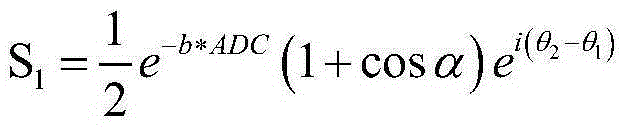Patents
Literature
337 results about "Single scan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
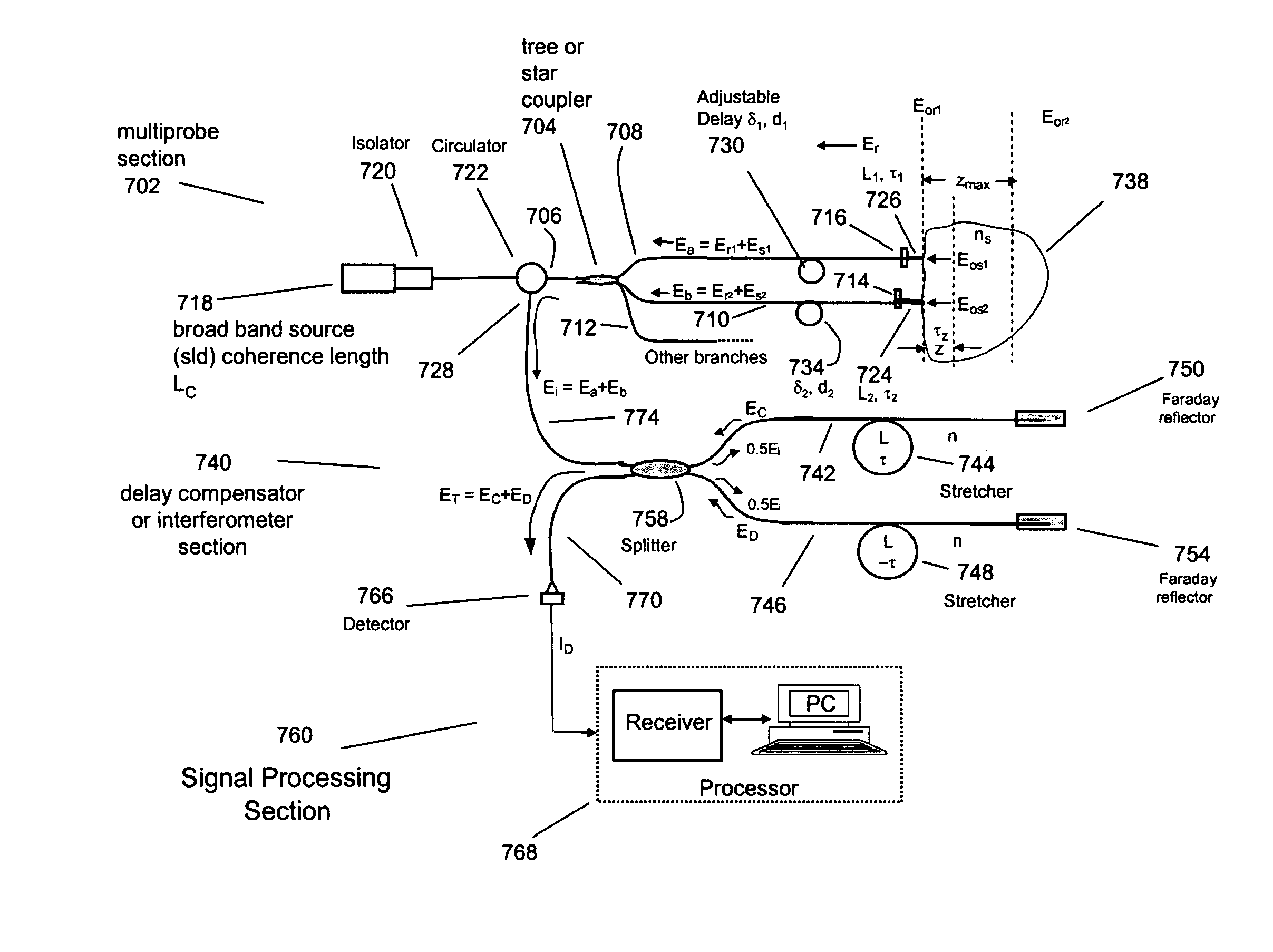
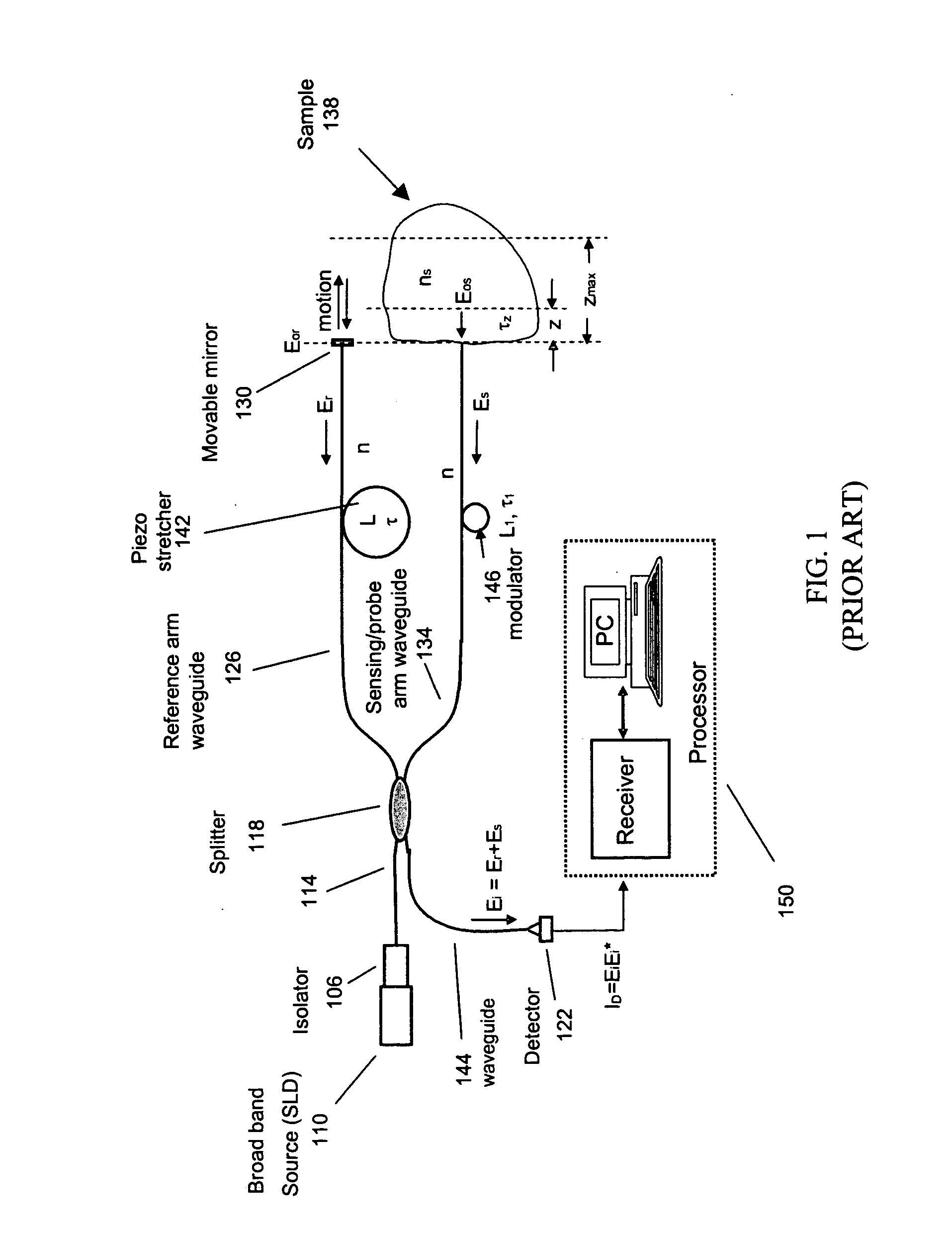
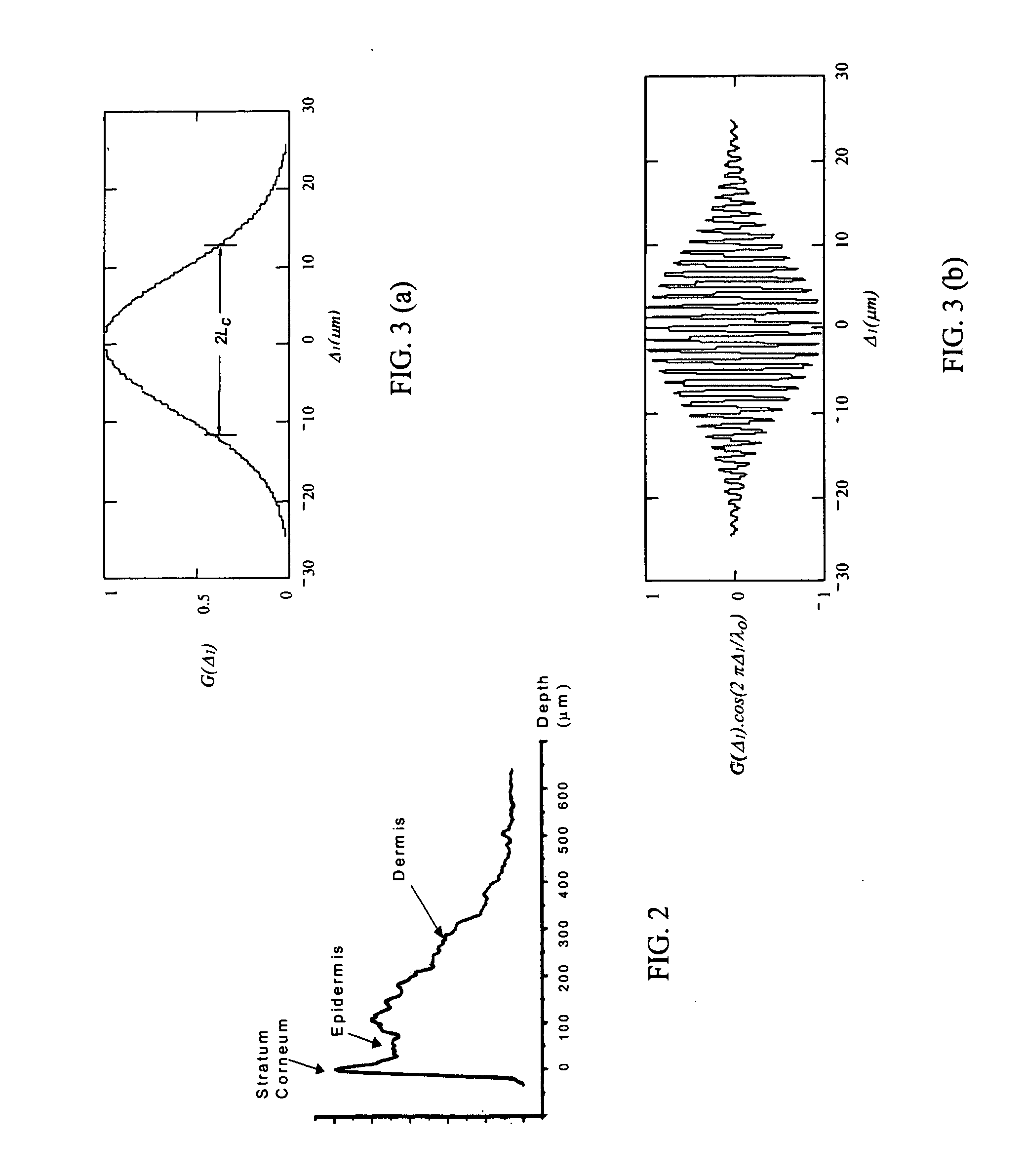
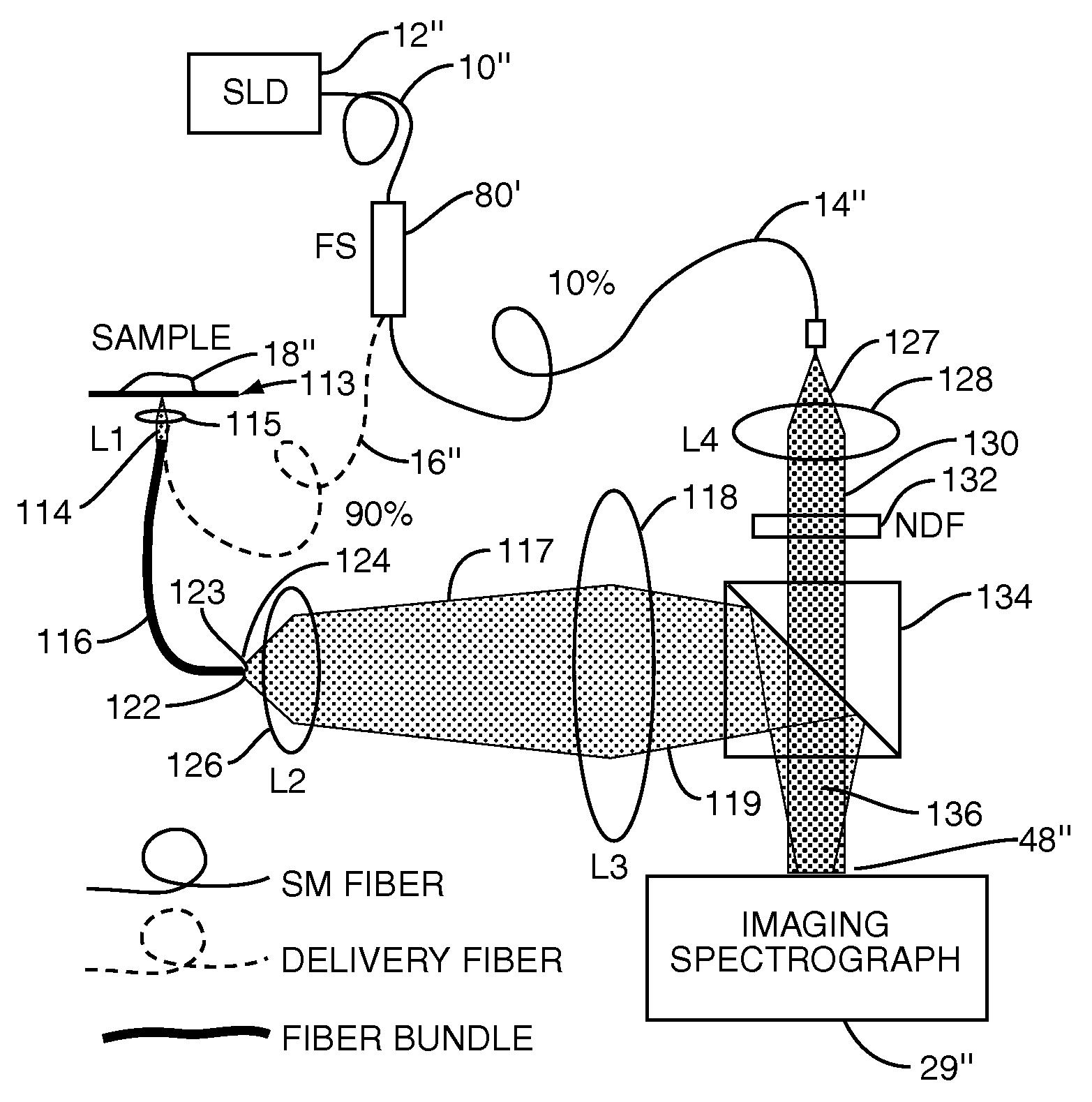
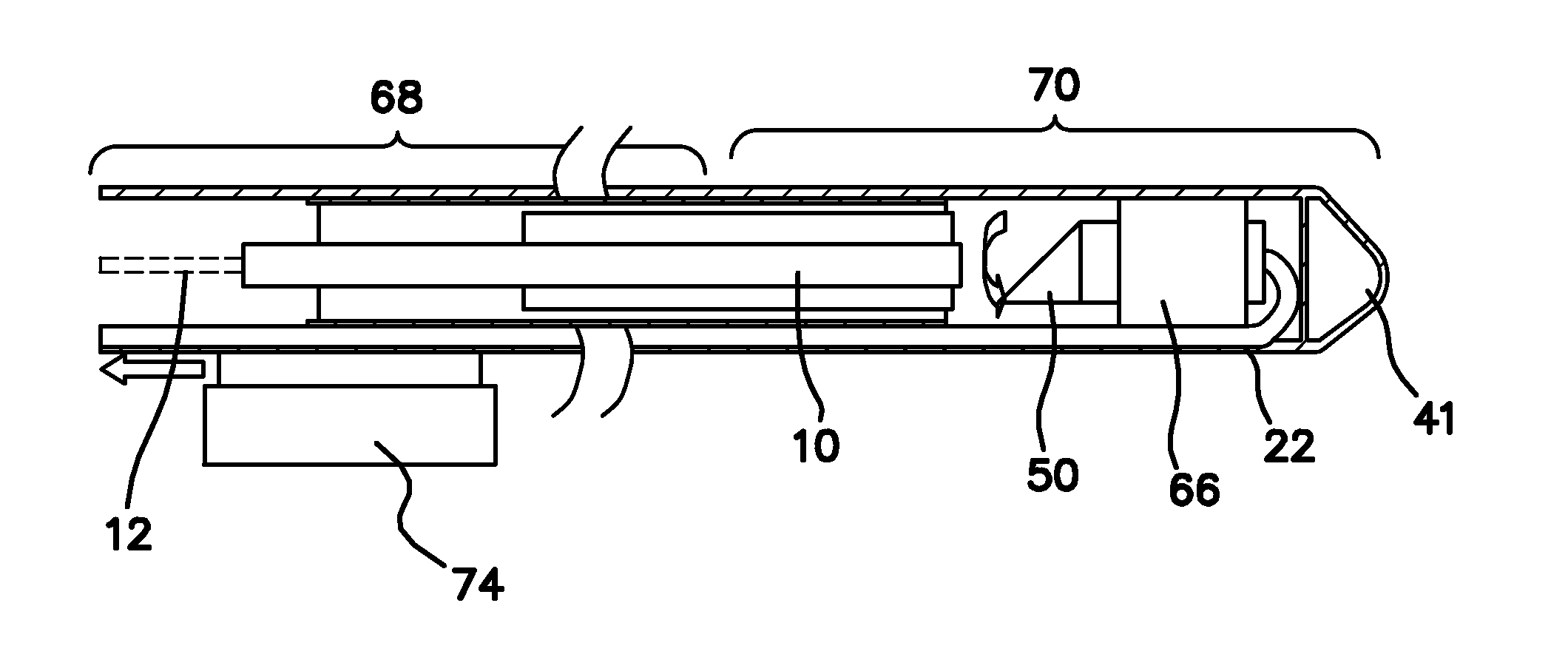
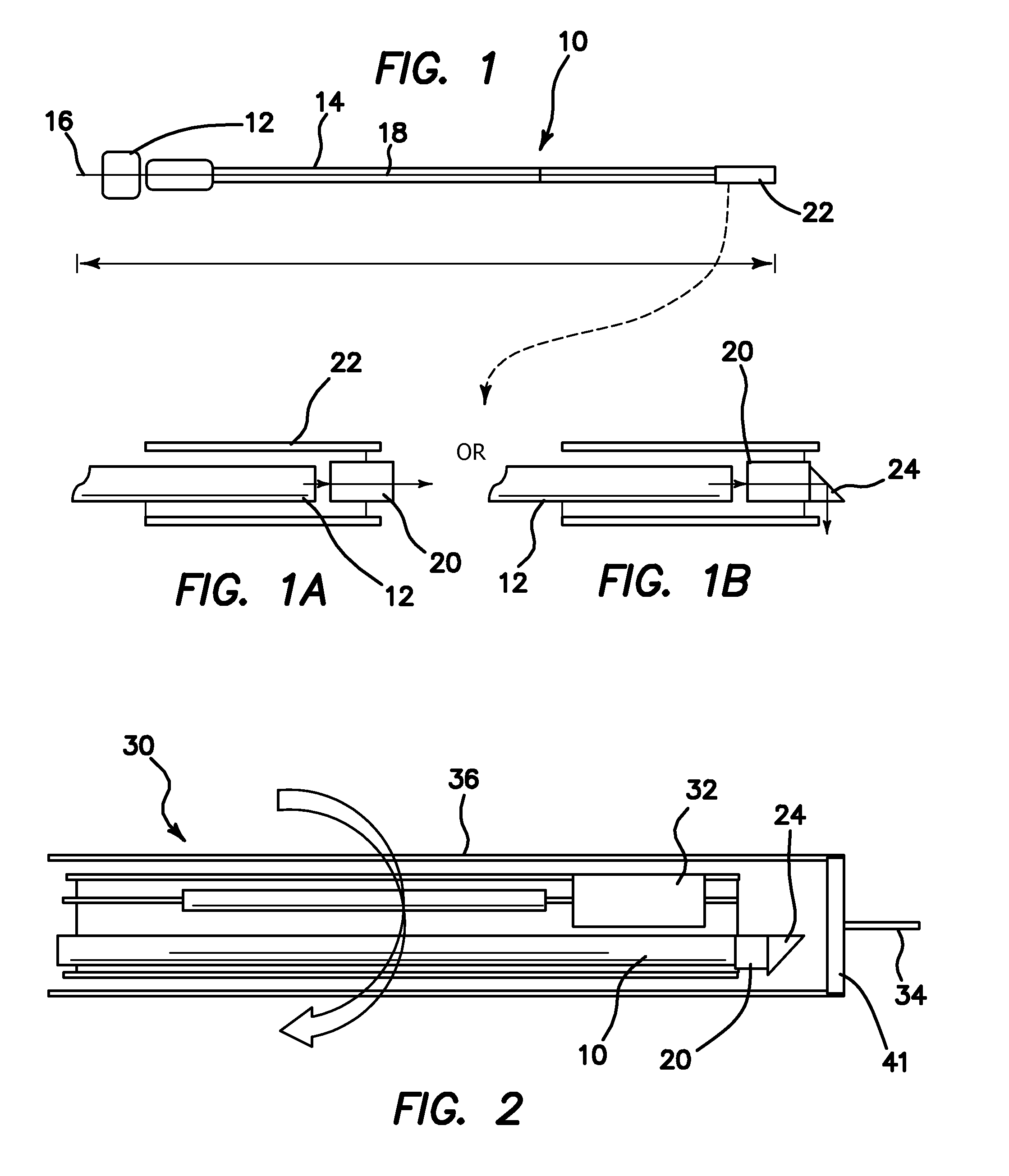
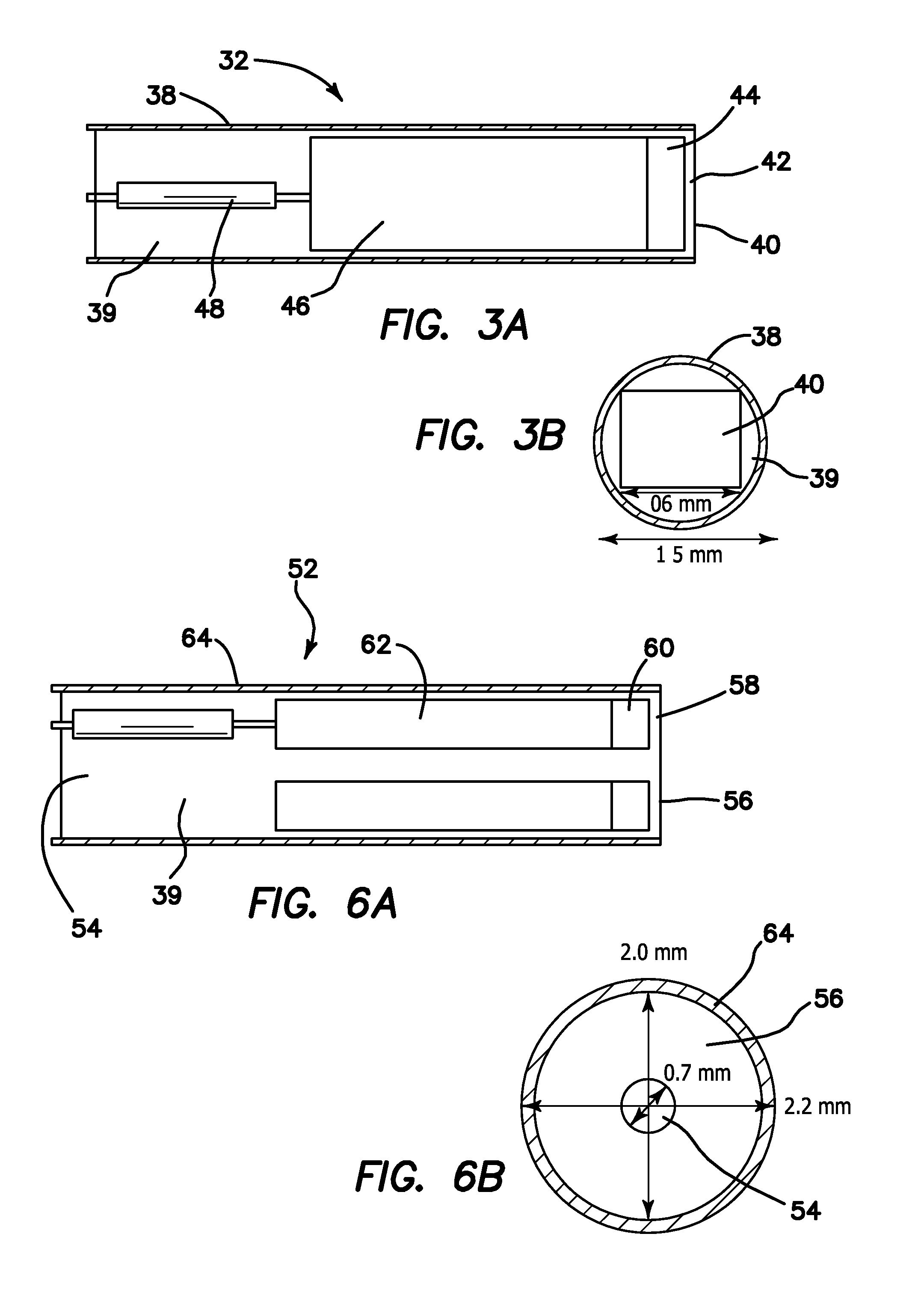
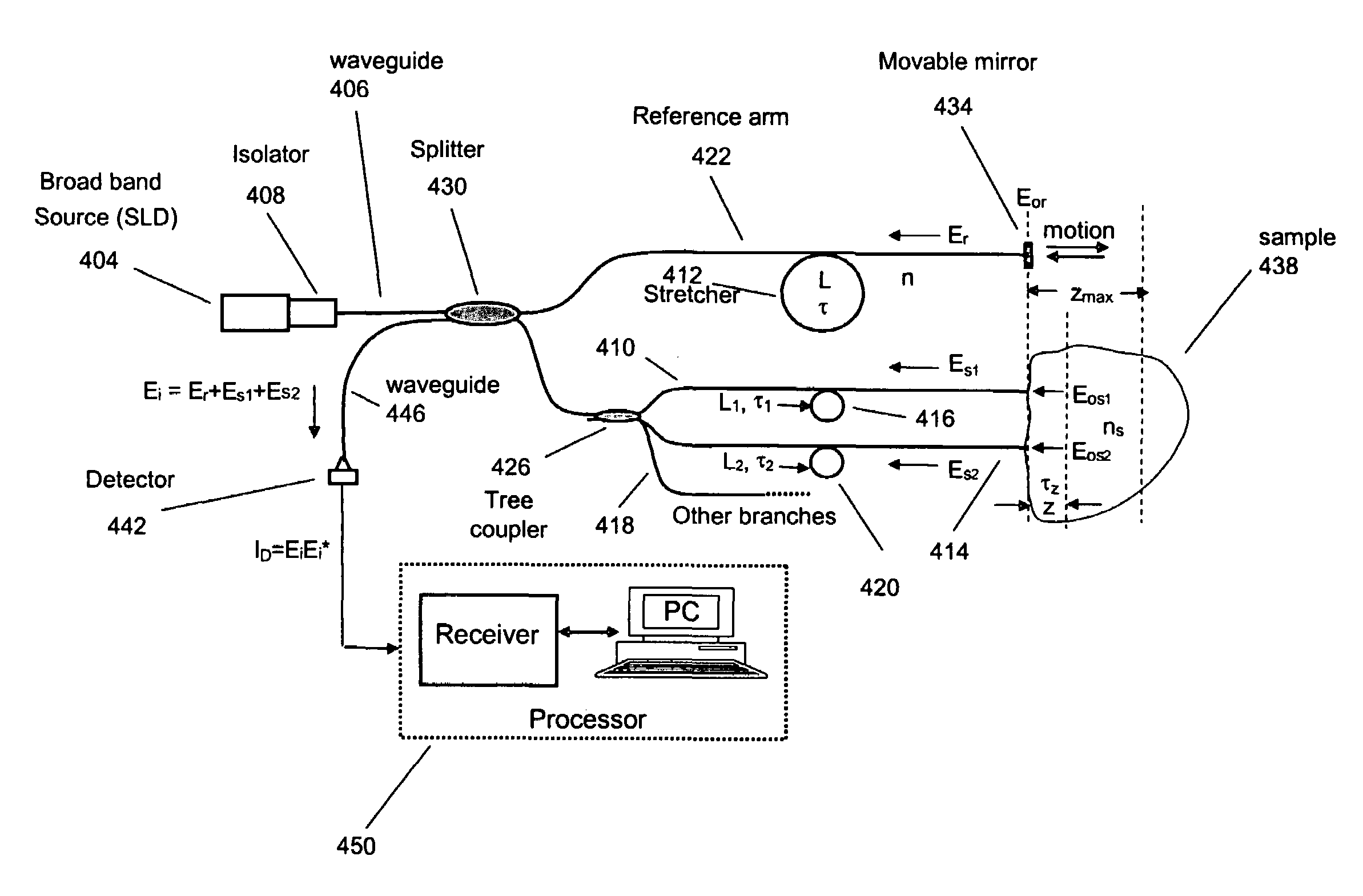
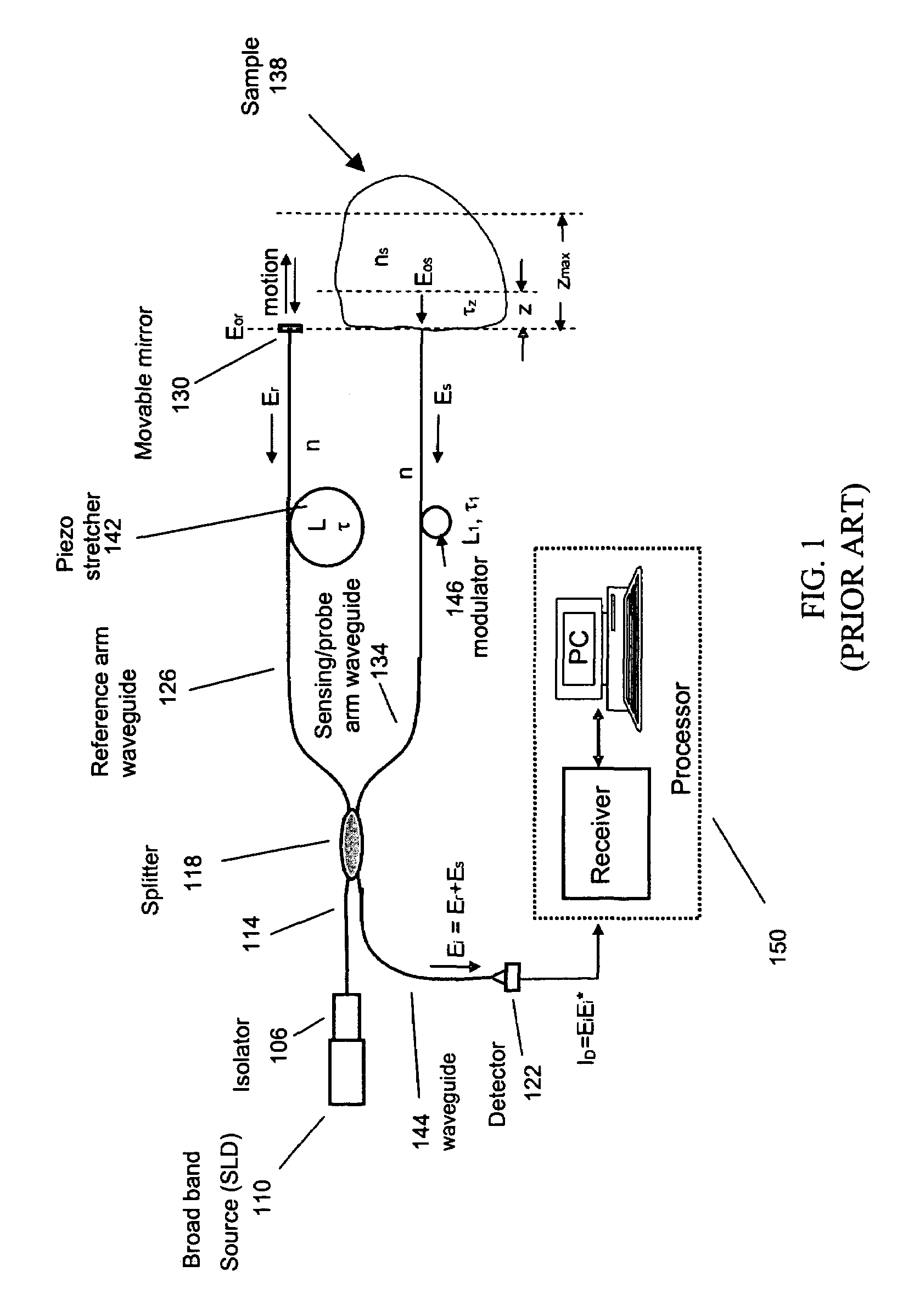
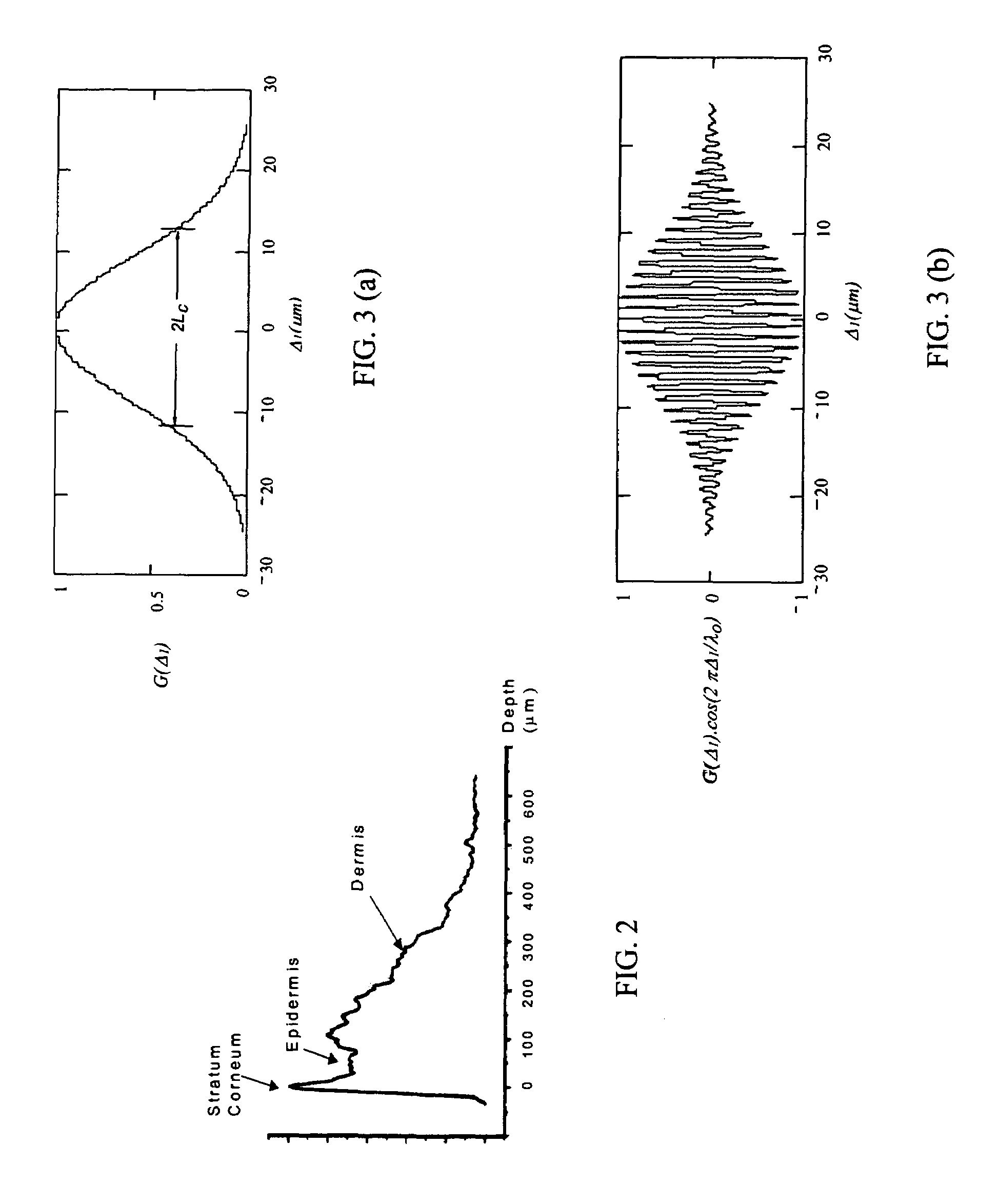
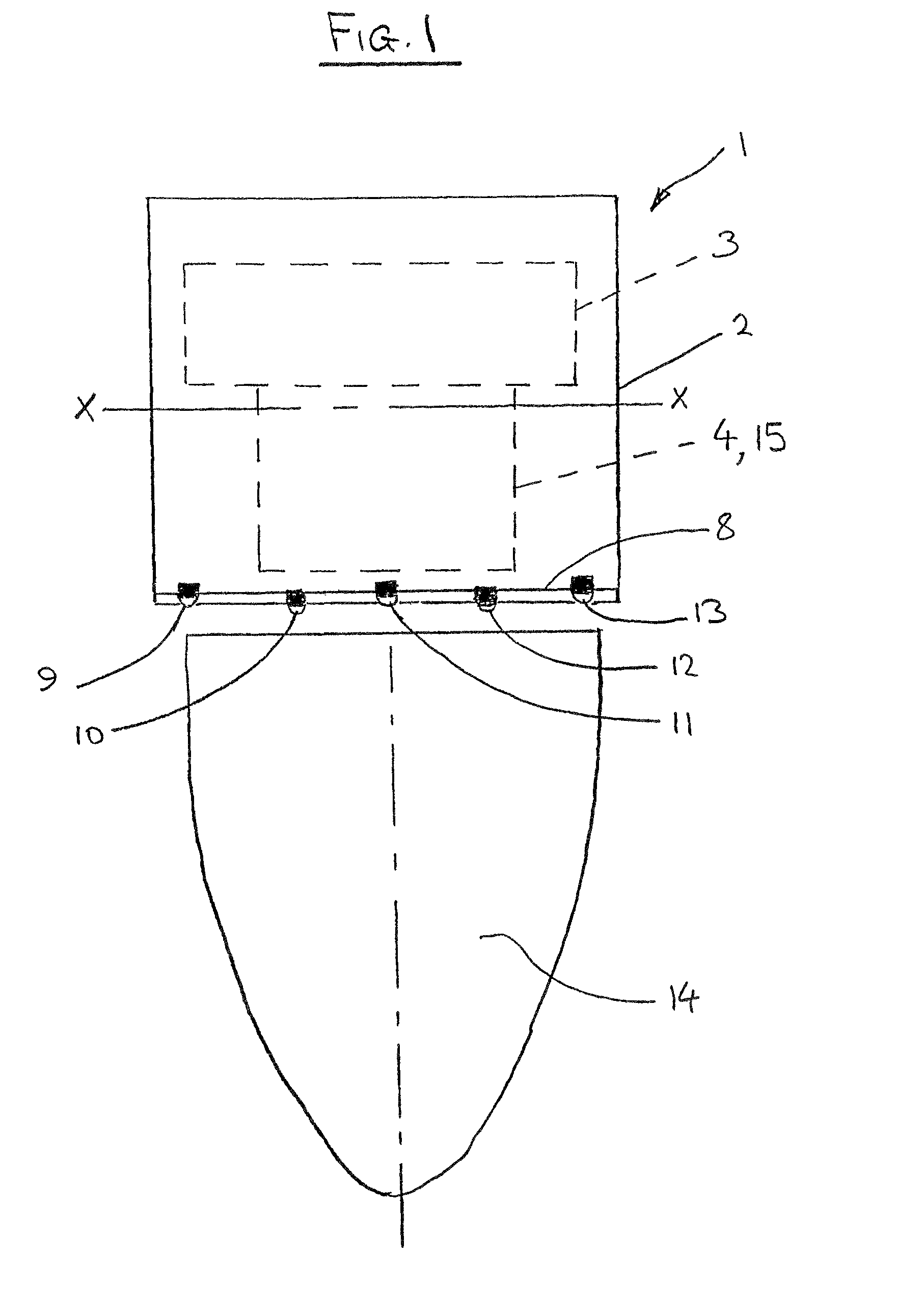
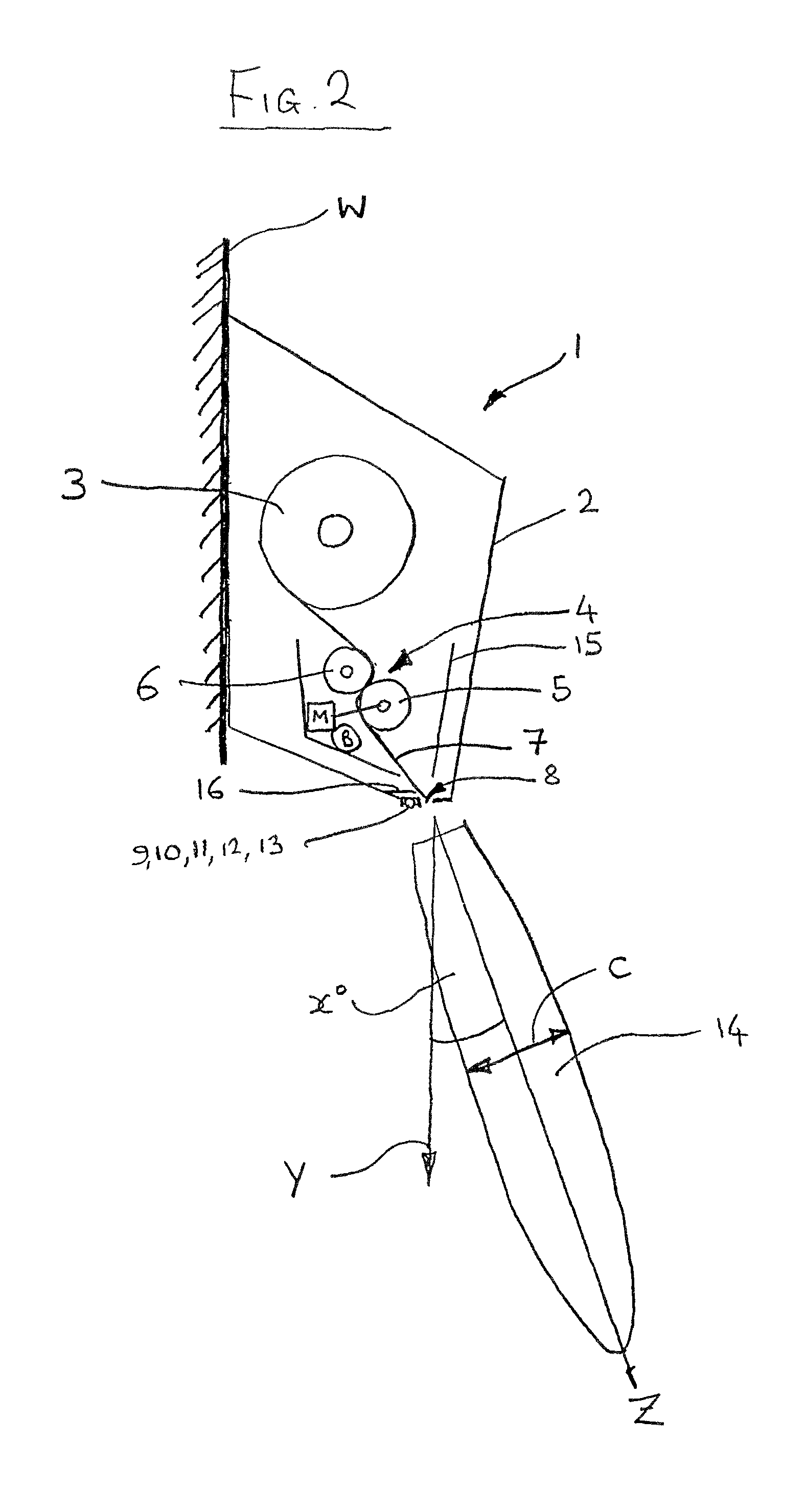
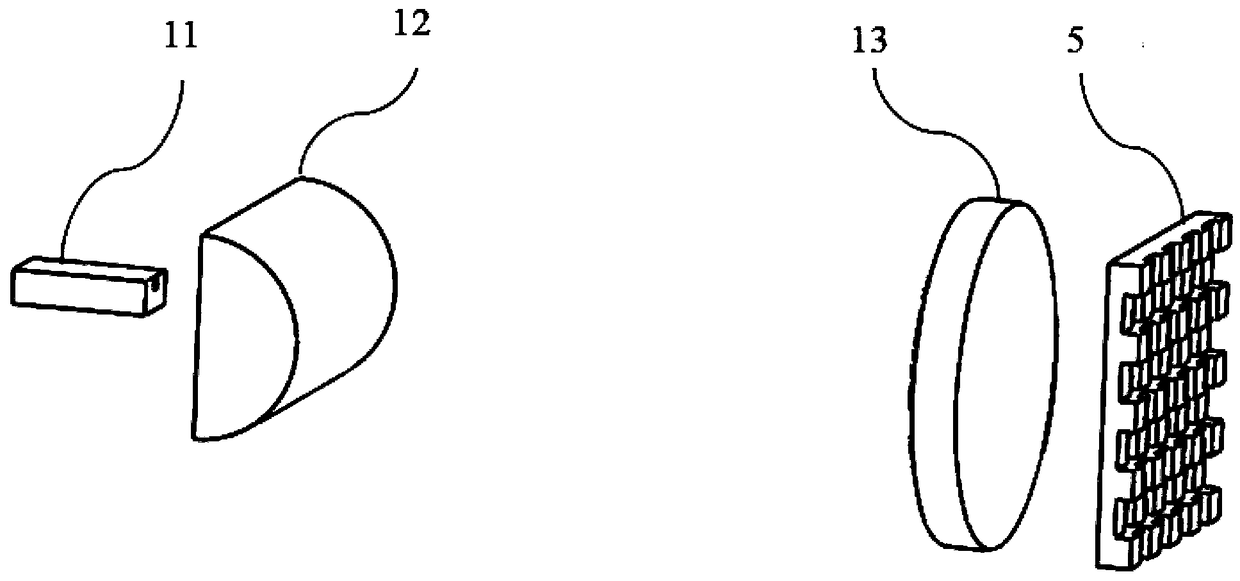
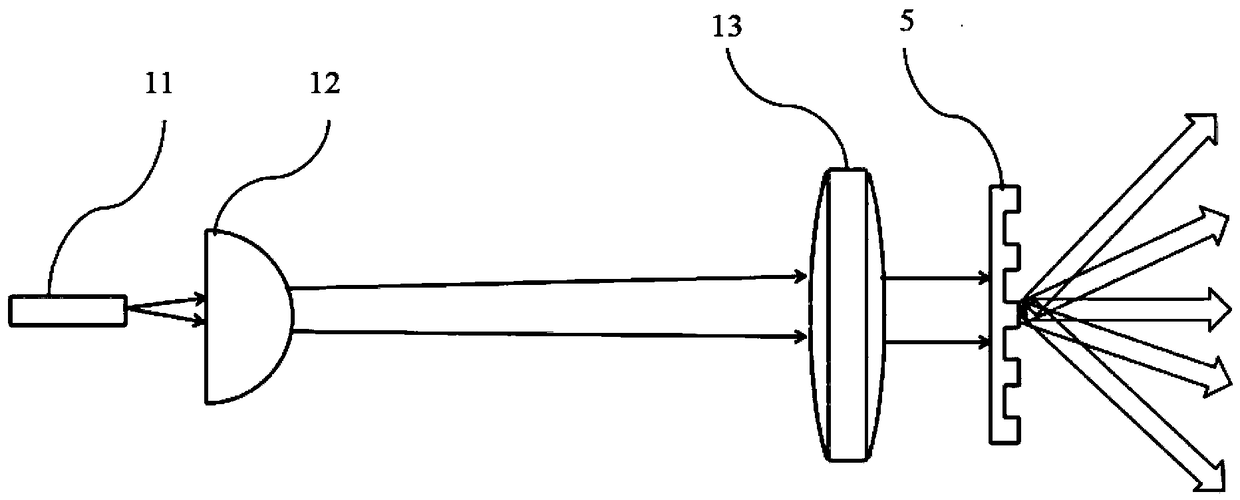
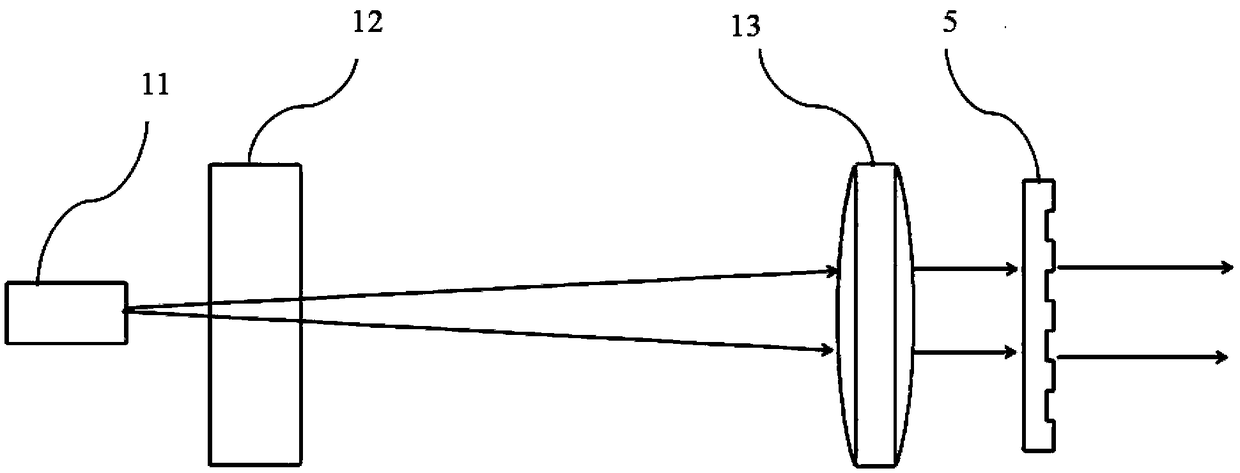
Single trace multi-channel low coherence interferometric sensor
InactiveUS20060103850A1Shorten the timeQuick identificationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringInterferometric sensorBorescope
Interferometers and autocorrelator based sensors are disclosed that are configured to have multiple sample arms which can be scanned and the backscattered low coherence source light from a sample resolved in a single sweep of one or more variable delays of the sensor. Borescopes and catheters capable of scanning multiple sections or areas of materials and tissues using these sensors are described.
Owner:MEDEIKON
Systems and methods for endoscopic angle-resolved low coherence interferometry
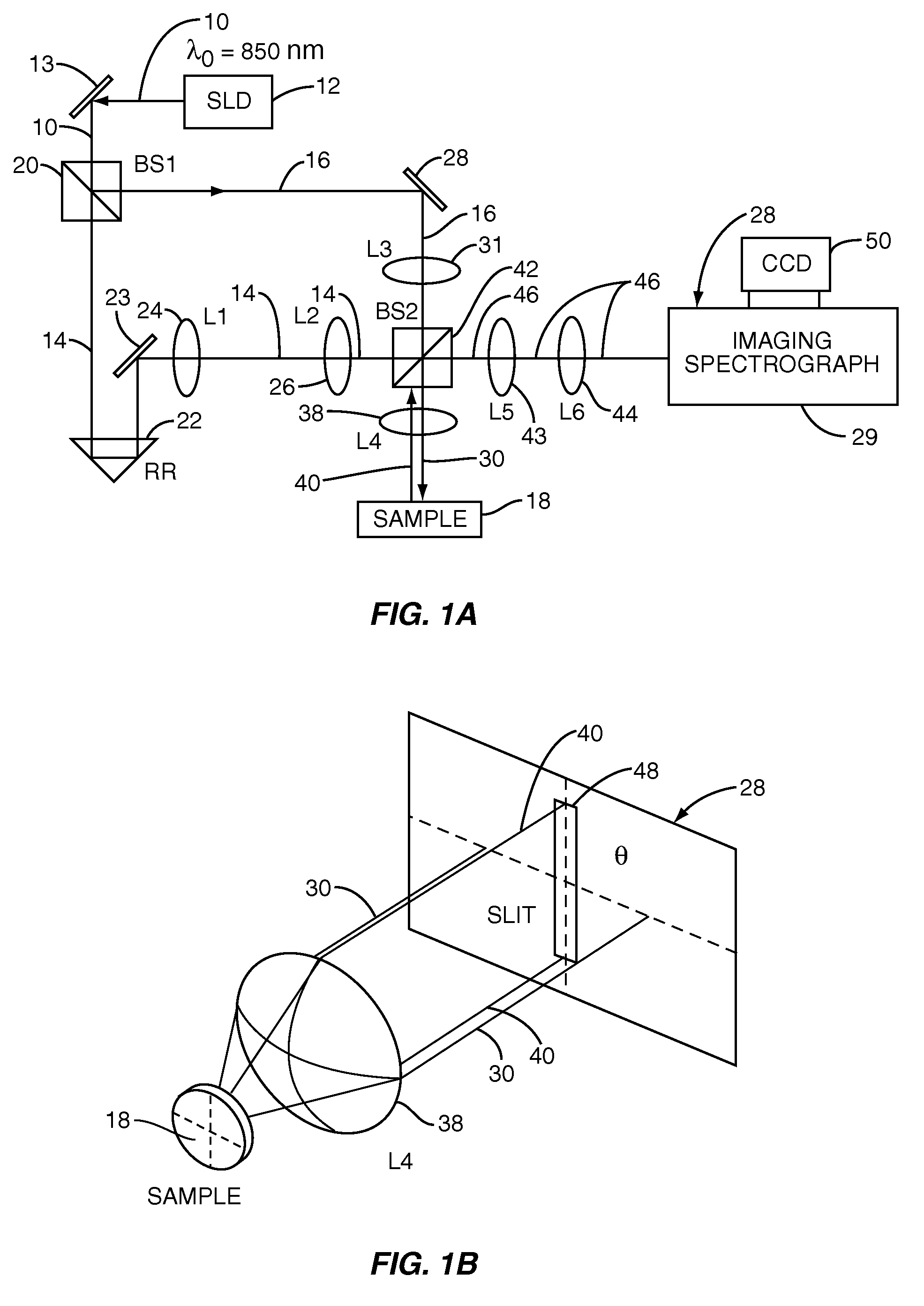
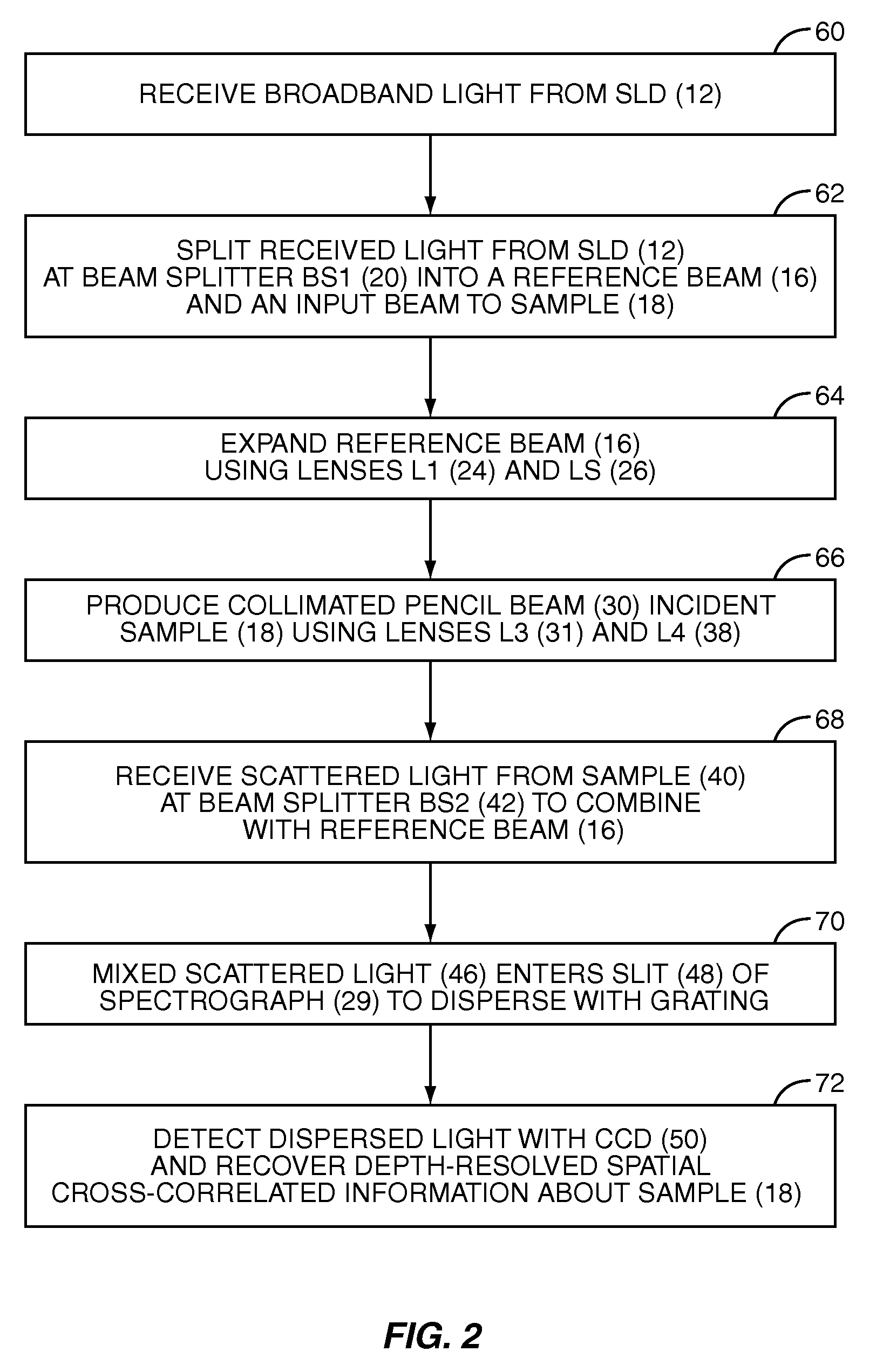
InactiveUS20070133002A1Fast resultsEnhance its widespread applicabilityRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyData acquisitionIn vivo
Fourier domain a / LCI (faLCI) system and method which enables in vivo data acquisition at rapid rates using a single scan. Angle-resolved and depth-resolved spectra information is obtained with one scan. The reference arm can remain fixed with respect to the sample due to only one scan required. A reference signal and a reflected sample signal are cross-correlated and dispersed at a multitude of reflected angles off of the sample, thereby representing reflections from a multitude of points on the sample at the same time in parallel. Information about all depths of the sample at each of the multitude of different points on the sample can be obtained with one scan on the order of approximately 40 milliseconds. From the spatial, cross-correlated reference signal, structural (size) information can also be obtained using techniques that allow size information of scatterers to be obtained from angle-resolved data.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS20110098572A1High resolution imagingEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
An imaging probe for a biological sample includes an OCT probe and an ultrasound probe combined with the OCT probe in an integral probe package capable of providing by a single scanning operation images from the OCT probe and ultrasound probe to simultaneously provide integrated optical coherence tomography (OCT) and ultrasound imaging of the same biological sample. A method to provide high resolution imaging of biomedical tissue includes the steps of finding an area of interest using the guidance of ultrasound imaging, and obtaining an OCT image and once the area of interest is identified where the combination of the two imaging modalities yields high resolution OCT and deep penetration depth ultrasound imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
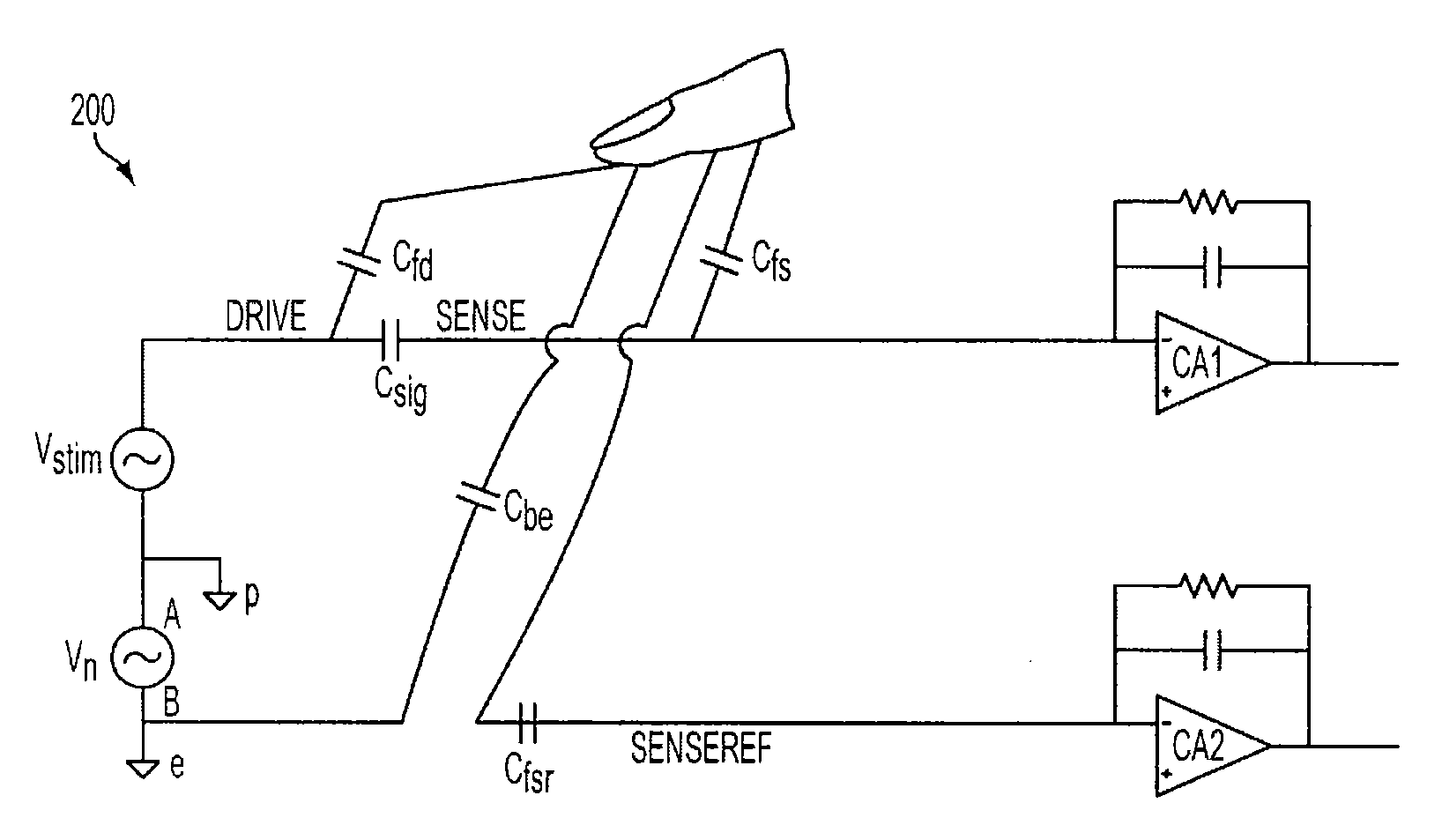
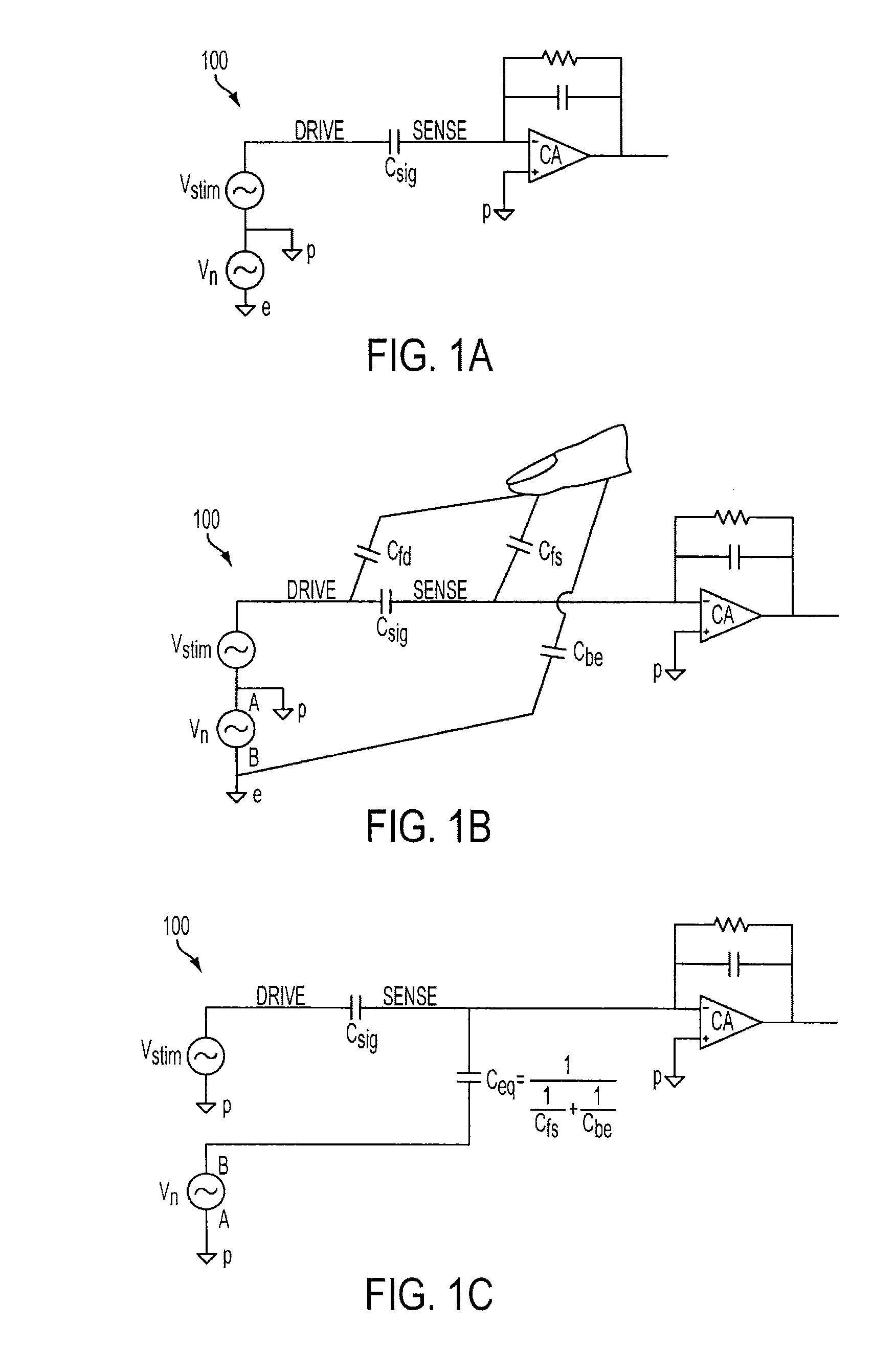
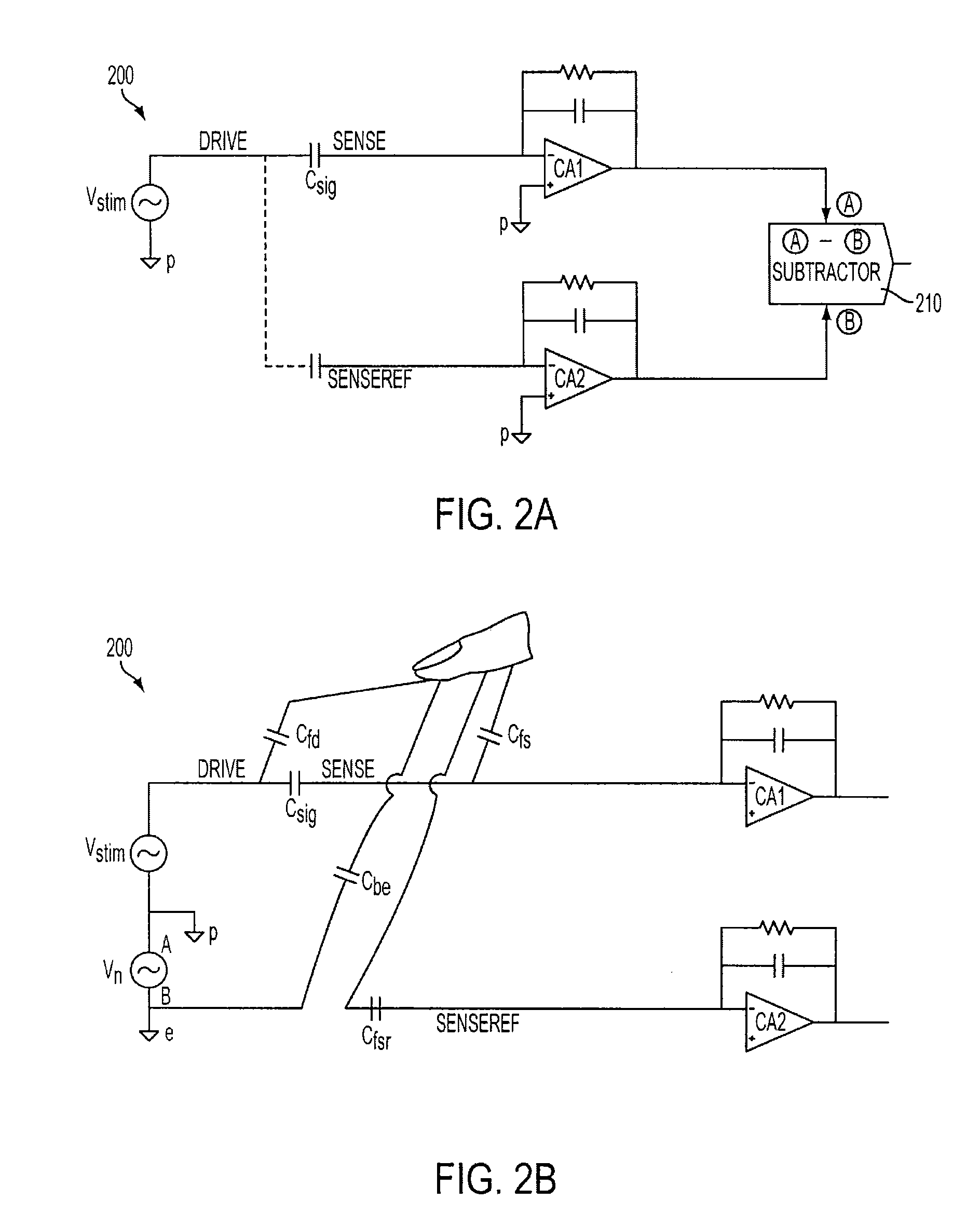
Differential sensing for a touch panel
ActiveUS20100079401A1Reduce adverse effectsHinder recognitionInput/output processes for data processingNoise levelEngineering
A touch panel can configured to reduce adverse effects associated with noise that can be injected into the panel when touched by performing a sensing operation at each sensor in both a panel-stimulated and non panel-stimulated state. The touch panel can detect a touch event by sensing touch in a non-stimulated state to quantify a noise level injected into the touch panel by the touch, and subtracting that noise level from a detection signal sensed in the stimulated state. In one embodiment, a sensing operation can be performed for a particular sensor at two successive time periods—one for each state—within a single scan cycle. In another embodiment, a sensing electrode configuration can be provided that enables a sensing operation to be performed for a particular sensor in both a panel-stimulated and non panel-stimulated state concurrently.
Owner:APPLE INC
Single trace multi-channel low coherence interferometric sensor
Interferometers and autocorrelator based sensors are disclosed that are configured to have multiple sample arms which can be scanned and the backscattered low coherence source light from a sample resolved in a single sweep of one or more variable delays of the sensor. Borescopes and catheters capable of scanning multiple sections or areas of materials and tissues using these sensors are described.
Owner:MEDEIKON
Method and system for providing a continuous motion sequential lateral solidification for reducing or eliminating artifacts, and a mask for facilitating such artifact reduction/elimination
InactiveUS20070020942A1Reduce and eliminate artifactArtifact is reduced and eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusComputer scienceGrain growth
An arrangement, process and mask for implementing single-scan continuous motion sequential lateral solidification of a thin film provided on a sample such that artifacts formed at the edges of the beamlets irradiating the thin film are significantly reduced. According to this invention, the edge areas of the previously irradiated and resolidified areas which likely have artifacts provided therein are overlapped by the subsequent beamlets. In this manner, the edge areas of the previously resolidified irradiated areas and artifacts therein are completely melted throughout their thickness. At least the subsequent beamlets are shaped such that the grains of the previously irradiated and resolidified areas which border the edge areas melted by the subsequent beamlets grow into these resolidifying edges areas so as to substantially reduce or eliminate the artifacts.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
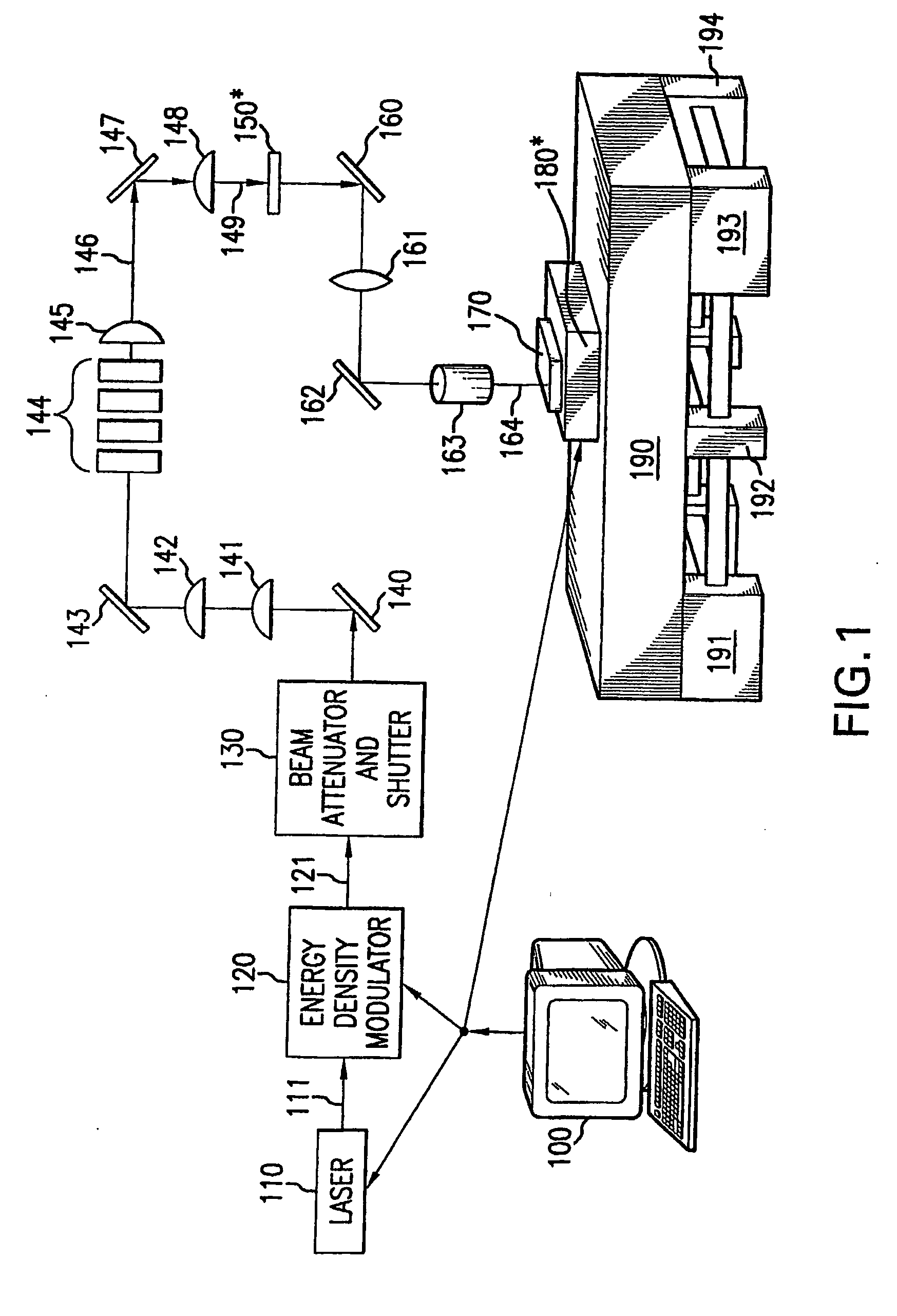
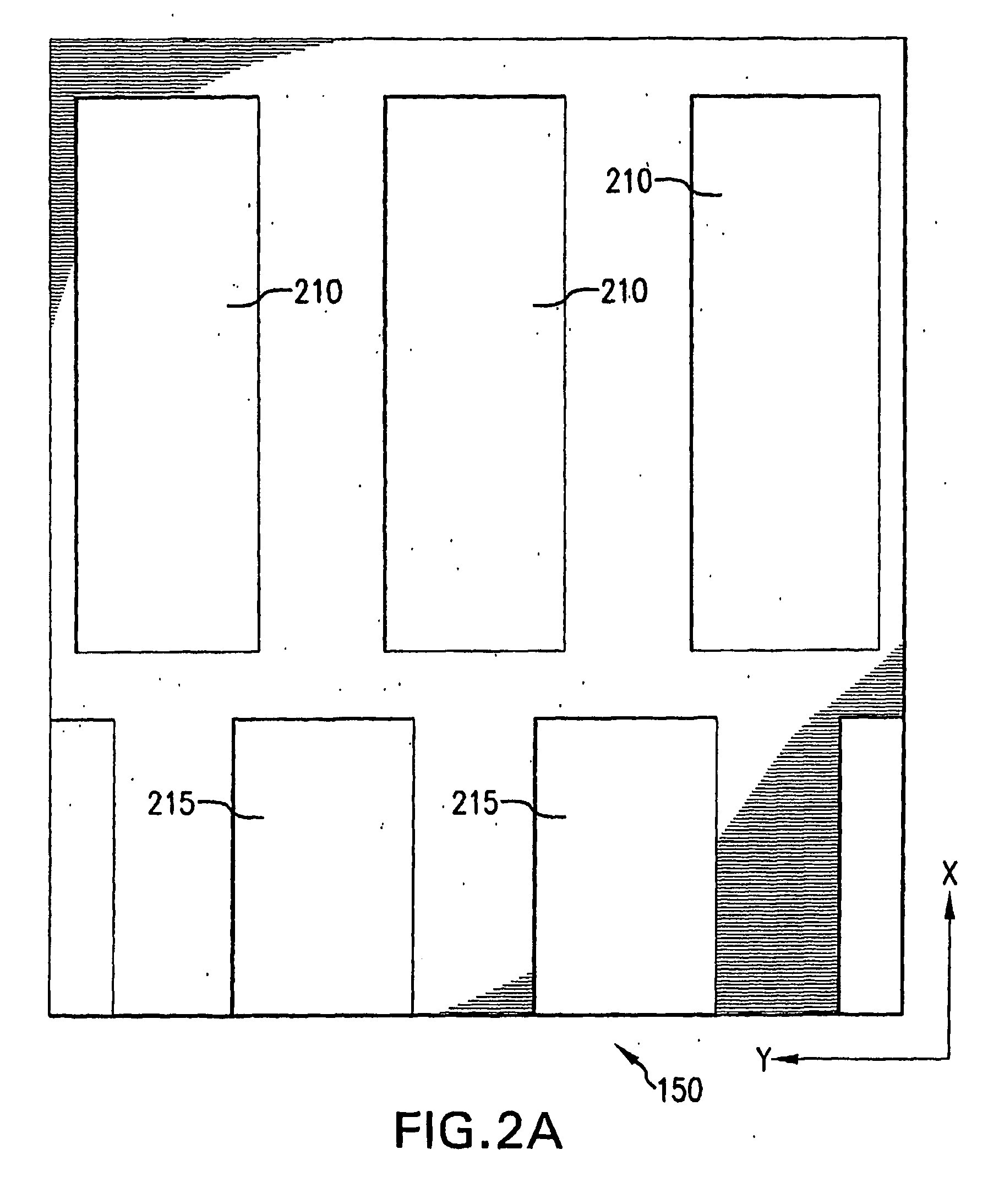
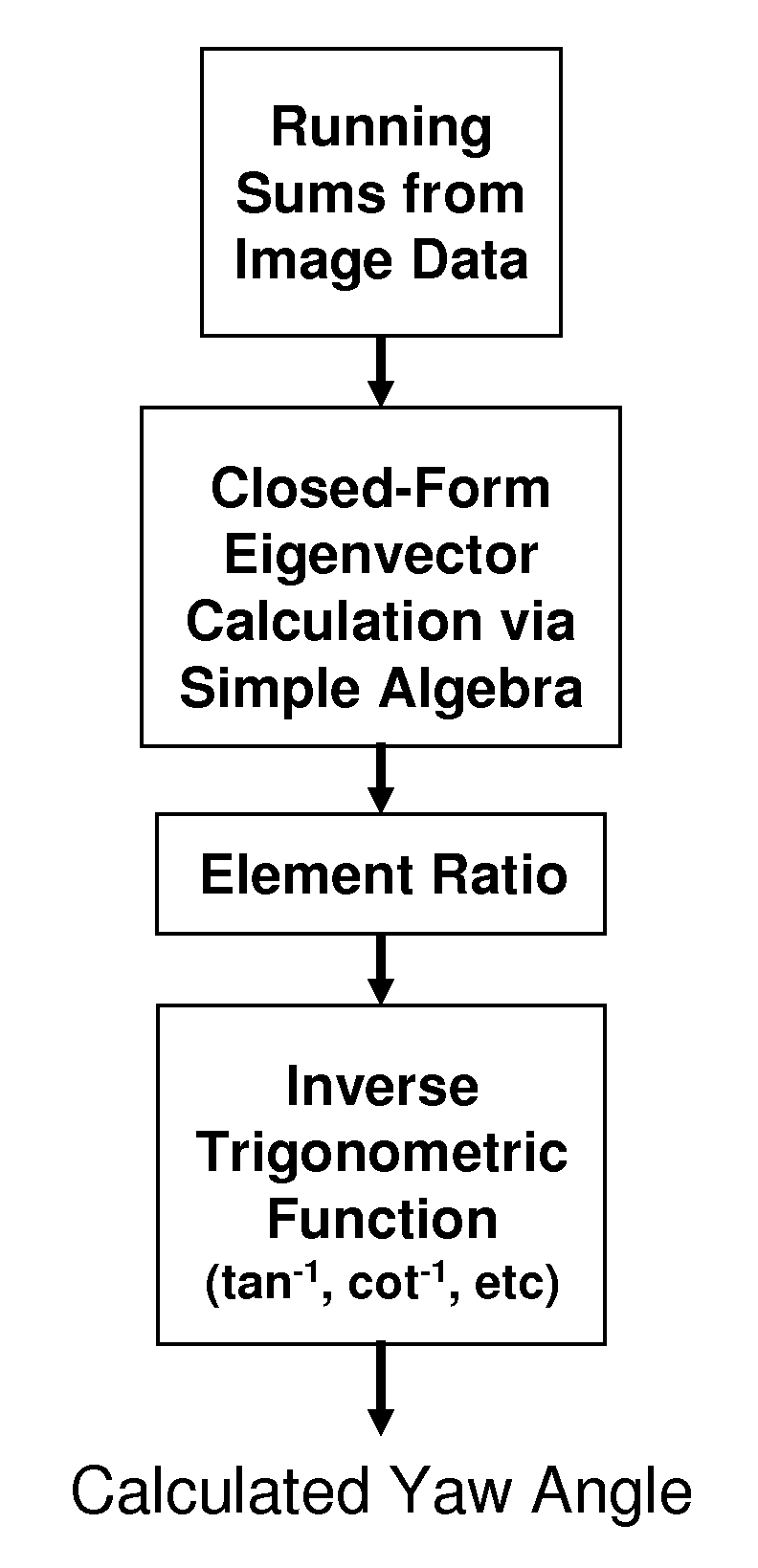
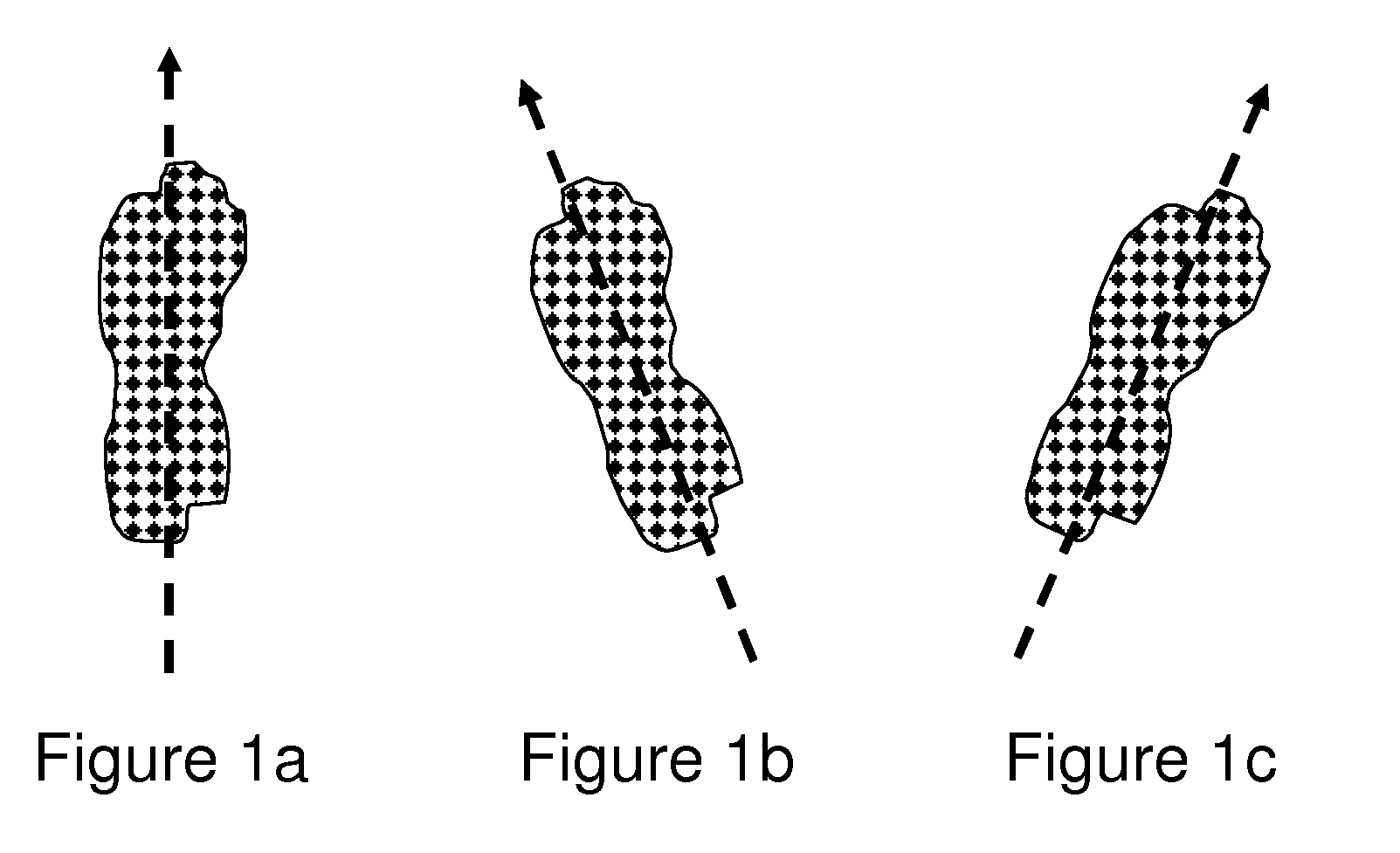
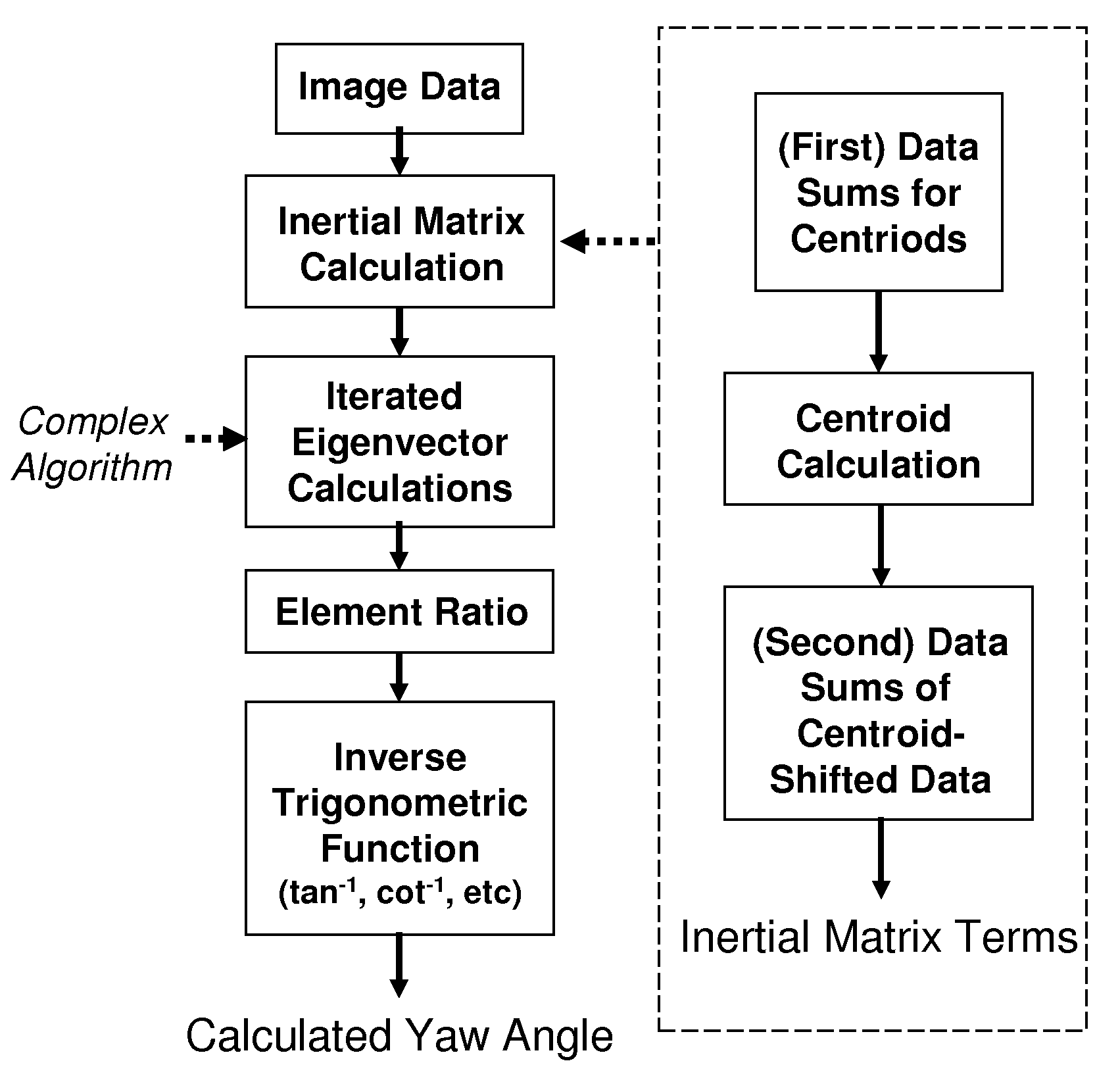
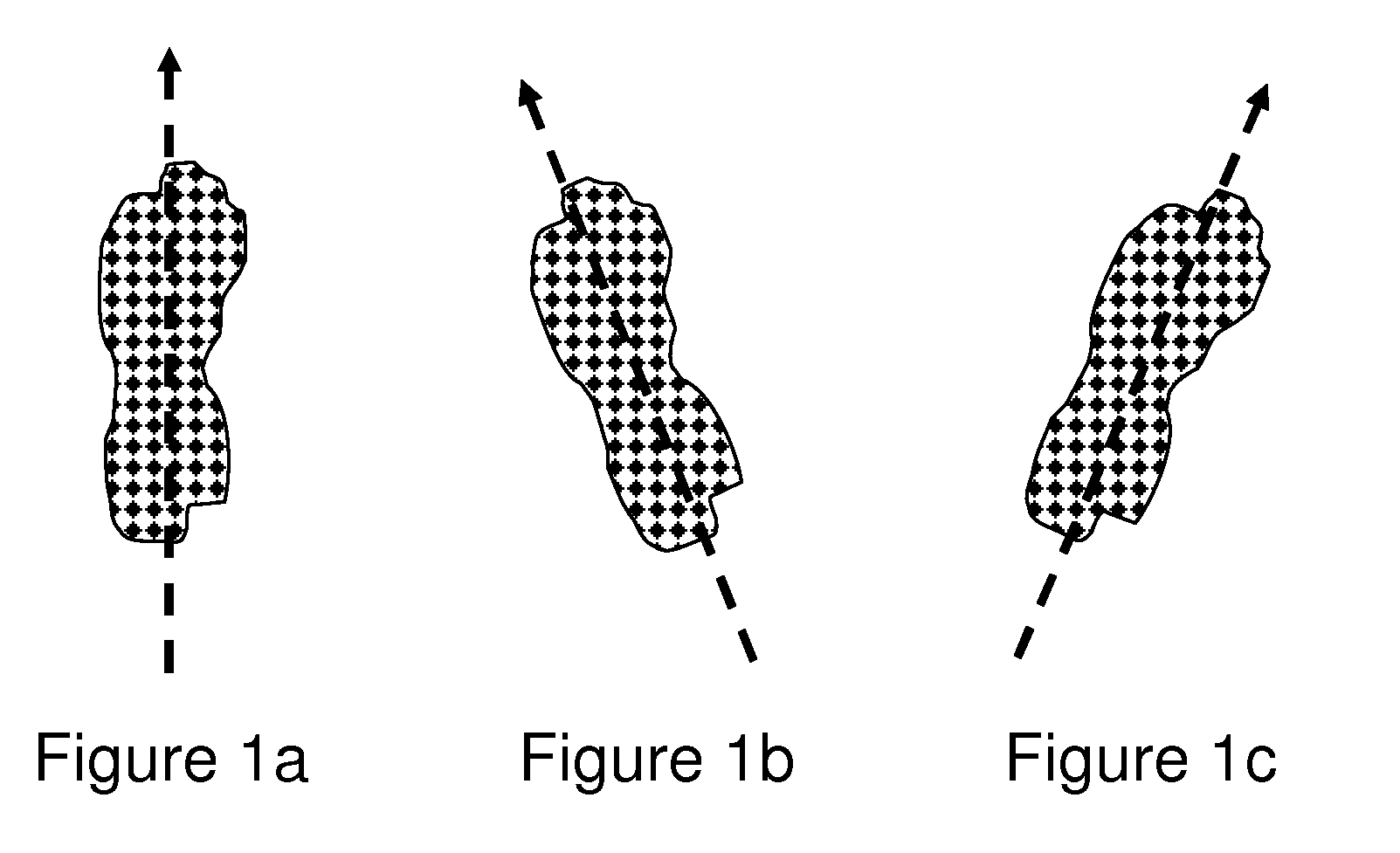
High-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size using running sums
A method for performing a high-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size on a processor using running sums is disclosed. Running sums are calculated and stored throughout each scan, and the results are obtained in closed form by simple post-scan computation. An algorithmic embodiment may execute on one or more hardware processors with limited or constrained computation power, available instruction cycles, available memory, etc. Exemplary hardware processors are found in one or more CPUs of a desktop, laptop, tablet, or handheld computing device, and may be an embedded processor or a signal processor chip. The resulting method may be used for touch or optical user interfaces, real-time image recognition, real-time machine vision, and other purposes.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
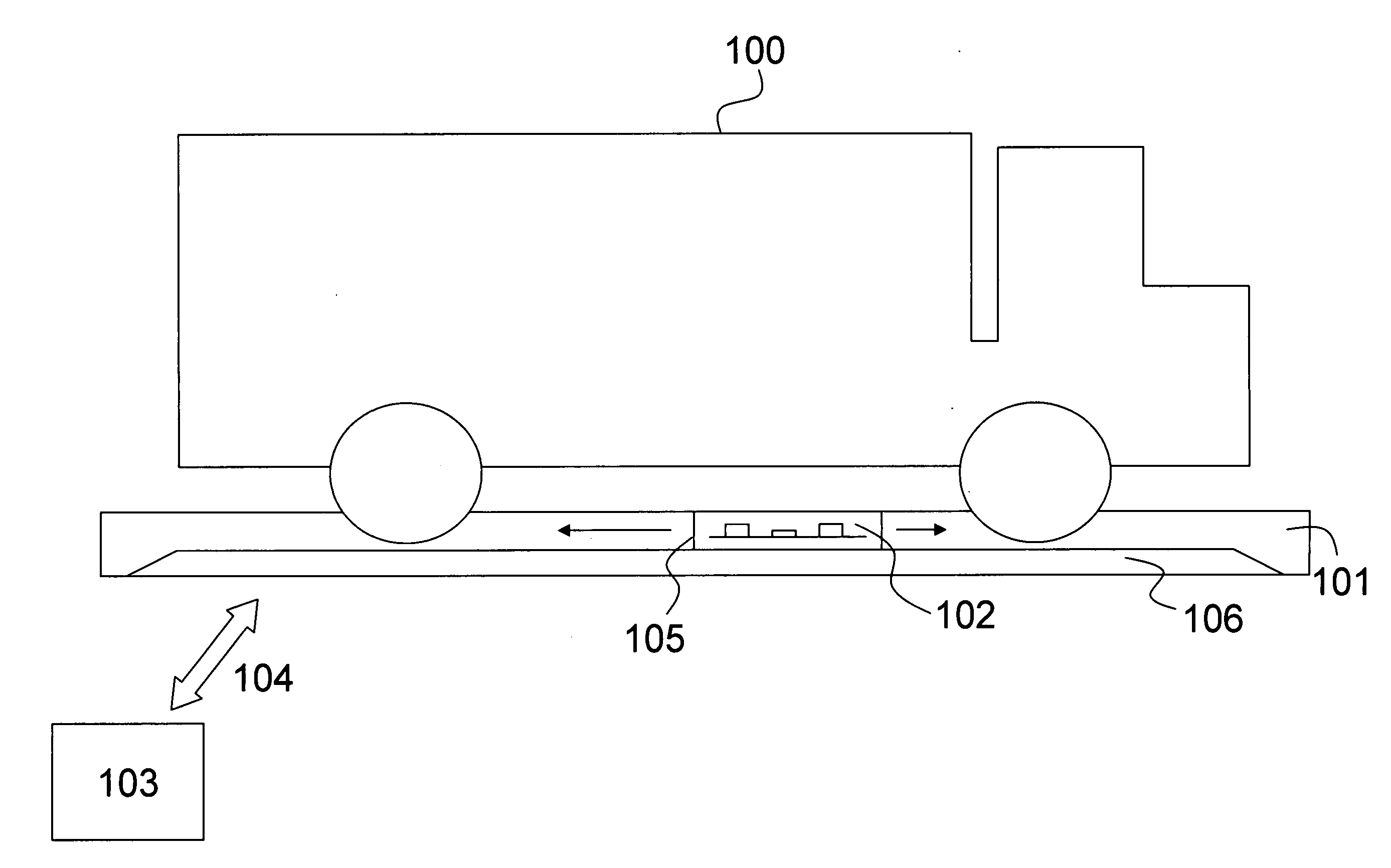
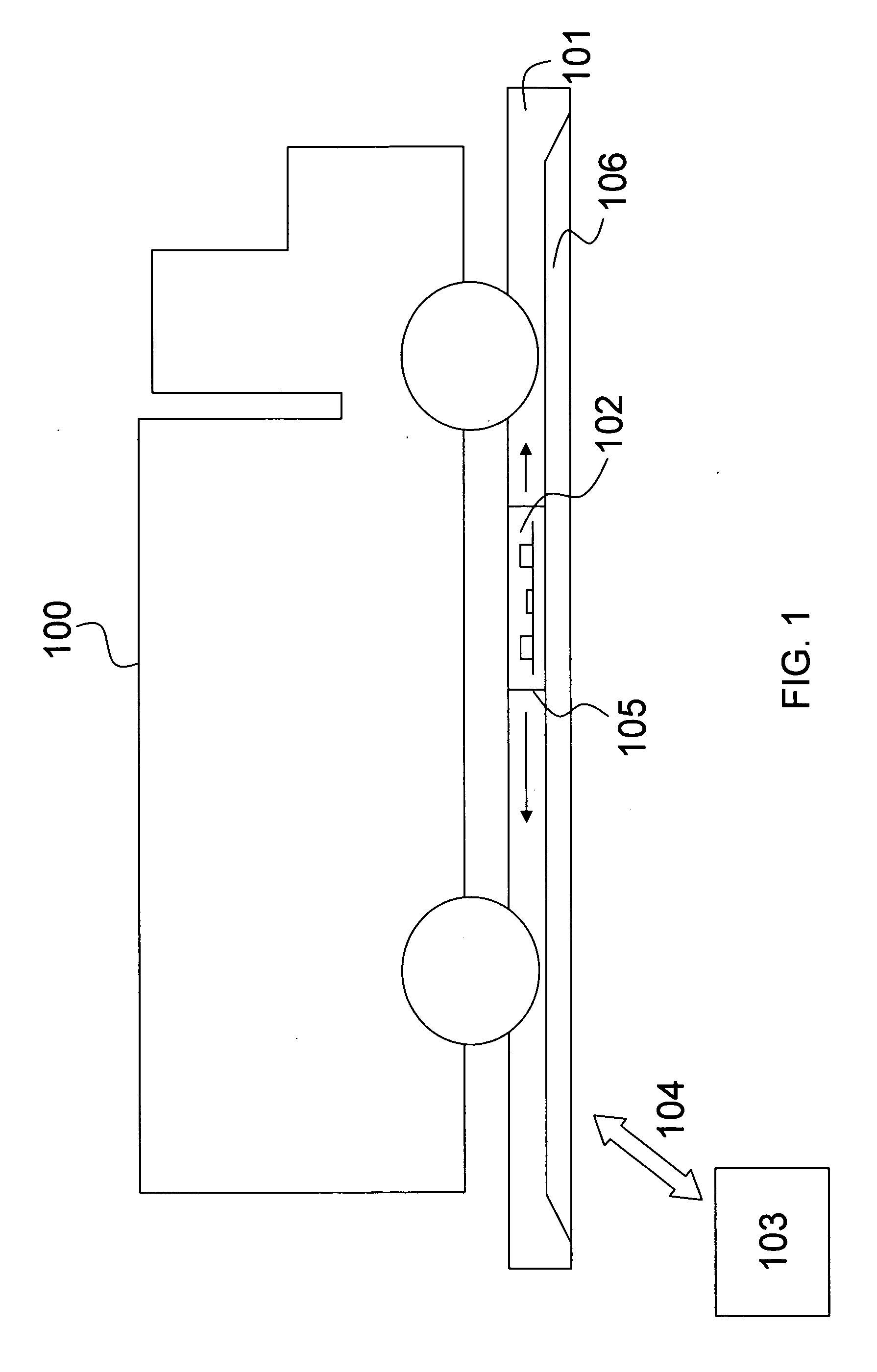
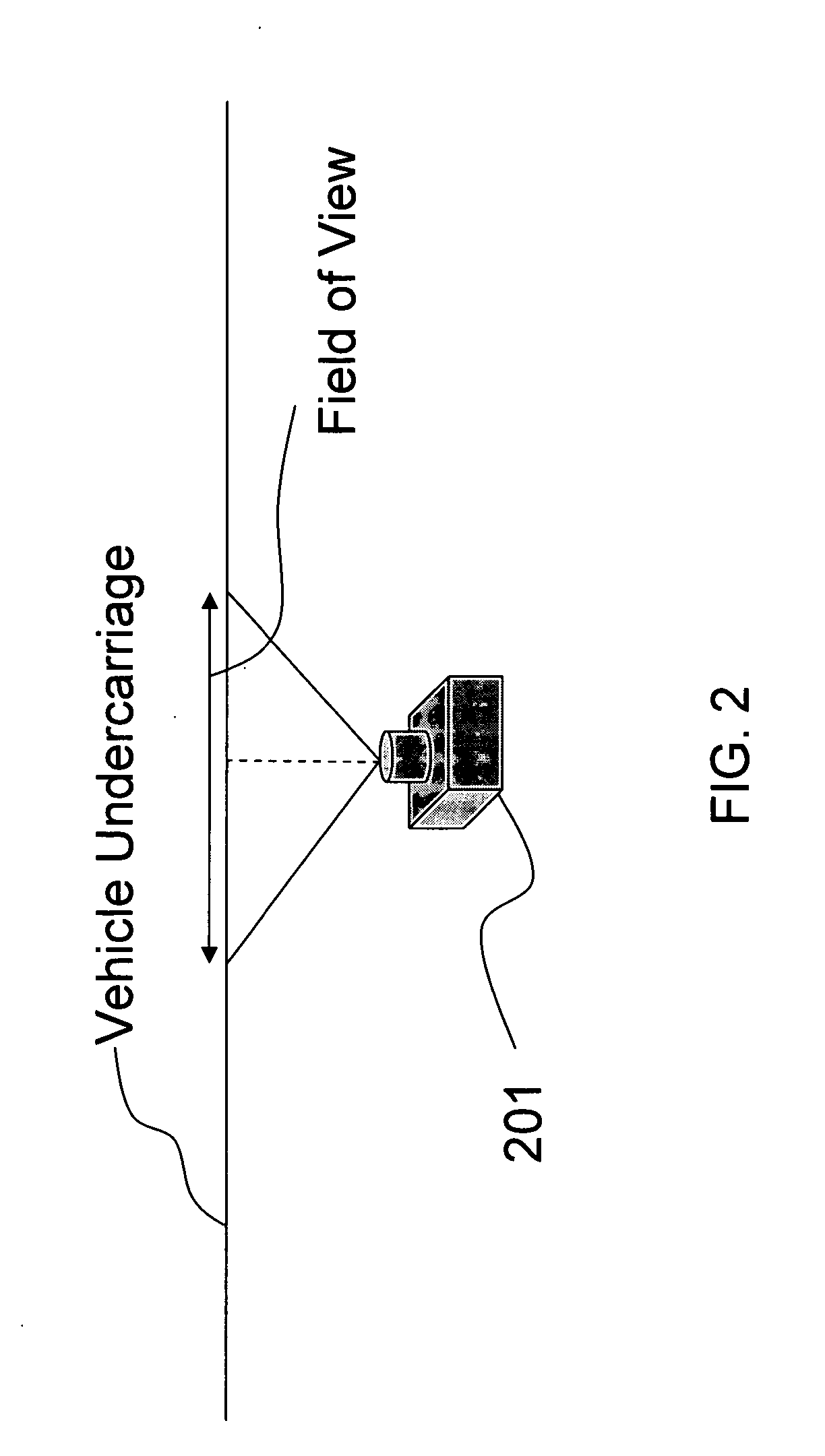
Under vehicle inspection system
InactiveUS20070040911A1Reliably and efficiently detectingMinimizing risk of physical harmColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsOptical axisEngineering
An under vehicle inspection system comprises a single camera adapted to capture a full width image of a vehicle undercarriage in a single scan. The camera has a viewing distance from the vehicle undercarriage, as measured along the optical axis of the camera, that is greater than a Euclidean distance between the camera and a point where the optical axis meets the vehicle undercarriage.
Owner:RILEY LARRY E
Multiple beam scanning imager
InactiveUS7209271B2Light provideCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationLight beamGrating pattern
A display apparatus includes a scanning assembly that scans about two or more axes, typically in a raster pattern. A plurality of light sources emit light from spaced apart locations toward the scanning assembly such that the scanning assembly simultaneously scans more than one of the beams. The light sources are positioned such that their beams each illuminate discrete regions of the image field that are substantially non-overlapping with respect to the other discrete regions. The image is thus formed from a set of “tiles”. By activating a first light source during a forward sweep of the mirror and activating a second light source during a reverse sweep of the mirror, two halves a common line can be written during a single sweep of the mirror. Shifting the position of the sources such that the two halves are aligned reduces raster pinch. In alternative embodiments, the same approach is used for imaging. Also, various approaches to controlling the frequency responses of the various scanners are described, including active control of MEMs scanners and passive frequency tuning.
Owner:MICROVISION
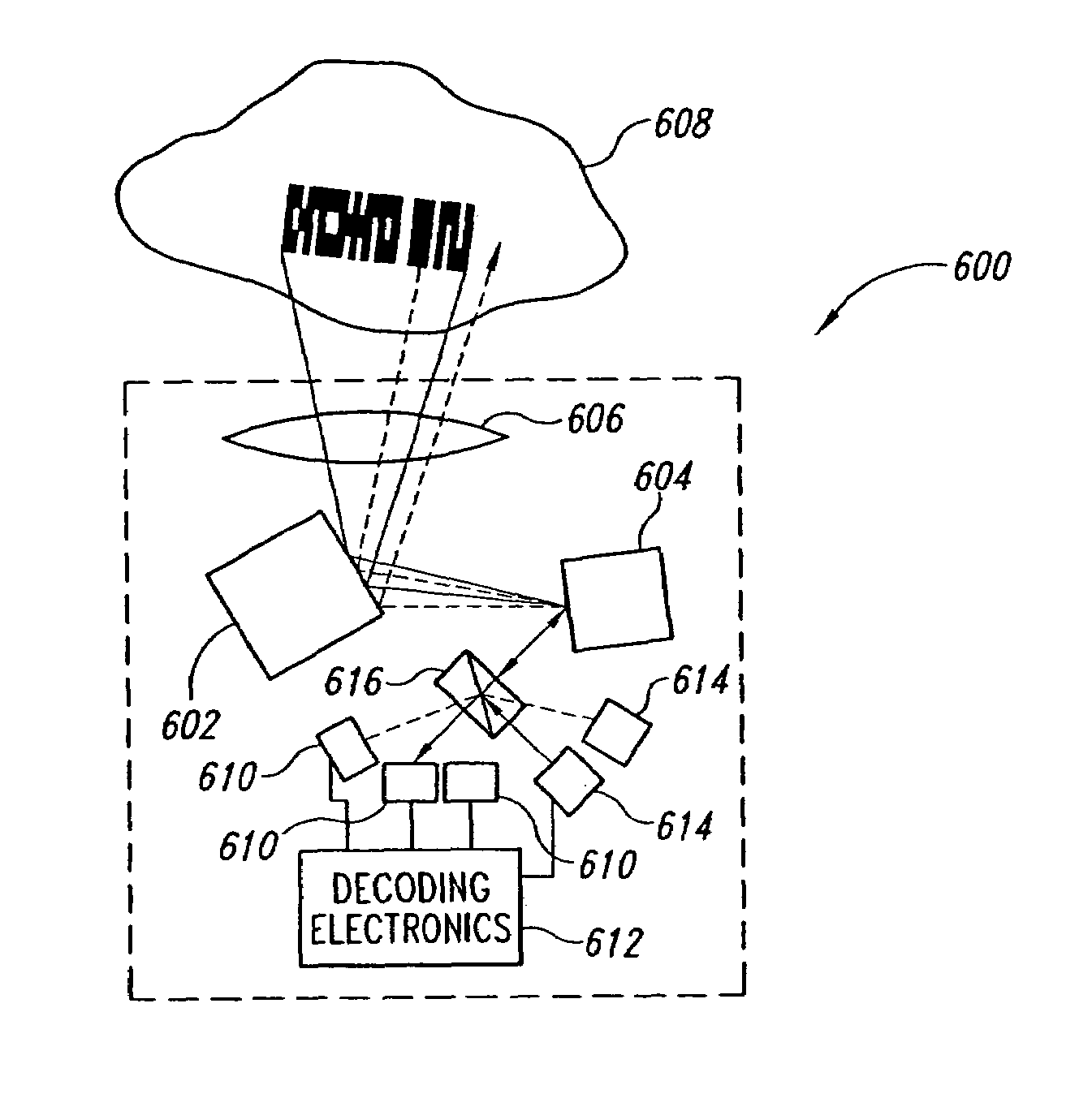
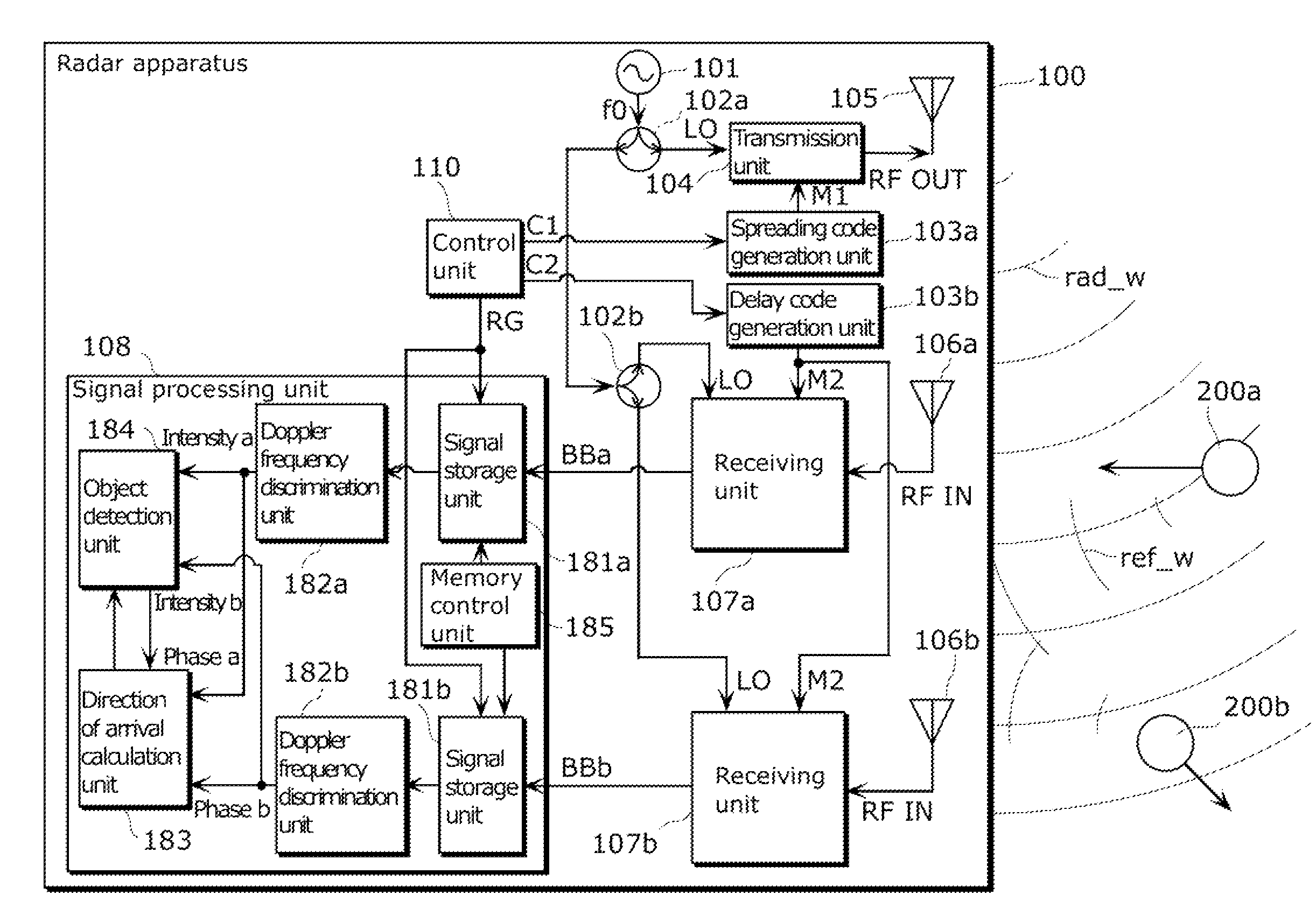
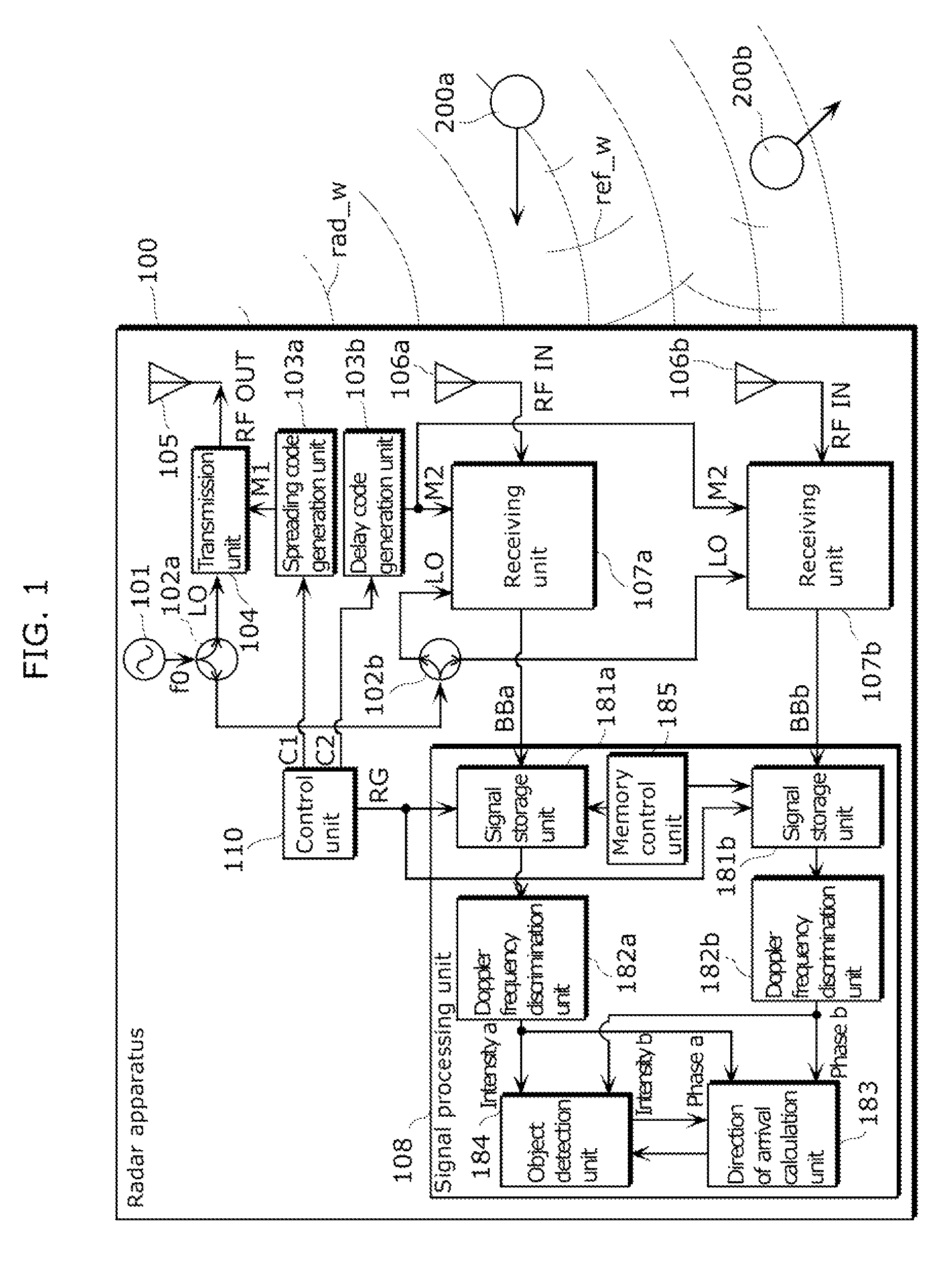
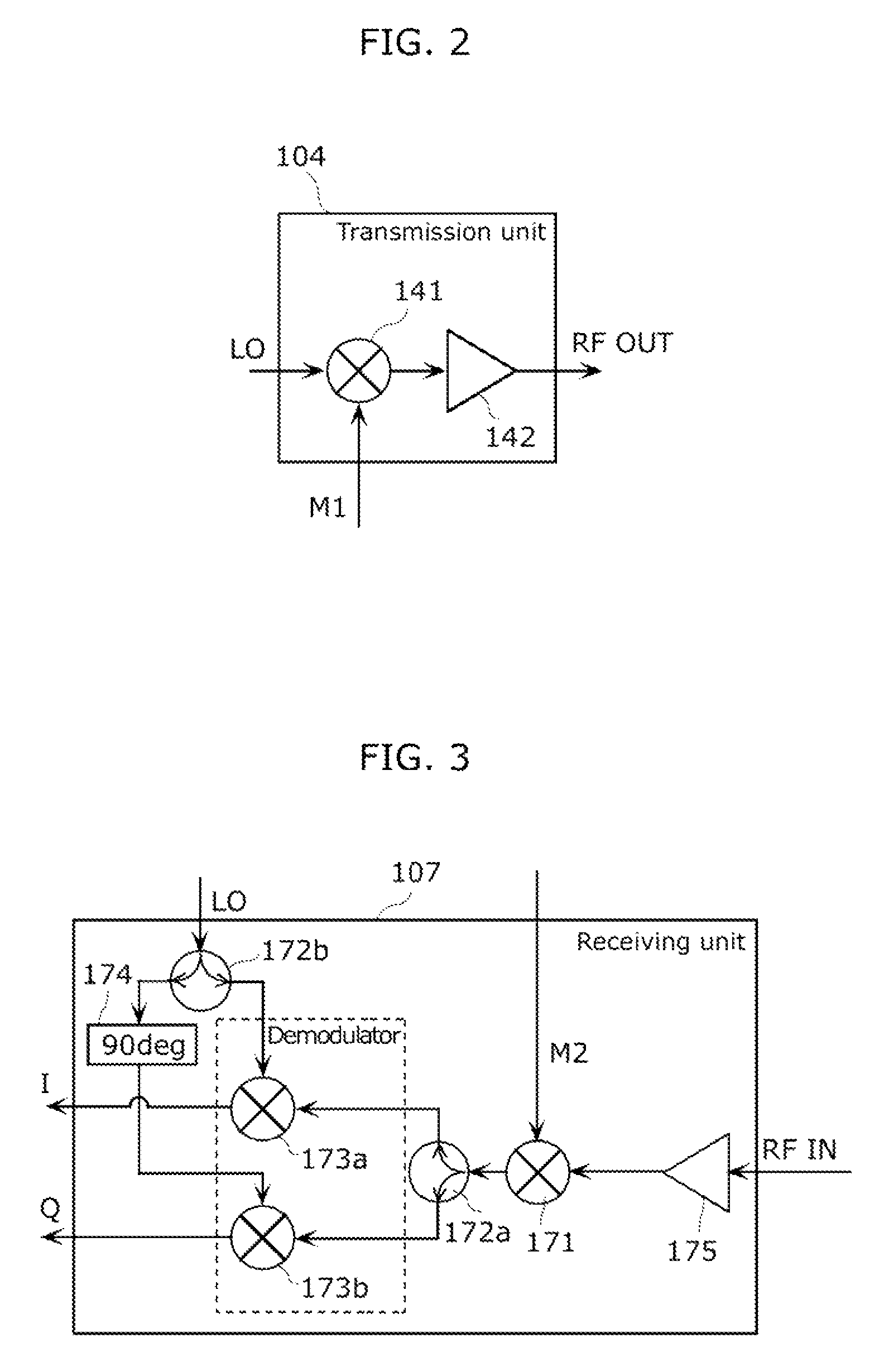
Radar imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program thereof
InactiveUS8686894B2Function increaseDirection findersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringRange gate
A radar imaging apparatus includes: (i) a delay code generation unit which repeats, for M scan periods, scan processing of generating, using a transmission code, N delay codes in a scan period for scanning N range gates having mutually different distances from the radar imaging apparatus; (ii) a signal storage unit which stores, in association with a range gate and a scan period, a baseband signal; (iii) a memory control unit which repeatedly writes, in the signal storage unit, for the M scan periods, N demodulated signals corresponding to a single scan period, and reads out a group of M demodulated signals corresponding to mutually different scan periods; (iv) a Doppler frequency discrimination unit which performs frequency analysis on demodulated signals having the same range gate; and (v) a direction of arrival calculation unit which estimates a direction of a target.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
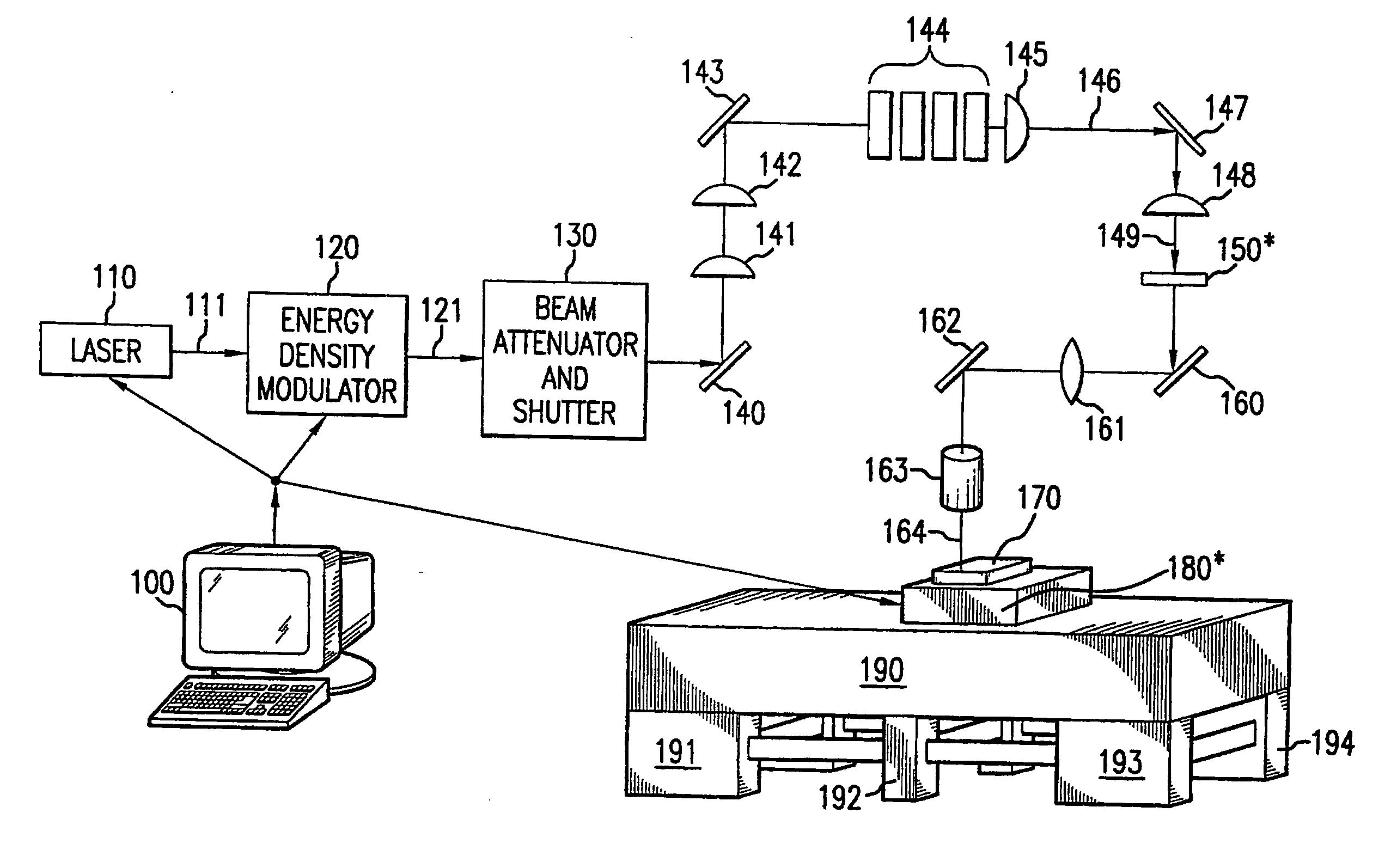
Single scan irradiation for crystallization of thin films
InactiveUS20050235903A1Improve propertiesSimple processFrom gel stateFrom solid stateLight beamOptoelectronics
A method of processing a polycrystalline film on a substrate includes generating a plurality of laser beam pulses, positioning the film on a support capable of movement in at least one direction, directing the plurality of laser beam pulses through a mask to generate patterned laser beams; each of said beams having a length l′, a width w′ and a spacing between adjacent beams d′, irradiating a region of the film with the patterned beams, said beams having an intensity that is sufficient to melt an irradiated portion of the film to induce crystallization of the irradiated portion of the film, wherein the film region is irradiated n times; and after irradiation of each film portion, translating either the film or the mask, or both, a distance in the x- and y-directions, where the distance of translation in the y-direction is in the range of about 1′ / n-δ, where δ is a value selected to form overlapping the beamlets from the one irradiation step to the next, and where the distance of translation in the x-direction is selected such that the film is moved a distance of about λ′ after n irradiations, where λ′=w′+d′.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Single scan irradiation for crystallization of thin films
InactiveUS7311778B2Improve propertiesSimple processFrom gel stateFrom solid stateLight beamOptoelectronics
A method of processing a polycrystalline film on a substrate includes generating a plurality of laser beam pulses, positioning the film on a support capable of movement in at least one direction, directing the plurality of laser beam pulses through a mask to generate patterned laser beams; each of said beams having a length l′, a width w′ and a spacing between adjacent beams d′, irradiating a region of the film with the patterned beams, said beams having an intensity that is sufficient to melt an irradiated portion of the film to induce crystallization of the irradiated portion of the film, wherein the film region is irradiated n times; and after irradiation of each film portion, translating either the film or the mask, or both, a distance in the x- and y-directions, where the distance of translation in the y-direction is in the range of about 1′ / n-δ, where δ is a value selected to form overlapping the beamlets from the one irradiation step to the next, and where the distance of translation in the x-direction is selected such that the film is moved a distance of about λ′ after n irradiations, where λ′=w′+d′.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
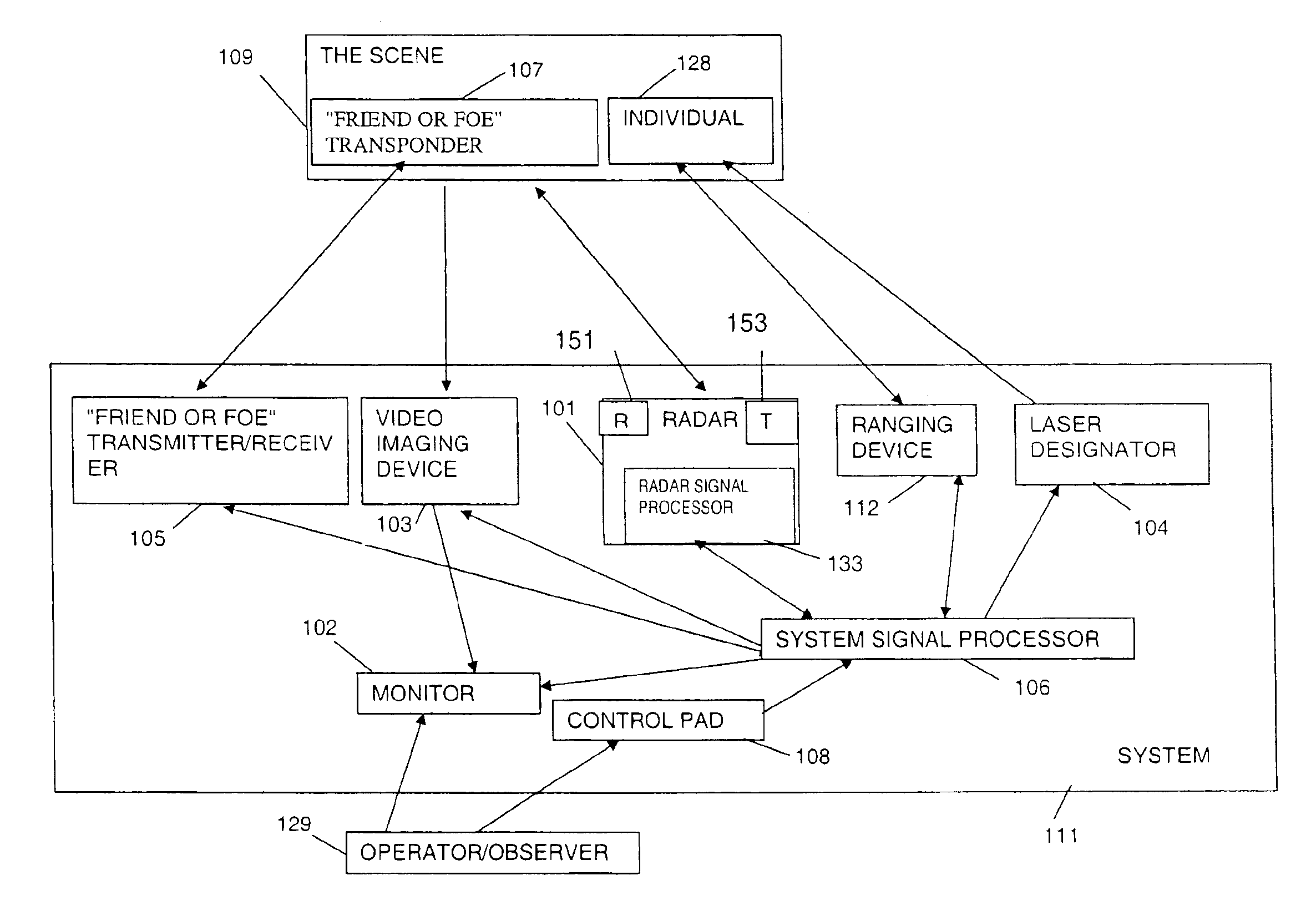
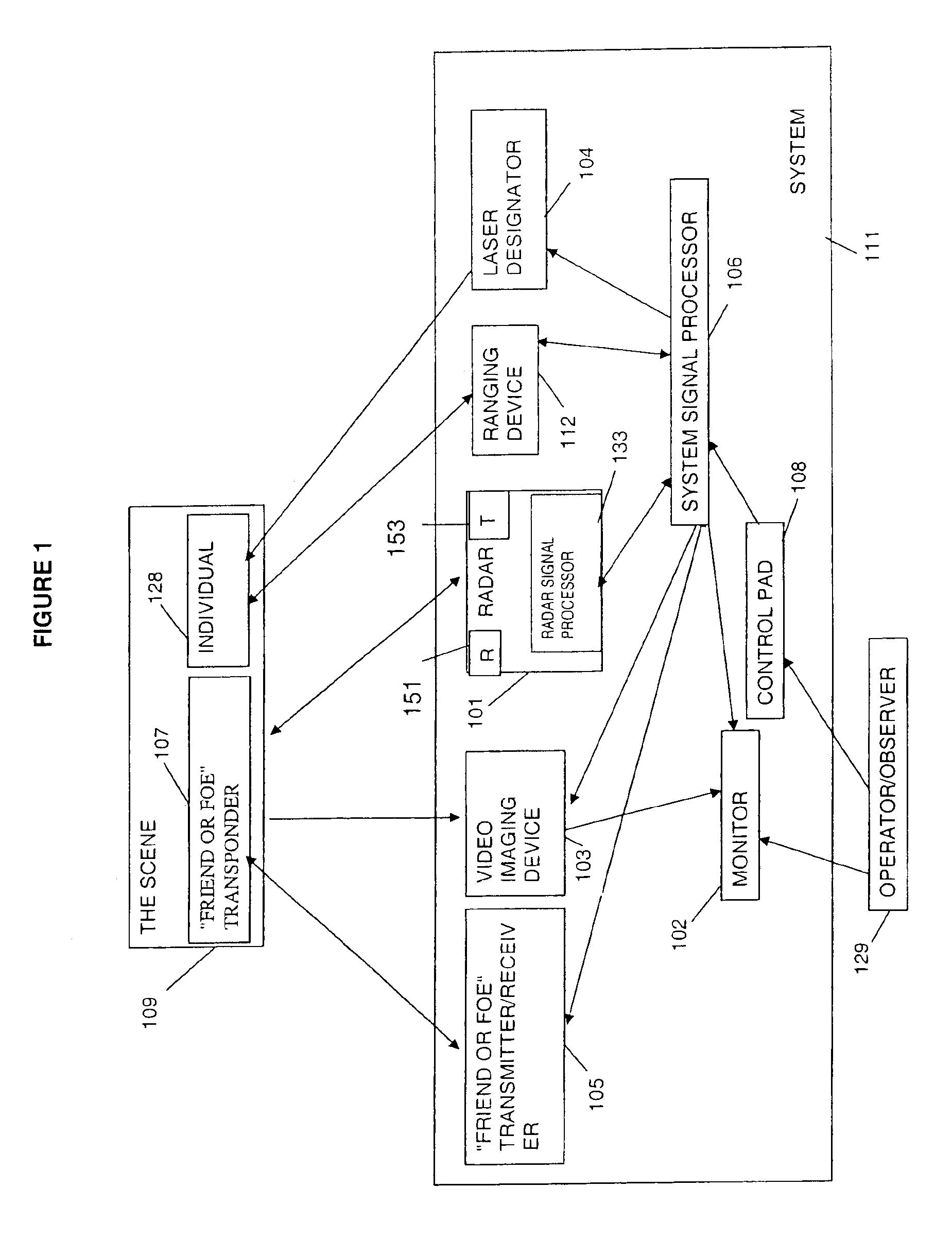
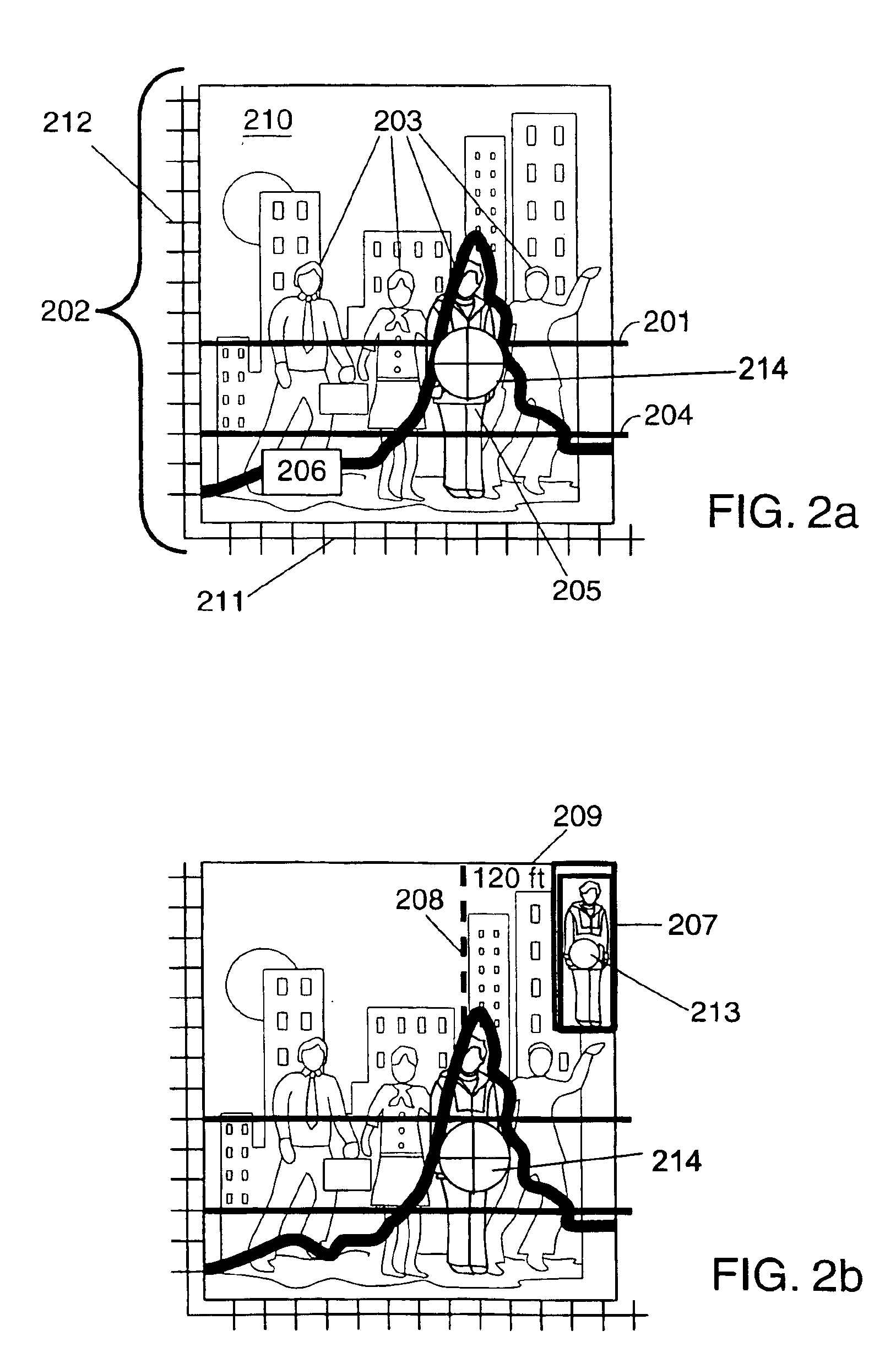
Methods and apparatus for detecting threats in different areas
Methods and apparatus for early detection and identification of a threat such as individuals carrying hidden explosive materials, land mines on roads, etc. are disclosed. Methods comprise transmitting radar signals in the direction of a potential threat, measuring the energy in reflected signals, dynamically generating a threat threshold value from signals received from multiple areas and comparing the energy in the reflected signals corresponding to different areas to the generated threat threshold value. The threat threshold value may be generated by averaging the weighted reflected energy measured from different areas during a single scan of a region including the different areas. The contribution to the threshold from different areas is weighted in some embodiments as a function of the distance from the transmitter and / or receiver to the particular area. Analysis of areas and treating different areas as segments facilitates accurate analysis and display of threat information.
Owner:KOSOWSKY LESTER
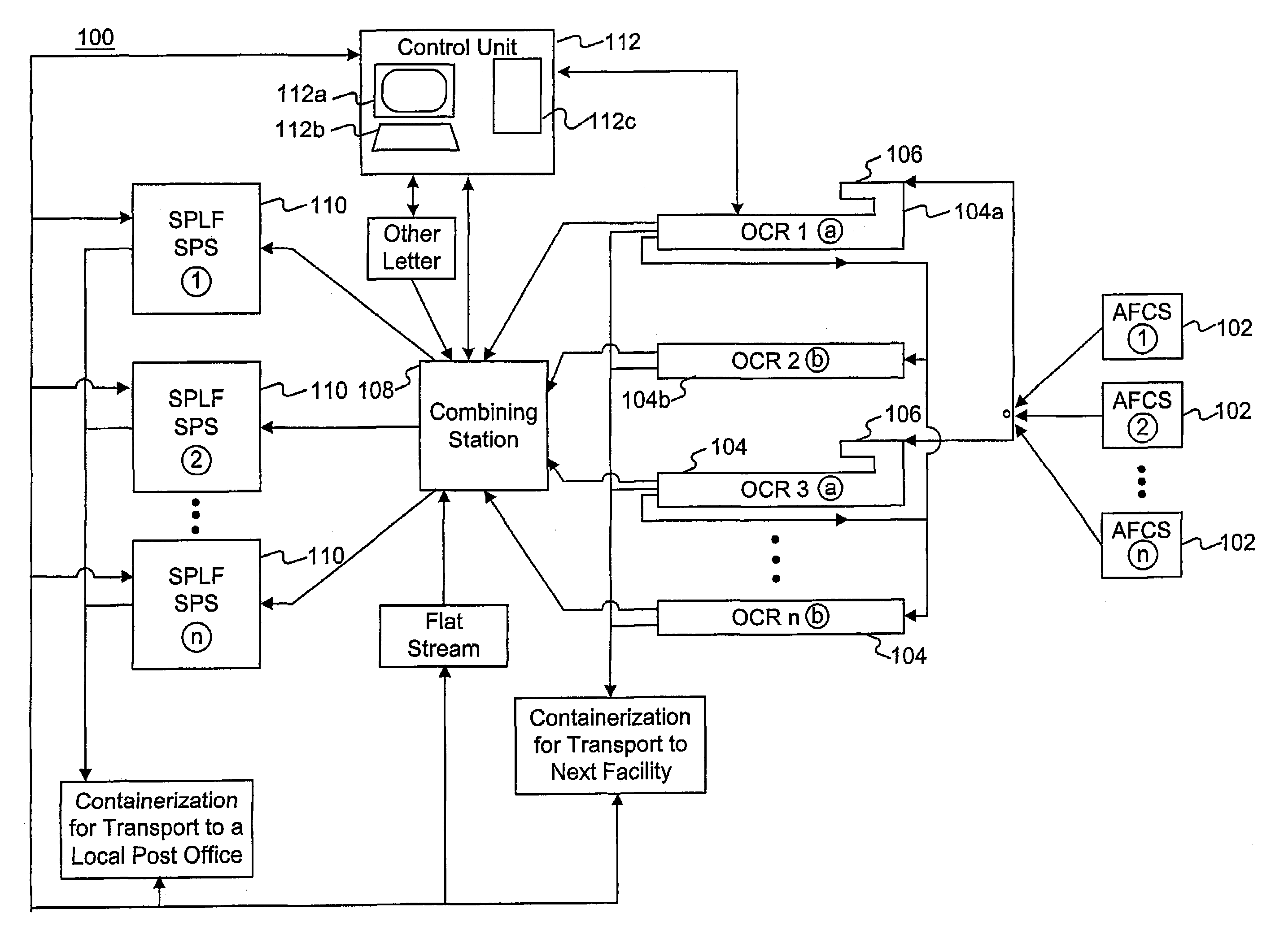
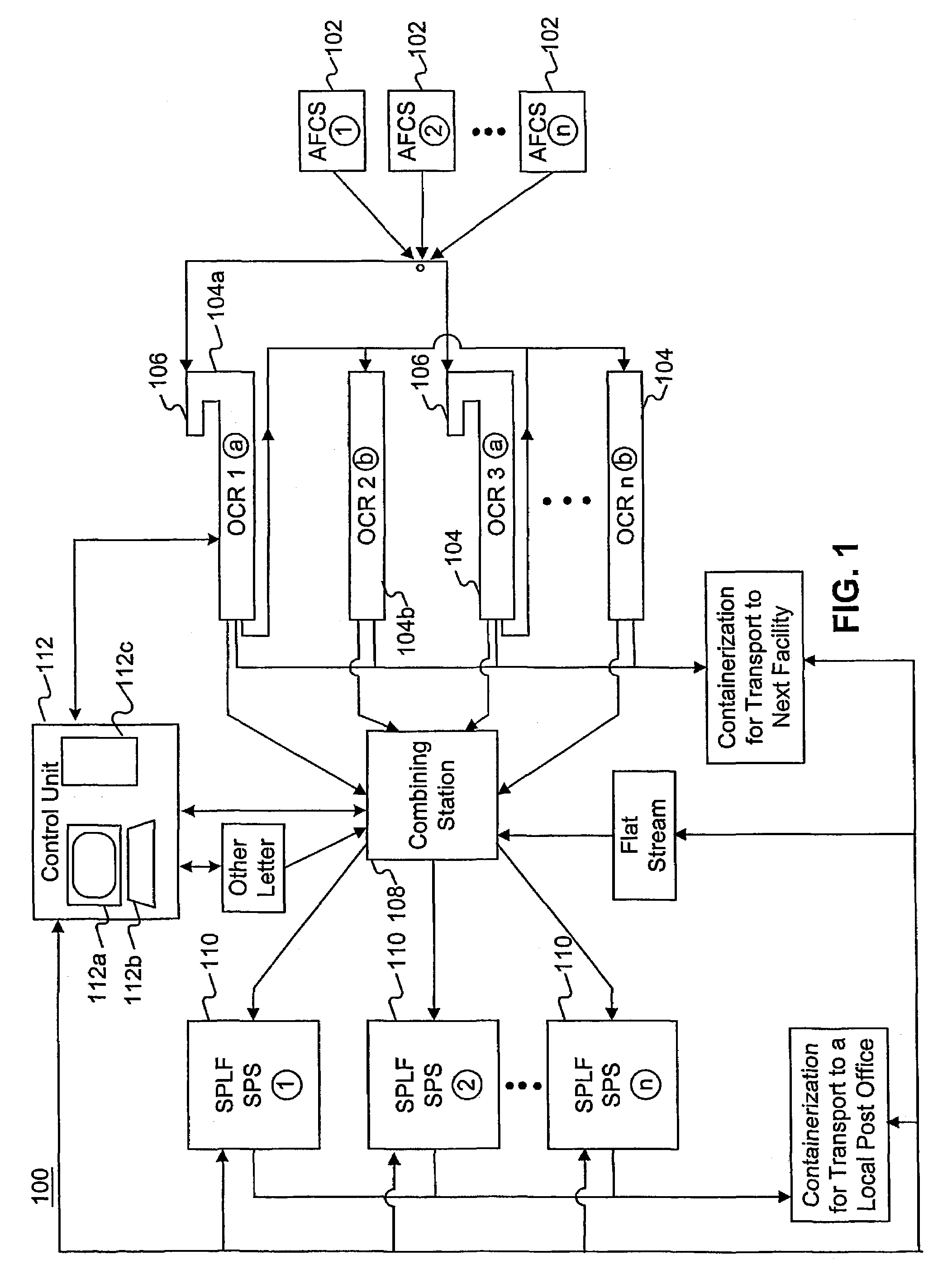
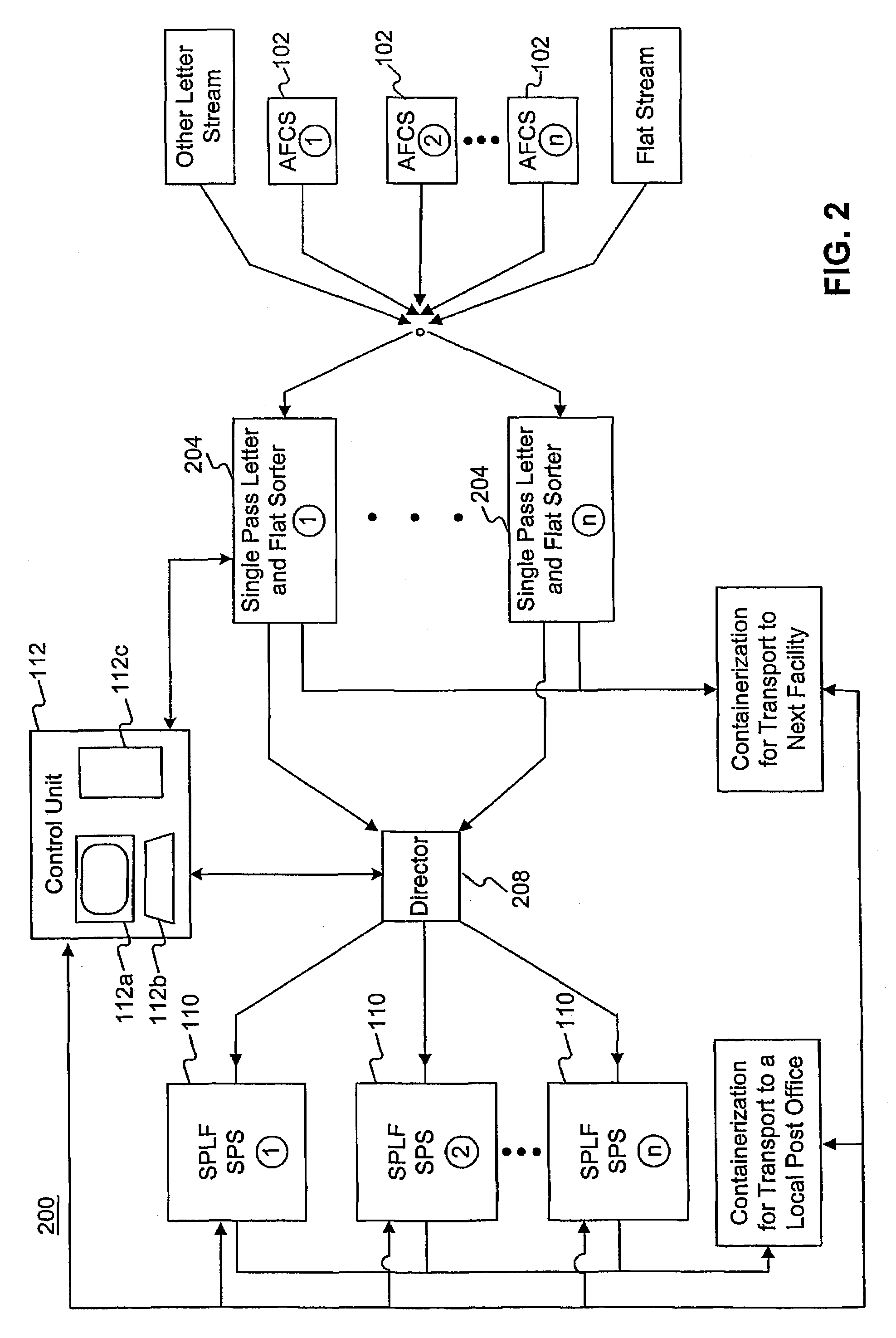
Method and system for single pass letter and flat processing
The sorting and packaging system comprises an induction and scanning system, a single pass sorting and packaging system for automatically sorting and packaging a plurality of mailpieces based on a single scan by the induction and sorting system, and a control unit connected to and controlling the induction and scanning system and the single pass sorting and packaging system. The single pass sorting and packaging system comprises at least one cell rack, at least one packaging system, and at least one delivery system. The cell rack is connected to the induction and scanning system by a transport sorting system. The cell rack comprises a plurality of cells and a purging system. The packaging system is connected to the cell rack and comprises a transport packaging system and a packaging unit. The delivery system is connected to the packaging system.
Owner:US POSTAL SERVICE
Between matching
InactiveUS8086597B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPath expressionSingle scan
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
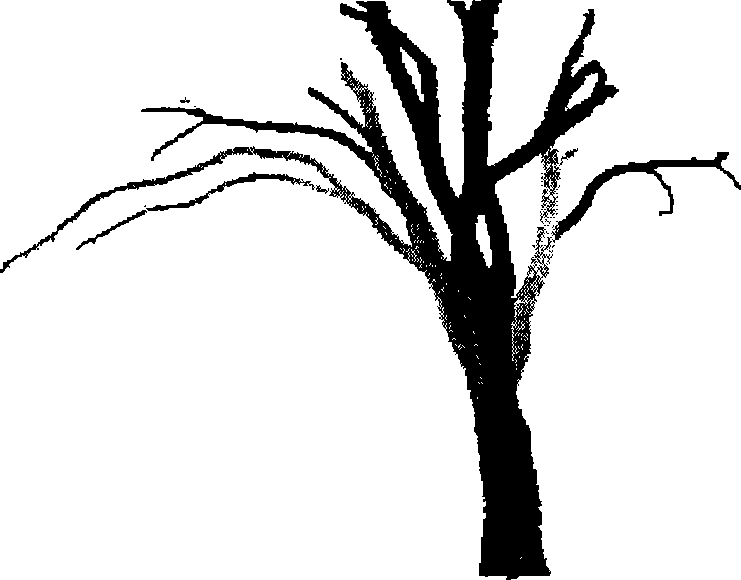
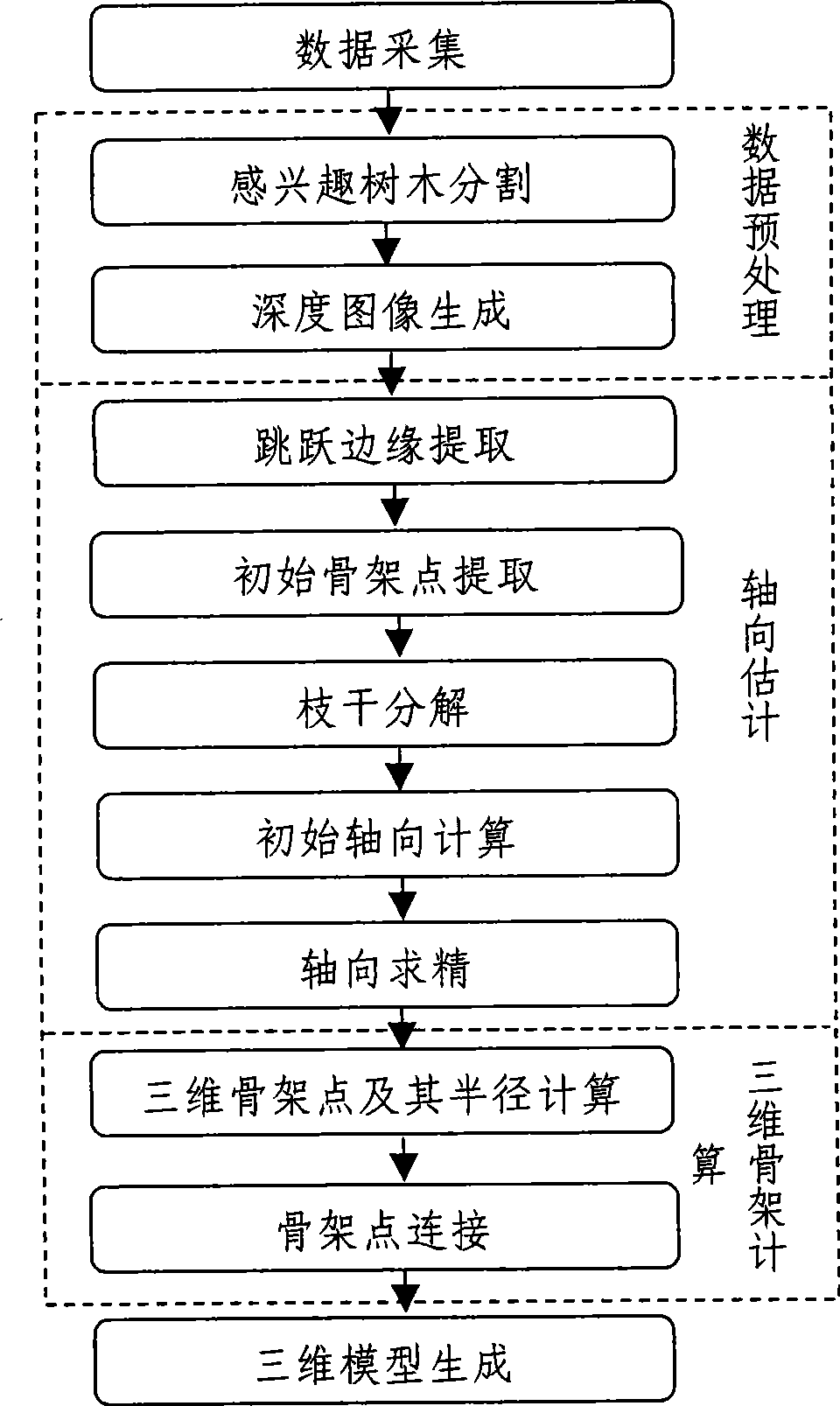
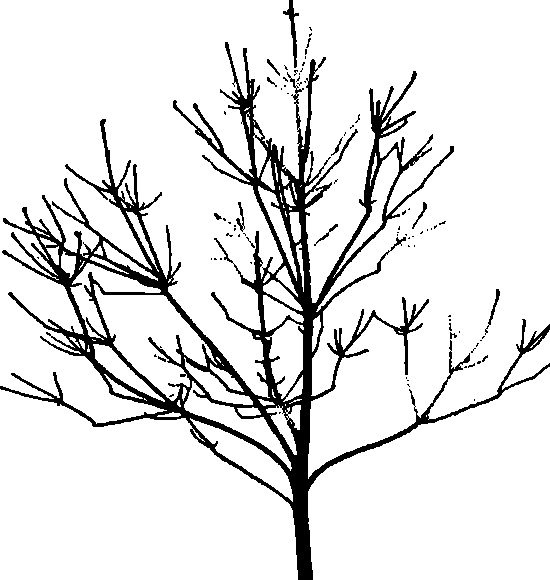
Tree measurement and reconstruction method based on single three-dimensional laser scanning
InactiveCN101488226AEasy to operateThe reconstruction results are accurate2D-image generationCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual technologyLaser scanning
The invention provides a method for measuring and reconstructing a tree based on single three-dimensional laser scanning, and relates to the technologies of computer graphs and computer vision. The method comprises steps of data preprocessing, axial estimation, three-dimensional framework computation and three-dimensional model generation. The method only utilizes single scanning data of a laser scanner to obtain branch shape and radius information faithful to the primary tree, carries out main operations in a two-dimensional image space, has simple and effective algorithm and accurate reconstruction result, and has important application values in the computer graphics application fields such as virtual reality, computer game, natural scene simulation, urban landscape design and the like and in the fields such as agriculture and forestry investigation, tree measurement, etc.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Automated dispenser with sensor arrangement
InactiveUS7795584B2Easy to detectImprove detection reliabilityRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesValue setControl system
Owner:SCA HYGIENE PROD AB
High-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size using running sums
A method for performing a high-performance closed-form single-scan calculation of oblong-shape rotation angles from binary images of arbitrary size on a processor using running sums is disclosed. Running sums are calculated and stored throughout each scan, and the results are obtained in closed form by simple post-scan computation. An algorithmic embodiment may execute on one or more hardware processors with limited or constrained computation power, available instruction cycles, available memory, etc. Exemplary hardware processors are found in one or more CPUs of a desktop, laptop, tablet, or handheld computing device, and may be an embedded processor or a signal processor chip. The resulting method may be used for touch or optical user interfaces, real-time image recognition, real-time machine vision, and other purposes.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
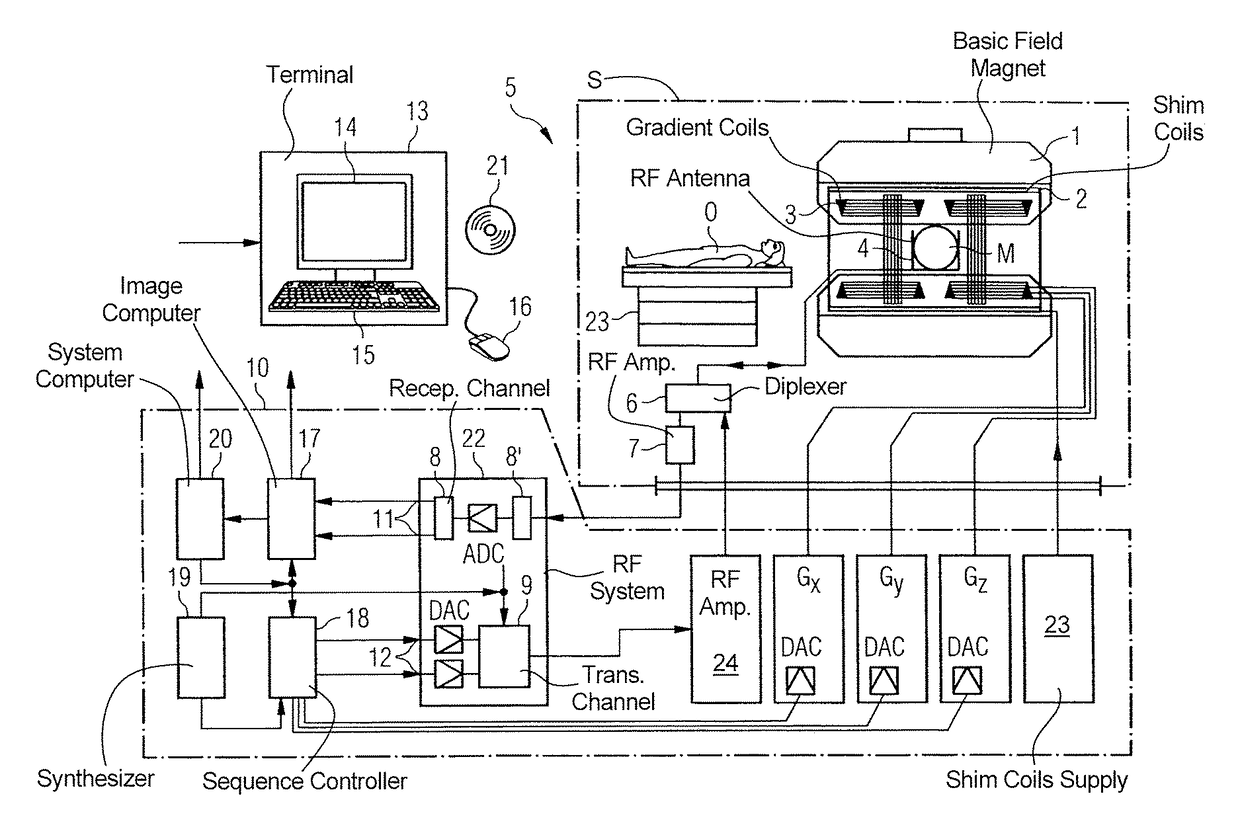
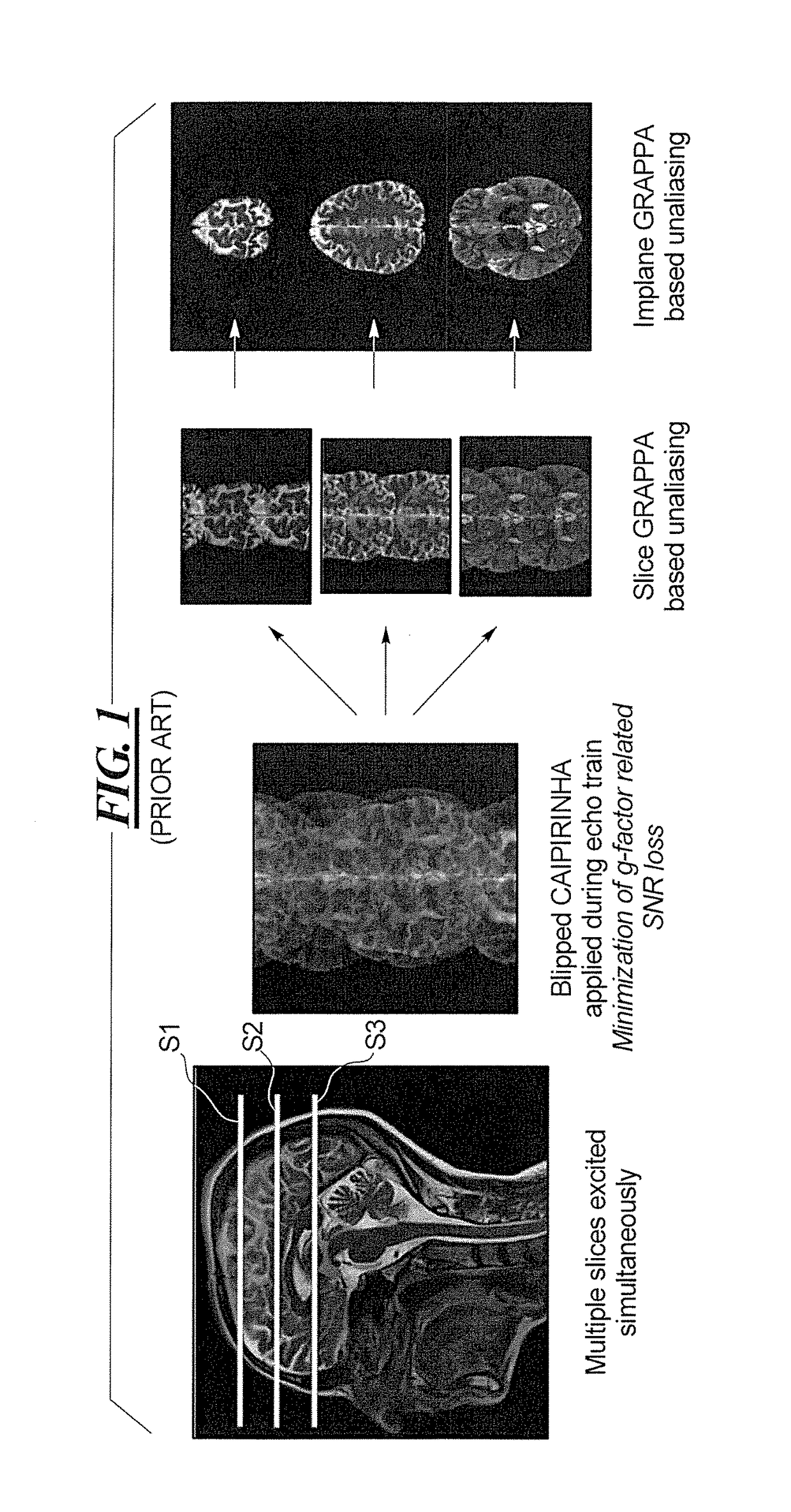
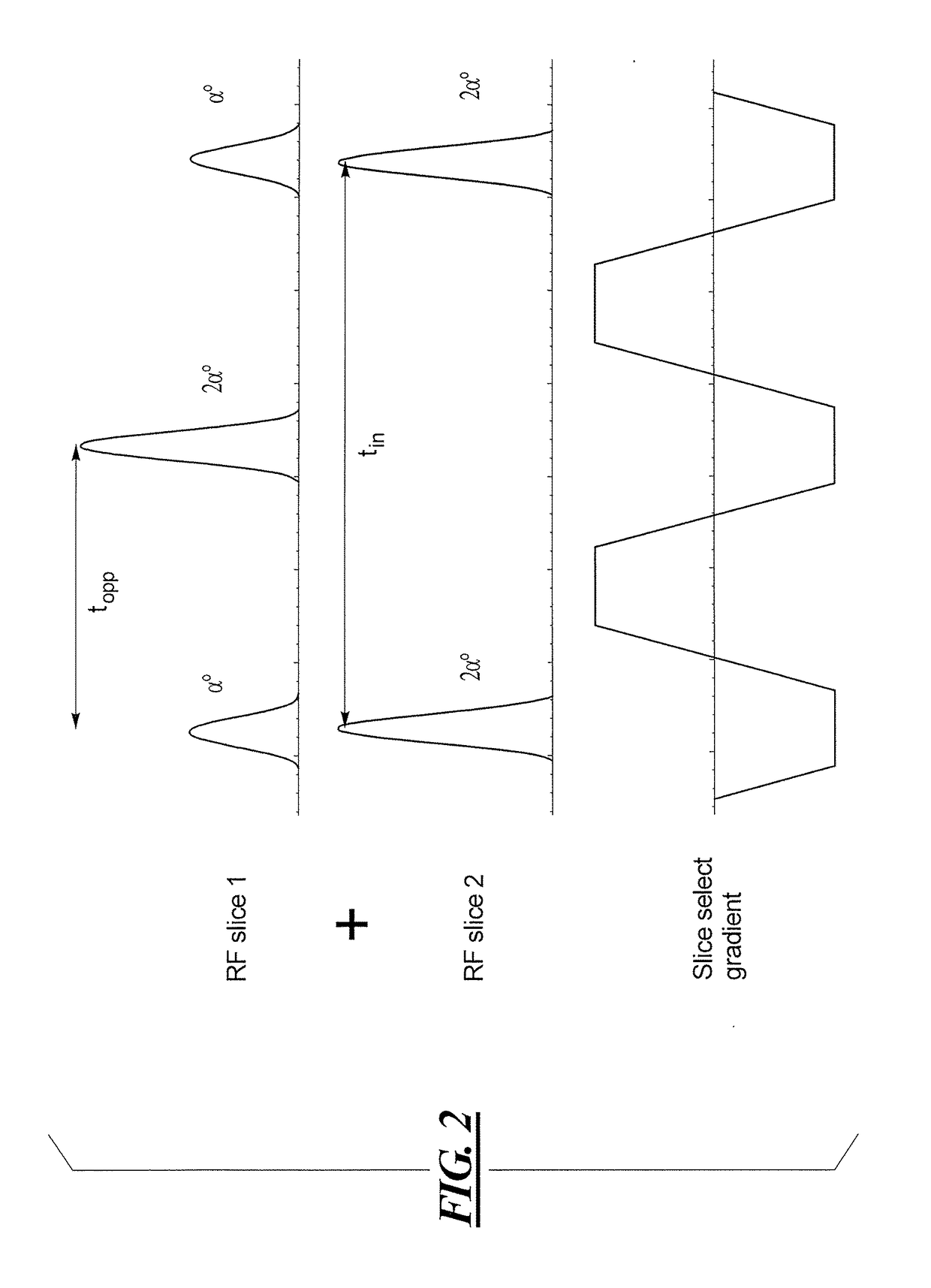
Multi-contrast simultaneous multislice magnetic resonance imaging with binomial radio-frequency pulses
ActiveUS20180024214A1Total acquisition time is halvedImage contrast will not sufferImage enhancementImage analysisMulti bandMulti slice
In a magnetic resonance apparatus and a method for operating the MR apparatus to acquire MR data in a single scan with different contrasts, nuclear spins in multiple slices of an examination subject are simultaneously excited in a single scan, with a simultaneous multi-slice acquisition sequence, in which a radio-frequency multi-band binomial pulse is radiated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Methods and systems for inspection of an entire wafer surface using multiple detection channels
ActiveUS7130036B1Scattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationEngineeringLight scattering
Methods for inspecting a wafer are provided. One method includes directing light to a center portion and an edge portion of a wafer in a single scan. The method also includes detecting light scattered from the center portion using a first detection channel and detecting light scattered from the edge portion using a second detection channel. Another method for inspecting an edge portion of a wafer includes scanning the edge portion of the wafer with light. The method also includes separately detecting different portions of light scattered from the edge portion. In addition, the method includes separating light scattered from edge features in the edge portion from other light scattered from the edge portion. The method further includes detecting defects in the edge portion of the wafer using the other scattered light.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
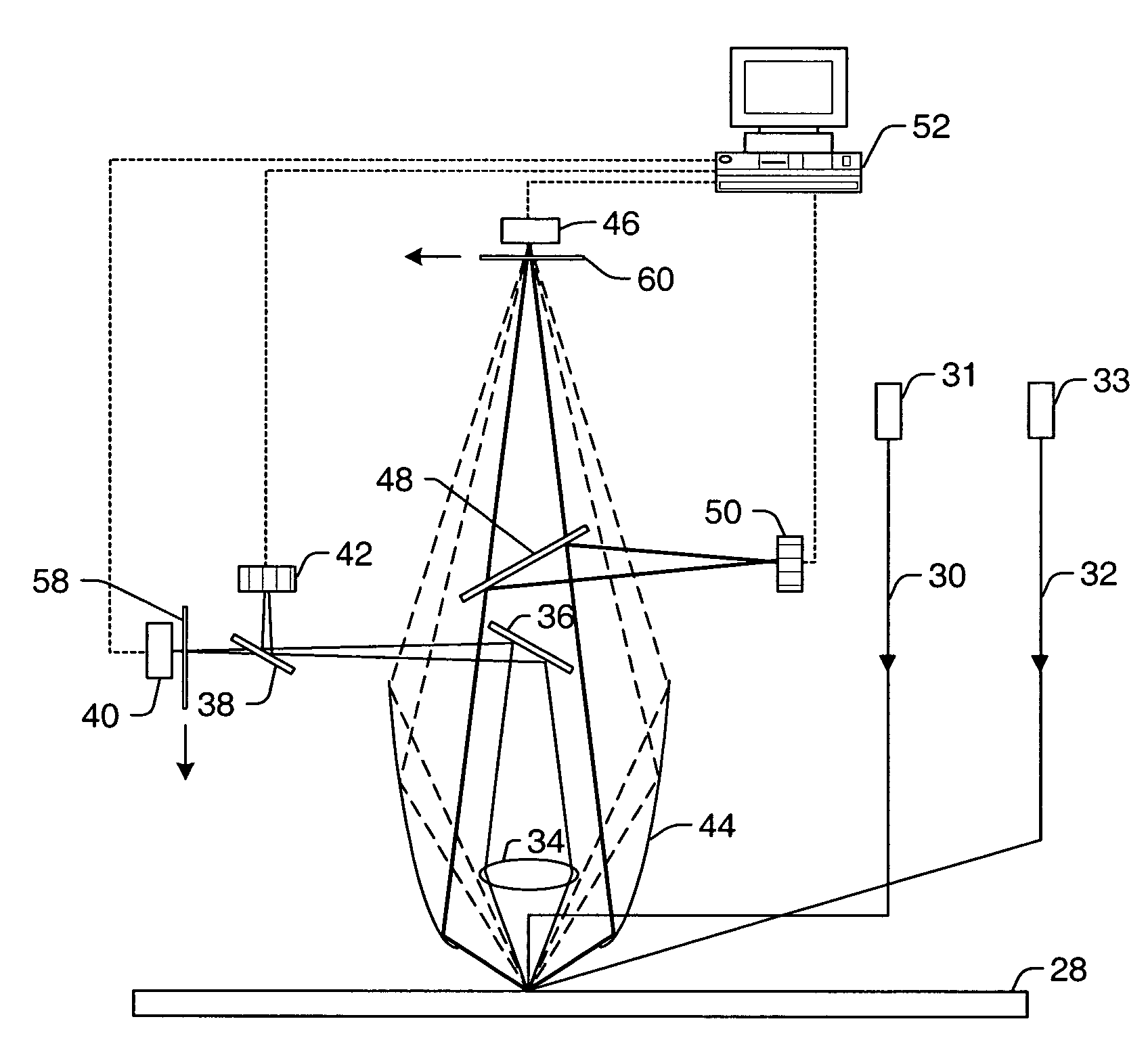
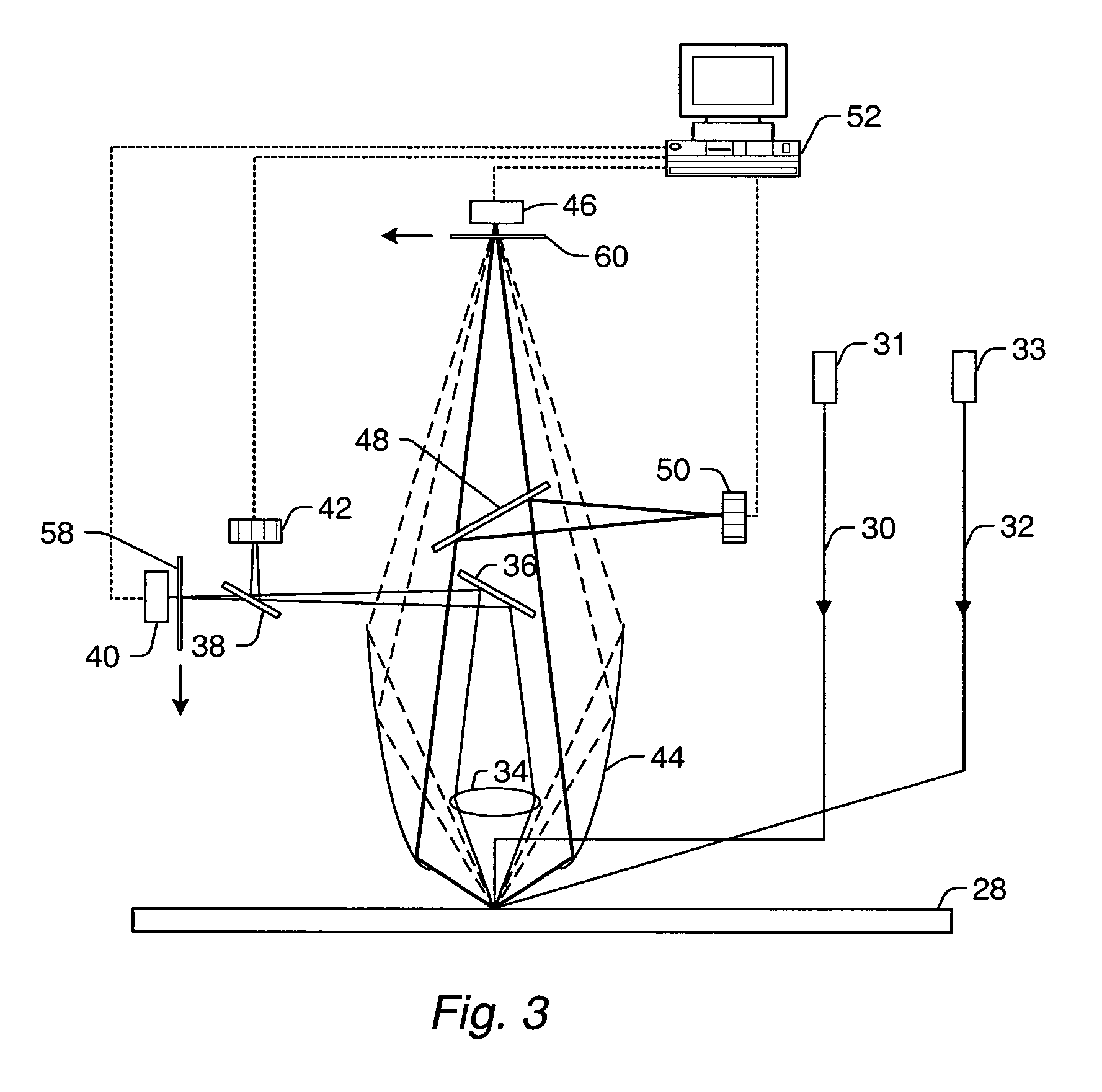
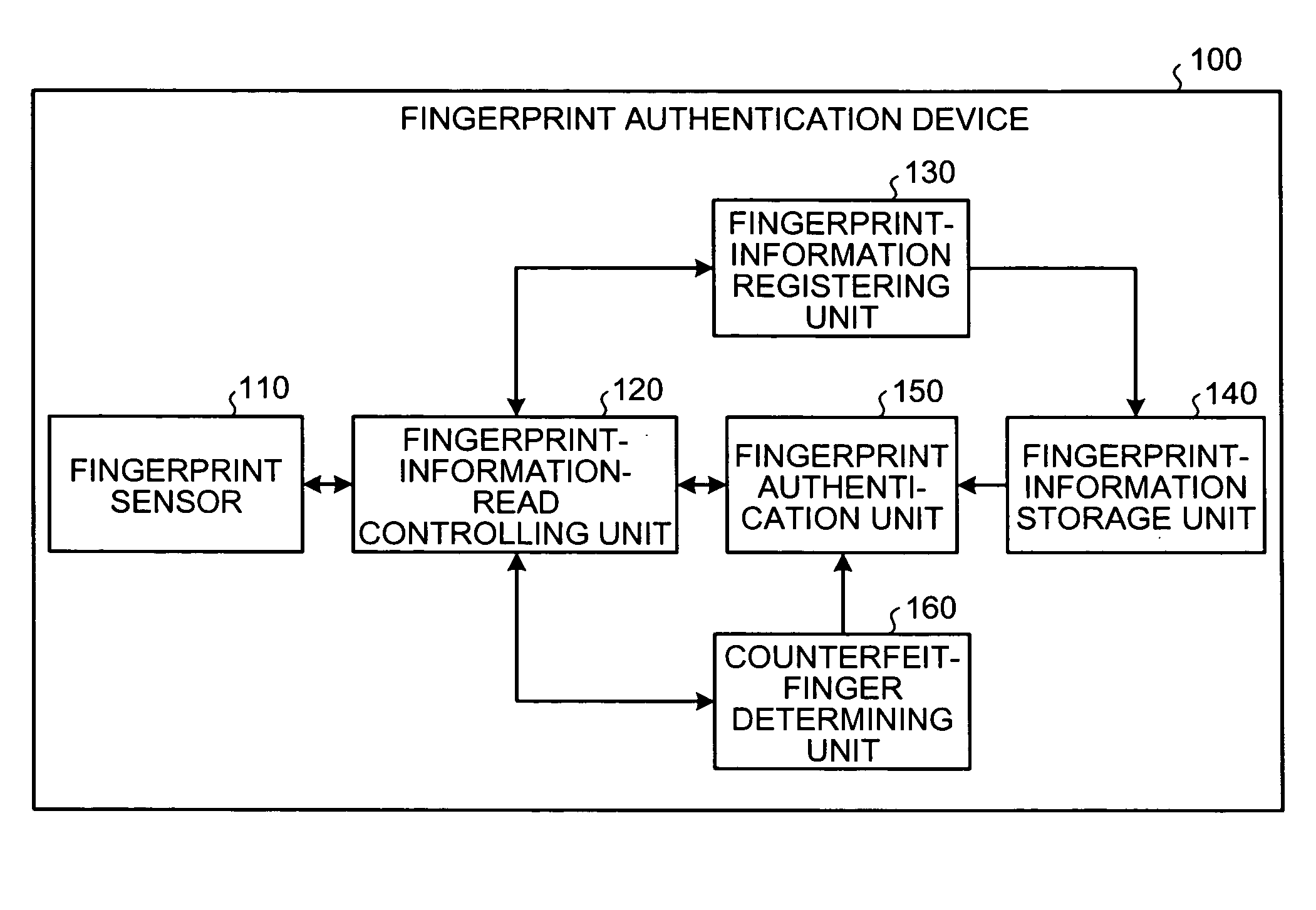
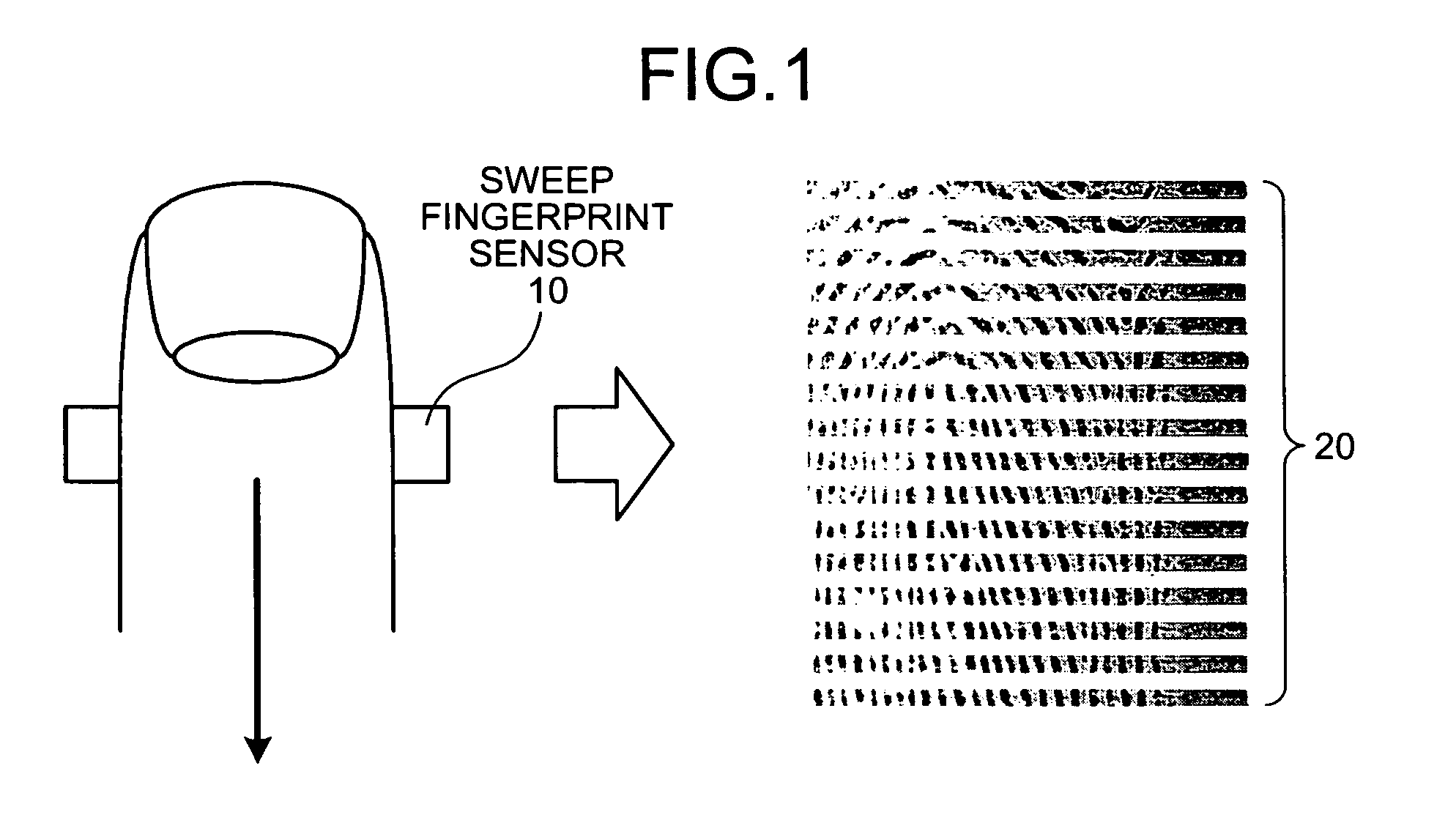
Fingerprint authentication device and information processing device
ActiveUS20070223791A1Digital data authenticationDetecting live finger characterPattern recognitionInformation processing
A fingerprint authentication device includes a sweep fingerprint sensor that acquires images of a fingerprint on a finger at at least two different sensitivity levels in a single scan, and a counterfeit-finger determining unit that determines whether the finger is counterfeit based on the images acquired by the sweep fingerprint sensor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20090195635A1Solve problemsInking apparatusOther printing apparatusTarget surfaceLight beam
A deflector deflects a light beam emitted from a light source including a plurality of light-emitting units. A scanning optical system focuses the light beam deflected by the deflector on a scanning target surface. A monitoring photoreceiver receives a part of a light beam deflected by the deflector and directed toward an area within a scanning area outside an image area. A detecting unit individually detects emission powers of at least two light-emitting units based on an output signal of the monitoring photoreceiver in a single sweep of scanning.
Owner:RICOH KK
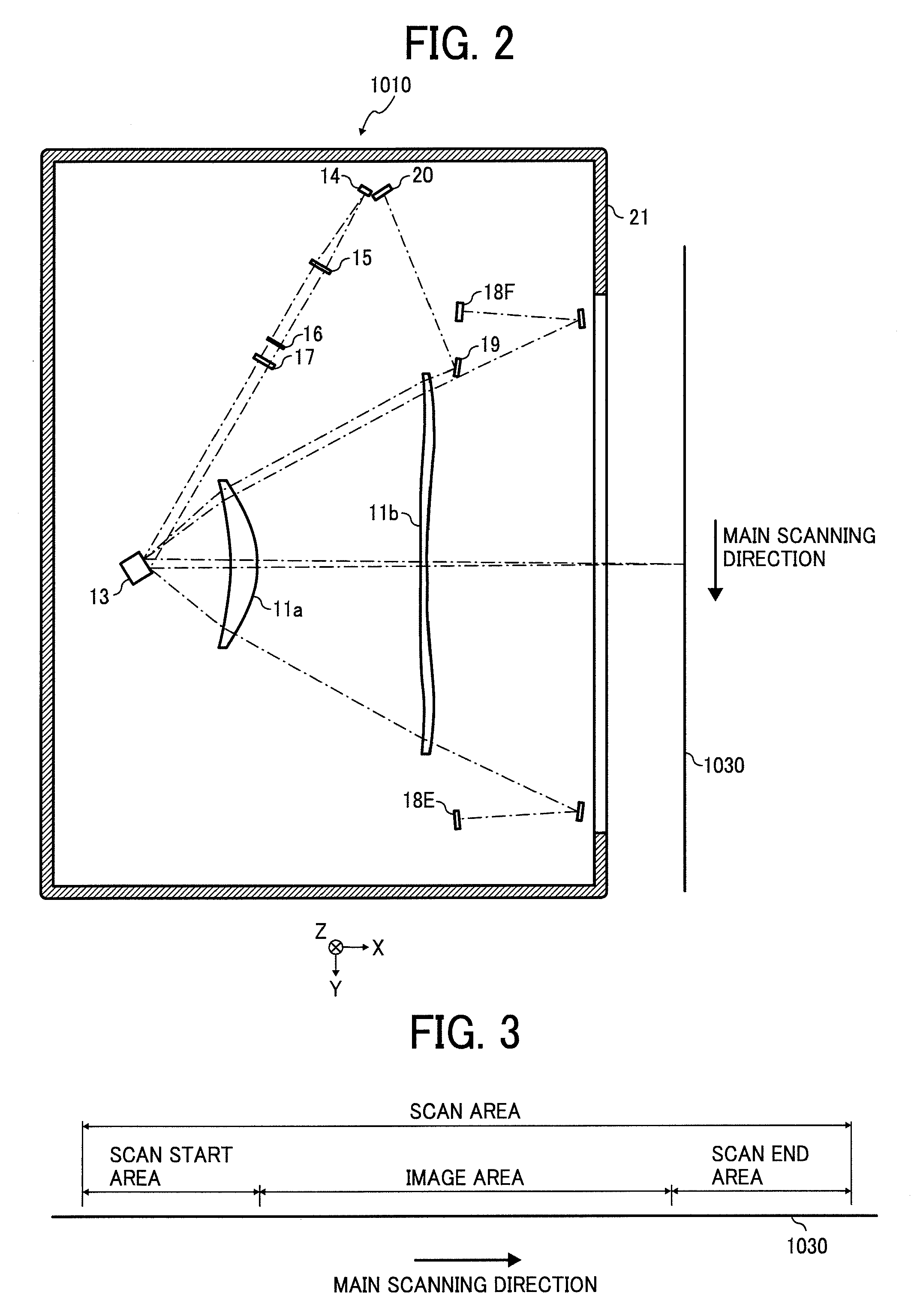
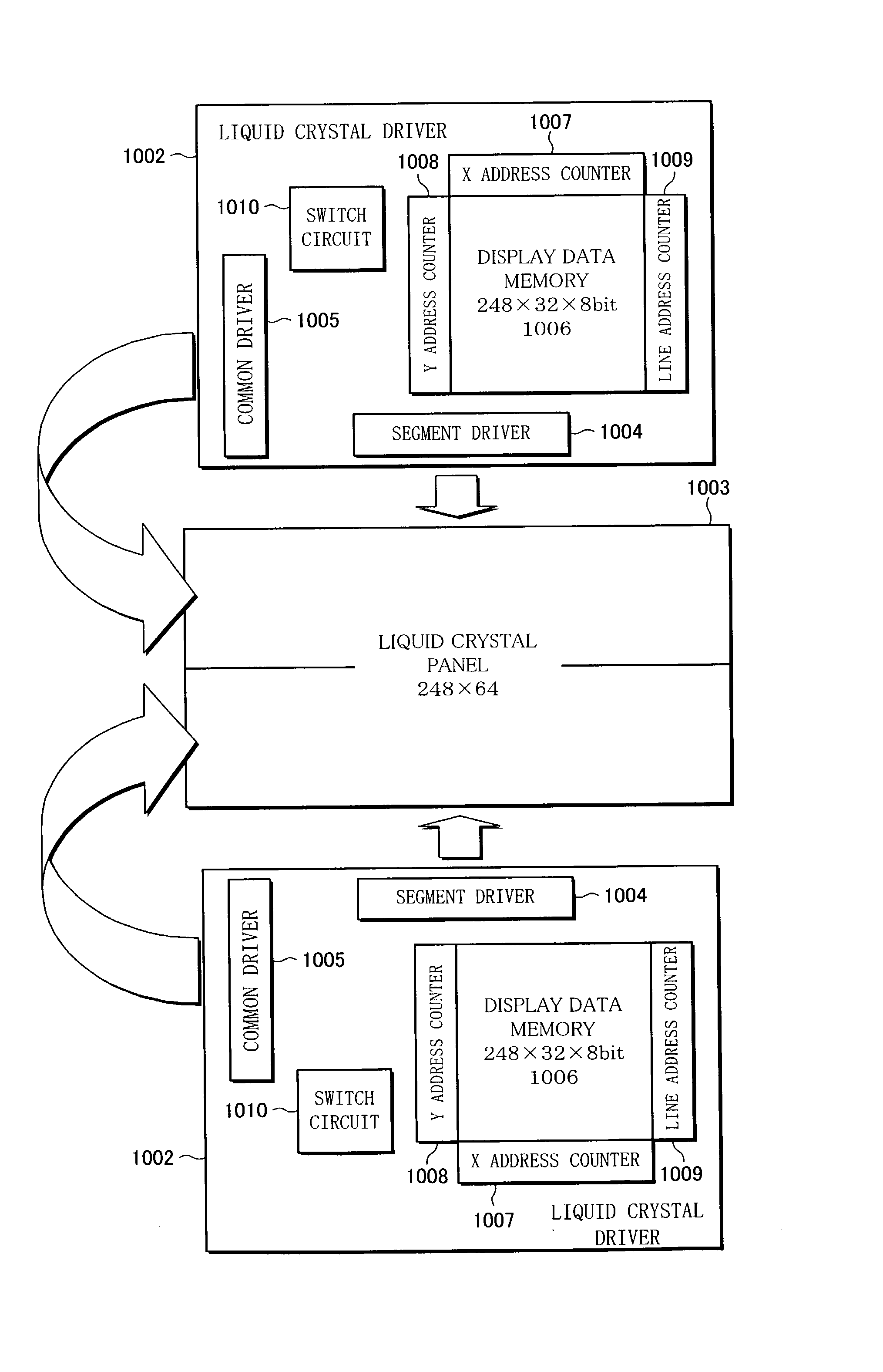
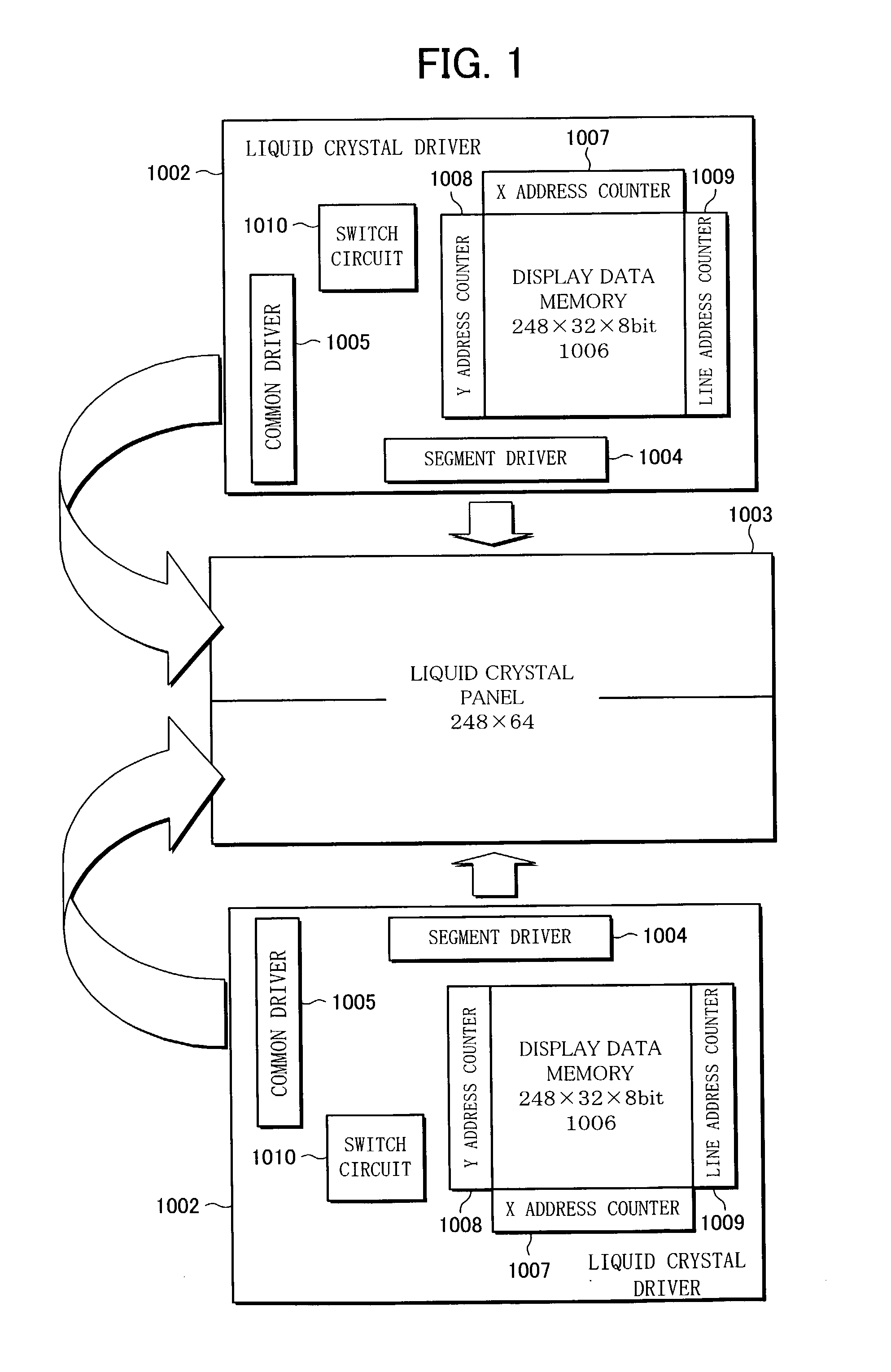
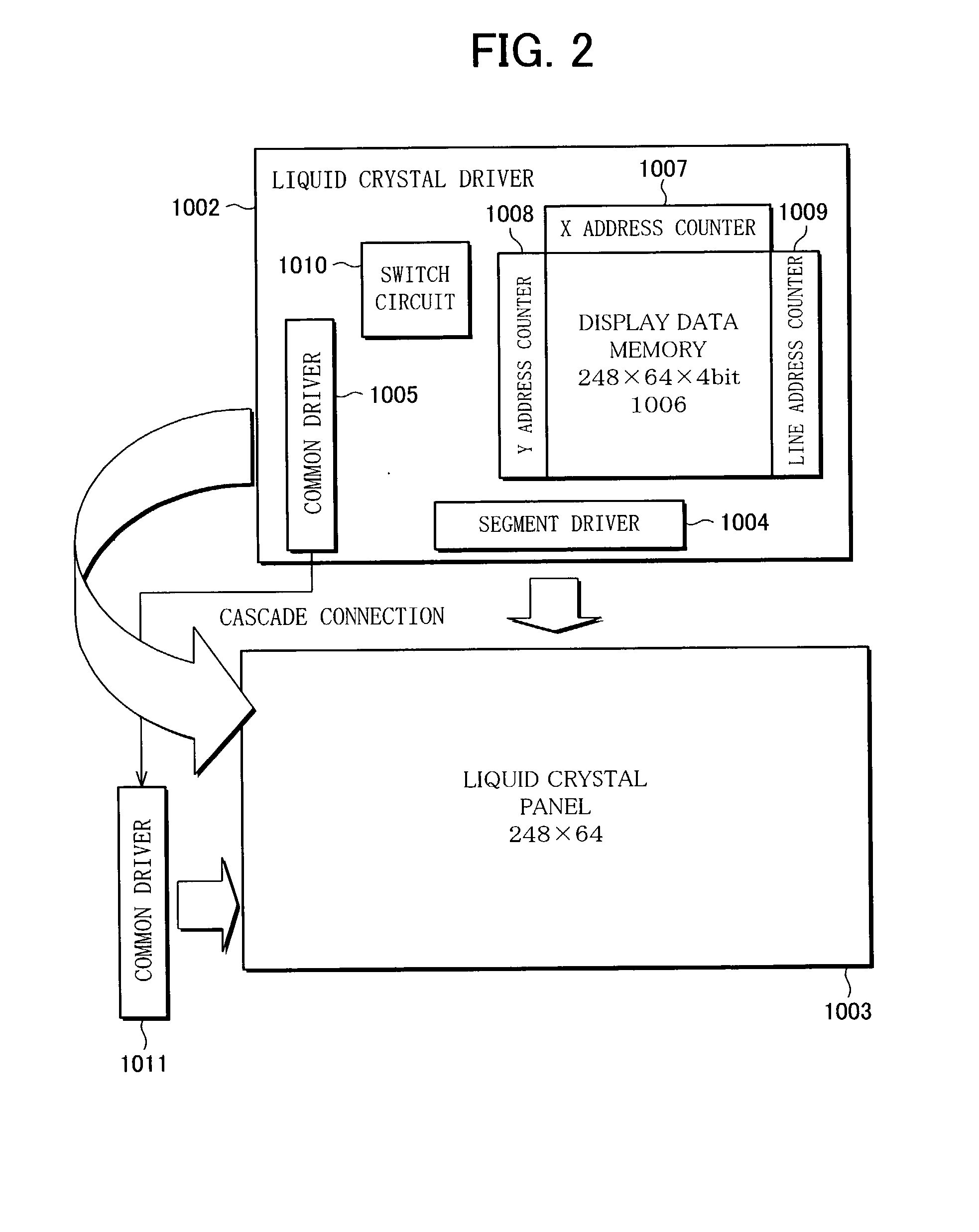
Liquid crystal driving devices
InactiveUS20030011549A1Low production costLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDual Scan
A liquid crystal driving device of the present invention is provided with a display data memory of a capacity that can be divided into two parts, and a switch circuit that is used to switch an addressing method of the display data memory between multi-tone display in a dual-scan and simple-tone display in a single-scan, so as to enable a driving IC to be shared between liquid crystal display devices that are used to display high-quality and multi-tone images and liquid crystal display devices that require less tone. Such a liquid crystal driving device can be used to reduce production cost of various types of liquid crystal display devices.
Owner:SHARP KK
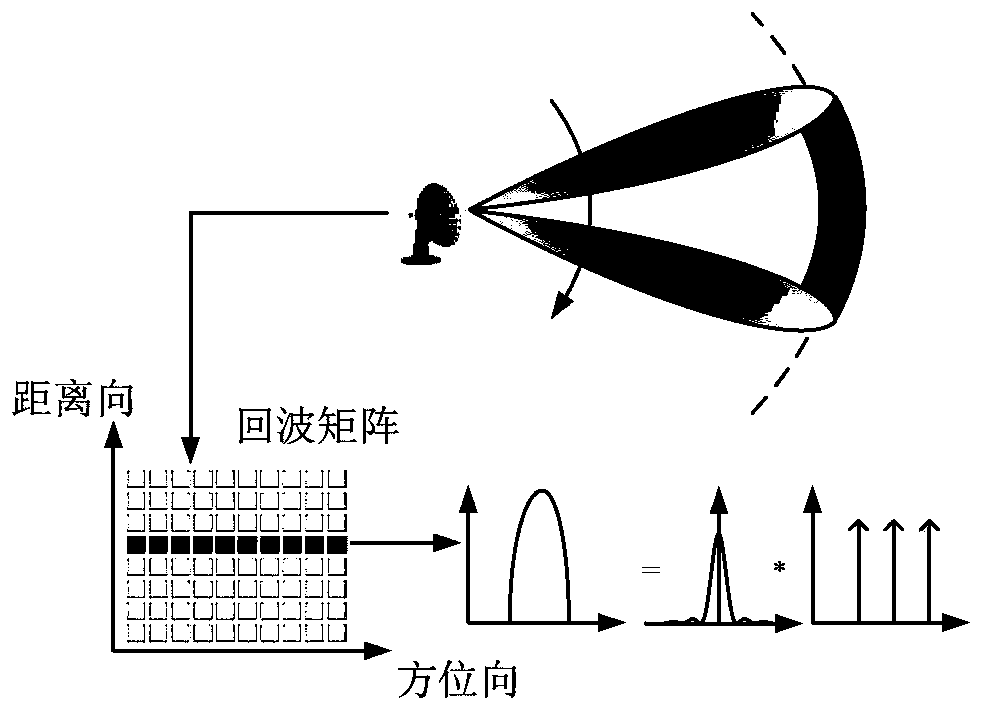
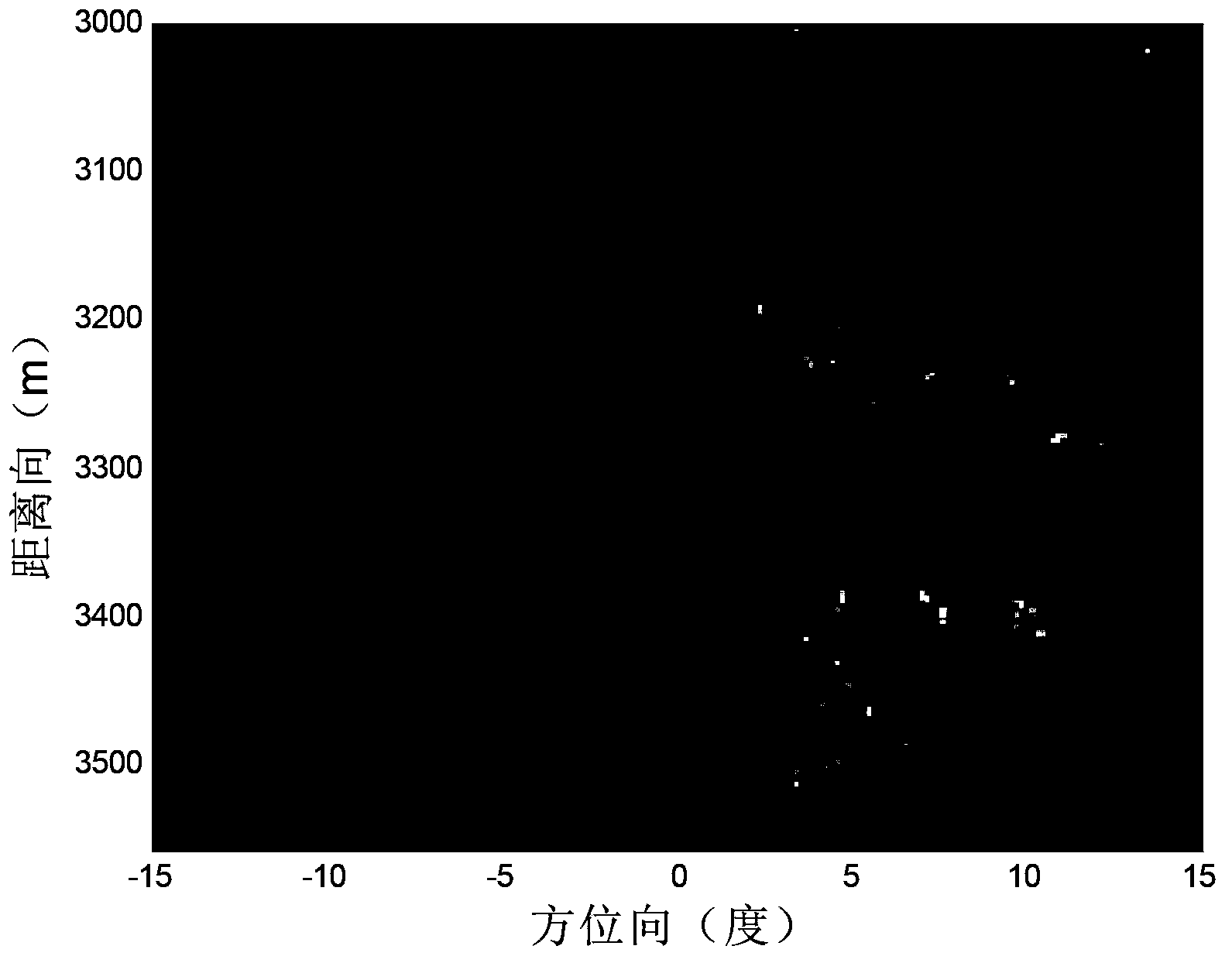
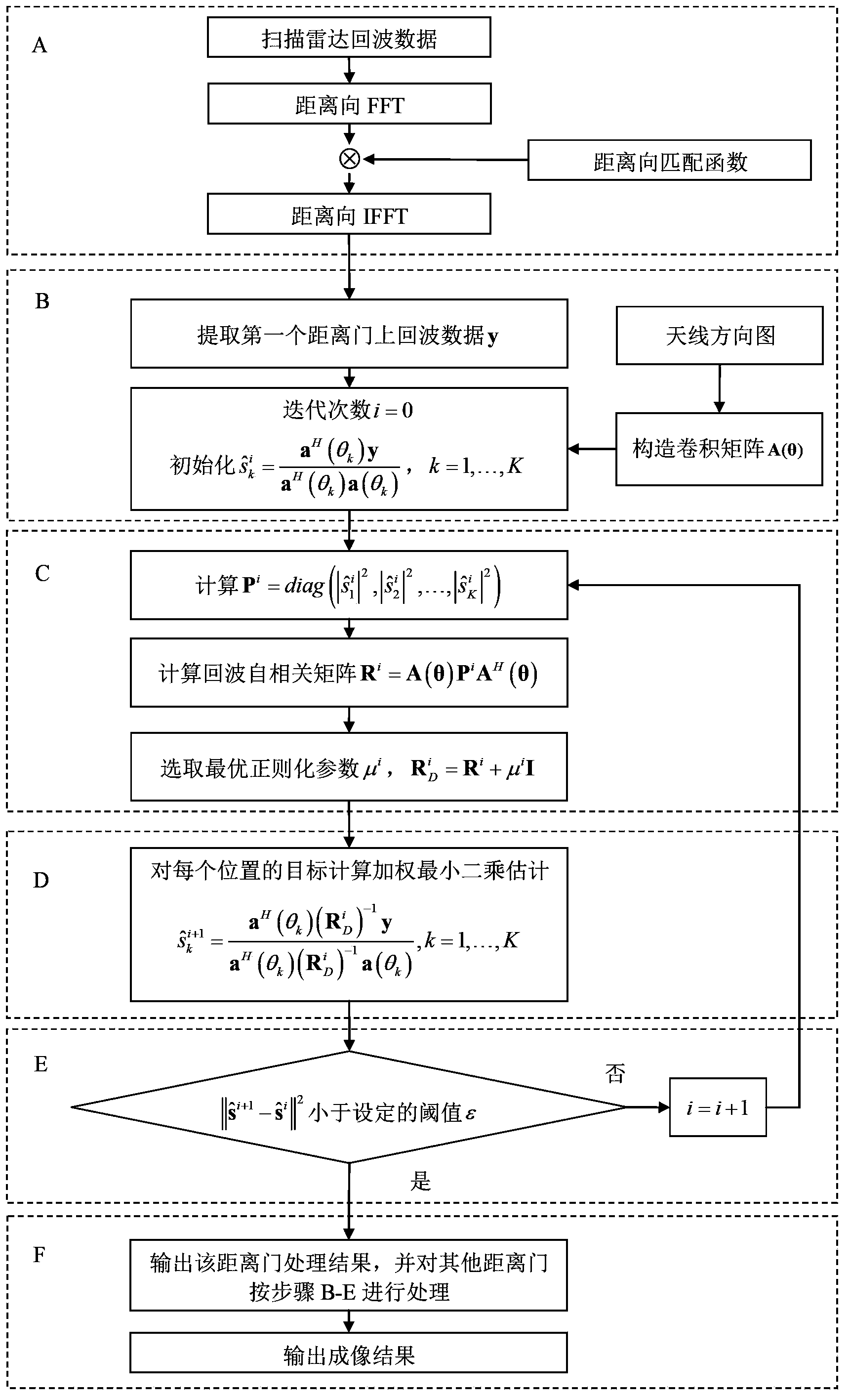
Scanning radar super-resolution imaging method
ActiveCN103412305AReduce signal to noise ratioImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Radar imaging
The invention discloses a scanning radar super-resolution imaging method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing distance-to-pulse compression; constructing a convolution matrix; initializing the convolution matrix; calculating an echo autocorrelation matrix; regularizing the echo autocorrelation matrix; performing orientation-to-parameter estimation; judging whether iteration is performed until a convergence state appears; and outputting super-resolution imaging results. According to the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method, an orientation-to-echo spectrum estimation model is constructed according to a radar antenna scanning process; a scanning radar imaging problem is converted into a parameter estimation problem; and amplitude and orientation estimation is performed on a site through an iteration self-adaptive method. Compared with an existing method, the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method can be applicable to low signal-to-noise ratio and has high robustness; and at the same time, with the scanning radar super-resolution imaging method adopted, robust imaging results can be obtained with a single times of scanning.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for three-dimensional surface inspection
An optical inspection system and method for inspecting a component on a printed circuit board (PCB) which determines three-dimensional information in a single scan. A first visual light source illuminates the PCB surface and component with a green light while a second visual light source illuminates the PCB and component with a blue light. At least one laser light source simultaneously illuminates the surface of the PCB with a narrow coherent red-light laser beam. The laser light source is mounted off vertical on a movable mount which enables the laser beam to be directed over an area of interest on the surface of the PCB. The system also includes a color scan camera mounted vertically above the PCB. The camera has red, green, and blue channels. The green and blue channels capture an image of the illuminated surface of the PCB which is used by a computer to determine two-dimensional information about the component. The red channel captures a path of the laser beam as it strikes the surface of the PCB and the component. The computer uses the path to determine height information for the component.
Owner:RUDOLPH TECHNOLOGIES INC
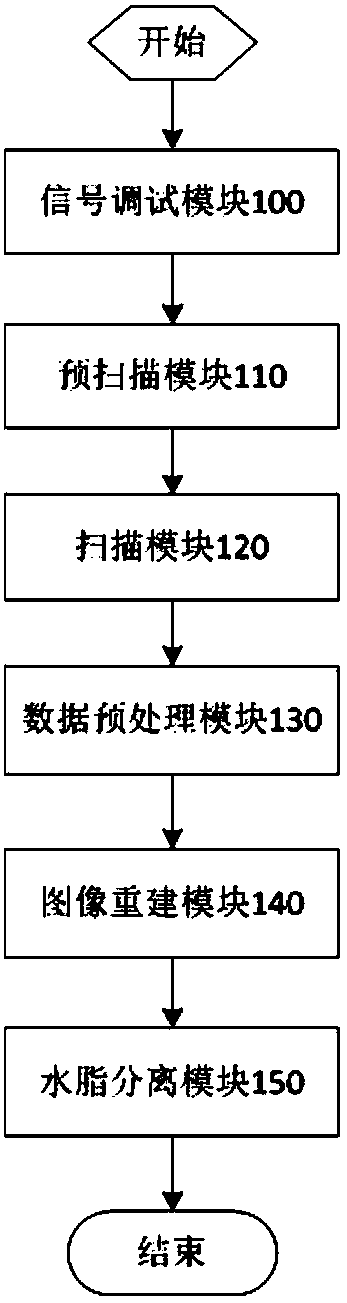
Synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN107271937AIncrease optionalityReduce dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsReconstruction methodT2 weighted
The invention discloses a synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A three-dimensional / two-dimensional fast multi-echo water-fat separation sequence and a signal debugging method, a pre-scanning method, a scanning method, a data preprocessing method and an image reconstruction method thereof can obtain a water-fat separation image and T2 weighted (T1 weighted or PD weighted) image by one-time scanning. The three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted synchronous scanning and calibration method can maximize the number of images obtained in a single scan, including, an in-phase image, a reverse-phase image, a fat image, a fat-pressed image water, a conventional T2 weighted (or T1 weighted / PD weighted ) image, and a T2weighted images, significantly shortens clinical scanning time and increases the selectivity of clinical scanning schemes, and has less reliance on the hardware performance of an MRI system.
Owner:南京拓谱医疗科技有限公司
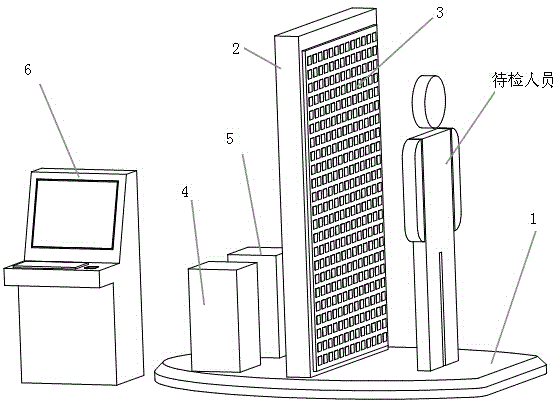
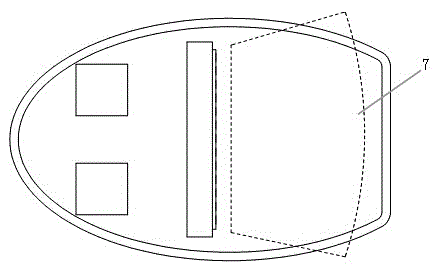
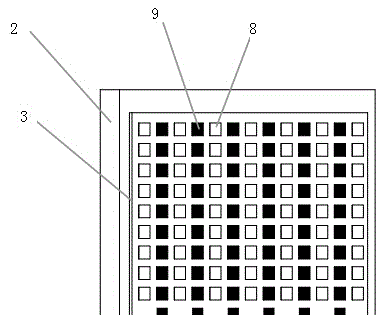
Surface-type millimeter wave scanning three-dimensional holographic imaging safety check system
InactiveCN104991283AShorten the timeNot easy to cause wear and tearOptical based geological detectionHolographic imagingSurface type
The invention relates to a surface-type millimeter wave scanning three-dimensional holographic imaging safety check system which comprises a millimeter wave signal emission driving module, a millimeter wave signal acquisition module, a millimeter wave signal processing module, a millimeter wave emission antenna and a millimeter wave reception antenna. The millimeter wave emission antenna and the millimeter wave reception antenna form a surface-type millimeter wave antenna array, wherein the surface-type millimeter wave antenna array is used for scanning a region to be detected; the millimeter wave emission antenna is connected with the millimeter wave signal emission driving module; the millimeter wave reception antenna is connected with the millimeter wave signal acquisition module; and the millimeter wave signal processing module is connected with the millimeter wave signal acquisition module. According to the surface-type millimeter wave scanning three-dimensional holographic imaging safety check system, through the surface-type millimeter wave antenna array, single scanning time is greatly reduced; and meanwhile, since equipment does need to be subjected to mechanical rotation, equipment wearing is not easy to cause, service time of the equipment is substantially prolonged and equipment fault is reduced.
Owner:深圳市太赫兹科技有限公司
Laser radar emitting system based on MEMS galvanometer
InactiveCN109343034APrecise control angleHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsRadarImage resolution
The invention discloses a laser radar emitting system based on a MEMS galvanometer. The system comprises a pulsed laser collimation emission module, a MEMS galvanometer, a reflecting mirror, a rotarymotor, and a diffraction beam splitting element. The pulsed laser collimation emission module emits collimated laser; the MEMS galvanometer, the pulsed laser collimation emission module, the reflecting mirror, and the diffraction beam splitting element are arranged correspondingly, so that the collimated laser incidents on the surface of the MEMS galvanometer to be reflected to form reflected light; the reflected light incidents on the reflecting mirror, and is reflected by the reflecting mirror to further incident on the diffraction beam splitting element, so that a quantity of uniform divergent light beams are formed; the reflecting mirror is connected to the rotary motor; and the rotary motor can drive the reflecting mirror to rotate. According to the laser radar emitting system based on the MEMS galvanometer, the rotation angle of the rotary motor is adjusted for multiple rounds of scanning; and the spatial range of angles between adjacent beams under a single scan can be filled, thereby greatly improving the spatial scanning resolution.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
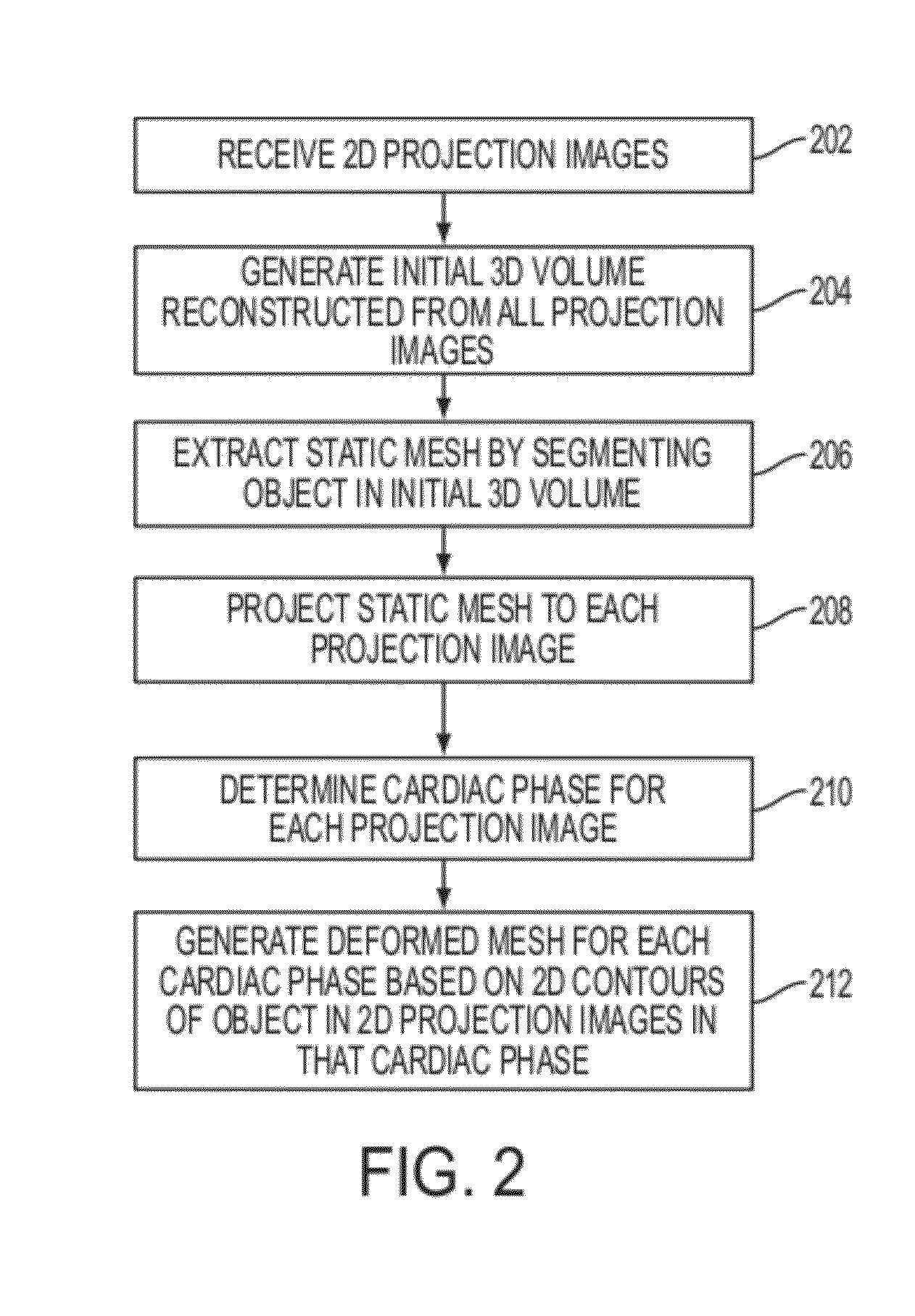
Method and System for 3D Cardiac Motion Estimation from Single Scan of C-Arm Angiography
A method and system for estimating 3D cardiac motion from a single C-arm angiography scan is disclosed. An initial 3D volume is reconstructed from a plurality of 2D projection images acquired in a single C-arm scan. A static mesh is extracted by segmenting an object in the initial 3D volume. The static mesh is projected to each of the 2D projection images. A cardiac phase is determined for each of the 2D projection images. A deformed mesh is generated for each of a plurality of cardiac phases based on a 2D contour of the object and the projected mesh in each of the 2D projection images of that cardiac phase.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
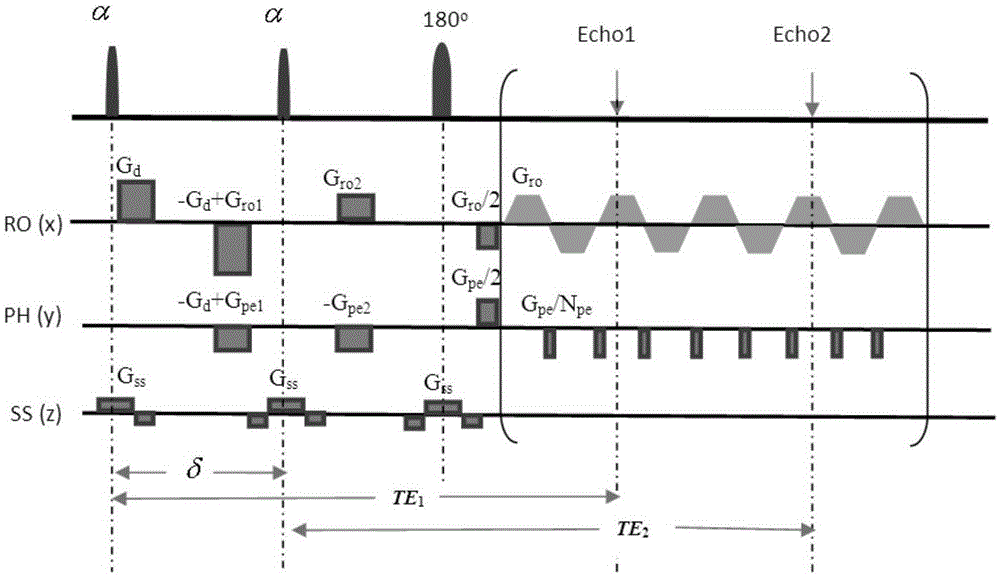
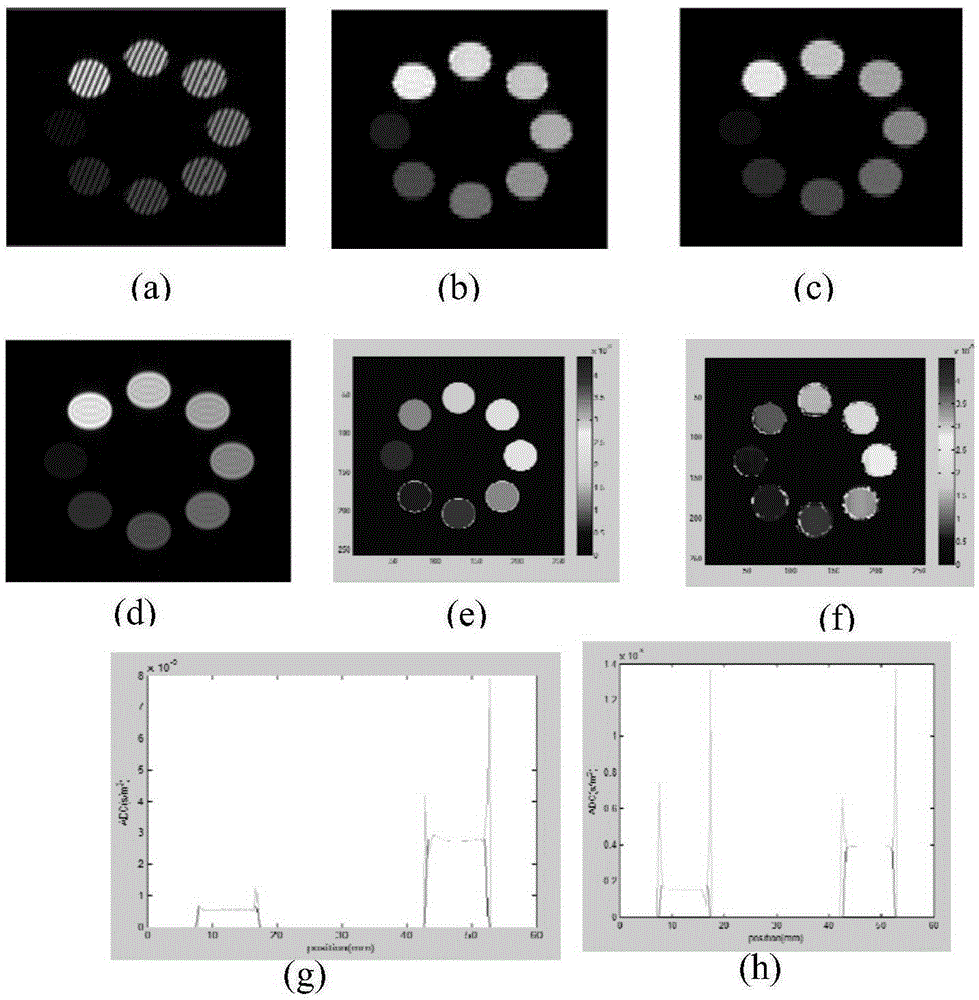
Single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echoes
The invention provides a single-scanning quantitative magnetic resonance diffusion imaging method based on dual echo, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. According to the method, two echoes with the same evolution time are generated through two small-angle excitation pulses with the same turning angle, so that the same transverse relaxation time is achieved; a displacement gradient is added after each excitation pulse to achieve central displacement of the two echo signals in a signal space, and a diffusion gradient is added after the first excitation pulse, so that diffusion reduction only exists in the first echo signal; accordingly, signals under different diffusion factors are obtained. The two echo signals are from one imaging slice, so that the two echo signals can be separated through priori knowledge of the two echo signals by matching sparse conversion with a corresponding separation algorithm. Finally, a quantitative ADC image is obtained by performing apparent diffusion coefficient calculation on two signals obtained through separation. Single-scanning quantitative ADC imaging is obtained through the method, and the quality of the obtained ADC image is good.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com