Patents
Literature
740 results about "Depolarization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biology, depolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell. Depolarization is essential to the function of many cells, communication between cells, and the overall physiology of an organism.
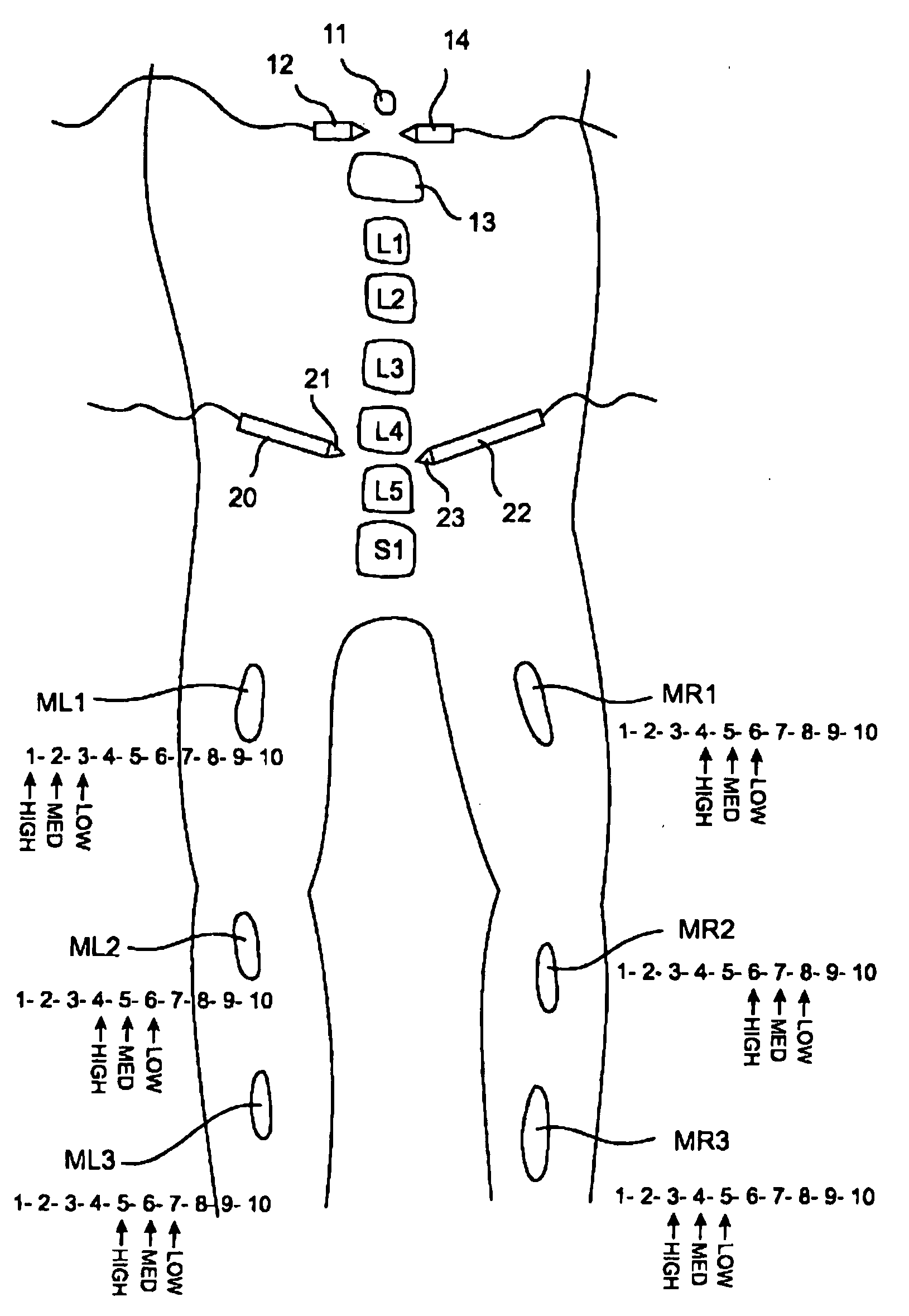
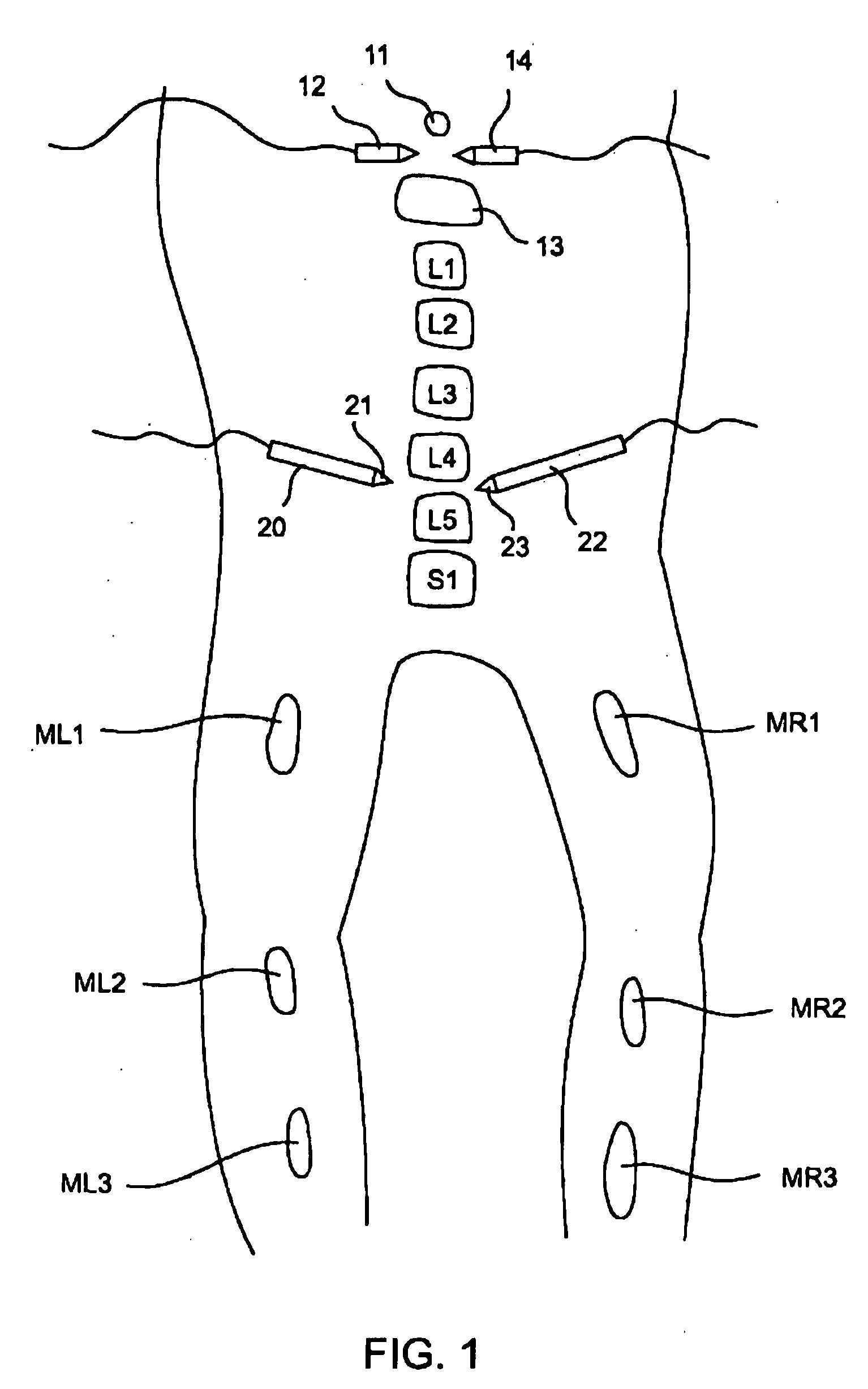
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20070293782A1Interpret accuracyLess sensitiveElectrotherapyElectromyographyPower flowMedicine
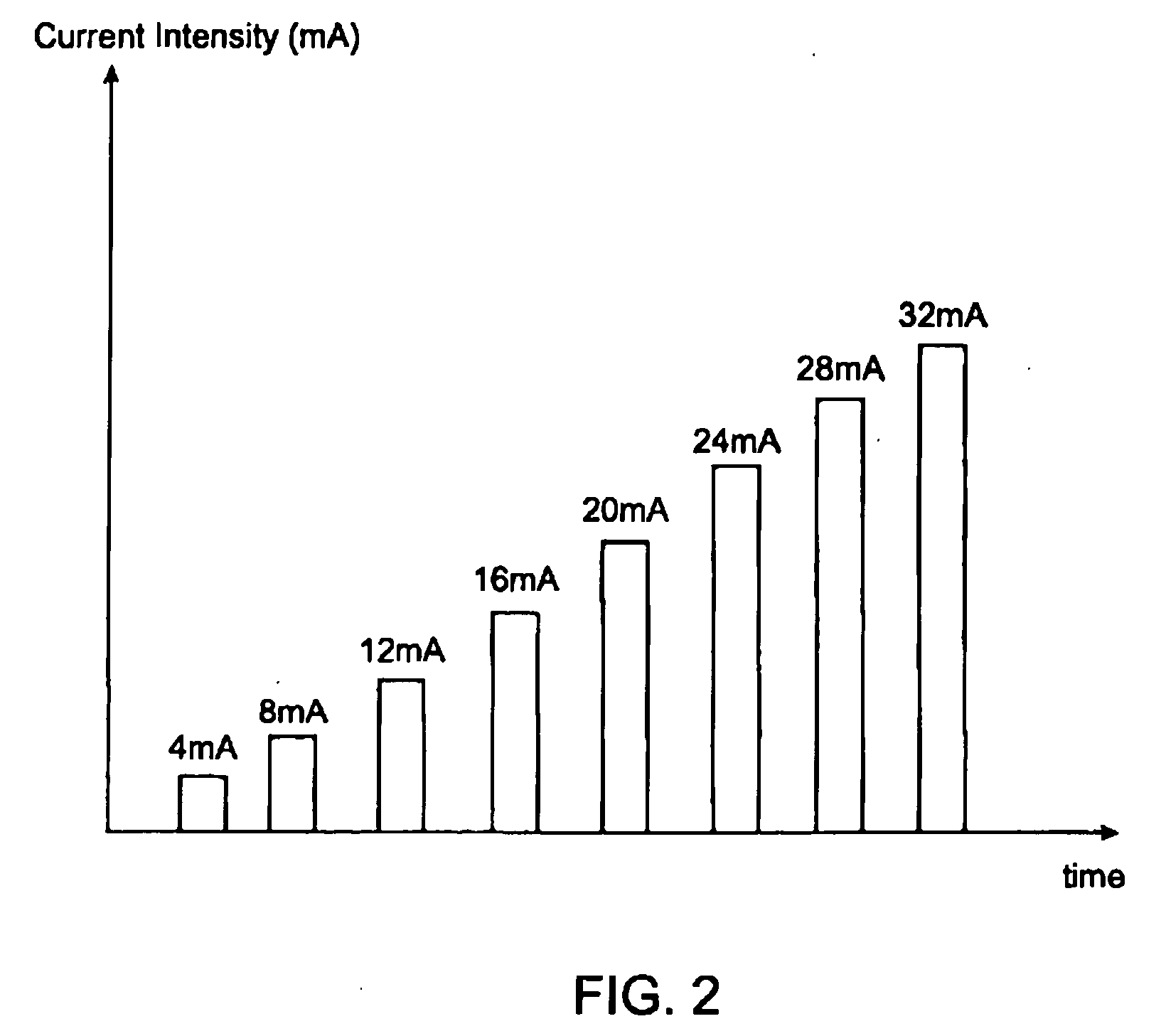
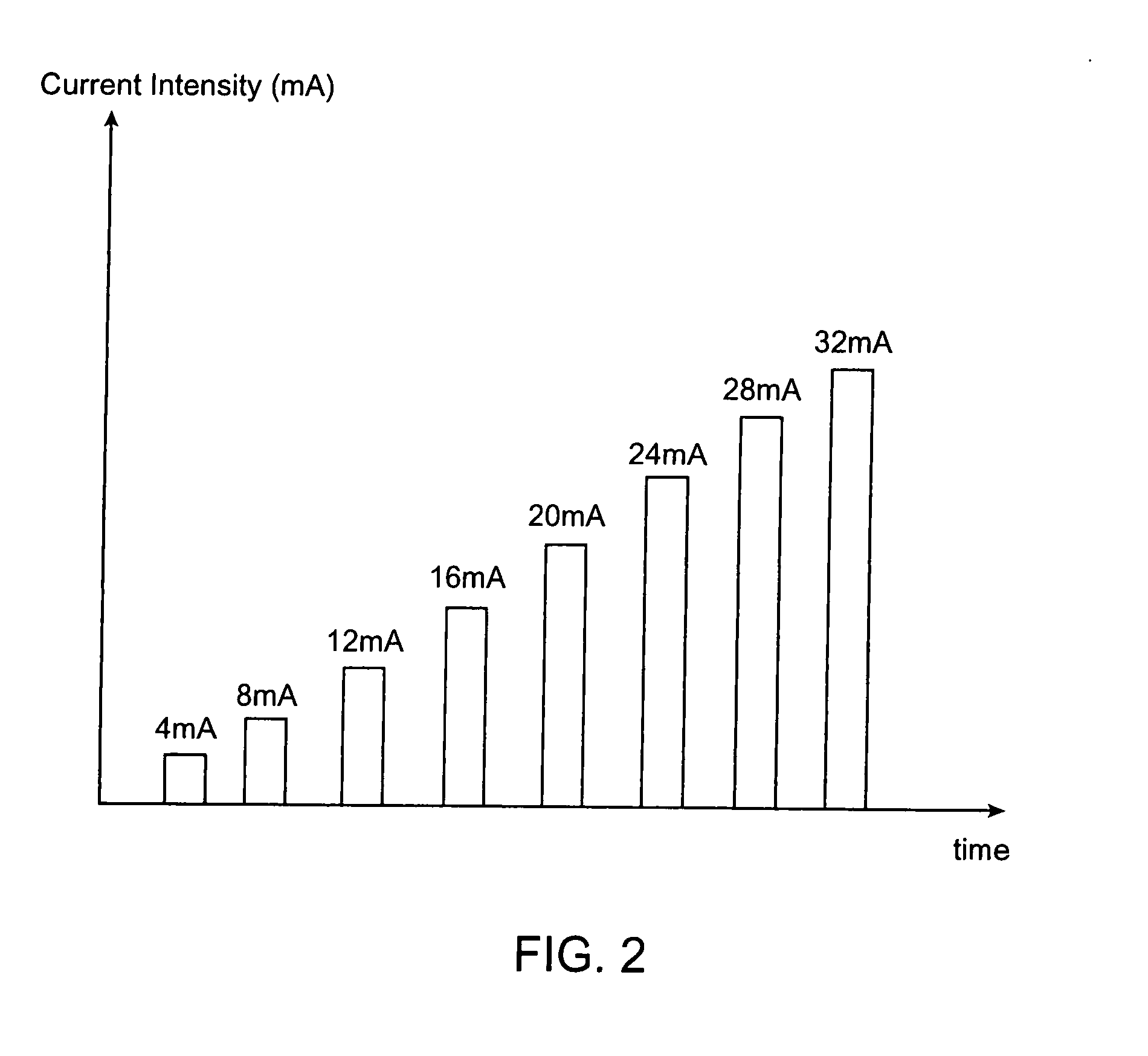
A method of determining relative neuro-muscular response onset value thresholds for a plurality of spinal nerves, comprising: depolarizing a portion of the patient's cauda equina; and measuring the current intensity level at which a neuro-muscular response to the depolarization of the cauda equina is detected in each of the plurality of spinal nerves. A method for detecting the presence of a nerve adjacent the distal end of at least one probe, comprising: determining relative neuro-muscular response onset values for a plurality of spinal nerves; emitting a stimulus pulse from a probe or surgical tool; detecting neuro-muscular responses to the stimulus pulse in each of the plurality of spinal nerves; and concluding that the electrode disposed on the distal end of the at least one probe is positioned adjacent to a first spinal nerve when the neuro-muscular response detected in the first spinal nerve is detected as a current intensity level less than or equal to a corresponding neuro-muscular response onset value of the first spinal nerve.
Owner:NUVASIVE
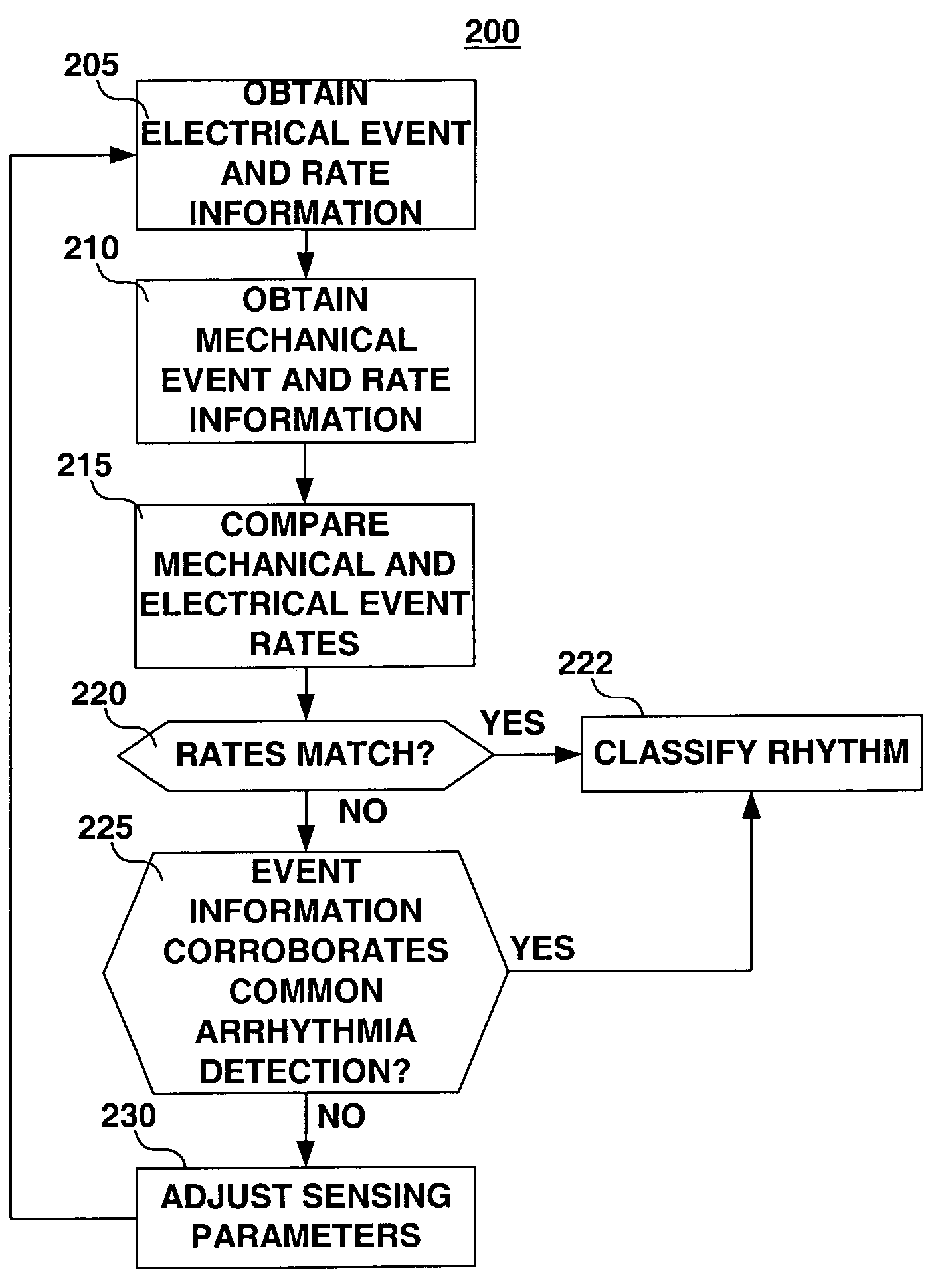
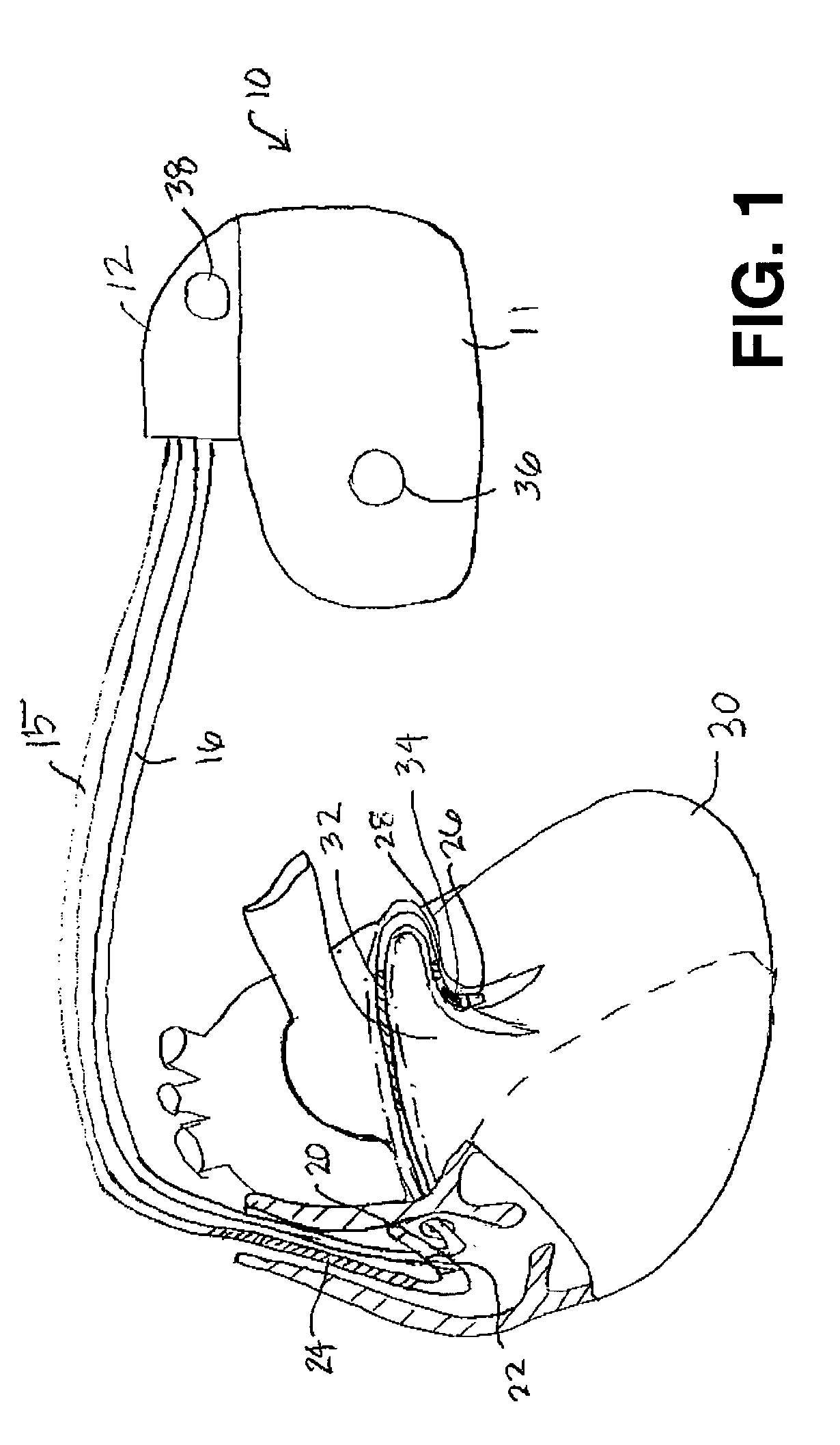
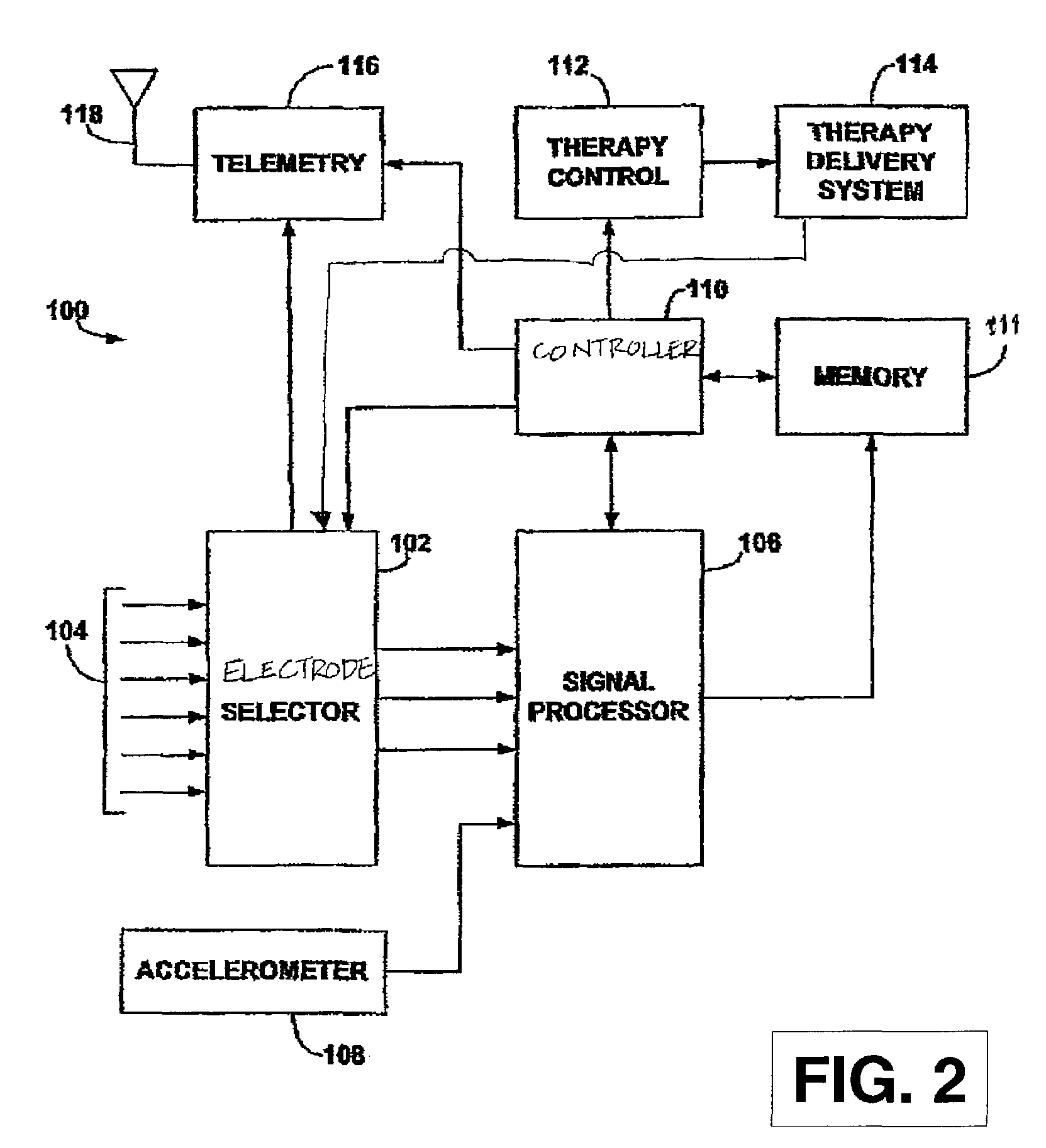
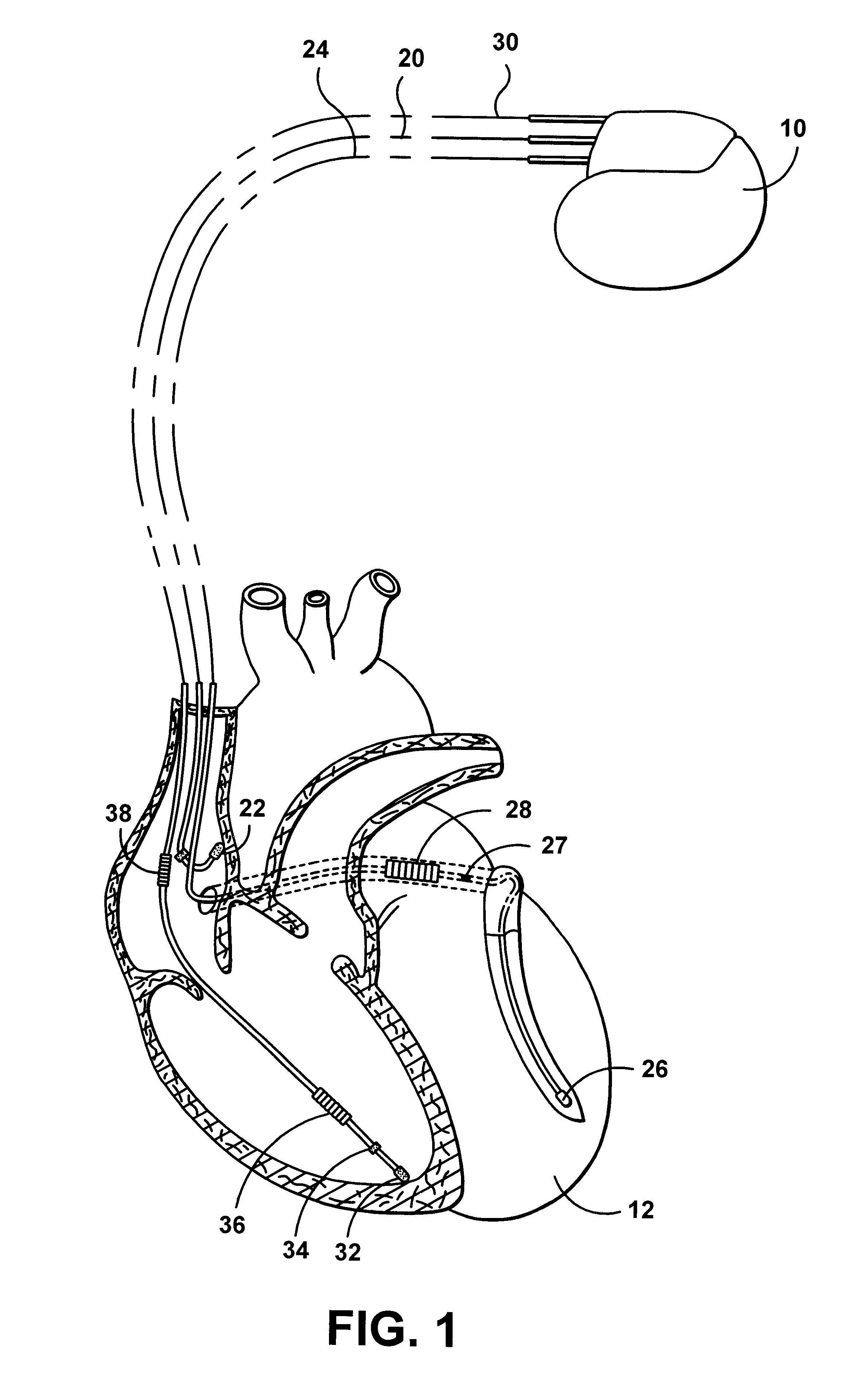
Use of accelerometer signal to augment ventricular arrhythmia detection
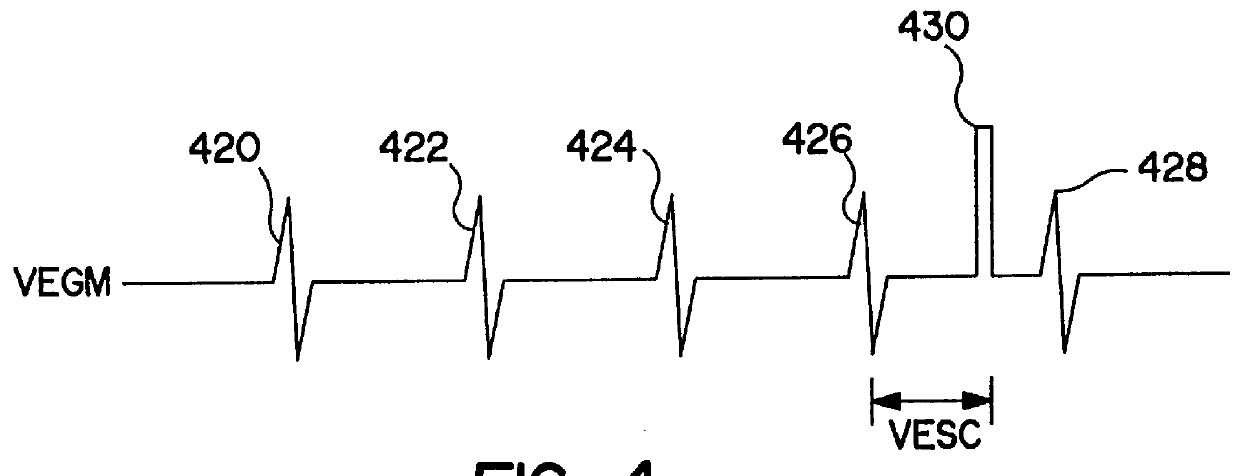
ActiveUS7130681B2Reliable detectionReliable classificationPerson identificationHeart stimulatorsEcg signalVentricular dysrhythmia
A system and method for detecting and discriminating atrial arrhythmias based on mechanical signals of cardiac wall motion and electrical signals of cardiac depolarizations. A mechanical event rate determined from sensed mechanical events is used to corroborate an electrical event rate determined from sensed EGM or ECG signals to classify the heart rhythm. If the event rates are not correlated, other parameterized data from the mechanical signal and electrical signal are evaluated to detect evidence of an arrhythmia. If electrical and mechanical event data do not corroborate a common arrhythmia condition, electrical and mechanical sensing parameters may be adjusted.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electromyography system
InactiveUS20080065178A1Reduce pressureInterpret accuracyElectromyographyInternal electrodesPower flowMedicine
A method of determining relative neuro-muscular response onset value thresholds for a plurality of spinal nerves, comprising: depolarizing a portion of the patient's cauda equina; and measuring the current intensity level at which a neuro-muscular response to the depolarization of the cauda equina is detected in each of the plurality of spinal nerves. A method for detecting the presence of a nerve adjacent the distal end of at least one probe, comprising: determining relative neuro-muscular response onset values for a plurality of spinal nerves; emitting a stimulus pulse from a probe or surgical tool; detecting neuro-muscular responses to the stimulus pulse in each of the plurality of spinal nerves; and concluding that the electrode disposed on the distal end of the at least one probe is positioned adjacent to a first spinal nerve when the neuro-muscular response detected in the first spinal nerve is detected as a current intensity level less than or equal to a corresponding neuro-muscular response onset value of the first spinal nerve.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Liquid crystal display
A normally-closed liquid crystal display includes a component to selectively absorb characteristic leakage light occurring at black representation. Therefore, when black is displayed, occurrence of unnecessary leakage light due to partial depolarization of polarized light caused by a component of an LCD panel can be suppressed. It is therefore possible to provide a liquid crystal display in which display performance of black is improved to clearly display black.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC +1
Single or multi-mode cardiac activity data collection, processing and display obtained in a non-invasive manner
InactiveUS7043292B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEasy to identifyElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorCardiac surface
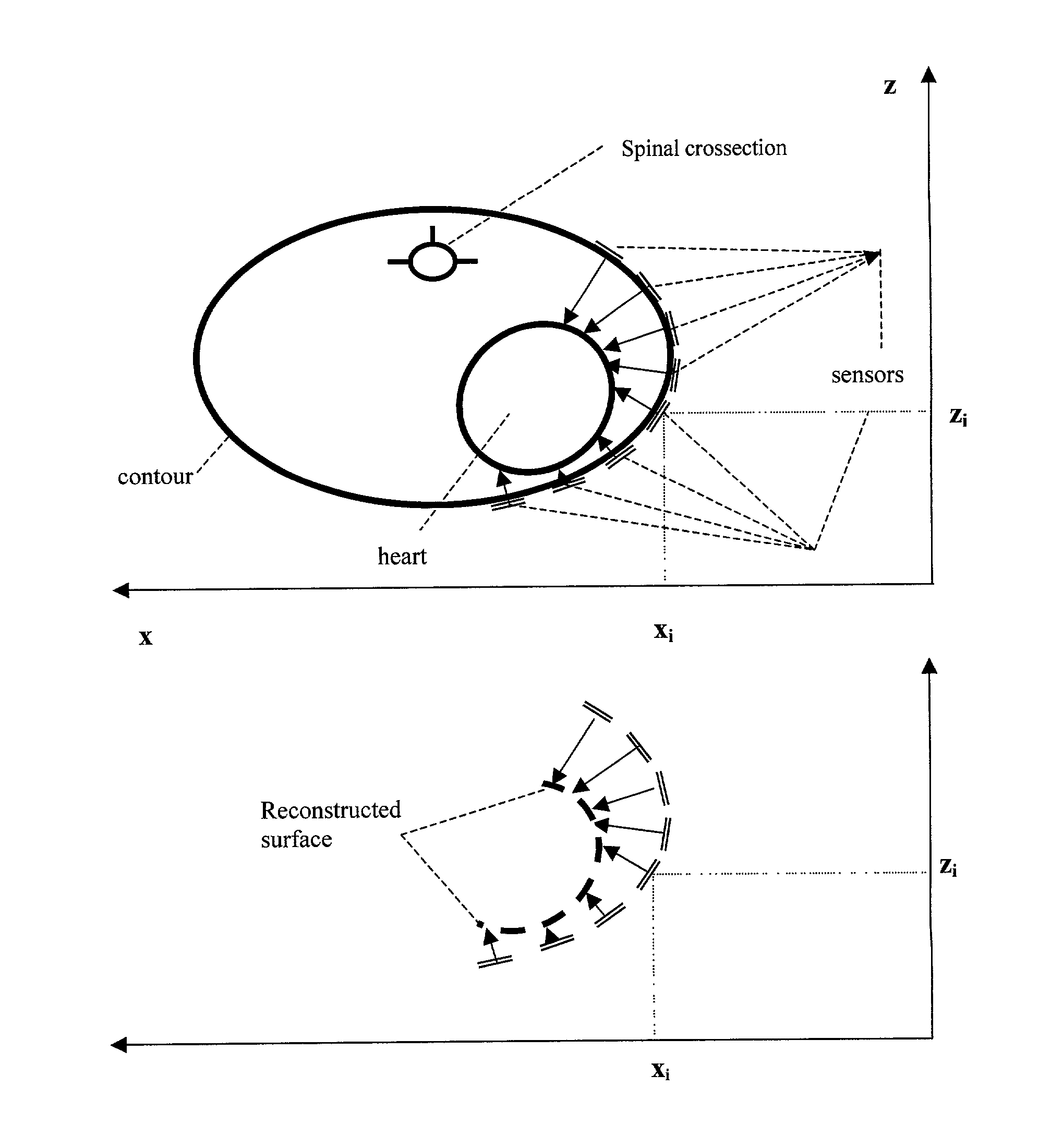
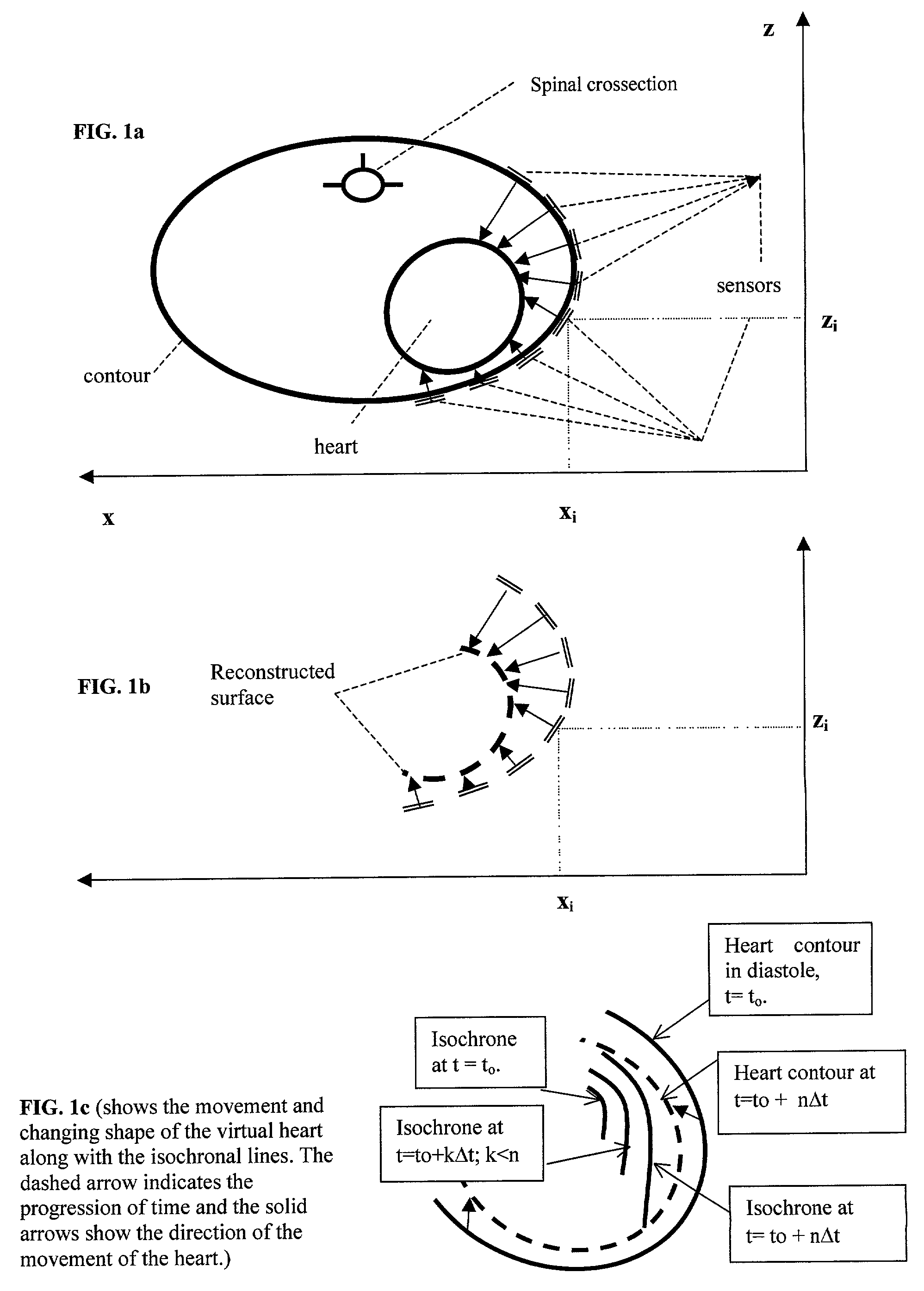
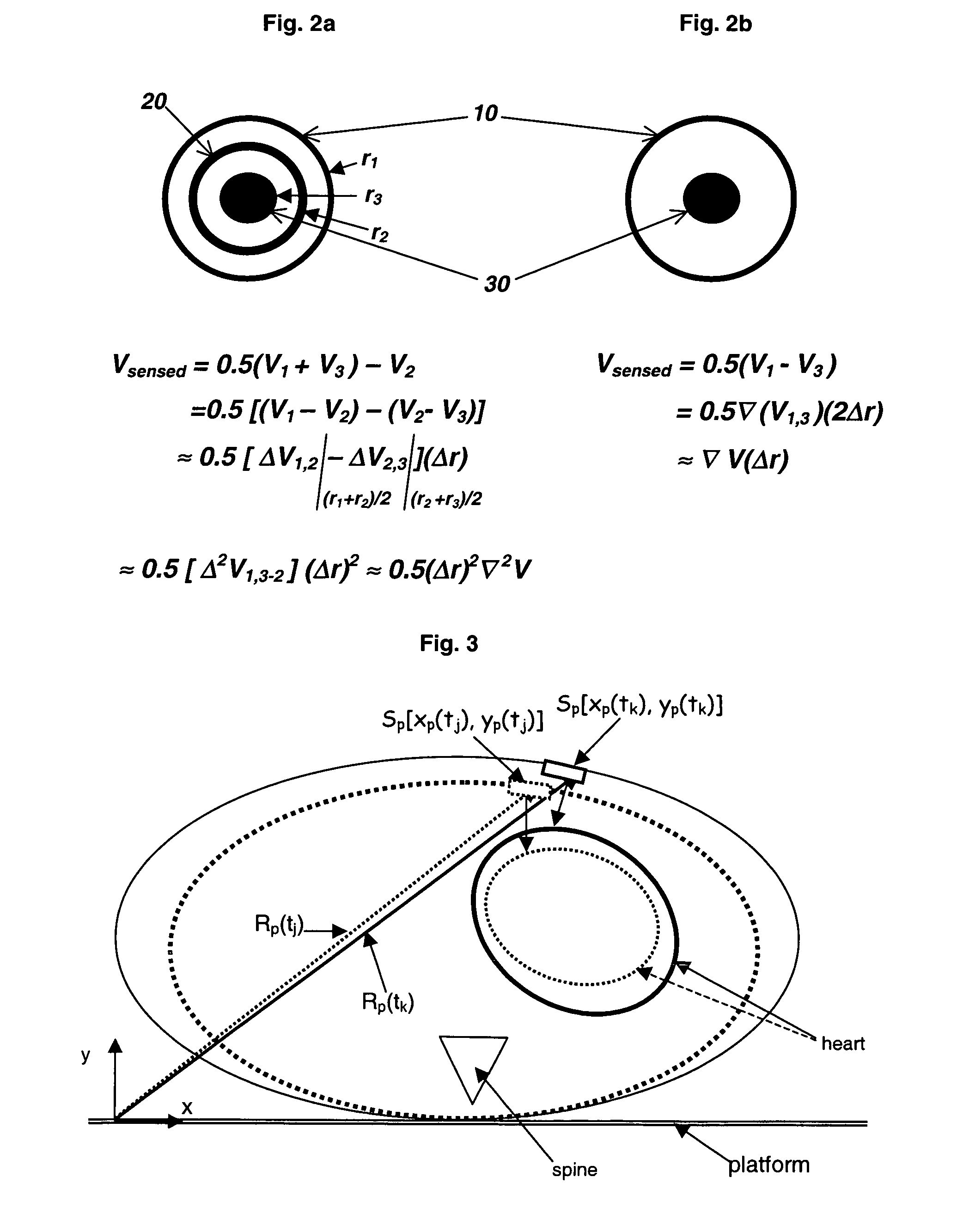
The method of presenting concurrent information about the electrical and mechanical activity of the heart using non-invasively obtained electrical and mechanical cardiac activity data from the chest or thorax of a patient comprises the steps of: placing at least three active Laplacian ECG sensors at locations on the chest or thorax of the patient; where each sensor has at least one outer ring element and an inner solid circle element, placing at least one ultrasonic sensor on the thorax where there is no underlying bone structure, only tissue, and utilizing available ultrasound technology to produce two or three-dimensional displays of the moving surface of the heart and making direct measurements of the exact sites of the sensors on the chest surface to determine the position and distance from the center of each sensor to the heart along a line orthogonal to the plane of the sensor and create a virtual heart surface; updating the measurements at a rate to show the movement of the heart's surface; monitoring at each ultrasonic sensor site and each Laplacian ECG sensor site the position and movement of the heart and the passage of depolarization wave-fronts in the vicinity; treating those depolarization wave-fronts as moving dipoles at those sites to create images of their movement on the image of the beating heart's surface; and, displaying the heart's electrical activity on the dynamically changing image of the heart's surface with the goal to display an approximation of the activation sequence on the beating virtual surface of the heart
Owner:TARJAN PETER P +2
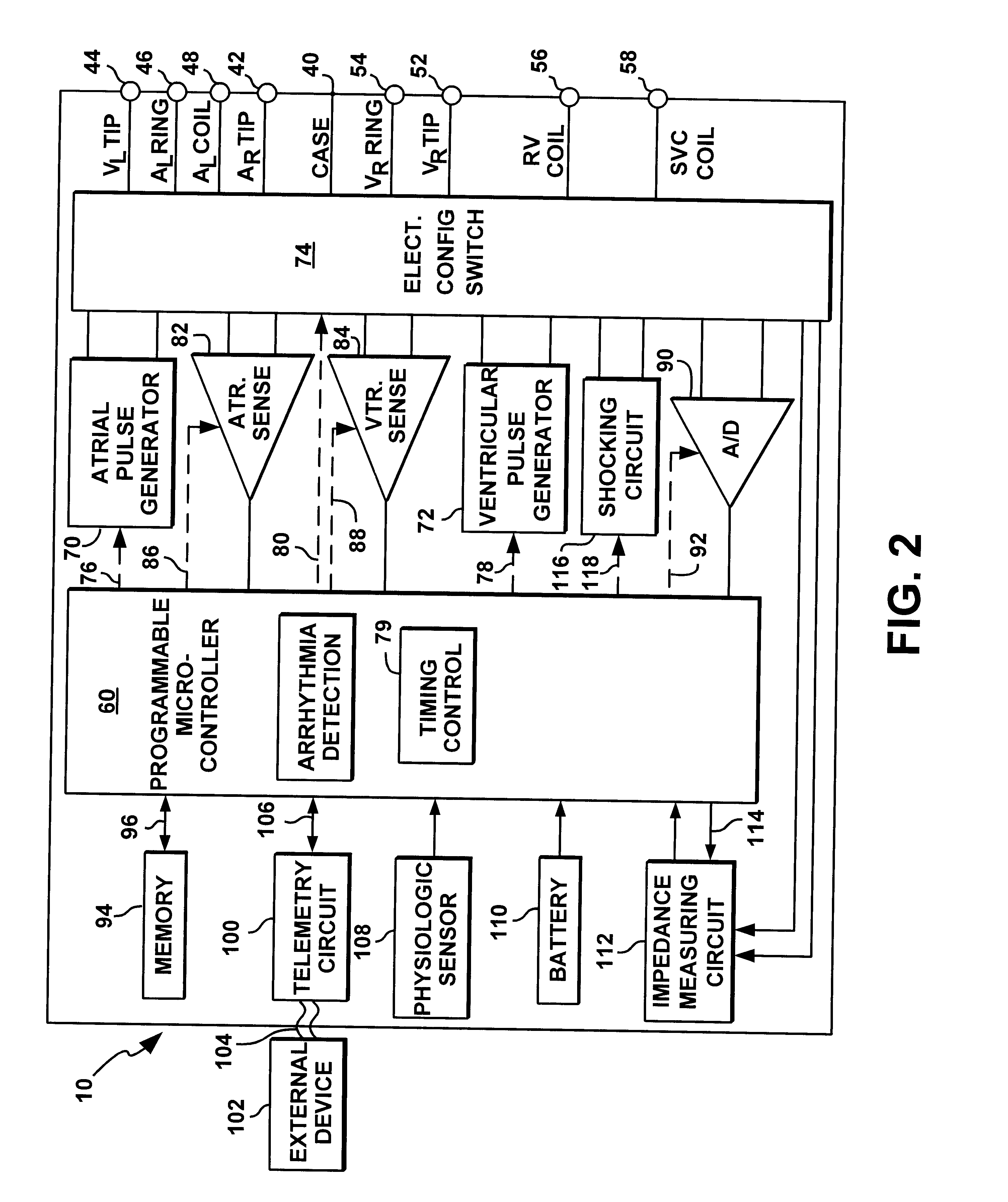
System and method for automatically selecting electrode polarity during sensing and stimulation
InactiveUS6477417B1Improve welfareImprove coordinationHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsElectricityElectrical battery
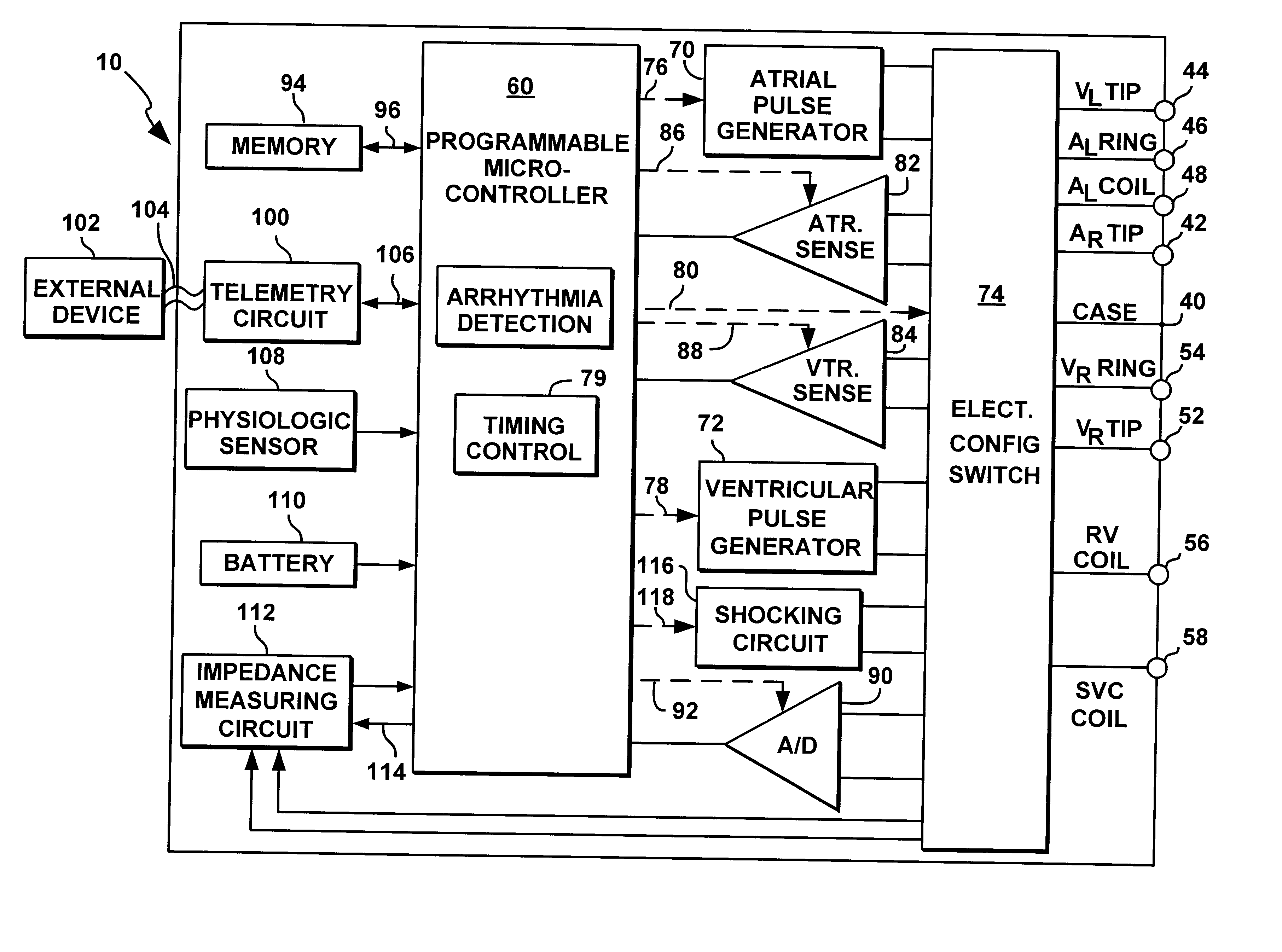
An implantable multi-chamber cardiac stimulation device includes flexibly programmable electrode stimulation configurations, and is capable of precisely controlling the stimulation sequence between multiple sites. The stimulation device provides a plurality of connection ports that allow independent connection of each electrical lead associated with a particular stimulation site in the heart. Each connection port further provides a unique terminal for making electrical contact with only one electrode such that no two electrodes are required to be electrically coupled. Furthermore, each electrode, whether residing on a unipolar, bipolar or multipolar lead, may be selectively connected or disconnected through programmable switching circuitry that determines the electrode configurations to be used for sensing and for stimulating at each stimulation site. The stimulation device allows for the programmable selection of each electrode terminal connection to a relatively positive or negative battery potential. In this way, each electrode, when electrically connected, may be programmed to act as the cathode or as the anode during sensing or stimulation delivery. Thus, directionality of the depolarization wave may be controlled by programming the cathode and anode assignments of the stimulation electrodes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
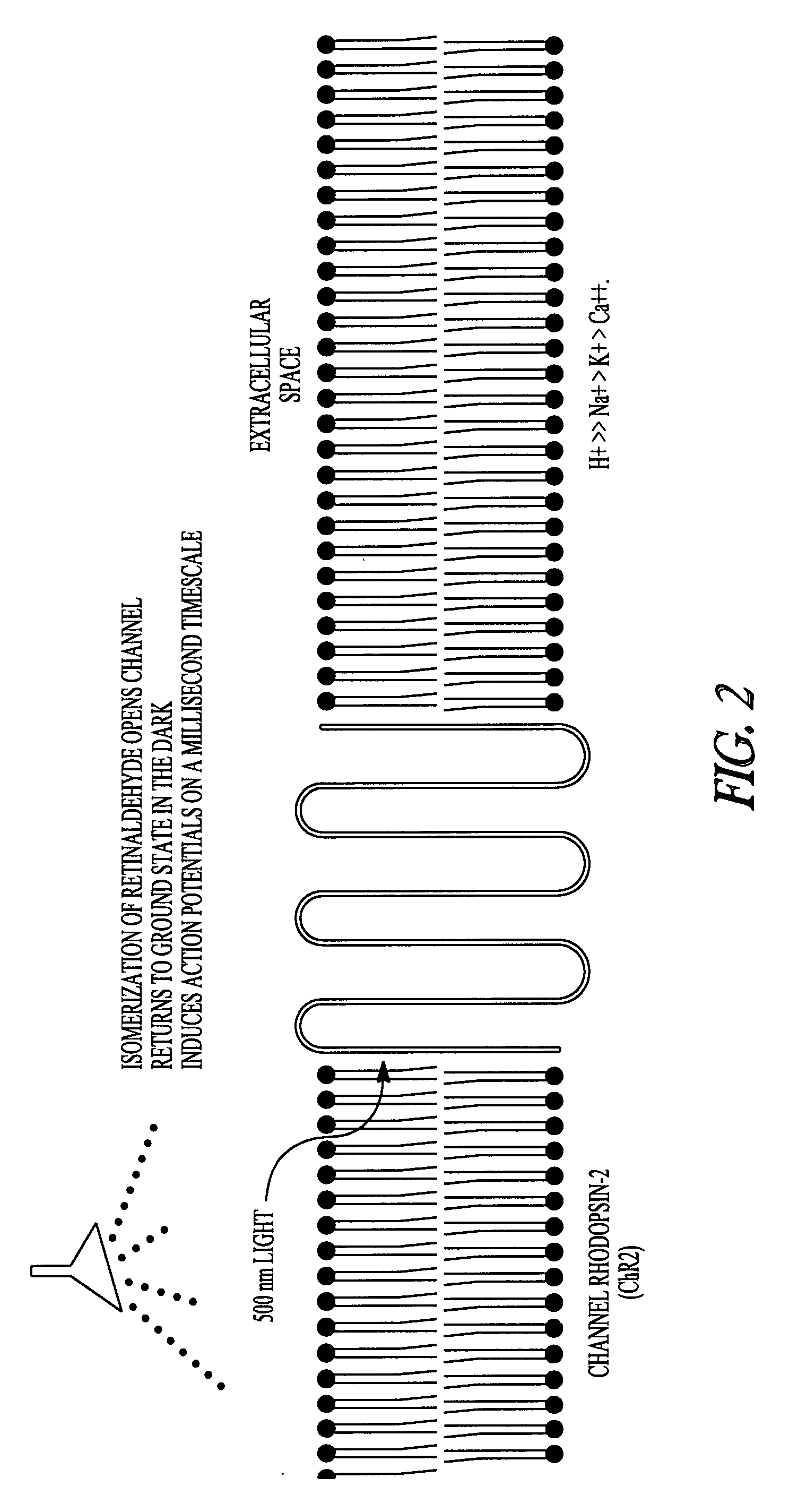
Optical depolarization of cardiac tissue
ActiveUS20090054954A1No painIncrease photosensitivitySurgical instrument detailsViruses/bacteriophagesManagement systemDepolarization
The invention provides a cardiac rhythm management system for stimulating a heart having photosensitive tissue, vectors useful to photosensitize cells expressing the vectors, and methods for light induced depolarization of cells.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
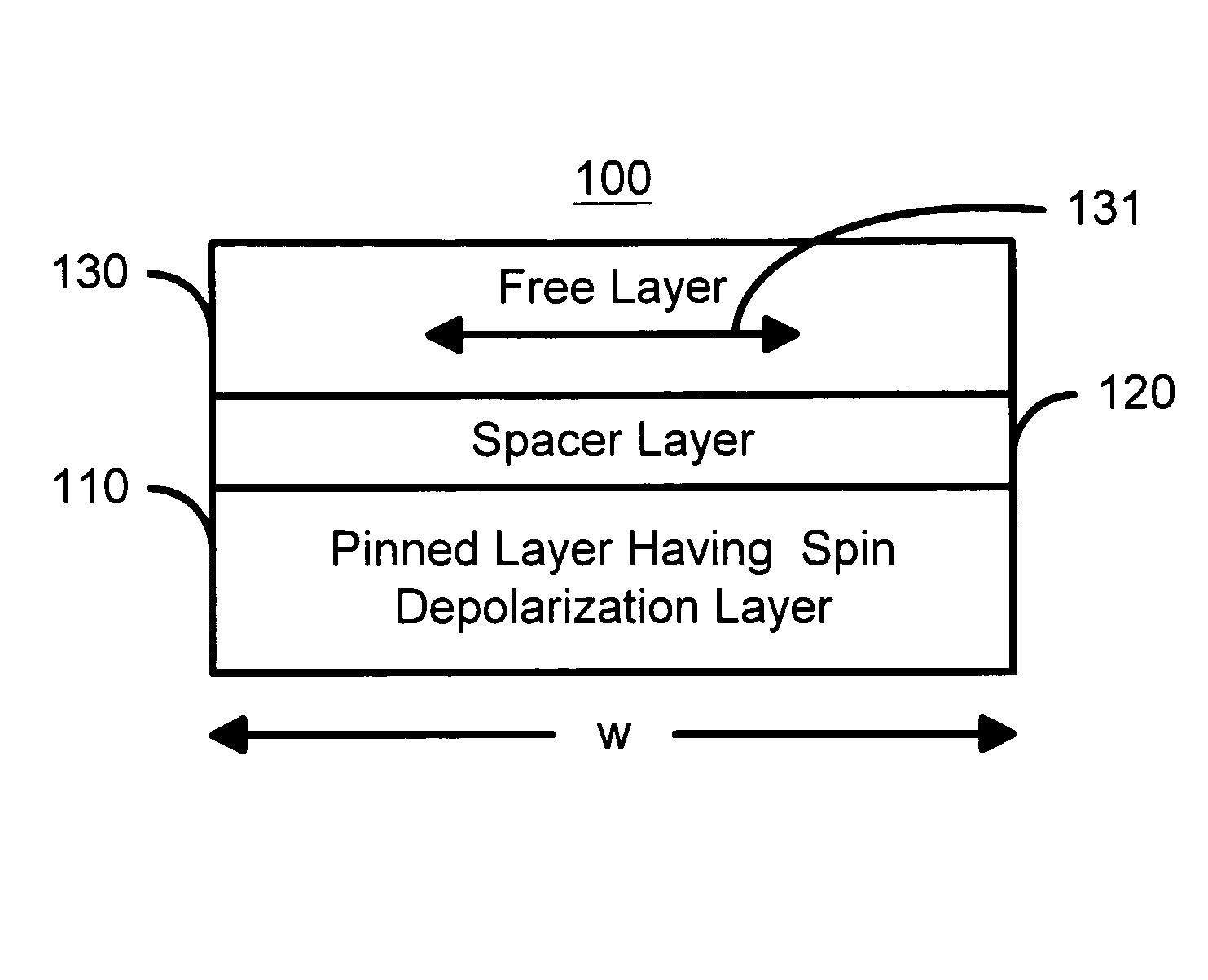
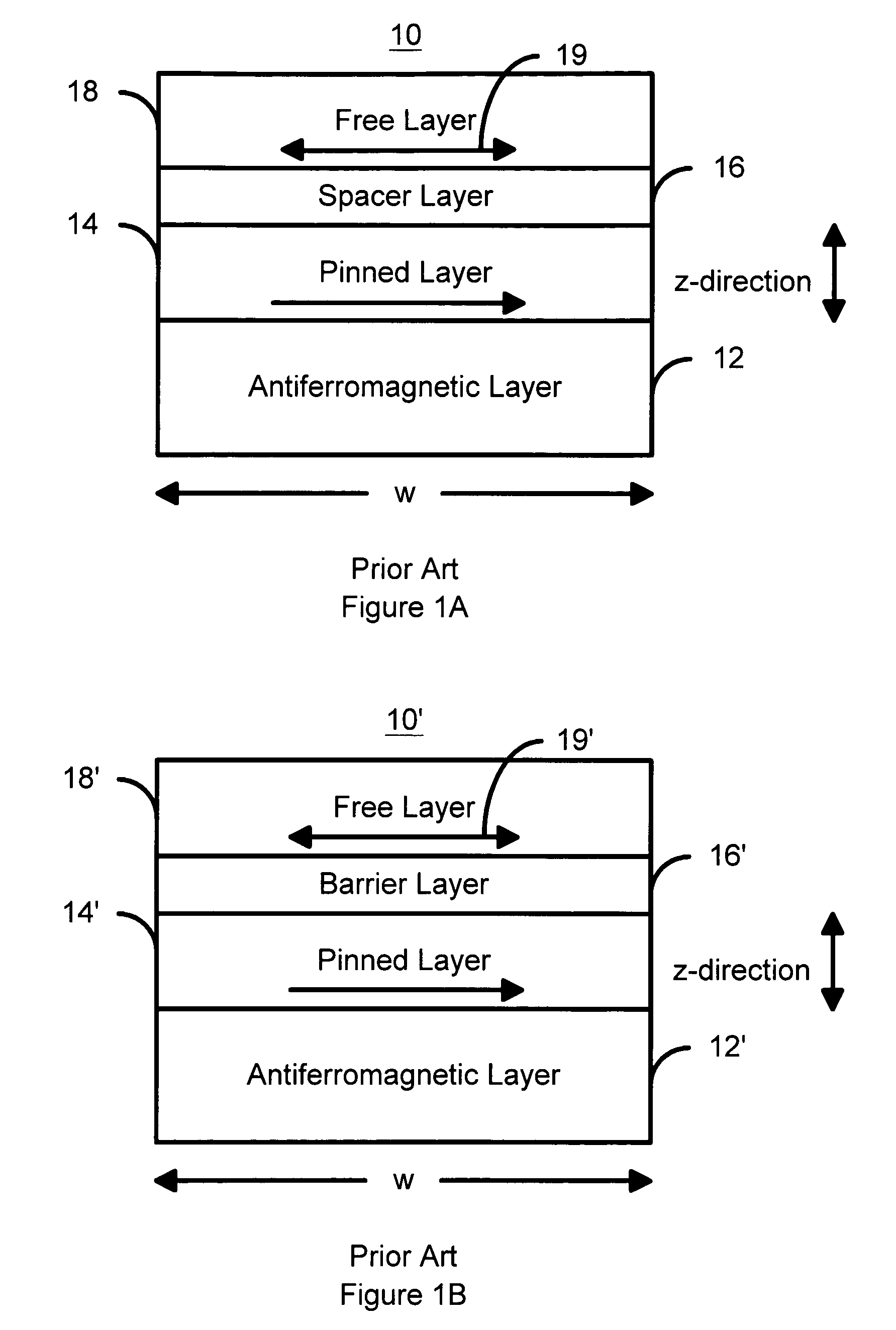
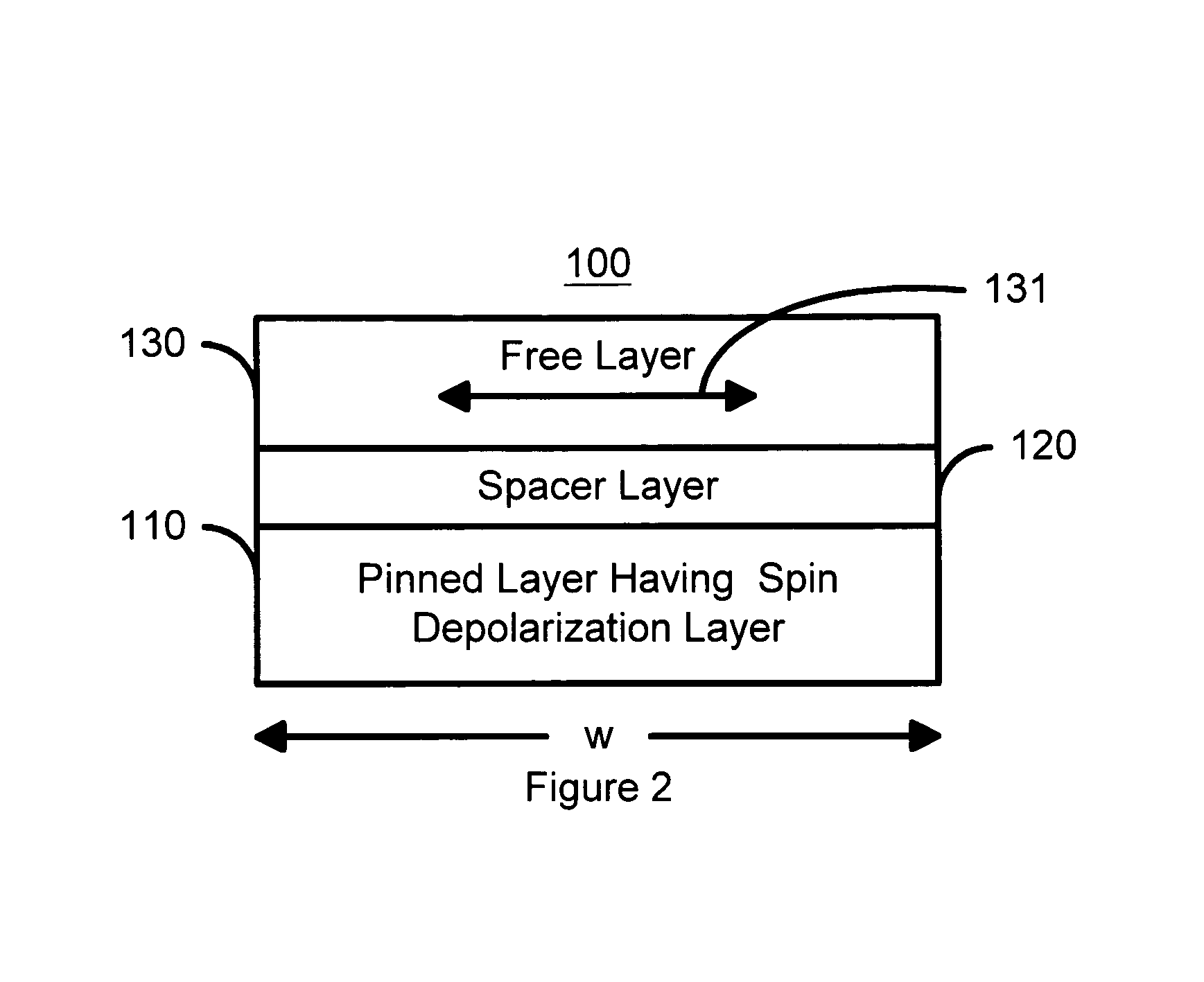
Spin transfer magnetic elements with spin depolarization layers
A method and system for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method and system include providing a free layer, a spacer layer, and a pinned layer. The free layer is ferromagnetic and has a free layer magnetization. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The pinned layer includes first and second ferromagnetic layers having first and second magnetizations, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a spin depolarization layer. Residing between the first and second ferromagnetic layers, the nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and promotes antiparallel orientations between the first and second magnetizations. The spin depolarization layer is configured to depolarize at least a portion of a plurality of electrons passing through it. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer magnetization to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Wavelet based feature extraction and dimension reduction for the classification of human cardiac electrogram depolarization waveforms
ActiveUS20080109041A1Improve accuracyPrecise processElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisCardiac pacemaker electrodeClassification methods
A depolarization waveform classifier based on the Modified lifting line wavelet Transform is described. Overcomes problems in existing rate-based event classifiers. A task for pacemaker / defibrillators is the accurate identification of rhythm categories so correct electrotherapy can be administered. Because some rhythms cause rapid dangerous drop in cardiac output, it's desirable to categorize depolarization waveforms on a beat-to-beat basis to accomplish rhythm classification as rapidly as possible. Although rate based methods of event categorization have served well in implanted devices, these methods suffer in sensitivity and specificity when atrial / ventricular rates are similar. Human experts differentiate rhythms by morphological features of strip chart electrocardiograms. The wavelet transform approximates human expert analysis function because it correlates distinct morphological features at multiple scales. The accuracy of implanted rhythm determination can then be improved by using human-appreciable time domain features enhanced by time scale decomposition of depolarization waveforms.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
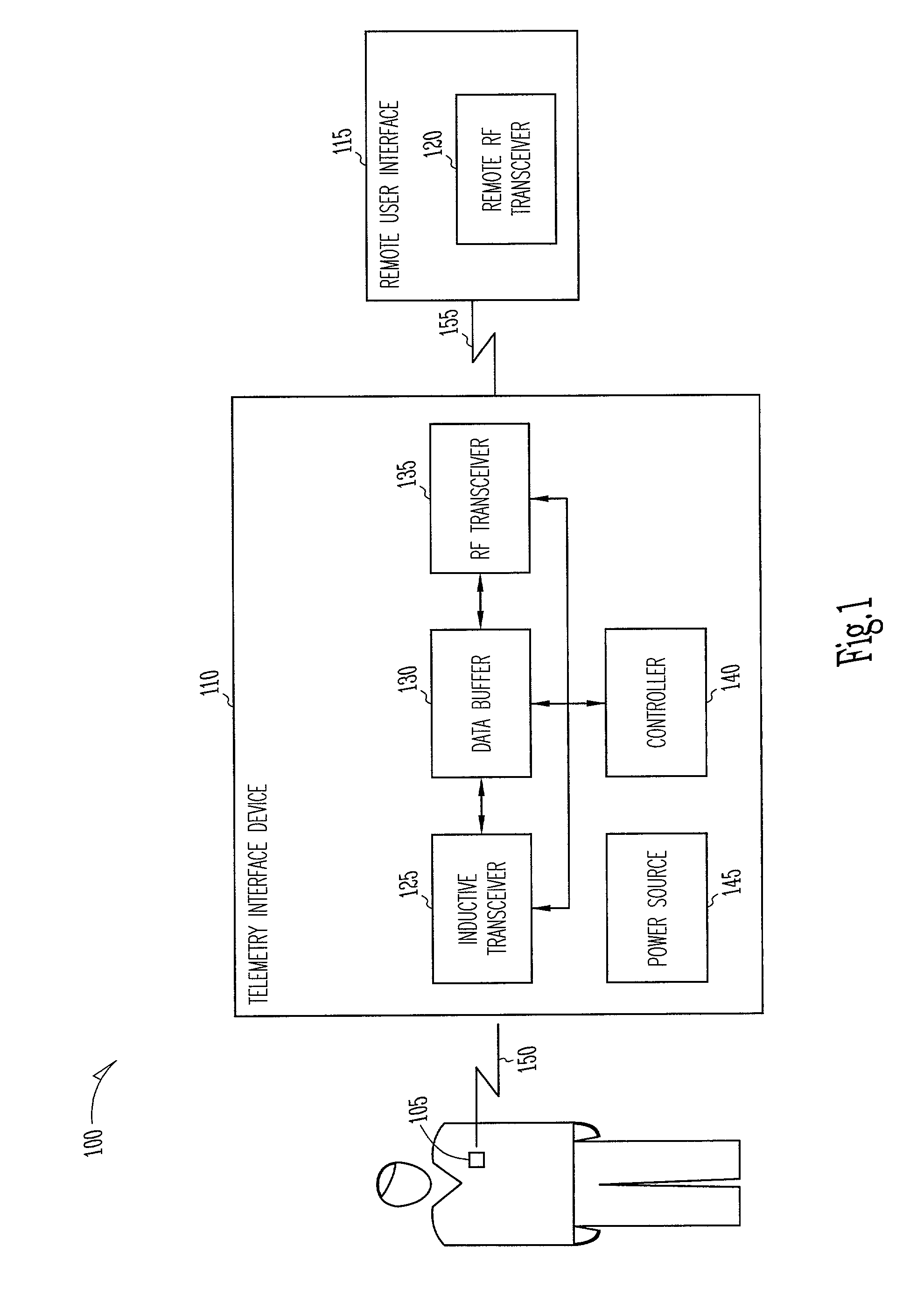
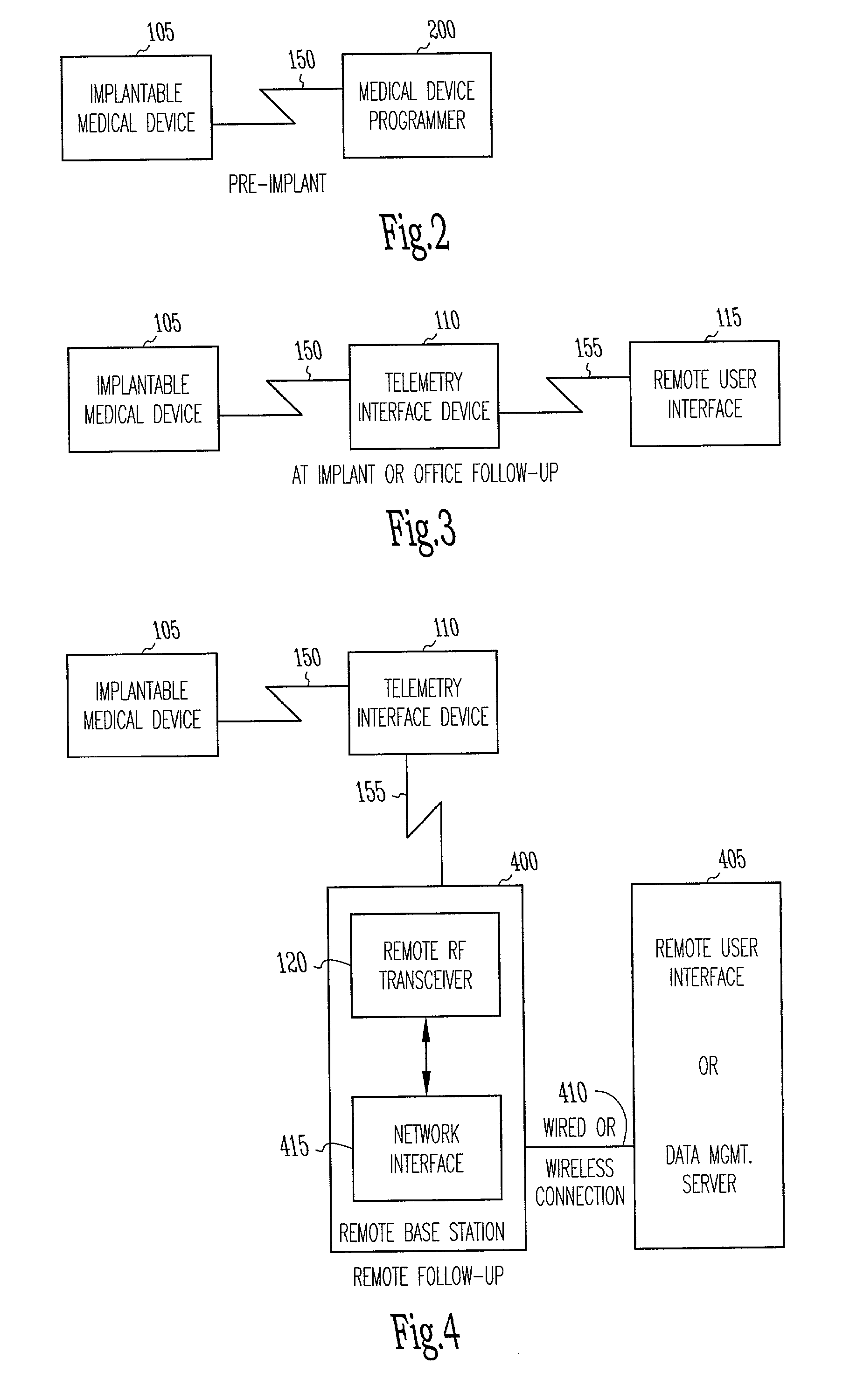
Two-hop telemetry interface for medical device
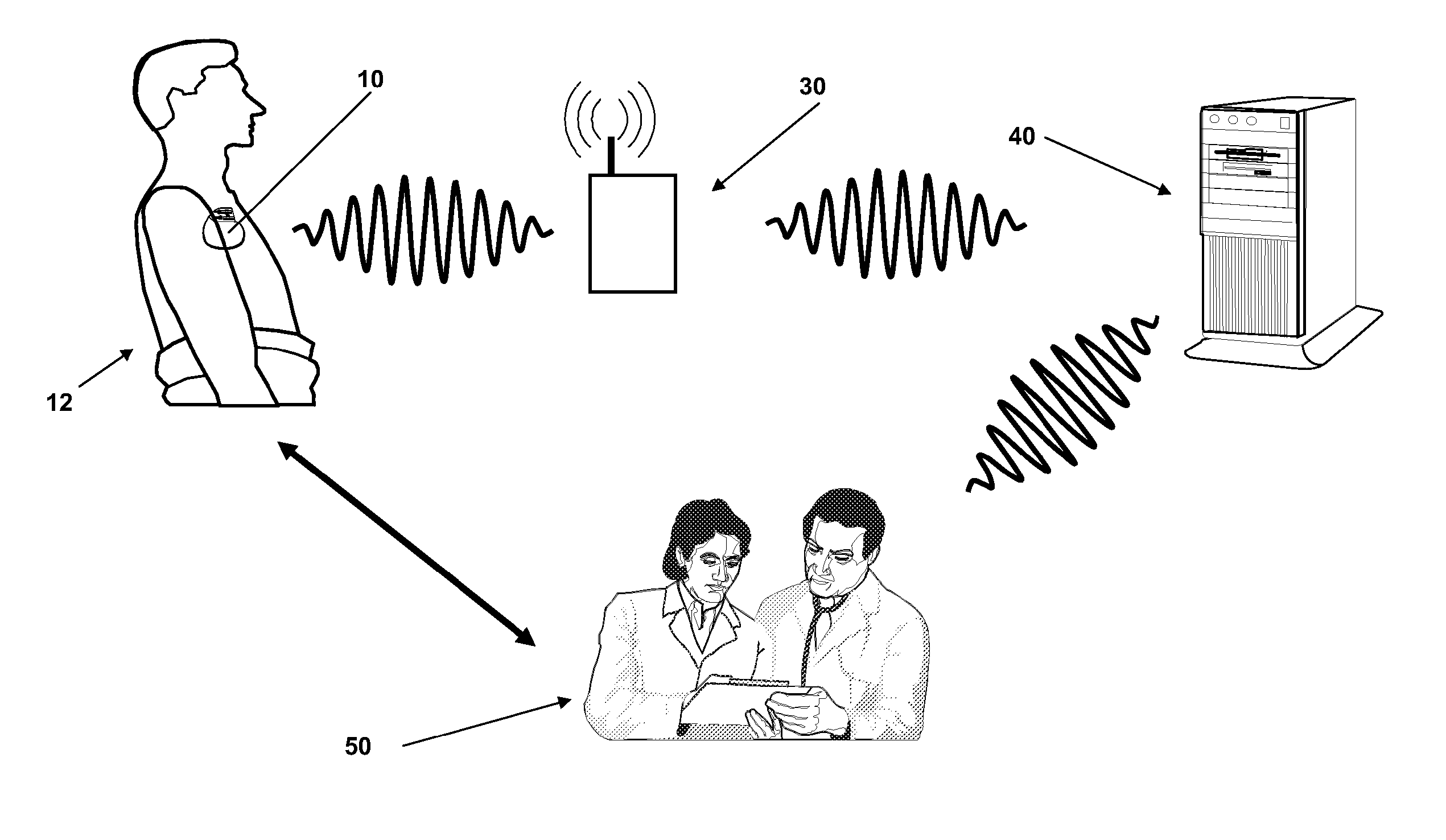
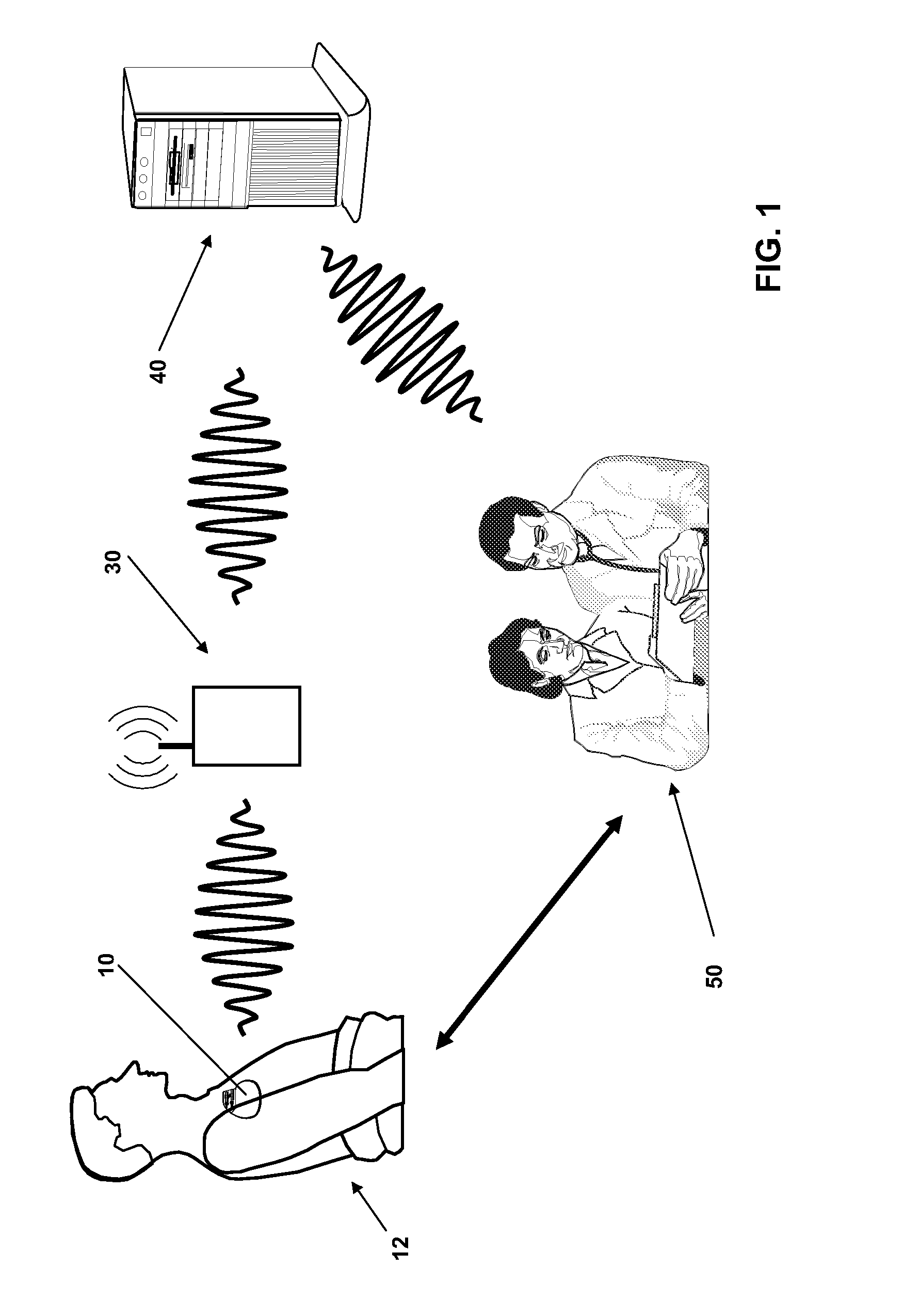
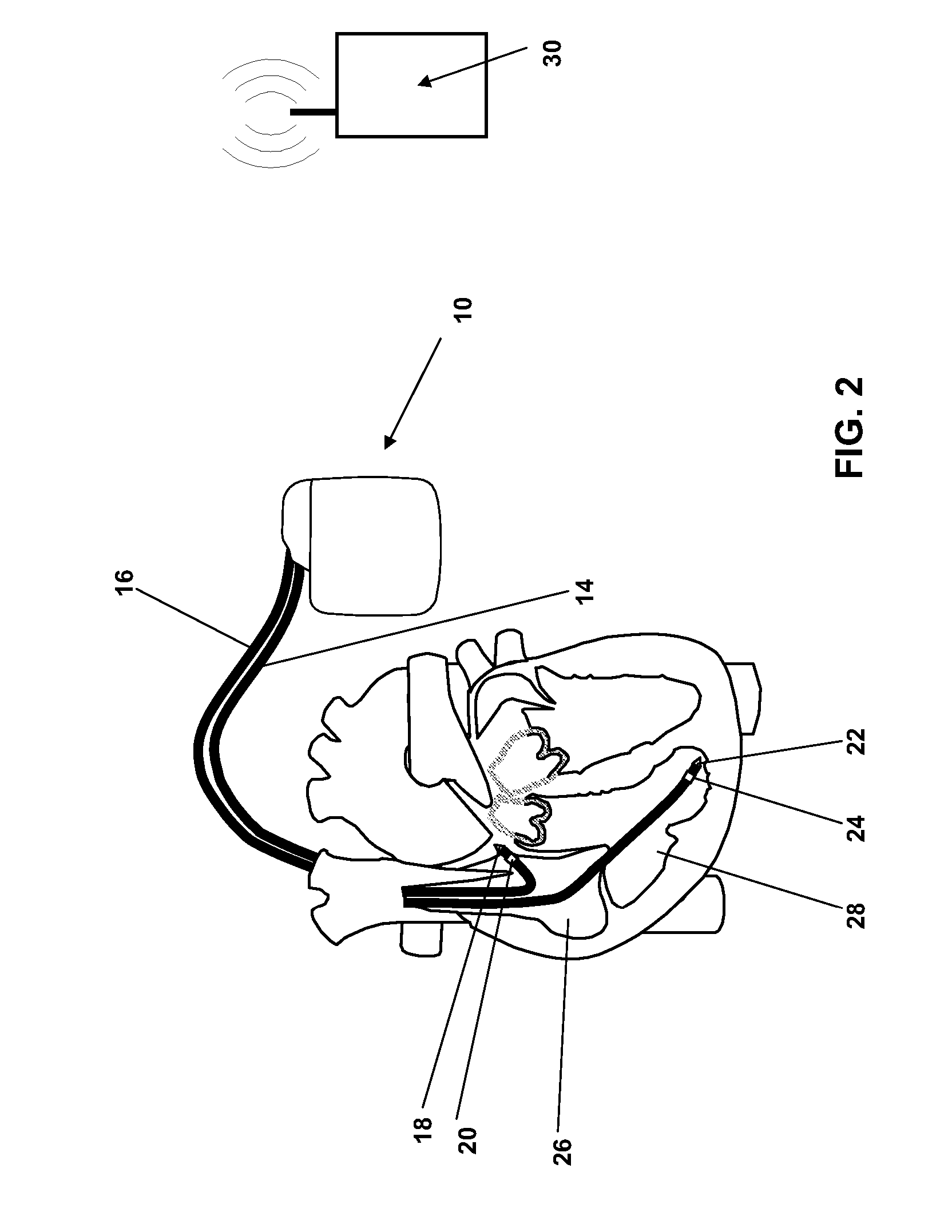
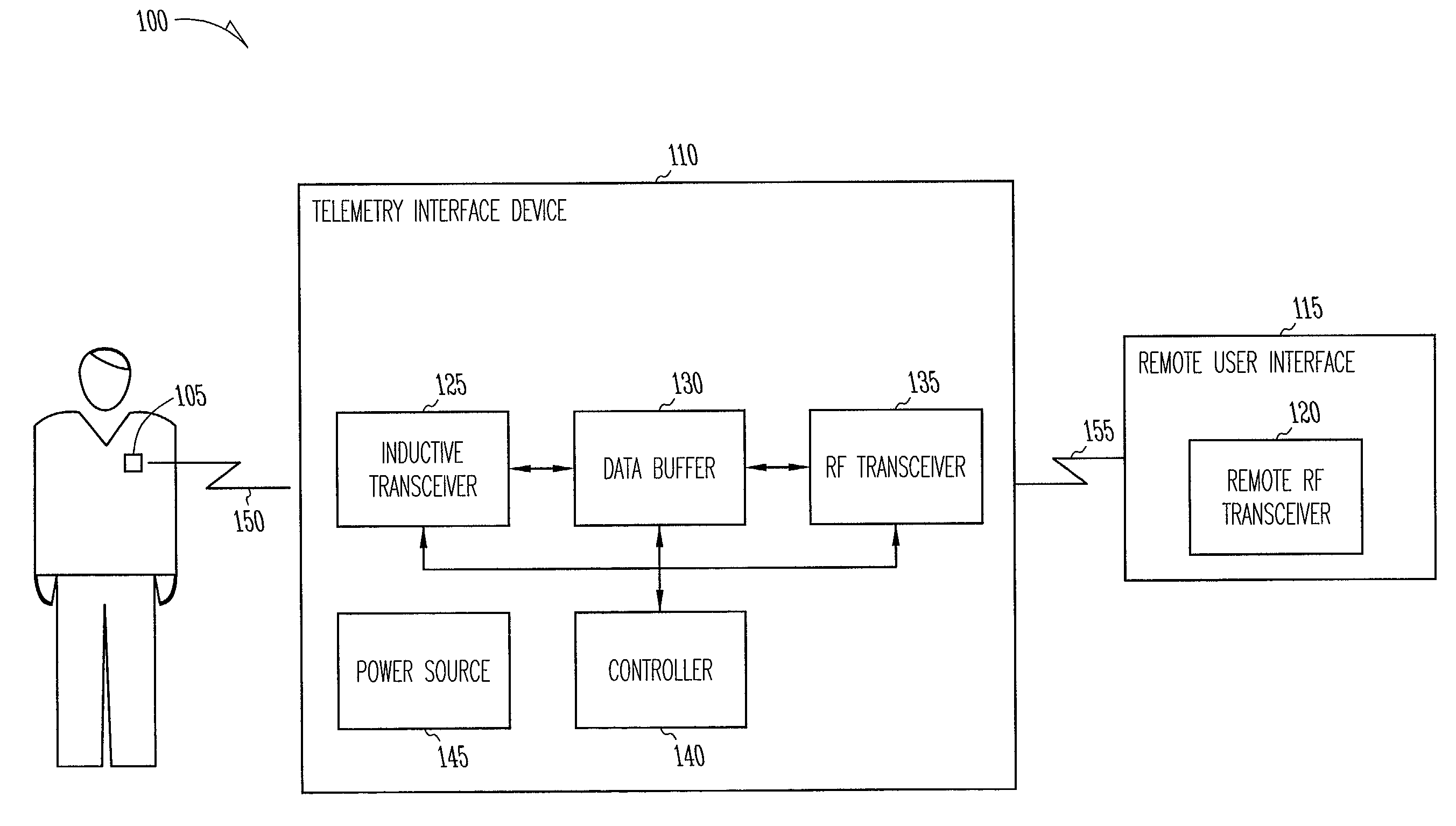
This document discusses a system that includes an intermediary telemetry interface device for communicating between a cardiac rhythm management system or other implantable medical device and a programmer or other remote device. One example provides an inductive near-field communication link between the telemetry interface and the implantable medical device, and a radio-frequency (RF) far-field communication link between the telemetry interface device and the remote device. The telemetry interface device provides data buffering. In another example, the telemetry interface device includes a data processing module for compressing and / or decompressing data, or for extracting information from data. Such information extraction may include obtaining heart rate, interval, and / or depolarization morphology information from an electrogram signal received from the implantable medical device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
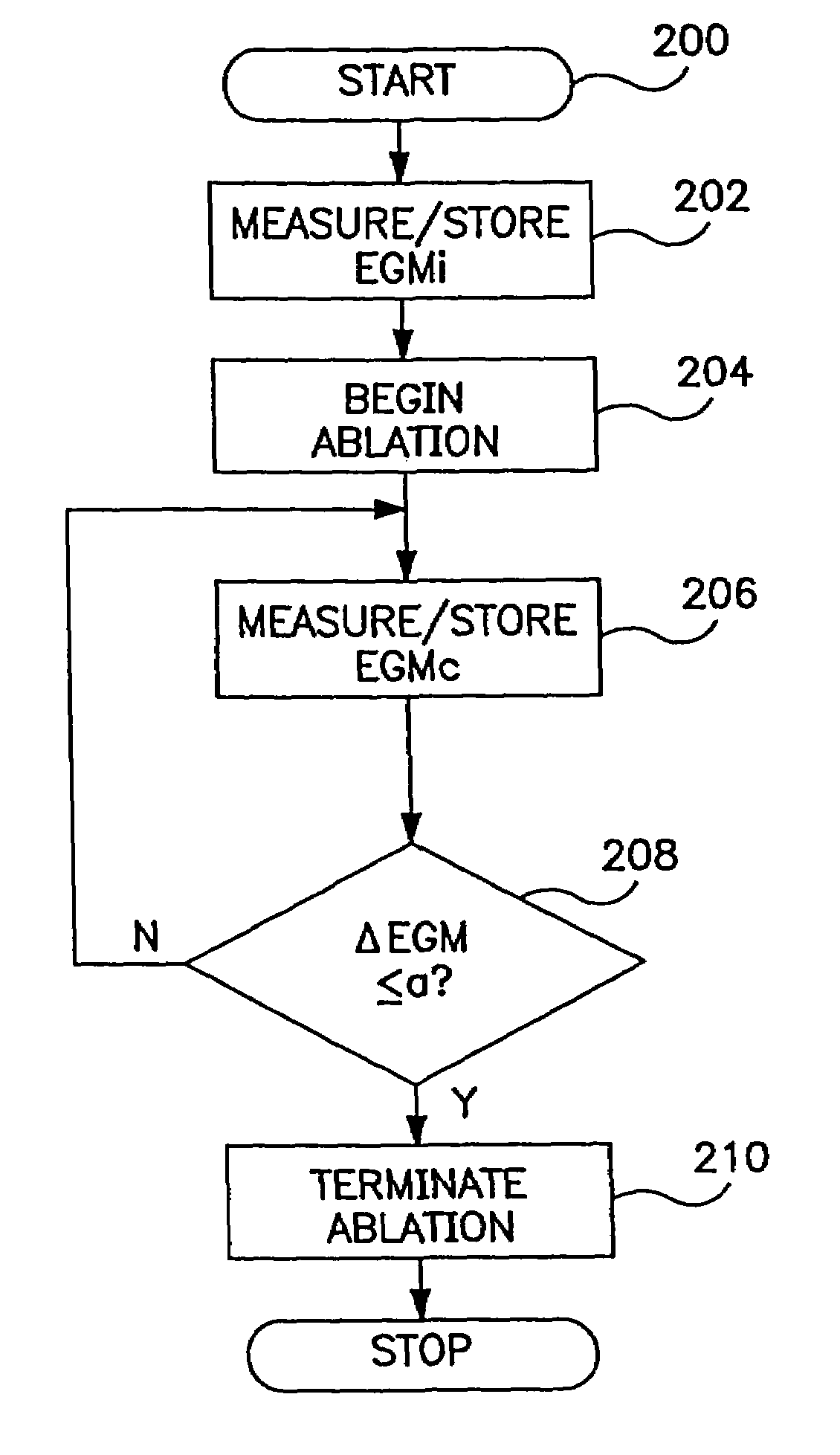
Ablation system and method of use
InactiveUS7029470B2Reducing applied powerGood application effectElectrotherapyBioelectric signal measurementBiomedical engineeringLesion
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the depolarization signal in a local electrogram taken using electrodes located adjacent the tissue to be ablated. Following onset of application of ablation energy to heart tissue, the local electrogram is measured with electrodes located adjacent tissue to be ablated so that the ablation energy to ablation elements can be selectively reduced or terminated when transmurality is detected.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ablation system and method of use
A system and method for creating lesions and assessing their completeness or transmurality. Assessment of transmurality of a lesion is accomplished by monitoring the depolarization signal in a local electrogram taken using electrodes located adjacent the tissue to be ablated. Following onset of application of ablation energy to heart tissue, the local electrogram is measured with electrodes located adjacent tissue to be ablated so that the ablation energy to ablation elements can be selectively reduced or terminated when transmurality is detected.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
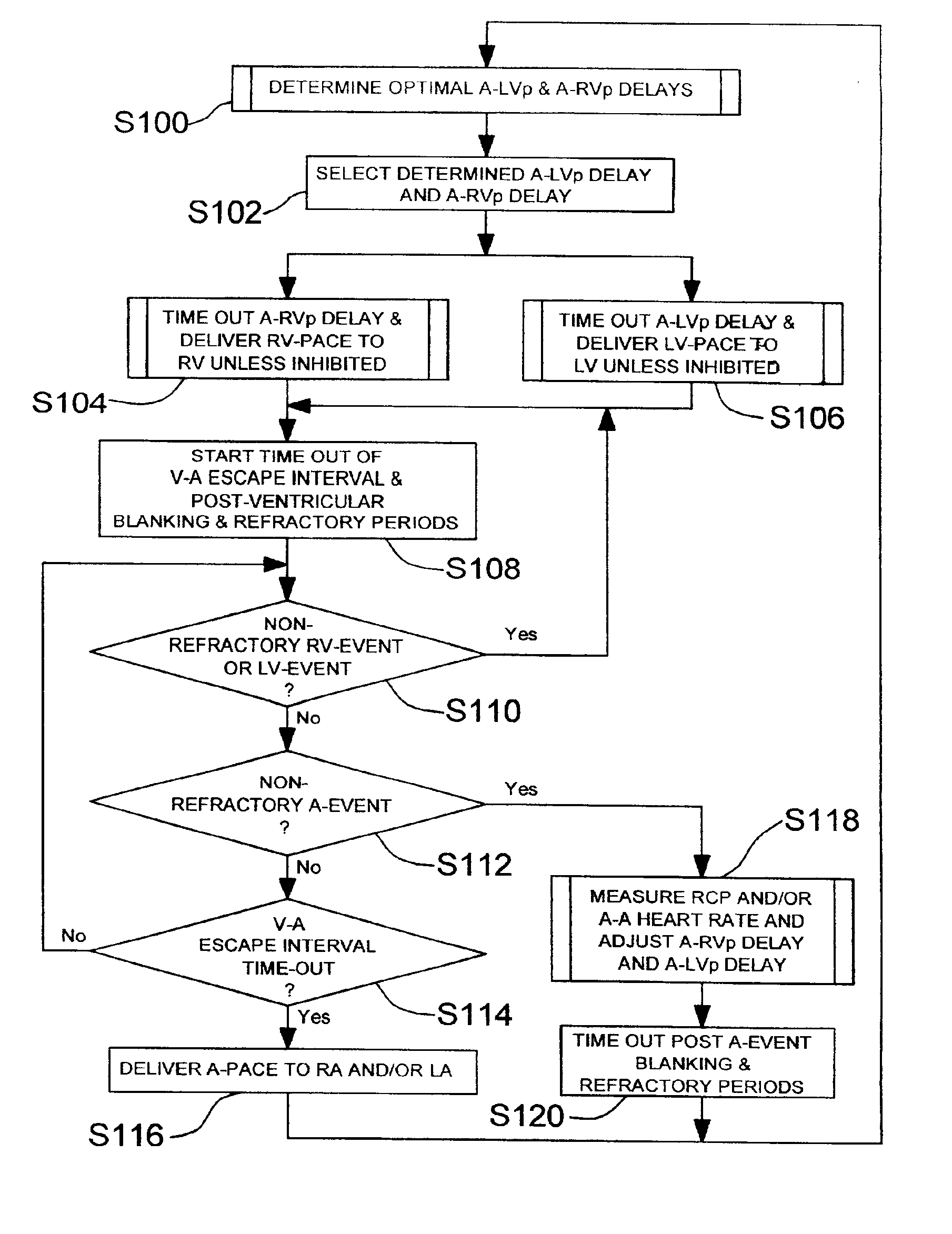
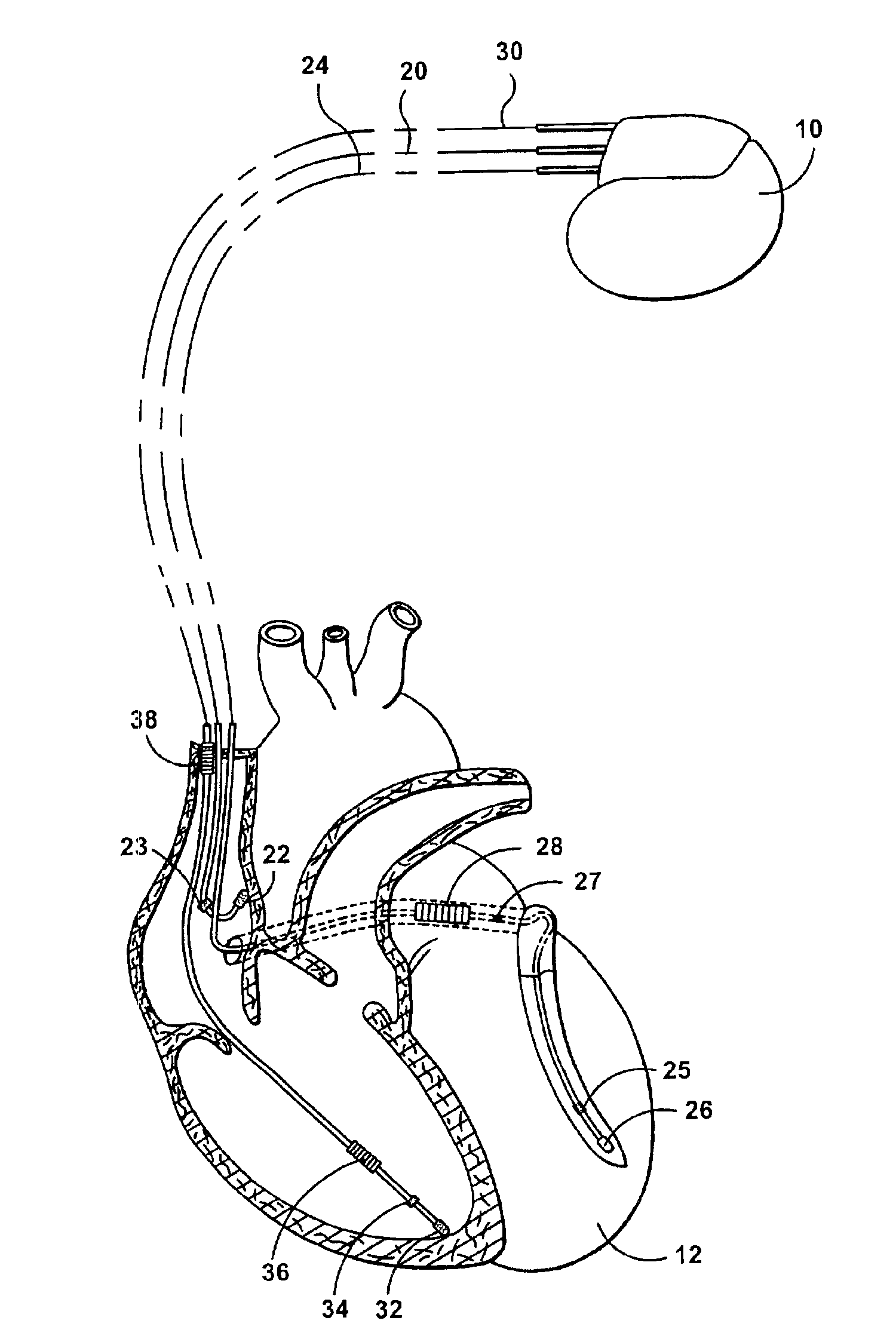
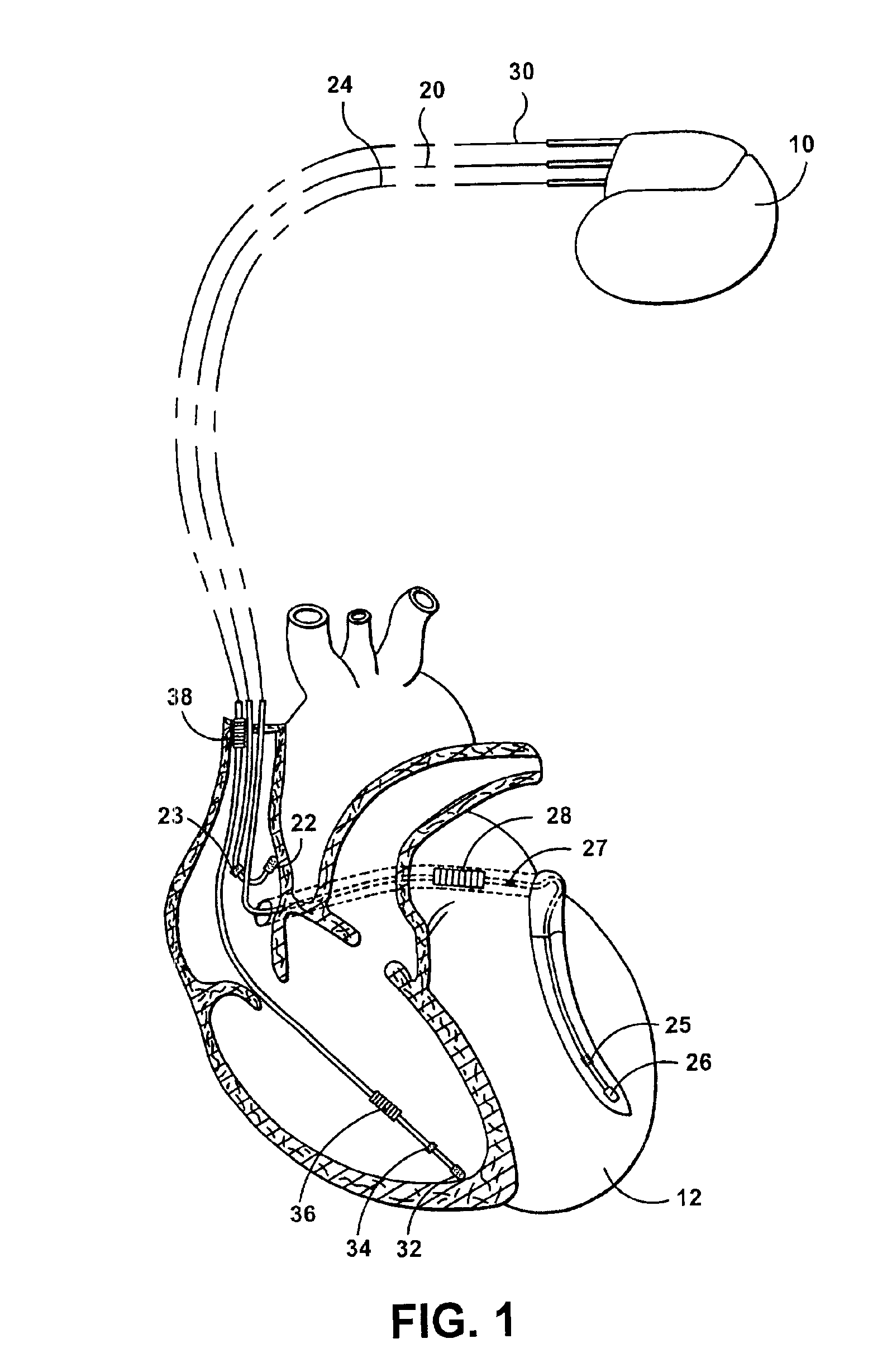
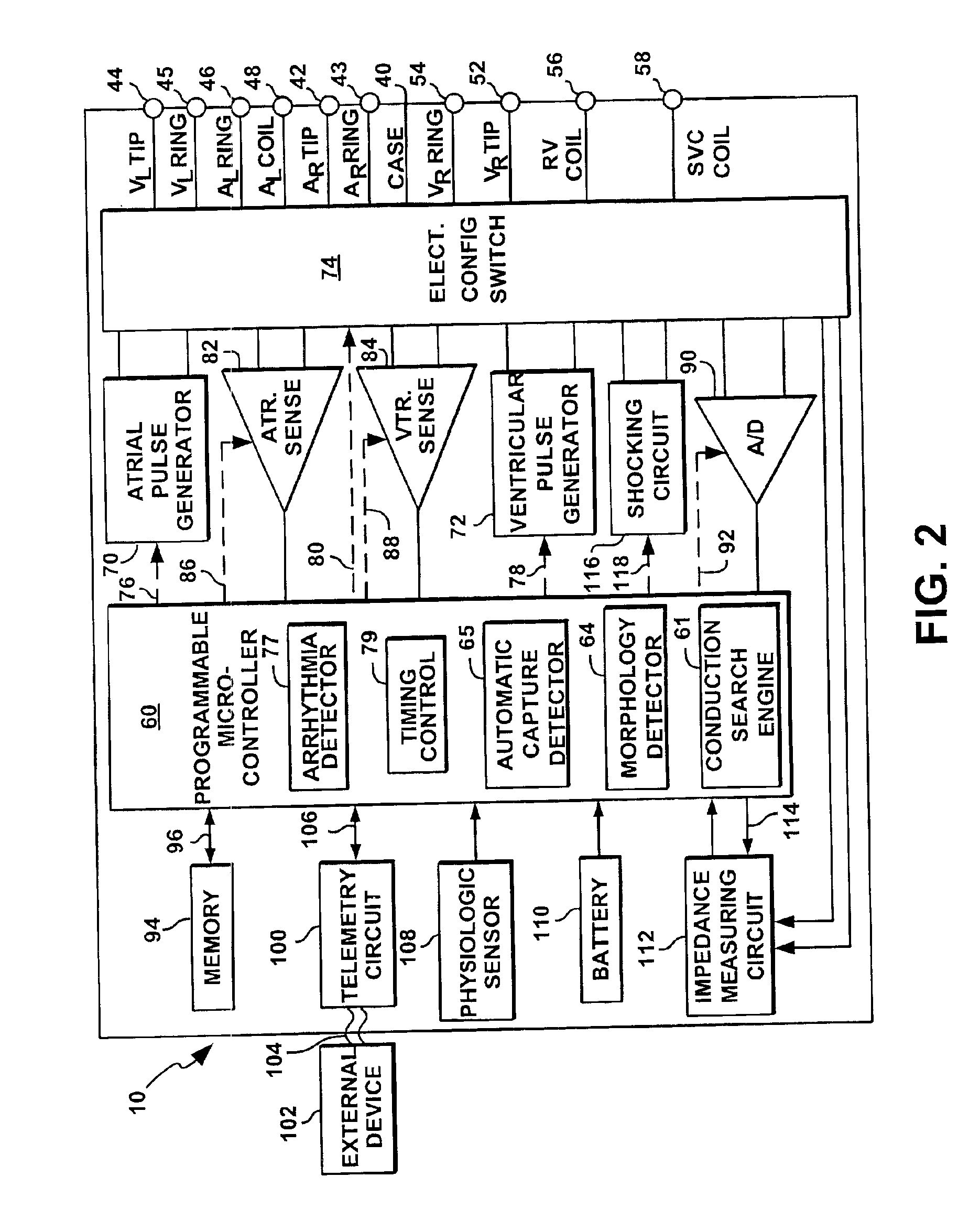
System and method for bi-ventricular fusion pacing
Bi-ventricular cardiac pacing systems and systems for improving cardiac function for heart failure patients that pace and sense in right and left ventricles of the heart and particularly pace in one of the right and left ventricles after an AV delay timed from a preceding atrial event and after a spontaneous depolarization in the other of the right and left ventricles to achieve fusion pacing. An A-RVp delay and an A-LVp delay are each determined from an intrinsic sensed A-RVs delay and an intrinsic A-LVs delay. If the derived A-LVp delay becomes substantially equal to or shorter than the intrinsic A-RVs delay, then the A-RVp delay is decremented to be shorter than the A-LVp delay. Bi-ventricular pacing of the RV and LV is then established closely timed to the intrinsic RV and LV depolarizations.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Lead with distal tip surface electrodes connected in parallel
InactiveUS7027852B2High pacing impedanceAdvantageous anode-to-cathode surface area ratioTransvascular endocardial electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringLow noiseWavefront
An body implantable stimulation lead is provided including tip electrode patterns and configurations producing low noise, clean sensed signals devoid of far field components, such sensed signals being generated irrespective of the direction of the incident depolarization wavefront. The invention also provides high pacing impedances and advantageous anode-to-cathode surface area ratios. Further, implantable leads utilizing the features of the present invention are particularly suitable for left side stimulation therapies.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
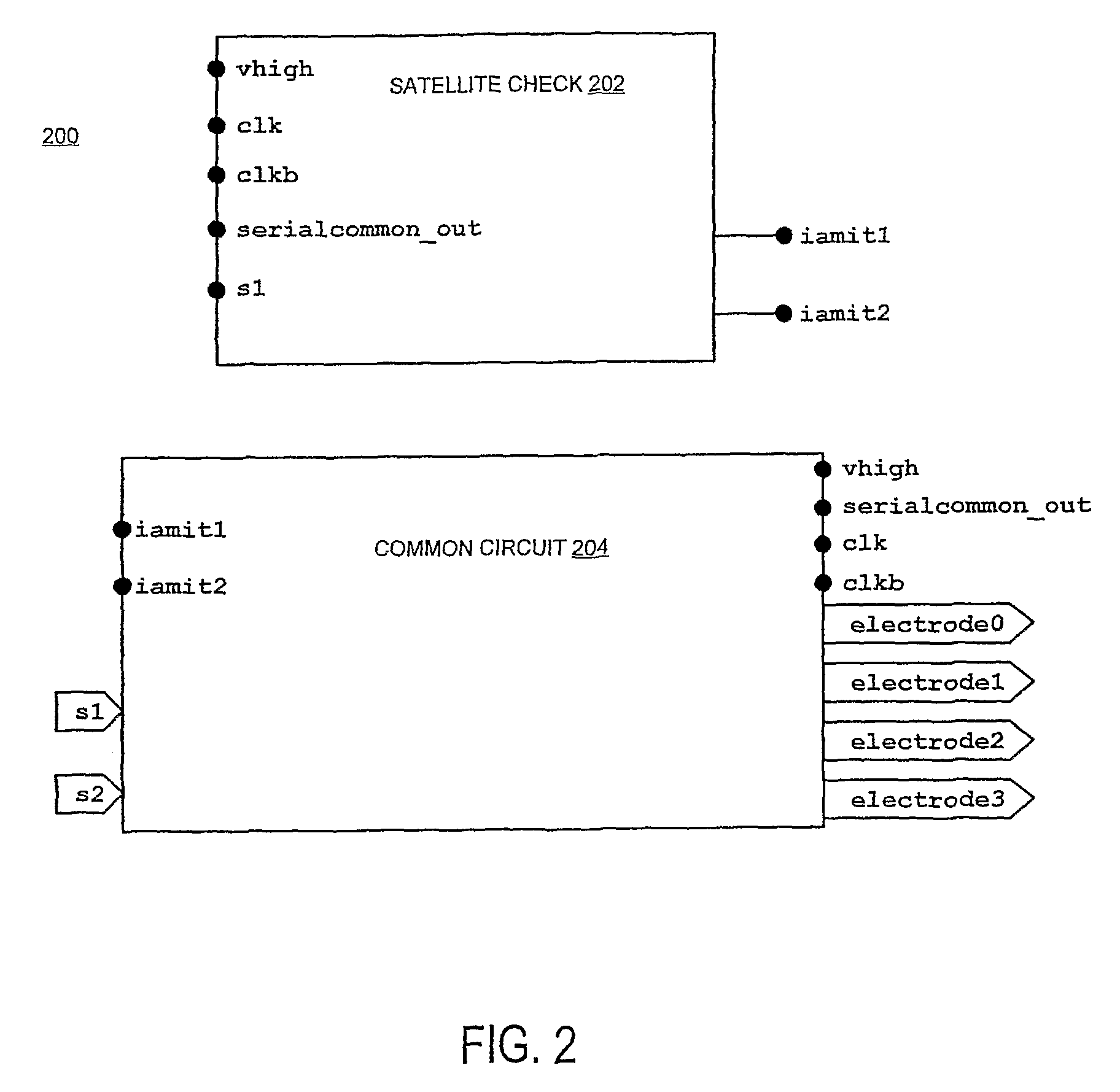
Measuring conduction velocity using one or more satellite devices
InactiveUS7983751B2Readily employedEase of evaluationElectrotherapySensorsClassical mechanicsNerve conduction velocity
A method for measuring the conduction velocity of a depolarization wave in a tissue employs a first satellite located within the tissue and a second that satellite is located within the tissue a distance away from the first satellite, e.g., by using the time of depolarization wave as reported from each satellite and the distance to determine velocity of the wave. Also provided are systems and kits that find use in accordance with the invention.
Owner:PROTEUS DIGITAL HEALTH INC
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20050140855A1Black luminance increaseContrast ratio is reducedNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDepolarization
A normally-closed liquid crystal display includes a component to selectively absorb characteristic leakage light occurring at black representation. Therefore, when black is displayed, occurrence of unnecessary leakage light due to partial depolarization of polarized light caused by a component of an LCD panel can be suppressed. It is therefore possible to provide a liquid crystal display in which display performance of black is improved to clearly display black.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Detecting ventricular noise artifacts in an active implantable medical device for pacing, resynchronization and/or defibrillation of the heart
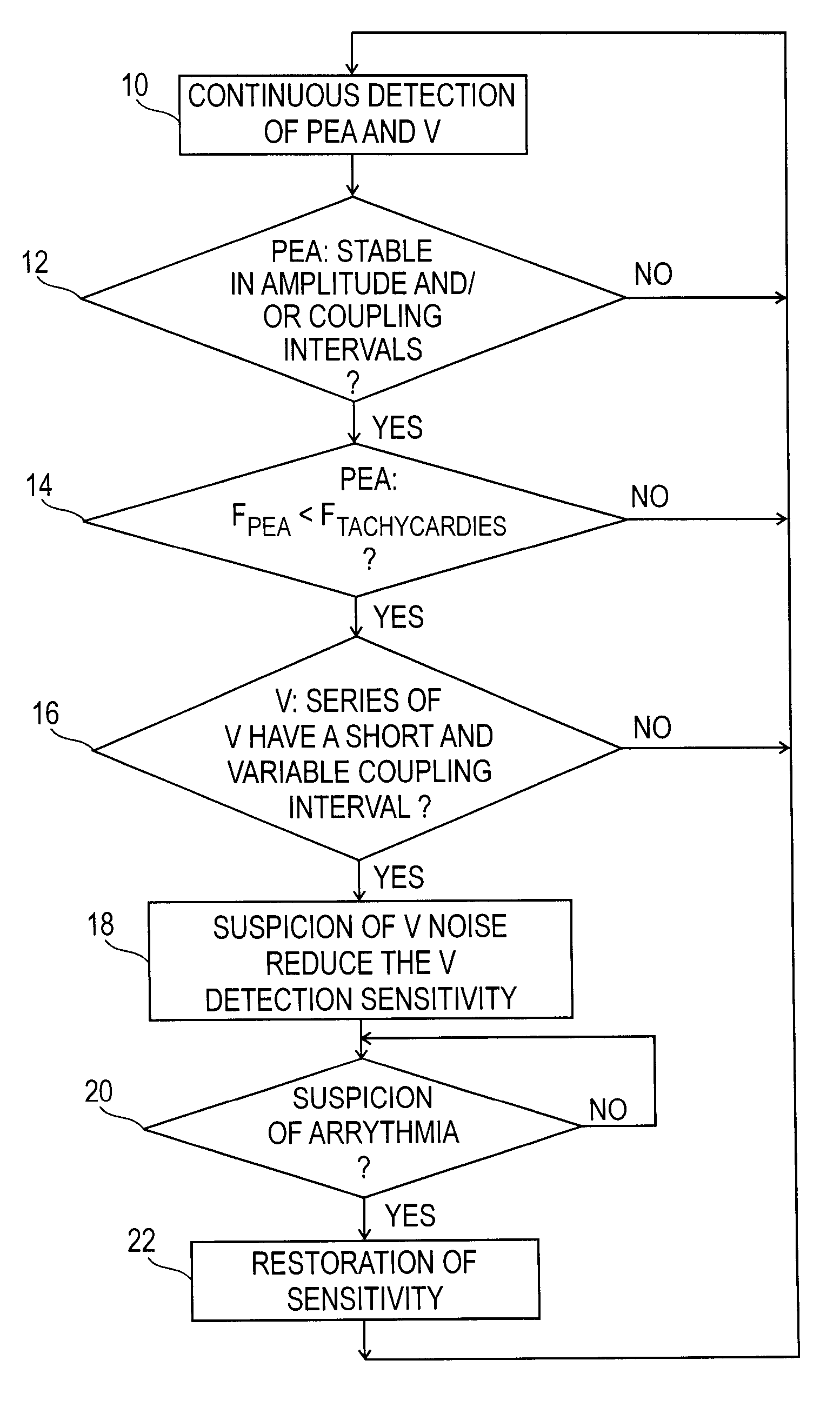
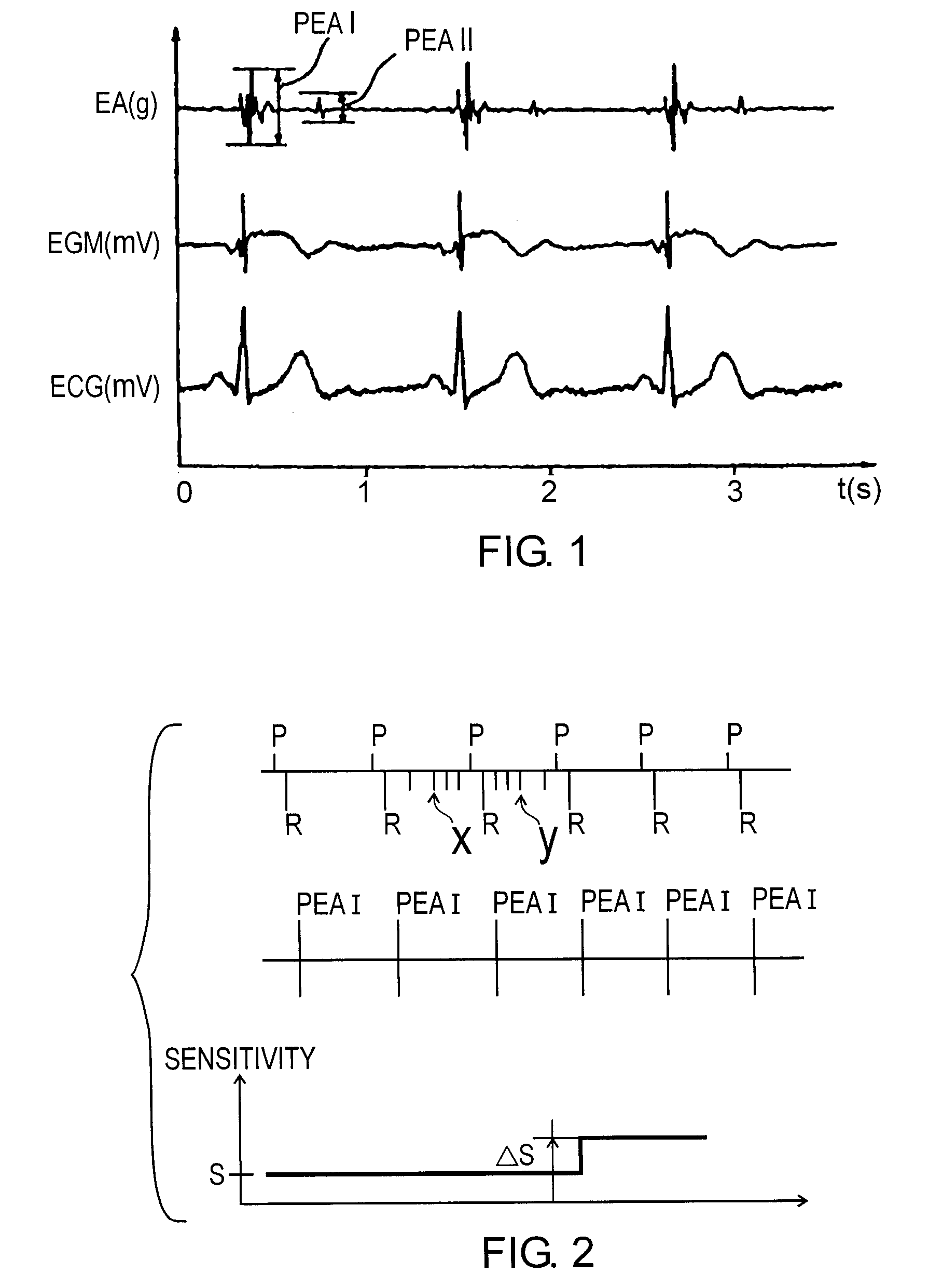
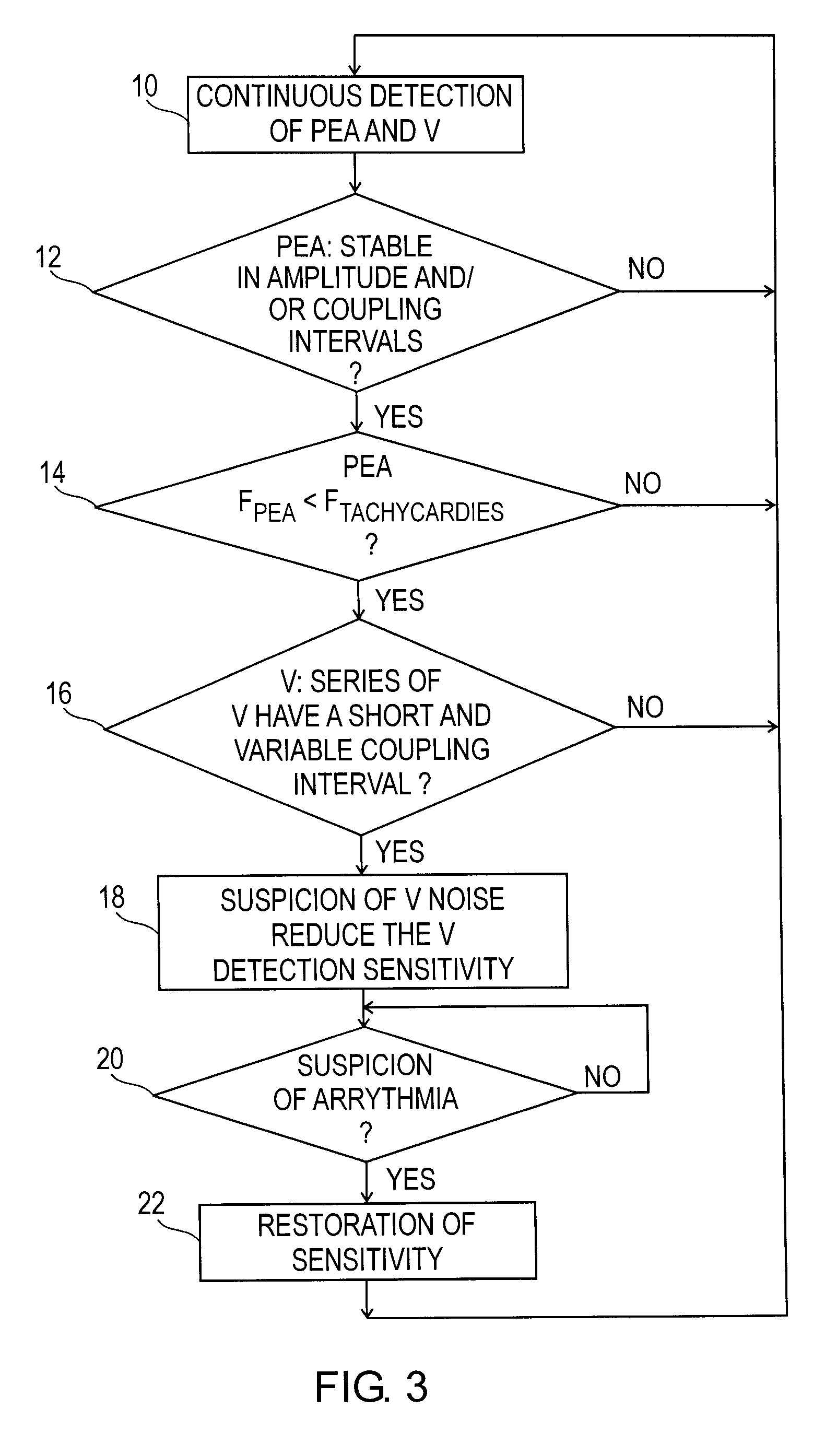
Sensing ventricular noise artifacts in an active implantable medical device for pacing, resynchronization and / or defibrillation of the heart. This device concerns sensing heart rhythm through an endocardial electrode collecting the depolarization potentials, and detecting the myocardium contractions through an endocardial acceleration sensor. The device searches for ventricular noise artifacts (X, Y) by correlating the signals representative of successive ventricular and atrial depolarizations (P, R) with the signals representative of successive acceleration peaks (PEA I). In case of a lack of correlation, a signal of suspicion of ventricular noise is delivered, which temporarily modifies the sensing sensitivity (S) of the sensing circuit.
Owner:SORIN CRM
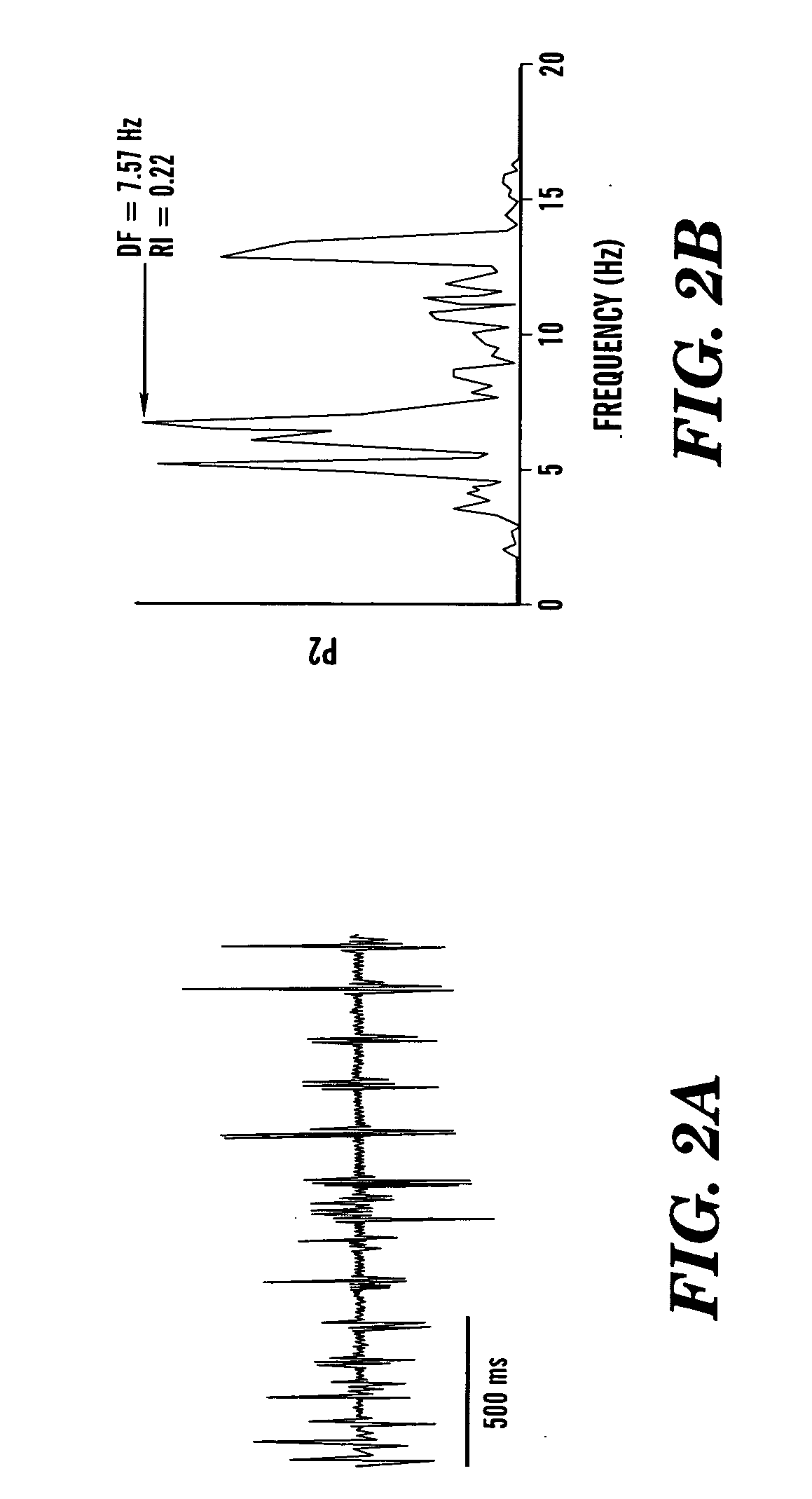
Method and algorithm for spatially identifying sources of cardiac fibrillation
InactiveUS20060122526A1Rapid and efficient and sensitiveElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAlgorithmDominant frequency
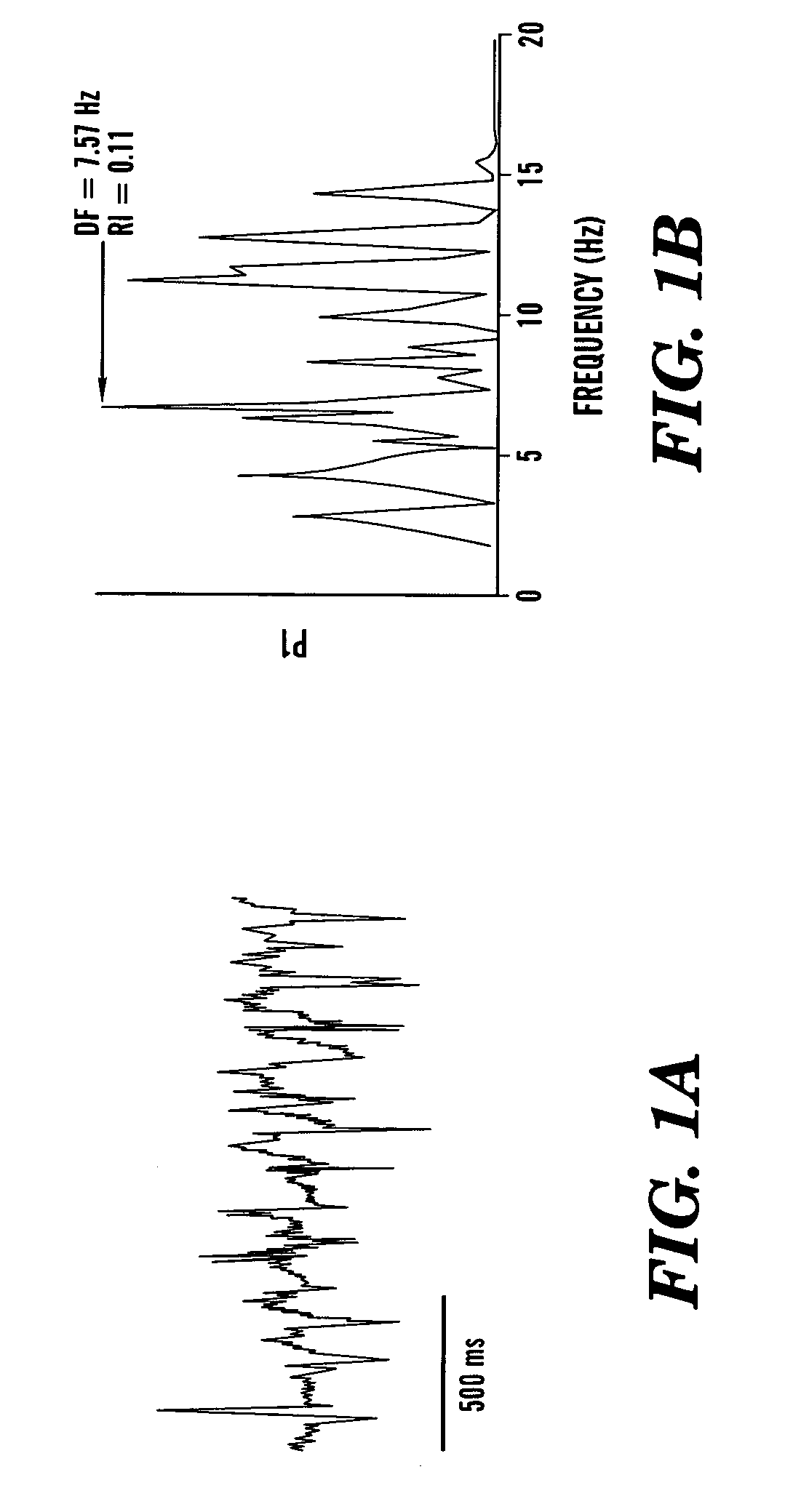
A method and computer program product comprising an algorithm adapted to execute a method of identifying the spatial coordinates of a sustaining source of fibrillatory activity in a heart by computing a set of point-dependent dominant frequencies and a set of point-dependent regularity indices for a set of products of point-dependent unipolar discrete power spectra and point-dependent bipolar discrete power spectra, derived by spectral analyses of corresponding unipolar and bipolar cardiac depolarization signals simultaneously acquired from a set of points of the heart. A maximum dominant frequency is selected whose associated coordinates identify the point of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity. The magnitude of the regularity index is interpreted to verify the identification of the spatial coordinates of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity. When indicated, surgical intervention is directed to the spatial coordinates of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
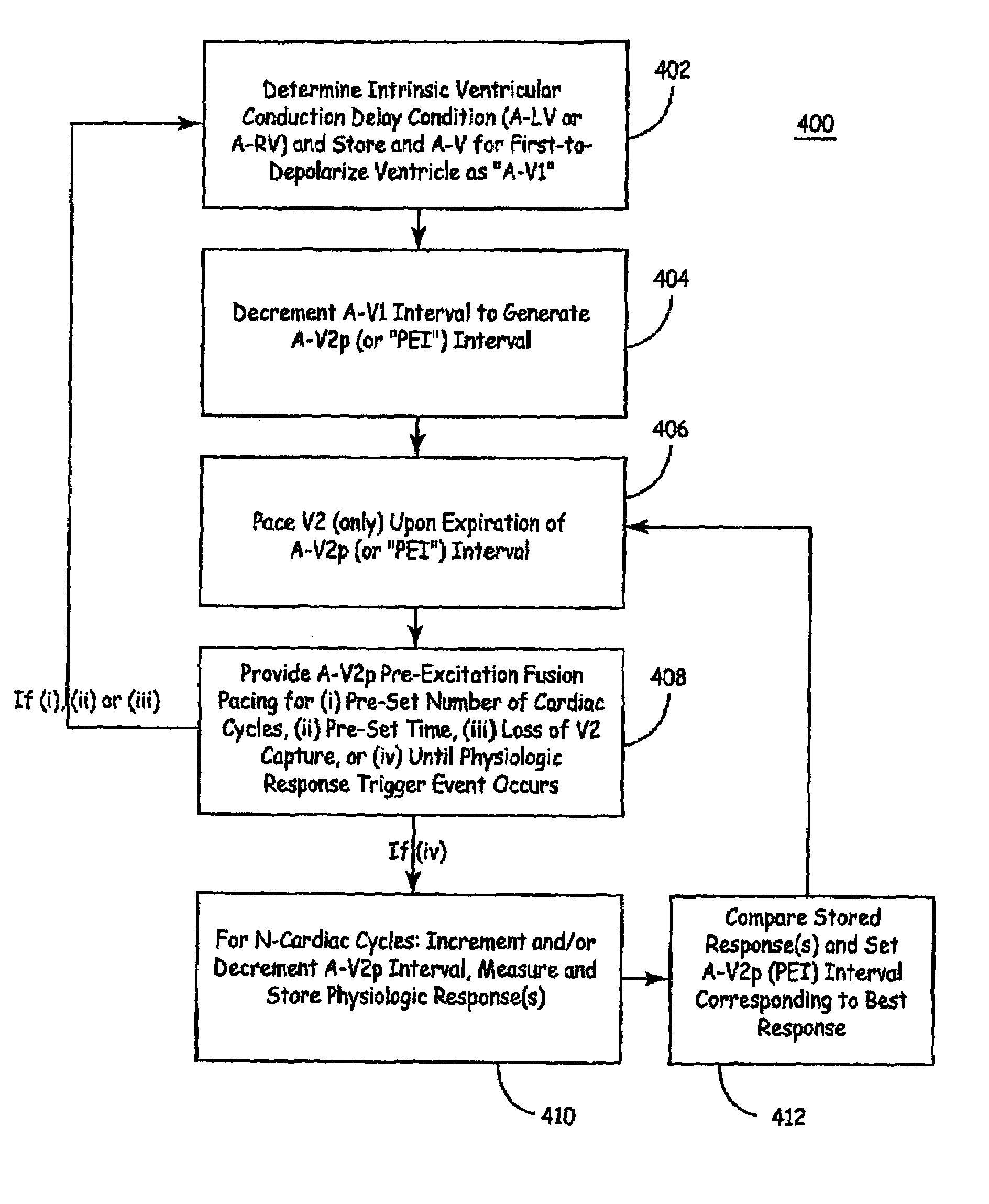
Apparatus and methods of energy efficient, atrial-based Bi-ventricular fusion-pacing
The bi-ventricular implantable pulse generator described and depicted herein enables hemodynamic efficiencies for patients suffering from intraventricular conduction delays or conduction blockage. The pulse generator effectively overcomes such conduction delay or block (e.g., left bundle branch block, “LBBB,” or right bundle branch block, “RBBB”) by delivering a novel form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). Specifically, a single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is triggered from an atrial event (e.g., intrinsic or evoked depolarization). The triggering event may emanate from the right atrium (RA) or the left atrium (LA). A single ventricular pre-excitation pacing stimulus is delivered prior to the intrinsic depolarization of the other ventricle and thus promotes intraventricular electromechanical synchrony during CRT delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and algorithm for spatially identifying sources of cardiac fibrillation
InactiveUS7117030B2Rapid and efficient and sensitiveElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAlgorithmDominant frequency
A method and computer program product comprising an algorithm adapted to execute a method of identifying the spatial coordinates of a sustaining source of fibrillatory activity in a heart by computing a set of point-dependent dominant frequencies and a set of point-dependent regularity indices for a set of products of point-dependent unipolar discrete power spectra and point-dependent bipolar discrete power spectra, derived by spectral analyses of corresponding unipolar and bipolar cardiac depolarization signals simultaneously acquired from a set of points of the heart. A maximum dominant frequency is selected whose associated coordinates identify the point of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity. The magnitude of the regularity index is interpreted to verify the identification of the spatial coordinates of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity. When indicated, surgical intervention is directed to the spatial coordinates of the sustaining source of fibrillatory activity.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
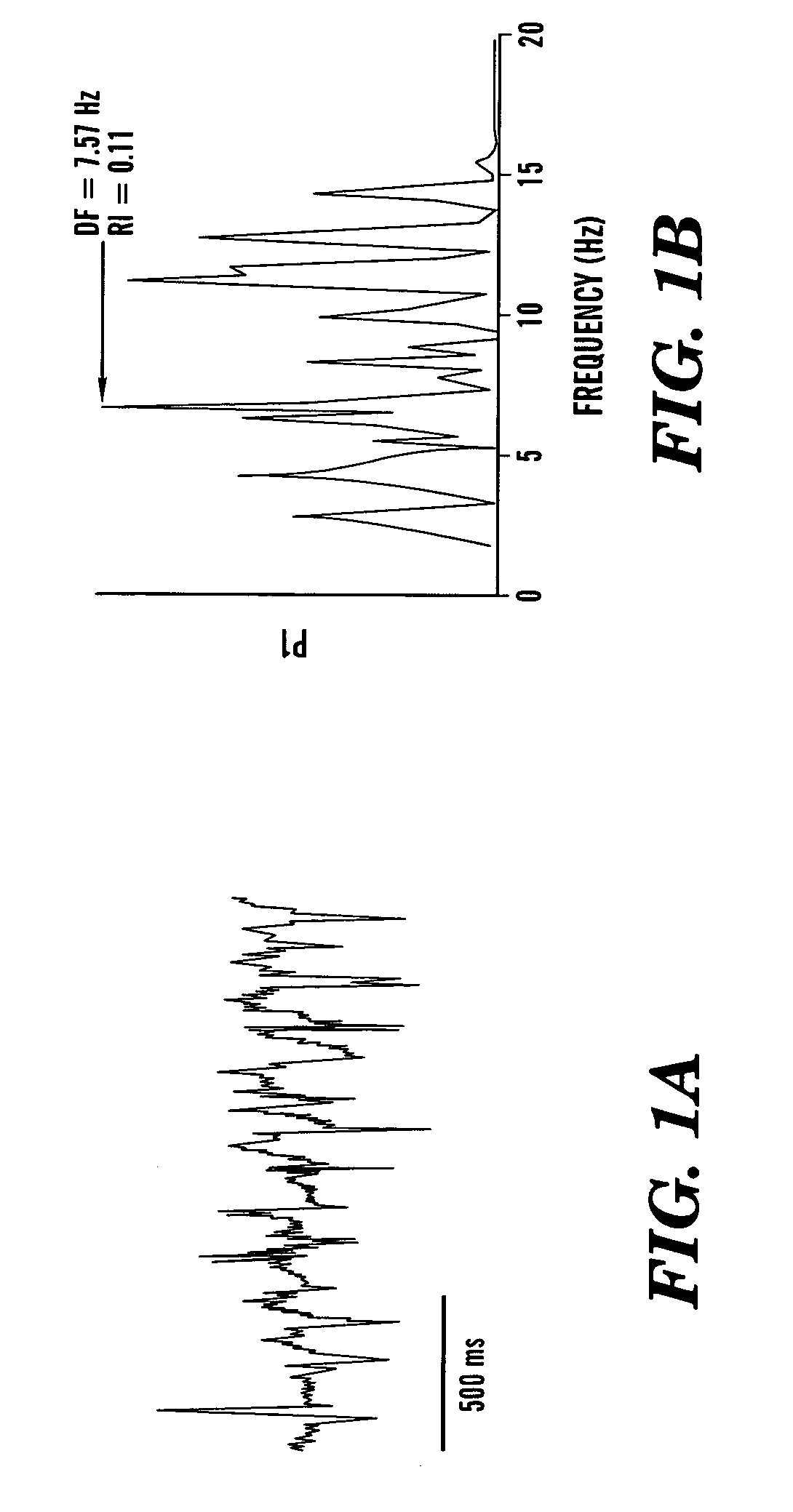
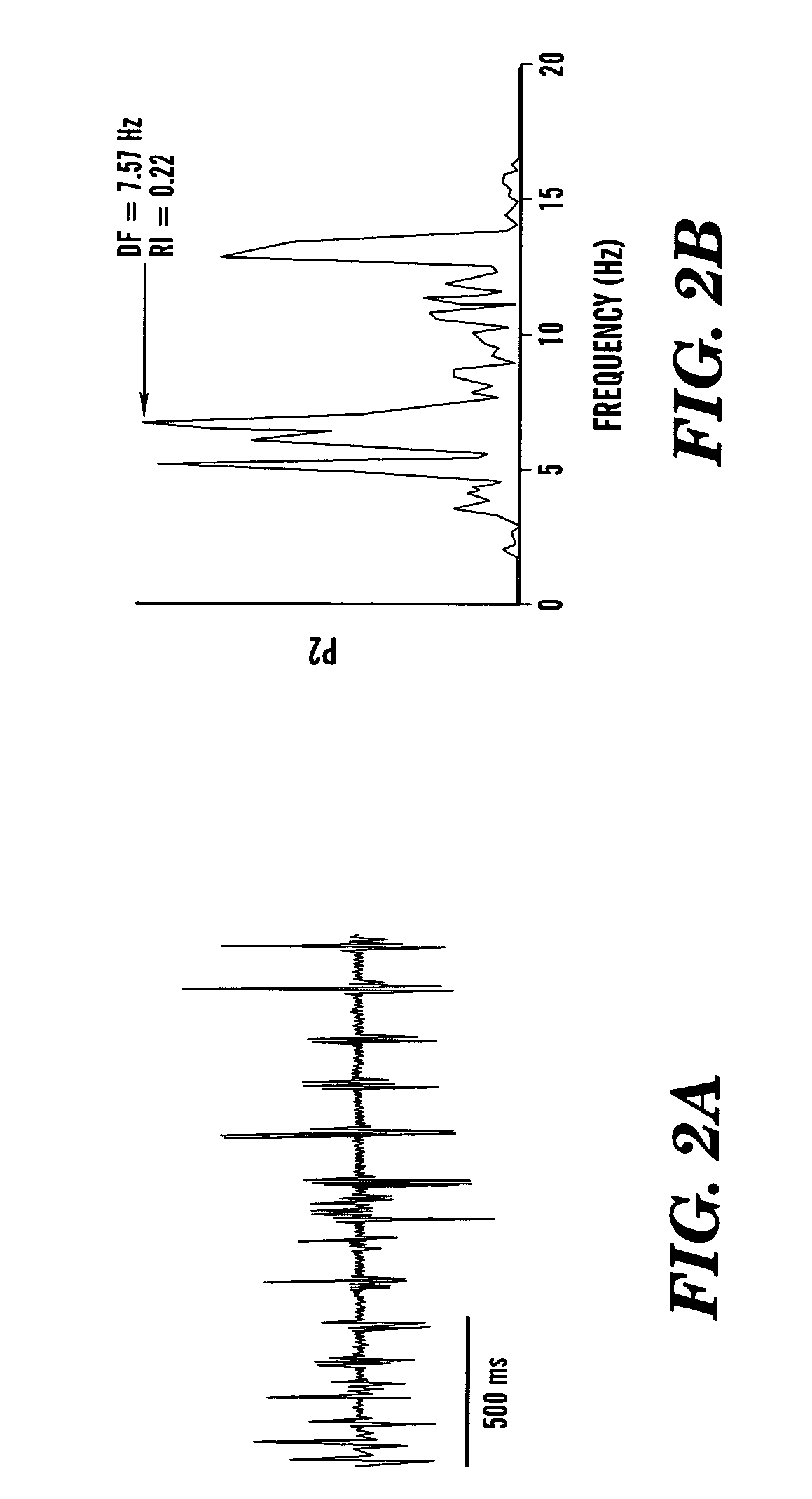
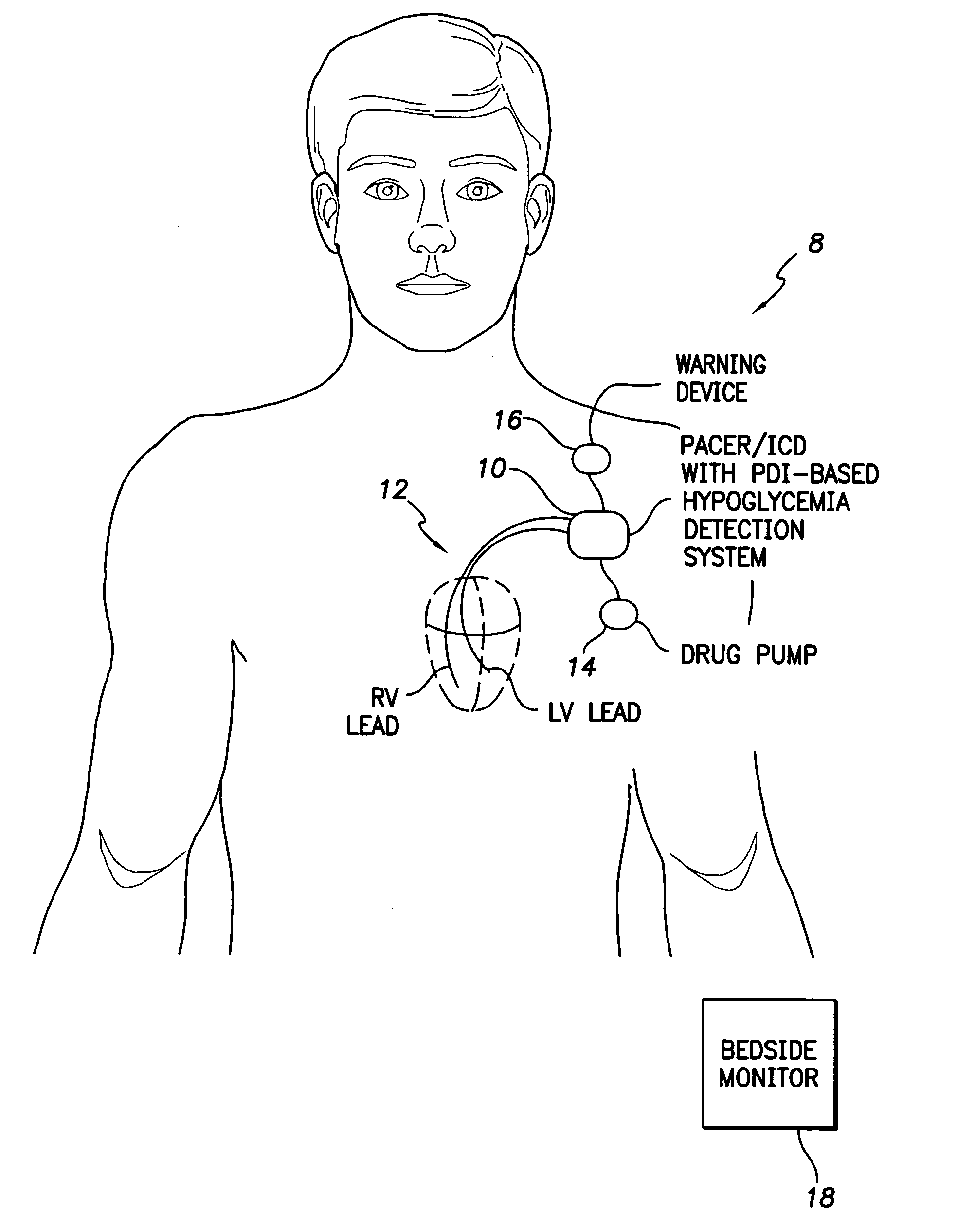
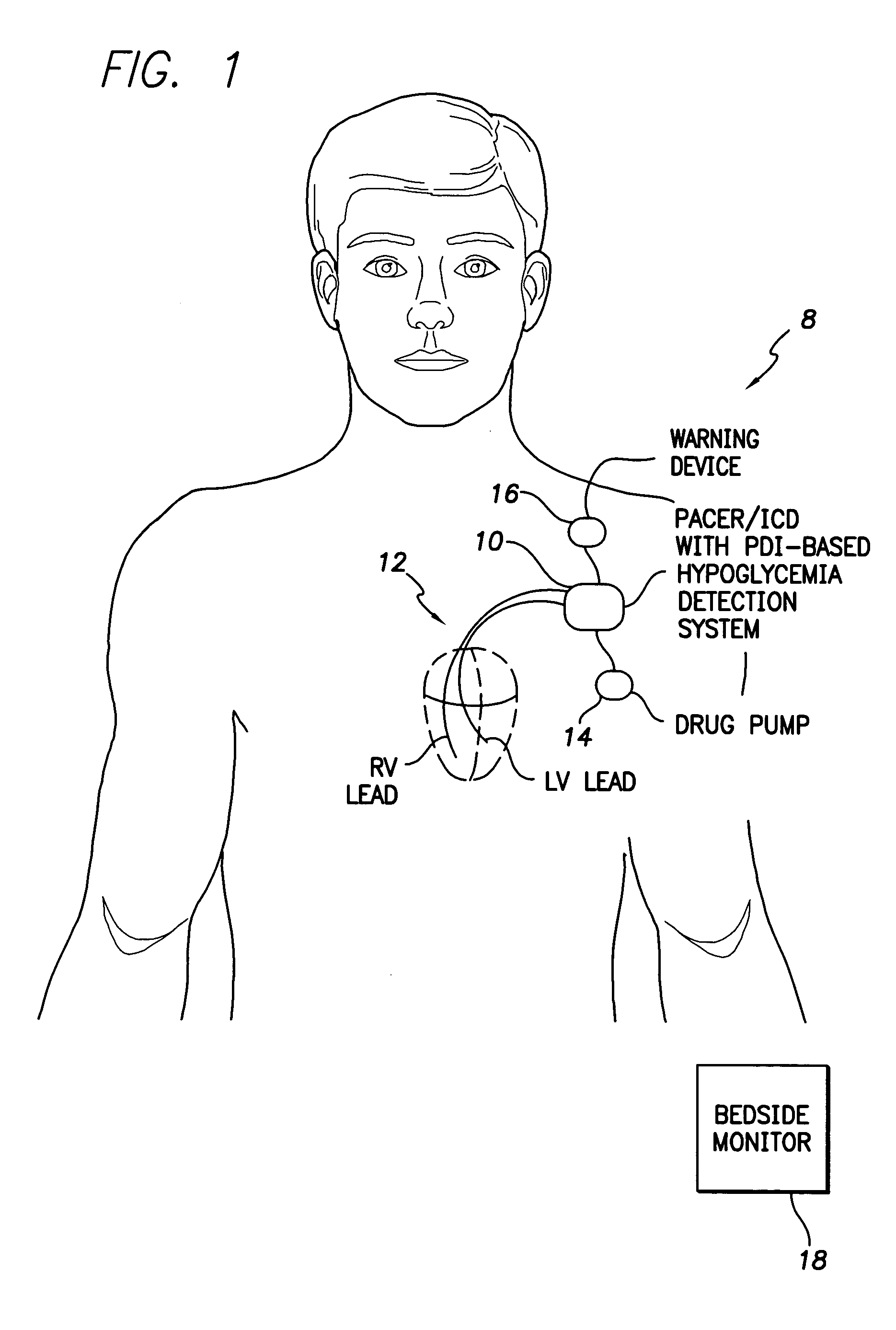
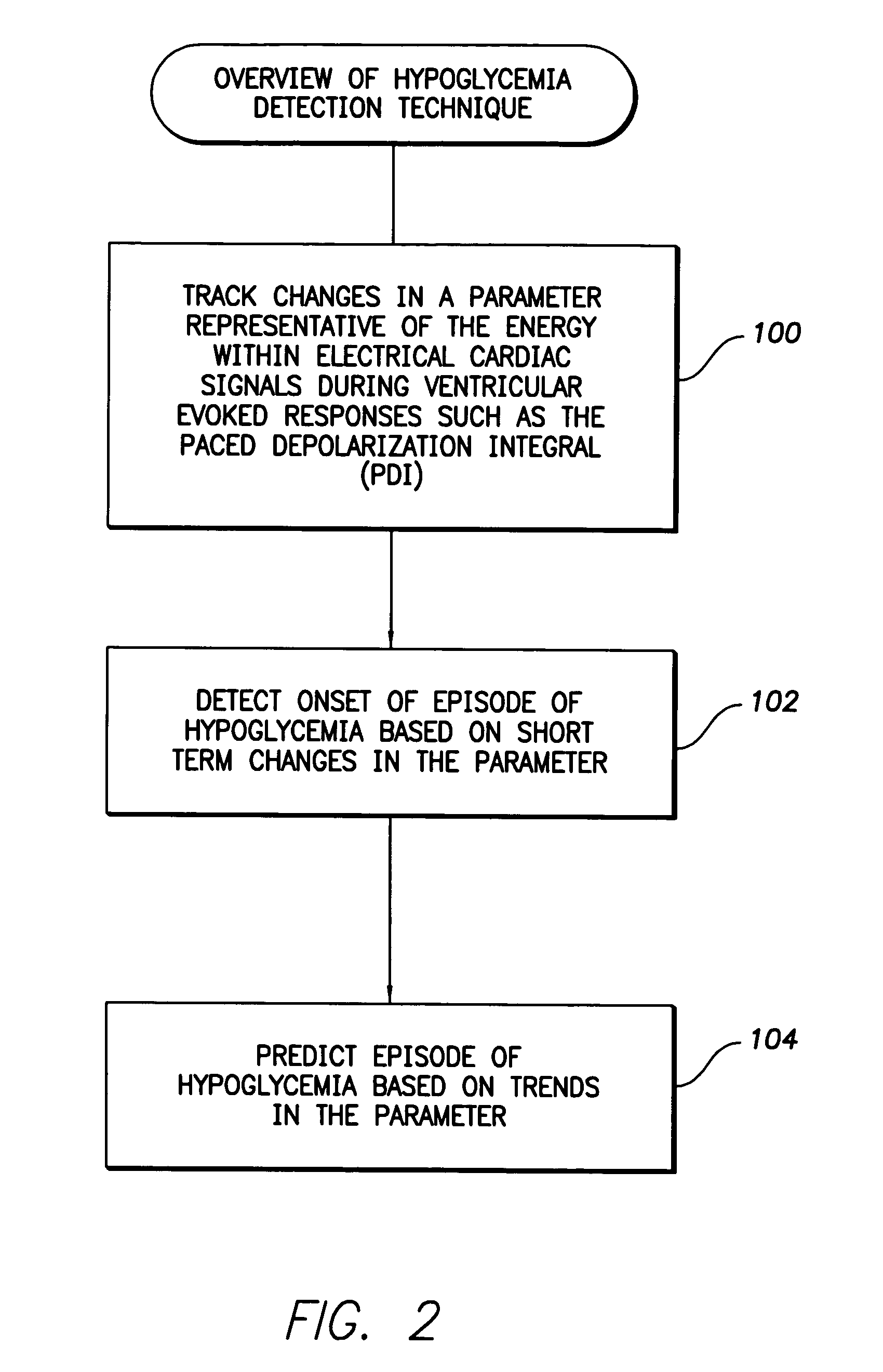
System and method for detecting hypoglycemia based on a paced depolarization integral using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20060247685A1Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrocardiographyMedical devicesCardiac pacemaker electrodeInsulin dependent
Techniques are provided for use with an implantable medical device such as a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter / defibrillator (ICD) for predicting and detecting hypoglycemia. In one example, the device tracks changes in a paced depolarization integral (PDI). A significant increase in PDI over a relatively short period of time indicates the onset of hypoglycemia (this can also be confirmed with QT changes). Upon detection of hypoglycemia, appropriate warning signals are generated to alert the patient. Certain therapies automatically provided by the implantable device may also be controlled in response to hypoglycemia. For example, if the patient is an insulin-dependent diabetic and the implantable device is equipped with an insulin pump capable of delivering insulin directly into the bloodstream, insulin delivery is automatically suspended until blood glucose levels return to acceptable levels. If the device is an ICD, it may be controlled to begin charging defibrillation capacitors upon detection of hypoglycemia so as to permit prompt delivery of a defibrillation shock, which may be needed if hypoglycemia triggers ventricular fibrillation. The detection techniques may be used in conjunction with other hypoglycemia detection techniques to improve detection specificity.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for low-voltage termination of cardiac arrhythmias by effectively unpinning anatomical reentries
ActiveUS20060161206A1Difficulties terminating anatomical reentryEfficient managementElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsLower limitLow voltage
A method for extinguishing a cardiac arrhythmia utilizes destructive interference of the passing of the reentry wave tip of an anatomical reentry through a depolarized region created by a relatively low voltage electric field in such a way as to effectively unpin the anatomical reentry. Preferably, the relatively low voltage electric field is defined by at least one unpinning shock(s) that are lower than an expected lower limit of vulnerability as established, for example, by a defibrillation threshold test. By understanding the physics of the electric field distribution between cardiac cells, the method permits the delivery of an electric field sufficient to unpin the core of the anatomical reentry, whether the precise or estimated location of the reentry is known or unknown and without the risk of inducting ventricular fibrillation. A number of embodiments for performing the method are disclosed.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
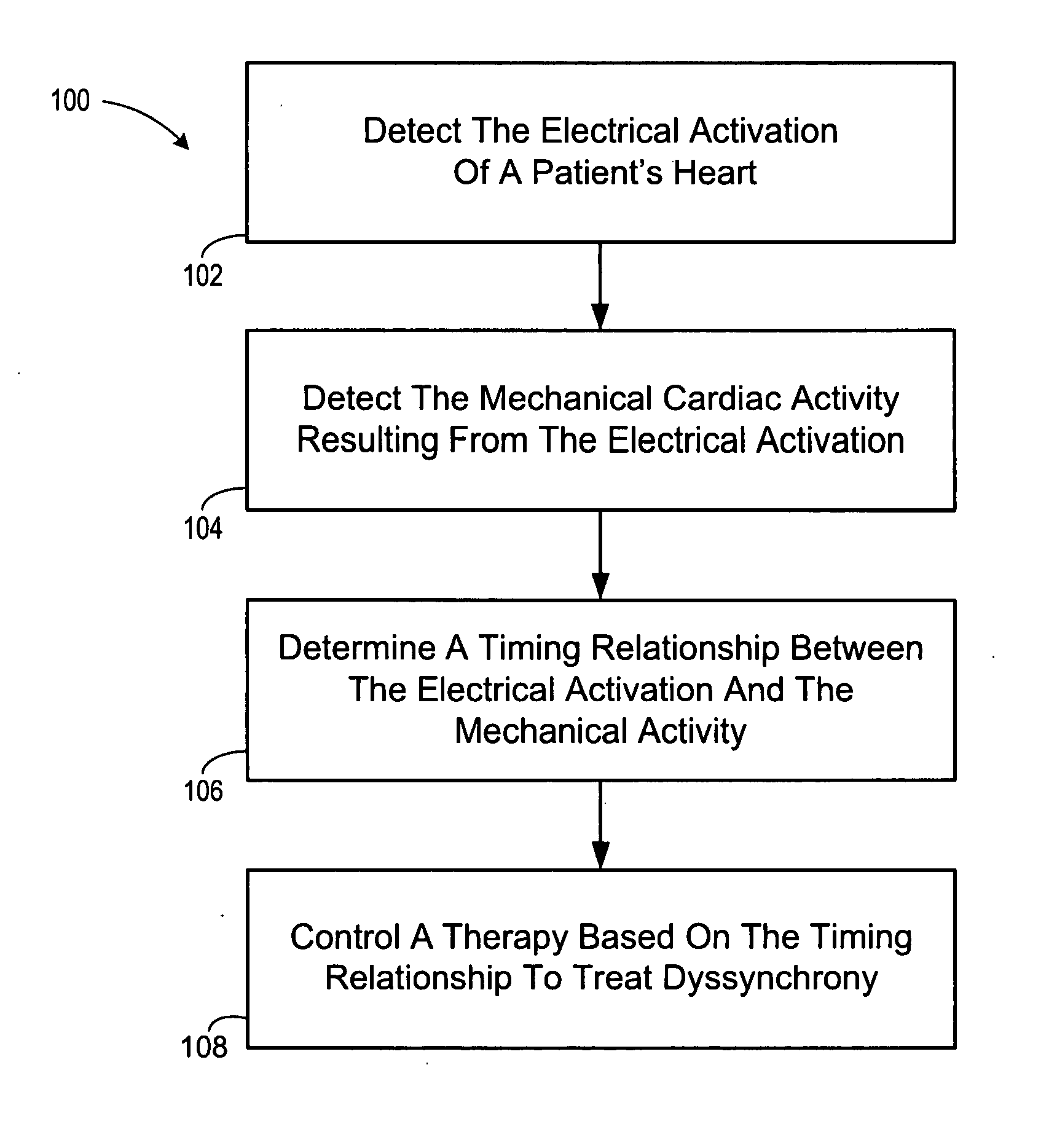
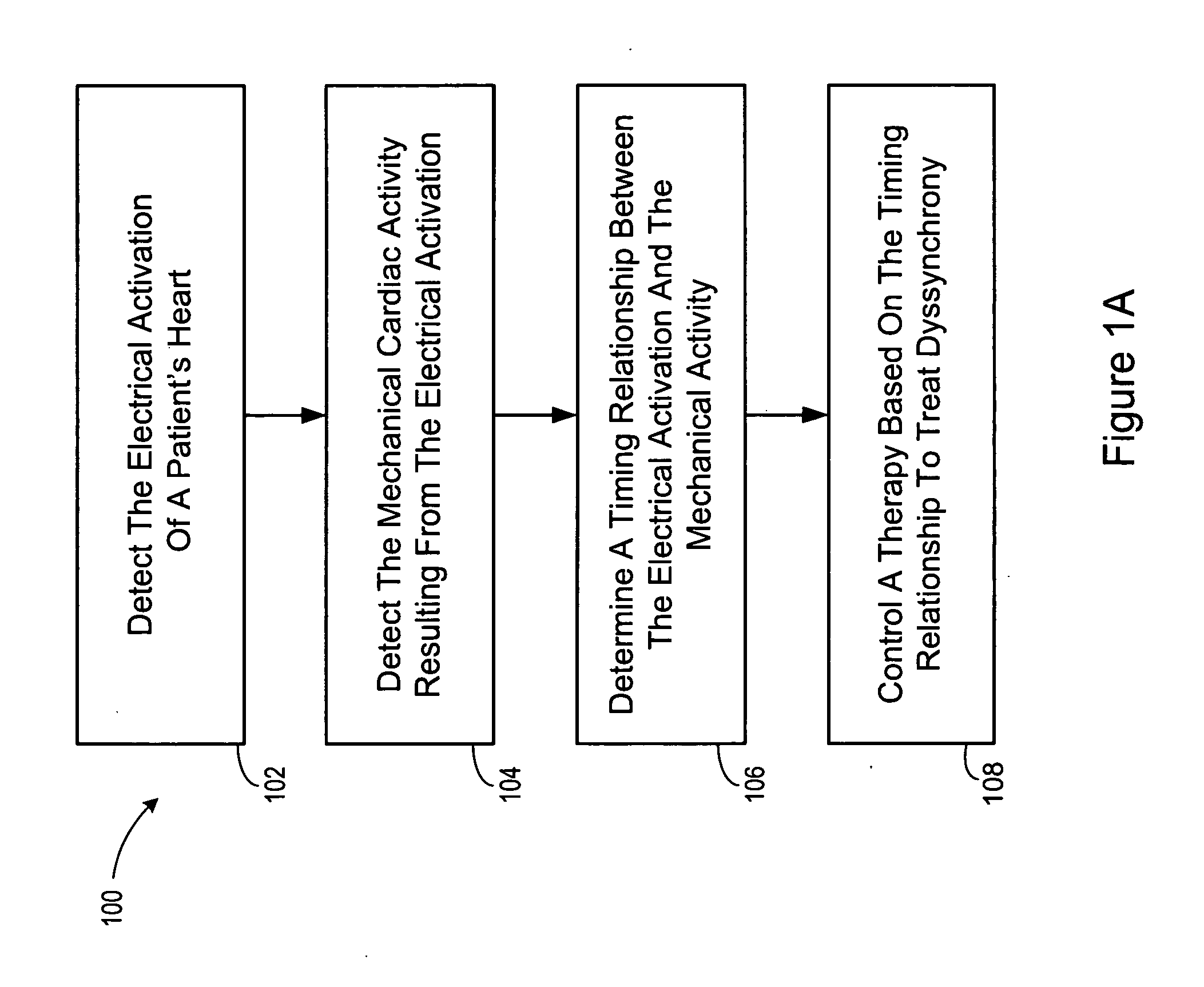
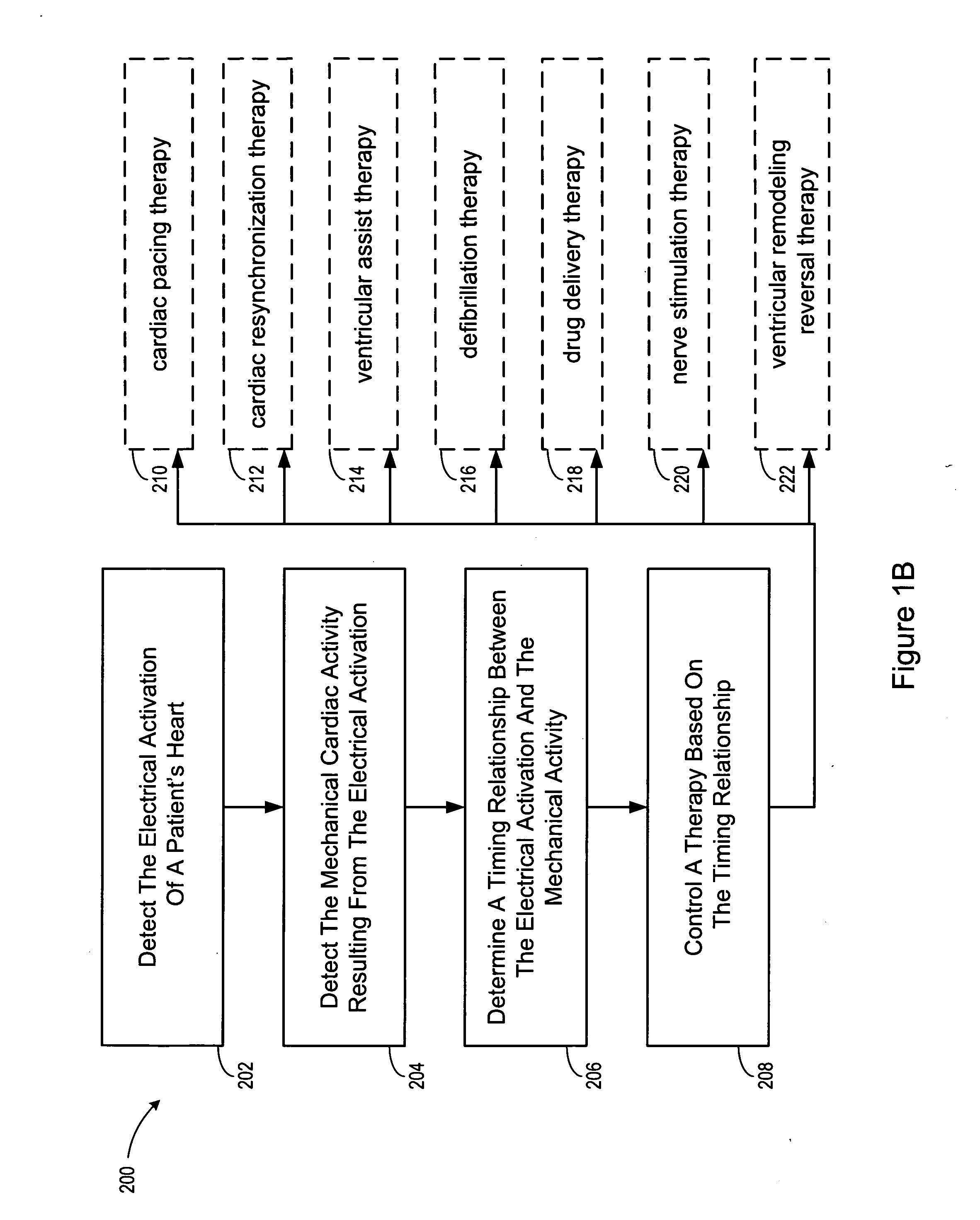
Method and apparatus for controlling cardiac therapy based on electromechanical timing
Devices and methods for therapy control based on electromechanical timing involve detecting electrical activation of a patient's heart, and detecting mechanical cardiac activity resulting from the electrical activation. A timing relationship is determined between the electrical activation and the mechanical activity. A therapy is controlled based on the timing relationship. The therapy may improve intraventricular dyssynchrony of the patient's heart, or treat at least one of diastolic and systolic dysfunction and / or dyssynchrony of the patient's heart, for example. Electrical activation may be detected by sensing delivery of an electrical stimulation pulse to the heart or sensing intrinsic depolarization of the patient's heart. Mechanical activity may be detected by sensing heart sounds, a change in one or more of left ventricular impedance, ventricular pressure, right ventricular pressure, left atrial pressure, right atrial pressure, systemic arterial pressure and pulmonary artery pressure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
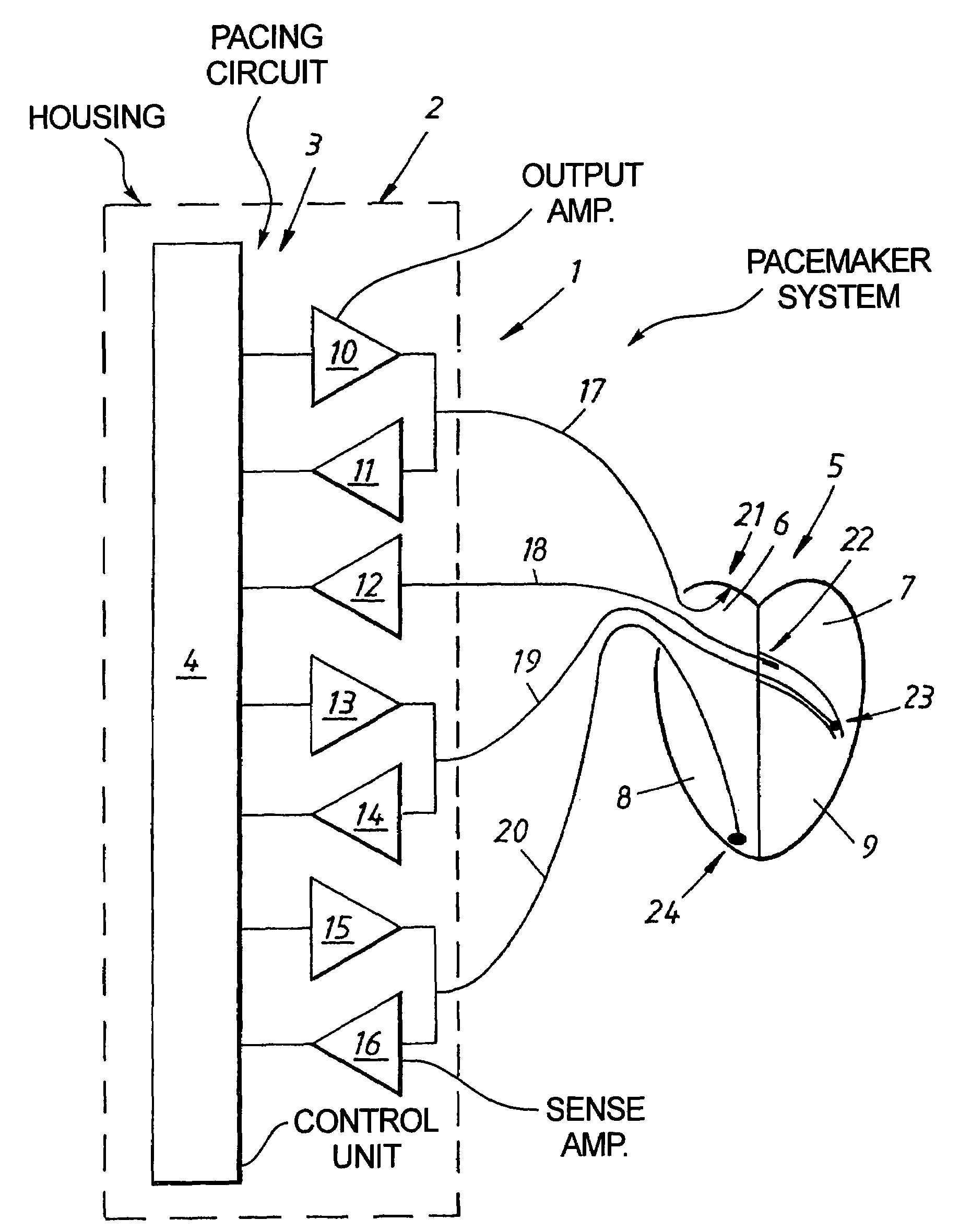
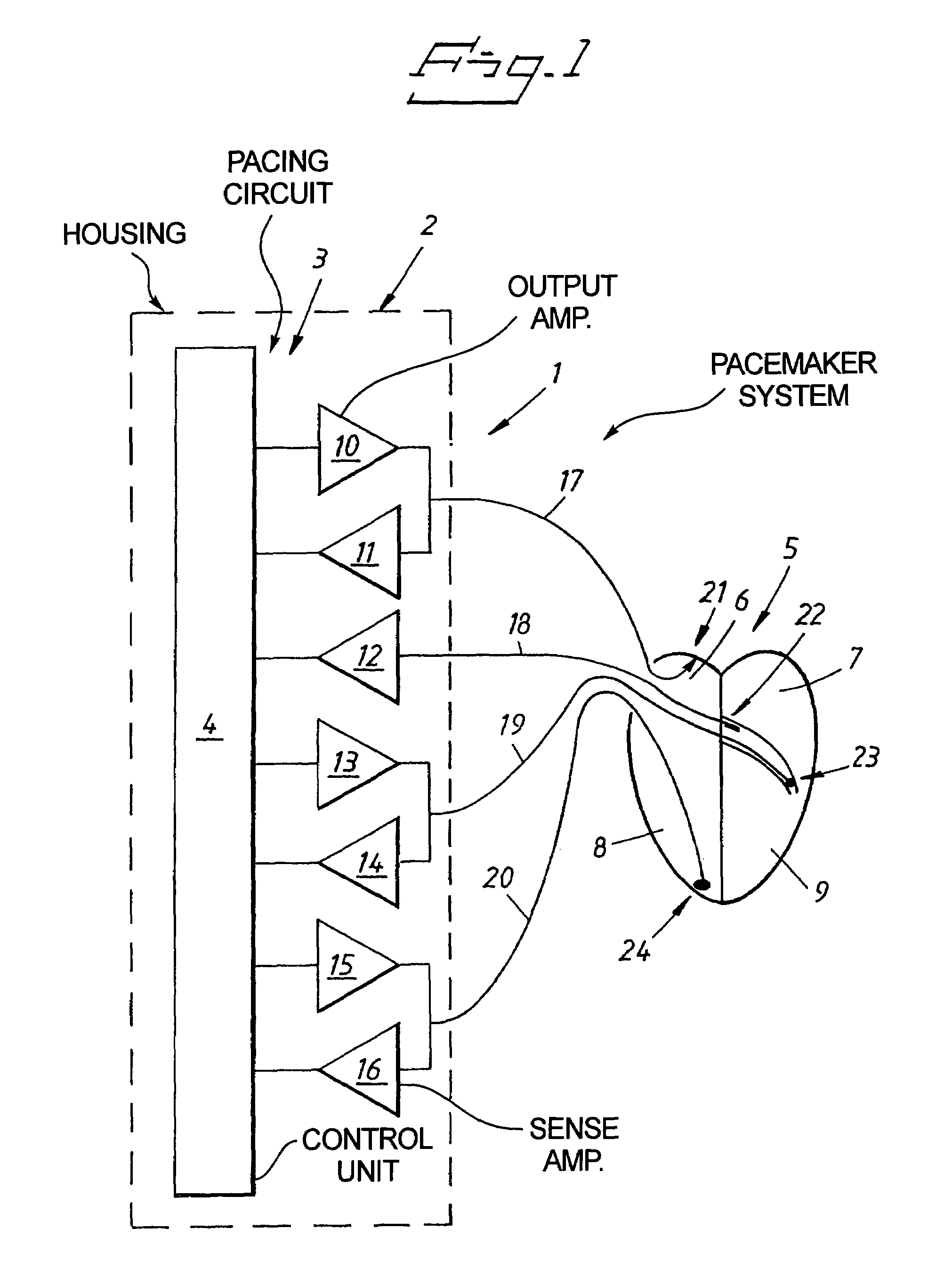
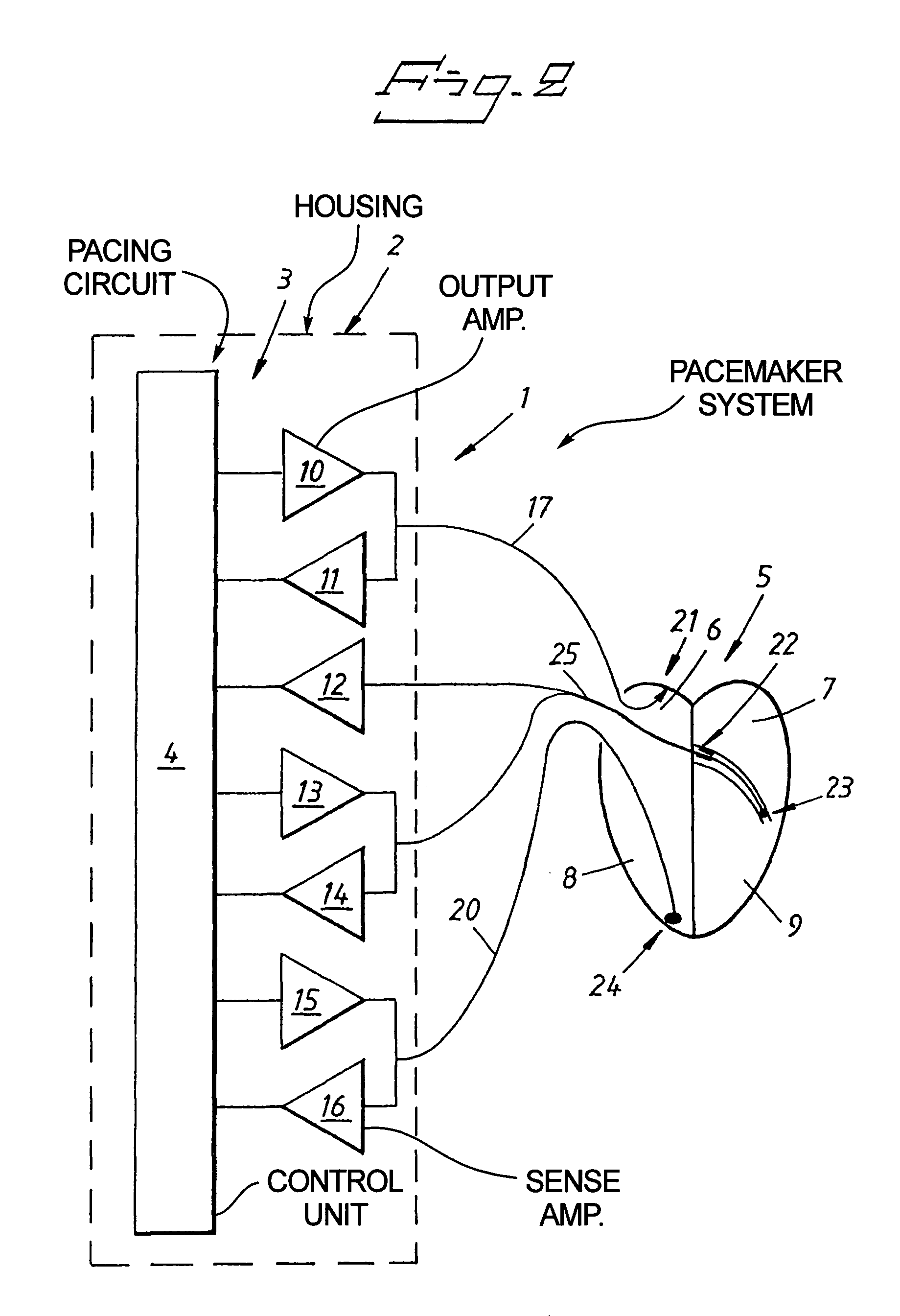
Cardiac stimulating device
An implantable cardiac stimulating device has a pacing circuit connected via an electrode lead system to a first electrode which stimulates and detects activity in the left ventricle, a second electrode to stimulate and detect activity in the right atrium, and to a third electrode to detect activity in the left atrium. Upon the occurrence of a paced or sensed depolarization of the right atrium, a first AV-delay is started. When the subsequent left atrial depolarization is detected, a new AV-interval is started that is optimized for the left side of the heart. Either the left ventricle only, or both ventricles, is paced at the optimized left side AV-interval.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
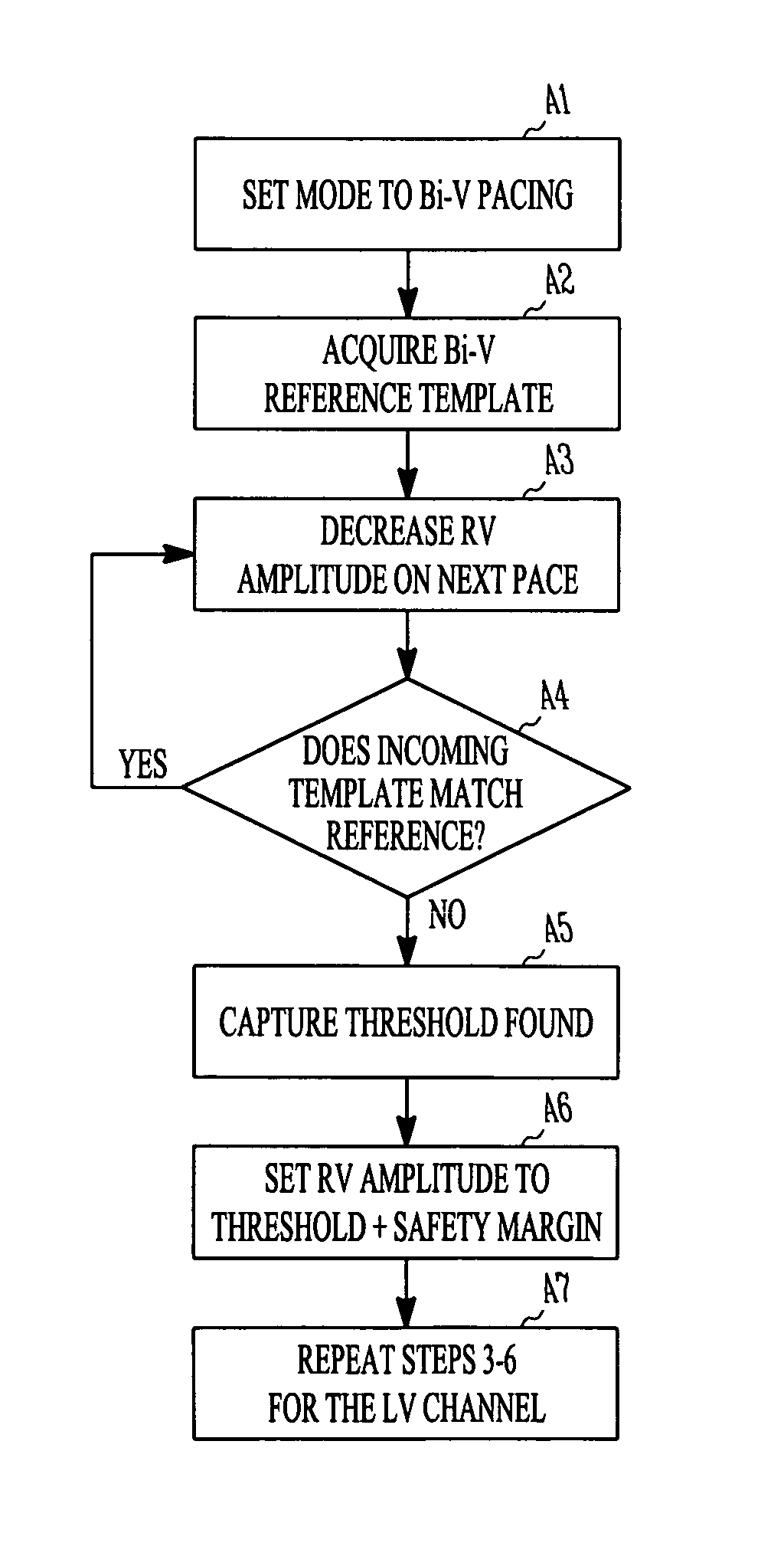
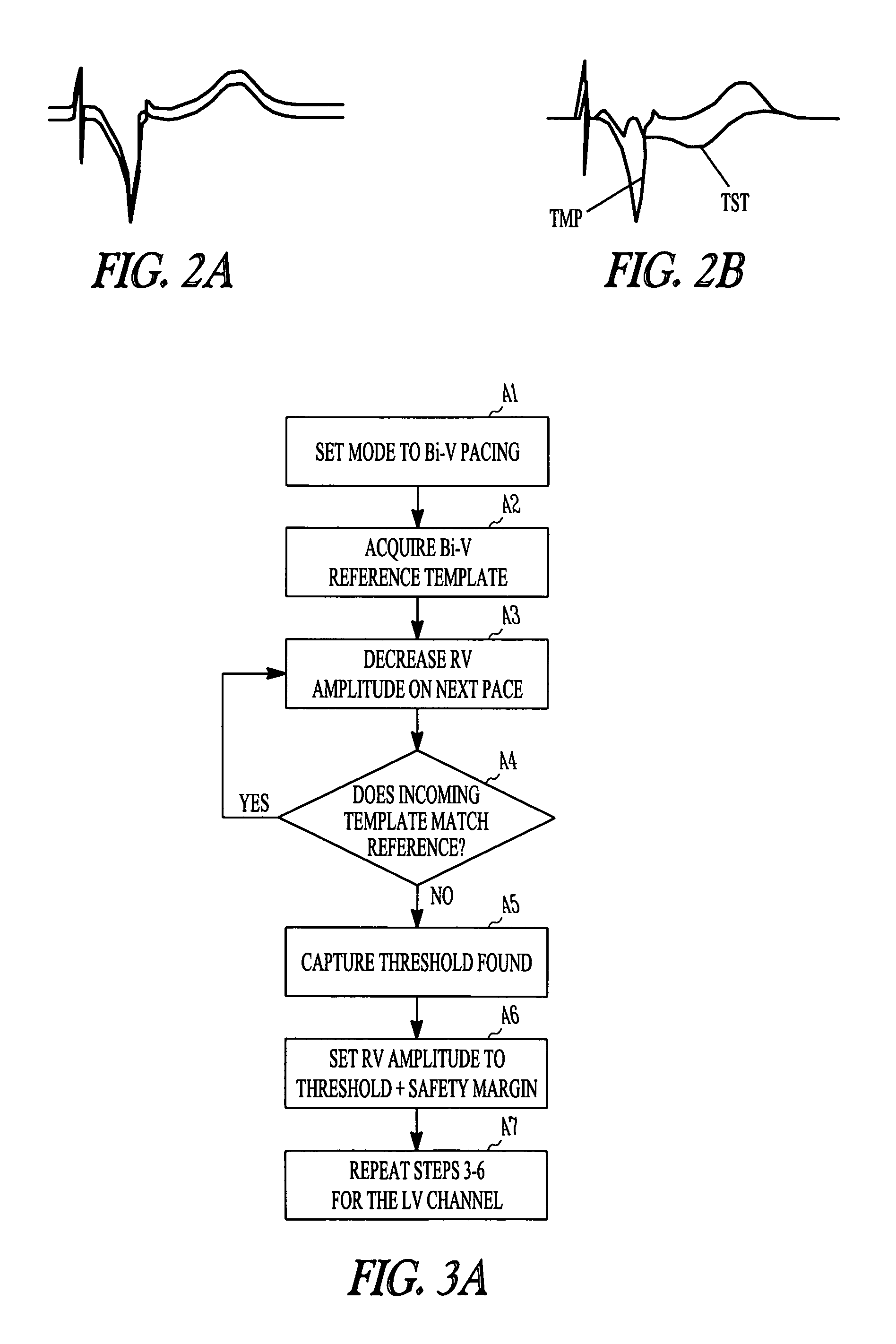
Method and apparatus for capture verification and threshold determination
An apparatus and method for verifying capture by a pacing pulse in which a test depolarization waveform recorded during a pacing event is compared with a template waveform representing capture by the pacing pulse. Capture verification in this manner may be used in pacemakers having multiple pacing channels for the atrial and / or ventricles where the multiple paces can interfere with conventional sensing of evoked responses in order to verify capture.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Implantable stimulation device and method for performing inter-chamber conduction search and conduction time measurement
InactiveUS6885893B1Improves cardiac stimulation device performanceAvoid negative effectsHeart stimulatorsConduction timeAtrial conduction
An implantable cardiac stimulation device and associated method set an atrial capture detection window by verifying that inter-atrial conduction is intact, and then measuring the inter-atrial conduction time. The measured inter-atrial conduction time may then be used for setting the atrial capture detection window. Capture verification of a stimulated atrial site is then implemented by detecting a conducted depolarization at another atrial site or in the opposite atrial chamber. A signal received during an atrial capture detection window is compared to a depolarization signal threshold or to a depolarization signal template in order to verify detection of a conducted depolarization signal as evidence of capture at the stimulated site. By sensing depolarization signal away from the stimulated site, the negative effects of lead polarization normally encountered when detecting an evoked response are avoided.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Hyperspectral polarization profiler for remote sensing
InactiveUS6052187AMinimize healthMinimize problemsRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyFluorescenceLarge range
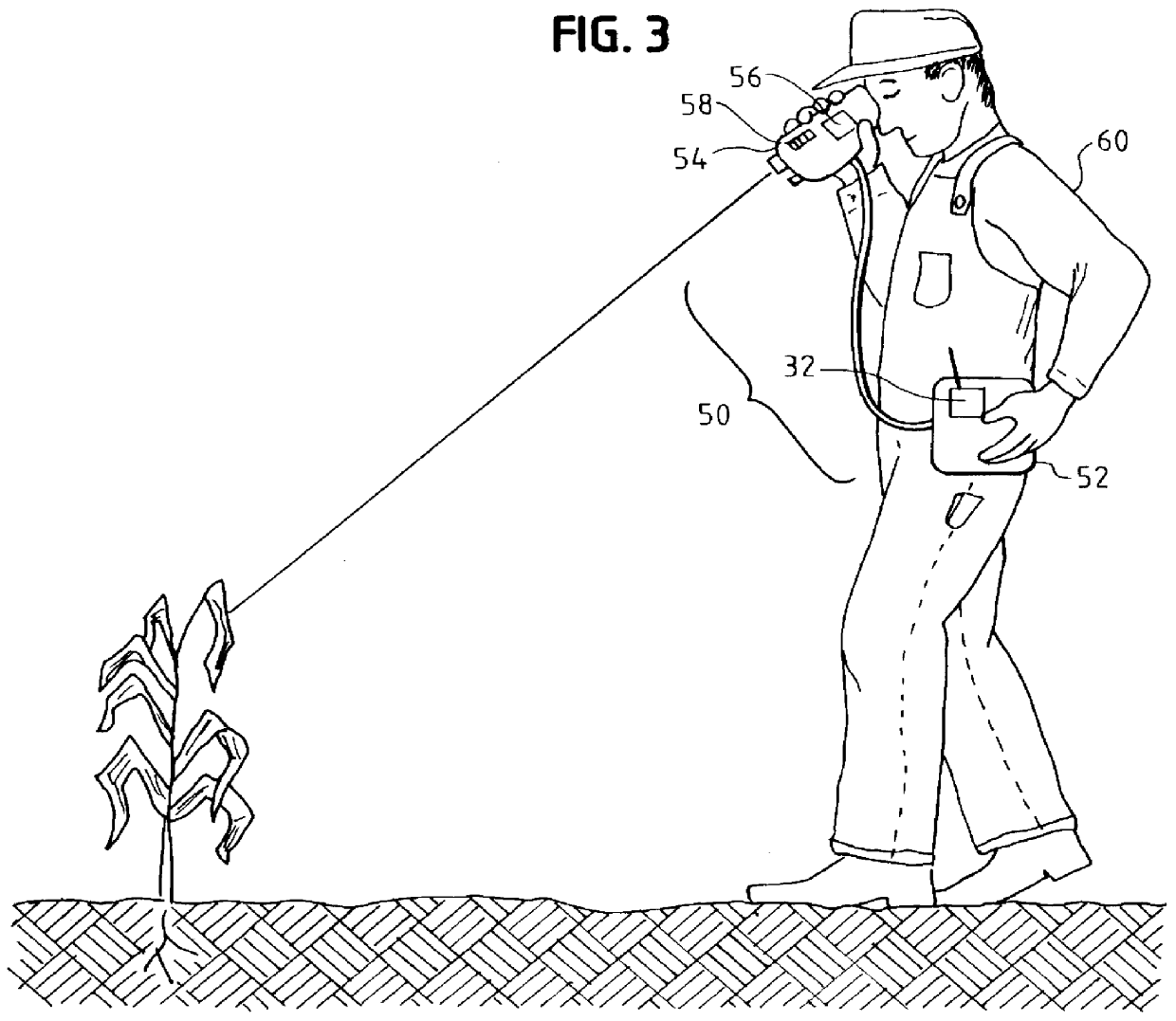
A device to provide hyperspectral reflection spectrum, hyperspectral depolarization, and hyperspectral fluorescence spectrum data in a portable, remote sensing instrument. The device can provide a large range of remotely-sensed optical property data, presently only obtainable in laboratories, in a low-cost field instrument. Among its many uses, the present invention can be used by farmers as a tool for determining the nitrogen content of crops to optimize fertilizer laydown.
Owner:CONTAINERLESS RES
Measurement of intracardiac impedance in a multisite-type, active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker, defibrillator and/or cardiovertor
InactiveUS6539261B2Minimizes additional circuitry requiredSimple and advantageous to realizeHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringPotential measurementElectricity
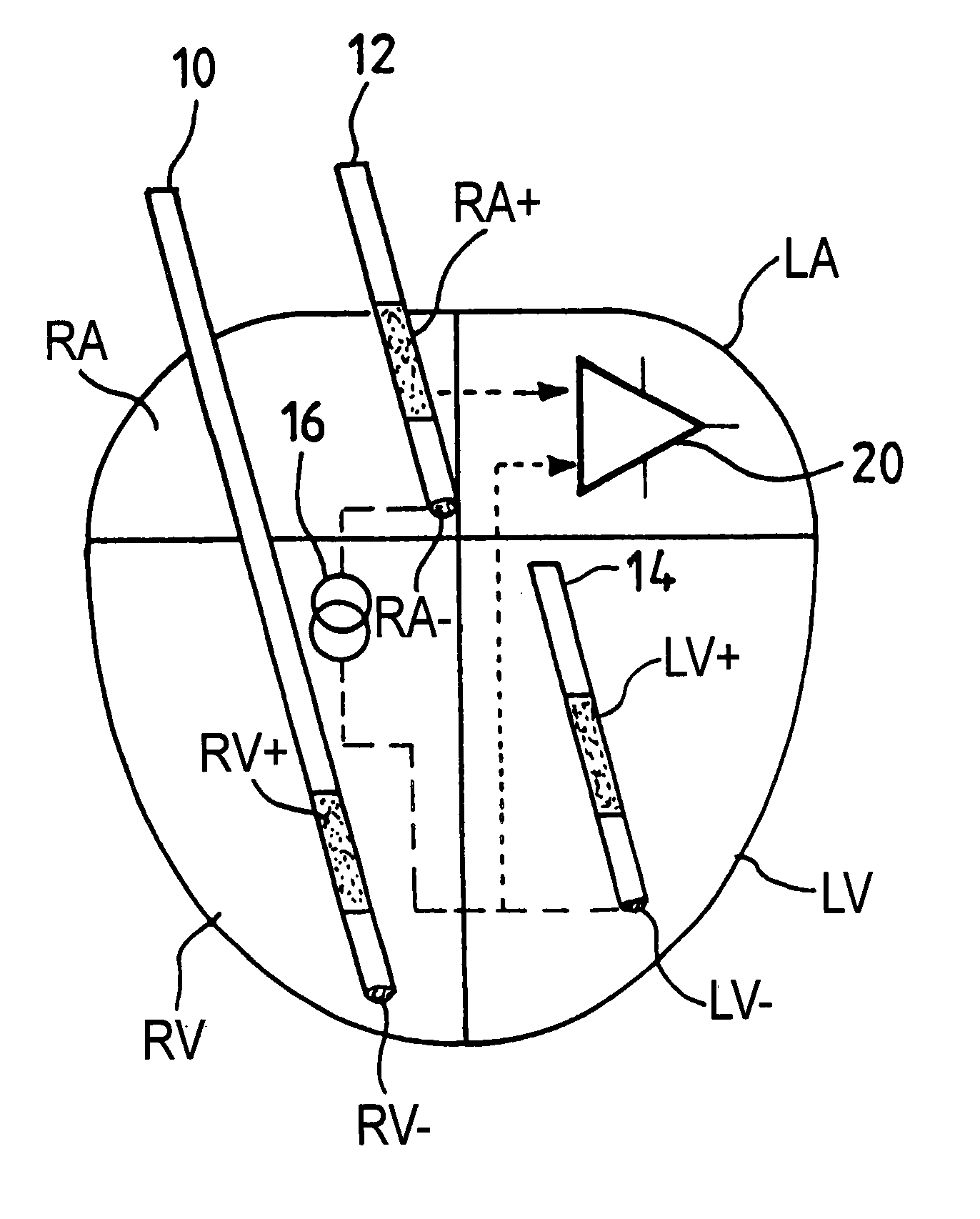
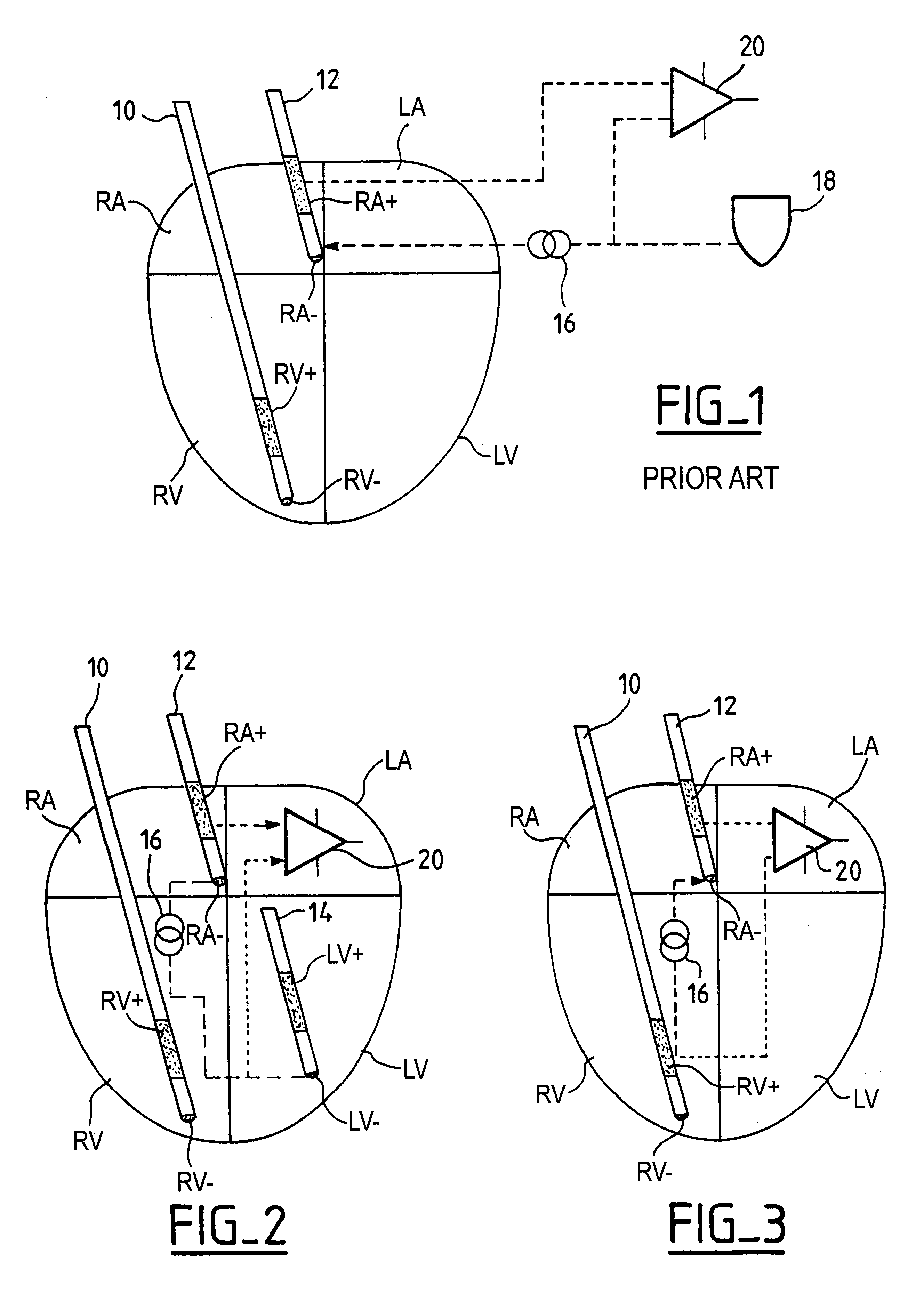
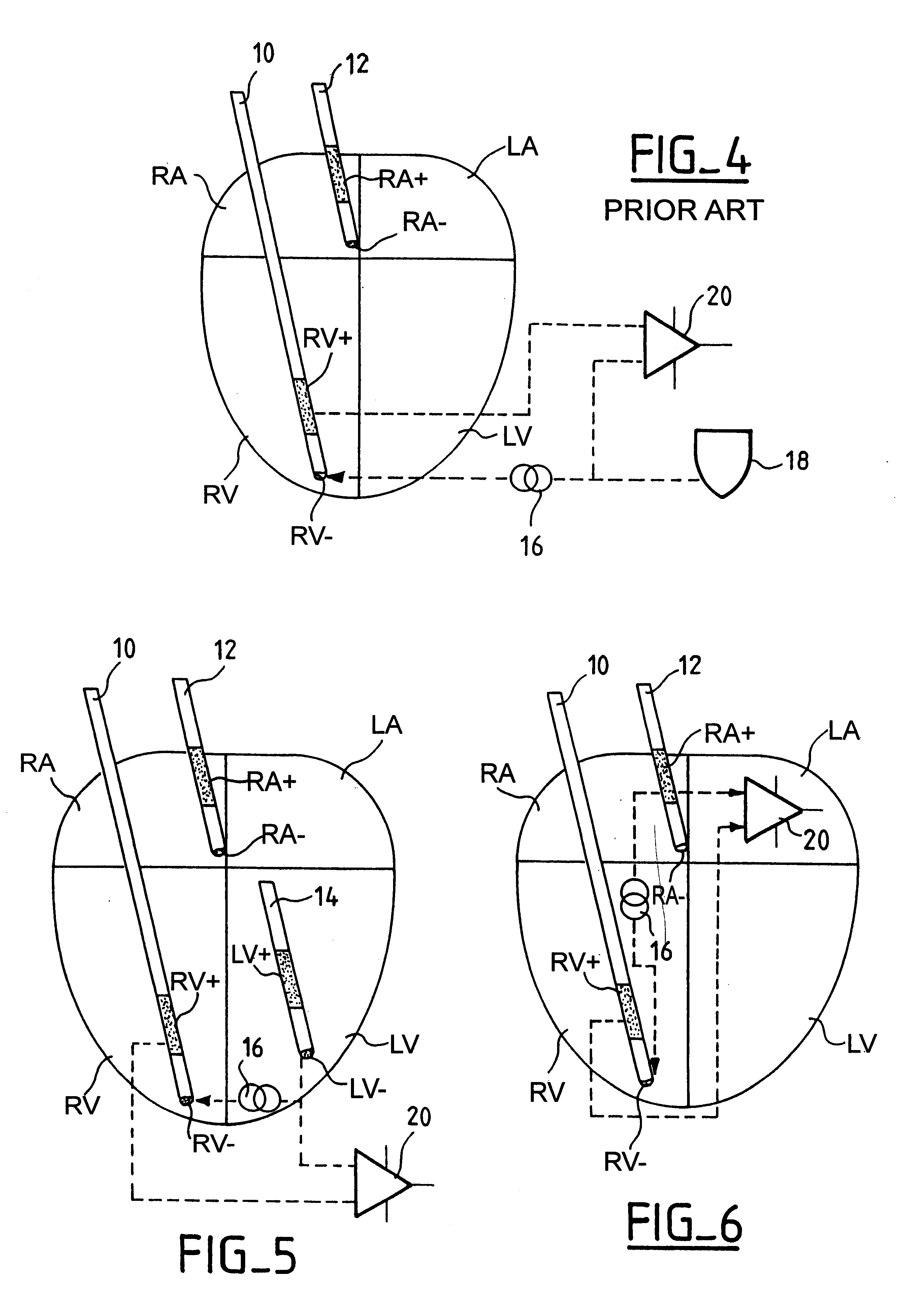
An active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker, defibrillator or cardioveter of the multisite type, including a circuit for measuring intercardiac impedance. Electrodes are placed in at least one ventricular site and one atrial site, and are connected to a circuit for the collection of cardiac signals, to detect a depolarization potential, as well as to a stimulation circuit, to apply stimulation pluses to at least some of the aforementioned sites. The measurement of a trans-pulmonary bio-impedance is obtained by injecting a current from an injection circuit (16) between the case (18) of the device and a first atrial (RA-) (or ventricular) site, and measuring a differential potential (20) between the case (18) and a point of measurement located in a second atrial (RA+) (or ventricular) site using a collection circuit. Switches are selectively operable to isolate the case (18) from the current injection and measurement of potential circuits, and to connect them to a common reference potential site, atrial or ventricular (LV-), which is distinct from the sites (RA-,RA+) to which are also connected these circuits, so as to allow a measurement of intracardiac impedance from the signal delivered by the differential potential measuring circuit. The switching is obtained by connections to an electric ground, operating independently of the current injection circuit and the differential potential measuring circuit.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Method and apparatus for synchronization of atrial defibrillation pulses
A method and apparatus for detecting and treating atrial fibrillation. In response to detecting atrial fibrillation, the device derives an escape interval based on one or more preceding intervals between ventricular depolarizations. The escape interval is initiated in response to a ventricular depolarization, and in response to the expiration of the escape interval, an atrial cardioversion pulse is delivered. In one embodiment of the invention, the cardioverting pulse is delivered immediately upon expiration of the derived escape interval. In a second embodiment of the invention, a ventricular pacing pulse is delivered on expiration of the escape interval, with an atrial cardioversion pulse following after a short delay.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
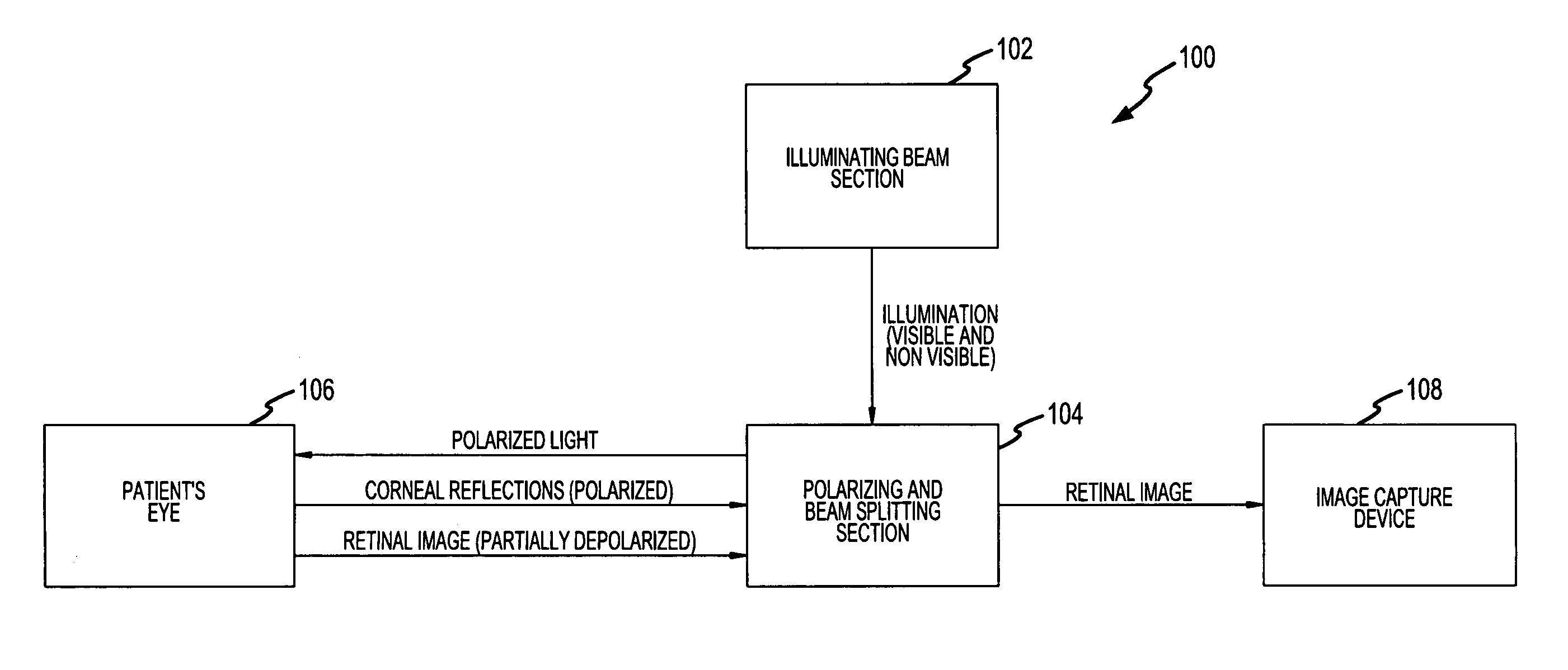
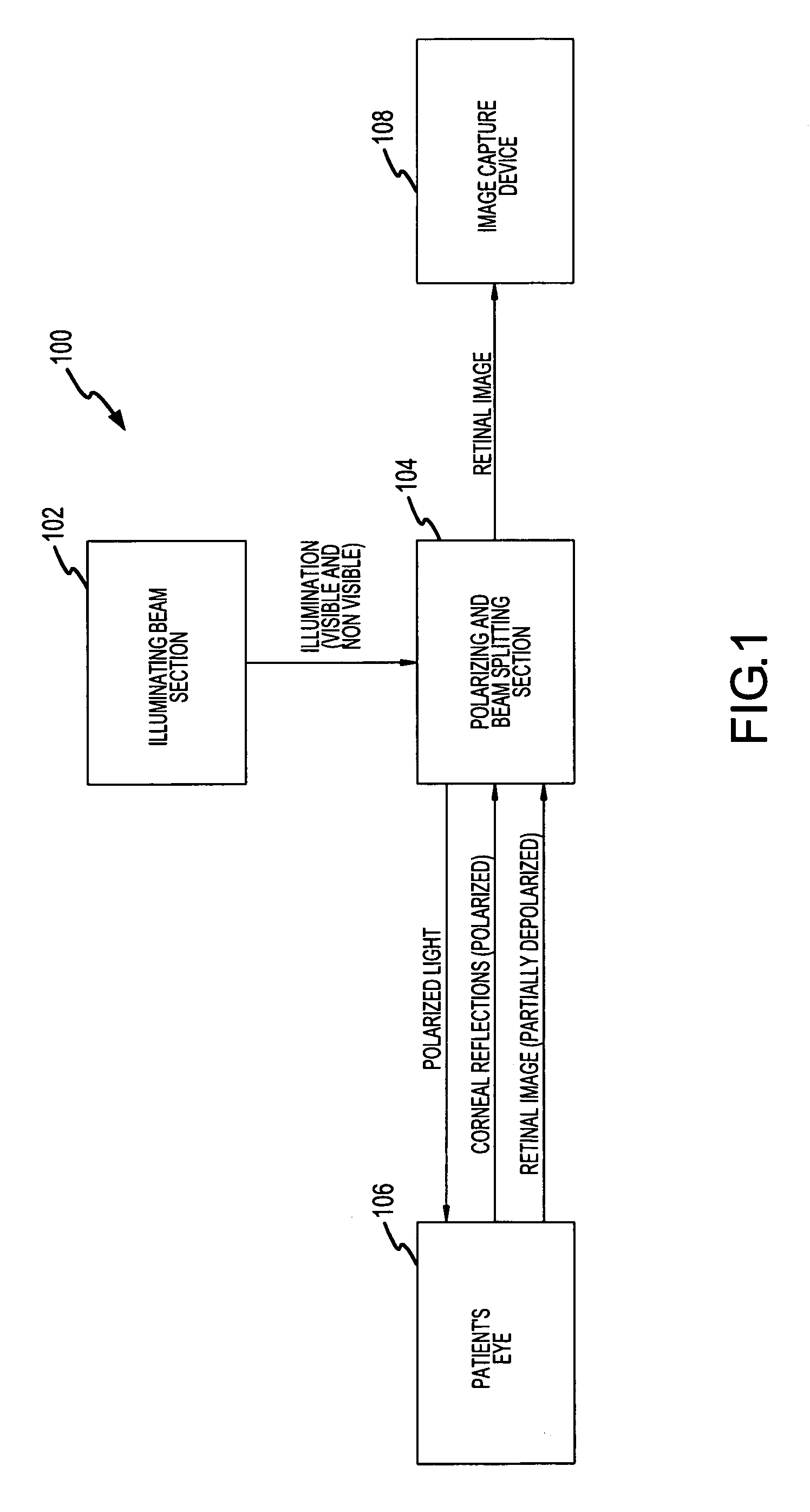
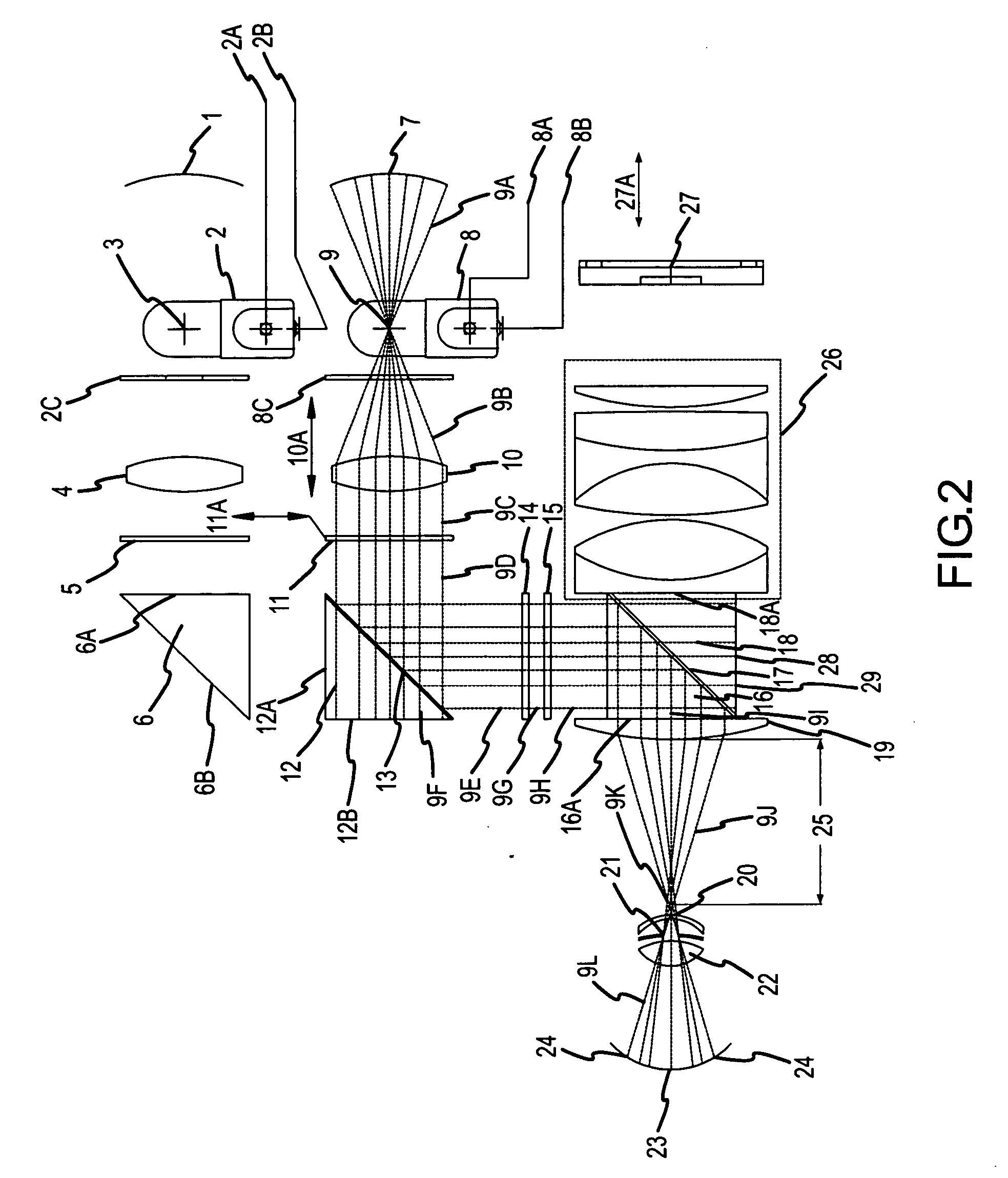
Hand held device and methods for examining a patient's retina
A hand held device for examining a patient's retina. In one example, the device generates visible or non-visible illuminating beams having desired spectral content. The illuminating beams are then polarized to generate polarized light beam(s) that are directed towards the patient's retina. At the patient's eye, a portion of the polarized beam is partially reflected by the cornea and travels back to the device, and another portion of the polarized beam enters the eye through the undilated pupil, illuminates the patient's retina, and generates a reflected retinal image (generally de-polarized) which also travels back to the device. The device receives the retinal image and transmits certain portions of the retinal image on through to an image detector (i.e., CCD or CMOS); and the device deflects the received polarized corneal reflections away from the image capture device. Hence, the image capture device receives retinal images but does not receive the polarized corneal reflected light.
Owner:OCUTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com