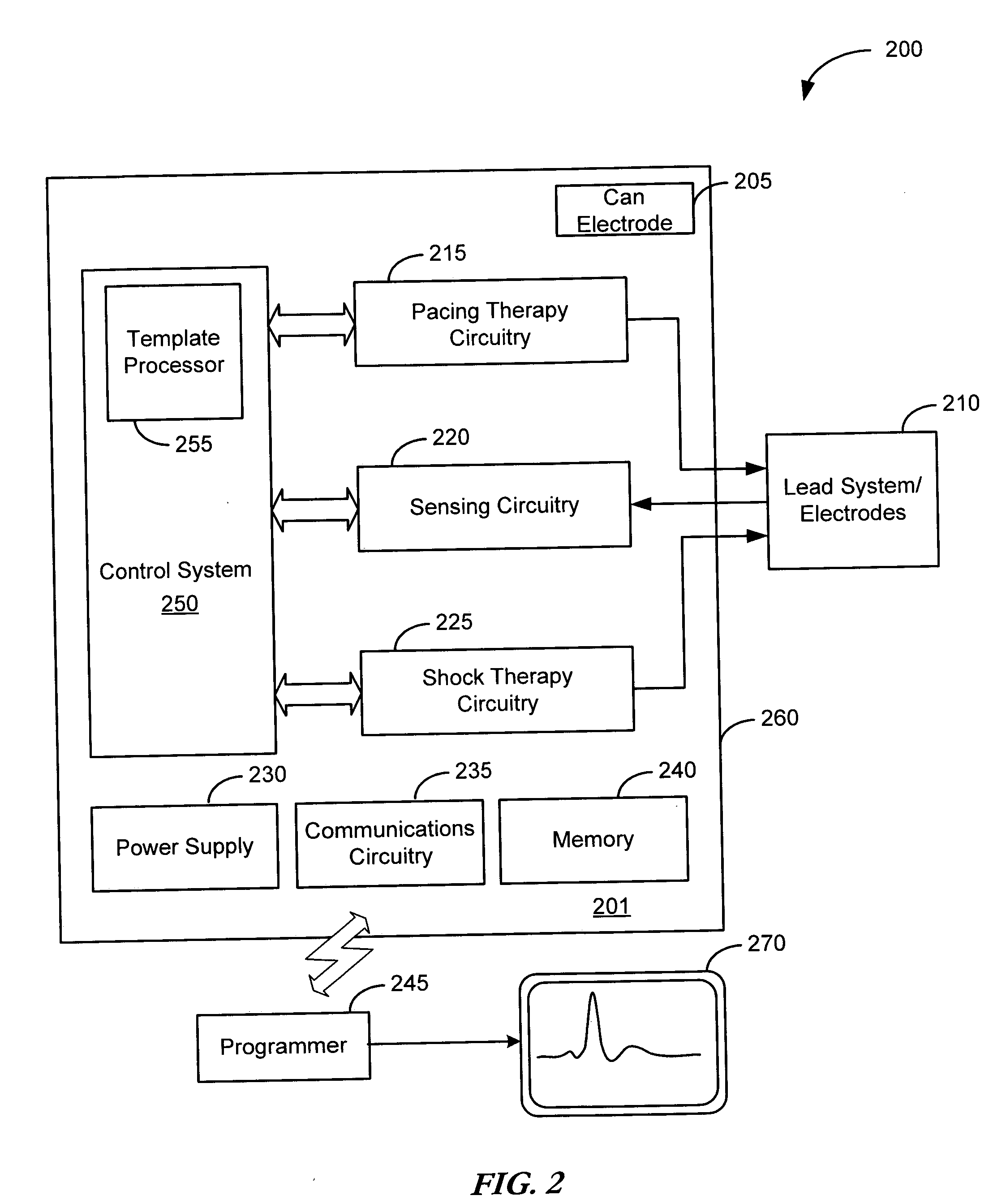
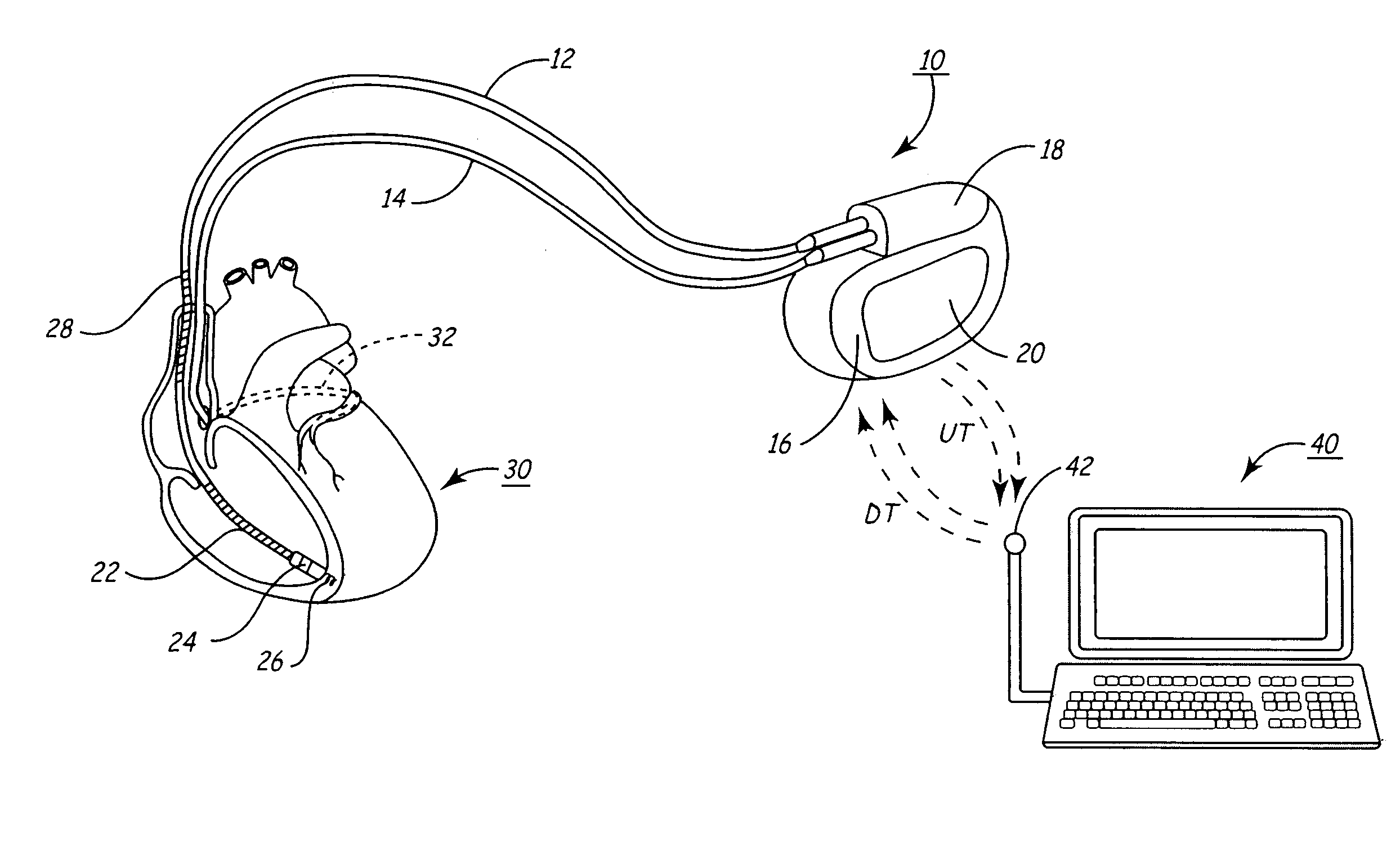
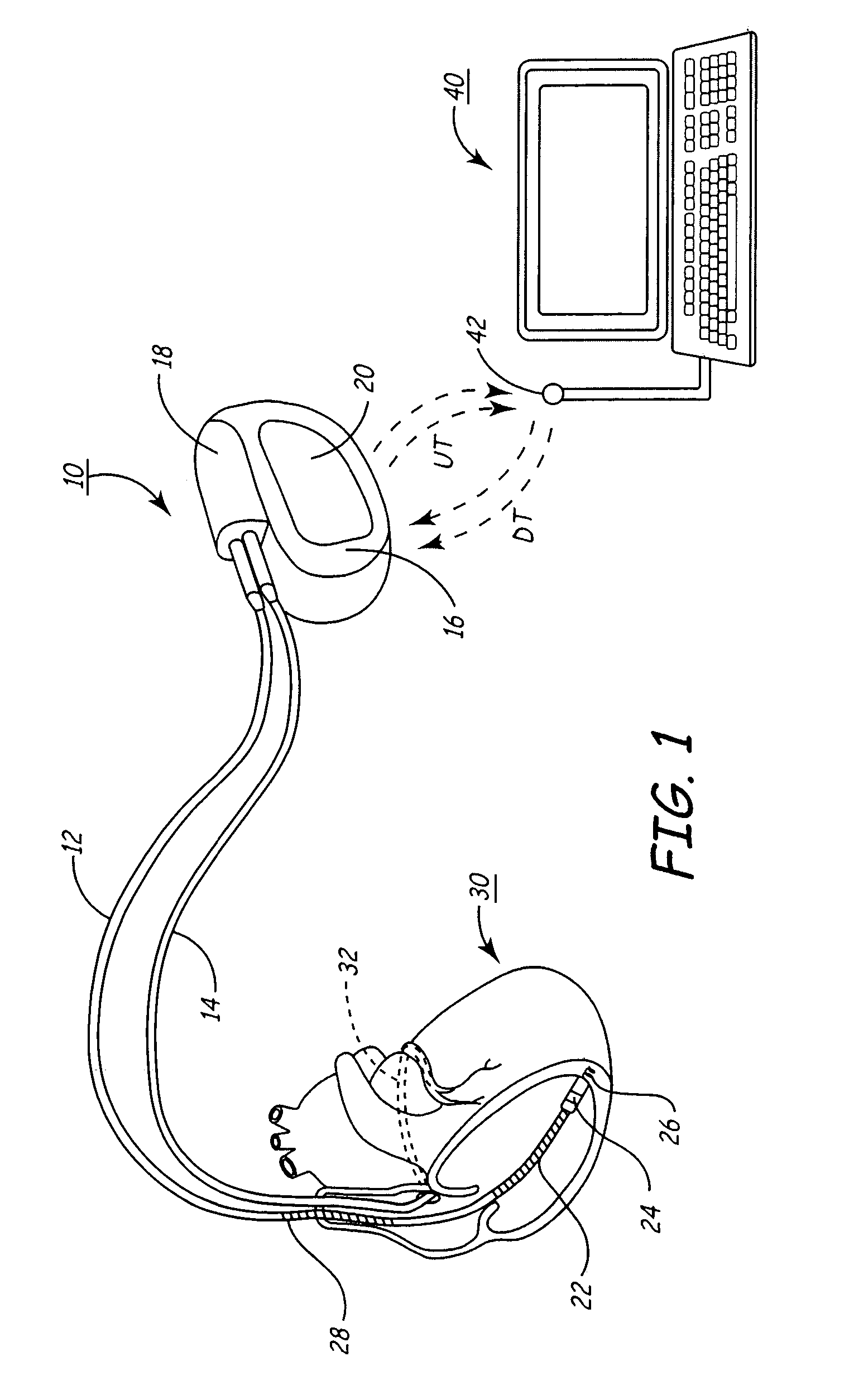
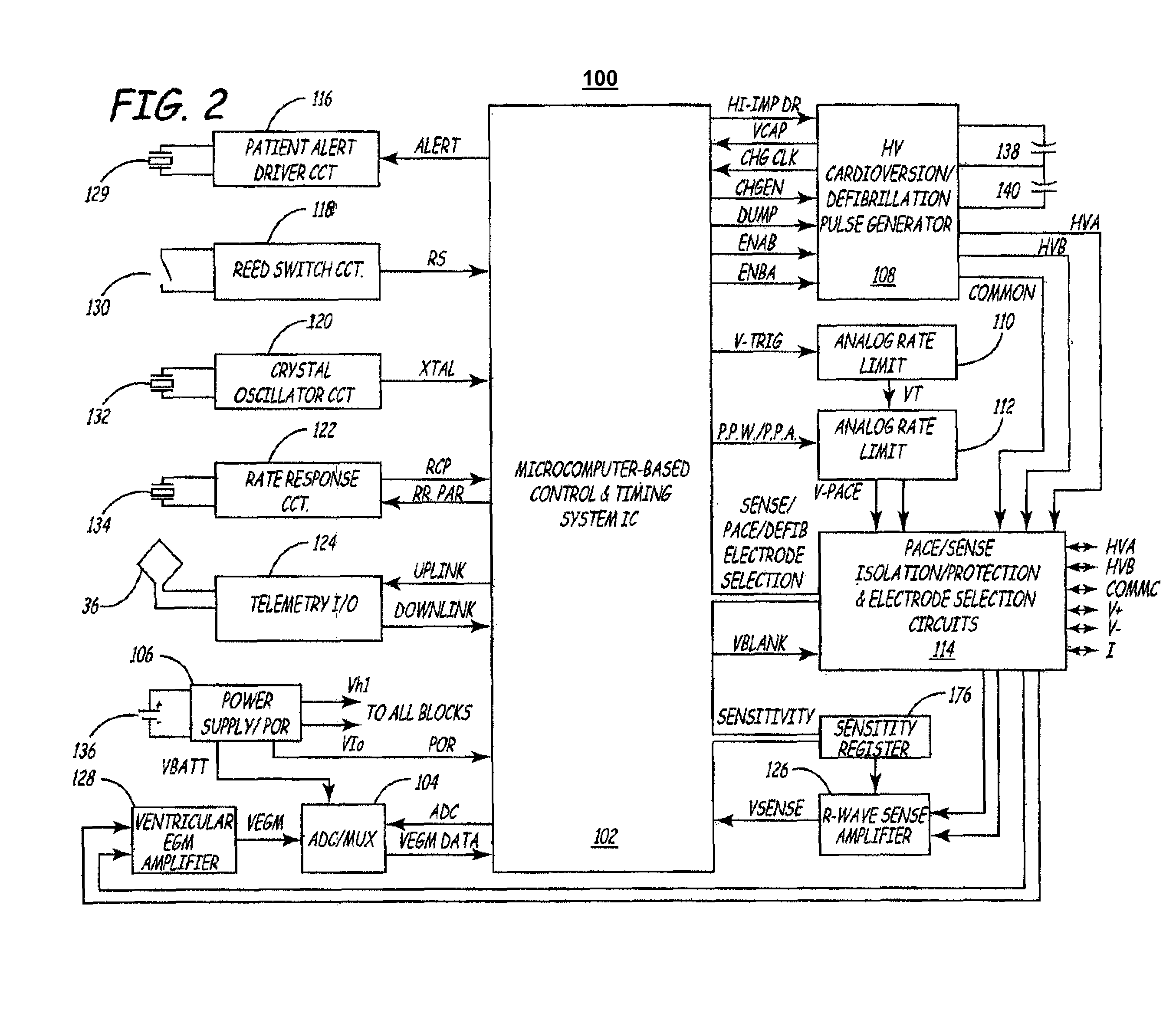
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Antitachycardia Pacing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
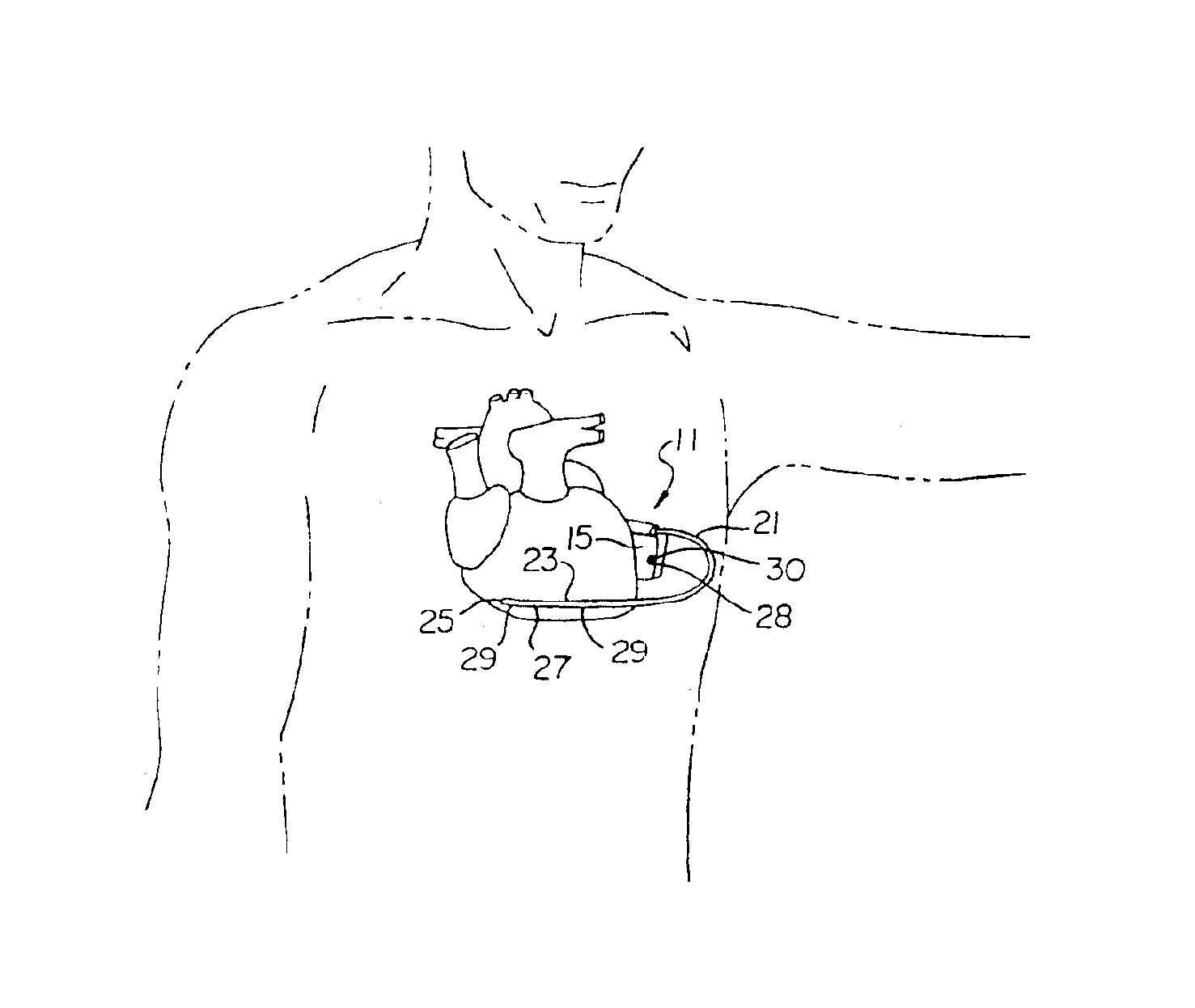
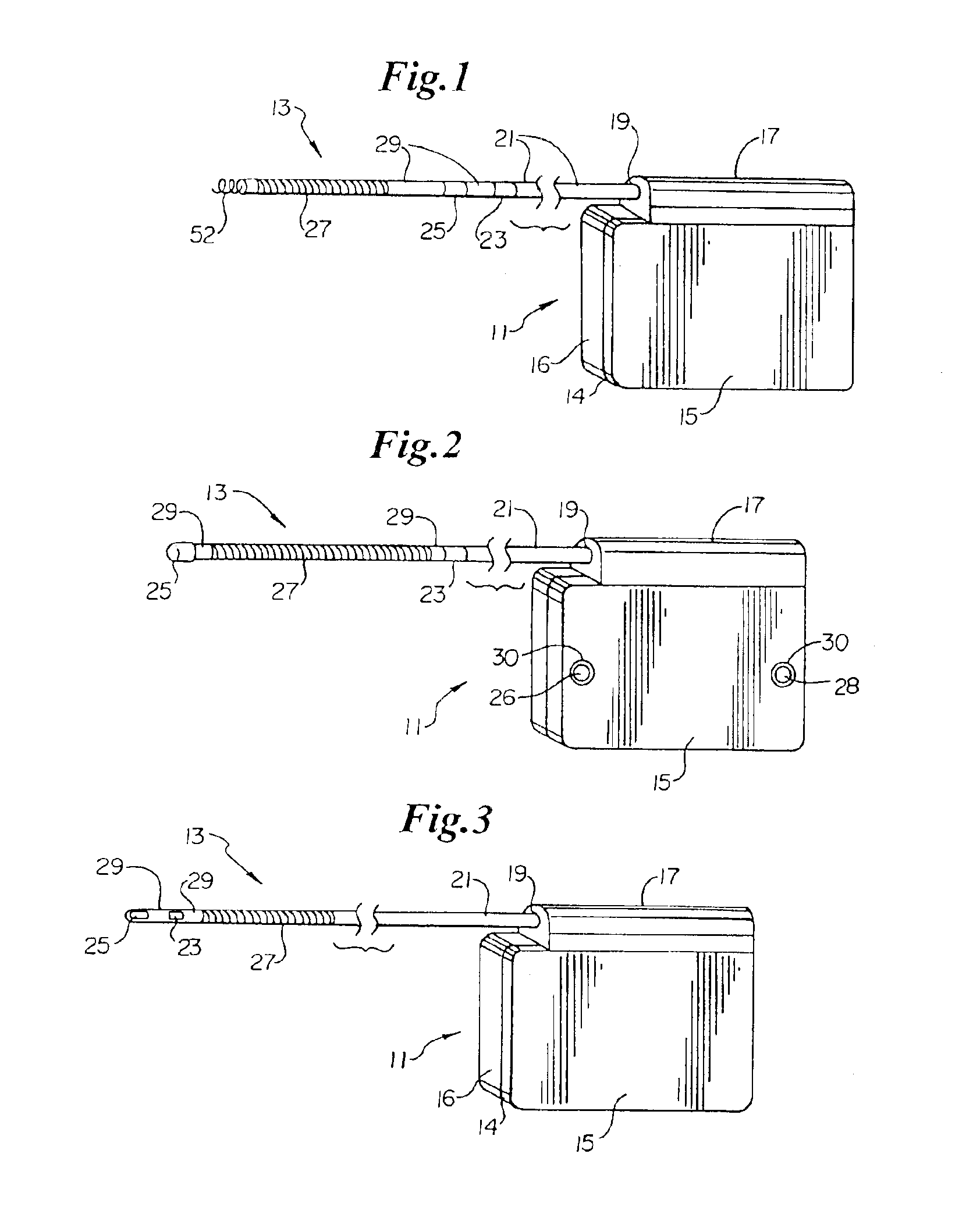
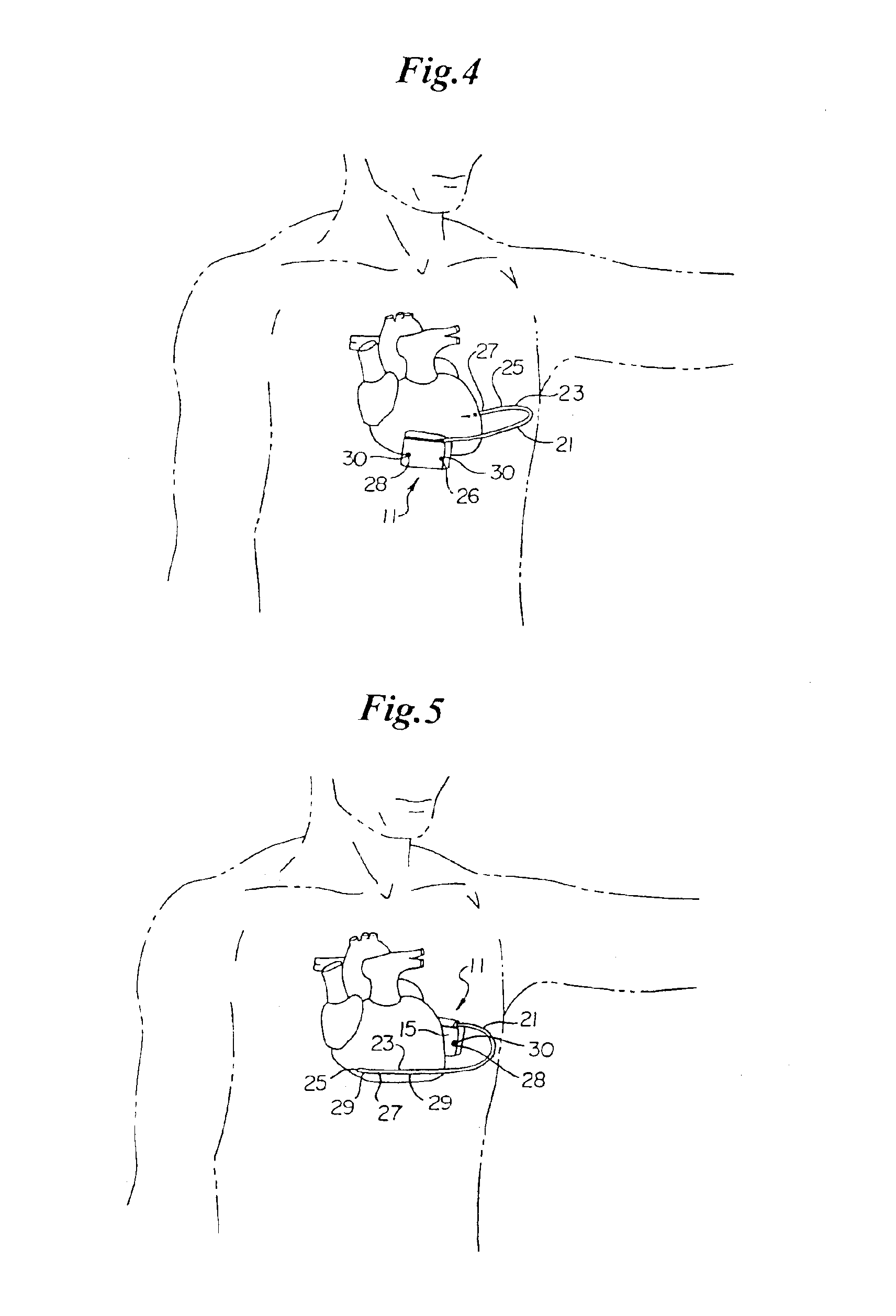
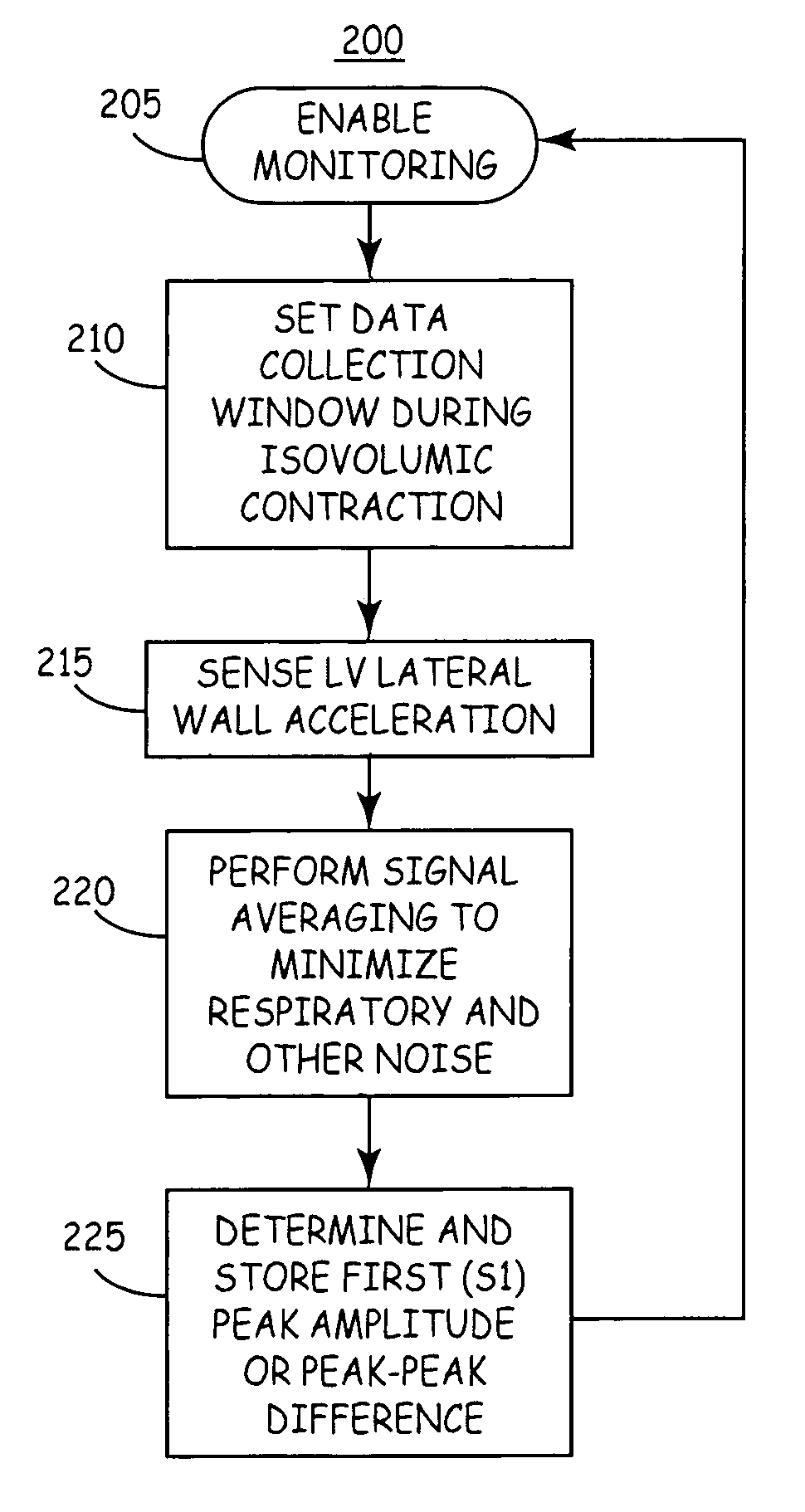
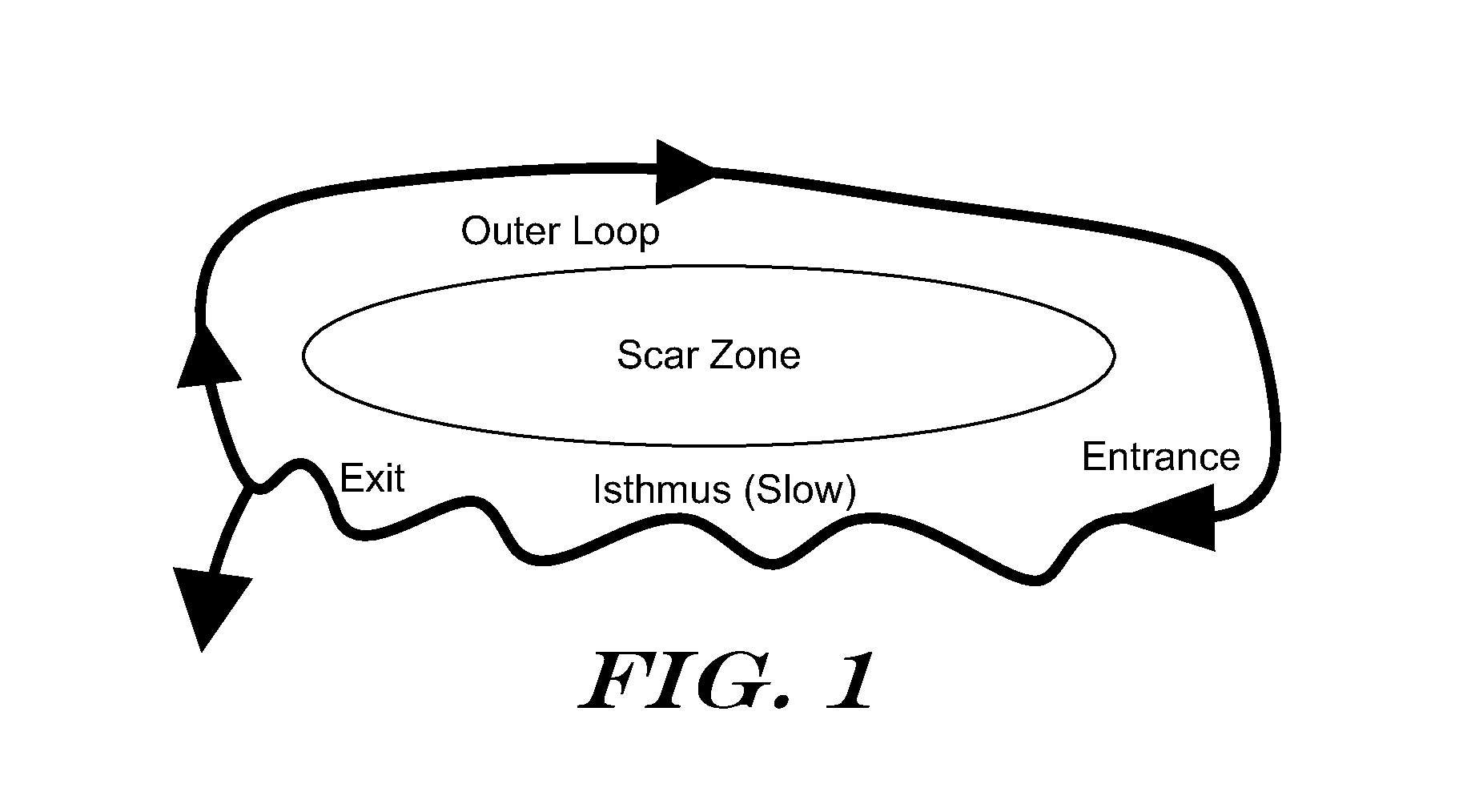
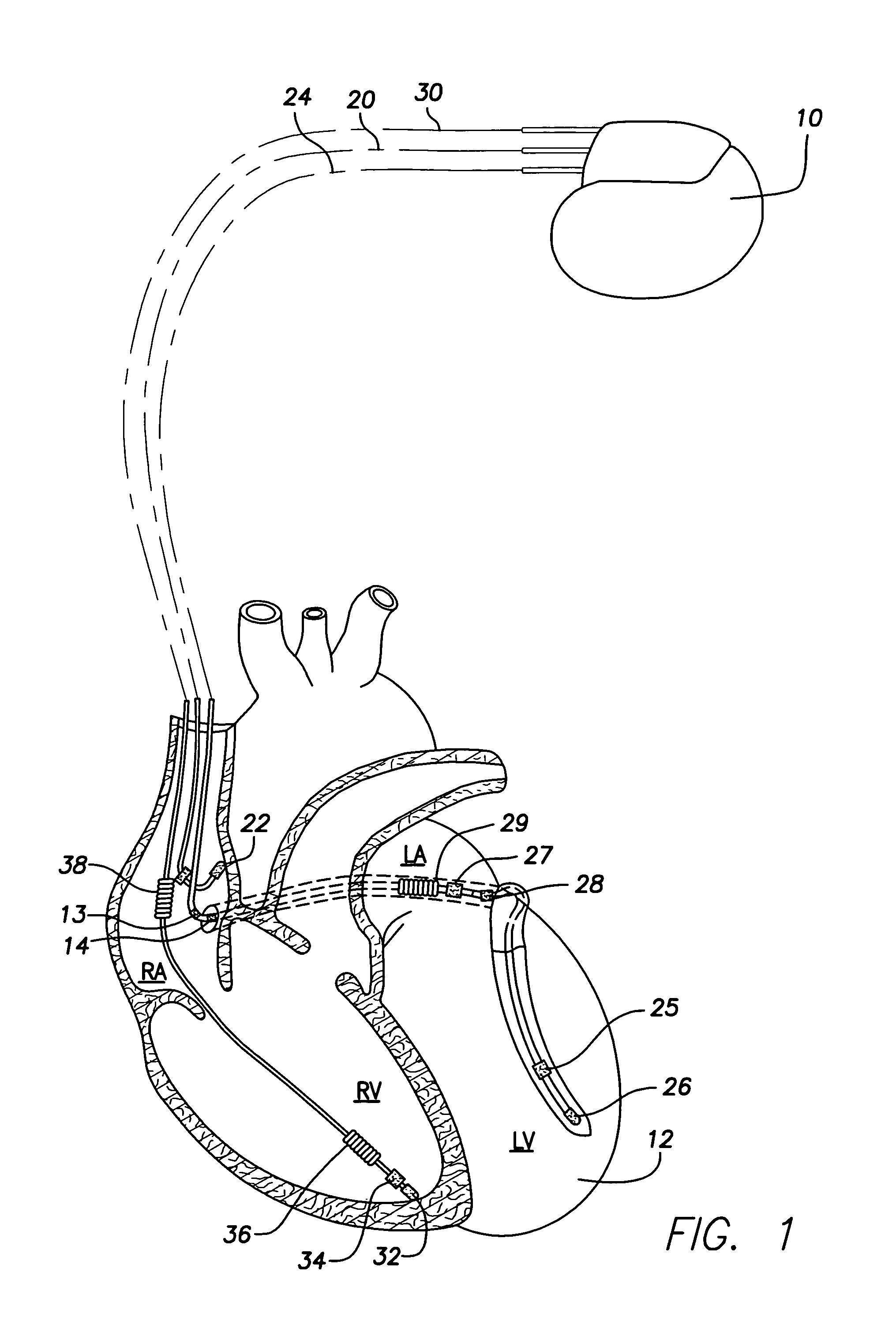
Delivery of electrical impulses to the heart at a faster rate than the intrinsic rate during an episode of tachycardia, in an attempt to terminate the abnormal tachycardia. (ACC)
Biphasic waveform for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
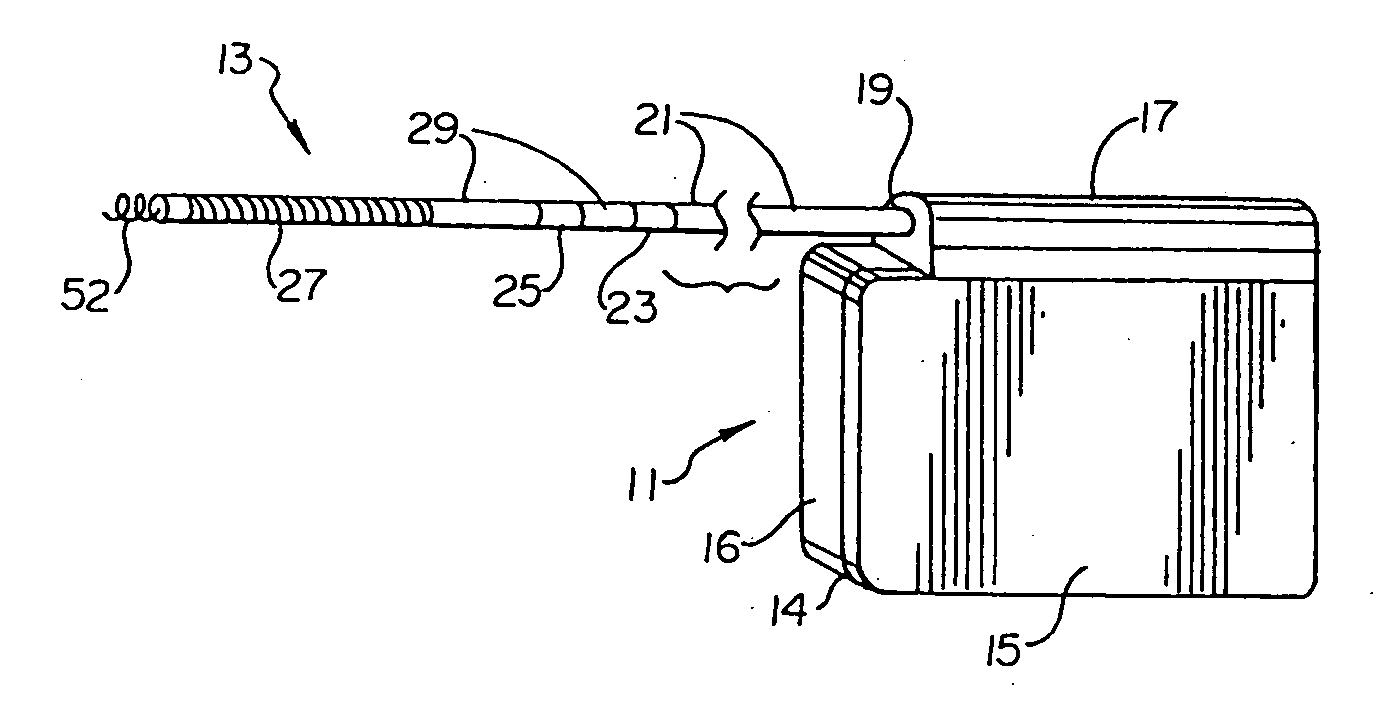
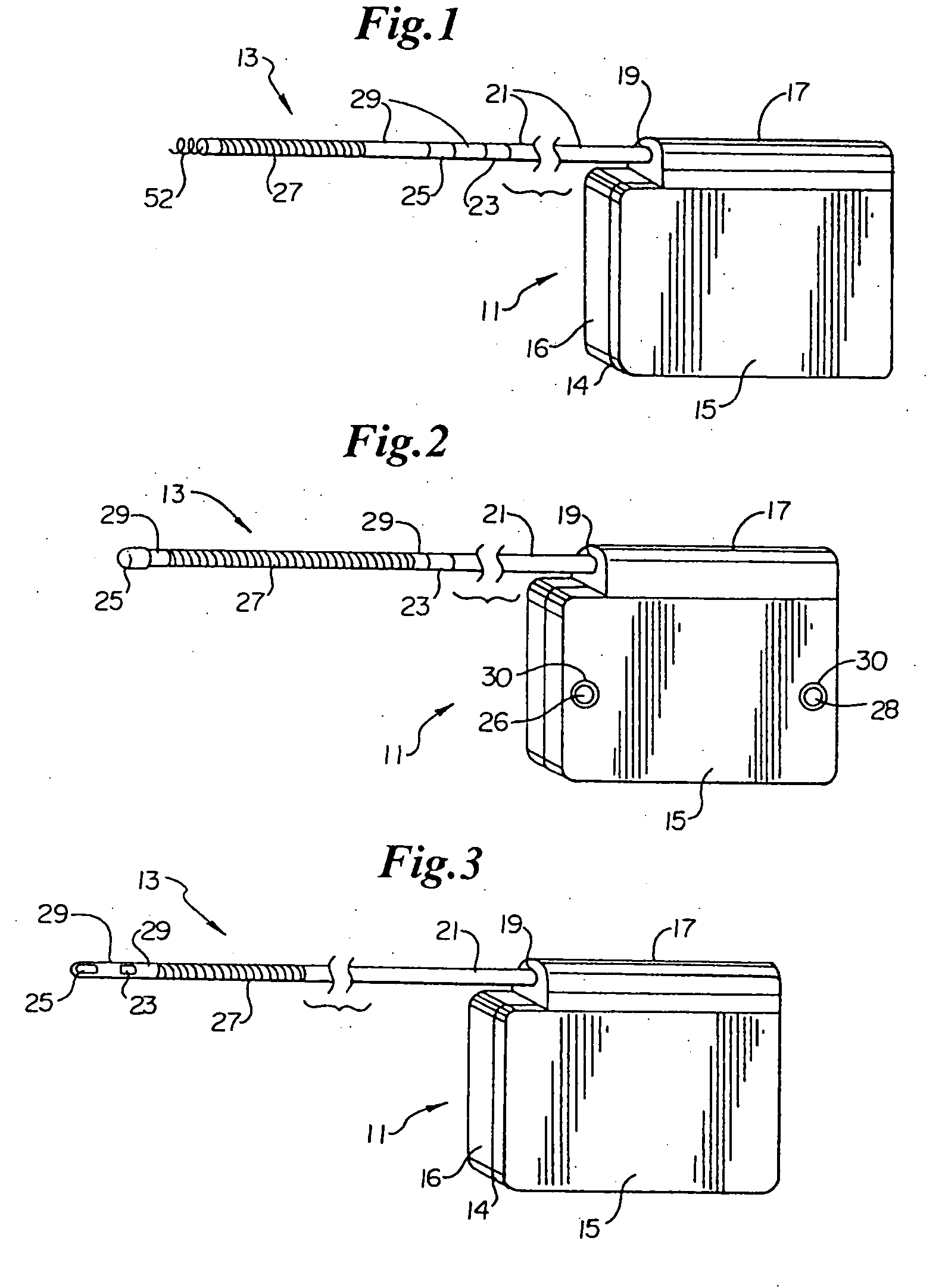
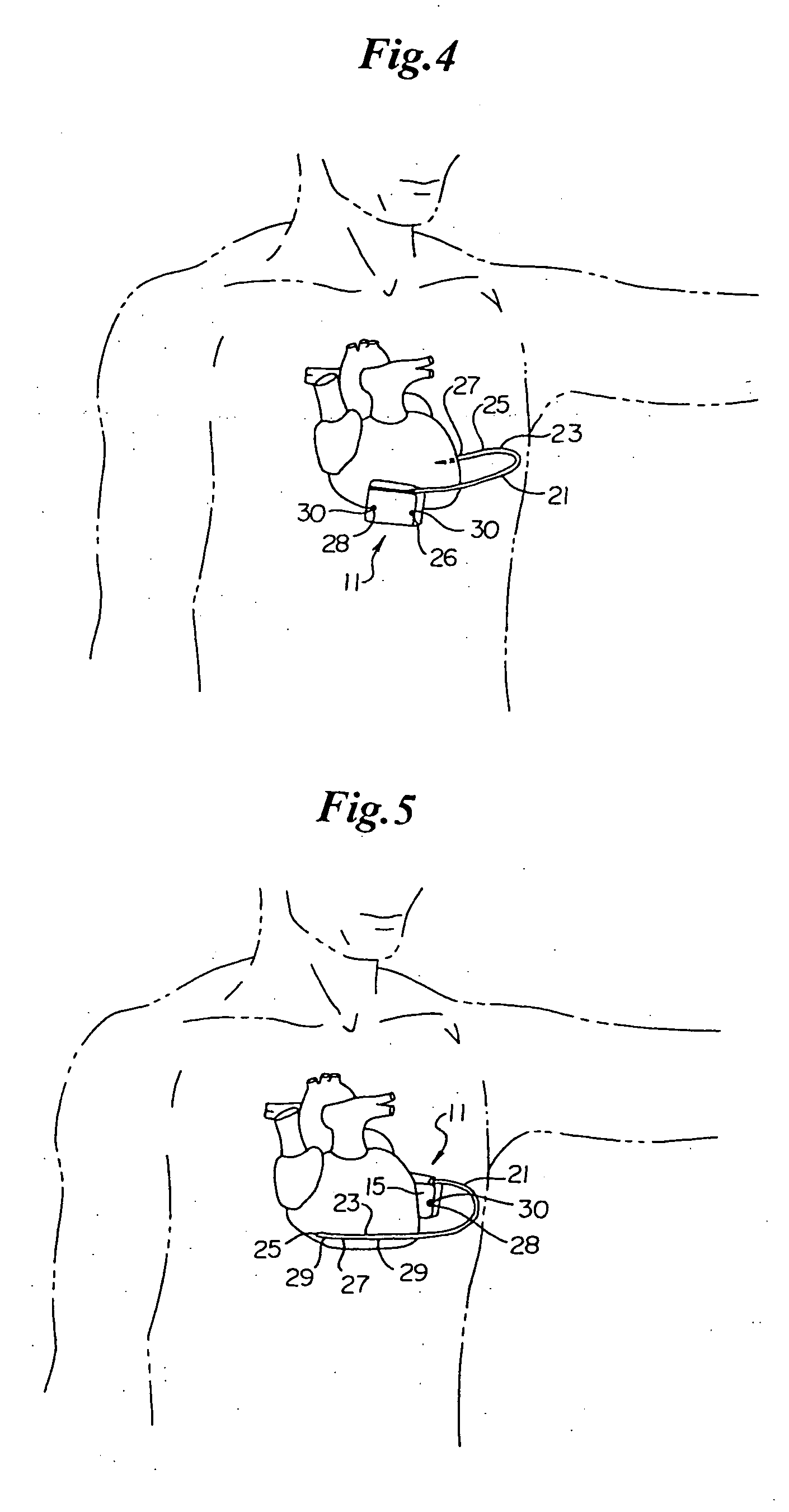
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathorasic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
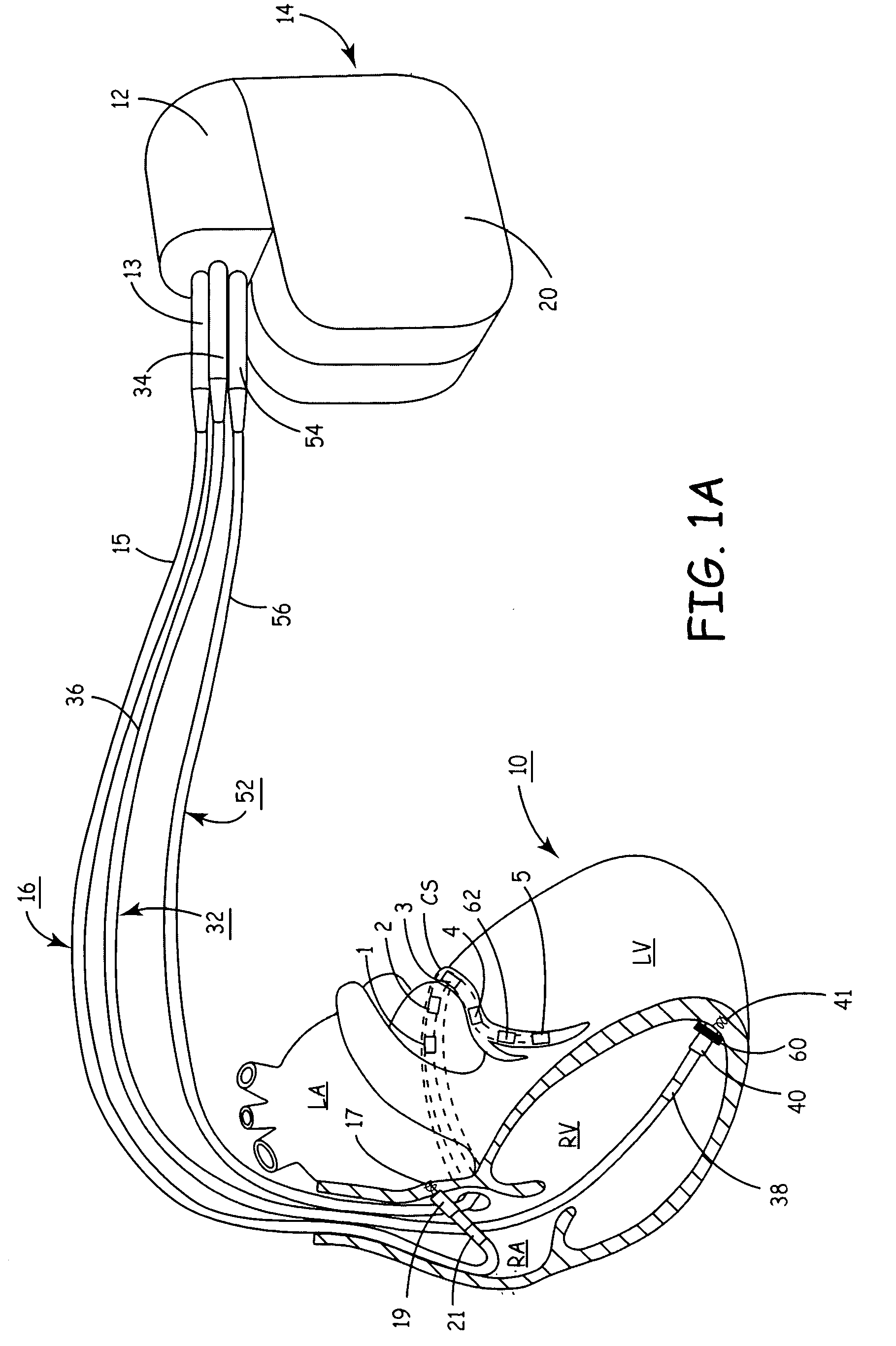
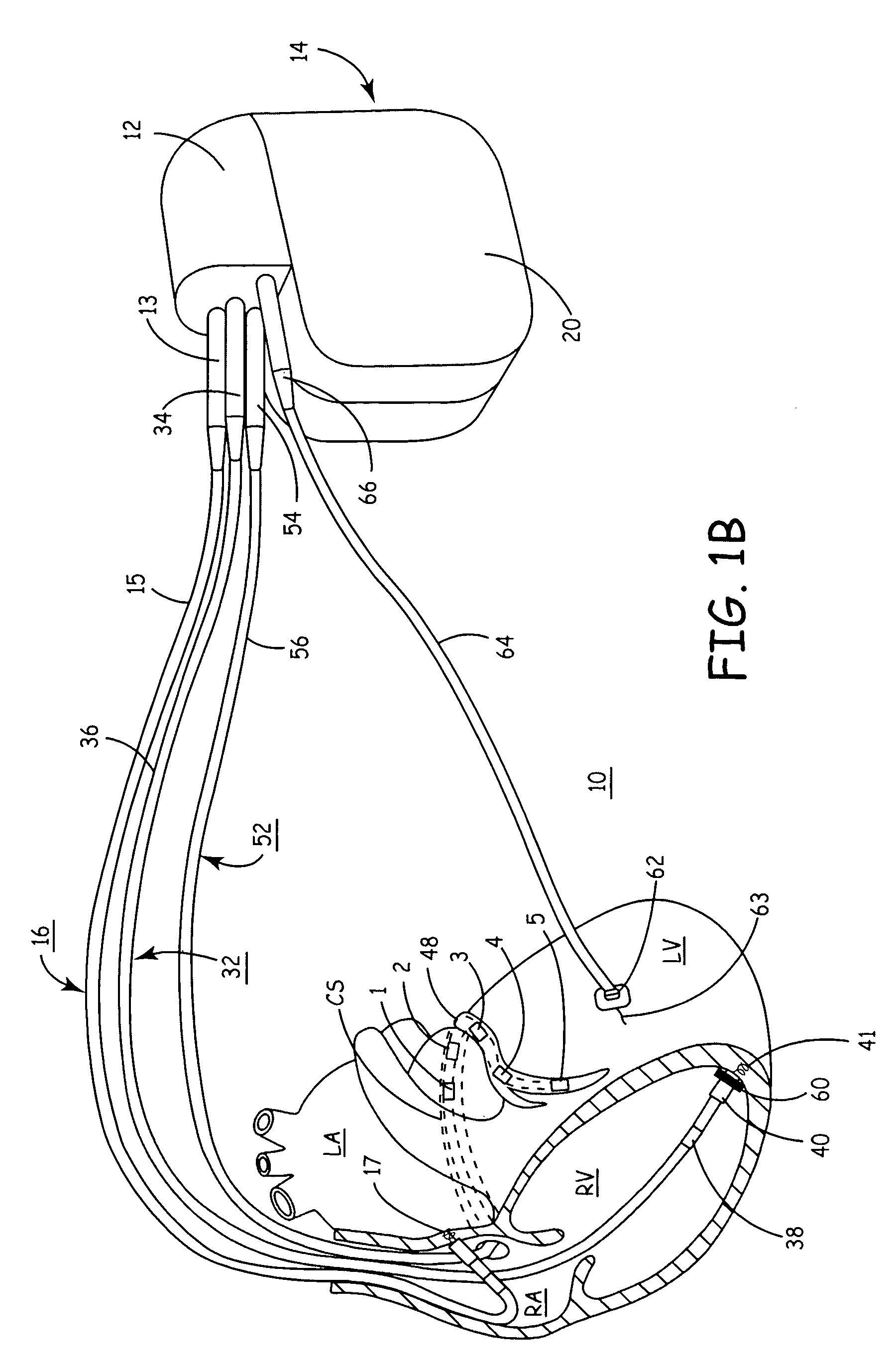
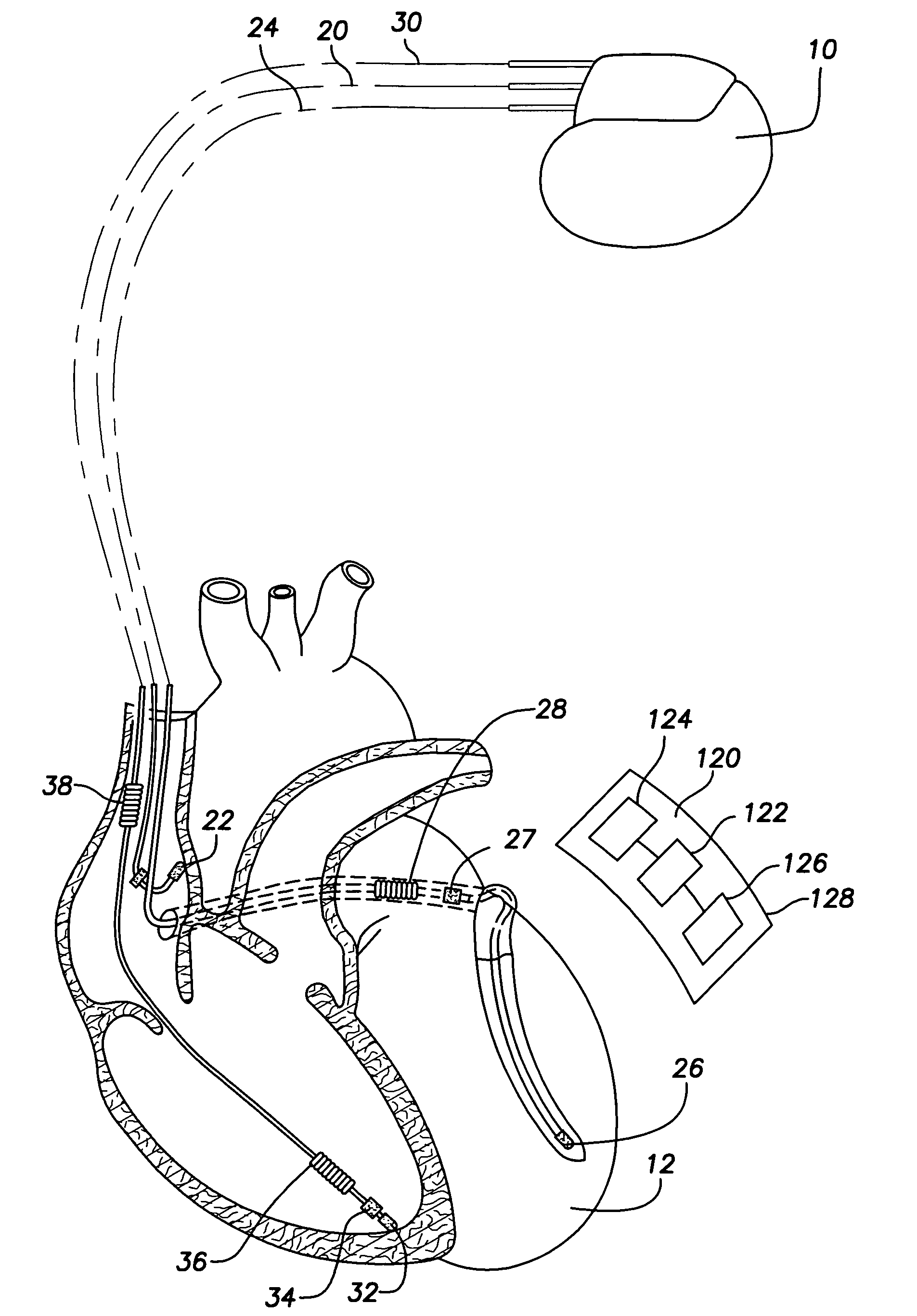
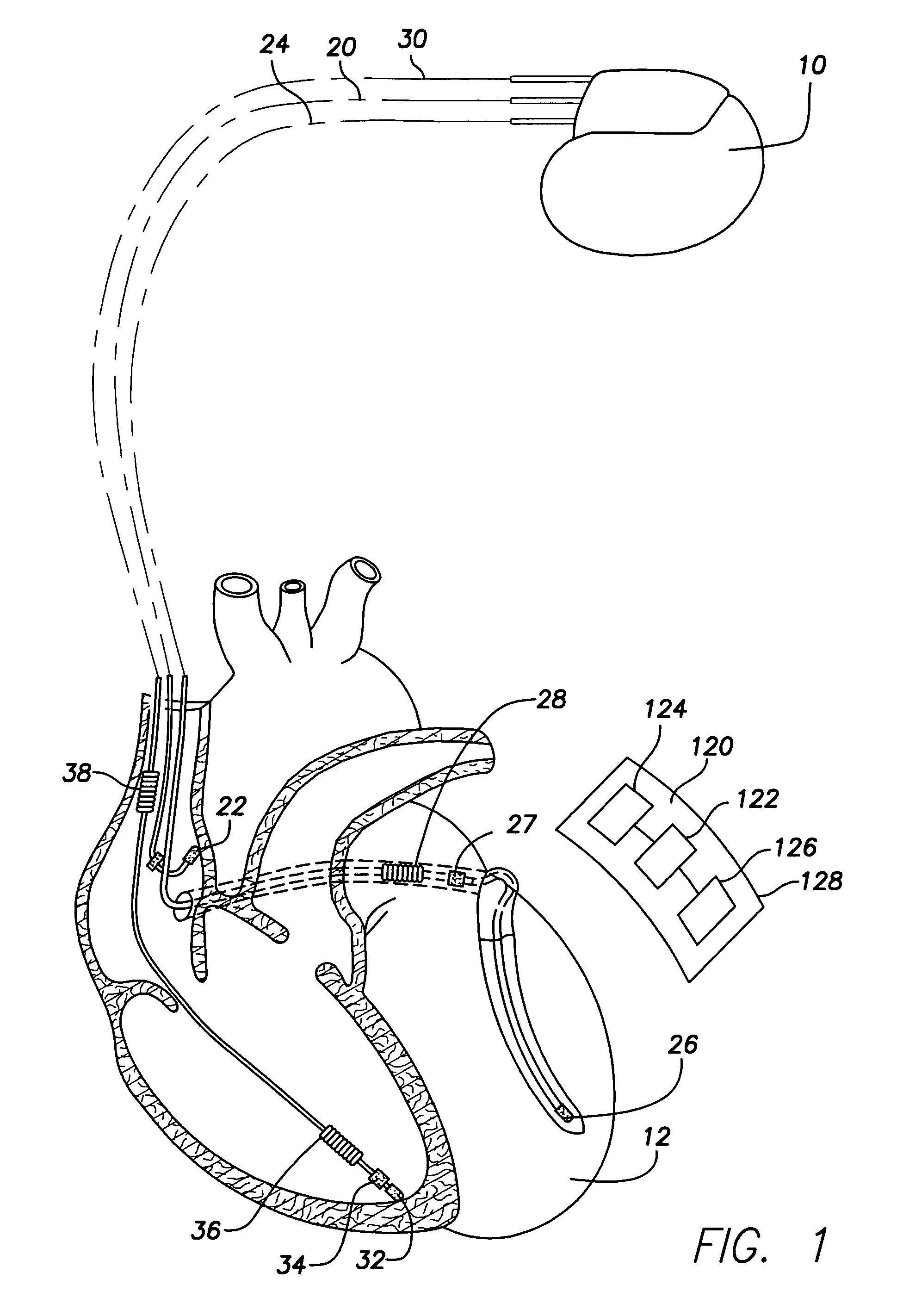
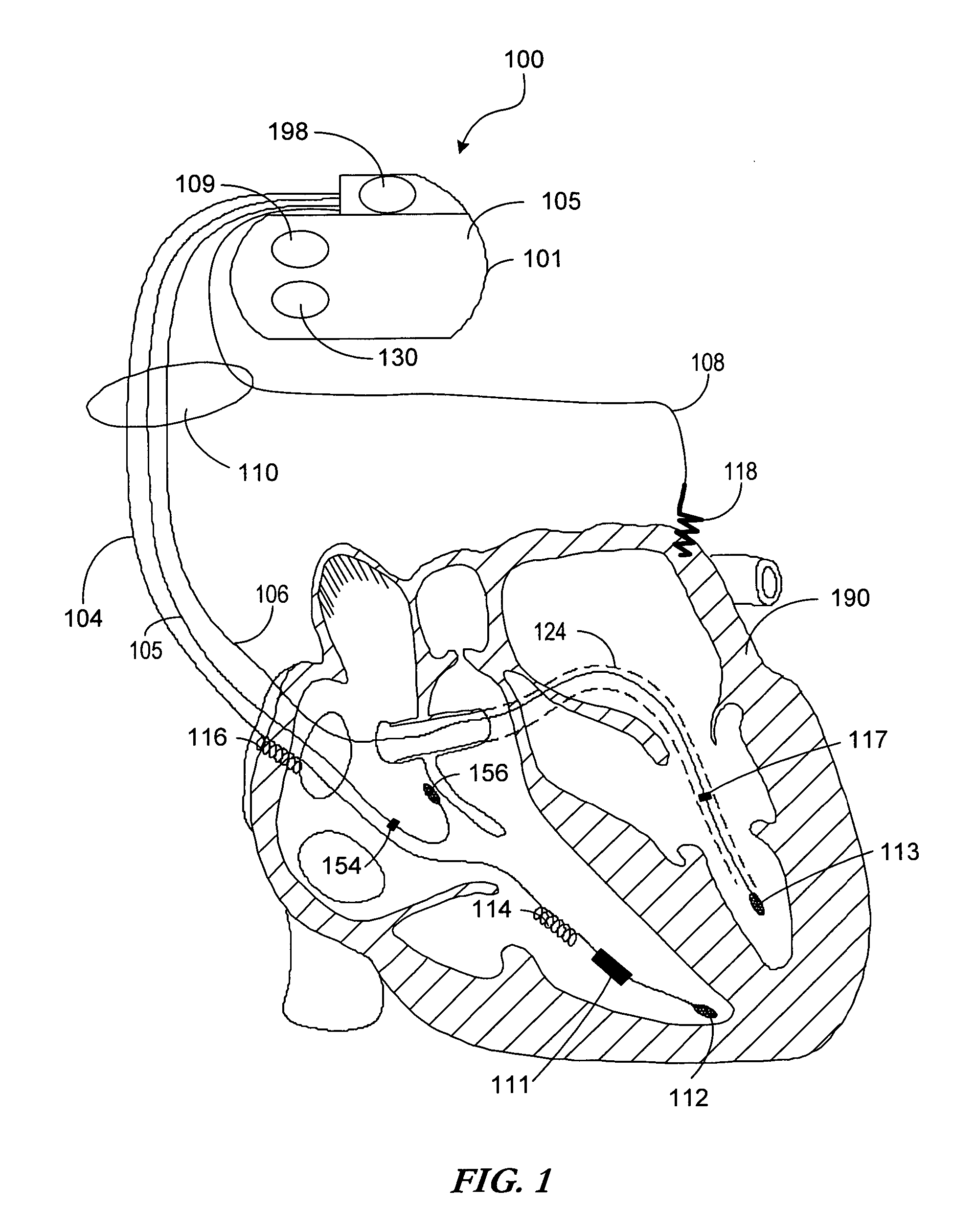
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS20050090870A1Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
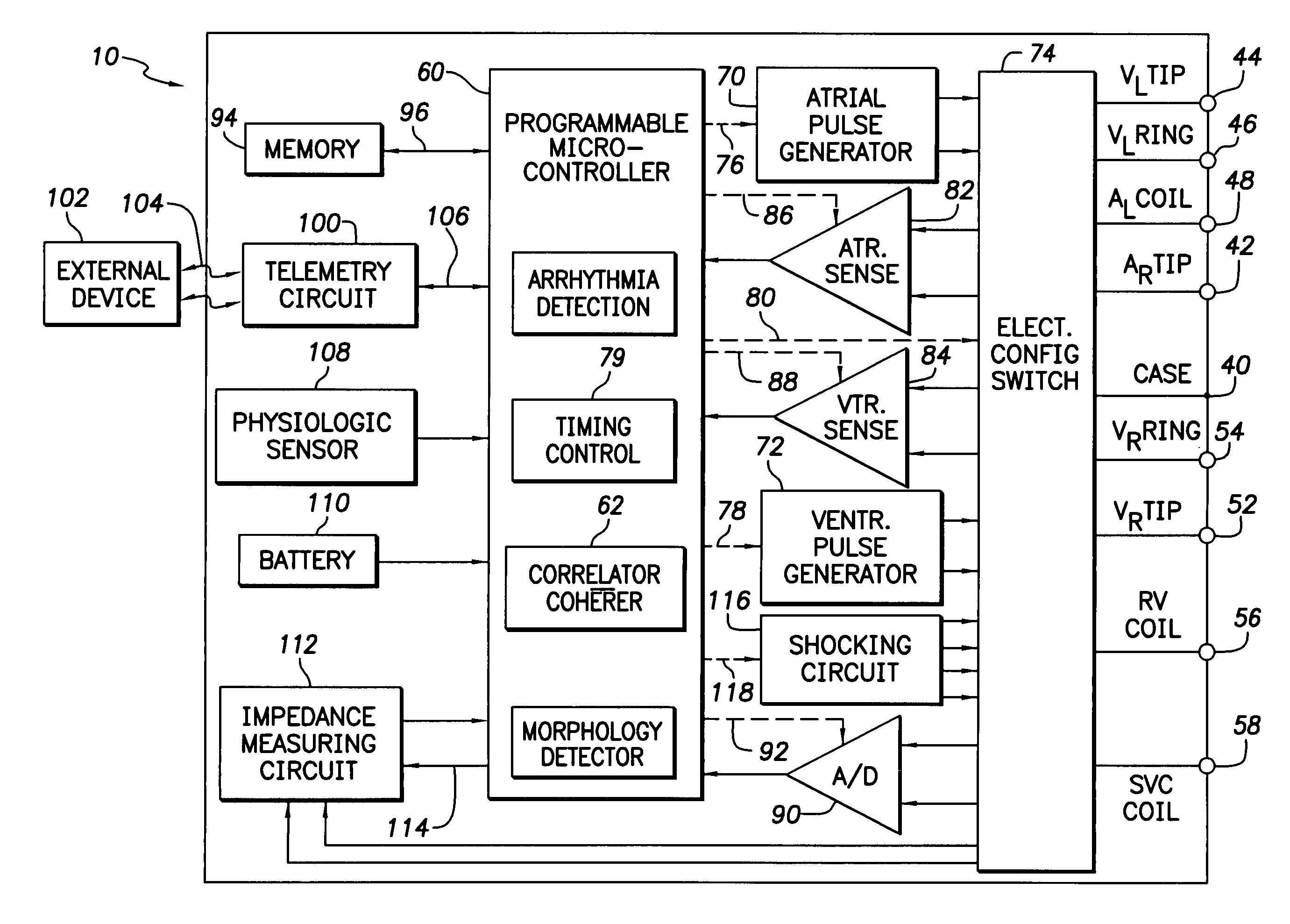
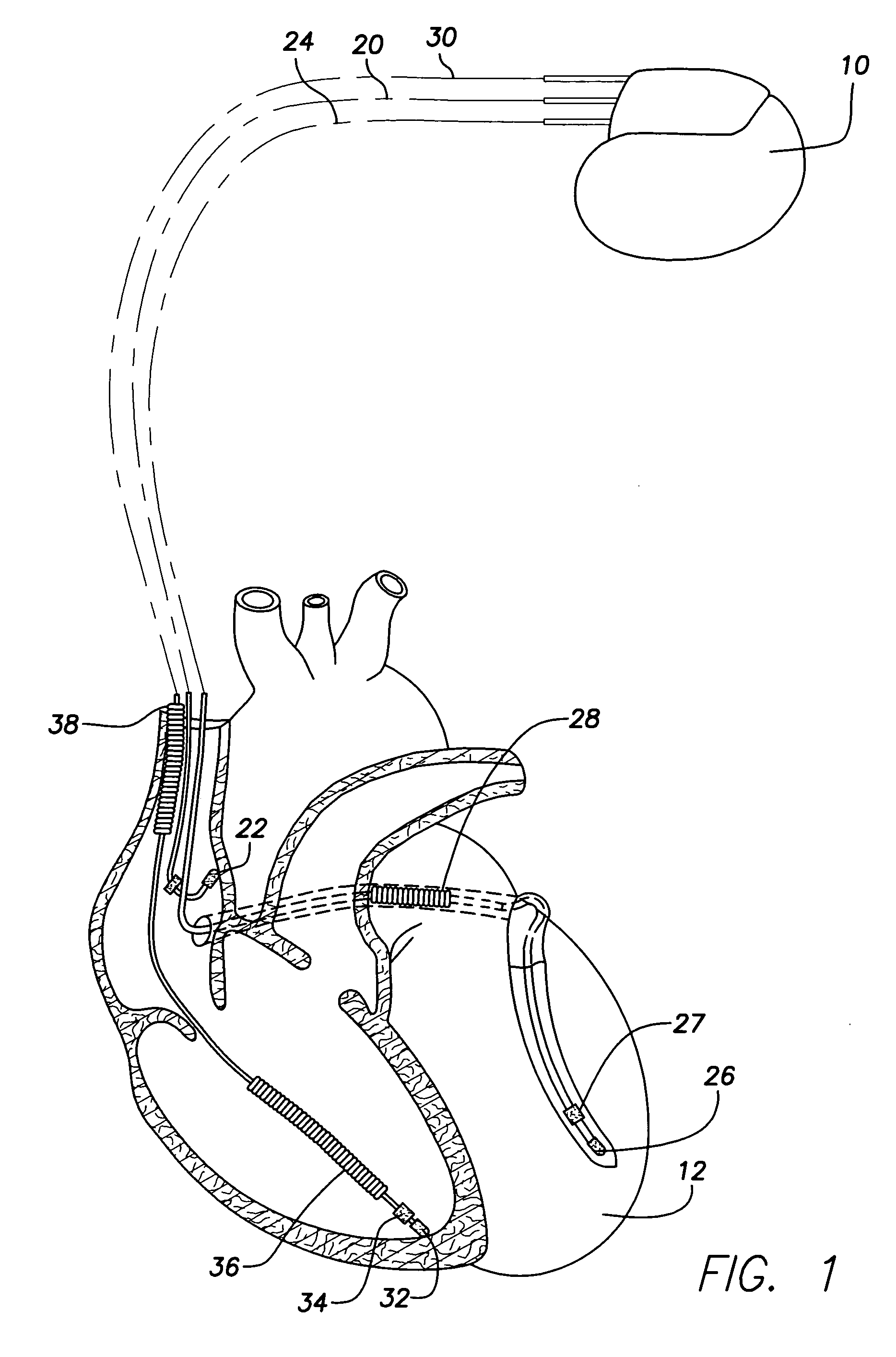
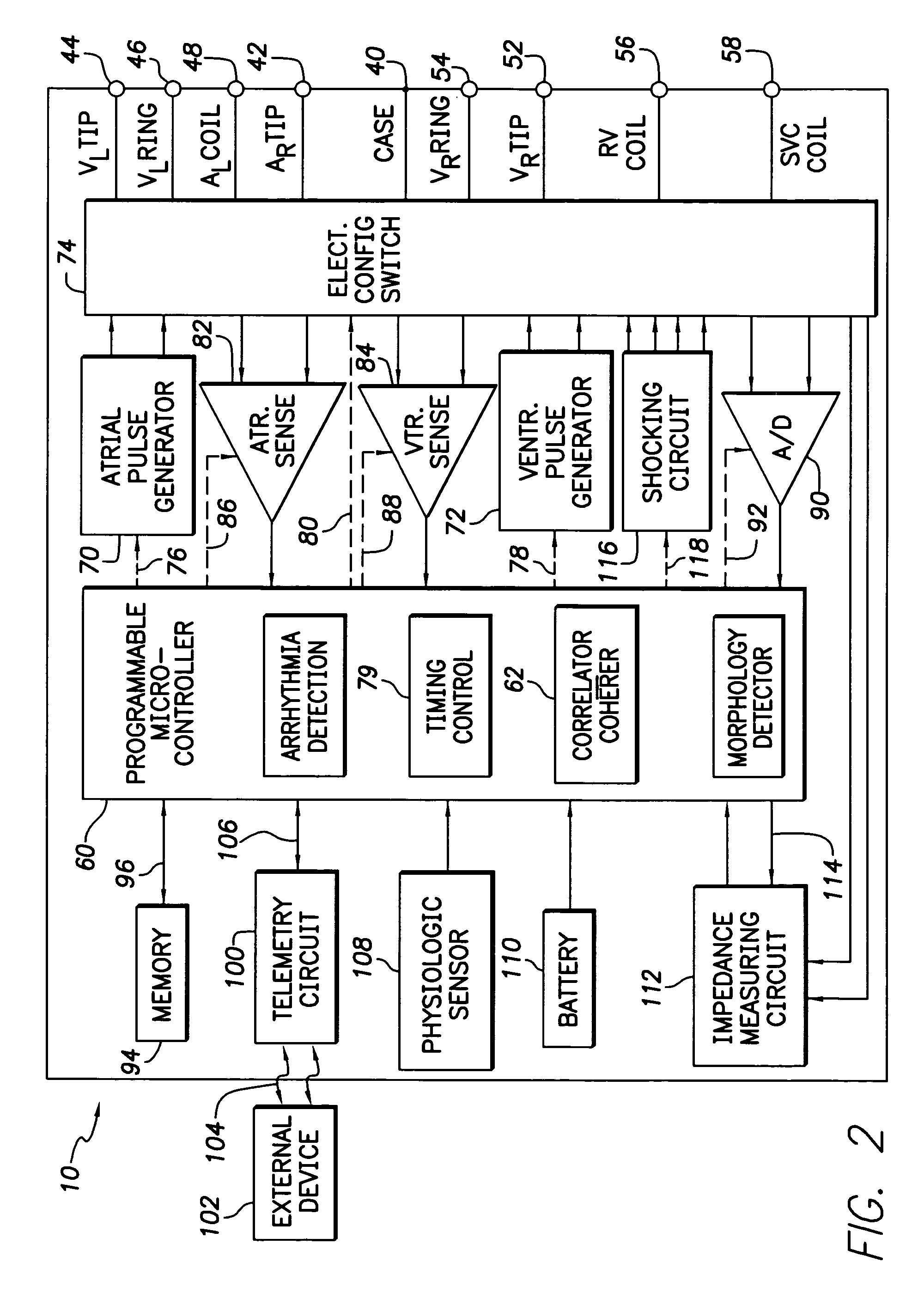
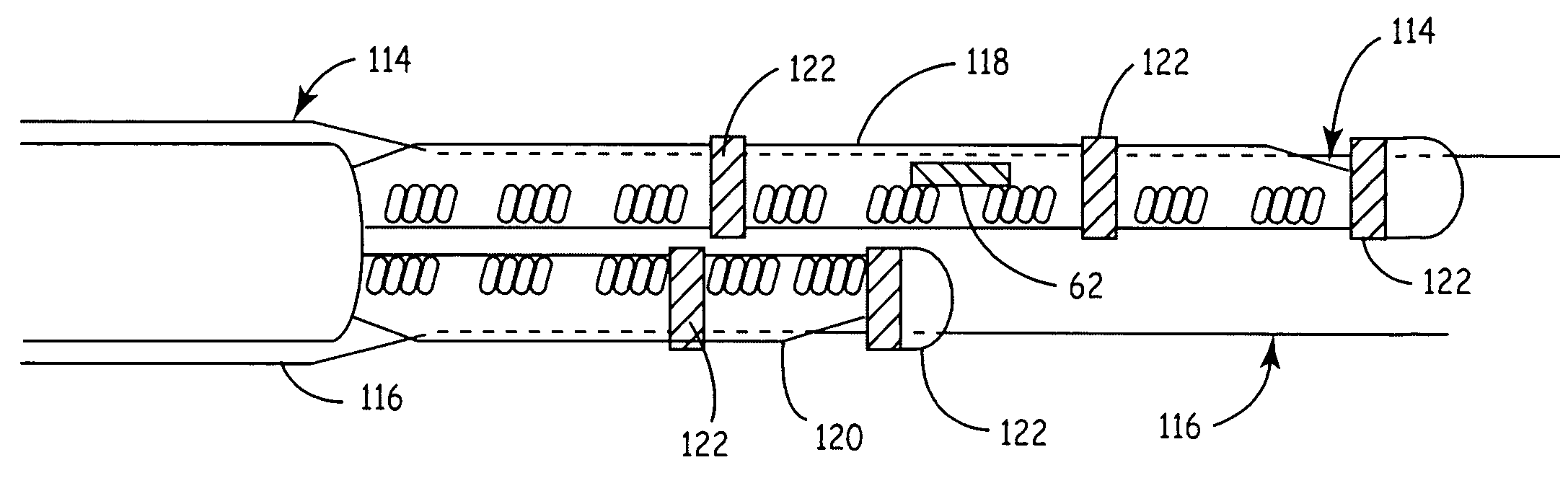
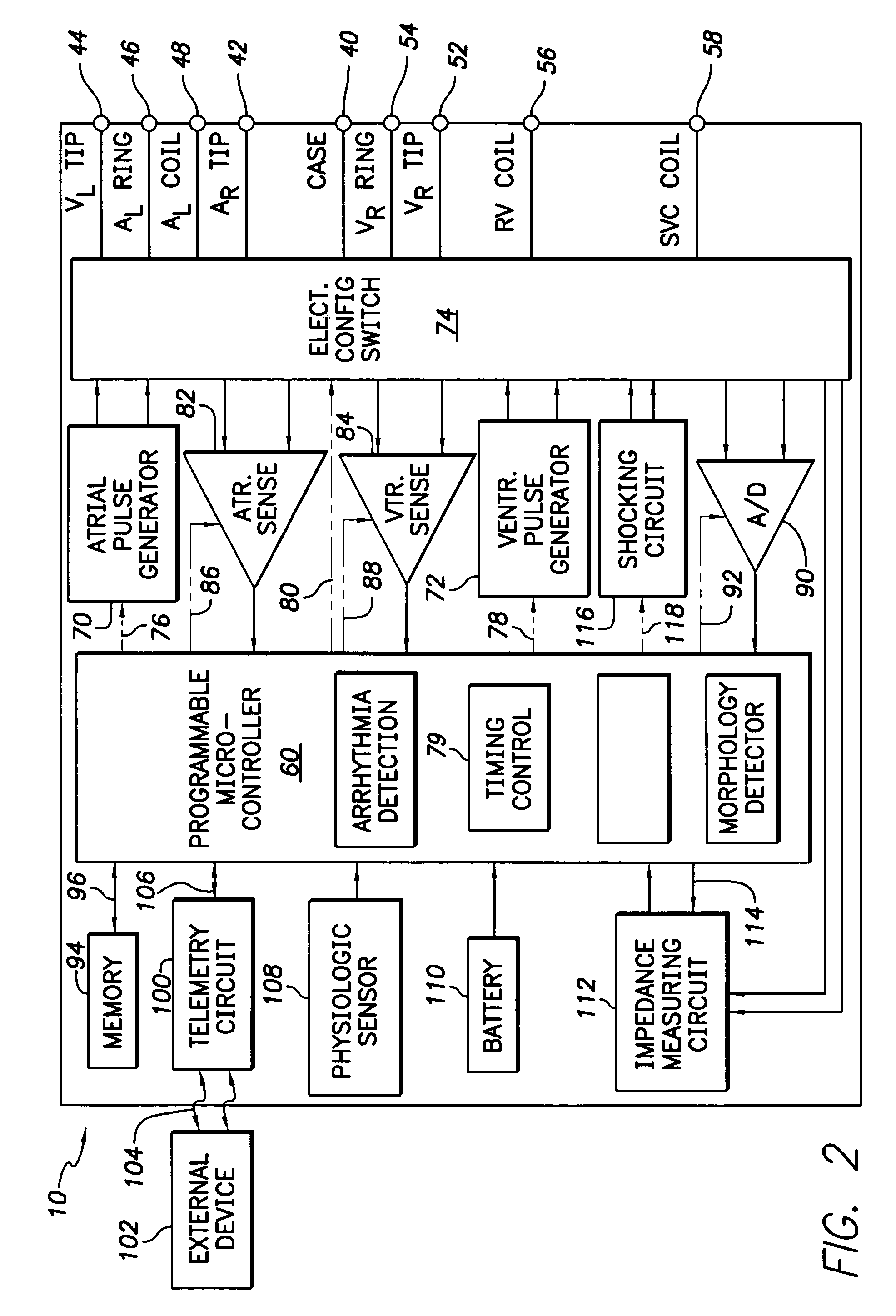
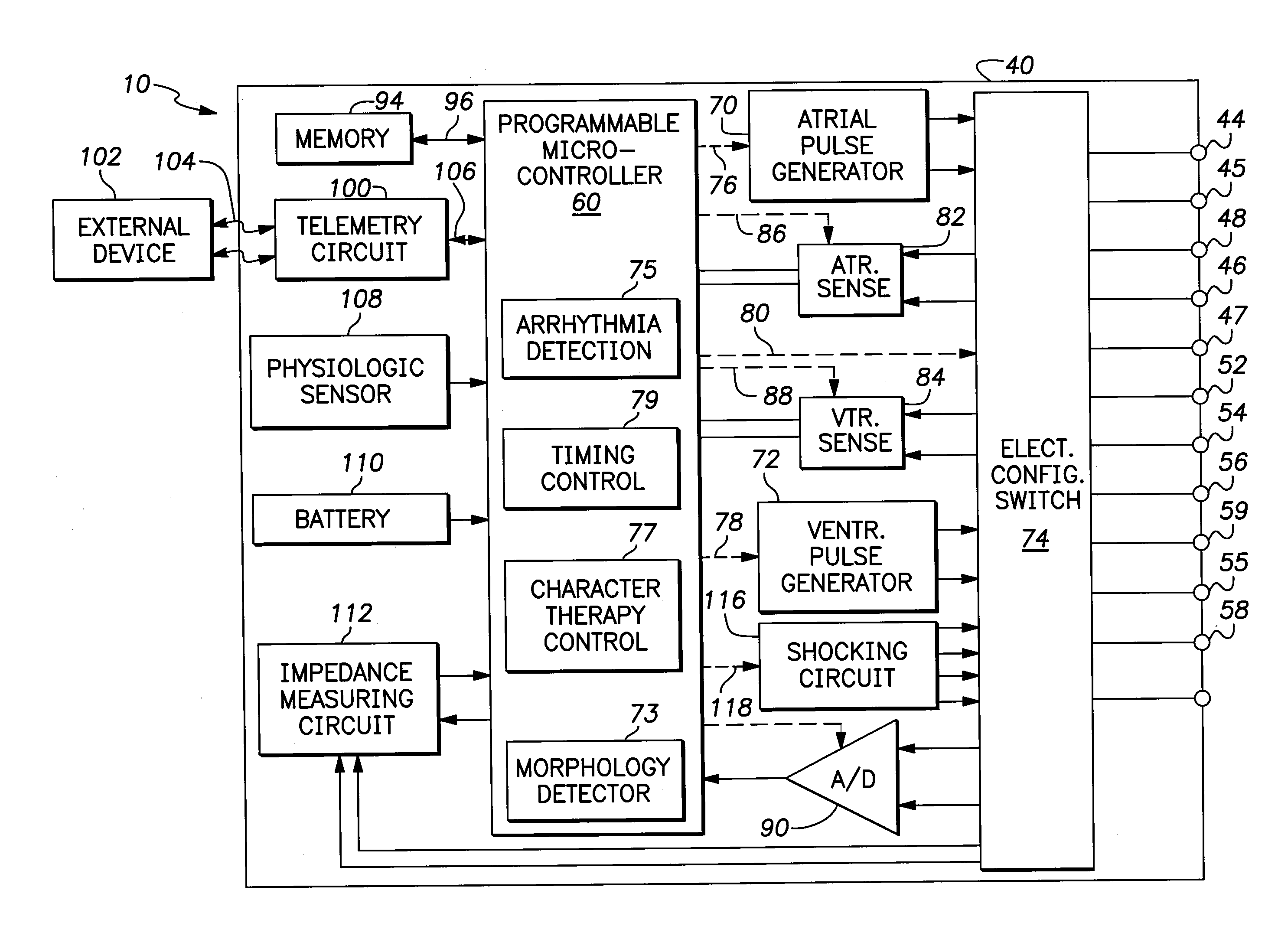
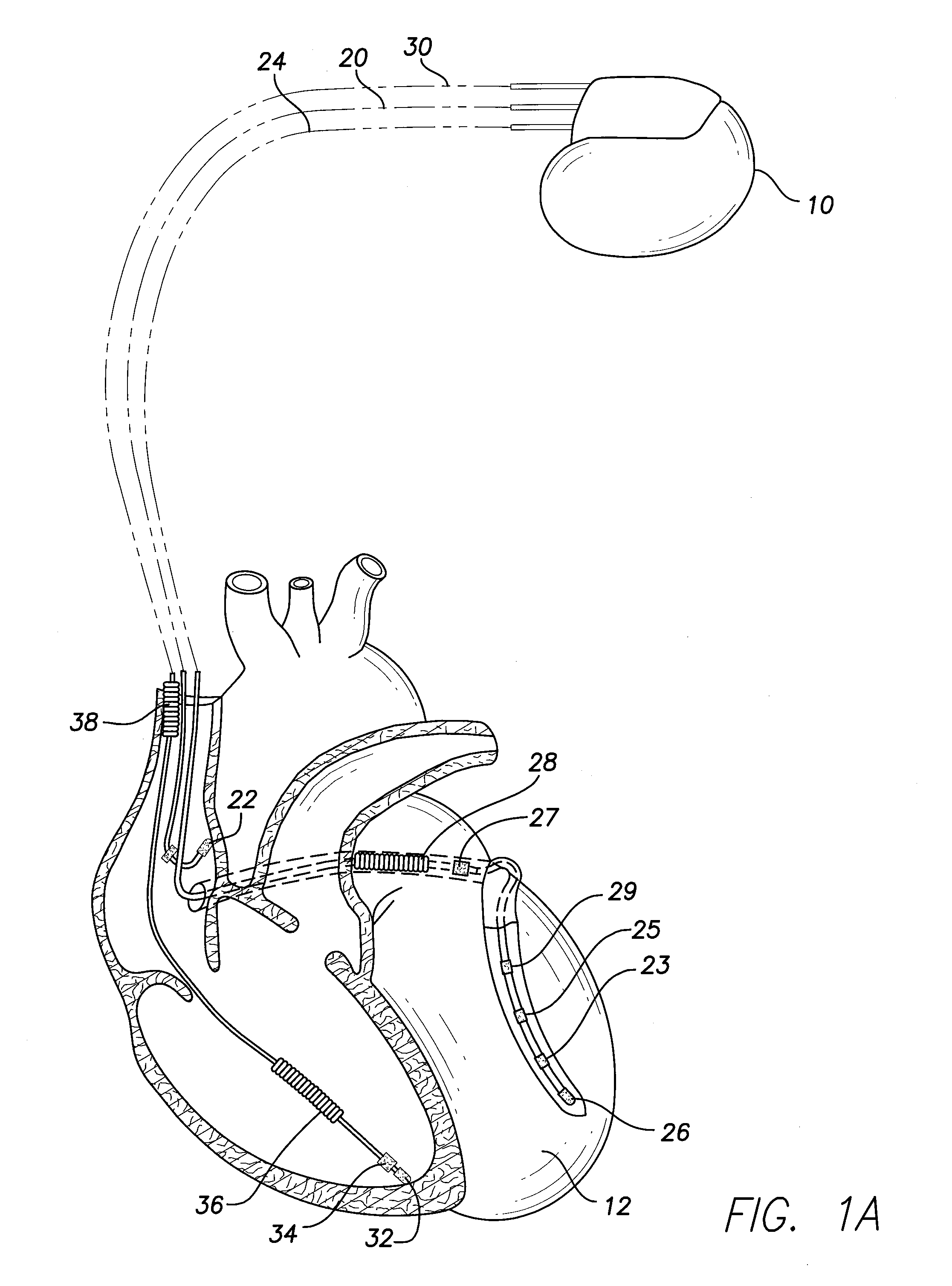
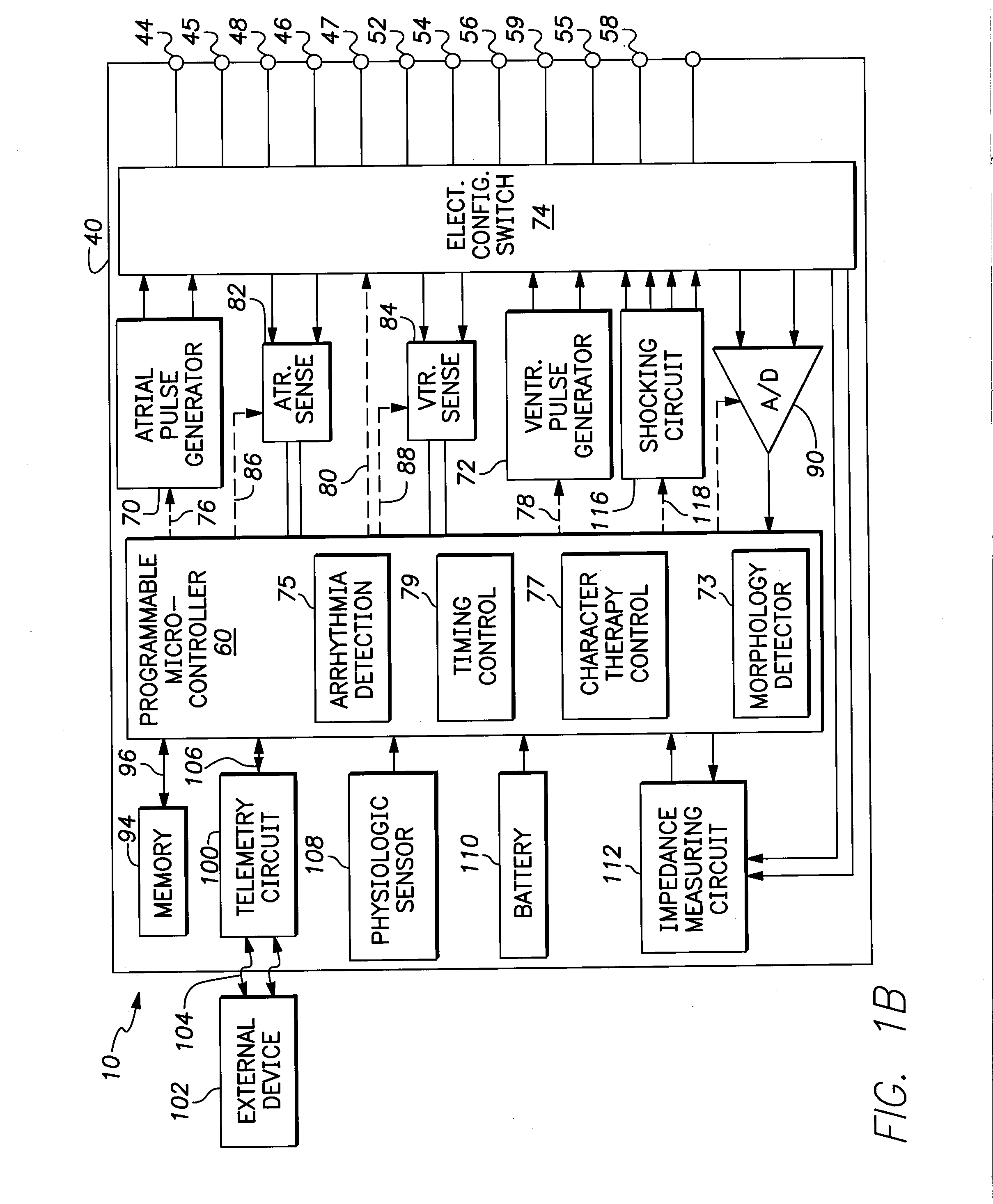
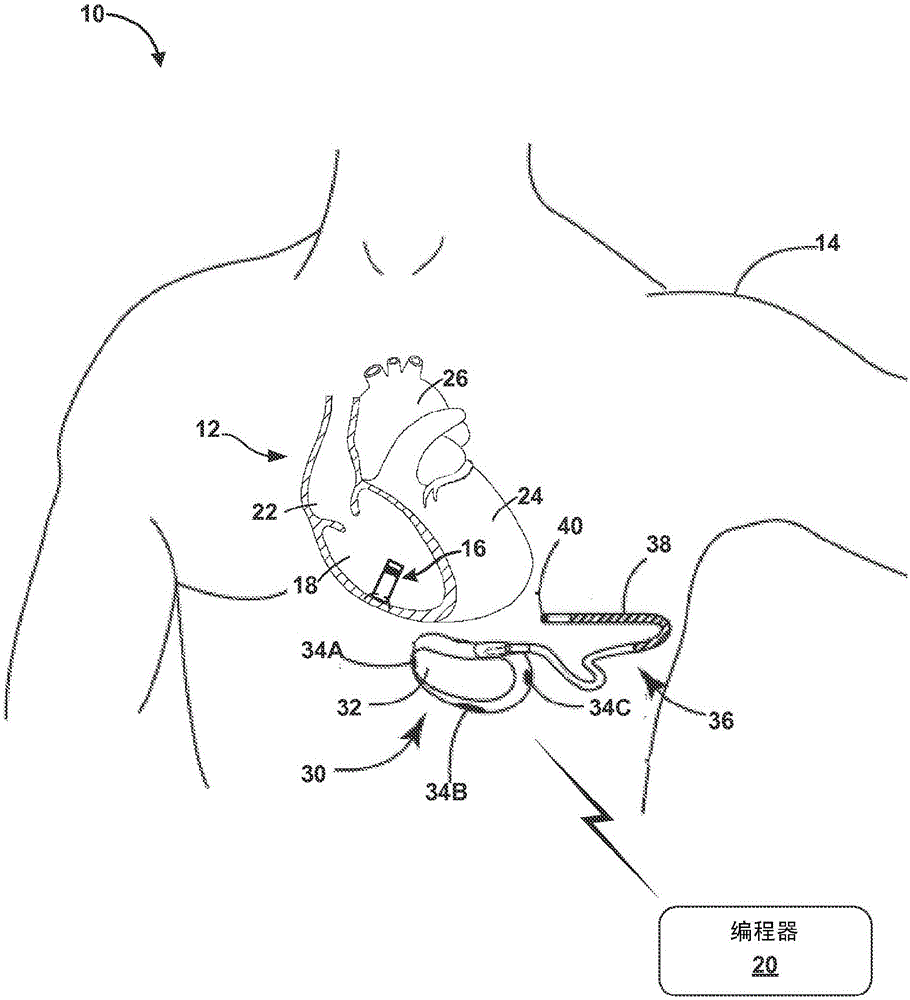
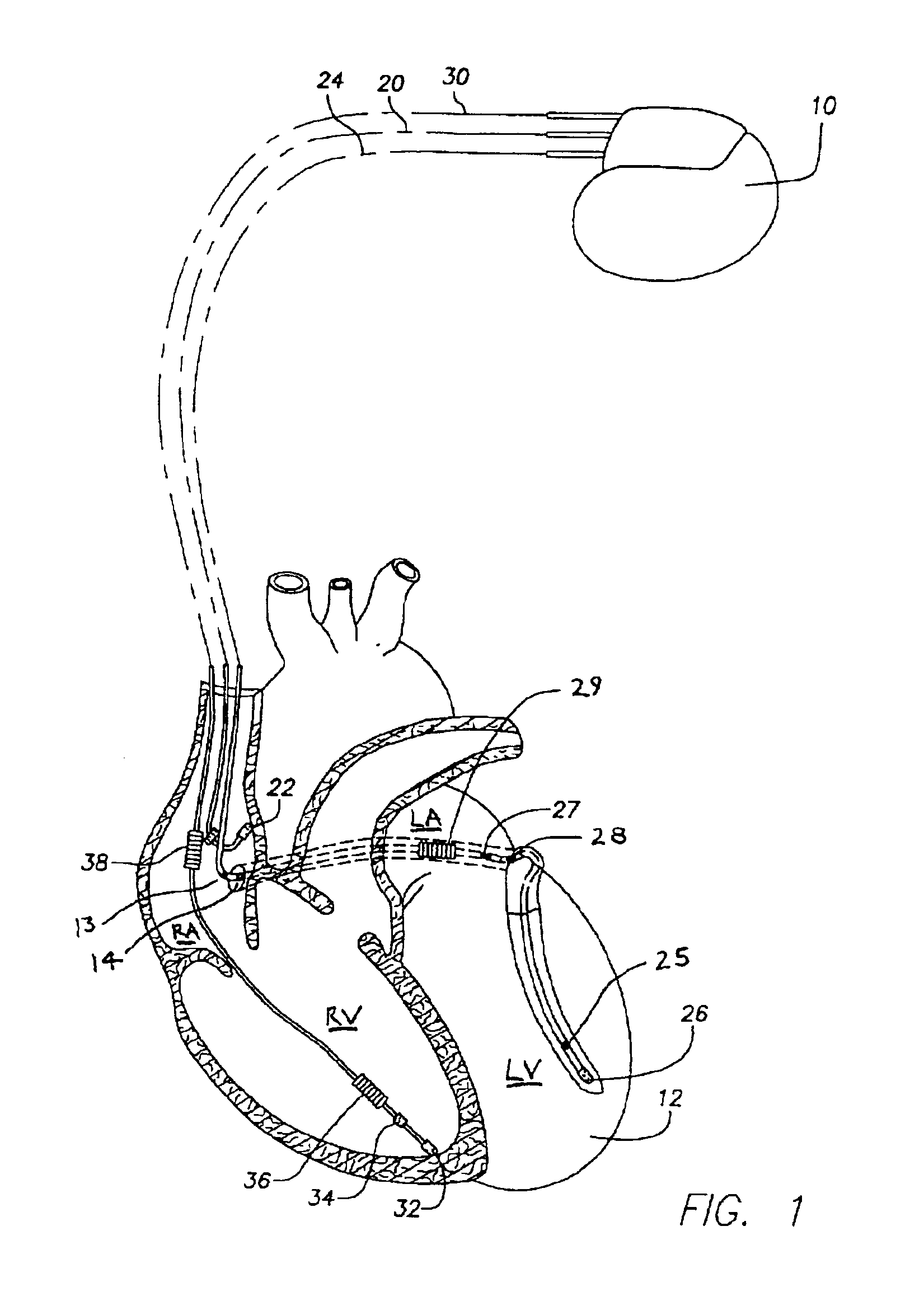
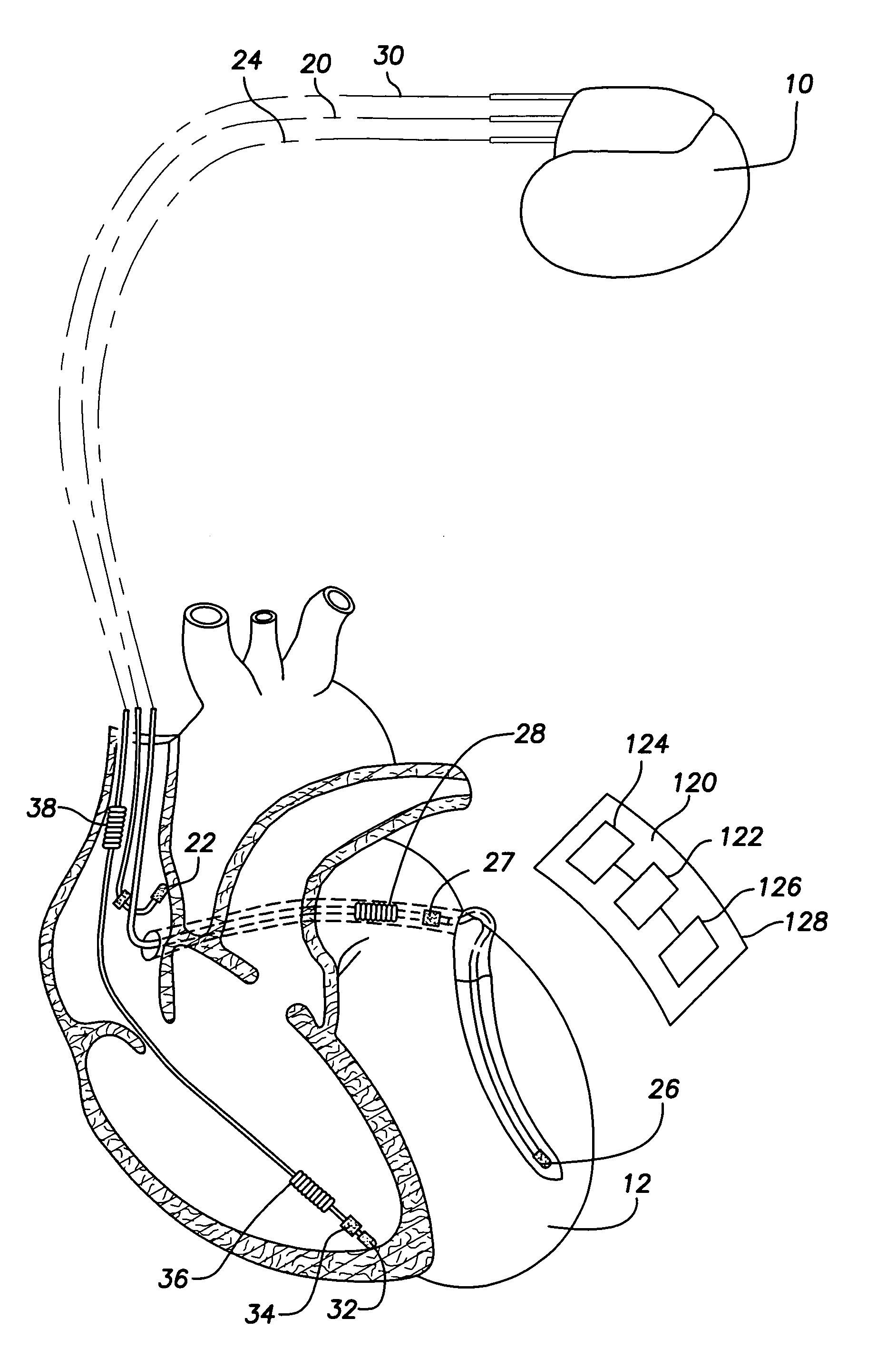
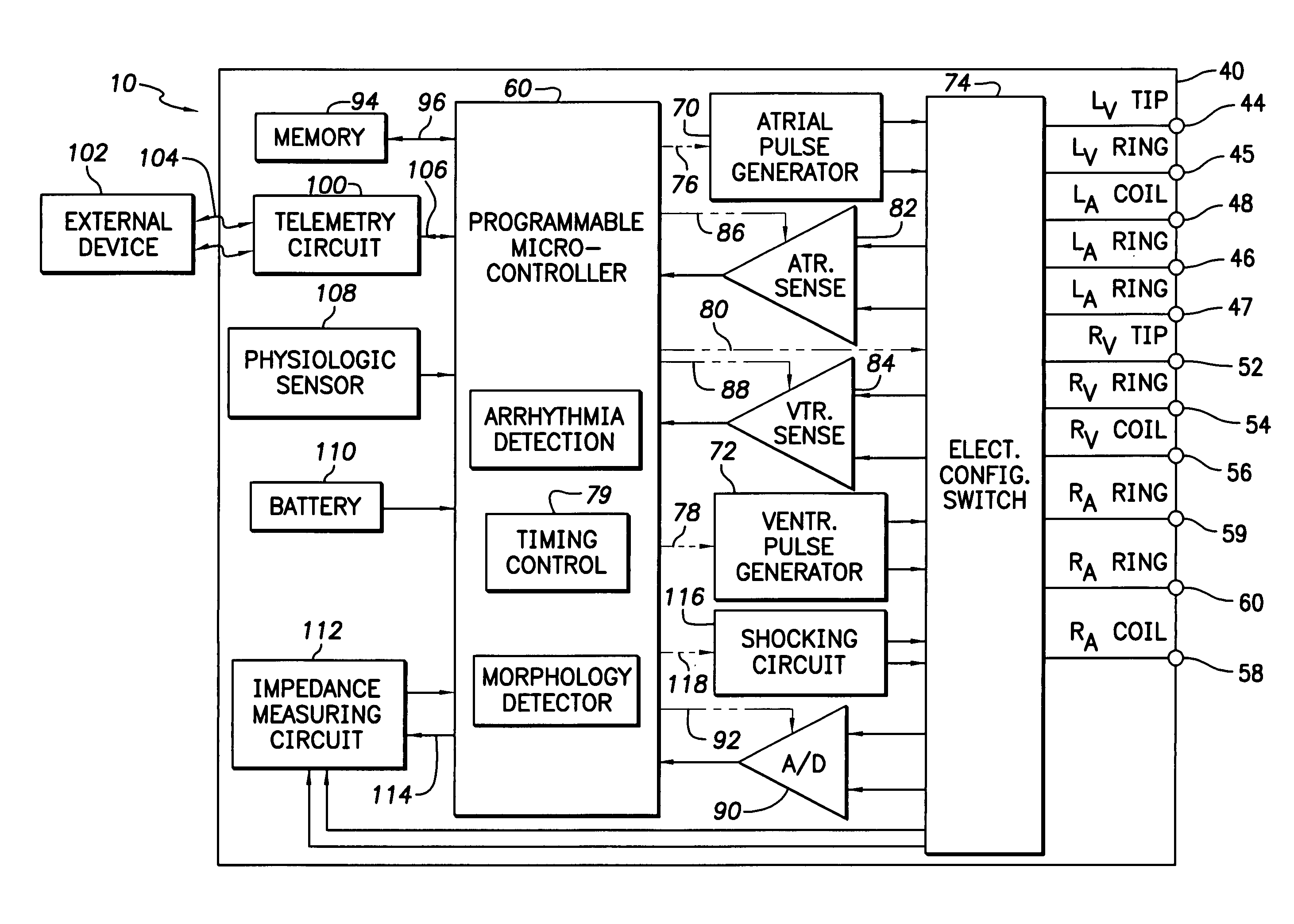
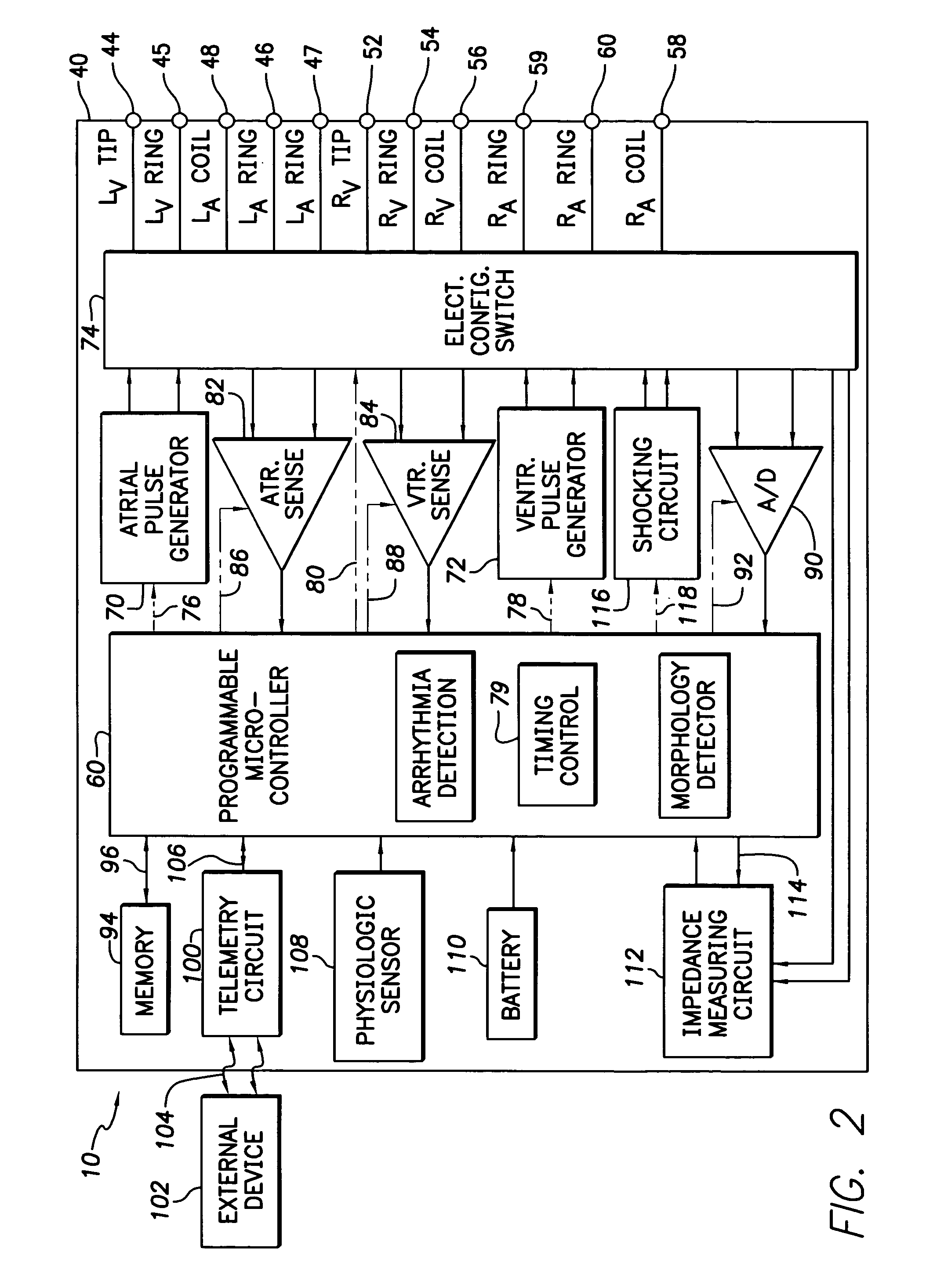
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Antitachycardia Pacing Pulse from a Subcutaneous Defibrillator
Devices and methods for single therapy pulse (STP) therapy for tachyarrythmia are disclosed. The STP therapy can be delivered from a far-field position to allow a “global” capture approach to pacing. Due to the global capture in STP, a series of pulses, which is indicative of conventional anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) delivered by transvenous systems, becomes unnecessary. One to four pulses at most are needed for STP, and after delivery of the one to four pulses, therapy delivery can be interrupted to determine whether the previously delivered therapy has been successful.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
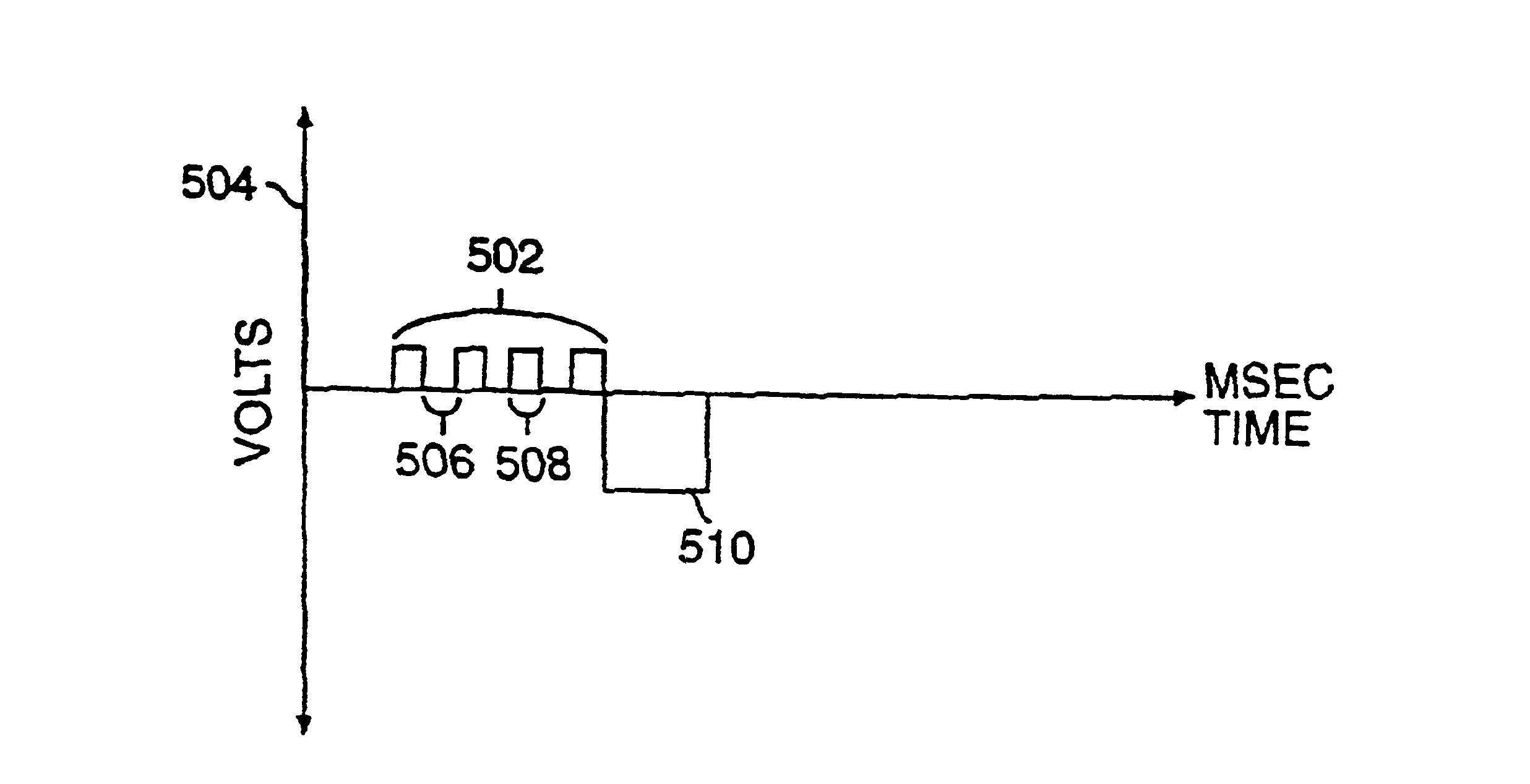
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter- defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
Implantable cardiac stimulation device and method that discriminates between and treats atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation
An implantable cardiac stimulation device discriminates and treats accelerated atrial arrhythmias of a patient's heart. The device includes a sensing circuit that senses cardiac activity of one of the patient's atria to provide an atrial activity signal, a detector that detects an accelerated atrial arrhythmia of the patient's heart, and a classifying circuit that measures relative correspondence between successive P waves of the atrial activity signal to classify the detected accelerated atrial arrhythmia as either atrial tachycardia or atrial fibrillation. A therapy circuit provides anti-tachycardia pacing therapy responsive to a classified atrial tachycardia and defibrillation therapy responsive to a classified atrial fibrillation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Reconfigurable, fault tolerant multiple-electrode cardiac lead systems
InactiveUS7142919B2Easy to detectEfficient deliveryElectrocardiographyEpicardial electrodesLead systemVentricular tissue
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for assessing ventricular function on a chronic basis using a plurality of electrodes disposed on or about a left ventricle and / or a right ventricle—and optionally, at least one mechanical or metabolic sensor—all operatively electrically coupled to an implantable medical device. The plurality of electrodes are preferably spaced-apart so that at least one electrode is disposed electrical communication with a discrete volume of ventricular tissue. In one embodiment, the discrete volume of tissue is defined by multiple longitudinal and axial planes as known and used in the medical arts. Thus, according to the present invention, at least one electrode couples to appropriate sensing circuitry and essentially provides a localized electrogram (EGM) that, when compared to other EGMs, provides for configurable, localized delivery of therapeutic pacing stimulus, diverse impedance-sensing vectors, various diagnostic information regarding myocardial function and / or anti-tachycardia pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
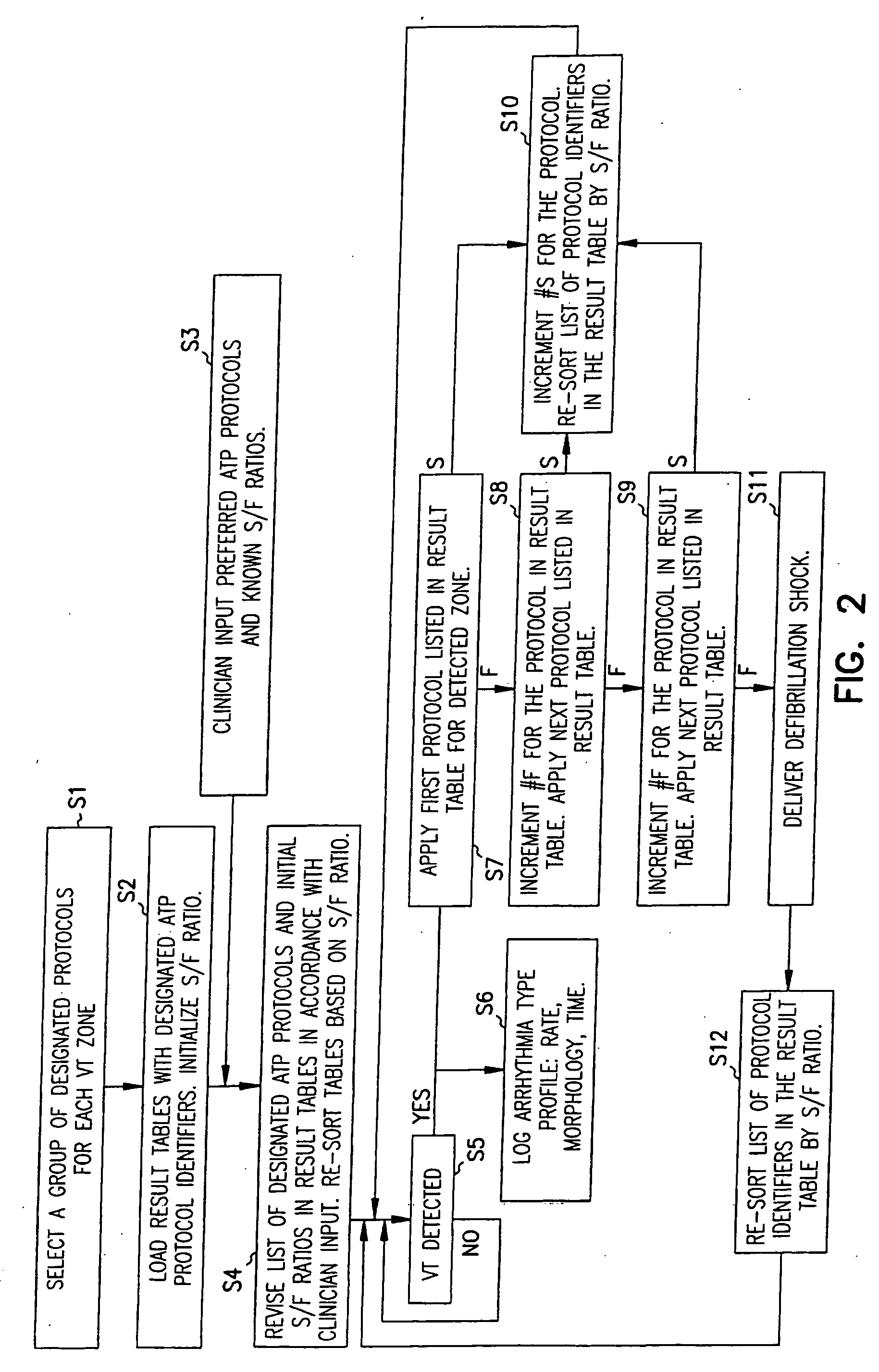
Adapative anti-tachycardia therapy apparatus and method
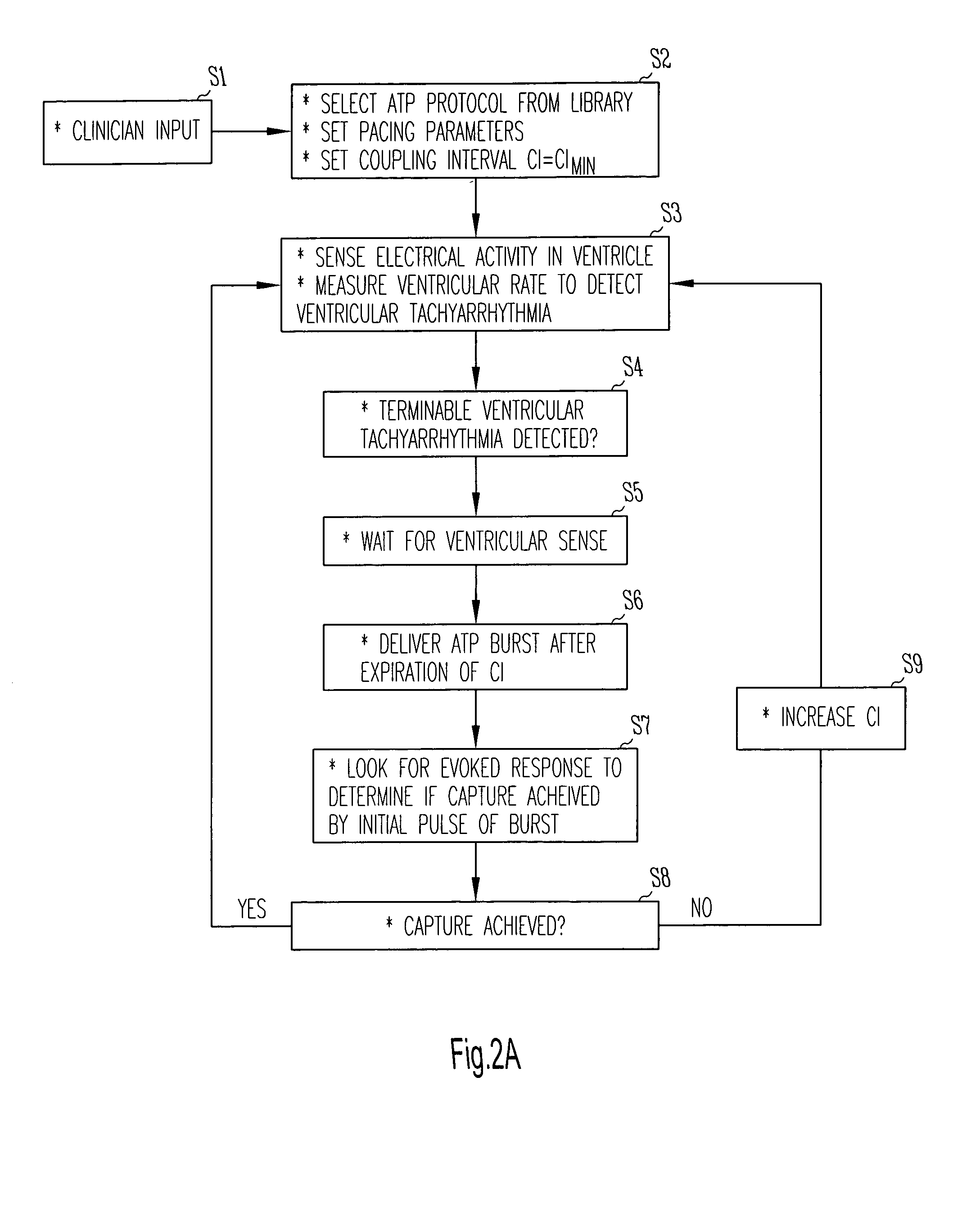
A method and apparatus for delivering anti-tachycardia pacing in an adaptive manner is disclosed. A cardiac rhythm management device, such as an implantable pacemaker, having anti-tachycardia pacing capability delivers anti-tachycardia pacing therapy in accordance with a selected pacing protocol upon detection of a terminable arrhythmia. The protocol is selected from a library of available protocols. A record of the successes and failures of each available protocol in converting tachyarrhythmias is maintained in a result table for use in selecting the protocol.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulation device providing anti-tachycardia pacing therapy and method
An implantable subcutaneous cardiac device includes at least two subcutaneous electrodes adapted for placement external to a heart beneath the skin of a patient. The device further includes an arrhythmia detector that detects a sustained tachyarrhythmia of the heart and a pulse generator that delivers anti-tachycardia pacing pulses to the subcutaneous electrodes in response to detection of a sustained tachyarrhythmia. The pacing pulses preferably have waveforms devoid of any exponential voltage decay and include rounded or substantially constant portions to minimize pain.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
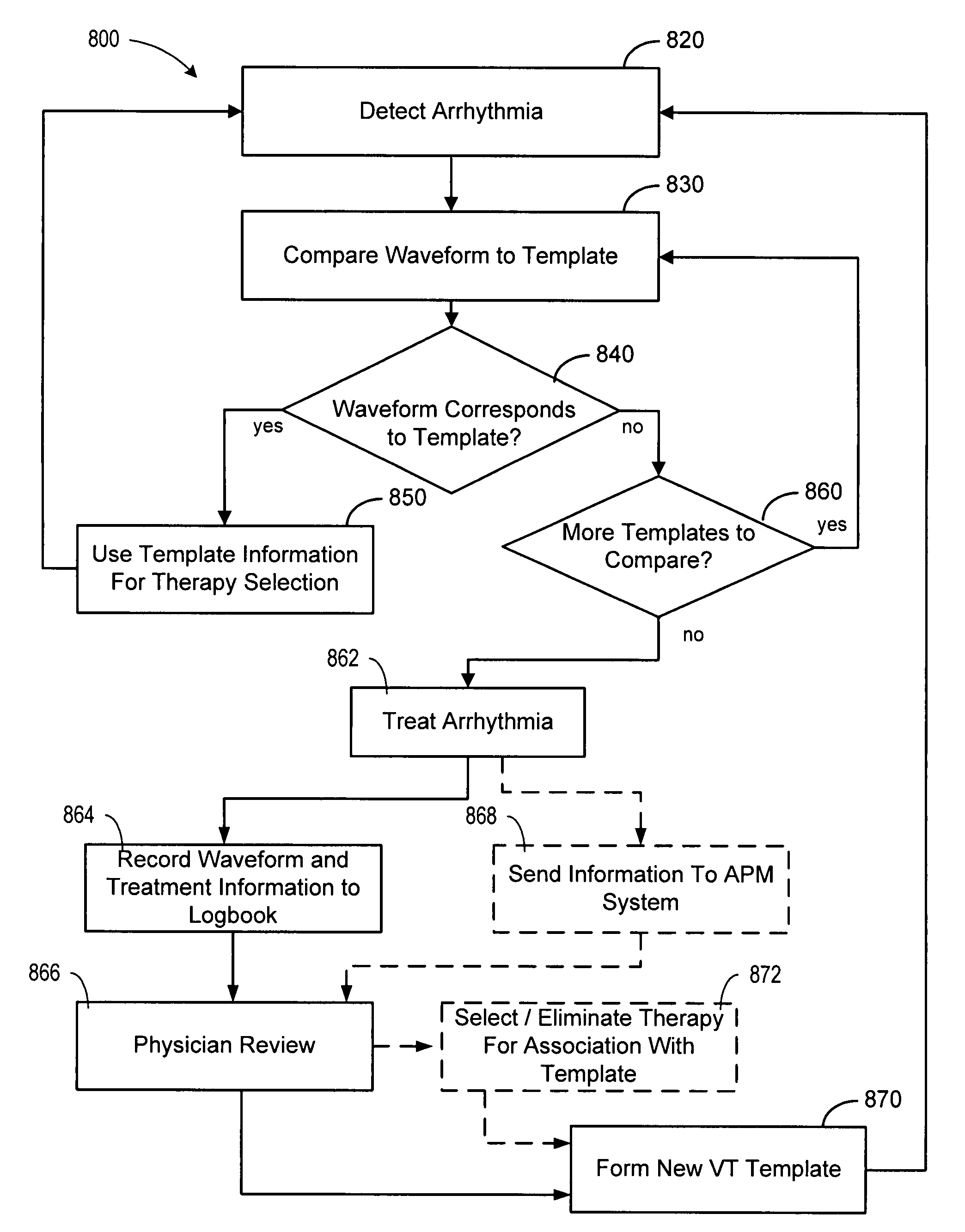
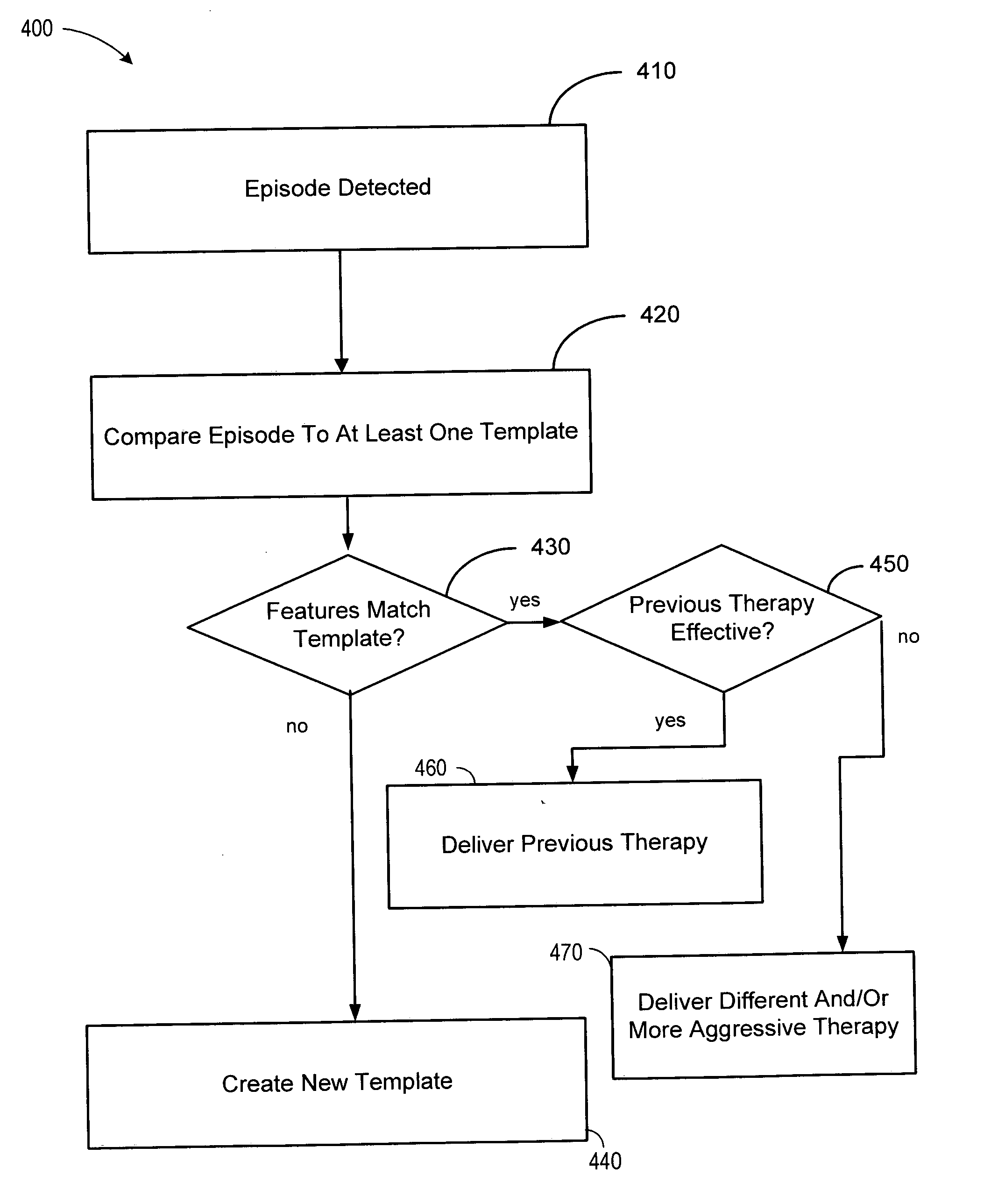
Cardiac tachyarrhythmia therapy selection based on patient response information
Cardiac treatment methods and devices providing templates representative of past tachyarrythmia events, each template associated with a therapy. A cardiac waveform is detected, and if it corresponds to a particular template associated with a previous therapy that was satisfactory in terminating a past event, the previous therapy is delivered again. If unsatisfactory, the previous therapy is eliminated as an option. If, for example, the previous therapy was an antitachycardia pacing therapy unsatisfactory in terminating the past tachyarrythmia event, delivery of the antitachycardia pacing therapy is eliminated as an option. Instead of ATP therapy, one or more of a cardioversion, defibrillation, or alternate anti-tachycardia pacing therapy may be associated with the particular template. Cardiac waveforms and templates may correspond in terms of one or more of morphology, timing, drug regimen, medication, neural activity, patient activity, hemodynamic status, cardiac tissue impedance, transthoracic impedance, or other information corresponding to the episode.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
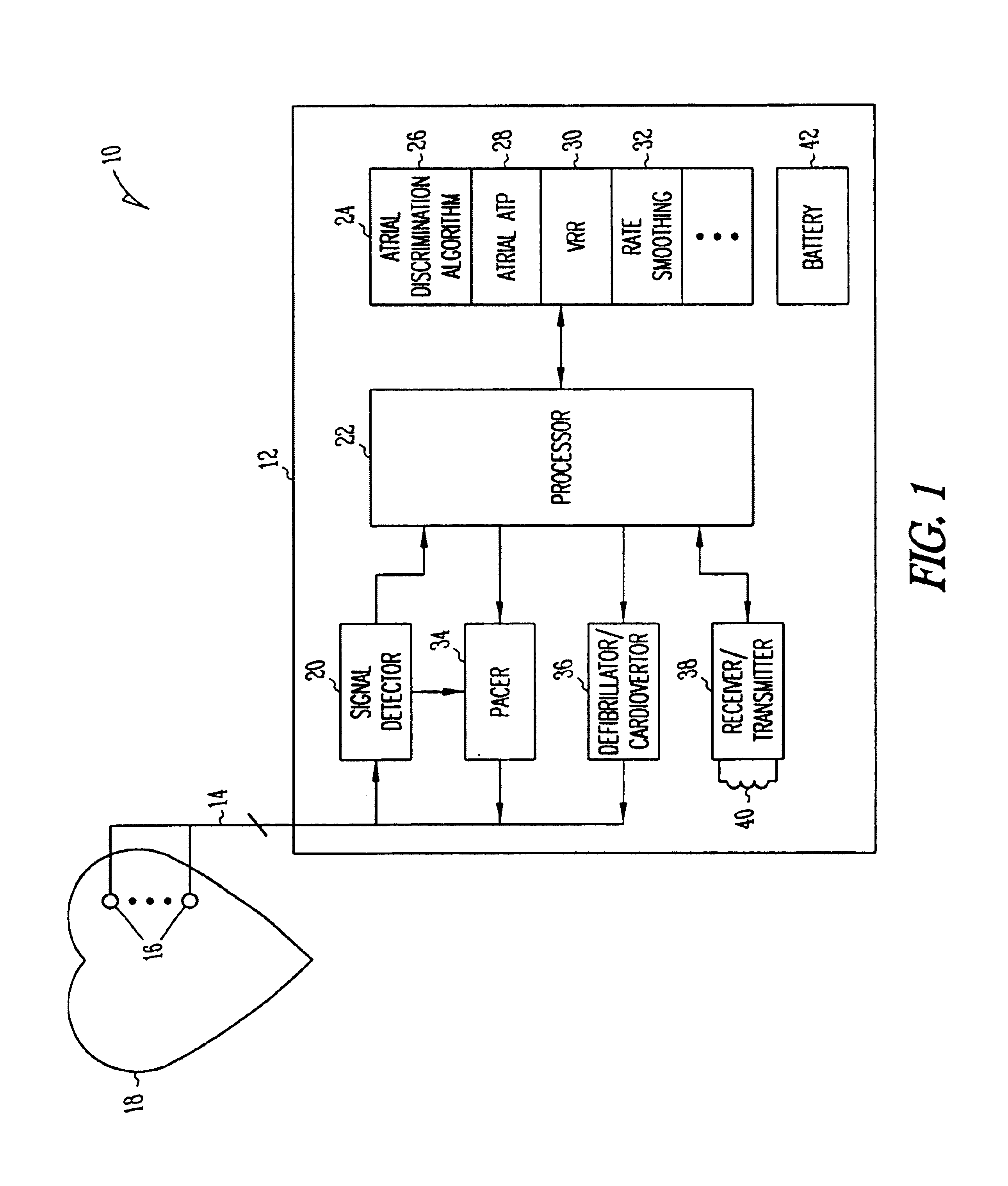
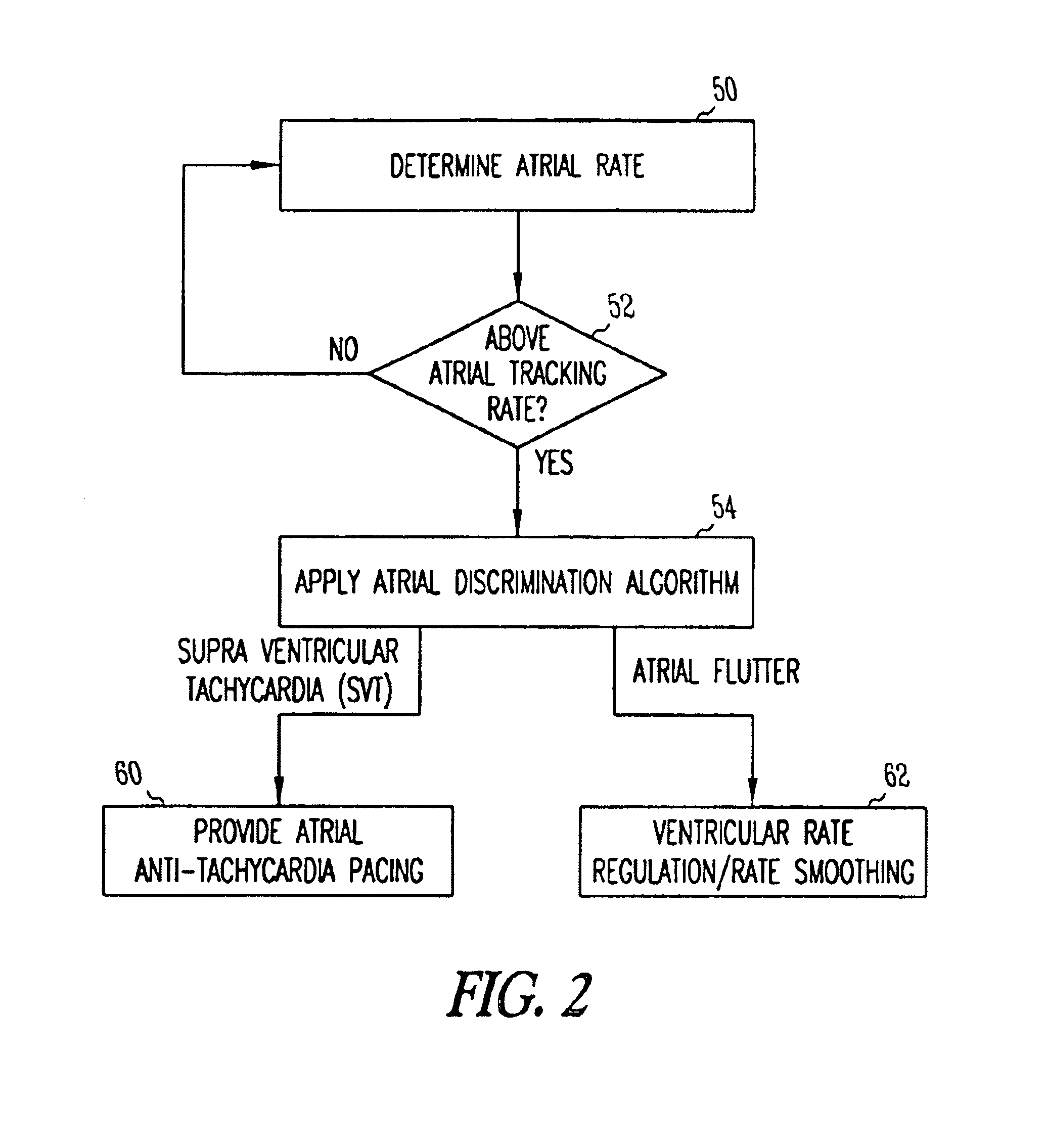
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
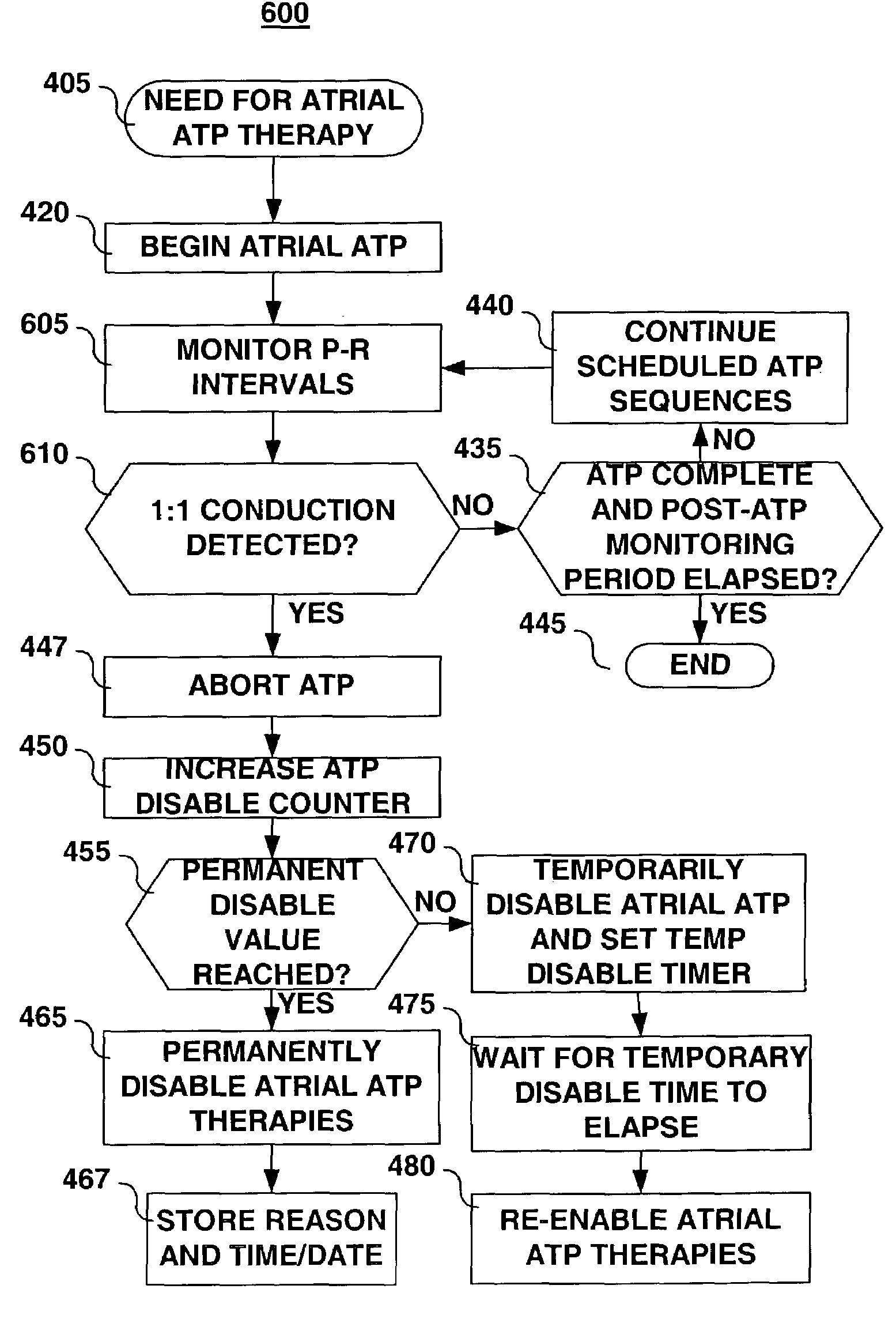
Method for elimination of ventricular pro-arrhythmic effect caused by atrial therapy
A system and method are provided for controlling atrial anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) delivery based on detection of ventricular pro-arrhythmia during or immediately after atrial ATP. Ventricular pro-arrhythmia is detected based on one or more criteria relating to pro-arrhythmic changes including, but not limited to, ventricular rate changes, R-wave morphology changes, and / or 1:1 or nearly 1:1 atrial-ventricular conduction patterns persisting at high ventricular rates. Upon detecting ventricular pro-arrhythmia, a current atrial ATP sequence is aborted. Atrial ATP therapies may subsequently be temporarily or permanently disabled.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for multi-site anti-tachycardia pacing
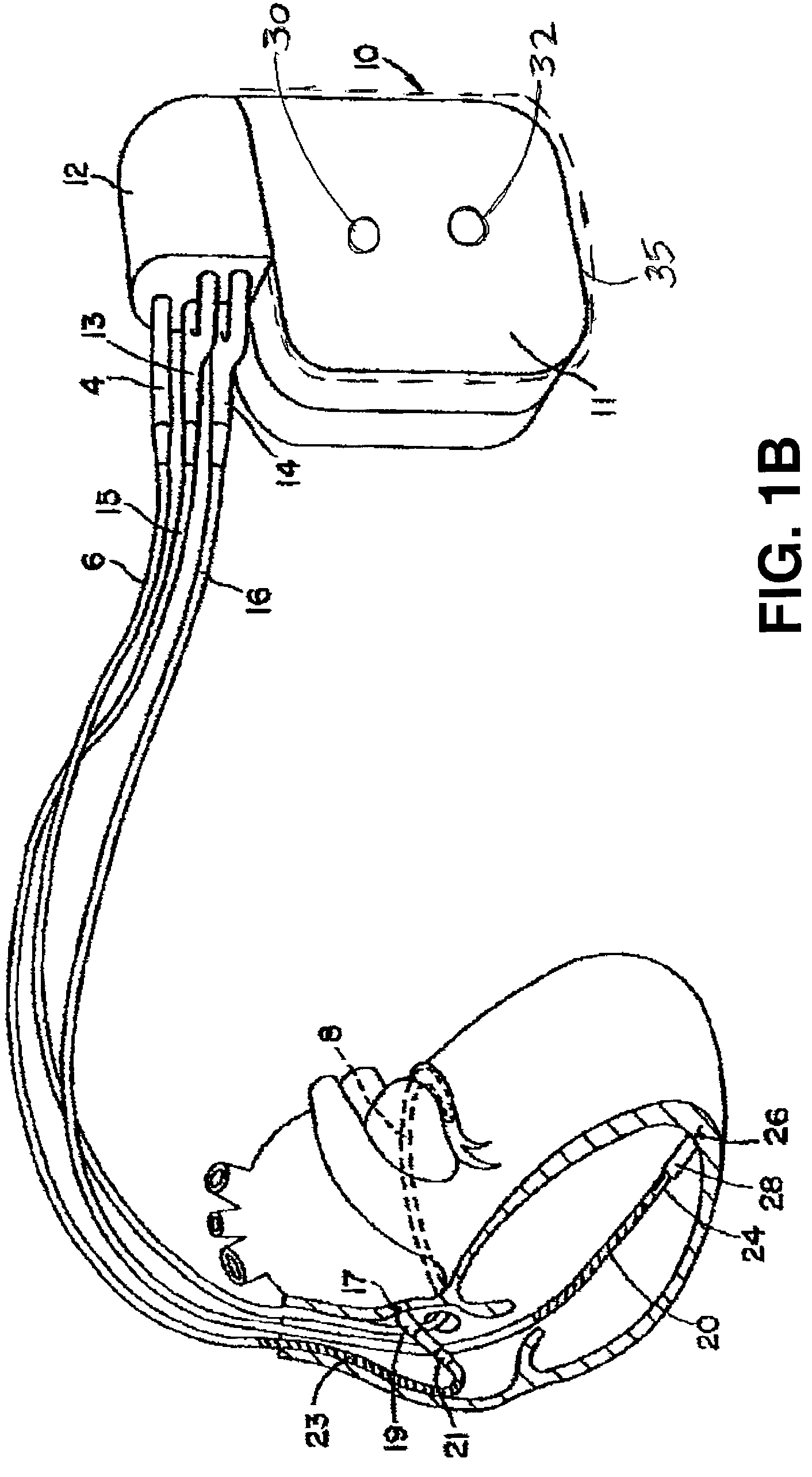
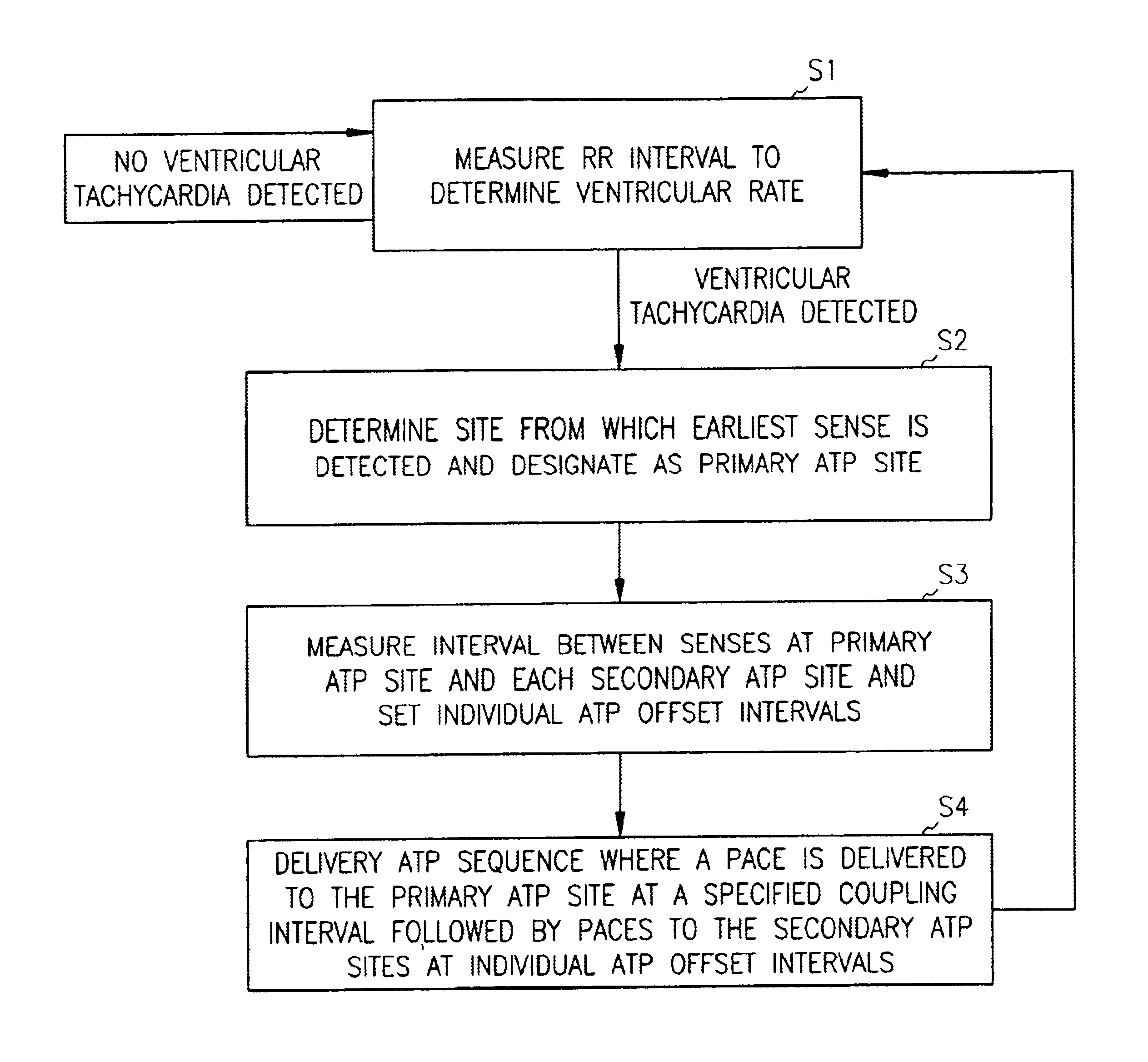
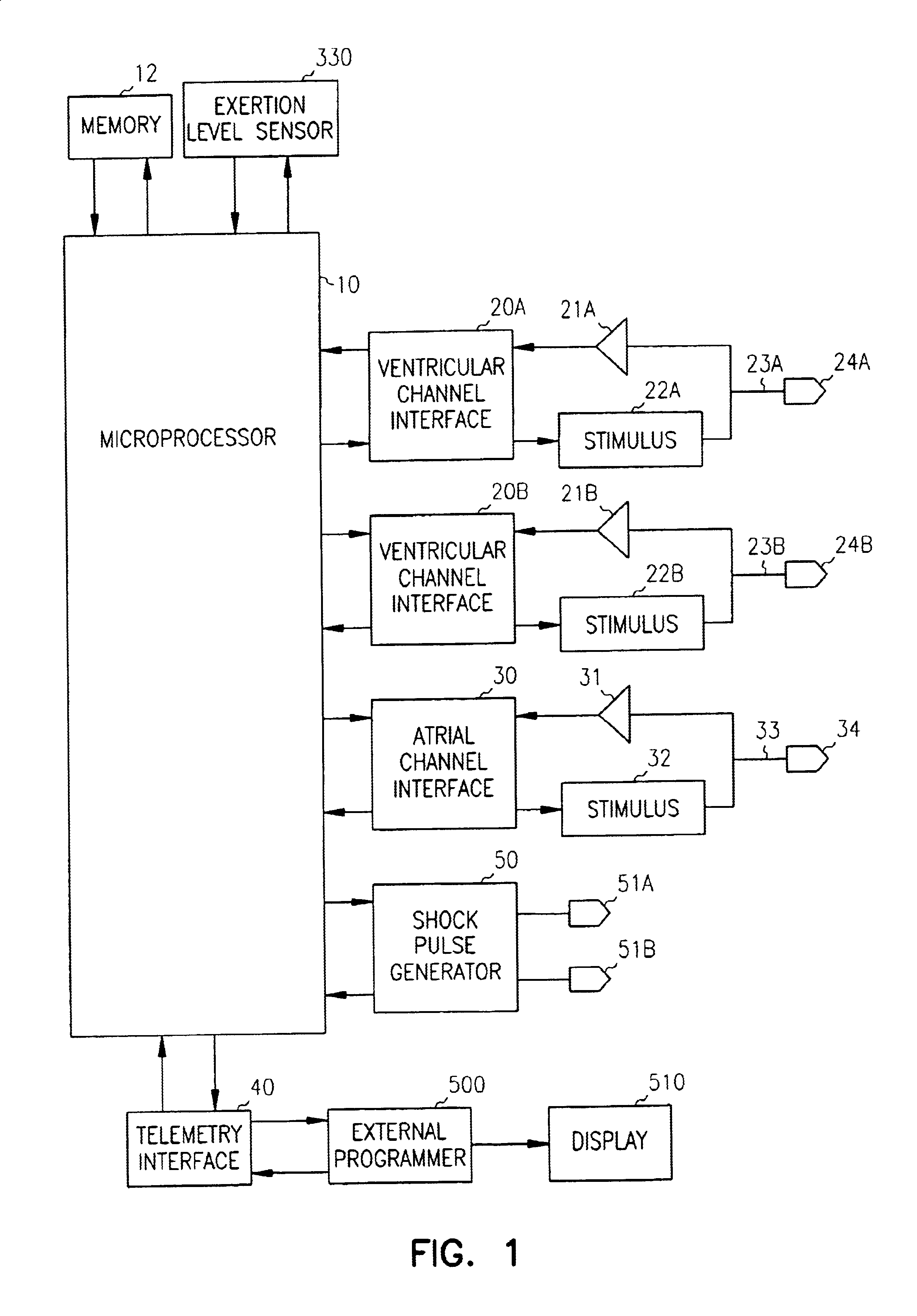
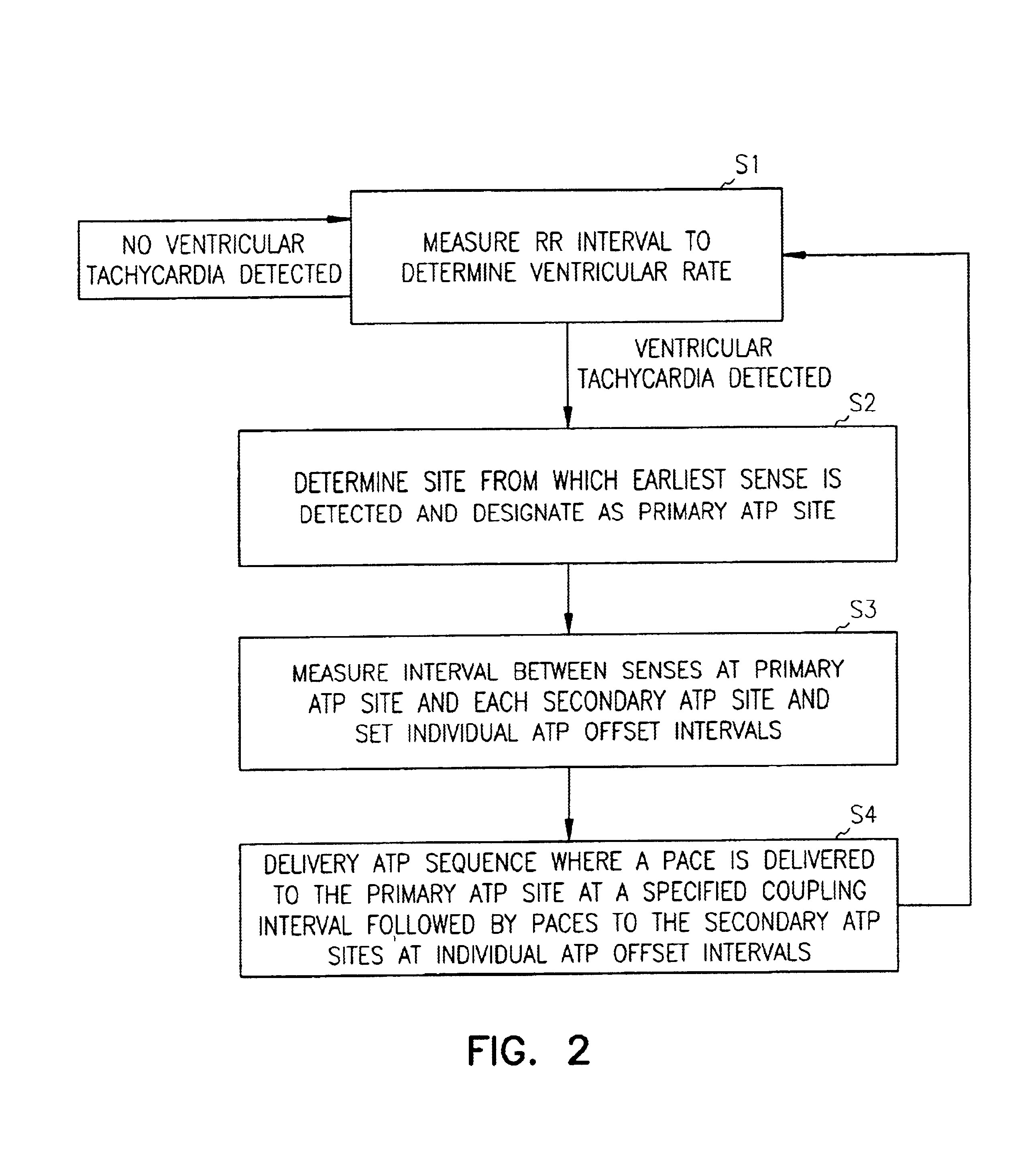
InactiveUS6885890B2Efficiently terminatesIncrease probabilityHeart stimulatorsMulti siteVentricular contraction
An apparatus and method for treating ventricular tachycardia in which paces are delivered to the ventricles at multiple pacing sites in accordance with an anti-tachycardia pacing protocol. Paces are delivered at a selected offset interval in a manner that both resynchronizes ventricular contractions and increases the probability of terminating the tachycardia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Current waveforms for anti-tachycardia pacing for a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
A power supply for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for subcutaneous positioning between the third rib and the twelfth rib and using a lead system that does not directly contact a patient's heart or reside in the intrathoracic blood vessels and for providing anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the heart, comprising a capacitor subsystem for storing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy for delivery to the patient's heart; and a battery subsystem electrically coupled to the capacitor subsystem for providing the anti-tachycardia pacing energy to the capacitor subsystem.
Owner:CAMERON HEALTH
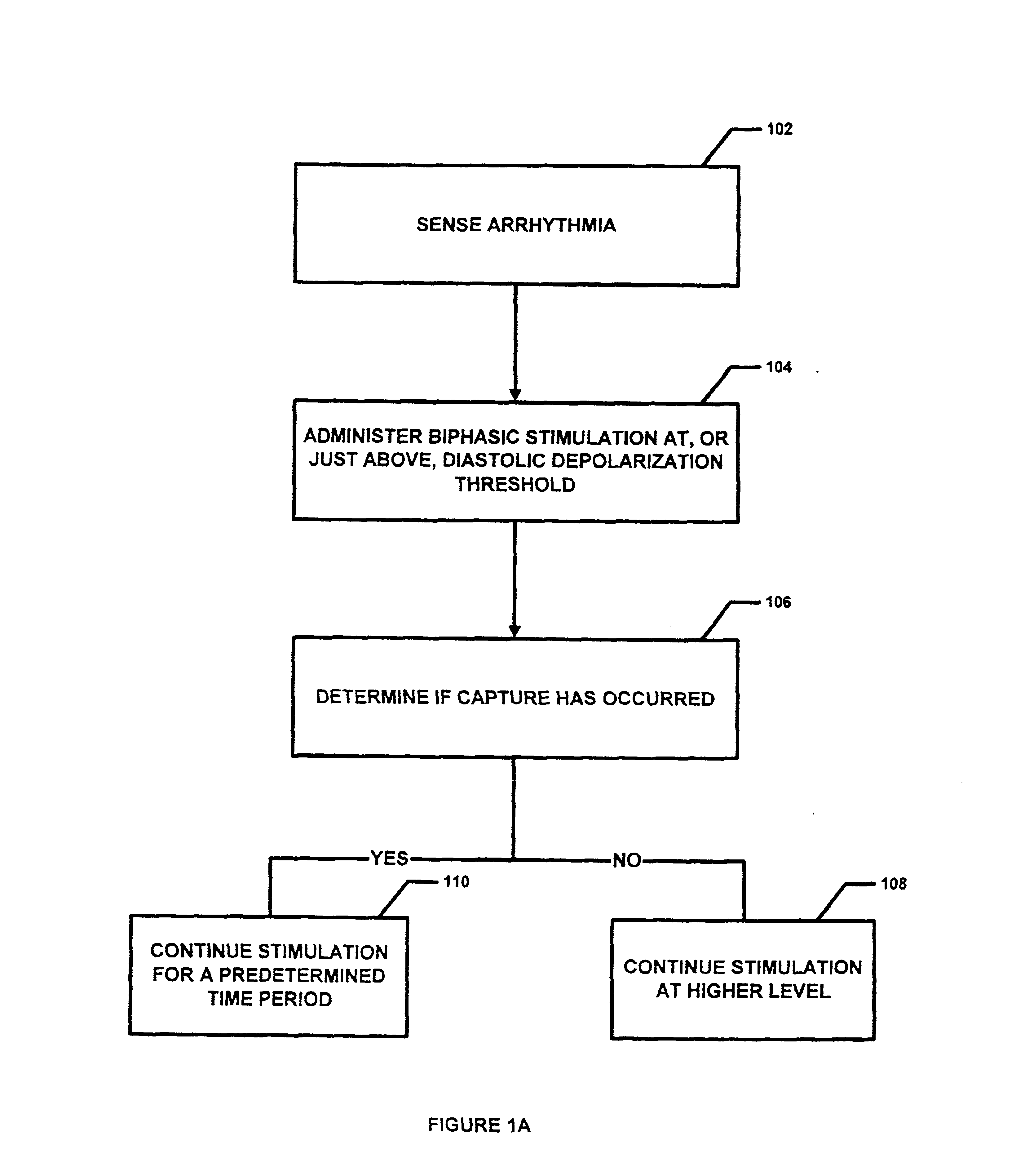
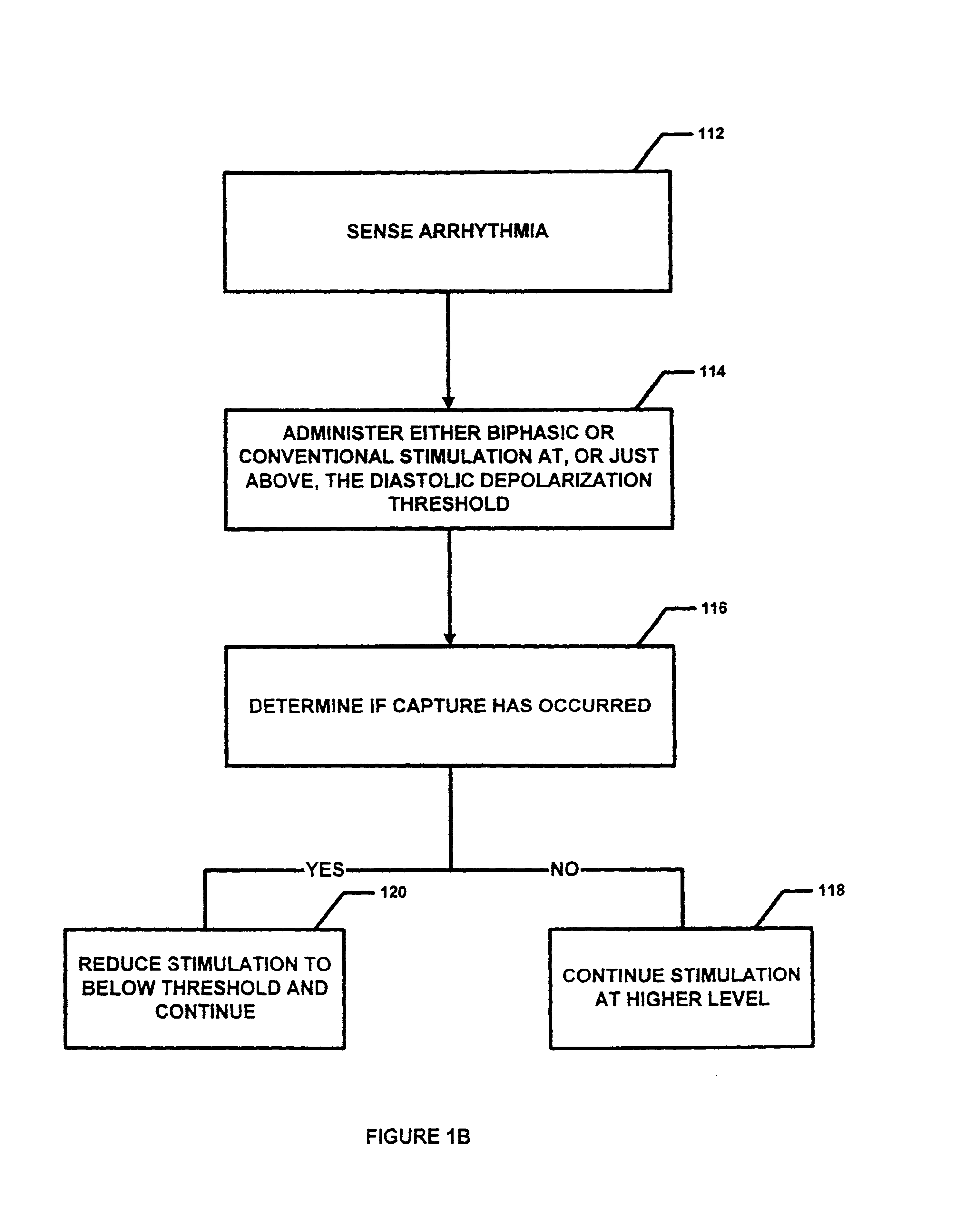
Antitachycardial pacing
InactiveUS6895274B2Facilitate conductionIncrease contractilityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsTreatment effectThreshold potential
Protocols for antitachycardial pacing including biphasic stimulation administered at, or just above, the diastolic depolarization threshold potential; biphasic or conventional stimulation initiated at, or just above, the diastolic depolarization threshold potential, reduced, upon capture, to below threshold; and biphasic or conventional stimulation administered at a level set just below the diastolic depolarization threshold potential. These protocols result in reliable cardiac capture with a lower stimulation level, thereby causing less damage to the heart, extending battery life, causing less pain to the patient and having greater therapeutic effectiveness. In those protocols using biphasic cardiac pacing, a first and second stimulation phase is administered. The first stimulation phase has a predefined polarity, amplitude and duration. The second stimulation phase also has a predefined polarity, amplitude and duration. The two phases are applied sequentially. Contrary to current thought, anodal stimulation is first applied and followed by cathodal stimulation. In this fashion, pulse conduction through the cardiac muscle is improved together with the increase in contractility.
Owner:MR3 MEDICAL LLC
Cardiac tachyarrhythmia therapy selection based on patient response information
Cardiac treatment methods and devices providing templates representative of past tachyarrythmia events, each template associated with a therapy. A cardiac waveform is detected, and if it corresponds to a particular template associated with a previous therapy that was satisfactory in terminating a past event, the previous therapy is delivered again. If unsatisfactory, the previous therapy is eliminated as an option. If, for example, the previous therapy was an antitachycardia pacing therapy unsatisfactory in terminating the past tachyarrythmia event, delivery of the antitachycardia pacing therapy is eliminated as an option. Instead of ATP therapy, one or more of a cardioversion, defibrillation, or alternate anti-tachycardia pacing therapy may be associated with the particular template. Cardiac waveforms and templates may correspond in terms of one or more of morphology, timing, drug regimen, medication, neural activity, patient activity, hemodynamic status, cardiac tissue impedance, transthoracic impedance, or other information corresponding to the episode.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Inter-episode implementation of closed loop ATP
Improved methods and apparatus for providing optimal anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) regimens in response to the return cycle length (RCL) exhibited by an exploratory ATP sequence initially applied upon detection of the tachycardia episode are disclosed. When a tachycardia episode is detected, an exploratory ATP sequence comprising a burst of pacing pulses is delivered, and an exploratory RCL is measured following delivery of the exploratory ATP sequence. A database of successful and unsuccessful ATP regimens associated with stored exploratory RCL values. The measured exploratory RCL and database are utilized to formulate an ATP regimen that is more likely than not to convert the tachycardia episode to NSR.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for ATP Treatment Utilizing Multi-Electrode Left Ventricular Lead
An implantable medical device includes a lead configured to be located proximate to the left ventricle (LV) of the heart, the lead including multiple LV electrodes to sense cardiac activity at multiple LV sensing sites. The a detection module to detect an arrhythmia that represents at least one of a tachycardia and fibrillation based at least in part on the cardiac activity sensed at the multiple LV sensing sites. The ATP therapy module to identify at least one of an ATP configuration or an ATP therapy site based on the cardiac sensed activity at the LV sensing sites, the ATP therapy module to control delivery of antitachycardia pacing (ATP) therapy at the ATP therapy site. The ATP therapy module delivers a stimulus to electrodes at one or more of an LV site, right ventricular (RV) site and right atrial (RA) site, the detection module to sense evoked responses at the LV sensing sites, the ATP therapy module to designate the ATP therapy site to include at least the LV sensing site with a shortest activation time relative to the one or more LV site, RV site and RA site where the stimulus is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for leadless pacing and shock therapy
ActiveCN105102060ATransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart defibrillatorsCardioversionsElectrical stimulations
Techniques and systems for monitoring cardiac arrhythmias and delivering electrical stimulation therapy using a subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator (SICD) and a leadless pacing device (LPD) are described. For example, the SICD may detect a tachyarrhythmia within a first electrical signal from a heart and determine, based on the tachyarrhythmia, to deliver anti-tachyarrhythmia shock therapy to the patient to treat the detected arrhythmia. The LPD may receive communication from the SICD requesting the LPD deliver anti-tachycardia pacing to the heart and determine, based on a second electrical signal from the heart sensed by the LPD, whether to deliver anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to the heart. In this manner, the SICD and LPD may communicate to coordinate ATP and / or cardioversion / defibrillation therapy. In another example, the LPD may be configured to deliver post-shock pacing after detecting delivery of anti-tachyarrhythmia shock therapy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
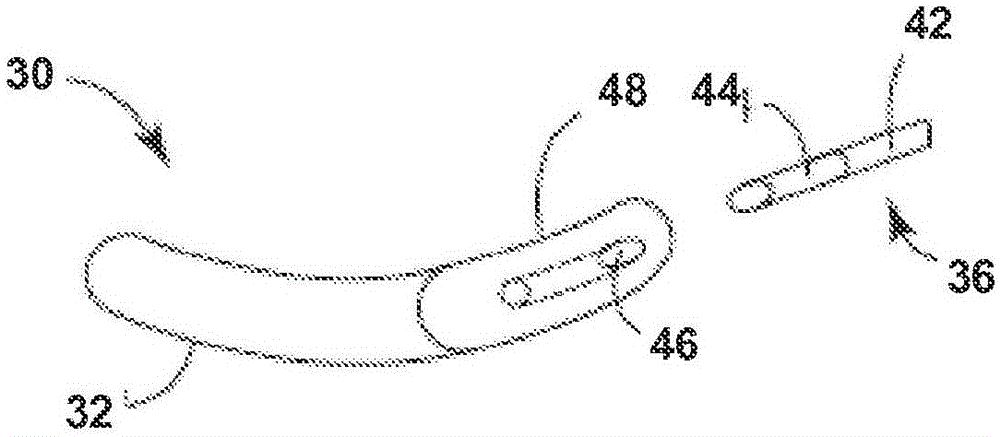
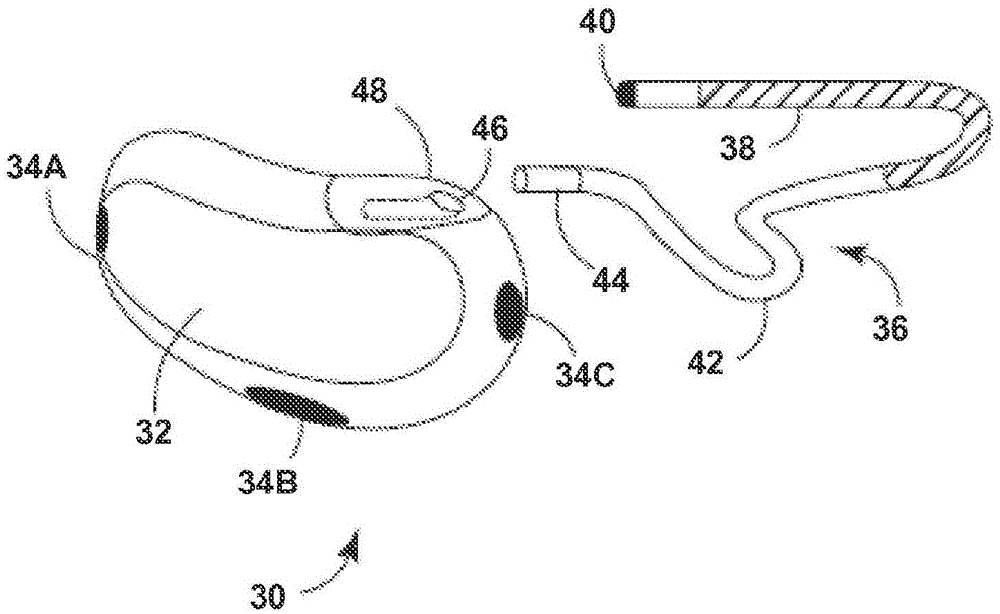
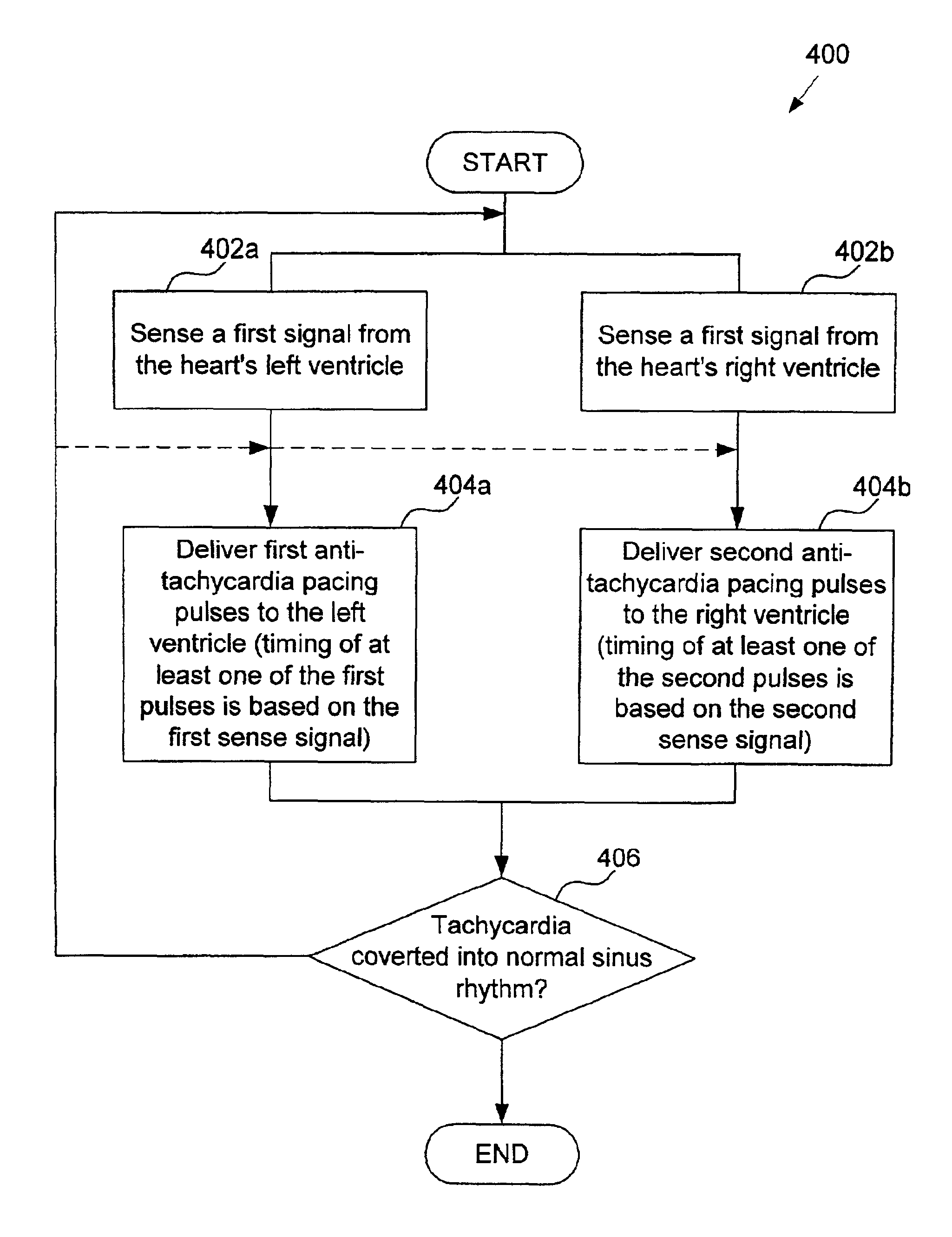
Anti-tachycardia pacing methods and devices
Improved methods and devices perform anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a ventricular tachycardia (VT) to normal sinus rhythm. In one embodiment of the invention bi-ventricular (BV) ATP is employed. In this embodiment the right ventricle and left ventricle of a patient's heart are independently paced based on signals sensed in each chamber.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
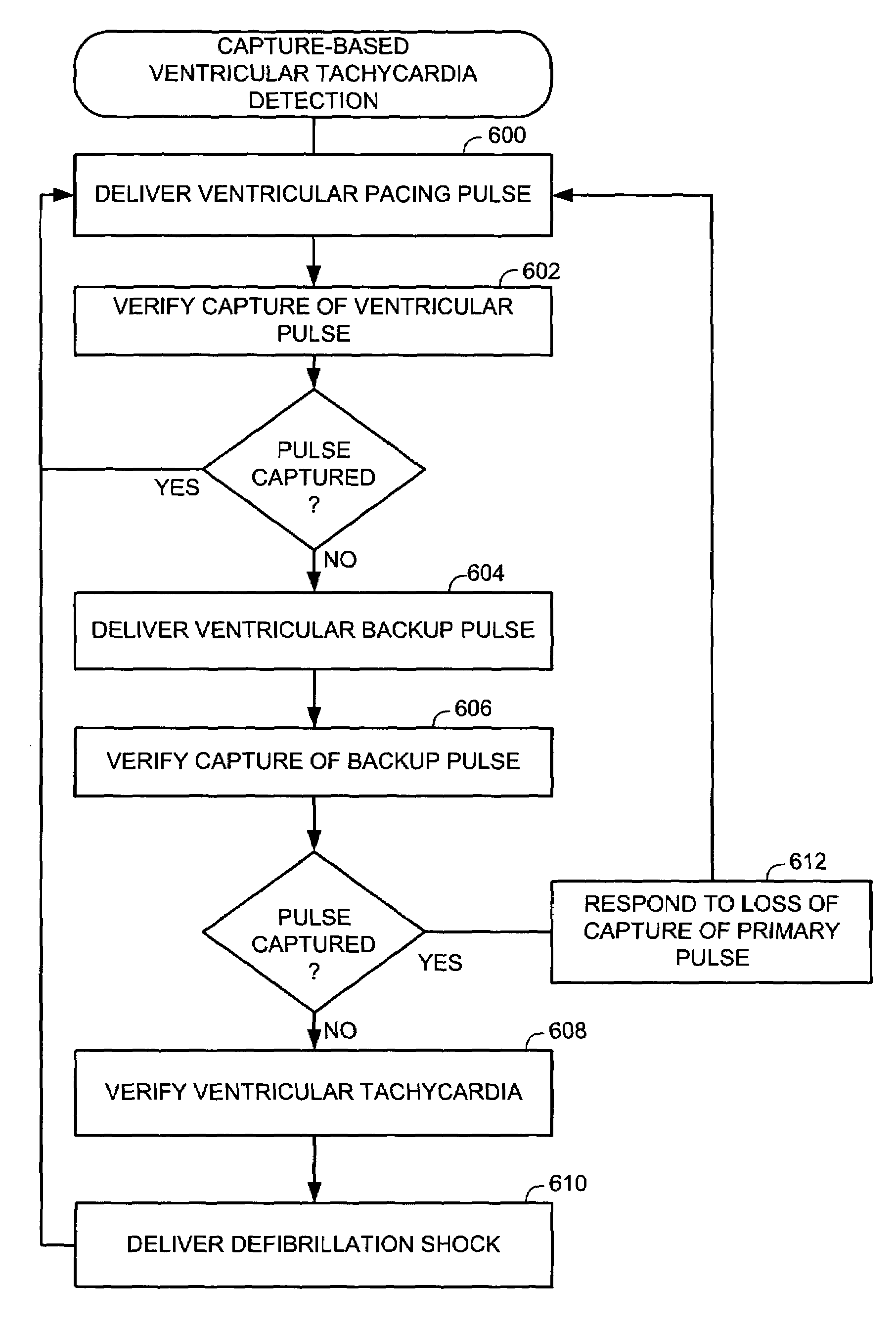
System and method for providing preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7363081B1Easy to detectReliably detecting the onset of an atrial tachycardiaHeart stimulatorsAtrial pacingAntitachycardia Pacing
Techniques for enabling both preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing (ATP) within an implantable device are provided. The device gains the benefits of overdrive pacing for preventing the onset of a tachycardia and, if one nevertheless occurs, ATP is employed to terminate the tachycardia. In particular, a technique is provided for promptly detecting the onset of atrial tachycardia during preventive overdrive pacing based on loss of capture of atrial pacing pulses. A technique is also provided for using detection of loss of capture of atrial or ventricular pacing pulses to trigger automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP. A setup technique determines whether to enable the automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP within a particular patient. Also, techniques are provided for verifying loss of capture of atrial or ventricular backup pacing pulses and for detecting low amplitude ventricular fibrillation based on loss of capture of ventricular backup pacing pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for providing preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing using an implantable cardiac stimulation device
InactiveUS7212855B1Easy to detectReliably detecting the onset of an atrial tachycardiaInternal electrodesExternal electrodesVentricular pacingAntitachycardia Pacing
Techniques for enabling both preventive overdrive pacing and antitachycardia pacing (ATP) within an implantable device are provided. The device gains the benefits of overdrive pacing for preventing the onset of a tachycardia and, if one nevertheless occurs, ATP is employed to terminate the tachycardia. In particular, a technique is provided for promptly detecting the onset of atrial tachycardia during preventive overdrive pacing based on loss of capture of atrial pacing pulses. A technique is also provided for using detection of loss of capture of atrial or ventricular pacing pulses to trigger automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP. A setup technique determines whether to enable the automatic switching from overdrive pacing to ATP within a particular patient. Also, techniques are provided for verifying loss of capture of atrial or ventricular backup pacing pulses and for detecting low amplitude ventricular fibrillation based on loss of capture of ventricular backup pacing pulses.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Inter-episode implementation of closed loop ATP
Improved methods and apparatus for providing optimal anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) regimens in response to the return cycle length (RCL) exhibited by an exploratory ATP sequence initially applied upon detection of the tachycardia episode are disclosed. When a tachycardia episode is detected, an exploratory ATP sequence comprising a burst of pacing pulses is delivered, and an exploratory RCL is measured following delivery of the exploratory ATP sequence. A database of successful and unsuccessful ATP regimens associated with stored exploratory RCL values. The measured exploratory RCL and database are utilized to formulate an ATP regimen that is more likely than not to convert the tachycardia episode to NSR.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods to optimize Anti-tachycardial pacing (ATP)
ActiveUS20160030743A1Increase probabilitySlow repolarization rateHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityCardiac arrest rhythm
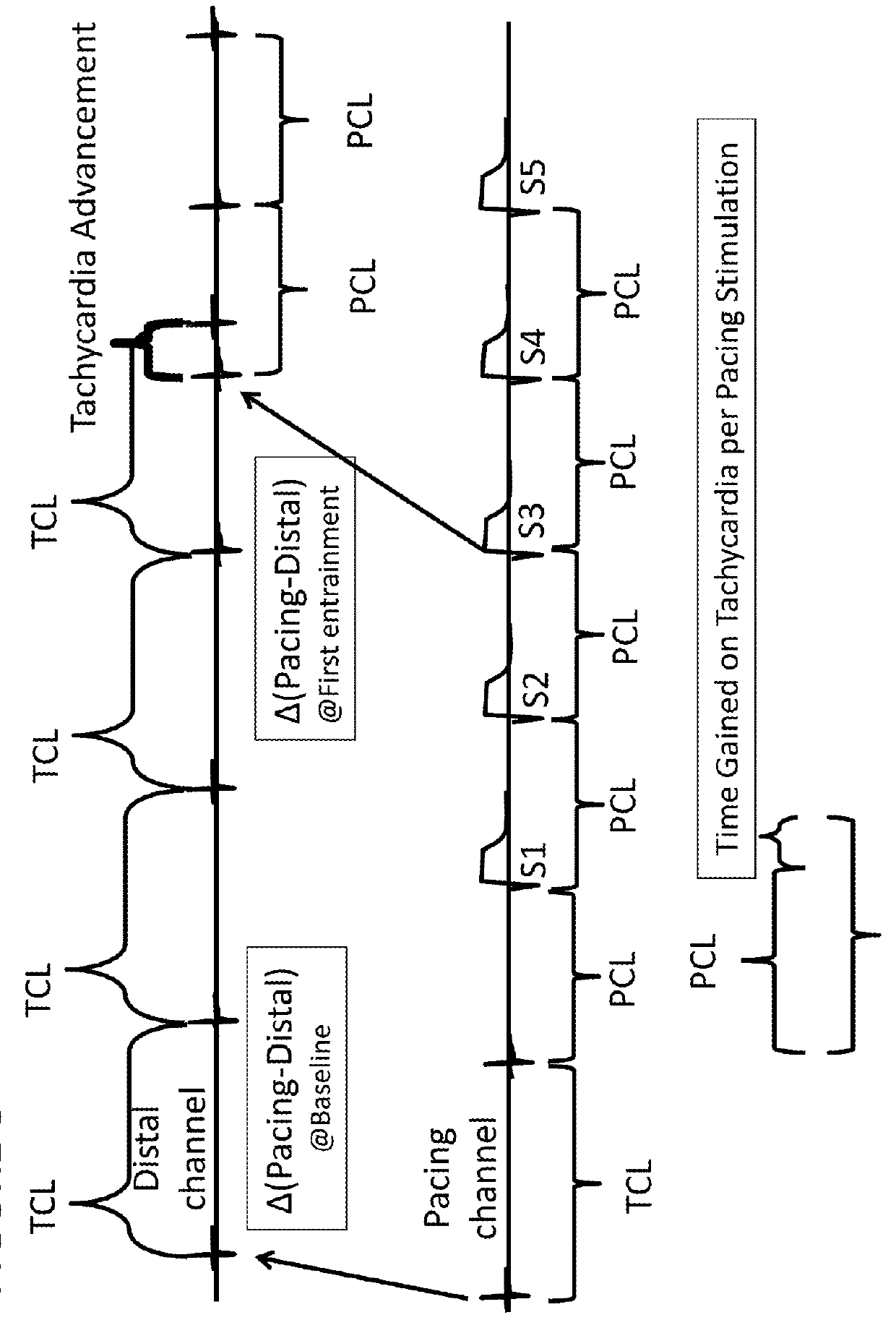
Apparatus, systems and methods are provided for prevention and / or remediation of cardiac arrhythmias, e.g. optimizing anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) algorithms. More particularly, implantable devices are provided that measure and treat cardiac arrhythmias. By monitoring the ATP attempt from additional electrodes, far-field morphology analyses, and / or measuring the return interval from a failed ATP attempt; the devices may estimate when entrainment has occurred, the amount of delay within the reentrant tachycardia, and / or tachycardia termination / acceleration. These variables and occurrences can be used to optimize the first and / or subsequent ATP attempts. Furthermore, other exemplary embodiments describe methods to integrate electrical restitution properties into the design of ATP pacing algorithms to facilitate tachycardia termination.
Owner:CARDIOFLOW TECH
Subcutaneous cardiac stimulation device providing anti-tachycardia pacing therapy and method
An implantable subcutaneous cardiac device includes at least two subcutaneous electrodes adapted for placement external to a heart beneath the skin of a patient. The device further includes an arrhythmia detector that detects a sustained tachyarrhythmia of the heart and a pulse generator that delivers anti-tachycardia pacing pulses to the subcutaneous electrodes in response to detection of a sustained tachyarrhythmia. The pacing pulses preferably have waveforms devoid of any exponential voltage decay and include rounded or substantially constant portions to minimize pain.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
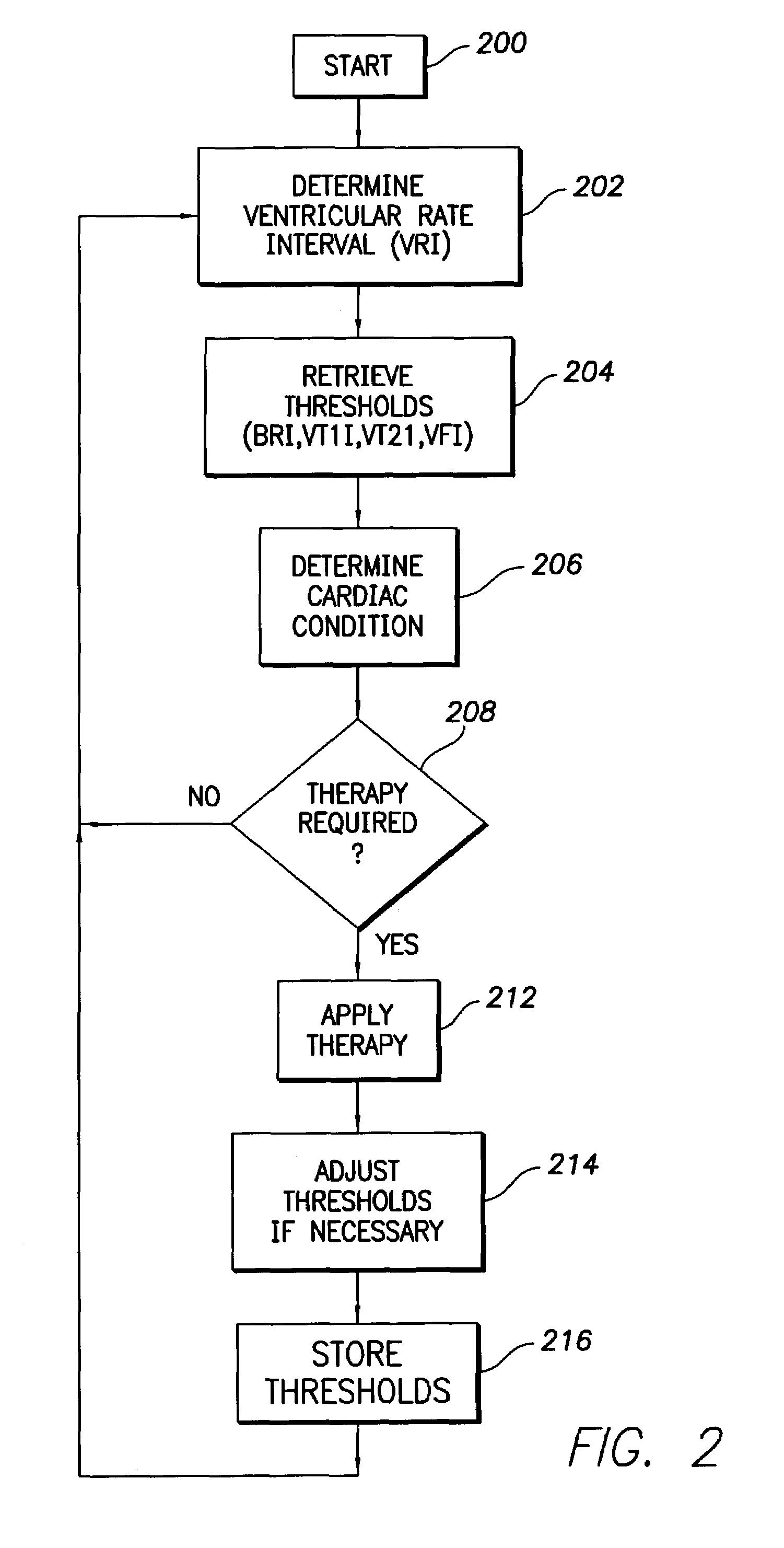
Implantable cardioversion device with a self-adjusting threshold for therapy selection
In an implantable cardioversion device, the condition of the patient's heart is determined from an intrinsic ventricular parameter, such as the ventricular rate, and therapy is provided with a pulse generator, including, for instance, antitachycardia pacing therapy or defibrillation shocks. Initially, the conditions, i.e., ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, are determined using predetermined values for a set of thresholds defining the various conditions. Thereafter, the thresholds are changed by increasing or decreasing the therapy thresholds from the predetermined values based on the morphology of the sensed ventricular signals.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
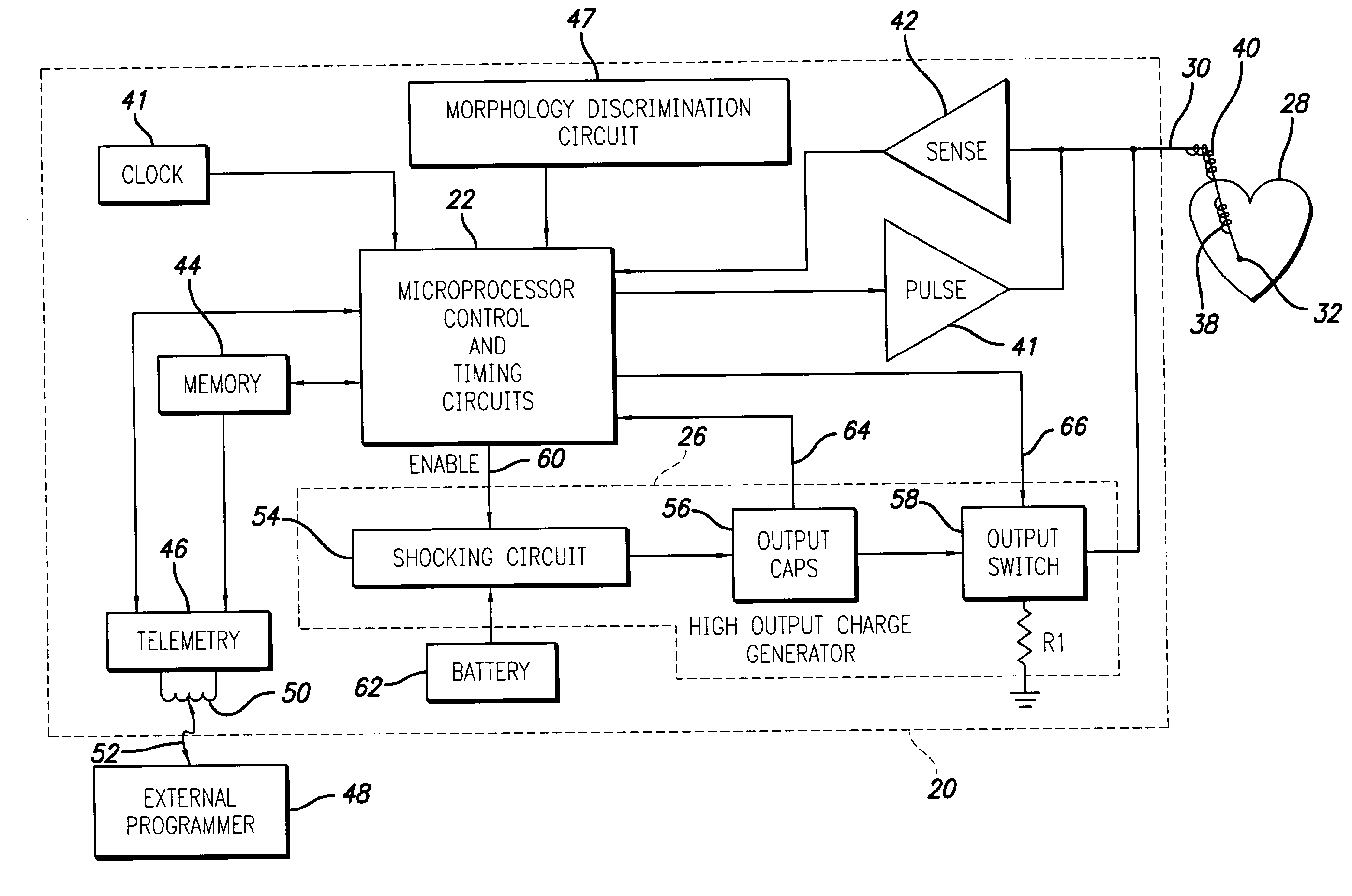
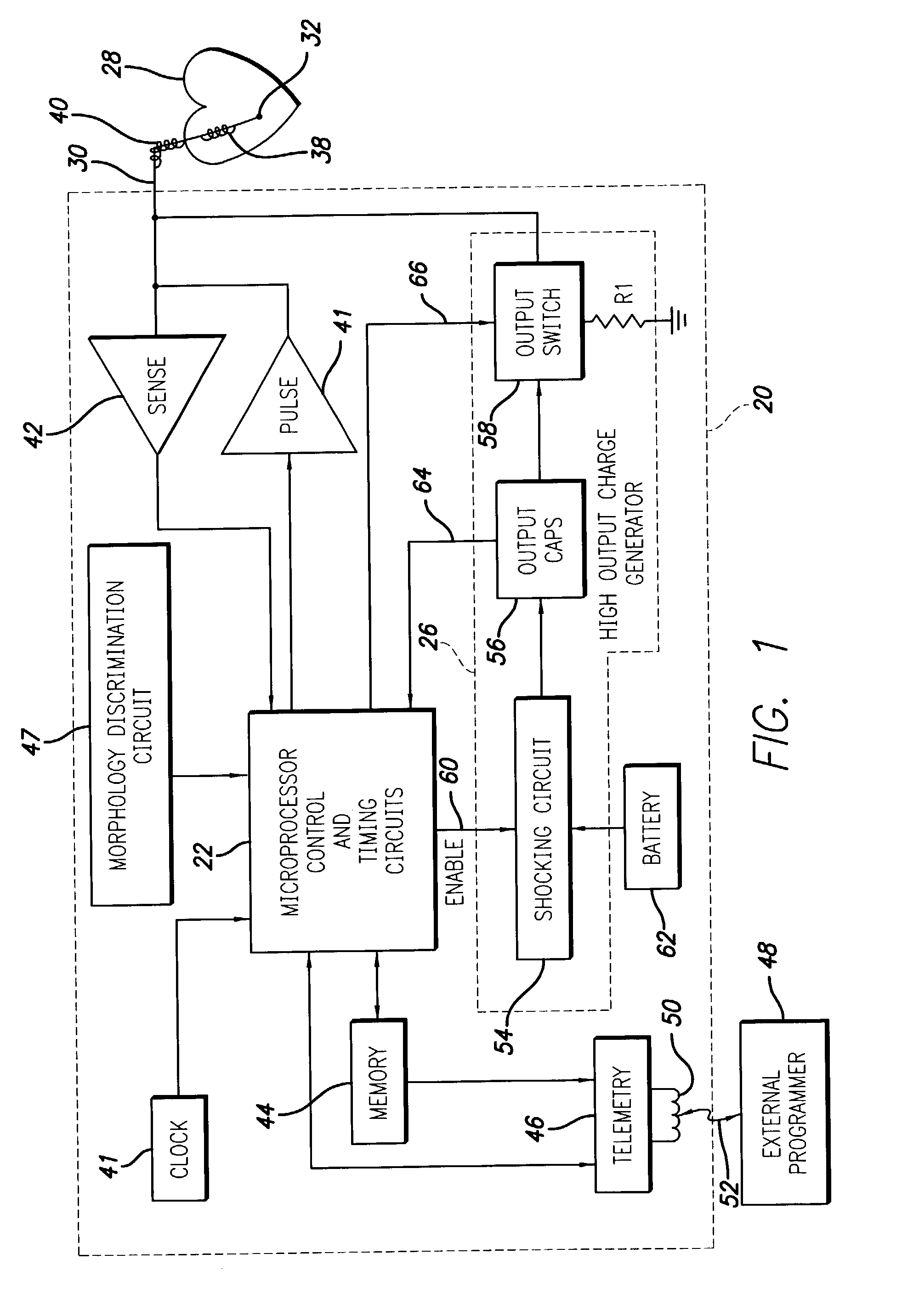
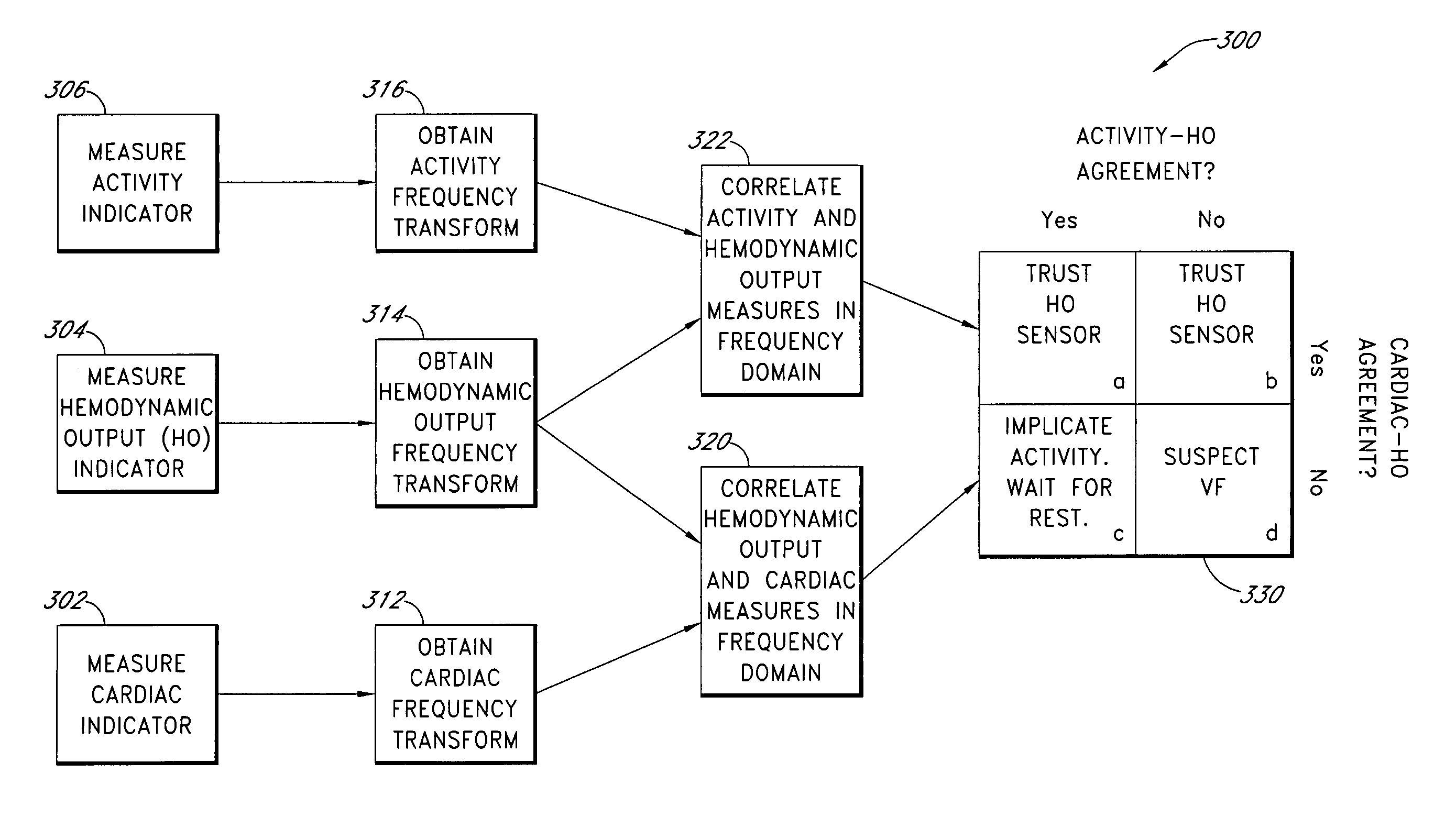
Opto-electrical coherence detection of hemodynamically compromising arrhythmia
InactiveUS7596412B1Readily note commonalityCharging capacity is limitedCatheterCharacter and pattern recognitionFast Fourier transformPhase shifted
System and methods for assessing sensed signals for determining a reliability measure of their accuracy with respect to a patient's true physiological status. As one example, the signals can include multiple, independently obtained signals, such as an electro-chemically based measure of cardiac activity and a plethysmography based measure of hemodynamic output which typically exhibit different morphologies and varying phase shifts with respect to each other. One manner of assessing the signals is to transform them into the frequency domain, such as via a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), and evaluate them, such as by a coherence determination, to determine the degree of their mutual agreement. This can be used to assess the reliability of the sensing. Therapy can be delivered under certain observed conditions, such as a condition of hemodynamic insufficiency where anti-tachycardia pacing and / or shocking therapy can be delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Synchronized atrial anti-tachy pacing system and method
A system and method for an implantable cardiac pacing device provide for delivery of anti-tachycardia pacing of the atrium upon detection of atrial tachycardia combined with automatic re-synchronization of ventricular pacing directly following the last atrial pulse of the anti-tachycardia scheme. At the onset of delivery of the ATP train or like scheme of ATP, an appropriate ventricular pacing interval is calculated to enable asynchronous pacing of the ventricle during the ATP and synchronous delivery of the next ventricular pulse at a delay following the end of the ATP train. Upon determination of AT, an algorithm is used to calculate if a ventricular pacing interval can be found that meets maximum and minimum pacing criteria and also provides that the next ventricular pace pulse following the end of the ATP train will follow the last atrial pulse of the train by a suitable AV delay. If such a suitable pacing interval is found, the ventricular pacing interval is set to a temporary value and the train is delivered. If such a pacing interval cannot be initially determined the system waits for one more atrial sense and then repeats the determination to find such a suitable ventricular pacing interval.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electrical cardiac output forcer
InactiveUS20050197676A1Maintain consciousnessLife maintenanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac cell
An electrical method and apparatus for stimulating cardiac cells causing contraction to force hemodynamic output during fibrillation, hemodynamically compromising tachycardia, or asystole. Forcing fields are applied to the heart to give cardiac output on an emergency basis until the arrhythmia ceases or other intervention takes place. The device is used as a stand alone external or internal device, or as a backup to an ICD, atrial defibrillator, or an anti-tachycardia pacemaker. The method and apparatus maintain some cardiac output and not necessarily defibrillation.
Owner:GALVANI
Method and system for automatic anti-tachycardia pacing
InactiveUS20050070967A1Promote resultsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeMotor evoked potentials monitoring
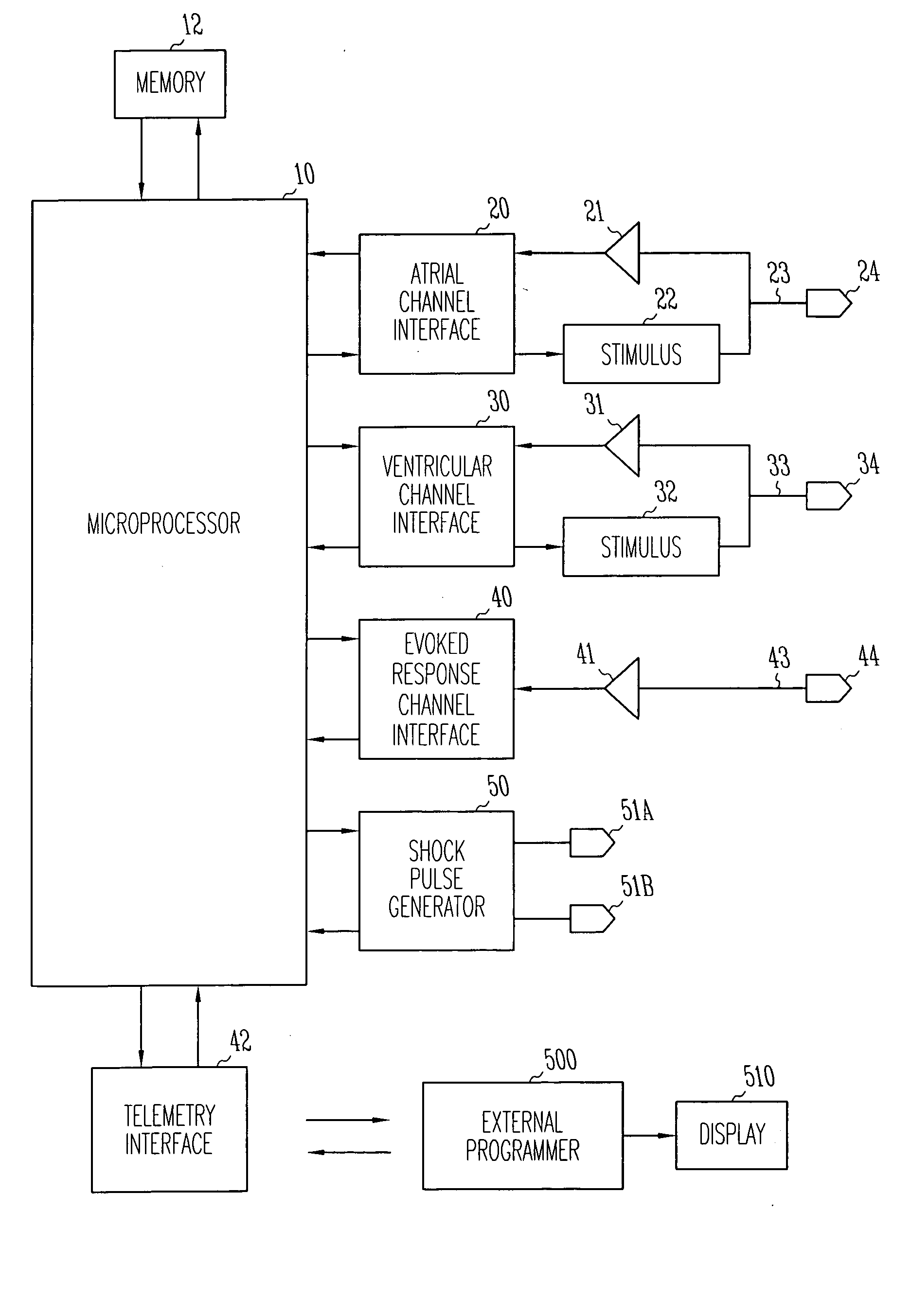
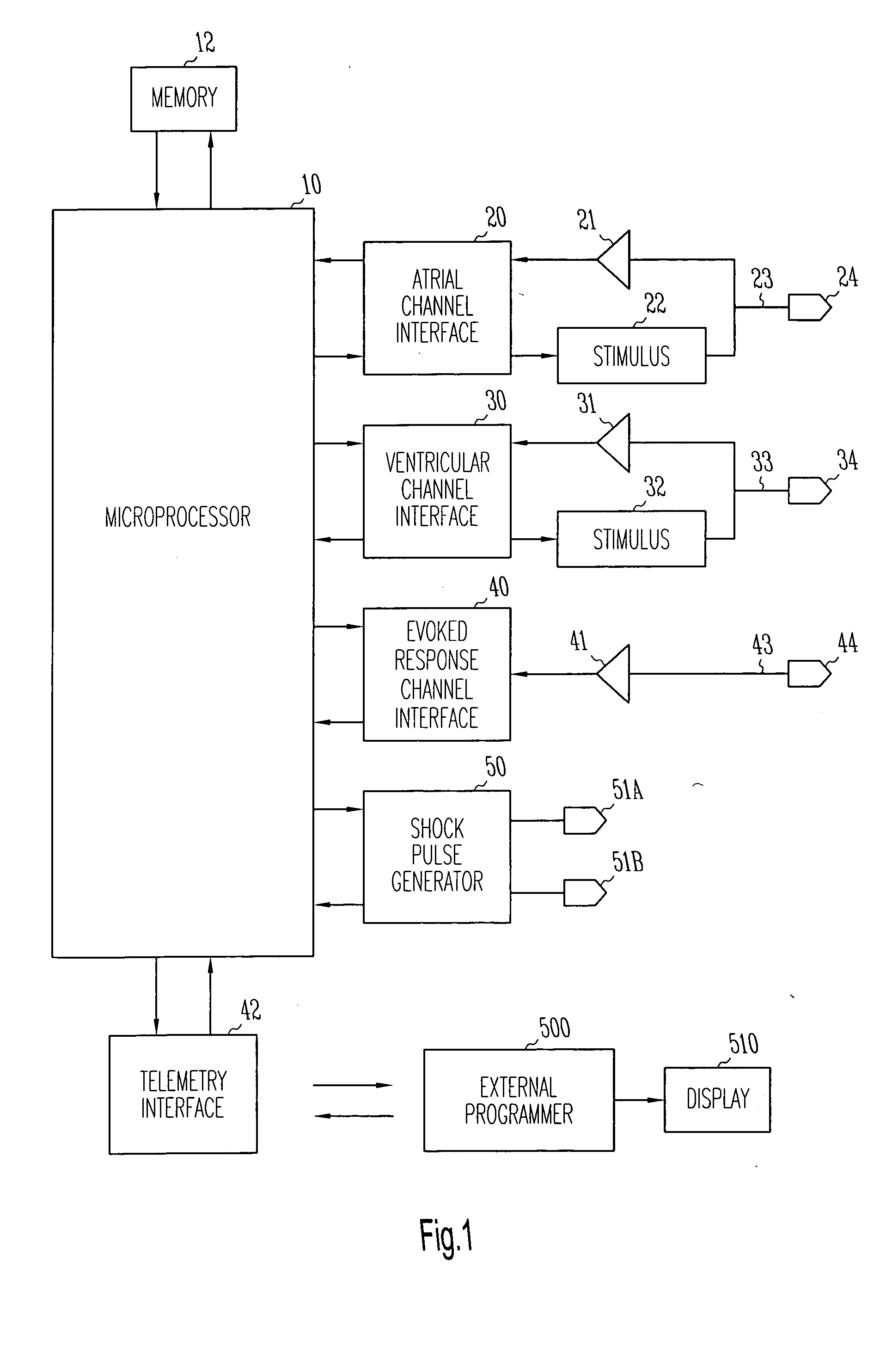
A method and system for delivering anti-tachycardia pacing is disclosed. A cardiac rhythm management device, such as an implantable pacemaker having anti-tachycardia pacing capability, delivers anti-tachycardia pacing therapy in accordance with an anti-tachycardia pacing protocol upon detection of a terminable arrhythmia. The anti-tachycardia pacing is delivered as a burst of one or more pacing pulses at a specified coupling interval after a sensed ventricular polarization. By sensing if an evoked potential occurs, the device can determine whether or not the anti-tachycardia pacing burst has captured the ventricle and can adjust the coupling interval and / or other parameters accordingly.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Anti-tachycardia pacing method and apparatus for multi-chamber pacing
Improved methods and devices perform tachycardia detection and anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) to convert a tachycardia (e.g., VT or AT) to normal sinus rhythm. According to one embodiment, an anti-tachycardia pacing method includes sensing, during sinus rhythm, first and second cardiac signals at first and second sites, respectively, in a patient's heart. The first and second sites include left and right ventricles or left and right atria, for example. The method further includes sensing third and fourth cardiac signals at the first and second sites, respectively, during a tachycardia (e.g., ventricular tachycardia or atrial tachycardia). The cardiac signals are processed to provide respective values. One or more anti-tachycardia pacing pulses are delivered at the site closest to the reentrant circuit based on a comparison of a first ratio of the first and third values and a second ratio of the second and fourth values. Unipolar sensing of the cardiac signals may be employed by, for example, shorting together pairs of electrodes implanted at each site.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com