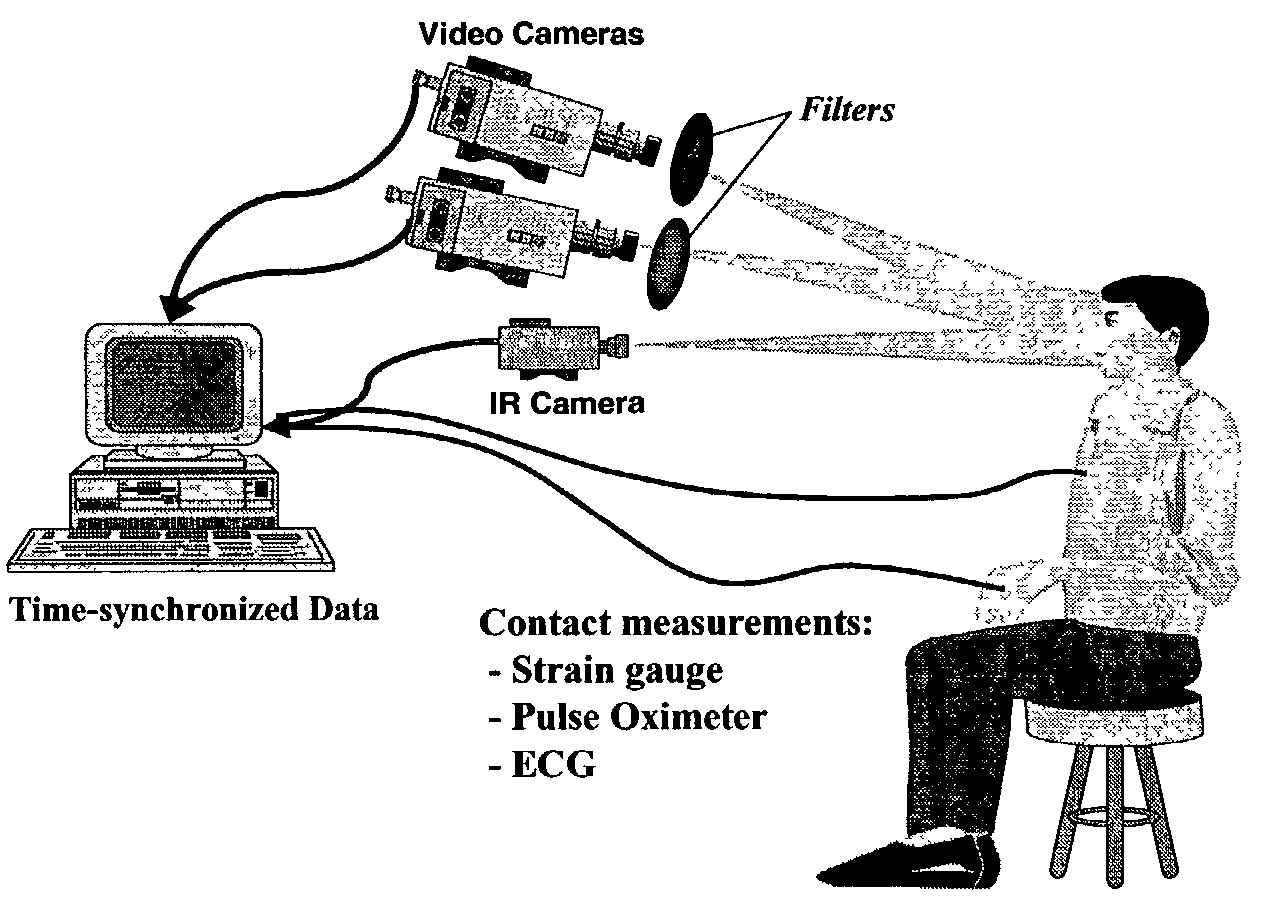
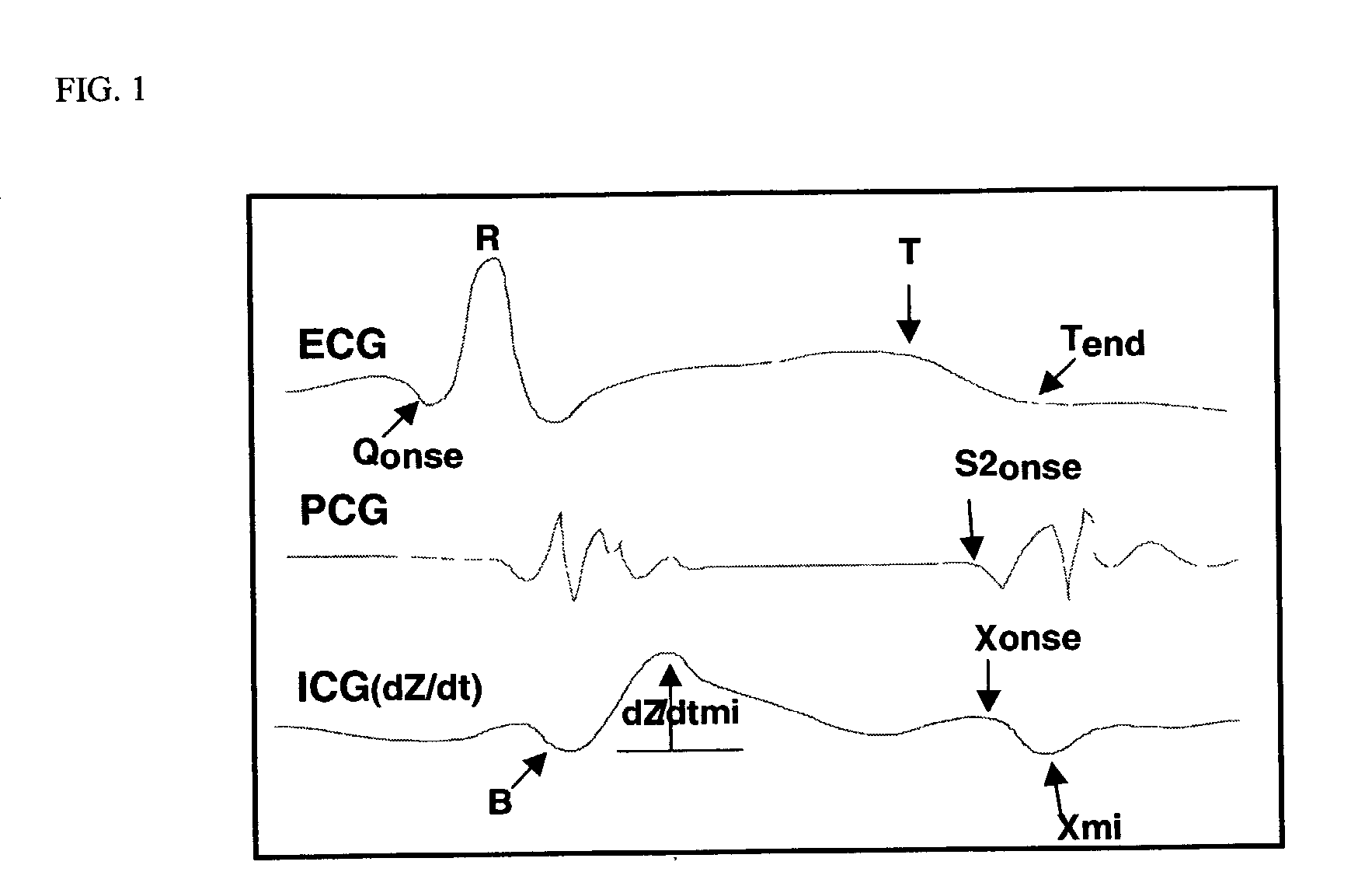
Patents
Literature
493 results about "Heart sounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
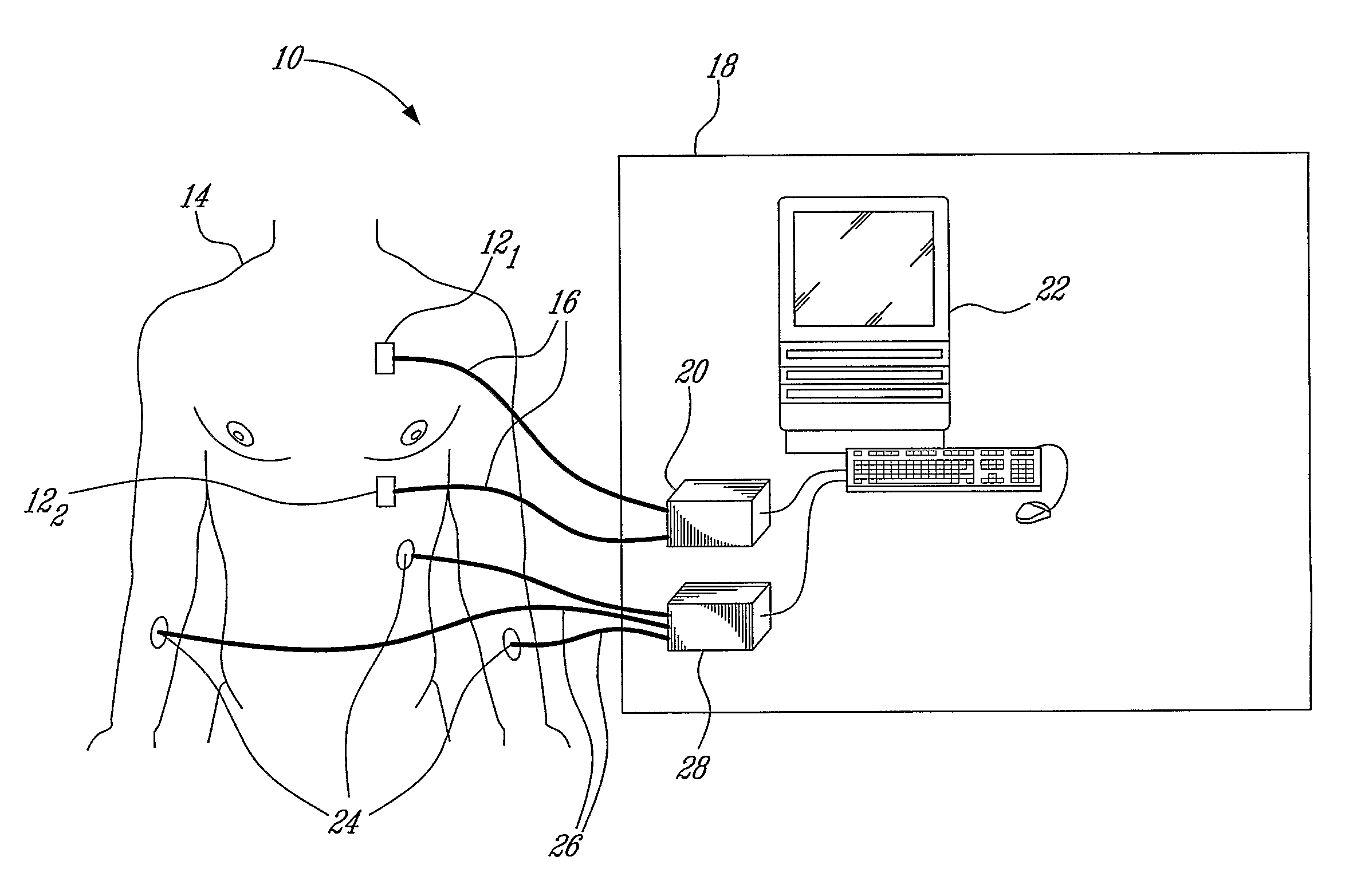
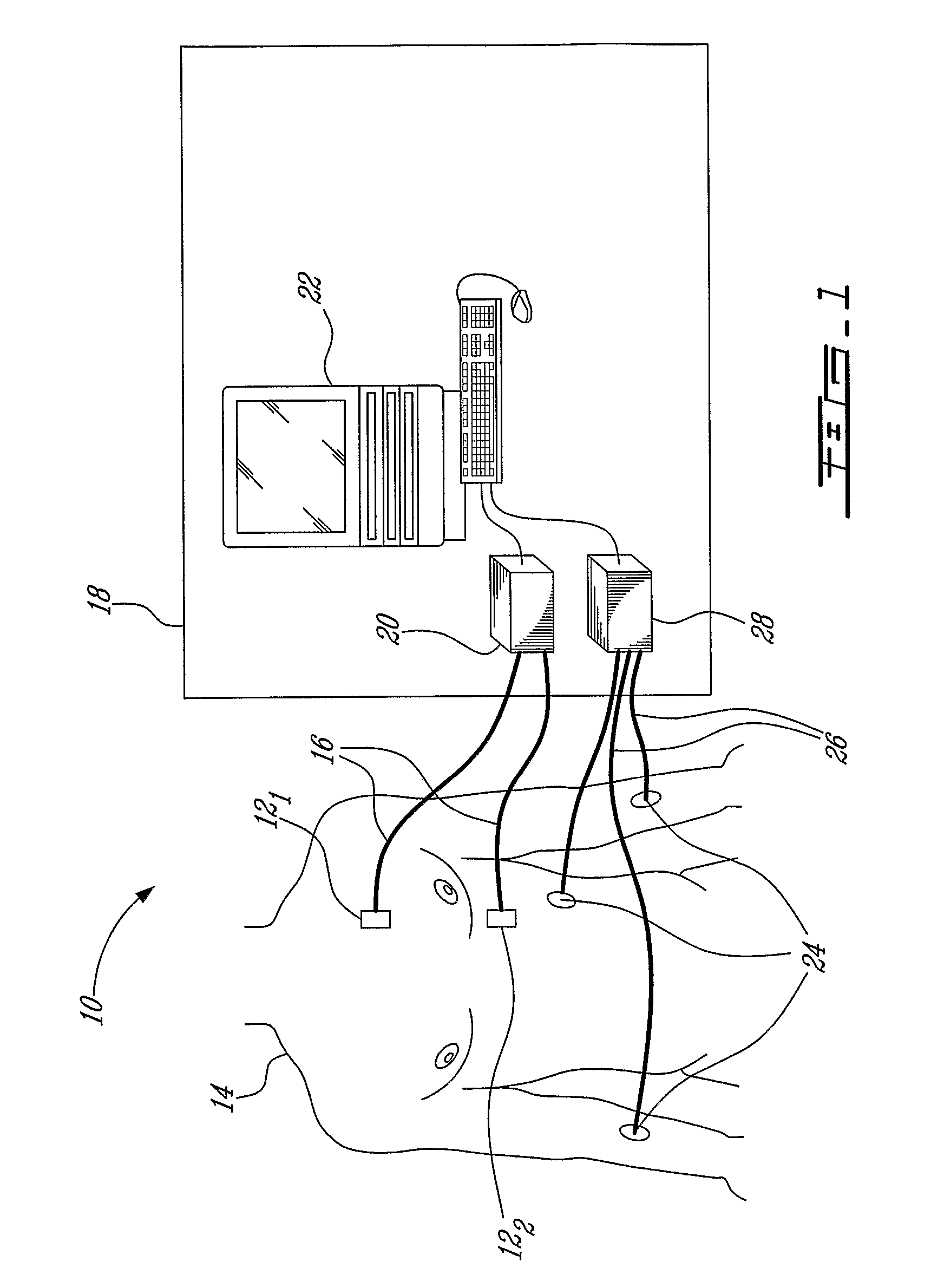
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stethoscope to listen for these unique and distinct sounds that provide important auditory data regarding the condition of the heart.
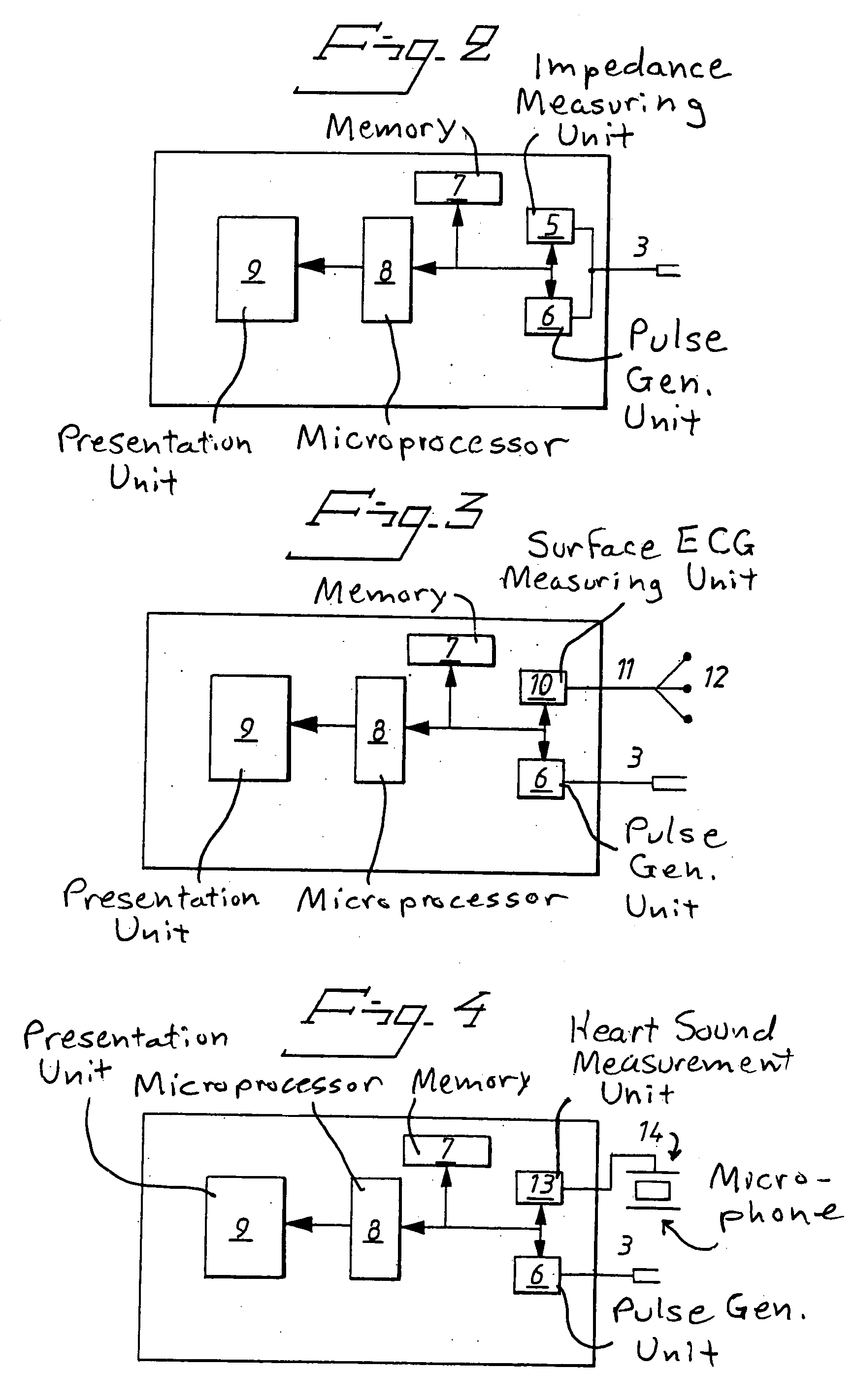
Non-invasive measurement of second heart sound components
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Glycemic control monitoring using implantable medical device
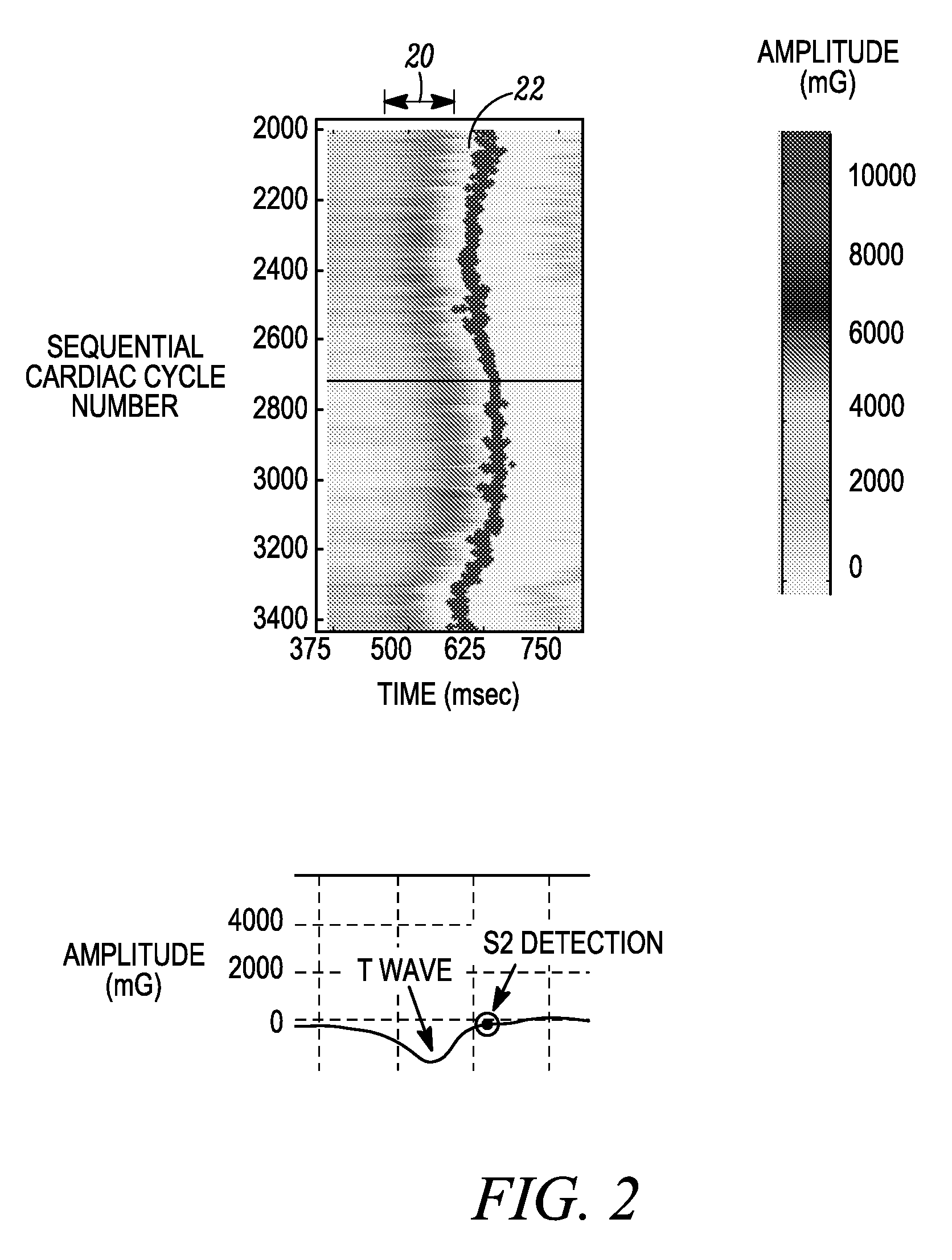
An apparatus for monitoring a patient's blood glucose level. The apparatus includes an implantable medical device having a controller and an implantable heart sounds sensor configured to transmit signals to the controller of the implantable medical device. The controller is configured to determine if a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic based on the signals from the heart sounds sensor. A method is also disclosed that includes sensing the patient's heart sounds, determining the amplitude of the S2 heart sound, determining the length of the interval from the S1 heart sound to the S2max heart sound, determining the length of the interval from the S1 heart sound to the S2end heart sound, and determining the patient's blood glucose status based on the patient's heart sounds.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Heart sound simulator
The disclosure includes systems and methods directed toward simulating heart sounds. The system can include an optical sensor configured to obtain data for generating a plurality of plethysmograph waveforms at a first frequency. The heart sound simulator can also include a processor in communication with the sensor. The processor can be configured to generate a heart sound signal based on at least one of the plurality of plethysmograph waveforms.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Heart sound simulator
The disclosure includes systems and methods directed toward simulating heart sounds. The system can include an optical sensor configured to obtain data for generating a plurality of plethysmograph waveforms at a first frequency. The heart sound simulator can also include a processor in communication with the sensor. The processor can be configured to generate a heart sound signal based on at least one of the plurality of plethysmograph waveforms.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Identification by analysis of physiometric variation
Methods involving extraction of information from the inherent variability of physiometrics, including data on cardiovascular and pulmonary functions such as heart rate variability, characteristics of ECG traces, pulse, oxygenation of subcutaneous blood, respiration rate, temperature or CO2 content of exhaled air, heart sounds, and body resonance, can be used to identify individual subjects, particularly humans. Biometric data for use in the methods can be obtained either from contact sensors or at a distance. The methods can be performed alone or can be fused with previous identification algorithms.
Owner:LEIDOS
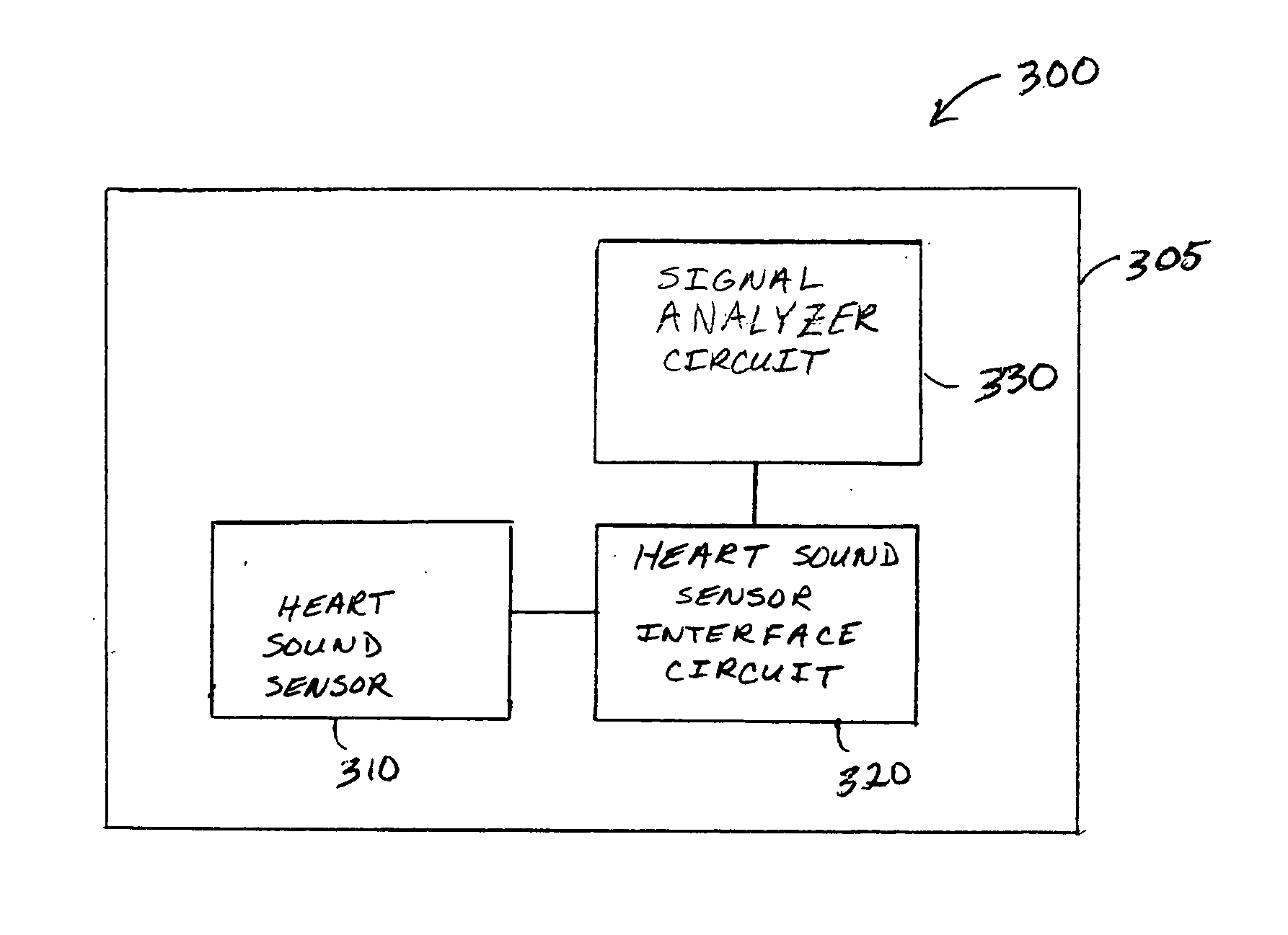
Ischemia detection using a heart sound sensor
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD) includes an implantable heart sound sensor to produce an electrical signal representative of at least one heart sound. The heart sound is associated with mechanical activity of a patient's heart. Additionally, the IMD includes a heart sound sensor interface circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor to produce a heart sound signal, and a signal analyzer circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor interface circuit. The signal analyzer circuit measures a baseline heart sound signal, and deems that an ischemic event has occurred using, among other things, a measured subsequent change in the heart sound signal from the established baseline heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
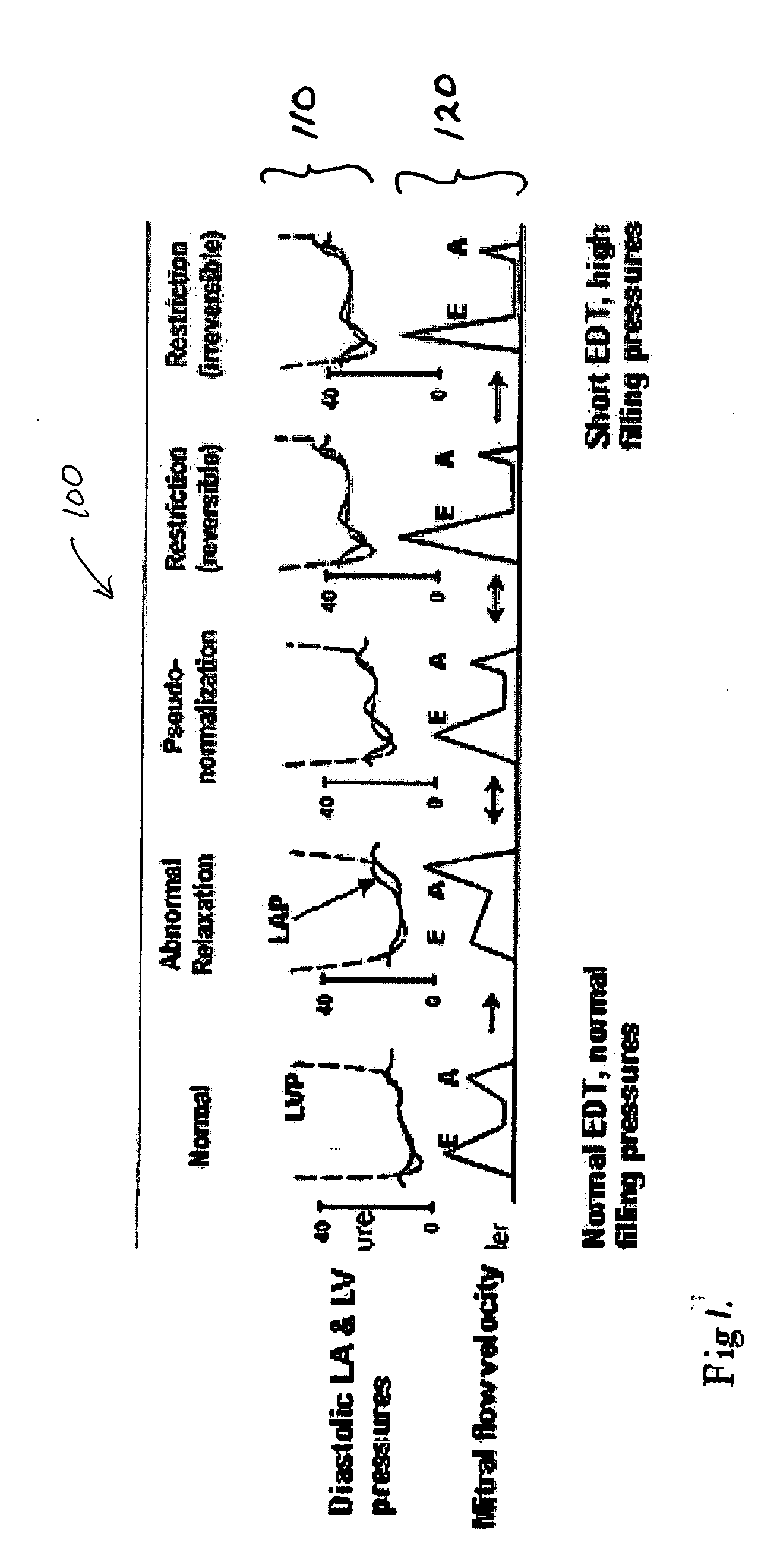
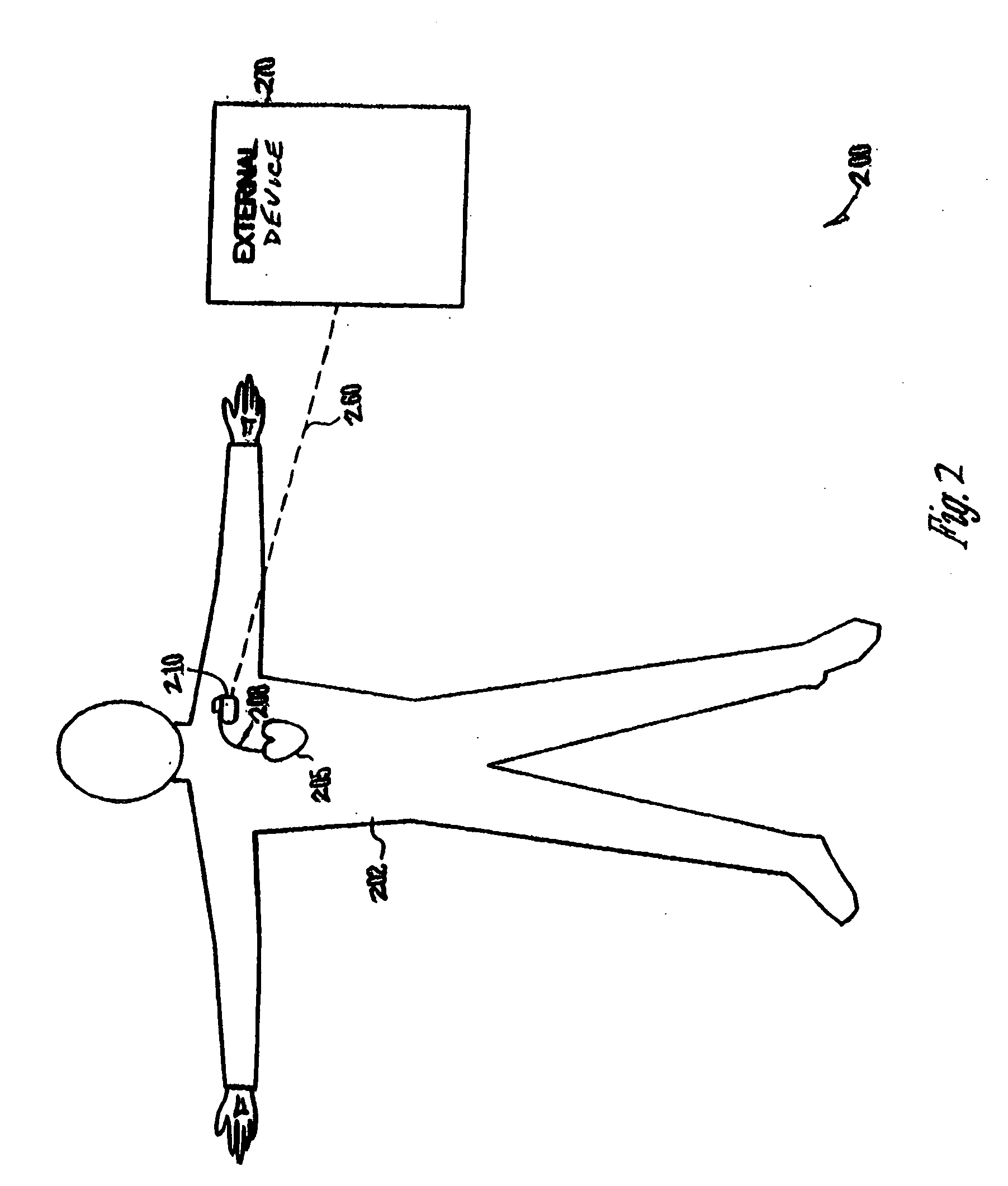
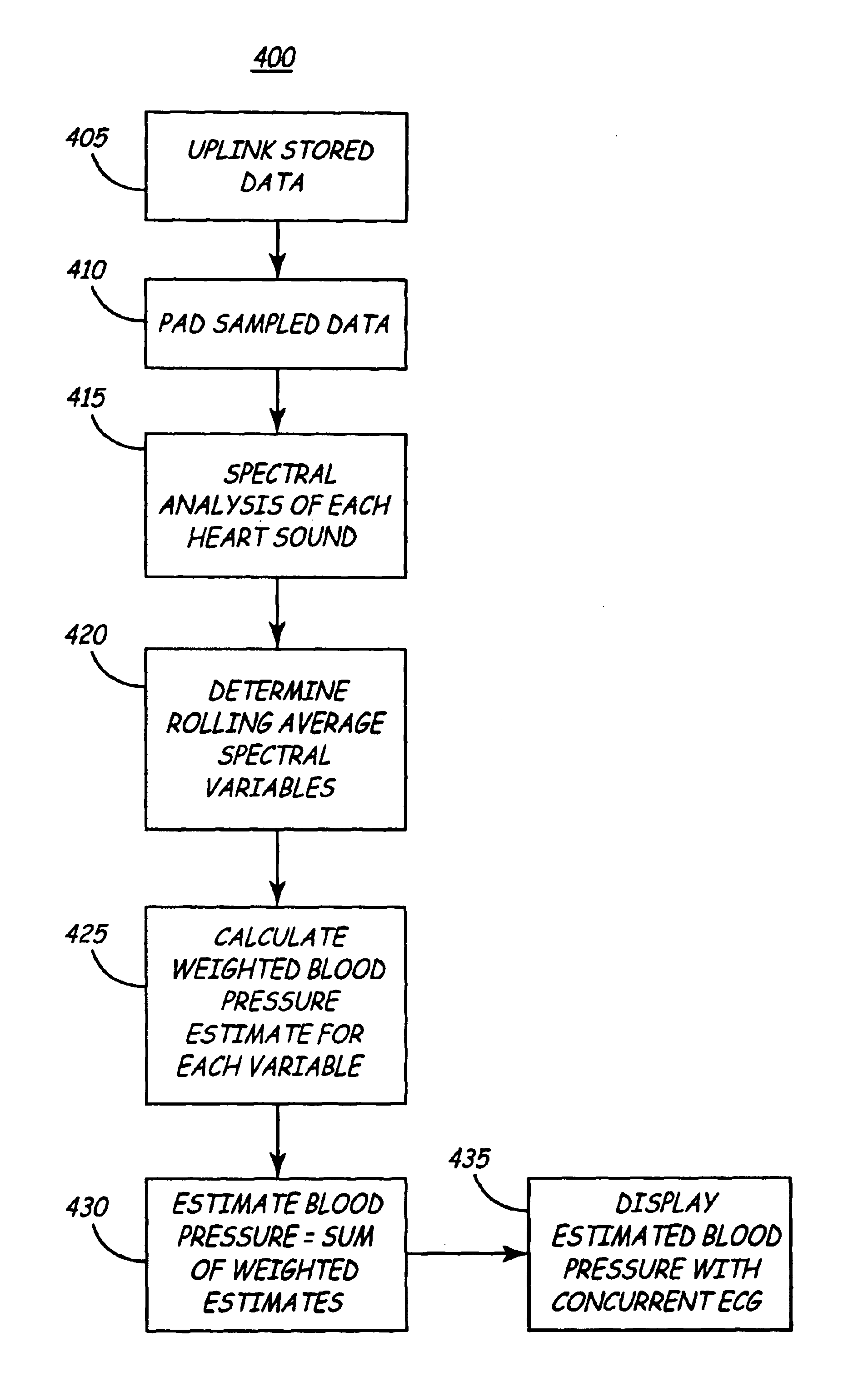
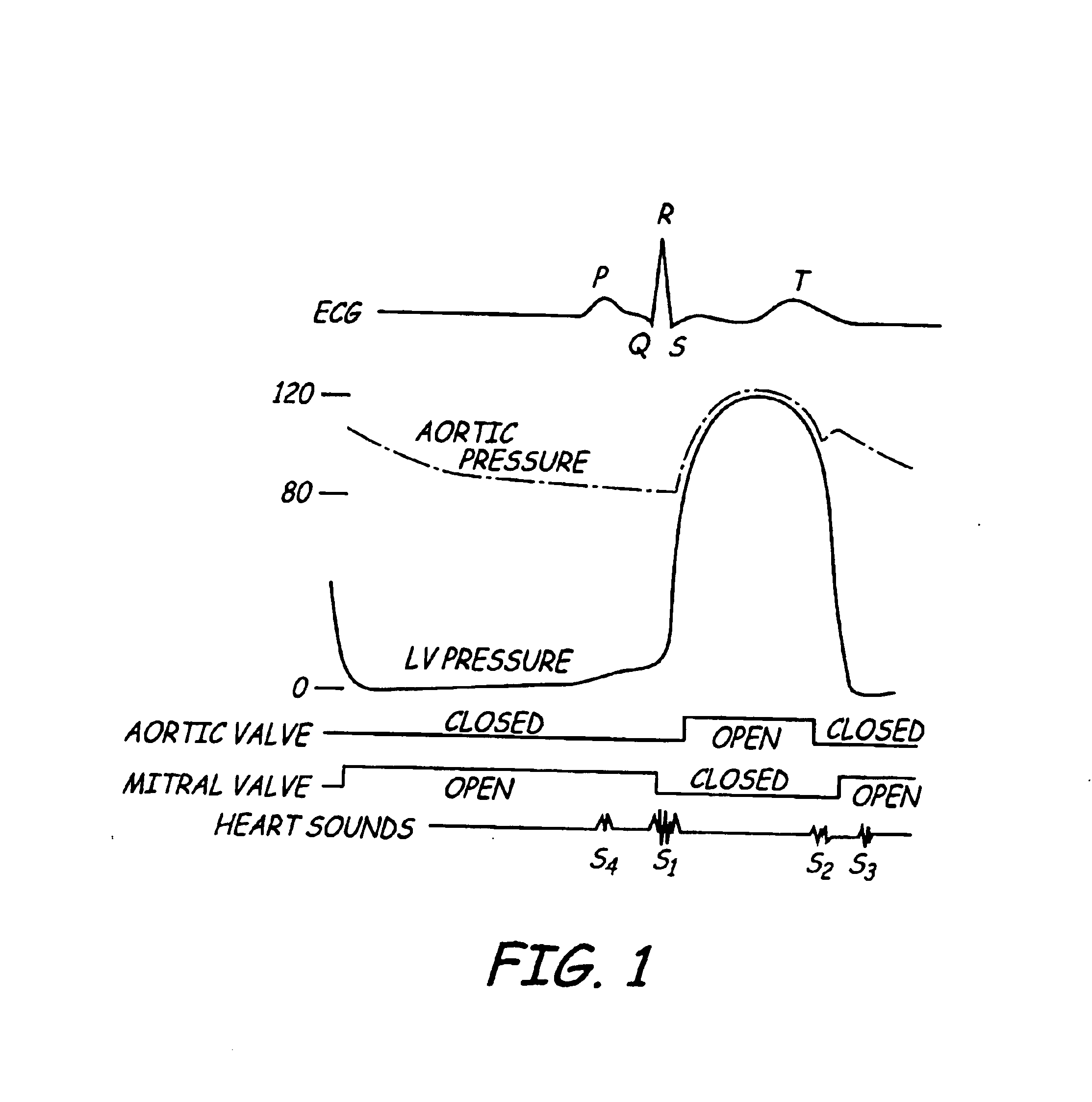
Apparatus and method for chronically monitoring heart sounds for deriving estimated blood pressure
ActiveUS6869404B2Simplified and minimized in sizeElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsRegression analysisT wave
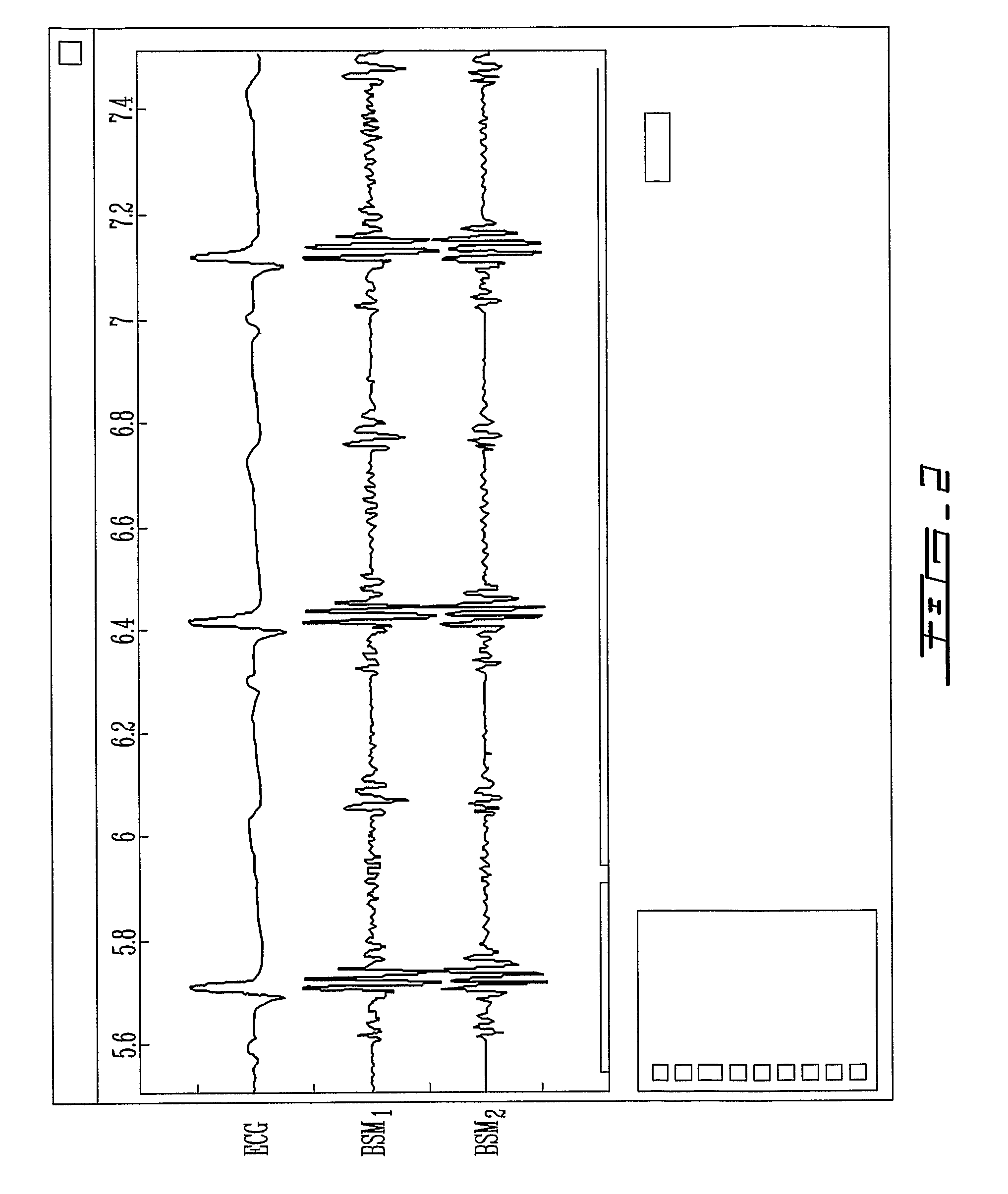
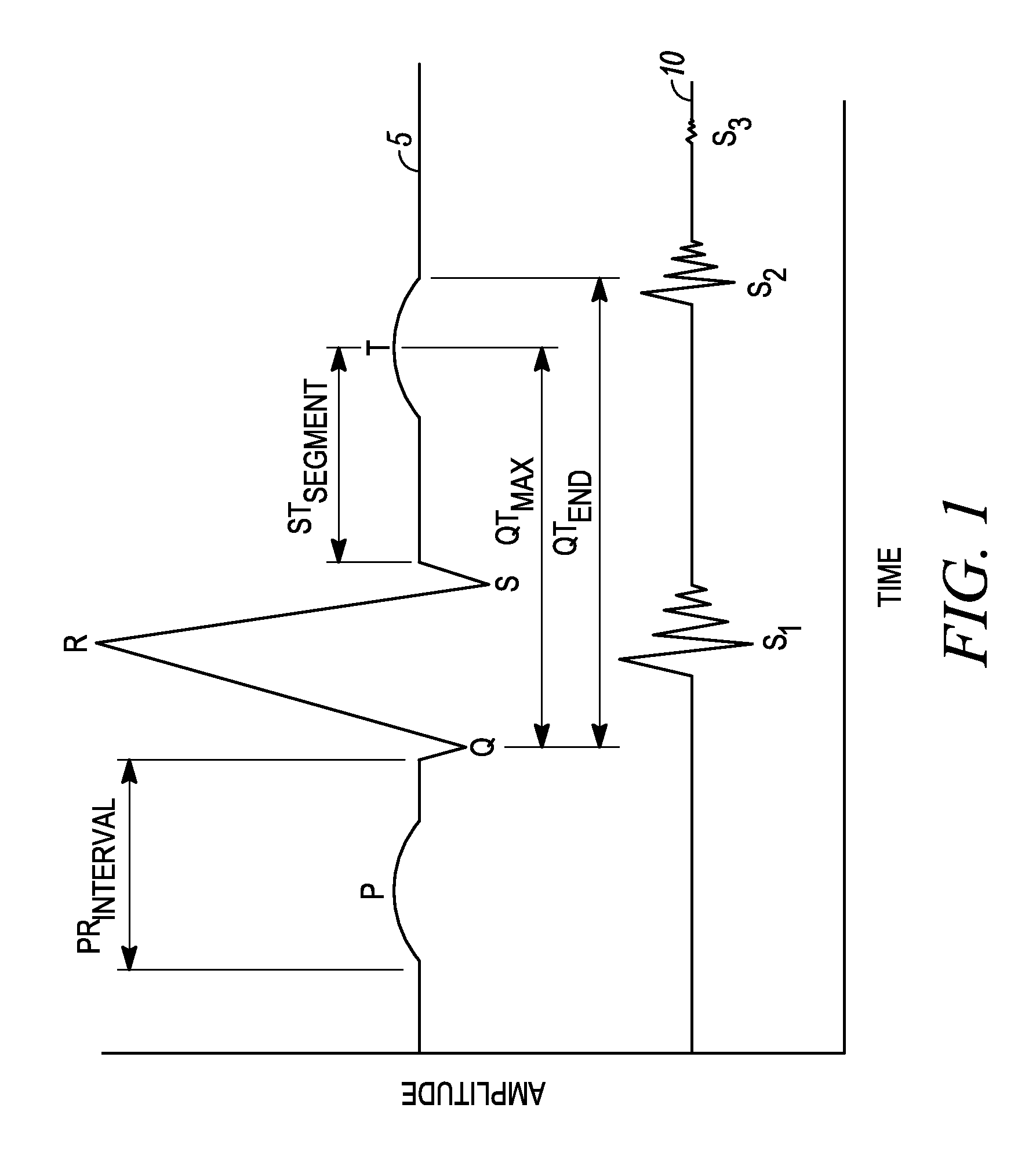
A minimally invasive, implantable heart sound and ECG monitor and associated method for deriving blood pressure from heart sound data. The device is equipped with an acoustical sensor for detecting first and second heart sounds which are sampled and stored during sensing windows following R-wave and T-wave detections, respectively. ECG and heart sound data are stored in a continuous, looping memory, and segments of data are stored in long-term memory upon an automatic or manual data storage triggering event. Estimated blood pressure is calculated based on custom spectral analysis and processing of the first and second heart sounds. A calibration method includes measuring a patient's blood pressure using a standard clinical method and performing regression analysis on multiple spectral variables to identify a set of best fit weighted equations for predicting blood pressure. Concurrent ECG and estimated blood pressure may be displayed for review by a physician.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
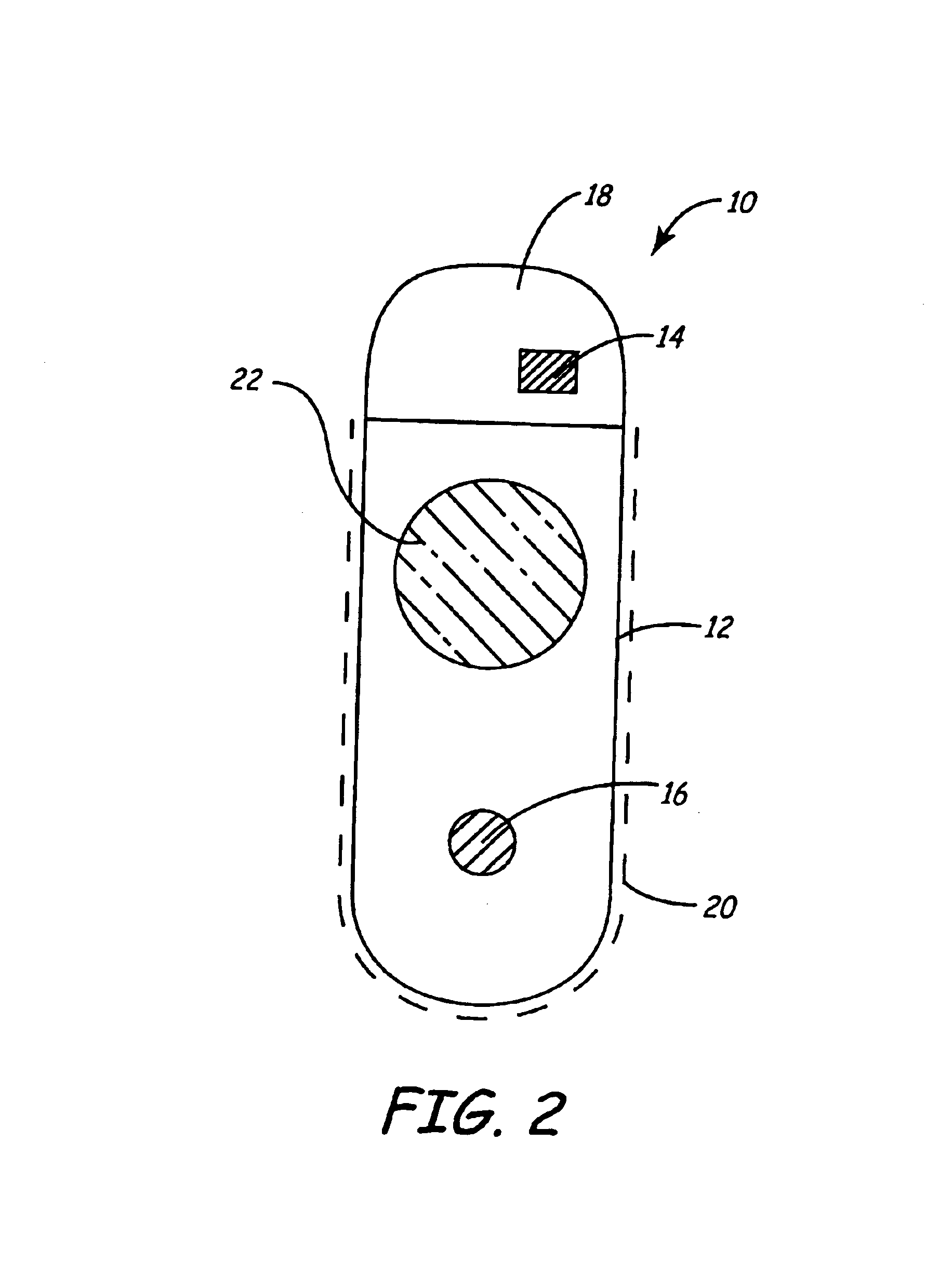
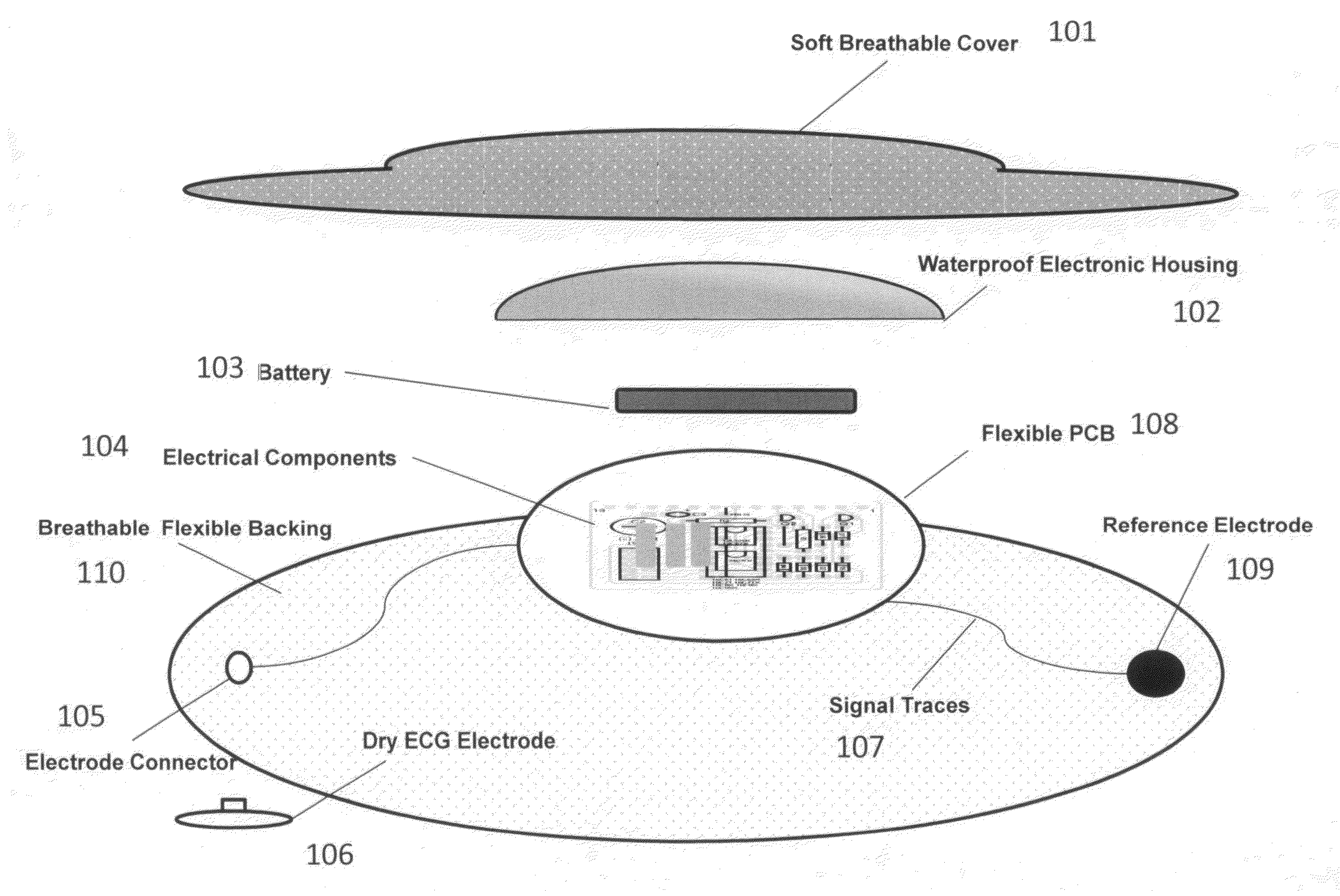
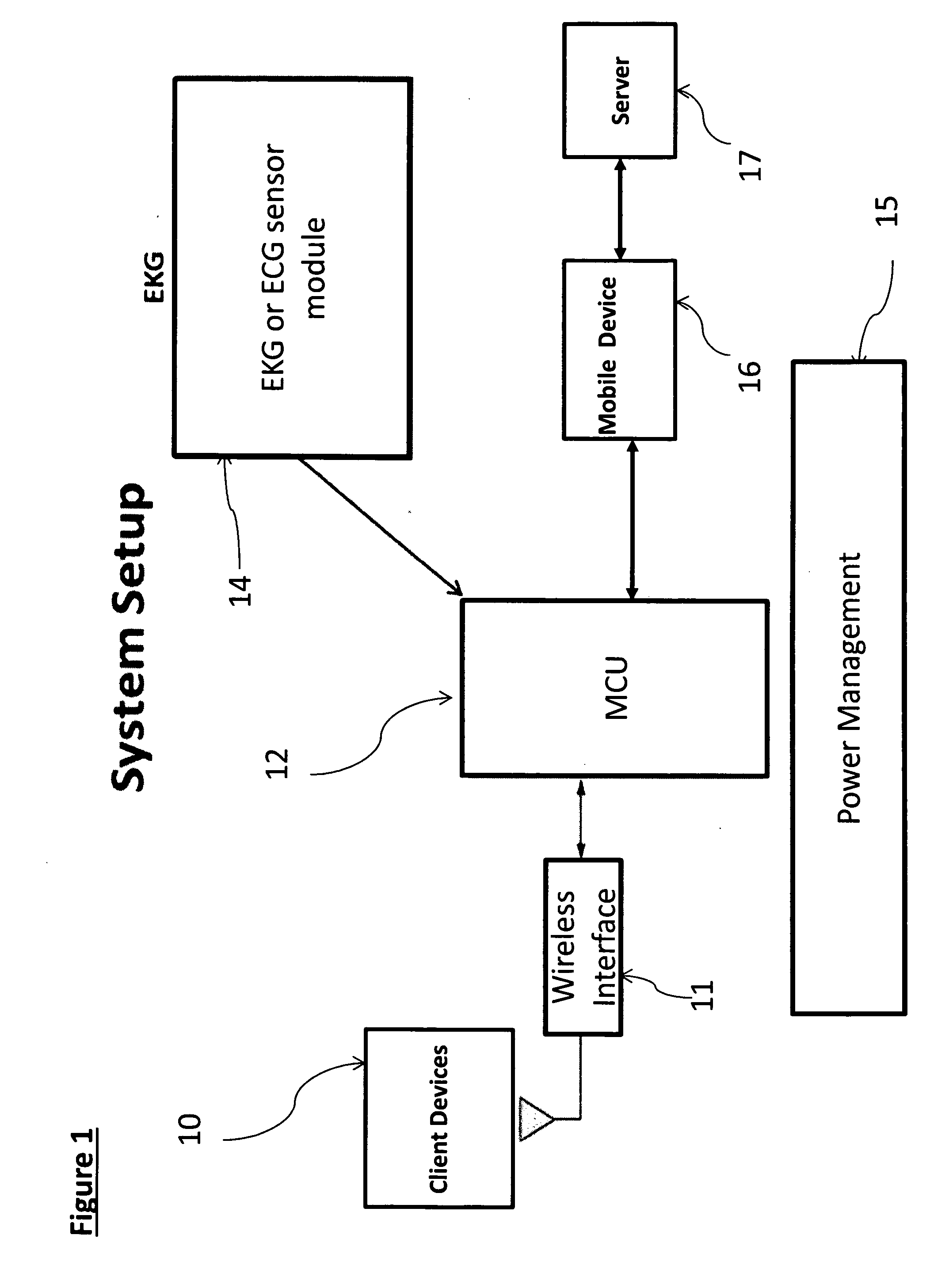
Wearable heart failure monitor patch
InactiveUS20150057512A1ElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationSleep disordered breathingHeart sounds
The invention is directed to a system for acquiring electrical footprint of the heart, electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG), heart sound, heart rate, nasal airflow and pulse oximetry incorporated into a mobile device accessory. The ECG and heart sound signals are conveniently acquired and transmitted to a server via the mobile device, offering accurate heart failure analysis, and sleep disorder breathing indication.
Owner:RIJUVEN
Breathing sound analysis for detection of sleep apnea/popnea events
Apparatus for use detection of apnea includes a microphone mounted in the ear of the patient for detecting breathing sounds and a second external microphone together with an oximetric sensor. A transmitter at the patient compresses and transmits the signals to a remote location where there is provided a detector module for receiving and analyzing the signals to extract data relating to the breathing. The detector uses the entropy or range of the signal to generate an estimate of air flow while extracting extraneous snoring and heart sounds and to analyze the estimate of air flow using Otsu's threshold to detect periods of apnea and / or hypopnea. A display provides data of the detected apnea / hypopnea episodes and related information for a clinician.
Owner:TR TECH
Determining a patient's posture from mechanical vibrations of the heart
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
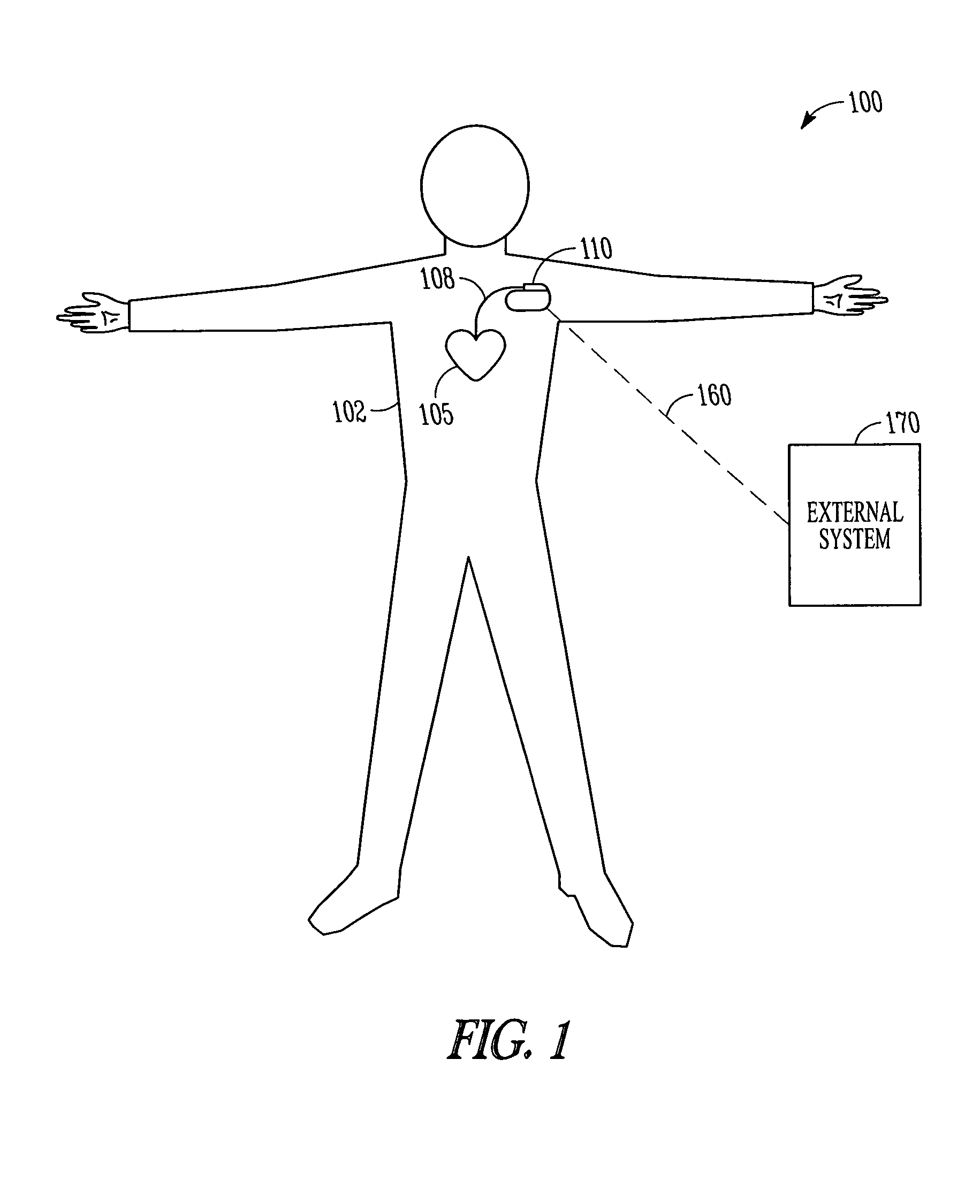
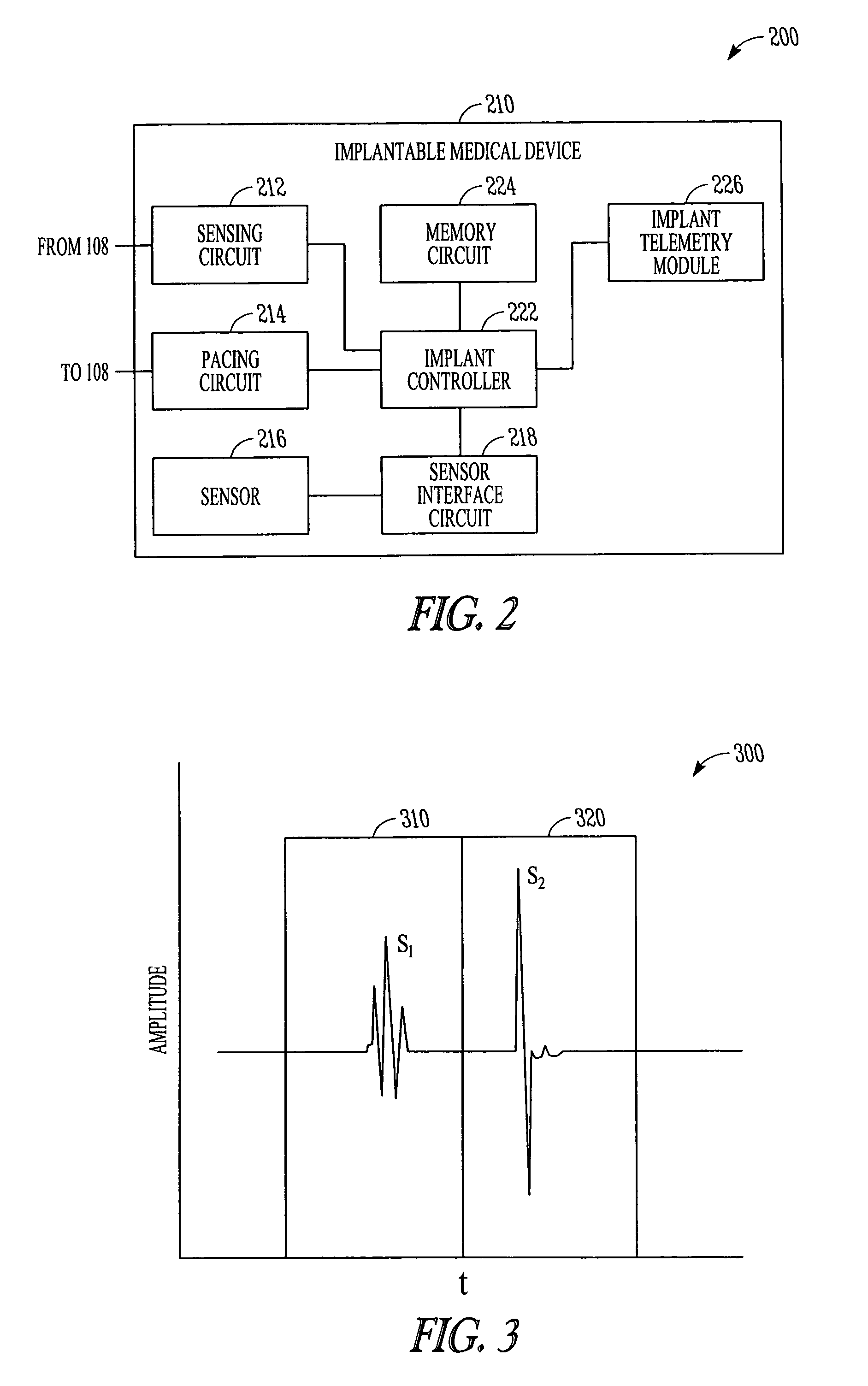
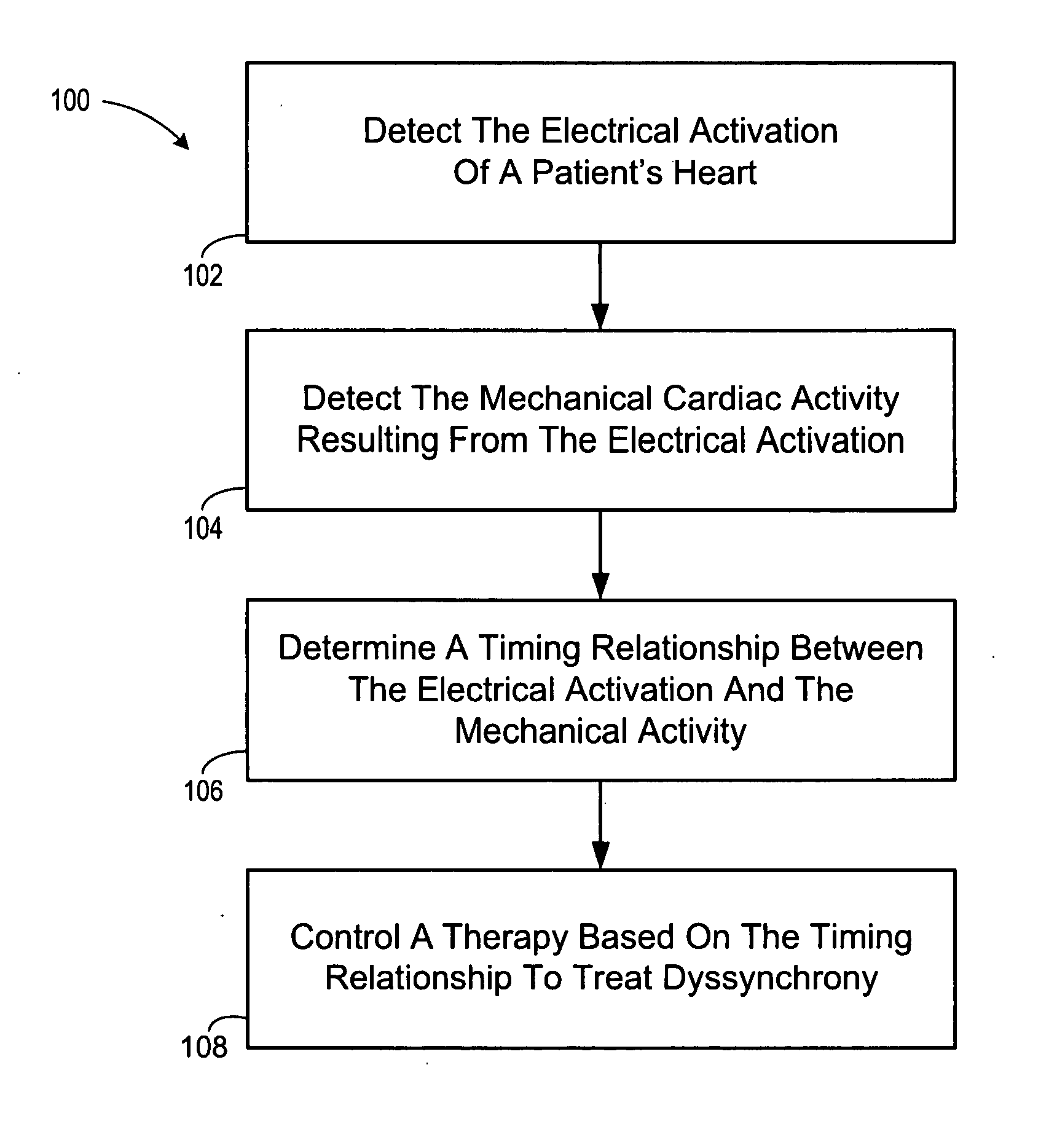
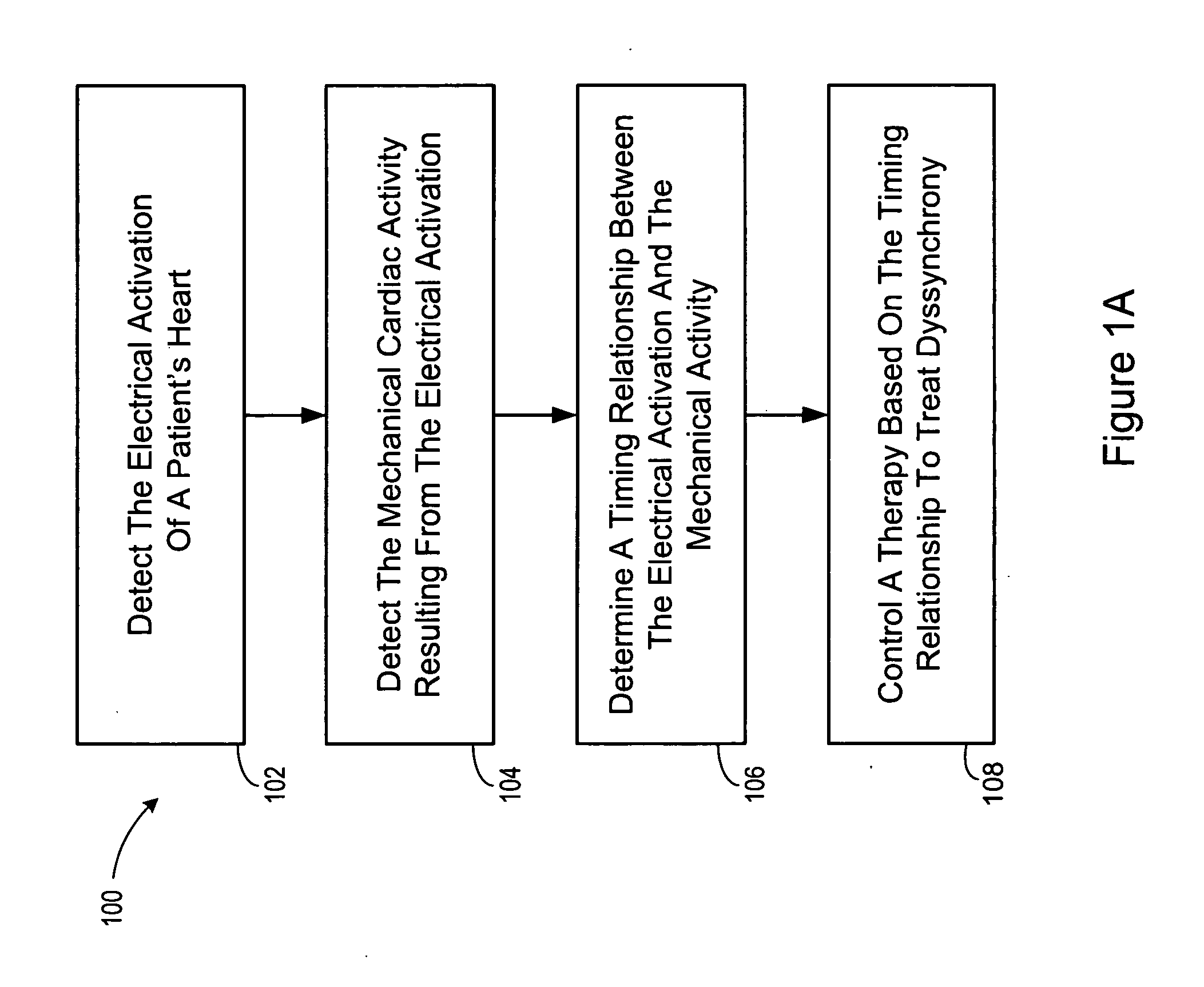
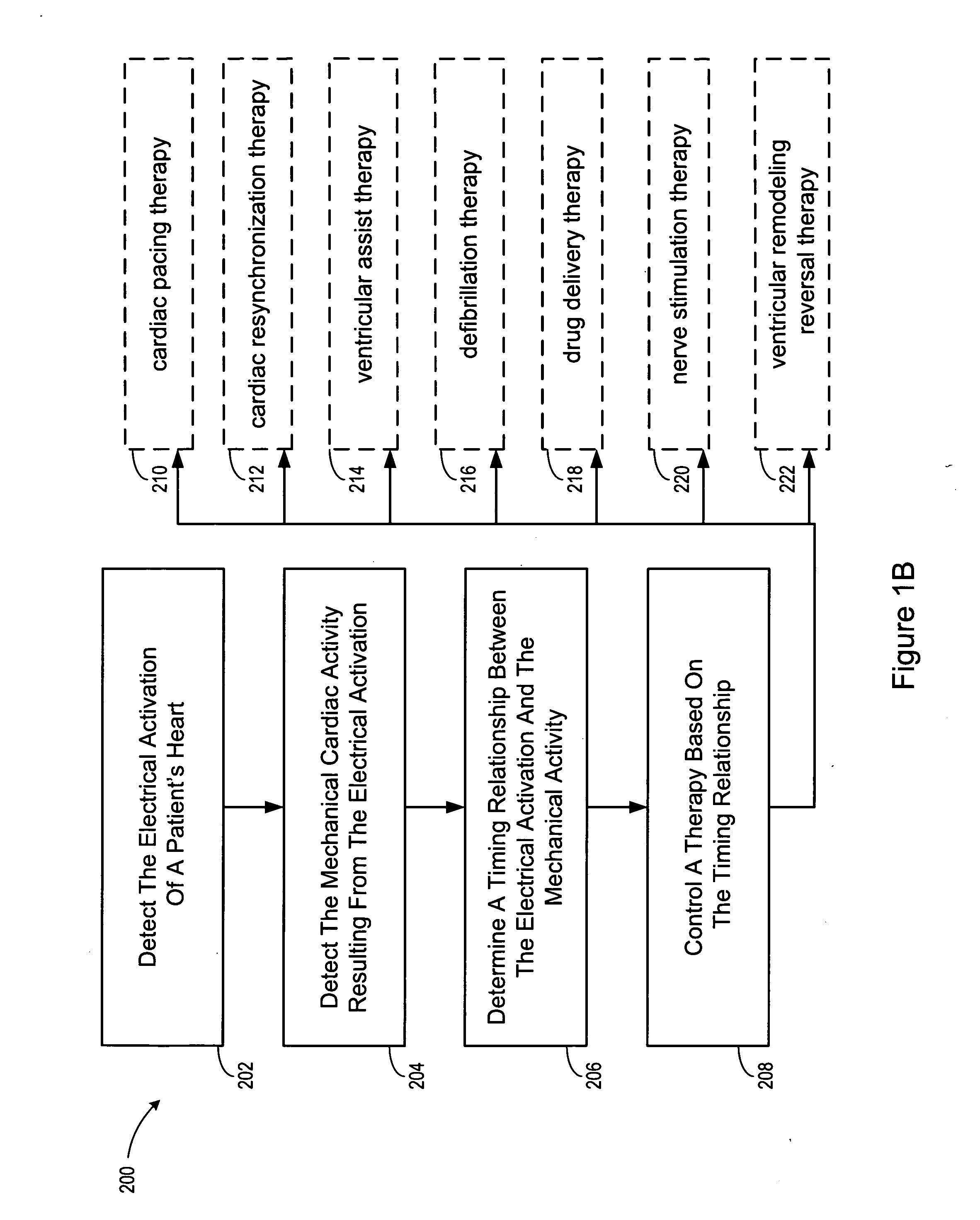
Method and apparatus for controlling cardiac therapy based on electromechanical timing
Devices and methods for therapy control based on electromechanical timing involve detecting electrical activation of a patient's heart, and detecting mechanical cardiac activity resulting from the electrical activation. A timing relationship is determined between the electrical activation and the mechanical activity. A therapy is controlled based on the timing relationship. The therapy may improve intraventricular dyssynchrony of the patient's heart, or treat at least one of diastolic and systolic dysfunction and / or dyssynchrony of the patient's heart, for example. Electrical activation may be detected by sensing delivery of an electrical stimulation pulse to the heart or sensing intrinsic depolarization of the patient's heart. Mechanical activity may be detected by sensing heart sounds, a change in one or more of left ventricular impedance, ventricular pressure, right ventricular pressure, left atrial pressure, right atrial pressure, systemic arterial pressure and pulmonary artery pressure.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
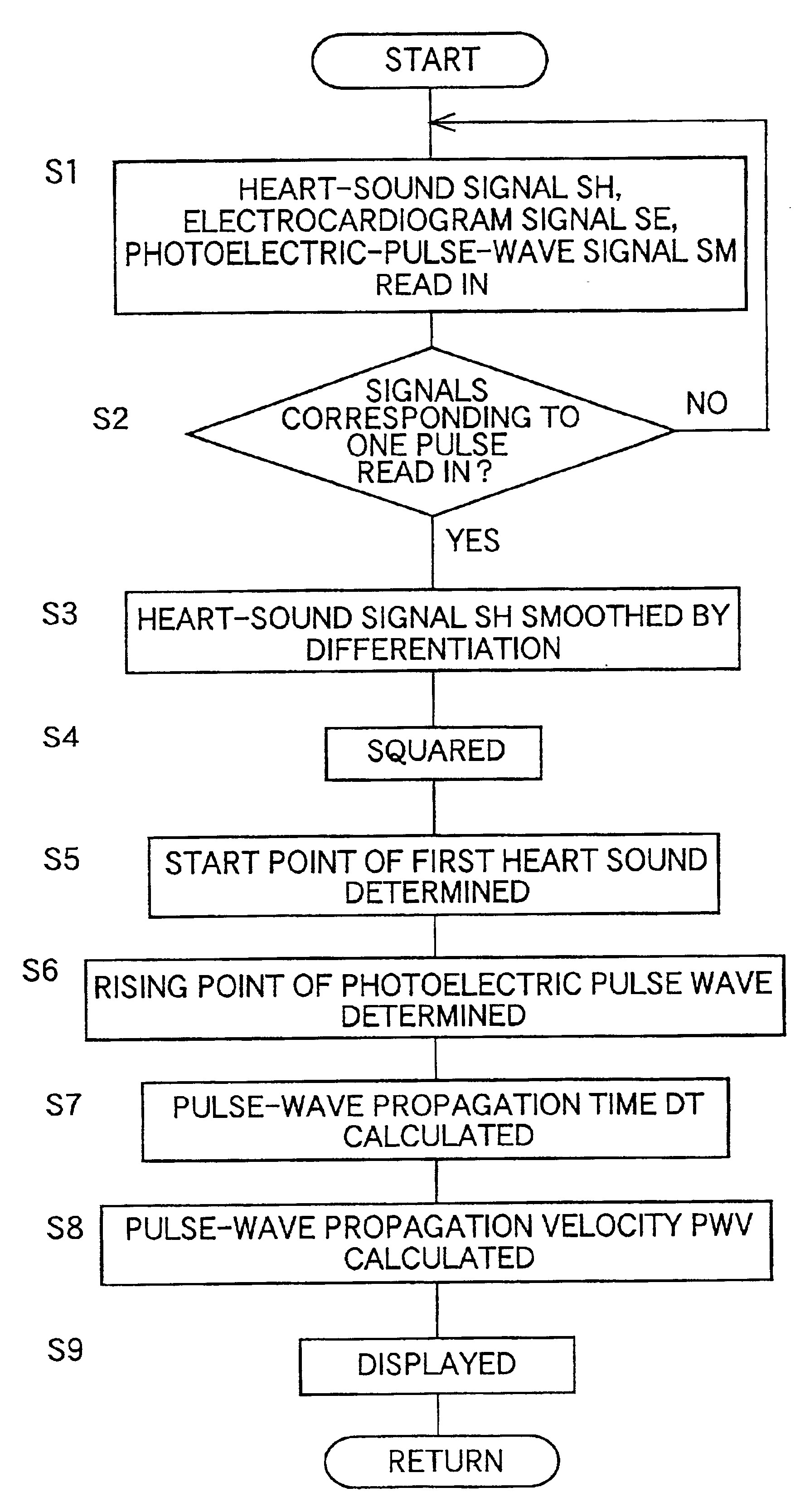
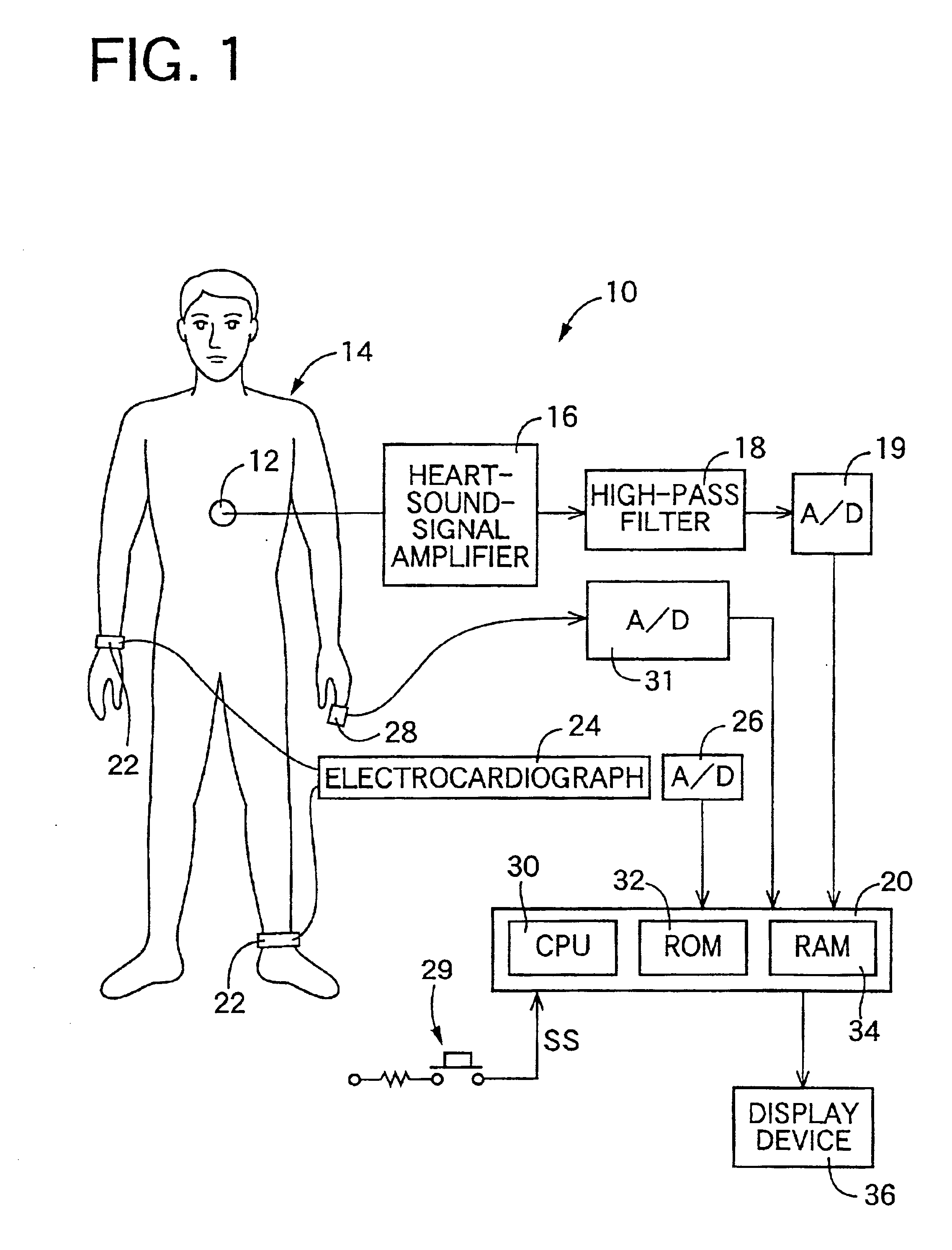
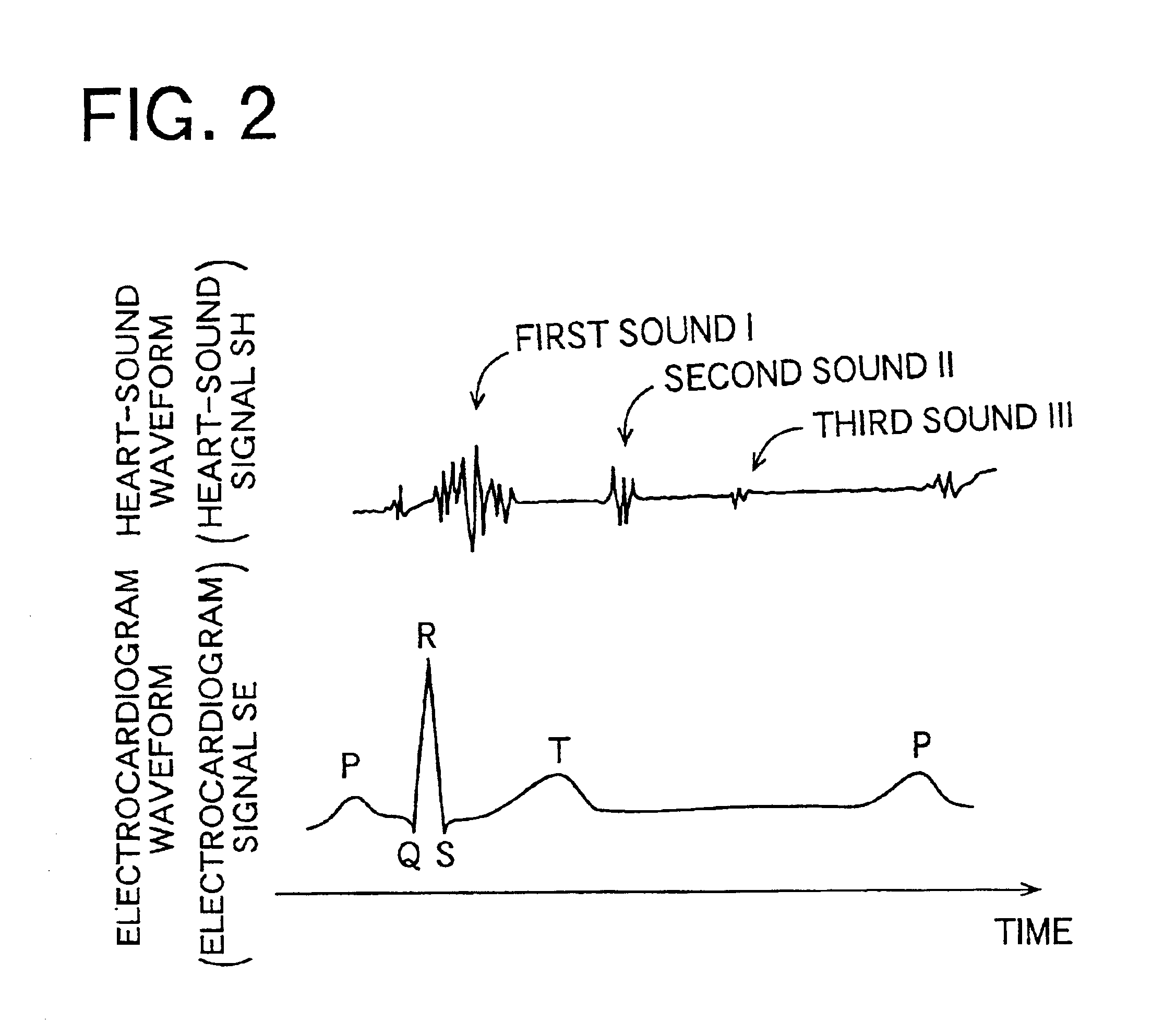
Heart-sound detecting apparatus and pulse-wave-propagation-velocity-relating-information obtaining system using the heart-sound detecting apparatus
InactiveUS6845263B2Accurately determineAccurately determinedElectrocardiographyStethoscopeBiological bodyHeart sounds
A heart-sound detecting apparatus, including: a heart-sound microphone which detects a plurality of heart sounds produced by a heart of a living subject and outputs a heart-sound signal representative of the detected heart sounds; a smoothing device for smoothing, by differentiation, a waveform of the heart-sound signal output from the heart-sound microphone; a squaring device for squaring an amplitude of the smoothed waveform with respect to a base line of the heart-sound signal; and a start-point determining device for determining a start point of a first heart sound I as one of the detected heart sounds, based on that the squared amplitude is greater than a prescribed threshold value.
Owner:OMRON HEALTHCARE CO LTD
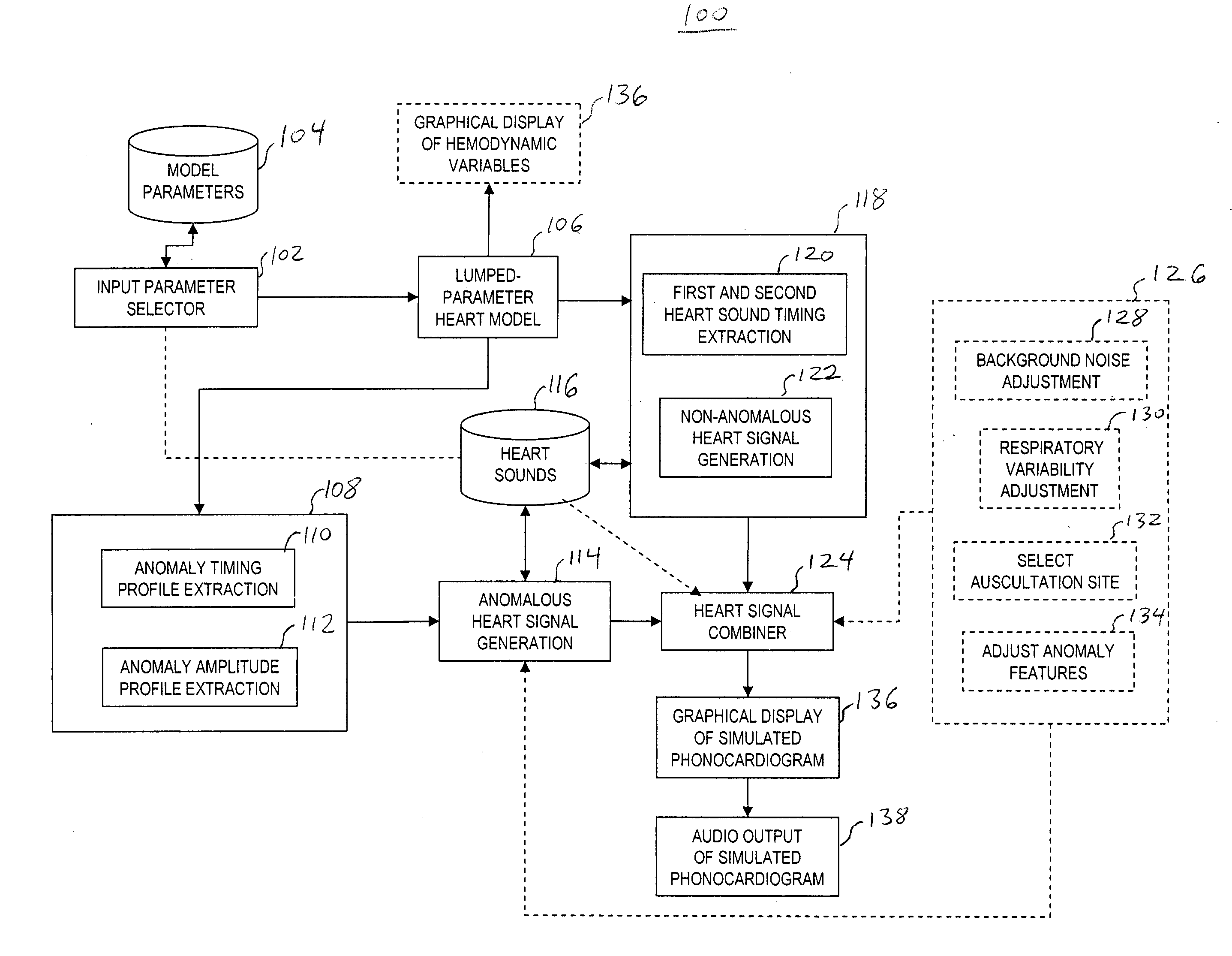
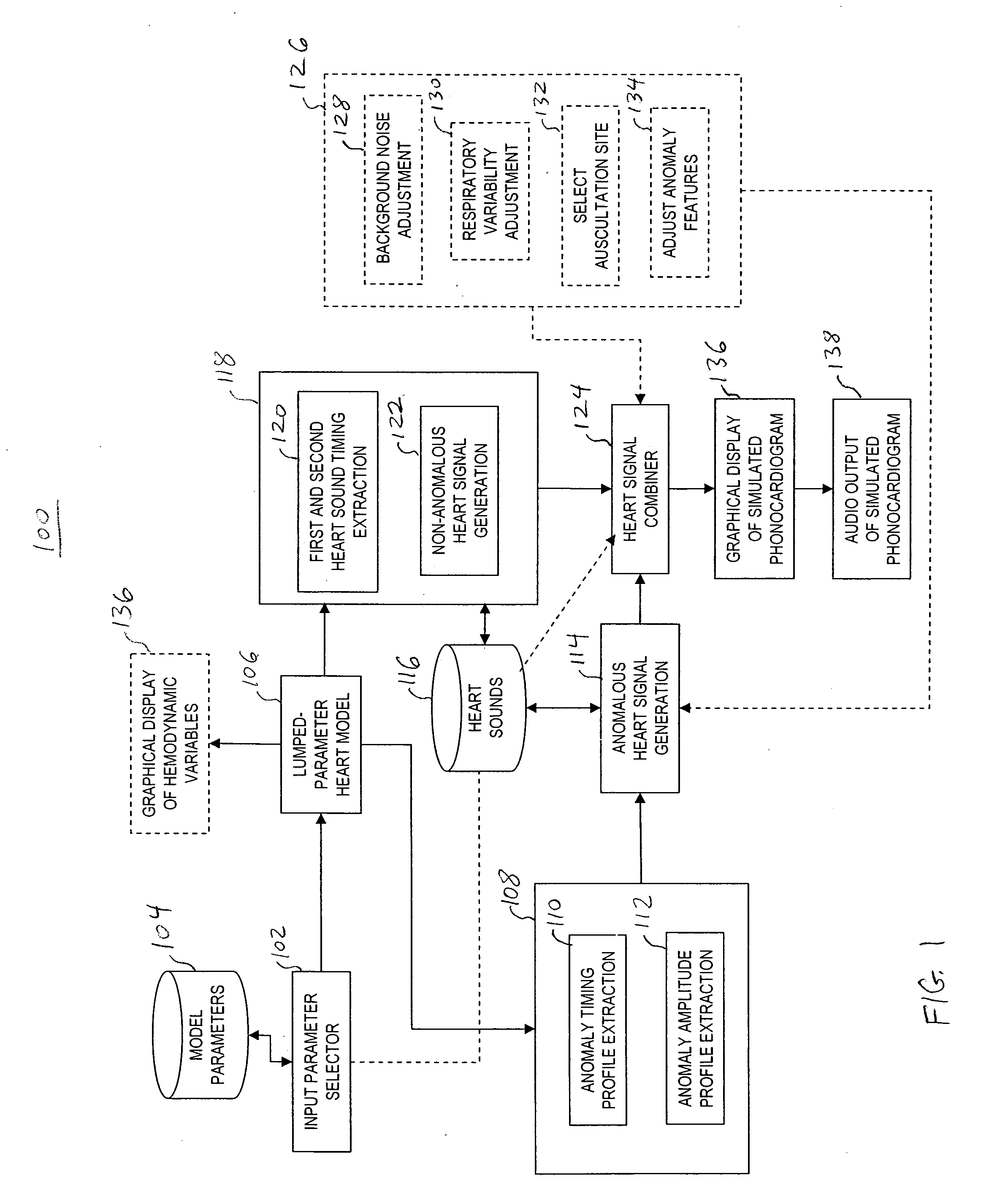
Automatic generation of heart sounds and murmurs using a lumped-parameter recirculating pressure-flow model for the left heart
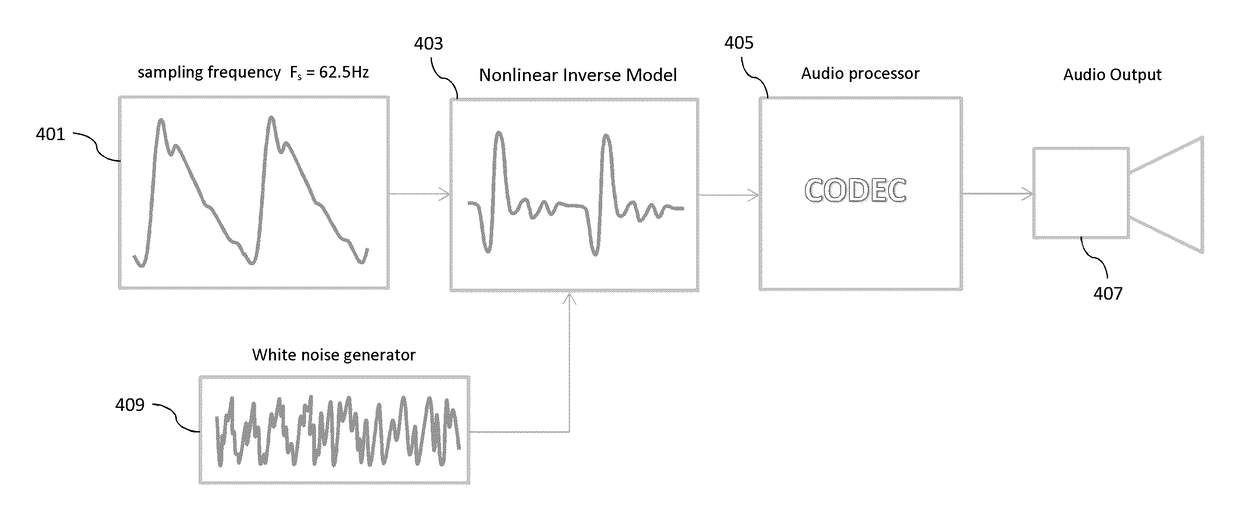
Methods and systems for simulating a phonocardiogram (PCG) signal that includes an anomalous condition are provided. The method generates pressure and flow signals from a lumped-parameter heart model responsive to anomaly parameters. The anomaly parameters represent the anomalous condition. A timing profile or the timing profile and an amplitude profile are extracted from at least one of the generated pressure and flow signals. An anomalous signal is generated using the anomaly parameters and the extracted timing profile or timing profile and amplitude profile. The anomalous signal is time-aligned and combined with a predetermined non-anomalous signal to represent the PCG signal.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Breathing sound analysis for detection of sleep apnea/popnea events
ActiveUS20080243014A1Cancellation effectAuscultation instrumentsMedical automated diagnosisHypopneaRelevant information
Apparatus for use detection of apnea includes a microphone mounted in the ear of the patient for detecting breathing sounds and a second external microphone together with an oximetric sensor. A transmitter at the patient compresses and transmits the signals to a remote location where there is provided a detector module for receiving and analyzing the signals to extract data relating to the breathing. The detector uses the entropy or range of the signal to generate an estimate of air flow while extracting extraneous snoring and heart sounds and to analyze the estimate of air flow using Otsu's threshold to detect periods of apnea and / or hypopnea. A display provides data of the detected apnea / hypopnea episodes and related information for a clinician.
Owner:TR TECH
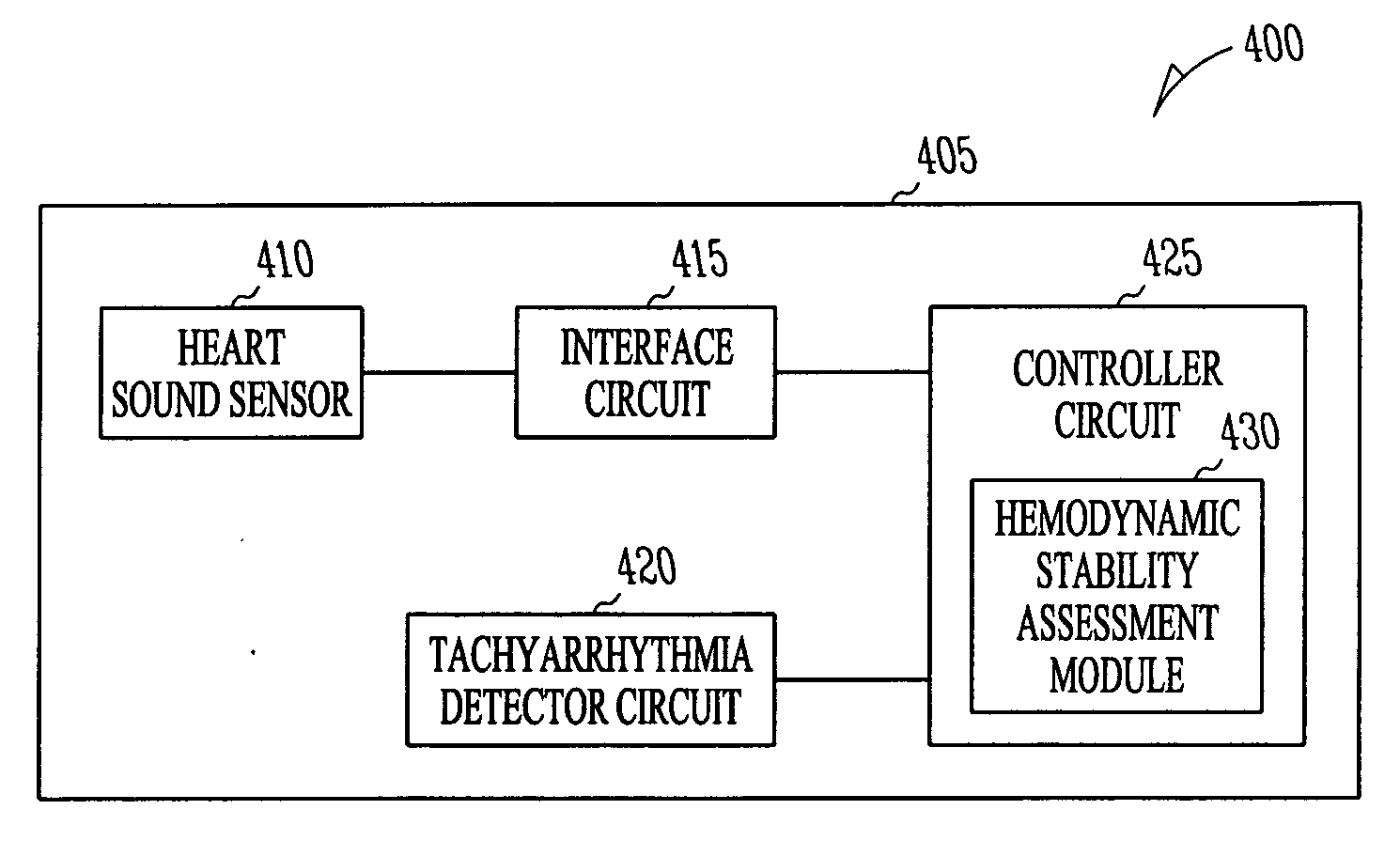
Hemodynamic stability assessment based on heart sounds
ActiveUS20070239218A1Measurement stabilityStethoscopeCatheterVentricular TachyarrhythmiasHeart sounds
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes an implantable sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of mechanical activity of a heart of a subject and a controller circuit coupled to the sensor. The IMD also includes a heart sound sensor interface circuit to produce a heart sound signal, a tachyarrhythmia detector, and a controller circuit. The controller circuit includes a hemodynamic stability assessment module configured to determine that at least one episode of ventricular tachyarrhythmia is detected in a subject and obtain a measurement of hemodynamic stability of the ventricular tachyarrhythmia from the heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method for correction of posture dependence on heart sounds
A system to monitor heart sounds. The system comprises an implantable heart sound sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of at least one heart sound, a heart sound sensor interface circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor to produce a heart sound signal, an implantable posture sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of a patient's posture, and a controller circuit, coupled to the heart sound sensor interface circuit and the posture circuit. The controller circuit is operable to measure at least one heart sound in correspondence with at least one sensed patient posture.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
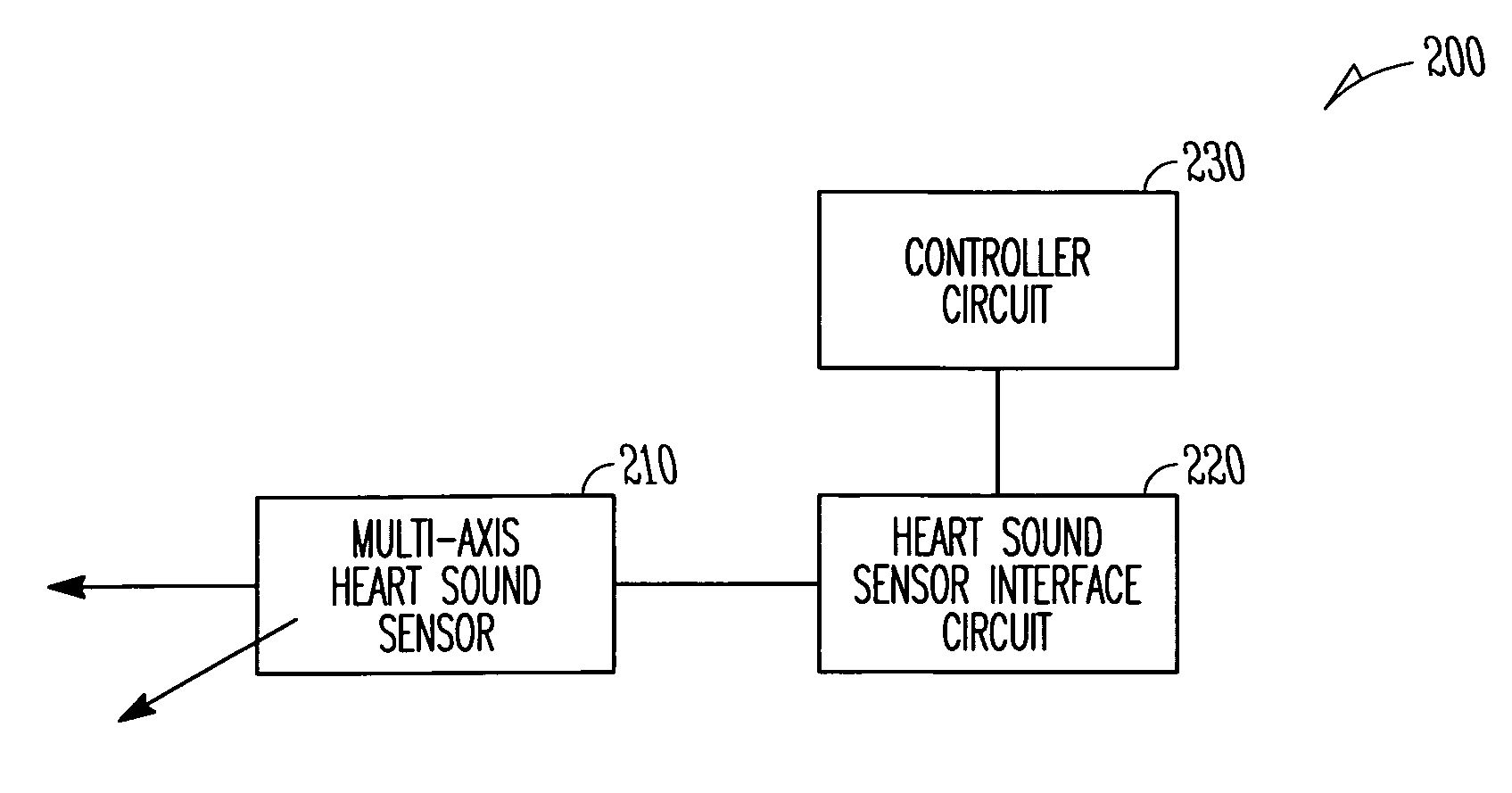
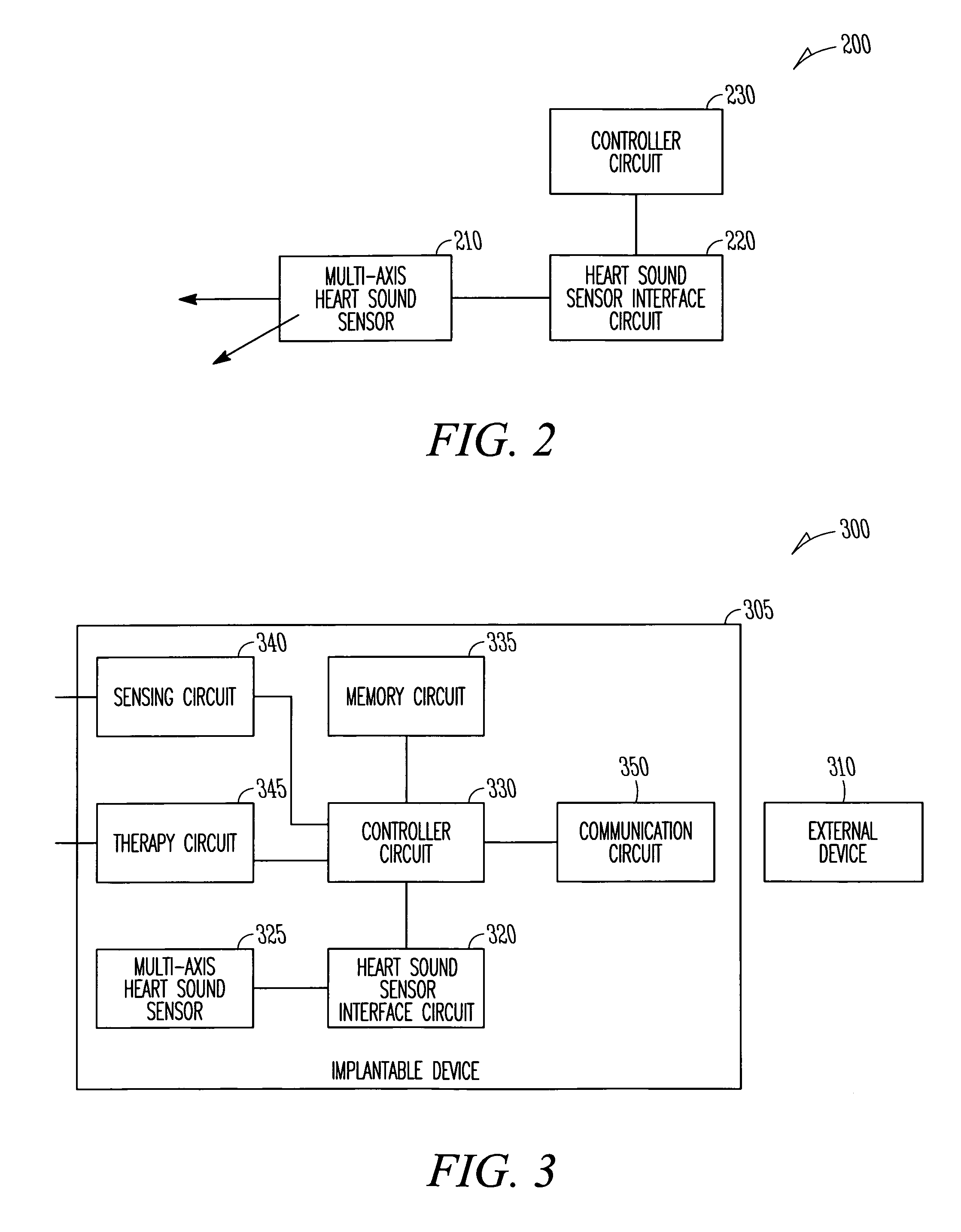
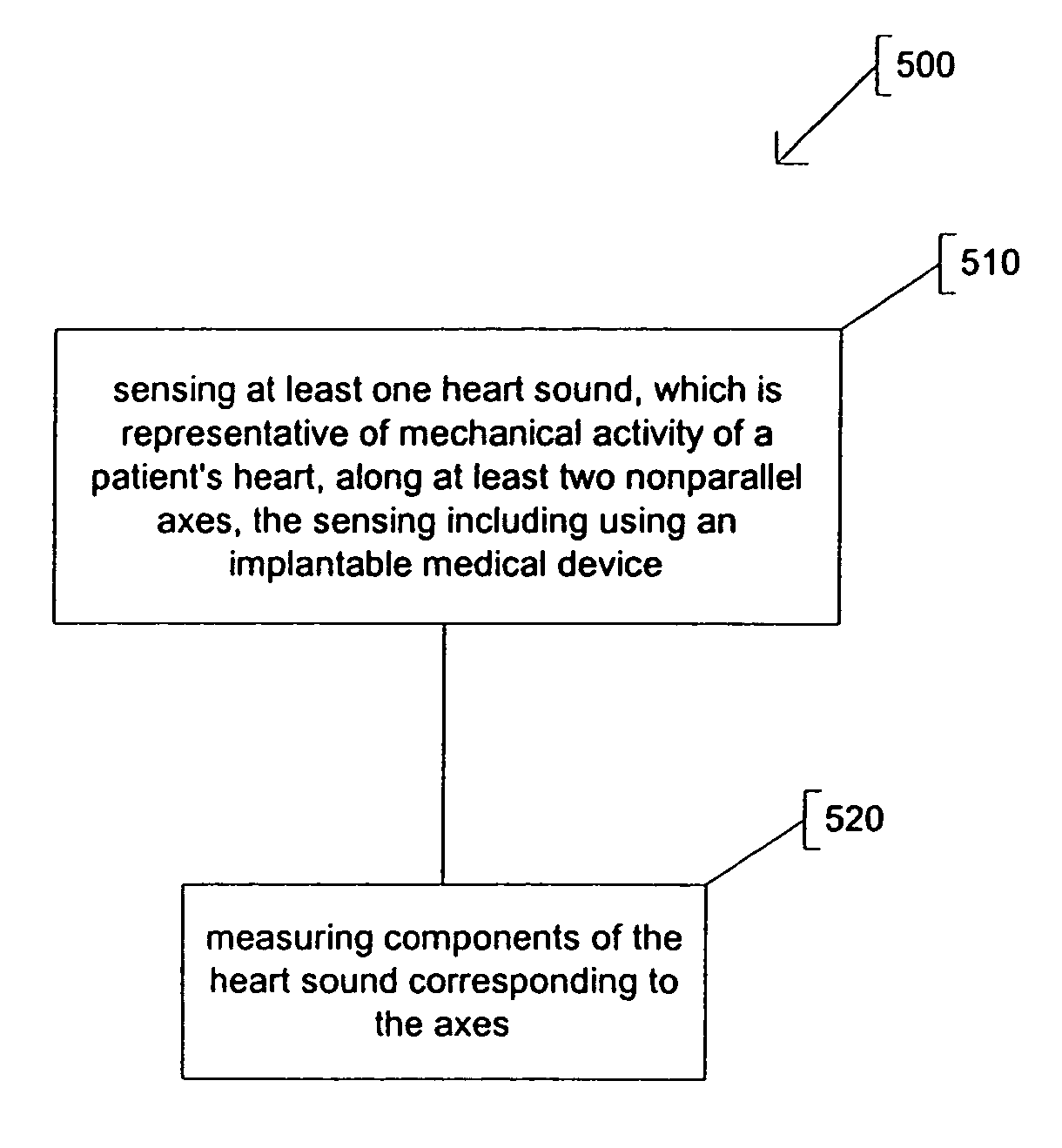
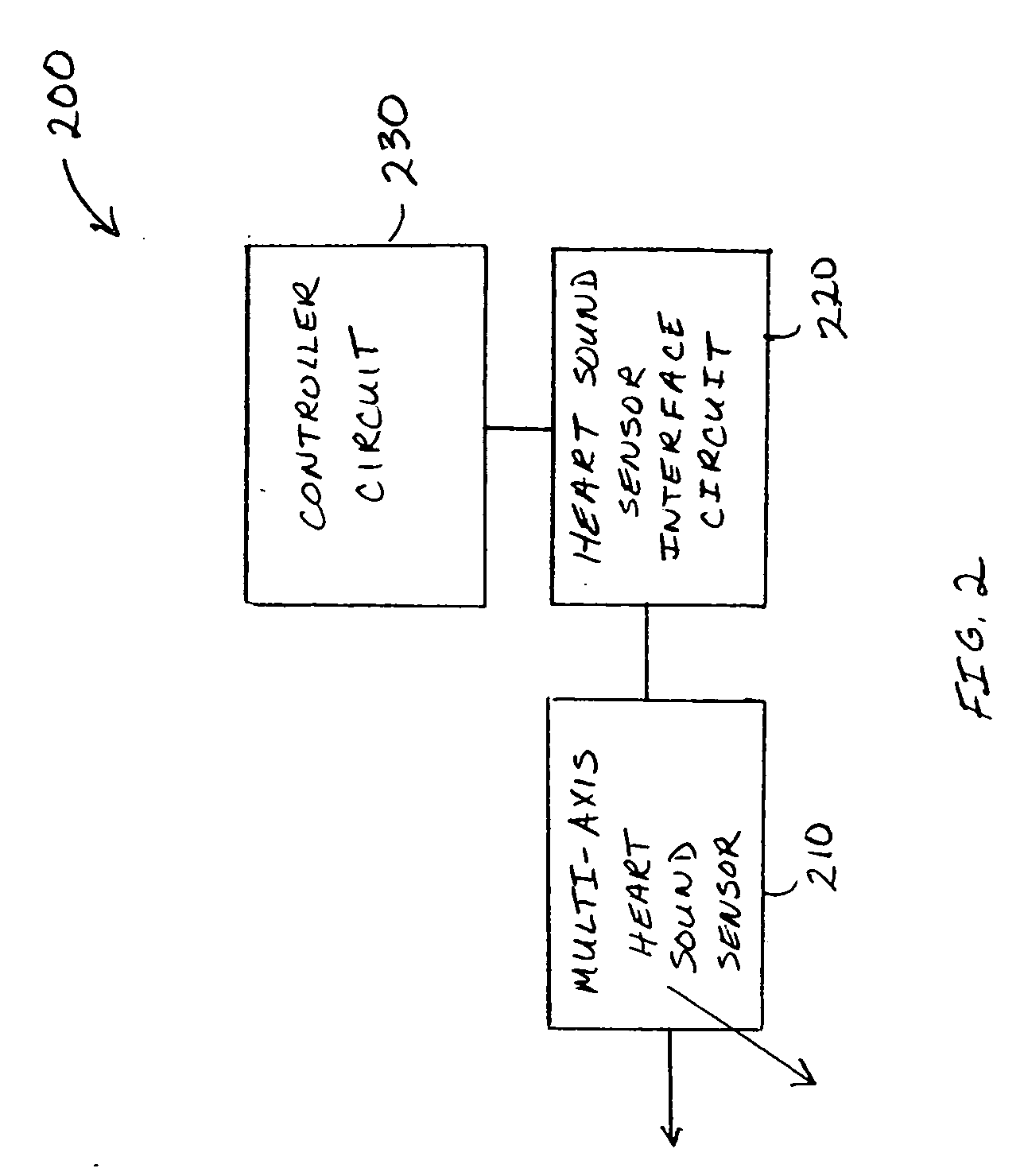
Systems and methods for multi-axis cardiac vibration measurements
A system to monitor heart sounds, such as to detect a worsening condition of heart failure decompensation. The system comprises a medical device that includes an implantable multi-axis heart sound sensor, operable to produce, for each of at least two nonparallel axes, an electrical signal representative of at least one heart sound, the heart sound associated with mechanical activity of a patient's heart. The device further includes a controller circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor. The controller circuit measures components of the heart sound that respectively correspond to each of the axes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Breathing sound analysis for estimation of airlow rate
InactiveUS20080243017A1Cancellation effectAuscultation instrumentsMedical automated diagnosisHypopneaRelevant information
Apparatus for use detection of apnea includes a microphone mounted in the ear of the patient for detecting breathing sounds and a second external microphone together with an oximetric sensor. A transmitter at the patient compresses and transmits the signals to a remote location where there is provided a detector module for receiving and analyzing the signals to extract data relating to the breathing. The detector uses the entropy or range of the signal to generate an estimate of air flow while extracting extraneous snoring and heart sounds and to analyze the estimate of air flow using Otsu's threshold to detect periods of apnea and / or hypopnea. A display provides data of the detected apnea / hypopnea episodes and related information for a clinician.
Owner:TR TECH
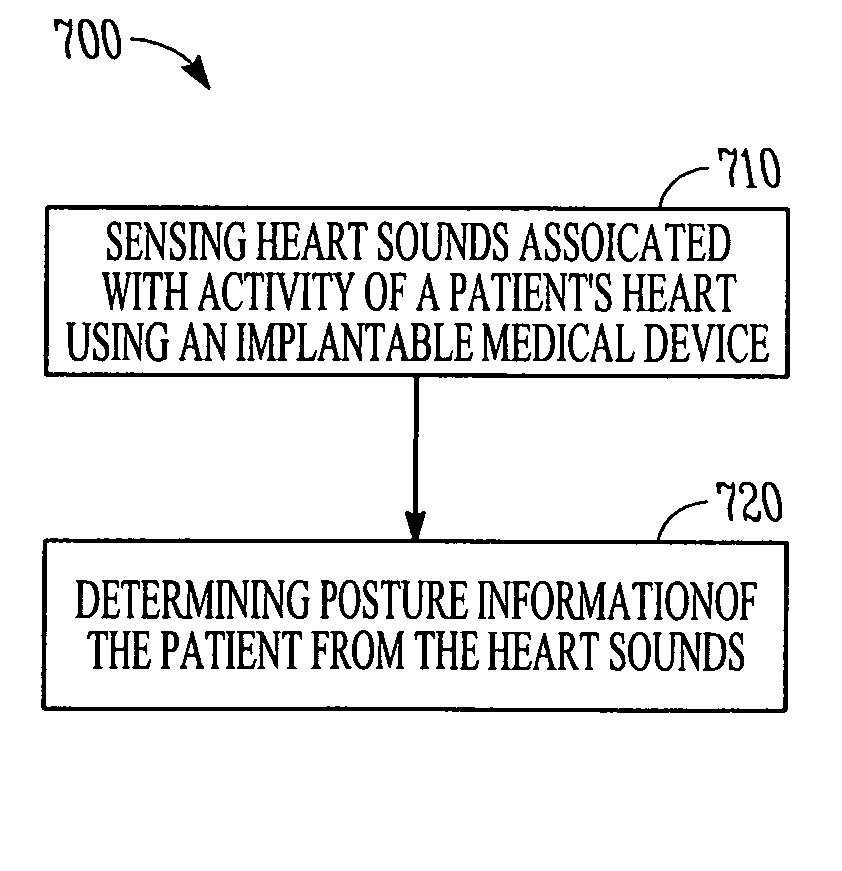
Determining a patient's posture from mechanical vibrations of the heart
A system for determining a patient's posture by monitoring heart sounds. The system comprises an implantable medical device that includes a sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of heart sounds, a sensor interface circuit coupled to the sensor to produce a heart sound signal, and a controller circuit coupled to the sensor interface circuit. The heart sounds are associated with mechanical activity of a patient's heart and the controller circuit is operable to detect a posture of the patient from a heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
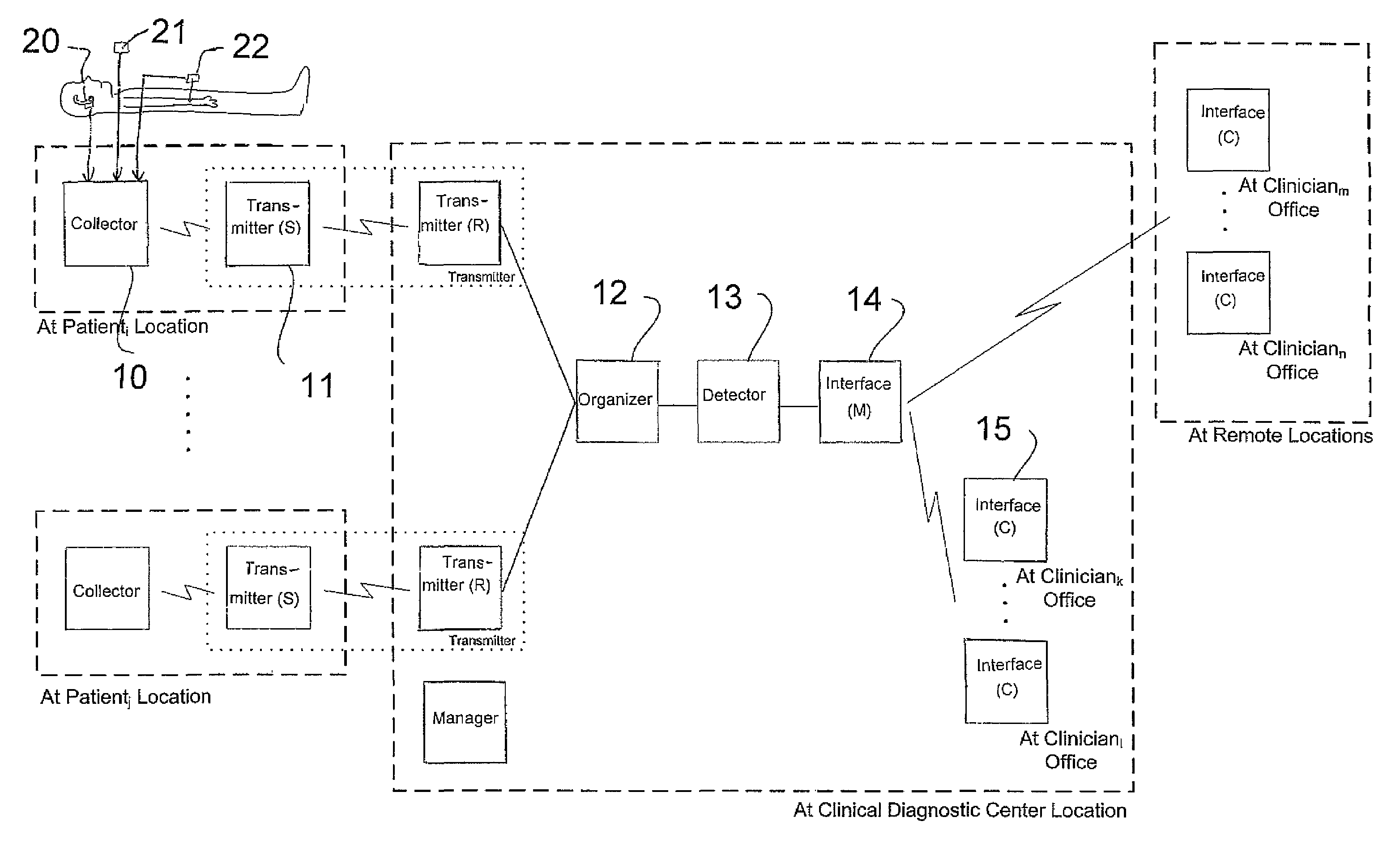
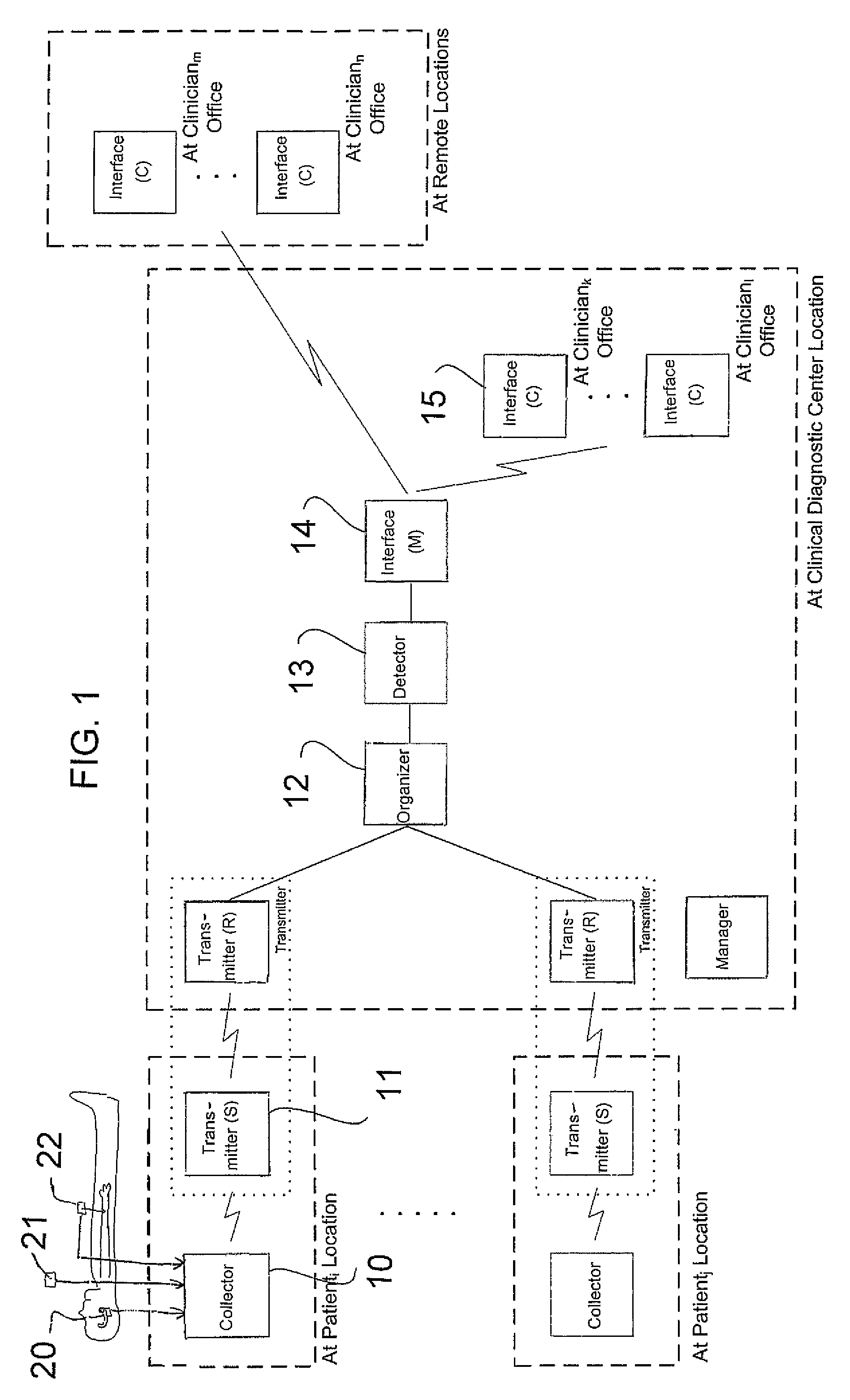
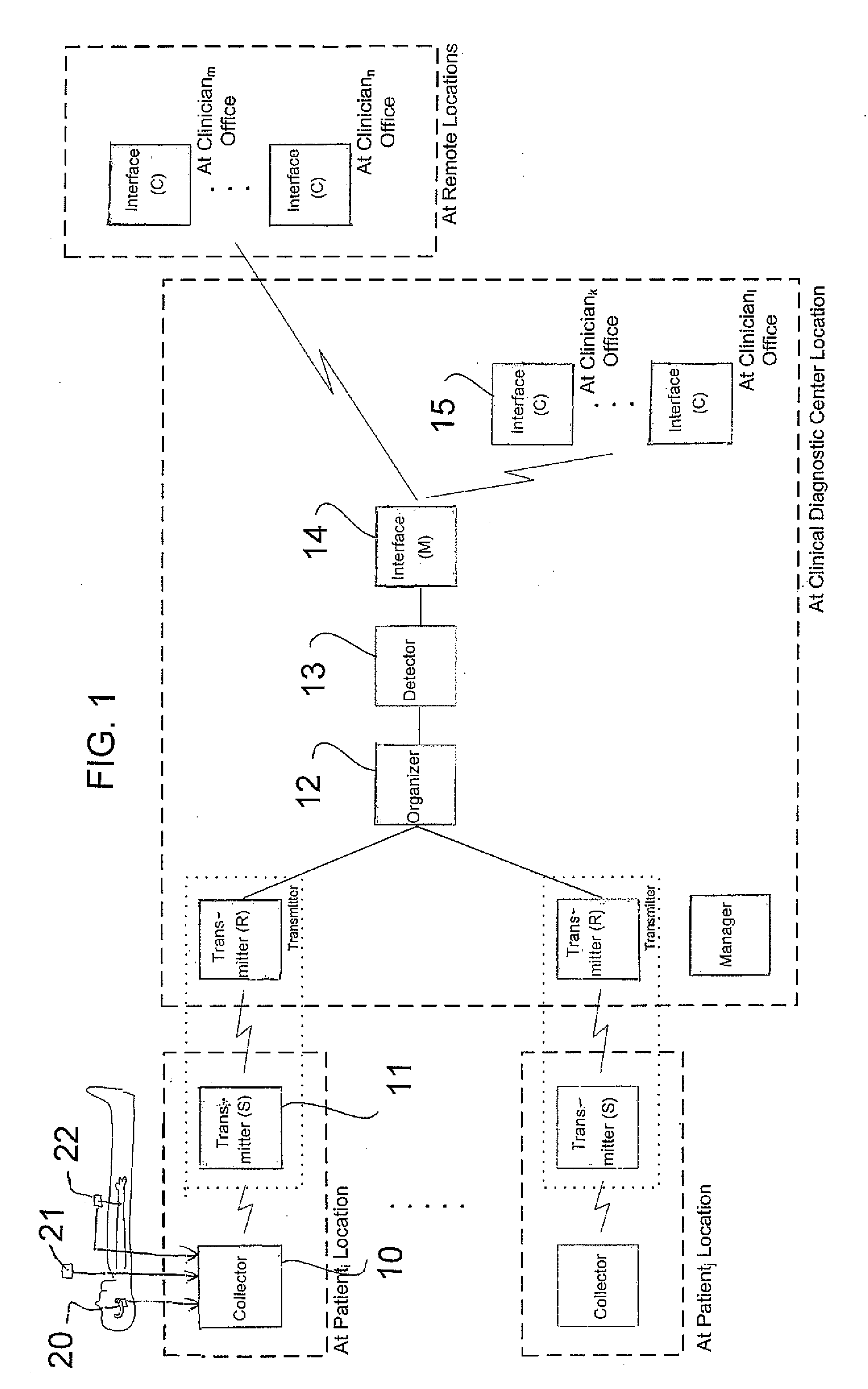
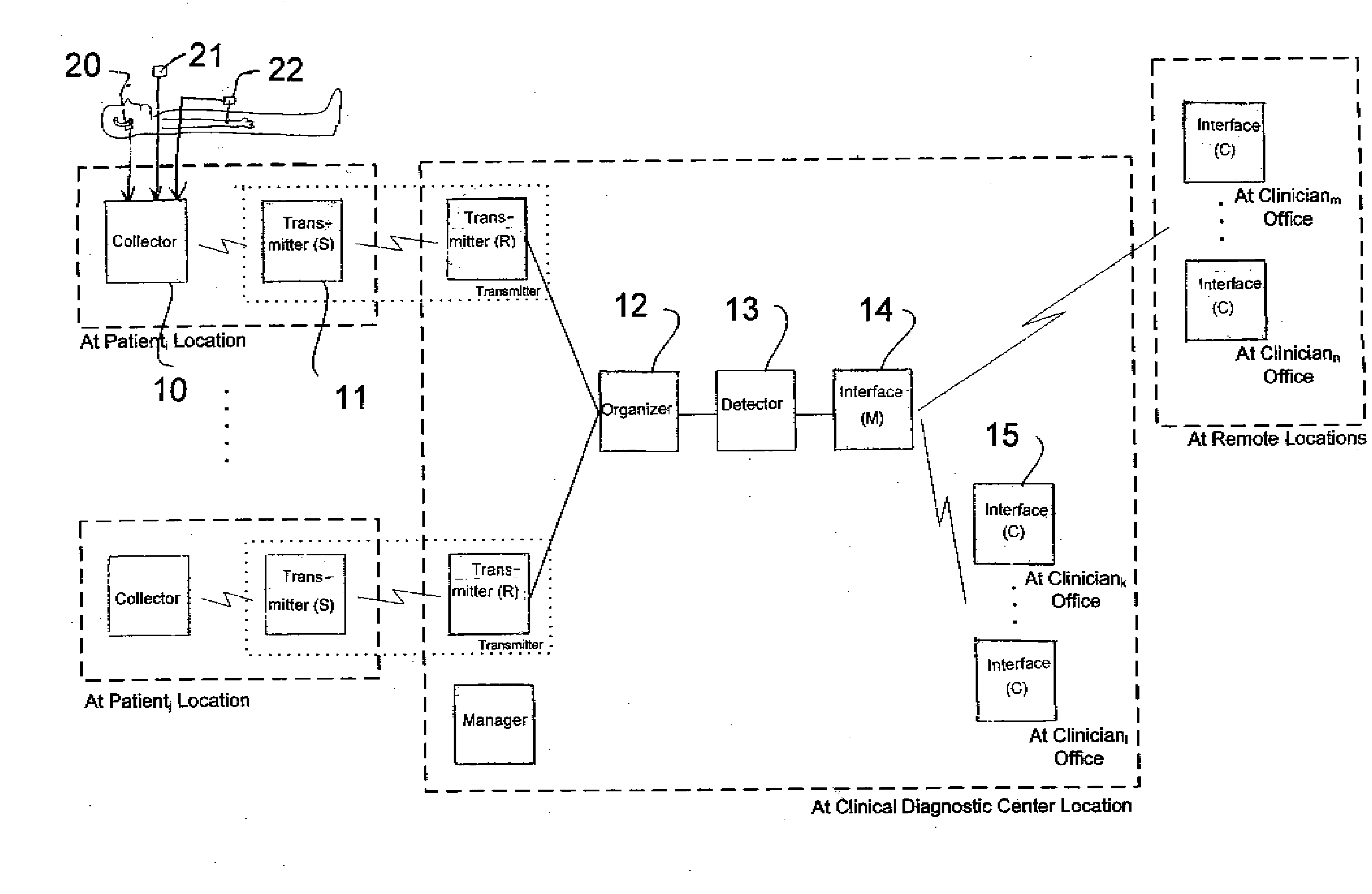
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring Body Temperature, Respiration, Heart Sound, Swallowing, and Medical Inquiring
InactiveUS20090024004A1Reduce mortalityMaintain qualityAuscultation instrumentsMedical automated diagnosisMedicineDisplay device
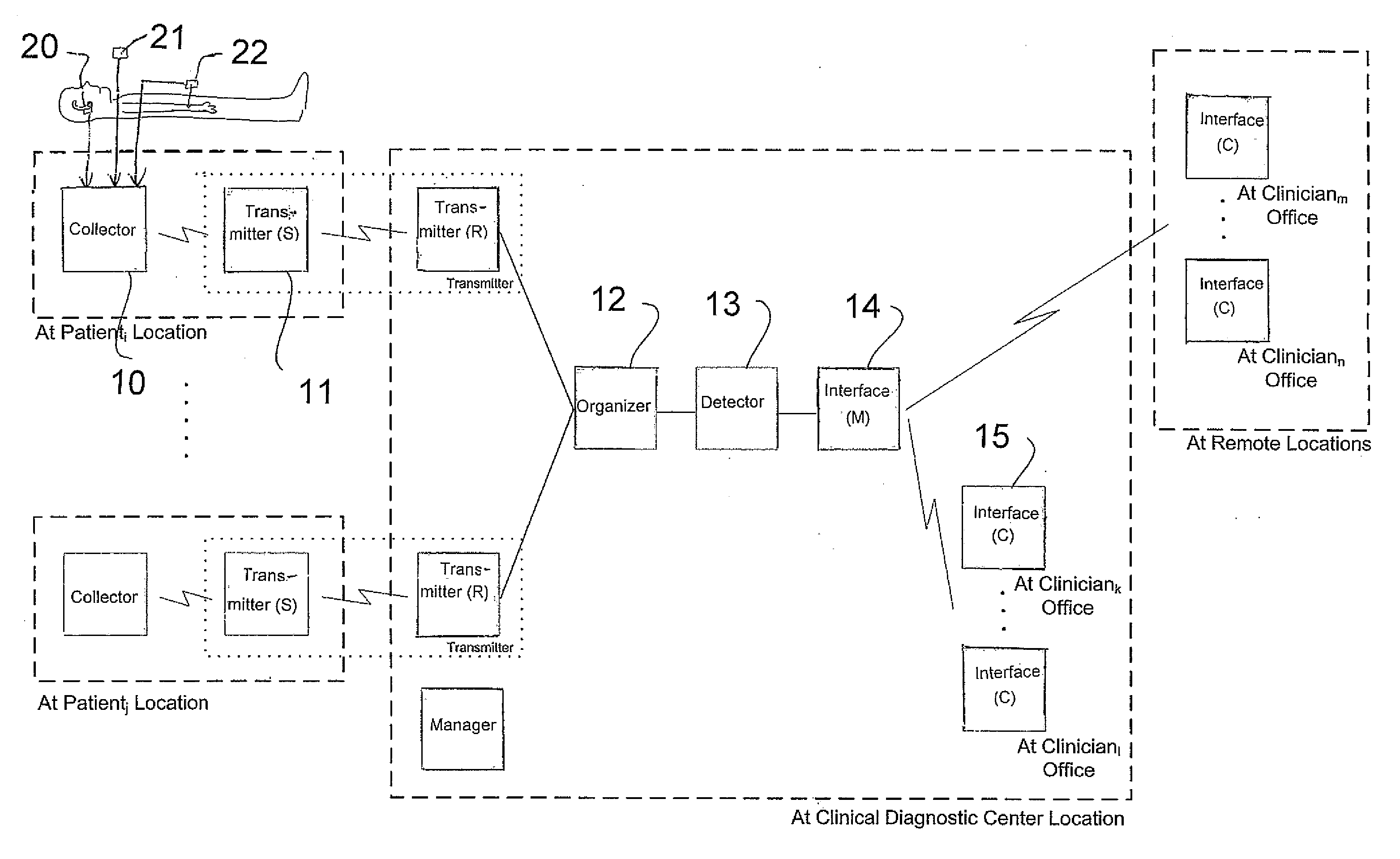
The invention provides a method as well as a device for the monitoring of body temperature, respiration, heart sound, swallowing, and offering medical inquiries. It comprises a sensor, a monitoring device, and medical devices. Installing proper sensors on the user's body and making the users wear necessary medical devices. The sensors attached to the user's body will be sensing the physical conditions and send the data collected to the monitoring device for security and protection. It can also allow the user or the medical personnel conduct two-way inquiries or treatment through displaying device, or the monitoring device can control the medical devices and assist the treatment. Furthermore, the data can be transferred to the medical system in the distant end and the user's data and be updated immediately and reduce errors happened in keying in the data. Doctors will be able to proceed with medical treatment according to the data and prevent abrupt accidents in patients as well as further protecting the security of the user.
Owner:YANG CHANG MING
Method and apparatus for continuously measuring blood pressure
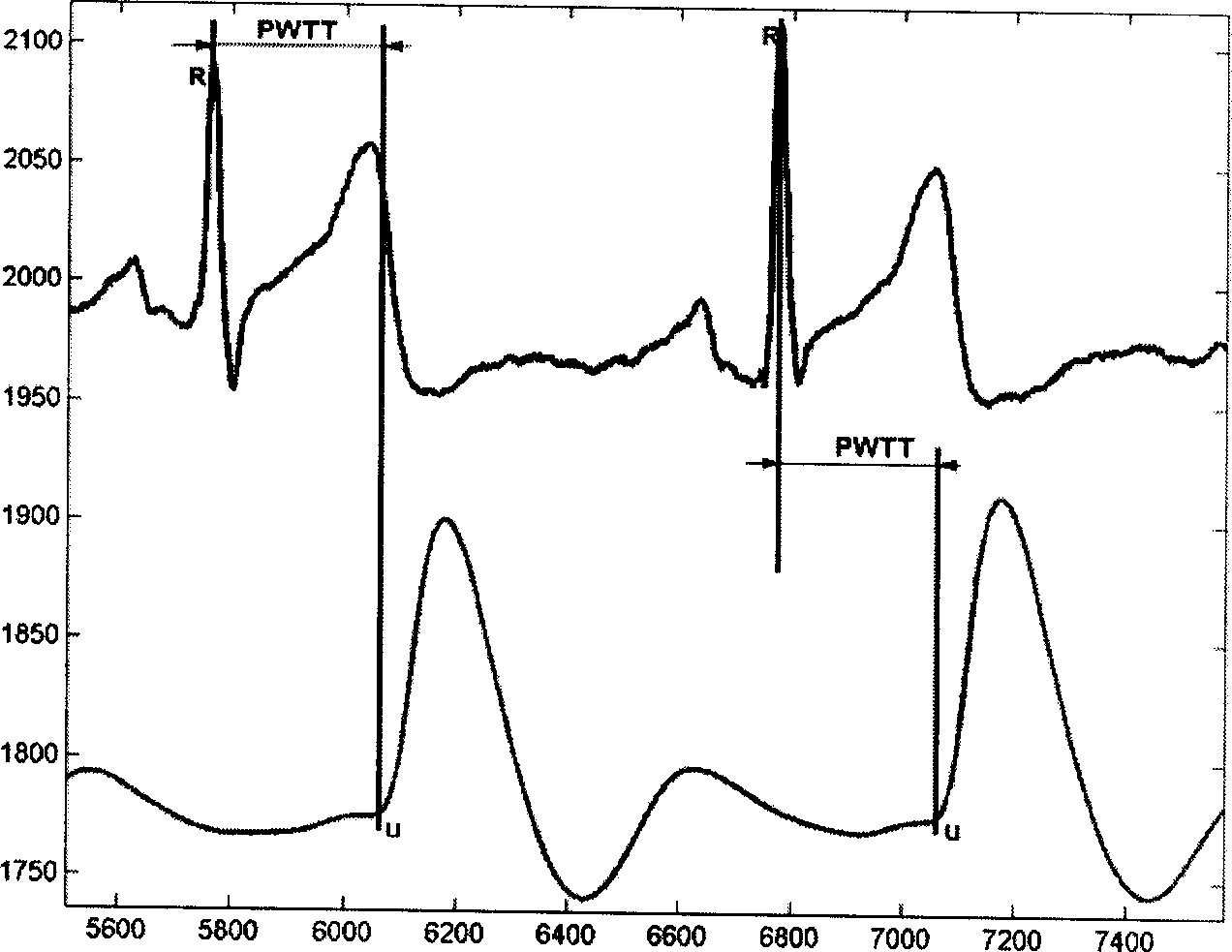
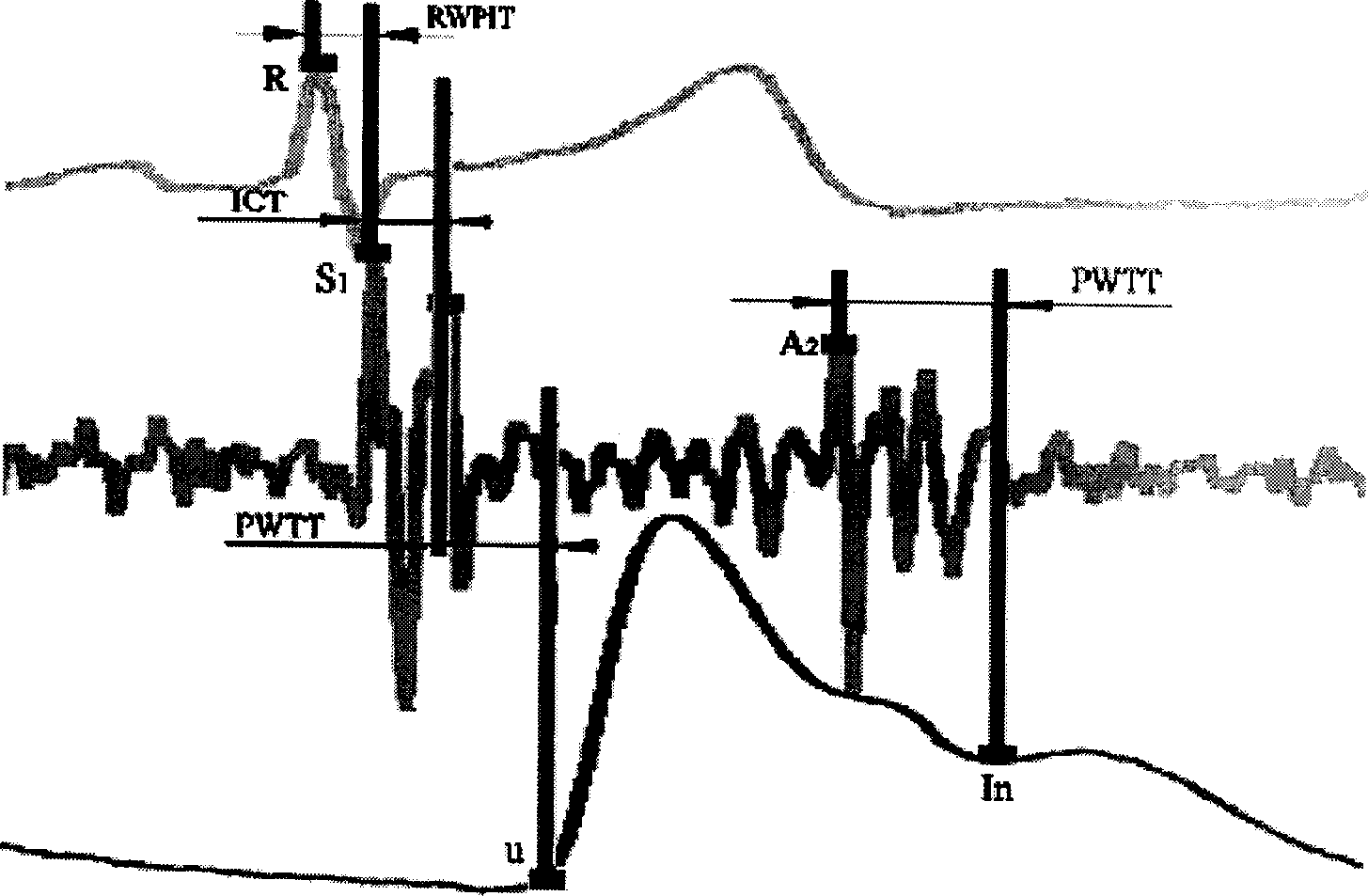
InactiveCN1849998AExclude positiveEliminate distractionsEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPersonalizationCardiac cycle
The present invention relates to a method for continuously measuring blood pressure and its equipment. Said method is characterized by that it creates a regression equation between pulse wave conduction time and arterial pressure: BP=a+b*PWTT for measurand person; and utilizes personalization correction technique to define intercept and regression coefficient b of measurand person. Besides, said invention also provides a method for continuously obtaining pulse wave conduction time PWTT by using pulse wave of human body, electrocardiogram signal and phonocardiogram signal and its concrete steps. Said method can raise accuracy for continuously measuring blood pressure, and can be used for measuring head blood pressure.
Owner:AVIATION MEDICINE INST AIR FORCE PLA +1
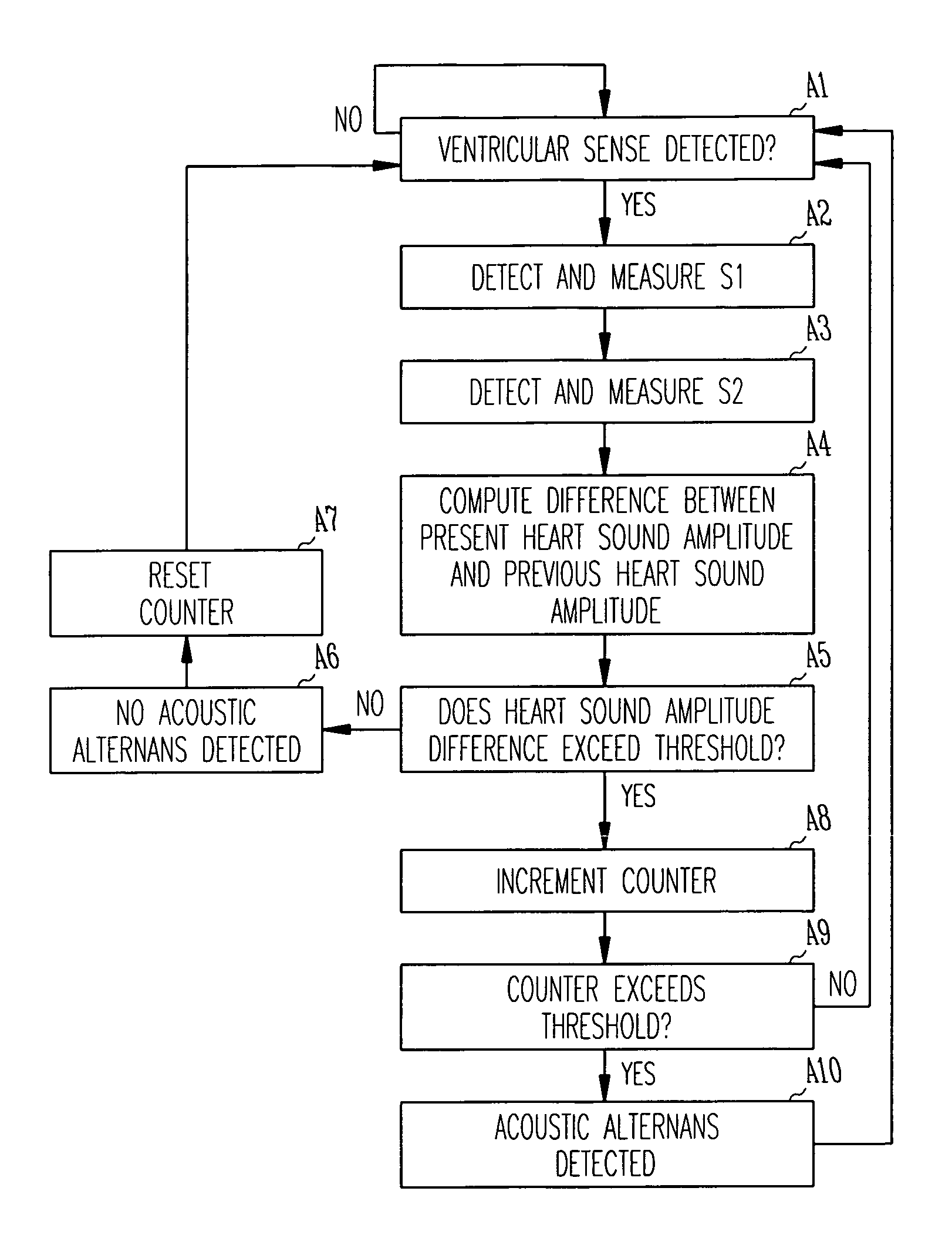
Method and apparatus for detecting acoustic oscillations in cardiac rhythm
A cardiac rhythm management device is configured to detect oscillations in cardiac rhythm by measuring the amplitudes of heart sounds during successive heart beats. Upon detection of acoustic alternans, the device may adjust its operating behavior to compensate for the deleterious effects of the condition.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
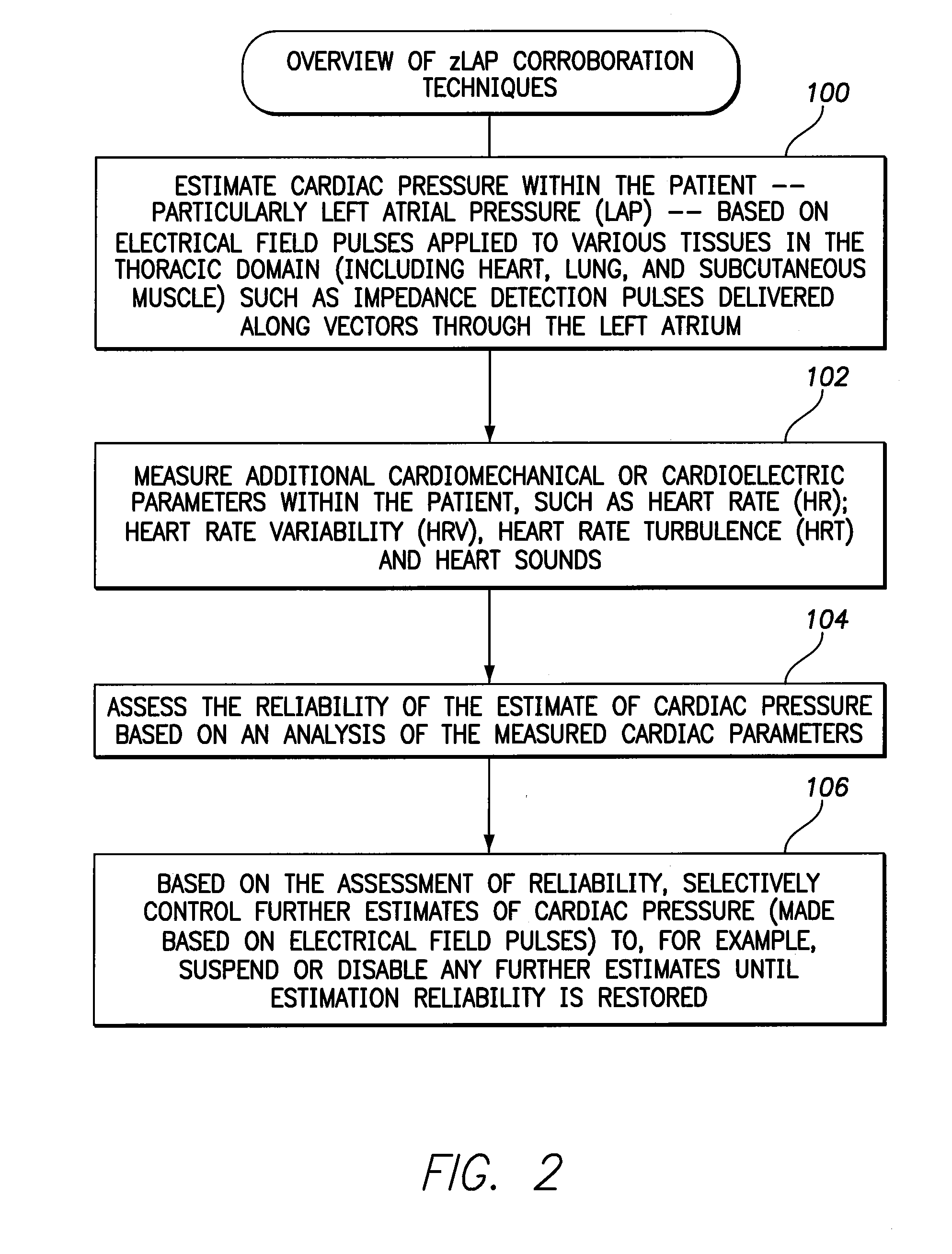
Systems and methods for corroborating impedance-based left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates for use by an implantable medical device
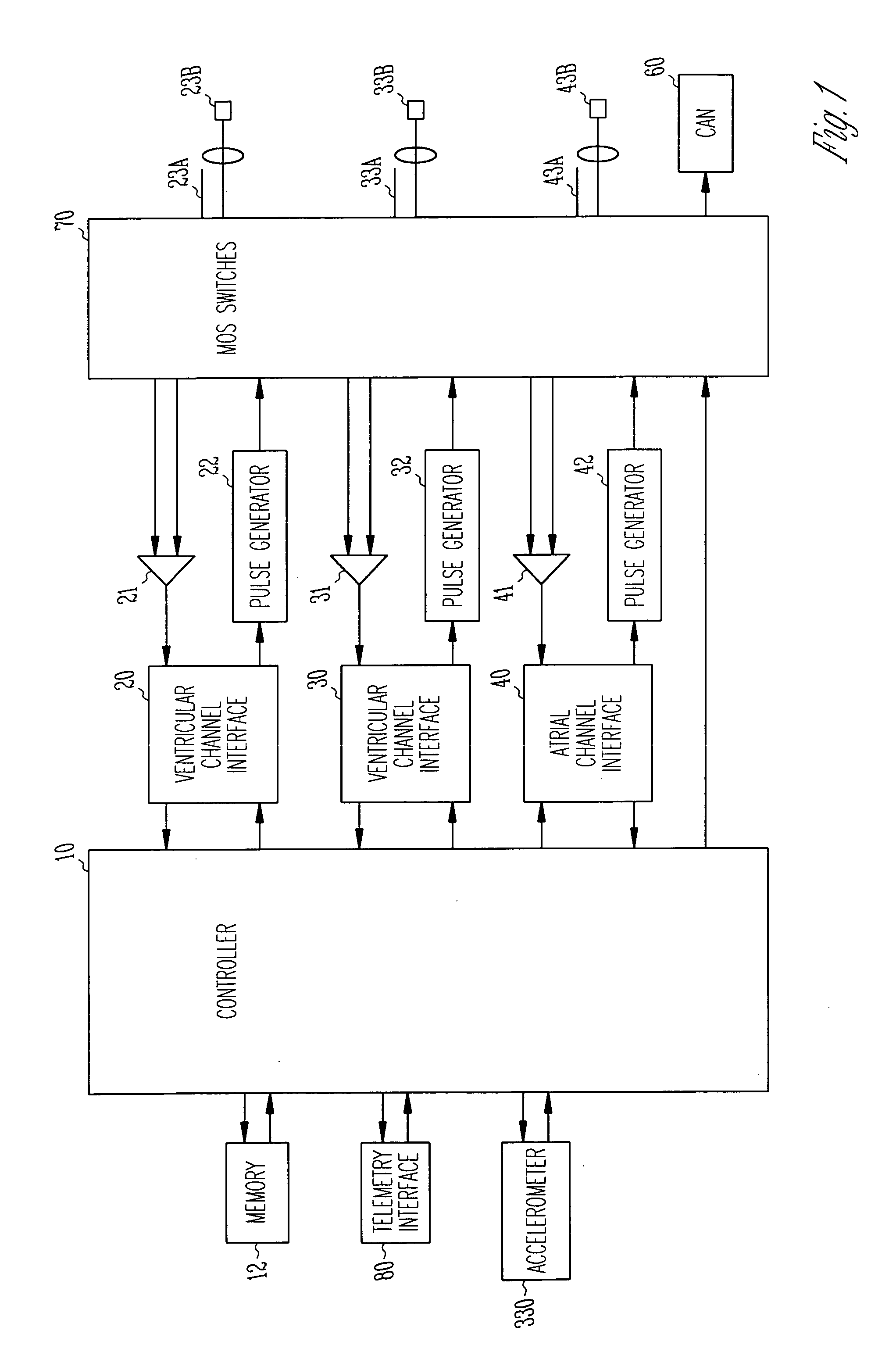
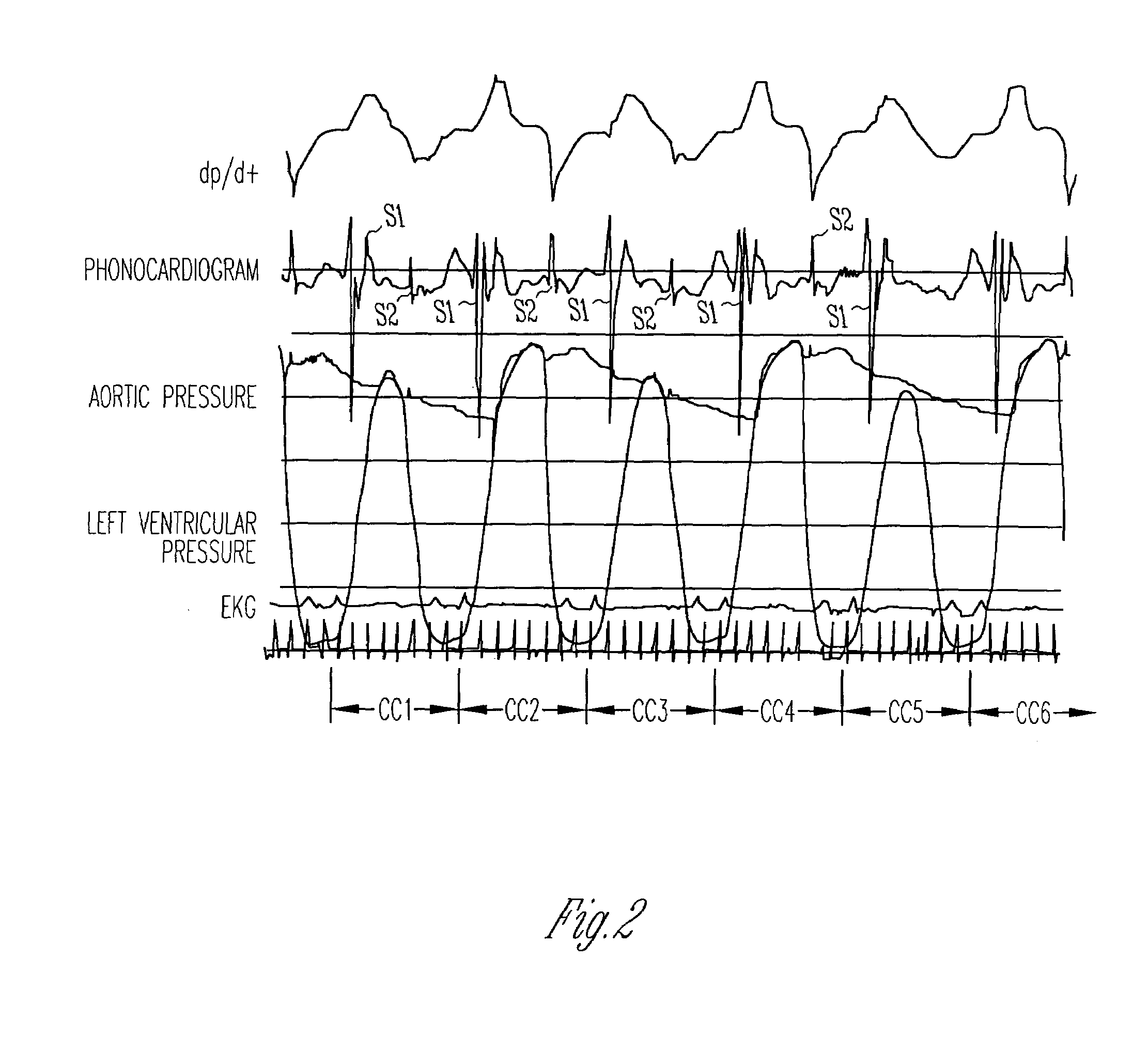
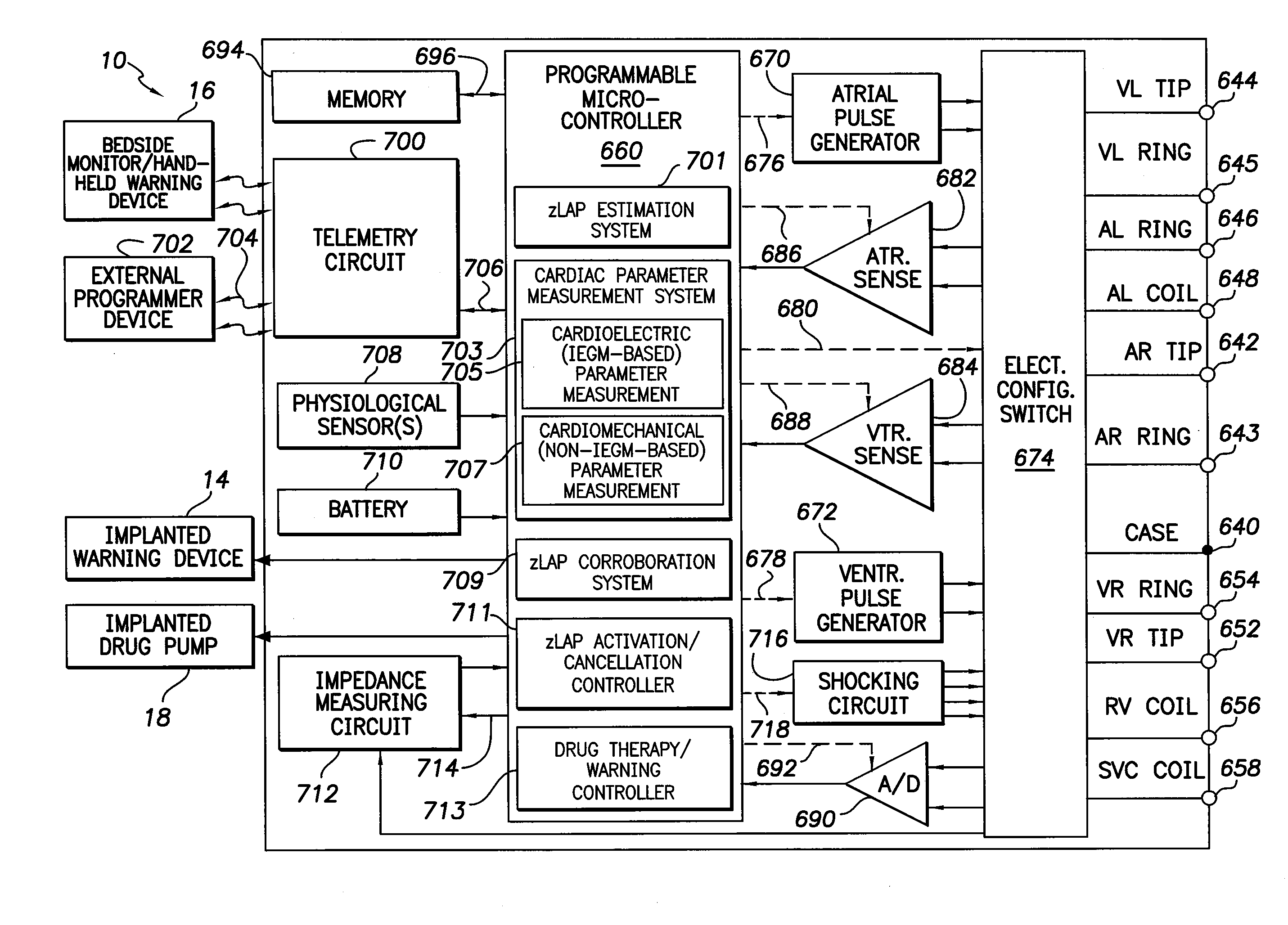
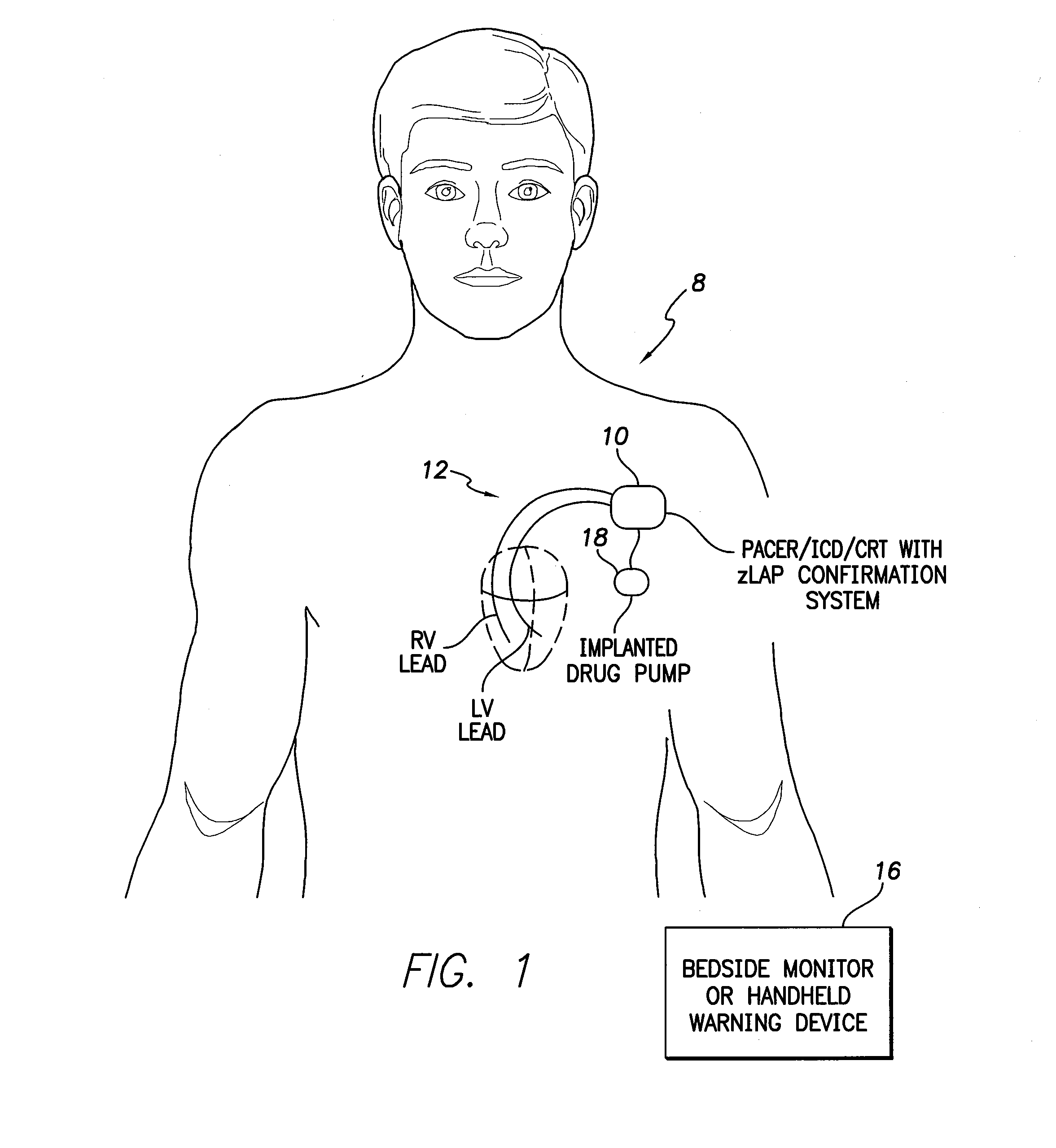
Various techniques are provided for assessing the reliability of left atrial pressure (LAP) estimates made by an implantable medical device based on impedance values or related electrical values. In one example, various cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters are used to corroborate LAP estimation in circumstances where the LAP estimates deviate from an acceptable, satisfactory or otherwise healthy range. The cardioelectric parameters include, e.g.: ST elevation; heart rate (HR); heart rate variability (HRV); T-wave alternans (TWA); QRS waveform parameters; P-wave duration; evoked response (ER) parameters; and intrinsic PV / AV / VV conduction delays. The cardiomechanical parameters include, e.g.: heart rate turbulence (HRT); cardiogenic impedance signals; heart sounds; and non-LAP blood pressure measurements, such as aortic pressure measurements. The device compares the cardioelectric and cardiomechanical parameters against corresponding baseline values to determine whether variations in the parameters corroborate the LAP estimates. If not, the LAP estimates are selectively cancelled or suspended, or the overall procedure is re-calibrated.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
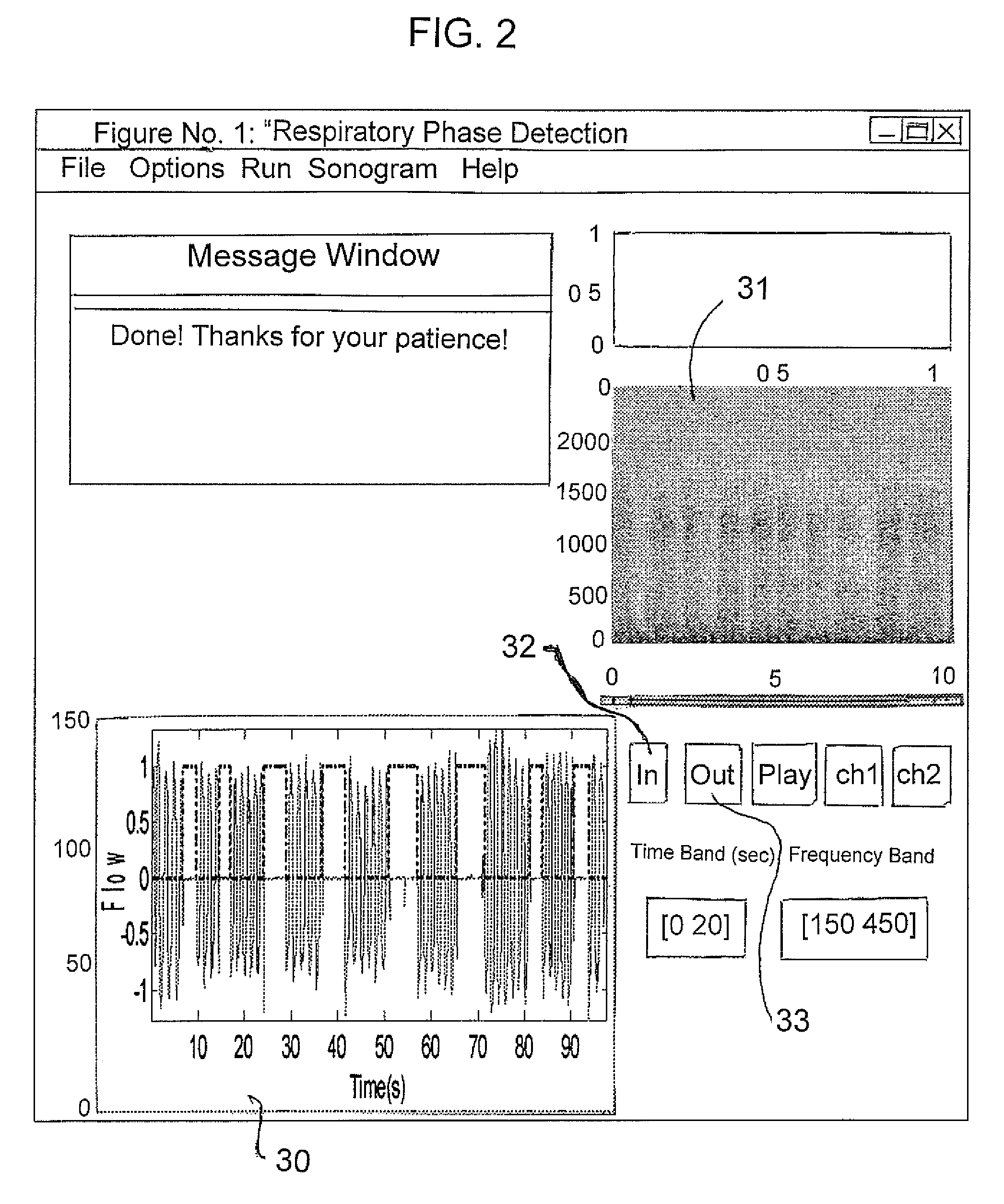
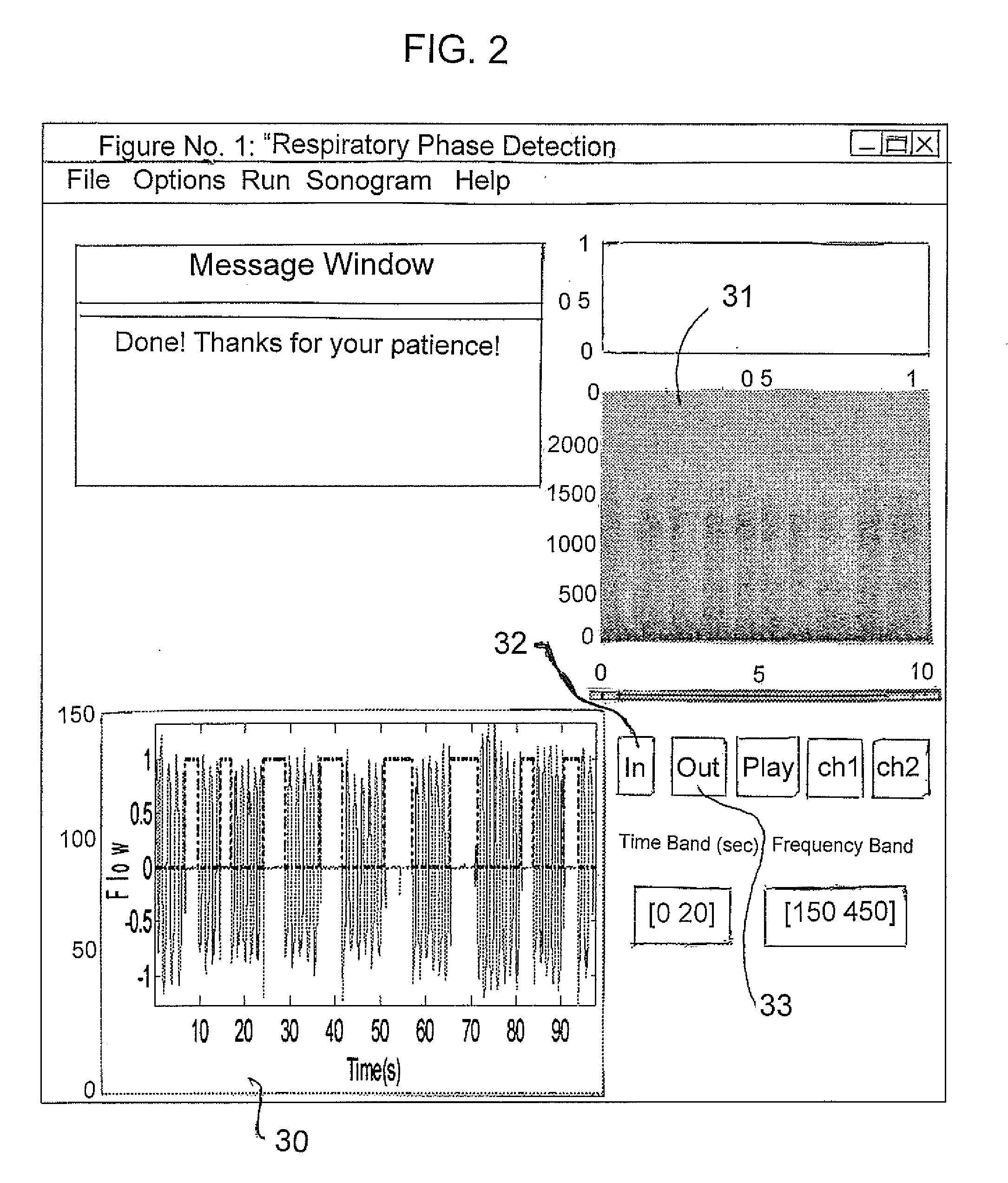
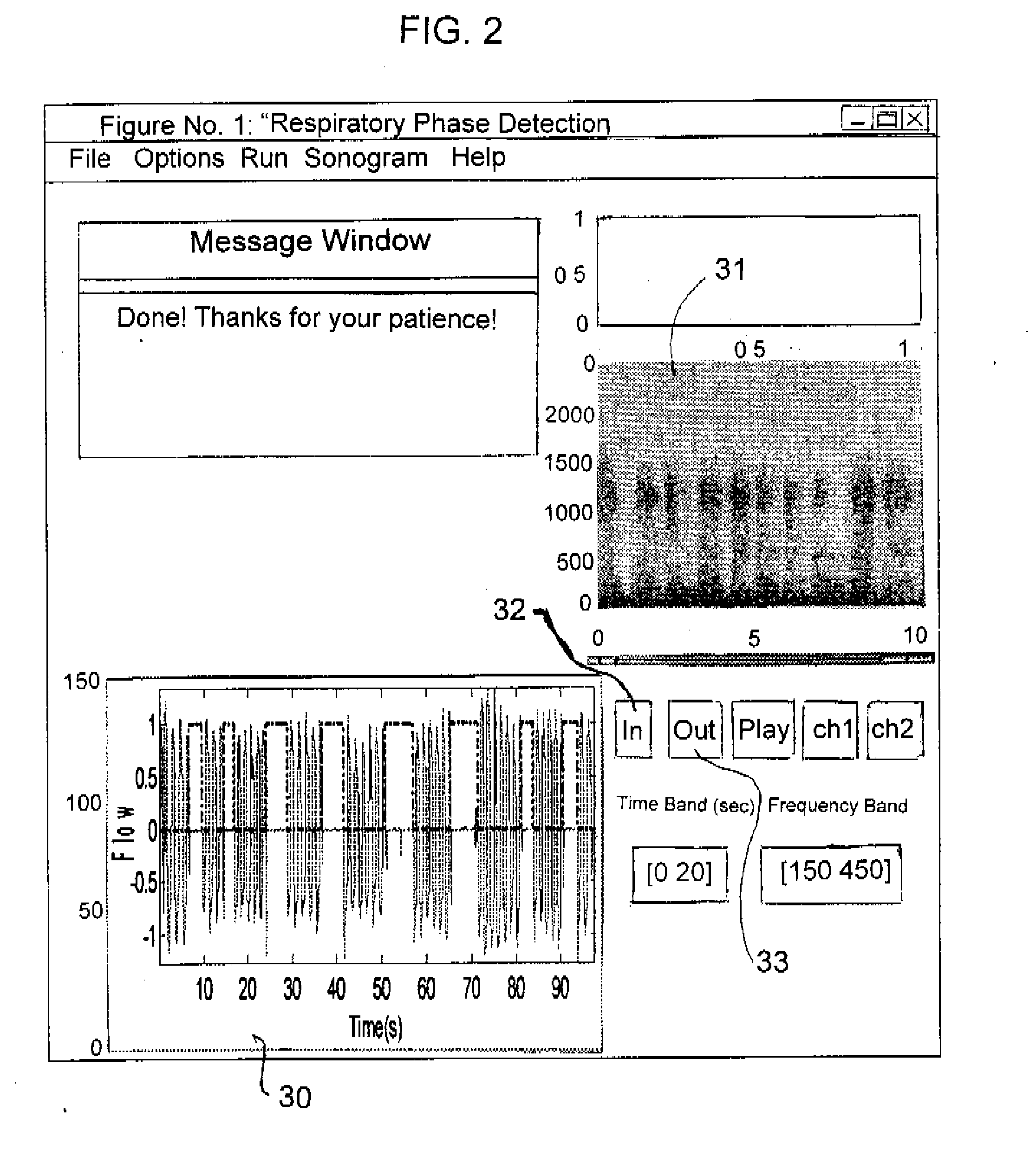
Methods and systems for monitoring respiration
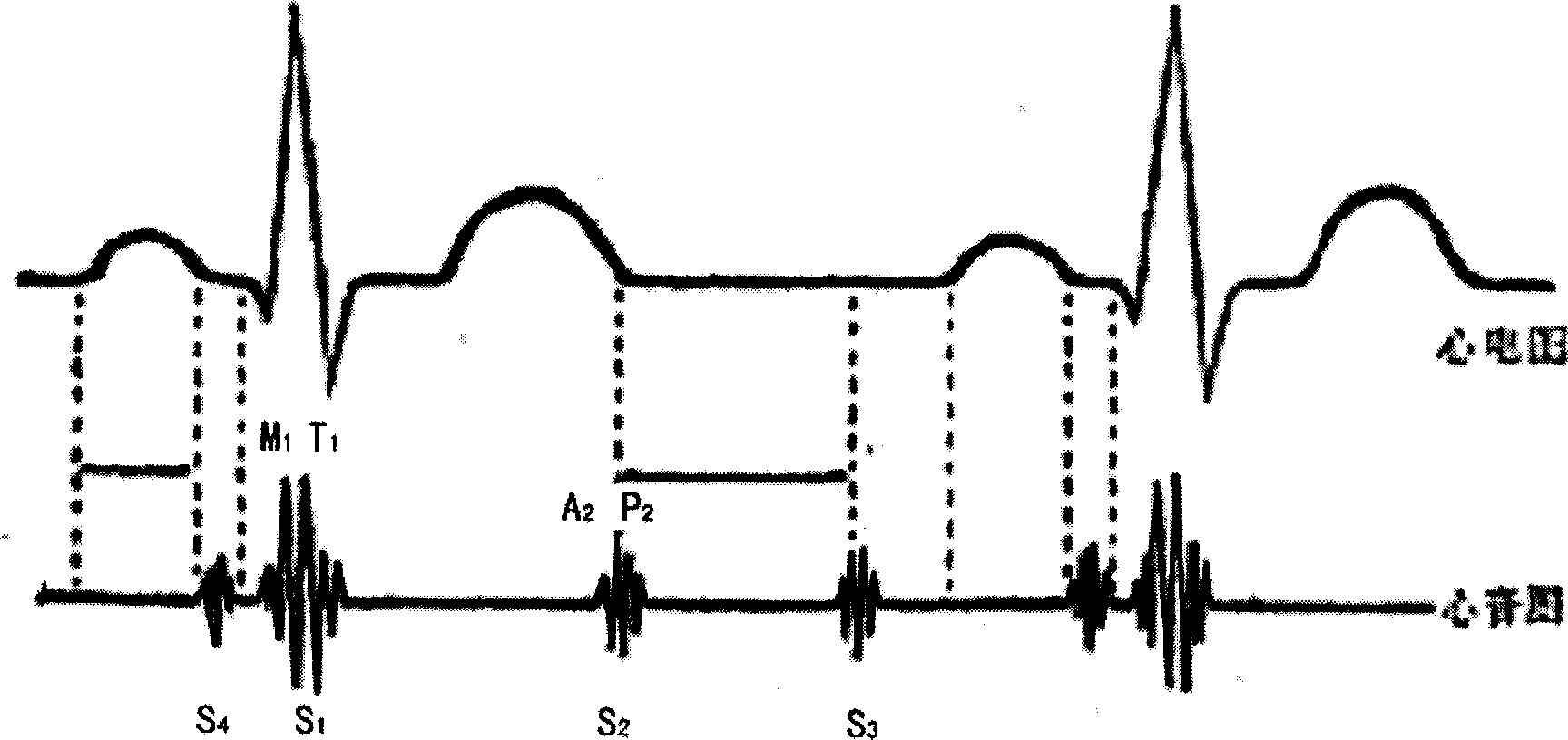
A method for determining respiration rate in a patient can include various parts. The respiration rate can be determined by measuring the heart's S2 split. The S2 split can be identified by observing the timing of the heart sounds. Other respiration related information, such as respiration phase and the occurrence of apnea, can be identified as well. A respiration monitor of this type may be useful for monitoring sub-acute patients, and outpatients. A sensor for the respiration monitor and an electrode for an ECG monitor may be combined into a single probe.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST INFORMATION TECH
Systems and methods for multi-axis cardiac vibration measurements
A system to monitor heart sounds, such as to detect a worsening condition of heart failure decompensation. The system comprises a medical device that includes an implantable multi-axis heart sound sensor, operable to produce, for each of at least two nonparallel axes, an electrical signal representative of at least one heart sound, the heart sound associated with mechanical activity of a patient's heart. The device further includes a controller circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor. The controller circuit measures components of the heart sound that respectively correspond to each of the axes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
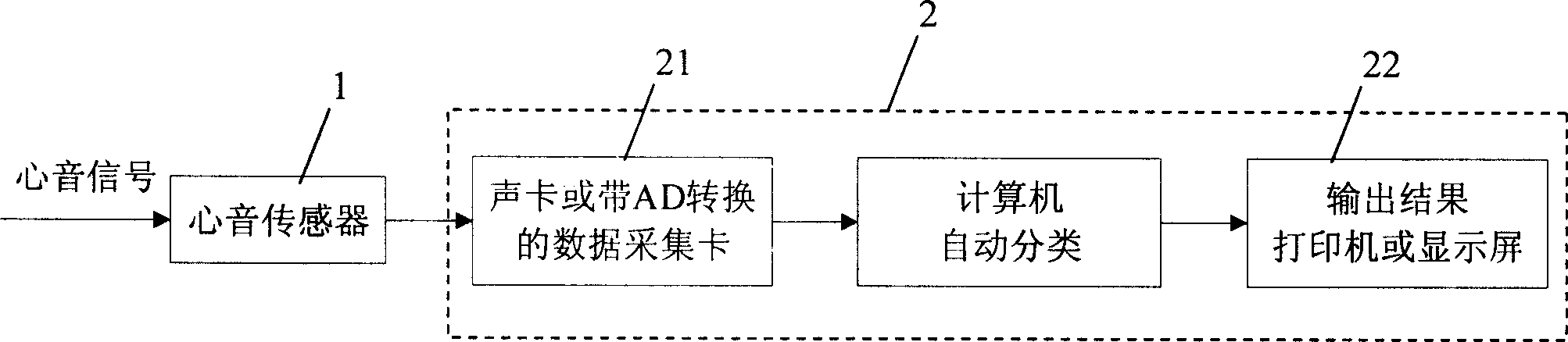
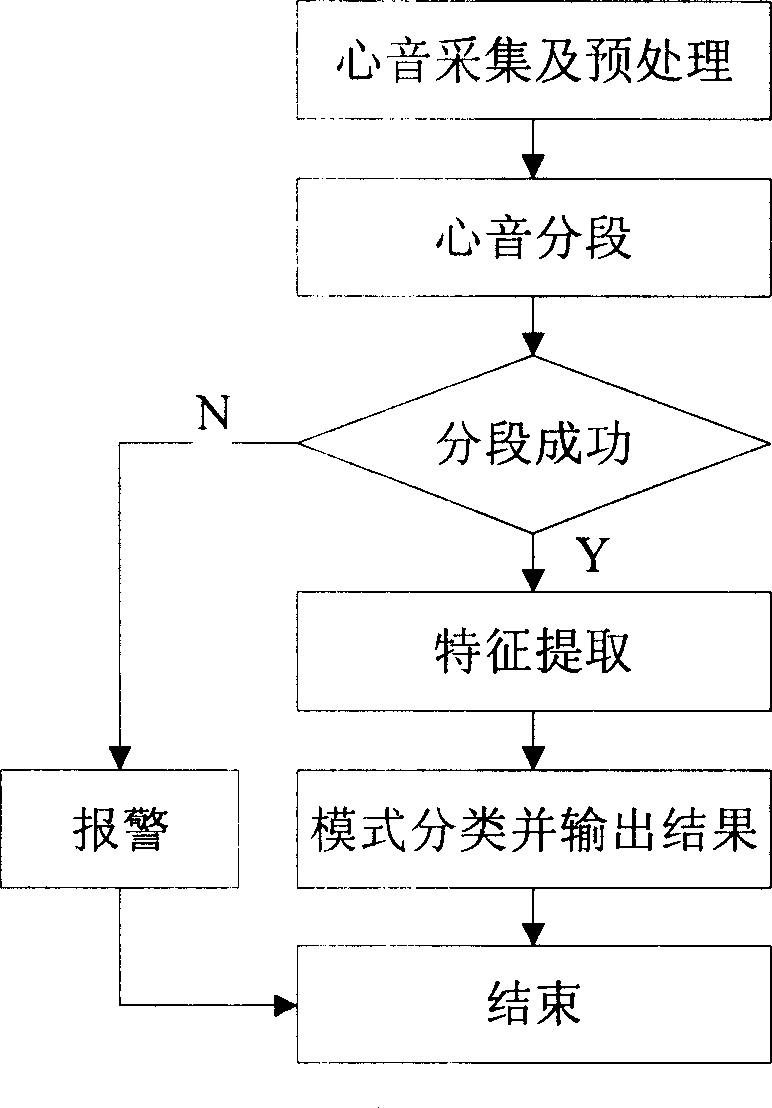
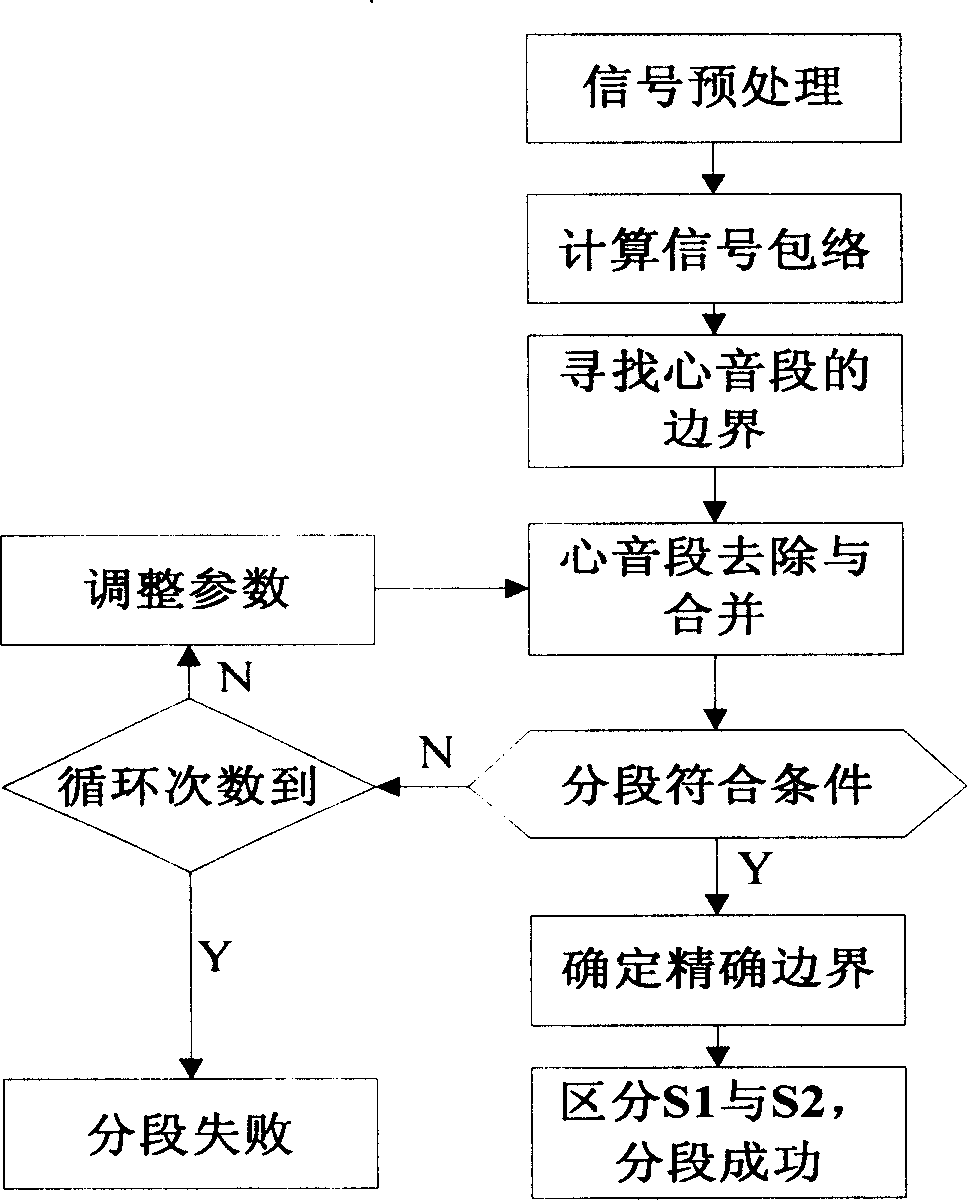
Heart disease automatic classification system based on heart sound analysis and heart sound segmentation method
The present invention relates to a heart disease automatic classification system based on heart sound analysis. It includes the following several portions: heart sound sensor, it is used for converting heart sound vibration signal of tested person into electric signal and outputting said electric signal; computer with multimedia function, it is connected with heart sound sensor by means of data acquisition card and can be used for recording the heart sound signal of tested person which is outputted by heart sound sensor and storing said signal in storage unit; and heart sound sectionalization program, heart sound characteristics extraction program and classification device which are mounted in the computer. Said invention also provides its working principle and its concrete operation method.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
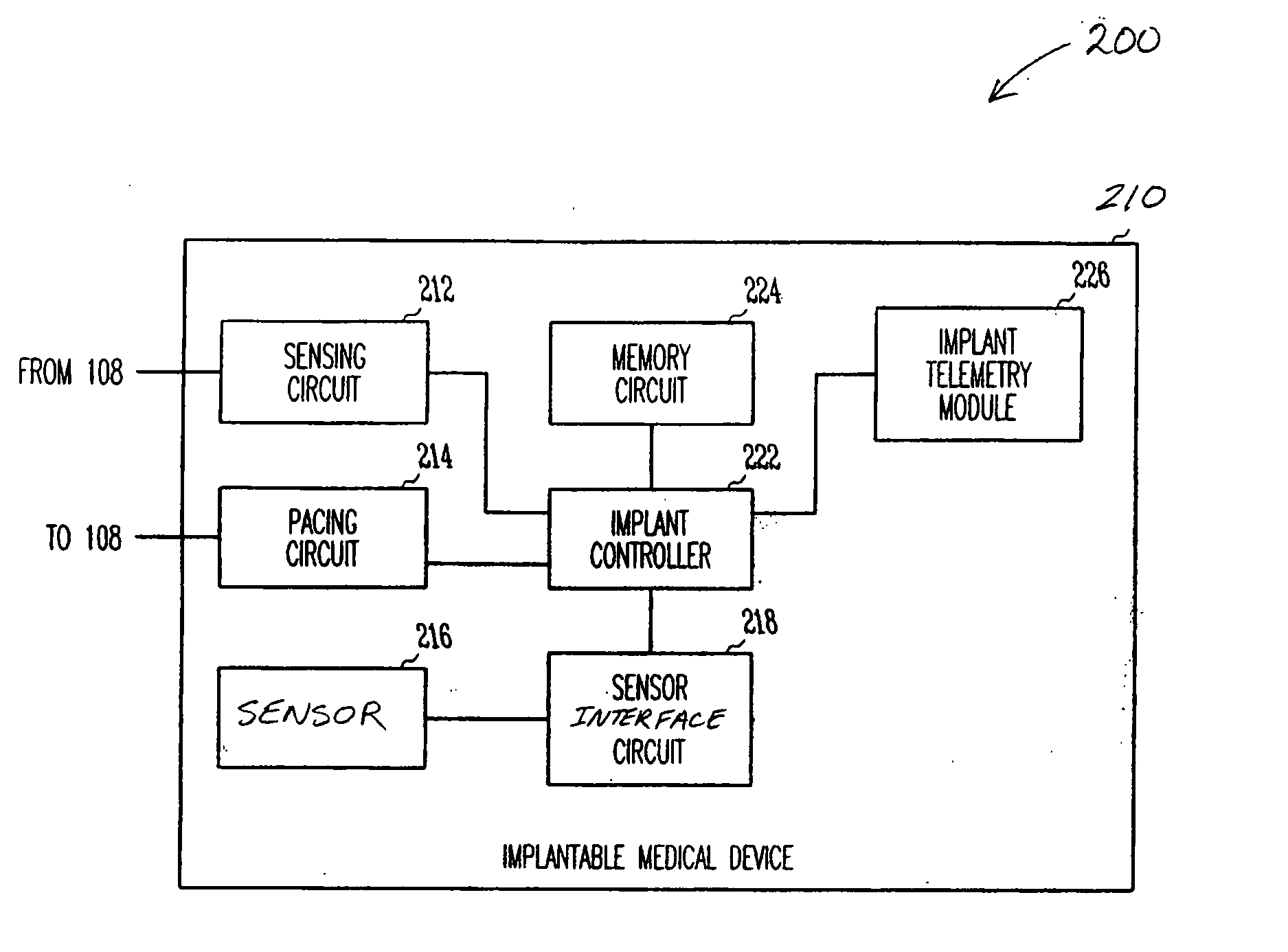
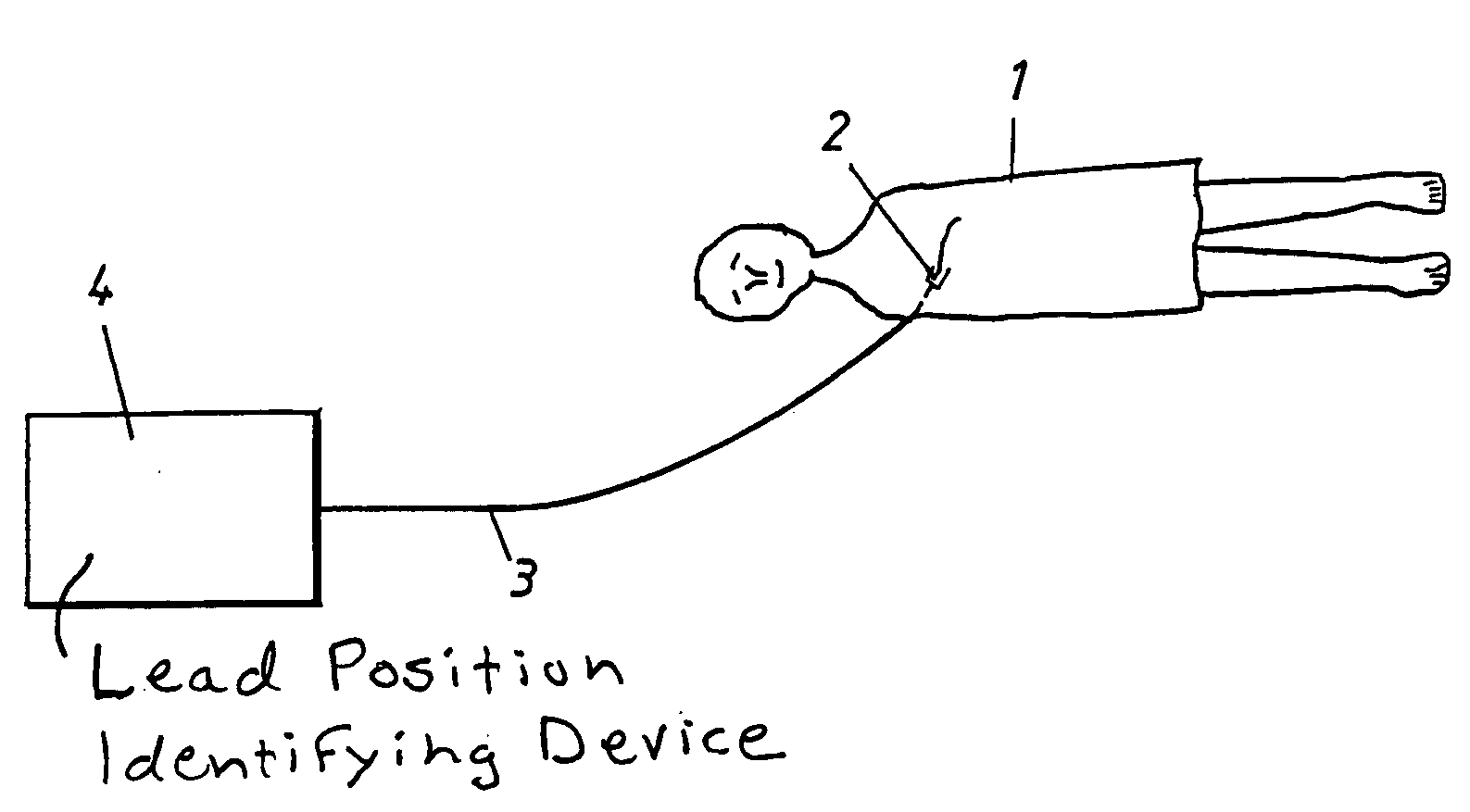
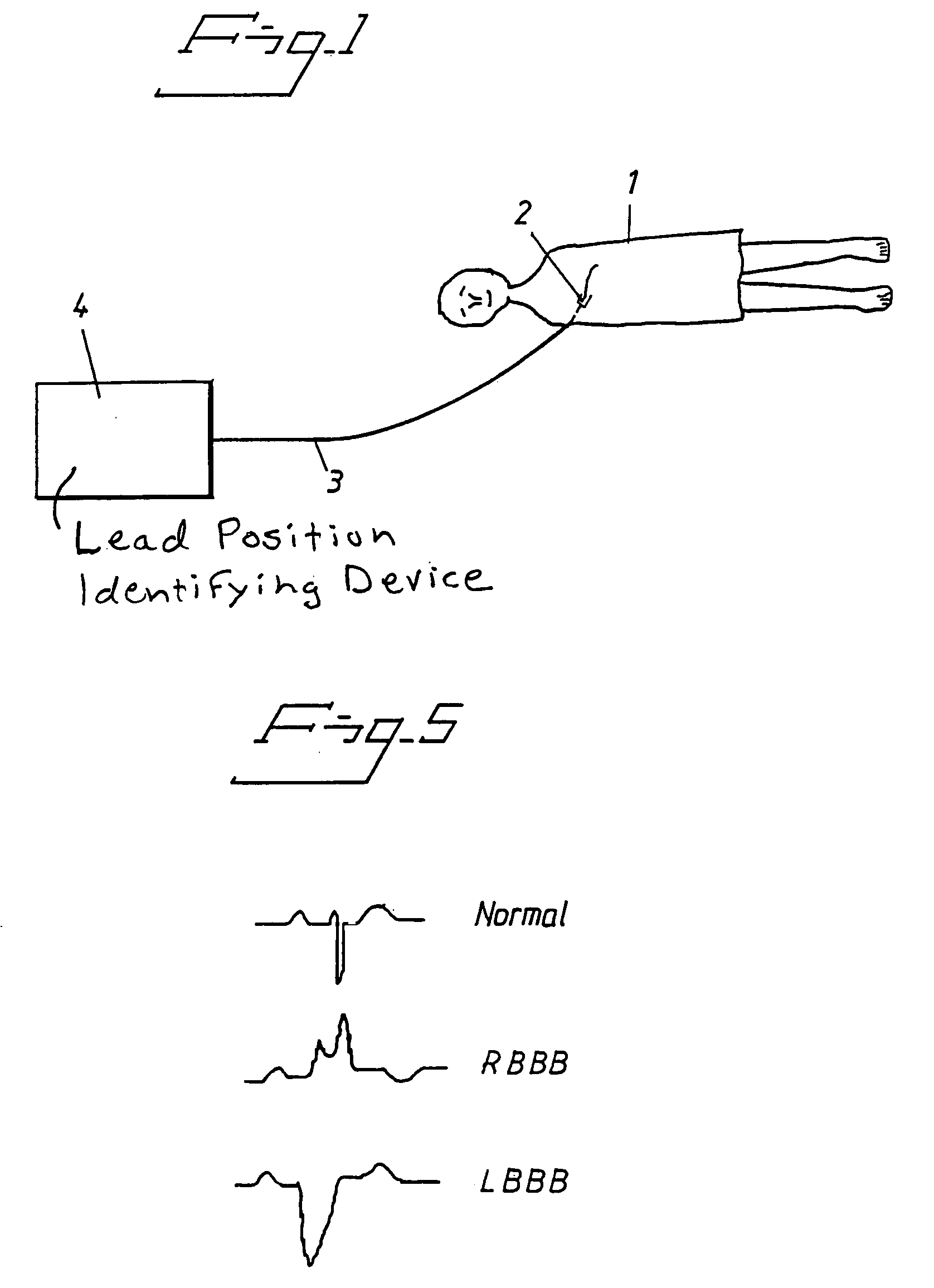
Arrangement and Method for Evaluating Operational Effectiveness of Implantable Medical Electrode Leads for Different Lead Placements
InactiveUS20080249375A1Improved and simplifiedElevated PSAElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalOperational effectiveness
In a method and an arrangement for evaluating operational effectiveness of an implantable medical device for different lead placements associated with the medical device, a measuring unit records signals that are characteristic of cardiac activity at respectively different lead positions, and these signals are stored. A processor accesses the stored signals and, from the stored signals, determines a measure of cardiac activity at each of the lead positions. The recorded signals may be intracardiac ECG signals, surface ECG signals, heart sound signals obtained from a microphone, or impedance signals. The lead position at which the best hemodynamic behavior of the heart is identified from the analysis of the stored signals, and is determined as being the optimum site for placement of the electrode leads.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Heart Monitoring Systems, Apparatus and Methods Adapted to Detect Myocardial Ischemia
Embodiments include heart monitoring systems, apparatus, and methods adapted to detect myocardial ischemia. An apparatus includes at least one first-tier sensor / analyzer adapted to sense a first input related to cardiac function, and to produce a first-tier trigger signal when the first input indicates myocardial ischemia. In an embodiment, a first-tier sensor / analyzer includes an ECG sensor / analyzer. In another embodiment, a first-tier sensor / analyzer includes a patient activator. An apparatus further includes at least one second-tier sensor / analyzer adapted to sense a second input related to cardiac function, and to produce a second-tier trigger signal when the second input indicates myocardial ischemia. In an embodiment, a second-tier sensor-analyzer includes a heart sound sensor / analyzer. A triggering element is adapted to produce a response-invoking signal in response to the first-tier trigger signal and the second-tier trigger signal. The response-invoking signal may invoke a patient alert, a message to an external system, and / or a cardiac stimulus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
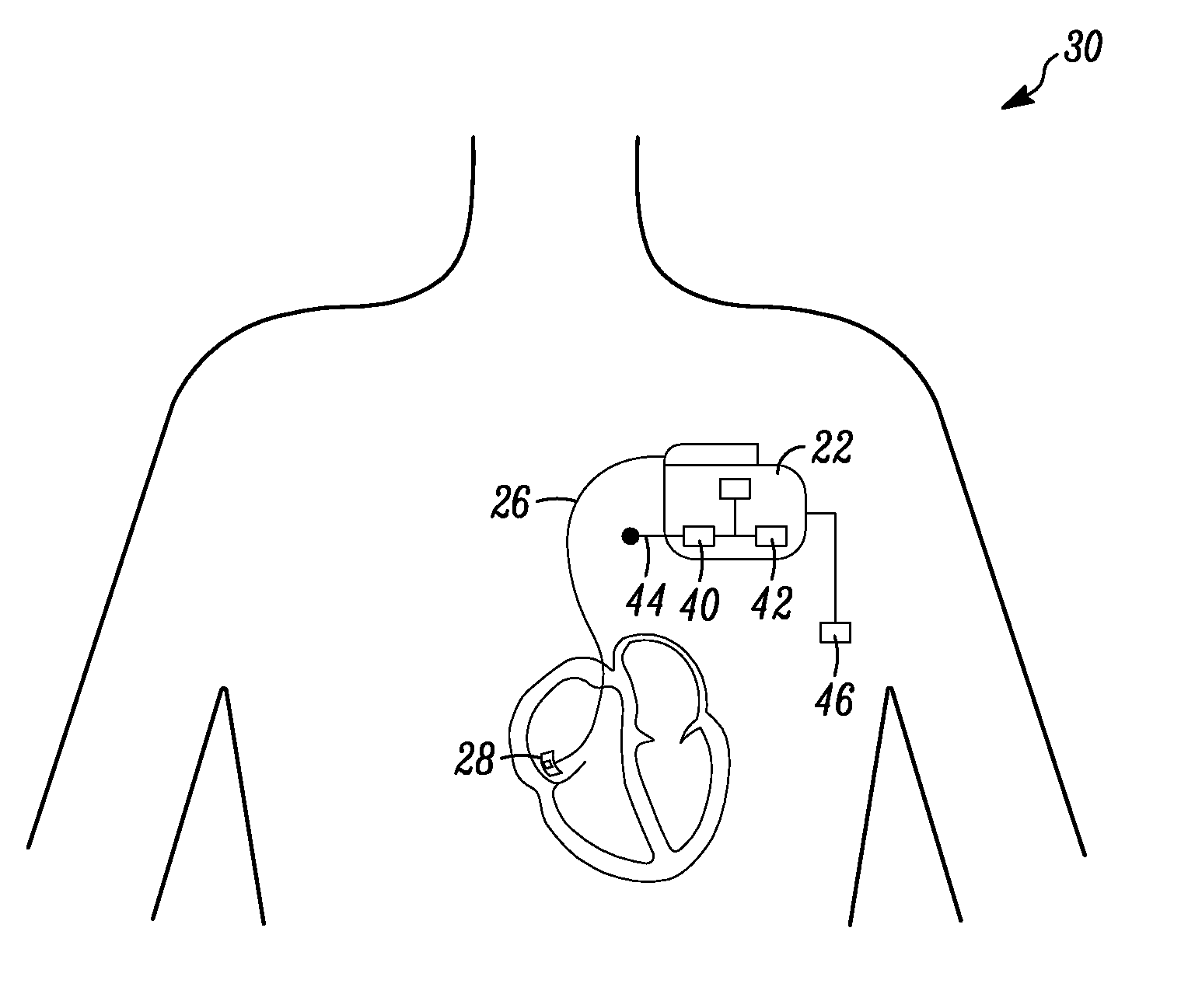
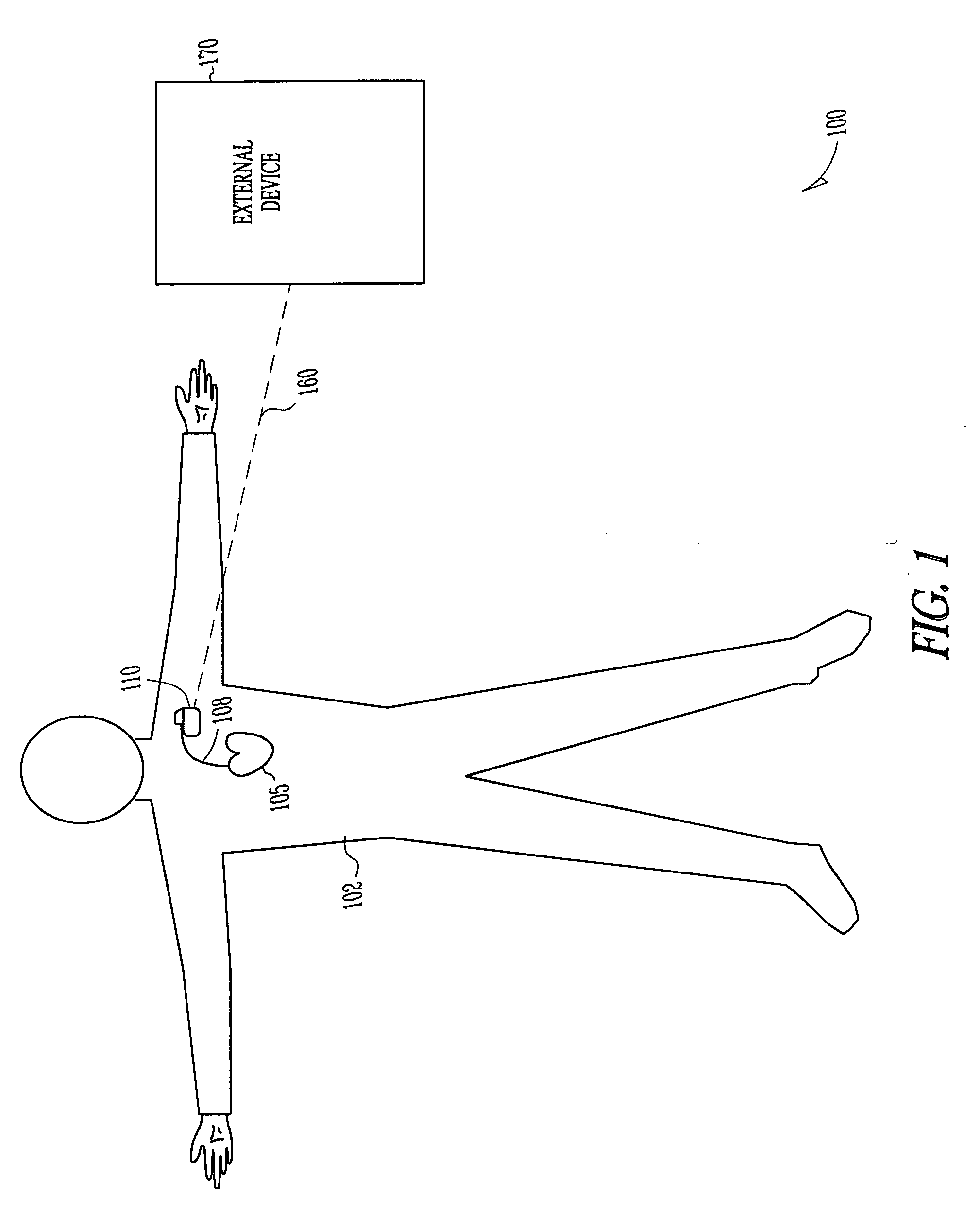
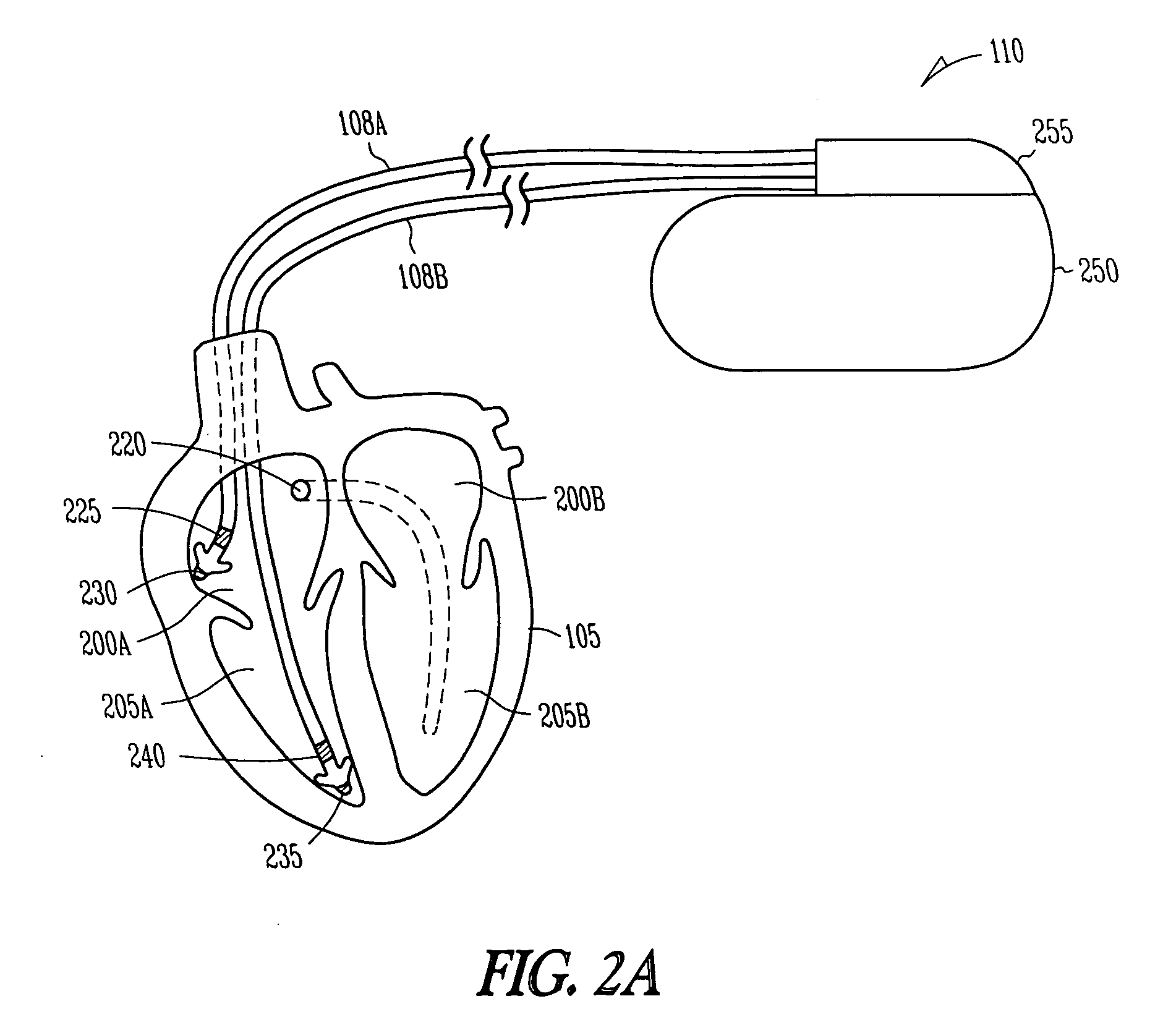
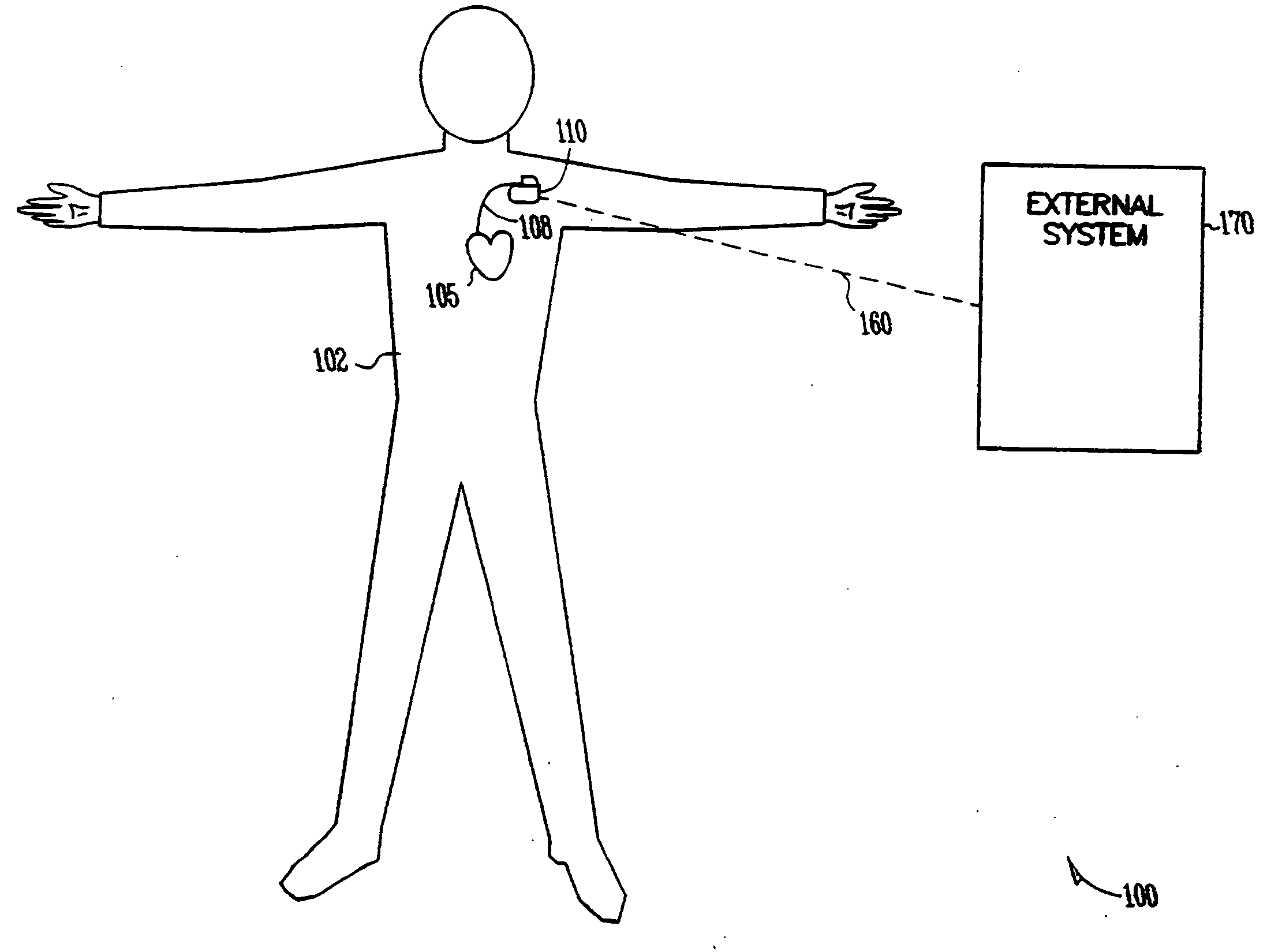
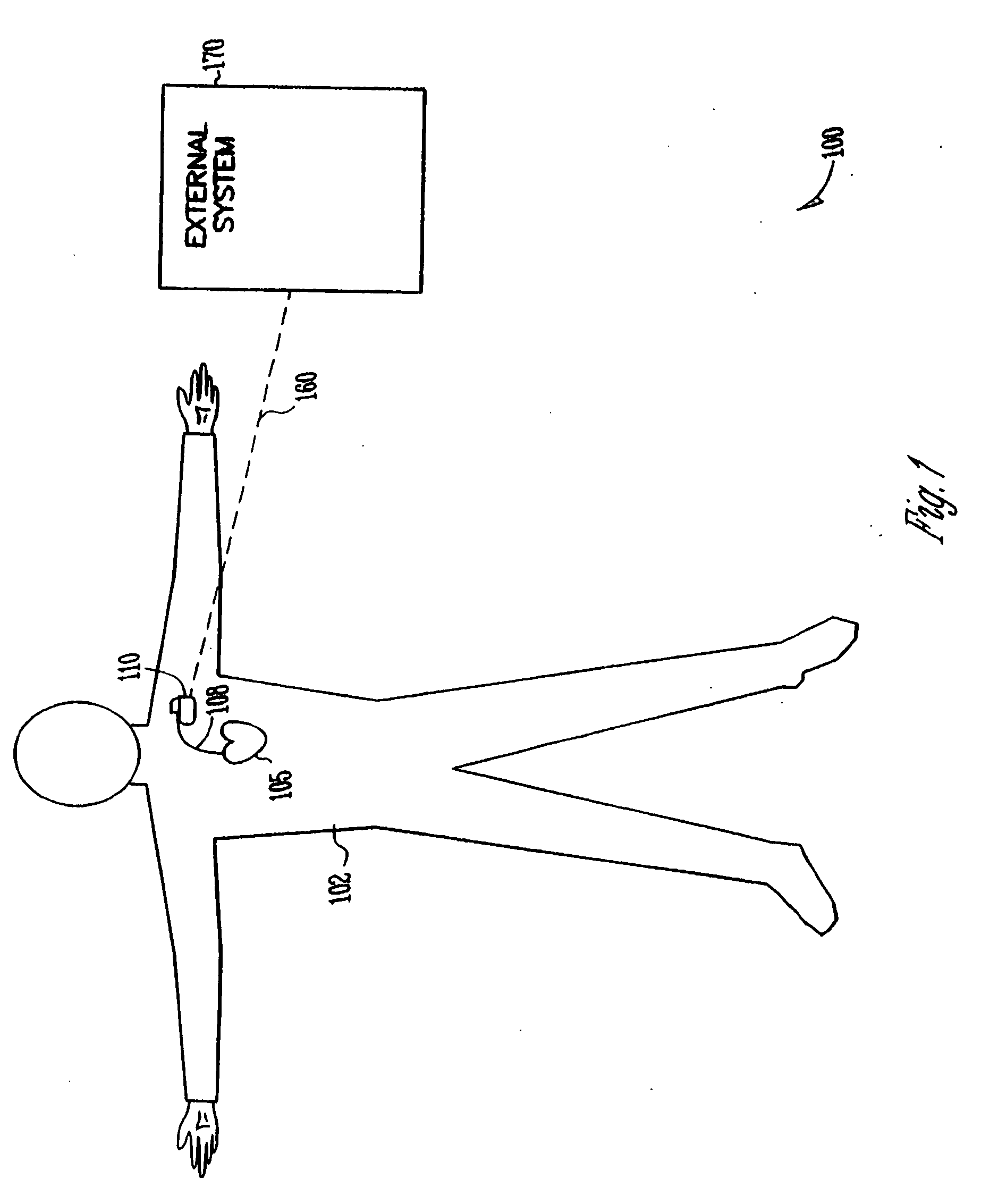
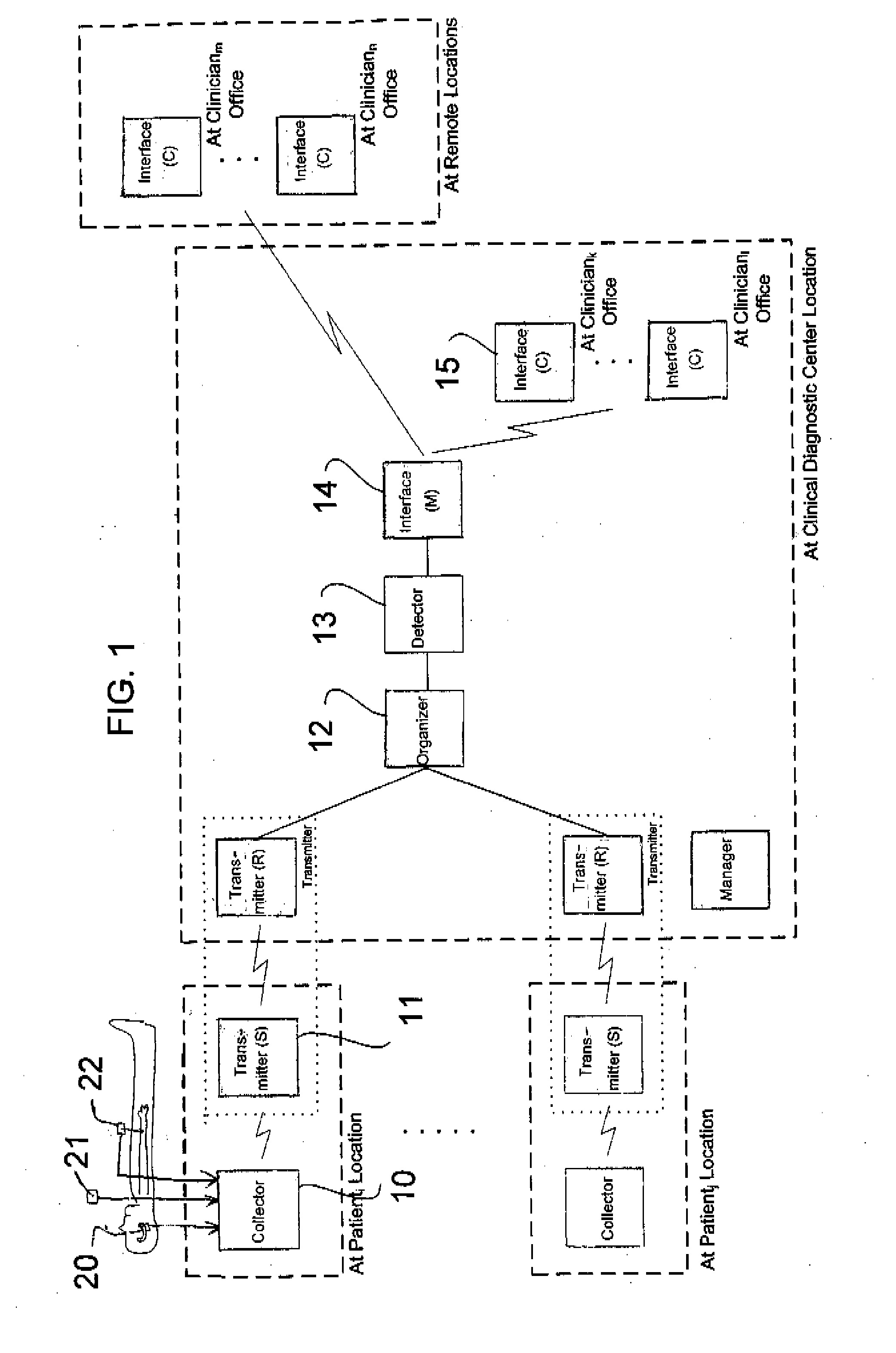
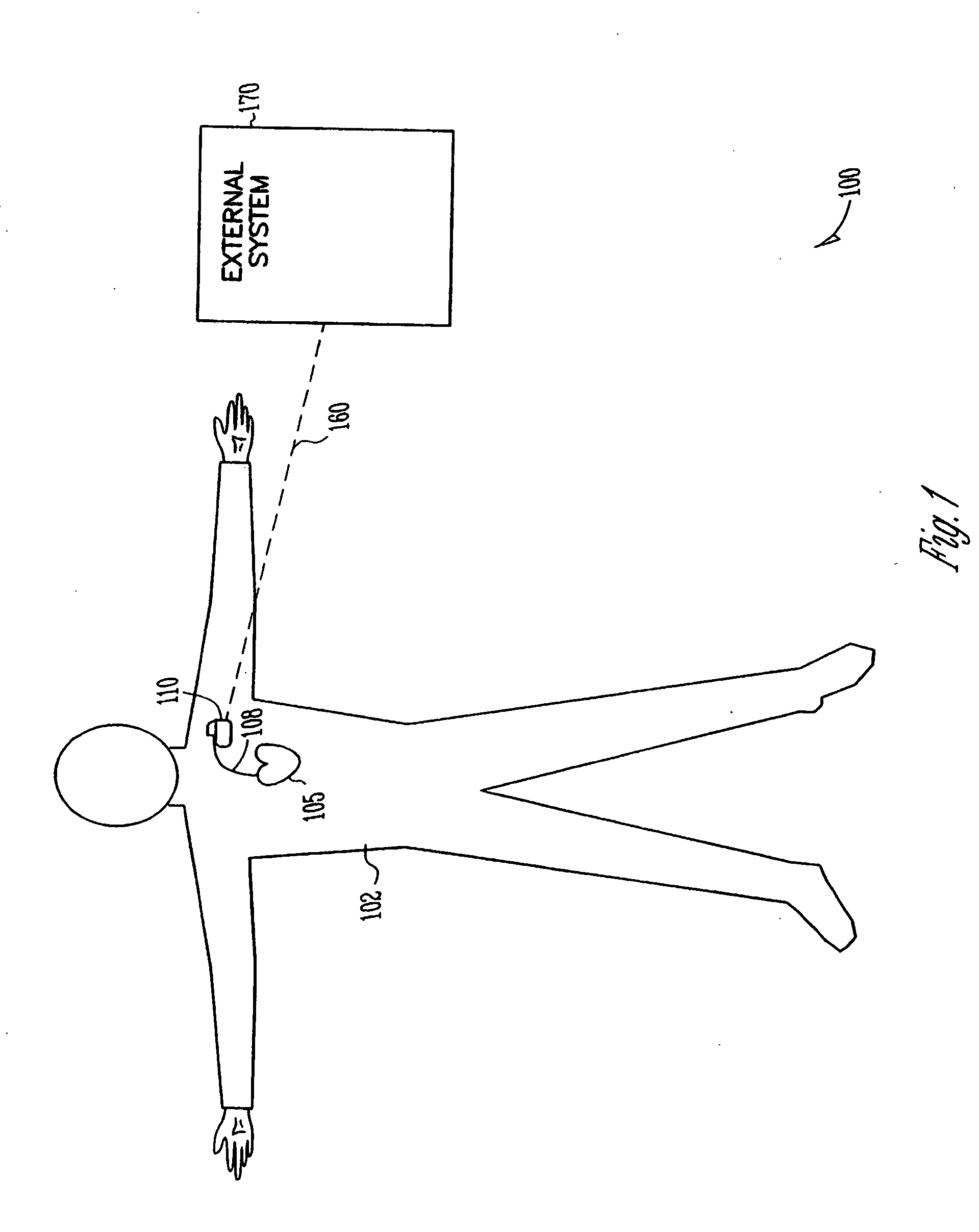
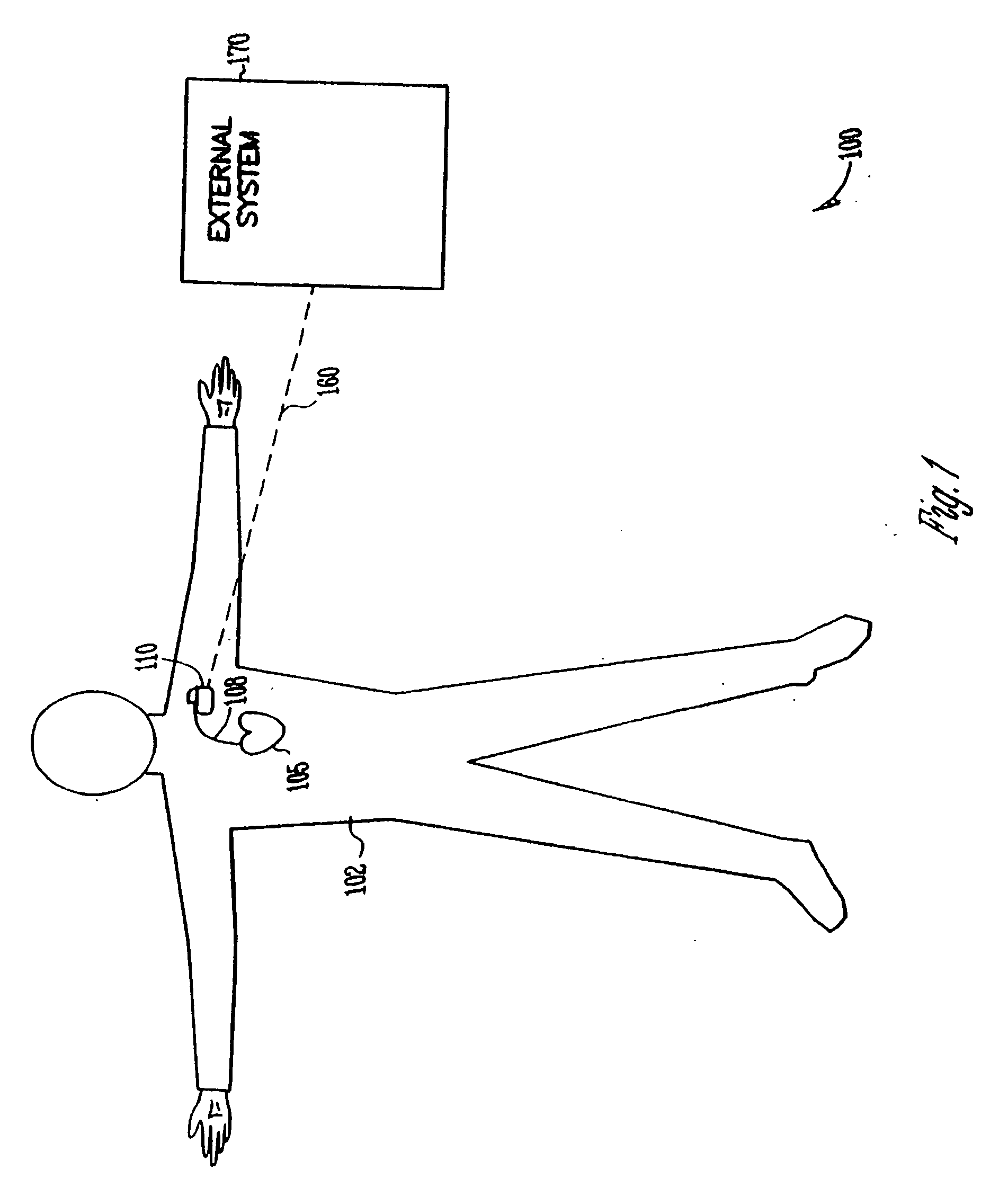
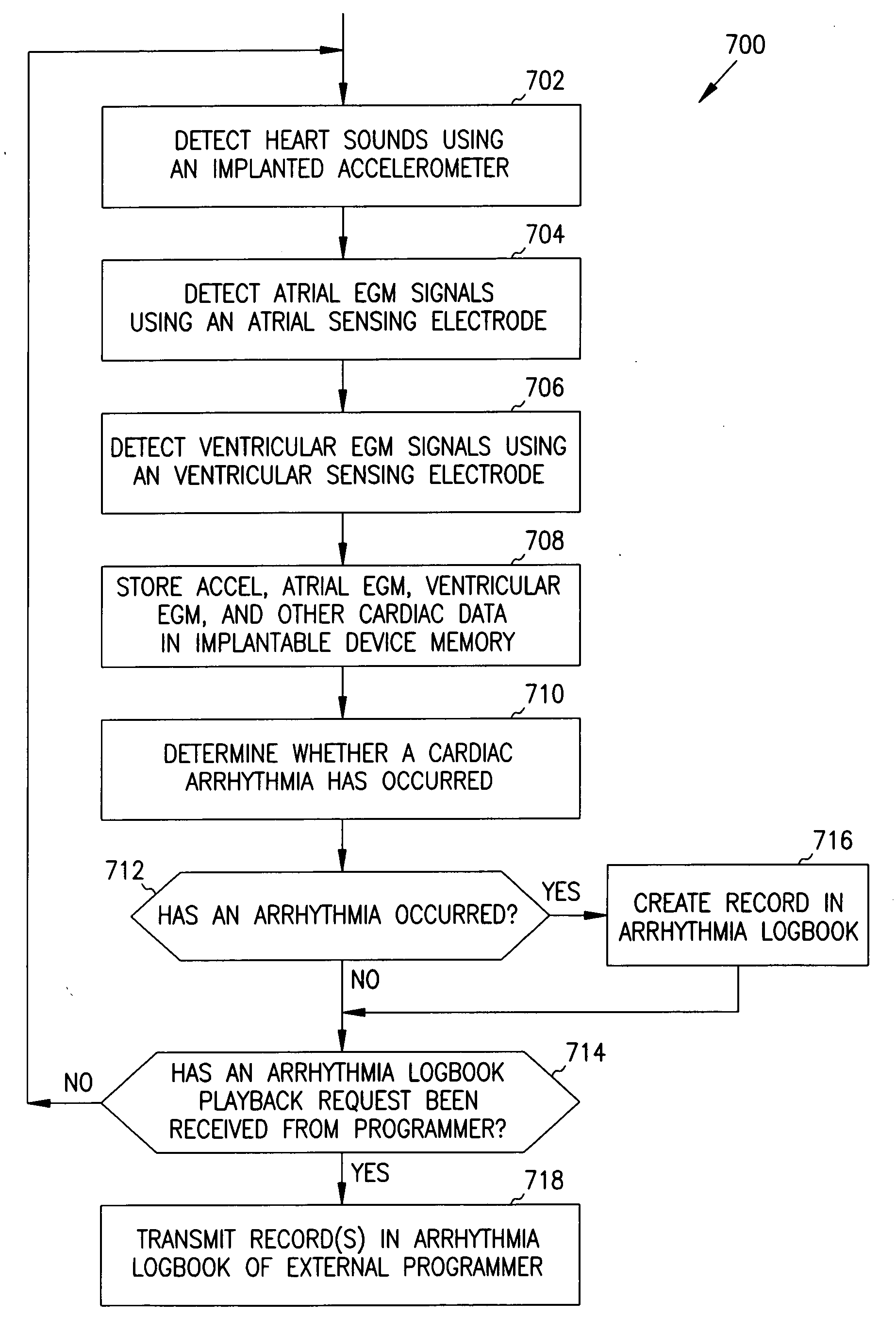
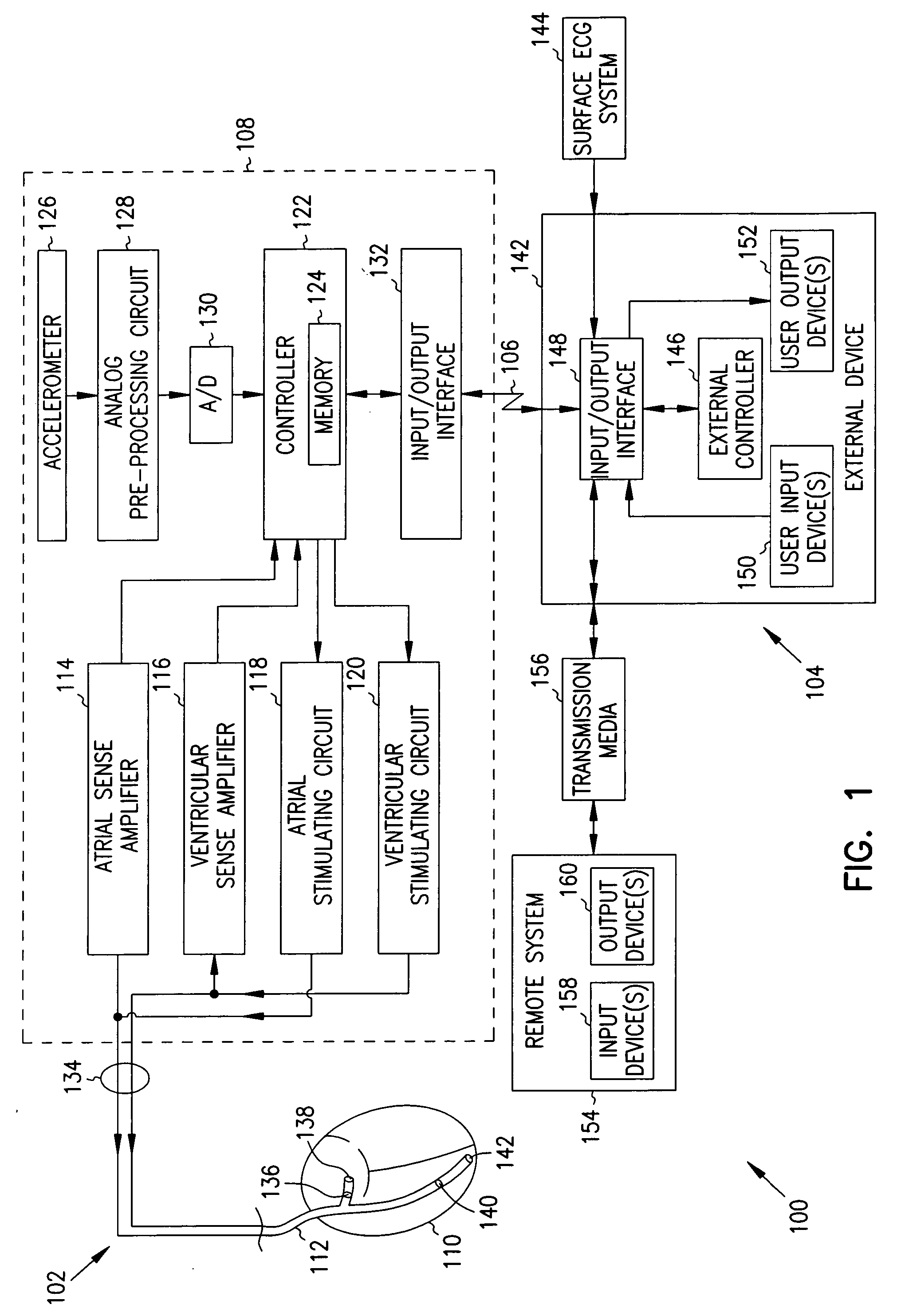
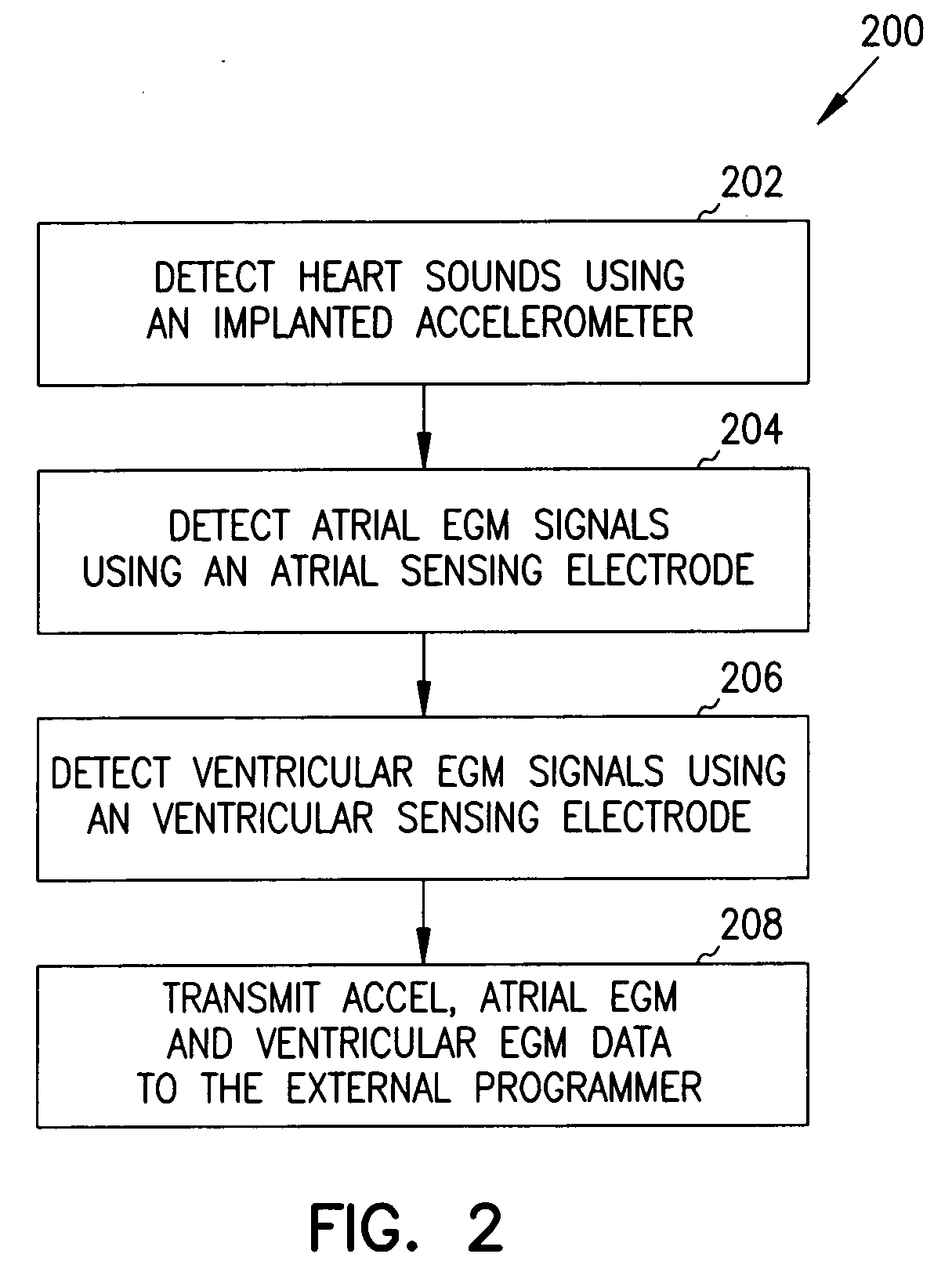
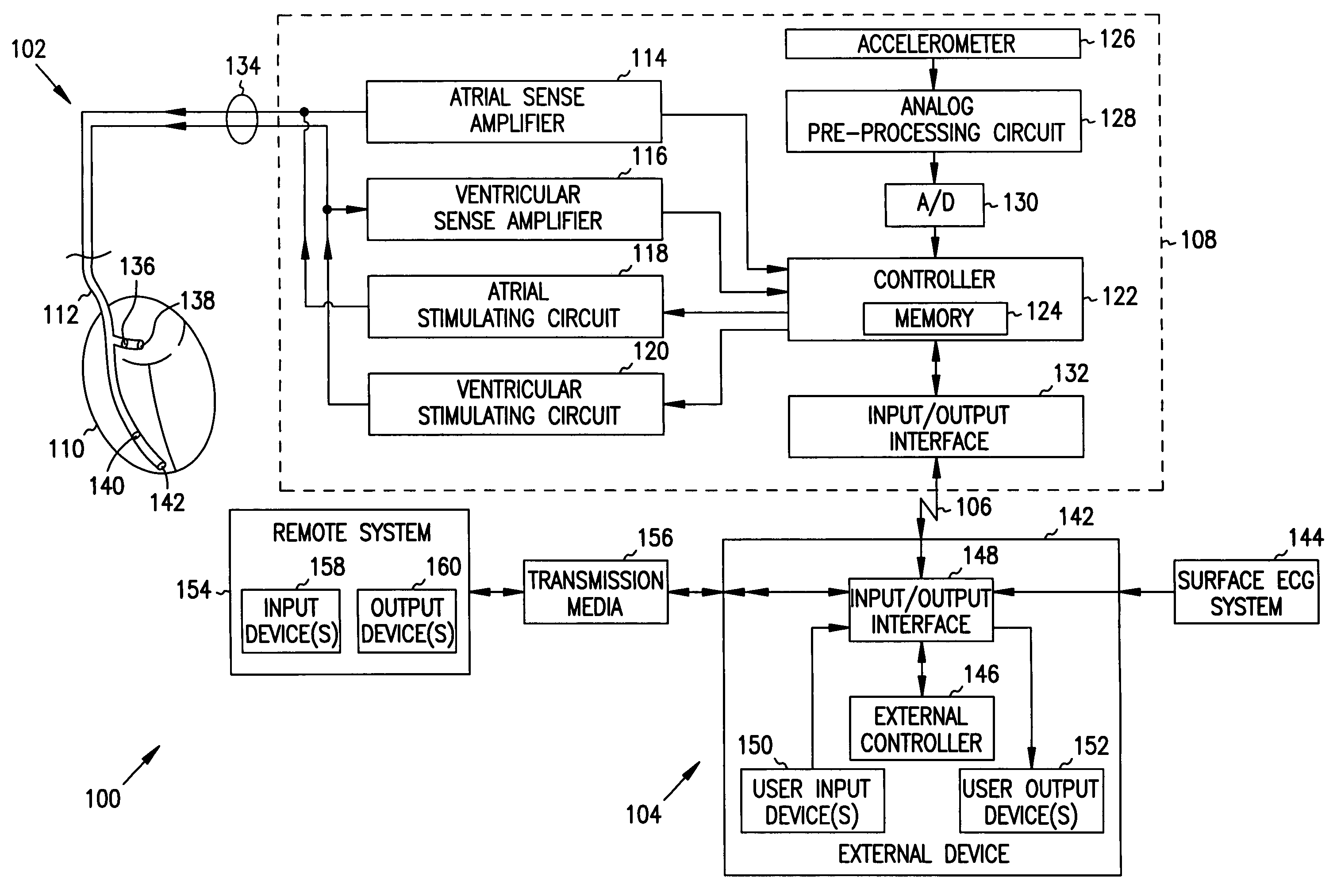
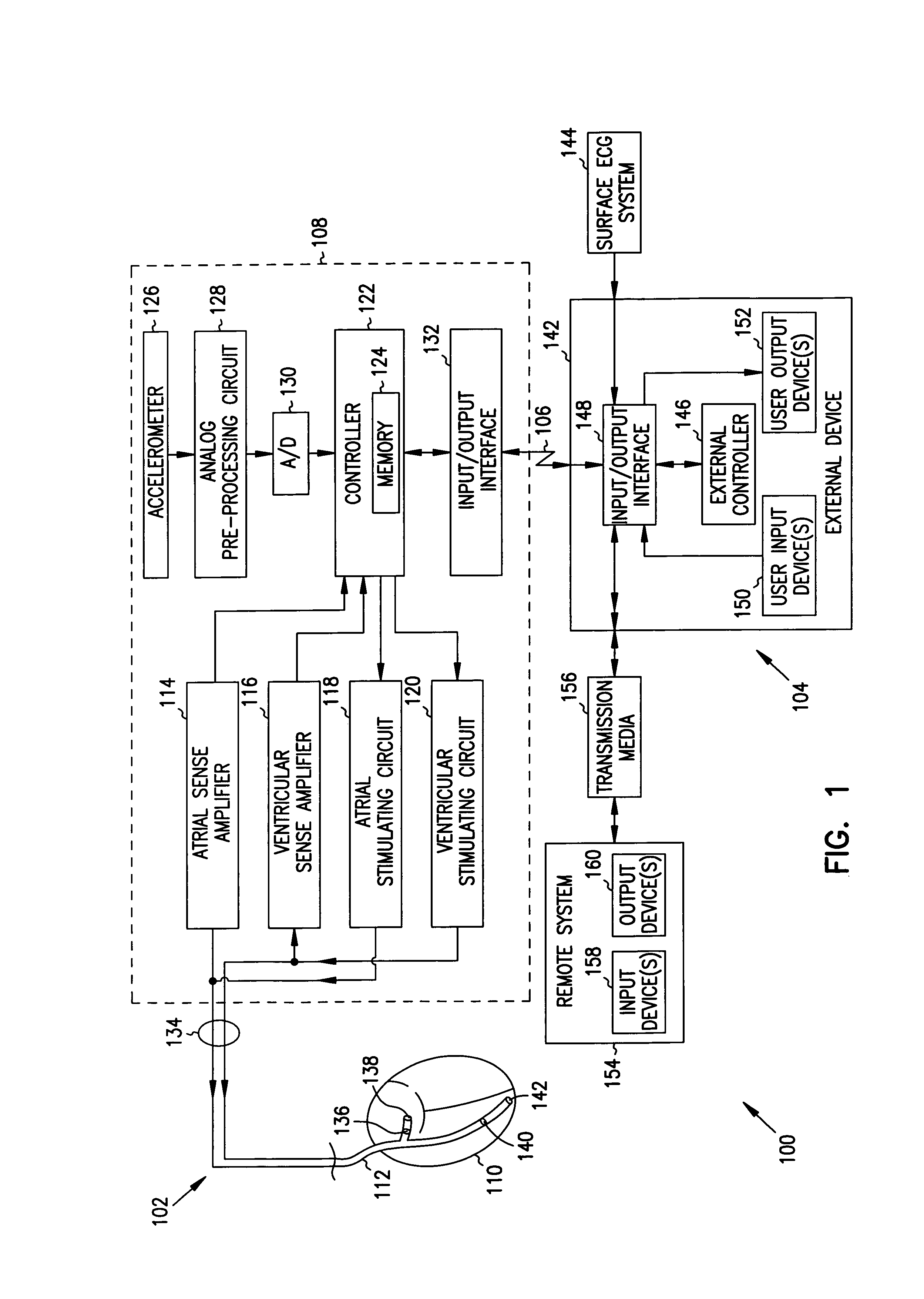
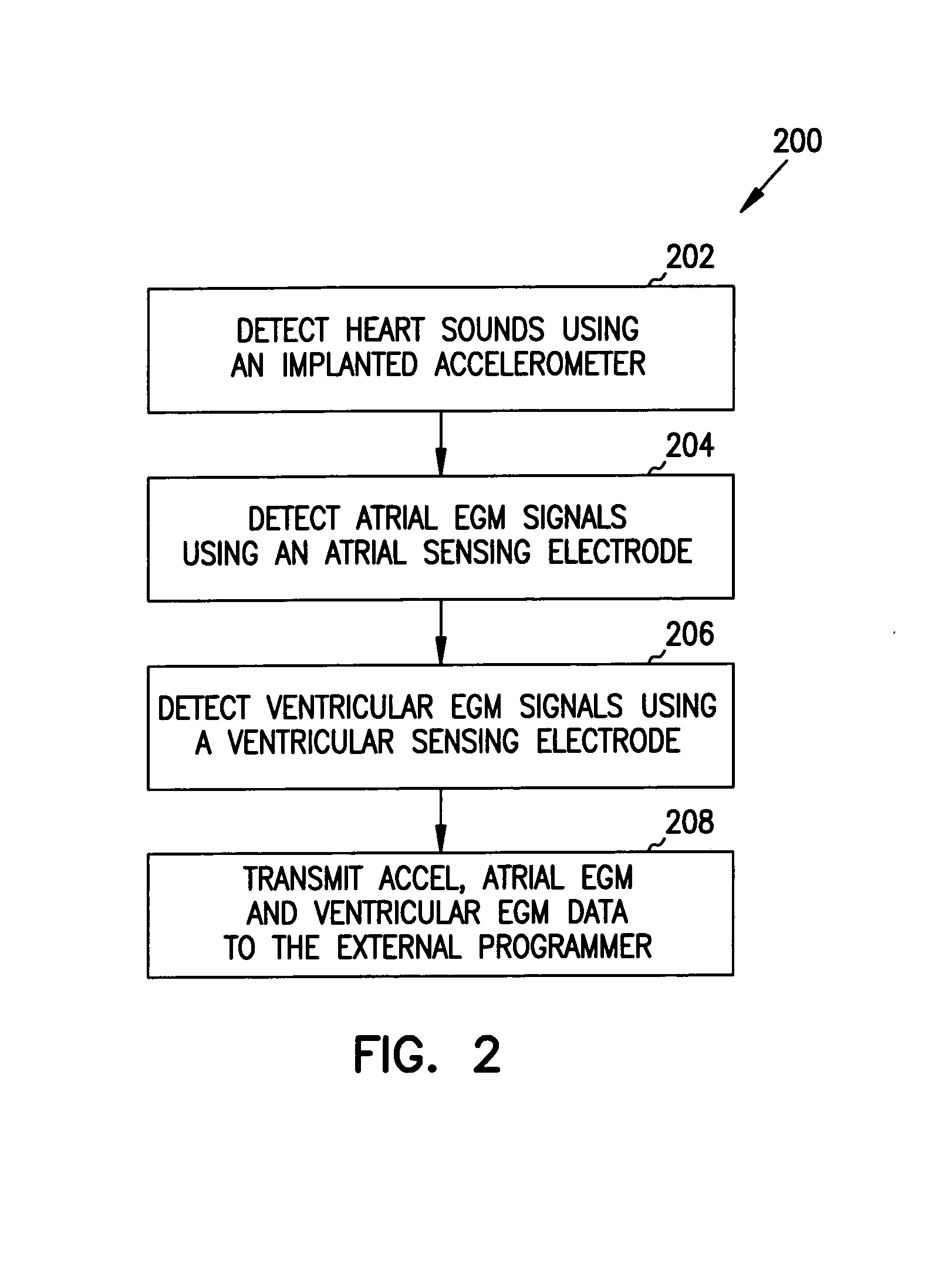
Apparatus and method for outputting heart sounds
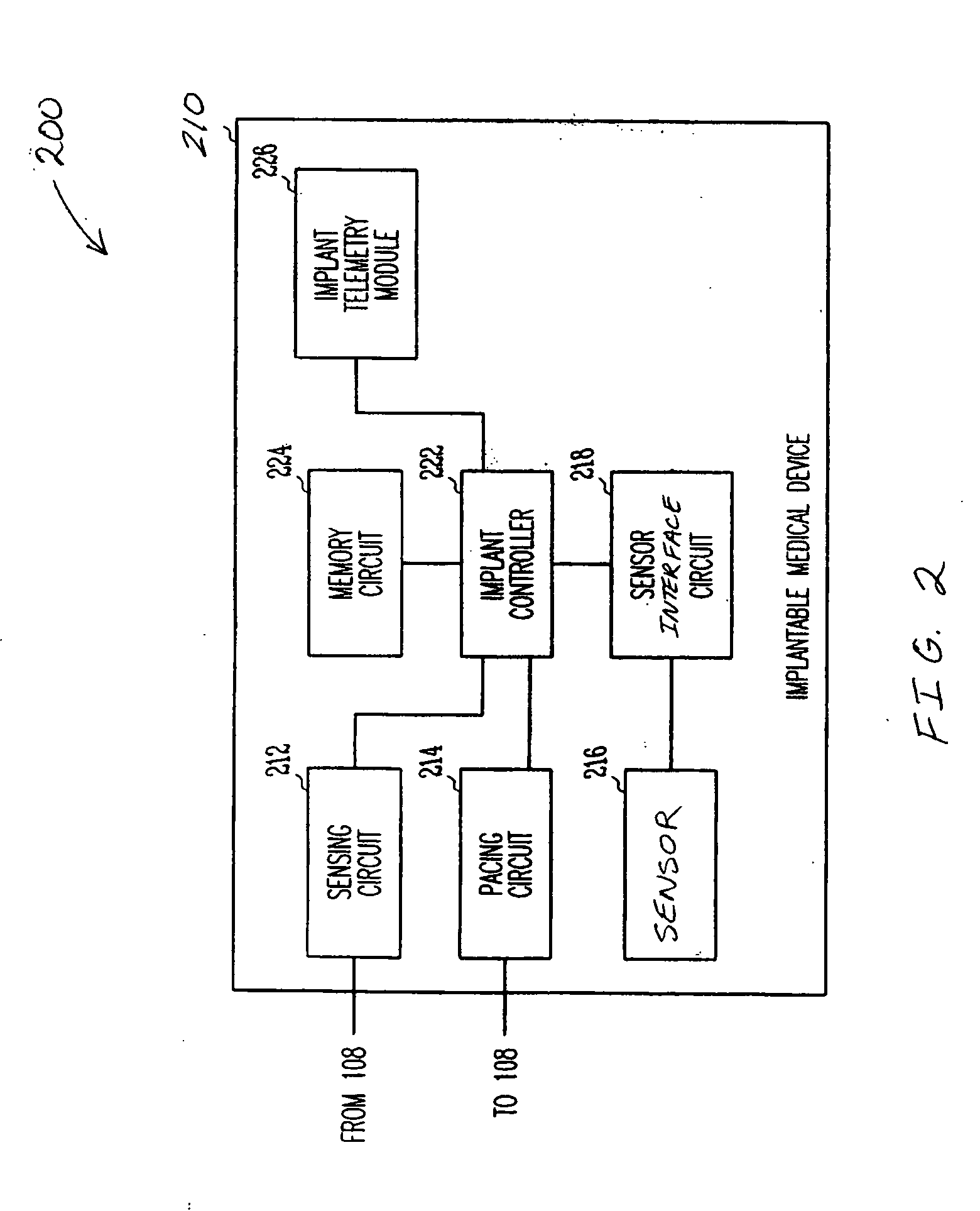
An apparatus for outputting heart sounds includes an implantable system and an external system. The implantable system includes a sensor for generating sensed signals representing detected heart sounds, an interface circuit and a control circuit for receiving the sensed signals, generating data representing the heart sounds therefrom, and transmitting the data to the external system via the interface circuit. The external system includes an interface circuit for communicating with the implantable system, and a control circuit for receiving the data representing the heart sounds and for generating control signals that cause an output device to generate outputs representing the sounds. The implantable system may also include a sensor(s) for detecting cardiac electrical signals. In this case, outputs representing the cardiac electrical signals are also output.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus and method for outputting heart sounds
An apparatus for outputting heart sounds includes an implantable system and an external system. The implantable system includes a sensor for generating sensed signals representing detected heart sounds, an interface circuit and a control circuit for receiving the sensed signals, generating data representing the heart sounds therefrom, and transmitting the data to the external system via the interface circuit. The external system includes an interface circuit for communicating with the implantable system, and a control circuit for receiving the data representing the heart sounds and for generating control signals that cause an output device to generate outputs representing the sounds. The implantable system may also include a sensor(s) for detecting cardiac electrical signals. In this case, outputs representing the cardiac electrical signals are also output.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com