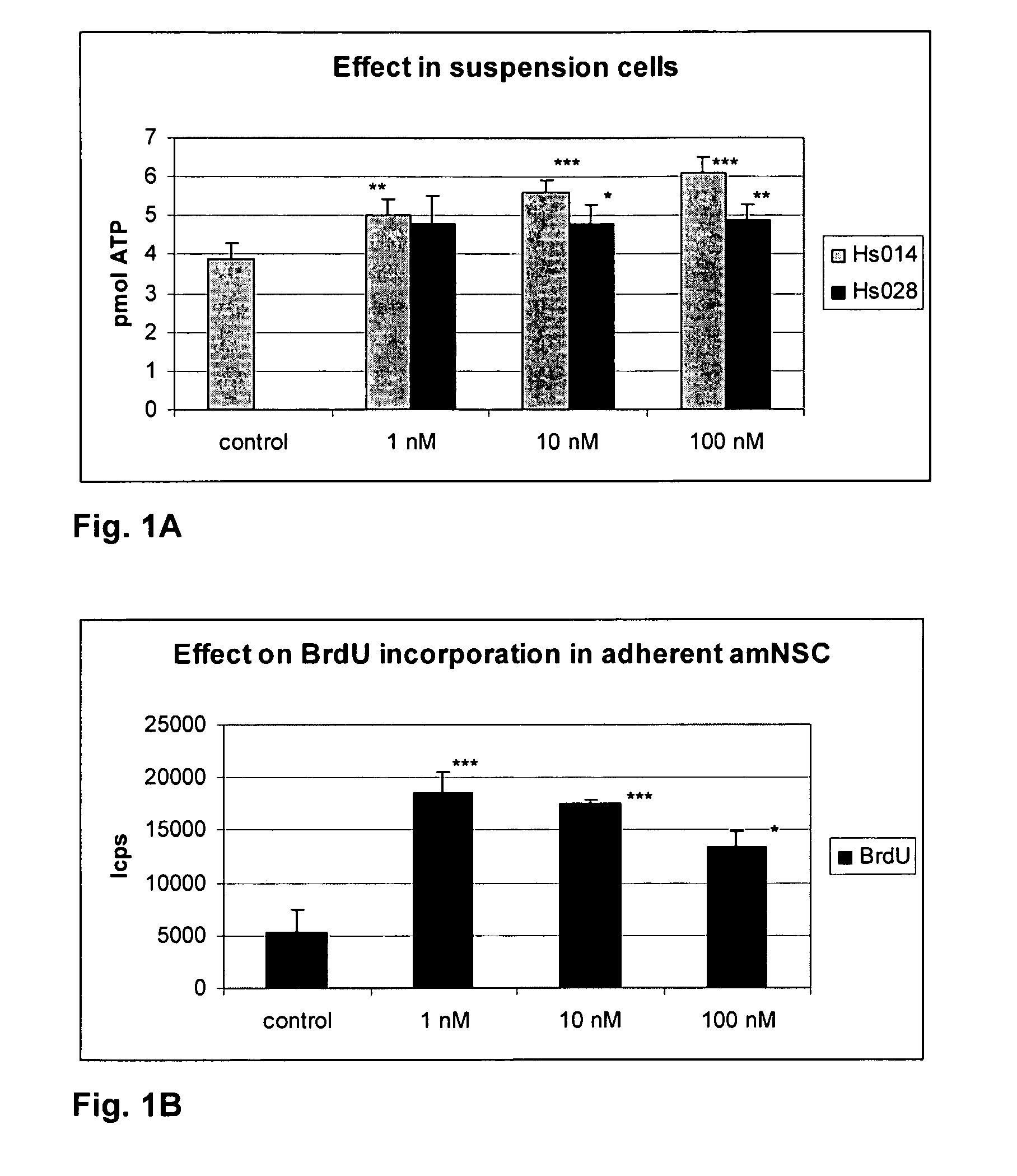
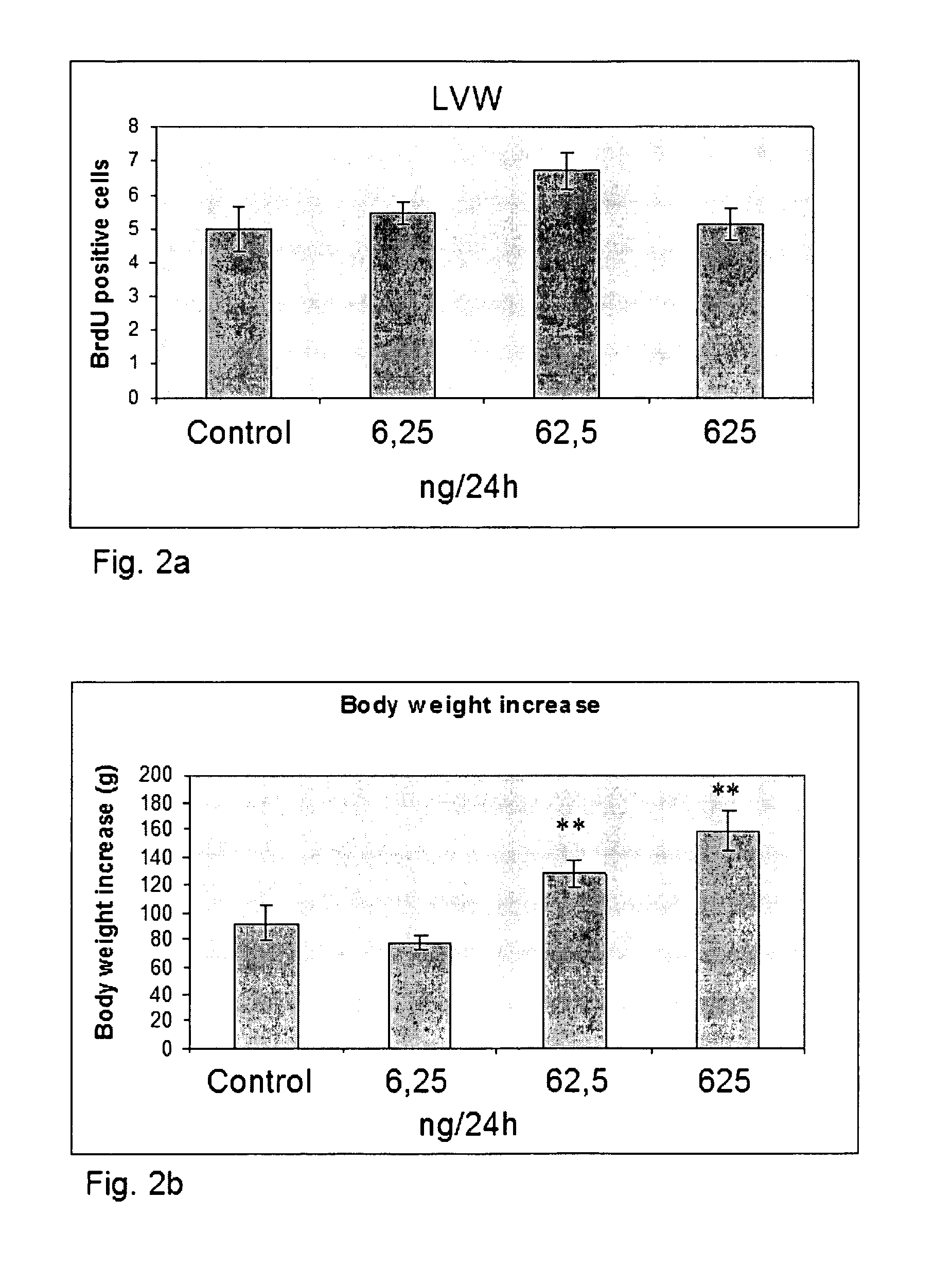
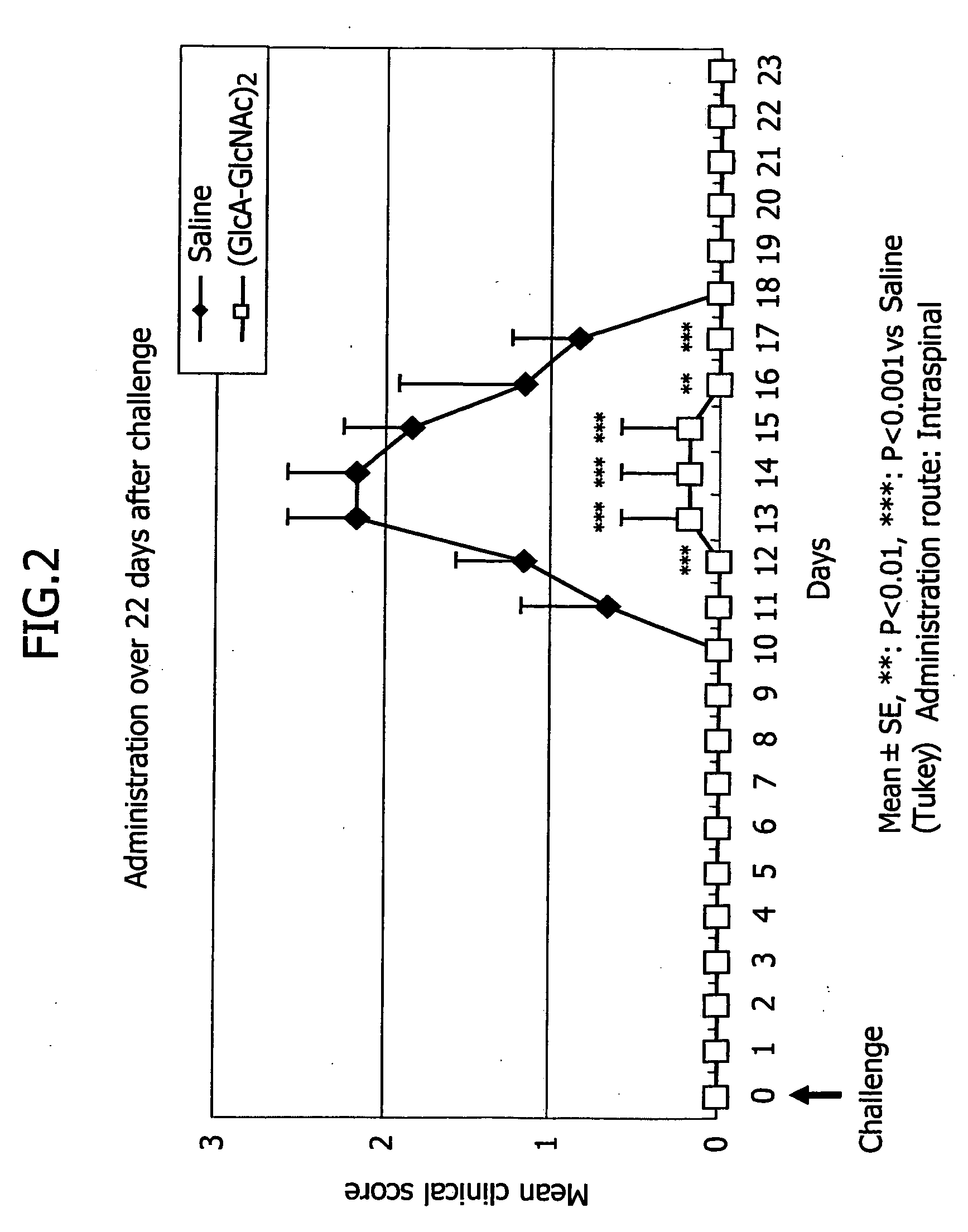
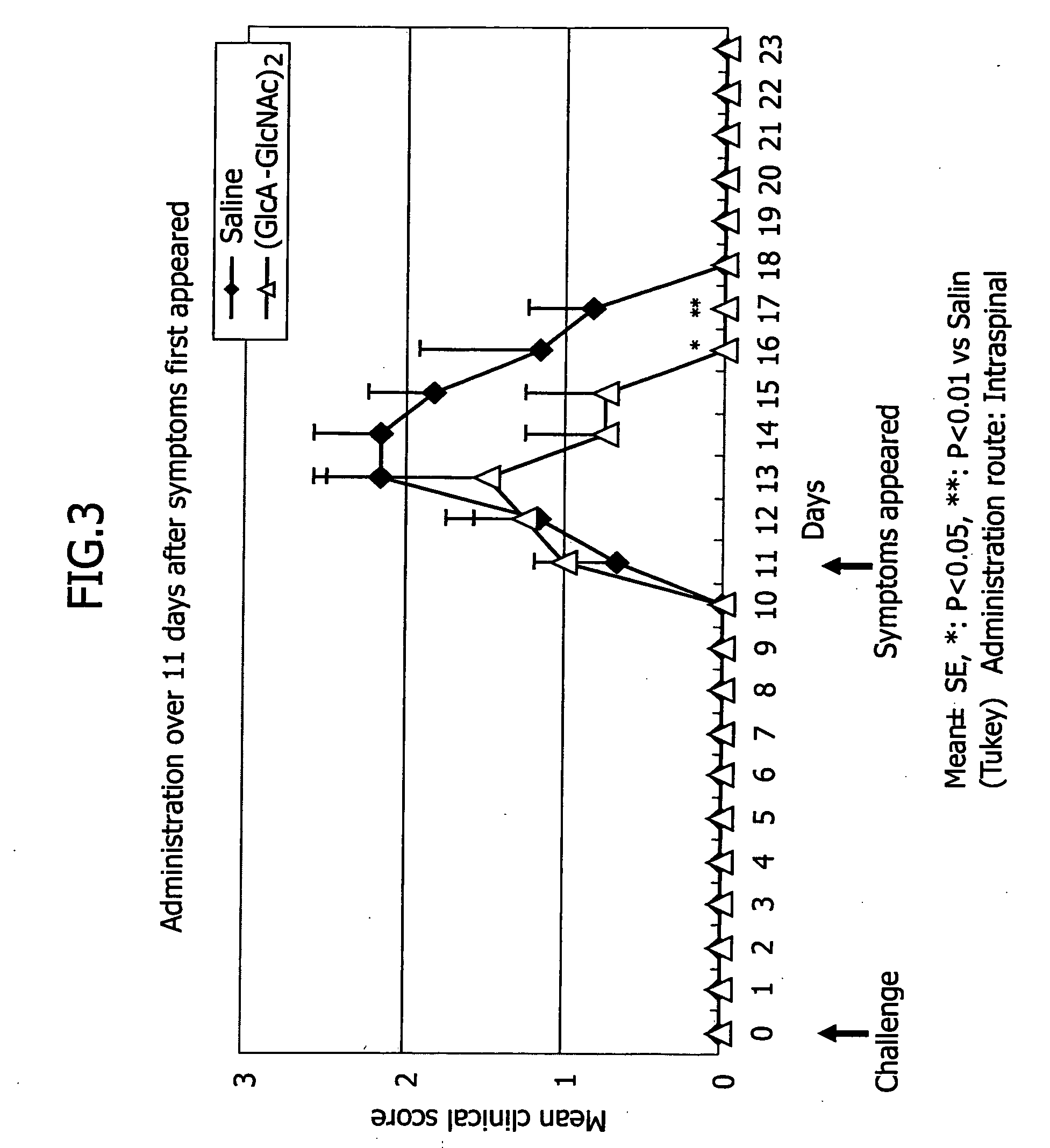
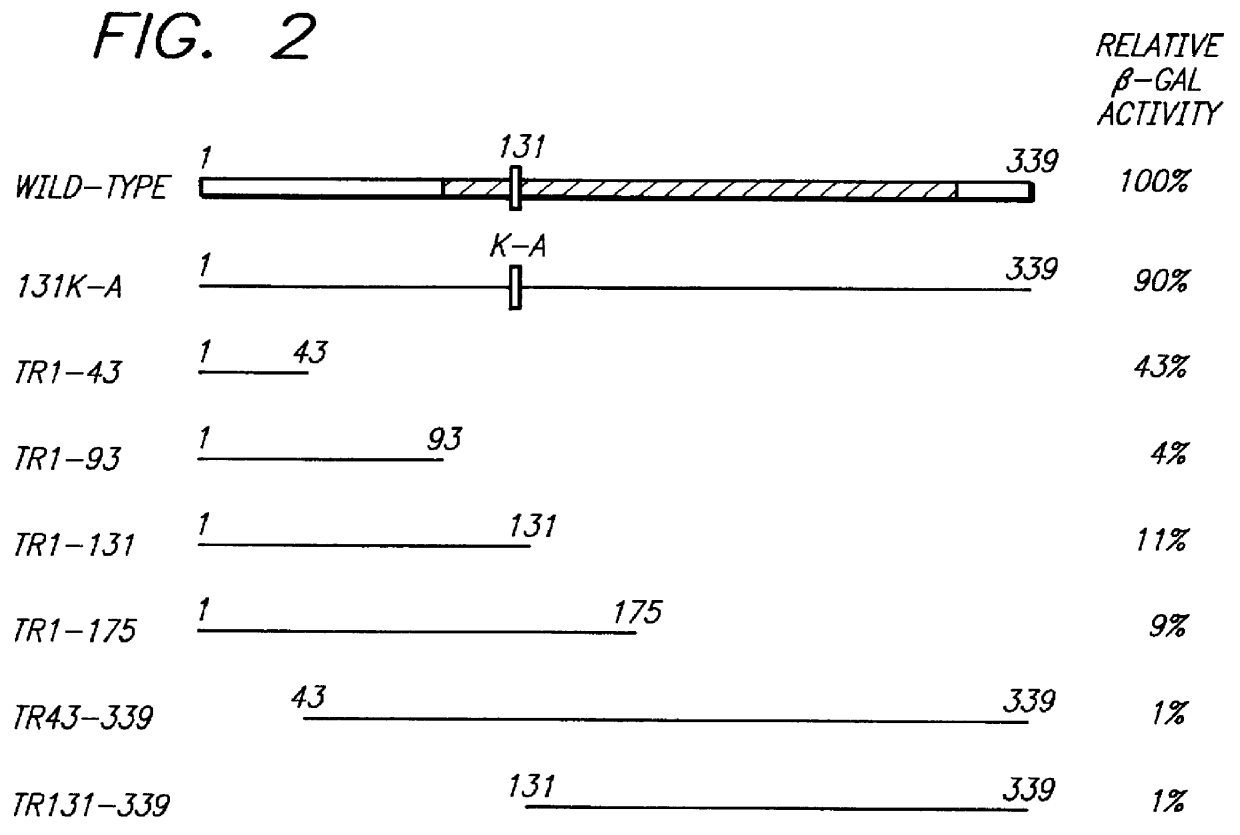
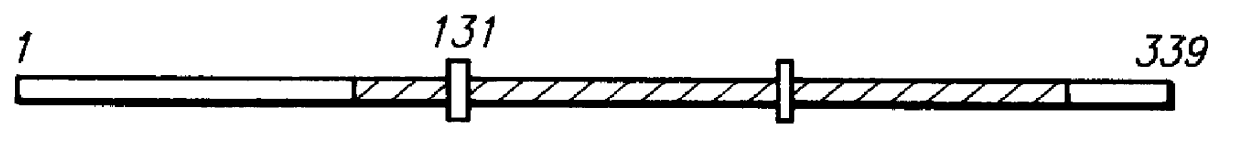
Patents
Literature
111results about How to "Reduce cell viability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production of proteins by cell culture
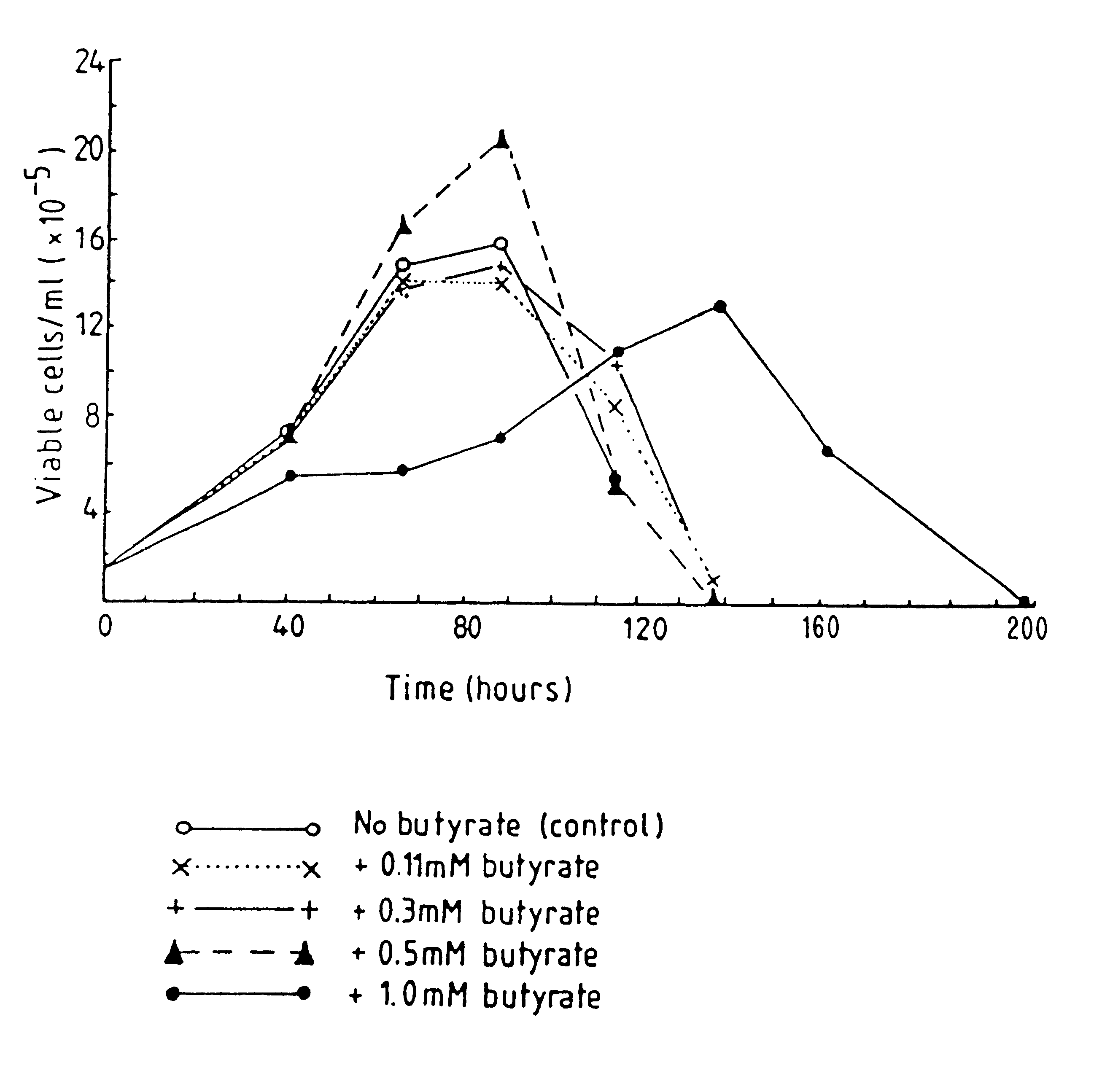
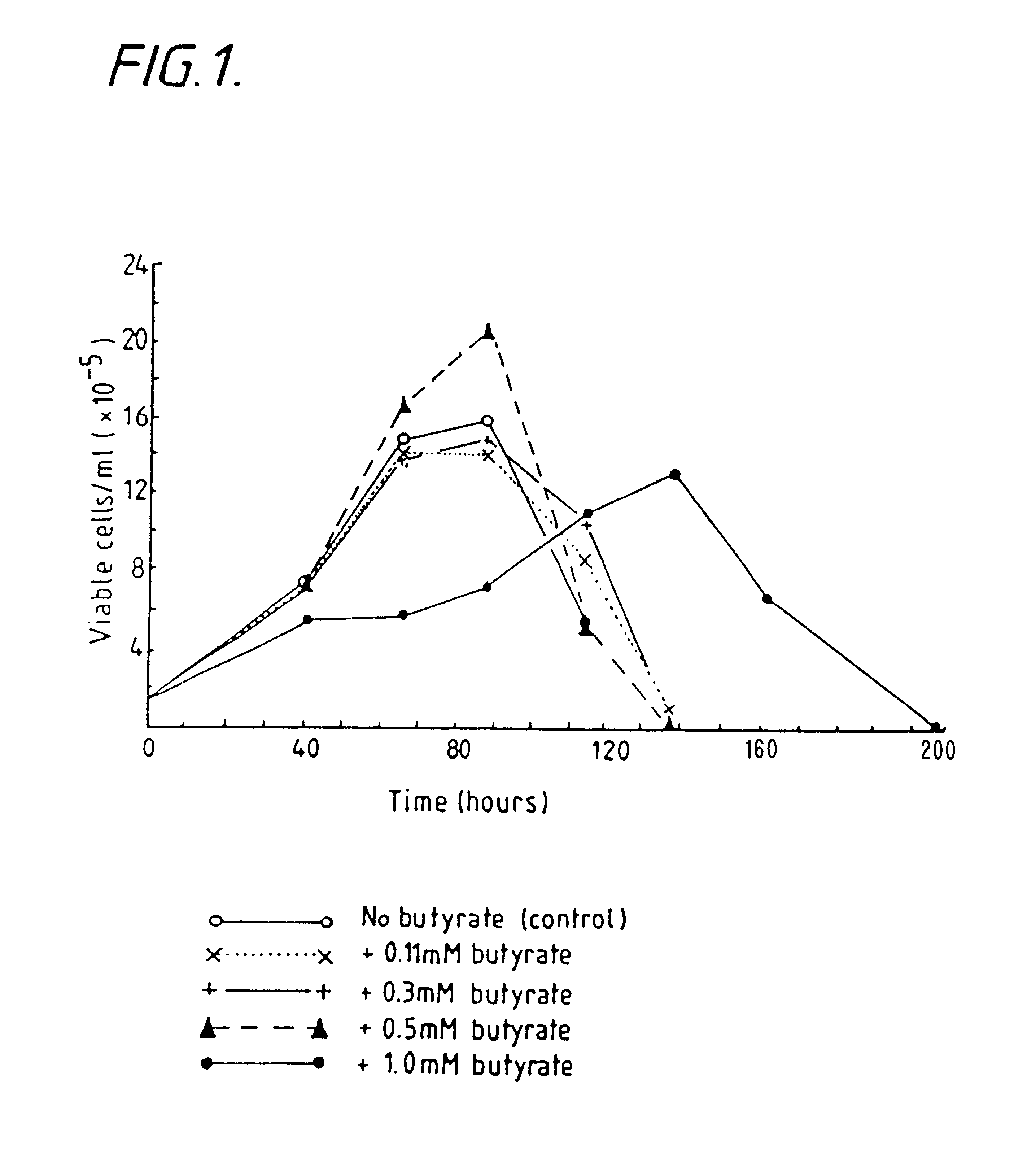
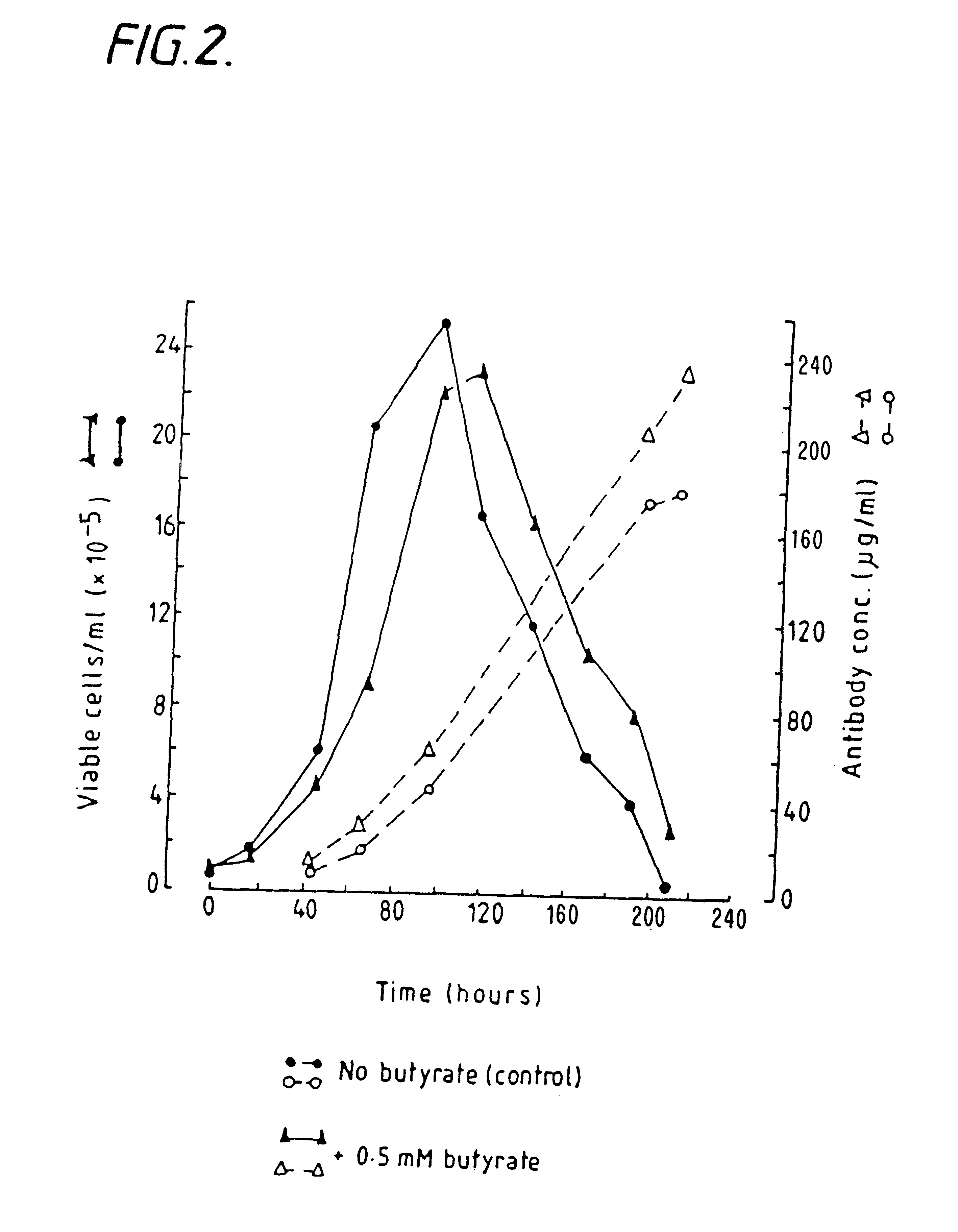
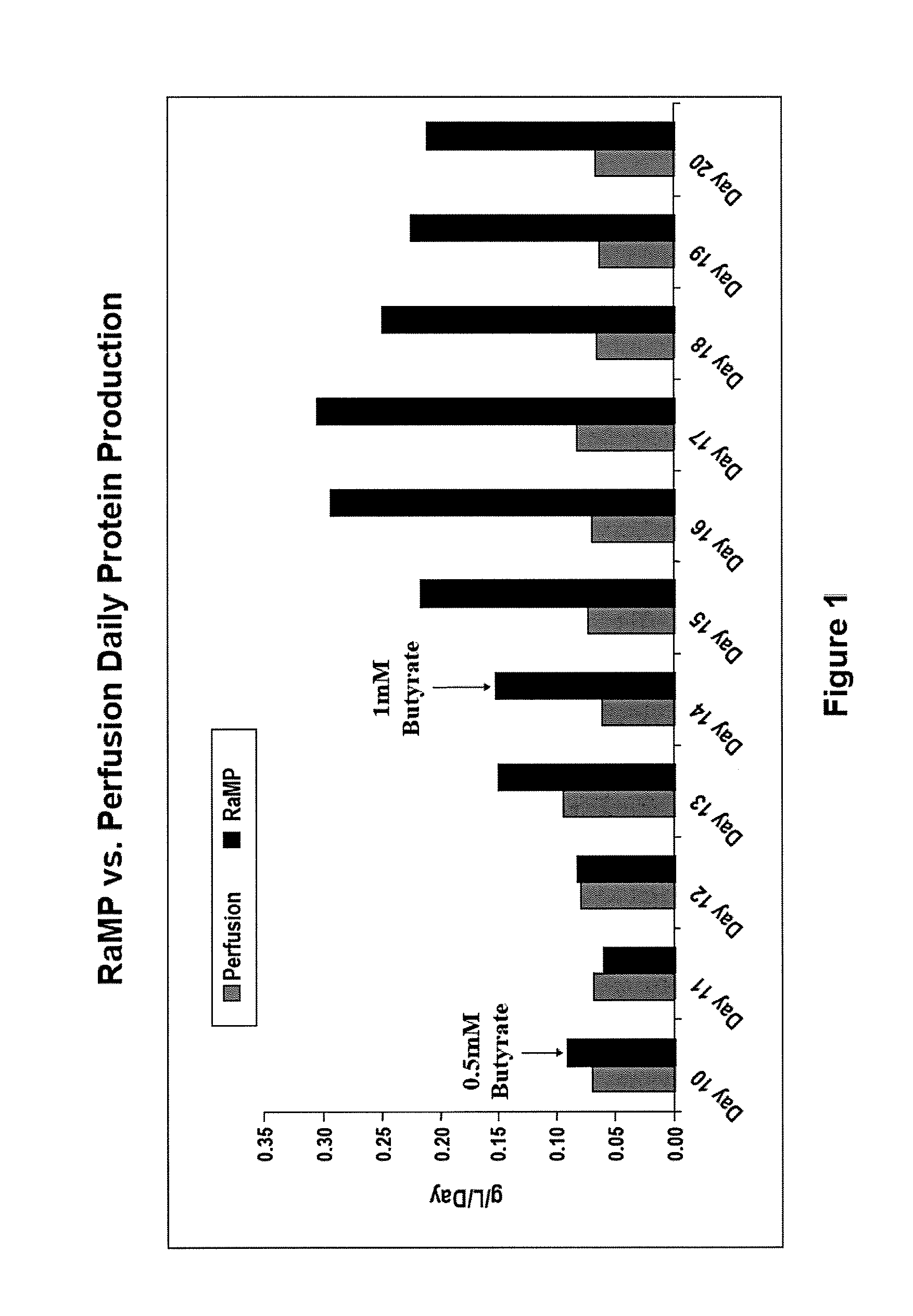
InactiveUS6413746B1High protein yieldReduce cell viabilityImmunoglobulins against blood group antigensPeptide/protein ingredients3D cell cultureBiochemistry
Methods for obtaining a protein by culture of hybridoma cells, wherein said protein is an immunoglobulin, are disclosed. The methods involve culturing animal hybridoma cells in continuous presence of an alkanoic acid or salt thereof, which enhances protein production, wherein said alkanoic acid or salt thereof is present at 2 concentration range of 0.1 mM to 200 mM.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Recombinant mutants of rhabdovirus and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050260601A1Decrease in cancer cell viabilityReduce cell viabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsGlycoproteinMutant
The present invention relates to recombinant Rhabdoviridae, isolated nucleic acids, vectors, cells and compositions comprising same. The recombinant Rhabdoviridae, isolated nucleic acids, vectors, cells and compositions express Rhabdoviral proteins including a mutated matrix protein (M) and / or a mutated glycoprotein (G), in addition to expression of at least one foreign nucleic acid. The present invention also relates to methods of use thereof, including their use in vivo, in anti-cancer applications, such as in the treatment of gliomas. The recombinant Rhabdoviridae of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy and vaccine applications.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Elongase gene and method for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS7179647B2High trafficImprove abilitiesCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsBiological bodyBiotechnology
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID No: 1 or its homologs, derivatives or analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacyiglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
BTLA nucleic acids
InactiveUS7304149B2Decrease autoreactive lymphocyte activityEnhanced signalCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesLymphocyteInhibitory receptors
The present invention provides a novel lymphocyte inhibitory receptor termed BTLA which is expressed on both T and B cells, and identifies B7 family member B7x as interacting with BTLA to attenuate lymphocyte activity. Methods and compositions for modulating BTLA-mediated negative signaling and interfering with the interaction of BTLA and B7x for therapeutic, diagnostic and research purposes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
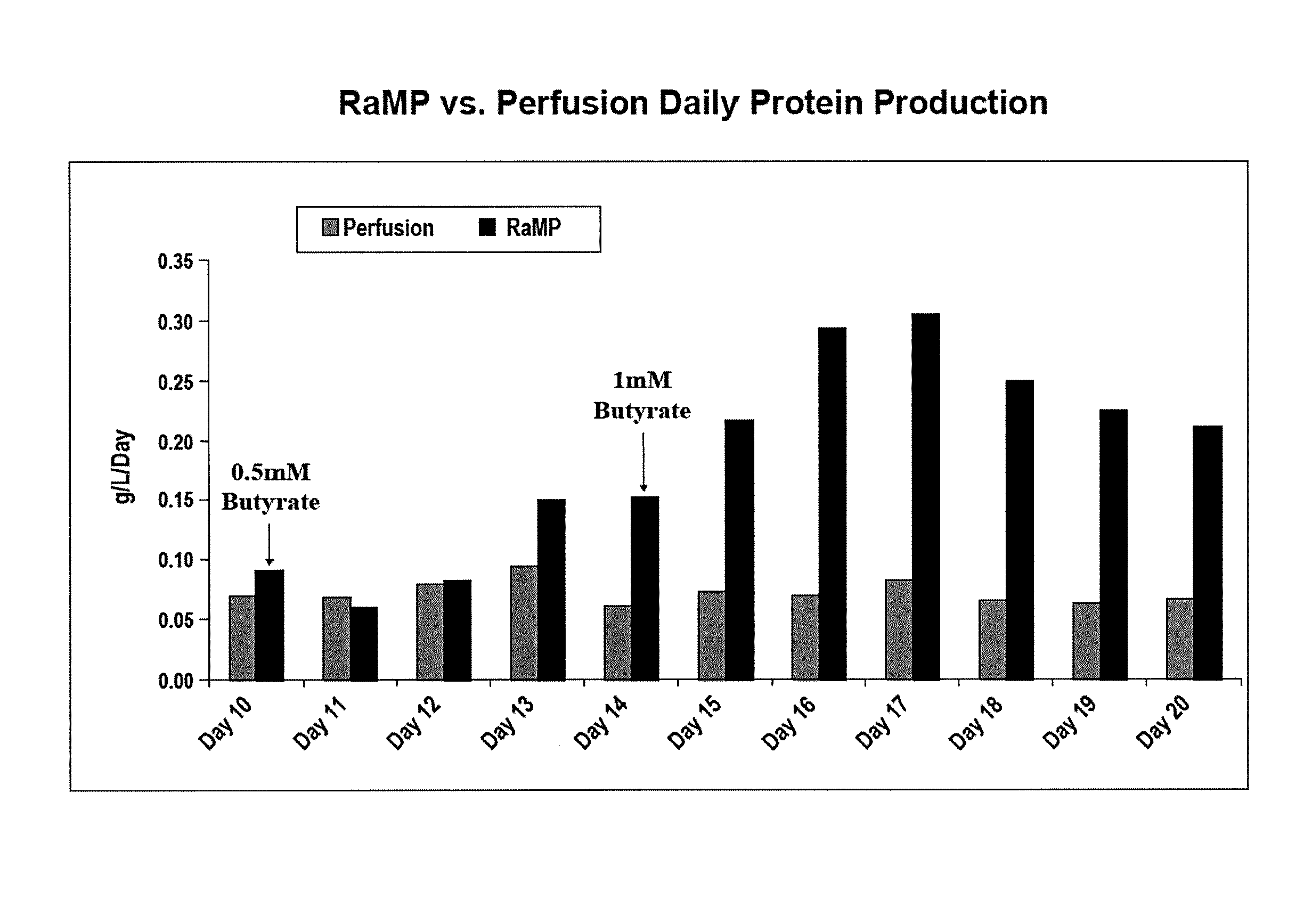
Intensified Perfusion Production Method
InactiveUS20080206819A1Increase cell densityIncrease productionGenetically modified cellsCulture processCulture cellPerfusion
The invention comprises a process for producing a protein of interest in a perfusion system using induction agents without a substantial loss of cell viability. The invention also comprises methods of growing cells in a perfusion system using induction agents without a substantial loss of cell viability.
Owner:RAVEN BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Method for preparing fecal sample, fecal sample preparation solution, and feces collection kit
InactiveCN102131928AConducive to preservationAvoid decompositionMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyOrganic acidOrganic solvent
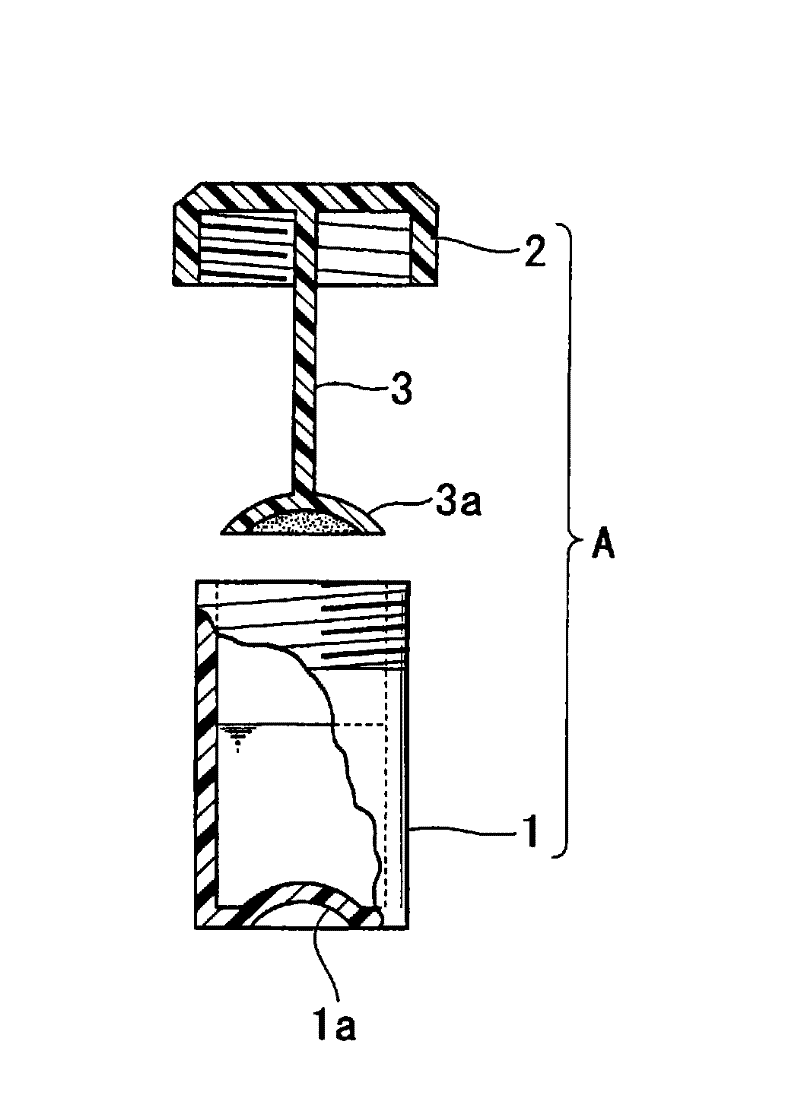
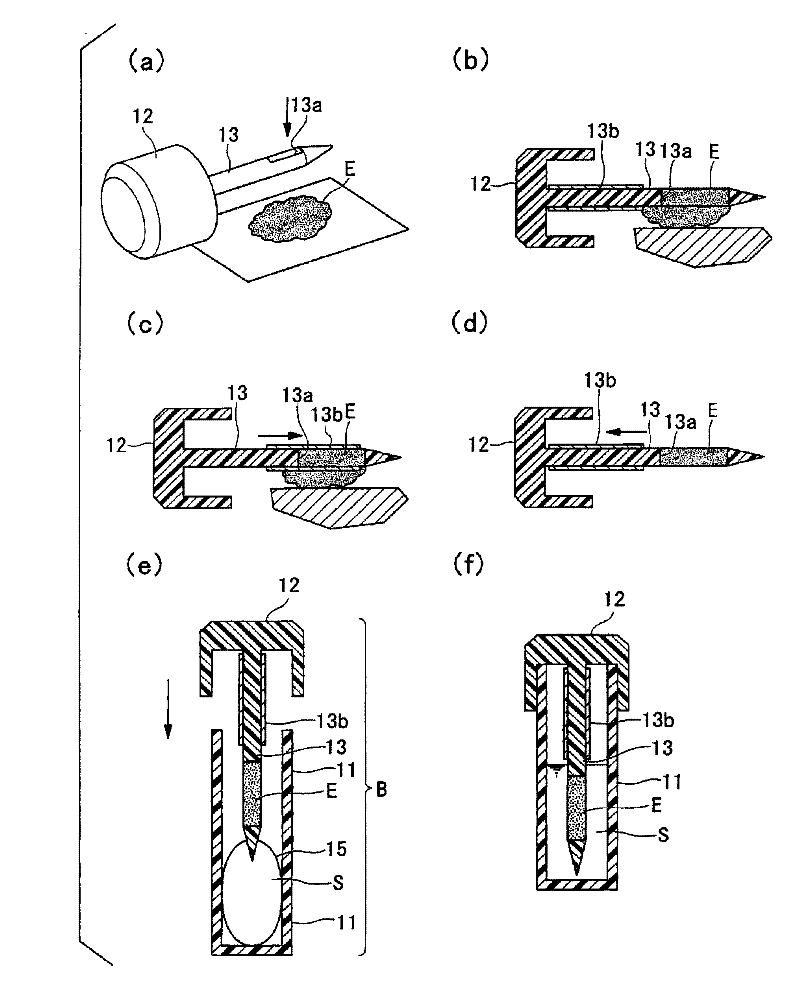
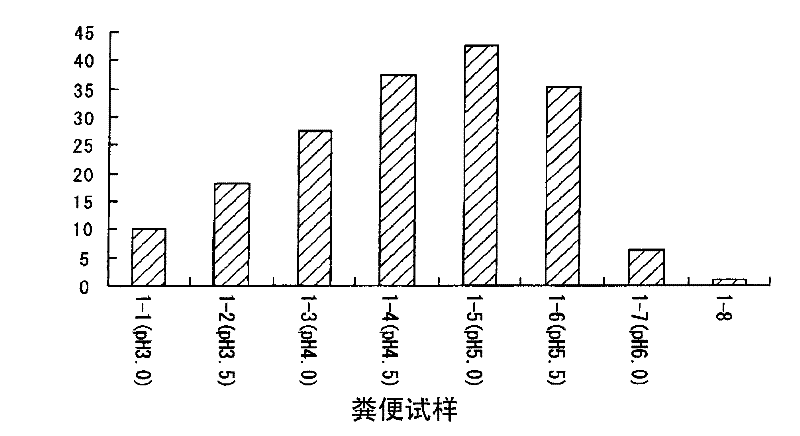
Provided is a method for preparing a fecal sample which can stably store a nucleic acid contained in feces without the need of any complicated procedure. Also disclosed is a fecal sample preparation solution to be used in the method. Further disclosed is a feces collection kit. Still further disclosed is a method for collecting a nucleic acid from feces by using a fecal sample prepared by the above-mentioned method and analyzing the nucleic acid. Feces collected is mixed with a fecal sample preparation solution containing, as an active ingredient, a water-soluble organic solvent containing an organic acid, thereby preparing a fecal sample which can store a nucleic acid contained therein satisfactorily.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Dried food products formed from cultured muscle cells
Dehydrated, edible, high-protein food products formed of cultured muscle cells that are combined (e.g., mixed) with a hydrogel (e.g., a plant-derived polysaccharide) are described. These food products may be formed into a chip (e.g., snack chip), that has a protein content of greater than 50%. One or more flavorants may also be included.
Owner:FORK & GOODE INC
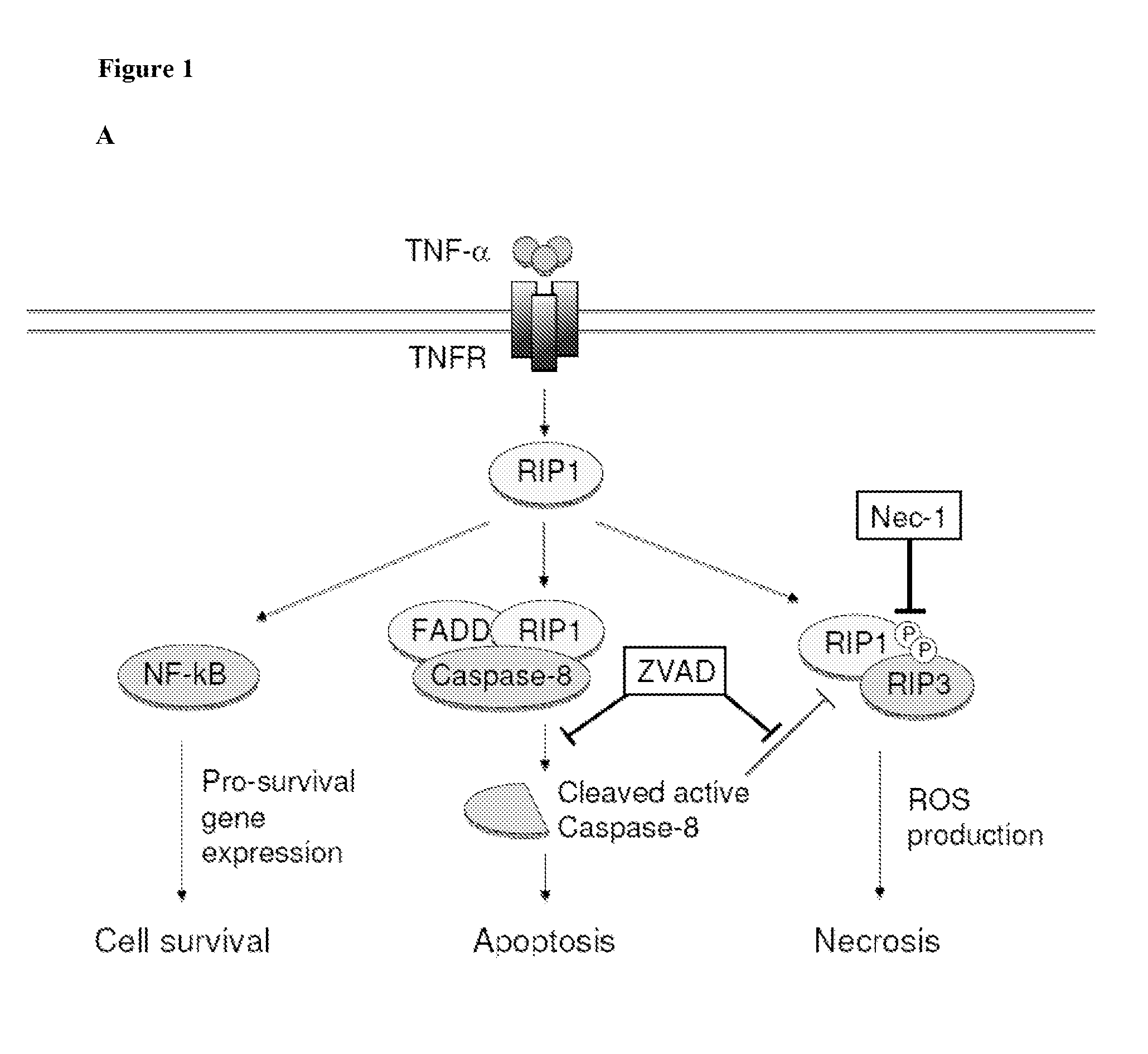
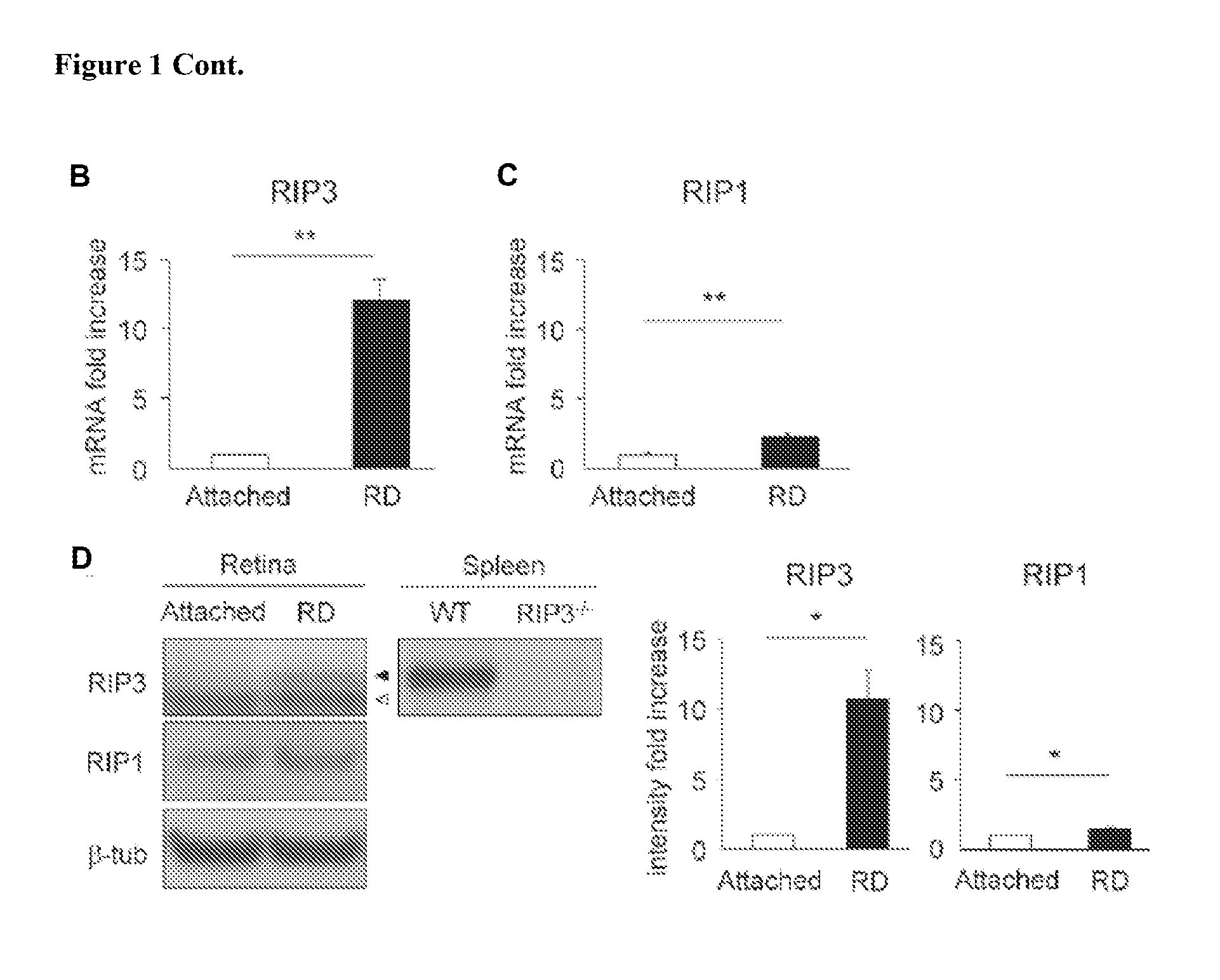
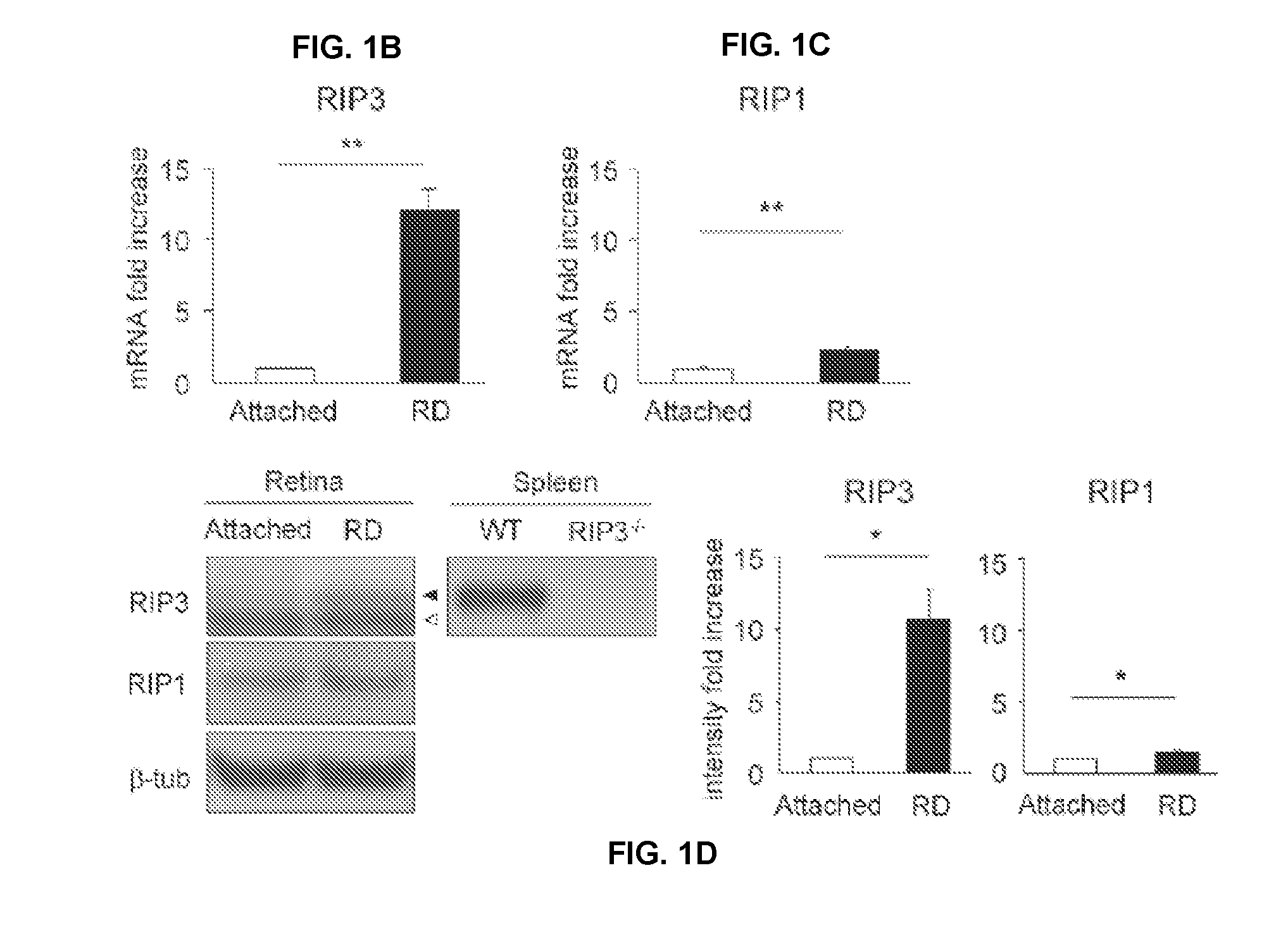
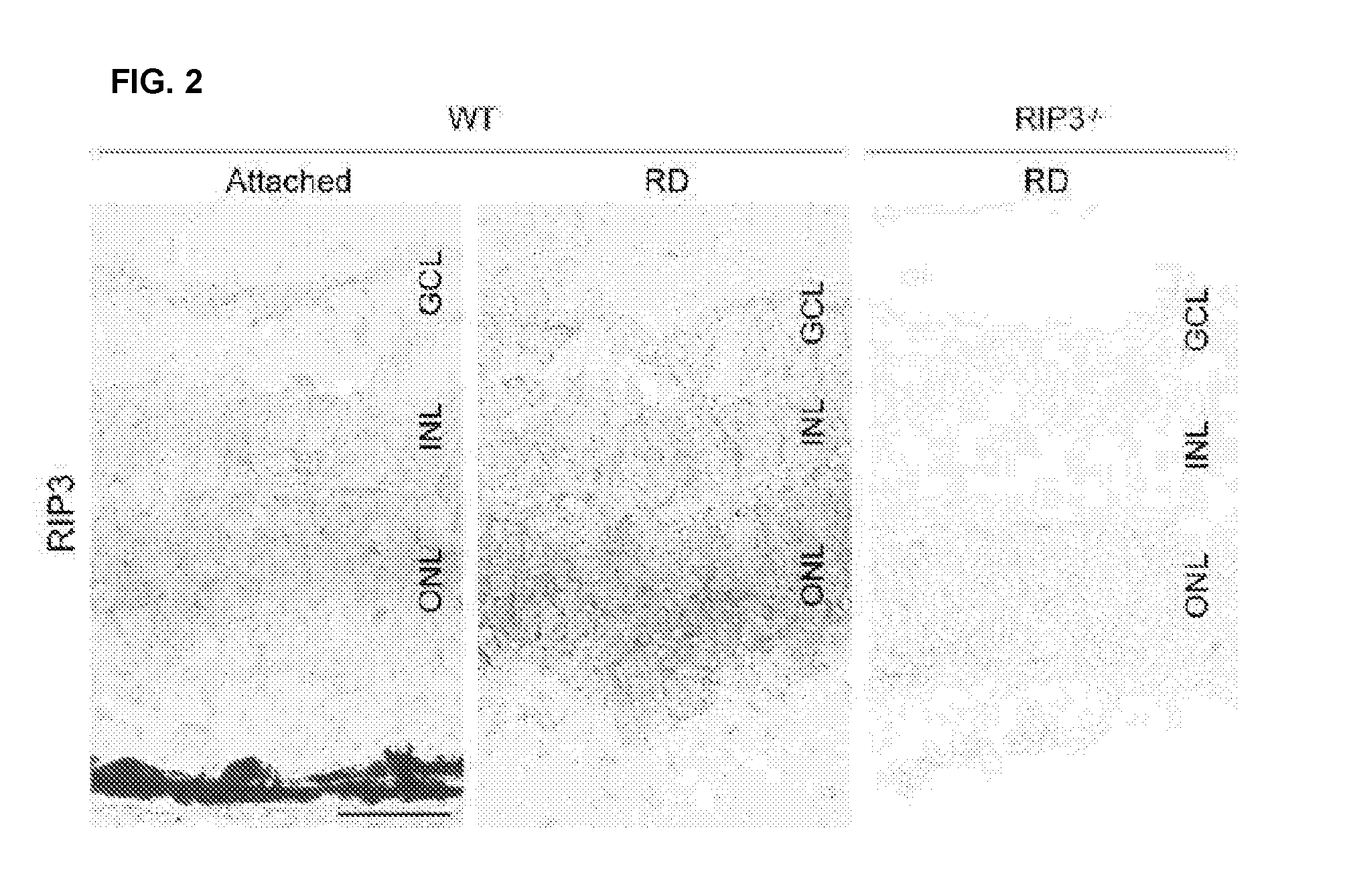
Methods and compositions for preserving photoreceptor and retinal pigment epithelial cells
InactiveUS20130137642A1Reduce and prevent of and cell viabilityReduce cell viabilitySenses disorderDipeptide ingredientsRetinitis pigmentosaRetinal pigment epithelial cell
Provided are methods and compositions for maintaining the viability of photoreceptor cells and / or retinal pigment epithelial cells in a subject with an ocular disorder including, for example, age-related macular degeneration (AMD) (e.g., dry or neovascular AMD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), or a retinal detachment. The viability of the photoreceptor cells and / or the retinal pigment epithelial cells can be preserved by administering a necrosis inhibitor either alone or in combination with an apoptosis inhibitor to a subject having an eye with the ocular condition. The compositions, when administered, maintain the viability of the cells, thereby minimizing the loss of vision or visual function associated with the ocular disorder.
Owner:VAVVAS DEMETRIOS +3
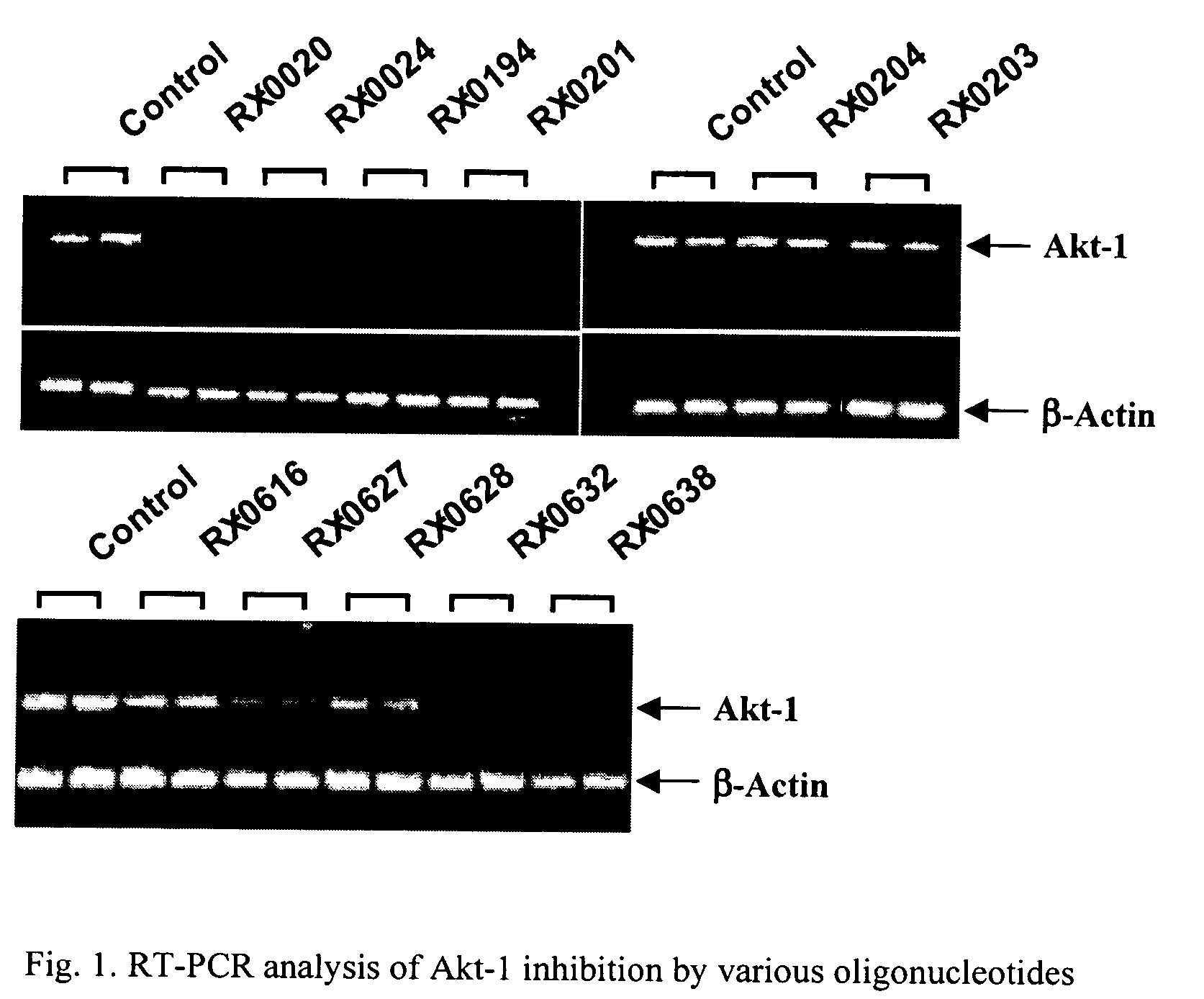
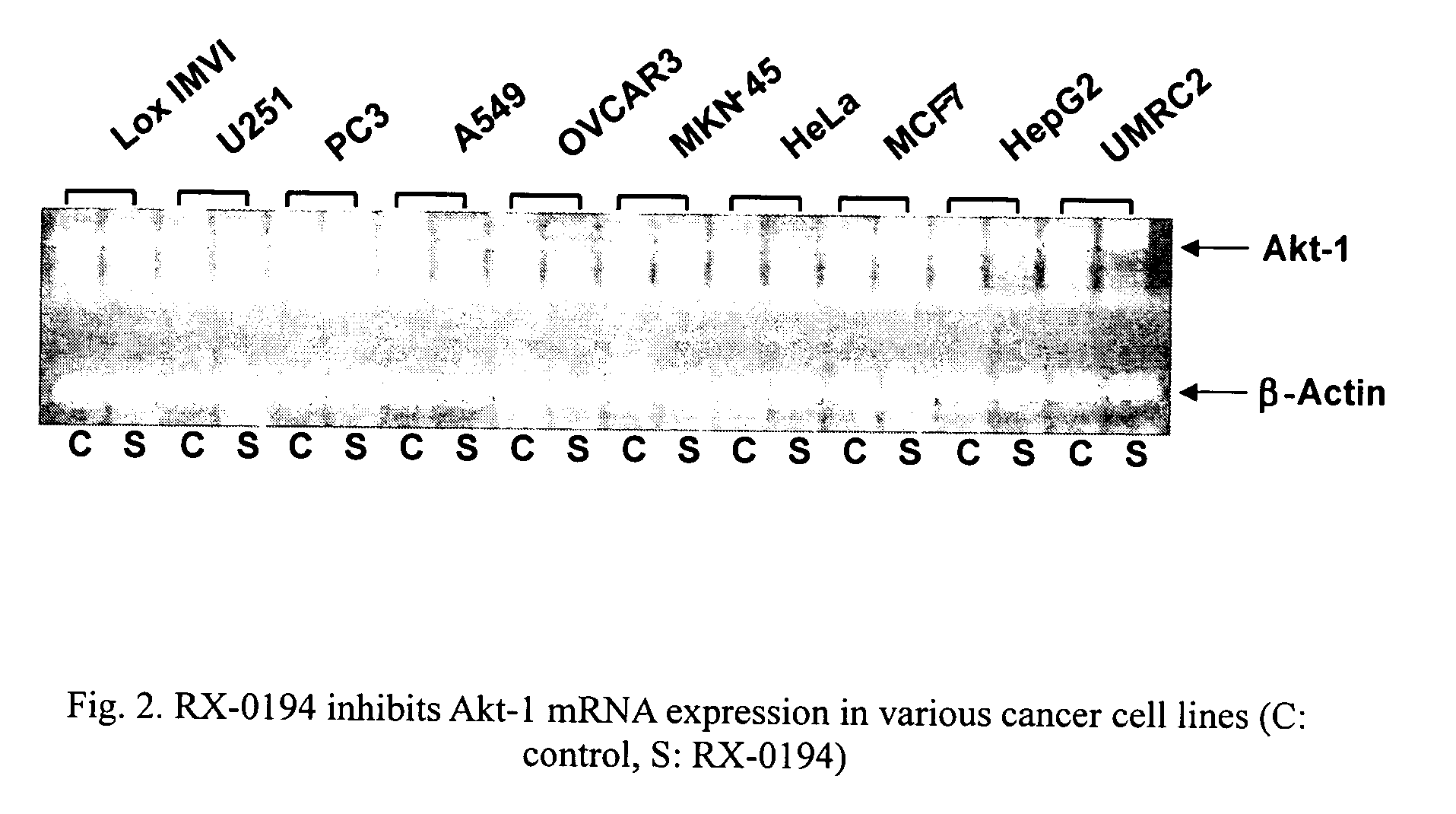
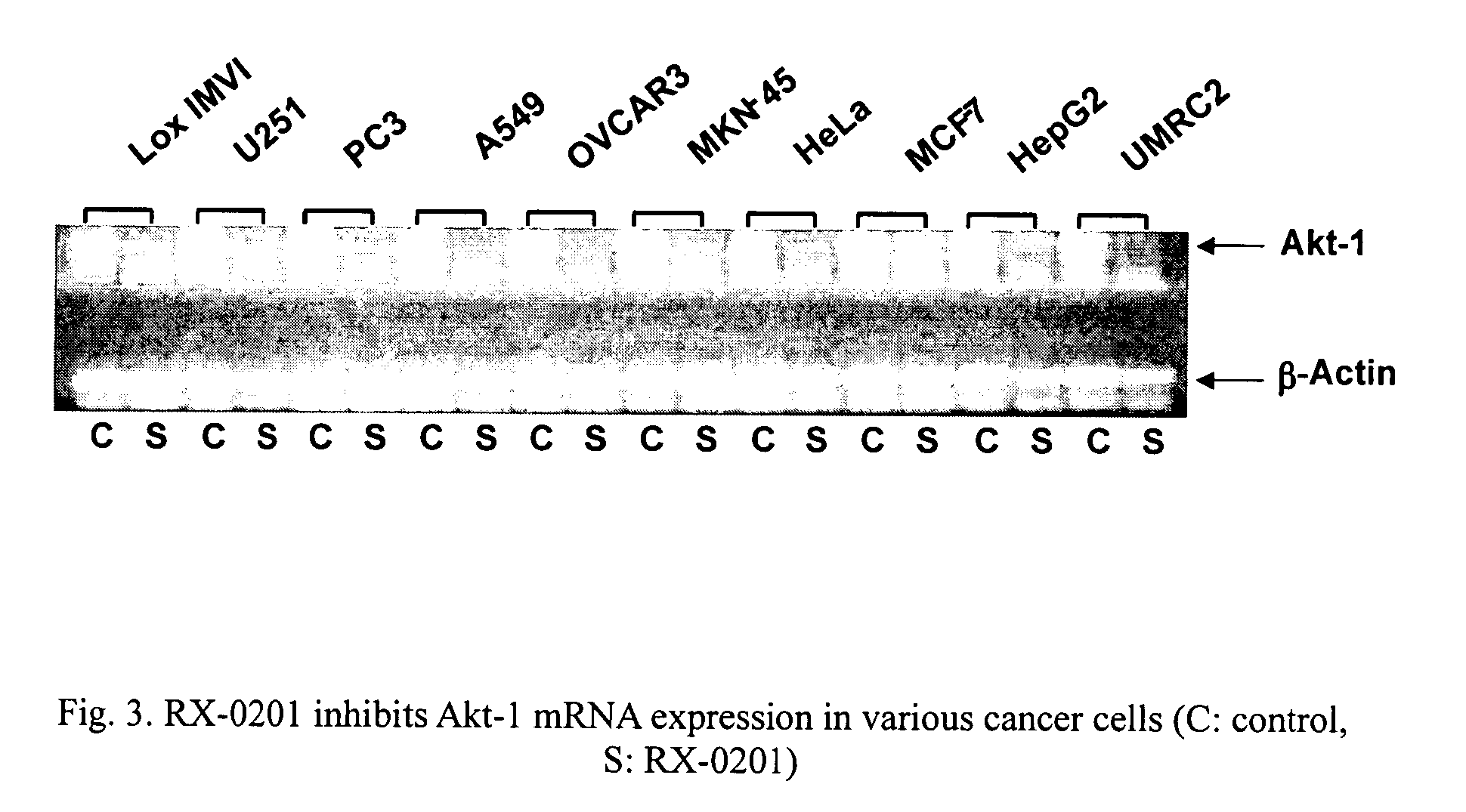
Use of antisense oligonucleotides to inhibit the expression of human Akt-1
ActiveUS7122527B2Modulate expressionReduce cell viabilitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsCancer cell linesCancer cell
New antisense oligonucleotide compounds inhibit expression of Akt-1 and also induce cytotoxicity in several cancer cell lines.
Owner:OCUPHIRE PHARM INC
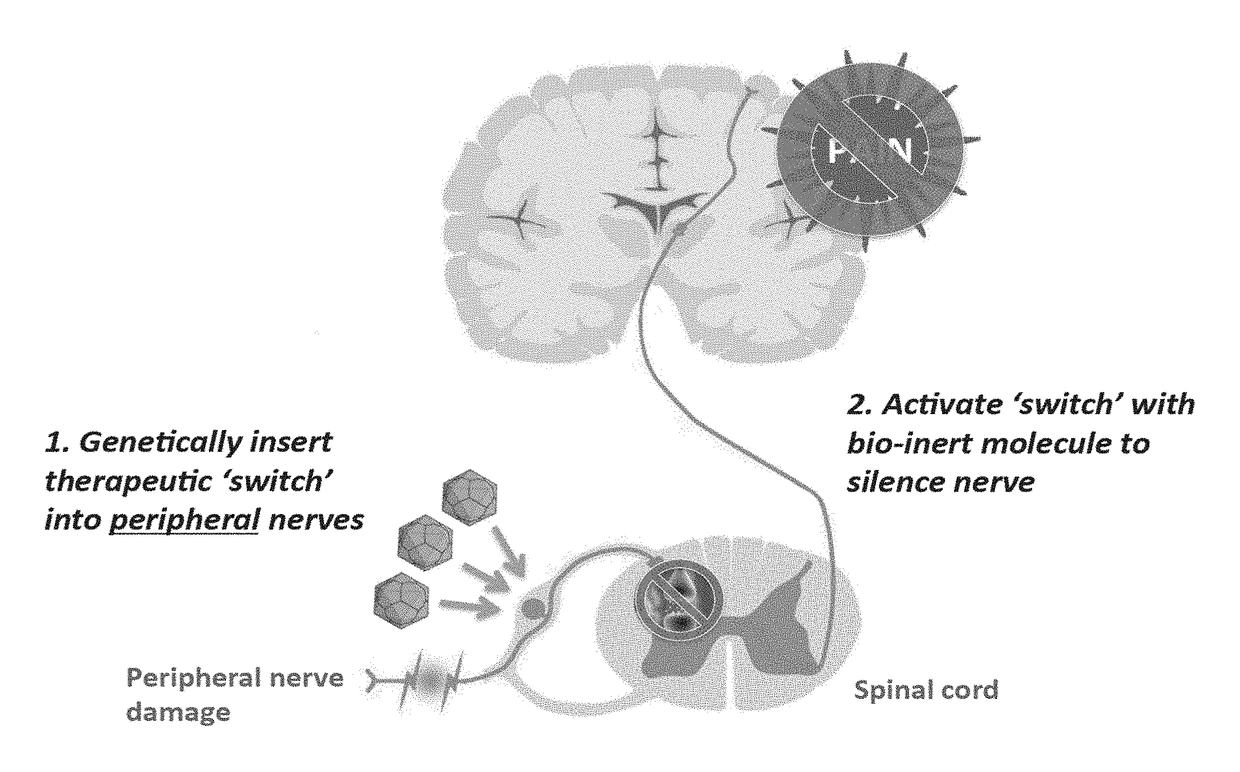
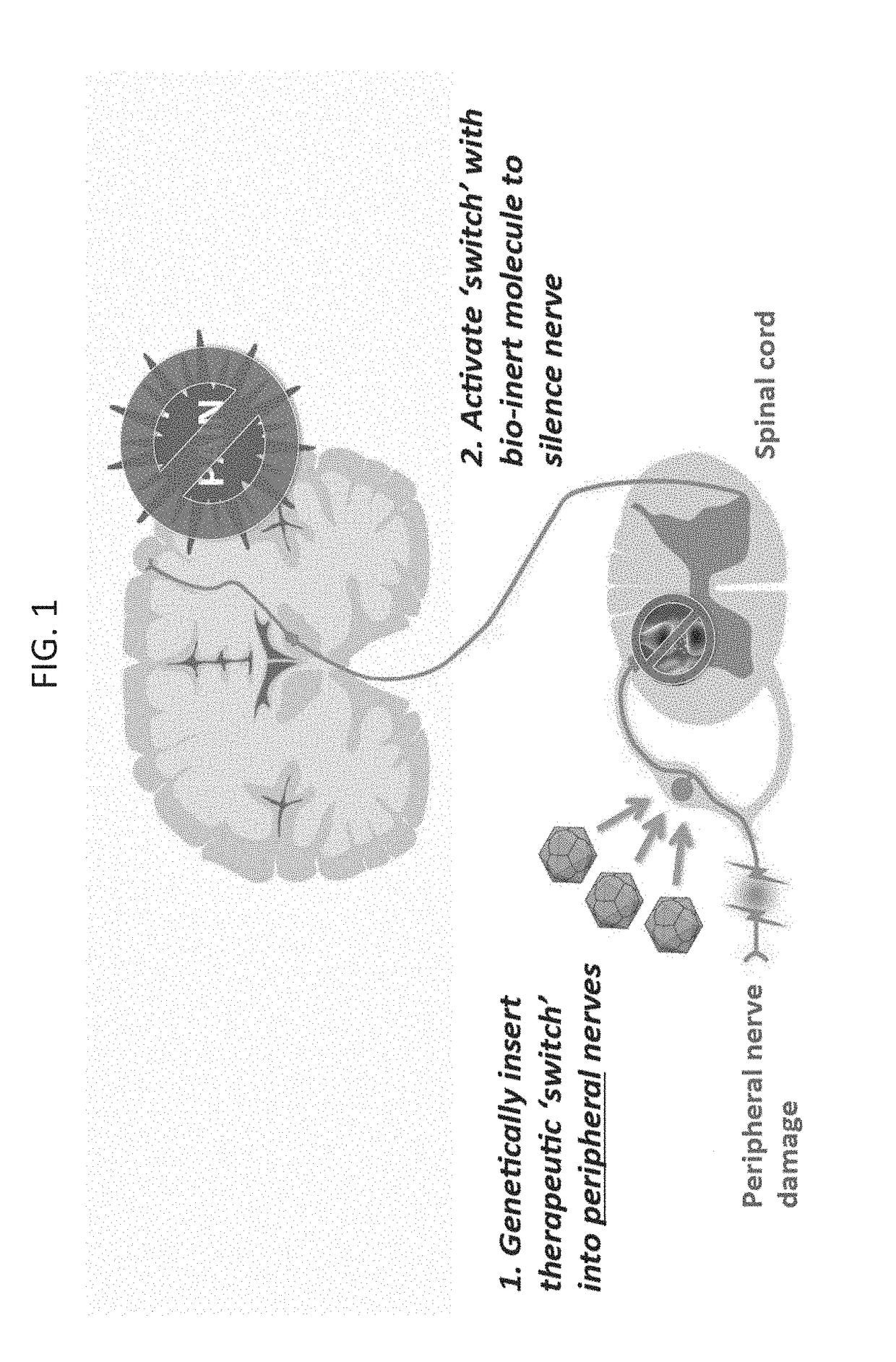
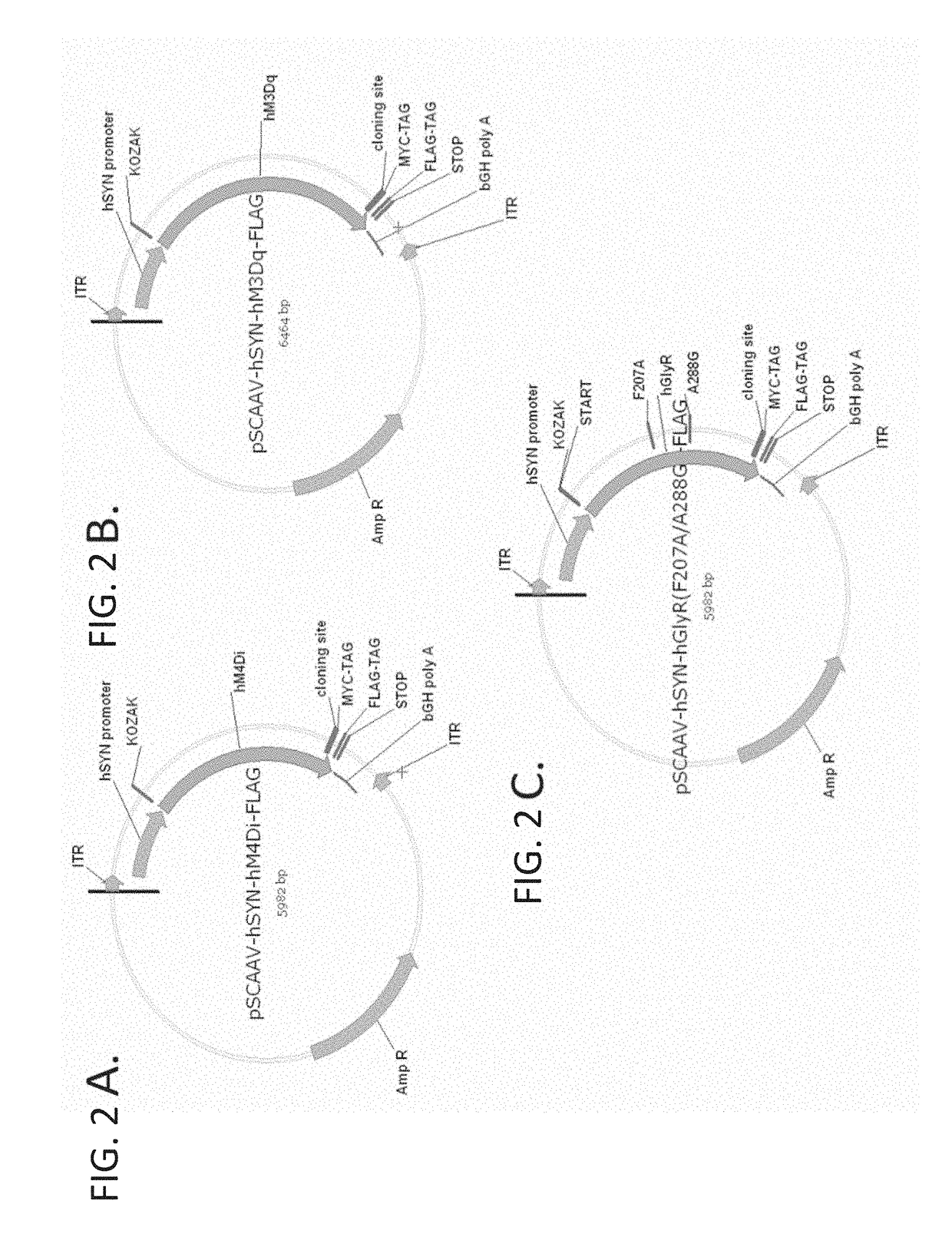
Compositions and methods for treating neurological disorders
InactiveUS20180193414A1Reduce cell viabilityReduced activityNervous disorderVectorsDiseasePain controlling
The present invention generally provides vectors, compositions, and methods of using the same for treating neurological disorders, including managing pain. The compositions and methods include the use of G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels to treat neurological indications including pain, epilepsy and satiety disorders. The compositions and methods further include the use of synthetic ligands to activate the G protein-coupled receptors and ligand-gated ion channels in the treatment of neurological disease.
Owner:CODA BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
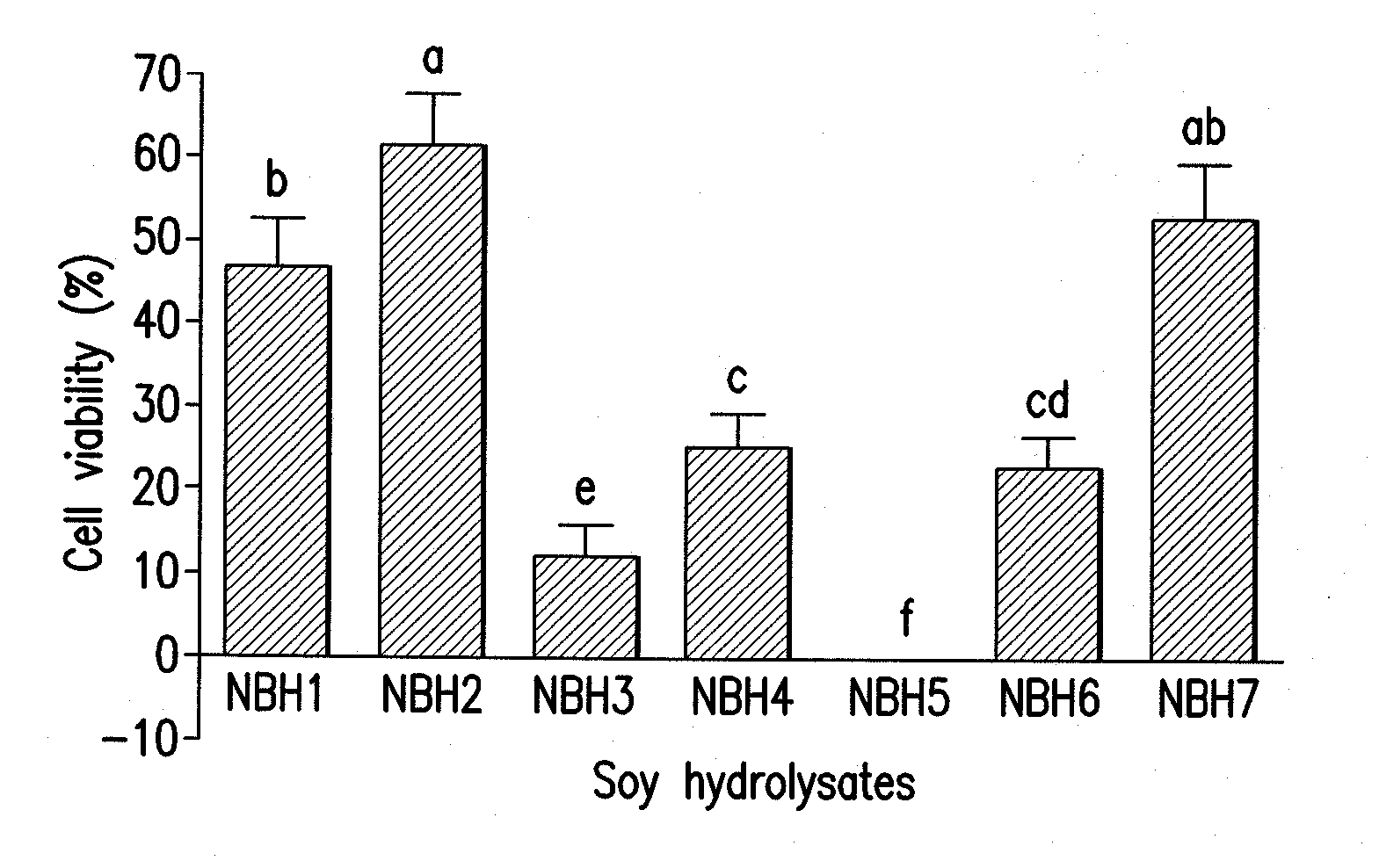
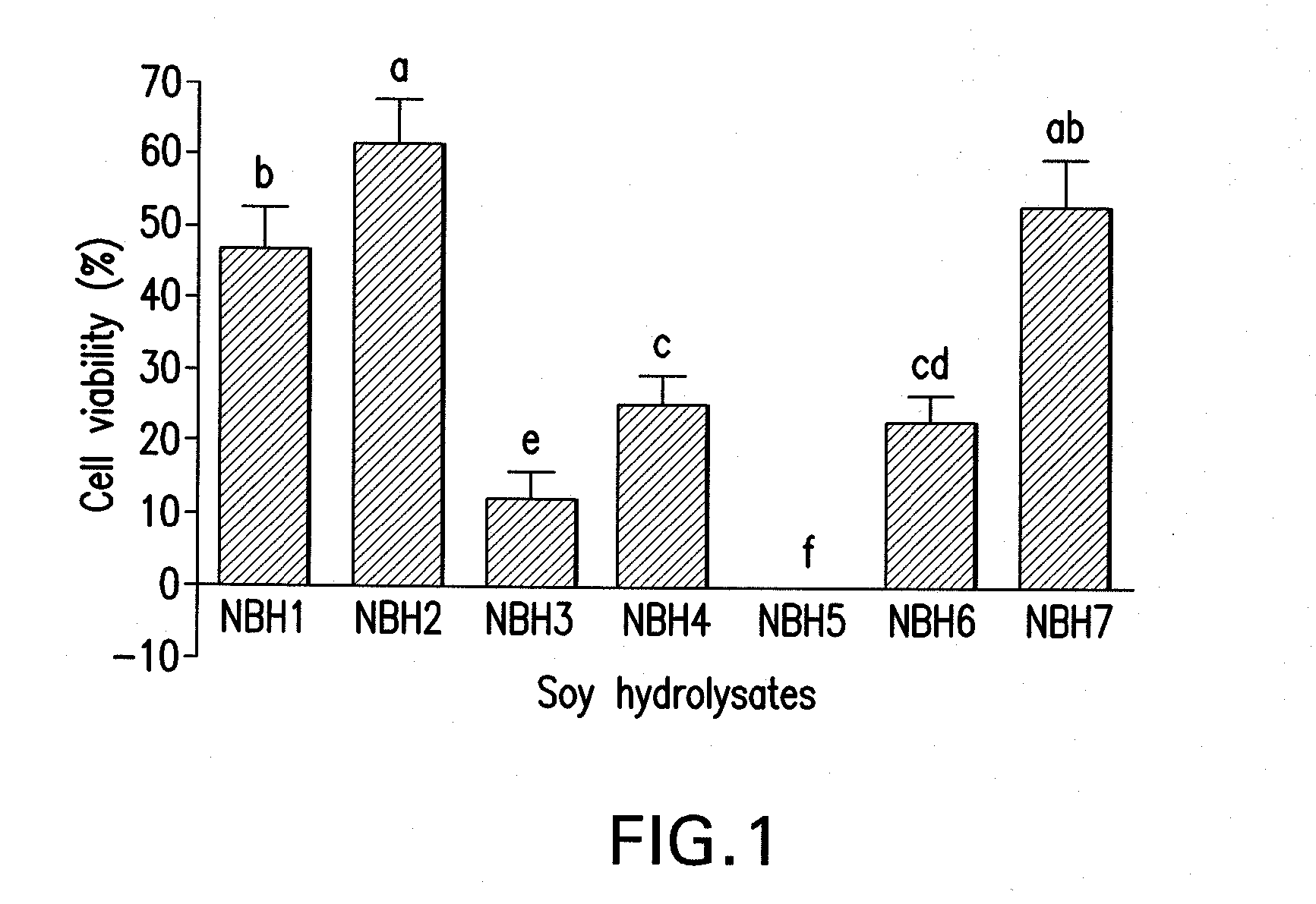
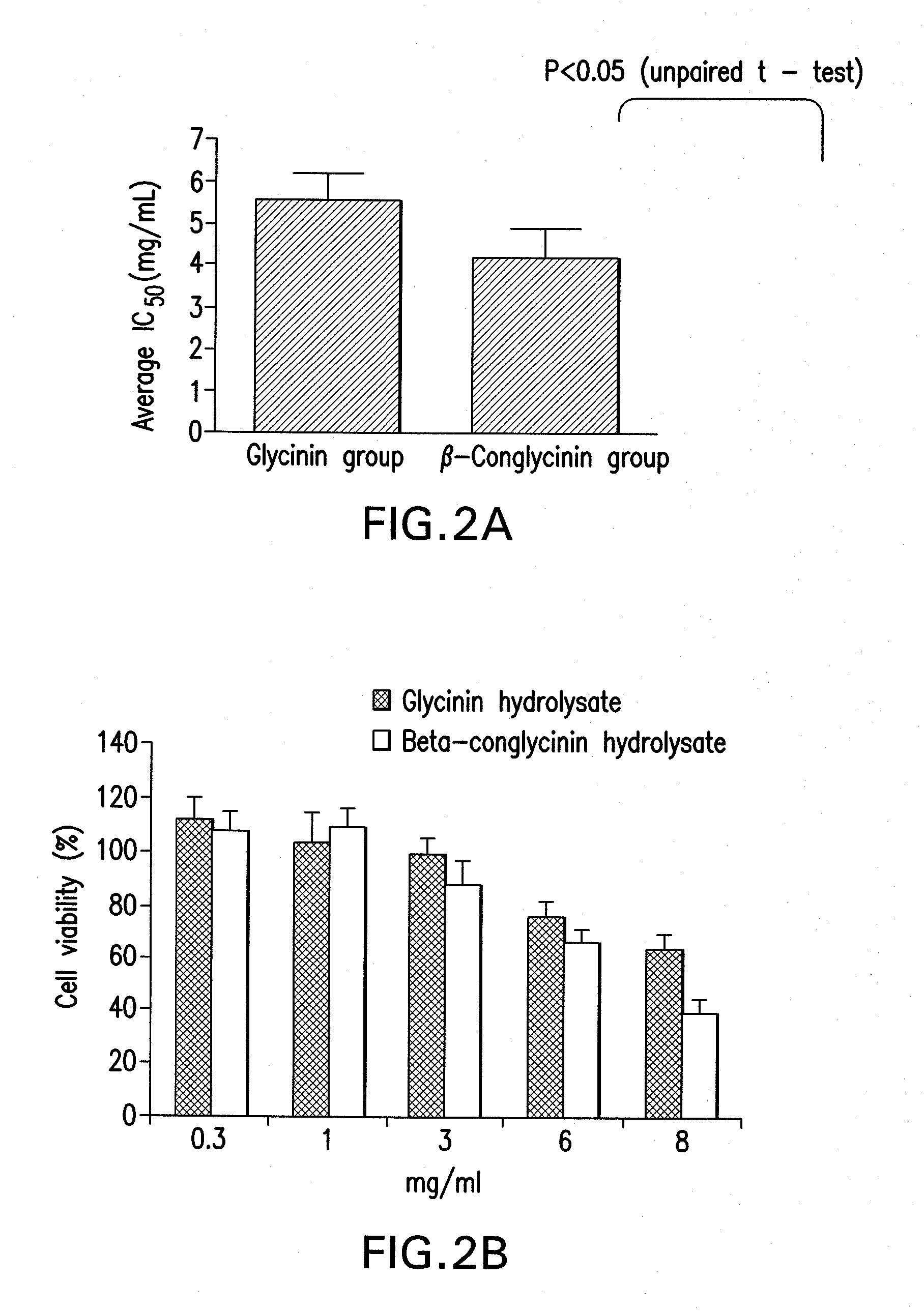
Method of selecting soybeans with enhanced bioactivity and compositions for reducing cancer cell viability
InactiveUS20110136745A1Lower cholesterol levelsReduce joint painPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHealth indexCancer cell
The invention provides a method that uses enzyme-treatment of whole soybeans or partially defatted soybeans to select soybeans with improved bioactivity or bioactivities. The invention further provides a soybean plant and seed with a non-transgenic mutation conferring enhanced bioactivity as an hydrolysate when compared to hydrolysate from other seeds, for instance in a cell-based assay, including reduced cancer cell viability; increased LDL receptor activity; reduced lipid accumulation; increased adiponectin expression; decreased FAS and LPL expression; reduced production of NO and PGE2, and expression of iNOS and COX-2; higher antioxidant activity; promotion of growth of bifidobacteria; and inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria; for instance when compared to other seeds tested as hydrolysates. The invention also provides soybean plants for use in producing seeds that have an overall improved bioactivity compared to other seeds as hydrolysates by combining effects on several bioactivity assays in a health index. The invention also provides products derived from, and parts of, these plants and uses thereof. Methods for producing such plants are also provided, as well as methods for standardizing or assuring quality control of soybean products with enhanced bioactivity for humans and animals.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method of preserving tissue equivalent and tissue equivalent preserved in frozen state
InactiveUS20030118982A1Improve cell activityImprove viabilityDead animal preservationTissue regenerationCell adhesionBiology
A method for cryopreservation of a tissue equivalent whereby the viability of frozen cells and the biological activity of thawed cells are improved and the steps are simplified; and a cryopreserved tissue equivalent obtained by the method. Cells suspended in a cryopreserving solution are inoculated into a matrix and then frozen before the cells adhere to the matrix.
Owner:MENICON CO LTD
Cell Suspension Preparation Technique and Device
InactiveUS20100196334A1Rapid and efficient and simple to prepare and applyReduce complexityBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDonor tissueBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides for methods and devices suitable for producing a transplantable cellular suspension of living tissue suitable for grafting to a patient. In applying the method and / or in using the device, donor tissue is harvested, subjected to a cell dissociation treatment, cells suitable for grafting back to a patient are collected and dispersed in a solution that is suitable for immediate dispersion over the recipient graft site.
Owner:AVITA MEDICAL LTD
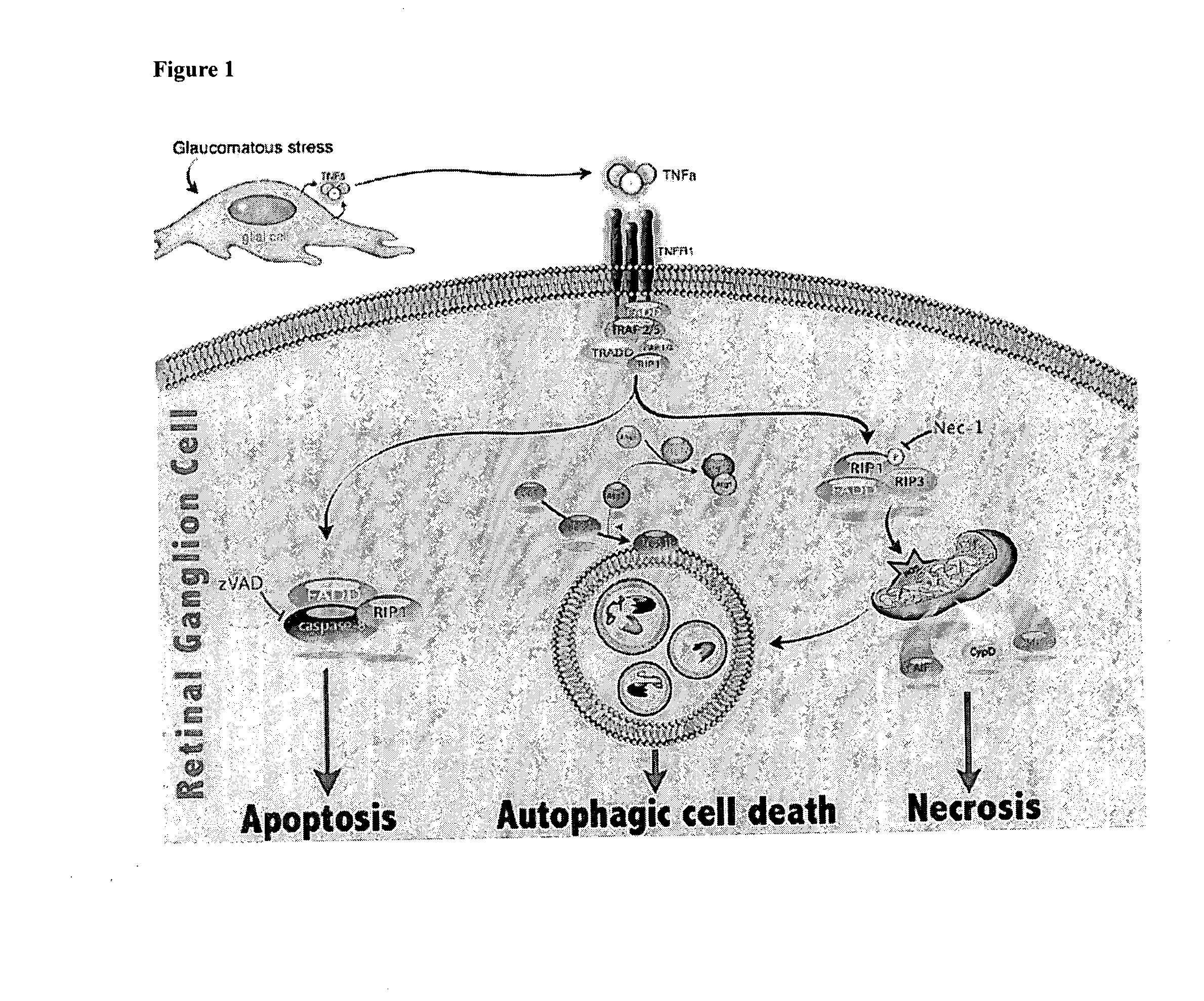
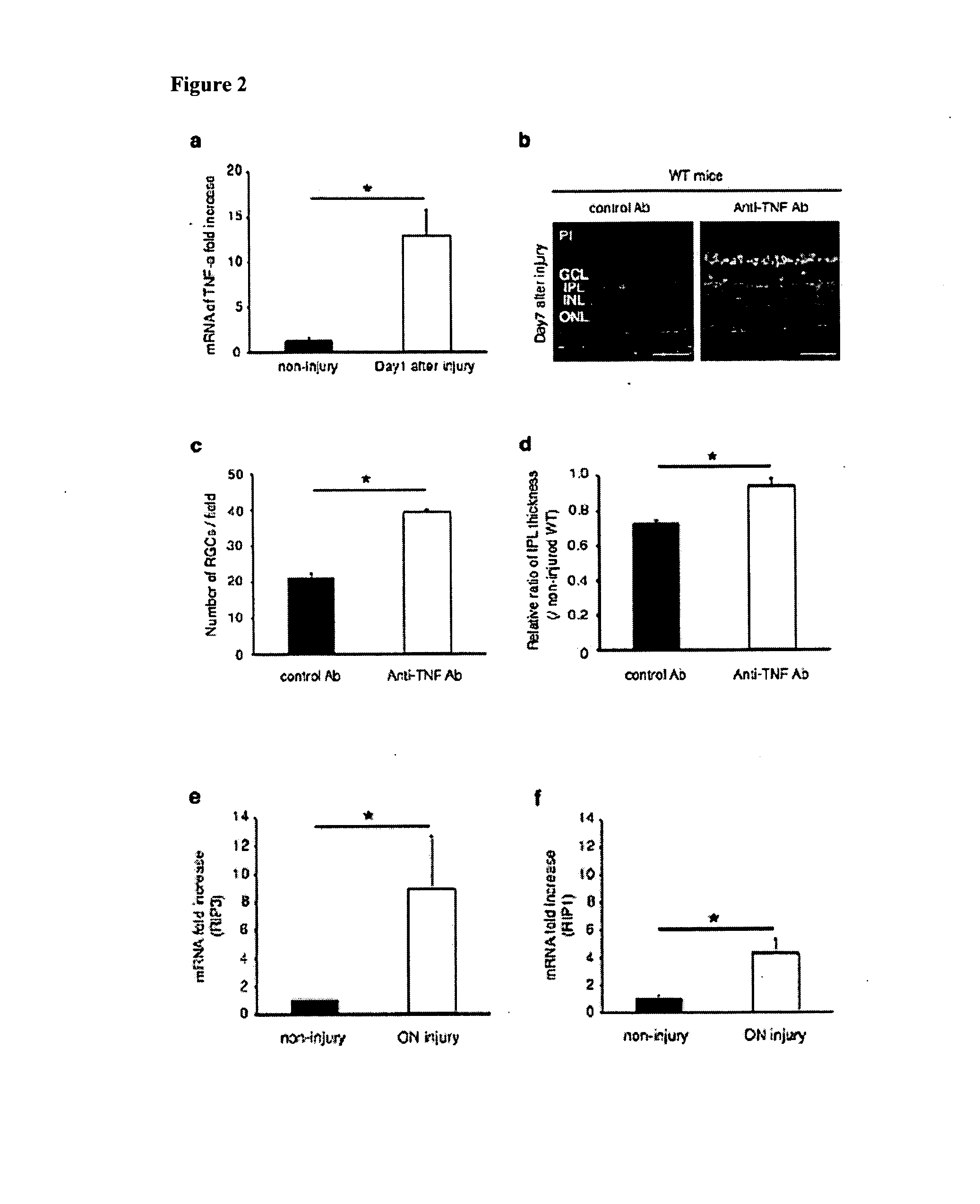
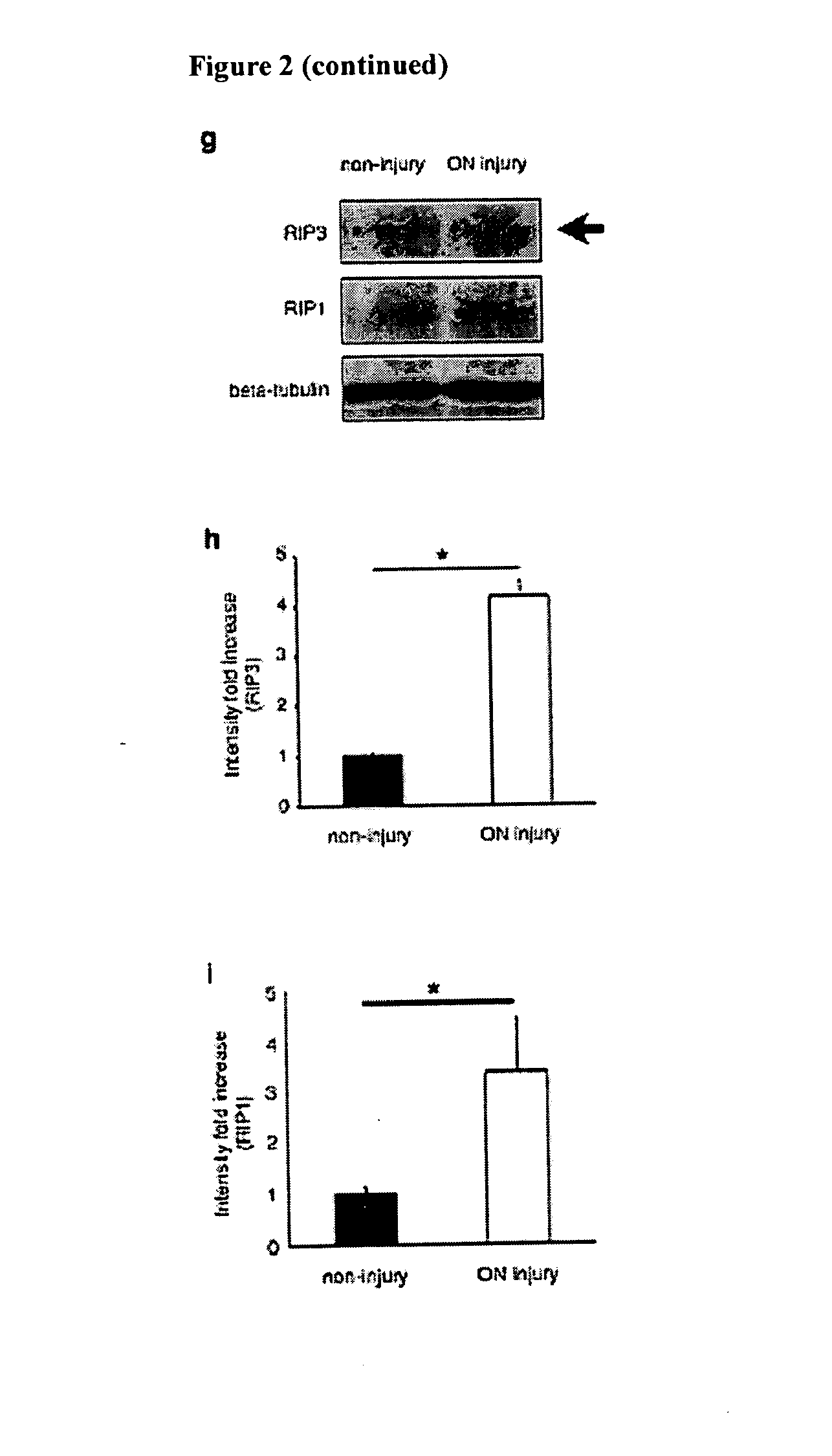
Methods and compositions for preserving retinal ganglion cells
InactiveUS20140024598A1Reduce visionReduce cell viabilityBiocideSenses disorderGlaucomaApoptosis Inhibitor
Provided are methods and compositions for maintaining the viability of retinal ganglion cells in a subject with an ocular disorder including, for example, glaucoma and optic nerve injury. The viability of the retinal ganglion cells can be preserved by administering a necrosis inhibitor either alone or in combination with an apoptosis inhibitor to a subject having an eye with the ocular condition. The compositions, when administered, maintain the viability of the cells and / or promote axon regeneration, thereby minimizing the loss of vision or visual function associated with the ocular disorder.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS EYE & EAR INFARY
Treatment of disease or injury of the nervous system using agents that decrease the activity of the melanocortin 4 receptor
InactiveUS20100129319A1Reduce cell viabilityDecrease intracellular responseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNervous systemIn vitro
Novel methods are provided for modulating CNS cell neogenesis in the CNS cells in vitro or in vivo, involving the use of agents that decrease the activity of the melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R). When the methods of the invention are applied to a subject such as a human, it may be used for reducing a symptom of a CNS disorder.
Owner:NEWRON SWEDEN
Cosmetic uses of electromagnetic radiation
ActiveUS20090012508A1Improve immune cell viabilityIncrease the number of cellsSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyWrinkle skinFine line
A method of cosmetically treating a superficial area of mammalian skin by irradiating the skin with a source of divergent electromagnetic radiation of between 900 nm to 1500 nm, and use of electromagnetic radiation of specified wavelengths. The cosmetic treatment includes reducing or alleviating or removing or diminishing wrinkles or fine lines, rejuvenating skin, retarding or reversing visible signs of aging, improving skin elasticity, tone, texture and appearance and beautifying facial, breast, arm, buttock, thigh, stomach or neck skin.
Owner:VIRULITE
Dried food products formed from cultured muscle cells
ActiveUS20150216216A1Reduce cell viabilityMeat/fish preservationFood shapingBiotechnologyHigh protein food
Dehydrated, edible, high-protein food products formed of cultured muscle cells that are combined (e.g., mixed) with a hydrogel (e.g., a plant-derived polysaccharide) are described. These food products may be formed into a chip (e.g., snack chip), that has a protein content of greater than 50%. One or more flavorants may also be included.
Owner:FORK & GOODE INC
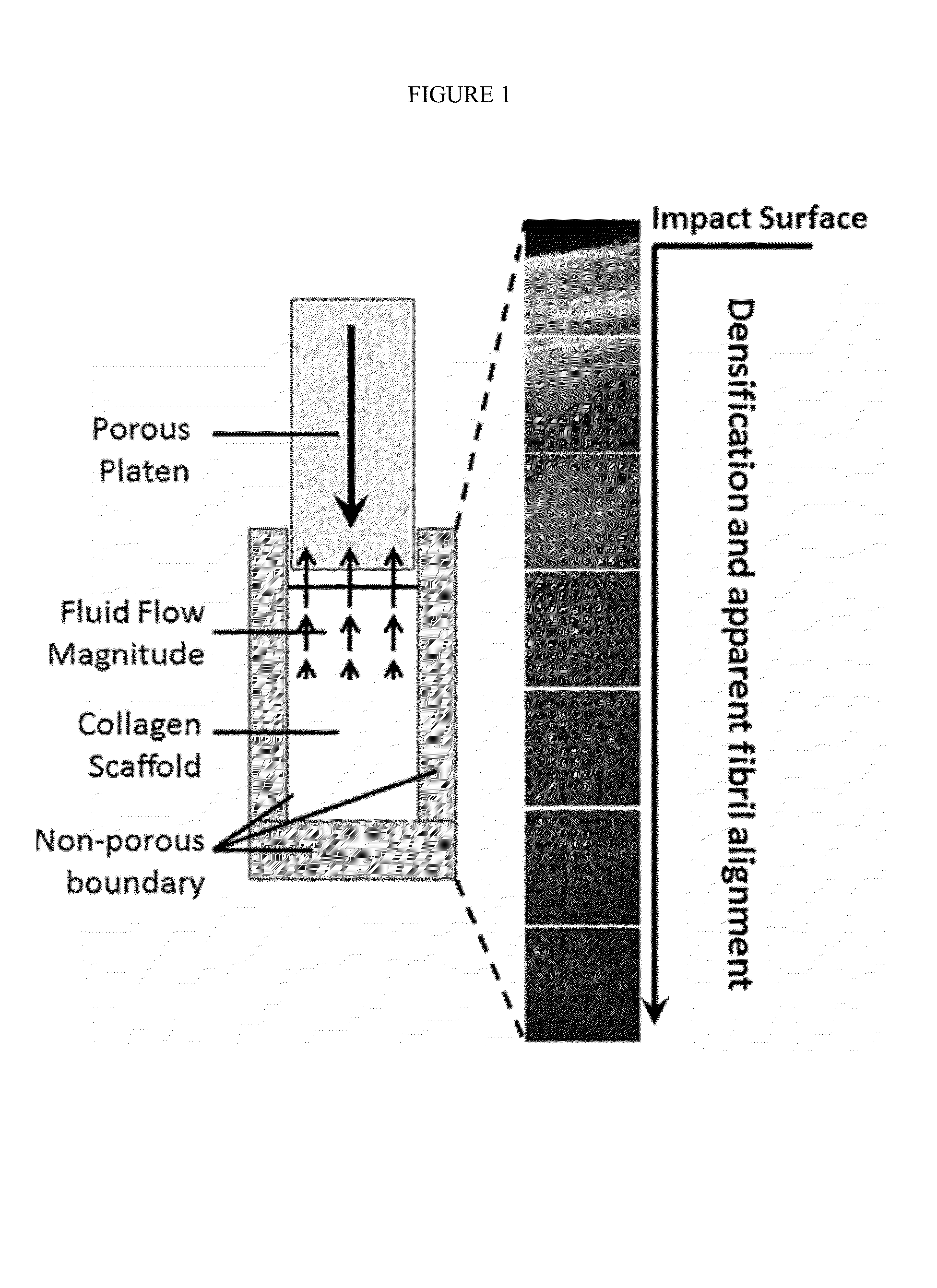
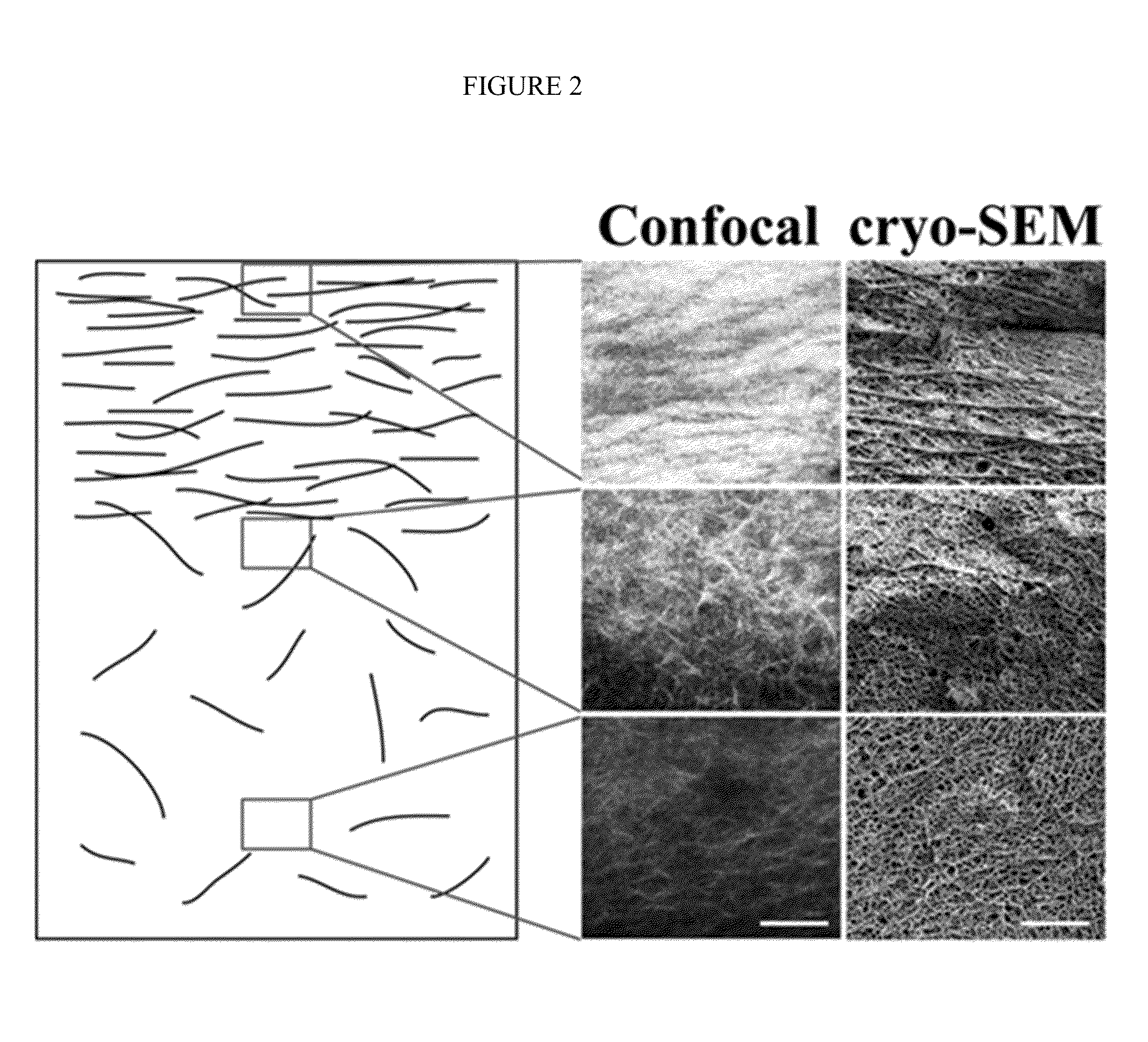
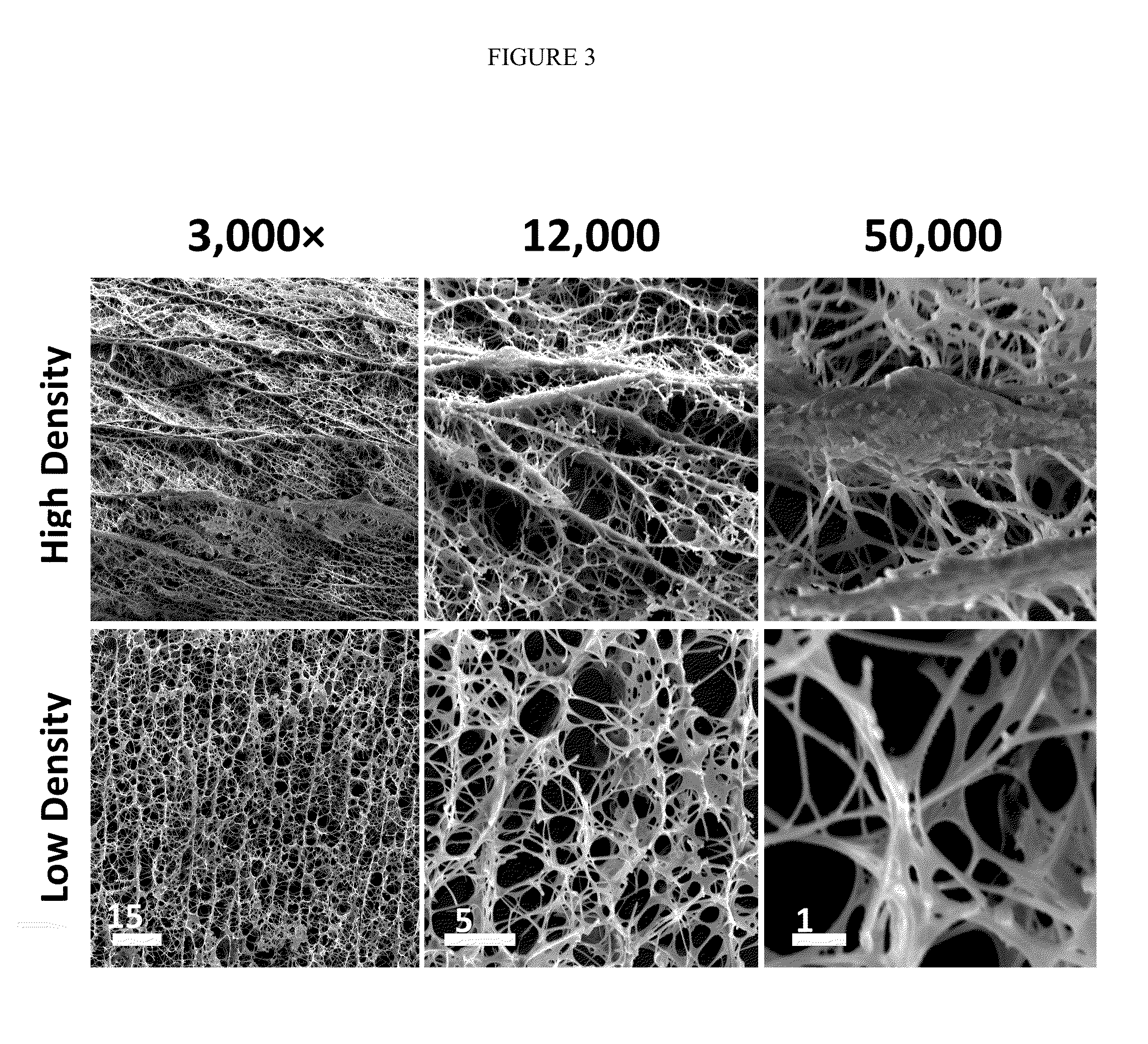
Collagen compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20150105323A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove overall strengthPeptide/protein ingredientsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringCollagenan
The present disclosure provides an engineered collagen composition comprising collagen, wherein the collagen composition is compressed to form a gradient of at least one physical property. Methods of using and of manufacturing the engineered collagen compositions of the present disclosure are also provided.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Pharmaceutical agent containing hyaluronan as an active ingredient
InactiveUS20070099867A1Easy to produceLow costOrganic active ingredientsBiocideN-AcetylglucosamineBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
A pharmaceutical composition containing hyaluronan as an active ingredient is provided. A preferred hyaluronan is a tetrasaccharide (HA4) containing 2 units, with a single unit being -D-glucuronic acid-β-1,3-D-N-acetylglucosamine-β-1,4-.
Owner:SHISEIDO CO LTD
Disruption of the mammalian Rad51 protein and disruption of proteins that associate with mammalian Rad51 for hindering cell proliferation
InactiveUS6057104AInhibit cell proliferationReduce cell viabilityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEmbryo
When a mutation, designated rad51M1, was generated in the mouse MmRAD51 gene, mutant embryos died shortly after implantation. rad51M1 cells exhibited hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation, reduced proliferation, programmed cell death and chromosome loss. The disruption of MmRad51 protein-protein interactions stopped cell proliferation and / or reduced cell viability. Several proteins that interact with MmRad51 have been identified including, for example Brca2 and M96. Additionally, Rad51 self-associates via the N-terminal region. When a single residue was changed from a conserved lysine to an alanine, the alteration proved toxic to cells. Moreover, a rad51 allele that lacked the RecA homology region was also deleterious to cells. In view of the above, it is clear that inhibiting MmRad51 function or the function of any molecule that associates with MmRad51, or any molecule in the Rad51 or Rad52 pathways, hinders cell proliferation and / or viability. Accordingly, molecules capable of blocking these critical DNA repair pathways may be effective as therapeutics for inhibiting cell proliferation.
Owner:LEXICON PHARM INC
Chemopreventive, Anticancer and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pinoresinol-Rich Olives
InactiveUS20090048187A1Reduce incidenceBroad spectrum of propertyBiocideOrganic chemistryPinoresinolPolyphenol
The present invention relates to a composition and method for preventing and treating cancer and modulating cell proliferation using compositions extracted from pinoresinol-rich Olea europaea Caiazzana olives. The present invention provides contacting one or more cells with a pharmaceutical effective amount of a polyphenolic composition isolated from Olea europaea Caiazzana olives. The polyphenolic composition includes one or more polyphenolic compounds extracted from Olea europaea Caiazzana olives.
Owner:UNIV DI NAPOLI +1
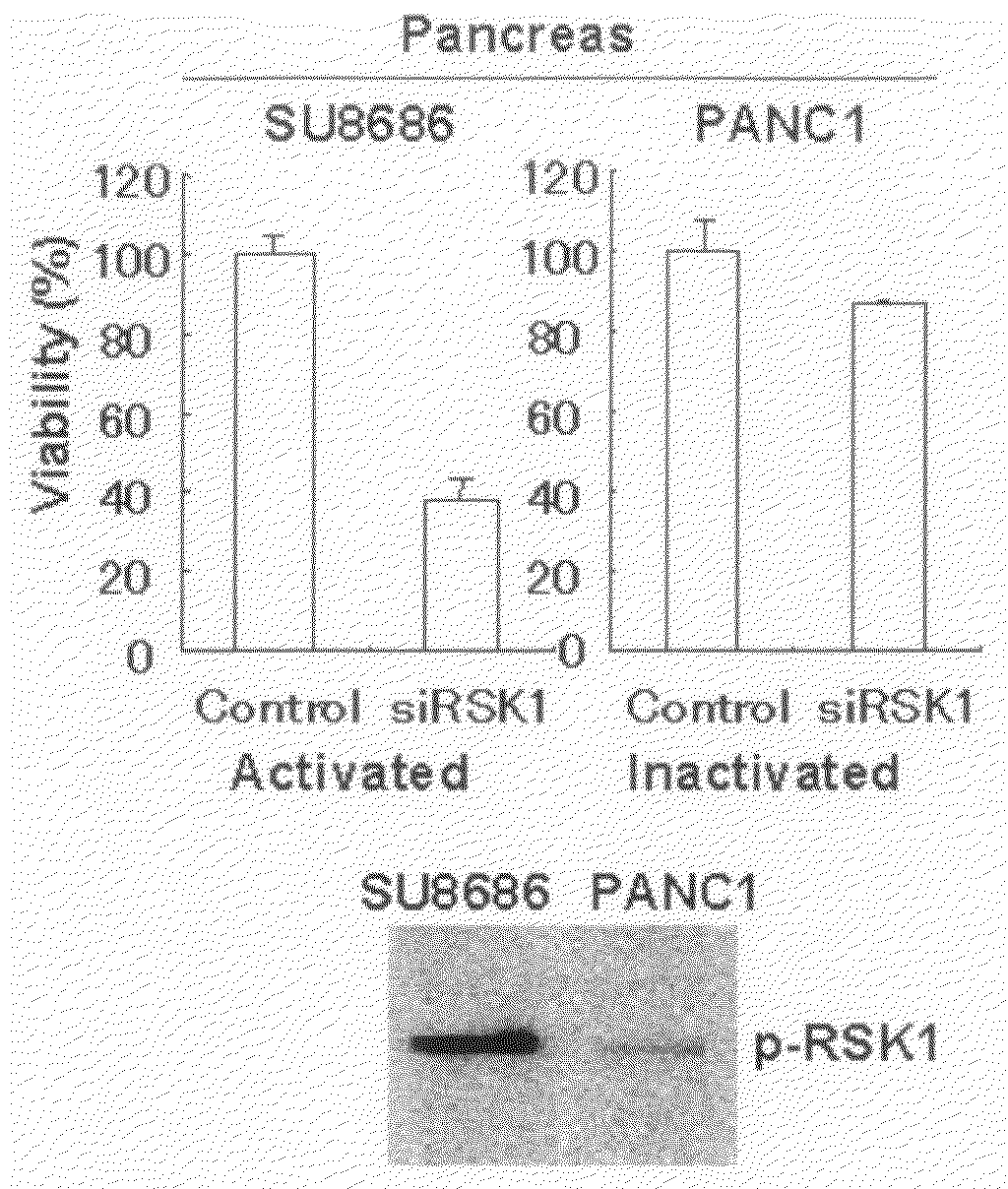
Method for evaluation of compound using RSK1
InactiveUS20100151050A1Reduce necessary doseEliminate side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellCisplatin
A method for evaluation of a compound comprising the steps of introducing an RSK1 gene into a cell to prepare a cell capable of expressing RSK1, contacting a compound to be evaluated with the cell, and detecting the specific binding of the compound to RSK1; and a compound given by the method. The compound can be used as a potentiator of cisplatin. The method enables to find a gene which acts specifically on a cell of cancer induced by the abnormality in p53 or enhanced MAPK pathway and to evaluate a compound by using the gene.
Owner:MSD KK
Methods and compositions for preserving photoreceptor and retinal pigment epithelial cells
ActiveUS20160250189A1Prevent photoreceptor lossLoss of functionSenses disorderDipeptide ingredientsRetinitis pigmentosaInhibitor of apoptosis
Provided are methods and compositions for maintaining the viability of photoreceptor cells and / or retinal pigment epithelial cells in a subject with an ocular disorder including, for example, age-related macular degeneration (AMD) (e.g., dry or neovascular AMD), retinitis pigmentosa (RP), or a retinal detachment. The viability of the photoreceptor cells and / or the retinal pigment epithelial cells can be preserved by administering a necrosis inhibitor either alone or in combination with an apoptosis inhibitor to a subject having an eye with the ocular condition. The compositions, when administered, maintain the viability of the cells, thereby minimizing the loss of vision or visual function associated with the ocular disorder.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS EYE & EAR INFARY
Targeted non-viral DNA insertions
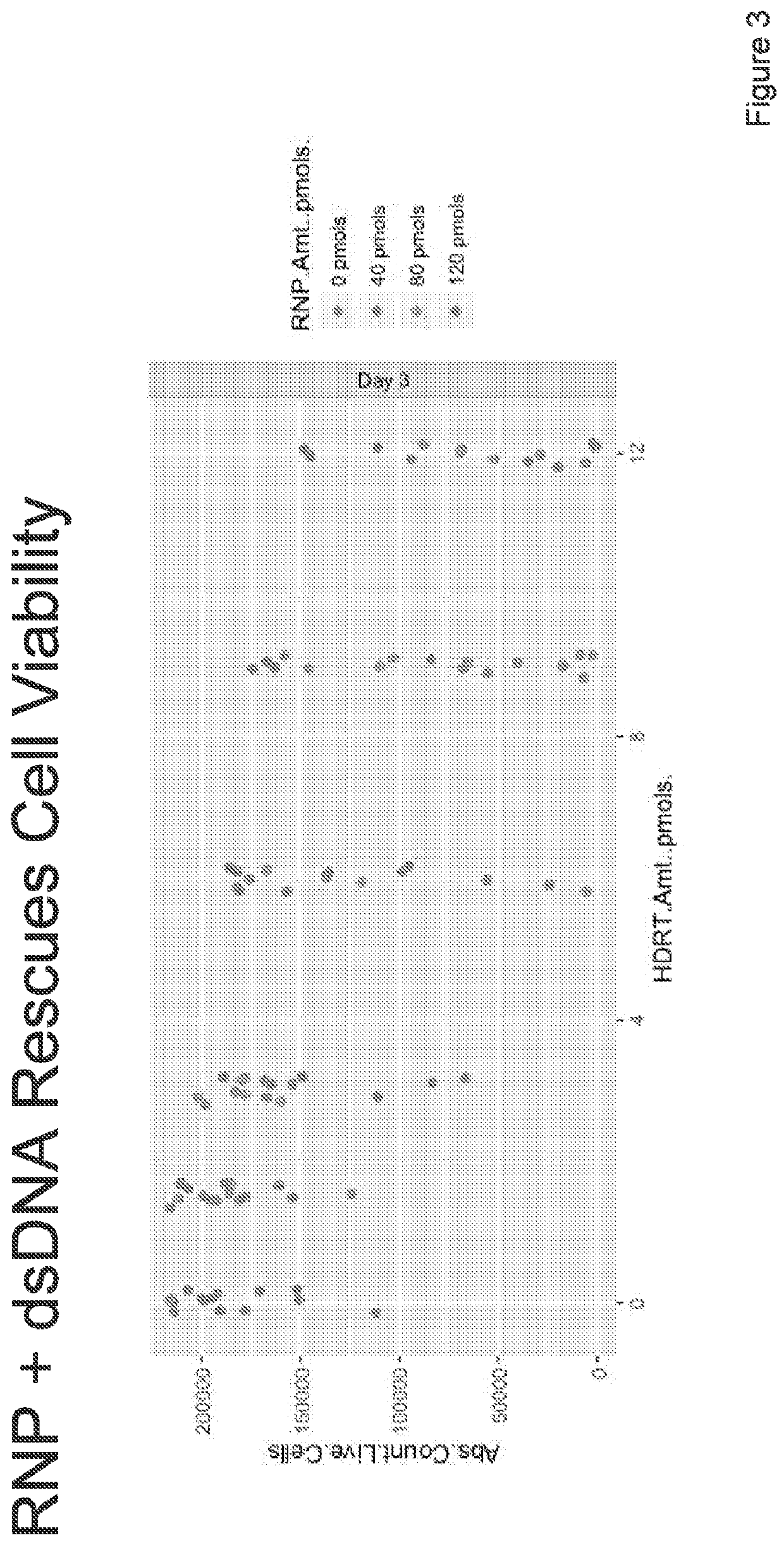
InactiveUS20200362355A1Reduce off-target effectsReduce cell viabilityActivity regulationHydrolasesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Provided herein are methods and compositions for editing the genome of a cell. In some embodiments, a nucleotide sequence of at least 200 nucleotides in length is inserted into a target region in the genome of a cell.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Human Neutralizing Anti-Kit Antibodies and Uses Thereof
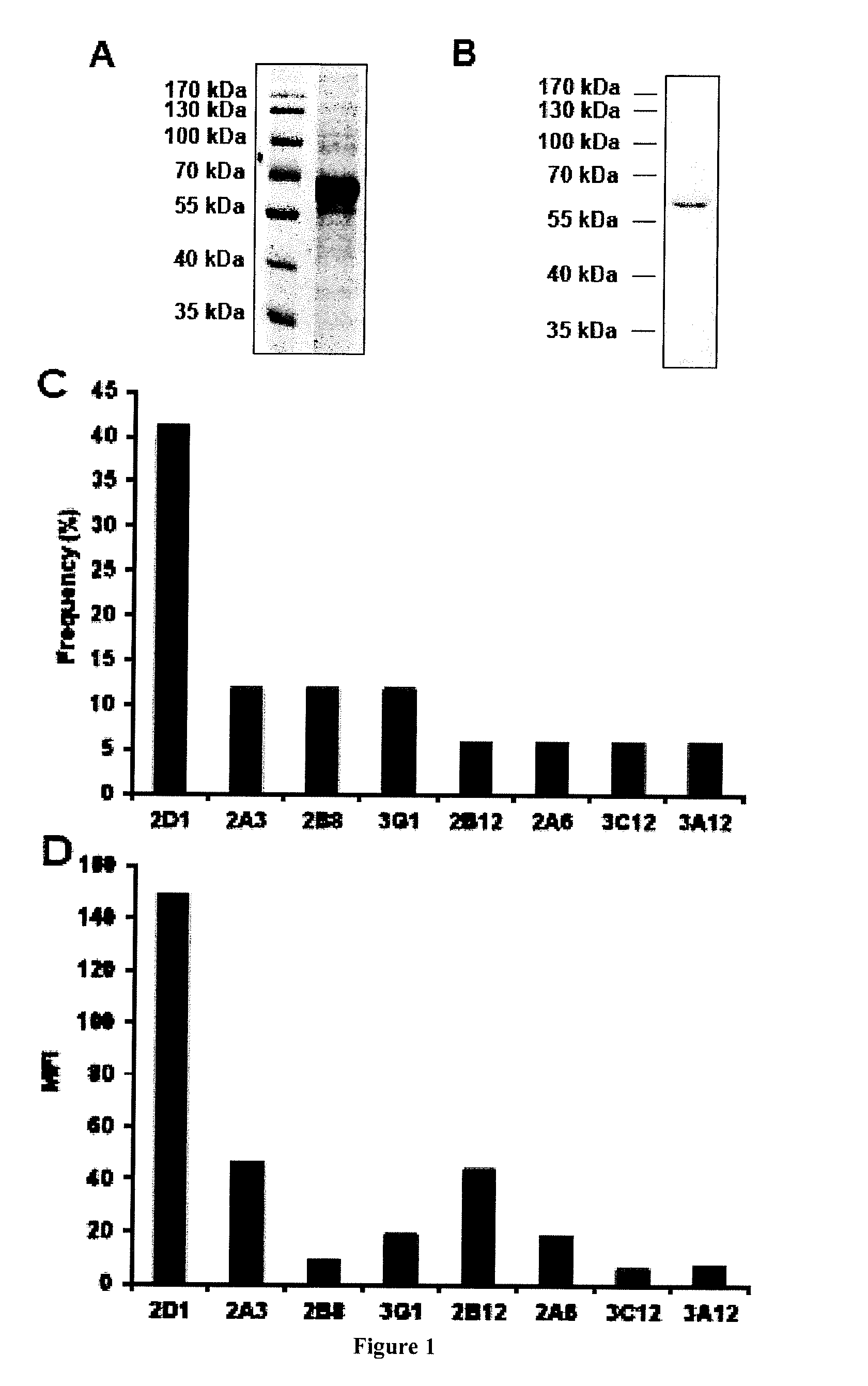
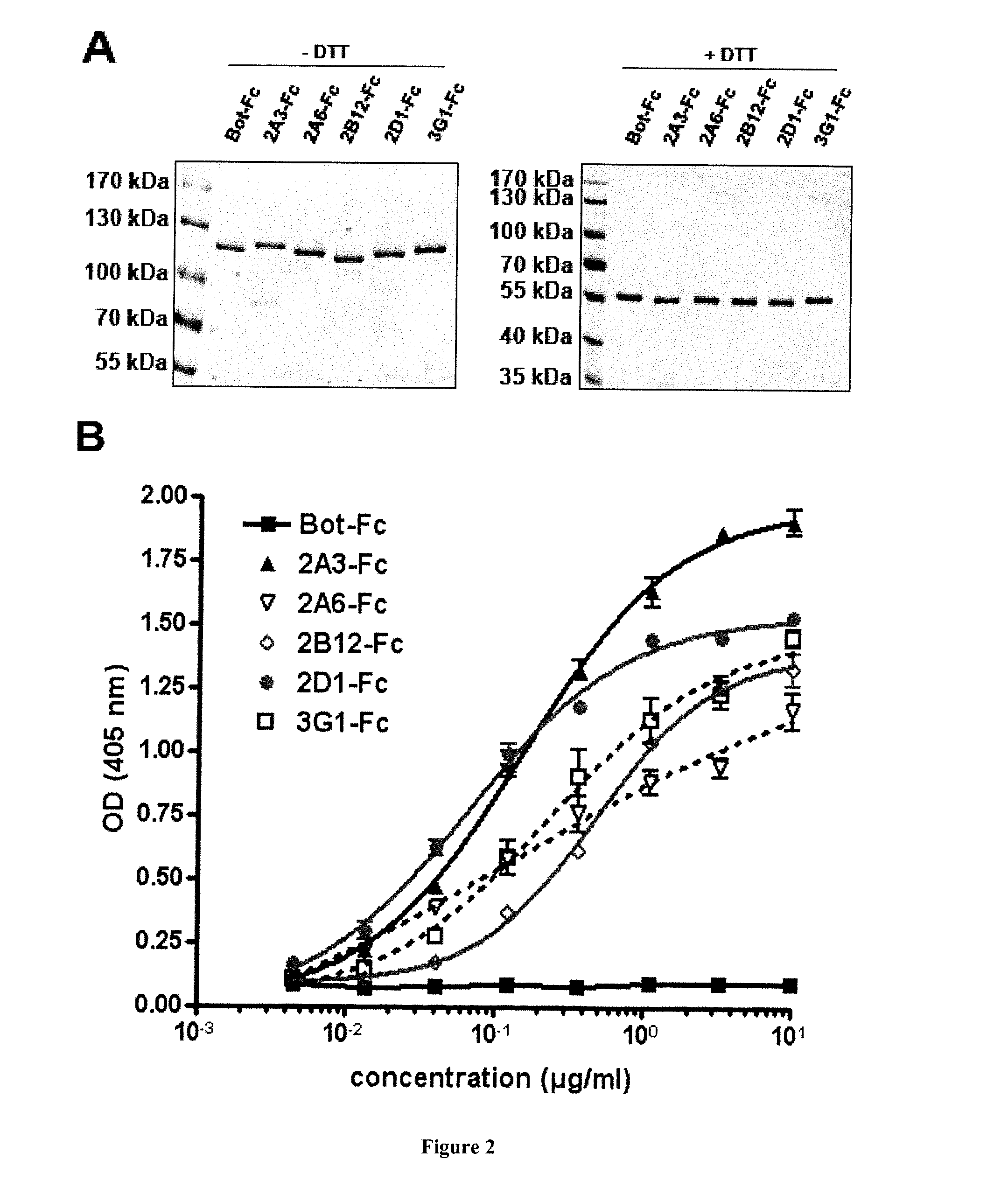
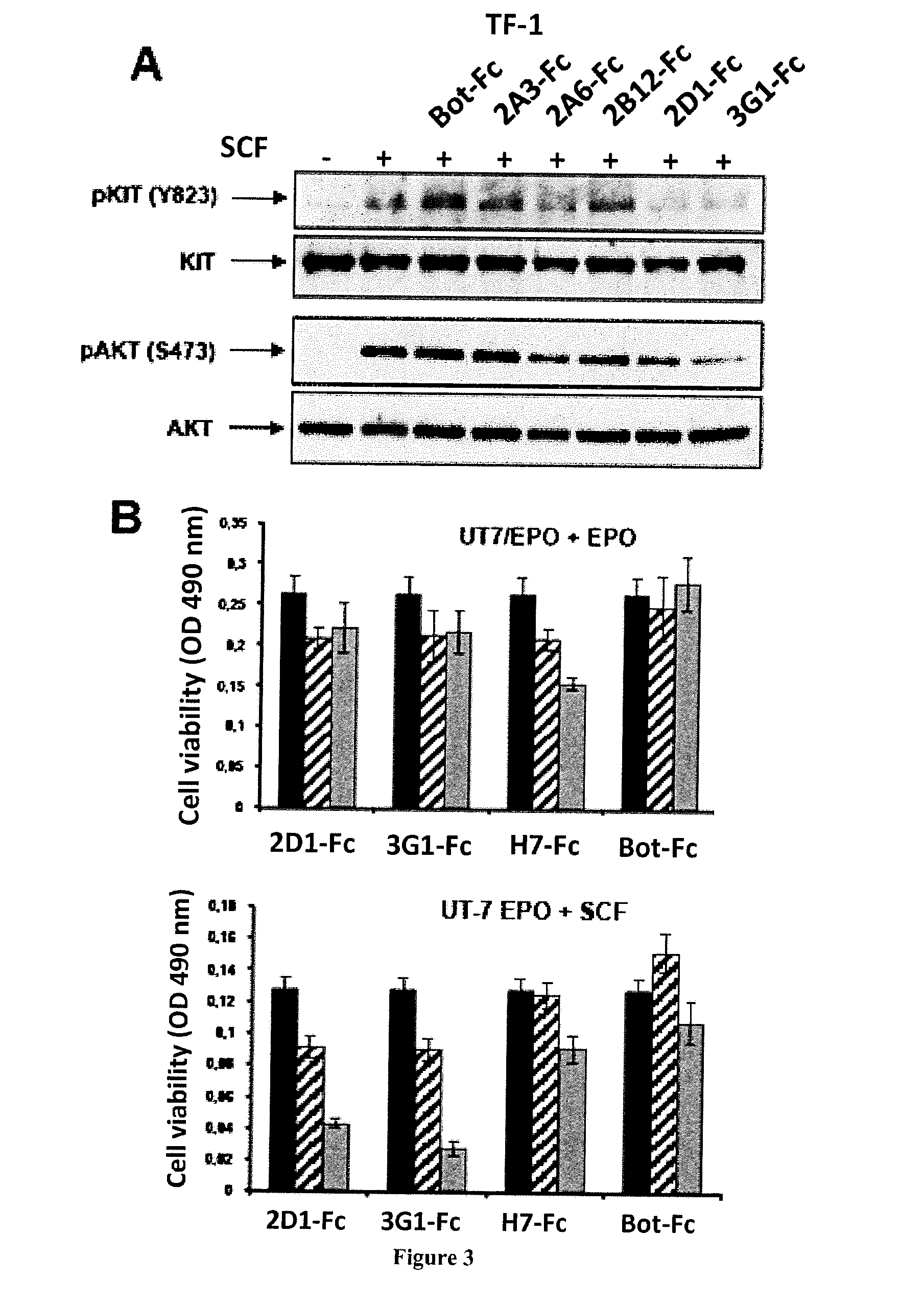
InactiveUS20160264680A1Avoid signalingReduced viabilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainBiology
The invention relates to human neutralizing anti-KIT antibodies and uses thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to an antibody comprising a heavy chain variable region comprising SEQ ID NO: 2 in the H-CDR1 region, SEQ ID NO: 3 in the H-CDR2 region and SEQ ID NO: 4 in the H-CDR3 region; and a light chain variable region comprising SEQ ID NO: 6 in the L-CDR1 region, SEQ ID NO: 7 in the L-CDR2 region and SEQ ID NO: 8 in the L-CDR3 region. The invention also relates to an antibody comprising a heavy chain variable region comprising SEQ ID NO: 10 in the H-CDR1 region, SEQ ID NO: 11 in the H-CDR2 region and SEQ ID NO: 12 in the H-CDR3 region; and a light chain variable region comprising SEQ ID NO: 14 in the L-CDR1 region, SEQ ID NO: 15 in the L-CDR2 region and SEQ ID NO: 16 in the L-CDR3 region.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +5
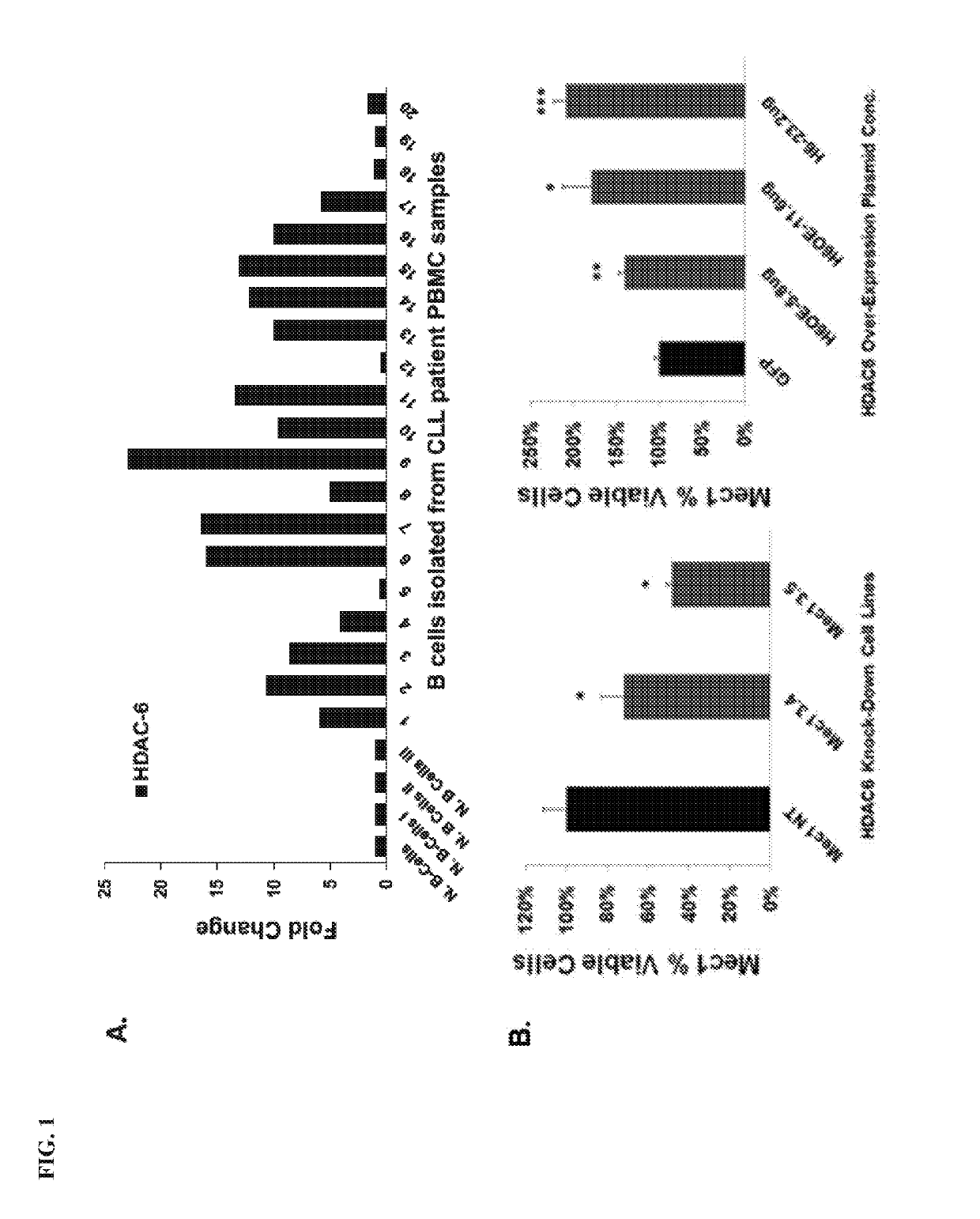
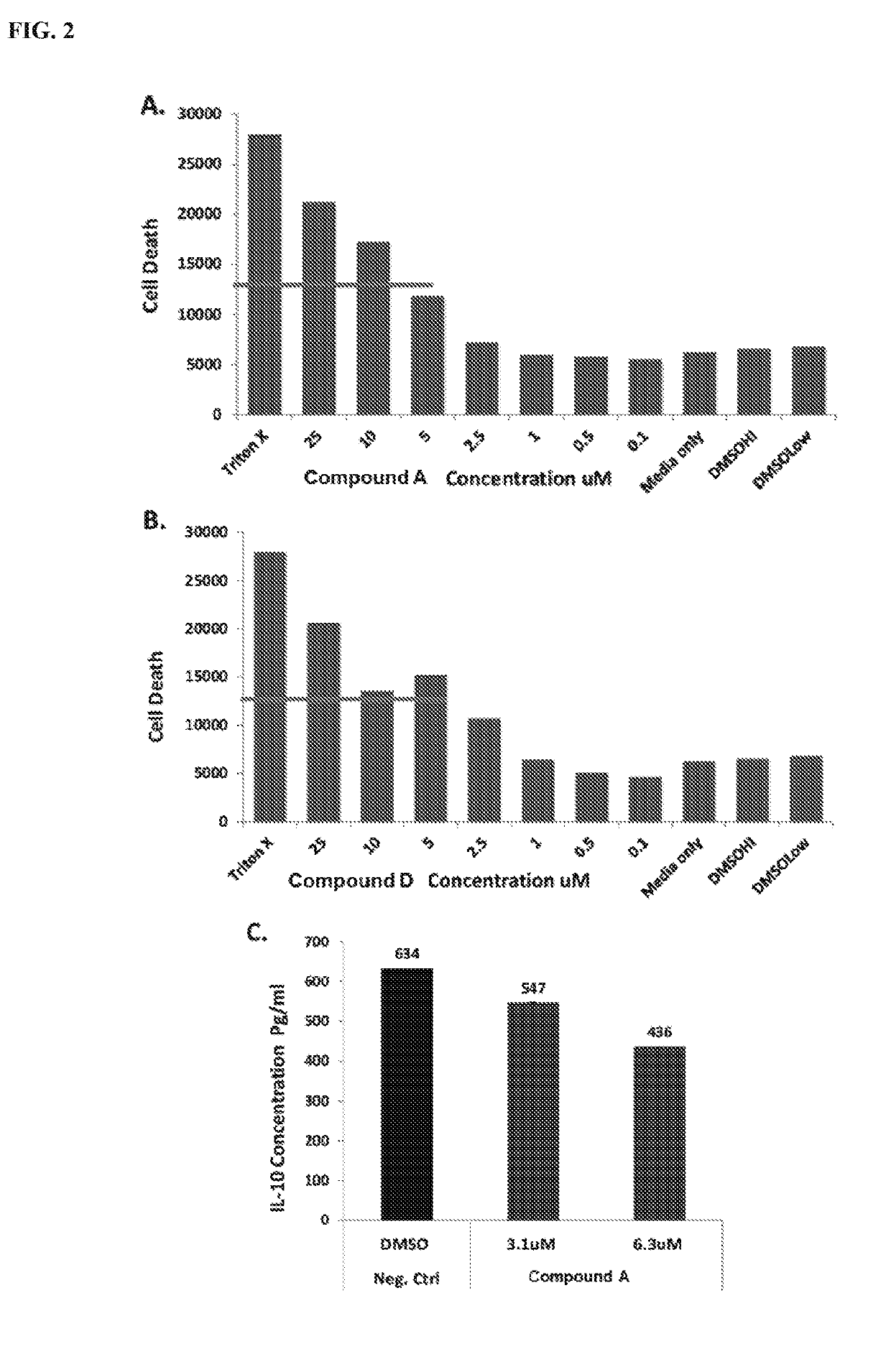
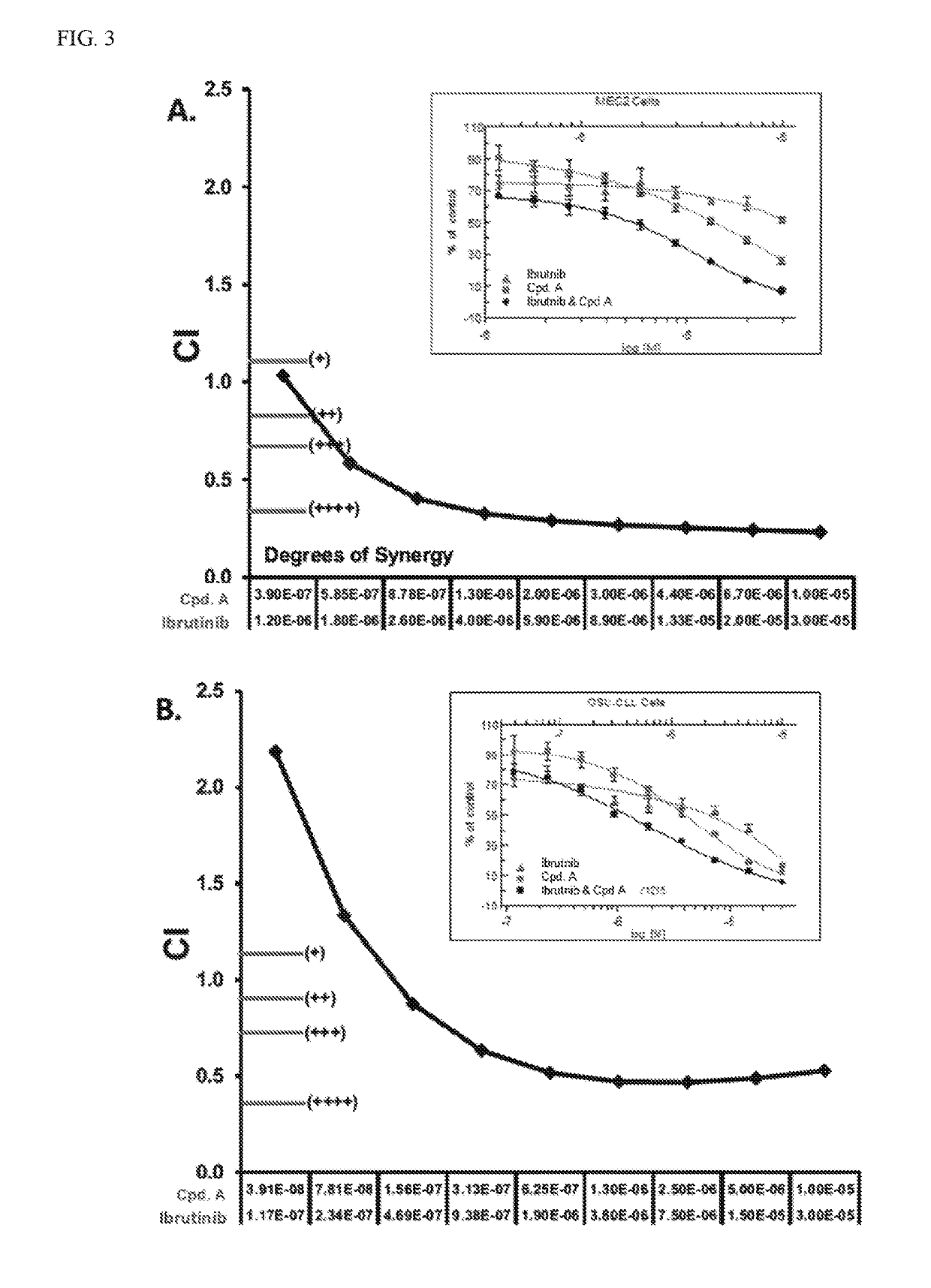
HDAC inhibitors, alone or in combination with btk inhibitors, for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia
PendingUS20190209559A1Reduce cell viabilityAltered expressionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHDAC inhibitorChronic lymphoblastic leukemia
Disclosed are histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, or combinations comprising an HDAC inhibitor and a Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a subject in need thereof. Also provided herein are methods for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia in a subject in need thereof comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an HDAC inhibitor, or a combination comprising an HDAC inhibitor and a BTK inhibitor. Other related methods are disclosed.
Owner:ACETYLON PHARMA +1
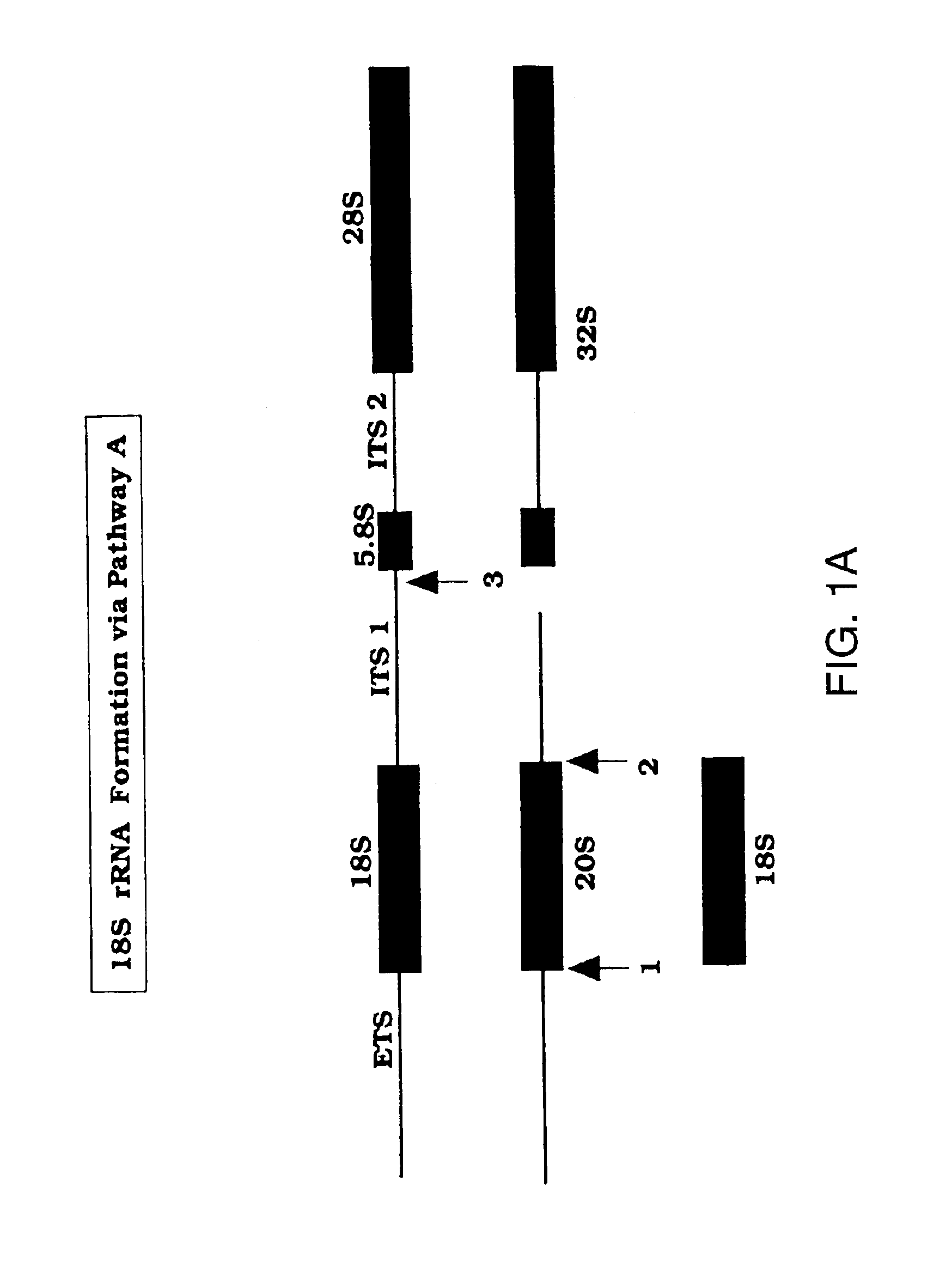
Methods to screen for antibiotic agents and their use in treatment of opportunistic infections
InactiveUS6913889B2Sufficient distanceReduce cell viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiparasitic agentsAntibiotic AgentsRibosome Subunits
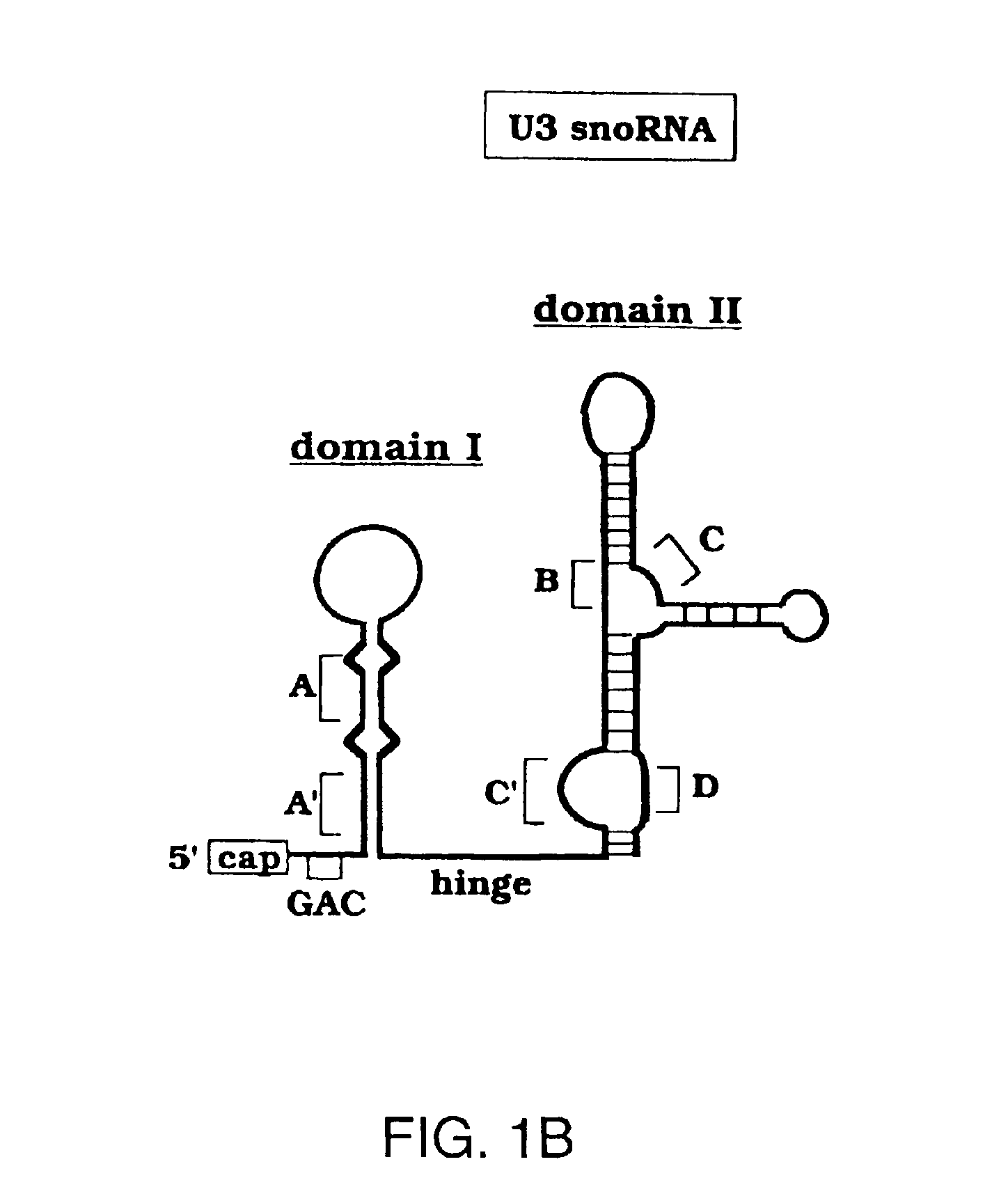
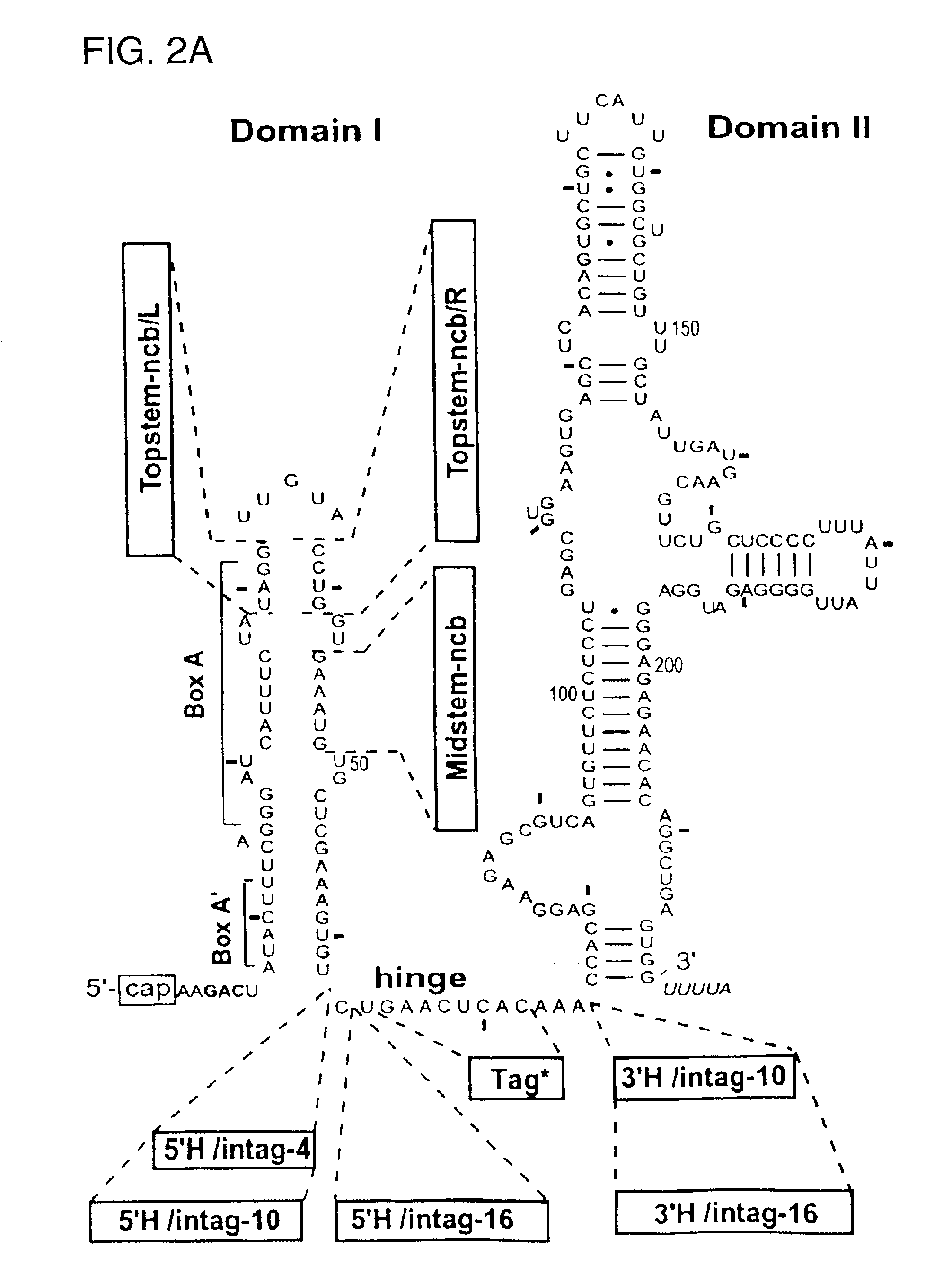
The present invention provides novel targets in eukaryotic cells for antibiotic agents and methods for identification of antibiotic agents affecting such targets and the use of the identified antibiotic agents in treatment of opportunistic infections in eukaryotic hosts. The invention is based upon the identification of species specific 5′ hinge and 3′ hinge regions of U3 small nucleolar ribonucleic acid (snoRNA). The present invention discloses that the external transcribed spacer (ETS) of the ribosomal RNA precursor (pre-rRNA) comprises sequences that are complementary to the 5′ and 3′ hinge regions of U3 snoRNA. The invention further discloses that sequence substitutions of the 5′ hinge or 3′ hinge region of U3 snoRNA severely compromise or fully inhibit the cleavage events at sites 1 and 2 in rRNA processing necessary to form mature 18S rRNA which is a vital component of the small subunit of ribosomes of all eukaryotes.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
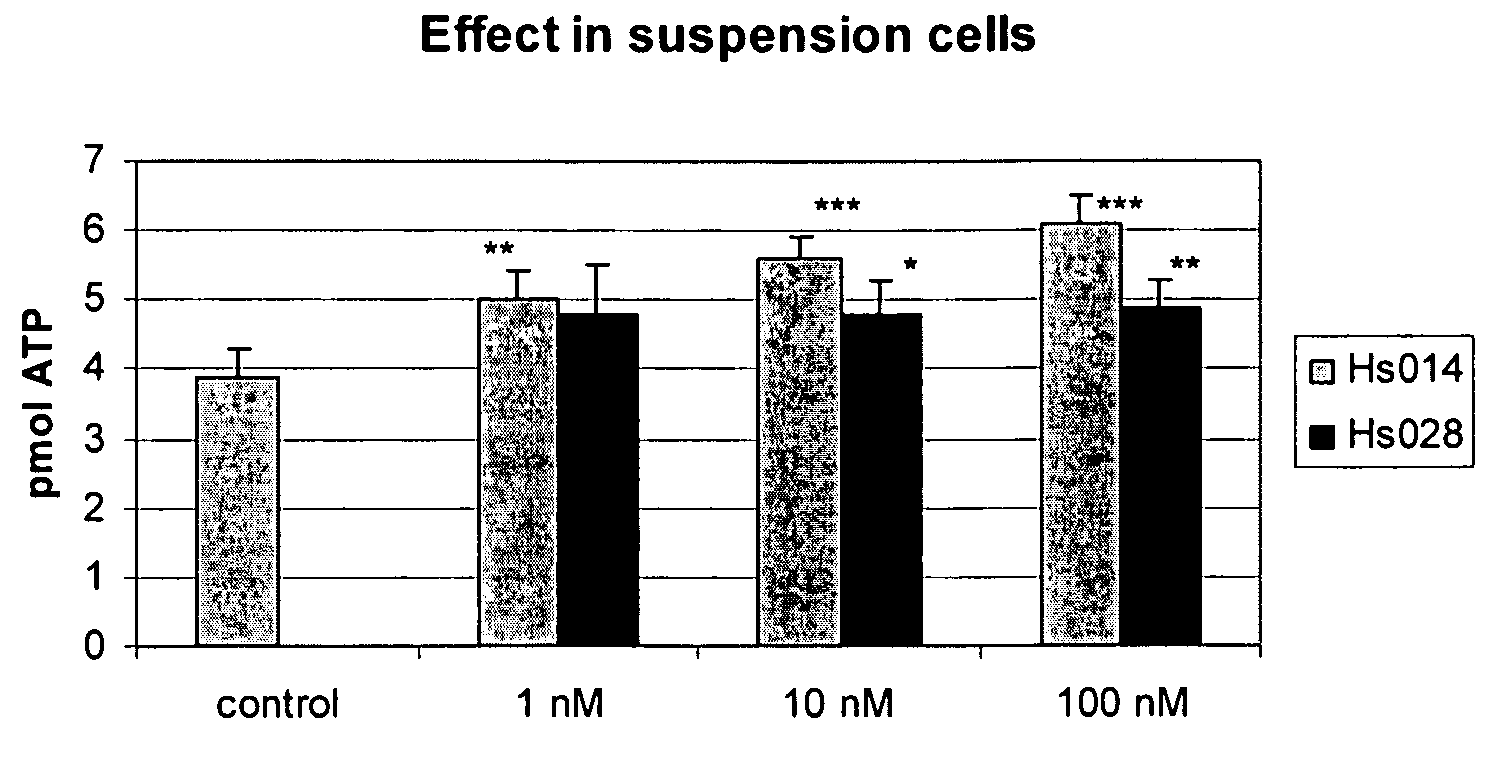
Methods of evaluating cell culture additives
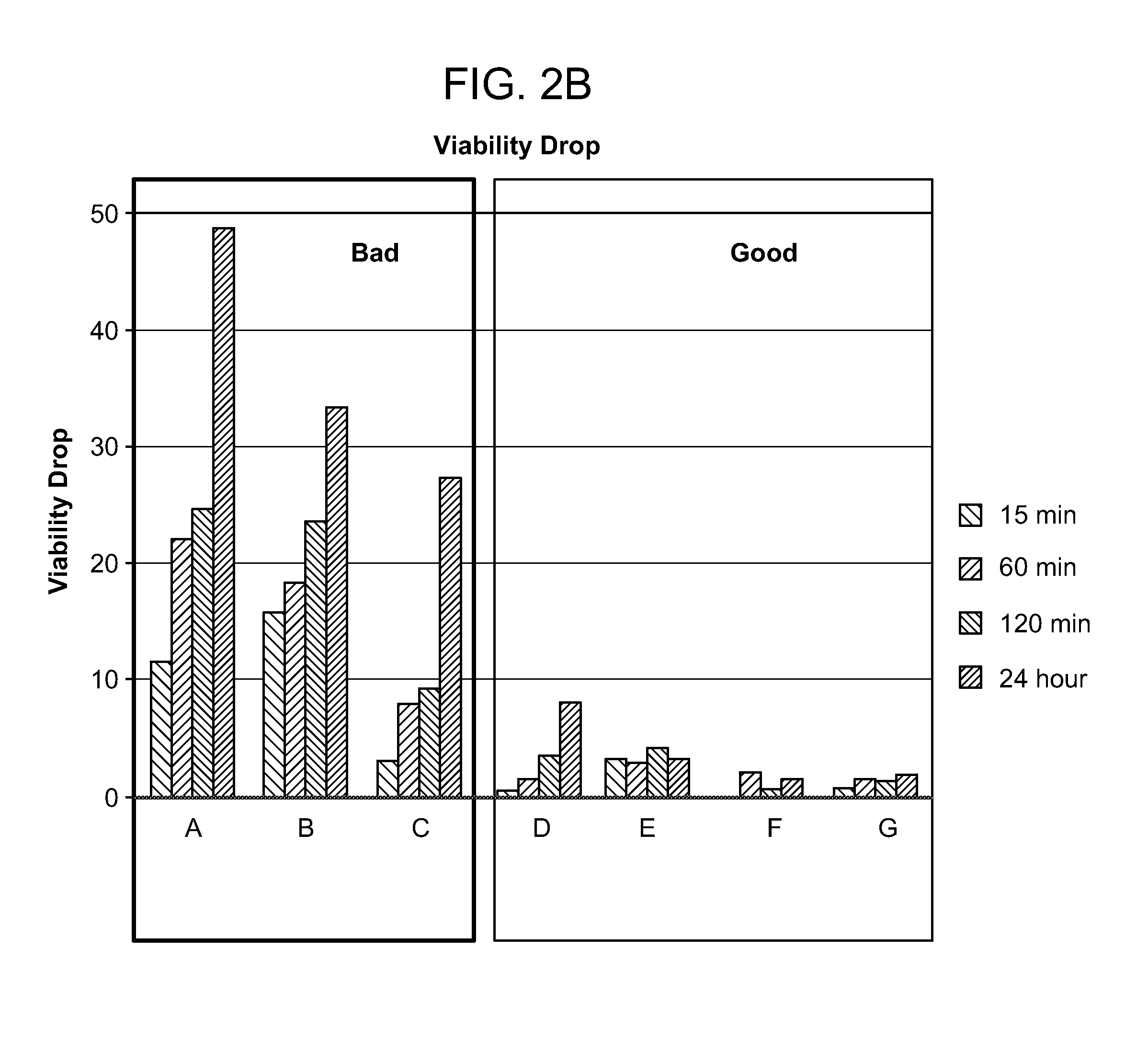
InactiveUS20160131634A1Reduce dropDrop in cell viabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiochemistry apparatusCell growthTime-Consuming
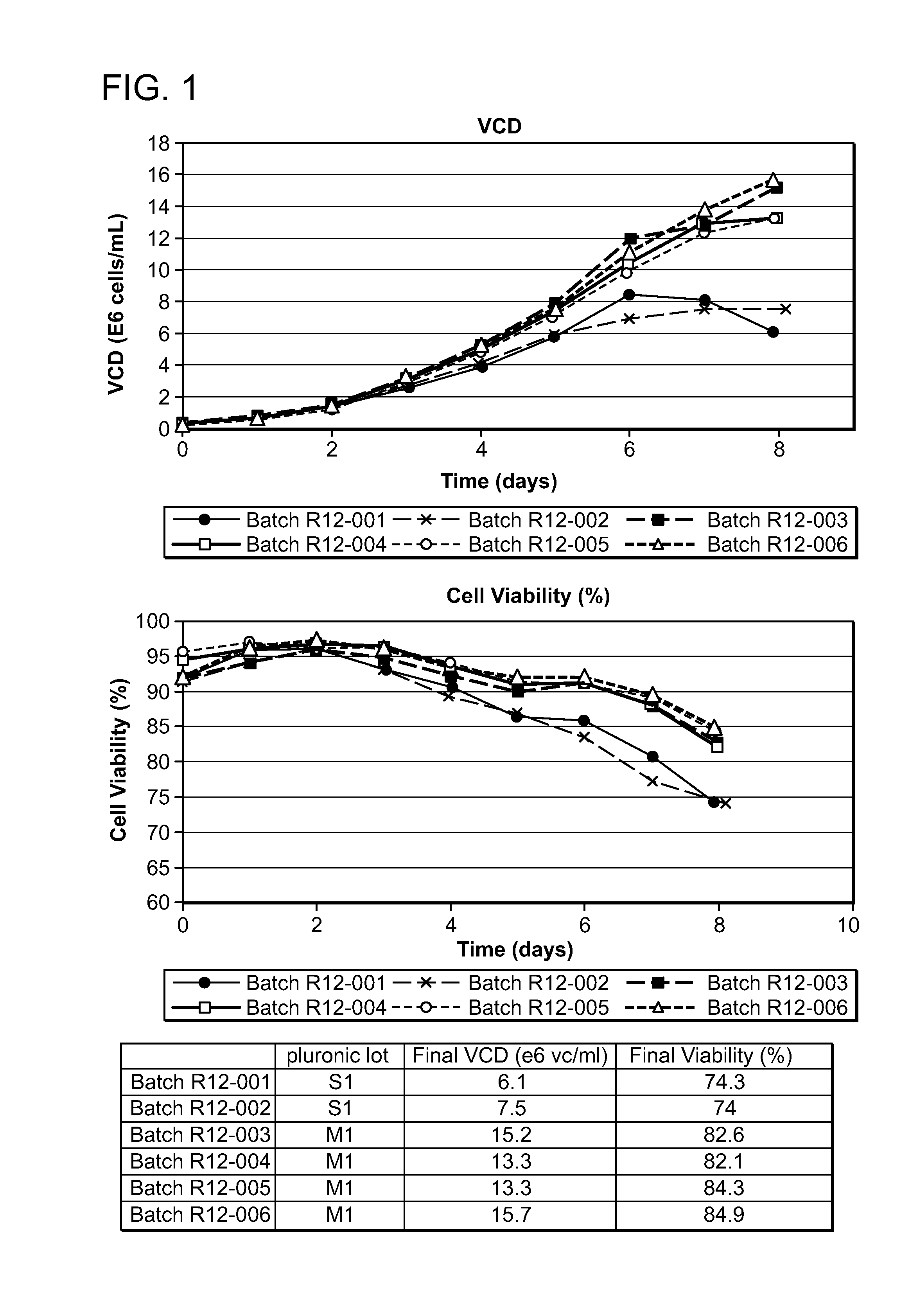
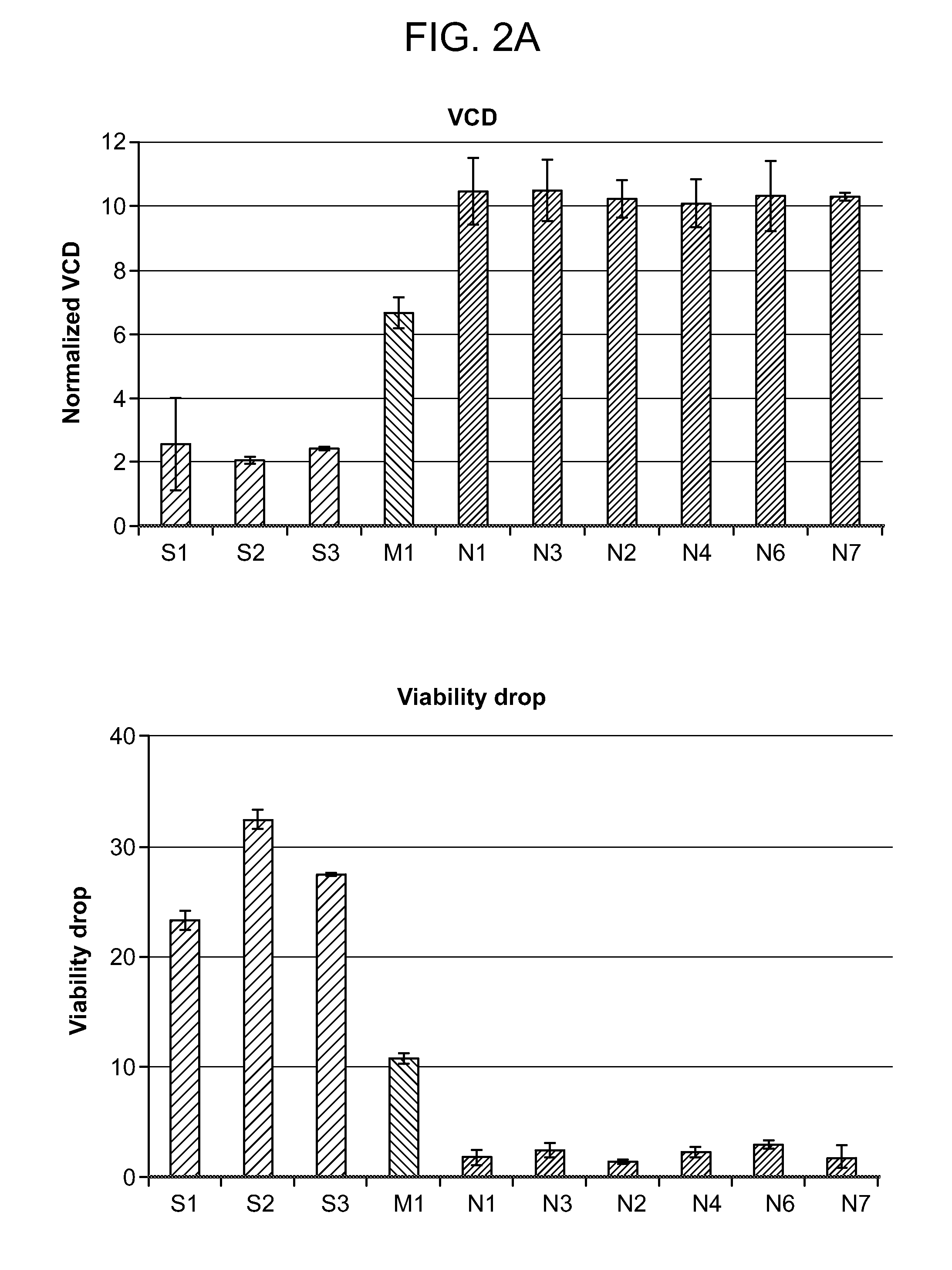
The present disclosure shows, unexpectedly, that variations in cell culture performance in large-scale cell culture systems such as, for example, those used in commercial manufacturing processes, in some instances, can be attributed to often subtle variations among shear-protectant additives used during cell culture. Assessing the quality of shear-protective additives using such large-scale systems, however, is inaccurate, time-consuming and costly. To solve the problem identified, the present disclosure provides methods and compositions for evaluating the suitability of shear-protectant additives without resorting to large scale cell growth and / or protein production tests.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Method for regulating osmotic stress of Pseudomonas glabrata
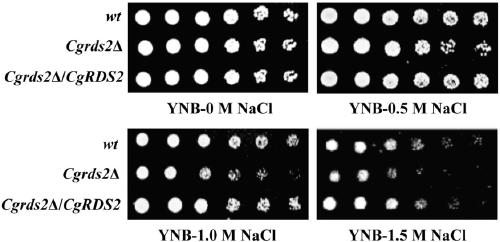
ActiveCN109266566AReduced integrityImprove integrityFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for regulating osmotic pressure stress of Pseudomonas glabrata, belonging to the field of bioengineering. The invention regulates the osmotic stress resistance of Pseudomonas glabrata by overexpressing or deleting the coding gene CgRDS2 of the native transcription factor. The results showed that the biomass, cell viability and membrane integrity of Pseudomonas glabrata decreased by 23%, 46% and 47.6%, respectively, under osmotic stress compared with wild-type strain after the deletion of CgRDS2 gene. After overexpression of CgRDS2 gene, the biomass increased by10%, cell viability increased by 39% and cell membrane integrity increased by 12.1% under 1.5 M NaCl stress.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for enhancing triplex and nuclease-based gene editing
PendingUS20210338815A1Reduced and low off-target modificationFacilitate entryOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesDna antibodyPotentiator
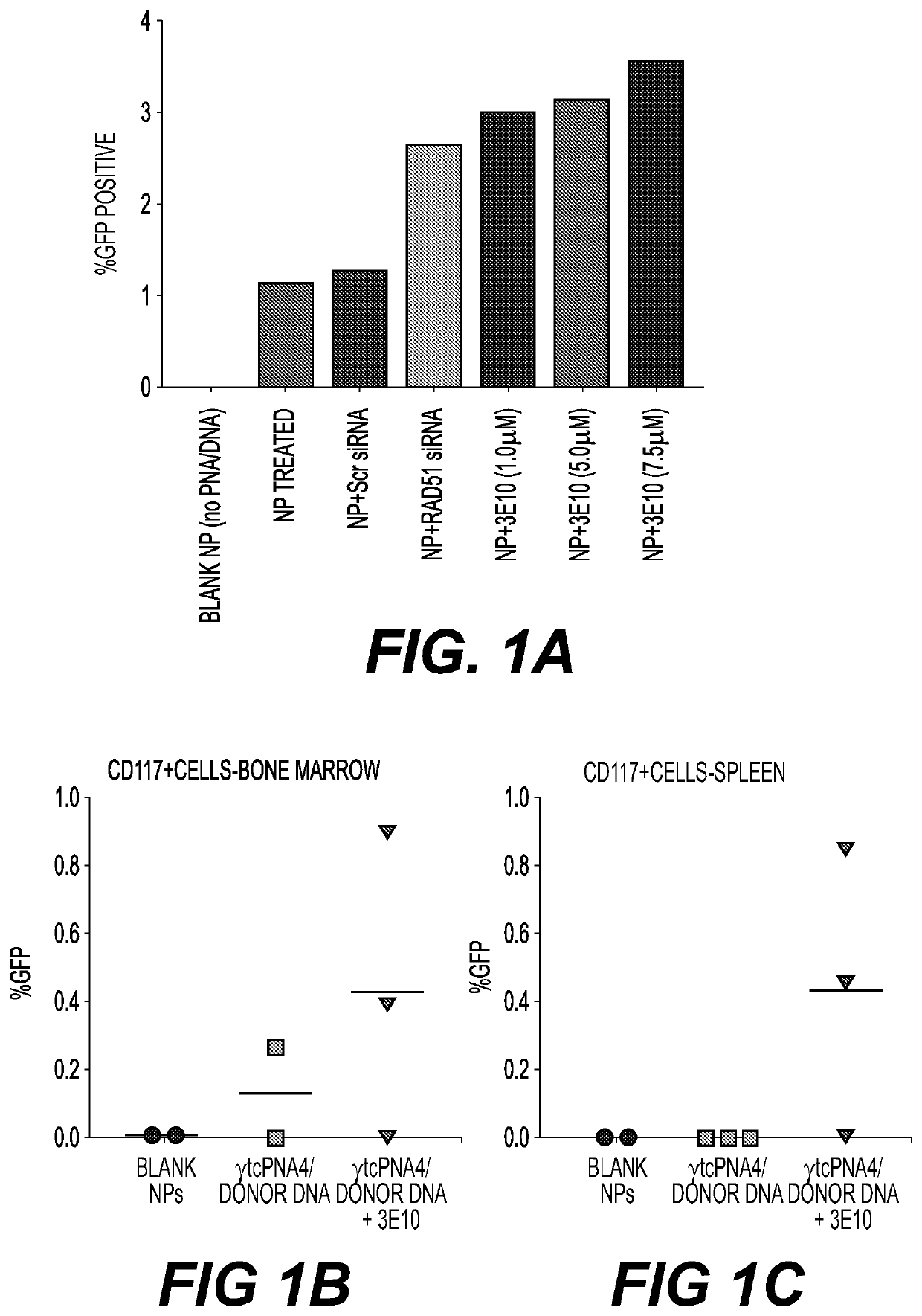
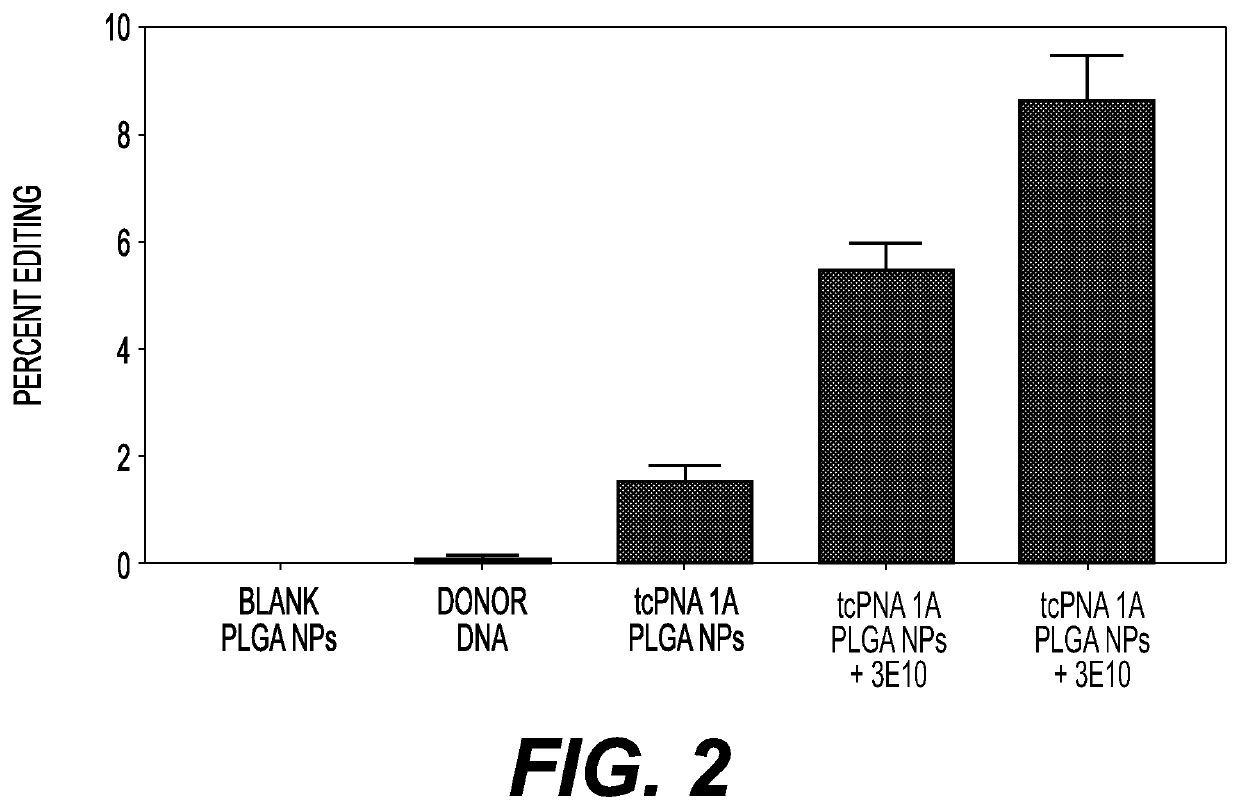
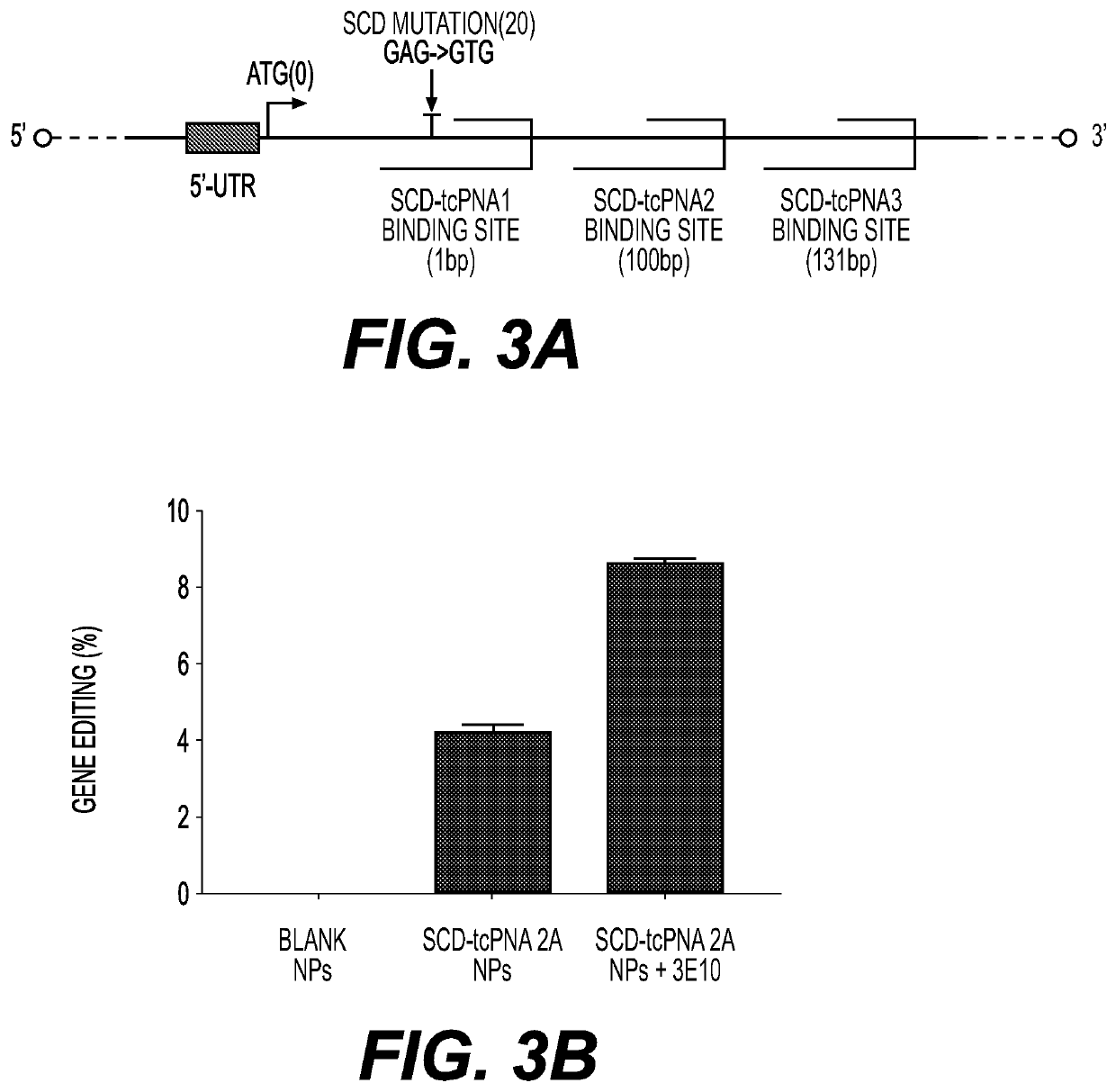
Compositions for improved gene editing and methods of use thereof are disclosed. In a preferred method, gene editing involves use of a cell-penetrating anti-DNA antibody, such as 3E10, as a potentiating agent to enhance gene editing by nucleases and triplex forming oligonucleotides. Genomic modification occurs at a higher frequency when cells are contacted with the potentiating agent and nuclease or triplex forming oligonucleotide, as compared to the absence of the potentiating agent. The methods are suitable for both ex vivo and in vivo approaches to gene editing and are useful for treating a subject with a genetic disease or disorder. Nanoparticle compositions for intracellular delivery of the gene editing compositions are provided and are particularly advantageous for use with in vivo applications.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com