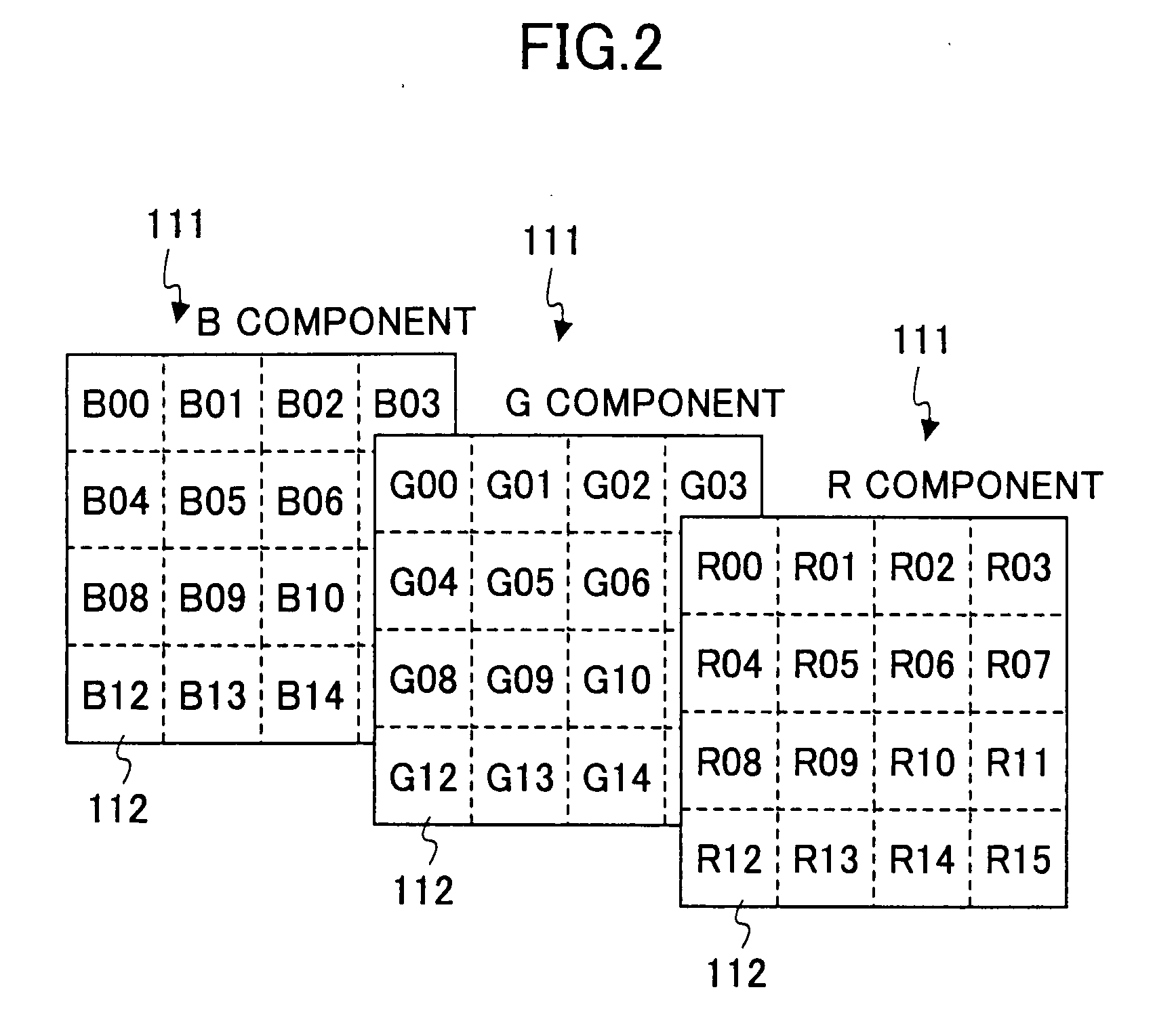
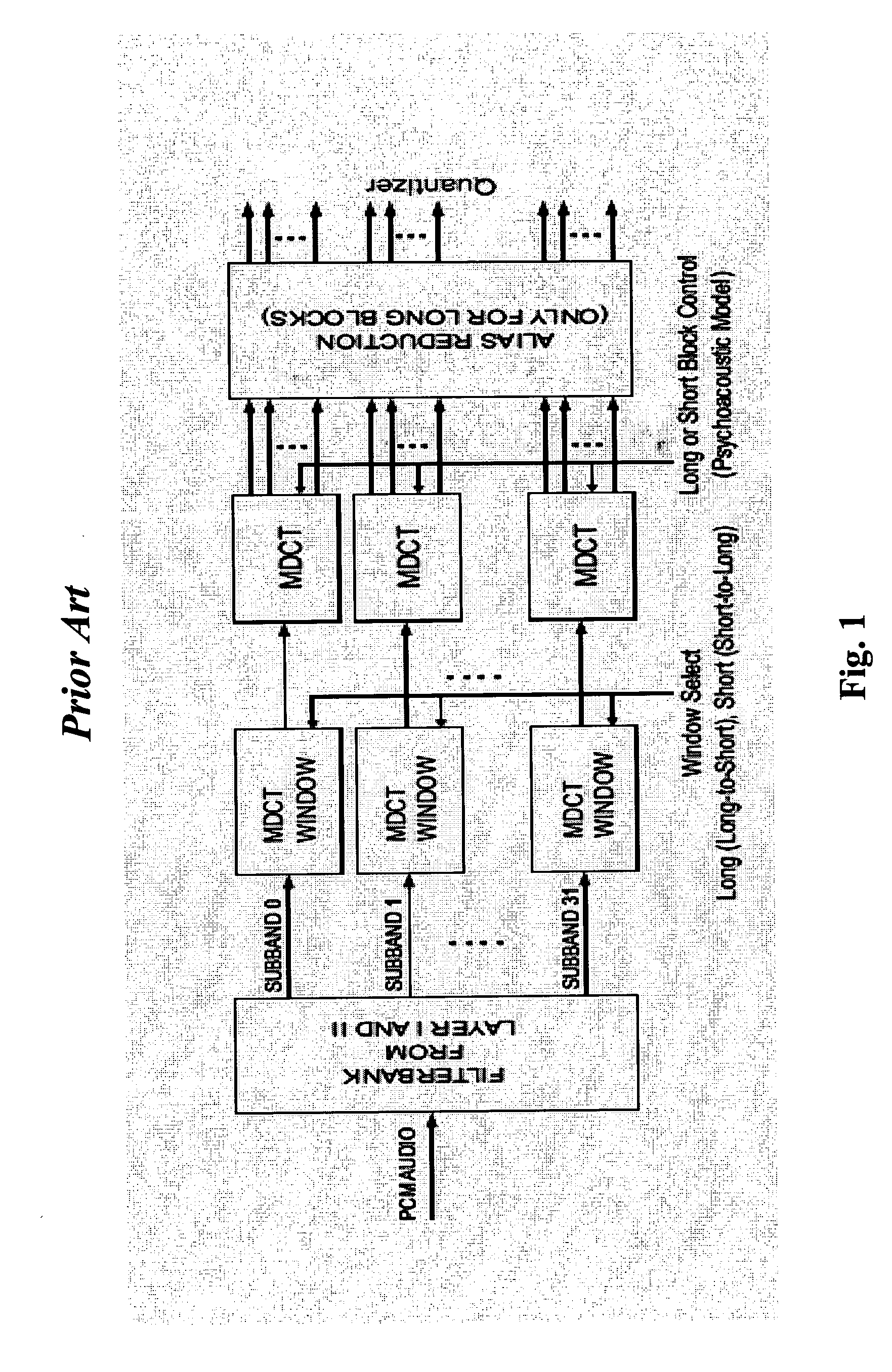
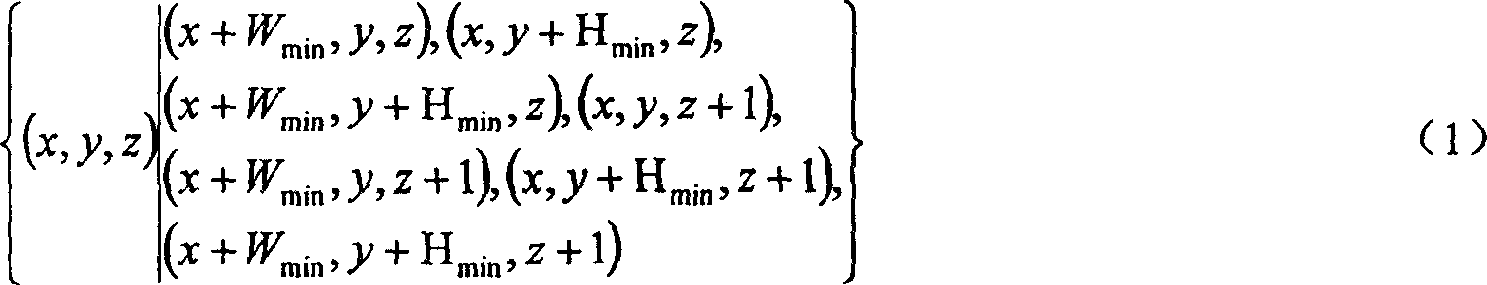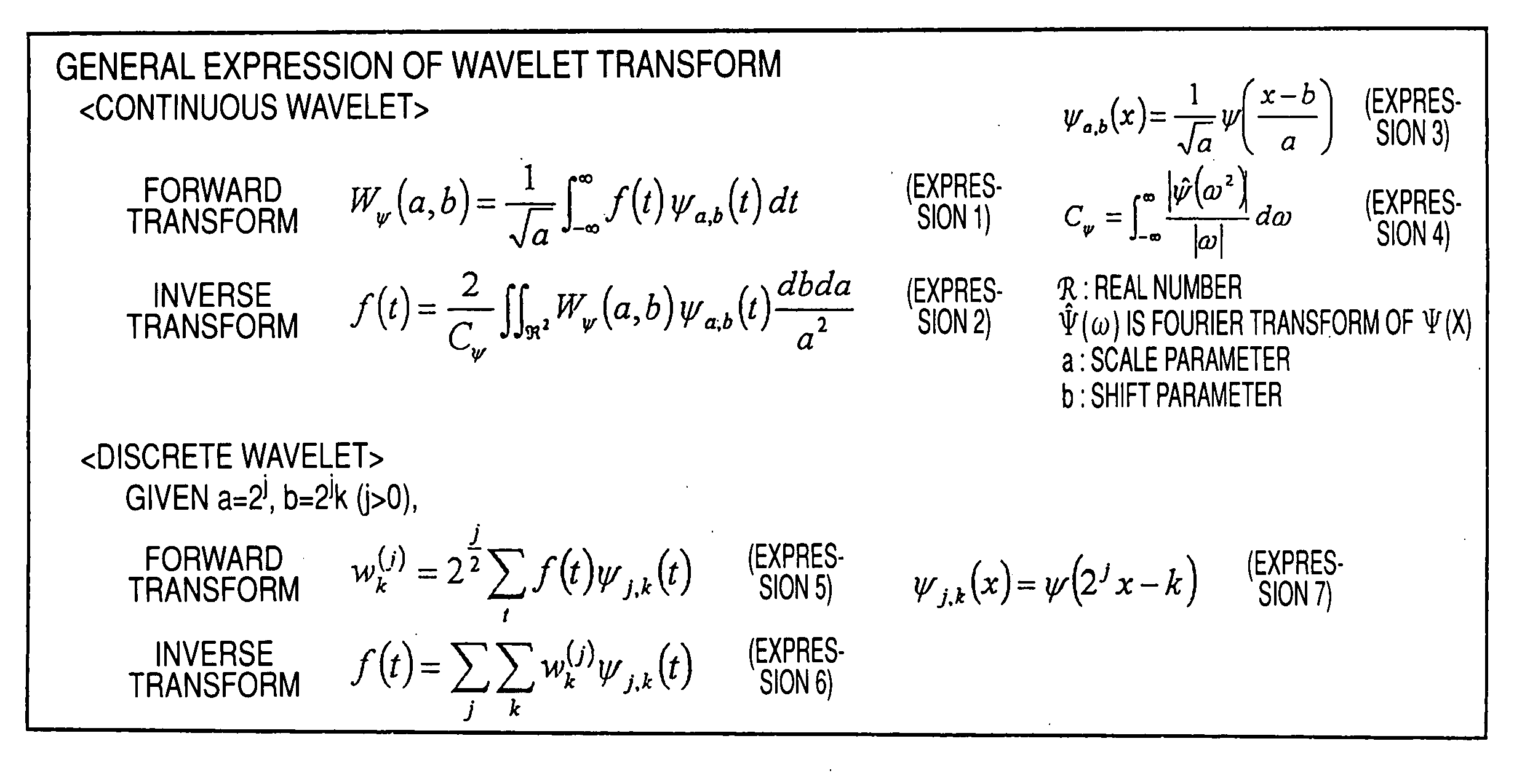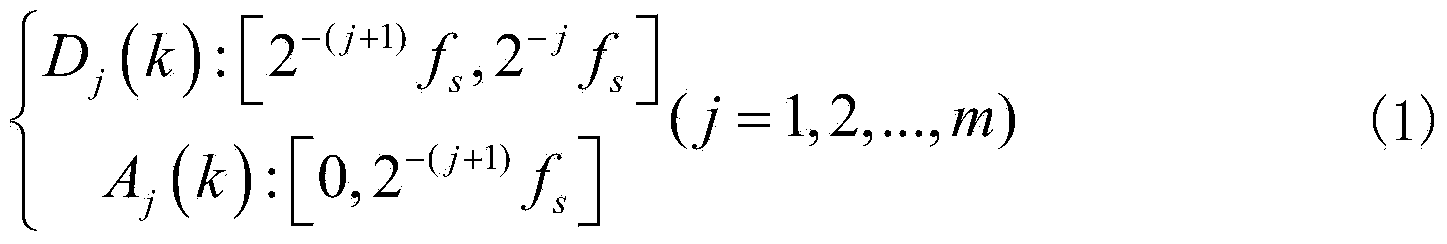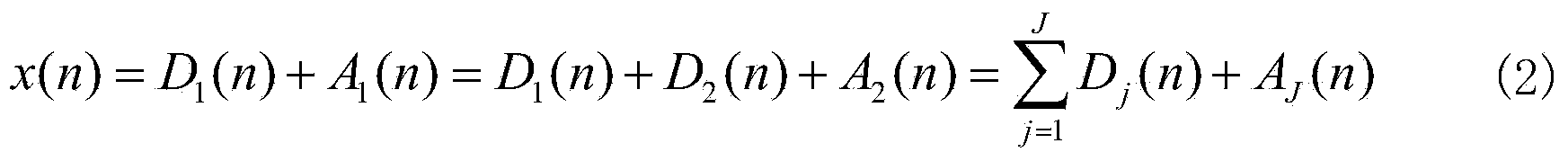Patents
Literature
733 results about "Discrete wavelet transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
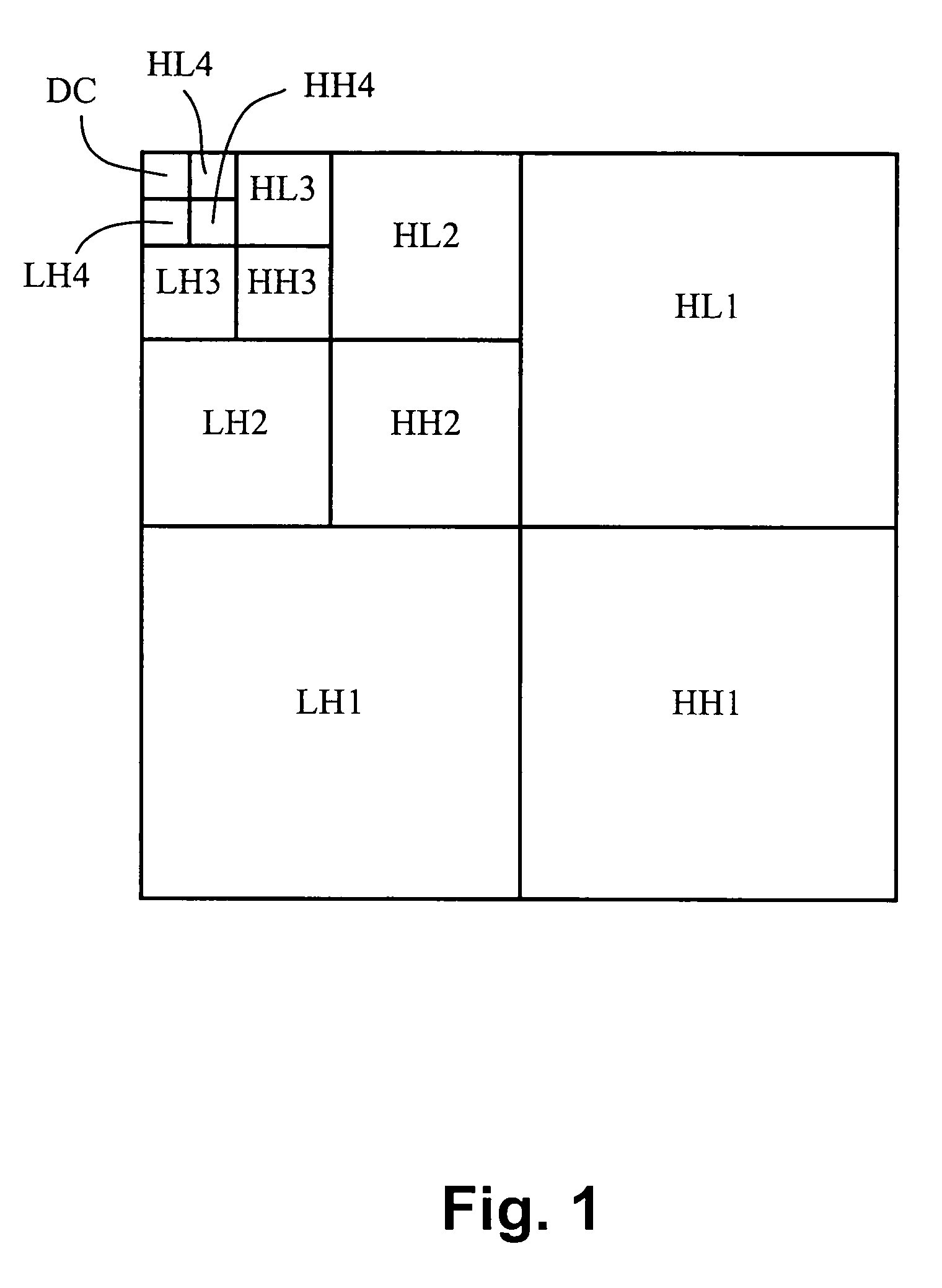
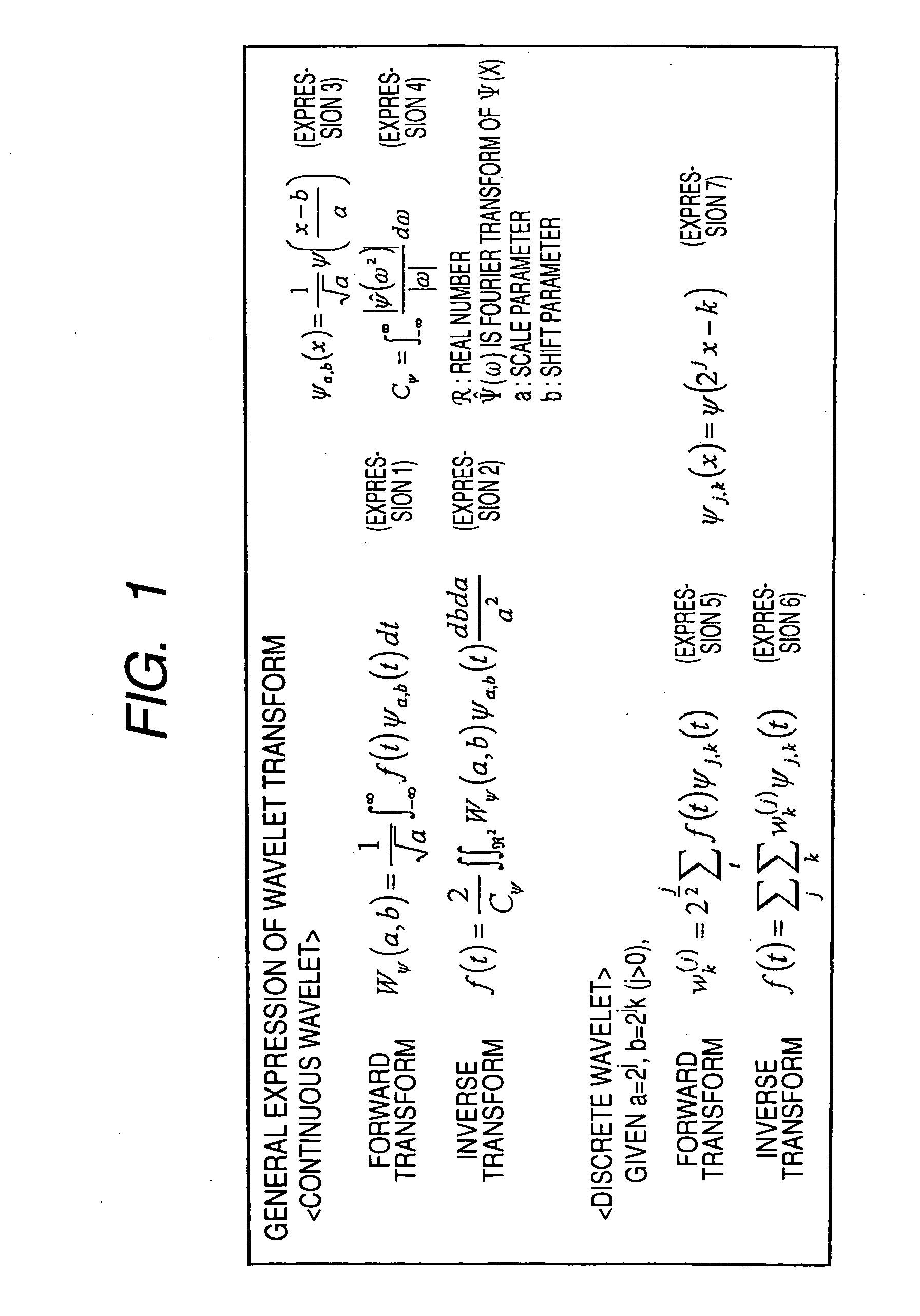
In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal resolution: it captures both frequency and location information (location in time).
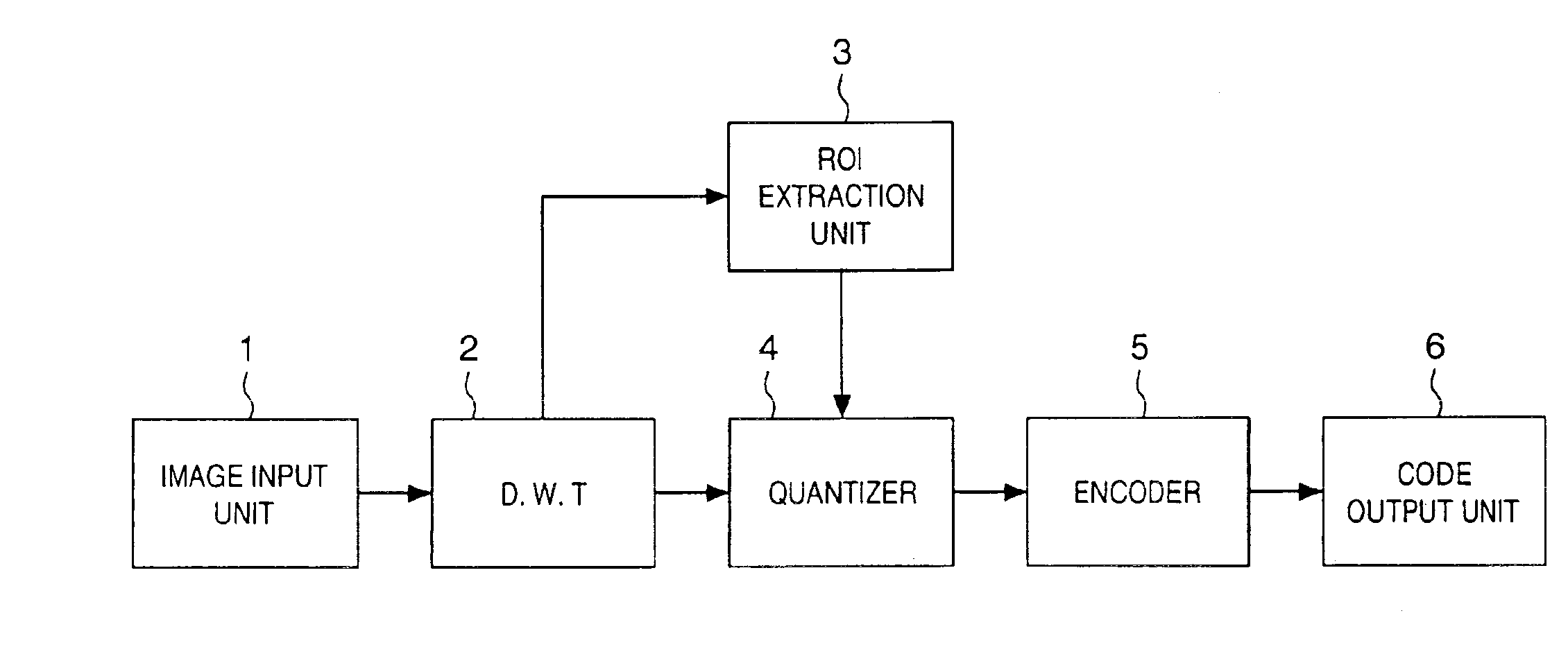
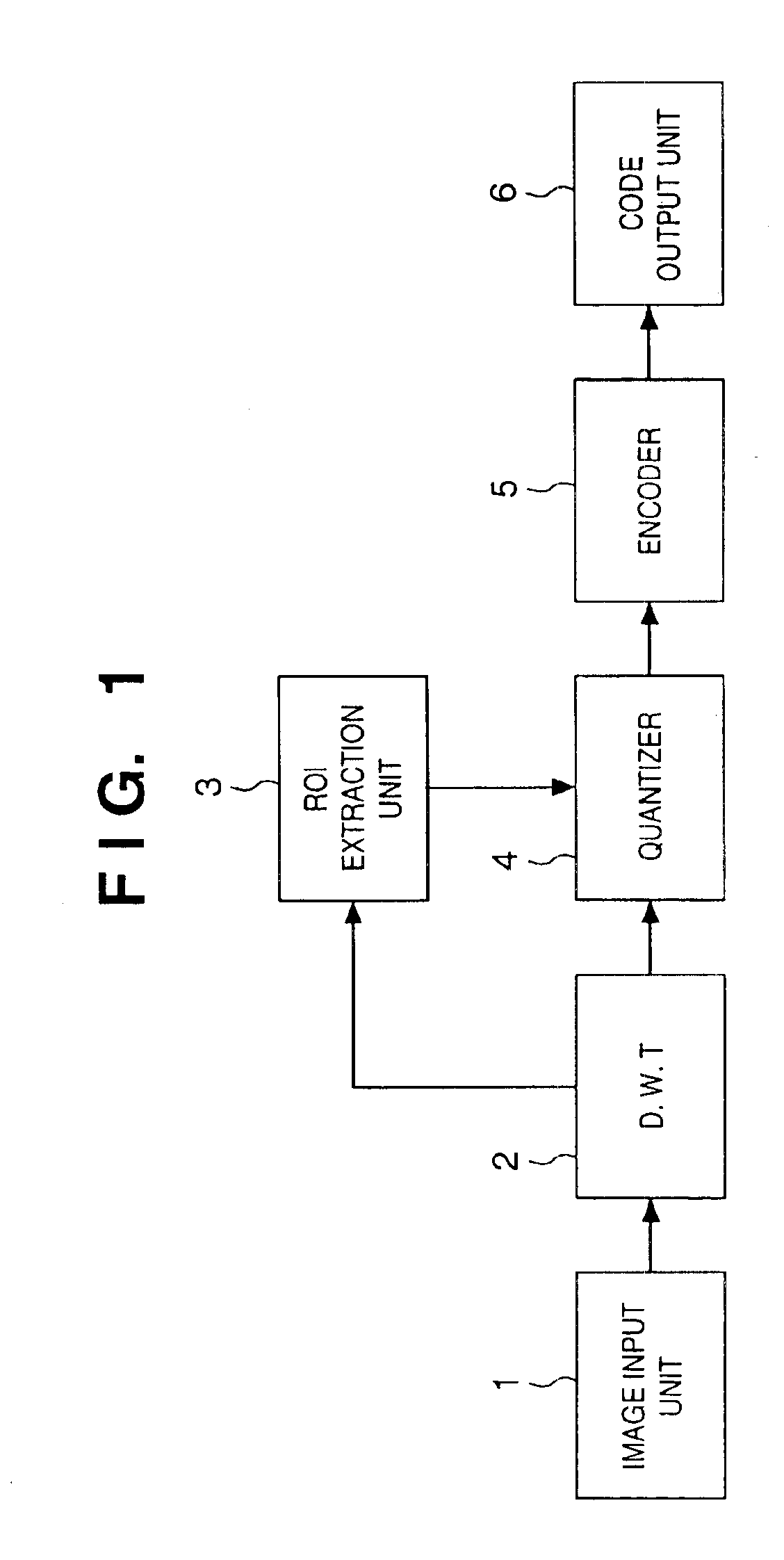
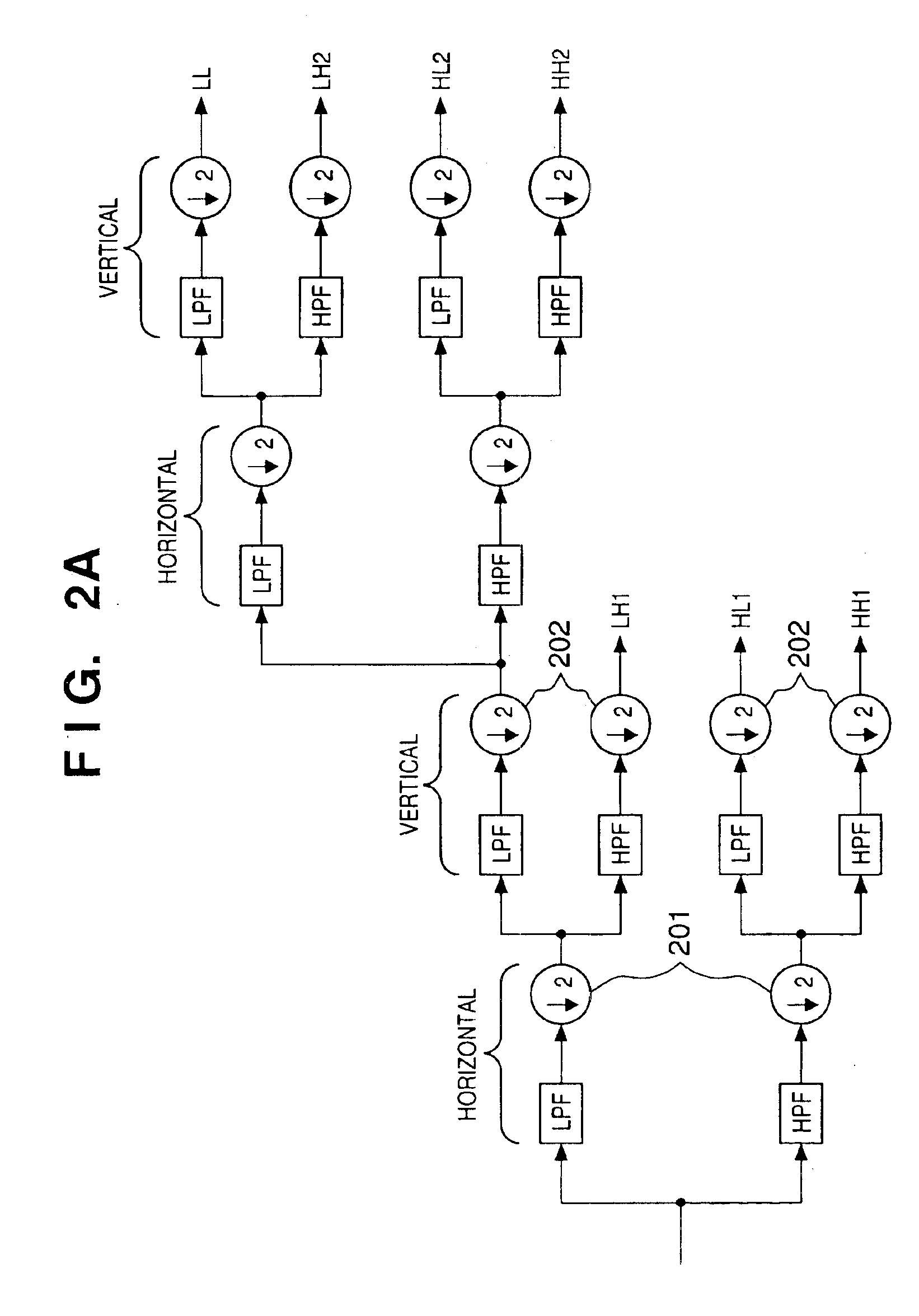
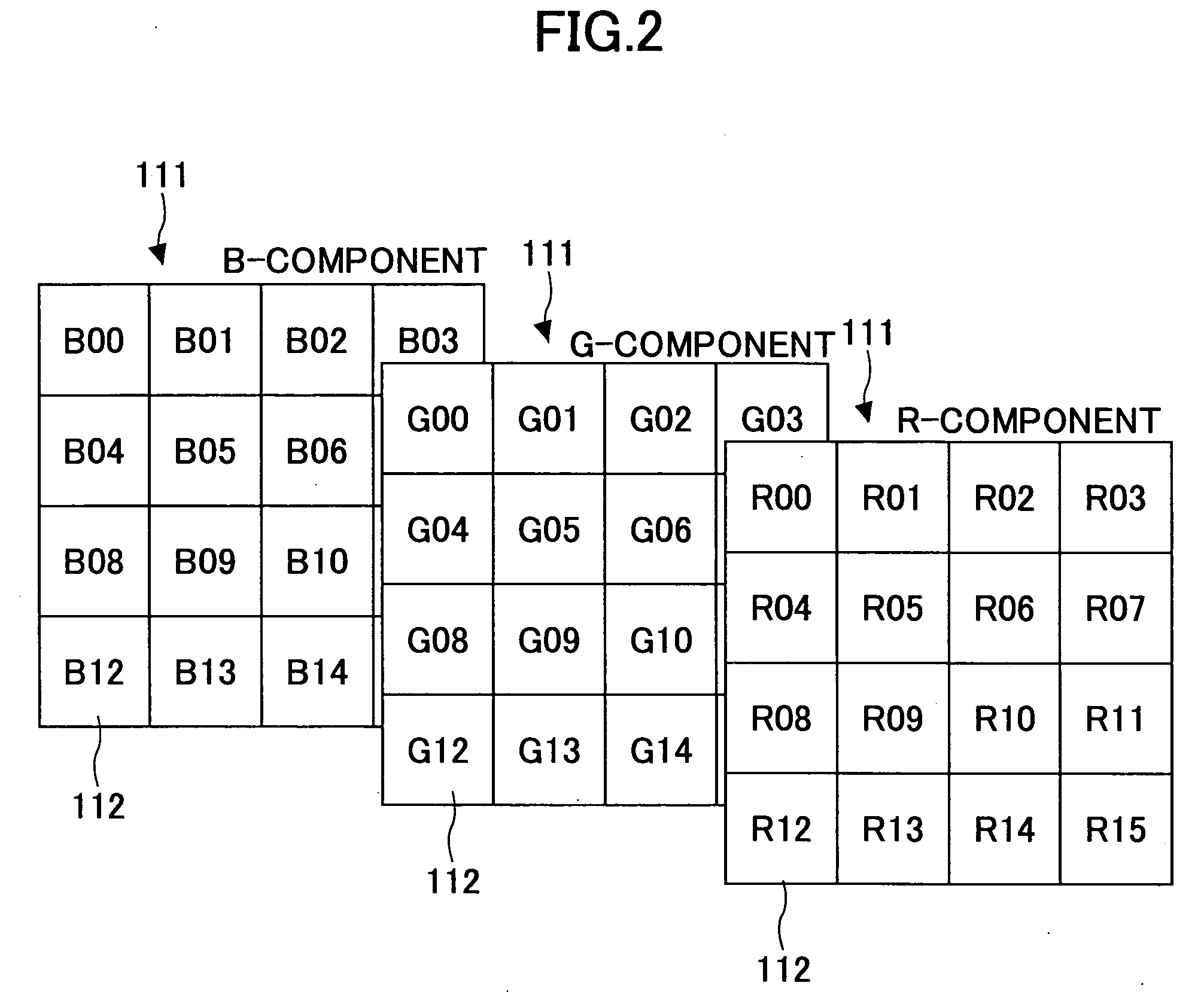
Image encoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS6937773B1Without placing a burden upon the userColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorTransformation unit
An image signal is input from an image input unit and is divided into different spatial frequency bands by applying a discrete wavelet transform thereto using a discrete wavelet transformation unit. On the basis of values of spatial frequency components, a region-of-interest extracts a region of interest by obtaining a distribution of motion vectors in the input image. A quantization unit applies quantization processing to the extracted region of interest and different quantization processing to other regions, and an encoder encodes the quantized image signal. Alternatively, motion of an image contained in the input image may be detected and the region of interest may be obtained based upon motion of this image.
Owner:CANON KK
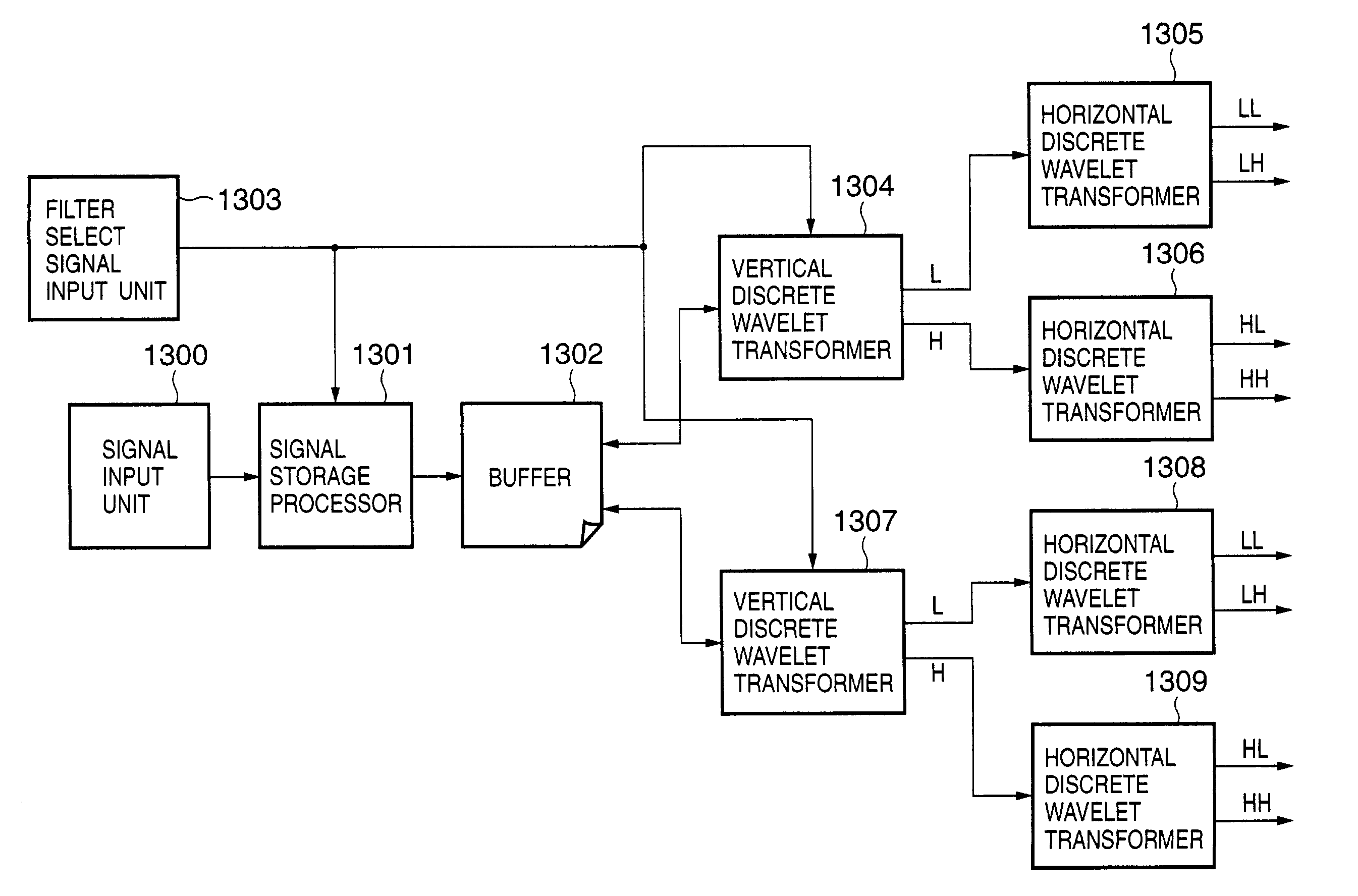
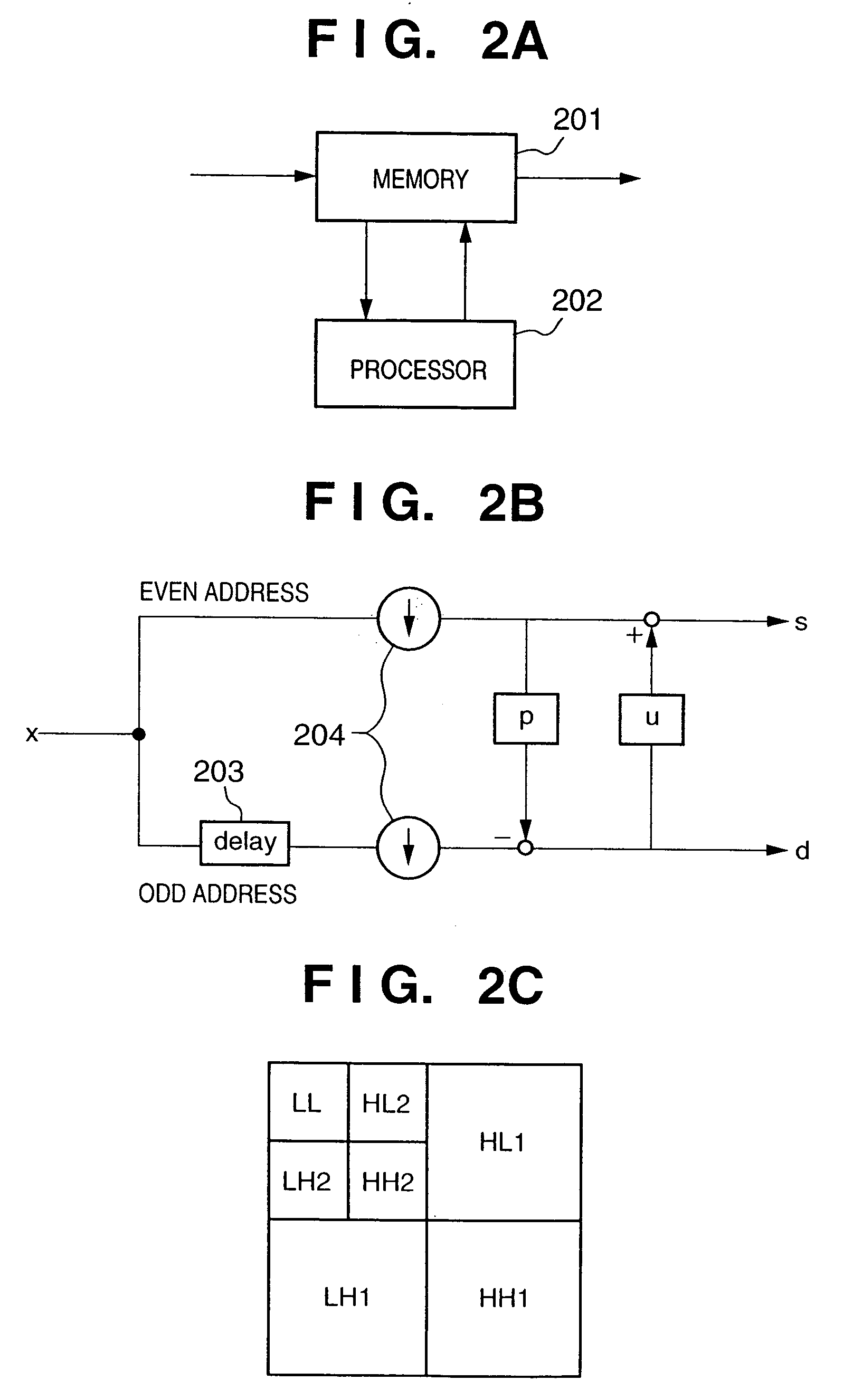
Signal processing apparatus and method, program, and storage medium
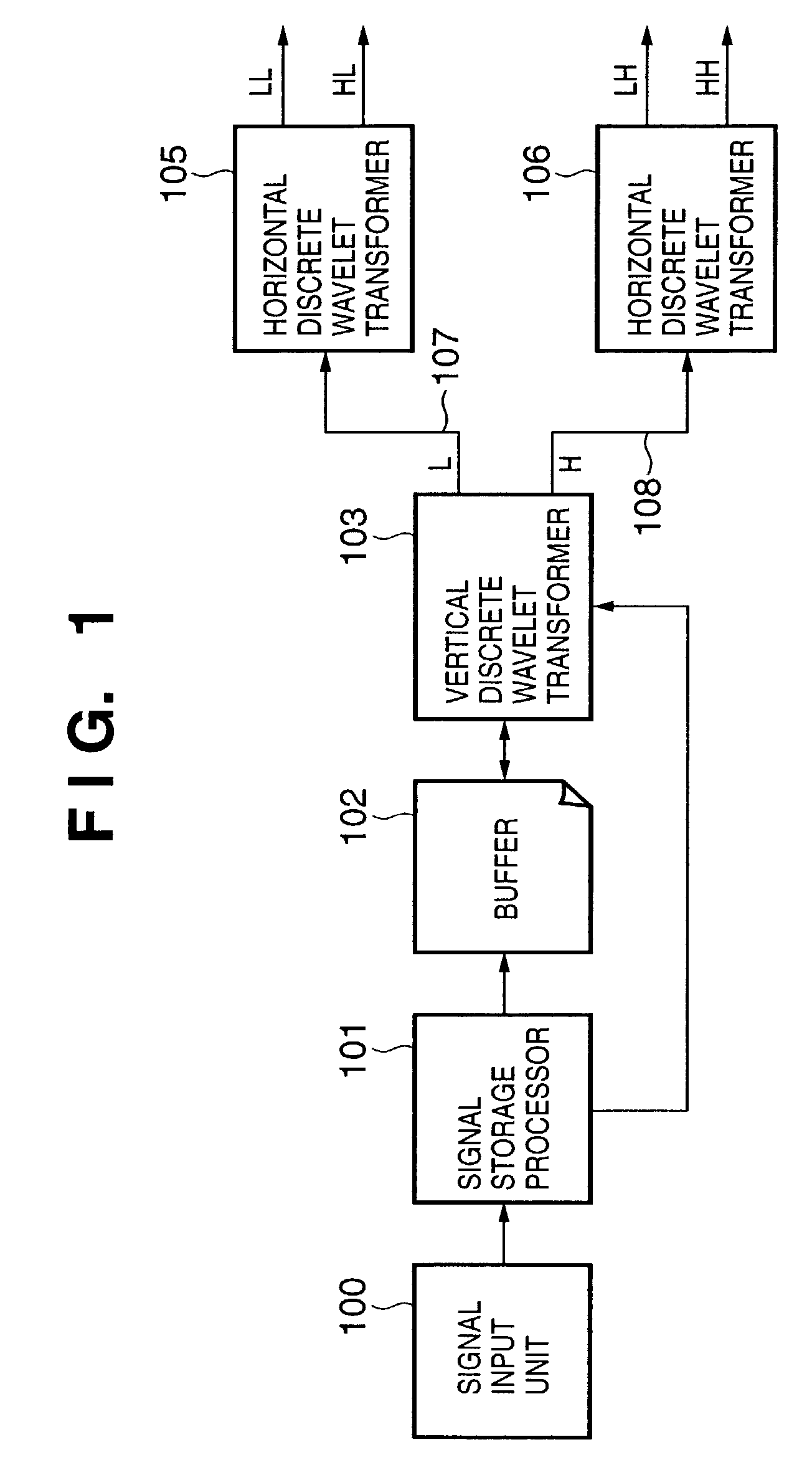
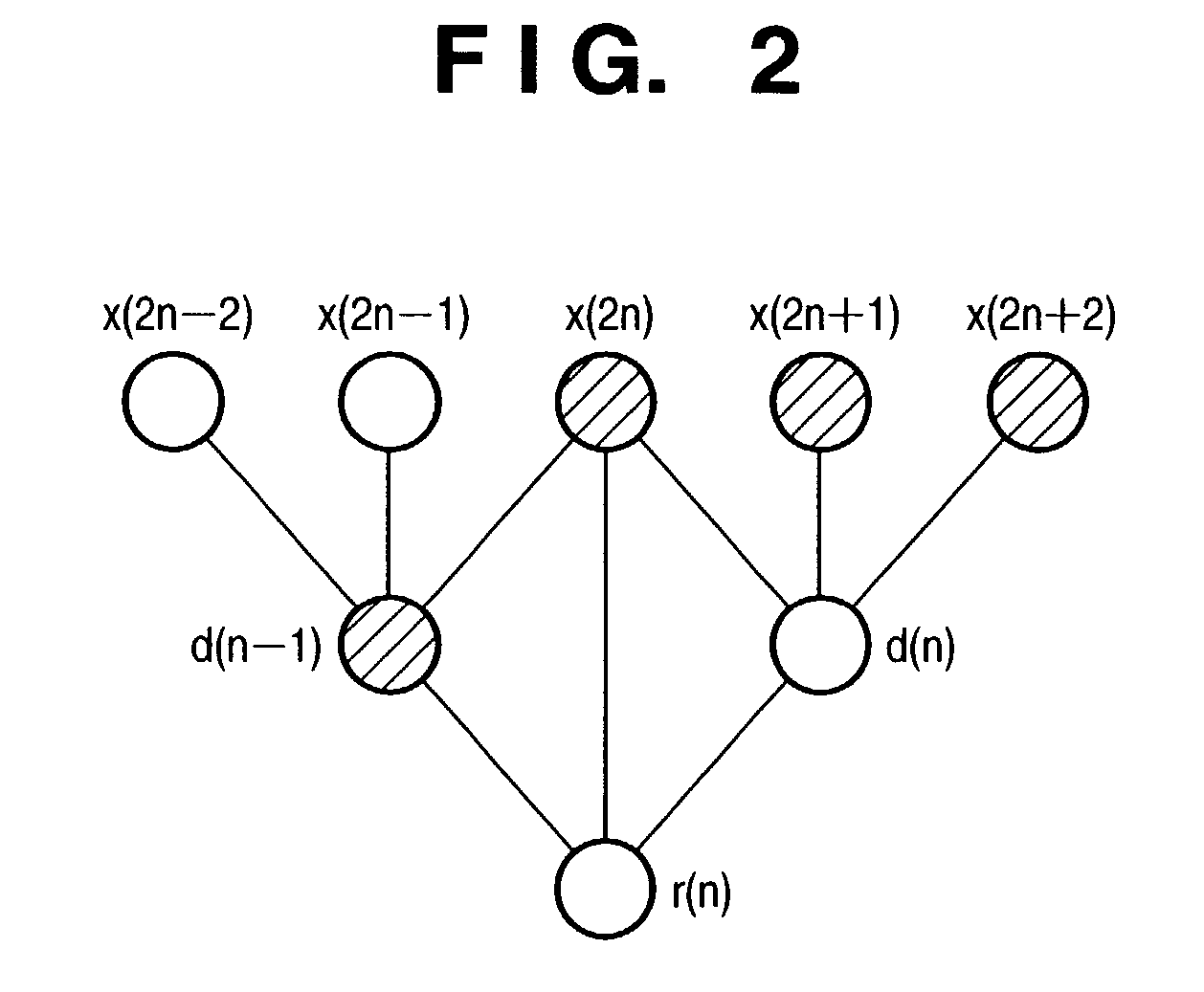
A signal storage processor (101) stores signals input from a signal input unit (100) in a buffer (102) for respective lines. A vertical discrete wavelet transformer (103) reads out an index value L from the signal storage processor (101), and obtains a reference address B from the value L. If L=2, B=2. If L=4, B=0. Furthermore, the vertical discrete wavelet transformer (103) reads out the i-th column of sets of data, which are stored in the buffer (102) and are continuous in the vertical direction (i.e., data read out from four addresses (addresses in the buffer (102)) i×4+B, i×4+mod((B+1),4), i×4+mod((B+2),4), and i×4+mod((B+3),4)), and computes the one-dimensional discrete wavelet transforms of the readout data.
Owner:CANON KK
Progressive image transmission using discrete wavelet transforms
InactiveUS6847468B2Convenient previewImprove the level ofDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationDecompositionImage transfer
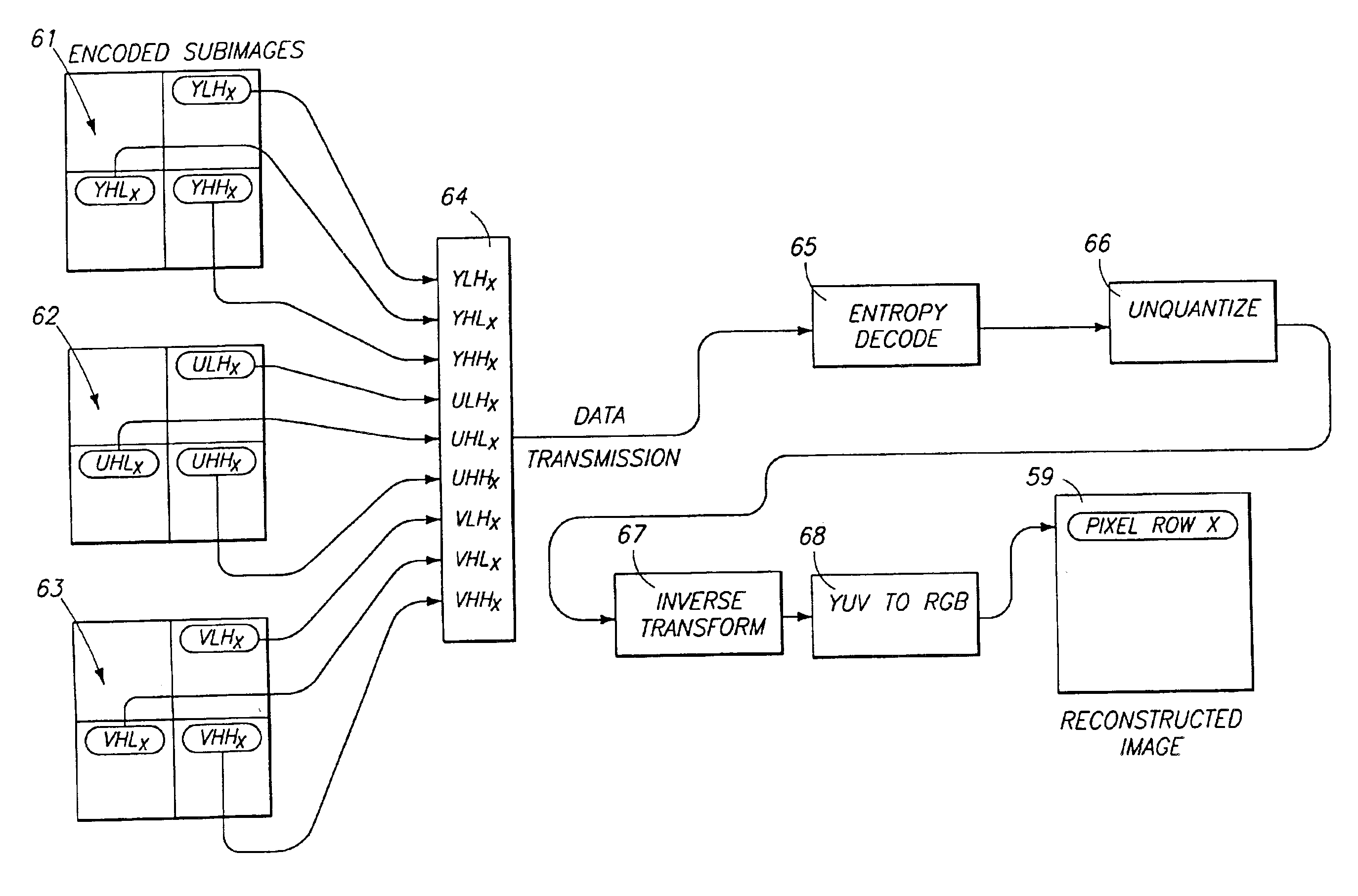
Disclosed herein is a method of storing and of progressively transferring a still image so that it can be conveniently previewed during the transfer and so that a user can terminate the transfer at an early stage if the image turns out to be undesirable. The methods of the invention include transforming the image into a plurality of decomposition levels using a discrete wavelet transform. Each decomposition level comprises a plurality of subimages which allow reconstruction of an image representation of the still image. The decomposition levels are transmitted beginning with a base decomposition level providing a low level of image resolution and then proceeding with decomposition levels providing increasingly higher levels of image resolution. Within each decomposition level, rows of the various subimages are arranged or interlaced together in contiguous blocks, so that all data for a single row, at a single decomposition level, is transmitted together. At the receiving end of the transfer, the row blocks are reconstructed and displayed as they are received. The invention enables the initial display of a low resolution image which is gradually updated and sharpened, on a row-by-row basis, until a desired high resolution is achieved. The user may terminate the transfer at any point.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
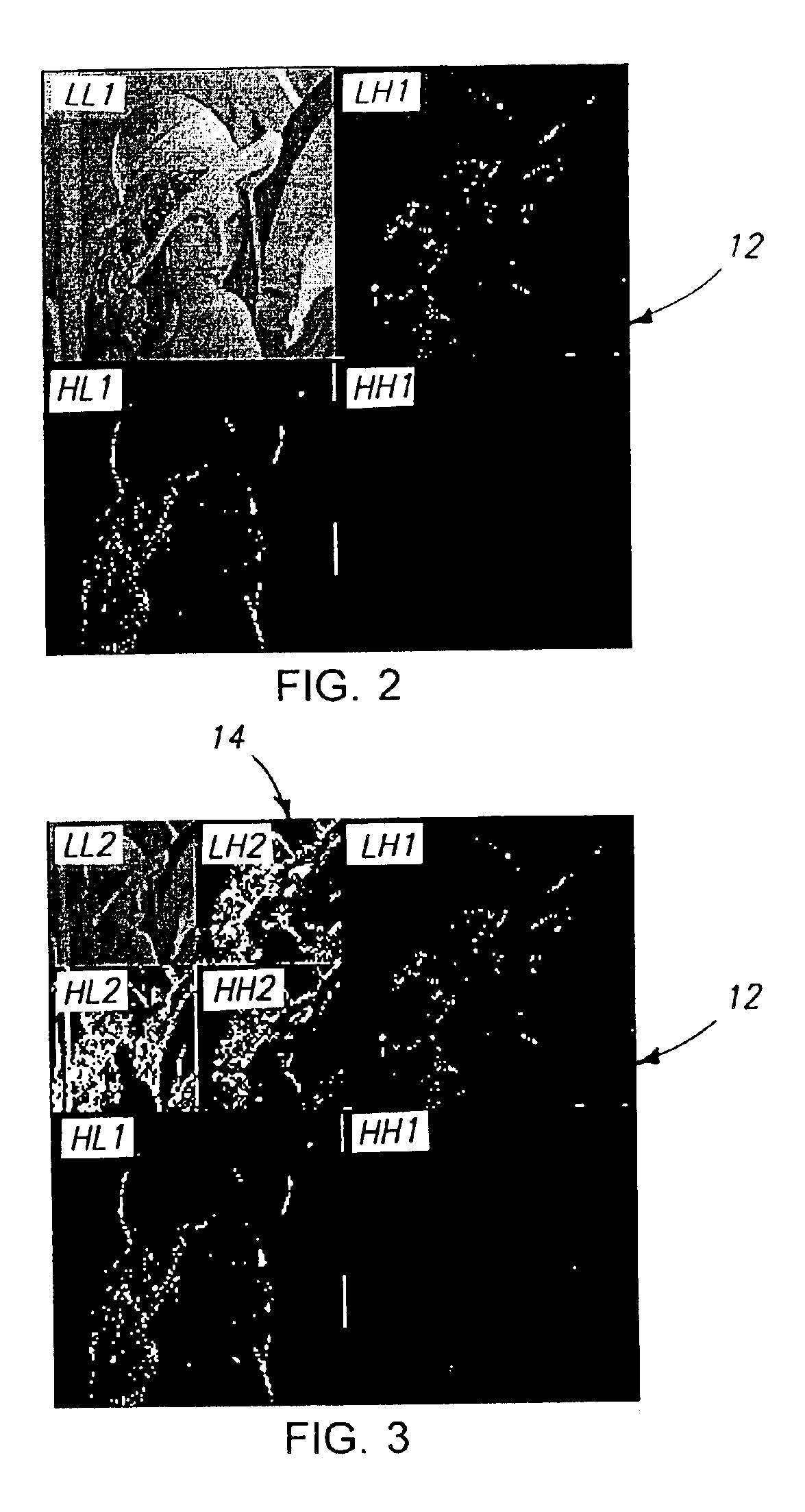
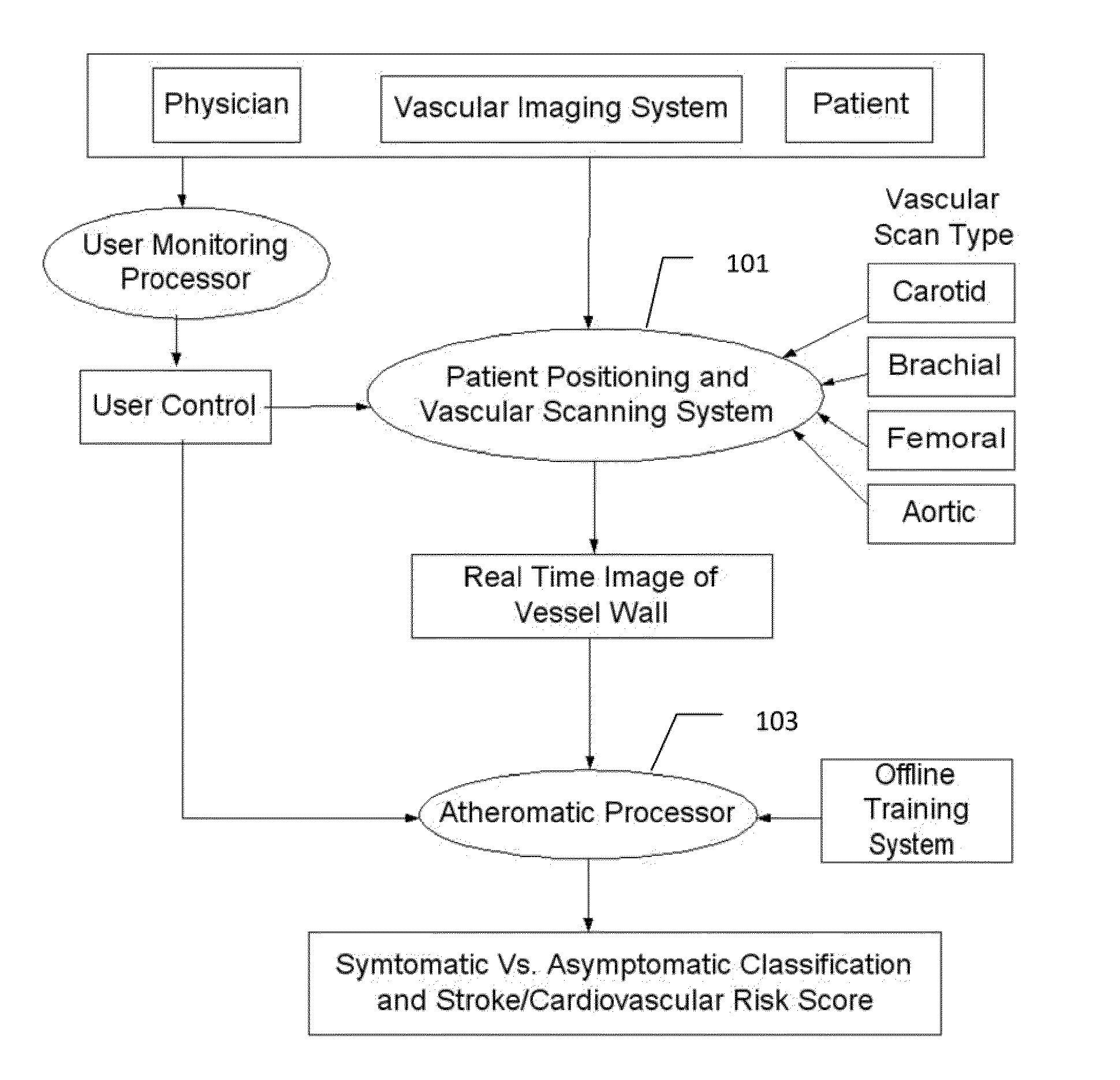
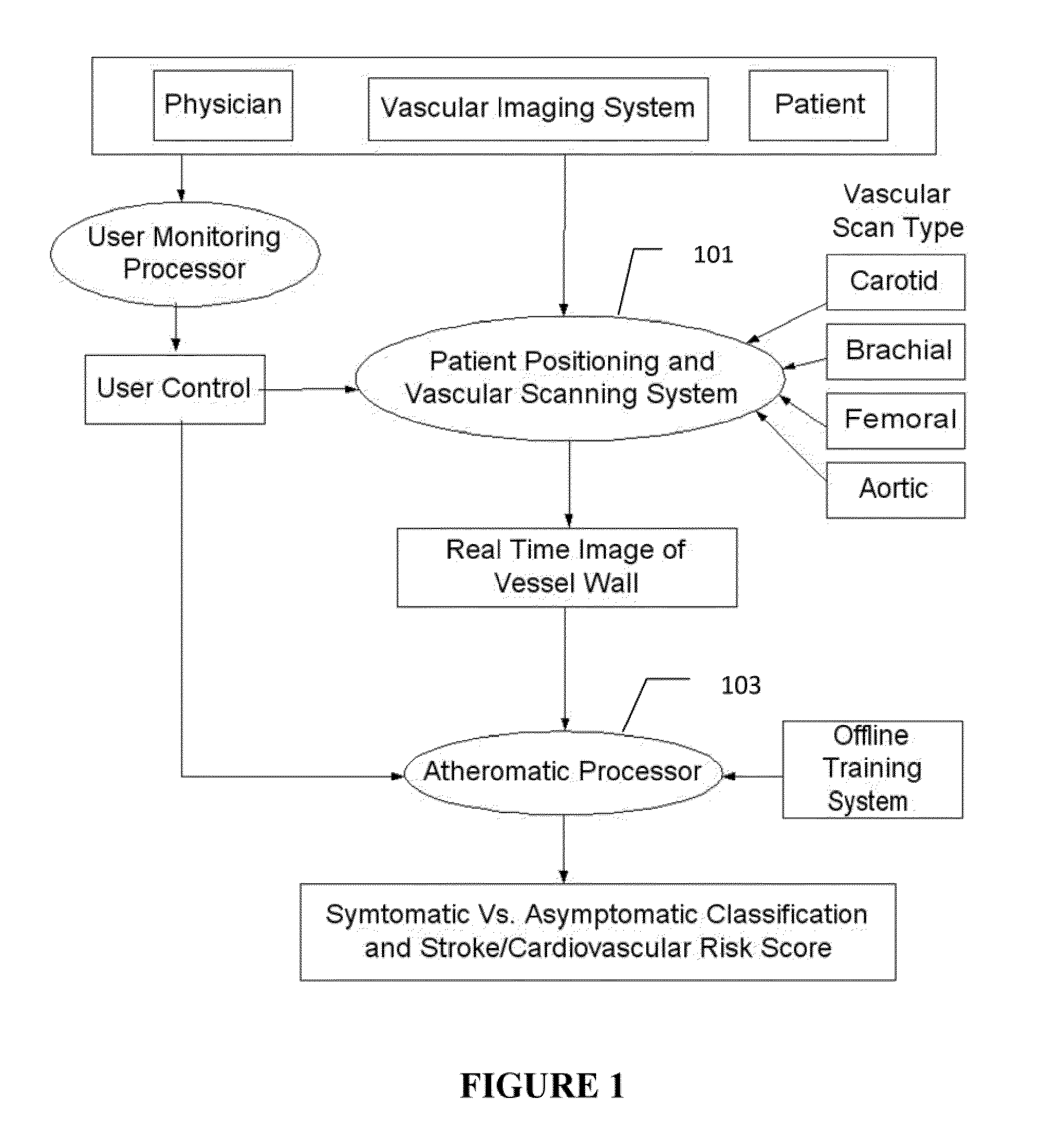
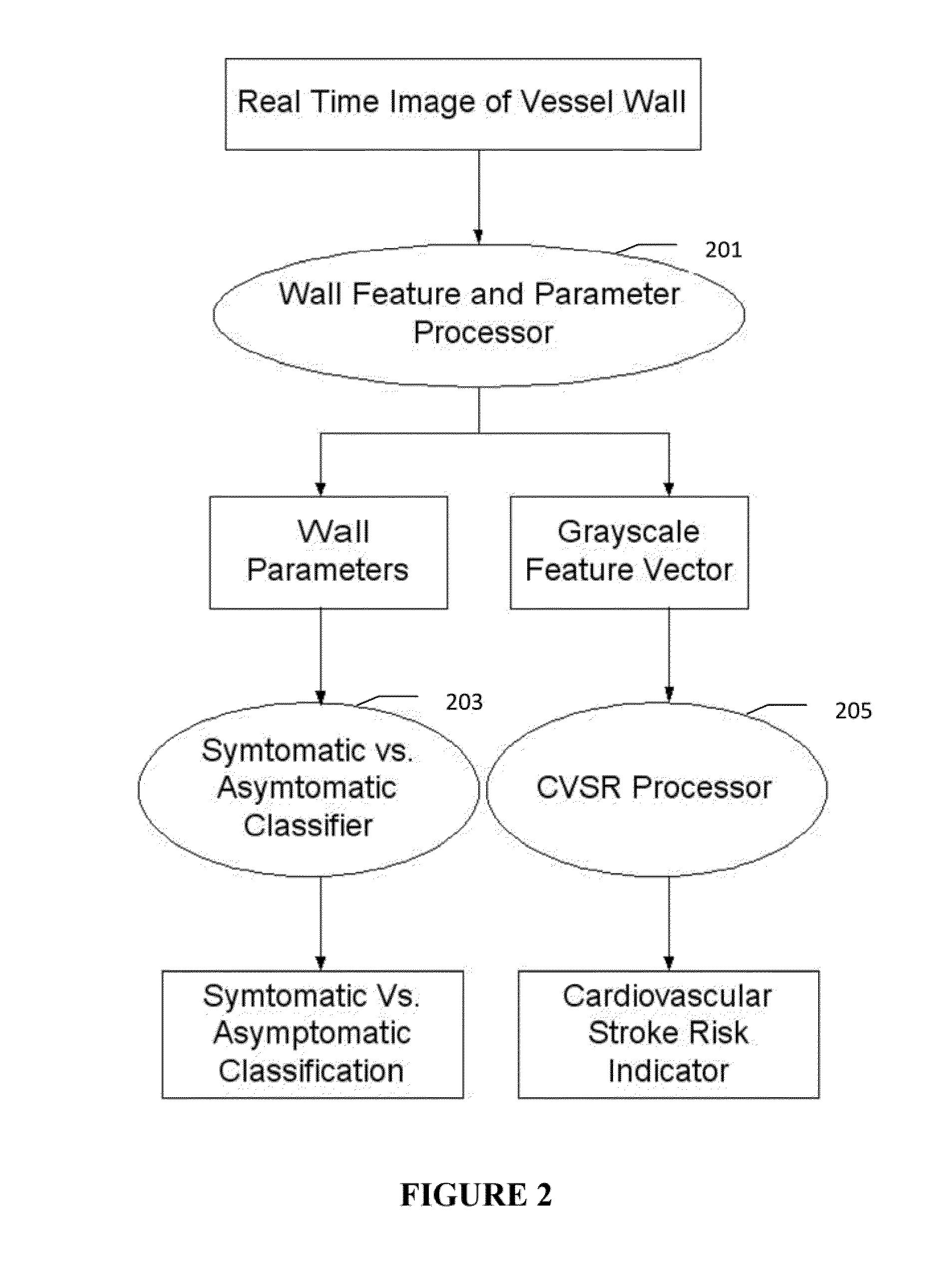
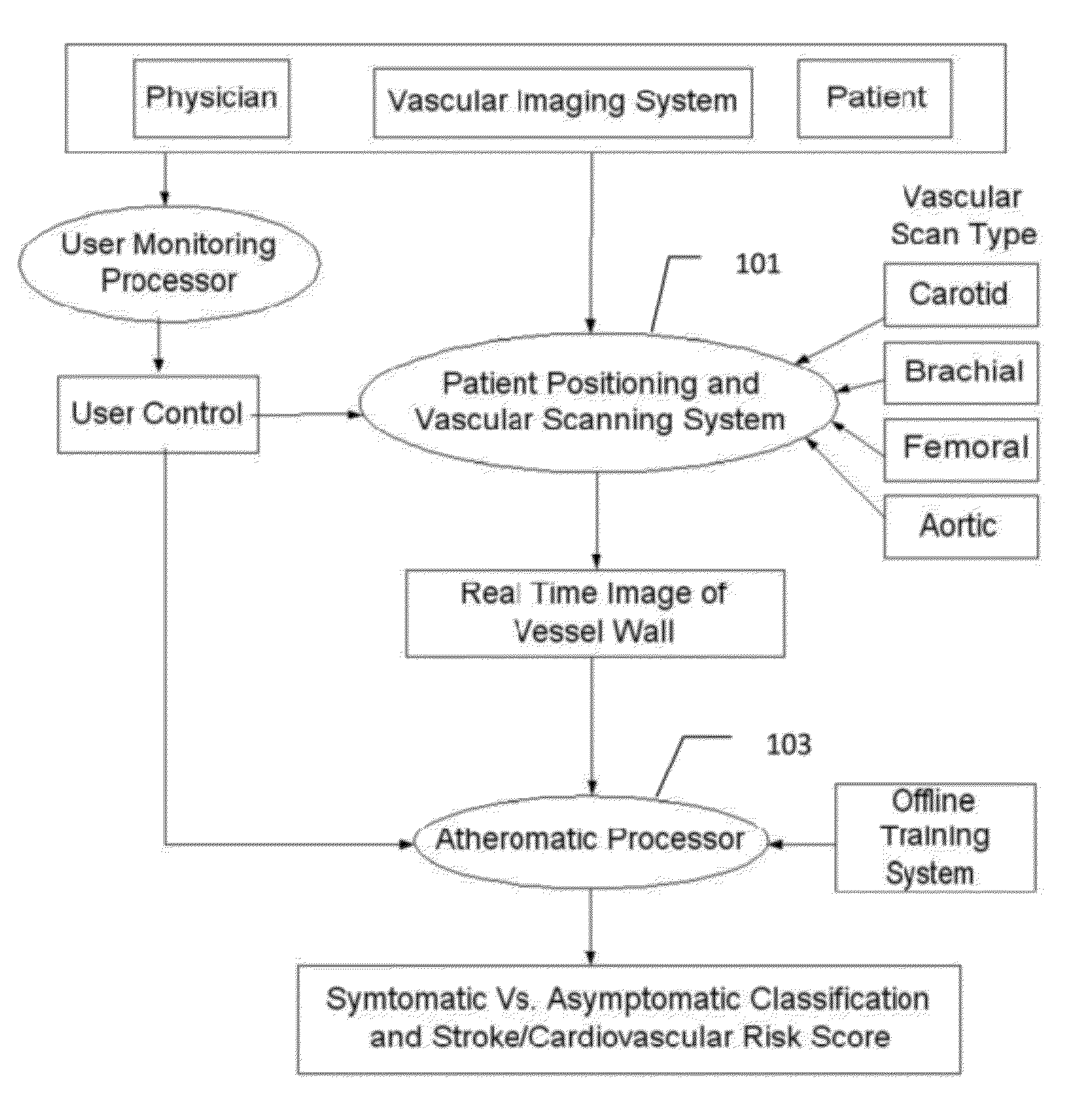
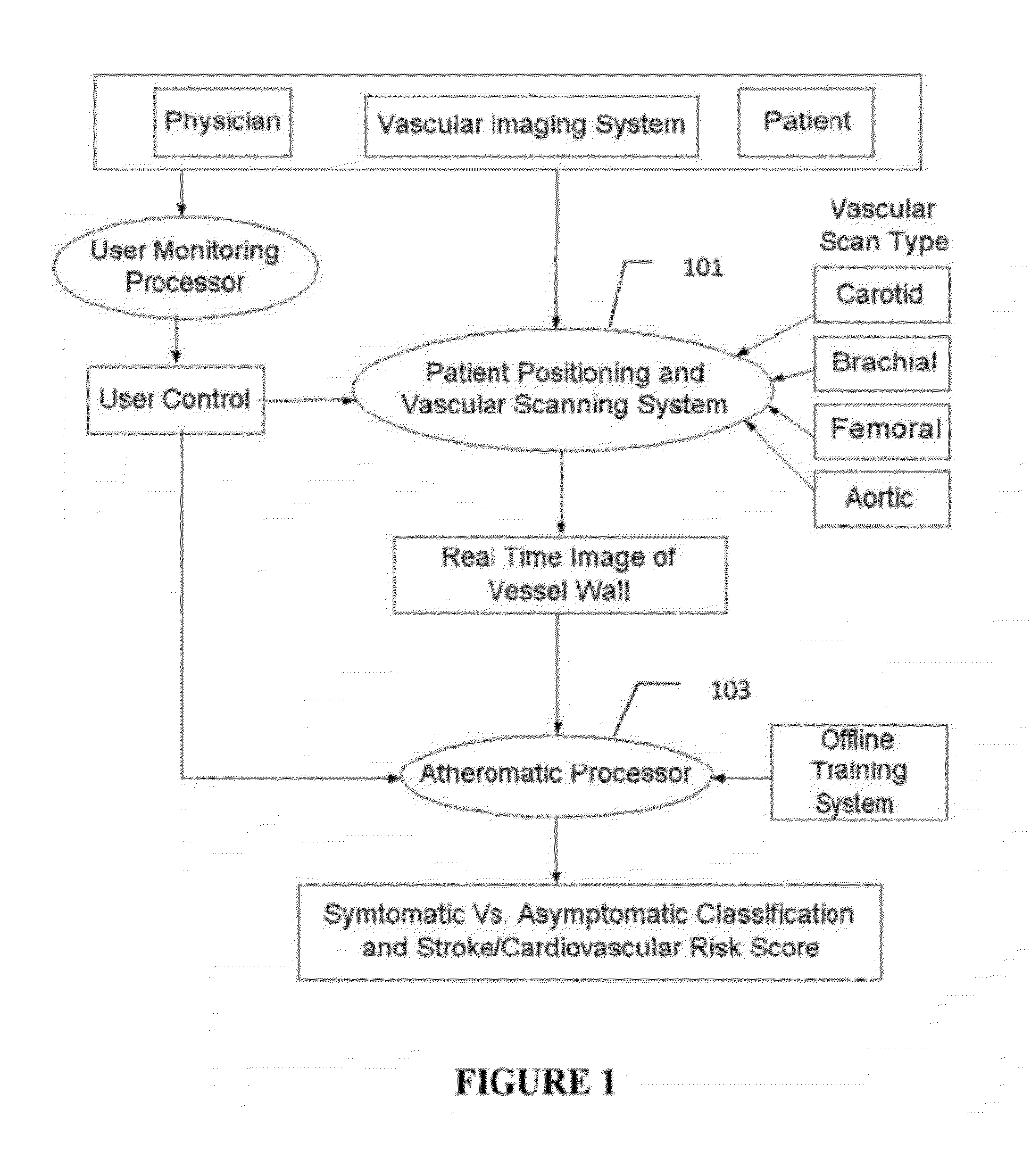
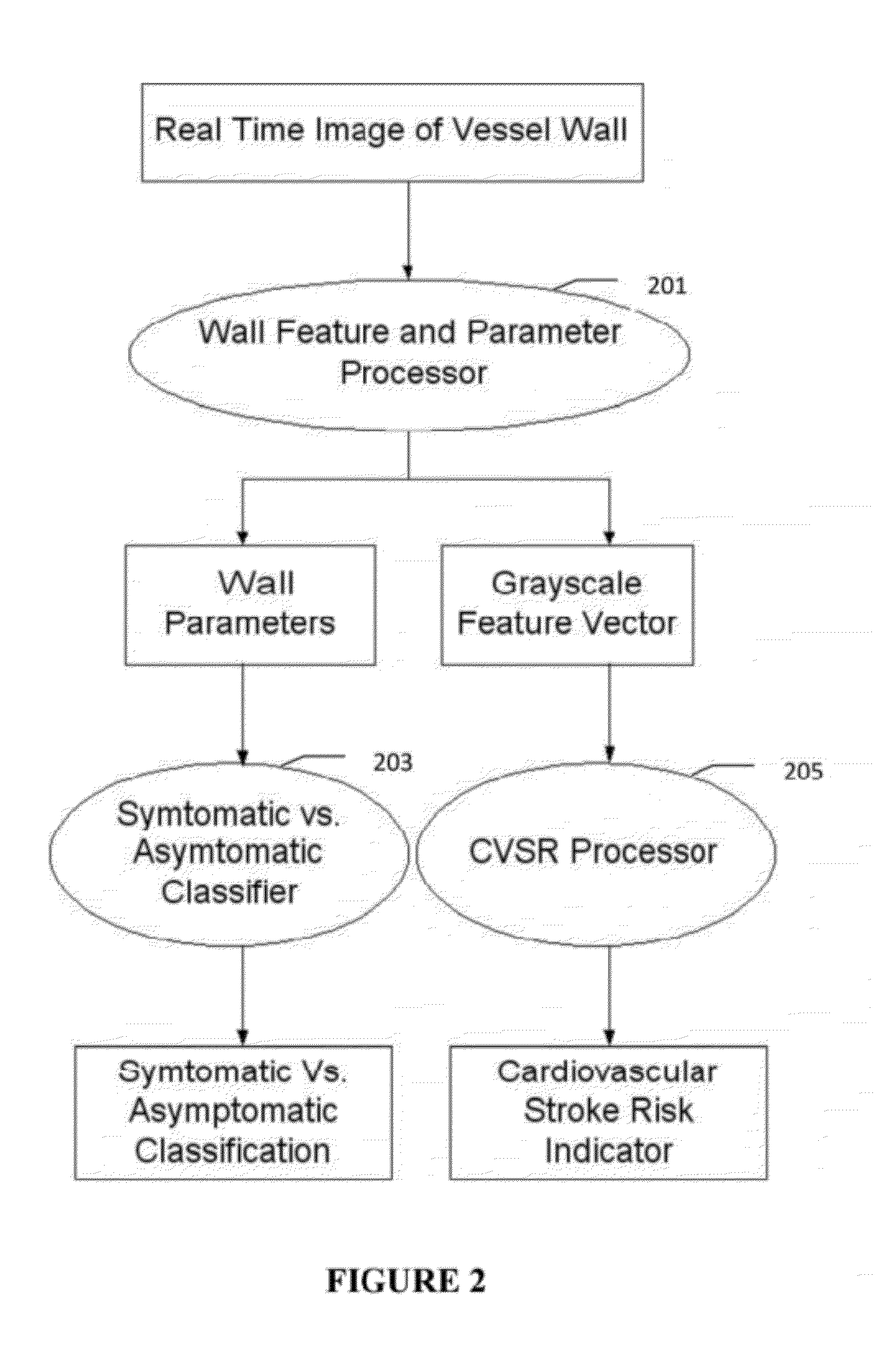
Imaging based symptomatic classification and cardiovascular stroke risk score estimation
InactiveUS20110257545A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementGround truthCross modality
Characterization of carotid atherosclerosis and classification of plaque into symptomatic or asymptomatic along with the risk score estimation are key steps necessary for allowing the vascular surgeons to decide if the patient has to definitely undergo risky treatment procedures that are needed to unblock the stenosis. This application describes a statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular stroke risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which computes: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line from the Database of similar Atherosclerotic Wall Region images. The off-line Classifier is trained from the significant features from (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability, selected using t-test. Symptomatic ground truth information about the training patients is drawn from cross modality imaging such as CT or MR or 3D ultrasound in the form of 0 or 1. Support Vector Machine (SVM) supervised classifier of varying kernel functions is used off-line for training. The Atheromatic™ system is also demonstrated for Radial Basis Probabilistic Neural Network (RBPNN), or Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier or Decision Trees (DT) Classifier for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification. The obtained training parameters are then used to evaluate the test set. The system also yields the cardiovascular stroke risk score value on the basis of the four set of wall features.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Tree-structure-based grade tree aggregation-divided video image compression method
InactiveCN1581977ASolve the amount of image dataSolve lengthImage codingTelevision systemsCompression methodVideo image
The method includes steps: first at encoding end, obtaining distribution of image energy on time and frequency domain through discrete wavelet transform; based on correlation between wavelet coefficient, wavelet coefficient in each order is divided according to tree structure; SPIHT encoding is carried out for wavelet coefficient of each tree; encoding result is deposited on encoding end momentarily; finally, results of encoding each tree are synthesized as a code stream in use for storing or transferring. The invention realizes video compression in high compression ratio and low degree of distortion by using less memory space, particular suitable to dedicated system realized through hardware.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
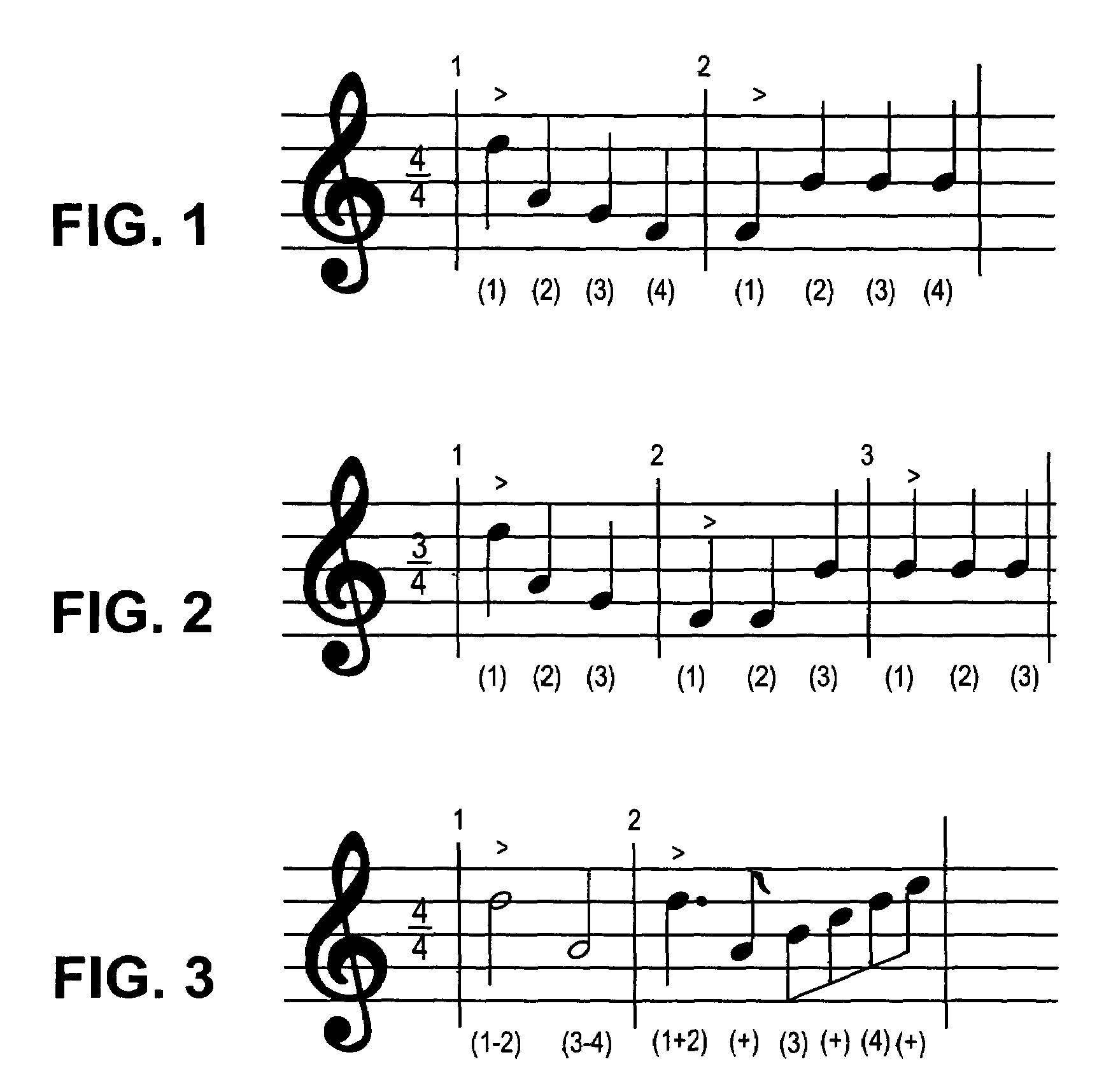
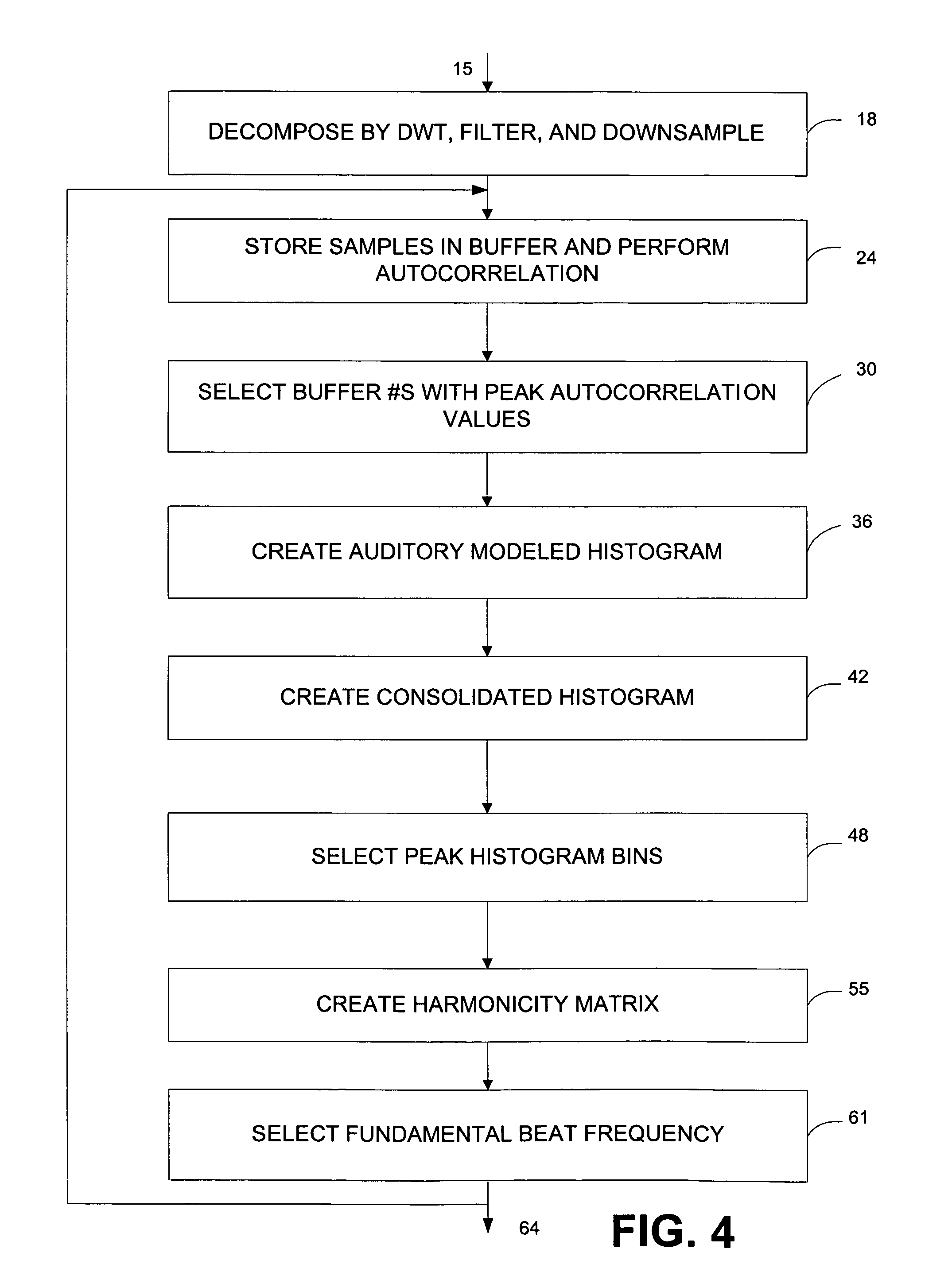
Method and apparatus for synchronizing audio and video components of multimedia presentations by identifying beats in a music signal
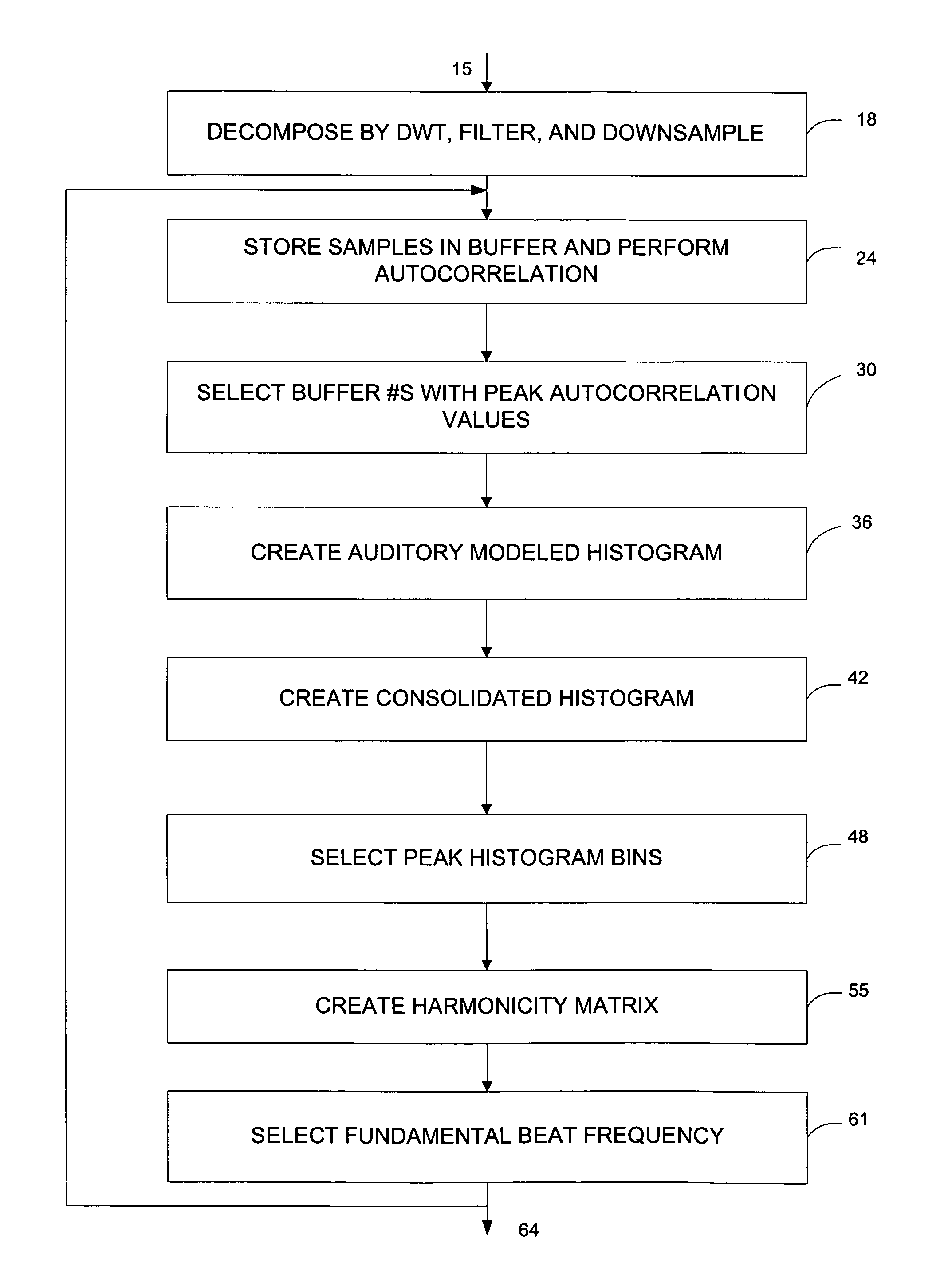
Methods and systems for detecting a fundamental beat frequency in a predetermined time interval of a music signal are disclosed. The frequency may be detected by processing a music signal with the discrete wavelet transform to obtain a set of coefficients. A subset of the coefficients may be processed to obtain a plurality of candidate beat frequencies contained in the corresponding portion of the music signal. Harmonic relationships between the candidate beat frequencies may be determined, and the fundamental beat frequency may then be determined based upon the determined harmonic relationships.
Owner:8324450 DELAWARE +1
Methods for performing fast discrete curvelet transforms of data
ActiveUS7840625B2The process is fast and accurateImprove representationComplex mathematical operationsDigital transformationArray data structure
Fast digital implementations of the second generation curvelet transform for use in data processing are disclosed. One such digital transformation is based on unequally-spaced fast Fourier transforms (USFFT) while another is based on the wrapping of specially selected Fourier samples. Both digital transformations return a table of digital curvelet coefficients indexed by a scale parameter, an orientation parameter, and a spatial location parameter. Both implementations are fast in the sense that they run in about O(n2 log n) flops for n by n Cartesian arrays or about O(N log N) flops for Cartesian arrays of size N=n3; in addition, they are also invertible, with rapid inversion algorithms of about the same complexity.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Voice recognition method facing specific crowd
ActiveCN101944359AImprove effectivenessImprove recognition accuracySpeech recognitionFrequency spectrumFeature extraction
The invention discloses a voice recognition method facing a specific crowd. The method comprises the following steps of: first, sampling a voice signal and converting the voice signal to a digital signal from an analogue signal; then, pre-weighting, windowing, en-framing and performing front-end processing of endpoint detection on the digital voice signal; later on, performing feature extraction on the voice signal by adopting discrete wavelet transform; and finally, performing voice recognition on the feature-extracted voice signal by adopting a discrete hidden Markov model after training a sample. In the processes of performing the front-end processing and the feature extraction on the voice signal, spectrum features and pronunciation characteristics of different target crowds are fully taken into consideration and the process of extracting voice information is optimized, so that a processing process and an information extracting process can be simplified; and therefore, recognition precision is ensured, simultaneously calculation amount and information storage capacity in the recognition process are greatly reduced, and the voice recognition on an embedded platform is realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU PINGPONG INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Imaging Based Symptomatic Classification Using a Combination of Trace Transform, Fuzzy Technique and Multitude of Features
InactiveUS20120078099A1Improve accuracyMaximum accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsGray levelRadiology
A statistical (a) Computer Aided Diagnostic (CAD) technique is described for symptomatic versus asymptomatic plaque automated classification of carotid ultrasound images and (b) presents a cardiovascular risk score computation. We demonstrate this for longitudinal Ultrasound, CT, MR modalities and extendable to 3D carotid Ultrasound. The on-line system consists of Atherosclerotic Wall Region estimation using AtheroEdge™ for longitudinal Ultrasound or Athero-CTView™ for CT or Athero-MRView from MR. This greyscale Wall Region is then fed to a feature extraction processor which uses the combination: (a) Higher Order Spectra; (b) Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT); (c) Texture and (d) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Local Binary Pattern; (b) Law's Mask Energy and (c) Wall Variability. Another combination uses: (a) Trace Transform; (b) Fuzzy Grayscale Level Co-occurrence Matrix and (c) Wall Variability. The output of the Feature Processor is fed to the Classifier which is trained off-line.
Owner:ATHEROPOINT
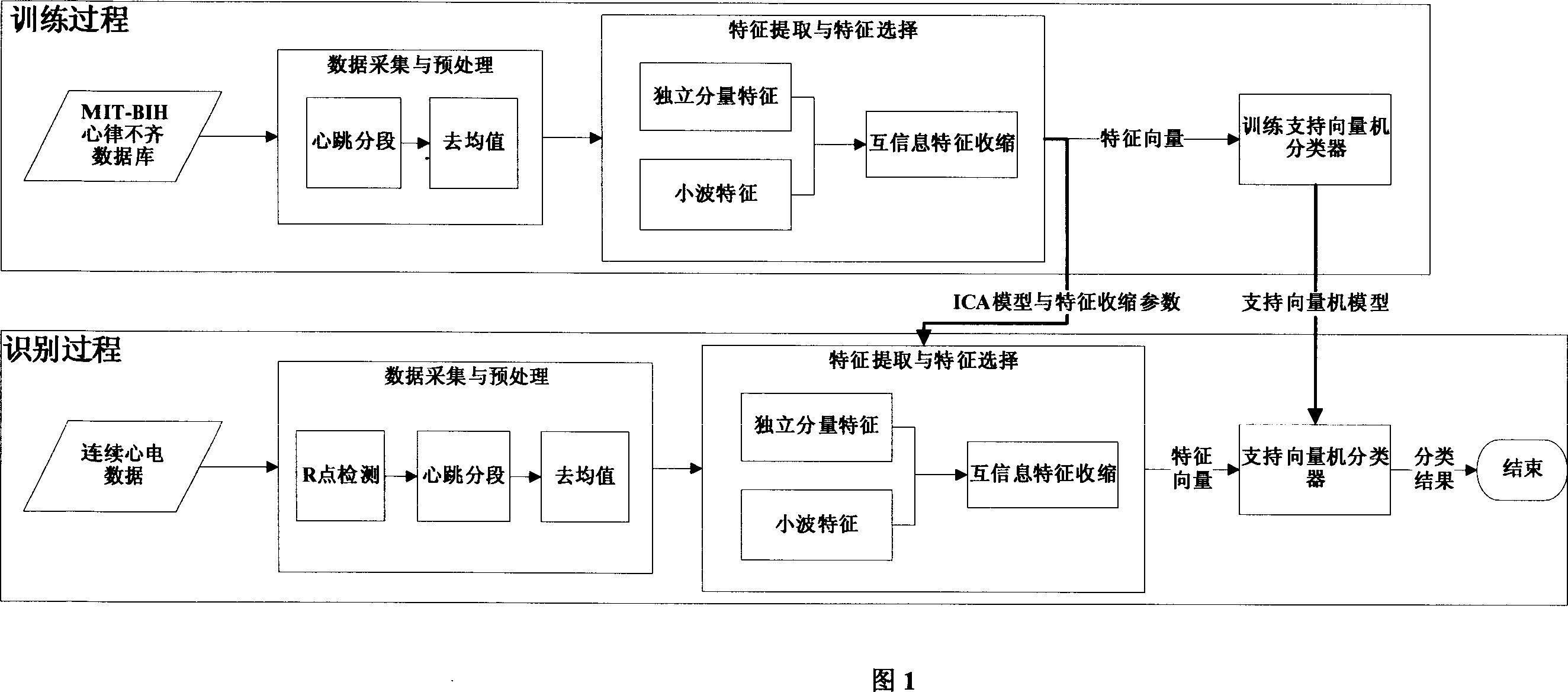
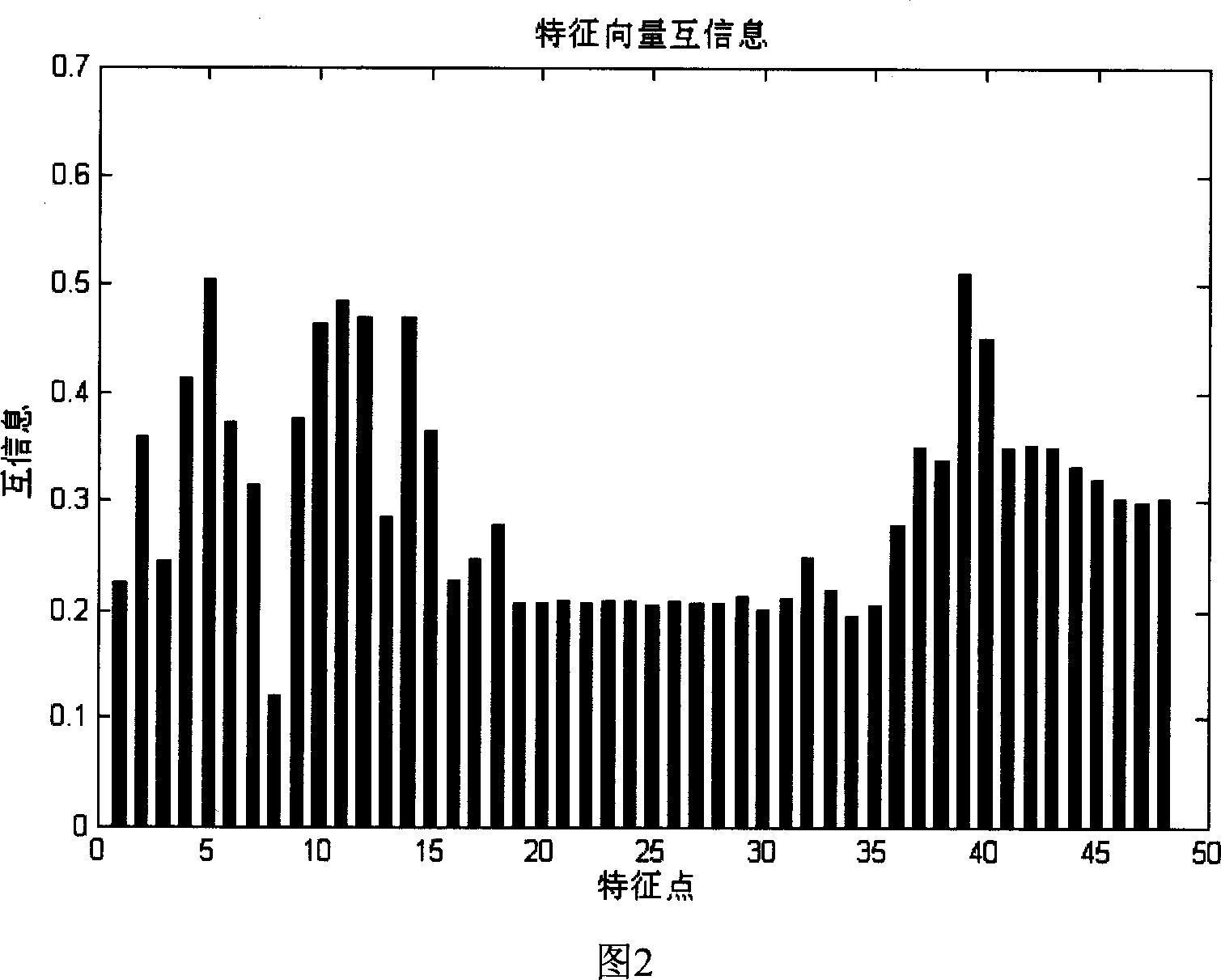
Abnormal electrocardiogram recognition method based on ultra-complete characteristics
InactiveCN1951320AImprove the accuracy of automatic recognitionGuaranteed recognition effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData segmentVector mode
The invention relates to an abnormal cardioelectric recognize method based on ultra-complete character. Wherein. it first uses secondary sample wavelet to process R-point check on the cardioelectric data, segments and pretreats the cardioelectric data based on the R-point position; then uses independent component method and disperse wavelet convert method to extract one ultra-complete character group from each heart beat, and contract the character via communication method; at last uses the vector method to train the extracted character to obtain one vector mode, to automatically recognize and classify the new heart beat data.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Machine learning-based wireless sensing motion identification method
InactiveCN106407905AImprove recognition accuracyRobustCharacter and pattern recognitionData acquisitionColumn vector
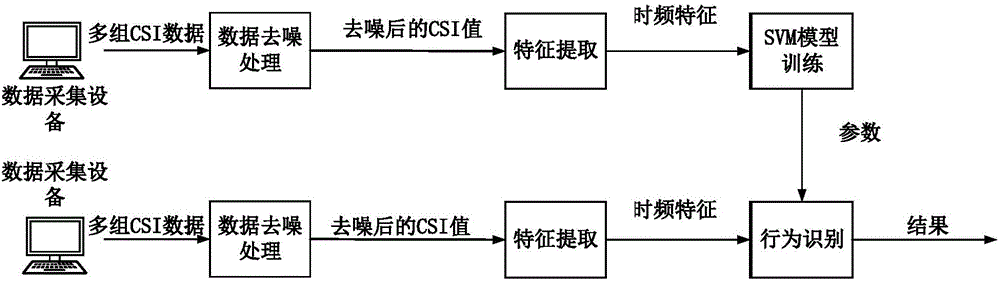
The invention discloses a machine learning-based wireless sensing motion identification method which comprises the following steps: a step of data collection, a step of data denoising operation, a step of feature extraction and a step of SVM model training and identifying operation. During data collection operation, absolute value of a group of CSI data collected on each sampling point is obtained and is read into a 30*Nr*Nt matrix form. A PCA mode is mainly adopted for the data denoising operation. Feature extraction operation can be conducted based on discrete wavelet transformation. To make SVM model training convenient, training samples are subjected to Kmeans clustering operation via the machine learning-based wireless sensing motion identification method, n clustering centers can be used as word bags, and voting operation is performed based on feature vectors and best matching items of all the word bags; when the matrix form feature vectors are converted into column vectors, SVM model training can be realized conveniently. The machine learning-based wireless sensing motion identification method is a human body behavior identification method which is high in identification accuracy and high in robustness for environment change.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
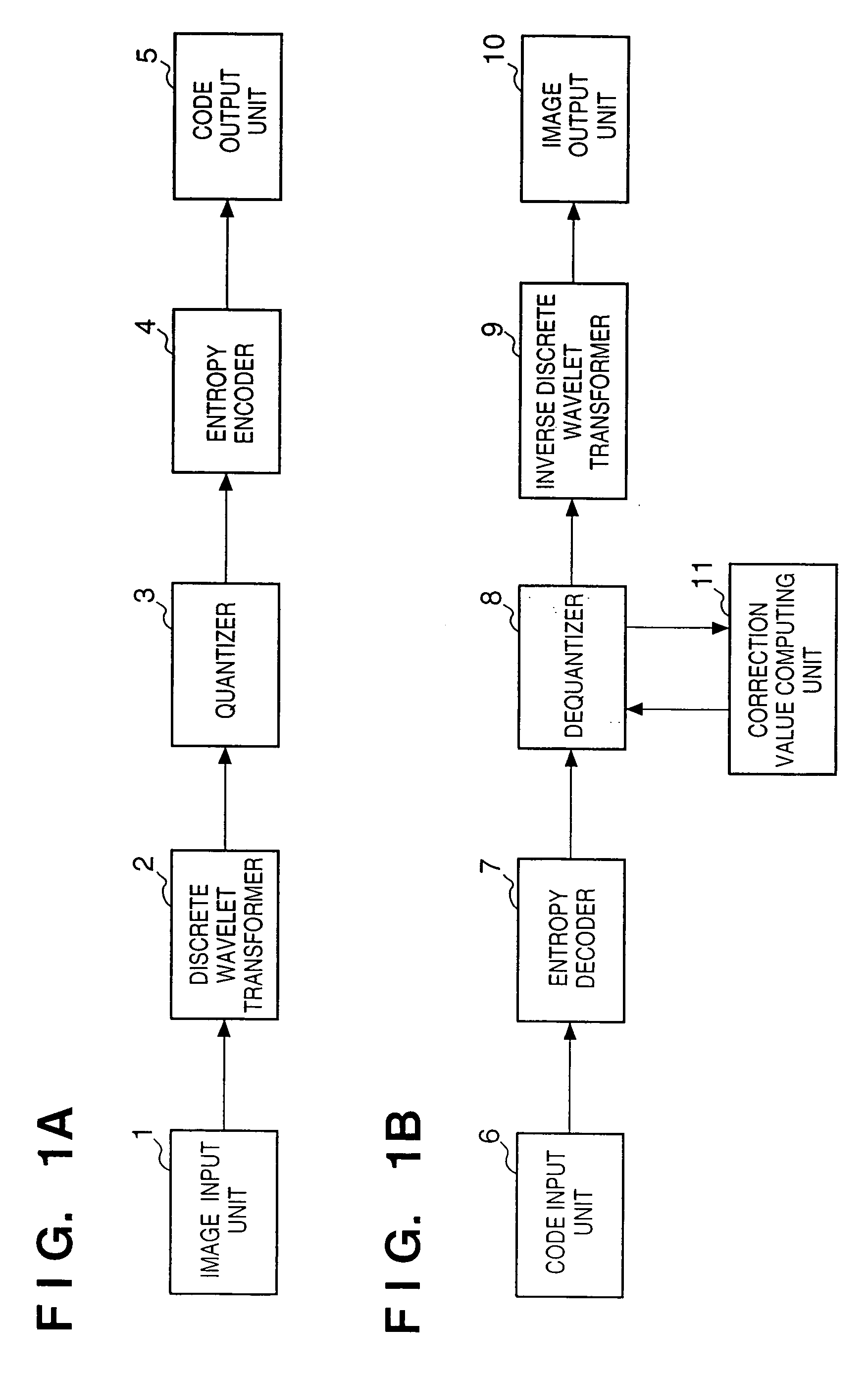
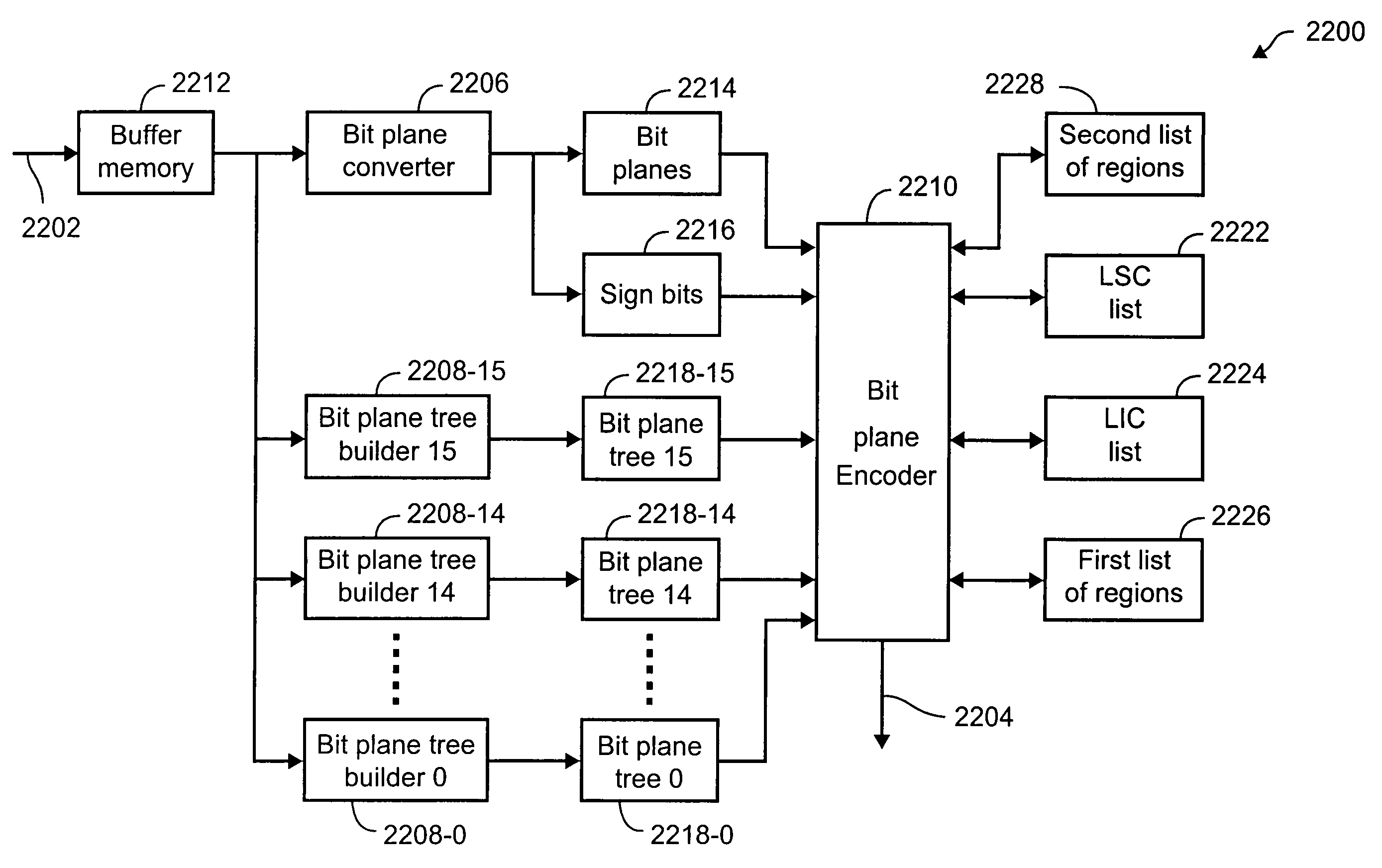
Information processing method, apparatus and storage medium for receiving and decoding a code sequence obtained by encoding an image
InactiveUS6947600B1Improve image qualityHigh image qualityCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsInformation processingBit plane
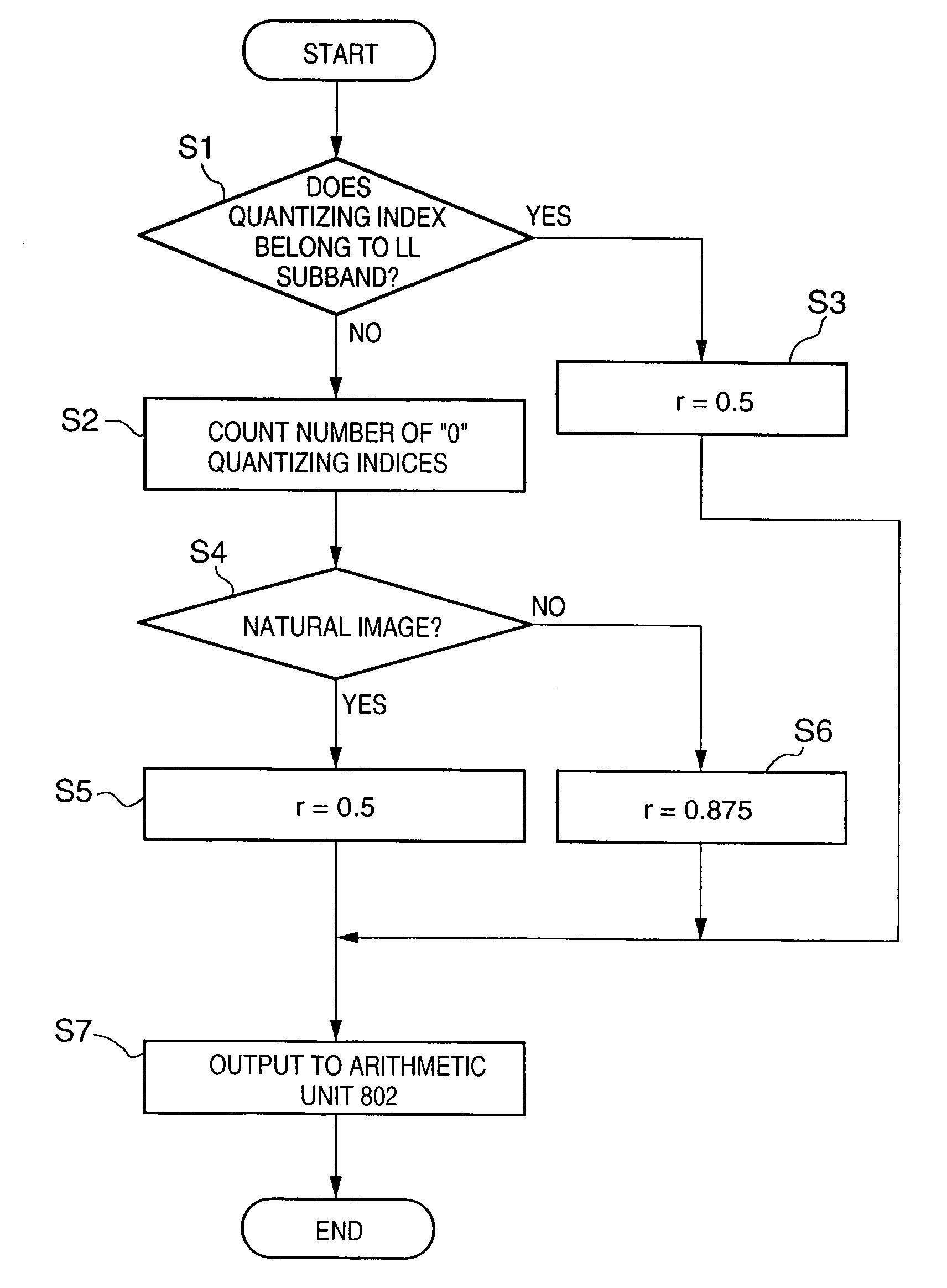
An entropy decoder receives a code sequence which is obtained by breaking up coefficients that have undergone discrete wavelet transformation into bit planes, and encoding the bit planes, and entropy-decodes the code sequence. A correction value computing unit determines correction values used to correct dequantized values in a dequantizer in accordance with the number of quantization indices decoded by the entropy decoder. The dequantizer receives the quantization indices decoded by the entropy decoder, and generates a series of coefficient sequences that represent an image by correcting and dequantizing the quantization indices on the basis of the values of the quantization indices and the correction values obtained by the correction value computing unit. A predetermined inverse discrete wavelet transformer restores an image by computing the inverse transforms of the coefficient sequences obtained by the dequantizer, and outputs the restored image to an image output unit.
Owner:CANON KK
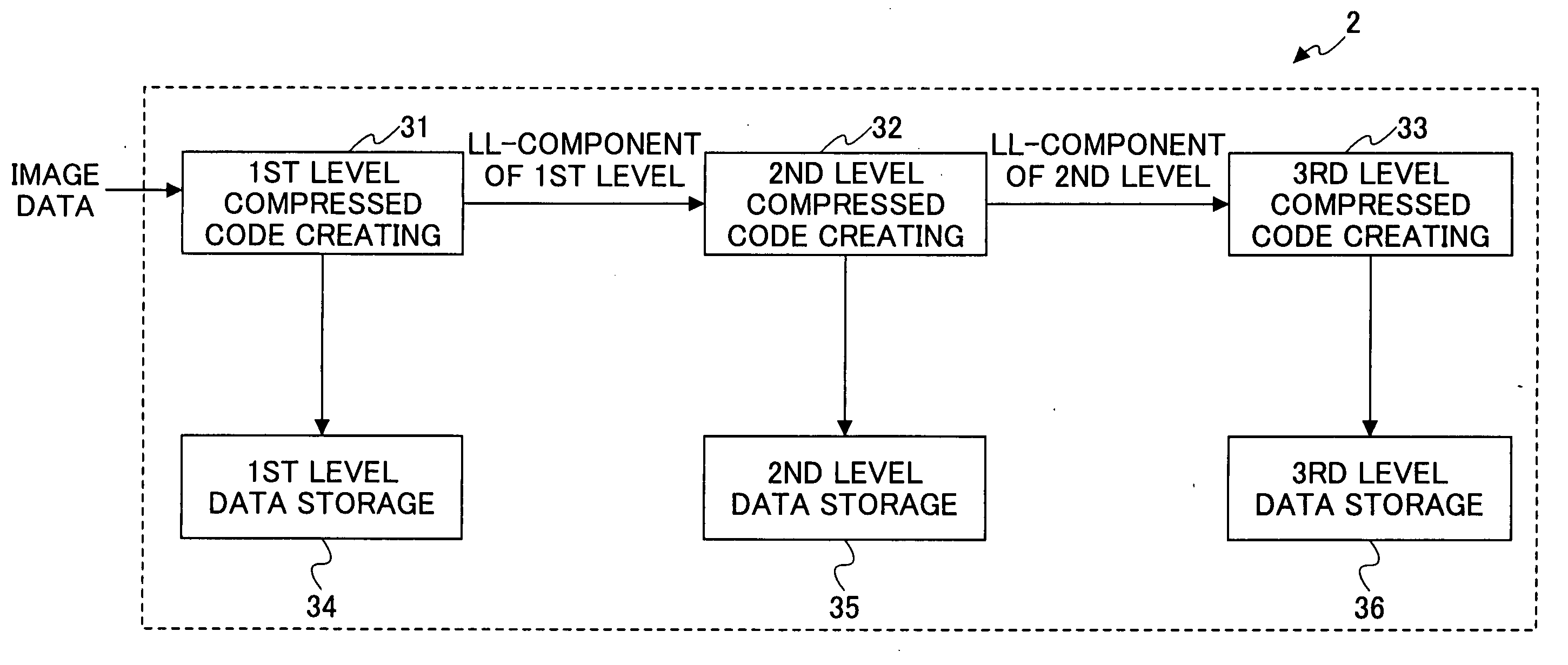
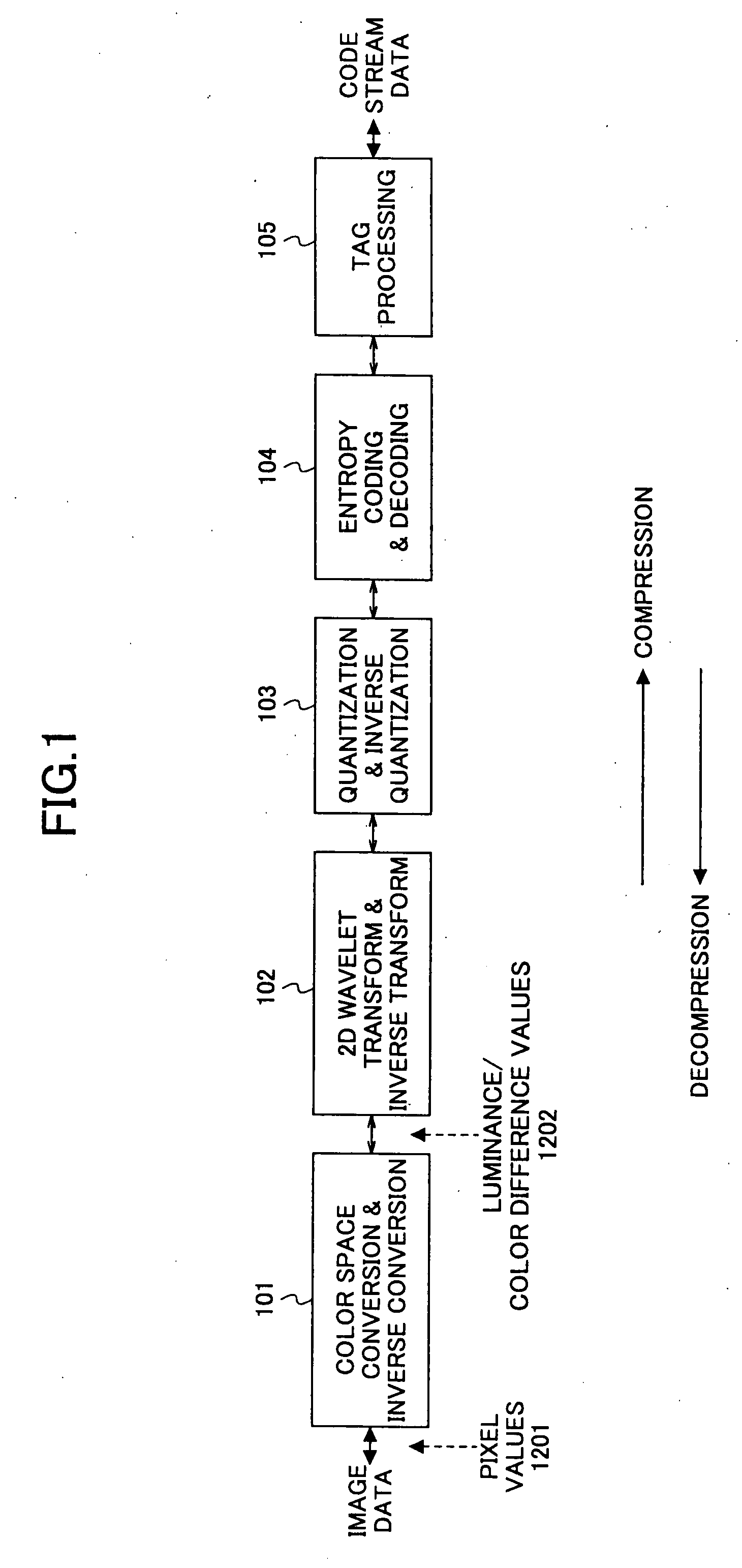
Image processing apparatus and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20050036701A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionImaging processingImaging data
An image processing apparatus hierarchically compresses and codes image data by subjecting pixel values of the image data to a discrete wavelet transform, quantization and coding for each of one or a plurality of rectangular regions into which the image data is divided. The image processing apparatus includes a hierarchical coding unit to compress and code the image data in a state where the image data is divided for each hierarchical layer, to obtain compressed codes, and a distributively storing unit to distributively store the compressed codes that are divided for each hierarchical layer by the hierarchical coding unit.
Owner:RICOH KK
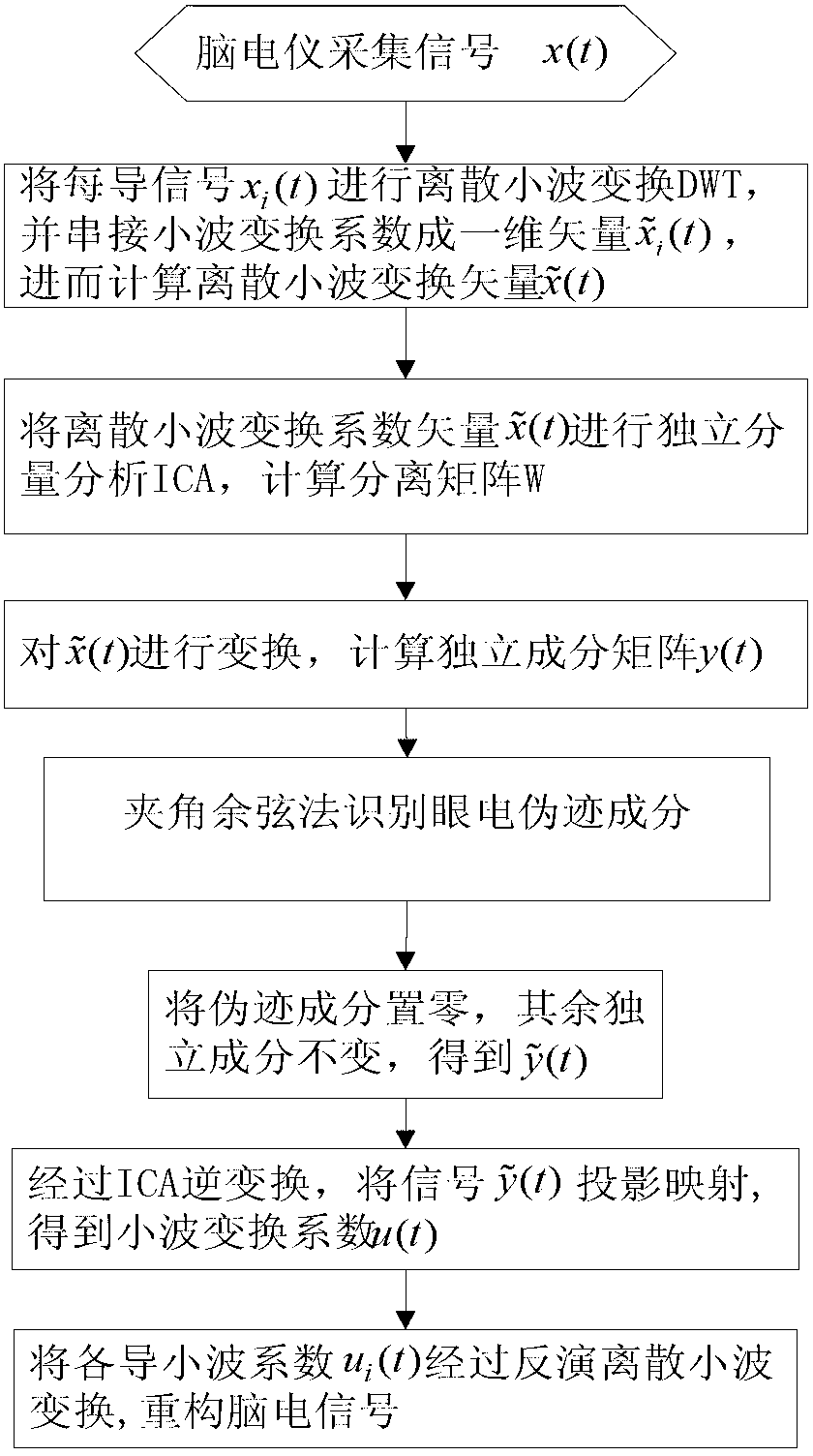
Method for rapidly and automatically identifying and removing ocular artifacts in electroencephalogram signal
InactiveCN102697493AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce iterative processDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectro oculogramFastica algorithm
The invention provides a method for rapidly and automatically identifying and removing ocular artifacts in an electroencephalogram signal and belongs to the technical field of biological information and the method is mainly applied to a process of acquiring and preprocessing the electroencephalogram signal. The method comprises the following specific steps of: carrying out discrete wavelet transformation on an acquired multi-channel electroencephalogram signal and an electro-oculogram signal to obtain multi-scale wavelet coefficients; using the wavelet coefficients connected in series as an input for analyzing an independent component, and rapidly acquiring the independent component by using a negative entropy criterion-based Fast ICA (Independent Component Analysis) algorithm; identifying the ocular artifacts through a cosine method, performing zero resetting on the independent component, and projecting the other components through ICA inverse transformation and returning to all electrodes of an original signal; and finally obtaining the electroencephalogram signal for removing the ocular artifacts through inversion of the wavelet transformation. By utilizing the method for rapidly and automatically identifying and removing the ocular artifacts in the electroencephalogram signal, the problems that an ICA method is poor in discrete effect and low in convergence rate when beingapplied to noisy electroencephalogram signals are solved, and the function of rapidly and automatically identifying and removing the ocular artifacts in the electroencephalogram signal is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Encoding method and apparatus
InactiveUS6978048B1More disadvantagePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionAlgorithmEngineering
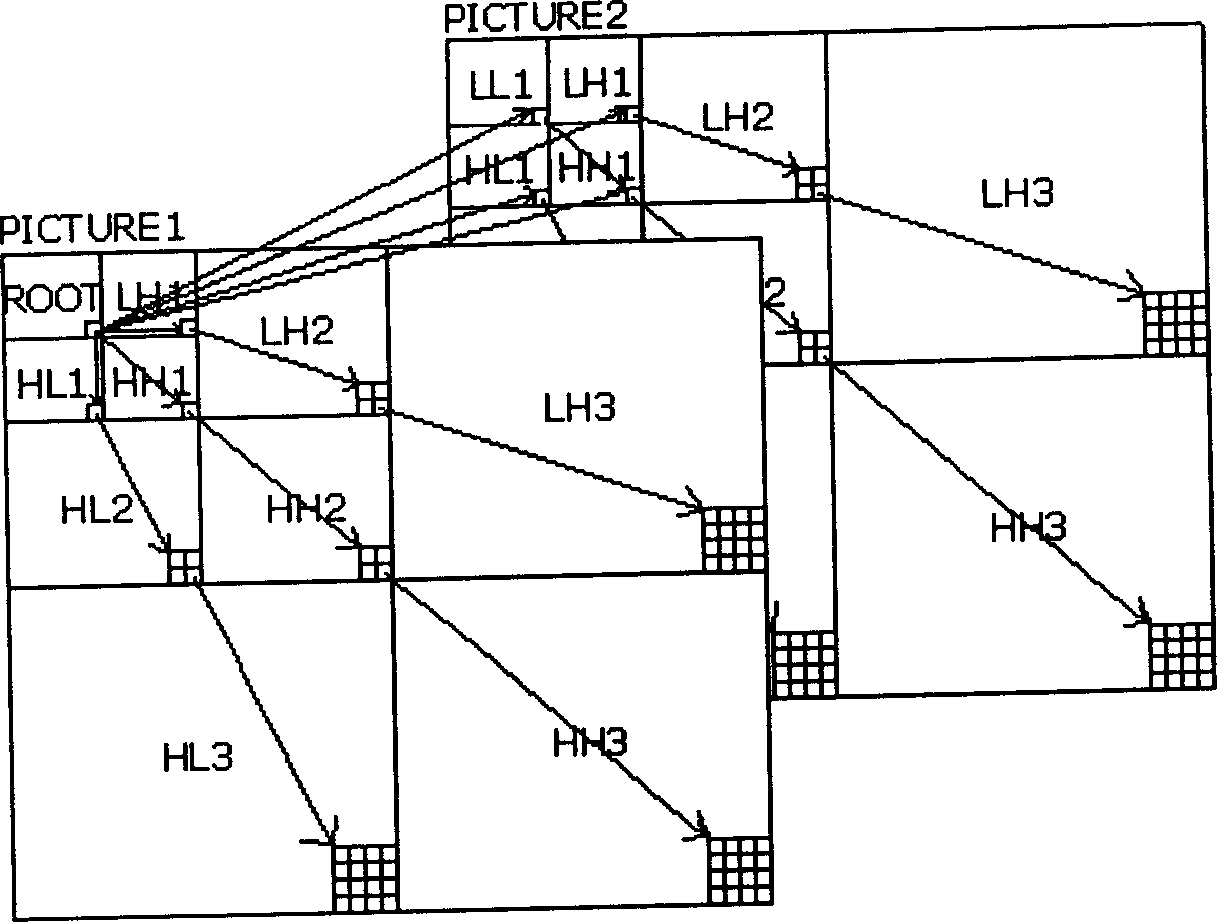
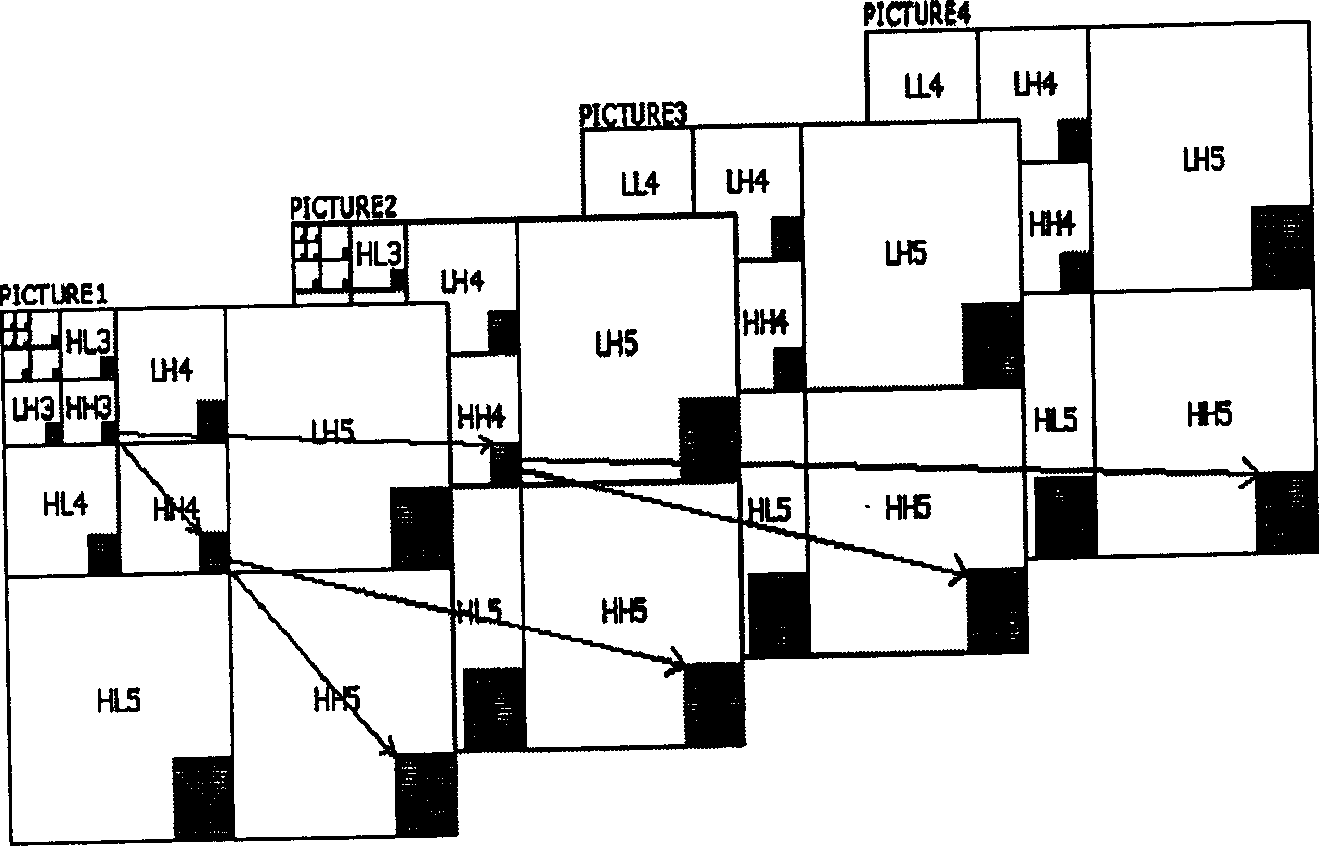
A method of encoding an digital image (502) by a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to a predetermined level of decomposition on a block by block basis, each block (1501, 1504, 1506) having a specified size in number of coefficients, is disclosed. The image is divided into tiles, each having dimensions required to produce the number of coefficients in a first dimension of the transformed block at the predetermined level of decomposition, and less than the number of coefficients in a second dimension of the transformed block. At a particular DWT level, tiles are decomposed. HH, HL and LH subband coefficients are accumulated to form blocks of specified size, and these are encoded to a bit stream (402). A predetermined number of associated LL subband coefficients are similarly accumulated, the process performed recursively per DWT level until the predetermined decomposition level is attained, and the corresponding LL subband coefficients encoded to the bit stream (402).
Owner:CANON KK
Compressing a signal that represents a physical attribute
ActiveUS20180075622A1LessEfficiently obtainedCode conversionImage codingImproved methodComputer science
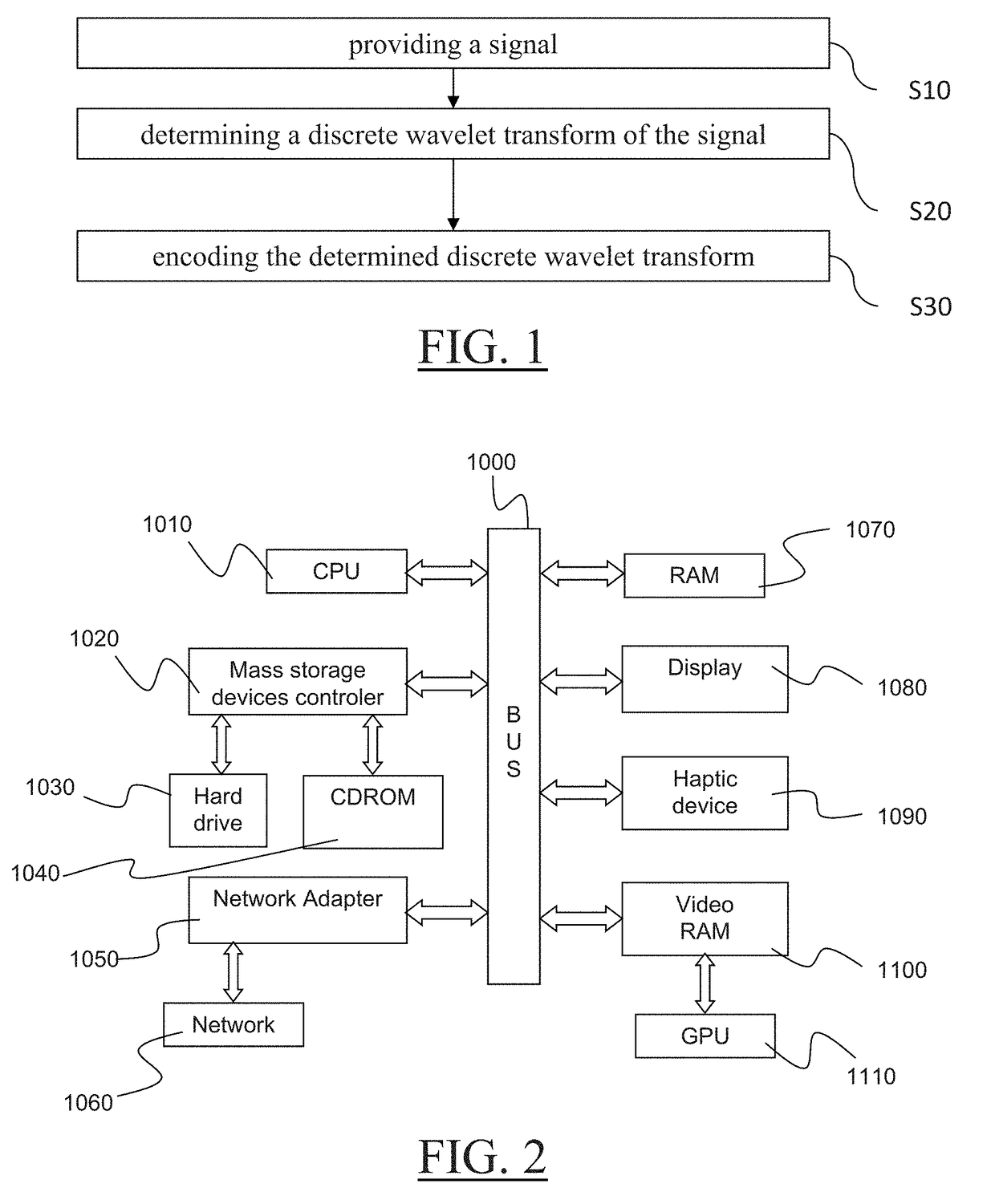
The invention notably relates to a computer-implemented method for compressing data representing values of a physical attribute in a predetermined space. The method comprises providing a signal that includes a mapping from leaf cells of a hierarchical subdivision of the predetermined space each onto a respective coefficient representative of a value of the physical attribute at the respective leaf cell. The method also comprises determining a discrete wavelet transform of the signal and encoding the determined discrete wavelet transform. The method provides an improved way to compress a modeled object that represents a real object.
Owner:DASSAULT SYSTEMES
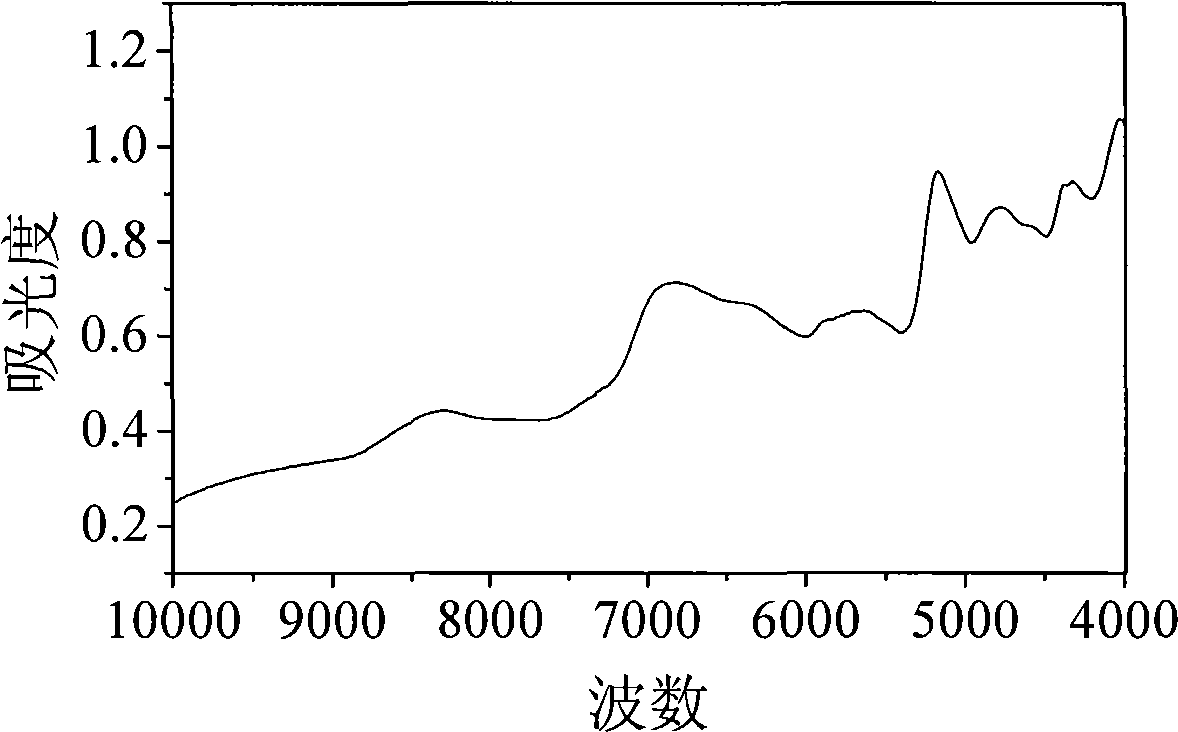
Near infrared spectrum analyzing method based on isolated component analysis and genetic neural network
InactiveCN101520412AImprove forecast accuracyRich Chemometric MethodsBiological neural network modelsColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredMetrology
The invention discloses a near infrared spectrum analyzing method based on the isolated component analysis and genetic neural network, which comprises the following steps for the acquired near infrared spectrum: firstly, effectively compressing spectrum data by using wavelet transform; secondly, extracting an independent component and a corresponding mixed coefficient matrix of a near infrared spectrum data matrix by using an isolated component analysis method; thirdly, building a three-layer BP neutral network, using the mixed coefficient matrix of a training sample as the input and correspondingly measured component concentration matrix as the output, and optimizing a neutral network structure by adopting a genetic algorithm, and obtaining a GA-BP neutral network by the training of the training sample; fourthly, predicting and analyzing the measured component concentration of the predicted set sample by using the GA-BA neutral network. The method enriches the chemical measurement method, widens the application range of the isolated component analysis and has favorable application prospect.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
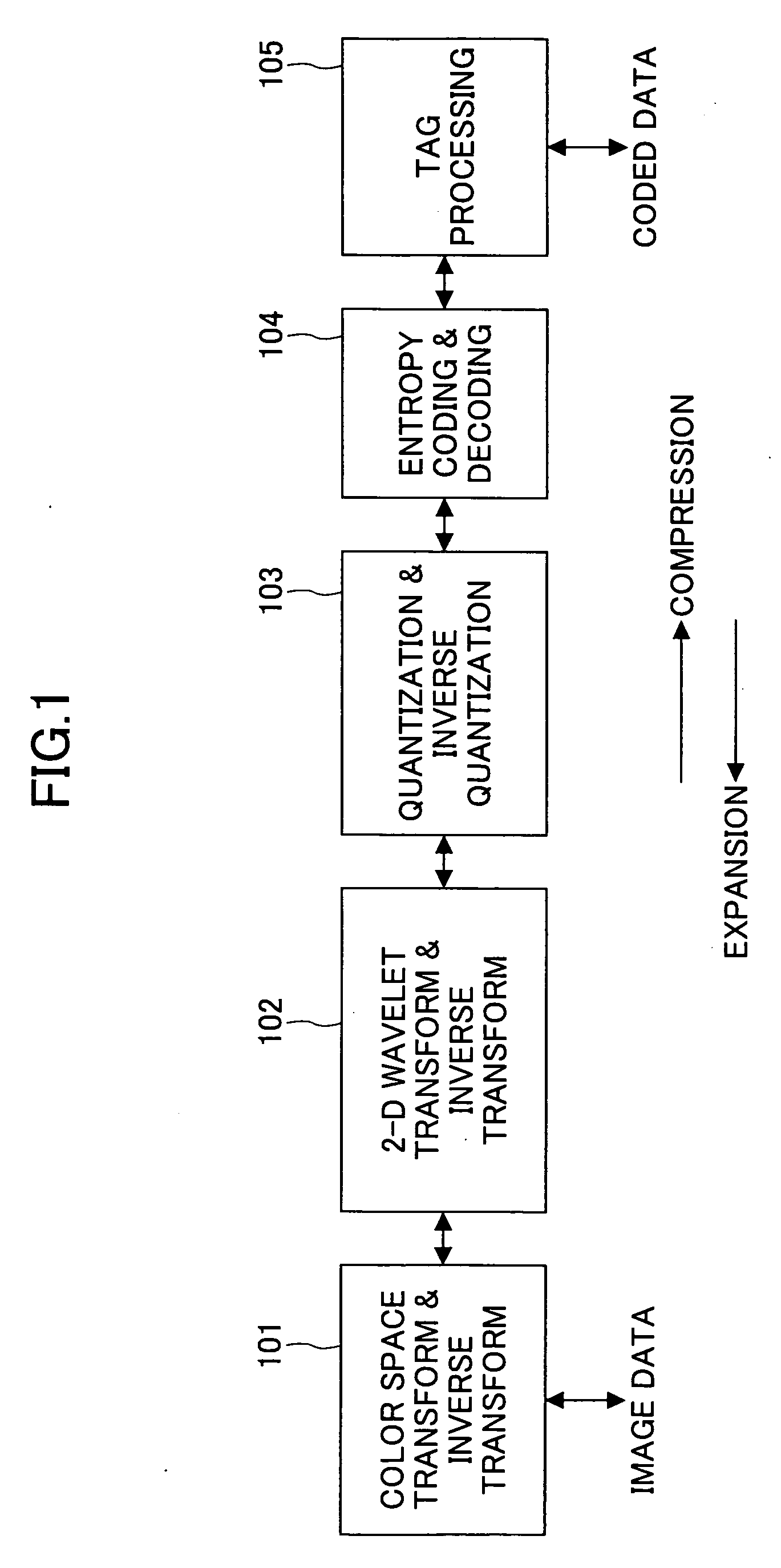
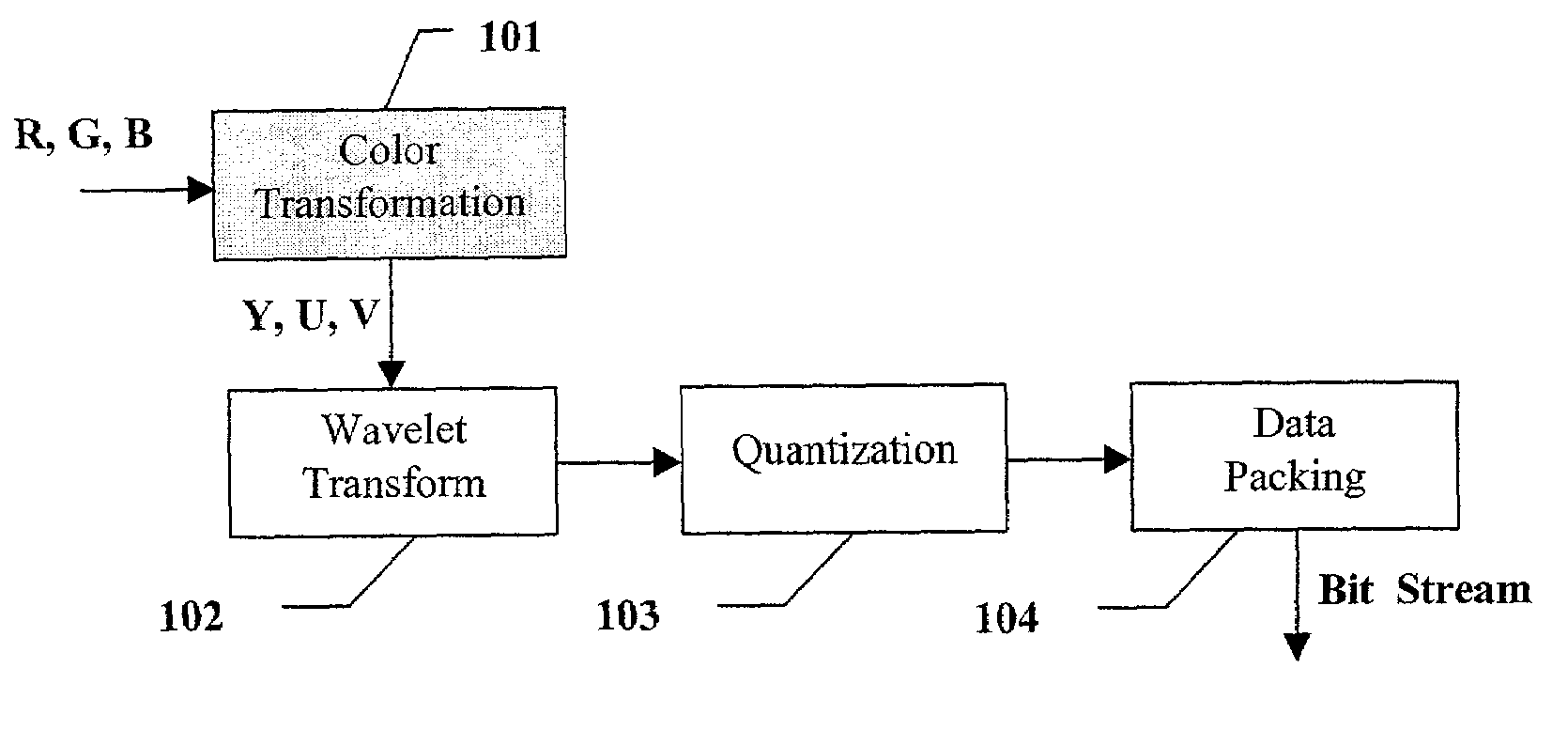
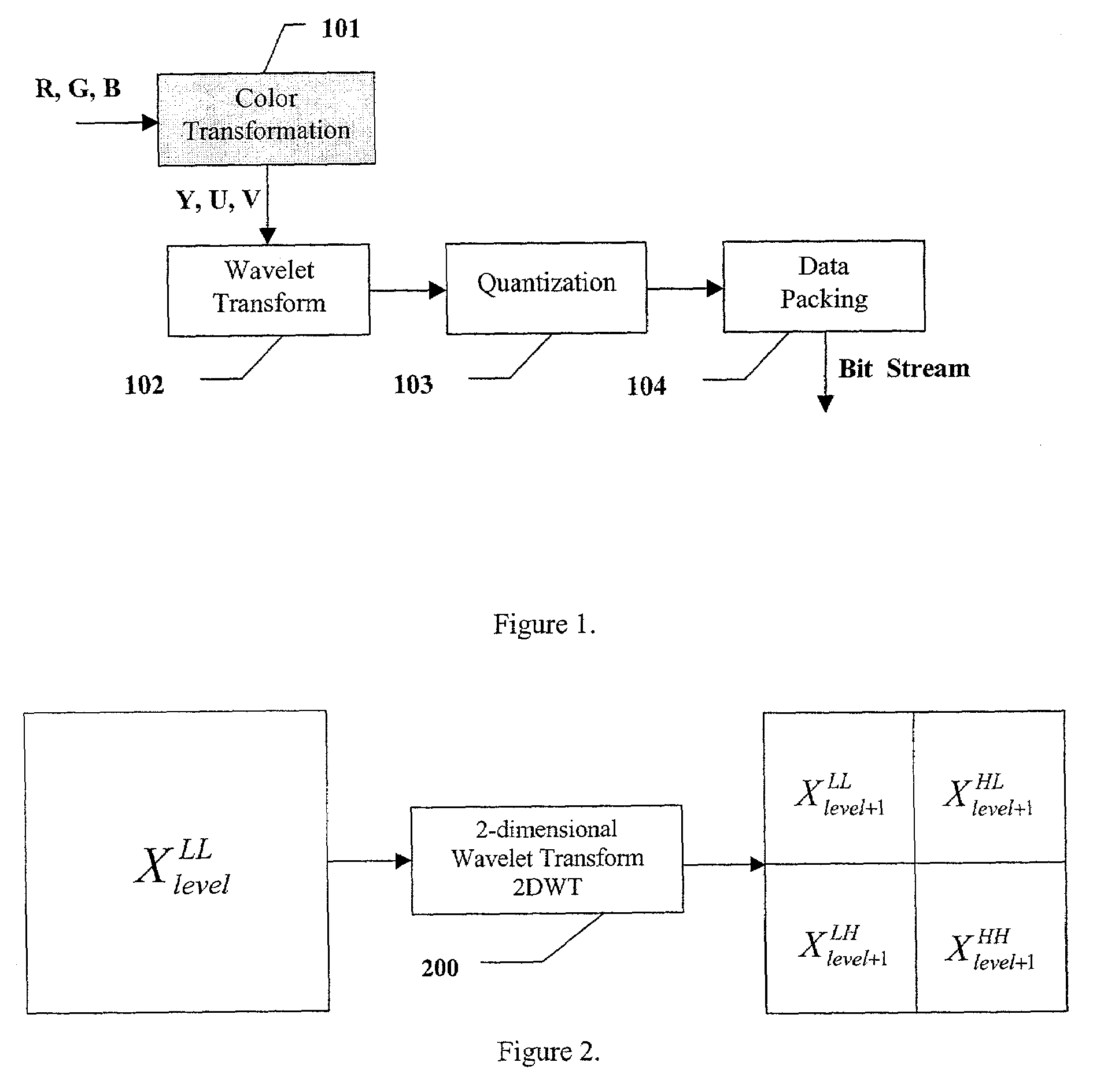
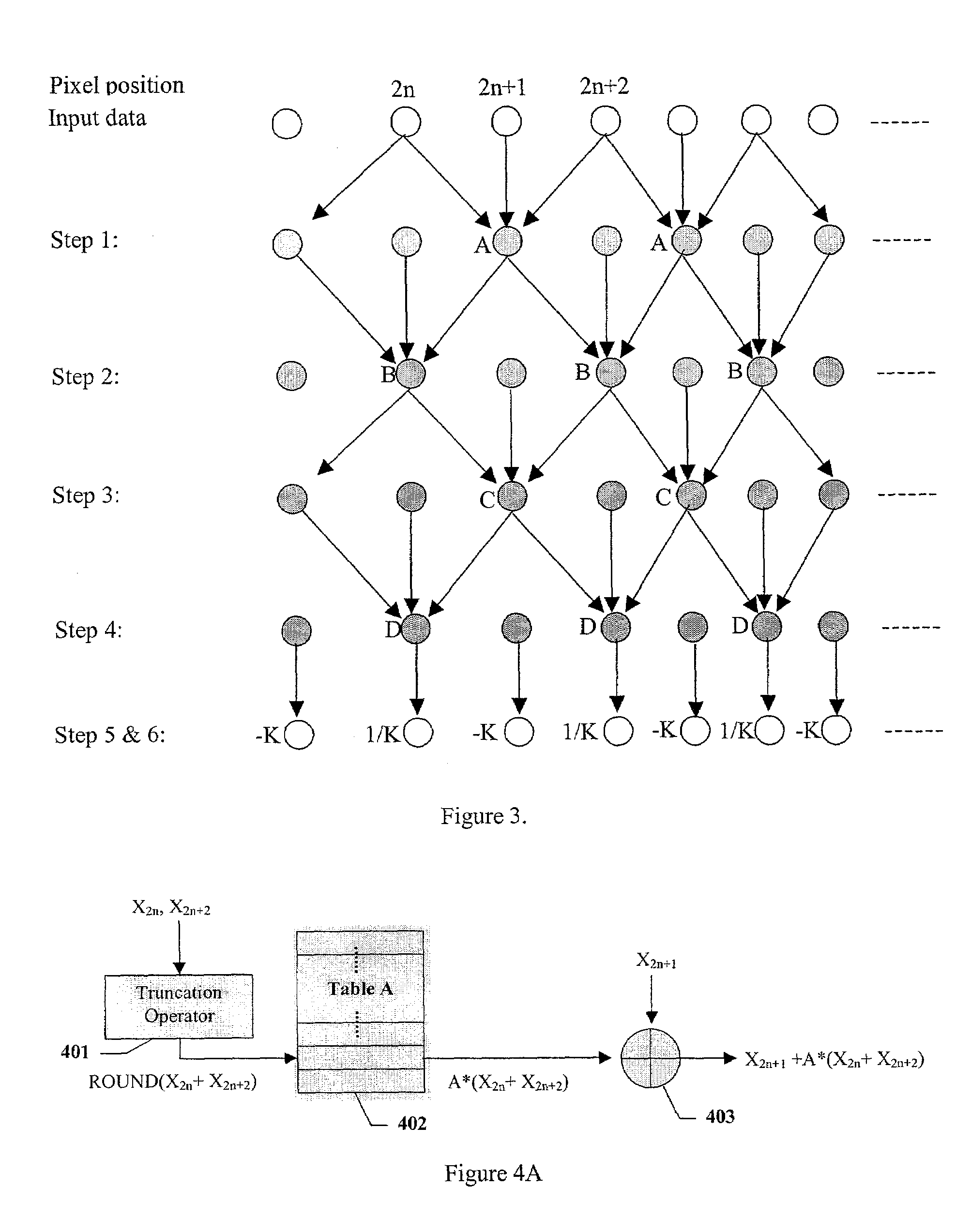
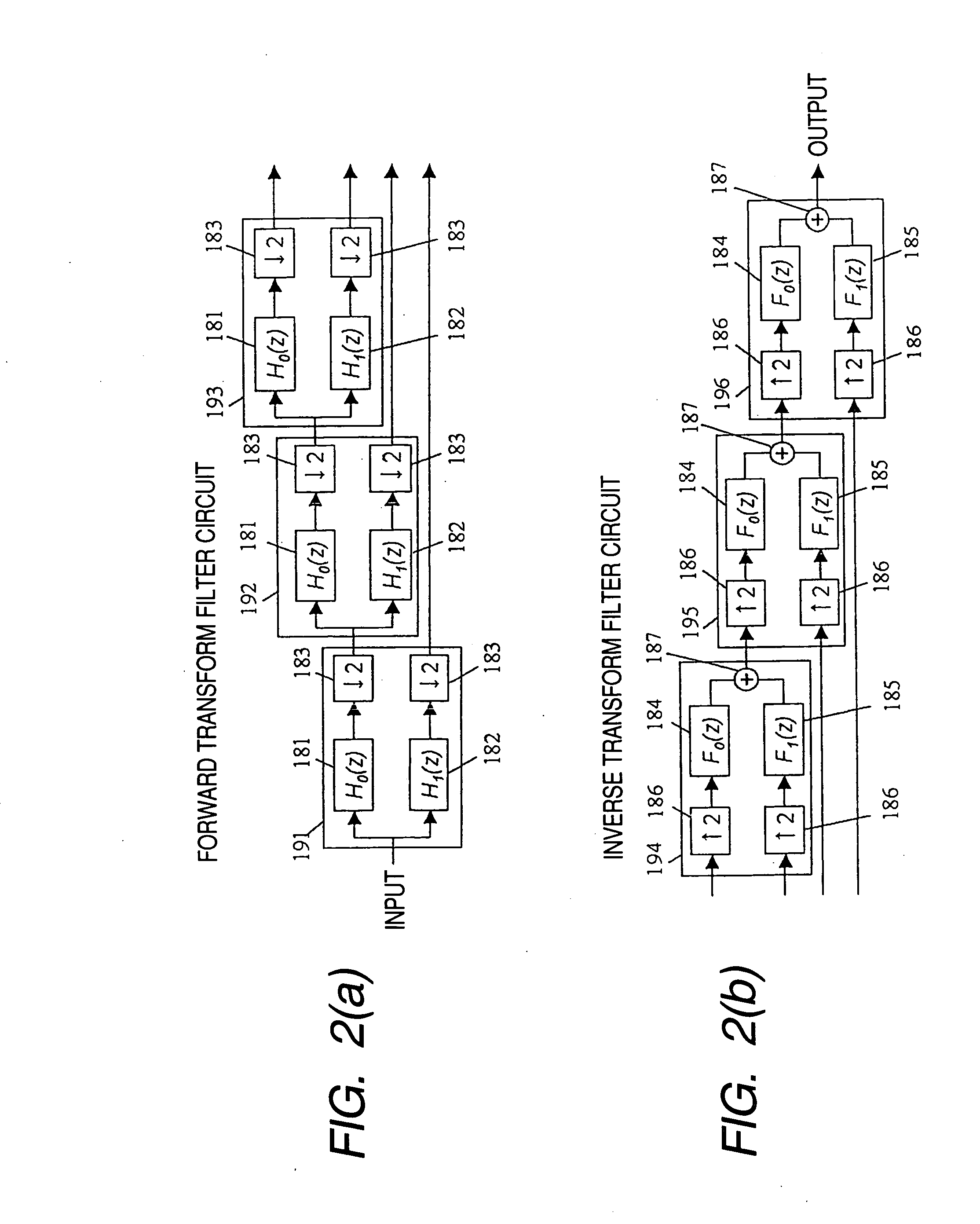
Apparatus and method for image/video compression using discrete wavelet transform
The inventions provides a method for compressing image data comprising the steps of: performing a color transformation of the data; wavelet-transforming the color-transformed data via division and multiplication operations being substituted with six lookup tables in order to provide a series of wavelet coefficients in different levels of wavelet transformation subbands; quantizing in accordance with a special equation the wavelet coefficients which fall above a predetermined threshold value to provide a series of quantized wavelet coefficients; applying an entropy coding to the quantized wavelet coefficients with a particular Huffman table; and compressing the coded wavelet coefficients to provide compressed data.
Owner:TECHSOFT TECH
Anti-interference method for high-frequency partial discharge signal detection
InactiveCN103675617AEliminate the effects ofHigh extraction rateTesting dielectric strengthDecompositionComputer science
The invention discloses an anti-interference method for high-frequency partial discharge signal detection. The anti-interference method includes the steps of 1, building partial discharge signal simulation testing circuit system to acquire signals which are generated from local discharge pulse signals carrying noises after passing through the partial discharge signal simulation testing circuit system, and analyzing characteristics of the signals within a wavelet domain to acquire optimal parameter that is denoised by a discrete wavelet transform based threshold process; 2, acquiring the field partial discharge signals carrying noises, and acquiring the coefficient of the partial discharge signals within the wavelet domain by denoising the partial discharge signals carrying noises by the discrete wavelet transform based threshold process according to the optimal parameter; 3, performing wavelet reconstruction according to the coefficient of the partial discharge pulse signals within the wavelet domain to acquire the denoised partial discharge signals. The signals are denoised by firstly performing threshold processing to decomposition coefficients of different dimensions by threshold selection and then performing wavelet transform.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
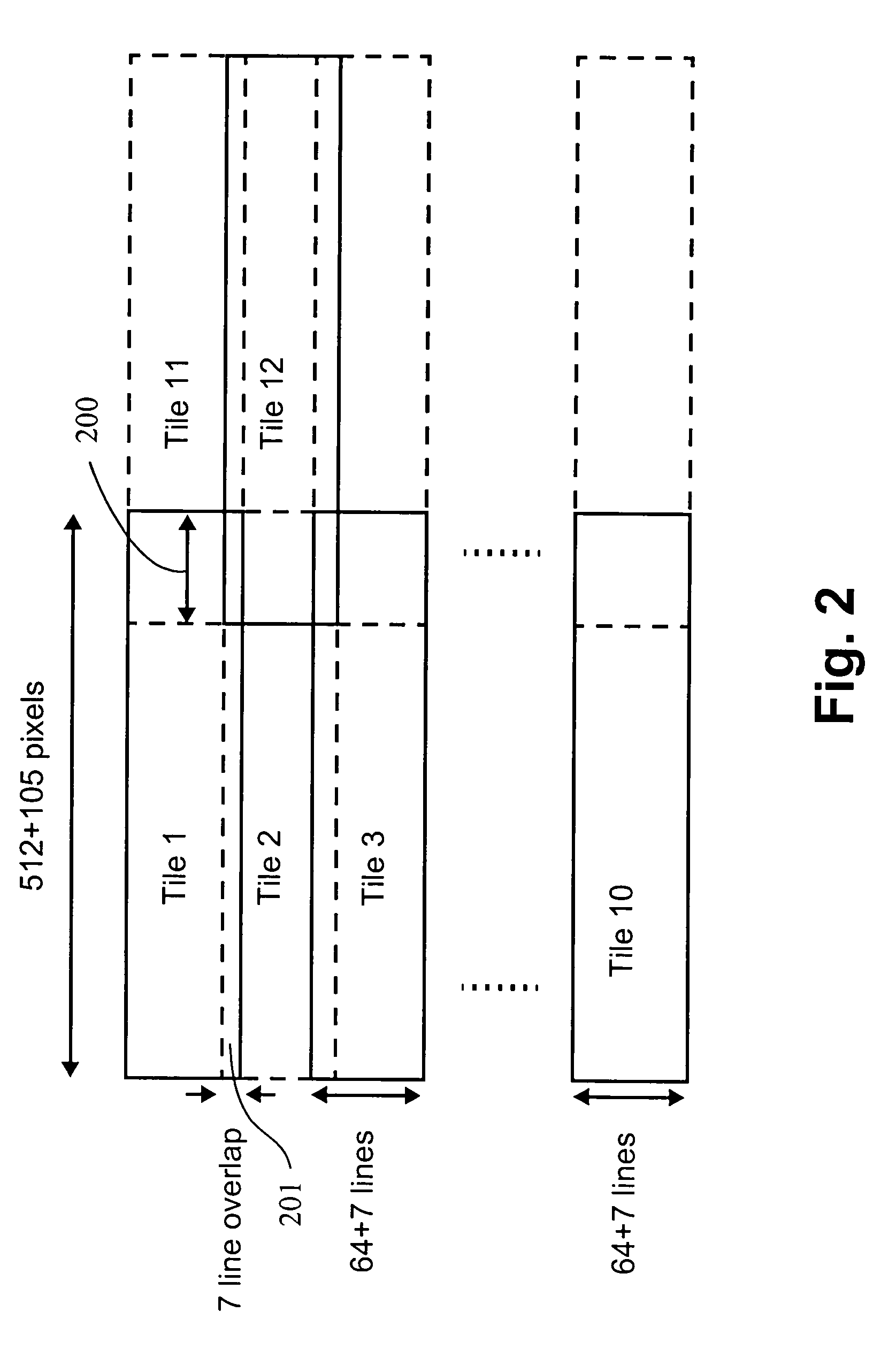
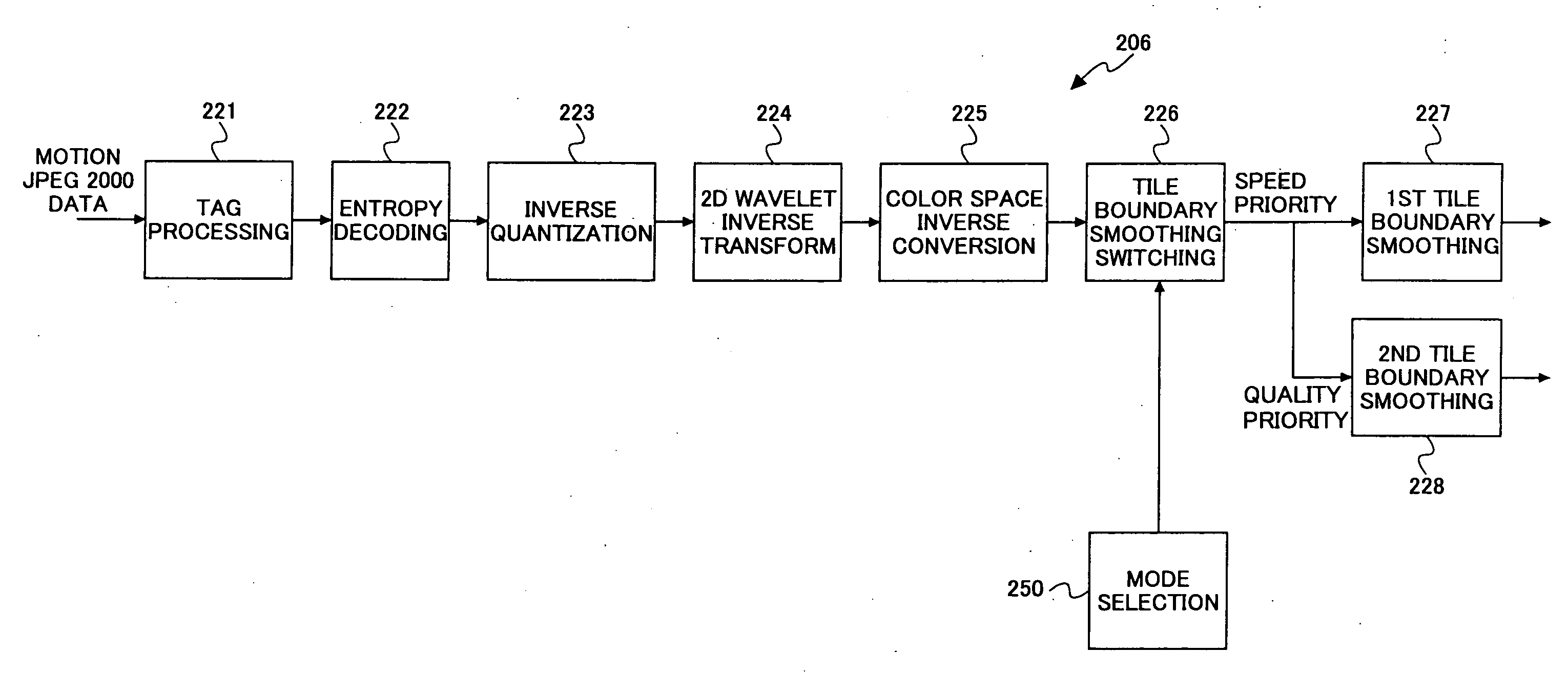
Image decoding technique for suppressing tile boundary distortion
InactiveUS20080131013A1Makes tile boundaries less conspicuousAvoid smoothImage enhancementImage codingLow-pass filterComputer science
An image decoding device for decoding a hierarchically encoded compressed code obtained by dividing an image into a plurality of tiles and performing discrete wavelet transform on the pixel values of the image tile by tile includes a tile boundary smoothing part that performs smoothing of tile boundary distortion on the image after the decoding by application of a low-pass filter. The tile boundary smoothing part controls the degree of smoothing of the low-pass filter according to the ratio of the decoding quantity to the entire quantity of the compressed code. The decoding quantity is the portion of the compressed code which portion is to be decoded.
Owner:RICOH KK
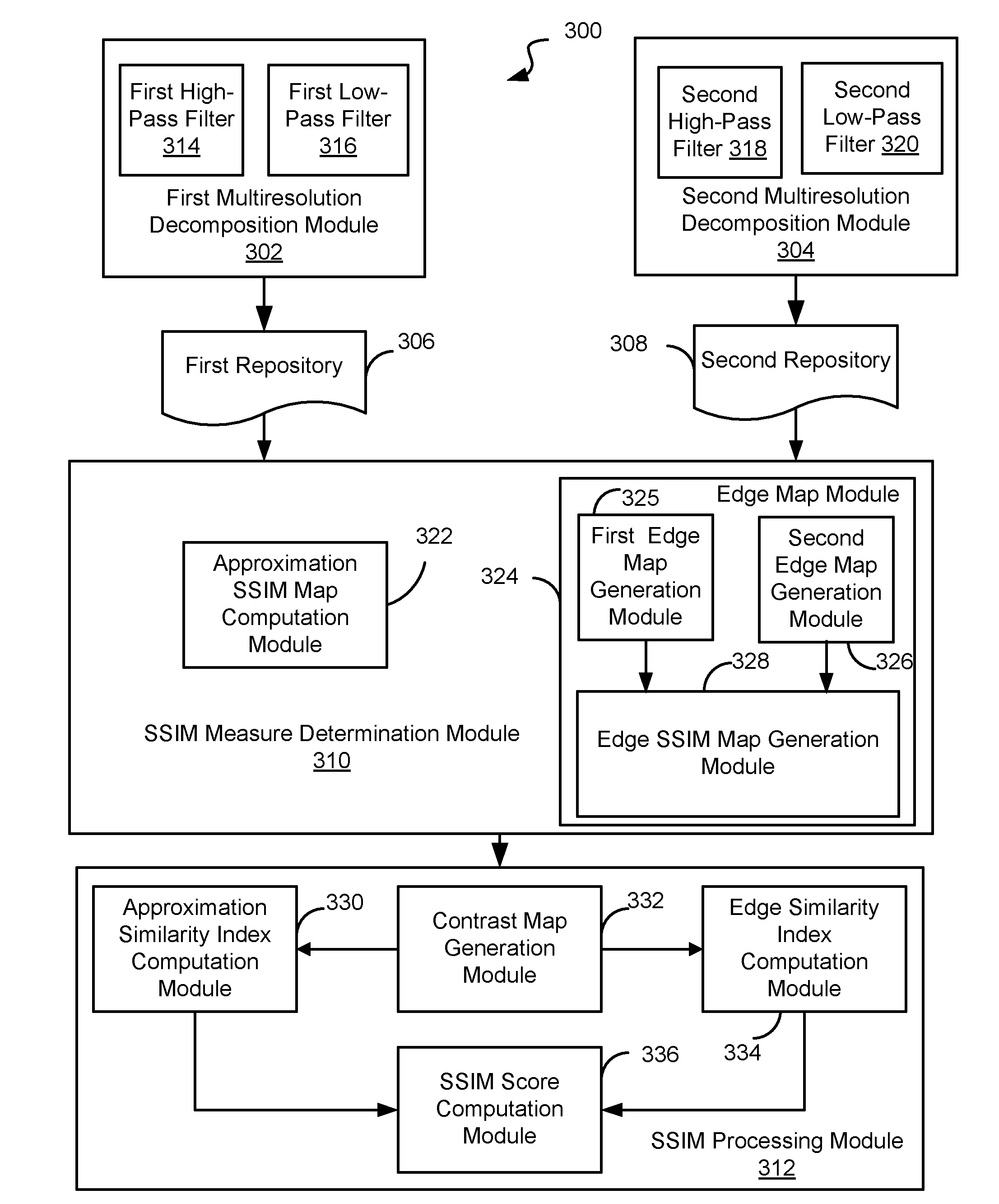
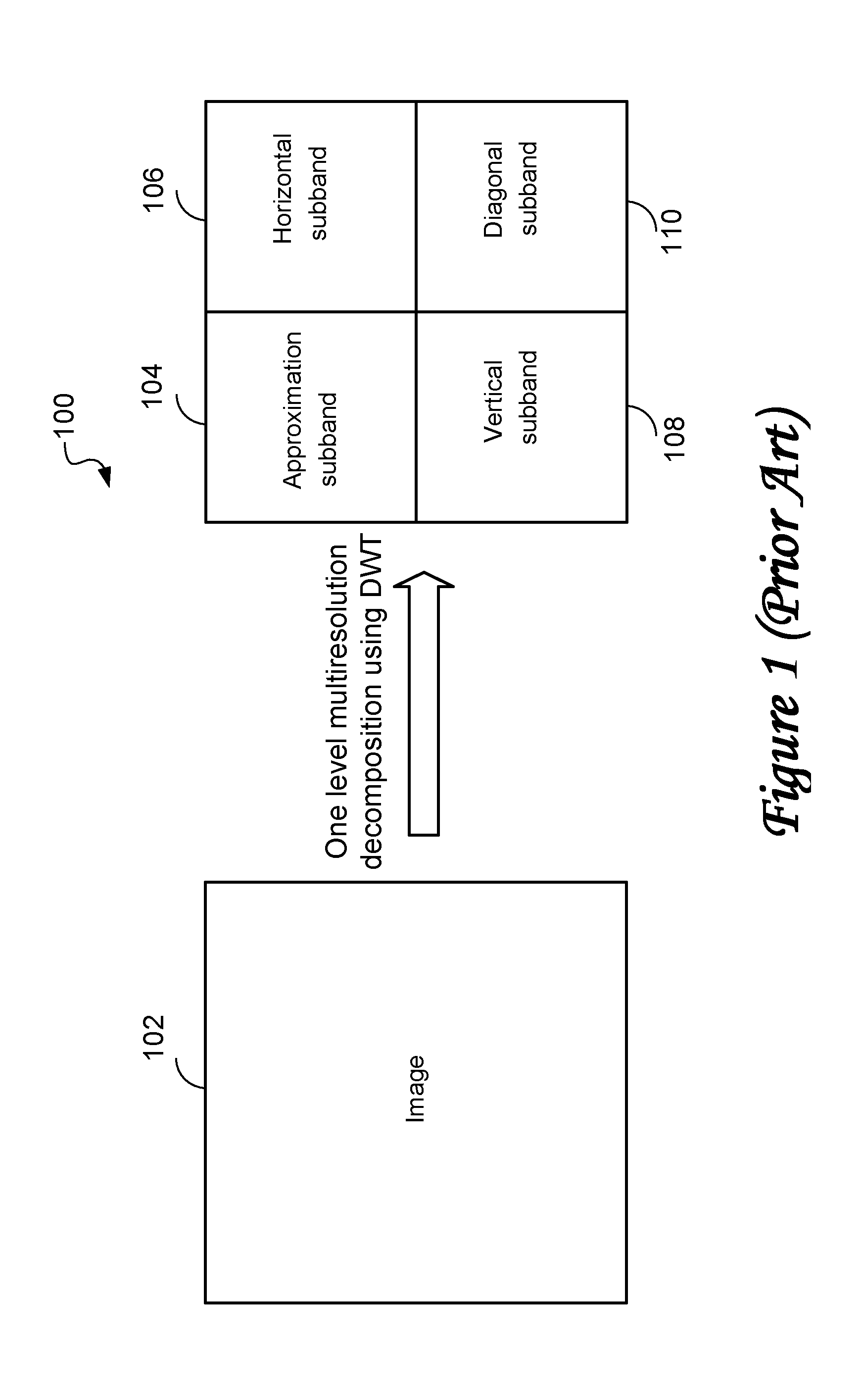
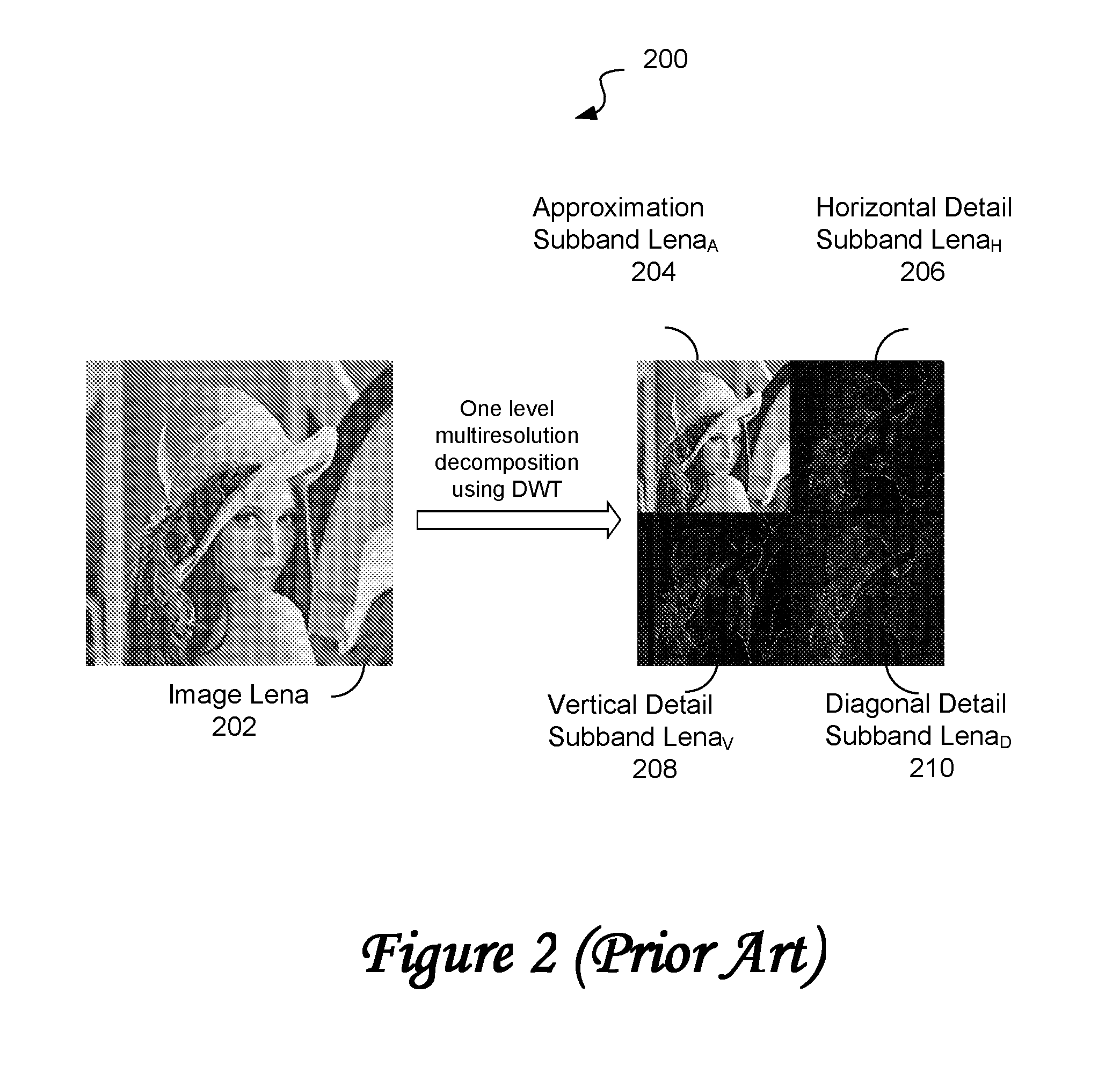
Method and system for determining structural similarity between images
Method and system for low complexity assessment of quality of an image are presented. By performing multiresolution decomposition of images using, for example, a discrete wavelet transform, and determining a metric based on a structural similarity index or a structural similarity map, a structural similarity score, characterizing similarity between images with a high degree of accuracy, is produced. The processing time is much smaller in comparison to that required by other methods producing image quality metrics of comparable accuracy.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
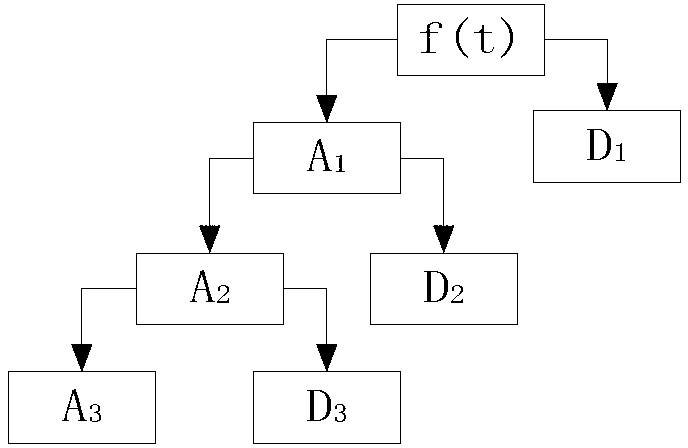
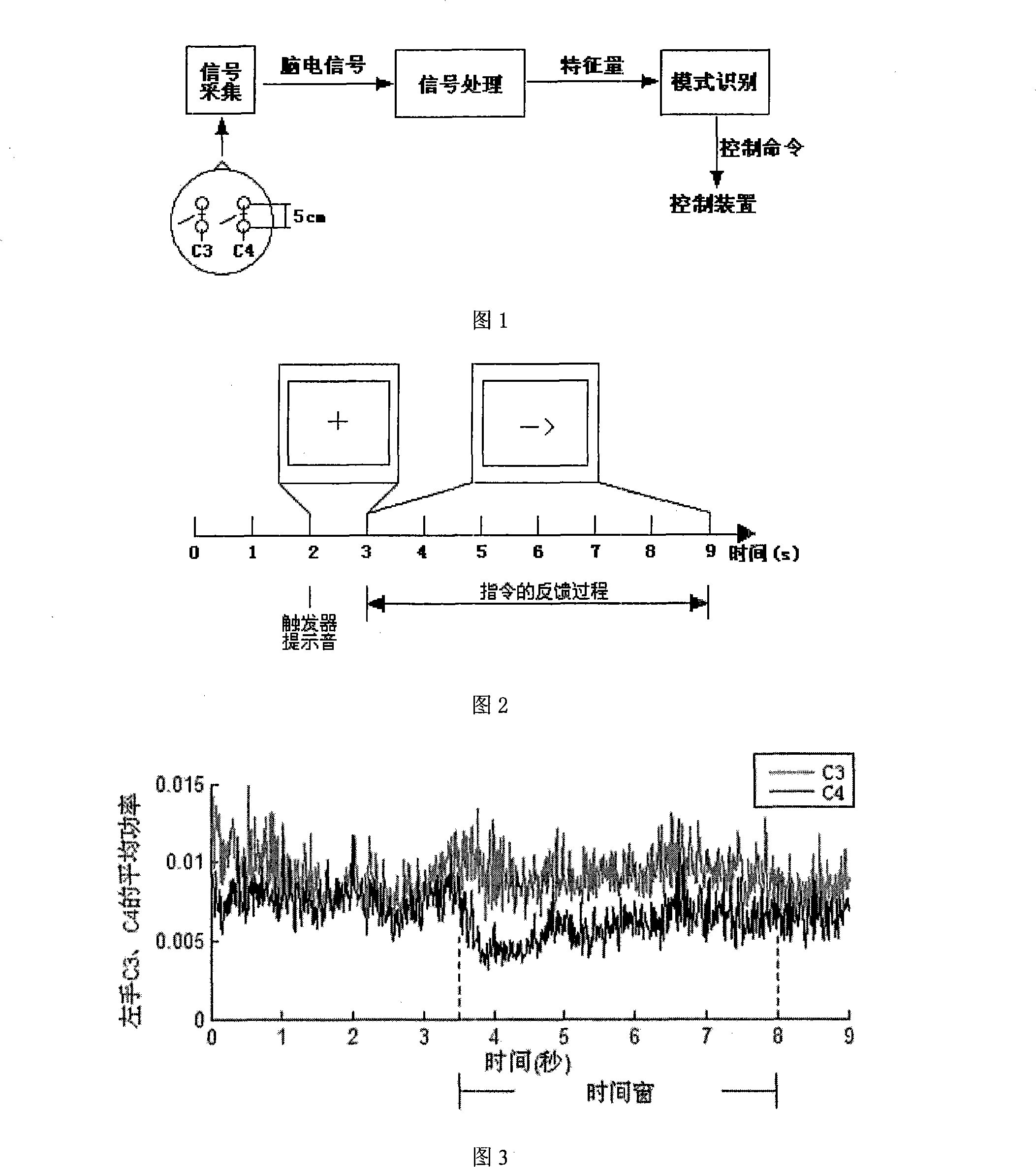
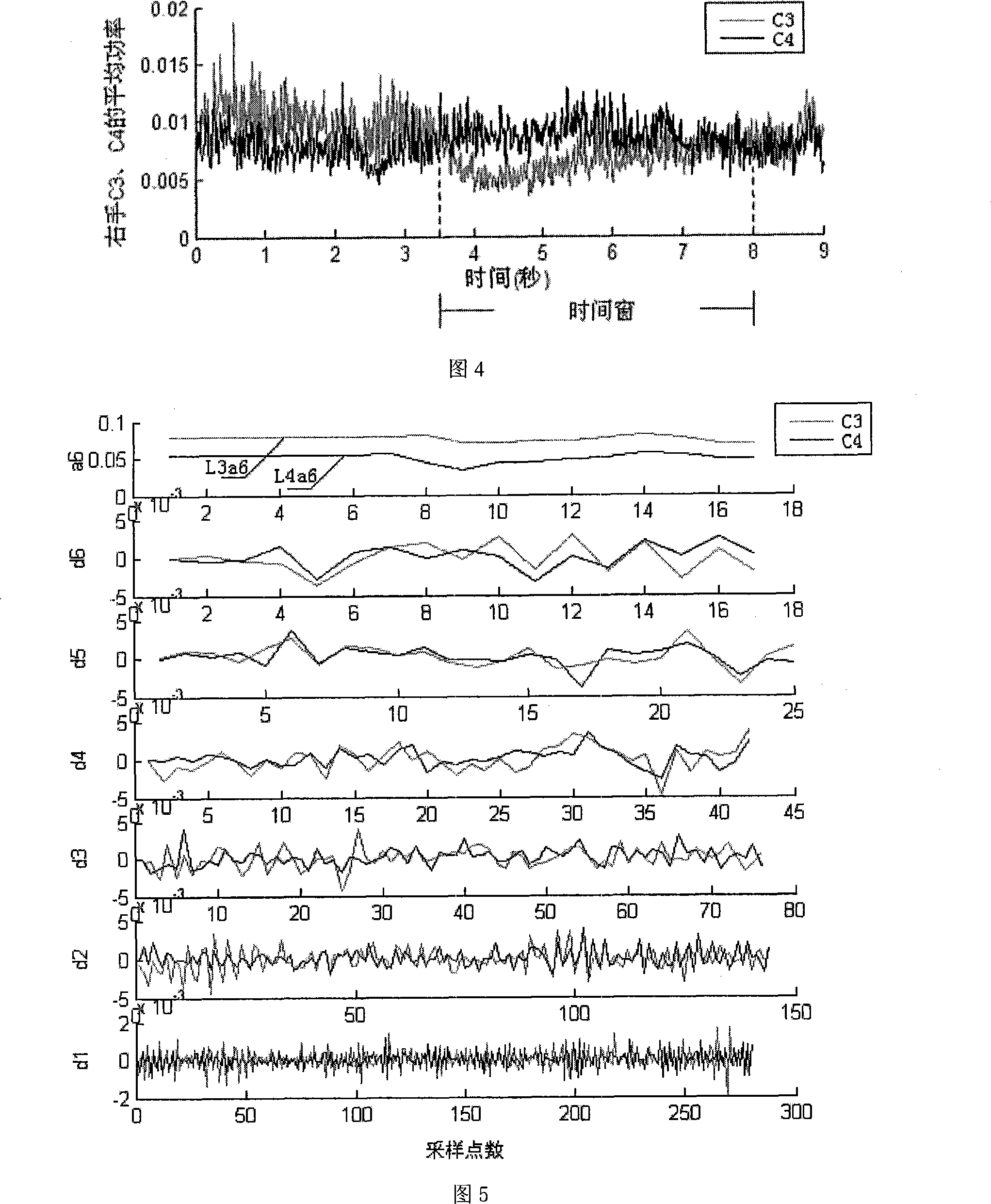
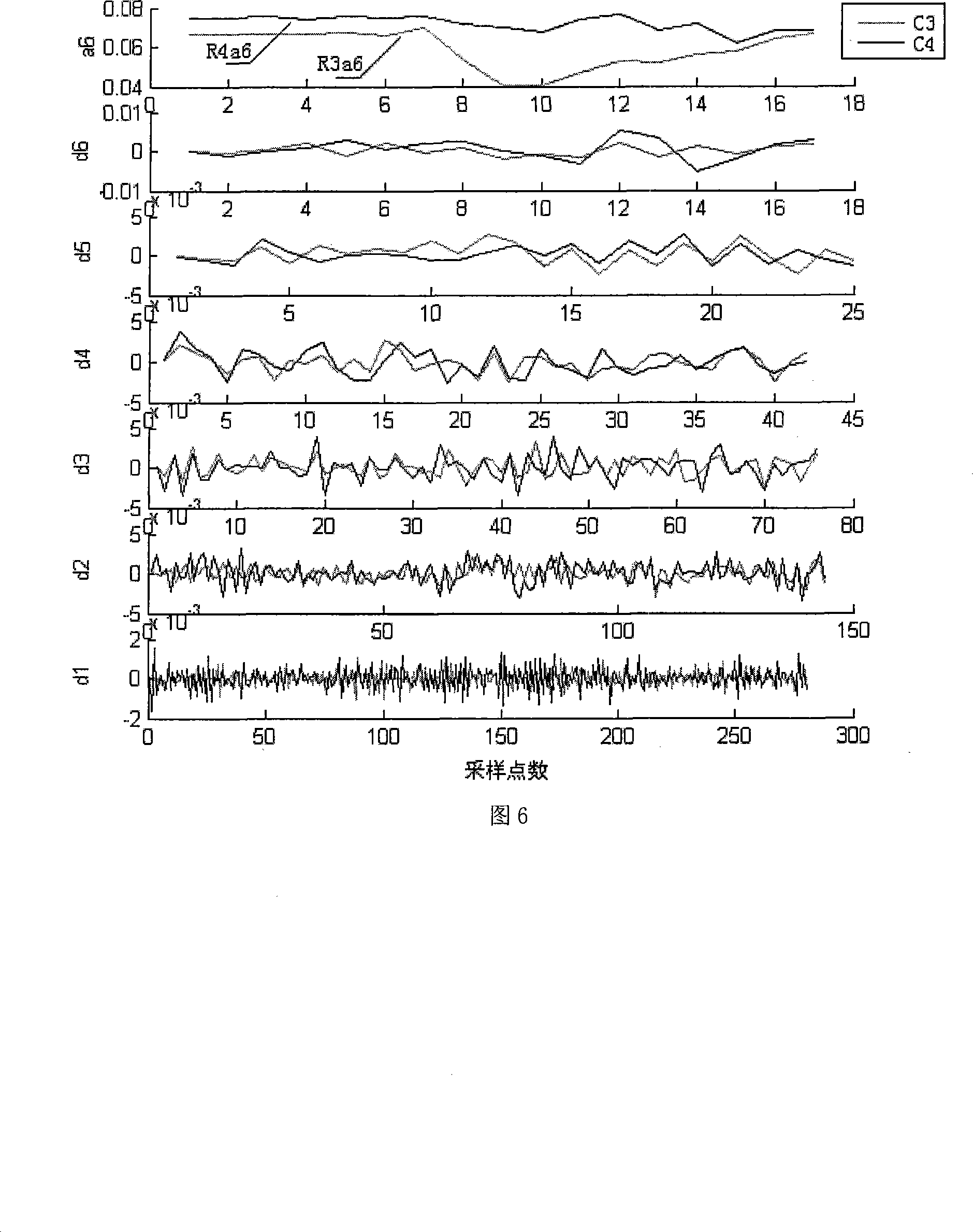
Brain wave characteristic extraction method based on wavelet translation and BP neural network
InactiveCN101221554AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEasy to identifyInput/output for user-computer interactionBiological neural network modelsEnergy variationBrain computer interfacing
The invention discloses an extraction method for brain-computer interface system imagination action EEG signal features, in particular to an EEG feature extraction method based on a wavelet transform and a BP neural network. The invention takes the energy change caused by imagination action thinking to be a feature distinguishing the imagination movements of a left hand and a right hand, respectively calculates the point-to-point average power of the entire samplings of the EEG signal obtained from C3 and C4 channels by the left hand and the right hand through the imagination (thereinafter called as C3 and C4 of the left hand and the right hand) within 0 to 9s according to the average power formula. A time window is arranged, a discrete dyadic wavelet transform is made to the data of a section provided with the window, an approximation signal a6 on a sixth size is selected to be taken as a signal feature; a BP neural network is used as a classifier to classify. The method of the invention adopting the wavelet transform and the BP neural network to extract the potential of the imagination movement helps to improve the signal / noise ratio and the identification correction rate of the potential of the imagination action; in addition, the wavelet transform is a linear transform, has a quick calculation speed, and is suitable for on-line analysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
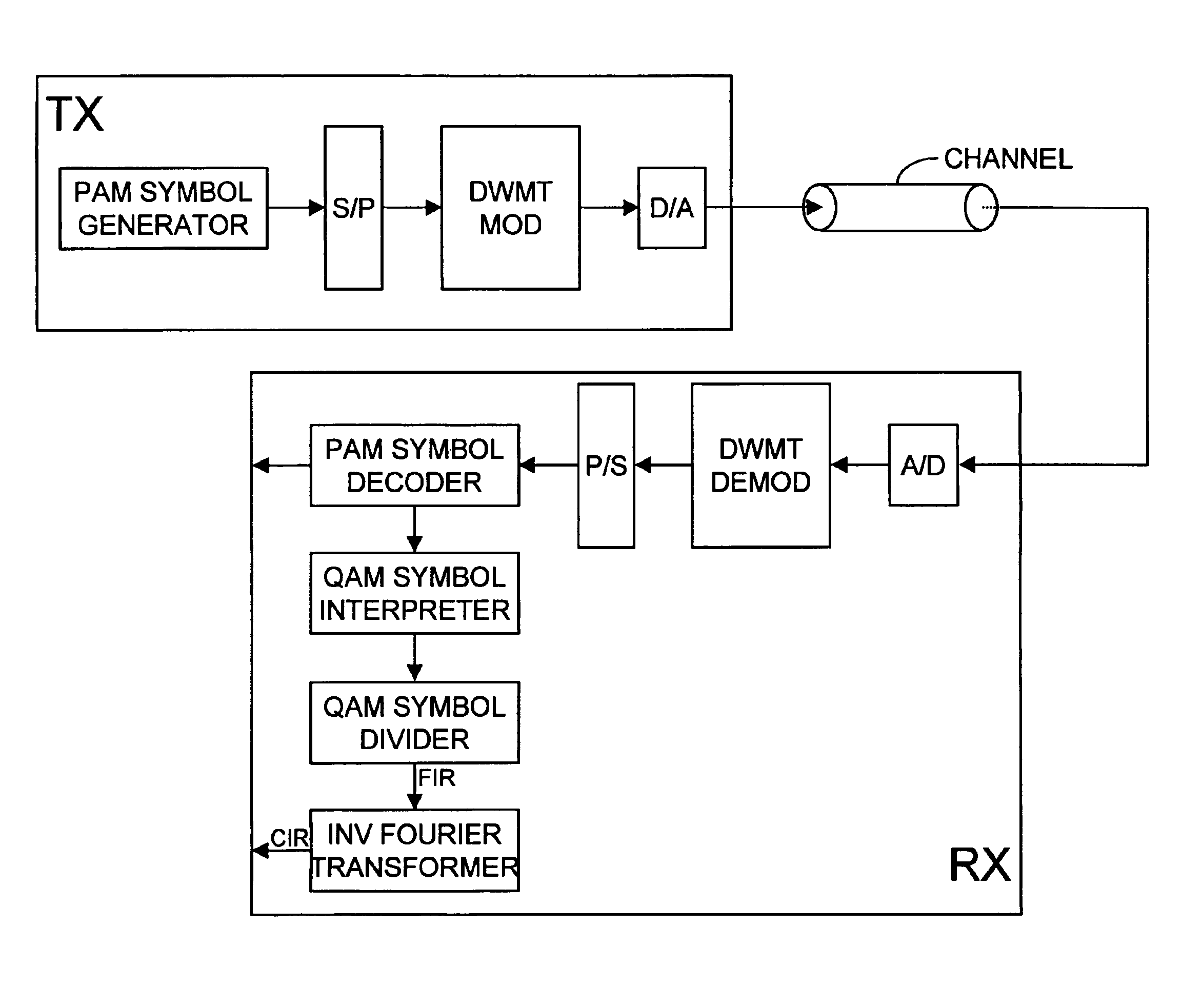
Method to determine a channel characteristic, and discrete wavelet transmitter and receiver to perform the method
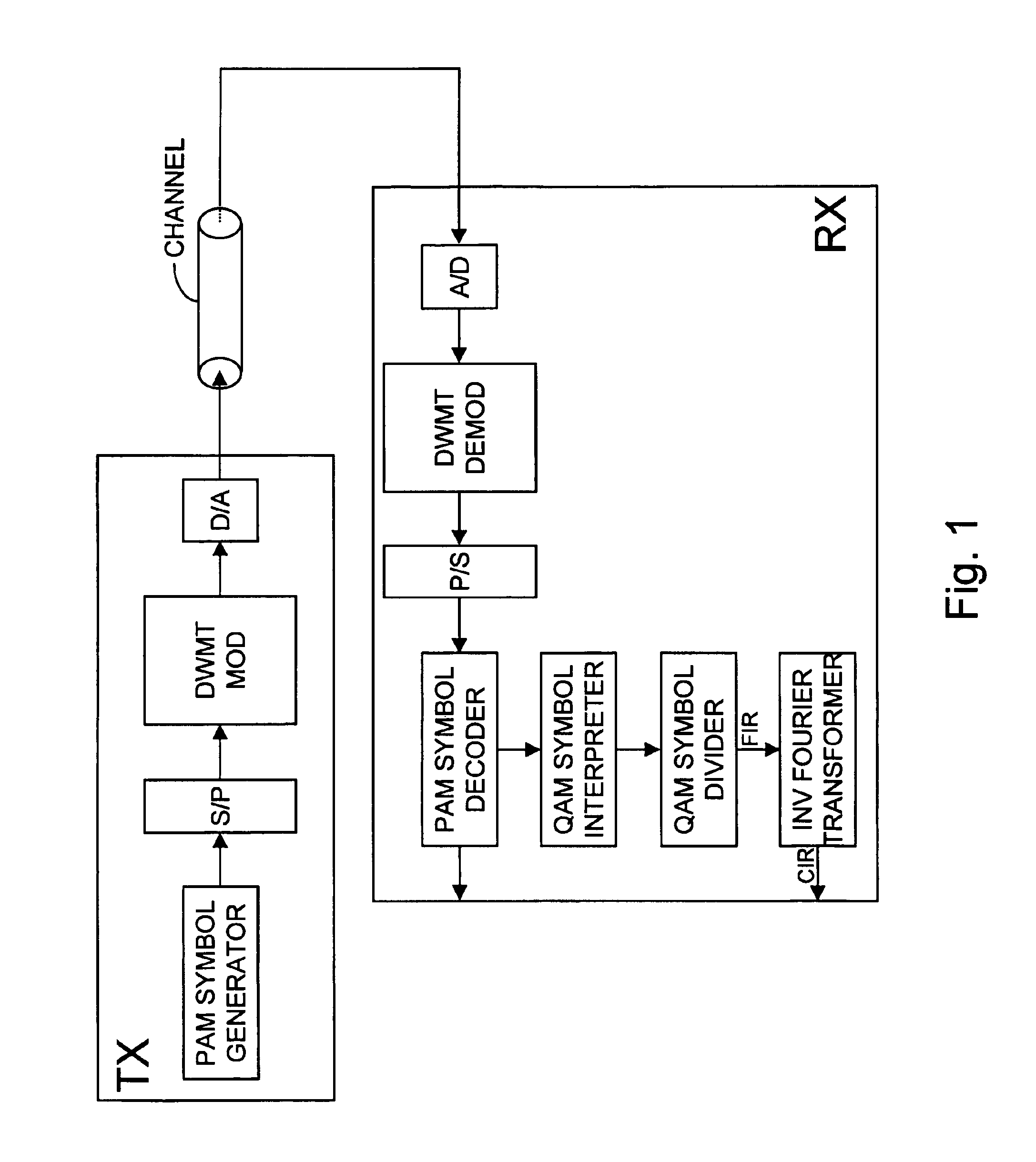
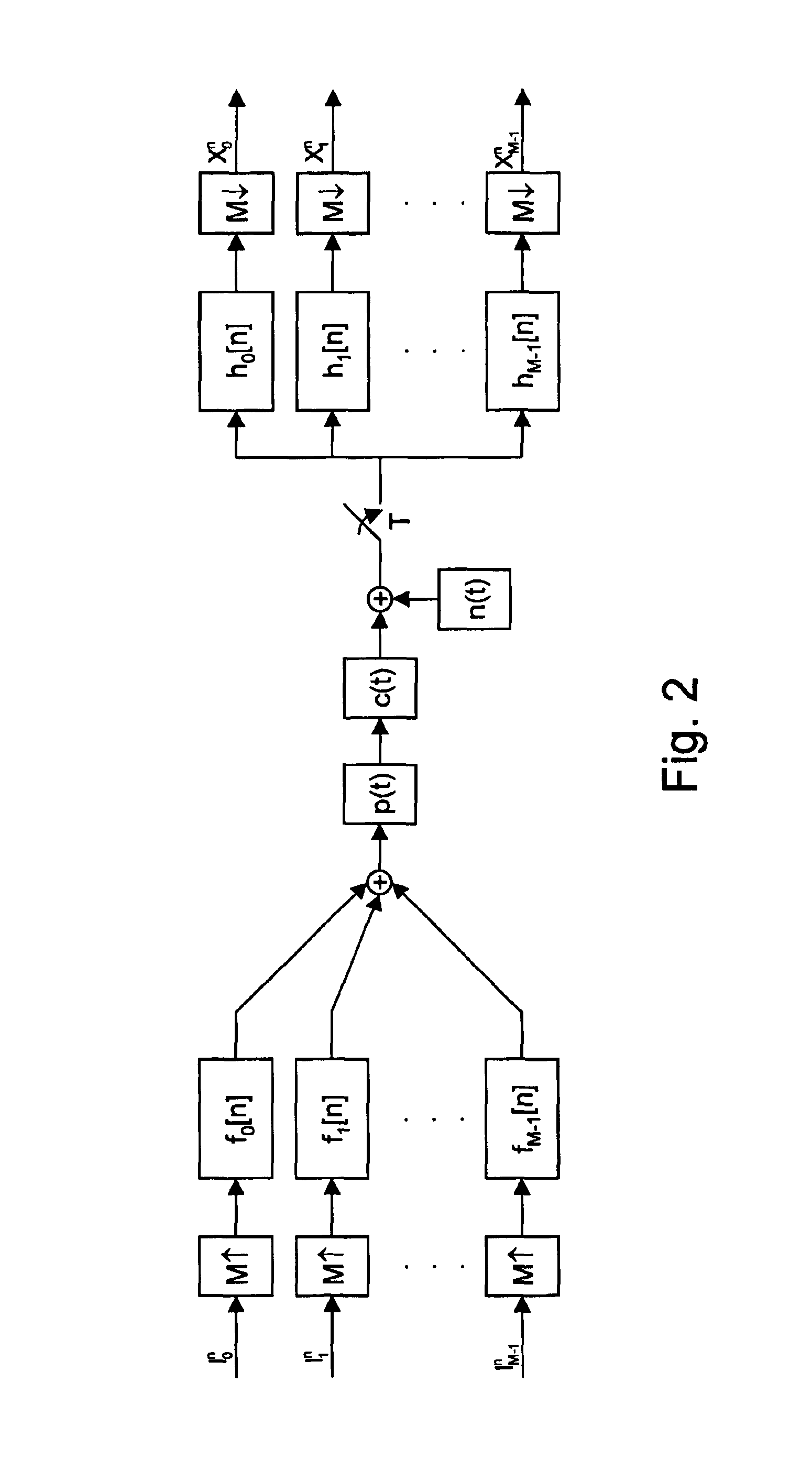
InactiveUS6952441B2Modulated carrier system with waveletsBaseband system detailsEngineeringFilter bank
To determine the channel characteristic of a channel (CHANNEL) between a transmitter (TX) and a receiver (RX), a predetermined periodic signal of pulse amplitude modulated symbols is modulated on waveforms by a cosine modulated filter bank (DWMT MOD) in the transmitter (TX), and the waveforms are transmitted over the channel (CHANNEL). In the receiver (RX), the received pulse amplitude modulated symbols are demodulated from the waveforms by a cosine modulated filter bank (DWMT DEMOD), pairs of the received pulse amplitude modulated symbols are combined to form received quadrature amplitude modulated symbols, and the received quadrature amplitude modulated symbols are divided by the transmitted predetermined pulse amplitude modulated symbols considered pairwise as transmit quadrature amplitude modulated symbols. So, samples of the channel characteristic are generated.
Owner:RPX CORP
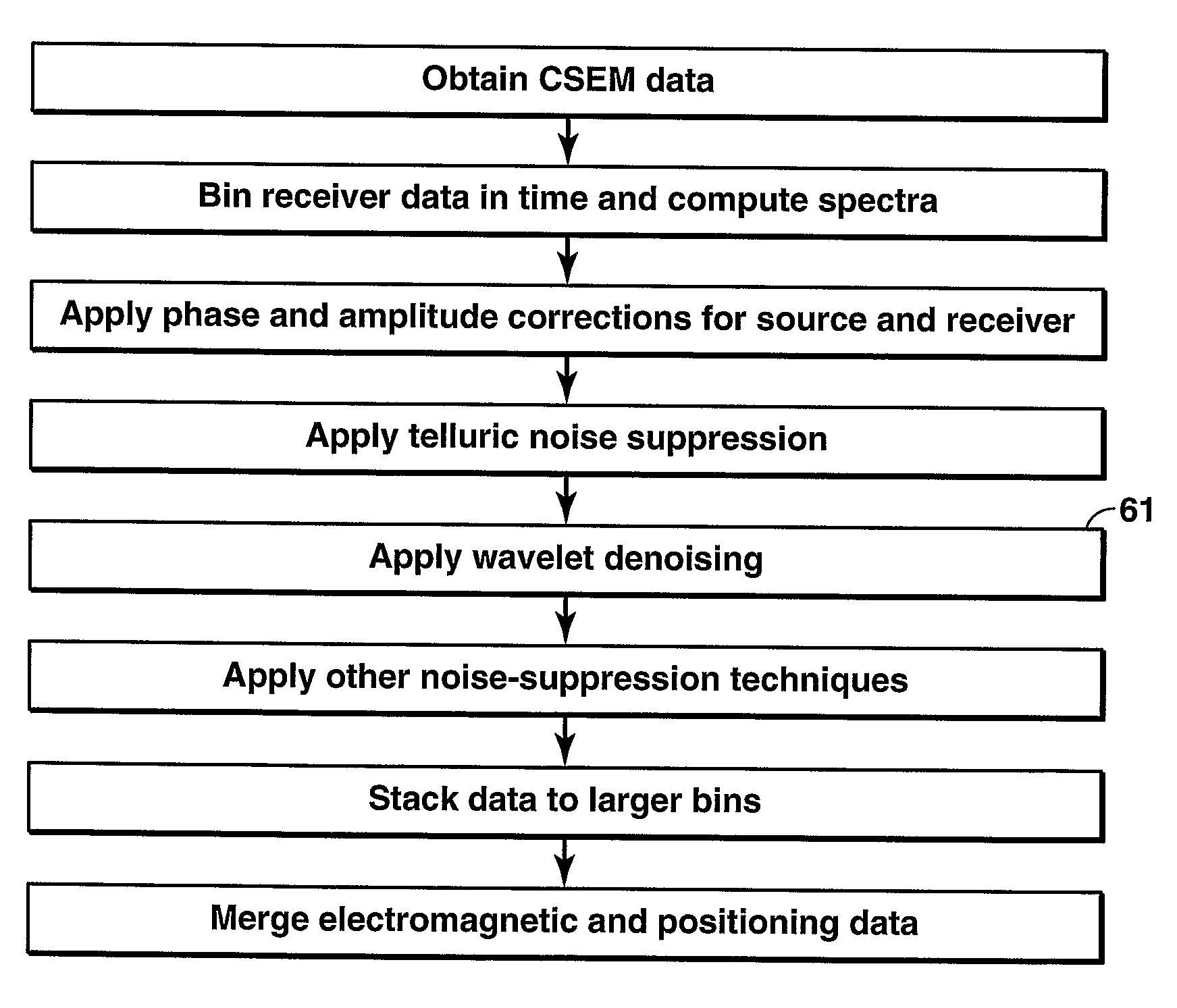
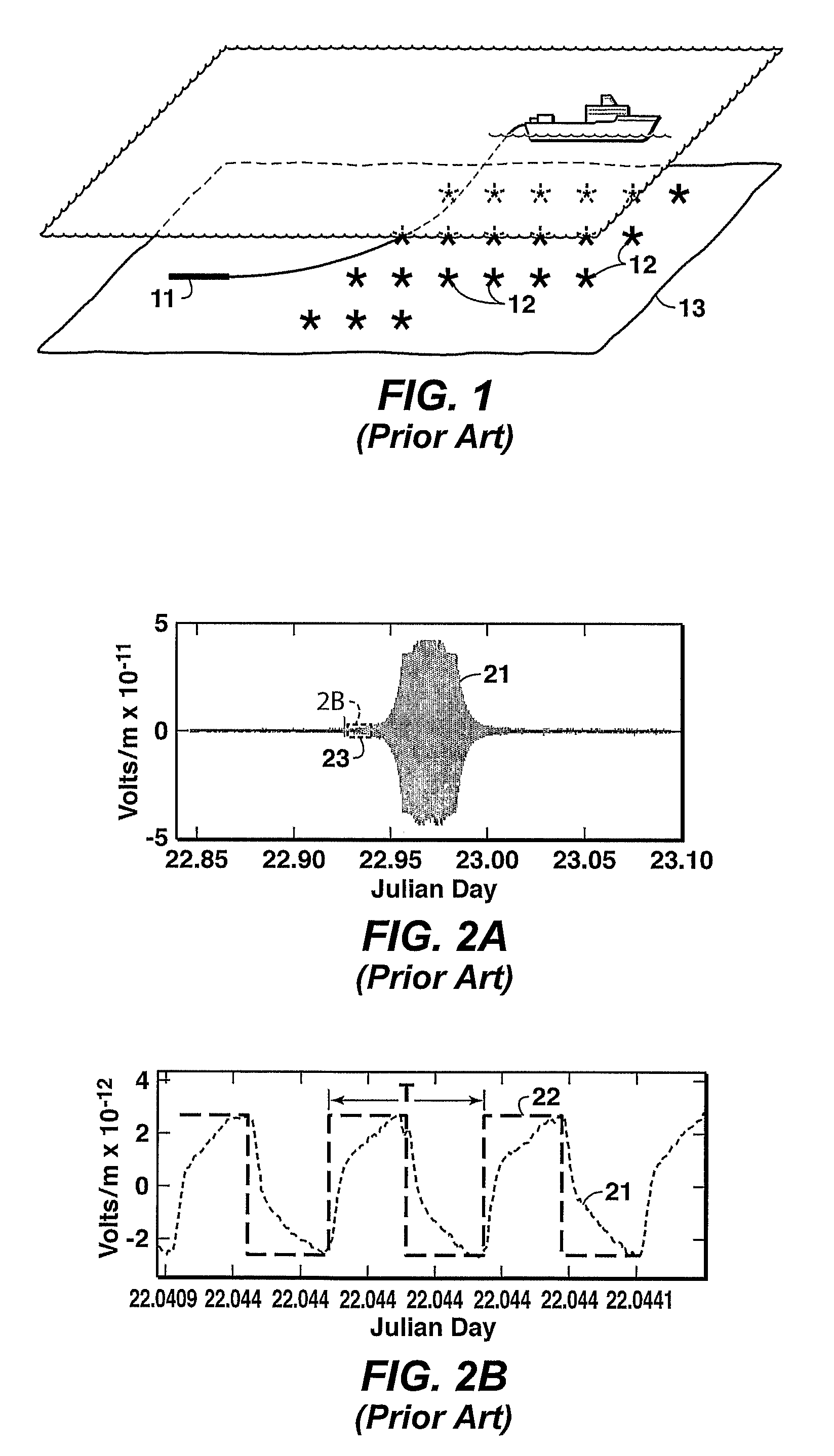
Method for Wavelet Denoising of Controlled Source Electromagnetic Survey Data
InactiveUS20090103395A1Weakening rangeSeismology for water-covered areasDetection using electromagnetic wavesWavelet denoisingControlled source electro-magnetic
Method for denoising a receiver signal from a controlled source electromagnetic survey. A discrete wavelet transform is performed on the signal, and the resulting detail coefficients are truncated using a selected threshold value, which may be zero. Further levels of decomposition may be performed on the approximation coefficients from the preceding level. After the final level of decomposition, a denoised signal is restructured by performing the inverse wavelet transformation on the last set of approximation coefficients combined with the thresholded detail coefficients accumulated from all levels of decomposition.
Owner:WILLEN DENNIS W
Apparatus and method for inserting/extracting capturing resistant audio watermark based on discrete wavelet transform, audio rights protection system using the same
InactiveUS20090125310A1Easy to detectVarious distortionTelevision system detailsBroadcast systems characterised by watermarksAudio watermarkProtection system
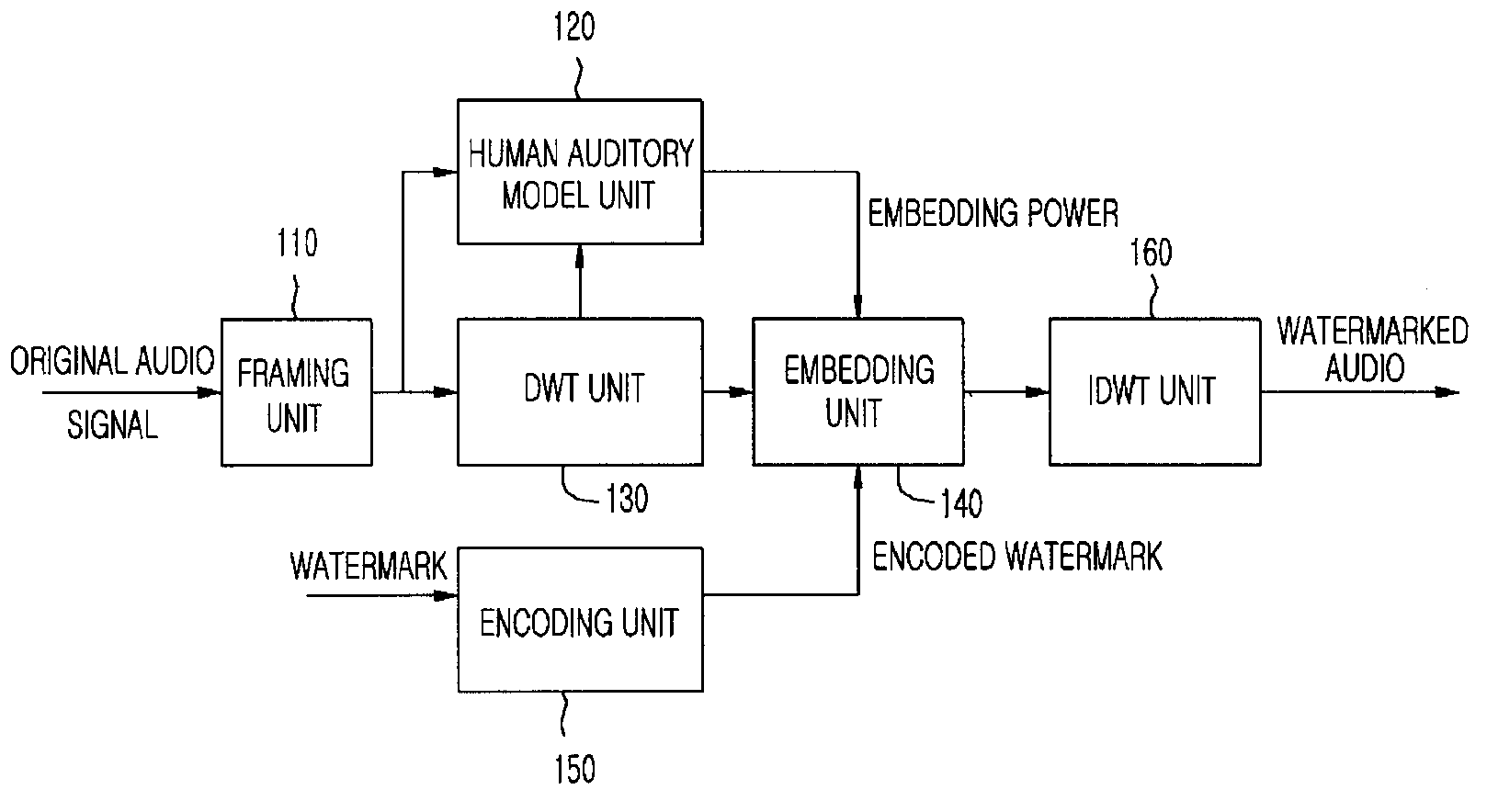
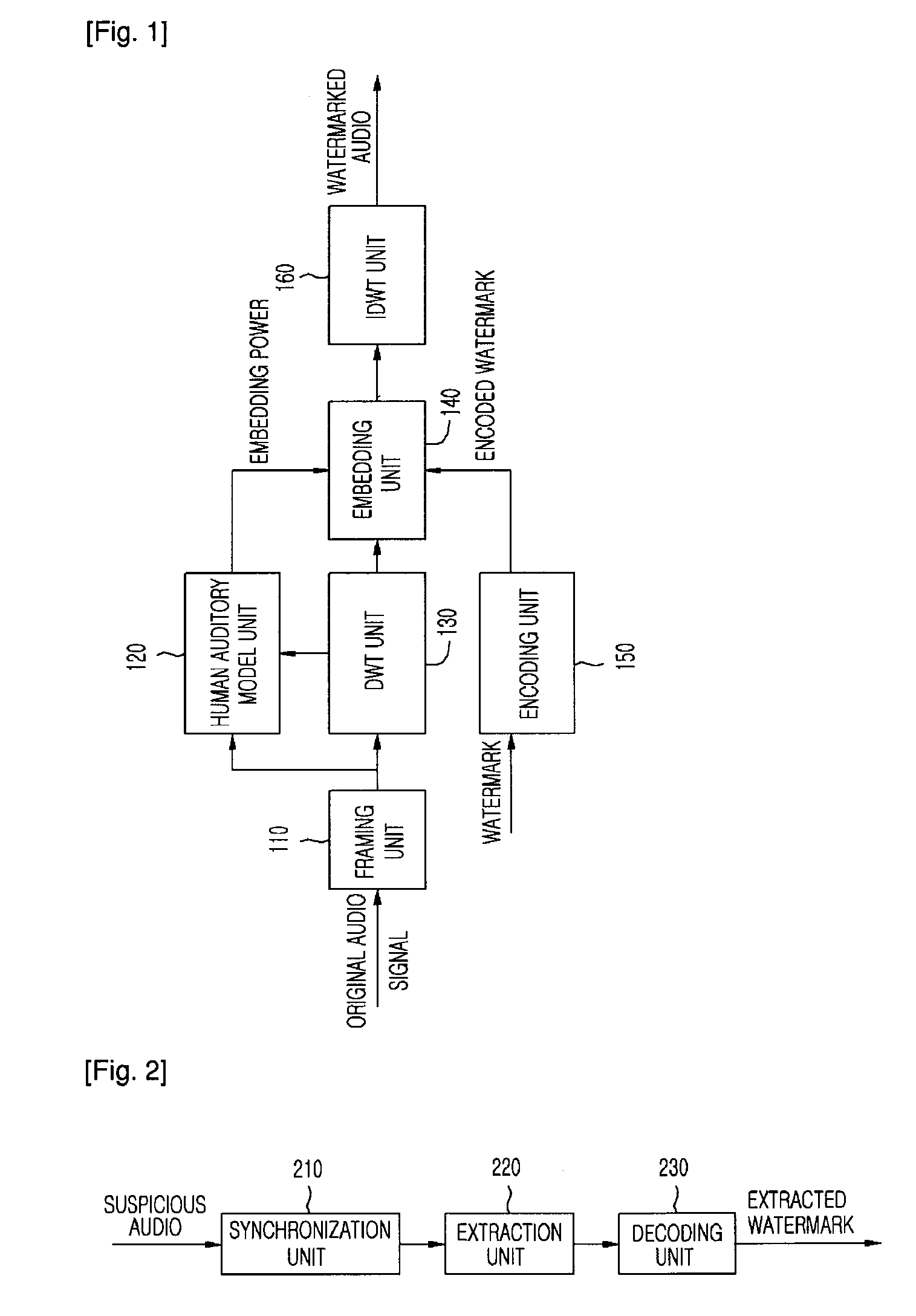
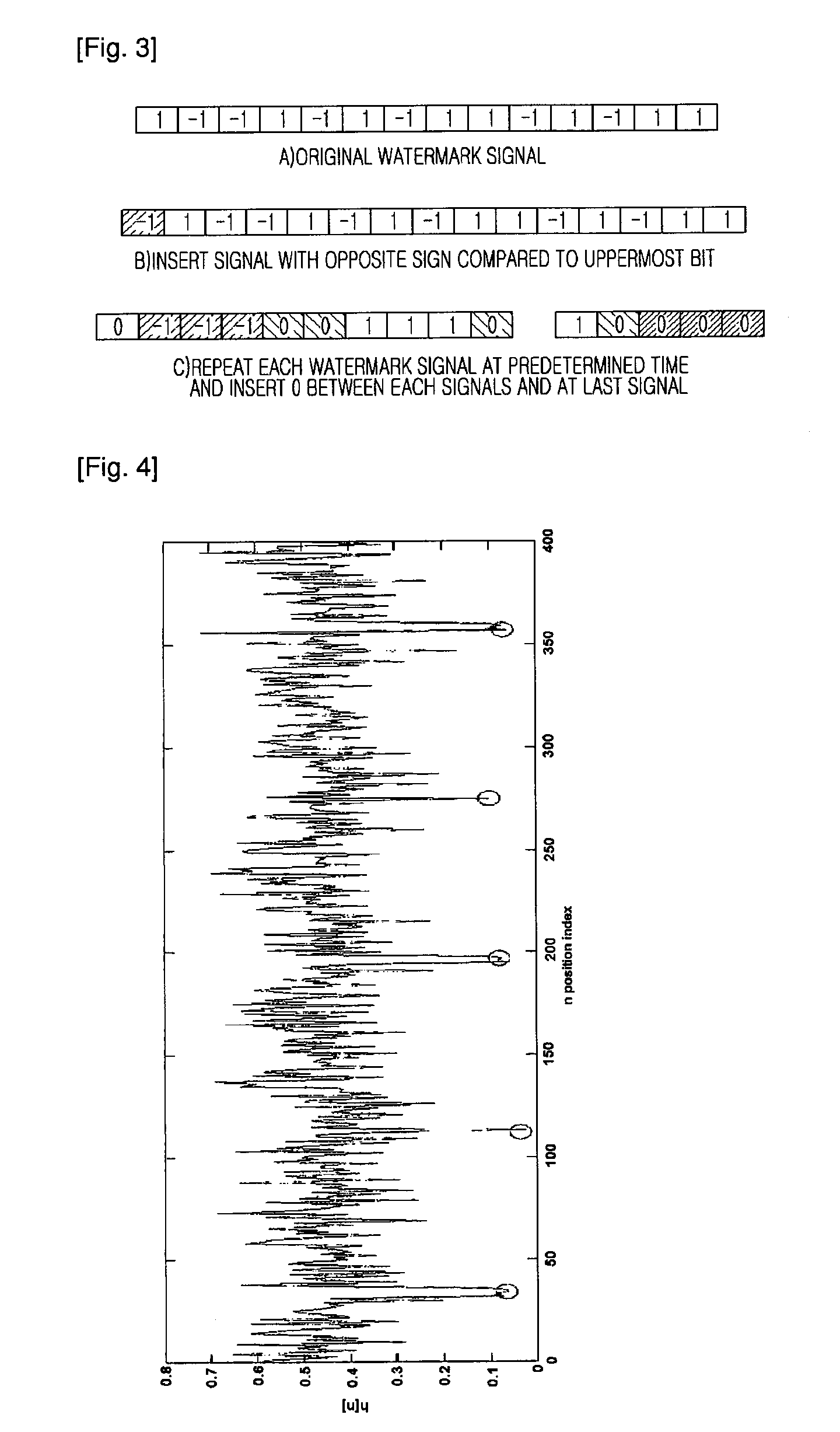
An apparatus and method for embedding and extracting a capturing-resistant audio watermark based on discrete wavelet transform, and a copyright management system using the same are provided. The apparatus for embedding a wavelet based audio watermark includes: a framing unit for dividing an input audio signal into small signals with a regular length; a discrete wavelet transform unit for calculating an mean value of wavelet coefficients by transforming the small signals based on a discrete wavelet transform; and an embedding unit for changing the calculated mean value according to a watermark where a synchronization signal is inserted and inserting the watermark into the audio signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Traffic information providing system, a traffic information expressing method and device
InactiveUS20060064233A1High resolutionAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsTime functionInformation representation
The invention has as an object to provide a traffic information providing system capable of compressing traffic information represented at an arbitrary detail level to a data volume corresponding to a different communications environment. The traffic information providing system includes: traffic information providing apparatus including means for generating sampling data from traffic information represented by a function of distance from a reference position on a road or a function of time and means for performing discrete wavelet transform on the sampling data to convert the traffic information to scaling coefficients and wavelet coefficients; and traffic information utilization apparatus for performing inverse wavelet transform on the scaling coefficients and wavelet coefficients received from the traffic information providing apparatus to restore the traffic information. The receiving party can restore coarse or minute information within the range of the received information even in case the traffic information providing apparatus has provided scaling coefficients and wavelet coefficients without considering the communications environment and reception state.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
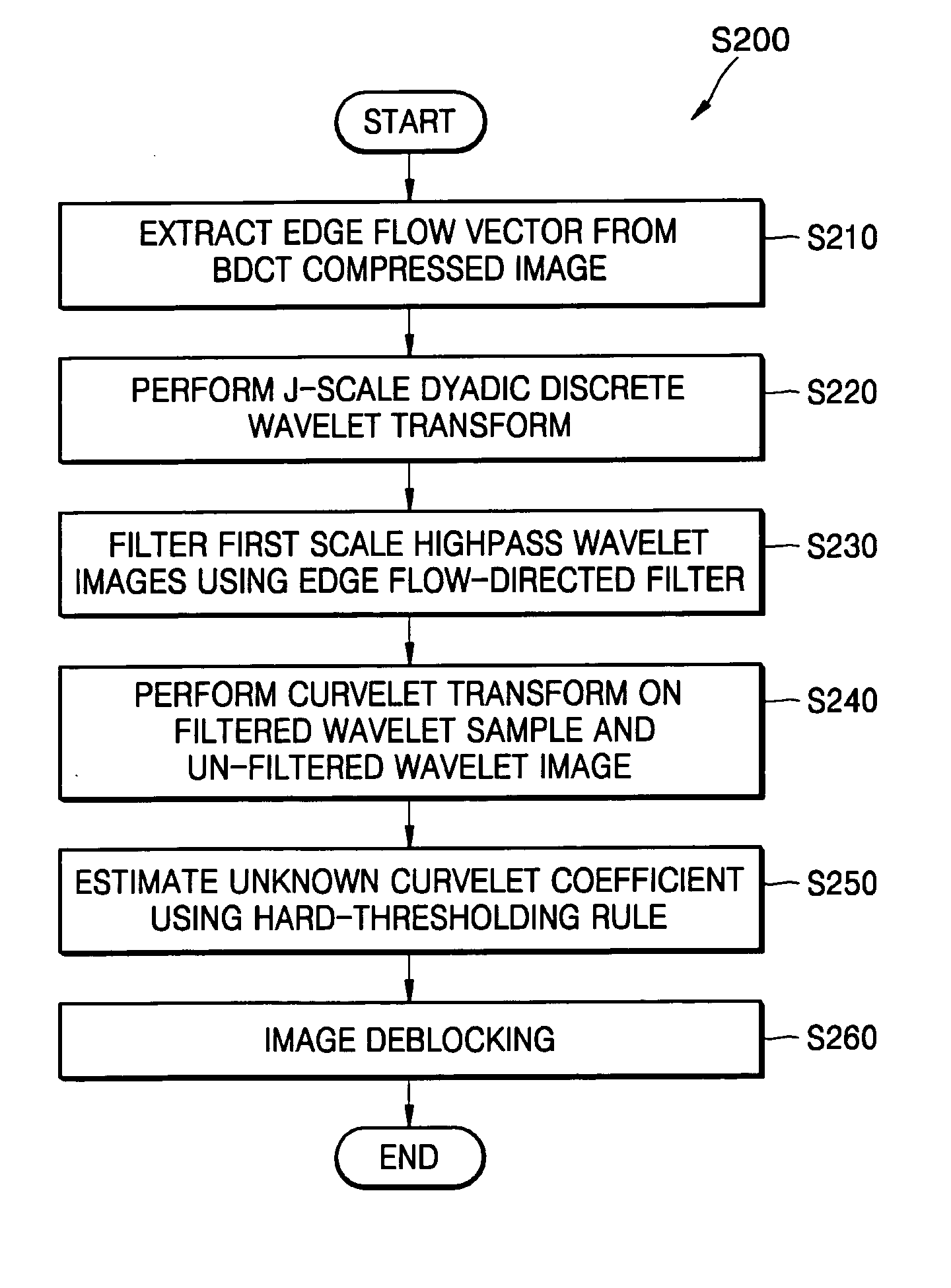
Deblocking method and apparatus using edge flow-directed filter and curvelet transform
InactiveUS20050286795A1Protect edge informationCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsDiscrete cosine transformWavelet
A deblocking method and apparatus using an edge flow-directed filter and curvelet transform for deblocking Block Discrete Cosine Transform (BDCT) compressed images. The deblocking method includes: extracting an edge flow vector from a Block Discrete Cosine Transform (BDCT) compressed image to identify a direction of changes in image attributes; performing a dyadic discrete wavelet transform on the BDCT compressed image; selectively filtering a highpass wavelet image among dyadic discrete wavelet transform compressed images according to an edge flow direction of an edge pixel; performing a curvelet transform on an image including the selectively filtered highpass wavelet image and wavelet images other than the highpass wavelet image; and estimating an original image before being BDCT compressed using the curvelet transform.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
System and method for audio data compression and decompression using discrete wavelet transform (DWT)
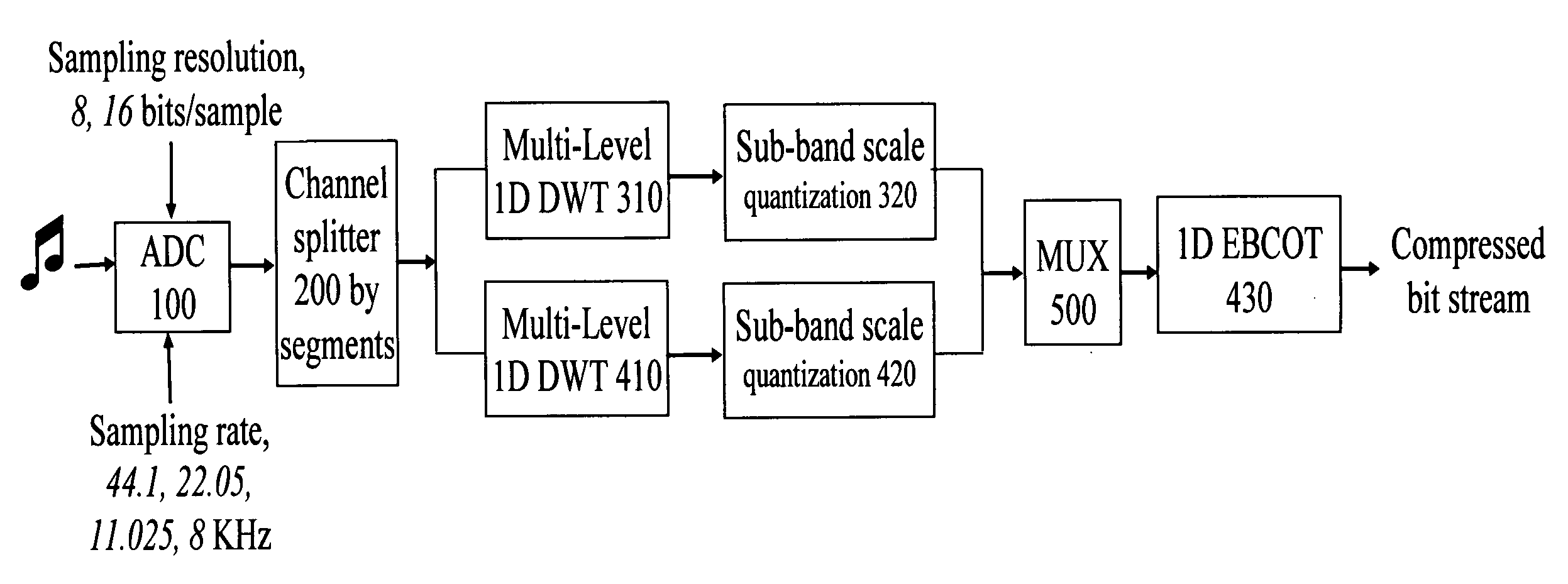
InactiveUS20060238386A1Less or no latency)Simple methodSpeech analysisCode conversionData compressionMultiplexing
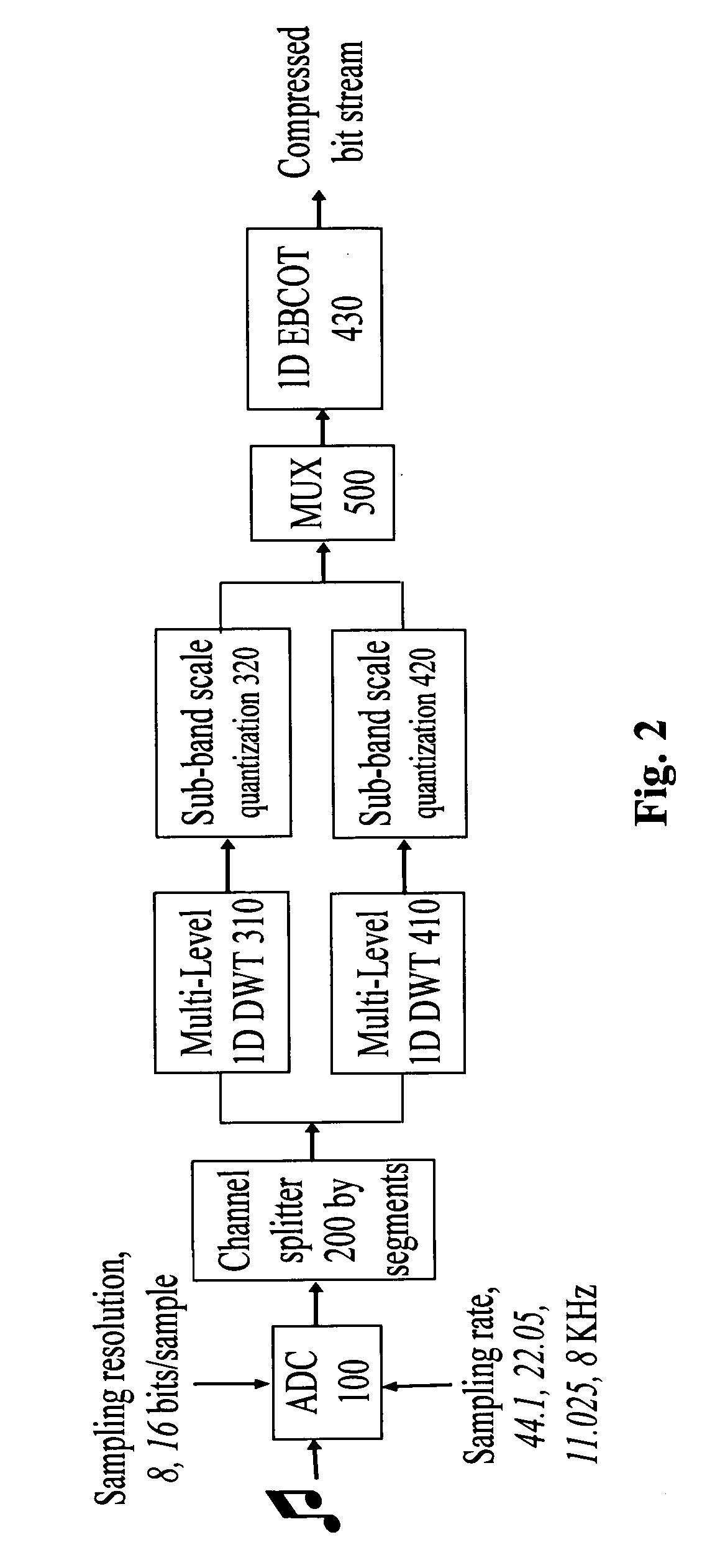
A system for audio data processing including sub-systems for compression and for de-compression. The compression sub-system includes an AD converter, a segment-based multi-channel splitter splitting and segmenting signals into channels each with segments, multi-level 1D discrete wavelet transformers each discrete wavelet transforming for a respective channel each segment thereof in sequence and recursively through a predetermined number of filtering levels into wavelet coefficients, quantizers, a multiplexer multiplexing quantized wavelet coefficients into 2-D arrays, and an embedded block coder coding the 2-D arrays into code blocks, discarding some of the code blocks, truncating a bit stream embedded in each remaining code block, and stringing the truncated bit stream embedded in each remaining code block into a compressed data stream. Another compression sub-system includes a non-segment-based multi-channel splitter, and a plurality groups of 1D discrete wavelet transformers.
Owner:TECHSOFT TECH
Power system electric transmission line fault diagnosis method
ActiveCN103713237AStable and economical operationImprove troubleshooting speedFault locationInformation technology support systemPhase currentsElectric power system
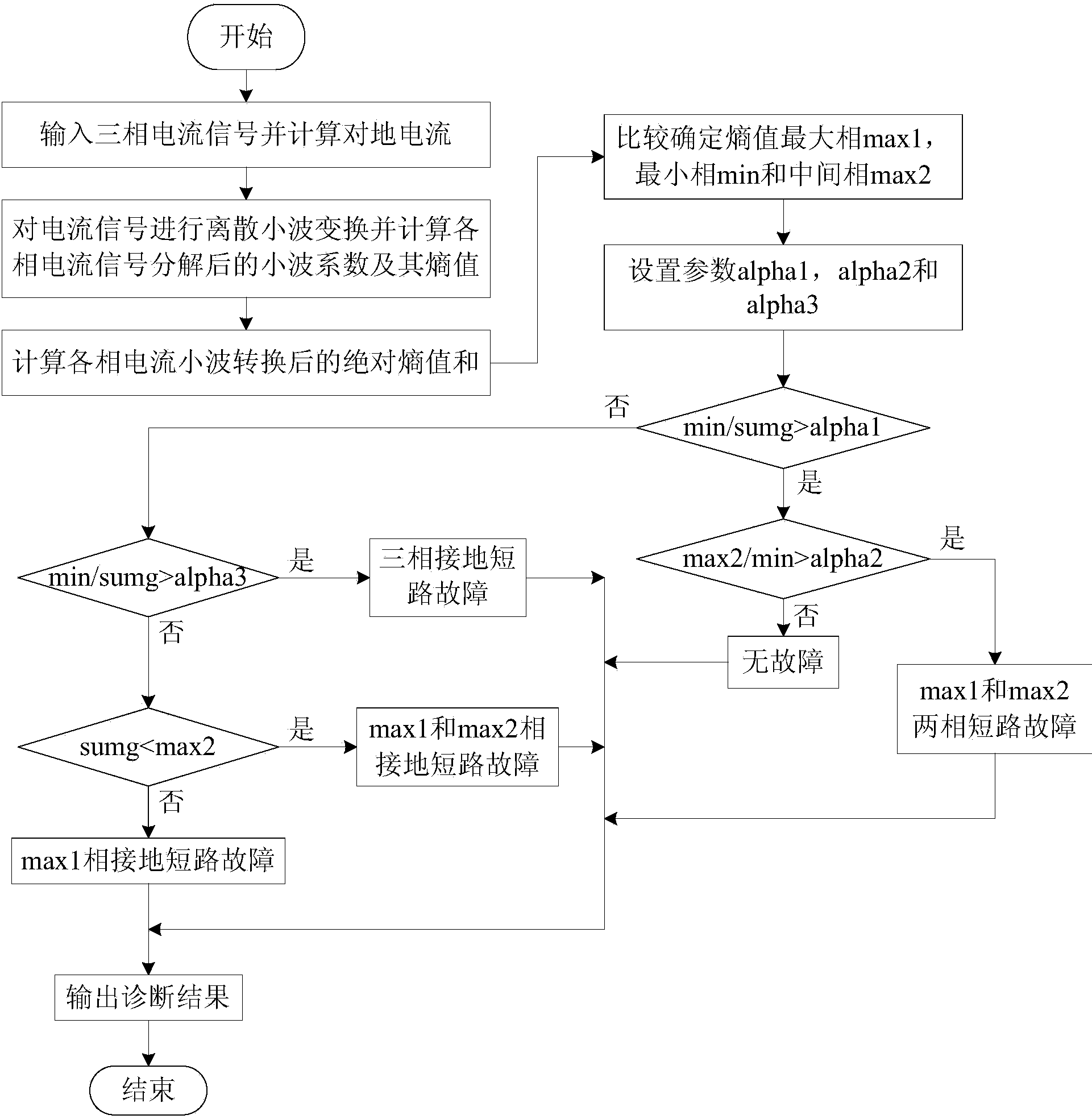
The invention discloses a novel power system electric transmission line fault diagnosis method. The method includes the steps that first, fault recording wave signals of an electric transmission line are extracted, and a three-phase current value and a discrete value of an earth current of the electric transmission line are obtained through discrete wavelet transform; then, according to a wavelet function db10, the wavelet coefficient entropy of each phase current is calculated, the sum of the wavelet coefficient absolute entropy of all the phase currents is calculated, and the largest value phase, the smallest value phase and the medium value phase of the three values are determined through comparison. According to the designed algorithm, the type and the phase of a fault which happens to a circuit where input current signals are located are judged. The algorithm relates to three parameters, and the parameters are set through a training set; model accuracy verification is performed through a test set, and meanwhile the parameters are corrected. With the method, whether a fault happens to the circuit and the type of the fault can be fast judged, and therefore good assistance effect is played for on-site dispatch personnel to fast and accurately position a fault area after the fault happens, and the security and the stability of the electric transmission line can be improved easily.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Apparatus for predicting state of health of battery pack by using discrete wavelet transform
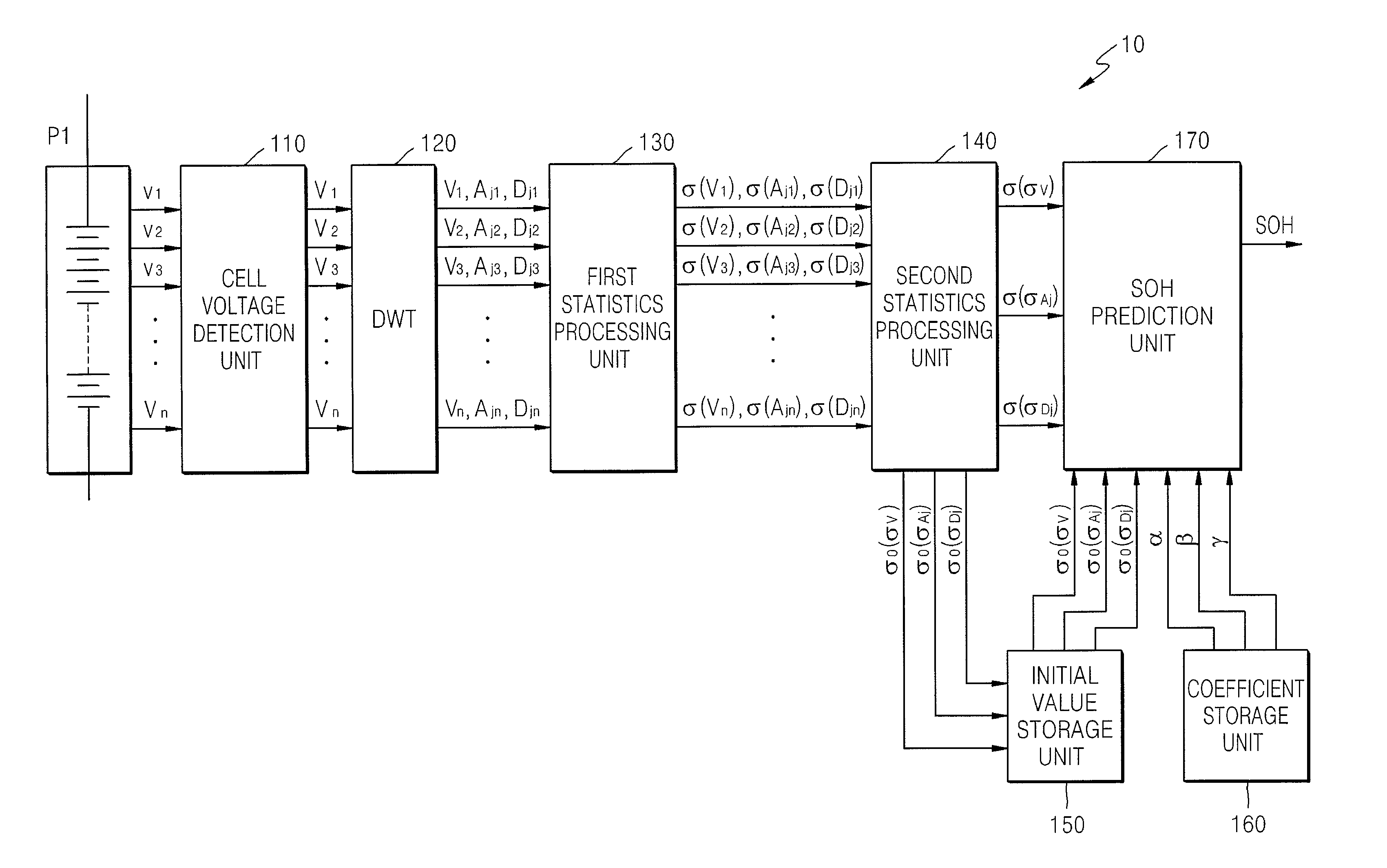
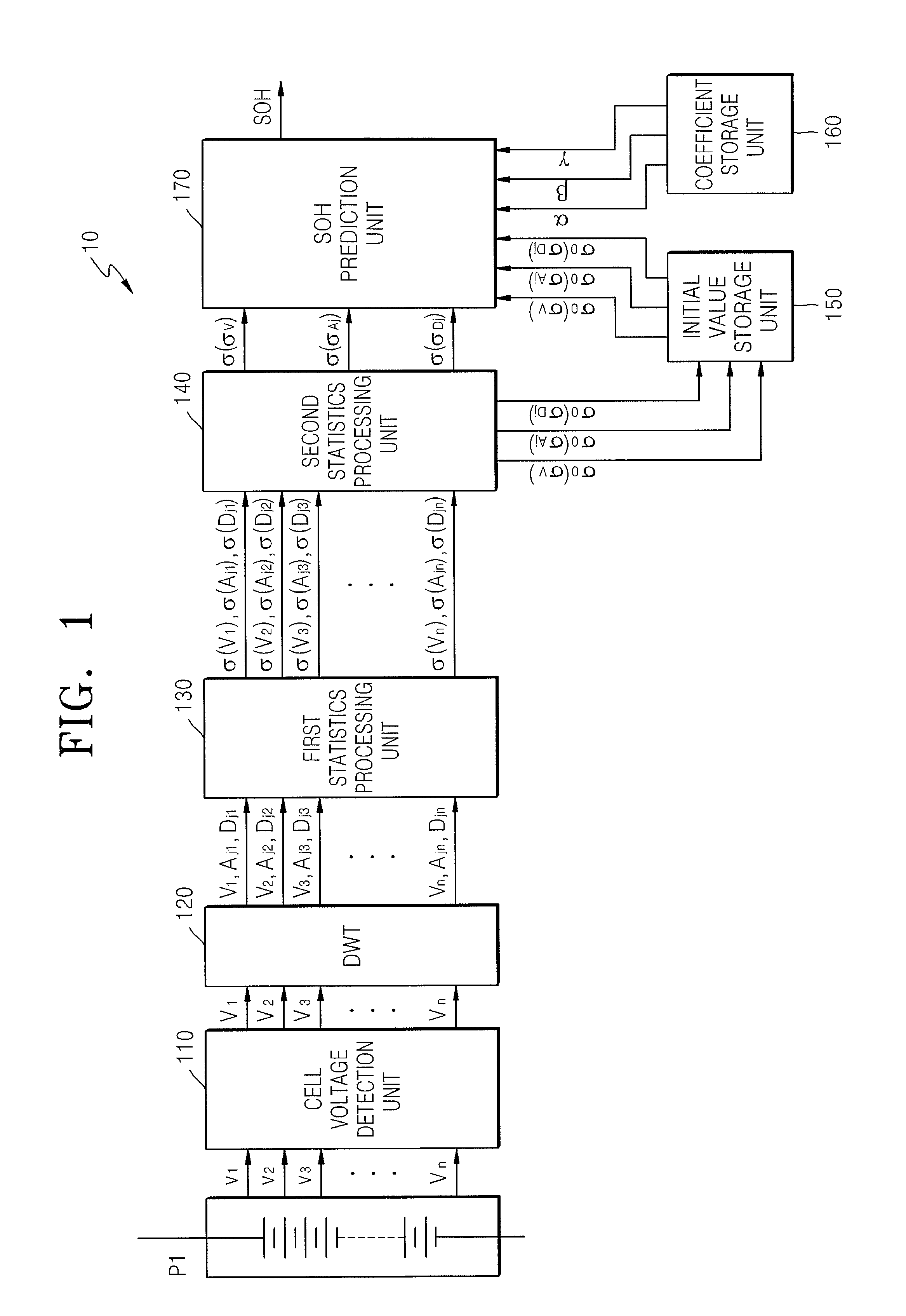
A method of predicting a state of health (SOH) of a battery pack is provided. The method includes: obtaining at least one of charging voltage data or discharging voltage data for each of a plurality of selected cells of the battery pack; wavelet transforming the at least one of charging voltage data or discharging voltage data to obtain low frequency component voltage data and high frequency component voltage data; calculating respective standard deviations of at least two from among the at least one of charging voltage data or discharging voltage data, the low frequency component voltage data, and the high frequency component voltage data; and predicting the SOH of the battery pack based on the calculated standard deviations.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com