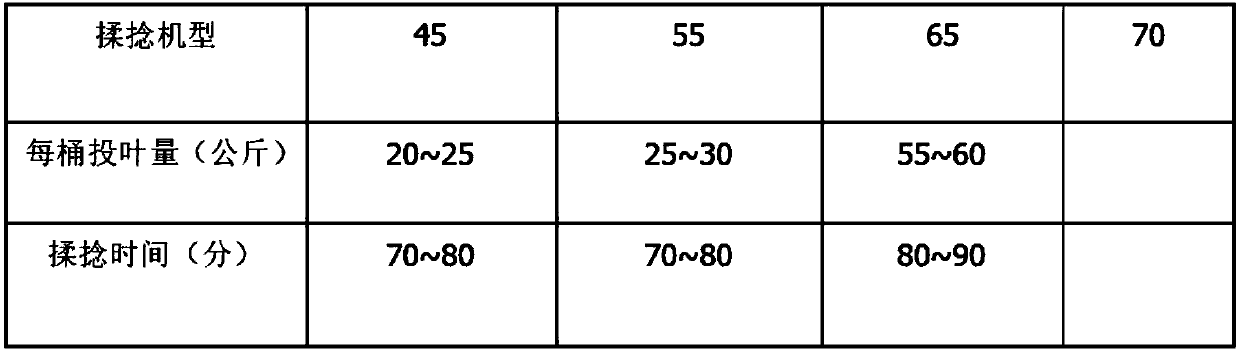
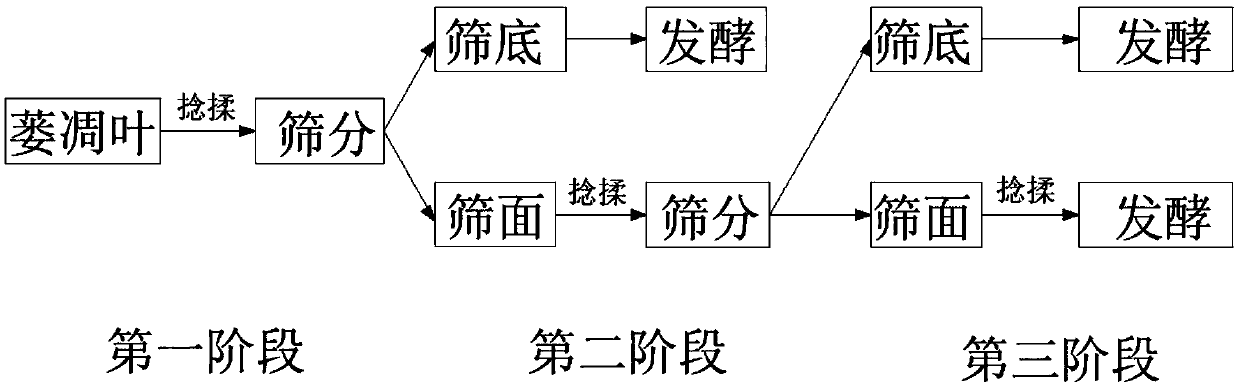
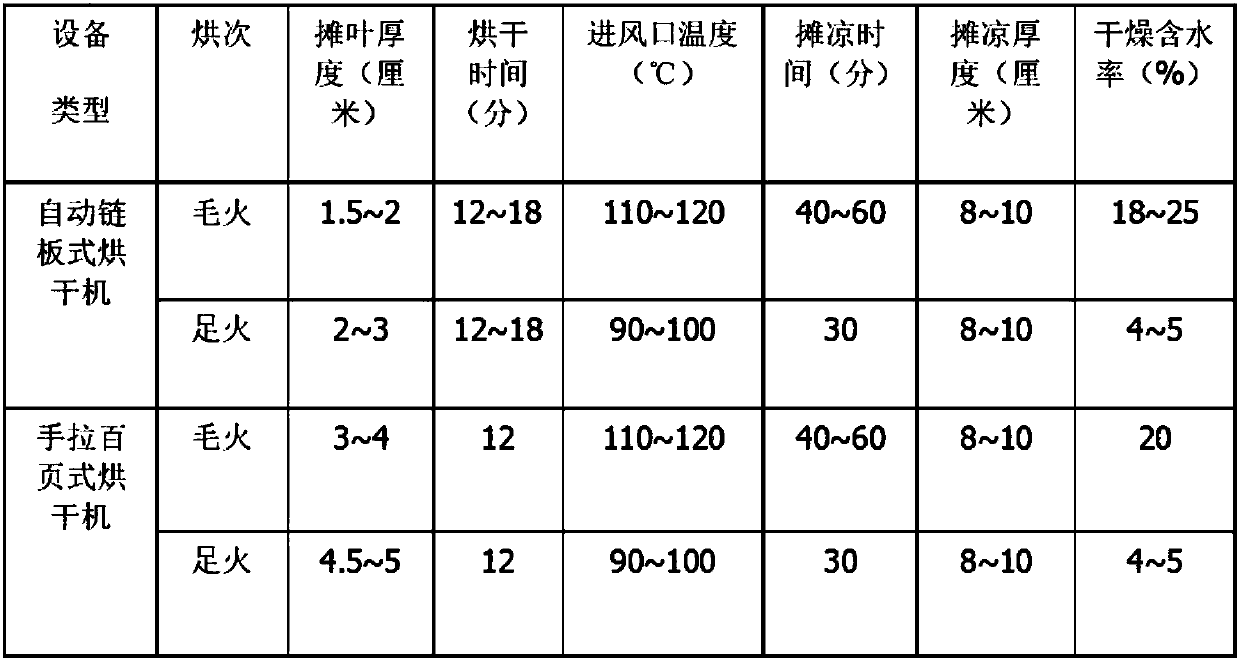
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Leaf cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
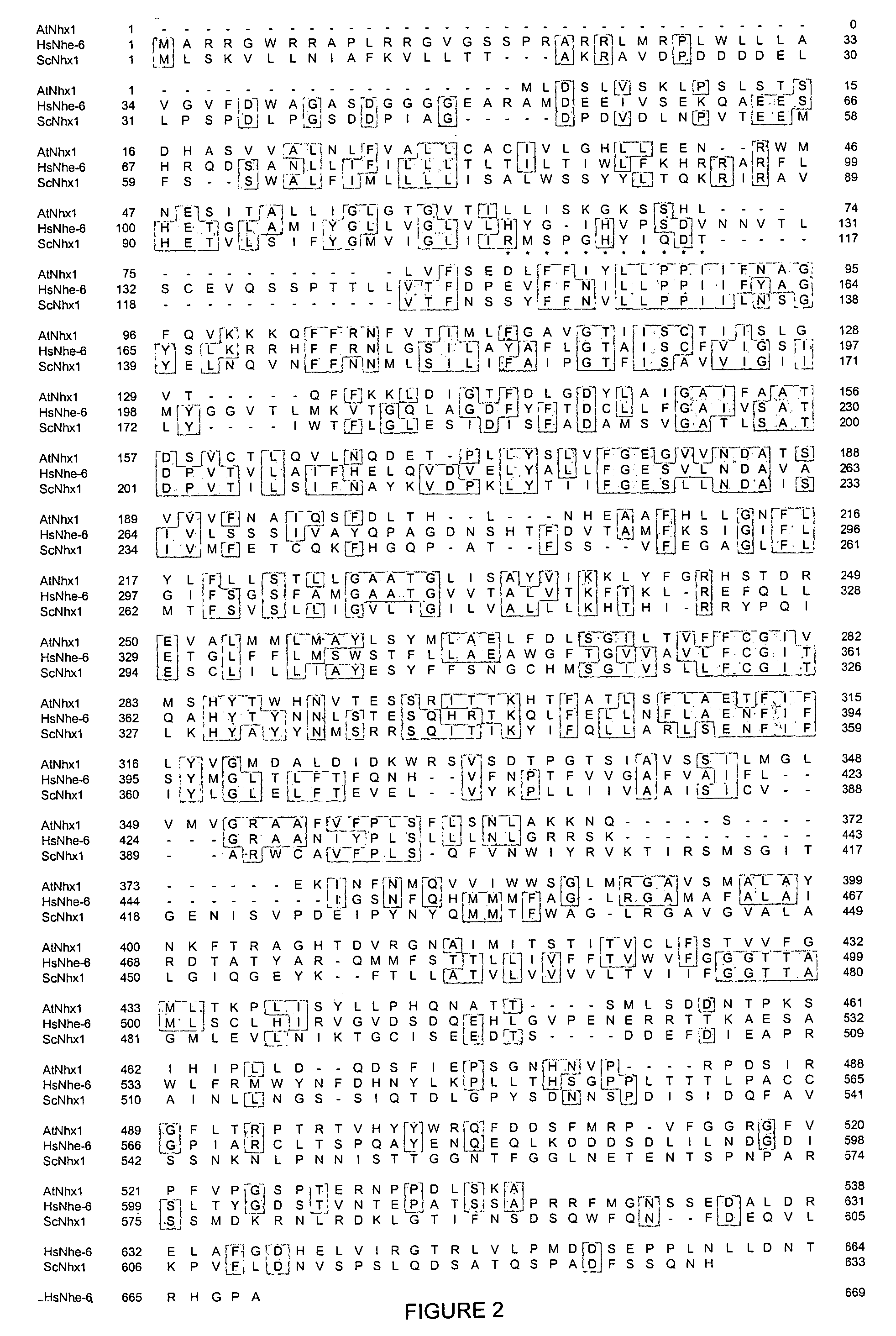
Leaf Cell Components. Like other plant cells, the leaf cell is eukaryotic. In addition to a nucleus within a membrane, a leaf cell has mitochondria, a central vacuole and sometimes chloroplasts containing cholorophyll. Cytoplasm is contained within a cell wall. Deciduous leaves are thin and flat to facilitate photosynthesis and respiration.
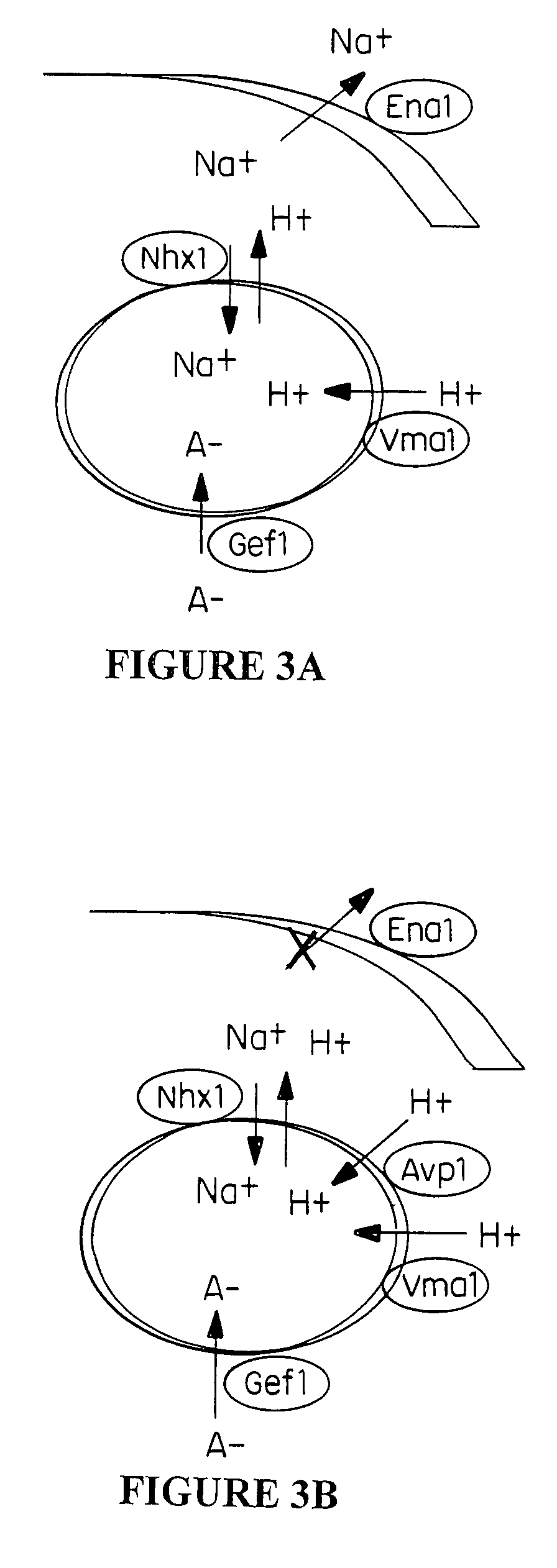
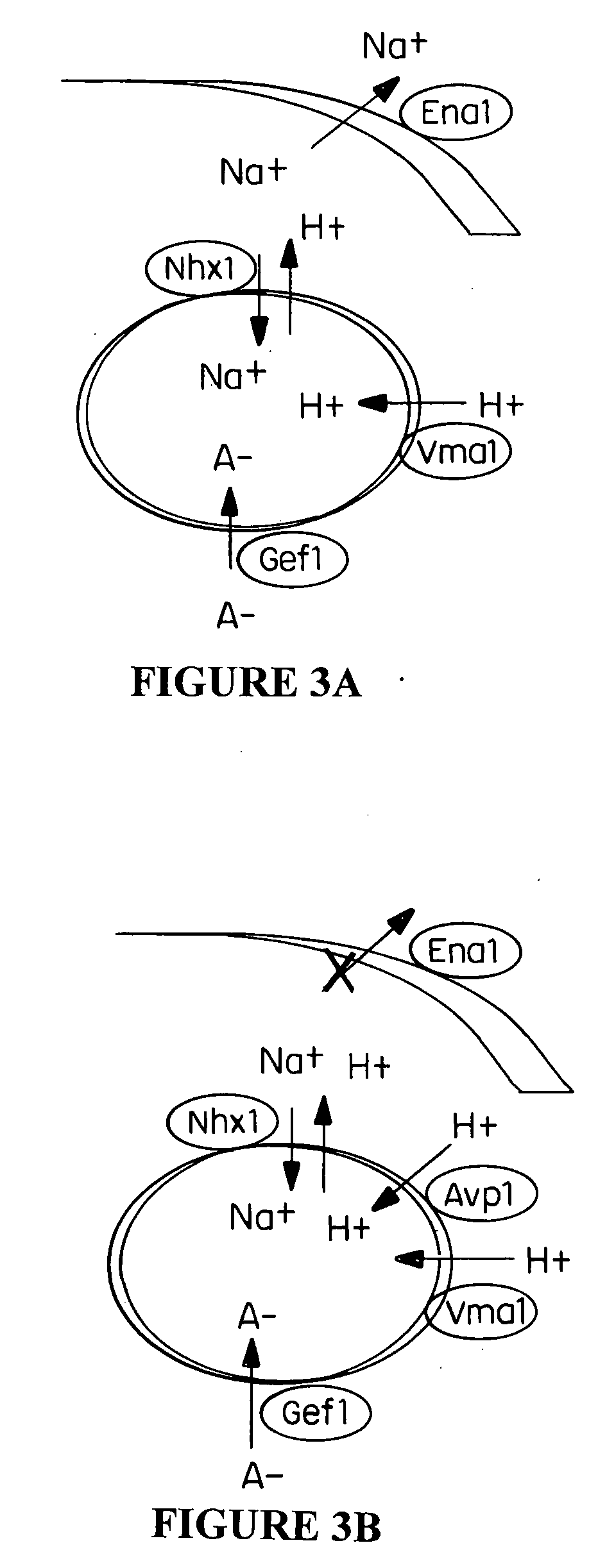
Plant cells and plants overexpressing vacuolar proton pyrophosphatases
InactiveUS8058515B2Increase planting yieldIncrease in sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationHalotoleranceLeaf cell
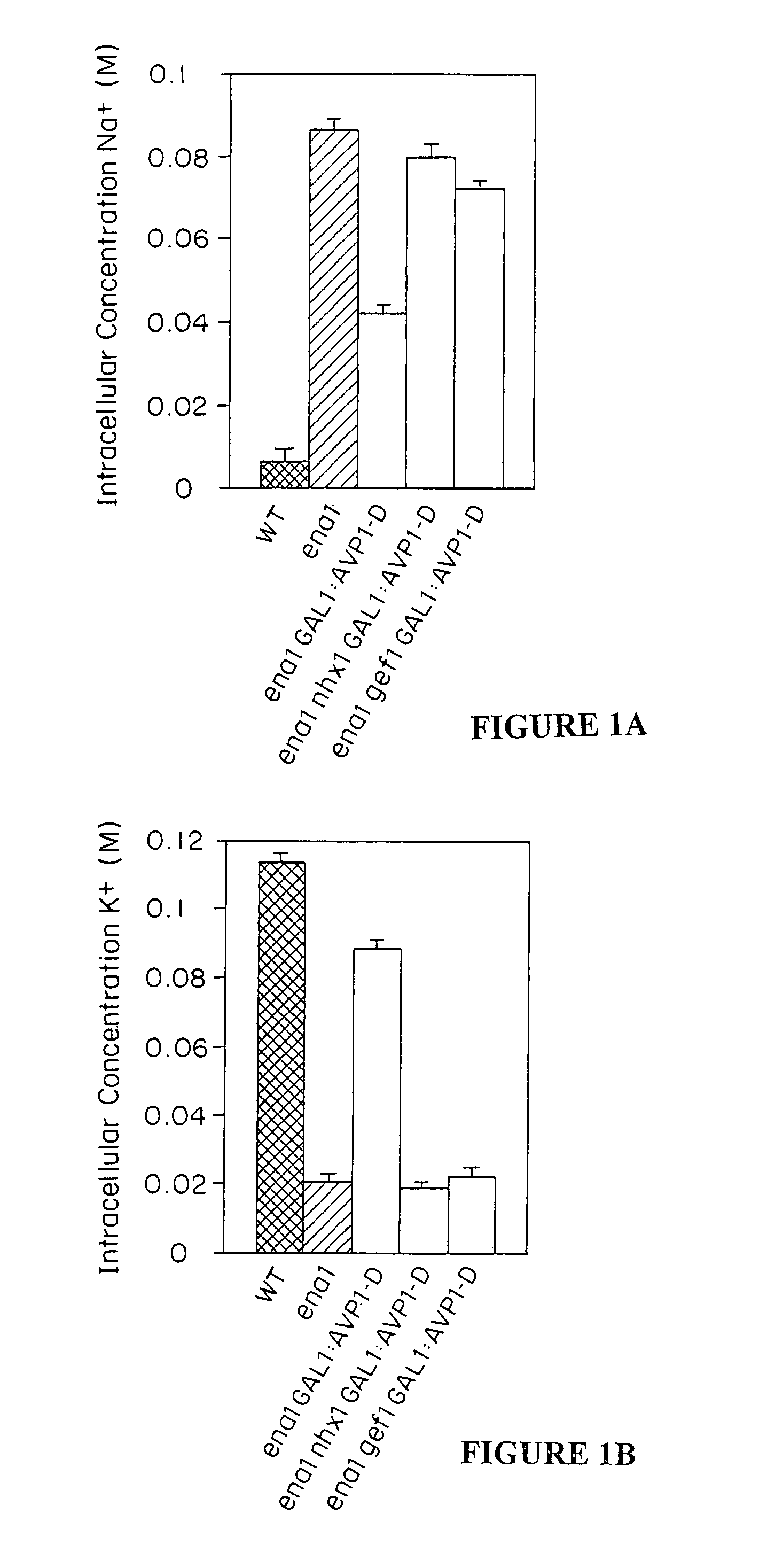
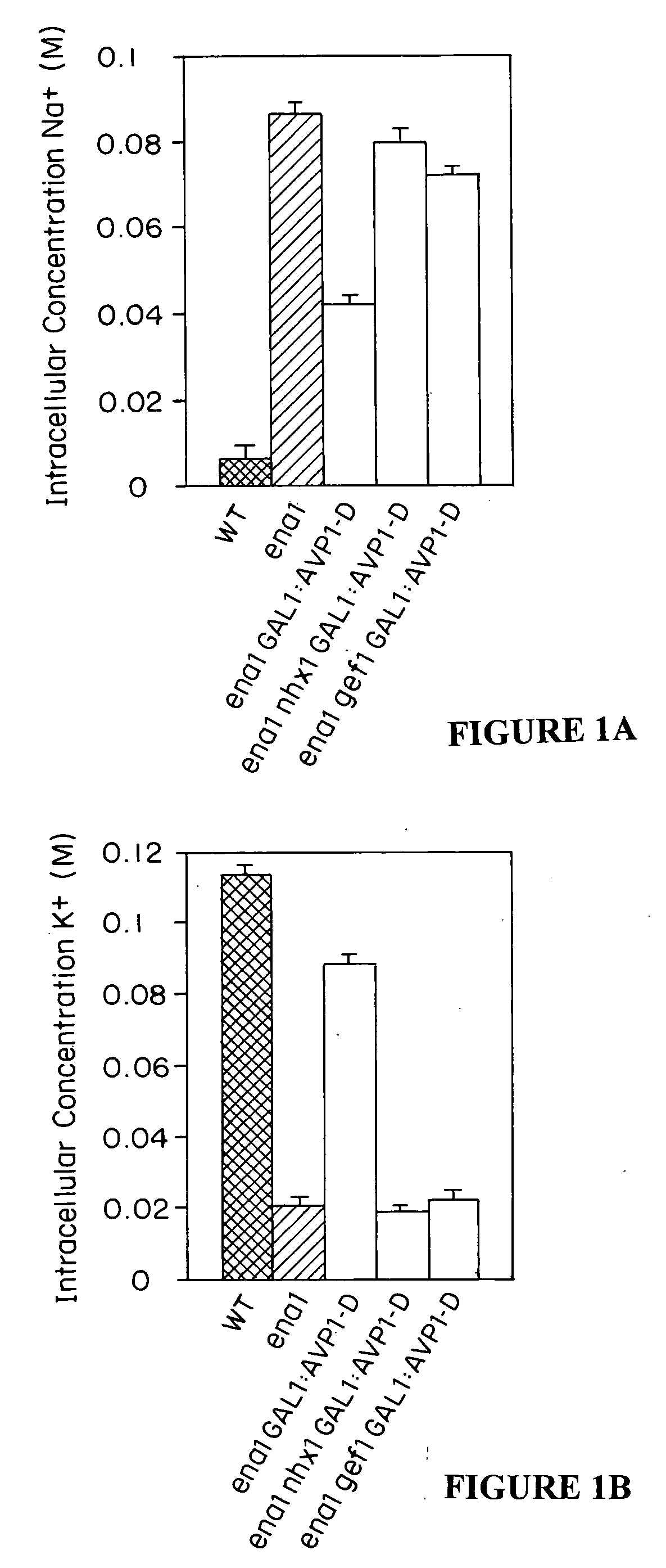
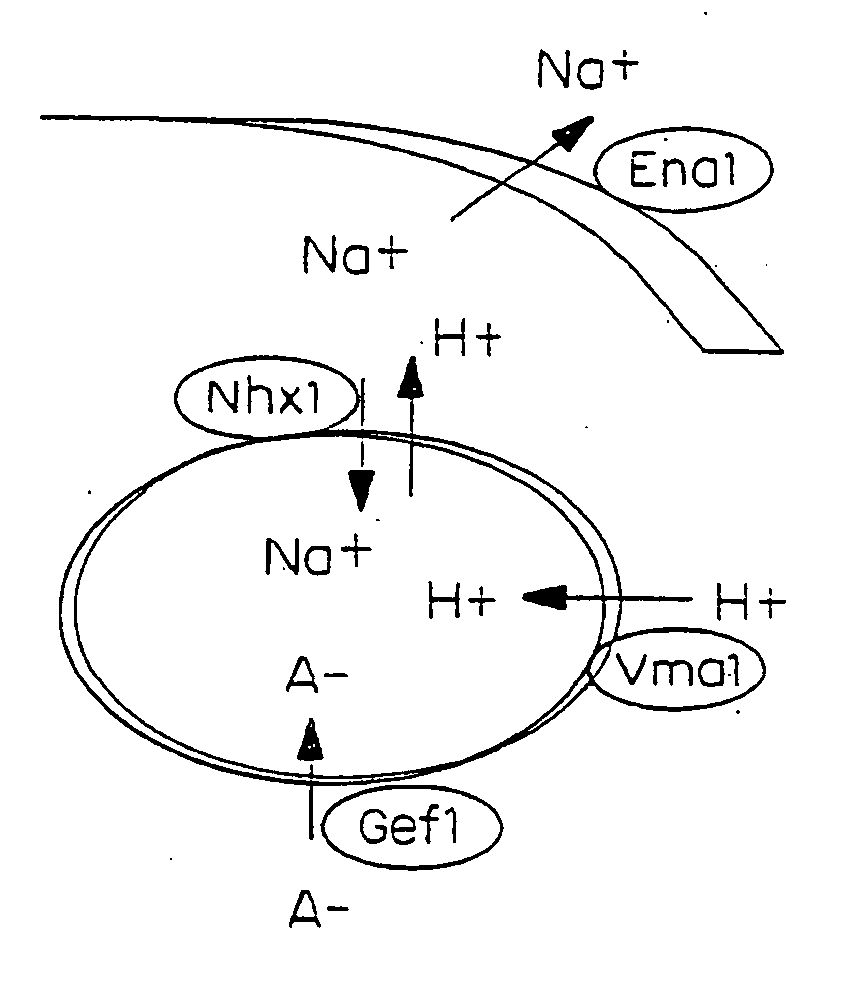
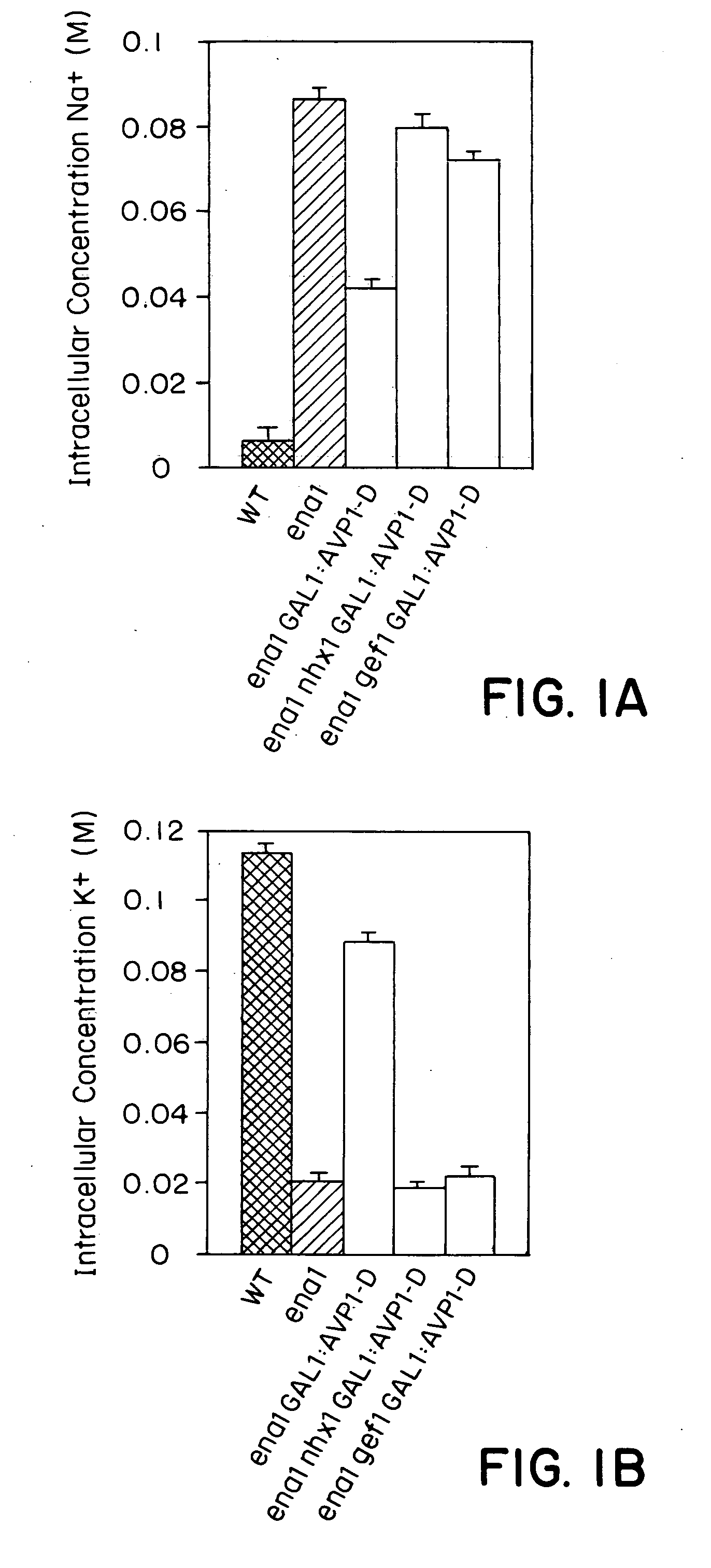
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plants grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cells, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which increases expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cells are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. The present invention also relates to a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased salt tolerance.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Moss scanning electron microscope observation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104374626ASimple methodEasy to storePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionCritical point dryingHistiocyte
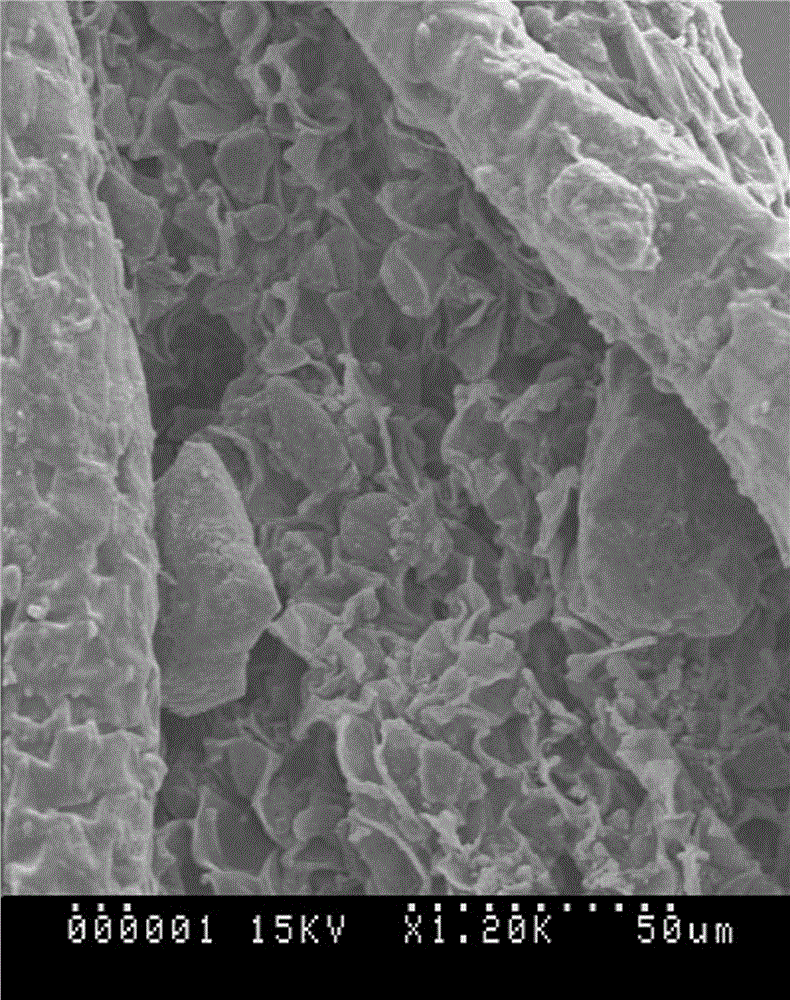
The invention relates to a preparation method of moss scanning electron microscope observation material. The method includes: sorting, to be more specific, sorting moss materials from biological crusts, and stripping leaves after cleaning; fixing, to be more specific, fixing the leaves in glutaraldehyde solution, and washing with buffer solution; dehydrating step by step with alcohol with gradient concentration; replacing, to be more specific, placing the leaves in ethanol-isoamyl acetate mixture for replacing, and placing the leaves in isoamyl acetate solution for replacing; critical point drying; loading onto a table. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and practical, and good in effect, the glutaraldehyde solution serving as the fixing solution is good in fixing effect on polysaccharide, glycoprotein, microtubule and the like, tissue cells do not become brittle after fixing, the influence of leaf cell surface tension can be avoided by the critical point drying, and the microstructures of samples are well preserved; reference is provided for the preparation of ideal moss samples, and the technical blank of related fields in China is filled.
Owner:刘永英
Extracting method and application for adenium obesum leaf cell extract
InactiveCN104622759AHigh yieldLess impuritiesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSolventActive ingredient
The invention discloses an extracting method for an adenium obesum leaf cell extract. The extracting method comprises the following steps: taking fresh adenium obesum leaves and crushing the fresh adenium obesum leaves; feeding raw material powder into a supercritical extraction kettle to perform supercritical CO2 extraction; taking and feeding an extracting mixture into a supercritical separation kettle to perform separation; adding separation products into distilled water to distill, and condensing and recycling steam to obtain the adenium obesum leaf cell extract. The extract is applied to a skin care product. Compared with the prior art, the extracting method can quickly extract much adenium obesum leaf cell extract on the premise of not damaging natural active ingredients of the adenium obesum, so that the yield is high, the impurities are few, solvent residues are avoided, and the natural characteristics of the extract are kept.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
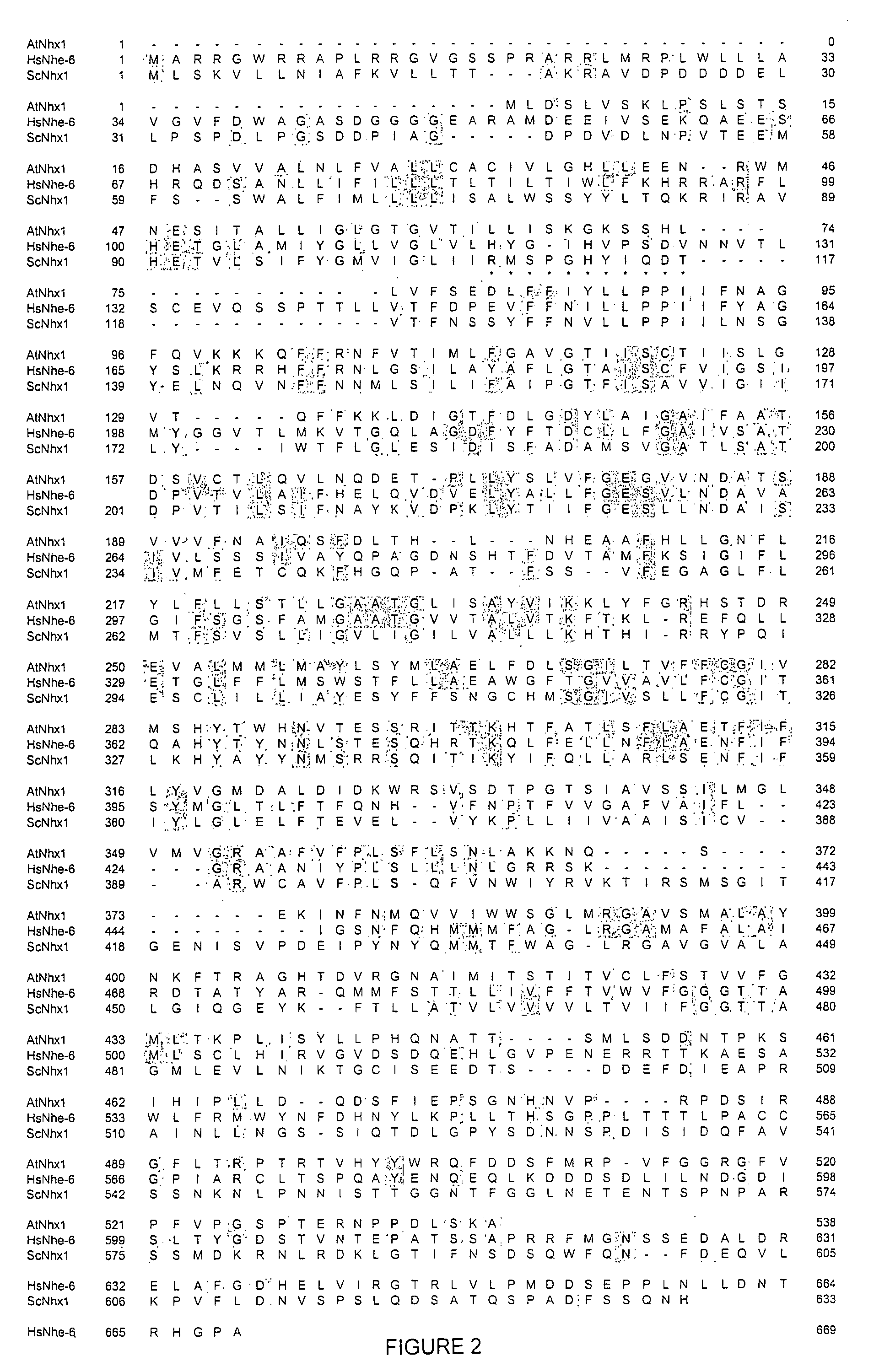
Proton transporters and uses in plants
InactiveUS20050262598A1Increase planting yieldIncreased flower sizeBryophytesClimate change adaptationPlant cellWild type
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. The present invention also relates to a construct comprising an AVP1 gene operably linked to a chimeric promoter designed to overexpress AVP1 or designed to down regulate endogenous pyrophosphatase. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, and a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water comprising introducing into one or more cells of a plant nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Preparation method and application of jasmine plant leaf cell extract
InactiveCN104622758AStrong penetrating powerPromote dissolutionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsLeaf cellFacial cream
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a jasmine plant leaf cell extract. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting jasmine plant leaves as raw materials; (2) weighing ethanol 10-15 times as much as the weight of the jasmine plant leaves, mixing the ethanol with the jasmine plant leaves to prepare feed liquid, and putting the feed liquid in an environment with a vacuum degree of 0.4-0.6 MPa, reacting for 1-15 minutes at a temperature of 50-60 DEG C and ultrasonic power of 420W; (3) filtering and collecting to obtain the jasmine plant leaf cell extract. In the invention, the jasmine plant leaf cell extract is extracted by a vacuum coupling ultrasonic extraction method, the extraction time is shortened, the product yield is high, the working efficiency is high and the product is safe; the jasmine plant leaf cell extract is added in such cosmetics as facial cream to achieving anti-aging and anti-ultraviolet beautifying effects.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
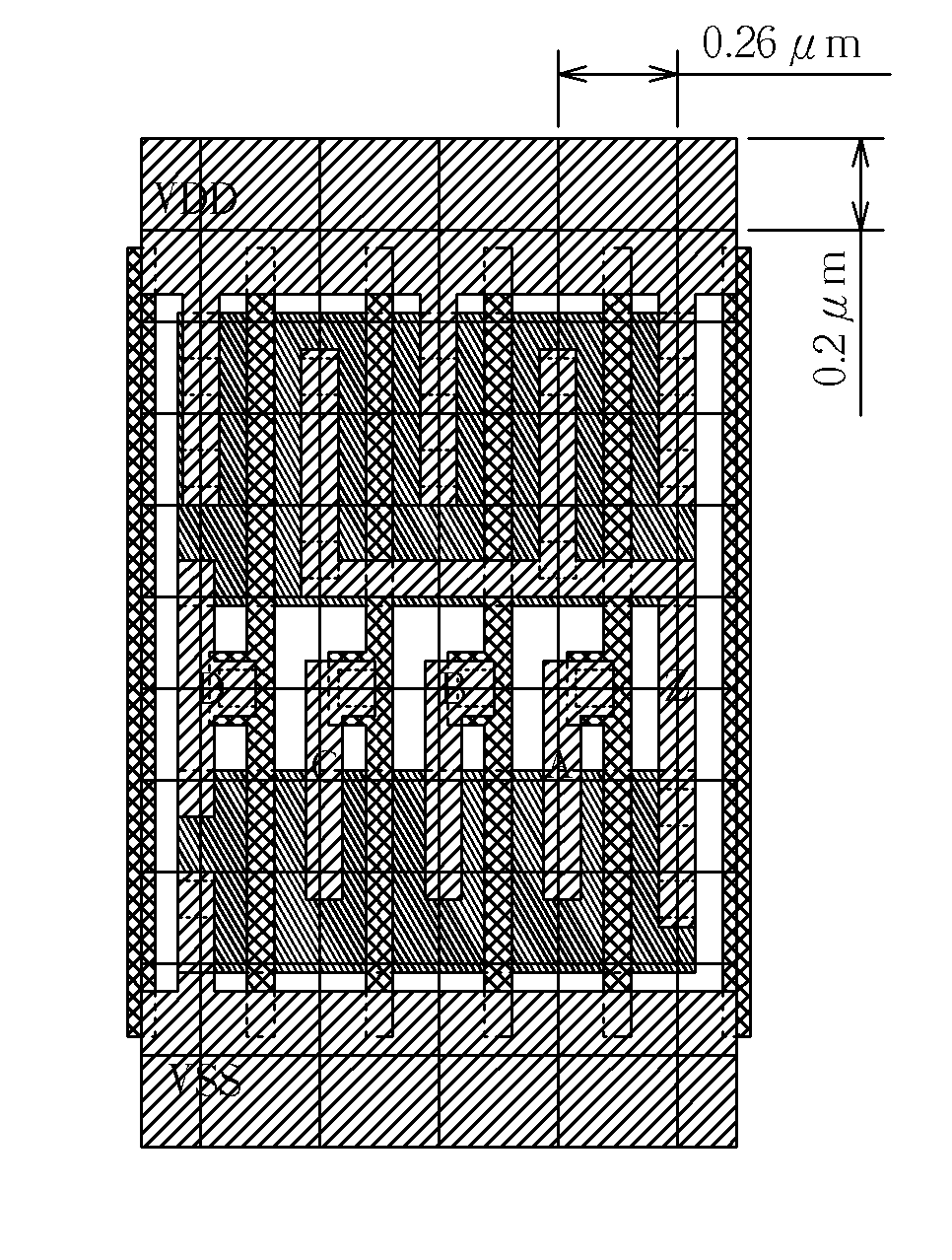
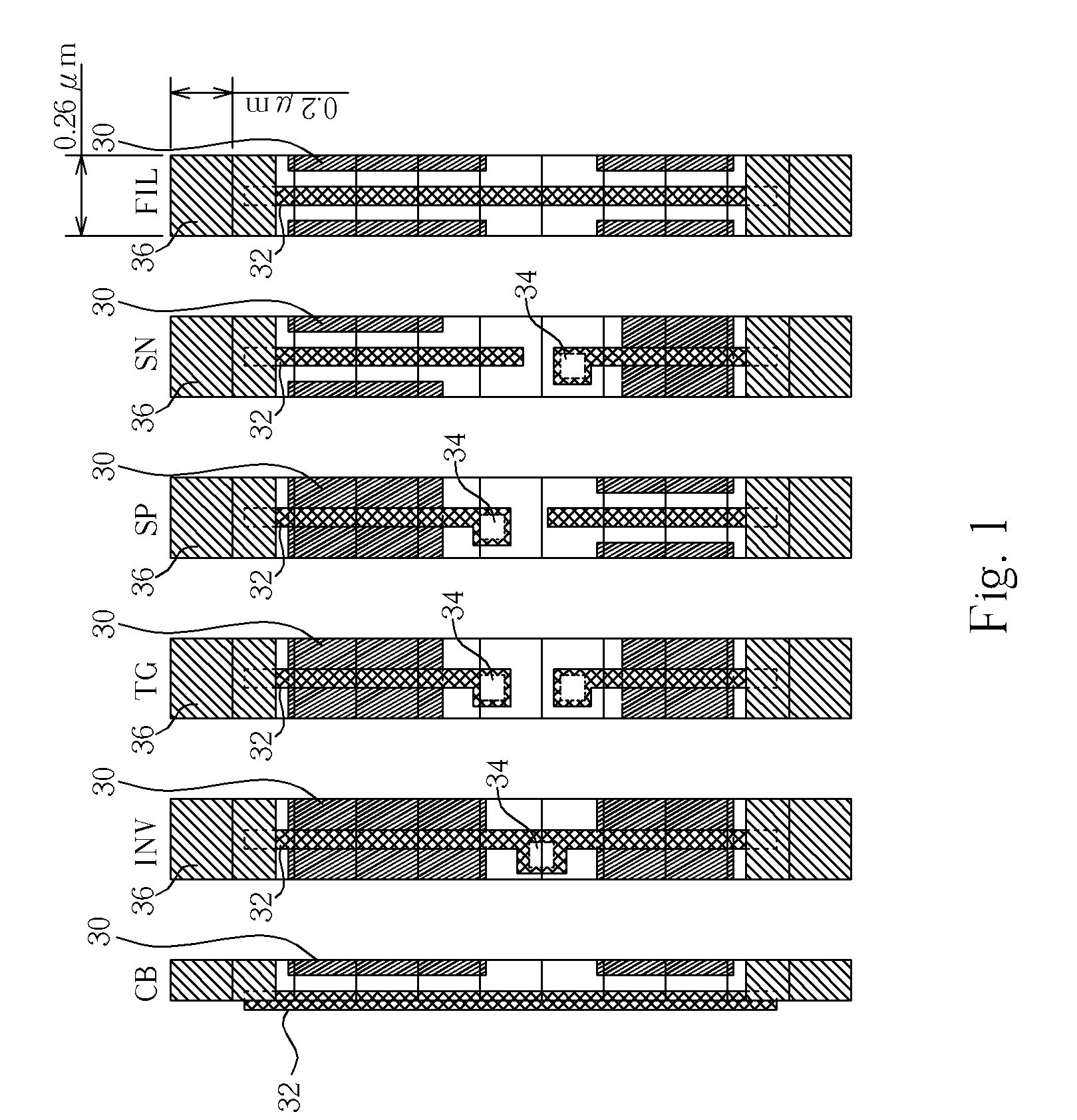
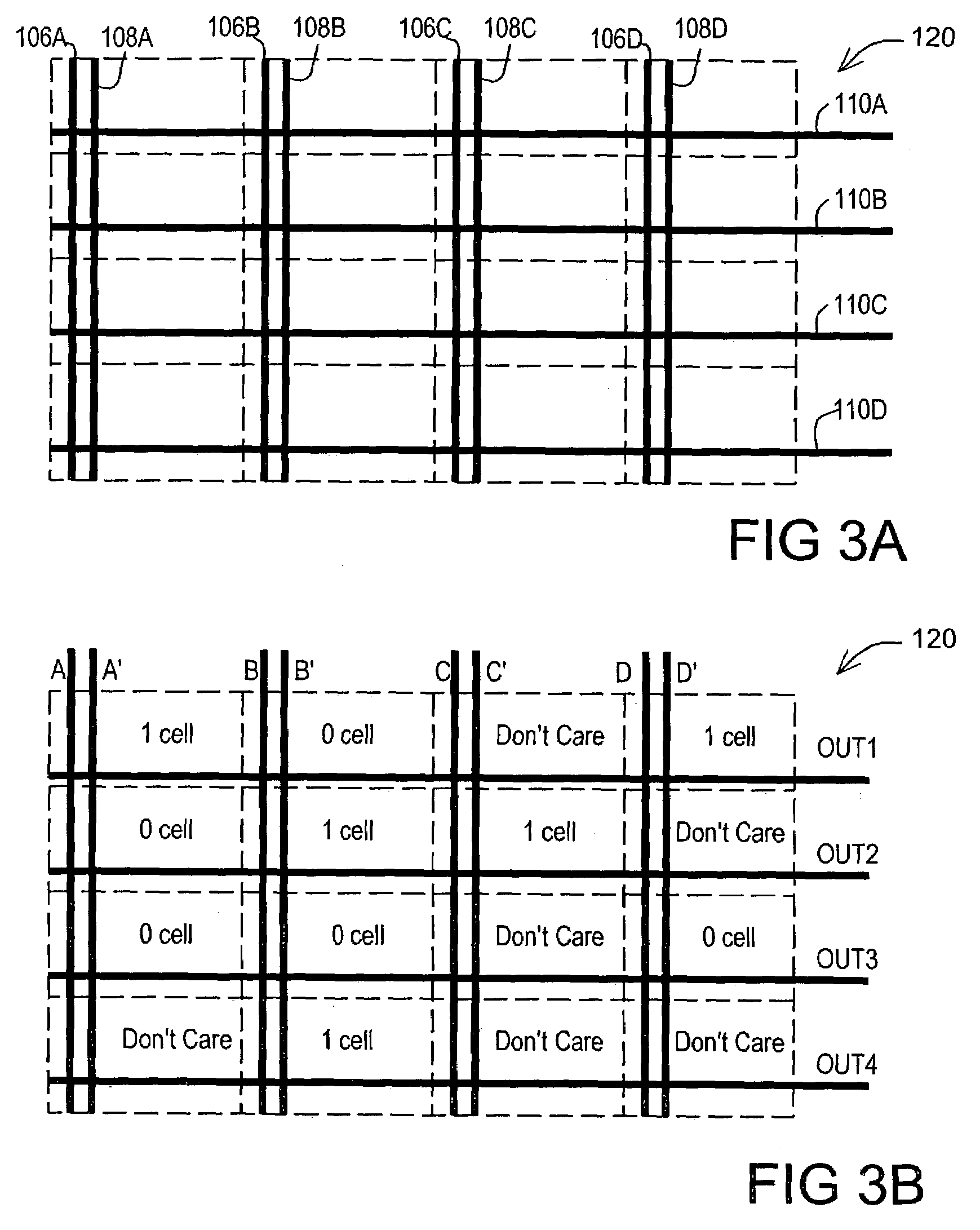
Method of generating a standard cell layout and transferring the standard cell layout to a substrate
ActiveUS7562326B2Reduce creation timeImprove efficiencyCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLeaf cellEngineering
A method of generating a standard cell layout includes analyzing a circuit of a standard cell layout and obtaining an analysis result, selecting a plurality of leaf cell layout according to the analysis result, and piecing together the leaf cell layouts to generate the standard cell layout.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
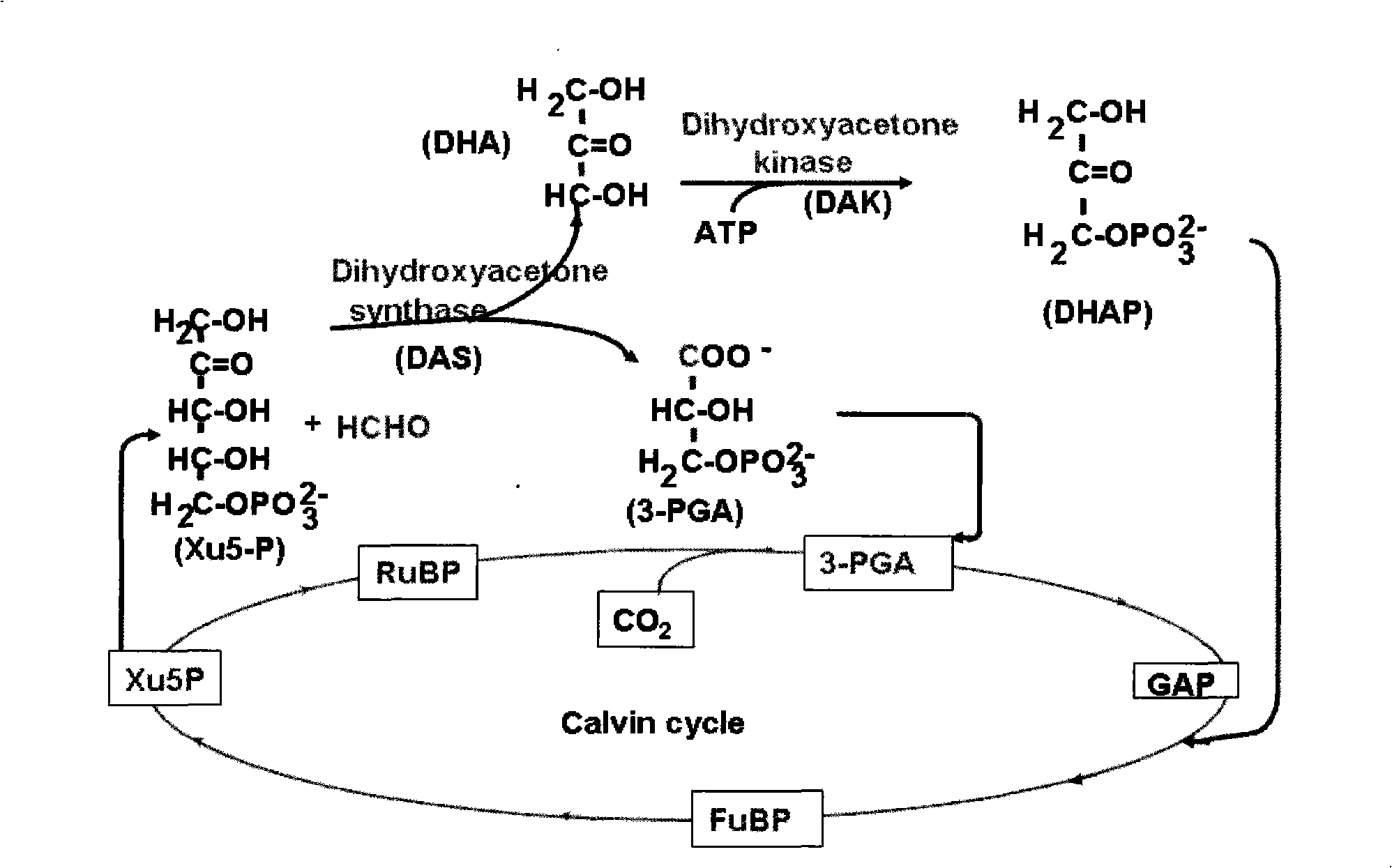
Method for improving plant absorption and tolerance methanal, plant expression vector and application
InactiveCN101270364APromote absorptionImprove toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionLeaf cellSpecific function
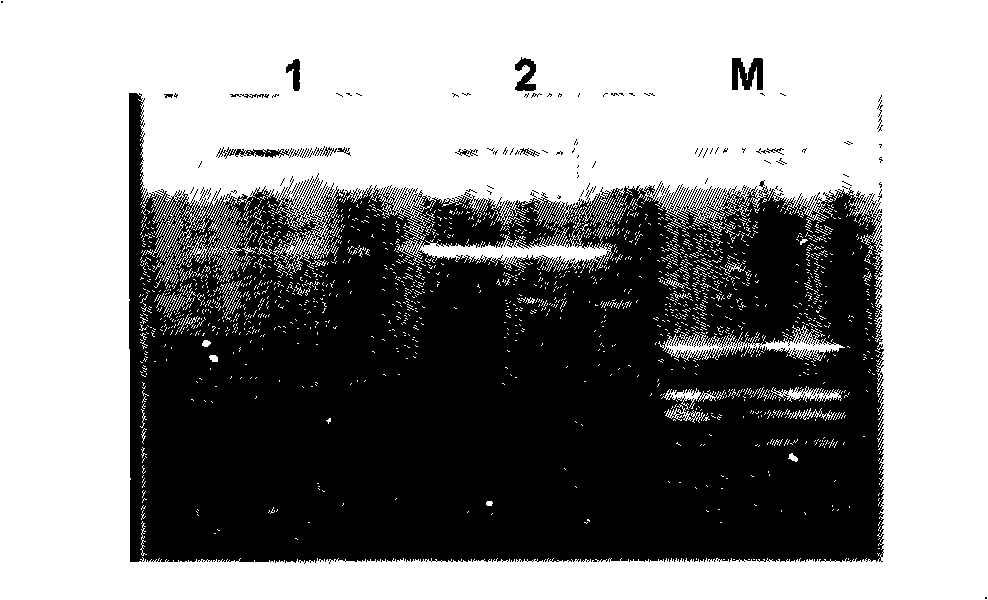
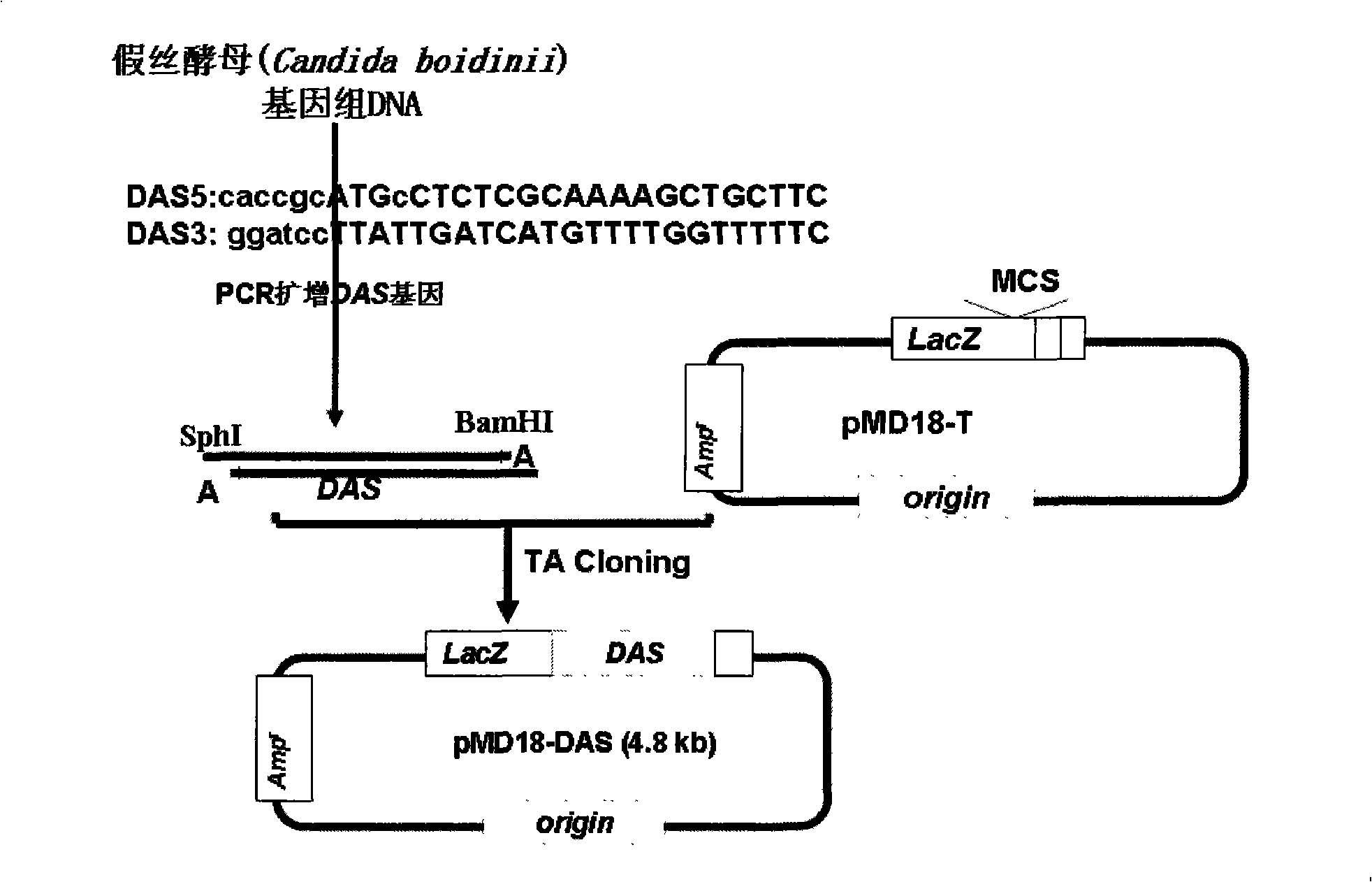
The invention discloses a method for improving assimilation of formaldehyde and tolerance to formaldehyde of a plant, expression vectors and application of the plant, which belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. In the method, double genes containing DAS and DAK are fed into the chloroplasts of plant leaf cells, thus establishing a formaldehyde assimilation path, and a mechanism to assimilate formaldehyde with the photosynthesis of the plant so as to detoxicate formaldehyde in plant cells, create decorative plants with the specific function of decontaminating formaldehyde in indoor air and controlling the pollution of formaldehyde in indoor air, and maintain health of human bodies. The expression vectors of the plant are vector pK2-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAS and vector pH2-35S-PrbcS-*T-DAK. Compared with the control plant, the plant can thrust up in the environment polluted by formaldehyde, the quantity of formaldehyde assimilated is increased by 20 to 70 percent, and the speed to assimilate formaldehyde is improved by 16 to 27 percent.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for inducing flavonoids and terpene lactones to accumulate in plant leaves by using methyl jasmonate and application
ActiveCN110024787AIncrease contentSimple methodBiocidePlant growth regulatorsLeaf cellBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
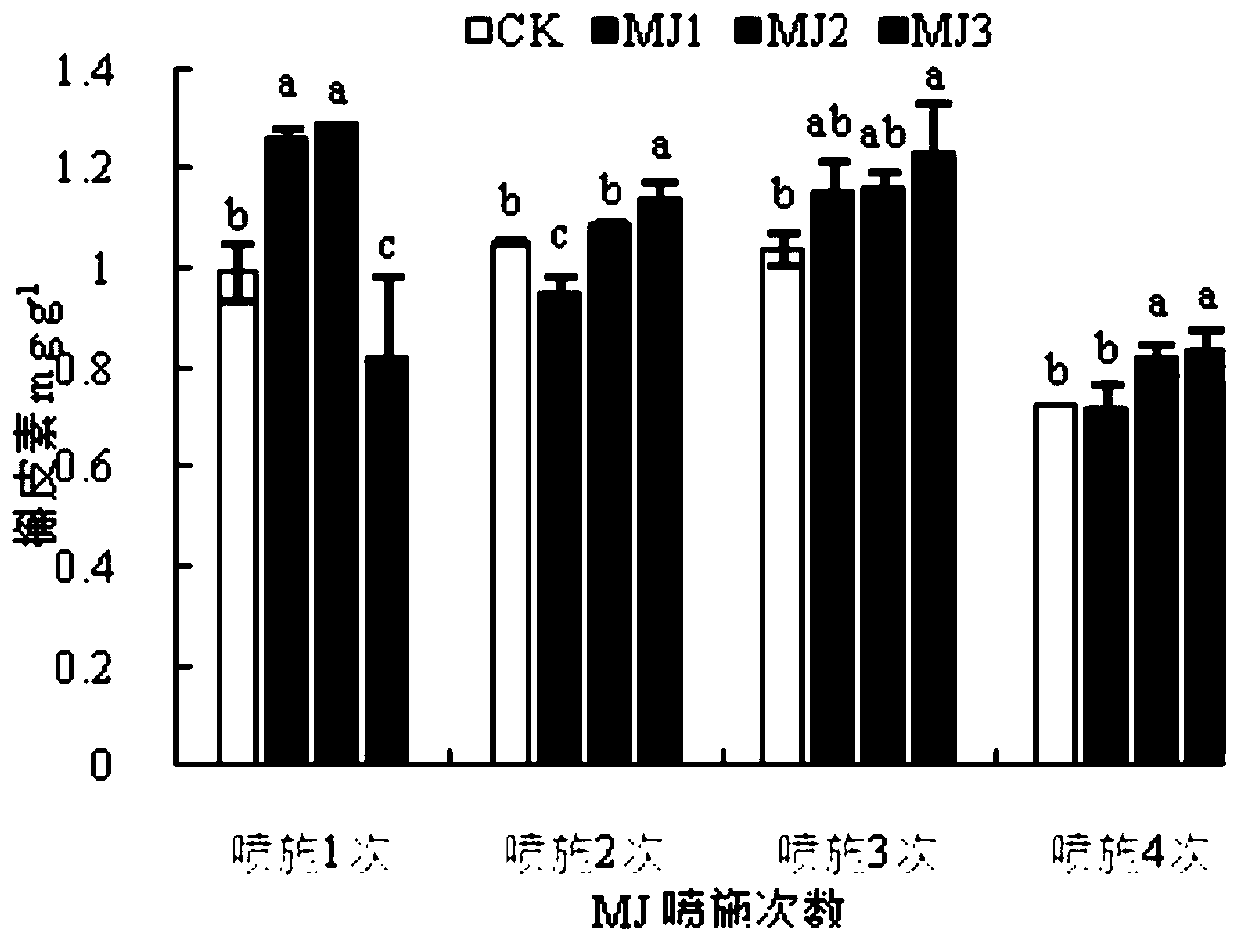
The invention discloses a method for inducing flavonoids and terpene lactones to accumulate in plant leaves by using methyl jasmonate and application, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following step: when plant leaf cells are completely mature, spraying a 20-80mg / L methyl jasmonate solution onto the plant leaves for 1-2 times, so that a ginkgo biloba extractwith high active ingredient content can be obtained from the treated plant leaves through a conventional method. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being simple and easy toimplement, low in cost, free of pollution, stable and efficient; the flavonoids and terpene lactones obtained after regulation and control by the method disclosed by the invention are high in content;wherein the contents of quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, total flavonoids, ginkgo terpene lactone A, ginkgo terpene lactone B and total terpene lactone are respectively increased by 29.84%, 18.08%, 35.94%, 26.24%, 30.36%, 60.65% and 35.41% compared with a control group.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
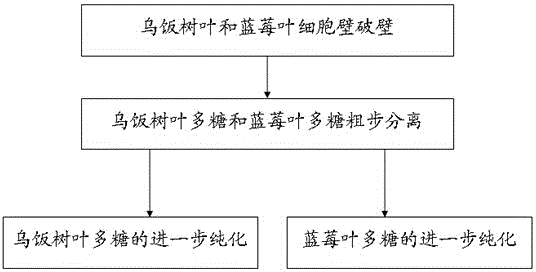
Separation and purification method for Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf polysaccharide and blueberry leaf polysaccharide
InactiveCN105777927AImprove developmentRegulate the micro-ecological environmentMetabolism disorderDigestive systemBiotechnologyVaccinium bracteatum
The invention discloses a separation and purification method for Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf polysaccharide and blueberry leaf polysaccharide. The method includes the steps that fresh Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaves and blueberry leaves are adopted as raw materials, cell disruption is carried out through the ultrasonic technology, extraction of polysaccharide is carried out with an alkaline solution, crude polysaccharide purification is carried out with composite biological enzymes, and pure natural plant polysaccharide ingredients are obtained. The method includes the four steps of Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf and blueberry leaf cell wall disruption, primary separation of Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf polysaccharide and blueberry leaf polysaccharide, purification of Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf polysaccharide and purification of blueberry leaf polysaccharide. The Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf polysaccharide and blueberry leaf polysaccharide products obtained after separation and purification with the method mainly have the effects of growth and development promotion, virus resistance, immune function enhancement, regulation and control of the intestinal microecological environment and promotion of development of immune organs on the human body.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGYUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Extraction method and application of myrrh leaf cell extract
ActiveCN104706553AReduce consumptionSimple processCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyCell extraction
The invention discloses an extraction method and application of a myrrh leaf cell extract. The extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) drying and crushing myrrh leaves; (2) performing enzymolysis, to be specific, uniformly mixing myrrh leaves, cellulase, tween-80 and water, and reacting for 50-110 minutes at 40-70 DEG C in the vacuum degree of (-0.4)-(-0.8)MPa; (3) filtering and concentrating the obtained mixture; (4) extracting, to be specific, performing extraction on the concentrated liquid by using a microwave method under the conditions that the microwave output power is 200-500W and the frequency is 3000MHz, filtering the extract, drying the filter residues, and grinding the filter residues into powder, so as to obtain the myrrh leaf cell extract. An anti-aging cosmetic consisting of the myrrh leaf cell extract extracted by using the extraction method, hyaluronic acid and the like has the effects of preventing aging, removing free radicals, and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Wire trimmed programmable logic array
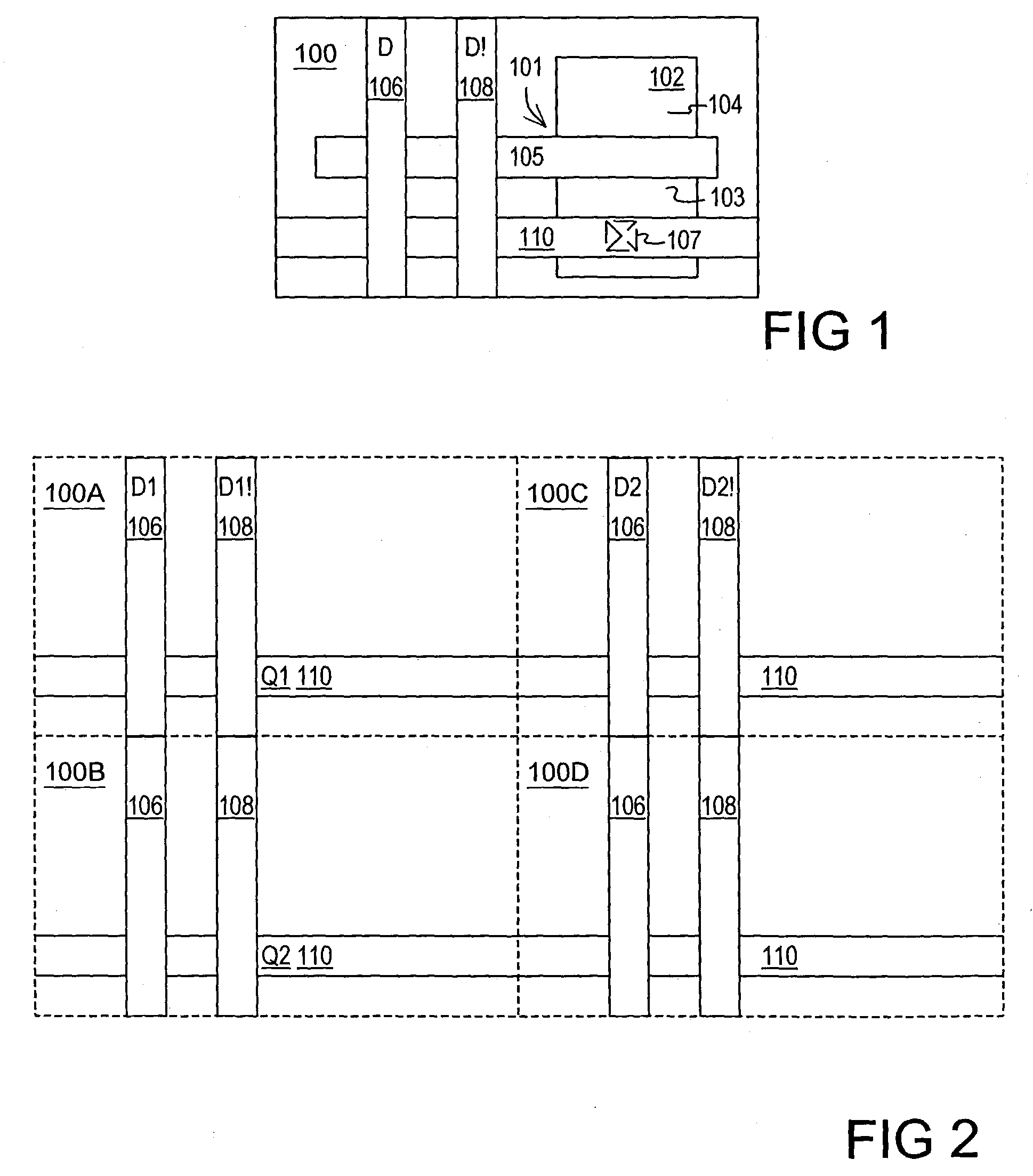
InactiveUS7225422B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCAD circuit designElectricityLeaf cell
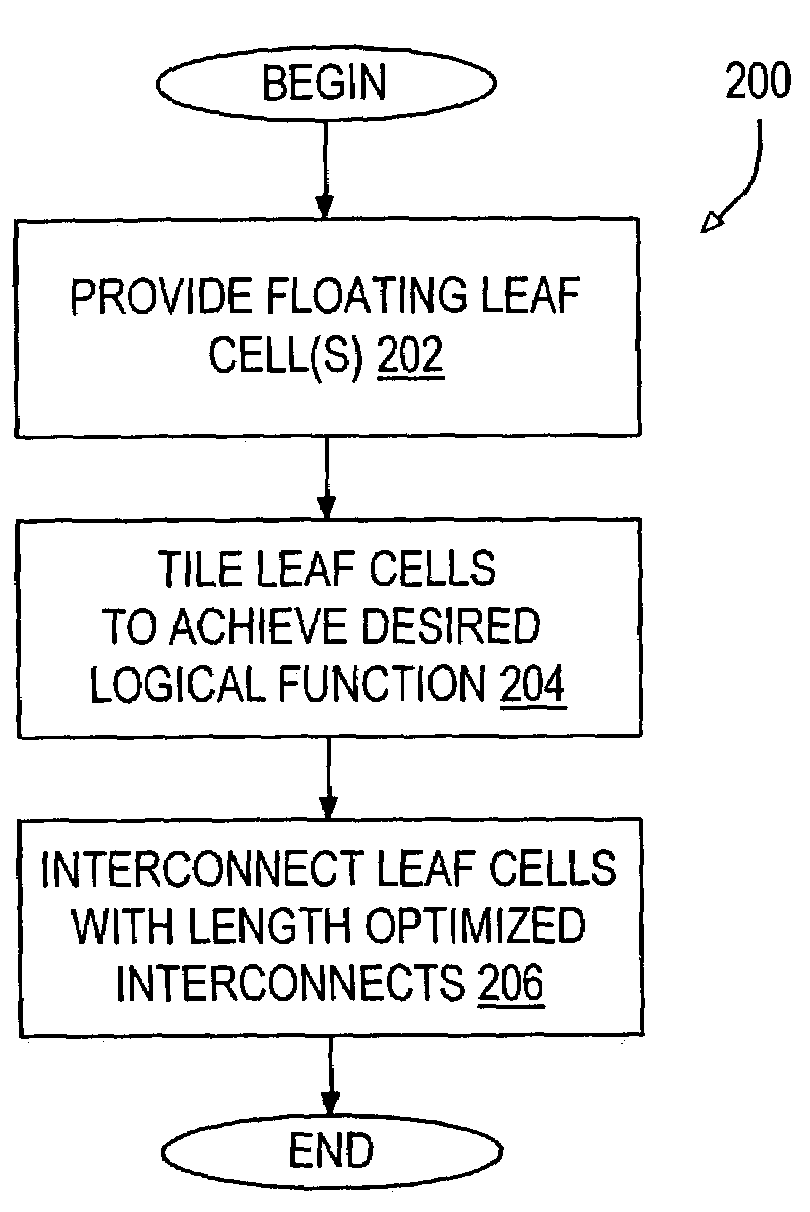
A method of designing a logic circuit includes providing a leaf cell having at least one transistor. The leaf is suitable for use as a 1-cell or a 0-cell in the logic circuit. A first array of abutting leaf cells is tiled using at least one 1-cell and at least one 0-cell to define at least one logical expression by the relative positions of the array cells. Length optimized interconnects are added to the array. Each length optimized interconnect terminates at a last leaf cell in the array to which the interconnect makes contact. The leaf cell may be a floating leaf cell in which any pair of abutting cells are electrically isolated from one another until the length optimized interconnects are added to the design. The leaf cell array likely includes a set of rows and a set of columns in which the leaf cells in each row and the set of columns each correspond to an input of the logical expression.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for making high-fermentation elder leaf black tea
The invention discloses a method for making high-fermentation elder leaf black tea. The method comprises the following steps: taking elder leaves of Wuyi rock tea trees as raw materials, picking fresh leaves, performing secondary wilting, performing alternative operations on three-time rolling and three-time fermentation, drying and the like. According to the invention, the unique rolling and wilting process is adopted, so that the elder leaf cells are uniformly and fully destroyed, and due to long-term fermentation, lots of substances contained in the elder leaves are fully oxidized and transformed, chemical changes of principle polyphenols and subsidiary transformation and accumulation of substances such as free amino acids, theanine, polysaccharides and the like are formed, the sufficiency and uniformity of tea leaf fermentation are effectively guaranteed, and the color, aroma, taste and shape of the tea leaves are improved, so that the made elder leaf black tea is tight and uniform in strip, oily in color, orange red and bright in soup, similar to dry aroma of longan, mellow in taste and obvious in sweetness after drinking tea.
Owner:武夷学院
Method of analyzing heavy metal pollution of vegetable based on reactive oxygen species level
The invention provides a method of evaluating the heavy metal pollution of vegetable based on reactive oxygen species level by analyzing the fluorescence intensity of reactive oxygen species in vegetable cells through adopting laser scanning confocal microscope technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) marking reactive oxygen species in vegetable leaf cells by adopting 2',7'-dichorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA); 2) analyzing the reactive oxygen species level in vegetable leaf cells by adopting the laser scanning confocal microscope technology; 3) fixing instrument acquisition parameters by taking the fluorescence intensity of reactive oxygen species in the non-polluted vegetable leaves according with the national standard; 4) further acquiring the fluorescence density value of the vegetable leaf to be detected according to the instrument parameter, performing statistic analysis on the fluorescence intensity value of vegetable to be detected and the standard vegetable fluorescence intensity value so as to confirm whether the vegetable is polluted by heavy metal.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for extracting high-quality genome DNA from dry suriana maritime leaf and kit thereof
The invention provides a method for extracting genome DNA from a dry suriana maritime leaf and belongs to the biotechnology field. Specifically, the extraction method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: grinding and crushing dry leaf cells, extracting DNA by adopting a two-step process, removing impurities and purifying the DNA. By adopting the extraction method provided by the invention, secondary metabolism products, such as polyphenol and polysaccharide, rich in a dry tissue sample can be effectively removed, and finally the high-quality genome DNA is obtained. The DNA extraction method provided by the invention has the advantages that polyvinylpyrrolidone is added, polyphenol substances can be more effectively removed, and quality of the genome DNA is obviously improved. The DNA extraction method provided by the invention is applicable to extraction of genome DNA from dry leaves of trees such as suriana maritime.
Owner:ANNOROAD GENE TECH BEIJING +2
Actinidia arguta leaf tea with antioxidant and hypoglycemic effects and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104171168ASolve the inconcentration of the harvest periodEasy to carryTea substituesLeaf cellPhenolic content in tea
The invention discloses actinidia arguta leaf tea with antioxidant and hypoglycemic effects and a preparation method thereof. The characteristics of the actinidia arguta leaf are combined on the basis of a traditional tea making process; the processing time limit of the actinidia arguta leaf is prolonged by technological means such as quick freezing; the enzyme activity is inhibited; tea polyphenol is protected; the problems that the harvest time of tender leaves of the actinidia arguta is not concentrated and the active components such as the tea polyphenol are oxidized after long-term placement are solved; meanwhile, the leaf cell membrane is damaged; further emission of green stink of the actinidia arguta leaf is facilitated; the color, flavor, taste and nutrient hygienical components of the actinidia arguta leaf are prevented from being damaged to the maximal extent; the actinidia arguta leaf tea is easy to carry and take; and the actinidia arguta leaf is utilized, so as to prepare a tea product which is convenient to carry and store, and easy to be accepted by widespread consumers, and has the antioxidant and hypoglycemic effects.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
Preparation method of fermented blueberry leaf tea
InactiveCN103461579ARealize industrializationAchieve scaleTea substituesTemperature controlLeaf cell
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fermented blueberry leaf tea. The method comprises the following steps: (1) plucking fresh blueberry leaves growing in late April to late October; (2) withering fresh leaves: carrying out back natural withering on the fresh leaves to water content of the fresh leaves reaching 60%-65%; (3) rolling the fresh leaves by a manual or mechanical manufacture method to break leaf cells and overflow leaf juice, controlling temperature below 35 DEG C during the rolling process, and rolling the leaves into tight round straight cords; (4) fermenting the rolled fresh leaves, with air humidity controlled at above 90% and temperature no higher than 35 DEG C, for 4-6 h; and (5) drying the leaves by three stages including 180 DEG C rapid high temperature drying, 110 DEG C forced air drying, and low temperature stoving to realize complete drying, and controlling water content at about 5%. The blueberry leaf tea produced by the invention has advantages of thin tight uniform cords, bright soup color, bright red brewed leaves, mellow taste with slight sweetness and sourness, high and fresh aroma and abundant functional nutrients.
Owner:ANHUI HUI KING FOOD
Preparation method and application of lotus leaf cell secondary metabolite freeze-dried powder
ActiveCN104706554ASimple production processSimplify production stepsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of lotus leaf cell secondary metabolite freeze-dried powder. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a lotus leaf cell strain, namely, cooperatively digesting sterile lotus leaves by using cellulase and pectinase so as to obtain the lotus leaf cell strain; (2) culturing a great amount of lotus leaf cells, namely, 1) performing primary culture by using a #I sterilization culture medium, and 2) performing suspension culture by using a #II sterilization culture medium, so as to obtain a lotus leaf cell culture; (3) collecting the lotus leaf cell culture so as to prepare lotus leaf cell secondary metabolite freeze-dried powder, and applying the lotus leaf cell secondary metabolite freeze-dried powder to anti-aging cosmetics. By using a lotus leaf cell culture method and due to the cooperative application of cellulase and pectinase, secondary metabolite in the culture can be finally collected, and not only is the production process simplified, but also the lotus leaf cell culture efficiency and quality are improved; meanwhile the product is high in security and can be stably produced for a long time; the lotus leaf cell secondary metabolite freeze-dried powder has an anti-aging function when being used in cosmetics.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Vacuolar pyrophosphatases and uses in plants
InactiveUS20080104733A1Improve toleranceLarge plant sizeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesWild typePlant cell
The present invention relates to a transgenic plant which is tolerant to a salt, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. The present invention also relates to a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake, comprising one or more plant cells transformed with exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant. Also encompassed by the present invention are transgenic progeny and seeds of the transgenic plants described herein. Progeny transgenic plant grown from seed are also described. Plant cells (e.g., root cells, stem cell, leaf cells, flower cells, fruit cells and seed cells) comprising exogenous nucleic acid which alters expression of vacuolar pyrophosphatase in the plant cell are also the subject of the present invention. Also encompassed by the present invention are methods of making a transgenic plant described herein. Transgenic plants produced by the methods of making a transgenic plant as described herein are also a subject of the present invention. The present invention also relates to a method of bioremediating soil, a method of increasing the yield of a plant, a method of making a plant which is larger than its corresponding wild type plant, a method of producing a transgenic plant which grows in salt water, and a method of producing a transgenic plant with increased Pi uptake. The transgenic plants of the present invention can also be used to produce double transgenic plants which are tolerant to a salt, or have increased Pi uptake.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES +2
Cold-resistant agent for brassica rapa L. seedlings and application method of cold-resistant agent
InactiveCN104798788AImprove cold resistancePromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAridChemical control
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural production, and particularly relates to a cold-resistant agent for brassica rapa L. The cold-resistant agent for the brassica rapa L. seedlings is mainly characterized by comprising raw materials as follows: 15-25 mg / L of ABA (abscisic acid) and the balance of water, wherein the purity of the ABA (abscisic acid) is higher than or equal to 99.9%. The cold-resistant agent aims to solve the problem that the brassica rapa L. in the northern cold and arid regions is vulnerable to low-temperature freezing damage, growth of the overground part and the root system of the brassica rapa L. is promoted with chemical control means, especially the thickening growth of roots, the outstanding performance refers to increase of dry matter accumulation, and safe wintering of the brassica rapa L. is guaranteed; meanwhile, permeability (relative electrical conductivity) of leaf cell membranes as well as accumulation of membrane lipid peroxidation malonaldehyde can be reduced, so that the low-temperature freezing degree of leaves of the brassica rapa L. is reduced, the cold resistance of the brassica rapa L. is remarkably improved, and the cold-resistant agent has great practical significance on brassica rapa L. production.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Magnesium-nitrogen-doped carbon dots, preparation method thereof and application of magnesium-nitrogen-doped carbon dots in improvement of photosynthesis of plants
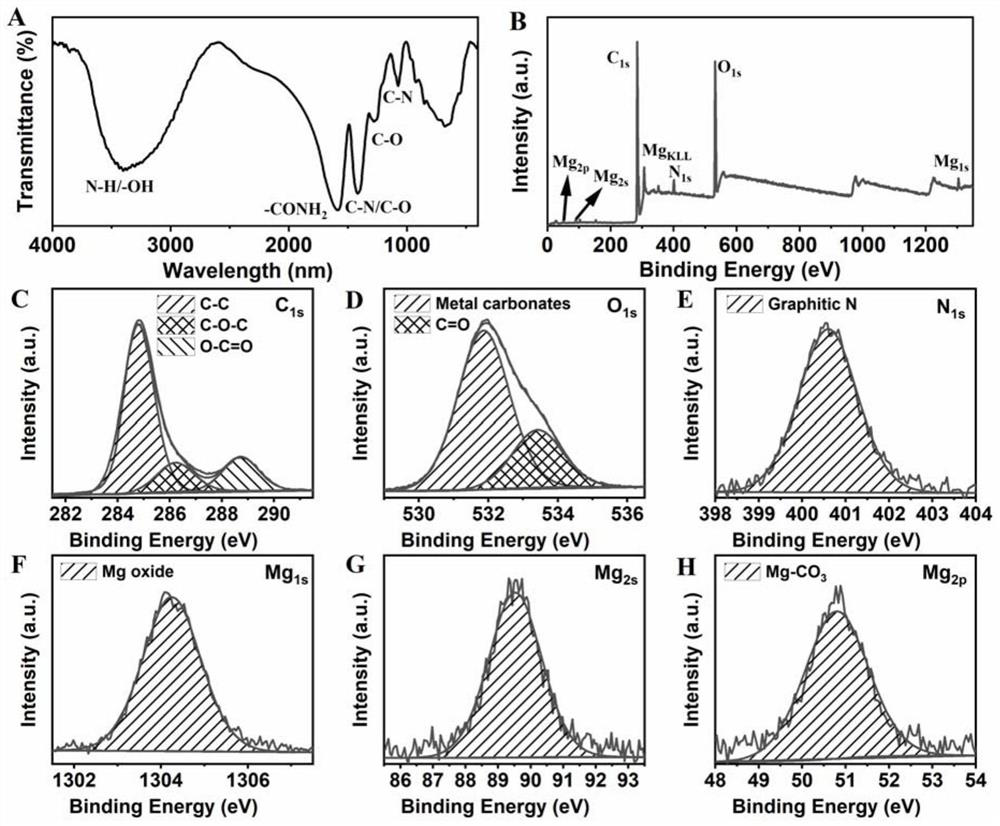
ActiveCN113201330AImprove photosynthetic activityPromote growthNanoopticsNano-carbonFreeze-dryingChloroplast
The invention belongs to the field of nano material biological effect research, and discloses a magnesium-nitrogen-doped carbon dot, a preparation method thereof and application of the magnesium-nitrogen-doped carbon dot in improvement of plant photosynthesis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving citric acid, ethanolamine and magnesium hydroxide in ultrapure water, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, pouring the treated system into a reaction kettle, and conducting reacting at 200 DEG C for 6 hours; after the reaction is finished, conducting cooling to room temperature, filtering a product by using a filter head with the pore diameter of 0.22 [mu]m, and then conducting dialyzing for 12 hours; and conducting freeze-drying to obtain the magnesium-nitrogen doped carbon dots. After the carbon dots are compounded with chloroplast, the excitation energy can be absorbed by the chloroplast for photosynthesis, so that the photosynthetic activity is improved. After the carbon dots are applied to rice plants through foliage spraying, Mg,N-CDs can be uniformly distributed in leaf cells, expression of related enzyme genes is regulated and controlled, synthesis and metabolism of chlorophyll in leaves are promoted, the activity of chlorophyll molecules is kept at a high level, and therefore the photosynthetic activity of the leaves is improved. Finally, the plant growth is obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
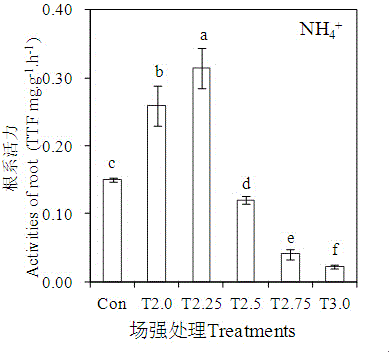
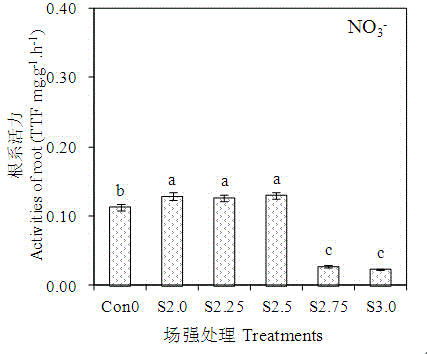
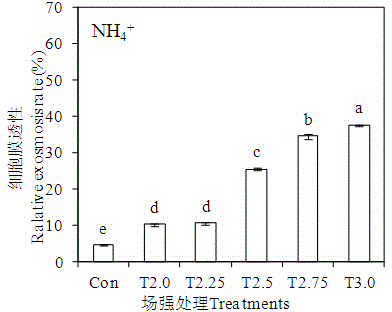
Method for promoting transplanted crops to absorb nutrients on basis of high-voltage electrostatic fields
ActiveCN104871845APromote absorptionSeed and root treatmentSaving energy measuresCell membraneHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method of promoting transplanted crops to absorb nutrients on the basis of high-voltage electrostatic fields. The method includes the following steps: 1 preparing seedling samples; 2 applying high voltage electric fields at different strengths to the samples; 3 measuring activity of seedling roots, penetration of leaf cell membranes and ionic concentration change of absorption liquid; 4 determining the optimum field intensity and treatment time which are favorable for nutrient absorption by the crops. The method of promoting transplanted crops to absorb nutrients on the basis of the high-voltage electrostatic fields can treat various different seedlings, determines the optimum field intensity and action time which can promote absorption of different nutrients for every kind of crop, and has the characteristics of being wide in application and simple to operate.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for determining plant leaf cell conveying capacity
ActiveCN108489867AGet Relative Call CapabilitiesGet Relative Carrying CapacitySurface/boundary effectMaterial impedanceCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a method for determining a plant leaf cell conveying capacity, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural engineering and crop information detection. A determining device comprises a support, foam plates, electrode plates, lead wires, an iron block and a plastic rod; the foam plates with the inlaid electrode plates are adhered onto the bottom end of the support andthe plastic rod; when in use, the method comprises the steps of connecting the electrode plates and an LCR tester through the lead wires; clamping a plant leaf to be measured through the two electrodeplates, determining the physiological resistance, physiological impedance and physiological capacitance of the plant leaf through a parallel-connection mode, and calculating physiological capacitivereactance according to the physiological capacitance of the plant leaf; further calculating physiological inductive reactance of the plant leaf; adopting a physiological resistance reciprocal of the plant leaf as a reference, and obtaining a relative electric capacity and a relative carrying capacity of a plant leaf cell; further acquiring a conveying capacity of the plant leaf cell. The method provided by the invention can be used for quickly, losslessly and quantitively detecting the conveying capacities of different plant leaf cells on line, filling the blank of representing a cell conveying capacity by utilizing biological physical indexes, and providing a mode for the quantitation of a cell membrane function.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of Yunnan congou black tea
The invention discloses a preparation method of Dianhong Gongfu tea. The method comprises the following steps: a. withering, b. rolling, c. fermentation, d. drying. The premise of forming the excellent quality of black tea. On the one hand, rolling is to form cords, and on the other hand, it is to break leaf cells. It is an important process for shaping the shape and forming the inner quality of Gongfu black tea. Fermentation is a process in which the tea polyphenols in tea are oxidized violently under the action of enzymes, and at the same time affect the changes of other ingredients in the tea, forming the unique color and aroma of black tea. Fermentation is the key process to form the quality of Gongfu black tea. Drying is the last process to fix and improve the quality of black tea, which has a great influence on the quality. These four key steps directly affect the quality of tea. By refining the production process of Dianhong Gongfu tea, it can obtain a better taste and save costs.
Owner:BAOSHAN GUDAOCHUN TEA BUSINESS LIMITED
Preservation method of rubber leaves
ActiveCN107873699AReduce degradationSolve shipping problemsDead plant preservationLeaf cellPreservation methods
The invention relates to a preservation method of rubber leaves. The method comprises the steps of leaf collecting, paraffin coating, bundling, sealing and casing. By the adoption of the method, rubber leaf samples can be preserved for 5-7 days, leaf cell nucleuses are hardly degraded, the rubber leaf samples meet sample standards of flow cytometry detection, and the purposes of leaf sample transformation and preservation in the flow cytometry detection process of a superior individual in a quite far long-distance rubber forest are addressed. The shelf life of the rubber leaf samples for the flow cytometry detection can be prolonged. Scientific researchers can intensively collect and detect the rubber leaf samples, and thus the round-trip costs in the sampling process are reduced. Moreover, the method has simple requirements for facilities and is simple in operation procedure and relatively low in operation cost.
Owner:YUNNAN INST OF TROPICAL CROPS
Method for extracting wild persimmon leaf tannin by ultrasonic wave auxiliary semi-bionic method
InactiveCN102344470APrevent oxidationMaintain physiological activityEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesUltrasonic assistedLeaf cell
The invention relates to a method for extracting tannin from wild persimmon leaves by an ultrasonic wave auxiliary semi-bionic method, which is mainly characterized in that the de-enzymed wild persimmon leaves are dried and smashed, ethanol and water as used as extraction solvents, and backflow extraction is carried out 3 times at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C by simulating the pH value of a gastrointestinal tract; and in the process of each extraction, ultrasonic waves are adopted for auxiliary treatment; and extracts in three times are combined and centrifuged, and then the obtained extract is concentrated and dried in a vacuum mode at the temperature of 50-60 DEG C to obtain the wild persimmon leaf tannin. In the semi-bionic extraction method of the invention, ultrasonic wave auxiliary extraction is adopted to make wild persimmon leaf cell tissues be wall-broken or deformed so as to increase the tannin yield, shorten the extraction time and keep the activity of the tannin.
Owner:余先纯
Application of exogenous melatonin to improvement of salt tolerance of beet seedlings
The invention provides application of exogenous melatonin to improvement of salt tolerance of beet seedlings. Beet KWS0143 is taken as a test material to research the relationship between melatonin and leaf cell membrane damage, an antioxidant enzyme system and an osmotic regulation substance of beet under salt stress and discuss the action mechanism of melatonin in resisting salt stress of plants. A foundation is laid for exploring the action of melatonin on the salt resistance mechanism of beet, and possibility is provided for actual production in salt land.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for appraising salinity tolerance potential by using stress resistance of isolated leaves
InactiveCN101706465ASmall scaleImprove screening efficiencyMaterial resistanceMembrane permeabilityLeaf cell
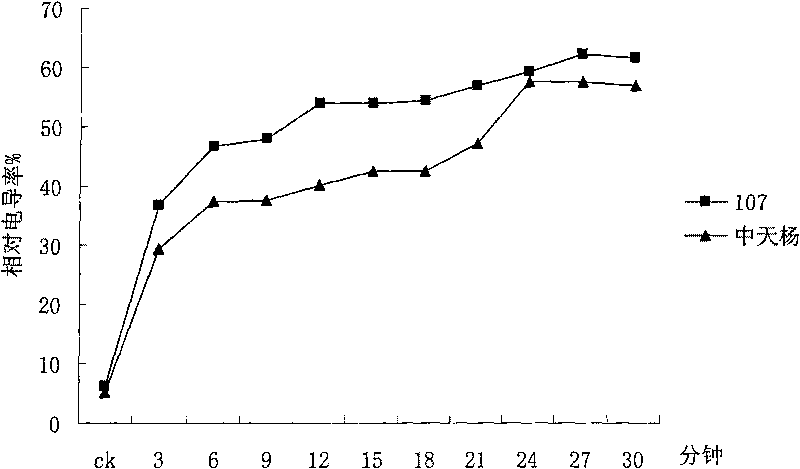
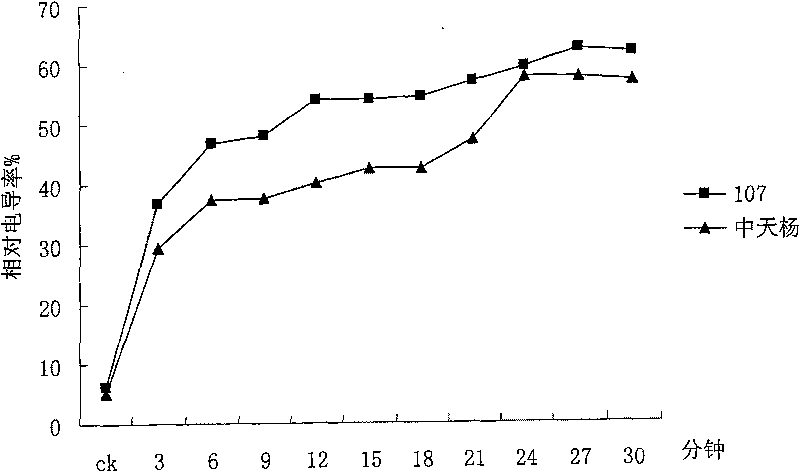
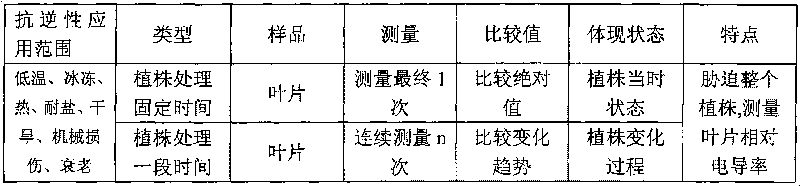
The invention discloses a method for appraising salinity tolerance potential by using stress resistance of isolated leaves. In the method, the leaves directly absorb NaCl, membrane permeability of leaf cells can be destroyed, and the magnitude of relative conductivity can precisely reflect the salinity tolerance of different poplar leaf cells. The membranes of poplar leaf cells are destroyed in high-salt condition, destruction degrees of cell membranes with different salinity tolerance are different, the more serious the destruction degree, the more the exudate in the cells; the destruction degrees of leaf cell membranes are judged on the basis of the relative conductivity of the isolated leaves in saline solution, thus judging genetypes of poplar with different salinity tolerance. The relative conductivity of the isolated leaves which are processed a certain time in high saline solution can rapidly and precisely reflect the salinity tolerance of the genetypes. By using the appraising technology, the salinity tolerance potential of the genetypes can be precisely judged by processing the leaves under certain salt concentration for 6-12min, thus saving labor and time, and having extremely high working efficiency and very wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Preparation method for peony leaf tea
InactiveCN107232372AGood effectReduce pigmentationPre-extraction tea treatmentTea substituesDiseaseAlkaloid
The invention discloses a preparation method for peony leaf tea. A processing technology of a mechanical method and a biological enzymolysis processing technology are comprehensively utilized. The methods, such as, stirring and ultrasonically vibrating, are firstly utilized to break the cell walls of microorganisms so as to release the beneficial matters from the cells, and then the biological enzymolysis technology is utilized to extract the beneficial matters, such as, flavonoids, polyphenols, polysaccharides and alkaloids in the peony leaf cells. According to the preparation method, the peony leaves and the blades with healthcare values are perfectly combined with each other. The peony leaf tea has various benefits to the human body as follows: excellent effects of relieving the symptoms, such as, throat itching, dry throat and irritable cough caused by pharyngitis and effects of detoxifying, beautifying, nourishing, relieving pigmentation, relieving fatigue, resisting against ageing, diminishing inflammation, preventing cancers, preventing and treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, and the like.
Owner:HENAN LUOYANG RED PEONY IND RES & DEV CO LTD
Application of ascorbic acid to improvement of plant photosynthesis efficiency
InactiveCN104886053APhotosynthetic characteristic parameters improvedImprove abilitiesBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyStoma
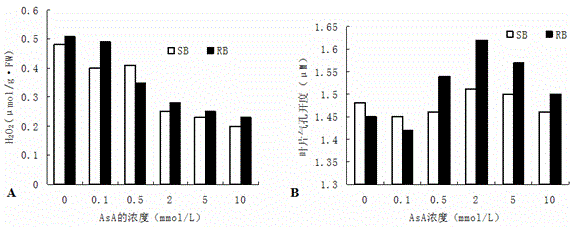
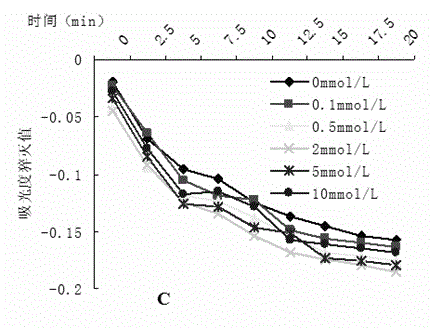
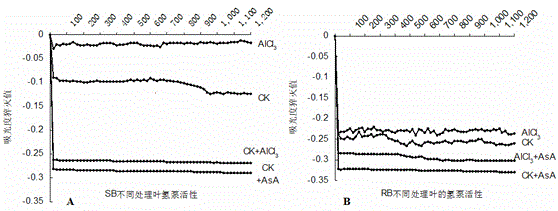
The present invention discloses novel application of ascorbic acid to improvement of plant photosynthesis efficiency. The invention is as below: using ascorbic acid solution with concentration gradient of 0.1,0.5,2,5,10 mmol / L to treat different varieties of plants for 24 hours, and respectively measuring physiological and biochemical parameters of leaves; stressing by using AlCl3 with different aluminum concentration gradients and different aluminum concentration gradients containing 2 mmol / L-ascorbic acid for 24 h, and measuring the photosynthetic characteristic parameters and physiological and biochemical indices of leaves respectively; and comparing the experimental results with the control plants. After ascorbic acid administration, H2O2 accumulation in aluminum sensitive soybean and Al tolerant soybean leaf cells decrease, and H + - pump activity and stomatal aperture and photosynthetic parameters are restored and improved; and these changes help promote plant stomatal opening and enhance photosynthesis and respiration of soybean, thereby enhancing the resistance to aluminum stress of plants.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Whitening and moisturizing mask and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110893169AGood whitening effectGood storage stabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyGlycerol
The invention belongs to the technical field of cosmetics, and provides a whitening and moisturizing mask and a preparation method thereof. The whitening and moisturizing mask comprises the followingcomponents in parts by weight: 2-5 parts of arbutin, 0.7-1.5 parts of tranexamic acid, 0.8-1.5 parts of a desert rose leaf cell extract, 1-3 parts of nicotinamide, 0.5-2 parts of a glycyrrhiza glabraroot extract, 5-20 parts of a ceramide nanoemulsion, 1.7-3.5 parts of ascorbic acid, 1-5 parts of a rhizoma menispermi extract, 0.9-2.5 parts of a luffa root extract, 0.5-2 parts of a manyflower gueldenstaedtid herb extract, 0.1-0.3 part of polyphosphate double salt, 0.9-2.5 parts of polyacrylic acid, 0.1-0.5 part of butanediol, 0.9-2.5 parts of glycerinum and 25-43 parts of water, wherein the ceramide nanoemulsion consists of the following components in parts by weight: 1-5 parts of ceramide, 2-10 parts of olive oil, 5-15 parts of glycerol, 3-8 parts of castor oil polyoxyethylene ether, 1.5-4parts of poloxamer and 35-62 parts of water. By adopting the technical scheme, the problem that in a mask in the prior art, ceramide is poor in dissolution and stability is solved.
Owner:广州微肽生物科技有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com