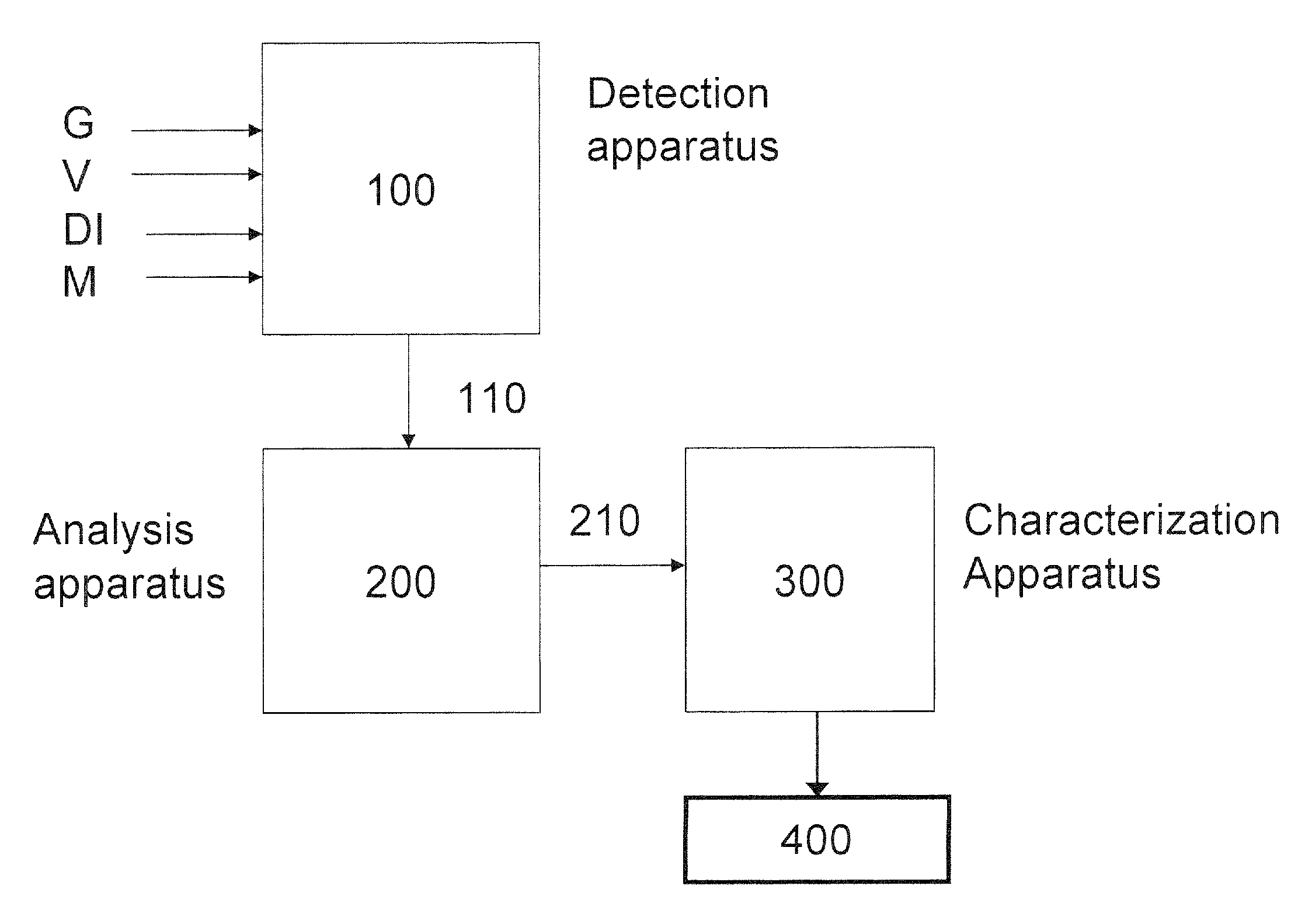
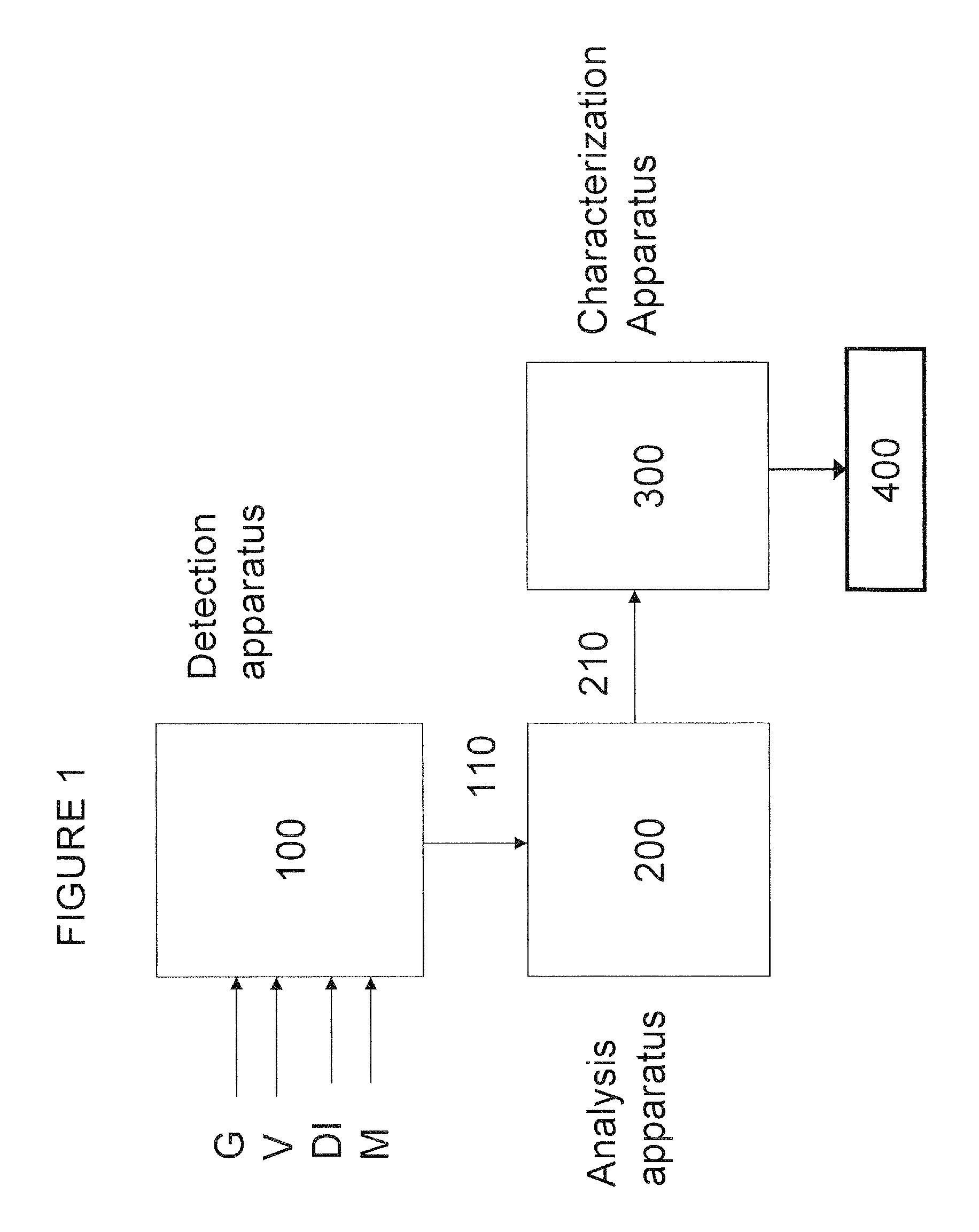
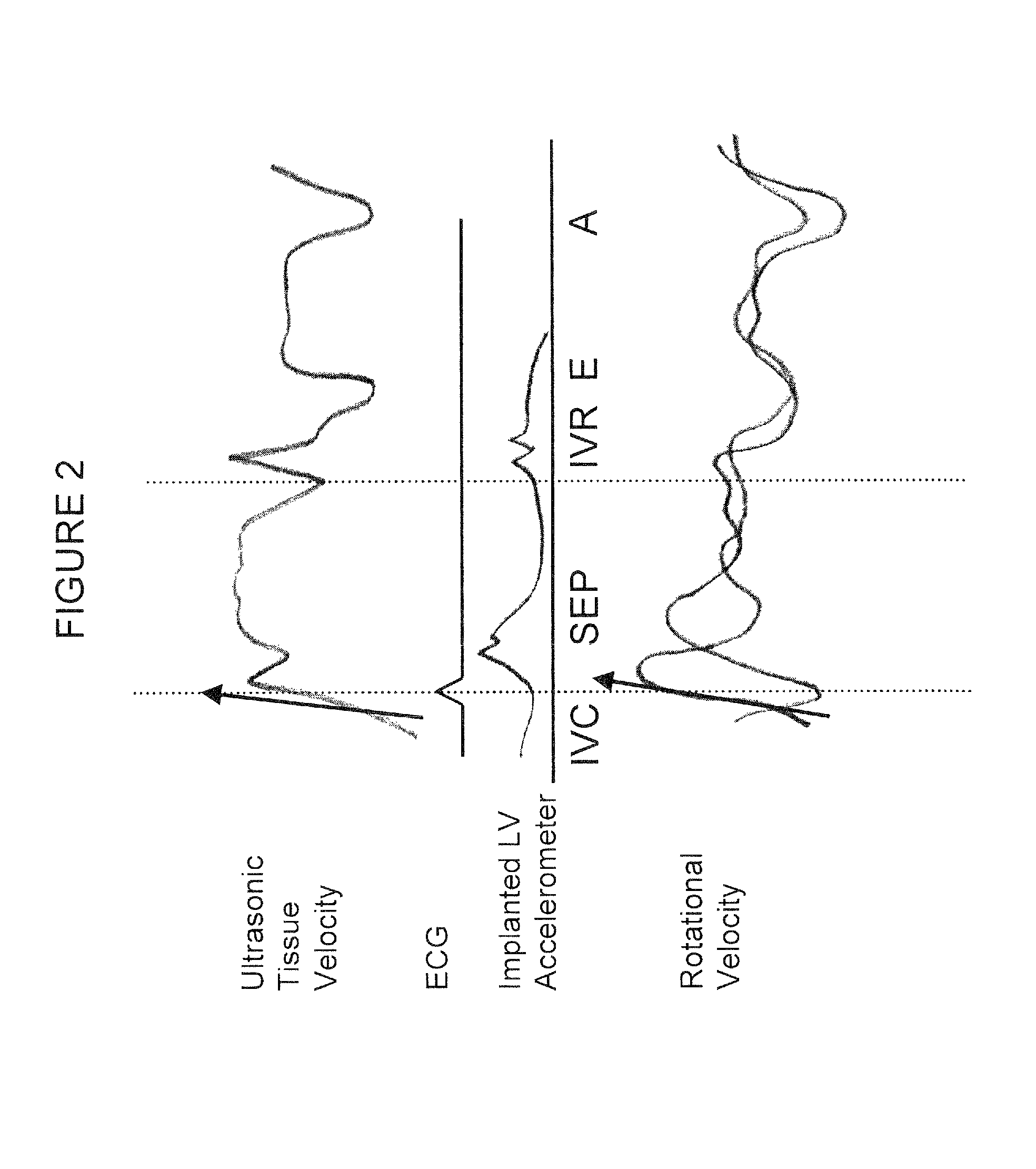
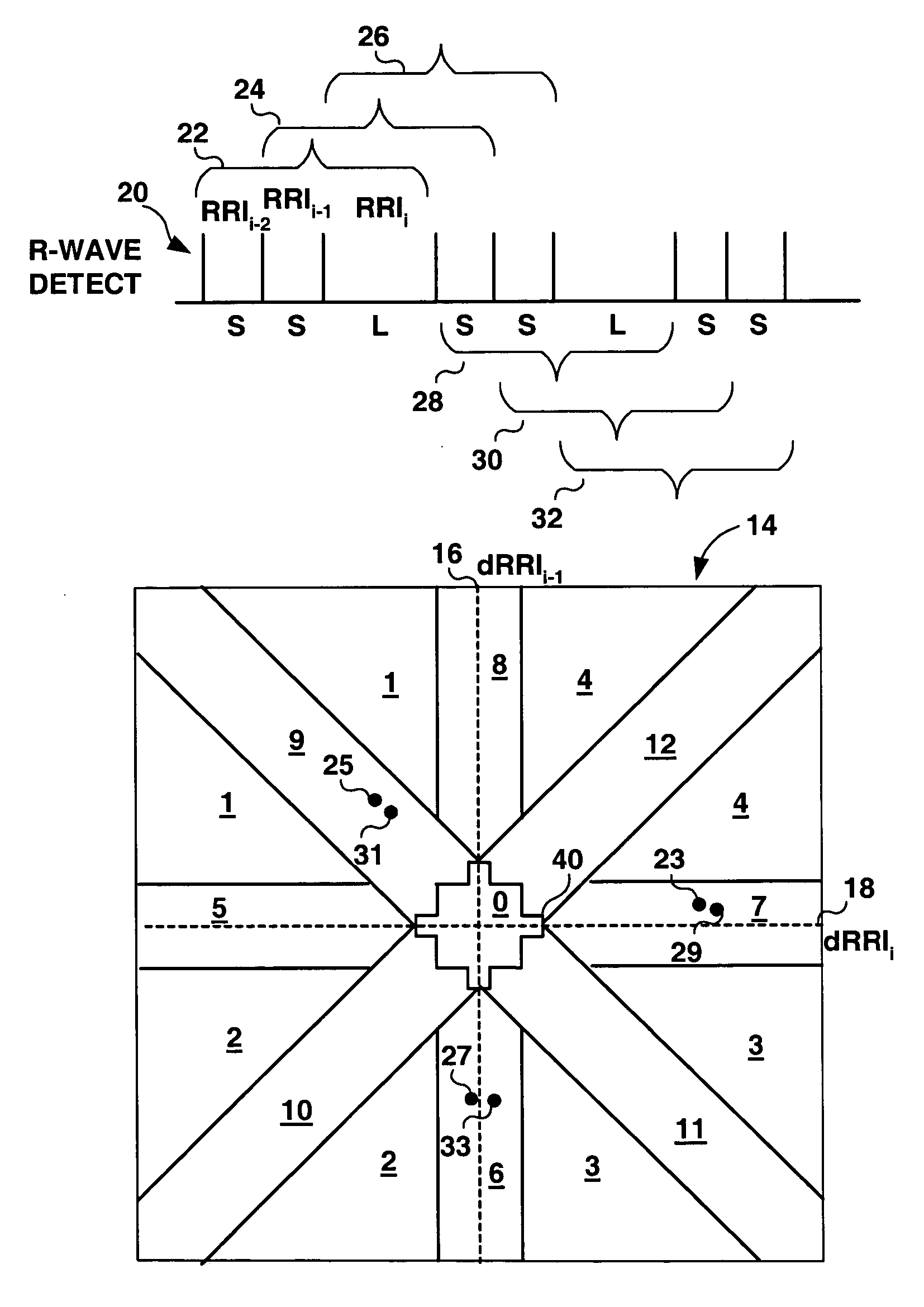
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Atrial arrhythmias" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
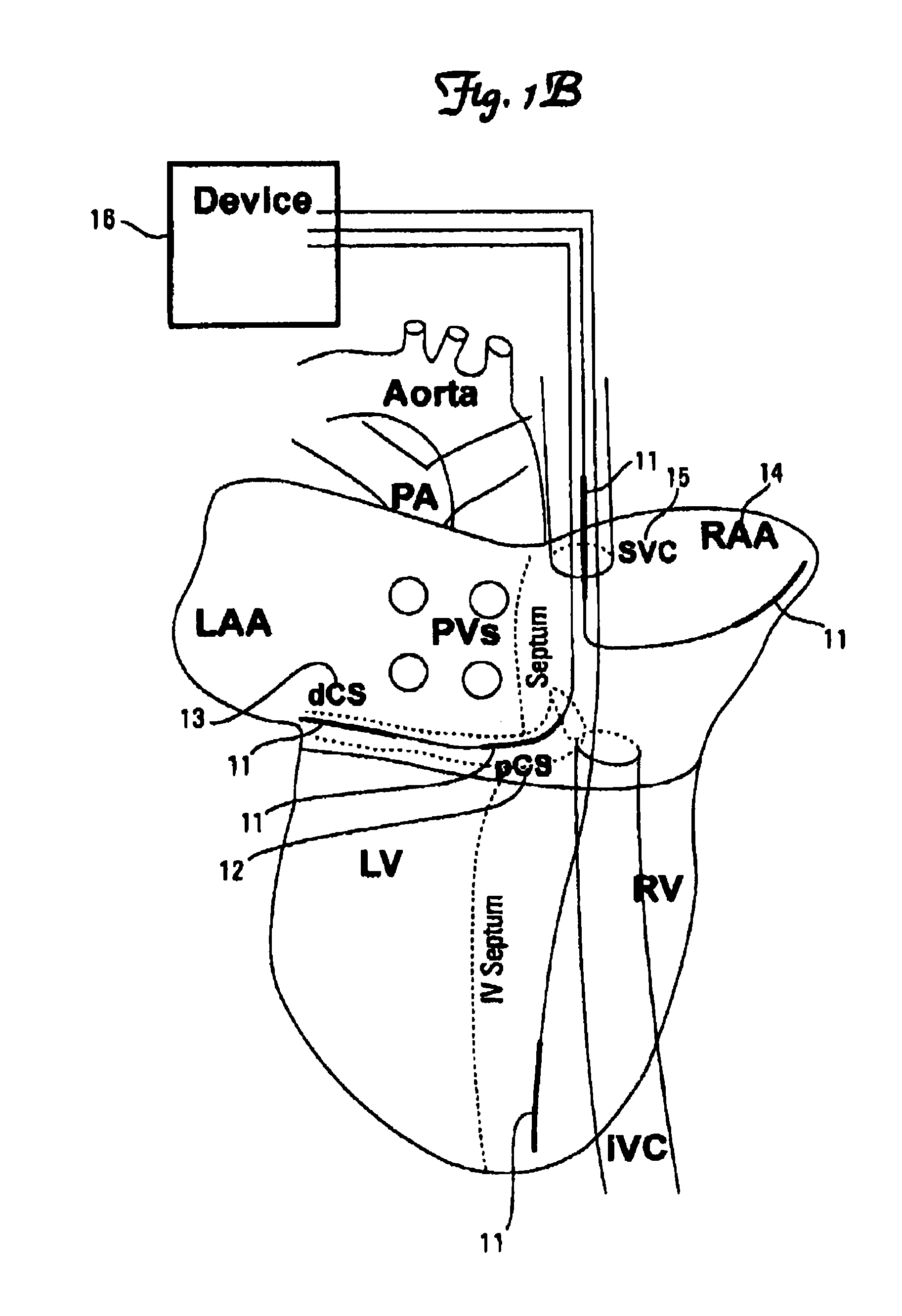
Arrhythmias are classified by their location in the heart and by their speed or rhythm. An atrial arrhythmia is an abnormality that occurs in one of the two upper chambers of the heart, the left or right atrium. Arrhythmias are associated with aging and typically happen more frequently during middle age.
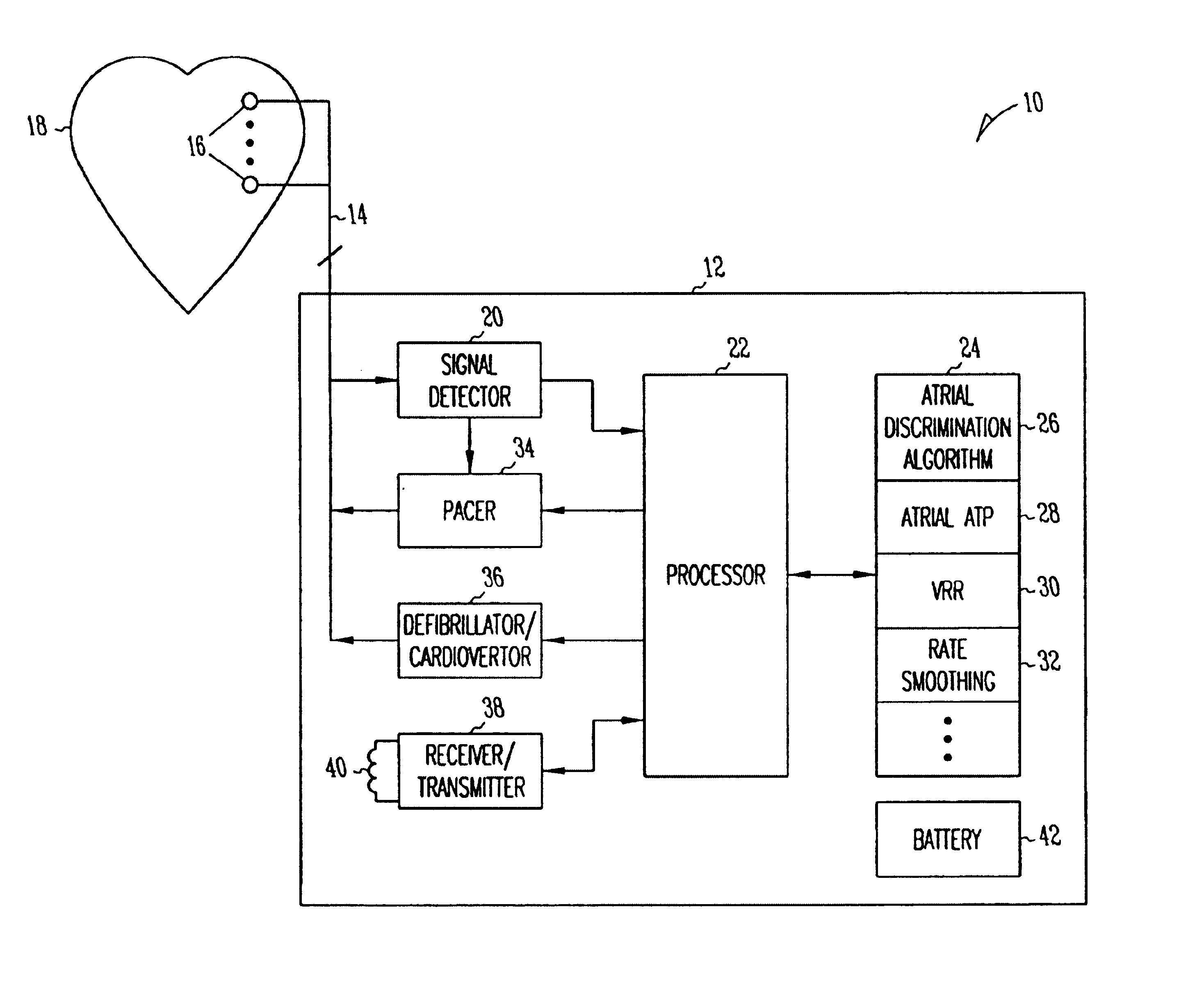
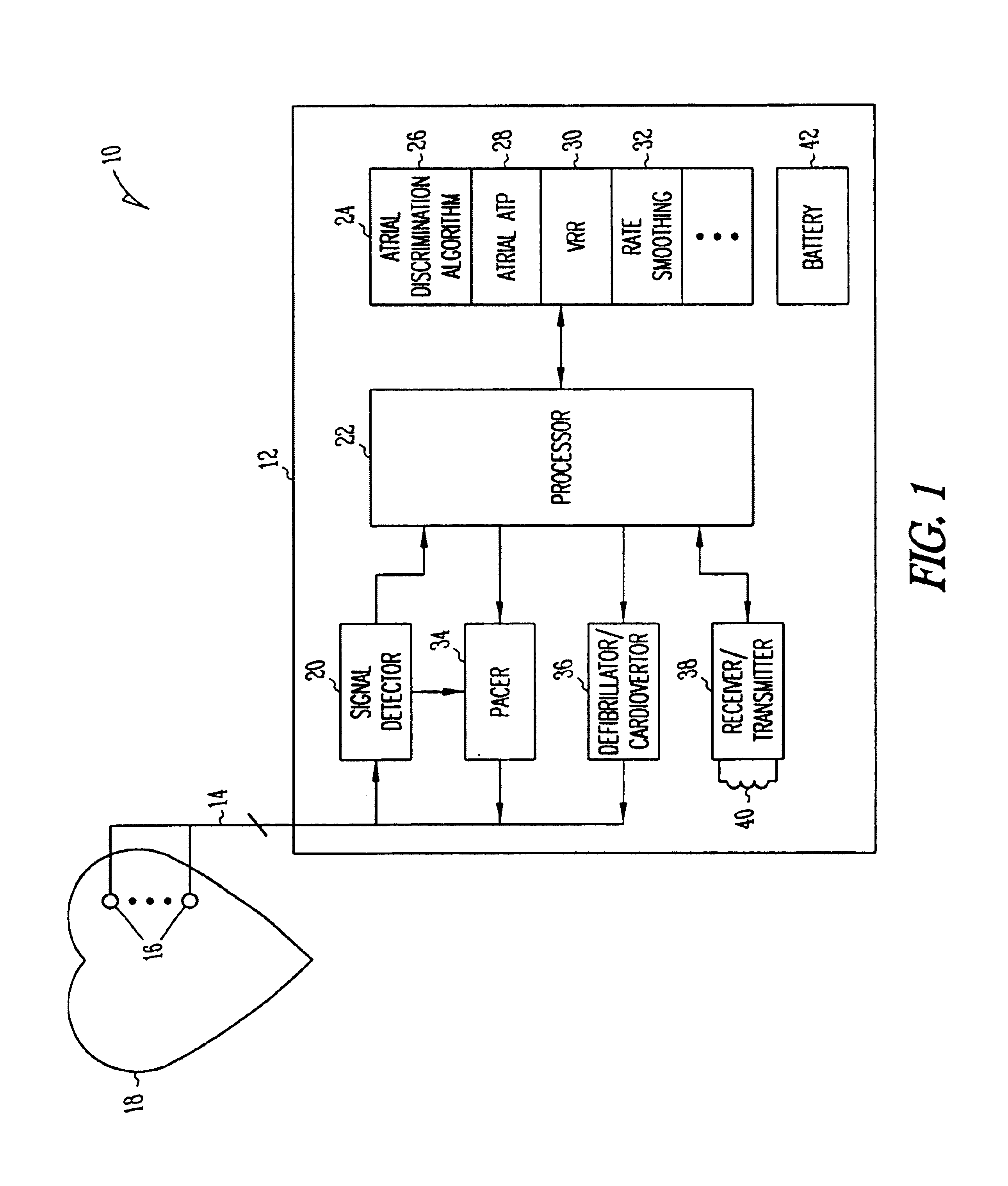
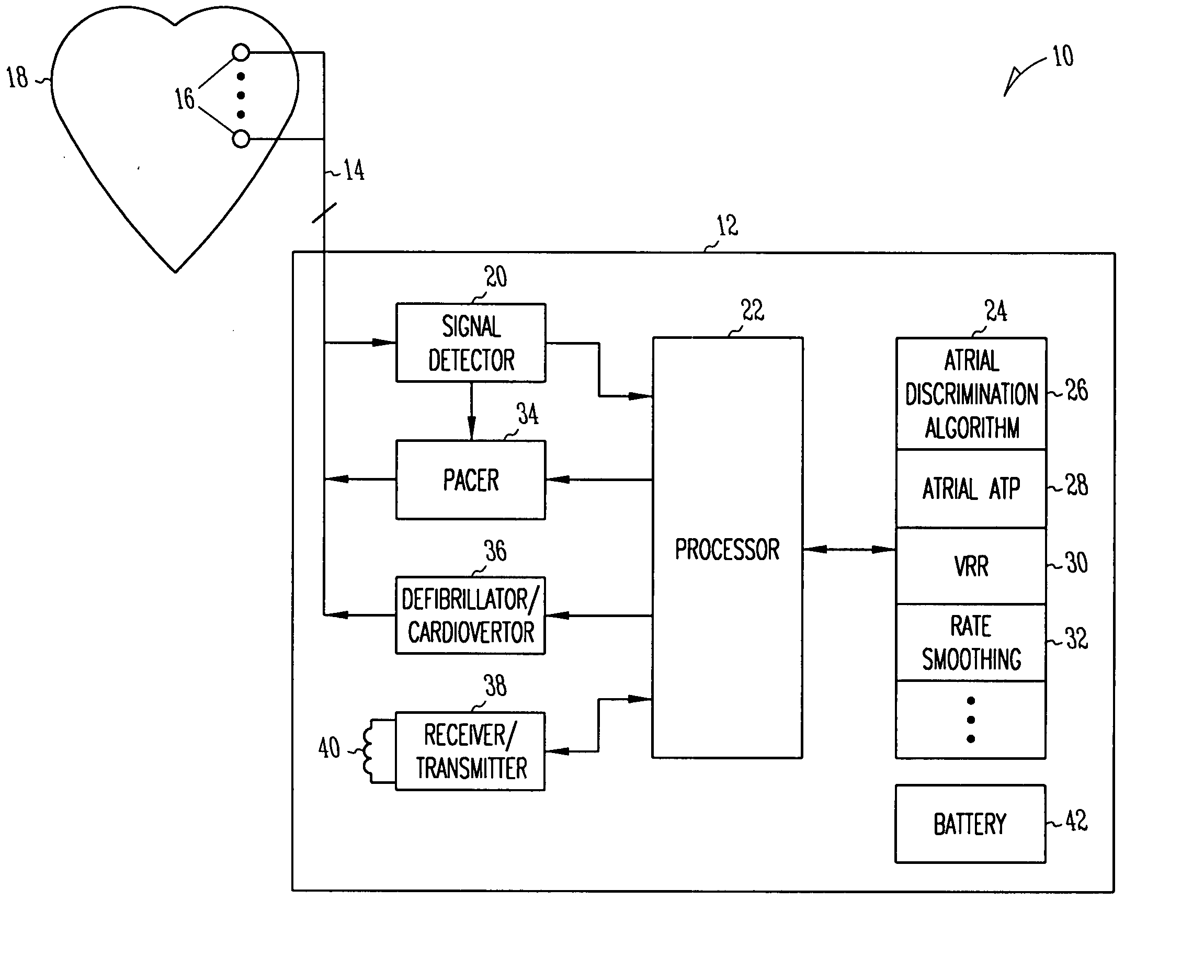
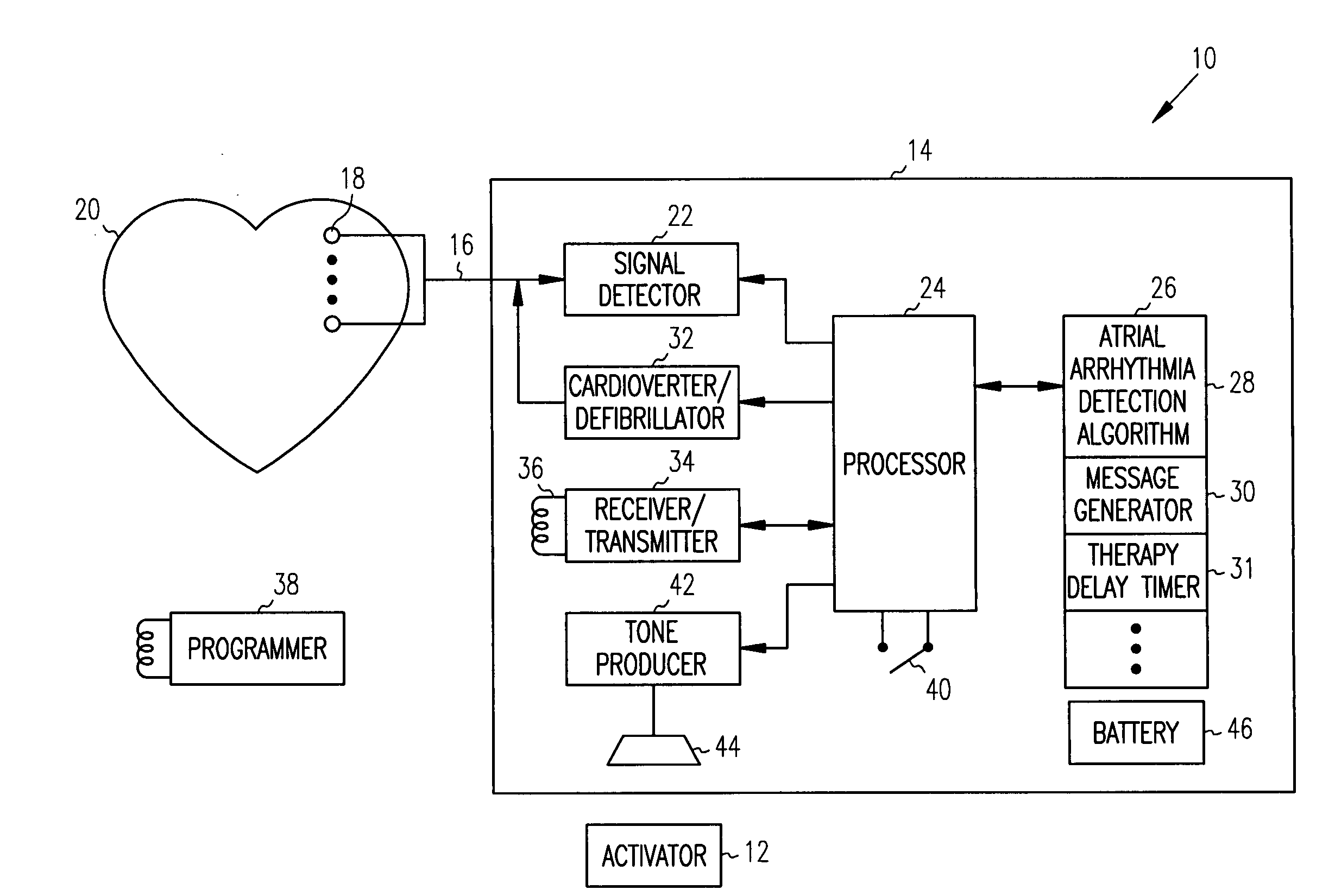
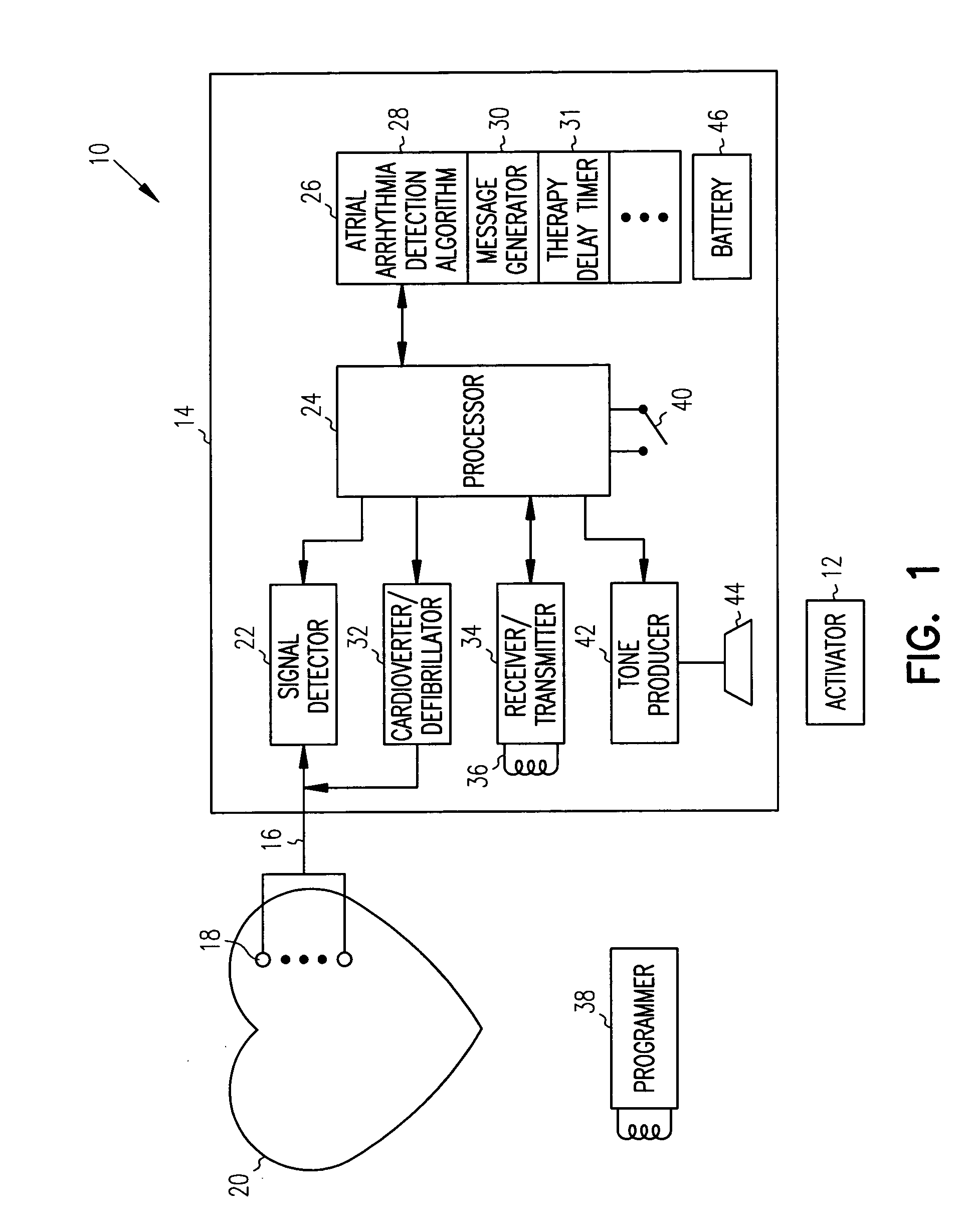
Use of accelerometer signal to augment ventricular arrhythmia detection
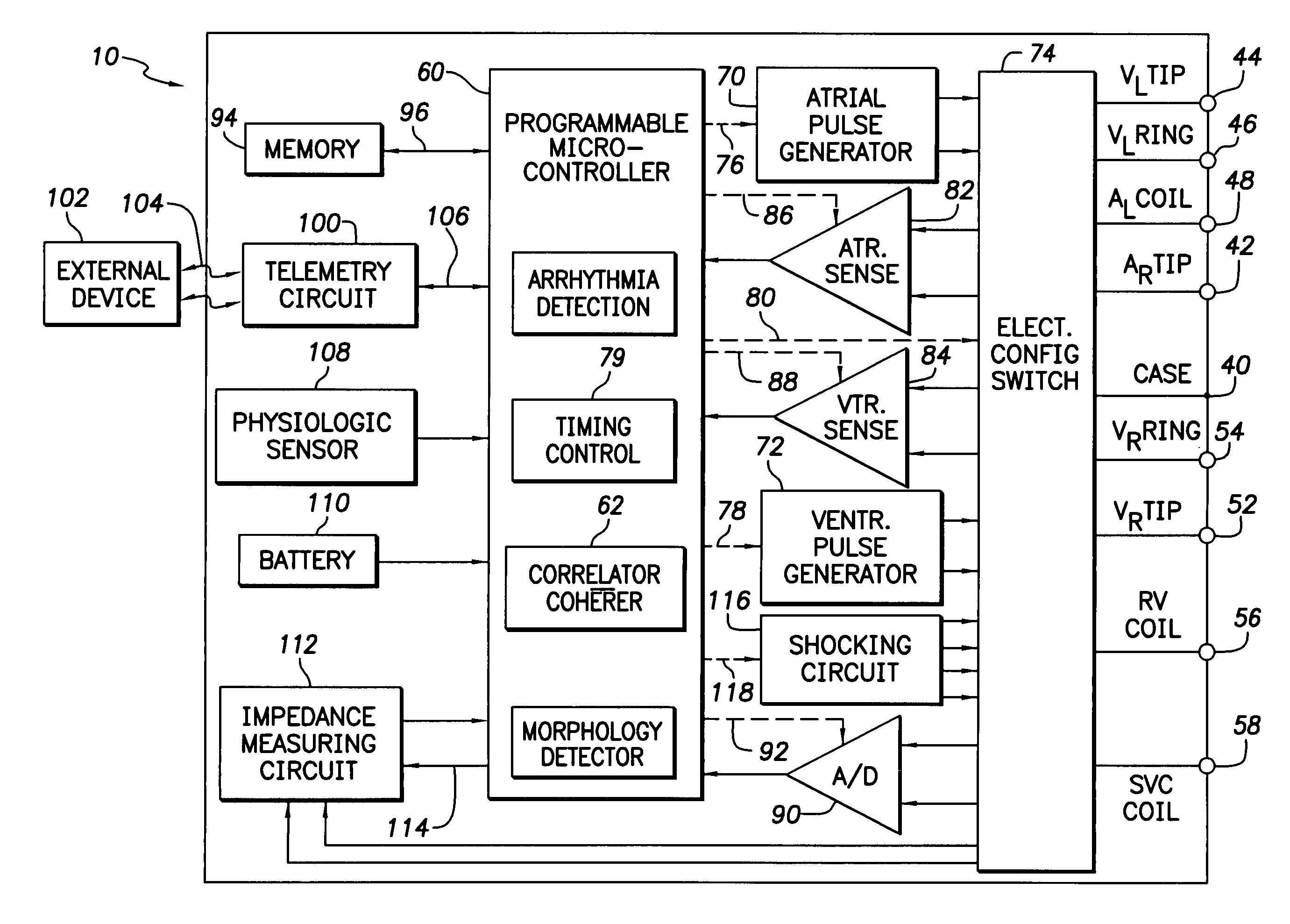
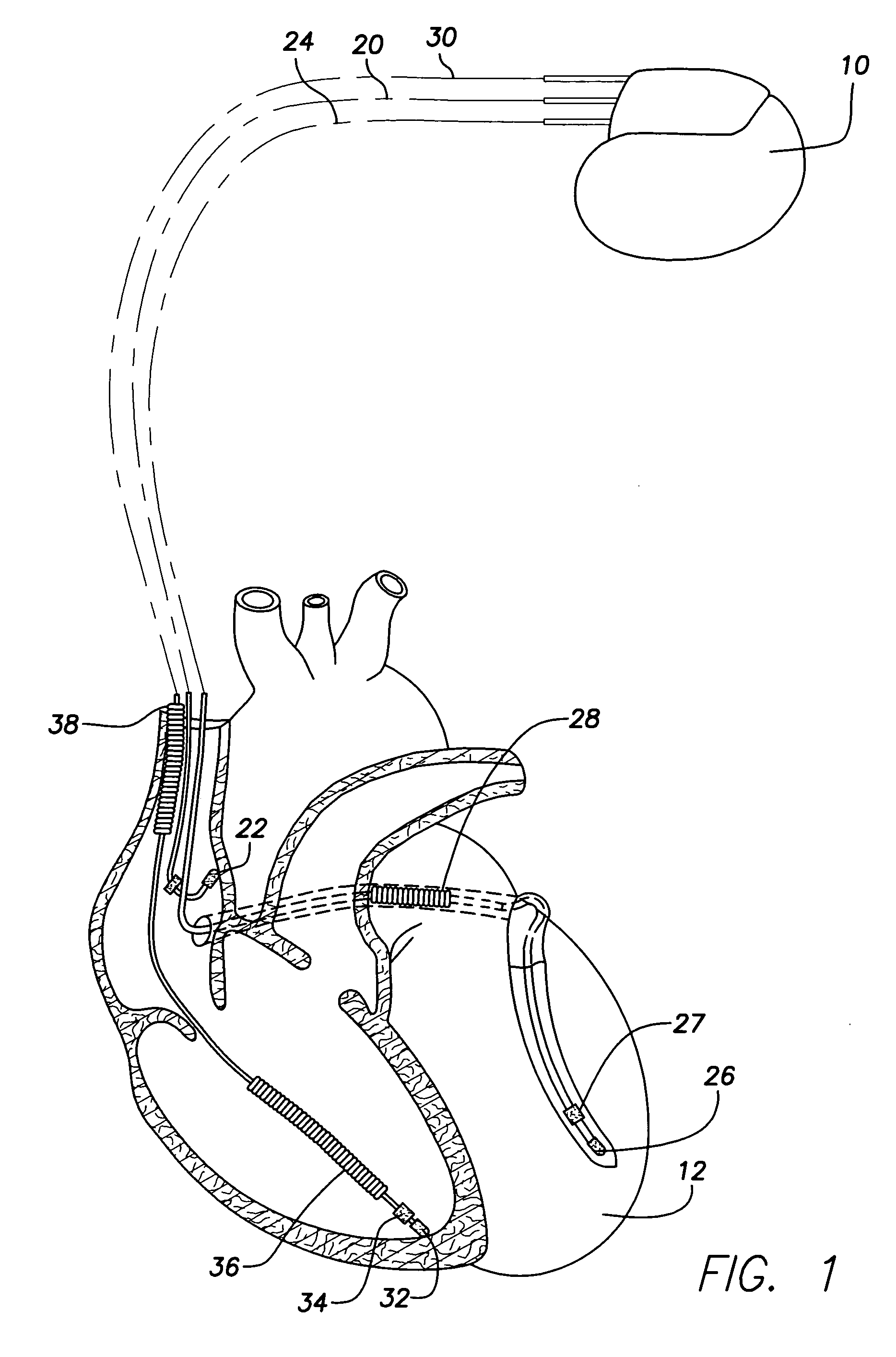
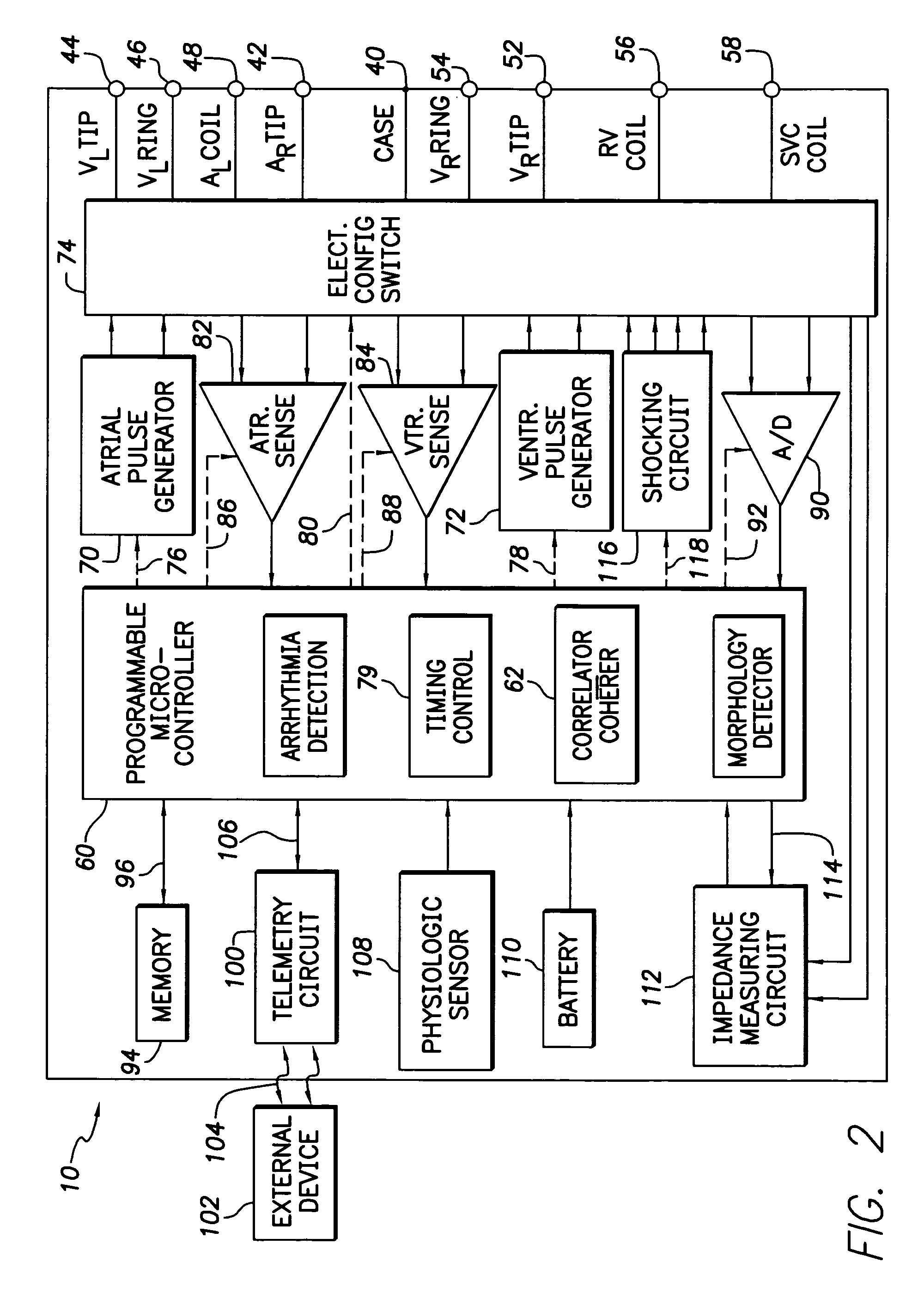
ActiveUS7130681B2Reliable detectionReliable classificationPerson identificationHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular dysrhythmia
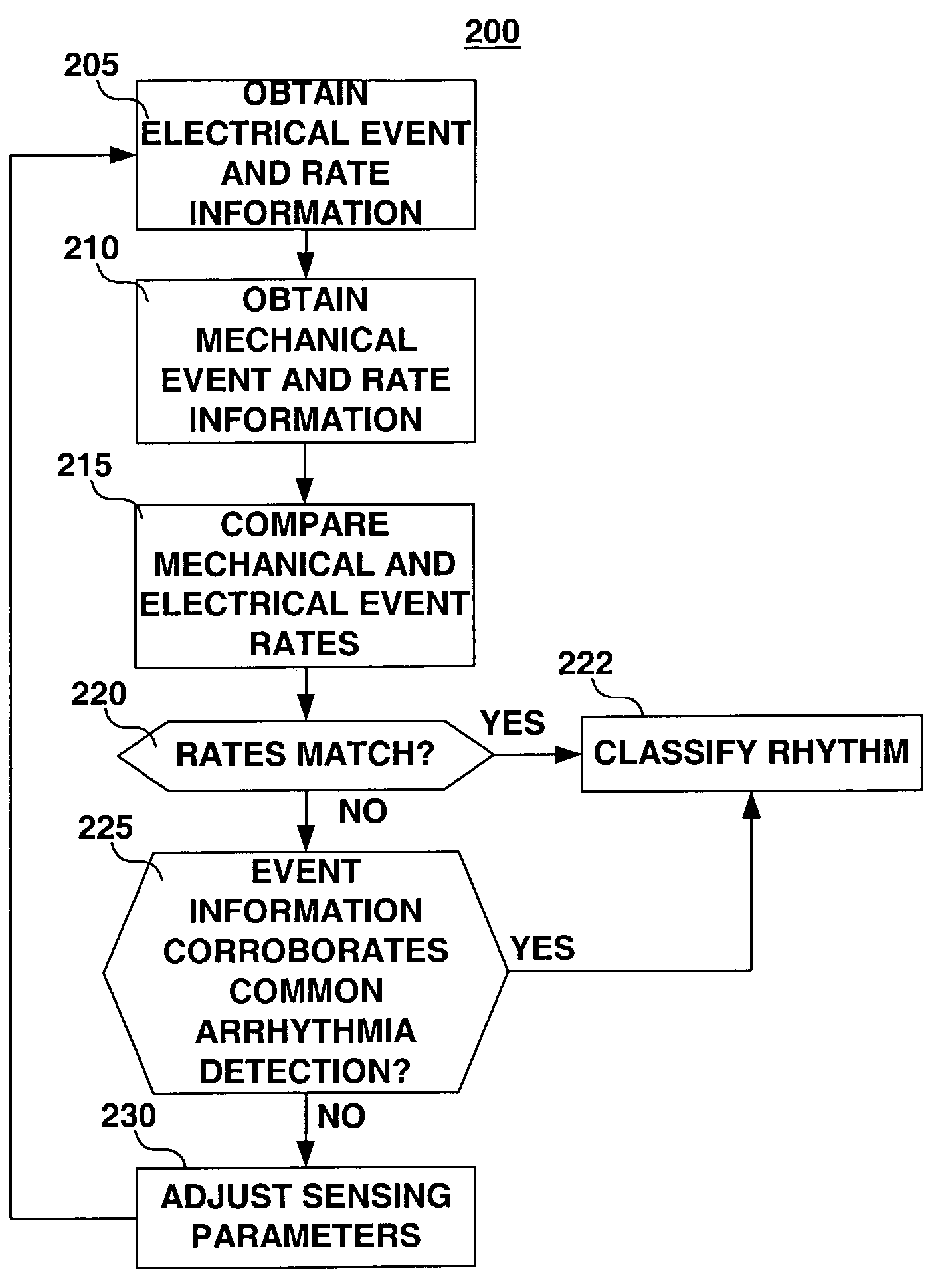
A system and method for detecting and discriminating atrial arrhythmias based on mechanical signals of cardiac wall motion and electrical signals of cardiac depolarizations. A mechanical event rate determined from sensed mechanical events is used to corroborate an electrical event rate determined from sensed EGM or ECG signals to classify the heart rhythm. If the event rates are not correlated, other parameterized data from the mechanical signal and electrical signal are evaluated to detect evidence of an arrhythmia. If electrical and mechanical event data do not corroborate a common arrhythmia condition, electrical and mechanical sensing parameters may be adjusted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
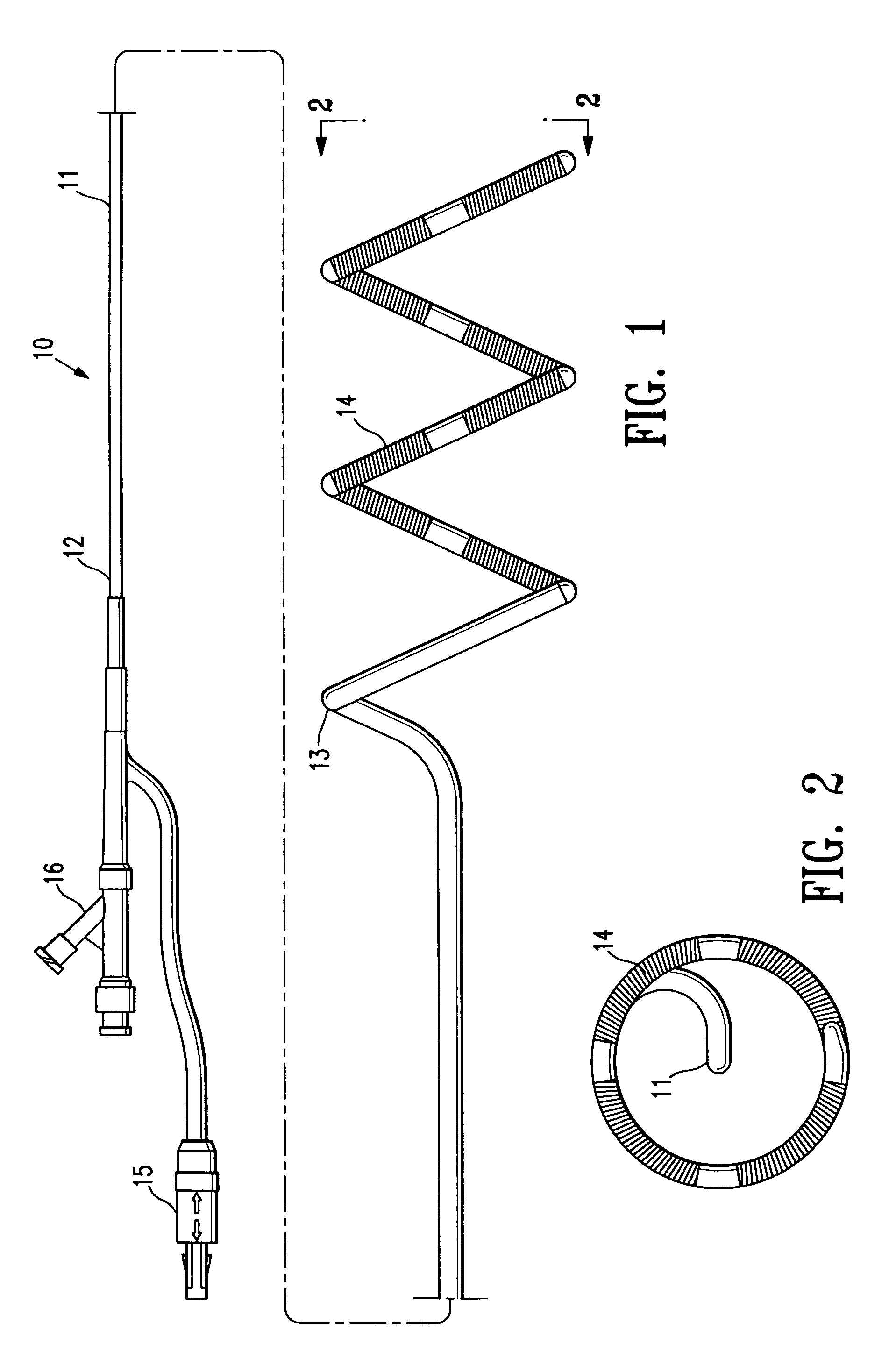
Helically shaped electrophysiology catheter
InactiveUS6972016B2Reduce configurationEasy to deployElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
An electrophysiology (EP) device suitable for ablating tissue within a patient's body lumen. The EP device of the invention generally comprises an elongated shaft having a distal shaft section with a helical shape and at least one electrode on an exterior portion thereof. One aspect of the invention comprises a method of performing a medical procedure, such as treating a patient for atrial arrhythmia, by forming a lesion using an EP device embodying features of the invention.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
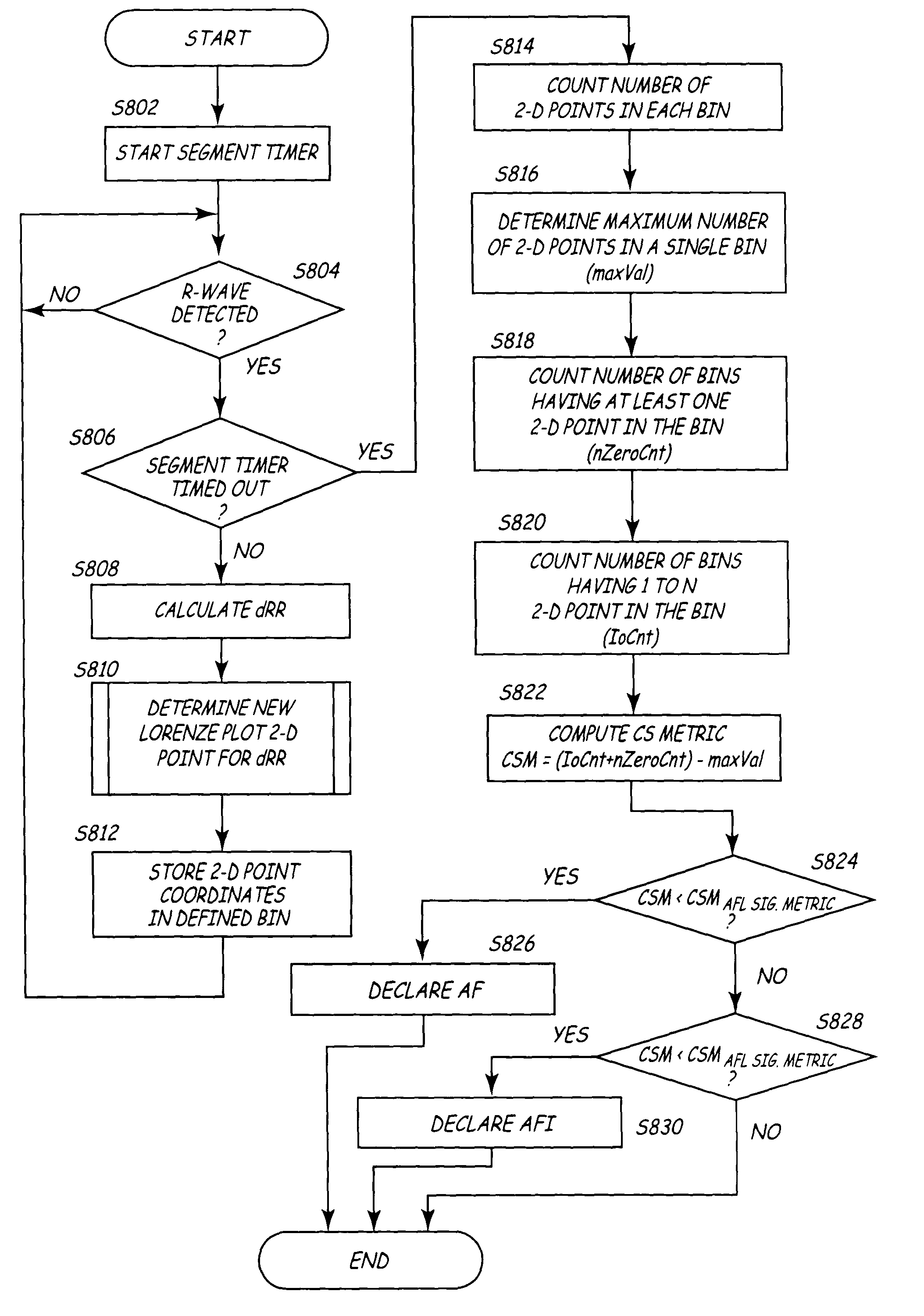
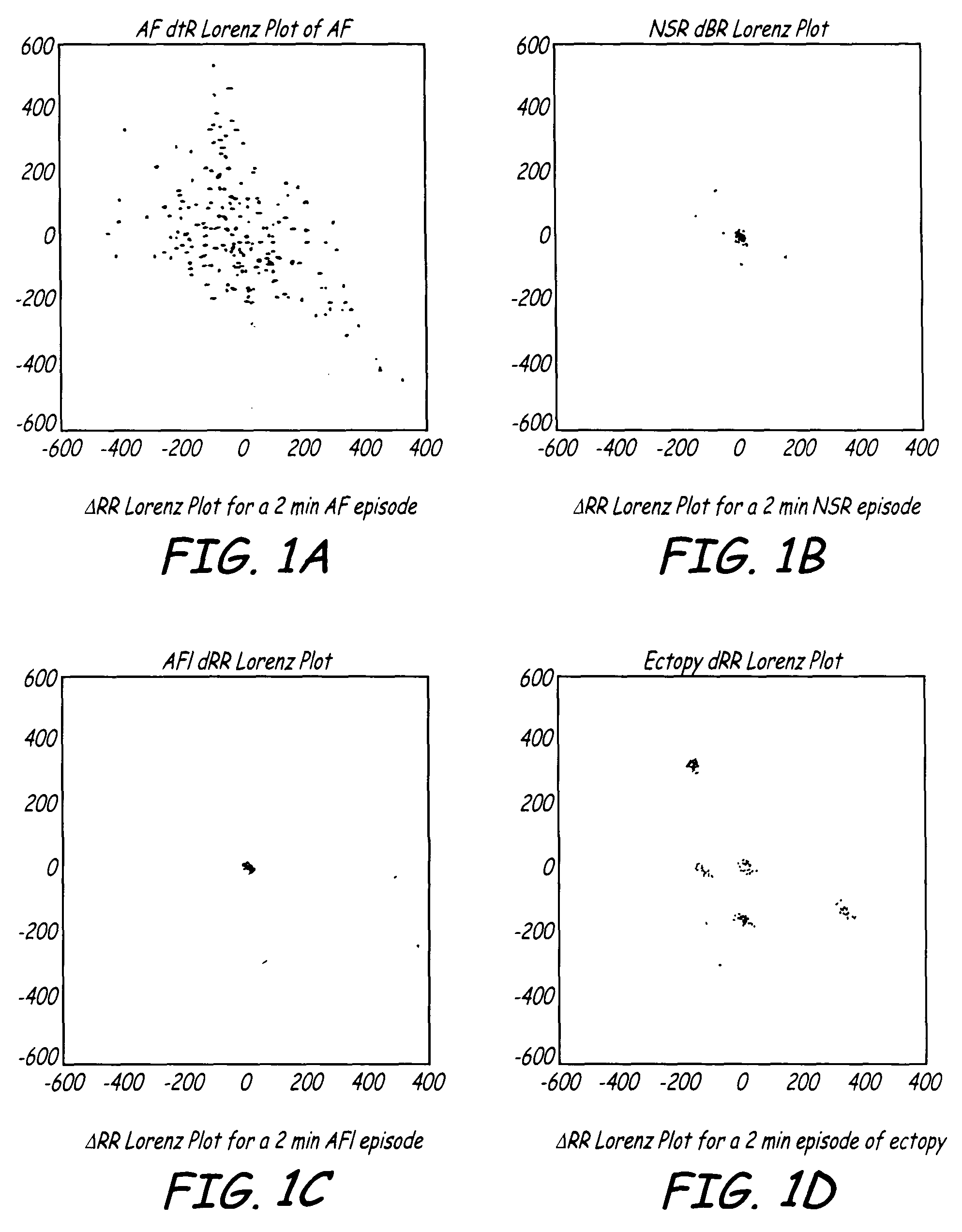
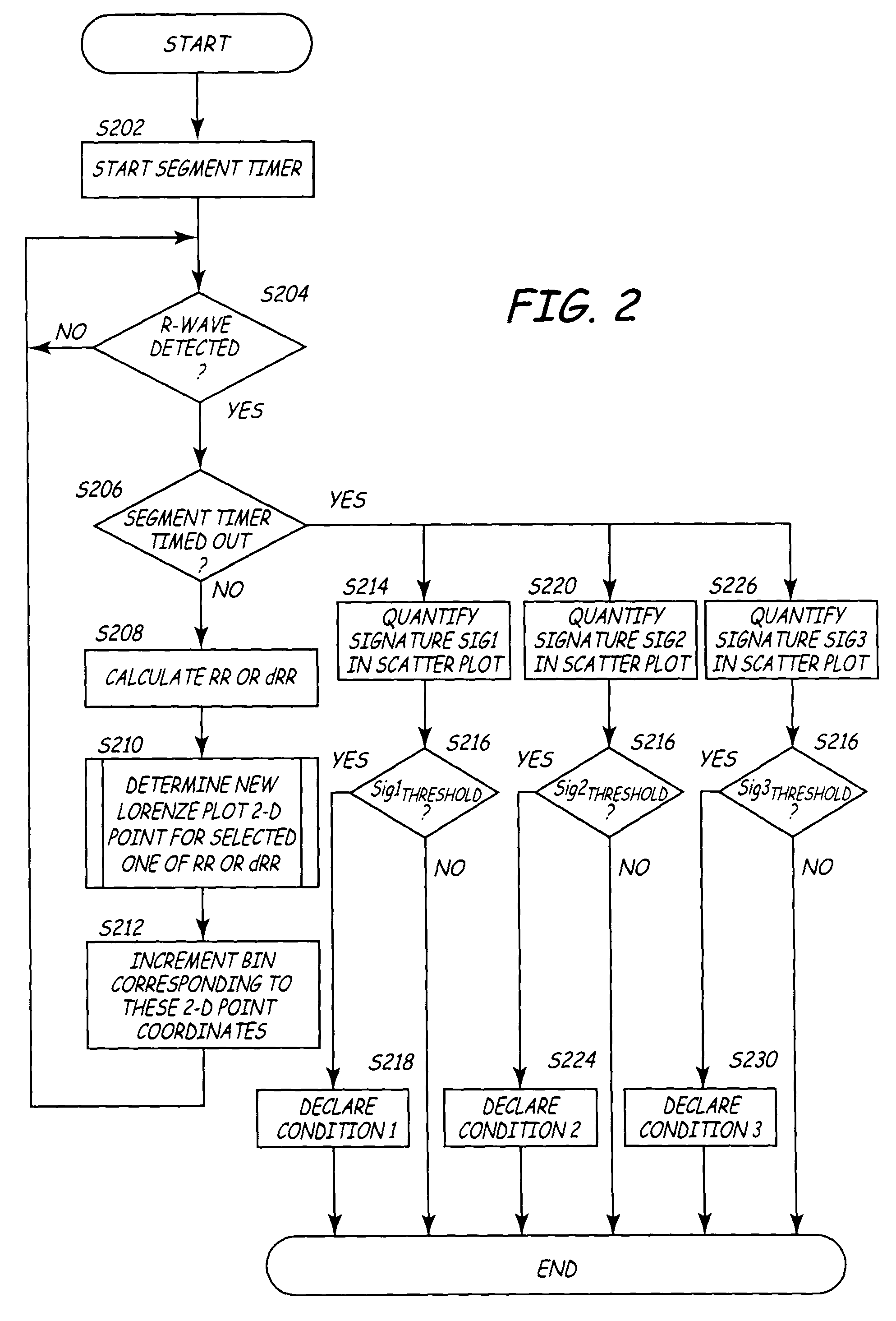
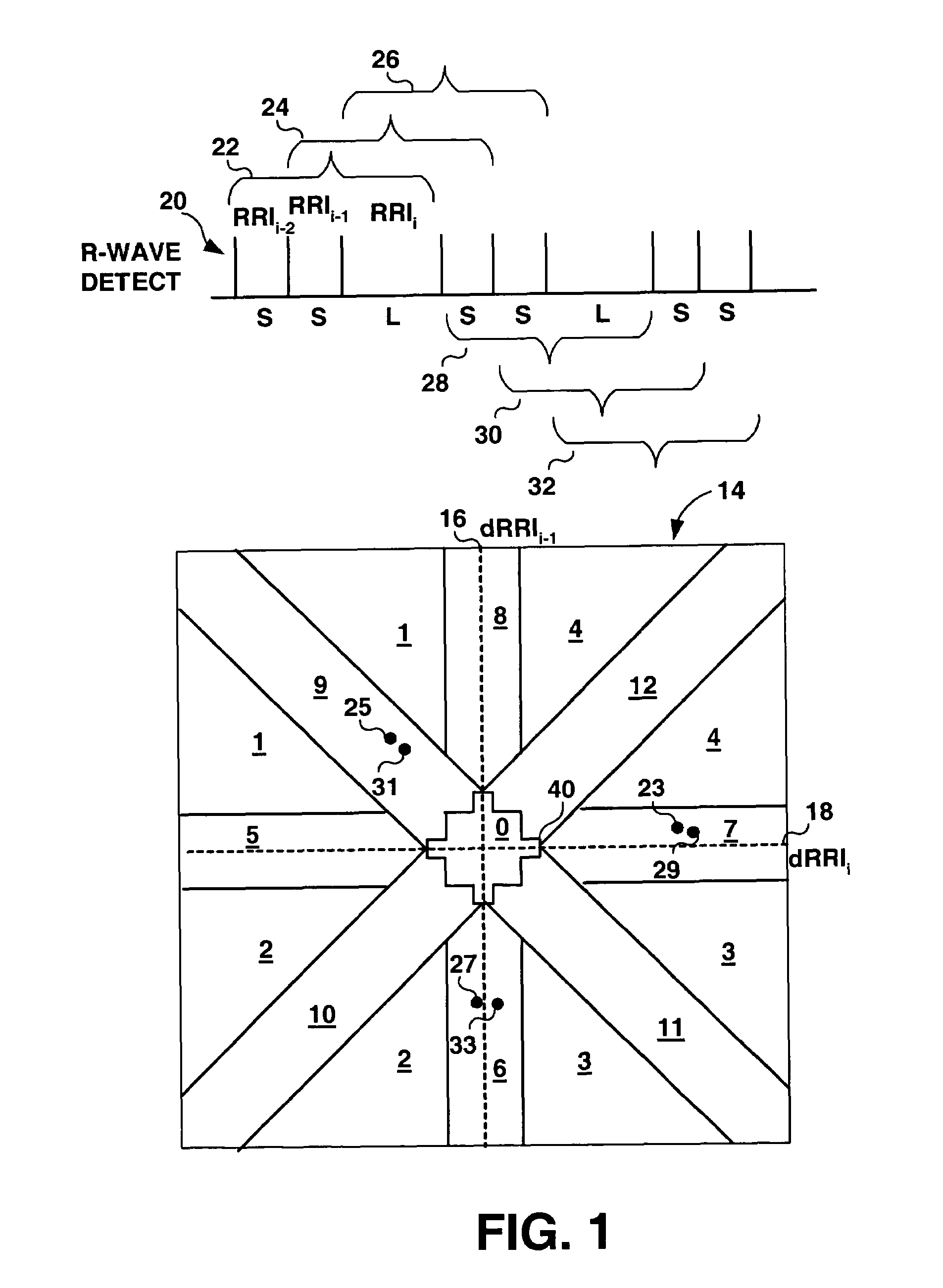
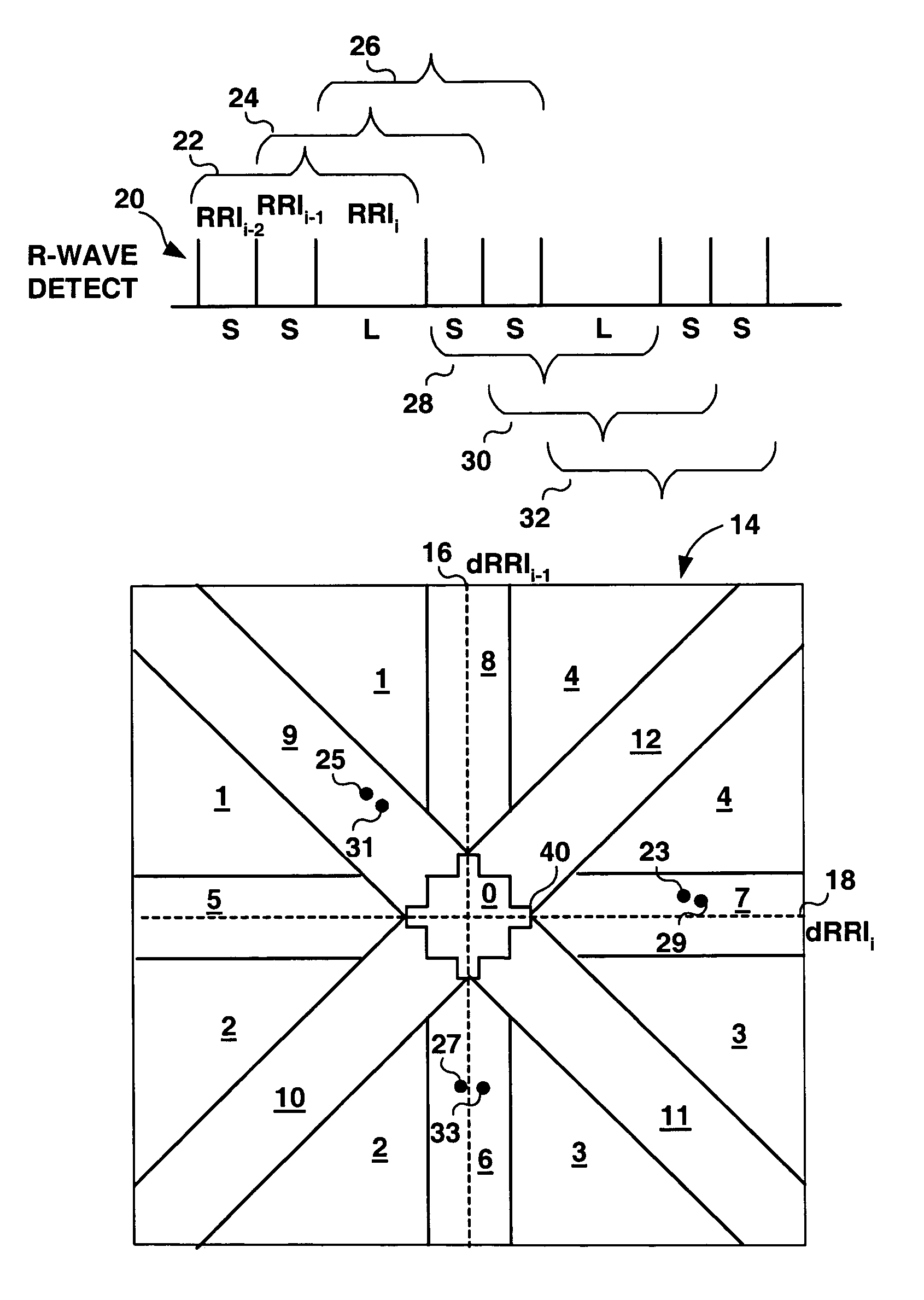
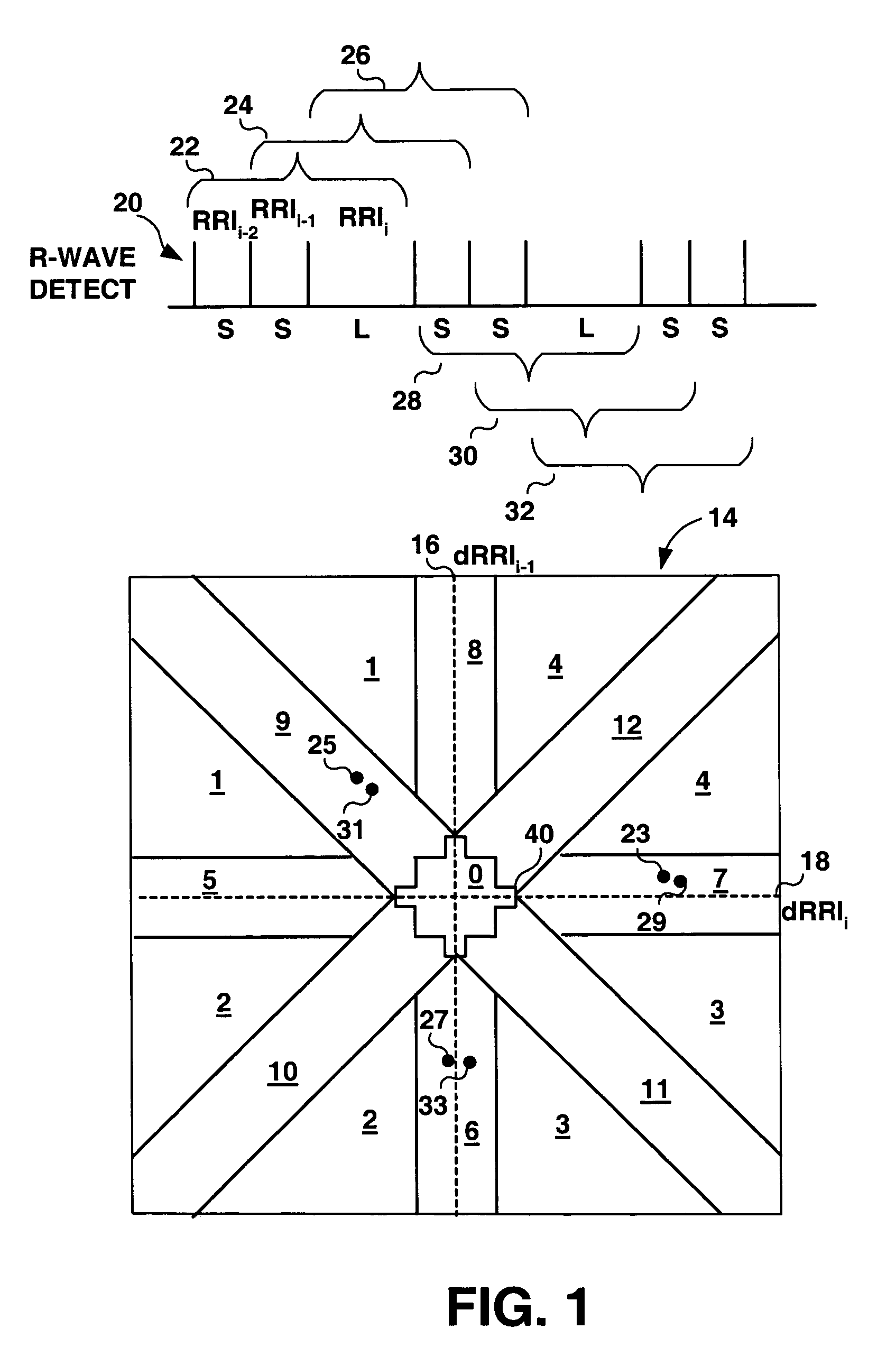
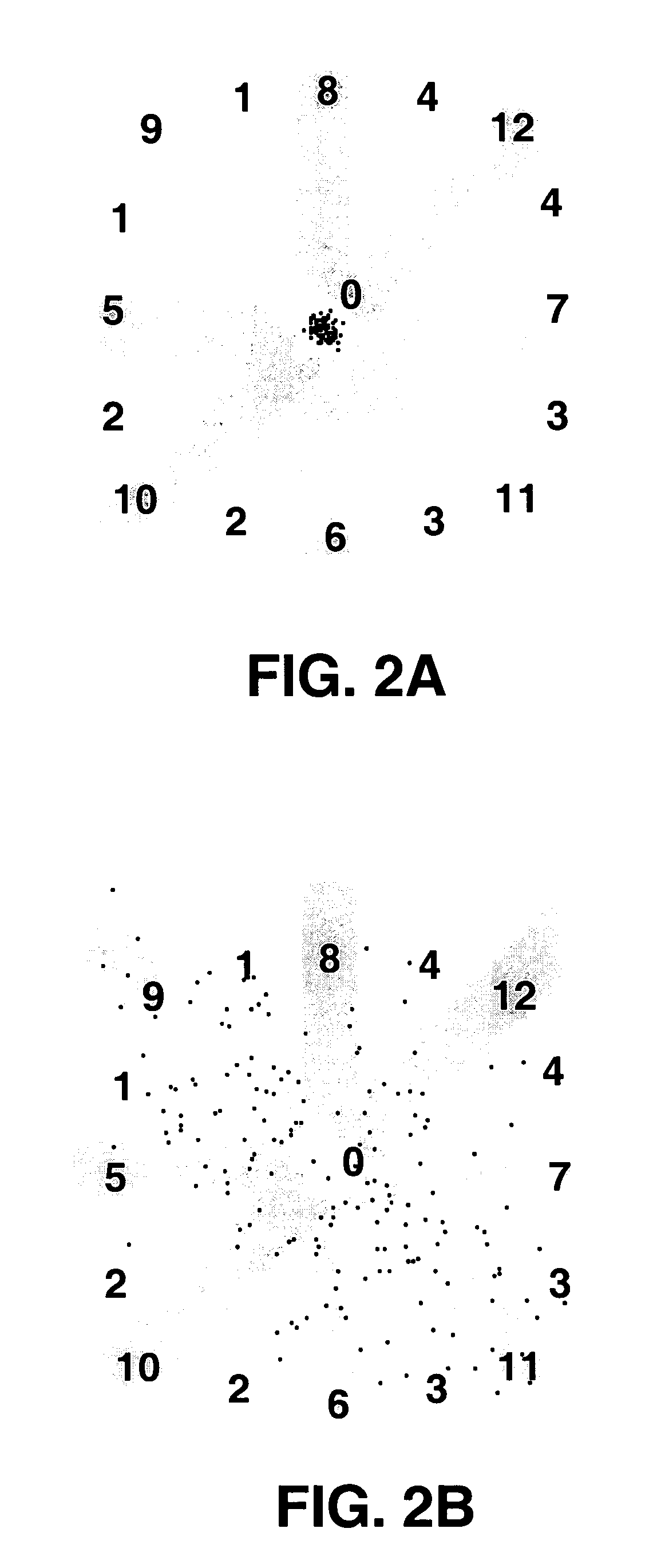
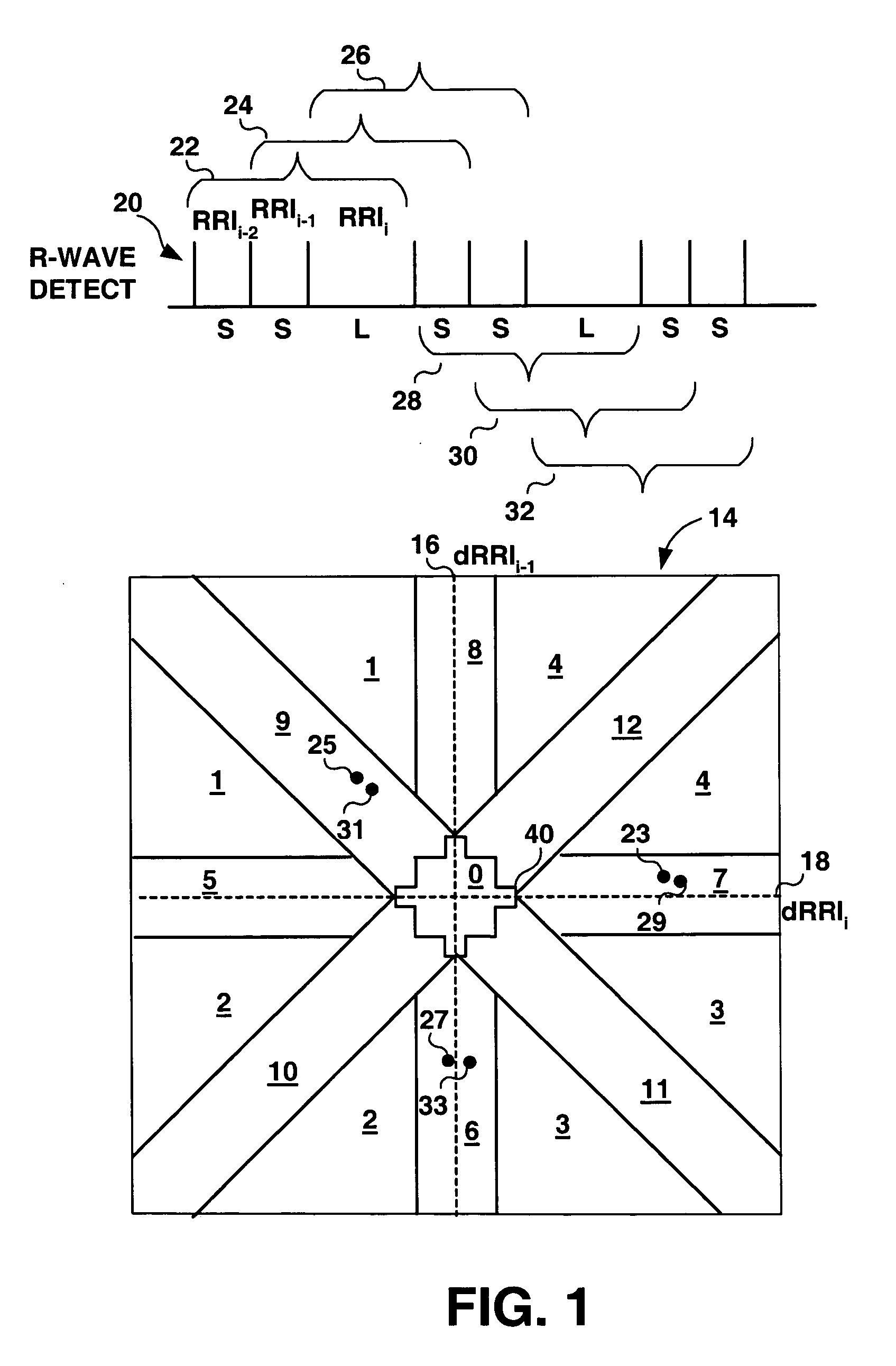
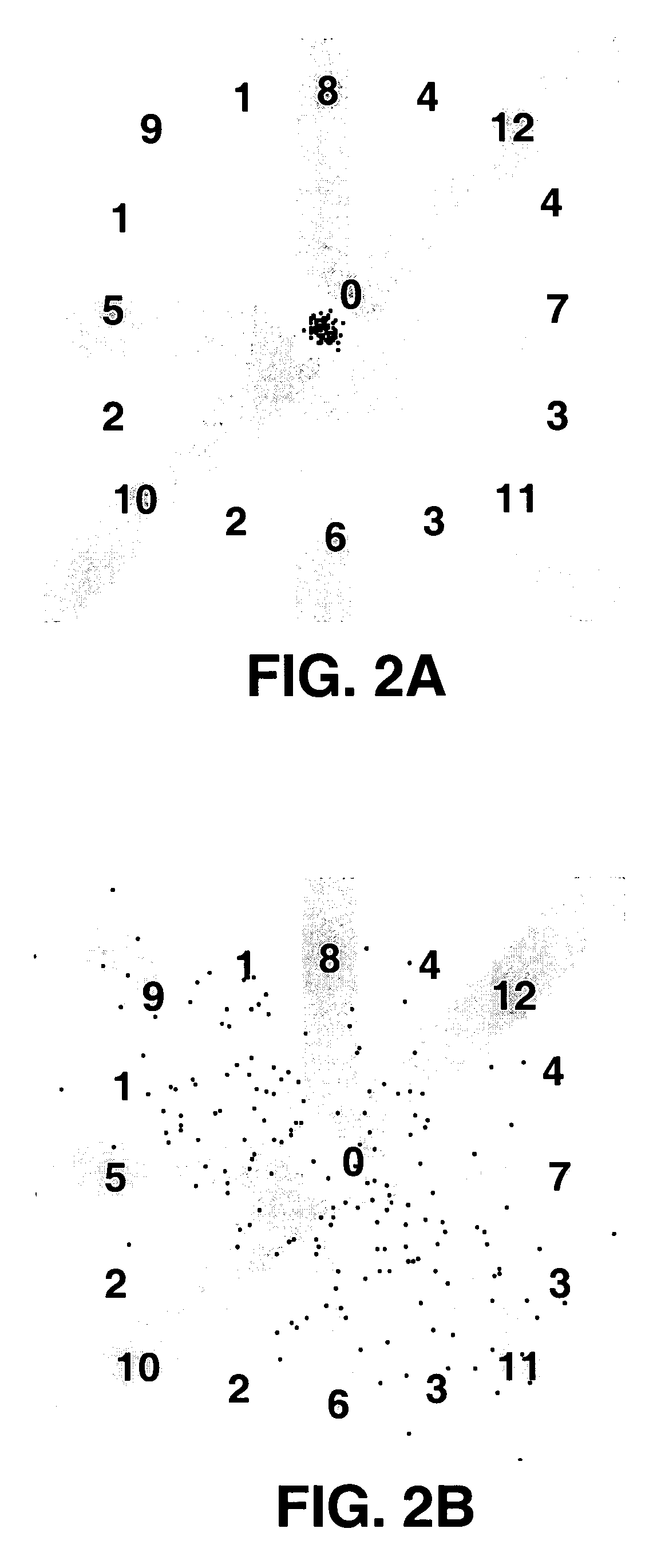
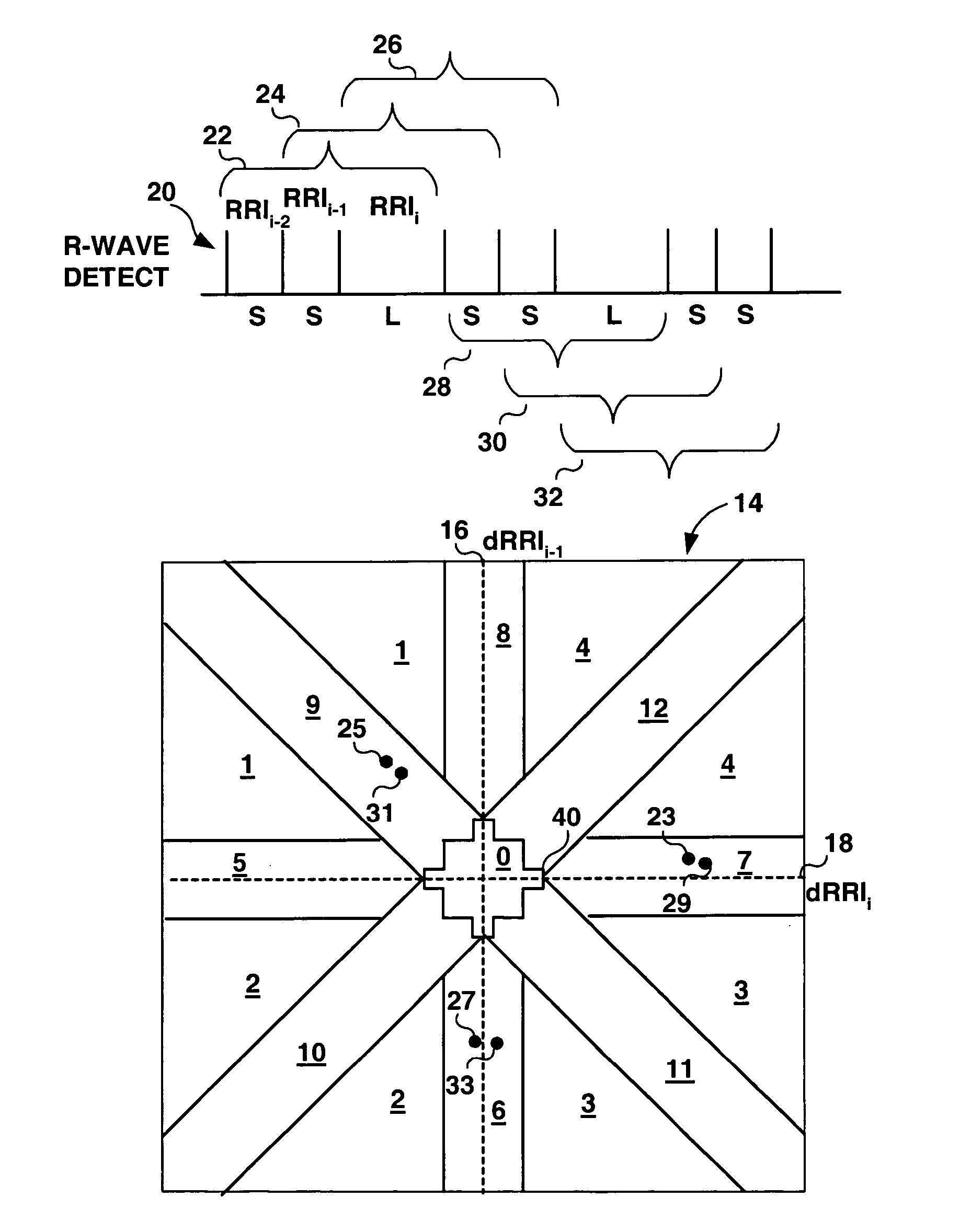
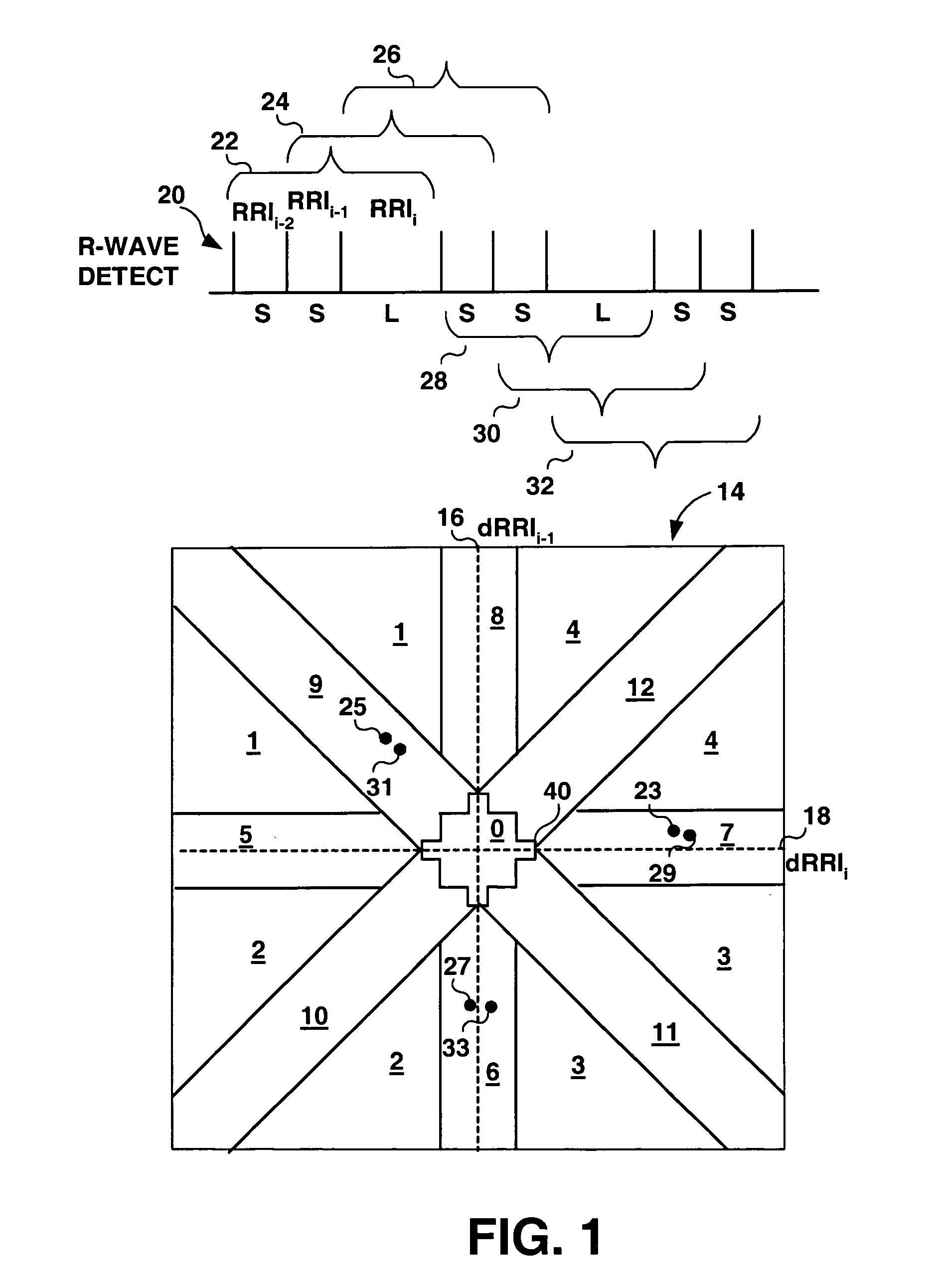
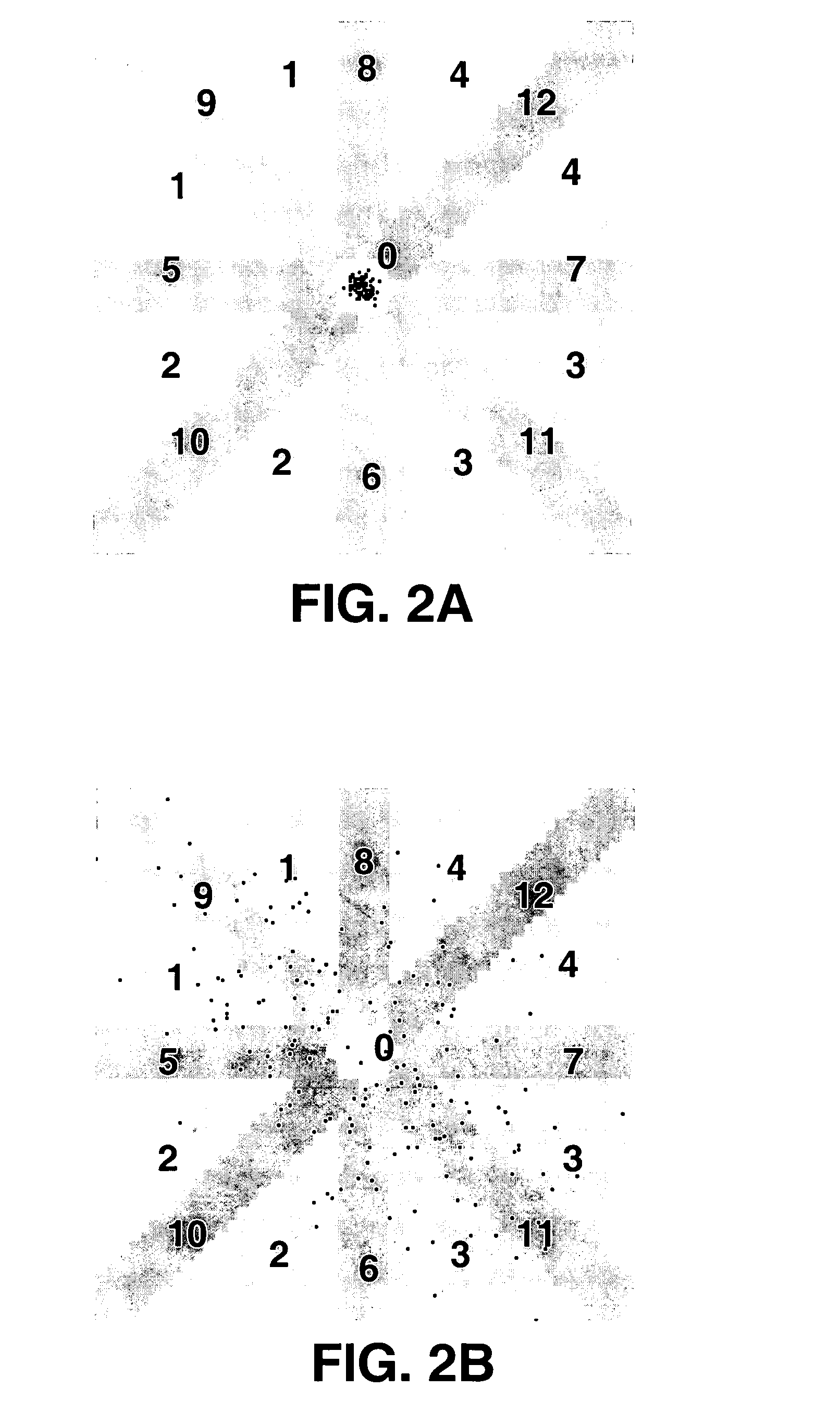
Algorithms for detecting atrial arrhythmias from discriminatory signatures of ventricular cycle lengths
ActiveUS7031765B2Enhances and improves detectionElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsCardiac arrhythmiaComputer science
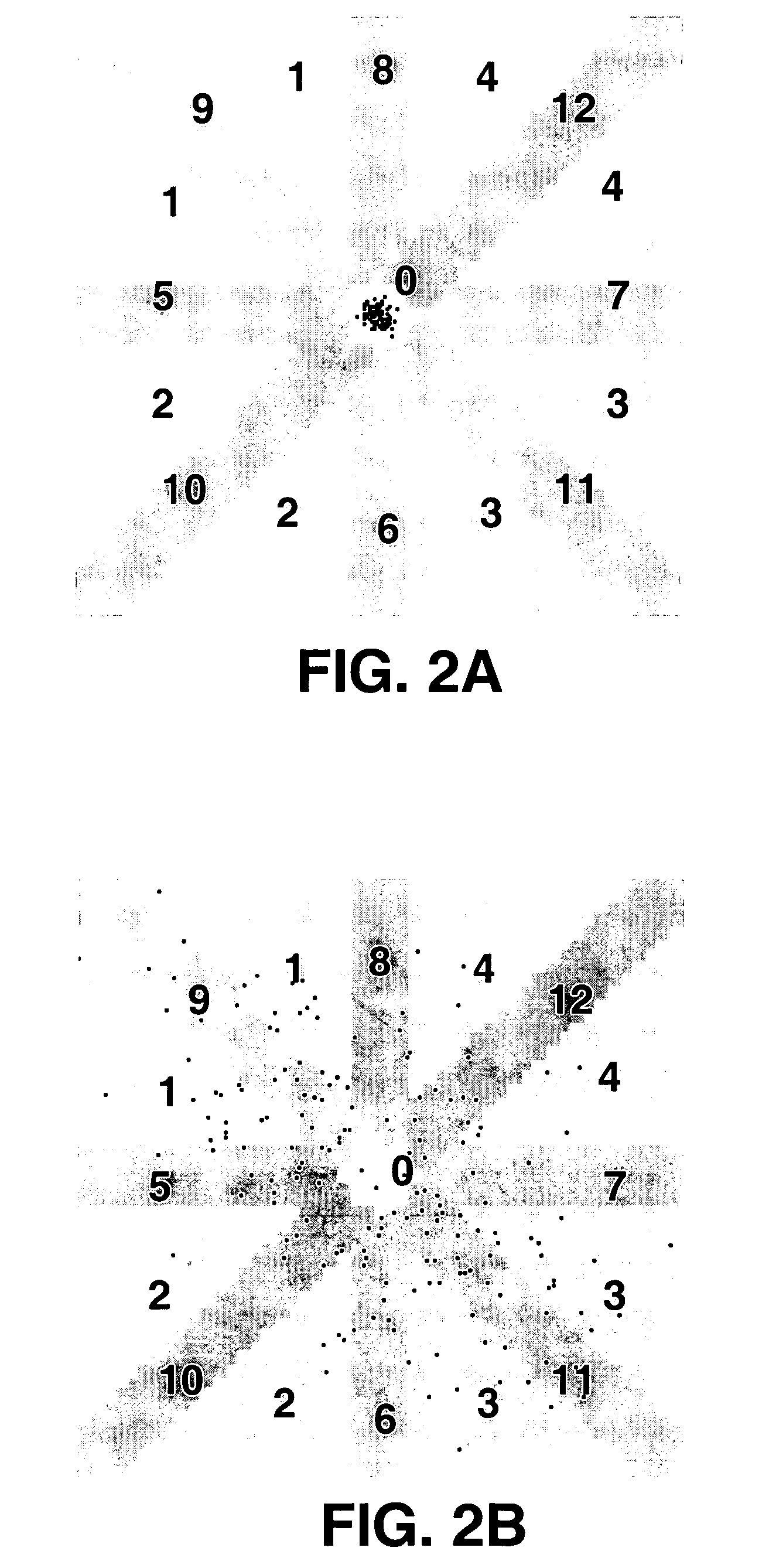
Detection of arrhythmias is facilitated using irregularity of ventricular beats measured by delta-RR (ΔRR) intervals that exhibit discriminatory signatures when plotted in a Lorenz scatter-plot. An “AF signature metric” is established characteristic of episodes of AF that exhibit highly scattered (sparse) distributions or formations of 2-D data points. An “AFL signature metric” is established characteristic of episodes of AFL that exhibit a highly concentrated (clustered) distribution or formation of 2-D data points. A set of heart beat interval data is quantified to generate highly scattered (sparse) formations as a first discrimination metric and highly concentrated (clustered) distributions or formations as a second discrimination metric. The first discrimination metric is compared to the AF signature metric, and / or the second discrimination metric is compared to the AFL signature metric. AF or HFL is declared if the first discrimination metric satisfies either one of the AF signature metric.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
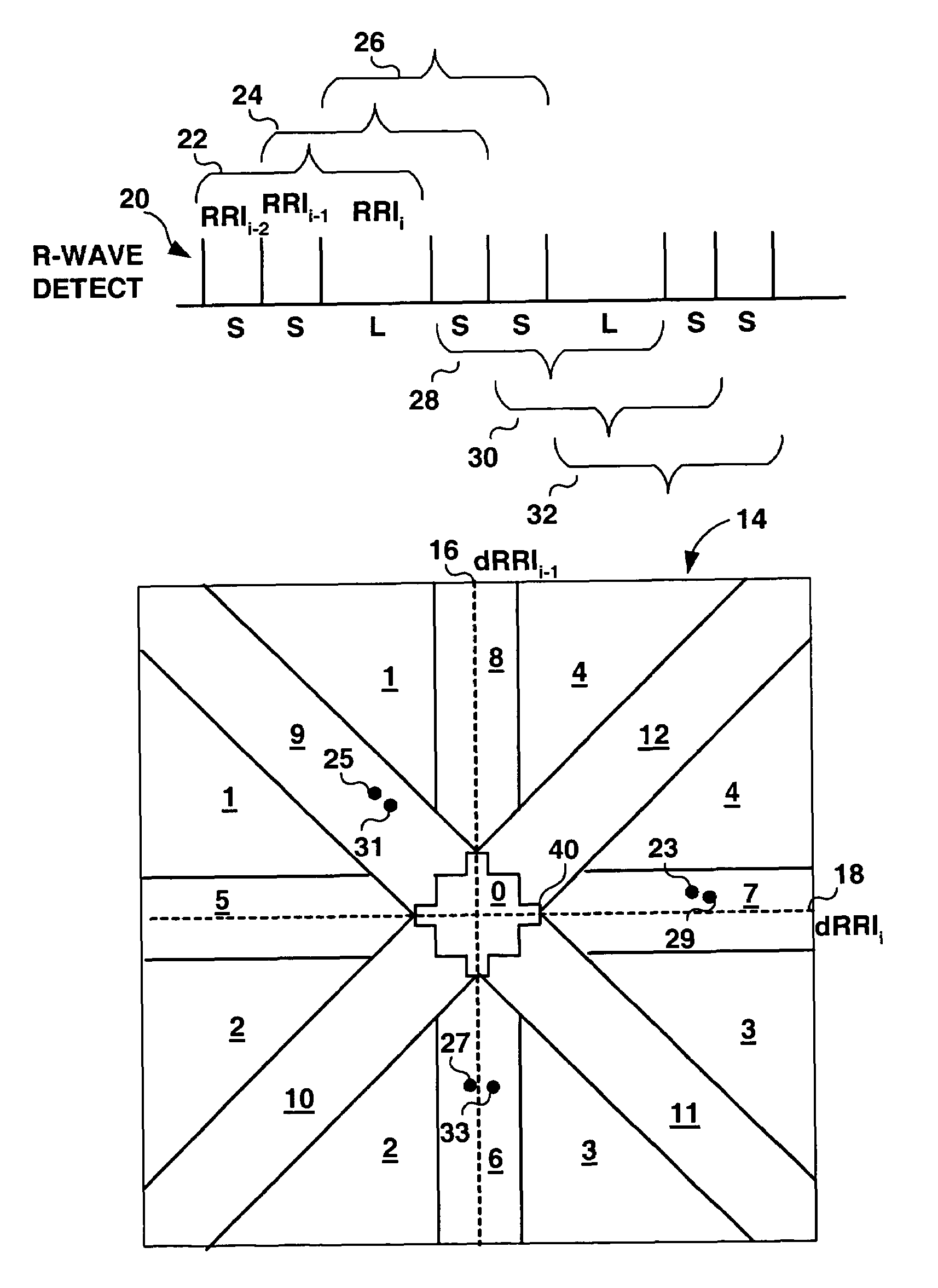
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Implantable cardiac stimulation device and method that discriminates between and treats atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation
An implantable cardiac stimulation device discriminates and treats accelerated atrial arrhythmias of a patient's heart. The device includes a sensing circuit that senses cardiac activity of one of the patient's atria to provide an atrial activity signal, a detector that detects an accelerated atrial arrhythmia of the patient's heart, and a classifying circuit that measures relative correspondence between successive P waves of the atrial activity signal to classify the detected accelerated atrial arrhythmia as either atrial tachycardia or atrial fibrillation. A therapy circuit provides anti-tachycardia pacing therapy responsive to a classified atrial tachycardia and defibrillation therapy responsive to a classified atrial fibrillation.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
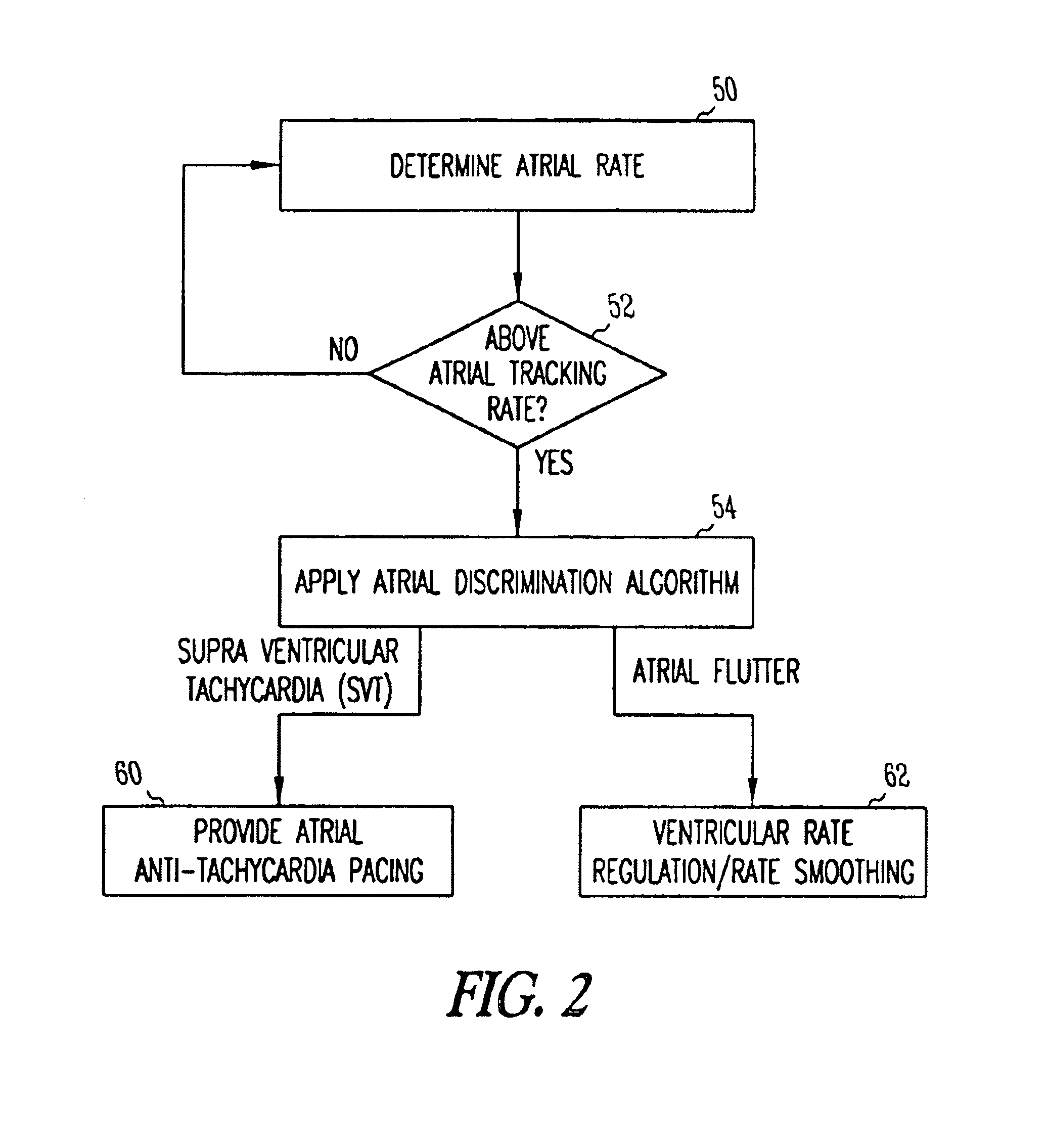
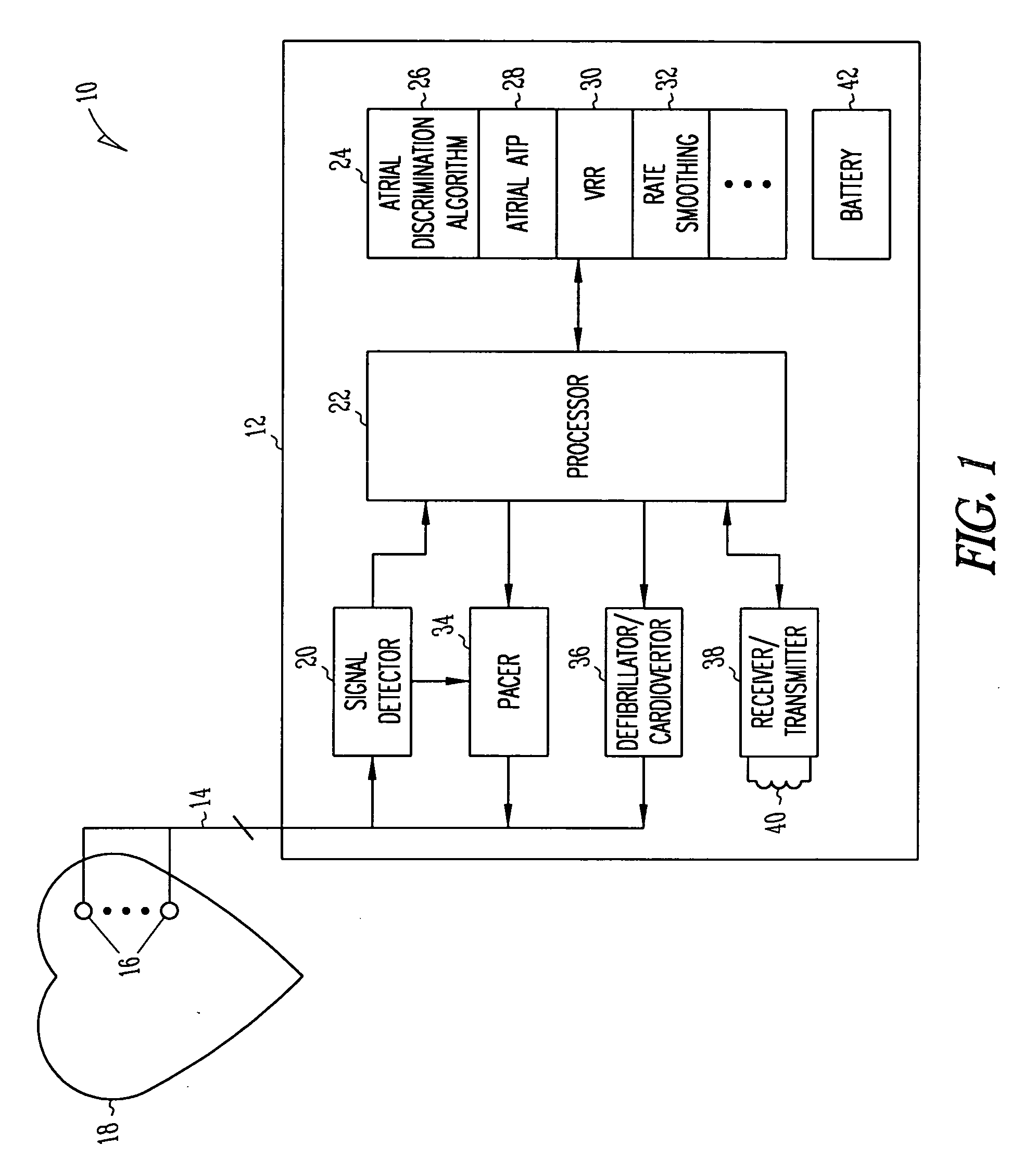
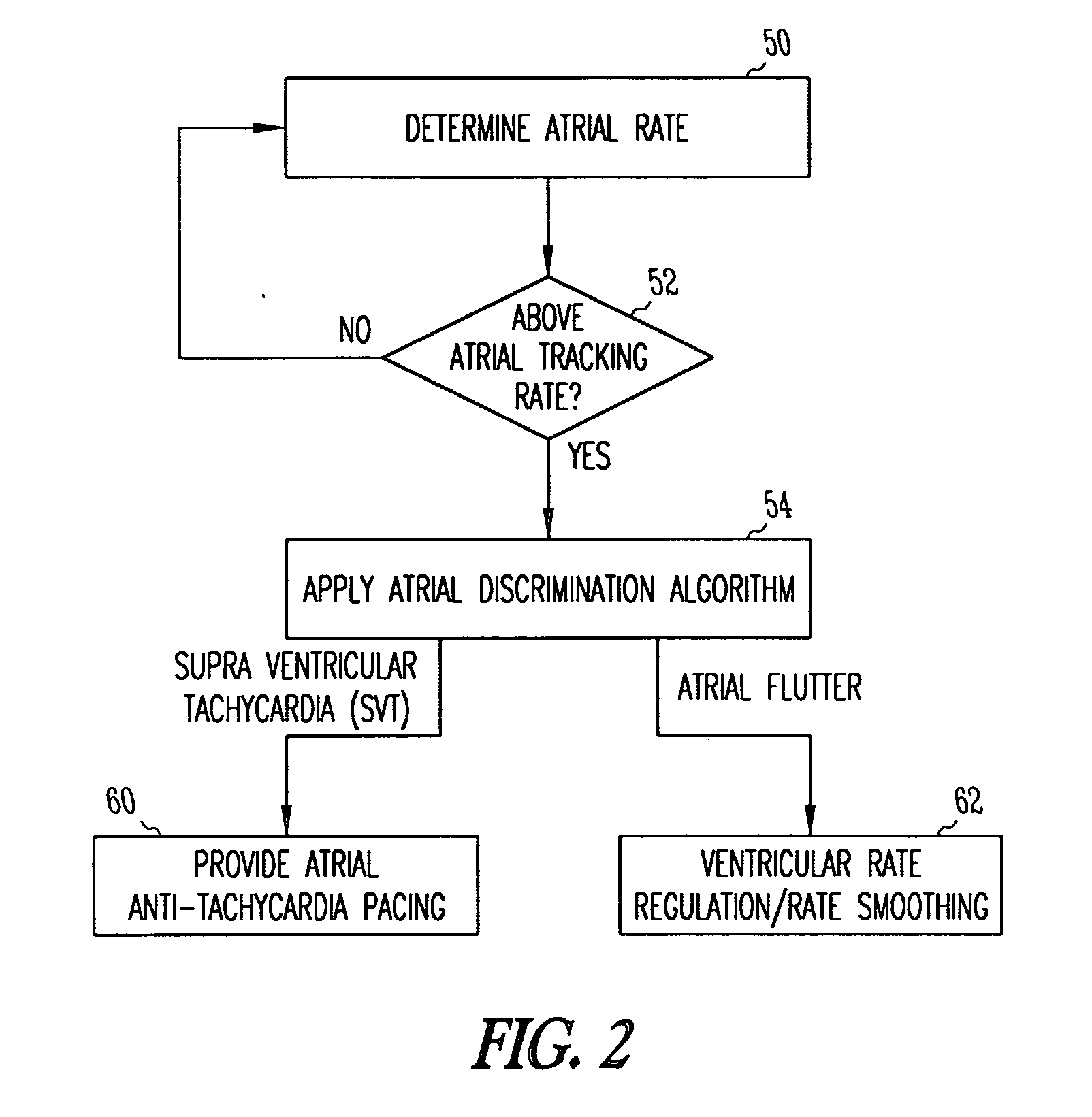
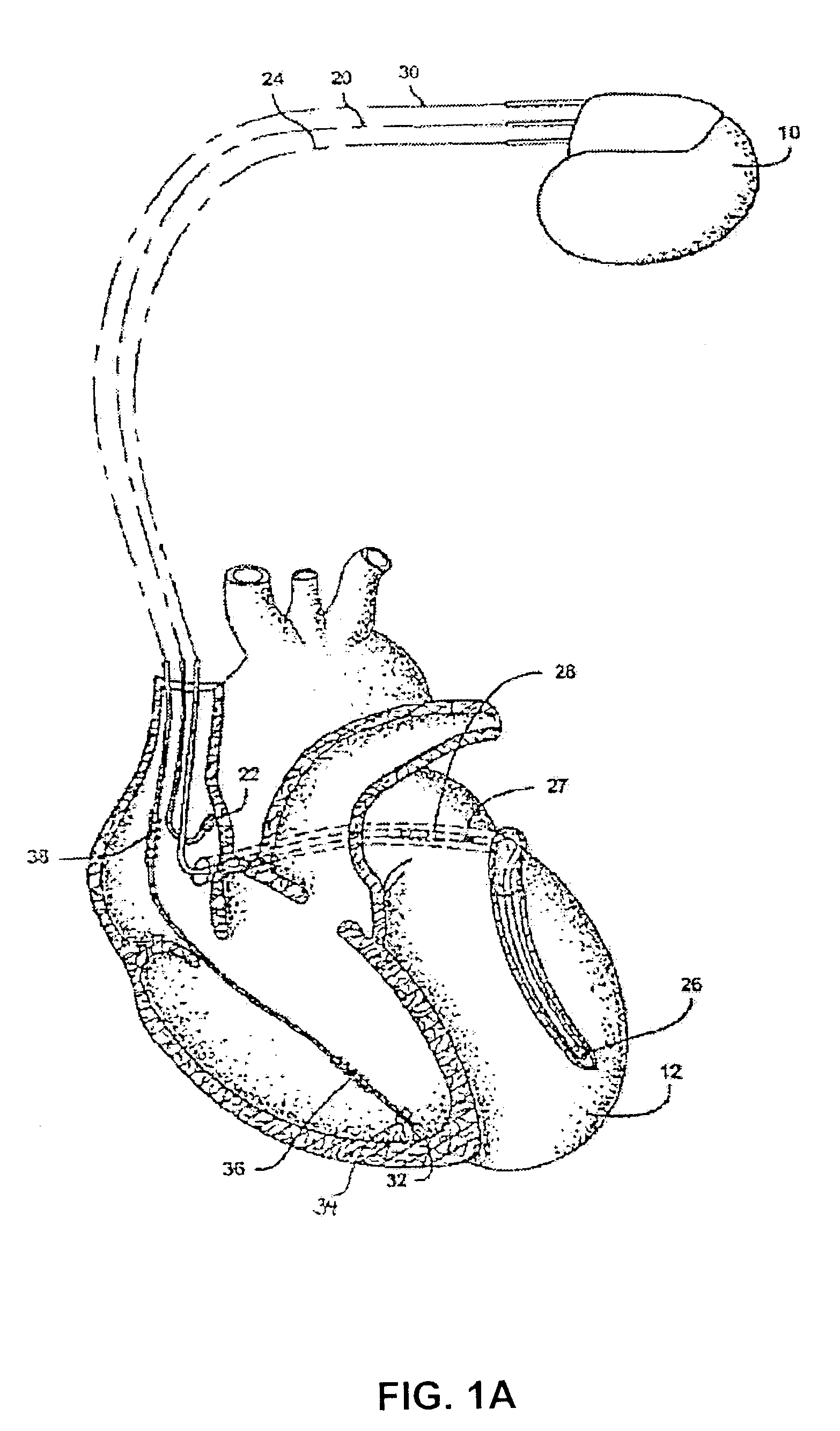
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
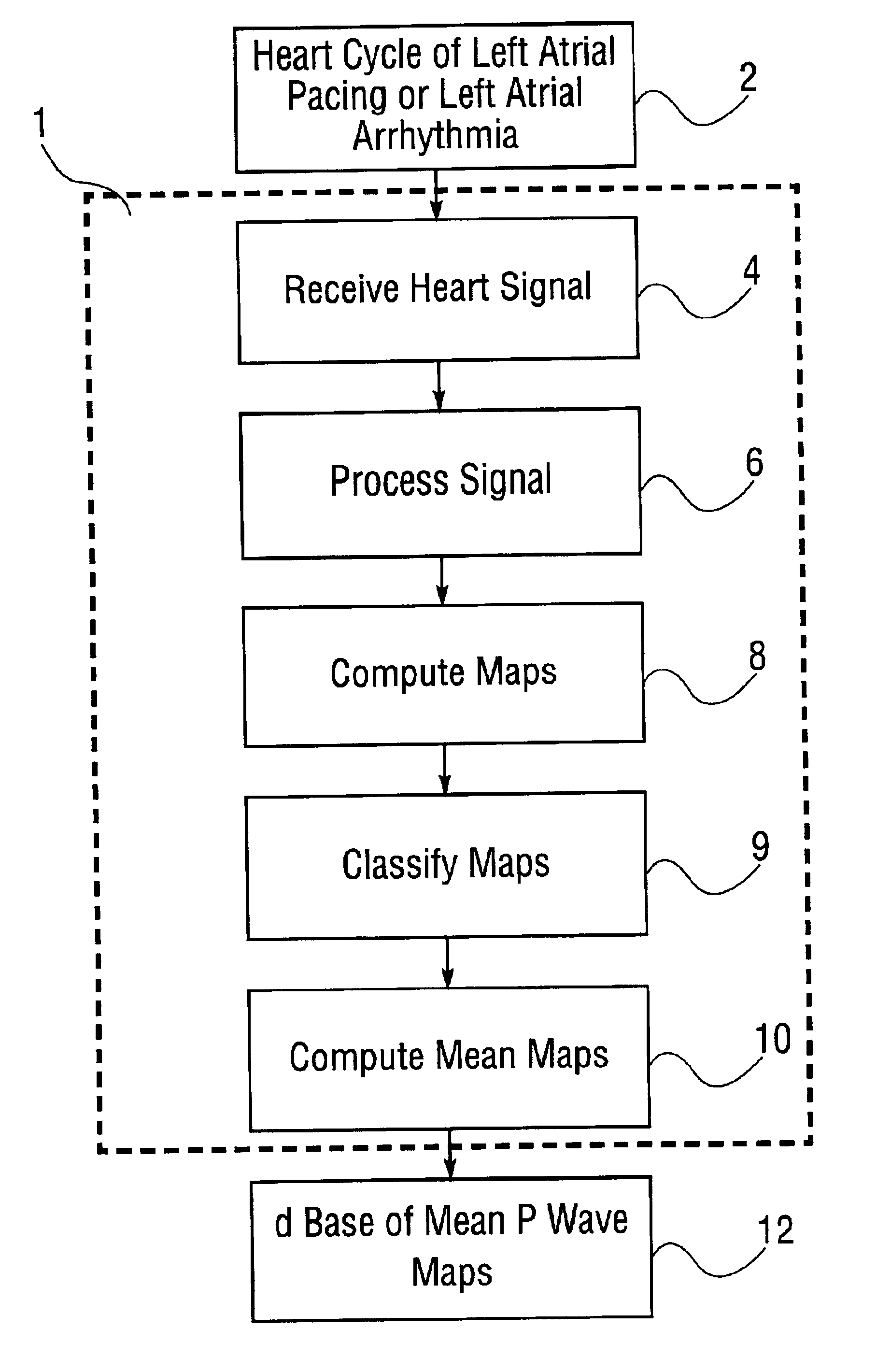
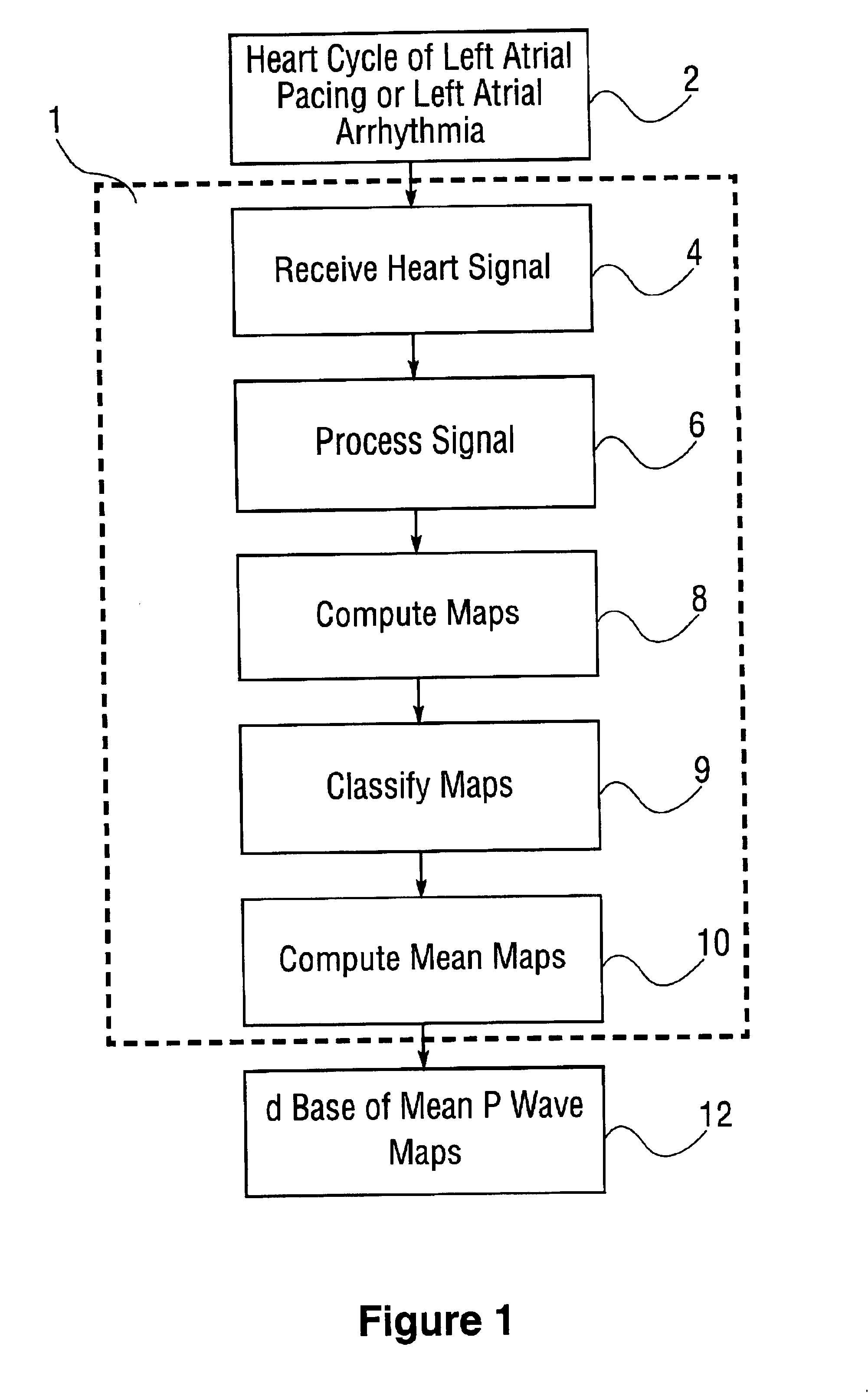
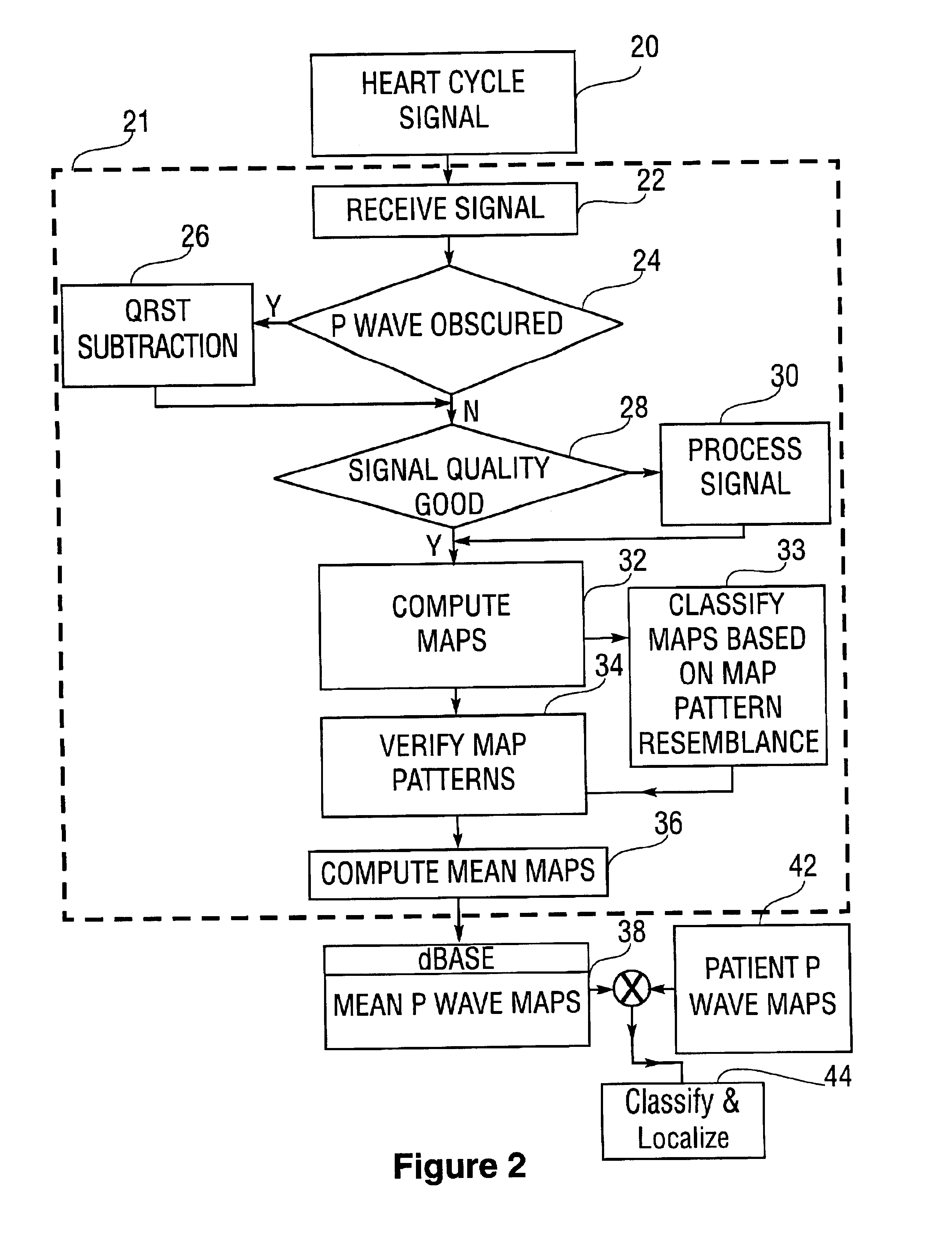
Database of body surface ECG P wave integral maps for localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias
InactiveUS6931273B2ElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyIsorhythmic Atrioventricular DissociationHypsarrhythmia
A system and method are provided for developing a database of body surface ECG P-wave maps for classification and localization of left-sided atrial arrhythmias. The system and method include generating and receiving P-wave data in a subject by left atrial pacing or receiving P-wave data in a subject during spontaneously occurring or induced left atrial arrhythmias; computing (e.g. potential or integral) maps of the P-wave data; classifying the maps specific to a left atrial ectopic origin; verifying the classification procedure; averaging the classified maps into mean maps; and storing and accessing the mean maps in the database. The mean maps of the P-wave data in the database can be used to automatically classify and localize P-wave data from a patient obtained during a left atrial arrhythmia such as atrial tachycardia, focal atrial fibrillation, or orthodromic atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for defining the effect of atrial arrhythmias on cardiac performance and directing therapy using a plurality of intrinsically and extrinsically derived signals
ActiveUS7963925B1Ensure complianceLess timelyElectrotherapyOrgan movement/changes detectionDigital signal processingPatient demographics
This invention describes methods and algorithms for processing a plurality of relevant signals / data intrinsic to a patient and / or derived from external diagnostic equipment for management of atrial arrhythmias. The intrinsic signals are acquired from intracardiac leads / sensors and analogous extrinsic data obtained from imaging equipment and patient demographics. These data are input into software algorithms that use digital signal processing to output informational data of clinical and technical relevance after comparisons are made to patients with access to this technology whose outcome under varying treatments is known. These combined data are used to define prognosis, make treatment suggestions, direct programming of cardiac devices and digitally convert intrinsically and extrinsically derived indices into a common metric. In a preferred embodiment, the intrinsically and extrinsically acquired data is utilized in the design of catheters and software algorithms for performing intracardiac procedures such as ablation of atrial arrhythmias.
Owner:STUART SCHECTER LLC
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A multi-layer method for detecting atrial arrhythmias using ventricular cycle length information that includes performing a base layer algorithm for detecting the onset and offset of an atrial tachyarrhythmia. The multi-layer method further includes one or more higher layer algorithms executed in response to a base layer detection to confirm or reject the base layer detection. The base layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia and the higher layer is designed to operate with high sensitivity and high specificity to atrial fibrillation and / or organized atrial tachycardia.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
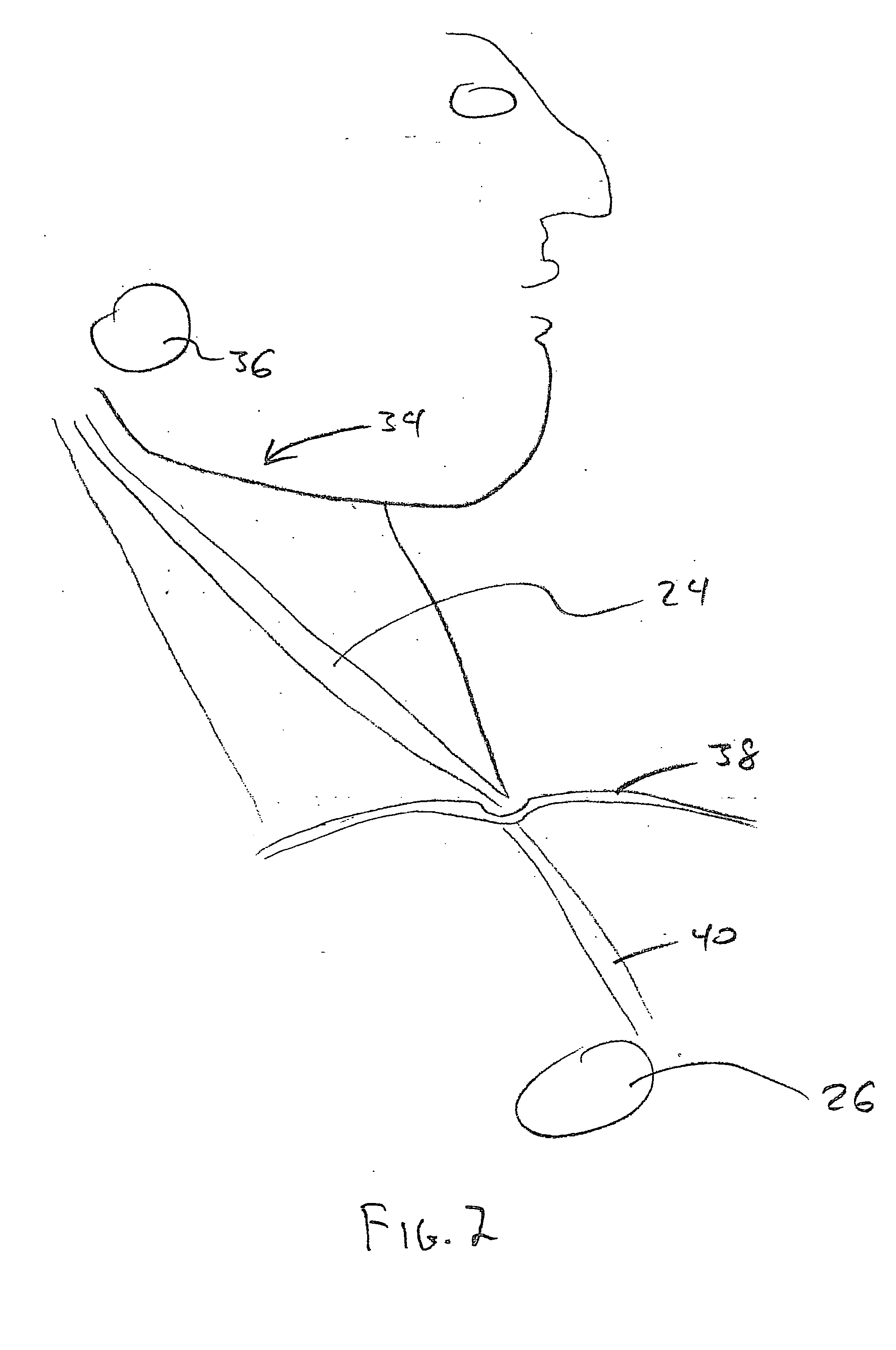
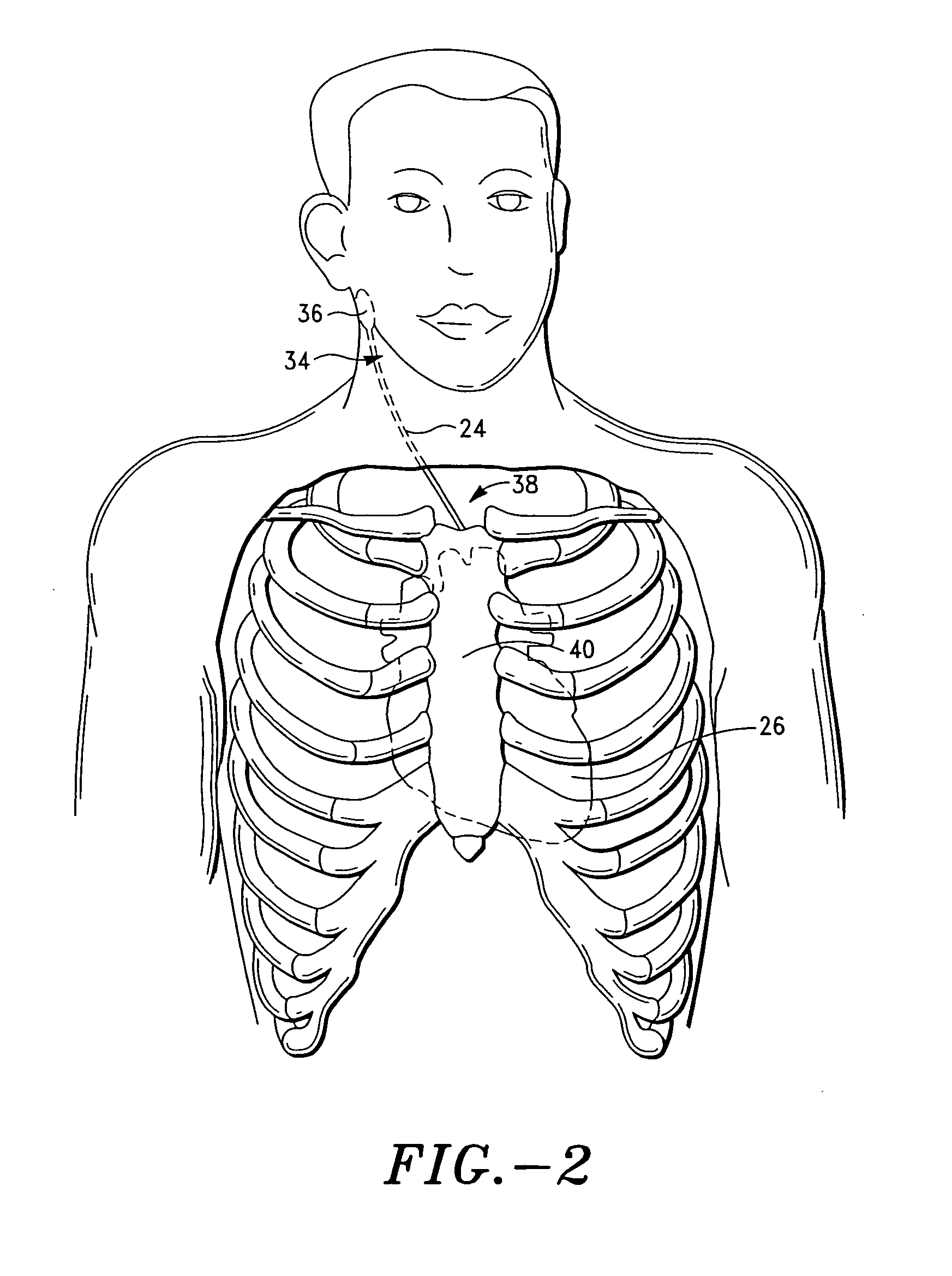
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:NEUROSIGNAL TECH
Device and procedure to treat cardiac atrial arrhythmias
A non-invasive vagal stimulation device and method. The device comprises a body having a vibration member. The stimulation is created by the vibration member which has a vibratory rate that can be adjusted from being off to a preferred operating range. The non-invasive stimulation method consists of placing the non-invasive stimulation device in the vicinity of the carotid artery bifrication where arises a carotid sinus and body which contain afferent sensory nerves that travel to medulla oblongata of brain, and either applying pressure in place, or moving the device along the target arm. The method can be accomplished either with the vibration feature of the device turned on or off.
Owner:ORTIZ & LOPEZ PLLC
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS7062325B1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
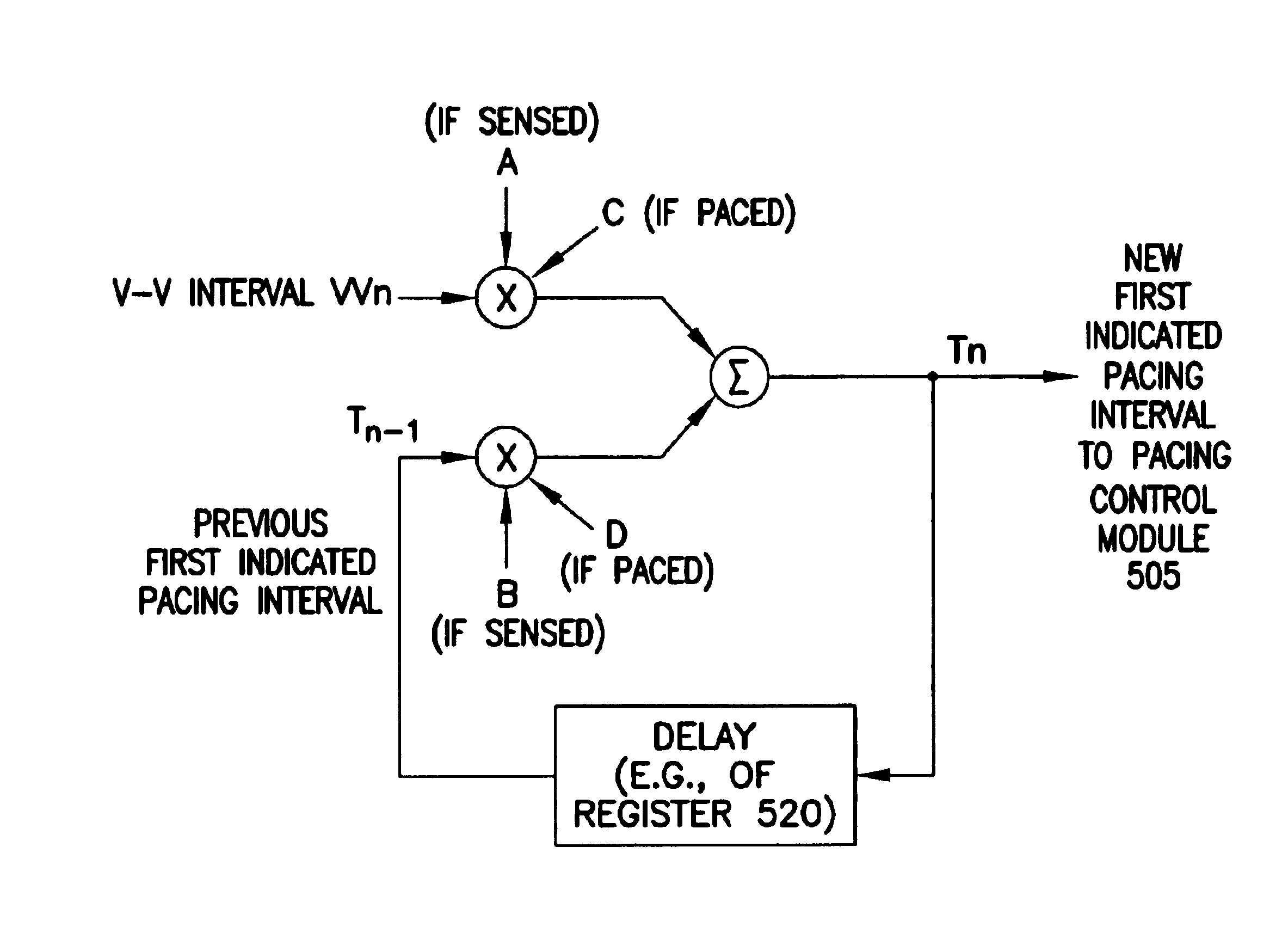
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V—V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and device for three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy
ActiveUS20110009916A1Reduction in energy required to convert atrial arrhythmiaExceeding pain thresholdEpicardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardioversionsThree stage
Methods and apparatus for a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy that treats atrial arrhythmias within pain tolerance thresholds of a patient. An implantable therapy generator adapted to generate and selectively deliver a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy and at least two leads operably each having at least one electrode adapted to be positioned proximate the atrium of the patient. The device is programmed with a set of therapy parameters for delivering a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy to the patient via both a far-field configuration and a near-field configuration of the electrodes upon detection of an atrial arrhythmia. The three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy includes a first stage for unpinning of one or more singularities associated with an atrial arrhythmia, a second stage for anti-repinning of the one or more singularities associated with the atrial arrhythmia, both of which are delivered via the far-field configuration of the electrodes, and a third stage for extinguishing of the one or more singularities associated with the atrial arrhythmia delivered via the near-field configuration of the electrodes.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method and device for three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy
ActiveUS20120209343A1Exceeding pain thresholdLower energy requirementsEpicardial electrodesHeart defibrillatorsThree stagePhases of clinical research
Methods and apparatus for a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy that treats atrial arrhythmias within pain tolerance thresholds of a patient. An implantable therapy generator adapted to generate and selectively deliver a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy and at least two leads, each having at least one electrode adapted to be positioned proximate the atrium of the patient. The device is programmed for delivering a three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy via both a far-field configuration and a near-field configuration of the electrodes upon detection of an atrial arrhythmia. The three-stage atrial cardioversion therapy includes a first stage for unpinning of one or more singularities associated with an atrial arrhythmia, a second stage for anti-repinning of the one or more singularities, both of which are delivered via the far-field configuration of the electrodes, and a third stage for extinguishing of the one or more singularities delivered via the near-field configuration of the electrodes.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method and apparatus for detection of tachyarrhythmia using cycle lengths
A method and apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias and discriminating atrial fibrillation (AF) and organized atrial tachycardia (OAT) that includes defining a threshold detection criteria for a cluster signature evidence metric corresponding to a Lorenz distribution of ventricular cycle lengths representative of AF or OAT. Using a signal containing VCL information, a number of consecutive ventricular cycle lengths are determined during a selected time interval for generating a one-dimensional or a two-dimensional histogram as a numerical representation of a Lorenz plot of VCLs. A number of cluster signature metrics are computed using the stored ventricular cycle length information, and a cluster signature evidence metric is computed from the cluster signature metrics. AF or OAT is detected if a comparative analysis of a corresponding cluster signature evidence metric meets a respective threshold detection criteria.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
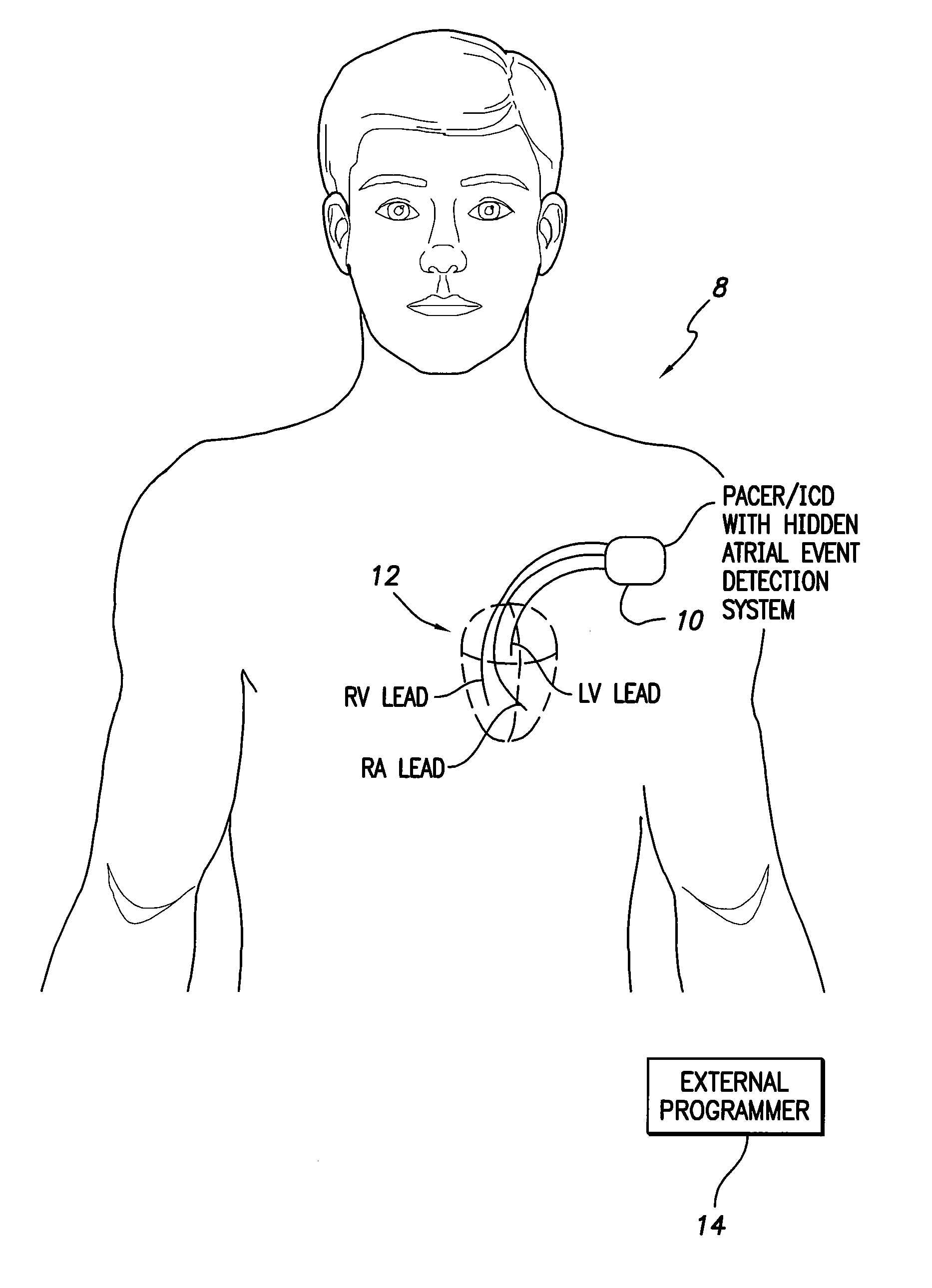
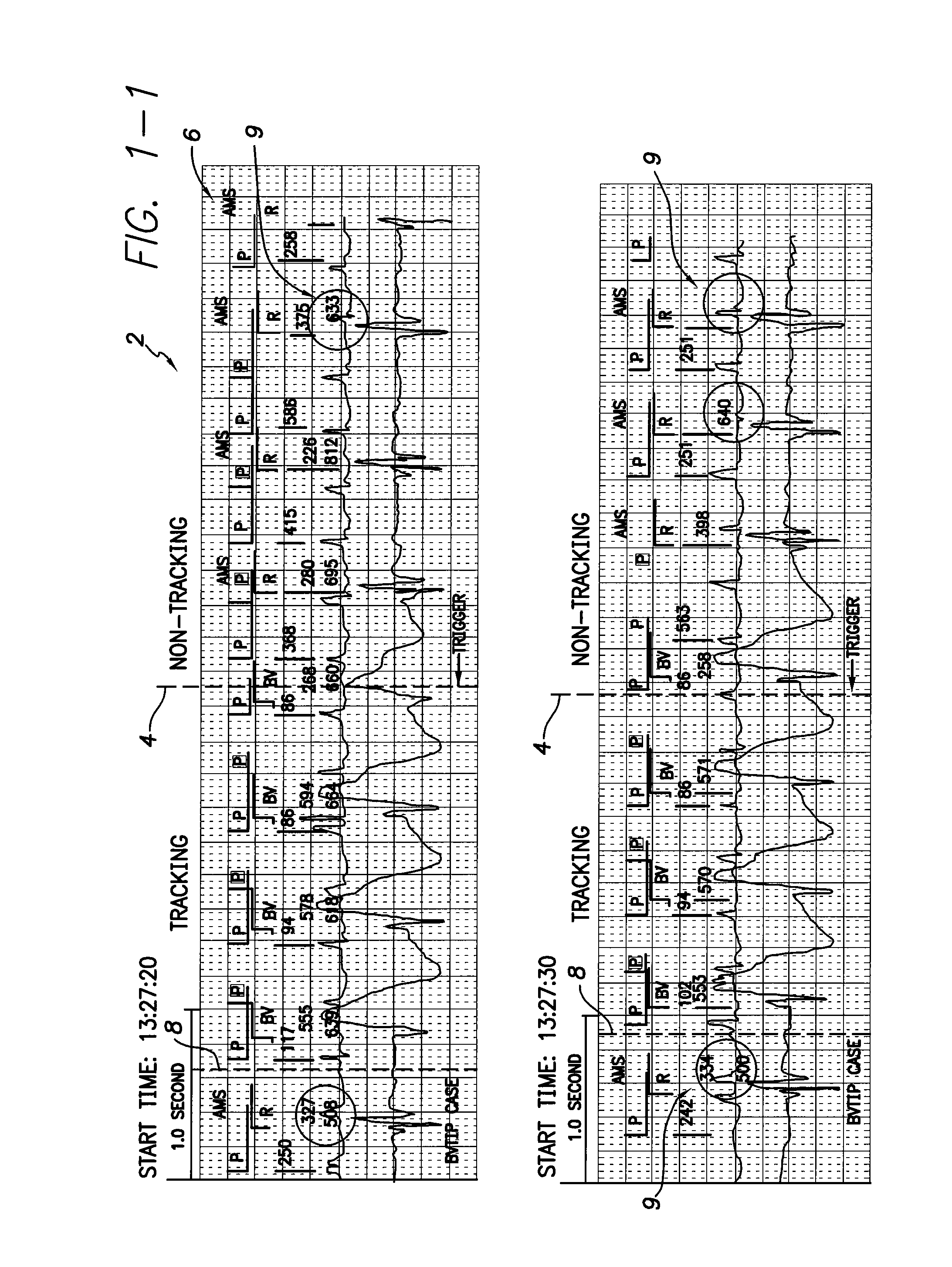
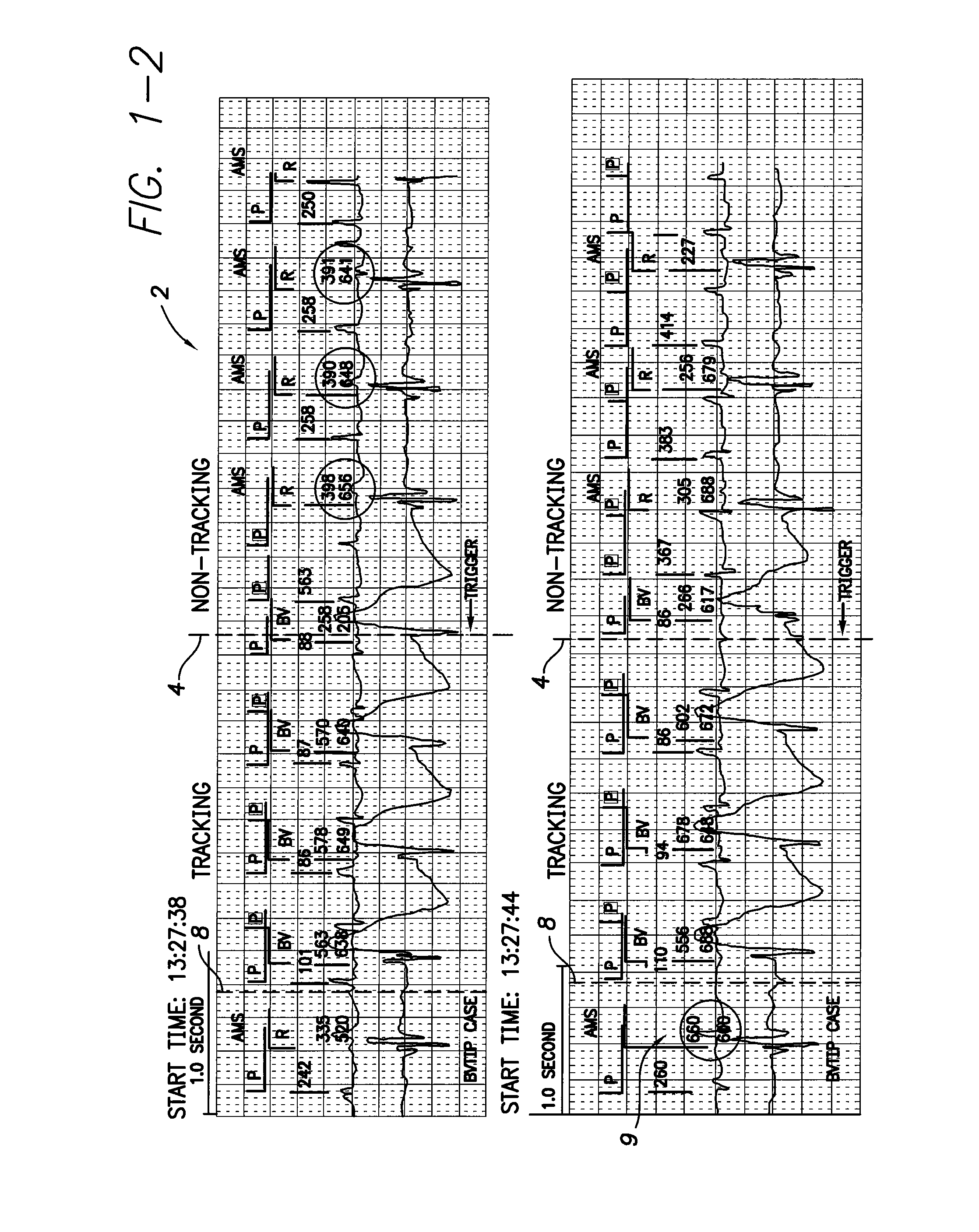
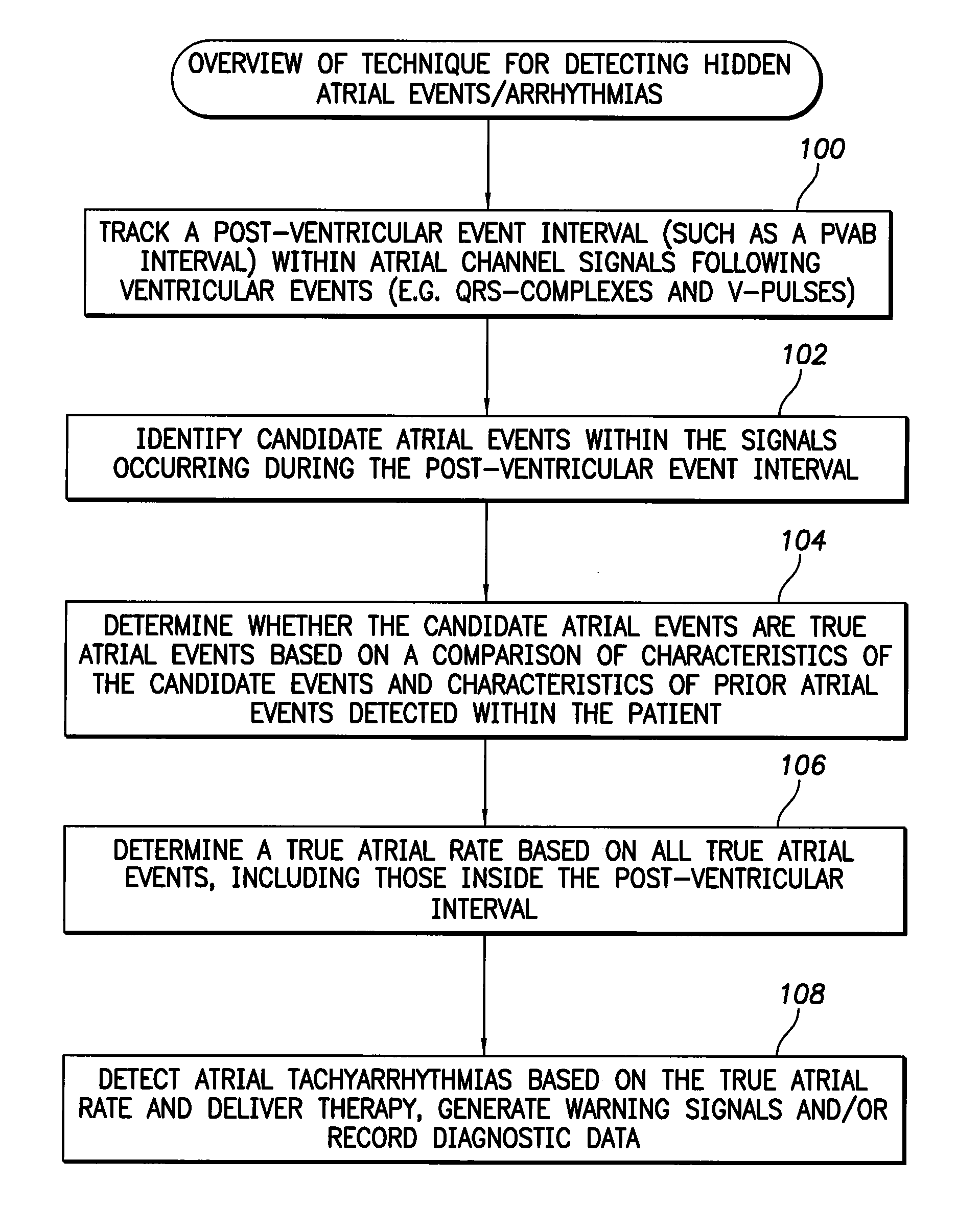
System and method for detecting hidden atrial events for use with automatic mode switching within an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20090281587A1Fast and accurate determinationMode switch oscillations can be reduced or eliminatedElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsMedical deviceMode switch
Techniques are provided for detecting atrial events that might be hidden due to the operation of a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or other atrial channel blanking interval. In one example, candidate atrial events are identified within signals occurring during the PVAB interval. Then, a determination is made as to whether the candidate atrial event is a true atrial event based on a comparison of characteristics of the candidate atrial event with characteristics of prior known atrial events within the patient. By comparing the characteristics of the “hidden” event with the characteristics of prior known atrial events within the patient, a quick and accurate determination can be made whether the event should be counted as a P-wave. In this manner, hidden atrial arrhythmias can be detected and mode switch oscillations can be reduced or eliminated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for detecting hidden atrial events for use with automatic mode switching within an implantable medical device
ActiveUS8233980B2Fast and accurate determinationMode switch oscillations can be reduced or eliminatedElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsMedical deviceMode switch
Techniques are provided for detecting atrial events that might be hidden due to the operation of a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or other atrial channel blanking interval. In one example, candidate atrial events are identified within signals occurring during the PVAB interval. Then, a determination is made as to whether the candidate atrial event is a true atrial event based on a comparison of characteristics of the candidate atrial event with characteristics of prior known atrial events within the patient. By comparing the characteristics of the “hidden” event with the characteristics of prior known atrial events within the patient, a quick and accurate determination can be made whether the event should be counted as a P-wave. In this manner, hidden atrial arrhythmias can be detected and mode switch oscillations can be reduced or eliminated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
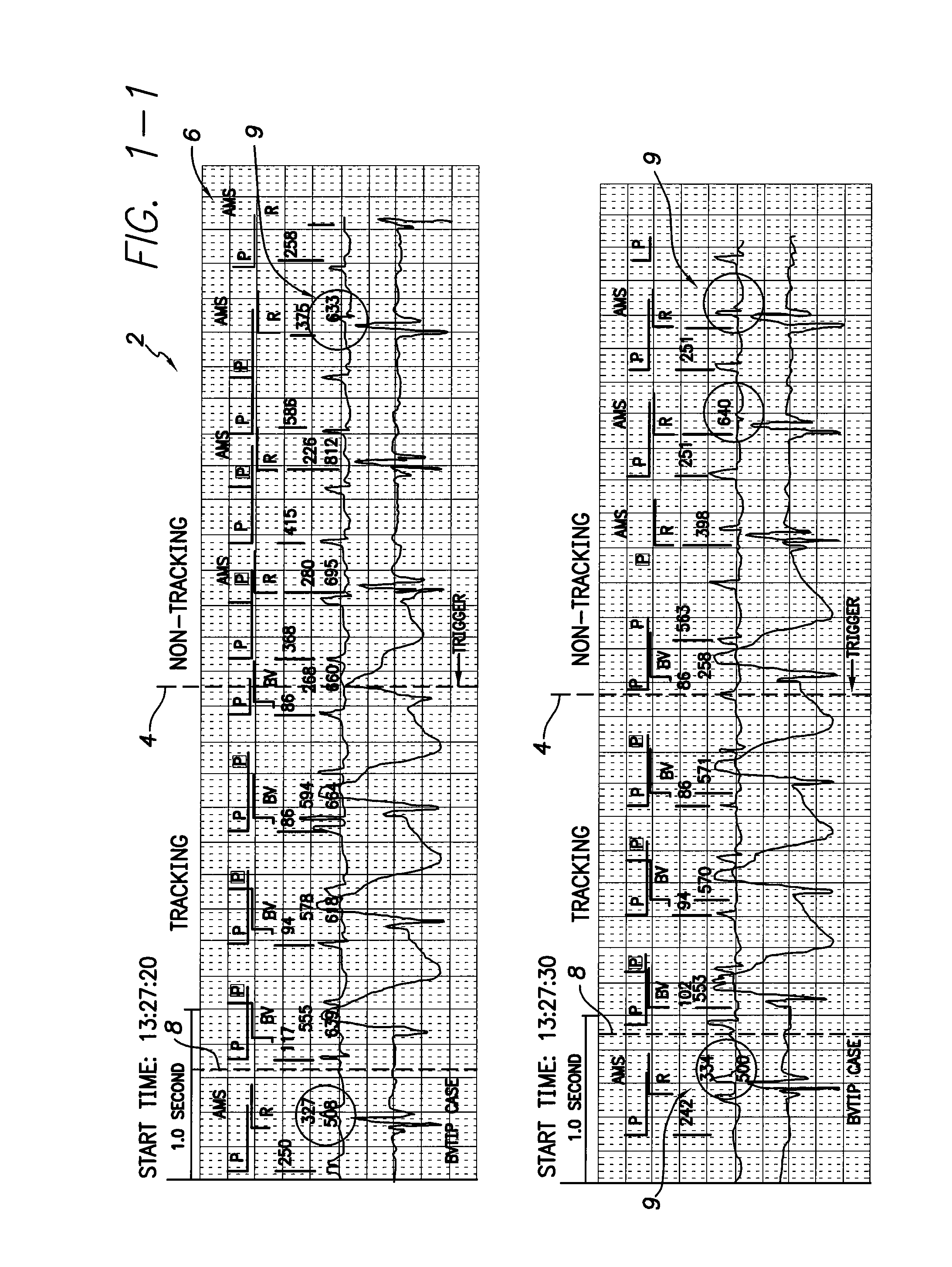
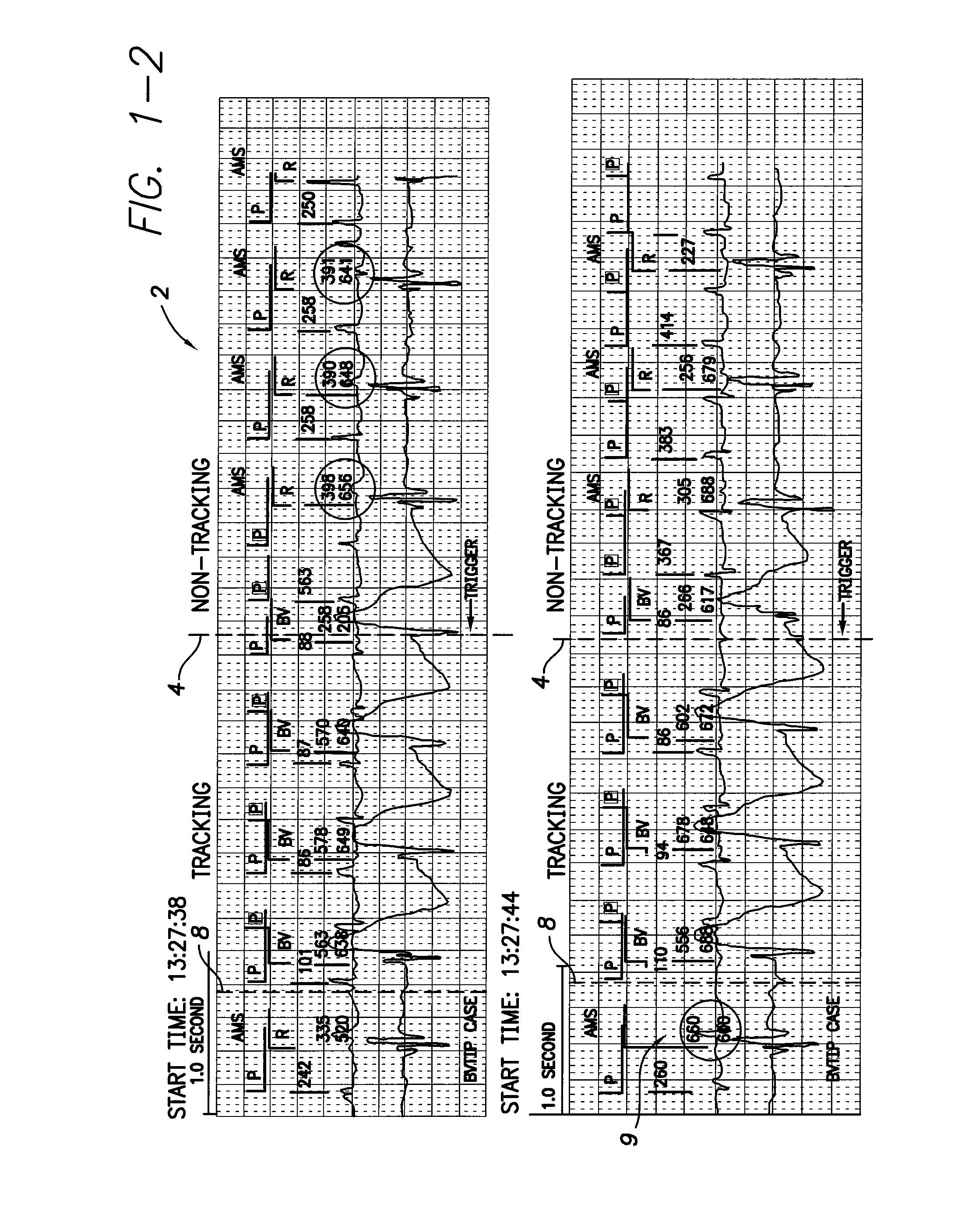
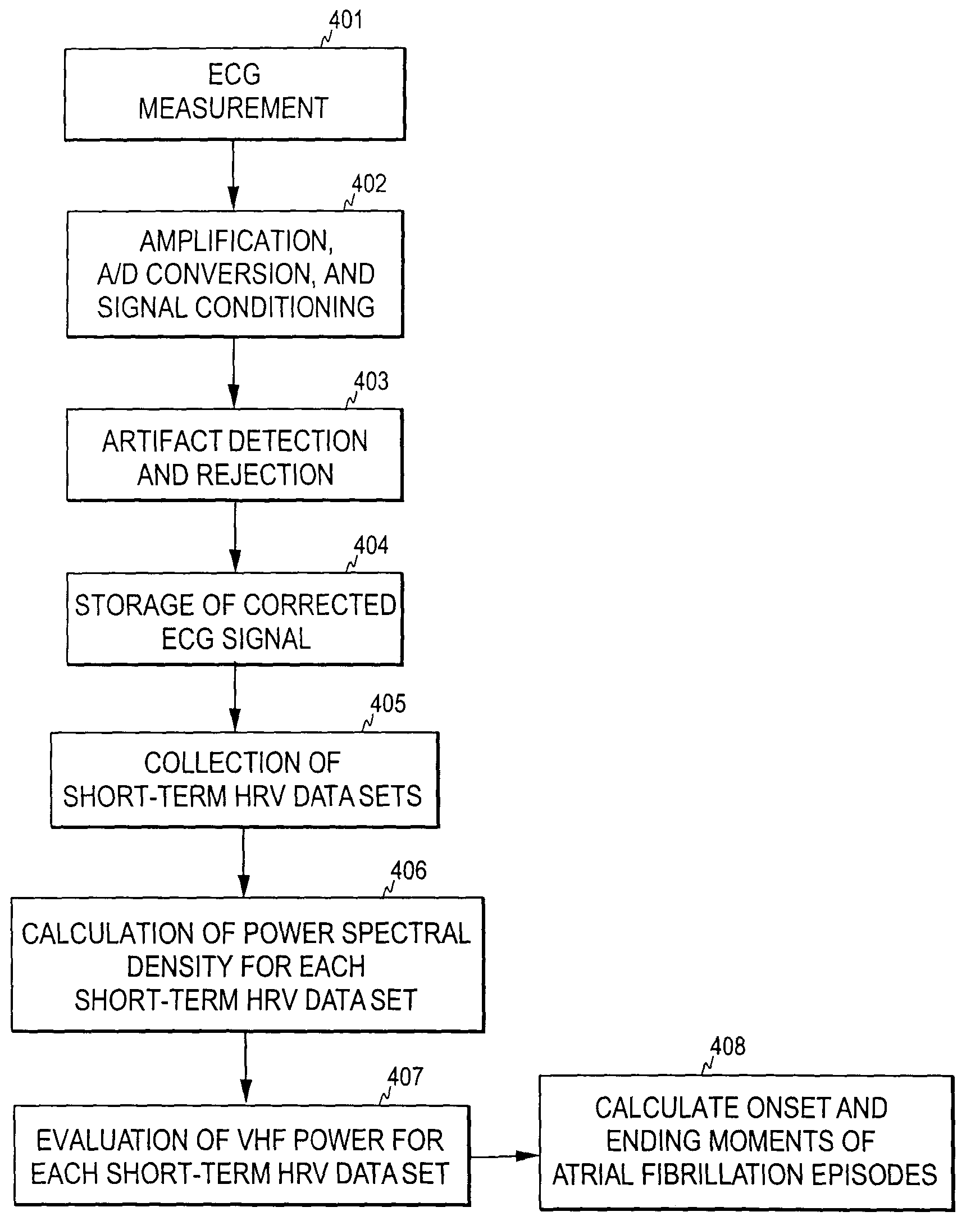
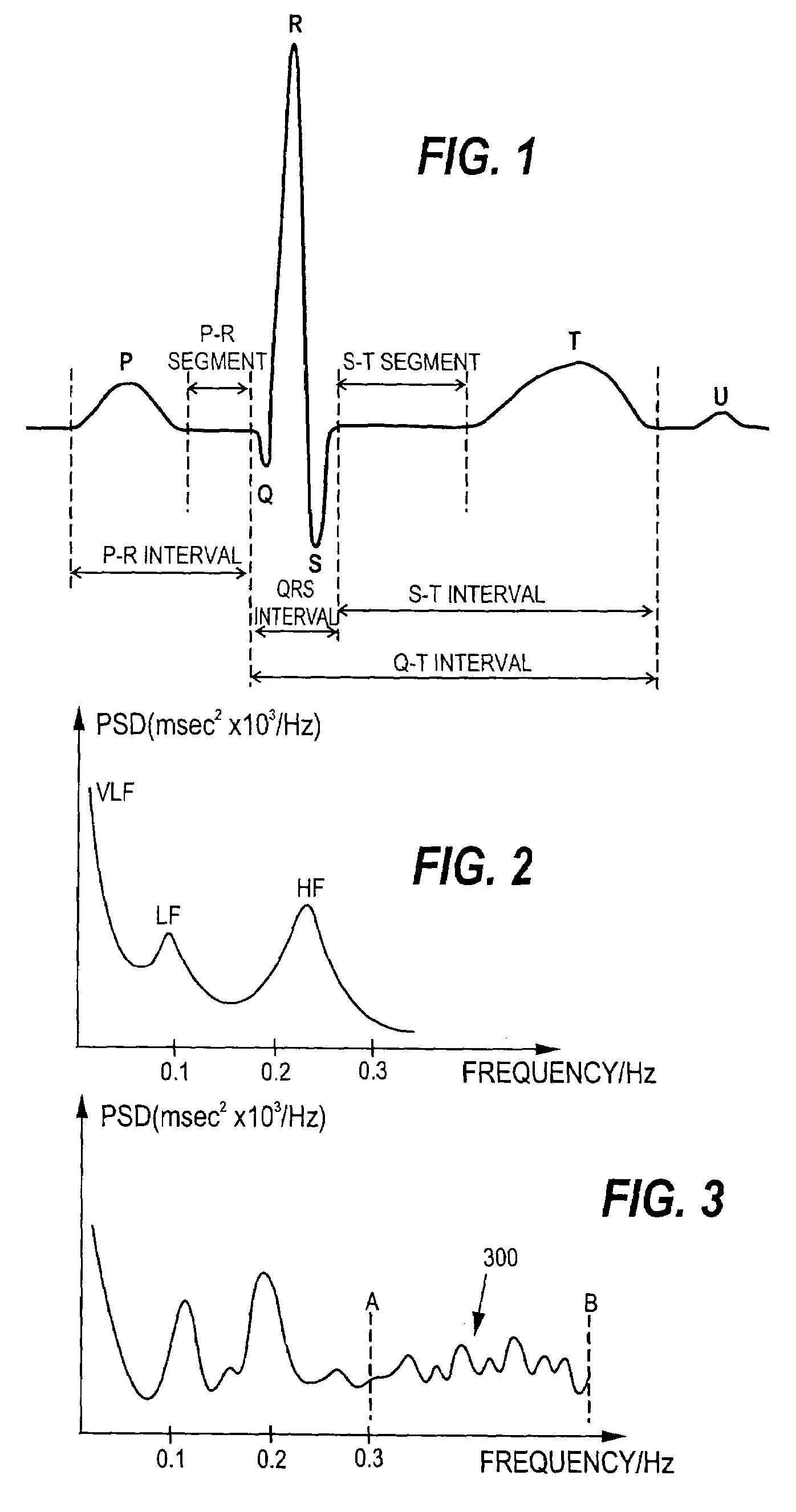
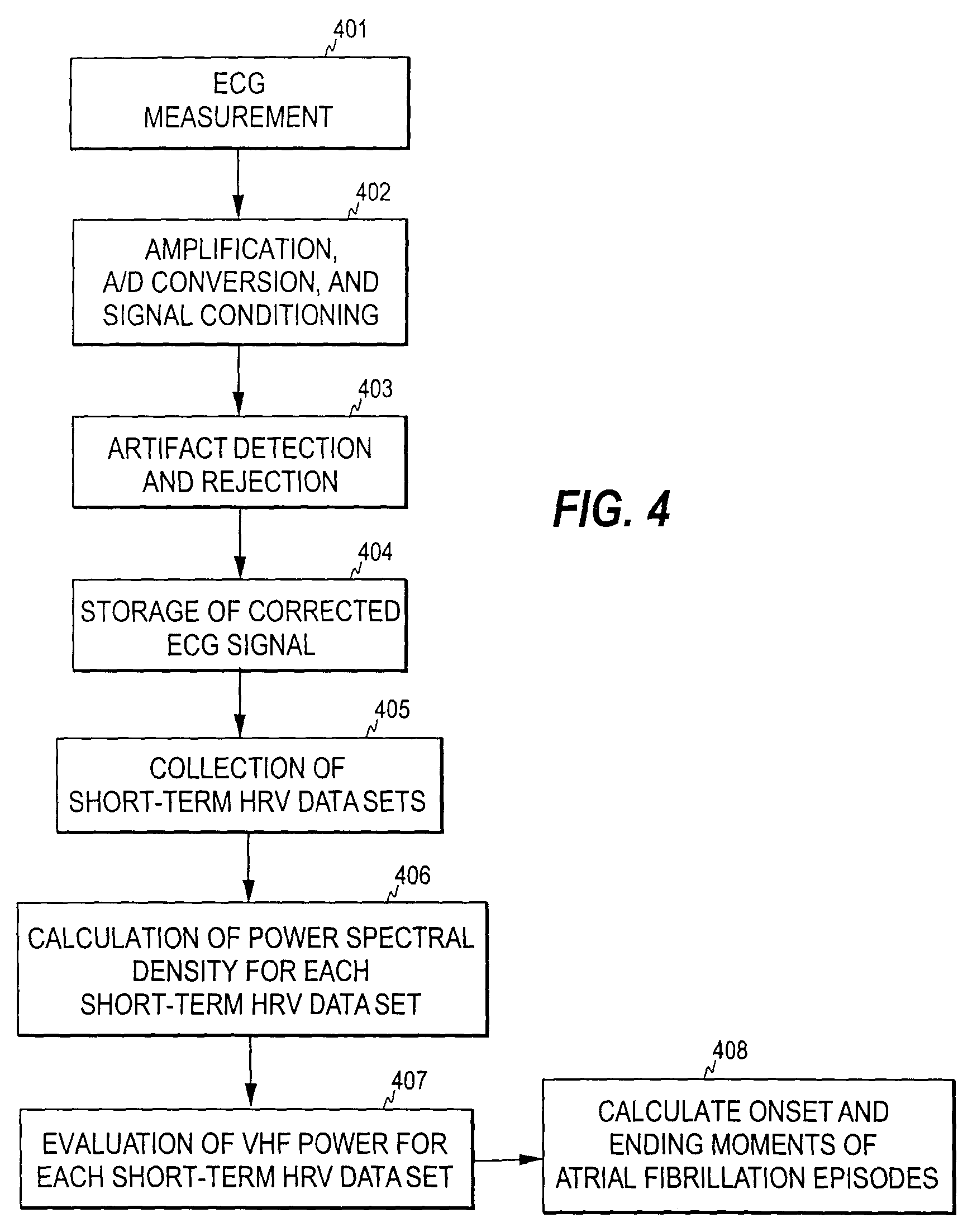
Detection of atrial arrhythmia
The invention relates to a method and system for detecting atrial arrhythmia, especially atrial fibrillations. Based on at least one electrical signal indicative of a heart's activity, a plurality of short-term HRV data sets are generated, one short-term HRV data set indicating the heart's rate variability within a time period of a given length, and two consecutive short-term HRV data sets having a given time difference. A frequency analysis of each short-term HRV data set is then performed and a power level corresponding to at least one selected frequency component in each short-term HRV data set is defined. The occurrence of the heart's atrial arrhythmia episodes are then estimated on the basis of the power levels defined.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
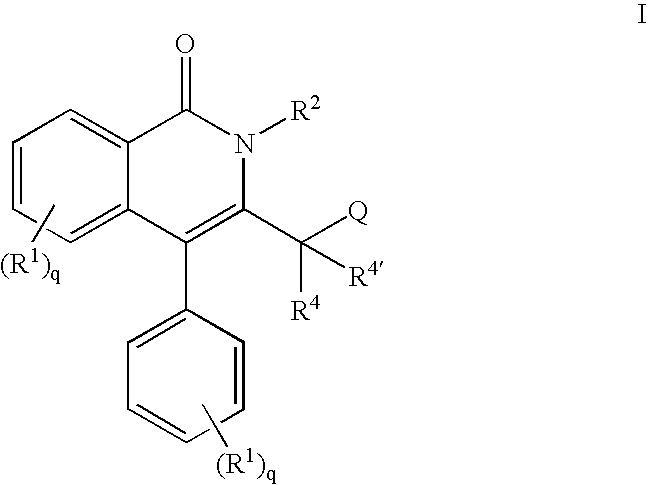
Isoquinolinone potassium channels inhibitors
The present invention concerns certain isoquinolinone compounds and their utility as inhibitors of voltage-dependent potassium channels or currents, such as Kv1.5 and IKur, that could serve as targets for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias especially atrial arrhythmias. The present invention also provide a method for treating or preventing conditions which respond to the inhibition of potassium channels or currents, such as cardiac arrhythmias and more especially atrial arrhythmias. The present invention further includes pharmaceutical formulations and a process of making a pharmaceutical composition comprising a compound of certain isoquinolinone or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates, crystal forms, and stereoisomers thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Atrial arrhythmia detection for an active implantable medical device
ActiveUS7113826B2Avoid detectionHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAtrial cavityCardiac pacemaker electrode
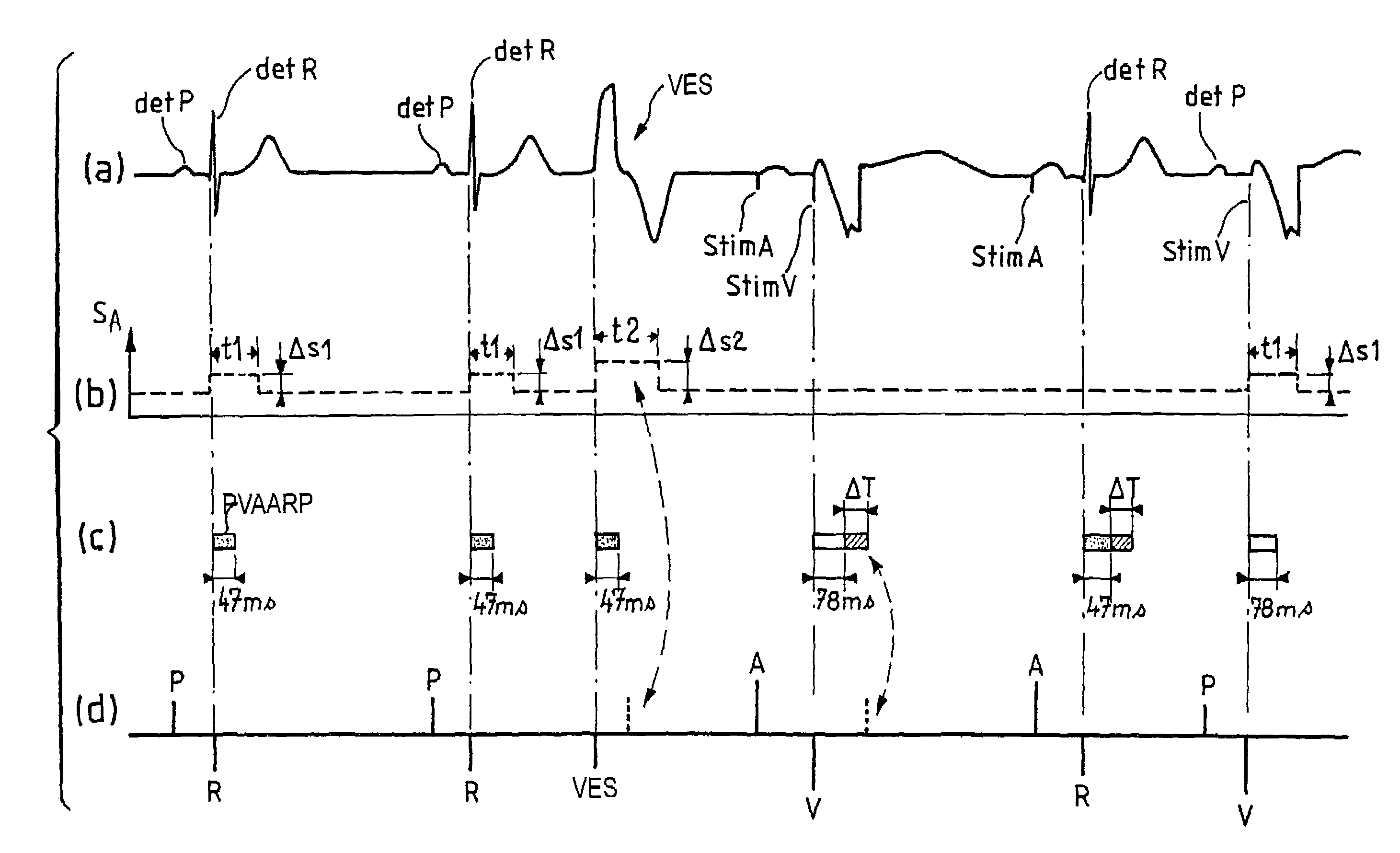
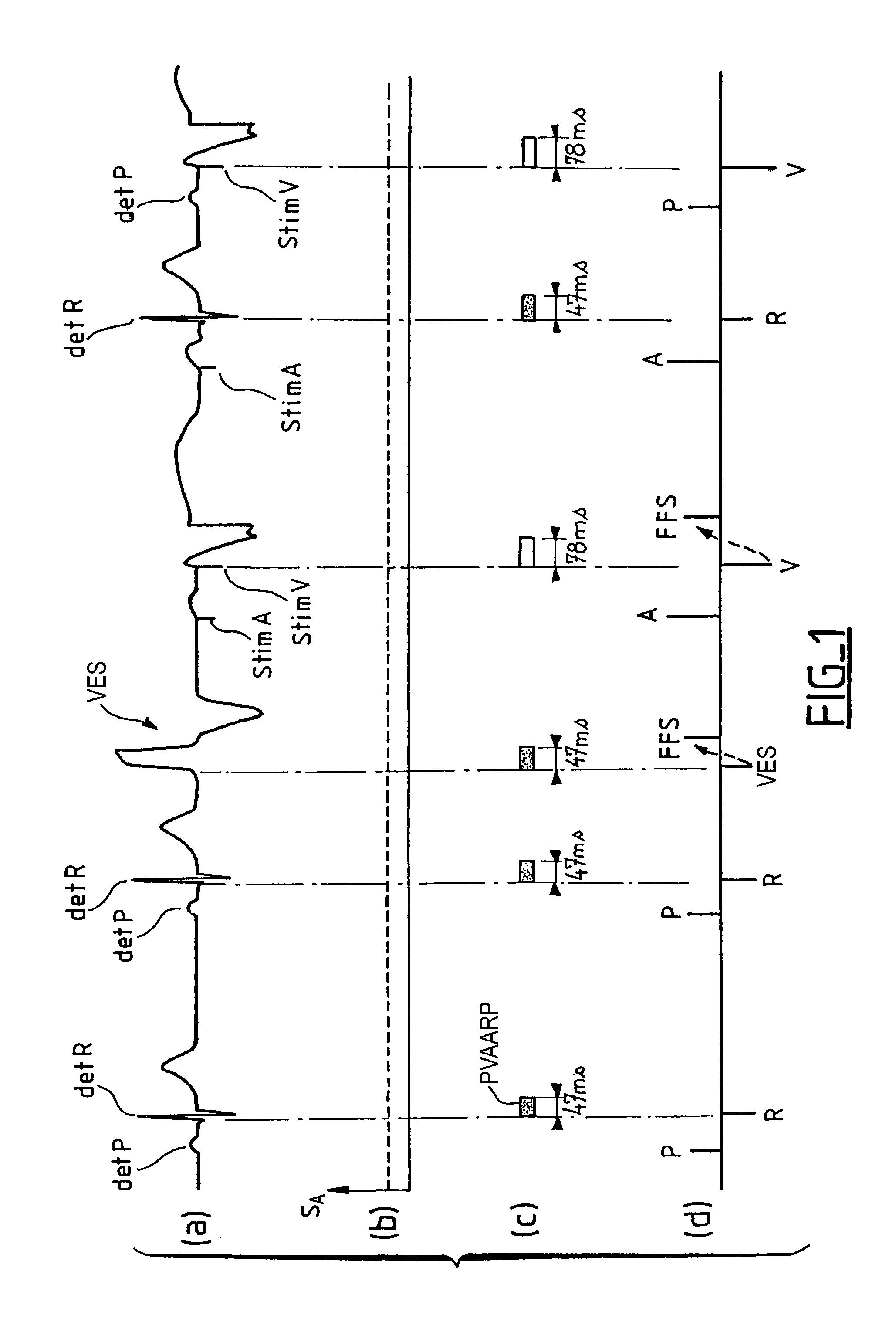
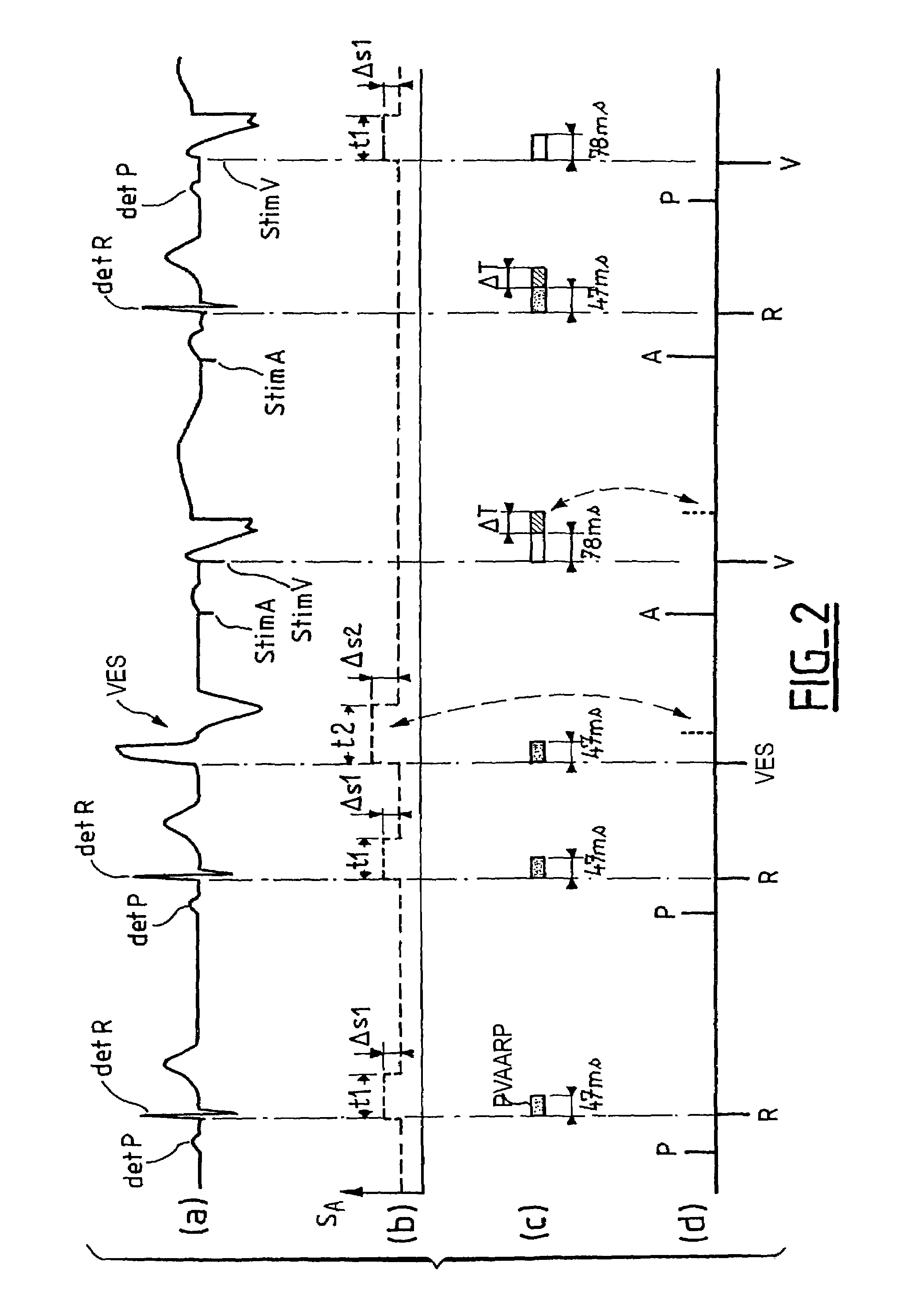
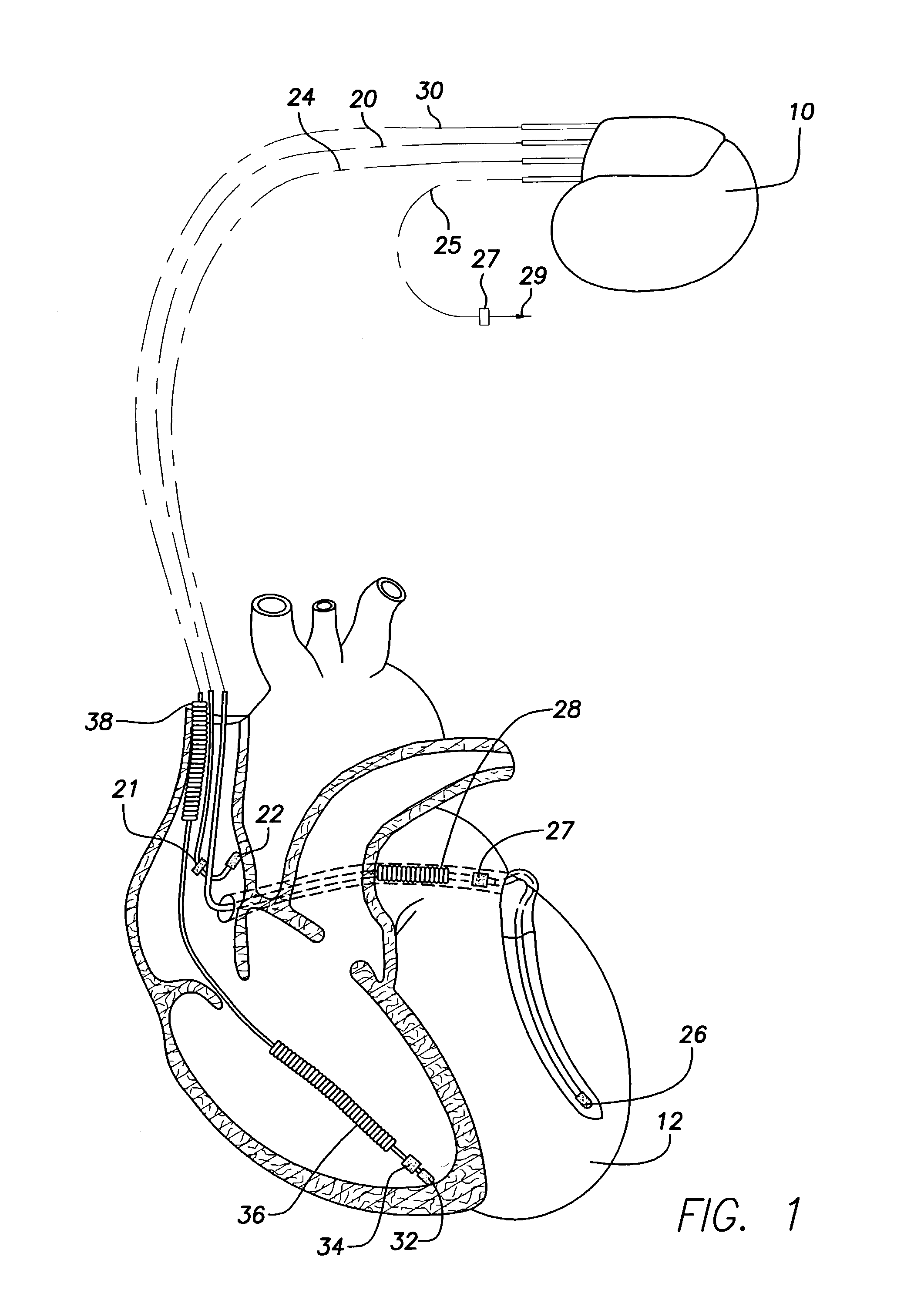
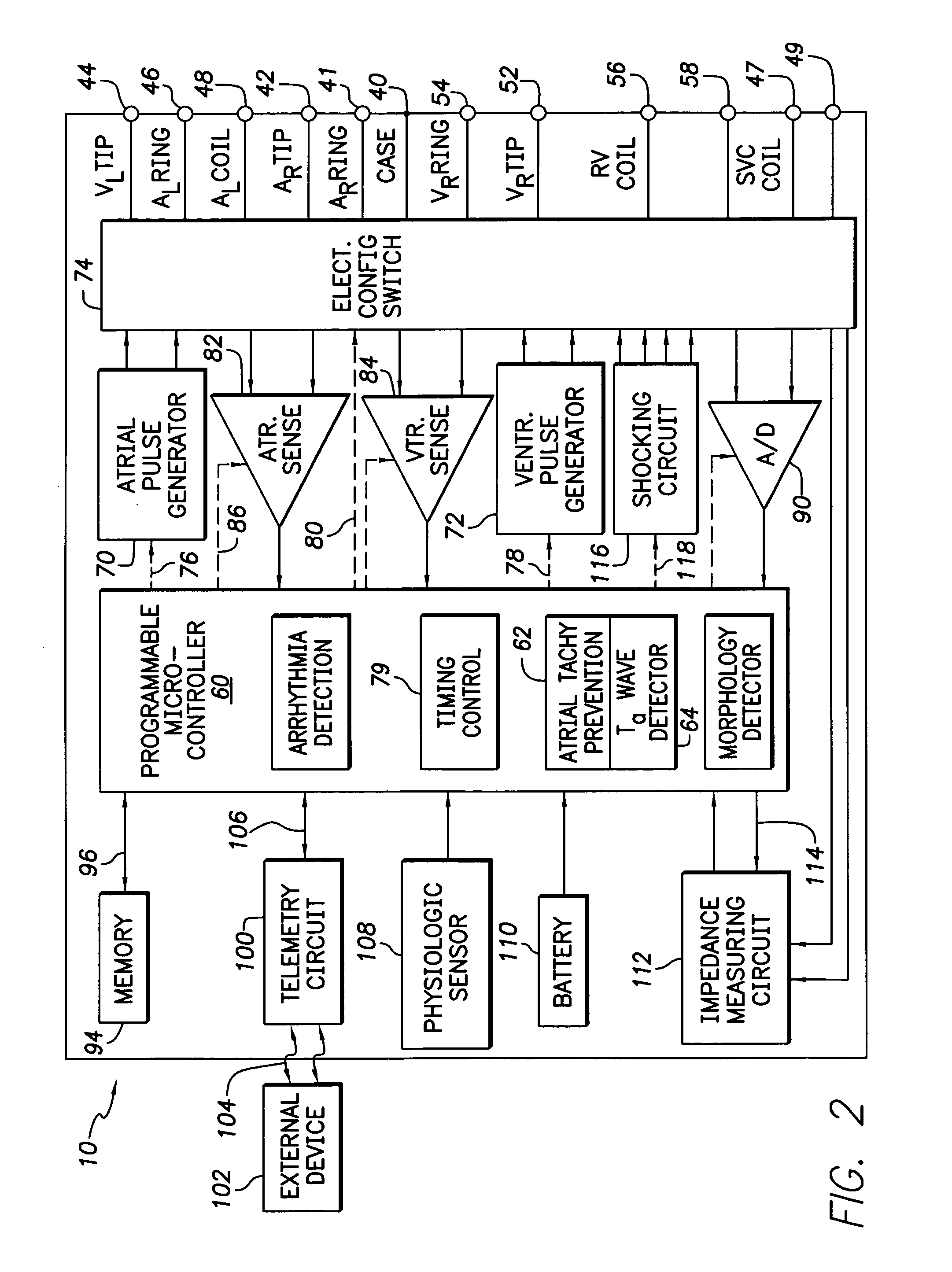
Apparatus for detecting atrial arrhythmias in the treatment of disorders of the heartbeat rate in active implantable medical devices of the pacemaker, cardioverter, defribillator and / or multisite type. This device includes conventional systems, circuits and control algorithm for detecting spontaneous and stimulated ventricular events (R, V) and atrial events (P, A), indicating the delivery of a ventricular and / or atrial event, and inhibiting the detection of atrial events after detection of a ventricular event throughout a post-ventricular atrial absolute refractory period (PVAARP). Detecting atrial events includes protecting against the detection of atrial signals that do not correspond to an atrial event that has actually occurred, in particular protecting against atrial detection of far-field signals caused by a ventricular event. The protection operates by a dynamic adjustment of the sensitivity of detection by temporarily raising (t1, t2) a detection threshold (ΔS1, ΔS2) after detection of a ventricular event without detection of a preceding (spontaneous or stimulated) atrial event during the same cardiac cycle.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Use of autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters inhibition and atrial parasympathetic fibers ablation for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to preserve drug effects
InactiveUSRE42961E1Increased occurrence of initiation of atrial flutterShorten the construction periodDiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsNervous systemRight atrium
Atrial arrhythmias, a major contributor to cardiovascular morbidity, are believed to be influenced by autonomic nervous system tone. The main purpose of this invention was to highlight new findings that have emerged in the study of effects of autonomic nervous system tone on atrial arrhythmias, and its interaction with class III antiarrhythmic drug effects. This invention evaluates the significance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation by determining the effects of autonomic nervous system using a vagal and stellar ganglions stimulation, and by using autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters infusion (norepinephrine, acetylcholine). This invention evaluates the autonomic nervous system effects on the atrial effective refractory period duration and dispersion, atrial conduction velocity, atrial wavelength duration, excitable gap duration during a stable circuit (such atrial flutter circuit around an anatomical obstacle), and on the susceptibility of occurrence (initiation, maintenance and termination) of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias in canine. This invention also evaluates whether autonomic nervous system activation effects via a local neurotransimitters infusion into the right atria can alter those of class III antiarrhythmic drug, sotalol, during a sustained right atrial flutter. This invention represents an emergent need to set-up and develop a new class of anti-cholinergic drug therapy for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to combine this new anti-cholinergic class to antiarrhythmic drugs. Furthermore, this invention also highlights the importance of a local application of parasympathetic neurotransmitters / blockers and a catheter ablation of the area of right atrium with the highest density of parasympathetic fibers innervation. This may significantly reduce the occurrence of atrial arrhythmias and may preserve the antiarrhythmic effects of any drugs used for the treatment of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing. Various embodiments are disclosed herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
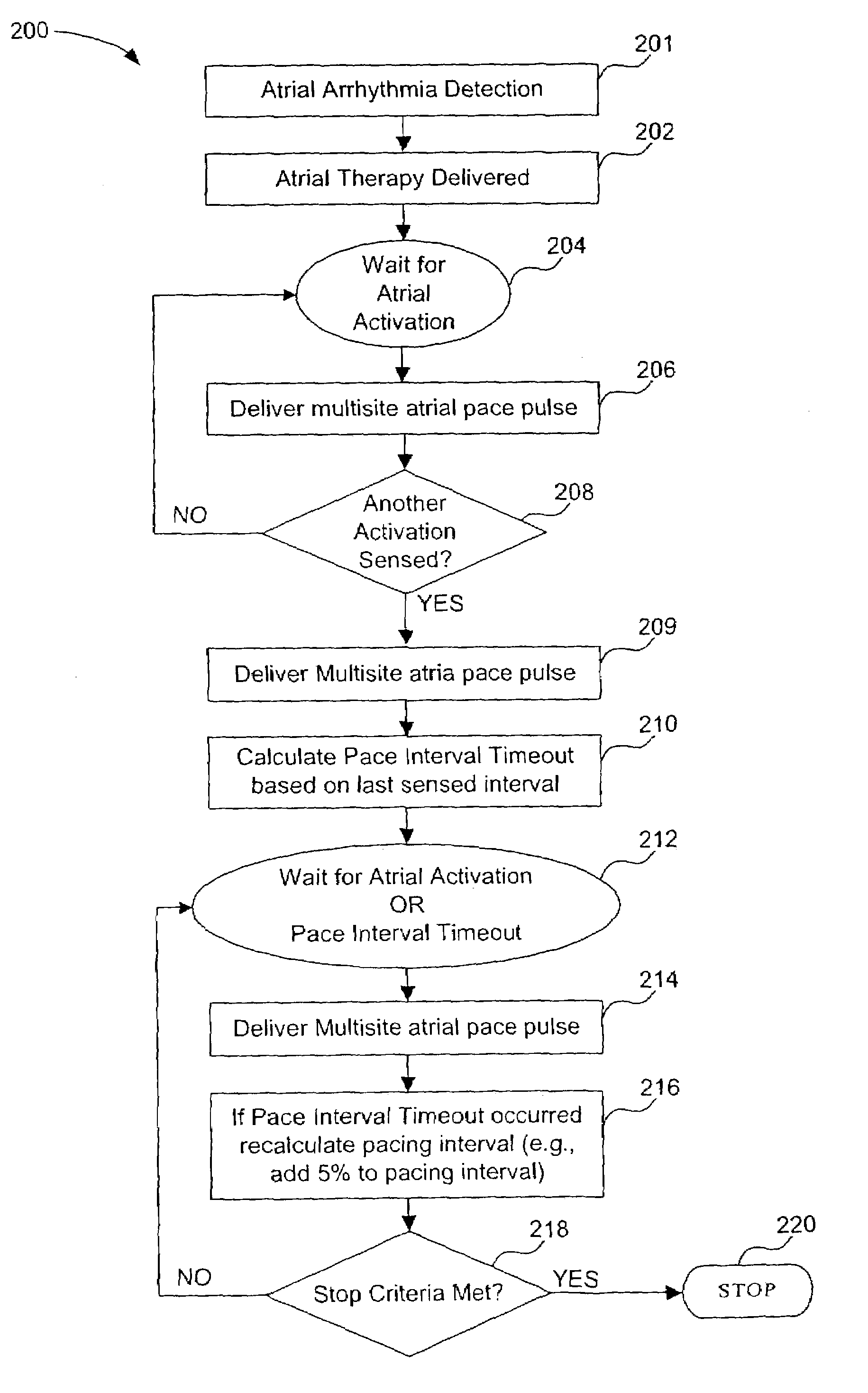
System and method for delivering post-atrial arrhythmia therapy
ActiveUS7136700B1Faster total activation timeReduce chanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsHypsarrhythmiaElectric energy
A system and method for applying atrial therapy to a human heart using a defibrillator includes detecting an atrial arrhythmia and delivering electrical energy to at least one atrium in response to a detected atrial arrhythmia. A first atrial activation is detected after delivering the electrical energy, occurrence of a detected first atrial activation defining a first moment. Finally, a first pacing pulse is delivered to a number of locations within the atria when the first atrial activation is detected. The first pacing pulse is delivered at a second moment substantially synchronous with the first moment.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for treating irregular ventricular contractions such as during atrial arrhythmia
InactiveUS20090076563A1Avoids unnecessary pacingAvoid rapid changesHeart stimulatorsPacing intervalVentricular contraction
A cardiac rhythm management system is capable of treating irregular ventricular heart contractions, such as during atrial tachyarrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. A first indicated pacing interval is computed based at least partially on a most recent V-V interval duration between ventricular beats and a previous value of the first indicated pacing interval. Pacing therapy is provided based on either the first indicated pacing interval or also based on a second indicated pacing interval, such as a sensor-indicated pacing interval. A weighted averager such as an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for sensed beats and differently adjusts the first indicated pacing interval for paced beats. The system regularizes ventricular rhythms by pacing the ventricle, but inhibits pacing when the ventricular rhythms are stable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
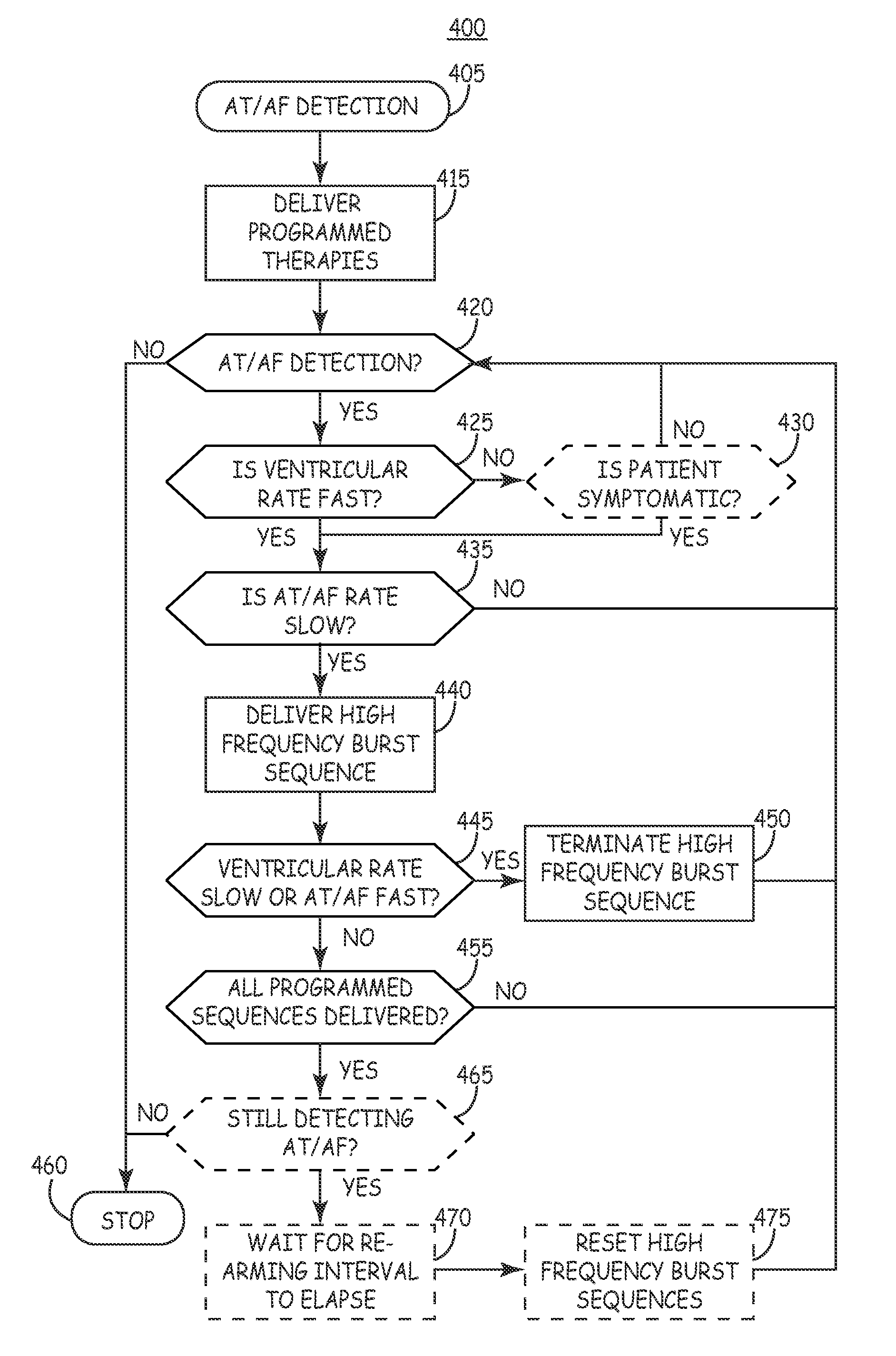
High frequency atrial burst pacing for improved ventricular rate control during atrial arrhythmias
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
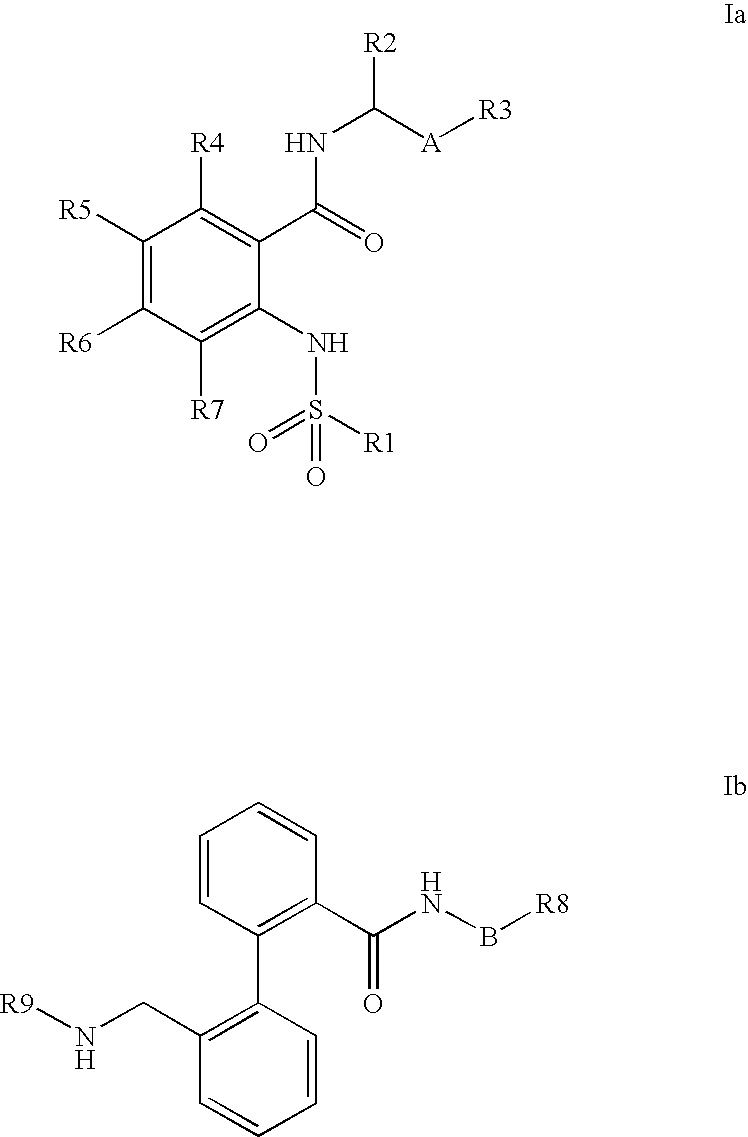
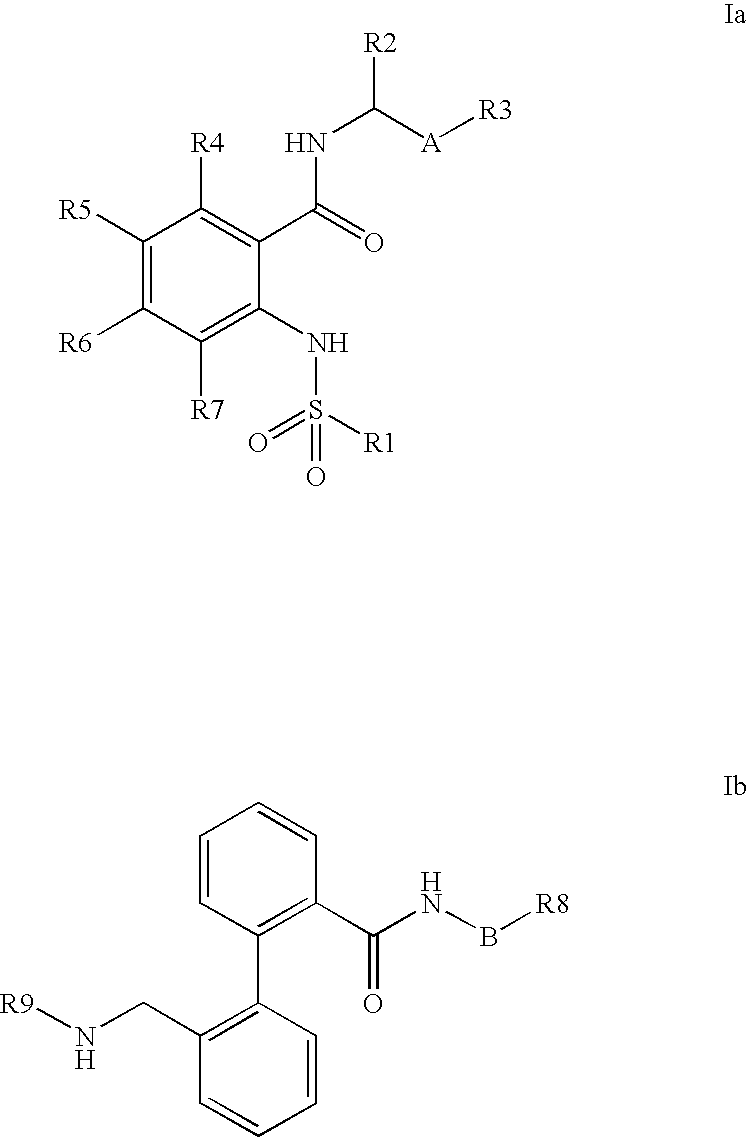
Combination of phenylcarboxylic acid amides with beta-adrenoreceptor blockers and their use for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias
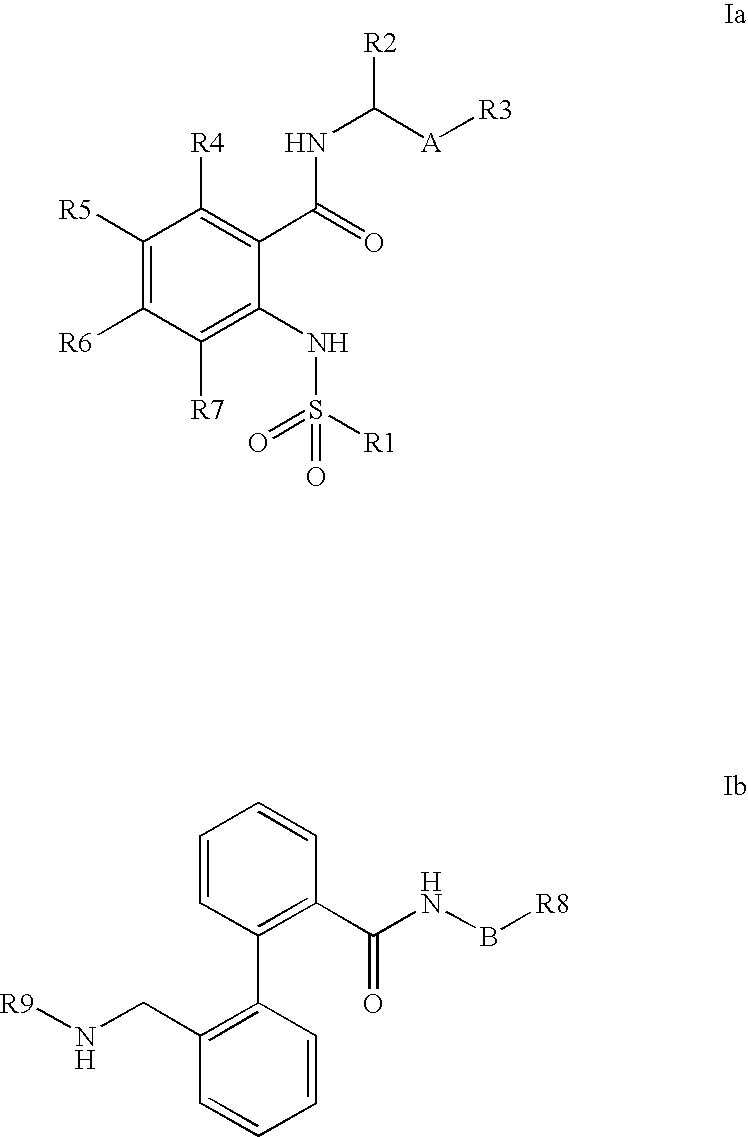
The invention relates to the combination of one or more beta-blockers and of one or more Kv1.5 blockers, in particular phenylcarboxamides of the formula la and / or lb and / or physiologically tolerable salts thereof, and the use of the combination for the treatment or prophylaxis of atrial arrhythmias.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Delay to therapy following patient controlled atrial shock therapy request
InactiveUS20060079939A1Provide slackOptimization mechanismHeart defibrillatorsImplanted devicePhysical therapy
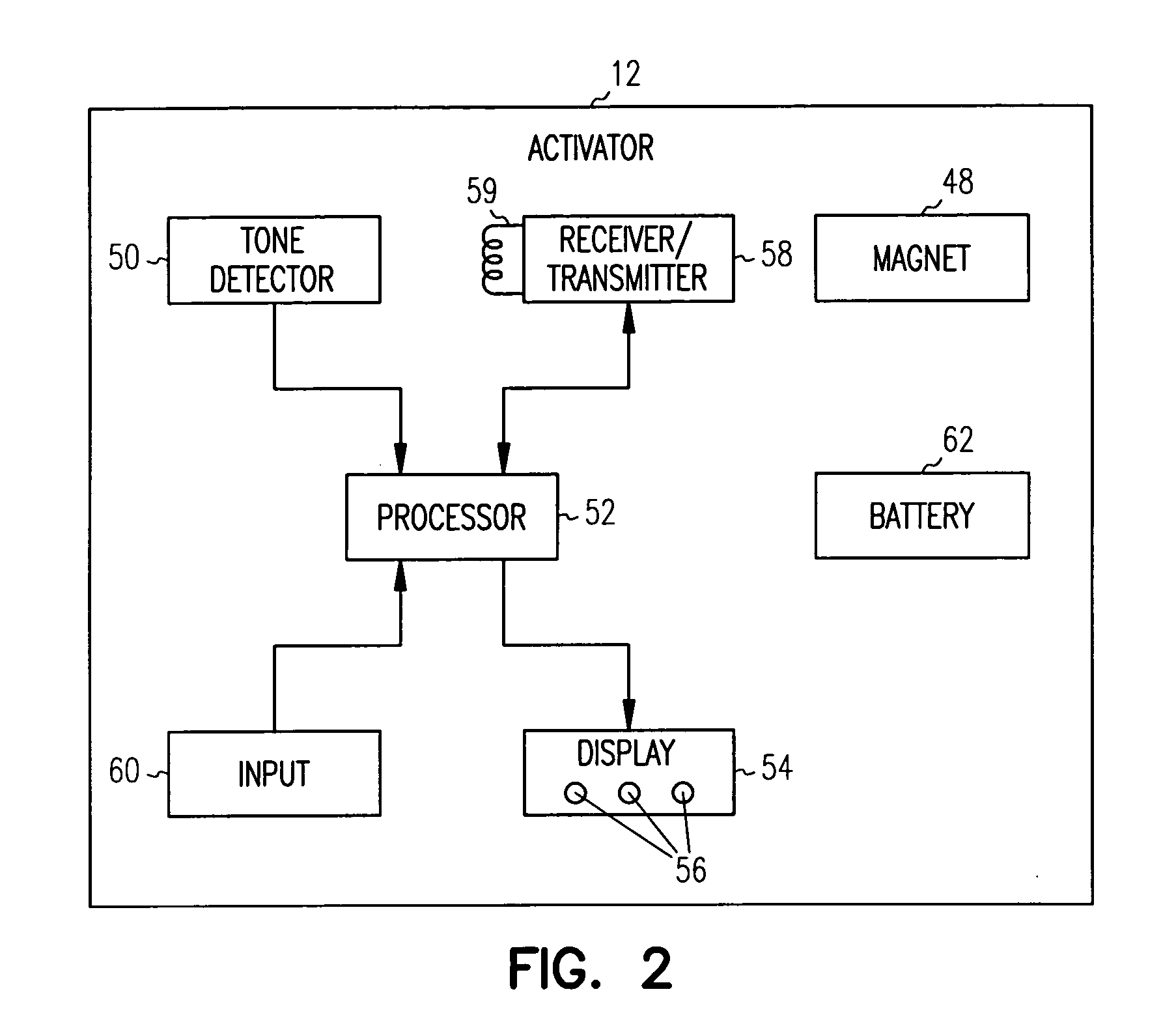
An implantable cardiac device detects a patient therapy request originating from external to the implantable device. A shock therapy delay period is timed in response to the detection of the patient therapy request. Atrial shock therapy is provided to the patient after expiration of the shock therapy delay period (if the presence of an ongoing atrial arrhythmia is detected). The patient therapy request may be provided by a patient activator including a magnet for operating a reed switch in the implanted device to provide the request. A patient activator including an input and receiver / transmitter circuitry may be employed to request the immediate providing of atrial shock therapy, and / or to set the duration the shock therapy delay period. By allowing specific delays to therapy after a therapy request, a patient can prepare for the requested therapy and thereby mitigate therapy discomfort.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and device for low-energy termination of atrial tachyarrhythmias
ActiveCN101939044APain threshold not exceededReduced defibrillation energyInternal electrodesExternal electrodesFully consciousEffective treatment
Methods for treating atrial arrhythmias can involve configuring an implantable arrhythmia treatment device. A device can be configured after implantation when the patient is fully conscious and after any pain suppression medication has worn off. The device is caused to apply a phased unpinning far field therapy to the patient in response to detection of an arrhythmia via a far field configuration of electrodes. An indication of a pain sensation of the patient and the effectiveness of the treatment in response to the therapy can then be received. In response, at least one of a set of therapy parameters is adjusted and the steps are repeated until it is determined that an effective treatment is provide at a pain sensation that is tolerable to the patient. The device is then programmed to automatically treat arrhythmias detected in the patient with the determined set of therapy parameters.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
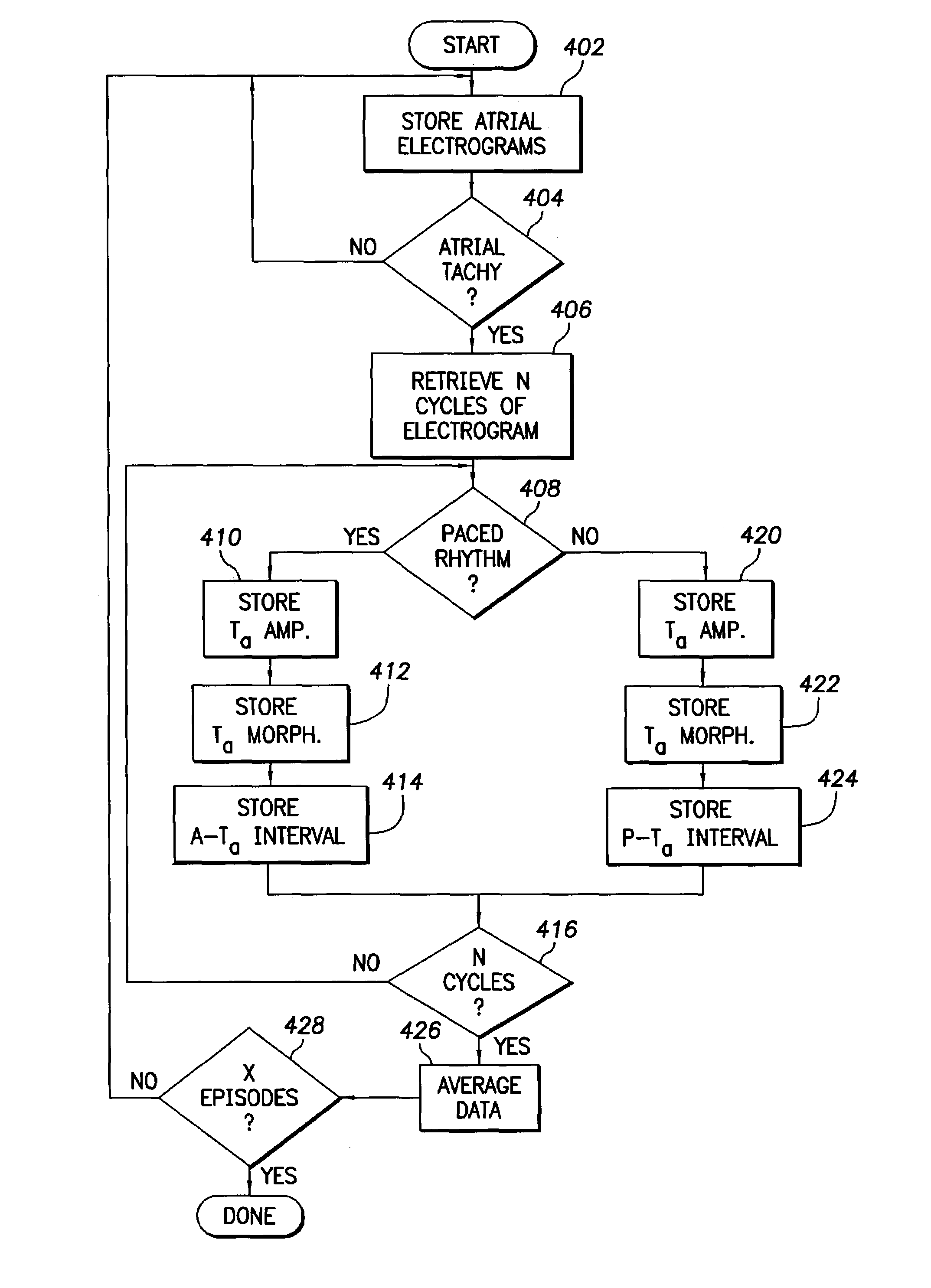
Implantable cardiac stimulation device, system and method that identifies and prevents impending arrhythmias of the atria
An implantable cardiac stimulation device includes a system that identifies and prevents the occurrence of impending atrial arrhythmias. A sensing circuit senses atrial activity of a patient's heart to provide an atrial activity signal. A processor compares the atrial activity signal to a predetermined standard indicative of an impending accelerated atrial arrhythmia to identify an impending accelerated atrial arrhythmia. A therapy circuit provides accelerated atrial arrhythmic preventive therapy to the patient when an impending accelerated atrial arrhythmia is identified. Data associated with the identification and therapy delivery is stored in a memory.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com