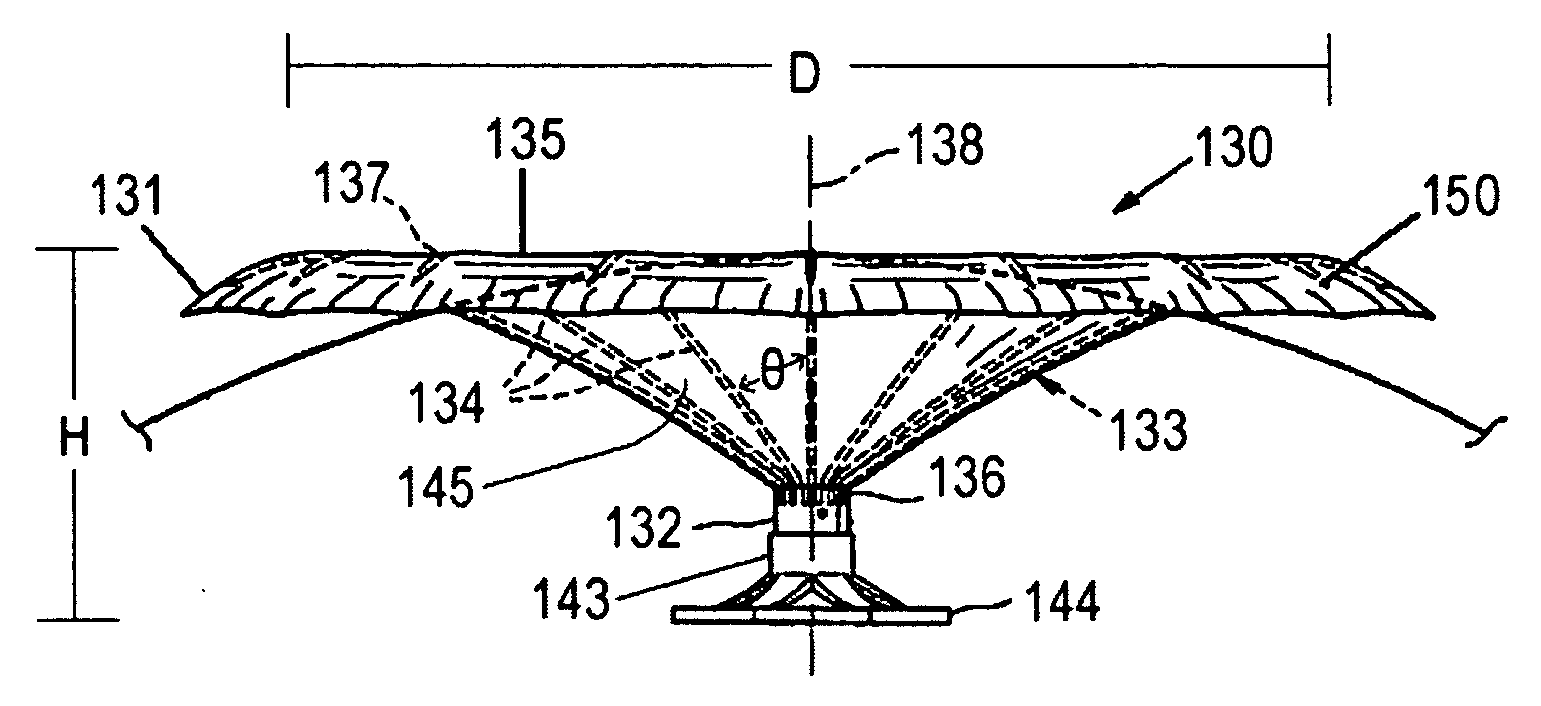
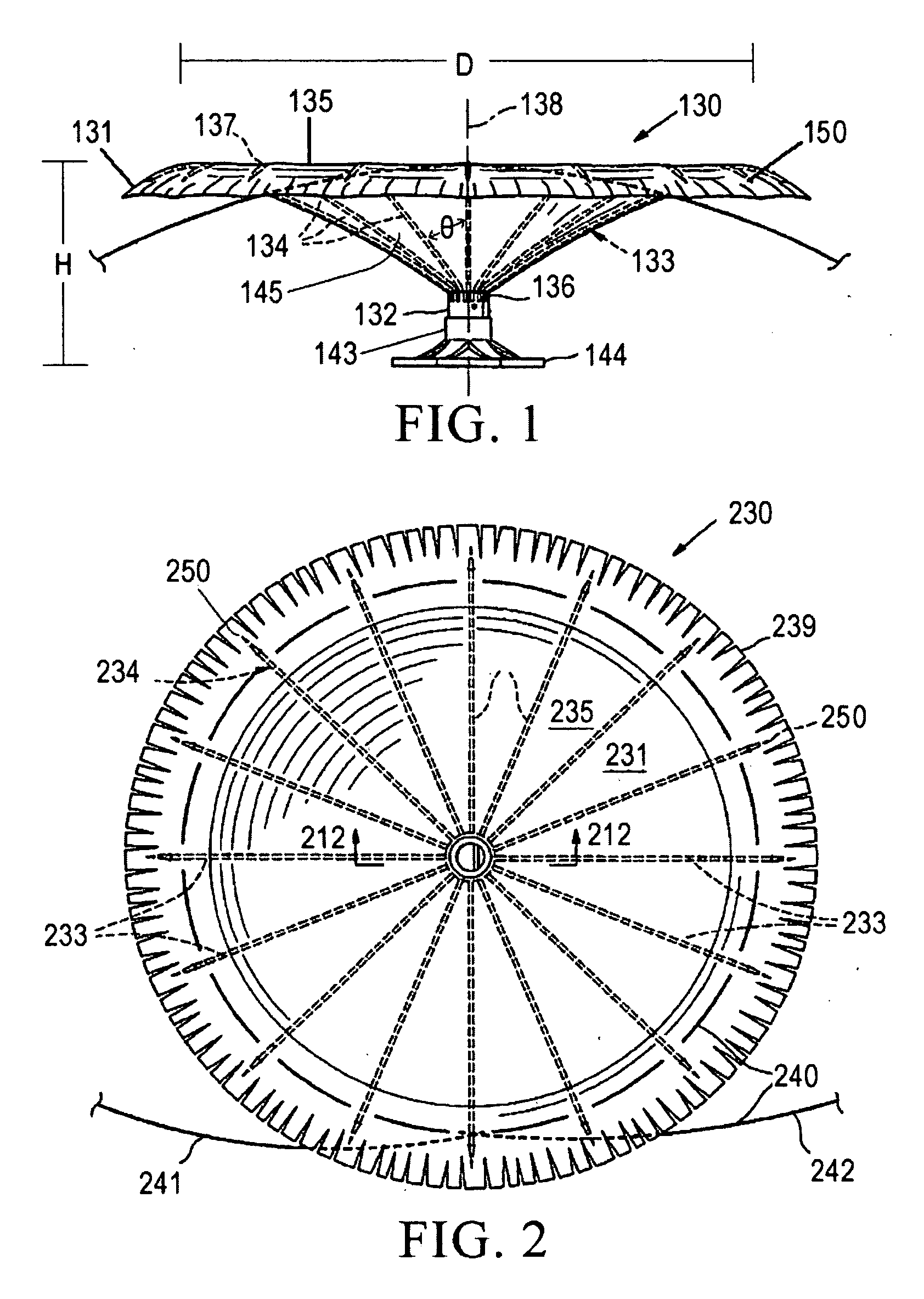
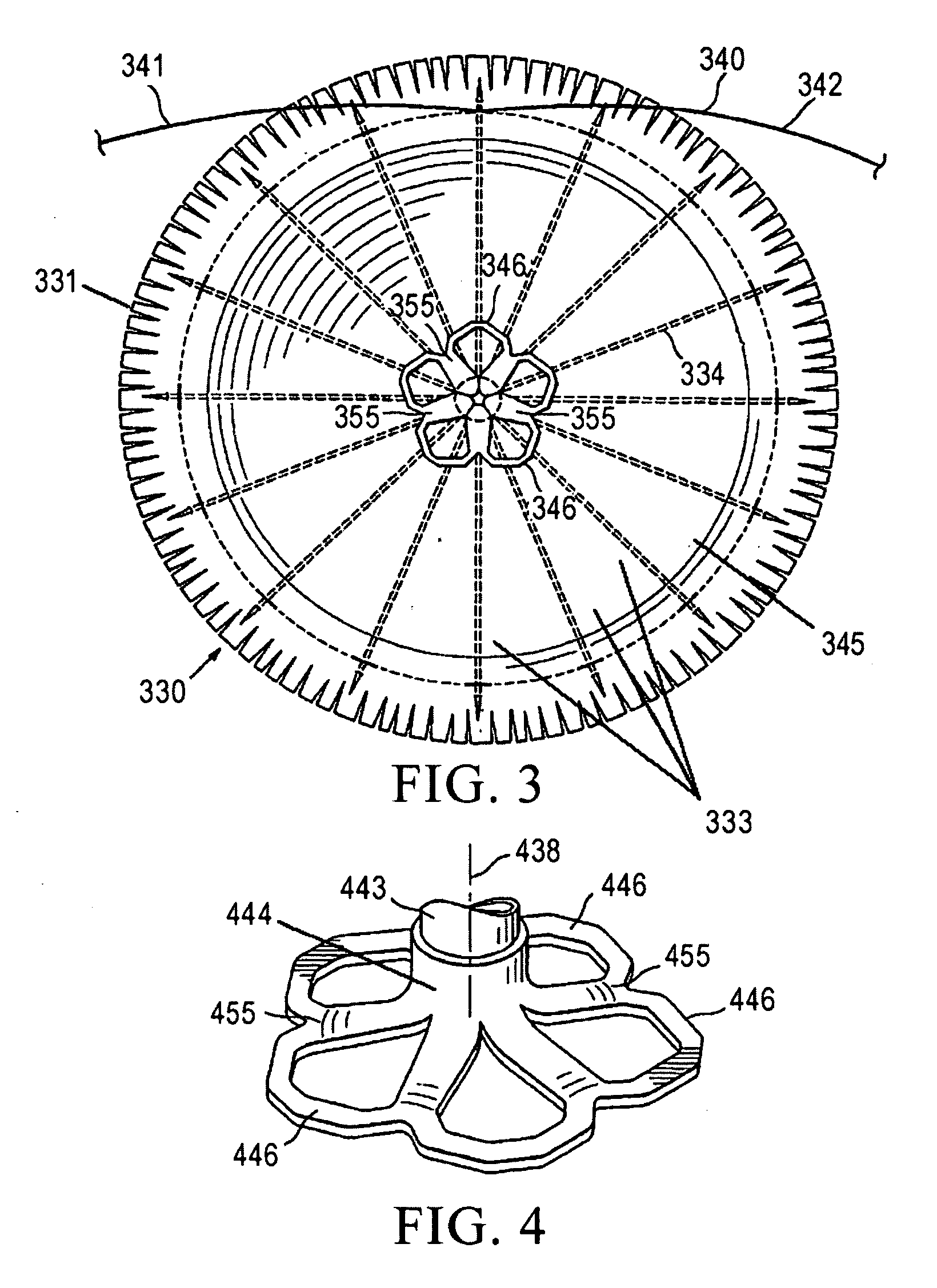
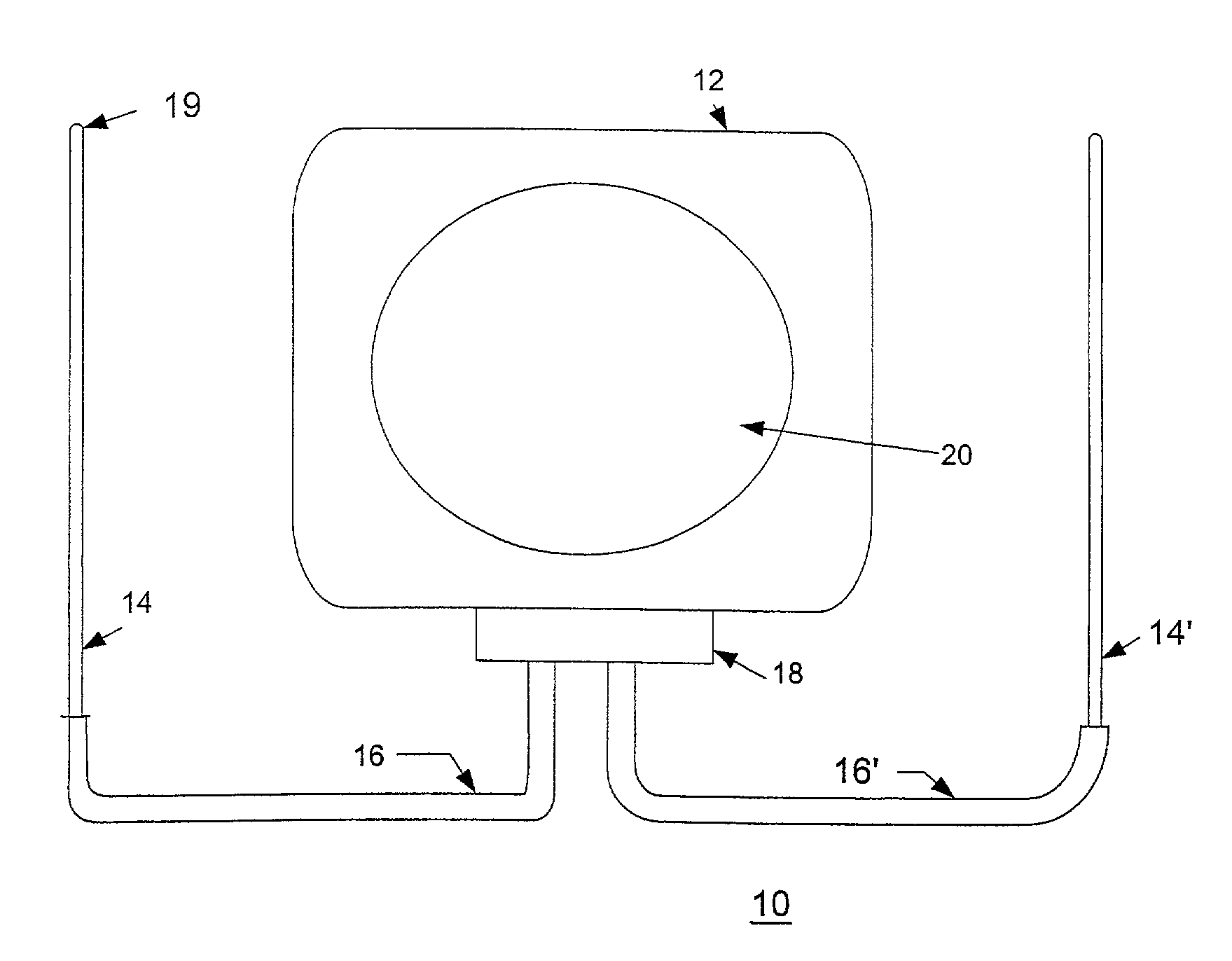
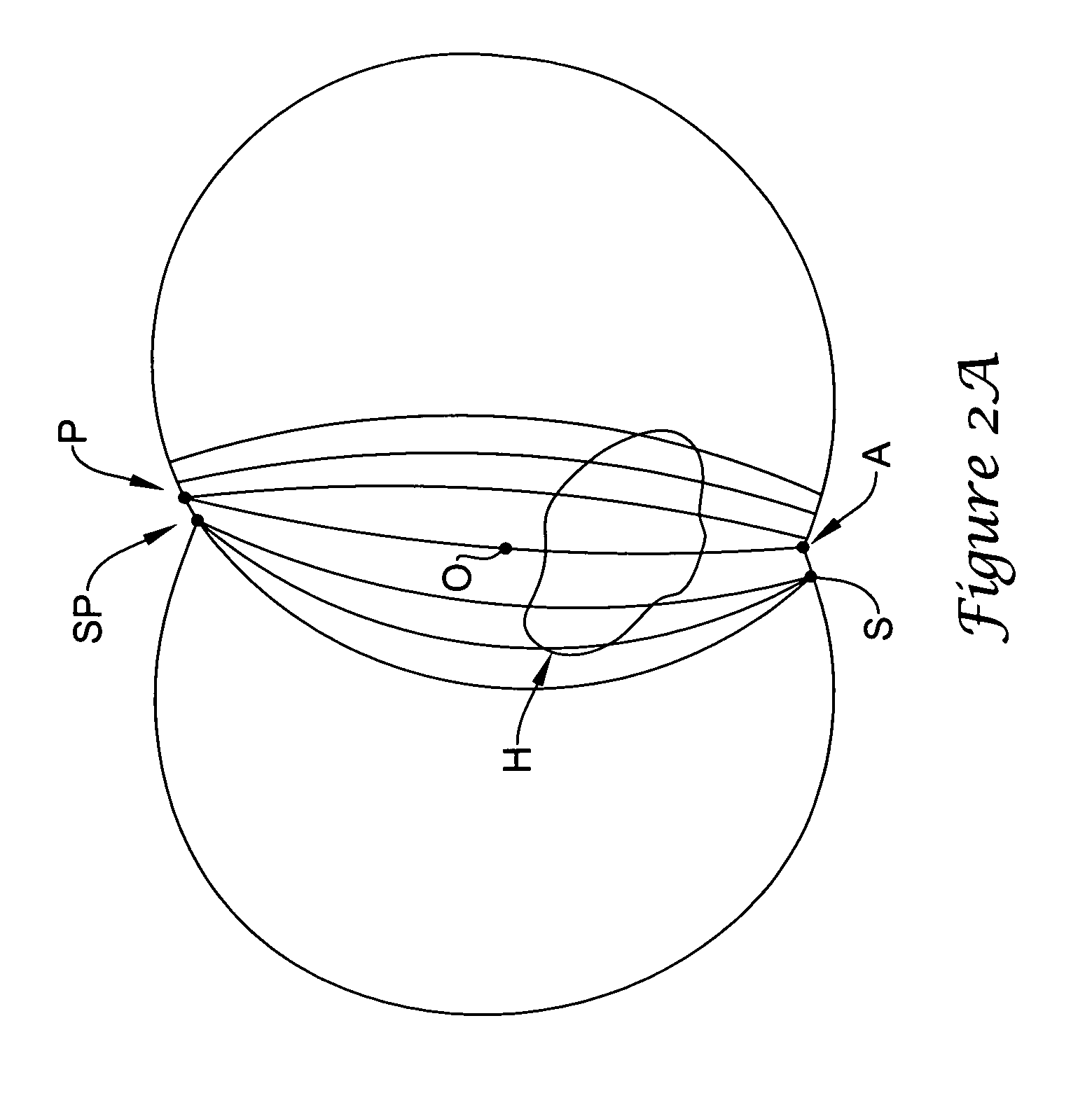
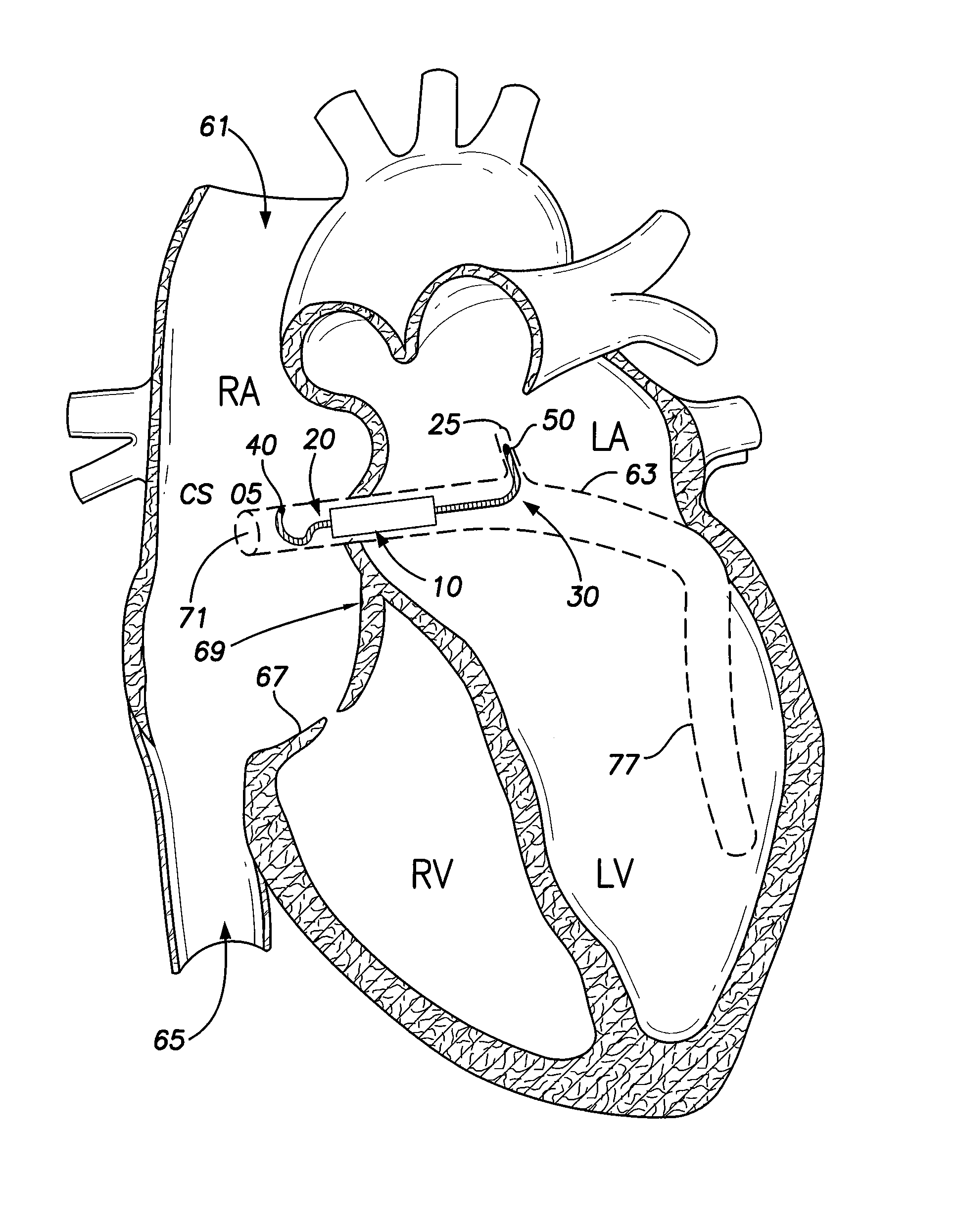
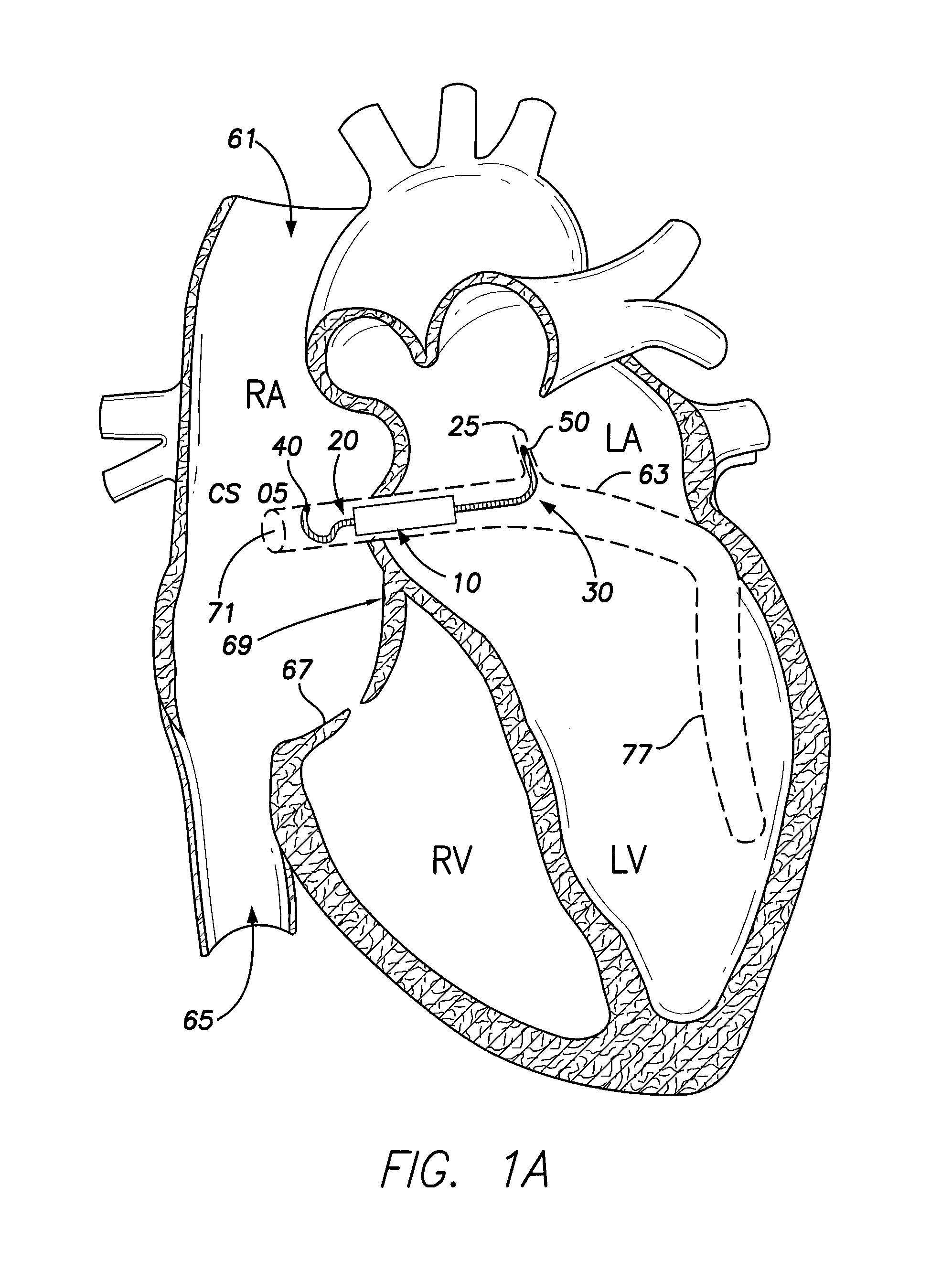
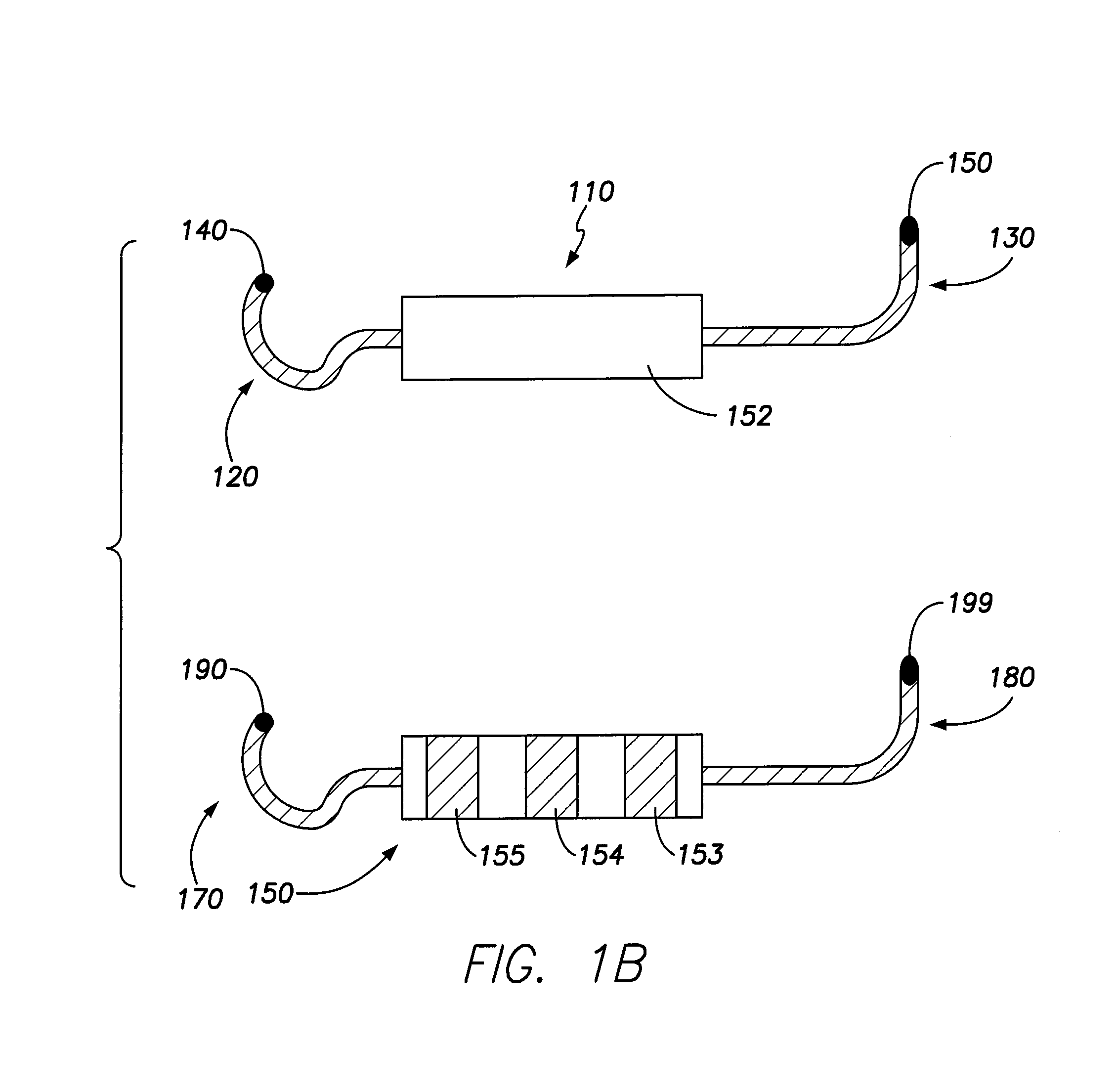
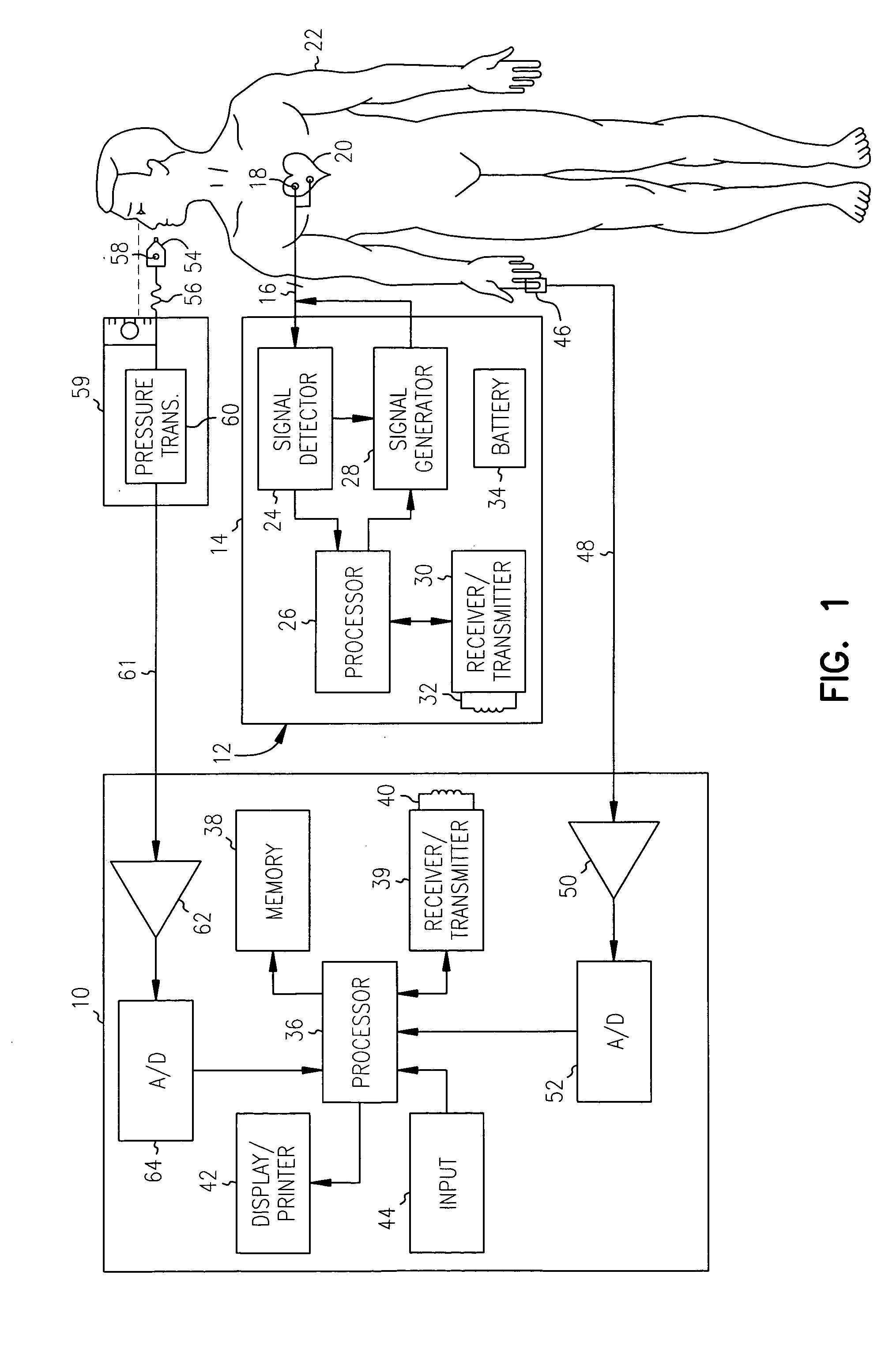
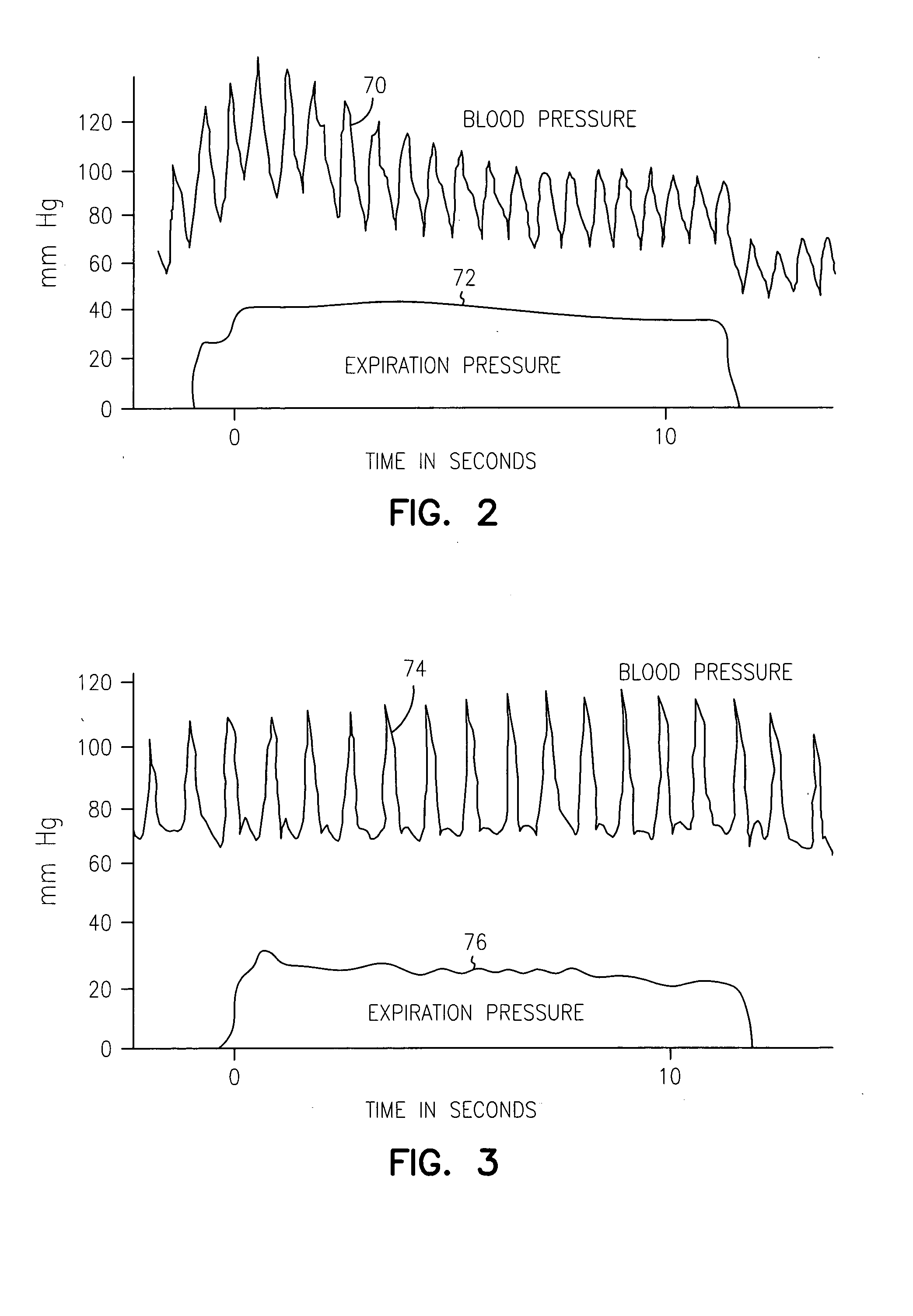
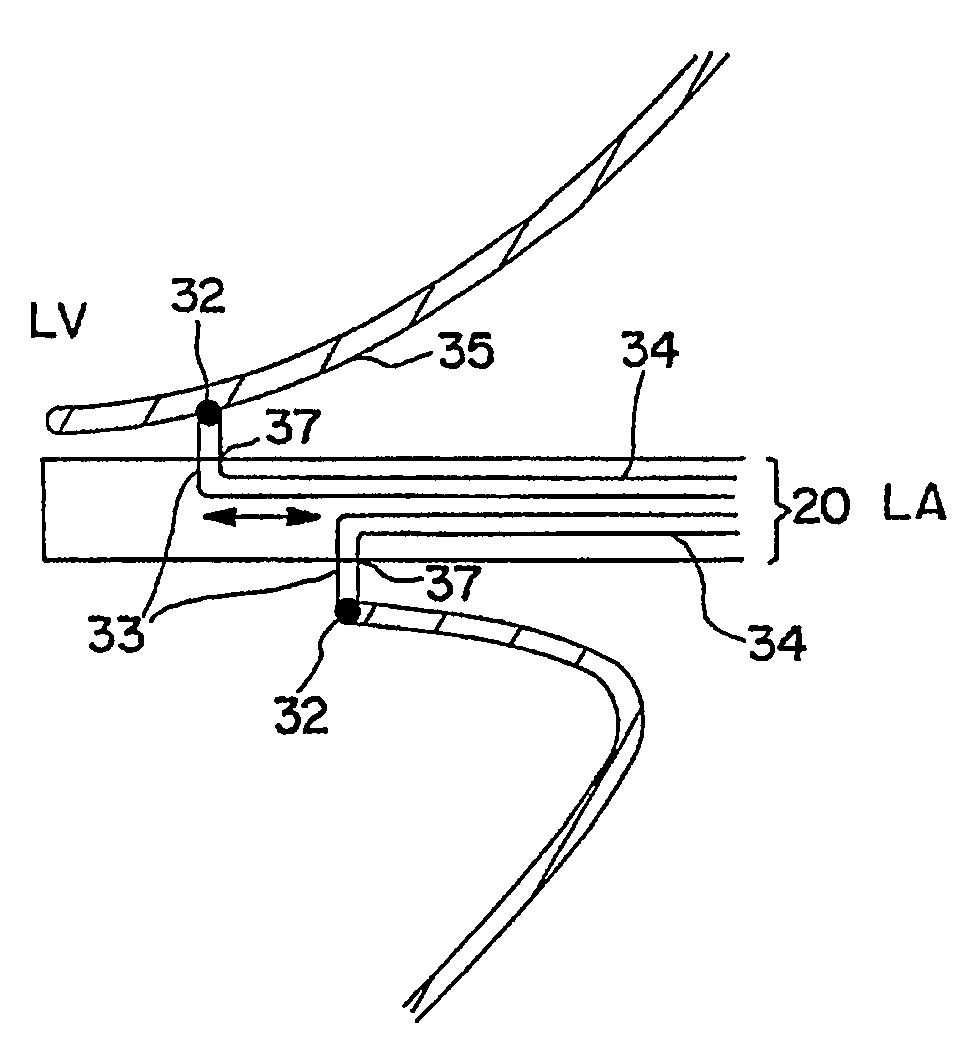
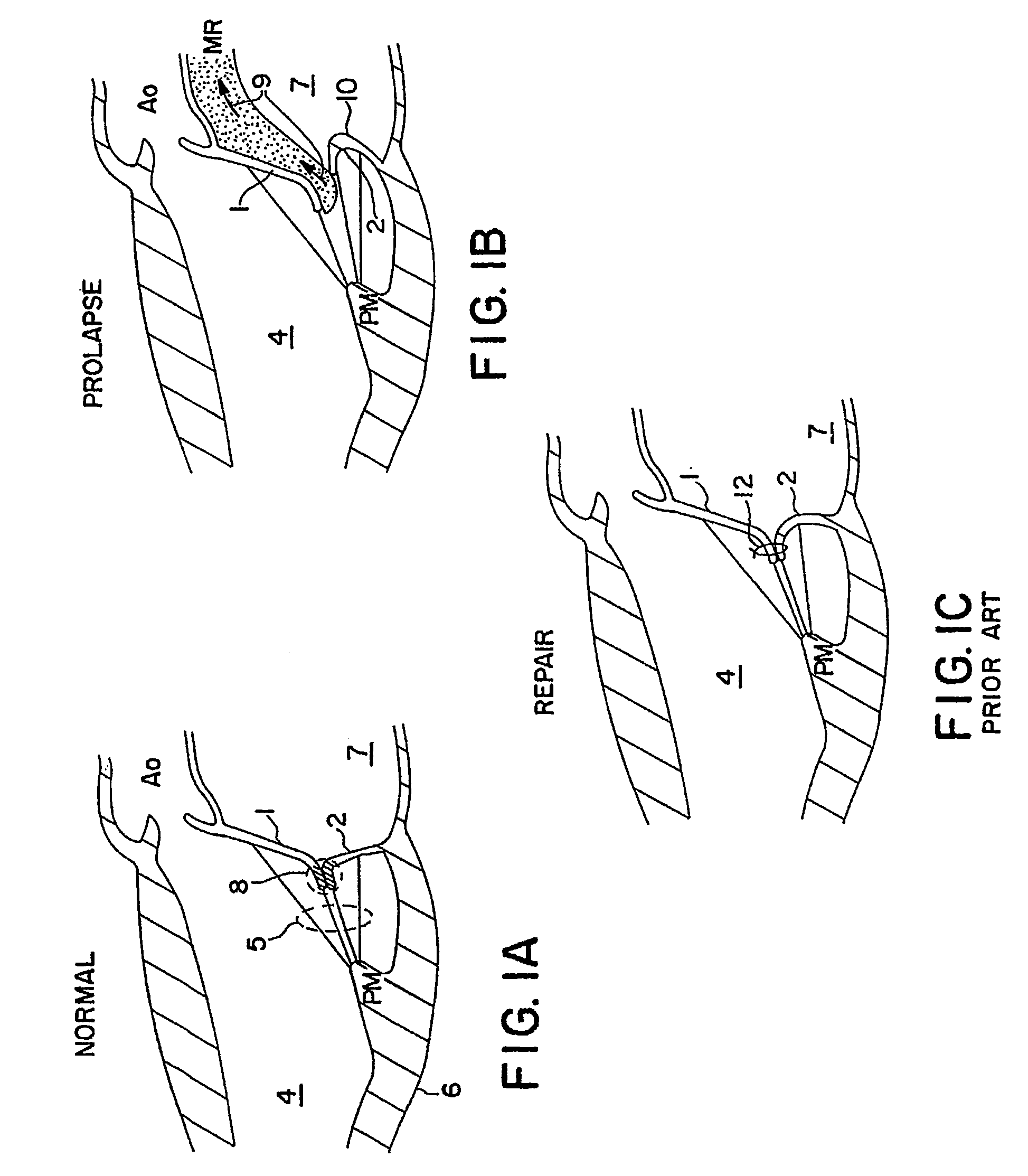
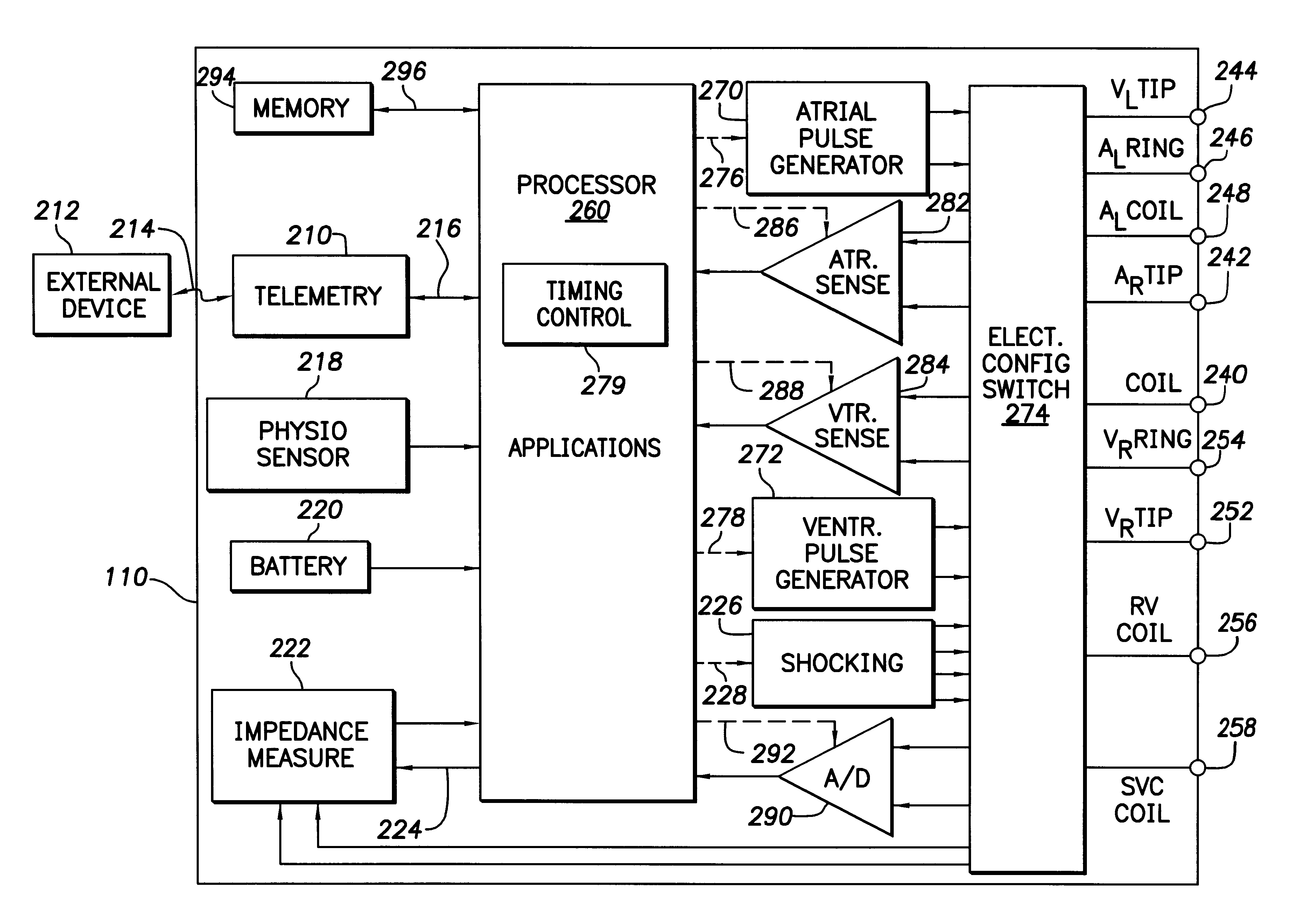
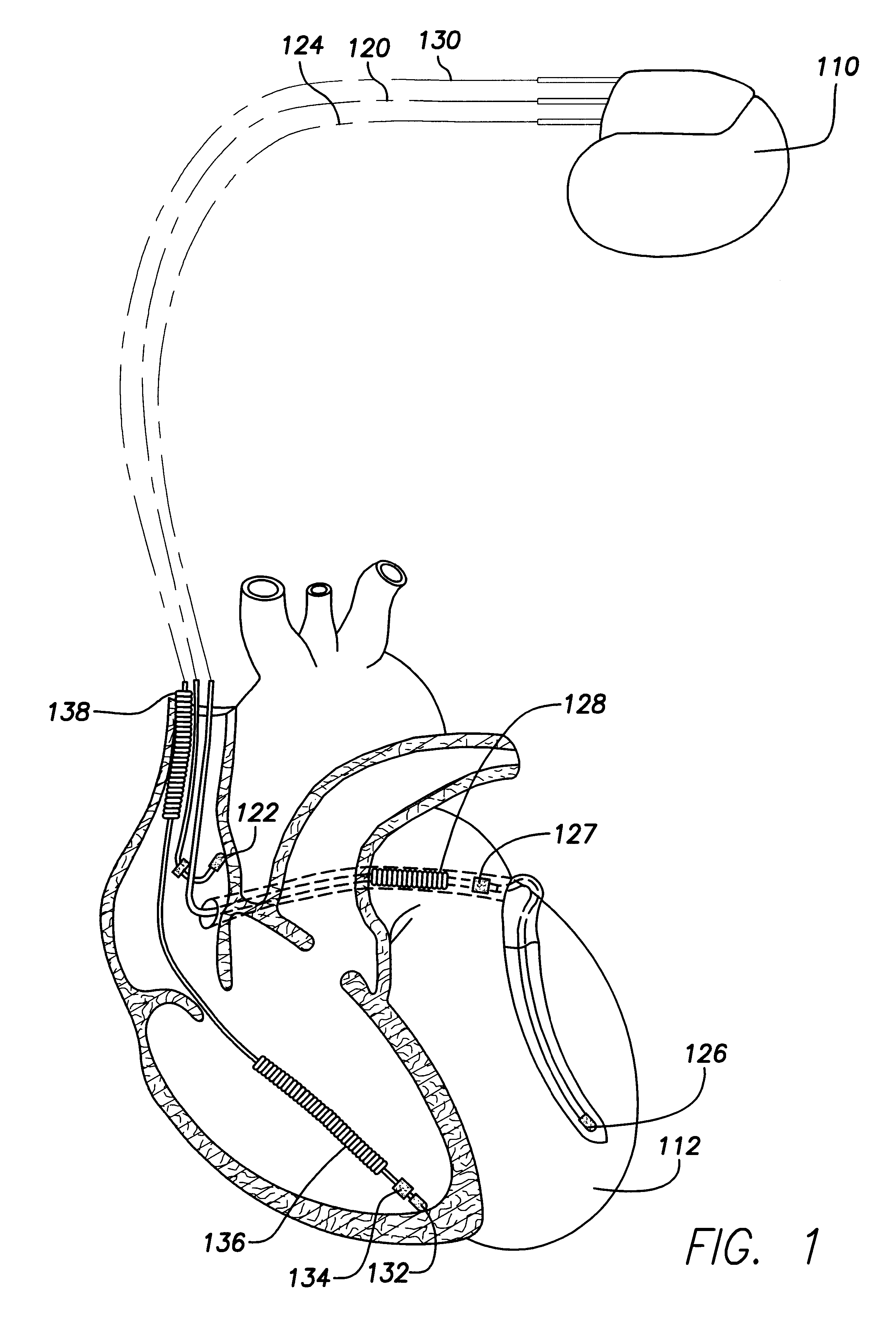
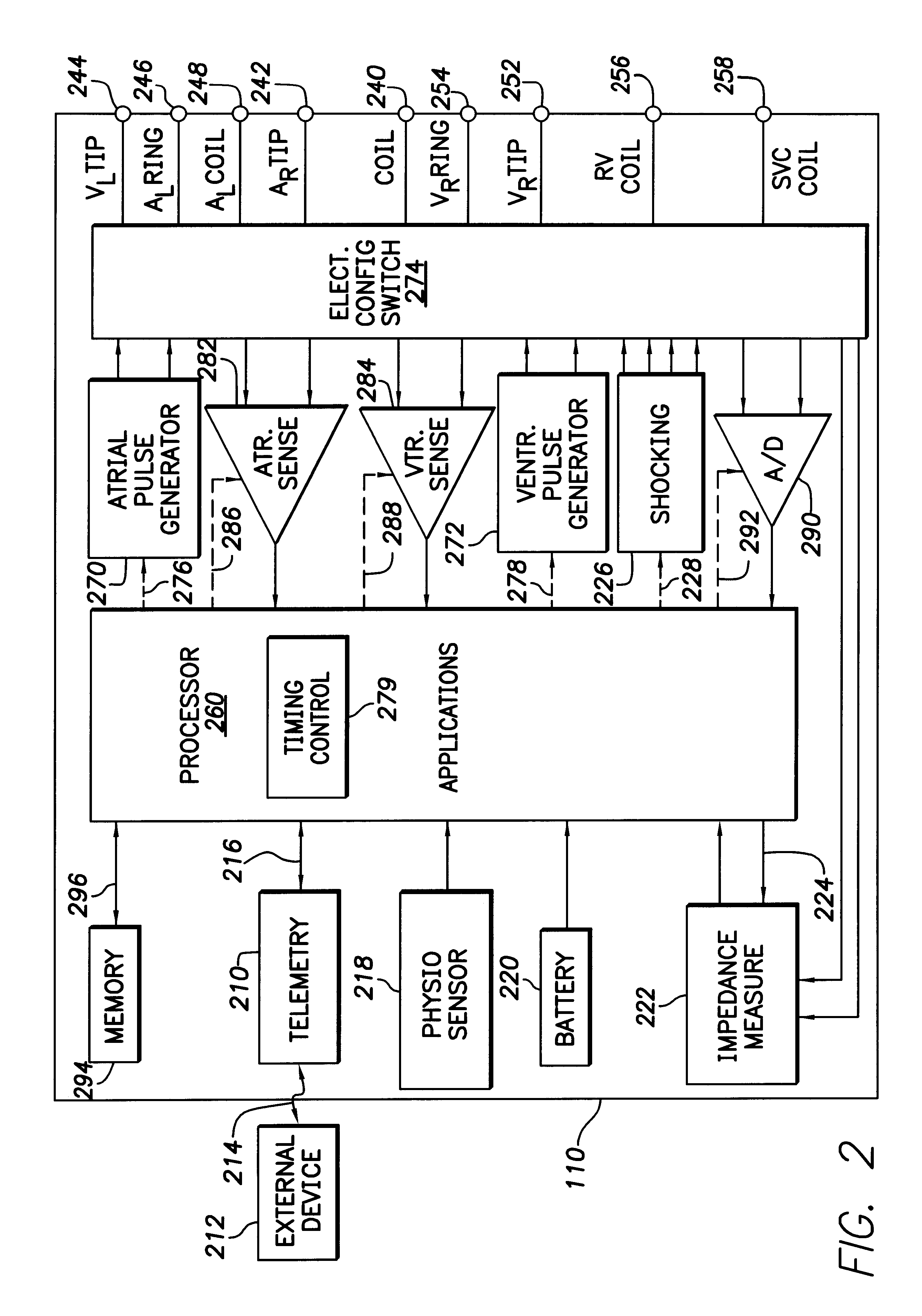
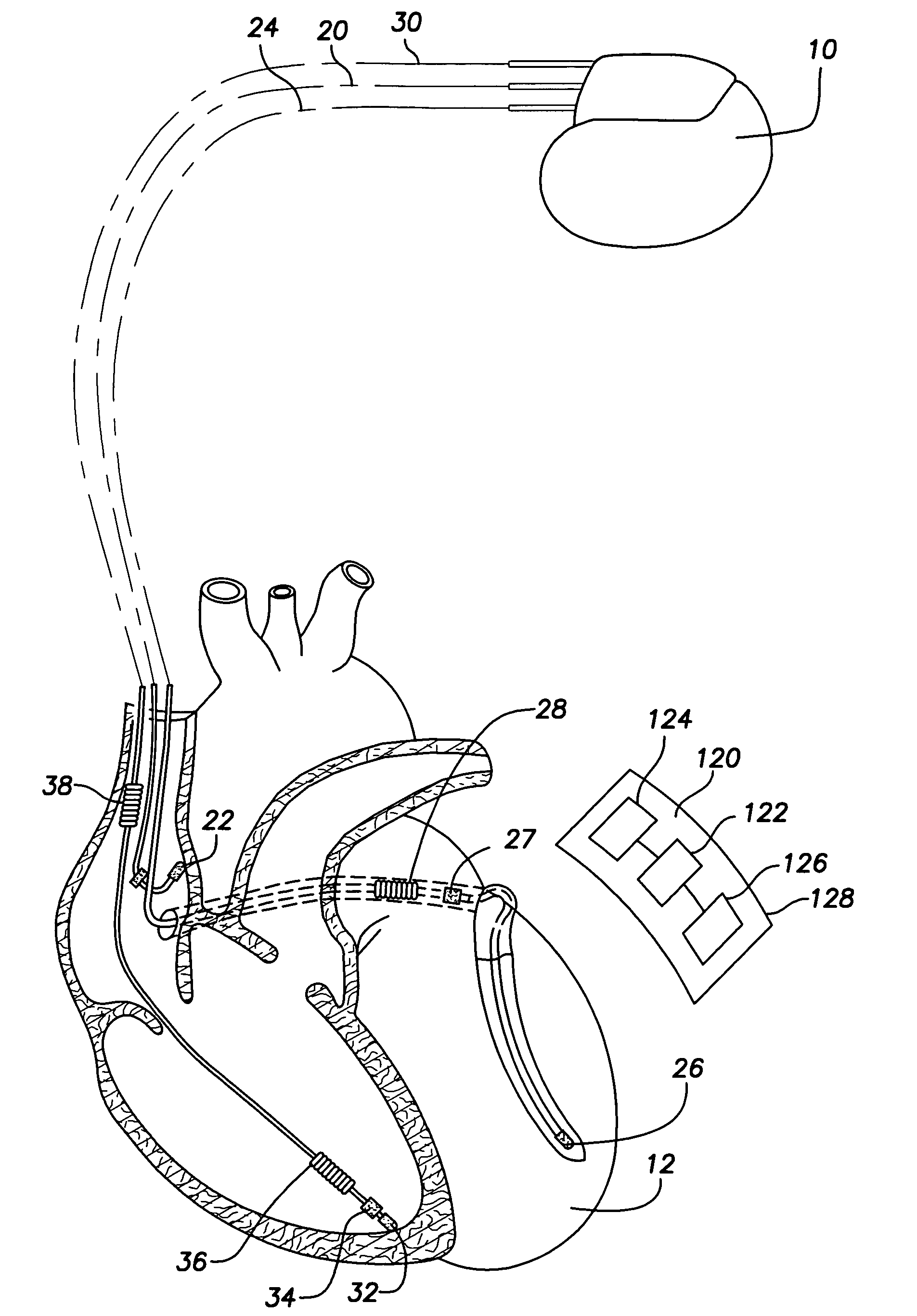
Patents
Literature
225 results about "Cardiac device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cardiac device is used to keep your heart beating with a normal rhythm. There are several types of devices available. If you have heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HF-rEF) and need a device, your doctor will let you know and talk with you about the best type to meet your needs.
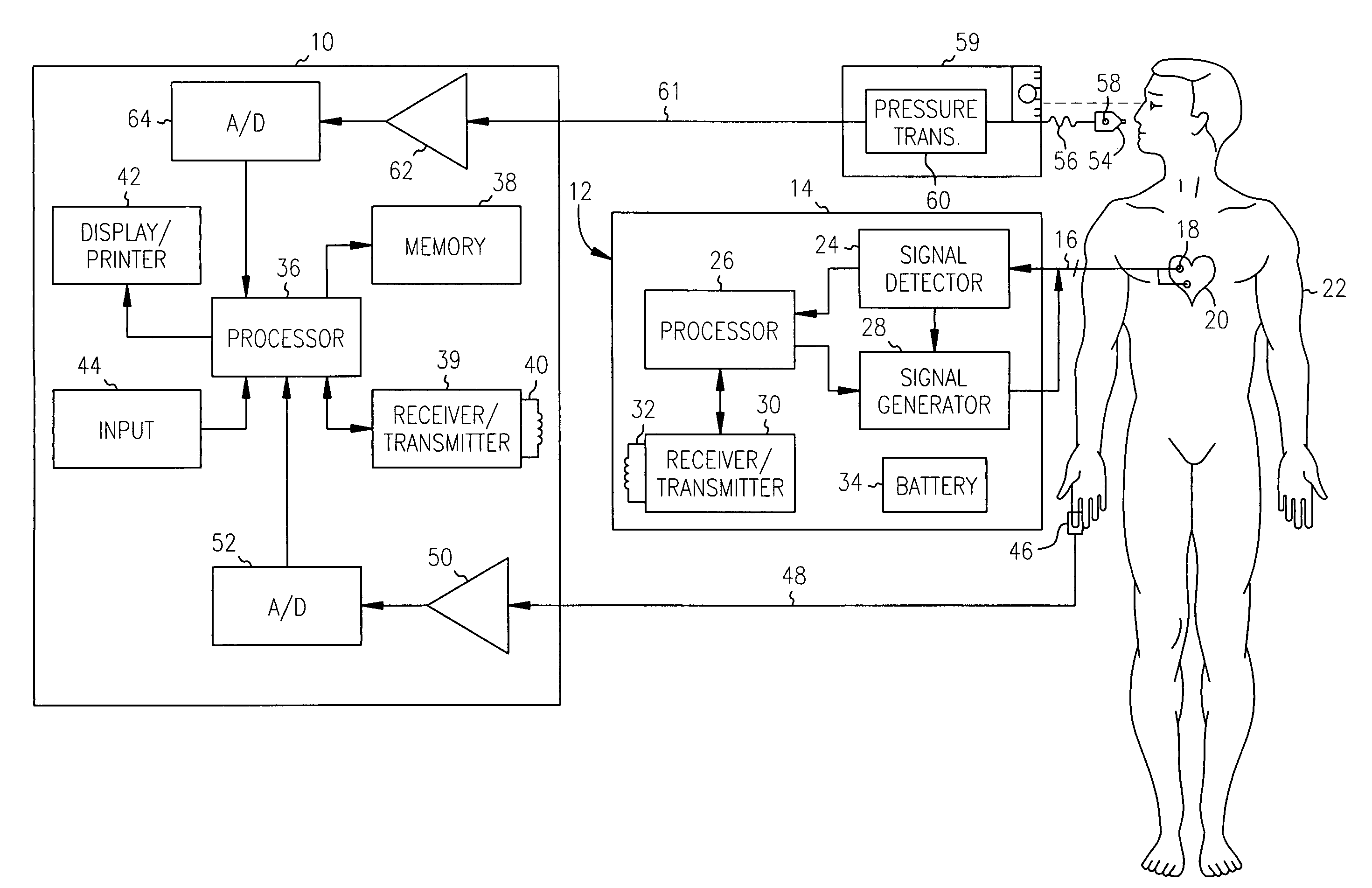
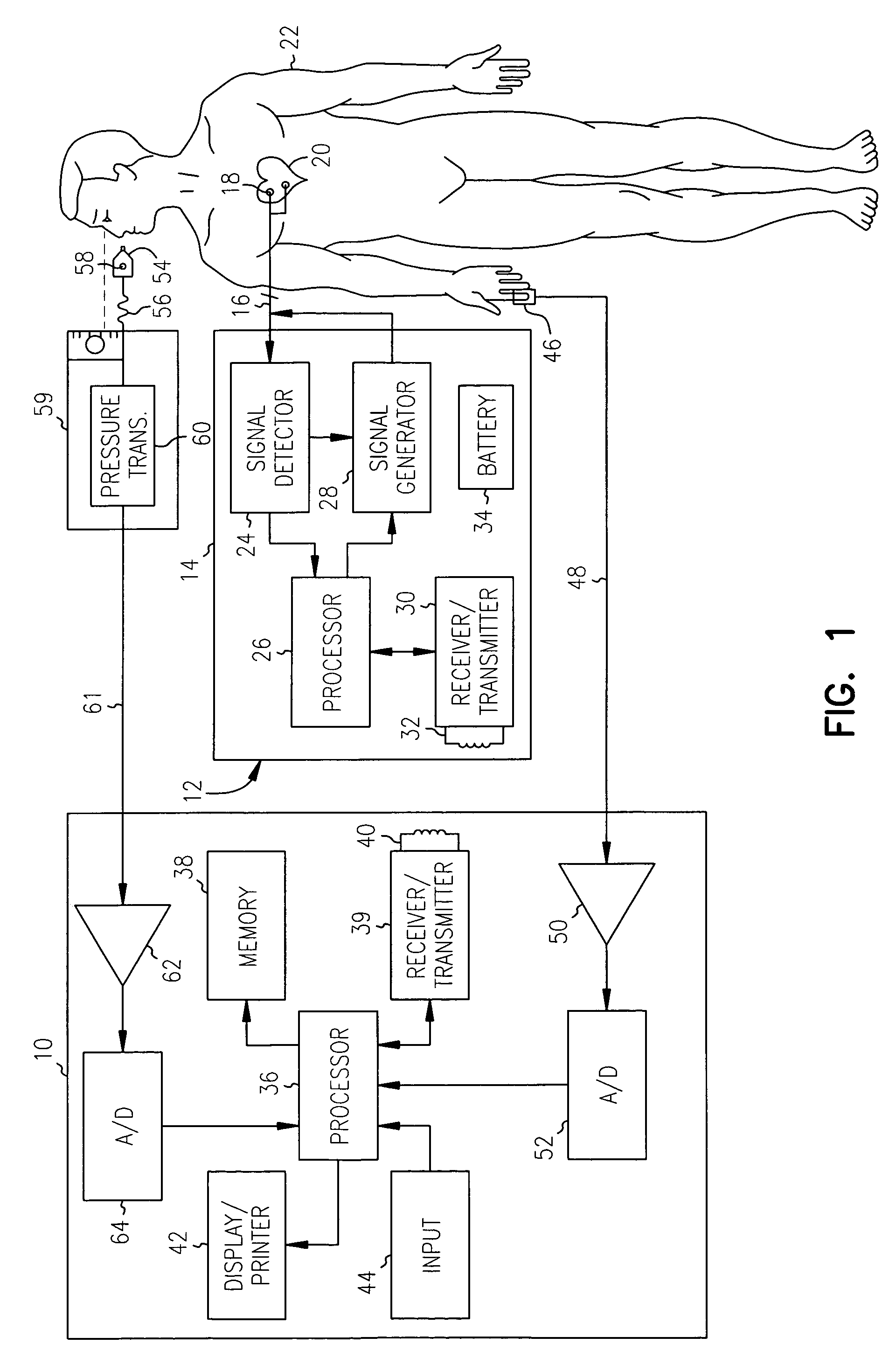
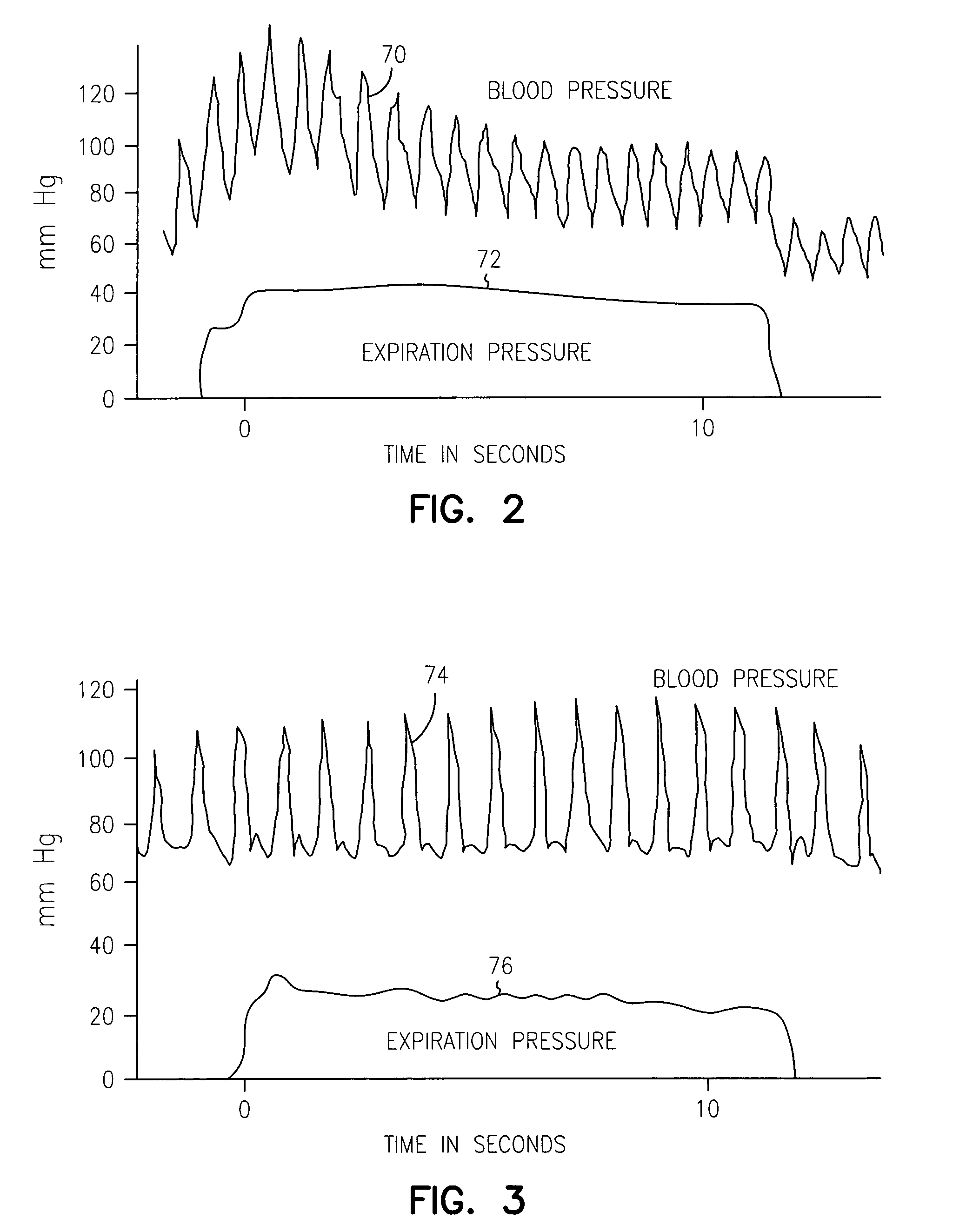
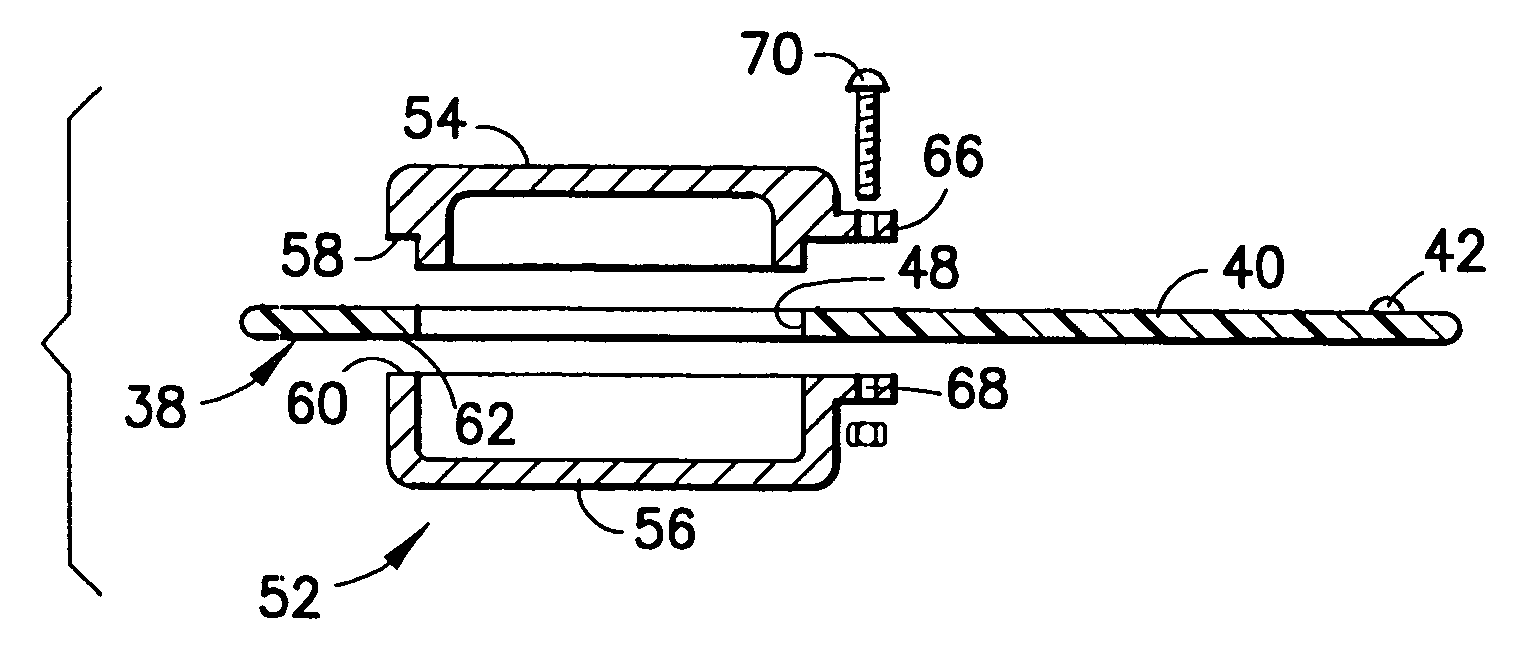
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070161846A1Reduced elastic recoilShorten speedHeart valvesInternal electrodesCardiac deviceDiastolic function
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulator device having an anteriorly positioned electrode
A subcutaneous cardiac device includes a subcutaneous electrode and a housing coupled to the subcutaneous electrode by a lead with a lead wire. The subcutaneous electrode is adapted to be implanted in a frontal region of the patient so as to overlap a portion of the patient's heart.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
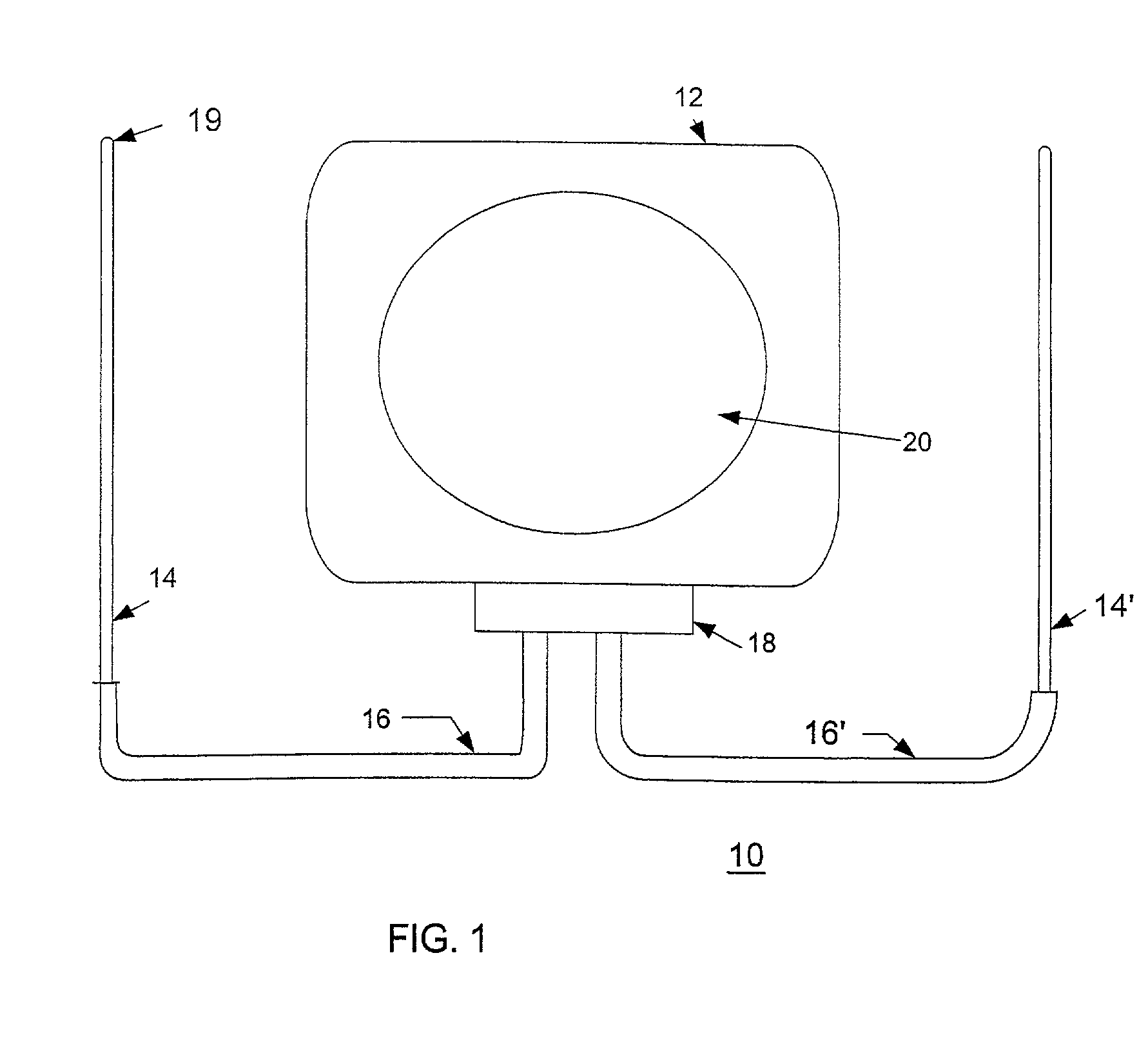
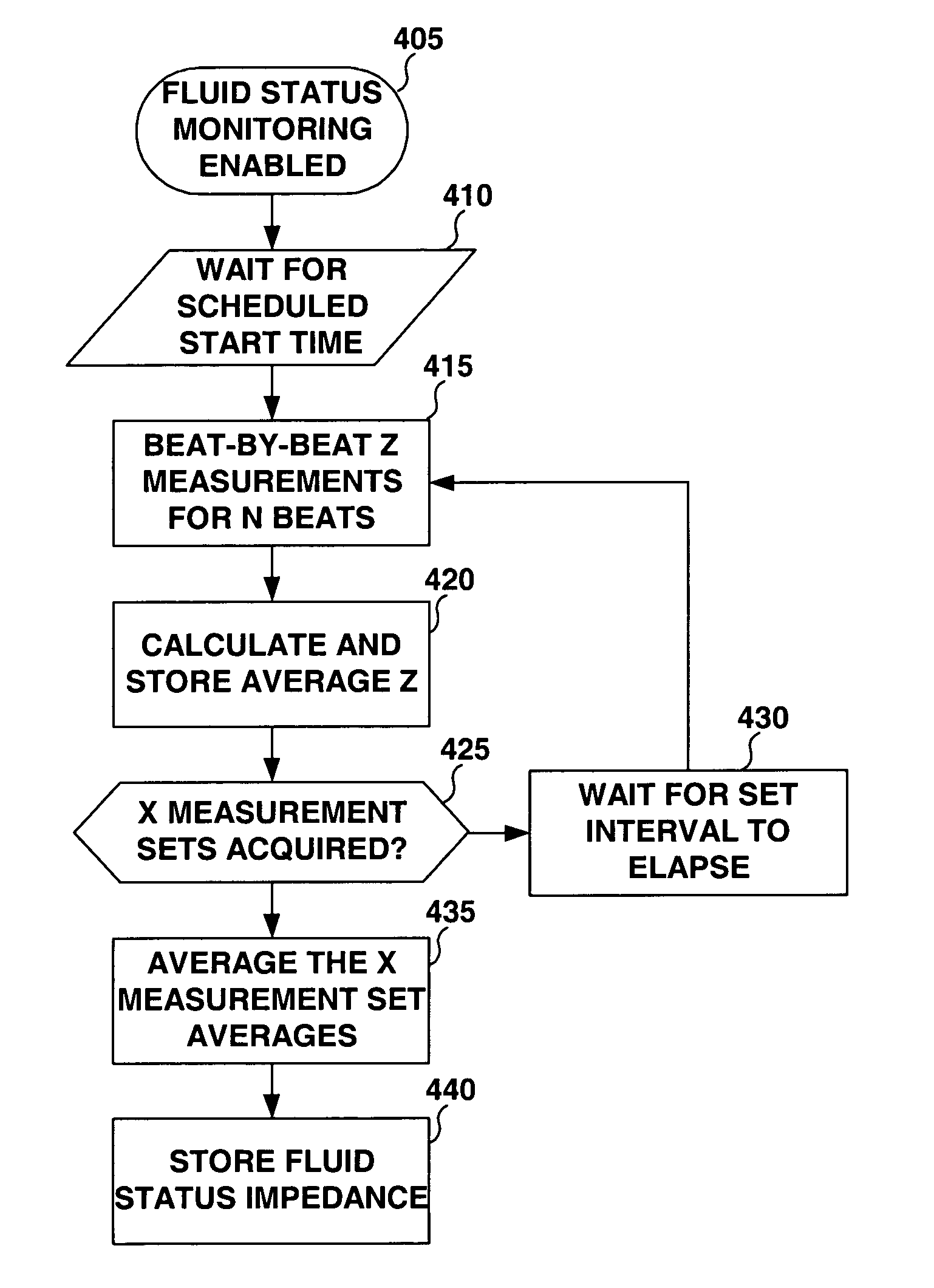
Method and apparatus for monitoring tissue fluid content for use in an implantable cardiac device
ActiveUS20050080460A1Easy to implementCancel noiseHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsThoracic FluidTissue fluid
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Manufacturing process of cellulose nanofibers from renewable feed stocks
InactiveUS20080146701A1High aspect ratioRaise the potentialMaterial nanotechnologyFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpCelluloseNatural fiber
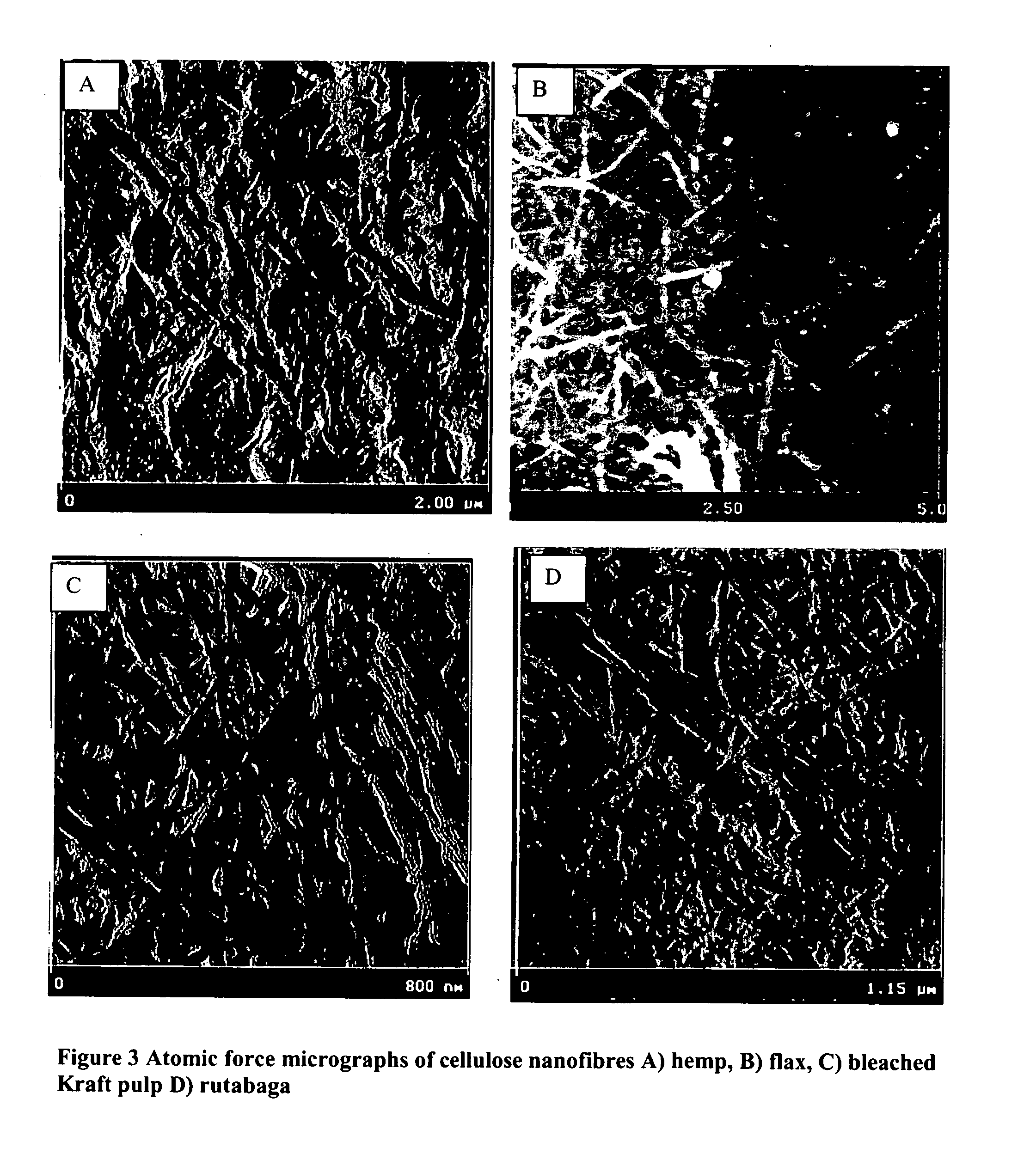
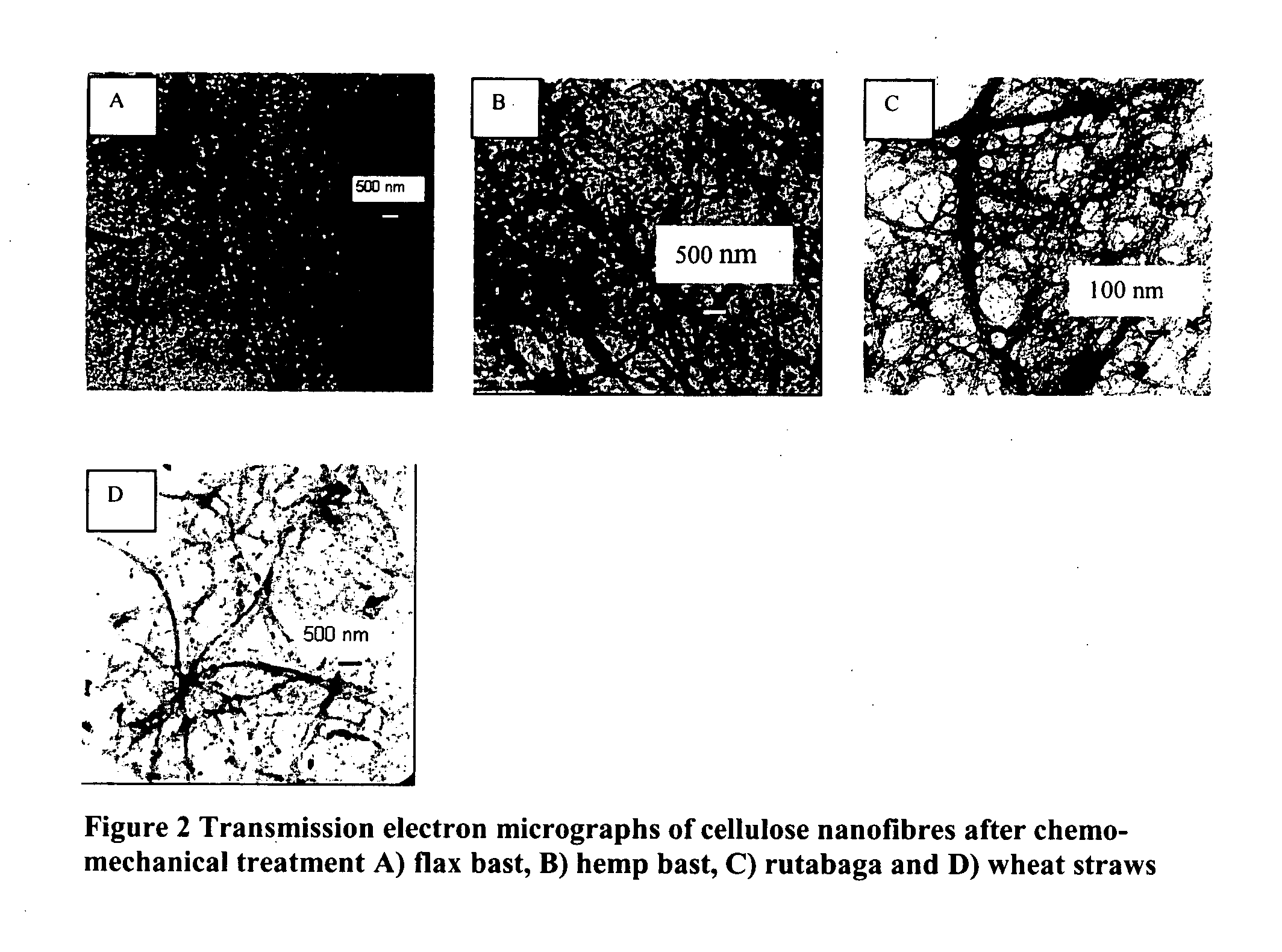
Cellulose nanofibers have been processed from renewable feedstock in particularly from natural fibers, root crops and agro fibers, wherein the pulp was hydrolysed at a moderate temperature of 50 to 90 degree C., one extraction was performed using dilute acid and one extraction using alkali of concentration less than 10%; and residue was cryocrushed using liquid nitrogen, followed by individualization of the cellulose nanofibers using mechanical shear force. The nanofibers manufactured with this technique have diameters in the range of 20-60 nm and much higher aspect ratios than long fibers. Due to its lightweight and high strength its potential applications will be in aerospace industry and due to their biodegradable potential with tremendous stiffness and strength, they find application in the medical field such as blood bags, cardiac devices, valves as a reinforcing biomaterial.
Owner:SAIN MOHINI M +1
Cardiac rhythm management device and sensor-suite for the optimal control of ultrafiltration and renal replacement therapies
ActiveUS20070175827A1ElectrotherapyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesUltrafiltrationOptimal control
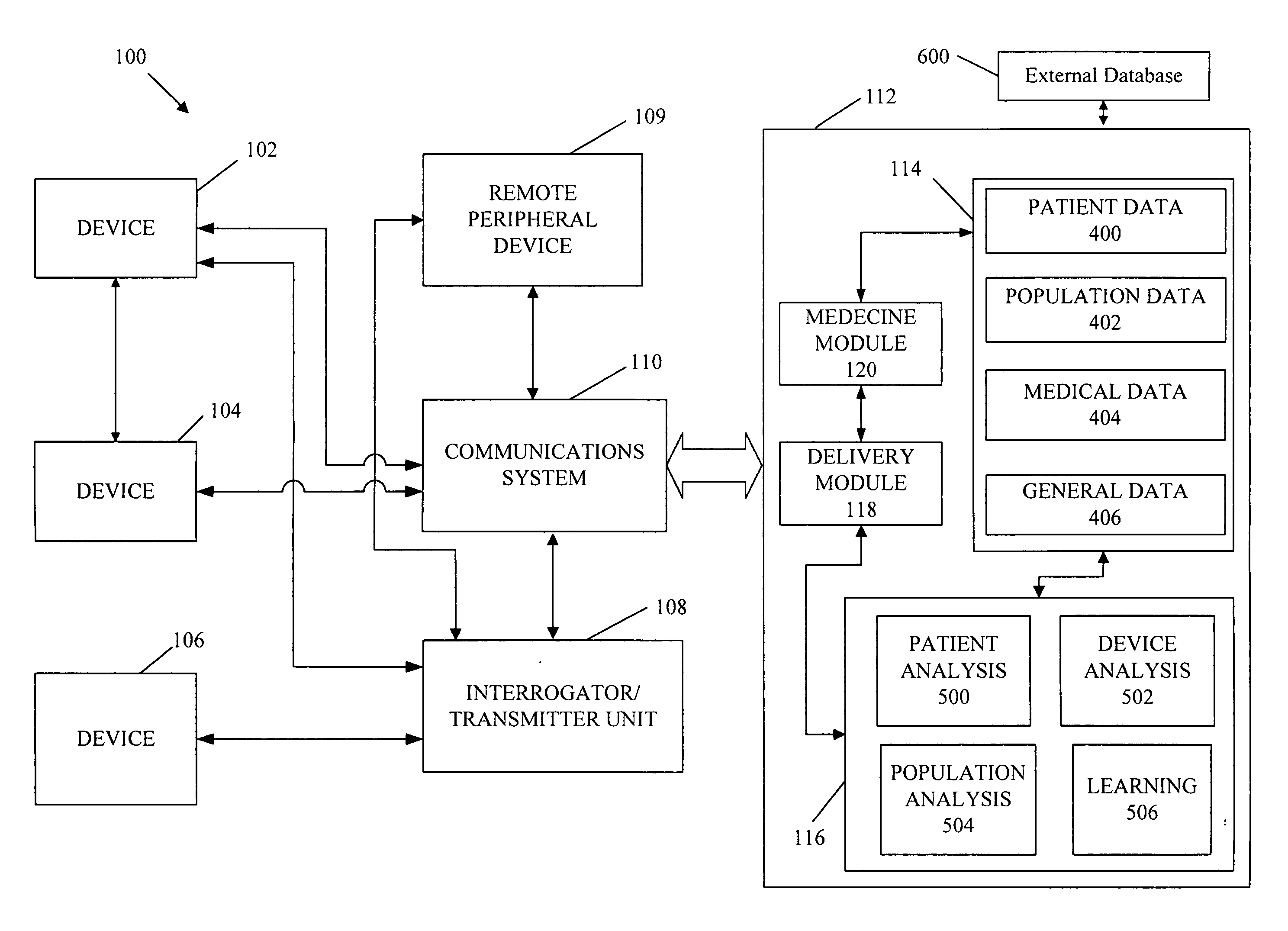
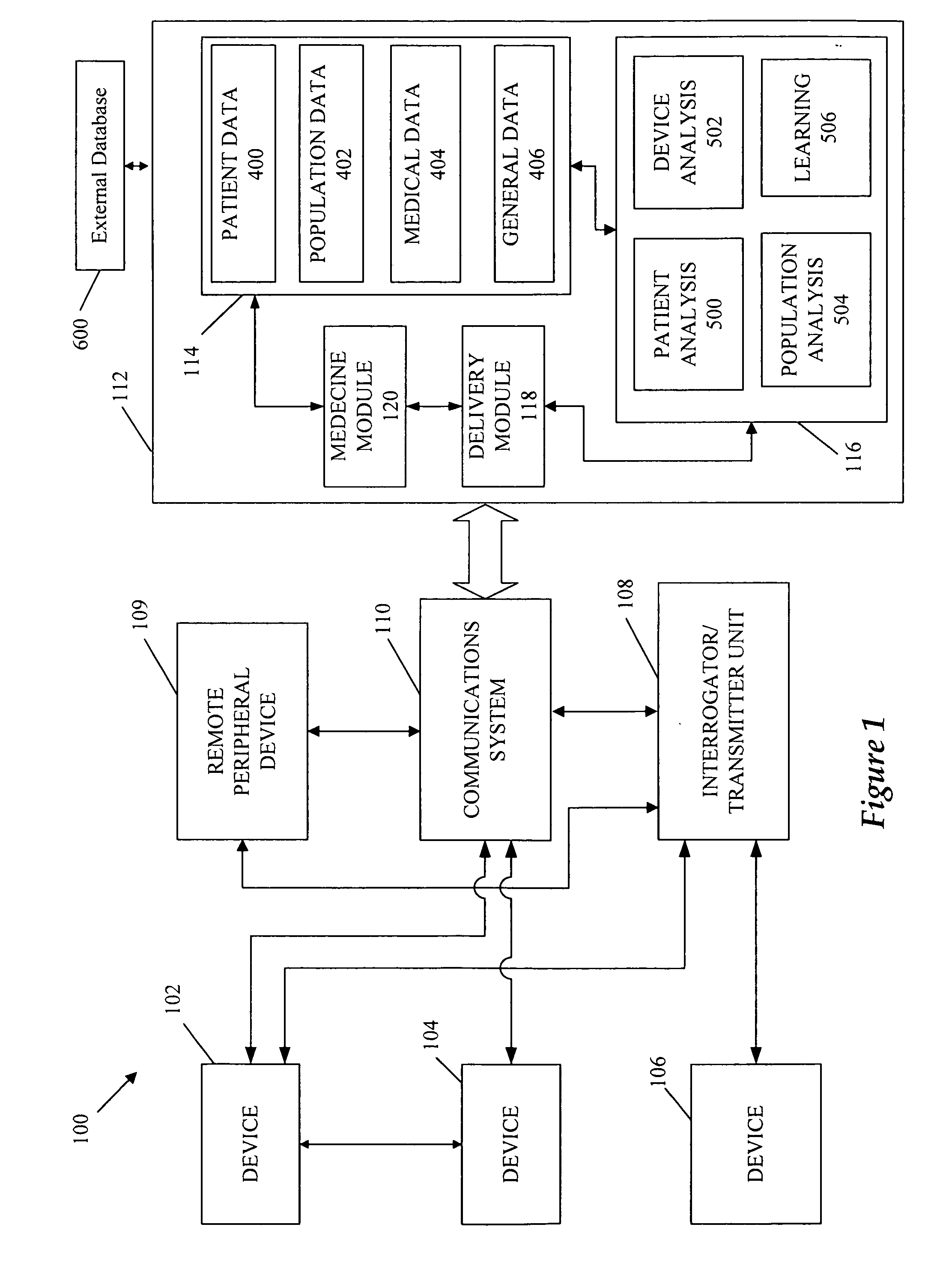
A cardiorenal patient monitoring system comprising, either implanted or non-implanted device(s), remote peripheral device(s), computer network(s), host, and communication means between the device(s), computer network(s), and host. The preferred embodiment shows an advanced patient monitoring system for using an implanted cardiac device and a dialysis machine in renal therapy. In addition, the method of advanced patient monitoring is in conjunction with the advanced patient monitoring system is disclosed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
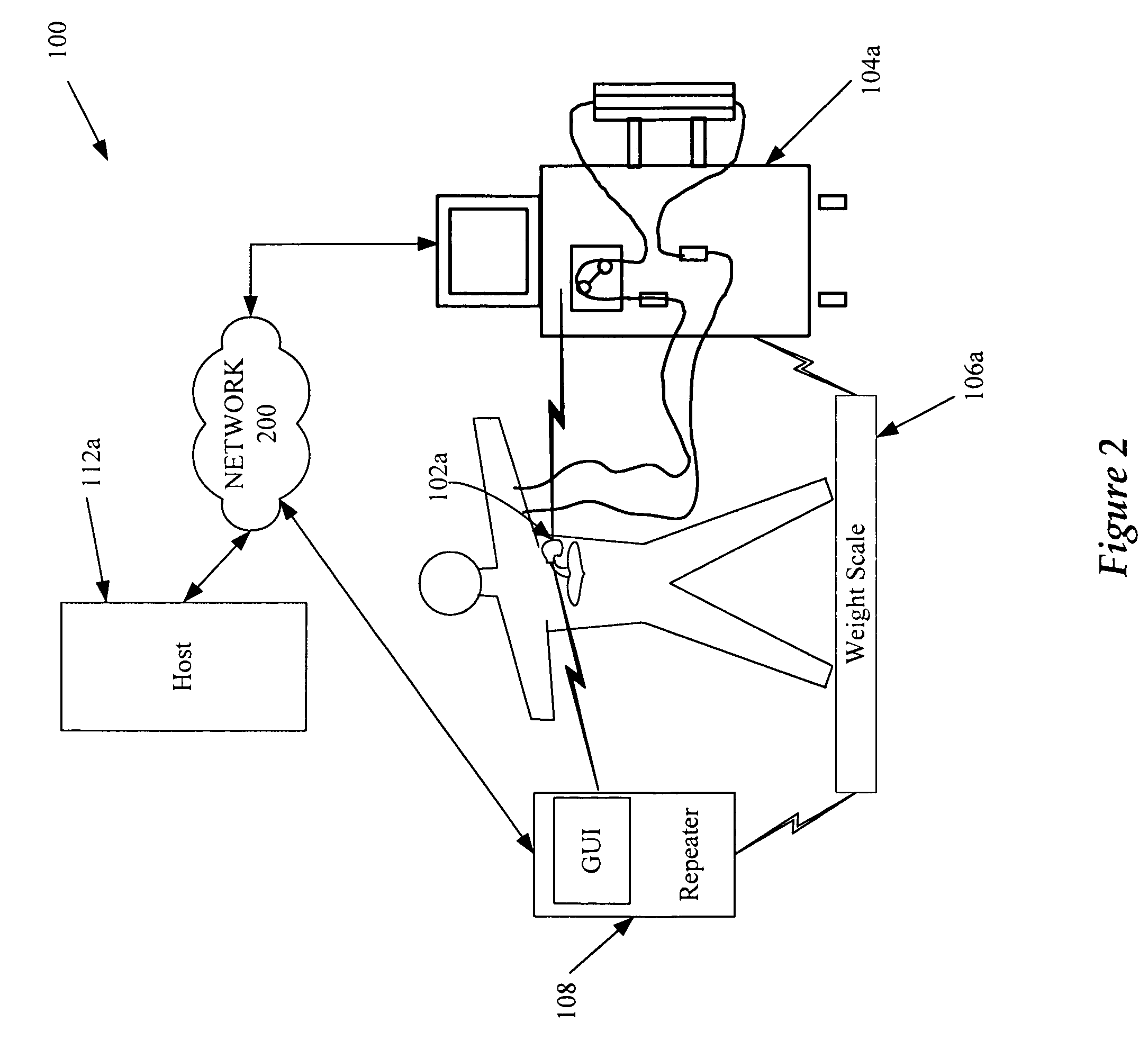
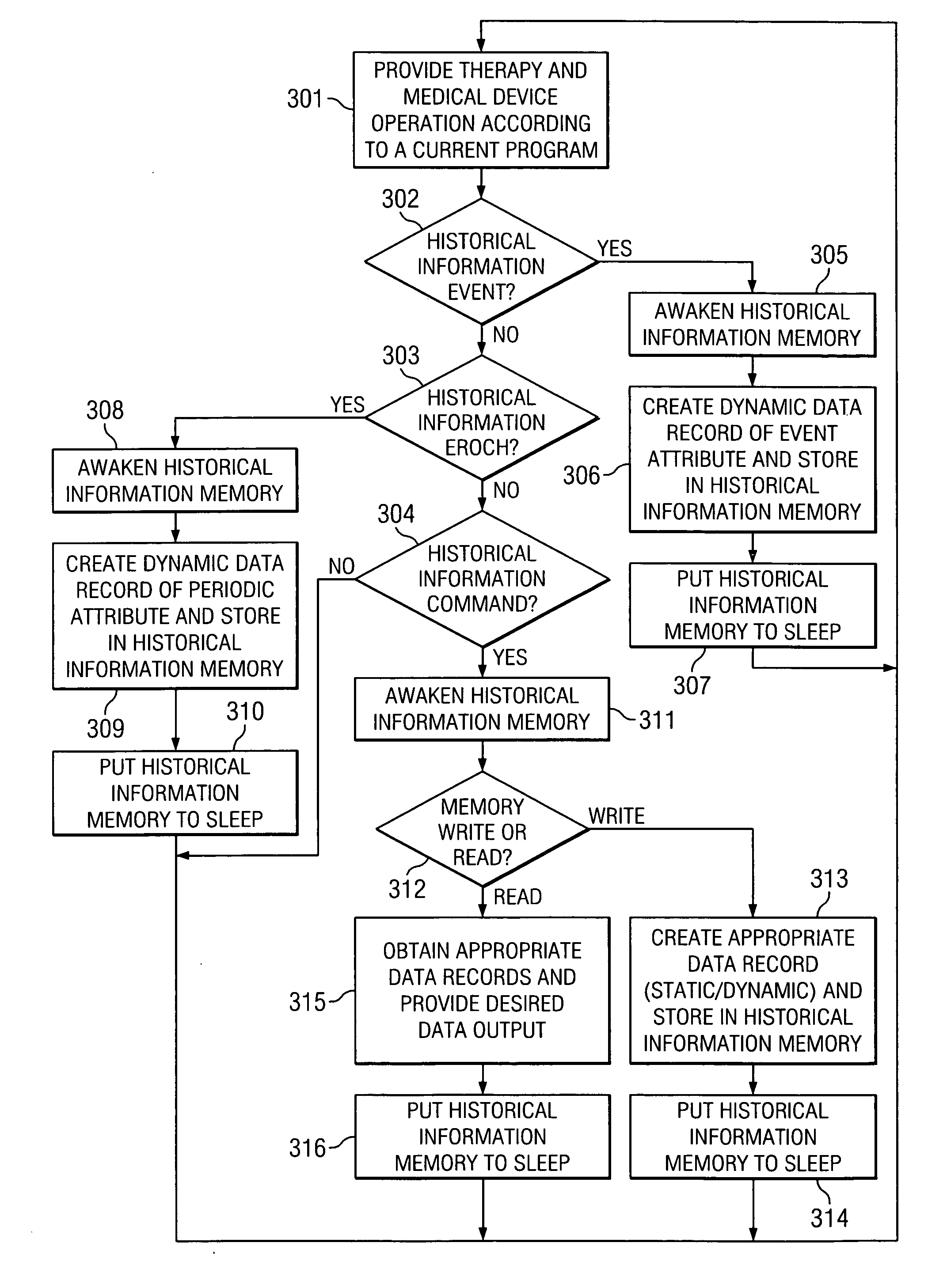
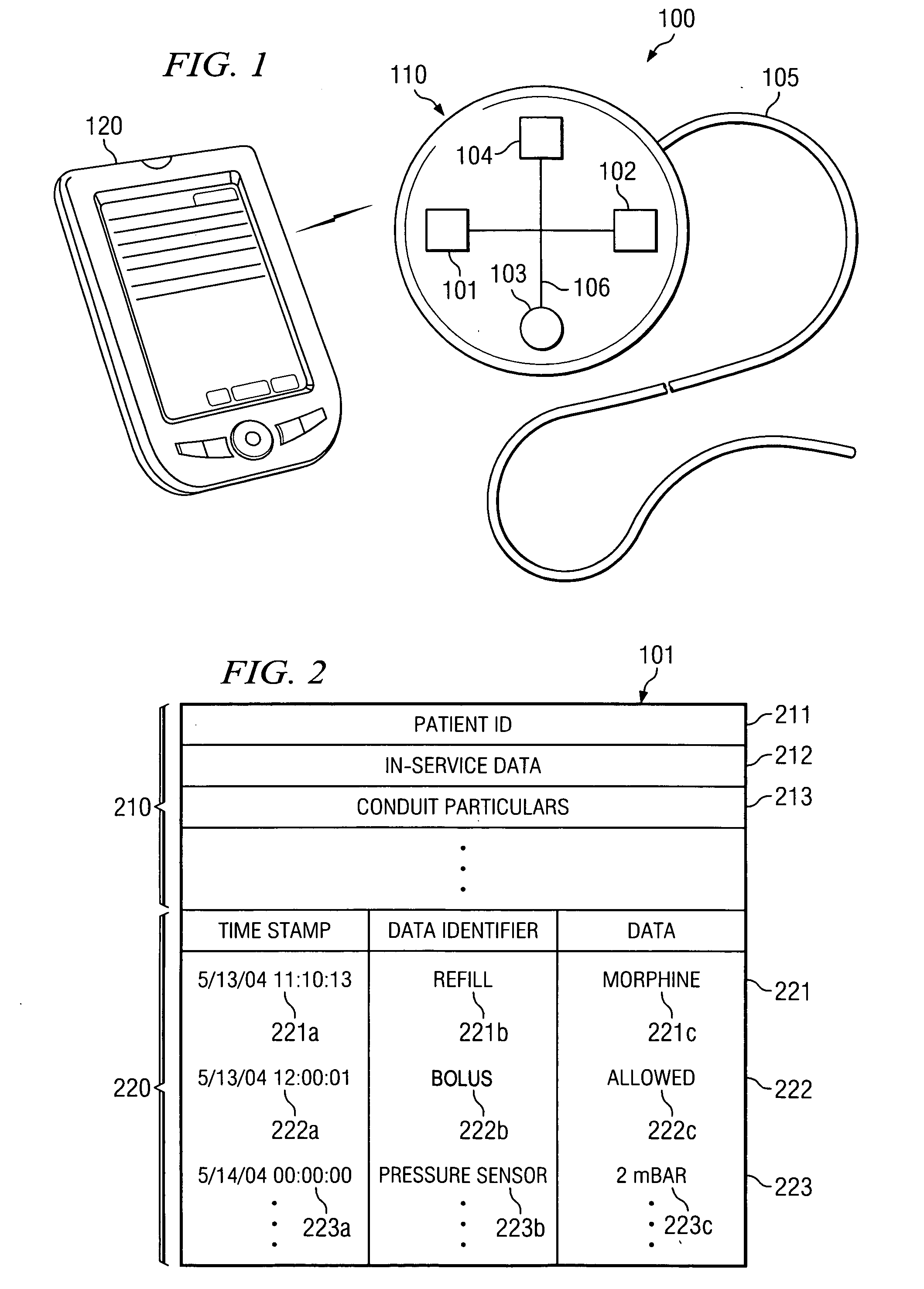
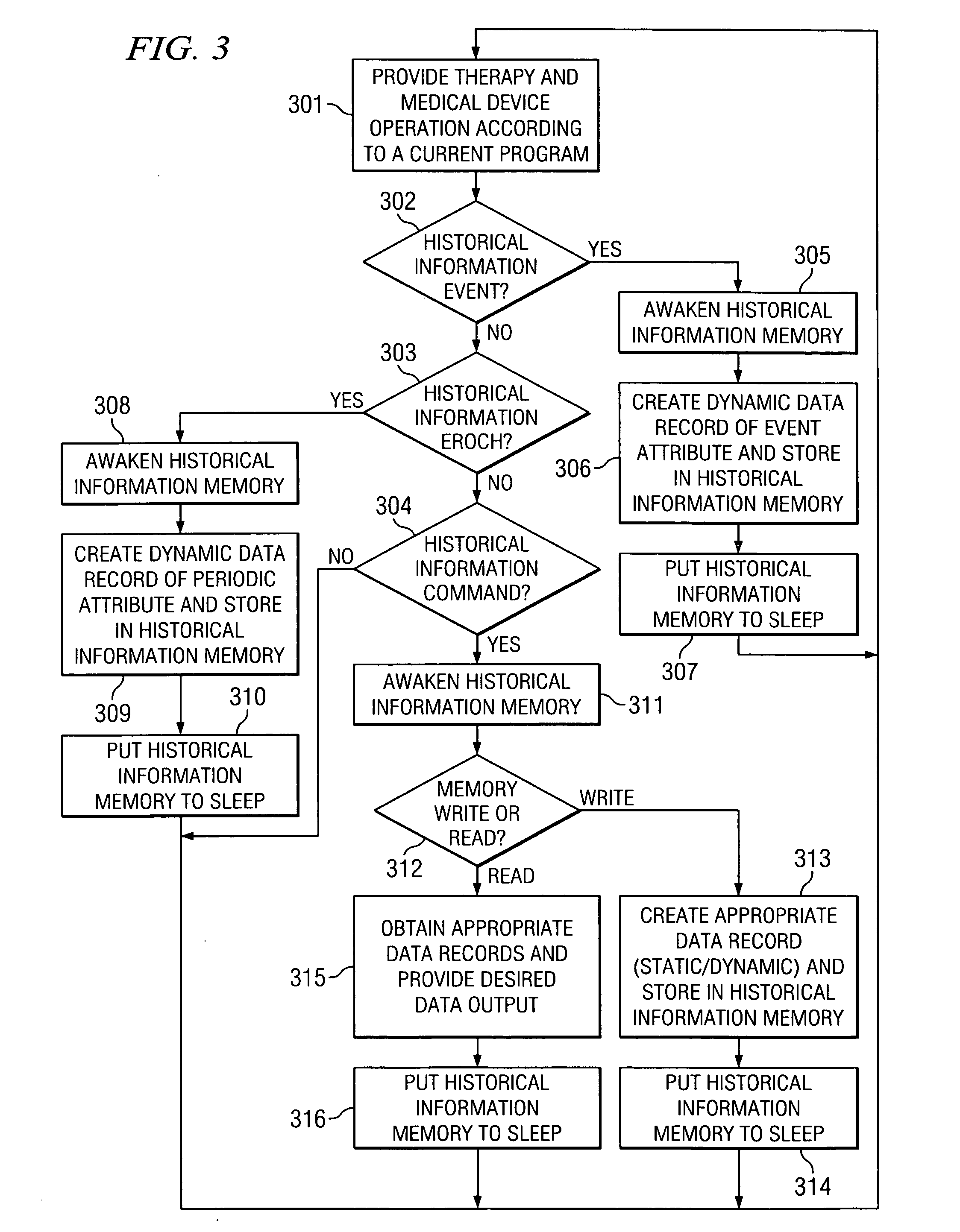
System and method of managing medical device historical data
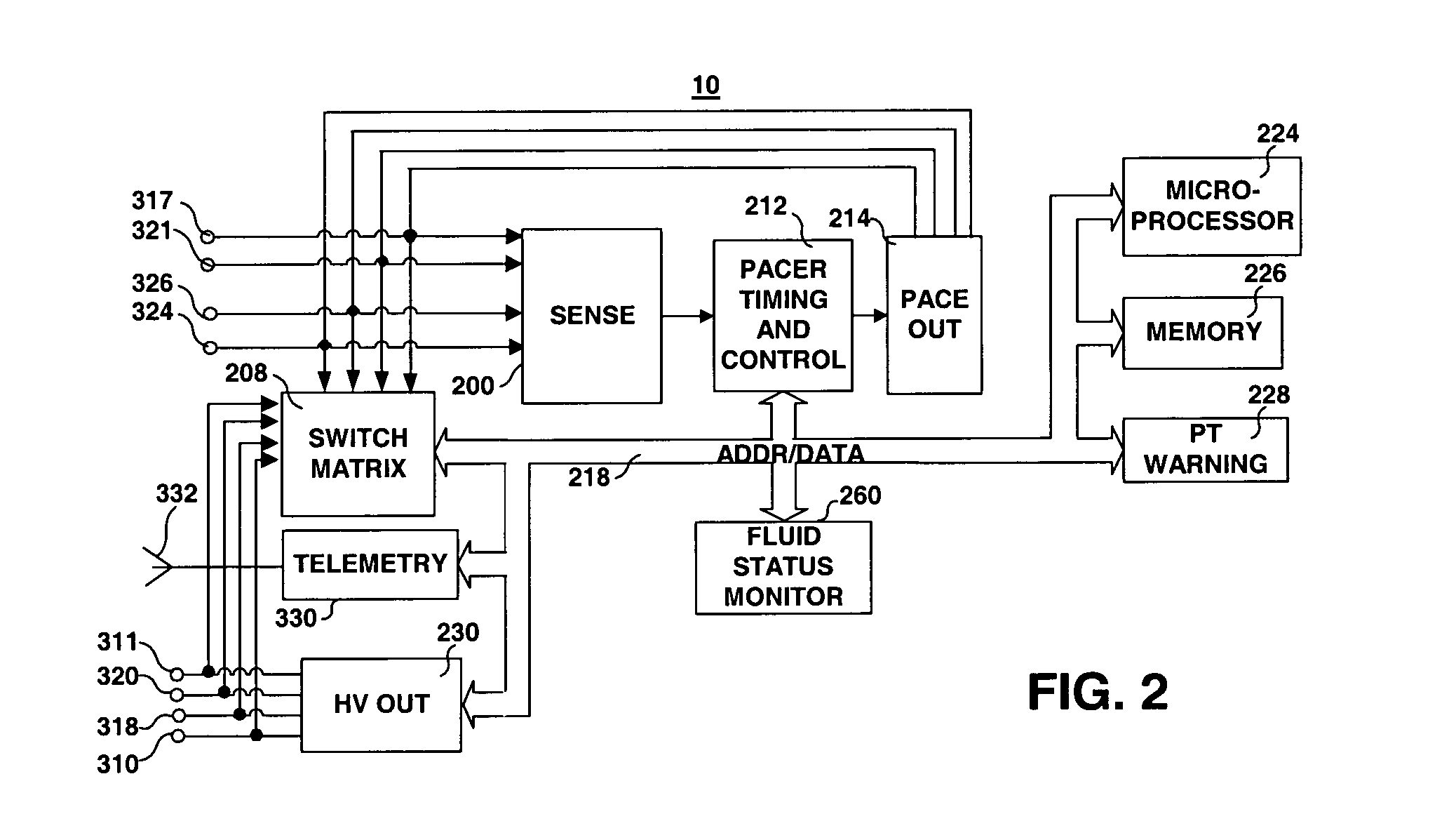
ActiveUS20050283210A1Eliminates and mitigates issueImprove insightsLocal control/monitoringHeart defibrillatorsCardiac deviceDynamic data
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide management of historical information associated with a medical device, such as an implantable neurostimulation pulse generator, drug pump, cardiac device, hearing enhancement device, or vision enhancement device. Such management of historical information includes storage of historical information within an associated medical device. Historical information stored within a medical device may provide a complete summary of the use, configuration, and operation of the medical device, e.g., information spanning the entire in-service life of the medical device. Historical information for which management is provided may include both static data and dynamic data. The historical information may be used in configuring the medical device, analyzing the operation of the medical device, autonomously altering operation of the medical device, etcetera.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
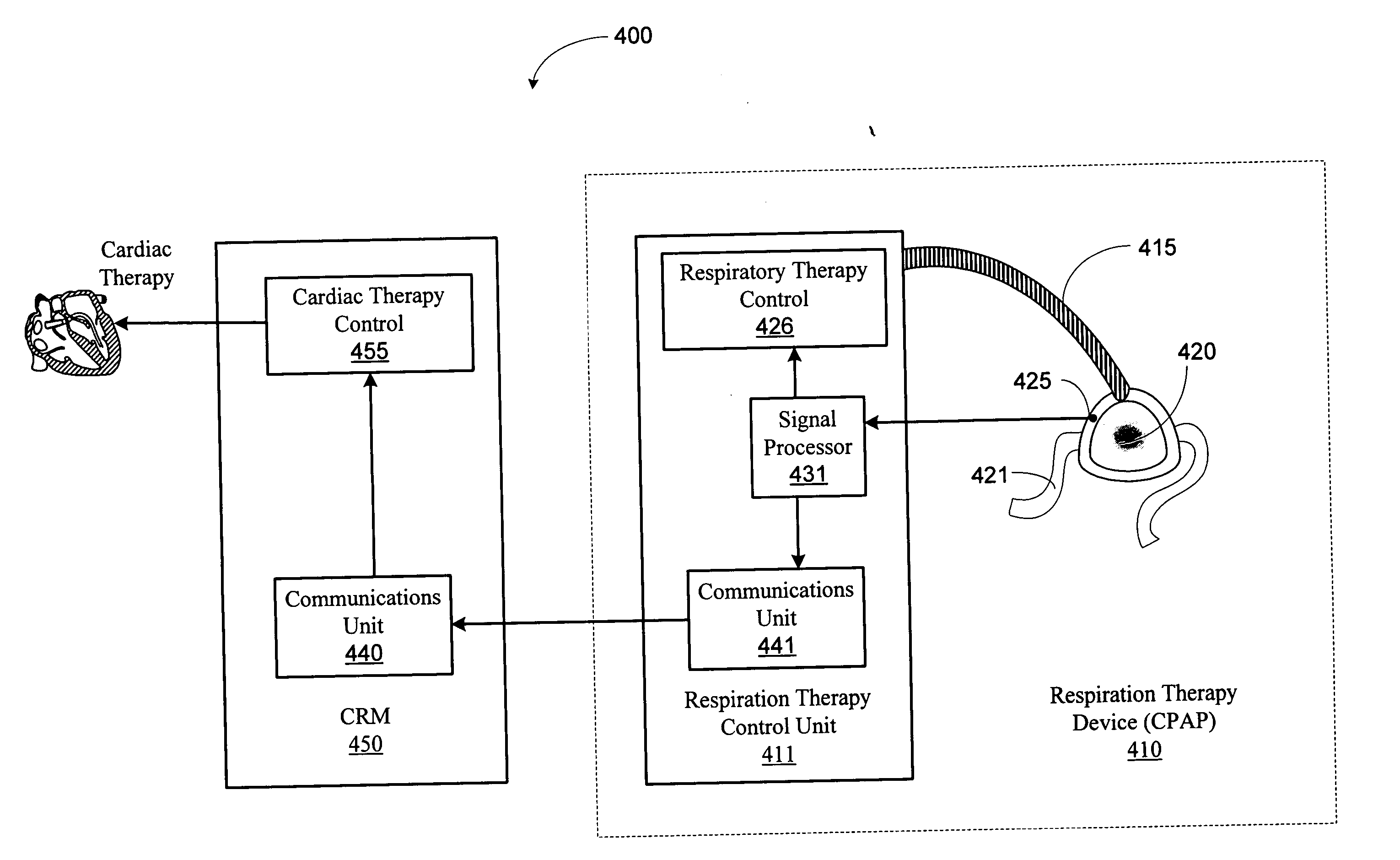
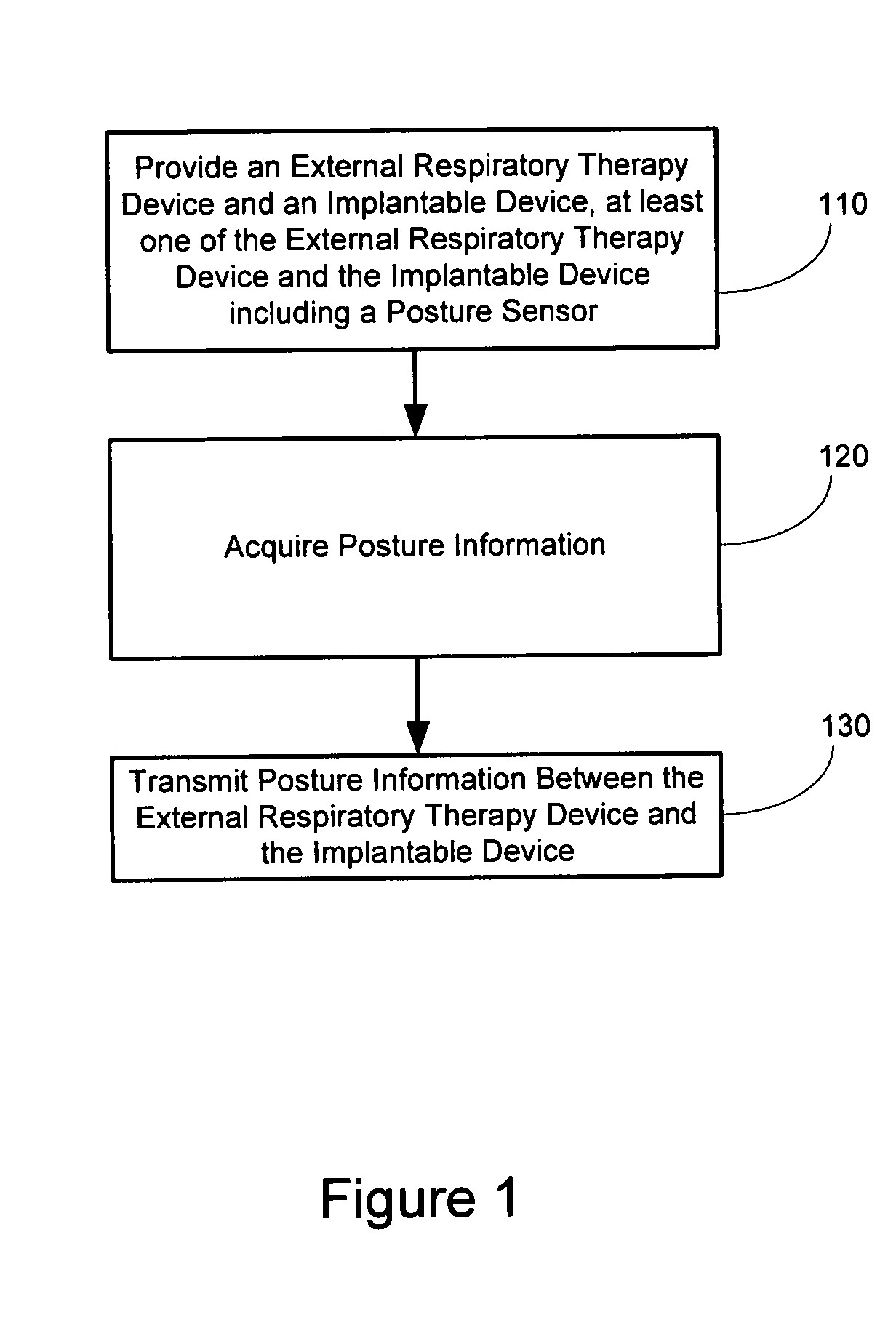
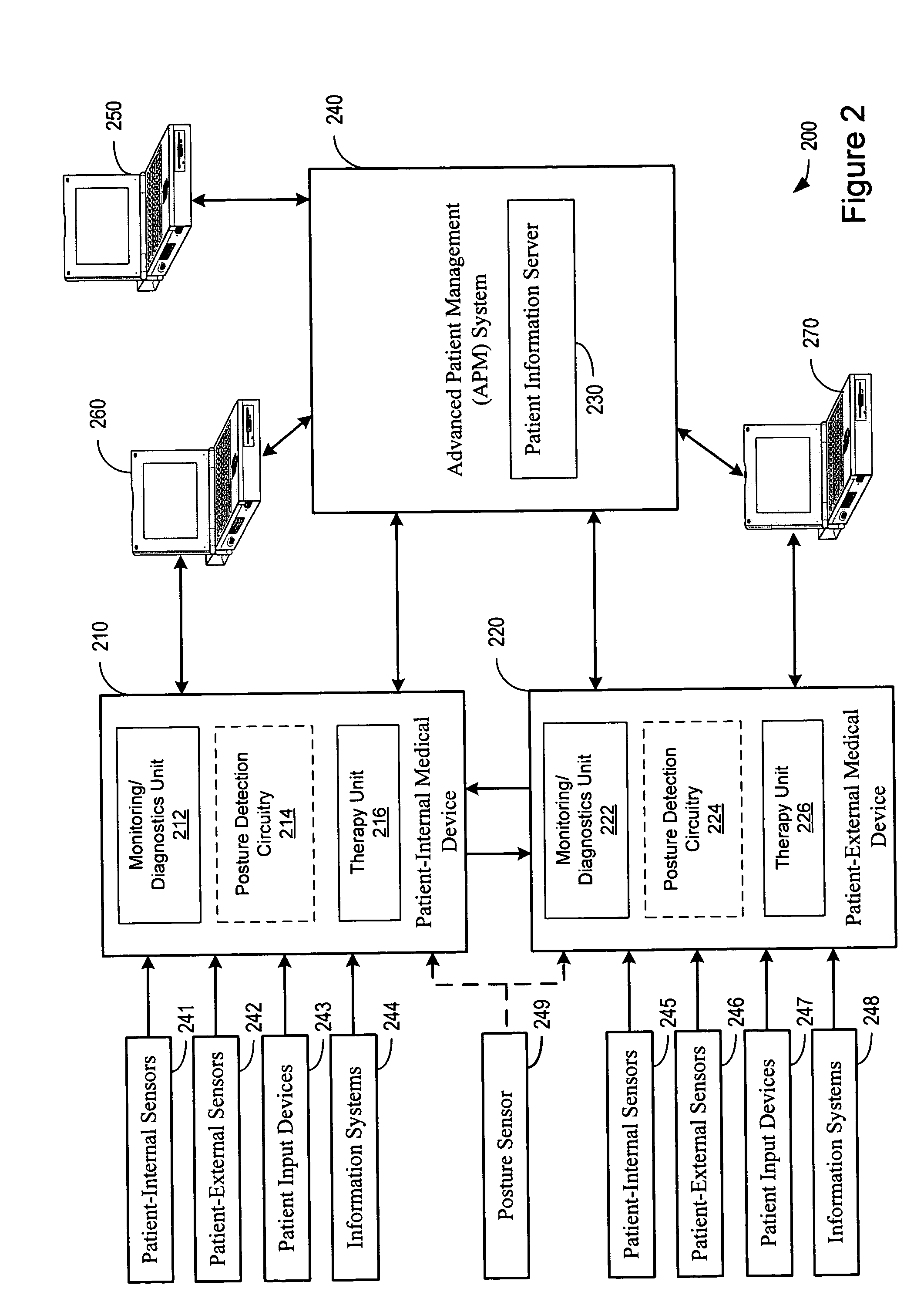
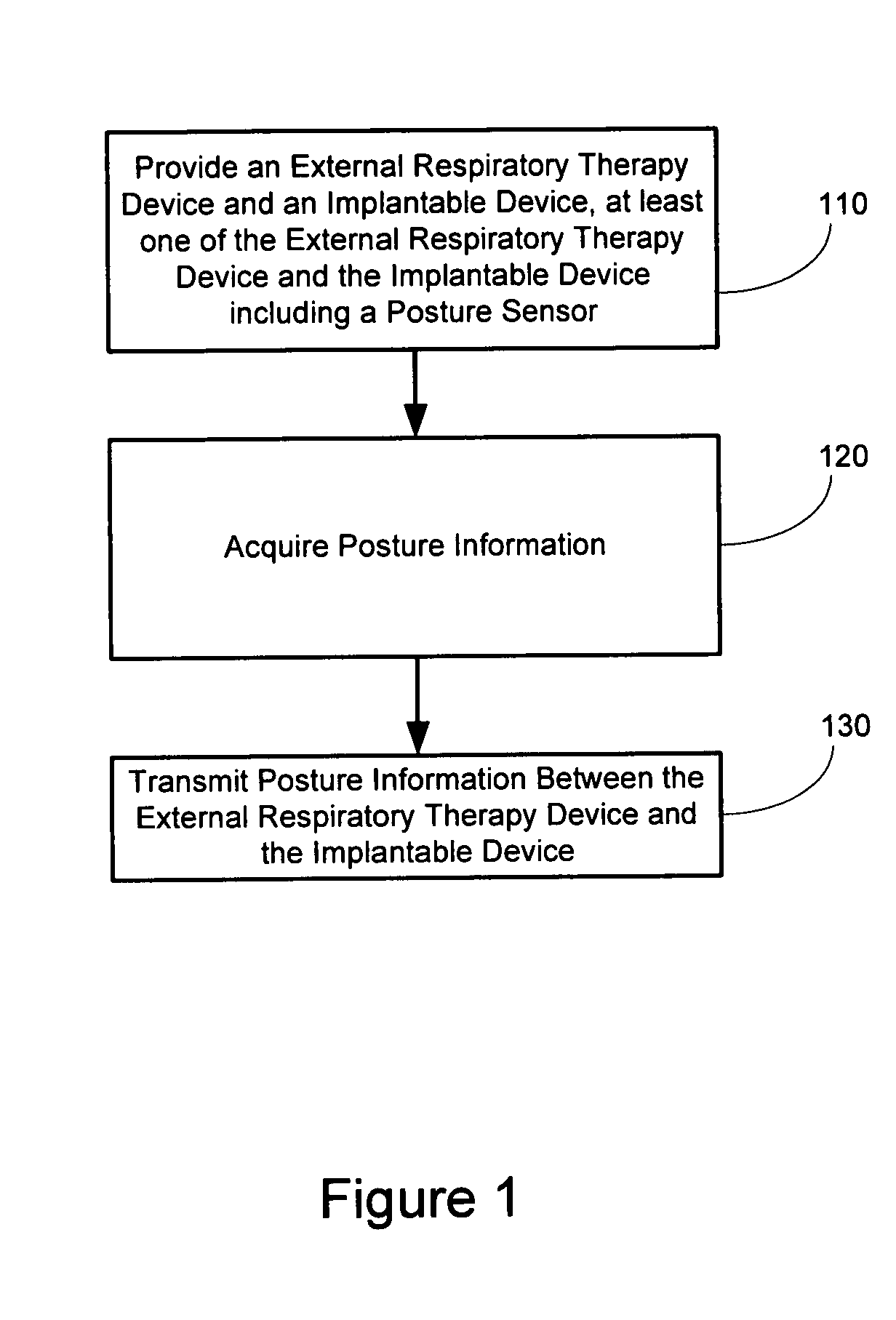
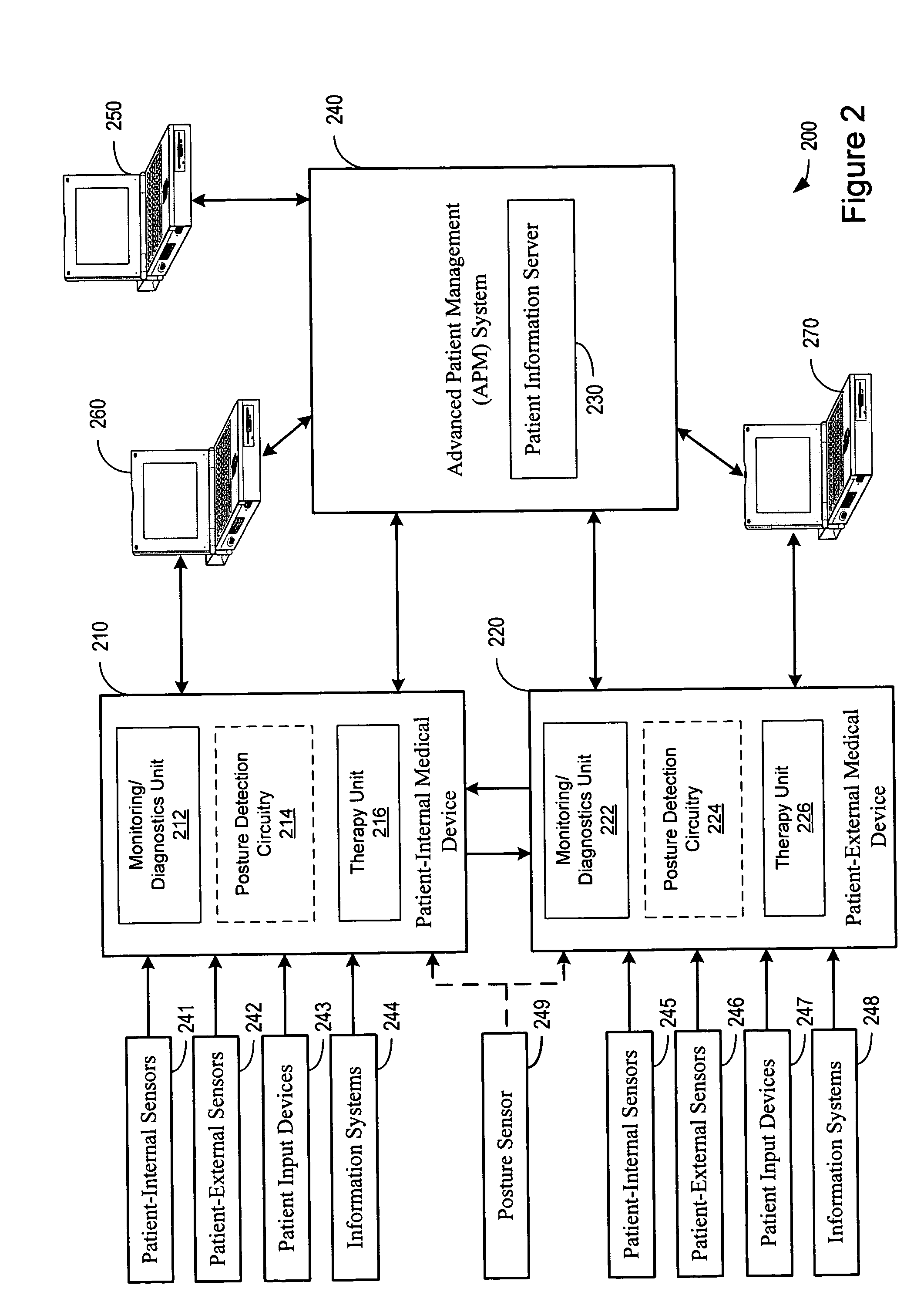
Posture detection system and method
InactiveUS20050145246A1Information transmissionRespiratorsElectroencephalographyImplanted deviceCombined use
A posture detection system includes an implantable device and a patient-external respiratory therapy device coupled via a communications channel. At least one of the implantable device and the patient-external respiratory therapy devices includes a posture detector. Posture information is transferred between the implantable device and the patient-external respiratory therapy device. The posture information may be used in connection with sleep detection or to modify therapy delivered by the implantable cardiac device and / or the patient-external respiratory therapy device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
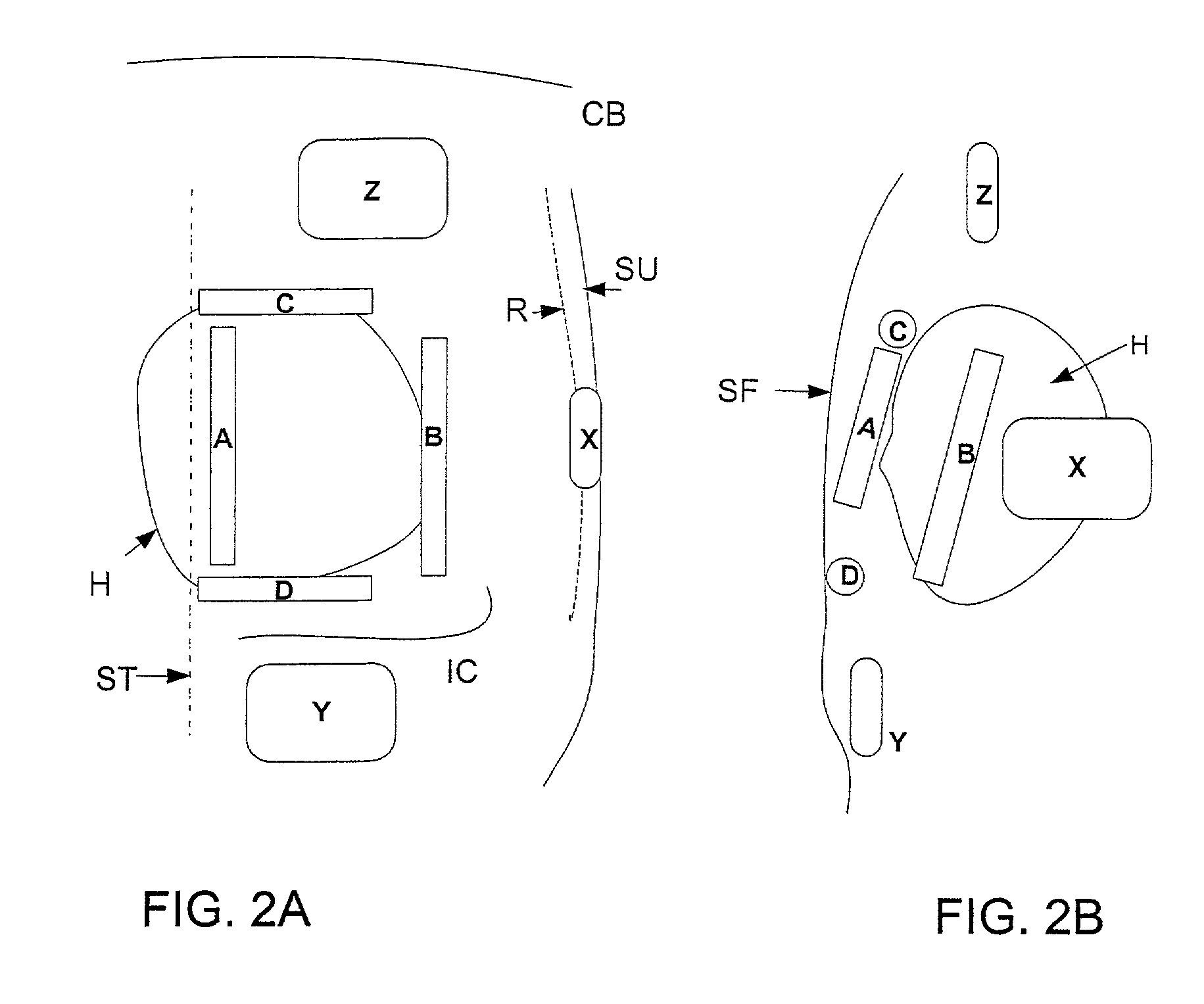
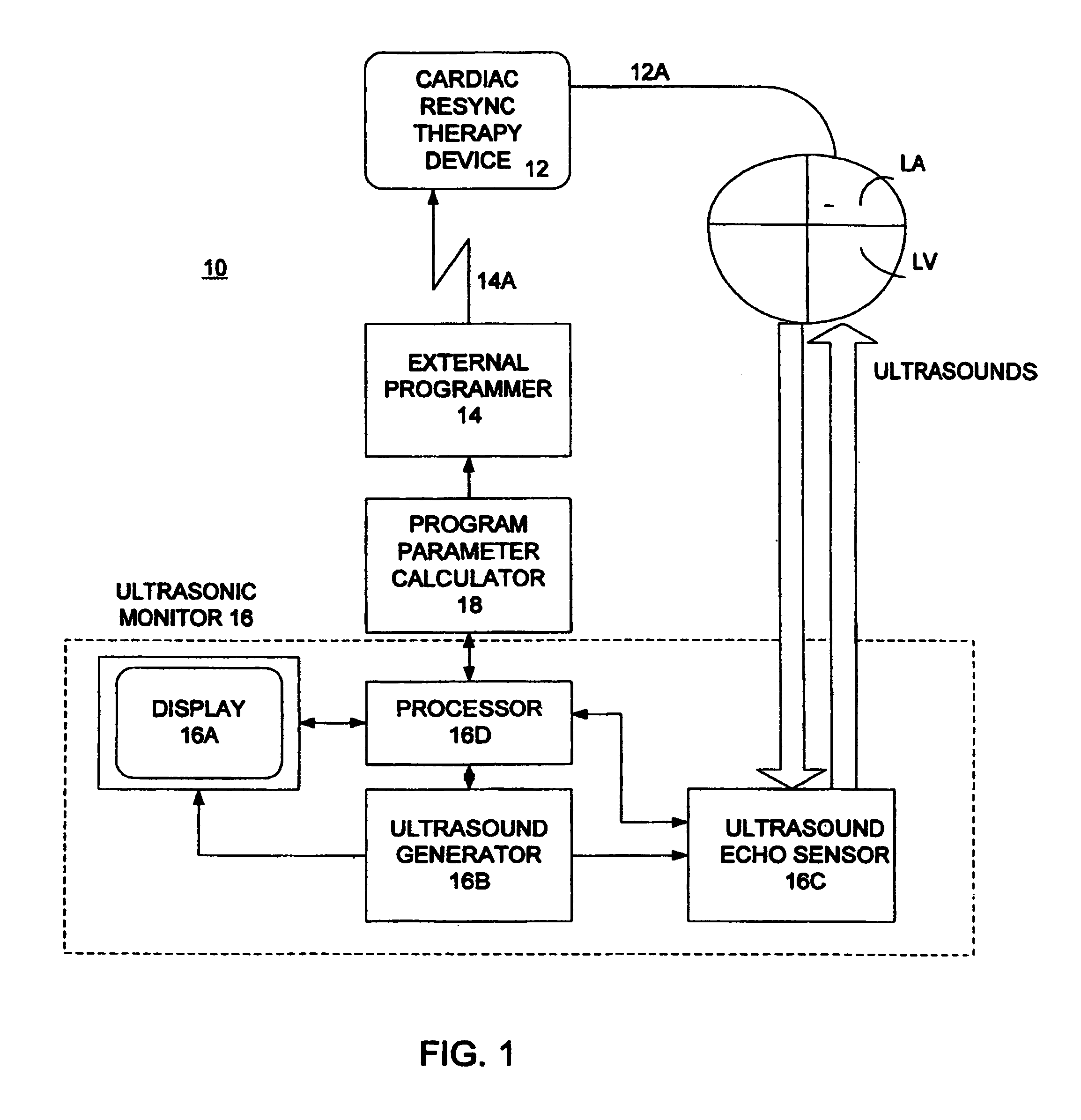
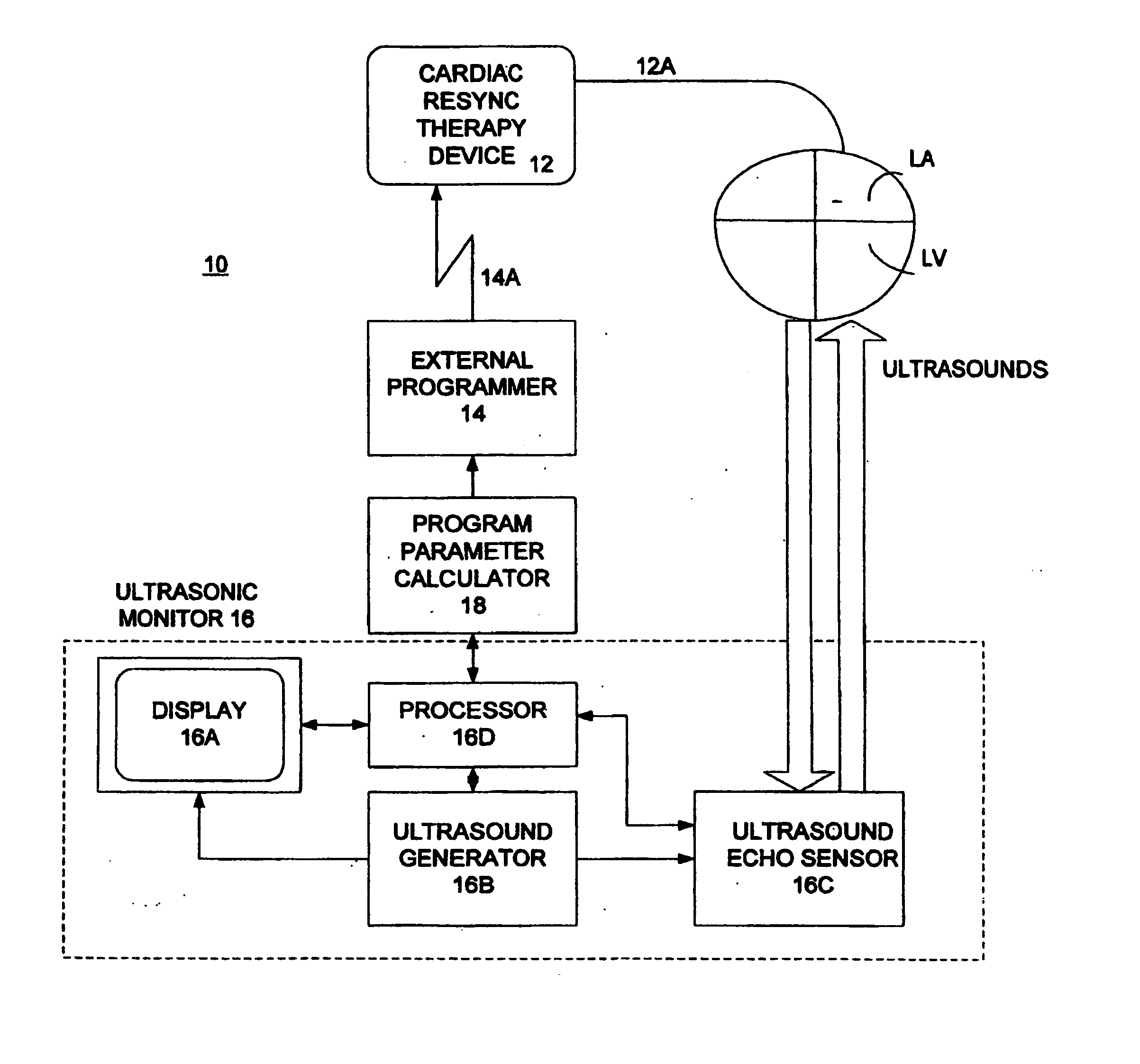
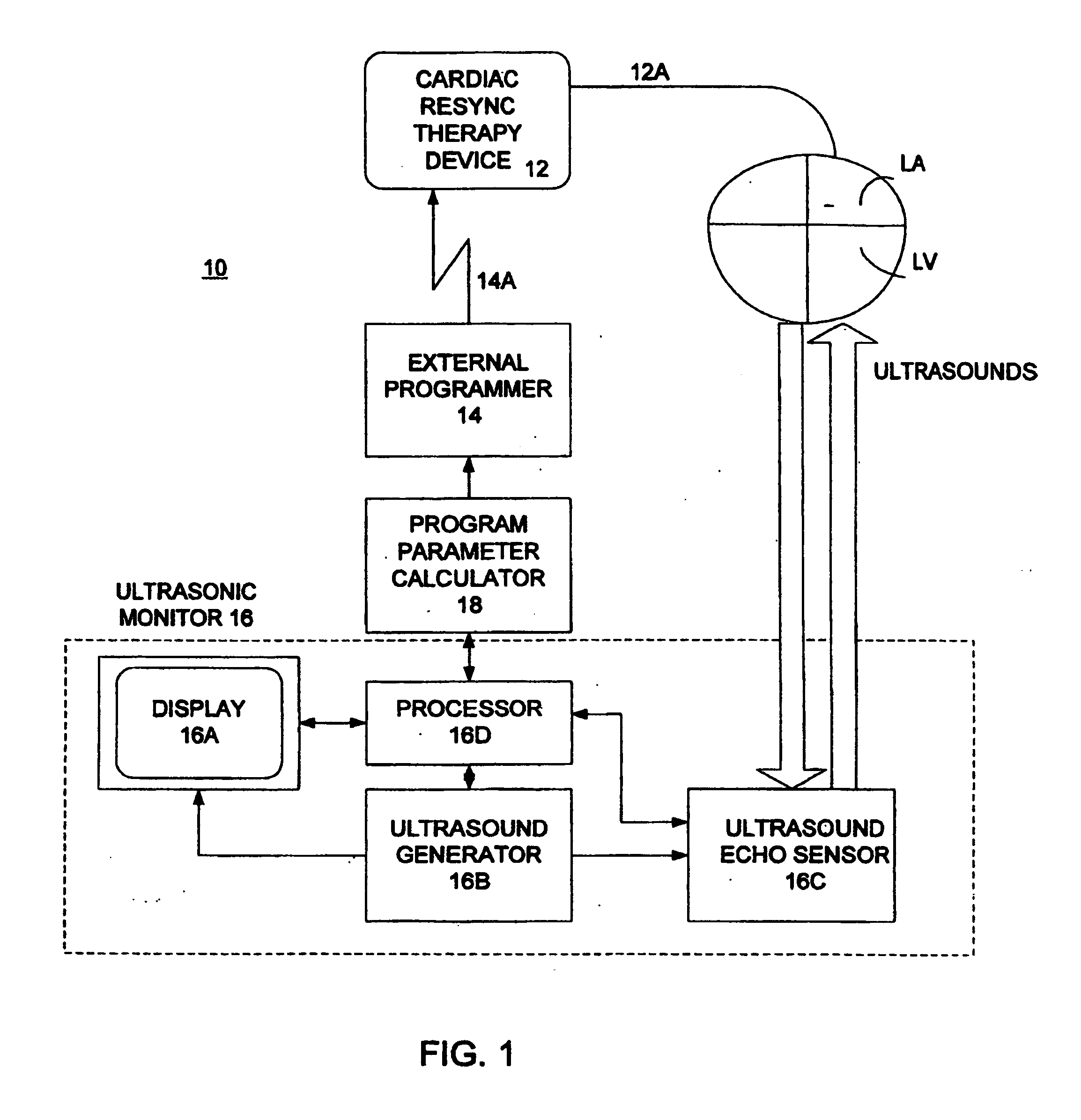
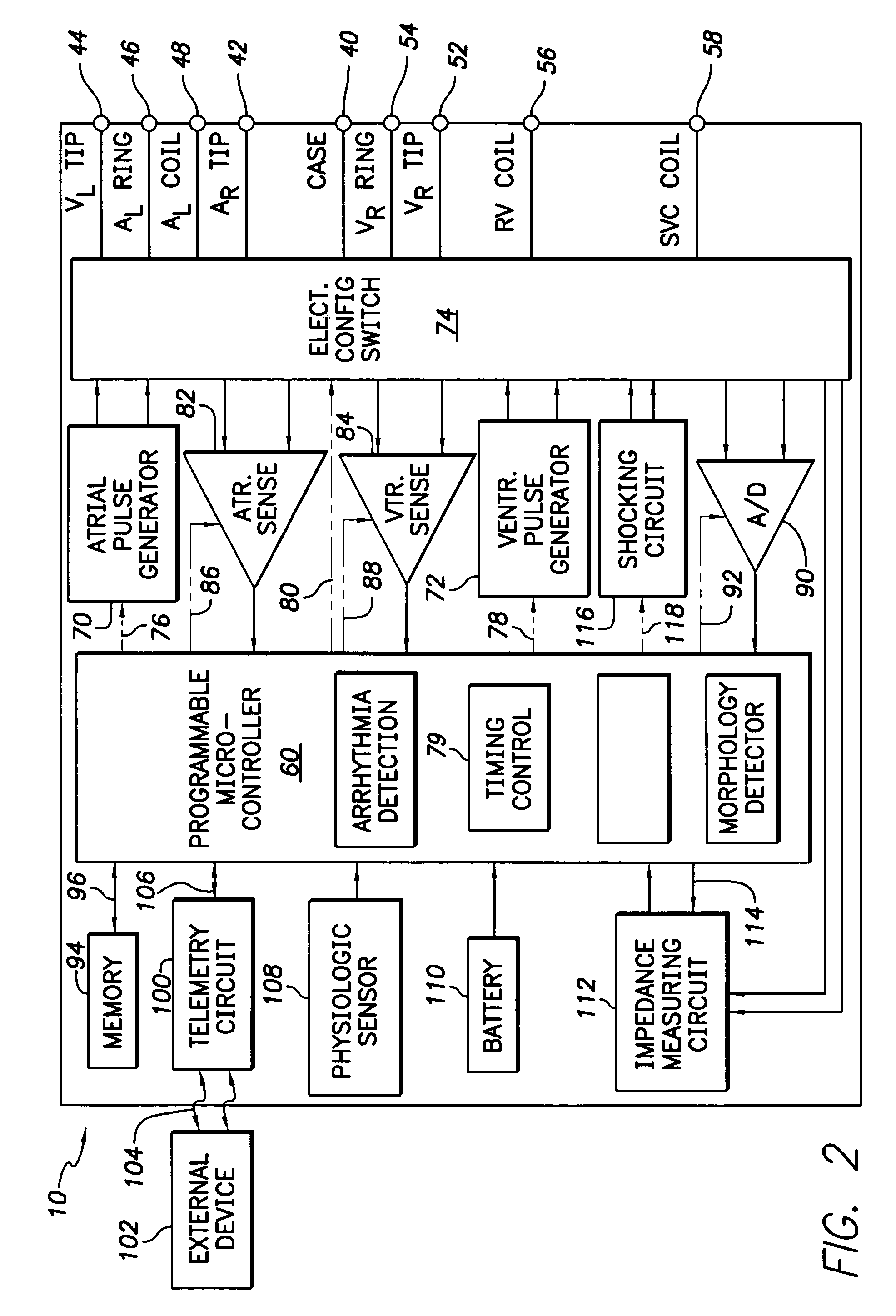
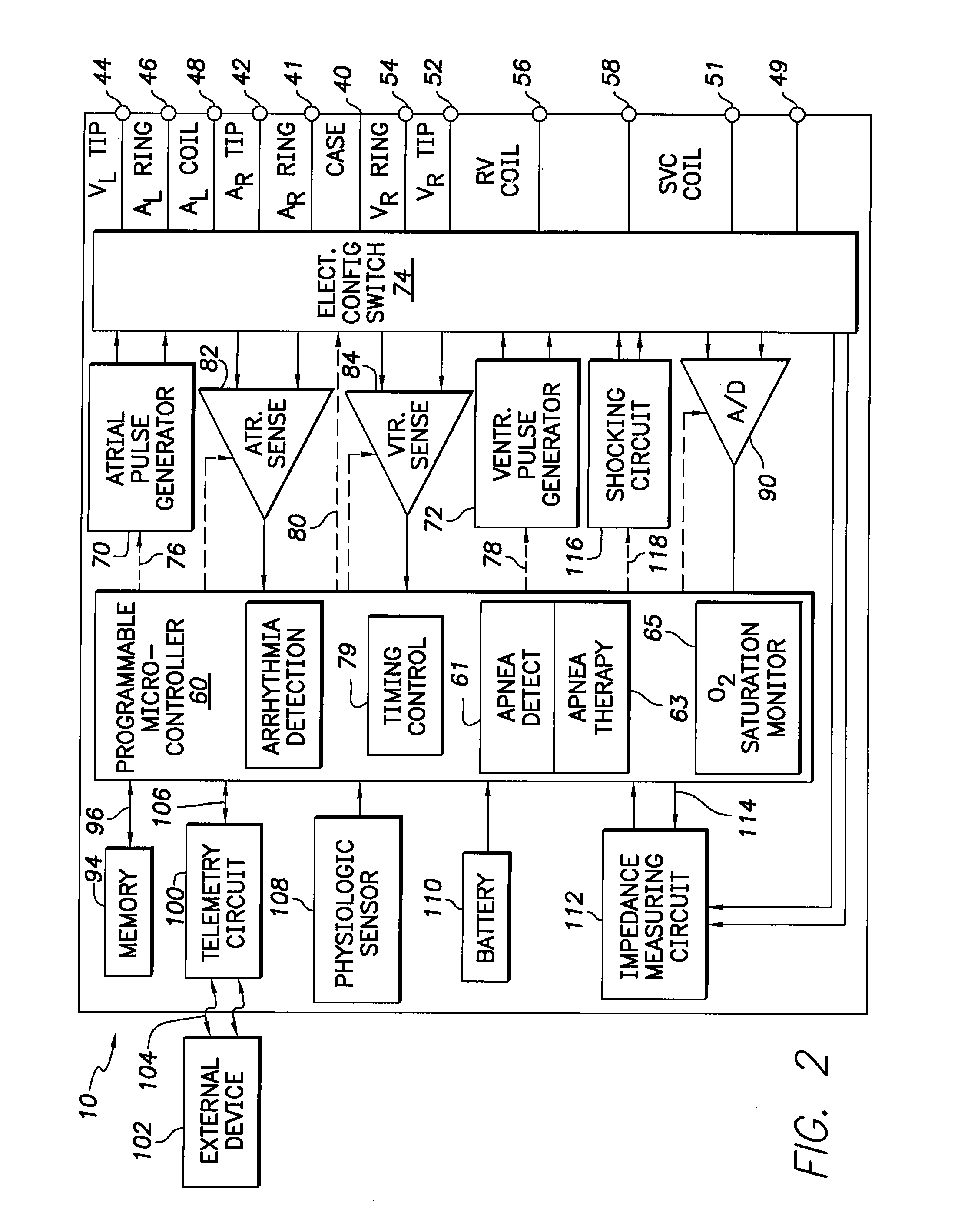
Optimization of impedance signals for closed loop programming of cardiac resynchronization therapy devices
What are described herein are implantable cardiac devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators that deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and to a method of optimizing acquisition of impedance signals between electrodes present on implanted lead systems. This system then automatically determines which electrodes or electrode combinations acquire impedance waveforms that have the best signal to noise ratio (highest fidelity) and characterize data most representative of dysynchronous electro-mechanical events. Using closed loop algorithms which provide electrograms and a variety of impedance data reflective of the patient's clinical status, the system autonomously modifies interval timing within the CRT device.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulator with small contact surface electrodes
InactiveUS7194302B2Reducing electrode interface resistanceReduce energy consumptionHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac activityCardiac device
A subcutaneous cardiac device includes two electrodes and a stimulator that generates a pulse to the electrodes. The electrodes are implanted between the skin and the rib cage of the patient and are adapted to generate an electric field corresponding to the pulse, the electric field having a substantially uniform voltage gradient as it passes through the heart. The shapes, sizes, positions and structures of the electrodes are selected to optimize the voltage gradient of the electric field, and to minimize the energy dissipated by the electric field outside the heart. More specifically, the electrodes have contact surfaces that contact the patient tissues, said contact surfaces having a total contact area of less than 100 cm2. In one embodiment, one or both electrodes are physically separated from the stimulator. In another embodiment a unitary housing holds the both electrodes and the stimulator. Sensor circuitry may also includes in the stimulator for detecting intrinsic cardiac activity through the same electrodes.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Intracardiac implantable medical device for biatrial and/or left heart pacing and method of implanting same
An intra-cardiac implantable medical device (IIMD) and method of implant are provided. The IIMD comprises a housing configured to be implanted entirely within a coronary sinus (CS) of the heart. The IIMD has at least one intra-cardiac device extension (ICDE).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac device and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7674222B2Lower the volumeImprove pressure-volume relationshipHeart valvesInternal electrodesCardiac deviceHeart disease
Devices and methods are described herein which are directed to the treatment of a patient's heart having, or one which is susceptible to heart failure, to improve diastolic function.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
InactiveUS20050043767A1Uniform peak amplitudeEasy to detectHeart stimulatorsCardiac dysfunctionAmplitude response
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
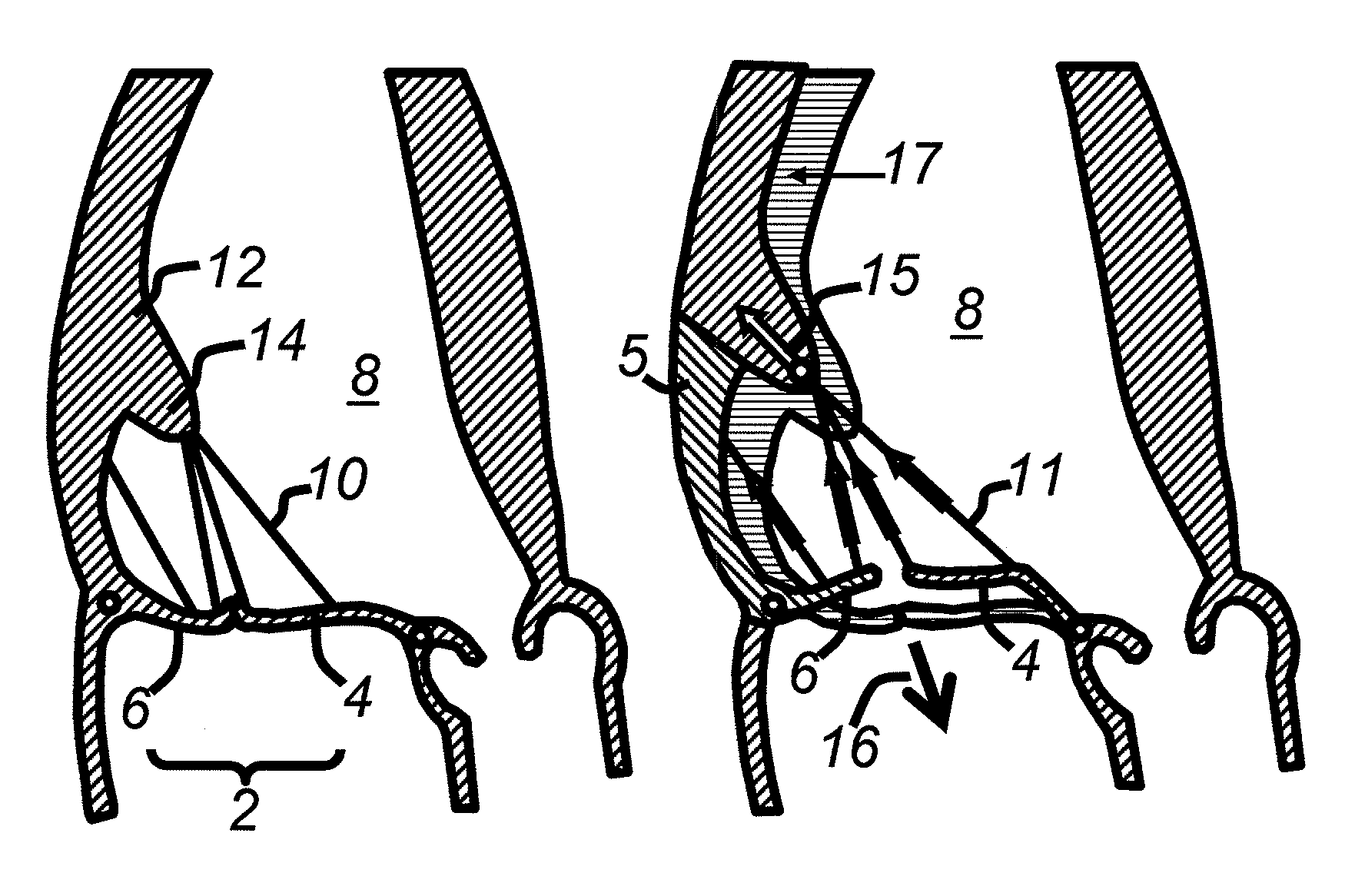
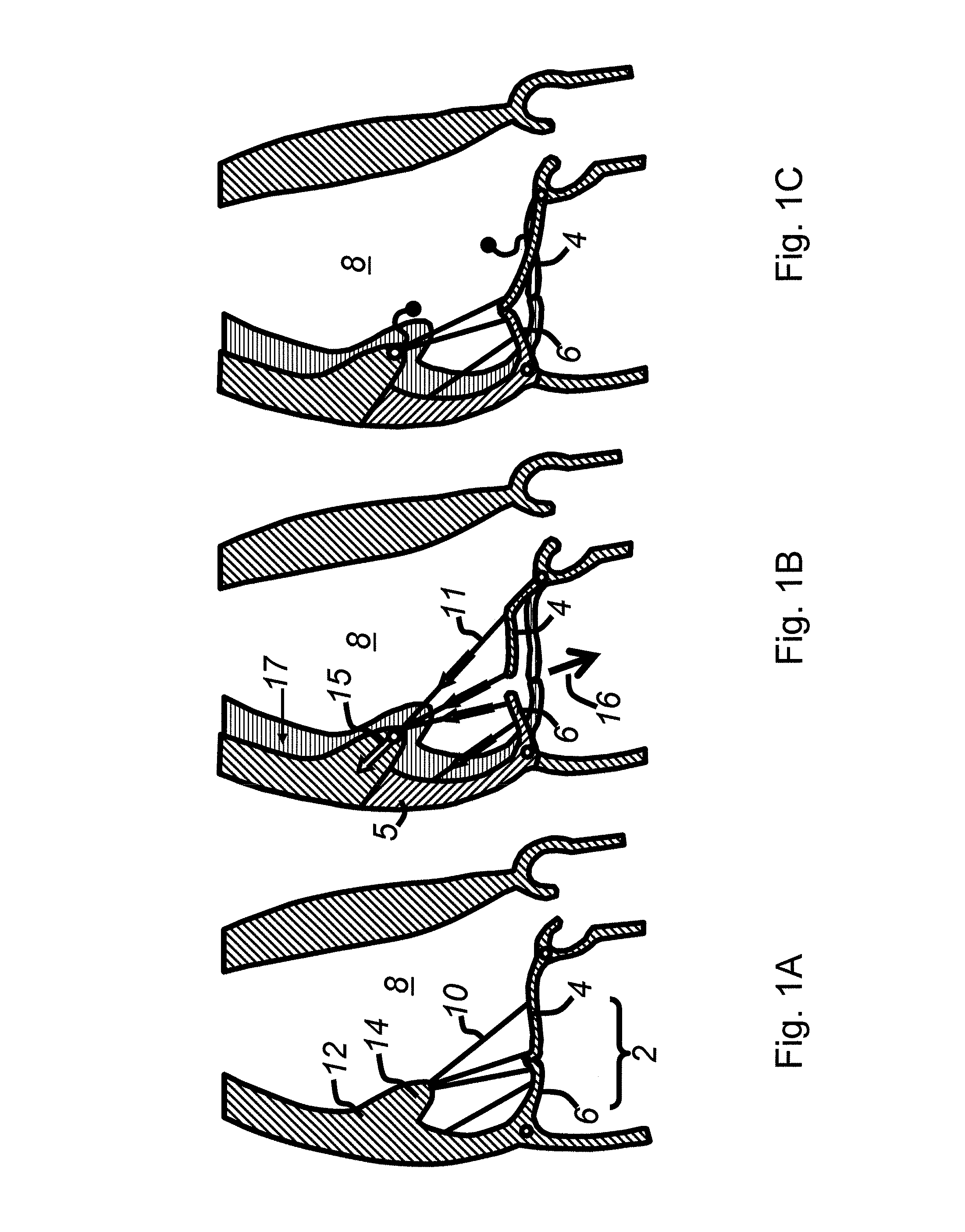
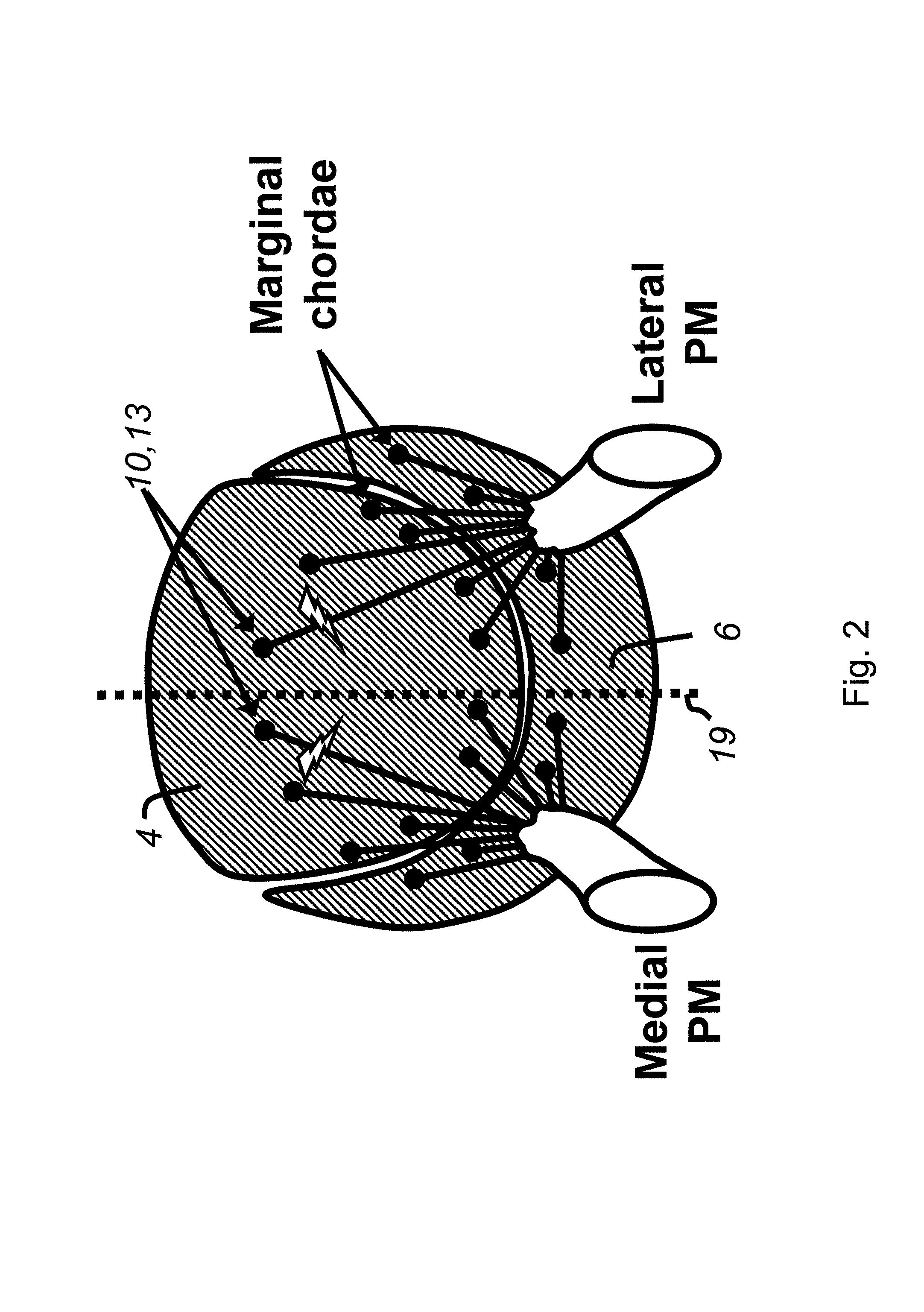
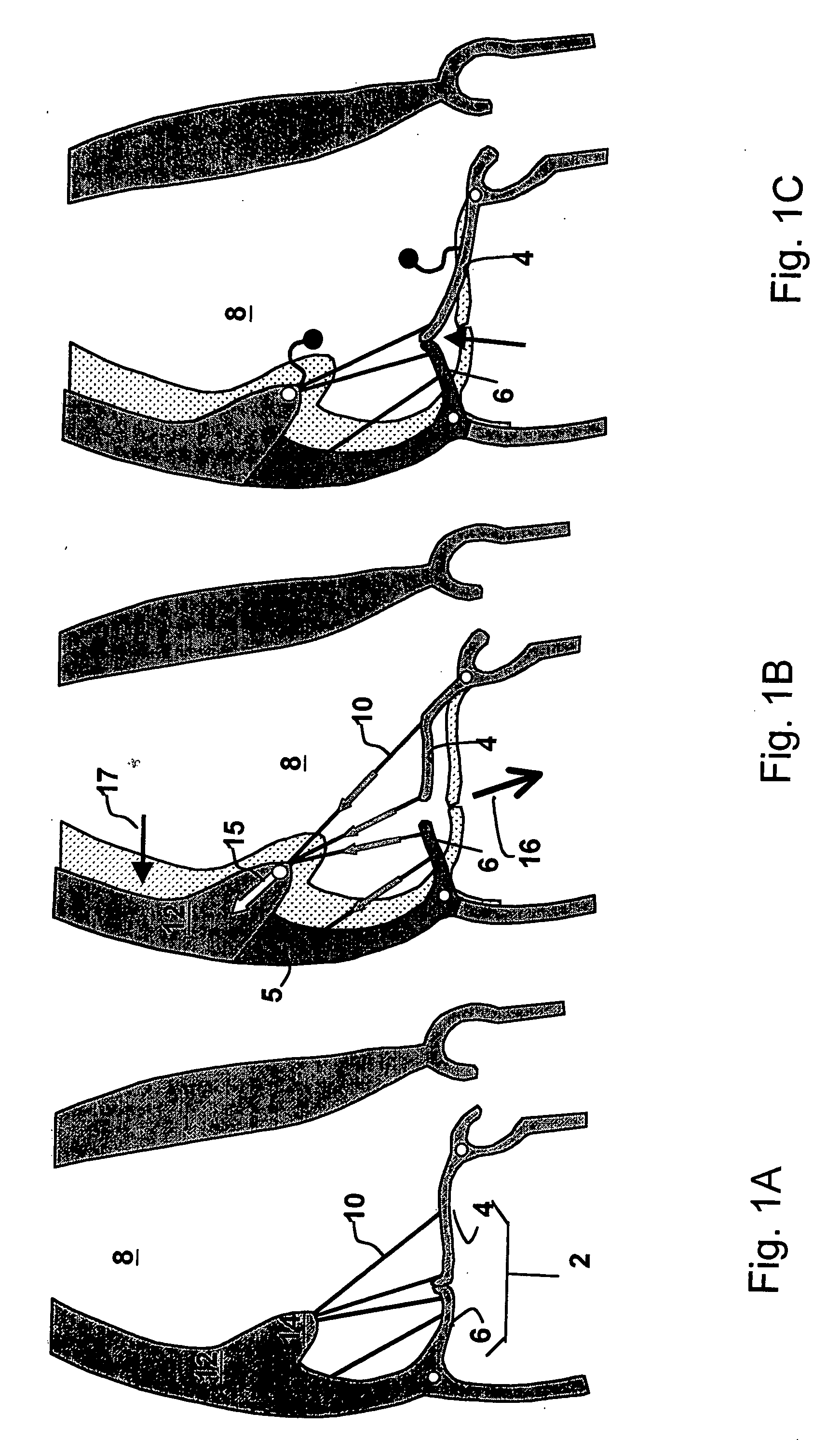
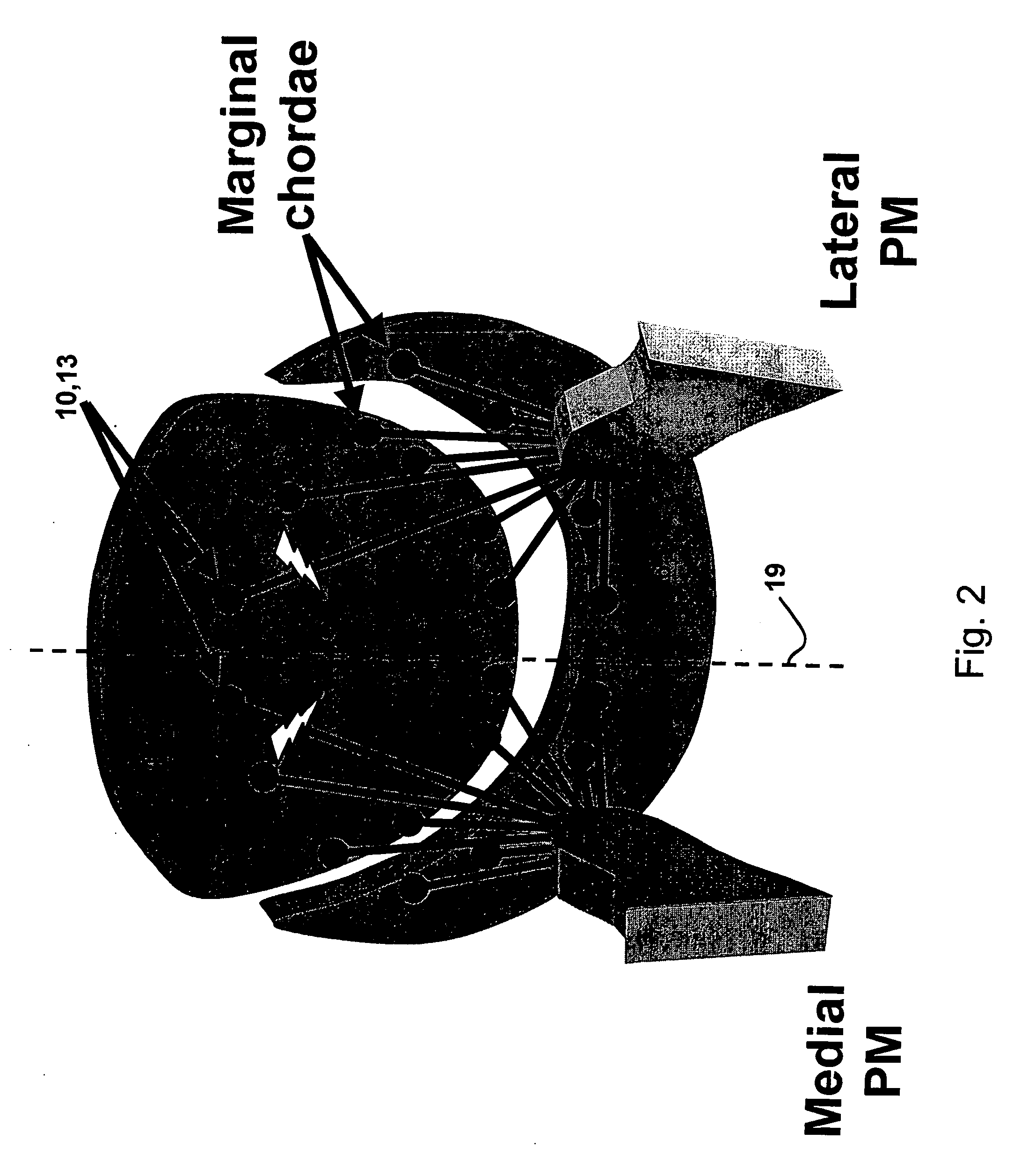
Cardiac devices and methods for percutaneous repair of atrioventricular valves
ActiveUS7559936B2Increase surface areaEffective applicationStaplesSurgical pincettesMitral valve leafletCardiac device
Novel apparatus and minimally invasive methods to treat The present invention provides methods and devices for grasping, stabilizing and fastening of cardiac valve leaflets to treat atrioventricular valve regurgitation, particularly mitral valve regurgitation, in the context of prolapse and / or flail mitral valve. Independent leaflet grasping elements provide the ability to reposition the leaflets for fastening and enough stability to prevent leaflet movement during fastening.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
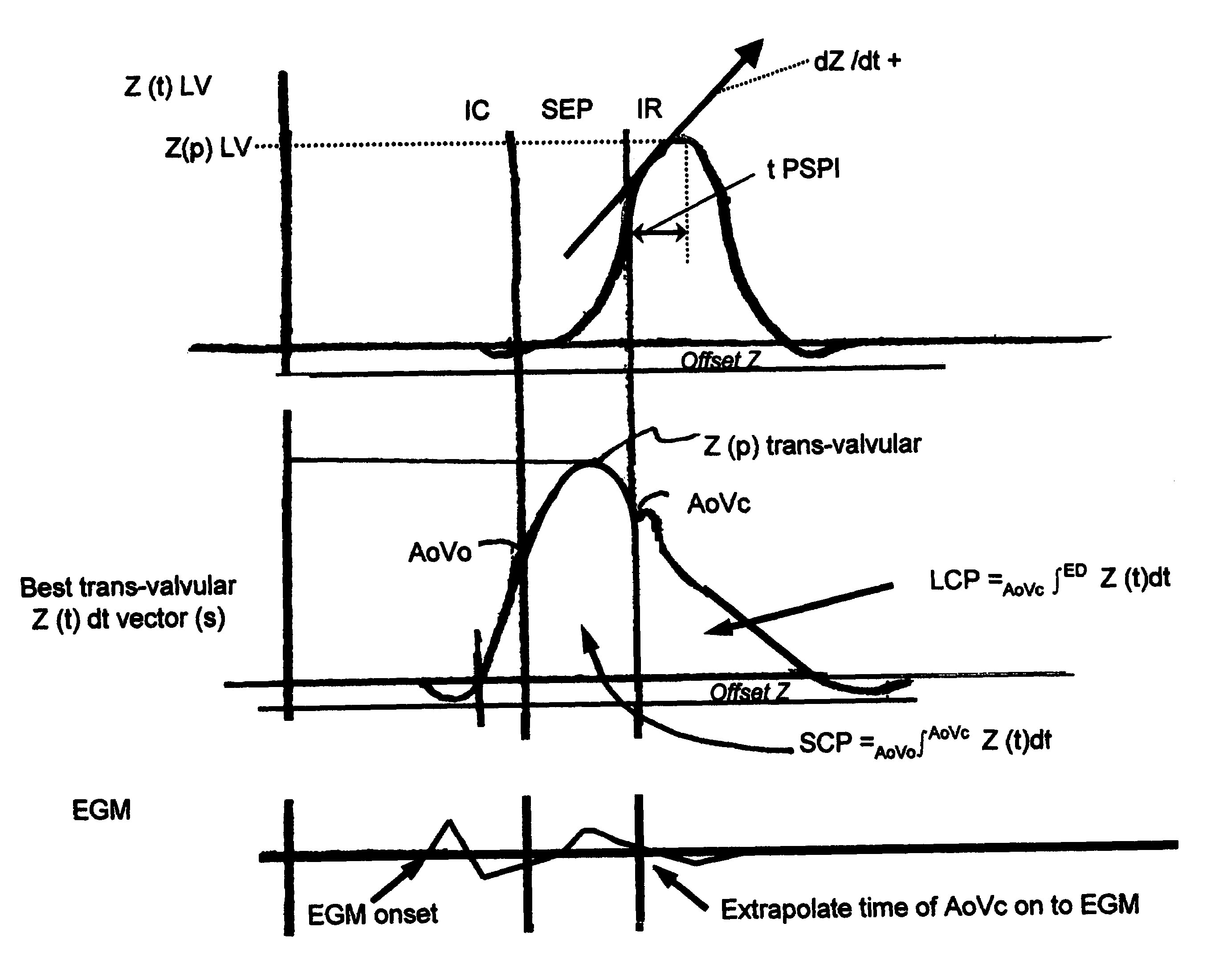
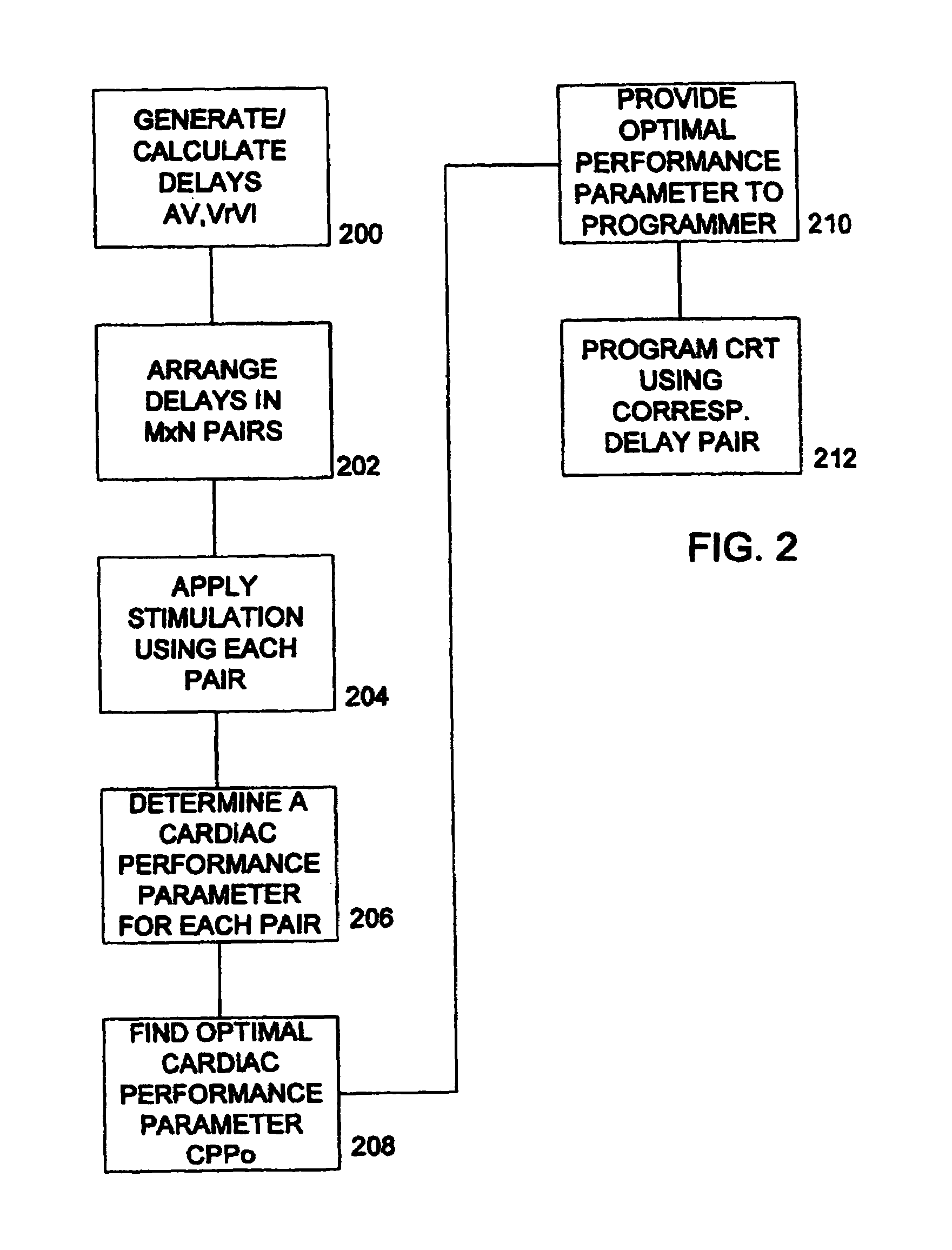
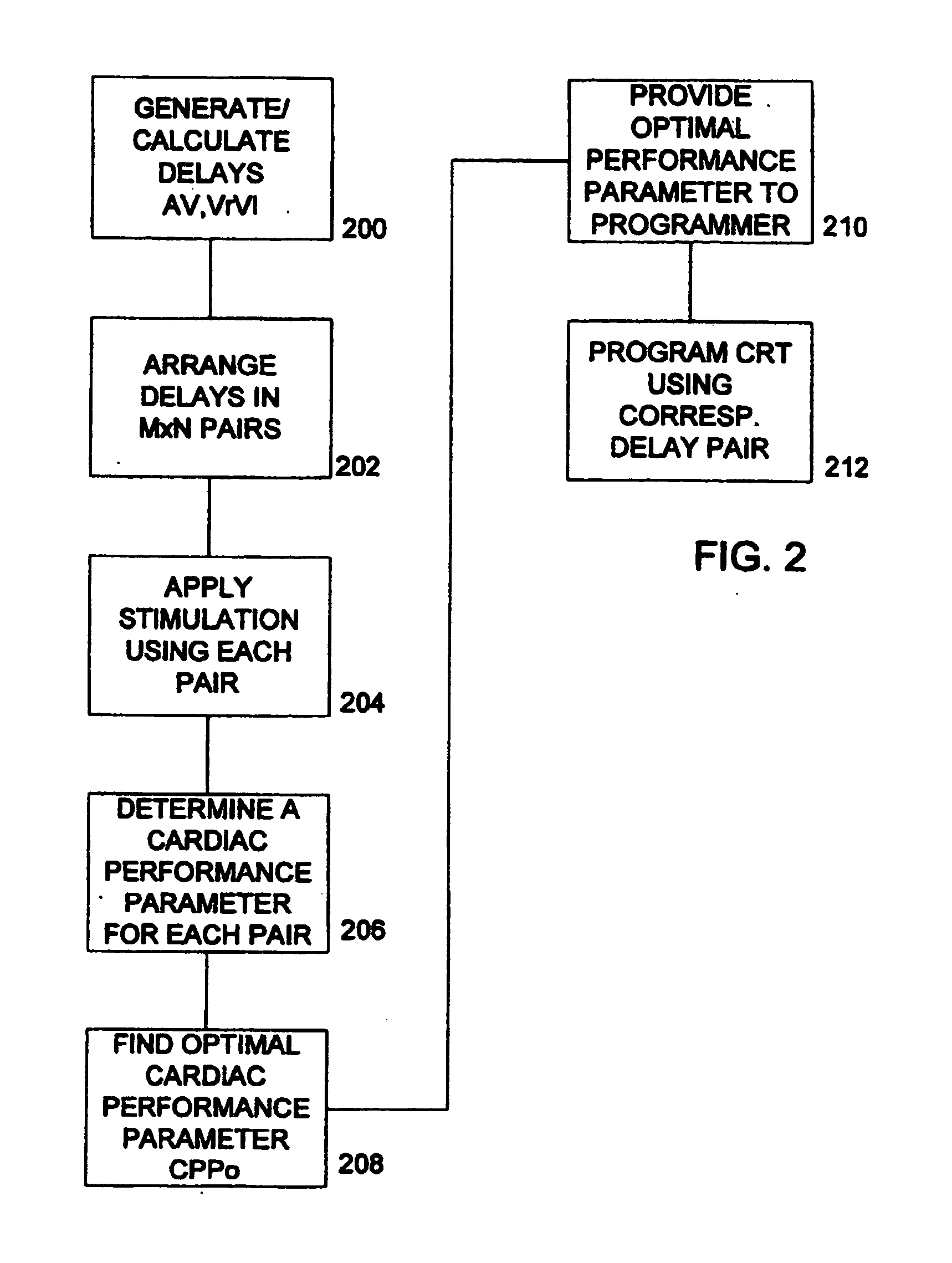
Optimization method for cardiac resynchronization therapy
ActiveUS6978184B1Shortening of pre-ejection periodIncrease in rate of contractionInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
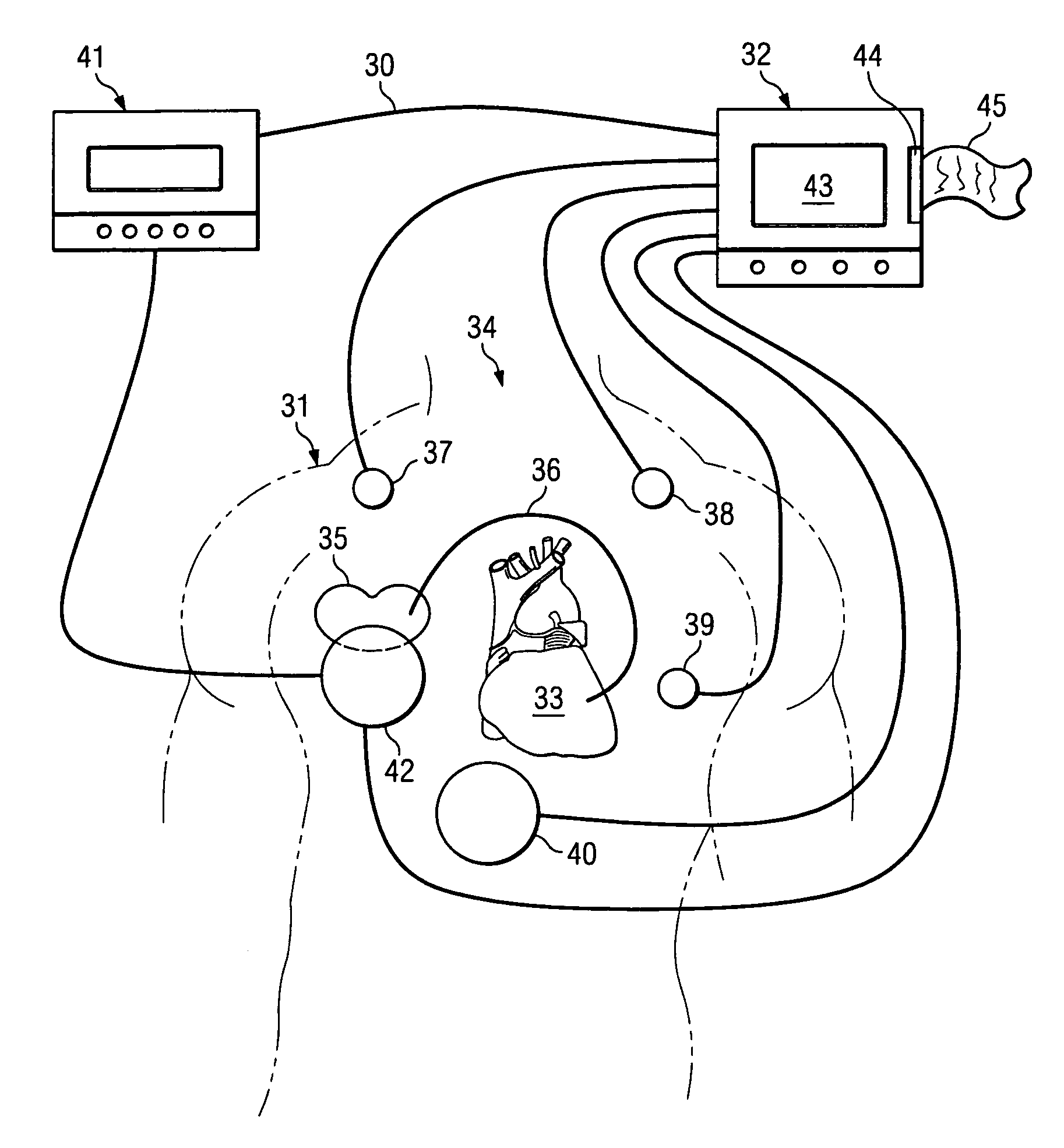
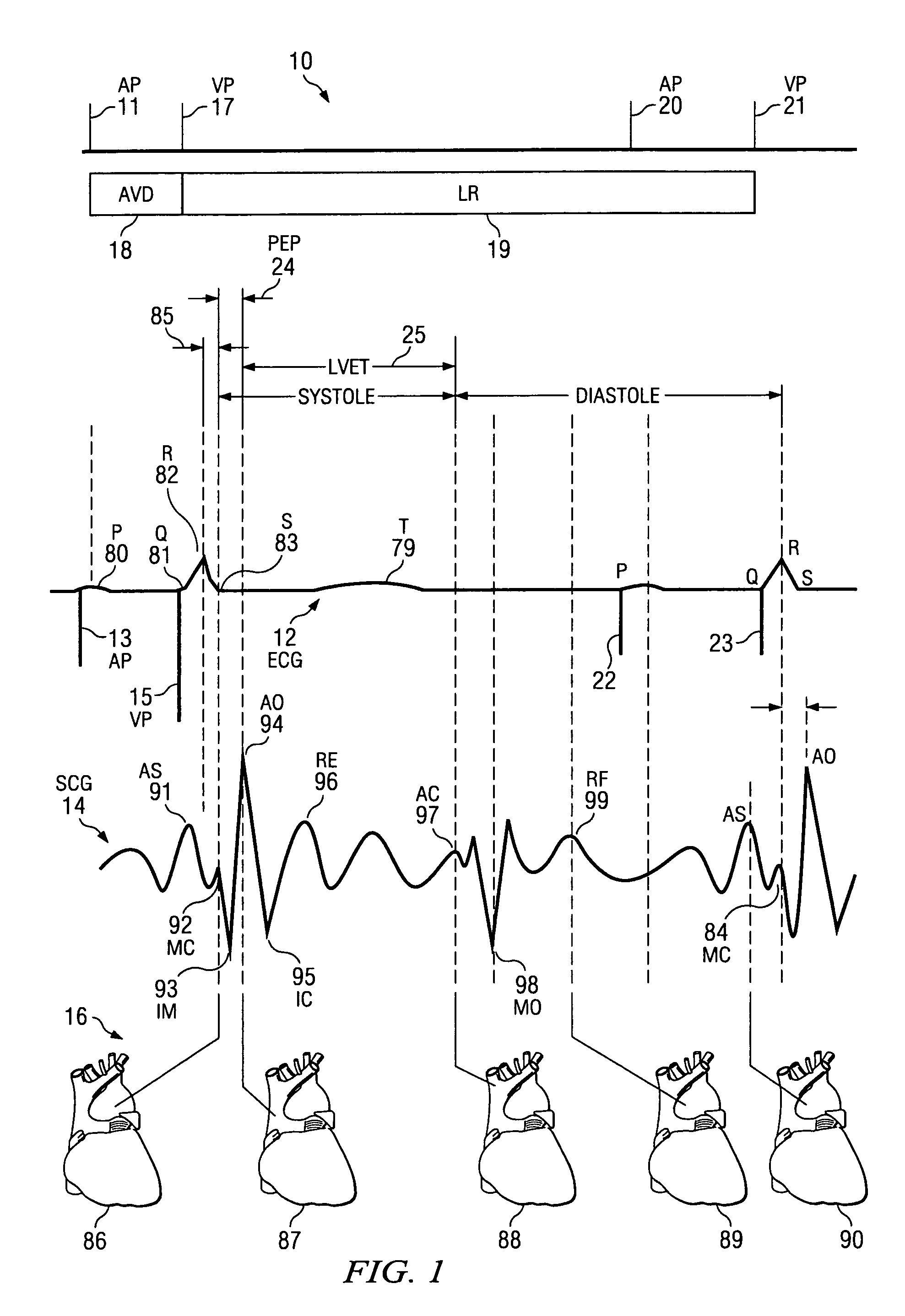
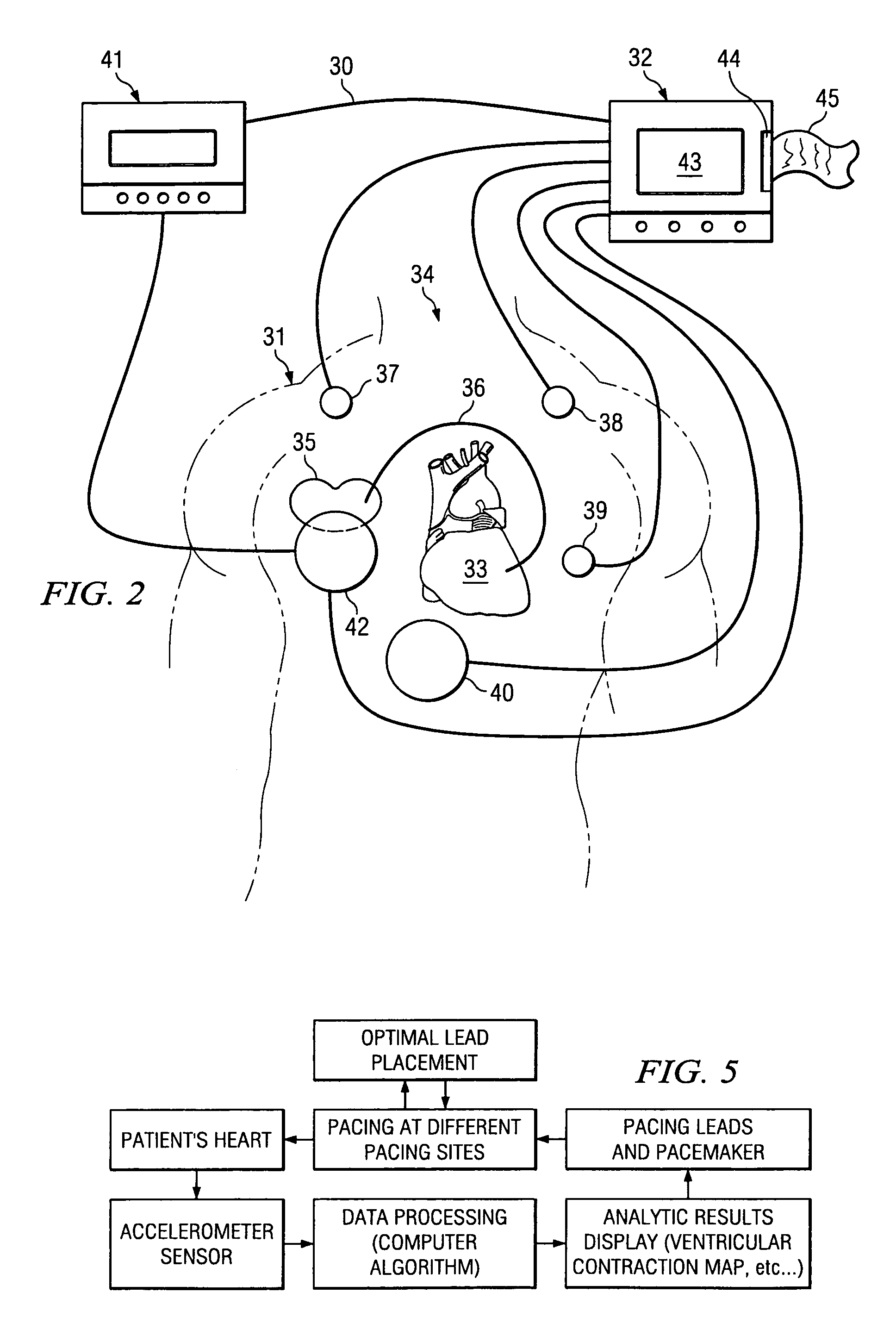
The patterns of contraction and relaxation of the heart before and during left ventricular or biventricular pacing are analyzed and displayed in real time mode to assist physicians to screen patients for cardiac resynchronization therapy, to set the optimal A-V or right ventricle to left ventricle interval delay, and to select the site(s) of pacing that result in optimal cardiac performance. The system includes an accelerometer sensor; a programmable pace maker, a computer data analysis module, and may also include a 2D and 3D visual graphic display of analytic results, i.e. a Ventricular Contraction Map. A feedback network provides direction for optimal pacing leads placement. The method includes selecting a location to place the leads of a cardiac pacing device, collecting seismocardiographic (SCG) data corresponding to heart motion during paced beats of a patient's heart, determining hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters based on the SCG data, repeating the preceding steps for another lead placement location, and selecting a lead placement location that provides the best cardiac performance by comparing the calculated hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters for each different lead placement location.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL +1
Non-invasive method and apparatus for cardiac pacemaker pacing parameter optimization and monitoring of cardiac dysfunction
A plethysmogram signal is sensed from a patient and provided to a programmer device for monitoring the condition of the patient and for optimizing pacing parameters of a cardiac device implanted in the patient. The programmer device analyzes the plethysmogram signal for cardiac performance associated with different pacing parameters. The cardiac performance is indicated by, for example, a pulse amplitude response, a degree of pulsus alternans, or irregularity in the pressure pulses detected in an atrial fibrillation patient. The pacing parameters resulting in the best cardiac performance are selected as the optimum pacing parameters. In one embodiment, the programmer device monitors a Valsalva maneuver performed by a patient. Optimum pacing parameters are derived by analysis of the plethysmogram signals obtained during performance of the Valsalva maneuver while the patient is paced using different pacing parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
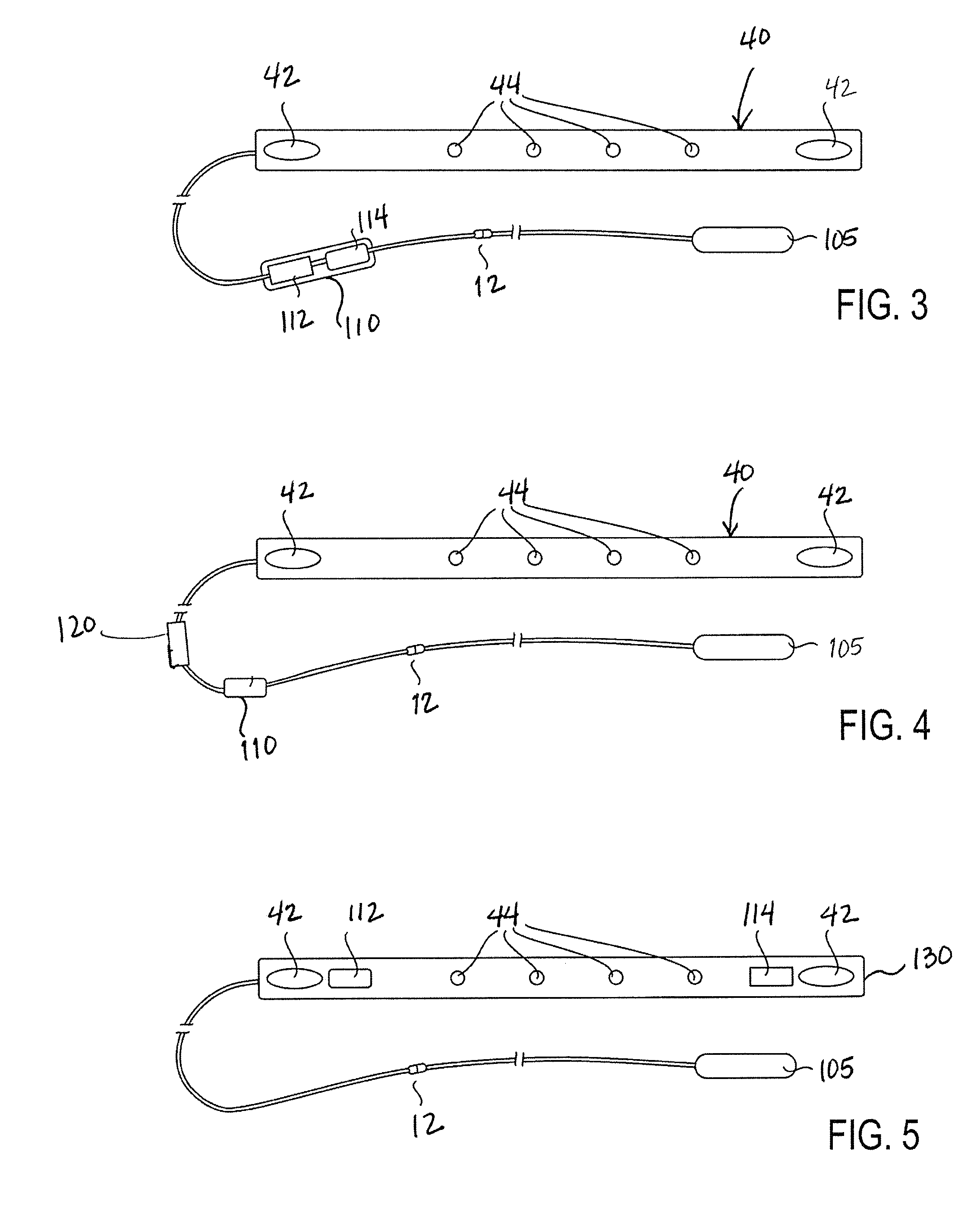
Implantable leadless cardiac device with flexible flaps for sensing
A technique for performing sensing operations in the body subcutaneously employs, in combination, the housing of an electrical stimulator such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator and an integral flap member of flexible insulative sheet material which has at least one arm projecting away therefrom to an extreme tip end. Each arm is rolled about itself from the tip end on a lateral axis transverse of the longitudinal axis of the arm into a compact unit adjacent the housing. An incision is made through the skin and a region beneath the skin enlarged to form a cavity. The compact unit is then inserted into the cavity and unrolled about the lateral axis of each arm so as to be laid flat under the skin. When positioned into a desired orientation, each flap member is sutured to the skin to maintain the desired orientation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
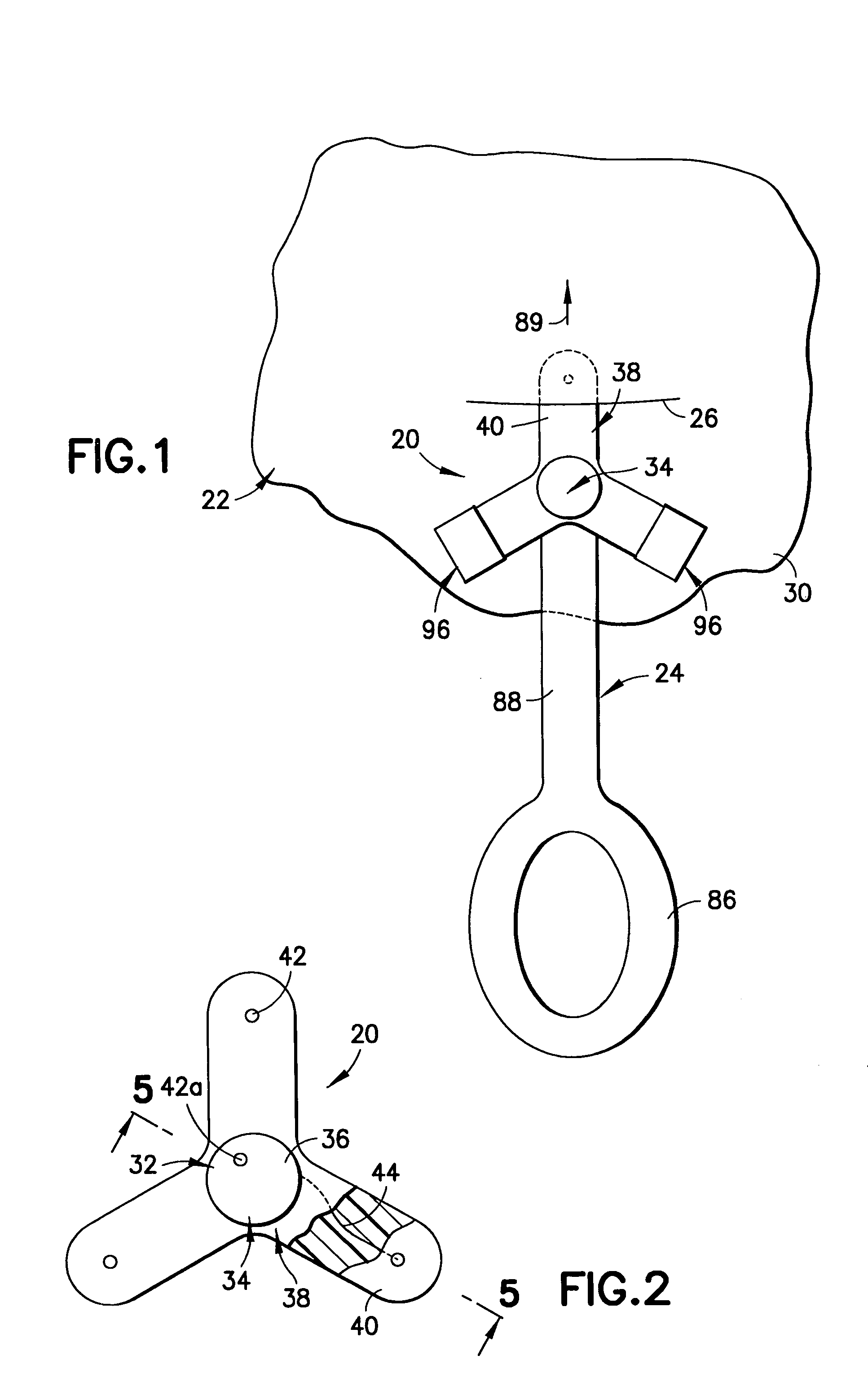
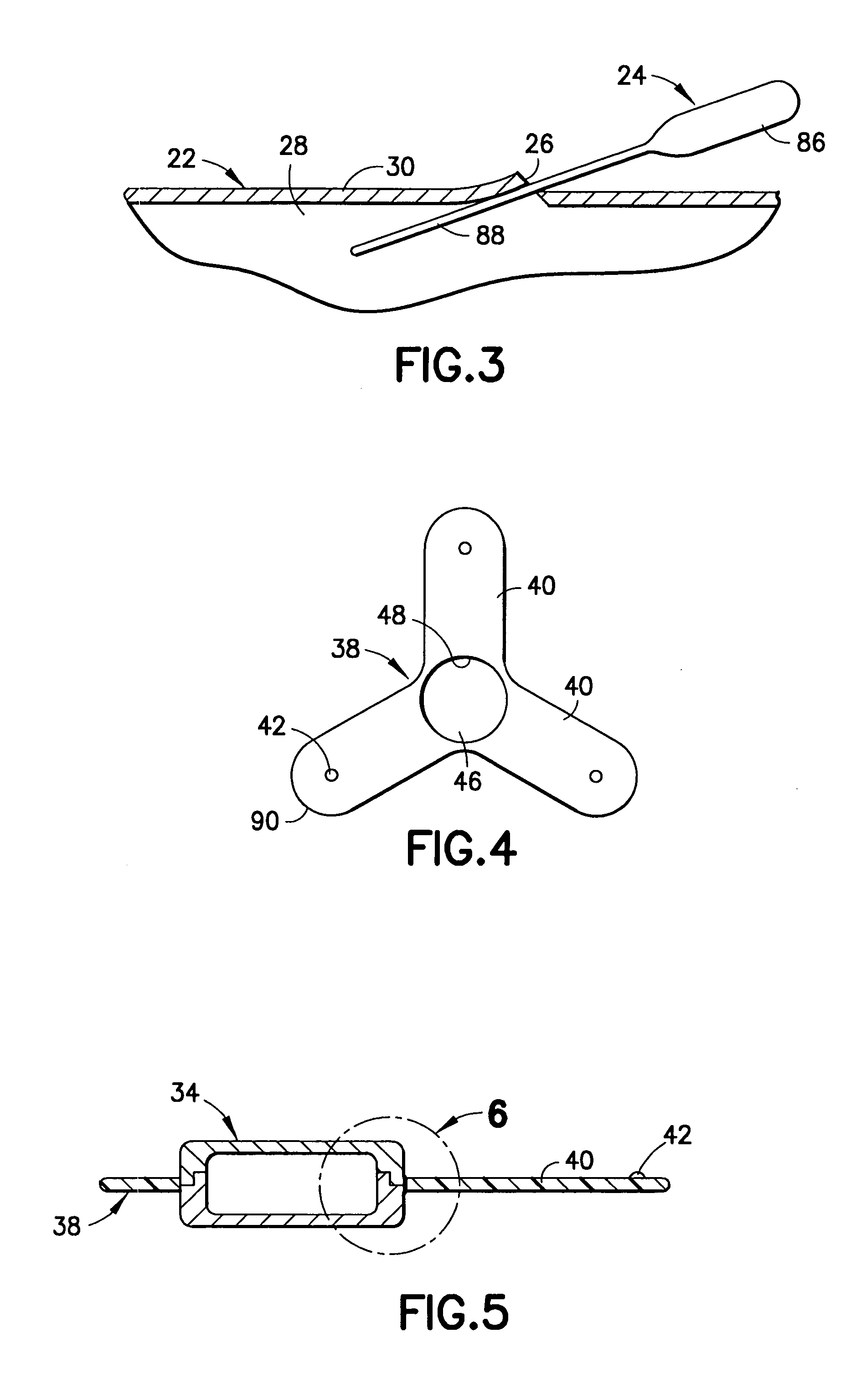
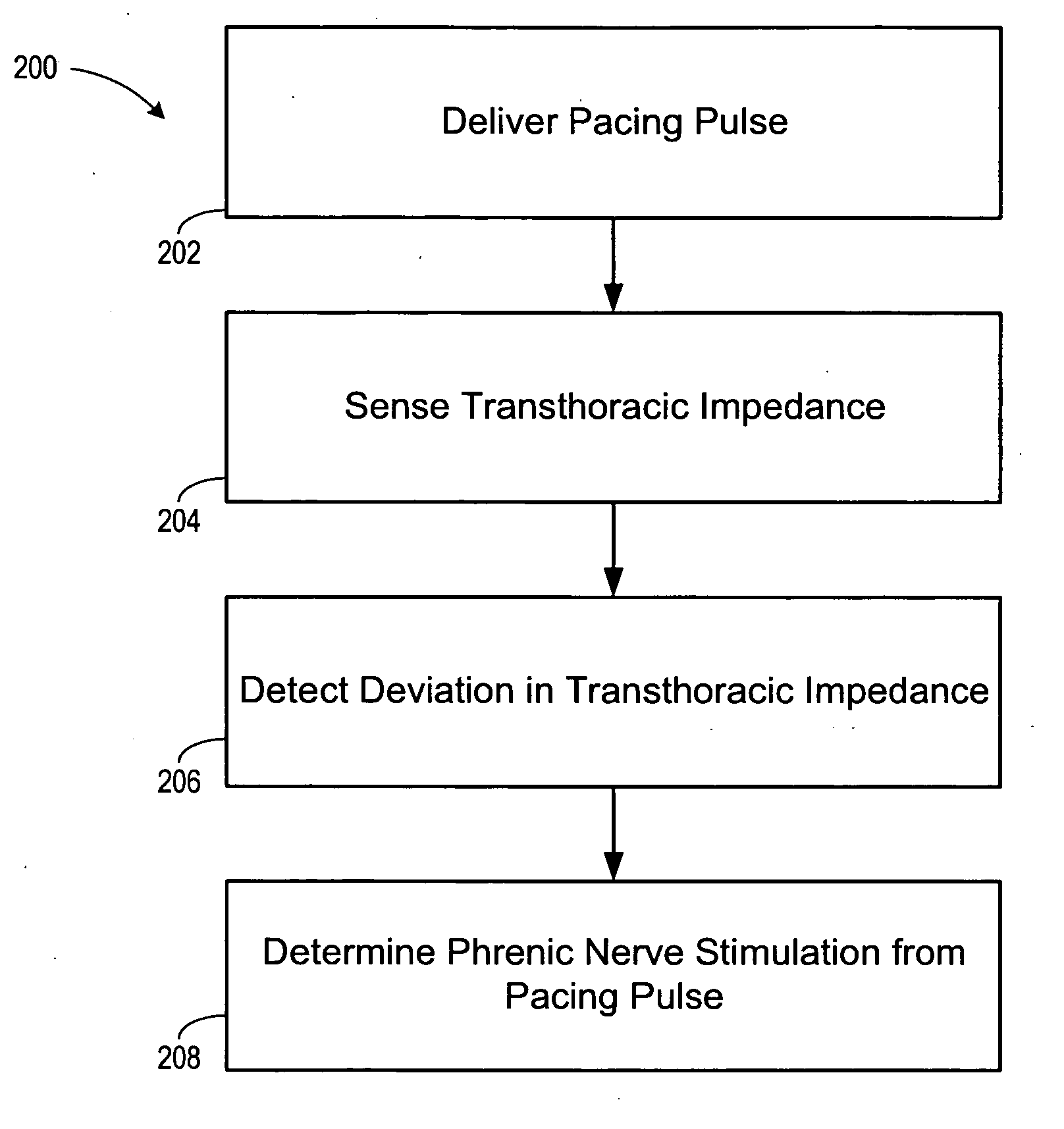
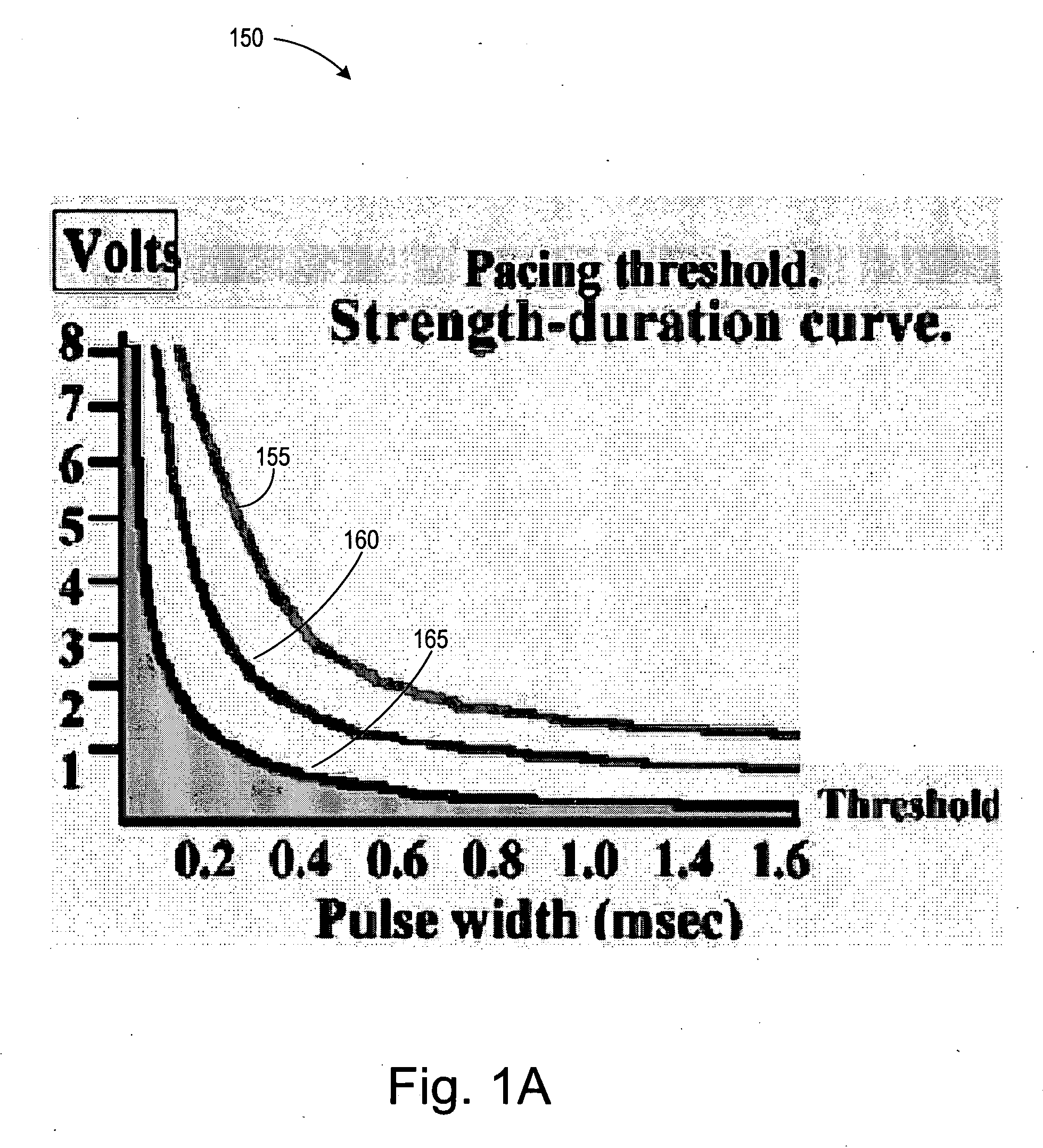
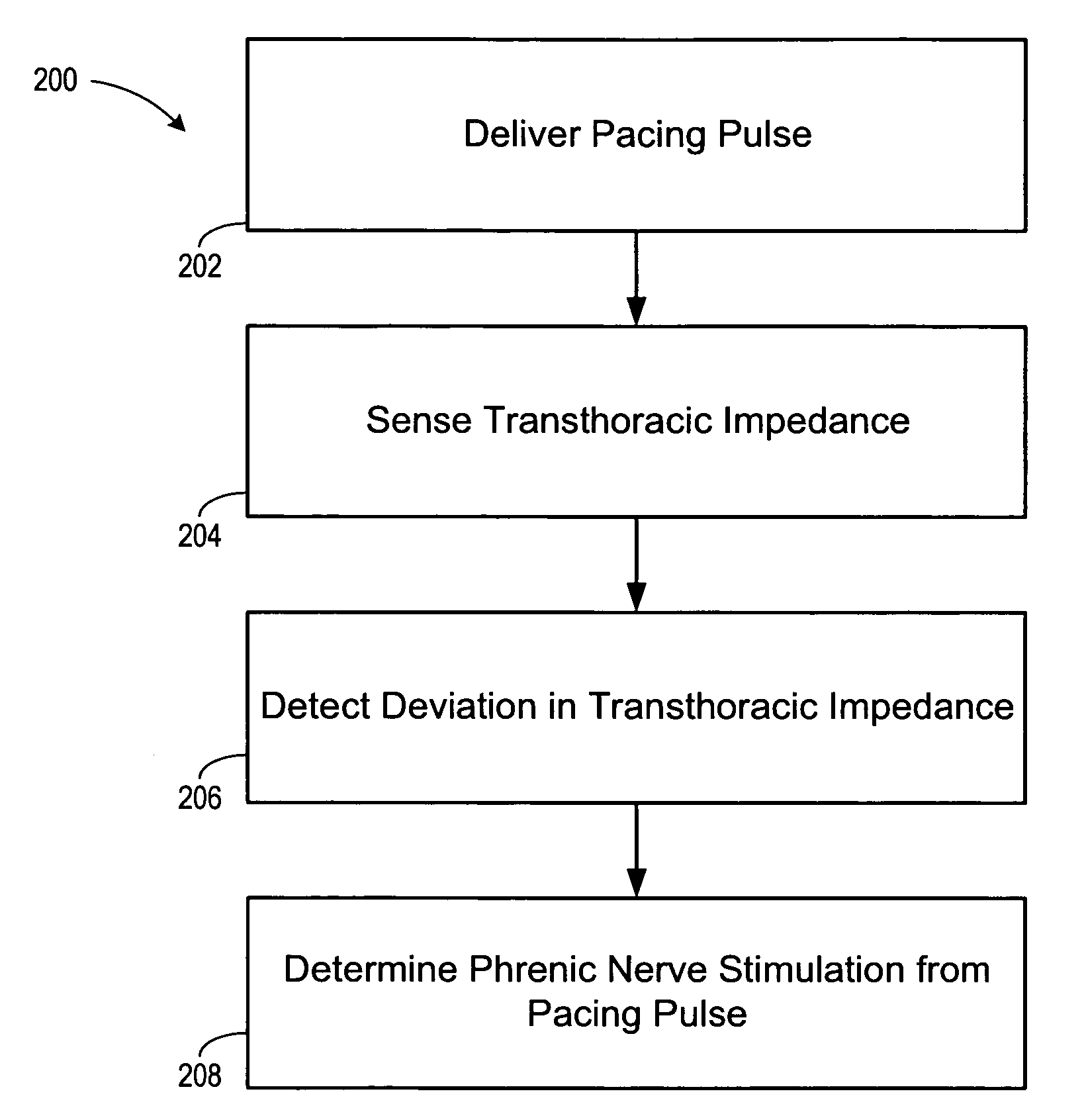
Implantable cardiac device and method for reduced phrenic nerve stimulation
ActiveUS20060241711A1Reducing phrenic nerve stimulationHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringStrength duration curveRadiology
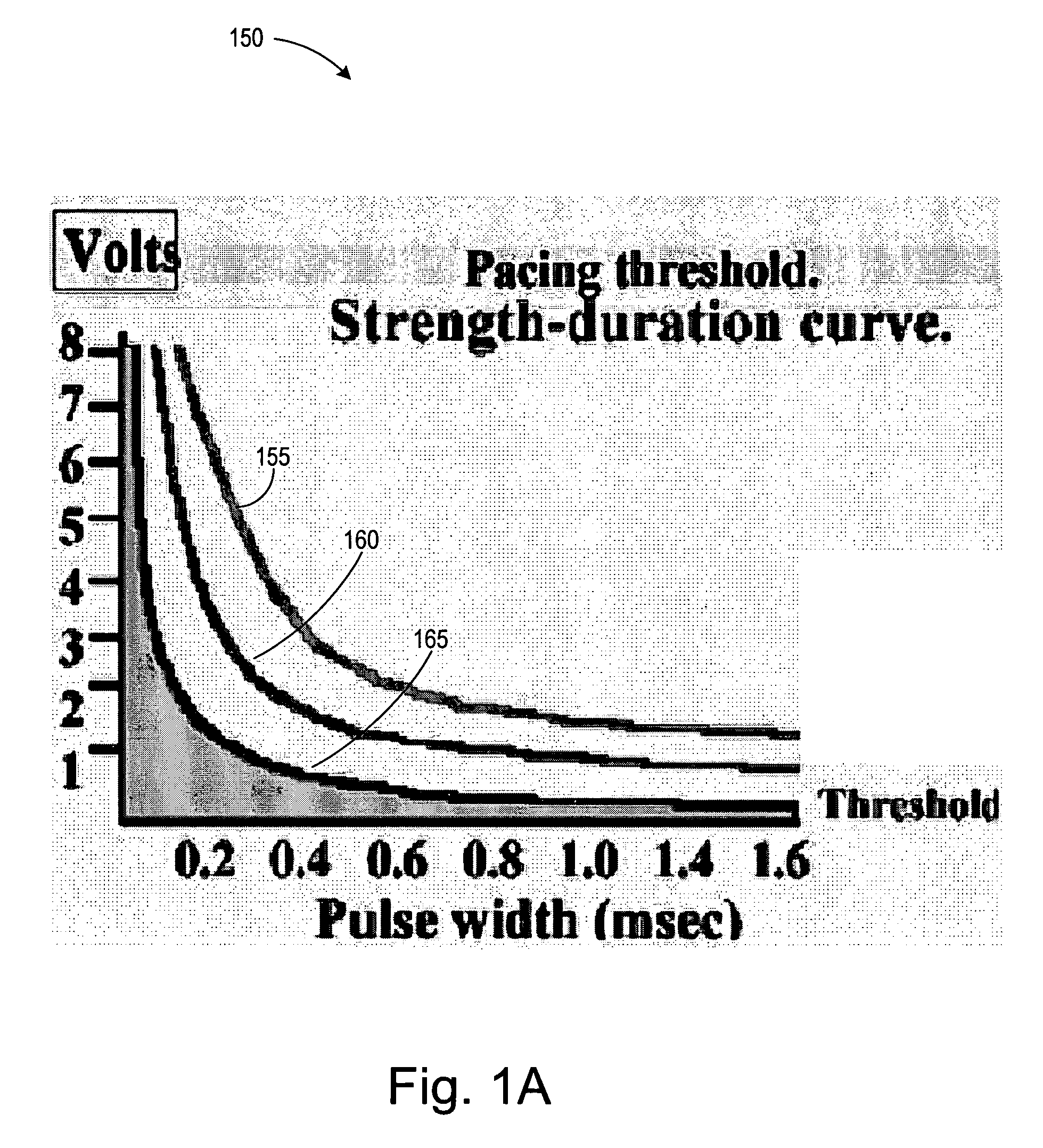
Methods and devices for reducing phrenic nerve stimulation of cardiac pacing systems involve delivering a pacing pulse to a ventricle of a heart. A transthoracic impedance signal is sensed, and a deviation in the signal resulting from the pacing pulse may be used to determine phrenic nerve stimulation. Methods may further involve detecting the phrenic nerve stimulation from the pacing pulse by delivering two or more pacing pulse to the ventricle of the heart, and determining a temporal relationship. A pacing vector may be selected from the two or more vectors that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing voltage and / or pulse width may be selected that provides cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. In other embodiments, a pacing pulse width and a pacing voltage may be selected from a patient's strength-duration curve that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Posture detection system and method
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Optimization of impedance signals for closed loop programming of cardiac resynchronization therapy devices
InactiveUS20050182447A1Reduce dysynchronyImprove congestive heart failure symptomElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCardiac pacemaker electrodeClosed loop
The present invention is related to implantable cardiac devices such as pacemakers and defibrillators that deliver cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and to a method of optimizing acquisition of impedance signals between electrodes present on implanted lead systems. This system then automatically determines which electrodes or electrode combinations acquire impedance waveforms that have the best signal to noise ratio (highest fidelity) and characterize data most representative of dysynchronous electromechanical events. Using closed loop algorithms which provide electrograms and a variety of impedance data reflective of the patient's clinical status, the system autonomously modifies interval timing within the CRT device.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac devices and methods for minimally invasive repair of ischemic mitral regurgitation
ActiveUS8292884B2Eliminate bendingEffective closureIncision instrumentsDiagnosticsChordae tendineaeAtrial cavity
Novel apparatus and minimally invasive methods to treat atrioventricular valve regurgitation that is a result of tethering of chordae attaching atrioventricular valve leaflets to muscles of the heart, such as papillary muscles and muscles in the heart wall, thereby restricting the closure of the leaflets. Catheter embodiments for delivering and positioning chordal severing and elongating instruments are described.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
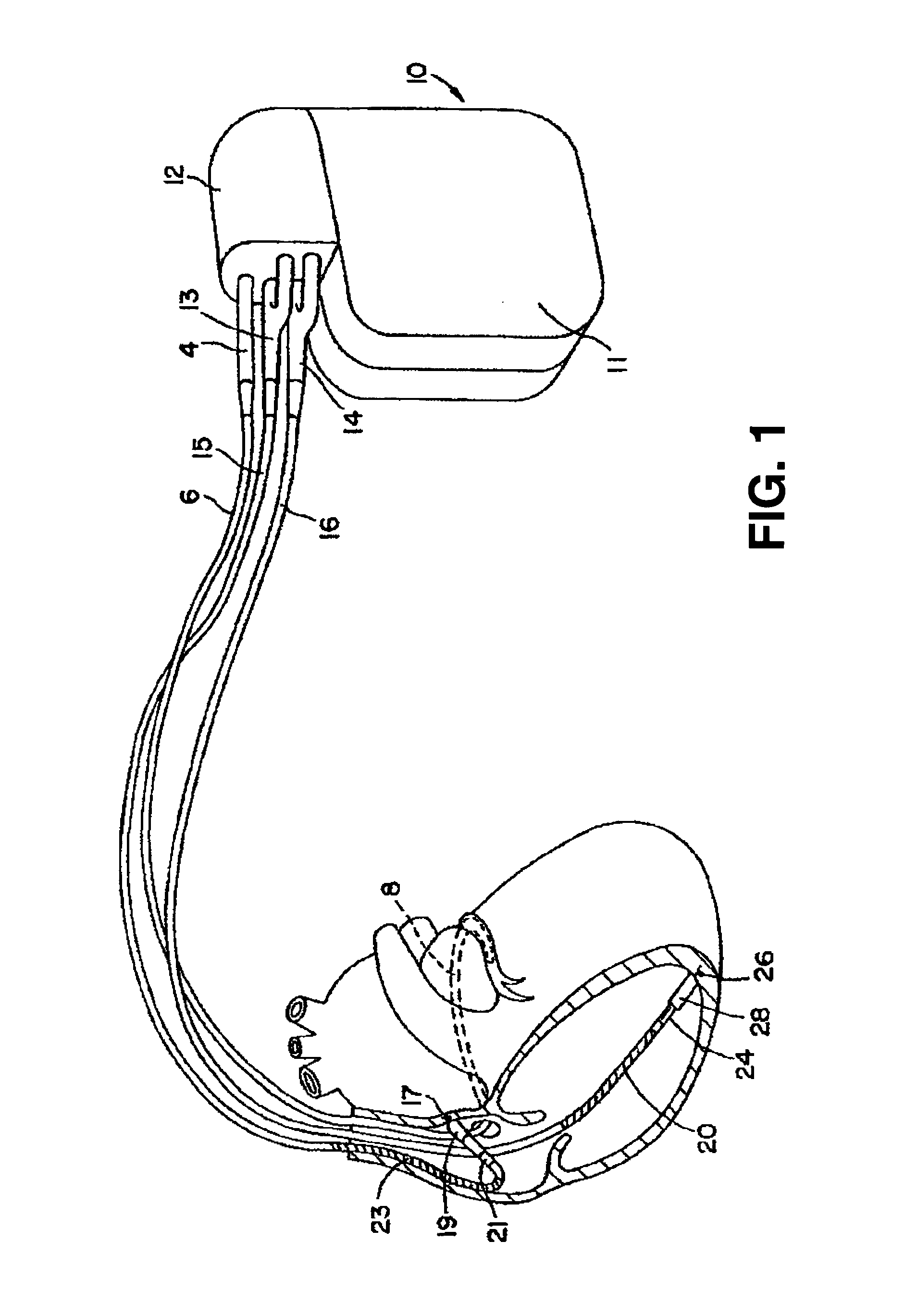
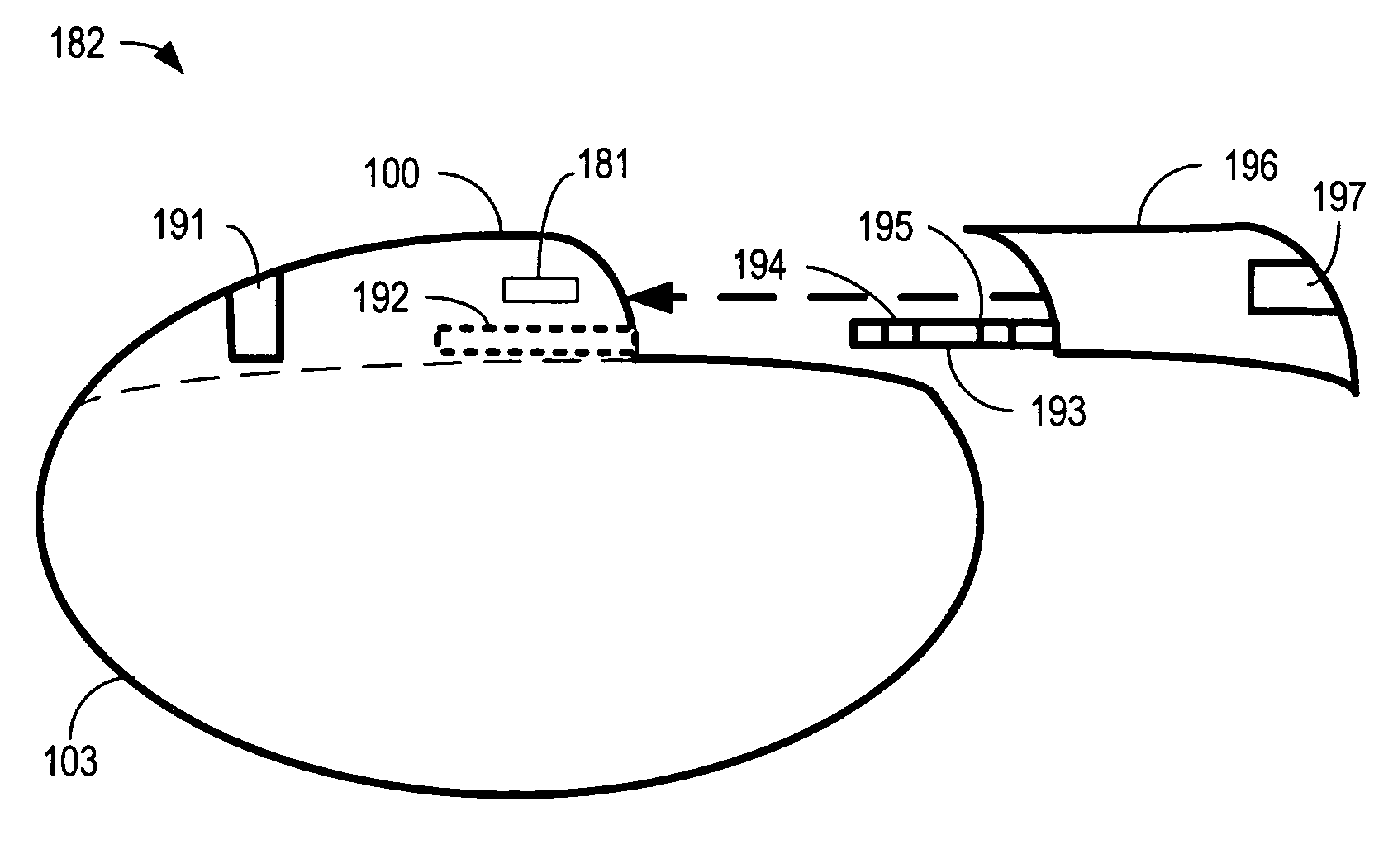
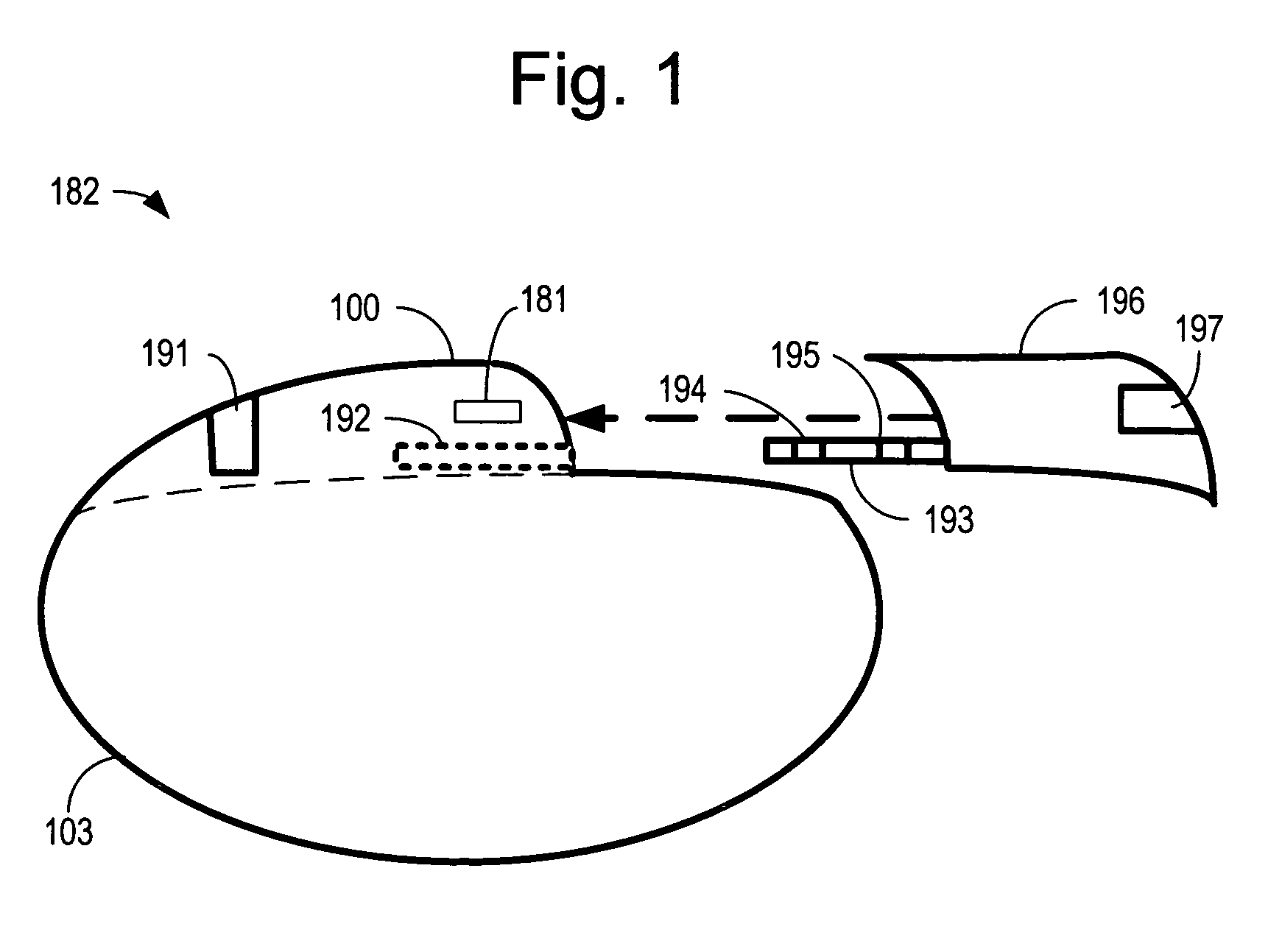
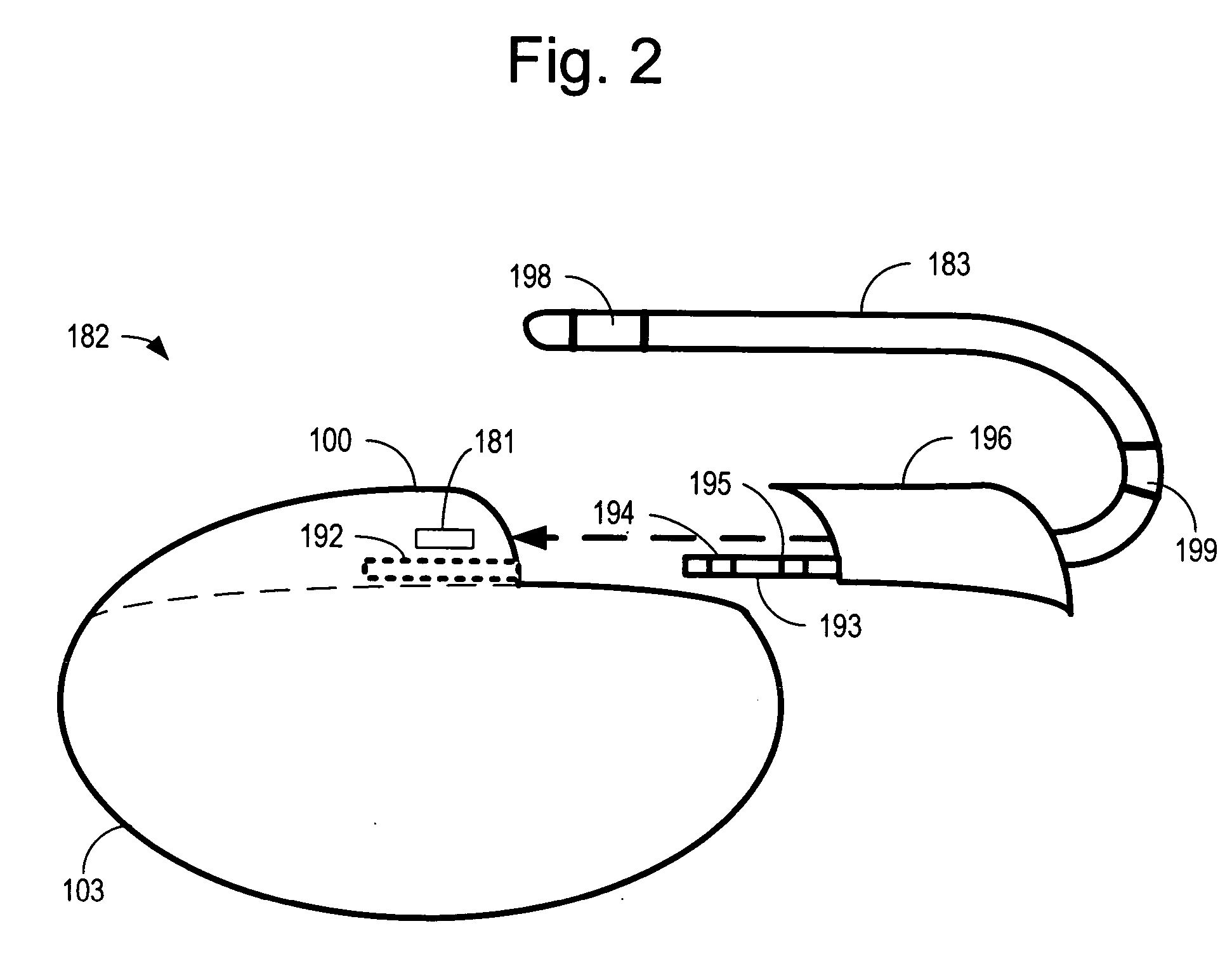
Implanted cardiac device for defibrillation
An implantable medical device for delivering electrical cardiac therapy includes a first implantable housing containing a battery. There is also a second implantable housing separate from the first implantable housing and containing at least one of: electronic circuitry adapted to evaluate and initiate electrical cardiac therapy, a storage capacitor and an electrode structure comprising a sensing electrode, a pacing electrode and a therapy electrode. There is a method of providing electrical cardiac therapy by implanting a first housing containing a battery into a first implantation site within the body. Then, implant a second housing separate from the first housing into a second implantation site within the body. The second housing contains at least one of: electronic circuitry adapted to evaluate and initiate electrical cardiac therapy; a storage capacitor and an electrode structure comprising a sensing electrode, a pacing electrode and a therapy electrode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Reconfigurable implantable cardiac monitoring and therapy delivery device
Methods and systems for implantable cardiac monitors reconfigurable to cardiac therapy devices. A device includes a housing with electrodes configured for cardiac activity sensing when the device is operated in monitoring mode, and sensing and energy delivery when operated in an energy delivery mode. A header may be configured to receive a cardiac lead, and may be associated with a switch to switch the device between monitoring and therapy modes in response to connecting one or more leads to the header. The device may include a transceiver that transmits the contents of the memory to a patient-external device. A method involves providing an implantable cardiac device configured to operate in a first mode as a loop recorder for monitoring cardiac activity and storing selected cardiac events, and operating in the second mode to monitor cardiac activity and provide cardiac stimulation therapy when the second mode is enabled.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Evoked response variability as an indicator of autonomic tone and surrogate for patient condition
Modern implantable cardiac stimulation devices include processing and data storage capabilities that may be exploited to track myocardial condition and autonomic tone. Implantable devices have a capability to measure and store electrogram information over a period of time in a relatively large capacity memory, with advances in technology allowing increases in memory size. The evoked response varies in amplitude and morphology with changes in autonomic tone, ventricular filling, paced rate, and other parameters. The implantable cardiac device can be configured to sense and accurately quantify the evoked response, derive parameters from the quantified evoked response, store the parameters over long time periods, and derive variability statistics from the parameters to assist in tracking the patient's condition over time, and guiding the patient's therapy.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulation device providing anti-tachycardia pacing therapy and method
An implantable subcutaneous cardiac device includes at least two subcutaneous electrodes adapted for placement external to a heart beneath the skin of a patient. The device further includes an arrhythmia detector that detects a sustained tachyarrhythmia of the heart and a pulse generator that delivers anti-tachycardia pacing pulses to the subcutaneous electrodes in response to detection of a sustained tachyarrhythmia. The pacing pulses preferably have waveforms devoid of any exponential voltage decay and include rounded or substantially constant portions to minimize pain.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
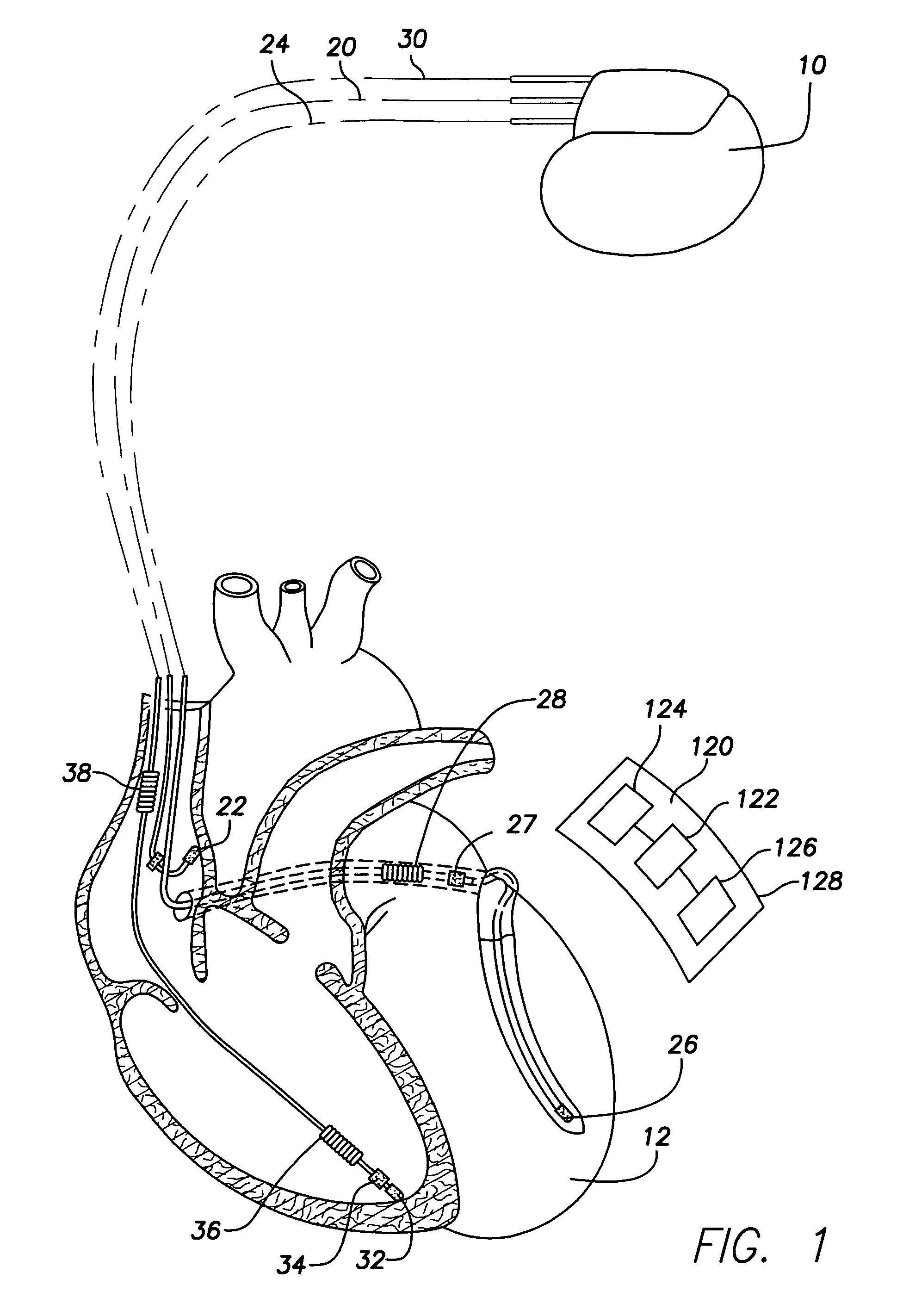
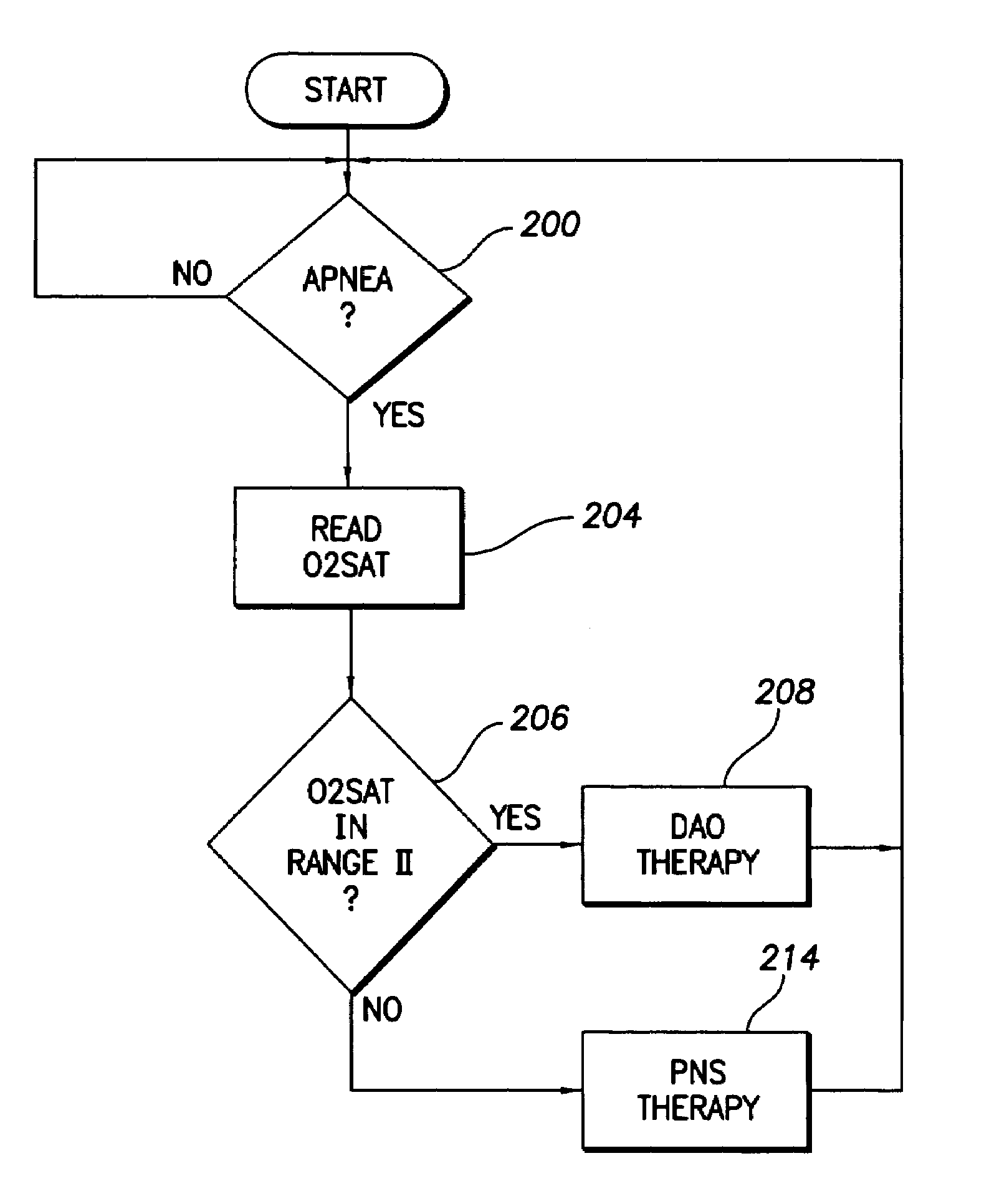
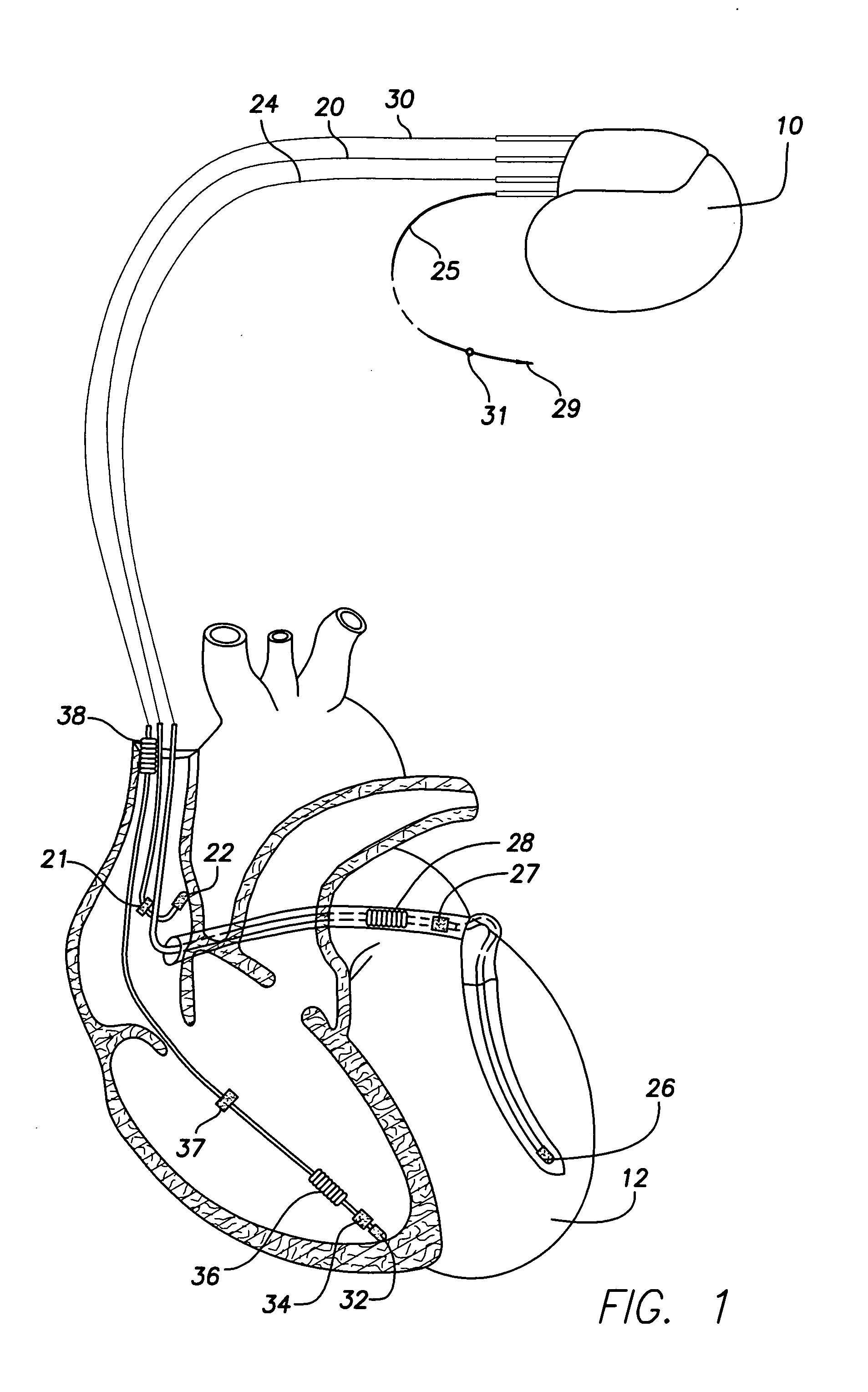
Implantable cardiac device with selectable tiered sleep apnea therapies and method
An implantable cardiac stimulation device treats apnea with either phrenic nerve stimulation pulses or cardiac stimulation pulses. The device includes an apnea detector that detects apnea of a patient, a blood oxygen saturation monitor that measures a blood oxygen saturation level of the patient responsive to detection of apnea, and a tiered therapy circuit that provides phrenic nerve stimulation pulses if the measured blood oxygen saturation level is within a first range and cardiac stimulation pulses if the measured blood oxygen saturation level is within a second range. The cardiac stimulation pulses are preferably provided in a DAO pacing mode.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac devices and methods for minimally invasive repair of ischemic mitral regurgitation
ActiveUS20060095025A1Eliminate bendingEffective closureIncision instrumentsHeart valvesChordae tendineaePapillary muscle
Novel apparatus and minimally invasive methods to treat atrioventricular valve regurgitation that is a result of tethering of chordae attaching atrioventricular valve leaflets to muscles of the heart, such as papillary muscles and muscles in the heart wall, thereby restricting the closure of the leaflets. Catheter embodiments for delivering and positioning chordal severing and elongating instruments are described.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
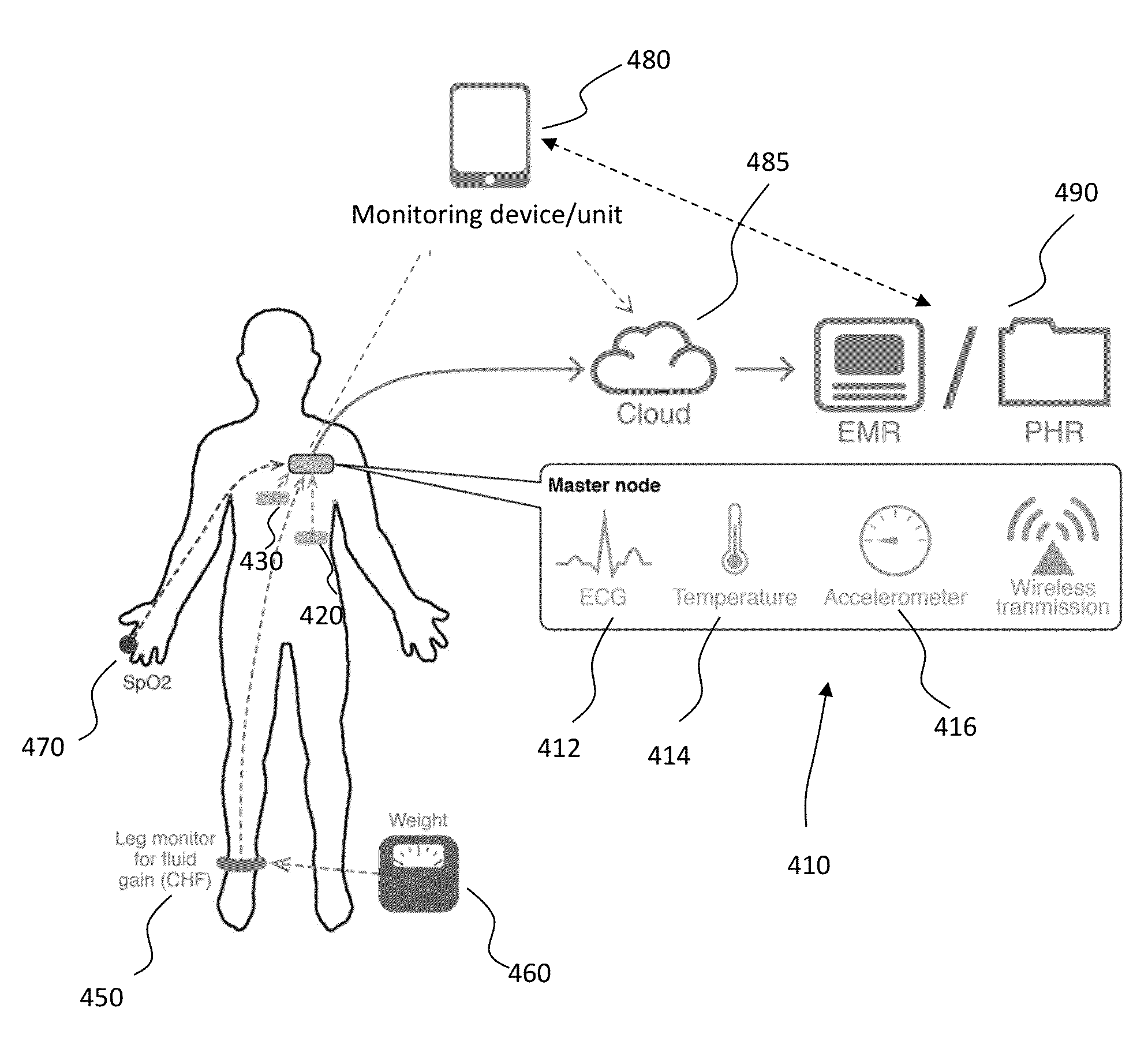
System and method for monitoring and diagnosing patient condition based on wireless sensor monitoring data
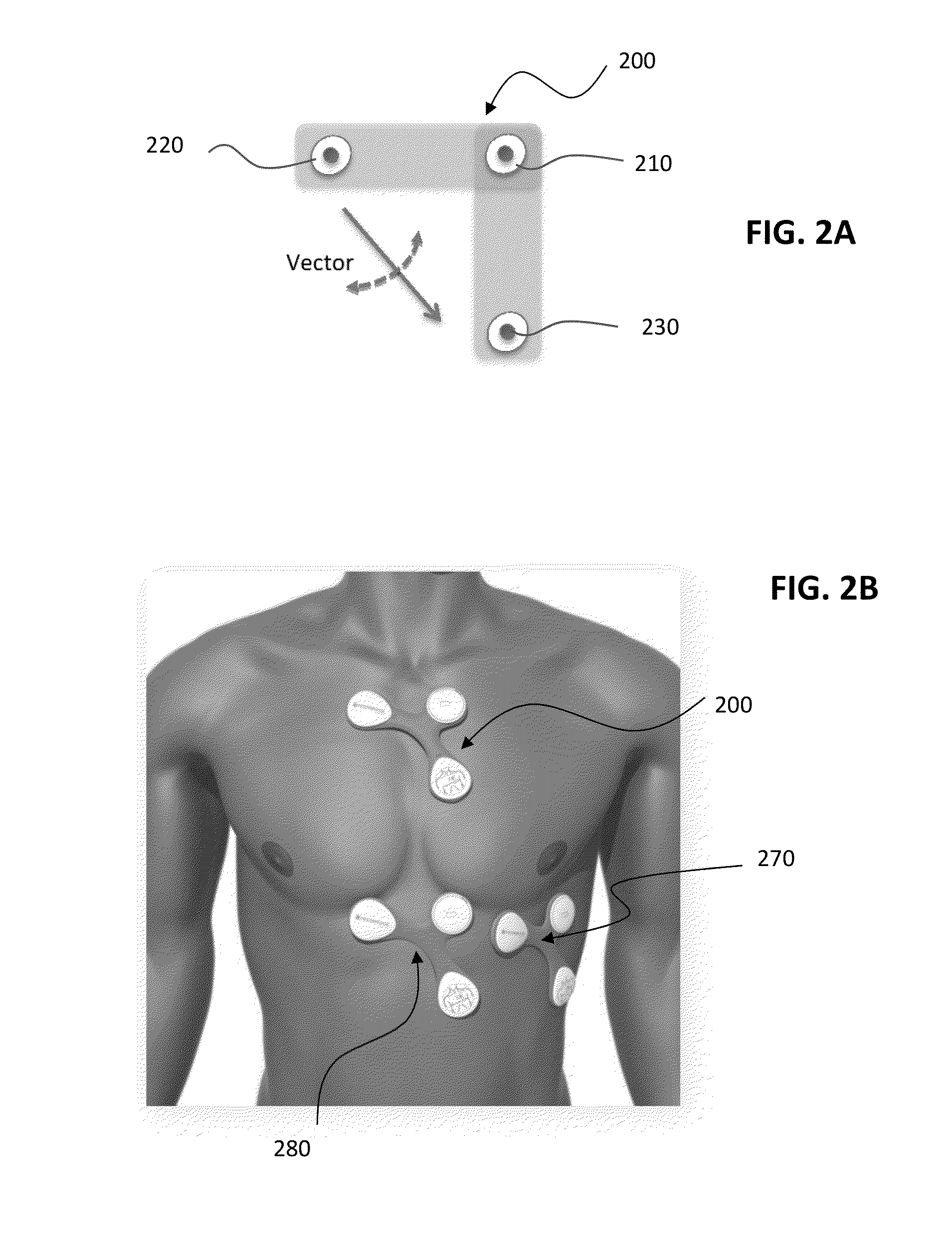
ActiveUS20140275928A1Maximize chanceMaximize magnitudeElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsLine sensorEcg signal
A device adapted to attach to a subject for detecting an ECG signal of the subject. The device includes a first, a second, and a third electrode, where the electrodes form an orthogonal configuration. Two channels of ECG data can be obtained using a common electrode, and can be further combined to obtain a further channel using vector mathematics. The channel combination can be performed at vector angles suitable for optimizing the detection of various features of the ECG spectra of the subject. A method of using an implantable cardiac device together with surface-attached wireless sensor(s) is also provided where the acquired data from the implantable cardiac device and from the surface-attached wireless sensor(s) are both used for diagnosing patient's heart conditions and administering appropriate therapies.
Owner:PEERBRIDGE HEALTH
Implantable cardiac device and method for reduced phrenic nerve stimulation
Methods and devices for reducing phrenic nerve stimulation of cardiac pacing systems involve delivering a pacing pulse to a ventricle of a heart. A transthoracic impedance signal is sensed, and a deviation in the signal resulting from the pacing pulse may be used to determine phrenic nerve stimulation. Methods may further involve detecting the phrenic nerve stimulation from the pacing pulse by delivering two or more pacing pulse to the ventricle of the heart, and determining a temporal relationship. A pacing vector may be selected from the two or more vectors that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. A pacing voltage and / or pulse width may be selected that provides cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation. In other embodiments, a pacing pulse width and a pacing voltage may be selected from a patient's strength-duration curve that effects cardiac capture and reduces the phrenic nerve stimulation.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Synchronization system between aortic valve and cardiac assist device
ActiveUS20060030747A1Achieve synchronizationControl devicesMedical devicesAccelerometerThoracic cavity
A cardiac assist device synchronization system includes a cardiac assist device and an acoustic or accelerometer sensor that provides a signal input to the cardiac assist device indicative of aortic valve closure. The cardiac assist device is coupled to a mammalian aorta and includes an inflatable chamber and a fluid pump. A fluid conduit is in communication between the chamber and the pump to provide for selective inflation of the chamber. A pump controller triggers the pump in counter-pulsation to a mammalian heart upstream from the aorta. A process for synchronizing a cardiac assist device in counter-pulsation with a left ventricle includes locating an acoustic or accelerometer sensor within a thoracic cavity of a mammal having the assist device coupled to the aorta of the mammal. Through the measurement of an acoustic or acceleration property of an aortic valve of the mammal, and the transmission of aortic valve closure measurement through a controller for the cardiac assist device, counter-pulsatile synchronization for the cardiac assist device is achieved.
Owner:KANTROWITZ ALLEN B +1
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
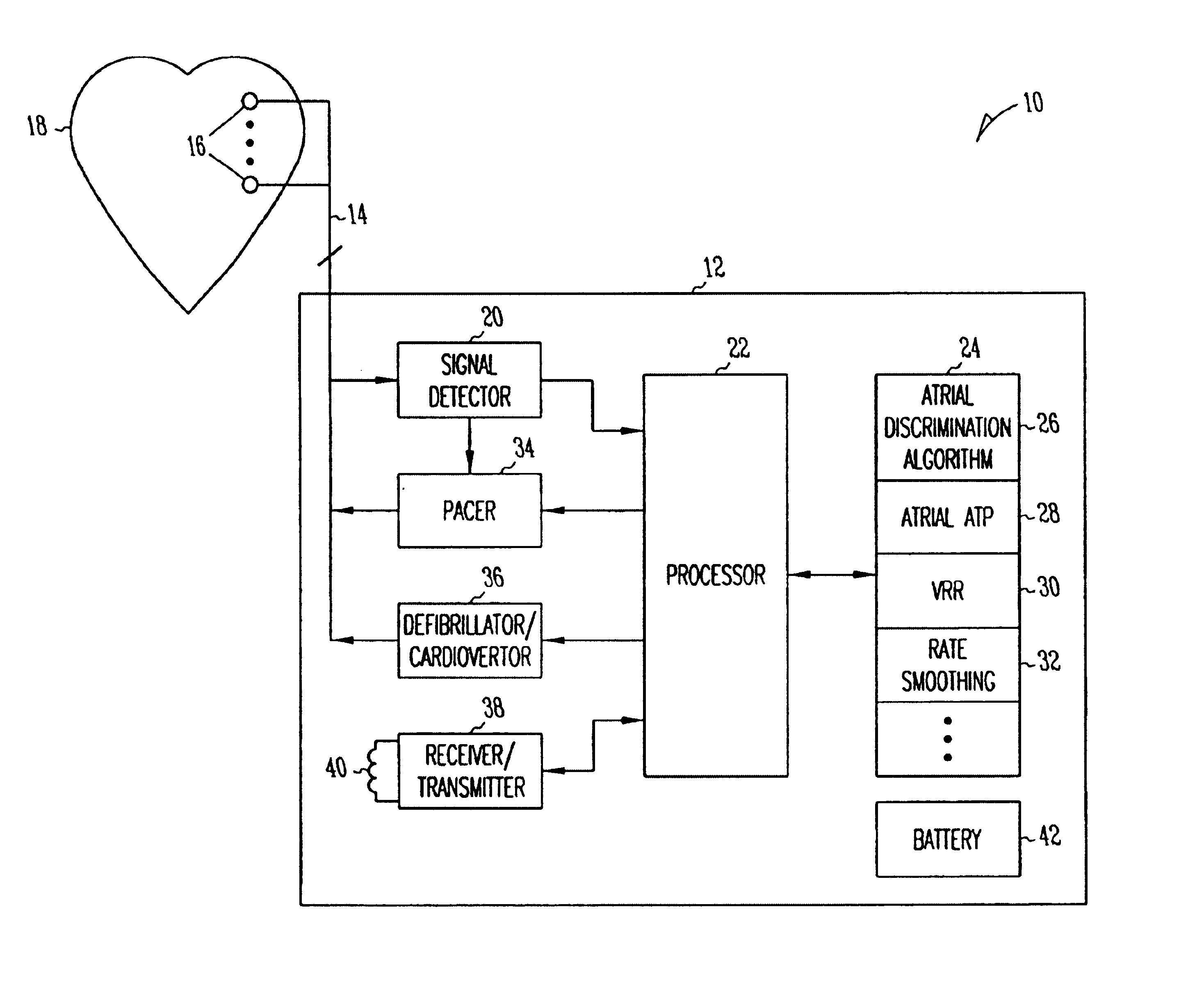
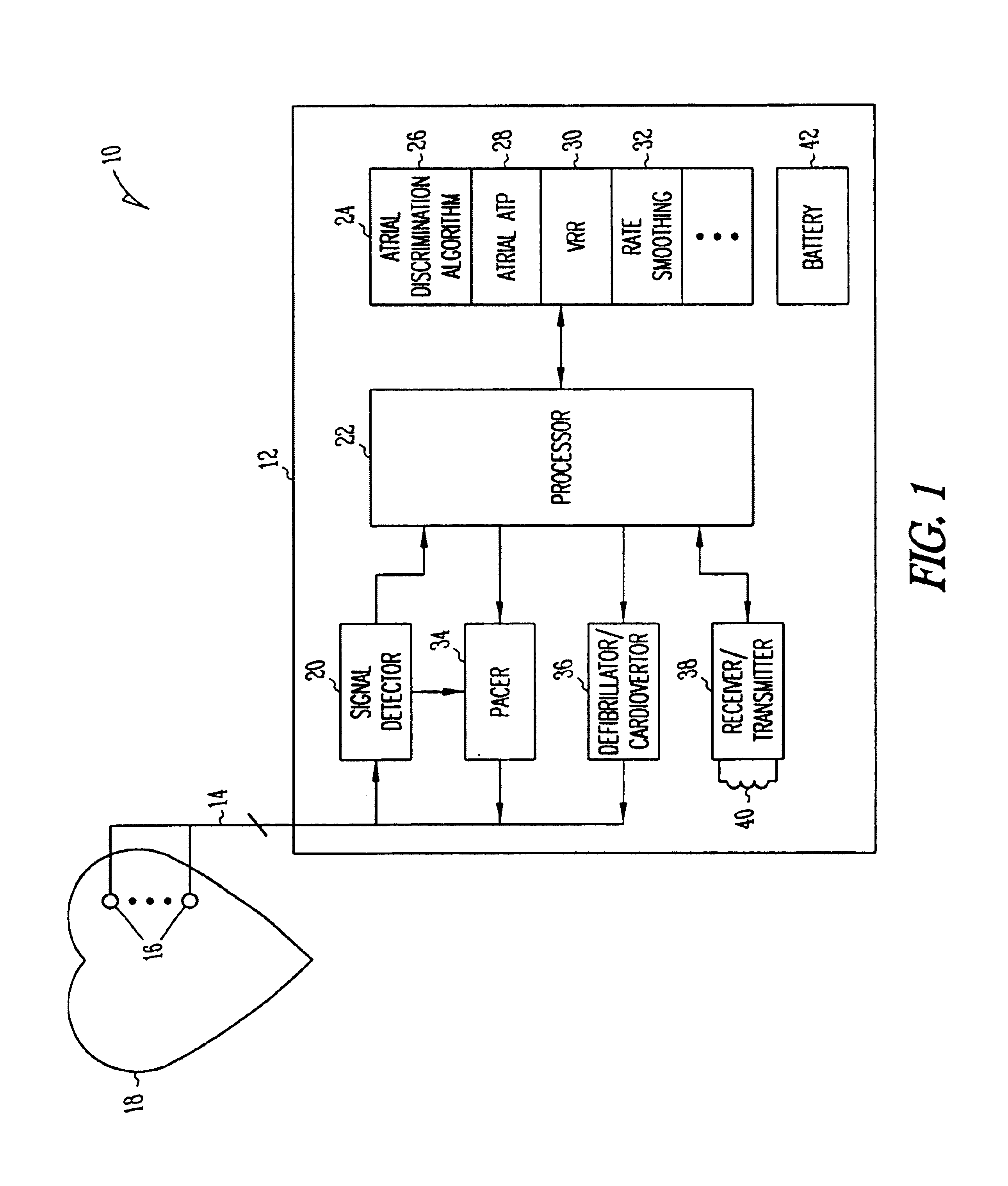
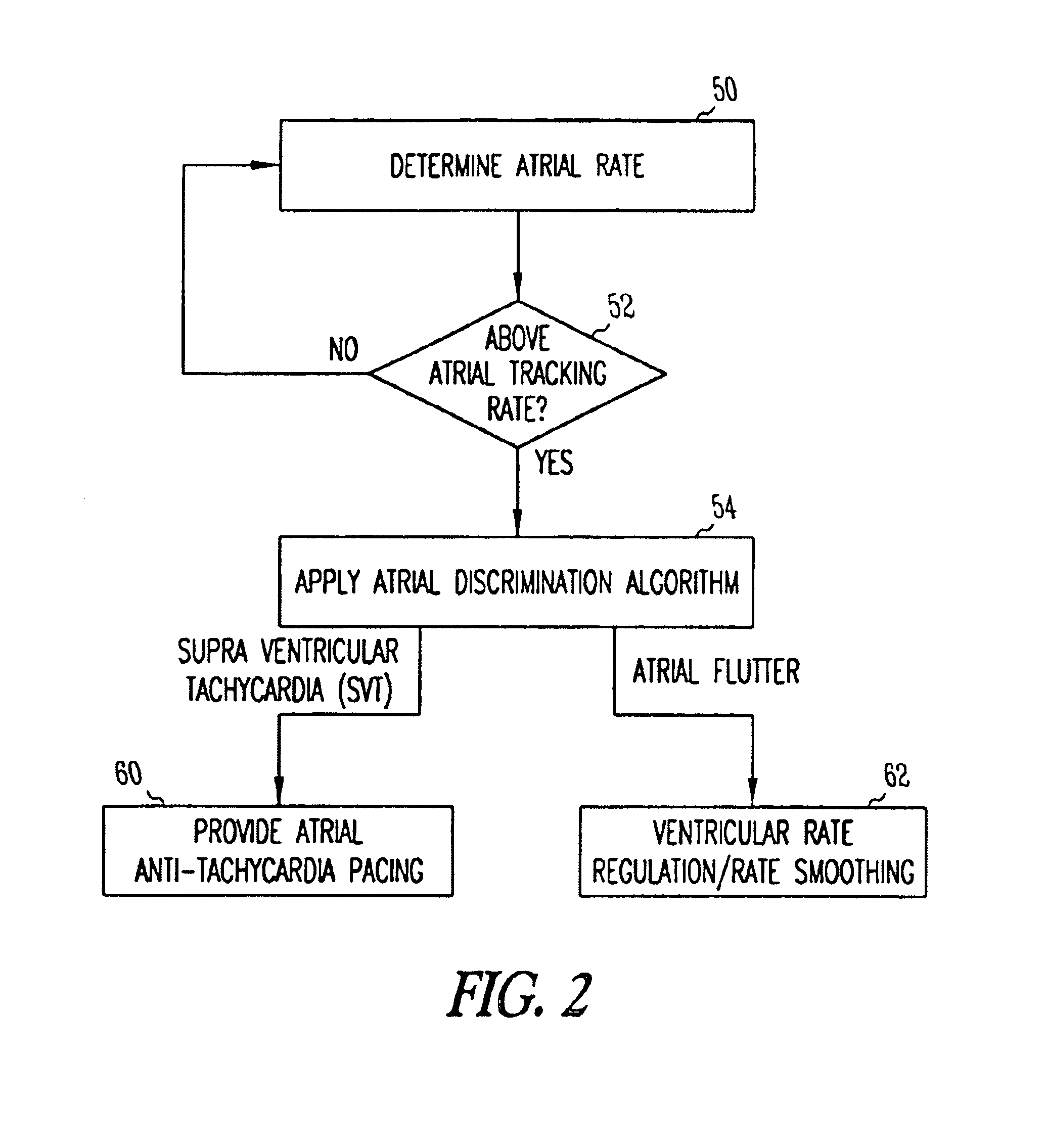
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com