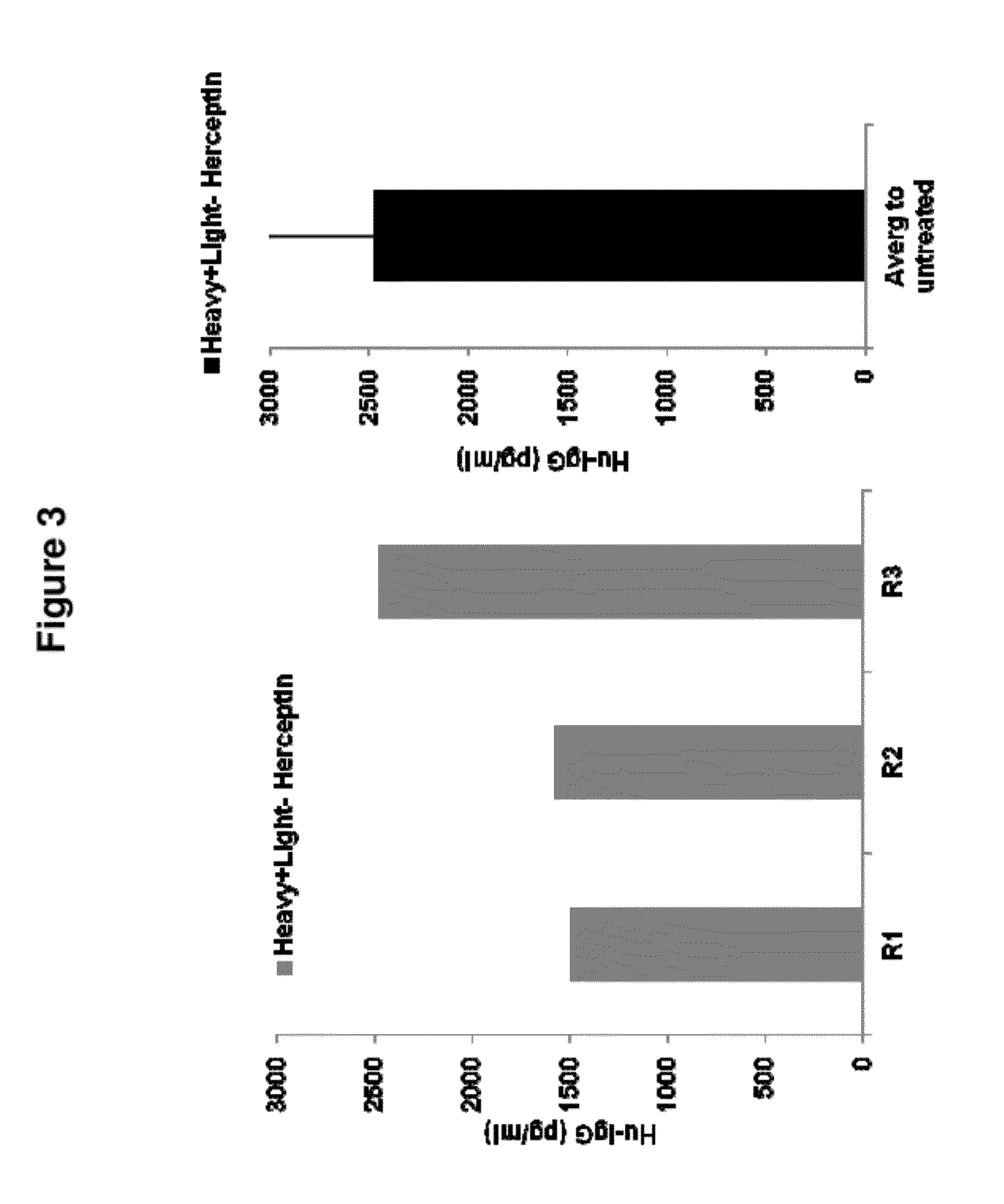
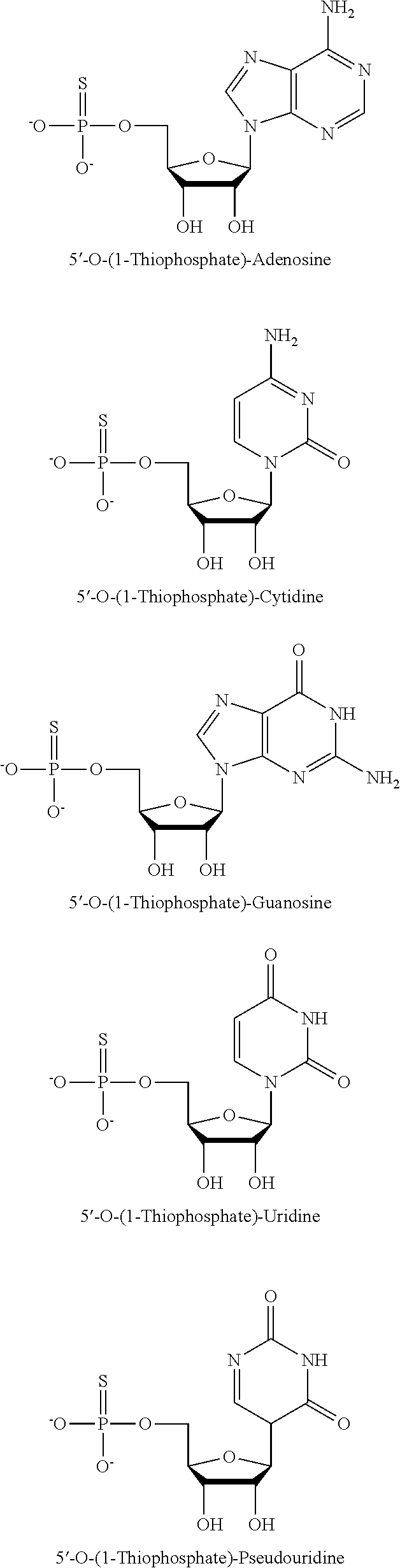
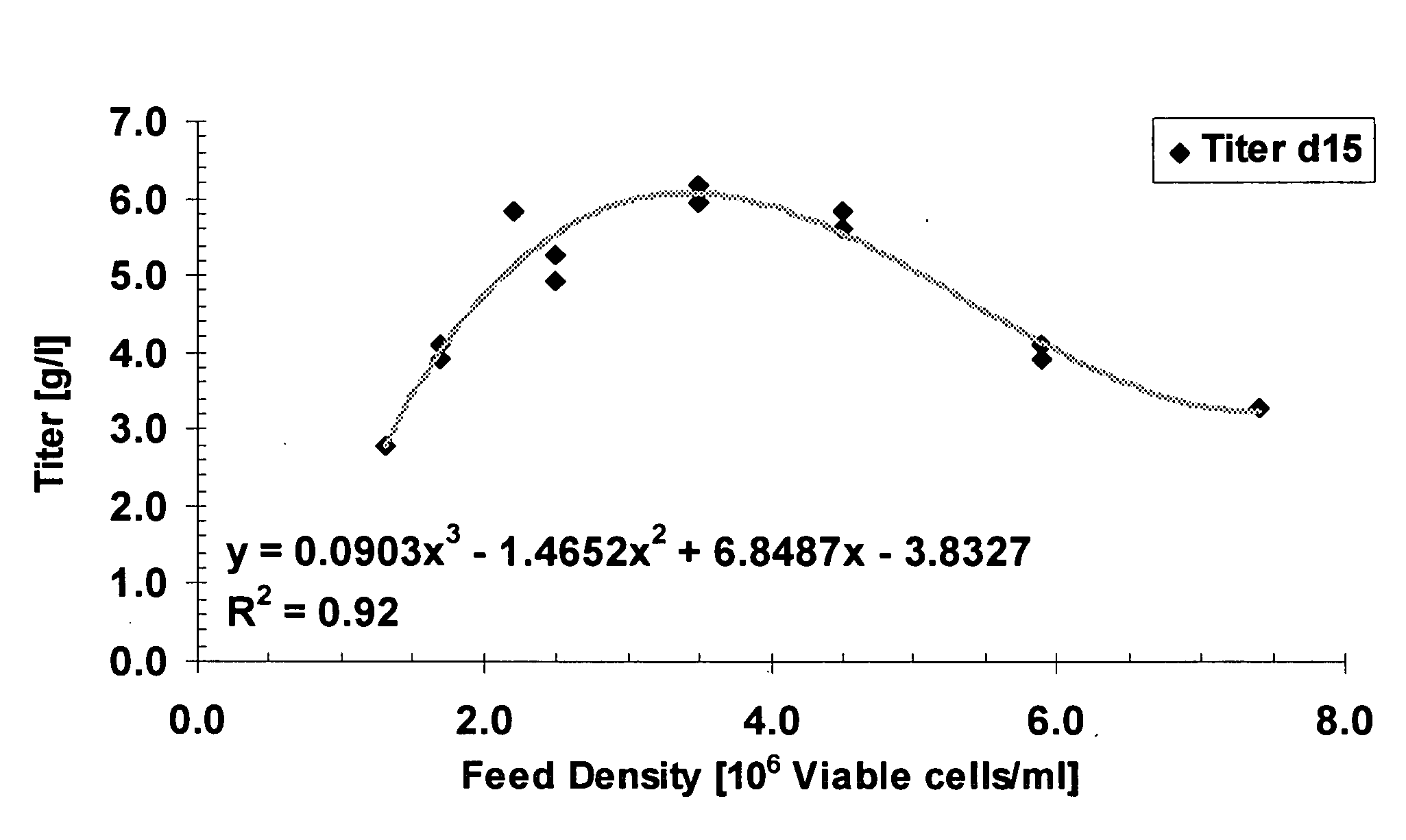
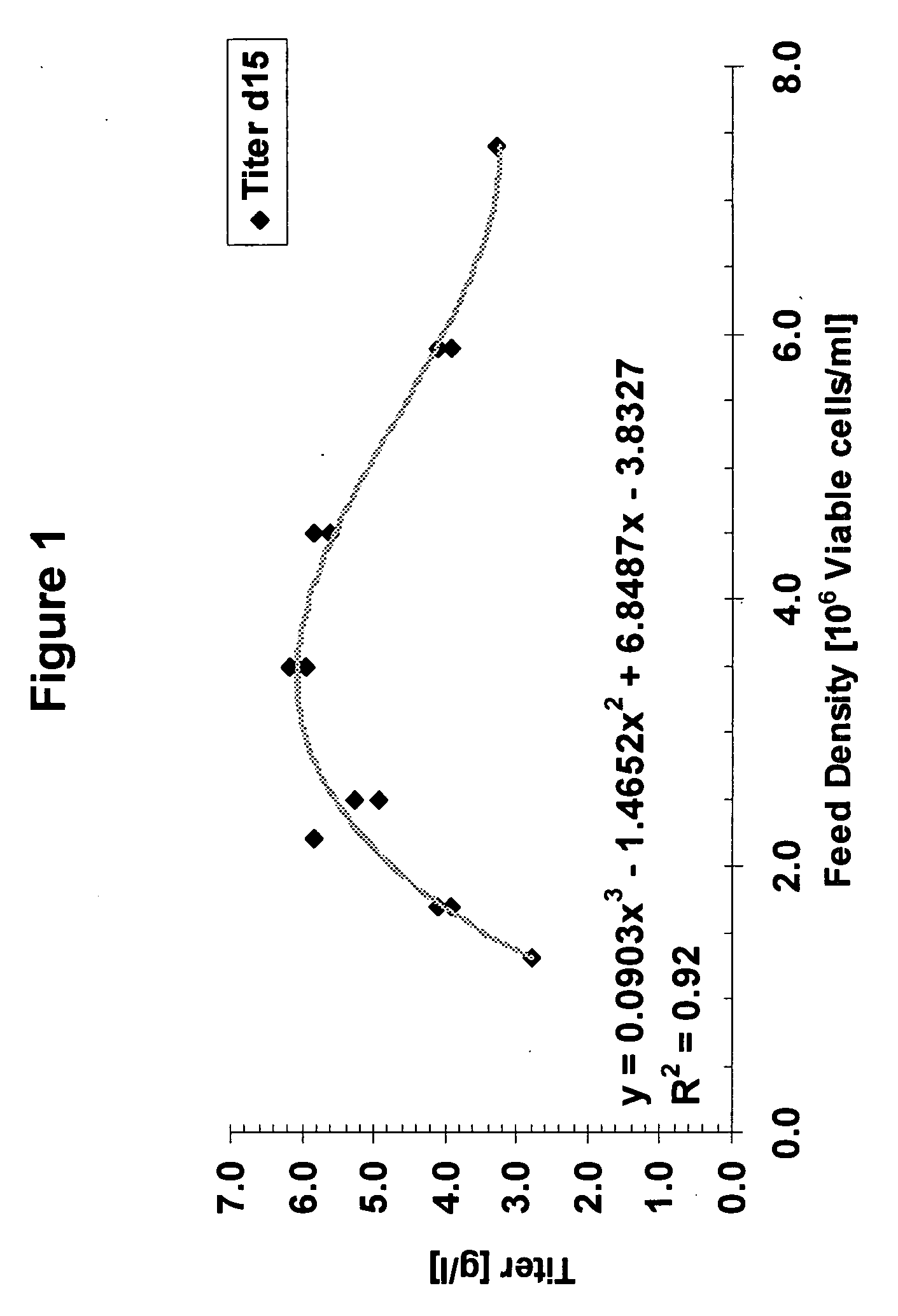
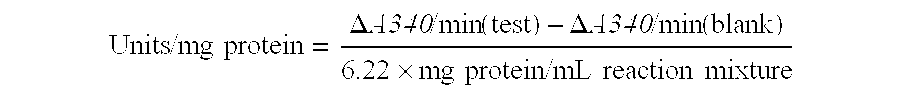Patents
Literature
3564 results about "Protein expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein production is the biotechnological process of generating a specific protein. It is typically achieved by the manipulation of gene expression in an organism such that it expresses large amounts of a recombinant gene. This includes the transcription of the recombinant DNA to messenger RNA (mRNA), the translation of mRNA into polypeptide chains, which are ultimately folded into functional proteins and may be targeted to specific subcellular or extracellular locations.
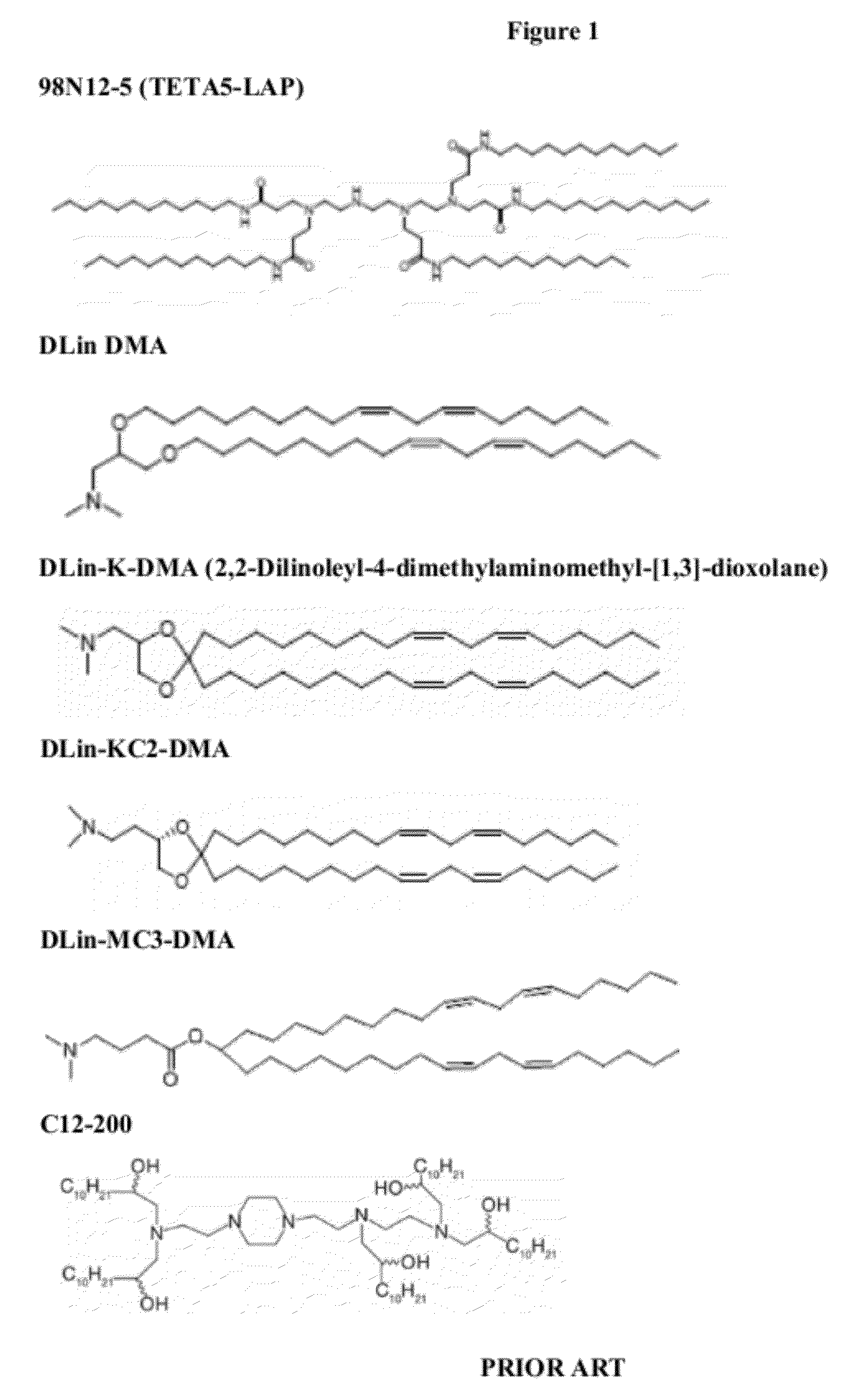
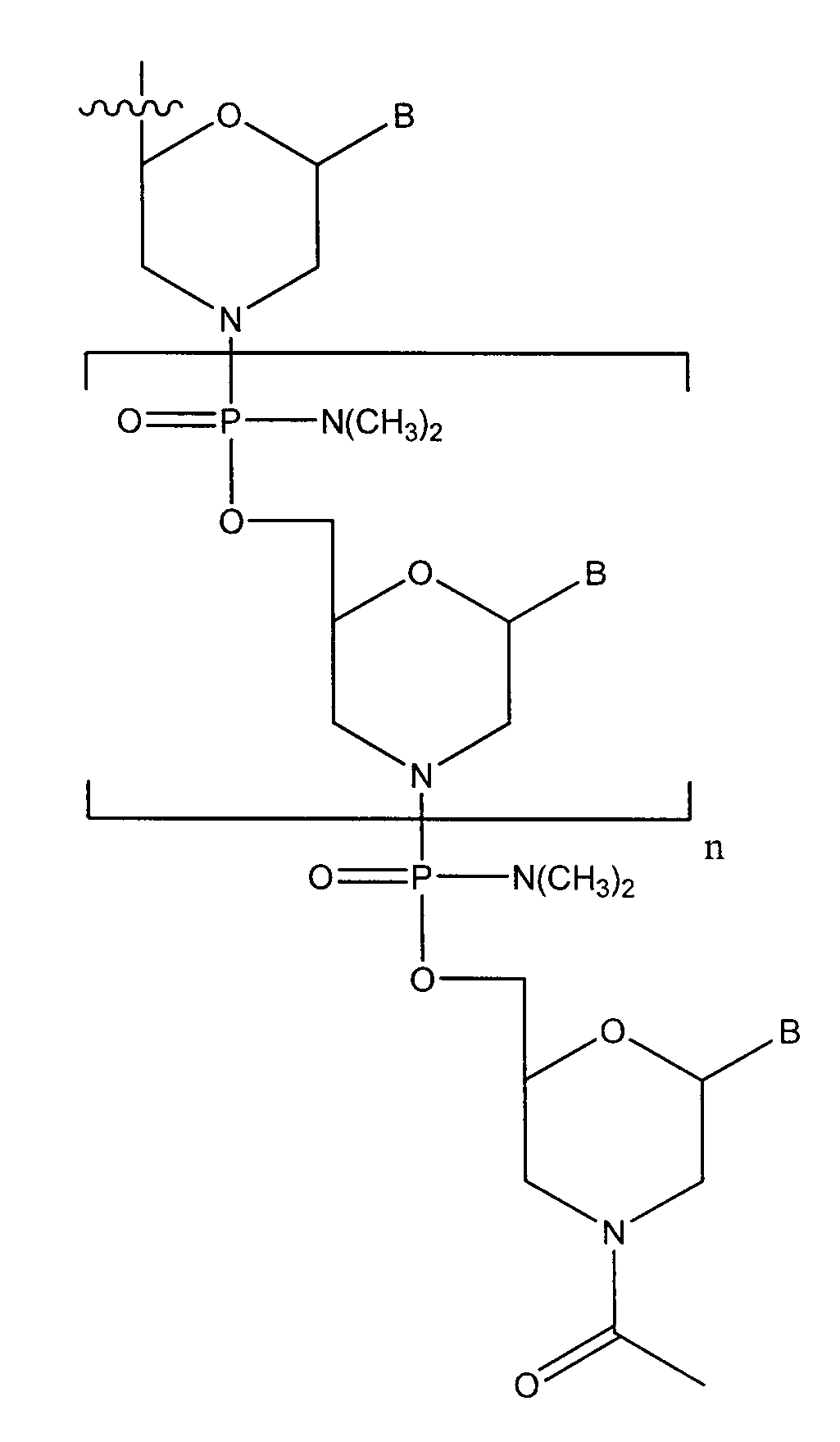
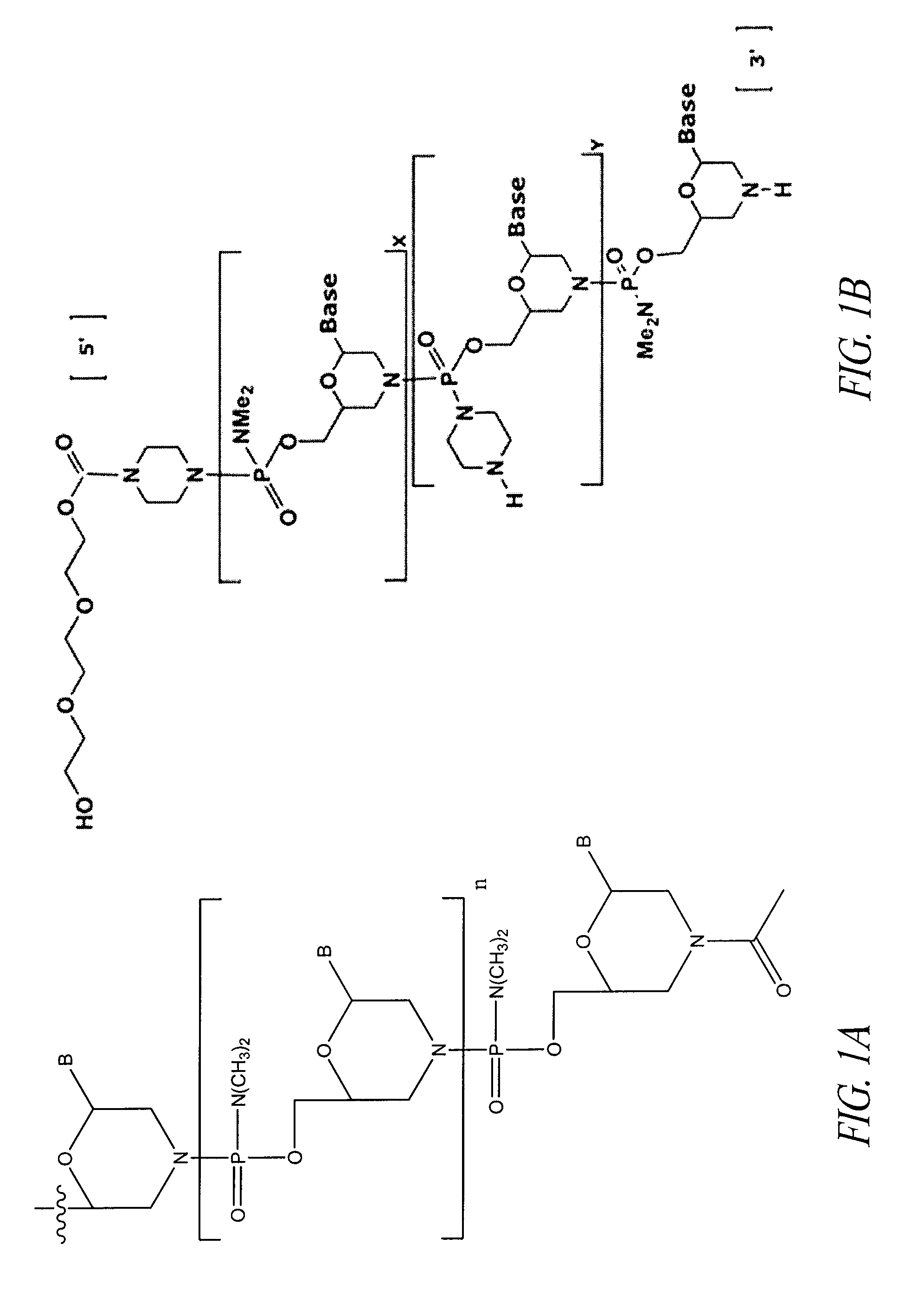
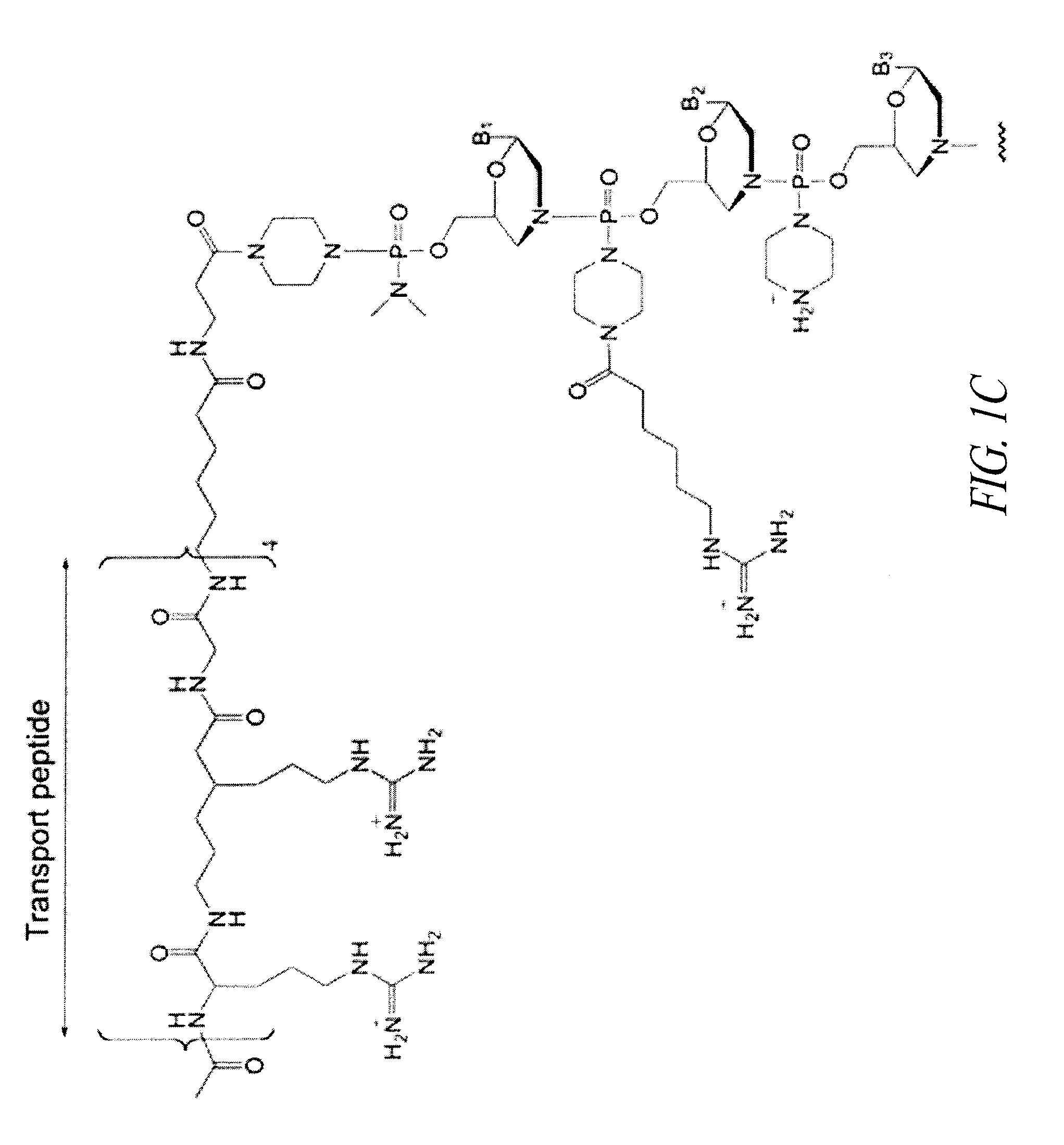
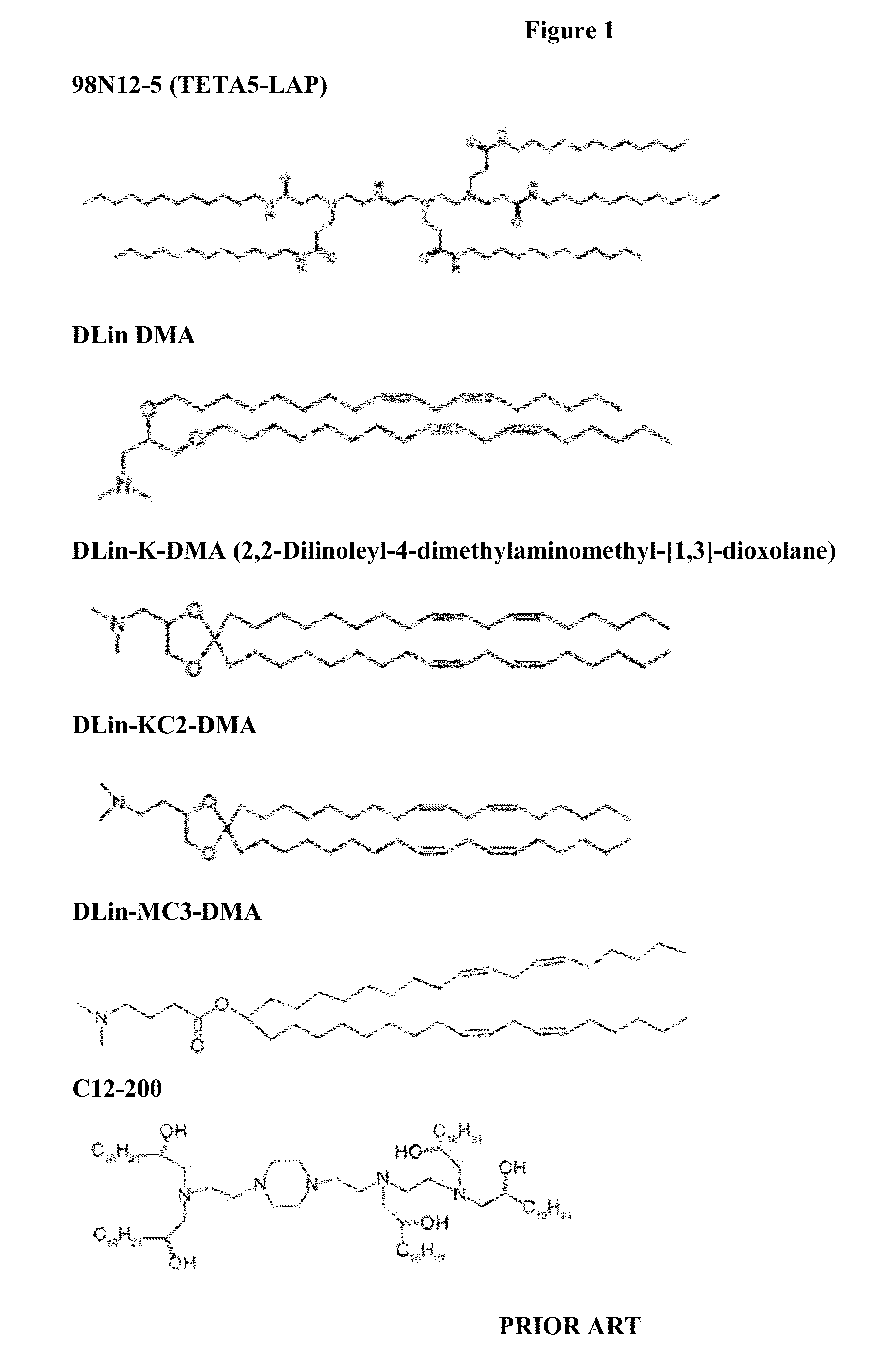
Delivery and formulation of engineered nucleic acids
ActiveUS20120251618A1Improve the level ofIncrease in level of polypeptideNervous disorderAntipyreticNucleic acidProtein expression
Provided are formulations, compositions and methods for delivering biological moieties such as modified nucleic acids into cells to modulate protein expression. Such compositions and methods include the delivery of biological moieties, and are useful for production of proteins.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
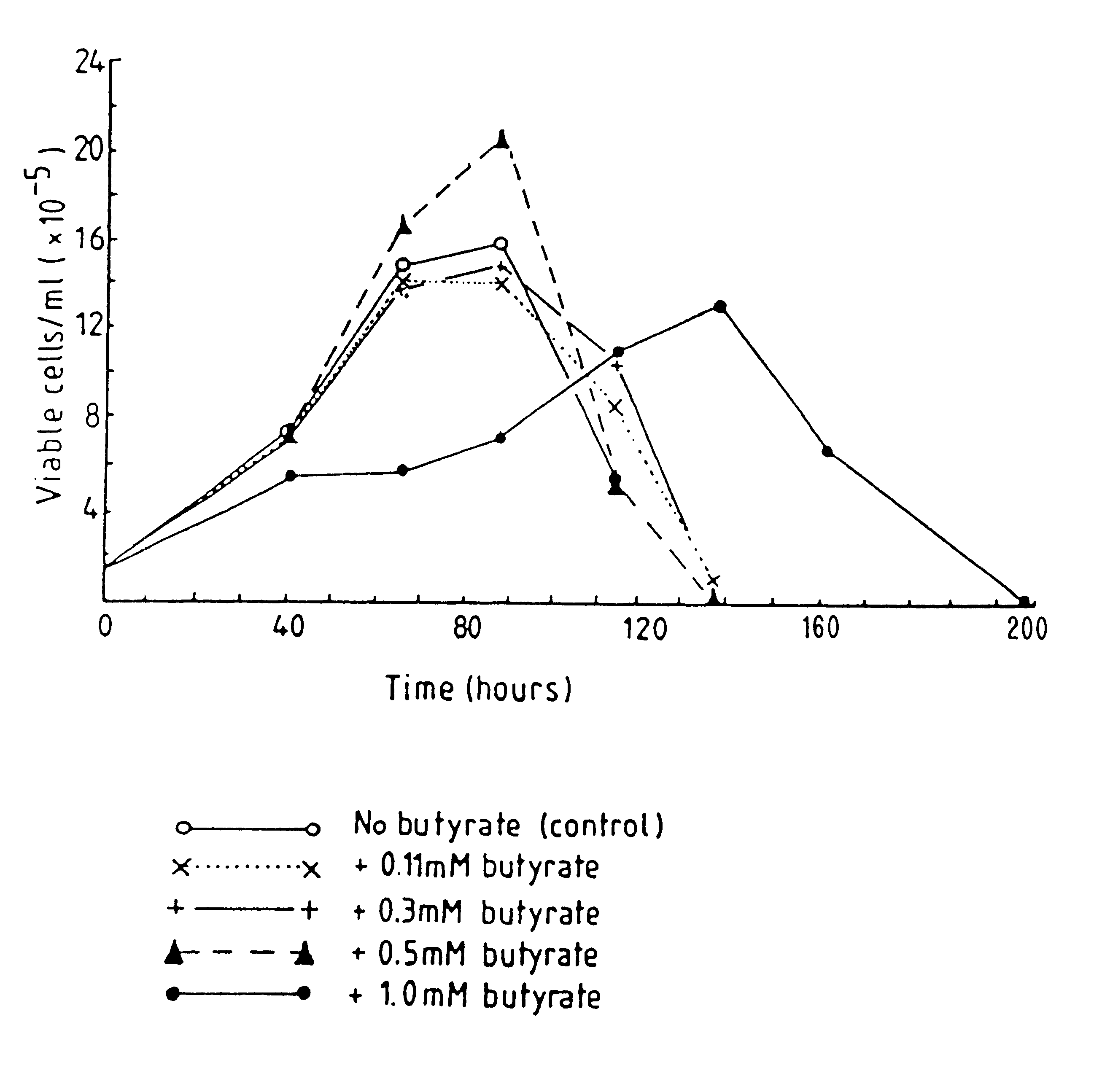
Production of proteins by cell culture
InactiveUS6413746B1High protein yieldReduce cell viabilityImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensPeptide/protein ingredients3D cell cultureBiochemistry
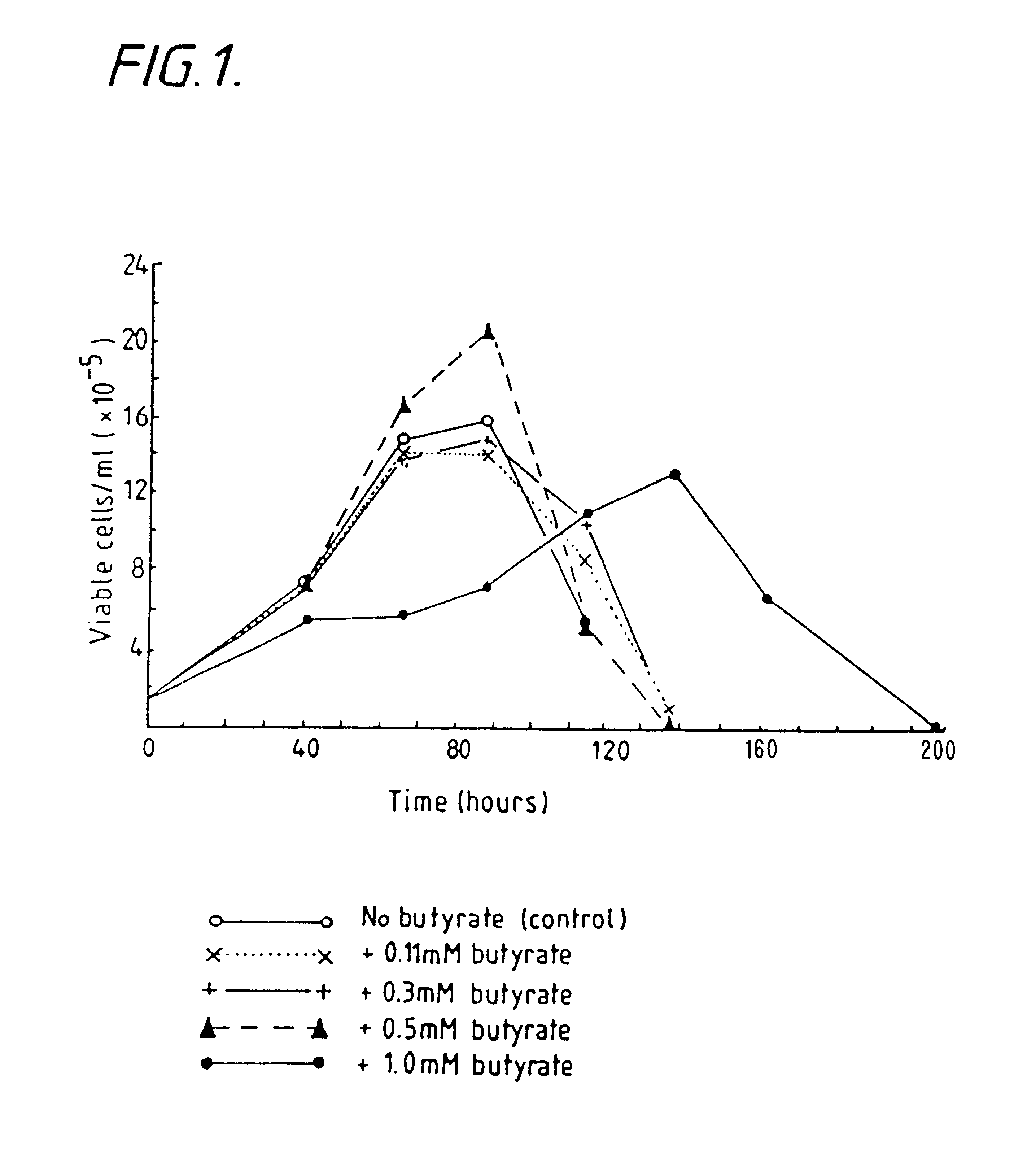
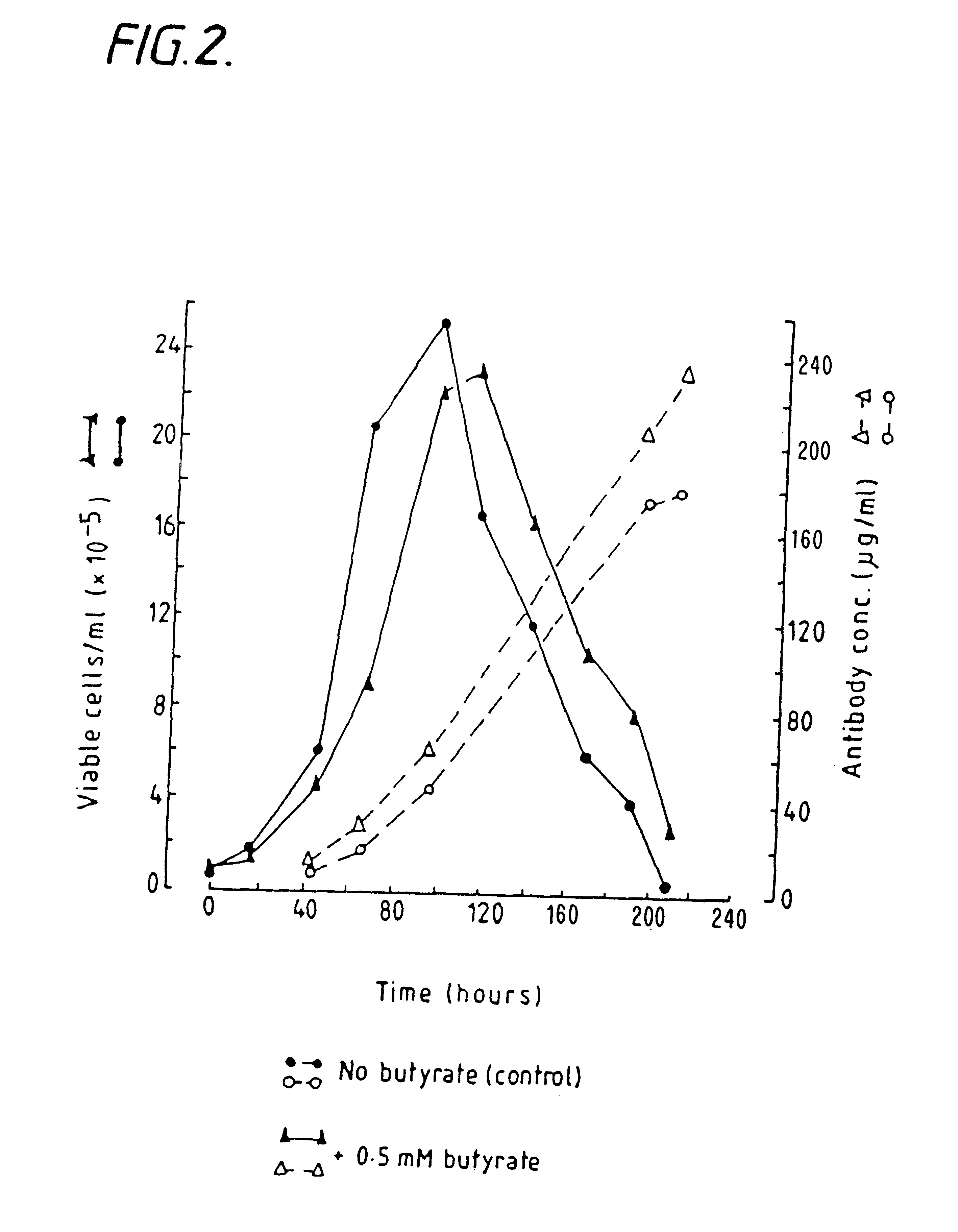
Methods for obtaining a protein by culture of hybridoma cells, wherein said protein is an immunoglobulin, are disclosed. The methods involve culturing animal hybridoma cells in continuous presence of an alkanoic acid or salt thereof, which enhances protein production, wherein said alkanoic acid or salt thereof is present at 2 concentration range of 0.1 mM to 200 mM.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Engineered nucleic acids and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20120237975A1Increase productionImprove translation efficiencySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMessenger RNABiology
Provided are compositions and methods for delivering biological moieties such as modified nucleic acids into cells to modulate protein expression. Such compositions and methods include the use of modified messenger RNAs, and are useful for production of proteins.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Process for discriminating between biological states based on hidden patterns from biological data
The invention describes a process for determining a biological state through the discovery and analysis of hidden or non-obvious, discriminatory biological data patterns. The biological data can be from health data, clinical data, or from a biological sample, (e.g., a biological sample from a human, e.g., serum, blood, saliva, plasma, nipple aspirants, synovial fluids, cerebrospinal fluids, sweat, urine, fecal matter, tears, bronchial lavage, swabbings, needle aspirantas, semen, vaginal fluids, pre-ejaculate.), etc. which is analyzed to determine the biological state of the donor. The biological state can be a pathologic diagnosis, toxicity state, efficacy of a drug, prognosis of a disease, etc. Specifically, the invention concerns processes that discover hidden discriminatory biological data patterns (e.g., patterns of protein expression in a serum sample that classify the biological state of an organ) that describe biological states.
Owner:ASPIRA WOMENS HEALTH INC +1
Engineered nucleic acids and methods of use thereof for non-human vertebrates
InactiveUS20140206752A1Sugar derivativesVector-based foreign material introductionCell biologyVertebrate
Provided are formulations, compositions, kits and methods for delivering biological moieties such as modified nucleic acids into cells to induce, reduce or modulate protein expression in non-human vertebrates.
Owner:MODERNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Cell culture improvements
ActiveUS20080227136A1Improve productivityImproved cell culture longevityGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture mediaImproved method
The invention describes improved methods and compositions for producing a recombinant protein, e.g., an antibody, in mammalian cell culture. In addition, the invention provides improved cell culture media, including improved production media, feed solutions, and combination feeds, which may be used to improve protein productivity in mammalian cell culture.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Oligonucleotide analogues having modified intersubunit linkages and/or terminal groups
ActiveUS20120065169A1Maintain good propertiesEnhanced cell deliveryAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseEnd-group
Oligonucleotide analogues comprising modified intersubunit linkages and / or modified 3′ and / or 5′-end groups are provided. The disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of diseases where inhibition of protein expression or correction of aberrant mRNA splice products produces beneficial therapeutic effects.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Modified polynucleotides for the production of factor ix
InactiveUS20130245103A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
Provided are formulations, compositions and methods for delivering biological moieties such as modified nucleic acids into cells to modulate protein expression. Such compositions and methods include the delivery of biological moieties, and are useful for production of proteins.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Methods and products related to the improved analysis of carbohydrates
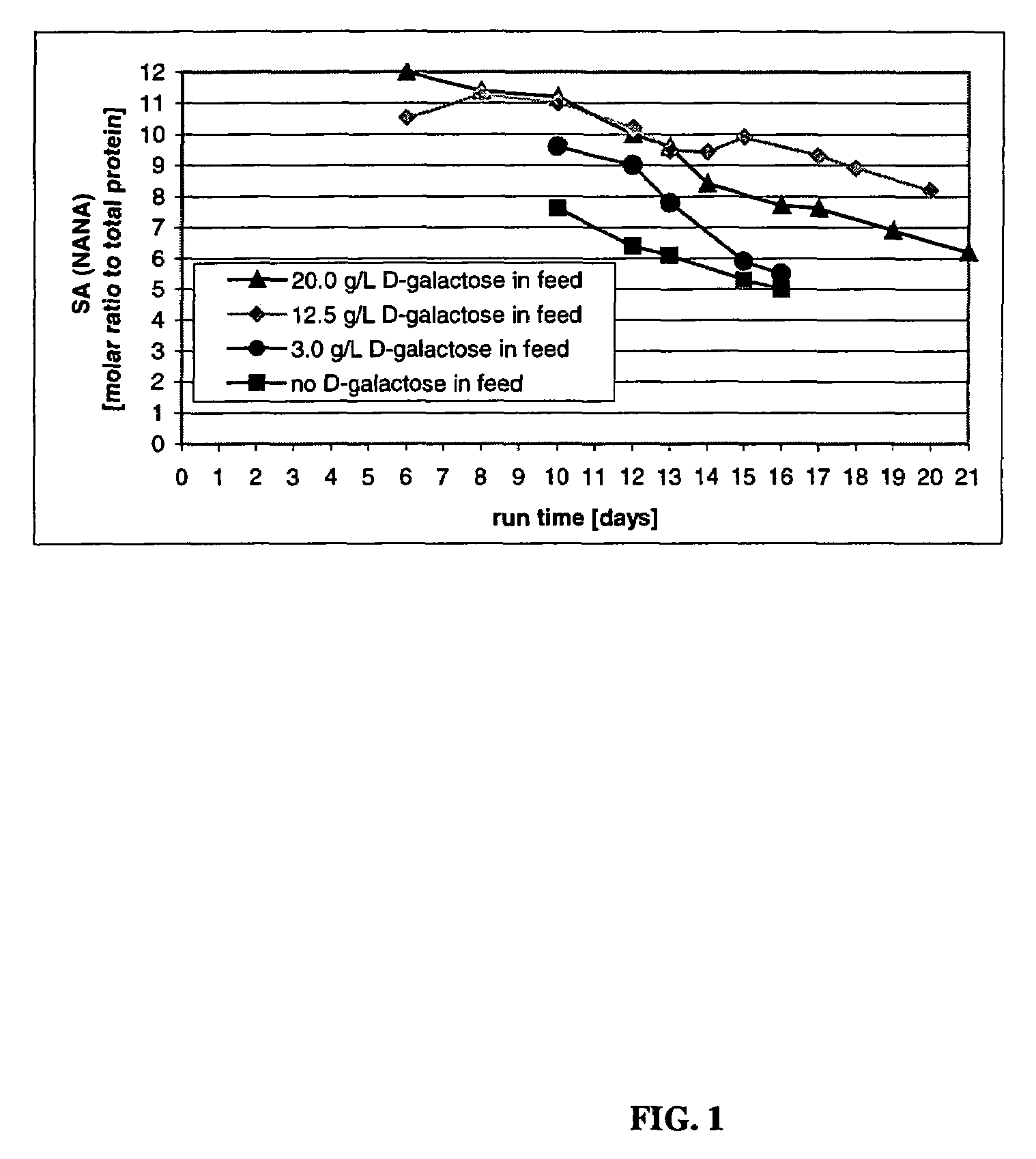
The invention relates, in part, to the improved analysis of carbohydrates. In particular, the invention relates to the analysis of carbohydrates, such as N-glycans and O-glycans found on proteins. Improved methods, therefore, for the study of glycosylation patterns on cells, tissue and body fluids are also provided. Information regarding the analysis of glycans, such as the glycosylation patterns on cells, tissues and in body fluids, can be used in diagnostic and treatment methods as well as for facilitating the study of the effects of glycosylation / altered glycosylation on protein function. Such methods are also provided. Methods are also provided to assess protein production processes, to assess the purity of proteins produced, and to select proteins with the desired glycosylation.
Owner:MOMENTA PHARMA +2
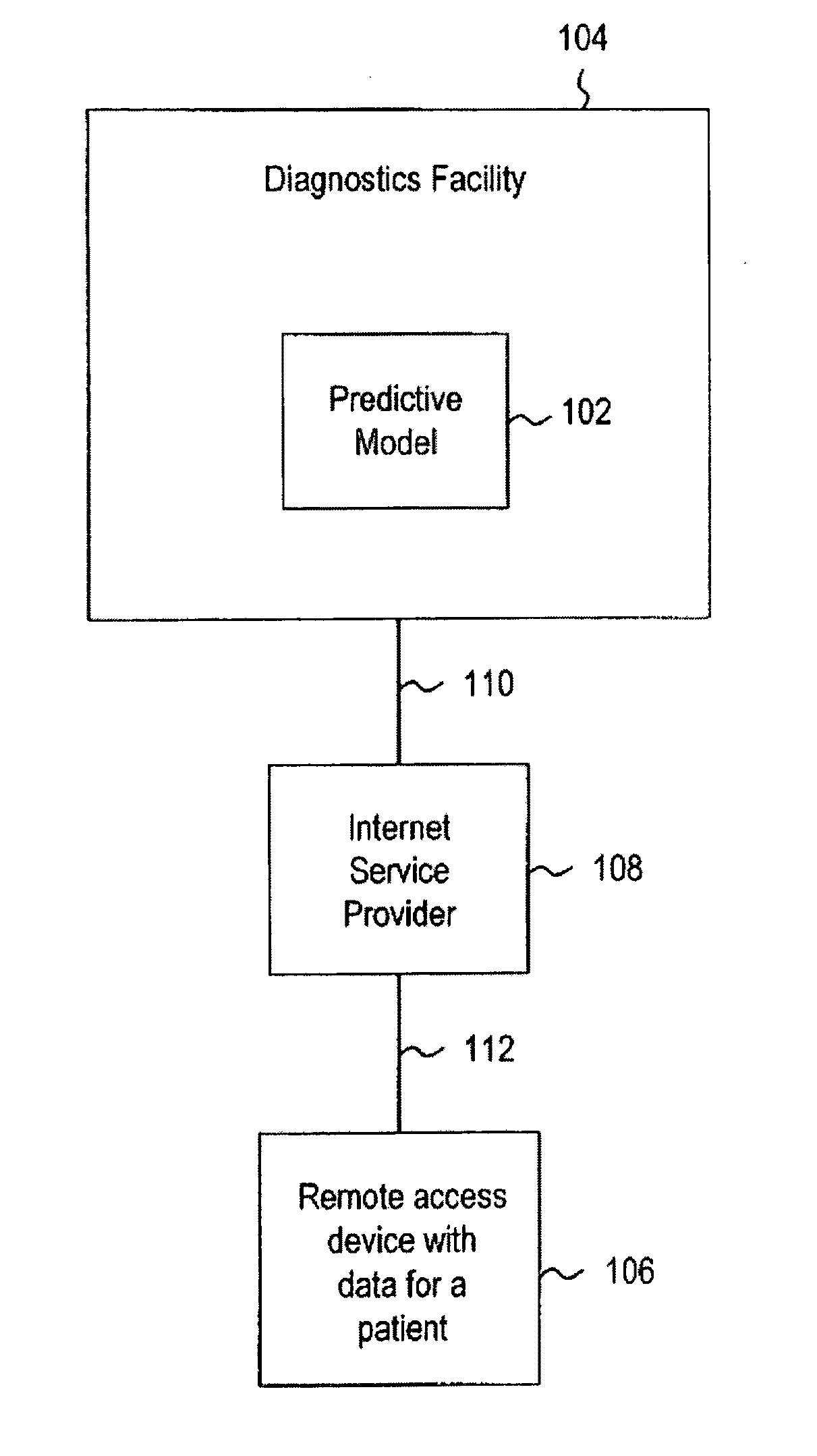
Systems and methods for treating, diagnosing and predicting the occurrence of a medical condition
ActiveUS20100184093A1Reliable and accurate image segmentationMedical simulationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImmunofluorescenceClinical information
Clinical information, molecular information and / or computer-generated morphometric information is used in a predictive model for predicting the occurrence of a medical condition. In an embodiment, a model predicts whether a patient is likely to have a favorable pathological stage of prostate cancer, where the model is based on features including one or more (e.g., all) of preoperative PSA, Gleason Score, a measurement of expression of androgen receptor (AR) in epithelial and stromal nuclei and / or a measurement of expression of Ki67-positive epithelial nuclei, a morphometric measurement of a ratio of area of epithelial nuclei outside gland units to area of epithelial nuclei within gland units, and a morphometric measurement of area of epithelial nuclei distributed away from gland units. In some embodiments, quantitative measurements of protein expression in cell lines are utilized to objectively assess assay (e.g., multiplex immunofluorescence (IF)) performance and / or to normalize features for use within a predictive model.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +1
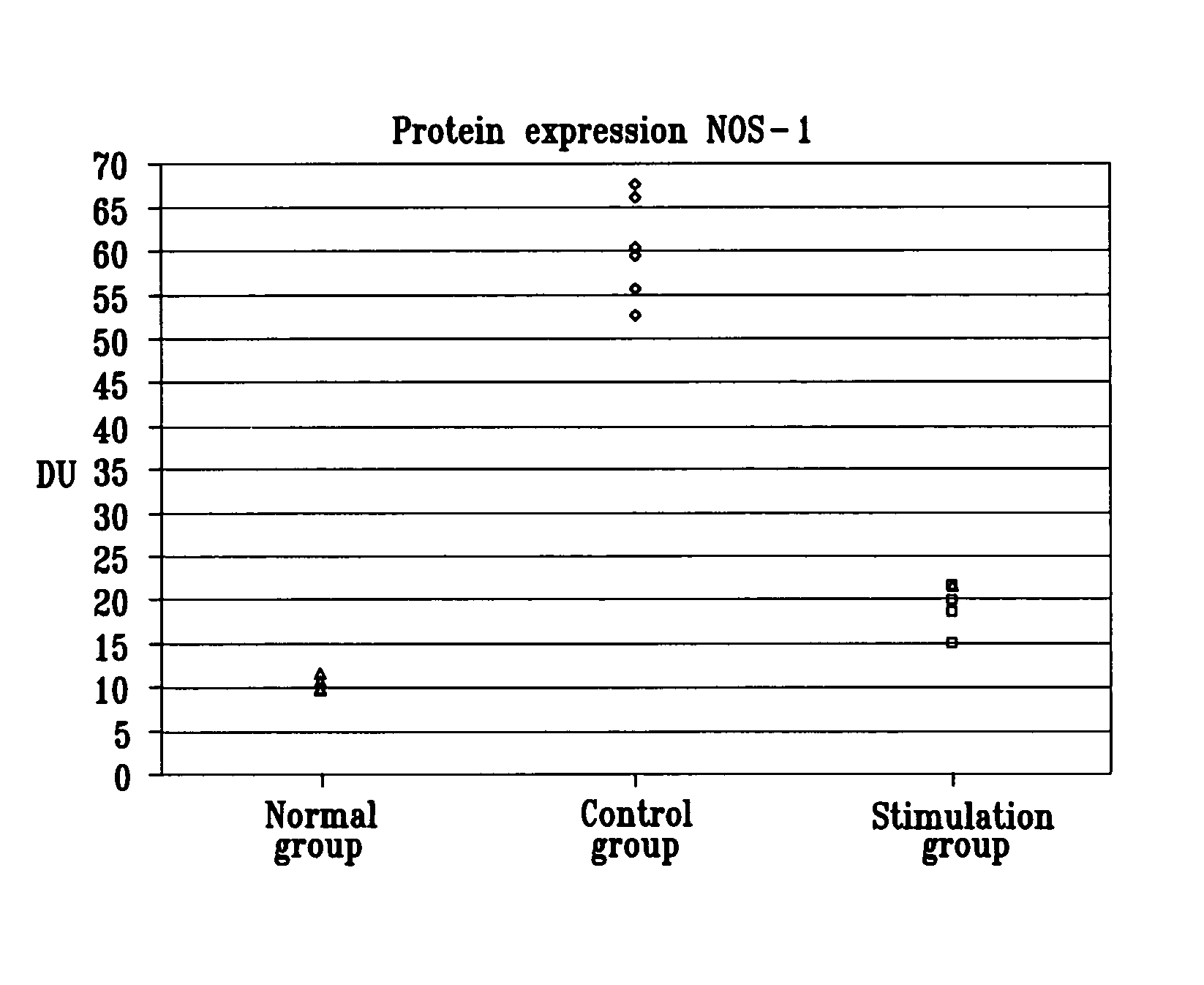
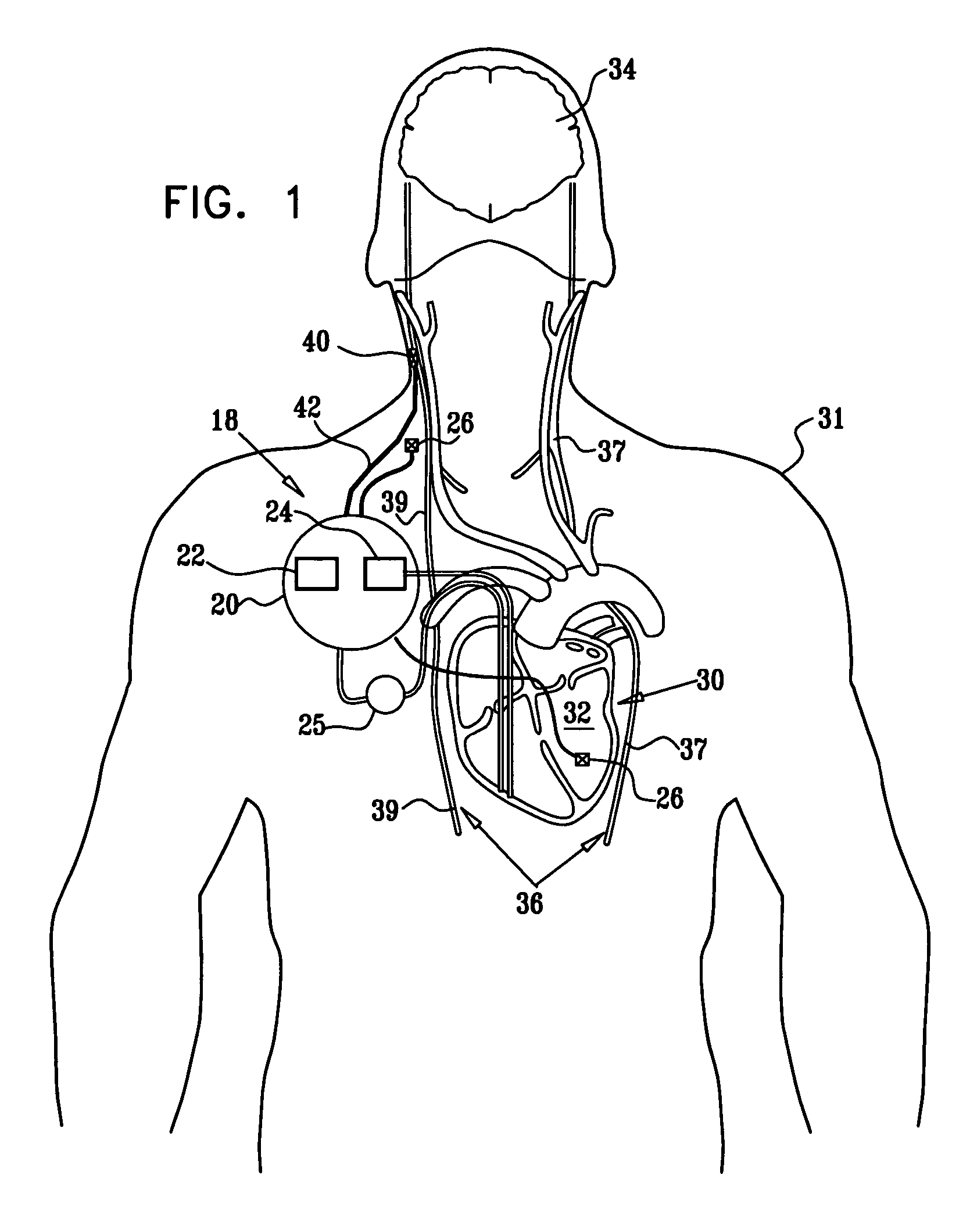
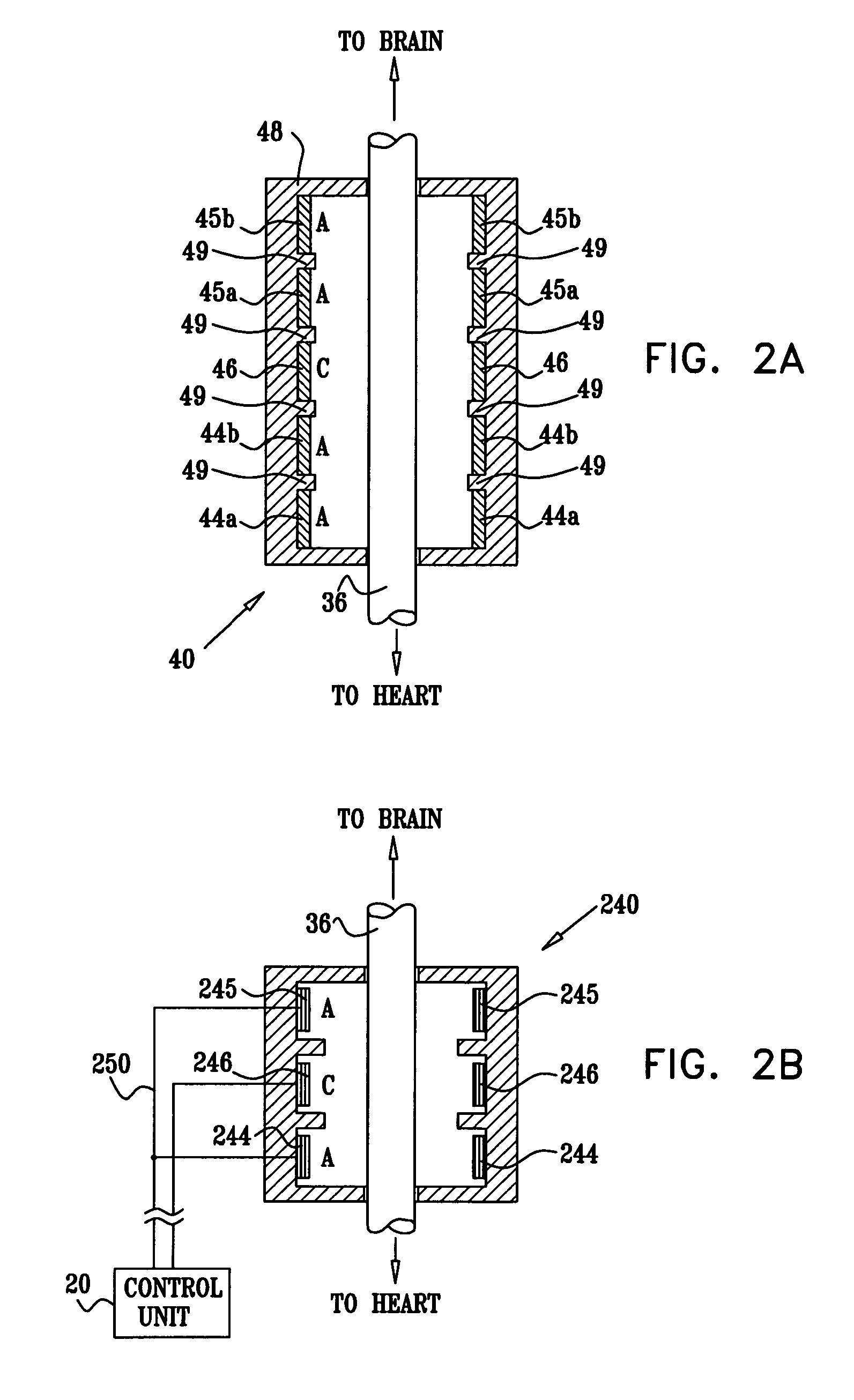
Nerve stimulation for treating disorders
InactiveUS7885709B2Minimize any unintended side effect of the signal applicationSuppresses afferent action potentialElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseasePower flow
This invention provides a method for treating a condition of a subject, comprising identifying the subject as suffering from heart failure; treating the heart failure by applying a stimulating current to parasympathetic nervous tissue of the subject, and configuring the stimulating current to change a level of protein expression of at least one NO synthase of the subject selected from the group consisting of: NOS-1, NOS-2, and NOS-3; and thereafter, measuring the level of the protein expression of at least one NO synthase, and evaluating an effectiveness of the current application by assessing at least one change in the level of the protein expression of at least one NO synthase.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Arrays of protein-capture agents and methods of use thereof
Owner:WAGNER PETER +3
Method of producing a plurality of isolated antibodies to a plurality of cognate antigens
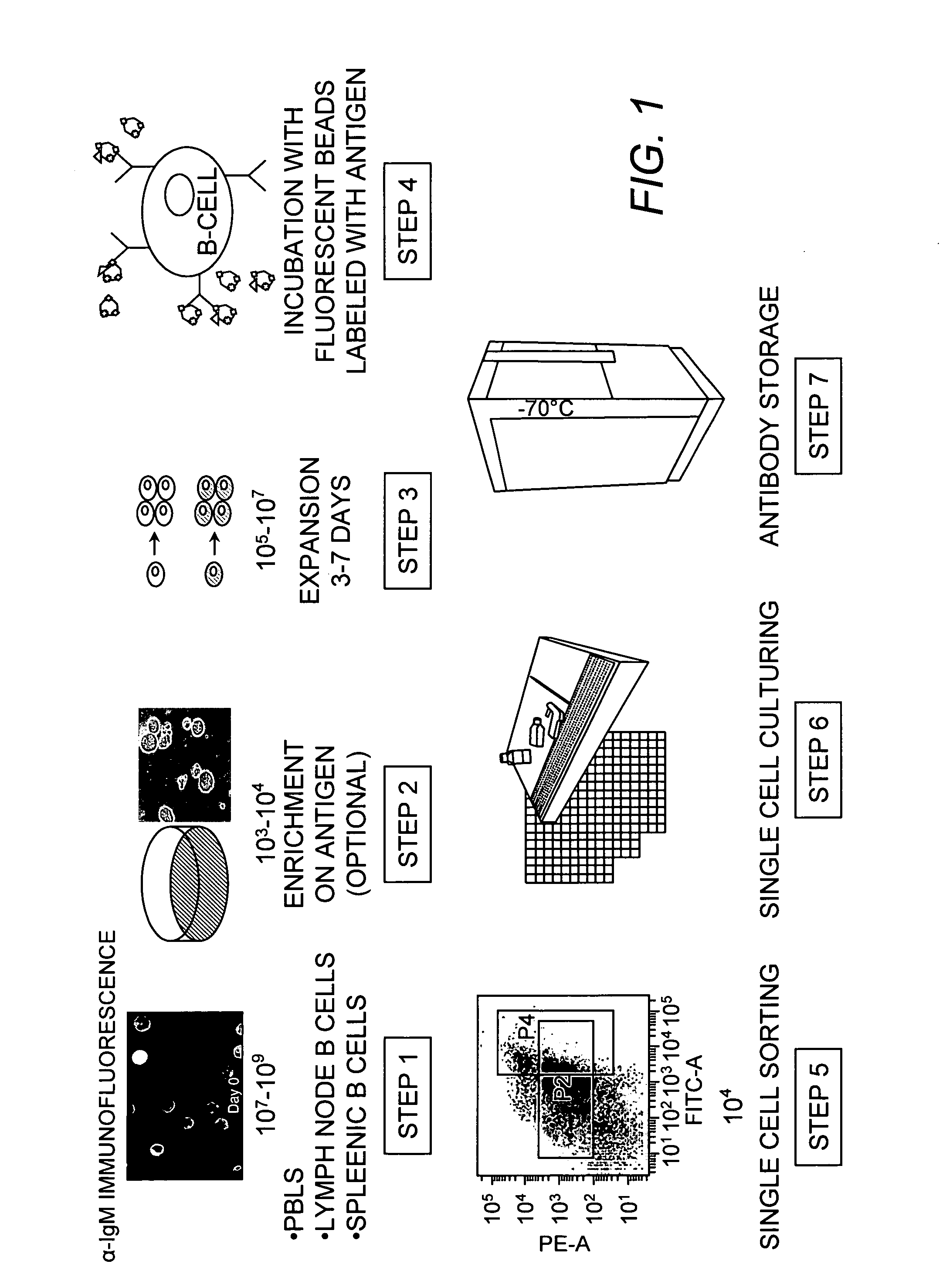
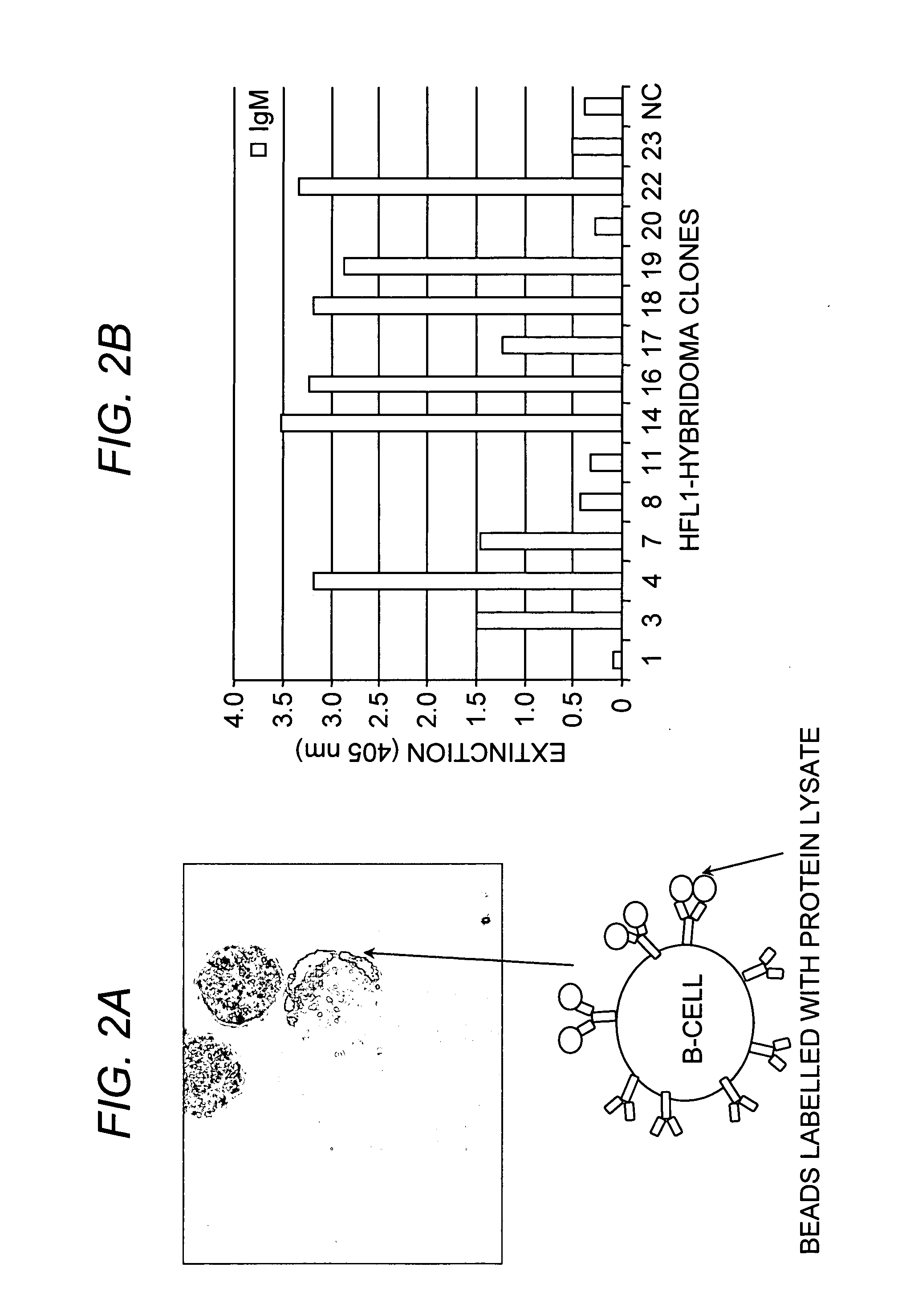
The present invention relates to a method for producing high affinity antibodies that are antigen-specific. The method involves binding a plurality of antibody-producing B-cells from a mammal to a plurality of cognate antigens; sorting the bound antibody-producing B-cell and cognate antigen; amplifying nucleic acid sequences encoding each antibody, or fragment thereof, from the B-cells; and expressing the each antibody in a protein expression system. Antibodies produced in this manner are useful in diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Owner:MONTECITO BIO SCI
Product quality enhancement in mammalian cell culture processes for protein production
ActiveUS7332303B2Low production costQuality improvementAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHigh cellBiotechnology
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Formulations comprising antisense nucleotides to connexins
InactiveUS7098190B1Reducing neuronal cell deathDown-regulated expressionNervous disorderSpecial deliveryNeuron cell deathWound healing
A therapeutic and / or cosmetic formulation comprising at least one anti-sense polynucleotide to a connexin protein together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or vehicle is useful in site specific down regulation of connexin protein expression, particularly in reduction of neuronal cells death, wound healing, reduction of inflammation, decrease of scar formation and skin rejuvenation and thickening.
Owner:COLLEGE LONDON UNIV
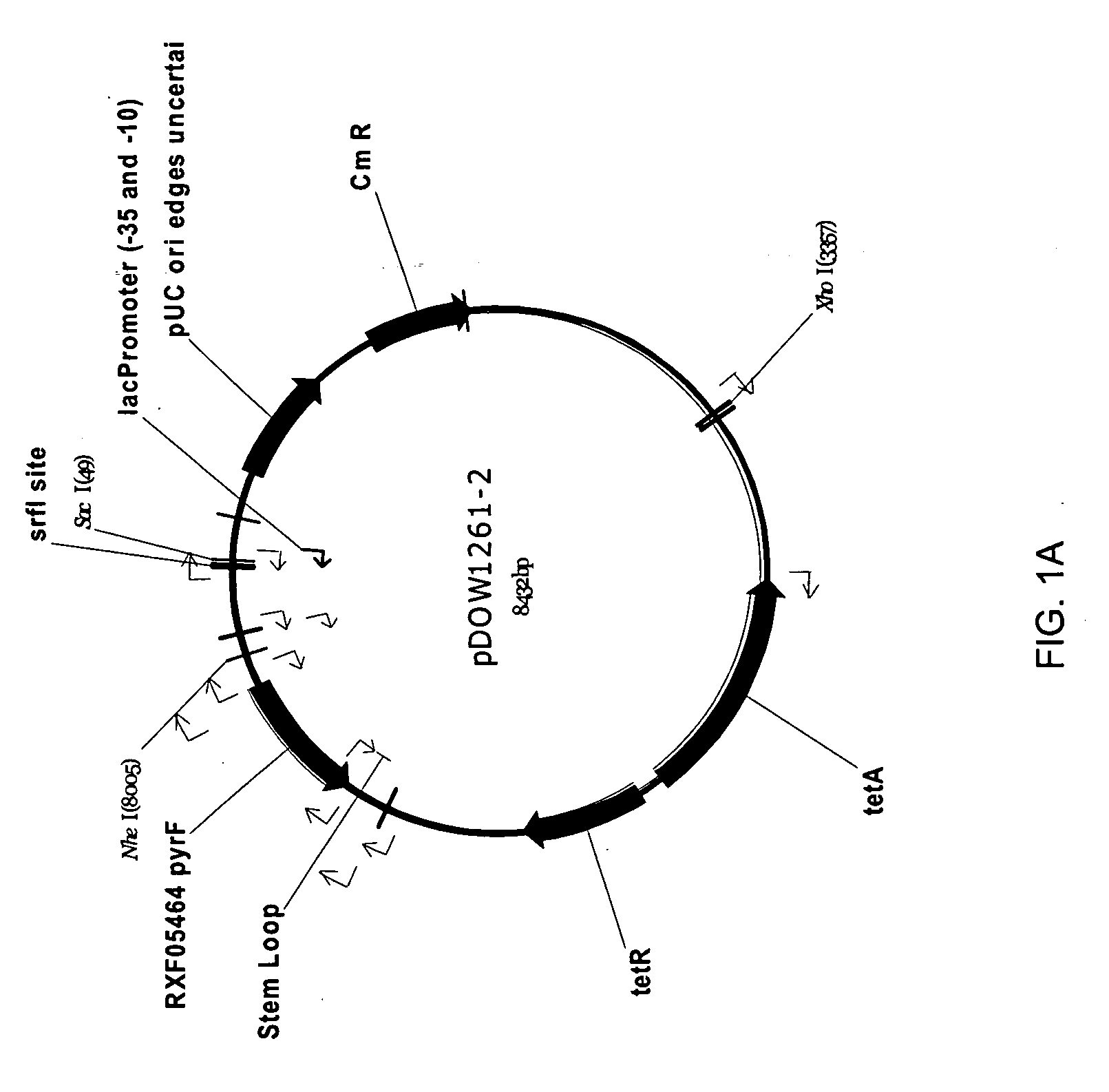
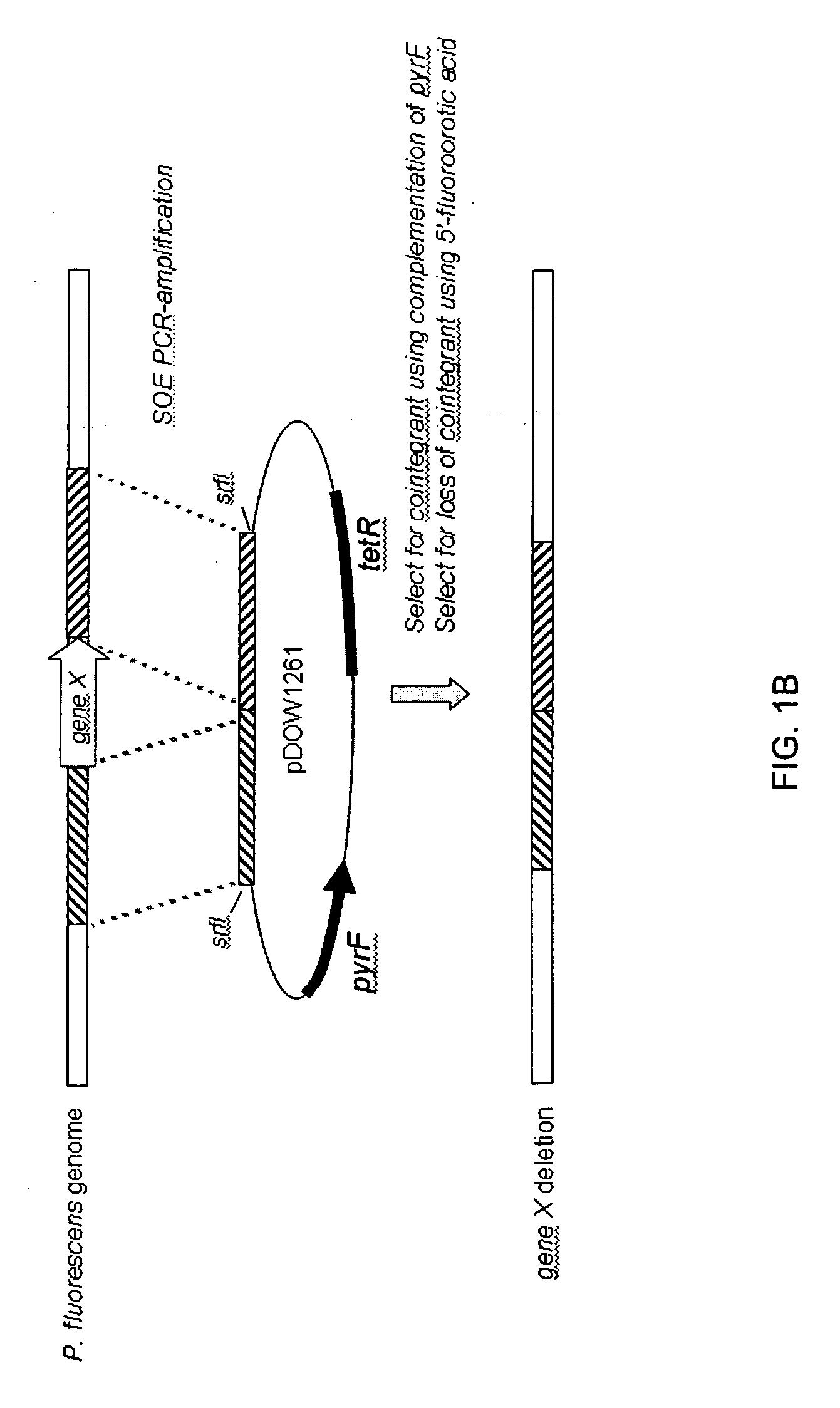
Protein expression systems
InactiveUS20050186666A1High protein yieldEfficient productionBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyRecombinant protein production
The present invention provides an improved expression system for the production of recombinant polypeptides utilizing auxotrophic selectable markers. In addition, the present invention provides improved recombinant protein production in host cells through the improved regulation of expression.
Owner:PFENEX
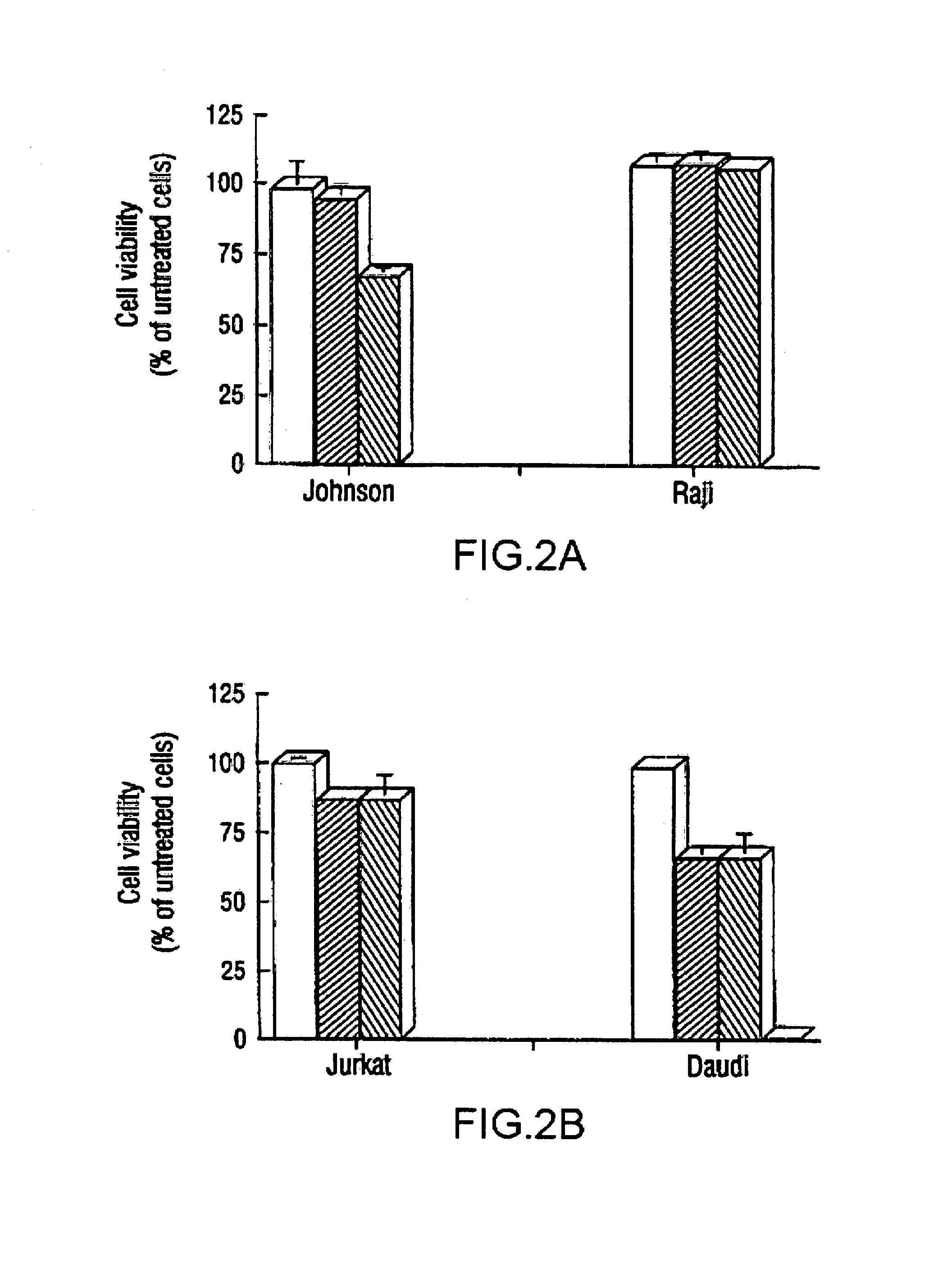
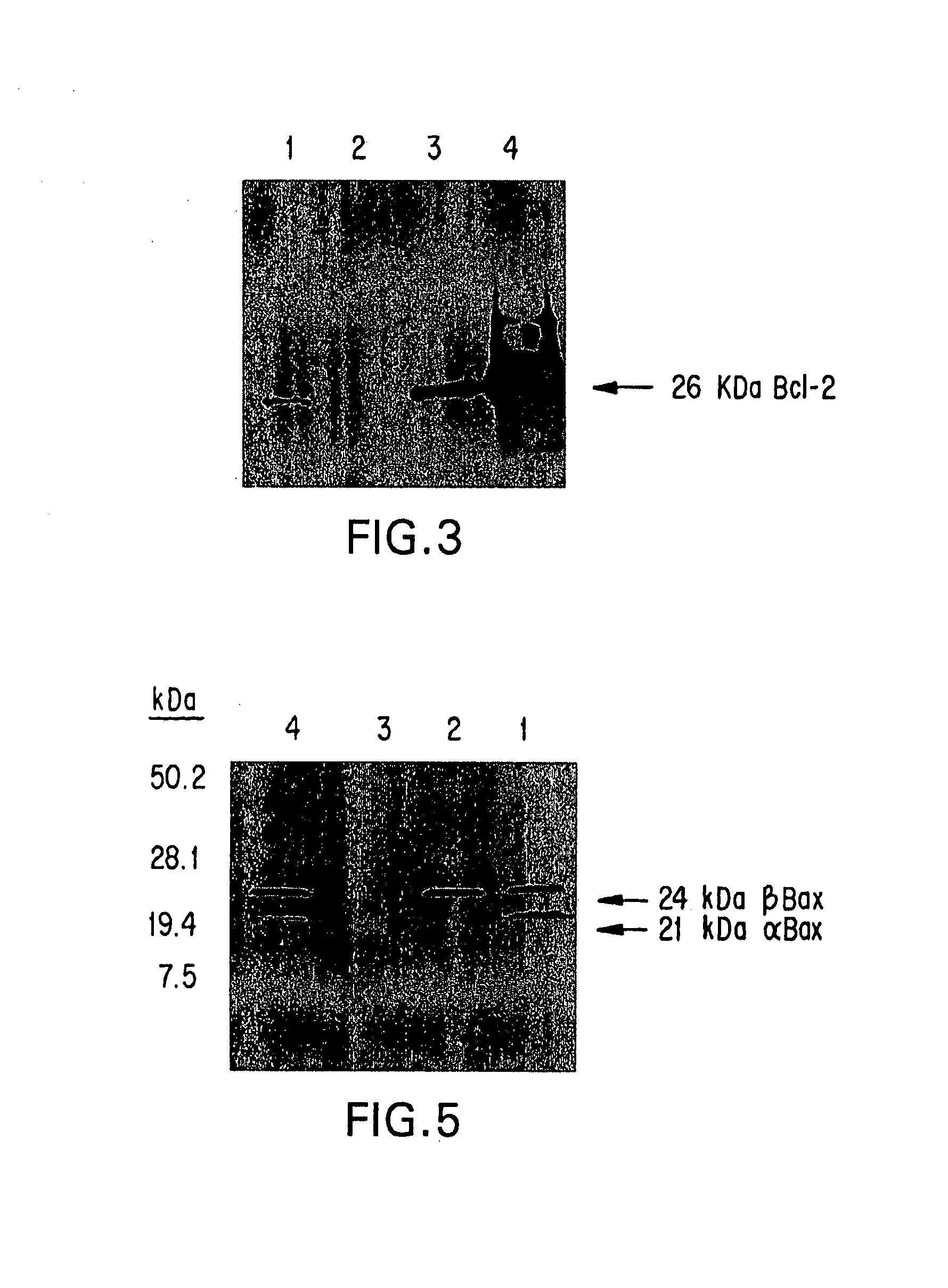
Inhibition of Bcl-2 protein expression by liposomal antisense oligodeoxynucleotides
InactiveUS7285288B1Lower the volumeIncrease the effective concentrationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention provides novel compositions and methods for use in the treatment of Bcl-2-associated diseases like cancer, specifically, in the treatment of follicular lymphoma (FL). The compositions contain antisense oligonucleotides that hybridize to Bcl-2 nucleic acids, the gene products of which are known to interact with the tumorigenic protein Bcl-2. Used alone, or in conjunction with other antisense oligonucleotides, these compositions inhibit the proliferation of FL cancer cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
ActiveUS20120289457A1Easy to transportImprove propertiesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
Oligonucleotide analogues conjugated to carrier peptides are provided. The disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of various diseases, for example diseases where inhibition of protein expression or correction of aberrant mRNA splice products produces beneficial therapeutic effects.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
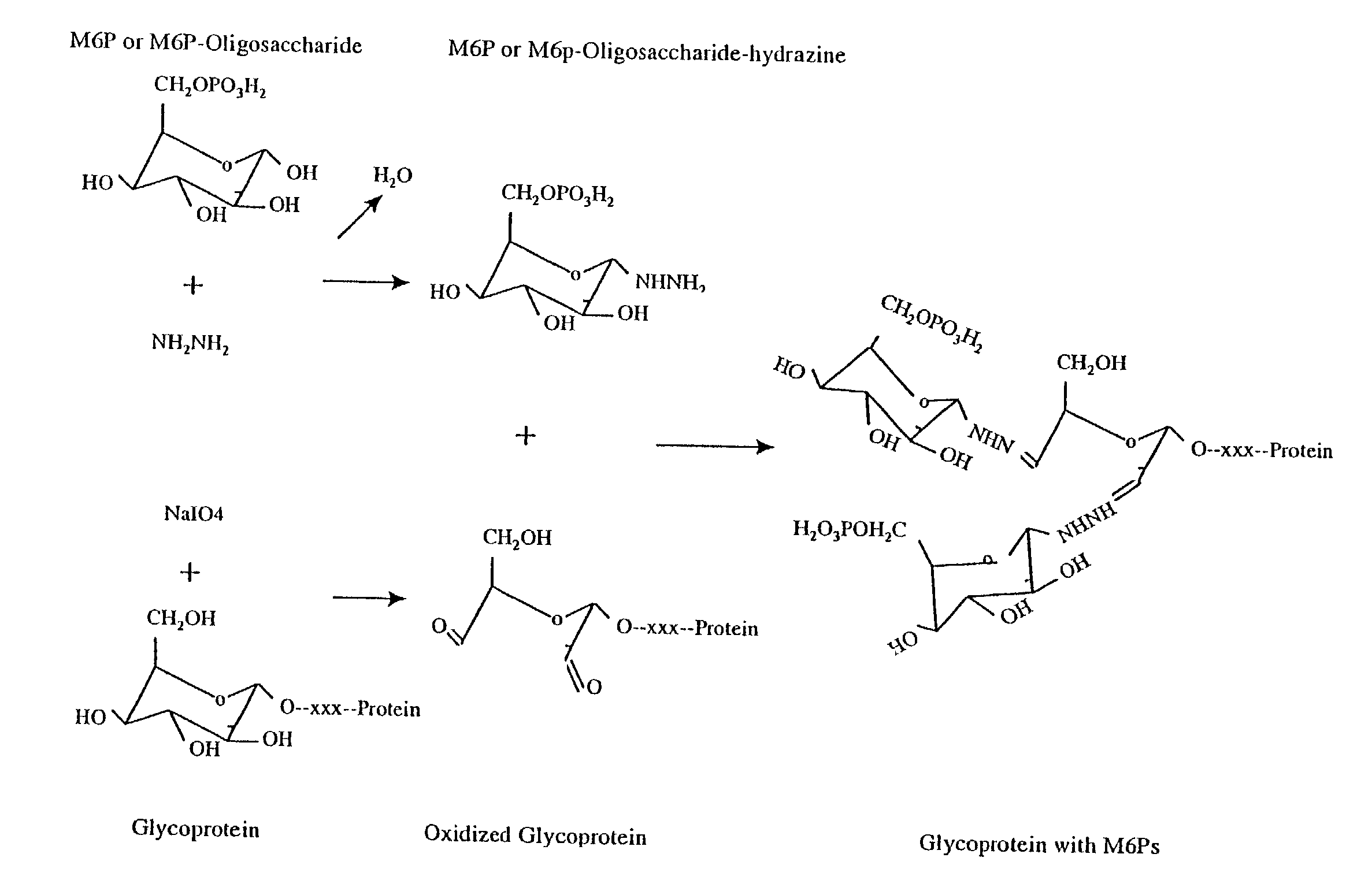
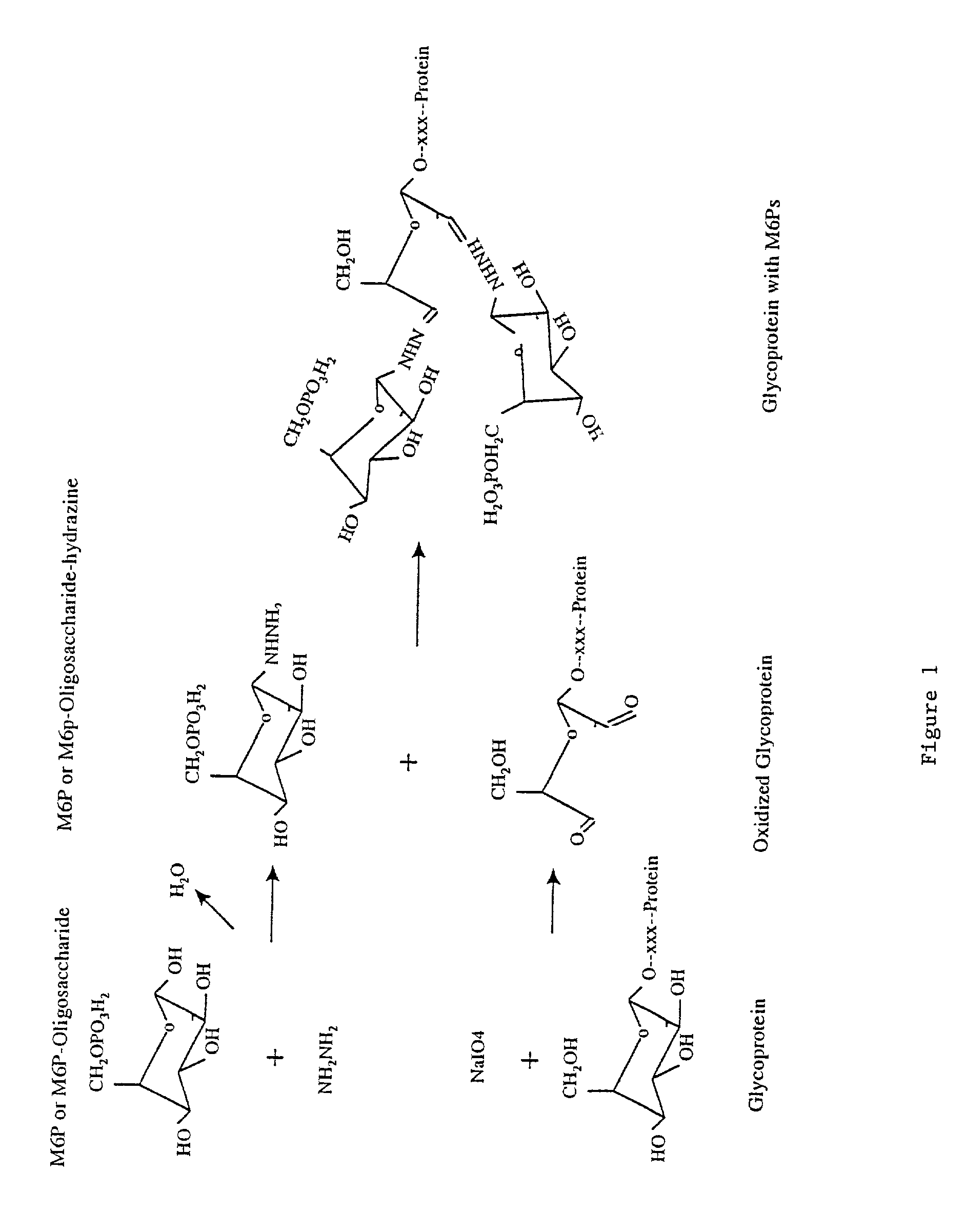
Methods for introducing mannose 6-phosphate and other oligosaccharides onto glycoproteins
InactiveUS7001994B2Well formedIncrease the cellular uptake of lysosomal enzymesHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphorylationPhosphoric acid
Methods to introduce highly phosphorylated mannopyranosyl oligosaccharide derivatives containing mannose 6-phosphate (M6P), or other oligosaccharides bearing other terminal hexoses, to carbonyl groups on oxidized glycans of glycoproteins while retaining their biological activity are described. The methods are useful for modifying glycoproteins, including those produced by recombinant protein expression systems, to increase uptake by cell surface receptor-mediated mechanisms, thus improving their therapeutic efficacy in a variety of applications.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Promoter and plasmid system for genetic engineering
This invention provides a series of low-copy number plasmids comprising restriction endonuclease recognition sites useful for cloning at least three different genes or operons, each flanked by a terminator sequence, the plasmids containing variants of glucose isomerase promoters for varying levels of protein expression. The materials and methods are useful for genetic engineering in microorganisms, especially where multiple genetic insertions are sought.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
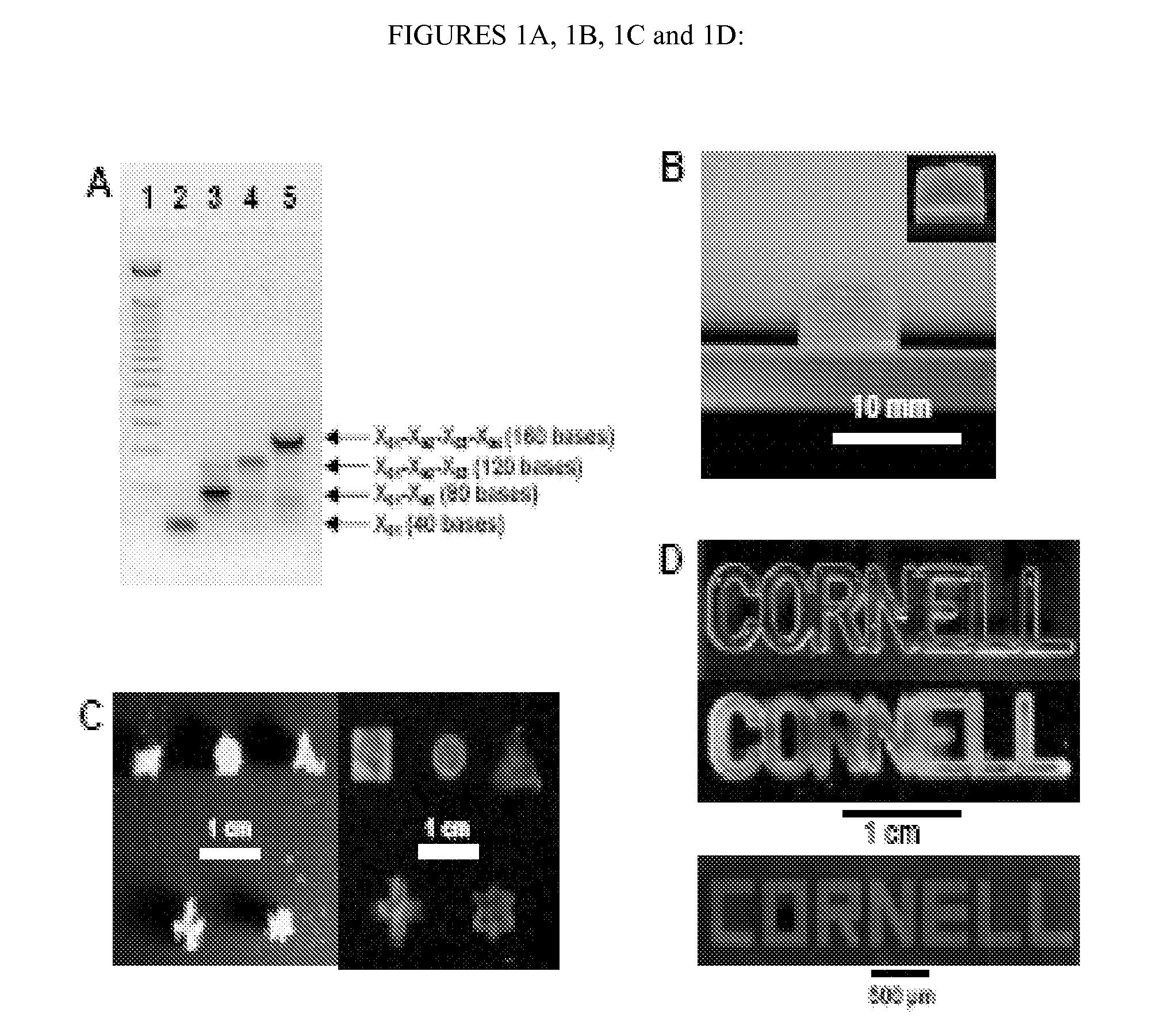
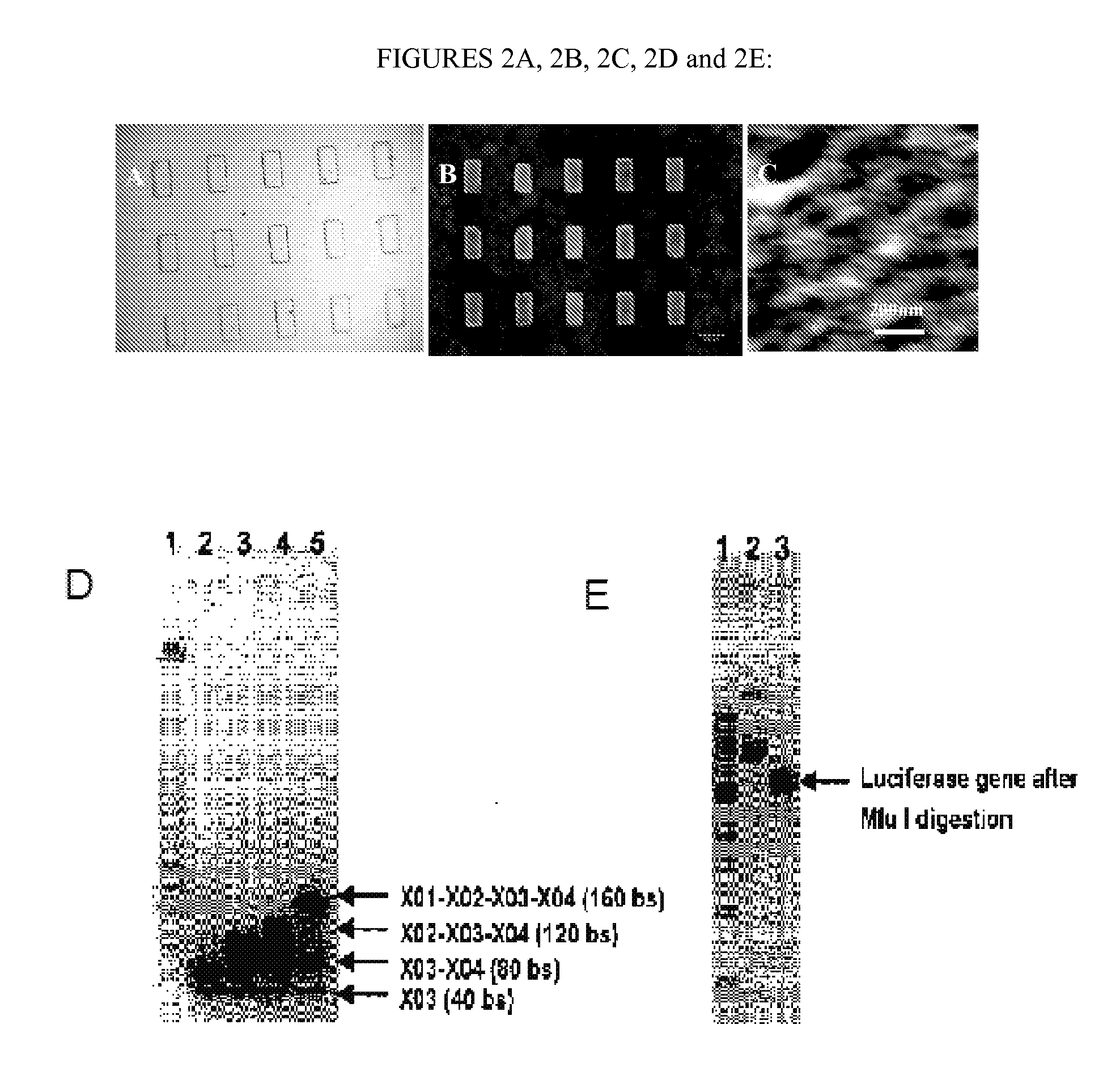
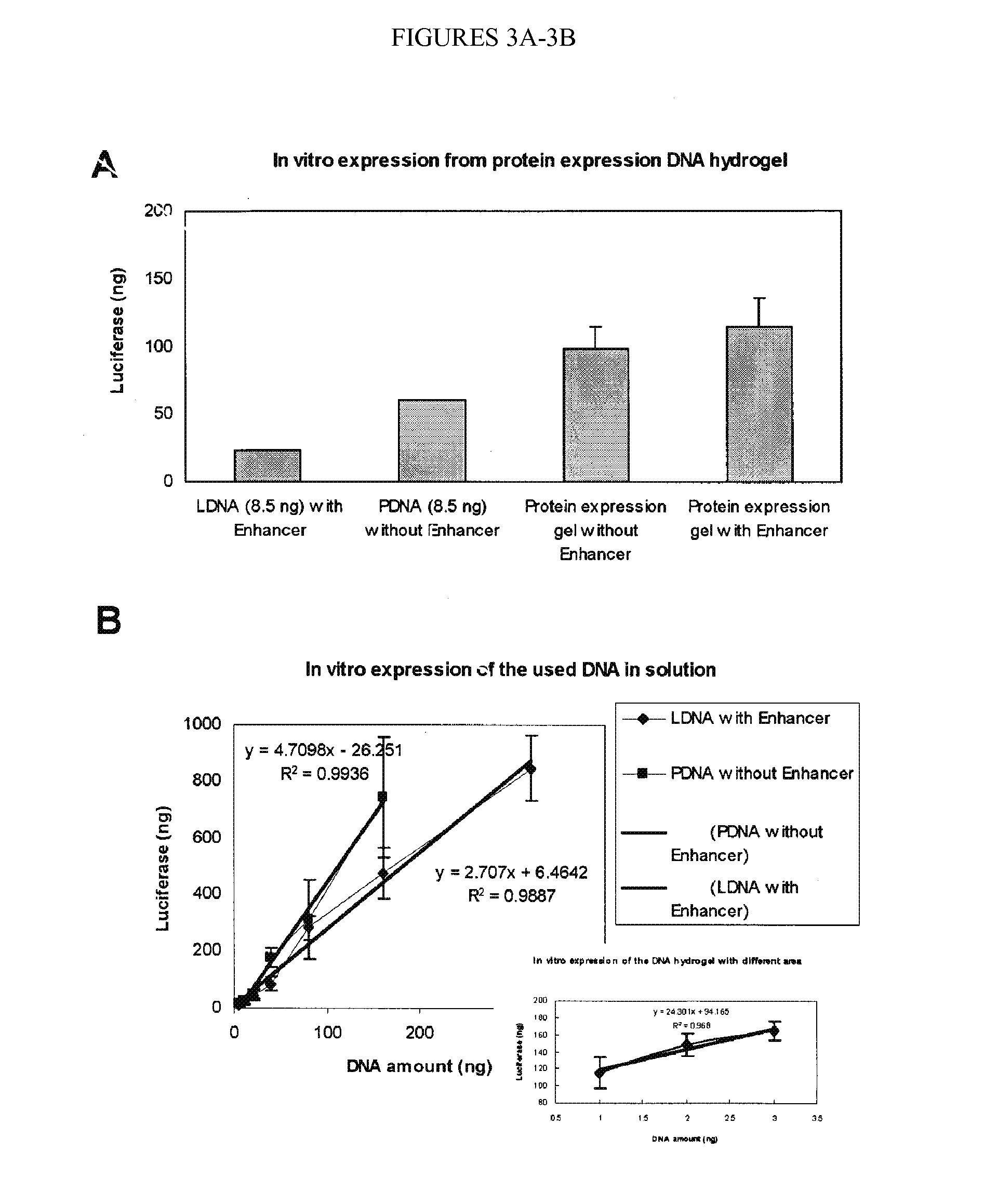
Nucleic Acid-Based Matrixes for Protein Production
InactiveUS20070117177A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological materialsCell-free protein synthesis
Various nucleic acid-based matrixes are provided, comprising nucleic acid monomers as building blocks, as well as nucleic acids encoding proteins, so as to produce novel biomaterials. Methods of utilizing such biomaterials include cell-free protein synthesis.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
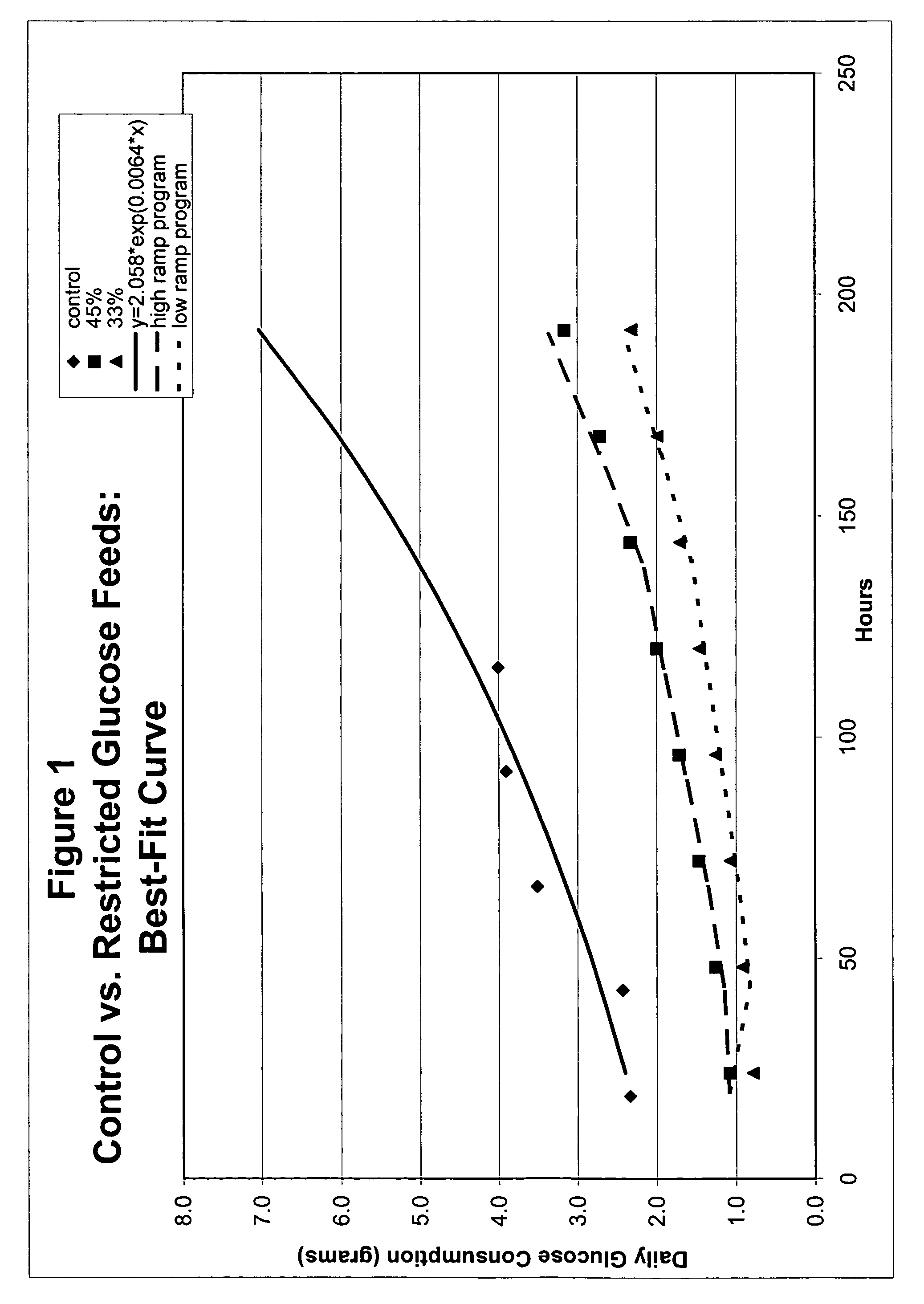
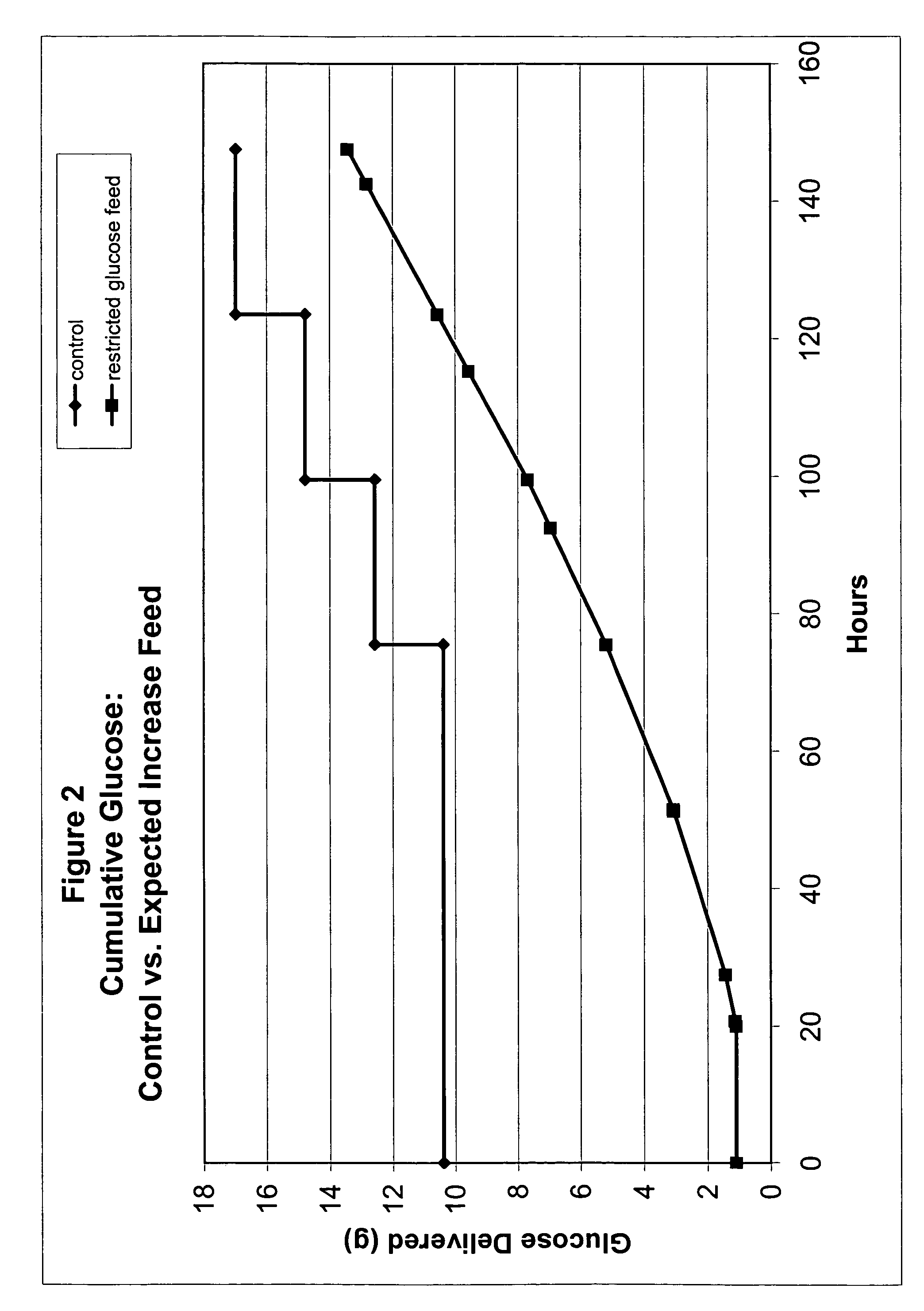
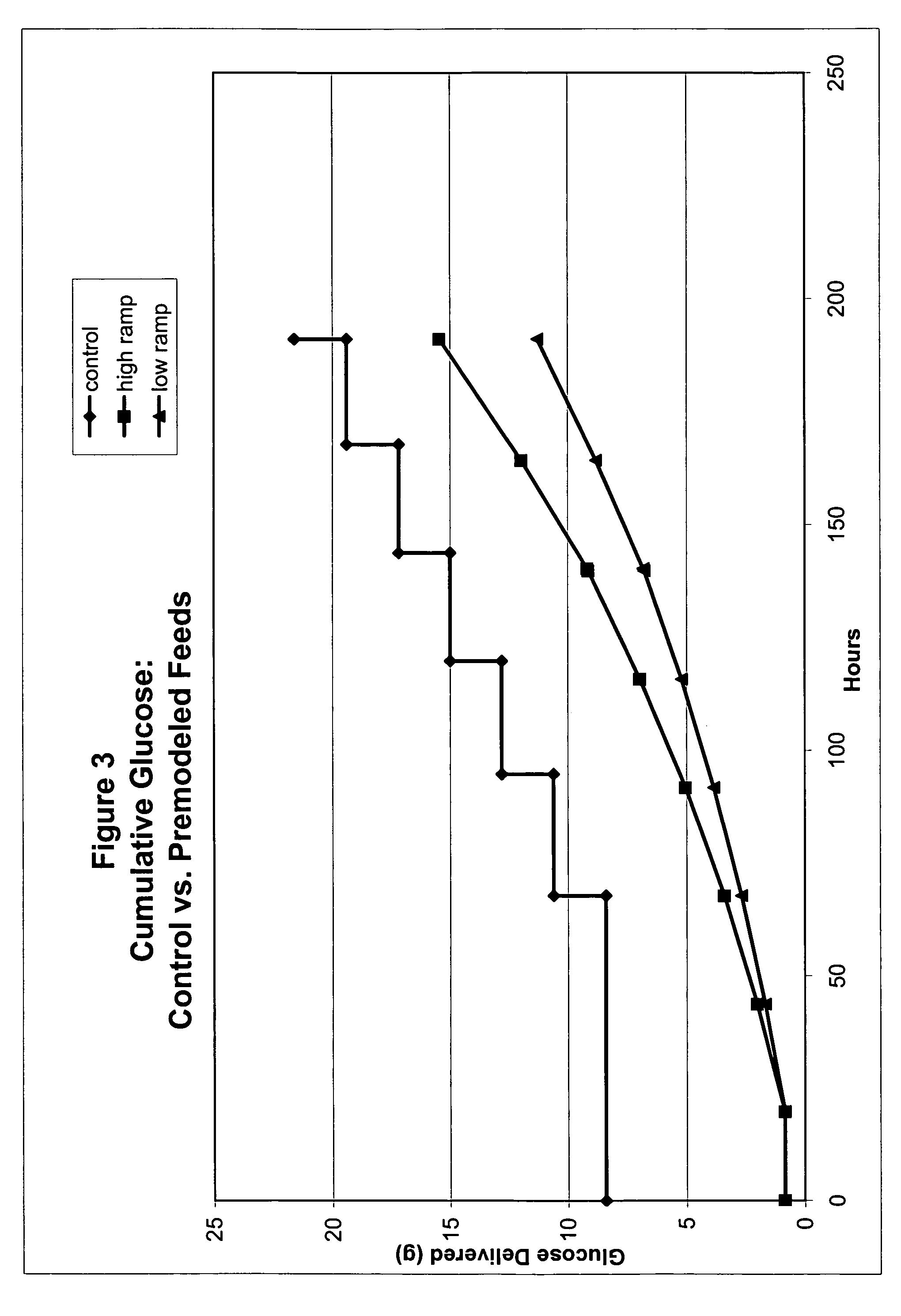
Restricted glucose feed for animal cell culture
ActiveUS7429491B2Promote productionFlexible controlCulture processCell culture mediaBiotechnologyBiochemistry
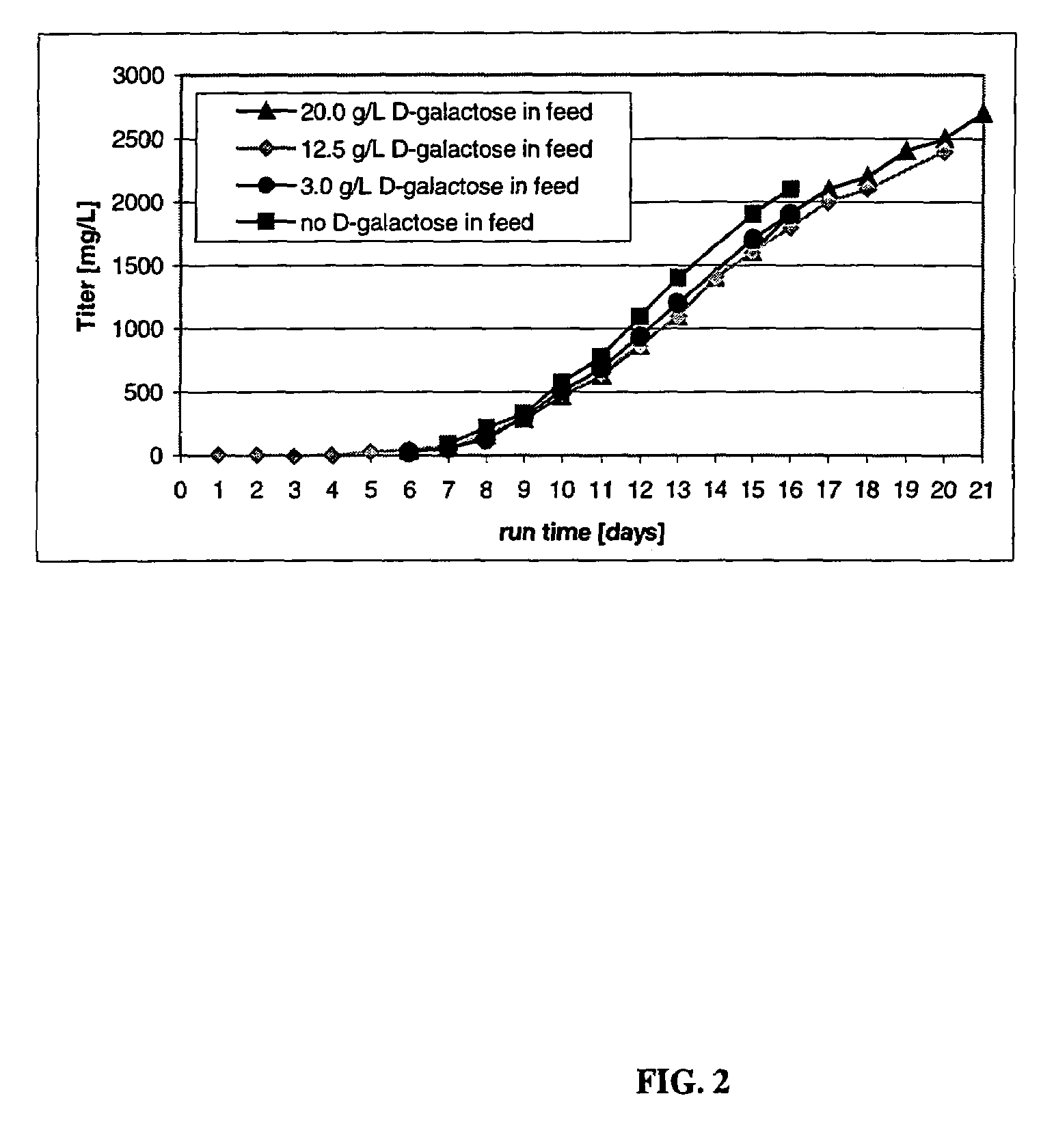
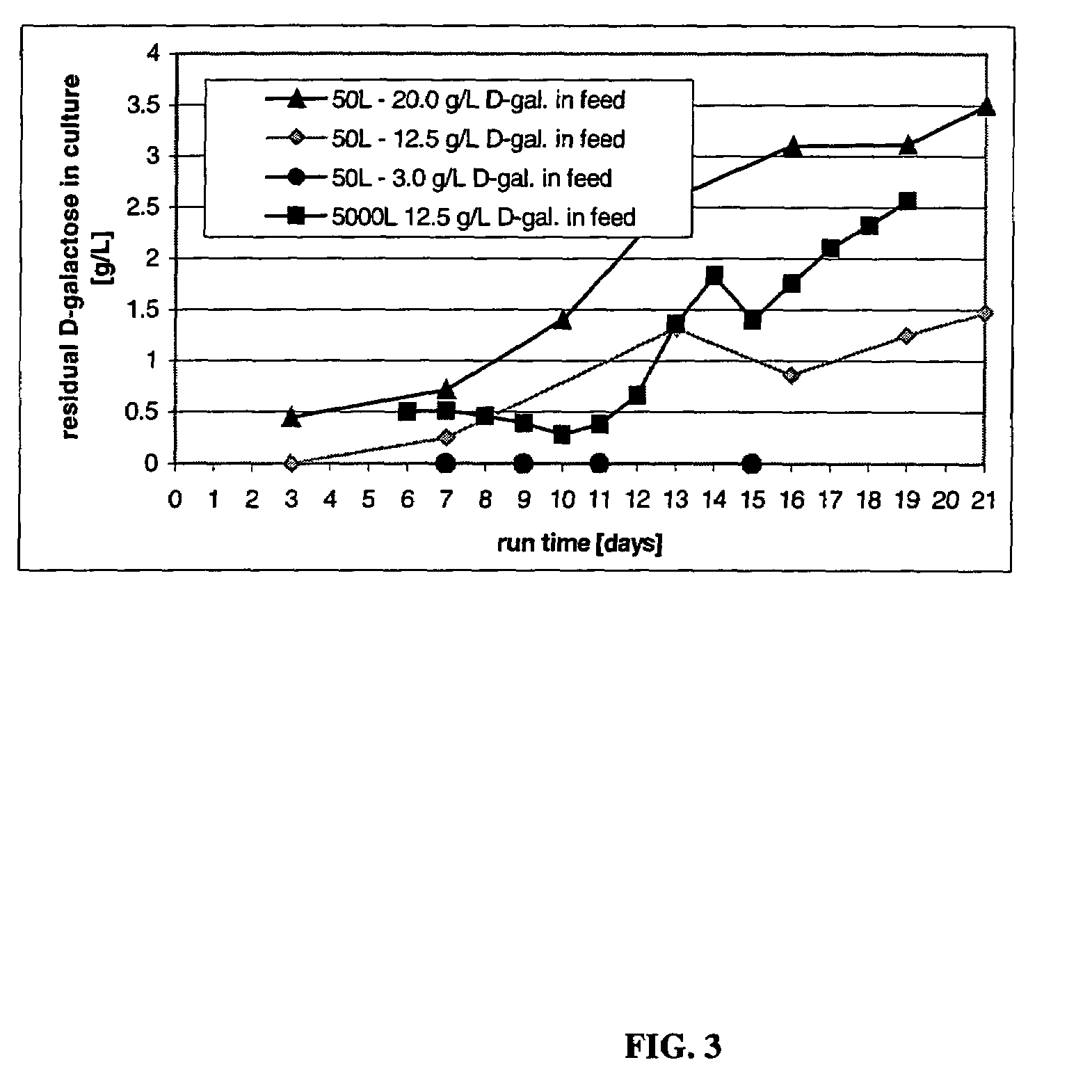
Methods of improving protein production in animal cell cultures are provided. Cell culture methods are presented wherein glucose is fed in a restricted manner to cell culture; this restricted feeding of glucose to the cell culture results in lactate production being controlled to a low level. The restricted feeding of glucose in a fed-batch process is not accomplished through a constant-rate feeding of glucose, and the restricted feeding need not depend on sampling. Instead, restricted feeding of glucose to the culture is accomplished through feeding of glucose to the culture at a rate that is a function of an expected or a premodeled rate of glucose consumption by the animal cells when exposed to medium containing a high level of glucose. Because lactate production is controlled to low levels, recombinant protein production is increased.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method of producing antibodies
InactiveUS20130244282A1Increase productionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMessenger RNAMoiety
Owner:MODERNATX INC
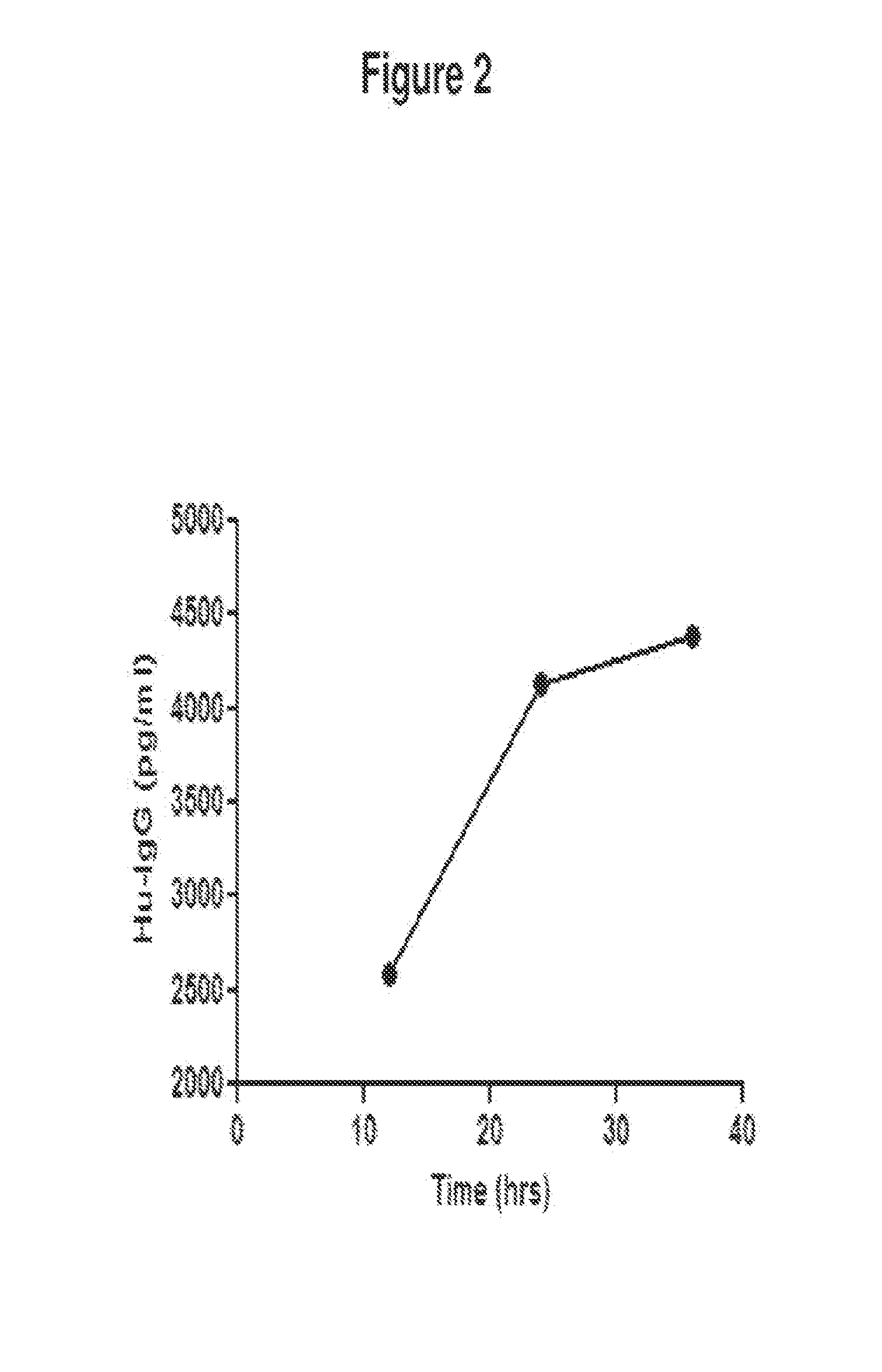
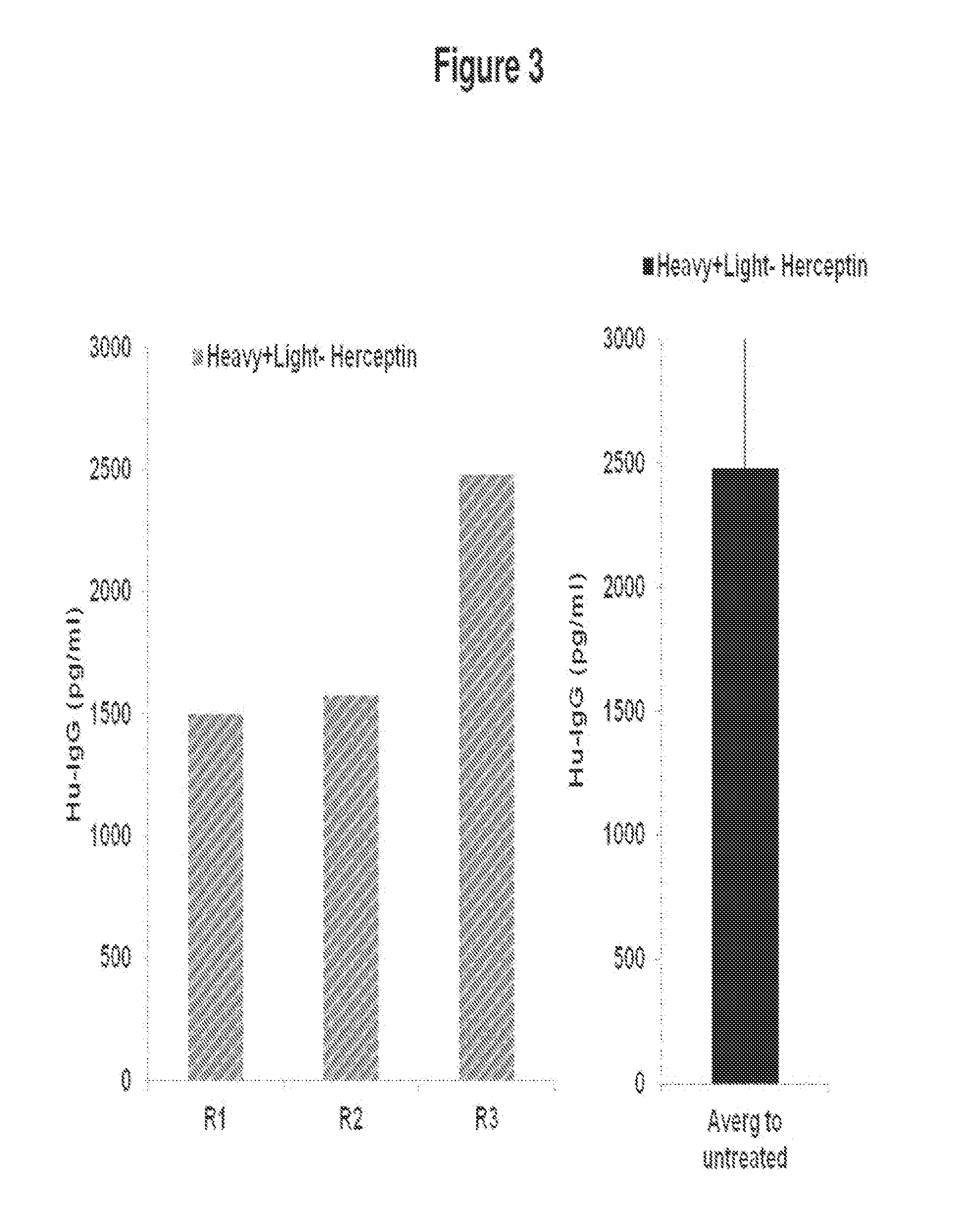
Nanoparticle delivery vehicle
A nanoparticle delivery vehicle, comprising a nanoparticle, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal and methods of modulating gene expression and protein expression employing the nanoparticle delivery vehicle. A representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter of about 30 nm or less, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the nucleus of a target cell. Another representative method includes providing a nanoparticle delivery vehicle comprising a nanoparticle having a diameter greater than or equal to about 30 nm, an active agent and a nuclear localization signal; and contacting a target cell with the nanoparticle delivery vehicle, whereby an active agent is delivered to the cytoplasm of a cell.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Recombinant expression of proteins from secretory cell lines
InactiveUS6110707AIncrease productionIncrease secretionHormone peptidesRecombinant DNA-technologyHeterologousDisease
The present invention a provides methods for production of heterologous polypeptides, for example amylin, using recombinantly engineered cell lines. Also described are methods engineering cells for high level expression, methods of large scale heterologous protein production, methods for treatment of disease in vivo using viral delivery systems and recombinant cell lines, and methods for isolating novel amylin receptors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Remedies for heart failure
InactiveUS7816511B2Preventing and treating heart failureInhibit deteriorationBiocideSugar derivativesCardiac failure therapyPharmaceutical drug
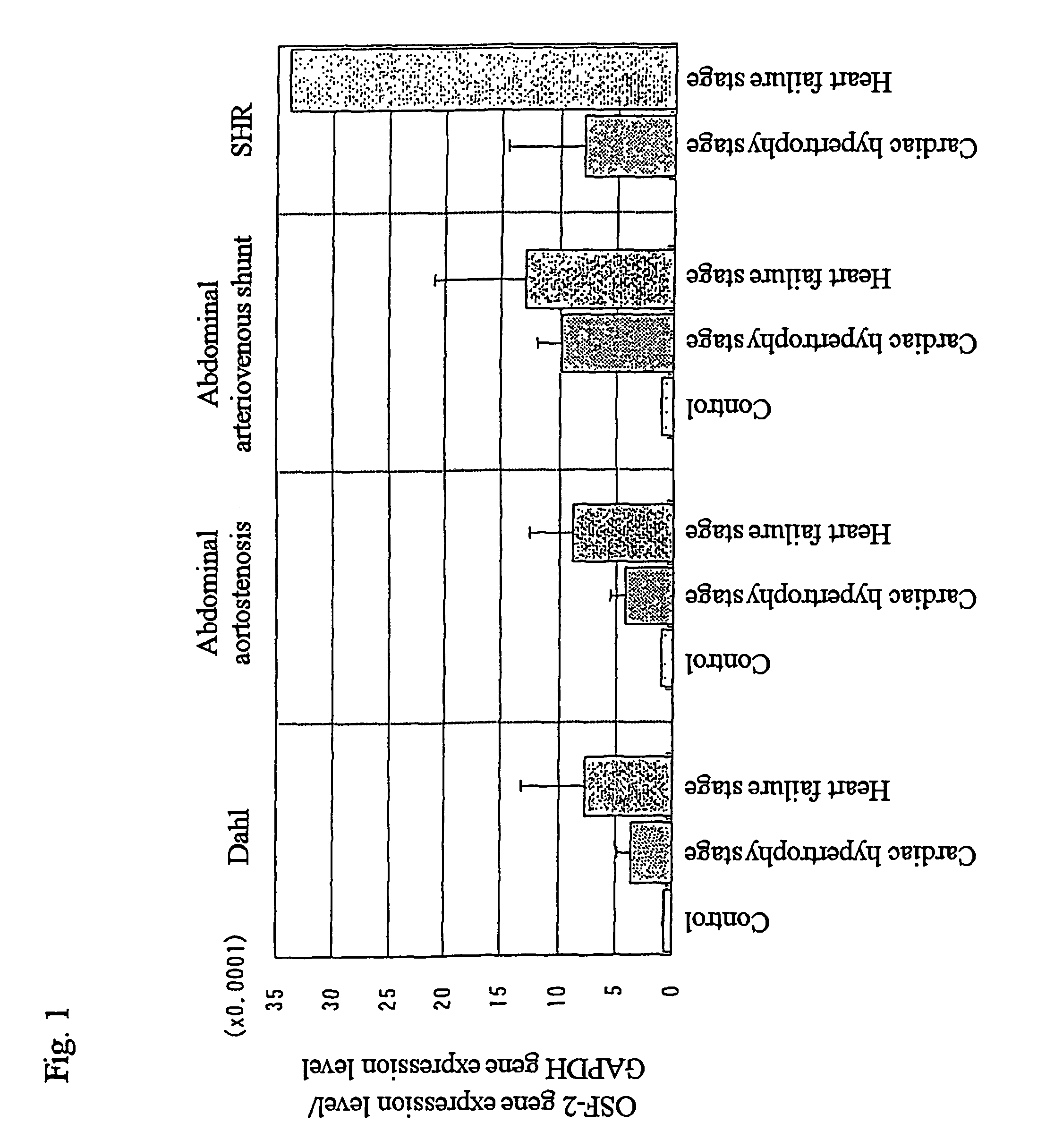
The present invention provides methods for screening drugs inhibiting the expression of OSF-2 gene or the production or function of the protein encoded thereby and therapeutic agents for heart failure having such effects. Useful methods for diagnosing heart failure can be provided by monitoring the expression or variation of said gene or the production of the protein encoded thereby. The present invention also provides transgenic animals with forced expression of OSF-2 gene and methods for studying changes in gene expression or protein production or the functions of various genes or proteins with the progress of the pathology of heart failure using them and novel therapeutic agents for heart failure.
Owner:ASUBIO PHARMA
Method for rapidly screening microbial hosts to identify certain strains with improved yield and/or quality in the expression of heterologous proteins
ActiveUS20080269070A1High yieldQuality improvementBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an array for rapidly identifying a host cell population capable of producing heterologous protein with improved yield and / or quality. The array comprises one or more host cell populations that have been genetically modified to increase the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein production, decrease the expression of one or more target genes involved in protein degradation, or both. One or more of the strains in the array may express the heterologous protein of interest in a periplasm compartment, or may secrete the heterologous protein extracellularly through an outer cell wall. The strain arrays are useful for screening for improved expression of any protein of interest, including therapeutic proteins, hormones, a growth factors, extracellular receptors or ligands, proteases, kinases, blood proteins, chemokines, cytokines, antibodies and the like.
Owner:PFENEX
Microfluidic devices for the controlled manipulation of small volumes
A method for conducting a broad range of biochemical analyses or manipulations on a series of nano- to subnanoliter reaction volumes and an apparatus for carrying out the same are disclosed. The invention is implemented on a fluidic microchip to provide high serial throughput. In particular, the disclosed device is a microfabricated channel device that can manipulate nanoliter or subnanoliter reaction volumes in a controlled manner to produce results at rates of 1 to 10 Hz per channel. The reaction volumes are manipulated in serial fashion analogous to a digital shift register. The invention has application to such problems as screening molecular or cellular targets using single beads from split-synthesis combinatorial libraries, screening single cells for RNA or protein expression, genetic diagnostic screening at the single cell level, or performing single cell signal transduction studies.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Non-specific binding resistant protein arrays and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6897073B2Effective resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological bodyCell biology
Arrays of protein-capture agents useful for the simultaneous detection of a plurality of proteins which are the expression products, or fragments thereof, of a cell or population of cells in an organism are provided. A variety of antibody arrays, in particular, are described. Methods of both making and using the arrays of protein-capture agents are also disclosed. The invention arrays are particularly useful for various proteomics applications including assessing patterns of protein expression and modification in cells.
Owner:ZYOMYX
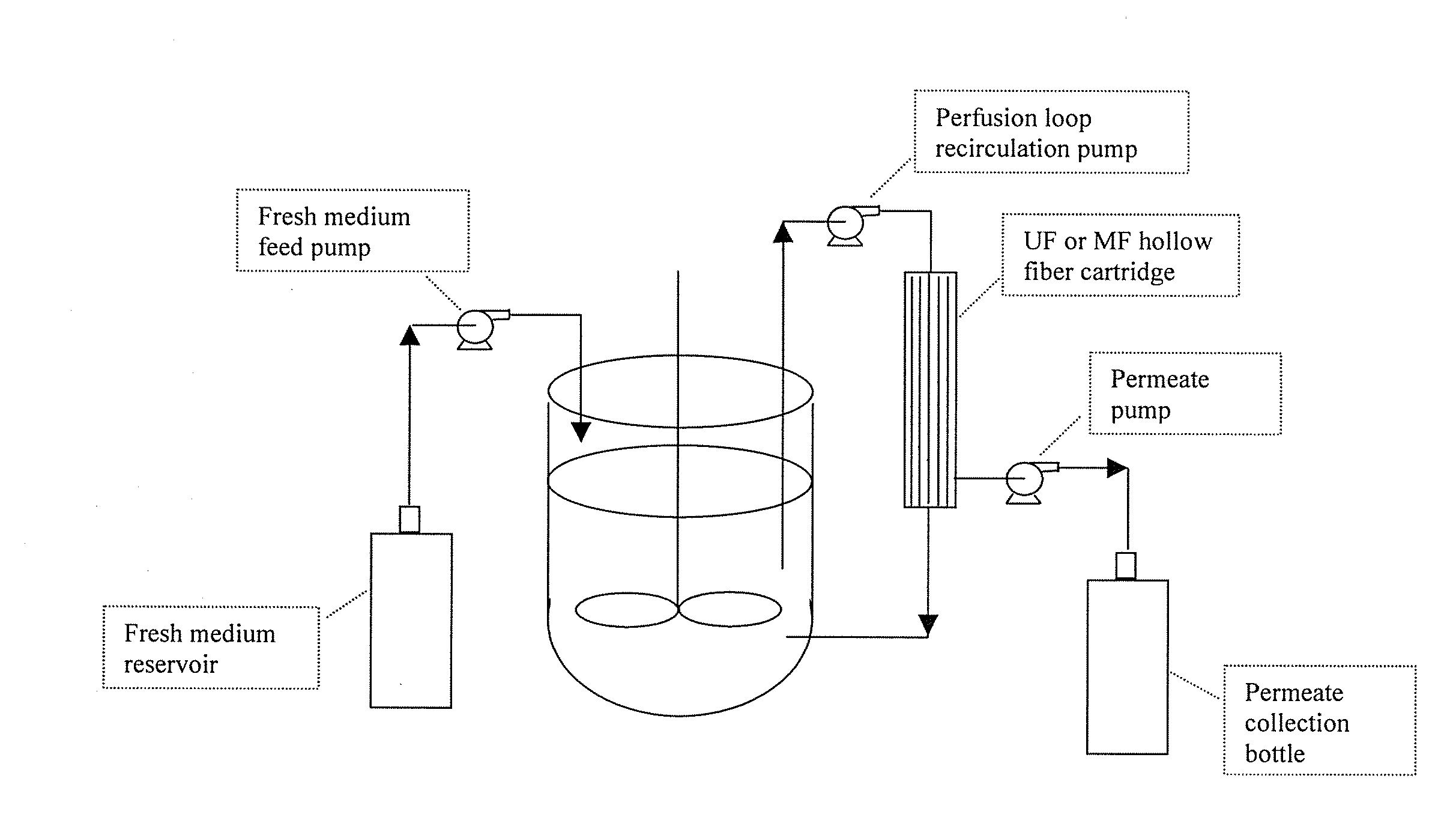
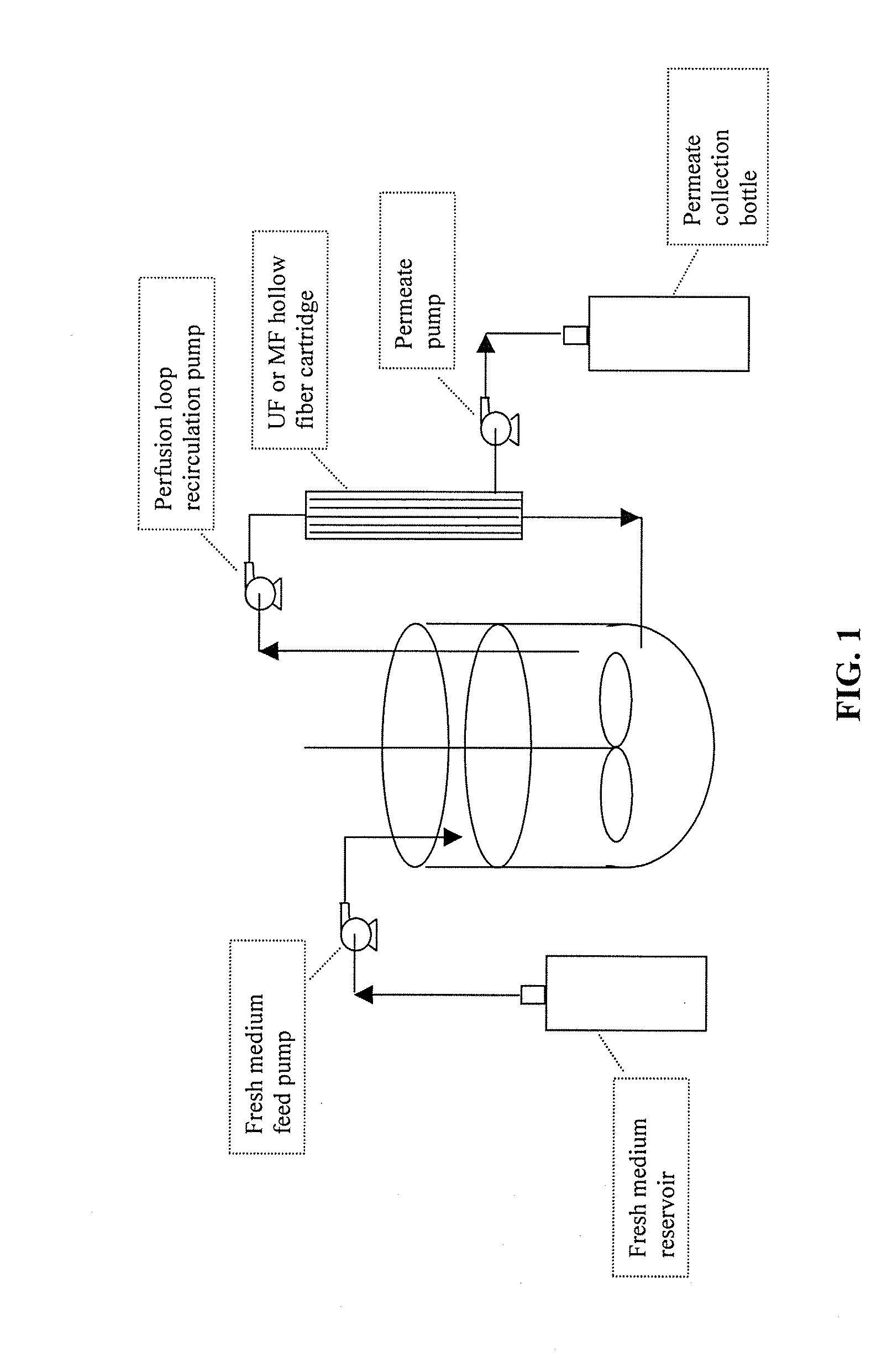
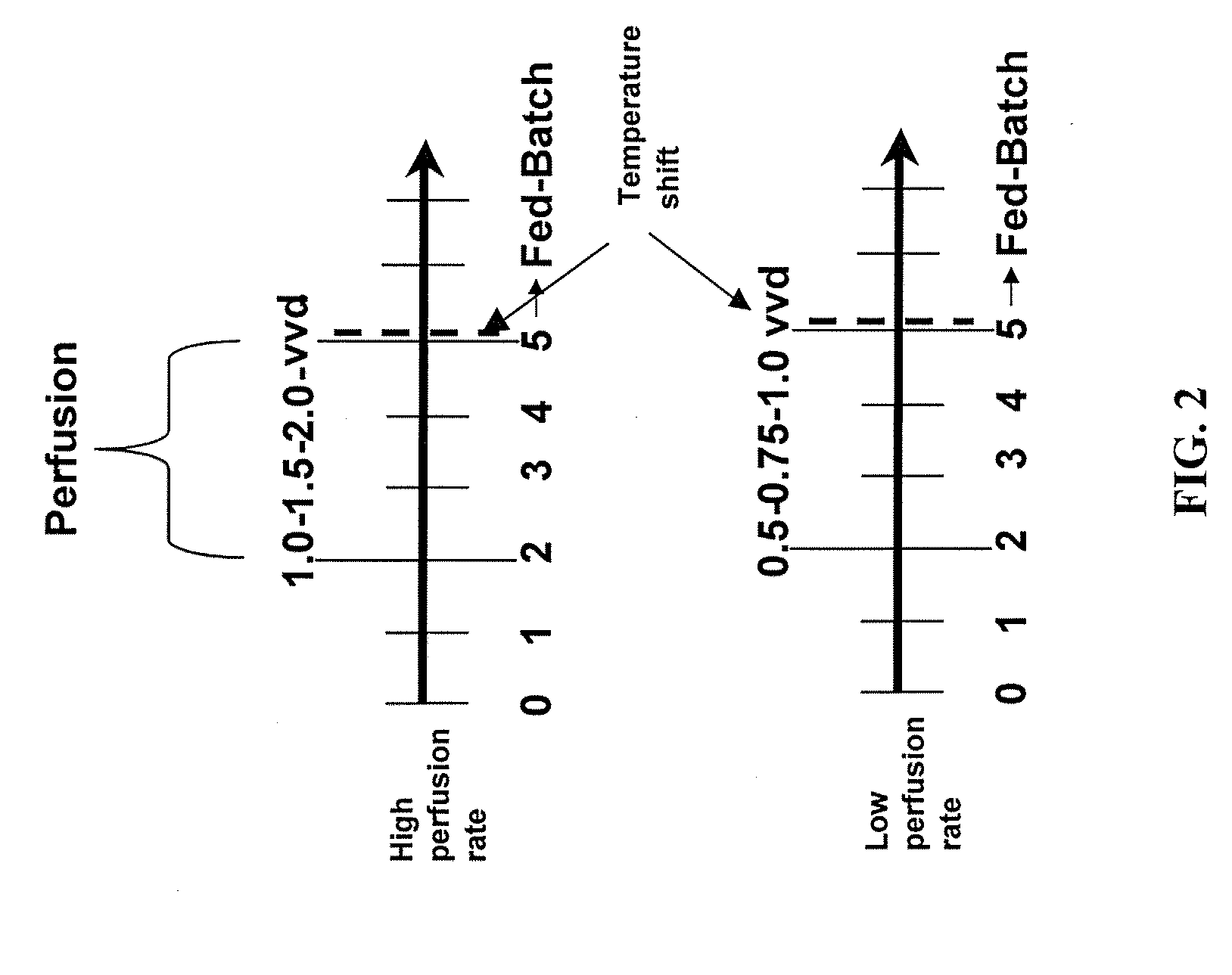
Use of perfusion to enhance production of fed-batch cell culture in bioreactors
InactiveUS20090042253A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationFeed pump
The invention relates to methods of improving protein production, e.g., large-scale commercial protein production, e.g., antibody production, utilizing a modified fed-batch cell culture method comprising a cell growth phase and a polypeptide production phase. The modified fed-batch cell culture method combines both cell culture perfusion and fed-batch methods to achieve higher titers of polypeptide products. Because the modified fed-batch cell culture method of the invention produces higher polypeptide product titers than fed-batch culture alone, it will substantially improve commercial-scale protein production. The invention also relates to a perfusion bioreactor apparatus comprising a fresh medium reservoir connected to a bioreactor by a feed pump, a recirculation loop connected to the bioreactor, wherein the recirculation loop comprises a filtration device, e.g., ultrafiltration or microfiltration, and a permeate pump connecting the filtration device to a permeate collection container.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com