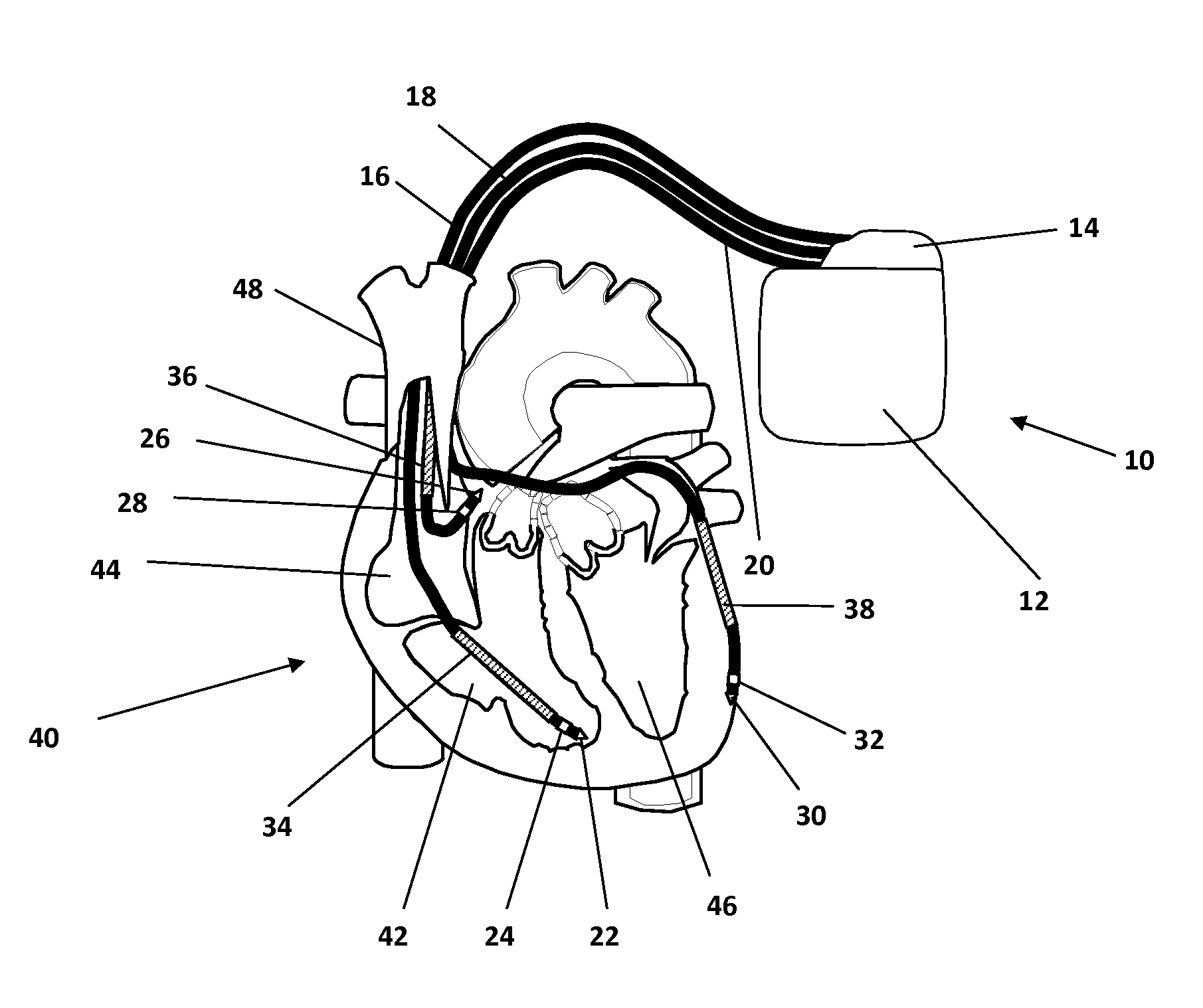
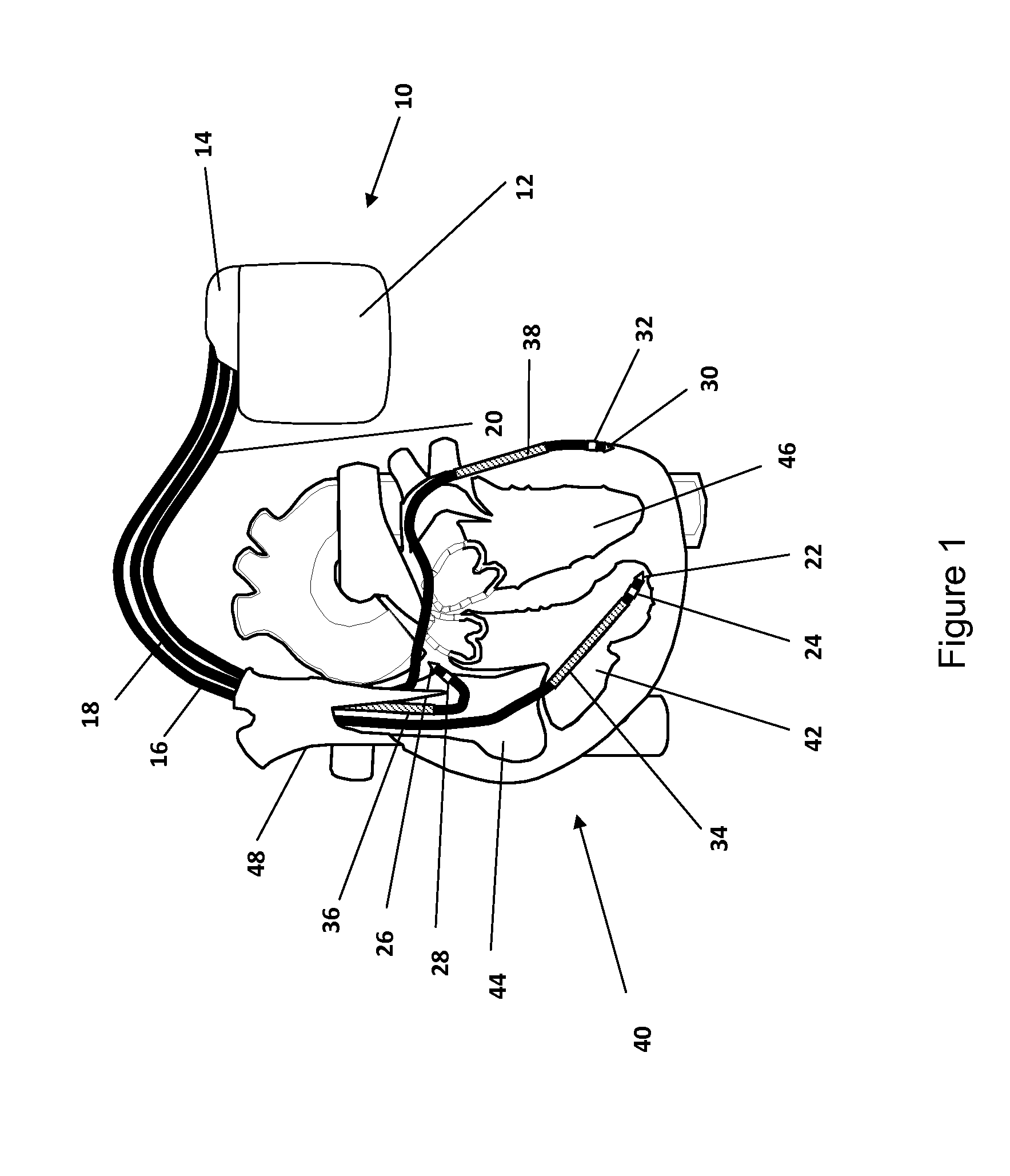
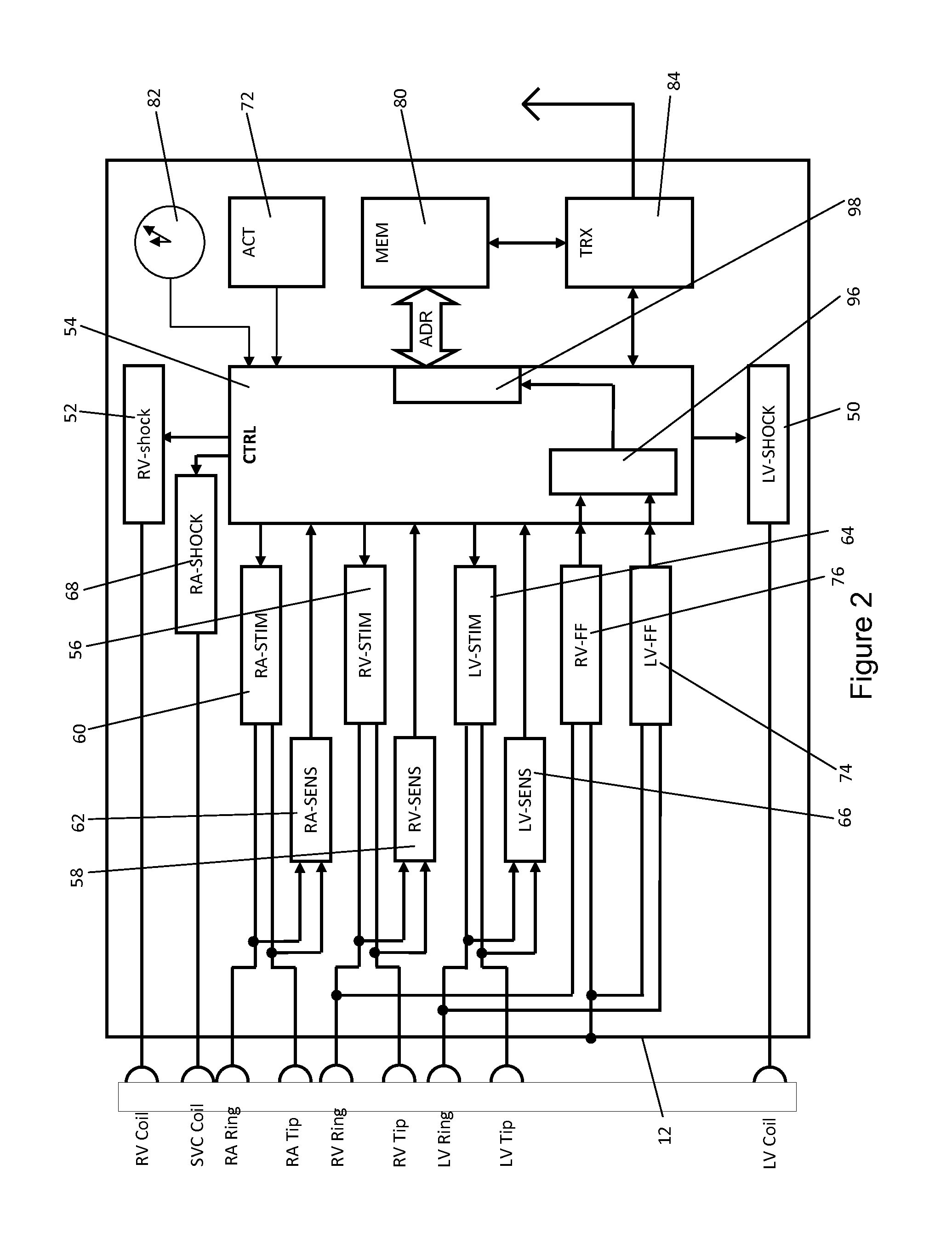
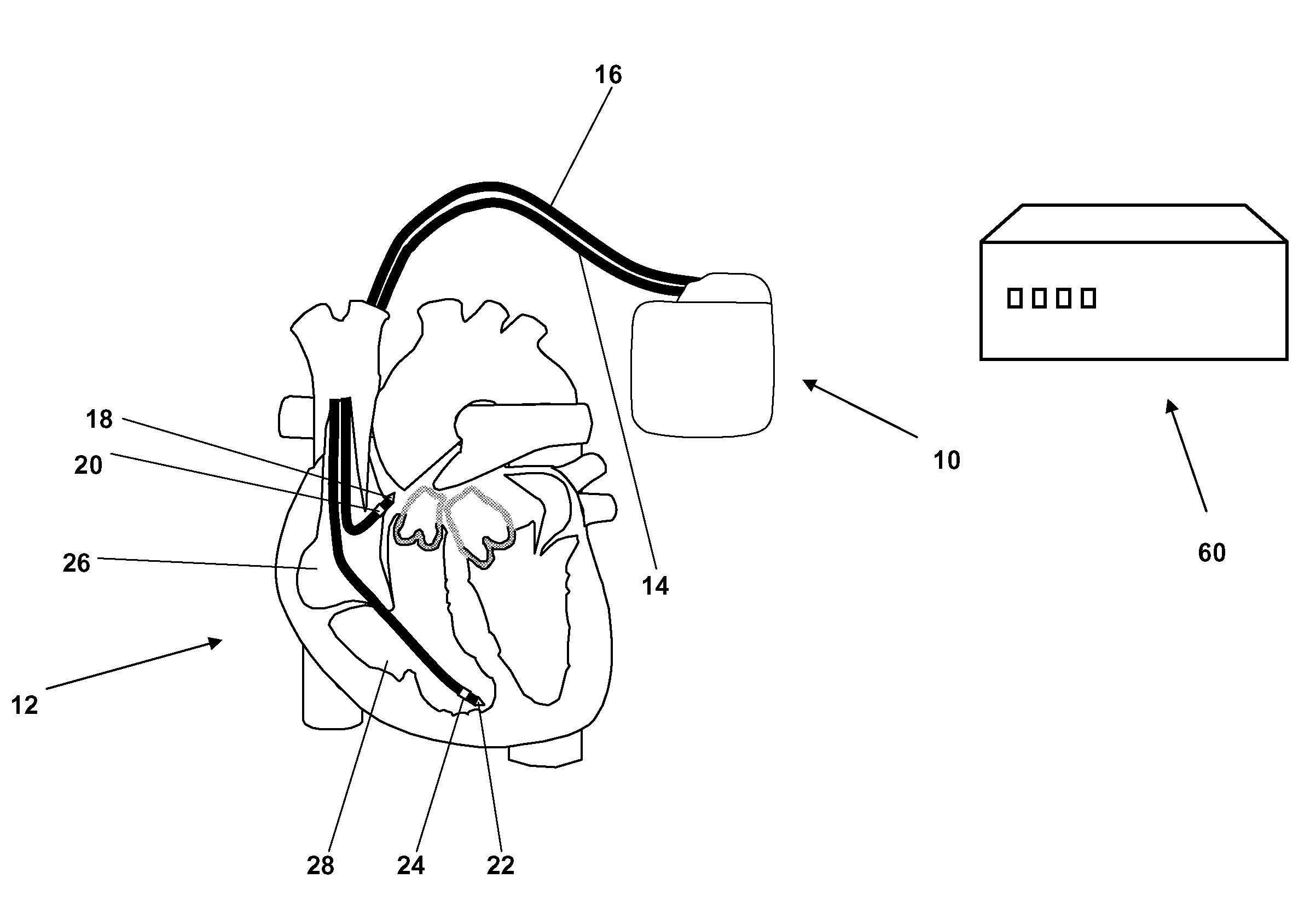
Patents
Literature
161 results about "Heart monitoring" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
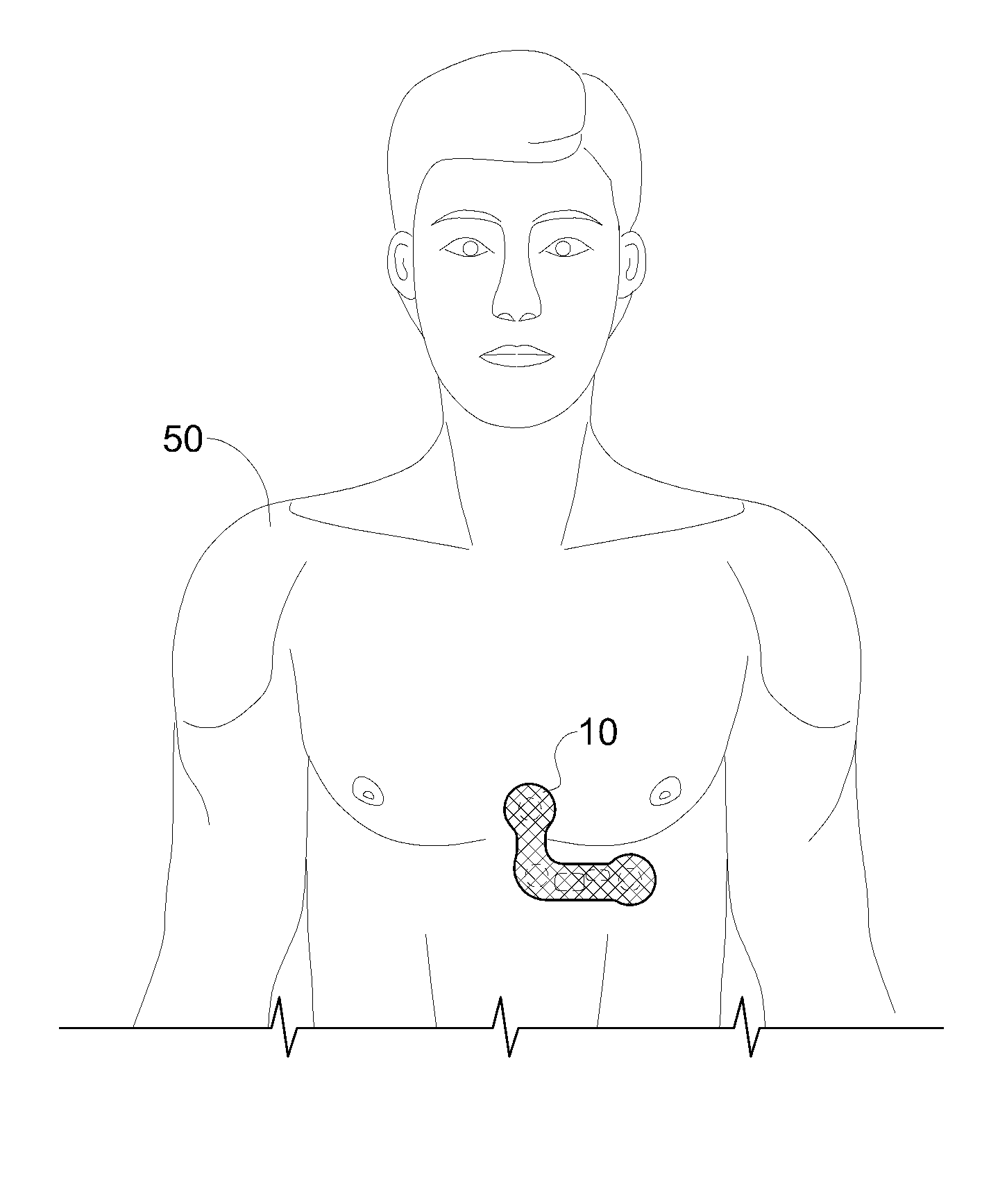
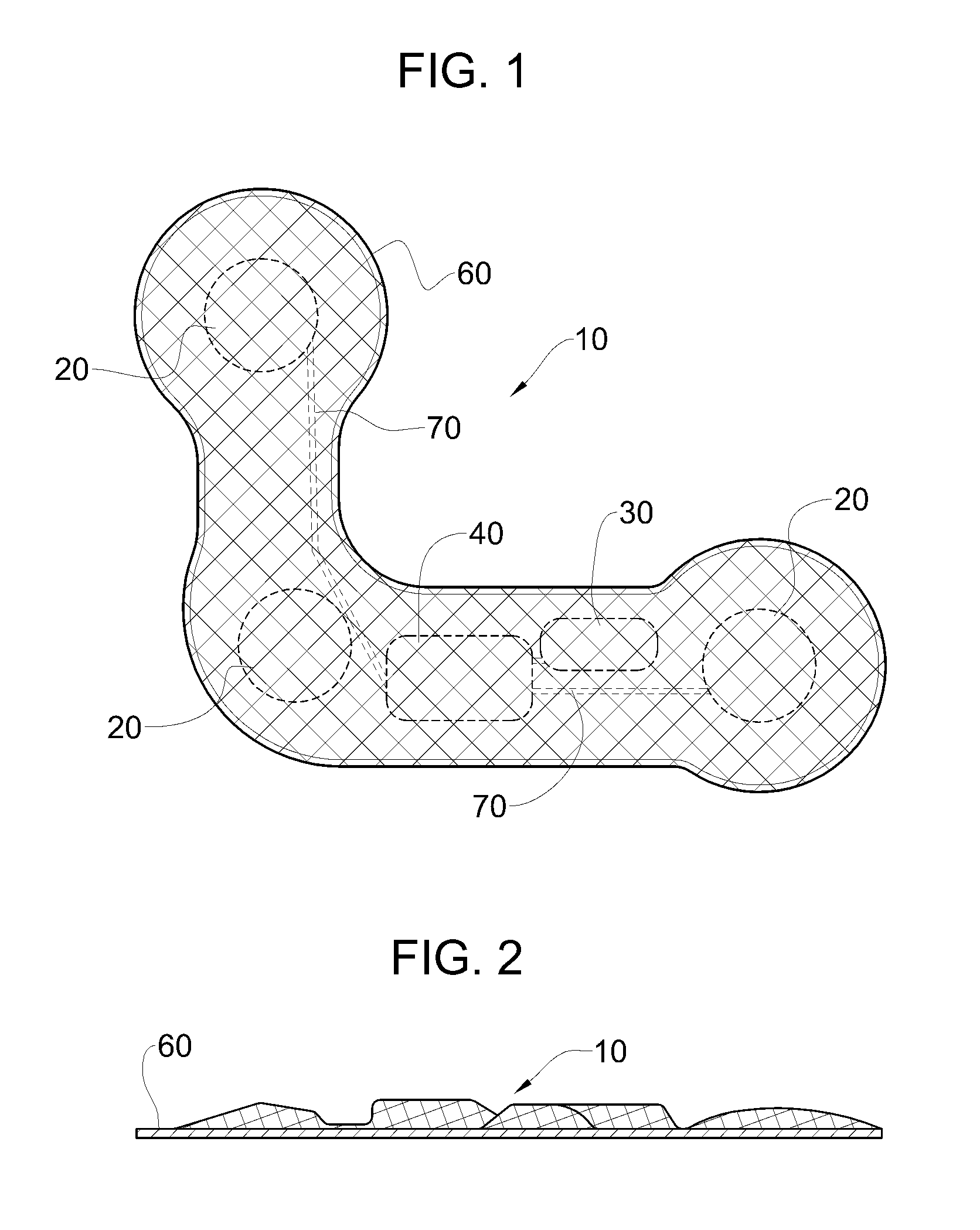
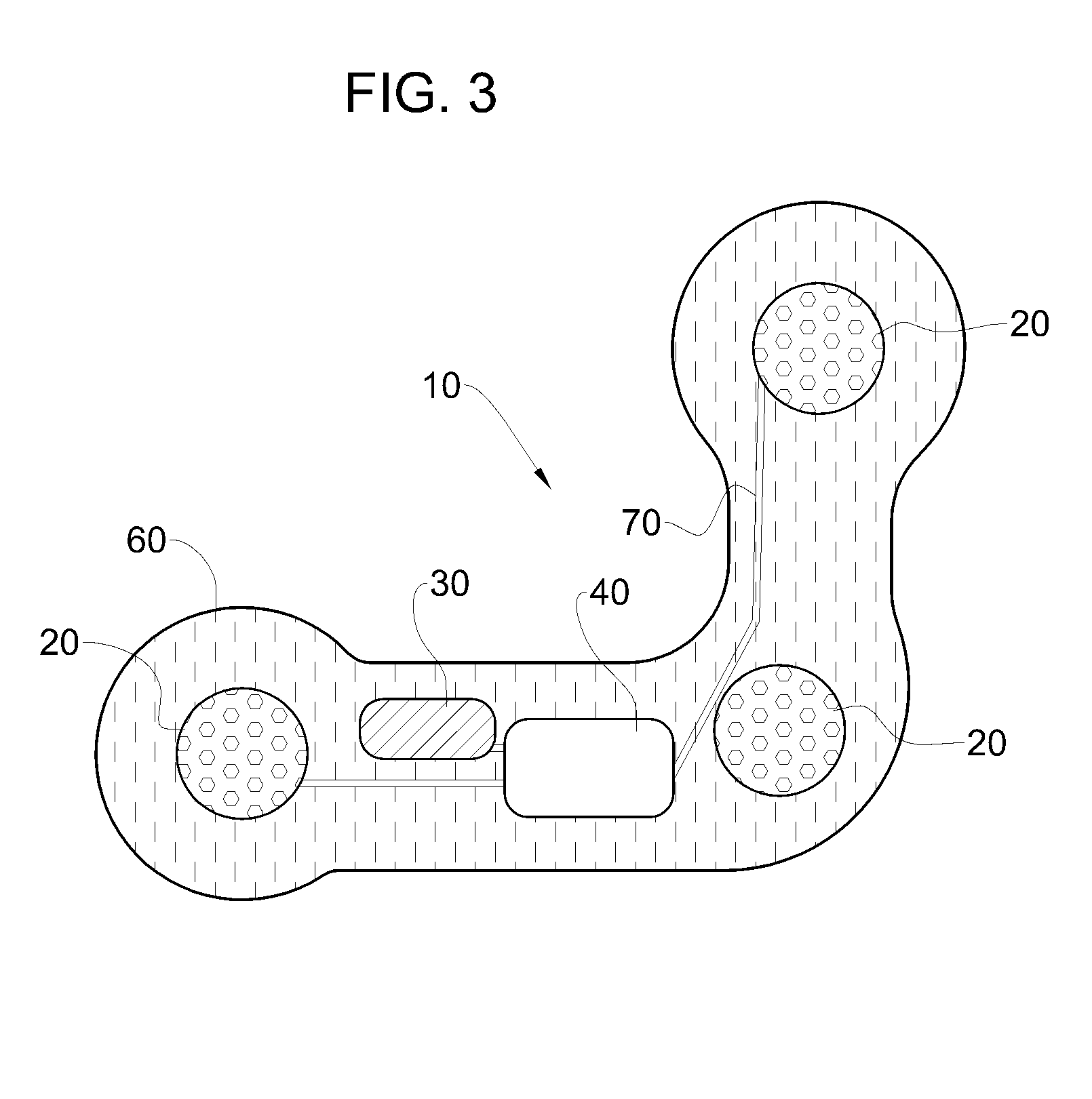
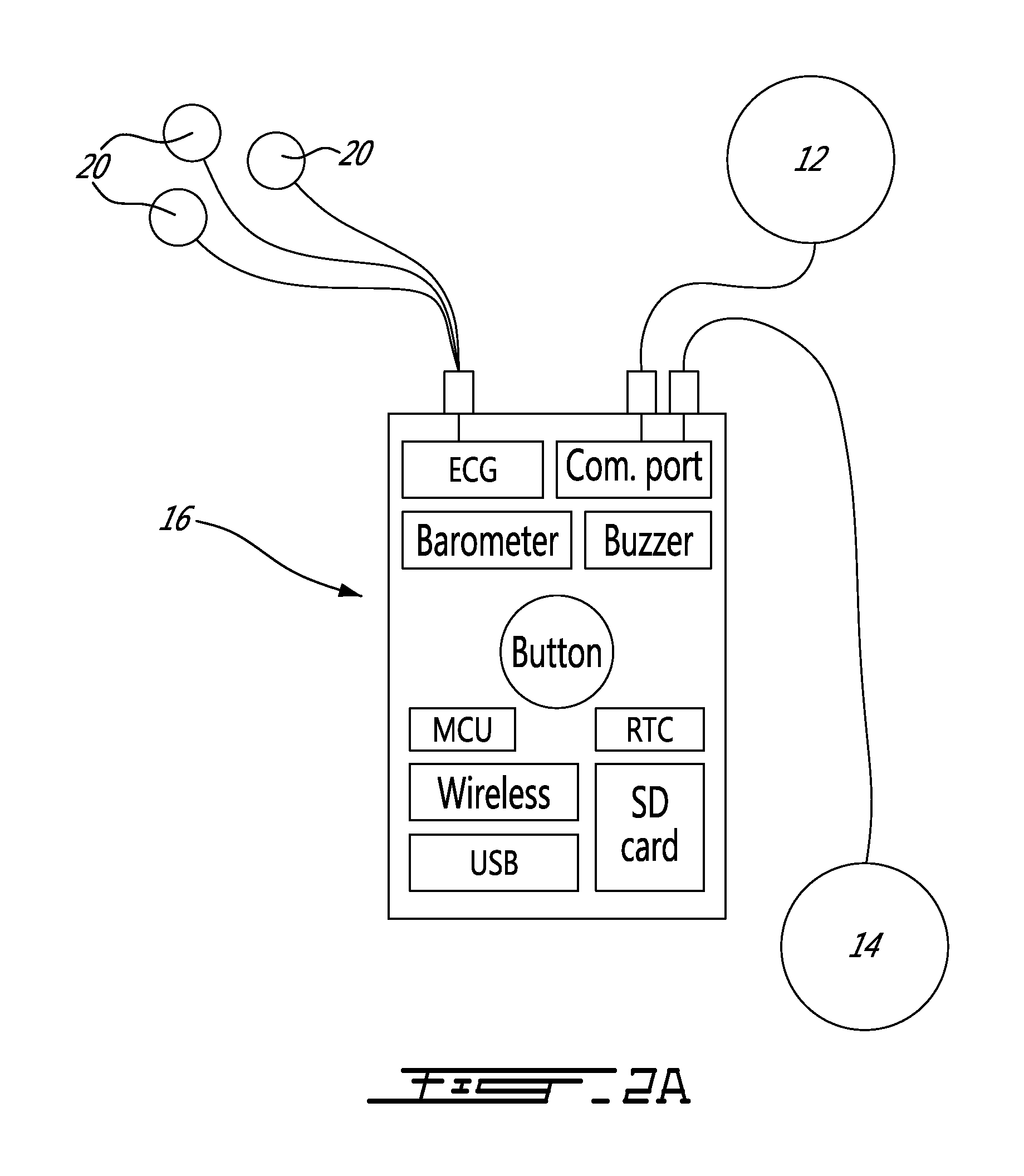
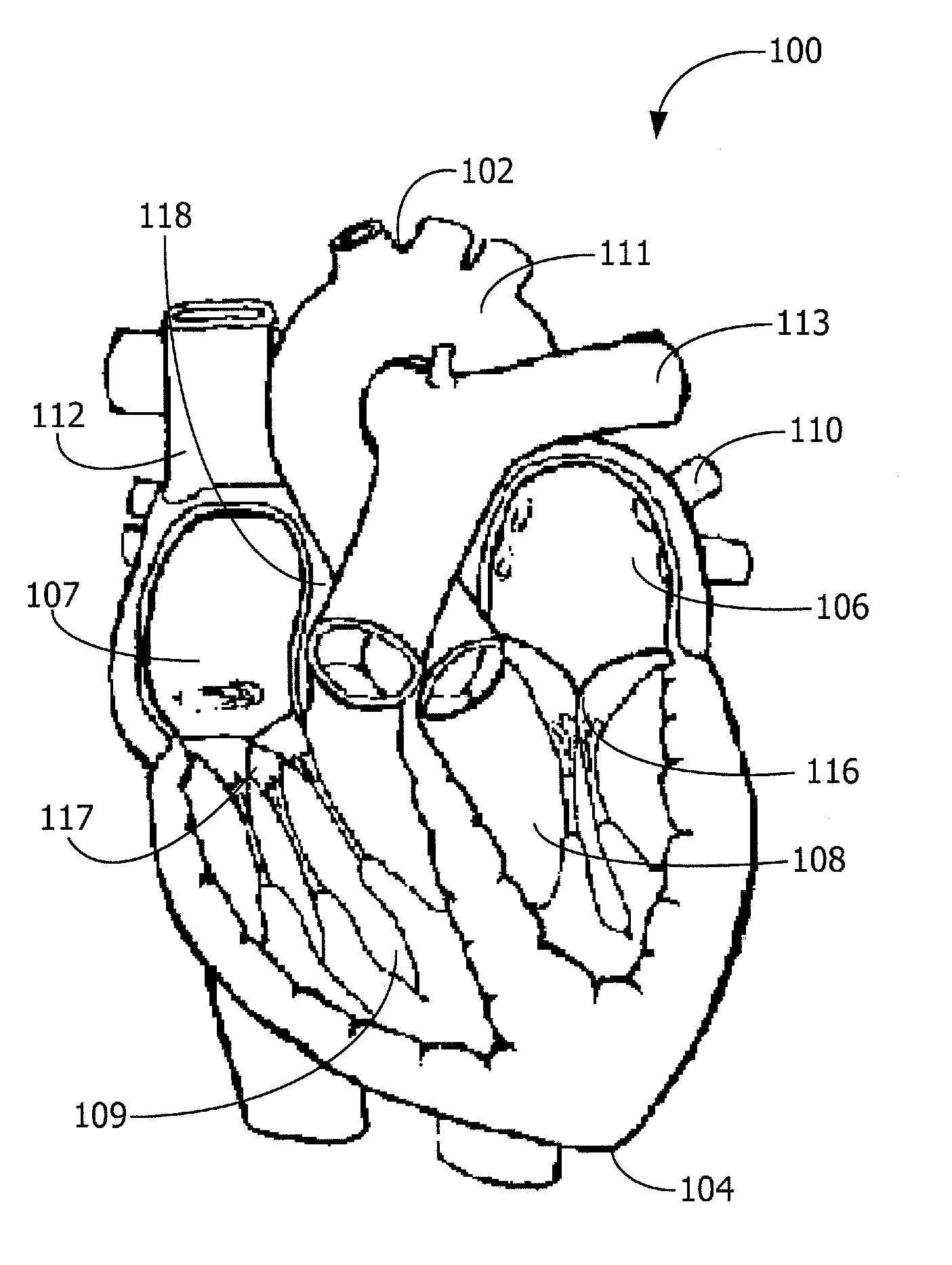
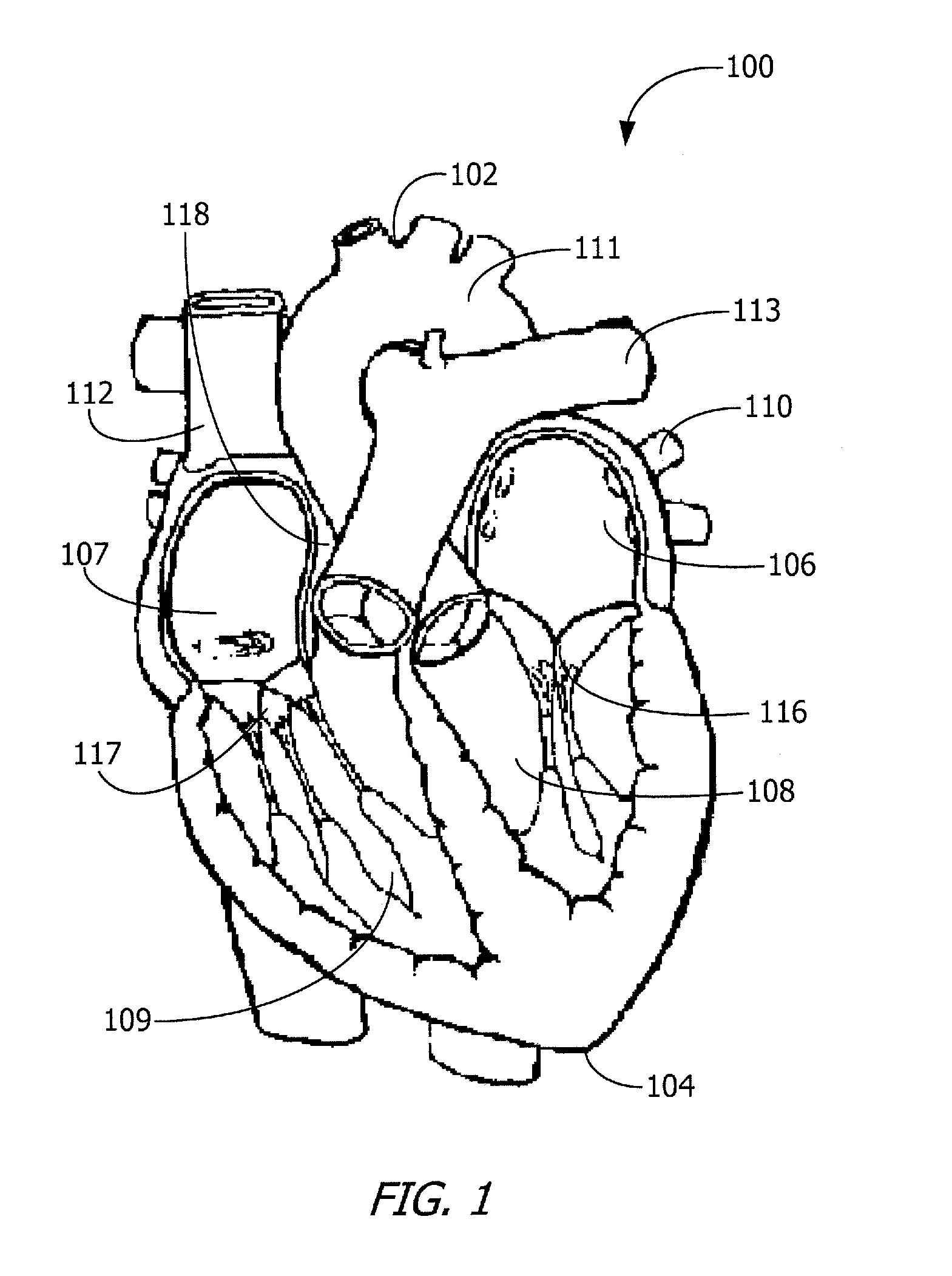
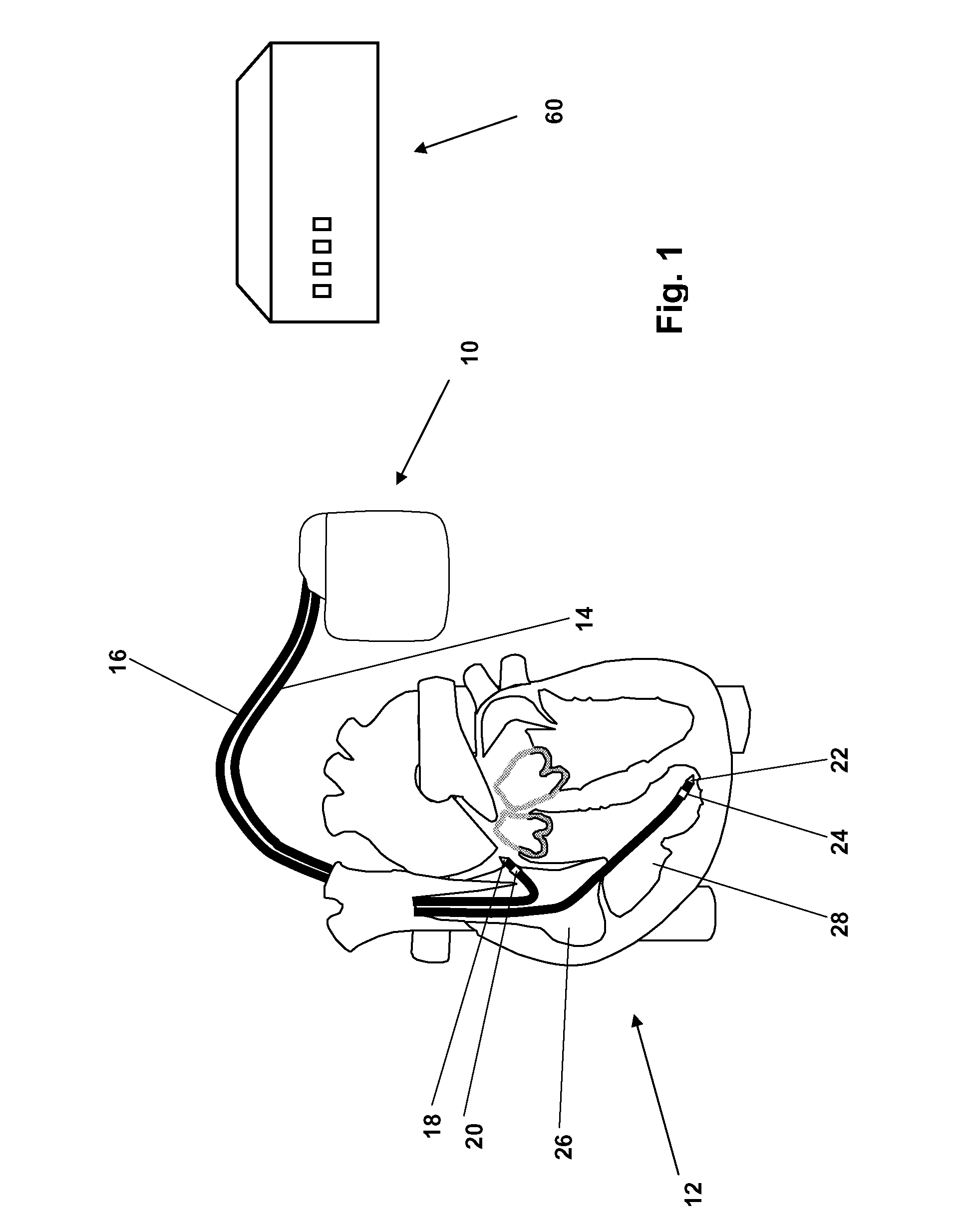
Heart monitoring body patch and system
InactiveUS20090062670A1Good adhesionEasily attached to patientElectrocardiographySensorsTransceiverHeart monitoring
Provided is a diagnostic patch system for monitoring and storing patient information, which includes sensors, a data storage unit, and a transceiver. Each of the sensors is attached to a skin to detect a patient data. The data storage unit is configured to store stream of the detected patient data from the plurality of sensors. The transceiver, connected with the sensors and the data storage unit, communicates the stream of the patient data with an analyzer, and the analyzer is configured to process and analyze the stream of the patient data. Two or more diagnostic patch systems can communicate with each other.
Owner:BIOSEVEN
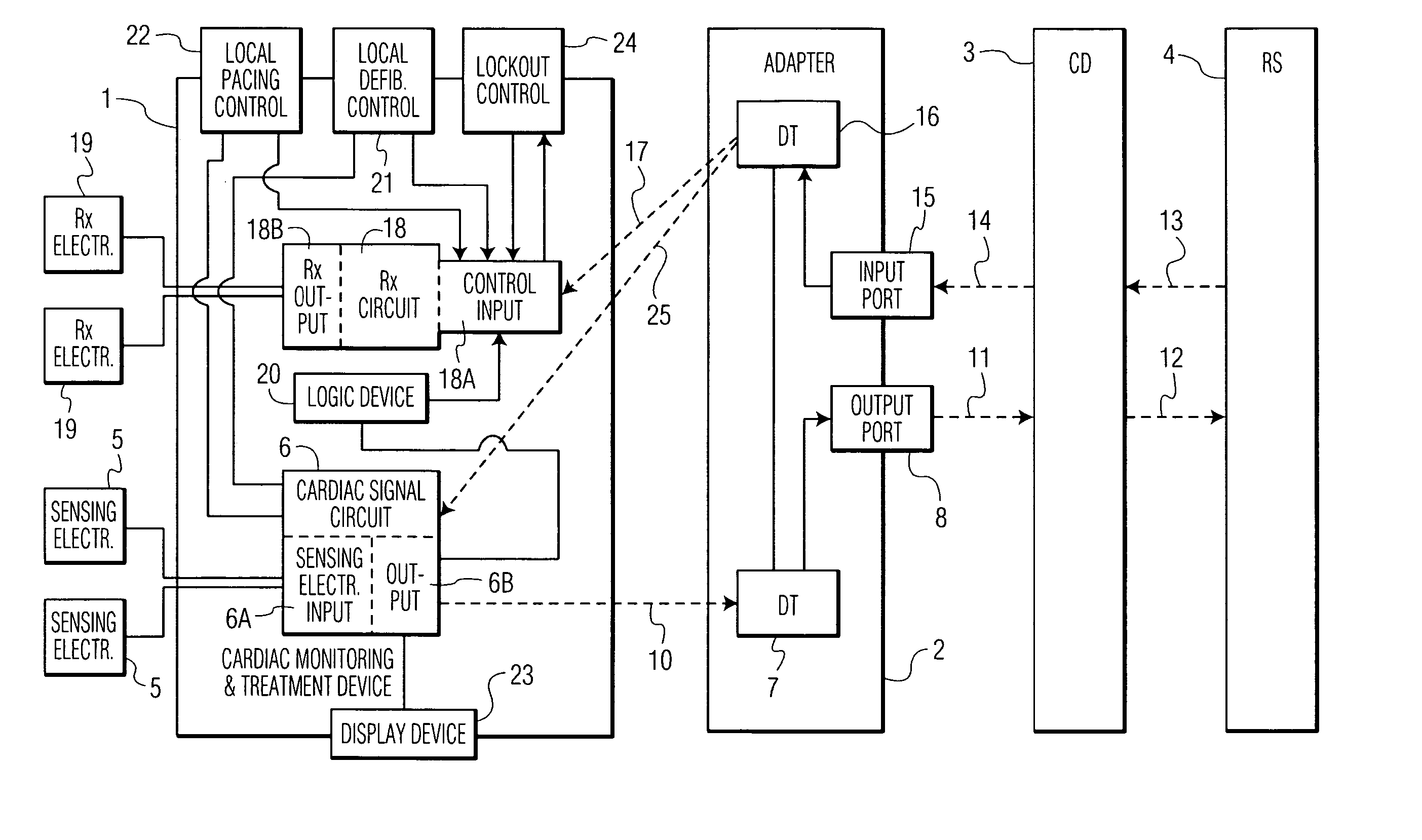
Control of a defibrillator and/or pacemaker
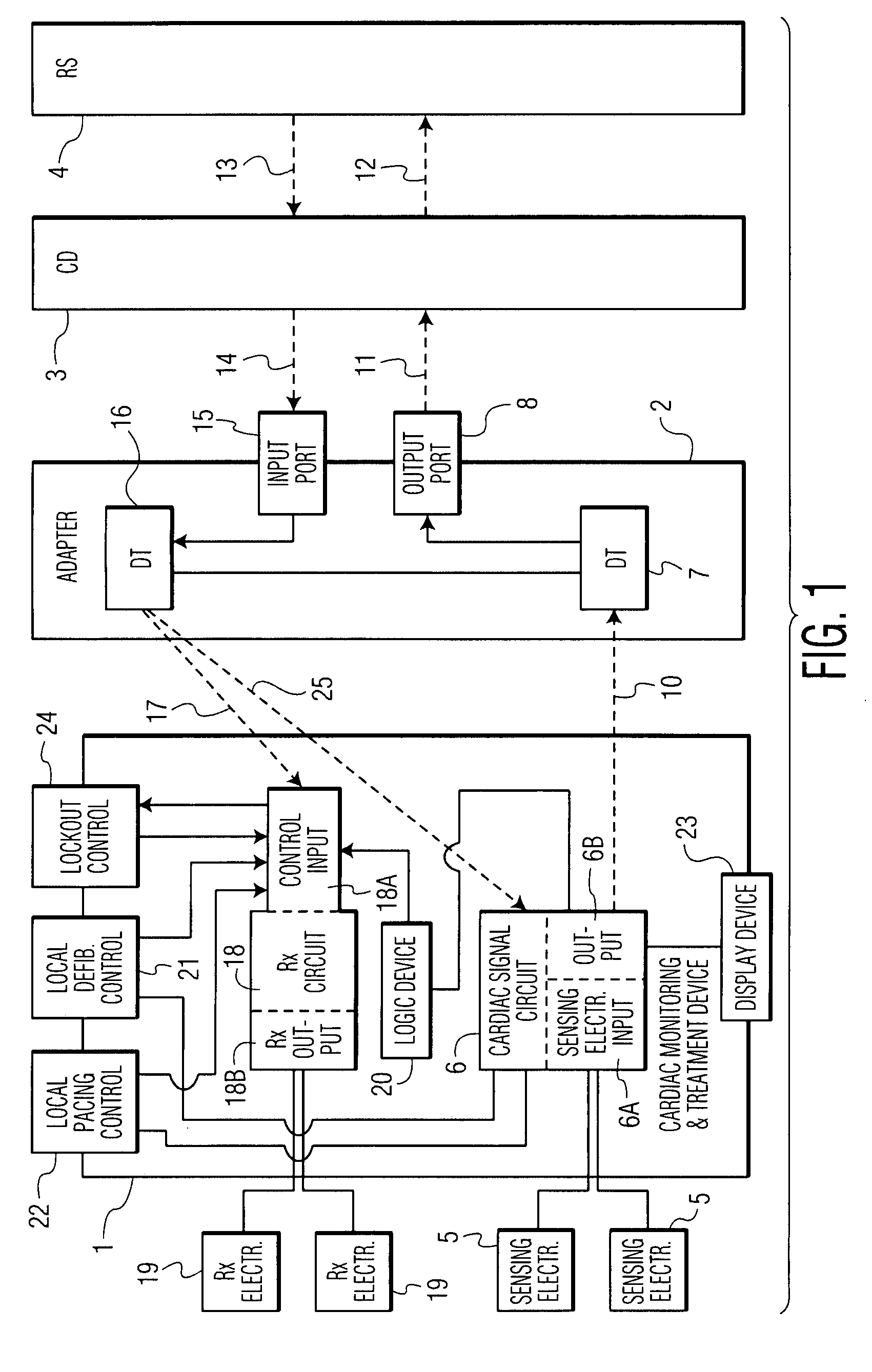
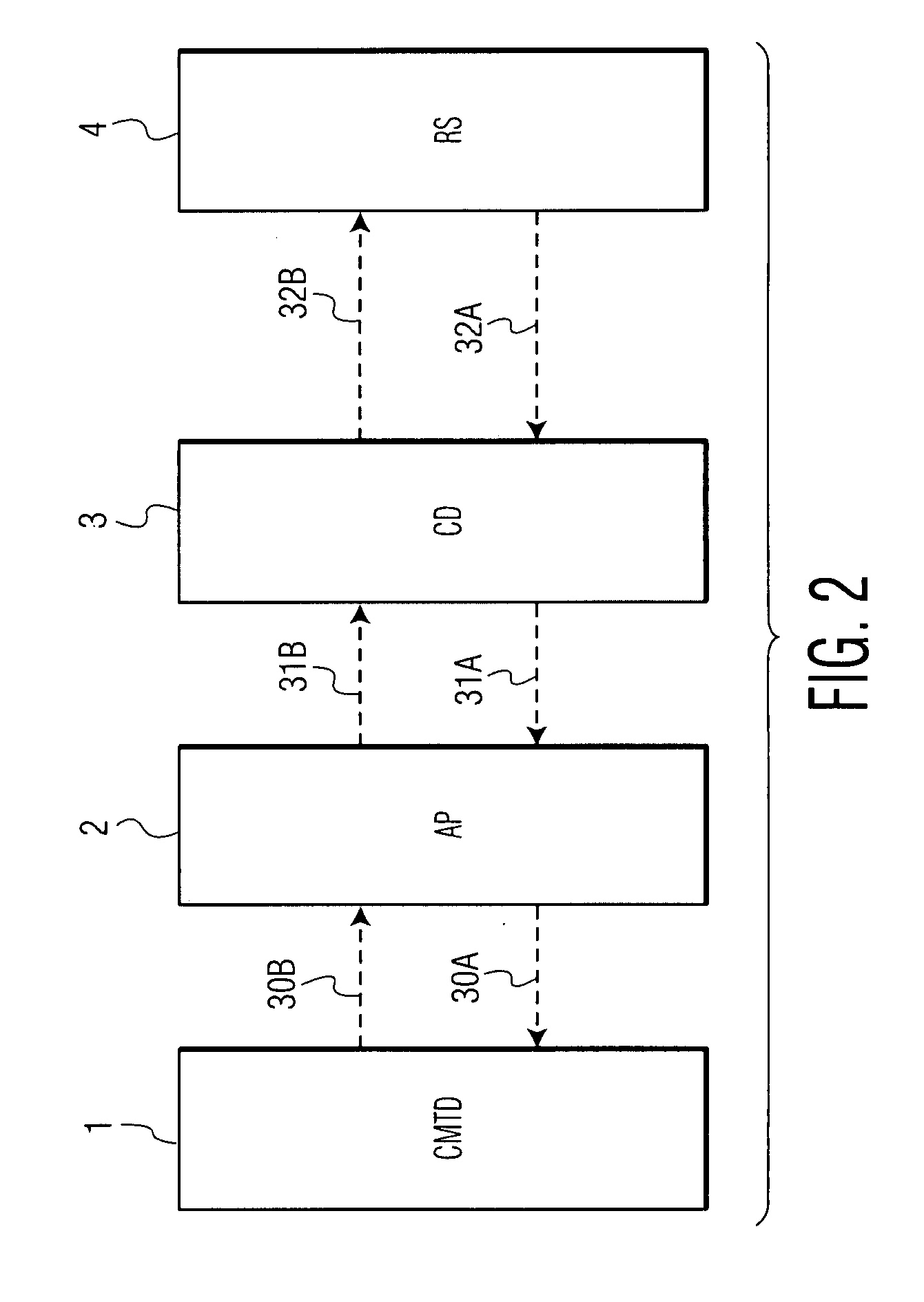
A cardiac monitoring and treatment apparatus allows a victim of a medical emergency access to a medical professional (MP) who can monitor, diagnose and treat the victim from a remote site. The apparatus includes a cardiac monitoring and treatment device (CMTD) coupled to an electronic adaptor designed to communicate with a local, first transmitting / receiving (T / R) device which, in turn, is adapted to electronically communicate with a remote, second transmitting / receiving (T / R) device used by the MP. The CMPD comprises a cardiac treatment circuit for effecting cardiac pacing and / or defibrillation and a cardiac signal circuit for receiving cardiac signals. The cardiac signals are (1) transmitted from the signal circuit to the second T / R device for evaluation by the MP, (2) the MP may transmit a control signal to the treatment circuit, and (3), in response thereto, the treatment circuit may generate one or more electrical pulses for treatment of the victim.
Owner:MATOS JEFFREY A
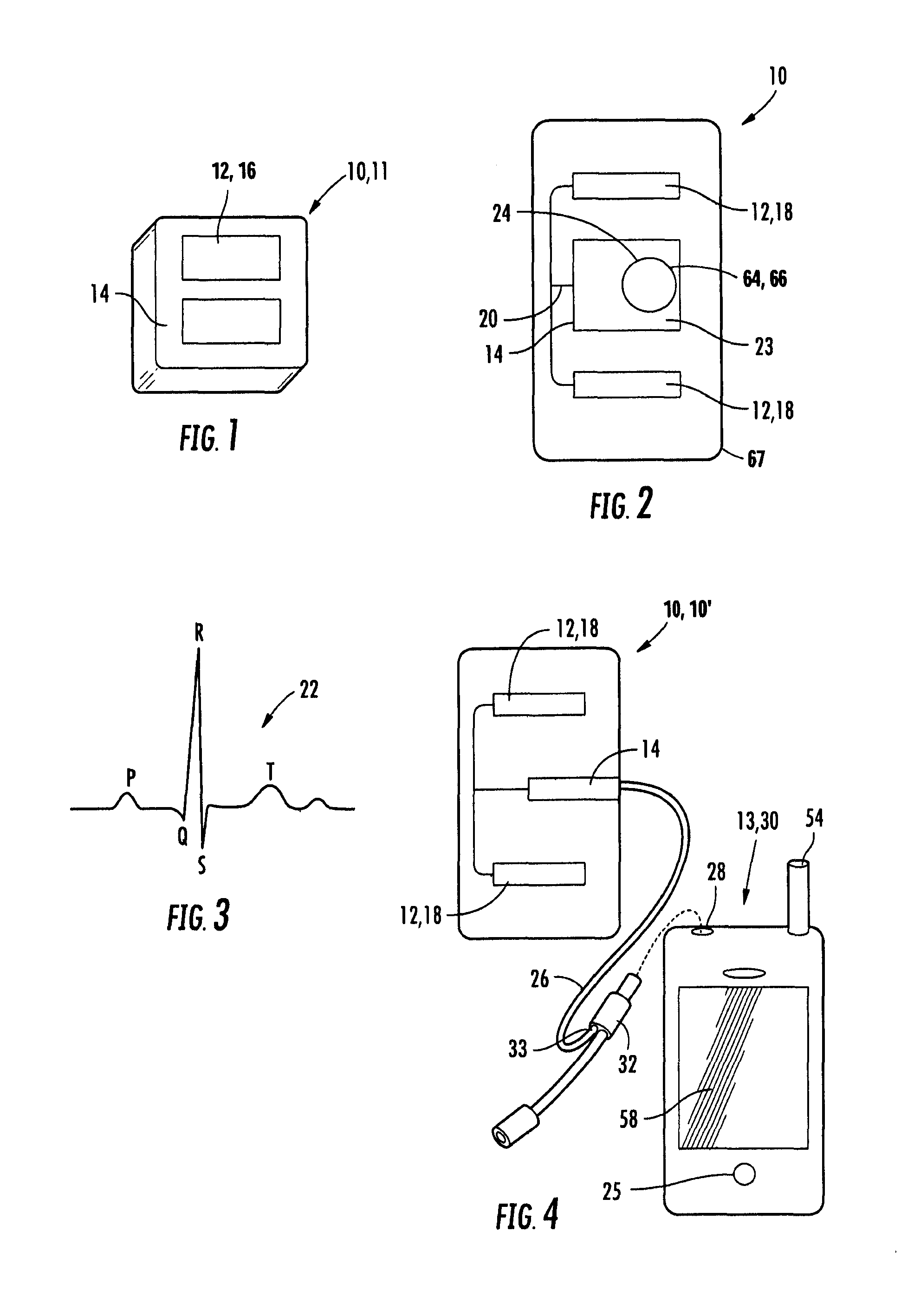
Heart monitoring system usable with a smartphone or computer
A personal monitoring device has a sensor assembly configured to sense physiological signals upon contact with a user's skin. The sensor assembly produces electrical signals representing the sensed physiological signals. A converter assembly, integrated with, and electrically connected to the sensor assembly, converts the electrical signals generated by the sensor assembly to a frequency modulated physiological audio signal having a carrier frequency in the range of from about 6 kHz to about 20 kHz.
Owner:ALIVECOR
Heart Monitoring System Usable With A Smartphone or Computer
A personal monitoring device has a sensor assembly configured to sense physiological signals upon contact with a user's skin. The sensor assembly produces electrical signals representing the sensed physiological signals. A converter assembly, integrated with, and electrically connected to the sensor assembly, converts the electrical signals generated by the sensor assembly to a frequency modulated physiological audio signal having a carrier frequency in the range of from about 6 kHz to about 20 kHz.
Owner:ALIVECOR
Cardiac monitoring system
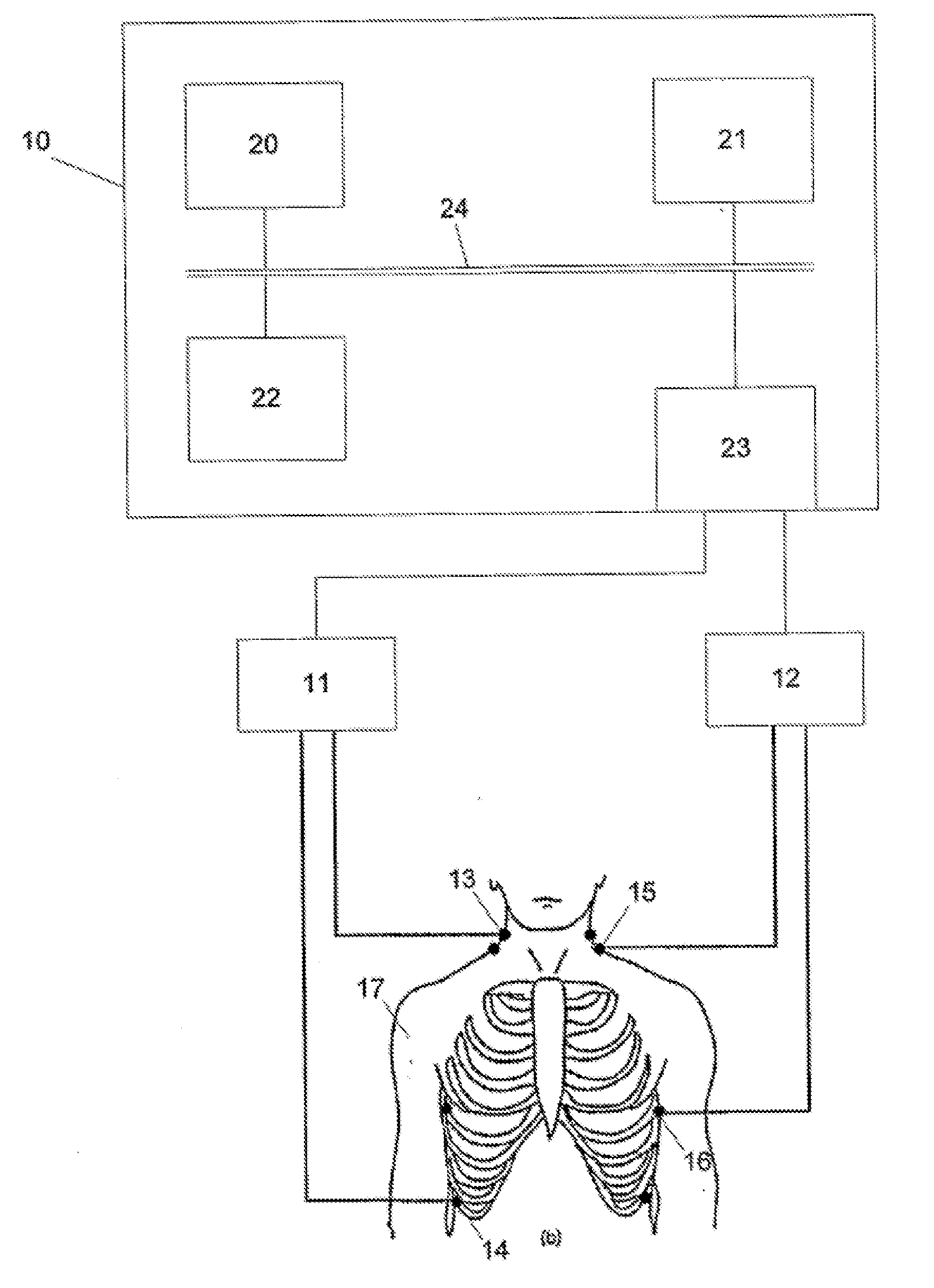
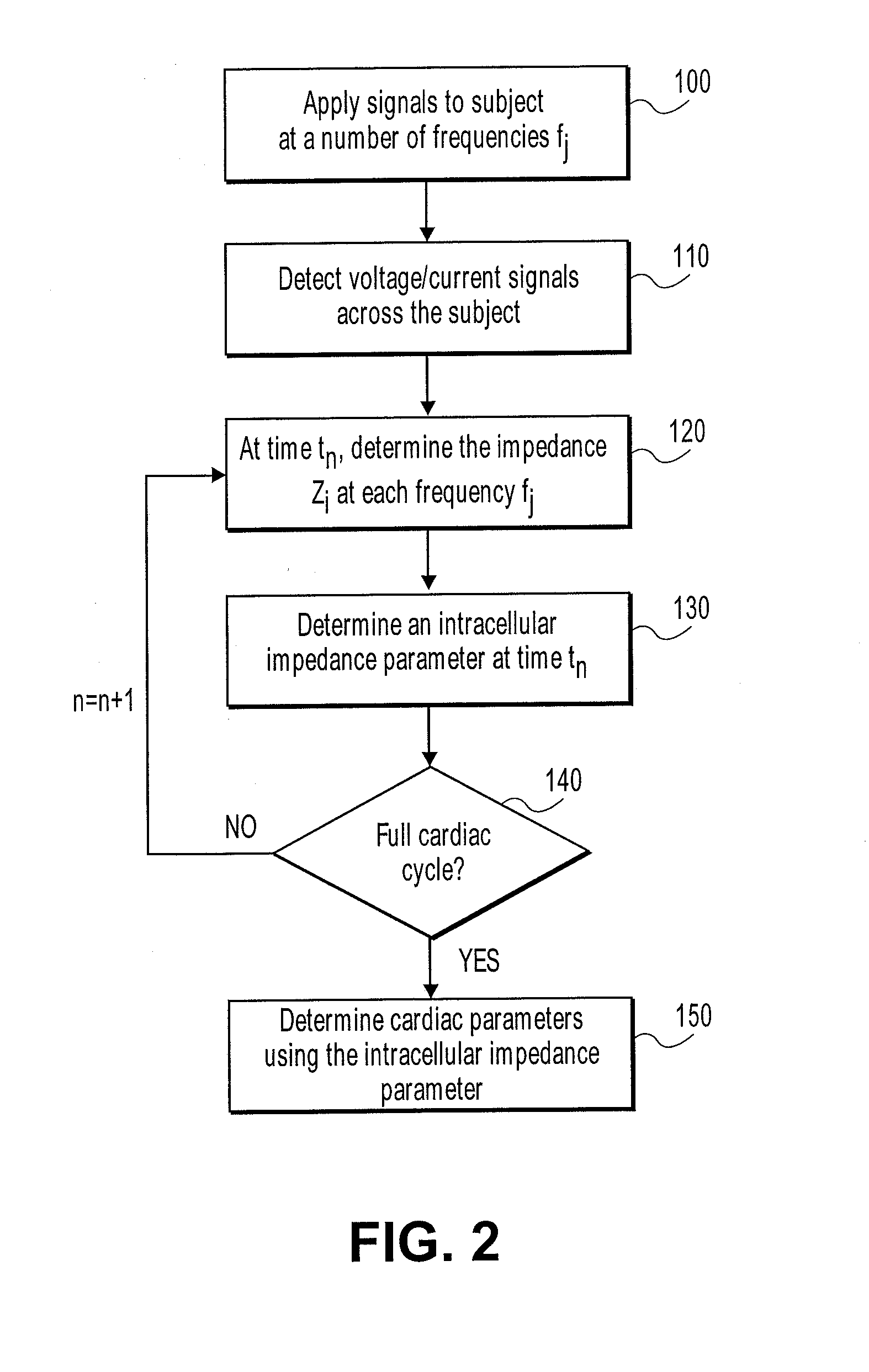
A method of analyzing cardiac functions in a subject using a processing system is described. The method may include applying one or more electrical signals having a plurality of frequencies to the subject and detecting a response to the applied one or more signals from the subject. A characteristic frequency can then be determined from the applied and received signals, and at least one component of the impedance (e.g., reactance, phase shift) can be measured at the characteristic frequency. Thus, the impedance or a component of impedance at a characteristic frequency can be determined for a number of sequential time instances. A new characteristic frequency may be determined within a cardiac cycle (e.g., with each sequential time instant) or the same characteristic frequency may be used throughout the cardiac cycle during which instantaneous values of impedance (or a component of impedance) are determined. These instantaneous values may be used to determine one or more indicia of cardiac function.
Owner:IMPEDANCE CARDIOLOGY SYST +1
Cardiac Monitoring And Therapy Using A Device For Providing Pressure Treatment Of Sleep Disordered Breathing
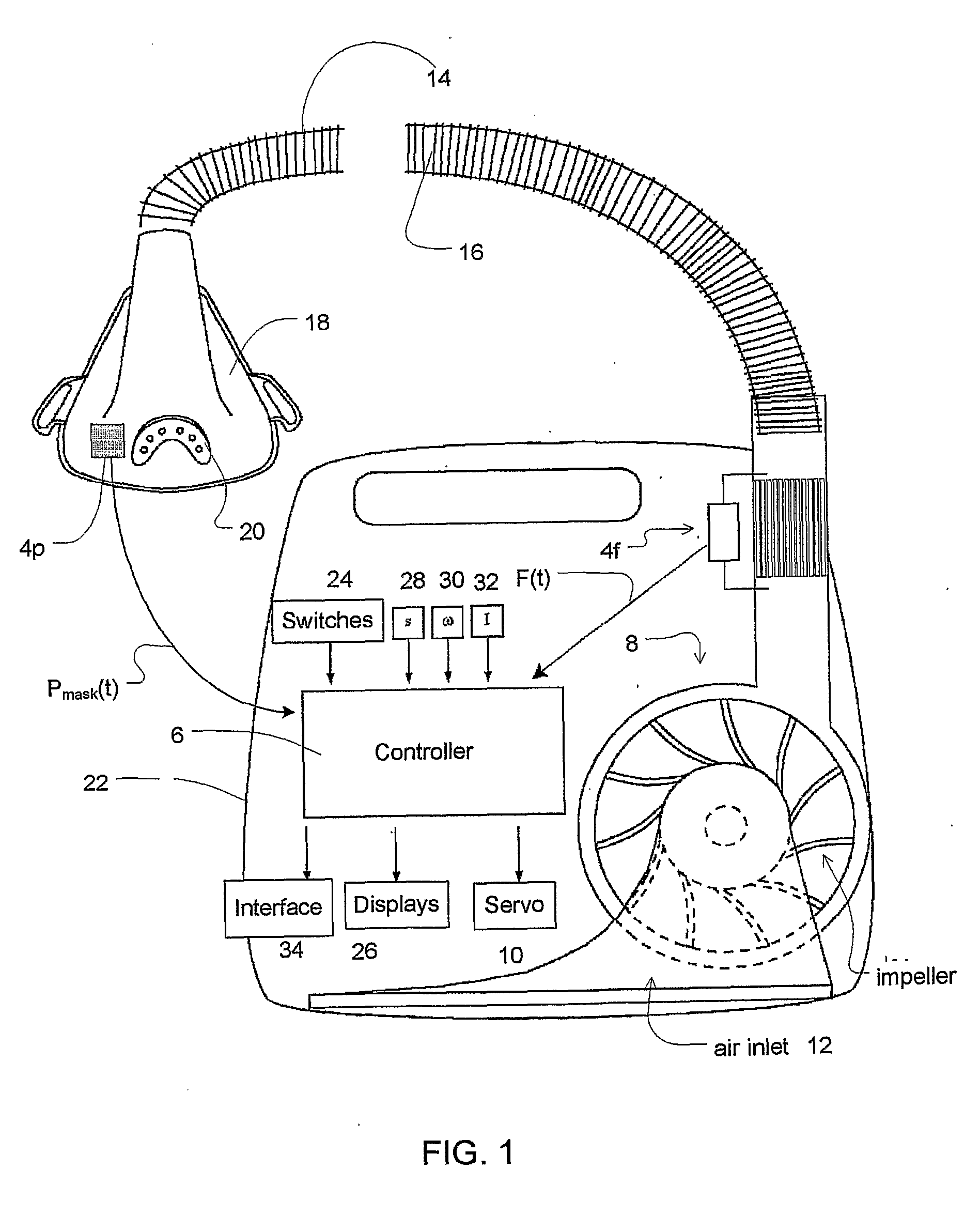
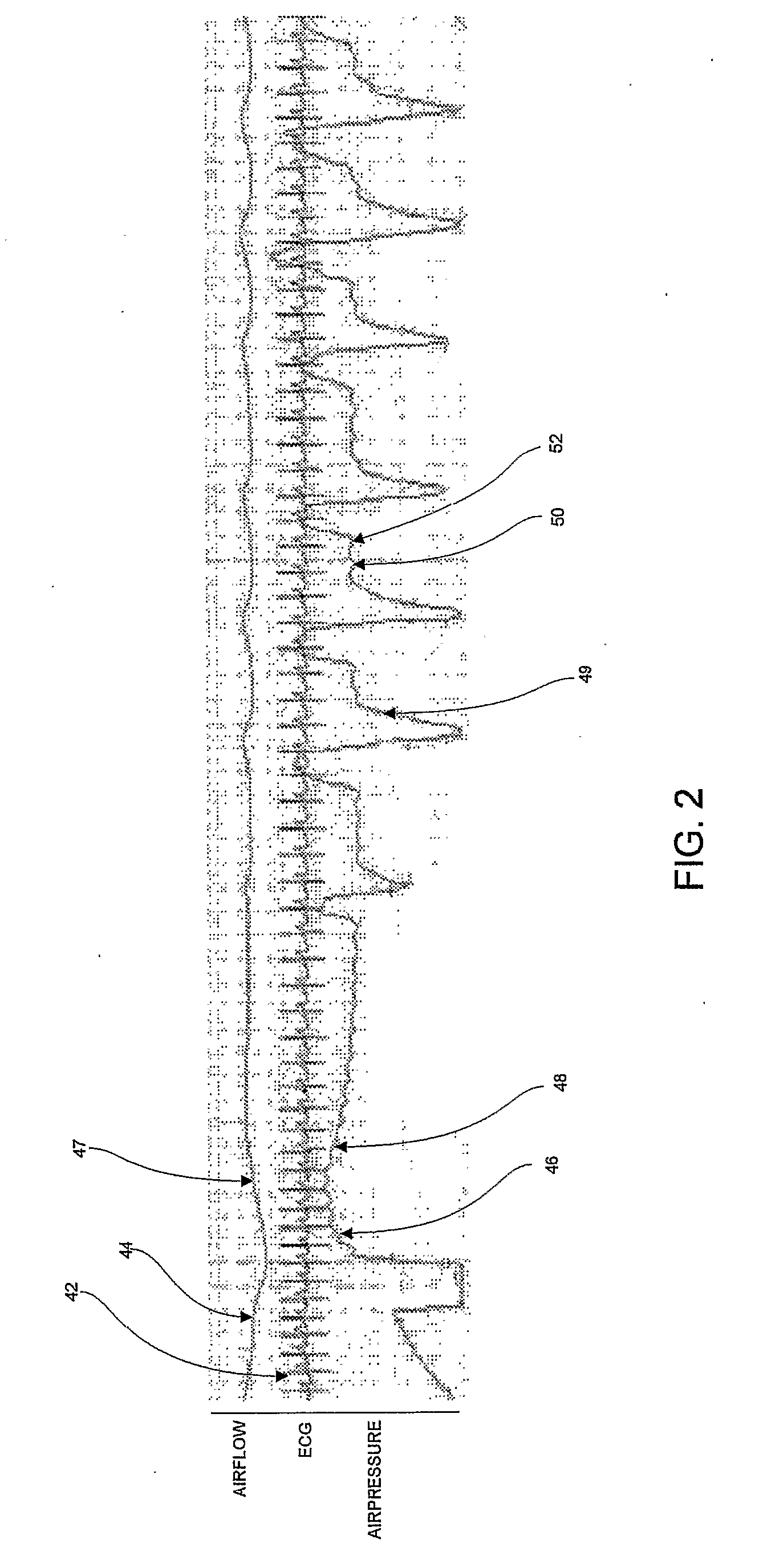
A method of using CPAP equipment to sense cardiogenic oscillations in a patient's airflow, and to monitor and treat the patient's cardiac condition. The apparatus diagnoses cardiac morbidity conditions, such as the existence of arrhythmias or other cardiac abnormalities, and influences and optimizes cardiac stroke volume. The apparatus further monitors pulse-transit time, changes in the heart pre-ejection period, and the duration of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:RESMED LTD
System and a method for cardiac monitoring
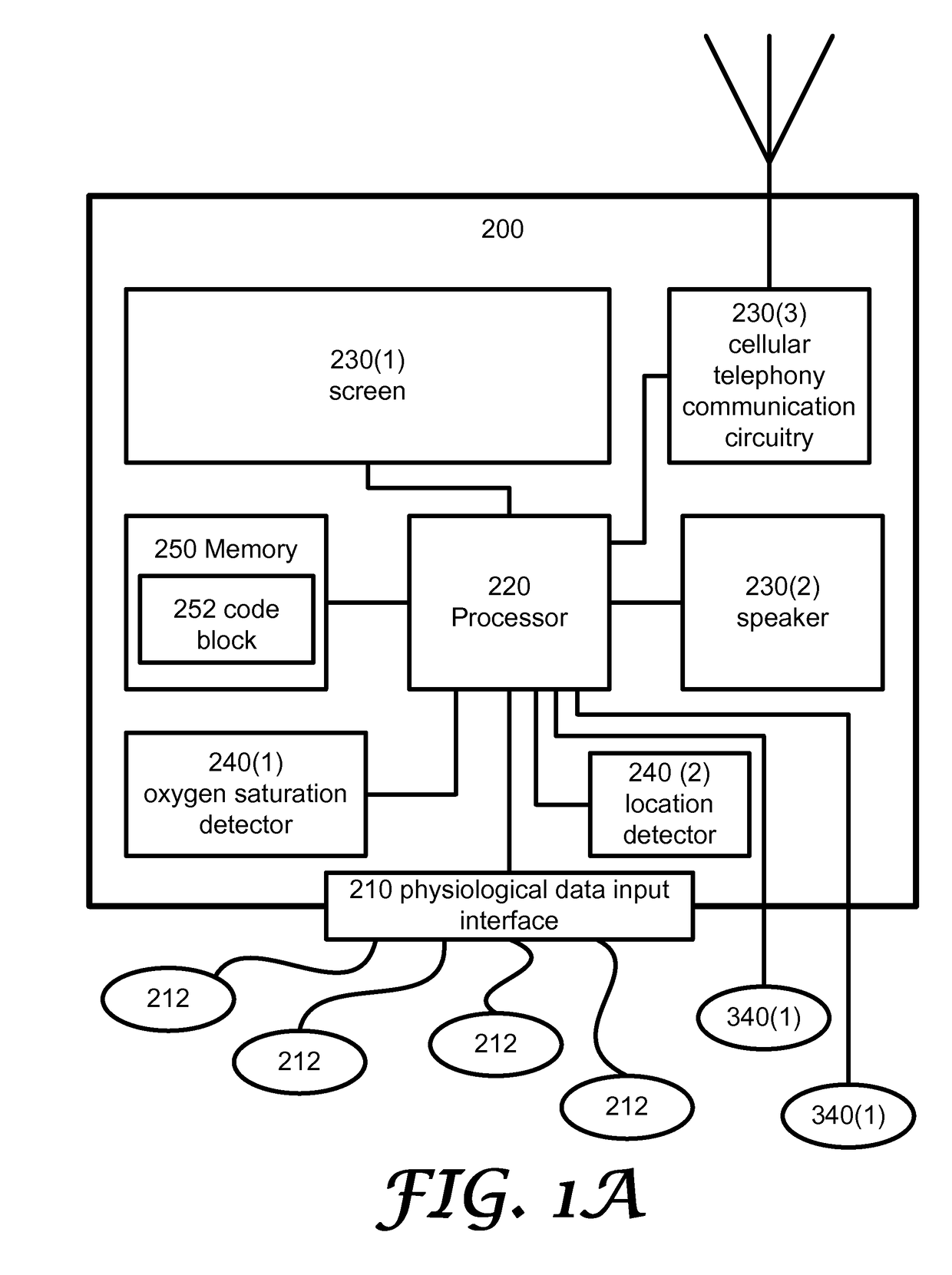
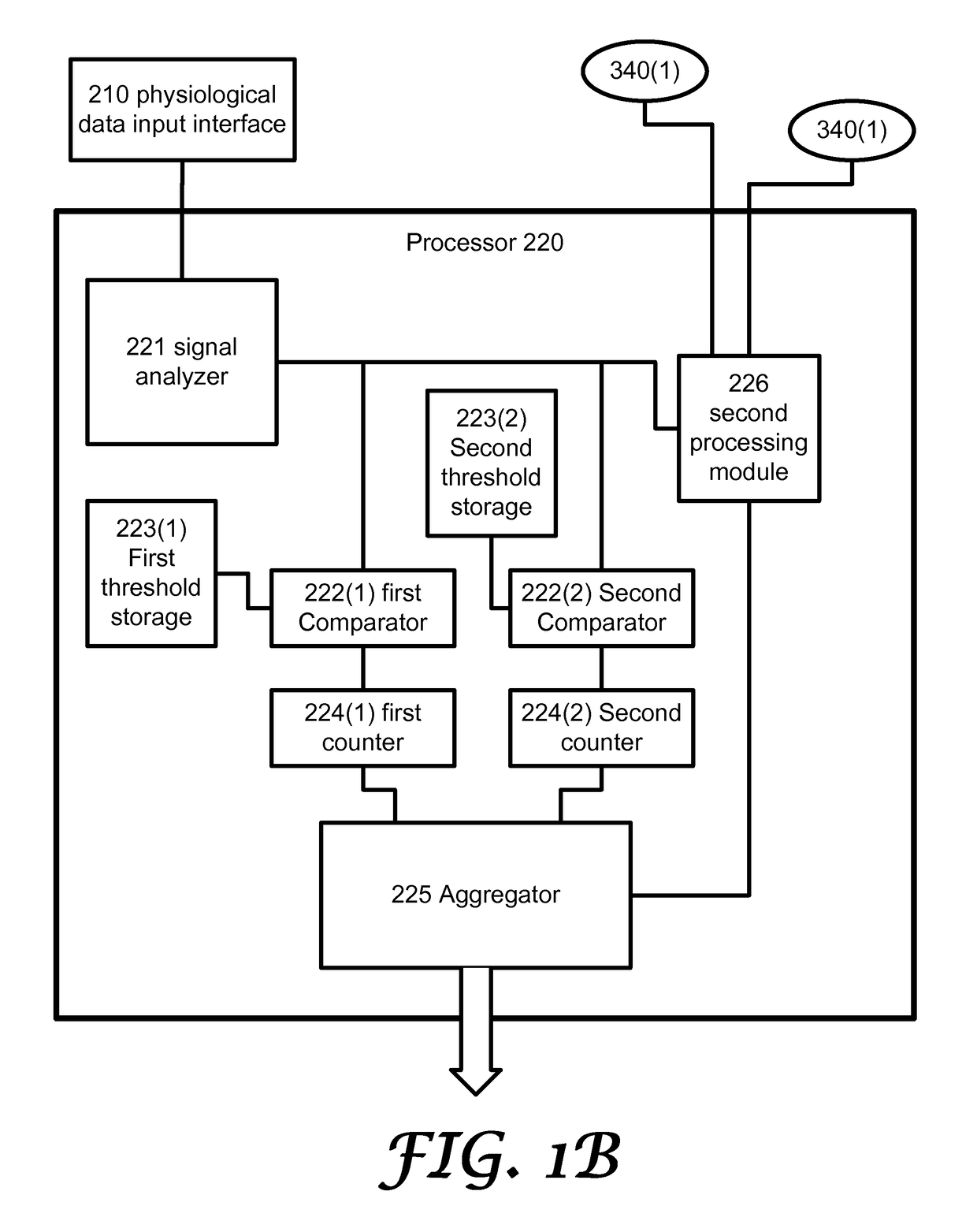
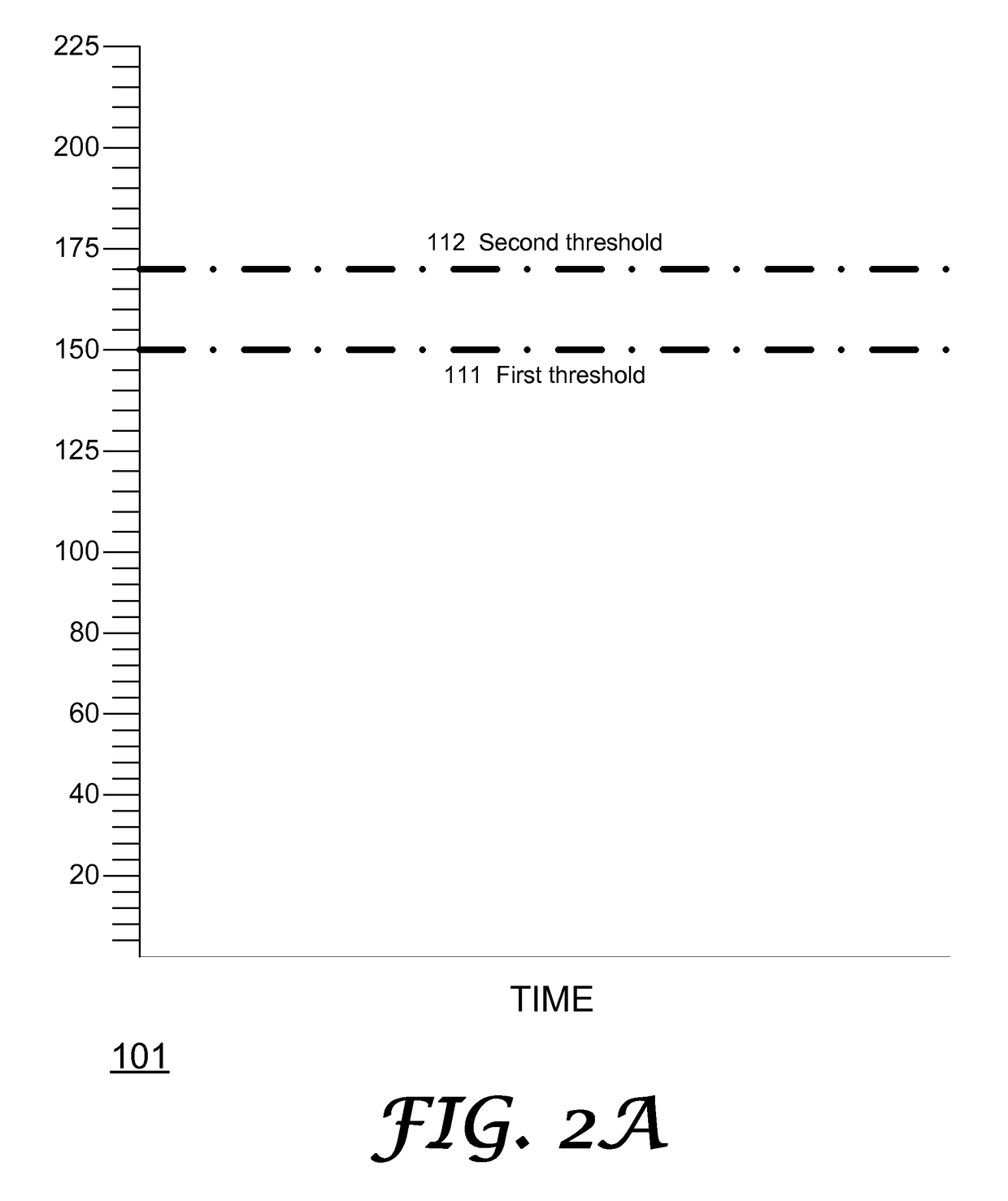
A system for monitoring a heart of a patient, the system includes: (i) a physiological data input interface, operative for receiving signals indicative of cardiac activity of the patient; (ii) a processor configured to process the signals to provide monitoring results; and (iii) an output interface operative to provide the monitoring results; wherein the monitoring results include information indicative of: (a) a heart rate of the patient during a monitoring period; (b) at least one first time period in which the heart rate of the patient exceeded a first threshold; and (c) at least one second time period in which the heart rate of the patient exceeded both the first threshold and a second threshold.
Owner:LIFEWATCH
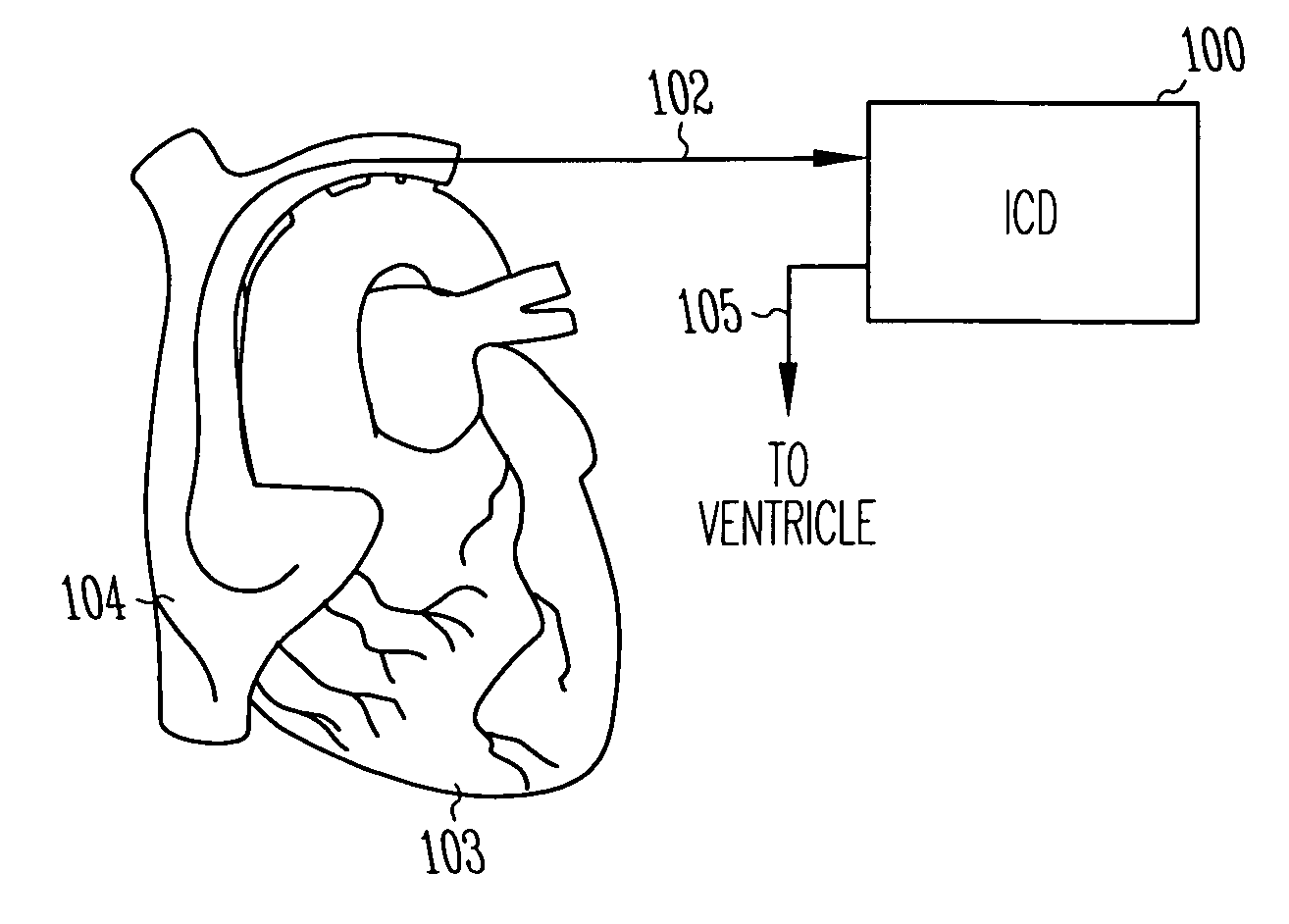
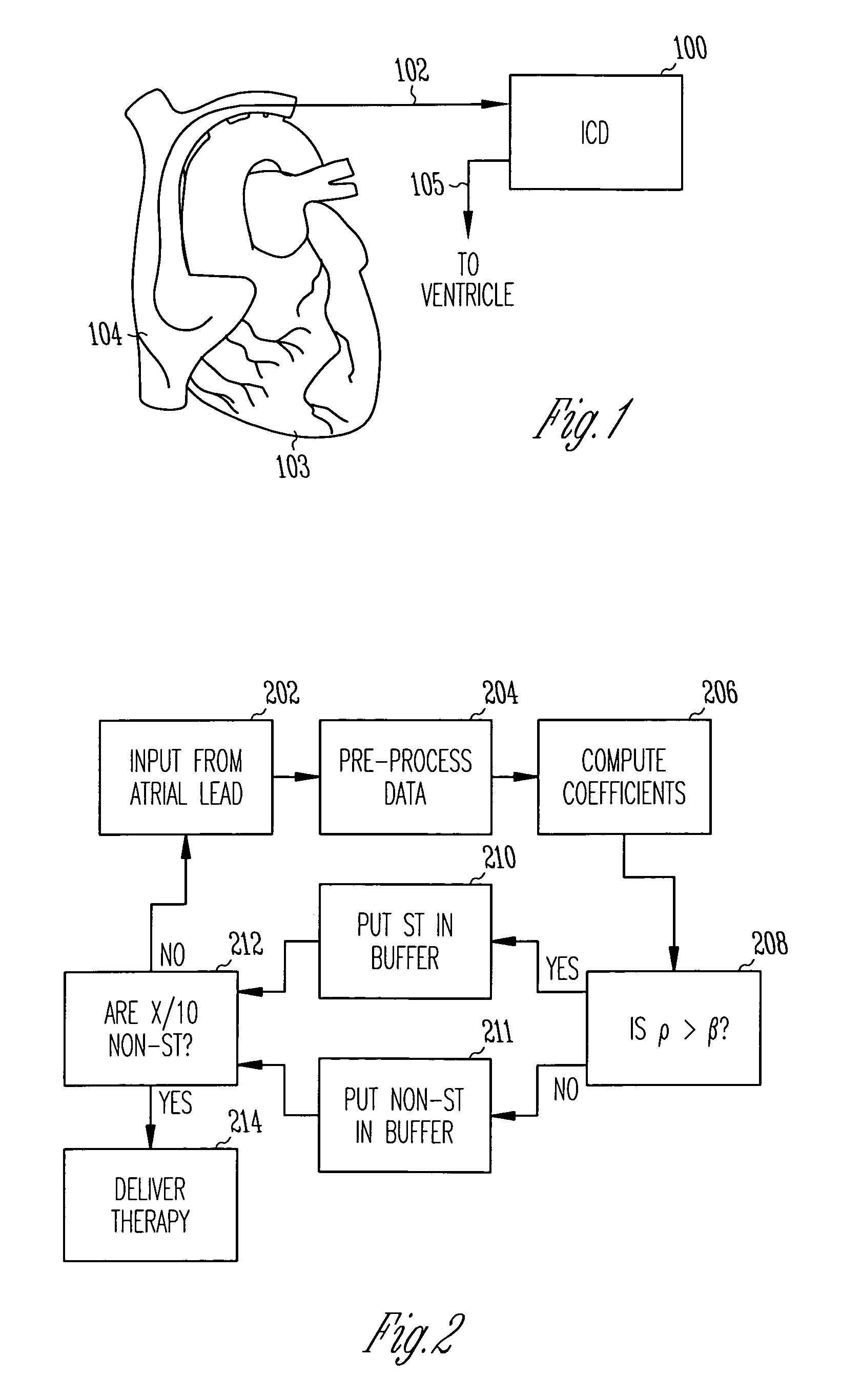
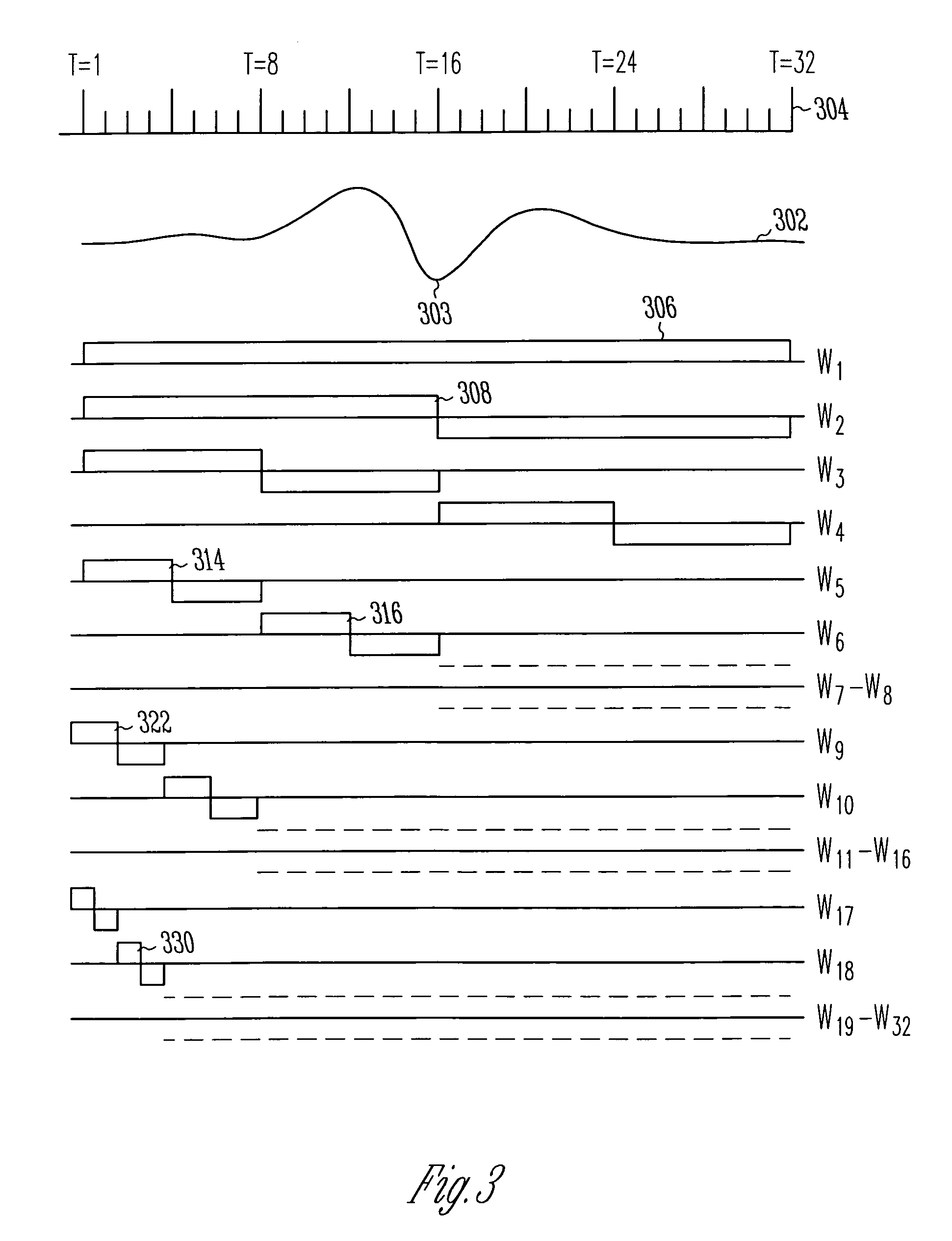
Heart Monitoring Systems, Apparatus and Methods Adapted to Detect Myocardial Ischemia
Embodiments include heart monitoring systems, apparatus, and methods adapted to detect myocardial ischemia. An apparatus includes at least one first-tier sensor / analyzer adapted to sense a first input related to cardiac function, and to produce a first-tier trigger signal when the first input indicates myocardial ischemia. In an embodiment, a first-tier sensor / analyzer includes an ECG sensor / analyzer. In another embodiment, a first-tier sensor / analyzer includes a patient activator. An apparatus further includes at least one second-tier sensor / analyzer adapted to sense a second input related to cardiac function, and to produce a second-tier trigger signal when the second input indicates myocardial ischemia. In an embodiment, a second-tier sensor-analyzer includes a heart sound sensor / analyzer. A triggering element is adapted to produce a response-invoking signal in response to the first-tier trigger signal and the second-tier trigger signal. The response-invoking signal may invoke a patient alert, a message to an external system, and / or a cardiac stimulus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
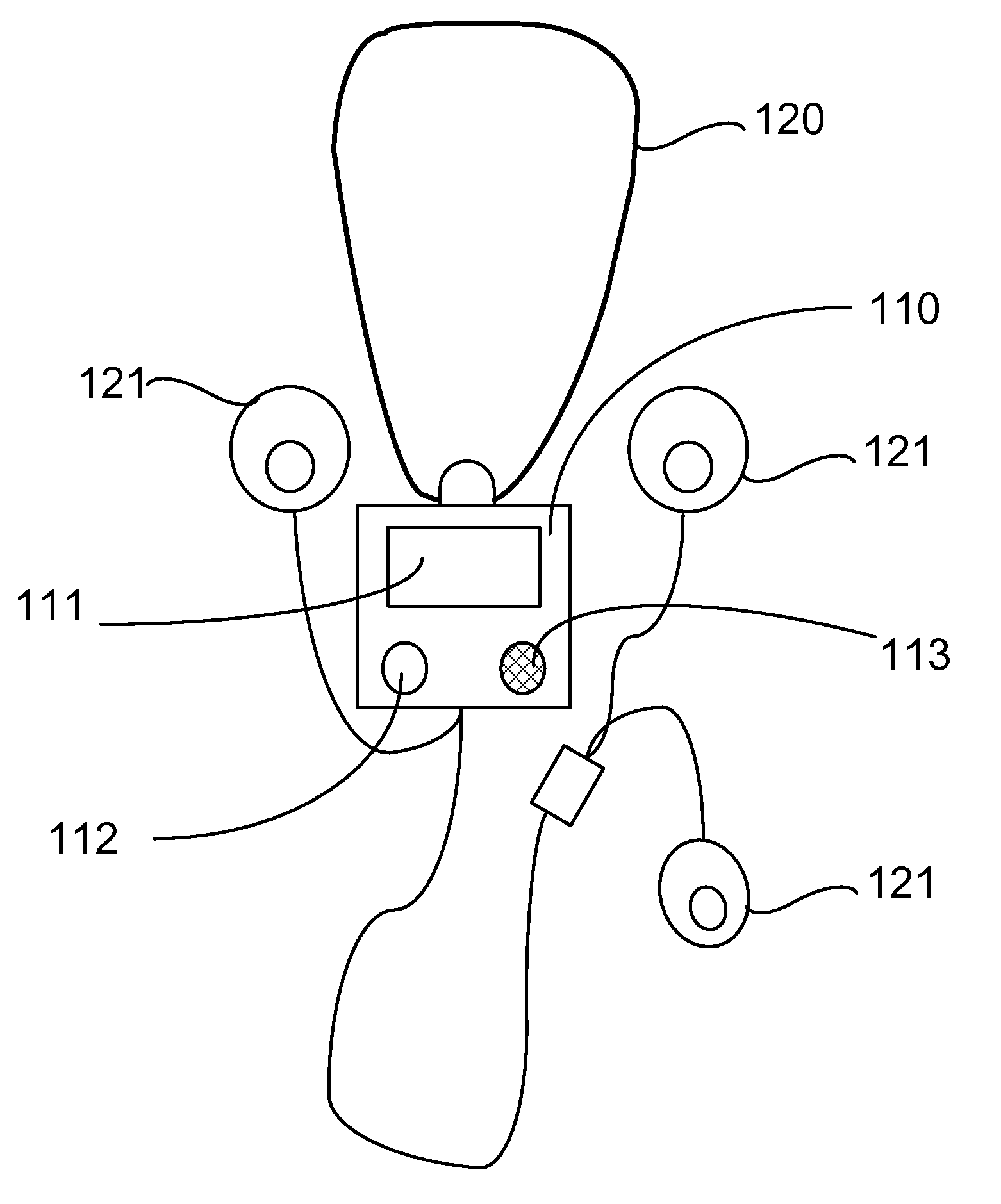
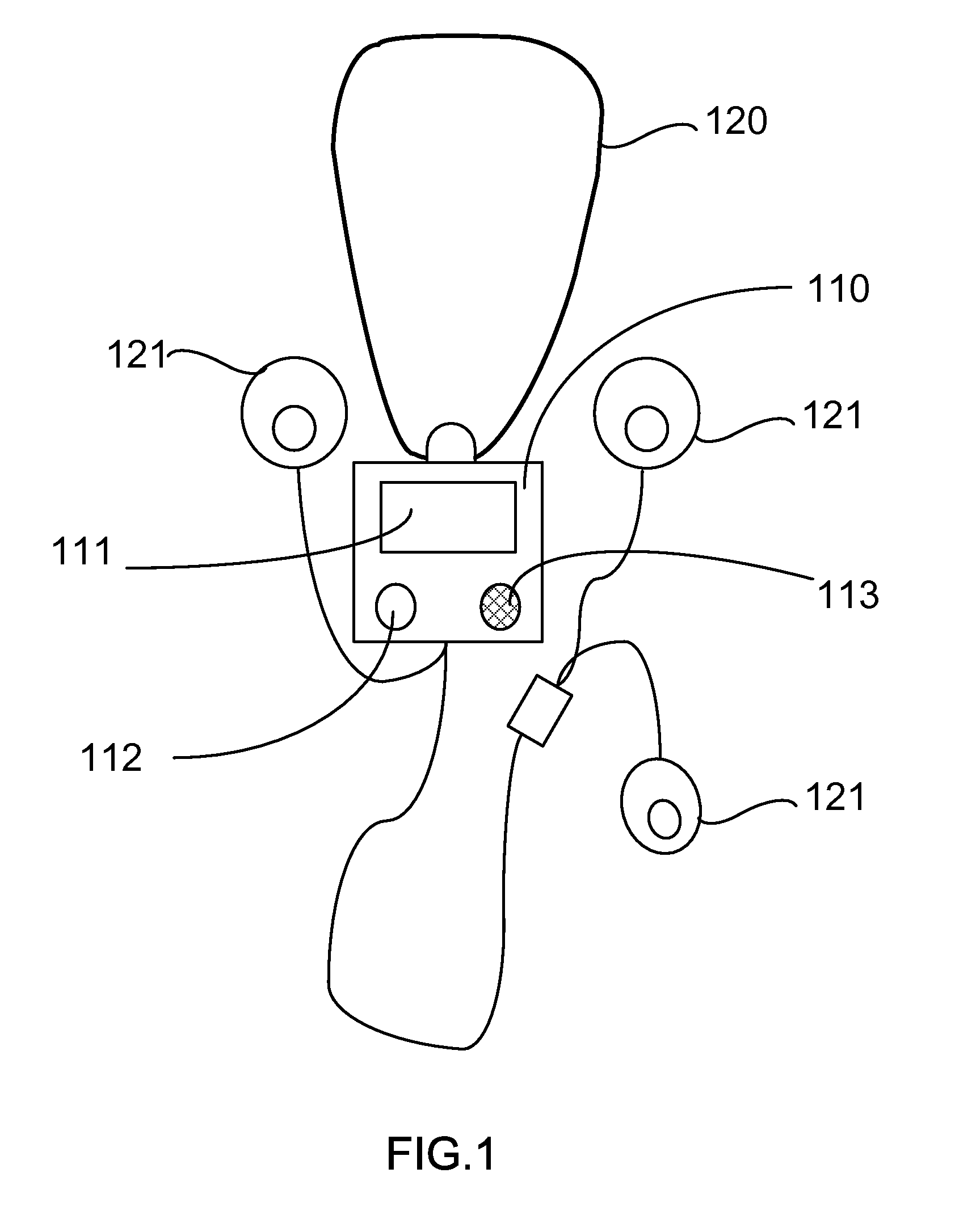
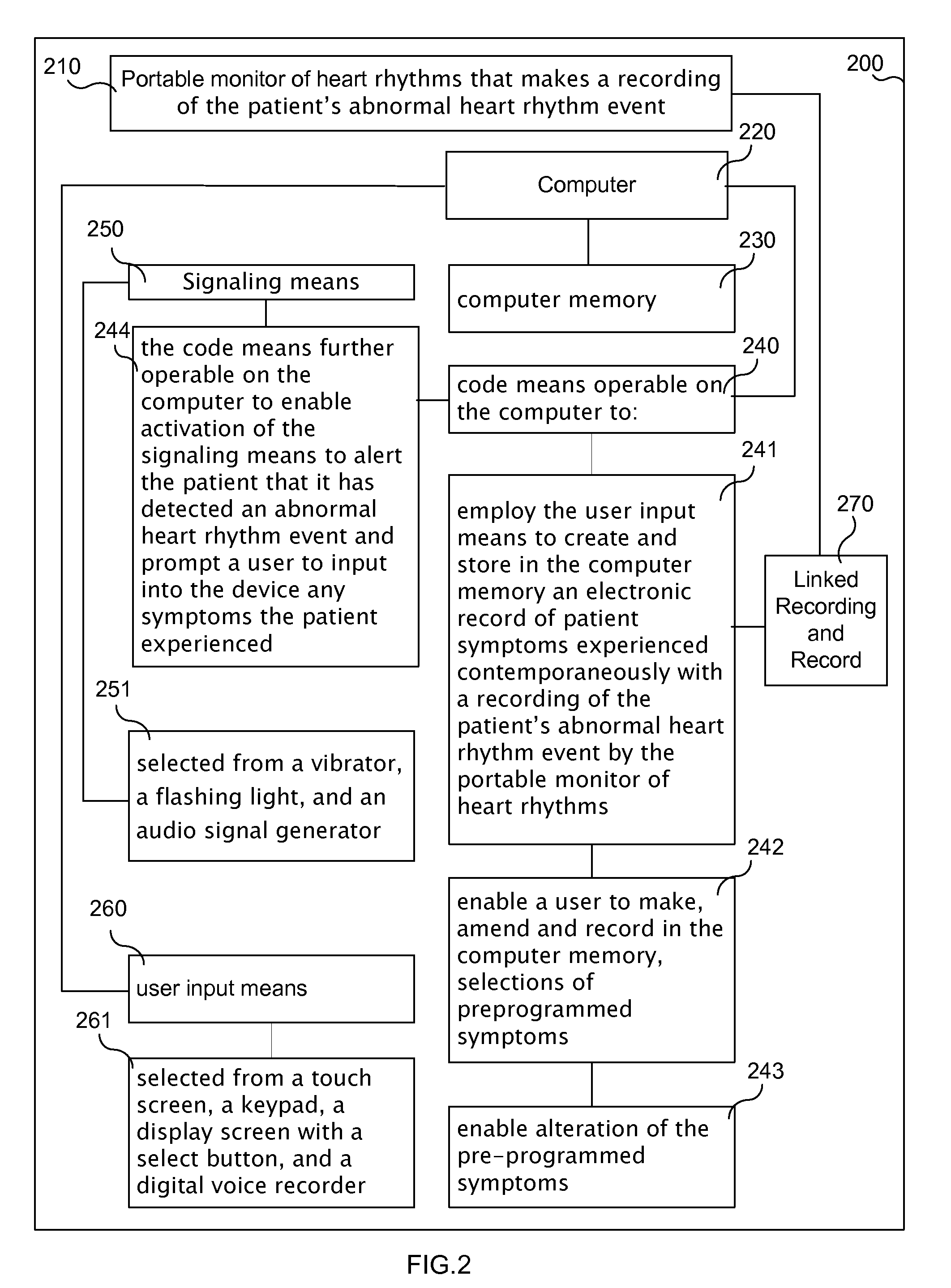
Symptom recording patient interface system for a portable heart monitor
A patient interface device contemporaneously records patient symptoms with an automated recording of heart rhythm data from a portable heart monitor. The patient interface device includes the portable heart monitor and a computer with a user input means to enter symptoms and store them in computer memory. Code means operable on the computer enables entry and recording of the symptoms. Where the portable heart monitor is activated automatically, a signaling means alerts the patient that it has begun recording and that symptoms experienced by the patient should be entered and recorded. Preferably, the electronic record of patient symptoms and the recording of the patient's abnormal heart rhythm event are linked such that they are accessed and used together.
Owner:LEVINE GLENN N
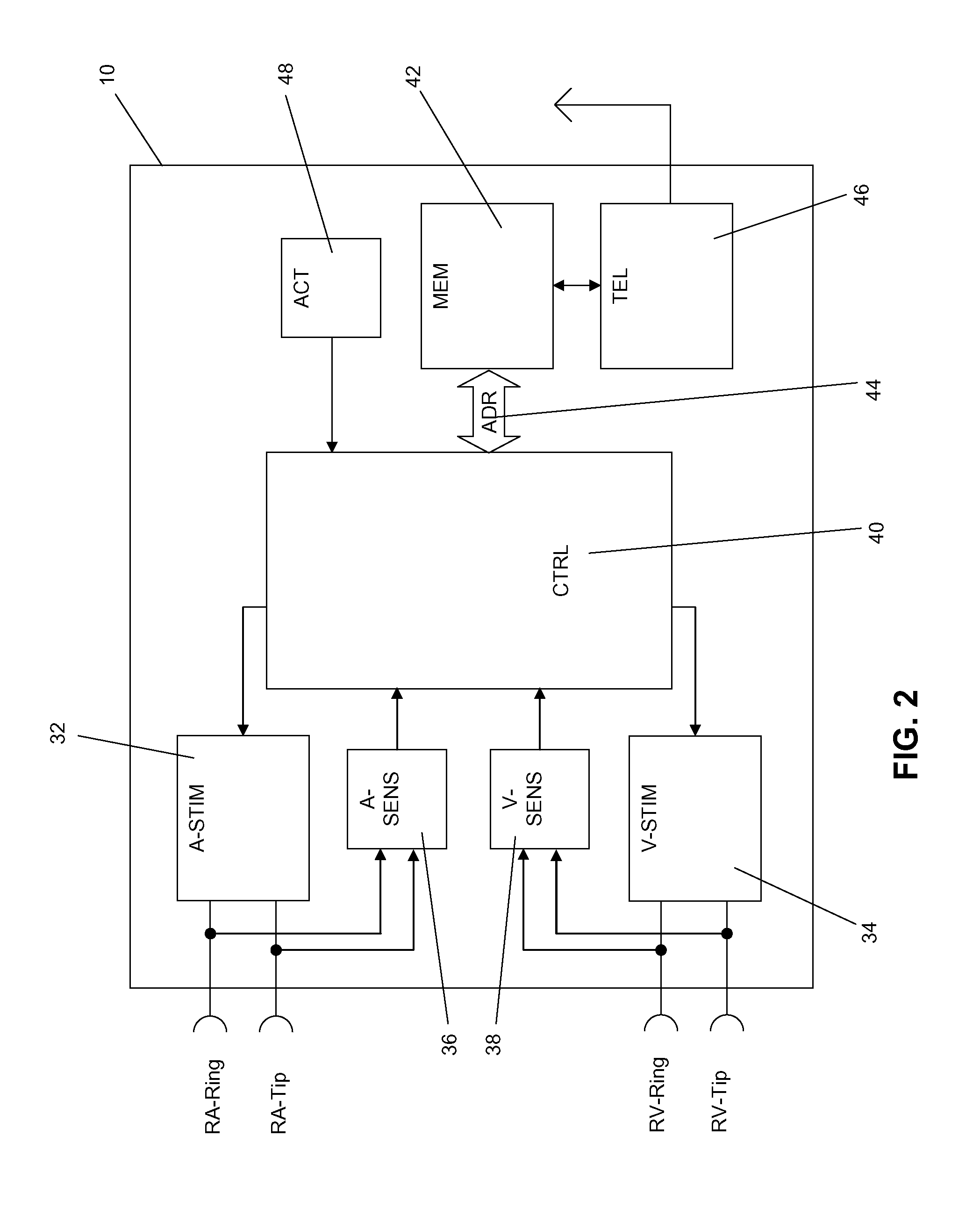
Heart monitoring system
ActiveUS20160220152A1Enhanced signalImprove analysisElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsHeart monitoringEngineering
A device that includes a sensor of angular motion configured to obtain an angular ballistograph signal indicative of rotational movement of a chest of a subject. Signal processing means are configured to generate from this angular ballistocardiograph signal measured values of an output parameter, which is indicative of cardiac operation of the subject.
Owner:PRECORDIOR OY +1
Monitoring system for sleep disordered breathing
ActiveUS20070265539A1Without excessive effortReliable informationElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringVentricular myocardiumSleep disordered breathing
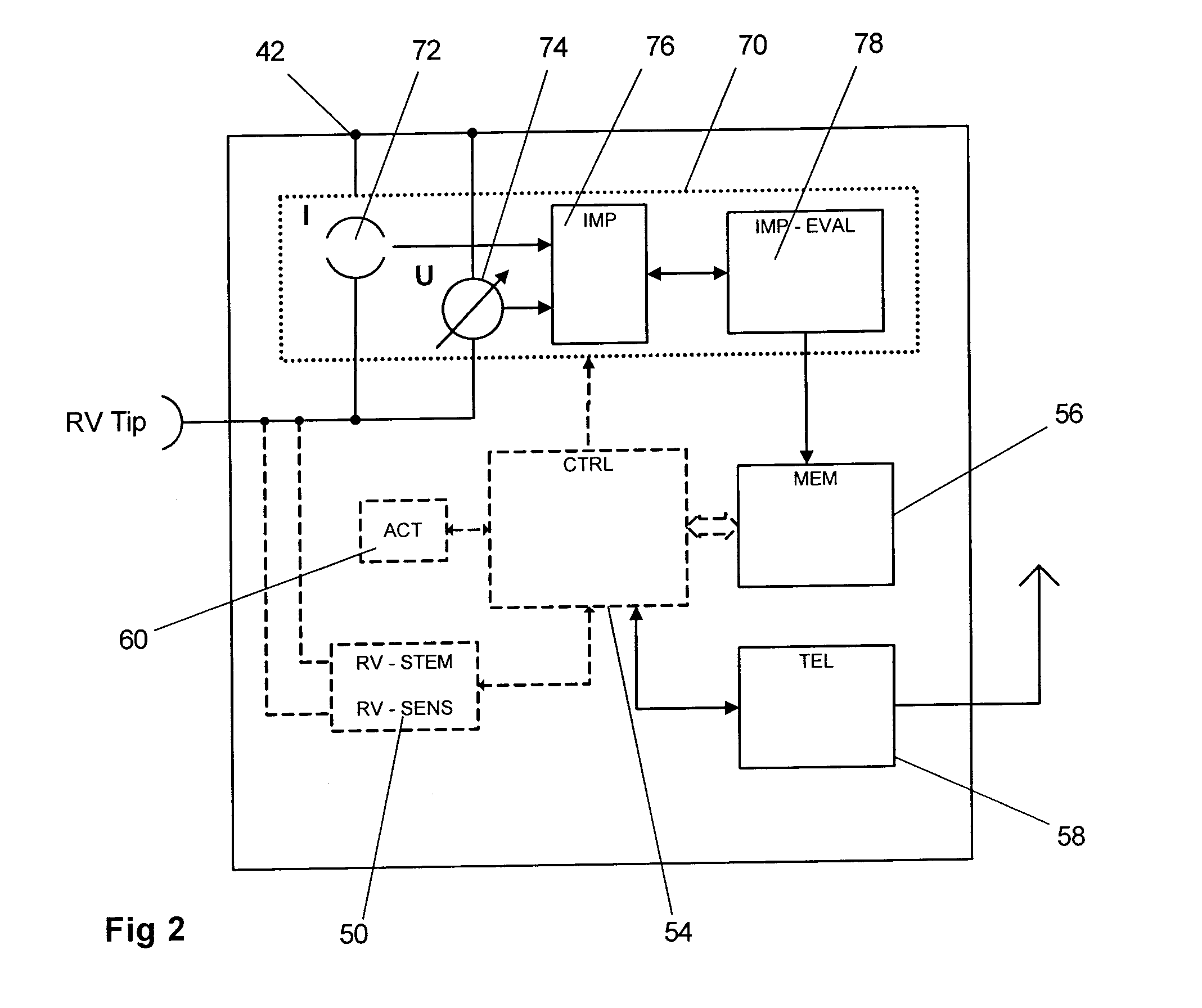
A heart monitoring system comprises a ventricular sensing stage sensing excitation or contraction of ventricular myocardium, an activity sensor unit determining a signal reflecting a patient's physical activity, a ventricular impedance or conductance measuring module, said modules comprising a current source unit adapted to provide a sub-threshold excitation current to the myocardium and comprising an impedance or conductance measurement unit for measuring the resulting voltage on said electrode at the myocardium, a signal generator module, a filter module, a memory, a control unit adapted to derive single measures |ΣZ| of magnitude of impedance or conductance change over a preset sample time interval, determine the variability TARVI in the impedance or conductance change, compare this variability and the activity sensor output signal with a threshold and recent history, determine if sleep disturbed breathing (SDB) is present, and log the SDB episode in the memory device.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Implantable heart monitors having flat capacitors with curved profiles
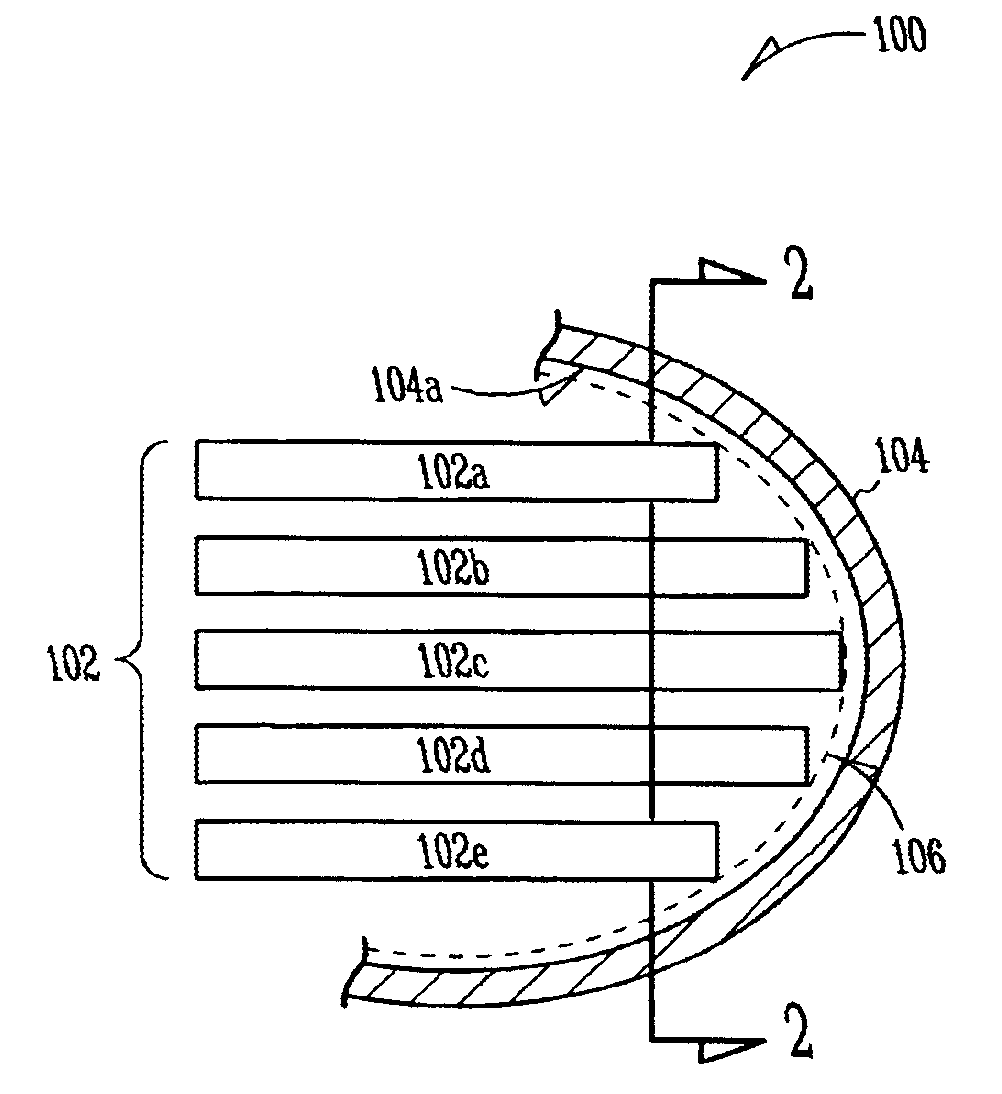
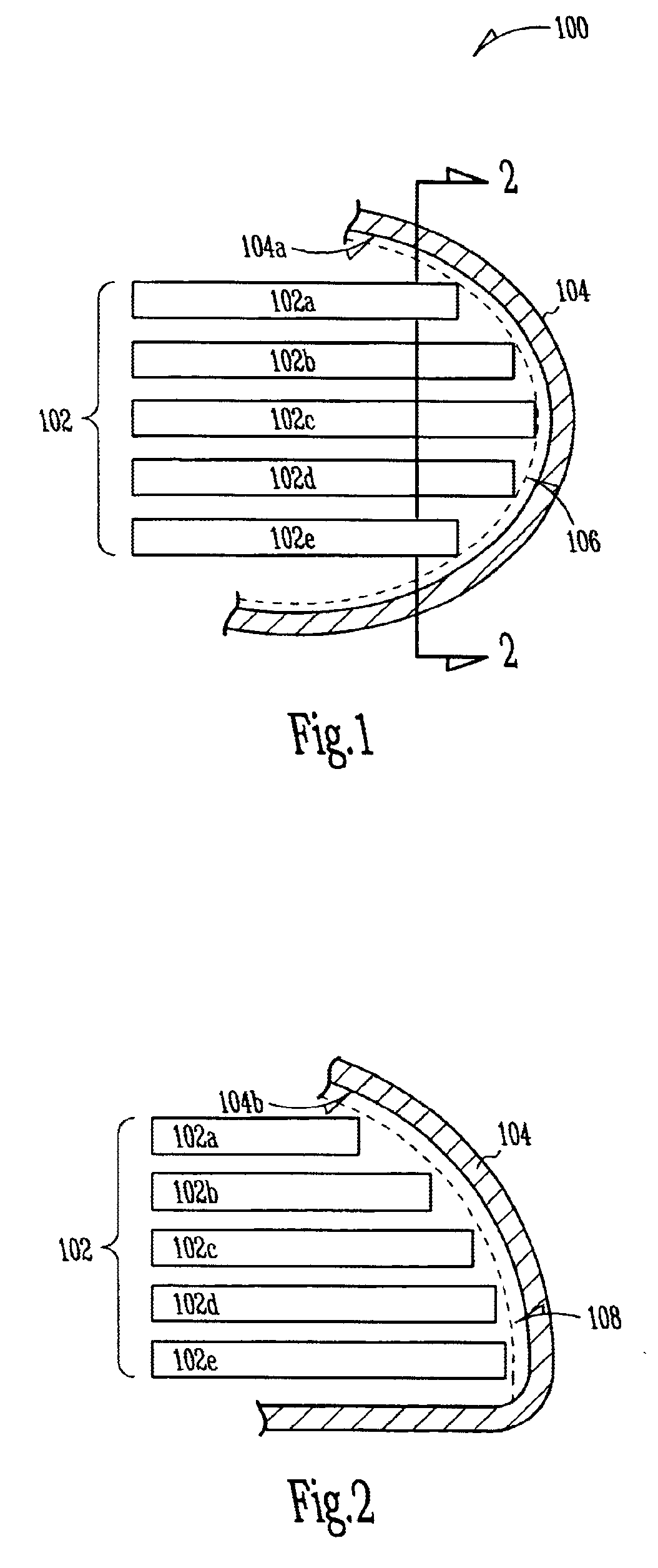
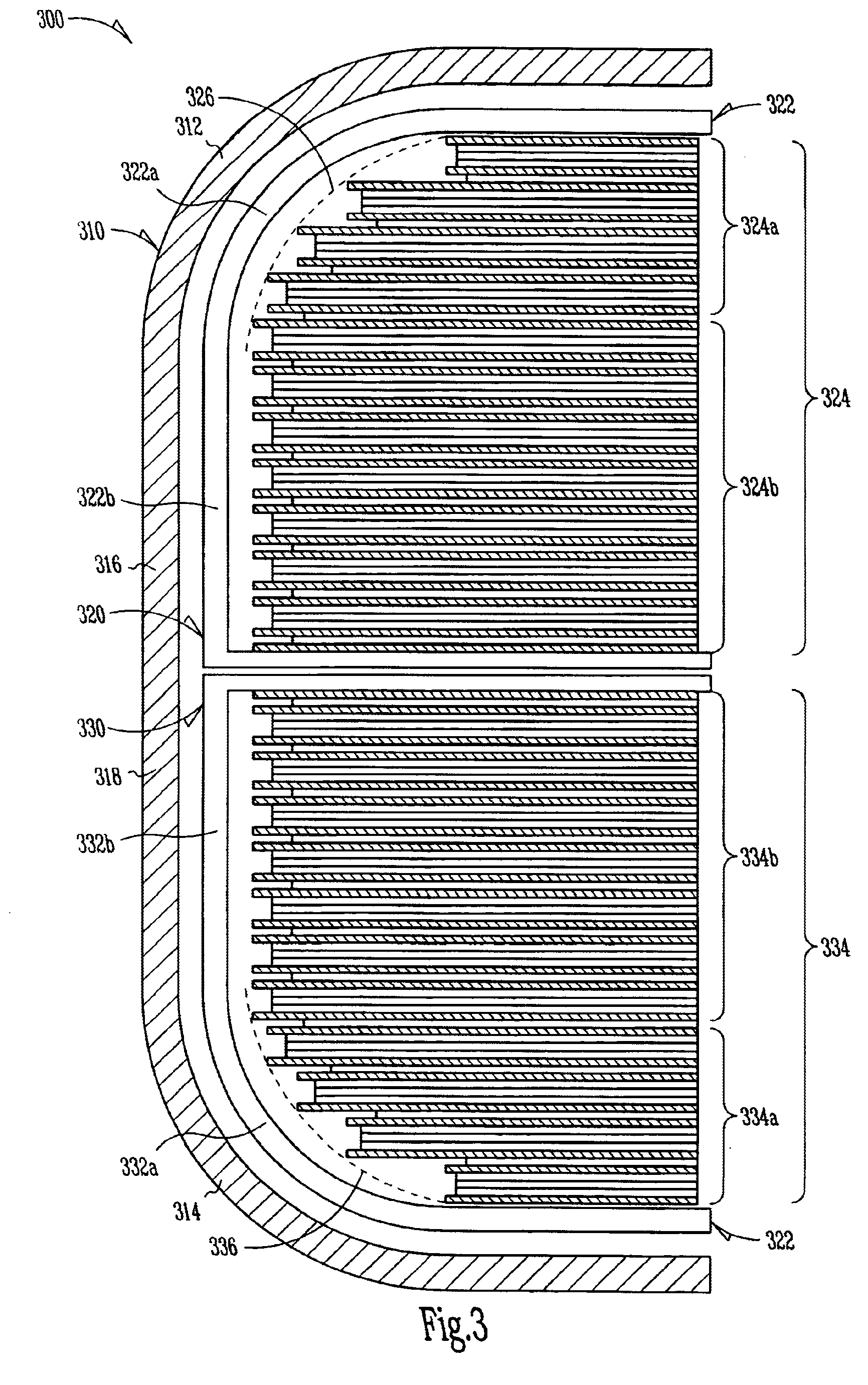
Implantable heart-monitoring devices, such as defibrillators, pacemakers, and cardioverters, detect onset of abnormal heart rhythms and automatically apply corrective electrical therapy, specifically one or more bursts of electric charge, to abnormally beating hearts. Critical parts in these devices include the capacitors that store and deliver the bursts of electric charge. Some devices use flat aluminum electrolytic capacitors have cases with right-angle corners which leave gaps when placed against the rounded interior surfaces of typical device housings. These gaps and voids not only waste space, but ultimately force patients to endure implantable devices with larger housings than otherwise necessary. Accordingly, the inventors devised several capacitor structures that have curved profiles conforming to the rounded interior surfaces of device housings. Some exemplary capacitor embodiments include two or more staggered capacitor elements, and other embodiments stagger capacitors of different types and / or sizes.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Medical device for controlled drug delivery and cardiac monitoring and/or stimulation
InactiveUS7917208B2Reduce frequencyHigh sensitivityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsMicrocontrollerCardioversions
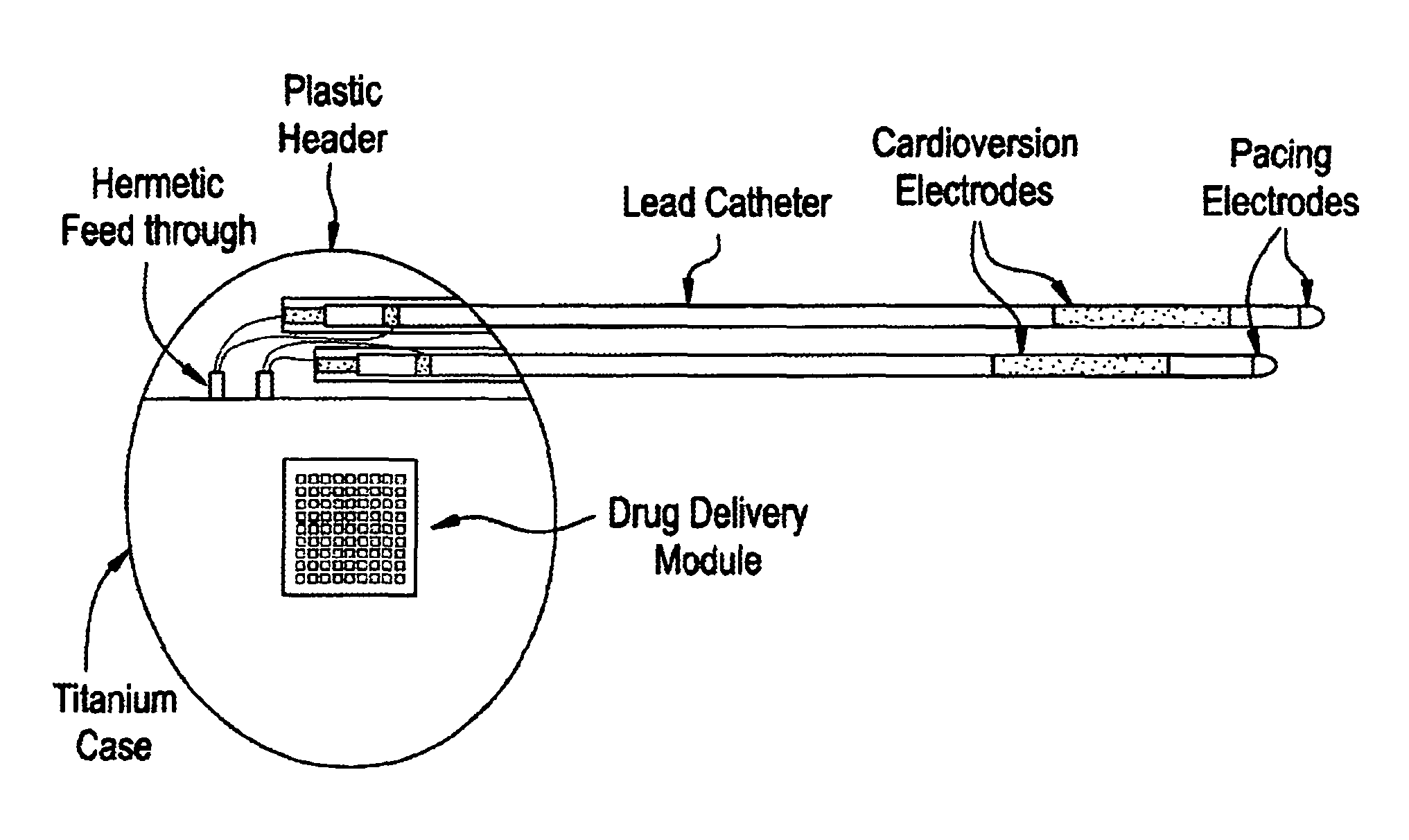
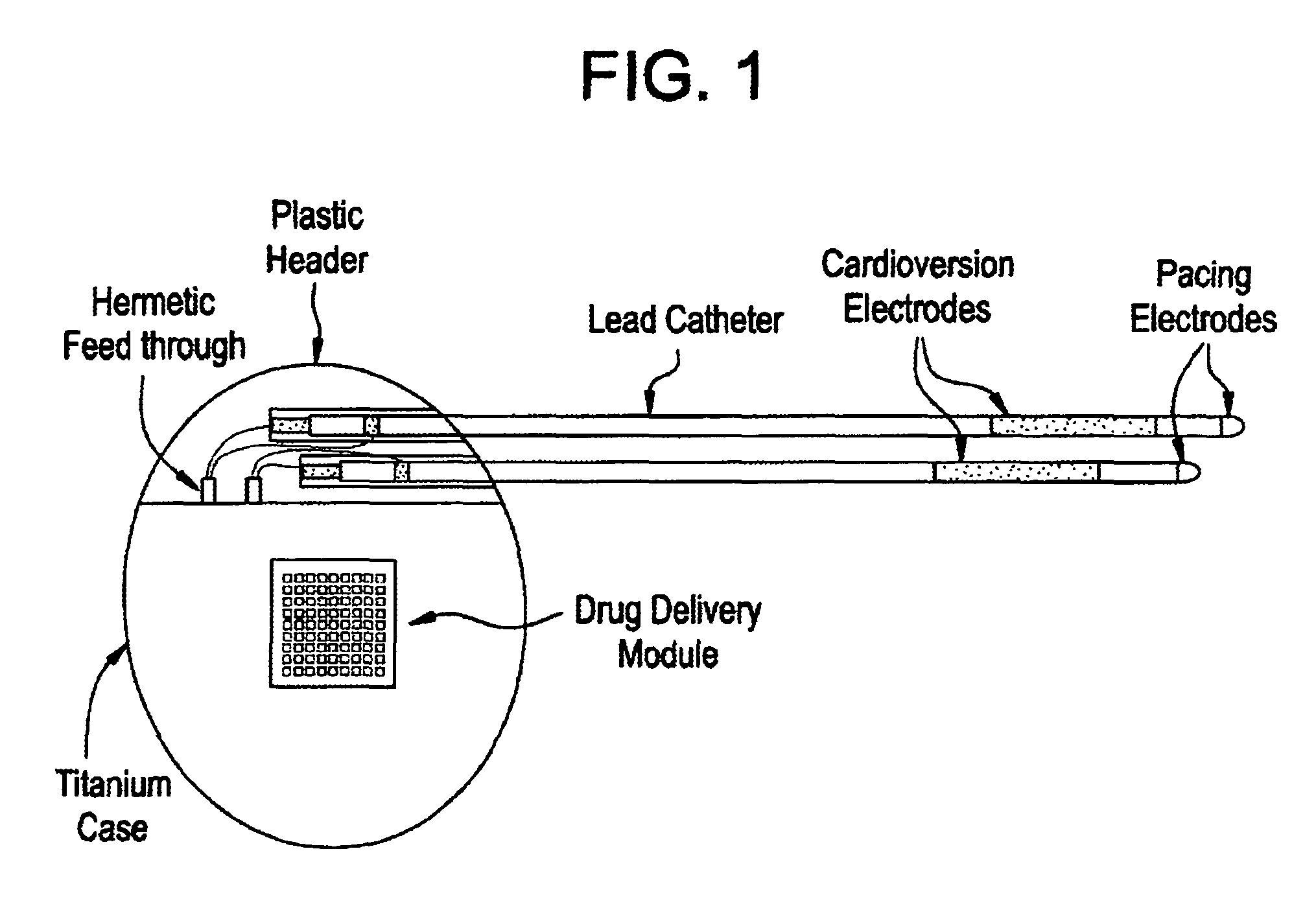
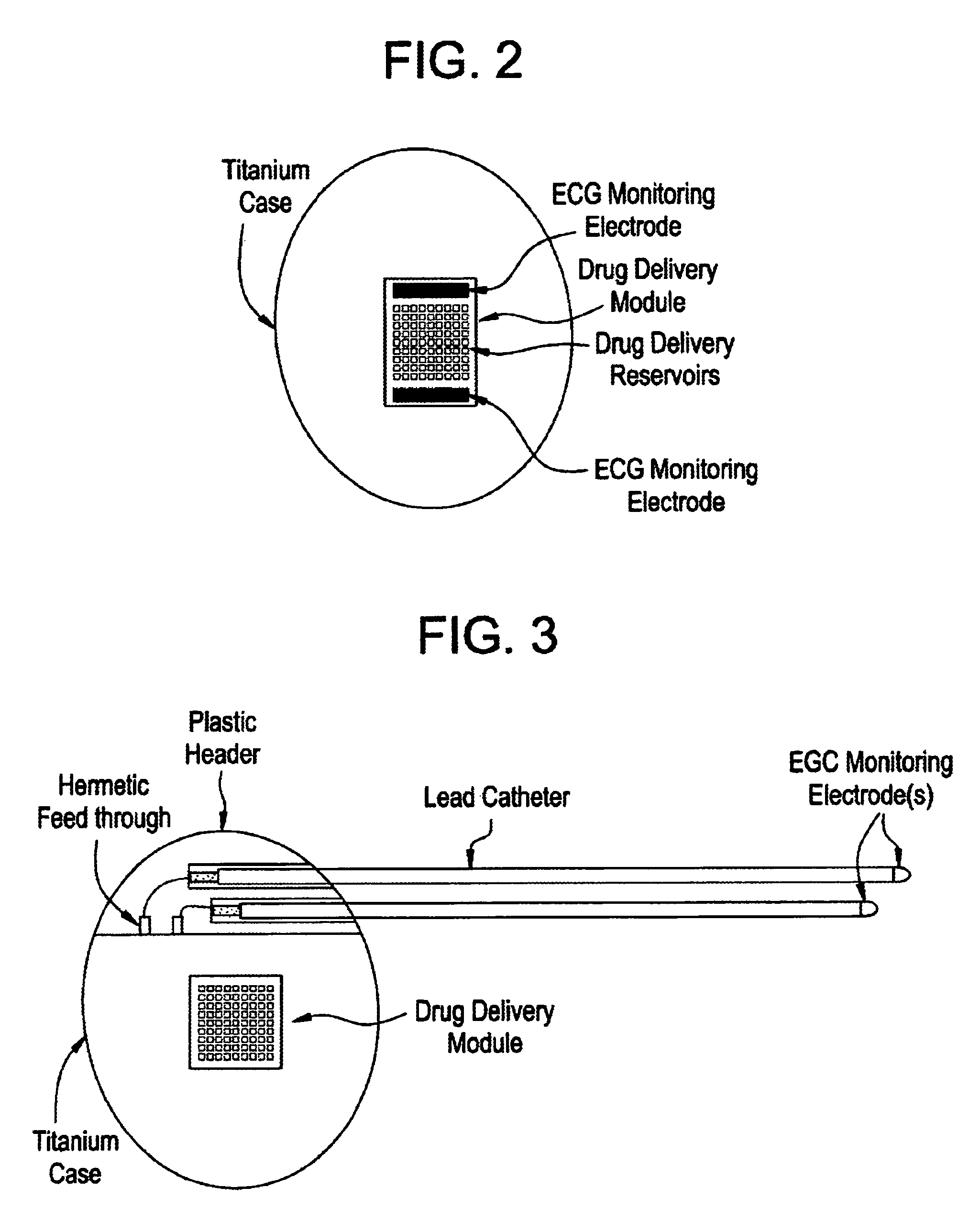
Medical device and methods are provided for controlled drug delivery in a cardiac patient. The device includes an implantable drug delivery module comprising reservoirs containing a drug and a control means for selectively releasing an effective amount of drug from each reservoir; one or more electrodes or sensors for cardiac monitoring, stimulation, or both; and a microcontroller for controlling operational interaction of the drug delivery module and the cardiac electrode. The electrodes may comprise ECG monitoring, cardioversion, or cardiac pacing electrodes. A medical device also is provided for controlled delivery of drug to a patient having congestive heart failure, which includes an implantable drug delivery module comprising a natriuretic peptide and a release mechanism for selectively releasing a pharmaceutically effective amount of the natriuretic peptide into the patient; and a microcontroller for controlling the release mechanism, for example, in response to one or more monitored patient parameters.
Owner:MICROCHIPS BIOTECH INC
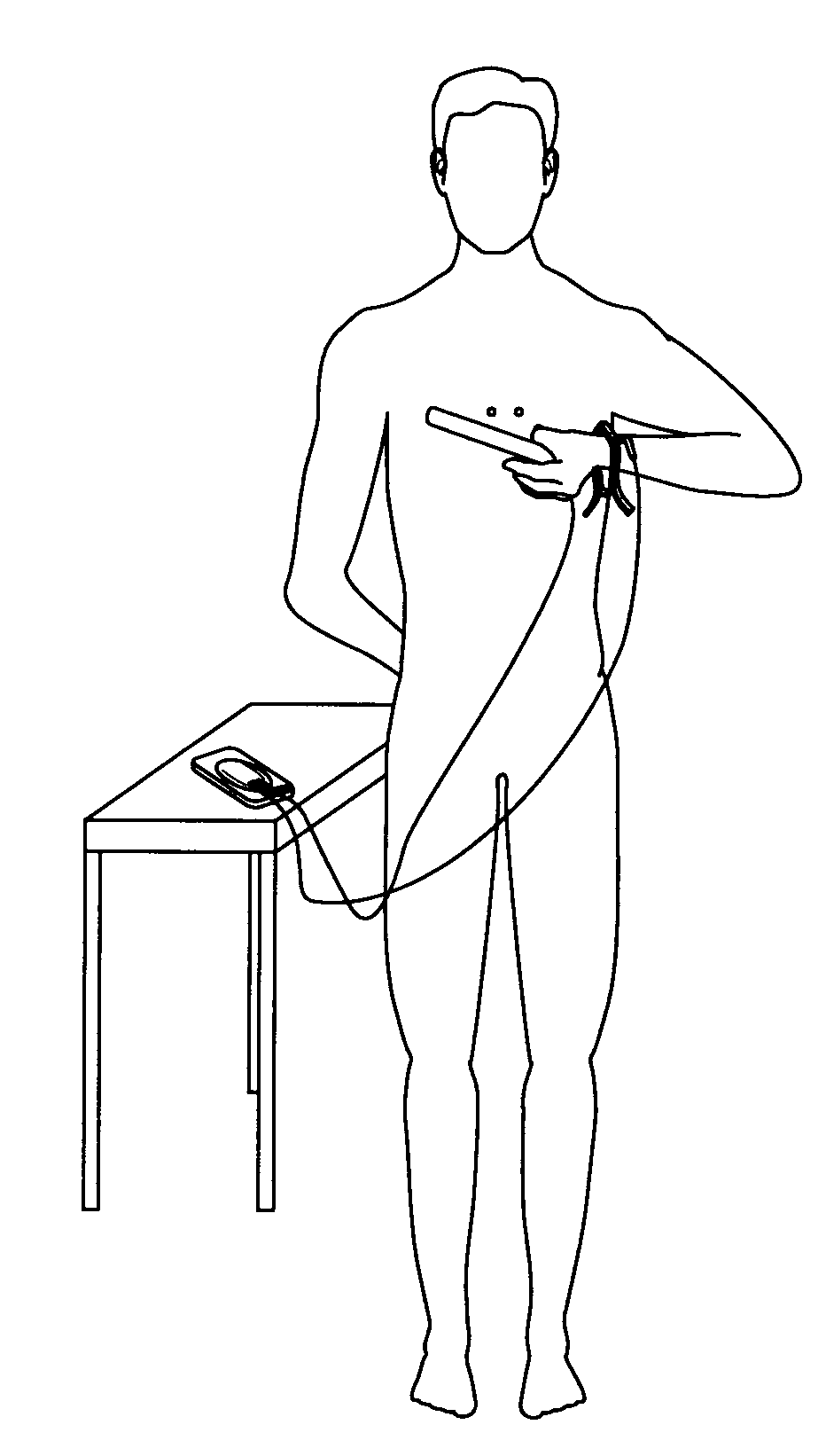
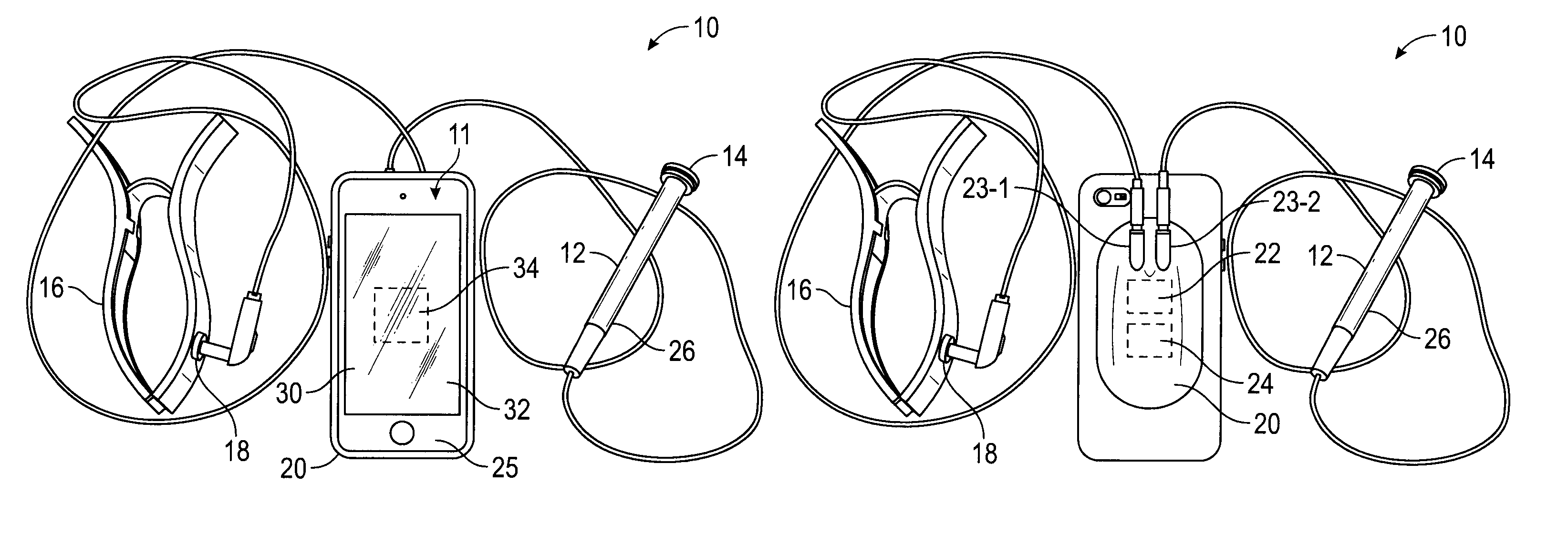
Two Electrode Apparatus and Methods for Twelve Lead ECG
Described herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for heart monitoring of a patient. The heart monitoring system can be used to take an electrocardiogram (ECG) using only two electrodes. A handheld device can be used to sequentially measure the electrical signal between different positions on a patient's body. The electrical signals can be processed and analyzed to prepare an ECG for the patient, including a 12-lead ECG.
Owner:ALIVECOR
System and method of aquiring blood-vessel data
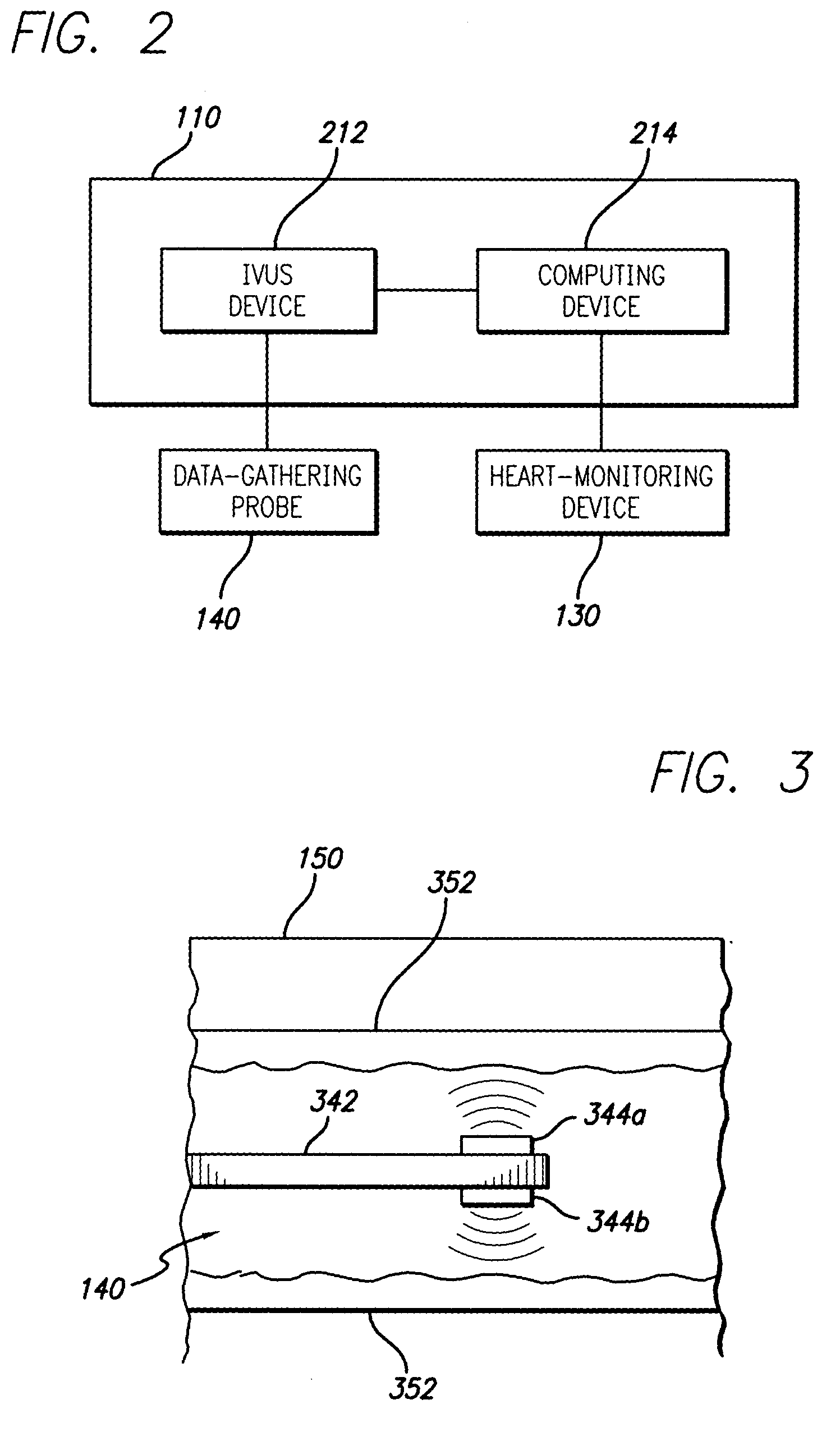
ActiveUS7927275B2Stable speedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementVascular ultrasoundData acquisition
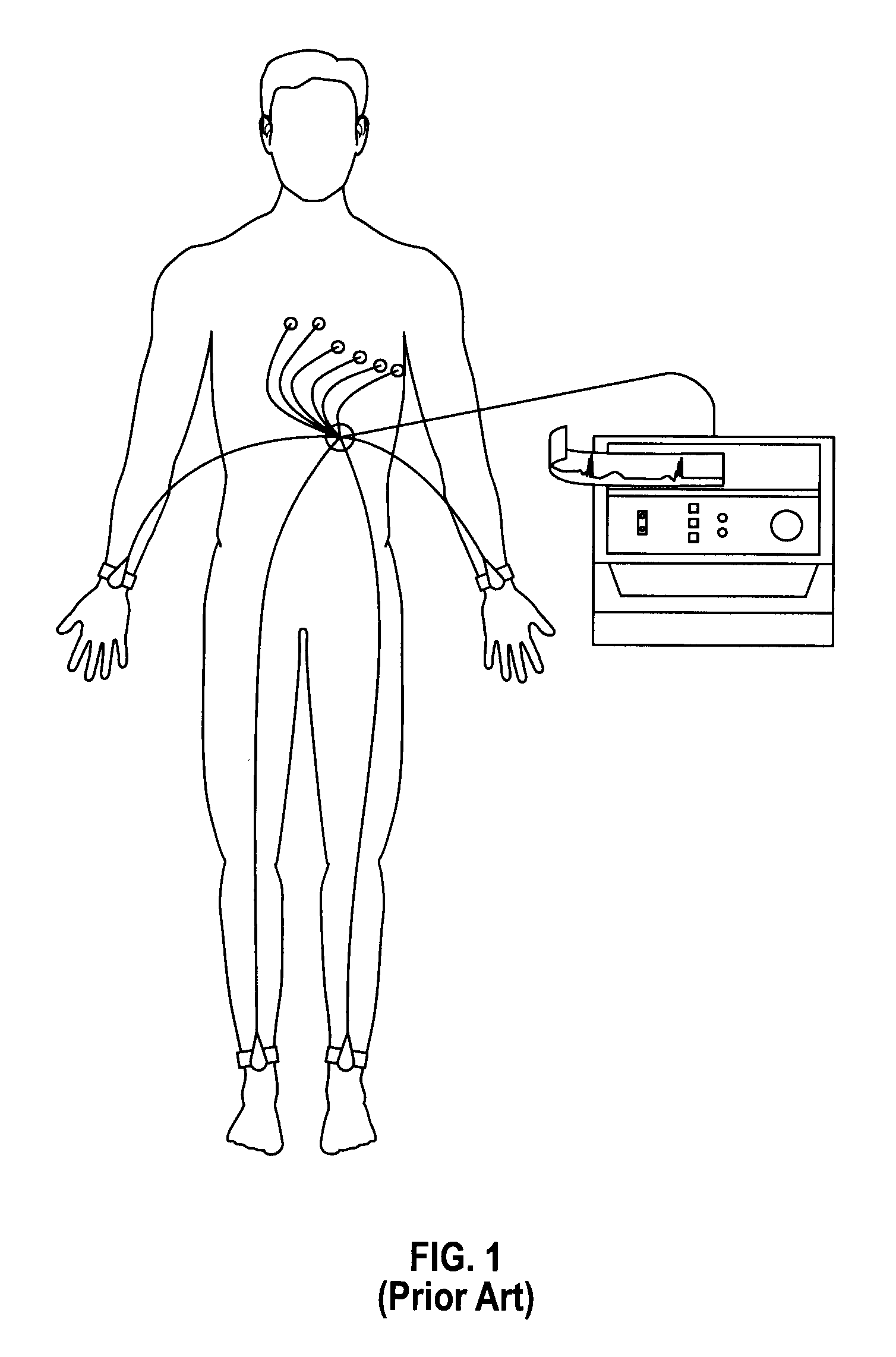
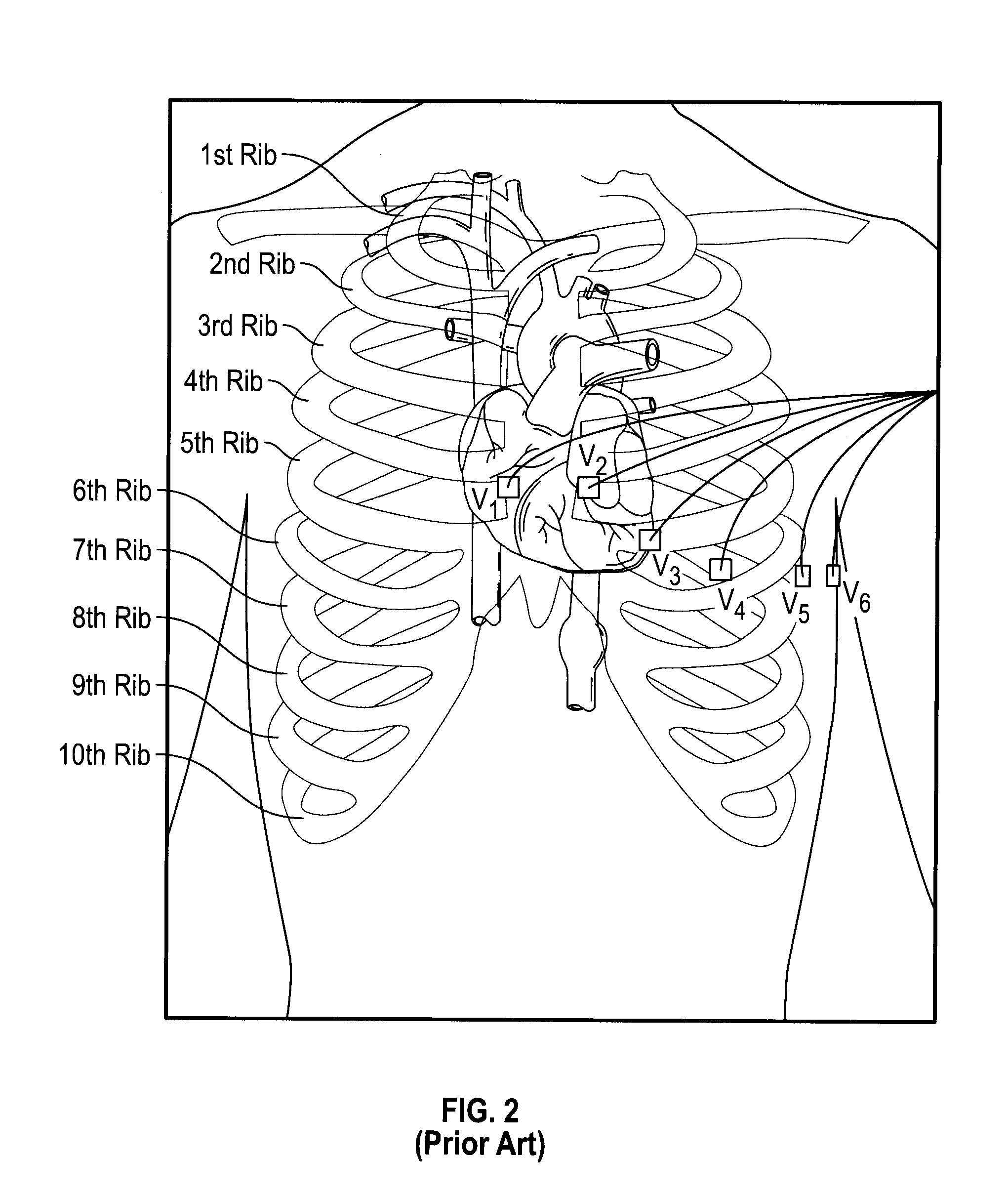
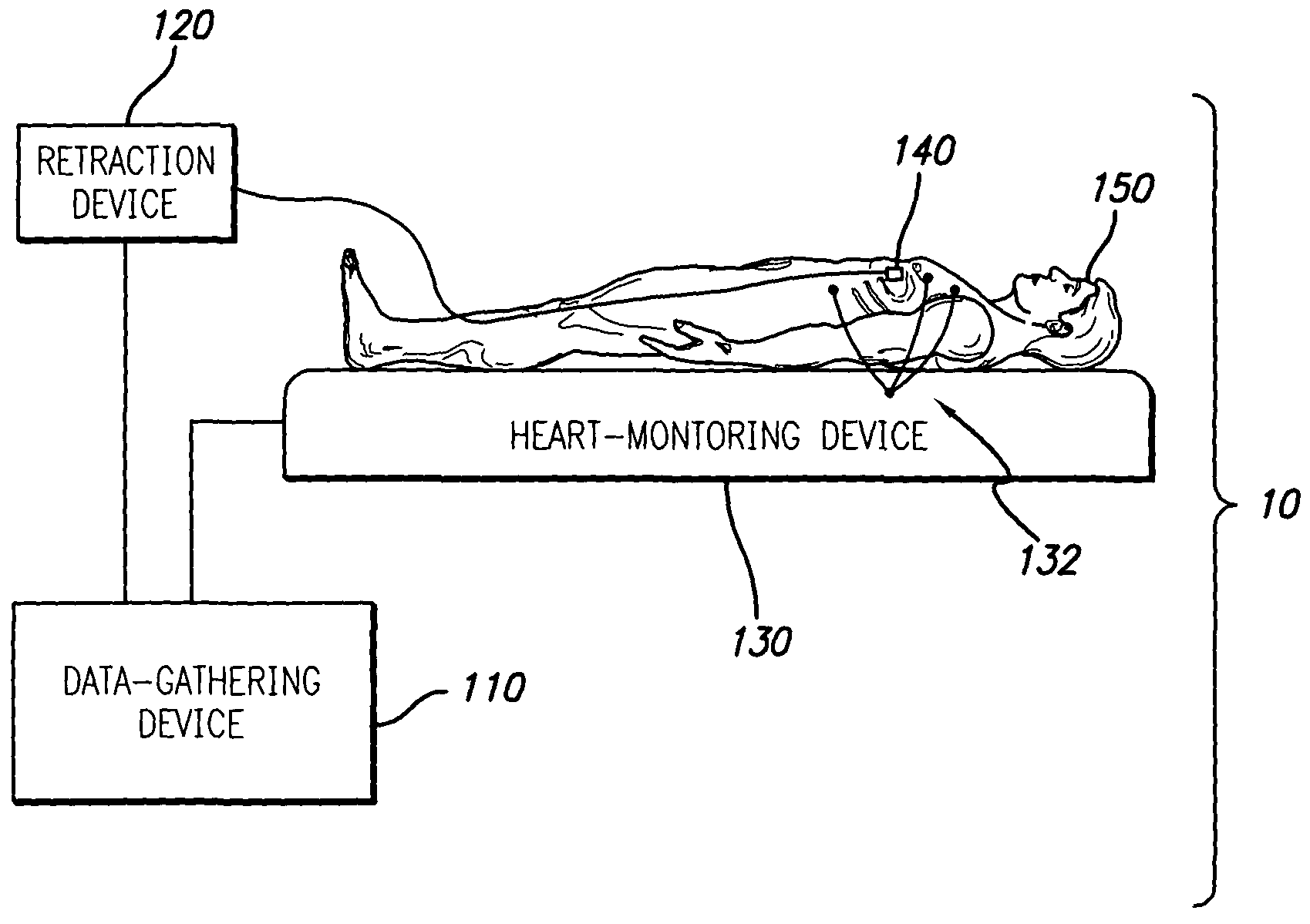
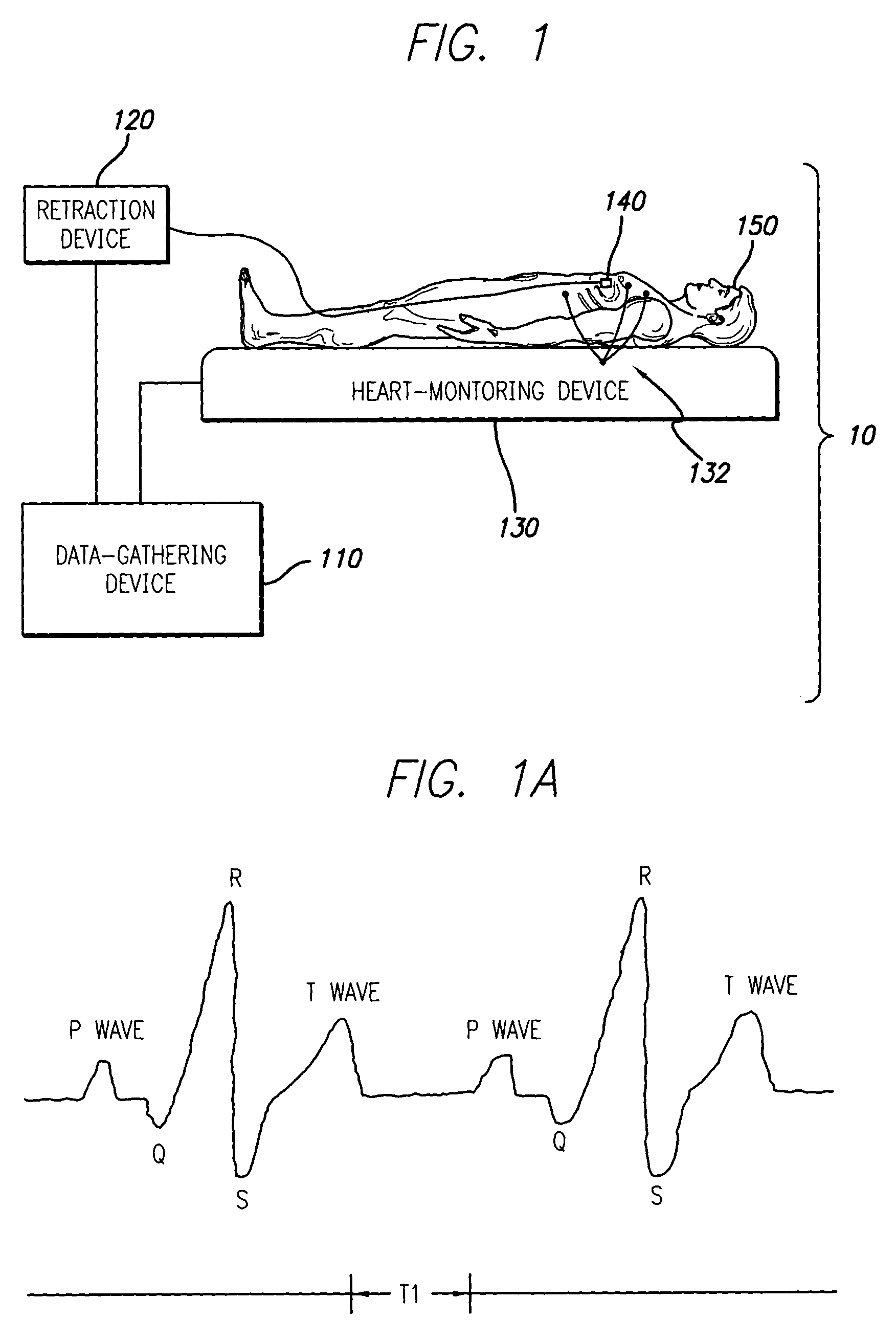
A system and method is provided for substantially synchronizing the acquisition of blood-vessel data to an identifiable portion of heartbeat data. Specifically, a data-gathering device is adapted to acquire heartbeat data and blood-vessel data from a heart-monitoring device and a data-gathering probe, respectively. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the blood-vessel data is acquired during a cyclical portion of the heartbeat data. By identifying a cyclical (or commonly reoccurring) portion of the heartbeat data and acquiring blood-vessel data during this cyclical portion (or during an interval that substantially corresponds thereto), the blood vessel can be analyzed as if it were standing still—i.e., not expanding and relaxing. In one embodiment of the present invention, the heart-monitoring device includes an EKG device, the data-gathering device includes an intra-vascular ultrasound (IVUS) device and a computing device, and the data-gathering probe includes at least one transducer. In another embodiment of the present invention, the data-gathering system further includes a retraction device adapted to move the data-gathering probe though a blood vessel at a substantially steady speed.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Integrated heart monitoring device and method of using same
InactiveUS20080249379A1Accurate measurementNo human intervention requiredElectrotherapyBlood flow measurement devicesElectricityBlood flow
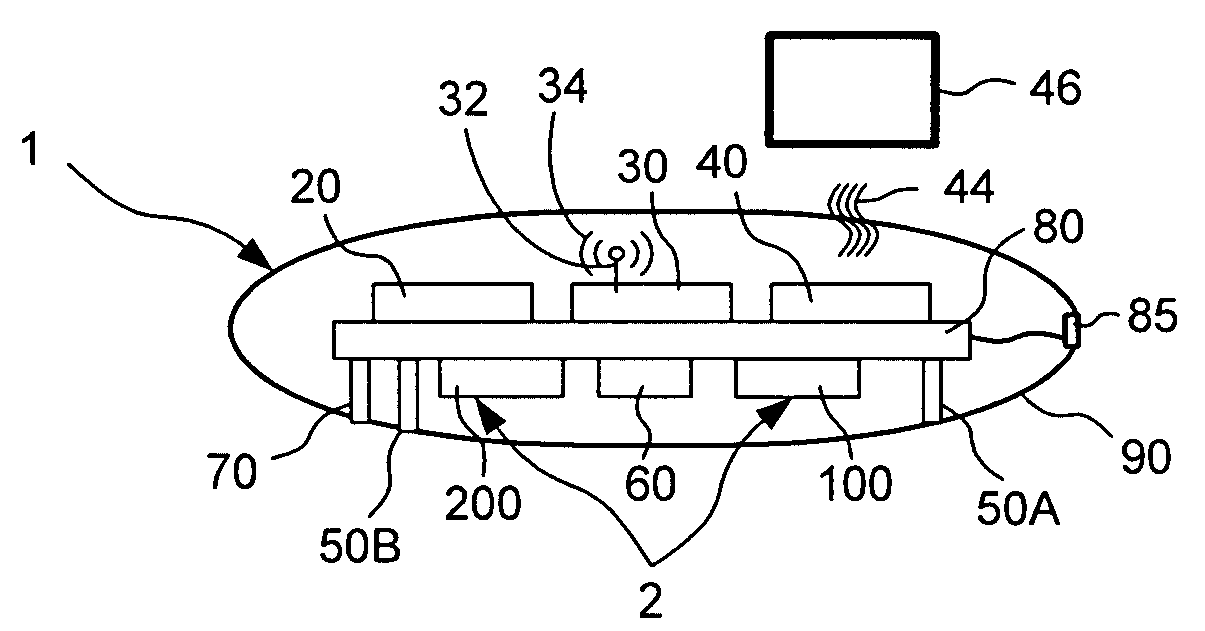
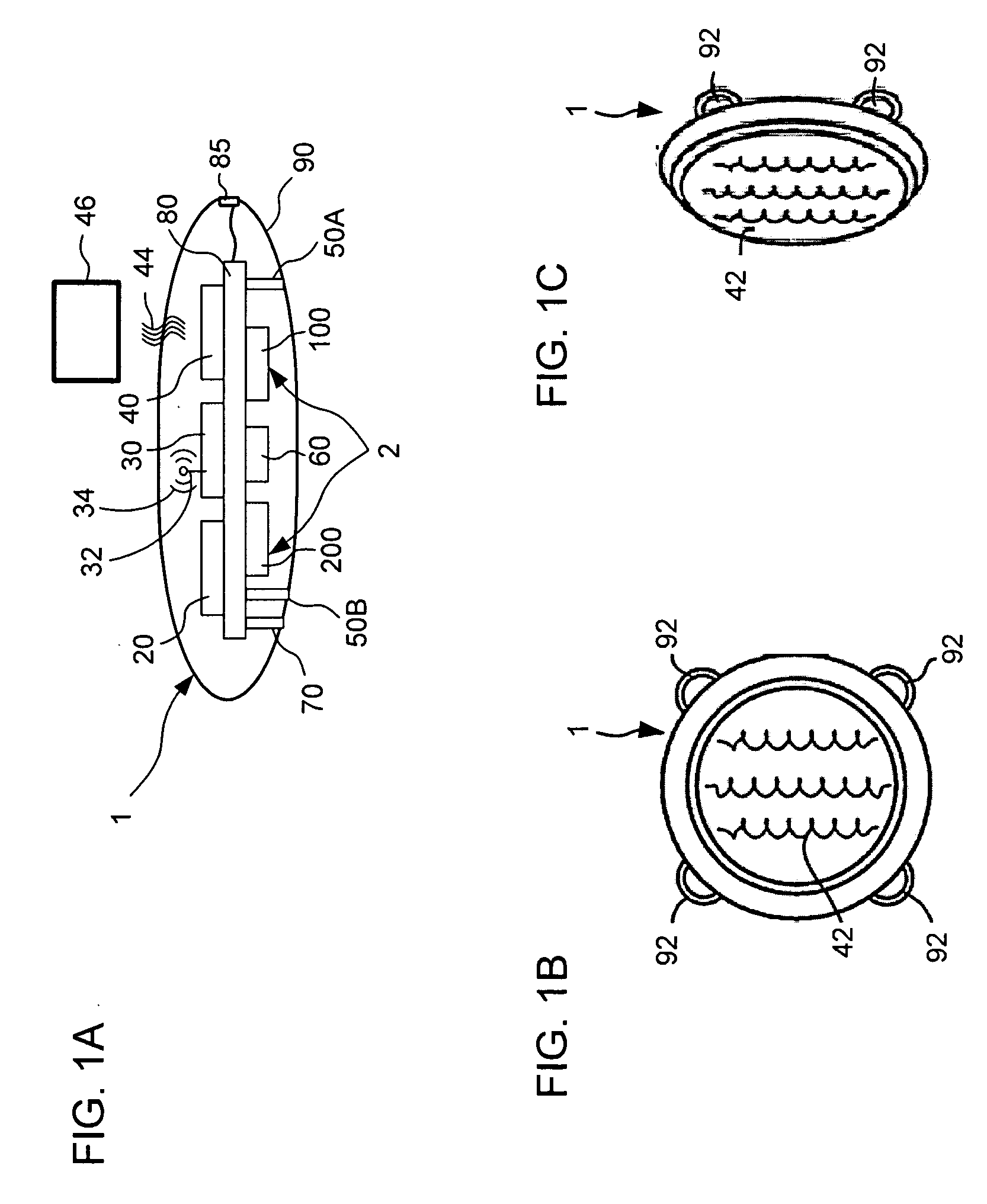
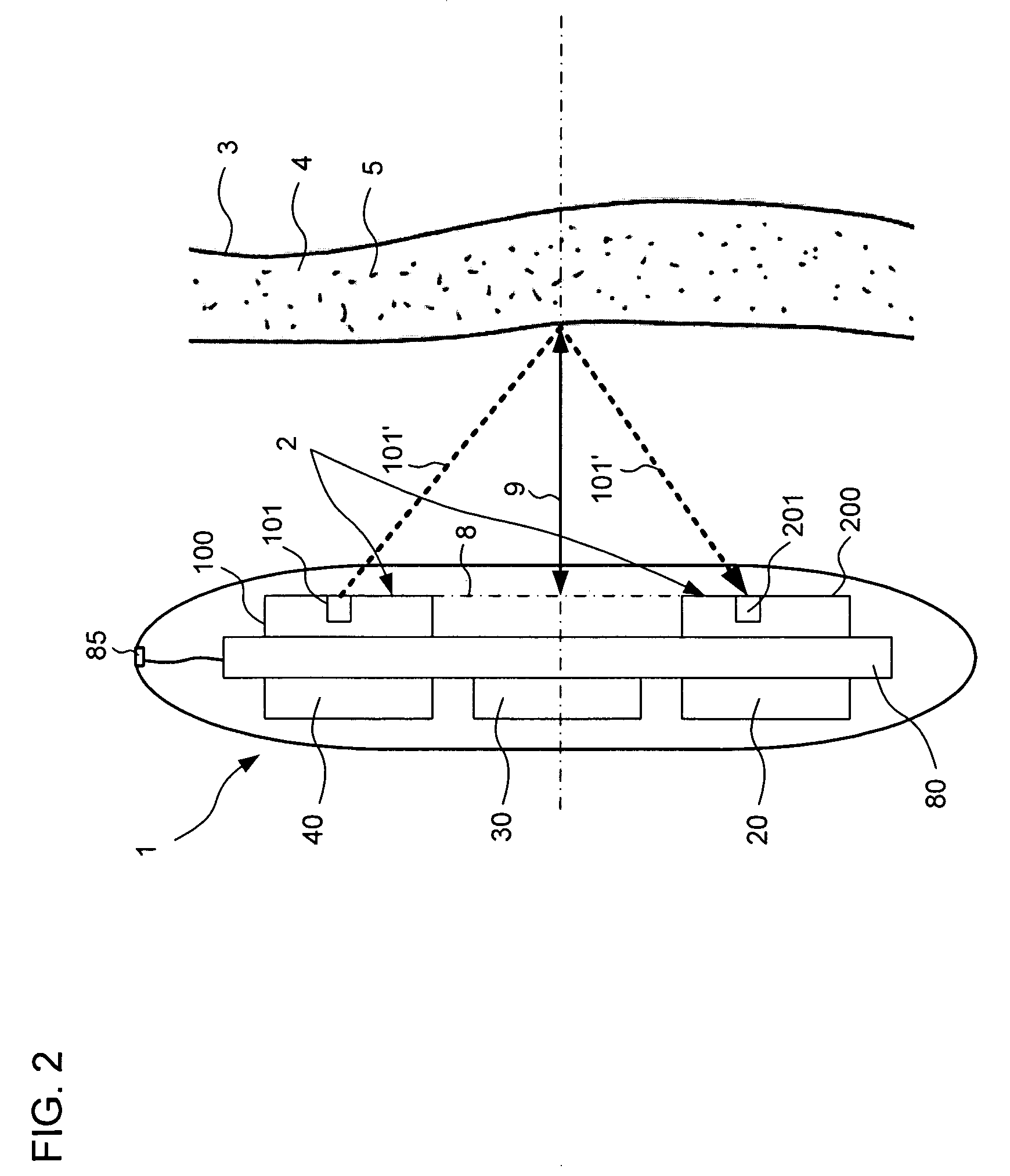
A device for monitoring the heart of a patient including a housing, a computing device, an optical sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a distance from the optical sensor to a vessel carrying blood, as well a diameter of the vessel, a Doppler sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a velocity of the blood through the vessel, and an ECG sensor adapted to provide signals to the computing device indicative of a plurality of electrical stimuli that cause the heart to pump. The computing device uses signals from the optical sensor, the Doppler sensor, and the ECG sensor to compute parameters including oxygen saturation of the blood, blood flow, blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output.
Owner:CARDIO ART TECH
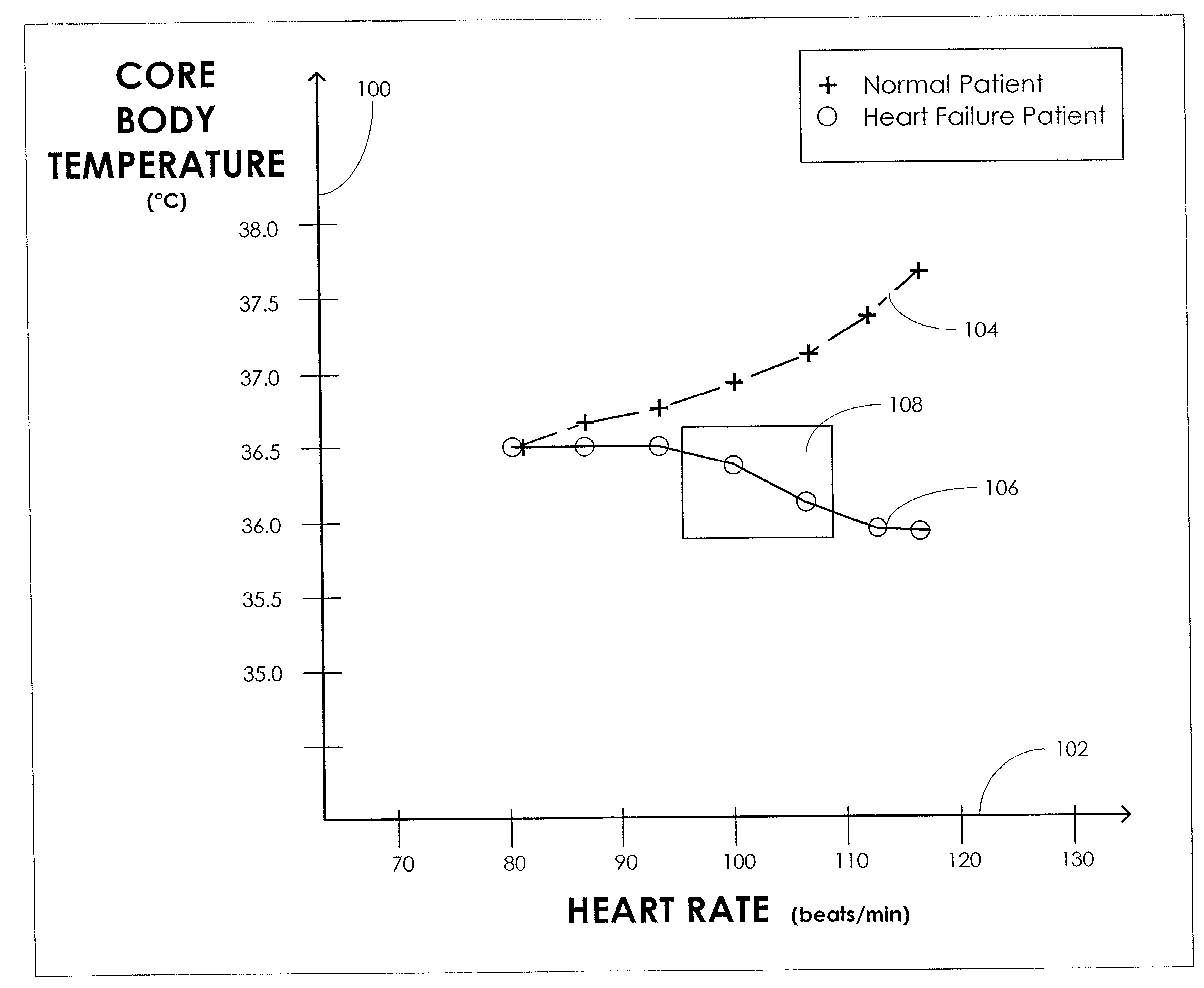
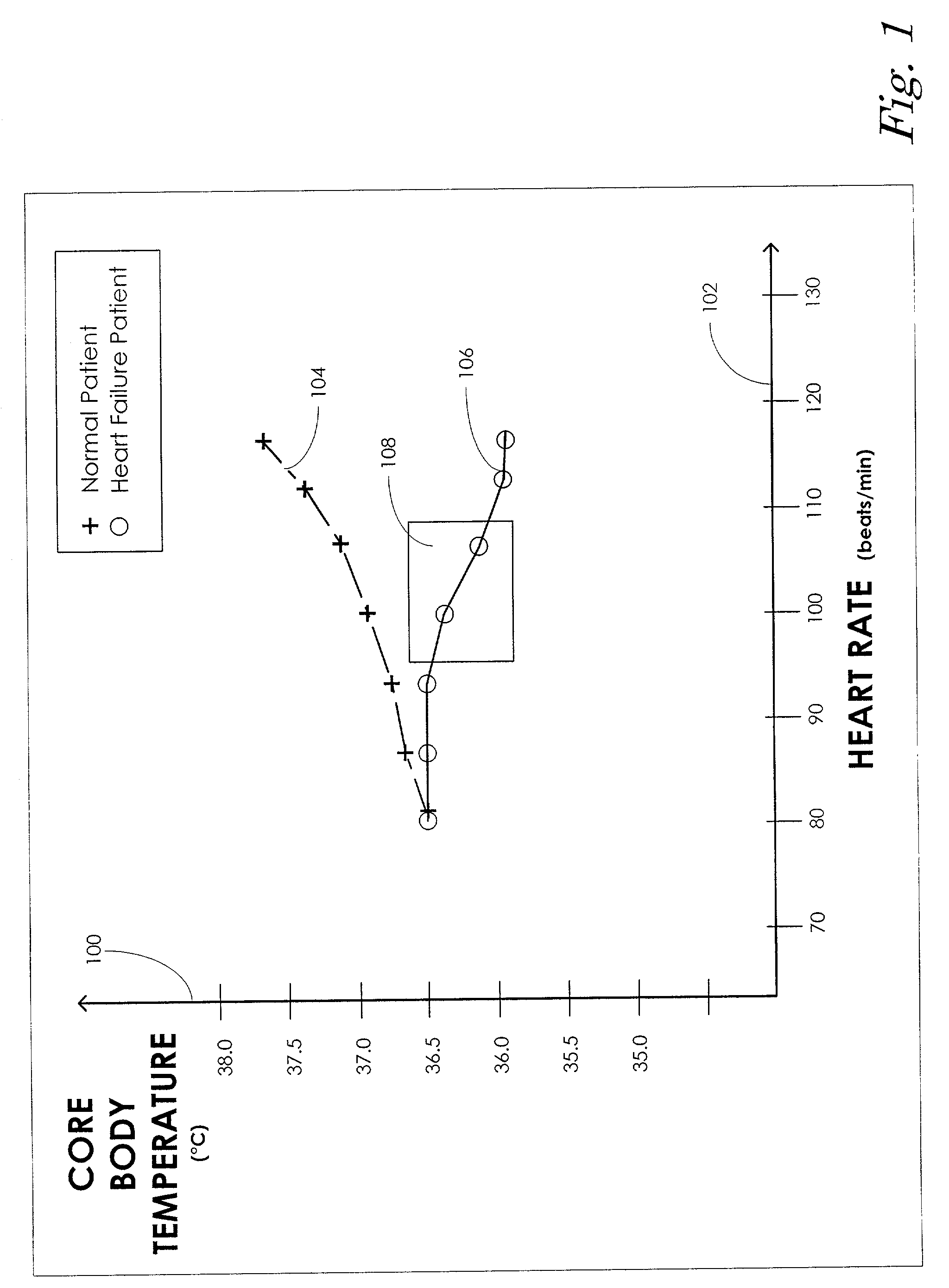
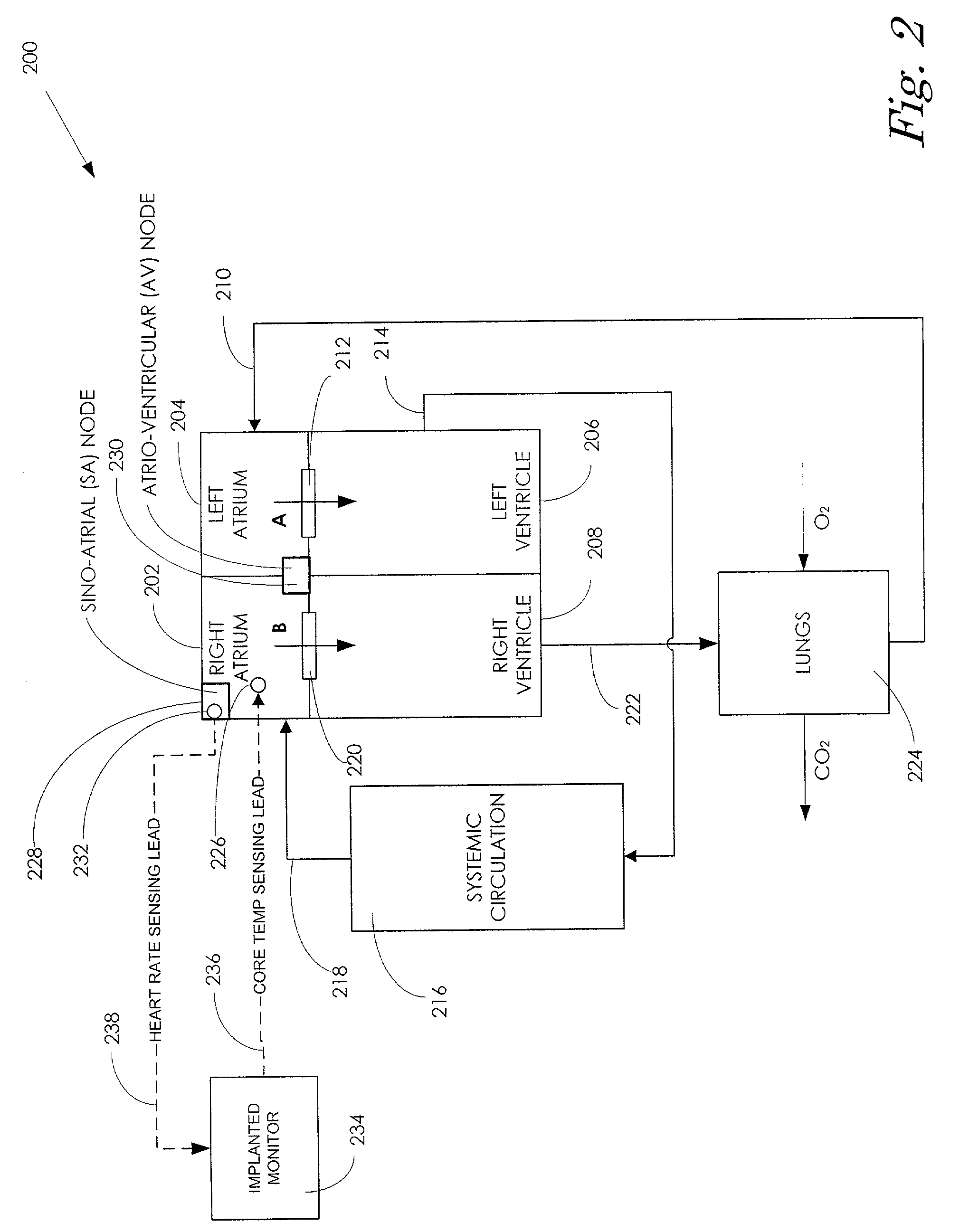
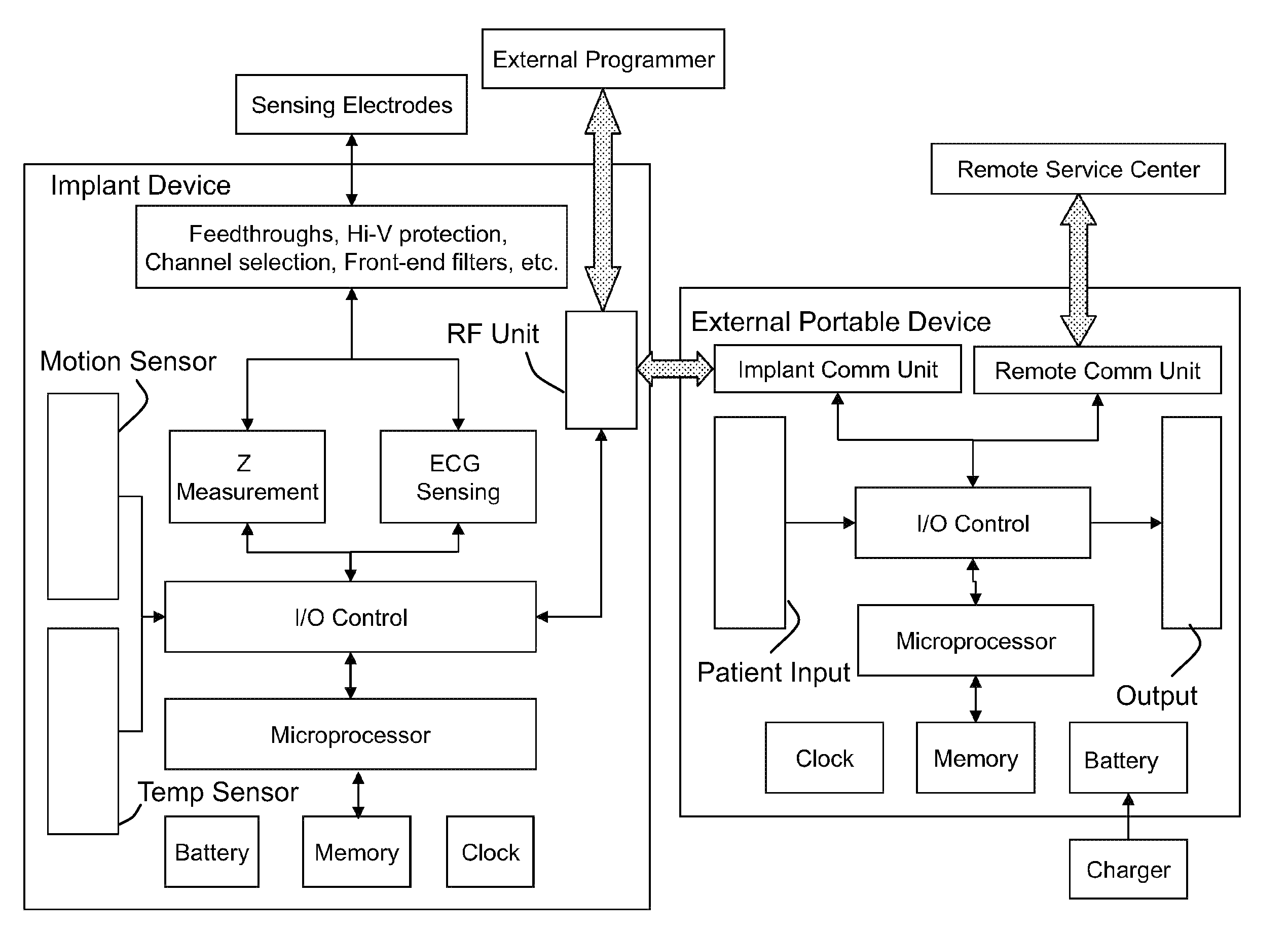
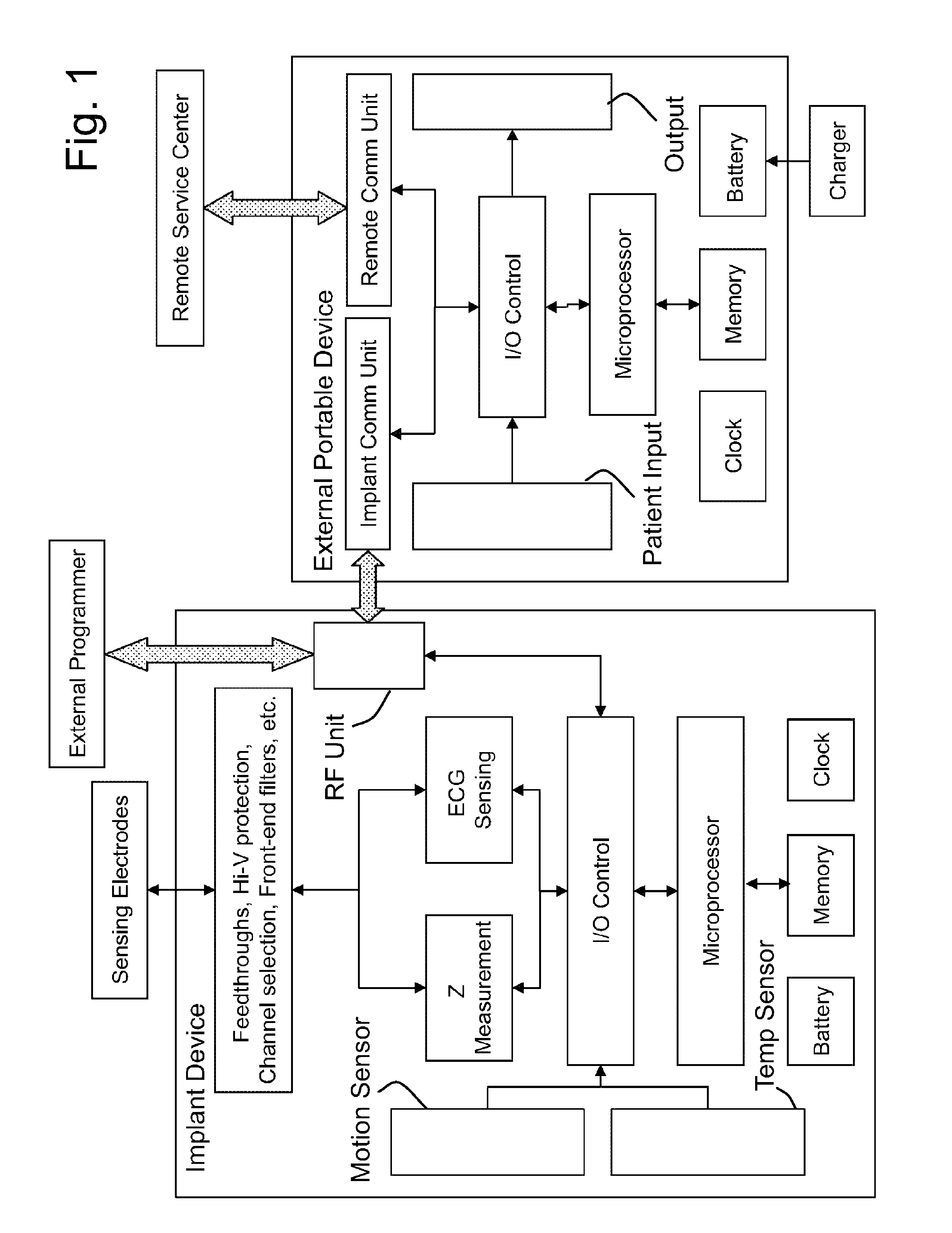
Core body temperature monitoring in heart failure patients
An implanted heart monitor includes sensors that measure various aspects of the heart failure patient's heart. A remote heart monitoring system connects the implanted heart monitor to a care provider, such as a physician. The data provided by the implanted heart monitor permits the care provider to obtain valuable data on the heart in order to make health care decisions affecting the heart failure patient's treatment. In many cases, the measurement of core body temperature and other patient data will enable the care provider to alter the patient's treatment to address the patient's condition. The implanted heart monitor can communicate over a wireless communication link with an external monitor. The implanted heart monitor may be implemented as part of a pacing device (i.e., pace maker) or may be a separate unit devoted to monitoring functions. The external monitor communicates with a monitoring station over a communication link. The monitoring station can operate as a centralized data collection unit, collecting data from multiple external monitors and multiple implanted heart monitors. Various other aspects of a heart failure patient's heart and / or body can be monitored, such as heart rate, blood pH levels, blood CO2 levels, and any other indications of the heart failure patient's activity. Various predetermined thresholds may be set to trigger alarms and / or data reports.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
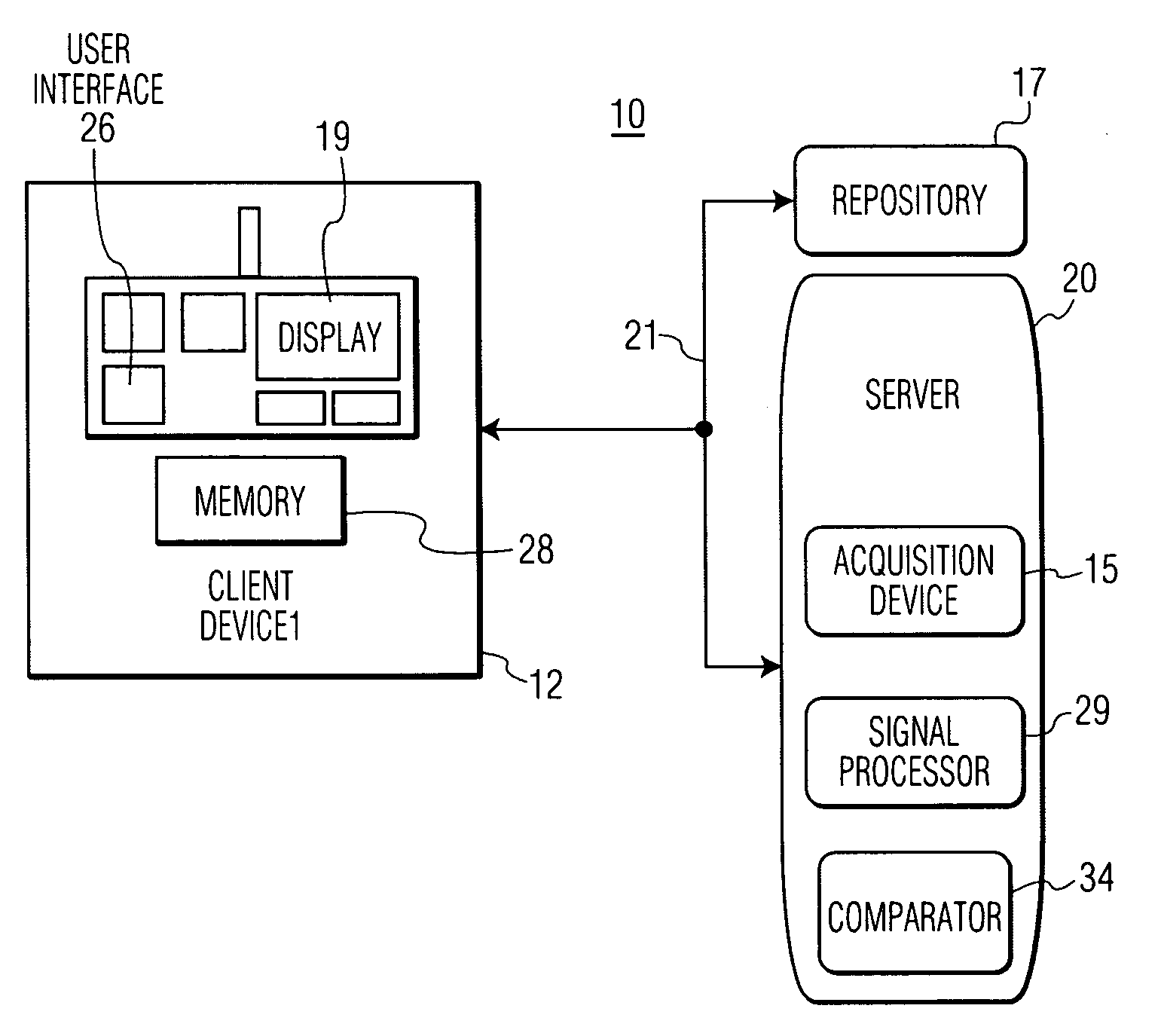
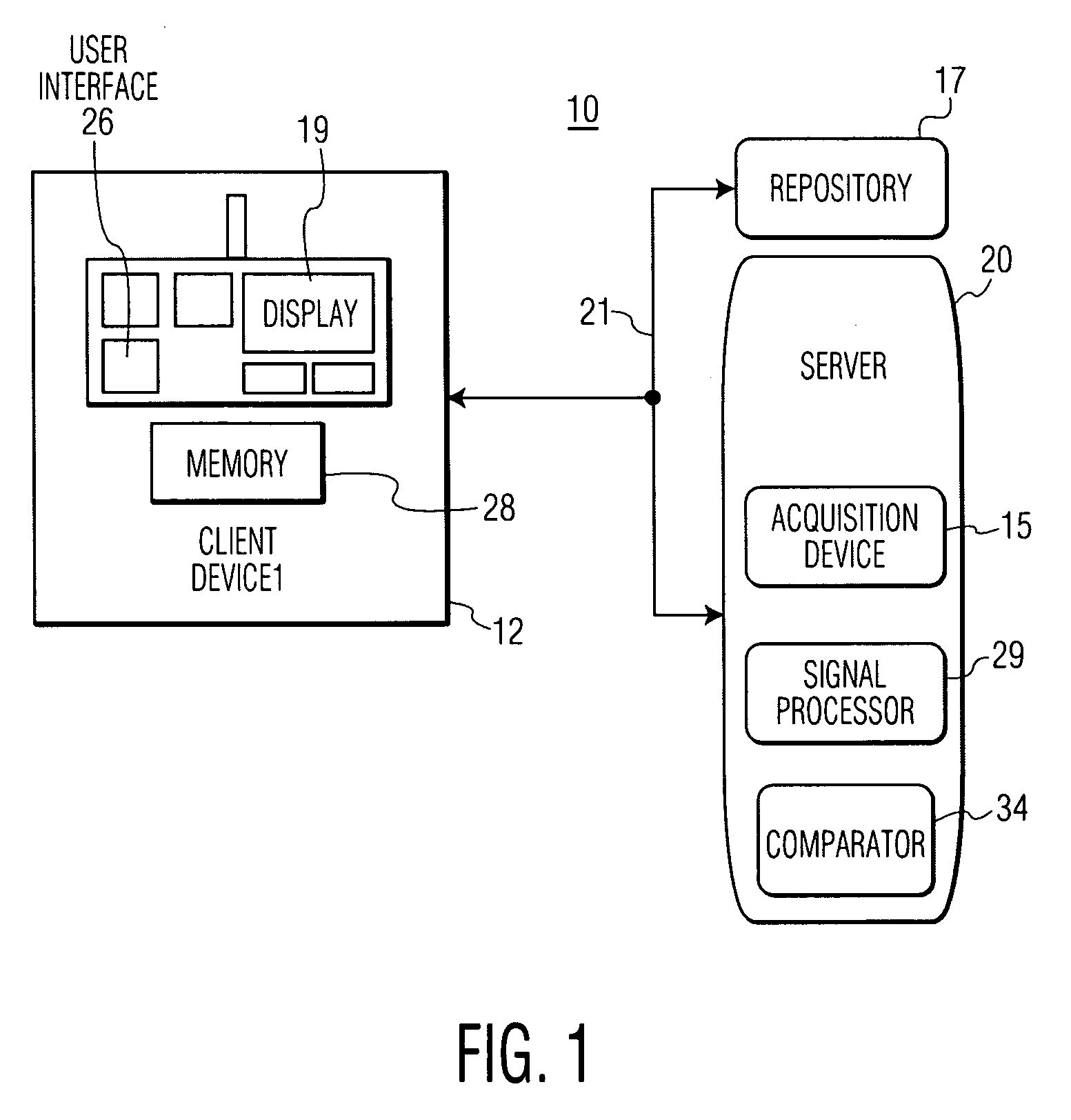
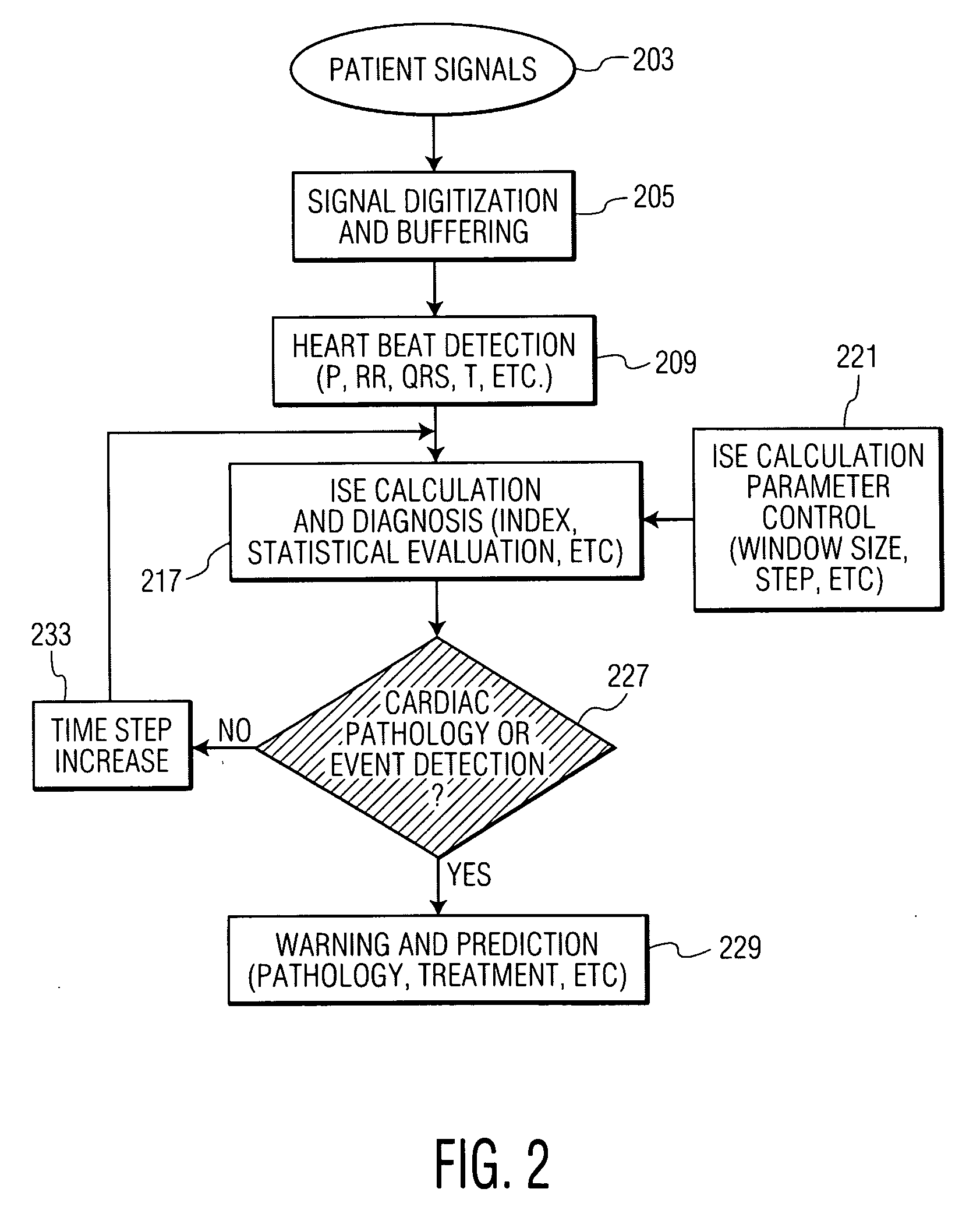
System for Heart monitoring, Characterization and Abnormality Detection
A system analyzes and characterizes cardiac electrophysiological signals by determining instantaneous signal entropy for identifying and characterizing cardiac disorders, differentiating cardiac arrhythmias, determining pathological severity and predicting life-threatening events. A system for heart monitoring, characterization and abnormality detection, includes an acquisition device for acquiring an electrophysiological signal representing a heart beat cycle of a patient heart. A signal processor derives an entropy representative value of the acquired electrophysiological signal within a time period comprising at least a portion of a heart beat cycle of the acquired electrophysiological signal and provides an entropy value as a function of the entropy representative value and the time period. A comparator generates data representing a message for communication to a destination device in response to the entropy value exceeding a predetermined threshold.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Systolic function monitoring utilizing slope of measured impedance
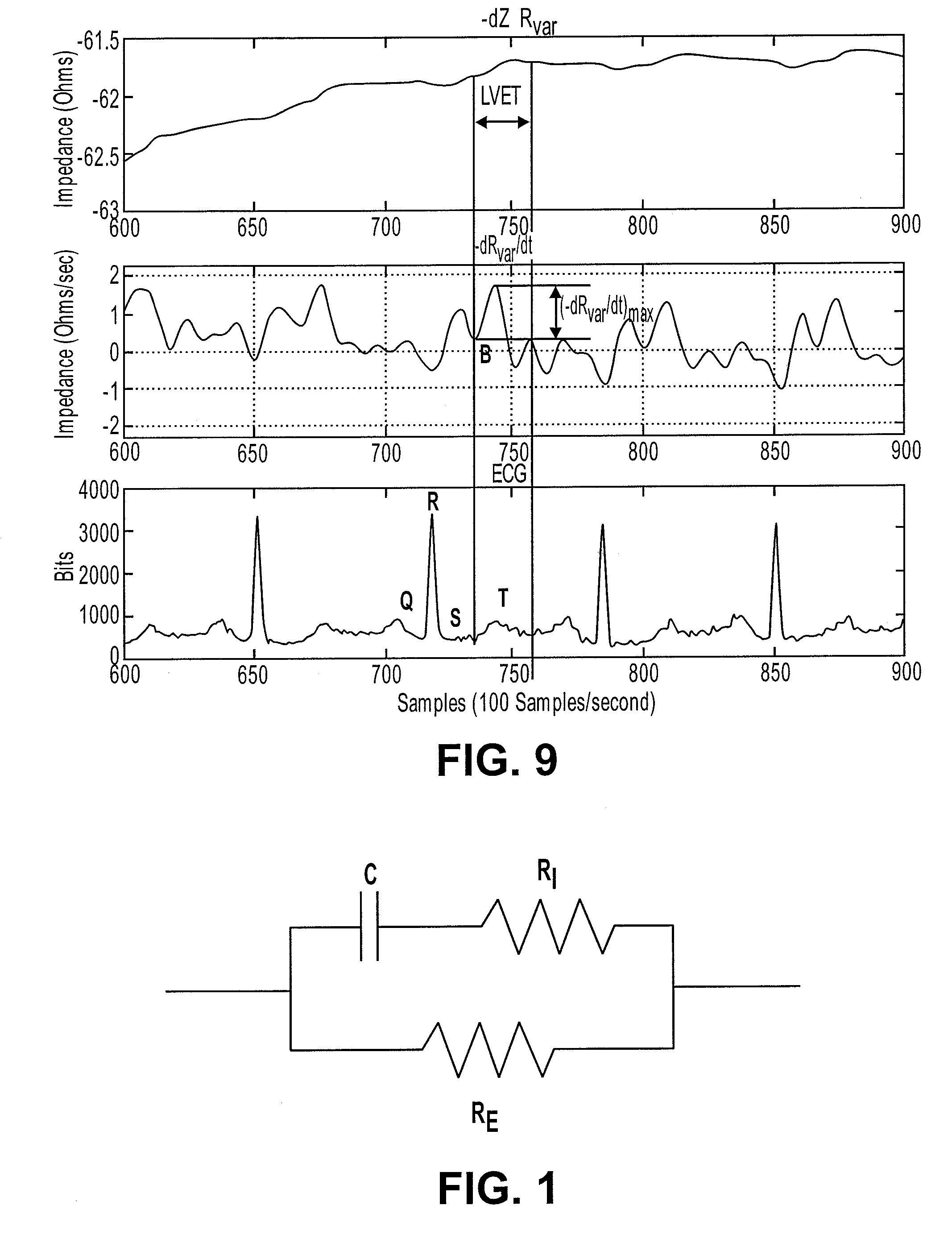
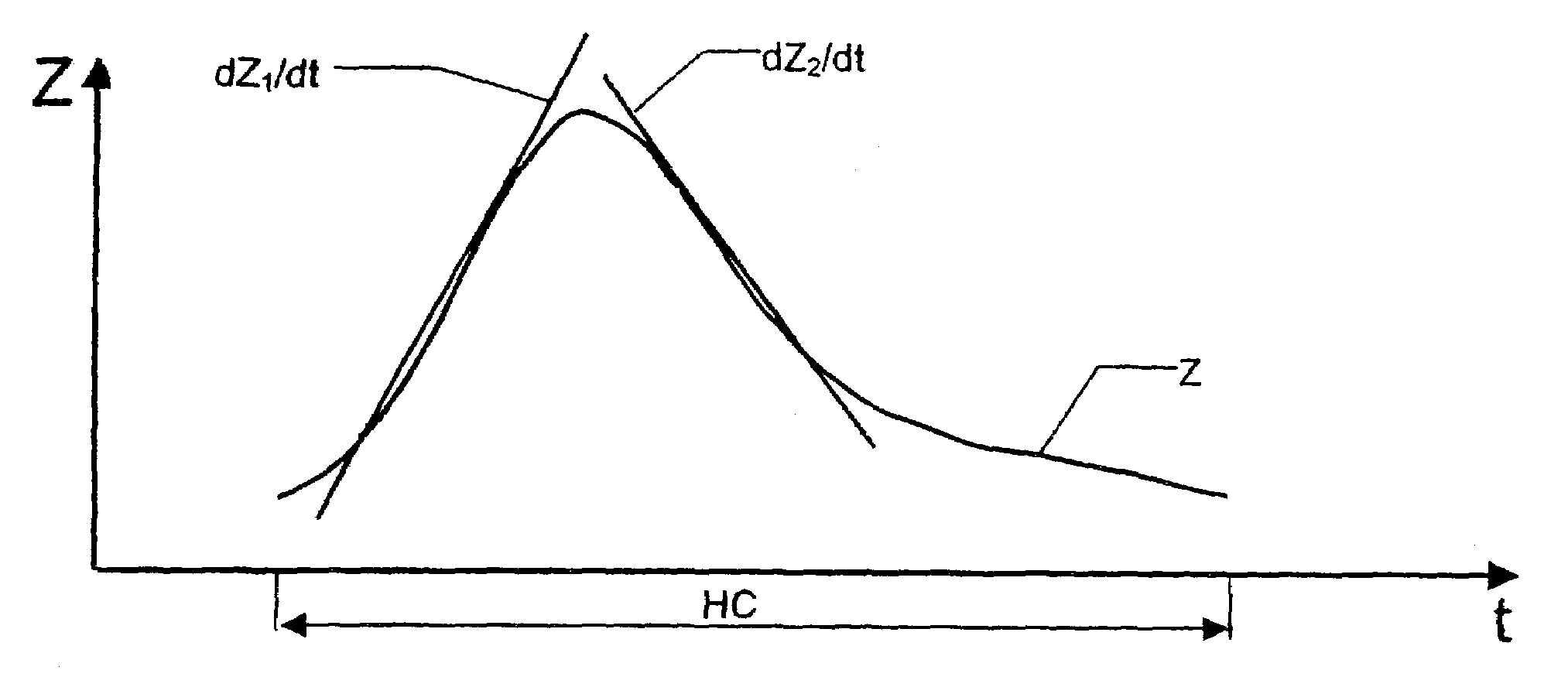
InactiveUS7146208B2Simple wayPossible to determineHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityHeart monitoring
A heart monitoring device has a control circuit, the control circuit being adapted to be electrically connected to electrode surfaces arranged at two different positions of the heart. The control circuit derives an impedance value indicative of the impedance between the electrode surfaces. Furthermore, the control circuit is arranged to determine and monitor a relationship between a positive rate of change and a negative rate of change of the impedance value. The device can, in particular, be used to detect and treat a systolic dysfunction of a heart.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
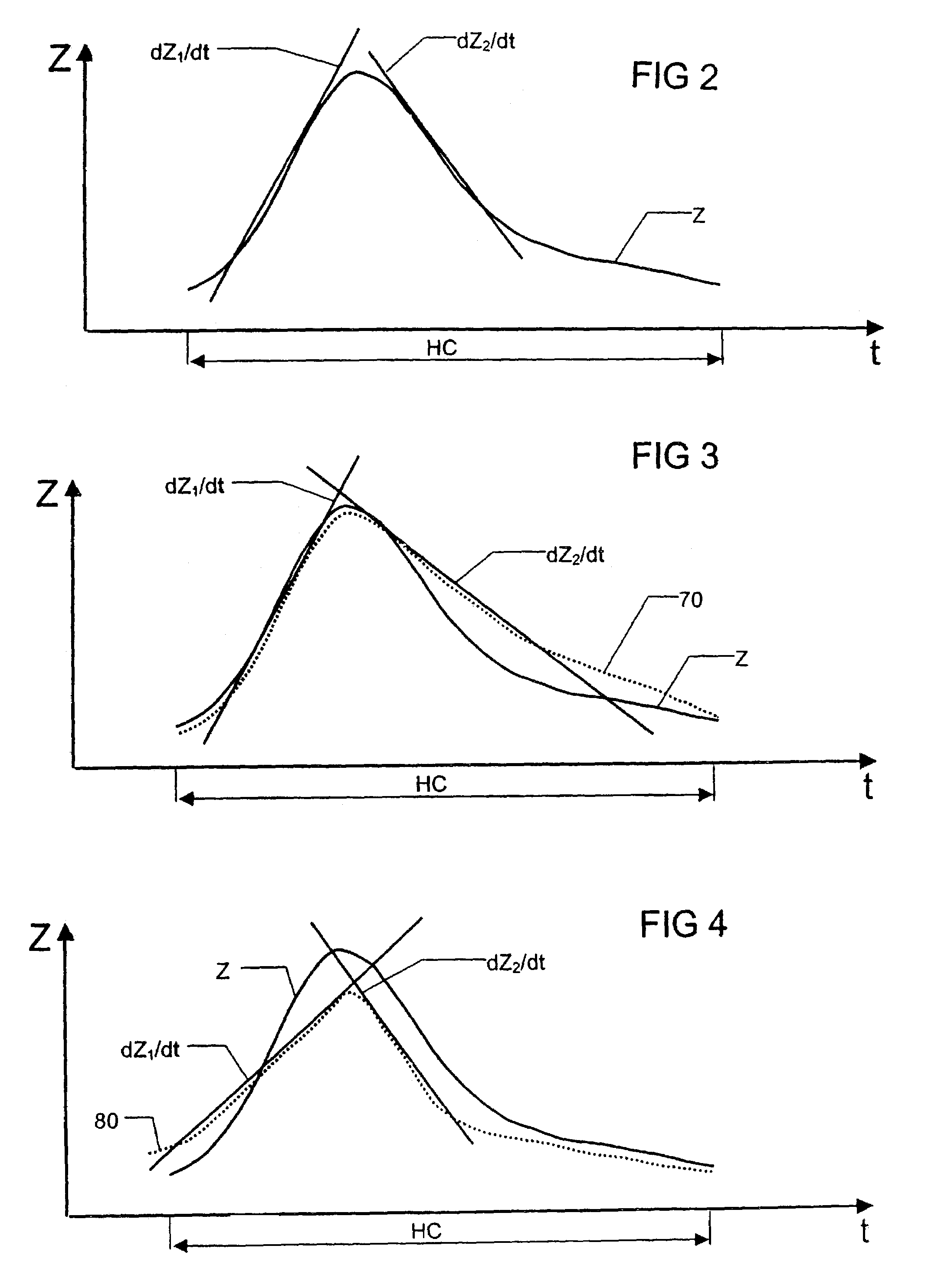
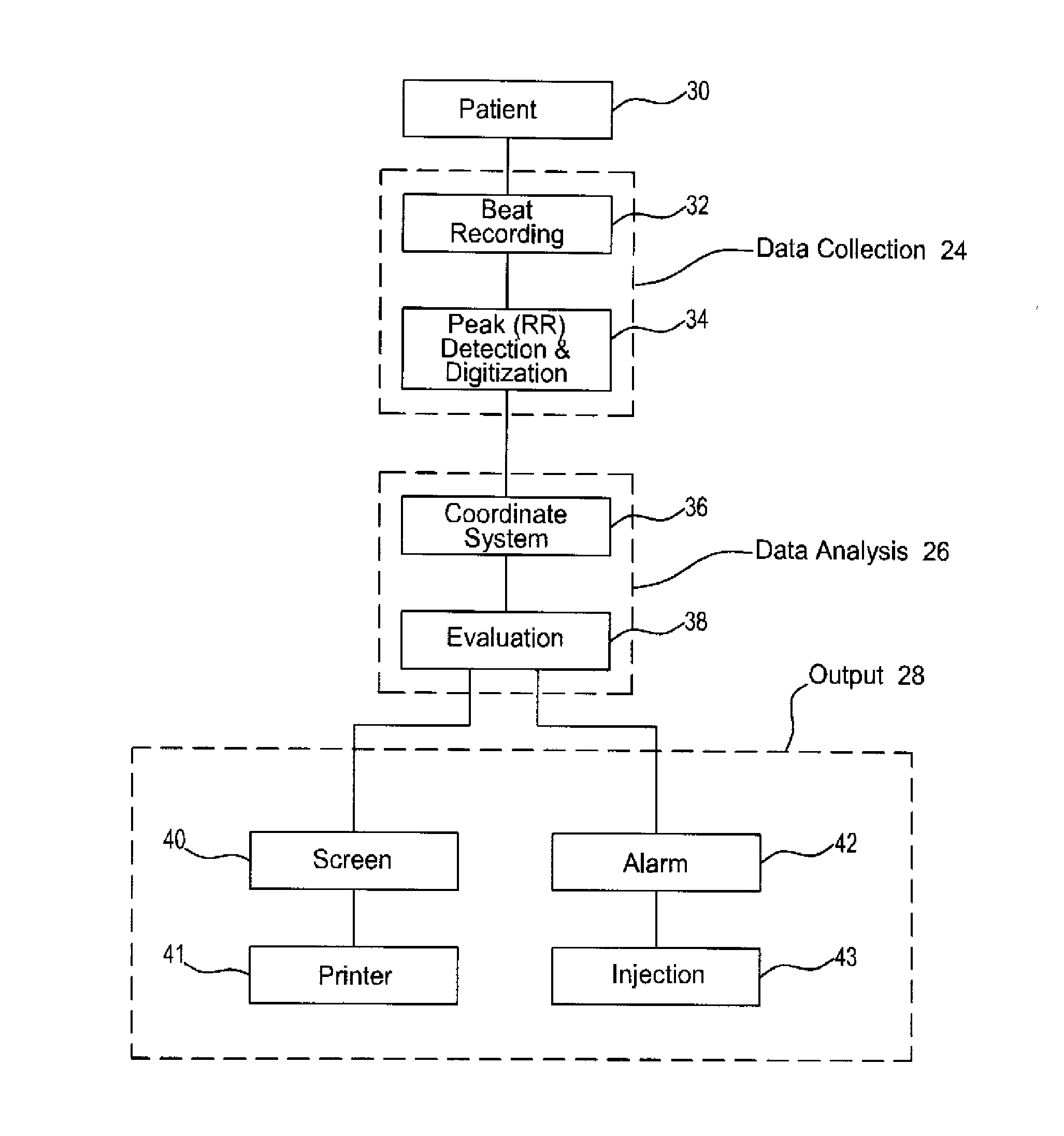
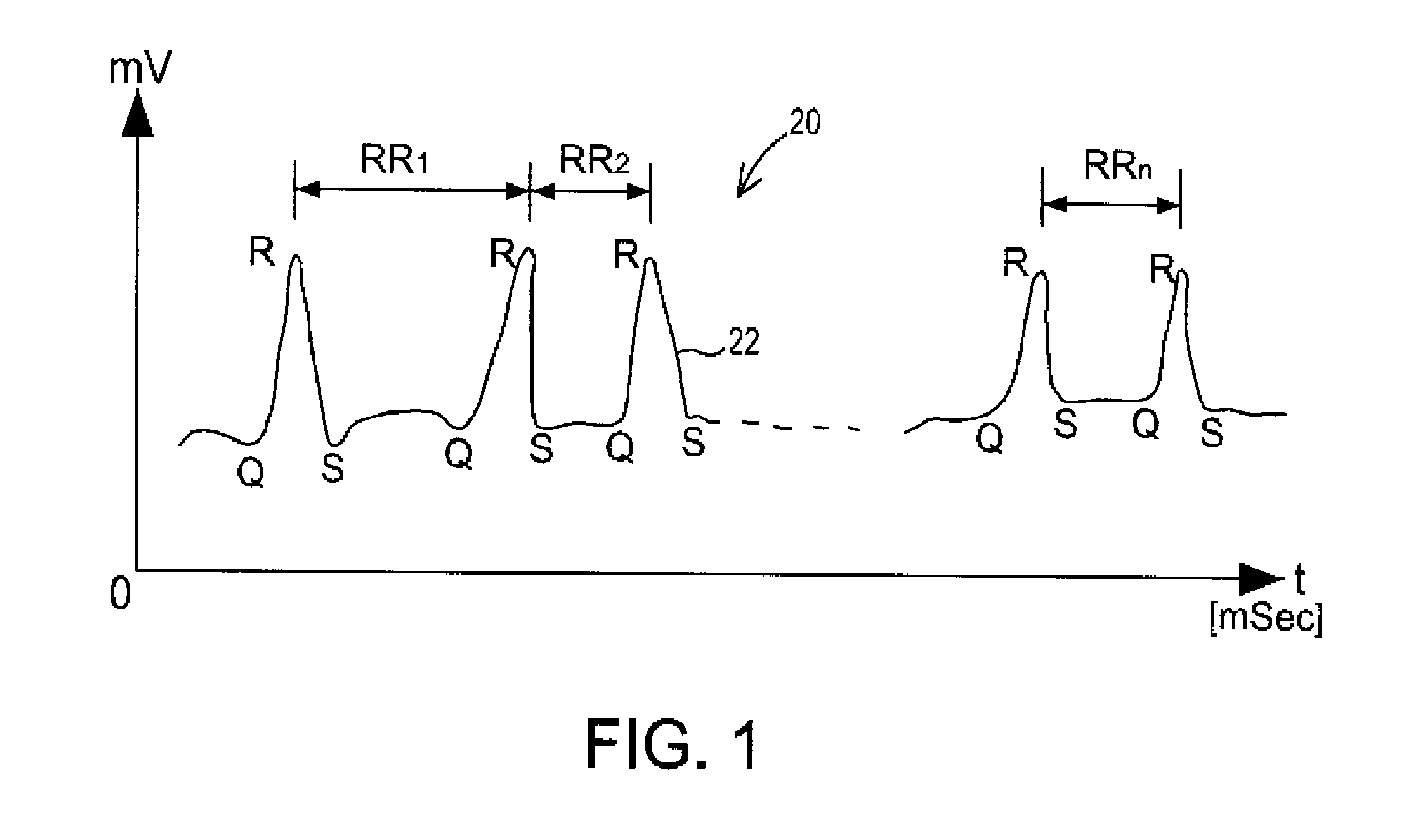
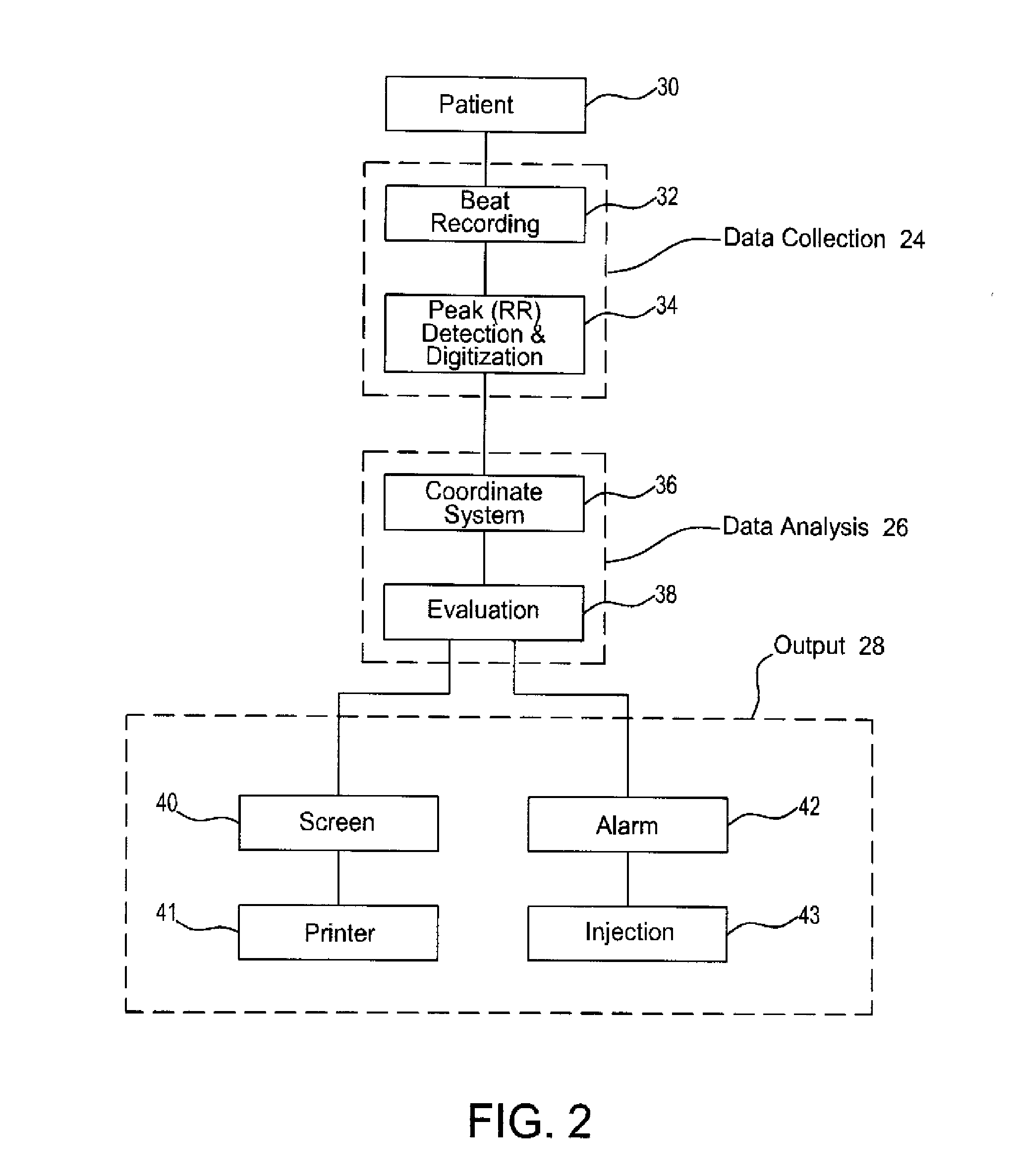
Heart rate variability sensor
A system for measuring heart rate variability (HRV) comprising 3 sub-systems: a data collection sub-system, a data analysis sub-system, and an output sub-system. A patient is connected to a heart monitoring device such as an ECG and the data collection sub-system records the patients heart beats, and an ECG chart is produced from which the patient's HRV value is derived by the data analysis sub-system. The present invention obtains the HRV value through calculation of a new parameter called relative density (RD). In accordance with the inventive method, data points are generated from the peak interval data of measured heart beats and the HRV relative density parameter (RD) is calculated by correlation between two subsets of data points.
Owner:LEV EL DIAGNOSTICS OF HEART DISEASE
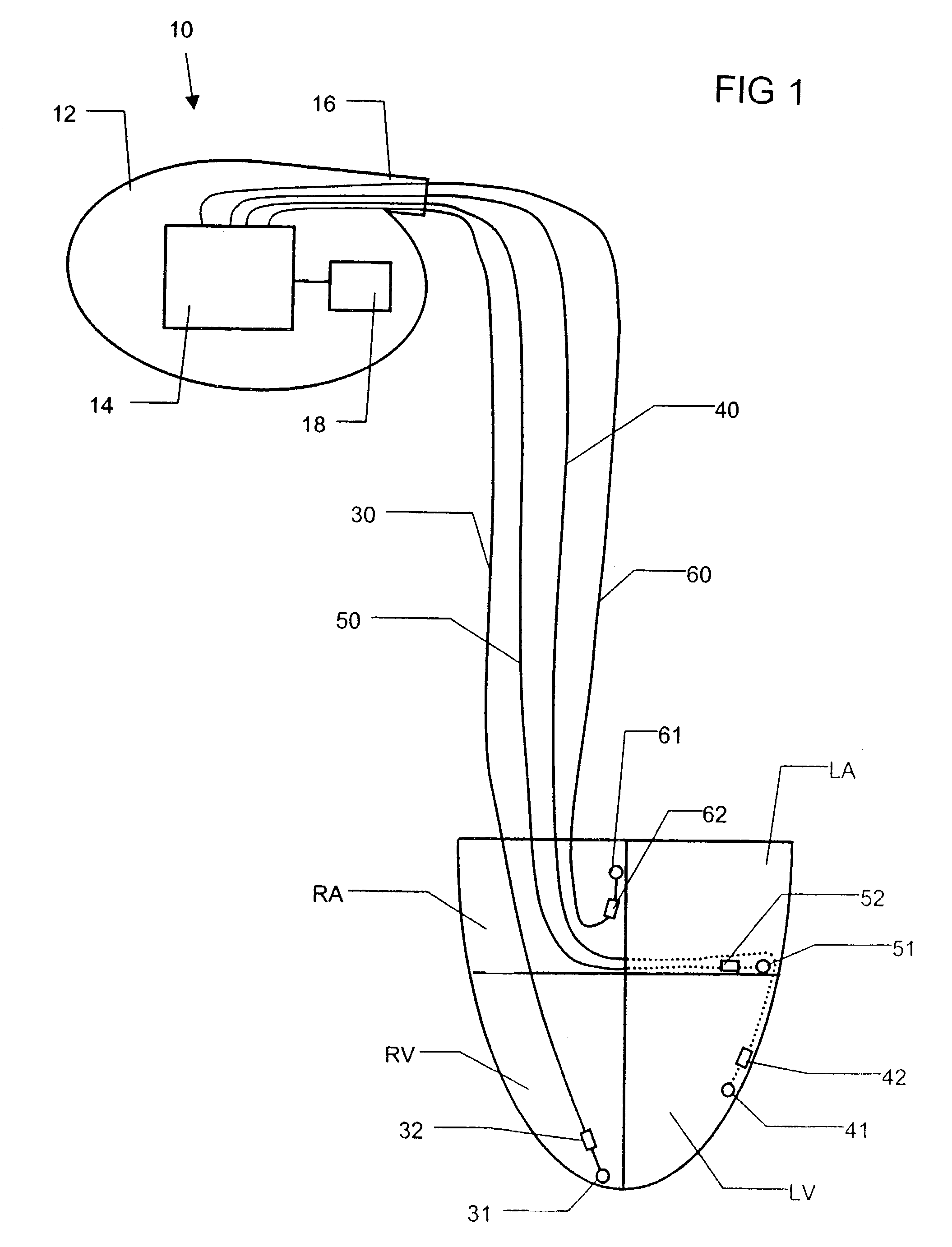
Distinguishing sinus tachycardia from atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter through analysis of atrial channel wavelet transforms
An implantable heart-monitoring device designed to distinguish two differing heart rhythms. The device comprises electrodes, a template, and first, second and third electronic mechanisms. The first electronic mechanism converts electrical representations of heartbeats from the electrodes into digital data and performs calculations including at least a partial discrete wavelet transform upon the digital data to generate a subset of discrete wavelet transform components including components for distinguishing the two differing heart rhythms and also demonstrated to be relatively low in variability from one patient to another. The template contains a corresponding subset of discrete wavelet transform components captured from at least one individual whose heart was beating in accordance with one of the two differing heart rhythms. The second electronic mechanism correlates the subset of transform components against the template components and provides a correlation value. The third electronic mechanism mathematically examines a time series of the correlation values and gives an indication of whether the first or second of the heart rhythms is present.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
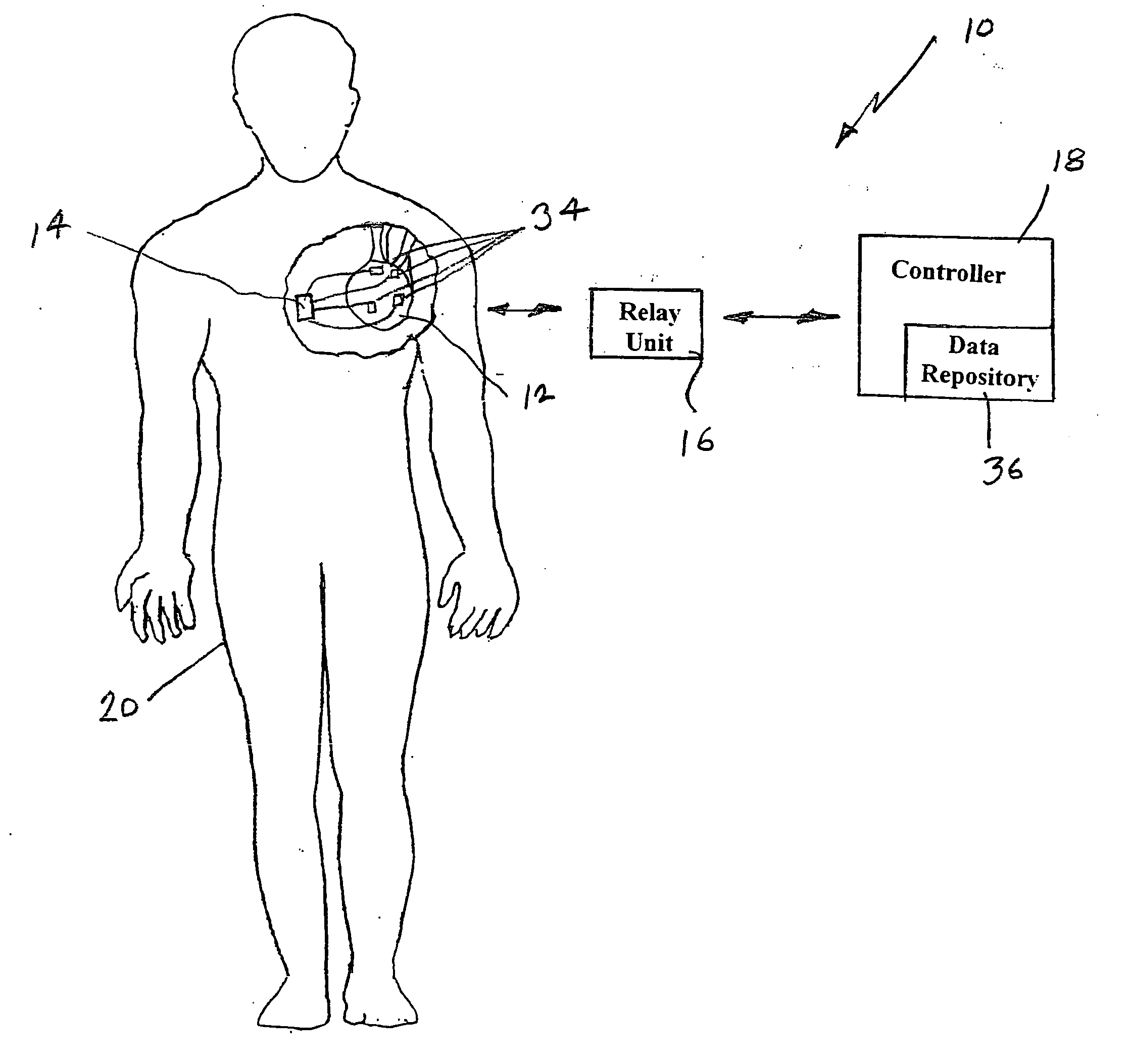
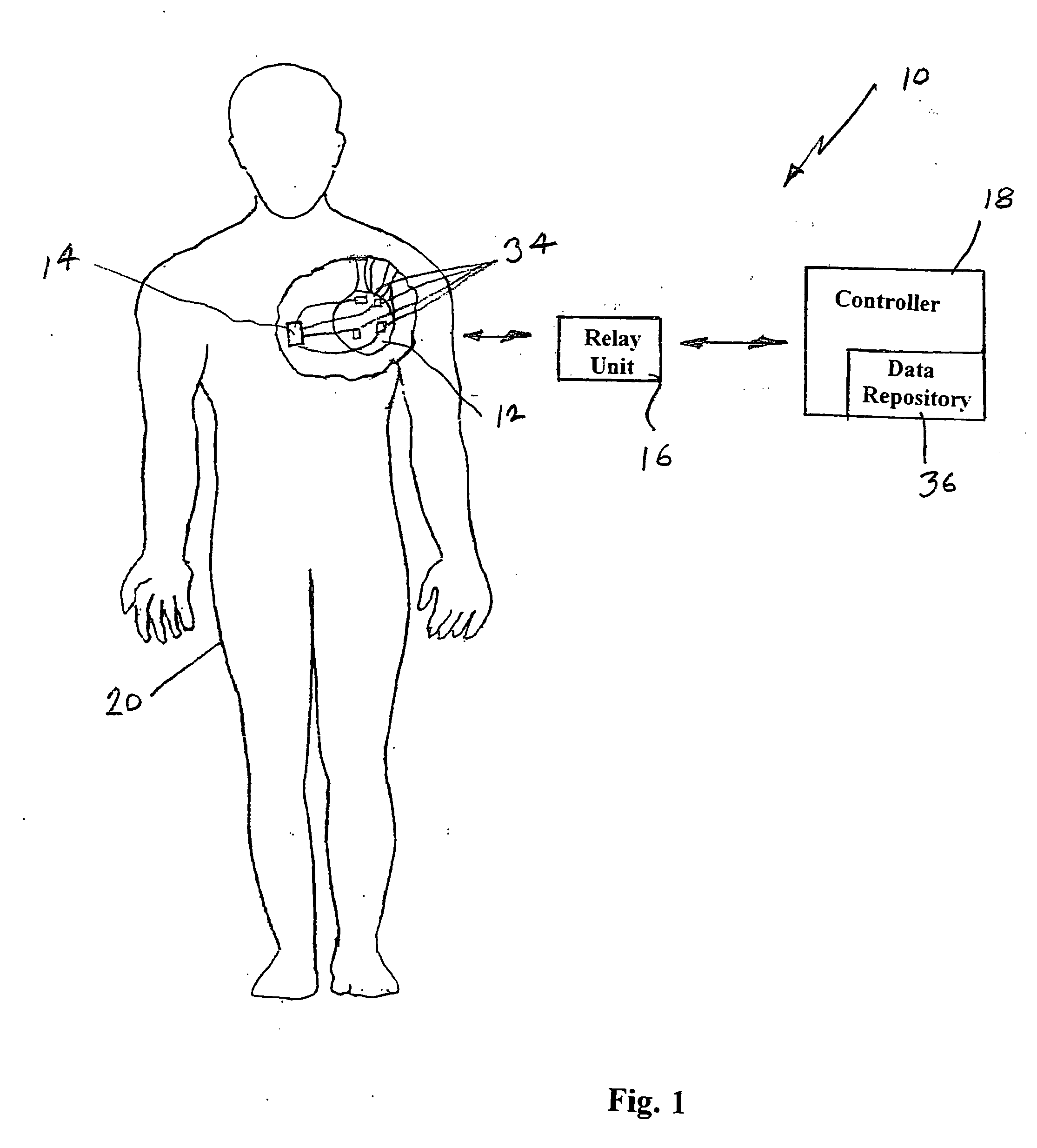
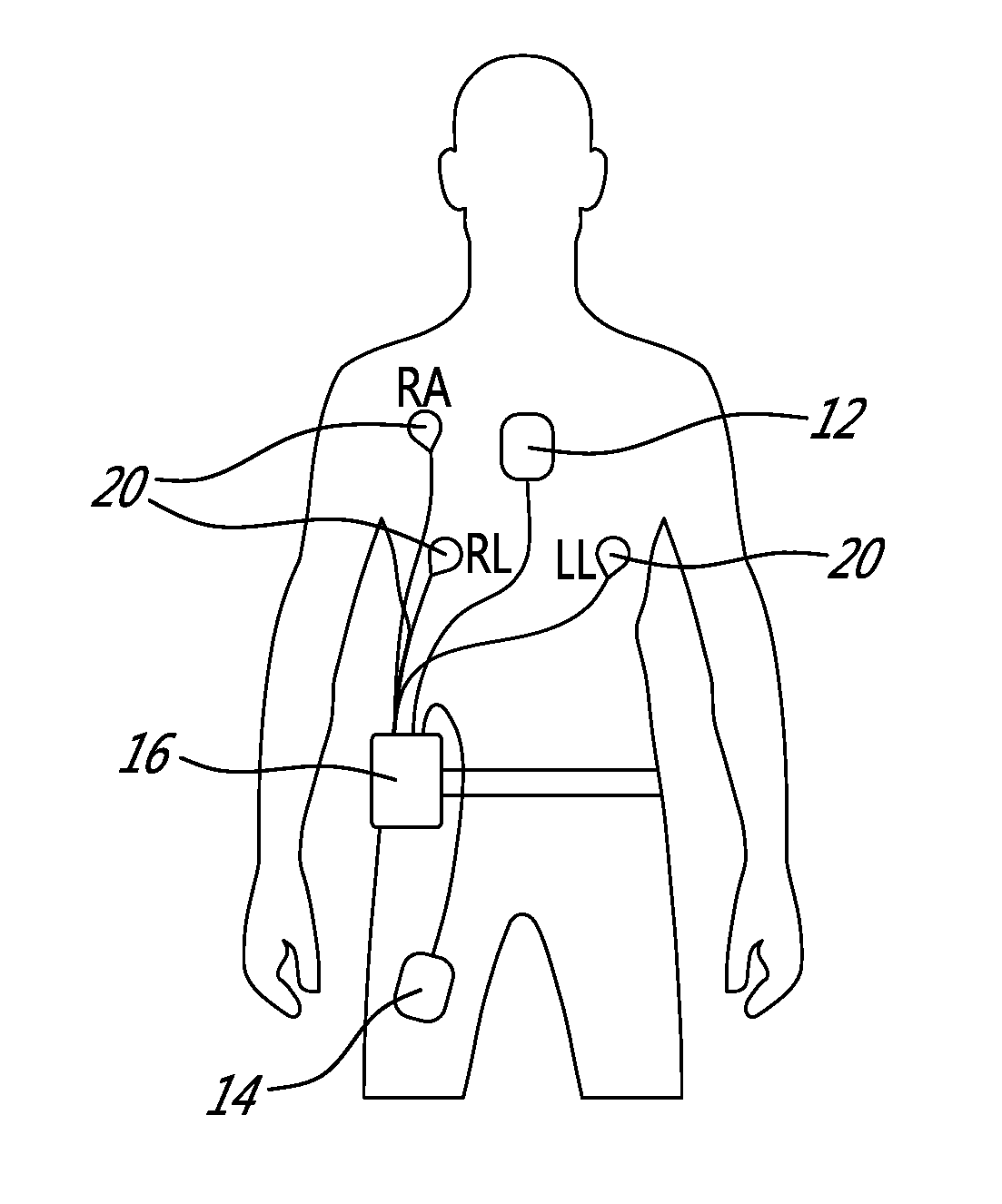
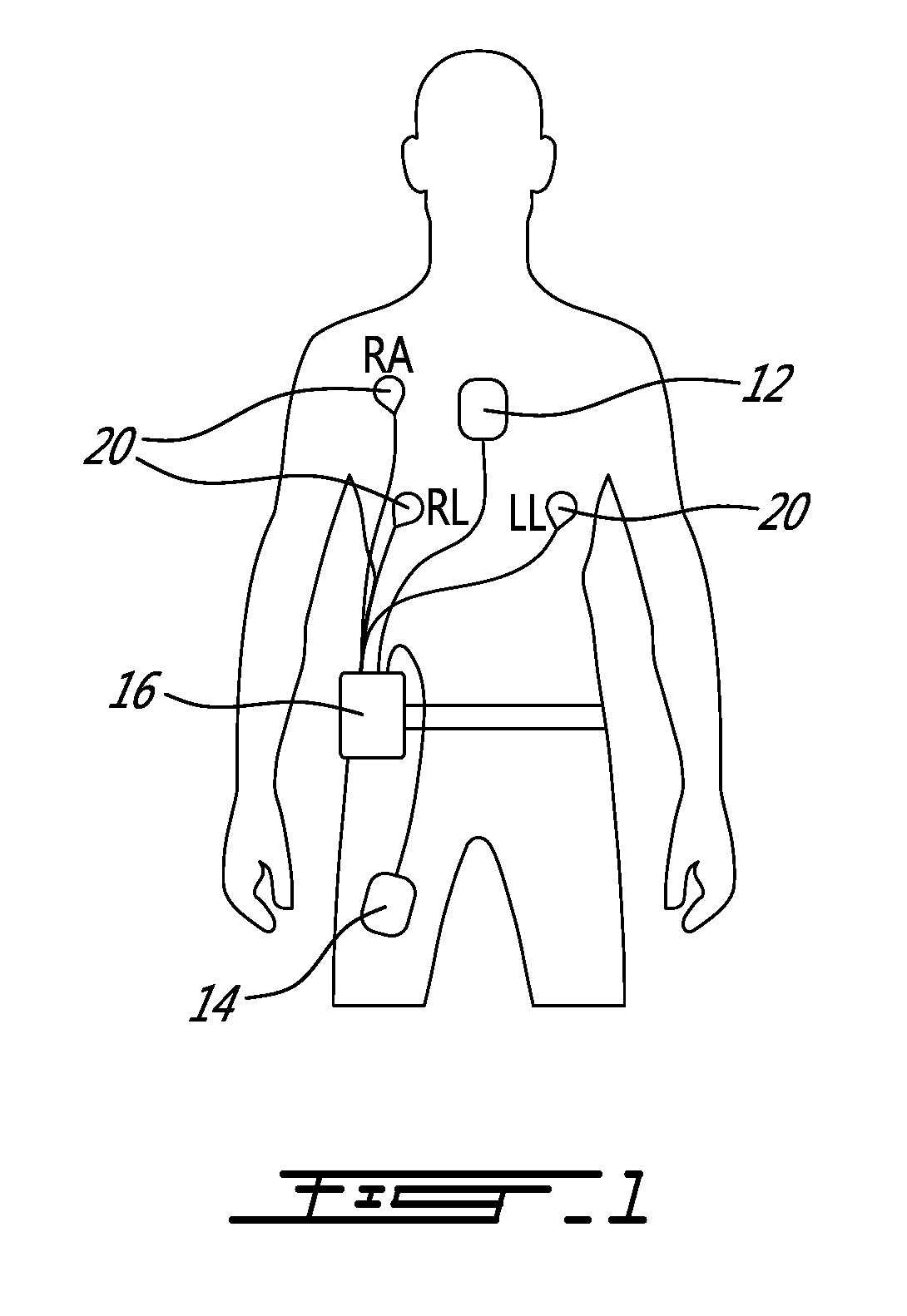
Systems, methods and computer program products for heart monitoring
ActiveUS20050234360A1Eliminate riskEffective diagnosisElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsHeart monitoringElectric signal
The present invention provides systems, methods and computer program products for monitoring a heart. According to one embodiment, the system includes an implantable registering unit. The registering unit comprises a first controller structured to register an electrical signal from the heart. The system includes a second controller in operable communication with the first controller. The second controller comprises a data repository structured to receive data corresponding to the registered electrical signal and being structured to store the data. The data repository stores data corresponding to a baseline electrical signal of the heart. The second controller is structured to receive the data from the first controller corresponding to the registered electrical signal and to compare the registered electrical signal to the baseline electrical signal to determine whether the heart is functioning properly.
Owner:COMPLETE MEDICAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Activity, posture and heart monitoring system and method
InactiveUS20150173654A1ElectrocardiographySensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationHeart monitoring
A system and a method for monitoring activity and posture of a person in correlation with the person's heat activity, comprising a) simultaneously detecting first linear accelerations and first angular speeds of rotation of an upper part of the person's body, second linear accelerations and second angular speeds of rotation of a lower part of the person's body, and the person's electrocardiogram signal; and b) determining the person's activity and posture from the first and second linear accelerations, the first and second angular speeds of rotation, and at least one of: i) a derivation signal, ii) heart rate and iii) a respiratory rate, of the person from the electrocardiogram signal.
Owner:SOLUTIONS NOVIKA
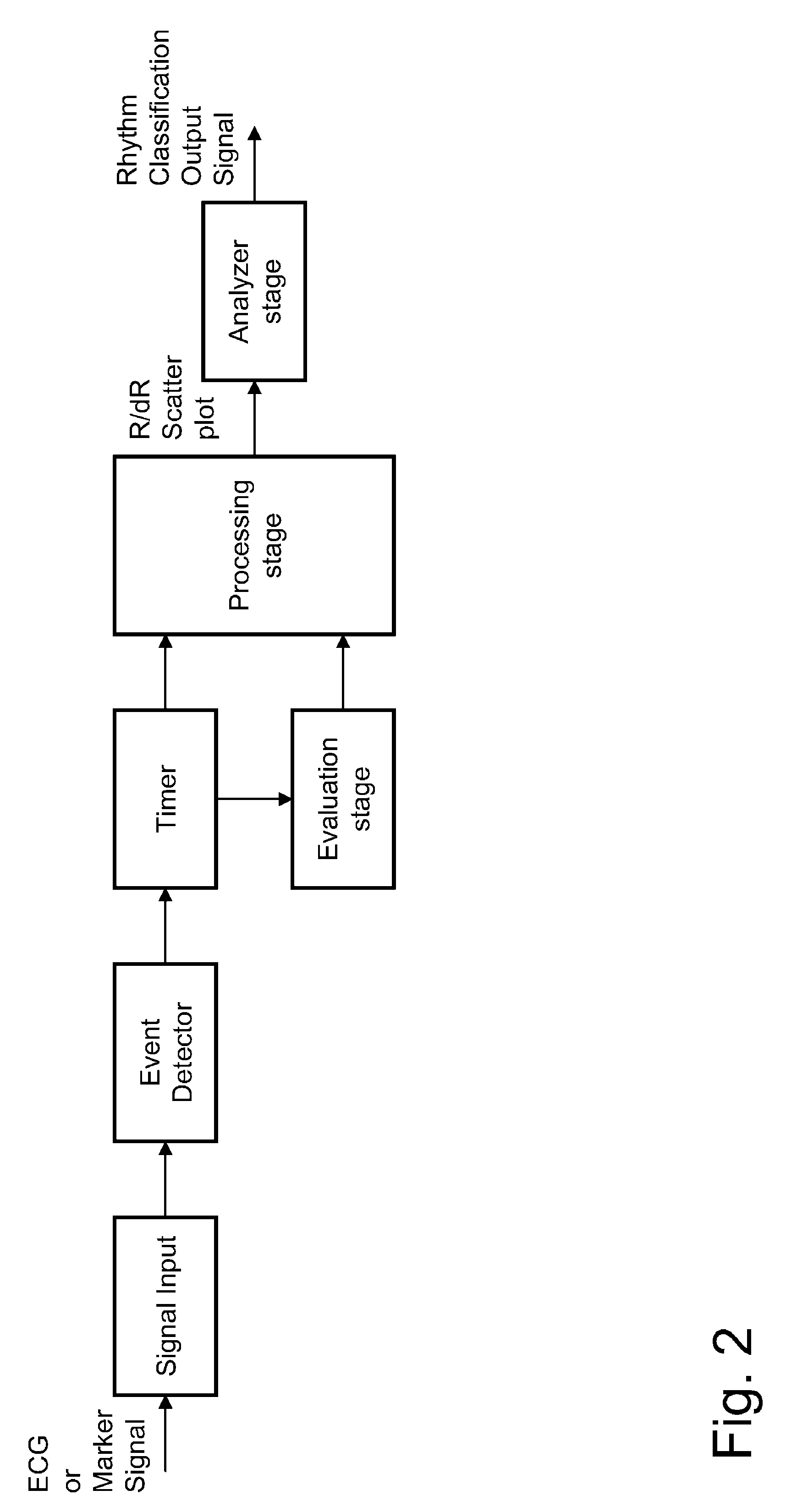
Heart monitoring device and method
InactiveUS8019407B2More robust cardiac rhythm classificationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsHeart monitoringComputer science
A heart monitor for processing input signals that represent periodically reoccurring events in a sequence of heart cycles. According to the invention graphical data representing a scatter plot of at least two dimensions, one dimension representing interval duration or its inverse and the other dimension representing change of duration or its inverse, respectively, are generated. The scatter plot comprises data points of which each data point represents heart interval duration or its inverse plotted against the change of duration with respect to a neighboring interval or the inverse of said change respectively.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Comprehensive System for Detection of Coronary Syndrome, Cardiac Ischemia and Myocardial Infarction
InactiveUS20100023081A1ElectrocardiographyAuscultation instrumentsCoronary arteriesCardiac functioning
Heart-monitoring systems, apparatus, and methods adapted to detect CS, CI and / or MI. In one embodiment, a system comprising at least two first-tier sensors capable of measuring and converting into signals at least two aspects related to cardiac function, at least one second-tier sensor that is also a first-tier sensor, at least one signal processor capable of transmitting a first-tier and second-tier trigger signal when coronary syndrome, cardiac ischemia or myocardial infarction has been detected, at least one communication device capable of communicating, at least one control element adapted to produce a first-tier and second-tier trigger signal when at least one first-tier sensor exceeds its threshold signal level, to exclude the signal from the first-tier sensor that exceeded its threshold and lower at least one threshold of the at least one first-tier sensor is provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
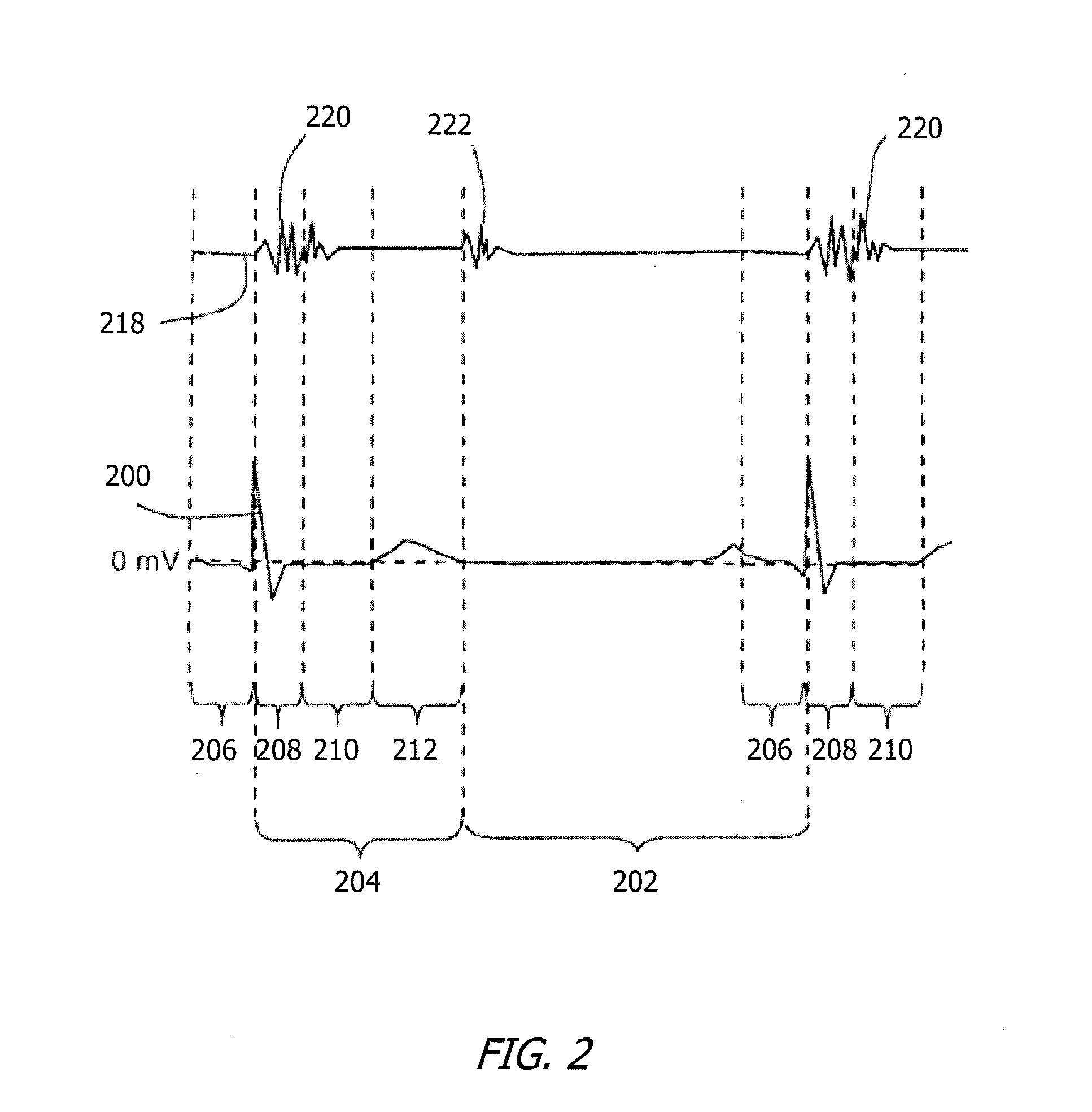
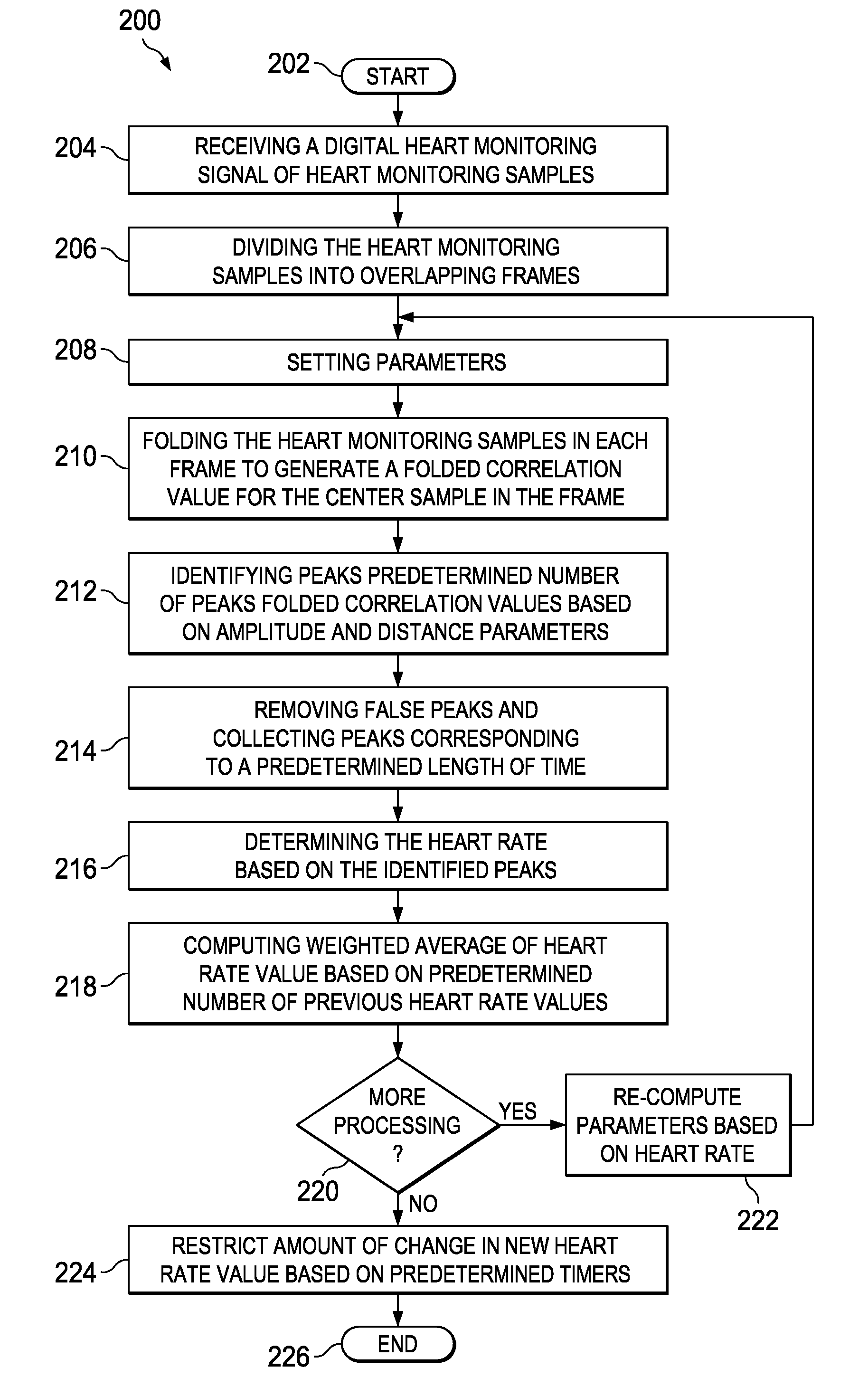
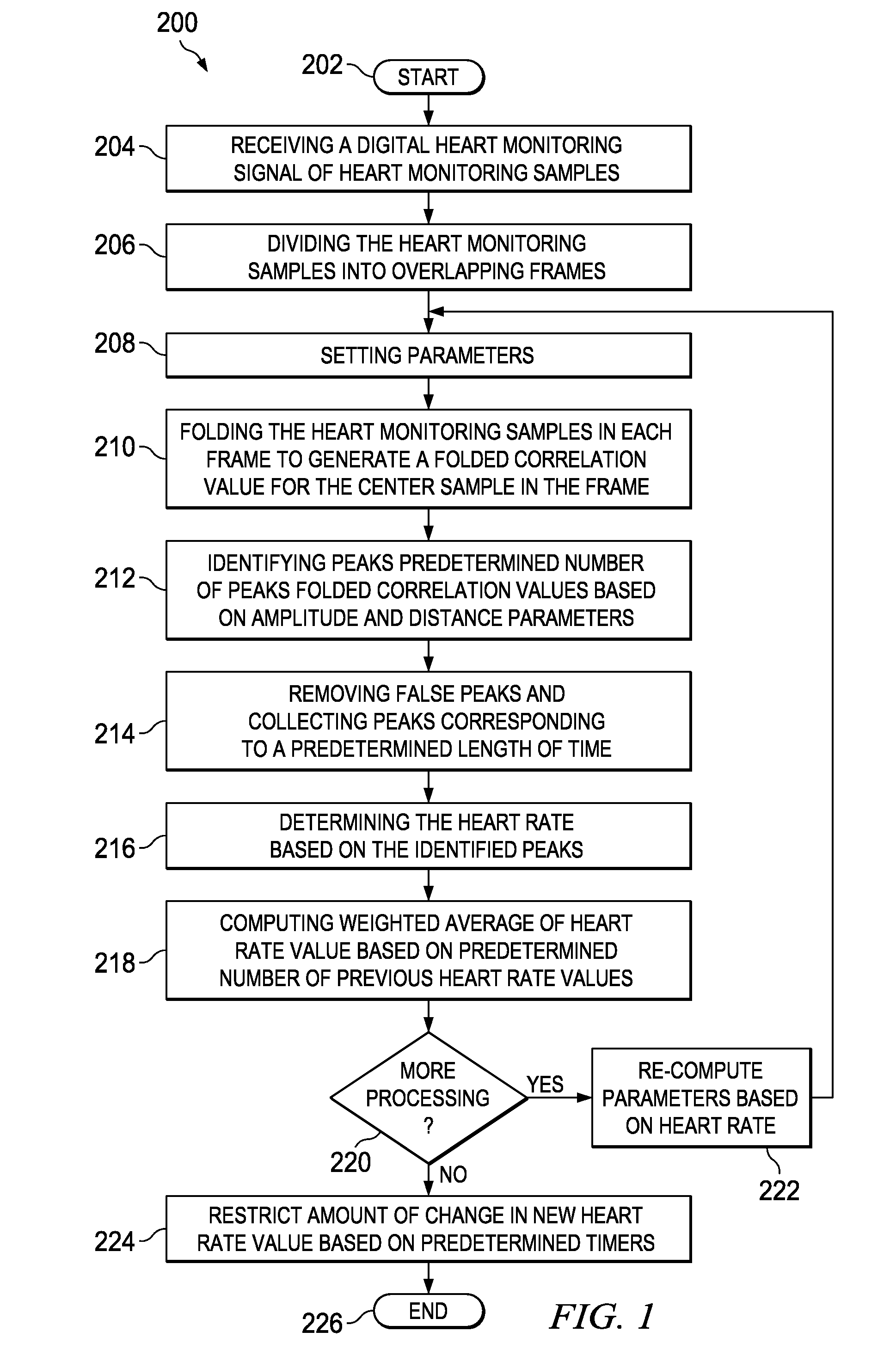
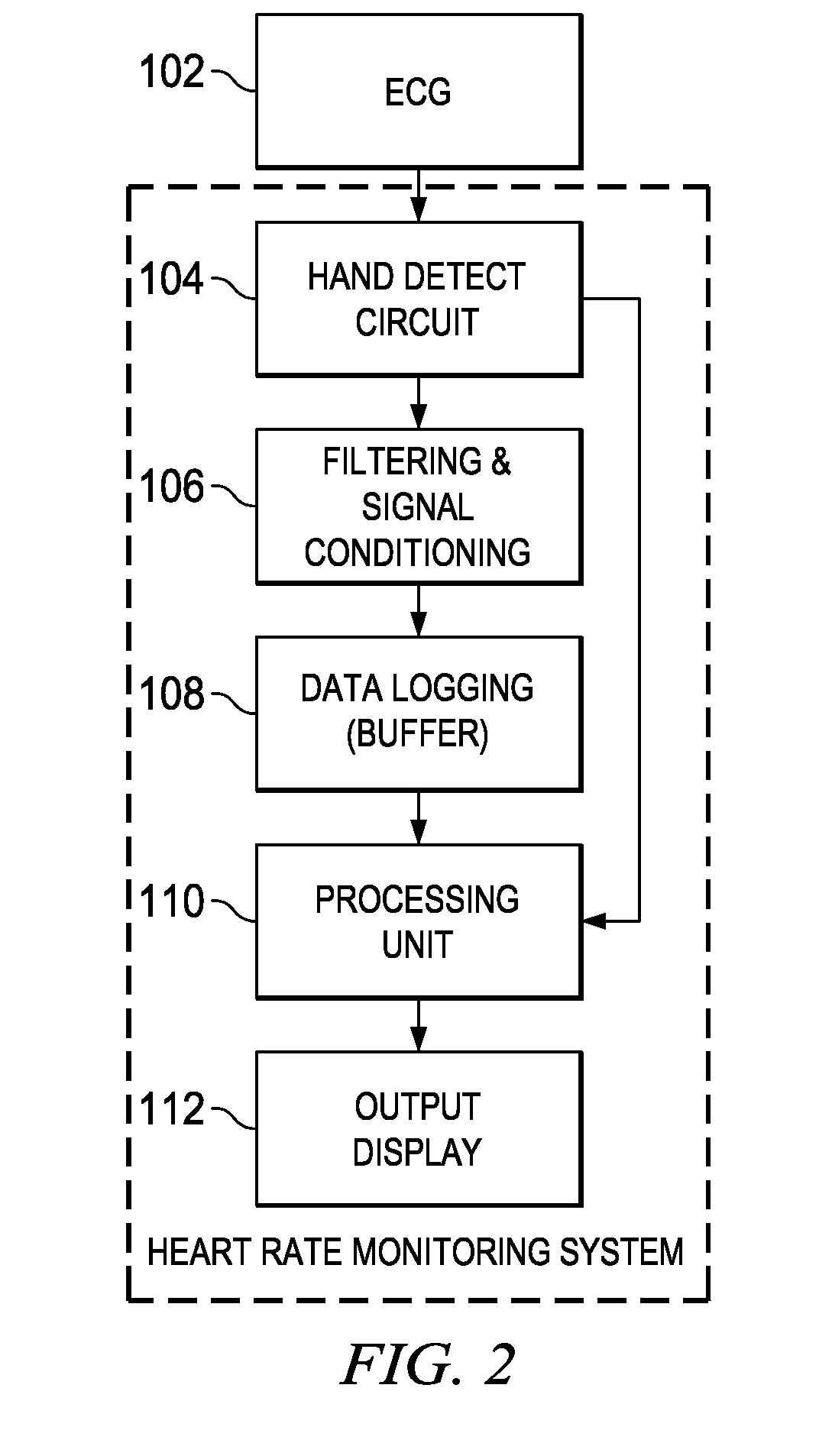
Method and Apparatus for Heart Rate Monitoring
A method and apparatus for monitoring heart rate. The method includes receiving a digital heart monitoring signal, determining the integrity of said signal with a “hand detect” signal that confirms electrical connection to the subject, dividing the digital heart monitoring signal into at least one frame, generating a folded correlation value for the center sample in the at least one frame, identify the number of peaks folded correlation values based on amplitude and distance parameters of the digital heart monitoring signal in the at least one frame, removing false peaks and collecting peaks corresponding to a length of time, determining the heart rate based on the identified peaks wherein the identified peaks relate to a minimum distance between valid heart beat peaks based on a heart rate estimate, computing the weighted average of heart rate value based on the number of previous heart rate values.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Two electrode apparatus and methods for twelve lead ECG
Described herein are methods, apparatuses, and systems for heart monitoring of a patient. The heart monitoring system can be used to take an electrocardiogram (ECG) using only two electrodes. A handheld device can be used to sequentially measure the electrical signal between different positions on a patient's body. The electrical signals can be processed and analyzed to prepare an ECG for the patient, including a 12-lead ECG.
Owner:ALIVECOR
System and method for heart monitoring
The present invention provides systems and methods for monitoring a heart. According to one embodiment, the system includes an implantable registering unit for registering an electrical signal from the heart. The system includes a local data unit in operable communication with registering unit. The local data unit may be placed in communication with a computer, which may be at a location remote from the local data unit. The computer is adapted to receive the data from the local data unit corresponding to the registered electrical signal and to compare the registered electrical signal to a reference electrical signal to determine whether the heart is functioning properly.
Owner:COMPLETE MEDICAL SOLUTIONS LLC
Device and method for fusion beat detection
ActiveUS20140207013A1Accurate assessmentFacilitate cardiac rhythm managementElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsFusion beatEngineering
A heart monitoring and / or therapy device for detecting and quantifying fusion beats, wherein the device includes an IEGM signal sensing channel that puts out a recorded IEGM signal and an evaluation unit operatively connected to said IEGM signal sensing channel that detects fusion beats. The evaluation unit comprises or is connected to a template memory including at least a first template electrogram signal and a second template electrogram signal. The evaluation unit compares the recorded IEGM signal with both, the first and the second template electrogram signal and determines at least a first degree of similarity reflecting the similarities between the recorded electrogram signal and the first template electrogram signal, and a second degree of similarity reflecting the similarities between the recorded electrogram signal and the second template electrogram signal. The evaluation unit then calculates a fusion index (FI) from the at least two degrees of similarity.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Heart monitoring system and method
A system for heart monitoring comprises an IEGM input for an intracardiac electrocardiogram (IEGM) that is connected to an active filtering stage that is adapted to transform an incoming IEGM into an output ECG signal. The active filtering stage is connected to a filter characterization stage that is adapted to process a recorded, patient specific IEGM template and a corresponding SECG template and to adapt the filter characteristics of said active filtering stage such that the filter characteristics best characterize the input-output relationship between the IEGM template and the corresponding SECG template. As a consequence, the active filtering stage is adapted to transform an incoming IEGM such that the output ECG signal closely resembles a morphology of a corresponding SECG.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com