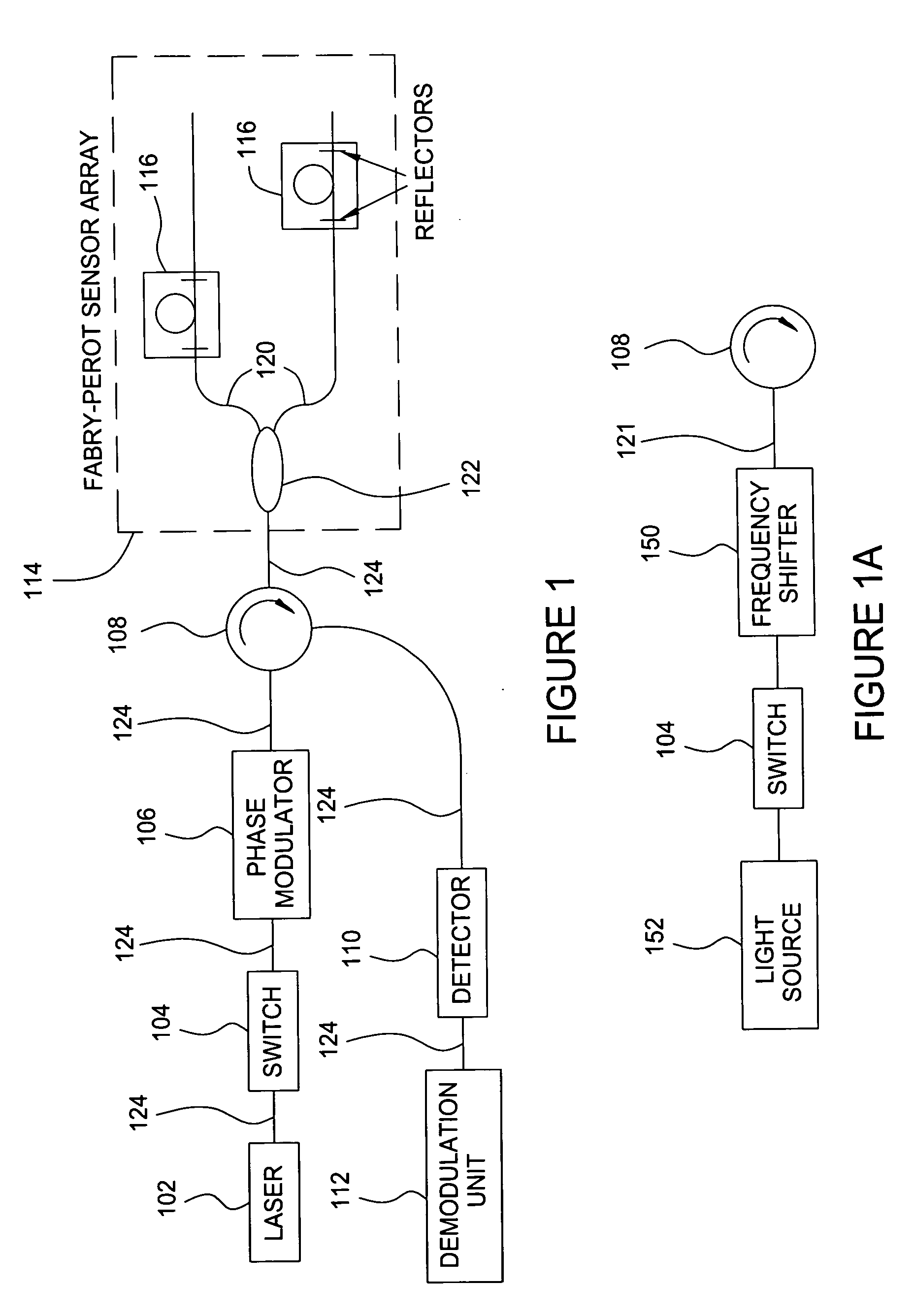
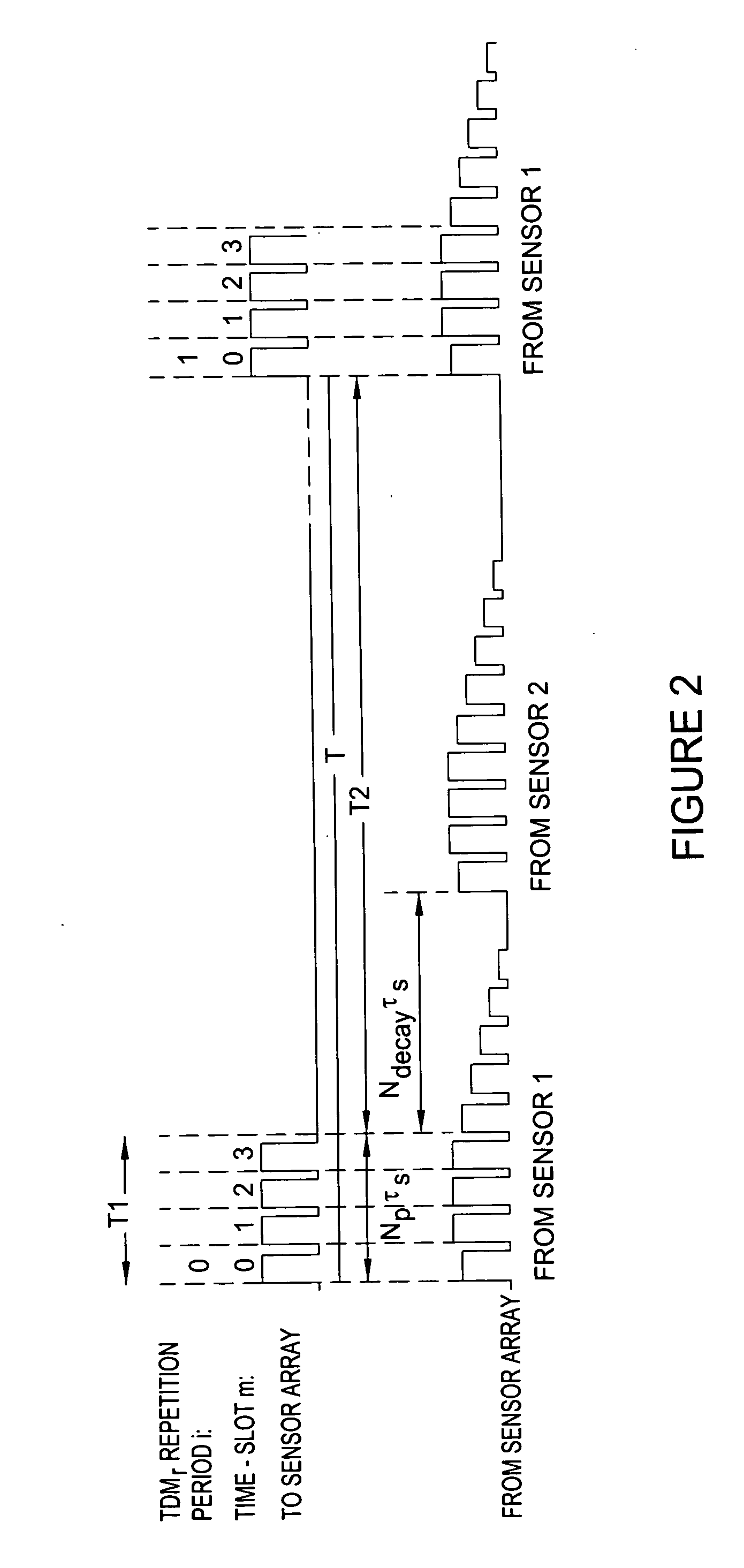
Method and apparatus for suppression of crosstalk and noise in time-division multiplexed interferometric sensor systems
ActiveUS20060181711A1Reduce crosstalkReduce noiseTime-division multiplexUsing optical meansPhase differenceInterferometric sensor
Unwanted signal components in time-division multiplexed (TDM) systems may lead to crosstalk and noise if these pulses overlap with signal pulses from an interrogated sensor. The crosstalk and noise are dominated by interference between the signal pulses from the interrogated sensor and the unwanted signal components and can be greatly reduced by suppressing this interference signal. The unwanted signal components may include overlapping pulses originating from different sets of interrogation pulses (repetition periods). Modulating the phase or frequency between the repetition periods so that the unwanted interference signal does not appear at frequencies from which the phase of the interrogated sensor is demodulated suppresses this interference. Other unwanted signal components include leakage light during dark periods of the duty cycle of an interrogation signal. Modulating the phase difference between the interrogation signal and the leakage light suppresses the interference between the leakage light and the interrogation signal.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Multi-pulse heterodyne sub-carrier interrogation of interferometric sensors
ActiveUS20050271395A1Increases allowable interrogation pulse duty-cycleImprove signal-to-noise ratioTime-division optical multiplex systemsUsing optical meansInterferometric sensorCarrier signal
A method for interrogating time-multiplexed interferometric sensors using multiple interrogation pulses so as to increases the allowable interrogation pulse duty-cycle and improve the signal-to-noise ratio. In each TDM repetition period a sequence of multiple interrogation pulses are generated. The pulses in the sequence are separated by a time that is equal to the sensor imbalance. The phase from pulse to pulse in each TDM time-slot is modulated at a different, linear rate such that the pulse in time-slot m will have an optical frequency that is shifted by mΔν, where Δν is the sub-carrier frequency. Because multiple reflections do not need to fade out the inventive method can enhance the signal-to-noise ratio of interferometric sensors such as inline Fabry-Perot sensors.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
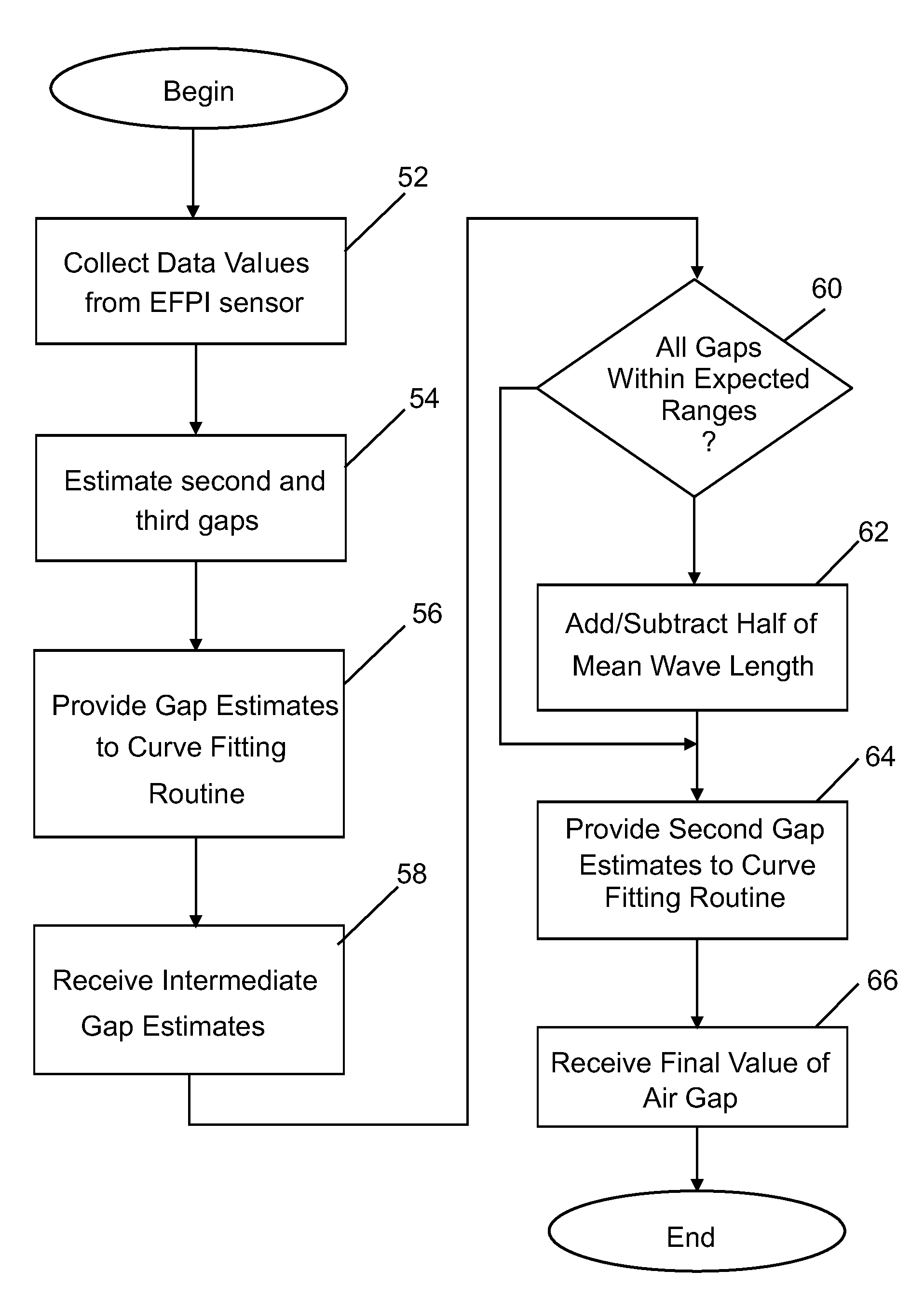
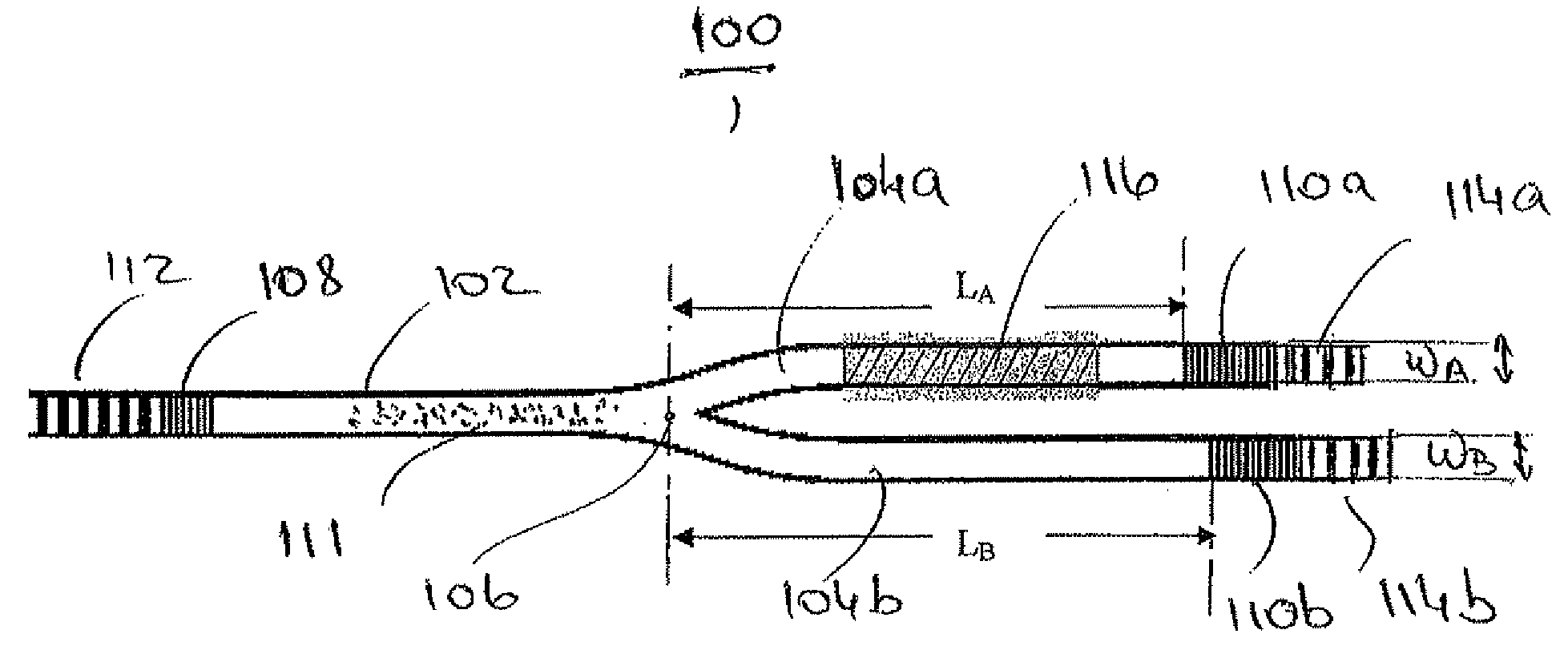
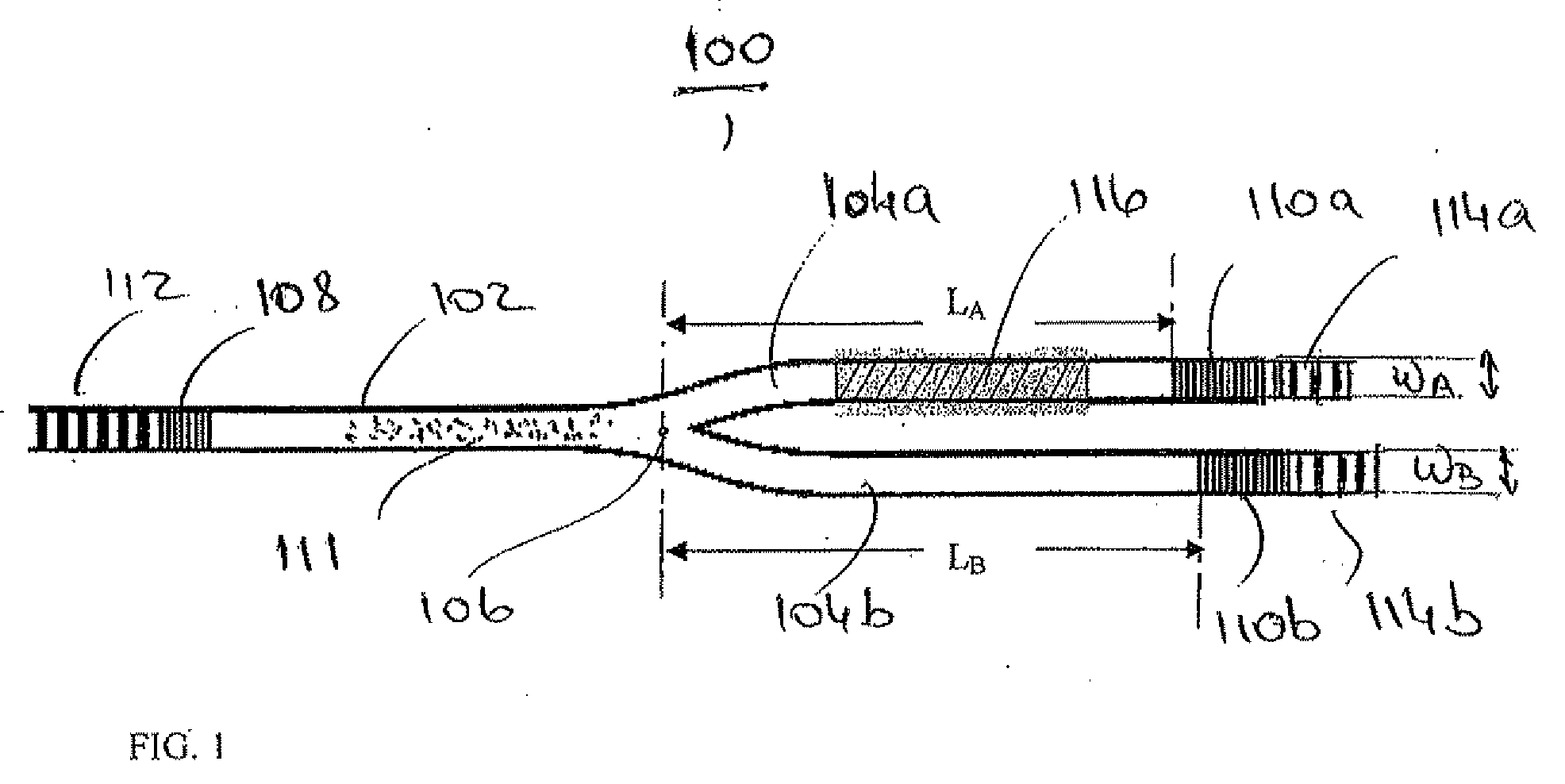
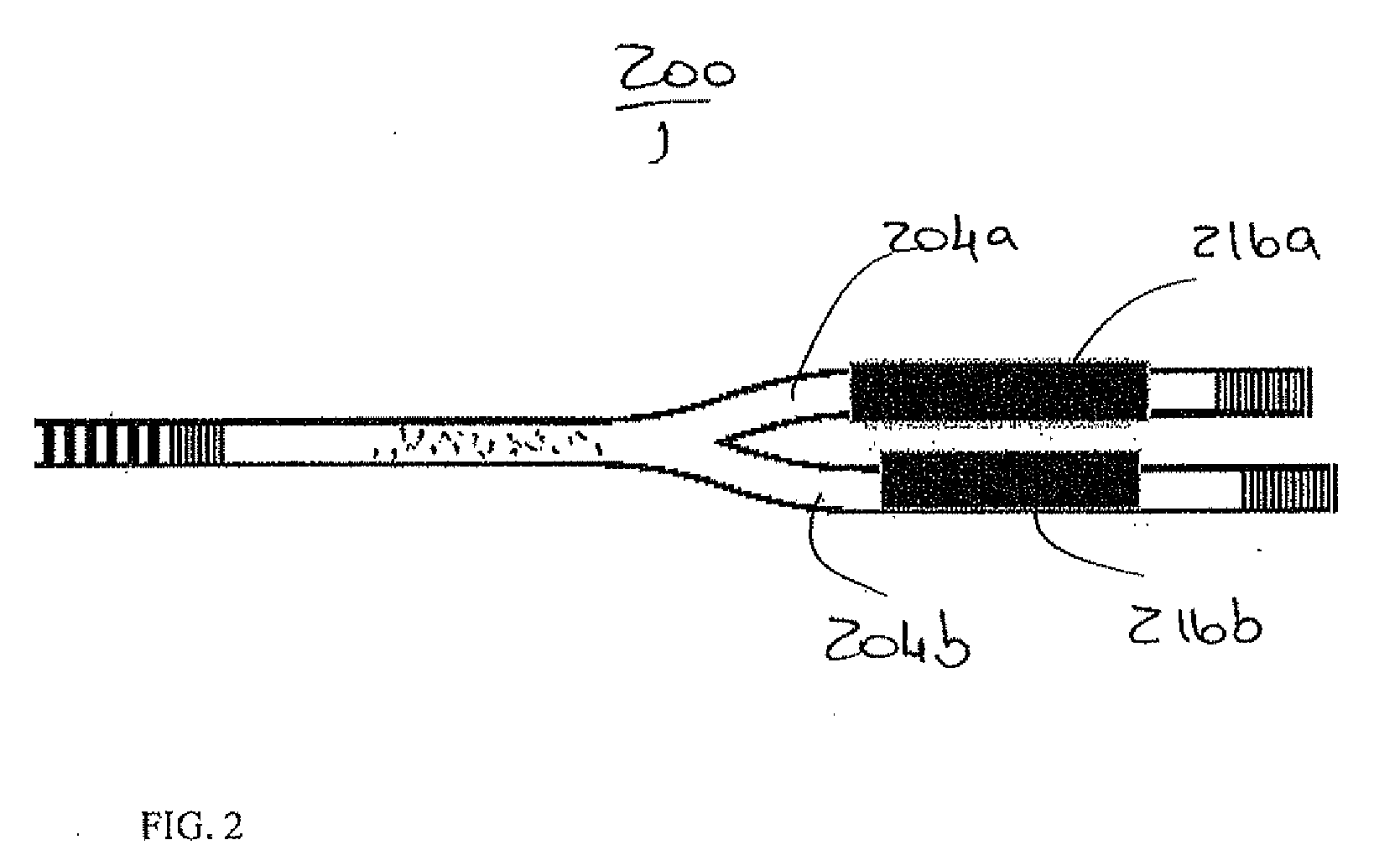
Multi-gap interferometric sensors
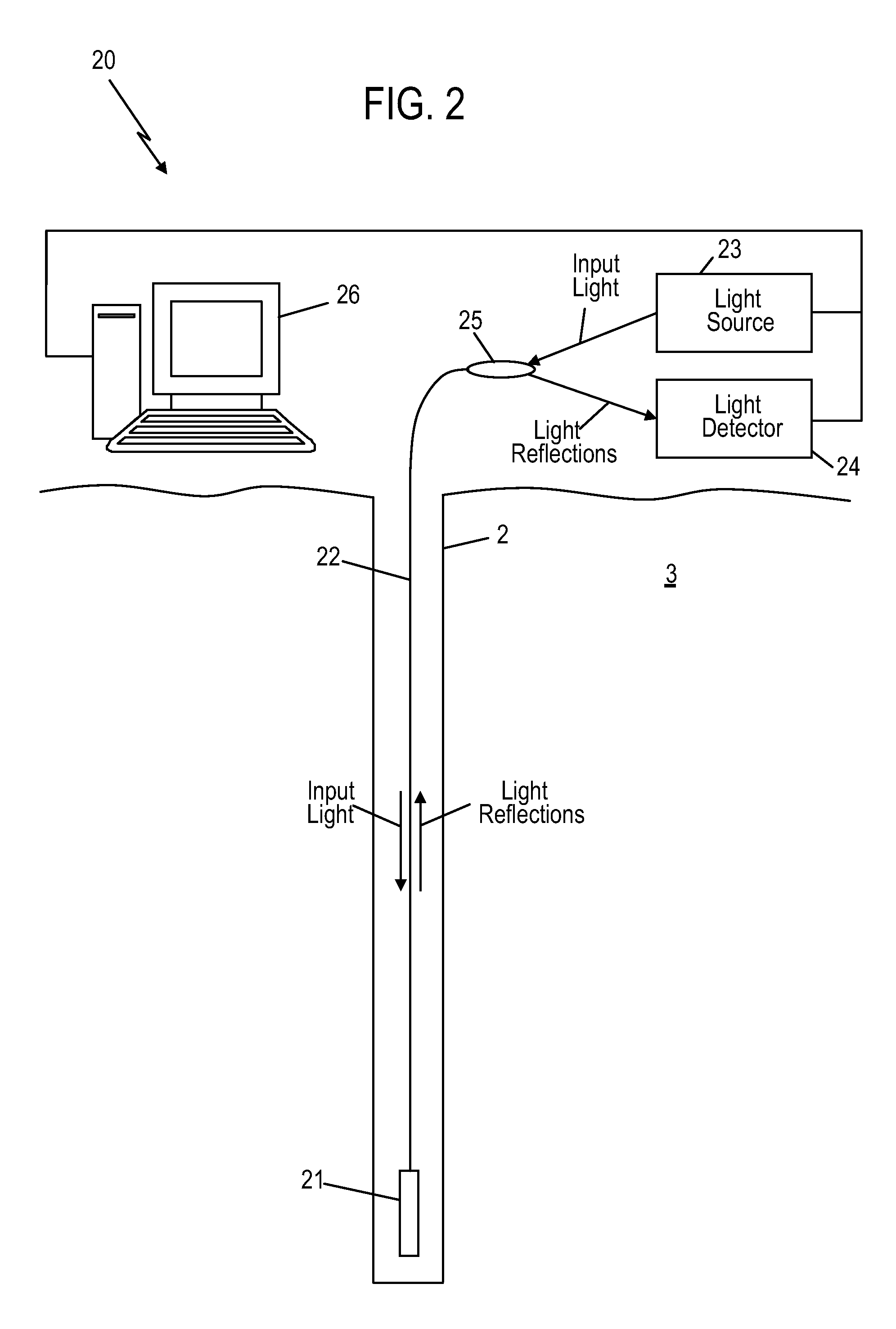
ActiveUS20110172959A1SurveyThermometers using material expansion/contactionInterferometric sensorLight guide
An apparatus for estimating a property includes a hollow core tube and an input light guide disposed at least partially within hollow core tube. The apparatus also includes a second gap disposed within the hollow core tube and separated from the input light guide by an air gap width. The second gap is formed of a first solid material and has a second gap width. The apparatus also includes a third gap disposed at least partially within the hollow core tube and being further from the input light guide than the second gap. The third gap is formed of a second solid material and has a third gap width.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Processing data from a distributed fibre-optic interferometric sensor system
ActiveUS20150100279A1Reduce noiseReduce optical powerSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceInterferometric sensorSensor system
A method of processing data from a distributed fibre-optic interferometric sensor system for measuring a measurand, the system comprising multiple interferometric sensors. The method comprises interrogating two or more of the multiple interferometric sensors to record a raw measurement time series for each of the sensors. The method further comprises calculating a common reference time series as a measure of central tendency of the raw measurement time series from two or more reference sensors, the reference sensors being selected from the multiple interferometric sensors. Finally, the method comprises compensating at least one raw measurement time series from a measurement sensor selected from the multiple interferometric sensors with the common reference time series to produce a compensated measurement time series, the measurement sensor being configured to be sensitive to the measurand. The invention further relates to a distributed fibre-optic interferometric sensor system.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Tracking algorithm for linear array signal processor for fabry-perot cross-correlation pattern and method of using same
ActiveUS20070064241A1Accurate trackingAccurate identificationInterferometersUsing optical meansInterferometric sensorTrack algorithm
An algorithm and method for calculating an interferometric gap is disclosed that comprises providing an interferometric sensor having a first gap and an interferometric correlation element having a second gap placed in series with the first gap. A correlation burst waveform is generated having a plurality of features wherein the shape of the burst waveform evolves across the range of the second gap. Means are provided for tracking the features across the entire range of gaps and determining the dominant peak or dominant valley to determine the first gap.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Hydrophone mandrel for precise placement of gratings
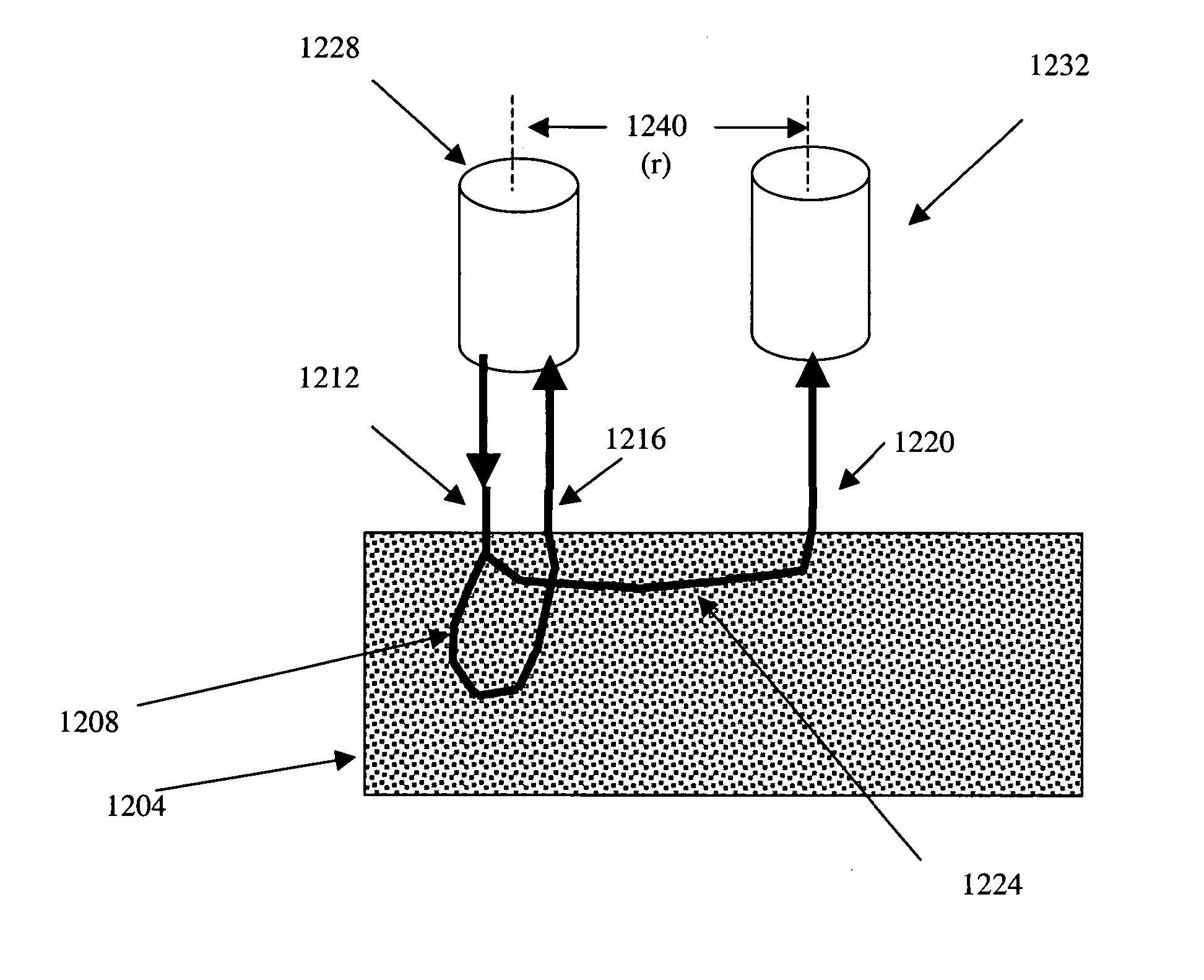
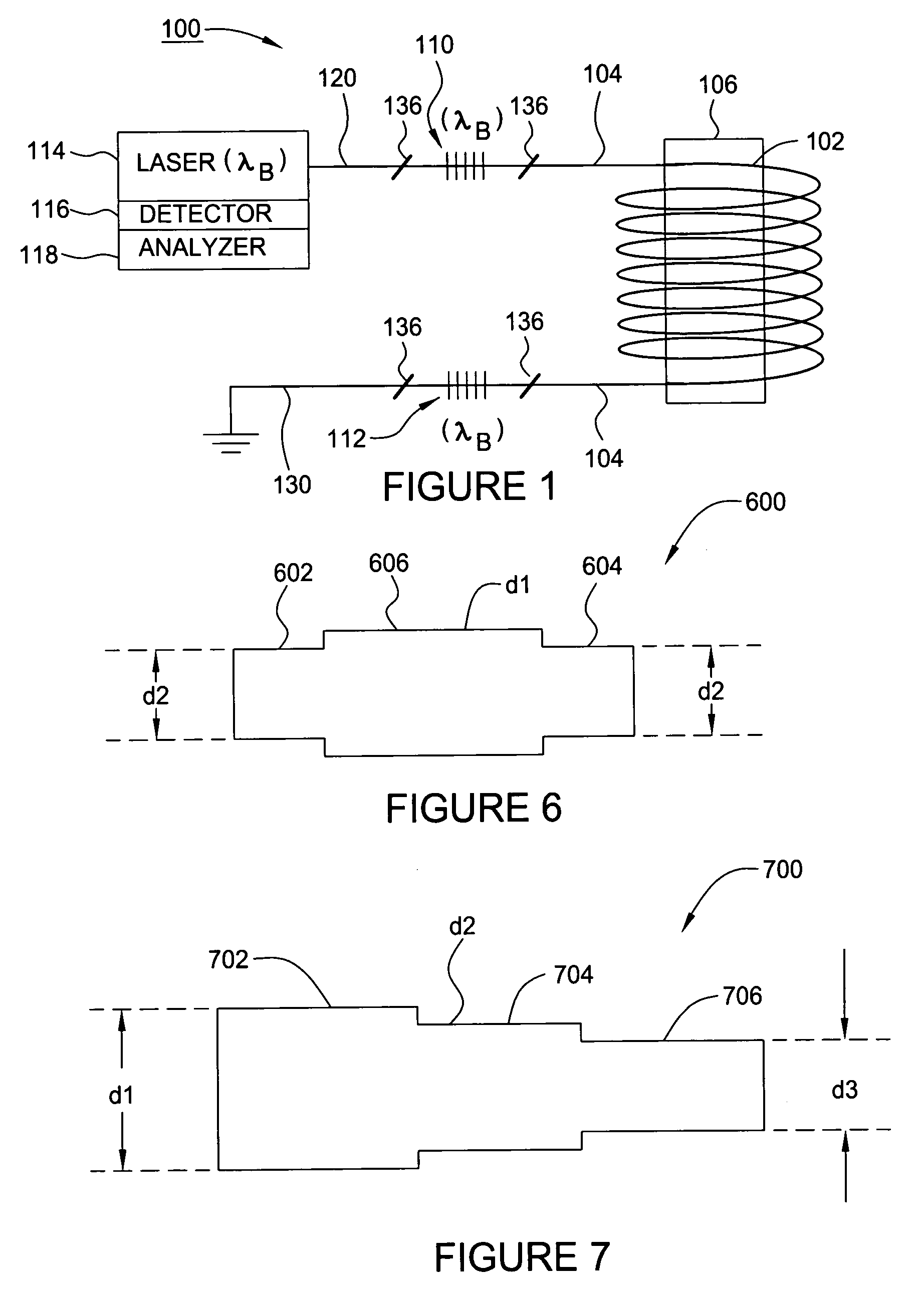
InactiveUS7116850B2Precise positioningReduce difficultyLaser detailsOptical signal transducersHydrophoneGrating
A method and apparatus for reducing the difficulty of controlling the length of a section of optical waveguide wrapped around a mandrel separating Bragg gratings forming an interferometric sensor are provided. The section of optical waveguide may be wrapped on a mandrel having at least two different outer diameters. The mandrel may also include one or more bores for receiving and protecting the Bragg gratings.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Fabrication method of miniature optical fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer with controllable cavity length
InactiveCN108332654ASolve the problems of difficult production and structural size controlHigh mechanical strengthUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyInterferometric sensorEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical fiber device fabrication, and discloses a fabrication method of a miniature optical fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer (FPI) with a controllable cavity length. A method in which a single mode optical fiber splices a hollow optical fiber (HCF) and a discharging taper is adopted to fabricate a miniature air cavity FPI. The structural size can becontrolled by adjusting a series of parameters such as an HCP length and various welding parameters such as a taper length, a two-fiber overlapping amplitude, a discharge parameter and the number of discharge times. By means of the method, the size-controllable, repeatable and efficient miniature air cavity Fabry-Perot interferometer can be obtained, and plays a vital role in an interference-typesensor based on Fabry-Perot. The method can make the microcavity level and perpendicular length of the FPI cover from a small value to a large value, and efficient fabrication can be achieved. By means of the method, according to user requirements, miniature air cavity FPIs with random sizes can be fabricated. Besides, a probe of the miniature air cavity FPI can be used for detection of parameterssuch as axial stress and temperature.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Active coherence reduction for interferometer interrogation
ActiveUS7433045B2Raise the barMoreUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyControl mannerInterferometric sensor
Methods and apparatus reduce coherence of an optical signal that is used to interrogate optical interferometric sensors. The optical field phasor of the interrogation source is modulated in a controlled manner to produce a broadened optical source power spectrum at the output of the source unit. The output from the source unit is launched into an optical sensor network, comprising a multiple of optical pathways from its input to the detection unit, where pairs of optical pathways form sensor interferometers. A compensating interferometer with delay difference similar to the sensor delay difference may be arranged in a serially coupled manner with the optical sensor network, either before or after the network. The coherence modulation may be performed through direct modulation of the source or through external modulation of the light with piezoelectric ring modulator, a Lithium niobate phase or intensity modulator, or an acoustooptic modulator.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
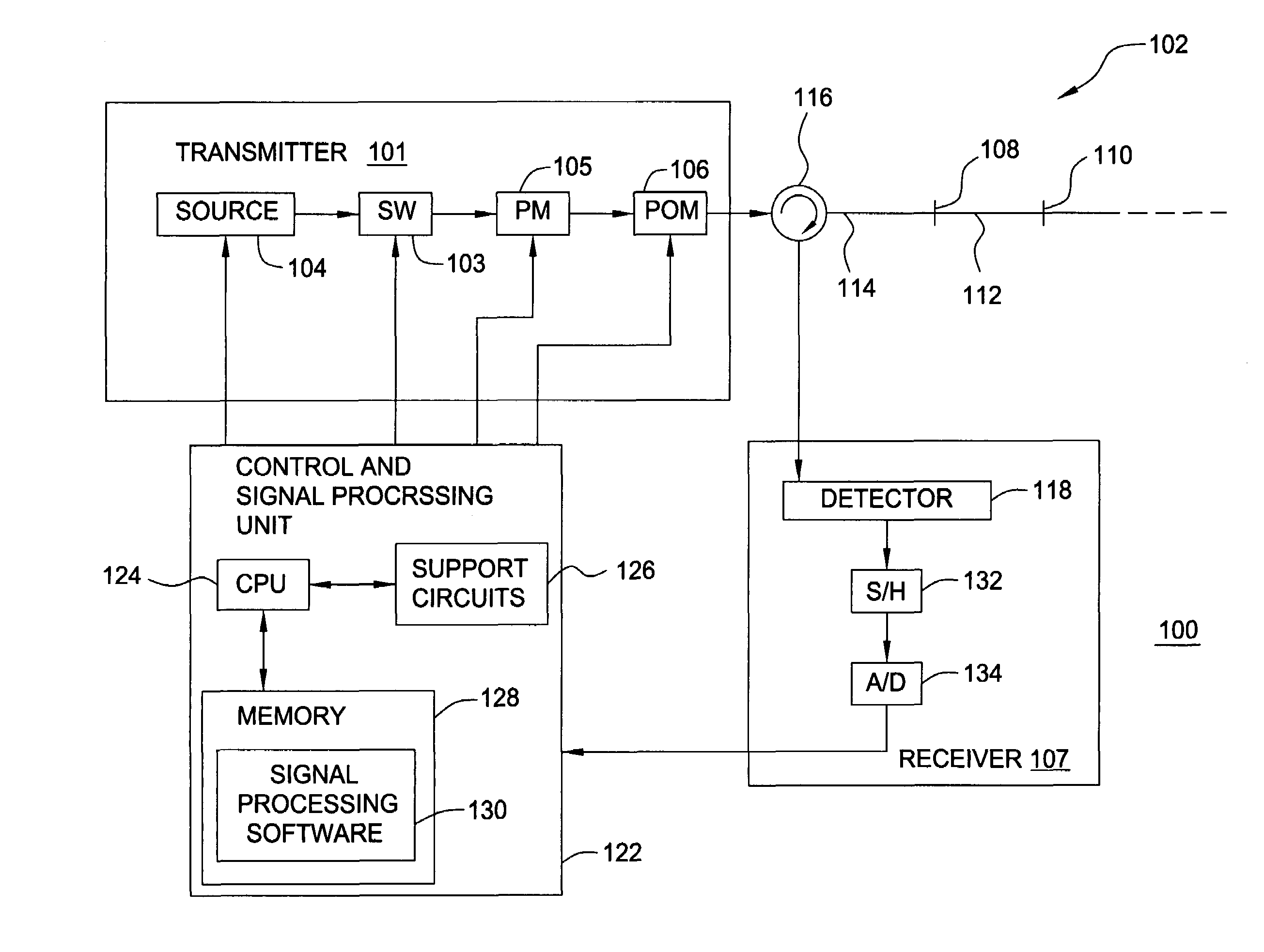
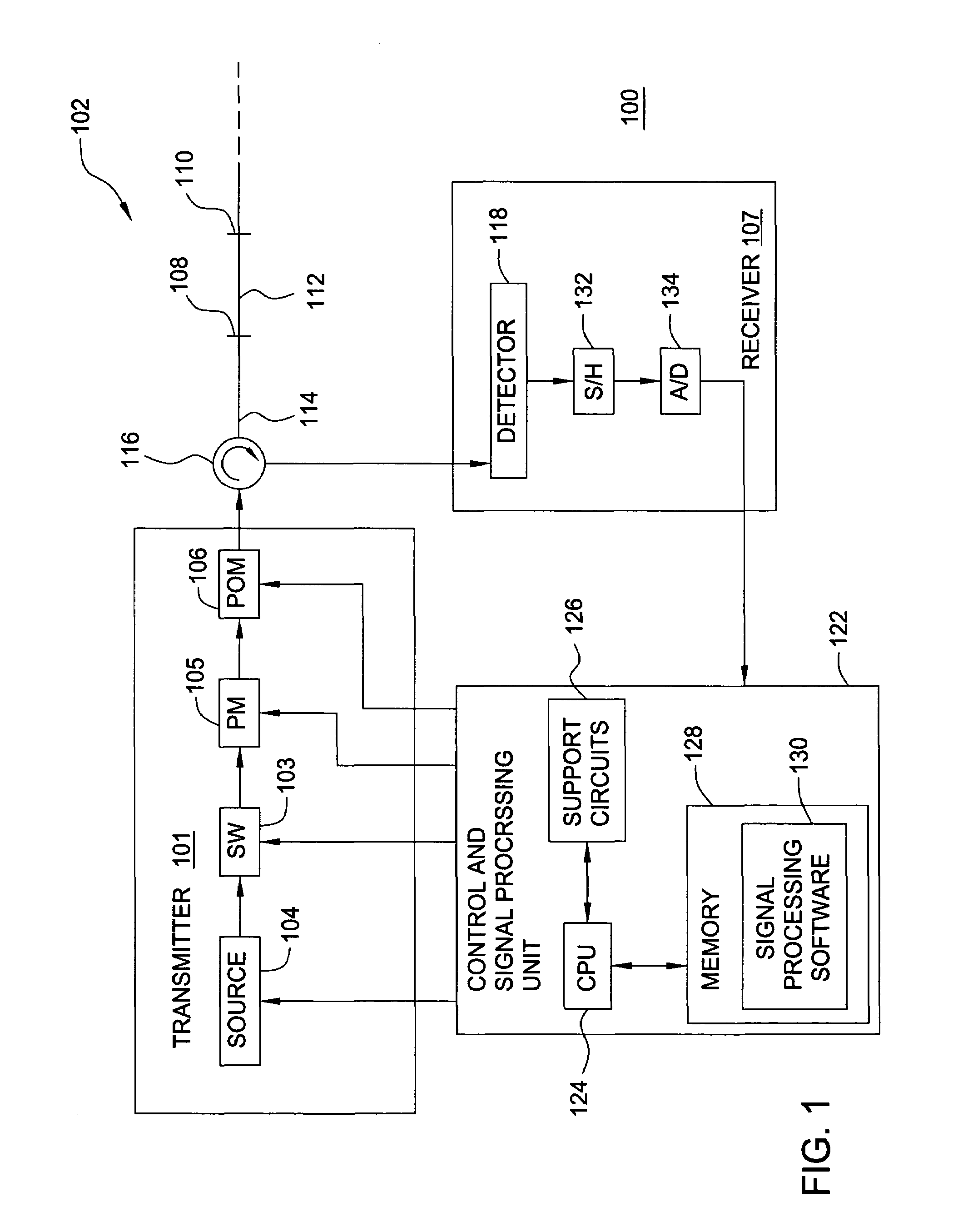
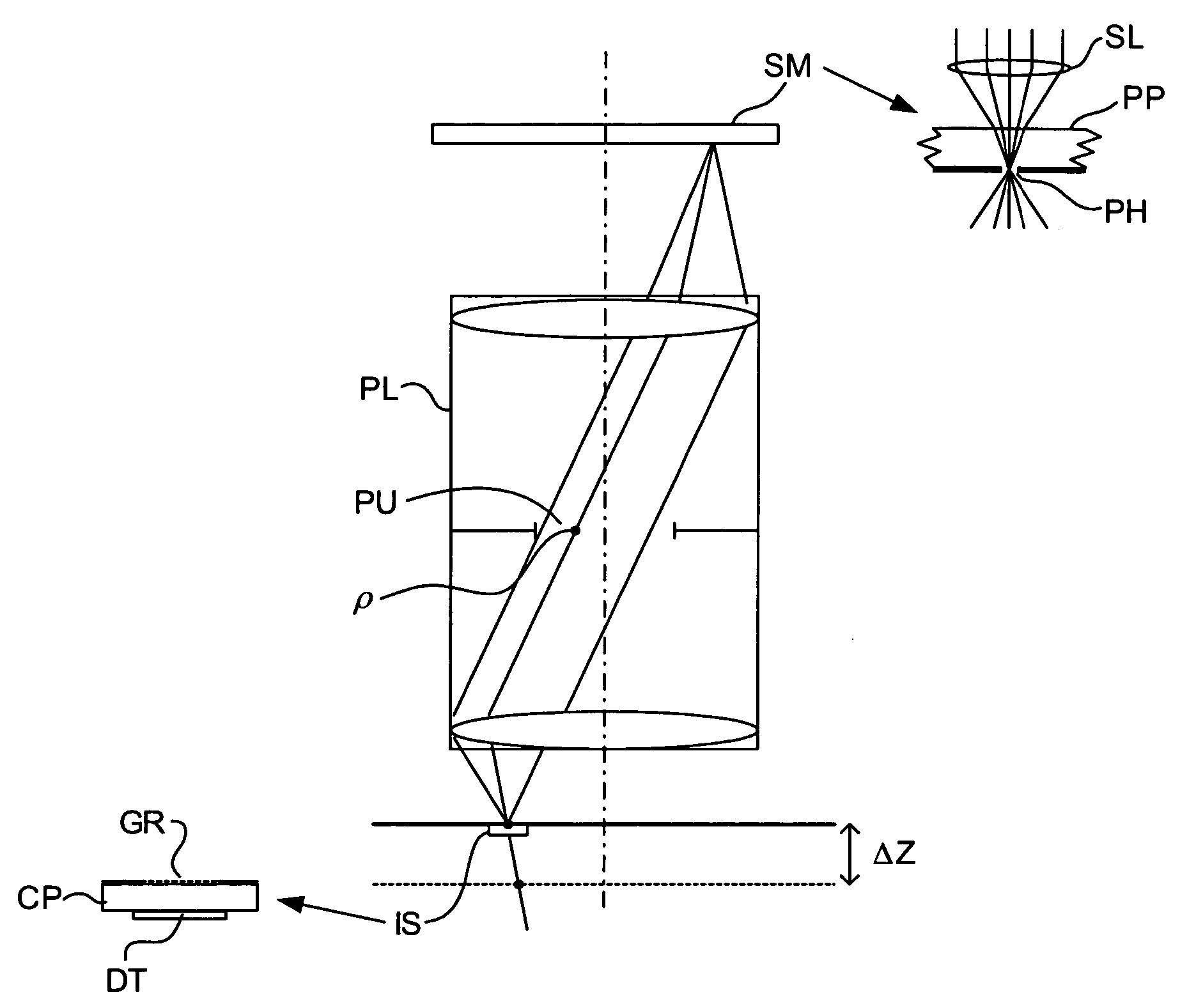
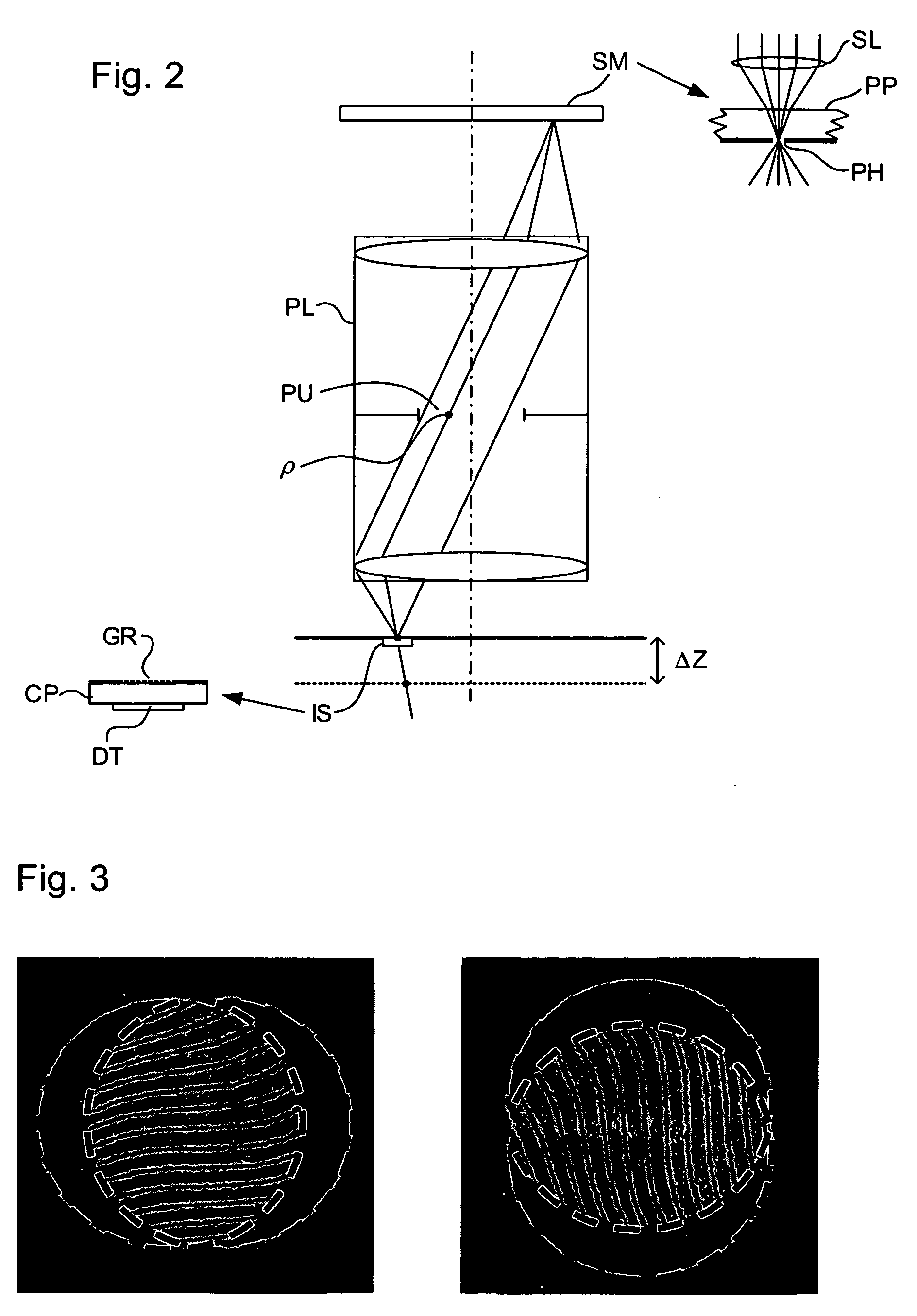
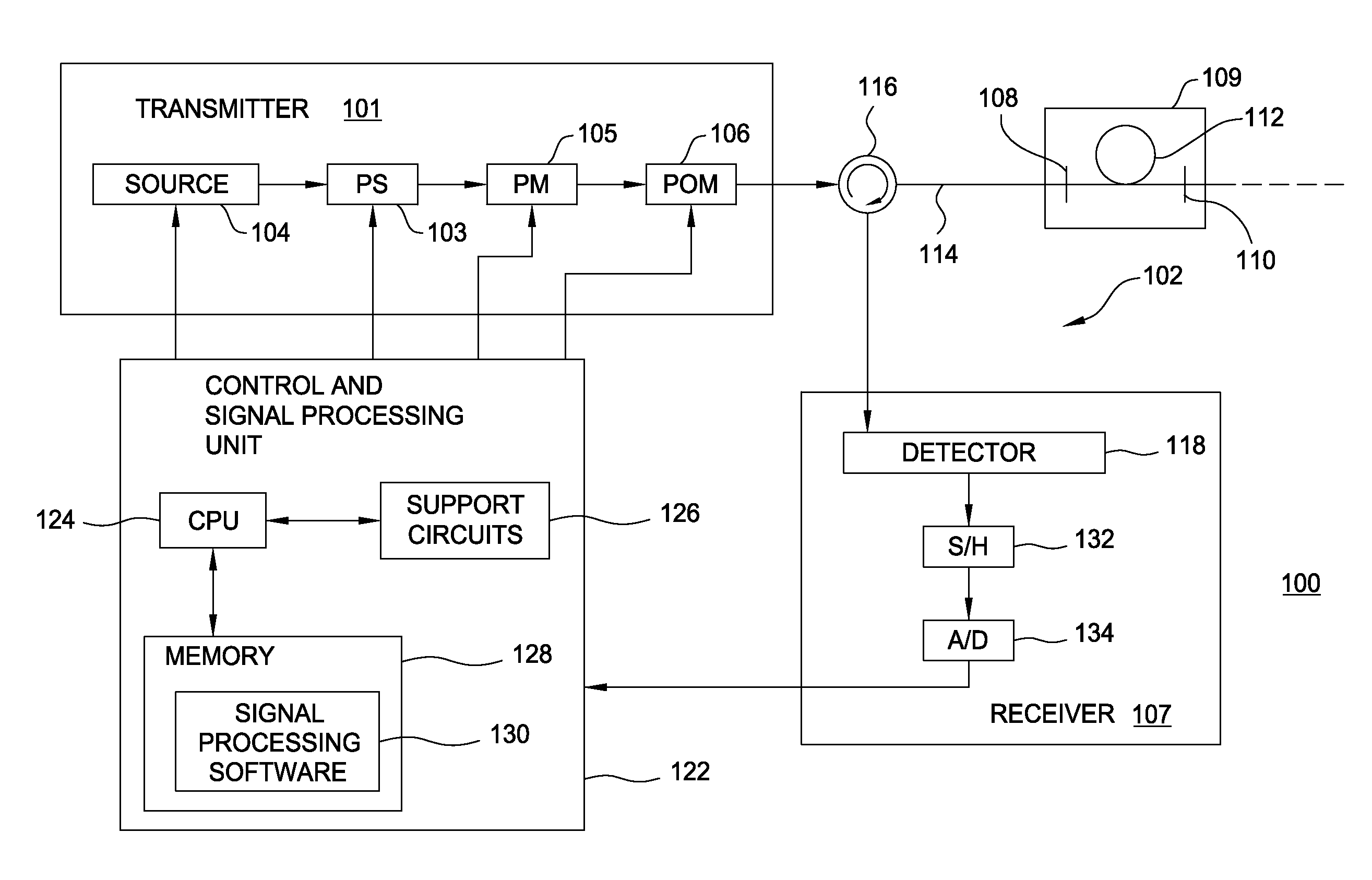
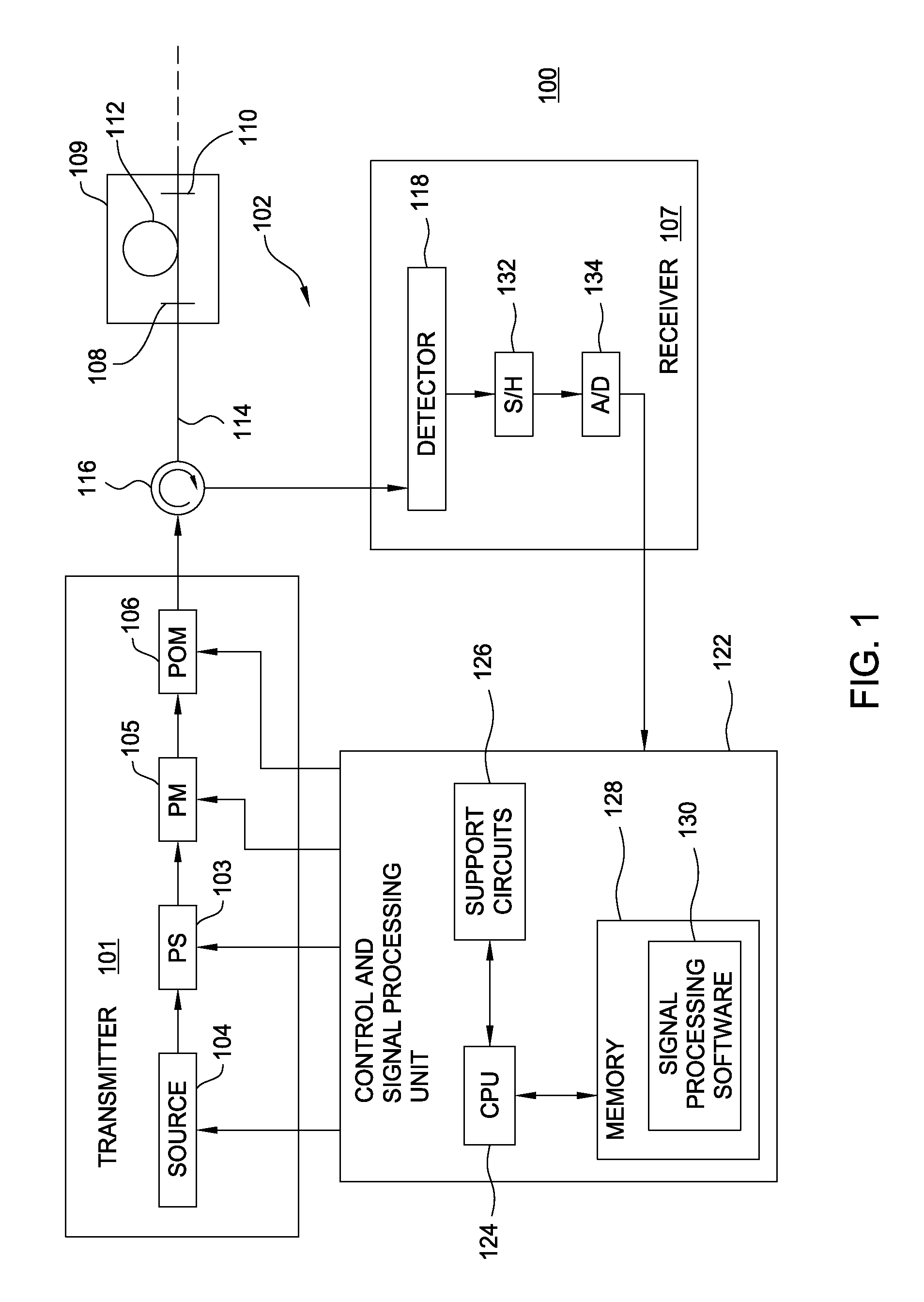
Lithographic apparatus, method of determining properties thereof and computer program
A lithographic apparatus is arranged to project a patterned radiation beam from a patterning device onto a substrate using a projection system. The lithographic apparatus comprises: an interferometric sensor for measuring the wavefront of the radiation beam at the level of the substrate, the interferometric sensor having a detector; an actuator for displacing the interferometric sensor in a direction along the optical axis; a first module for determining the change of phase of the wavefront at each of a plurality of locations on the detector of the interferometric sensor, the change of phase resulting from displacement of the interferometric sensor by the actuator between a first position and a second position; and a second module for determining, for each of the plurality of locations on the detector, the corresponding pupil location at the pupil plane of the projection system traversed by the radiation, using the change of phase determined by the first module and the value of the displacement of the interferometric sensor by the actuator, to produce a mapping between locations on the detector and corresponding pupil locations. Once the mapping has been obtained, the numerical aperture and telecentricity of the projection system can be measured.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
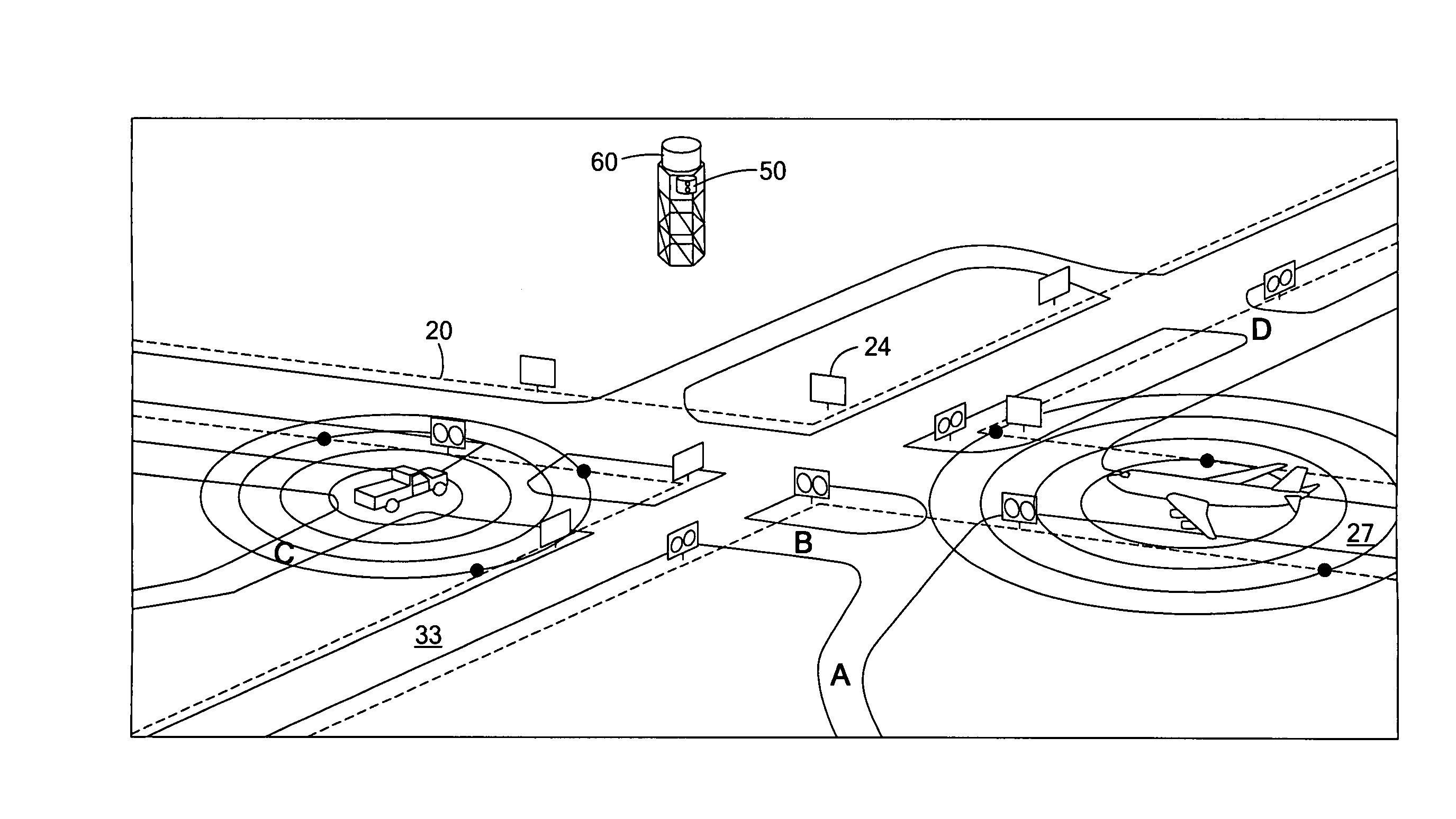
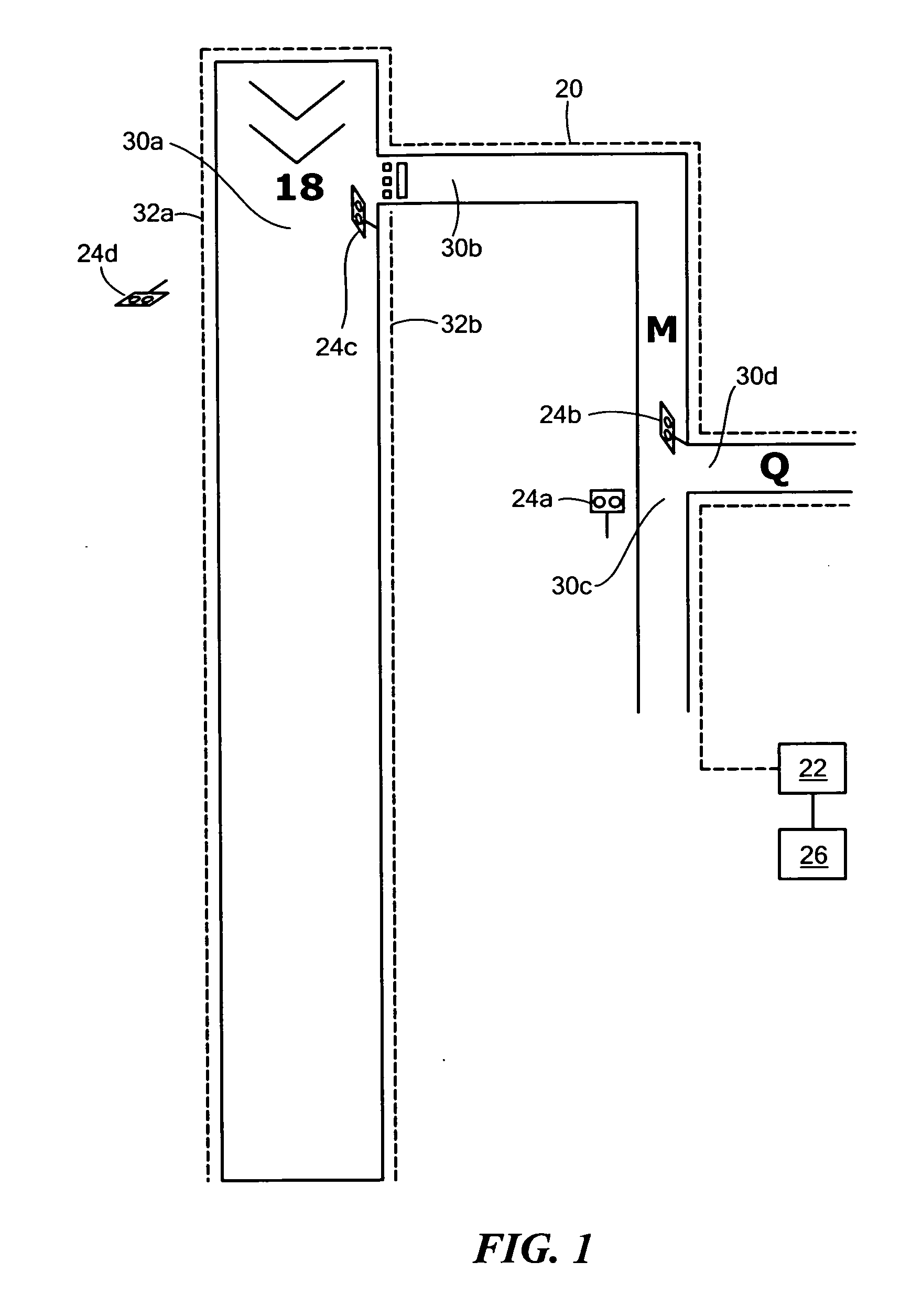
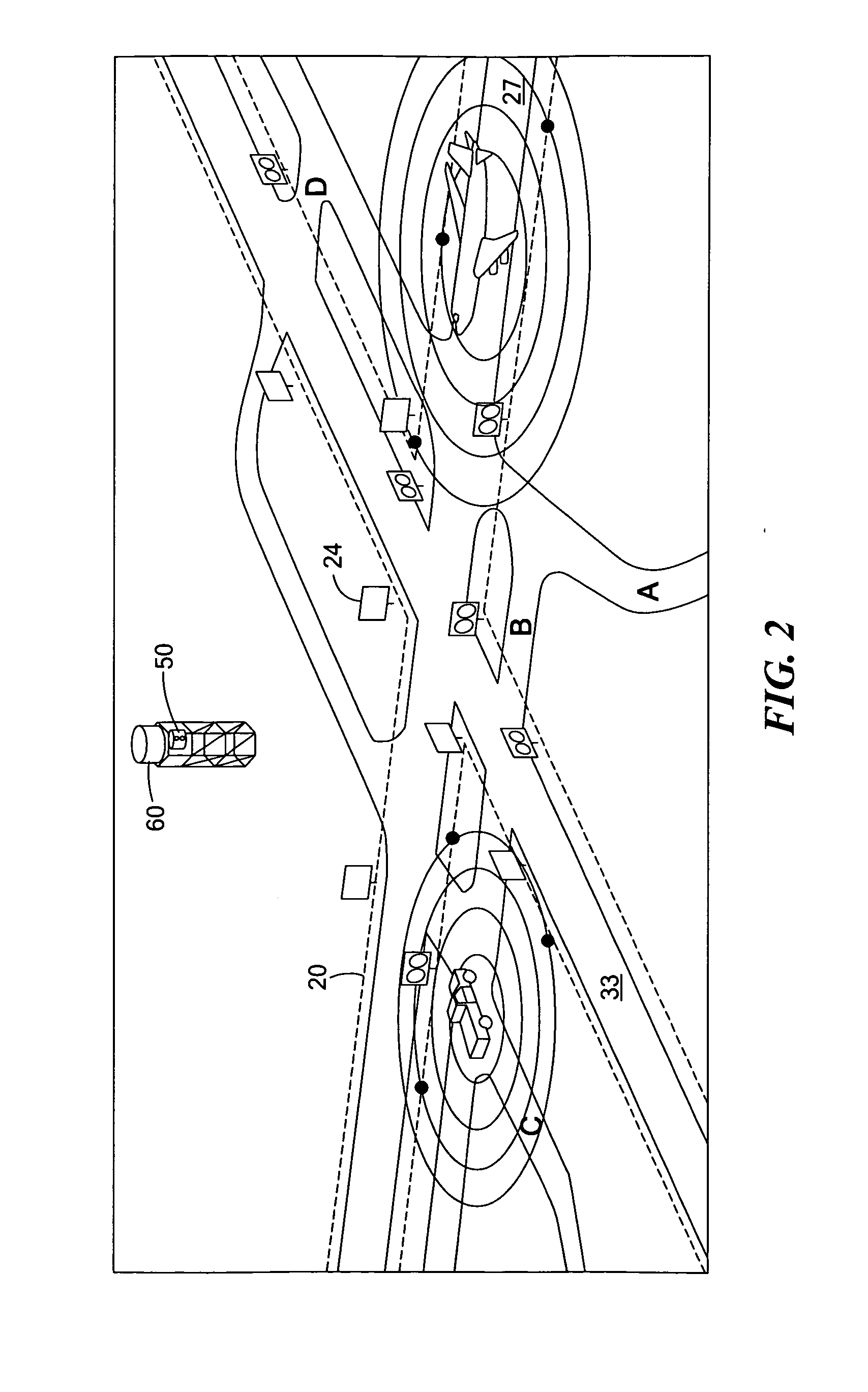
Airport incursion notification system
An airport incursion notification system includes a fiber optic configured as an interferometric sensor to detect noise and buried adjacent at least at select runways and taxiways of an airport. At least one interrogator unit is for determining the location of and classifying noises detected by the fiber optic. Indicators are present at least at select runway and taxiway intersections. A controller subsystem is responsive to the interrogator unit and is configured to activate one or more indicators if an incursion condition exists. Imaging and / or radar subsystems can also be employed.
Owner:FOSTER-MILLER
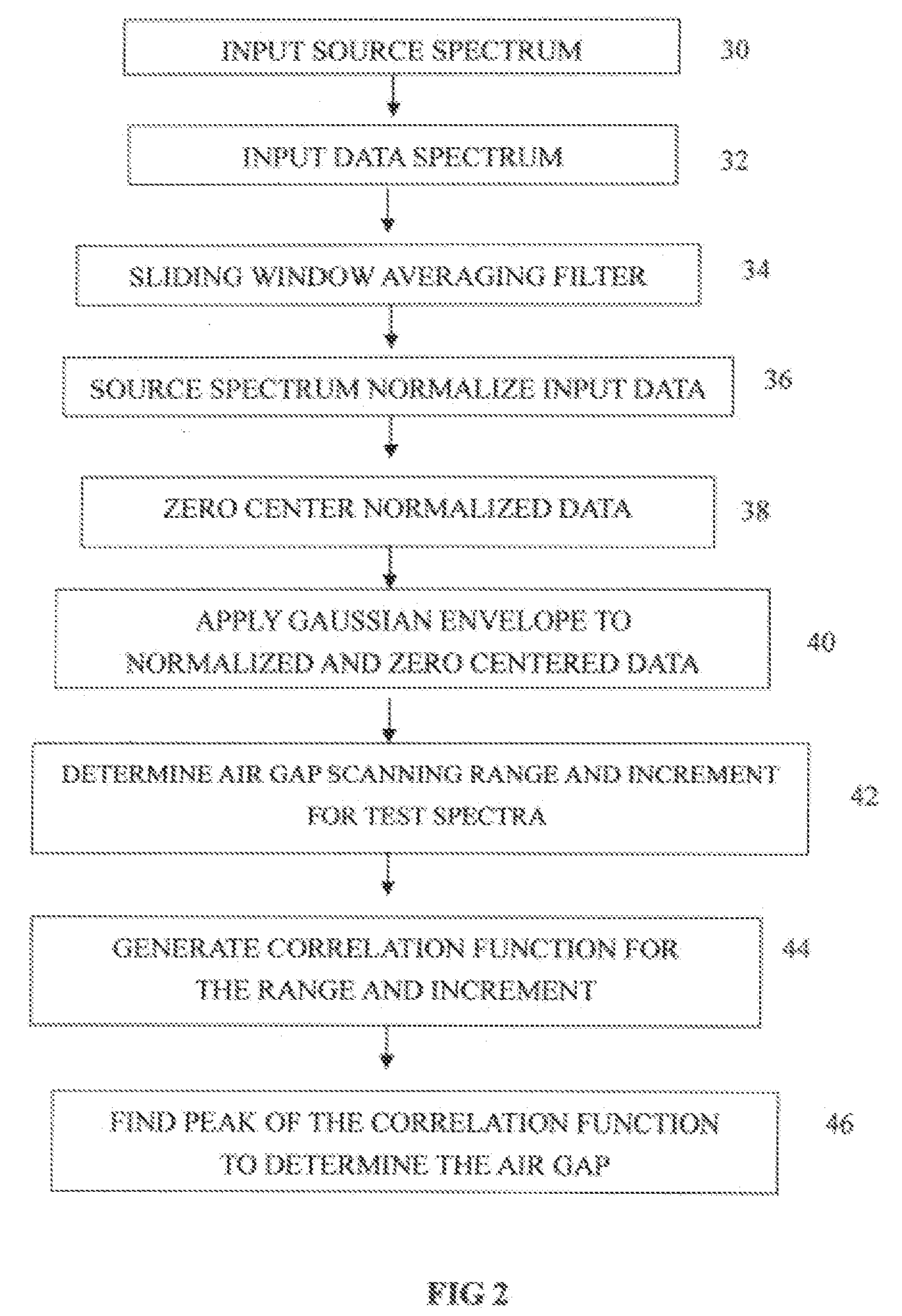
Method for demodulating signals from a dispersive white light interferometric sensor and its application to remote optical sensing
ActiveUS20080204759A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryInterferometric sensorCorrelation function
A method for demodulating signals from a dispersive, white light interferometer includes generating test interferometry spectra from an interferometer forming part of a sensor for various values of interferometer sensor optical path length. The various test spectra are correlated to a measured spectrum from the sensor to generate a correlation function. The sensor optical path length resulting in the correlation function value reaching a maximum is selected as the optical path length
Owner:ZIEBEL AS
Light-emitting intra-cavity interferometric sensors
InactiveUS20100231920A1Minimizes nonspecific binding effectMaximize sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansInterferometric sensorMach–Zehnder interferometer
Light-emitting intra-cavity interferometric (ICI) optical sensors based on channel waveguide structures which include an internal light emitting material and a functionalized region. In some embodiments, the waveguides are made of a sol-gel which incorporates the light emitting material. In some embodiments, the waveguide structure includes an ICI resonator backbone and the ICI sensor is a laser sensor. In some embodiments, the resonator backbone has an interferometric Y-branch shape. In some embodiments, the resonator backbone has a Mach Zehnder interferometer shape. In some embodiments, an ICI laser sensor has an interferometric arrayed waveguide grating shape. In some embodiments, an ICI sensor may be remotely optically pumped and remotely read.
Owner:TEL AVIV UNIV FUTURE TECH DEVMENT
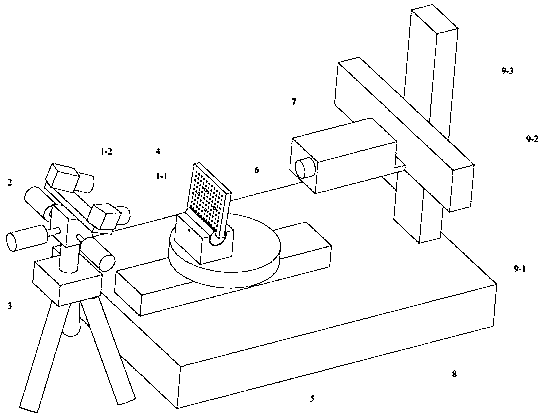
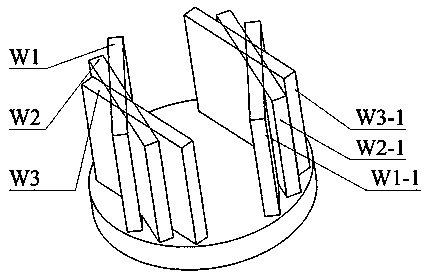
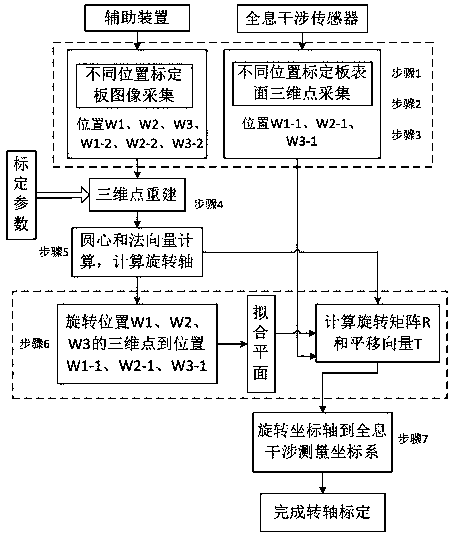
Calibration method for rotation axis of holographic interferometric four-axis measuring device
ActiveCN108507462AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyUsing optical meansInterferometric sensorHolographic interferometry
The invention relates to a calibration method for the rotation axis of a holographic interferometric four-axis measuring device. The error of fitting which is realized by means of the center of a standard ball is large, and as a result, the problem of inaccurate calibration of a rotation axis is brought about, while, with the measuring device of the invention adopted, the problem can be solved. The method is realized by means of a binocular stereoscopic image sensor and a planar target with a standard point. The method includes the following steps that: 1, the images of a planar target in a set of different positions are acquired; 2, a holographic interferometric sensor obtains the three-dimensional point cloud data of the planar target in the set of different positions; 3, the planar fitting of the planar target is carried out; 4, a set of vectors of a fitted plane and the rotation center of the fitted plane are obtained, the calibration value of the rotation axis is determined; 5, arotation matrix R and a translation vector T between two coordinate systems are solved; and 6, and the calibration of the rotation axis is completed in a unified manner in a coordinate system. The calibration method of the invention has high precision and high efficiency.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Adaptive mixing for high slew rates
ActiveUS20090111417A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansLocal oscillator signalLow-pass filter
A method and apparatus for demodulation of detected fringes from interferometric sensors with high slew rates are provided. A detected interference signal may be mixed with a local oscillator phasor to obtain a mixed signal, the local oscillator being controlled to produce a frequency that roughly matches the fringe frequency of the interference signal. A sensor phase estimate may be obtained from the detected interference signal or the mixed signal. The local oscillator signal can be computed from the sensor phase estimate. The mixed signal and the sensor phase estimate may be low pass filtered and decimated and the resulting decimated mixed signal and decimated sensor phase estimate may be processed and combined with moderate processing power requirements in an effort to accurately measure the sensor phase for the interferometric sensor.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com