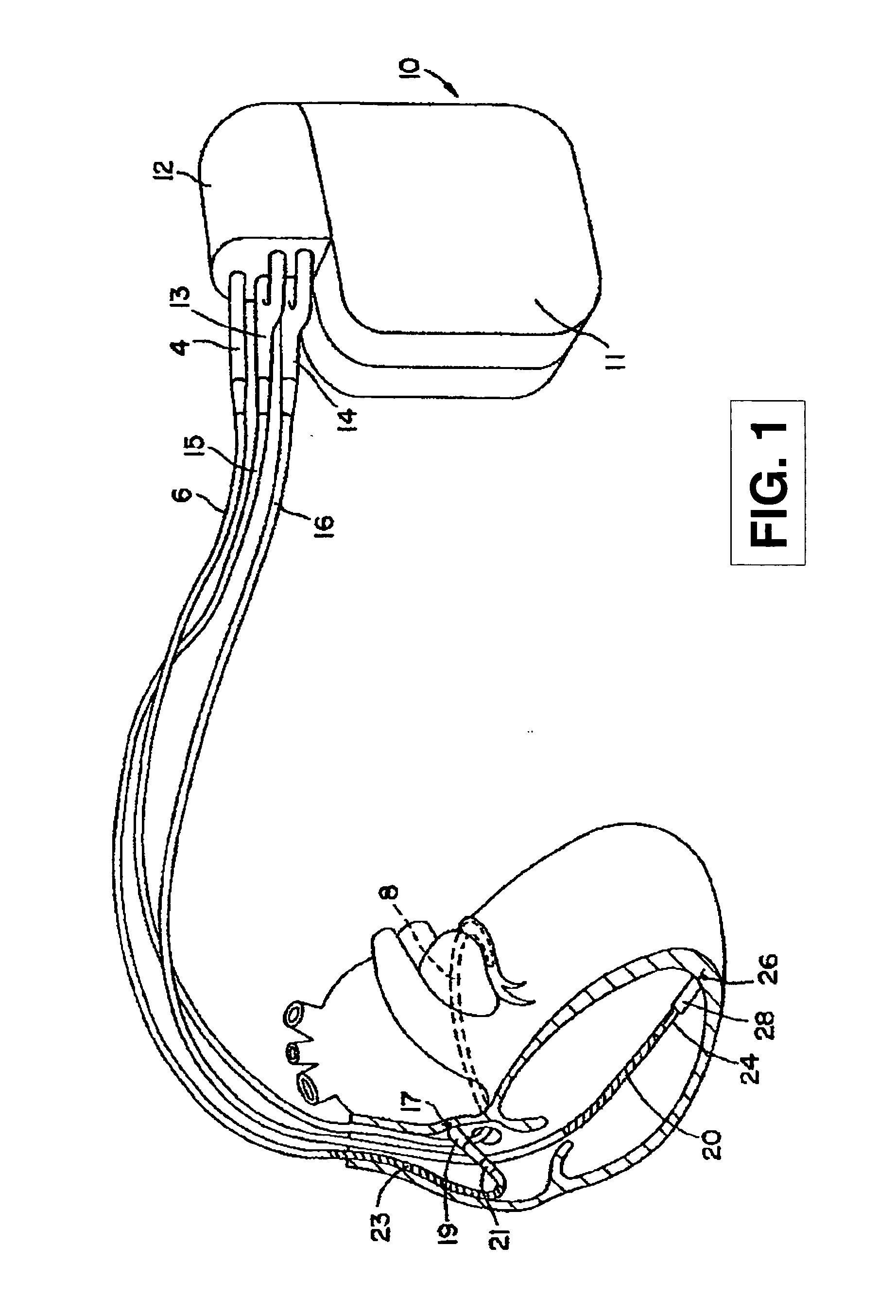
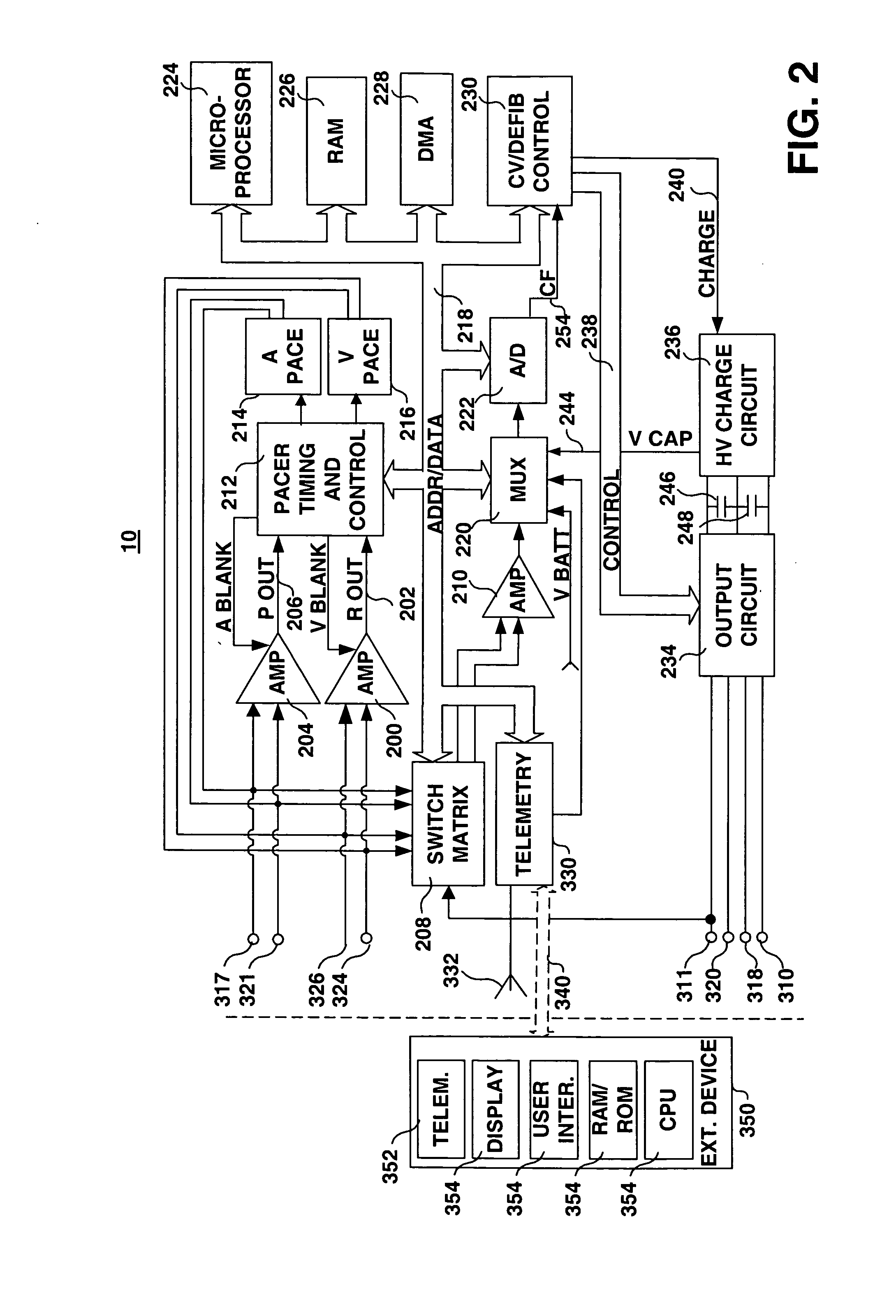
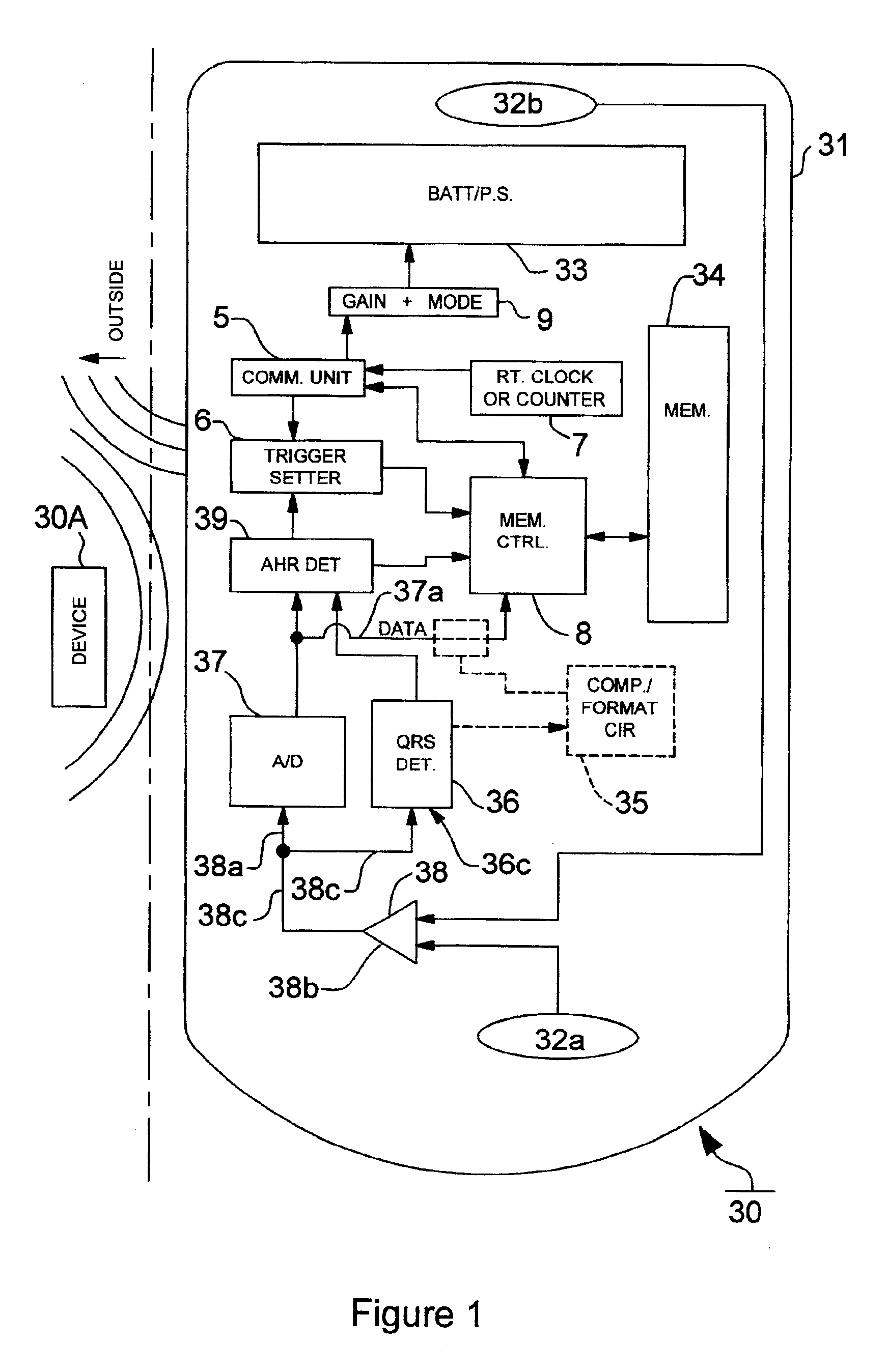
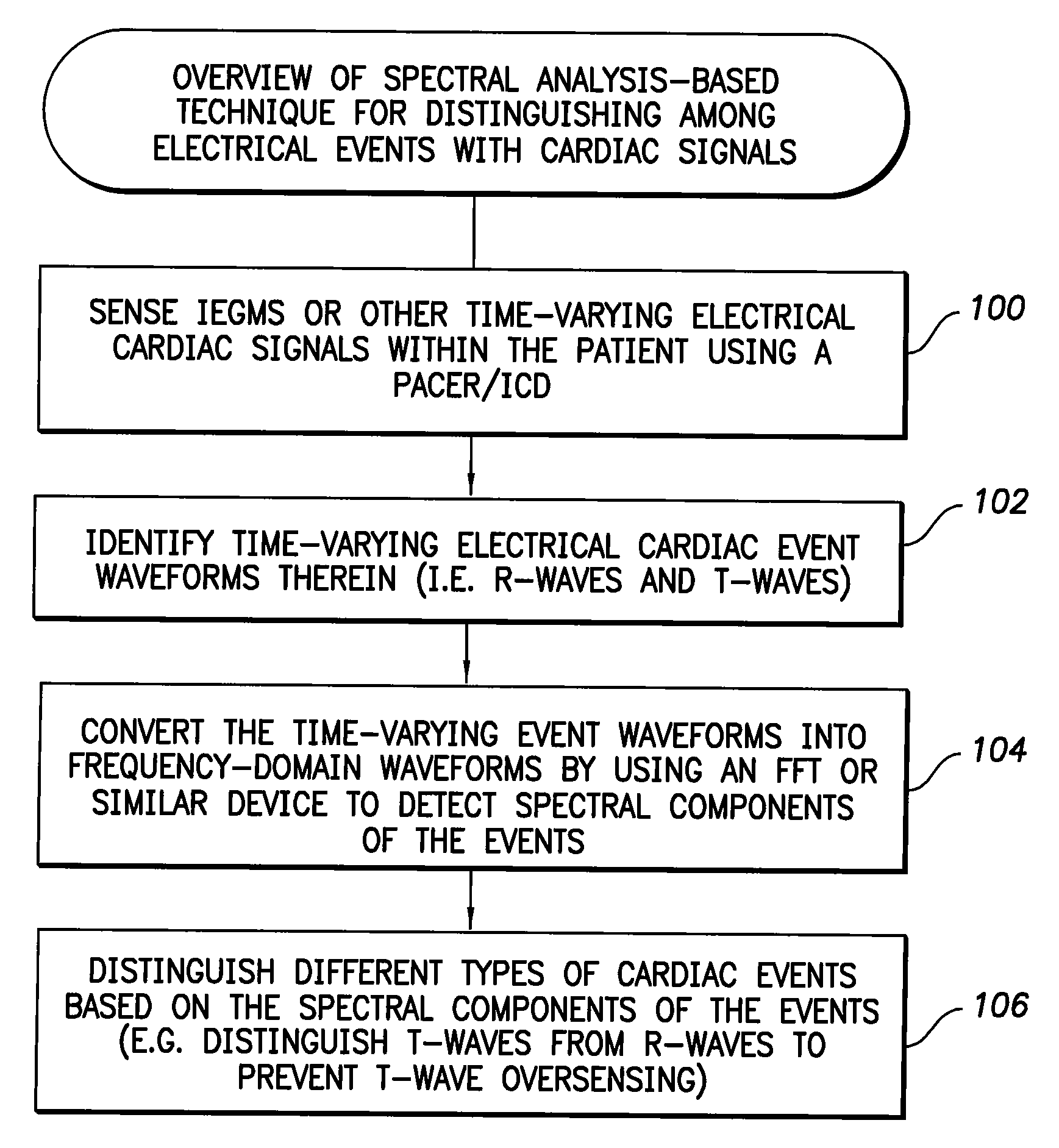
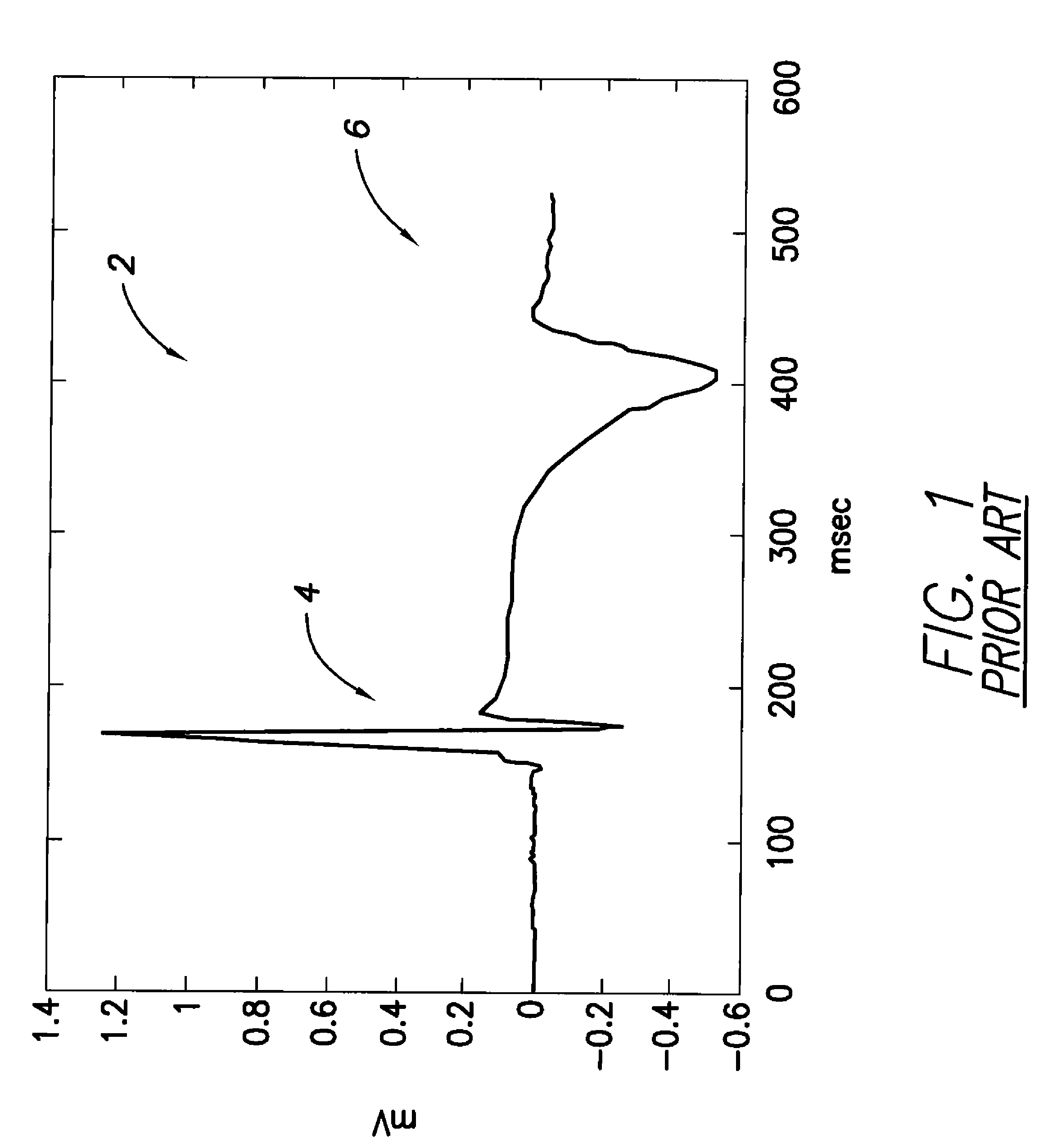
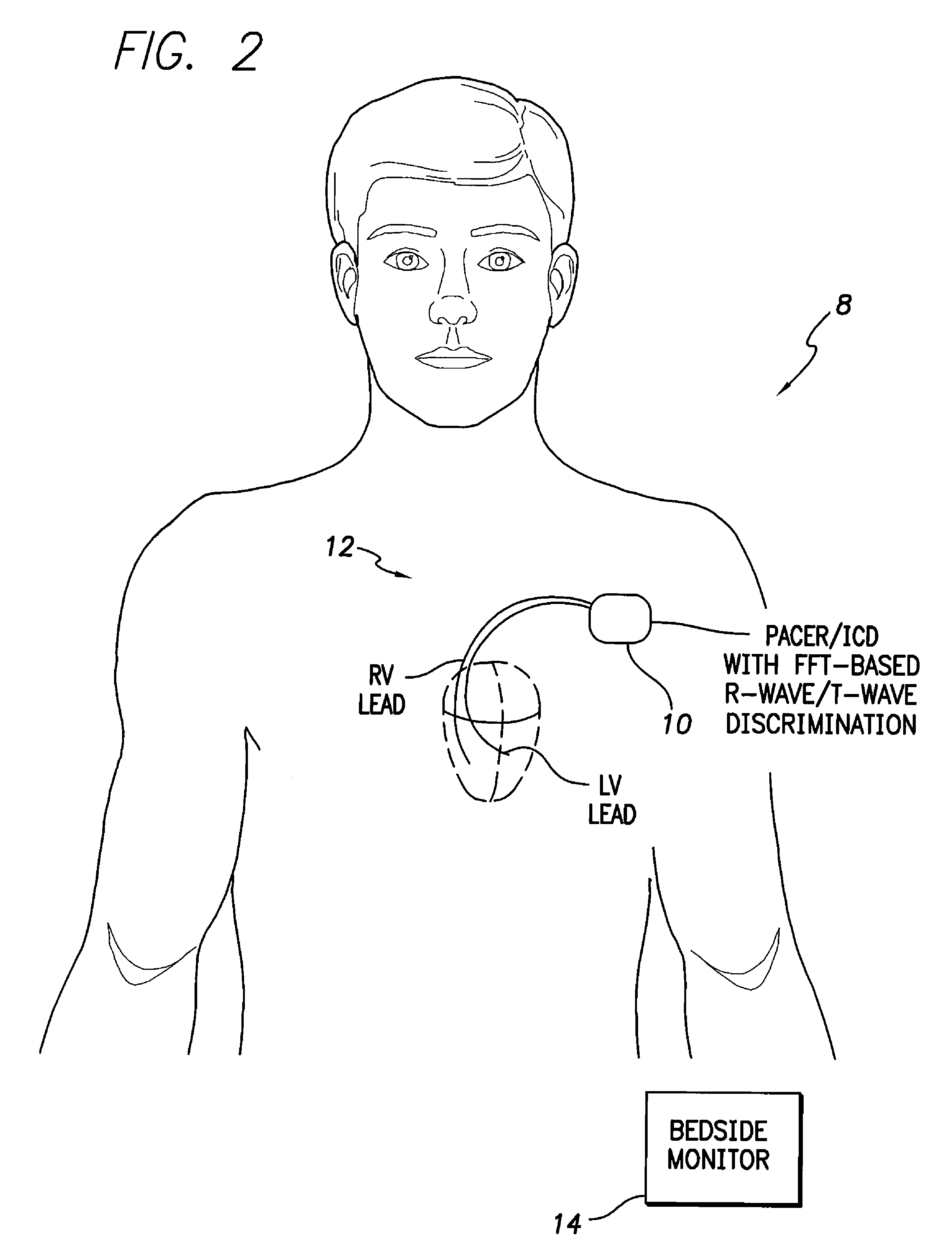
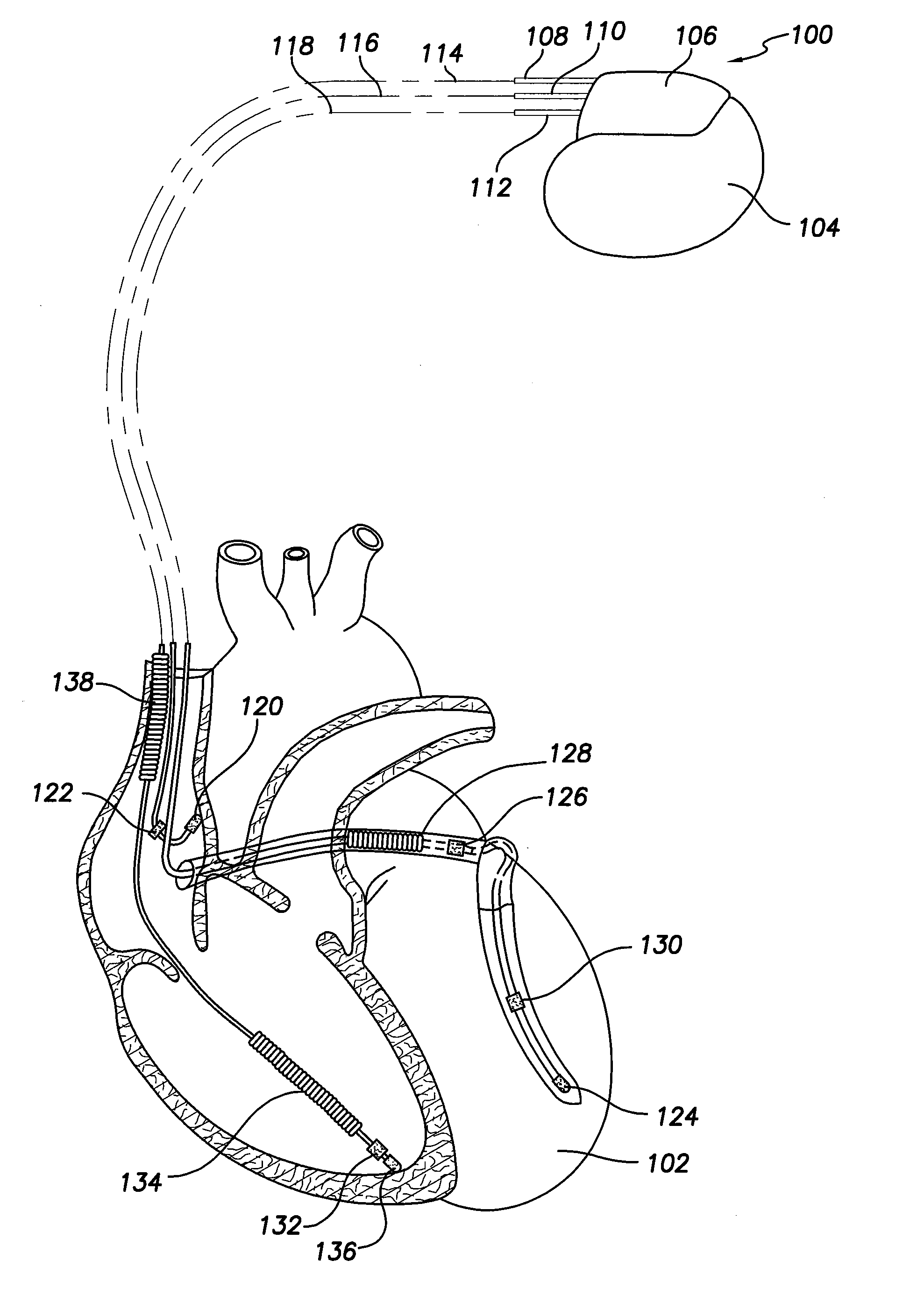
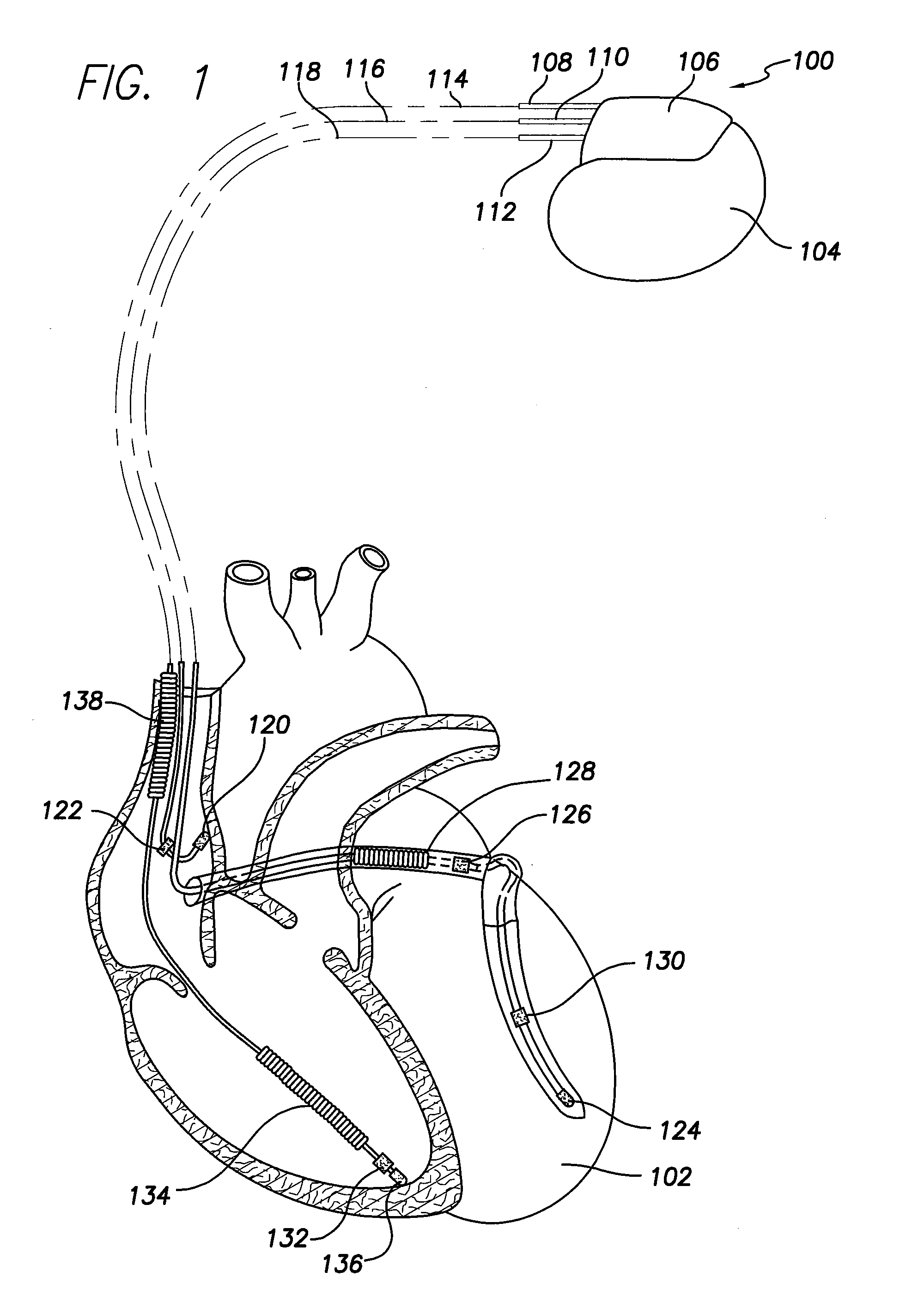
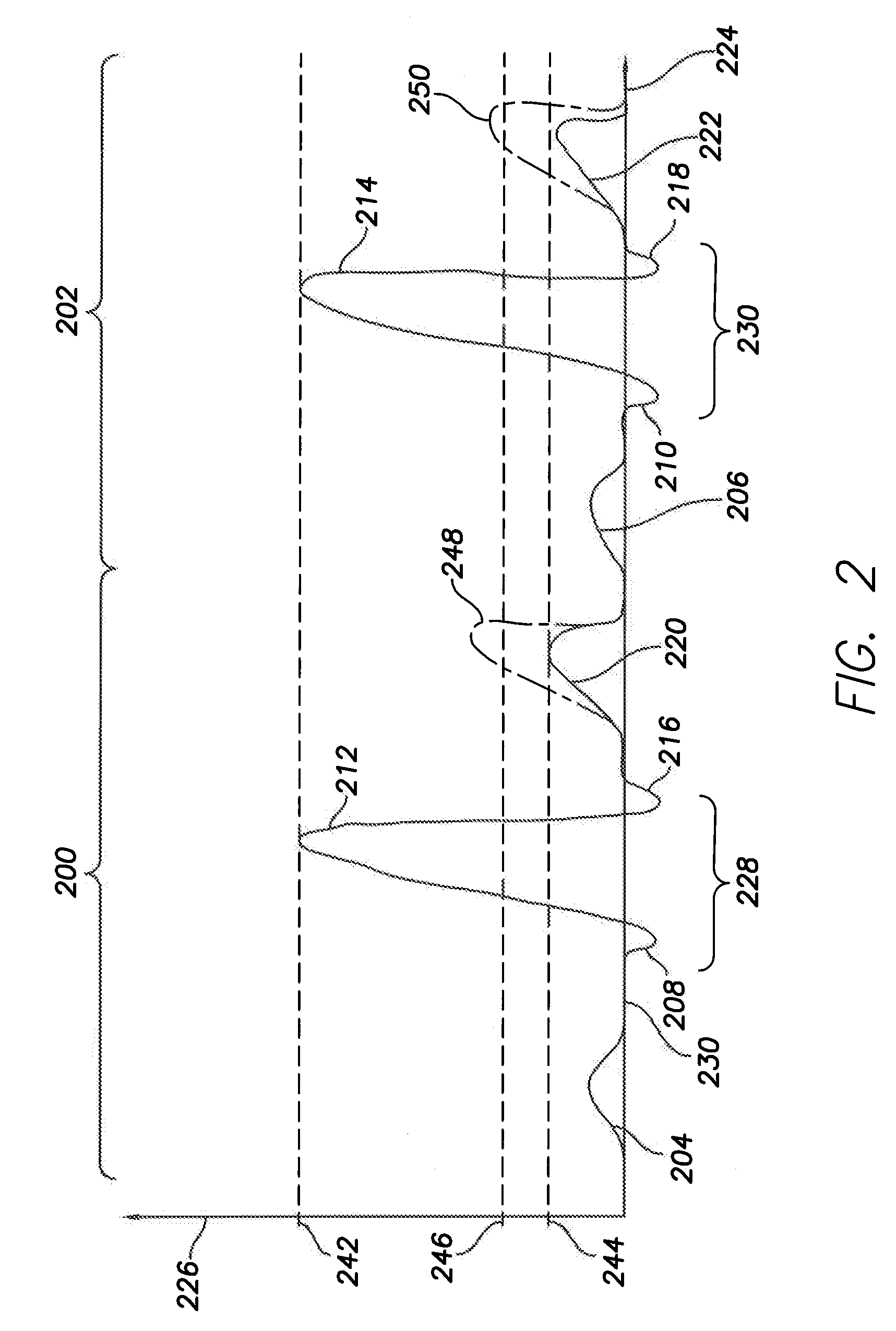
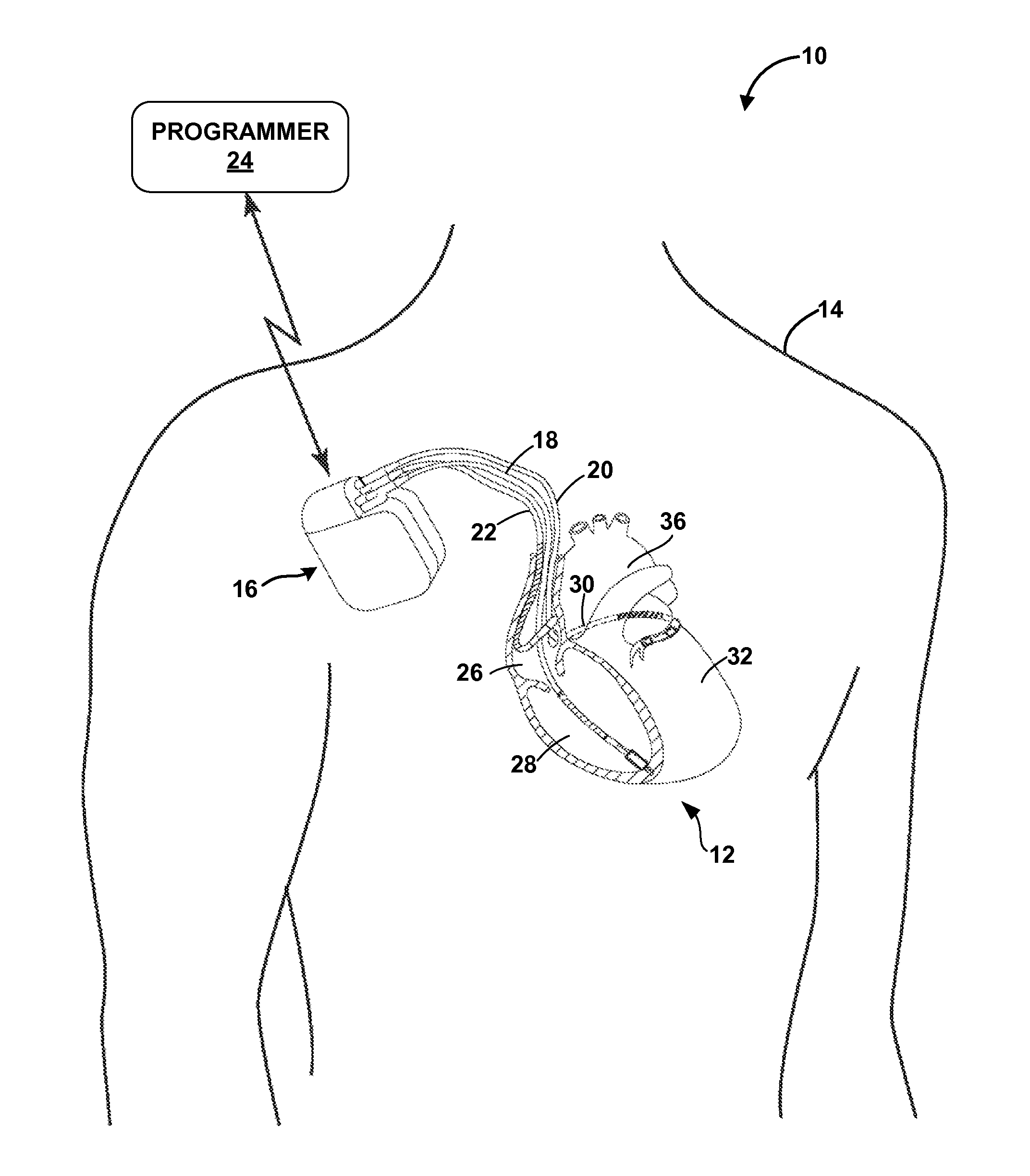
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Ventricular rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Most normal heart rates are in the range of 60 to 100 beats a minute. Ventricular tachycardia can result in rates as high as 170 beats a minute or even more.
Wavelet based feature extraction and dimension reduction for the classification of human cardiac electrogram depolarization waveforms
ActiveUS20080109041A1Improve accuracyPrecise processElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac pacemaker electrodeClassification methods
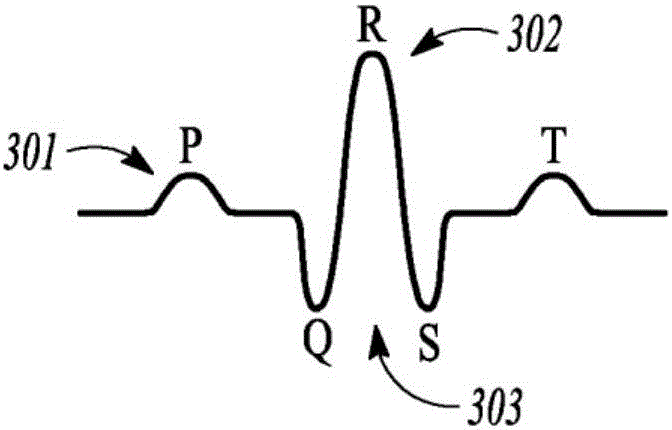
A depolarization waveform classifier based on the Modified lifting line wavelet Transform is described. Overcomes problems in existing rate-based event classifiers. A task for pacemaker / defibrillators is the accurate identification of rhythm categories so correct electrotherapy can be administered. Because some rhythms cause rapid dangerous drop in cardiac output, it's desirable to categorize depolarization waveforms on a beat-to-beat basis to accomplish rhythm classification as rapidly as possible. Although rate based methods of event categorization have served well in implanted devices, these methods suffer in sensitivity and specificity when atrial / ventricular rates are similar. Human experts differentiate rhythms by morphological features of strip chart electrocardiograms. The wavelet transform approximates human expert analysis function because it correlates distinct morphological features at multiple scales. The accuracy of implanted rhythm determination can then be improved by using human-appreciable time domain features enhanced by time scale decomposition of depolarization waveforms.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method and apparatus for generating a template for arrhythmia detection and electrogram morphology classification
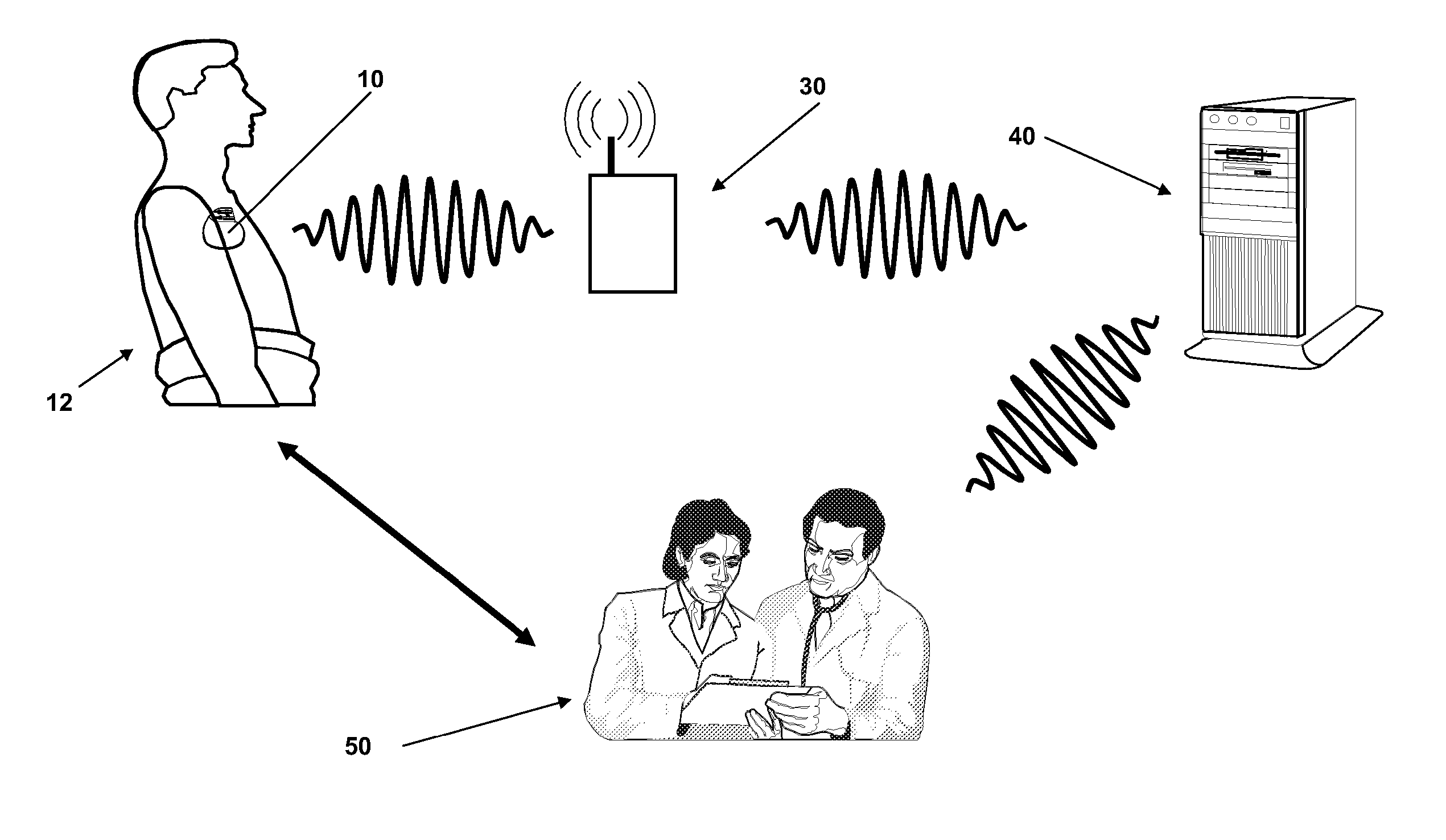
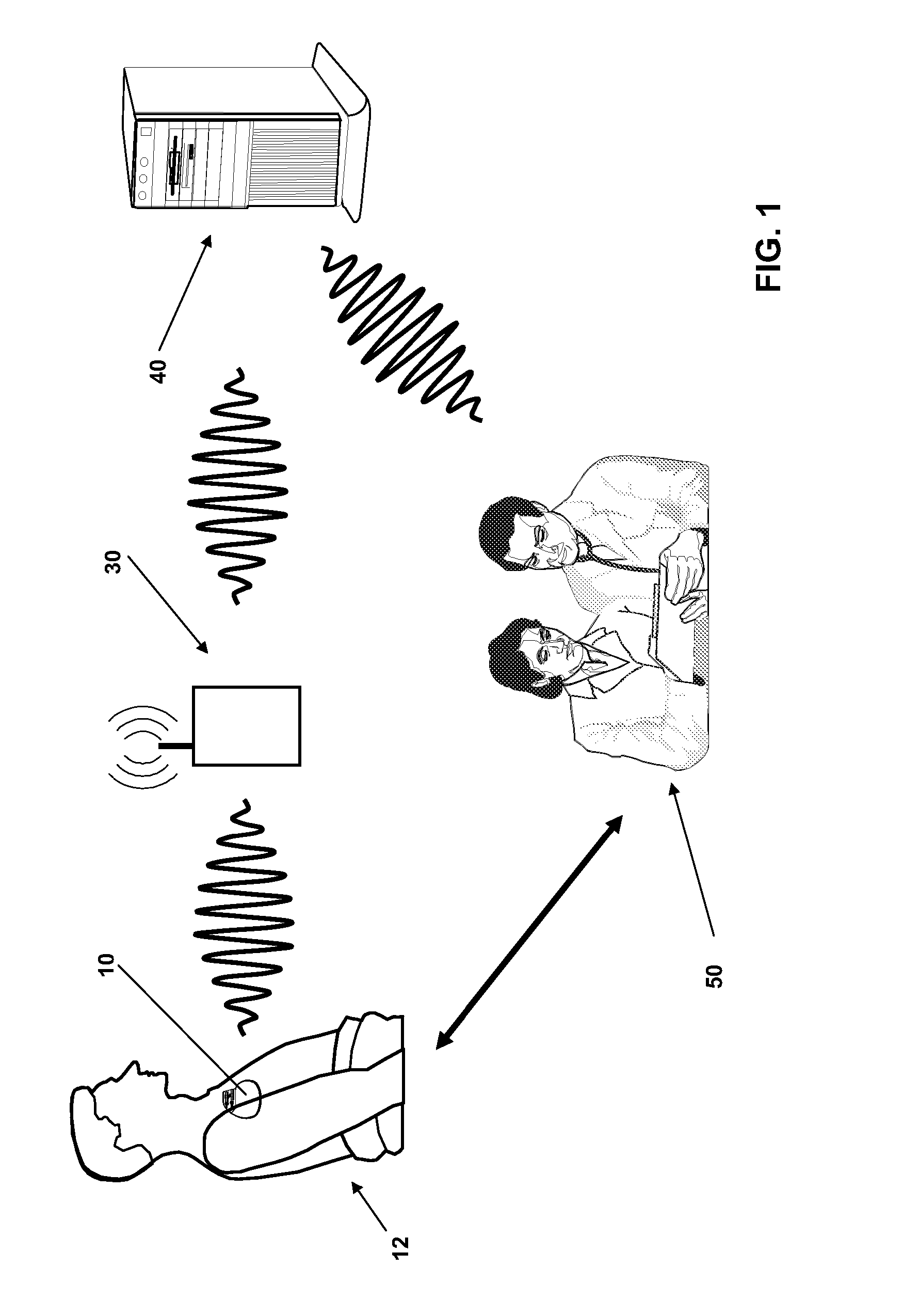
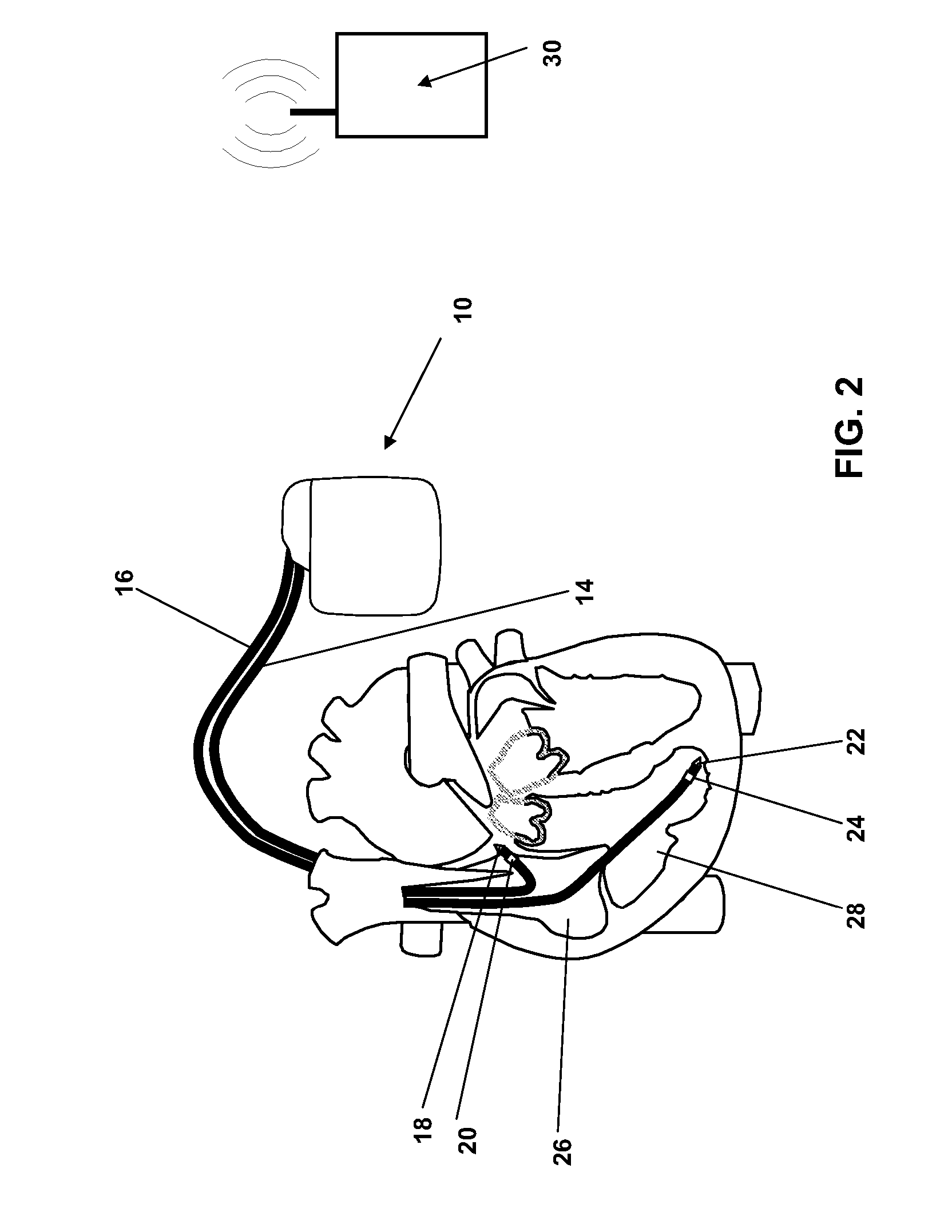
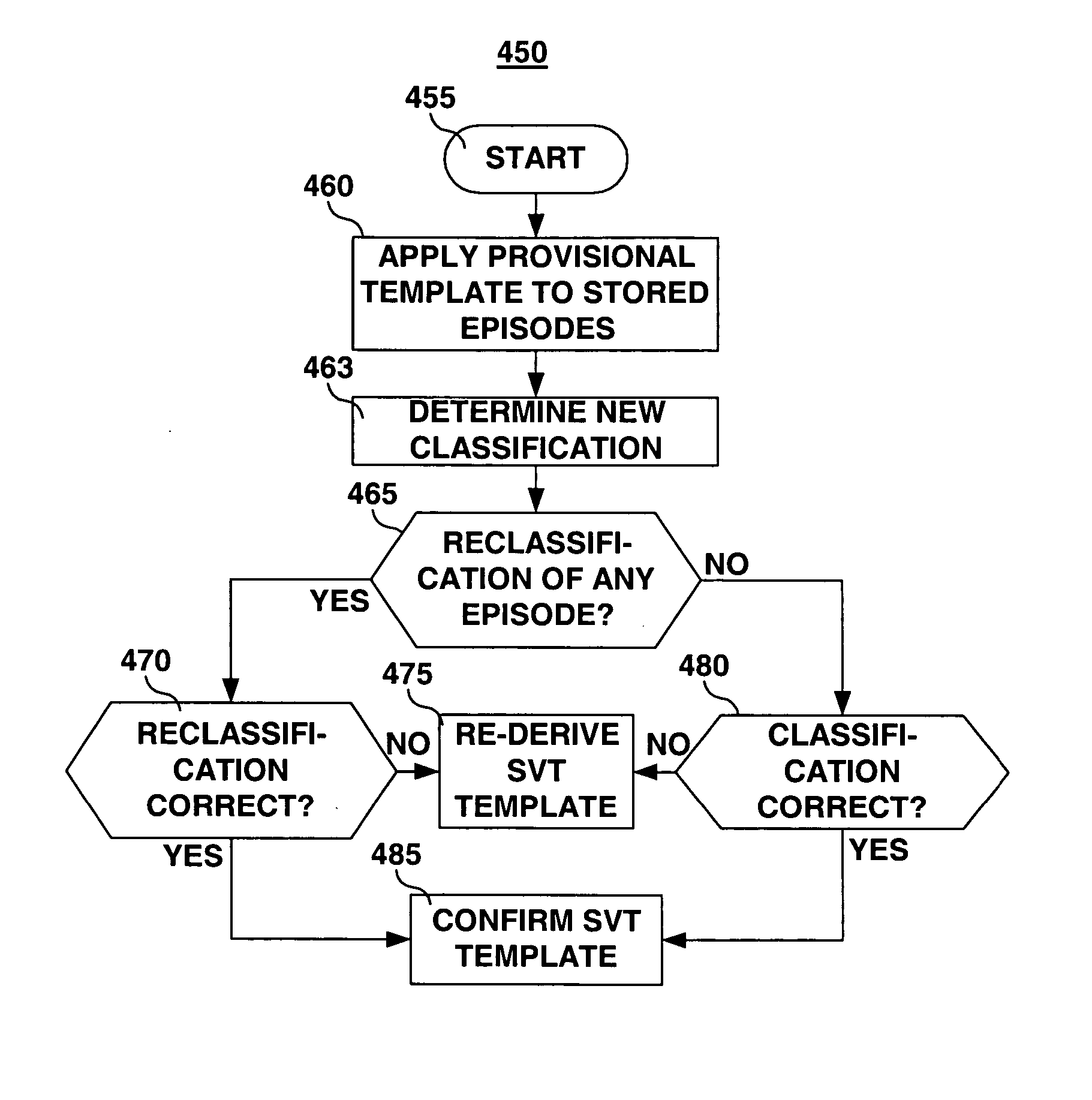
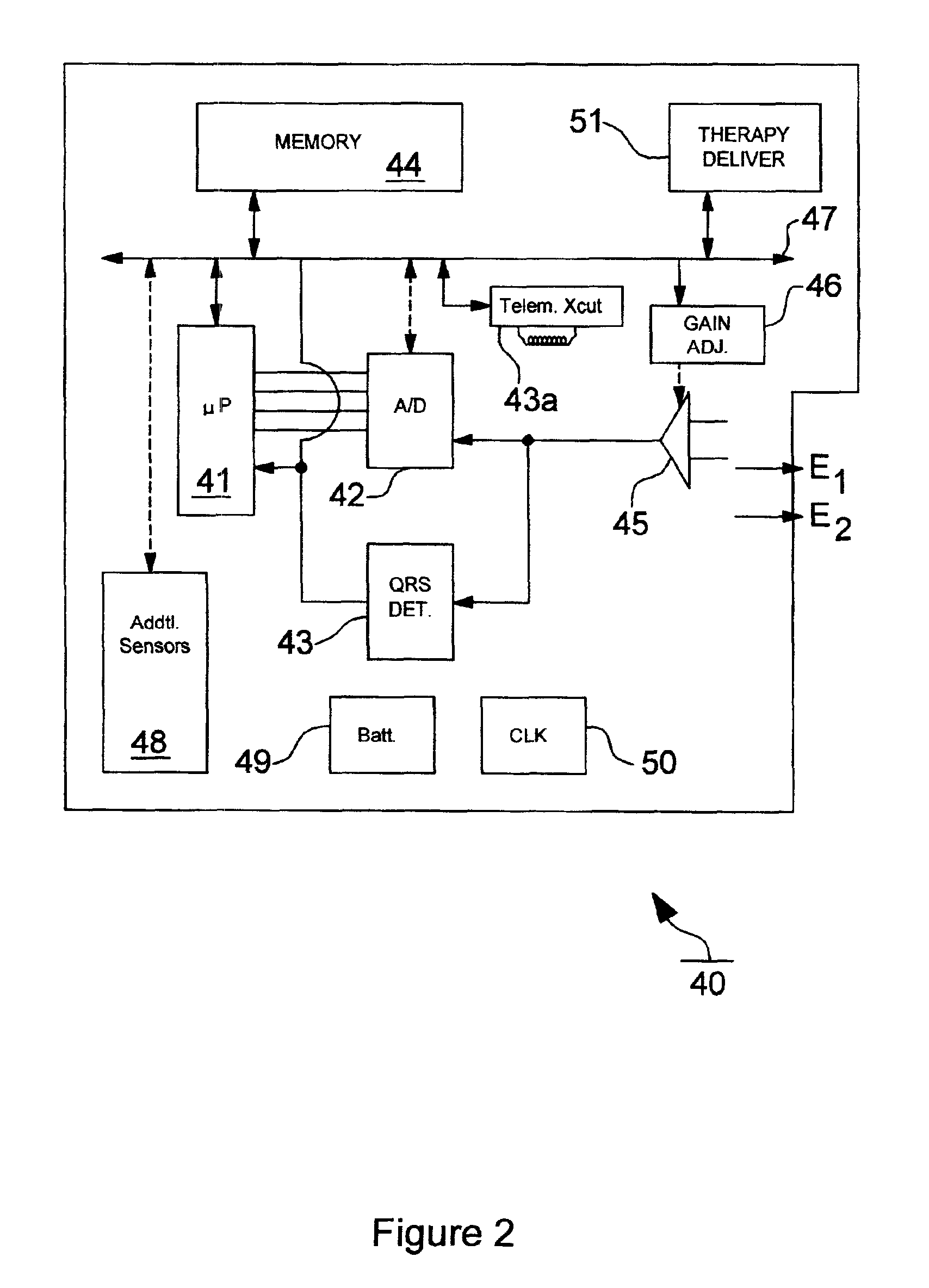
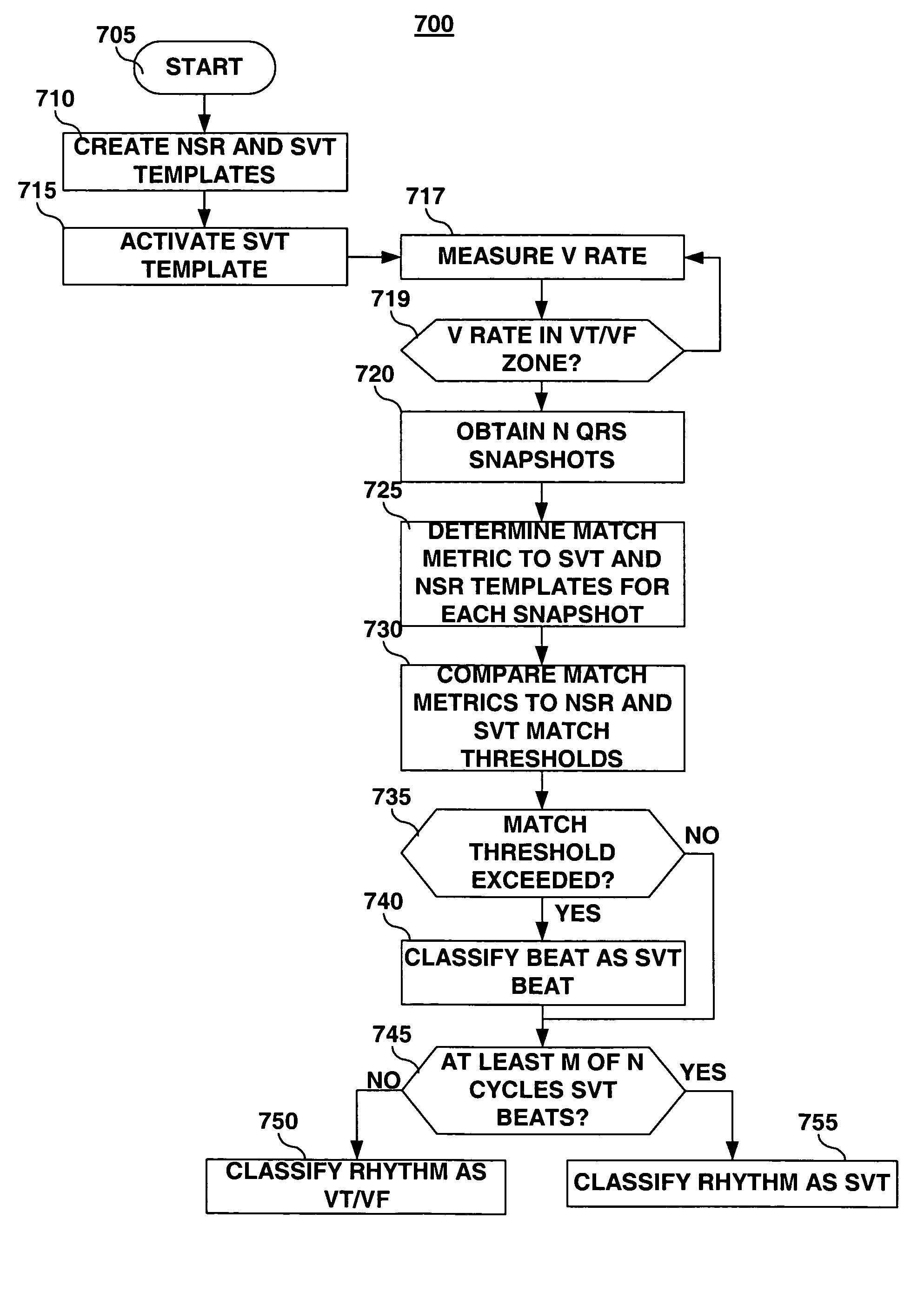
An implantable medical device and associated method for automatically generating morphology templates during fast cardiac rhythms, confirming a provisional template as a confirmed template, and using the confirmed template to classify subsequent detected arrhythmias. A provisional SVT template may be created during a fast ventricular rate and activated as a confirmed SVT template upon verification that the fast rate was due to an SVT. The confirmed SVT template may be used to discriminate SVT from VT / VF.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
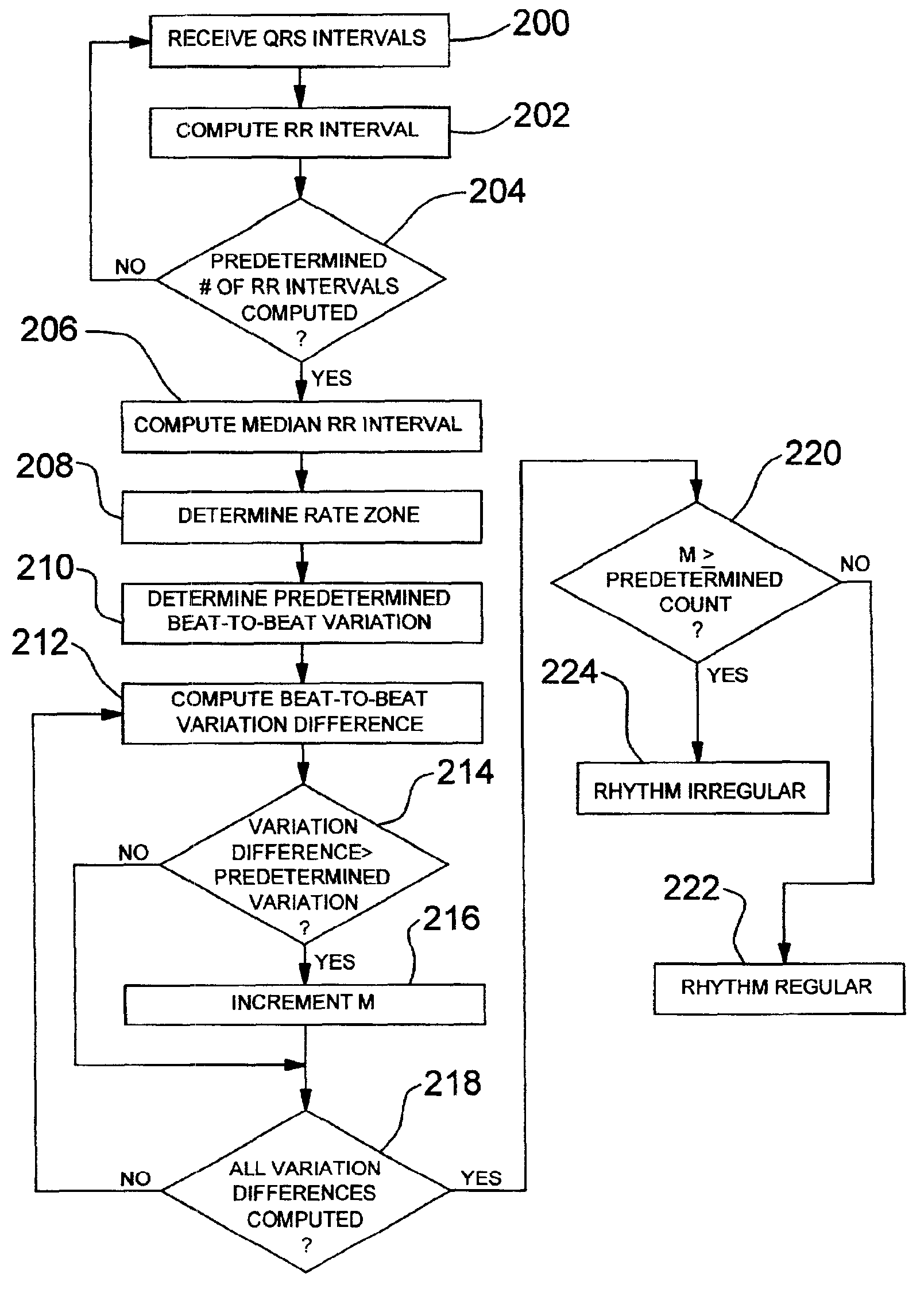
Method and apparatus for discrimination atrial fibrillation using ventricular rate detection
A method and apparatus for method for discriminating heart rhythms includes computing a first predetermined number of RR intervals from received QRS intervals, and computing a median RR interval corresponding to a predetermined number of the first predetermined number of RR intervals. A predetermined beat-to-beat variation and a corresponding predetermined count are determined based on the computed median RR interval. Beat-to-beat variation differences between the first predetermined number of RR intervals are computed and a determination is made as to whether the computed beat-to-beat variation differences are greater than the predetermined beat-to-beat variation, and as to whether a number of the computed beat-to-beat variation differences that are greater than the predetermined beat-to-beat variation is greater than the predetermined count. The heart rhythm is identified as an irregular rhythm in response to the number being greater than or equal to the predetermined count.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for generating a template for arrhythmia detection and electrogram morphology classification
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
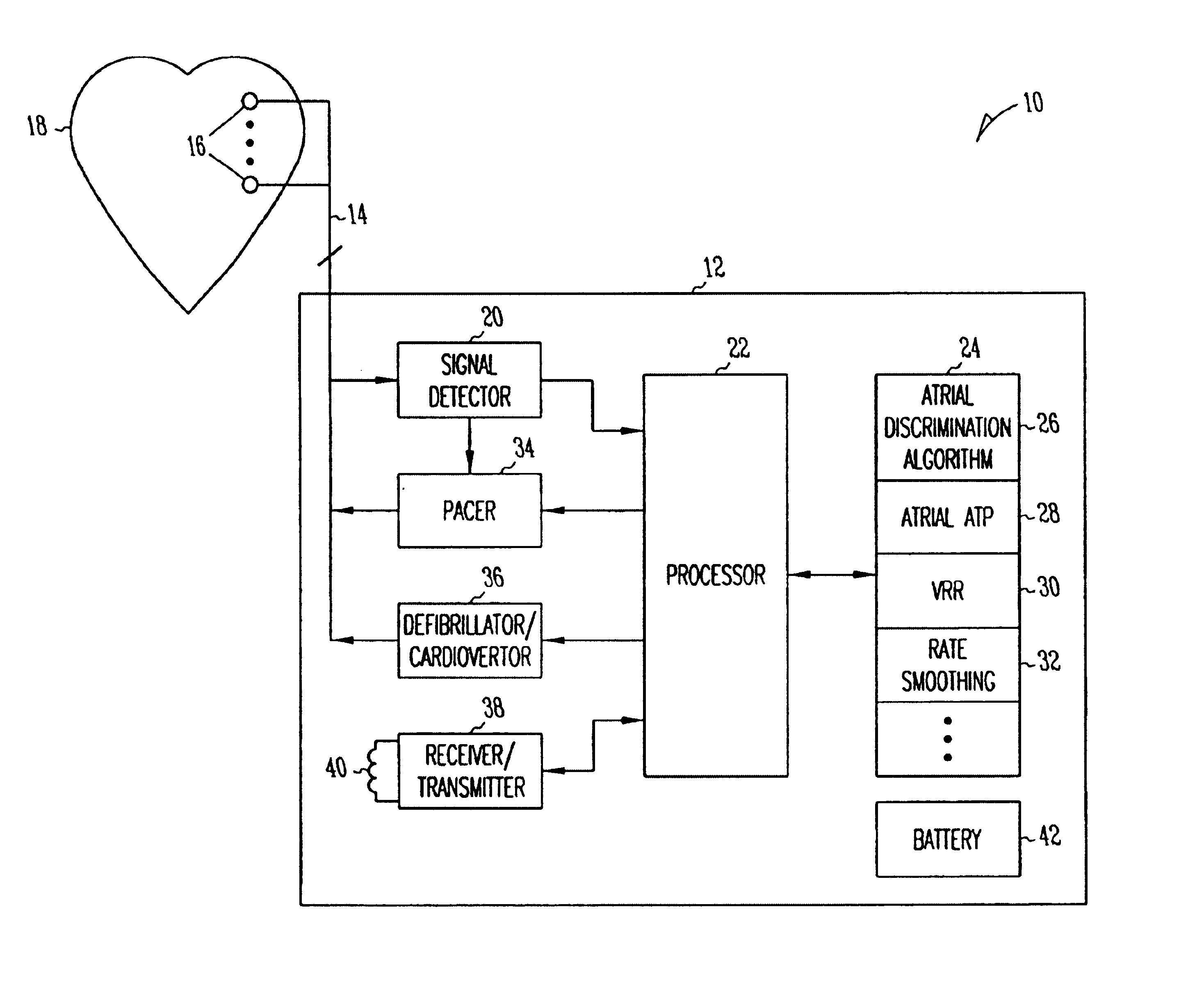
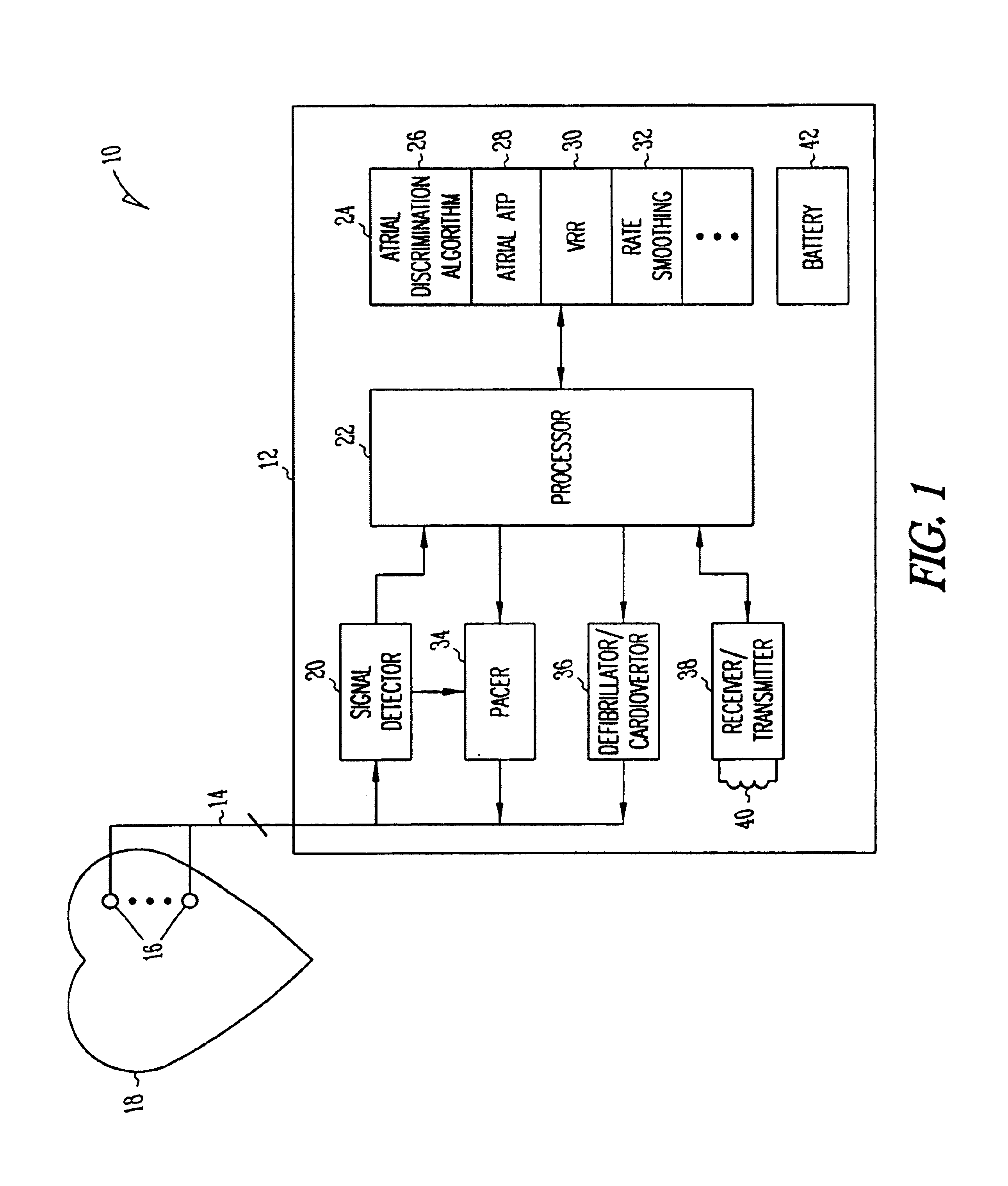
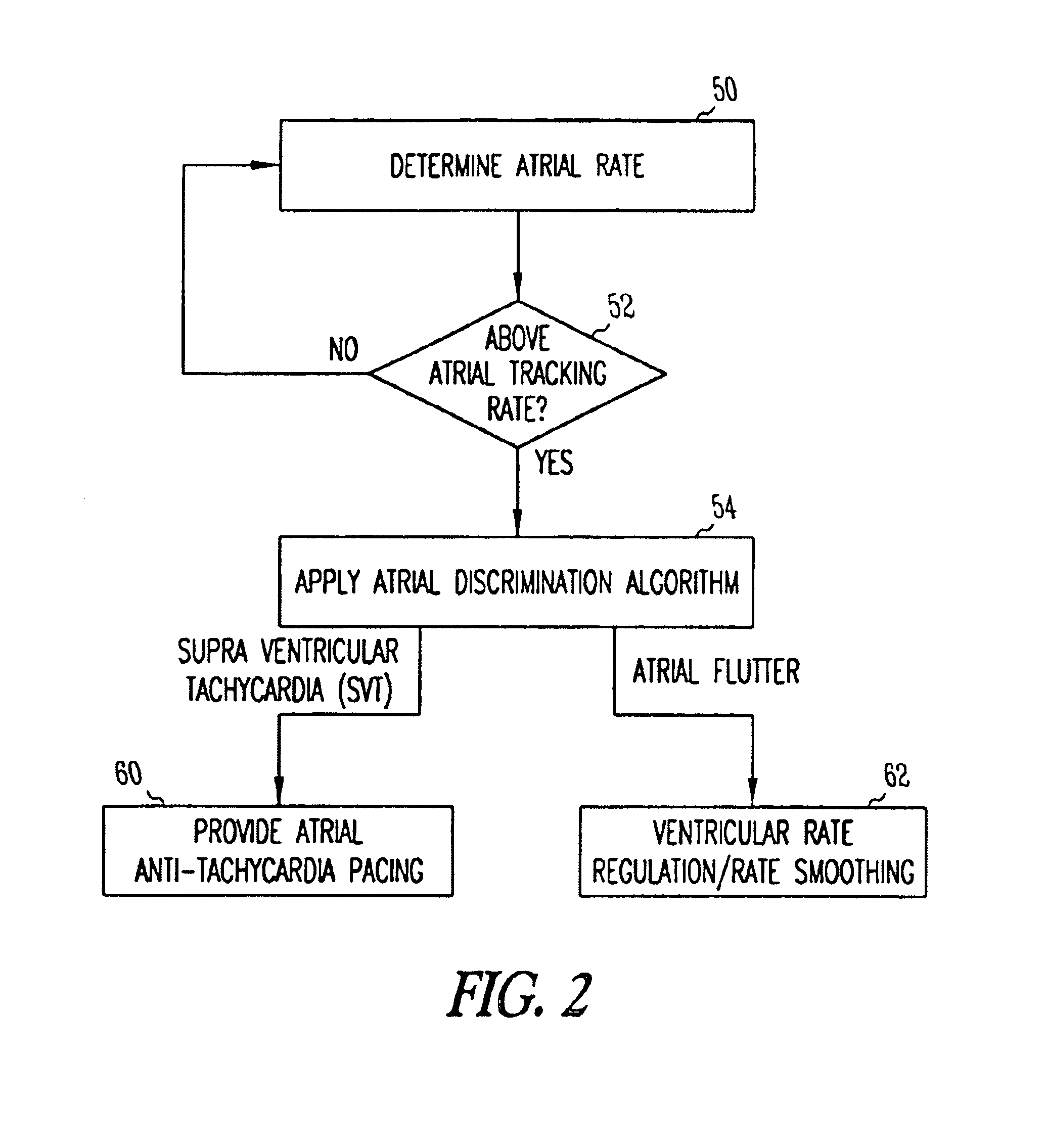
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for elimination of ventricular pro-arrhythmic effect caused by atrial therapy
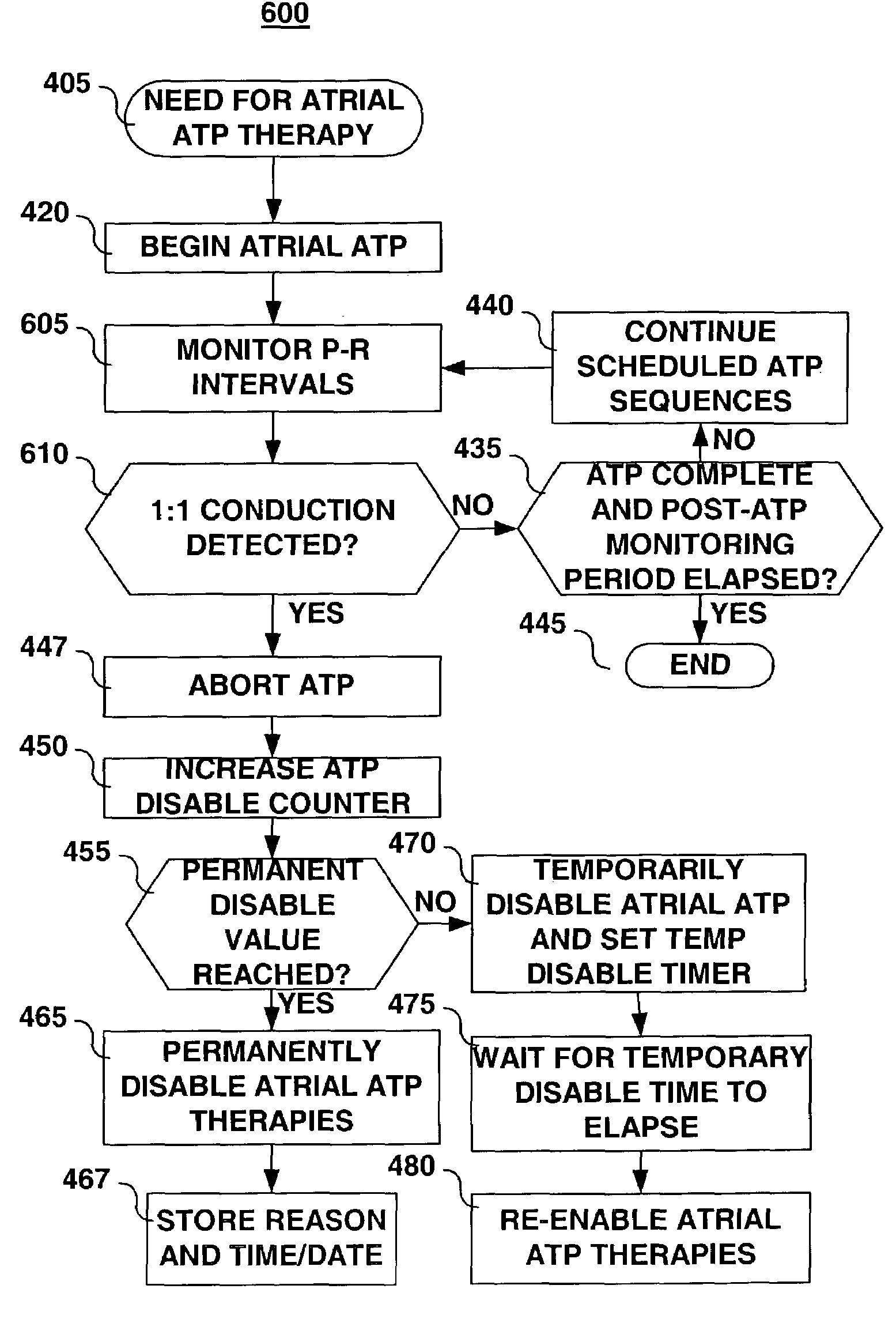
A system and method are provided for controlling atrial anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) delivery based on detection of ventricular pro-arrhythmia during or immediately after atrial ATP. Ventricular pro-arrhythmia is detected based on one or more criteria relating to pro-arrhythmic changes including, but not limited to, ventricular rate changes, R-wave morphology changes, and / or 1:1 or nearly 1:1 atrial-ventricular conduction patterns persisting at high ventricular rates. Upon detecting ventricular pro-arrhythmia, a current atrial ATP sequence is aborted. Atrial ATP therapies may subsequently be temporarily or permanently disabled.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
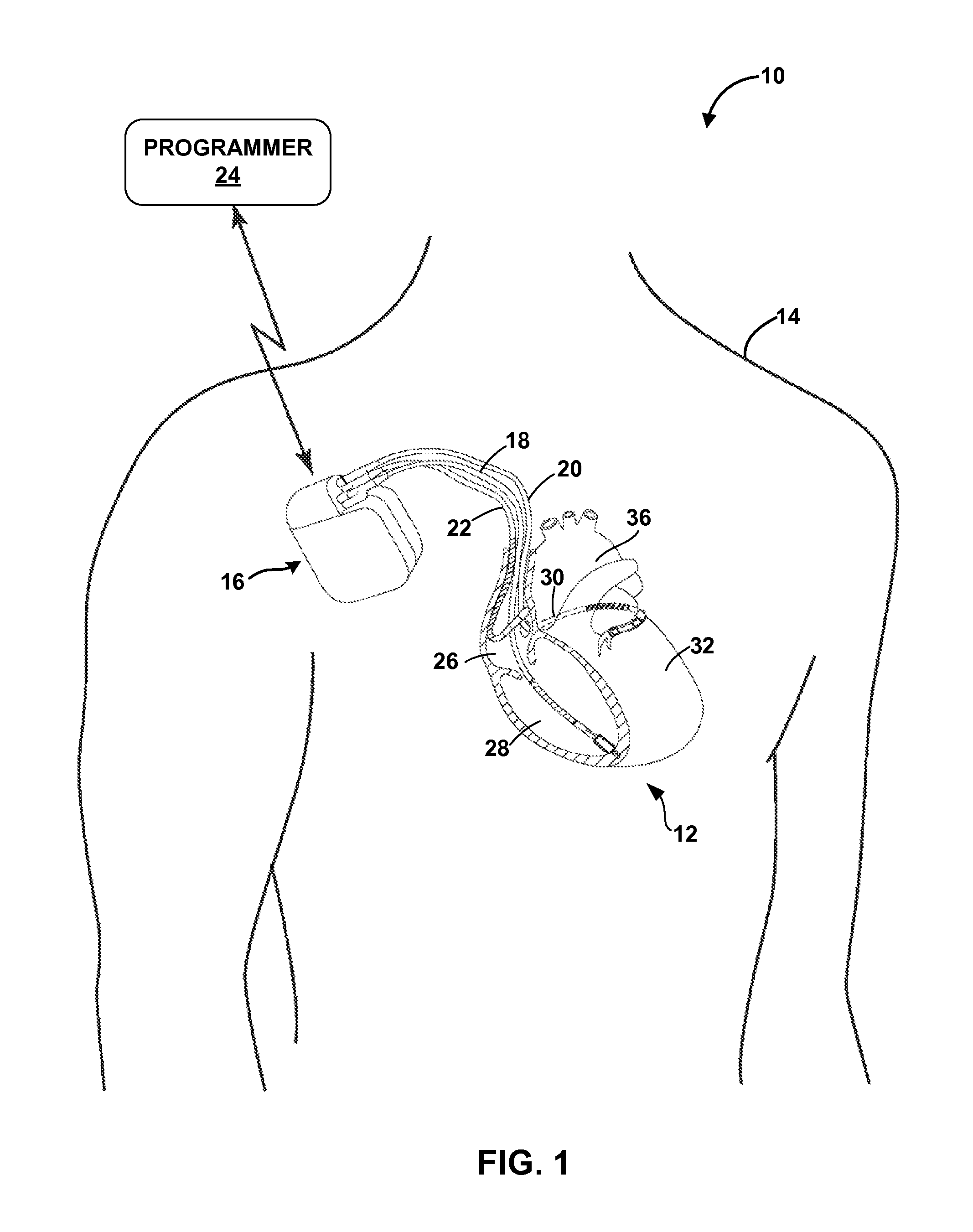
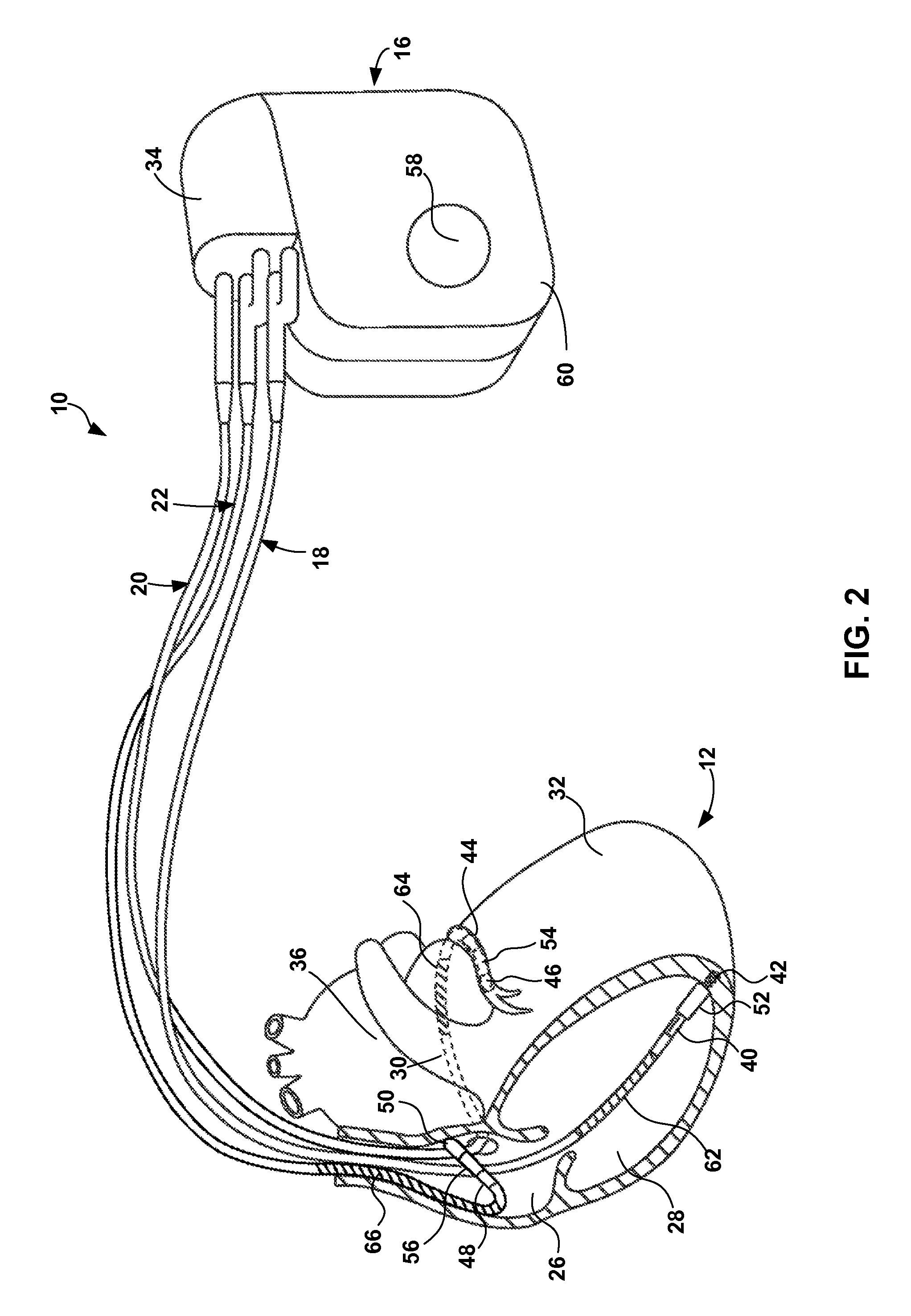
System and method for achieving regular slow ventricular rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation
InactiveUS20070083242A1Decrease ventricular rateEasy to adjustElectrotherapyVentricular rateAtrial cavity
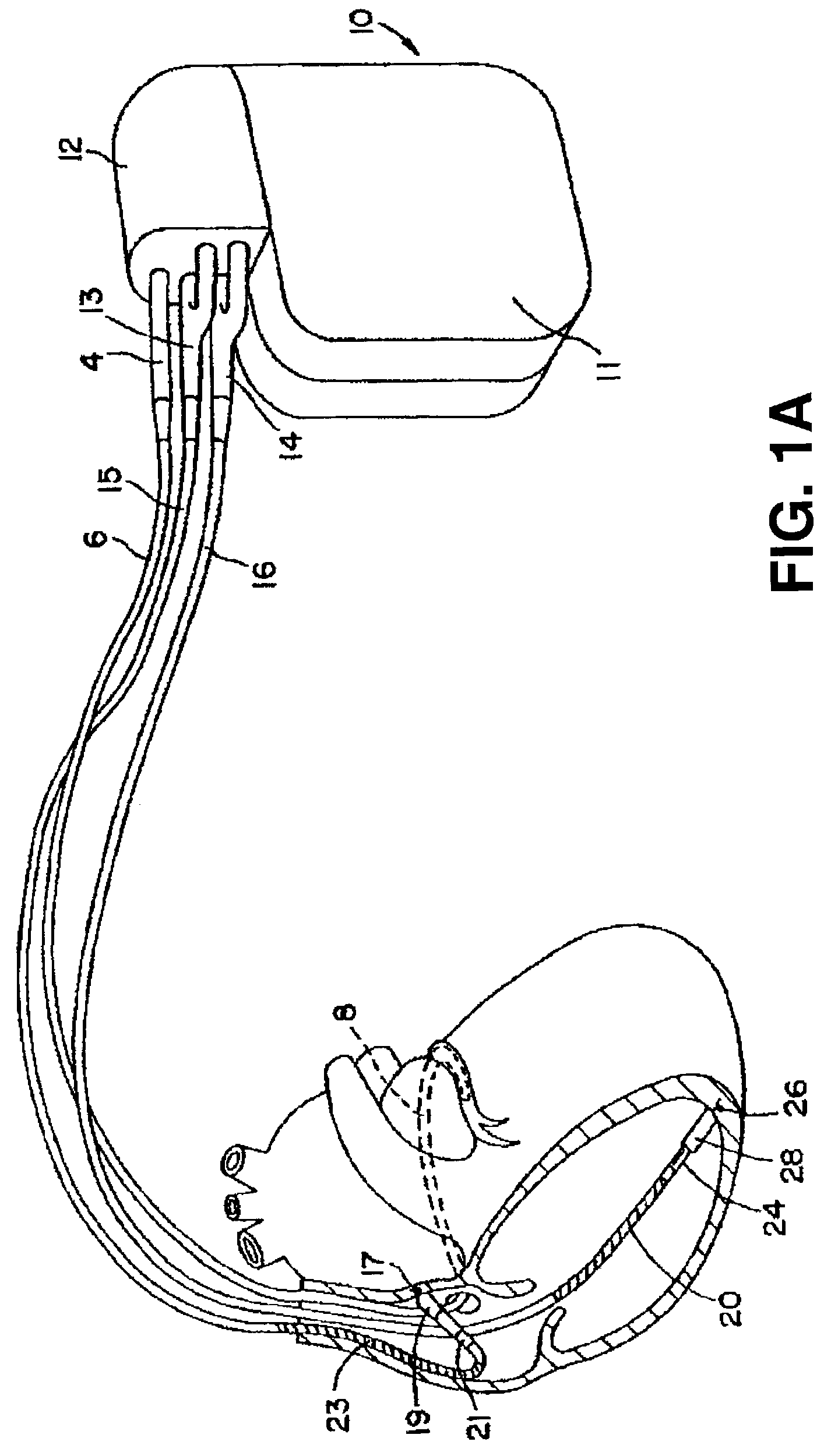
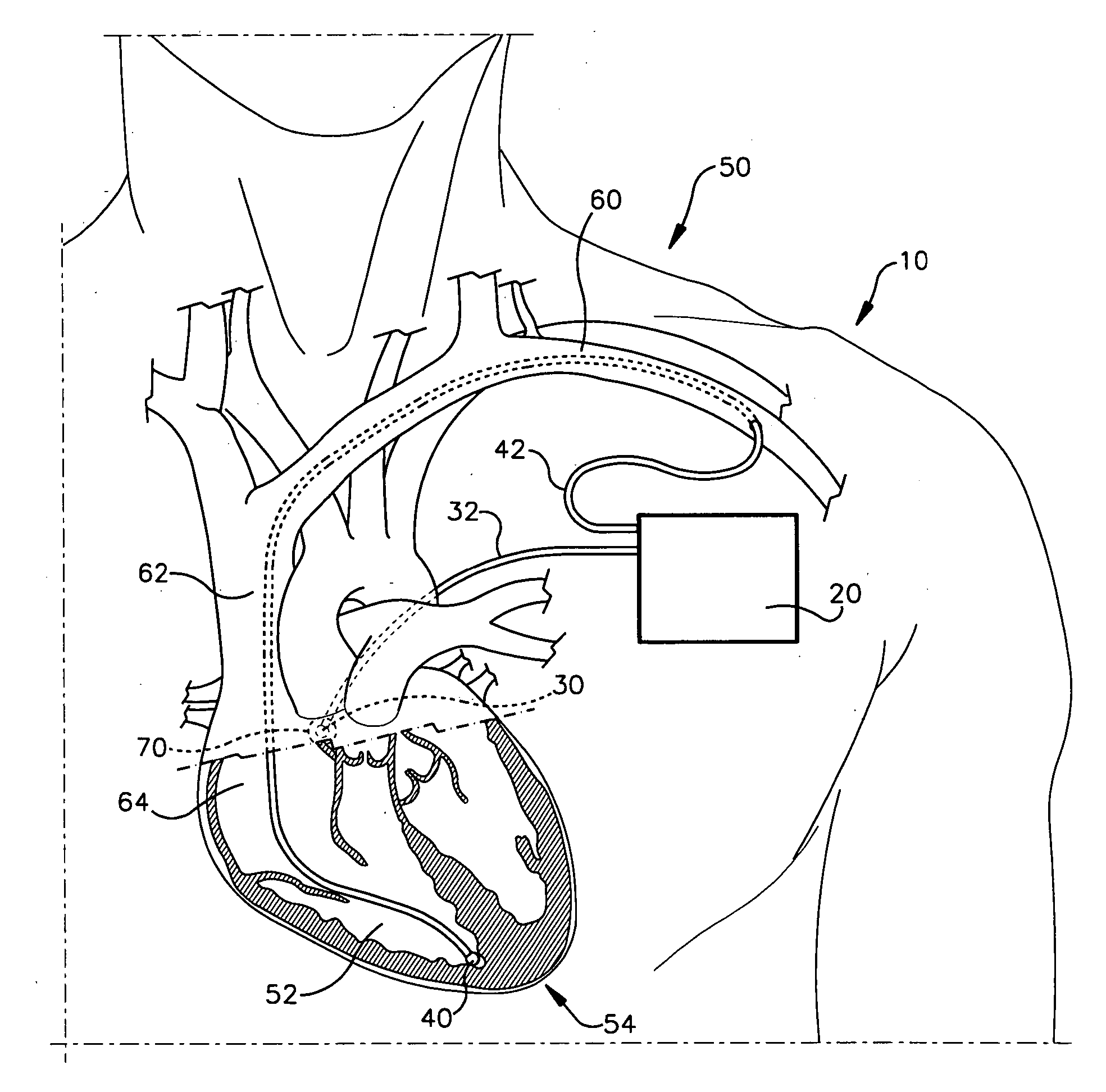
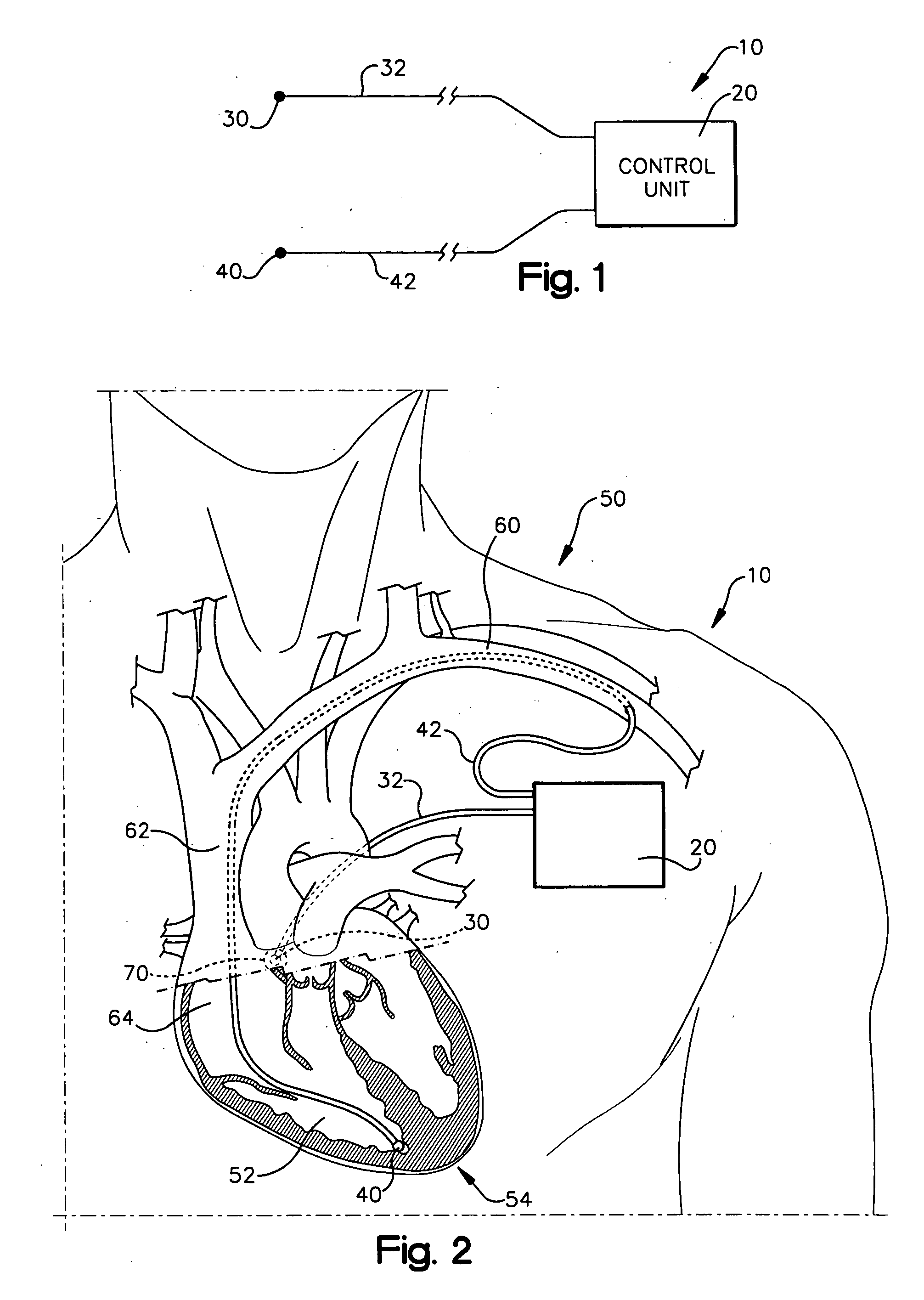
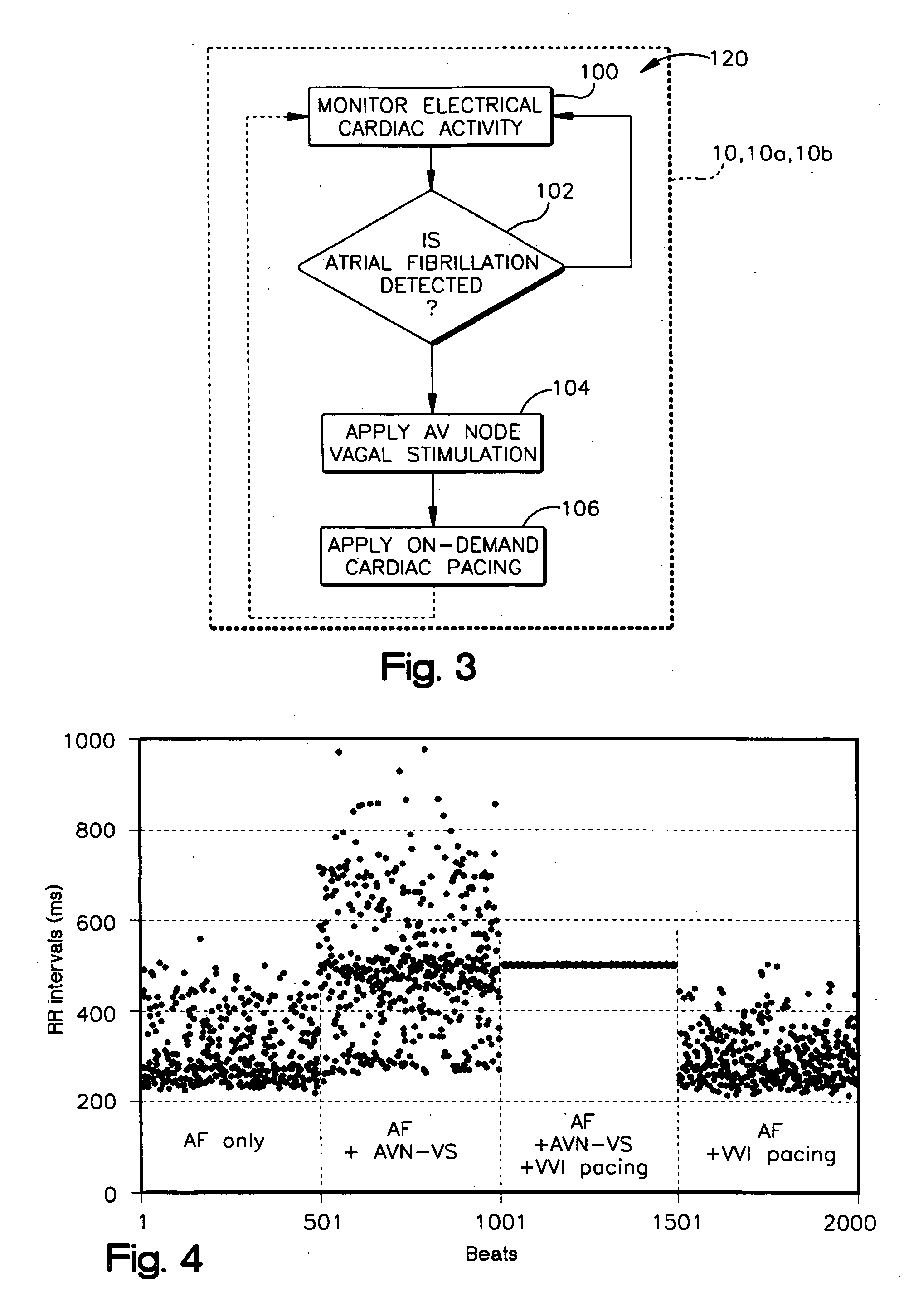
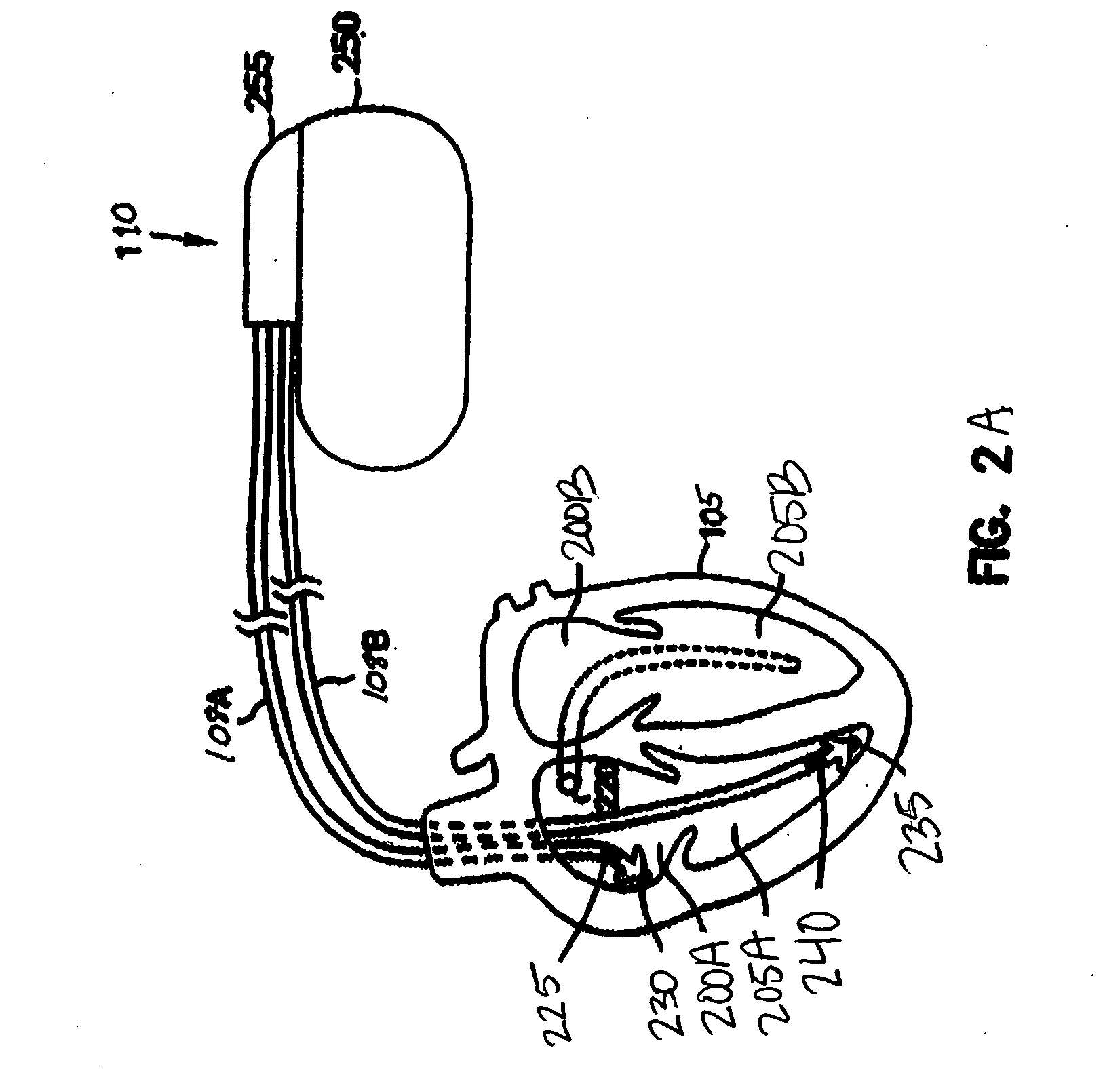
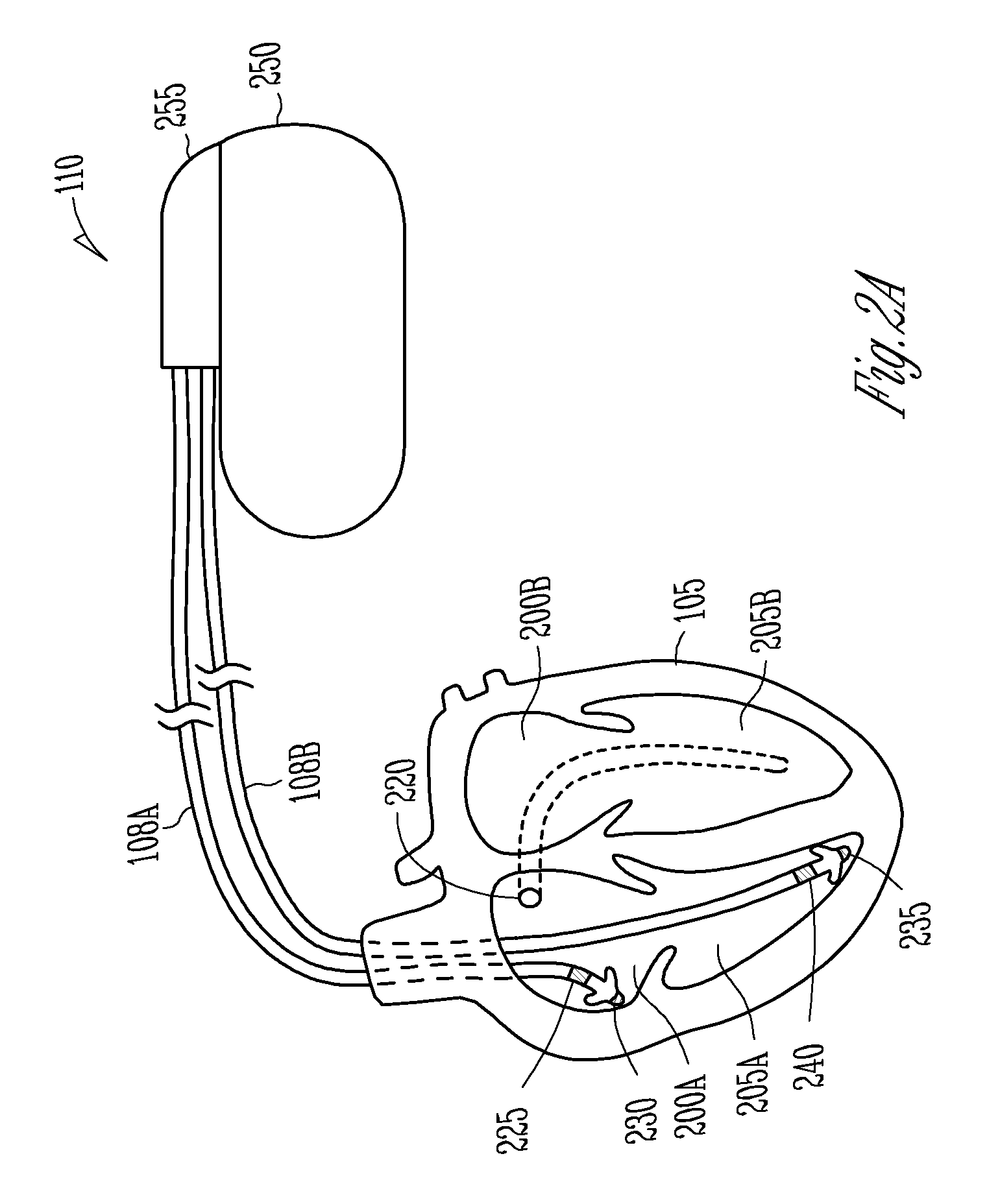
A system (10) for achieving a desired cardiac rate and cardiac rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation in a heart includes an atrial fibrillation (AF) detector (40) for detecting AF. The system also includes an atrioventricular node vagal stimulator (AVN-VS) (30) for stimulating vagal nerves associated with an atrioventricular (AV) node of the heart. The system further includes an on-demand pace maker (40) for providing ventricular pacing stimulation to the heart. A control unit (20) is operatively connected with the AF detection device, the AVN-VS device, and the on-demand pacing device. The control unit is responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the AVN-VS to stimulate the vagal nerves to help reduce the ventricular rate of the heart. The control unit is further responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the on-demand pace maker to help regulate the ventricular rate of the heart.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Zoneless tachyarrhythmia detection with real-time rhythm monitoring
A system including an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes a ventricular contraction sensing circuit that provides a sensed ventricular contraction signal, a timer circuit that provides a ventricular time interval between ventricular contractions, and a controller circuit coupled to the timer circuit, the controller circuit determines the ventricular contraction rate using the ventricular time interval. The controller circuit further includes a tachyarrhythmia detection module that declares tachyarrhythmia, in response to detecting a sudden rate increase, without comparing a ventricular rate or time interval to a respective tachyarrhythmia detection rate or time interval threshold.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for employing an FFT to distinguish R-waves from T-waves using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7813791B1Reduce and eliminate T-wave oversensingImprove detection reliabilityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsFast Fourier transformVentricular rate
A Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) converts time-varying event waveforms into the frequency domain waveforms to thereby decompose the events into their spectral components, which are analyzed to distinguish R-waves from T-waves. In some embodiments, the FFT is only activated if a ventricular tachyarrhythmia is already indicated. For example, an initial ventricular rate may be derived from a ventricular IEGM based on all events detected therein. The initial ventricular rate is compared against one or more thresholds representative of ventricular tachycardia (VT) and / or ventricular fibrillation (VF) to determine if VT / VF is indicated. If so, the FFT is activated to distinguish R-waves from T-waves and, in particular, to detect and eliminate T-wave oversensing. Then, the ventricular rate is re-determined based only on the rate of true R-waves. Therapy is delivered if VT / VF is still detected.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
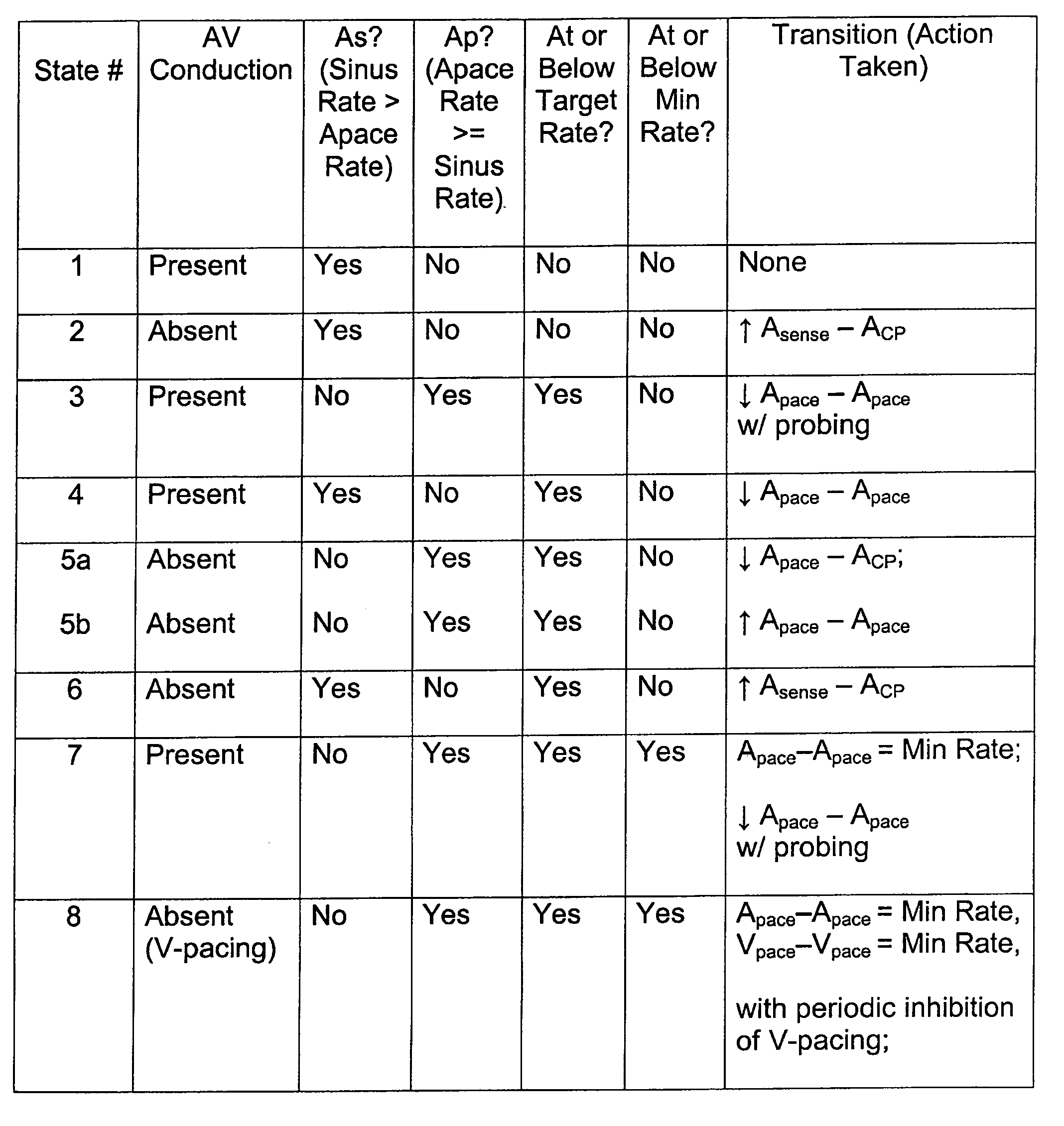
Method of optimizing mechanical heart rate during delivery of coupled or paired pacing
InactiveUS7286873B2Maximize their opportunityOptimize heart rateHeart stimulatorsVentricular ratePulse rate
A method of operating a cardiac pacing device that optimizes the mechanical heart rate using coordinated potentiation therapy while maximizing the opportunity for intrinsic AV conduction to occur. The method may include adjusting the timing of extra stimulus intervals during coupled or paired pacing to promote AV conduction and to effect changes in rate according to certain embodiments of the invention. Other embodiments may include adjusting the atrial pacing rate to achieve a desired target rate consistent with AV conduction. A mode switch to a dual-chamber pacing mode may be provided according to certain embodiments of the invention to ensure a ventricular rate that meets or exceeds a minimum mechanical rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Wavelet based feature extraction and dimension reduction for the classification of human cardiac electrogram depolarization waveforms
ActiveUS7751873B2Improving implant accuracyImprove accuracyElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisRhythmTime scale decomposition
A depolarization waveform classifier based on the Modified lifting line wavelet Transform is described. Overcomes problems in existing rate-based event classifiers. A task for pacemaker / defibrillators is the accurate identification of rhythm categories so correct electrotherapy can be administered. Because some rhythms cause rapid dangerous drop in cardiac output, it's desirable to categorize depolarization waveforms on a beat-to-beat basis to accomplish rhythm classification as rapidly as possible. Although rate based methods of event categorization have served well in implanted devices, these methods suffer in sensitivity and specificity when atrial / ventricular rates are similar. Human experts differentiate rhythms by morphological features of strip chart electrocardiograms. The wavelet transform approximates human expert analysis function because it correlates distinct morphological features at multiple scales. The accuracy of implanted rhythm determination can then be improved by using human-appreciable time domain features enhanced by time scale decomposition of depolarization waveforms.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method of optimizing mechanical heart rate during delivery of coupled or paired pacing
InactiveUS20060224197A1Optimize mechanical heart rateMinimum rateHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrial pacing
A method of operating a cardiac pacing device that optimizes the mechanical heart rate using coordinated potentiation therapy while maximizing the opportunity for intrinsic AV conduction to occur. The method may include adjusting the timing of extra stimulus intervals during coupled or paired pacing to promote AV conduction and to effect changes in rate according to certain embodiments of the invention. Other embodiments may include adjusting the atrial pacing rate to achieve a desired target rate consistent with AV conduction. A mode switch to a dual-chamber pacing mode may be provided according to certain embodiments of the invention to ensure a ventricular rate that meets or exceeds a minimum mechanical rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
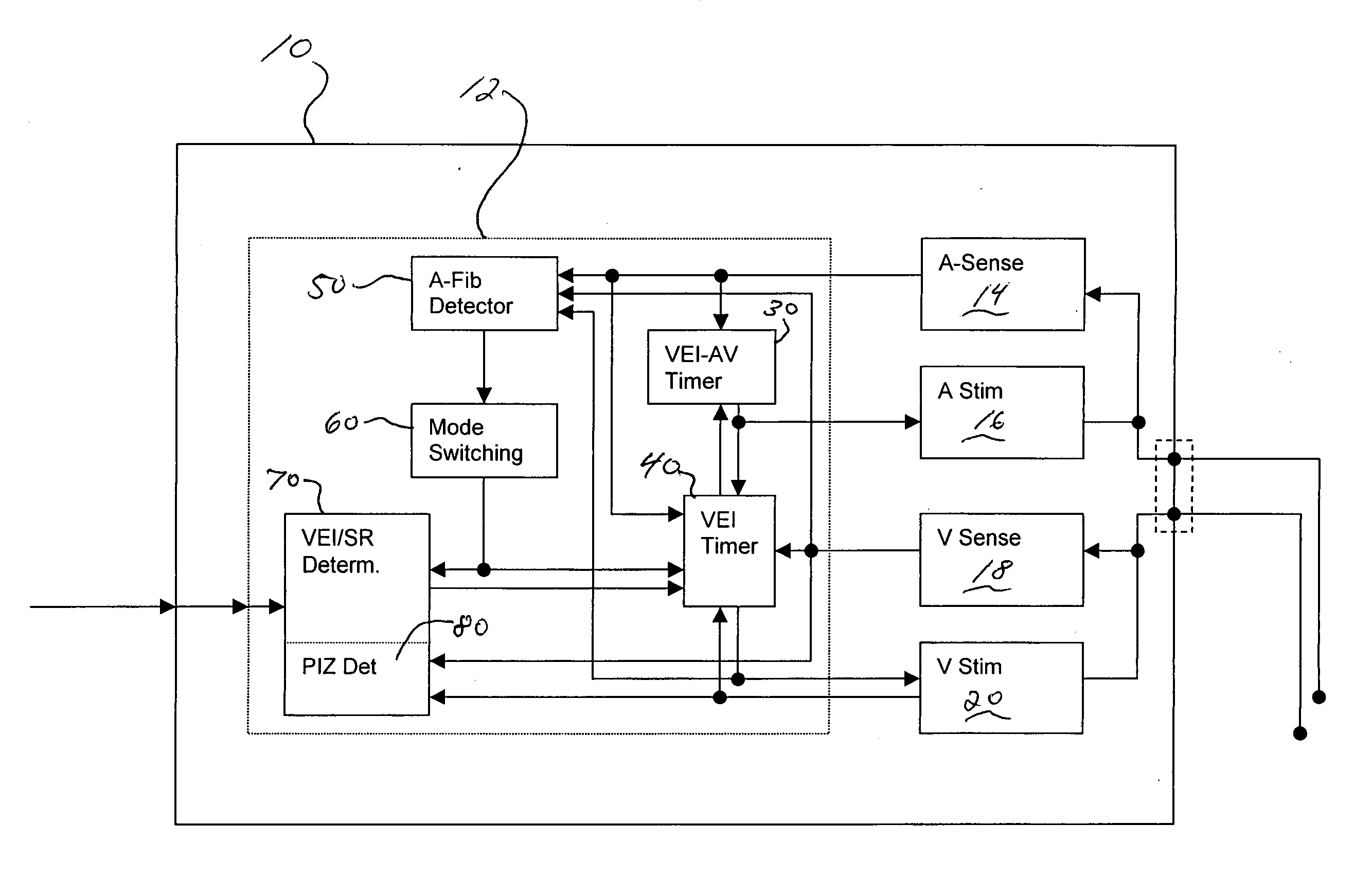
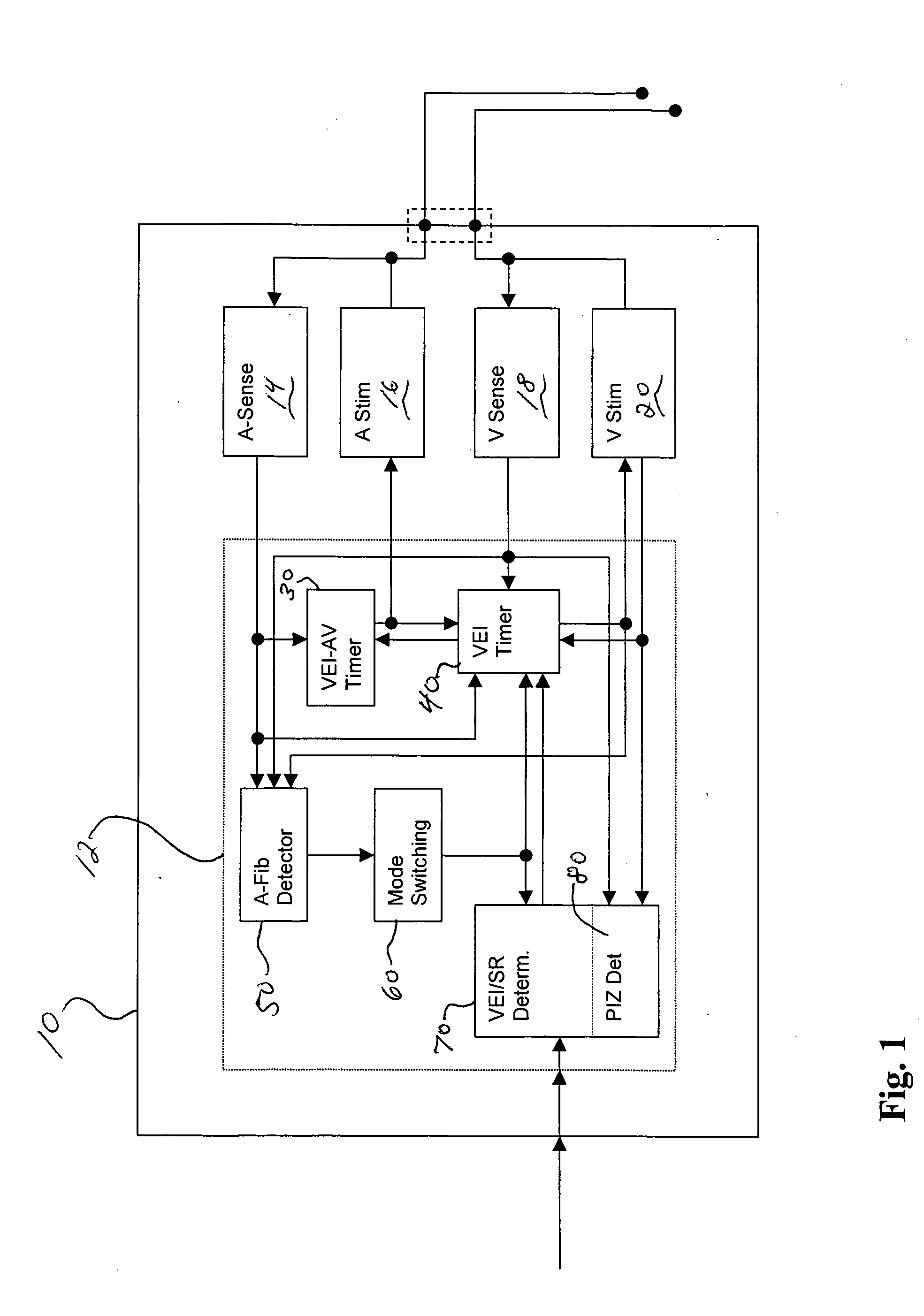
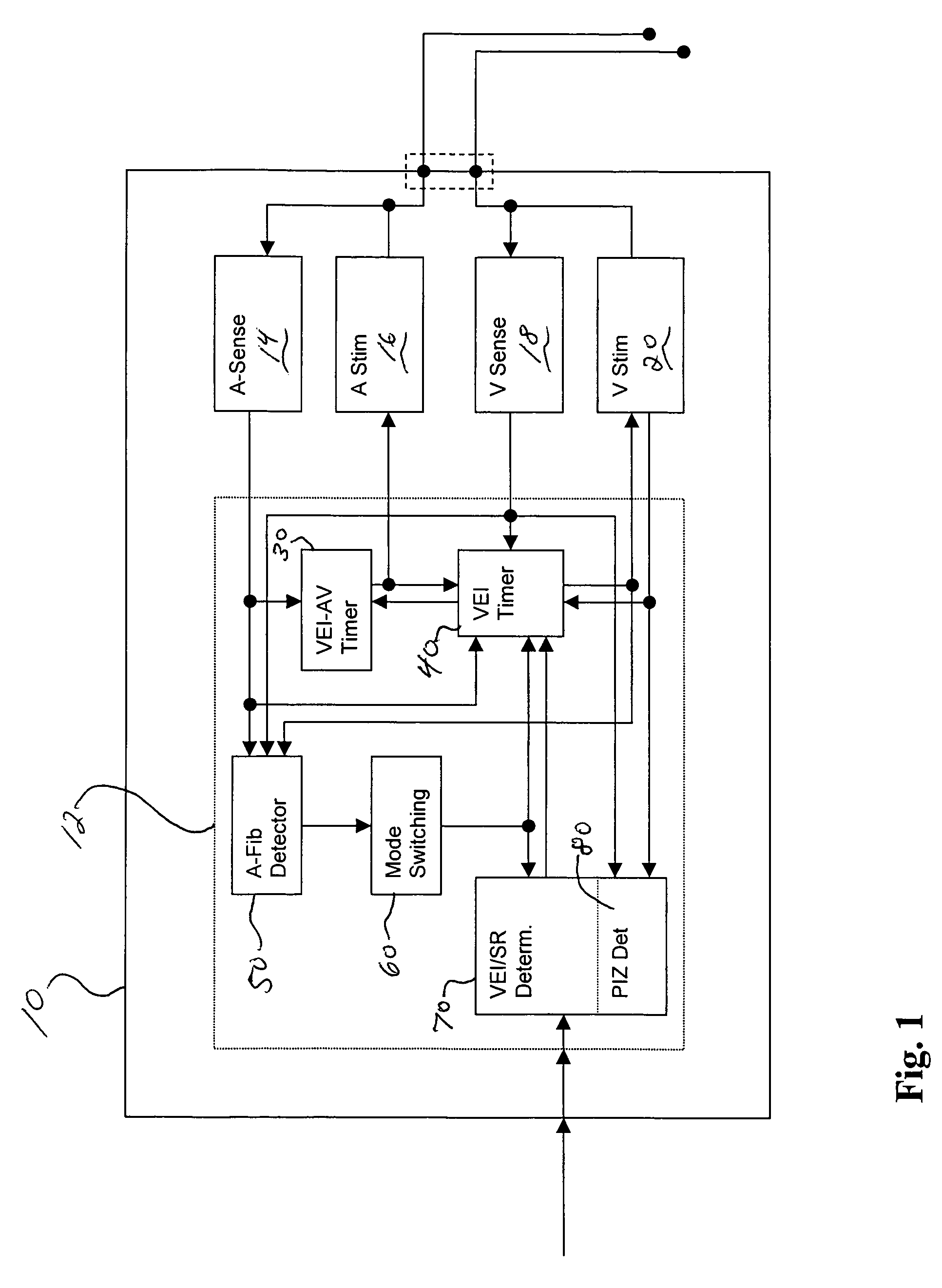
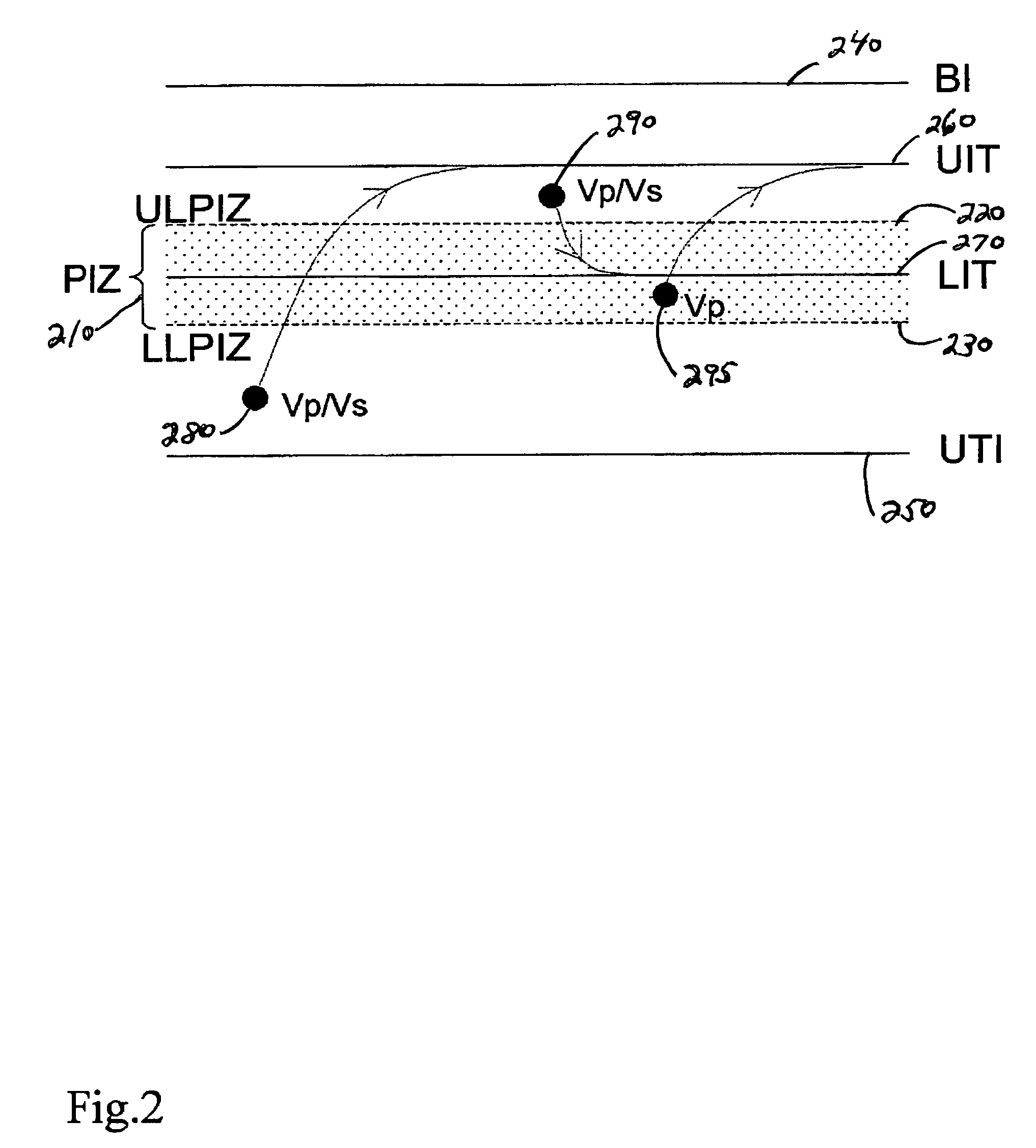
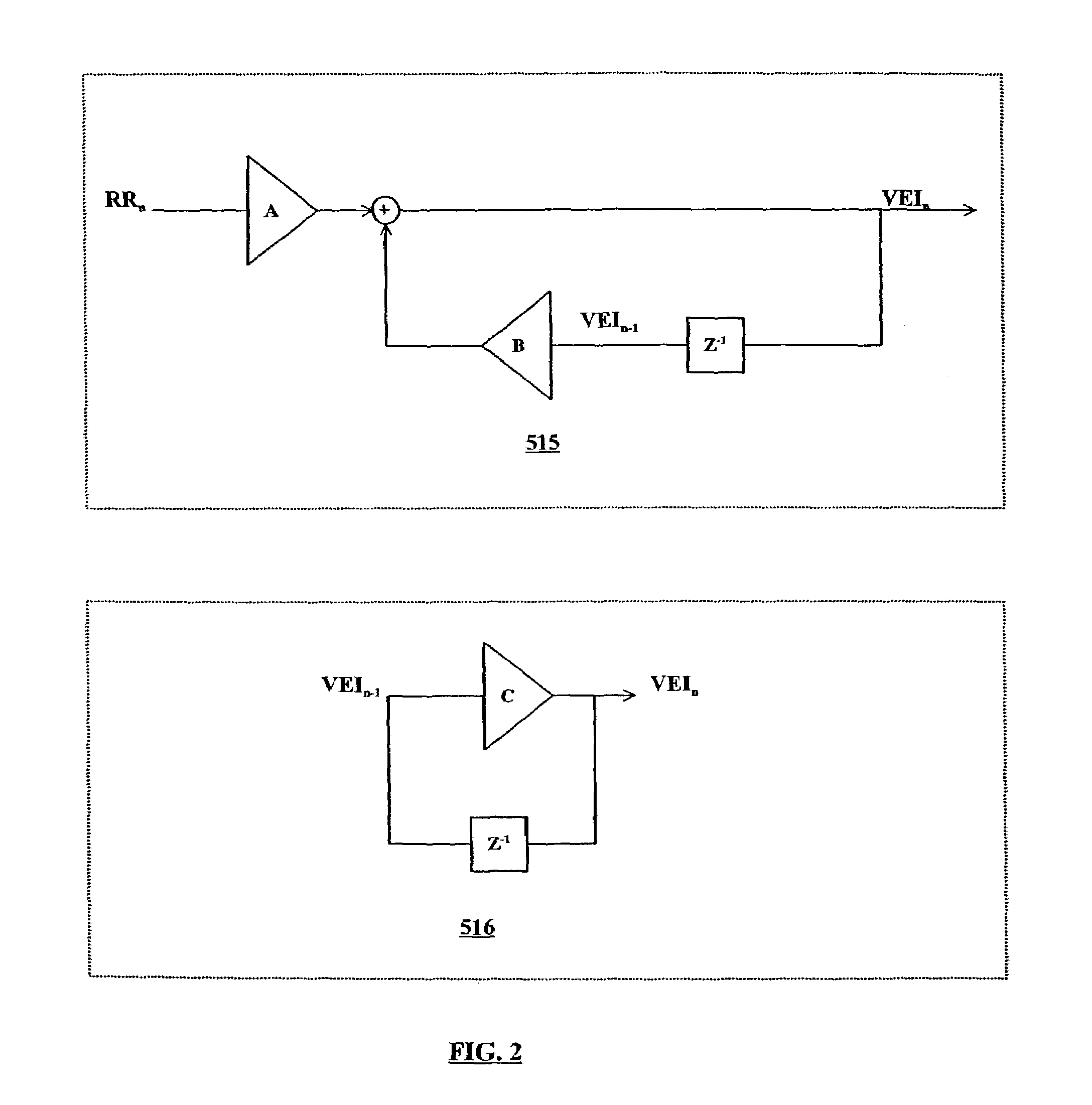
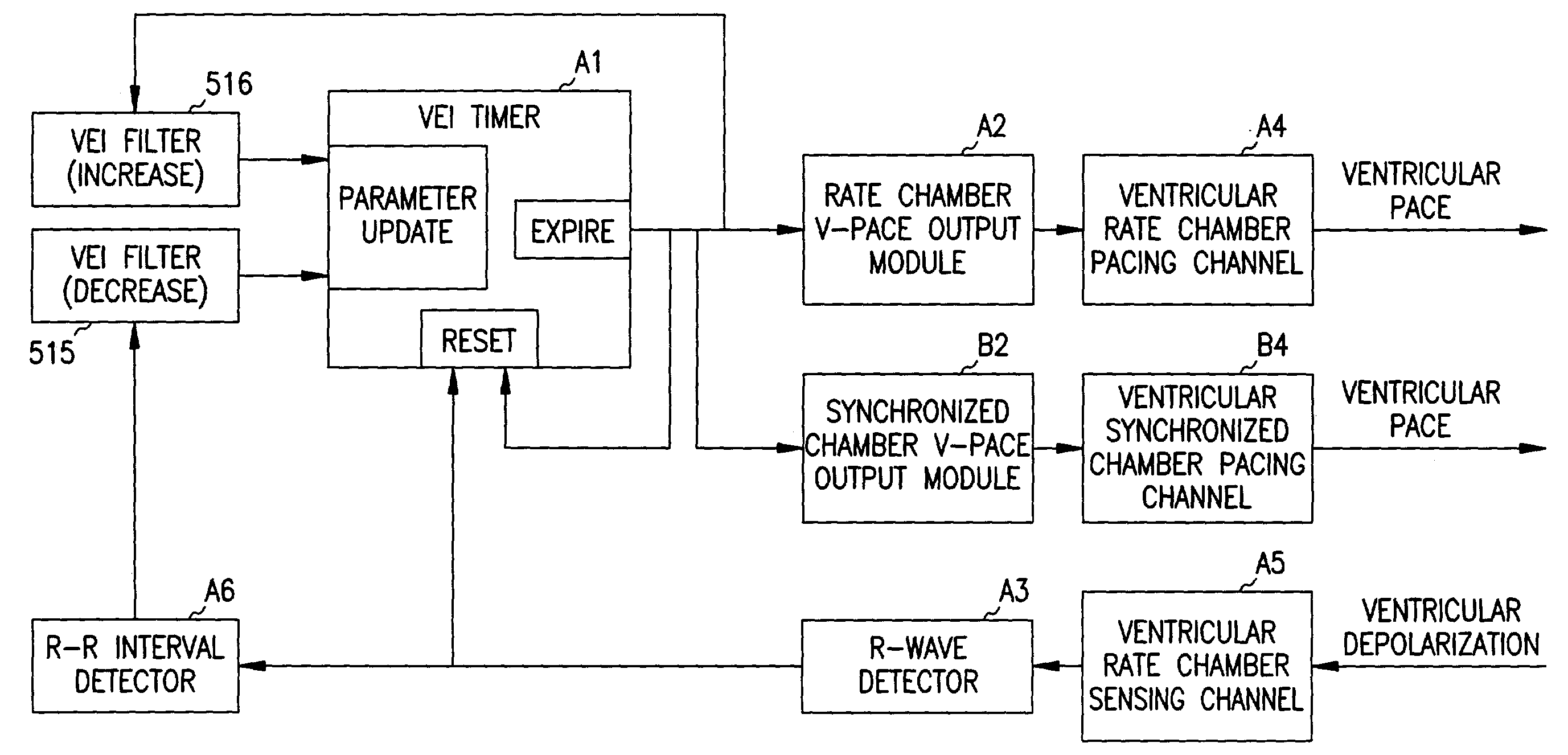
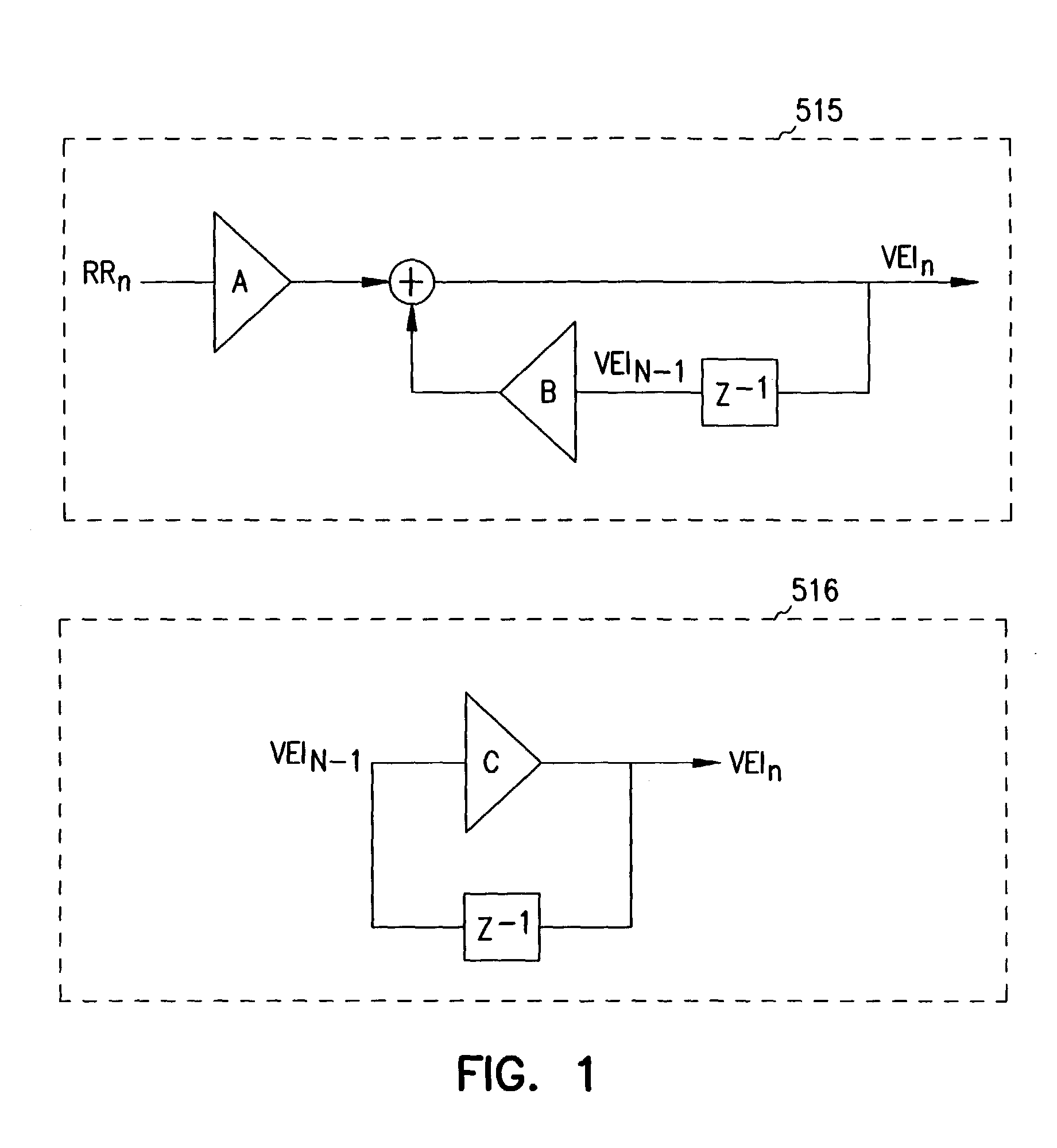
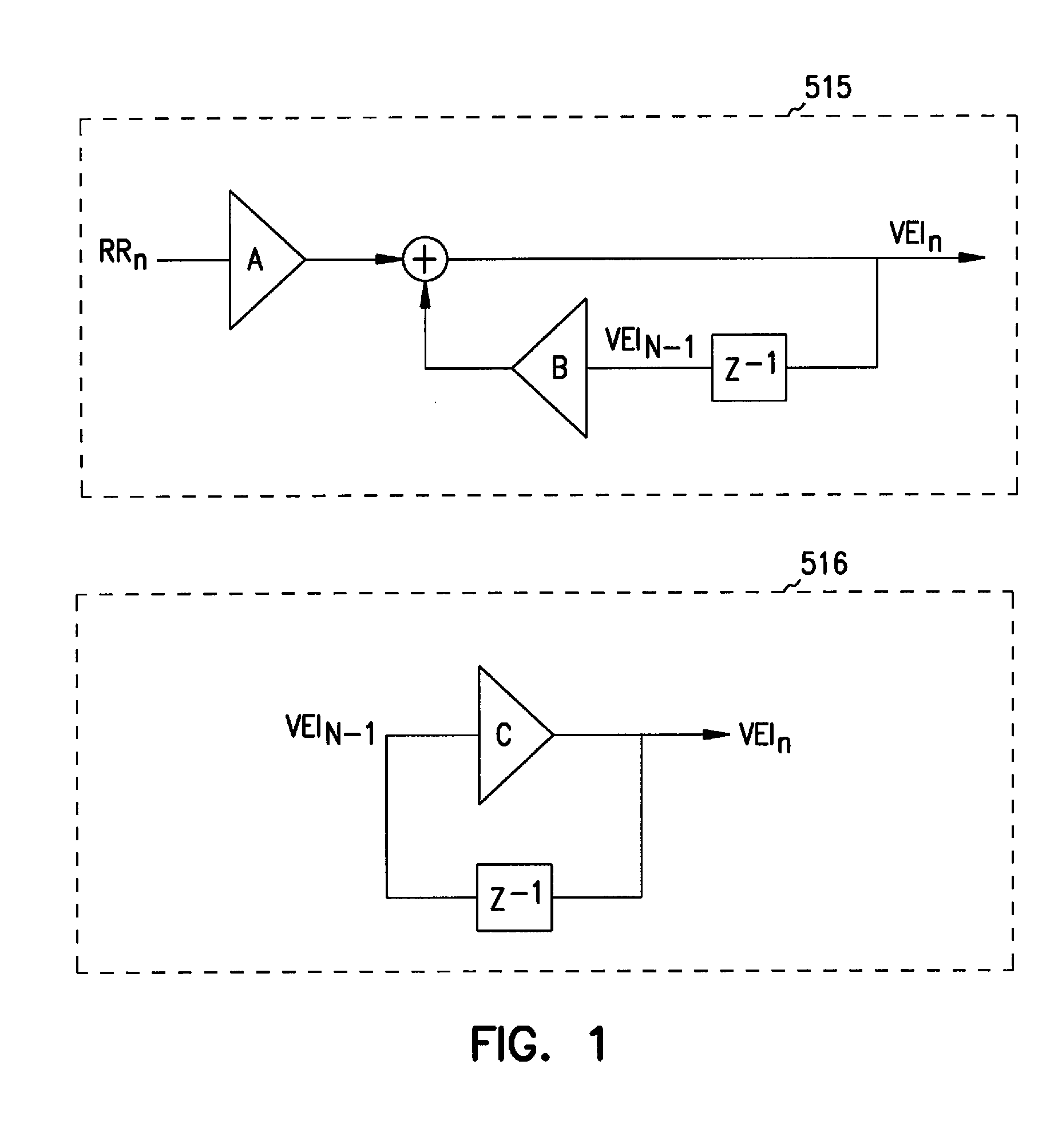
Adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation
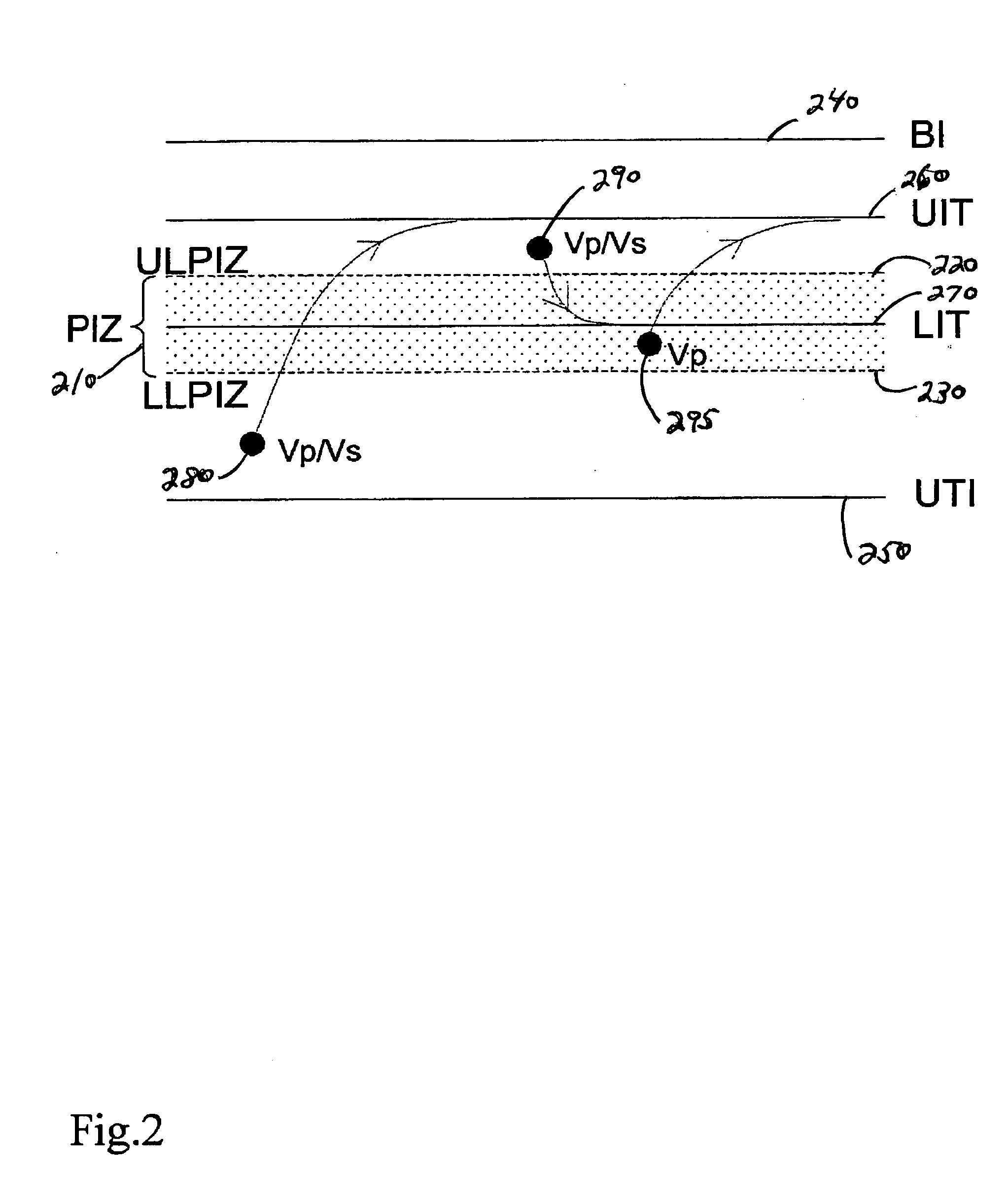
An implantable cardiac device is provided for adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation (AF). When AF is detected, the operation of the device is switched to non-atrial synchronized pacing mode such as DDI, DDIR, VDI, VDIR, VVI, or VVIR. The ventricular escape interval (VEI) is beat-by-beat modulated around a physiological interval zone (PIZ), which is determined by the pre-arrhythmia ventricular rate or the output of rate responsive sensor. The VEI remains unchanged if the preceding ventricular event is sensed and its RR interval is within the PIZ. Otherwise, the VEI is decreased asymptotically toward a lower interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is longer than the upper limit of the PIZ, or the VEI is increased asymptotically toward an upper interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is shorter than the upper limit of the PIZ. The step of incrementing or decrementing the VEI is adaptive to the absolute difference value between the preceding RR interval and the asymptotic interval threshold to ensure fast recovery of deviant RR interval toward the PIZ and to reduce the amount of high rate ventricular paces after a ventricular sense with very short coupling interval.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation
An implantable cardiac device is provided for adaptive ventricular rate smoothing during atrial fibrillation (AF). When AF is detected, the operation of the device is switched to non-atrial synchronized pacing mode such as DDI, DDIR, VDI, VDIR, VVI, or VVIR. The ventricular escape interval (VEI) is beat-by-beat modulated around a physiological interval zone (PIZ), which is determined by the pre-arrhythmia ventricular rate or the output of rate responsive sensor. The VEI remains unchanged if the preceding ventricular event is sensed and its RR interval is within the PIZ. Otherwise, the VEI is decreased asymptotically toward a lower interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is longer than the upper limit of the PIZ, or the VEI is increased asymptotically toward an upper interval threshold if the preceding RR interval is shorter than the upper limit of the PIZ. The step of incrementing or decrementing the VEI is adaptive to the absolute difference value between the preceding RR interval and the asymptotic interval threshold to ensure fast recovery of deviant RR interval toward the PIZ and to reduce the amount of high rate ventricular paces after a ventricular sense with very short coupling interval.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS7142915B2Less variabilityIncrease cardiac outputHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateBradycardia
A method and system for operating a cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed with conventional bradycardia pacing, ventricular resynchronization therapy, or anti-tachyarrhythmia therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
High frequency atrial burst pacing for improved ventricular rate control during atrial arrhythmias
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS7181278B2Less variabilityIncrease cardiac outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed within bradycardia pacemakers, ventricular resynchronization devices, or implantable cardioverter / defibrillators.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
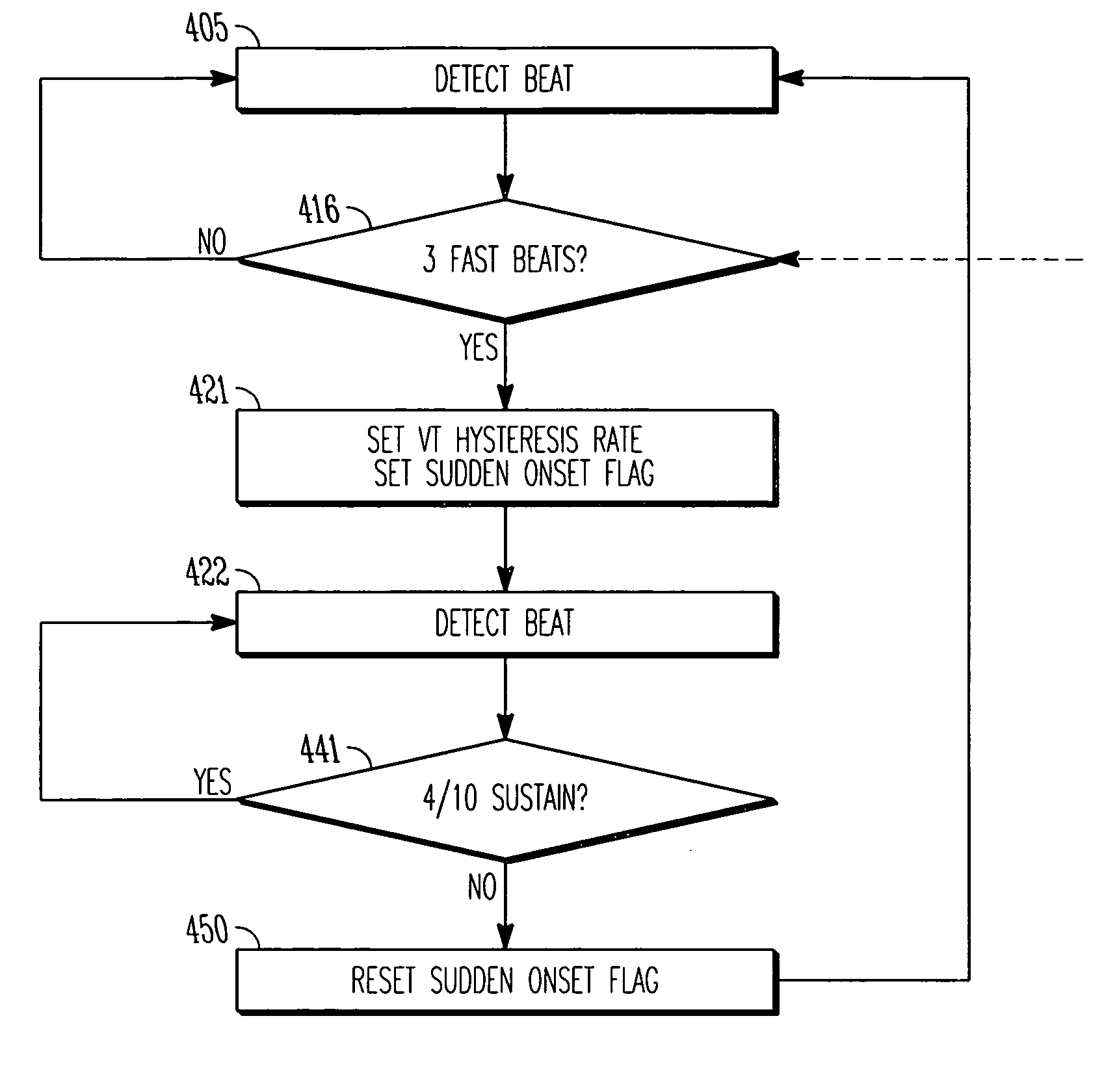
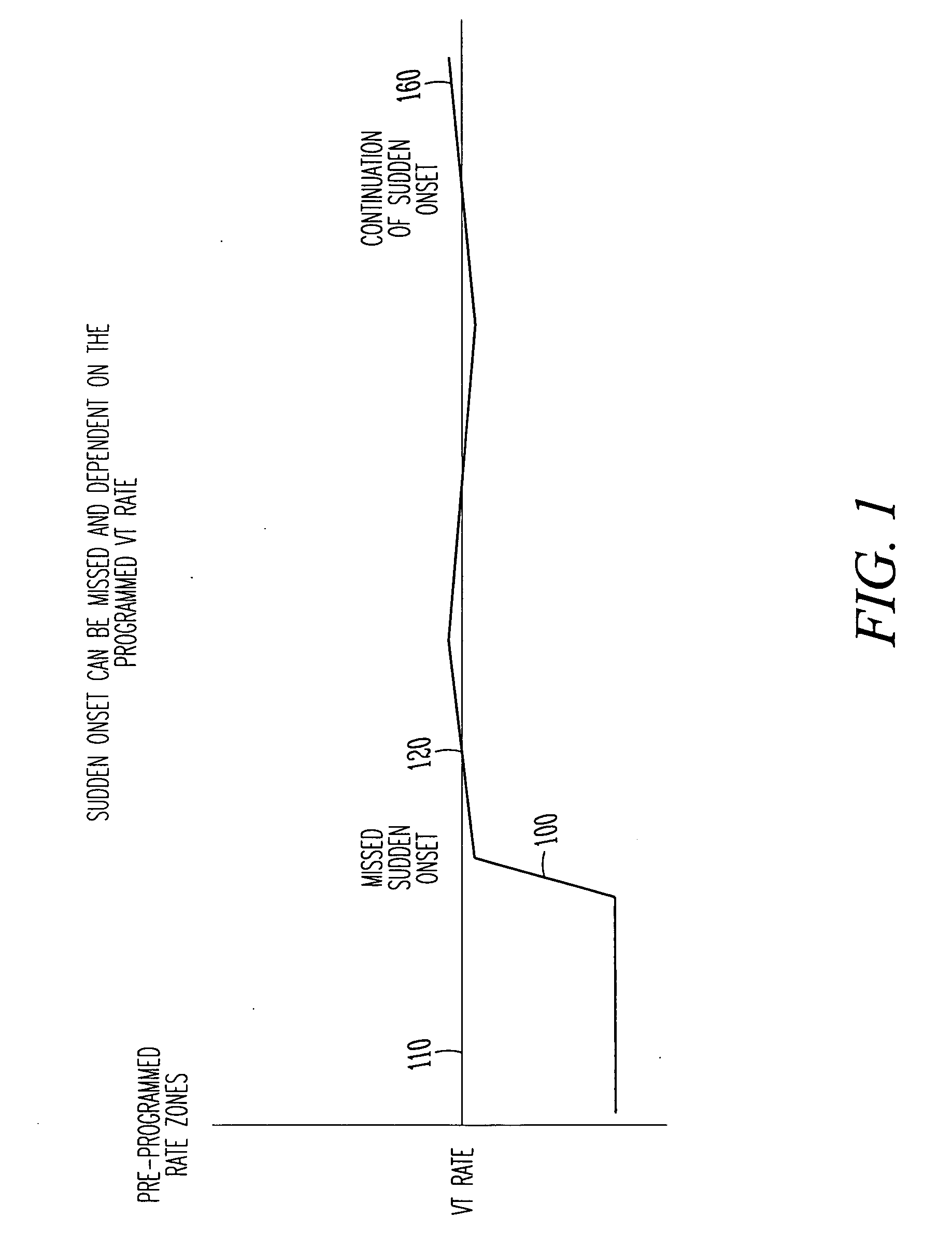
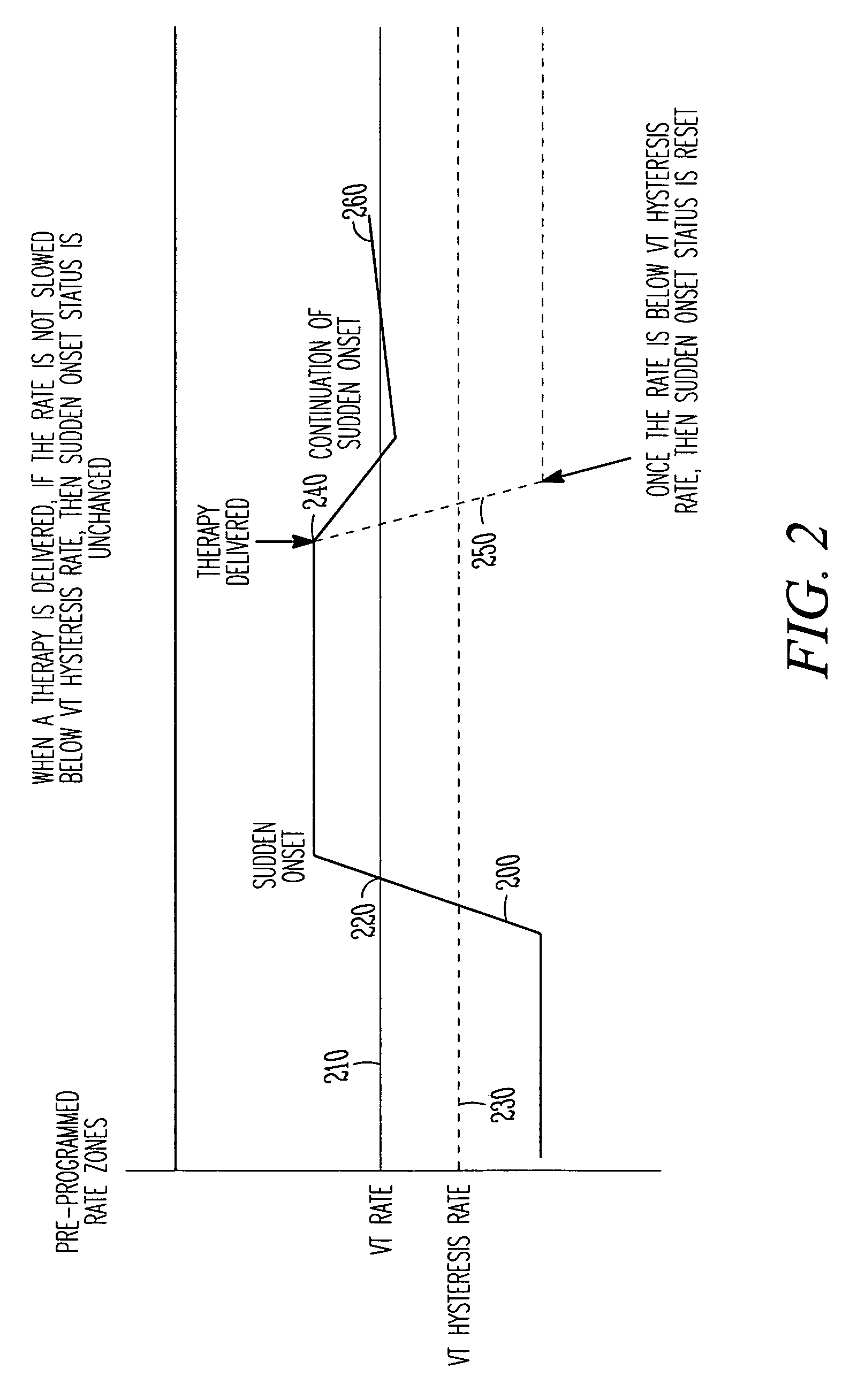
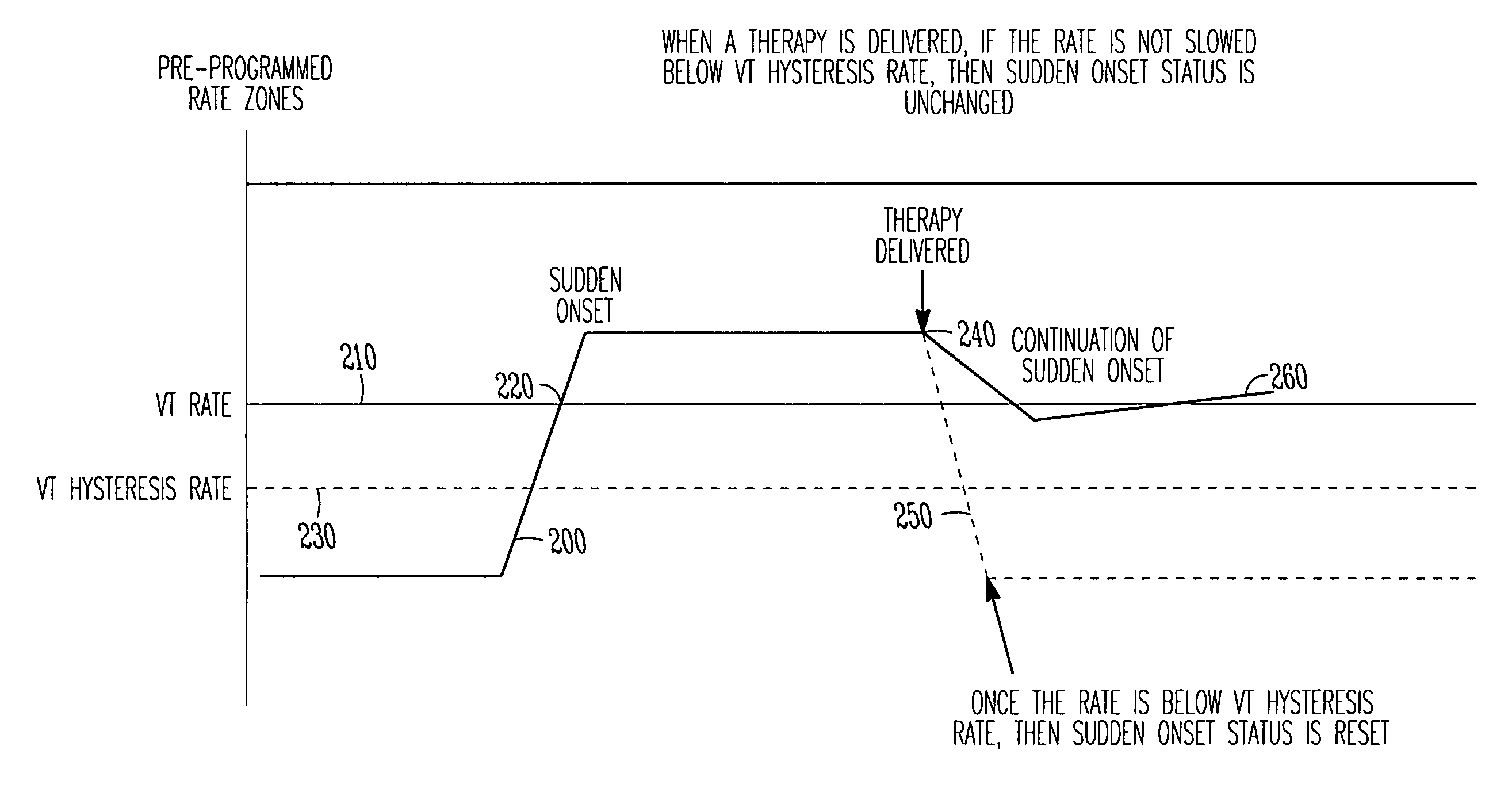
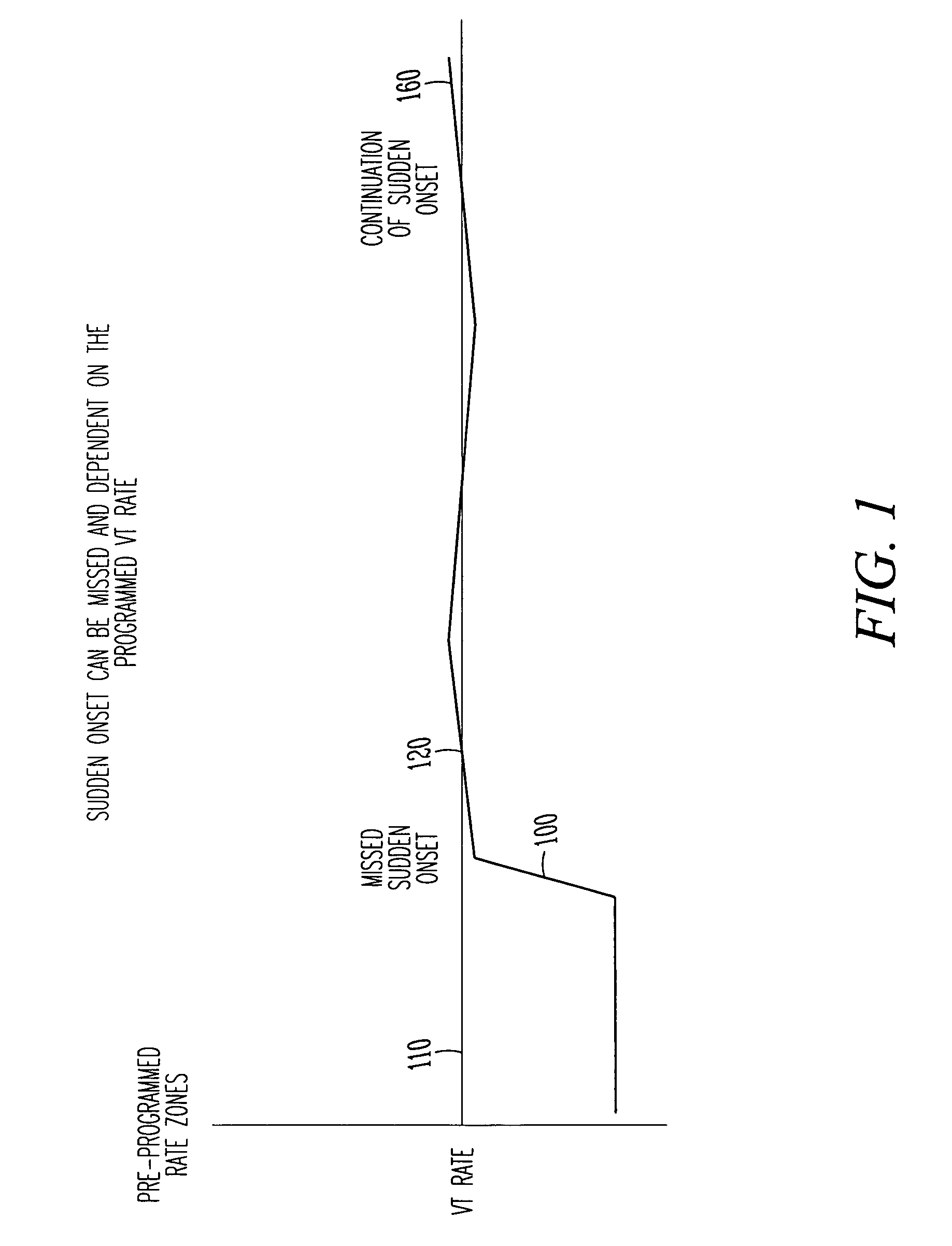
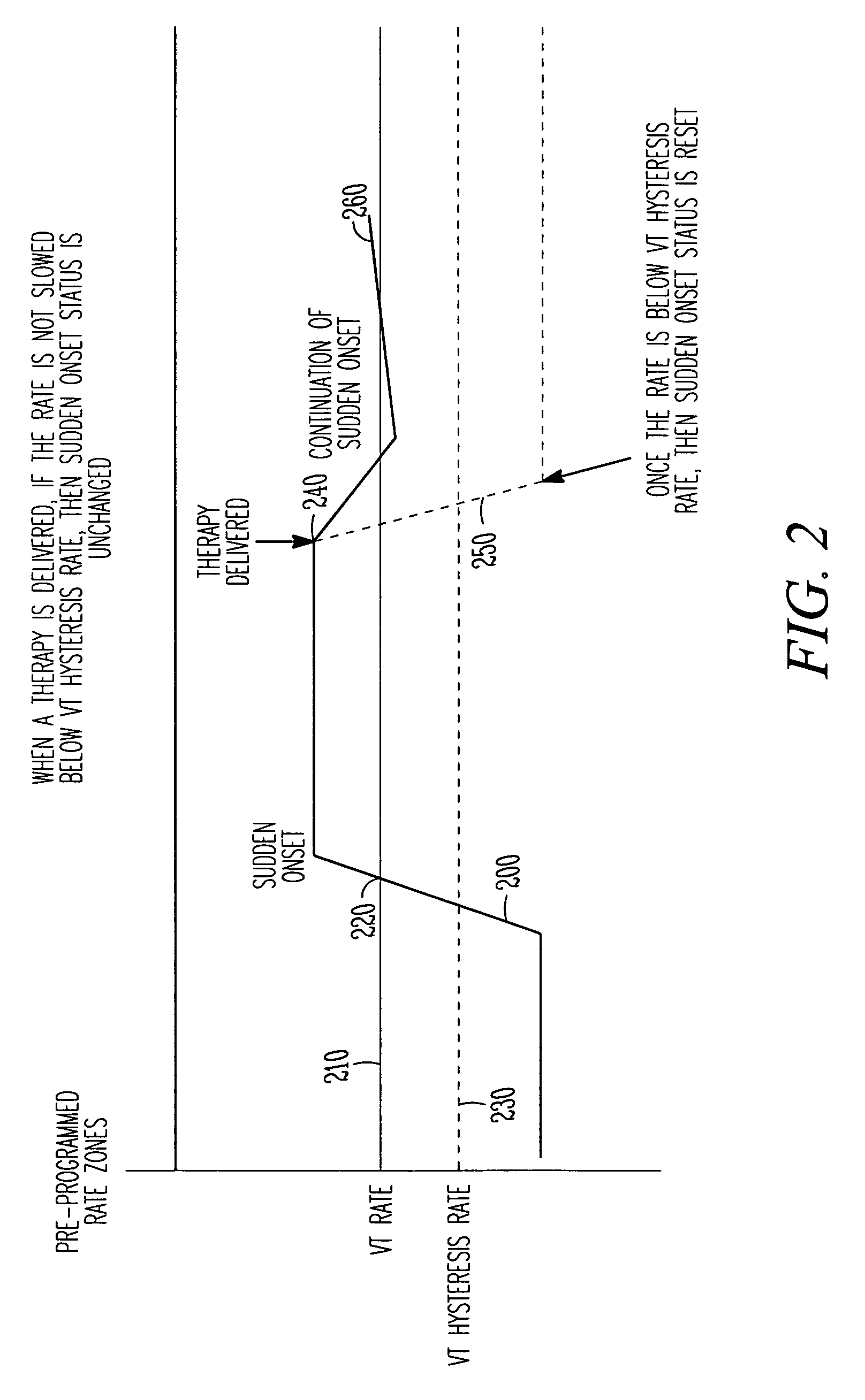
Tachyarrhythmia sudden onset detection with hysteresis
This document discusses, among other things, detection of a sudden onset of a tachyarrhythmia. A sudden onset of tachyarrhythmia is determined by monitoring changes in intrinsic ventricular rate, such as by using one or more sensing channels in the ICD. A lowest tachyarrhythmia rate threshold is accompanied by a slightly lower “hysteresis tachyarrhythmia rate threshold.” If a sudden onset of tachyarrhythmia is declared, the sudden onset status is not reset by the ventricular rate falling below the lowest tachyarrhythmia rate threshold, but is instead reset by the ventricular rate falling below the slightly lower hysteresis tachyarrhythmia rate threshold.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and Method for Achieving Regular Slow Ventricular Rhythm in Response to Atrial Fibrillation
InactiveUS20080300640A1Decrease ventricular rateEasy to adjustHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrioventricular node
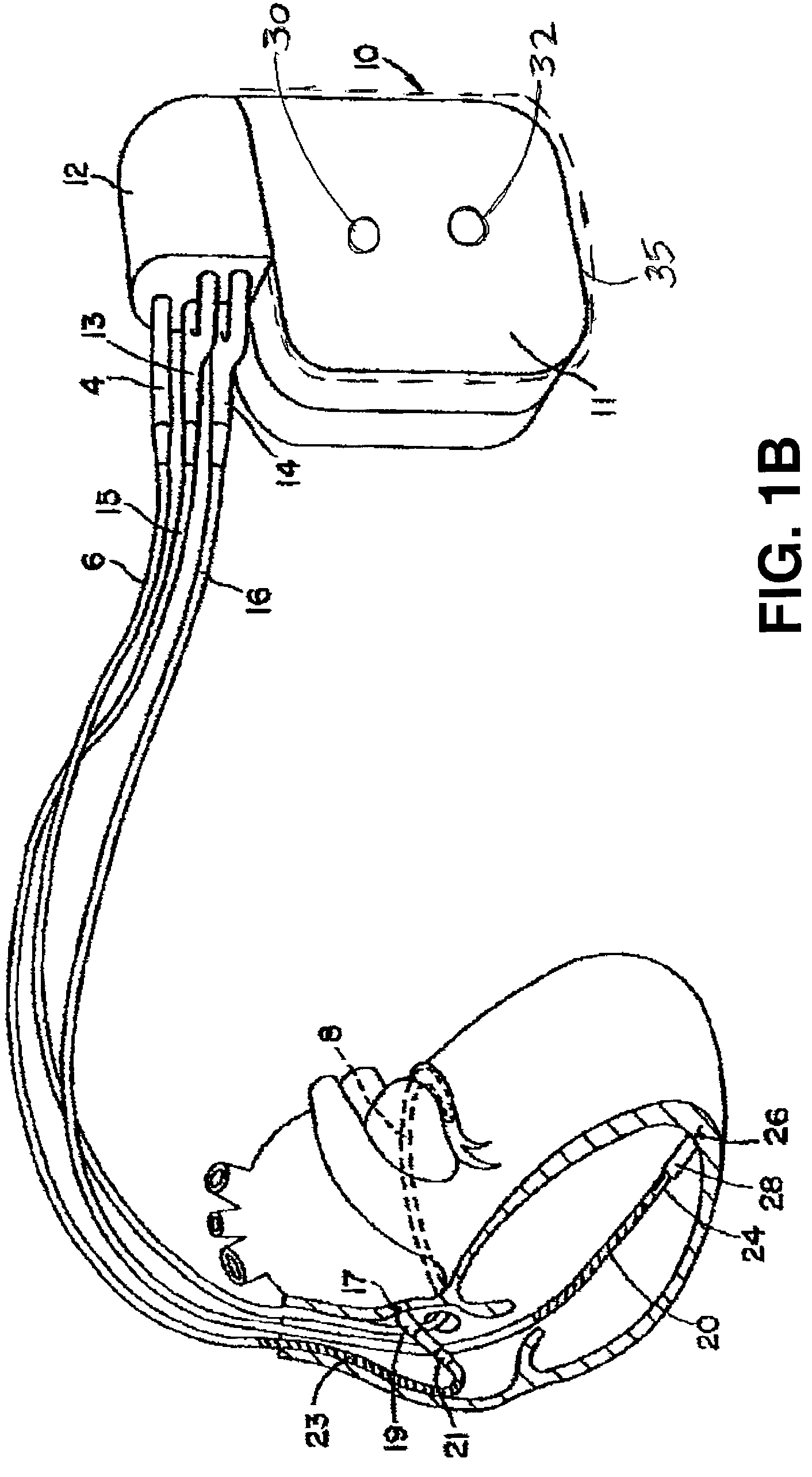
A system (10) for achieving a desired cardiac rate and cardiac rhythm in response to atrial fibrillation in a heart includes an atrial fibrillation (AF) detector (40) for detecting AF. The system also includes an atrioventricular node vagal stimulator (AVN-VS) (30) for stimulating vagal nerves associated with an atrioventricular (AV) node of the heart. The system further includes an on-demand pace maker (40) for providing ventricular pacing stimulation to the heart. A control unit (20) is operatively connected with the AF detection device, the AVN-VS device, and the on-demand pacing device. The control unit is responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the AVN-VS to stimulate the vagal nerves to help reduce the ventricular rate of the heart. The control unit is further responsive to AF detection by the AF detector to cause the on-demand pace maker to help regulate the ventricular rate of the heart.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
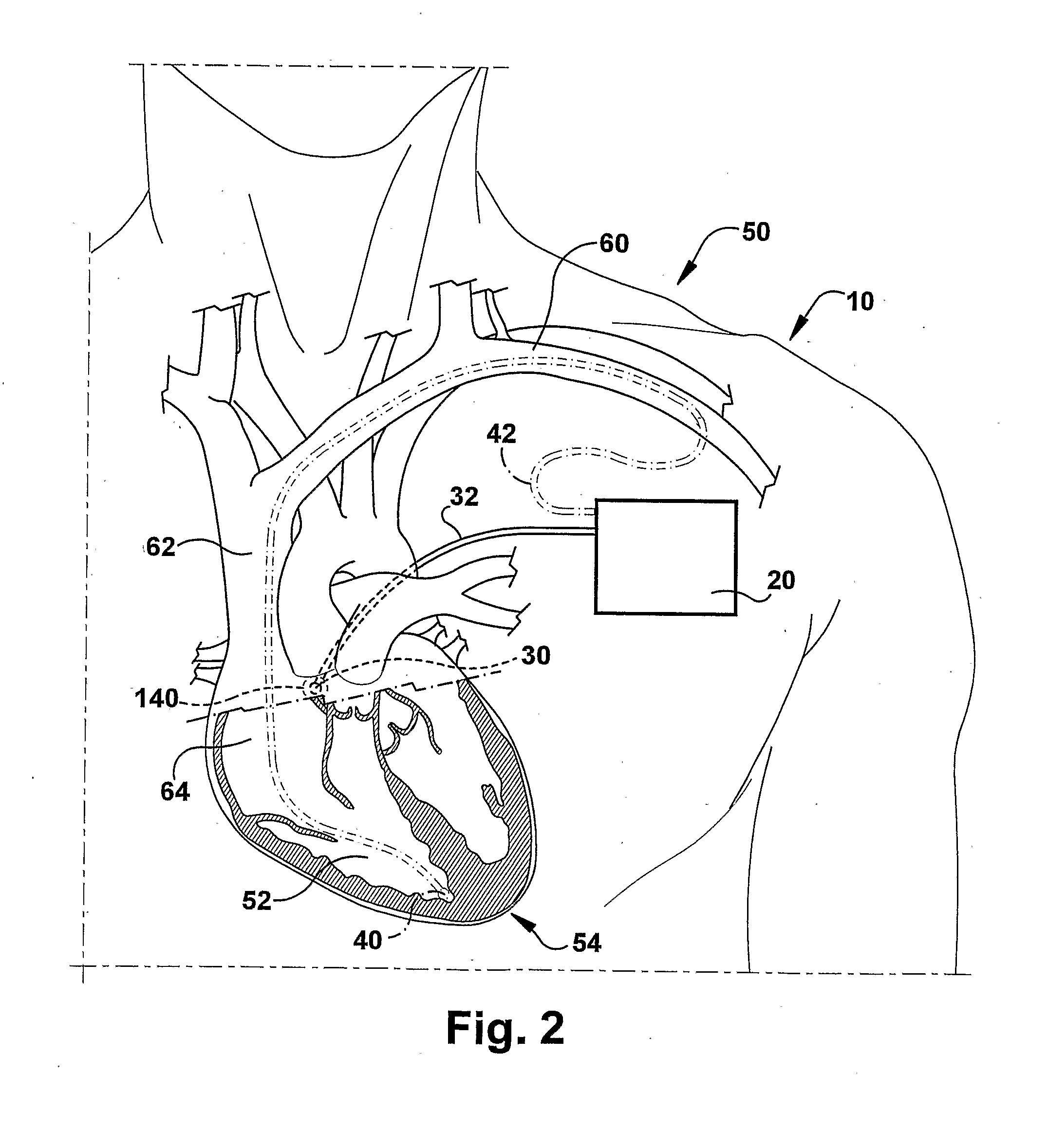
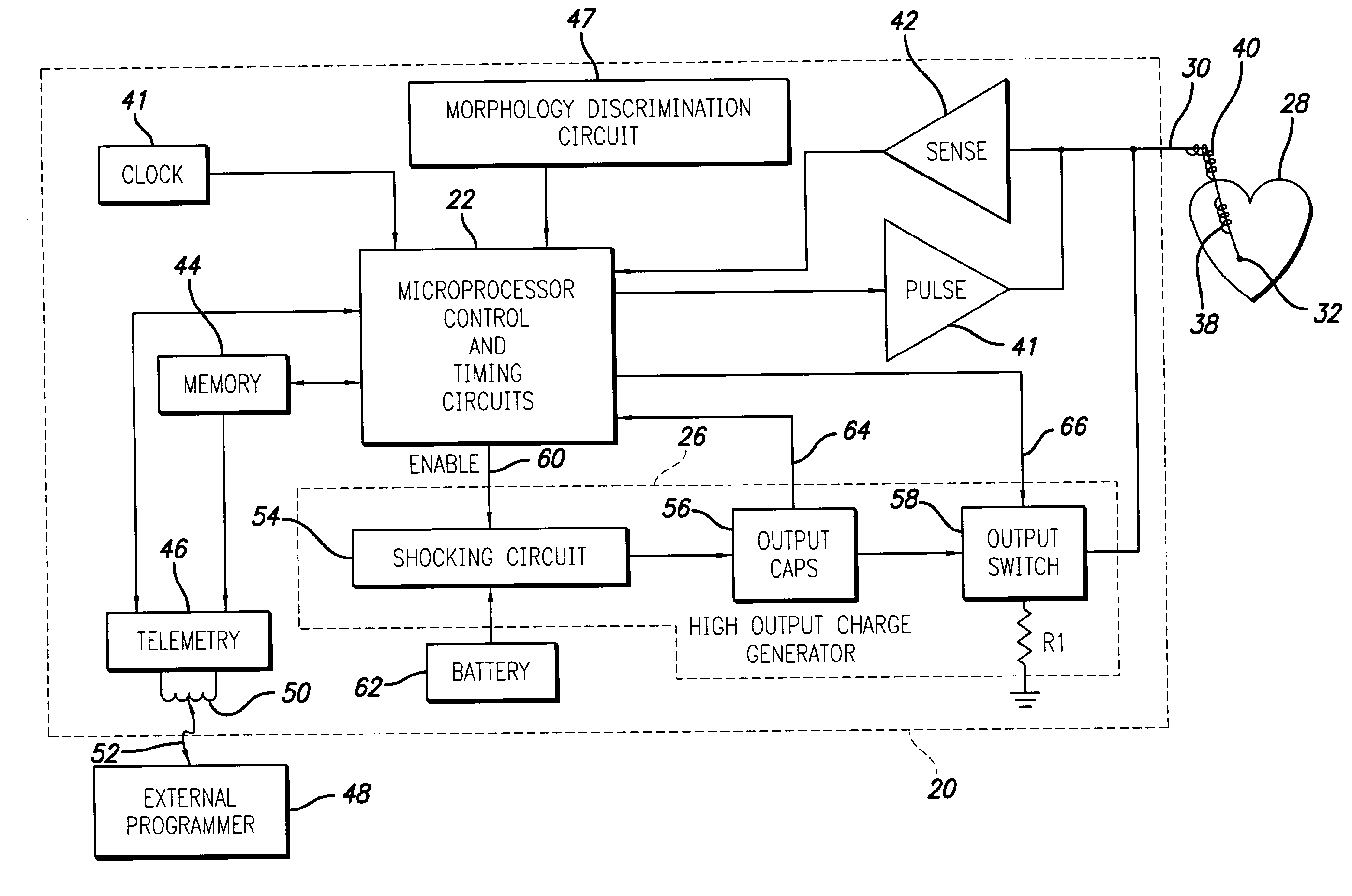
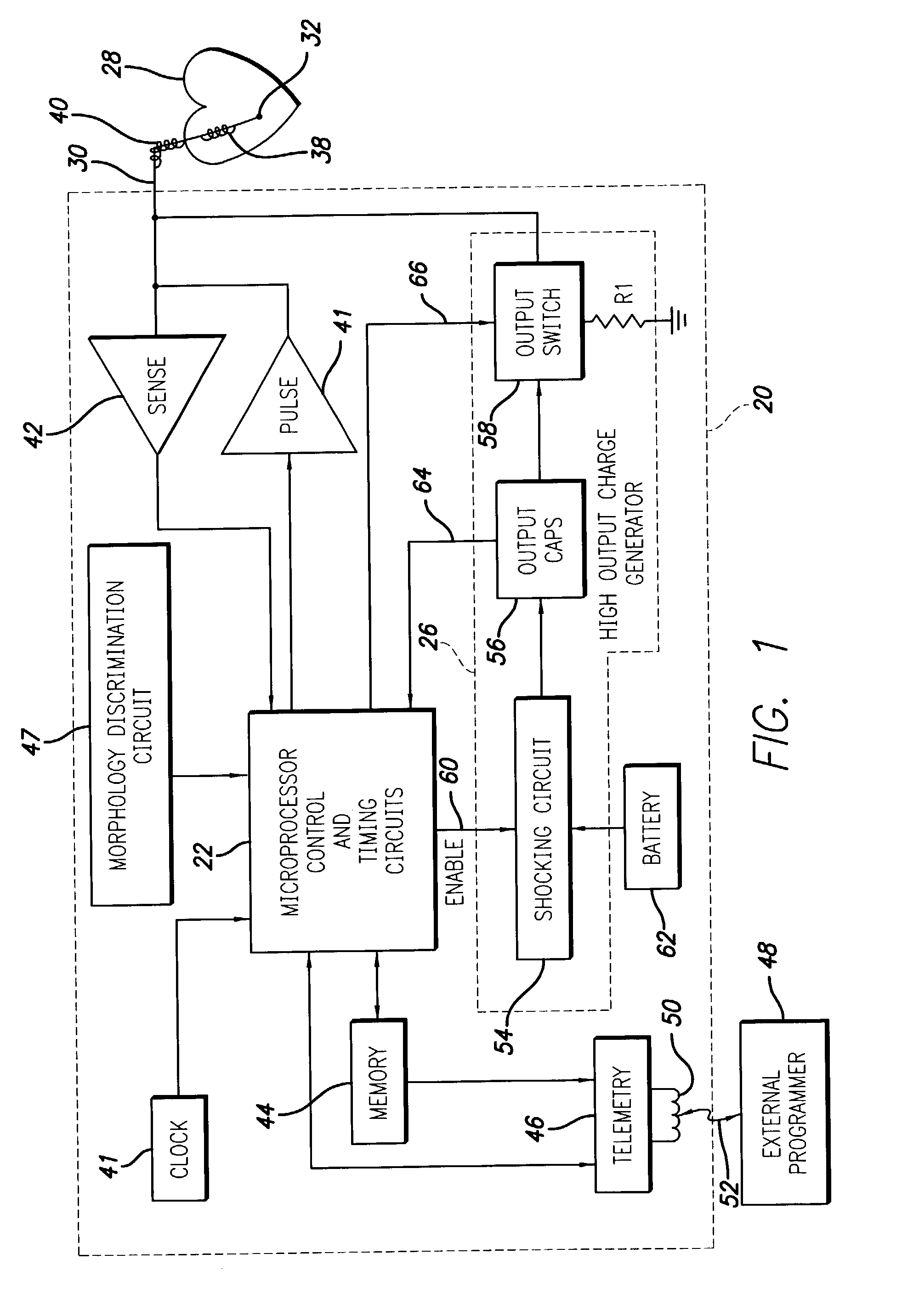
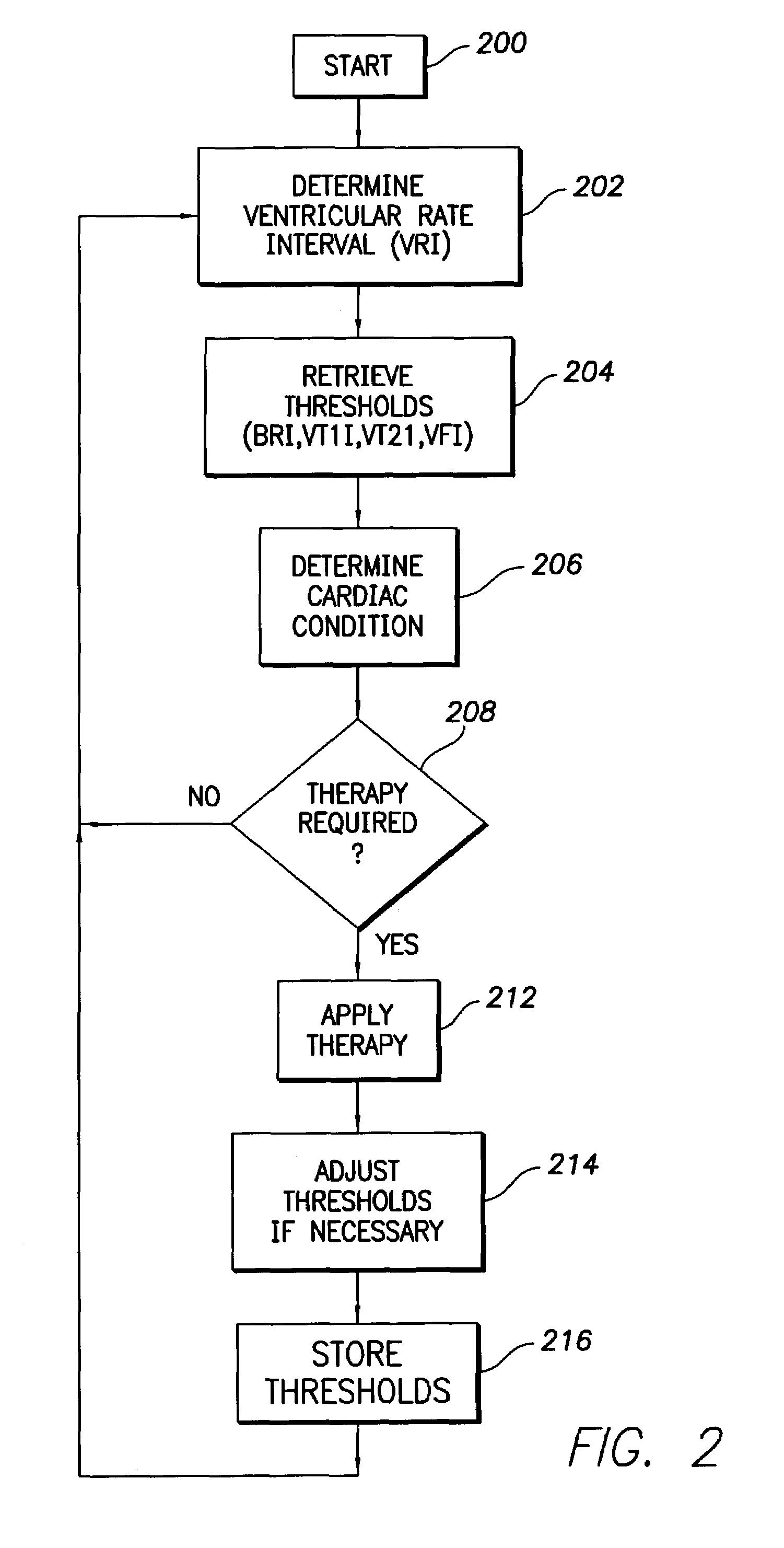
Implantable cardioversion device with a self-adjusting threshold for therapy selection
In an implantable cardioversion device, the condition of the patient's heart is determined from an intrinsic ventricular parameter, such as the ventricular rate, and therapy is provided with a pulse generator, including, for instance, antitachycardia pacing therapy or defibrillation shocks. Initially, the conditions, i.e., ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, are determined using predetermined values for a set of thresholds defining the various conditions. Thereafter, the thresholds are changed by increasing or decreasing the therapy thresholds from the predetermined values based on the morphology of the sensed ventricular signals.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Av nodal stimulation during atrial tachyarrhythmia to prevent inappropriate therapy delivery
ActiveCN103517734AHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationVentricular rateVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
The disclosure describes techniques for delivering electrical stimulation to decrease the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation. AV nodal stimulation is employed during an atrial tachyarrhythmia episode with rapid ventricular conduction to distinguish ventricular tachyarrhythmia from supraventricular tachycardia and thereby prevent delivering inappropriate therapy to a patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical device for reducing and diagnosing unnecessary cardiac pacing
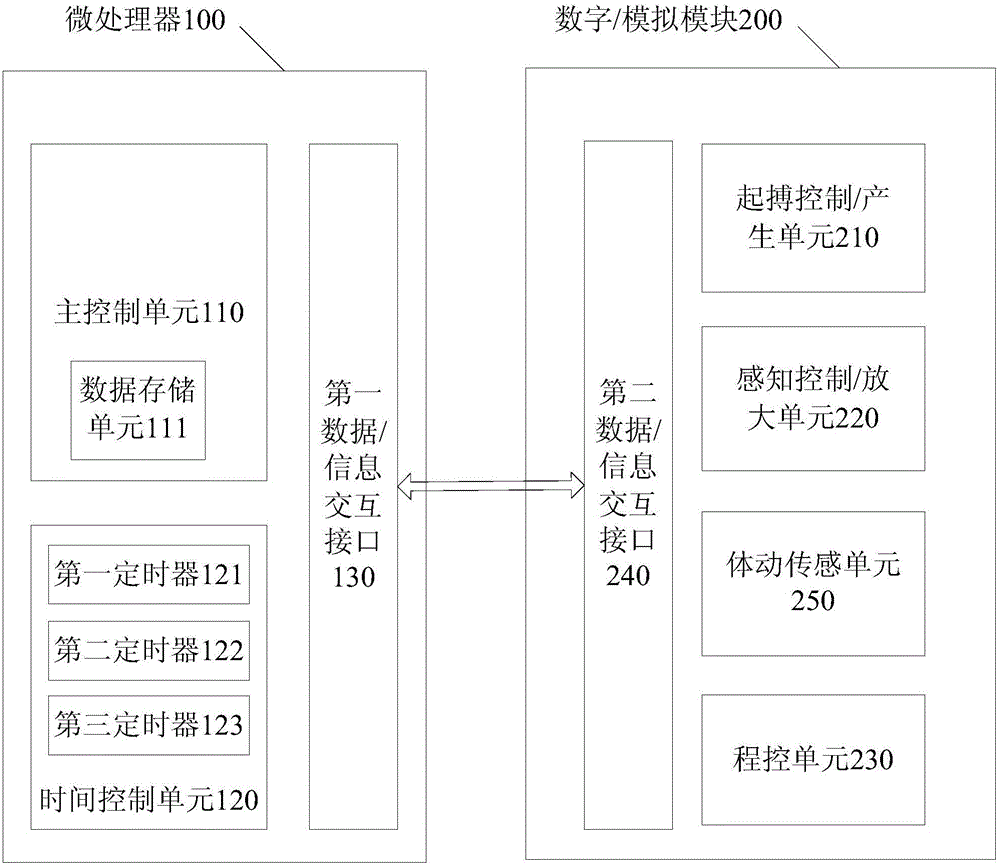
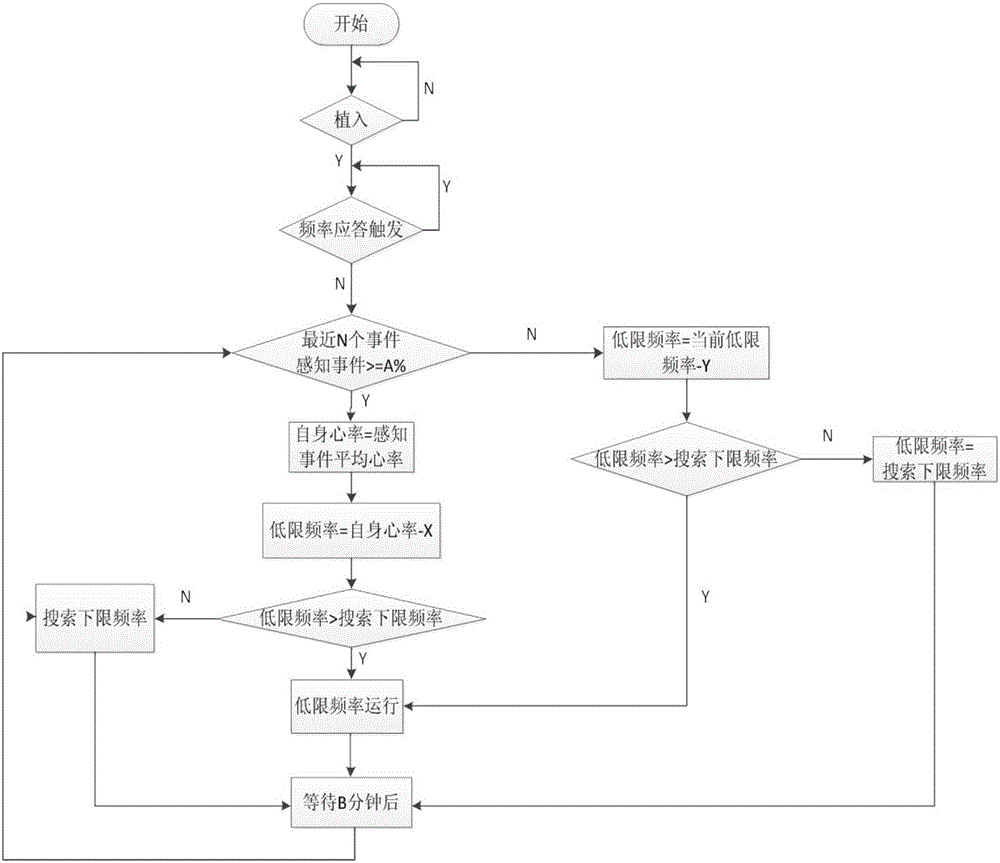
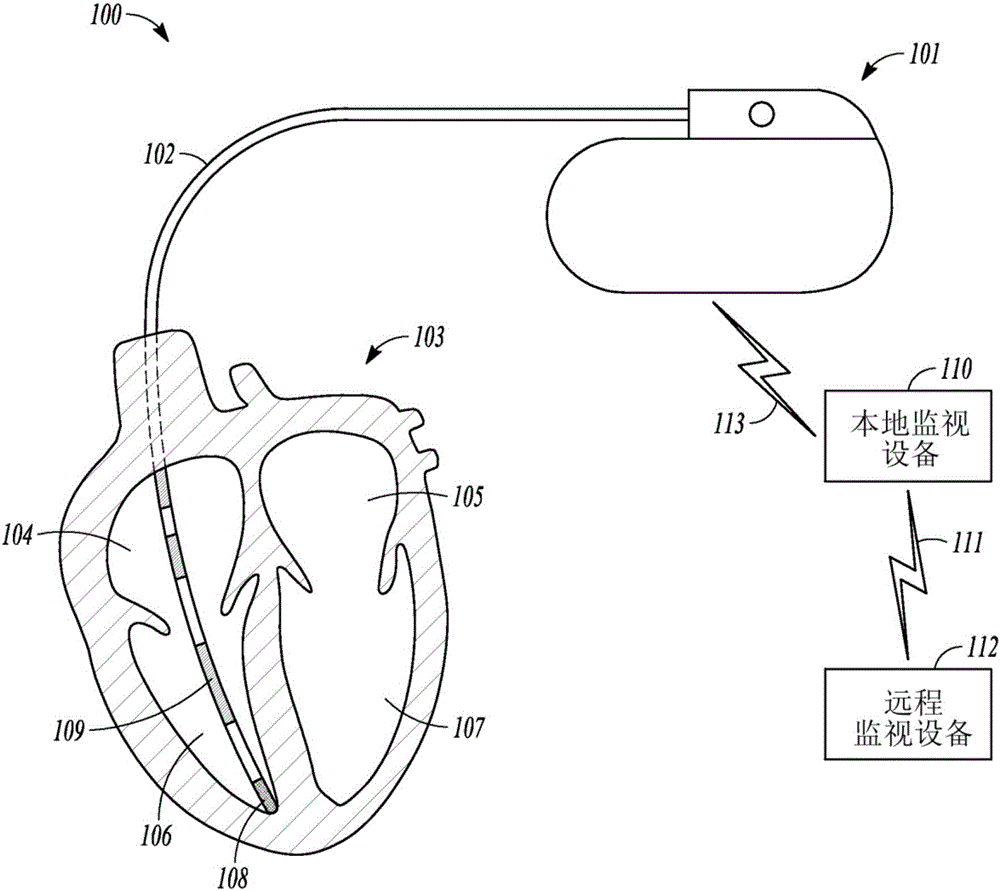
The invention provides a medical device for reducing and diagnosing unnecessary cardiac pacing. The medical device comprises a microprocessor and a digital / analog module connected to the microprocessor; a main control unit receives a sensing event when a sensing control / amplification unit is beyond a refractory period, or the main control unit measures an interval between the sensing event / a pacing signal and a last sensing event / a pacing signal after the main control unit transmits the pacing signal to a pacing control / generation unit, and a heart rate is obtained through multiple intervals; the main control unit determines a low limit frequency of the medical device according to the heart rate, and sets a pacing frequency of the medical device. The device pacing frequency set by the medical device updates with the change of the heart rate of a patient. The medical device of the invention is applied to a double-chamber-mode atrium low limit frequency and a single-chamber-mode ventricle low limit frequency, can effectively reduce unnecessary atrium / ventricle pacing to realize physiological pacing, can eliminate ventricle long intermittence during atrial fibrillation (AF), and relatively regulates a ventricular rate and reduces possible symptoms of the patient.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRMSHANGHAICO LTD
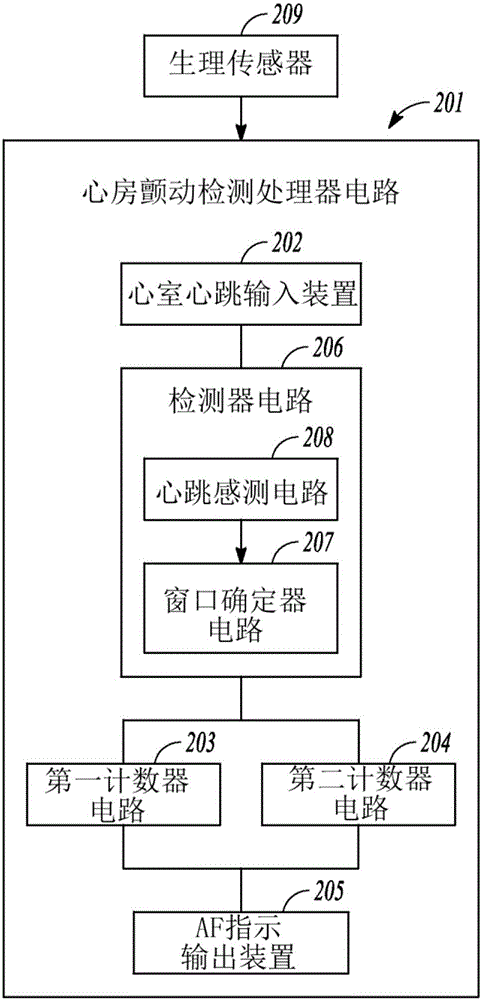
Atrial fibrillation detection using ventricular rate variability
Atrial fibrillation information can be determined from ventricular information or a ventricular location, such as using ventricular rate variability. An ambulatory medical device can receive indications of pairs of first and second ventricular rate changes of three temporally adjacent ventricular heart beats. A first count of instances of the pairs meeting a combined rate change magnitude characteristic and a second count of instances of the pairs in which both of the first and second ventricular rate changes are negative can be used to provide atrial fibrillation information.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Tachyarrhythmia sudden onset detection with hysteresis
This document discusses, among other things, detection of a sudden onset of a tachyarrhythmia. A sudden onset of tachyarrhythmia is determined by monitoring changes in intrinsic ventricular rate, such as by using one or more sensing channels in the ICD. A lowest tachyarrhythmia rate threshold is accompanied by a slightly lower “hysteresis tachyarrhythmia rate threshold.” If a sudden onset of tachyarrhythmia is declared, the sudden onset status is not reset by the ventricular rate falling below the lowest tachyarrhythmia rate threshold, but is instead reset by the ventricular rate falling below the slightly lower hysteresis tachyarrhythmia rate threshold.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and method for ventricular rate regularization
InactiveUS20070135853A1Less variabilityHigh outputHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateCardiac pacemaker electrode
A cardiac rhythm management device which employs pacing therapy to regularize the ventricular rhythm. Such ventricular rate regularization may be employed within bradycardia pacemakers, ventricular resynchronization devices, or implantable cardioverter / defibrillators.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Zoneless tachyarrhythmia detection with real-time rhythm monitoring
A method of using an implantable medical device (IMD) comprising monitoring a ventricular contraction rate of a subject, monitoring an atrial contraction rate of the subject, declaring tachyarrhythmia if the ventricular contraction rate exceeds the atrial contraction rate, and declaring a slow tachyarrhythmia when the ventricular rate is less than a specified tachyarrhythmia detection rate.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
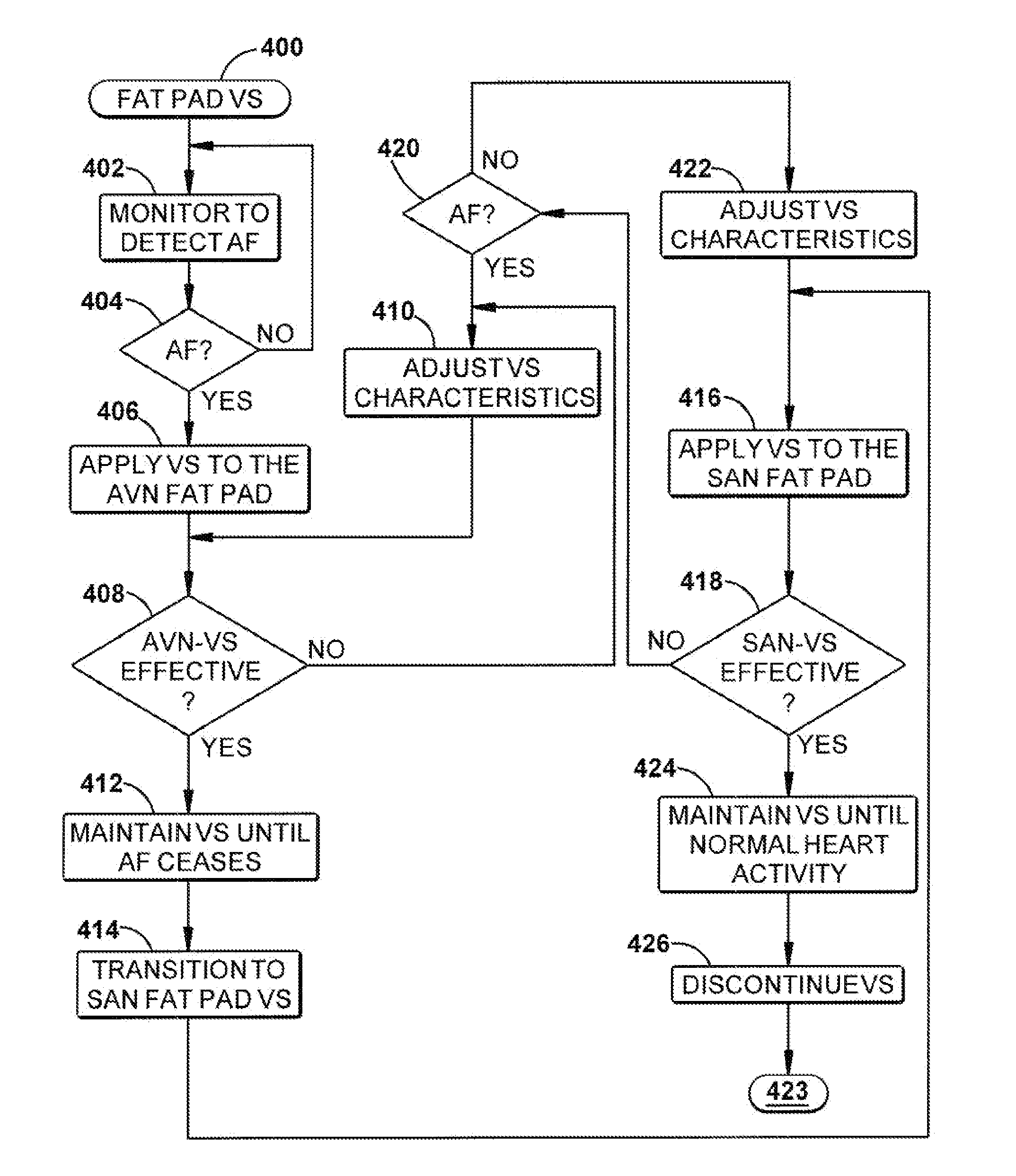
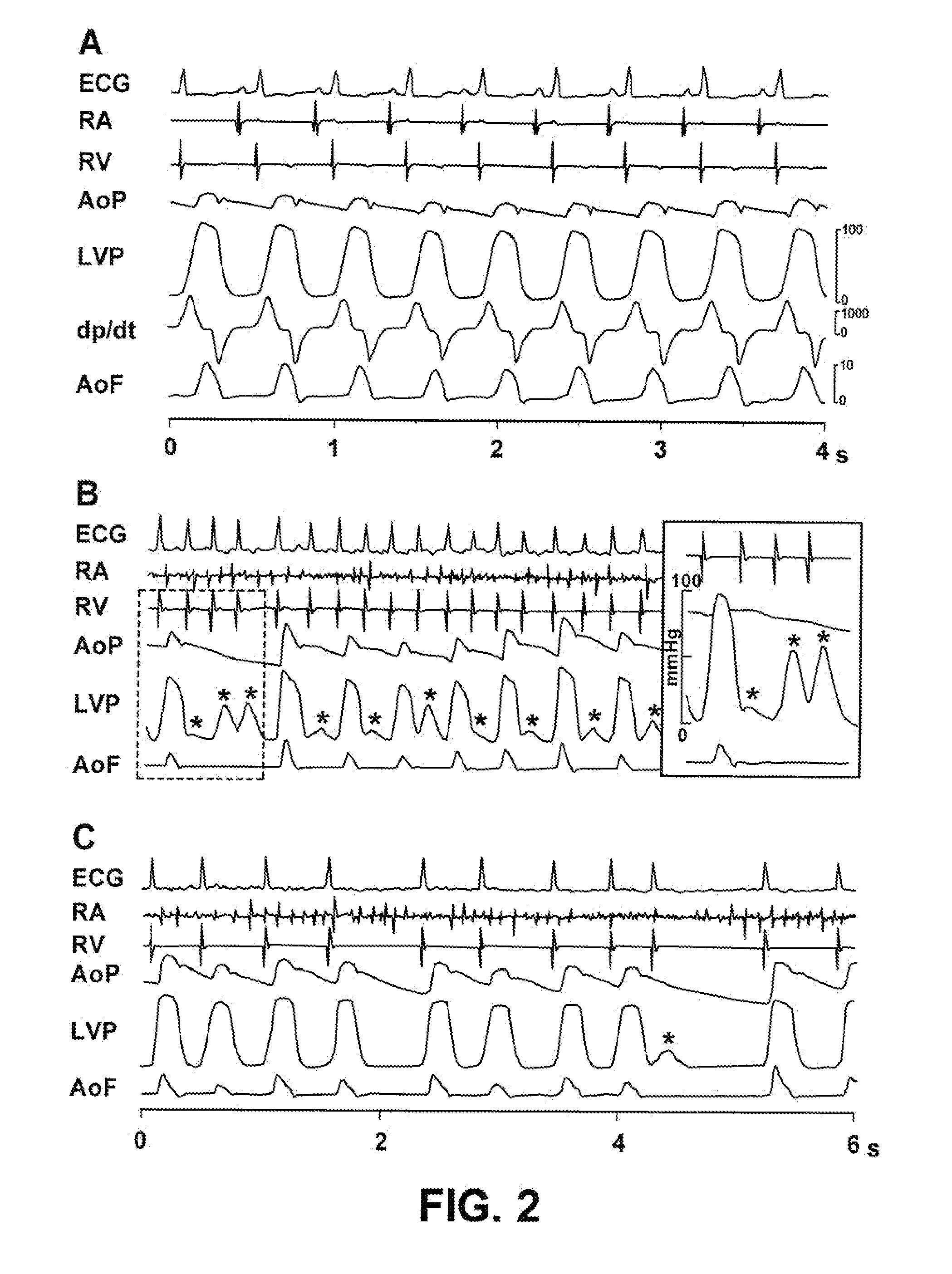
Control of cardiac arrhythmia by vagal stimulation at the atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodal fat pads of the heart
Vagal stimulation applied to the atrioventricular nodal (“AVN”) fat pad and the sinoatrial nodal (“SAN”) fat pad via epicardial leads is useful for controlling cardiac arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation (‘AF”). In the case of AF, for example, vagal stimulation may be applied initially to the AVN fat pad to reduce ventricular rate, and vagal stimulation may be applied to the SAN fat pad after restoration of sinus rhythm to control atrial rate. The technique is applicable to control acute AF and chronic AF. The vagal stimulation may be optimized for exciting ganglia in the fat pads to produce dromotropic and chronotropic effects in the atrioventricular node and the sinoatrial node, respectively. In addition, the SAN fat lead can also be used to pace the atrium in case of sinus bradycardia.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Methods and Systems for Discriminating Between Ventricular Waveforms When Ventricular Rate Exceeds Atrial Rate
A ventricular rate based on first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms within sensed ventricular waveforms is compared to an atrial rate. If the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate, the first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms are compared to a ventricular polarization complex template to obtain a first morphology indicator and a second morphology indicator. If a morphology match inconsistency is present, the amount by which the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate is compared to a threshold. If the threshold is exceeded, high-ventricular-rate therapy to the heart is inhibited. The ventricular polarization complex template may be a QRS-complex template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if each of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms do not match the QRS-complex template. Alternatively, the ventricular polarization complex template may be a T-wave template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if either of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms matches the T-wave template.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Vagal stimulation during atrial tachyarrhythmia to facilitate cardiac resynchronization therapy
InactiveUS20130138173A1Increased and variable ventricular rateMore intrinsic ventricular depolarizationsHeart stimulatorsVentricular rateAtrial cavity
The disclosure describes techniques for delivering vagal stimulation to decrease the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation. Decreasing the ventricular rate response during an atrial tachyarrhythmia may facilitate increased ventricular pacing for cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), and may also reduce the likelihood of inappropriately detecting a ventricular tachyarrhythmia during the atrial tachyarrhythmia. Furthermore, the vagal stimulation may augment vagal tone, which may facilitate long term left ventricular reverse remodeling and decrease atrial and ventricular arrhythmic burden in heart failure patients. An example system that delivers CRT comprises a processor that detects an atrial tachyarrhythmia in one or more atria of the heart, and monitors at least one of a ventricular rate or degree of ventricular pacing subsequent to the detected atrial arrhythmia. The processor controls a stimulation generator to deliver vagal stimulation based on the least one of a ventricular rate or degree of ventricular pacing.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method based on voting ensemble learning
ActiveCN111000553AGood effectReduce threatDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsClassification methodsTest set
An intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method based on voting ensemble learning in the invention is characterized by being realized through the following steps: a) carrying out data preprocessing; b) establishing a logistic regression model; c) establishing a decision tree model; d) establishing a support vector machine; e) establishing a naive Bayesian model; f) establishing a neuron model; g) establishing a k proximity model; and h) carrying out model integration. Finally, a model with the accuracy of not less than 80% is obtained, and the effect of the model is better than theeffect of the single model established in the steps b) to g). According to the intelligent electrocardiogram data classification method, enough data are firstly acquired from ccdd and are divided into a training set and a test set, then various models are established, and the model with accuracy of not less than 80% is finally obtained, thereby realizing intelligent identification and classification of normal, atrial fibrillation, atrial premature beat, accidental atrial premature beat, frequent atrial premature beat, atrial tachycardia and atrial fibrillation accompanied with rapid ventricular rate, and realizing early discovery and early treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:SHANDONG COMP SCI CENTNAT SUPERCOMP CENT IN JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com