Patents
Literature
361 results about "Cell extraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue engineering composite
InactiveUS6991652B2Facilitate formationNon-invasive methodBiocideCosmetic implantsTissue engineeringDamages tissue
The invention provides a biocompatible composite for use in a living subject for purposes of repairing damaged tissues and reconstructing a new tissue. The composite includes a biodegradable or absorbable three-dimensional support construct, a liquid or viscous fluid forming a gel matrix or viscous fluid when delivered to an area of interest in a living subject. The biodegradable construct provides an ideal surface for cell or cell extract attachment, while the gel matrix or viscous fluid acts as both a carrier material and a separator for maintaining the space between the constructs as well as the structural integrity of the developing issue.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND +1
Probe Compound for Detecting and Isolating Enzymes and Means and Methods Using the Same
InactiveUS20120231972A1Easy to useHighly sensitive and accurate and reproducible and robust high-throughputOrganic compound preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteFluorescence
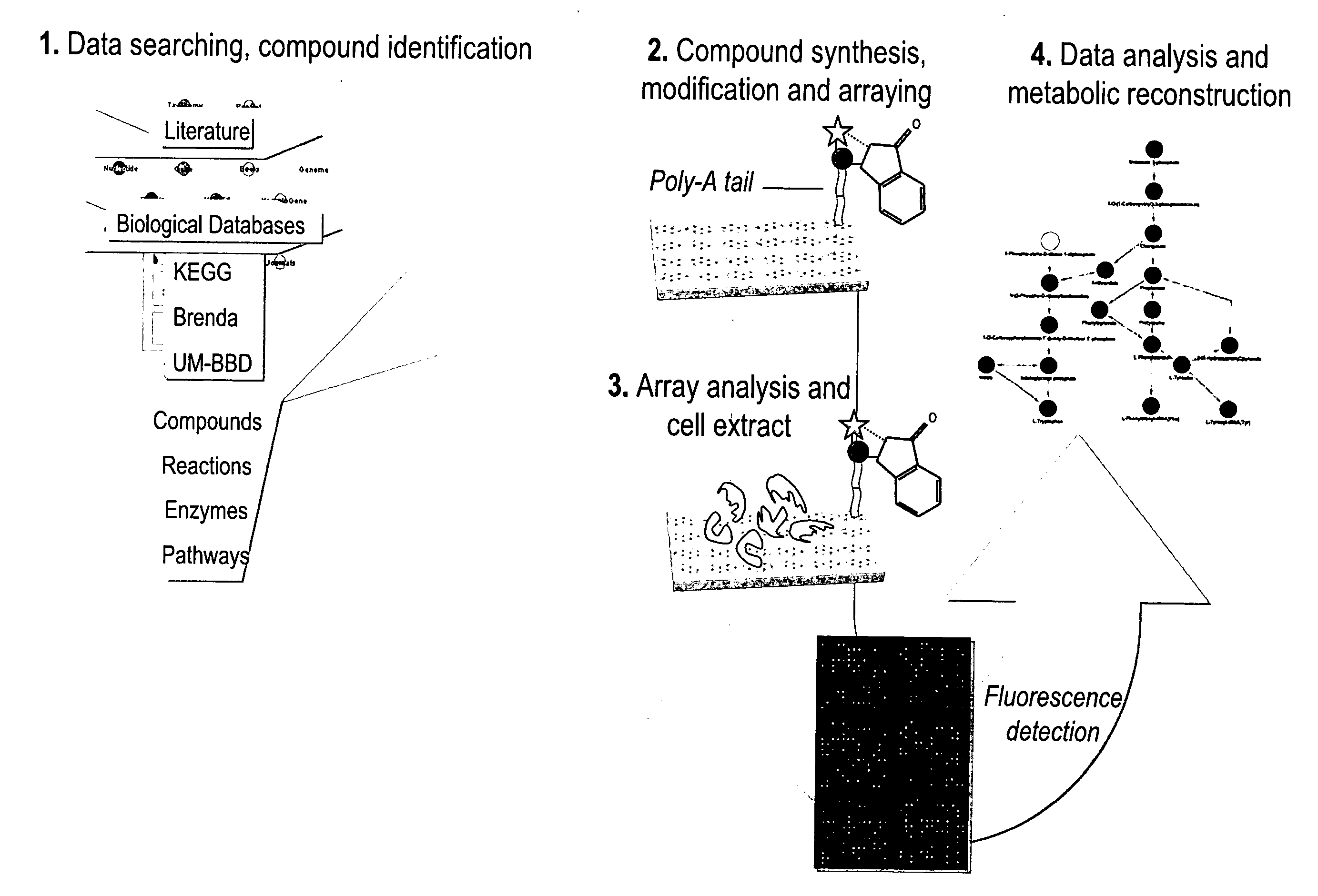
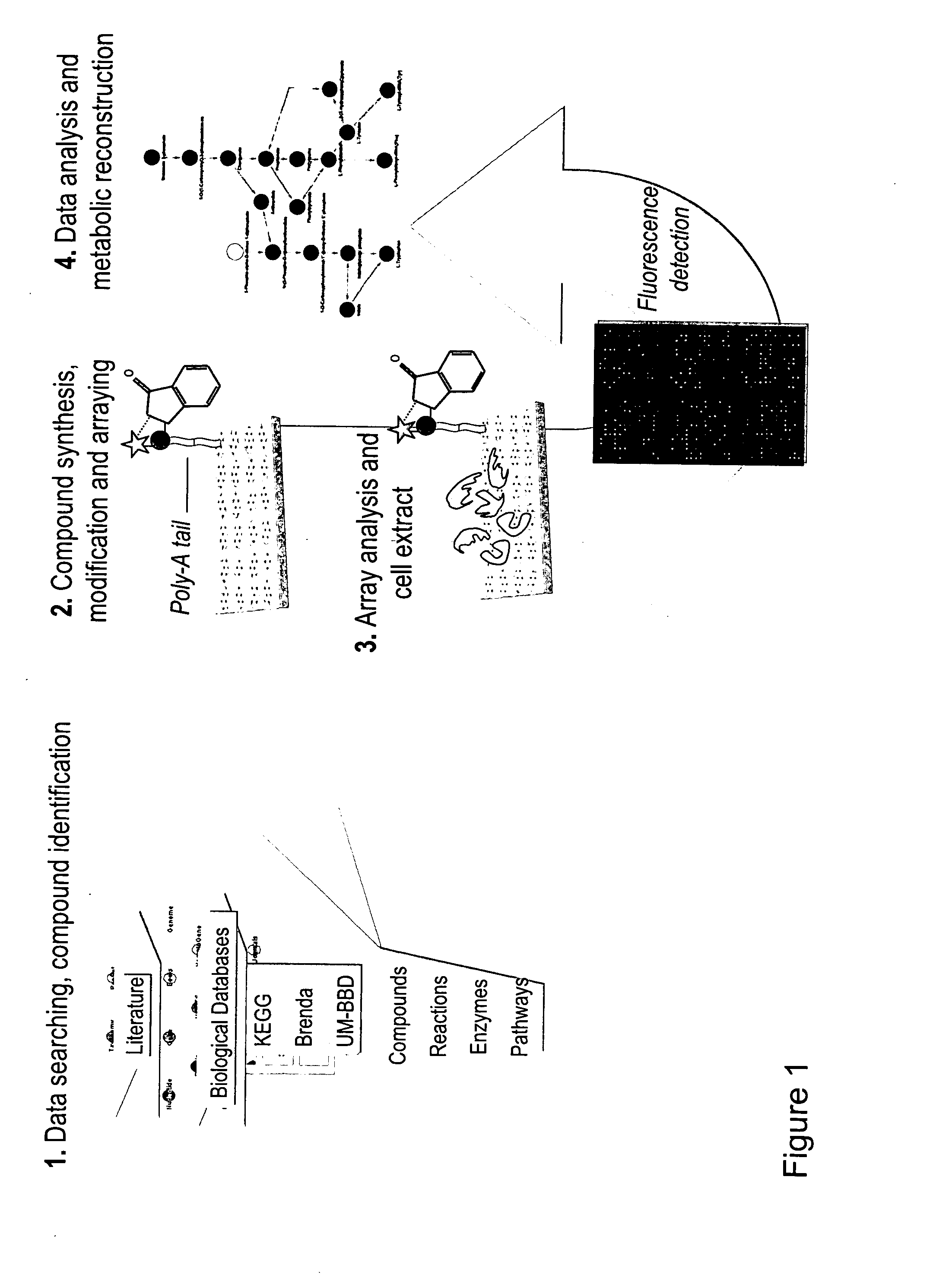
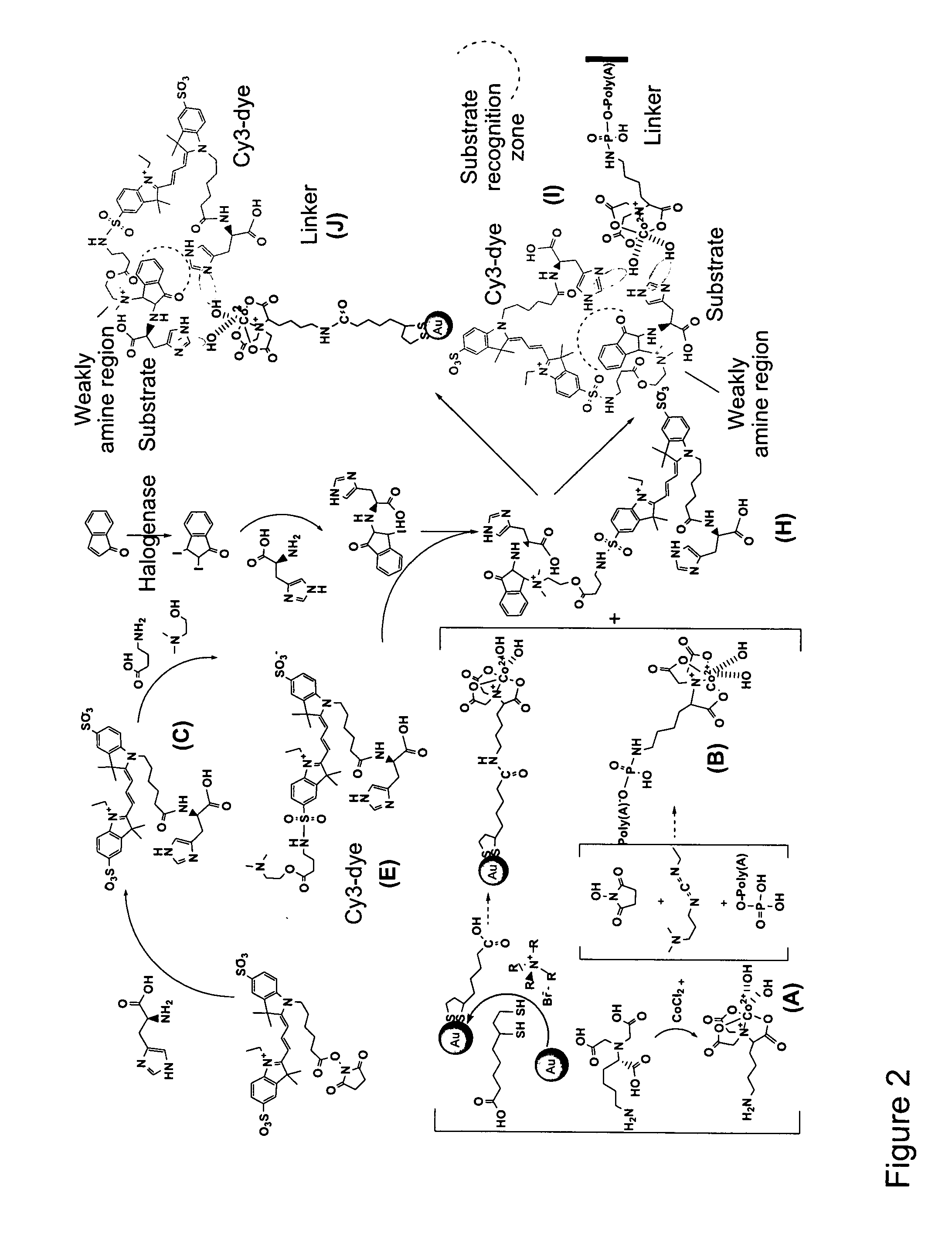
The present invention relates to a probe compound that can comprise any substrate or metabolite of an enzymatic reaction in addition to an indicator component, such as, for example, a fluorescence dye, or the like. Moreover, the present invention relates to means for detecting enzymes in form of an array, which comprises any number of probe compounds of the invention which each comprise a different metabolite of interconnected metabolites representing the central pathways in all forms of life. Moreover, the present invention relates to a method for detecting enzymes involving the application of cell extracts or the like to the array of the invention which leads to reproducible enzymatic reactions with the substrates. These specific enzymatic reactions trigger the indicator (e.g. a fluorescence signal) and bind the enzymes to the respective cognate substrates. Moreover, the invention relates to means for isolating enzymes in form of nanoparticles coated with the probe compound of the invention. The immobilisation of the cognate substrates or metabolites on the surface of nanoparticles by means of the probe compounds allows capturing and isolating the respective enzyme, e.g. for subsequent sequencing.
Owner:GESELLSCHAFT FUR BIOTECHNOLOGISCHE FORSCHUNG MBH GBF +1
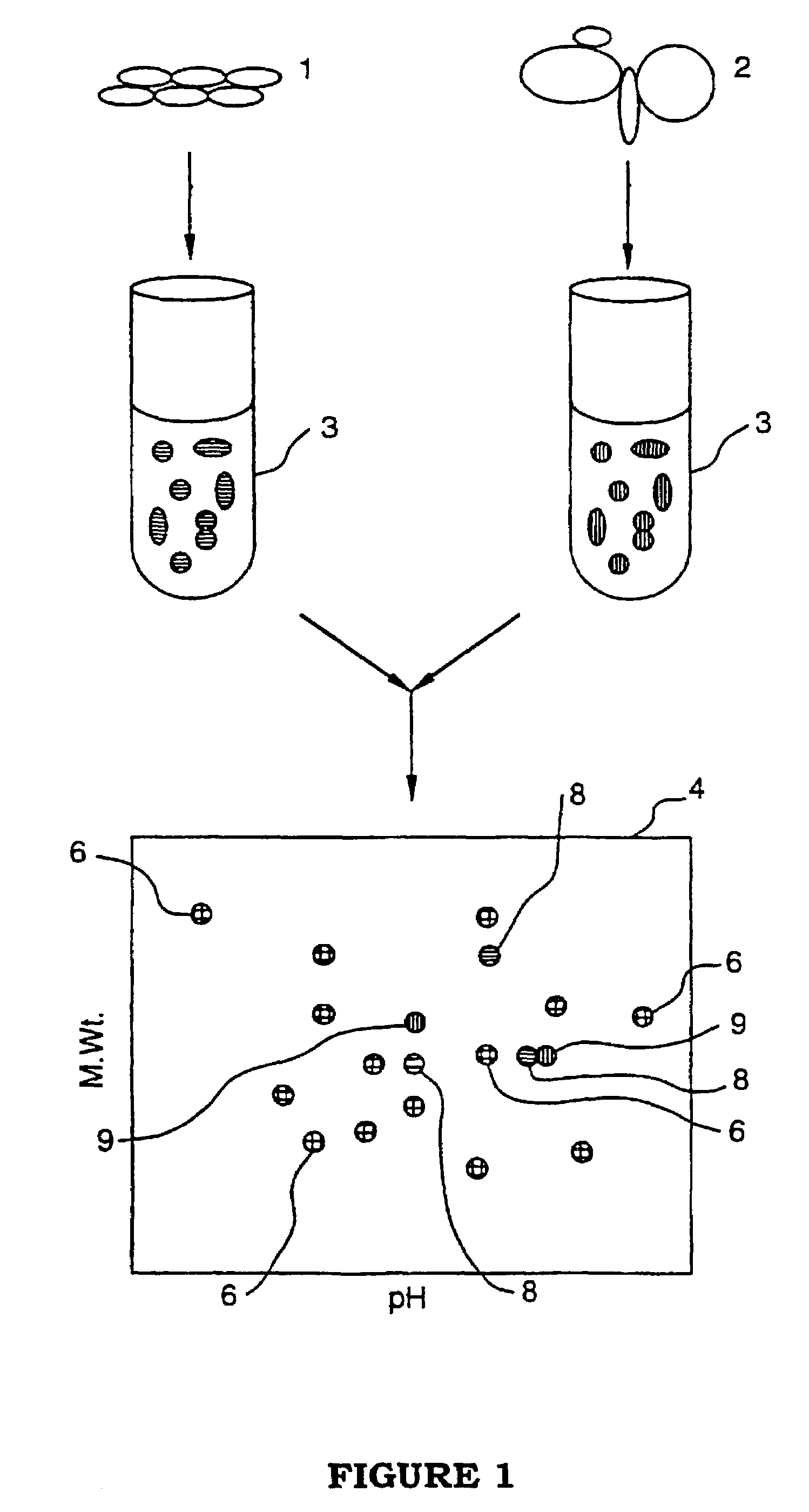
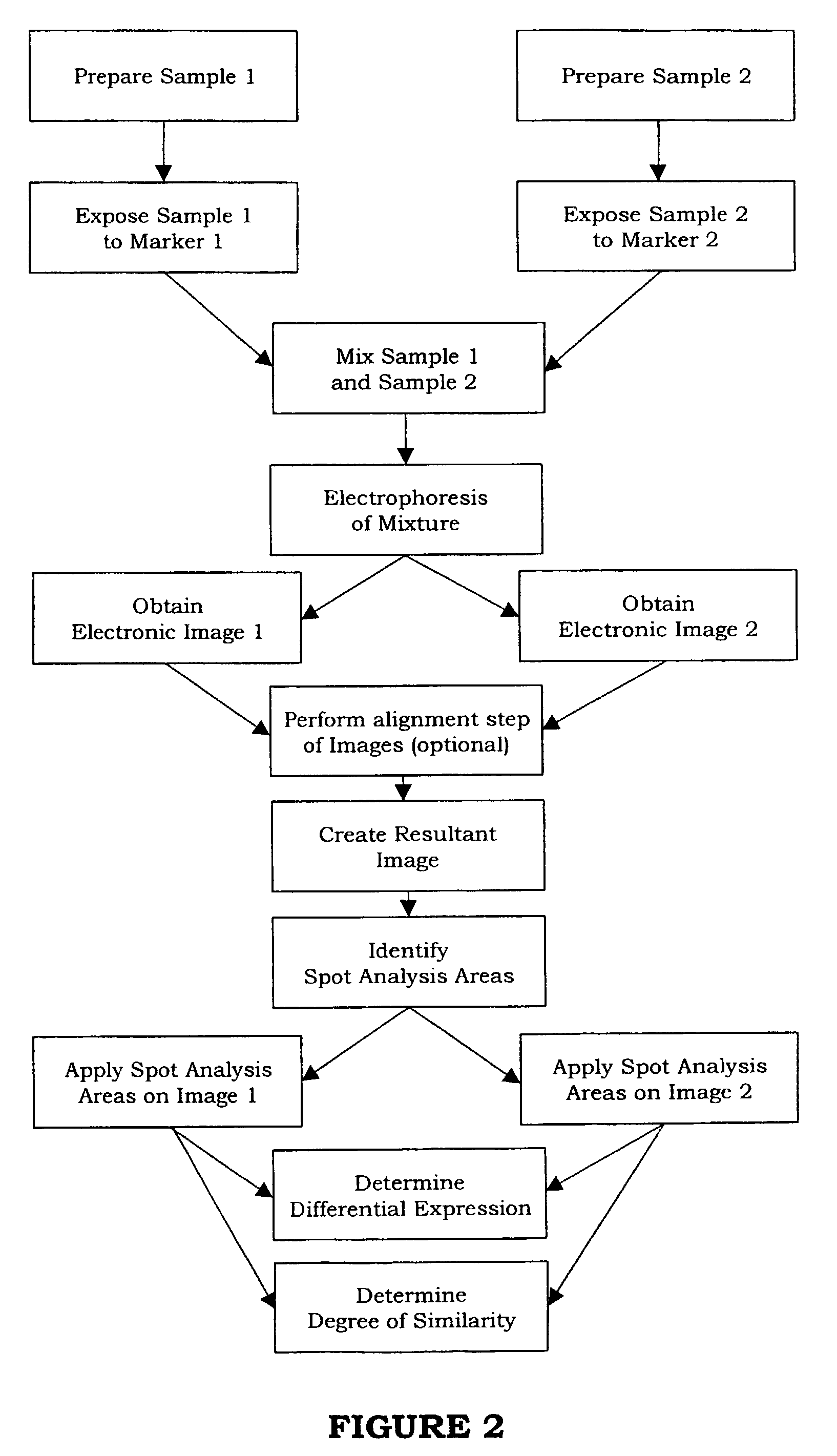
Method of analyzing cell samples, by creating and analyzing a resultant image
InactiveUS7155050B1High precisionVariation of resultImage analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementCell extractionPattern recognition
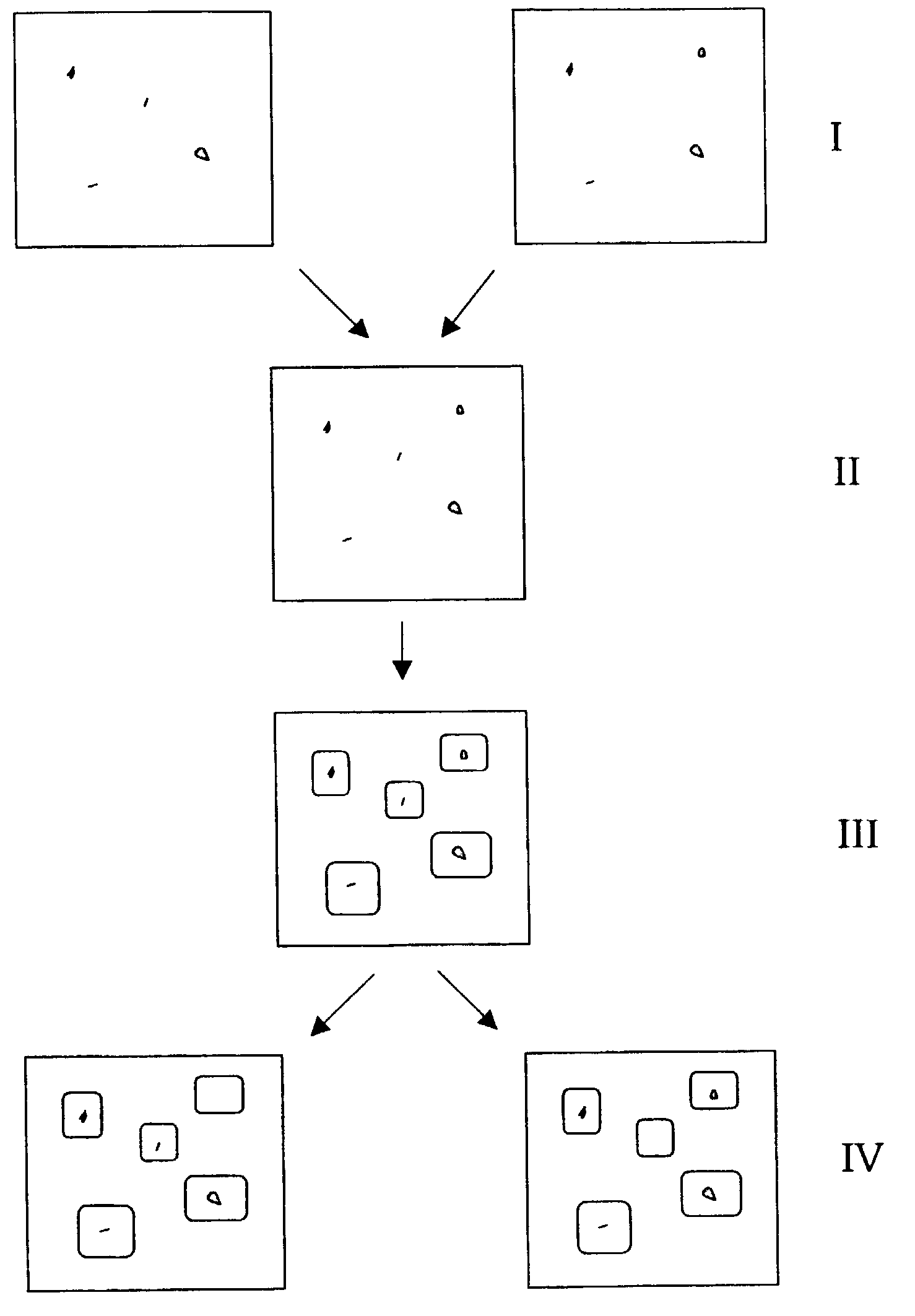
A method is provided for comparing multiple samples of cell extract containing a plurality of components. The method comprises the steps of preparing at least two samples of cell extract from at least two groups of cells and of exposing each of said sample of said cell extract to a different one of a set of matched markers, e.g. luminescent markers, to bind the marker to the cell extract to label the cell extract, each marker within said set of markers being capable of binding to the cell extract and can be individually detected from all other markers within said set. The samples are then mixed to form a mixture and said mixture is electrophoresed to separate the components within the cell extract. At least two electronic images of the electrophoresed mixture are obtained (I) by detection of the individual markers, each image being represented by detection of a marker different from the others. One resultant electronic image (Ires) of the obtained at least two electronic images is created (II) and analyzed in order to identify spot analysis areas (III). The identified spot analysis areas are applied on the respective at least two electronic images for evaluating said areas in order to detect spots representing components of said cell extracts (IV).
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
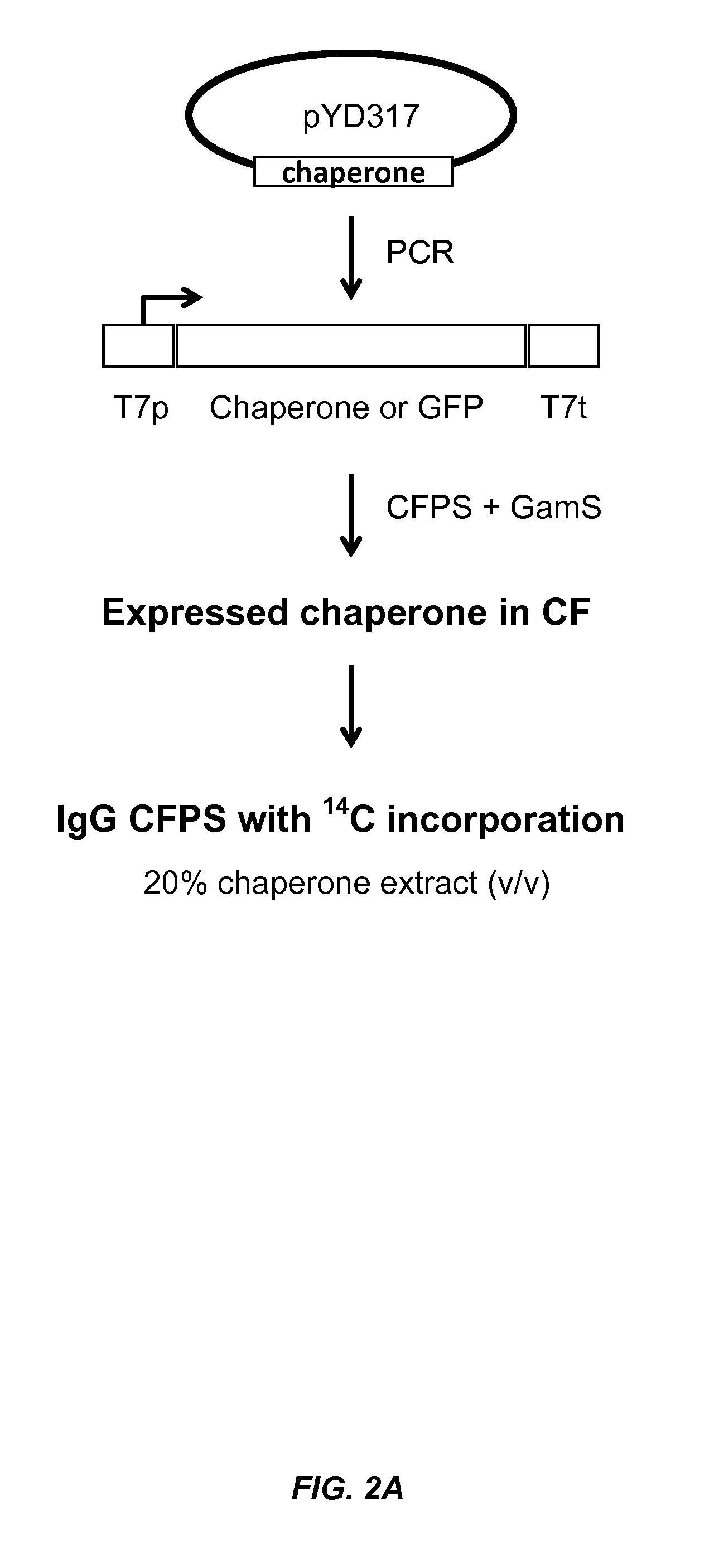
Expression of biologically active proteins in a bacterial cell-free synthesis system using bacterial cells transformed to exhibit elevated levels of chaperone expression
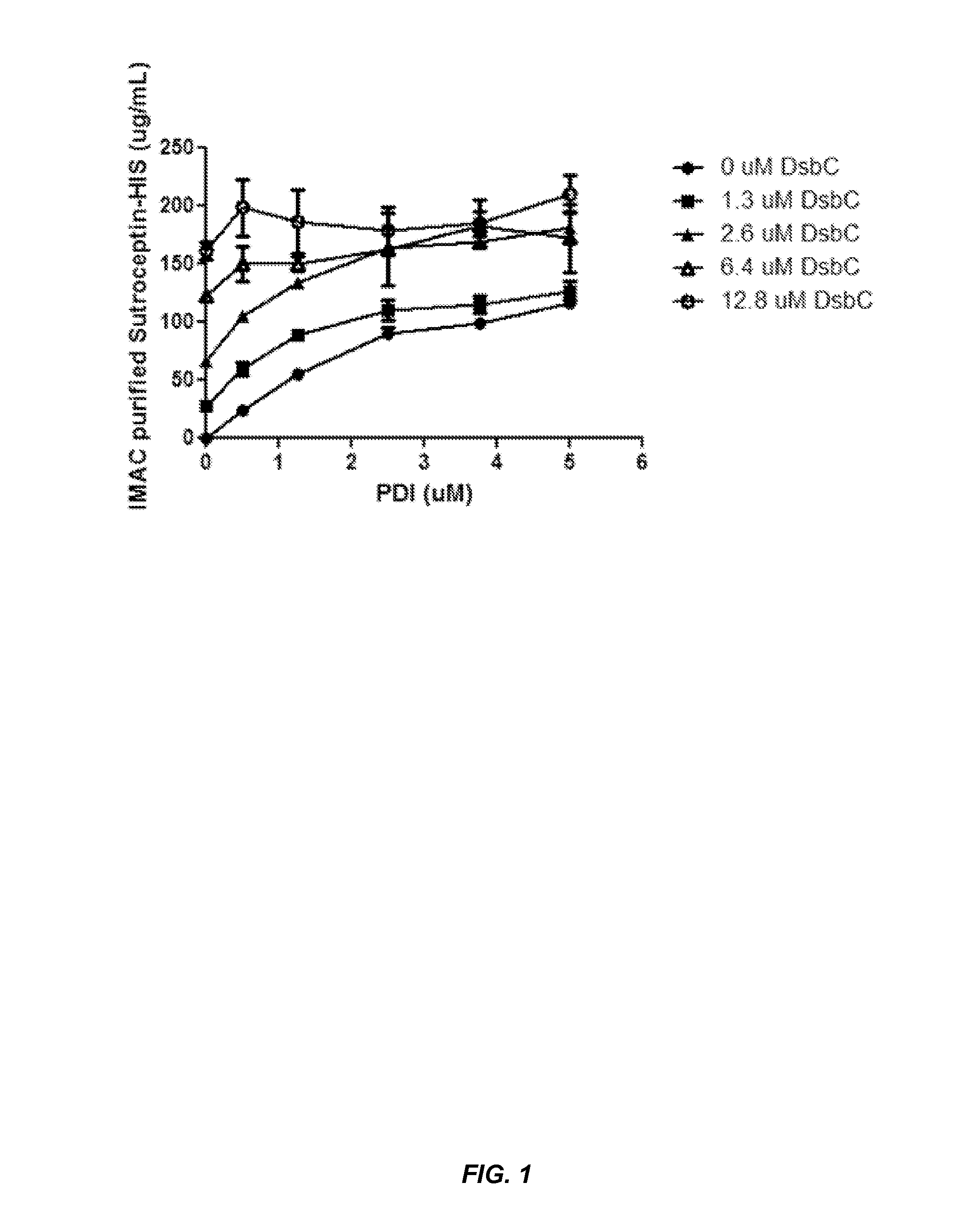
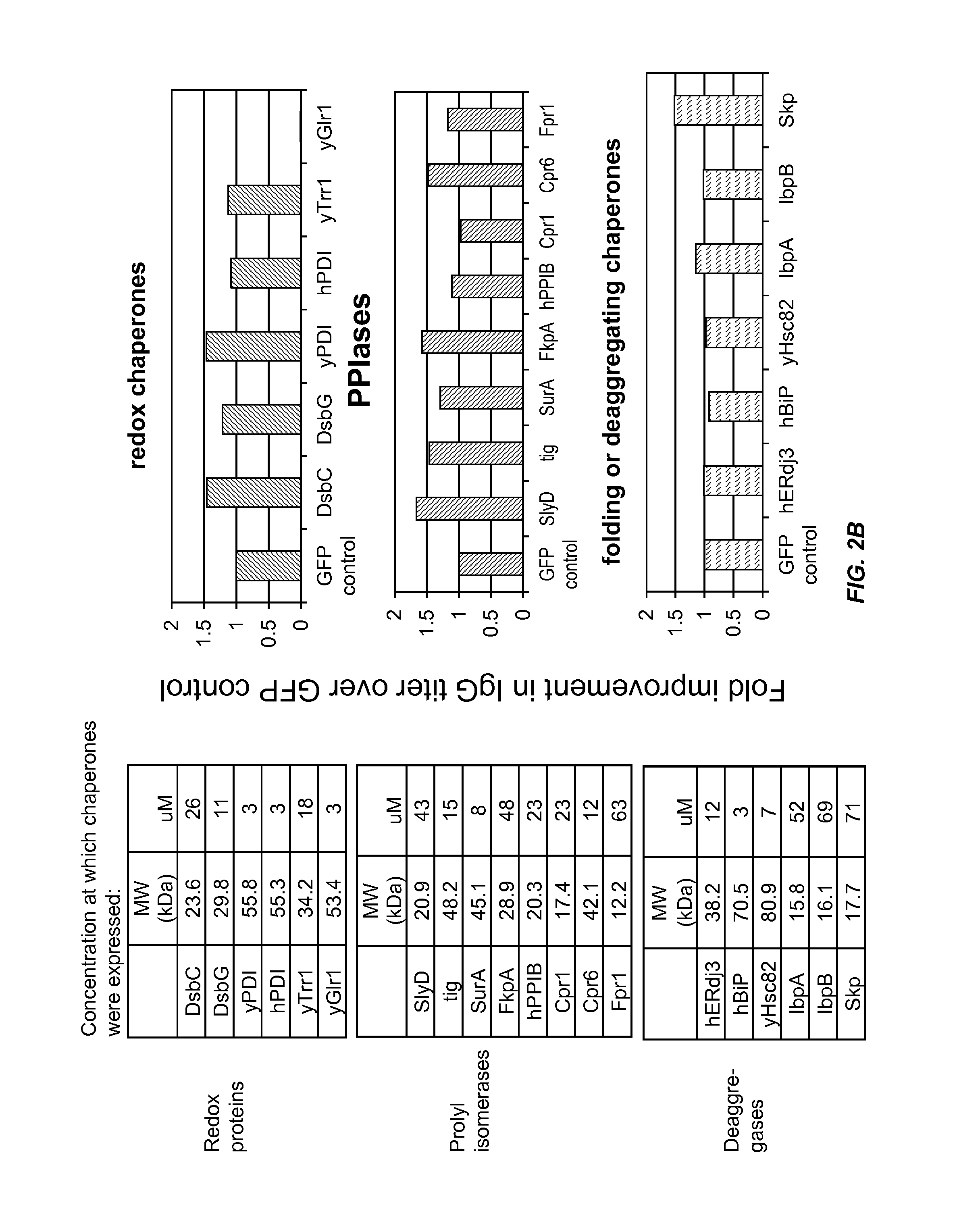
The present disclosure describes methods and systems for improving the expression of a properly folded, biologically active protein of interest in a cell free synthesis system. The methods and systems use a bacterial cell free extract having an active oxidative phosphorylation system, and include an exogenous protein chaperone. The exogenous protein chaperone can be expressed by the bacteria used to prepare the cell free extract. The exogenous protein chaperone can be a protein disulfide isomerase and / or a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. The inventors discovered that the combination of a protein disulfide isomerase and a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase produces a synergistic increase in the amount of properly folded, biologically active protein of interest.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology
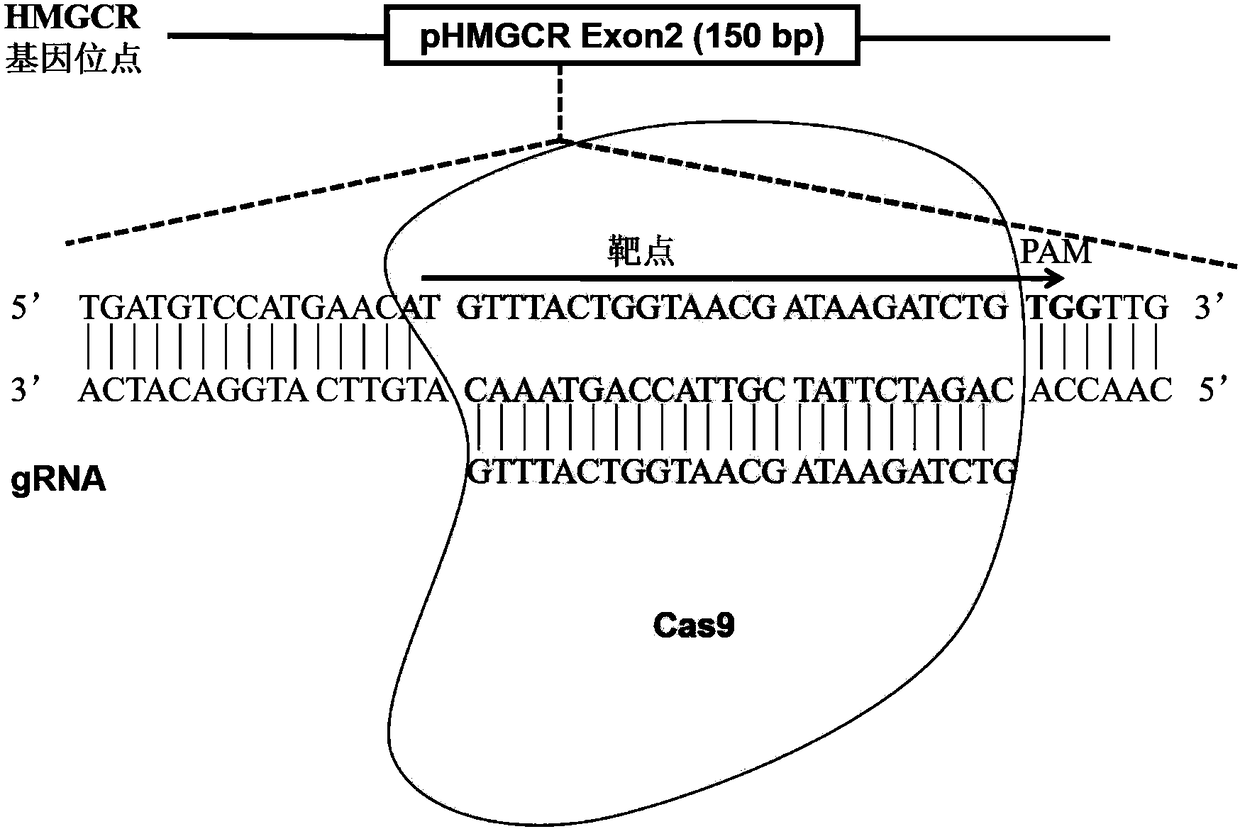
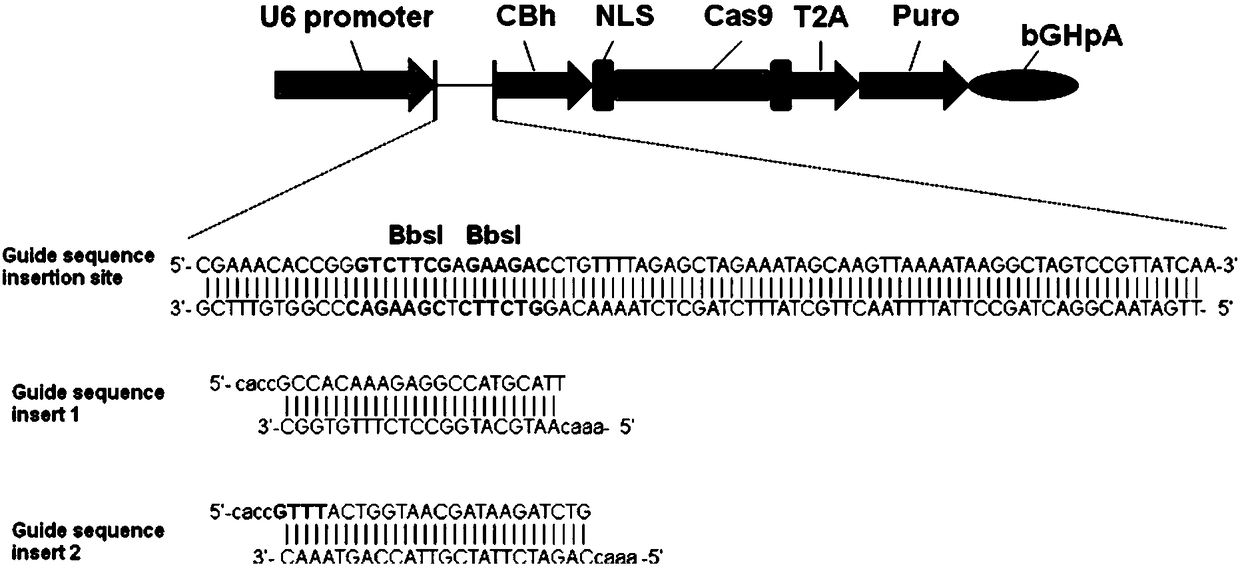
The invention relates to a method for achieving HMGCR gene knockout based on the CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The method is characterized in that two CRISPR / Cas9 target sequence aiming at the HMGCR gene isdesigned, a gRNA single chain is synthesized in vitro, annealing is performed to obtain two gRNA double-chain DNA target insertion fragments, the insertion fragments are inserted into PX459 (pSpCas9(BB)-2A-Puro)V2.0 vectors to obtain the two different-locus plasmids of the target HMGCR gene; the two plasmids are transfected into PK15 cells, puromycin is used to process the cells, the processed cell genome DNA is extracted to perform PCR amplification, the PCR product is denatured, annealing is performed, and then T7E1 is used to perform HMGCR gene knockout identification. The method has the advantages that method can be used for analyzing the expression conditions of sequence and mRNA after the HMGCR gene knockout, whether an off-target phenomenon exists or not can be verified by using amethod combining PCR and T7E1 enzyme treatment, and accordingly the specificity based on target sequence HMGCR-gRNA can be determined; the method is applicable to cell and animal models to achieve fixed-point HMGCR gene knockout, has a reference value to the knockout of other genes, and is good in effect, simple, economical, short in time and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Cartilage cell epimatrix three-dimensional porous sponge stent for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101496913AFacilitate in vitro constructionPromotes regeneration in the bodyBone implantCartilage cellsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold made of natural cartilage, which can compound cells further to construct tissue engineered cartilage, and can be used for clinically repairing cartilage defects. In the invention, conditions which can fully perform cell extraction and form a porous scaffold matrix are provided by processing cartilage into cartilage microfilaments, and then the cell extraction and solidification and / or strengthening treatment are performed to obtain the three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold which is completely decellurized. The antigenicity and cell components are removed in the natural cartilage, and an extracellular matrix component of the cartilage is retained to obtain the scaffold with appropriate pore diameter and porosity, suitable degradation rate, good biocompatibility and certain biomechanical strength. The scaffold has the advantages of broad material sources, low cost, simple and feasible preparation technology, and good repetitiveness; and the scaffold can be widely applied in the field of tissue engineering and has good clinical application prospect.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
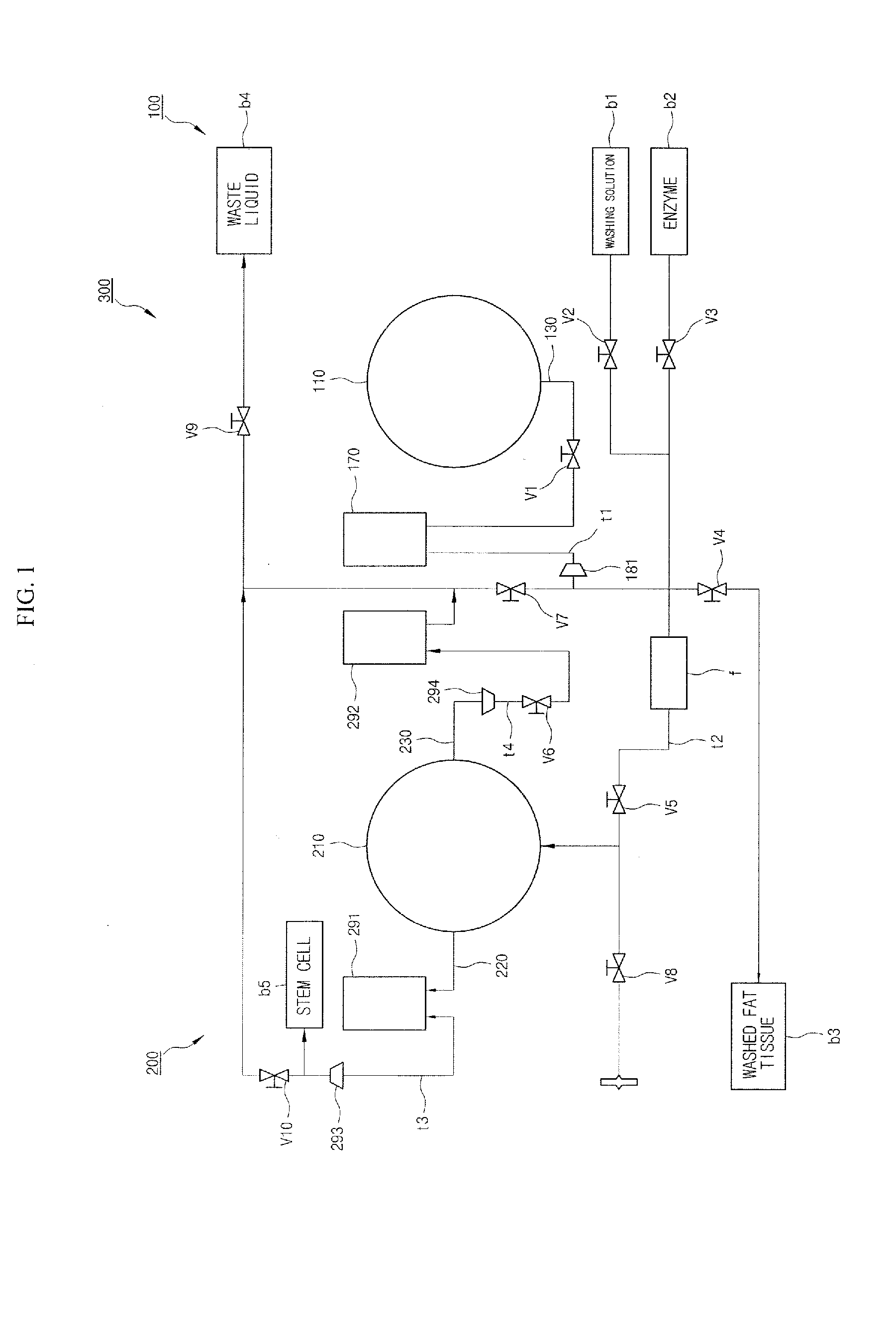
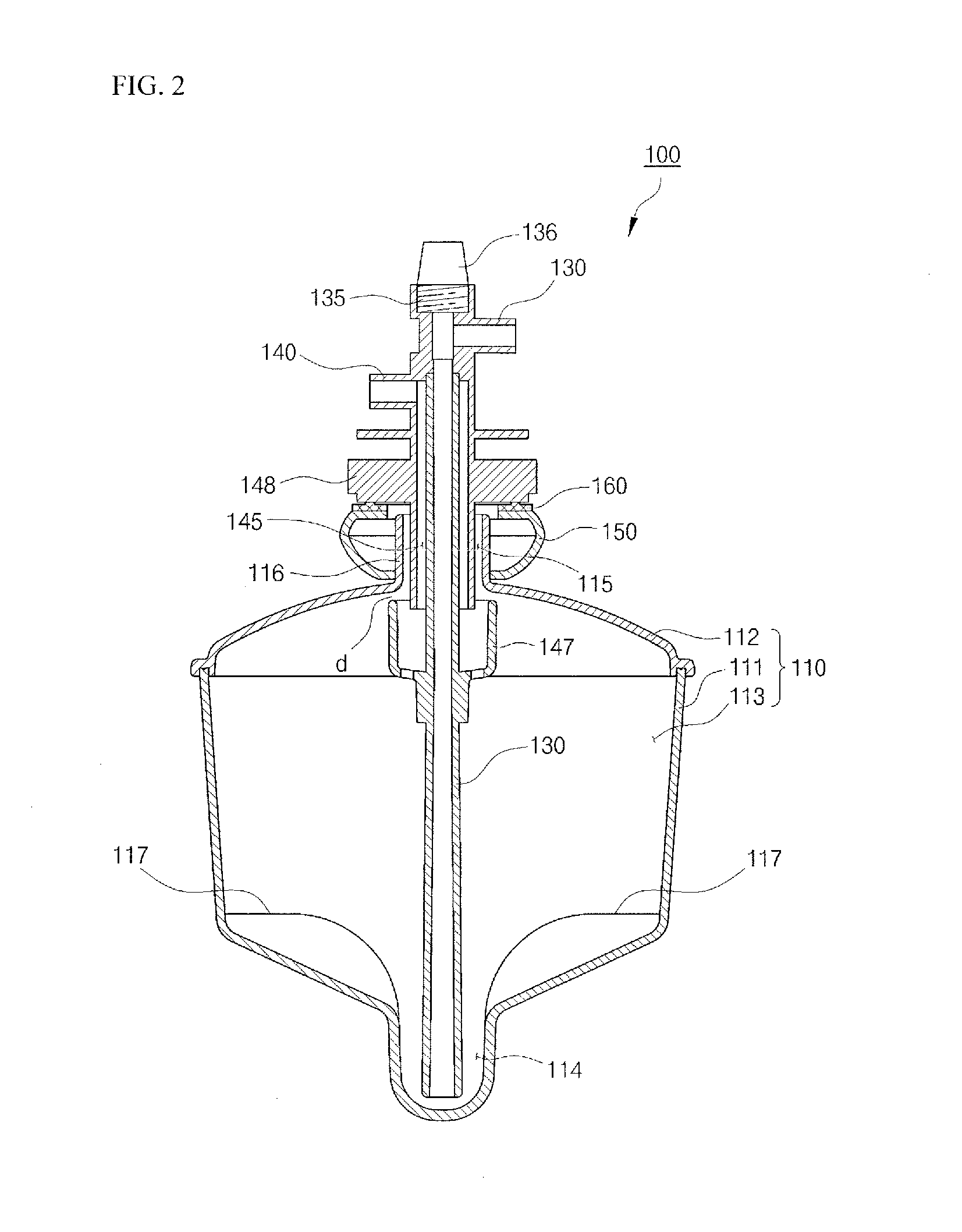
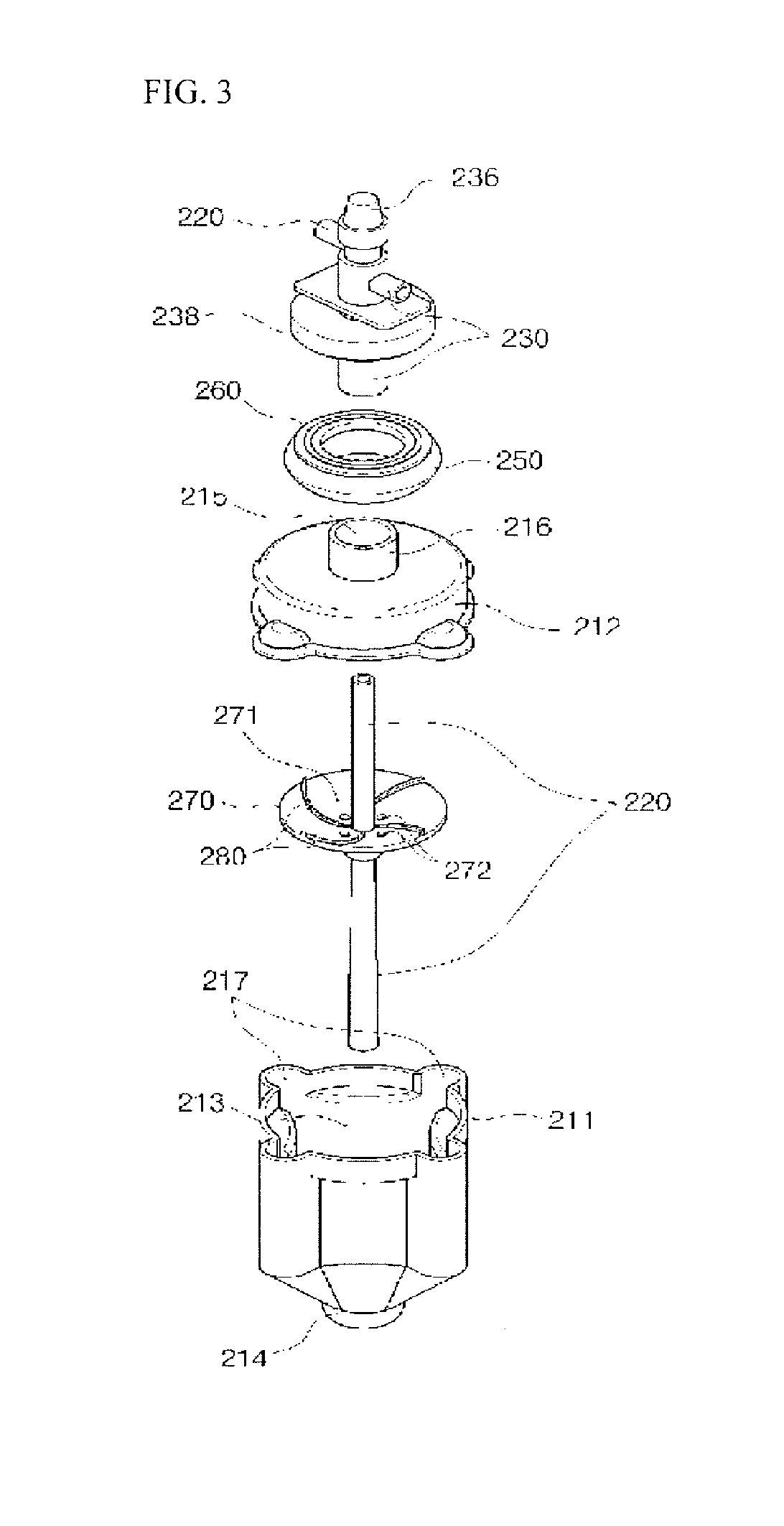
Regenerative cell extraction unit and regenerative cell extraction system
ActiveUS20120214659A1Improve efficiencyBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell extractionEngineering
Provided is a regenerative cell extraction system. The regenerative cell extraction system includes: a regenerative cell separation unit which separates fat tissue; and a regenerative cell extraction unit. The regenerative cell separation unit includes: a sub container which is rotated by a torque applied from an external source and includes a space in which fat tissue is housed; a hollow main pipe which is inserted into the sub container; and a pump which is connected to the main pipe. In addition, the regenerative cell extraction unit receives a regenerative cell-containing substance, which is obtained after the fat tissue is centrifuged by the regenerative cell separation unit, from the regenerative cell separation unit, and extracts regenerative cells from the substance by centrifuging the substance. The regenerative cell extraction unit includes: a main container which is rotated by a torque applied from an external source; a hollow first discharge pipe which is inserted into the main container; and a suction device which is connected to the first discharge pipe; and a plurality of protruding housing portions which bulge outwards along a radius direction with respect to a center of rotation of the main container to accommodate relatively heavy components among components separated from the substance.
Owner:PUREBIO & TECH +2
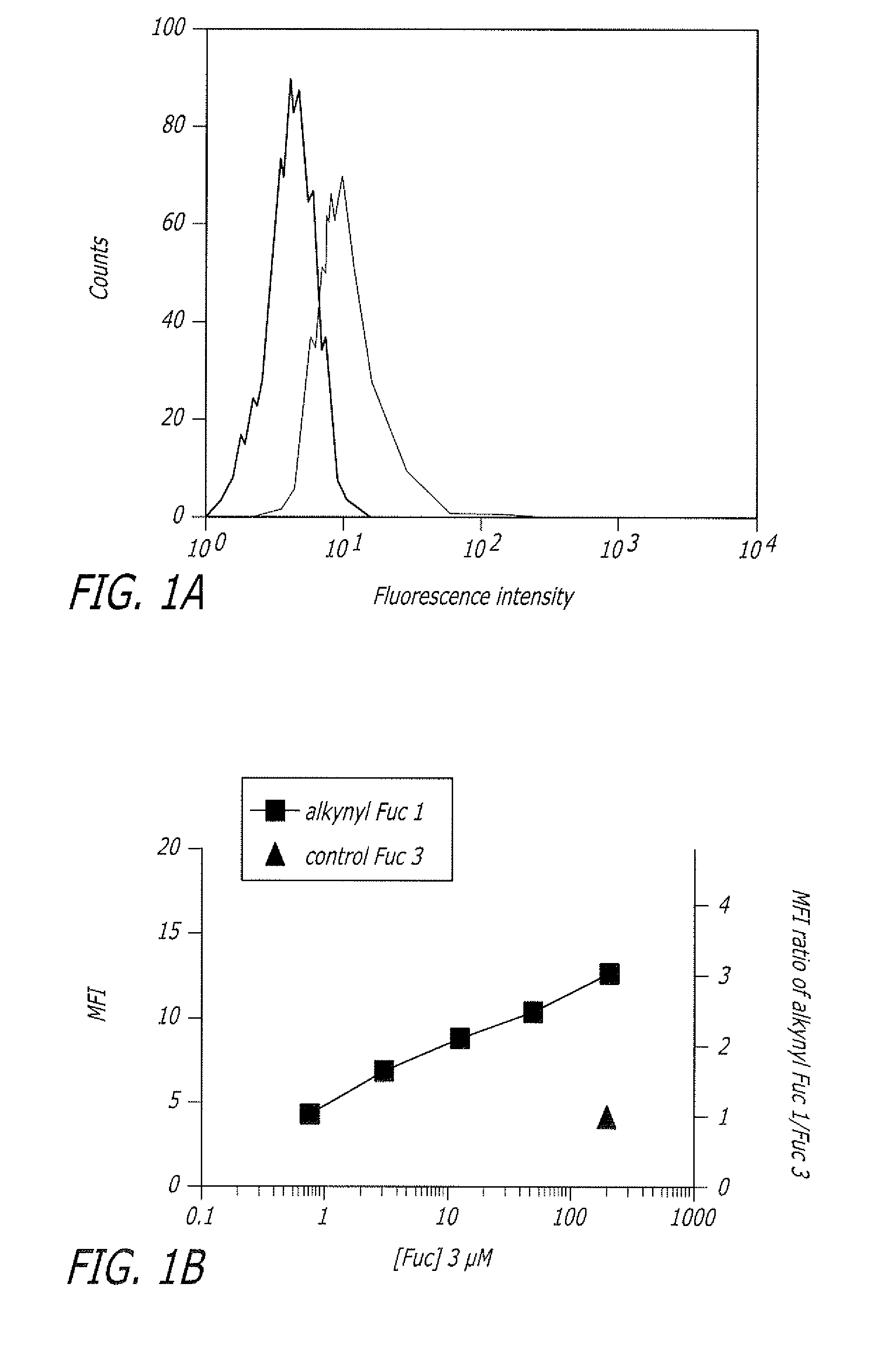
Alkynyl sugar analogs for the labeling and visualization of glycoconjugates in cells
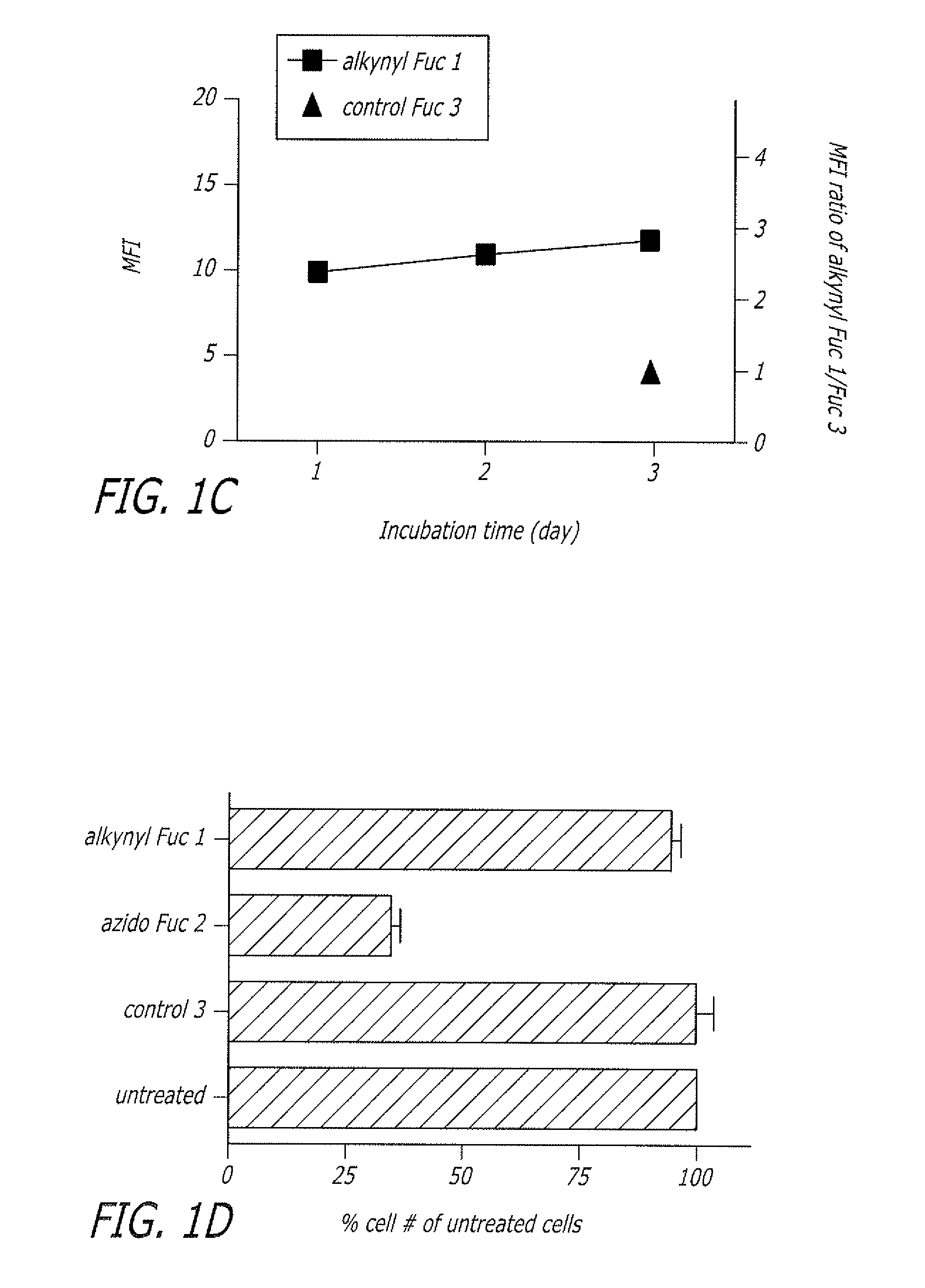
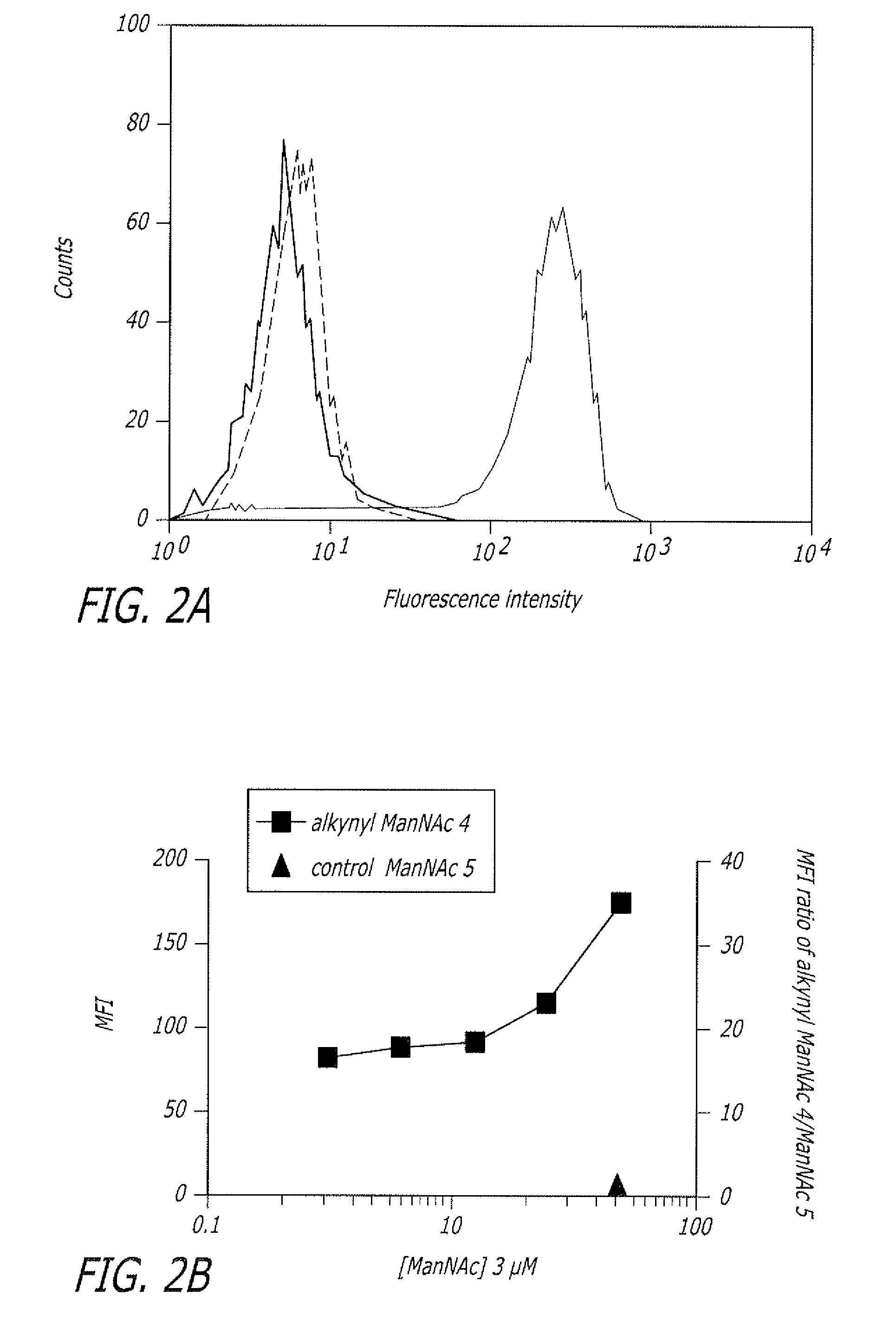
ActiveUS7960139B2Increased toxicitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceWestern blot
The present disclosure relates to a method for metabolic oligosaccharide engineering that incorporates derivatized alkyne-bearing sugar analogs as “tags” into cellular glycoconjugates. The disclosed method incorporates alkynyl derivatized Fuc and alkynyl derivatized ManNAc sugars into a cellular glycoconjugate. A chemical probe comprising an azide group and a visual probe or a fluorogenic probe is used to label the alkyne-derivatized sugar-tagged glycoconjugate. In one aspect, the chemical probe binds covalently to the alkynyl group by Cu(I)-catalyzed [3+2] azide-alkyne cycloaddition and is visualized at the cell surface, intracellularly, or in a cellular extract. The labeled glycoconjugate is capable of detection by flow cytometry, SDS-PAGE, Western blot, ELISA or confocal microscopy, and mass spectrometry.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Administration of cells and cellular extracts for rejuvenation
ActiveUS20090175927A1Prevent damage to skinImprove skin appearanceCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationDisease
The invention describes methods and agents for improving cosmetic appearance, for promoting, improving or restoring health of cells and tissues, preferably skin, and more preferably, for restoring aged or damaged skin to a healthy appearance. This invention relates to the use of cells and cellular extracts in rejuvenation and healing technologies thereby improving healing and regeneration of all bodily tissues and organs. The present invention relates to compositions and methods of managing, preventing, and treating scars. The invention also relates to prevention of deterioration, damage and malfunction of cells and tissues, and to promote, improve or exceed cellular function in order to promote, improve and exceed appearance, vitality and health. In some embodiments, the invention relates to compositions of cells, eggs, cell extracts, egg extracts, and extract components such as purified nucleic acids, polypeptides, lipids, carbohydrates or other natural products. Said components can also be synthesized. In other embodiments, the cells are differentiable cells preferably stem cells or eggs. In some embodiments, compositions are used in a method that comprises application of compositions to tissues, including skin and / or wounds after removal of tissue surface layers. In other embodiments, the invention relates to methods of dedifferentiation of cells and / or dedifferentiation followed by differentiation. In other embodiments, the invention relates to managing, preventing, and treating skin diseases.
Owner:REGENICS AS
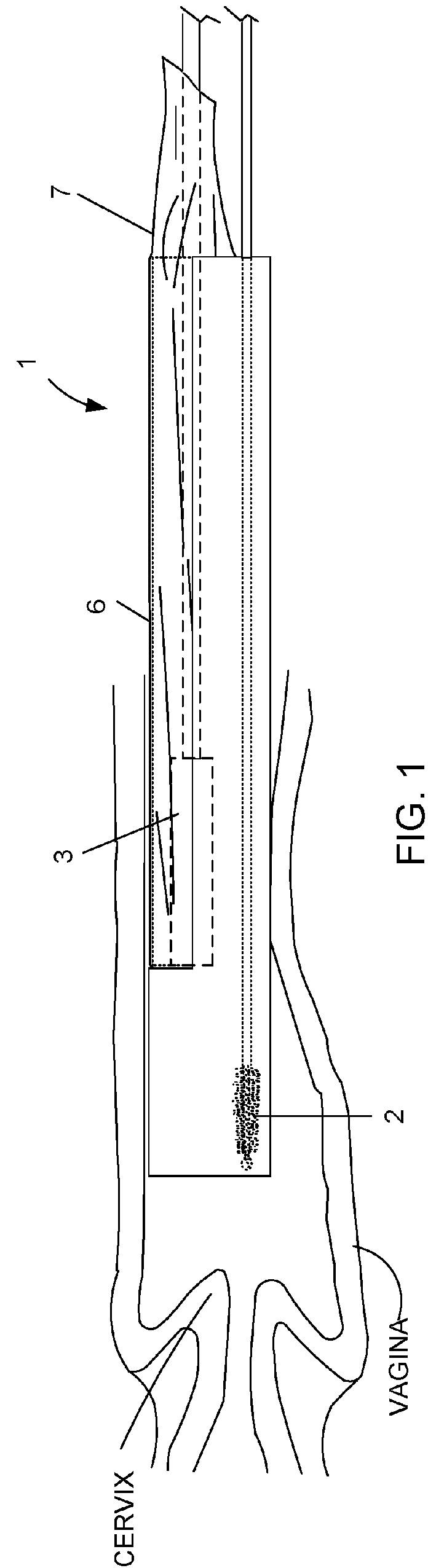
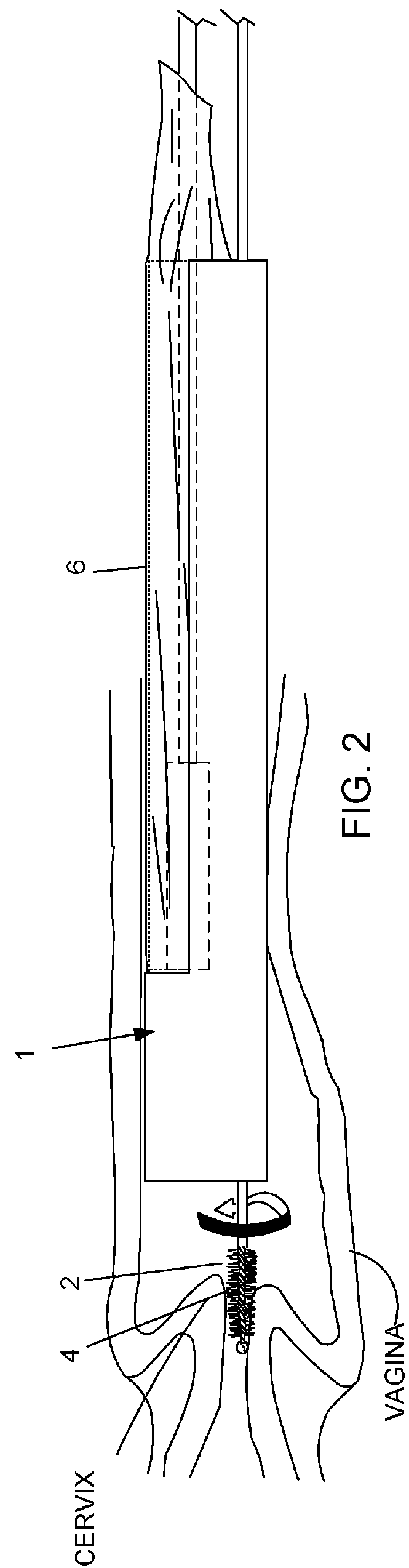
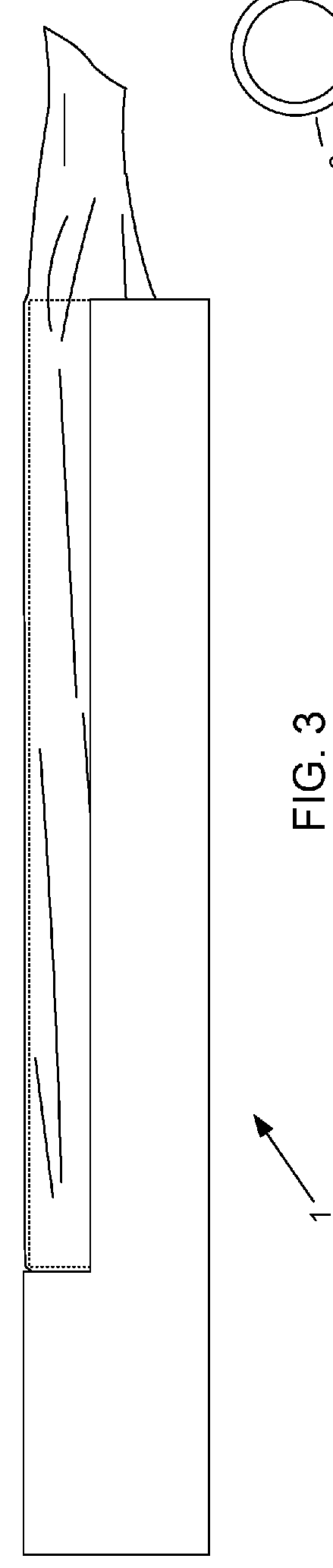
Device and method for conducting a pap smear test
A protective guide for protecting a cell extraction device during a Pap smear. A camera protective cover encloses a camera and a light emitting device. A thin, flexible transparent sheath encloses the camera cover. A cell extraction device cover encloses the cell extraction device. The location of the cervix is determined by utilizing the camera. The cell extraction device is pushed outward from the cell extraction device cover so that said cell extraction device head contacts the cervix and removes cells from the cervix. The cell extraction device is pulled back into the cell extraction device cover after the cells have been removed from the cervix. In a preferred embodiment the camera and light emitting device is an endoscope and the camera cover is an endoscope cover.
Owner:MILLARD MATTHEW D +2
Vascular substrate without cell in vascular tissue and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a blood vessel matrix for removing cell components in vascular tissue and a preparing method thereof. The invention provides a method which can remove the cell components in the vascular tissue and protect the structural integrity of the cell matrix at utmost. The method comprises the steps of cell extraction, detergent removing and enzyme treatment. The blood vessel cell removing matrix prepared by the invention has the advantages of excellent mechanical strength, proper porosity and low cytotoxicity and can successfully implant cells into the cell matrix, thereby providing a favorable tissue stent for the blood vessel tissue engineering.
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
Methods for improved in vitro protein synthesis with proteins containing non standard amino acids
ActiveUS20160060301A1Improves chaperone levelImproves translation functionPeptide-nucleic acidsBacteriaBiopolymerAmino acid
The invention relates to genomically recoded organisms, platforms for preparing sequence defined biopolymers in vitro comprising a cellular extract from a genomically recorded organism, and methods for preparing sequence defined biopolymers in vitro are described. In particular, the invention relates to genomically recoded organisms comprising a strain deficient in release factor 1 (RF-1) or a genetic homolog thereof and at least one of at least one additional genetic knock-out mutation, at least one additional upregulated gene product, or both at least one additional knock-out mutation and at least one additional upregulated gene product.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method for simultaneously treating multiple kinds of biological tissue
ActiveCN106267346AUniform treatmentSimple processTissue regenerationProsthesisCell extractionCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously treating multiple kinds of biological tissue. The method includes the steps of pretreating, degreasing, cell extraction, crosslinking and sterilization. The method for simultaneously treating the multiple kinds of biological tissue can simultaneously treat the multiple kinds of biological tissue, the batch-treated biological tissue amount is large, the treatment degree is uniform, the process is simple, industrialization is easy, and efficient production is achieved. According to the method for simultaneously treating the multiple kinds of biological tissue, use of strong acid, strong base and protease is completely avoided, natural three-dimensional collagen support fiber structures of extracellular matrixes of the multiple kinds of biological tissue can be reserved, and cell components, causing immunogenicity, in the tissue are removed. The biological tissue prepared through the method has good bio-compatibility and mechanical performance, compared with natural biological tissue, high degradation resistance is achieved, and the biological tissue can be used for repairing various kinds of soft tissue injuries.
Owner:SUZHOU HENRUI DISHENG MEDICAL CO LTD +1
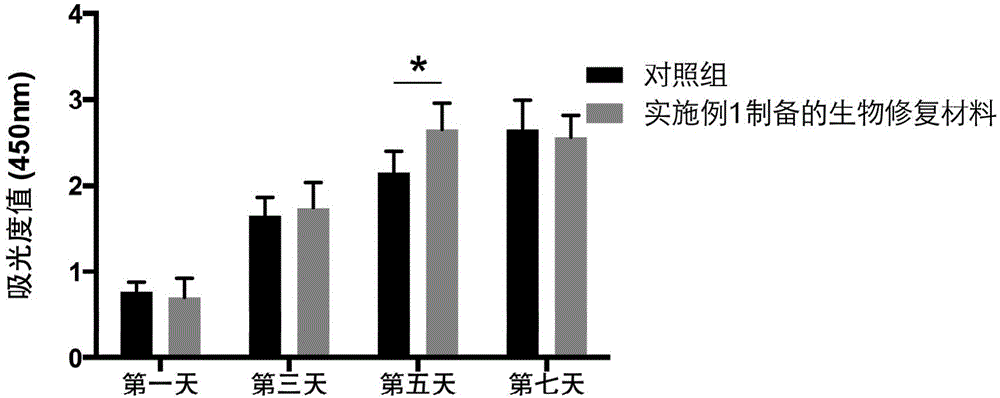
Biological repairing material for abdominal wall defect and preparation method of biological repairing material
InactiveCN104353111AAdjustment of mechanical propertiesImprove adhesionNon-woven fabricsProsthesisFiberCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medical engineering, and discloses a biological repairing material for an abdominal wall defect and a preparation method of the biological repairing material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing pre-treatment on the muscular tissue of rectus abdominis of a dead animal; (2) performing cell extraction treatment to prepare a skeletal muscle acellular matrix biological thin sheet; (3) dissolving the skeletal muscle acellular matrix biological thin sheet into pepsase for digestion; (4) performing electrostatic spinning on skeletal muscle acellular matrix microparticles obtained by digestion and polycaprolactone to obtain a polycaprolactone / skeletal muscle acellular matrix blended electrostatic spinning fiber film which is the biological repairing material disclosed by the invention. According to the method, a skeletal muscle acellular matrix from abdominal wall tissue and polycaprolactone are combined by an electrostatic spinning technology; the preparation materials can be degraded, and products from degradation are harmless to a human body; the prepared biological repairing material can well simulate constituents and the structure of an extracellular matrix and is good in biocompatibility and biomechanical property.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
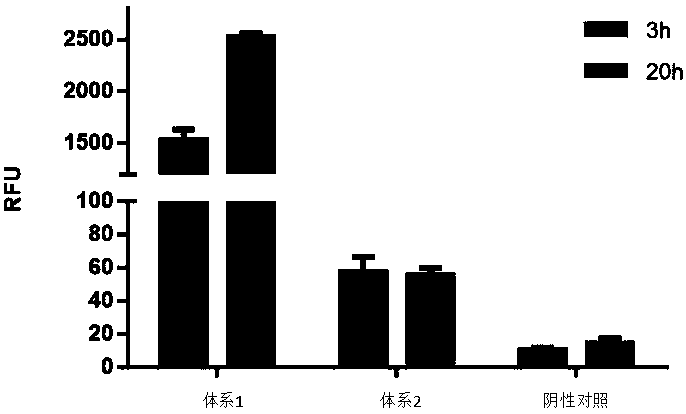
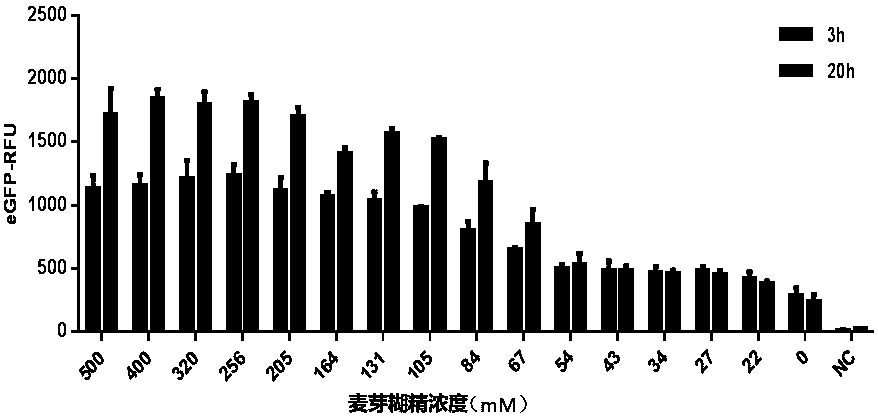
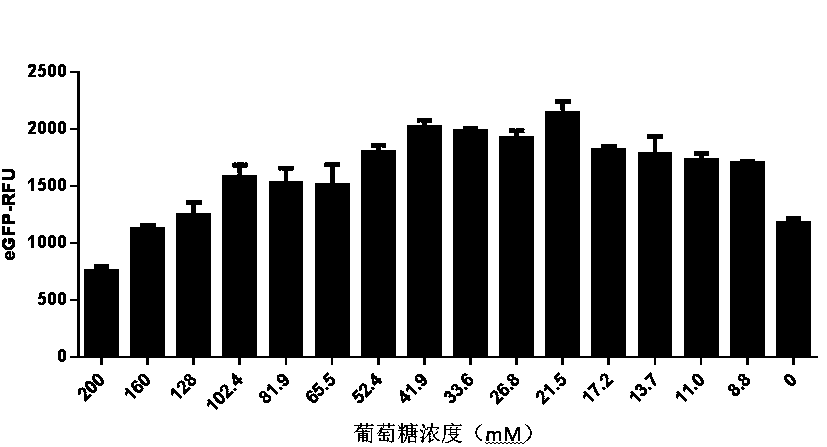
Optimized in vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application
ActiveCN111378708AIncrease productionLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetCell free
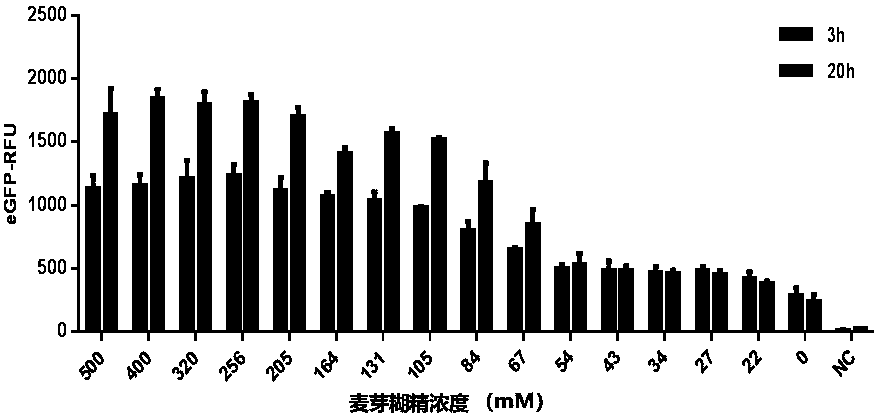
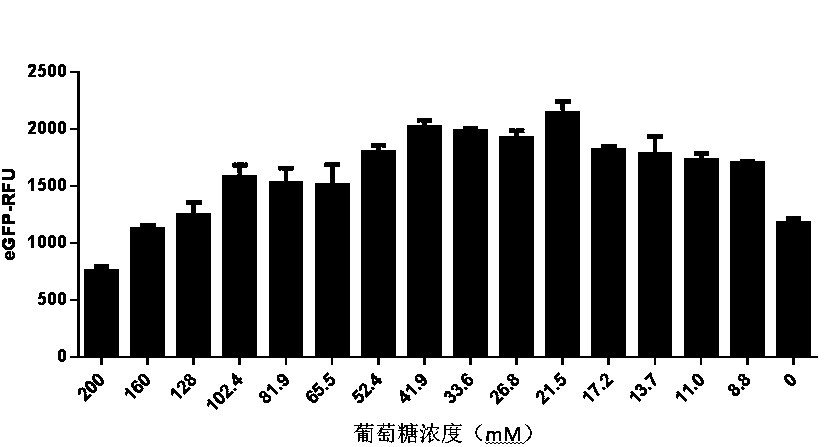
The invention discloses an optimized in vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises a cell extract, a carbohydrate material, a phosphate compound, a buffering agent and a DNA molecular template for encoding an exogenous protein, wherein the cell extract is a yeast cell extract inserted into a T7 RNA polymerase gene; the carbohydrate material is a mixture of glucose and maltodextrin; the buffering agent is a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane buffering agent; and the DNA molecule template is prepared by a nucleic acid isothermal amplification method, and a sequence as shown in SEQID NO.1 is inserted into the upstream of the coding sequence of the exogenous protein in the DNA molecular template. By optimizing, the cost of in vitro protein synthesis is reduced and the yield ofthe target protein is increased.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Culture method of hair follicle stem cell for treating baldness, as well as syringe
InactiveCN102586177ARich sourcesGrow fastInfusion syringesArtificially induced pluripotent cellsCell extractionFibroblast
The invention relates to the field of health-care, and in particular relates to a culture method of hair follicle stem cell for treating baldness, as well as a syringe. The culture method comprises the following steps: A, digesting excised hair follicles by utilizing separase; B, cutting bugle of follicles; C, digesting the follicle bugle by utilizing pancreatin; D, centrifugally collecting the follicle bulge obtained in the step C to obtain cells; E, culturing the cells in DEME (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium) culture solution, and primarily separating; F, culturing the product which is obtained in primary separation of the step E in a culture dish; and G, centrifugally collecting upper unattached keratinocyte and follicle fibroblast which are cultured in the step F, and culturing to obtain hair follicle stem cells. The syringe comprises a hair follicle stem cell extraction component and a syringe needle, wherein the hair follicle stem cell extraction component is used for quantitatively extracting hair follicle stem cells, and connected with the syringe needle; and the syringe needle is bent and blunt. According to the method and the syringe, hair growth under baldness situation can be improved.
Owner:北京雍禾植发技术研究院有限公司
In-vitro protein synthesis system, method of enhancing protein synthesis efficiency by using system and kit including system
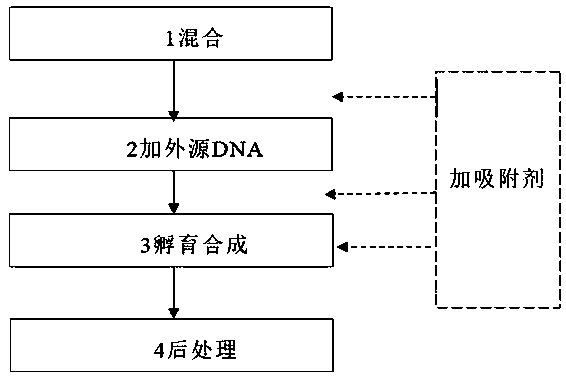
PendingCN110964736AHigh synthesis efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign proteinCell extraction
The invention provides an in vitro protein synthesis system, a kit and a preparation method. The in vitro protein synthesis system includes: (a) a cell extract; (b) an adsorbent used for enhancing protein synthesis efficiency; (c) amino acids; (d) nothing or NTPs; and (e) exogenous DNA molecules. A method for enhancing in vitro protein synthesis efficiency is provided. The method adopts the synthesis system and includes the following steps: (1) performing mixing; (2) adding the exogenous DNA molecules; (3) performing incubation synthesis; and (4) performing post-processing; and the method alsoincludes a step of adding the adsorbent after the step (1) or (2). In addition, the kit of the in vitro protein synthesis system is also provided. Therefore, the synthesis efficiency of foreign protein can be significantly enhanced.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
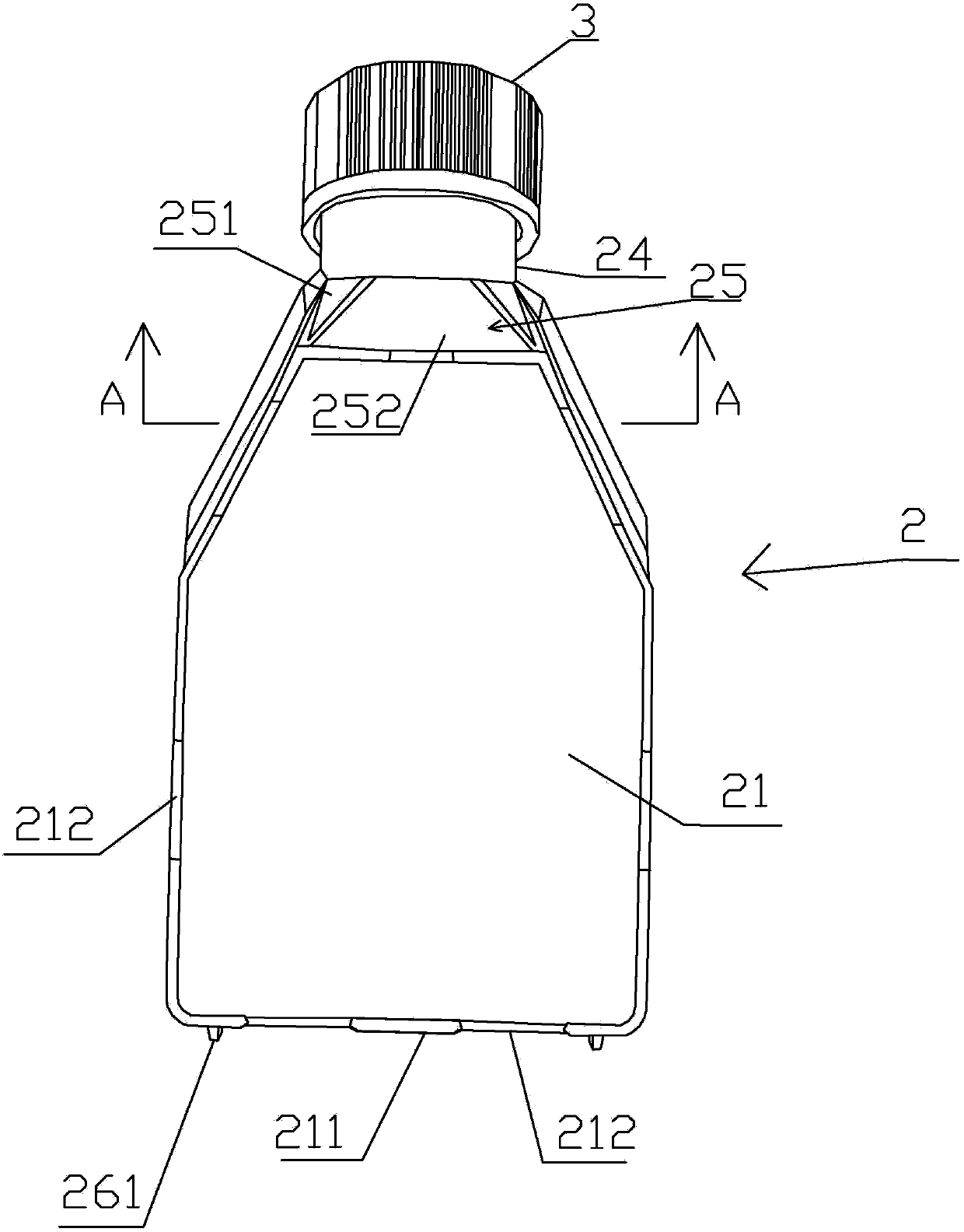
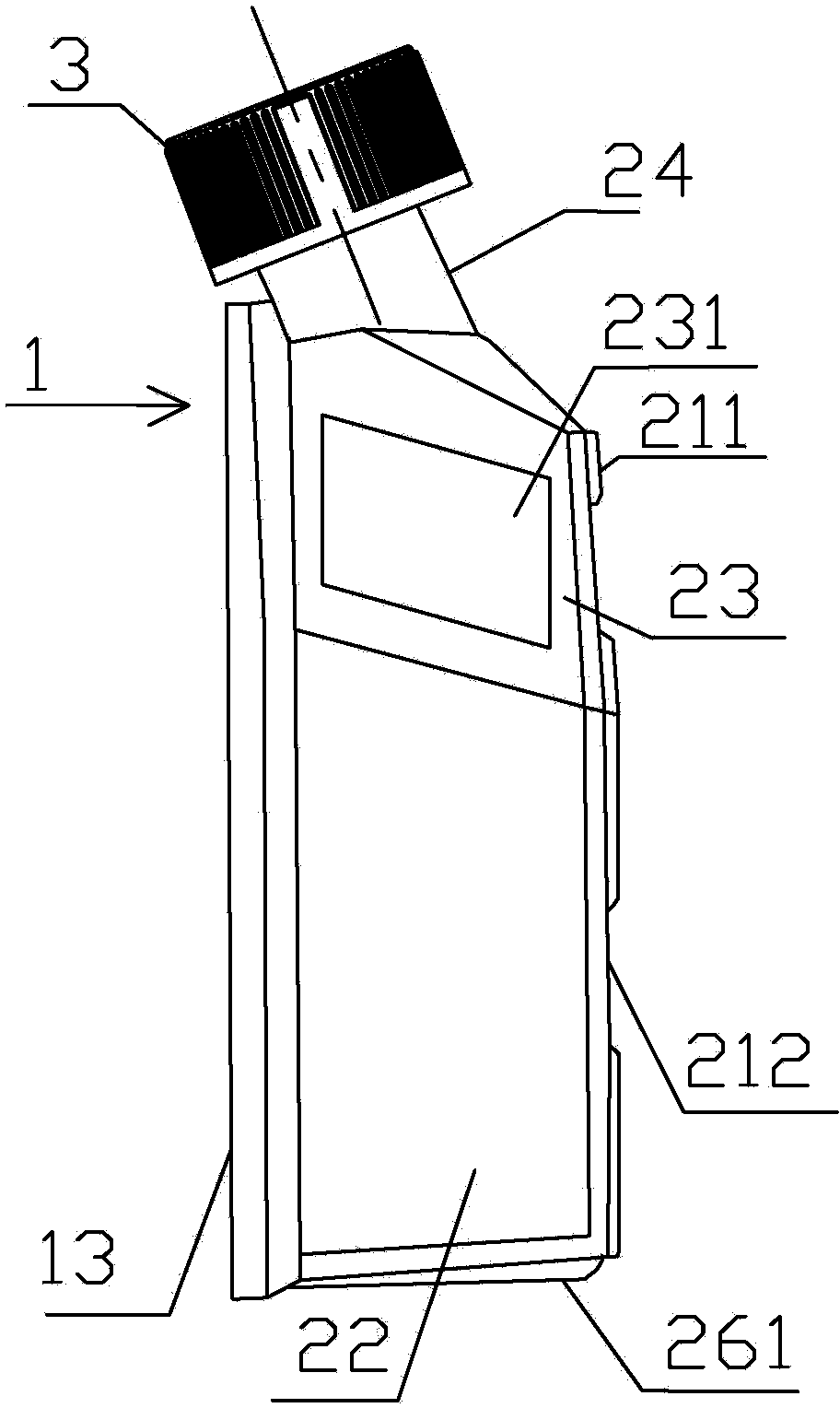
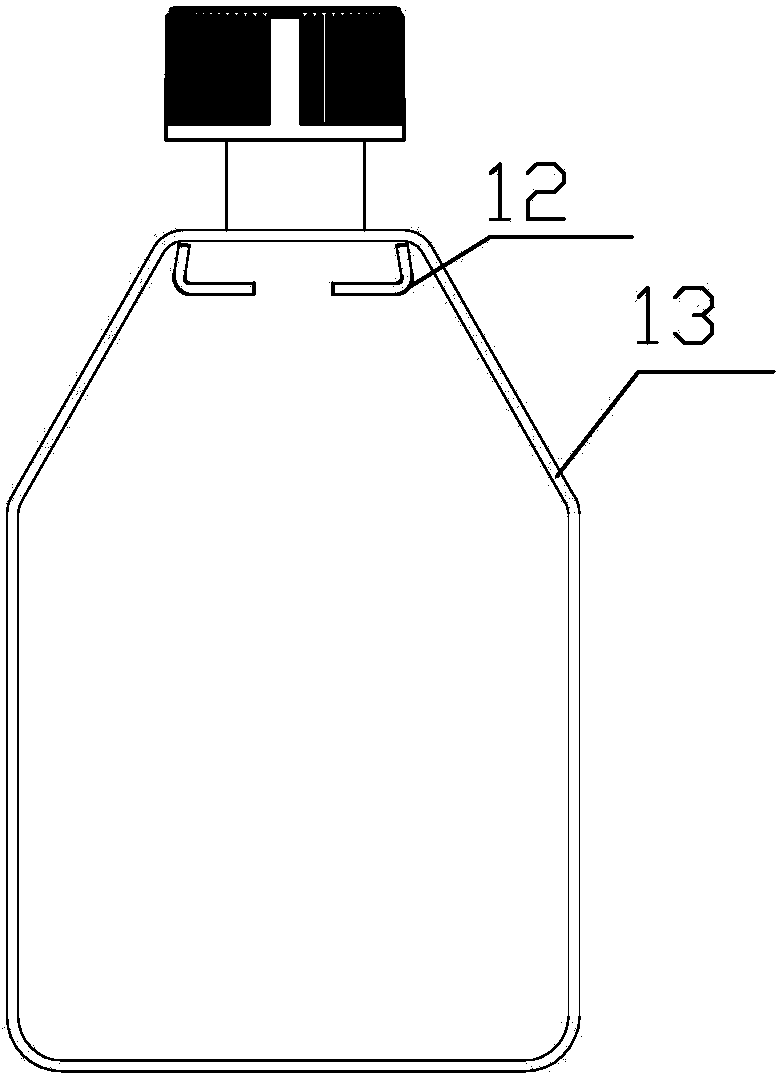
Cell culture bottle
InactiveCN103436441ASave spaceEasy to manageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell extractionPipette
The invention discloses a cell culture bottle. A clamping edge of a front panel of the cell culture bottle can be clamped and positioned between a clamping groove and a flanged edge of a back panel of another cell culture bottle; and thus, a plurality of culture bottles can be stored and moved in a piling mode, thereby saving the space of an incubator and facilitating the management. The joint of the cell culture bottle comprises two triangular plates and a trapezoidal plate, and the included angle formed by the trapezoidal plate and the front panel is 130 degrees; the lower side panel, bottom panel and upper side panel tilt towards the inner side of the bottle body, the bottleneck tilts towards the back panel, and a certain inclination angle is set; and when the cell culture bottle is arranged flatly, a pipette or cell scraper can touch all positions of the culture bottom surface, thereby facilitating the collection of cells, and preventing the culture bottle from generating dead area where cells can not be easily extracted. The invention solves the following problems: the plurality of cell culture bottles can not be easily managed and stored, the cell culture bottle generally has difficulty in cell extraction, and dead extraction areas can be easily generated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SORFA MEDICAL PLASTIC
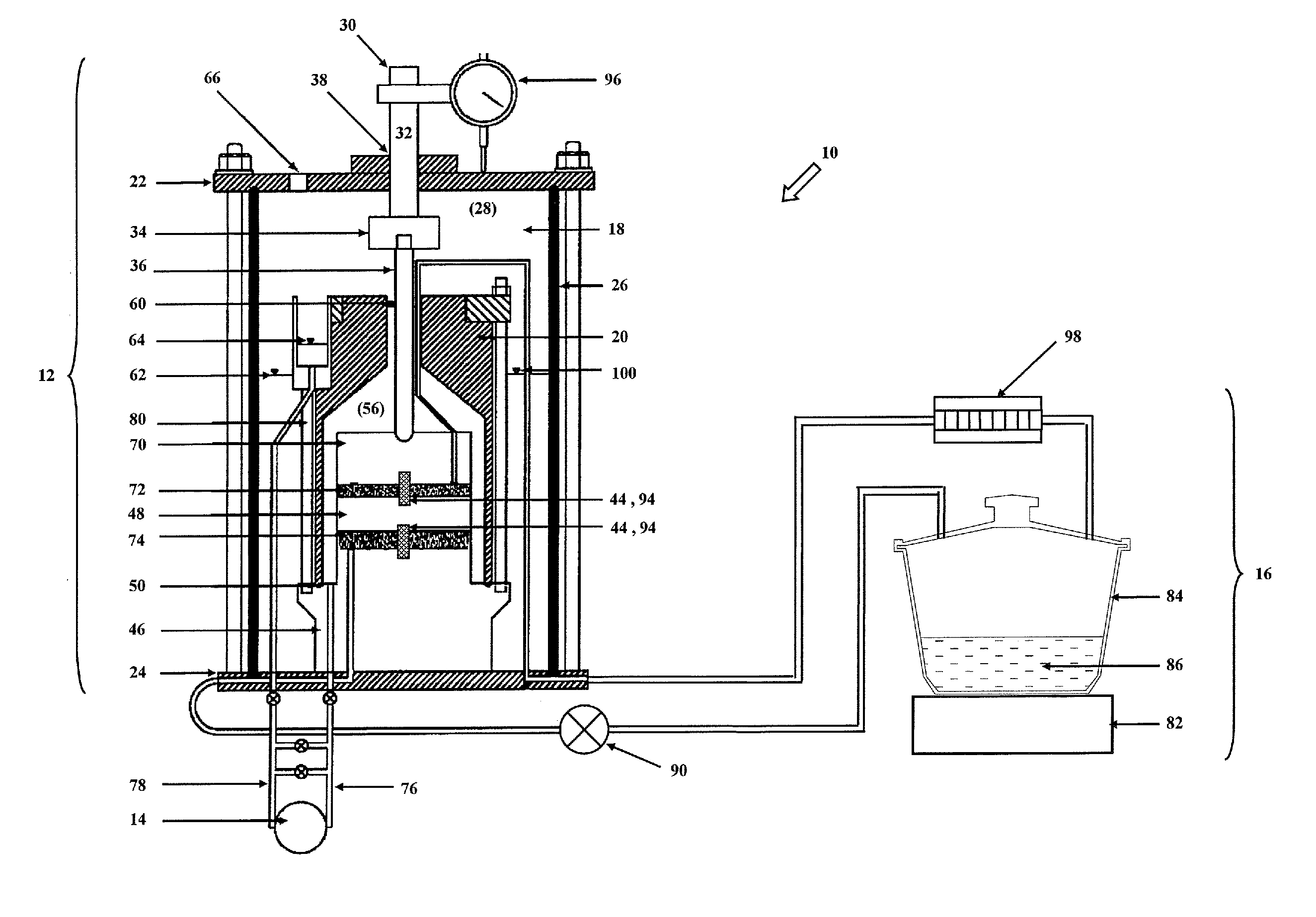
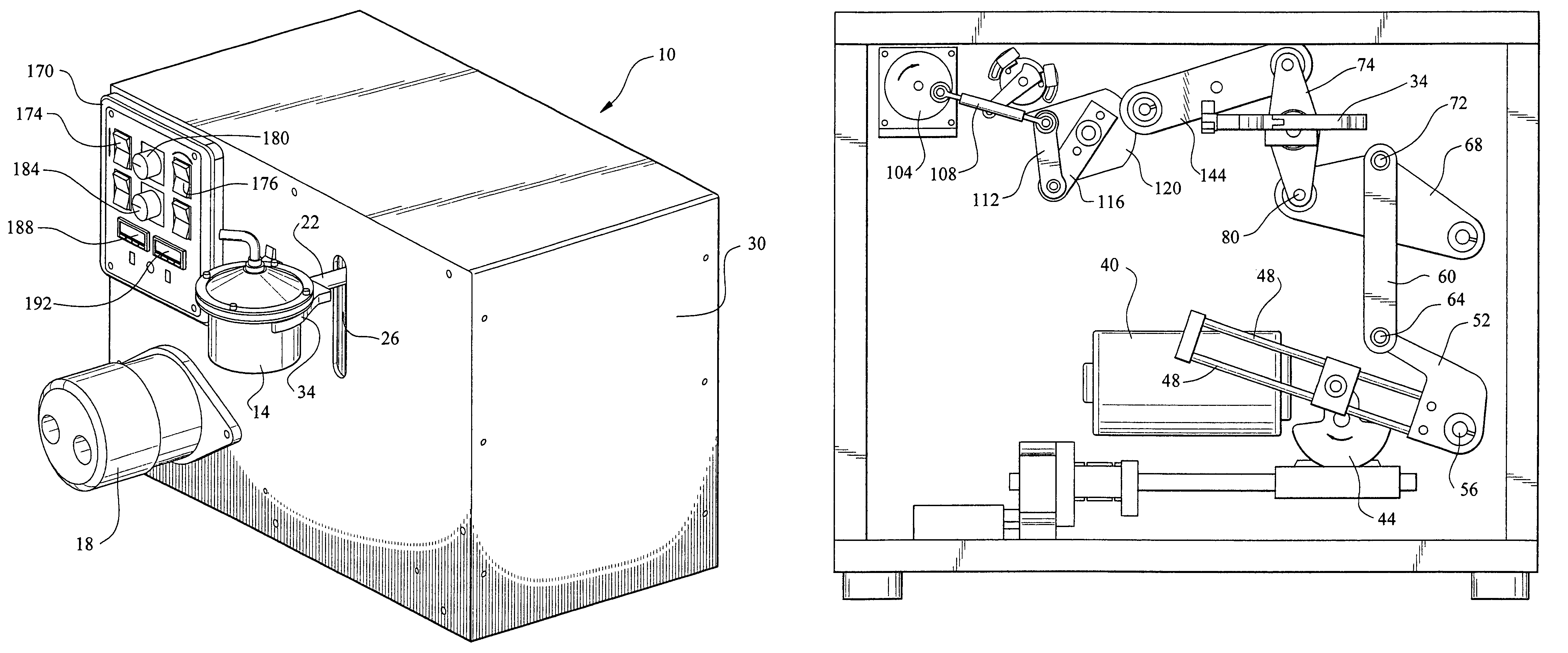
High suction double-cell extractor
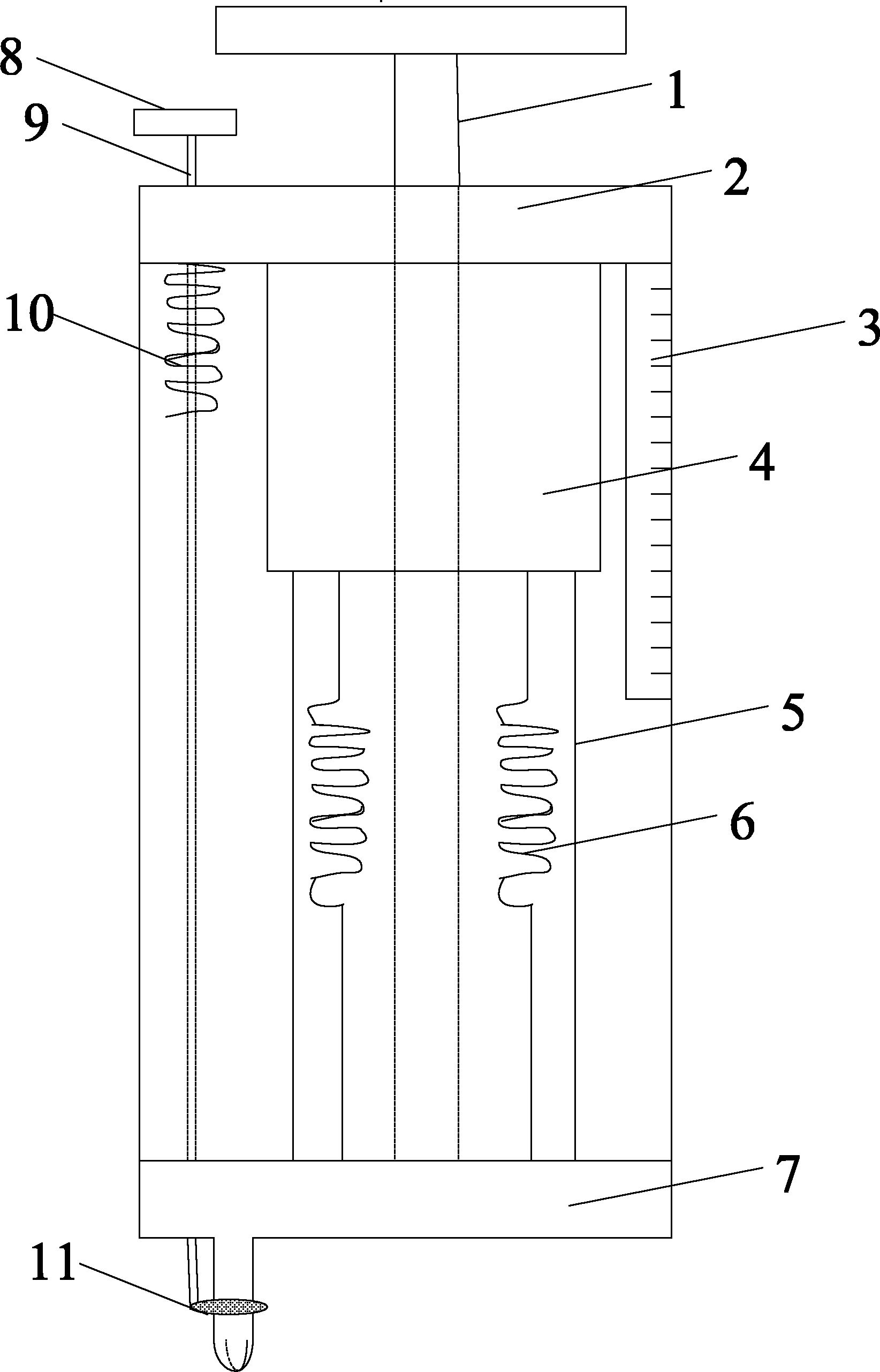
InactiveUS20090049924A1Great suctionEliminating expansionForce measurementMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCell extractionSuction stress
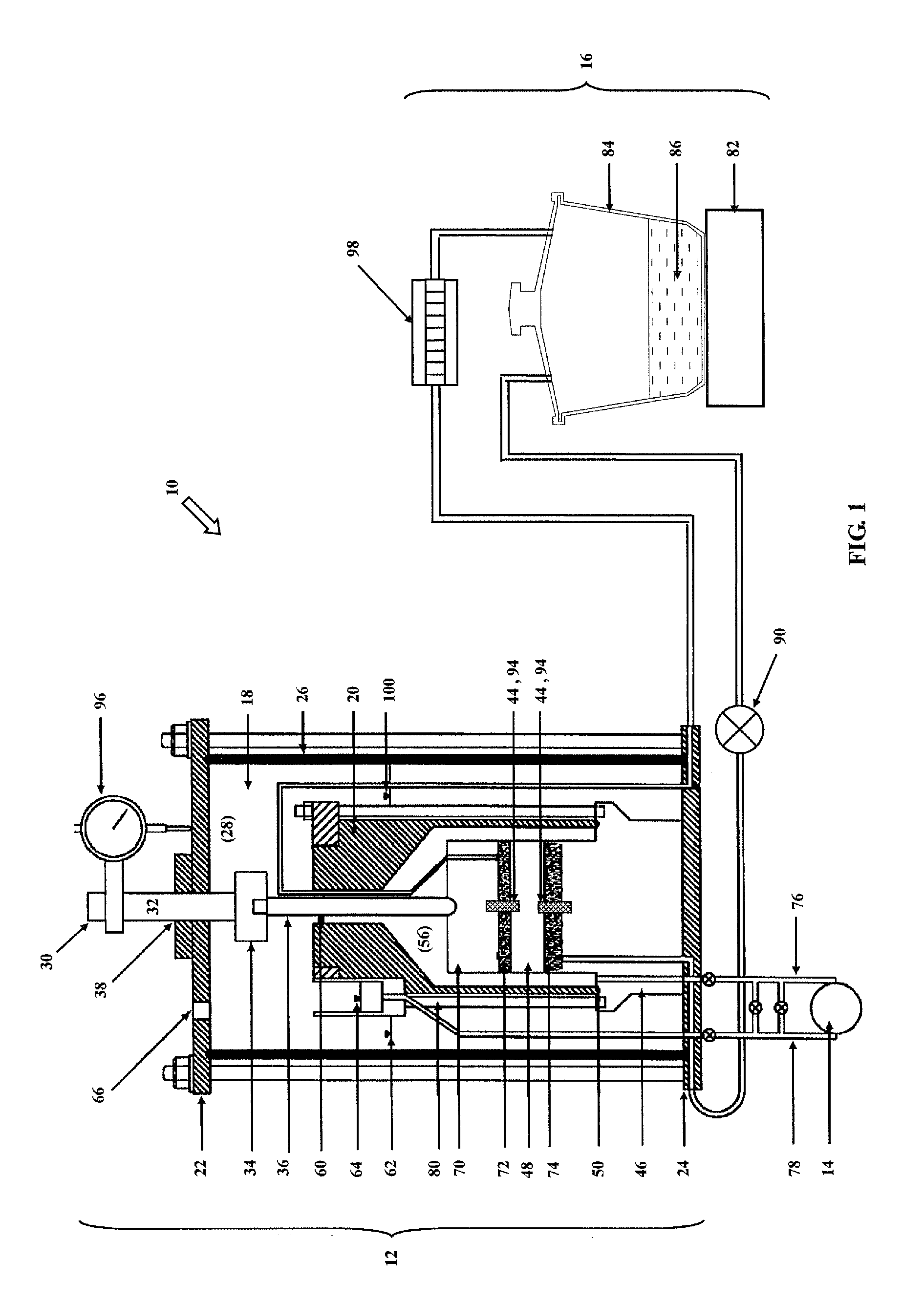
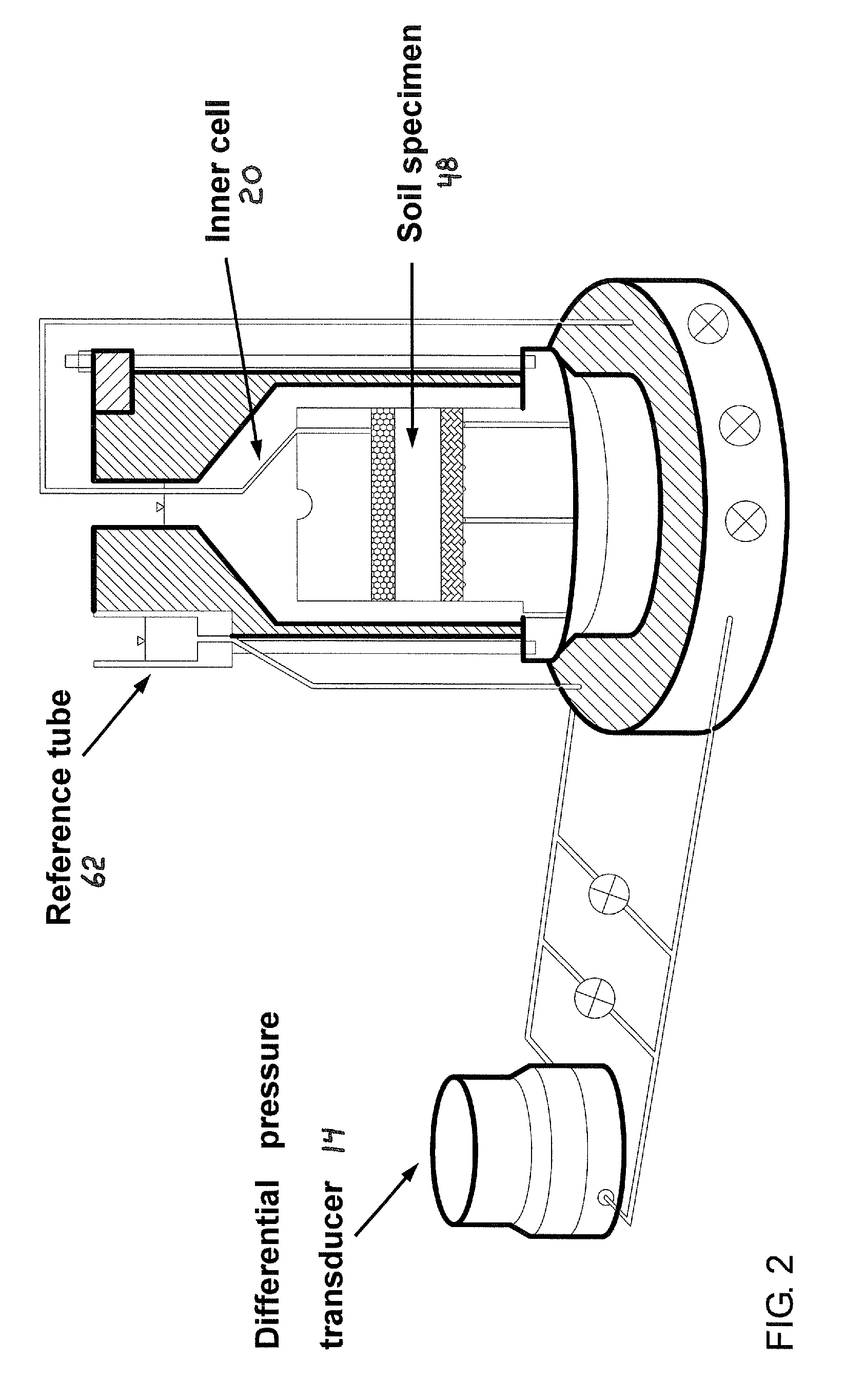
A high suction double-cell extractor includes an outer cell defining an outer chamber, and an open-ended inner cell defining an inner chamber. The inner chamber is bottle-shaped and has a neck. The high suction double-cell extractor also includes a vertical loading system for applying axial force on a soil specimen during extraction. The high suction double-cell extractor also includes a port for introduction of pressurized air supply into the outer and inner cells. The introduced pressurized air can apply cell pressure on the soil specimen during extraction. The high suction double-cell extractor also includes a relative humidity control system and a differential pressure detector system. The high suction double-cell extractor can be used to measure stress-dependent soil-water characteristics curve (SDSWCC) under various stress states three-dimensionally and more accurately, and under total suction up to 8,000 kPa.
Owner:EARTH PROD CHINA
Biodetection articles
Articles are provided for the detection of cells in a sample (610). The articles include a hydrogel (640) comprising a cell extractant. Methods of use are also disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
In-situ cell extraction and assay method
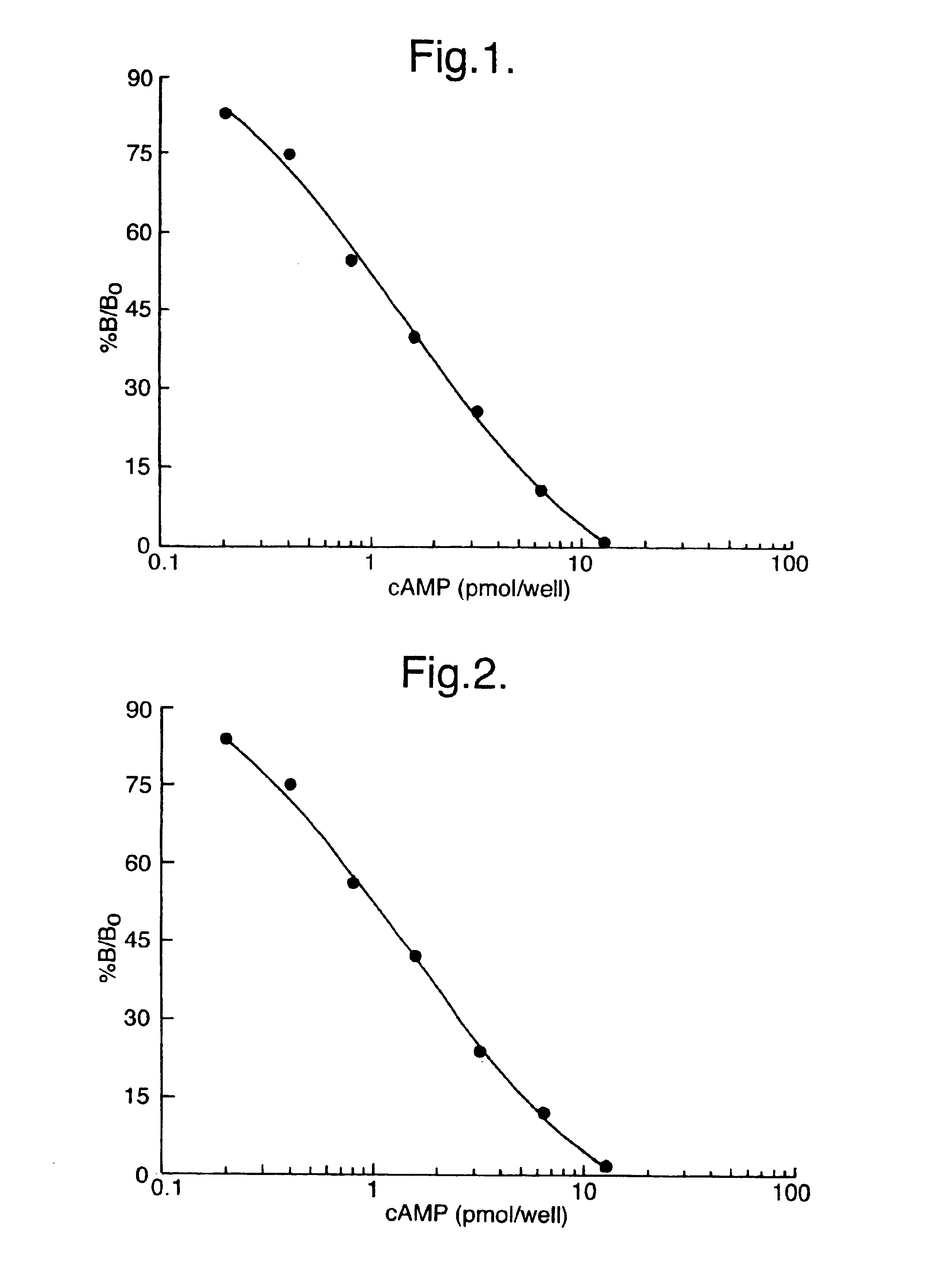
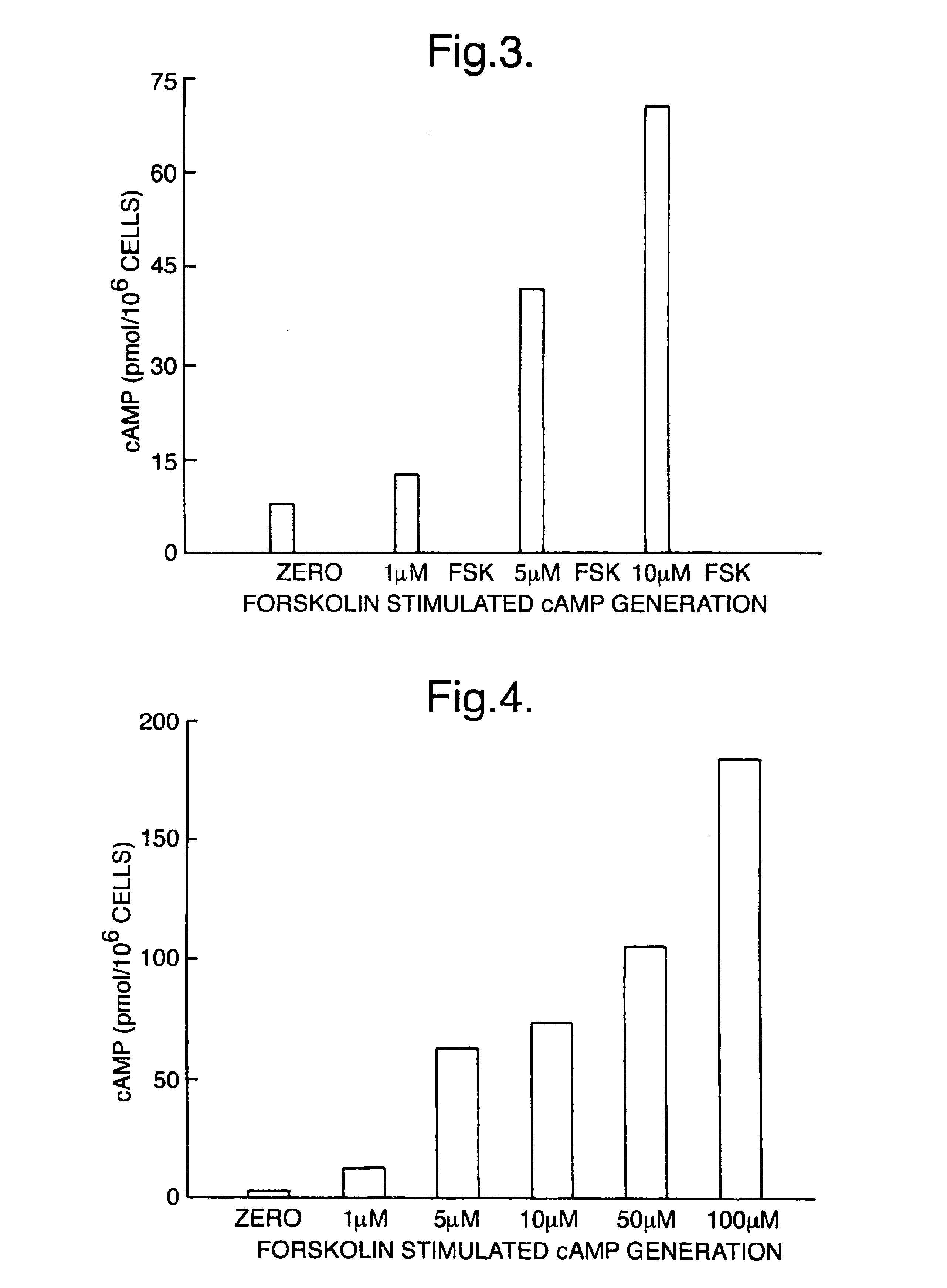
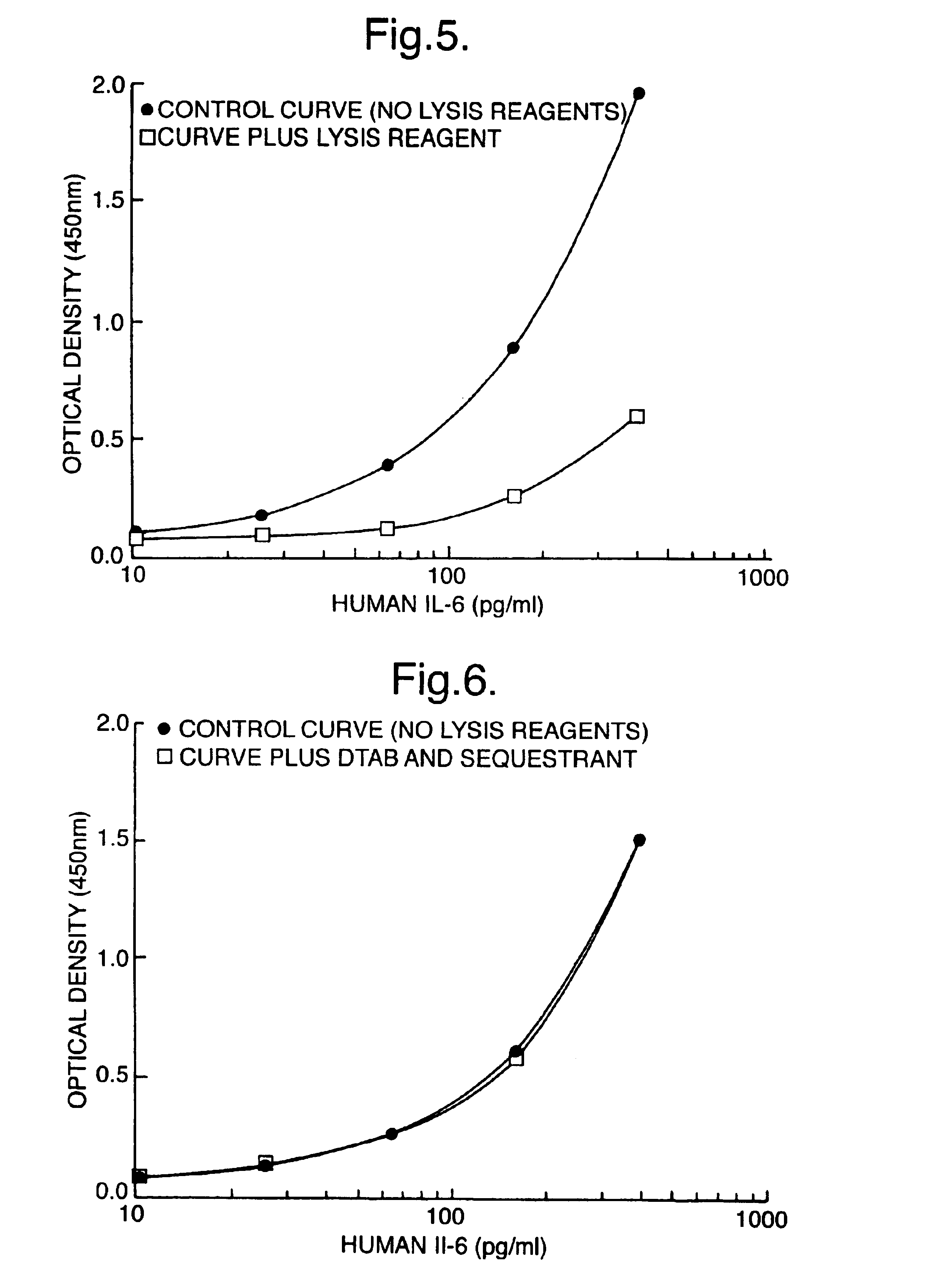
This invention provides a simple and convenient, single stage, single vessel cell extraction and assay method which is suitable for the extraction and measurement of a range of different types of analyte which occur as cellular components. The invention also provides kits of reagents suitable for performing cellular extraction and measurement as a single stage, single vessel process.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Orbital shaker for cell extraction
InactiveUS7188994B2Rotating receptacle mixersShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersCell extractionCrystallography
Owner:MIAMI UNIVERISTY OF +1
Isolated phospholipid-protein particles
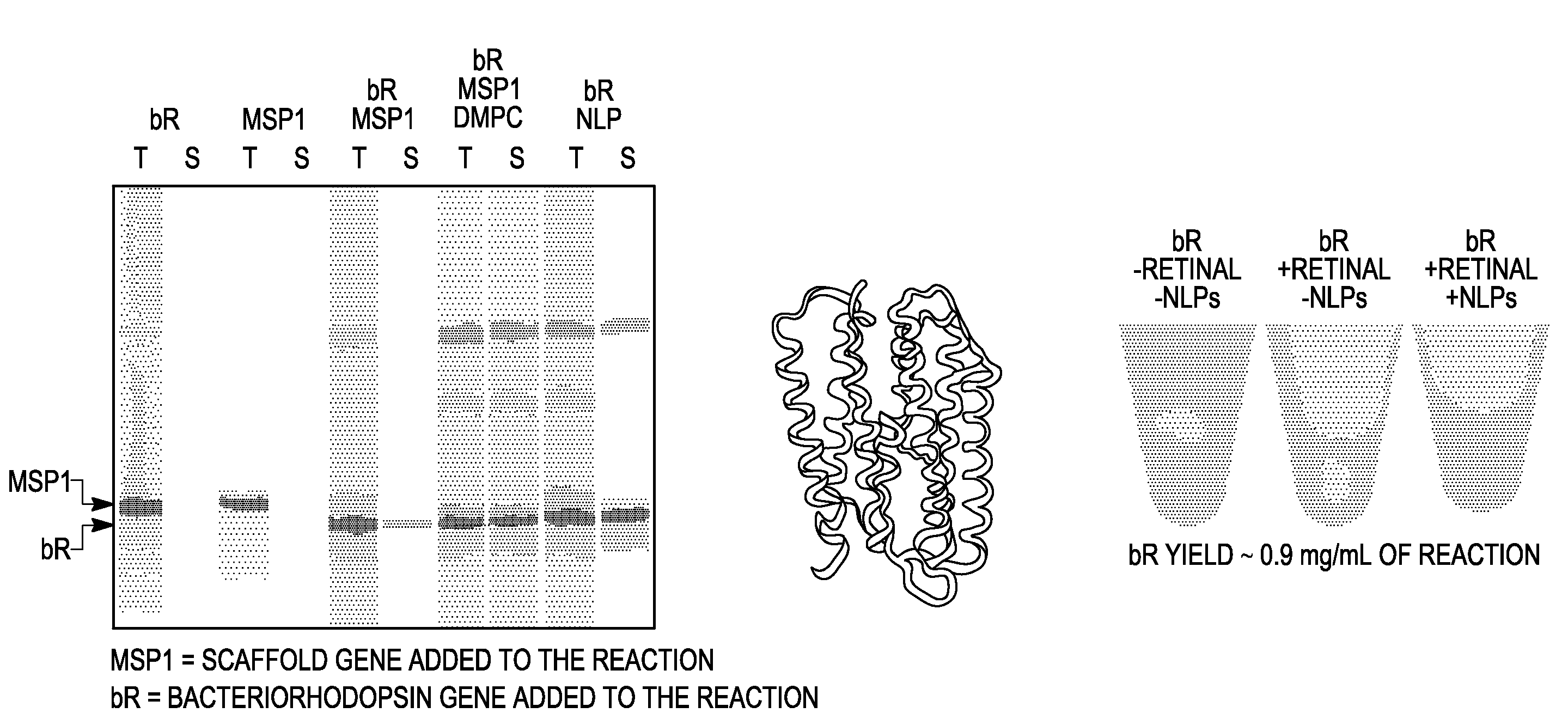
InactiveUS20080248565A1Speed up the processImprove solubilityPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesADAMTS ProteinsApolipoproteins E
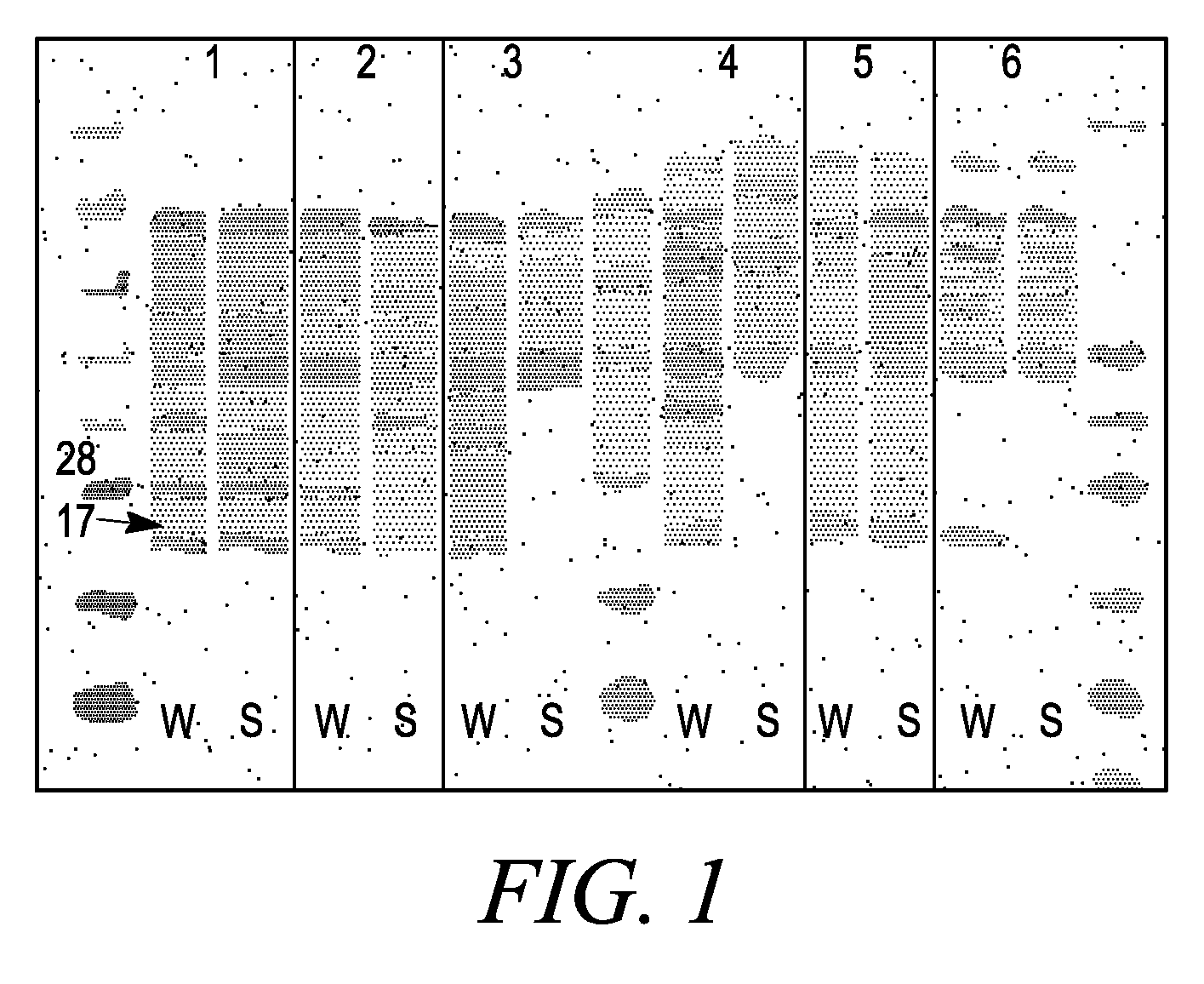
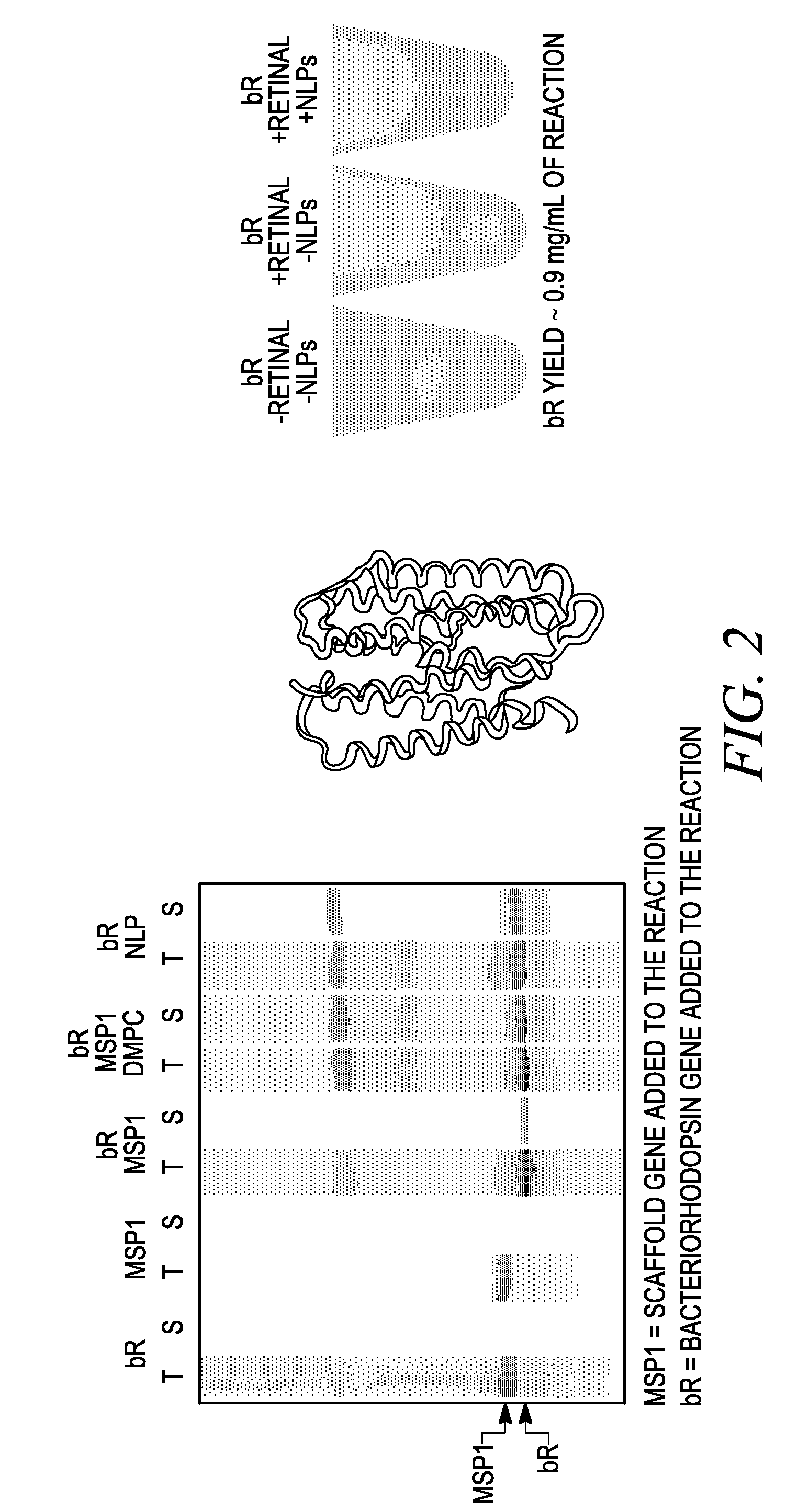
Systems and methods are provided for producing a protein of interest that is typically not amenable to expression in soluble form in in vitro expression systems. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of synthesizing proteins using in vitro protein synthesis systems that include a scaffold protein such as apolipoprotein or an amphipathic alpha helix containing (“AAHC”) protein, in which higher yields of soluble protein are produced than in the absence of the scaffold protein. The scaffold proteins may be provided in an in vitro protein synthesis system associated with lipid or not associated with lipid. The scaffold protein may be provided as a protein per se or may be encoded by a nucleic acid template and co-expressed with the protein of interest. The invention also provides compositions and kits for synthesis of proteins in soluble form, in which the compositions and kits include cell extracts for protein expression and isolation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
In-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application thereof
The present invention discloses an in-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises cell extract, carbohydrate and a phosphate compound, wherein the carbohydrate is maltodextrin, lactose, or a combination of the maltodextrin and glucose, or a combination of the lactose and the glucose, or a combination of the maltodextrin, the lactose and the glucose. ATP is provided for an in-vitro reaction by low-cost substances such as the glucose, the maltodextrin and the lactose instead of energy sources such as phosphoenolpyruvic acid, phosphocreatine and acetyl phosphate, so that whilethe cost is reduced, a mode of providing energy by slow release prolongs the reaction time and increases the yield of target protein.
Process for manufacturing a fermented food product using cell extracts
InactiveUS6649199B2Shorten still further the ripening phaseImprove propertiesMilk preparationCheese manufactureMicroorganismCell extraction
The invention relates to a process for manufacturing a fermented food product, which enables the maturation phase of said product to be shortened and its organoleptic to be improved. The process is characterized by the addition to the raw material of a cluster of cell extracts of its fermenting micro-organisms, which are either naturally present or added in live state. The proportion of each extract in the cluster is approximately equivalent to that of the corresponding micro-organism in the fermenting mixture.
Owner:BIOSAVEURS
Microcapsule biological feed
InactiveCN102511688AImprove qualityHigh in proteinAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyNutrient solution
The present invention relates to a microcapsule biological feed, which is characterized in that the microcapsule biological feed comprises, by weight, 40-50 parts of composite high protein powder, 5-10 parts of an algae single cell extract, 20-30 parts of microbial protein yeast, 20-25 parts of detoxification fermentation potato powder, a microecology nutrient solution, and a feeding attraction film coating agent. The microcapsule biological feed of the present invention has advantages of fine product quality, high efficiency, safety, environmental protection, production cost reducing, and the like. In addition, the biological product is adopted to replace the chemical antibiotic additive so as to improve the food safety probability.
Owner:郭伟 +2
Method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast
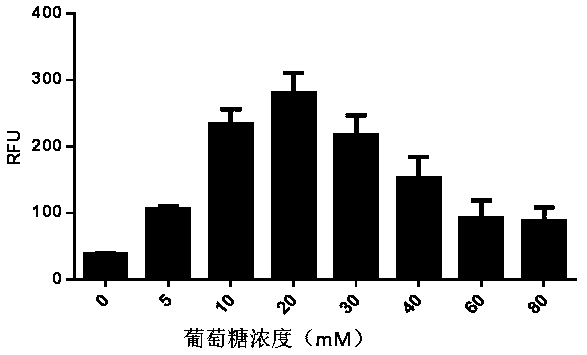
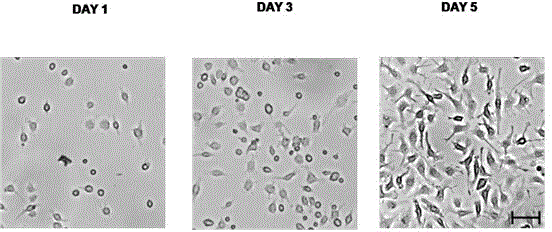
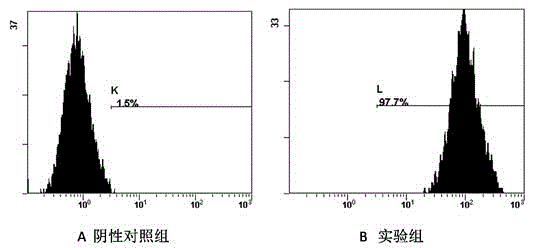
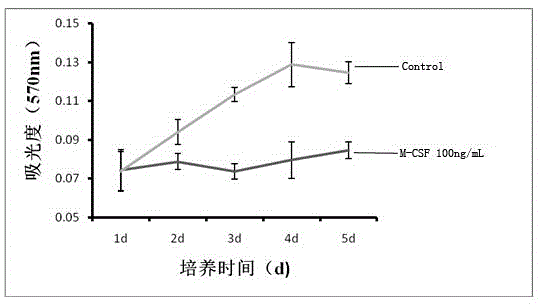
InactiveCN104651302AStable traitsLower requirementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteocyteCellular density
The invention belongs to the field of cell extraction and differentiation authentication, and discloses a method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast. The method comprises the following steps: (A) performing sterile myelomonocyte separation, culturing in a complete medium of 20-100ng / mLM-CSF, replacing the complete medium every other day, and observing the morphological characteristics of monocyte; (B) when the density of monocyte is 80-90%, taking out a part of the cells for surface antigen authentication; (C) drawing a growth curve of other cells and performing differentiation induction for osteoclast on other cells. The method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast is simple, convenient and reliable, low in requested condition requirements, low in cost and short in time, the extracted monocyte is stable in property, and C57BL / 6 mice myelomonocyte which is reliable and stable in resource can be provided for medical basis, clinical research, tissue engineering study, and the like.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
Form template definition method and form template definition apparatus
InactiveUS20110222776A1Work lessReduce workloadFinanceCharacter and pattern recognitionCell extractionComputer science
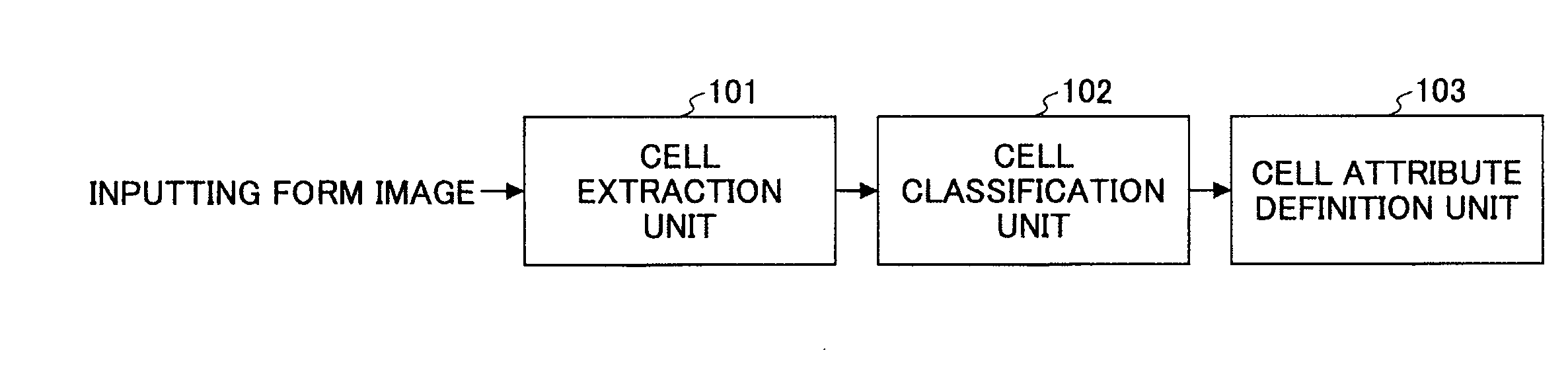
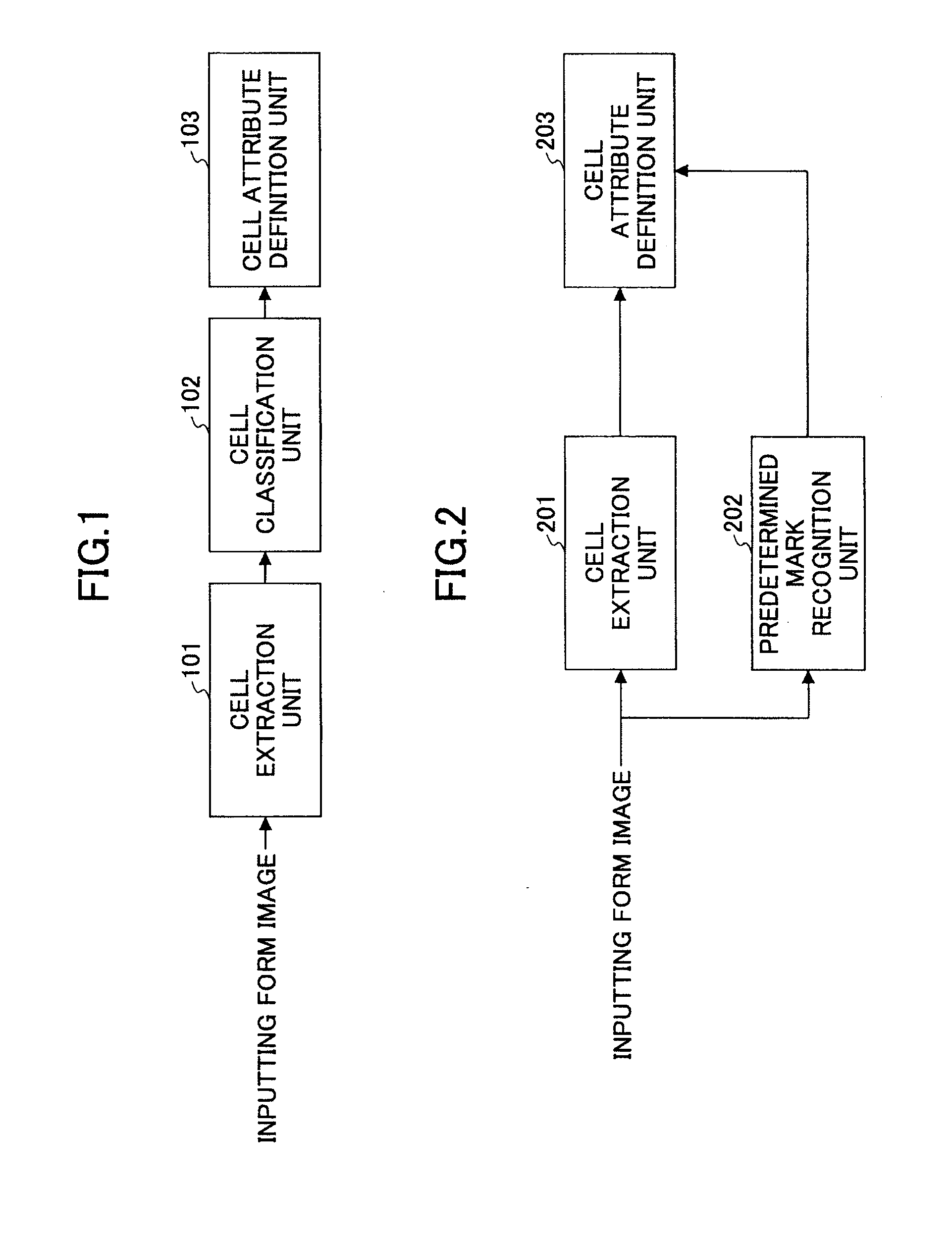
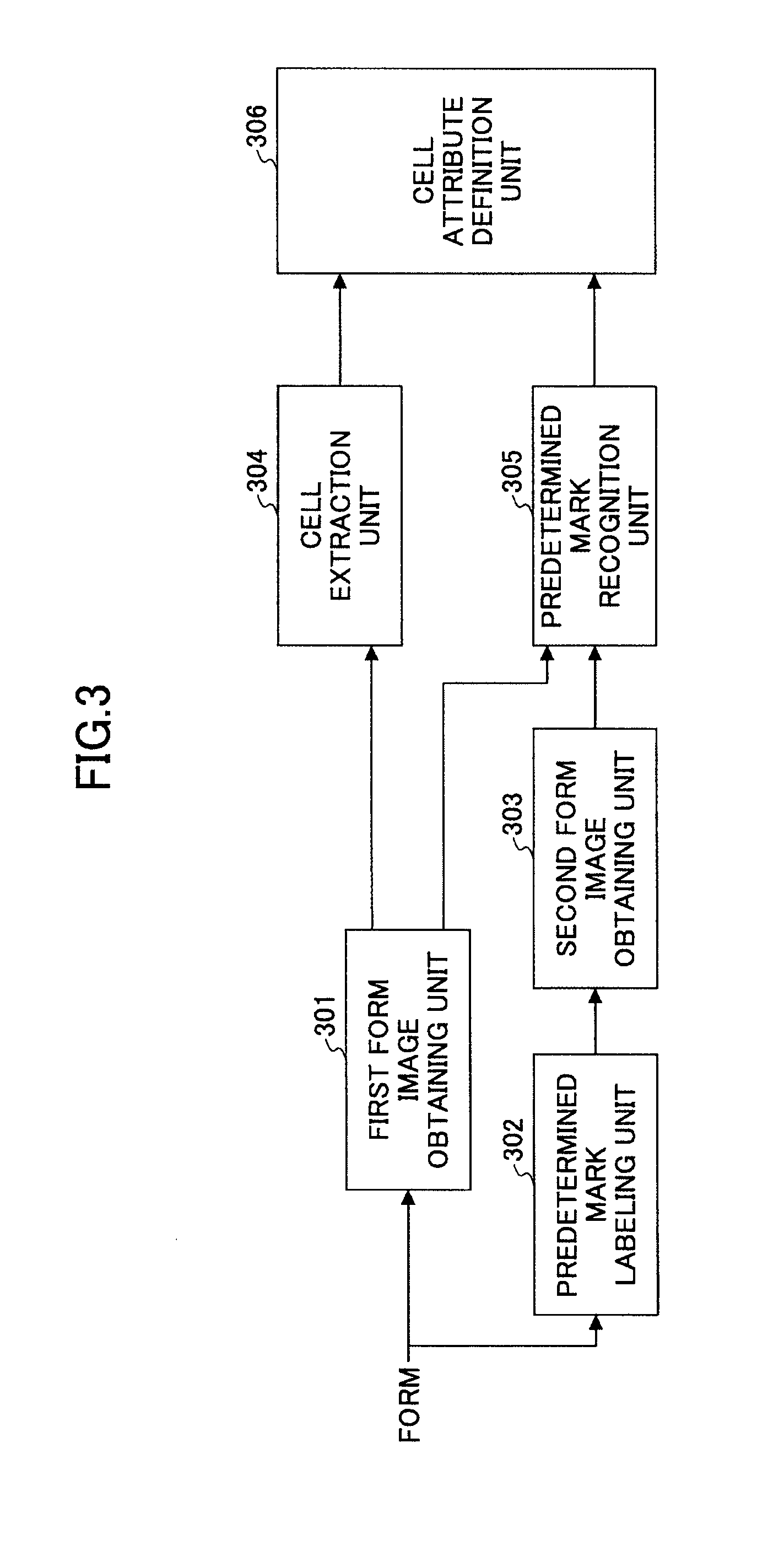
Disclosed are a form template definition method and a form template definition apparatus. The form template definition method comprises a cell extraction step of analyzing an image of a form so as to extract one or more cells from the image of the form; a cell classification step of classifying the extracted cells; and a cell attribute definition step of defining attributes of the extracted cells class by class. If an attribute of a first cell in one class is defined, then other cells in the class automatically copy the attribute of the first cell. As a result, the work amount of form template definition may be dramatically reduced by employing the form template definition method and form template definition apparatus.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for separating parenchyma cells from fibers in bamboo wood
The invention belongs to the field of separation of bamboo wood, and particularly relates to a method for separating parenchyma cells from fibers in bamboo wood. Currently, in industrial utilization of the bamboo wood, bamboo fibers are mainly used, and parenchyma cells are processed as waste, not only are resources wasted, but also the environment pollution problem is caused. According to the provided physical method for quickly separating the bamboo fibers and the parenchyma cells in an environment-friendly mode, the method specifically includes the following steps of 1, smashing; 2, screening; and 3, separation. By means of the separating method, the parenchyma cell extraction rate can reach 85% or so, and the purity can reach 95%. The dispersing media adopted in the method are wide in source, low in cost and easy to obtain.
Owner:INT CENT FOR BAMBOO & RATTAN
Biological membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105963782AAvoid damageQuality improvementTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberCell extraction
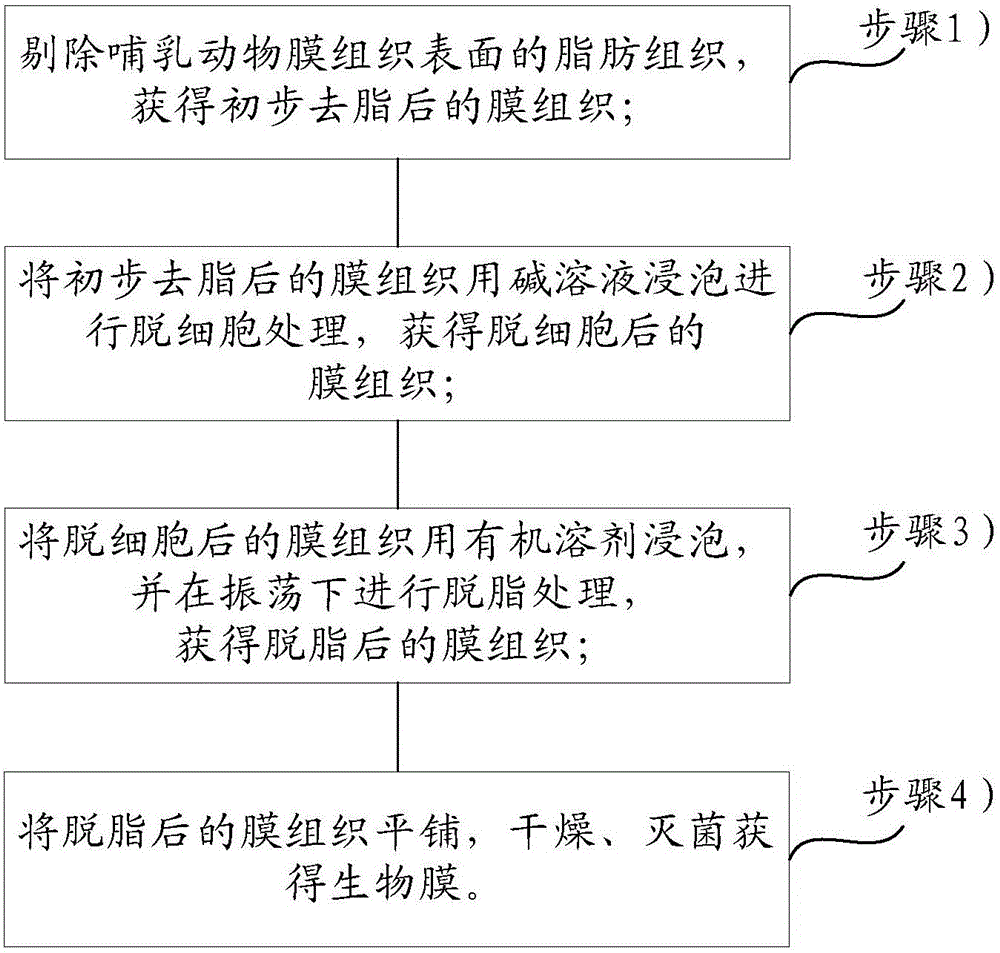
The invention relates to the technical field of tissue engineering, in particular to a biofilm and a preparation method thereof. This method has simple process, low cost, less damage to the collagen fibers of membrane tissue, and good decellularization effect. The obtained biofilm retains the natural double-layer structure of animal membrane tissue and can guide tissue regeneration. The clinical application of the membrane has created conditions. The embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing a biofilm, comprising: step 1) removing the fatty tissue on the surface of the mammalian membrane tissue to obtain the membrane tissue after the preliminary degreasing; step 2) treating the membrane tissue after the preliminary degreasing with alkali solution soaking for decellularization to obtain decellularized membrane tissue; step 3) soaking the decellularized membrane tissue in an organic solvent, and performing degreasing treatment under vibration to obtain degreased membrane tissue; step 4) degreasing The final membrane tissue was flattened, dried, and sterilized to obtain a biofilm.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com