Patents
Literature
667 results about "Excitation pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
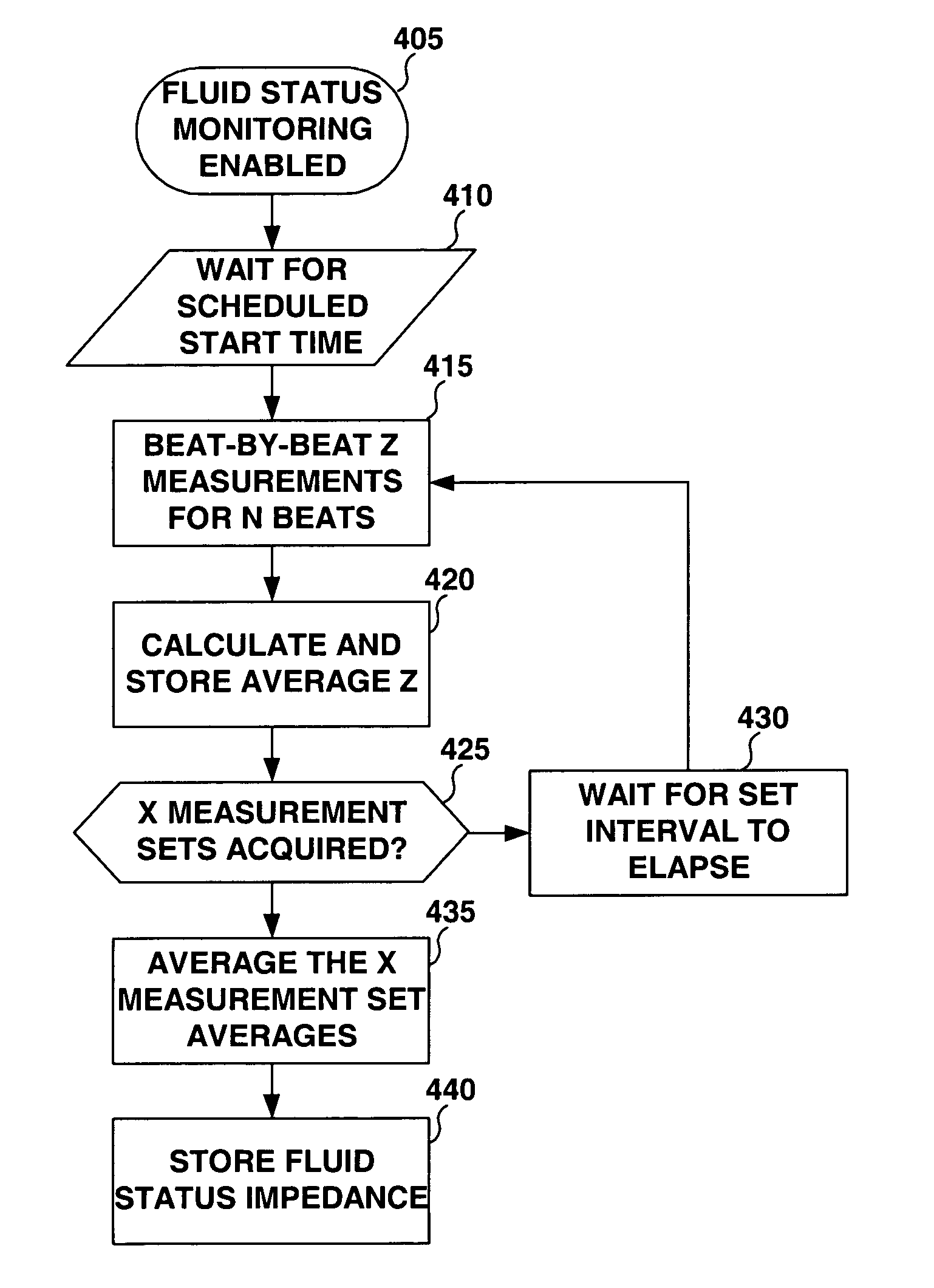
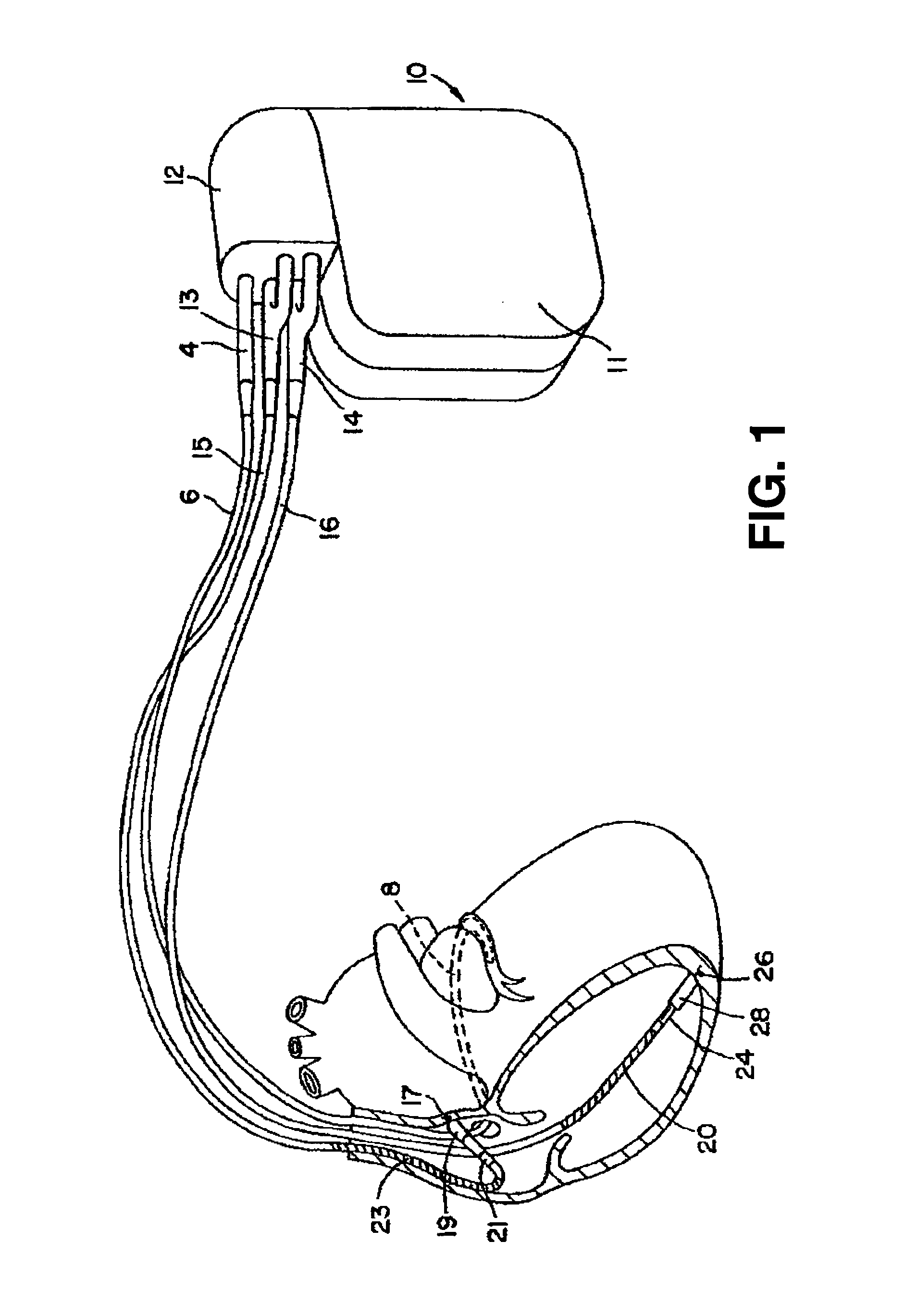
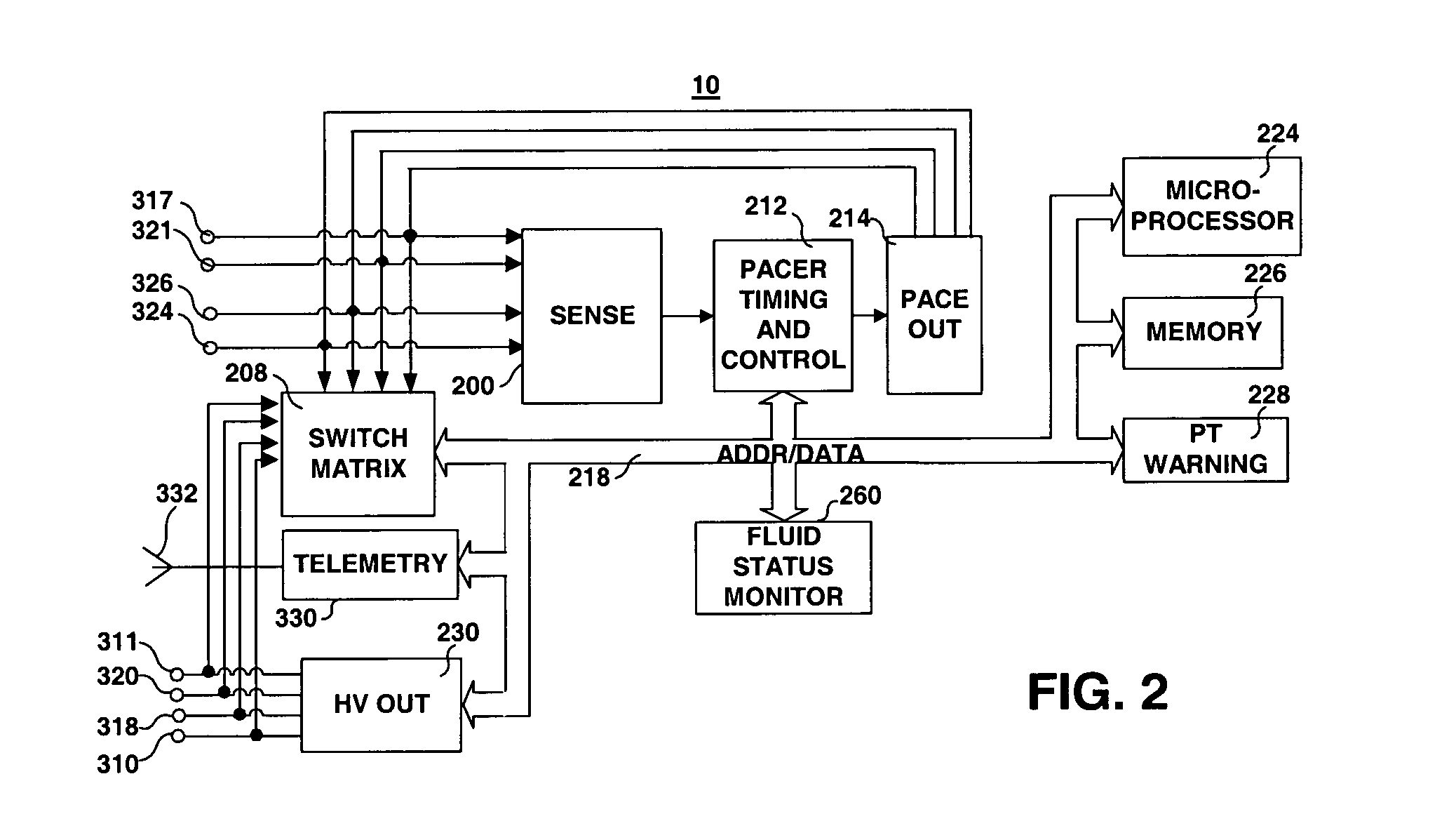
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS20050080460A1Easy to implementCancel noiseHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
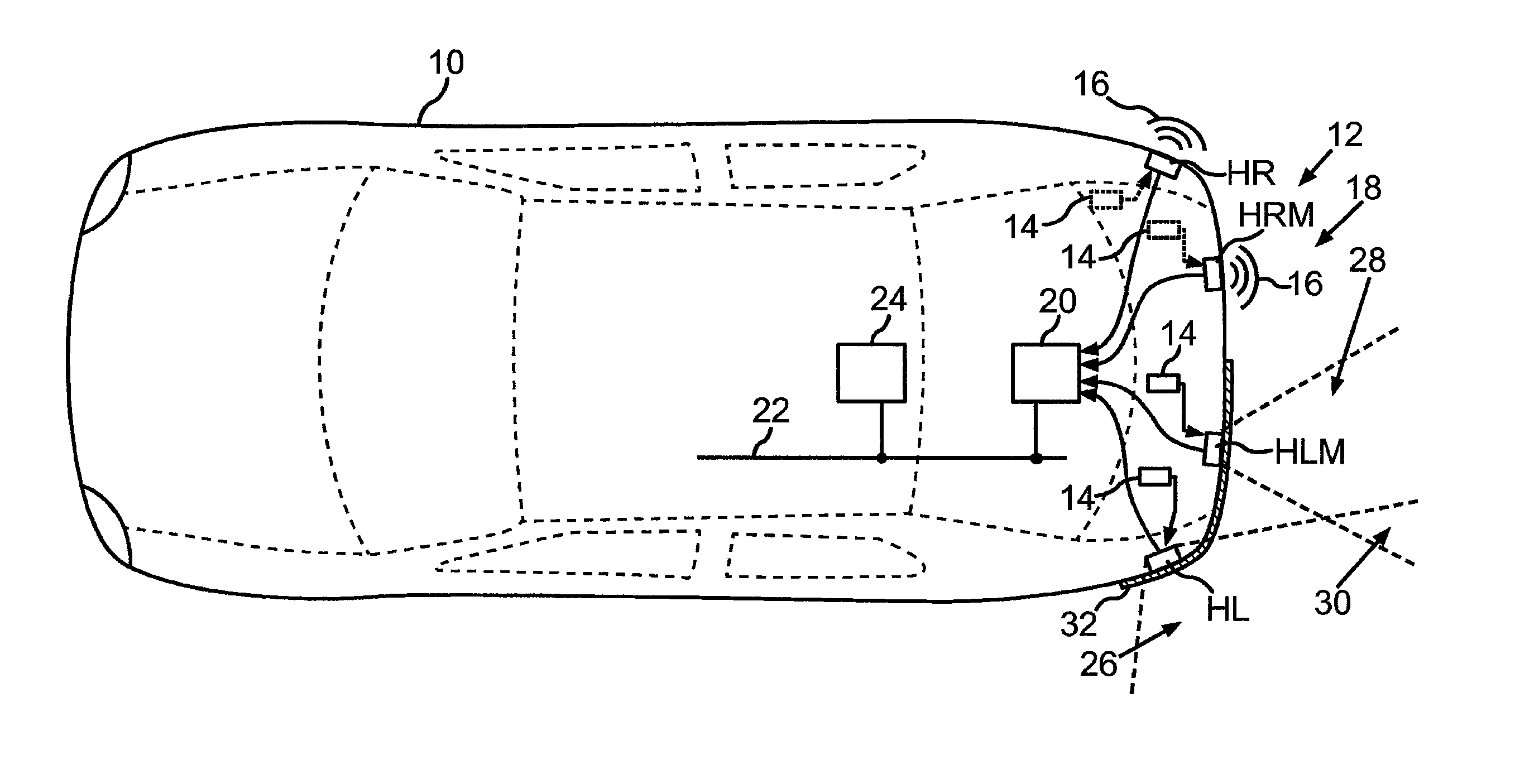
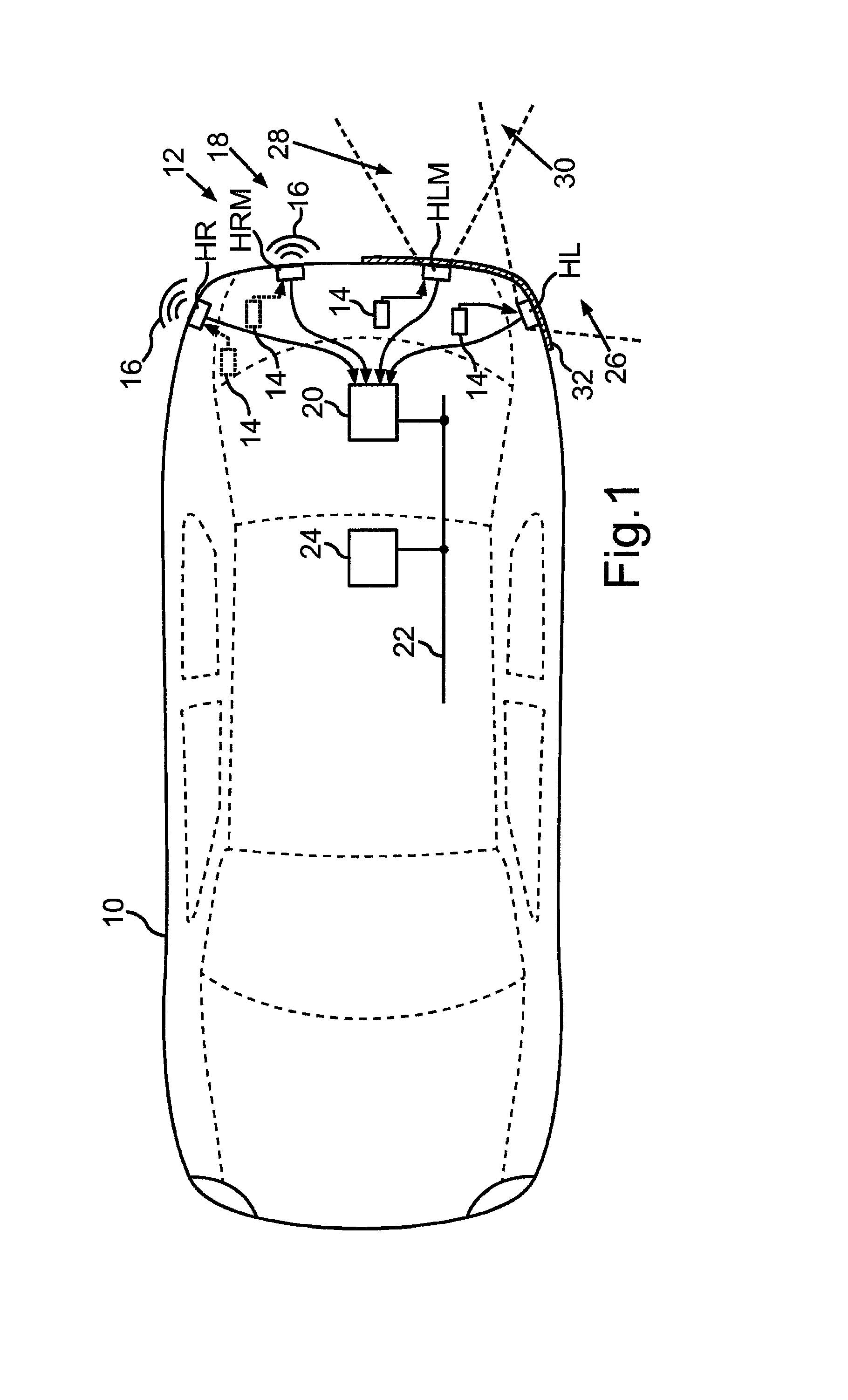
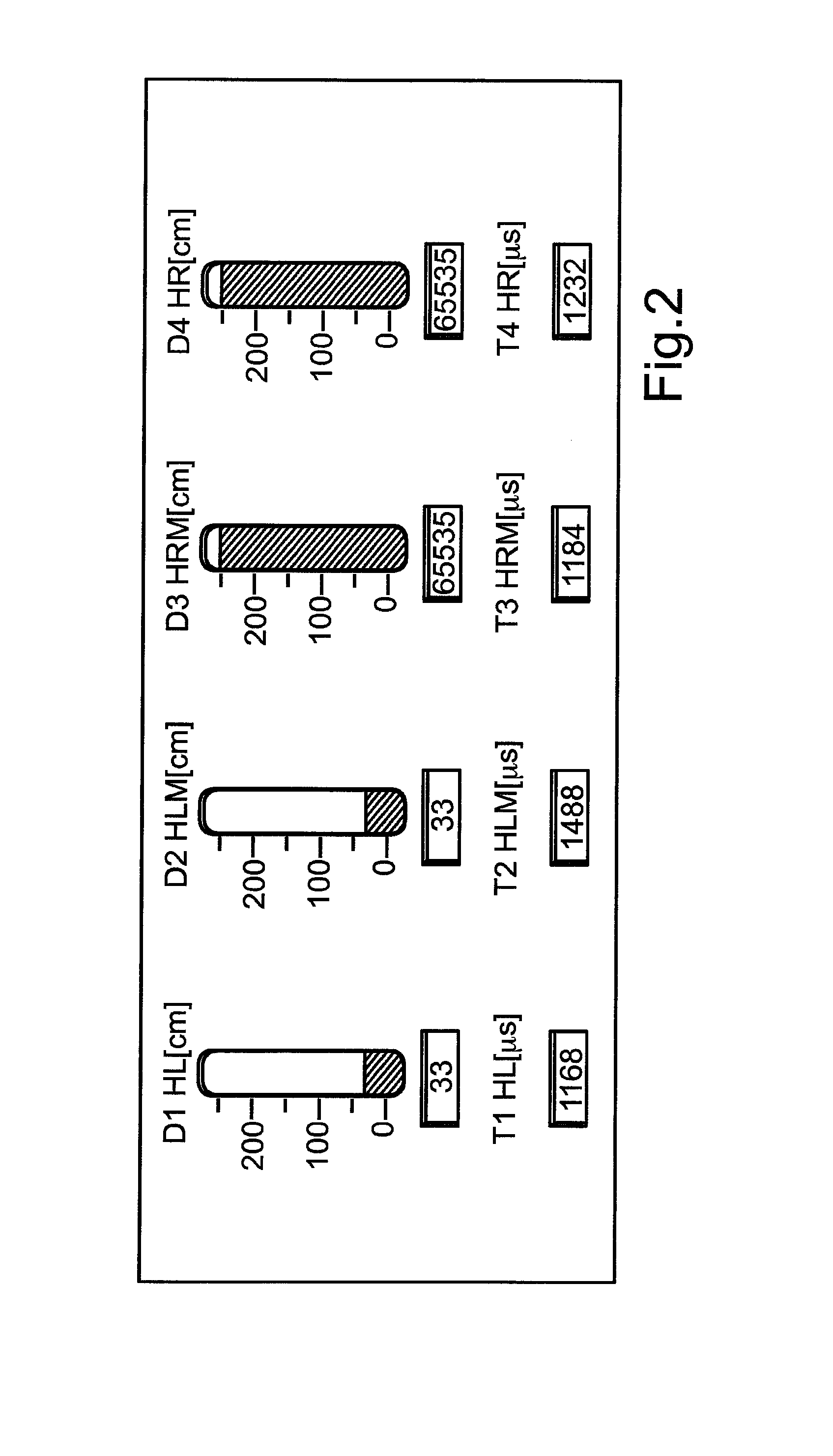
Motor Vehicle Having Occlusion Detection for Ultrasonic Sensors
ActiveUS20160291153A1Extended decay timeAvoid false activationAcoustic wave reradiationUltrasonic sensorOcclusion detection
In a method for checking a first ultrasonic sensor of a motor vehicle for an occlusion, a measuring signal of the first ultrasonic sensor is acquired by an evaluation unit, and from the measuring signal, a decay time of a natural oscillation of the diaphragm of the first ultrasonic sensor, brought about by an excitation pulse, is ascertained. From the measuring signal of either the first ultrasonic sensor or a second ultrasonic sensor, an echo produced by an object located in a sensing range of the first ultrasonic sensor is ascertained, and a distance value of the object is determined on the basis of the echo. An occlusion is signaled if the decay time is less than a predetermined threshold value which would be exceeded if ice and / or dirt were to adhere directly to the diaphragm, and if the distance value is less than a predetermined maximum value.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Travelling-wave nuclear magnetic resonance method
InactiveUS20110115486A1Convenient verificationImprove securityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceElectromagnetic electron wave
A method for acquiring an image or spectrum of a subject or object residing within the magnetic field of a magnetic resonance apparatus, comprises the steps of:executing a predetermined pulse sequence for applying gradient magnetic fields and for coupling in electromagnetic excitation pulses to induce nuclear magnetic resonance within the subject or object;detecting an electromagnetic signal resulting from said magnetic resonance; andconstructing at least one image or magnetic resonance spectrum of said subject or object from said detected electromagnetic signal.According to the invention, said coupling in of the electromagnetic excitation pulse and / or said detecting of the electromagnetic signal are carried out substantially by means of travelling electromagnetic waves.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Solid-State Quantum Memory Based on a Nuclear Spin Coupled to an Electronic Spin
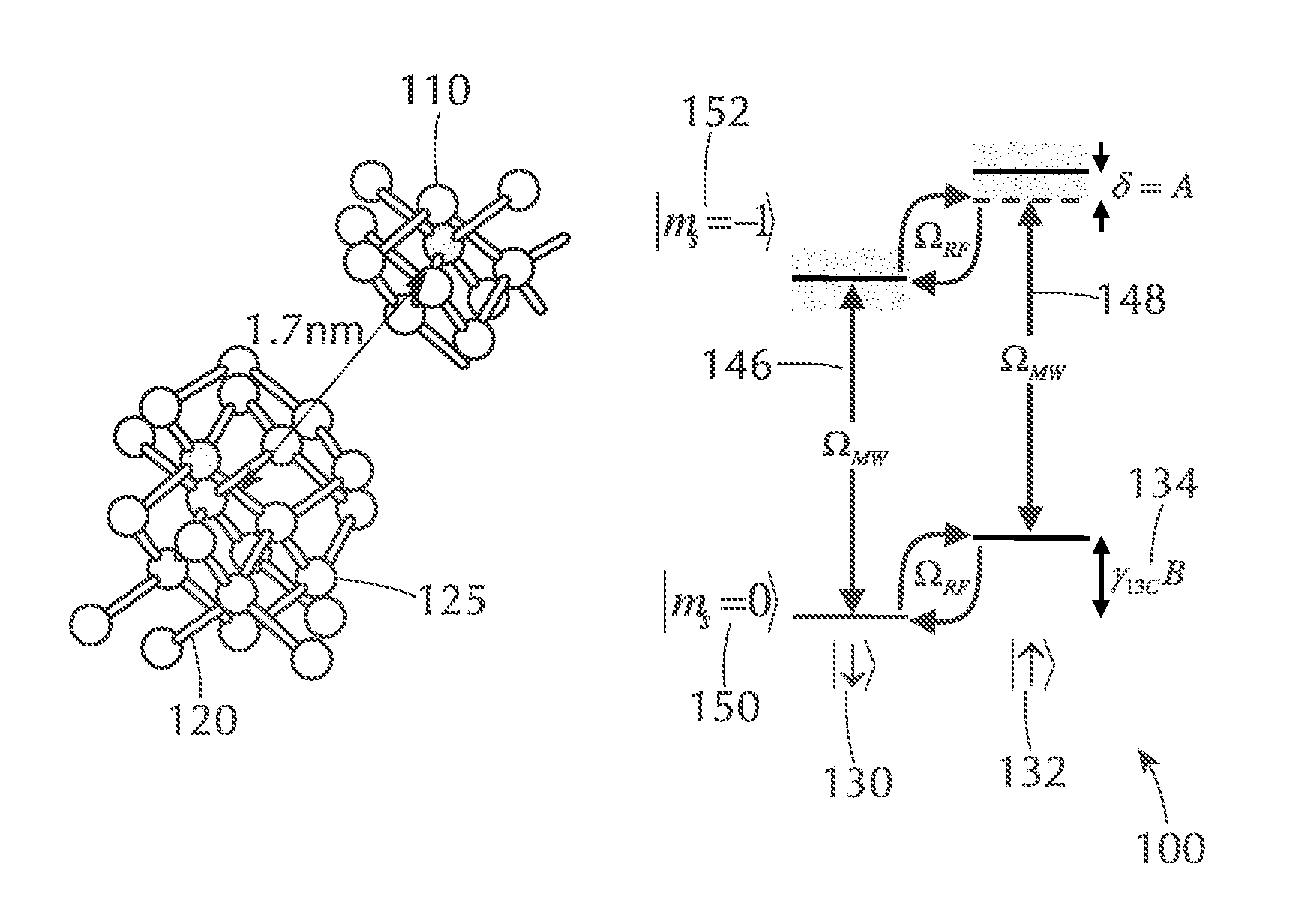
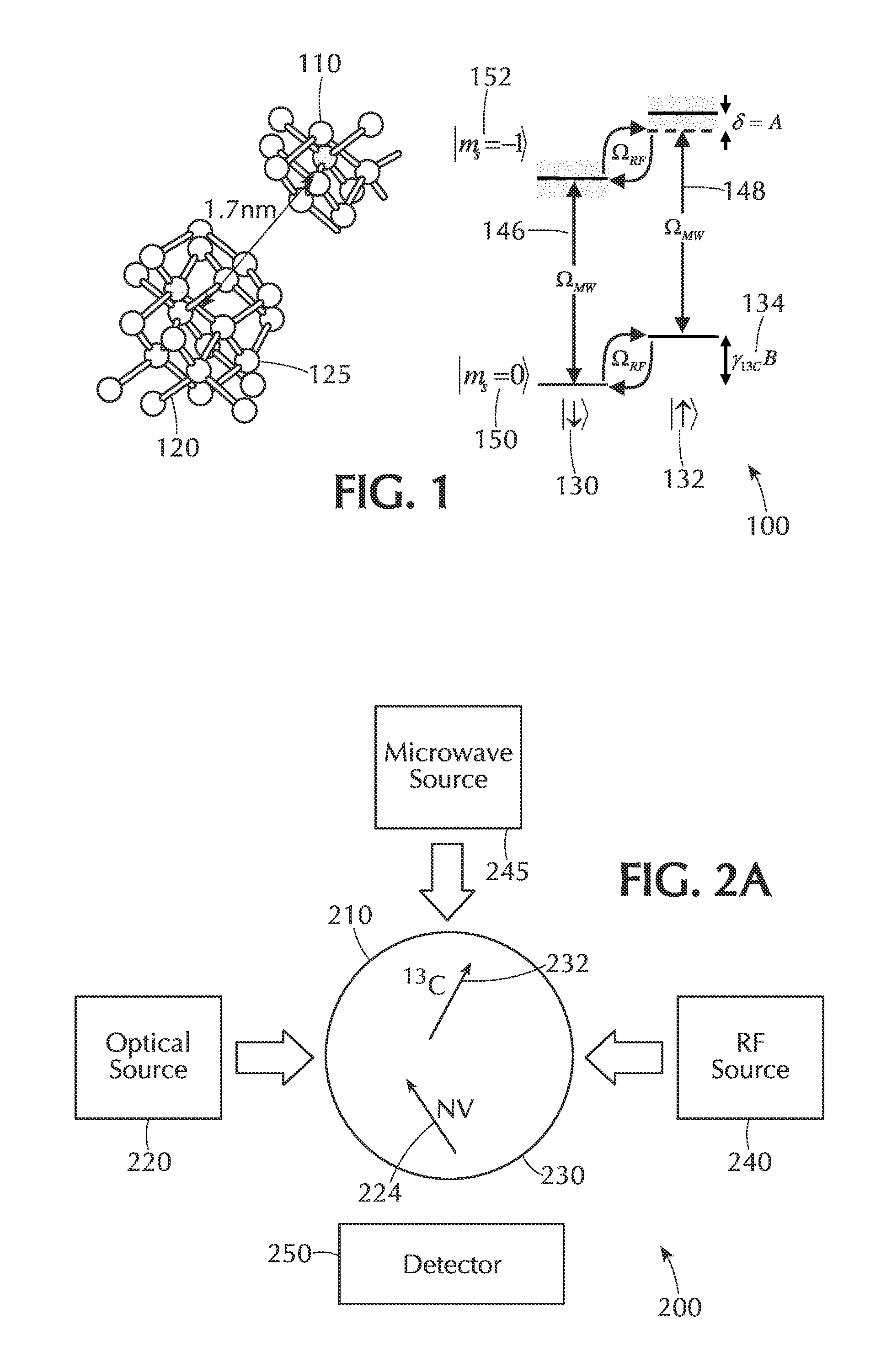
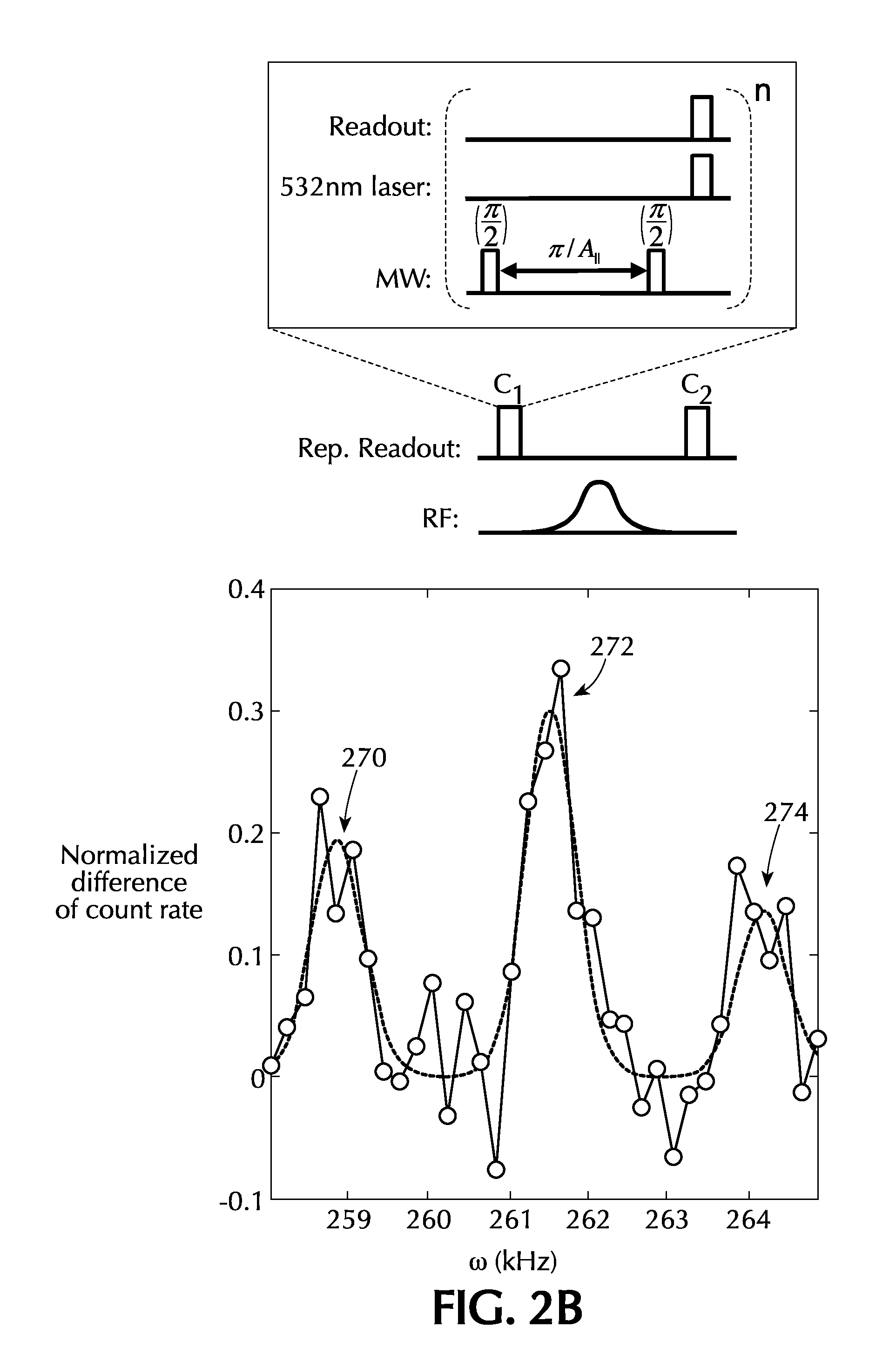
ActiveUS20150009746A1Effective decouplingHigh fidelity initializationQuantum computersNanoinformaticsOptical radiationElectronic spin
A system comprising a solid state lattice containing an electronic spin coupled to a nuclear spin; an optical excitation configuration which is arranged to generate first optical radiation to excite the electronic spin to emit output optical radiation without decoupling the electronic and nuclear spins; wherein the optical excitation configuration is further arranged to generate second optical radiation of higher power than the first optical radiation to decouple the electronic spin from the nuclear spin thereby increasing coherence time of the nuclear spin; a first pulse source configured to generate radio frequency (RF) excitation pulse sequences to manipulate the nuclear spin and to dynamically decouple the nuclear spin from one or more spin impurities in the solid state lattice so as to further increase the coherence time of the nuclear spin; a second pulse source configured to generate microwave excitation pulse sequences to manipulate the electronic spin causing a change in intensity of the output optical radiation correlated with the electronic spin and with the nuclear spin via the coupling between the electronic spin and the nuclear spin; and a detector configured to detect the output optical radiation correlated with the electronic spin and the nuclear spin so as to detect a nuclear spin state of the nuclear spin.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
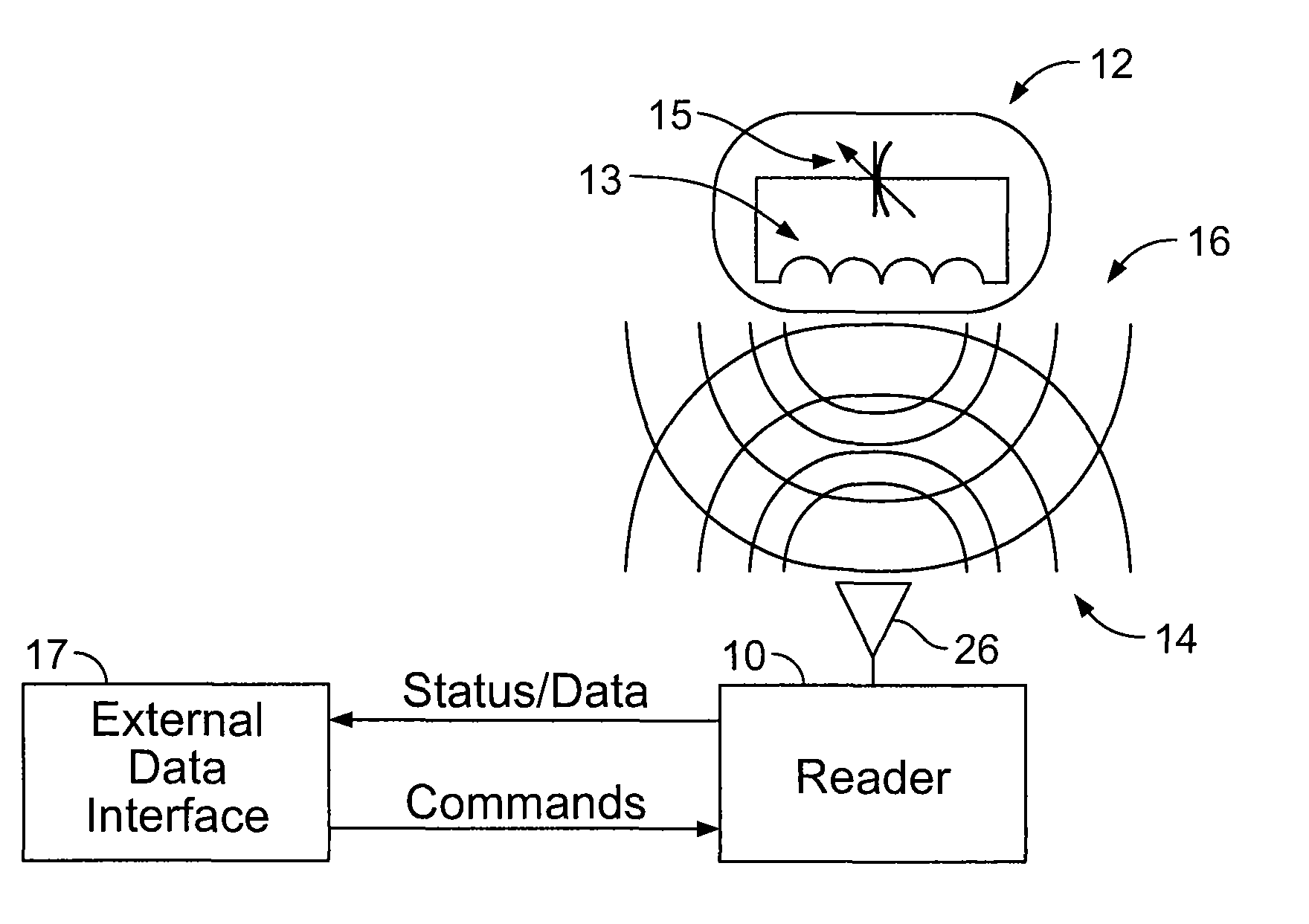
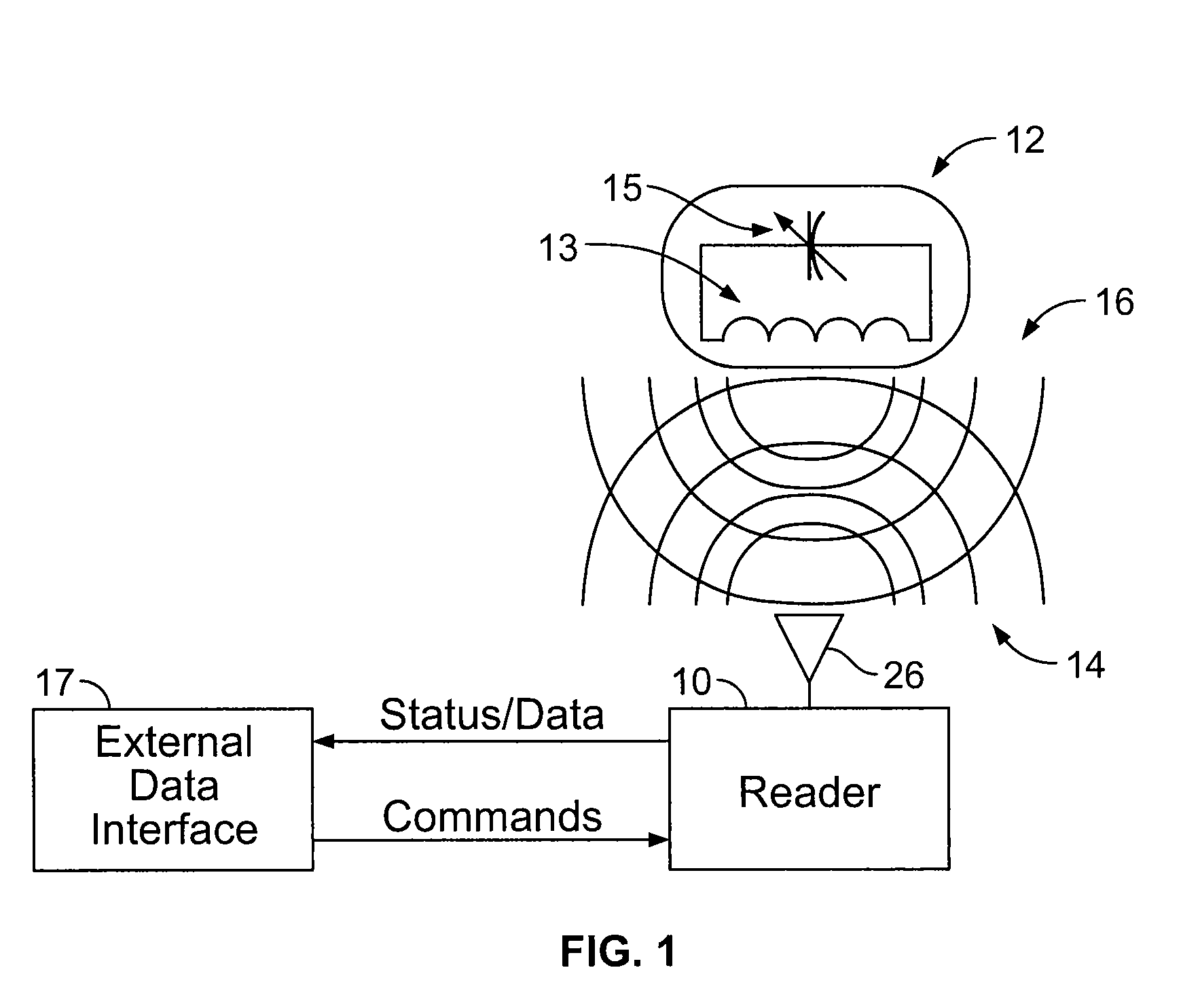
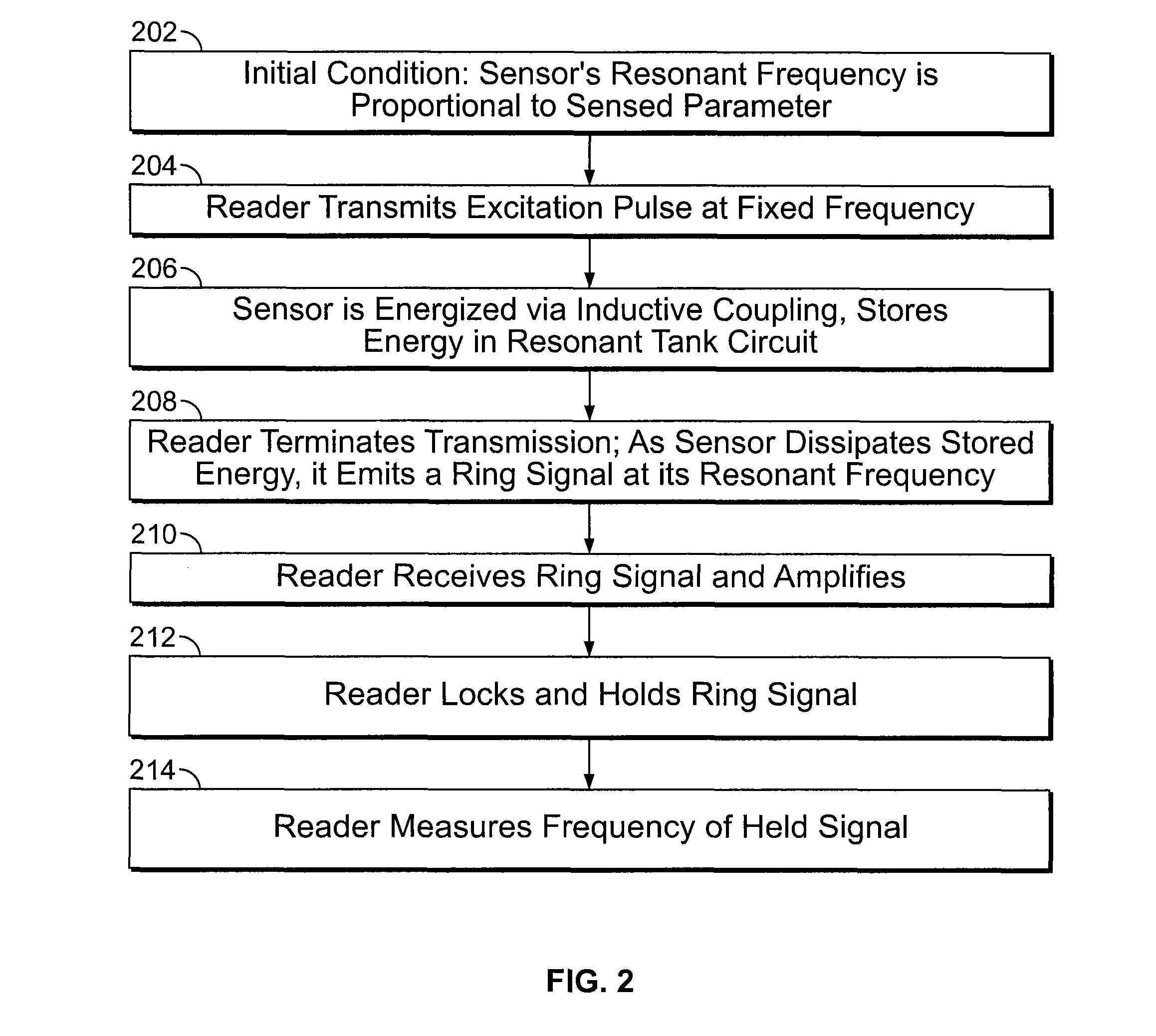
Wireless sensor reader
ActiveUS8493187B2Electric signal transmission systemsInertial sensorsFrequency determinationAlternative methods
A wireless sensor reader is provided to interface with a wireless sensor. The wireless sensor reader transmits a narrowband, fixed frequency excitation pulse to cause the wireless sensor to generate a ring signal. The ring signal corresponds to the value of the physical parameter being sensed. The wireless sensor reader receives and amplifies the ring signal and sends the signal to a phase-locked loop. A voltage-controlled oscillator in the phase-locked loop locks onto the ring signal frequency and generates a count signal at a frequency related to the ring signal frequency. The voltage-controlled oscillator is placed into a hold mode where the control voltage is maintained constant to allow the count signal frequency to be determined. The low power, simple circuitry required to generate the excitation pulse allows the reader to be a small, battery operated unit. Alternative methods of frequency determination are also disclosed.
Owner:ENDOTRONIX
Method, device and security system, all for authenticating a marking
InactiveUS7067824B2Guaranteed high speed operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioPaper-money testing devicesPhotometrySecurity systemAtomic physics
A luminescent probe marking is excited with at least one excitation pulse of at least one excitation source. The probe intensity values of emission intensity from emission radiation of the luminescent probe marking are measured in response to the excitation pulse(s) at time intervals. A probe intensity-versus-time emission function is formed of the probe intensity values, and the probe intensity-versus-time emission function is compared with at least one reference intensity-versus-time emission function after the probe intensity-versus-time emission function and the reference intensity-versus-time emission function have been normalized.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
Reduction of motion artifacts in NMR
ActiveUS20050248342A1Different sensitivityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic fluxMotion artifacts
NMR spin echo signals, acquired on a MWD logging tool, are susceptible to errors magnetic flux density has a gradient and the magnet on the logging tool is moving relative to the earth. The errors can be corrected by having the excitation pulse cover a smaller or a larger volume than the refocusing pulses. Correction may also be made by selective saturation, or by echo averaging.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Oil tank cleaning robot
InactiveCN102764750ARealize all-round cleaningCompact structureHollow article cleaningDrive wheelUltrasonic sensor
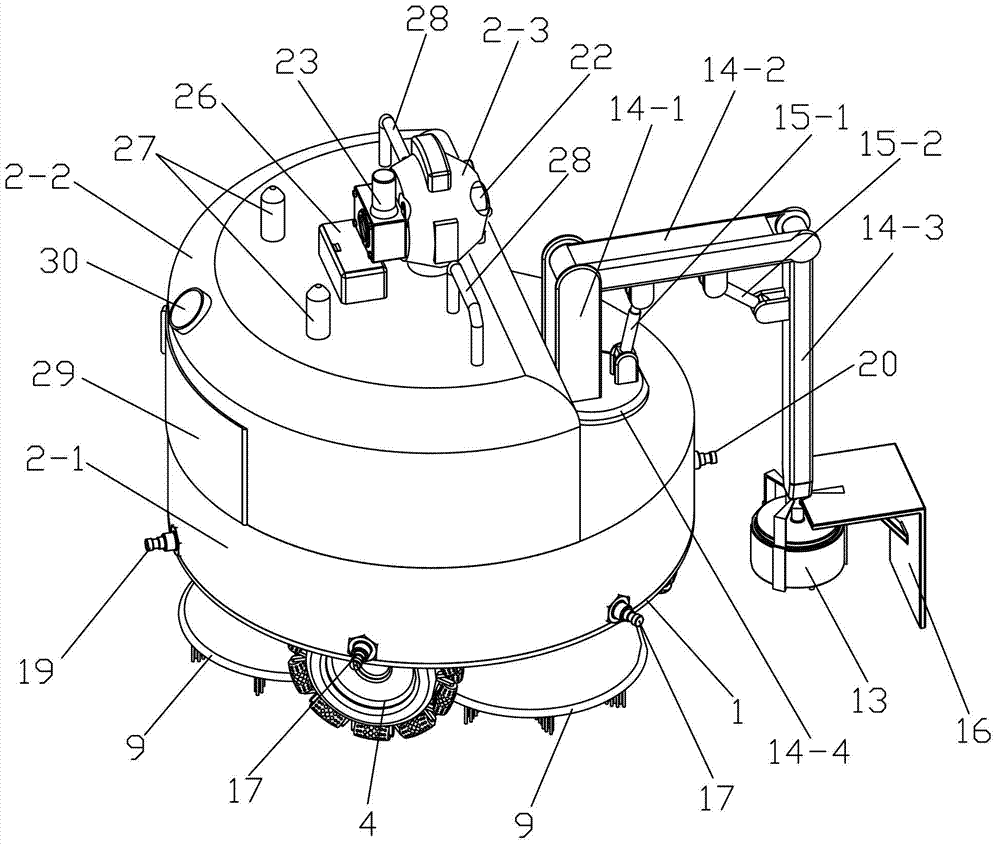
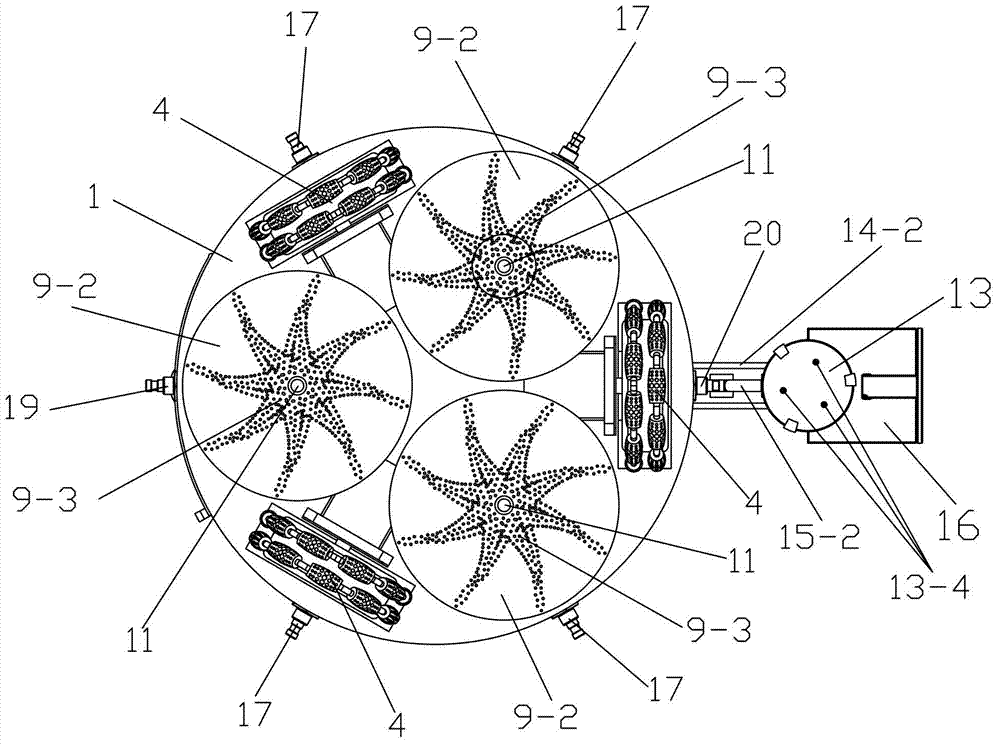
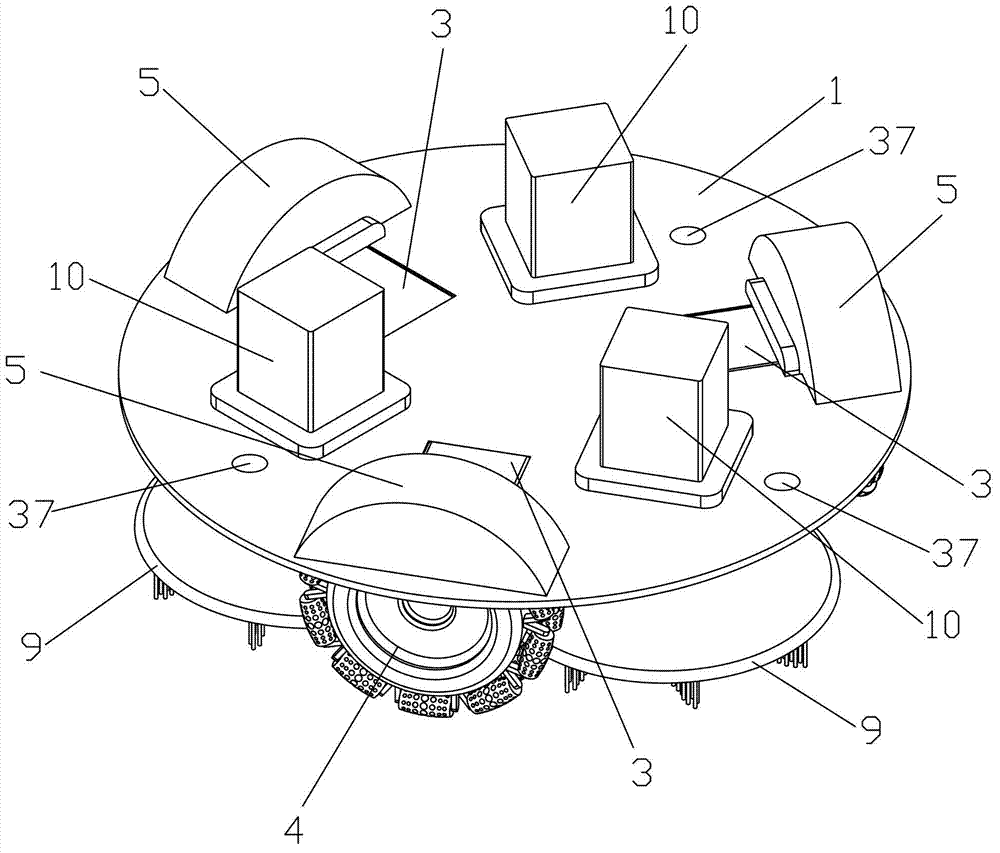
The invention discloses an oil tank cleaning robot. The robot comprises a robot body, a walking unit, a cleaning unit, a control unit, a sensing communication unit and a power supply unit, wherein the robot body comprises a base plate, a lower casing and an upper casing, the walking unit comprises three driving wheels and three driving wheel hydraulic motors, the cleaning unit comprises a cleaning device and a self-excitation pulse device, the cleaning device comprises three cleaning disk brushes and three cleaning disk brush hydraulic motors, the self-excitation pulse device comprises a pulse device hydraulic motor, a retractable beam assembly and a self-excitation oscillating pulse nozzle, the control unit is composed of a remote control portion and a robot body control portion, and the sensing communication unit comprises a pressure sensor, a temperature sensor, an infrared sensor, an ultrasonic sensor, a horizontal attitude sensor, a turbidity sensor, a camera and an oil-gas concentration monitor. The robot is novel in design, high in intelligent degree, high in working reliability, good in safety performance, energy-saving, environment-friendly, high in practicability, high in popularization and application value and capable of achieving omni-directional cleaning.
Owner:周利坤
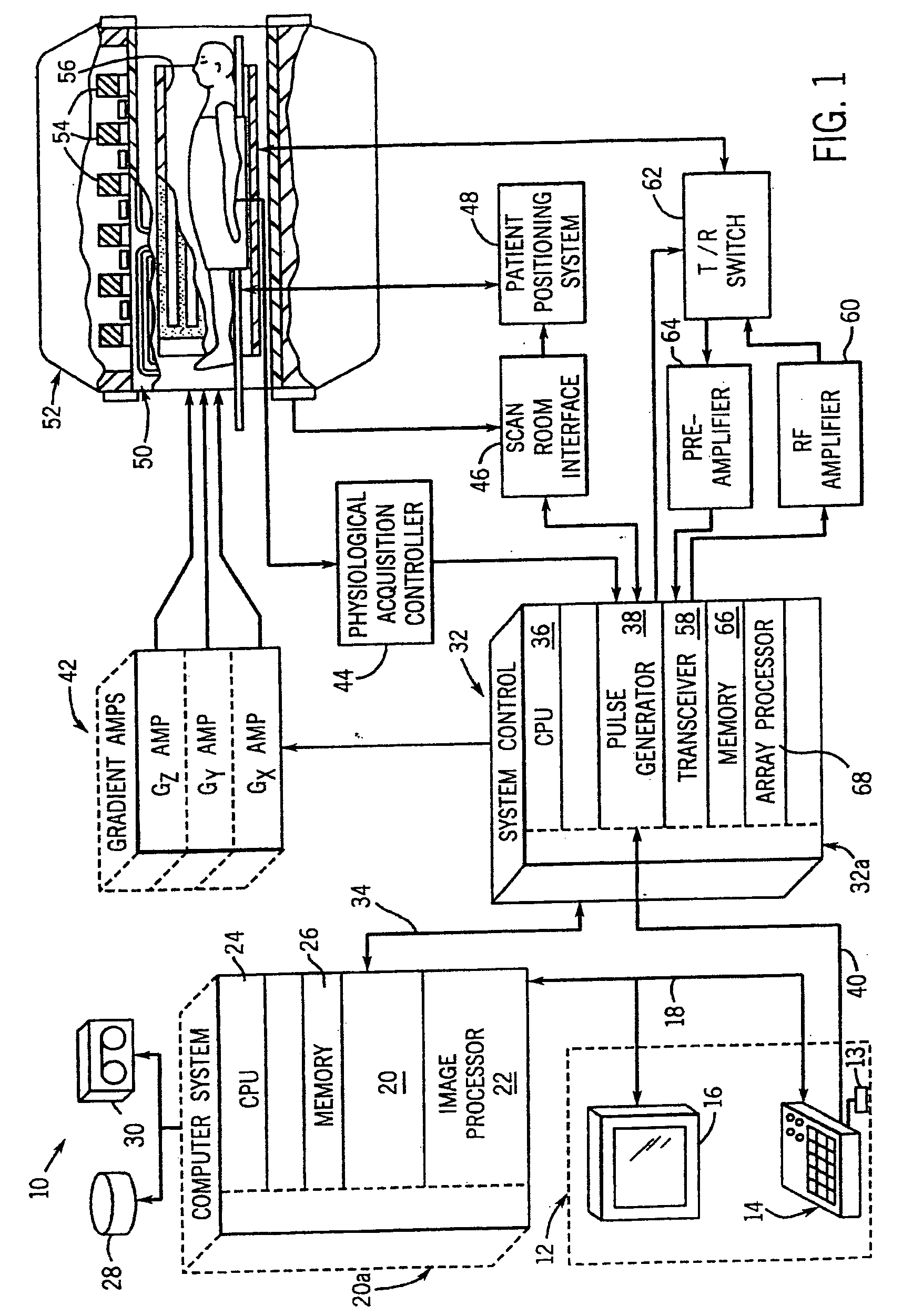
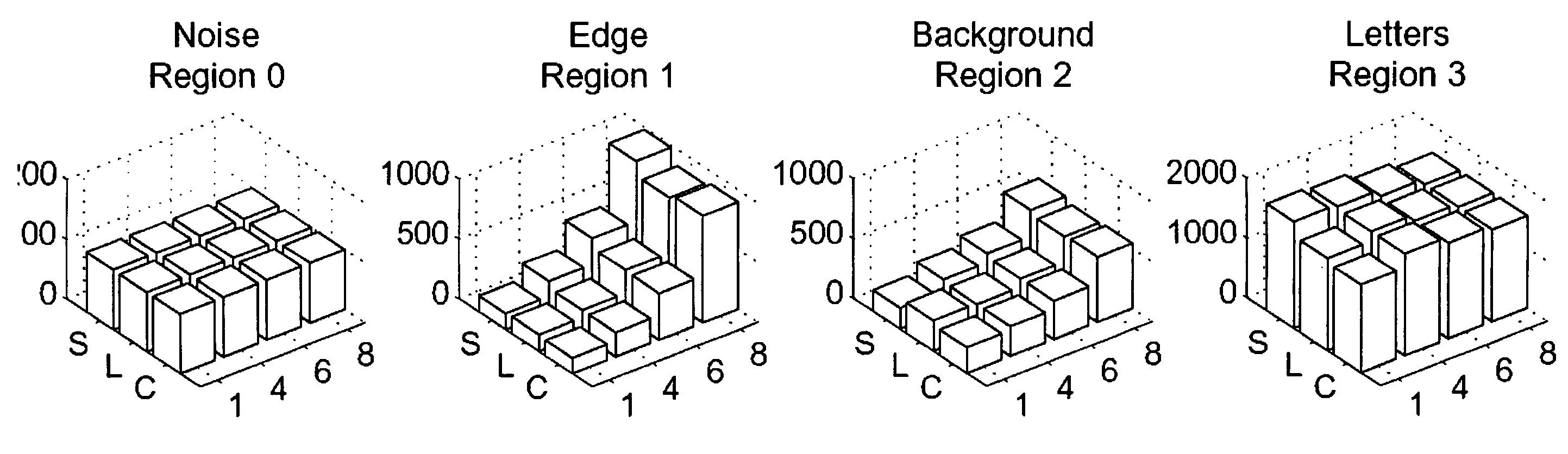
Method and apparatus to generate an RF excitation consistent with a desired excitation profile using a transmit coil array
ActiveUS20050110488A1Easy to manageFaithful productionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAudio power amplifierCoil array
A system composed of multiple transmit coils with corresponding RF pulse synthesizers and amplifiers is disclosed. A method of designing RF pulses specific to each transmit coil to induce spatiotemporal variations in a composite B1 field is also disclosed. The present invention supports faithful production of desired excitation profiles and accommodates the use of any coil array geometry. The present invention also supports reduction in excitation pulse length. Through effective B1 field maps for each transmit coil, mutual coupling and other inter-coil correlations are accounted for in the RF pulse design.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and control device to operate a magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS20130249548A1Reduce examination duration of SAR-limitedHigh resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceTomography
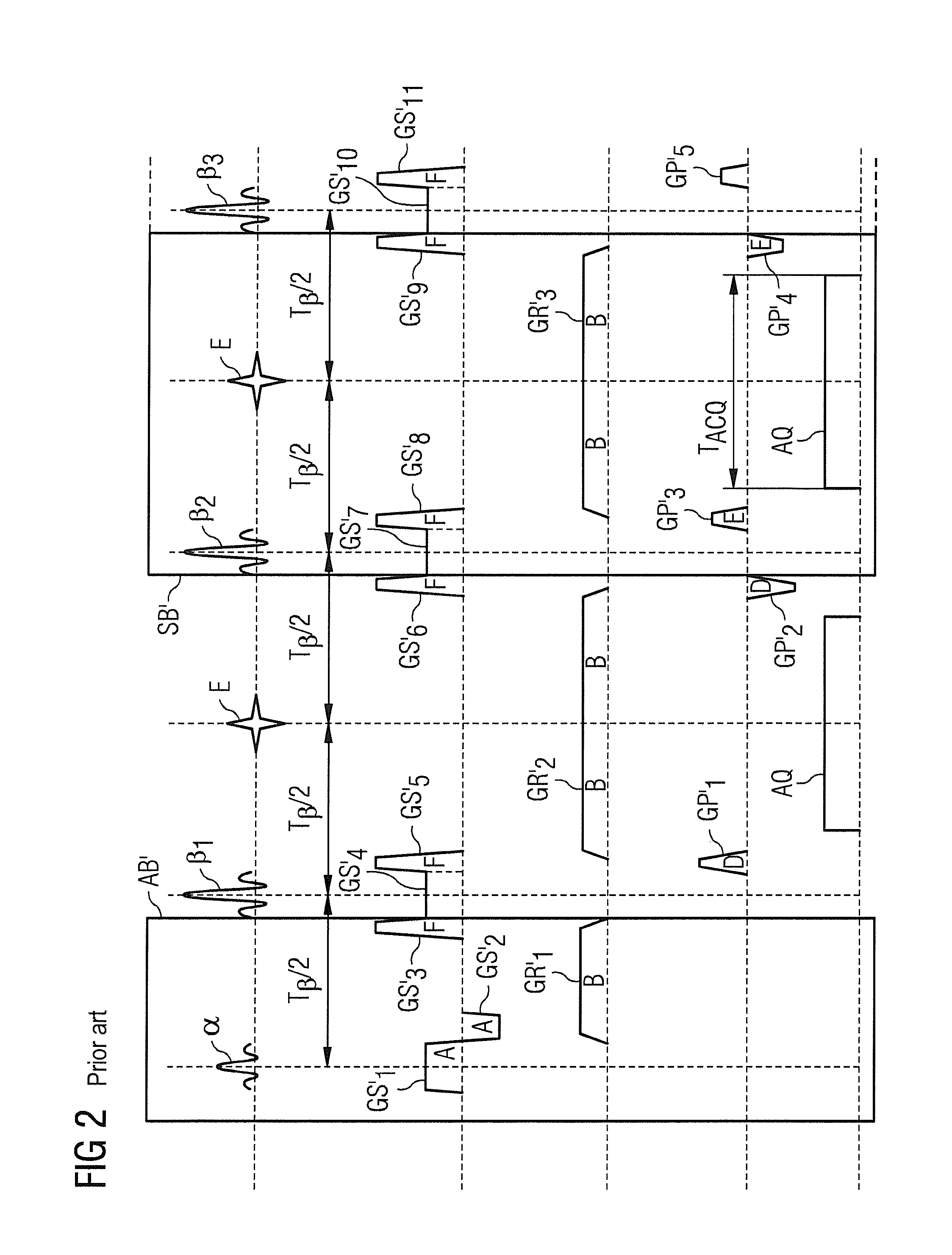
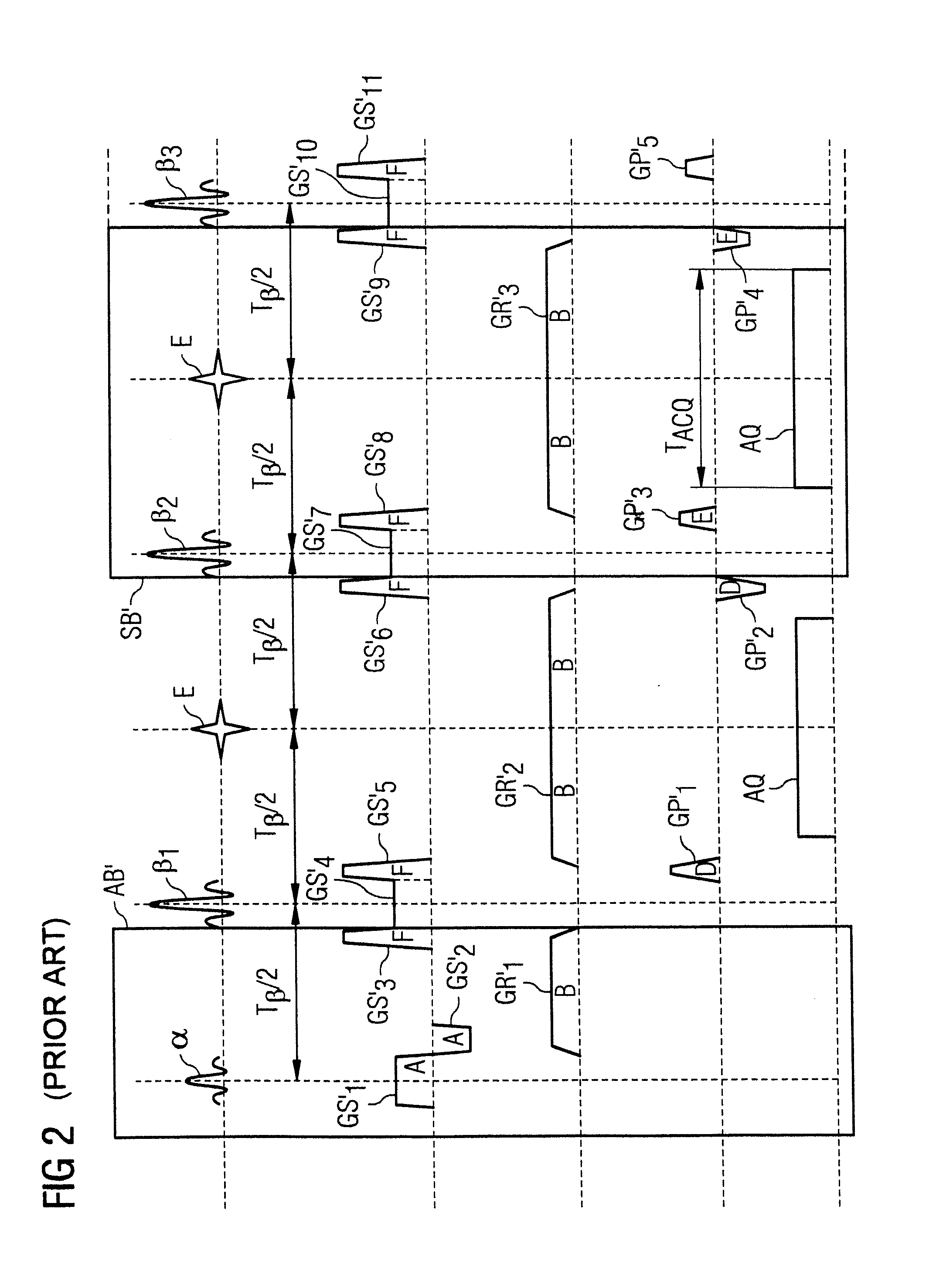
In a method and a control device for operation of a magnetic resonance tomography system to generate image data, multiple of slices in an examination subject are initially excited at a first time interval by a respective RF slice excitation pulse of a series of spatially selective slice excitation pulses. An RF refocusing pulse is then emitted at a second time interval after the first excitation pulse or after the last excitation pulse of the series of RF slice excitation pulses. At least one additional RF refocusing pulse is emitted at a third time interval after a preceding RF refocusing pulse. The third time interval is twice as long as the second time interval. The width of the RF refocusing pulses is selected to generate a number of chronologically separate echo signals per RF refocusing pulse for simultaneous refocusing of all excited slices.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and control device for operating a magnetic resonance system
ActiveUS20140210471A1Reduce decreaseEliminate the problemMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceEcho signal
In a method and a control device for operating a magnetic resonance imaging system, initially, in a sequence module, multiple slices are excited in an examination object by respective spatially selective RF slice excitation pulses whereby the time between two consecutive of these RF slice excitation pulses defines a first time interval. A preparation block follows the last excitation pulse. The preparation bloc radiates at least one RF refocusing pulse designed so that, for each of the slices, one echo signal is formed. The time interval between two consecutive echo signals is equal to the first time interval. Then, a second RF refocusing pulse is emitted at a second time interval after the last echo signal formed by the preparation block. The second RF refocusing pulse is designed so that, for each of the slices, one further echo signal is formed, and the time interval of two consecutive echo signals is equal to the first time interval. Subsequently, at least one further RF refocusing pulse is emitted at a third time interval after the preceding RF refocusing pulse for producing a number of temporally separated echo signals per refocusing pulse. The third time interval is selected so that the number of echo signals per RF refocusing pulse is twice as high as the number of excited slices.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
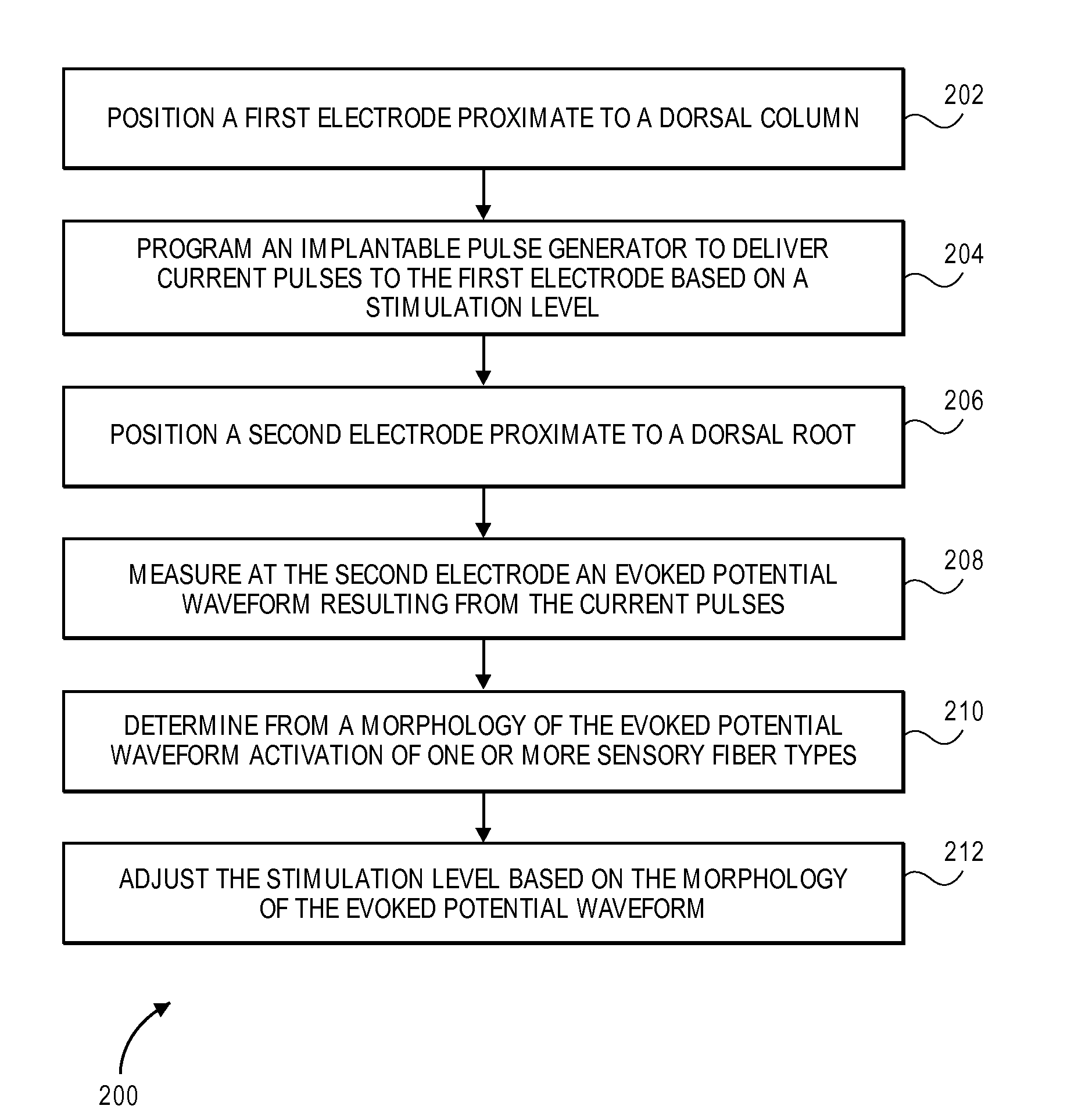
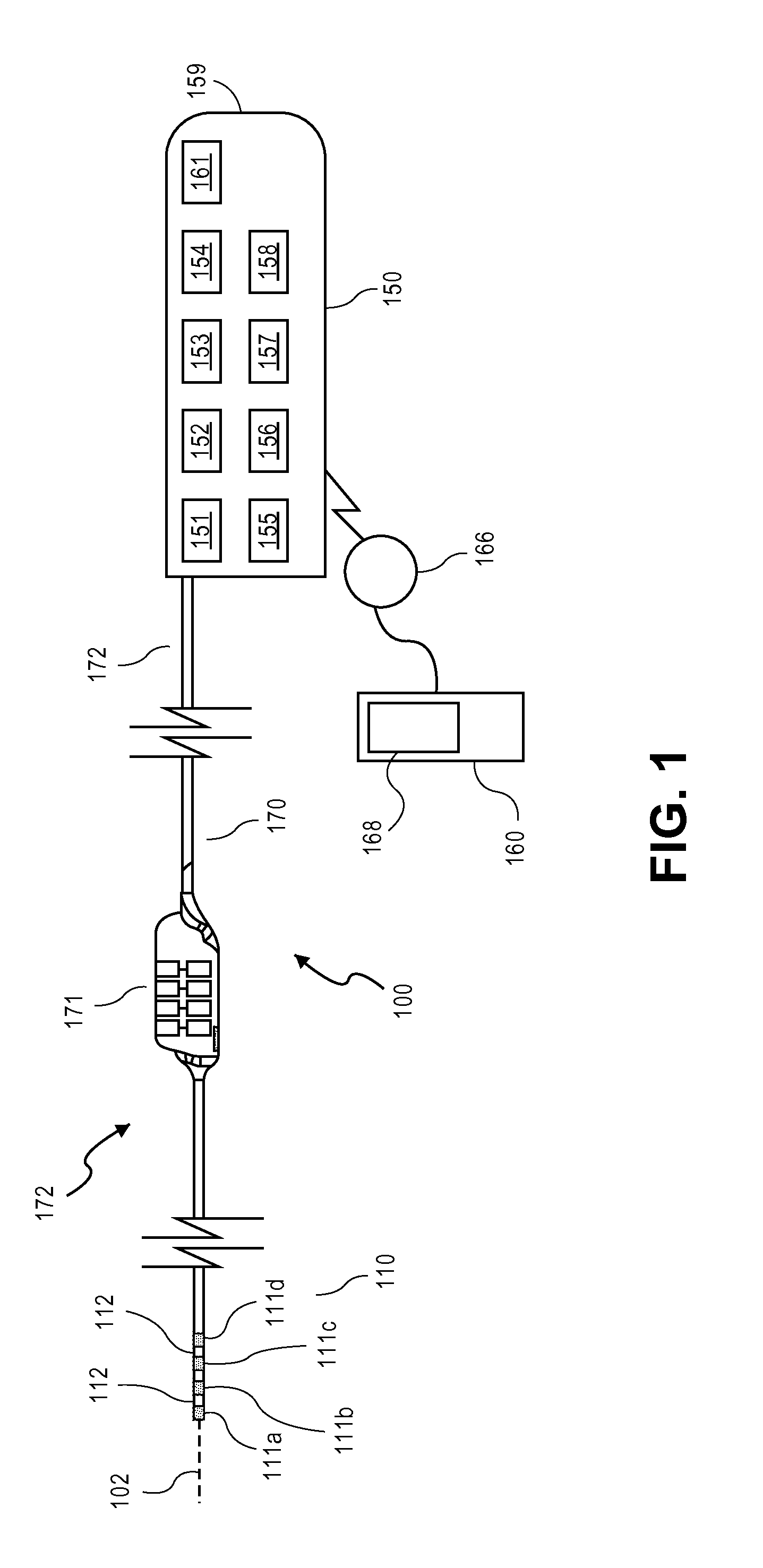
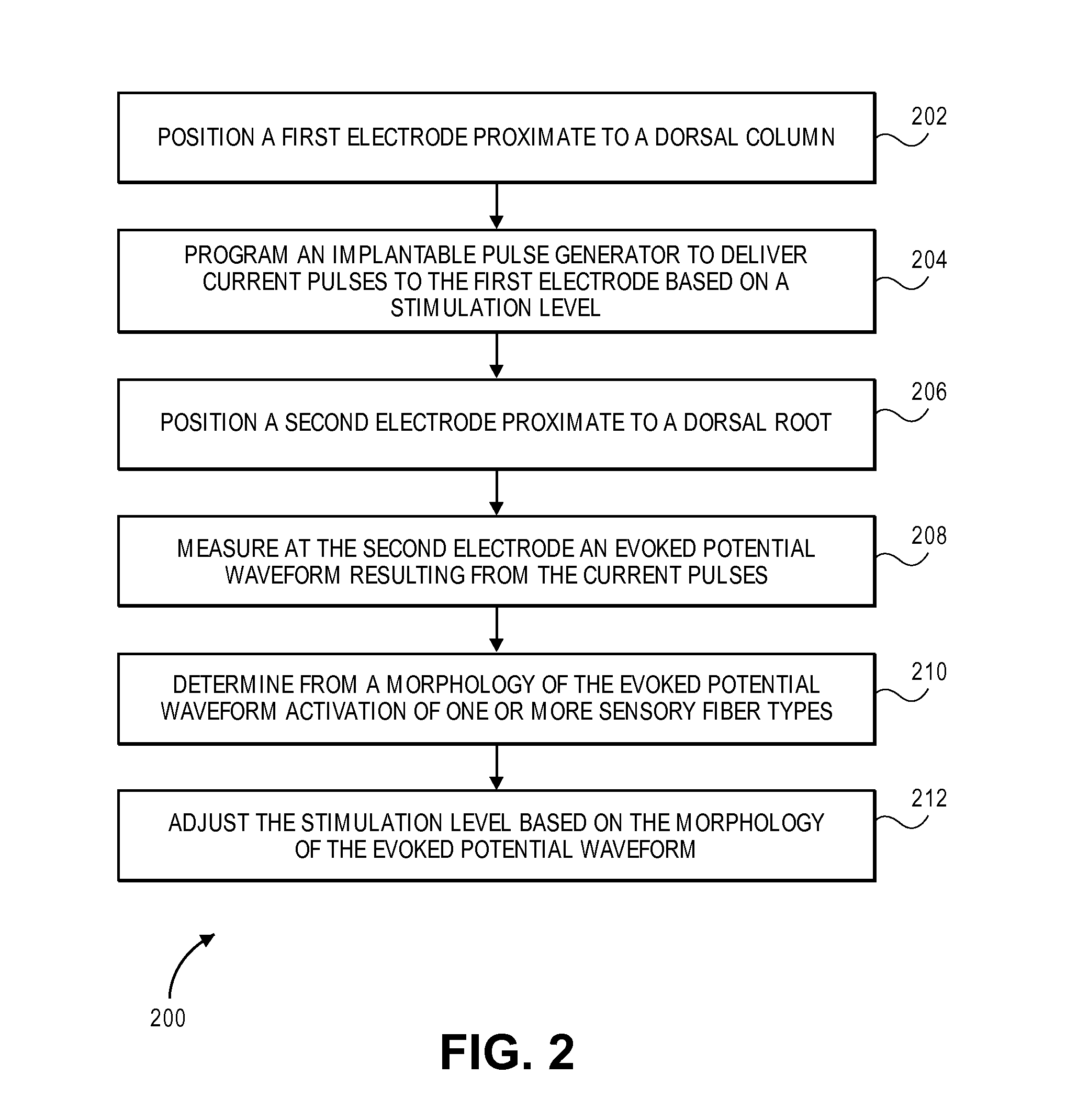
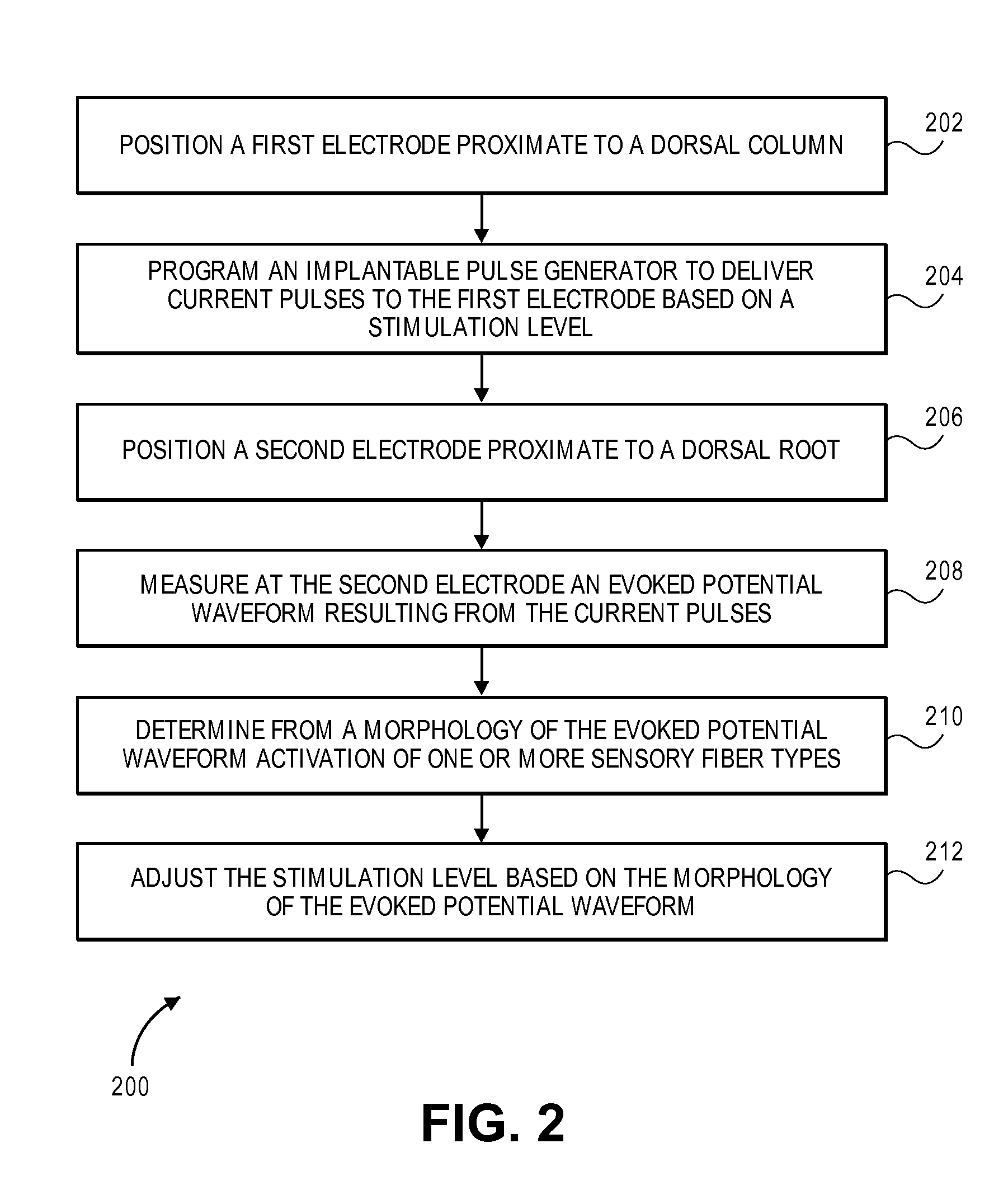
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
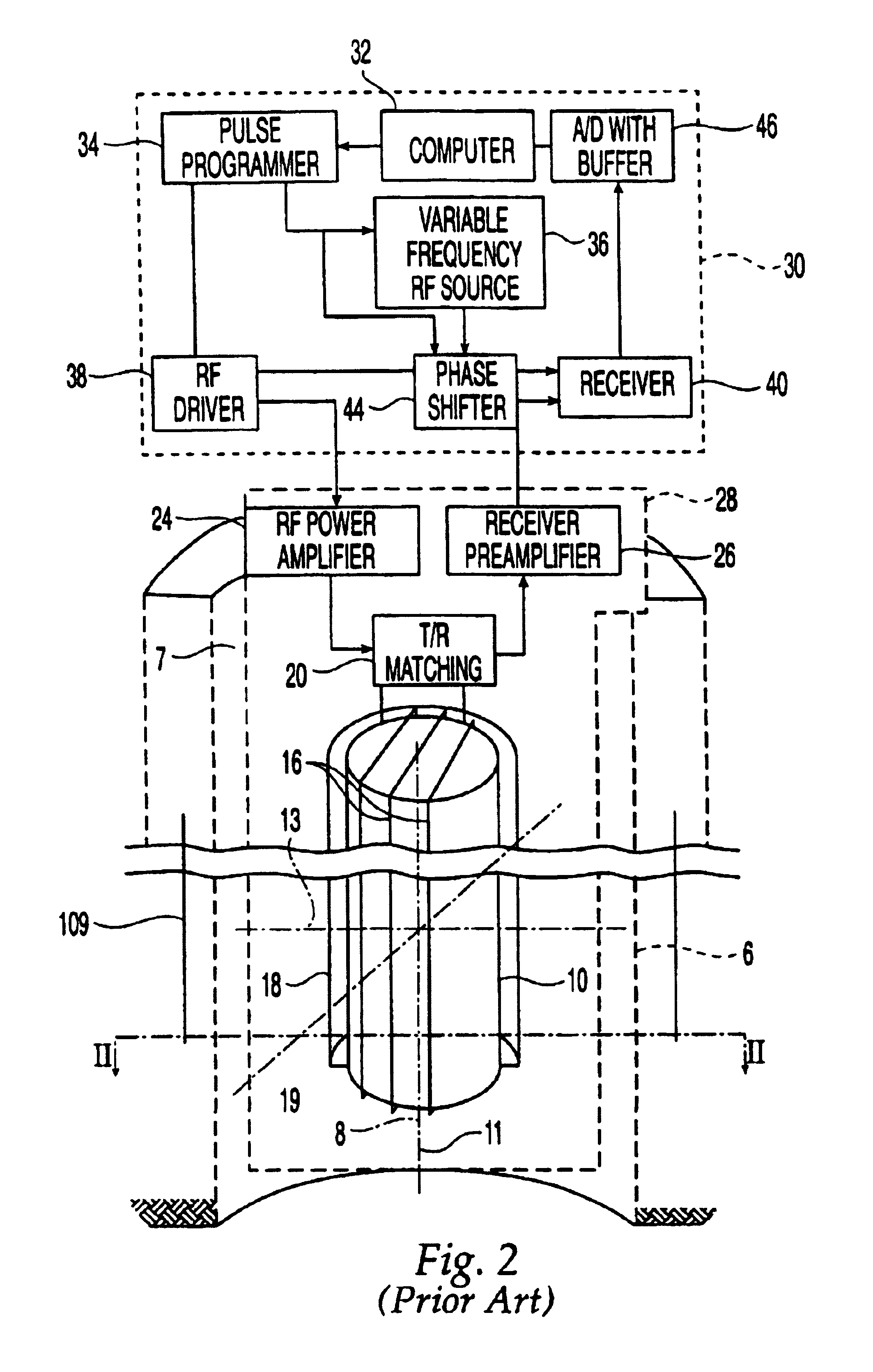
Method and apparatus for detecting diffusion sensitive phases with estimation of residual error in NMR logs
InactiveUS6956371B2High resolutionSuppress artifactsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingDiffusionRecovery period
A method and system are disclosed for NMR echo-train data acquisition and processing for enhanced tracking of the error in the signal due to magnetoacoustic effects, known as ringing, that are not cancelled out or otherwise corrected. In one aspect, the method enables correction of ringing signals in a single pass by way of collecting a composite signal that includes echoes due to pulses at least at two different frequencies. The choice of one or more of the frequencies, the phase of the pulses, and the recovery period enable cancellation of the ringing signal from the echoes, including the echo from an excitation pulse. In another aspect, the method encompasses providing protection against errors due to tool motion by saturating a relatively wide sensitive region with the echo signals collected from within this relatively wide sensitive signal. Preferred embodiments of the invention include one or more of the aforementioned aspects.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
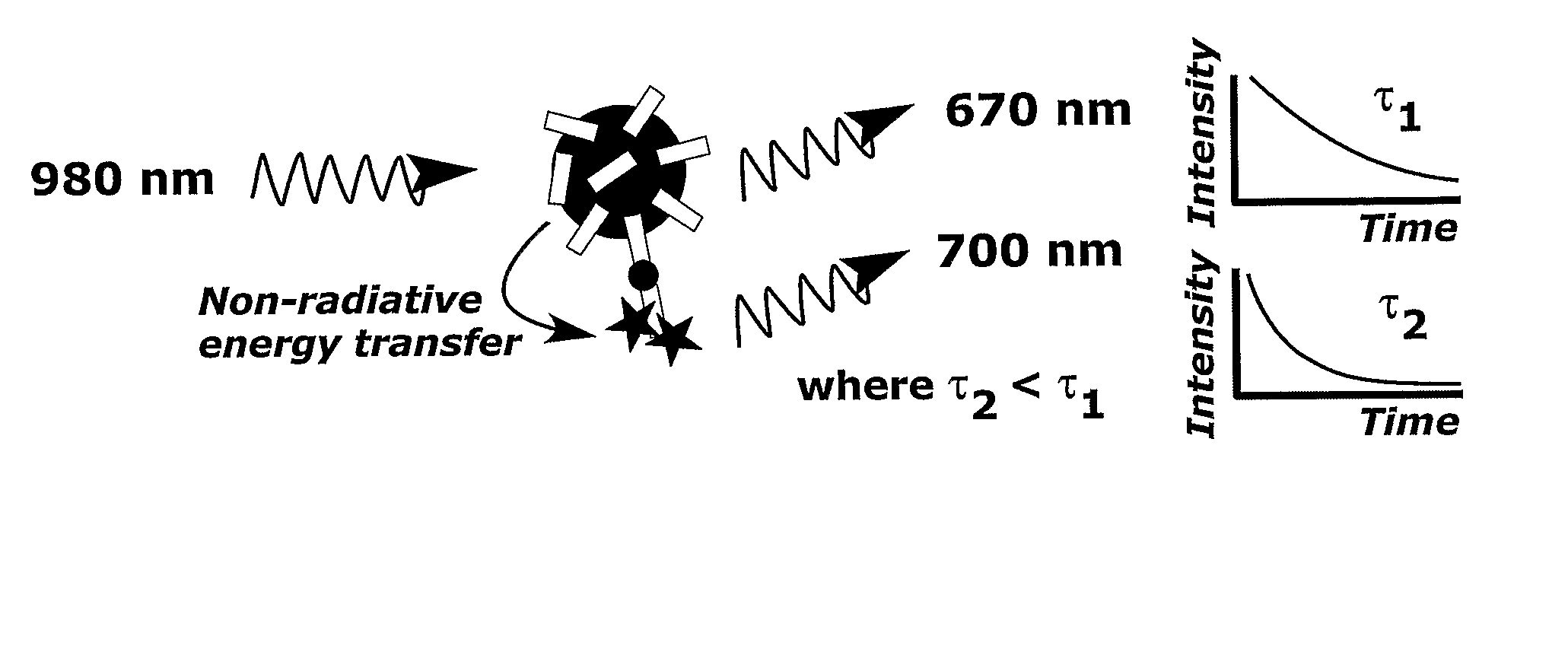
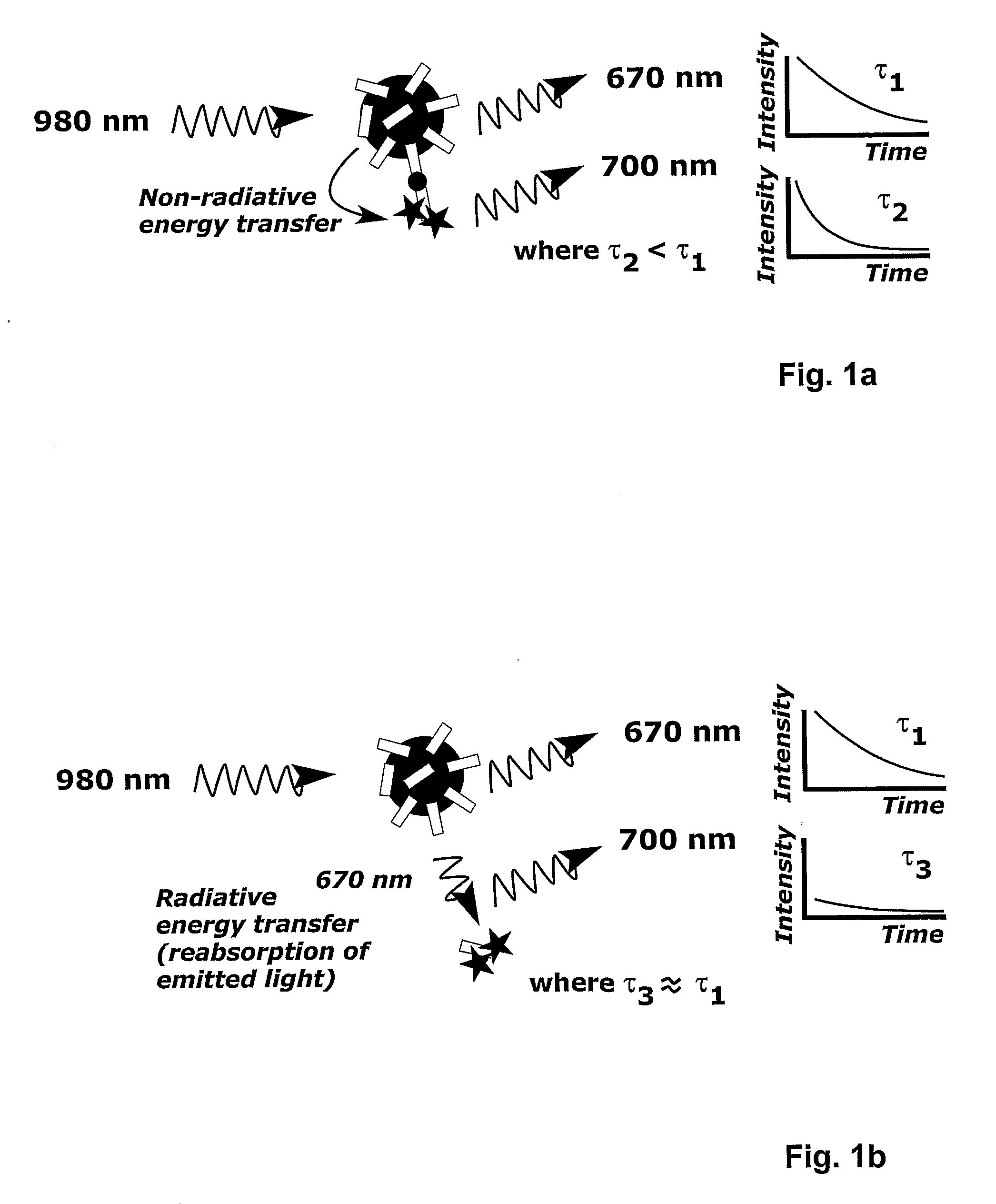
Correction Method and Measurement Device For Anti-Stokes Photoluminescence Measurement
This invention relates to a method to correct for error in an anti-Stokes photoluminescence measurement in a Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay. The method comprises the steps of exciting anti-Stokes photoluminescent molecules, ions, phosphors, chelates, or particles, i.e. donors of the assay, with one wavelength or multiple wavelengths of light wherein the wavelength or wavelengths are greater than that of an emission wavelength of acceptor molecules in the assay; measuring emission light signal at a wavelength, which is the emission wavelength of the acceptor molecules in the Foerster-type resonance energy-transfer assay, and which differs from the emission wavelength of the anti-Stokes photoluminescent donor in at least two different time windows; a first time window within the time window defined by the excitation light pulse, i.e. within the time window opening when the excitation light pulse is switched on and closing when the excitation light pulse is switched off, and a second time window to follow the first time window not at all overlapping with the time window defined by the excitation pulse; and correcting the emission light signal measured, comprising signals originating from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer, within the first time window by estimating the ratio of the signals from non-radiative and radiative energy transfer or the signal originating from radiative energy transfer using at least one emission light signal measured in the second time window. This invention also relates to the use of a device according to the method of the invention, a system for carrying out the method and a software product for the system.
Owner:HIDEX
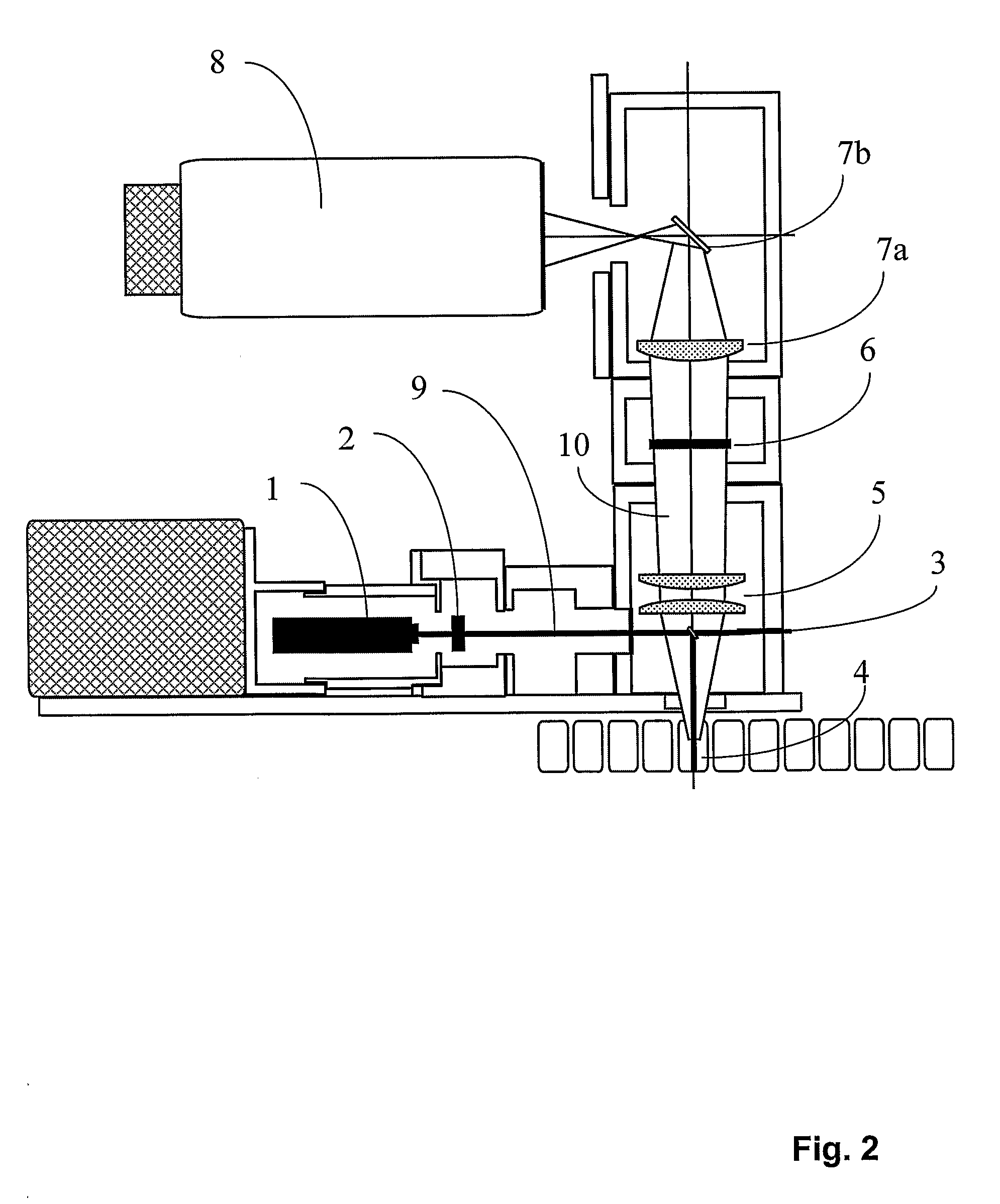
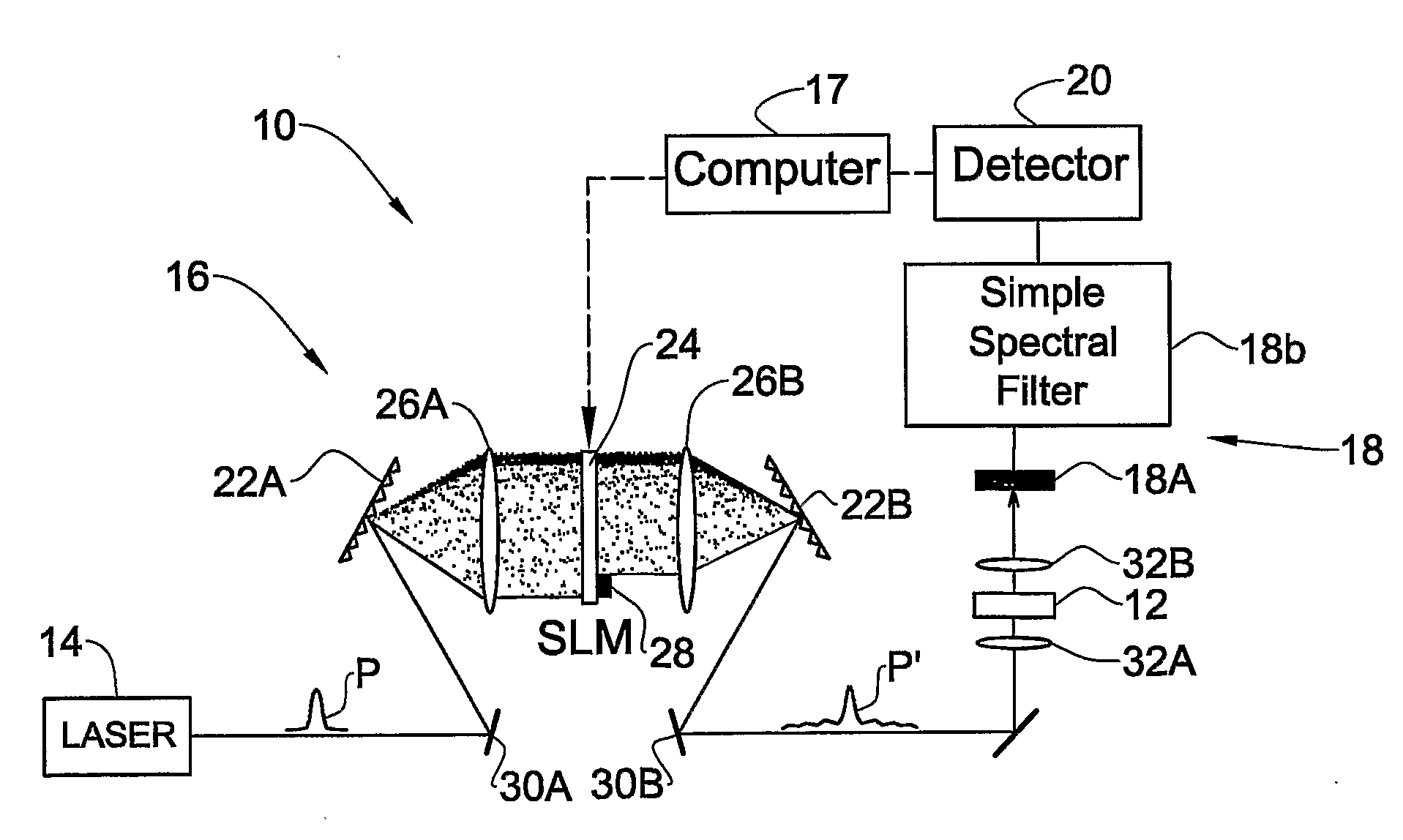
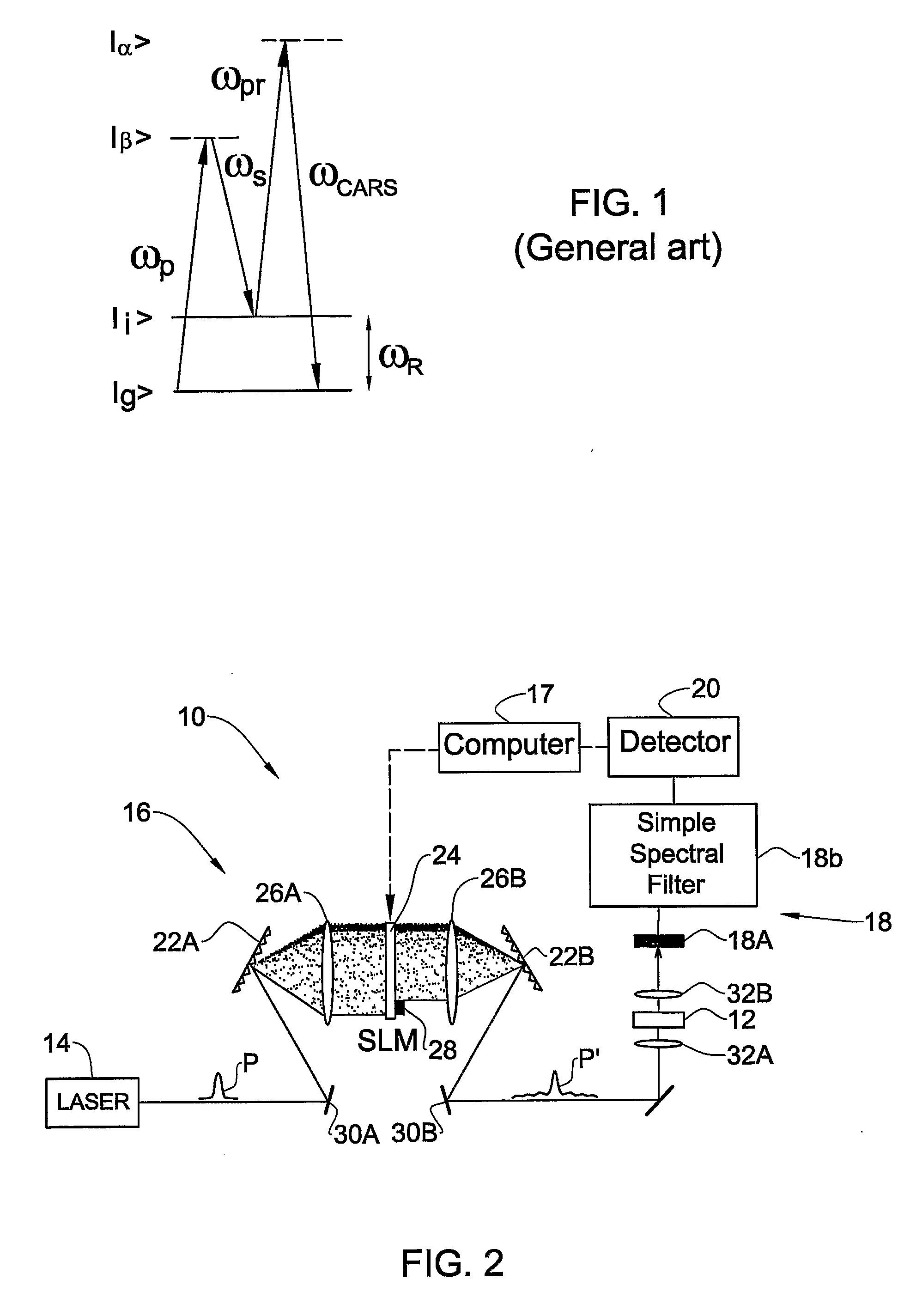
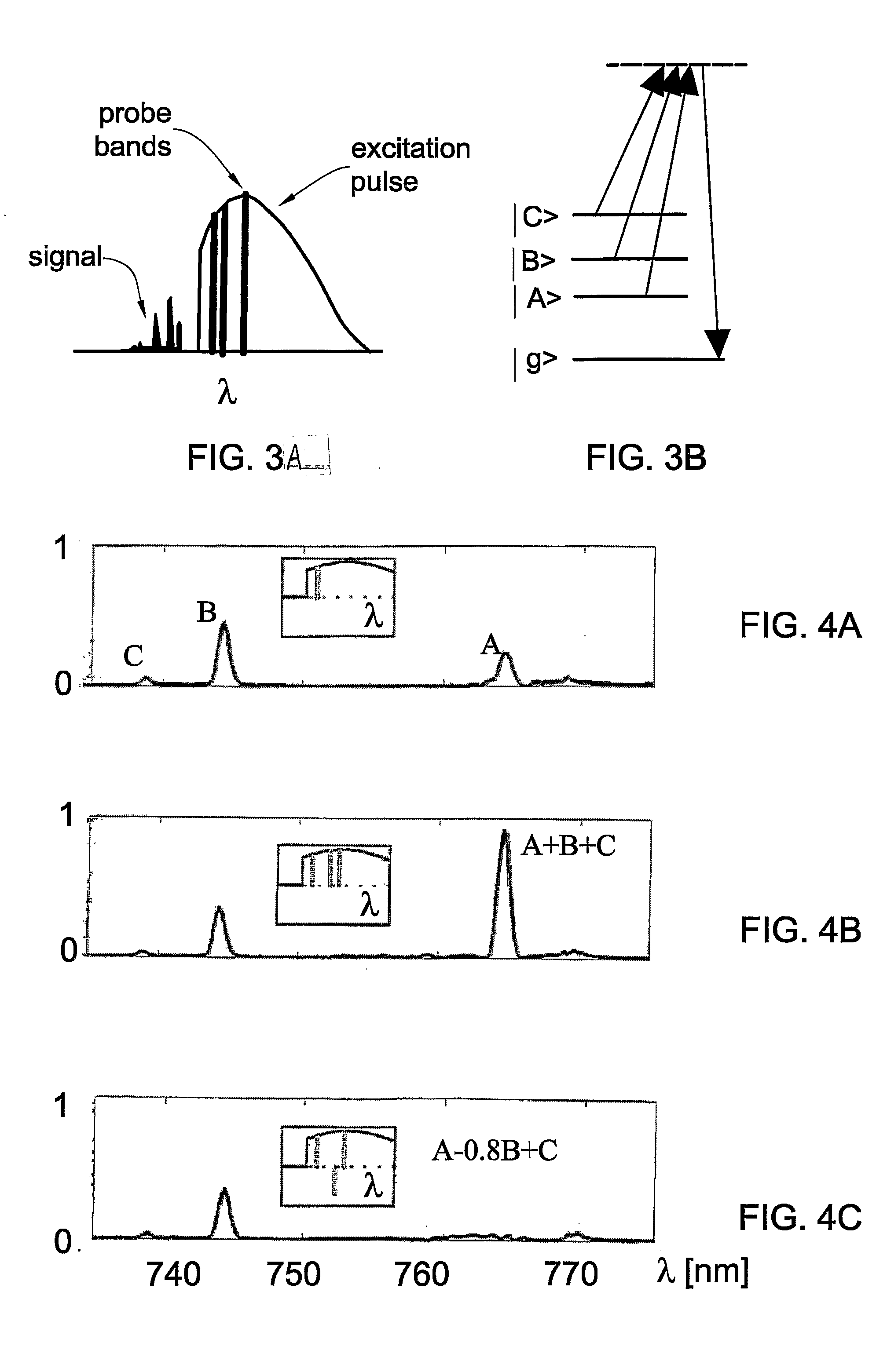
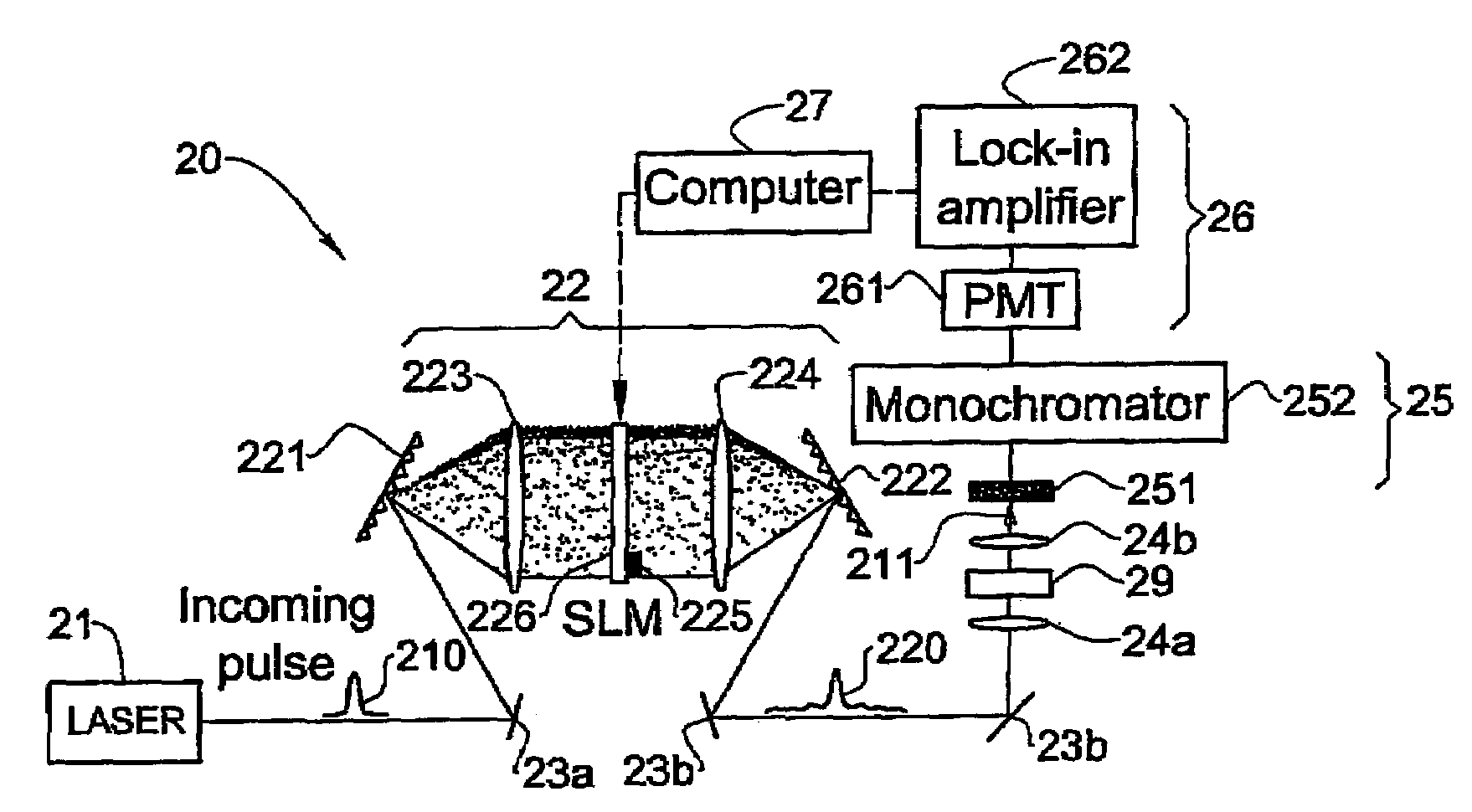
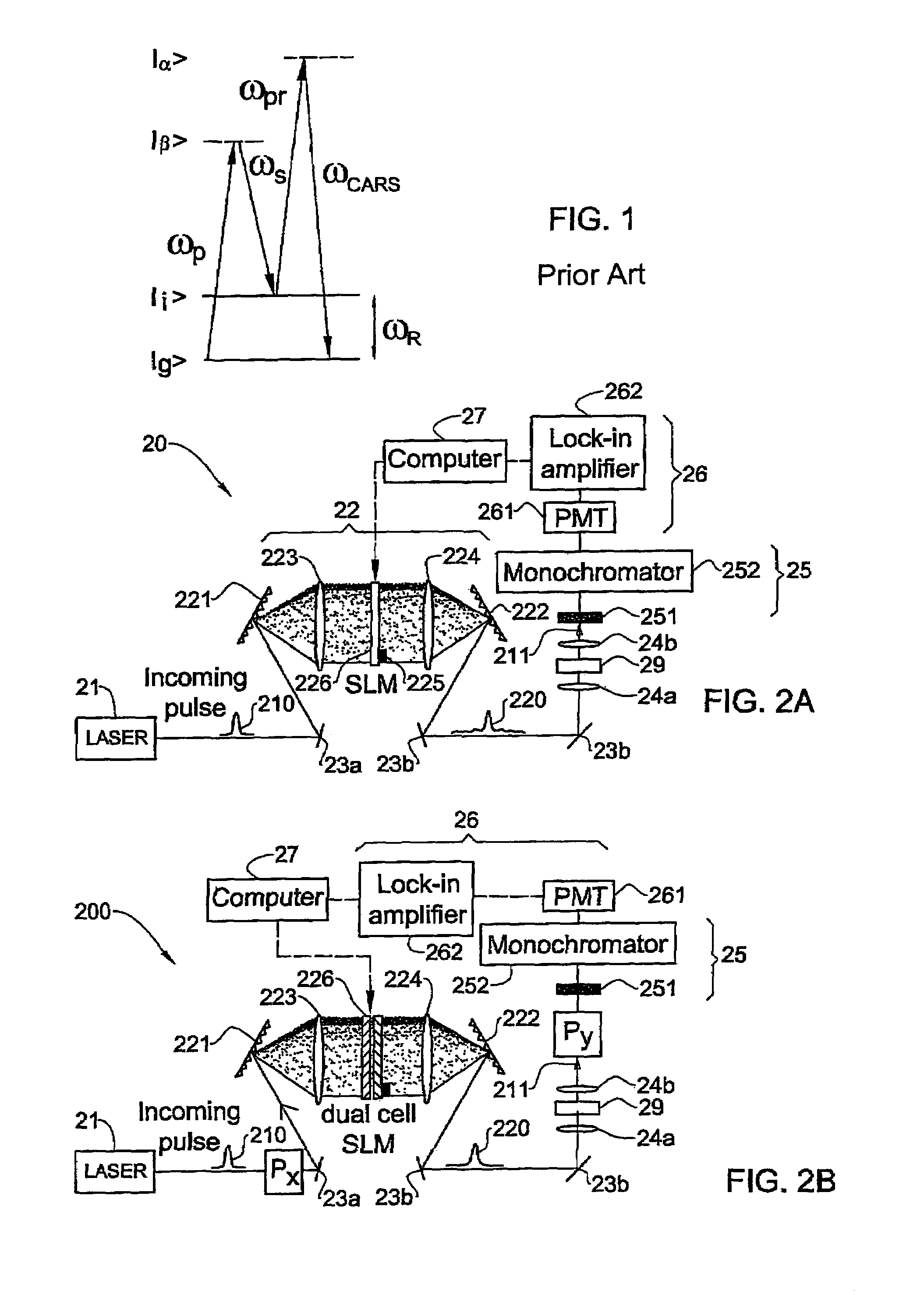
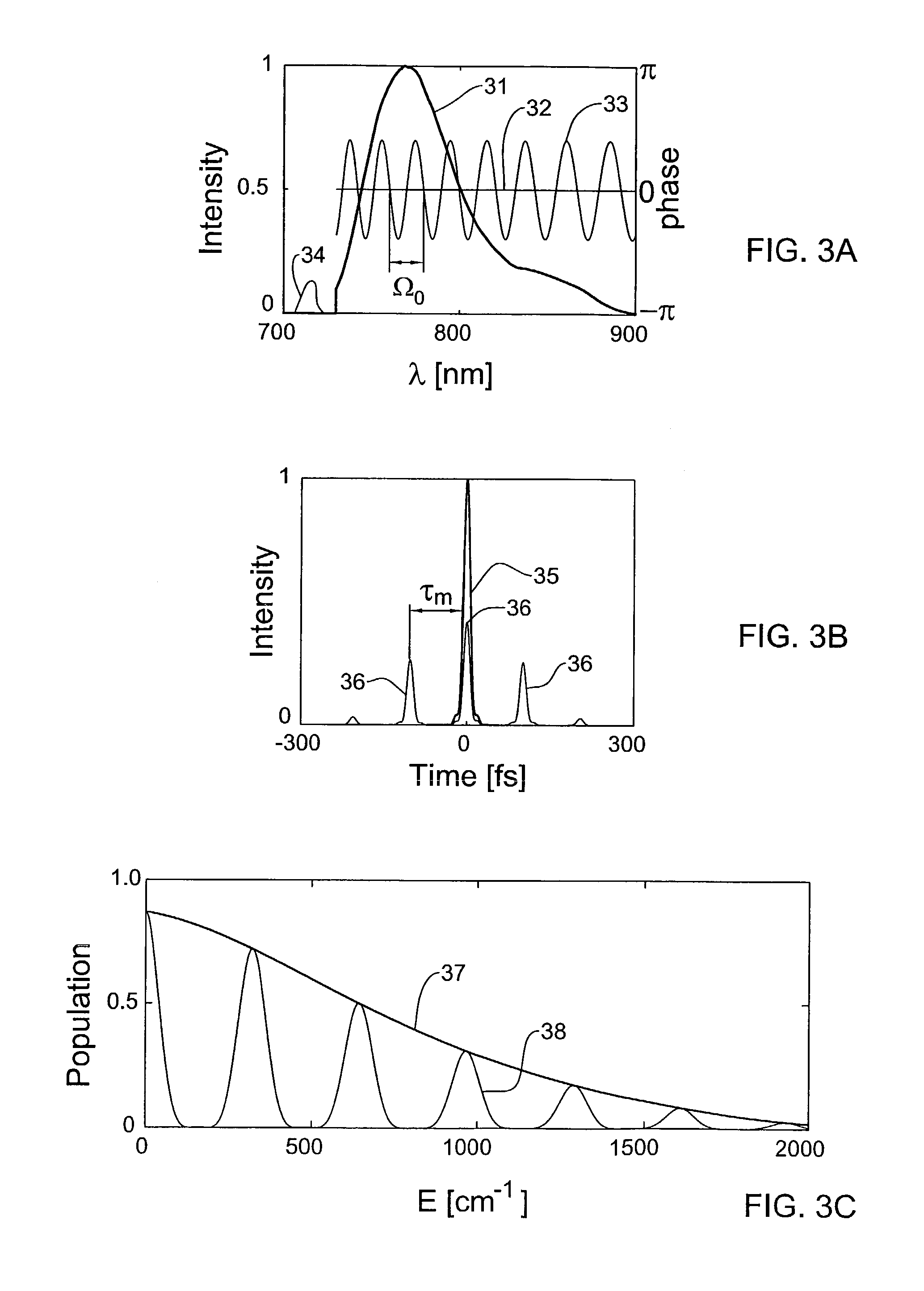
Coherently Controlled Nonlinear Raman Spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080309931A1Spectroscopic fingerprintEffective segmentationRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringLength waveRaman scattering
A method and system (10) are presented for producing exciting radiation (P′) to be used in producing an output coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering (CARS) signal of a medium (12). An input spectral phase coherent optical pulse (P), carrying a pump, a Stokes and a probe photon, is optically processed by adjusting spectral phase and polarization of wavelength components of the input pulse to produce a unitary optical exciting pulse (P′) that carries the pump photon, the Stokes photon and multiple probe photons and is capable of inducing interference between contributions from at least some of vibrational levels in the CARS signal.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Coherently controlled nonlinear Raman spectroscopy and microscopy
InactiveUS7256885B2High spectral resolutionReduce adverse effectsLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryMolecular physicsRaman scattering
A method and system are presented for producing an output coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering (CARS) signal of a medium. The method comprises generation of a unitary optical excitation pulse that carries a pump photon, a Stokes photon and a probe photon; and inducing a CARS process in the medium by exciting the medium by the at least one such unitary optical excitation pulse.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
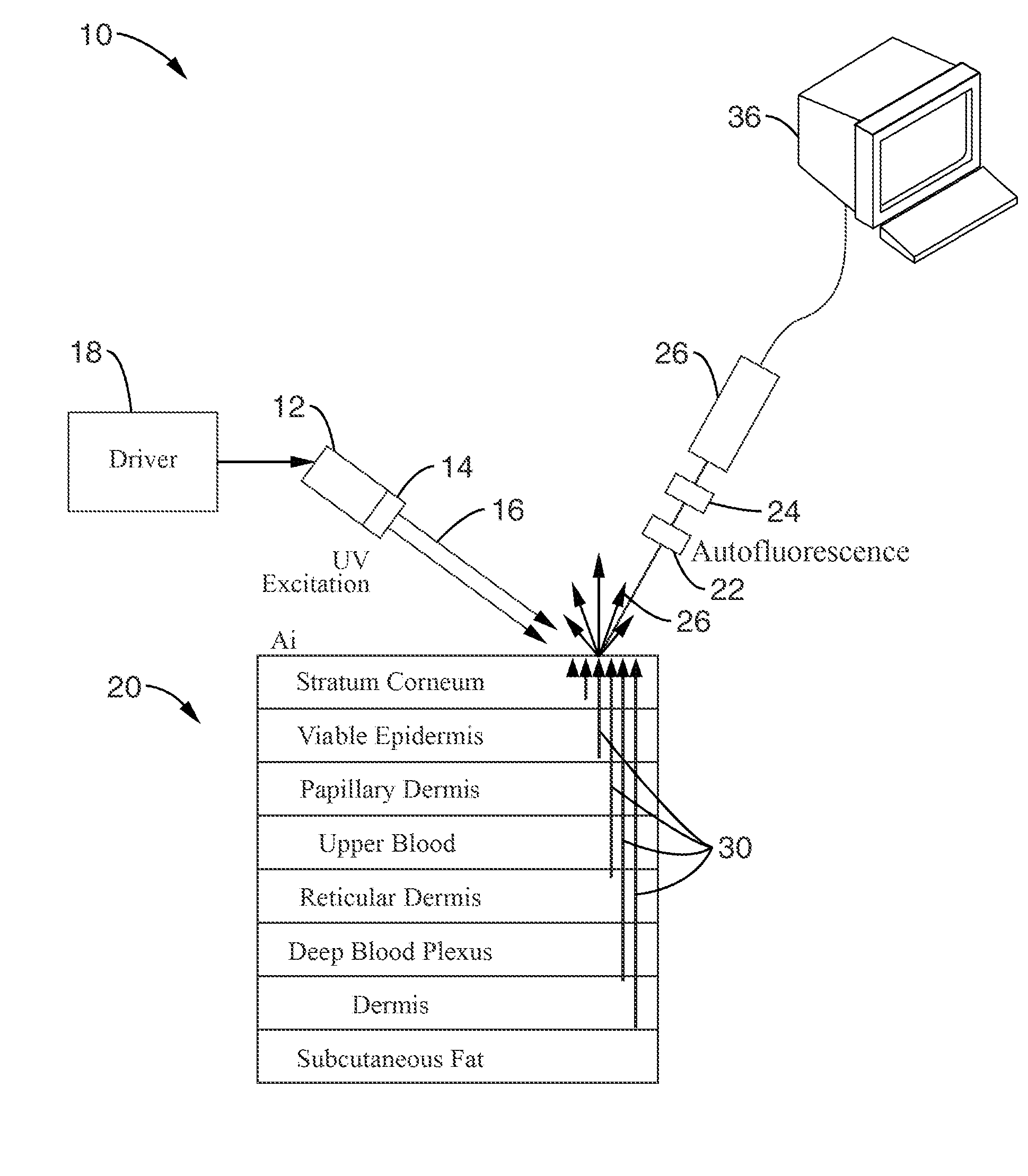
Time-resolved non-invasive optometric device for medical diagnostic
InactiveUS20070156037A1Remove restrictionsDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseFluorophore
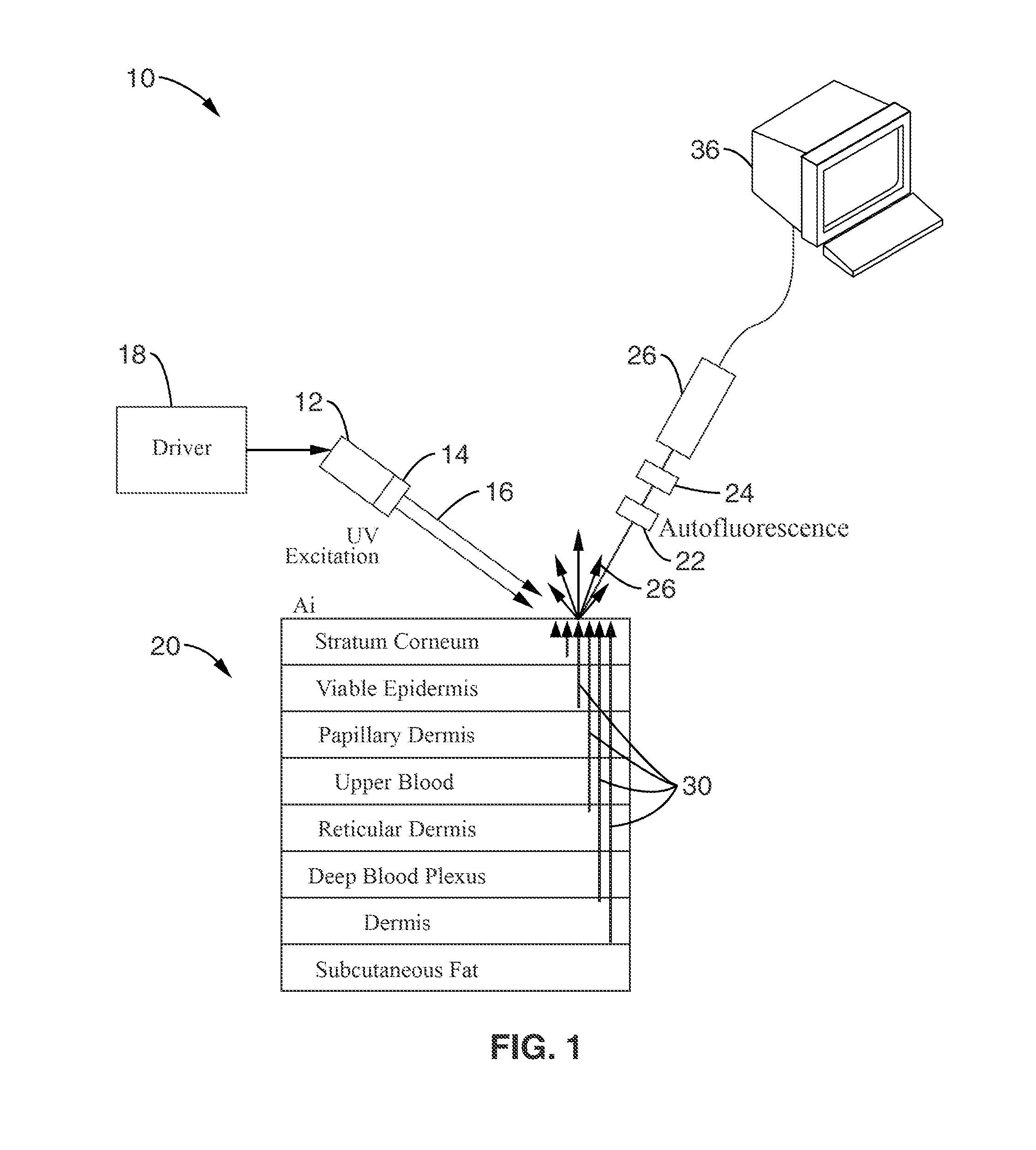
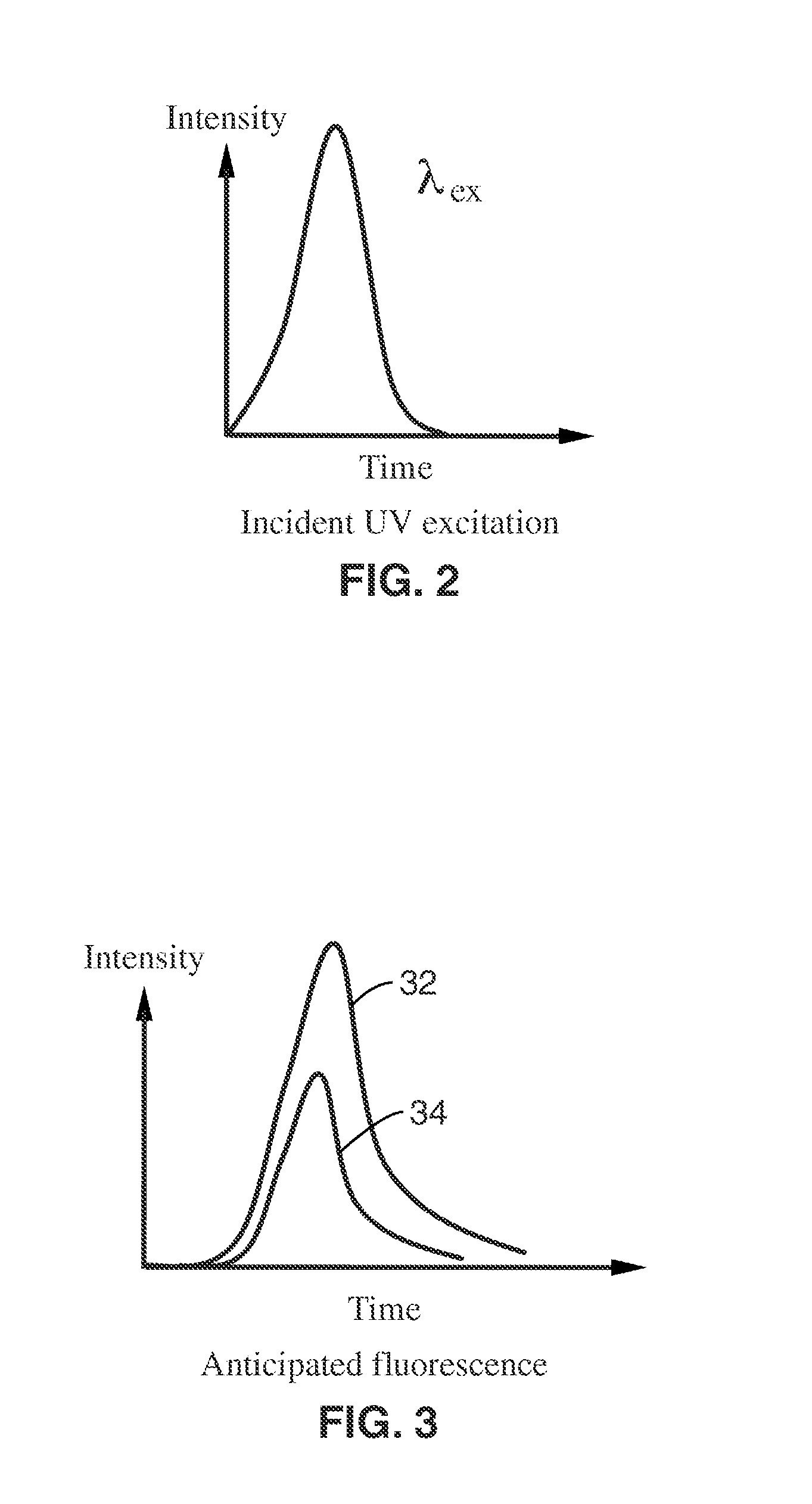
A time-resolved fluorescence device is described for the detection and diagnosis of various metabolic diseases in a noninvasive or minimally invasive manner. The device uses an ultra-short excitation pulse that comprises of a repetition of nanosecond pulses. The excitation pulse is directed incident onto a strategically selected area of the patient body such as the forearm, the feet, and the palm. This light interacts with the different layers of the skin. The absorbed light excites conditions of interest in the skin, which in turn generate a fluorescence signal, which is collected by a detector. A processor is coupled to the detector to measure the transient fluorescence intensity decay of the skin in terms of lifetimes, and the contribution of individual fluorophores to the overall fluorescence signal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for recording evoked responses from neurostimulation
Systems and methods for closed loop spinal cord stimulation are provided. The systems and methods position a first electrode proximate to a dorsal column. The first electrode is electrically coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The systems and methods further program the IPG to deliver excitation pulses to the first electrode based on a stimulation level. The excitation pulses are emitted from the first electrode. The systems and methods further position a second electrode proximate to a dorsal root. The second electrode is electrically coupled to the IPG. The systems and methods further measure at the second electrode a first evoked potential waveforms resulting from the excitation pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
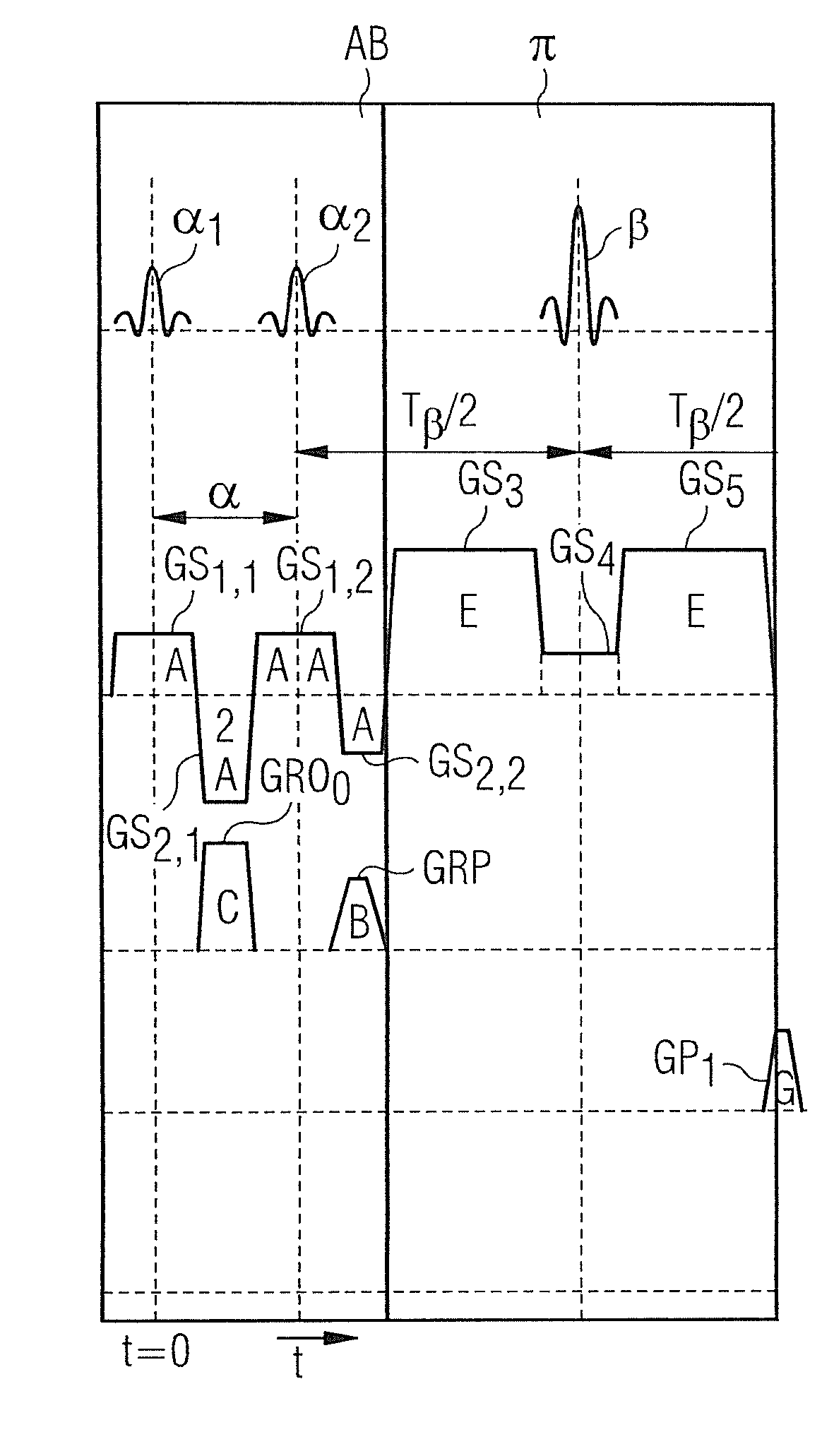
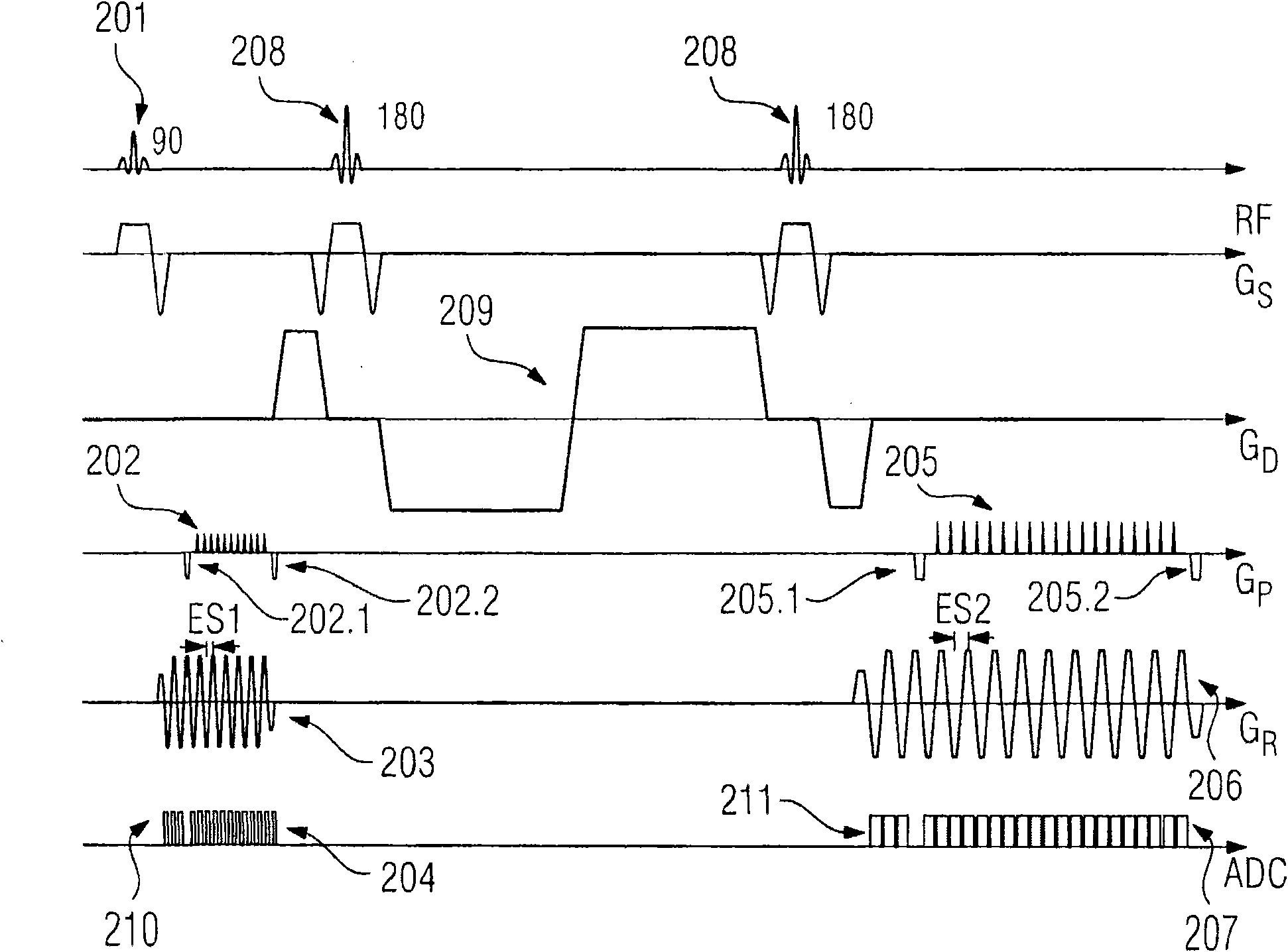
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method employing a true FISP sequence with improved off-resonant behavior of two spin ensembles
InactiveUS7020509B2Significant differenceImprove stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setPhase Code
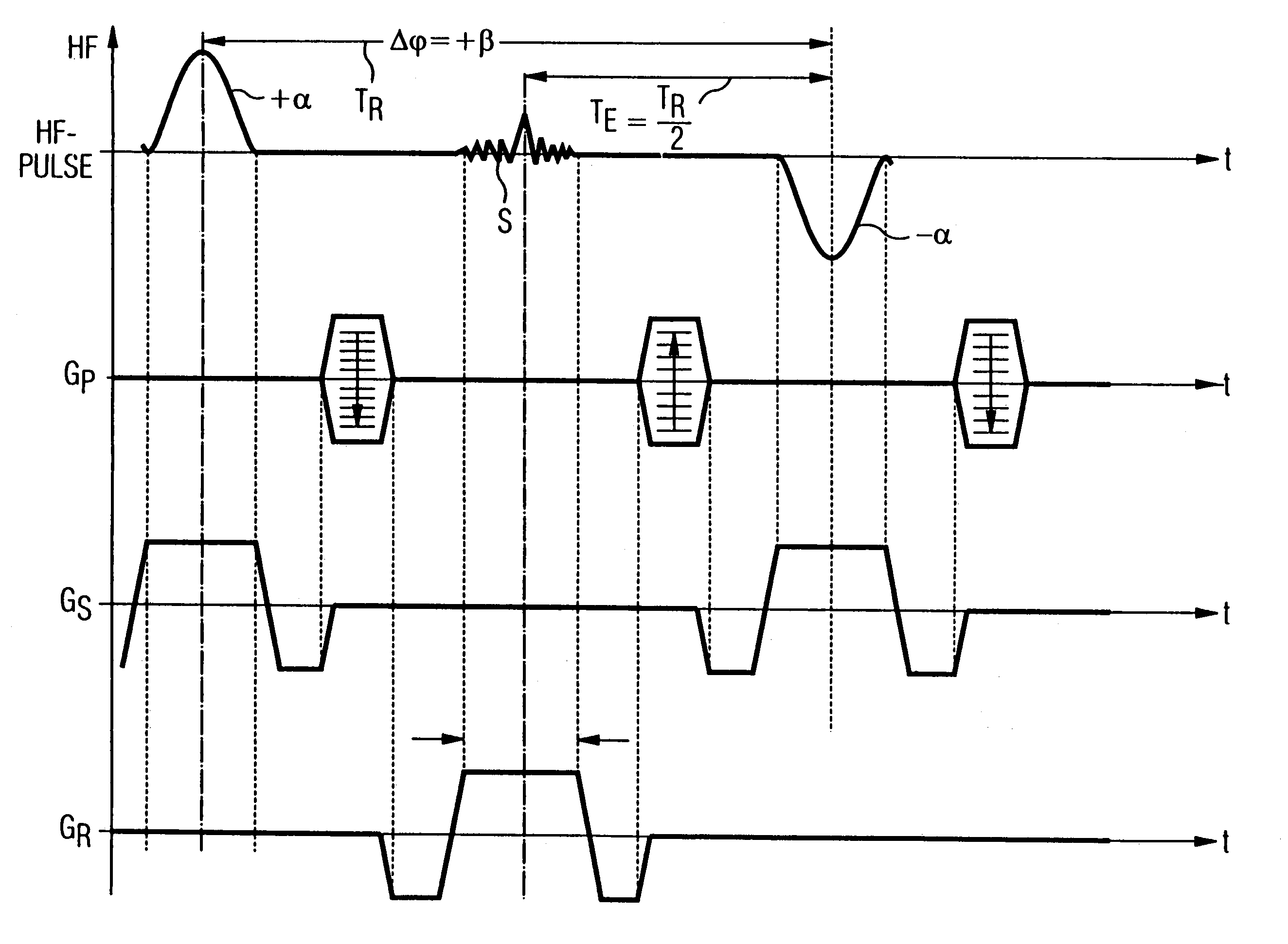
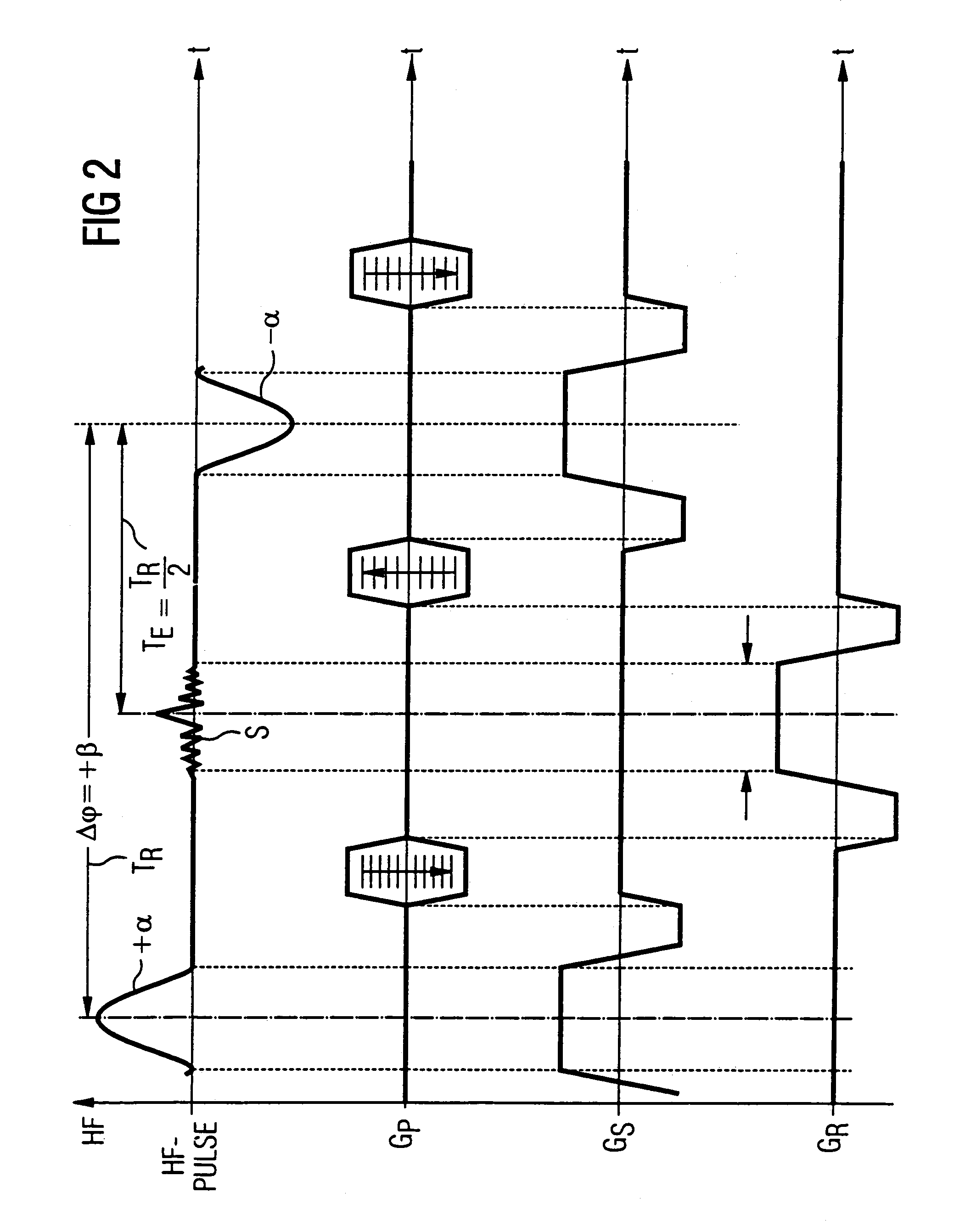
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus employing a FISP pulse sequence, the pulse sequence is repeated with a repetition time TR with different phase-coding gradient directions and with an alternating operational sign of the flip angle α. The gradient pulse trains are thereby completely balanced. A phase increment ΔΦ=β is generated in addition to the alternating operational sign of the flip angle α between successive excitation pulses, so that the steady state signals for a first and a second spin ensemble optionally have either identical or reversed signal polarities. A first dataset on the basis of identical signal polarities and a second dataset on the basis of reversed signal polarities are obtained by means of the free selection of the mutual signal polarities. A pure image of the first and the second spin ensembles is thus obtained by the addition and / or subtraction of the first and second datasets.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for NMR sensor with loop-gap resonator
InactiveUS20030151408A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonanceCapacitanceNon magnetic
A loop-gap resonator for providing an excitation pulse in a down hole nuclear magnetic resonating (NMR) tool for determining a parameter of interest in a formation adjacent a borehole. The loop-gap resonator is constructed having one or more capacitive gaps formed in a nonmagnetic conductive loop. The loop-gap resonator may be deployed down a bore in a measurement while drilling (MWD) configuration or in a wire line configuration. The MWD configuration may utilize a non-rotating sleeve rotationally associated with the drill string.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Photon counting multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system and counting method
InactiveCN103728446AAvoid interferenceEasy to assembleBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceTime resolved fluorescence immunoassayTime mark
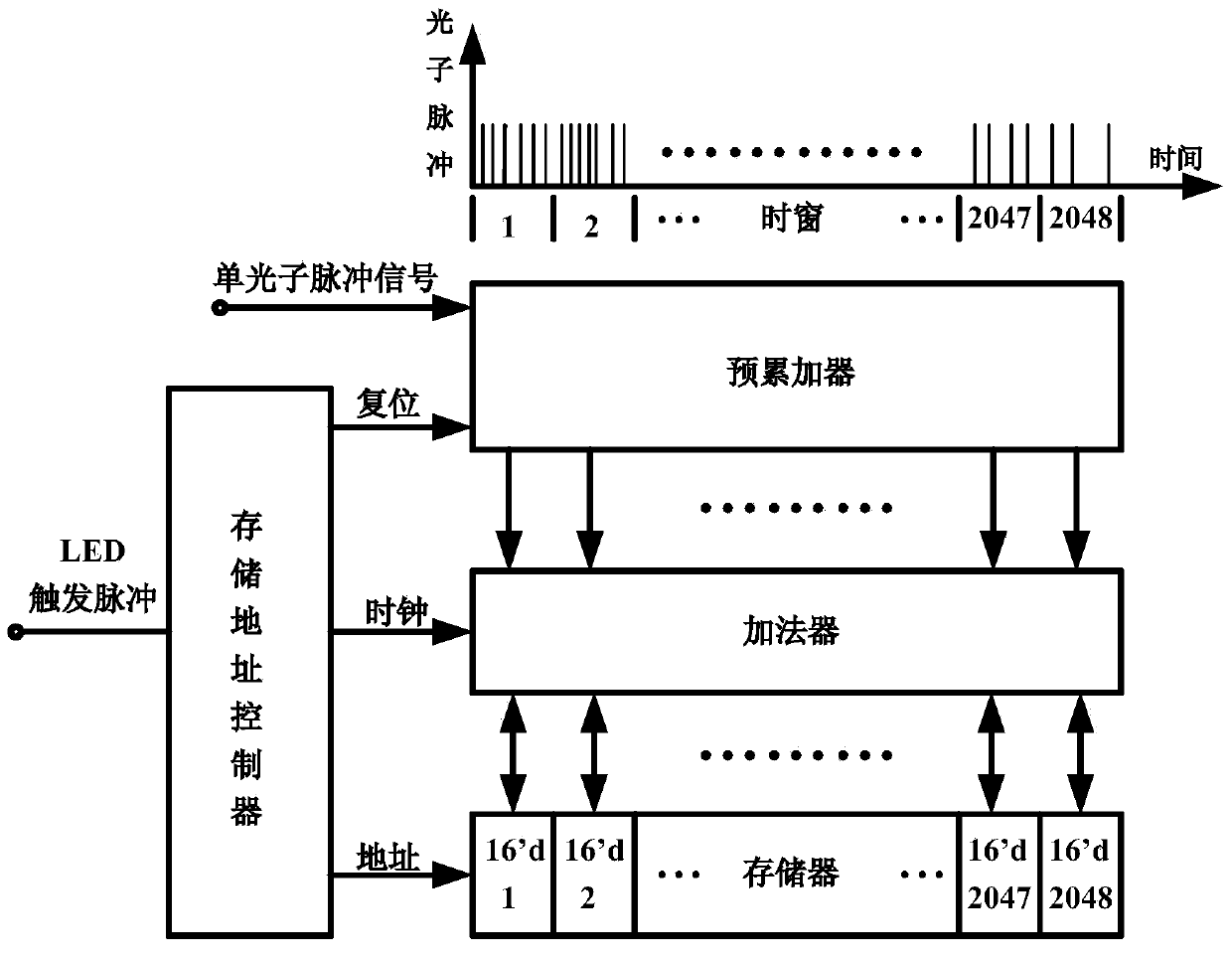
The invention belongs to the technical field of fluorescence immunoassay and relates to a photon counting multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system which comprises a light source module, a detection module and a time marked photon counting analysis / control module. At the same time, the invention relates to a counting method adopted by the system. The counting method of exciting a sample to be detected with pulse light, sending a fluorescence signal generated by the sample after excitation into a PMT (Photo Multiplier Tube) photon counting head and outputting a pulse signal comprises the following steps of taking cycles of the excitation pulse light as counting cycles, dividing each counting cycle into a plurality of time intervals with the same width, accumulating photons detected after sending excitation light pulses of each counting cycle into a memory corresponding to a corresponding time window, that is marking the positions of the photons in the pulse cycles with the intervals where the time windows are located, and uploading data in the memory into an upper computer after counting for the cycles. The multi-channel time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay system is low in cost and has very high sensitivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
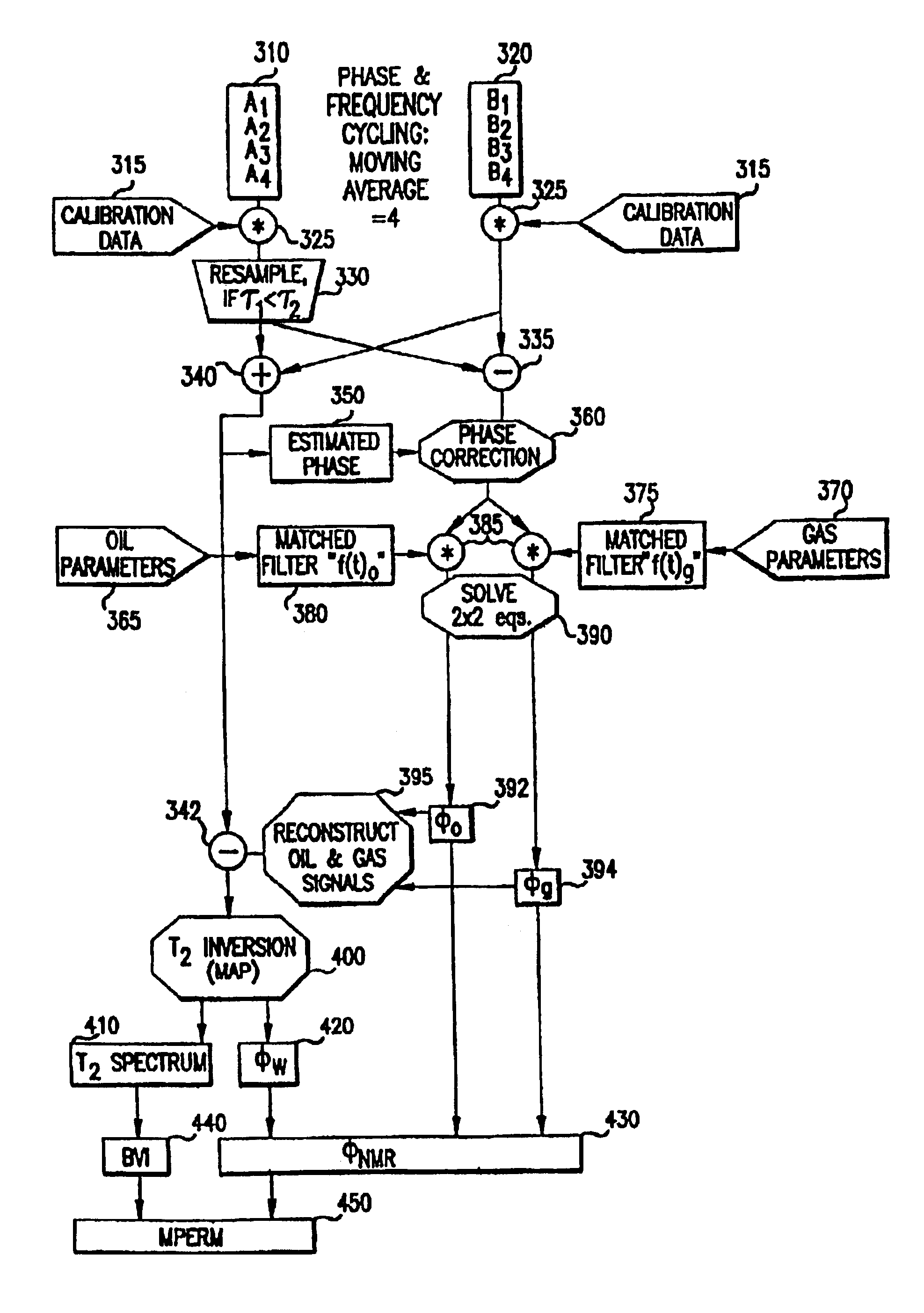
Objective oriented methods for NMR log acquisitions for estimating earth formation and fluid properties
InactiveUS6972564B2Long wait timeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMaterial analysis by using resonancePulse sequenceFormation evaluation
An objective oriented NMR logging method selects pulse sequences over a plurality of frequencies from a set of building blocks. The building blocks include trainlet sequences wherein each trainlet comprises an excitation pulse and a plurality of refocusing pulses, the total length of a trainlet being typically less than 10 ms. Another building block is a short CPMG or modified CPMG sequence and yet another building block is a regular CPMG or modified CPMG sequence. The modified CPMG sequences may have refocusing pulses with a tipping angle less than 180° to reduce the power consumption. Based on the logging objective (formation evaluation or FE, FE plus hydrocarbon typing, FE plus gas evaluation) the building blocks are combined at a plurality of frequencies with different wait times and TEs.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
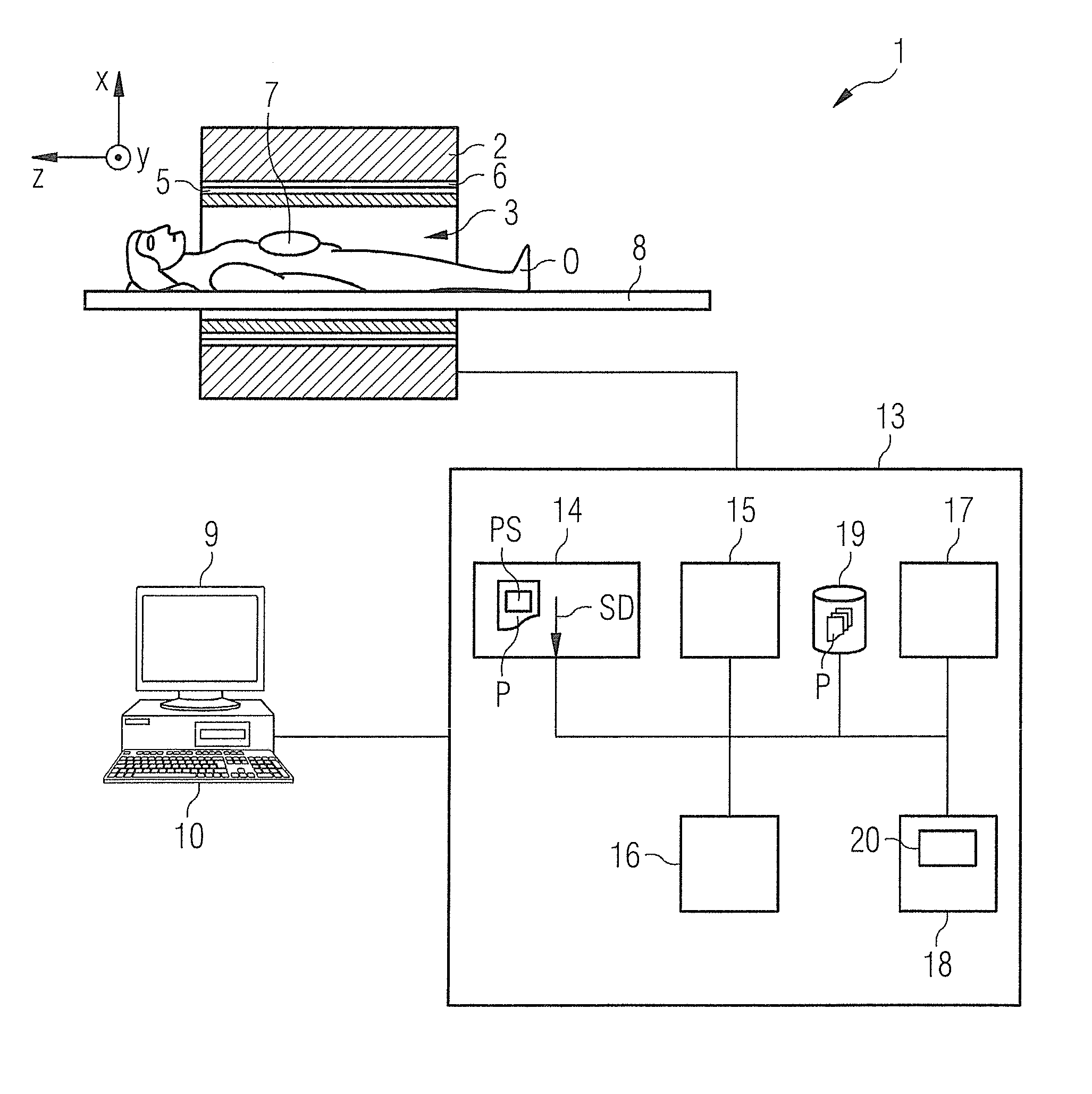
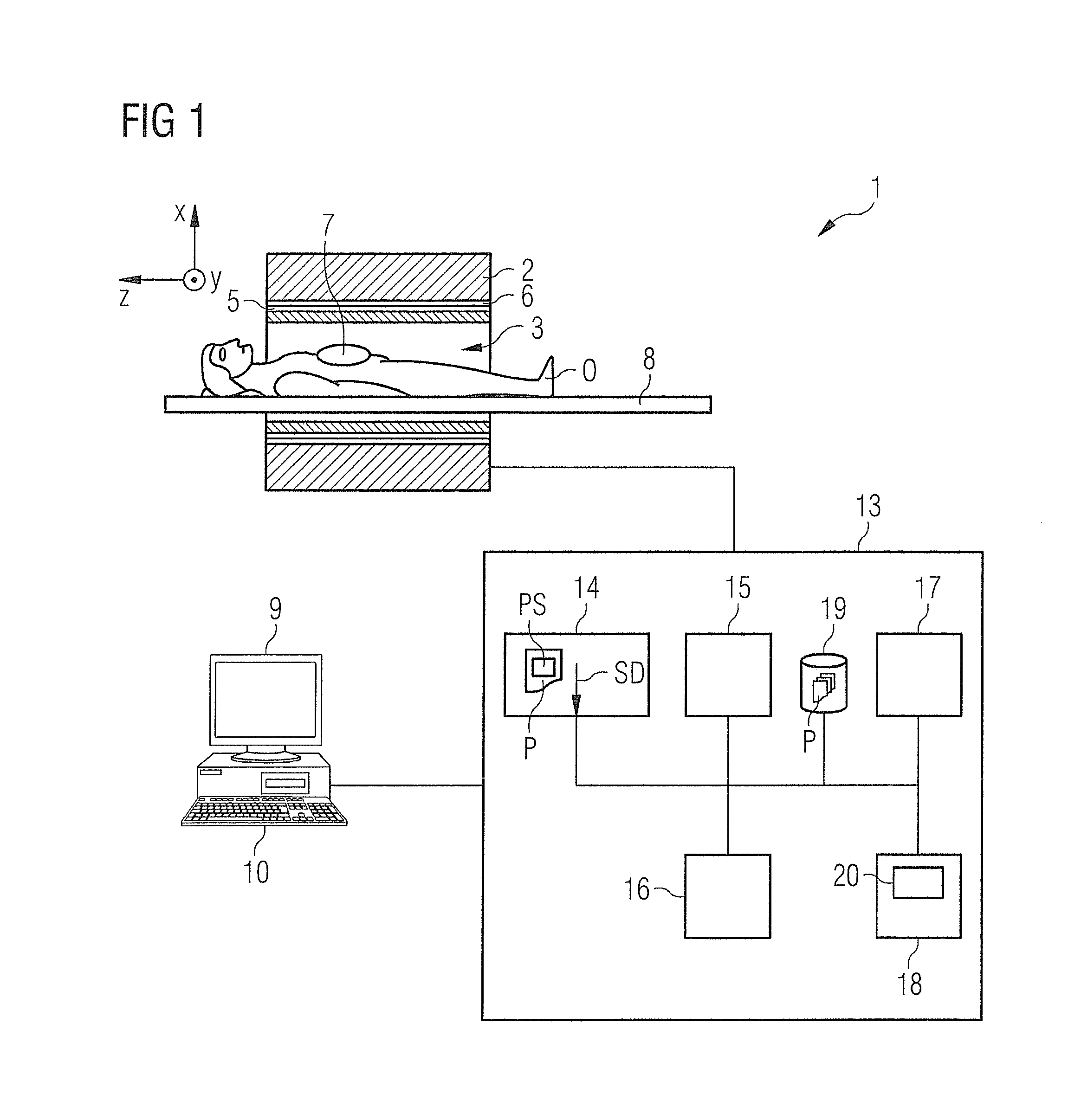
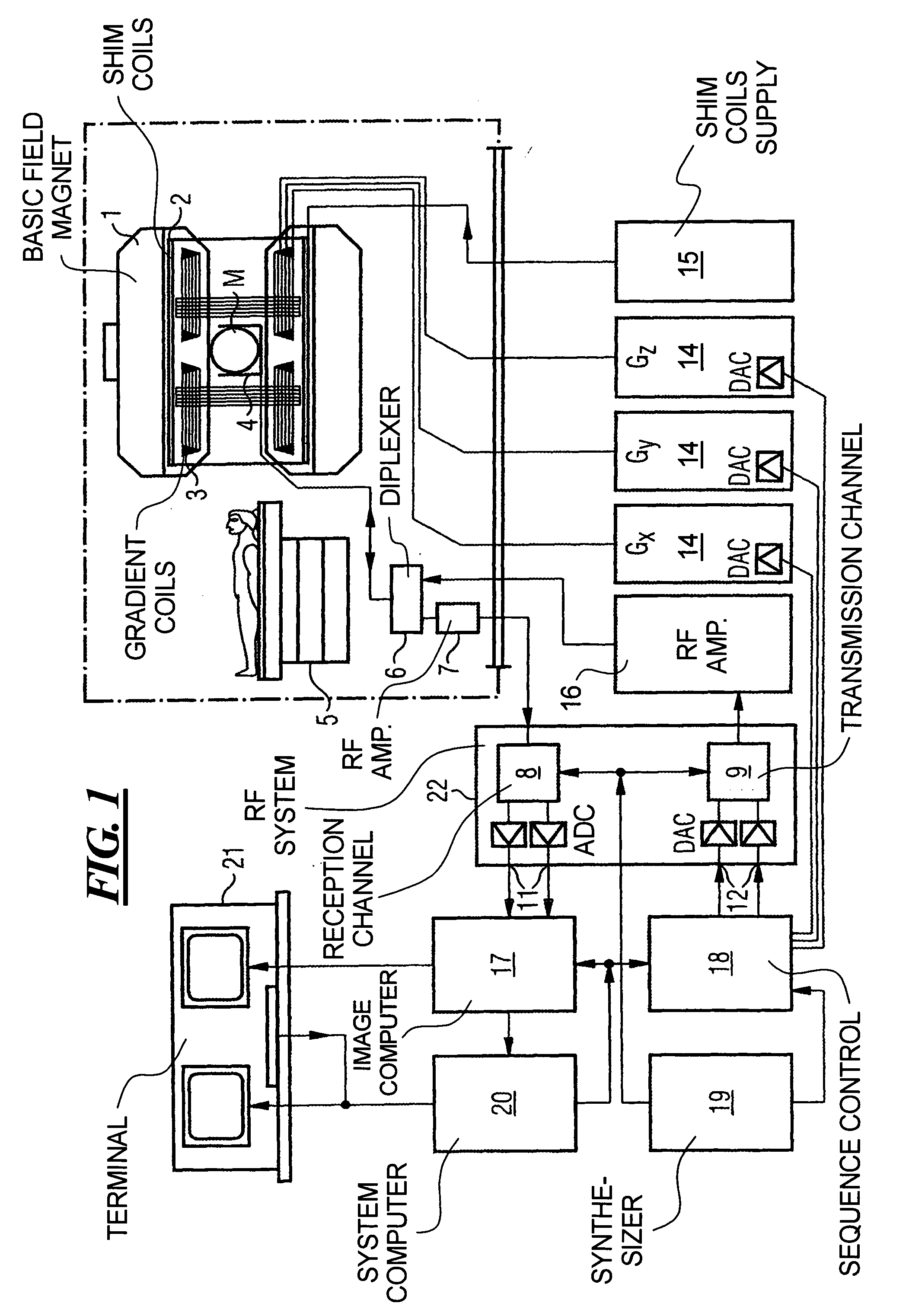
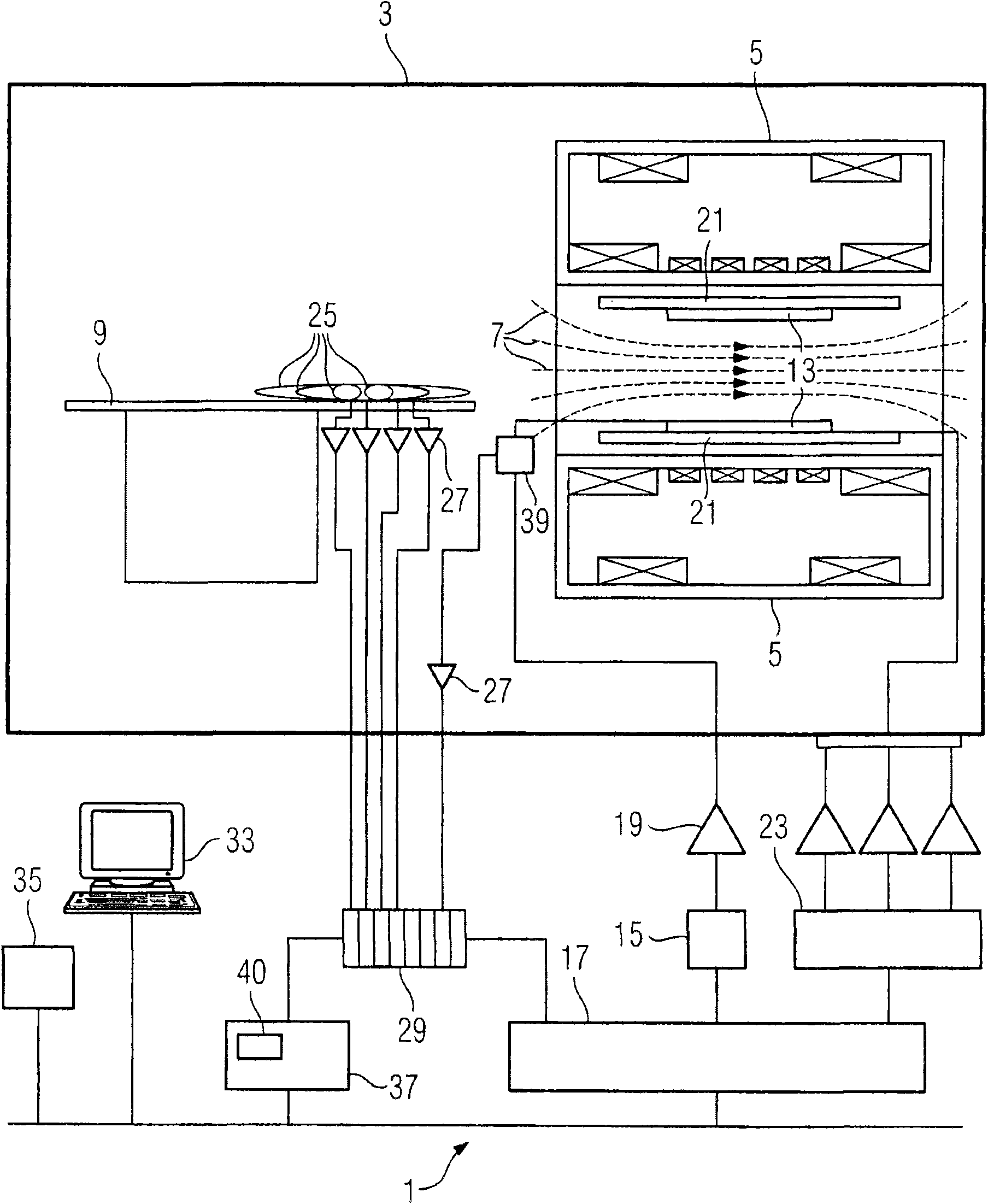
Method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the B1 field distribution
ActiveUS20050073304A1High overall measuring timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurement deviceSelective excitation
In a method and magnetic resonance tomography apparatus for spatially resolved measurement of the magnetic high frequency field distribution in the apparatus, a double echo high frequency pulse sequence with a first excitation pulse following by at least two refocusing pulses are emitted for generation of a first echo and a following second echo. At least the excitation pulse is slice selective. In an excitation layer defined by the slice selective excitation pulse a first echo image and second echo image are spatially resolved by using suitable gradient pulses for phase or frequency encoding Using the relationships of the amplitudes of the first and second echo image in the various locations the flip angles representing the field strength at the relevant locations in the relevant slice are determined.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
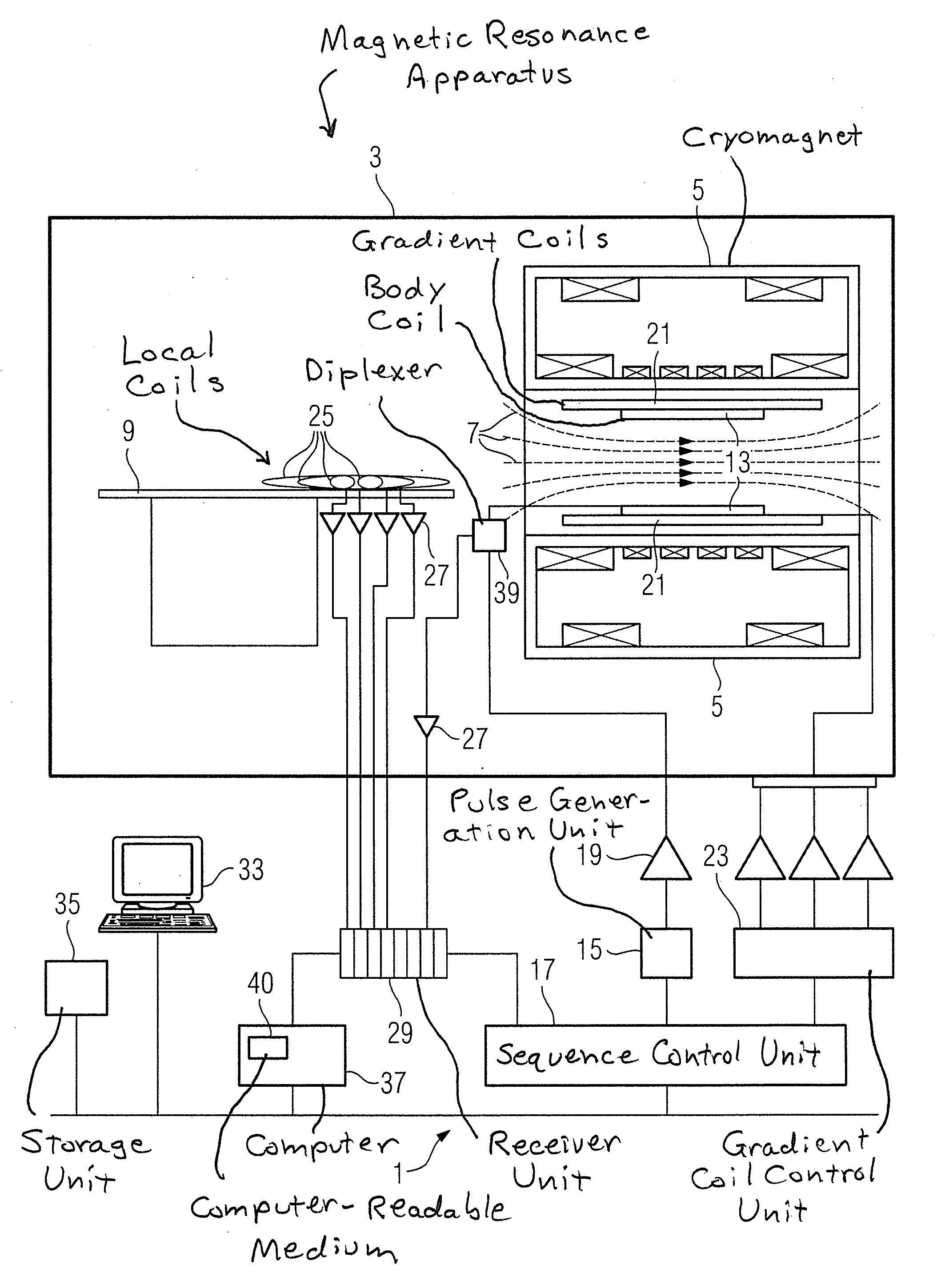
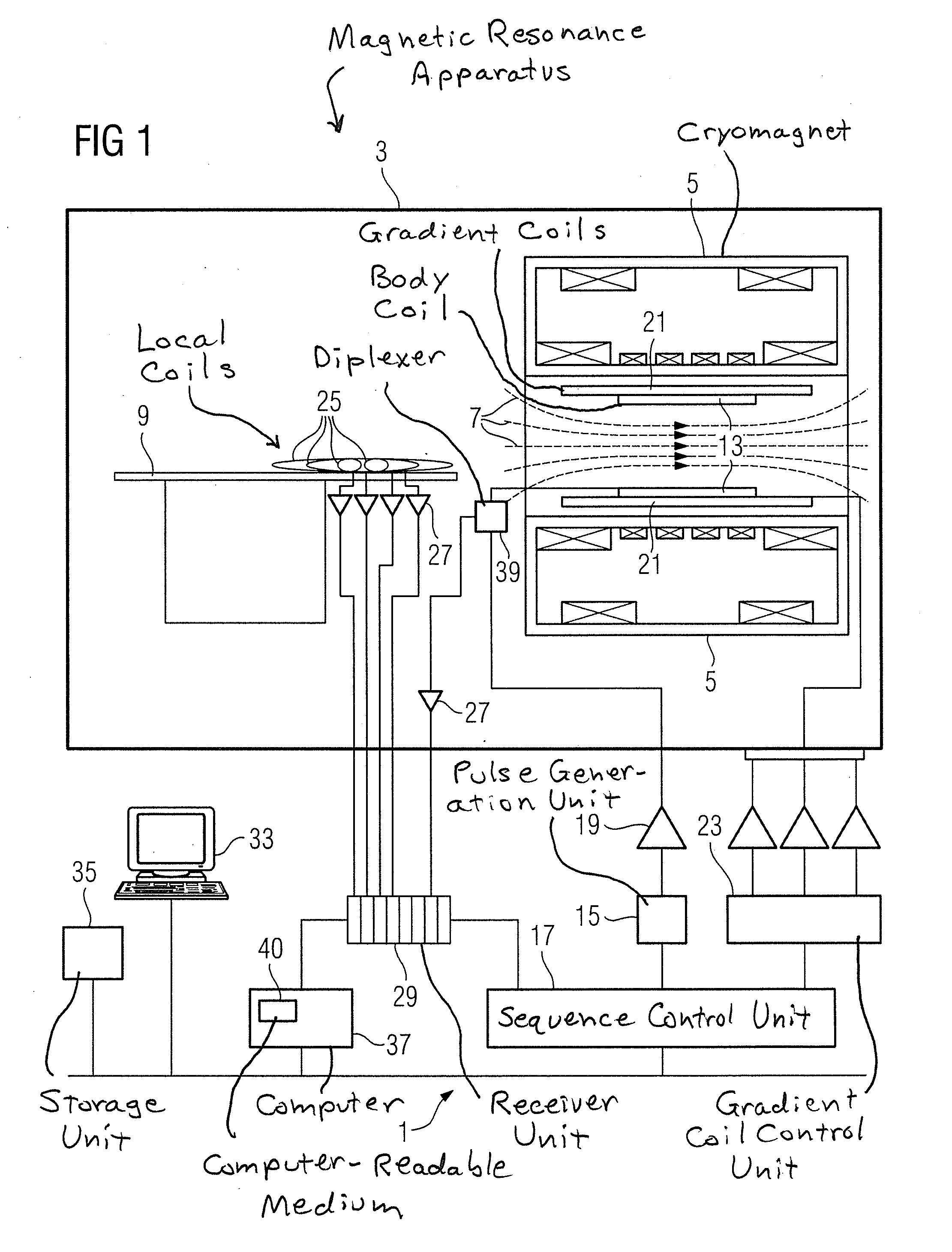
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus to generate an image using a parallel acquisition technique
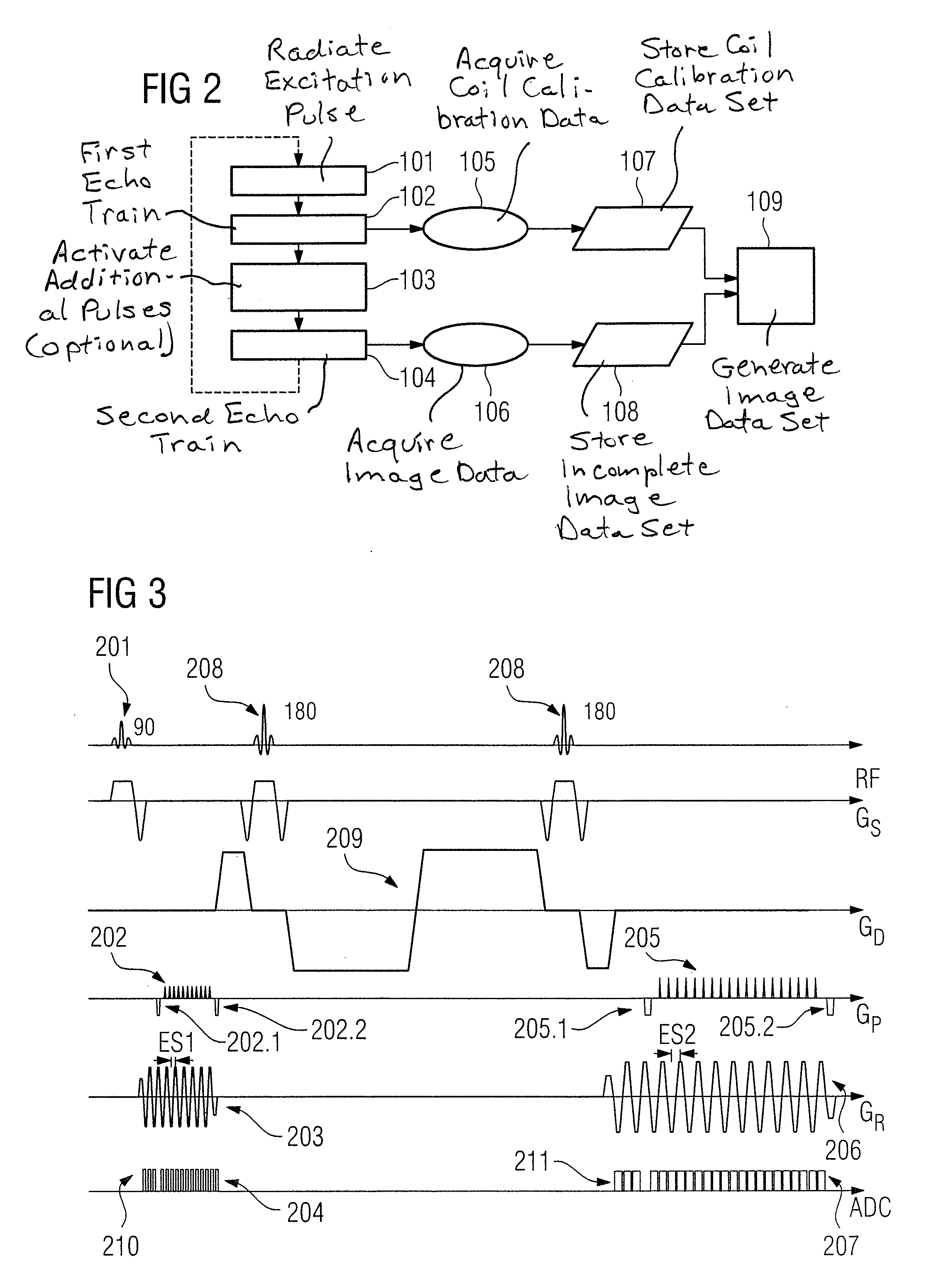
In a magnetic resonance method and apparatus to generate images by a parallel acquisition technique an excitation pulse is radiated into an examination subject, and a first echo train is generated after the excitation pulse, wherein the first echo train densely scans a segment of k-space to be scanned for an acquisition of coil calibration data. Coil calibration data are acquired by means of the first echo train. The acquired coil calibration data are stored in a coil calibration data set. A second echo train is generated after the same excitation pulse, wherein the second echo train undersamples a segment of k-space to be scanned for an acquisition of image data. Image data are acquired by means of the second echo train. The acquired image data are stored in an incomplete image data set. An image data set is generated by substituting data missing in the incomplete image data set due to the undersampling by means of a selected PAT reconstruction technique using the coil calibration data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
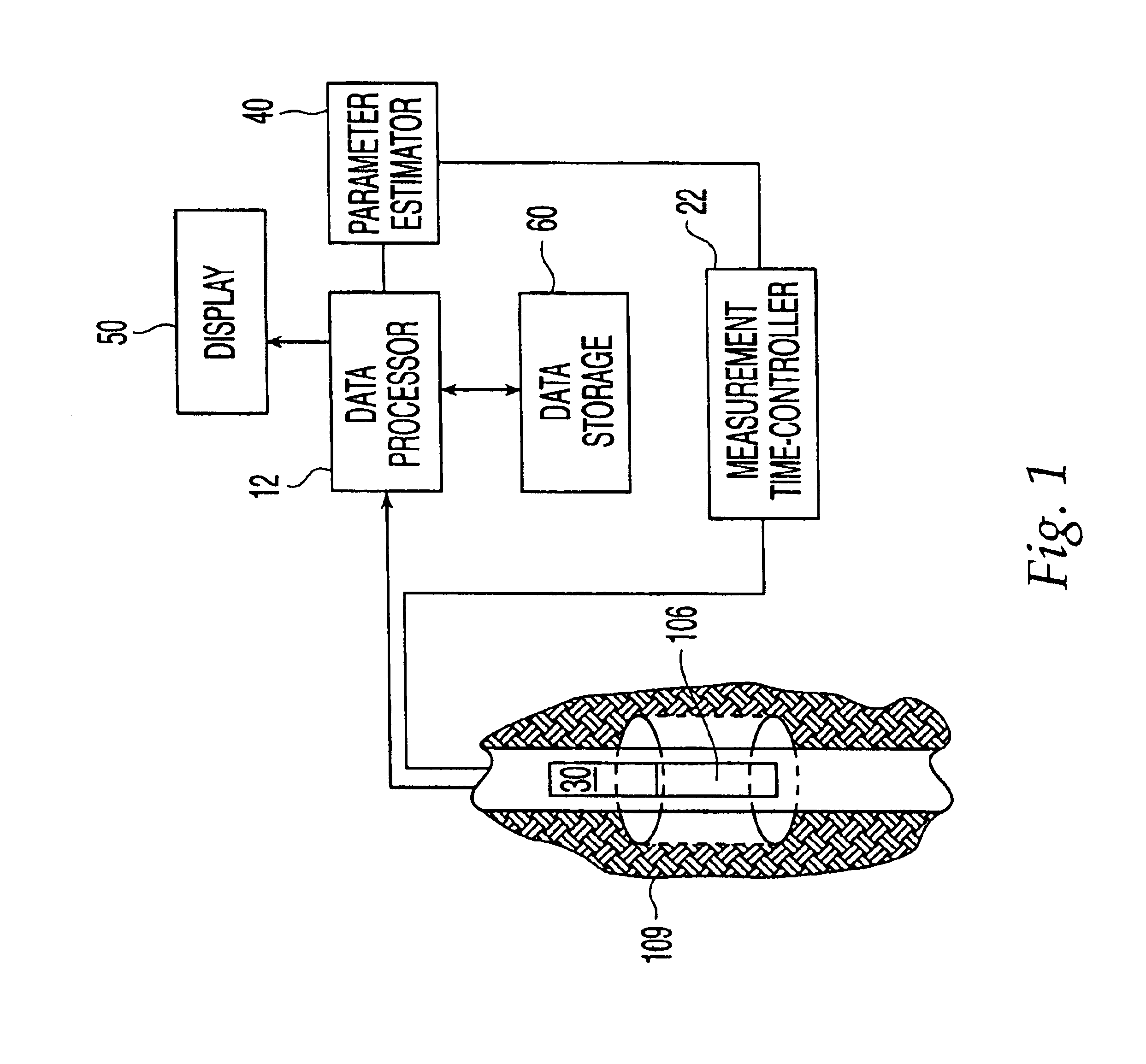
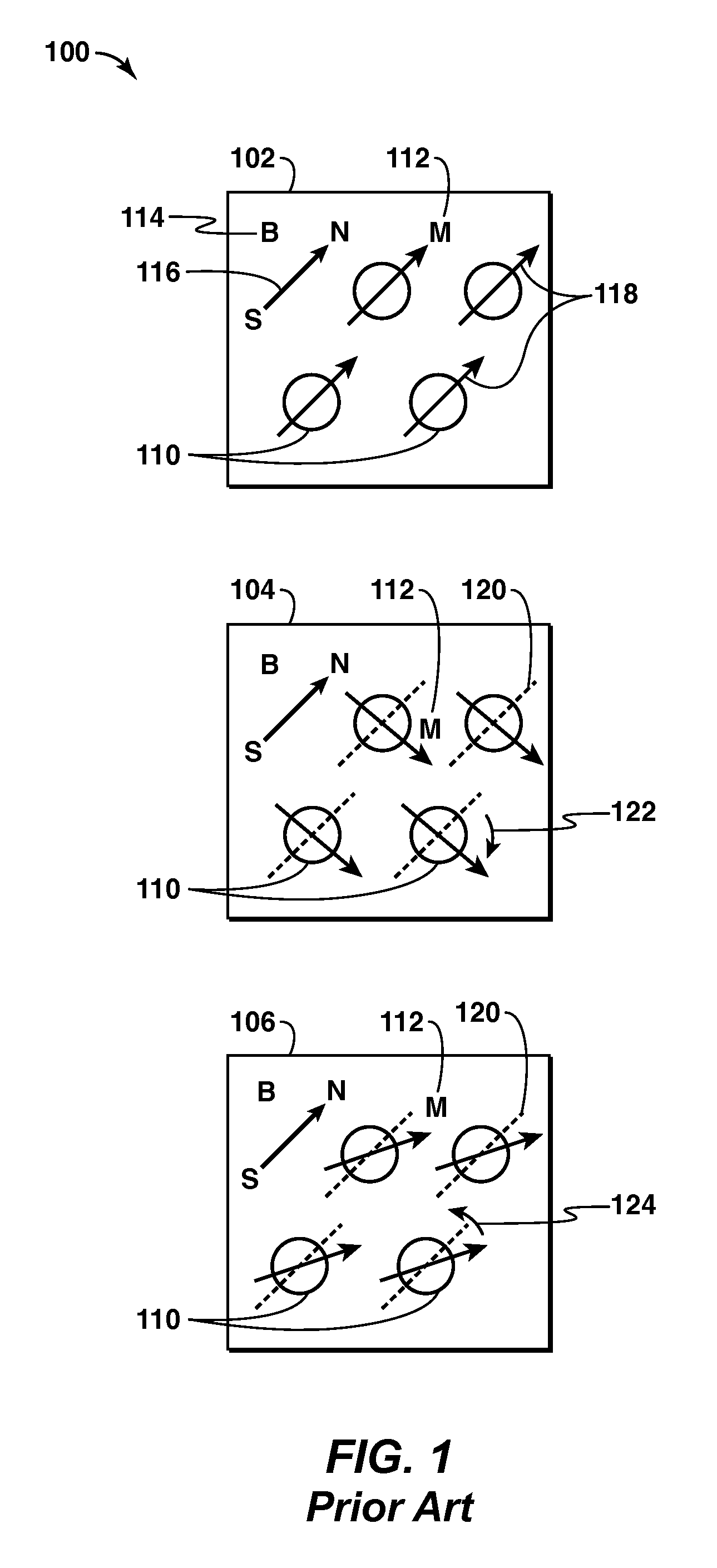
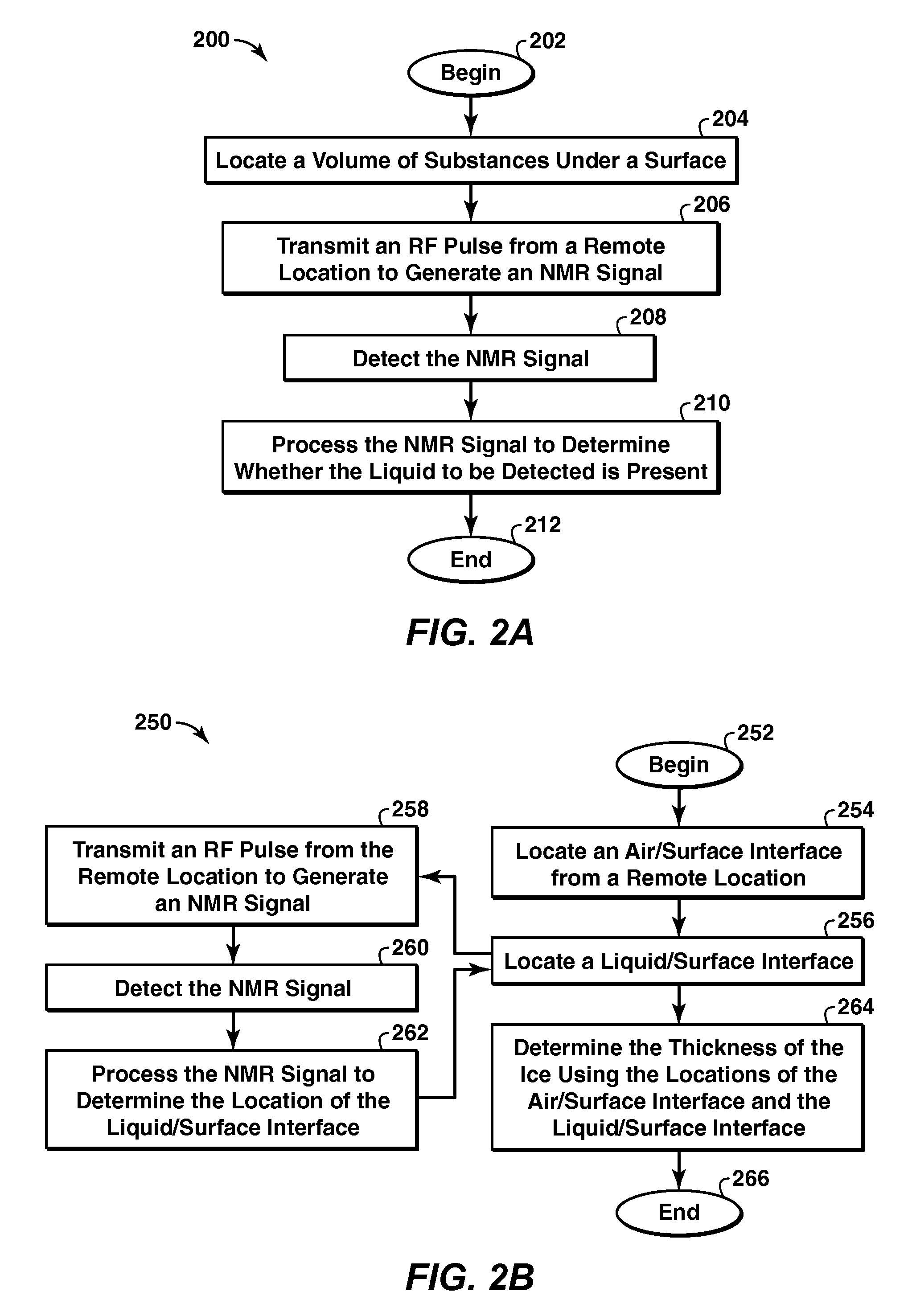
Method And Apparatus For Detection of A Liquid Under A Surface
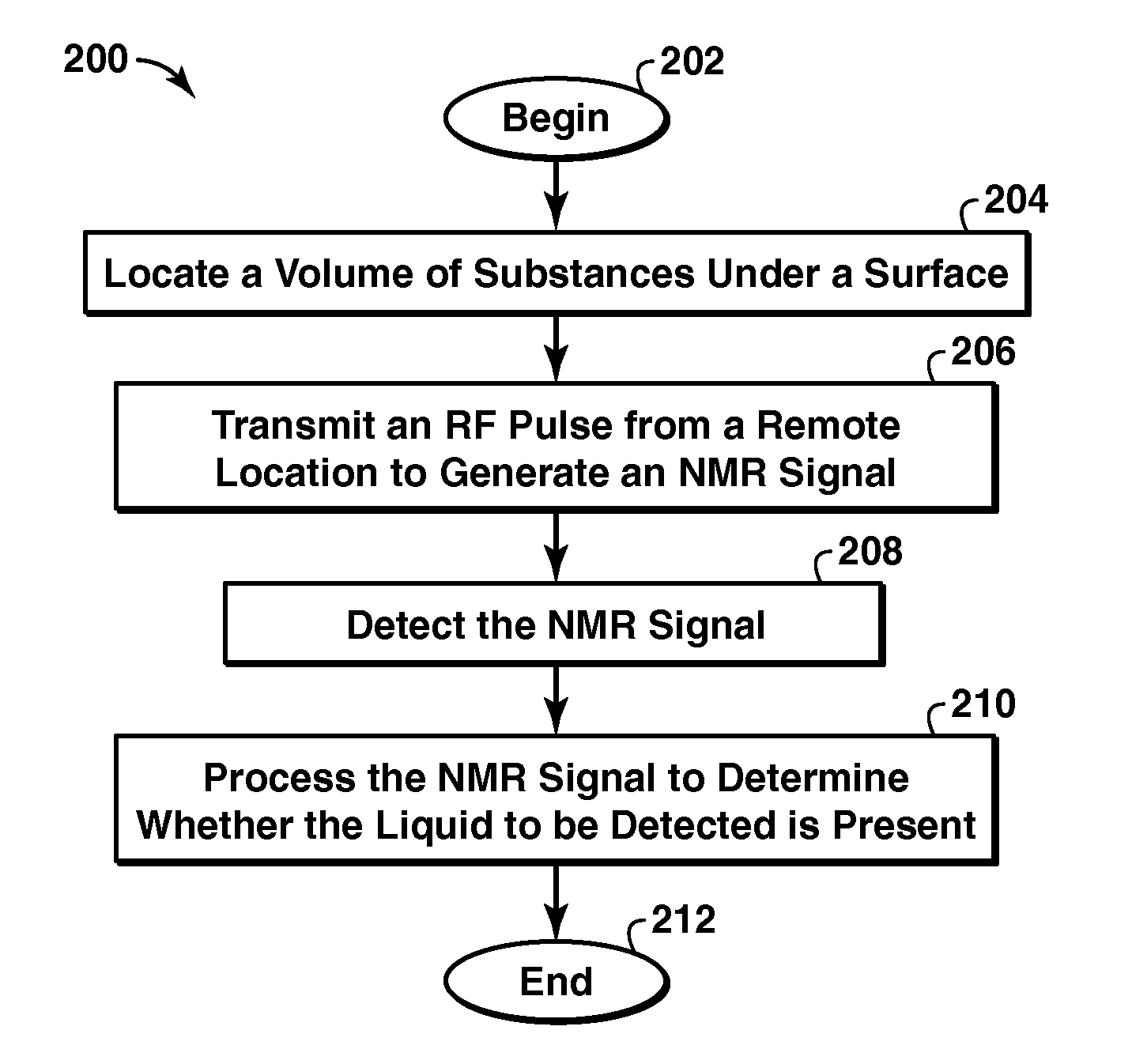
InactiveUS20110181279A1Water resource assessmentAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFuel oilTime element
Methods for detecting a liquid under a surface and characterizing Ice are provided The liquid may be a liquid hydrocarbon such as crude oil or fuel oil or mineral oil The surface may be ice, snow, or water, and the method may be practiced in an arctic region to detect oil spills, leaks, or seepages The methods may be used with a range finder to characterize marine ice The methods may include a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) tool with antenna to send a radio-frequency (RF) excitation pulse or signal into volume of substances being detected, detect an NMR response signal to determine the presence of the liquid of interest The NMR response may include a relaxation time element and an intensity level and may include a free induction signal (T2*), a spin echo signal (T2), a train of spin echo signals (T2), or a thermal equilibrium signal (T 1).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
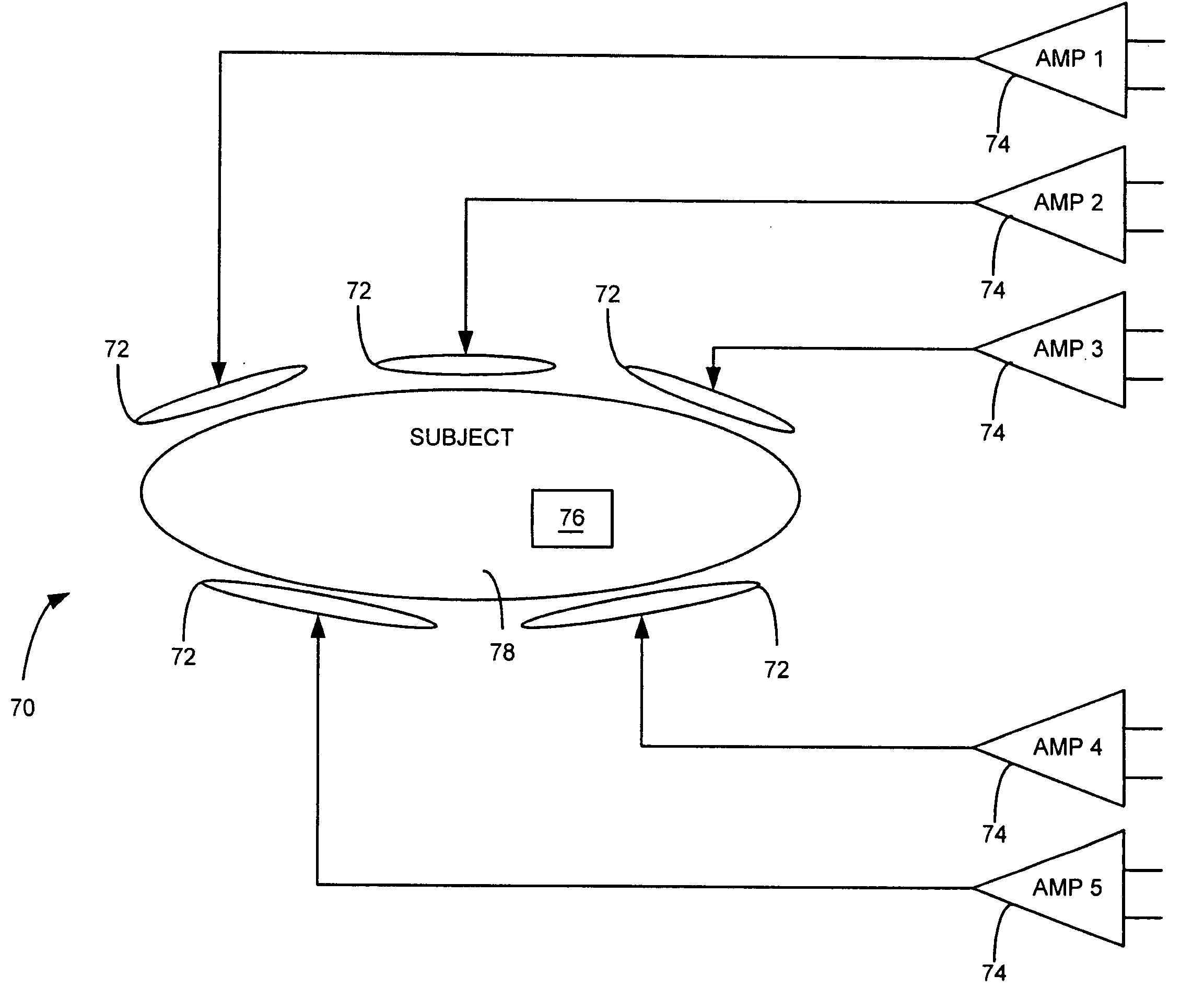
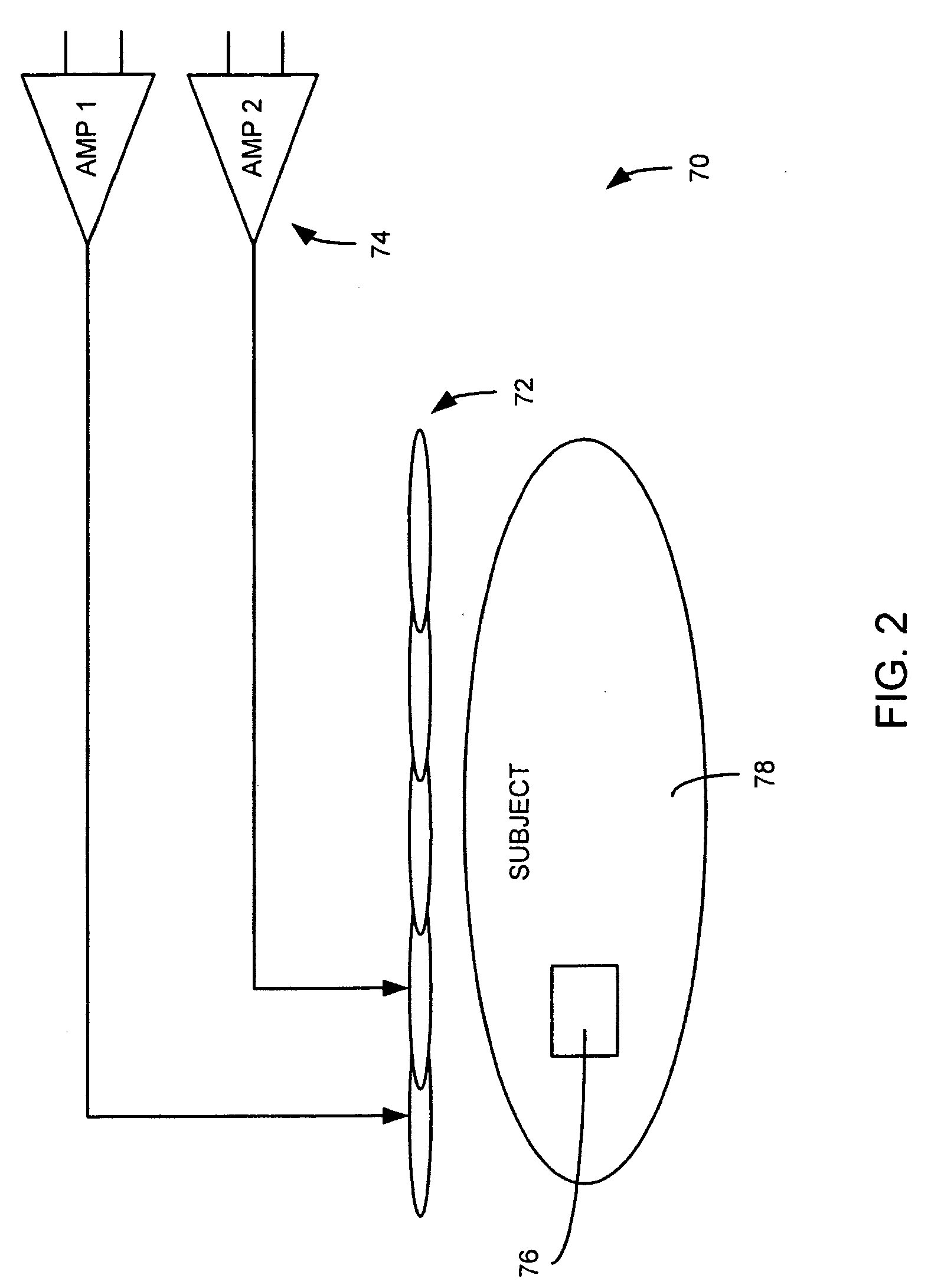
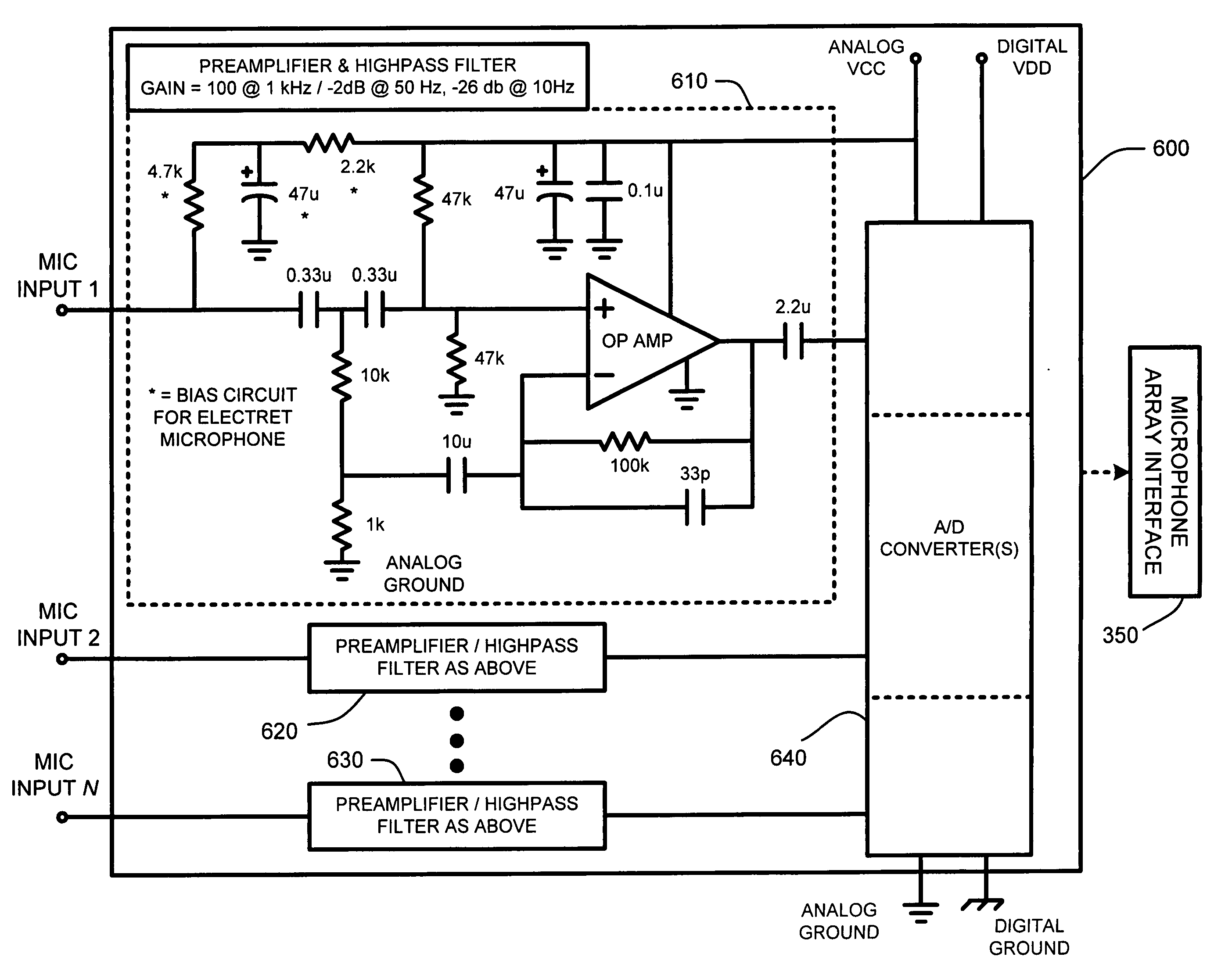
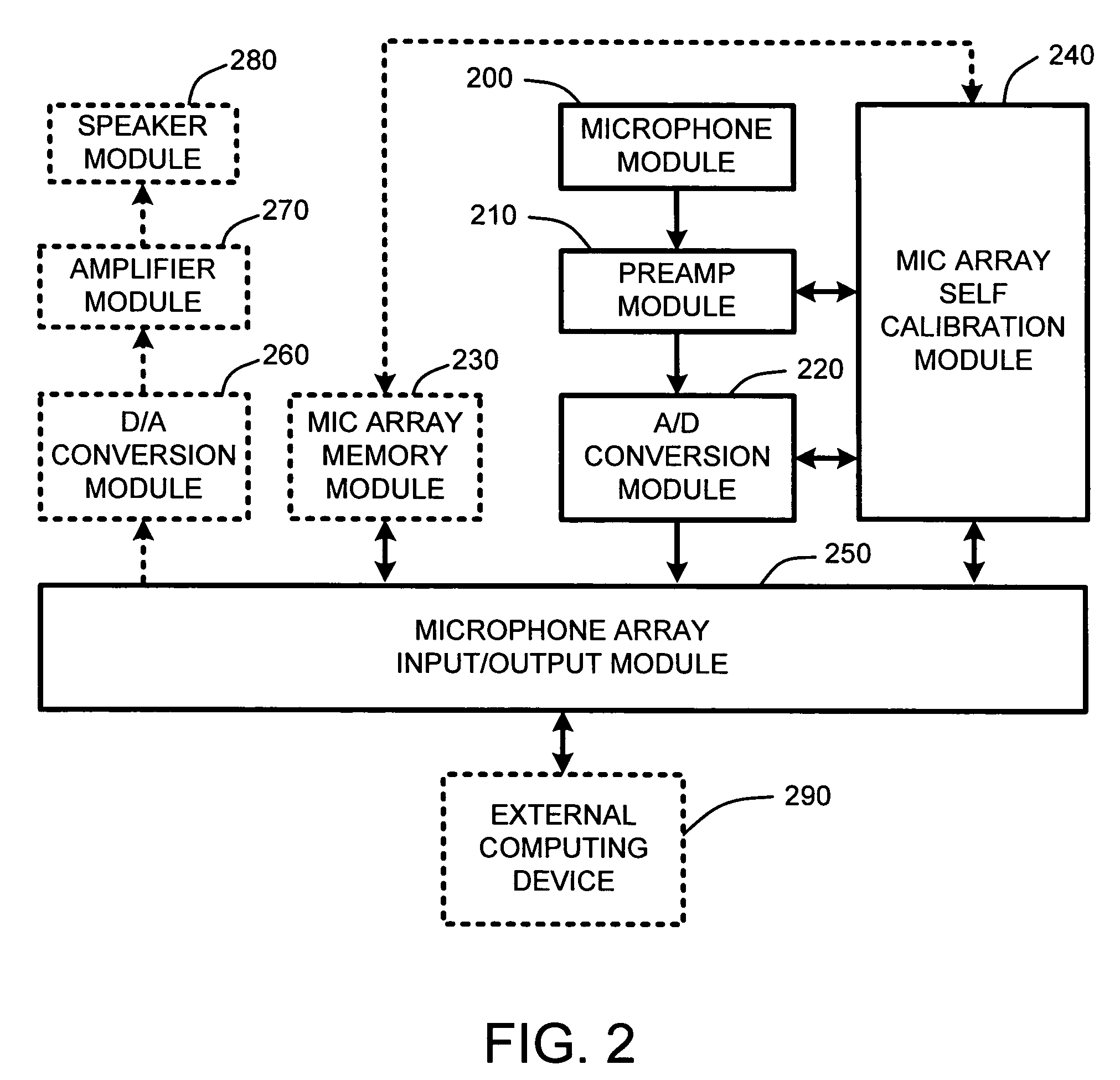
Analog preamplifier measurement for a microphone array
InactiveUS20050169483A1Increase costExtended test timeMicrophones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAudio power amplifierFft fast fourier transform
An analog preamplifier measurement system for a microphone array builds on conventional microphone arrays by providing an integral “self-calibration system.” This self-calibration system automatically injects an excitation pulse of a known magnitude and phase to all preamplifier inputs within the microphone array. The resulting analog waveform from each preamplifier output is then measured. A frequency analysis, such as, for example, a Fourier or Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), or other conventional frequency analysis, of each of the resulting waveforms is then performed. The results of this frequency analysis are then used to automatically compute frequency-domain compensation gains (e.g., magnitude and phase gains) for each preamplifier for matching or balancing the responses of all of the preamplifiers with each other.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus to generate an RF excitation consistent with a desired excitation profile using a transmit coil array
ActiveUS20050134268A1Easy to manageFaithful productionDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAudio power amplifierCoil array
A system composed of multiple transmit coils with corresponding RF pulse synthesizers and amplifiers is disclosed. A method of designing RF pulses specific to each transmit coil to induce spatiotemporal variations in a composite B1 field is also disclosed. The present invention supports faithful production of desired excitation profiles and accommodates the use of any coil array geometry. The present invention also supports reduction in excitation pulse length. Through effective B1 field maps for each transmit coil, mutual coupling and other inter-coil correlations are accounted for in the RF pulse design.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for designing RF excitation pulses in magnetic resonance tomography
InactiveUS7336145B1Promote resultsReduce peakMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionSingular value decompositionResonance
Waveforms for radio-frequency (RF) excitations pulses used in magnetic resonance imaging are designed according to a Least Squares QR (LSQR) algorithm or a Conjugate Gradient Least Squares (CGLS) algorithm, to solve the linear system of equations that arises in a multi-channel RF transmit arrangement. Better management of SAR and other factors is achieved with RF pulses designed according to these algorithms, compared to the conventionally employed singular value decomposition (SVD) algorithm.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Deacidifying method for paper cultural relics
InactiveCN102242530AAvoid damageDeacidification achievedOld paper after-treatmentInfusion methodNitrogen
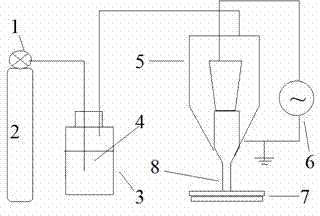
The invention discloses a de-acidifying method for paper cultural relics, which comprises the following steps of: 1) flatly spreading acidified paper cultural relics on a flat board; 2) injecting an ion source reagent including OH- and Ca<2+> into a bubbler, and importing a mixed gas of helium gas and nitrogen to serve as a carrier gas, and transmitting the ion source reagent to a plasma spray gun; 3) turning on a plasma excitation pulse power source, forming ion flames containing OH- and Ca<2+> at the muzzle of the plasma spray gun; and spraying the ion flames to scan the surface of the flattened paper cultural relics to perform deacidifying processing. In the method disclosed by the invention, a plasma discharging form is adopted under normal temperature and normal pressure work conditions, thereby complex and expensive vacuum equipment are avoided being used, and damages of an aqueous solution infusion method to a paper body are avoided; and the method disclosed by the invention can be used for realizing rapid large-area deacidifying processing and has the advantages of uniformity for de-acidification, stable process, and suitability for industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method, magnetic resonance apparatus and program to generate image using parallel acquisition technique
A method of generating an imaging by using a parallel acquisition technique comprises the following steps: an excitation pulse is radiated into an examination subject; a first echo train is generated after the excitation pulse, wherein the first echo train densely scans a segment of k-space to be scanned for an acquisition of coil calibration data; coil calibration data are acquired by means of the first echo train; the acquired coil calibration data are stored in a coil calibration data set; a second echo train is generated after the same excitation pulse, wherein the second echo train undersamples a segment of k-space to be scanned for an acquisition of image data; image data are acquired by means of the second echo train; the acquired image data are stored in an incomplete image data set; and a first image data set is generated by substituting data missing in the incomplete image data set due to the undersampling by means of a selected PAT reconstruction technique using the coil calibration data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com