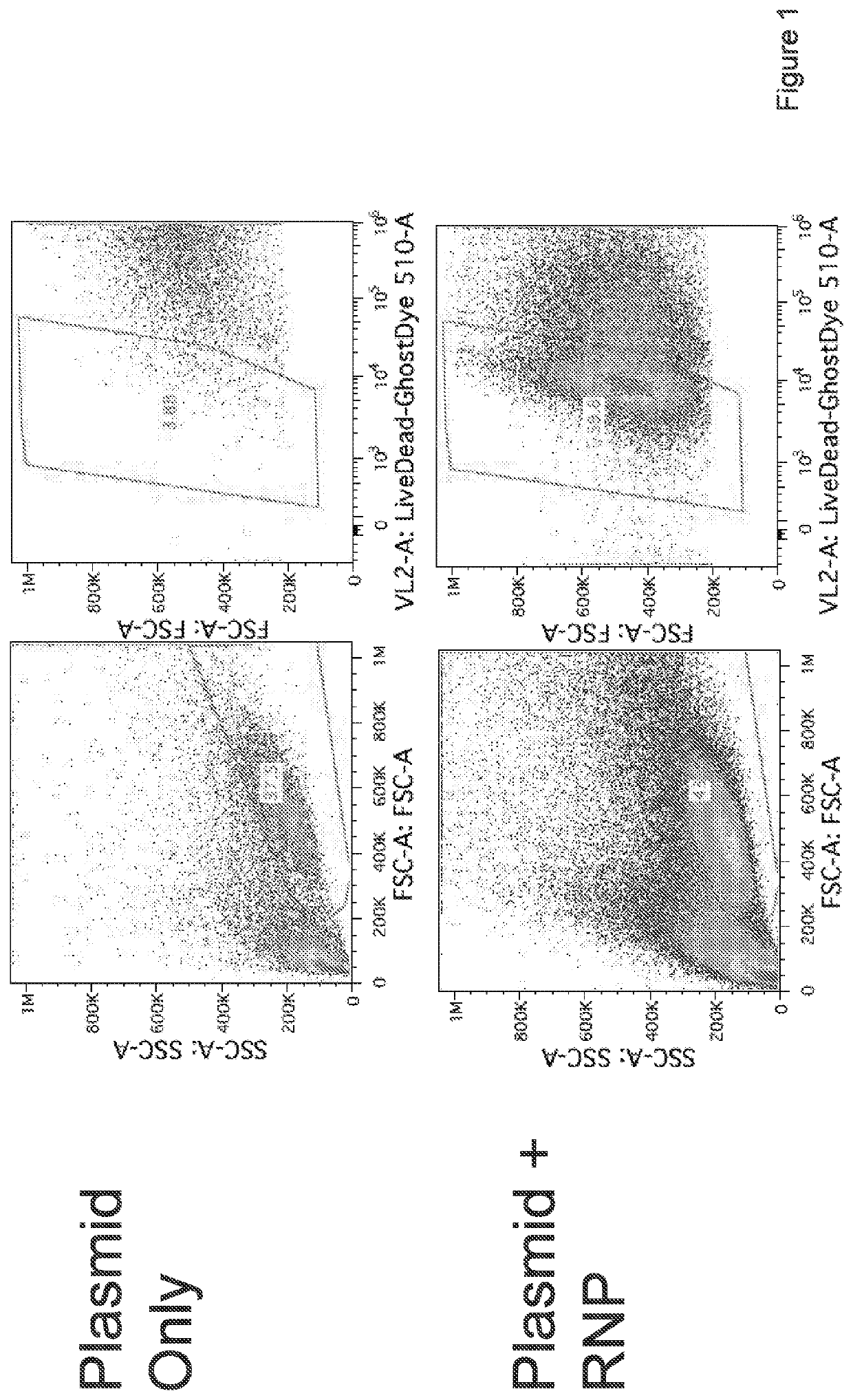
Targeted non-viral DNA insertions
a dna insertion and non-viral technology, applied in the field of targeted non-viral dna insertions, can solve the problems of protein to be knocked out of the frame, many applications cannot be served by this method, and mass cell death, so as to reduce the loss of cell viability and reduce the off-target
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0093]The following examples are provided by way of illustration only and not by way of limitation. Those of skill in the art will readily recognize a variety of non-critical parameters that could be changed or modified to yield essentially the same or similar results.
example i
[0094]The data provided in Example I were generated as outlined in the protocol below.[0095]Clinical protocols / donor consent were established[0096]Isolation of PBMCs was performed with SepMate using the manufacturer's protocol.[0097]Isolation of Bulk T Cells was performed with EasySep using the manufacturer's protocol.[0098]Freezing was performed with Bambanker medium using the manufacturer's protocol.[0099]20 million cells per mL[0100]Thawing[0101]1 mL Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium (RPMI) added on top of thawed cells, which were then combined and washed in media[0102]Cells rested in media only overnight prior to stimulation
Primary T Cell Culture
[0103]Media[0104]RPMI+10% FBS[0105]XVivo15+5% FBS; or[0106]Immunocult (Serum free)[0107]Useful for culturing cells in a serum free environment[0108]Stimulation[0109]1:1 CD3 / CD28 magnetic Dynabeads[0110]Ratios of 0.25:1 up to 2:1 can be used[0111]Magnetic bead removal prior to electroporation can improve efficiency[0112]Cytokines Pre...
example ii
Isolation of Human Primary T Cells for Gene Targeting
[0178]Primary human T cells were isolated from healthy human donors either from fresh whole blood samples, residuals from leukoreduction chambers after Trima Apheresis (Blood Centers of the Pacific), or leukapheresis products (StemCell). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from whole blood samples by Ficoll centrifugation using SepMate tubes (STEMCELL, per manufacturer's instructions). T cells were isolated from PBMCs from all cell sources by magnetic negative selection using an EasySep Human T Cell Isolation Kit (STEMCELL, per manufacturer's instructions). Unless otherwise noted, isolated T cells were stimulated and used directly (fresh). When frozen cells were used, previously isolated T cells that had been frozen in Bambanker freezing medium (Bulldog Bio) per manufacturer's instructions were thawed, cultured in media without stimulation for 1 day, and then stimulated and handled as described for freshly iso...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com